Patents
Literature
200 results about "Thermophotovoltaic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Thermophotovoltaic (TPV) energy conversion is a direct conversion process from heat to electricity via photons. A basic thermophotovoltaic system consists of a thermal emitter and a photovoltaic diode cell.
System and method for enhanced thermophotovoltaic generation
InactiveUS20050109386A1Reduce fossil fueled NOx emissionIncreasing burner efficiencyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPV power plantsThermophotovoltaicDistributed generation
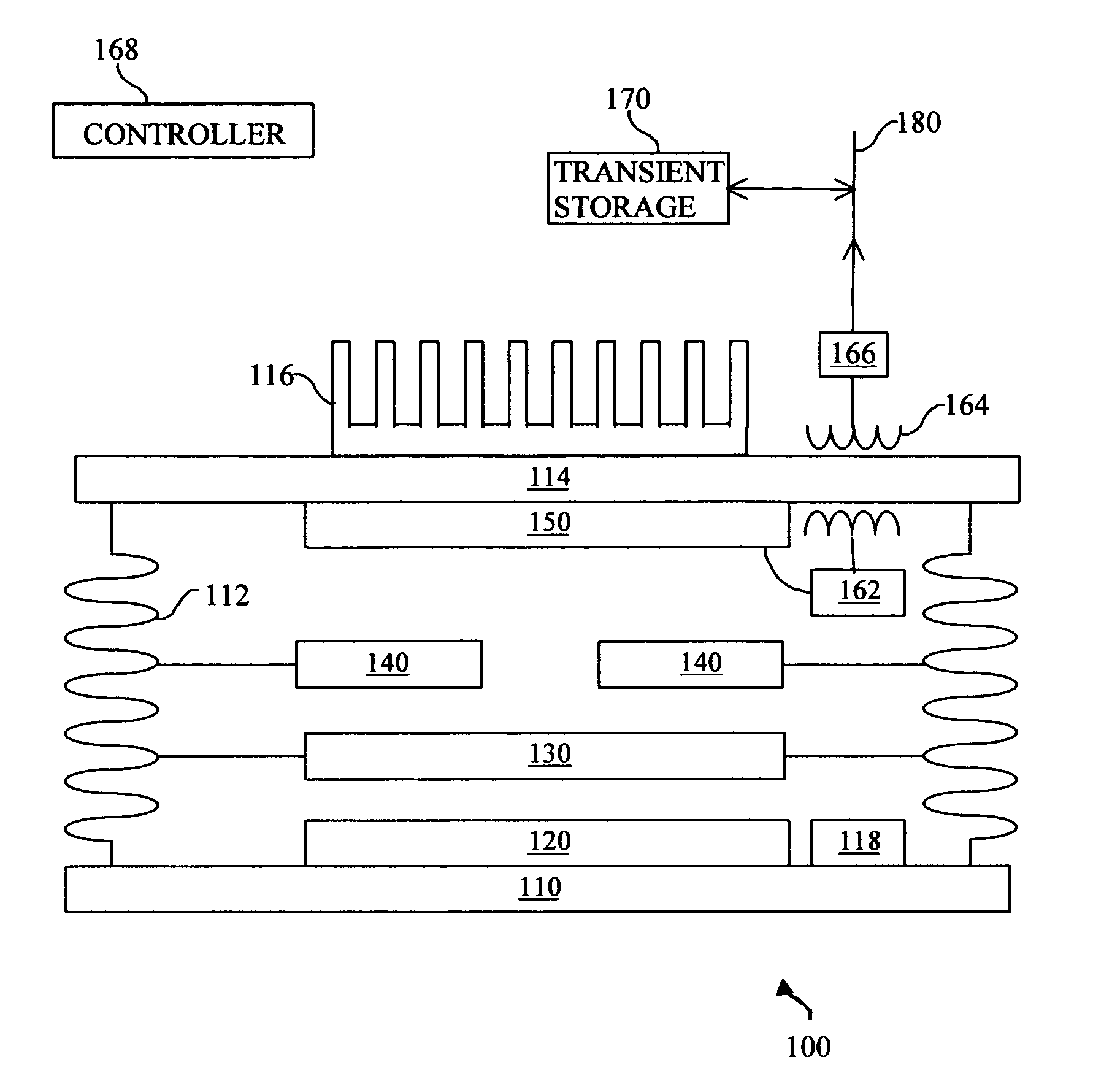
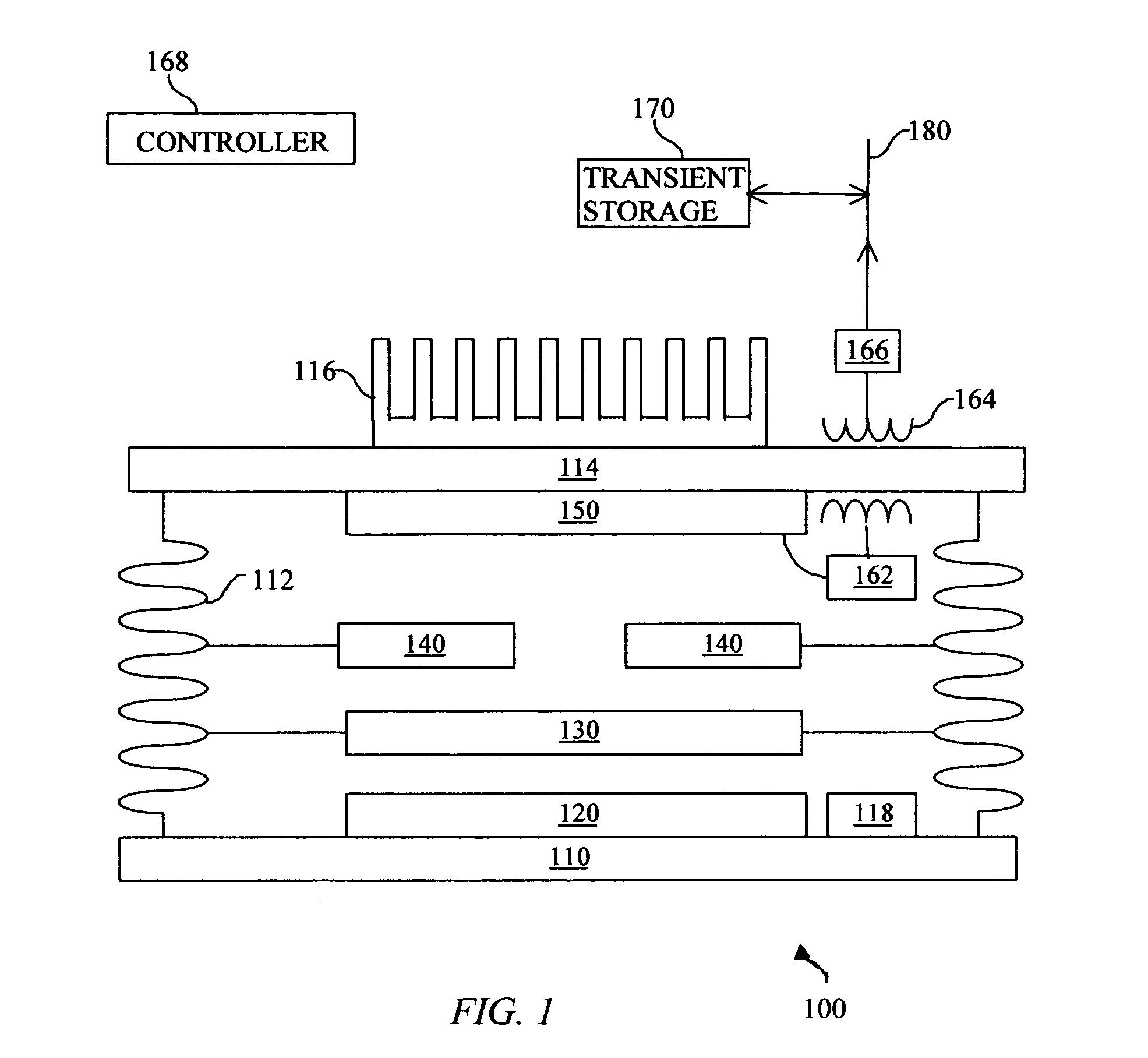
A system and method for lower cost, high efficiency, thermophotovoltaic distributed generation includes: an emitter, a photovoltaic cell, and transient electrical energy storage.
Owner:PRACTICAL TECH
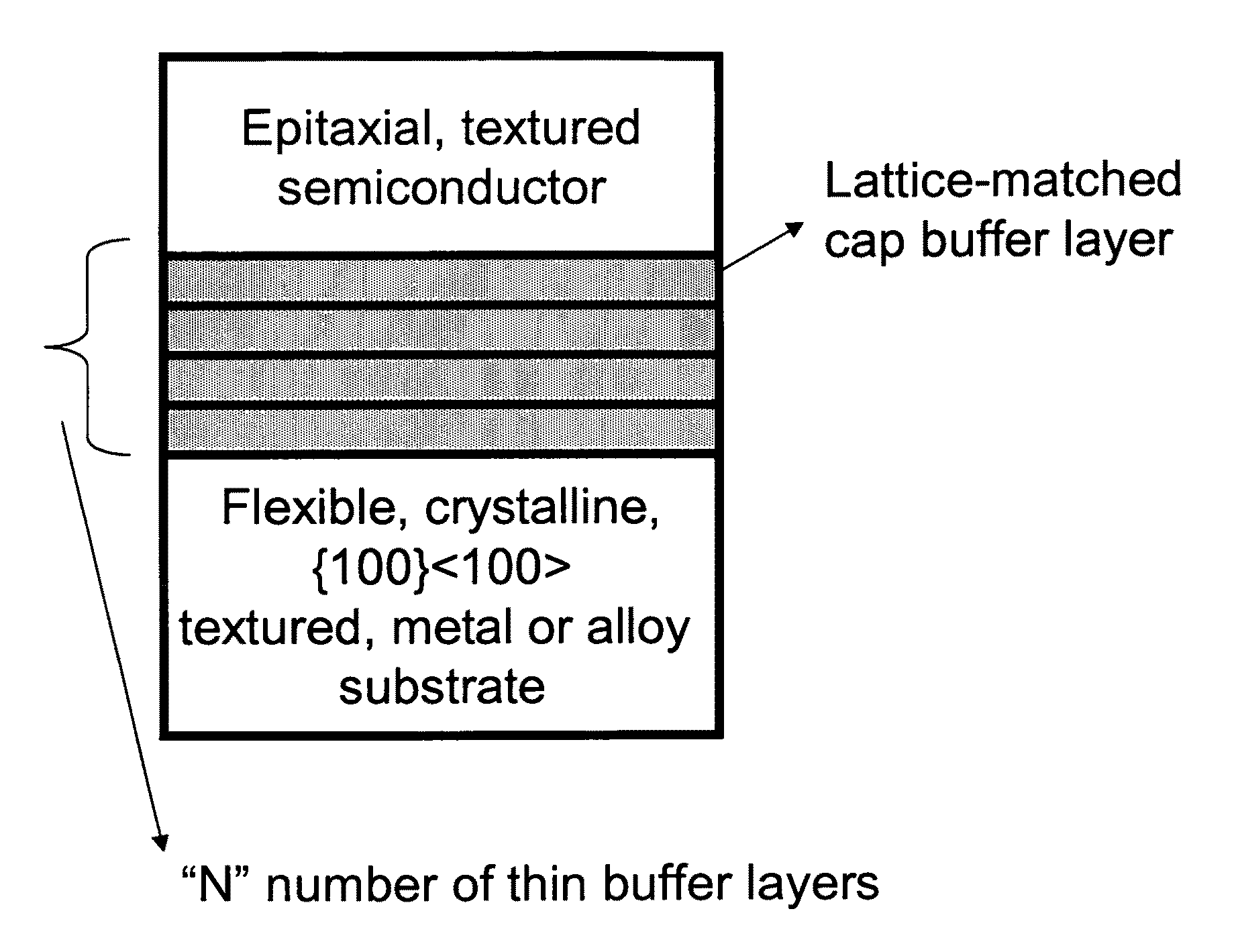
Novel, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS20080217622A1Good lattice matchingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, large-area, triaxially textured, single-crystal or single-crystal-like, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
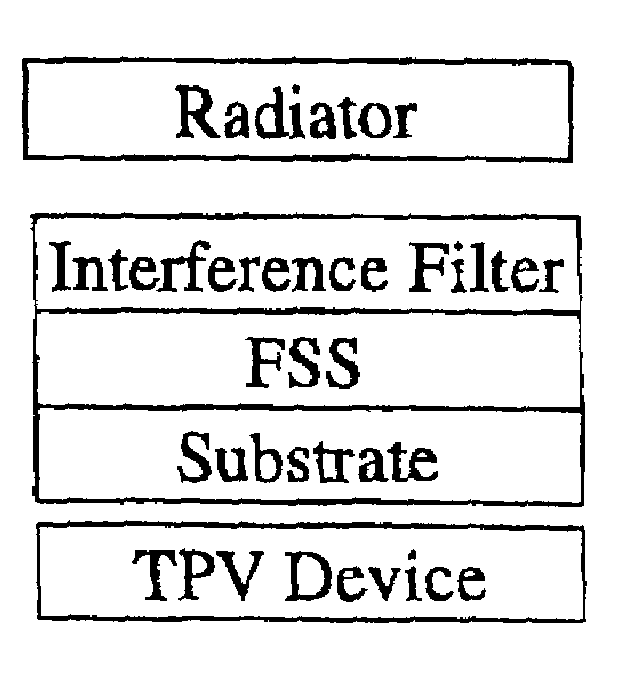
Tandem filters using frequency selective surfaces for enhanced conversion efficiency in a thermophotovoltaic energy conversion system
InactiveUS7166797B1High bandgap energyImprove reflectivityMirrorsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsTransmittanceLength wave
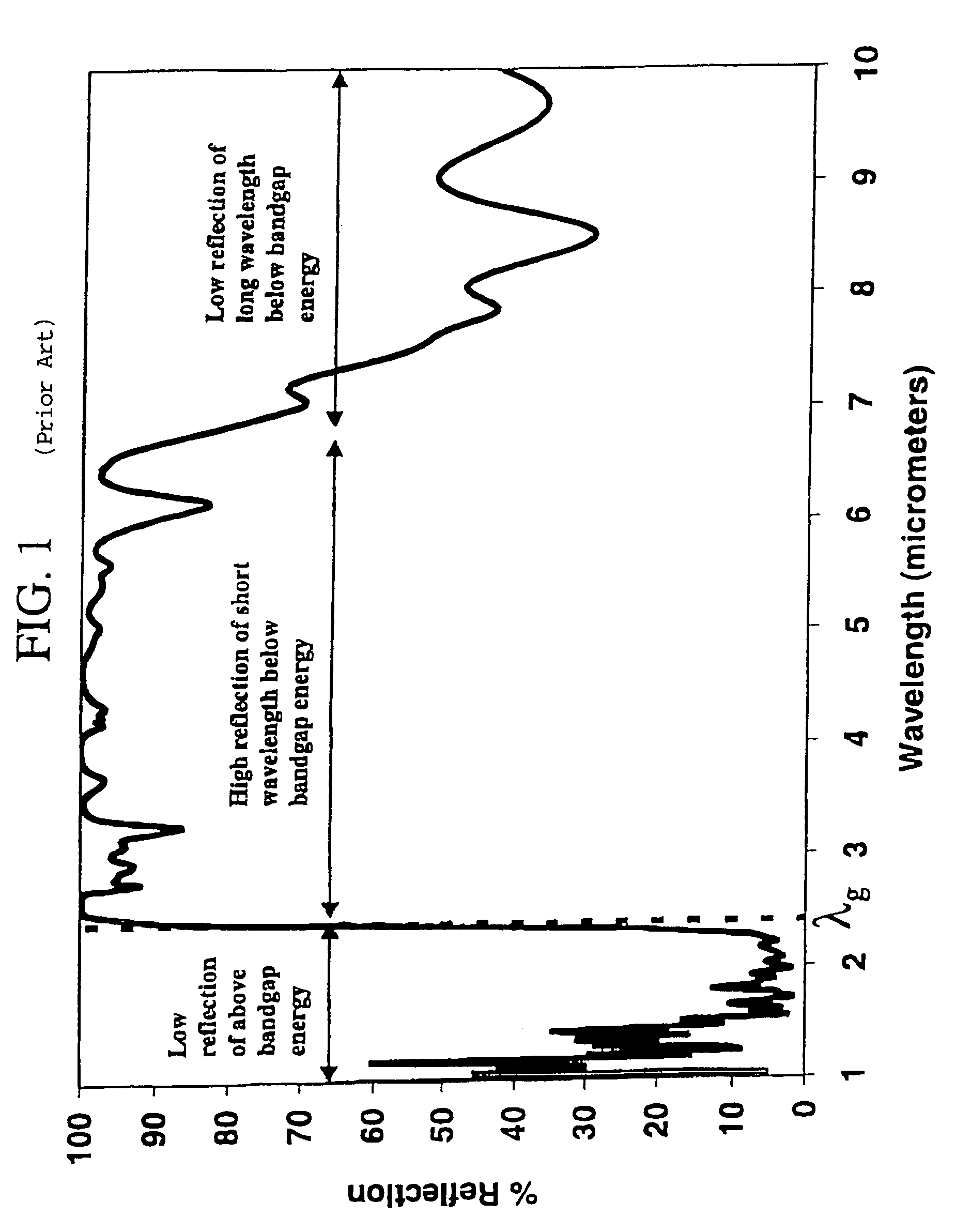
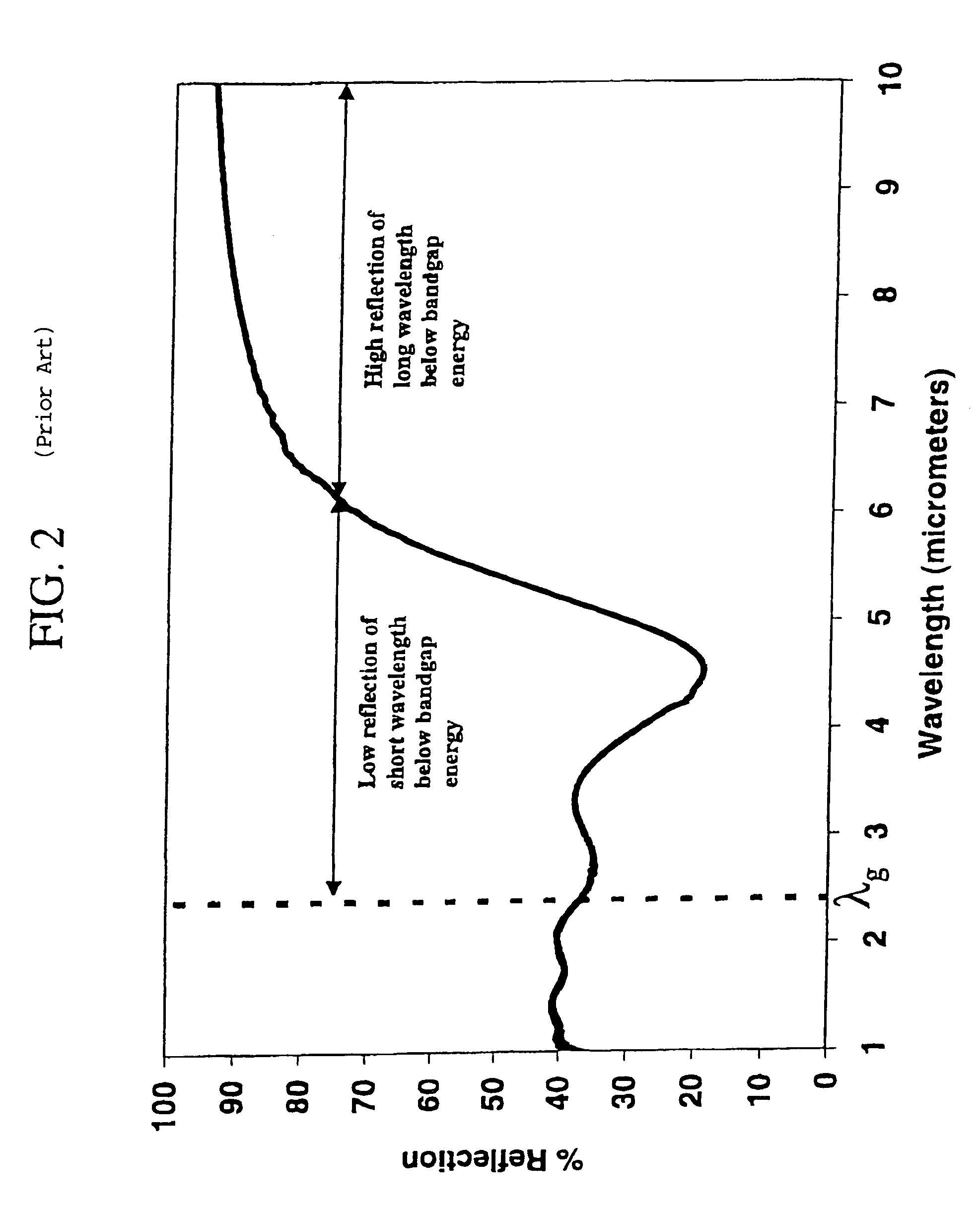
This invention relates to the field of thermophotovoltaic (TPV) direct energy conversion. In particular, TPV systems use filters to minimize parasitic absorption of below bandgap energy. This invention constitutes a novel combination of front surface filters to increase TPV conversion efficiency by reflecting useless below bandgap energy while transmitting a very high percentage of the useful above bandgap energy. In particular, a frequency selective surface is used in combination with an interference filter. The frequency selective surface provides high transmission of above bandgap energy and high reflection of long wavelength below bandgap energy. The interference filter maintains high transmission of above bandgap energy and provides high reflection of short wavelength below bandgap energy and a sharp transition from high transmission to high reflection.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
<100> or 45 degrees-rotated <100>, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS20110062446A1Good lattice matchingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, {100}<100> or 45°-rotated {100}<100> oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Thermophotovoltaic energy generation
ActiveUS20110284059A1Radiation/particle handlingPV power plantsElectromagnetic radiationThermophotovoltaic
Inventive systems and methods for the generation of energy using thermophotovoltaic cells are described. Also described are systems and methods for selectively emitting electromagnetic radiation from an emitter for use in thermophotovoltaic energy generation systems. In at least some of the inventive energy generation systems and methods, a voltage applied to the thermophotovoltaic cell (e.g., to enhance the power produced by the cell) can be adjusted to enhance system performance. Certain embodiments of the systems and methods described herein can be used to generate energy relatively efficiently.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Hybrid radiant energy aircraft engine
Hybrid aircraft propulsion systems are disclosed comprising an electrically driven ducted fan, a peripheral duct or enclosure, a combustion-produced source of radiant energy, radiant energy receivers or cold mirrors, and thermophotovoltaic or thermoelectric cell energy converters. An electric motor drives a partially or completely duct enclosed fan. Downstream and within the duct enclosure, radiant energy emitters irradiated receiver fins and thermophotovoltaic cells or thermoelectric cells. The receiver fins heat and expand the fan air, and the thermophotovoltaic cells or thermoelectric cells convert the radiant energy into electrical energy which is available to charge batteries and energize the fan motor. Thrust is provided via the acceleration of air by the fan and by the acceleration of air due to heat driven expansion.
