Patents
Literature
120results about How to "Increased Radiation Power" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
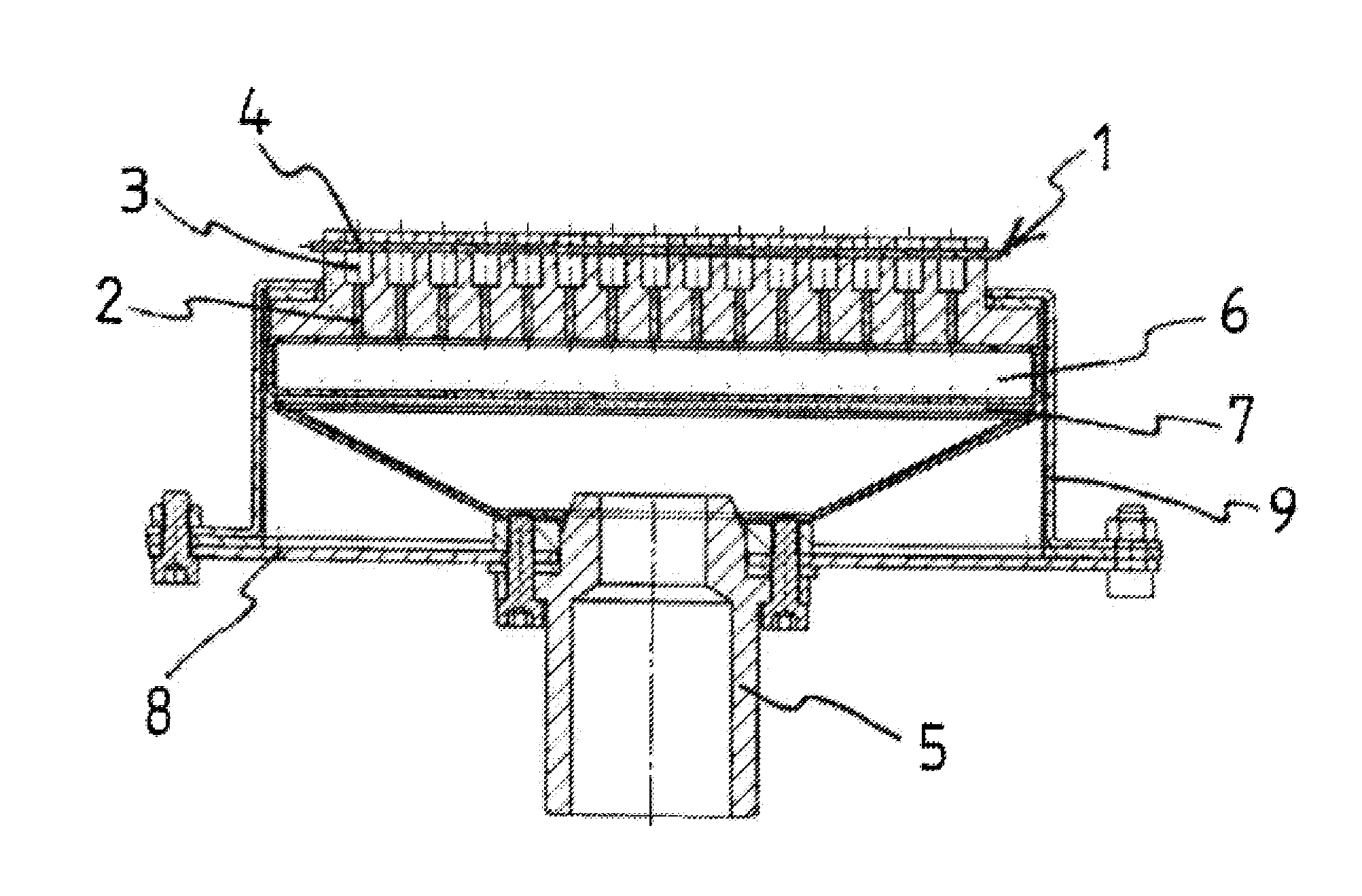
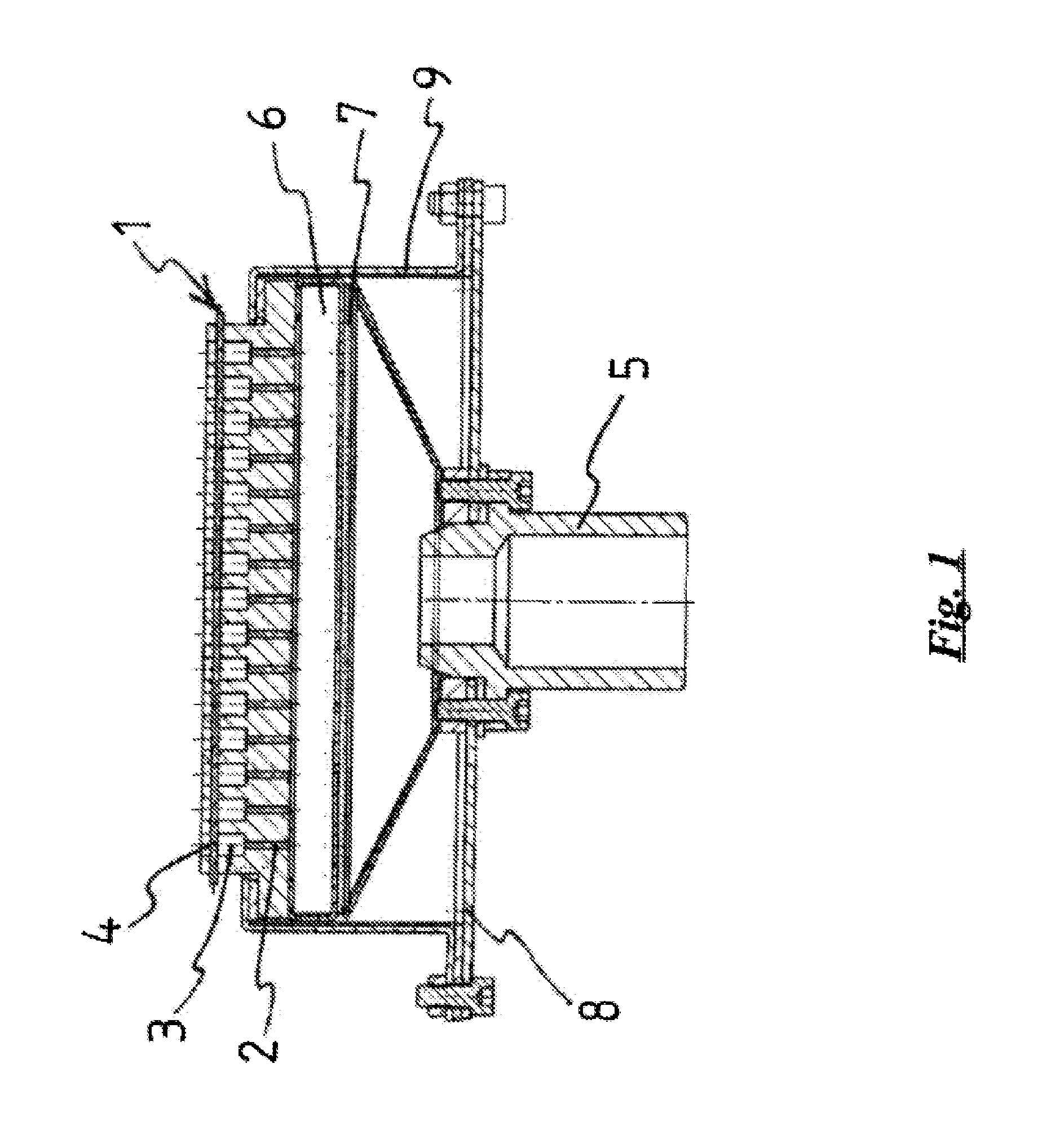
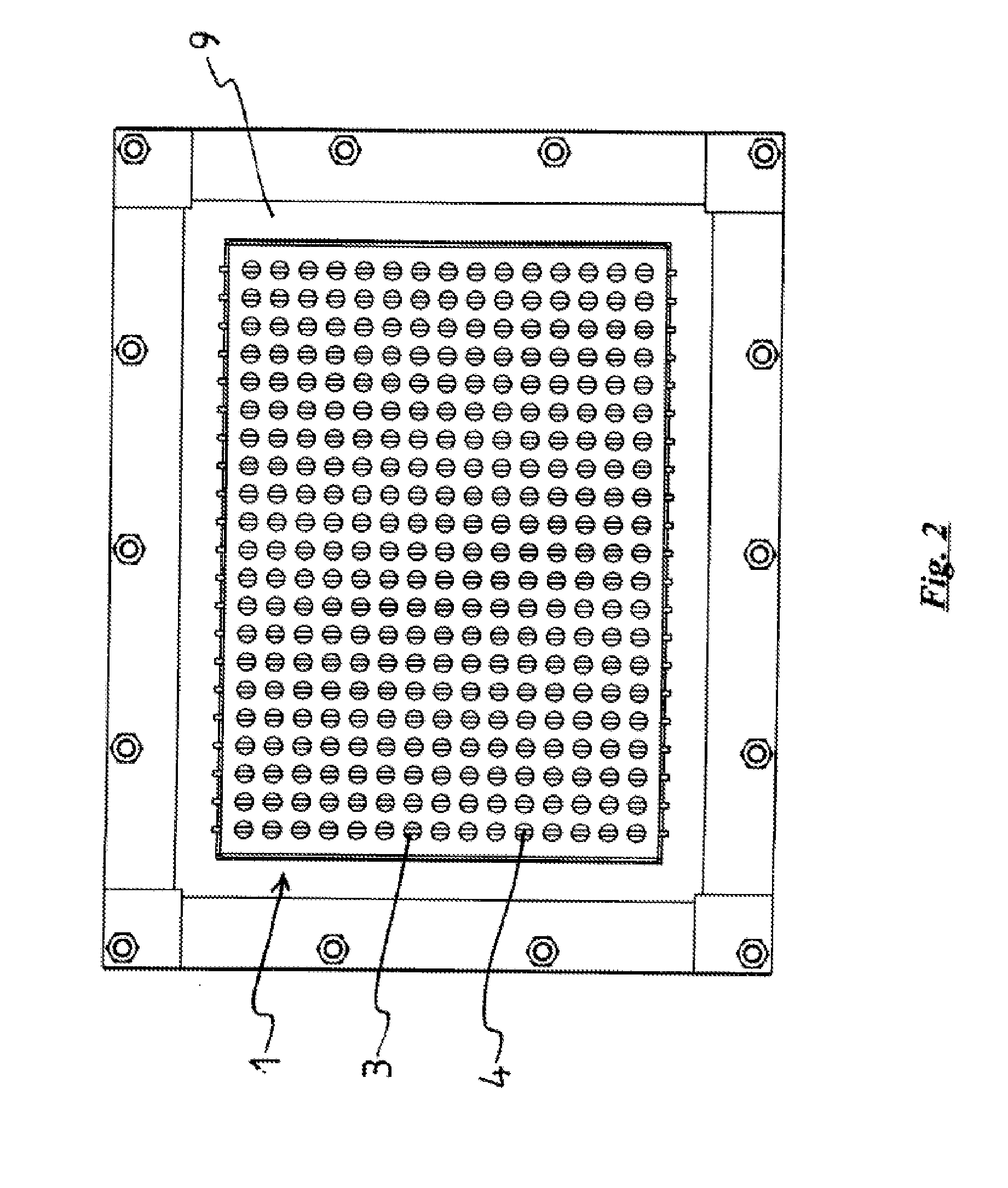
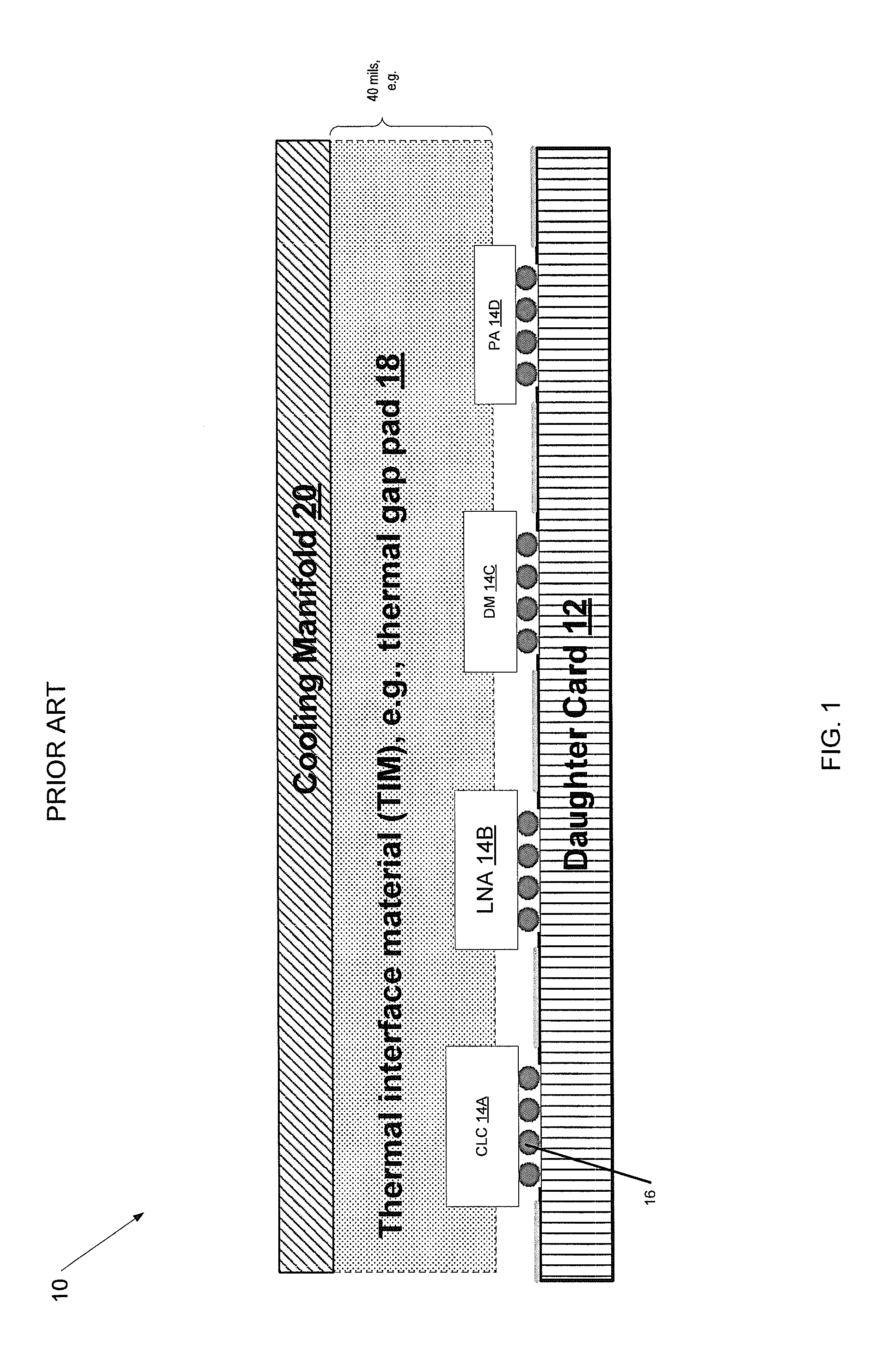
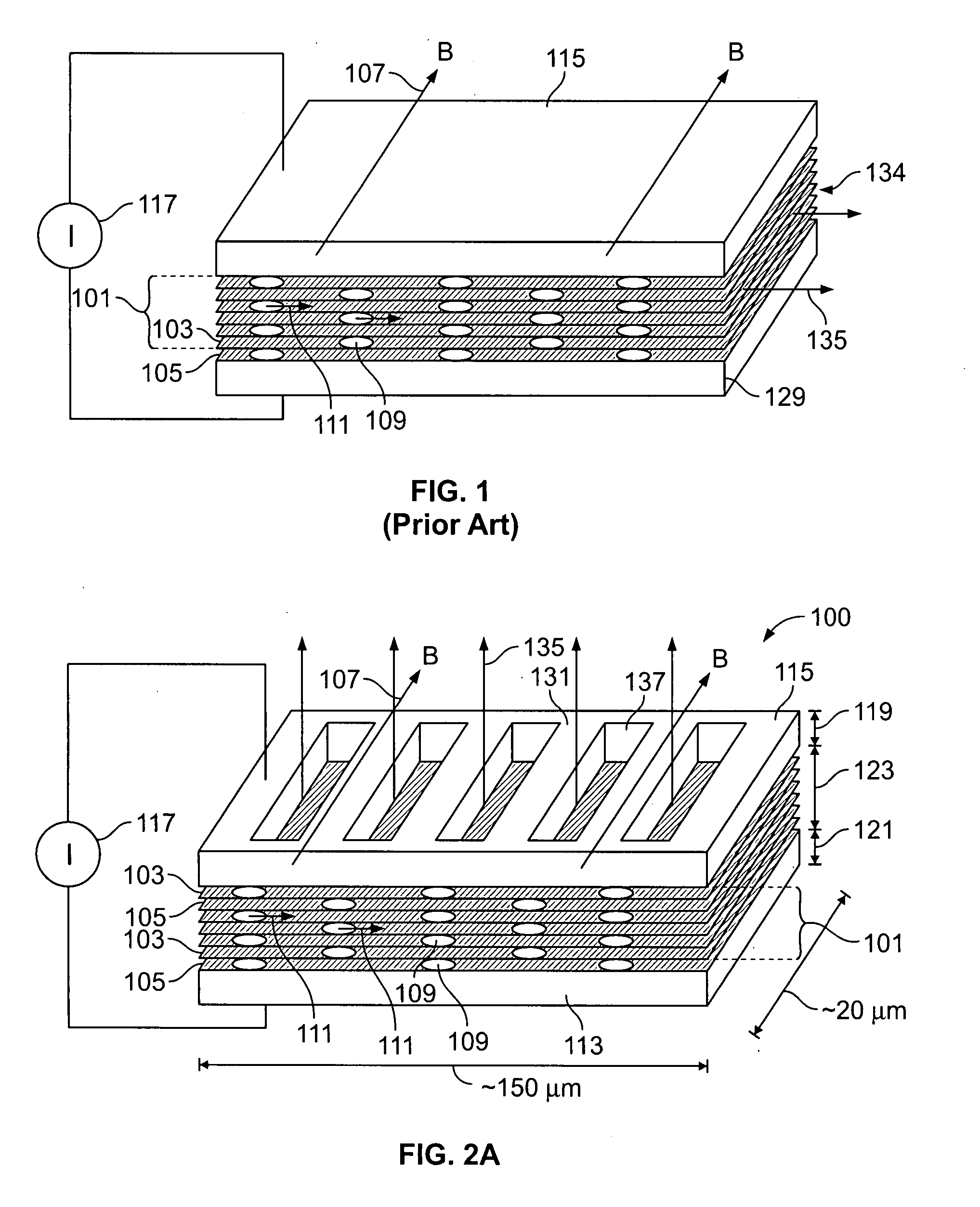
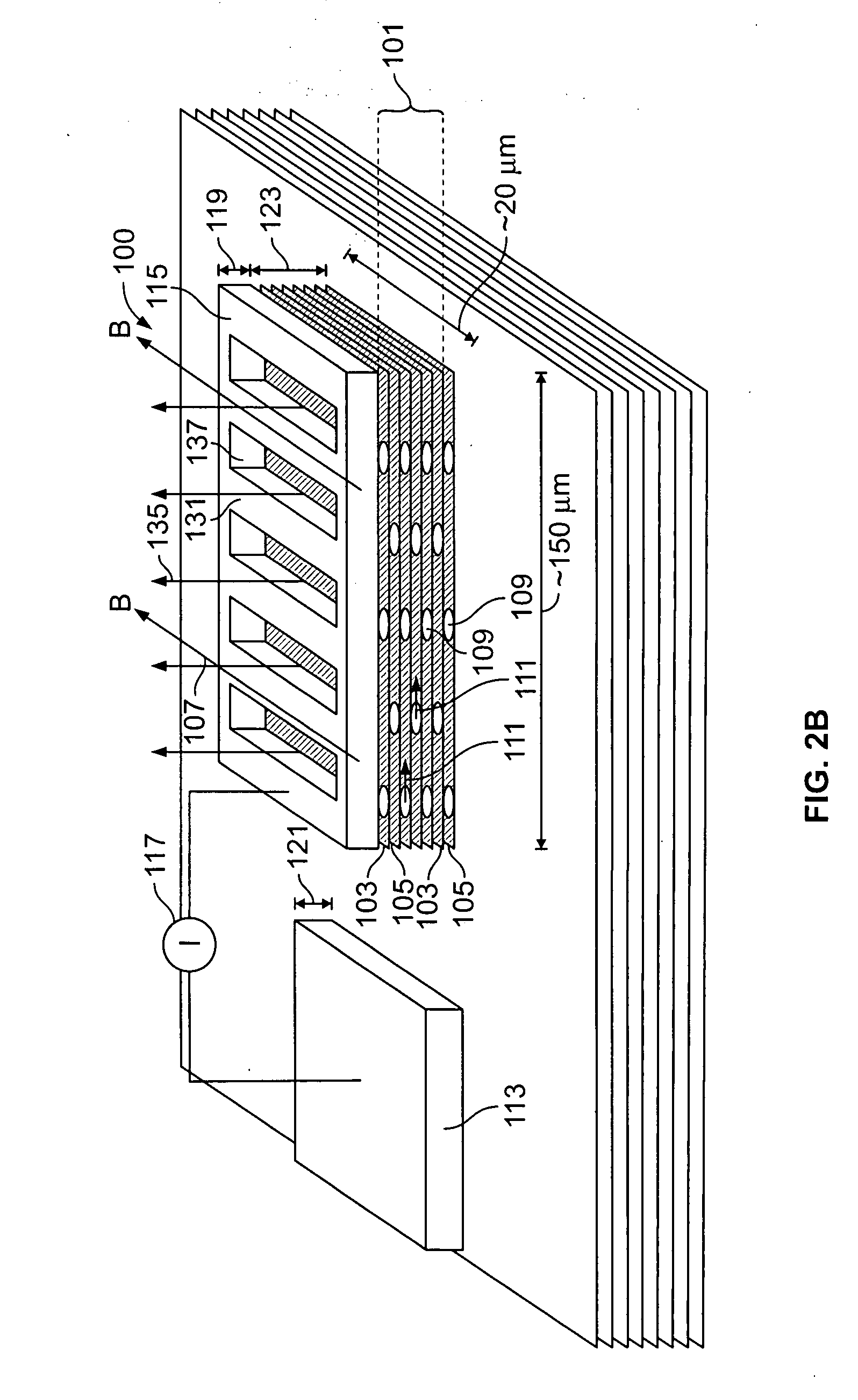
Radiant Burner
InactiveUS20120164590A1Improve energy efficiencyIncreased Radiation PowerBurner material specificationsGaseous fuel burnerCombustorOxygen
The invention relates to a burner, in particular a radiant burner, for the combustion of a gas mixture of fuel gas and an oxygen carrier gas, with a burner plate with passage channels for the throughflow of the gas mixture from a mixing chamber side to a combustion side, wherein, on the combustion side, combustion channels with an enlarged cross-section compared with the passage channels connect to the passage channels, wherein flow obstacles for a contact with the combustion flame are arranged in the combustion channels and the flow obstacles are made of a material which has a higher thermal conductivity than the material of the burner plate.
Owner:SANDVIK INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY AB
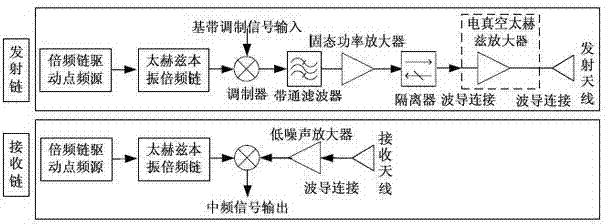
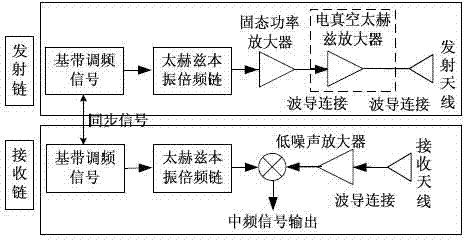
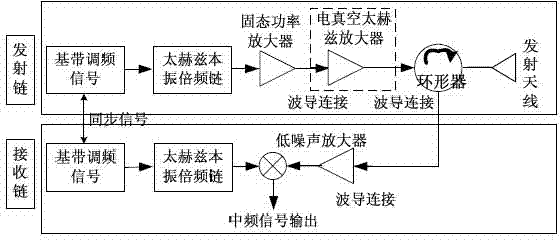
MMAOP framework applicable to terahertz radar and communication system
InactiveCN103901404AEasy to detectHigh Resolution Imaging CapabilityWave based measurement systemsTransmissionSpace powerSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a MMAOP framework applicable to a terahertz radar and communication system. The implementation mode that a multiplier, a mixer, an array, the quasi-optics and a parabolic antenna are combined is adopted for the MMAOP framework, an all-solid high-power terahertz radiation source is obtained, and meanwhile the MMAOP framework is applicable to the terahertz radar and communication system. A receiving link and a transmitting link of the framework are both obtained in an all-solid mode, and thus the MMAOP framework is good in repeatability and can be integrated and be smaller conveniently. According to the framework, the output power of the terahertz source is raised with an array space power synthesis method, and thus the expansibility is good; a small array can be adopted first to acquire medium output power, as the technology improves, the number of arrays is gradually increased, the output power of a single array element is raised, and thus the radiation power is raised.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS ENG CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
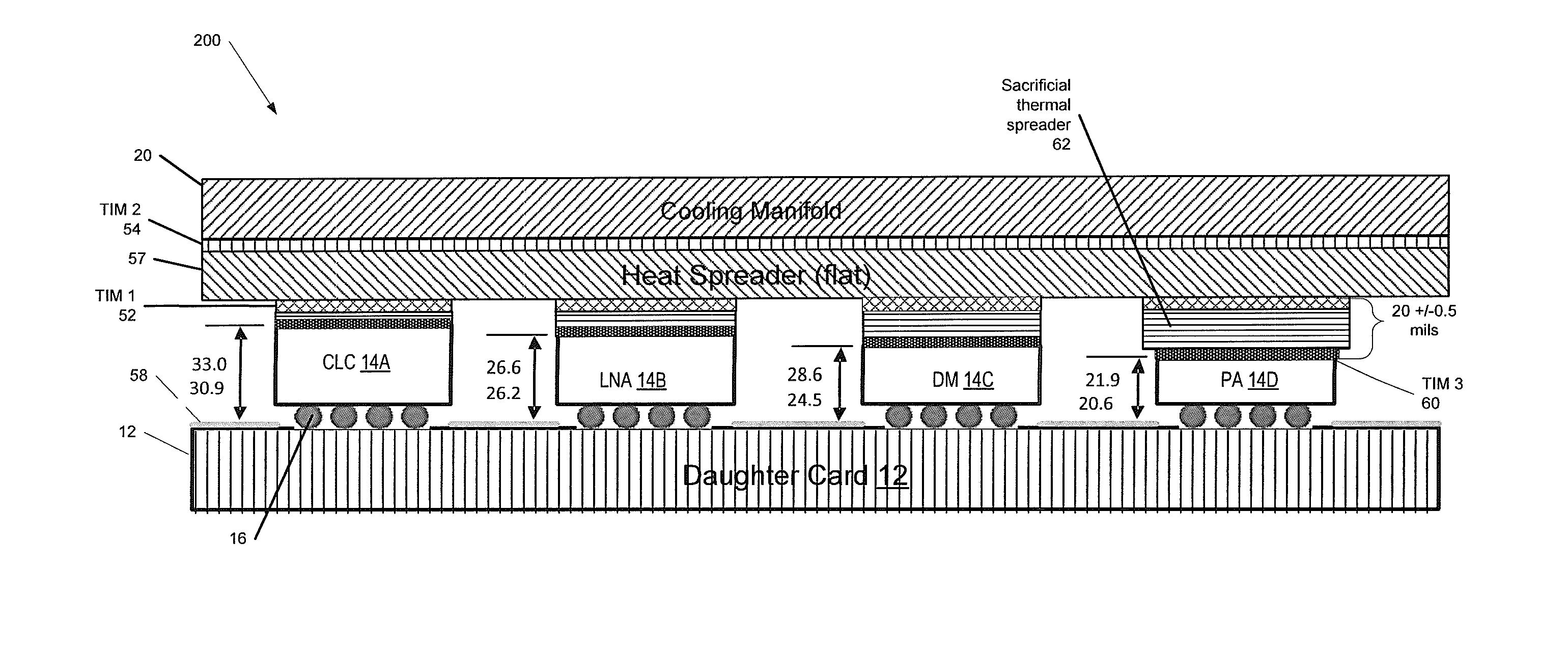
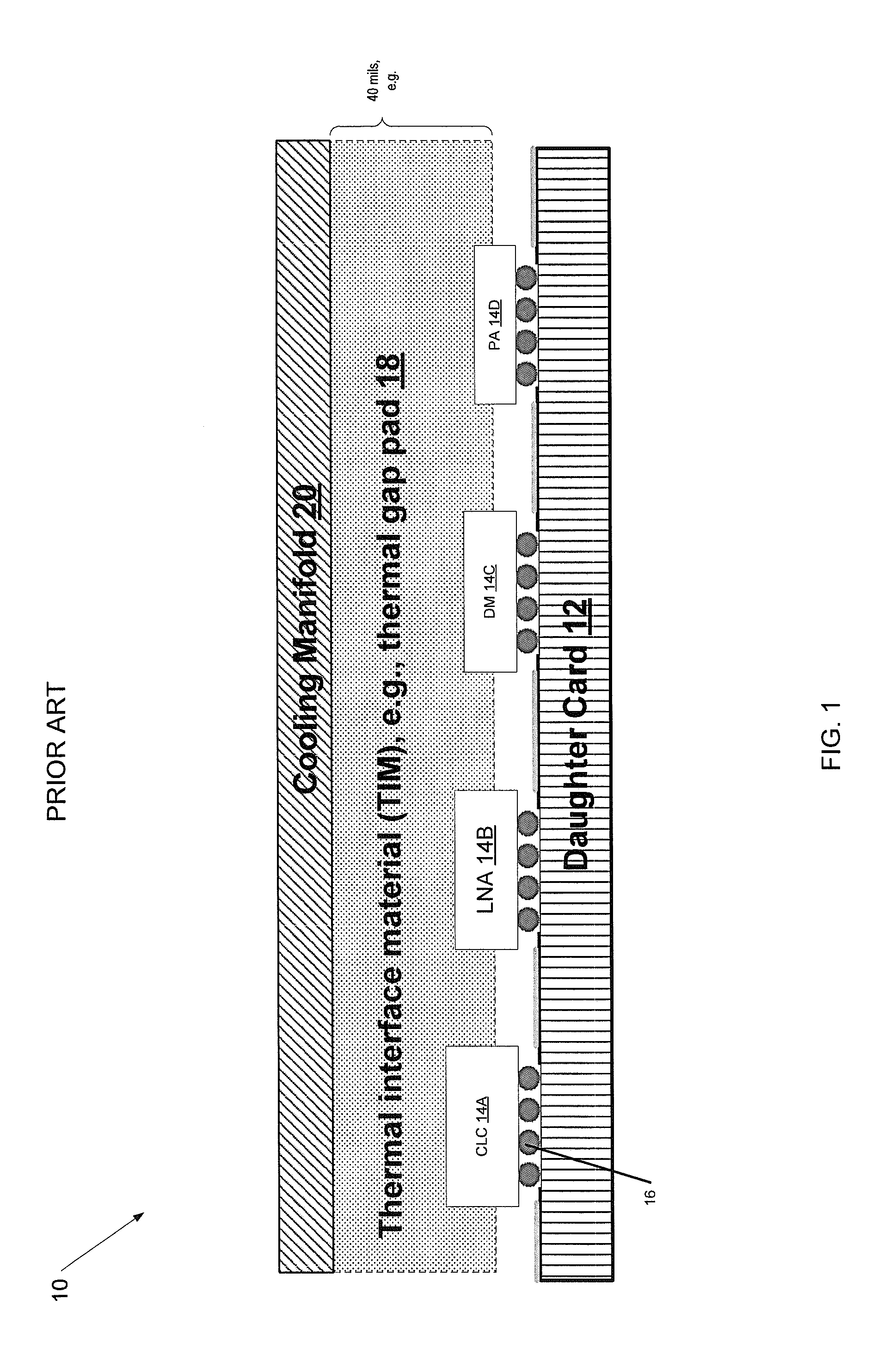
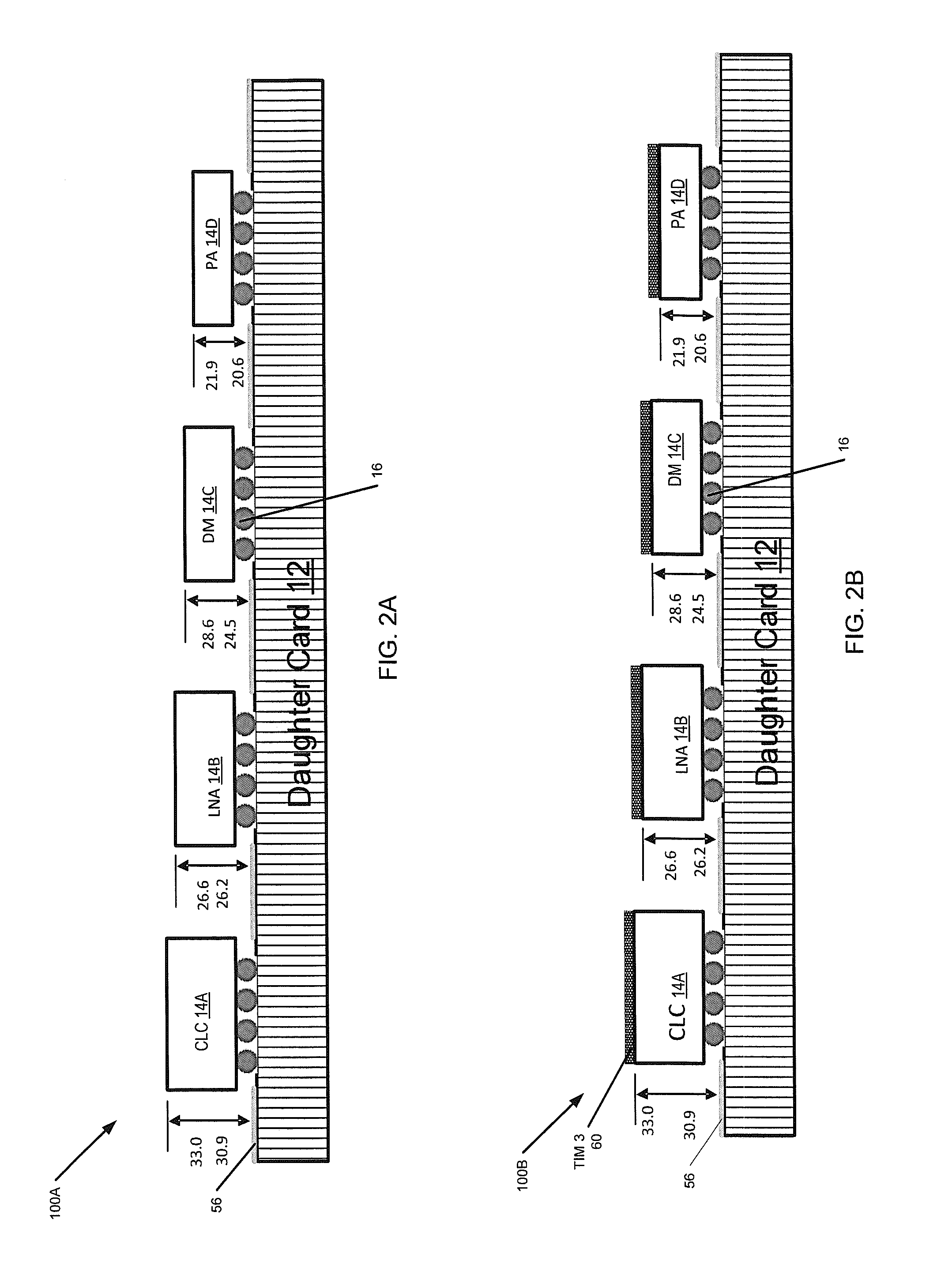
Conduction cooling of multi-channel flip chip based panel array circuits
ActiveUS20130258599A1Minimize thermal gapImprove thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor chipConduction cooling
