Patents
Literature
1203results about "Excitation process/apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
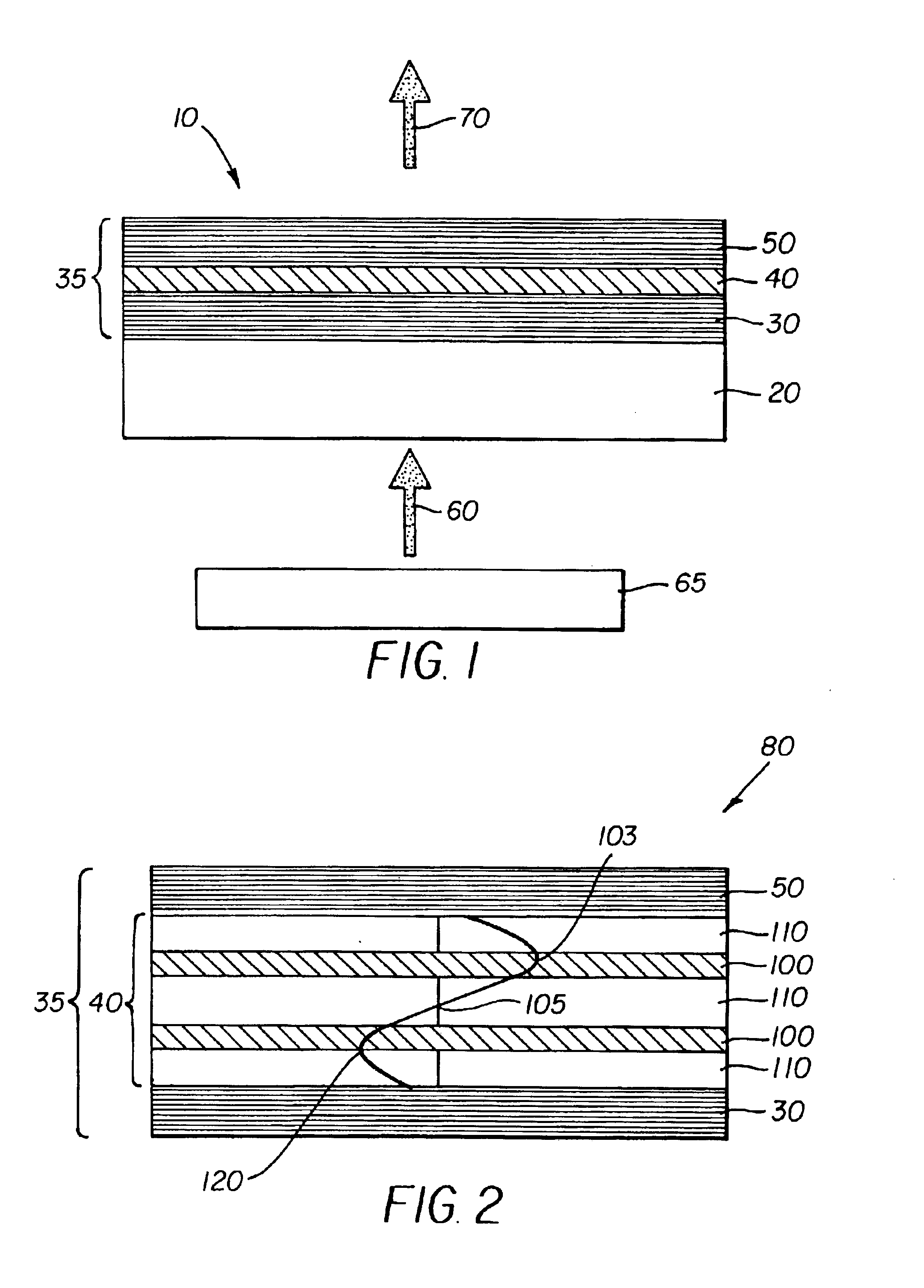
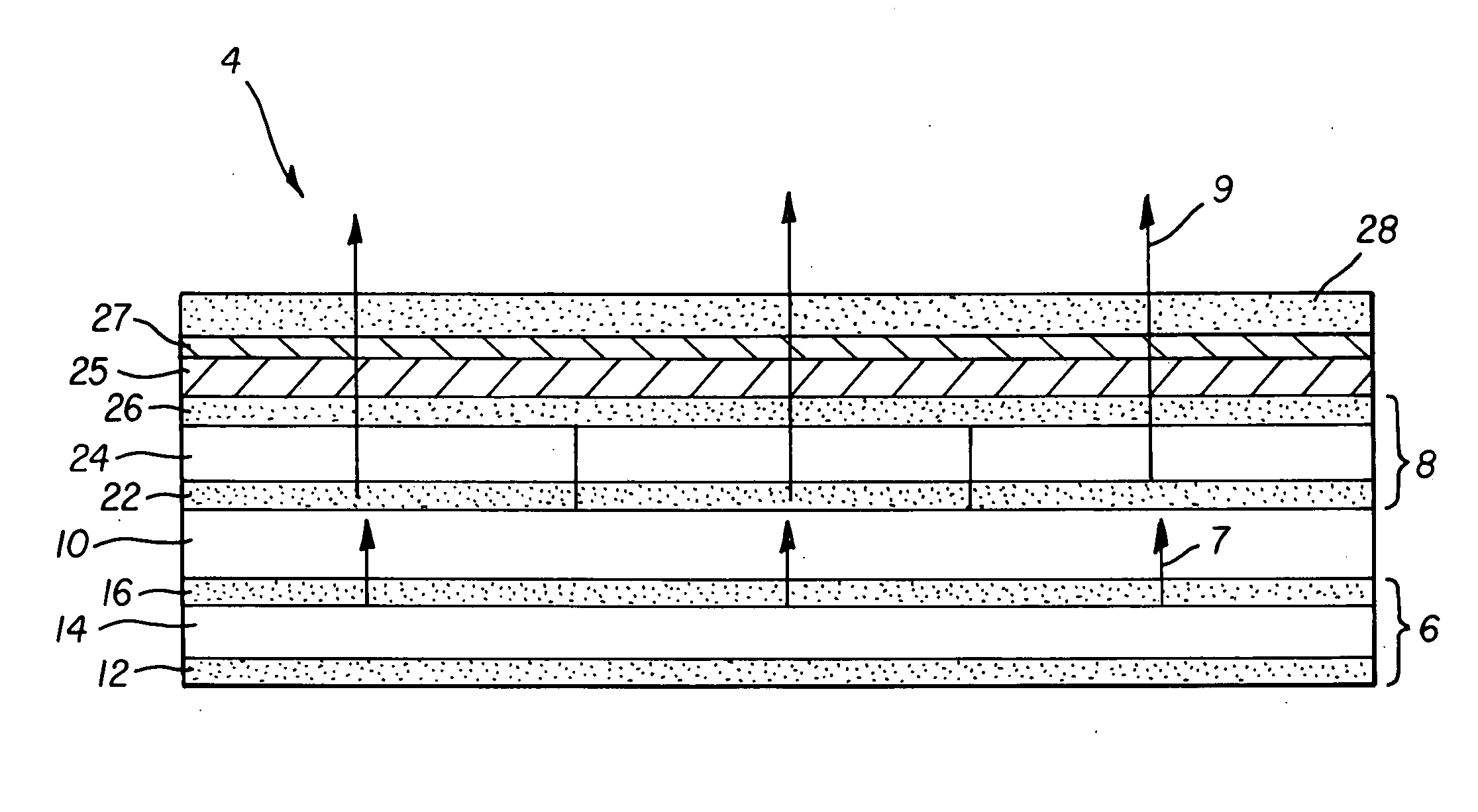
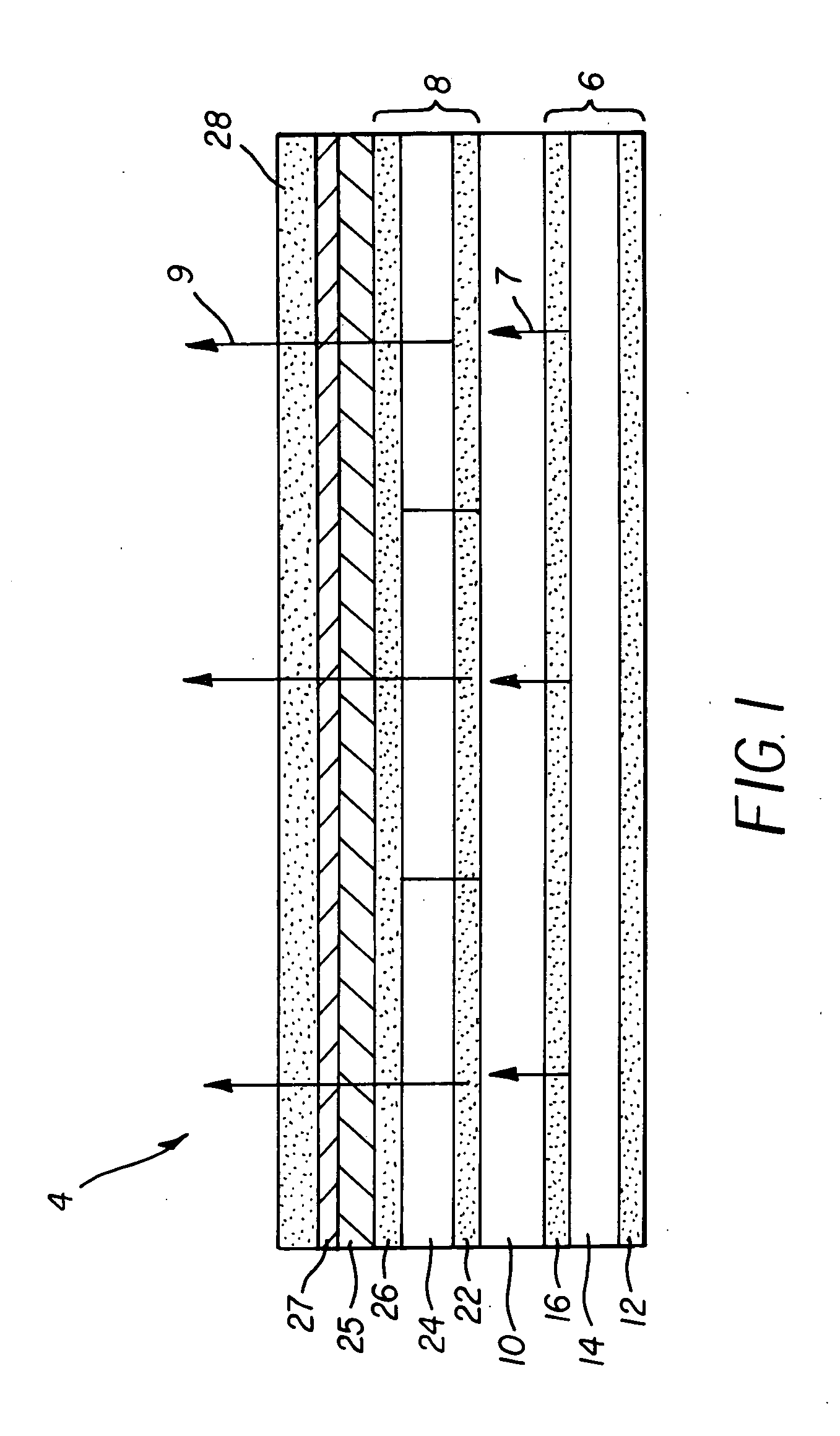
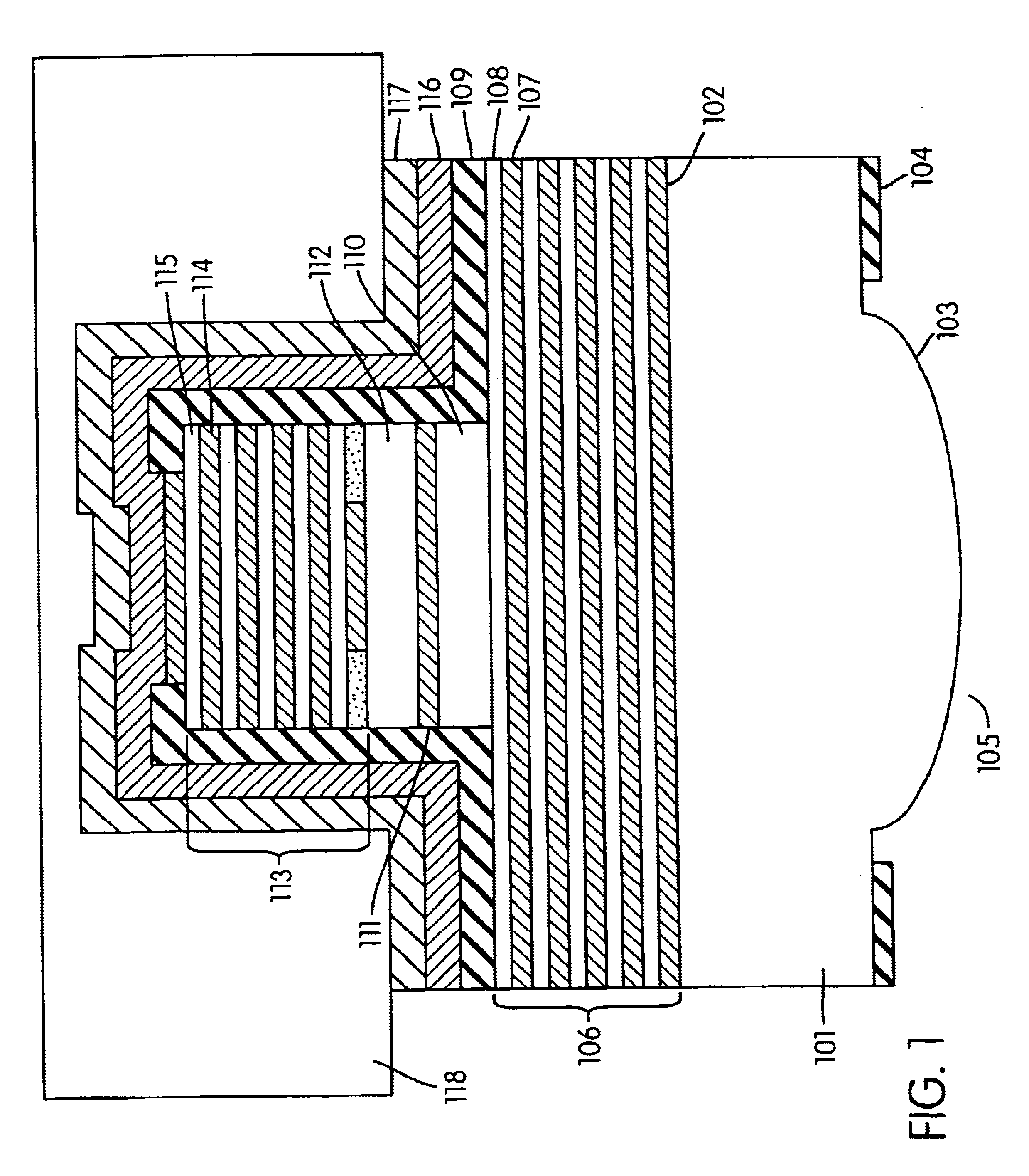
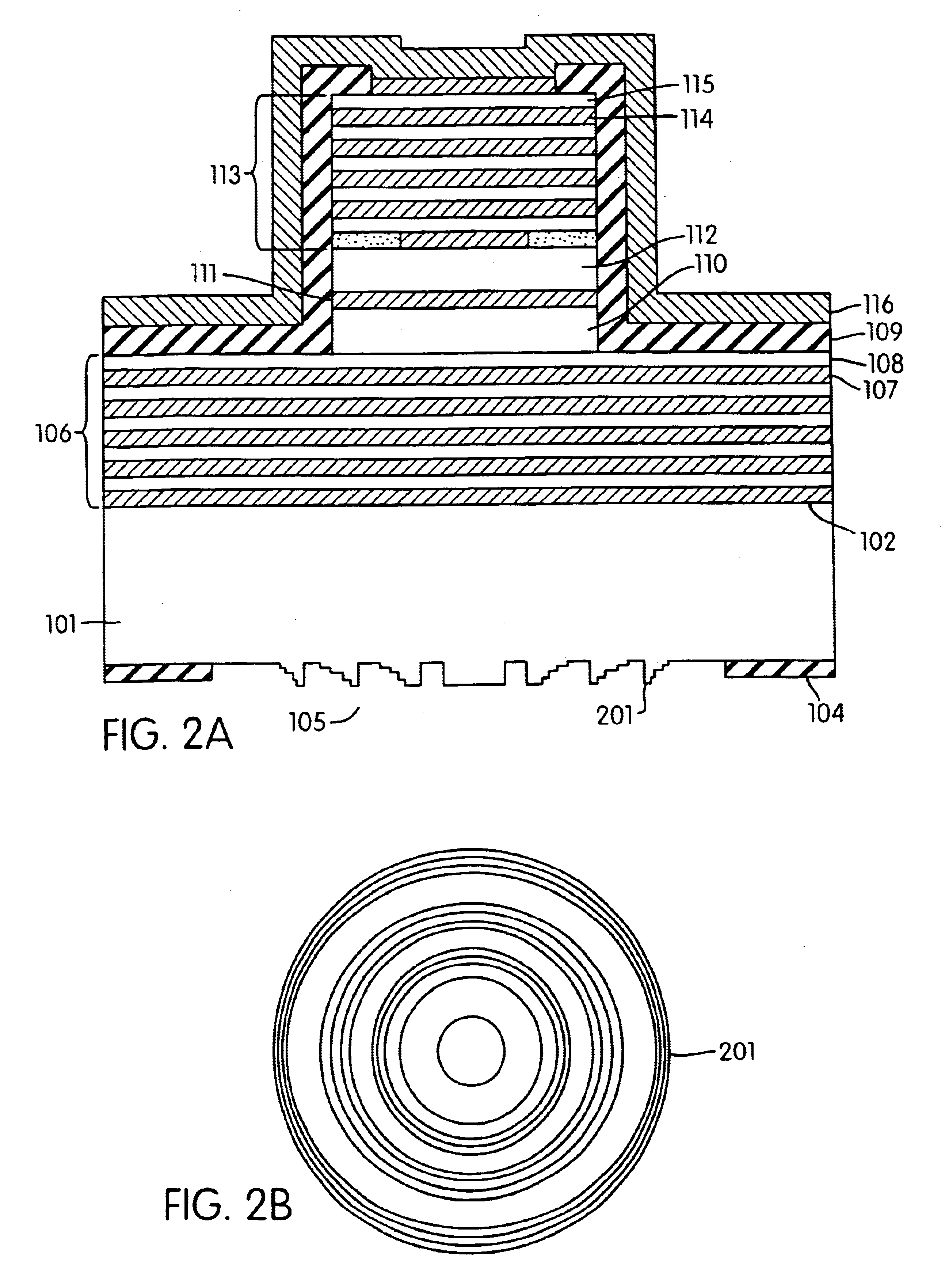
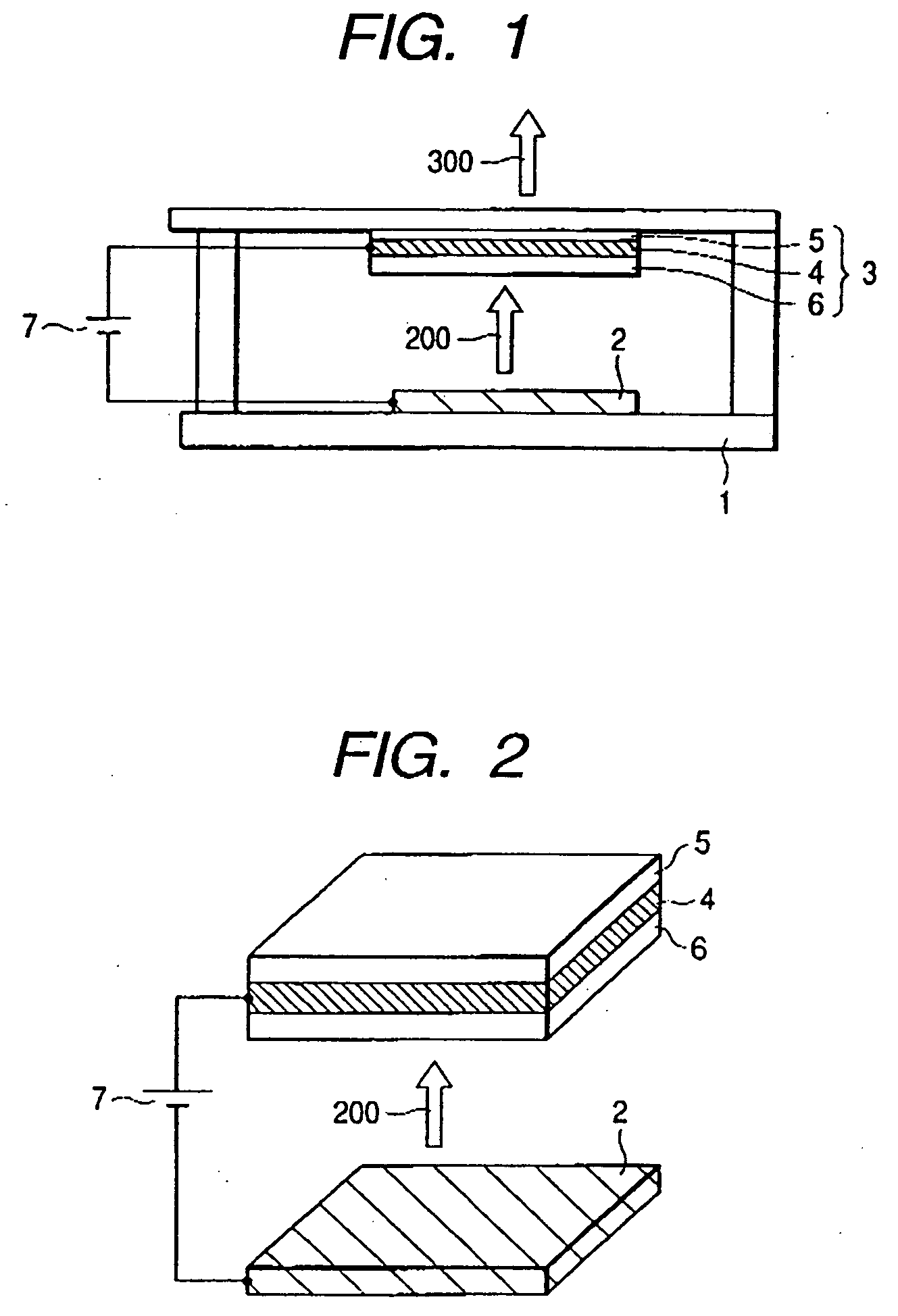
Organic vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
InactiveUS6160828ALaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserThin layer