Owner:SEPARATION DESIGN GROUP
Semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices on <100> oriented substrates
InactiveUS20080265255A1Improve performanceGood lattice matchingFinal product manufactureNanoinformaticsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices on {110}<100> textured substrates are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
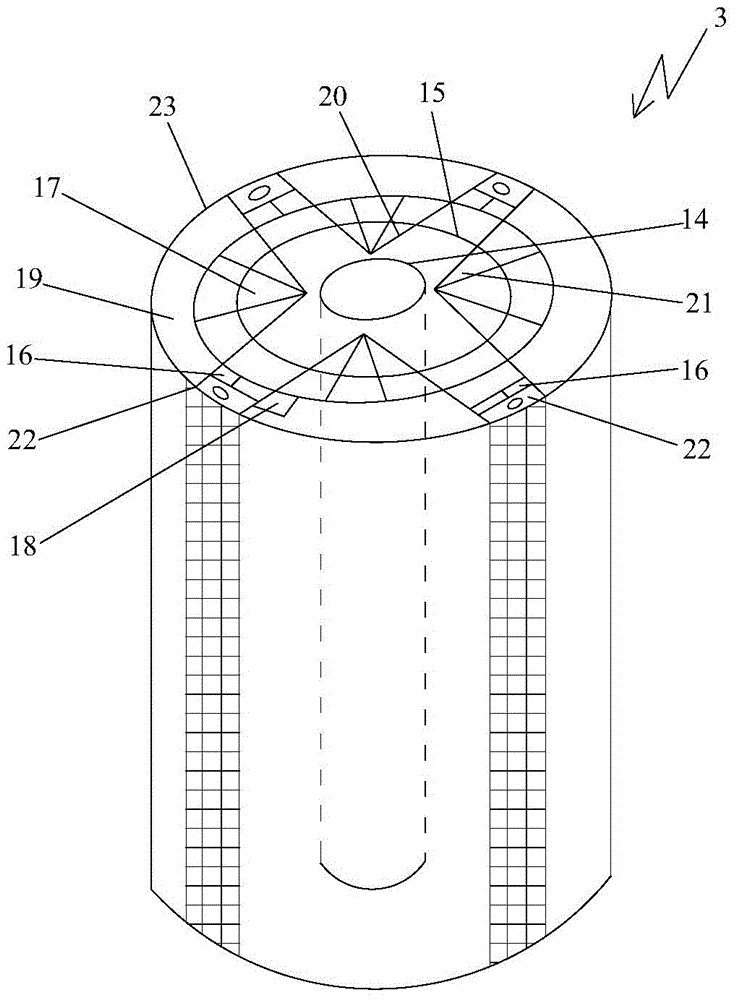
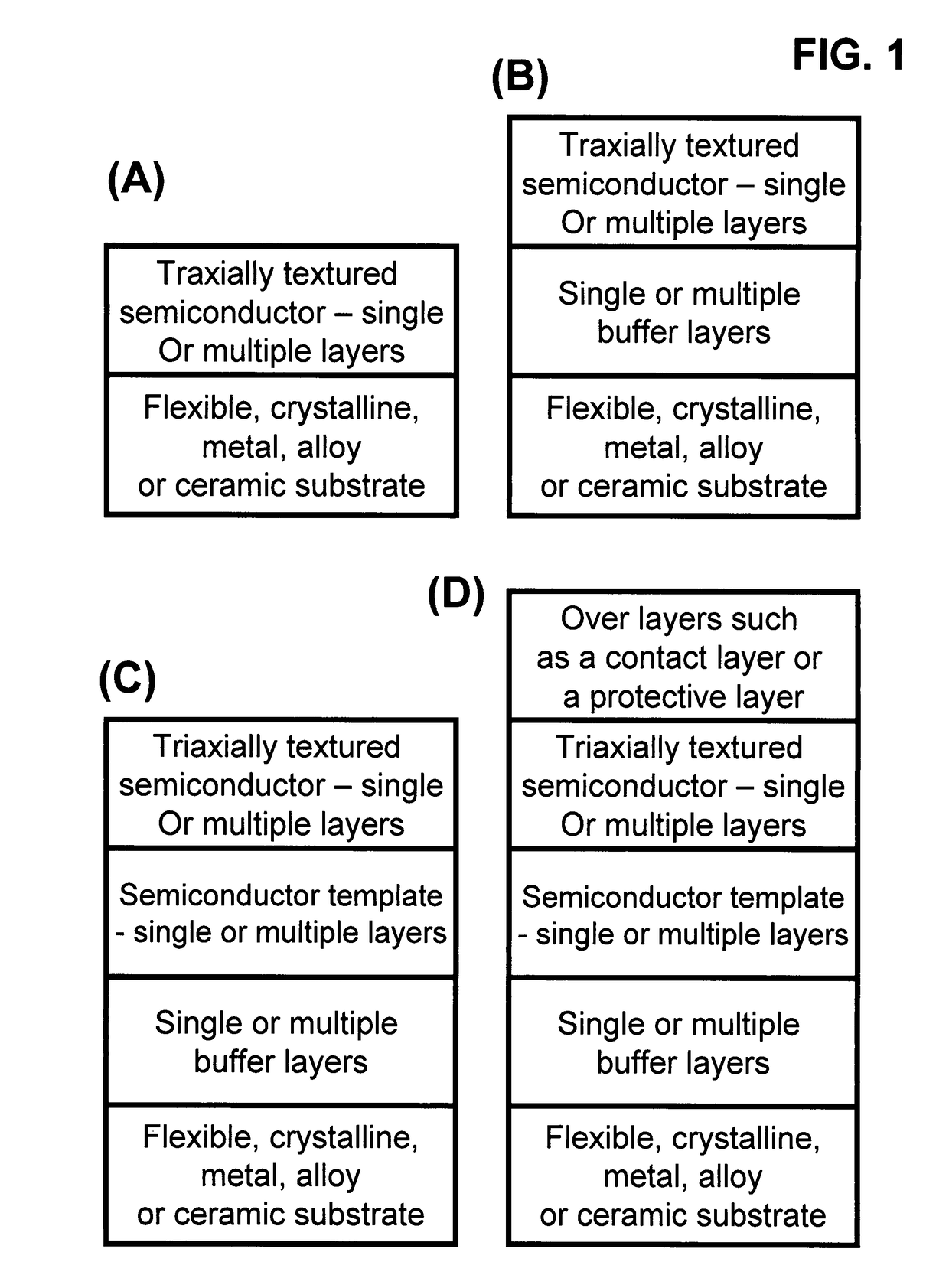
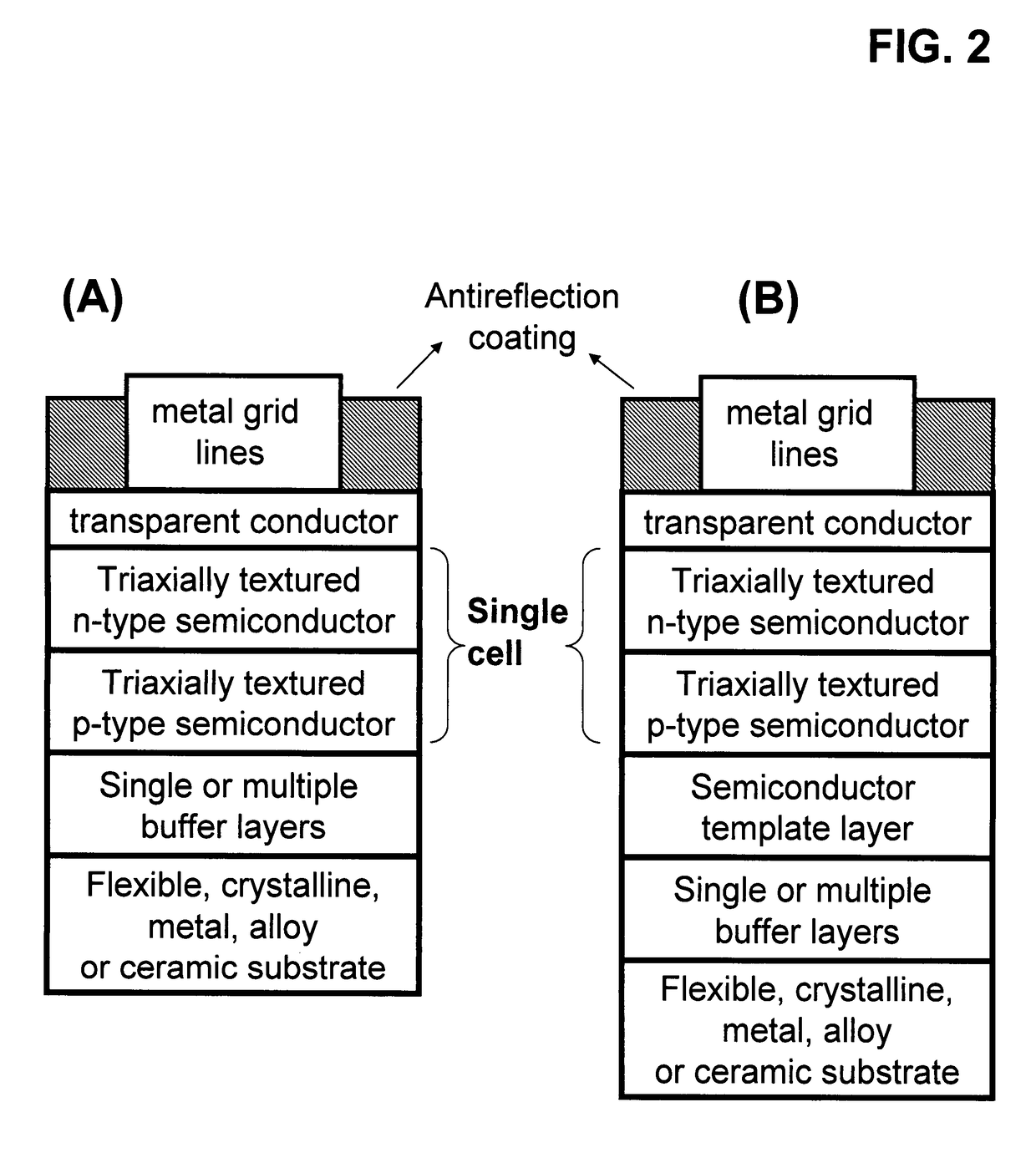
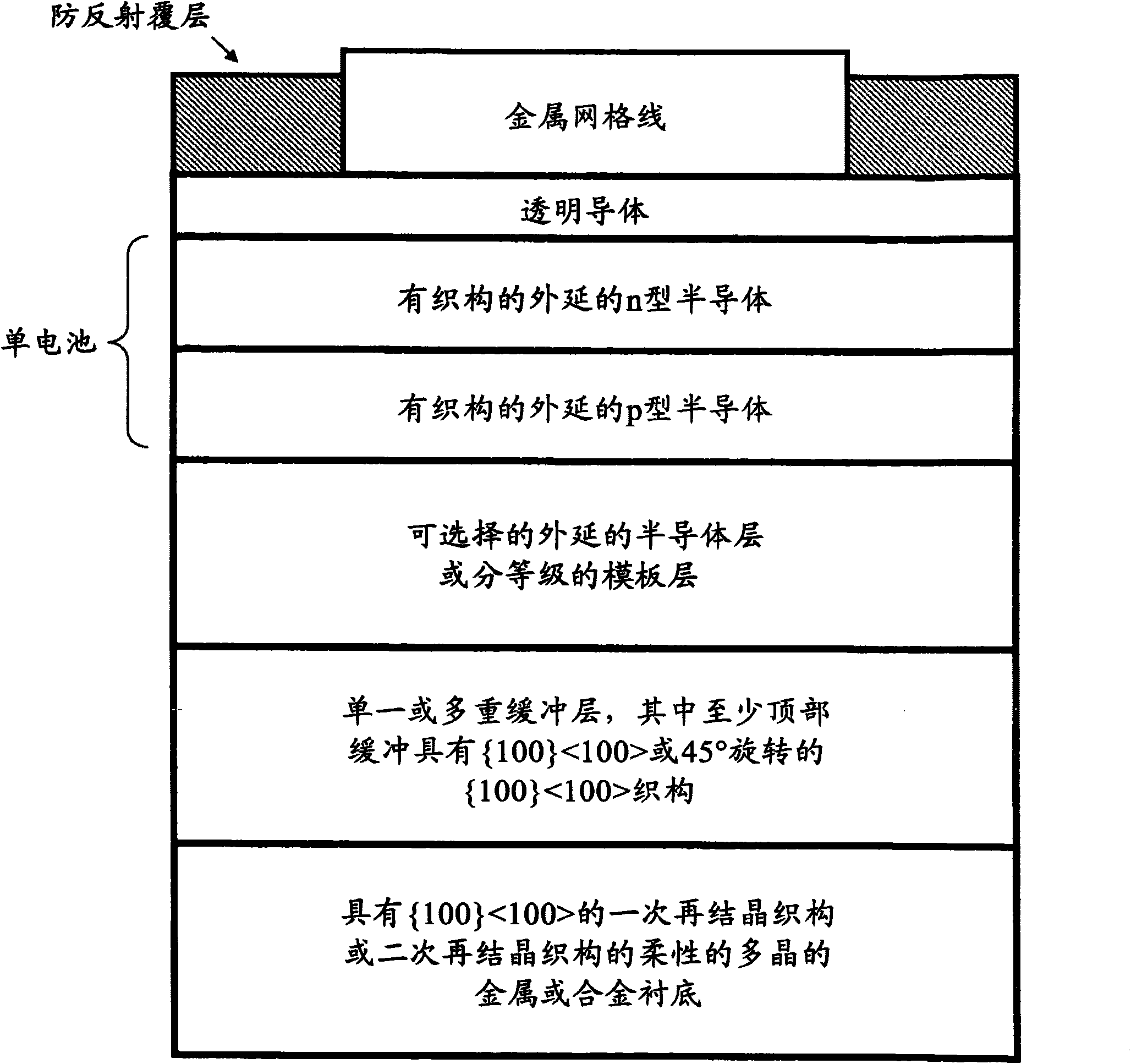
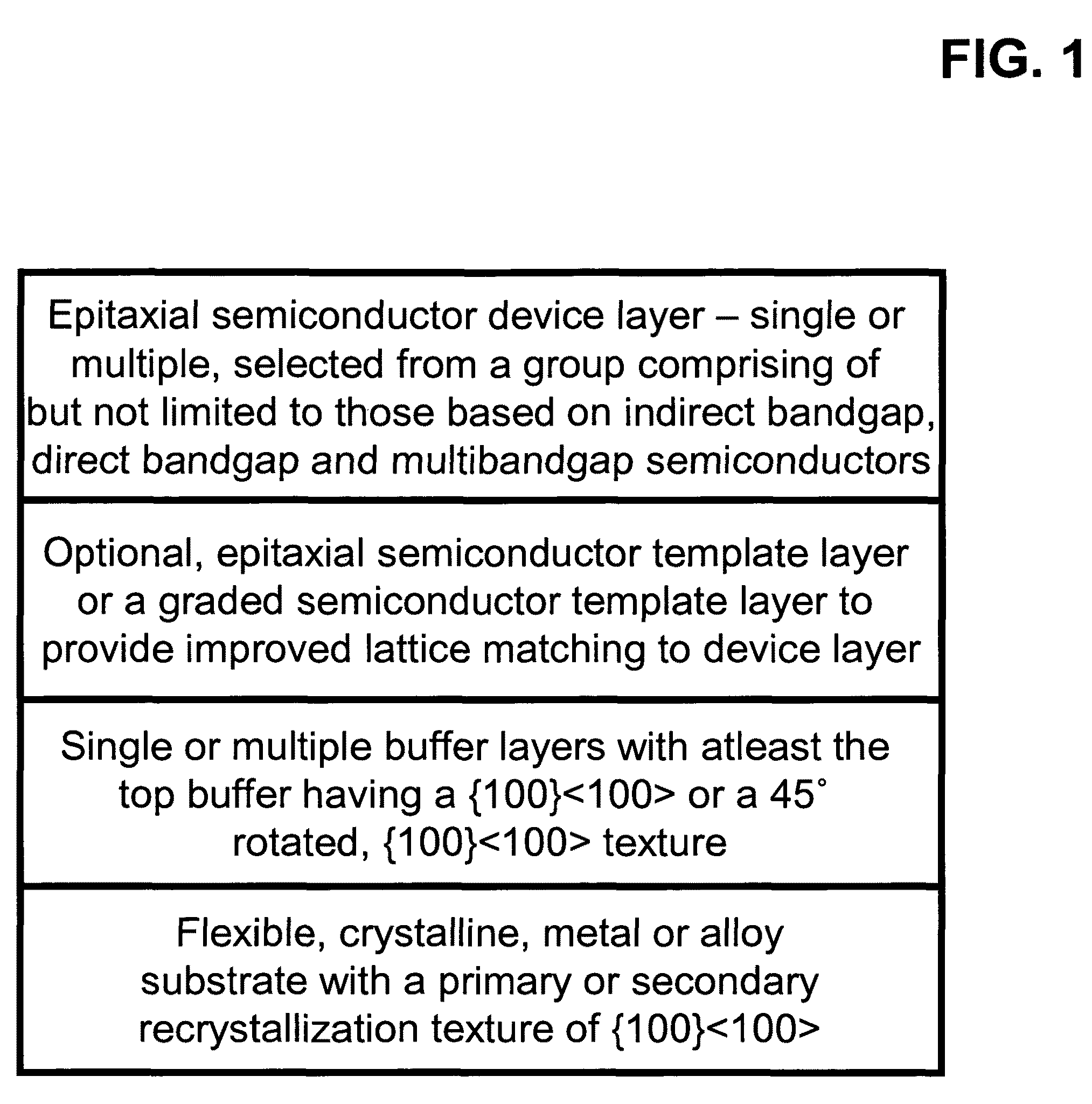
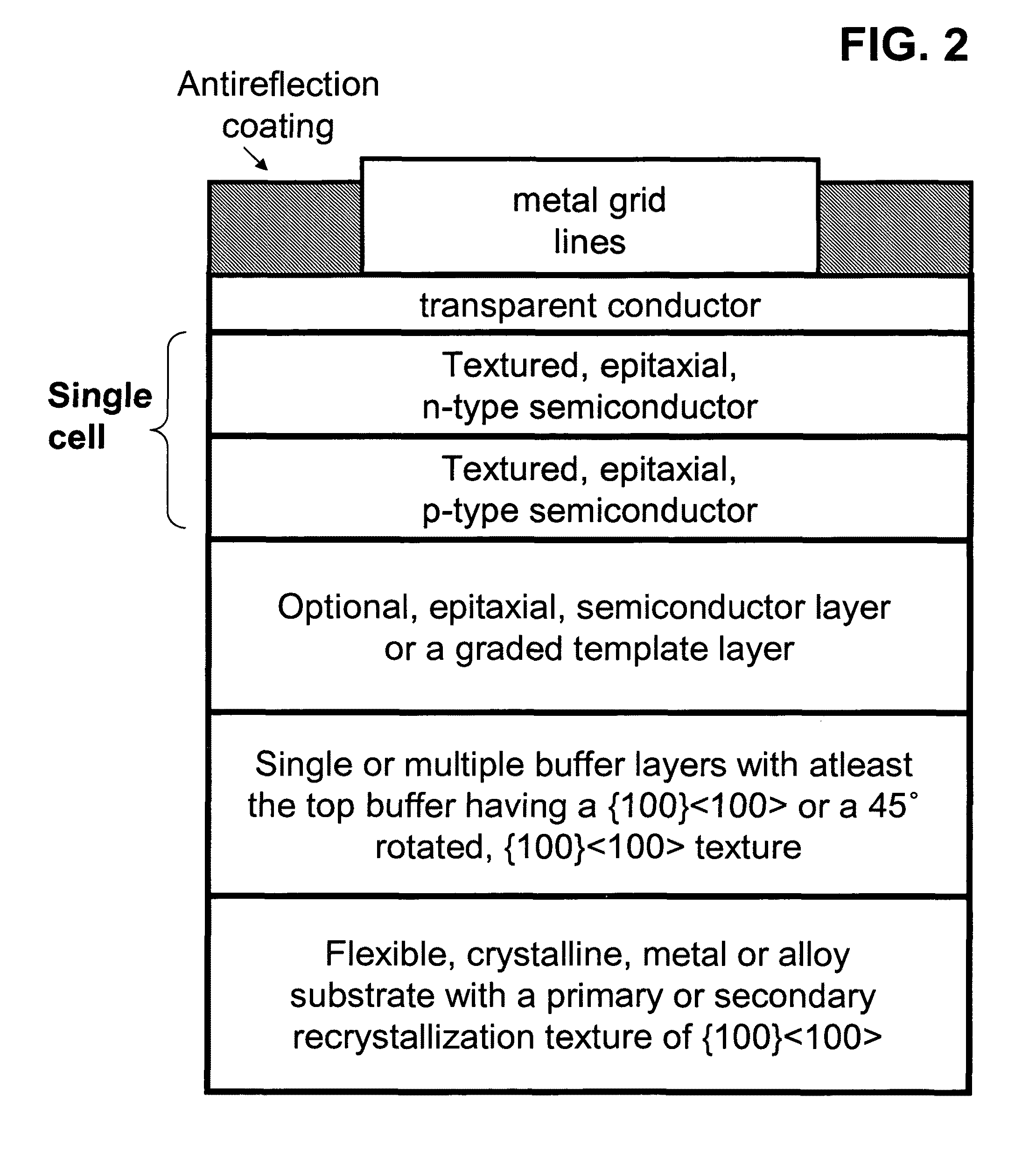
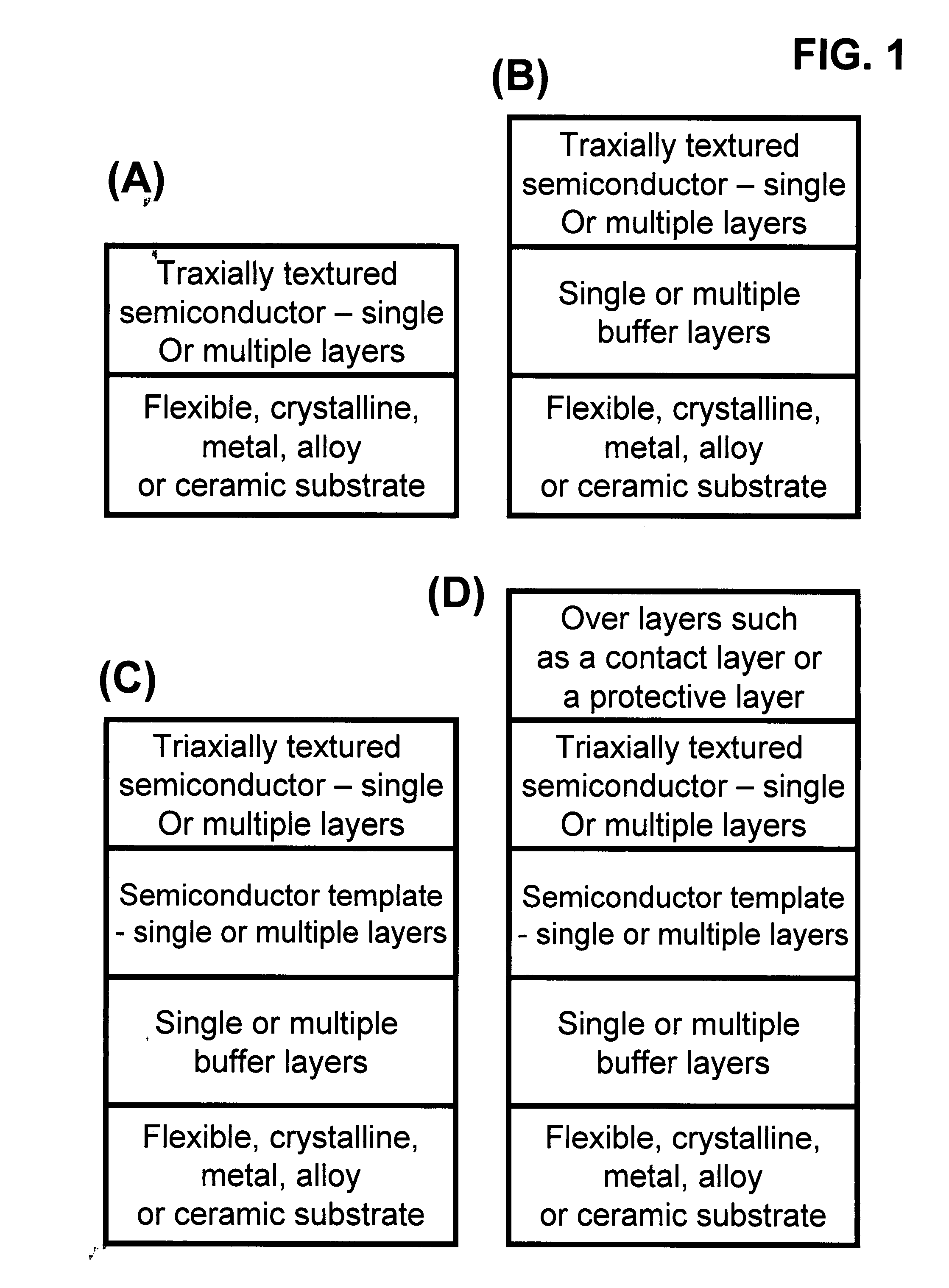
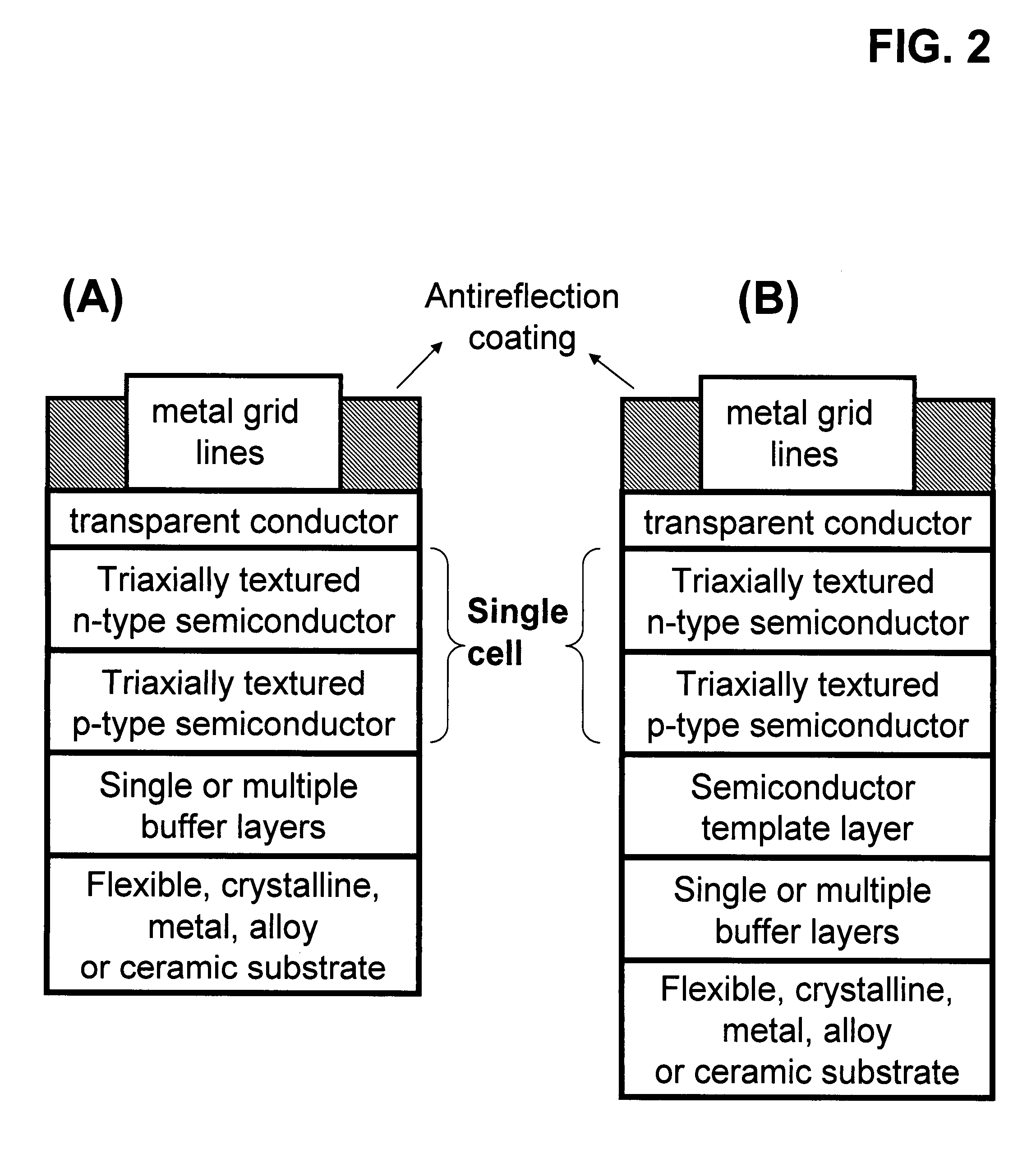
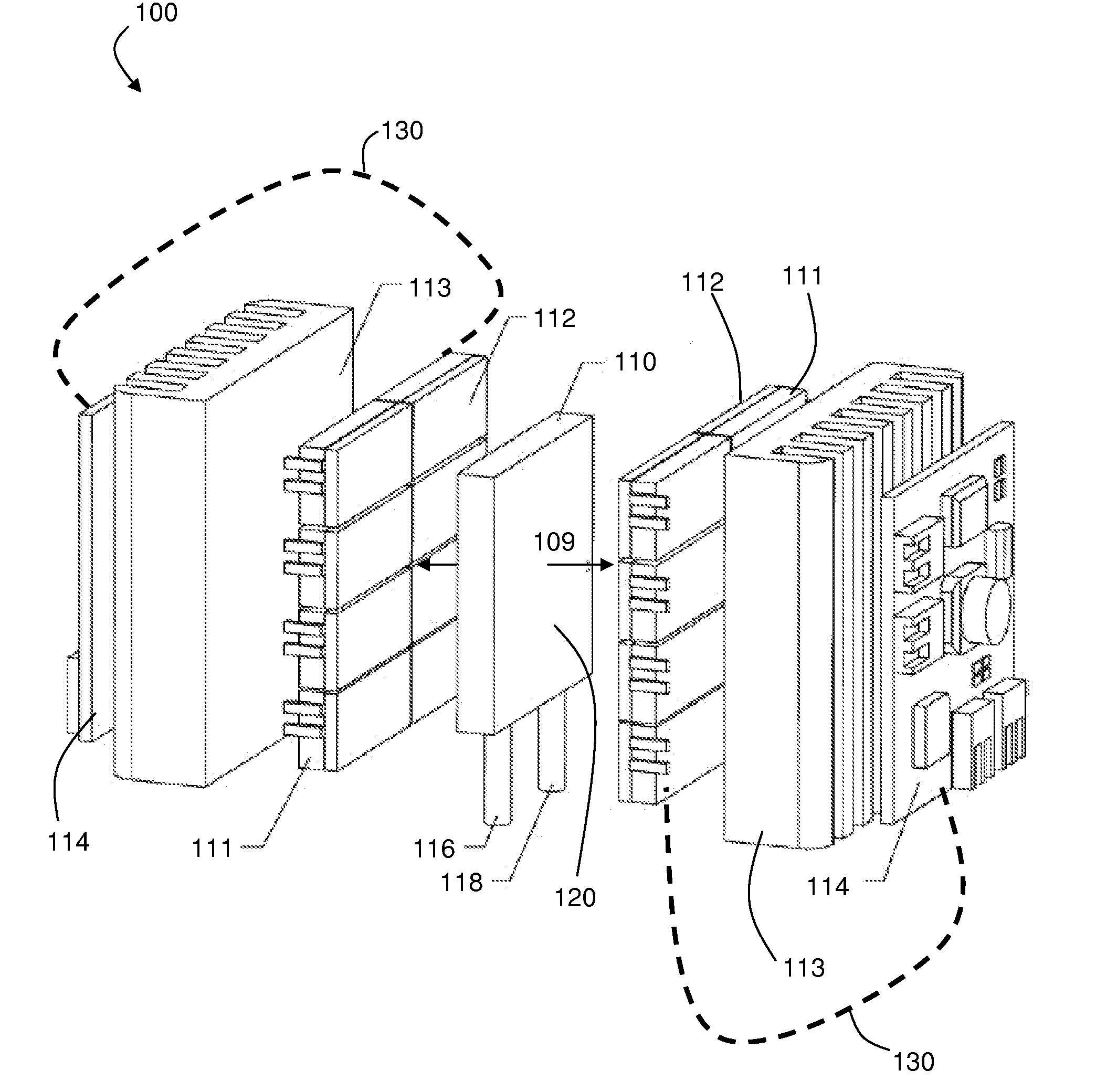
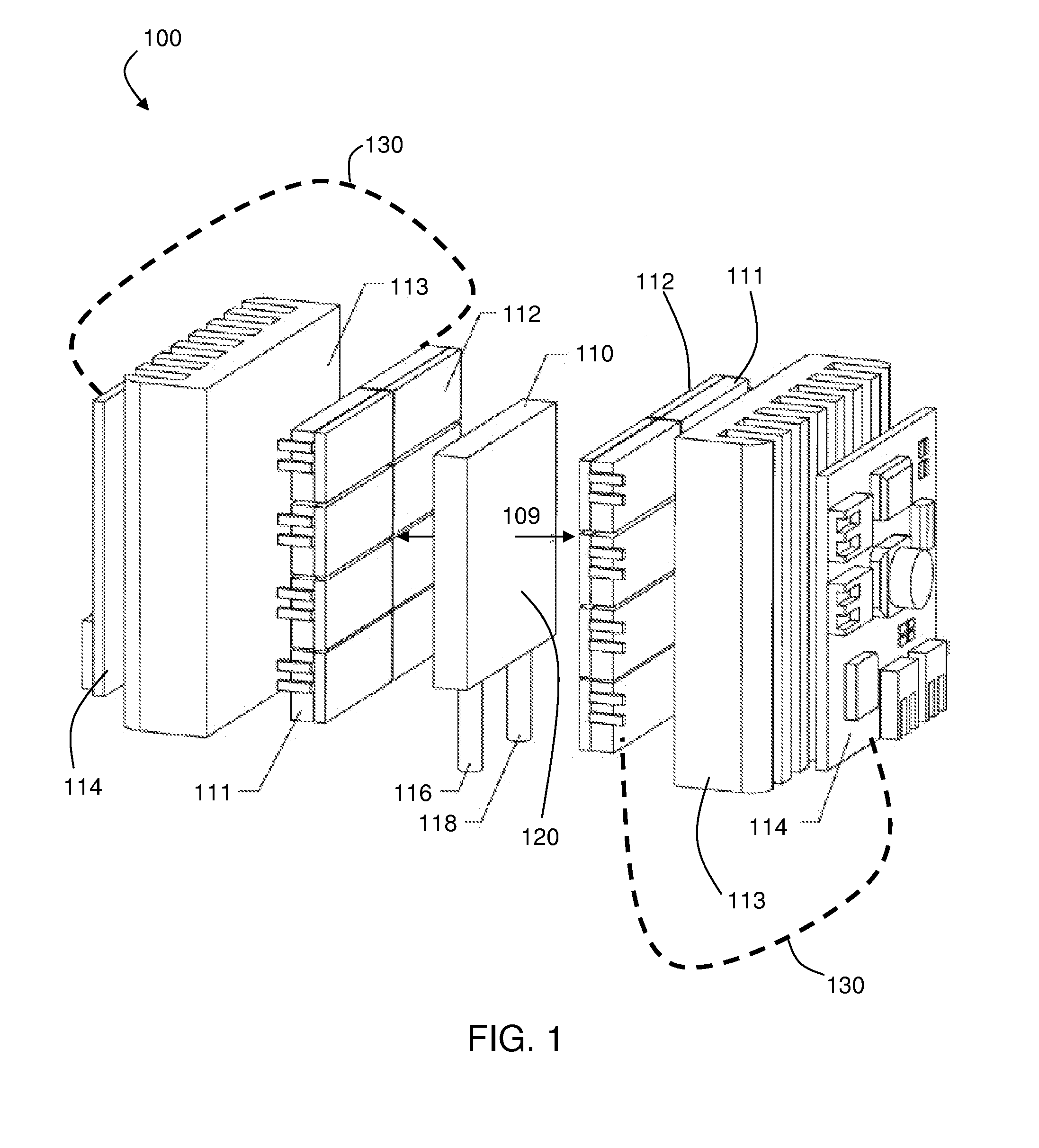
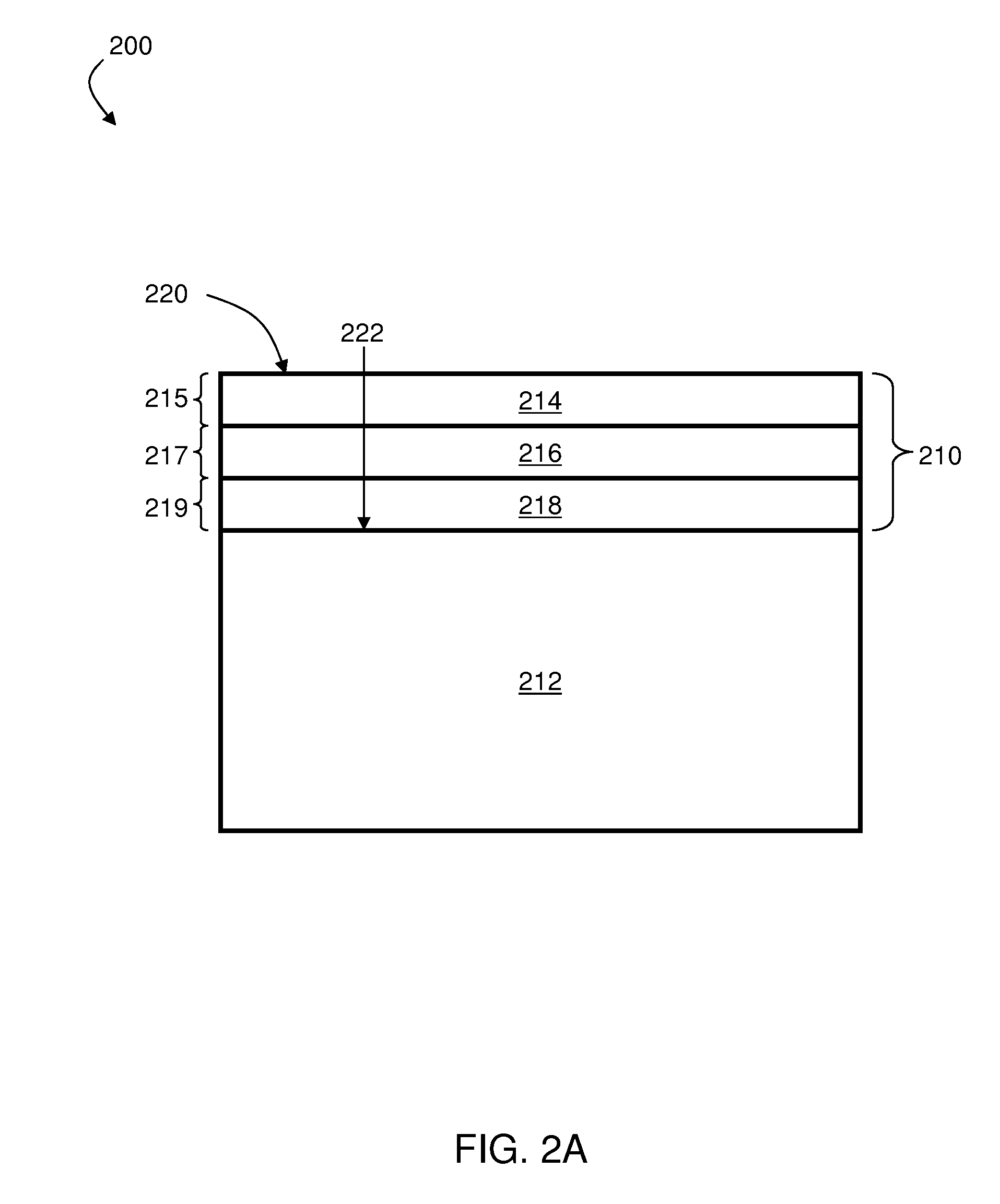
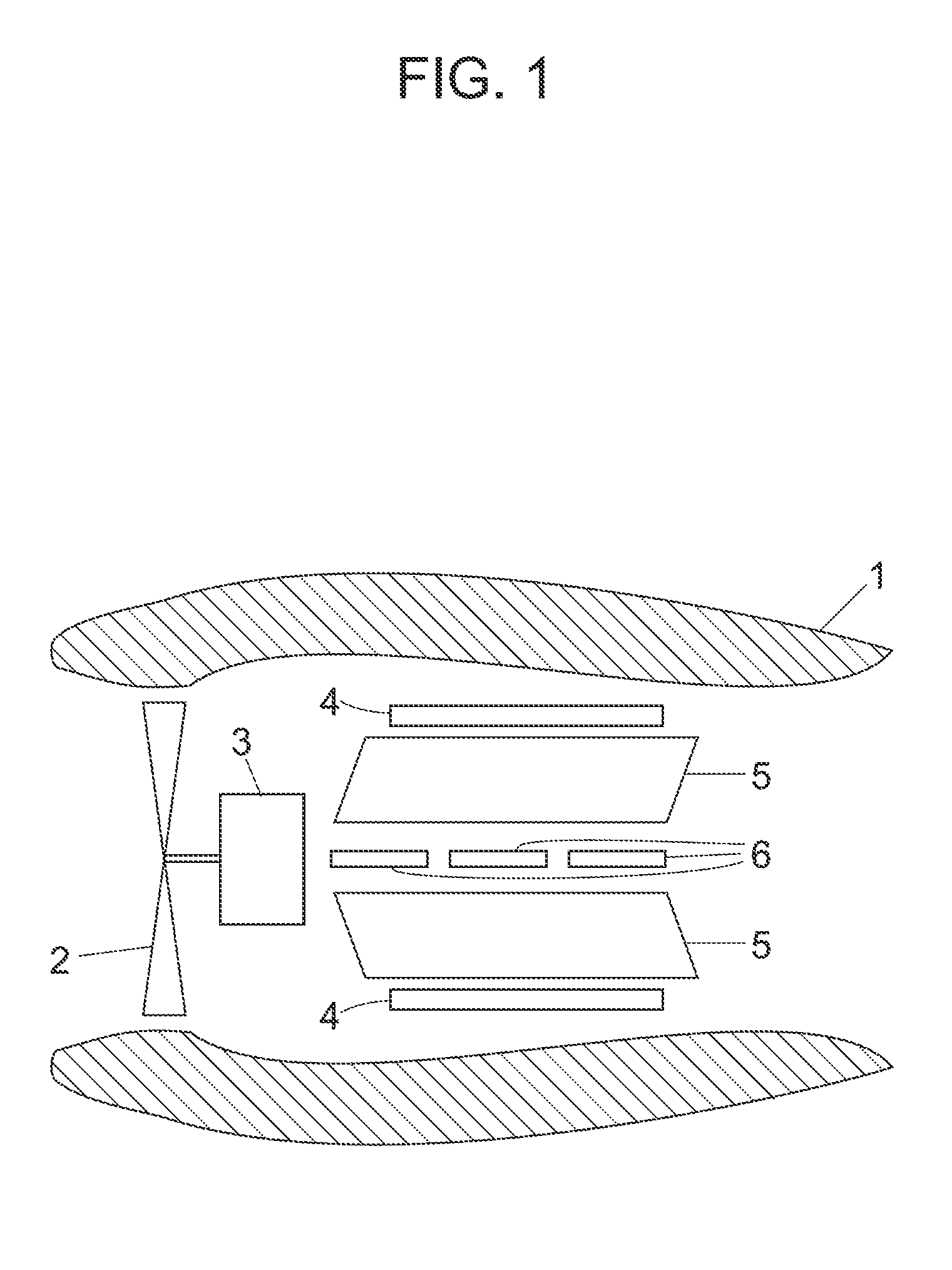
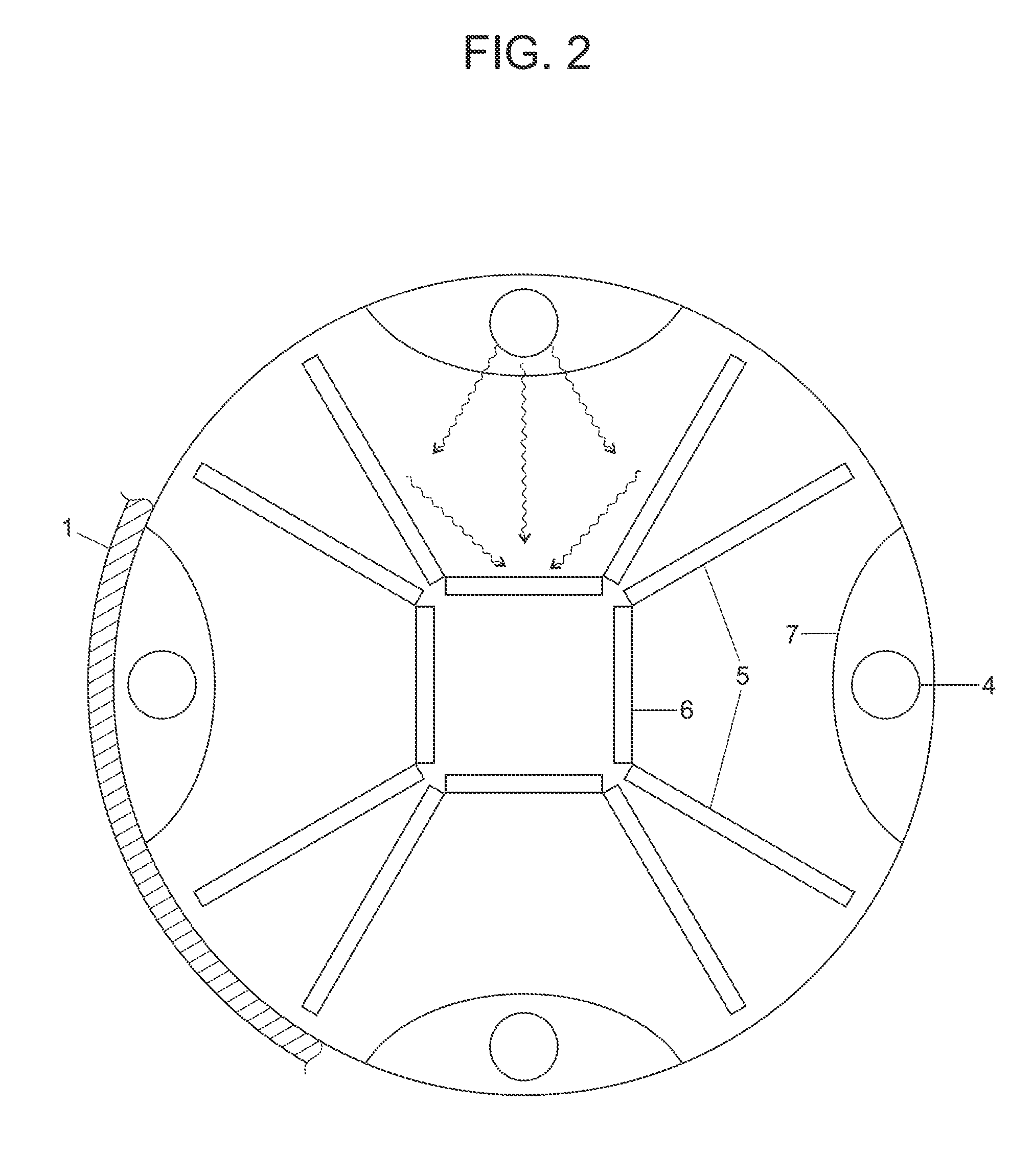
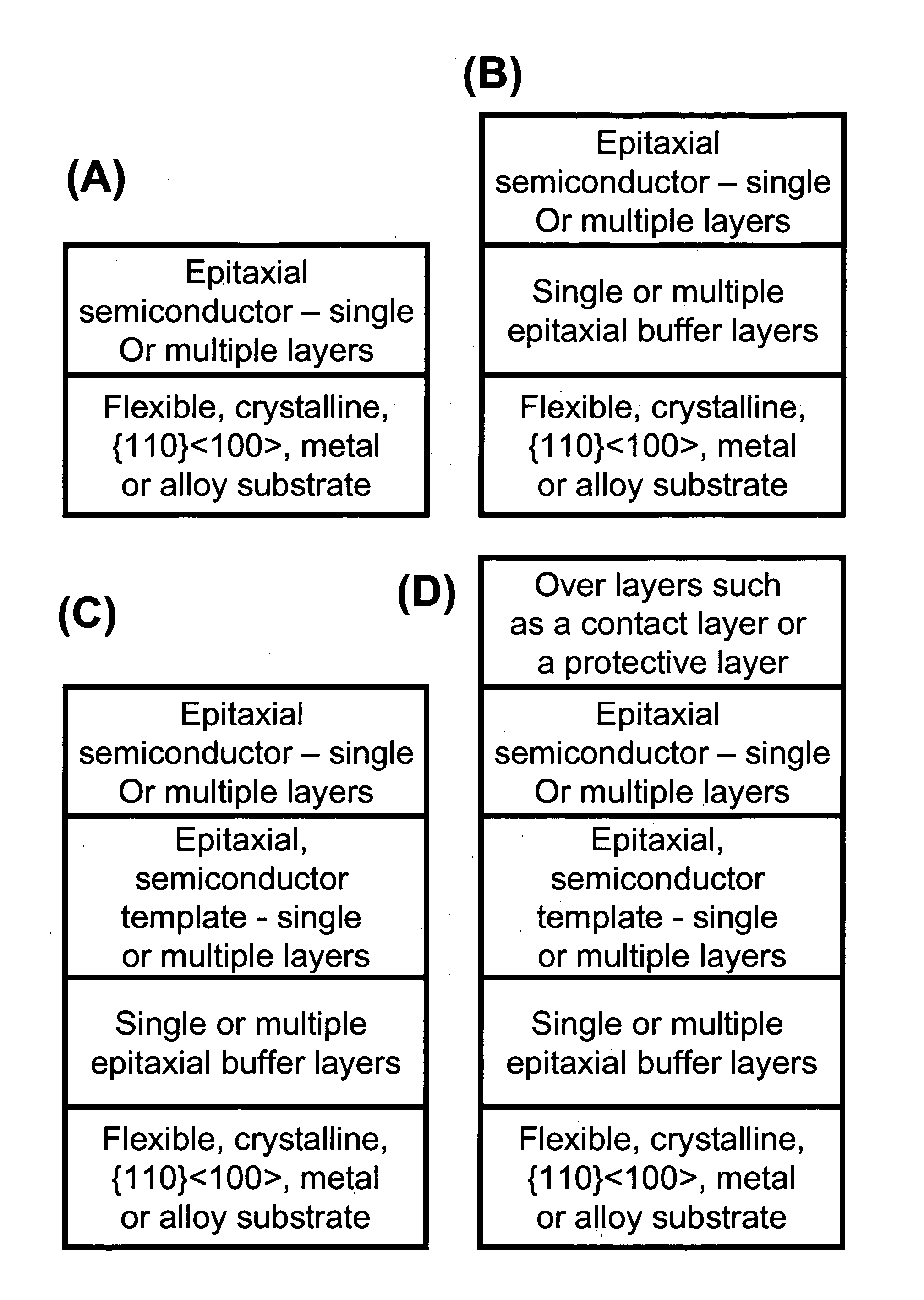
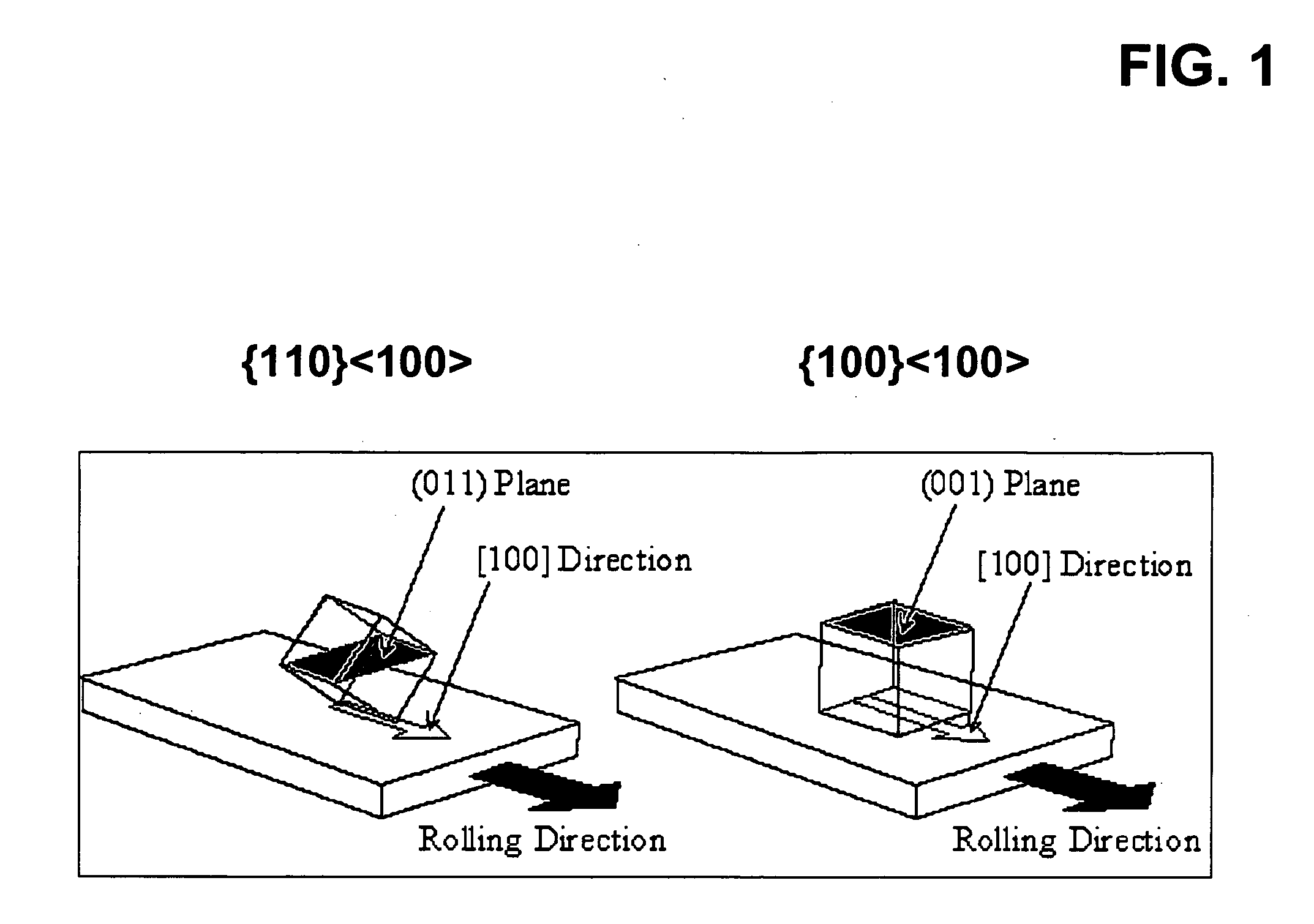
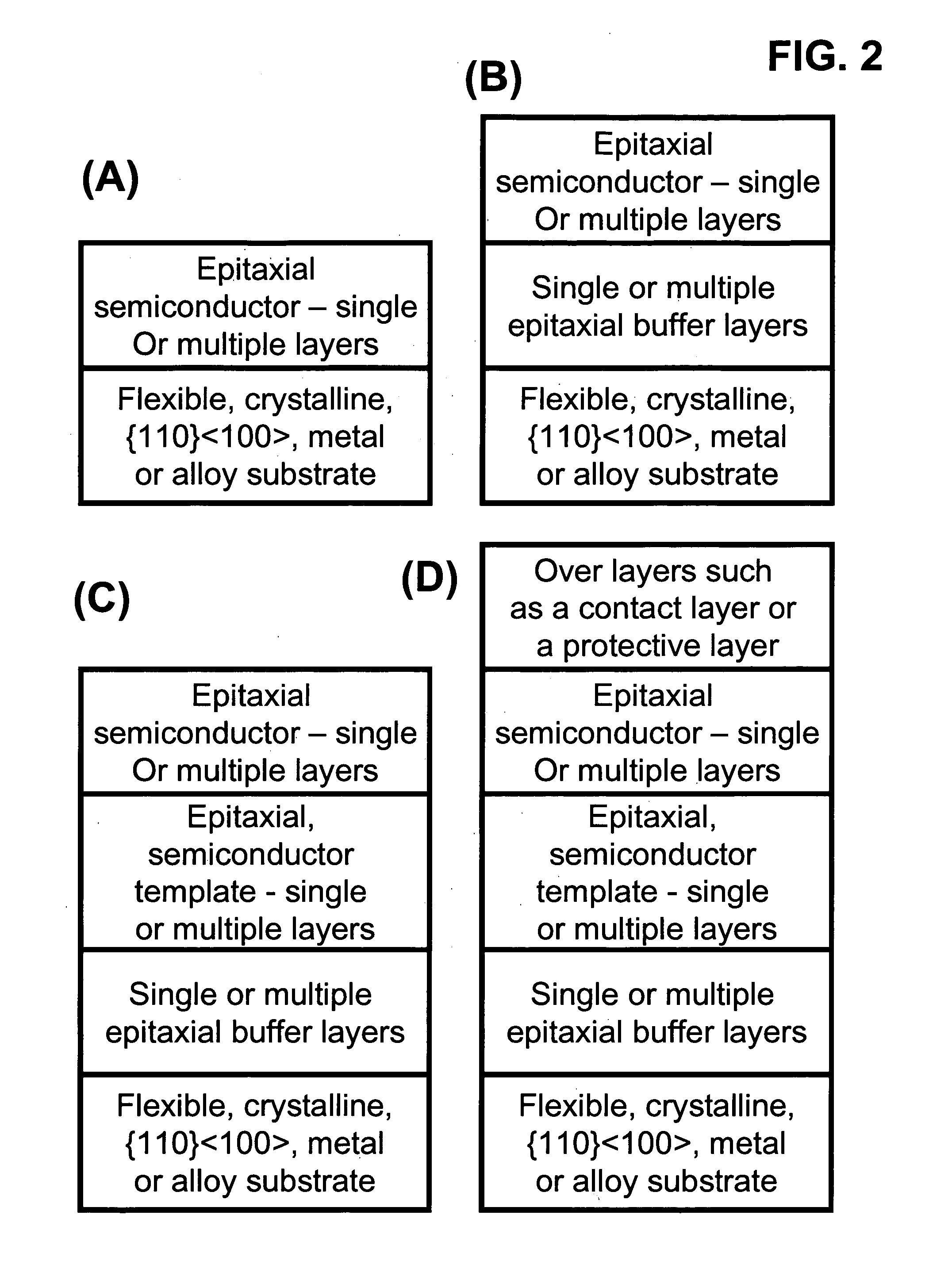
[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS20080230779A1Good lattice matchingSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
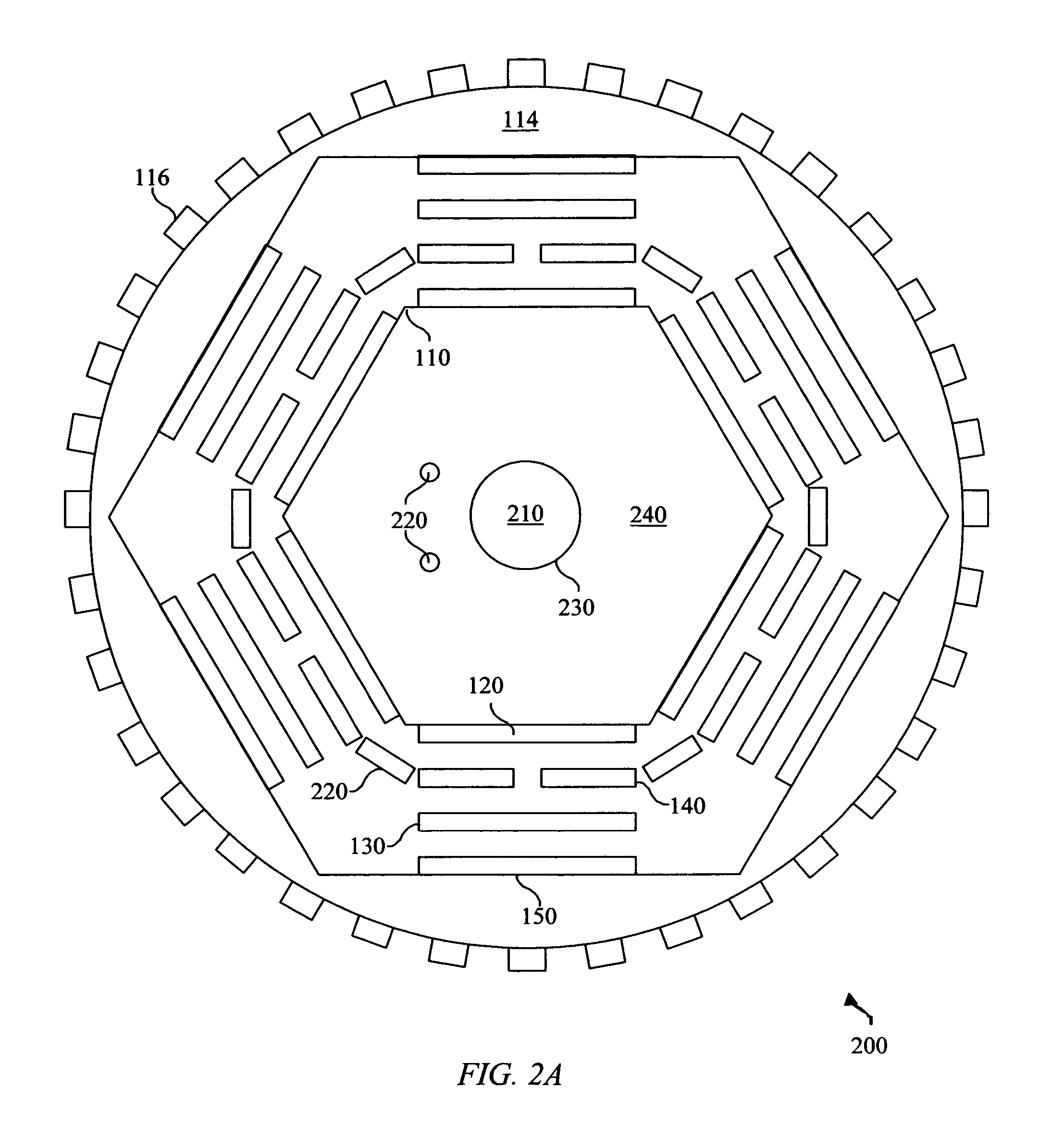
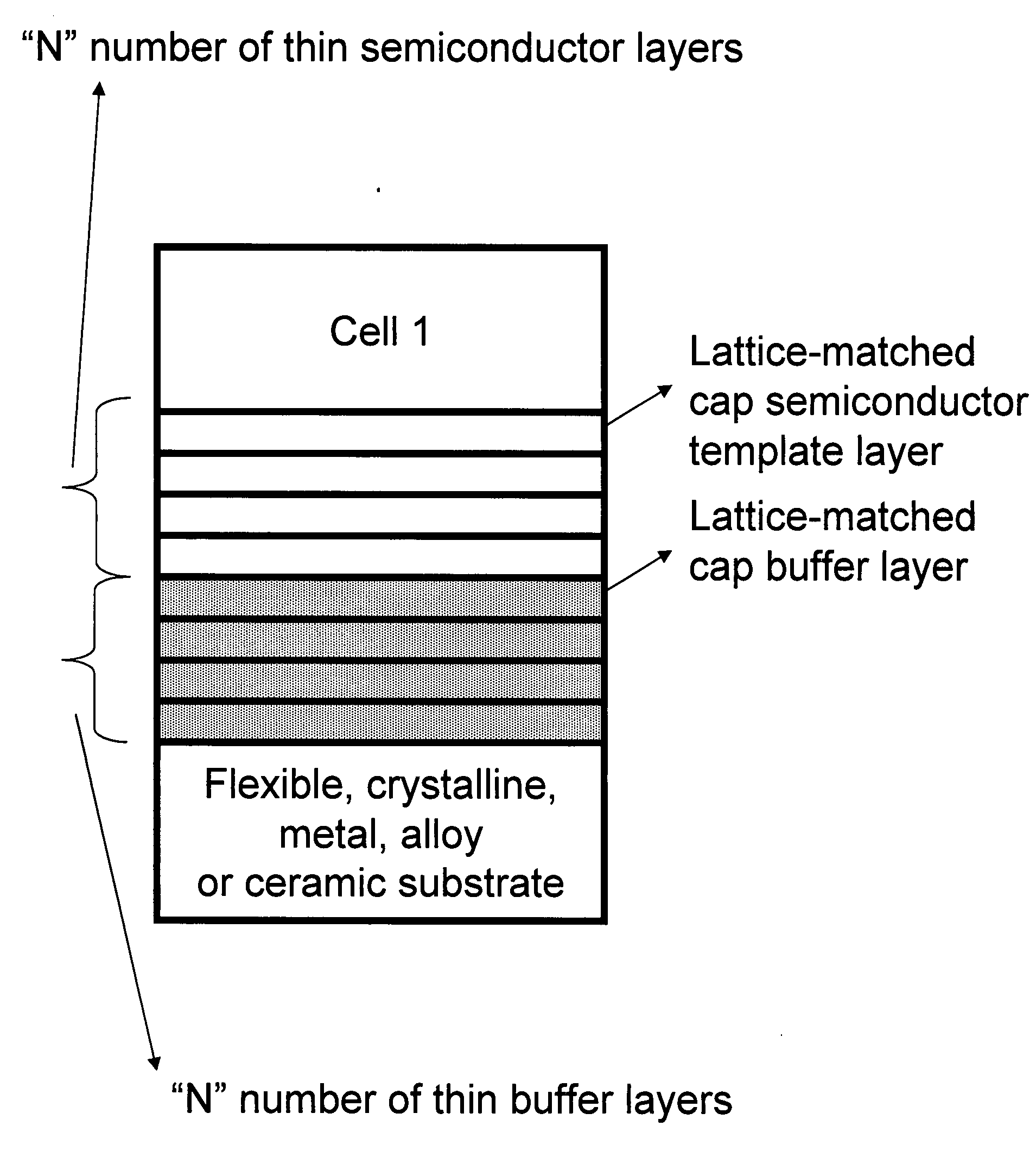
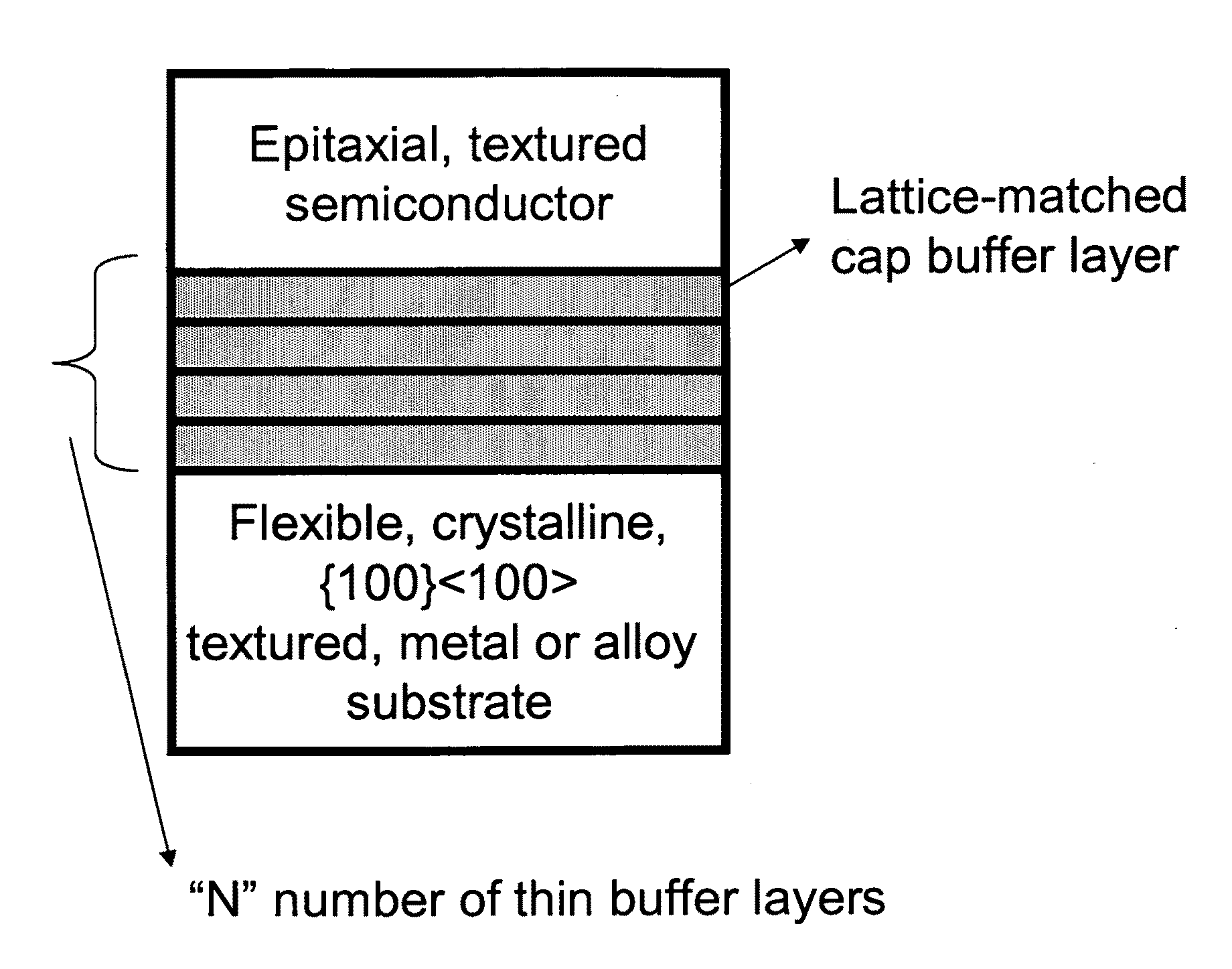
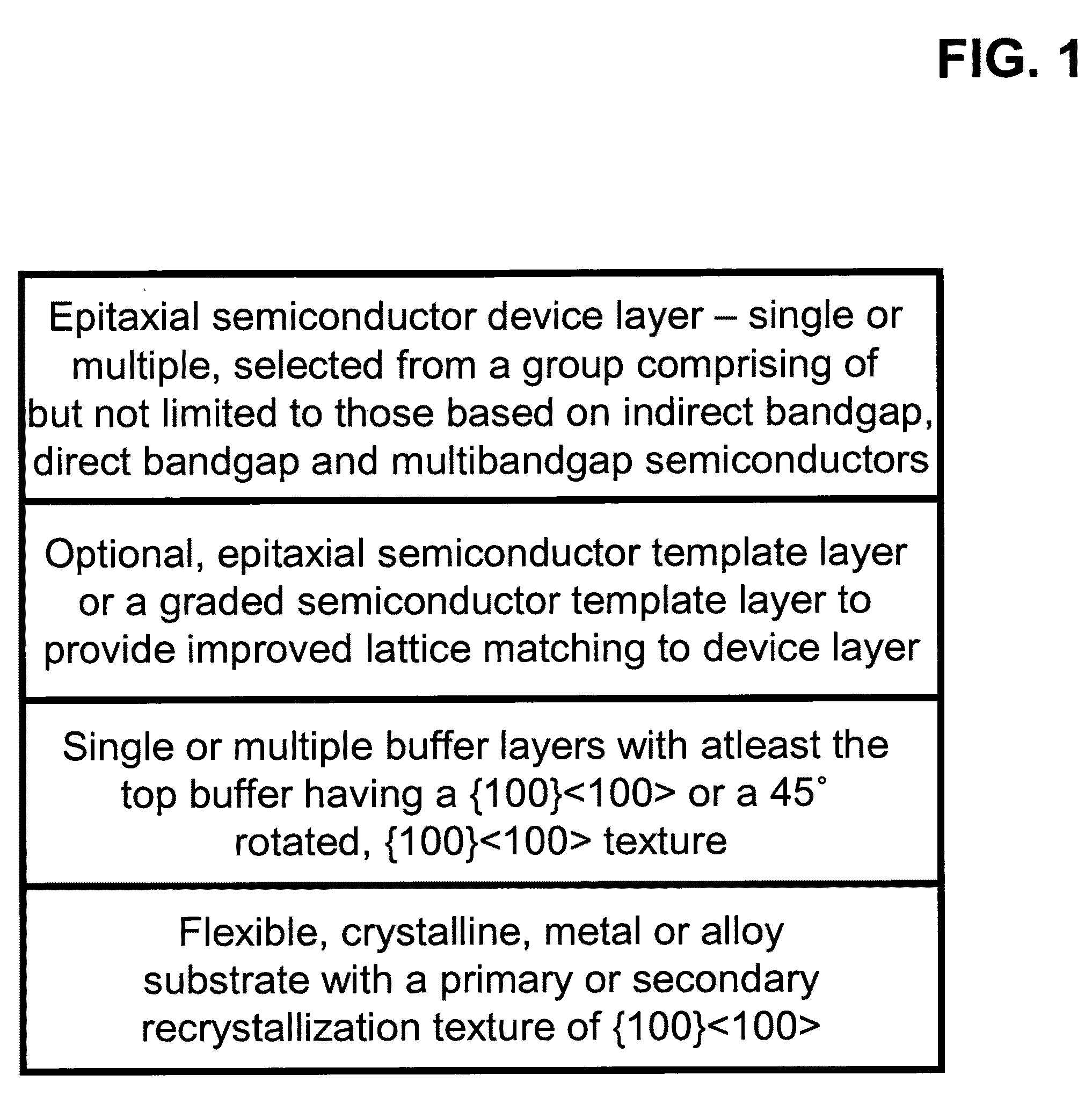
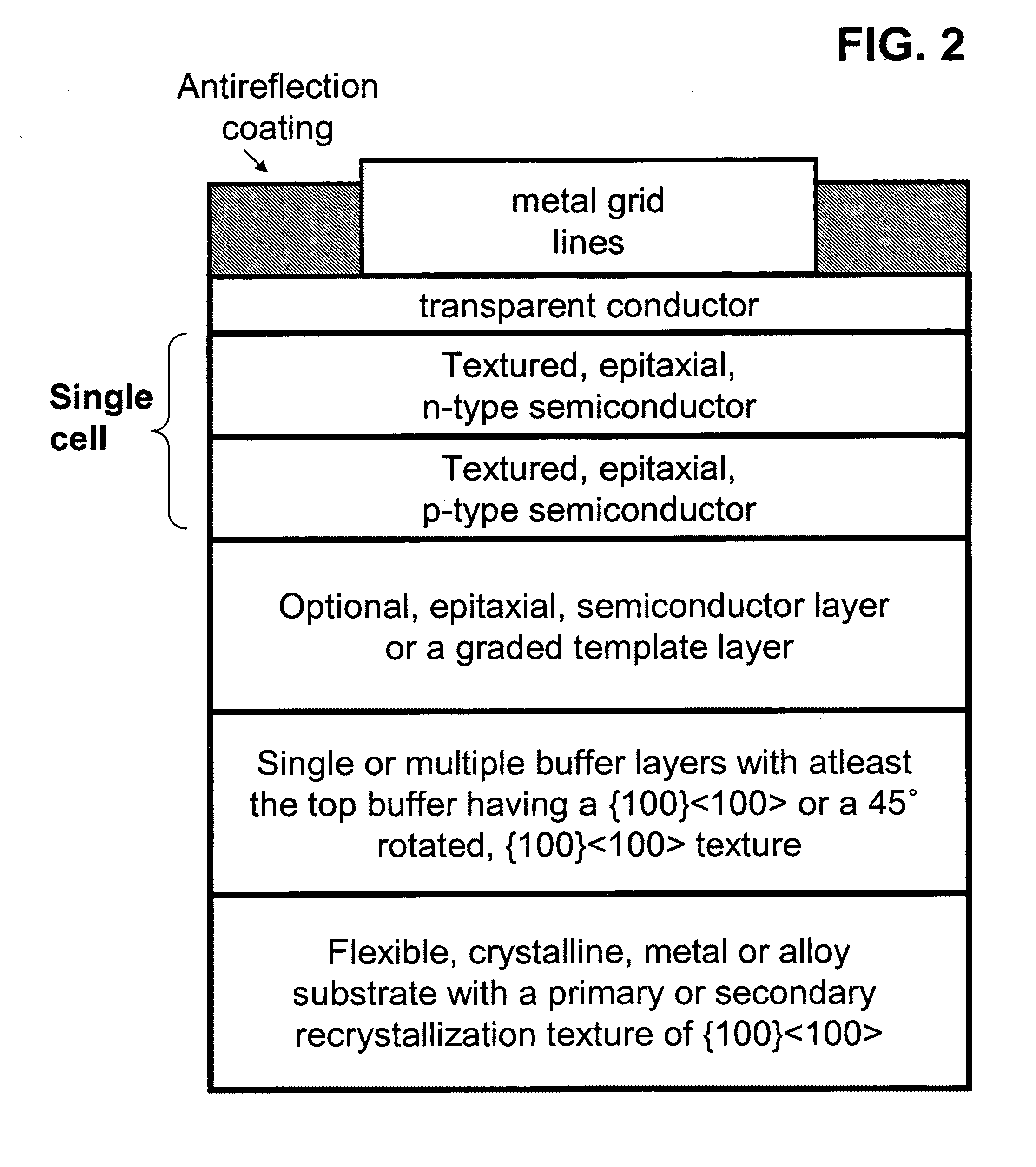
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, large-area, [100] or [110] textured, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Use of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to generate or exchange thermal, kinetic, electronic or photonic energy
The present disclosure concerns a means to use at least a form of electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions in a structure or material having one or more addressable frequencies to generate the exchange of thermal, kinetic, electronic or photonic energy. In some implementations this provides a means to use electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions to influence, cause, control, modulate, stimulate or change the state or phase of electrical, magnetic, optical or electromagnetic charge, emission, conduction, storage or similar properties. The method could include the use of light-matter interactions to generate electromagnetic excitation or light-matter interactions and concentrate extremely localized field effects or concentrated plasmonic field effects to cause an exchange of energy states in a material or structure. Said field effects could be used for excitation of surface electrons in metallic nanostructures causing said electrons to exchange energy states or said field effects could be used to mediate or stimulate photon emissions or to modulate photonic energy to excite or stimulate emissions of electrons. Said electron or photon emissions could be used to drive photochemical, photocatalysis, photovoltaic or thermophotovoltaic reactions.