A method of forming a heat-dissipating structure for semiconductor circuits is provided. First and second semiconductor integrated circuit (IC) chips are provided, where the first and second semiconductor chips each have first and second opposing sides, wherein the first and second semiconductor IC chips are configured to be fixedly attached to a top surface of a substantially planar circuit board along their respective first sides. The respective second opposing sides of each of the first and second semiconductor IC chips are coupled to first and second respective portions of a sacrificial thermal spreader material, the sacrificial thermal spreader material comprising a material that is thermally conductive. The first and second portions of the sacrificial thermal spreader material are planarized to substantially equalize a respective first height of the first semiconductor chip and a respective second height of the second semiconductor chip.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Fluorescent non-metallic particles encapsulated in a metallic coating
InactiveUS20090302235A1Easy to detectIncreased Radiation PowerPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersNano biosensorWavelength
The present invention relates to a particle comprising a non-metallic core having a fluorescent material and a metallic shell encapsulating the non-metallic core wherein the metallic shell has transparency for an electromagnetic radiation having a first wavelength to excite the said fluorescent material and reflectance for an electromagnetic radiation having a second wavelength emitted by the said fluorescent material to confine the electromagnetic radiation having the second wavelength in the metallic shell. This system allows for the excitation of optical cavity modes inside the particle even at sub-micron particle size. The cavity modes are extremely sensitive to any change of the dielectric environment of the particle. This sensitivity can be used for the construction of optical nano-biosensors. Another application of the system is that of a microscopic source for spherical light waves, which may find applications in digital inline holography and display technology.
Owner:FUJIREBIO CO LTD
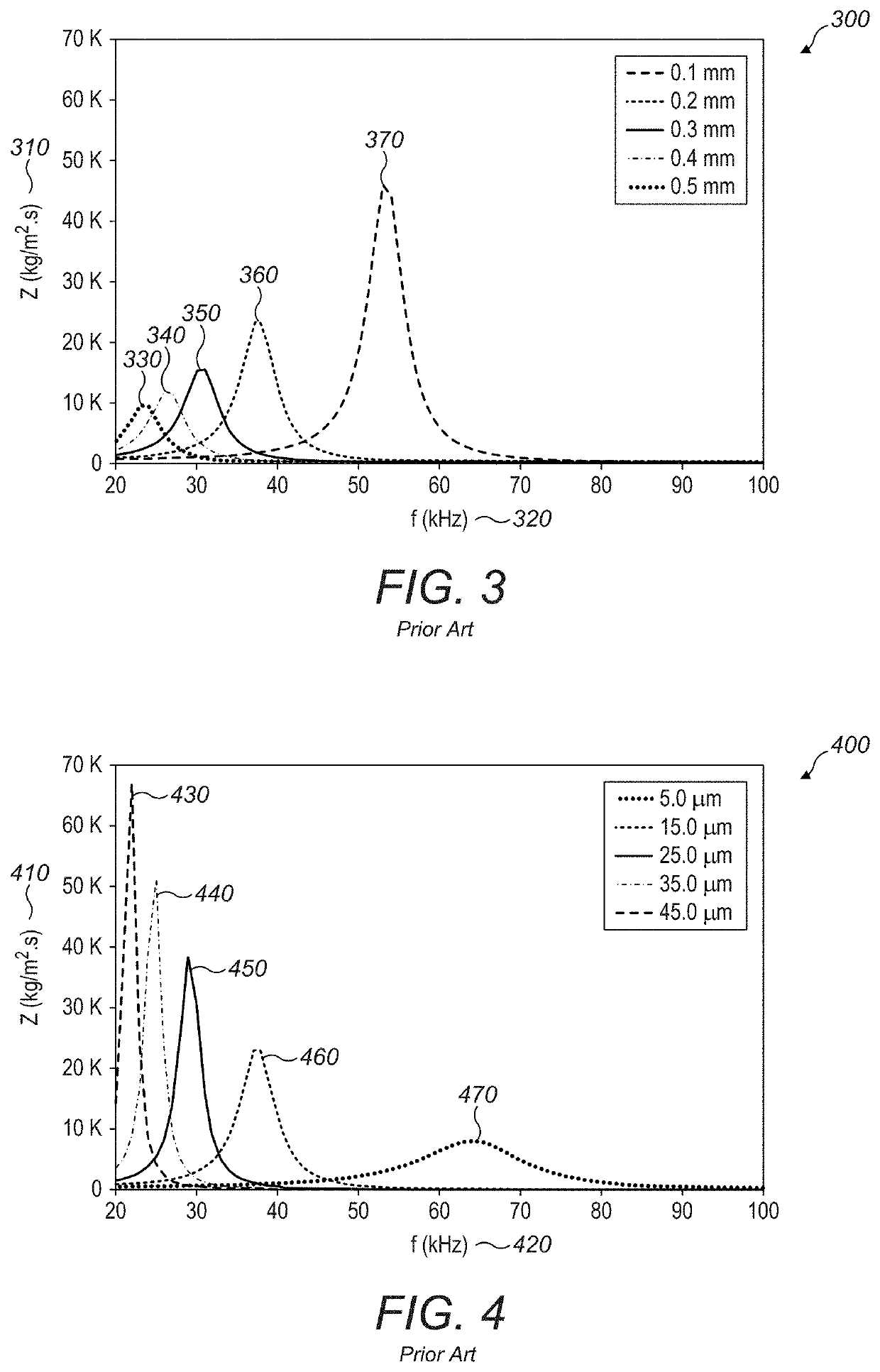
Blocking Plate Structure for Improved Acoustic Transmission Efficiency
ActiveUS20190342654A1Improve transmission efficiencyIncreased Radiation PowerLoudspeaker transducer fixingFlexible member pumpsAcoustic transmissionAcoustic medium
An acoustic matching structure is used to increase the power radiated from a transducing element with a higher impedance into a surrounding acoustic medium with a lower acoustic impedance. The acoustic matching structure consists of a thin, substantially planar cavity bounded by a two end walls and a side wall. The end walls of the cavity are formed by a blocking plate wall and a transducing element wall separated by a short distance (less than one quarter of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium at the operating frequency). The end walls and side wall bound a cavity with diameter approximately equal to half