Double-electron-beam double-grating based terahertz free electron laser source
A double electron injection and double grating technology, applied in the field of vacuum electronics, can solve the problem of low radiation power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
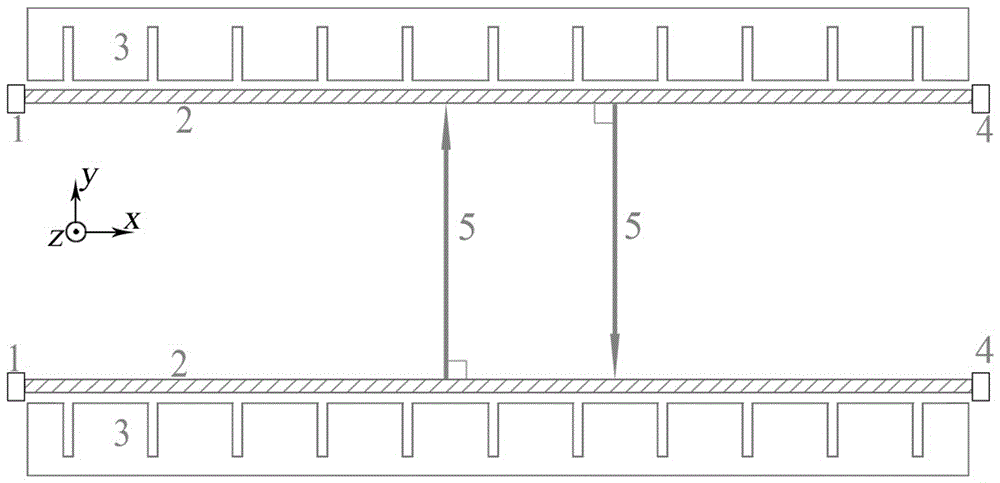
[0035] see figure 1 , a terahertz free electron laser source based on double electron injection and double gratings includes two sets of electron guns 1 with identical parameters, metal rectangular gratings 3 and collectors 4 . The two electron guns 1 correspond to the two collectors 4 respectively, a metal rectangular grating 3 is located between the electron gun 1 and the collector 4 on one side, and the other metal rectangular grating 3 is located between the electron gun 1 and the collector on the other side 4, two metal rectangular gratings 3 are symmetrical; the two metal rectangular gratings 3 form a variant open resonant cavity.
[0036] In this embodiment, the terahertz free electron laser source works in the fundamental mode, the radiation frequency is 0.32THz, and the radiation power is 10W.
[0037] The working parameters of the terahertz free electron laser source in this embodiment are as follows: the grating period is 0.13 mm, the gap width between the grating ...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The structure of the terahertz free-electron laser source based on double-electron injection and double-grating is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0042] In this embodiment, the terahertz free electron laser source works in the secondary mode, and the radiation frequency is 0.96 THz.
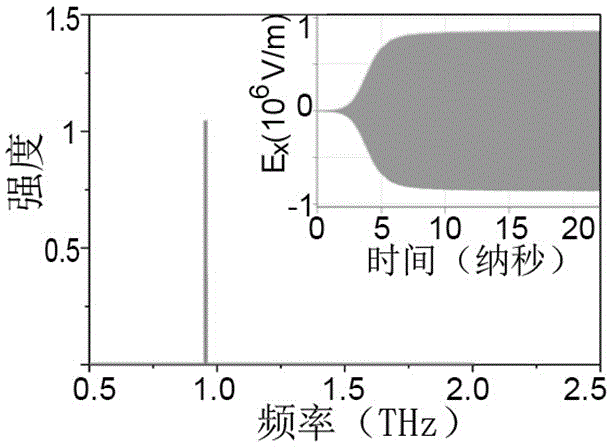
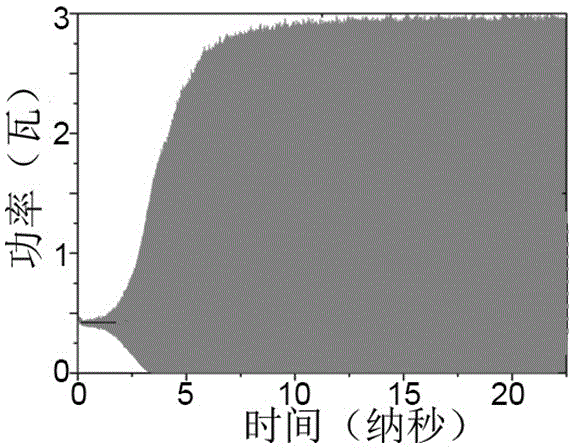
[0043] The specific implementation parameters and simulation results of this embodiment are as follows: the grating period is 0.13 mm, the gap width between the grating comb teeth is 0.013 mm, the grating comb tooth depth is 0.215 mm, and the distance between the two gratings is 2.2 mm; the cross-sectional size of the electron beam is 1mm*0.1mm, the electron beam acceleration voltage (i.e. working voltage) is 5 kV, and the current density is 50 amperes per square centimeter. figure 2 is the time-domain diagram and spectrum of the radiation field obtained by simulation, at this time, image 3 The time-domain diagram of the radiated power obtained by simulation shows that the average ...
Embodiment 3
[0045] The structure of the terahertz free-electron laser source based on double-electron injection and double-grating is the same as that in Embodiment 1.
[0046] In this embodiment, the terahertz free electron laser source works in the secondary mode, and the radiation frequency is 1.36 THz.
[0047] The specific implementation parameters and simulation results of this embodiment are as follows: the grating period is 0.1 mm, the gap width between the grating comb teeth is 0.01 mm, the grating comb tooth depth is 0.15 mm, and the distance between the two gratings is 1.8 mm; the electronic beam cross-sectional size is 1mm*0.1mm, the electron beam acceleration voltage (i.e. working voltage) is 6 kV, and the current density is 30 amperes per square centimeter. Figure 4 is the simulated radiation field diagram and spectrum, Figure 5 For the radiation power time domain diagram obtained by simulation, it can be seen that the average radiation power is about 1W.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Gap width | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com