Owner:DEFRIES ANTHONY +1
Solar thermophotovoltaic hydrogen generating device
InactiveCN101974764AIncrease temperatureImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyCellsEnergy inputEngineeringThermophotovoltaic
The invention provides a device for generating hydrogen by electrolyzing water by using a solar thermophotovoltaic system and belongs to the technical field of solar utilization and hydrogen production by electrolysis. The device consists of two main parts: an improved solar thermophotovoltaic system and a water electrolysis-based hydrogen generation system. The improved solar thermophotovoltaic system has higher conversion efficiency and high output power than a system based on common photovoltaic technology and can provide sufficient current power supply for a water electrolysis-based hydrogen generation device. The device uses the power generated by the system in hydrogen generation by electrolysis, the hydrogen is stored, and thus, the problem that the output of the photovoltaic power generator varies with the change of weather and the alternation of day and night. In addition, the cooling of a photovoltaic cell in the device is liquid cooling, the aqueous solution for electrolysis is preheated before being introduced into an electrolytic cell, the power consumption in an electrolysis process is reduced, and thus, the solar utilization rate is further improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Sub-micrometer gap thermophotovoltaic structure (MTPV) and fabrication method therefor
ActiveUS20100319749A1Reduce manufacturing costPrecise and uniform setting of gap dimensionPV power plantsThermoelectric device detailsEngineeringThermophotovoltaic
An MTPV thermophotovoltaic chip comprising a photovoltaic cell substrate, micron / sub-micron gap-spaced from a juxtaposed heat or infrared radiation-emitting substrate, with a radiation-transparent intermediate window substrate preferably compliantly adhered to the photovoltaic cell substrate and bounding the gap space therewith.
Owner:MTPV POWER CORP
Thermophotovoltaic power supply