of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium. In operation, a transducing element generates acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity. The transducing element may be an actuator which generates motion of an end wall in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the cavity to excite acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity, and the cavity geometry and resonant amplification increase the amplitude of the resulting pressure oscillation. The cavity side wall or end walls contain at least one aperture positioned away from the center of the cavity to allow pressure waves to propagate into the surrounding acoustic medium.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Conduction cooling of multi-channel flip chip based panel array circuits
ActiveUS8780561B2Gap minimizationImprove thermal conductivityPrinted circuit assemblingDigital data processing detailsSemiconductor chipConduction cooling
A method of forming a heat-dissipating structure for semiconductor circuits is provided. First and second semiconductor integrated circuit (IC) chips are provided, where the first and second semiconductor chips each have first and second opposing sides, wherein the first and second semiconductor IC chips are configured to be fixedly attached to a top surface of a substantially planar circuit board along their respective first sides. The respective second opposing sides of each of the first and second semiconductor IC chips are coupled to first and second respective portions of a sacrificial thermal spreader material, the sacrificial thermal spreader material comprising a material that is thermally conductive. The first and second portions of the sacrificial thermal spreader material are planarized to substantially equalize a respective first height of the first semiconductor chip and a respective second height of the second semiconductor chip.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
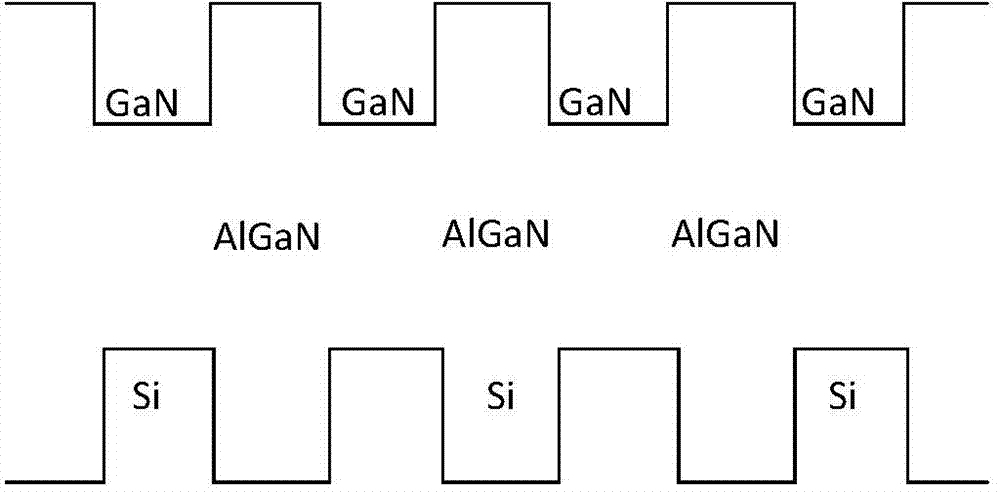
Epitaxial growth method of purple-light LED
InactiveCN103887380AReduce the difficulty of growingIncreased Radiation PowerSemiconductor devicesWavelength rangeCharge carrier
The invention provides an epitaxial growth method of a purple-light LED. The suitable wavelength range of the method is 365-420 nm, the growth difficulty of the purple-light LED can be greatly lowered, meanwhile, the radiation power of the purple-light LED can be increased and the reliability of purple-light LED devices is effectively improved. In the epitaxial growth method, an n-type AlGaN / GaN super lattice structure is adopted, potential-barrier-layer AlGaN and potential-well-layer GaN are doped alternately periodically, and therefore concentration of n-type carriers can be concentrated; the concentration of different layers change periodically, and periodic conductance changes enable currents to be diffused better; meanwhile, the conductance changing area is widened, so that the transmitting effect of an electric leakage channel with linear defects is weakened, forward voltage can be lowered, and ESD can be improved.