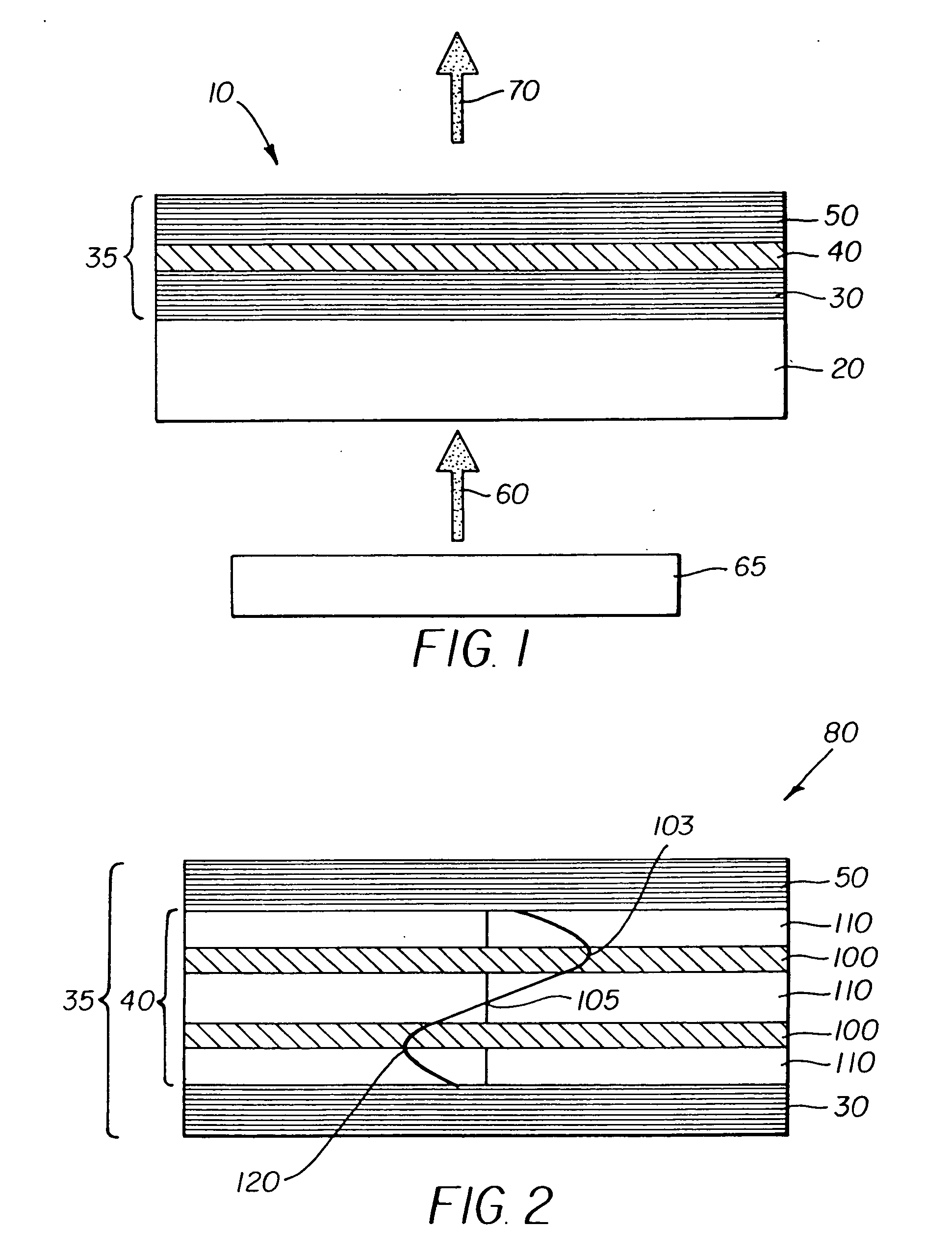
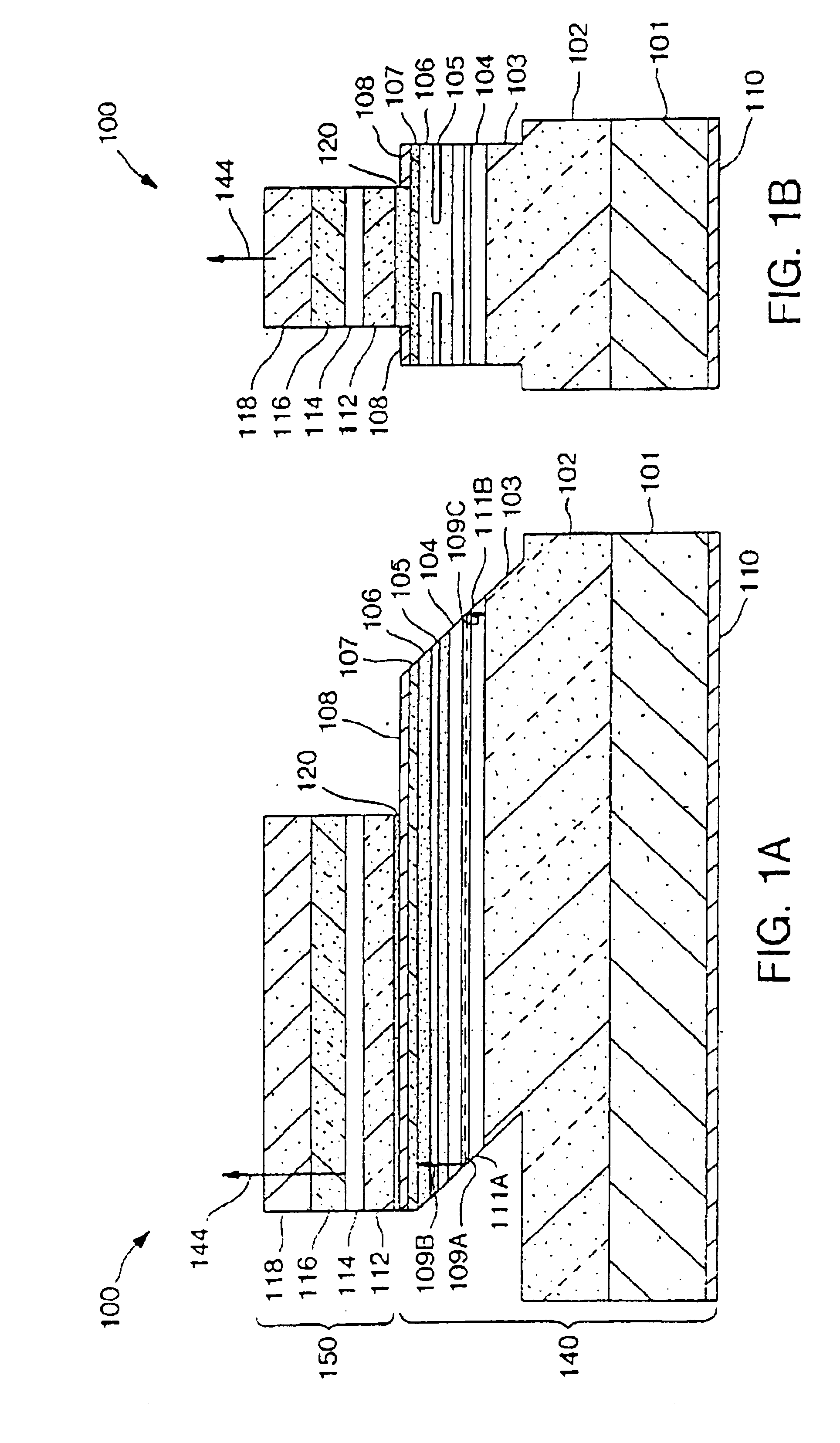
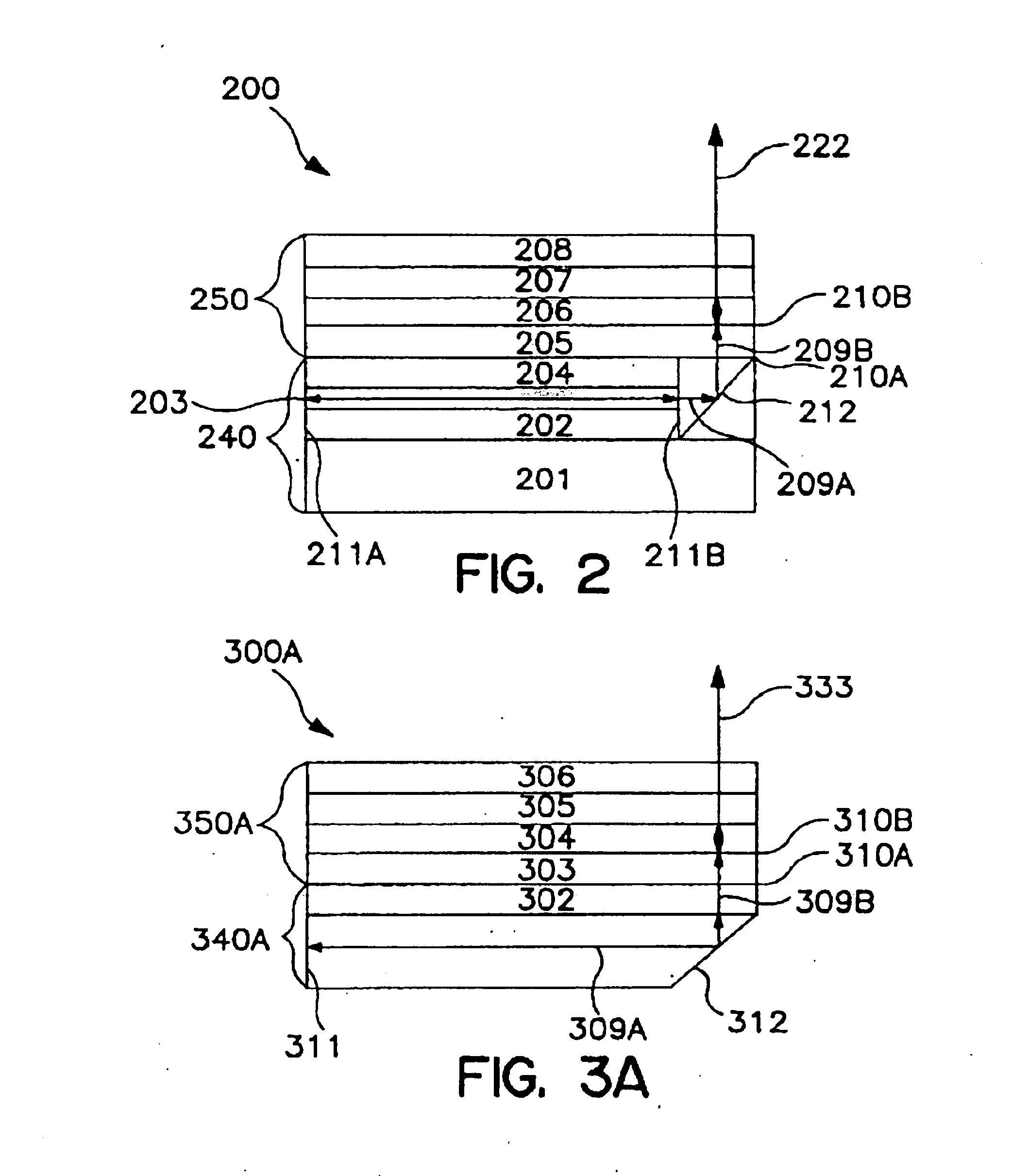
Organic vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers ("OVCSELs"), in which a thin layer of organic material is disposed between highly reflective mirrors to thereby form a vertical cavity within a stacked arrangement. The lasers of the present invention each comprise a first mirror layer; a layer of active organic material over the first mirror layer; and a second