A microthermophotovoltaic (micro-TPV) system is a novel micro power device. The system fully utilizes the high surface-to-volume ratio of a microcombustor, and is able to deliver and electrical power output of 0.5-10 W in a package of the order of centimeters. The system comprises mainly a combustor-emitter, a filter, a photovoltaic (PV) cell array, and cooling fins. The combustor-emitter functions to convert chemical energy into radiative heat energy. The filter is able to recycle a large part of the unusable energy that cannot be converted into electricity by the PV cell array. The PV cell array is used to convert radiative heat energy into electricity. The system has no moving parts. Its fabrication and assembly are relatively easy. As a result, it can be readily used as a power source of micro mechanical devices and portable devices, in which convenience and low cost reliability and ease of maintenance are the key factors of consideration.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
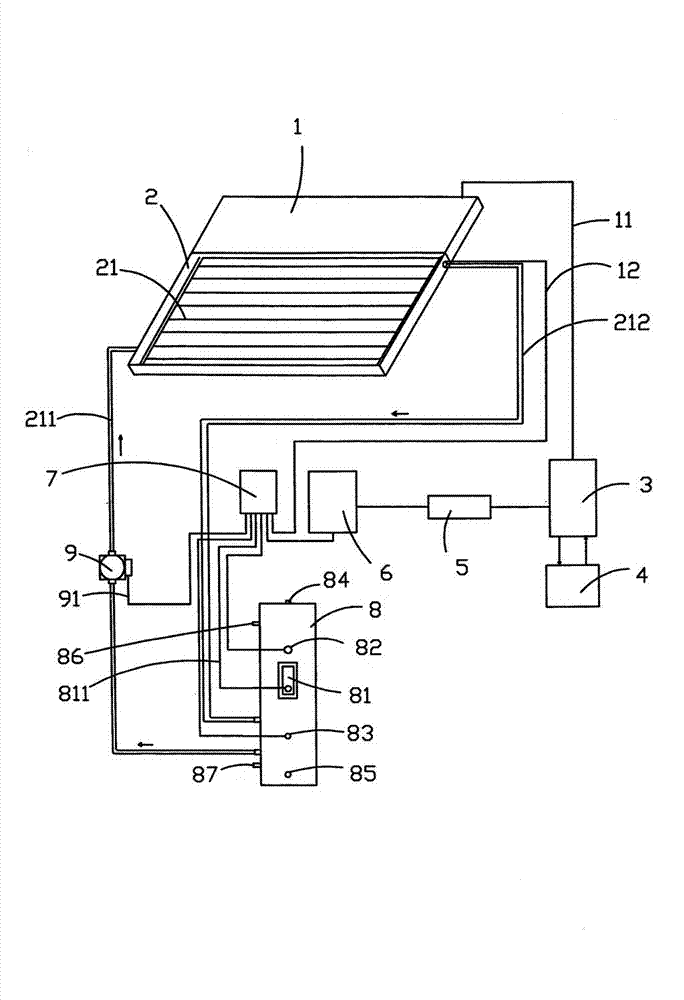
Split type flat-plate solar photothermal and photovoltaic system
InactiveCN102734943AMeet the requirement of continuous hot water supplyMeet the requirements for providing powerSolar heat devicesPhotovoltaicsCirculator pumpCollector device
The invention discloses a split type flat-plate solar photothermal and photovoltaic system, and belongs to the technical field of water heating equipment. The system comprises a solar photovoltaic generation component, a flat-plate solar thermal collector, an adjustment controller, a storage battery, an inverter, a power supply control cabinet, a controller, a water tank and a circulating pump, wherein the solar photovoltaic generation component is connected with one end of the flat-plate solar thermal collector; the flat-plate solar thermal collector is provided with a pipe type heat absorber; a water inlet and a water outlet of the pipe type heat absorber are connected with the water tank; the adjustment controller is connected with the inverter; the inverter is connected with the power supply control cabinet; the power supply control cabinet is connected with the controller; the storage battery is connected with the adjustment controller; an electric heater is arranged in the water tank and is in electrical connection with the controller; the water tank is provided with a tank upper water level sensor and a lower water level sensor; and the circulating pump is arranged on a pipeline and is in electrical connection with the controller through a circuit. The invention has the advantages that the system avoids light influence, and meets requirements of the water tank for continuous water supply.