Owner:西安利科光电科技有限公司
3G (third-generation) antenna of full-screen intelligent mobile phone and design method of 3G antenna
InactiveCN102694242AReduce volumeImprove performanceSimultaneous aerial operationsAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna designLow frequency band
The invention relates to a design method of a 3G (third-generation) antenna of a full-screen intelligent mobile phone and the corresponding antenna. The design method comprises the steps of arranging a high-frequency circuit and a low-frequency circuit of the antenna on a circuit board, wherein the high-frequency circuit and the low-frequency circuit are isolated through an isolating trough, and adjusting the length and the width of the isolating trough to control resonance between the high-frequency circuit and the low-frequency circuit; and arranging a feed point and a ground point, wherein the ground point is arranged on the external side of the feed point, i.e. close to the side of the circuit board; and after an arranged second isolating trough leads out high-frequency second resonance, adjusting the length or the thickness of the second isolating trough to adjust the low-frequency band of the antenna, so as to match with a radio-frequency power amplifier to realize high frequency and high sensitivity. The antenna designed by adopting the design method provided by the invention has the advantages that the volume is small, the performance is excellent and the problem that the low-frequency radiation power and the low-frequency receiving sensitivity of the antenna are decreased because a method of adding a parasitic element to increase bandwidth is adopted can be effectively avoided.
Owner:HUIZHOU SPEED WIRELESS TECH CO LTD
Device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle
ActiveUS20050075760A1The device operates reliablyImprove applicabilityDigital data processing detailsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsVisibilityDisplay device
The invention relates to a device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle, having a radiation source for infrared radiation for irradiating the surroundings of the vehicle, having an infrared-sensitive camera for taking images of at least part of the irradiated surroundings, having a display unit for displaying collected image data, and having a control unit for controlling the device. Furthermore, a sensing unit for a recommended maximum velocity vmax is provided and is connected to the control unit. A velocity sensor which is connected to the control unit is provided in such a way that the control unit causes the display to be switched off when the vehicle velocity v exceeds the maximum velocity vmax. The display is preferably switched on when the vehicle velocity v drops below the maximum velocity vmax. The sensing unit for a recommended maximum velocity vmax is preferably designed in such a way that the recommended maximum velocity vmax is determined from the road profile or from the driving behavior of the vehicle or from received radio signals. This device ensures that the vehicle with the device operates in a safe way for the user.
Owner:CHEMTRON RES
Modulation method based on elliptically spherical function
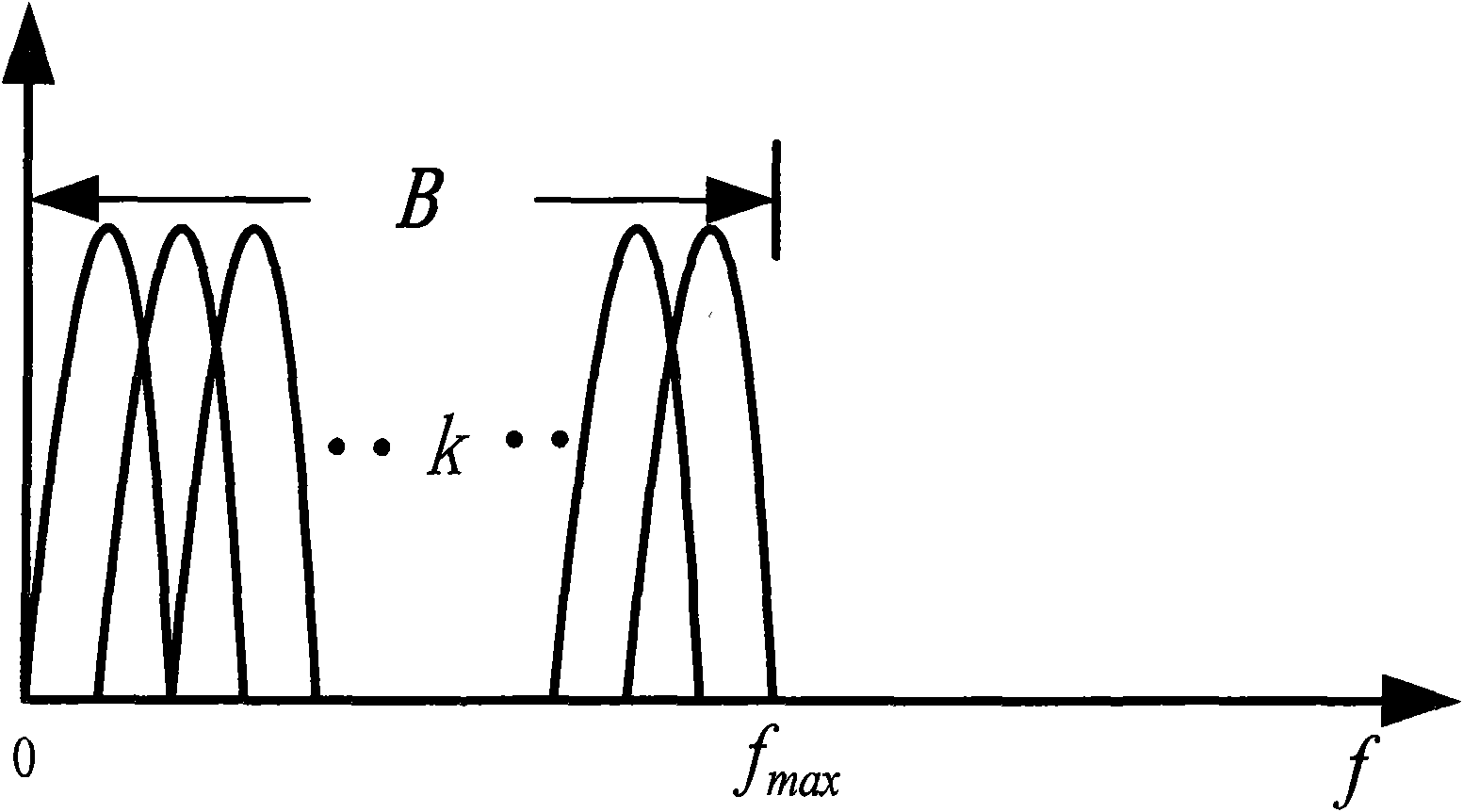
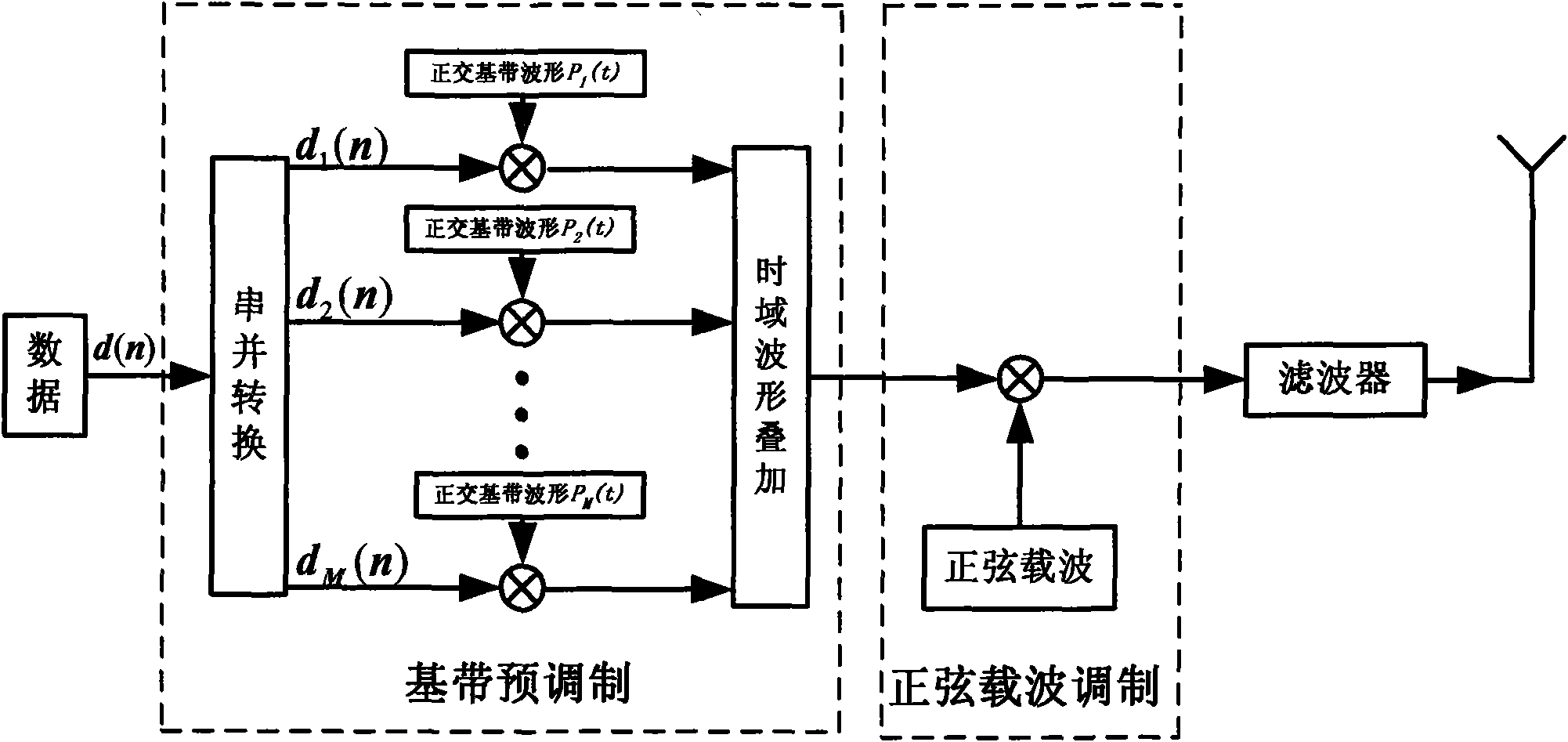
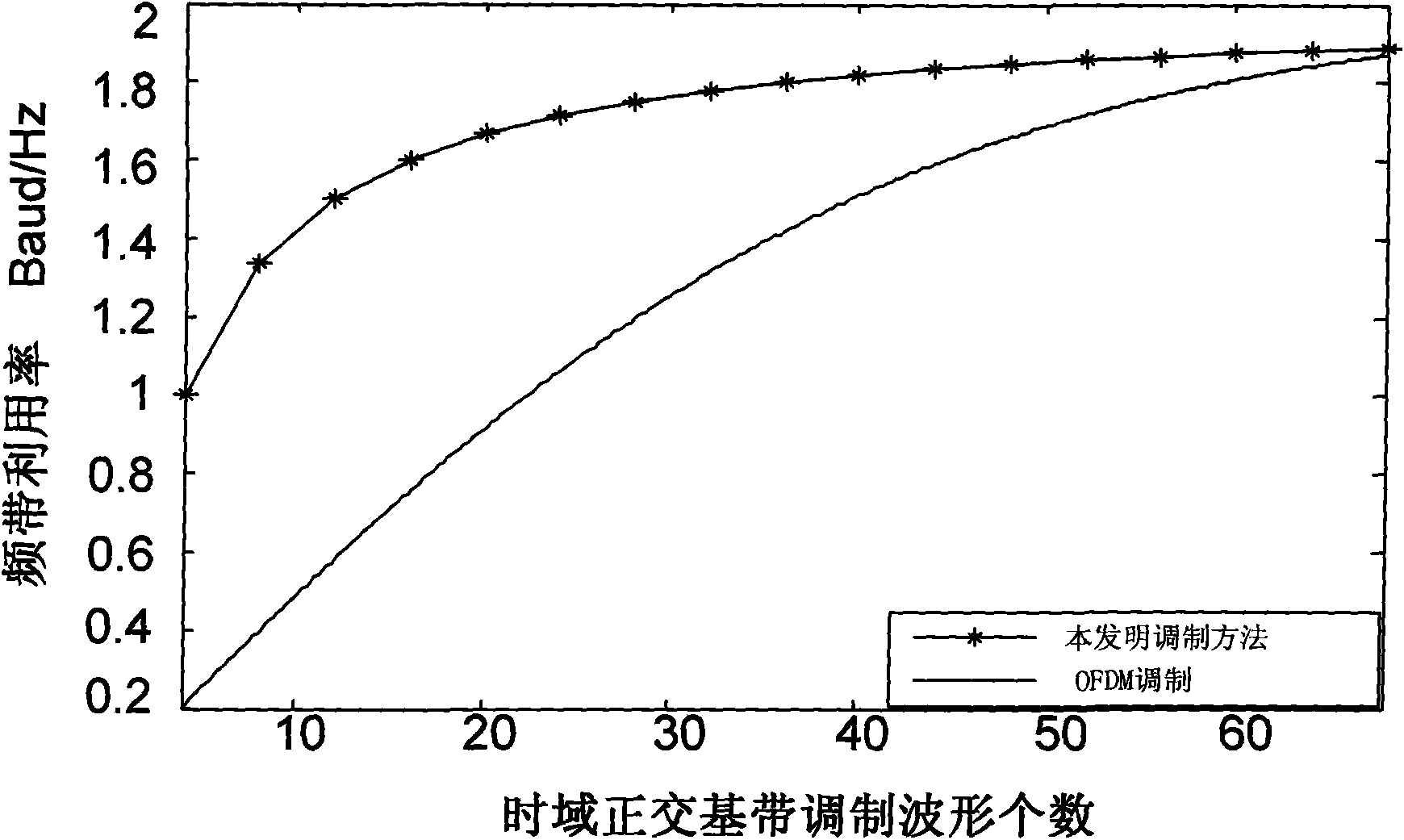
InactiveCN101552751AHigh unit frequency band utilizationImprove aggregation effectAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksFrequency spectrumCarrier signal
The invention provides a modulation method based on an elliptically spherical function. With the design of the multiplexing time-domain orthogonal base band modulation waveform, a multiplexing base band premodulation is carried out. Signals after the base band premodulation at each branch are superimposed and synthesized in a time domain to form a path of signals, and then sine-wave carrier modulation is carried out to move the frequency spectrum of the signal to radiation frequency band and then the frequency spectrum is output. The waveform of the base band modulation adopts the elliptically spherical function with limited time-domain duration time and approximately finite frequency band. The frequency band of a communication system can rapidly approach to the Nyquist rate with the increase in the number of the time-domain orthogonal base band modulation waveform. Simultaneously, the system has better power utilization rate and is convenient and easy to realize.