mirror layer over the layer of first active organic material. The active organic material lases when pumped to thereby produce laser light. The present invention provides for optical semiconductor lasers with desired properties such as narrow bandwidth emission, the minimal use of active organic materials, and the facilitation of wavelength tuning and electrical pumping.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV THE TRUSTEES OF
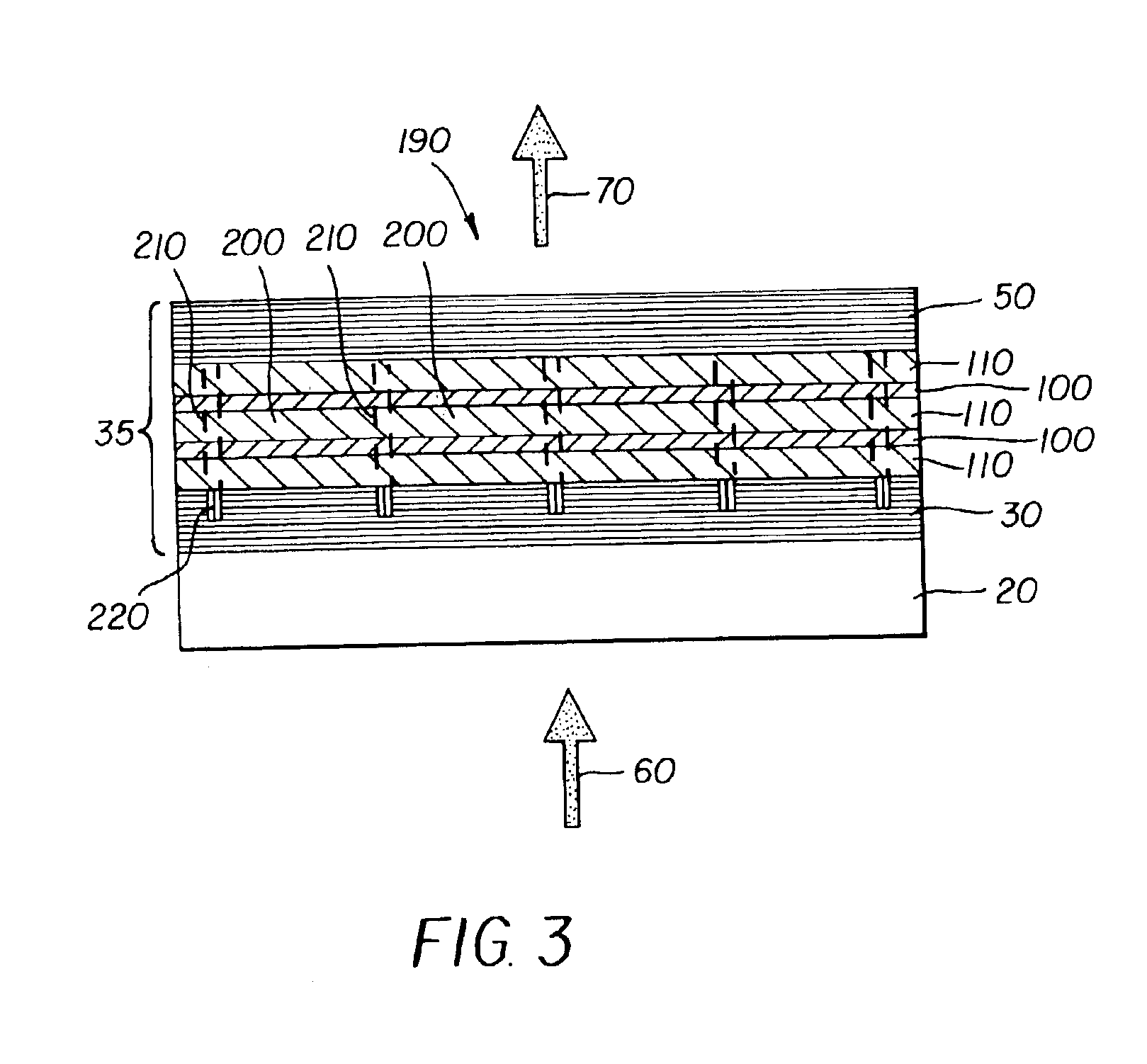