Owner:SUZHOU SUNSHINE SOLAR ENERGY
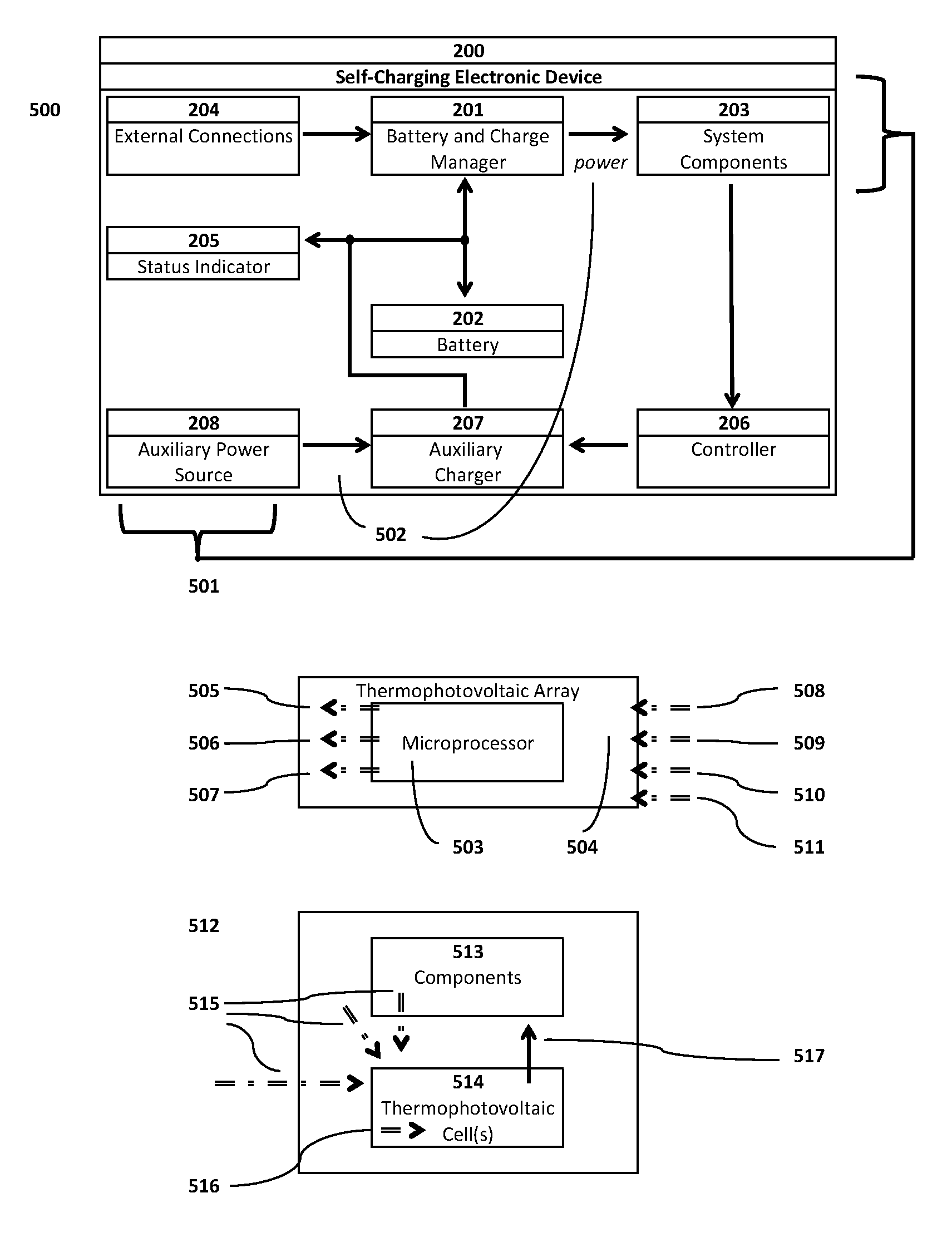
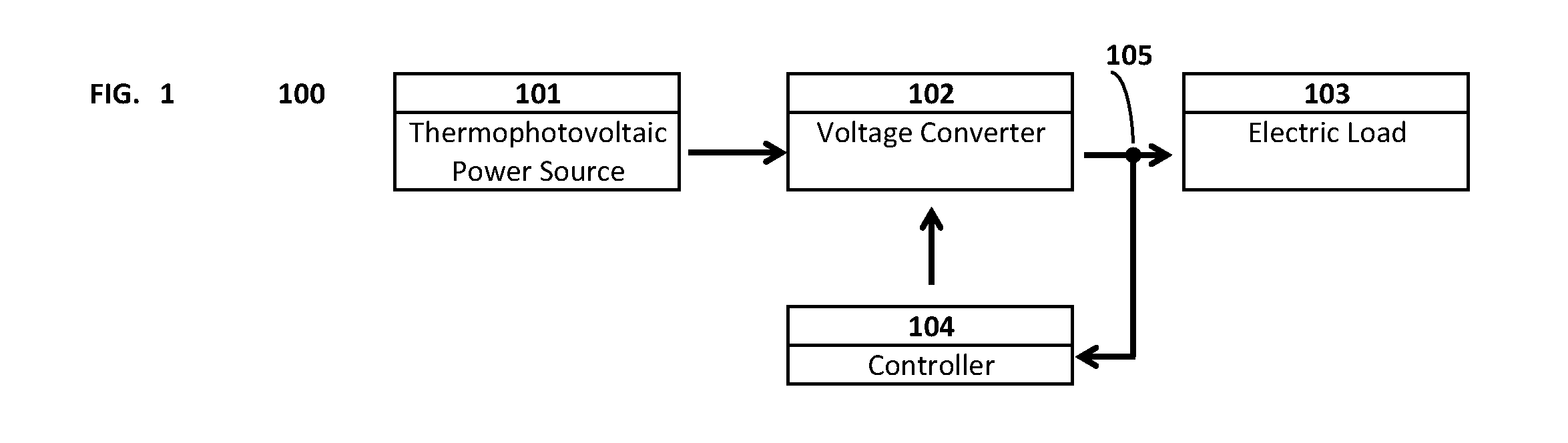
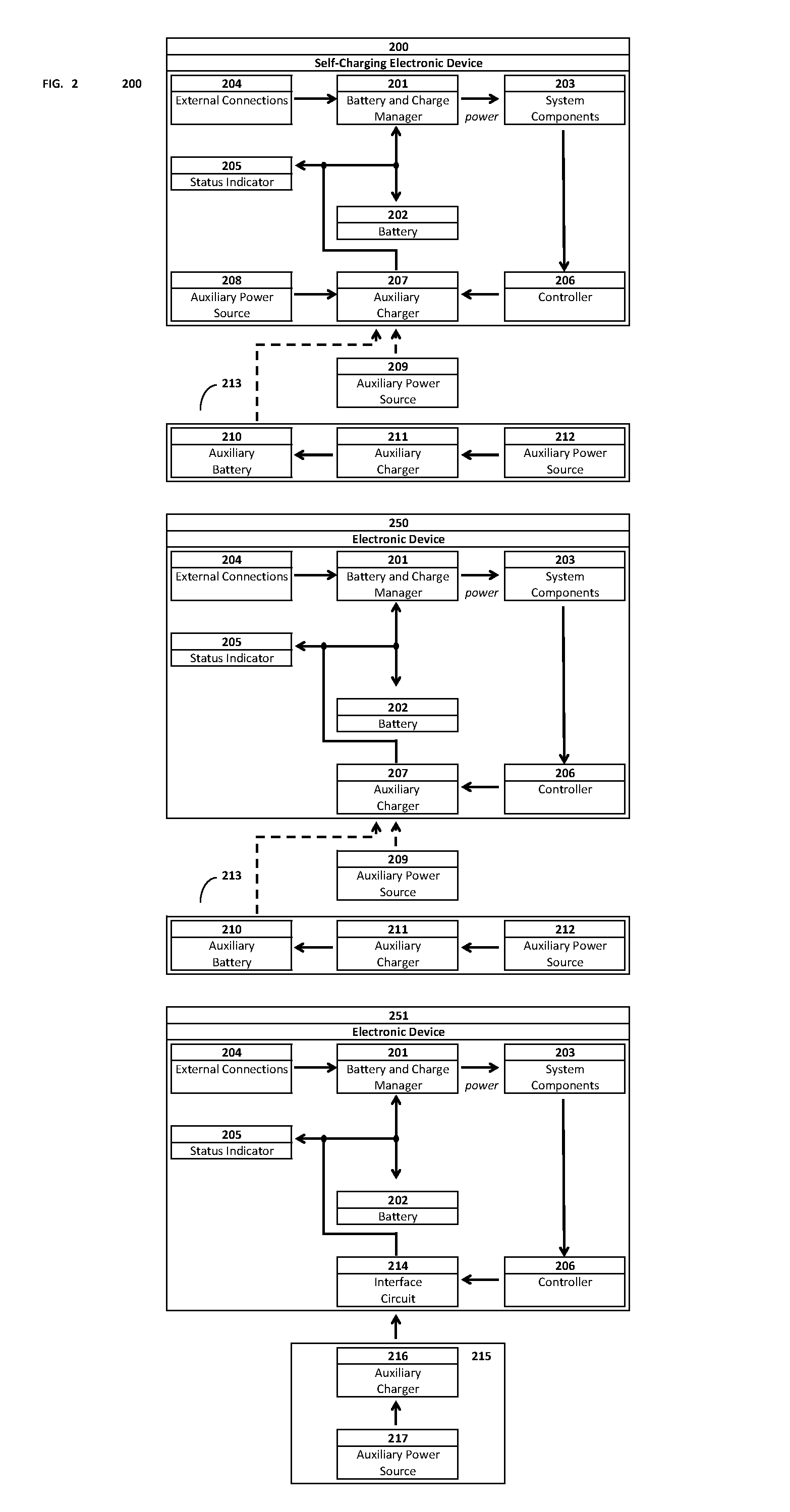
Self-charging electronic devices
ActiveUS20140097786A1Low efficiencyLow mobilityBatteries circuit arrangementsPV power plantsThermal energyElectrical battery
Self-powered portable electronic devices are disclosed that have the capacity to generate their own electrical power, store electrical charge, and distribute electrical power to similarly designed devices in close proximity. Devices generate power in part using one or more non-solar thermal energy sources that have increased stability and efficiency compared to current solar cell powered devices. Devices comprise components including, control processors, data storage, energy storage, dedicated energy and power management processors, and thermophotovoltaic cells that convert thermal energy into electrical power. Devices are capable of transmitting and receiving energy, power, voice and data information using standard frequencies associated with portable devices. Additionally, the invention discloses methods, systems, and apparatuses comprising circuitry that can control power generation from multiple thermophotovoltaic cells and traditional power sources.
Owner:PLAIN SIGHT INNOVATIONS LLC
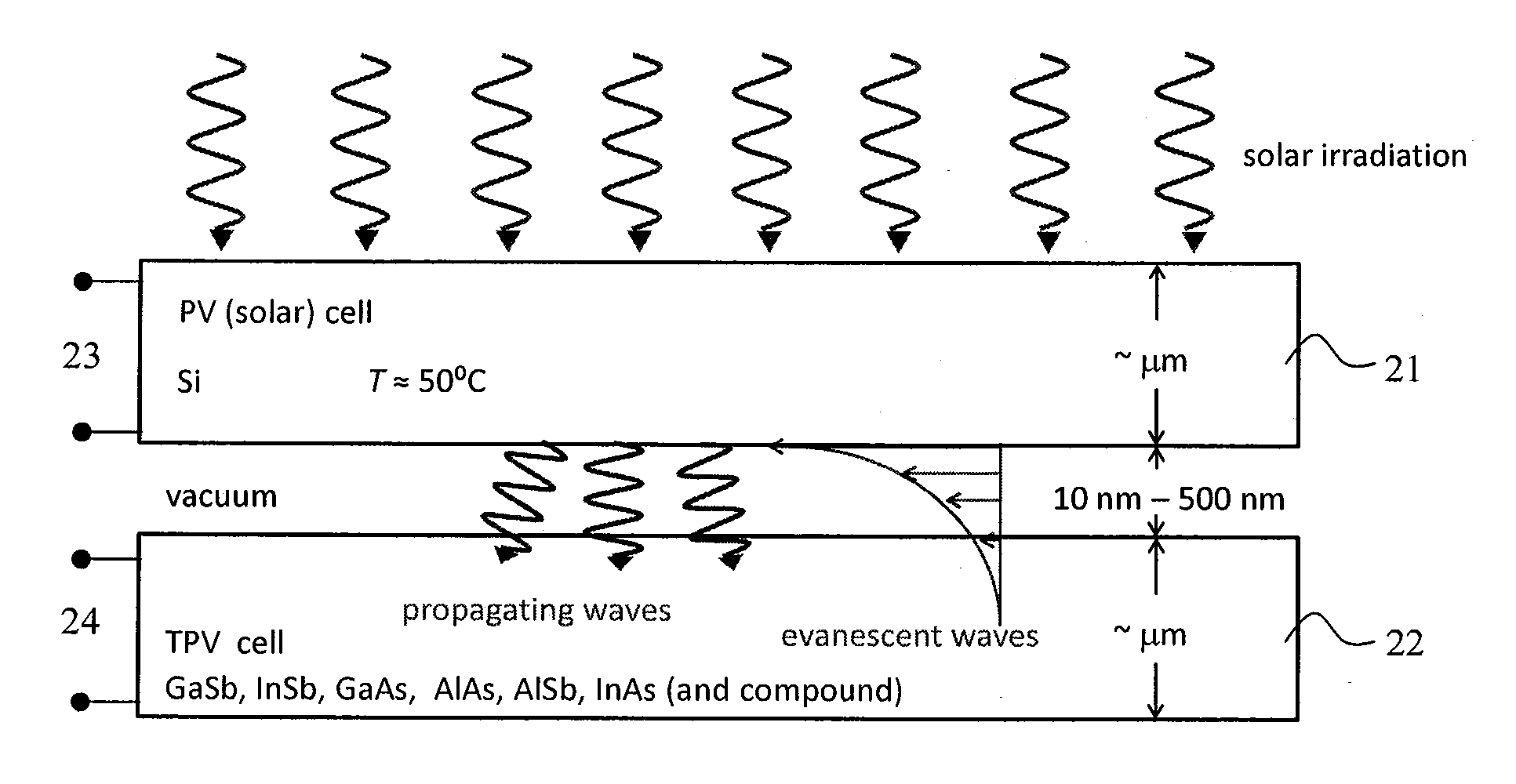
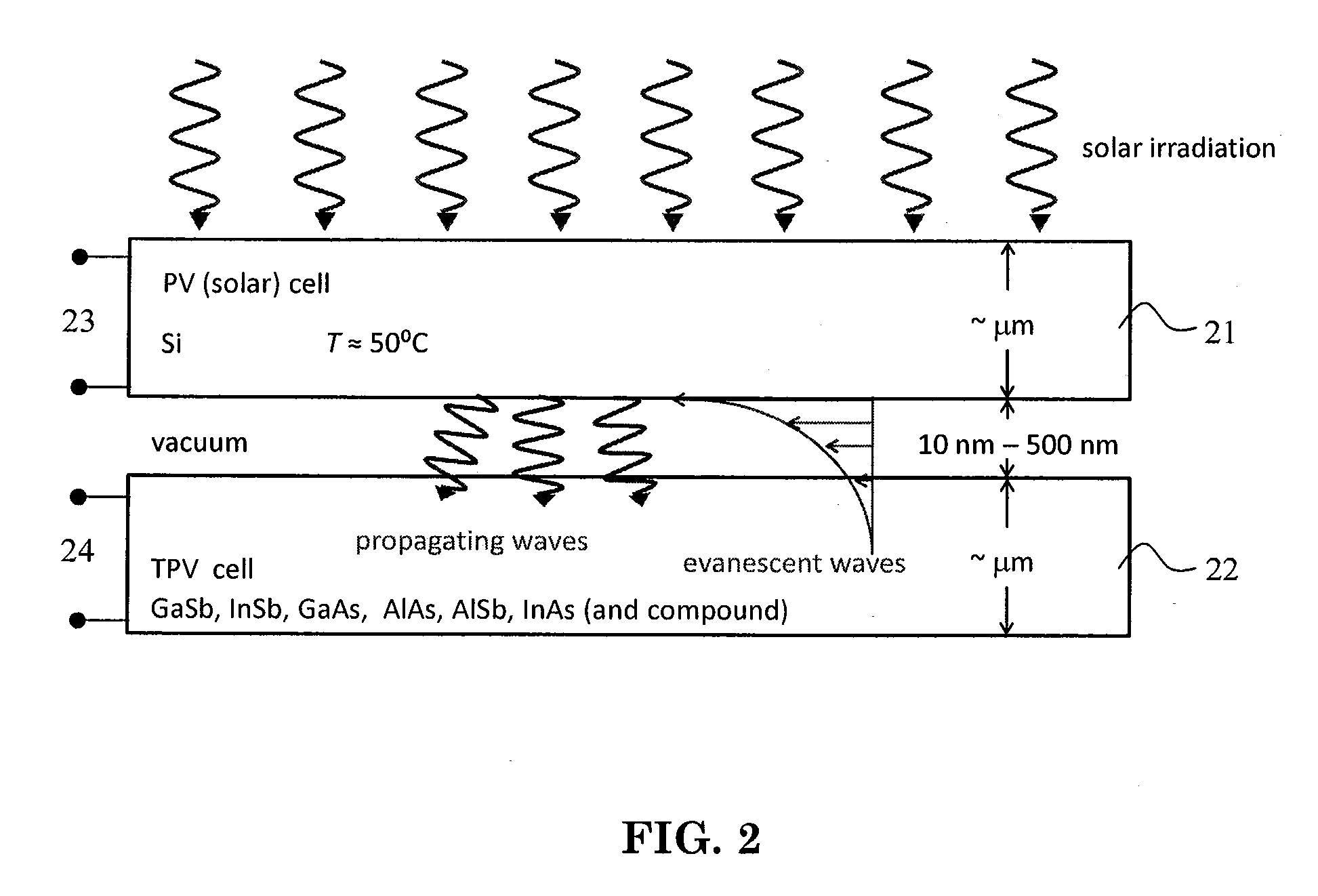
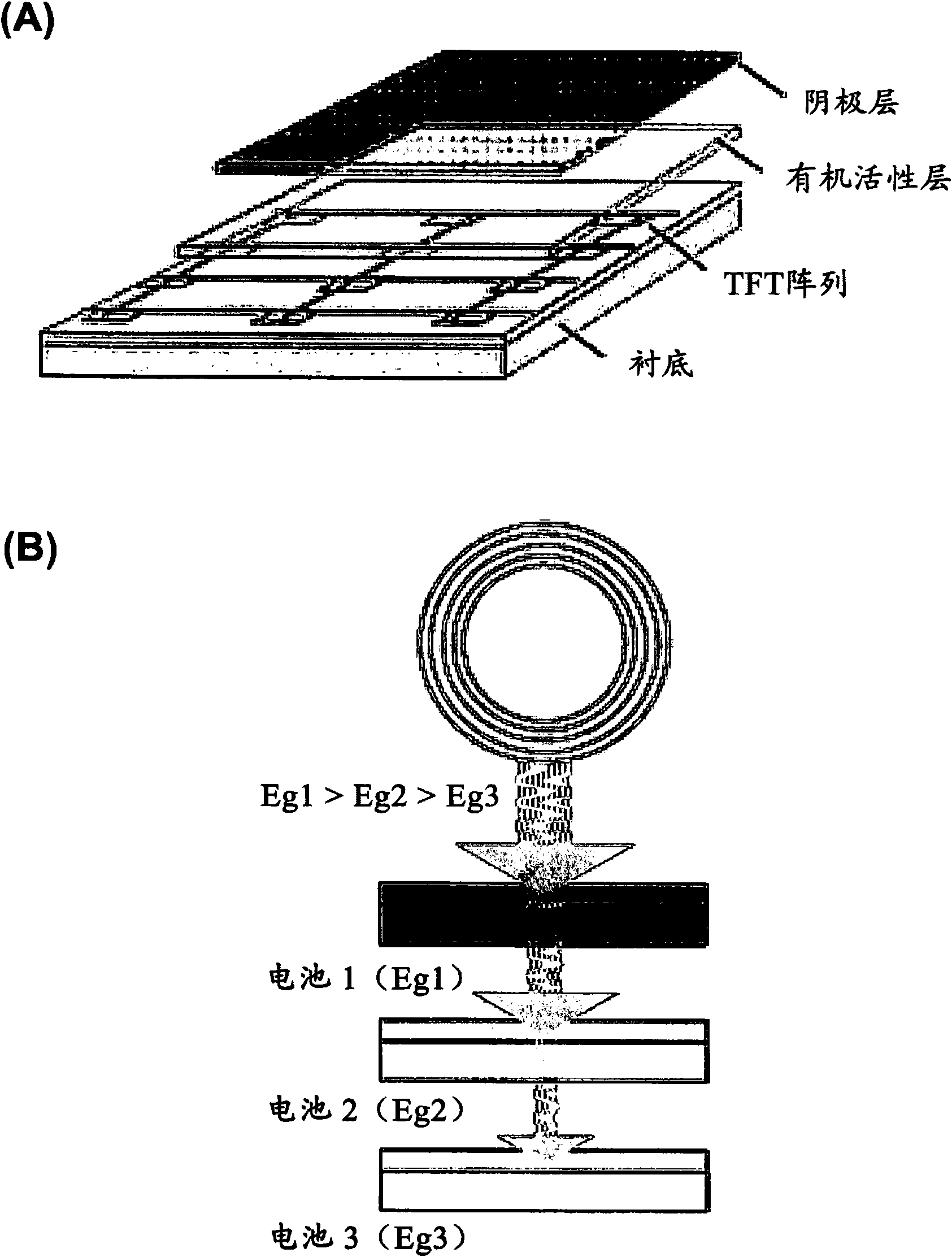
Cascaded Photovoltaic and Thermophotovoltaic Energy Conversion Apparatus with Near-Field Radiation Transfer Enhancement at Nanoscale Gaps
InactiveUS20100031990A1Improve efficiencyPhotovoltaicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy conversionEngineering
A cascaded photovoltaic / thermophotovoltaic energy conversion apparatus, a cascaded thermophotovoltaic energy conversion apparatus, and a method for forming the apparatuses are provided. The cascaded photovoltaic / thermophotovoltauc apparatus includes a photovoltaic device that receives solar radiation on an upper surface thereof and produces a first electric current output and a thermal radiation output, and a thermophotovoltaic device disposed a predetermined distance below a lower surface of the photovoltaic device, the thermophotovoltaic device receiving the thermal radiation output and converting the received thermal radiation output into a second electric current output. The cascaded thermophotovoltaic apparatus includes a radiator maintained at constant temperature via an external heat input on its upper surface and produces a thermal radiation output, and a thermophotovoltaic device disposed a predetermined distance below a lower surface of the radiator, the thermophotovoltaic device receiving the thermal radiation output and converting the received thermal radiation output into a first electric current output.
Owner:UNIV OF KENTUCKY RES FOUND
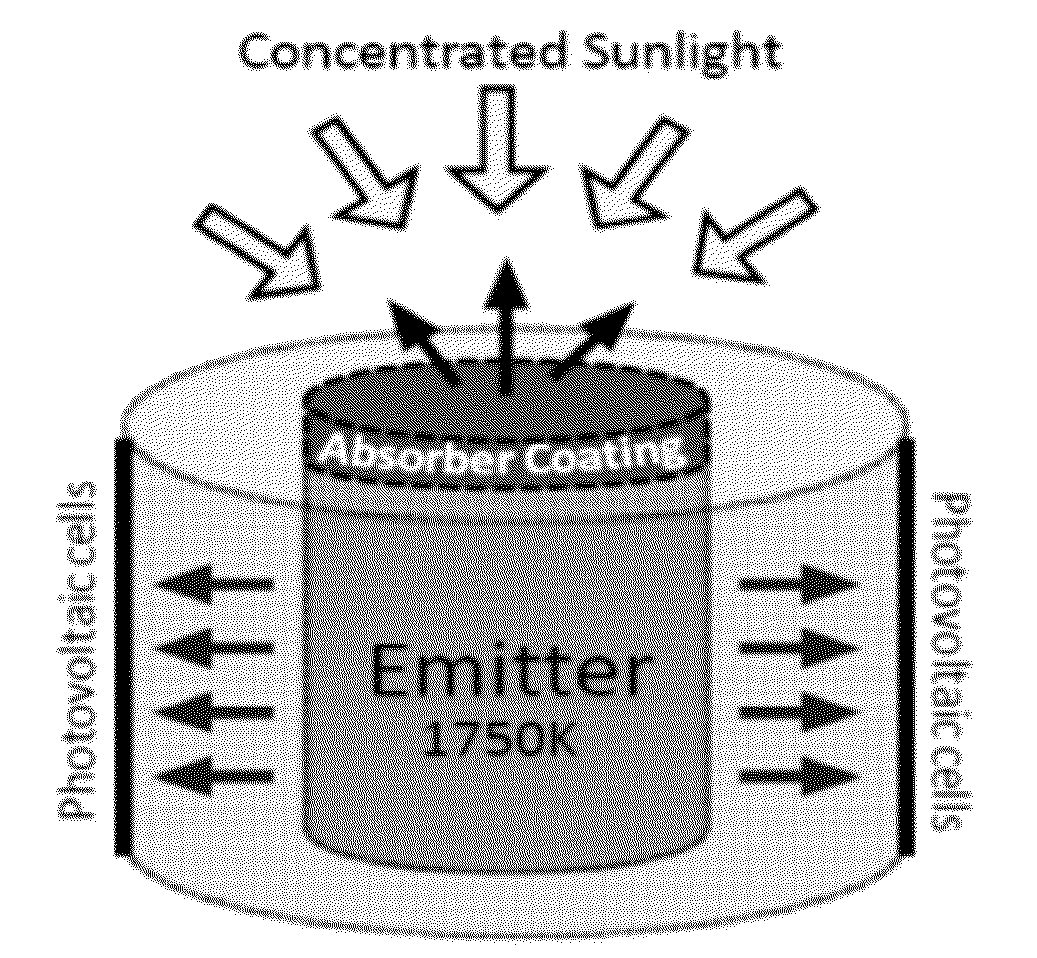
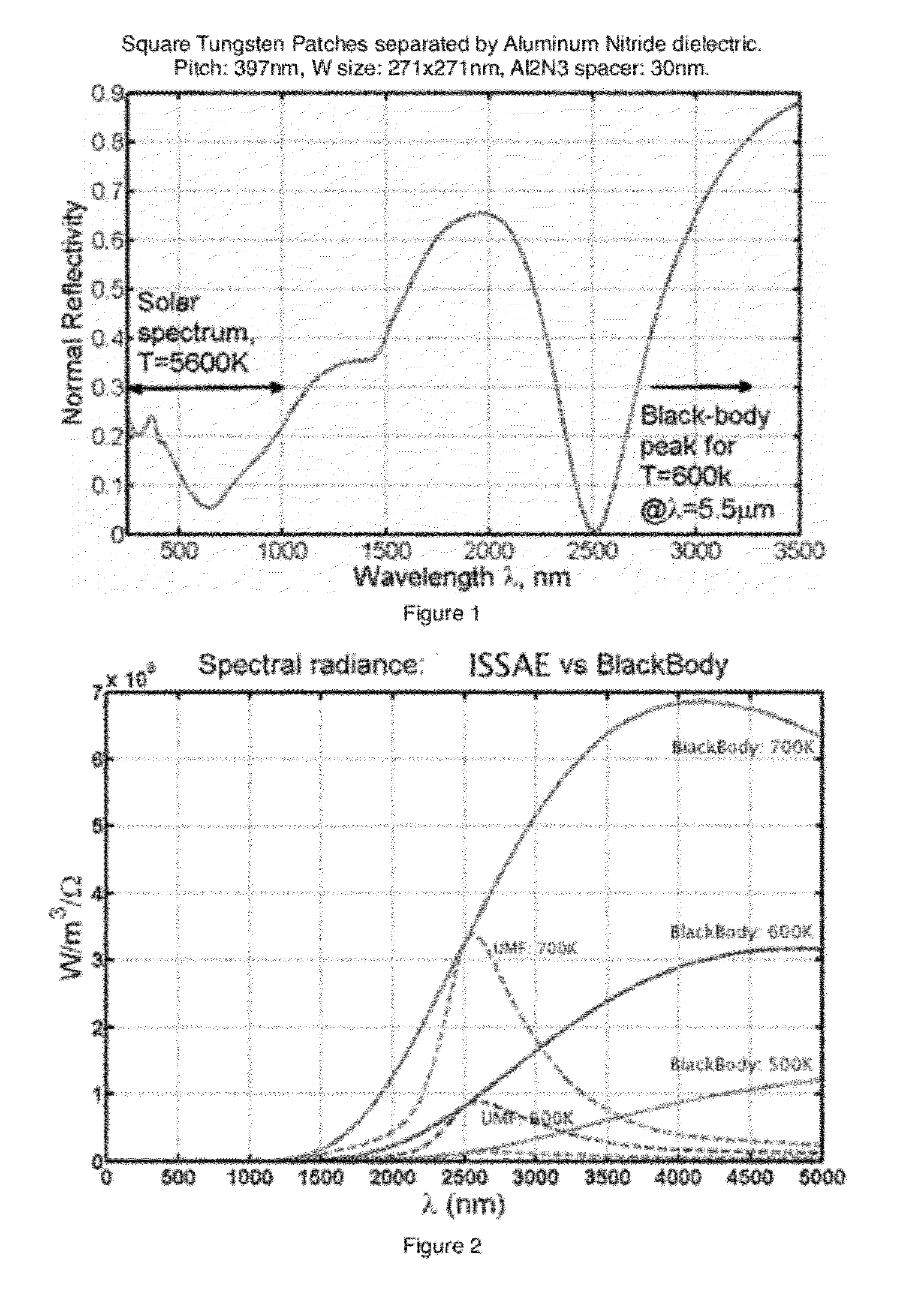
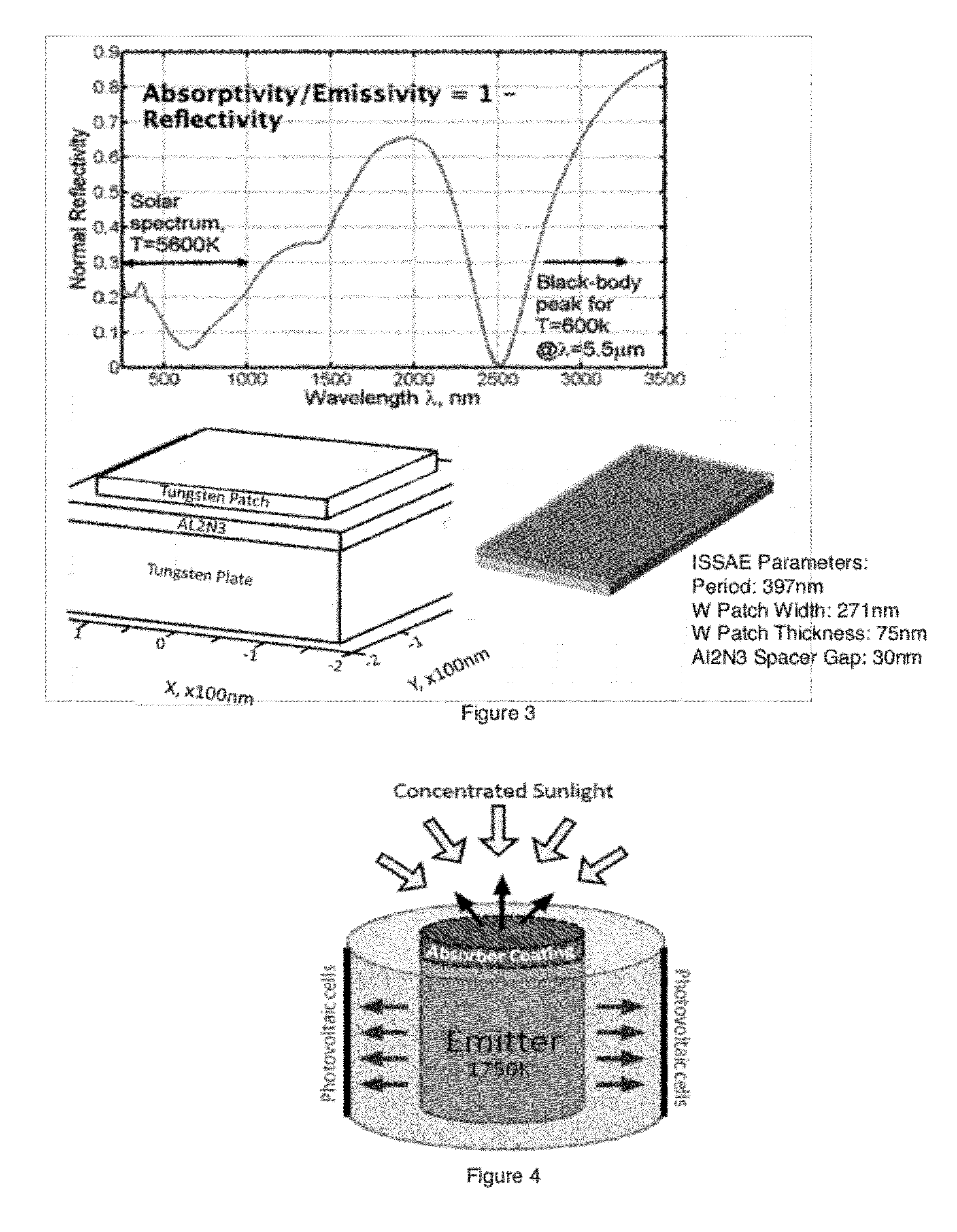
Thin-film integrated spectrally-selective plasmonic absorber/ emitter for solar thermophotovoltaic applications
ActiveUS20120312360A1Improve efficiencySolar heating energyPV power plantsThermophotovoltaicInfrared emitter
Thin-film integrated spectrally-selective plasmonic absorber / emitter (ISSAE) that is simultaneously (i) an efficient sunlight absorber; (ii) an efficient heat insulator that enables modest sunlight concentration to produce a high temperature by reducing infrared emission by a hot surface; (iii) a spectrally-selective infrared emitter that supplies infrared photons of the right energy to a targeted photovoltaic cell, thereby matching its bandgap. Additionally, said ISSAE is sufficiently thin to enable its use as a wrapping / cloaking material for use with hot storage pipes containing heat exchange fluid. Said ISSAE is incorporated into a number of solar-conversion apparatus, taking advantage of the unique properties of said ISSAE.