Owner:中国人民解放军海军航空大学航空作战勤务学院
Blocking Plate Structure for Improved Acoustic Transmission Efficiency
ActiveUS20210170447A1Improve transmission efficiencyIncreased Radiation PowerLoudspeaker transducer fixingFlexible member pumpsAcoustic transmissionAcoustic medium
An acoustic matching structure is used to increase the power radiated from a transducing element with a higher impedance into a surrounding acoustic medium with a lower acoustic impedance. The acoustic matching structure consists of a thin, substantially planar cavity bounded by a two end walls and a side wall. The end walls of the cavity are formed by a blocking plate wall and a transducing element wall separated by a short distance (less than one quarter of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium at the operating frequency). The end walls and side wall bound a cavity with diameter approximately equal to half of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium. In operation, a transducing element generates acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity. The transducing element may be an actuator which generates motion of an end wall in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the cavity to excite acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity, and the cavity geometry and resonant amplification increase the amplitude of the resulting pressure oscillation. The cavity side wall or end walls contain at least one aperture positioned away from the center of the cavity to allow pressure waves to propagate into the surrounding acoustic medium.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
Blocking plate structure for improved acoustic transmission efficiency
ActiveUS10911861B2Improve transmission efficiencyIncreased Radiation PowerLoudspeaker transducer fixingFlexible member pumpsAcoustic transmissionAcoustic medium
An acoustic matching structure is used to increase the power radiated from a transducing element with a higher impedance into a surrounding acoustic medium with a lower acoustic impedance. The acoustic matching structure consists of a thin, substantially planar cavity bounded by a two end walls and a side wall. The end walls of the cavity are formed by a blocking plate wall and a transducing element wall separated by a short distance (less than one quarter of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium at the operating frequency). The end walls and side wall bound a cavity with diameter approximately equal to half of the wavelength of acoustic waves in the surrounding medium. In operation, a transducing element generates acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity. The transducing element may be an actuator which generates motion of an end wall in a direction perpendicular to the plane of the cavity to excite acoustic oscillations in the fluid in the cavity, and the cavity geometry and resonant amplification increase the amplitude of the resulting pressure oscillation. The cavity side wall or end walls contain at least one aperture positioned away from the center of the cavity to allow pressure waves to propagate into the surrounding acoustic medium.
Owner:ULTRAHAPTICS IP LTD
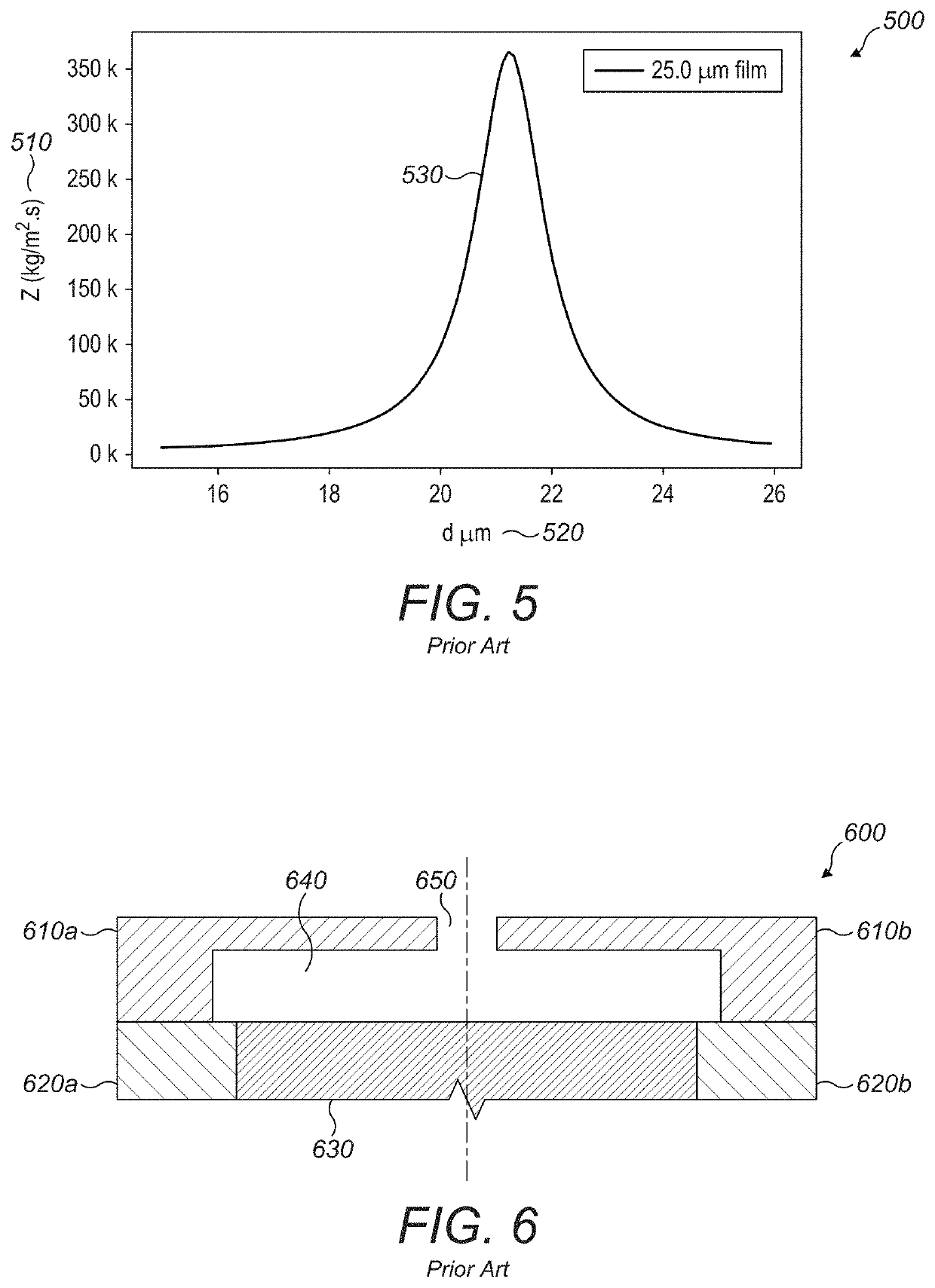
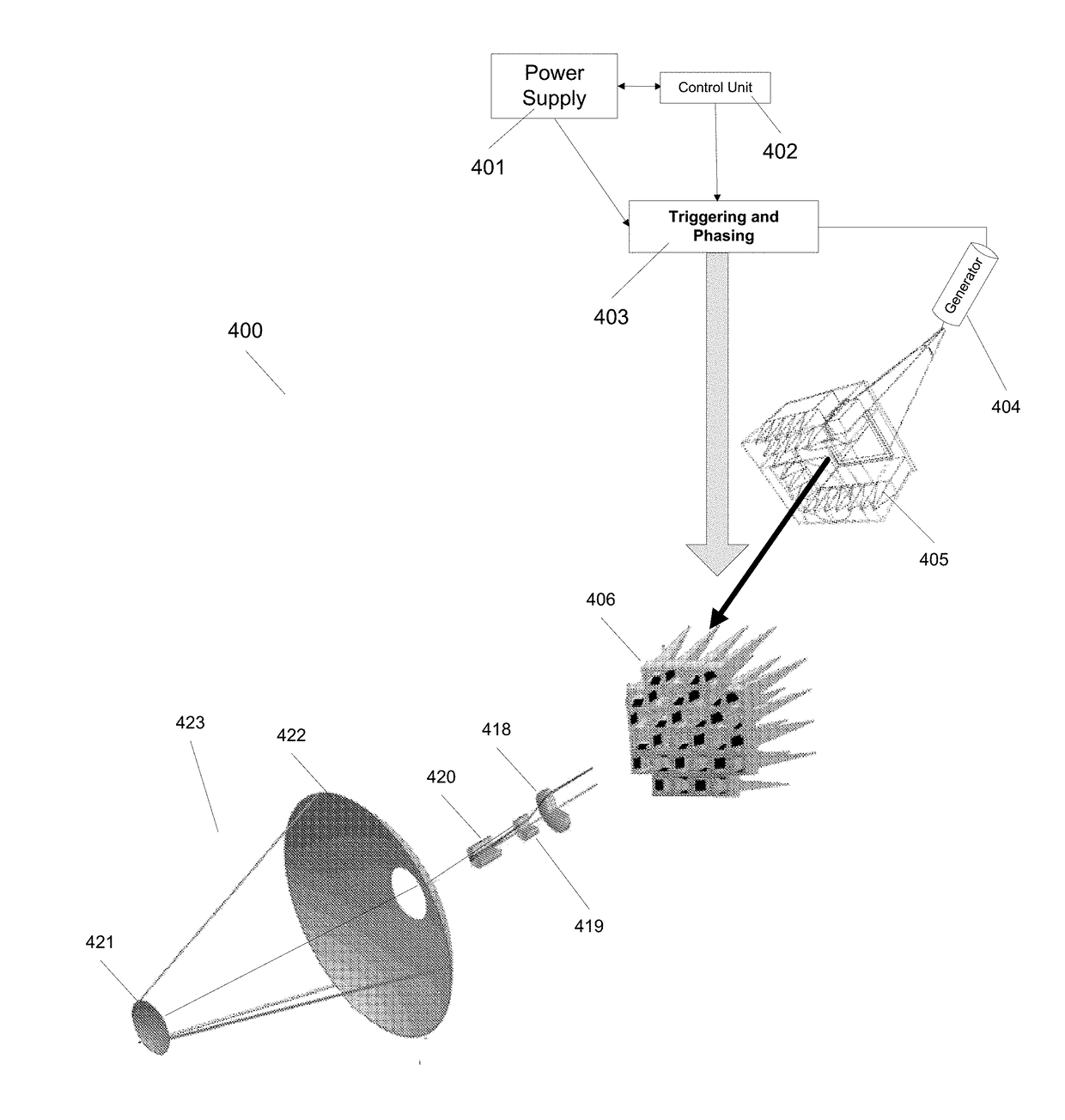
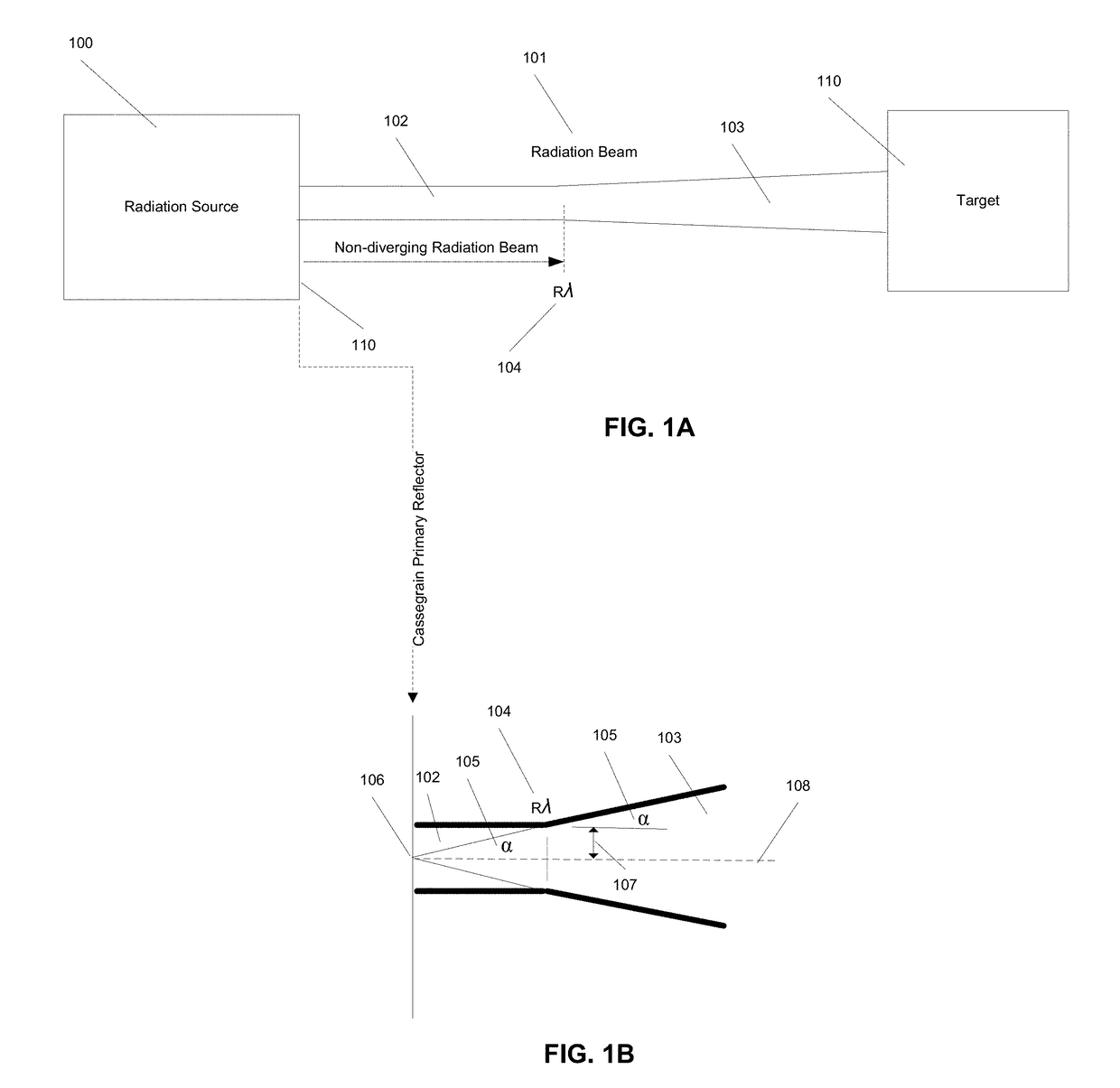
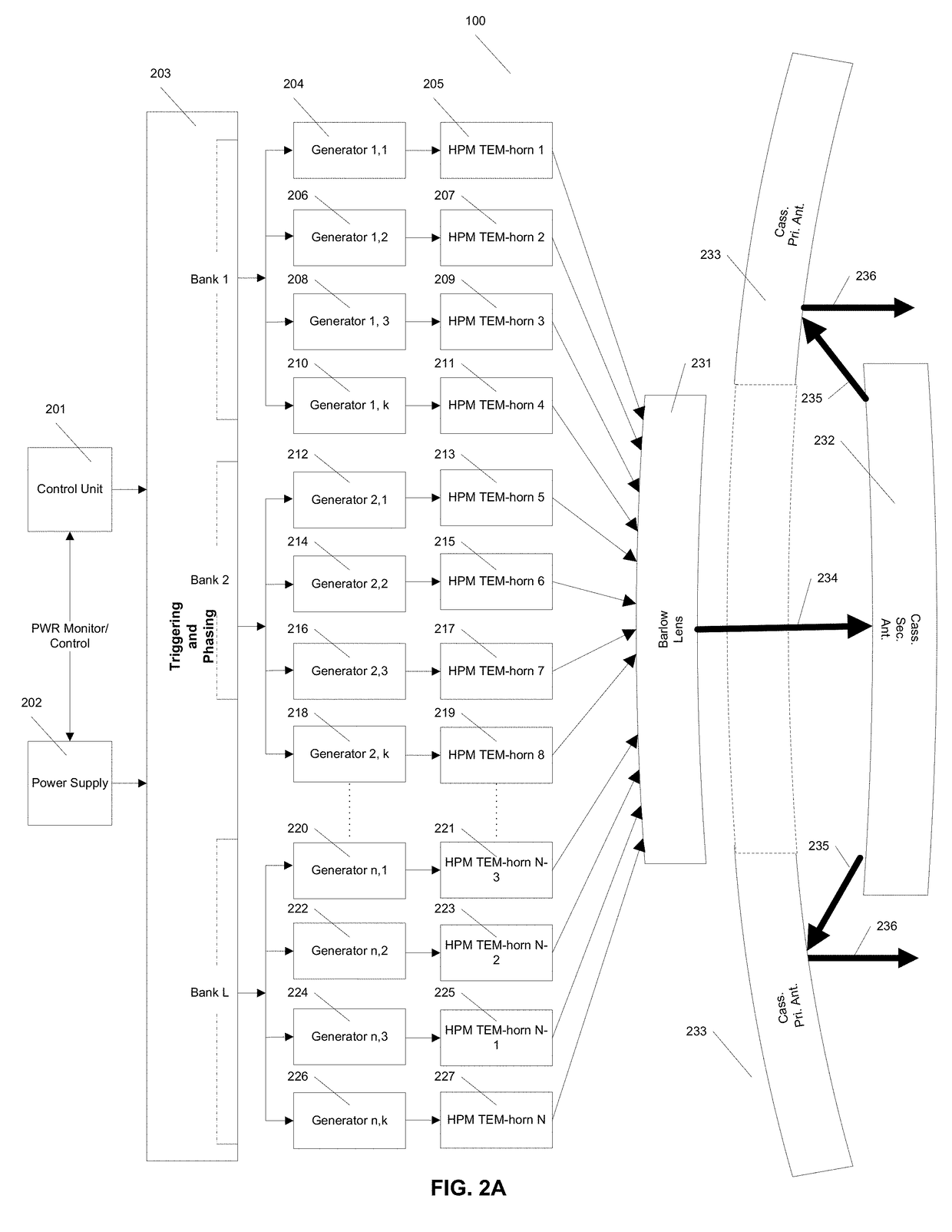
High Power Microwave Weapon System
ActiveUS20180058826A1Reduce ionizationIncreased Radiation PowerWaveguide hornsWeapons typesOptical frequenciesEngineering
This invention allows combining broadband GW(10+9 Watt), peak power to achieve MV / m(10+6 Volt / meter), and GV / m(10+9 Volt / meter), radiated E-fields, in the range of air or vacuum breakdown in the entire electromagnetic spectrum, including optical frequencies and beyond. Use of many antennas and independently triggered generators allows achieving GV / m field, while by preventing the E-field induced breakdown it provides control of peak power and energy content at targets. The achieved broadband MV / m E-field levels and energy density significantly exceed levels required for destruction of distant electronic targets; therefore this invention radically improves the effectiveness of the electromagnetic weapons. Furthermore, collimating multiplicity of MV / m beams allows reaching GV / m E-field that exceeds by orders of magnitude the air or vacuum breakdown needed for broadband plasma excitation at resonance plasma frequencies in the 300 GHz range, permitting energy efficient plasma research leading to fusion.
Owner:PODGORSKI ANDREW STAN
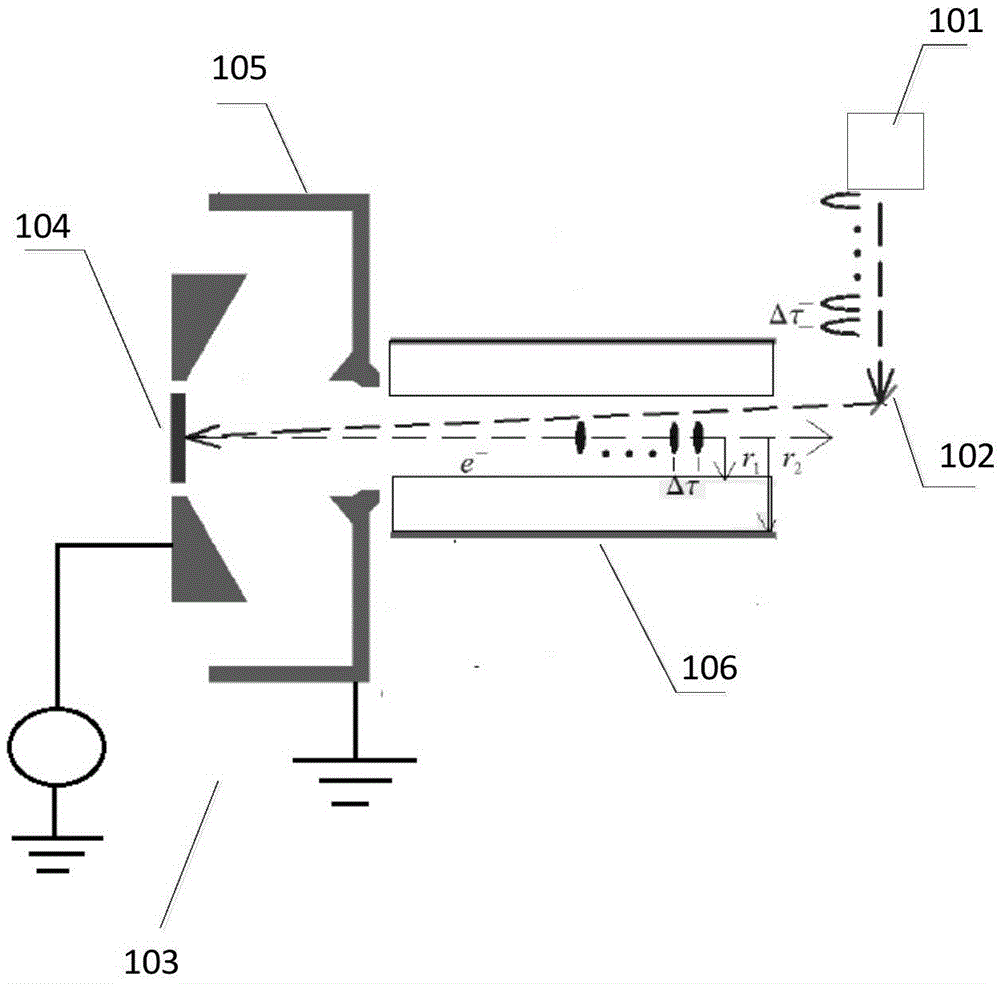
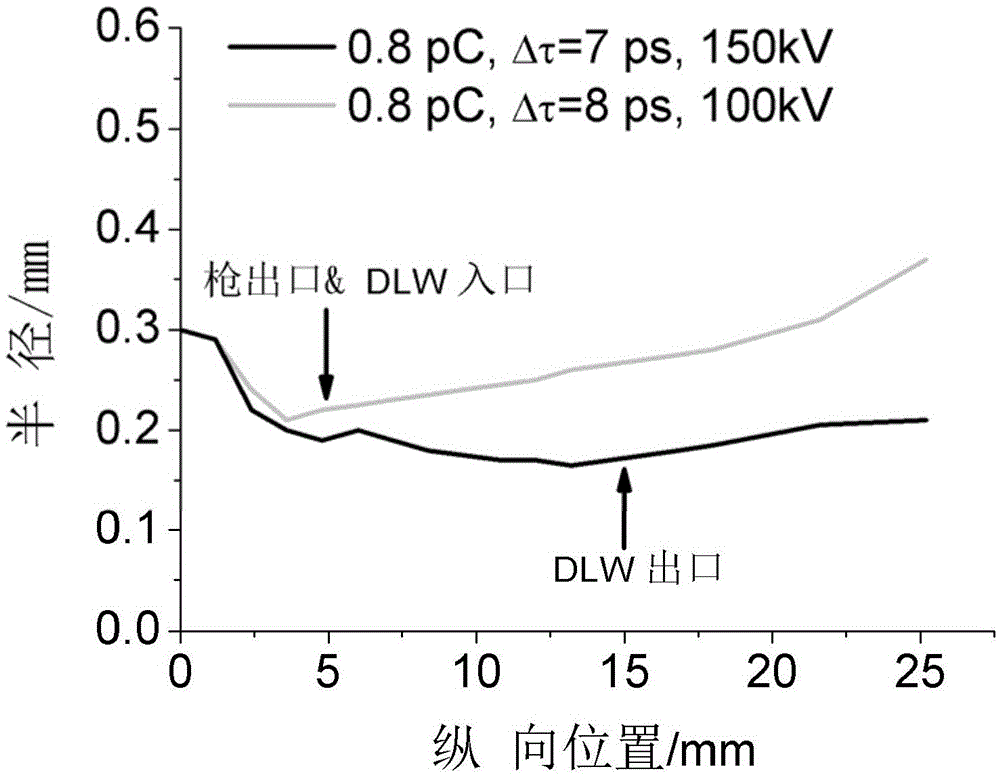
Non-relativistic electron beam induced dielectric waveguide-based terahertz radiation source
ActiveCN105655851AImprove energy conversion efficiencyIncreased Radiation PowerMasersRadiation frequencyResonance
The invention discloses a non-relativistic electron beam induced dielectric waveguide-based terahertz radiation source. The non-relativistic electron beam induced dielectric waveguide-based terahertz radiation source includes a pulse laser light source used for emitting a laser pulse string, a frequency adjusting device used for adjusting the repetition frequency of the laser pulse string, an electron gun and a dielectric waveguide; the cathode of the electron gun is used for absorbing the laser pulse string and transmitting an electron beam cluster string; a size-adjustable electric field formed between the cathode and anode of the electron gun is used for accelerating the emitting of the electron beam cluster string into the dielectric waveguide; the dielectric waveguide is excited by the electron beam cluster string to form terahertz radiation; and the repetition frequency of the laser pulse string and the radiation frequency of the dielectric waveguide form resonance. With the non-relativistic electron beam induced dielectric waveguide-based terahertz radiation source adopted, energy conversion efficiency between the electrons and radiations of the terahertz radiation source can be effectively improved, radiation power can be improved, radiation frequency is adjustable. The cost of the terahertz radiation source can be reduced.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