Organic vertical cavity laser and imaging system
InactiveUS6947459B2Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser light
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
High power optical apparatus employing large-mode-area, multimode, gain-producing optical fibers
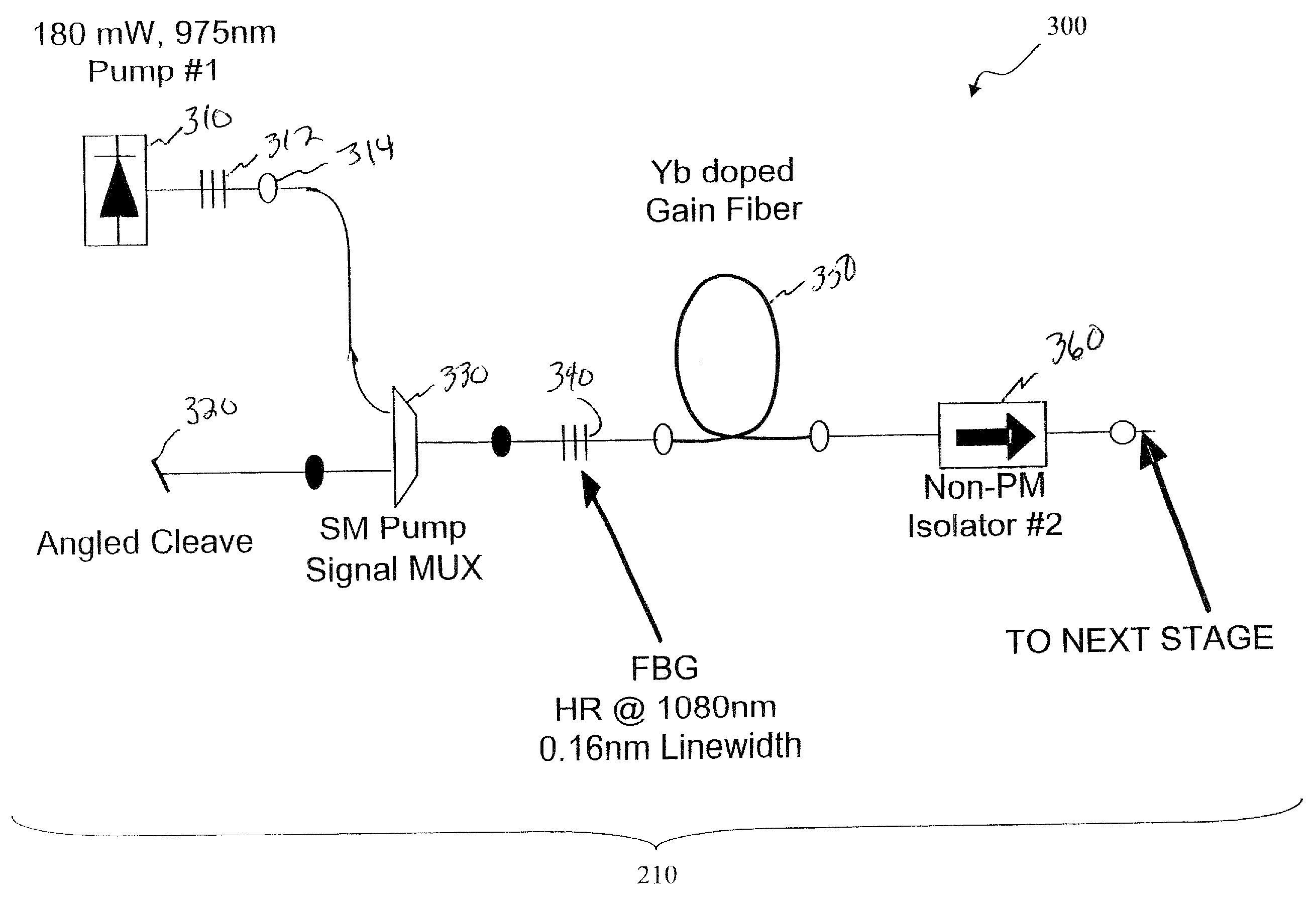
ActiveUS20080180787A1Promote absorptionIncrease brightnessExcitation process/apparatusCoupling light guidesFiberNanosecond
Optical apparatus includes a multimode, gain-producing fiber for providing