Owner:IP EQUITY MANAGEMENT LLC
Solar energy tower type optical-condensation heat-storage thermophotovoltaic power generation system
InactiveCN104993776ASolving Dispersion ProblemsReduce dosageSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersThermal insulationEngineering
The invention relates to a solar energy tower type optical-condensation heat-storage thermophotovoltaic power generation system. The system comprises a tower type solar heat collector field, an optical-condensation heat-storage thermophotovoltaic generator, a working medium circulating system, a generation output system and an intelligent central controller. The optical-condensation heat-storage thermophotovoltaic generator comprises a central reflector, a heat radiator, an optical filter, a thermophotovoltaic cell, a latticed phase change heat-storage box, a temperature sensor, a thermal insulation layer, an upper reflecting plate, a lower reflecting plate, a radiator and a housing. The tower type solar heat collector field comprises a tower and heliostats for collecting solar energy and reflecting the solar energy to the central reflector. The central reflector further reflects the solar condensation energy to the heat radiator. Heat radiation spectrums are then generated. Parts of the heat radiation spectrums pass through the optical filter and irradiate the thermophotovoltaic cell in an optically condensing way. The thermophotovoltaic cell further generates power. The disperse solar energy use problem is solved. The heat radiator can be kept in a high temperature state. The photoelectric conversion efficiency of the thermophotovoltaic system is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS7906229B2Good lattice matchingFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, large-area, triaxially textured, single-crystal or single-crystal-like, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
Semiconductor-based large-area flexible electronic devices
InactiveCN101981699AFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Novel articles and methods to fabricate the same resulting in flexible, {100}<100> or 45 DEG -rotated {100}<100> oriented, semiconductor-based, electronic devices are disclosed. Potential applications of resulting articles are in areas of photovoltaic devices, flat-panel displays, thermophotovoltaic devices, ferroelectric devices, light emitting diode devices,, computer hard disc drive devices, magnetoresistance based devices, photoluminescence based devices, non-volatile memory devices, dielectric devices, thermoelectric devices and quantum dot laser devices.
Owner:阿米特·戈亚尔
Micro parallel plate burner with preheating channel
InactiveCN101539293AImprove temperature distributionIncrease enthalpyGaseous fuel burnerCombustion chamberHydrogen
The invention belongs to the field of micro-power electromechanical systems (MEMS), particularly relates to a micro parallel plate burner with a preheating channel. The micro parallel plate burner with a preheating channel consists of a parallel plate burning chamber, a preheating channel and a quartz shade, which are arranged from inside to outside, wherein the upper half section of the parallel plate burner is an oxy-hydrogen premixing zone; and the quartz shade is double-layered and internally vacuumized. Fuels and oxidant can be preheated before being mixed by the preheating channel, thereby more stable burning is realized; and the double-layered vacuumized quartz shade not only can make most of photons generated on the radiation surface of the burner pass through, but also play a heat insulation role, so that the whole transformation efficiency and the working performance of micro thermophotovoltaic systems are greatly improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Heterojunction thermophotovoltaic cell based on Ga-In-As-Sb quarternary semiconductor
InactiveCN101521238AIncrease the open circuit voltageImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesHeterojunctionThermophotovoltaic