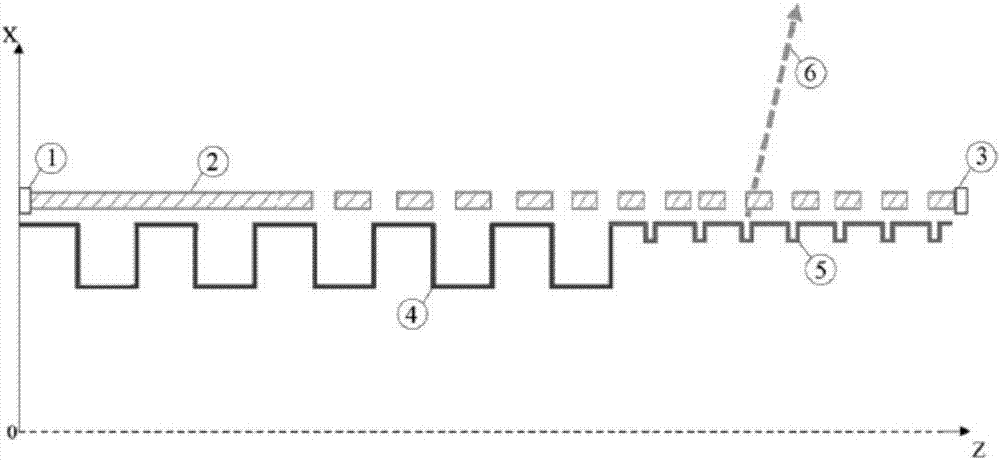
Smith-Purcell electromagnetic radiation source based on two rectangular gratings
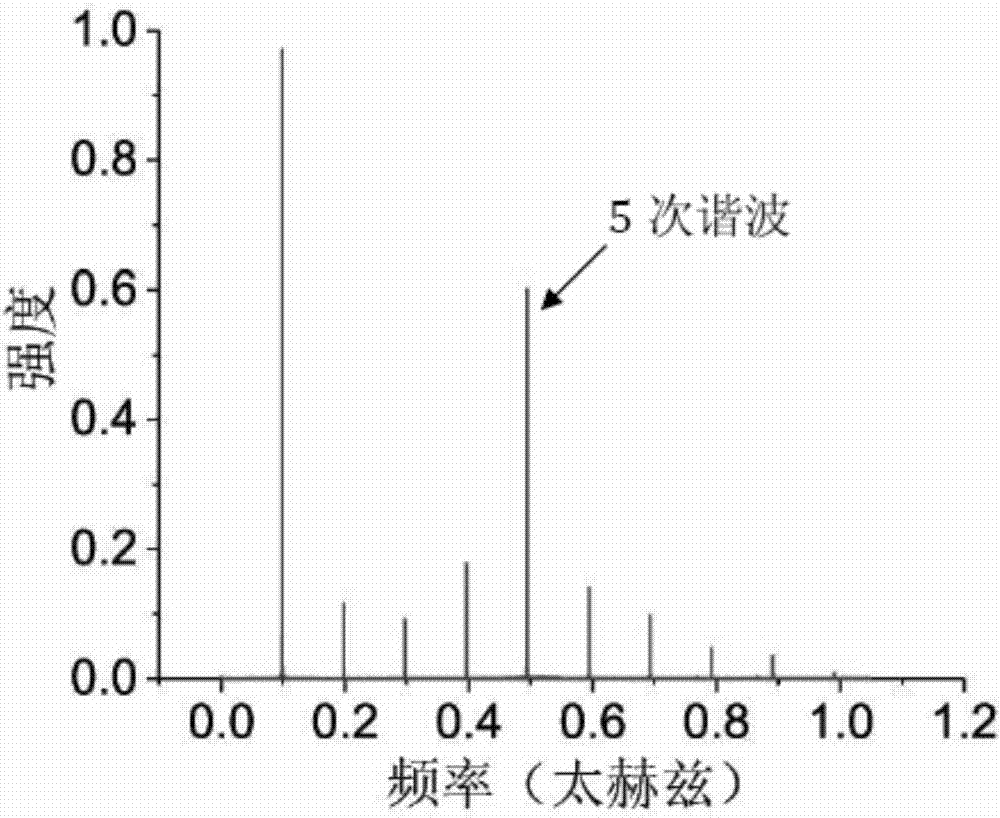
InactiveCN107093538AIncreased radiation frequencyRaise the frequency of radiationTransit-tube electron/ion gunsTransit-tube collectorsFree-electron laserElectromagnetic radiation
The invention discloses a Smith-Purcell electromagnetic radiation source based on two rectangular gratings, which comprises an electron gun used for generating a rectangular ribbon-shaped electron beam, a large-size flat metal rectangular grating, a small-size flat metal rectangular grating and a collecting electrode, and is characterized in that the electron gun is opposite to the collecting electrode, the large-size flat metal rectangular grating and the small-size flat metal rectangular grating are sequentially placed between the electron gun and the collecting electrode, and the distance between the upper surface of the large-size flat metal rectangular grating and the rectangular ribbon-shaped electron beam is equal to the distance between the upper surface of the small-size flat metal rectangular grating and the rectangular ribbon-shaped electron beam; the constant-speed rectangular ribbon-shaped electron beam generated by the electron gun skims over the upper surface of the large-size flat metal rectangular grating and the upper surface of the small-size flat metal rectangular grating and finally gets into the collecting electrode. Compared with a traditional Smith-Purcell free electron laser, the Smith-Purcell free electron laser can be enabled to operate at higher harmonic waves, and the radiation frequency is improved by 2-3 times.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Telemetry ground station pointing calibration method
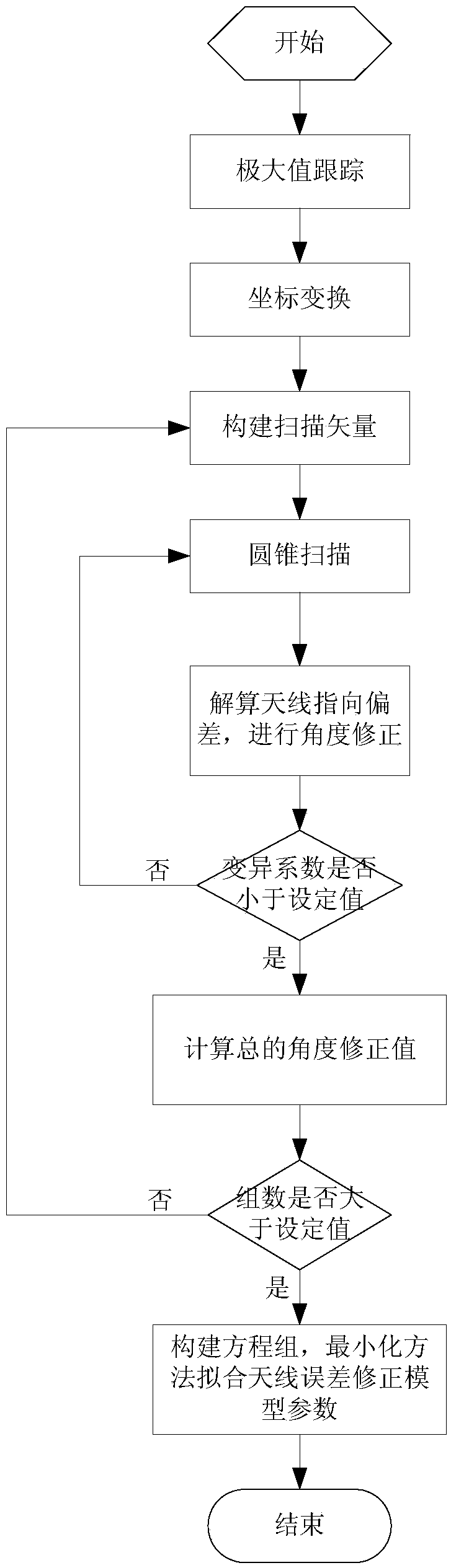
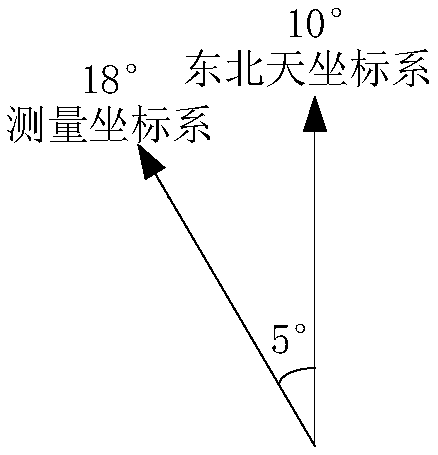
ActiveCN109631945AThe calibration process is simpleSave manpower and material resourcesMeasurement devicesAngular degreesGround station
The invention provides a telemetry ground station pointing calibration method. The method comprises the following steps that firstly, maximum tracking is carried out by utilizing solar radiation powerreceived by an antenna, then an antenna pointing angle is converted from a measurement coordinate system to an east-north-up coordinate system by utilizing the angle of the sun under the east-north-up coordinate system, a vector is scanned by utilizing the direction vector of the sun relative to a measurement and control station at the calibration moment, then an antenna is controlled to carry out cone scanning, iterative calculation is carried out through a solar radiation power variation coefficient so as to obtain a pointing deviation correction value of the corresponding scanning period,moreover, iteration correction is carried out on the antenna pointing direction, and finally, the above processes are repeated at different moments to obtain a plurality of groups of calculation values; and an equation set is constructed by utilizing an antenna pointing error correction model, a plurality of parameters in the error correction model are obtained through a minimization parameter fitting method, and an angle deviation value calculated through the error correction model is the pointing deviation of the antenna each time when the antenna is pointed in the follow-up process.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF TELEMETRY +1
Device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle
InactiveUS20050073431A1Increase awarenessImprove securityAnti-collision systemsCathode-ray tube indicatorsVisibilityDisplay device
The invention relates to a device for improving the visibility conditions in a motor vehicle, having a radiation source for infrared radiation for irradiating the surroundings of the vehicle, having an infrared-sensitive camera for taking images of at least part of the irradiated surroundings, having a display unit for displaying collected image data, and having a control unit for controlling the device. In this context, the control unit is embodied in such a way that, while the device is operating, the display represents image data in a chronologically limited fashion by means of controlled switching on and switching off, and in the process the switching off of the representation of images on the display is made gradual. The gradual switching off is carried out in particular by changing the brightness limiting values, the contrast limiting values and / or by increasing or reducing the noise of the image data to be represented. Furthermore, the gradual switching off preferably has a time-dependent or velocity-dependent profile. This device ensures that the vehicle with the device operates in a very safe way for the user.
Owner:DAIMLER AG
Terahertz photoconductive phased-array antenna system
ActiveCN106450750AIncreased Radiation PowerImprove controllabilityAntenna arraysAntennas earthing switches associationDelayed timeOptical fiber coupler
The invention relates to a terahertz photoconductive phased-array antenna system. The system comprises a laser source, an optical fiber coupler, a light delay controller and a terahertz photoconductive array antenna, wherein the optical fiber coupler is used for coupling the pump light generated by the laser source into an optical fiber; the light delay controller is used for controlling the delaying time of the pump light outputted by the optical fiber coupler and generating N beams of pump light at different delaying time; N is a natural number more than 1; the terahertz photoconductive array antenna is used for receiving the N beams of pump light at different delaying time outputted by the light delay controller; each beam of pump light is focused and irradiated on a corresponding bias antenna unit and then the terahertz irradiation is stimulated and generated. According to the terahertz photoconductive phased-array antenna system, the light delay controller is introduced into a pump light path of the photoconductive antenna array and the radiation phase is controlled so as to increase the radiation power of the array antenna and change the direction angle of the wave beam.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