gain to signal light propagating in the core of the fiber, and a pump source for providing pump light that is absorbed in the core, characterized in that (i) the pump source illustratively comprises a low brightness array of laser diodes and a converter for increasing the brightness of the pump light, (ii) the pump light is coupled directly into the core, and (iii) the area of the core exceeds approximately 350 μm2. In one embodiment, the signal light propagates in a single mode, and the pump light co-propagates in at least the same, single mode, both in a standard input fiber before entering the gain-producing fiber, and a mode expander is disposed between the input fiber and the gain-producing fiber. In another embodiment, multiple pumps are coupled into the core of the gain-producing fiber. The pumps may generate light of the same wavelength or of different wavelengths. In accordance with a particular embodiment of our invention, we have demonstrated amplification of nanosecond optical pulses at 1545 nm in a single clad Er-doped fiber having a core area of 875 μm2; the core was pumped by a high brightness Raman laser at 1480 nm; and the pulses had a record peak power of several hundred kW.
Owner:OFS FITEL LLC
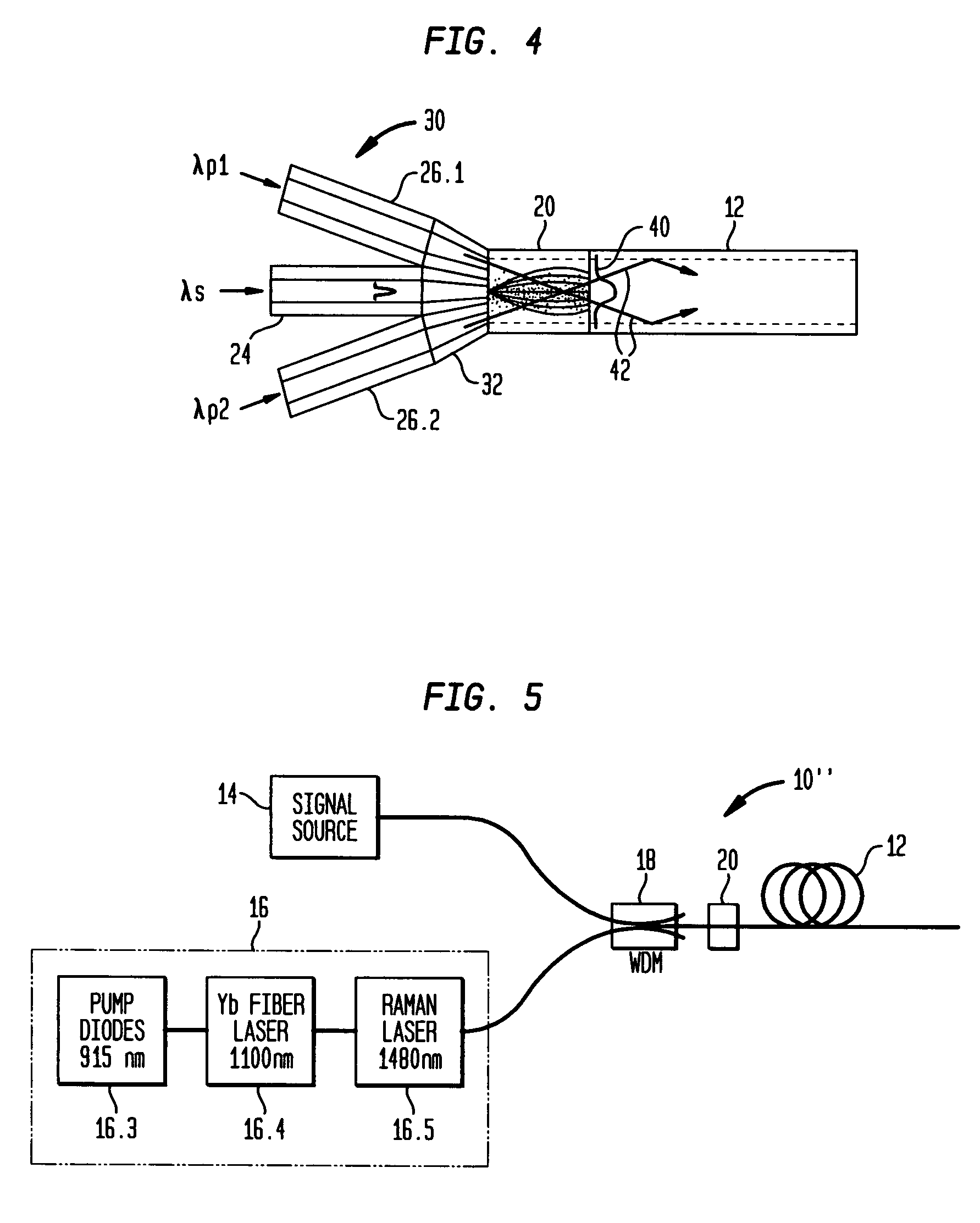
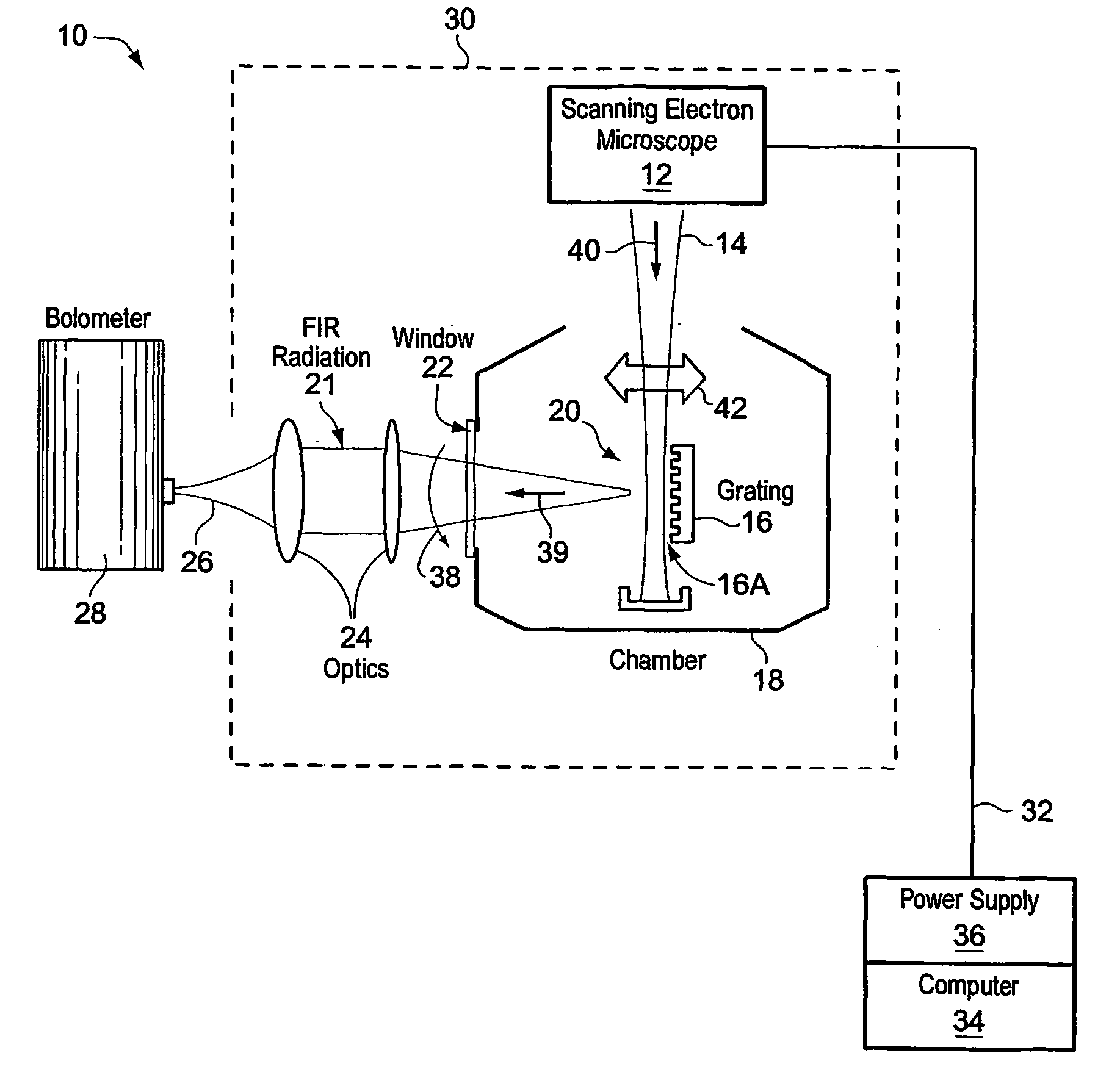
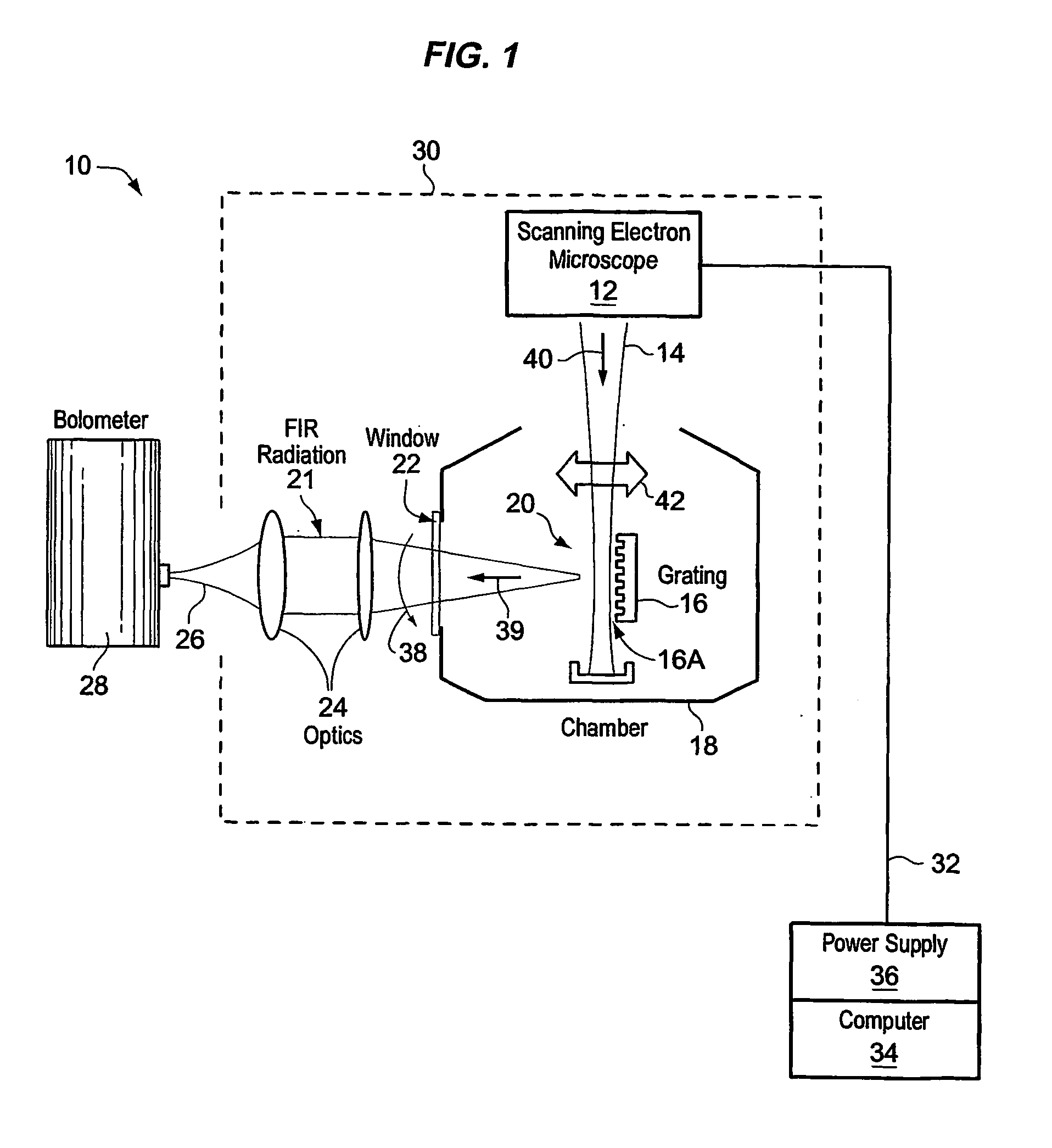
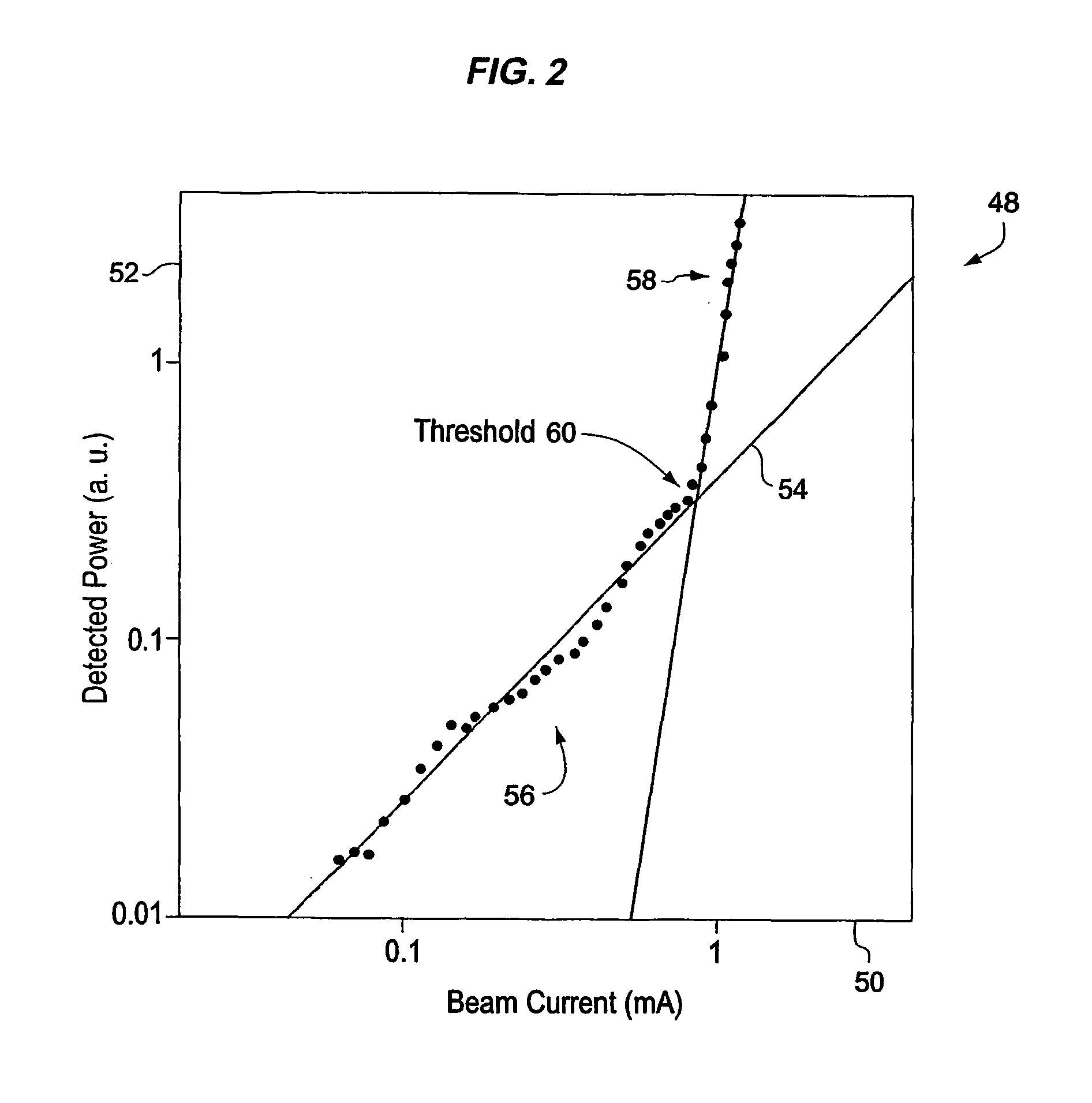
Free electron laser, and associated components and methods