The invention belongs to the field of thermophotovoltaic technology, in particular to a high conversion efficiency heterojunction thermophotovoltaic cell based on the Ga[x]In[1-x]As[1-y]Sb[y] quarternary semiconductor matched with crystal lattices. The heterojunction thermophotovoltaic cell sequentially comprises a back electrode, an N type substrate, an N type wide bandgap Ga[x1]In[1-x1]As[1-y1]Sb[y1] active layer, a lightly doped P<-> type narrow bandgap Ga[x2]In[1-x2]As[1-y2]Sb[y2] active layer, a heavily doped P<+> type wide bandgap Ga[x3]In[1-x3]As[1-y3]Sb[y3] limiting layer and an upper electrode in the shape of a grizzly bar from top to bottom. Furthermore, a P type GaSb window passivating layer is additionally arranged between the P<+> type wide bandgap limiting layer and the upper electrode in the shape of the grizzly bar, and an N type GaSb back limiting layer is additionally arranged between the N type substrate and the N type wide bandgap active layer. The heterojunction thermophotovoltaic cell which is used for low temperature radiator thermophotovoltaic systems has the advantages of good stability and high safety coefficient, and can be applied to the fields of spaceflight, military affairs, industry, life, and the like.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage composite power generation device
InactiveCN106452287AReduced reflection lossImprove light harvesting efficiencyPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationThermal energyMicro nano
The invention relates to a micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage composite power generation device which comprises two types: a laser type micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage composite power generation device and a solar concentration type micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage composite power generation device, wherein the laser type micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage composite power generation device implements composite power generation by use of laser for wireless transmission of energy; the laser type micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage composite power generation device comprises a laser part, a micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage part, a thermal battery part, a thermal energy power generation part and an intelligent controller; and the micro-nano light trap honeycomb energy storage part can generate a light trap effect as well as absorb laser or solar concentration and store and convert the energy transmitted by laser or solar concentration, and can transmit and provide work energy to the thermal battery part and the thermal energy power generation part respectively in the daytime or at night. The device can outward output comprehensive electric quantity generated by thermophotovoltaic power generation and thermal energy power generation.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
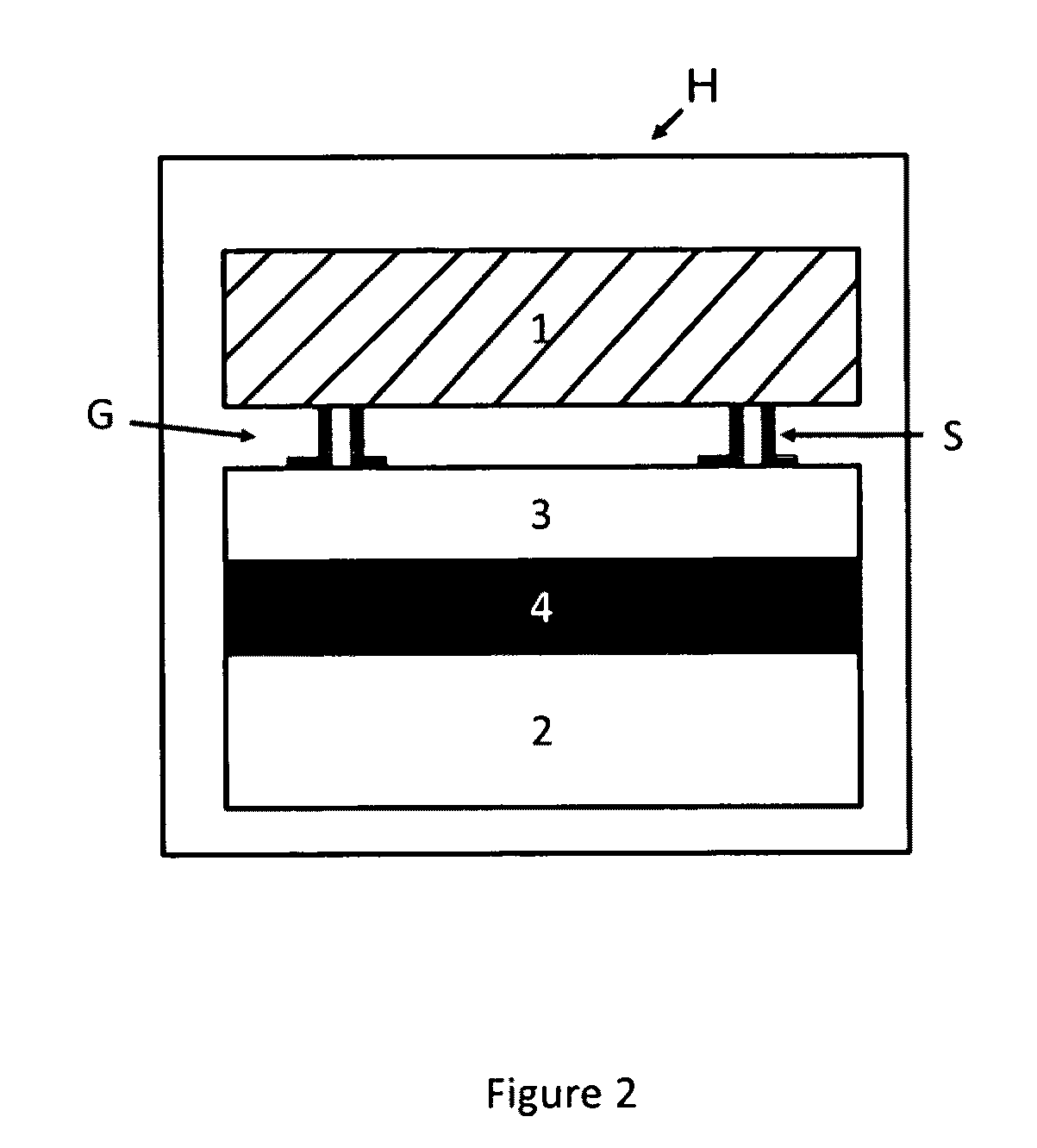
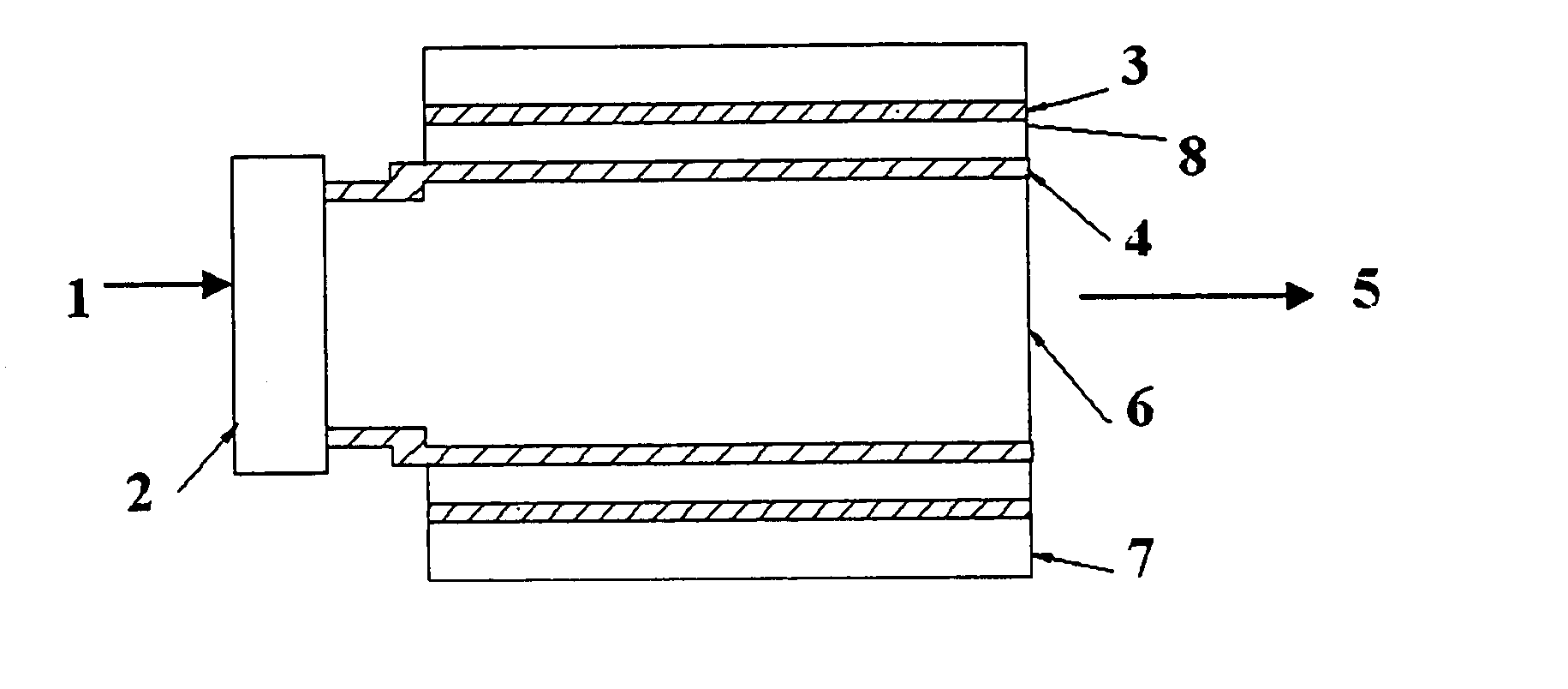
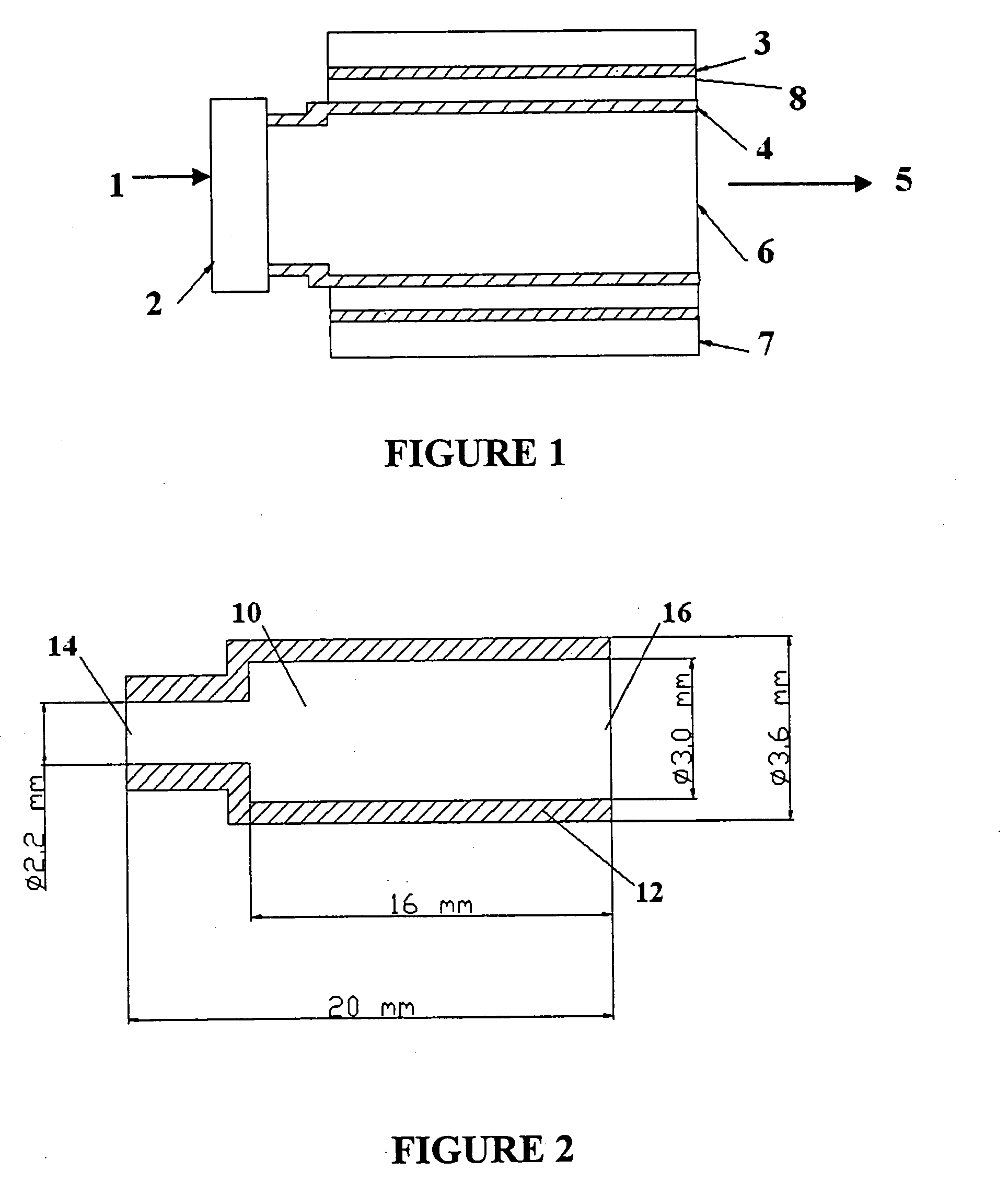
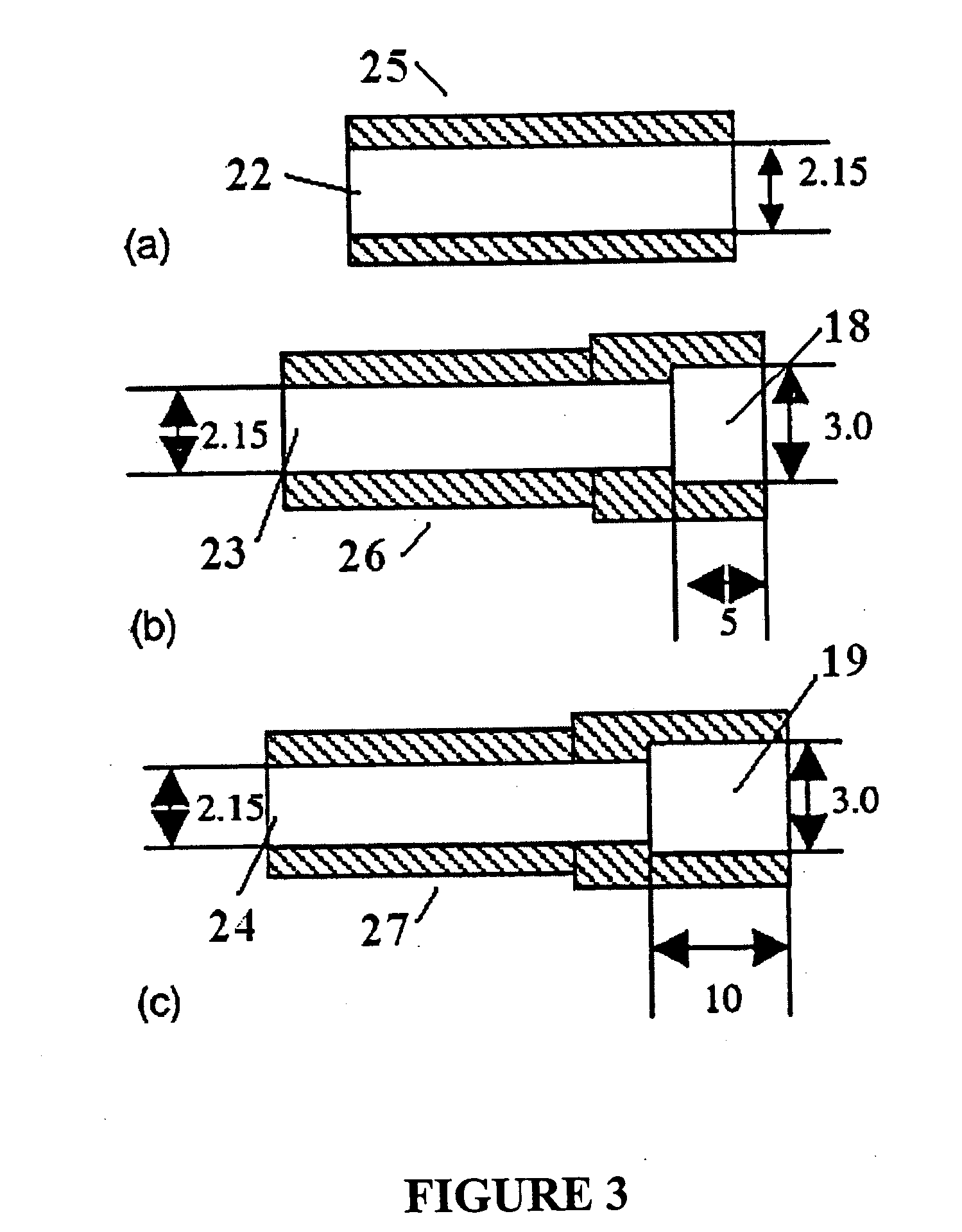
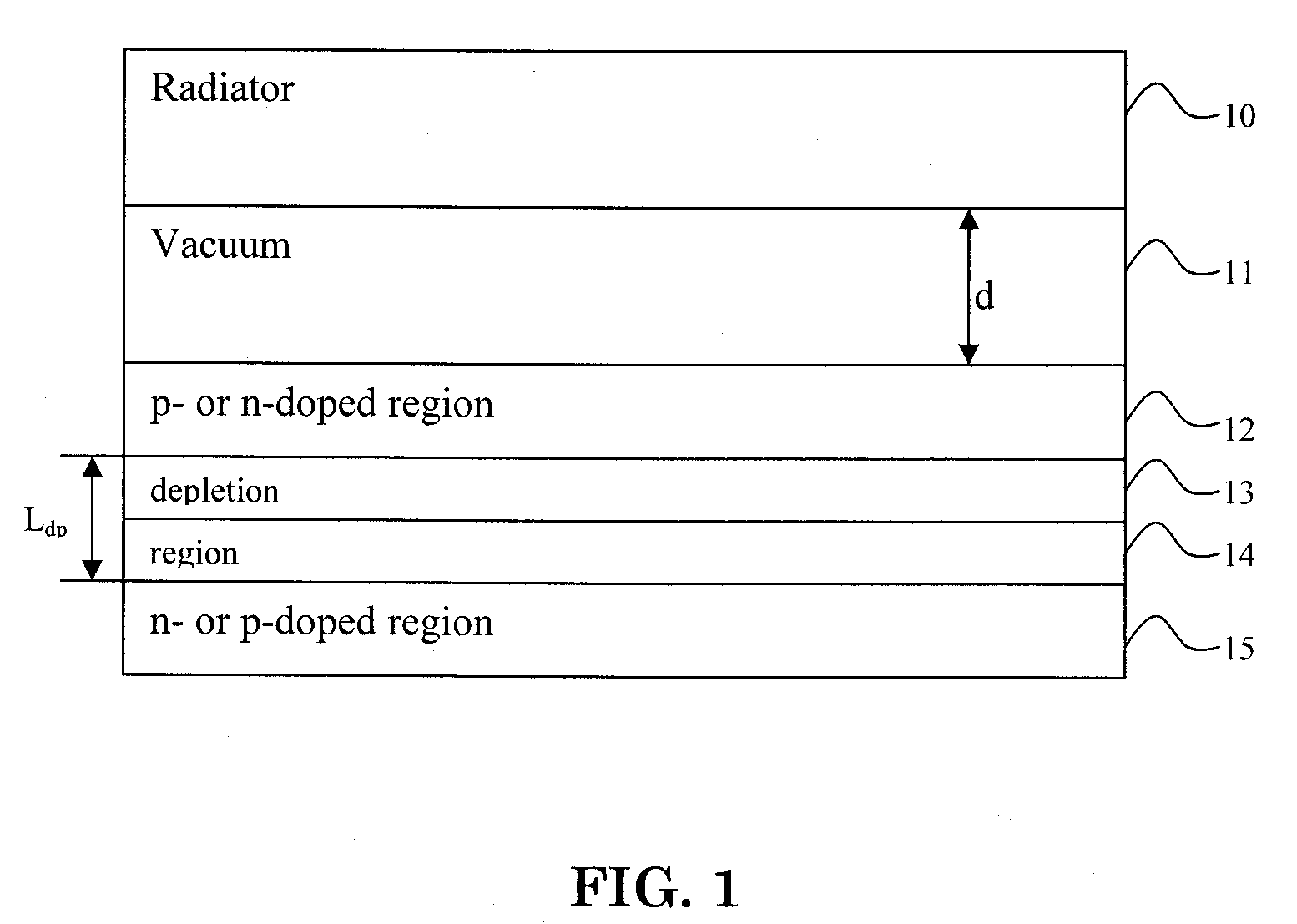
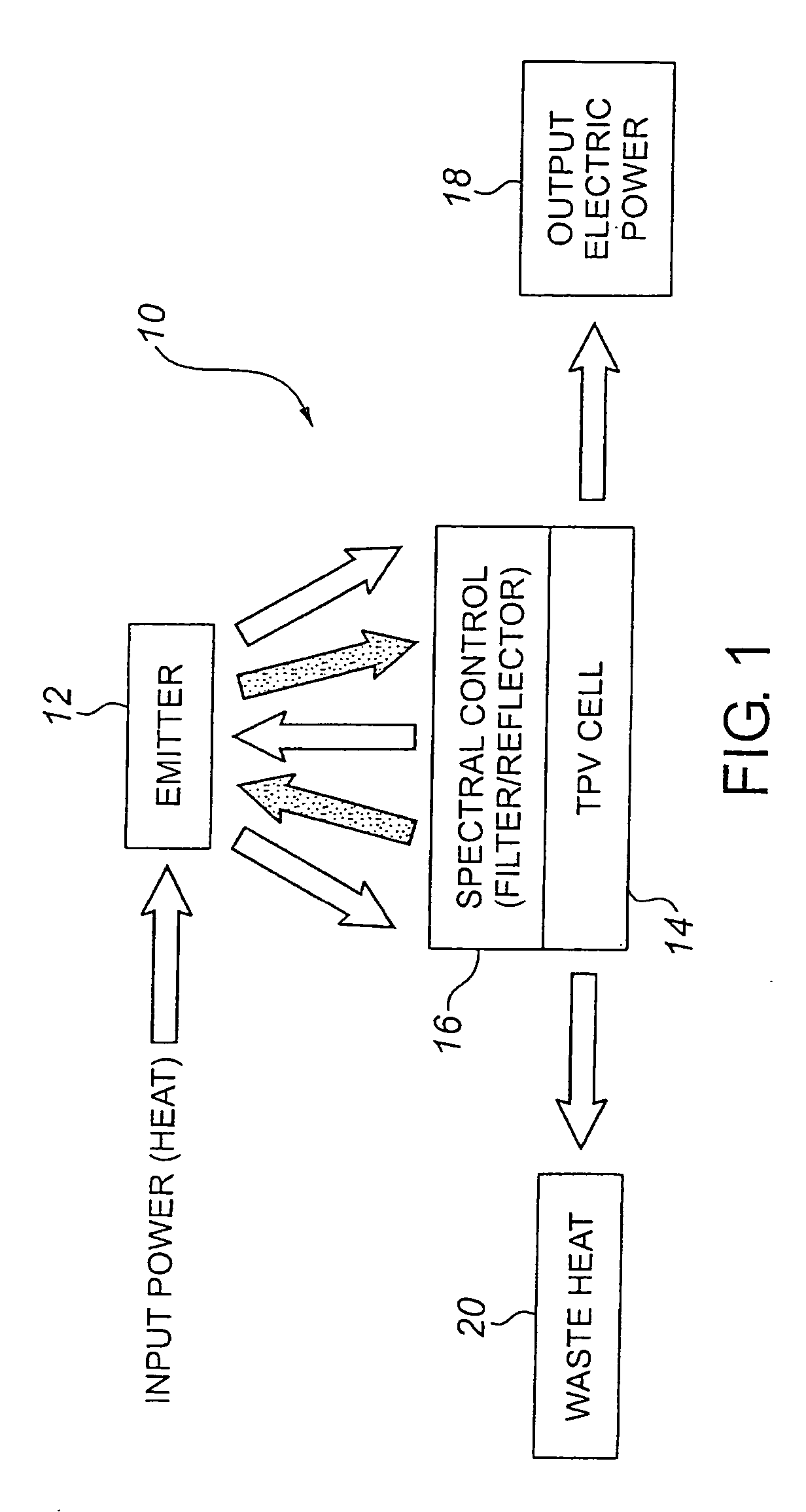
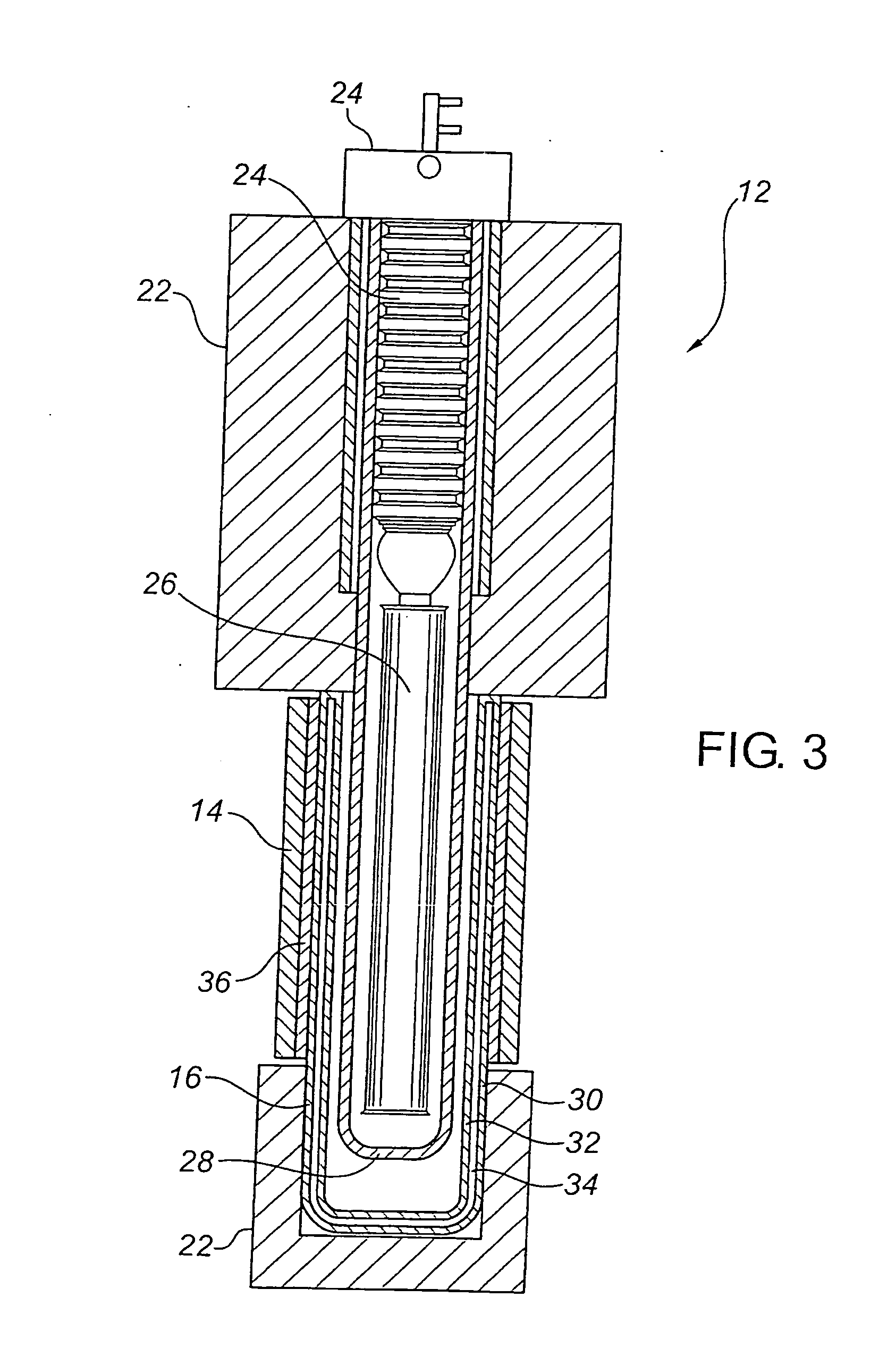
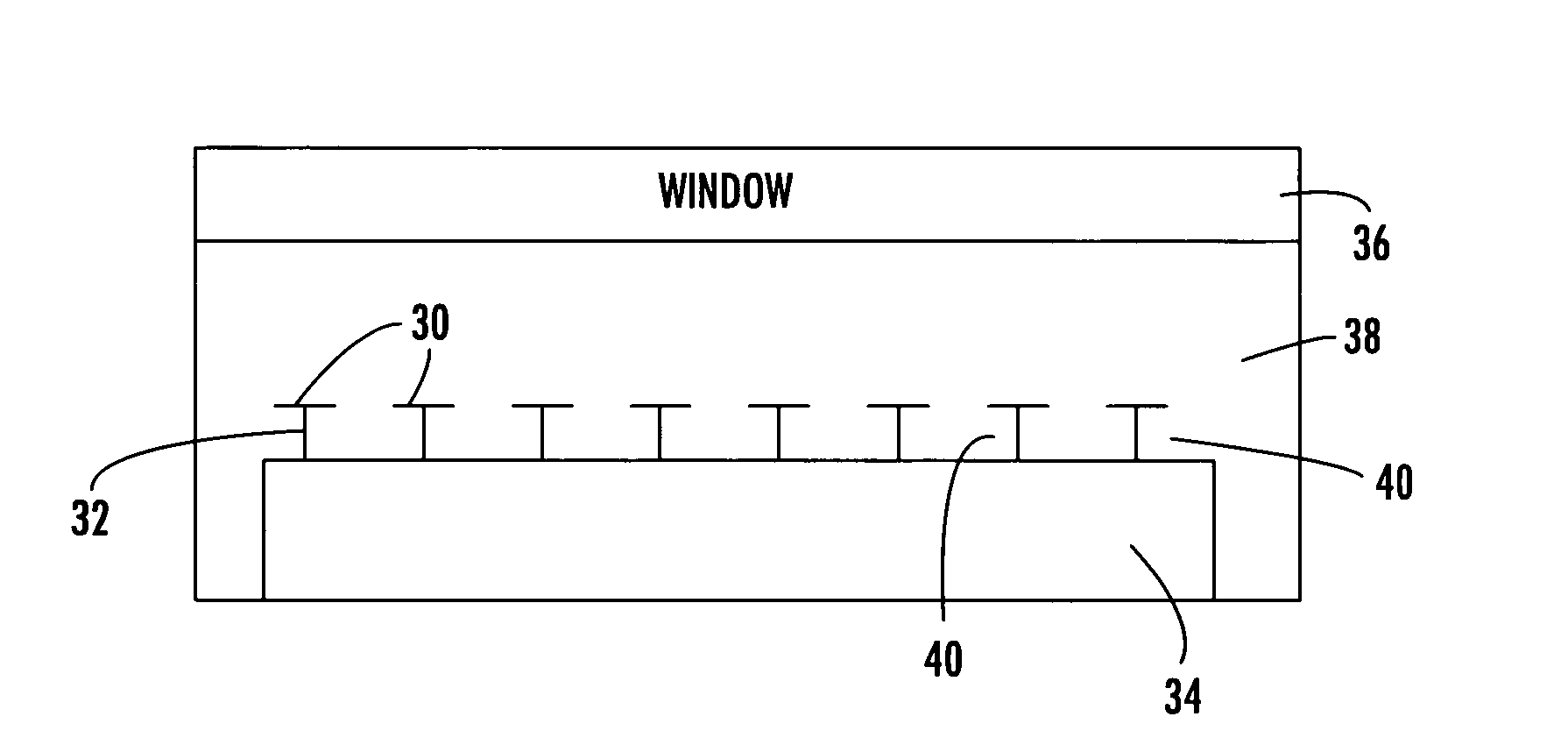
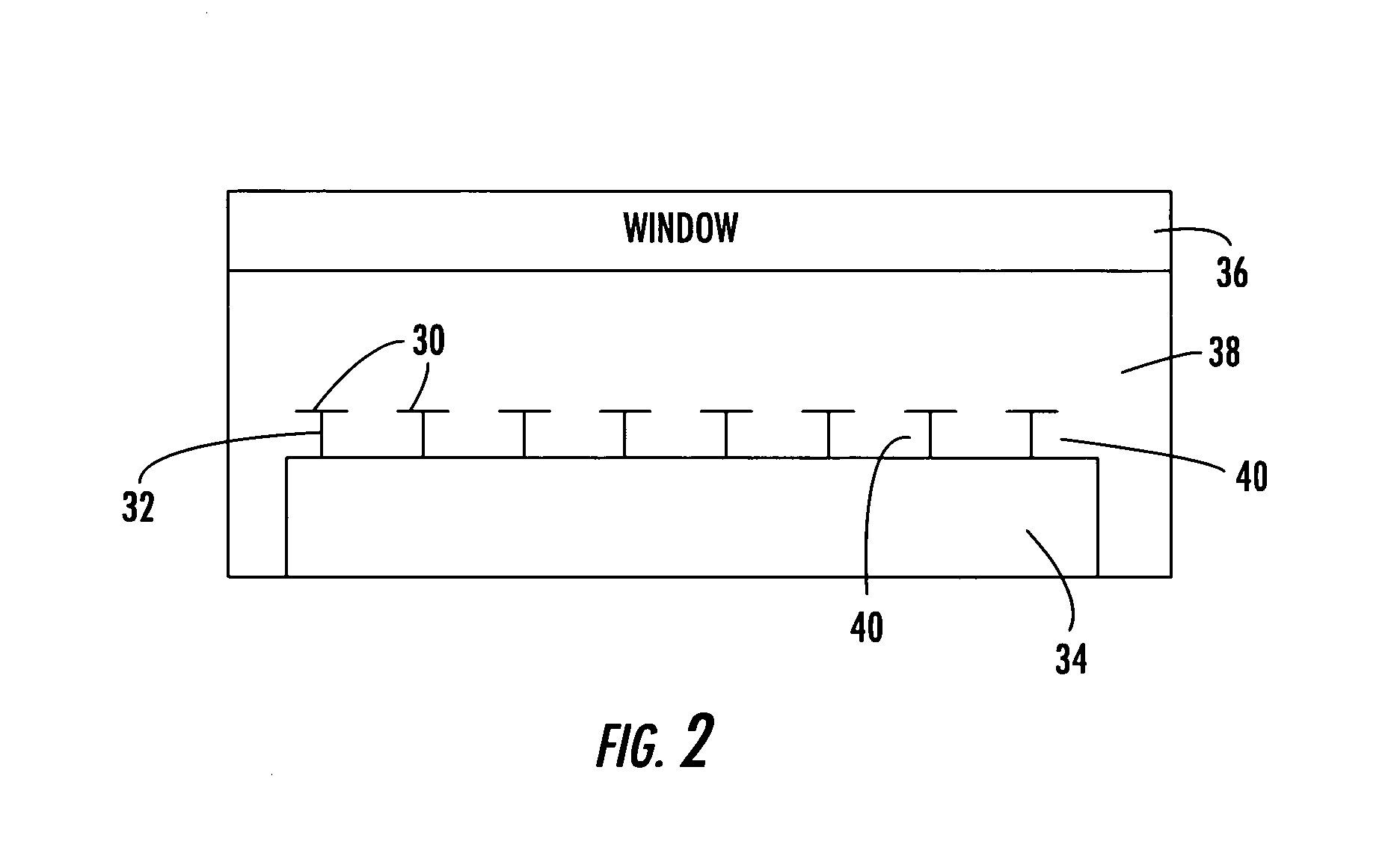
Thermophotovoltaic device
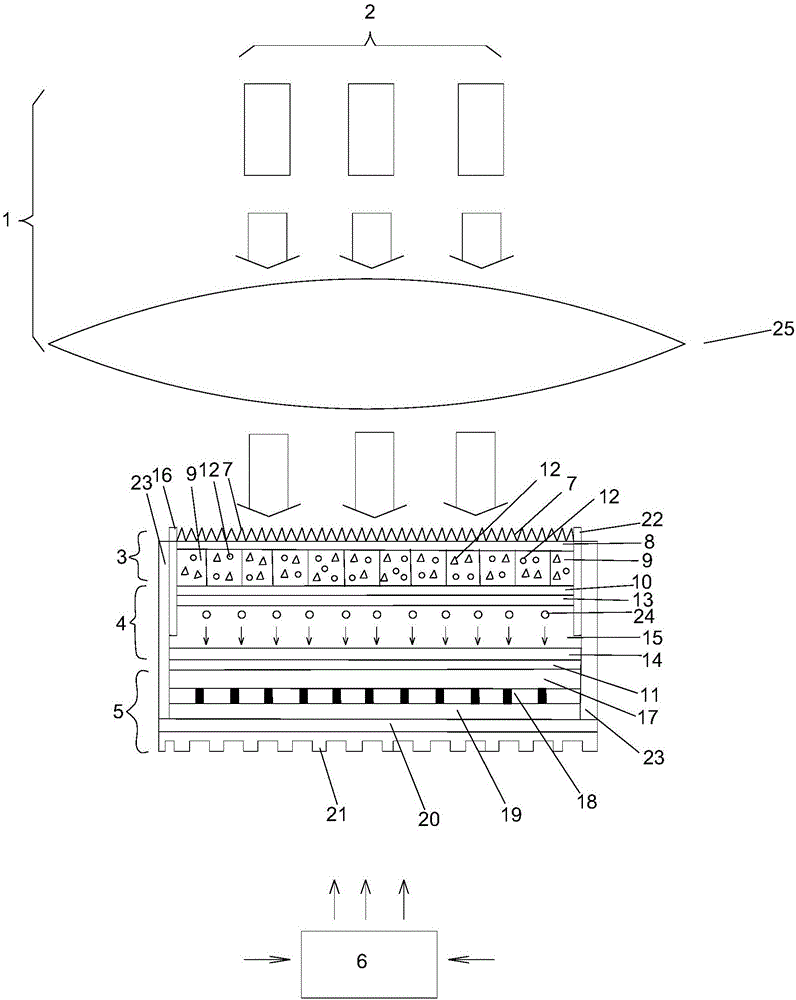
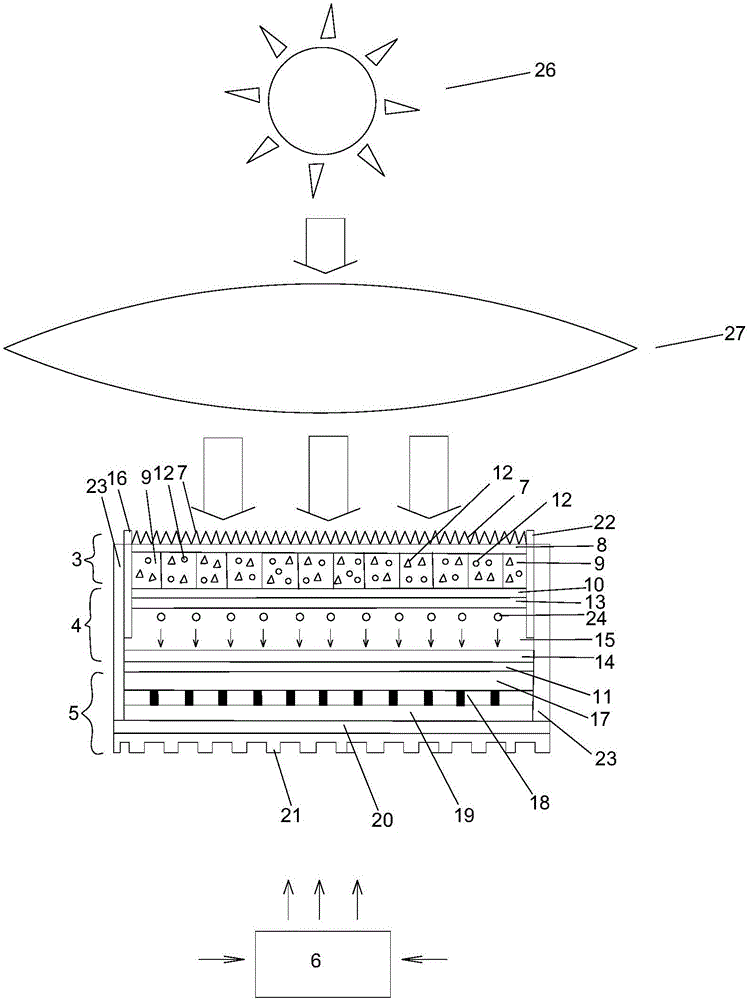
InactiveUS20060107995A1Prevent heat transferReduce conductivityPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationEngineeringConvection heat
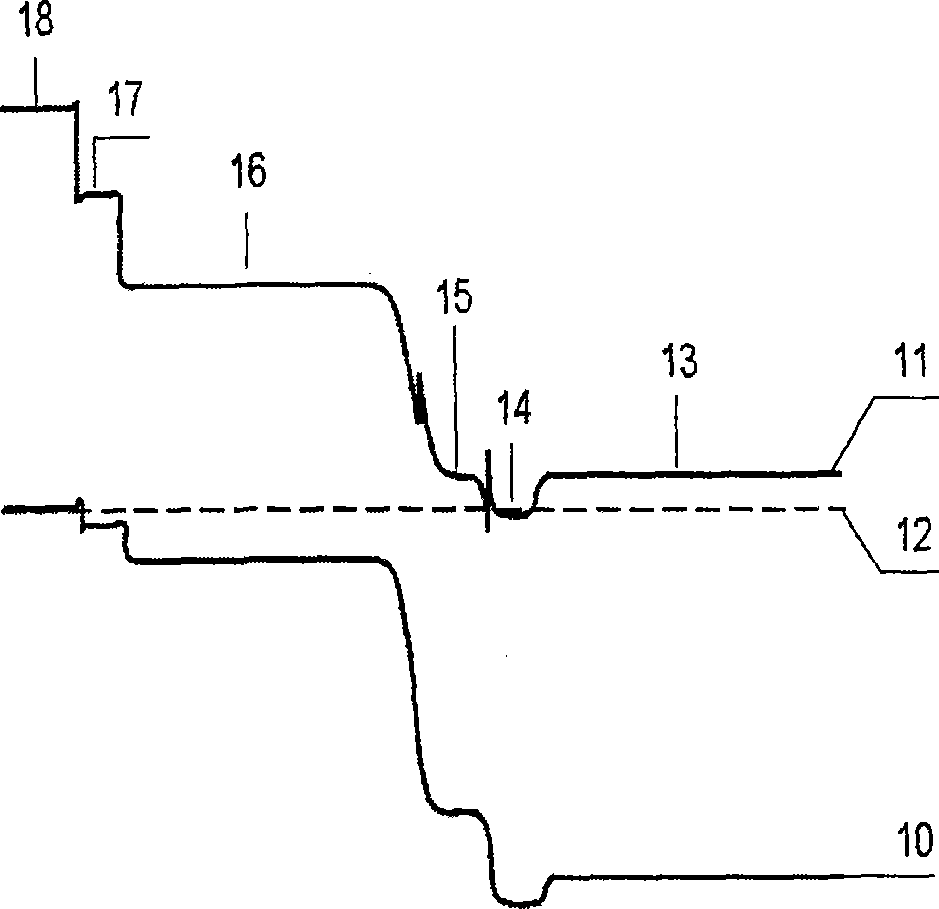
A thermophotovoltaic device (10) includes an energy source (12) compatible with thermophotovoltaic cells and thermophotovoltaic cells (14). A filter (16), adapted to filter out long wavelength energy, is positioned between the energy source (12) and the thermophotovoltaic cells (14). The filter (16) has dual walls (30 &32) with a low conductivity space (34) between the walls (30 &32) which is adapted to break the convection heat transfer path from the energy source (12) to the thermophotovoltaic cells (14).
Owner:KOVACIK GARY +2
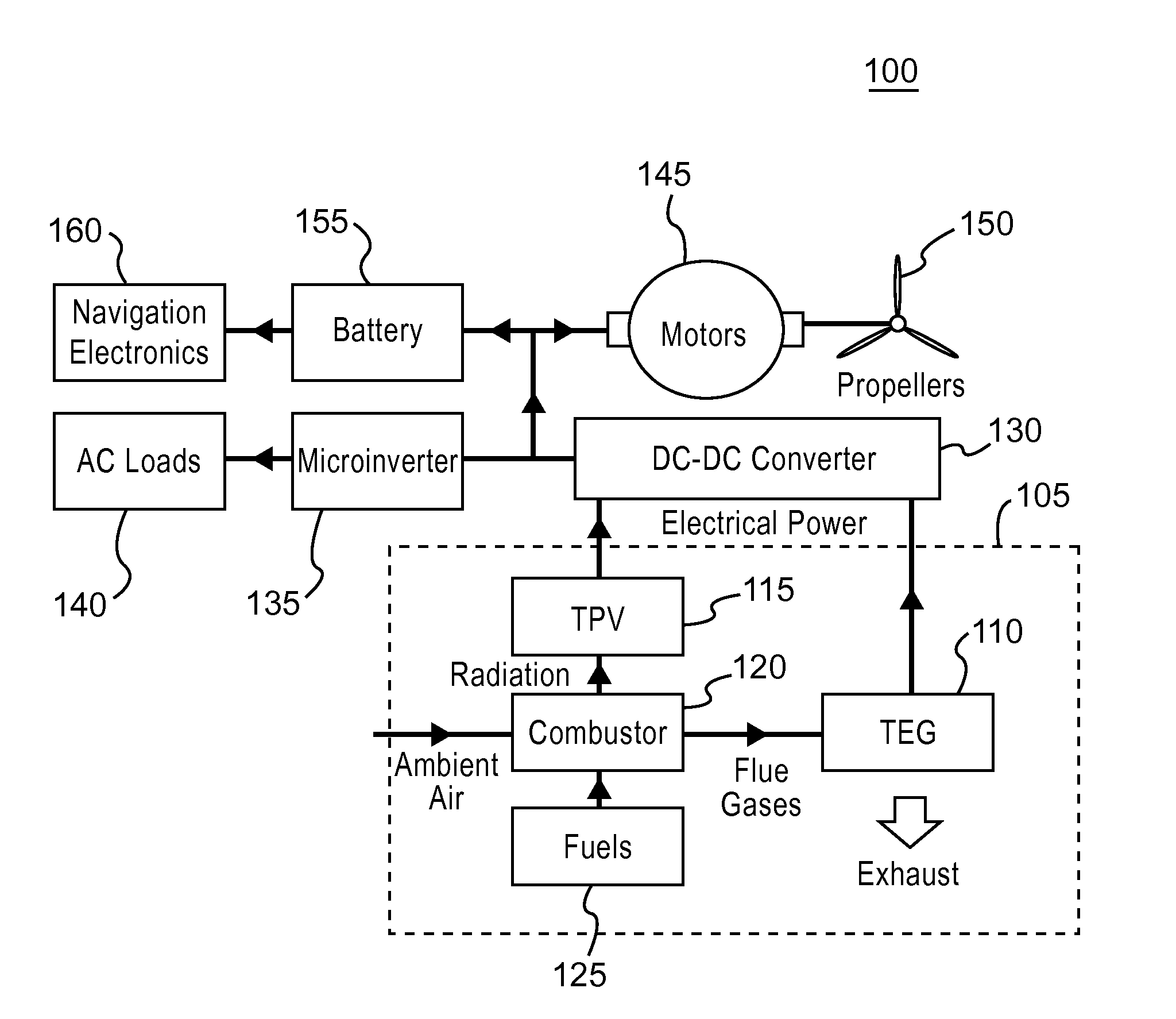
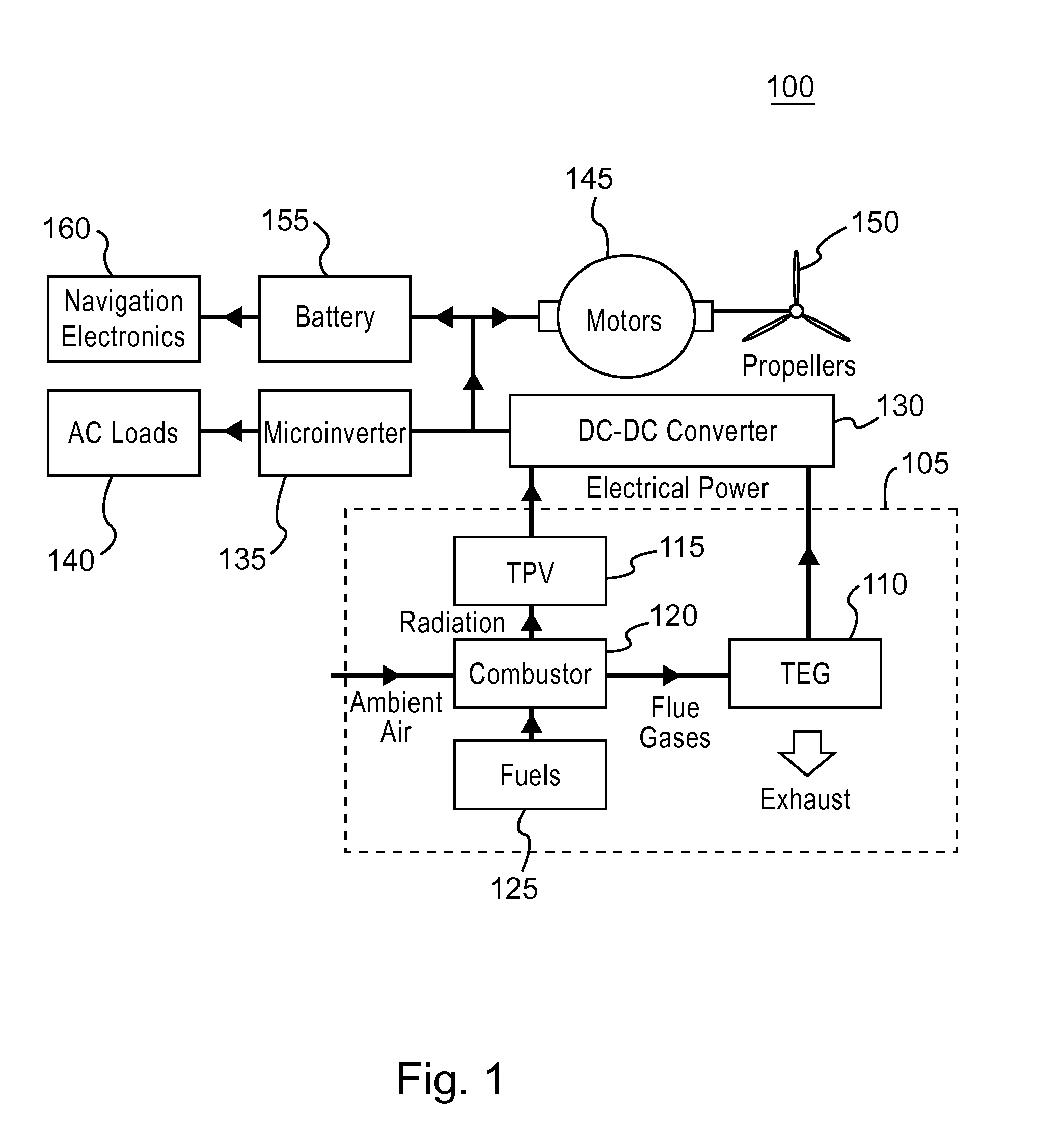
Hybrid propulsion power system for aerial vehicles
ActiveUS20160090184A1Thermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectPV power plantsElectric powerSolid-state
This disclosure generally relates to a hybrid solid-state propulsion system for aerial vehicles. The hybrid propulsion system includes a combustor, a thermophotovoltaic generator, and a thermoelectric generator. The combustor burns a chemical based fuel to produce radiation and heat that are converted into electricity used to power the aerial vehicle. The thermophotovoltaic generator is positioned to receive radiation and remnant heat generated by flames in the combustor while the thermoelectric generator receives heat from exhausted flue gases from the combustor.