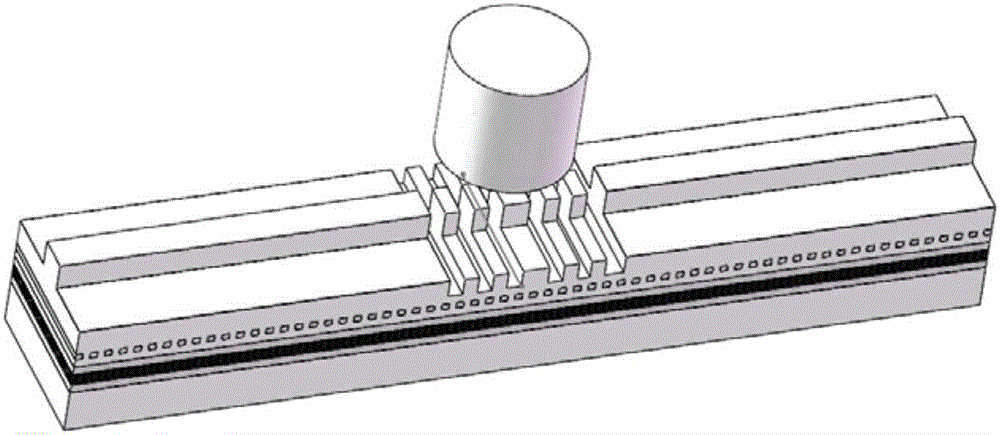
Terahertz radiation source based on special Smith-Purcell effect
ActiveCN105826150ALow densityCompact structureTubes with velocity/density modulated electron streamTransit-tube circuit elementsGratingTerahertz radiation
The invention discloses a terahertz radiation source based on a special Smith-Purcell effect. The terahertz radiation source comprises an electronic gun (1), metal rectangular gratings (3), a collector (4), a metal flat reflector (6) and an output port (8), wherein the electronic gun (1) is opposite to the collector (4), the metal rectangular gratings (3) are arranged between the electronic gun (1) and the collector (4), the metal flat reflector (6) is disposed above the metal rectangular gratings (3), and the output port (8) is arranged at the metal flat reflector (6). According to the invention, the oscillation-starting current density of an electron beam can be substantially reduced, through adjusting the distance from the reflector to the gratings, the terahertz radiation source can work at a lowest mold or a secondary mode in a controllable way, the structure is simple, required work voltages are low, huge external additional equipment is unnecessary, and miniaturization and integration are quite easily realized.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Metallic Layer-by-Layer Photonic Crystals for Linearly-Polarized Thermal Emission and Thermophotovoltaic Device Including Same
ActiveUS20100294325A1Overcome problemsIncreased Radiation PowerRadiation pyrometryPV power plantsGratingPhotonics
Metallic thermal emitters consisting of two layers of differently structured nickel gratings on a homogeneous nickel layer are fabricated by soft lithography and studied for polarized thermal radiation. A thermal emitter in combination with a sub-wavelength grating shows a high extinction ratio, with a maximum value close to 5, in a wide mid-infrared range from 3.2 to 7.8 μm, as well as high emissivity up to 0.65 at a wavelength of 3.7 μm. All measurements show good agreement with theoretical predictions. Numerical simulations reveal that a high electric field exists within the localized air space surrounded by the gratings and the intensified electric-field is only observed for the polarizations perpendicular to the top sub-wavelength grating. This result suggests how the emissivity of a metal can be selectively enhanced at a certain range of wavelengths for a given polarization.
Owner:IOWA STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Double-electron-beam double-grating based terahertz free electron laser source
ActiveCN105938972ACompact structureEasy to implementExcitation process/apparatusResonant cavityGrating
The invention relates to a double-electron-beam double-grating based terahertz free electron laser source. The laser source comprises two groups of electron guns, metal rectangular gratings and collectors with totally-consistent parameters; the two electron guns are corresponding to the two collectors respectively; one metal rectangular grating is positioned between the corresponding electron gun and the correcting collector on one side while the other metal rectangular grating is positioned between the corresponding electron gun and the correcting collector on the other side; the two metal rectangular gratings are symmetrical; and a variable open resonant cavity is formed by the two metal rectangular gratings. The uniform-velocity band-shaped electron beams generated by the electron guns skim over the surfaces of the metal rectangular gratings and finally enter the collectors; the two electron beams generate two special Smith-Purcell radiating waves along the perpendicular direction on the surfaces of the metal rectangular gratings respectively; the two special Smith-Purcell radiating waves are reflected back and forth between the two metal rectangular gratings to form a resonant mode in the open resonant cavity, and are converted into electromagnetic wave energy; and the electromagnetic wave energy is amplified and finally output through a port.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Terahertz wave generator based on graphene
PendingCN106299979AIncreased Radiation PowerIncrease antenna gainSolid masersAntenna gainEngineering
The invention discloses a terahertz wave generator based on graphene. The teraHertz wave generator comprises a substrate, a graphene film and a terahertz photoconductive antenna, wherein the graphene film is formed on the substrate and the terahertz photoconductive antenna is used for coupling Sierpinski fractal geometrical shape of the terahertz wave. According to the invention, bar-shaped electrodes are arranged at the two ends of inverse fractal antenna; a bias voltage is applied between the electrodes; the graphene film is pumped through femtosecond pulse laser; the electron motion in the graphene film is excited; the terahertz wave is irradiated under the effect of the bias voltage; the terahertz wave is coupled with the free space through the photoconductive antenna. Due to the high electronic mobility and the characteristic of easily generating terahertz wave of the graphene and the coupling function of the photoconductive antenna with similar characteristic, the emission efficiency of terahertz wave is increased, the antenna gain is increased, the power consumption and propagation loss of the antenna are reduced and the radiant power of the terahertz wave is increased.
Owner:郭玮
THz radiation reinforcing method through light line array
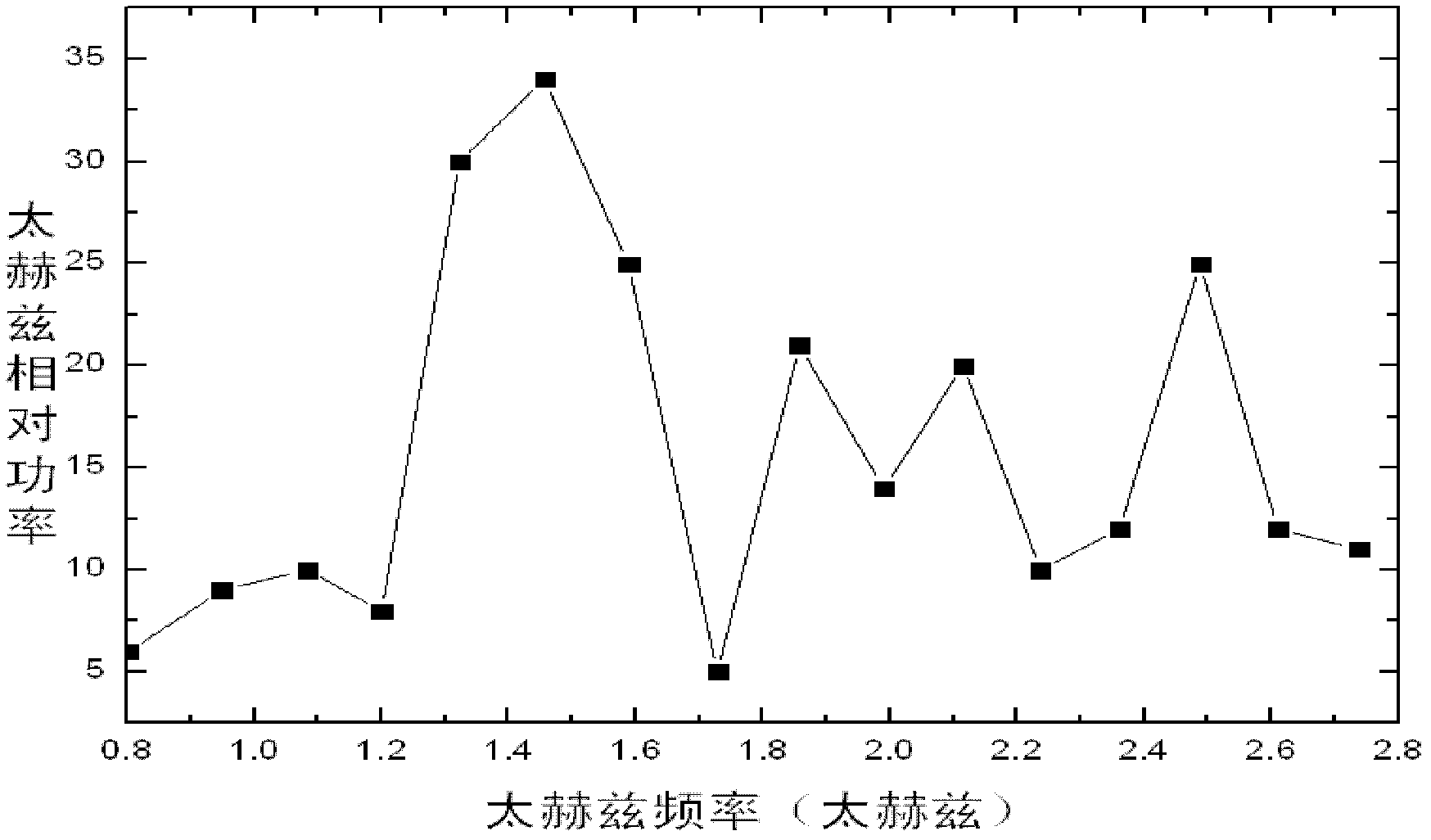
ActiveCN103411903AIncreased Radiation PowerHigh light wave powerOptical detectionColor/spectral properties measurementsFemto second laserMechanical engineering
The invention relates to a THz radiation reinforcing method through a light line array, which comprises the following steps: calibrated femtosecond laser are focused by a focusing lens to generate light line; a BBO crystal is mounted behind the focusing lens to generate a two-color field; a step-type phase plate is mounted in front of the focusing lens to generate controllable light line array to reinforce the THz radiation. Compared with the conventional THz radiation reinforcing method, the method provided by the invention has the advantage that a simple, compact, and feasible structure is provided; the generated THz is impulse light wave, has higher average power and signal-to-noise ratio compared with THz generated without the phase plate, and can be applied to THz remote detection; the THz radiation reinforcing method can reinforce THz radiation power, increases the signal-to-noise ratio, and can be applied to THz spectral analysis.
Owner:天津理特光电科技有限公司
Space-borne plasma antenna generation and emission device and communication method
ActiveCN103730723AImprove mobilityIncrease flexibilityRadiating elements structural formsPlasma jetPlasma antenna
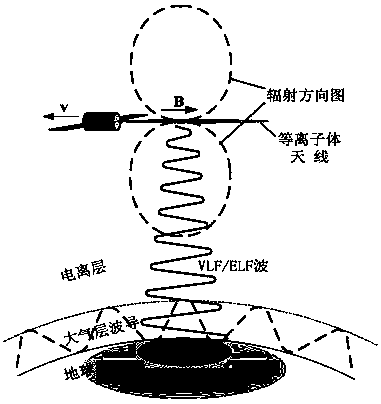
The invention relates to a space-borne plasma antenna generation and emission device and a communication method. The device comprises a discharge tube, solenoid coils, an antenna, an air chamber, a radio frequency (RF) power source, a VLF / ELF wave feed source and a matching network. Space-borne plasma antenna submarine communication is used, and super-long plasma jet flows are jetted from a low-orbit satellite to be used as the VLF / ELF transmitting antenna, so that the device has high elusiveness, flexibility and maneuverability, weaknesses of foundation / shore-based submarine communication are prevented, and communication requirements of strategic nuclear submarines are fully met.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF SPACECRAFT ENVIRONMENT ENG
Tunable, superconducting, surface-emitting teraherz source
InactiveUS20070244012A1Enhances active surface areaIncreased Radiation PowerSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-stateJosephson vortex
A compact, solid-state THz source based on the driven Josephson vortex lattice in a highly anisotropic superconductor such as Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8 that allows cw emission at tunable frequency. A second order metallic Bragg grating is used to achieve impedance matching and to induce surface emission of THz-radiation from a Bi2Sr2CaCu2O8 sample. Steering of the emitted THz beam is accomplished by tuning the Josephson vortex spacing around the grating period using a superimposed magnetic control field.
Owner:UCHICAGO ARGONNE LLC
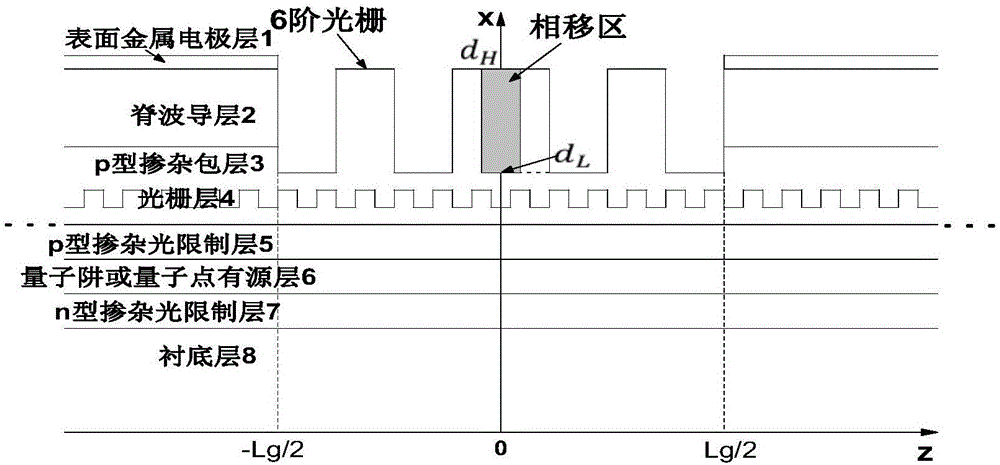
High-order surface grating surface-emitting semiconductor laser
ActiveCN106848836AImprove production efficiencyReduce manufacturing difficultyLaser optical resonator constructionResonant cavityPhase shifted
The invention discloses a high-order surface grating surface-emitting semiconductor laser. The laser comprises a surface metal electrode layer, a ridge waveguide layer, a p-type doped cladding layer, a grating layer, a p-type doped optical confinement layer, a quantum well or quantum dot active area, an n-type doped optical confinement layer and a substrate layer, which are sequentially arranged, wherein a first-order grating is distributed on the grating layer; a high-order surface grating for coupling optical energy resonating along the horizontal direction to the perpendicular direction for output is distributed above the first-order grating in the center of a resonant cavity. The length of the high-order surface grating positioned above the grating layer in the center of the resonant cavity of the laser is (9 to 100) microns. A traveling wave mode in the resonant cavity of the laser is coupled into a radiation mode to realize surface output of laser by the high-order surface grating. The surface output light of the laser is directly coupled with a fiber core of a standard single-mode optical fiber. A segment of central phase shift is introduced into the center of the high-order surface grating, so that the coupling efficiency of the high-order surface grating surface-emitting laser and the standard single-mode optical fiber can exceed 50 percent.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Measuring transducer for obtaining position data and method for its operation
InactiveUS20130264472A1Increase tolerance of mechanicalImprove reliabilityMaterial analysis by optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyTransducerLight source
A measuring transducer for obtaining position data, with a transmit / receive unit having a plurality of light sources for scanning a dimensional scale, wherein the transmit / receive unit includes several light sources, in particular at least one light source having a plurality of emitters.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Epitaxial structure of near-infrared VCSEL laser and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN107093841AIncreased Radiation PowerImprove response rateLaser detailsLaser active region structureOhmic contactActive layer
The invention provides an epitaxial structure of a near-infrared VCSEL laser. The structure comprises a GaAs substrate. A GaAs buffer layer, an N-type doped DBR, an active layer, an oxidation limiting layer, a P-type doped DBR and an ohmic contact layer are successively deposited on the GaAs substrate. The active layer successively comprises a limiting layer, a waveguide layer, a quantum well, a symmetrical waveguide layer and a symmetrical limiting layer. The quantum well is formed by multiple groups of quantum well layers. A thick barrier layer is arranged between the two adjacent groups of quantum well layers. A thickness of the thick barrier layer is greater than 50nm. In the epitaxial structure of the near-infrared VCSEL laser, through inserting the plurality of thick barrier layers in an active area quantum well, leakage losses of a carrier are reduced, a compound probability of an active area carrier is increased, a differential gain of the active area is improved and radiation power of the VCSEL laser is increased. Simultaneously, a limiting factor of active area photon is increased and a response rate of the VCSEL laser is improved.
Owner:张永
Angle tuning-free THz collinear difference frequency radiation system based on cadmium telluride
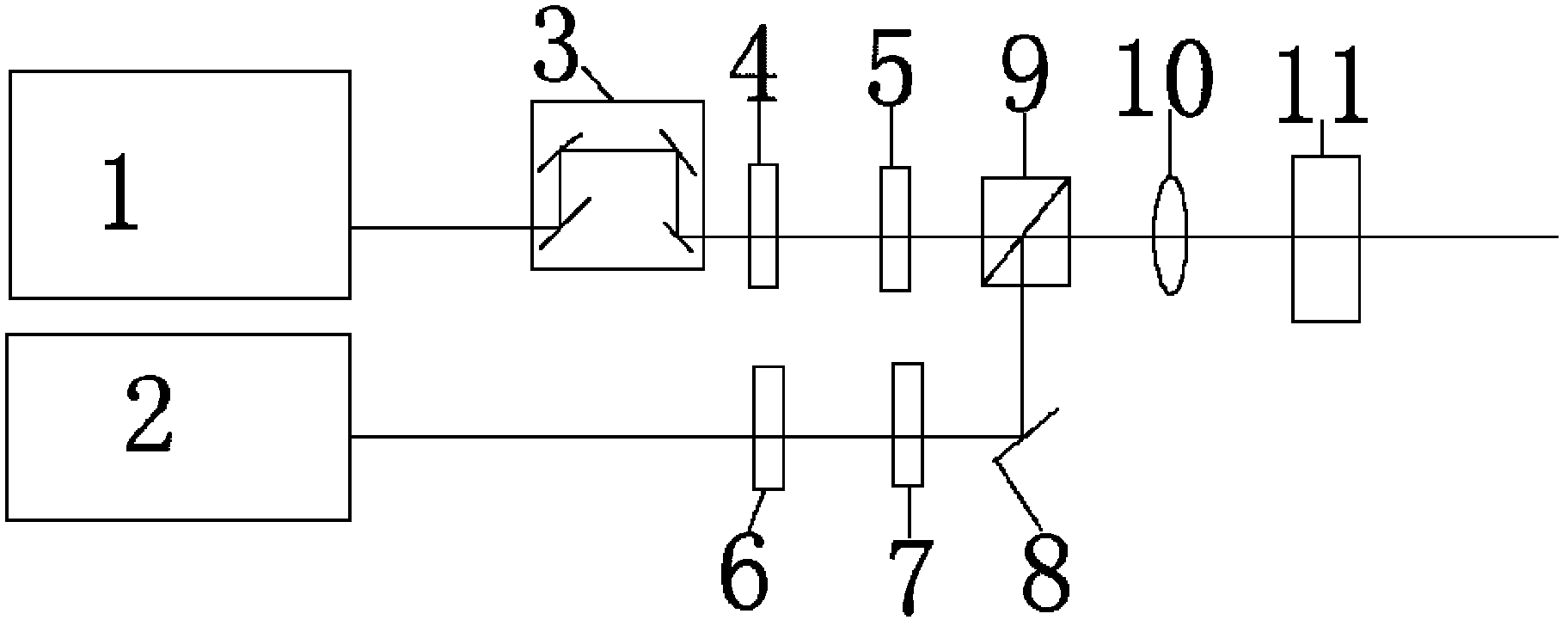
InactiveCN102570247AReduce the difficulty of operationImprove stabilitySolid masersNon-linear opticsBirefringent crystalLine width
The invention discloses an angle tuning-free nanosecond laser collinear difference frequency THz radiation system based on cadmium telluride crystals. The system can achieve THz light radiation without angle tuning by particularly using the principle of nonlinear optical collinear difference frequency and quasi-phase matching technology, and the wavelength tuning range of the system is 0.80THz to 2.74THz. The system not only has the characteristics of high power, quasi-continuity, narrow line width, room temperature operation and so on, but also has the advantages of convenient wavelength tuning by only tuning the output wavelength of a tunable laser, high easiness in adding an external infrared resonant cavity, compact structure, easy construction, high system stability, high convenience for actual large-scale application and so on in comparison with a radiation system using birefringent crystals as THz crystals and a parametric oscillation source based on lithium niobate crystals.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECHNICAL PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mercury-free metal halide high-pressure discharge lamp
InactiveUS20090230867A1Accelerate evaporationIncreased Radiation PowerSolid cathode detailsGas discharge lamp detailsNoble gasHalogen
A mercury-free metal halide high pressure discharge lamp having a transparent and gastight sealed discharge vessel and two electrodes which protrude into the discharge vessel and are arranged in the discharge vessel opposite one another, with the discharge vessel being filled with a lamp filling which has: at least one noble gas, at least the elements of iron and zinc, as well as at least one halide, with the halide comprising bromide, and with the percentage of the bromide being at least 14 mole percent of the total halogen quantity and the following relationship applying to the ratio of molar density of zinc D in μmol / cm3 and electric field strength E in V / cm between the electrodes: 0.005≦D / E≦0.200.
Owner:BLV LICHT UND VAKUUMTECHNIK GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com