Owner:REEBEEZ
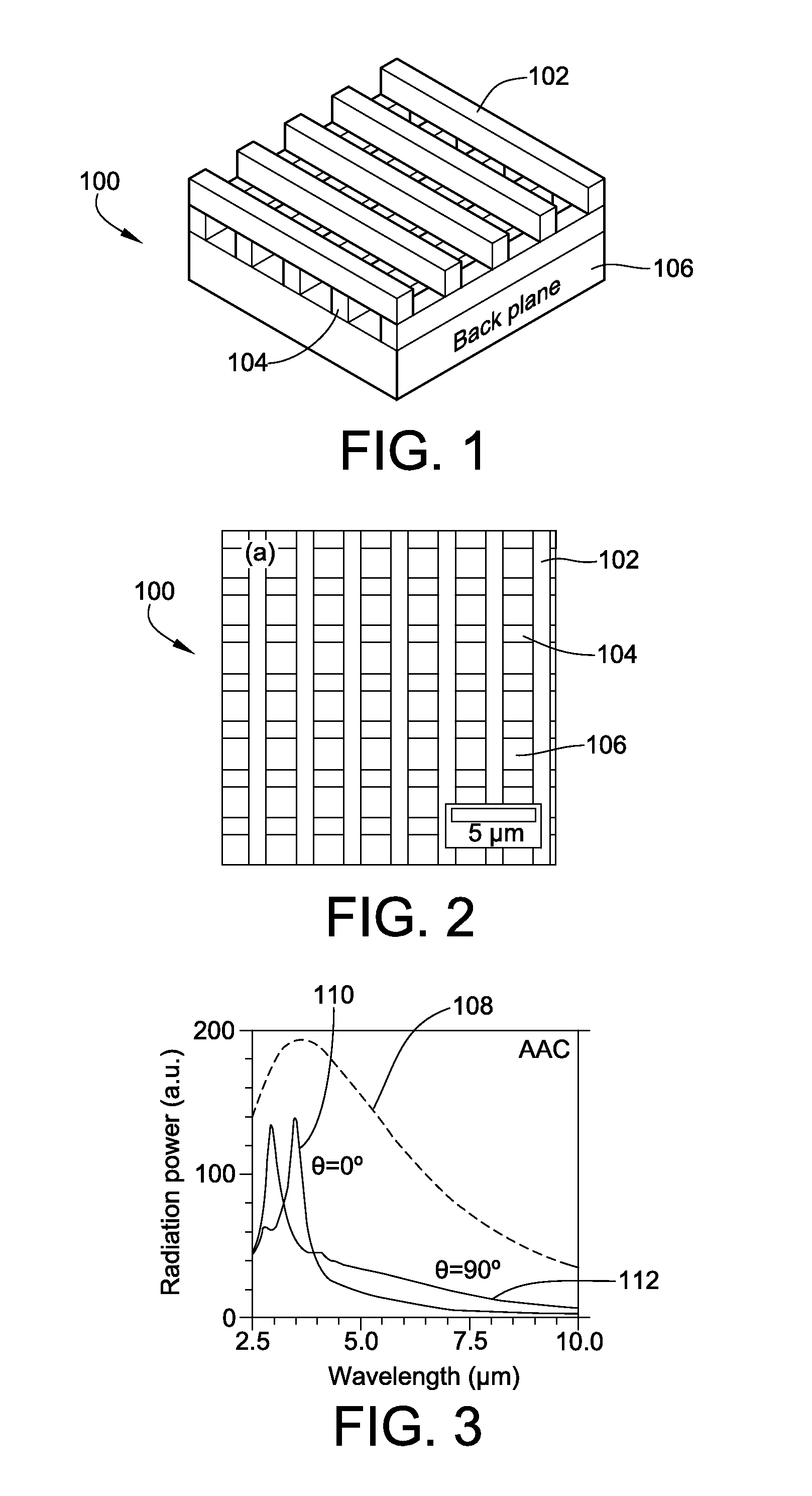
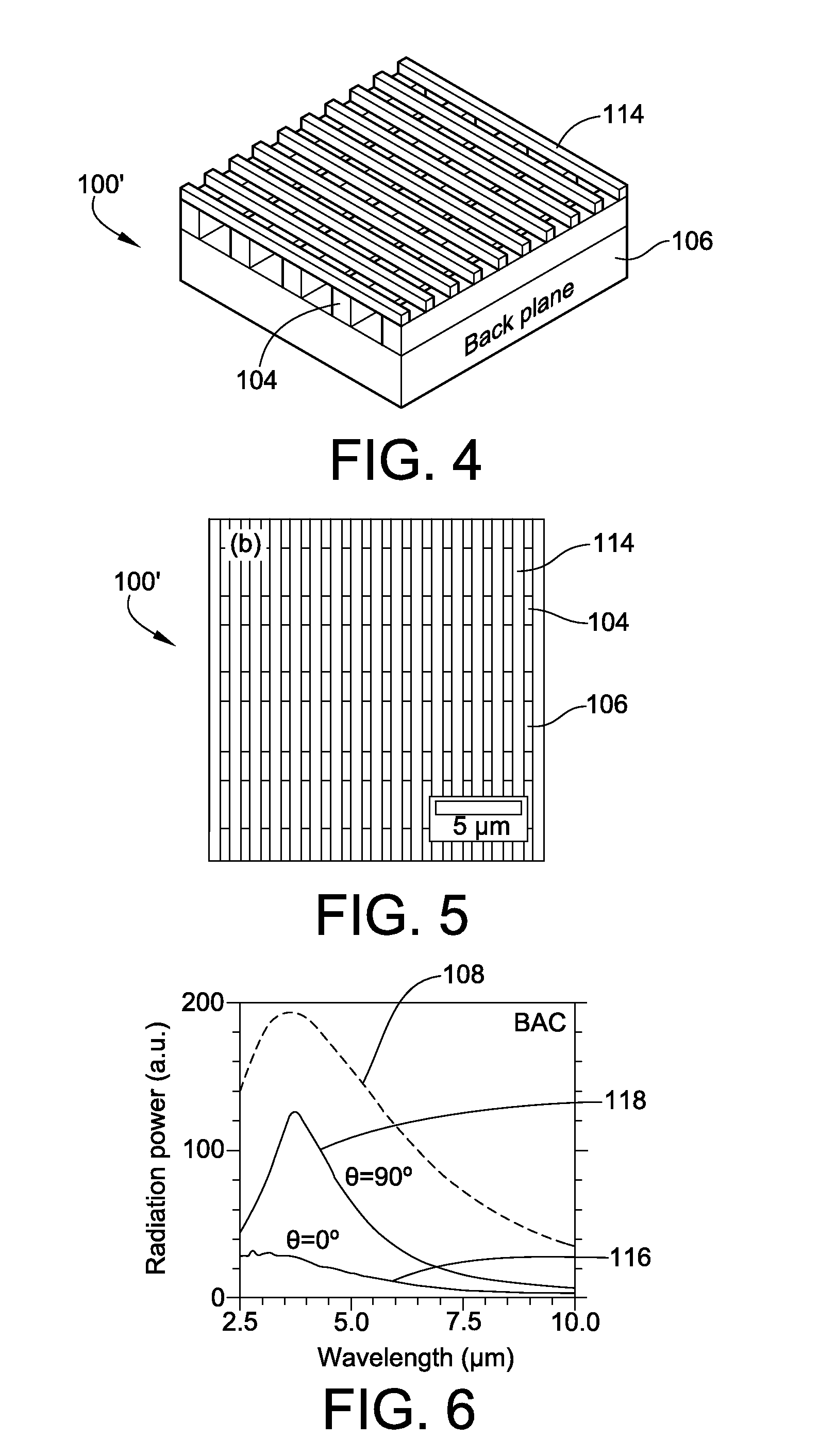
Metallic Layer-by-Layer Photonic Crystals for Linearly-Polarized Thermal Emission and Thermophotovoltaic Device Including Same
ActiveUS20100294325A1Overcome problemsIncreased Radiation PowerRadiation pyrometryPV power plantsGratingPhotonics
Metallic thermal emitters consisting of two layers of differently structured nickel gratings on a homogeneous nickel layer are fabricated by soft lithography and studied for polarized thermal radiation. A thermal emitter in combination with a sub-wavelength grating shows a high extinction ratio, with a maximum value close to 5, in a wide mid-infrared range from 3.2 to 7.8 μm, as well as high emissivity up to 0.65 at a wavelength of 3.7 μm. All measurements show good agreement with theoretical predictions. Numerical simulations reveal that a high electric field exists within the localized air space surrounded by the gratings and the intensified electric-field is only observed for the polarizations perpendicular to the top sub-wavelength grating. This result suggests how the emissivity of a metal can be selectively enhanced at a certain range of wavelengths for a given polarization.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
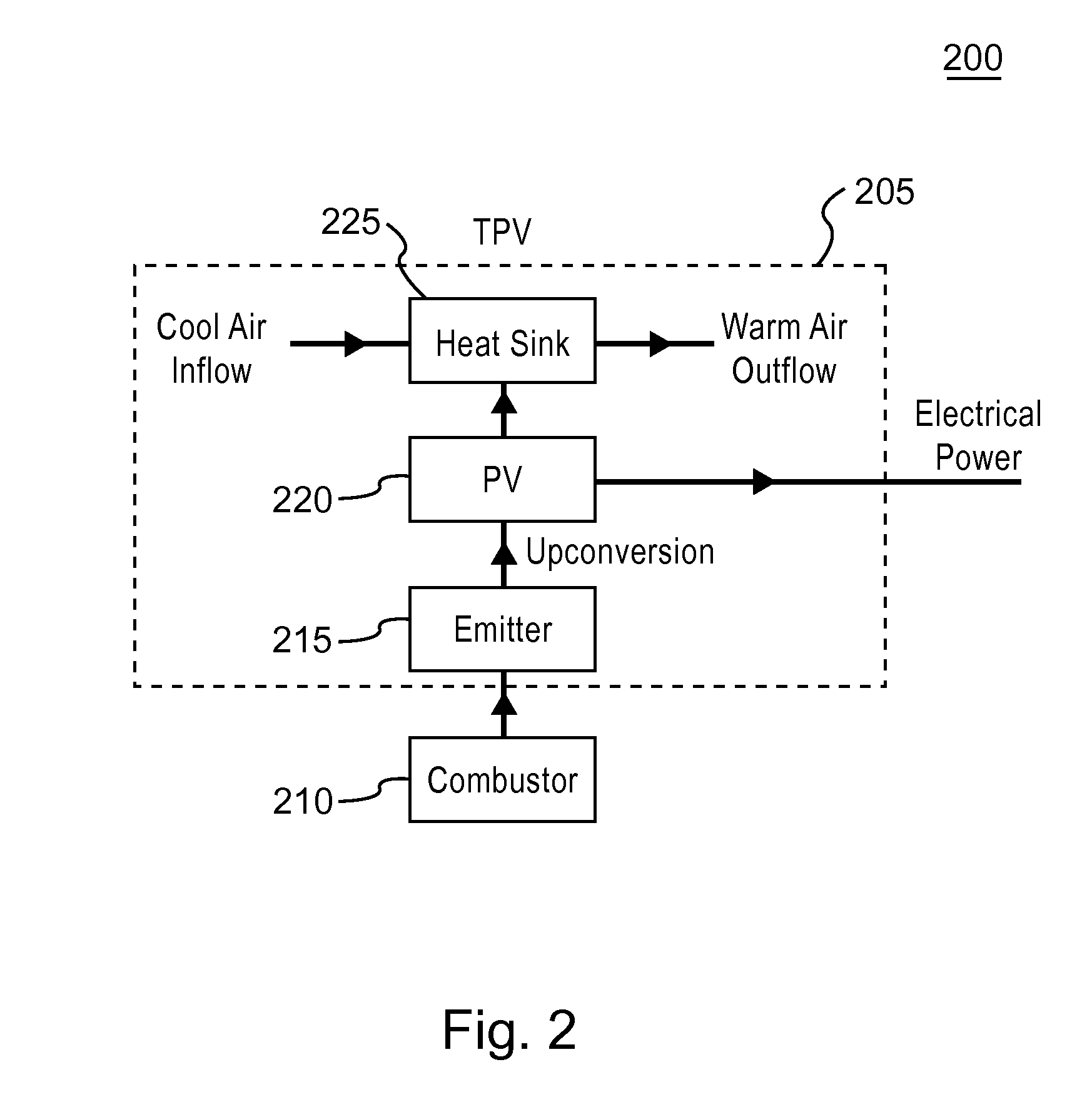
Method and device for selectively emitting photons
A selective emitter for a thermophotovoltaic system includes a heat source and a semiconductor layer having a thickness less than about 10 microns in thermal communication with the heat source. The heat source provides thermal energy to the semiconductor layer, which emits photons having a selected wavelength that is suitable for conversion into electrical energy by a thermophotovoltaic converter, in response to receiving thermal energy.
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
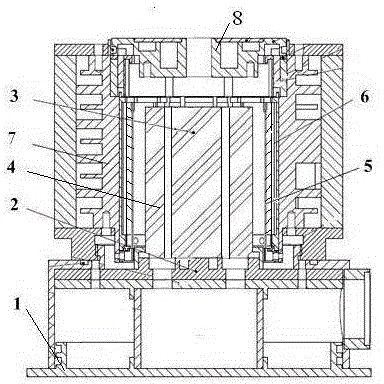
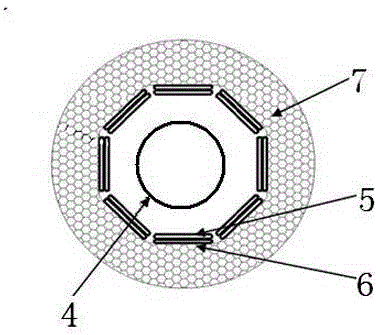
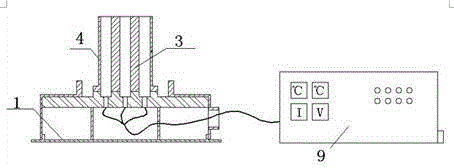
Electric heating type universal thermophotovoltaic system
ActiveCN103151963AImprove general performanceImprove control efficiencyPhotovoltaicsPhotovoltaic energy generationElectricityTemperature control
The invention discloses an electric heating type universal thermophotovoltaic system, which comprises a support frame, a heat insulation gasket, a heating pipe, a heat radiator, a filter, a thermophotovoltaic cell, a radiator, heat insulation sealing covers and a temperature control device, wherein the support frame is arranged beneath, the heating pipe is arranged at the center above the support frame, the heat radiator, the filter, the thermophotovoltaic cell and the radiator are respectively and sequentially arranged around the heating pipe from the interior to the exterior in an axial way, the heat insulation sealing covers are arranged in the inner side of the radiator and above the heating pipe, the heat radiator, the filter and the thermophotovoltaic cell, the heat insulating gasket is arranged between the heating pipe and the support frame, and the temperature control device is connected with the heating pipe and the heat radiator. The electric heating type universal thermophotovoltaic system has the advantages that the conversion efficiency and the output power are high, the recovery and utilization efficiency of energy is improved, and the system can be directly suitable for any heat source.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF SPACE POWER SOURCES
{100}<100> or 45°-rotated {100}<100>, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices
InactiveUS8178221B2Good lattice matchingSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHard disc drivePhotoluminescence
Owner:GOYAL AMIT
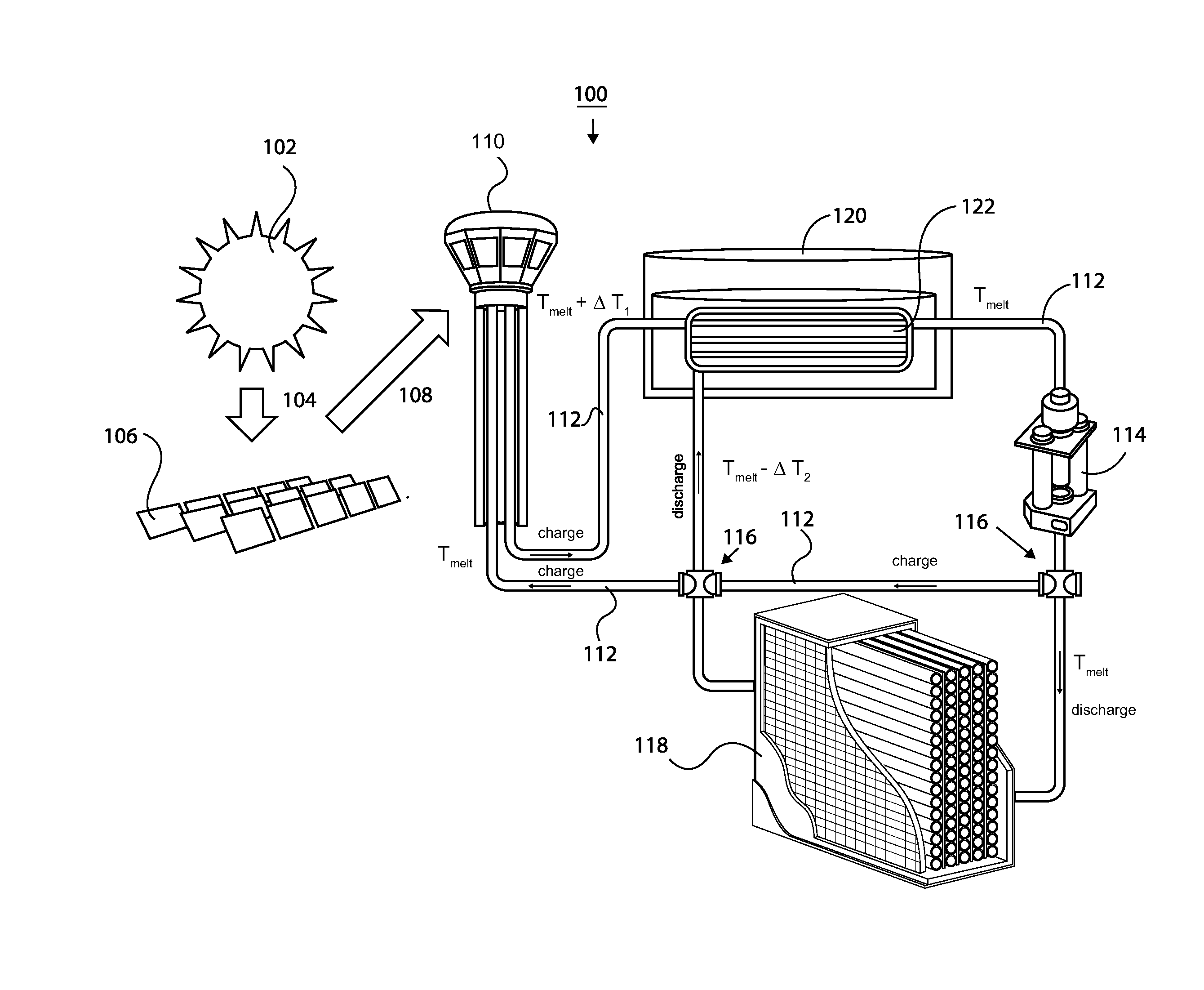
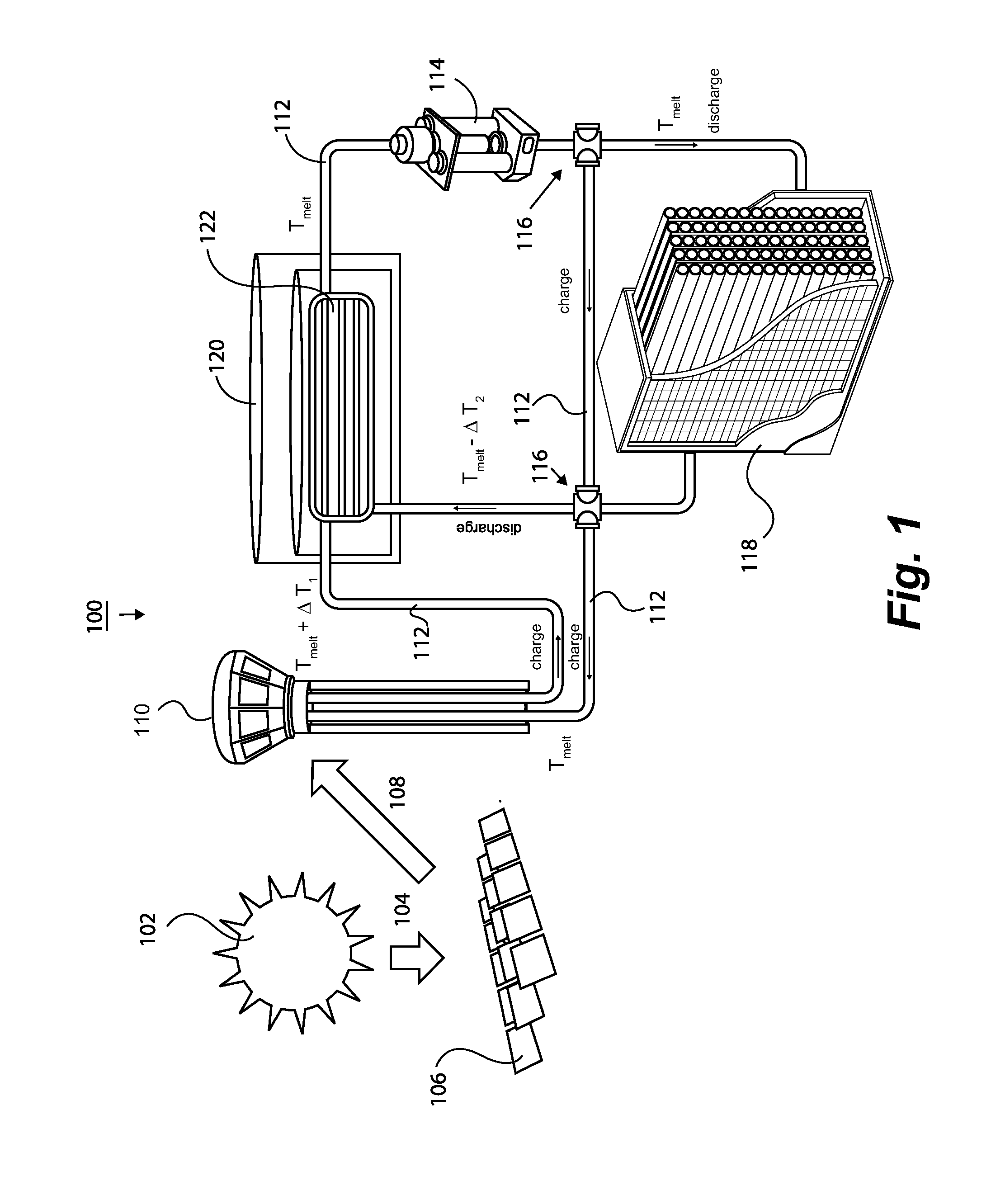
Systems and methods for thermophotovoltaics with storage
InactiveUS20160197574A1Maximizing exergetic efficiencyLow costSolar heating energyThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentEngineeringThermophotovoltaic
Systems and methods for thermophotovoltaics with storage are disclosed. In one embodiment, includes a heat generating device configured to generate heat for a heat transfer fluid and a thermal storage device configured to receive the heat transfer fluid from the heat generating device via fluid delivery devices and cause, by the heat of the heat transfer fluid, a thermal storage material to store at least a portion of the heat of the heat transfer fluid. The system can also include a power block having a thermal emitter and a thermophotovoltaic device. The power block can be configured to receive the heat transfer fluid via the fluid delivery devices and cause, by the heat of the heat transfer fluid, the thermal emitter to emit a plurality of photons to a photovoltaic element of the thermophotovoltaic device.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Micron gap thermal photovoltaic device and method of making the same
ActiveUS20080223435A1Easy to manufactureImprove heat insulationPV power plantsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhysicsPhotovoltaics
Owner:CHARLES STARK DRAPER LABORATORY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/05ef1fe0-6ace-42a2-8058-990b1467d89a/US20080230779A1-20080925-D00000.png)
![[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/05ef1fe0-6ace-42a2-8058-990b1467d89a/US20080230779A1-20080925-D00001.png)
![[100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices [100] Or [110] aligned, semiconductor-based, large-area, flexible, electronic devices](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/05ef1fe0-6ace-42a2-8058-990b1467d89a/US20080230779A1-20080925-D00002.png)