A system generates FIR laser radiation. An electron source generates an electron beam. A grating horn interacts with the electron beam to produce the FIR laser radiation. The grating horn may comprise a flat base and a pair of grating elements attached to the base, each of the grating elements being ruled with a grating period, the grating elements oriented in phase and in substantial symmetry about a normal to the flat base.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
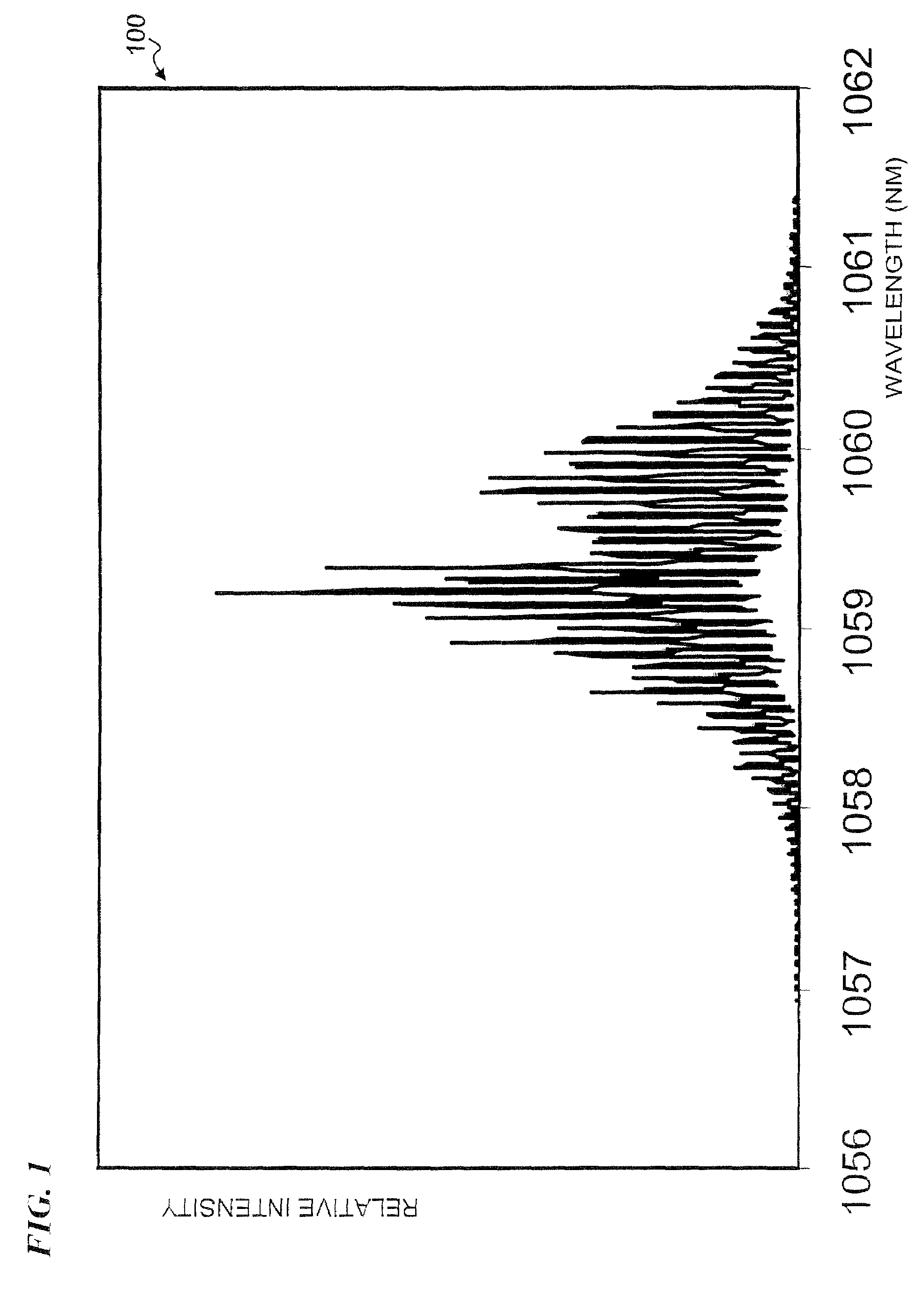
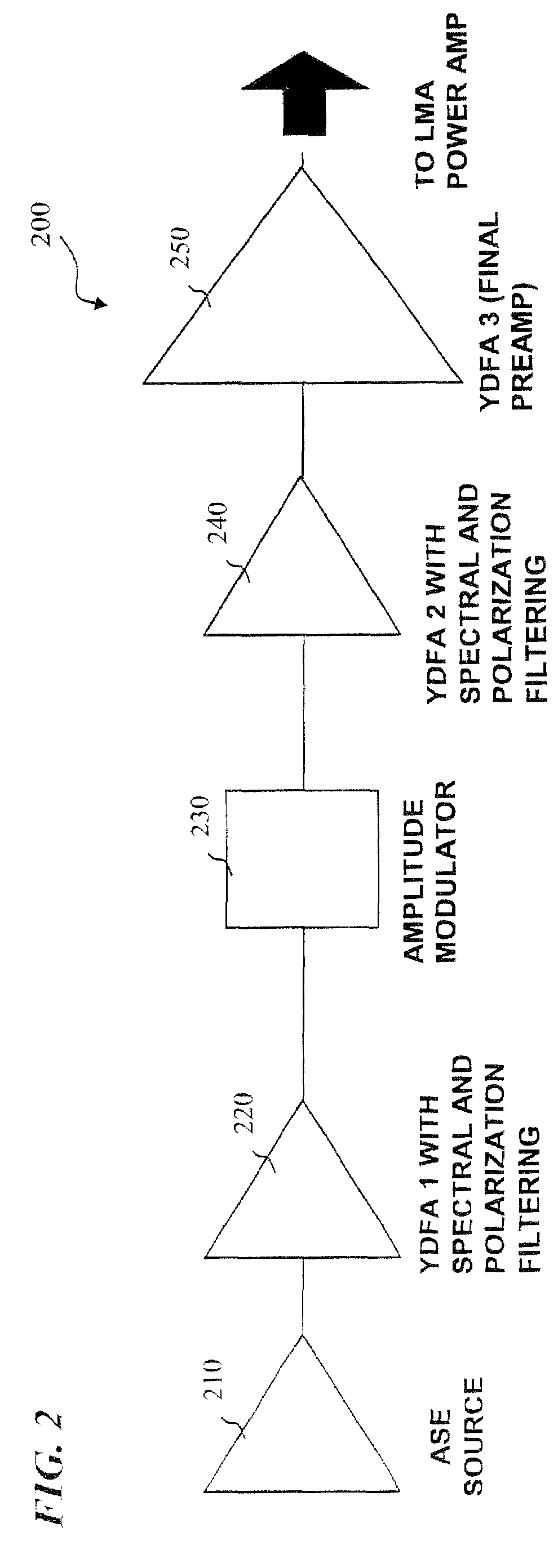
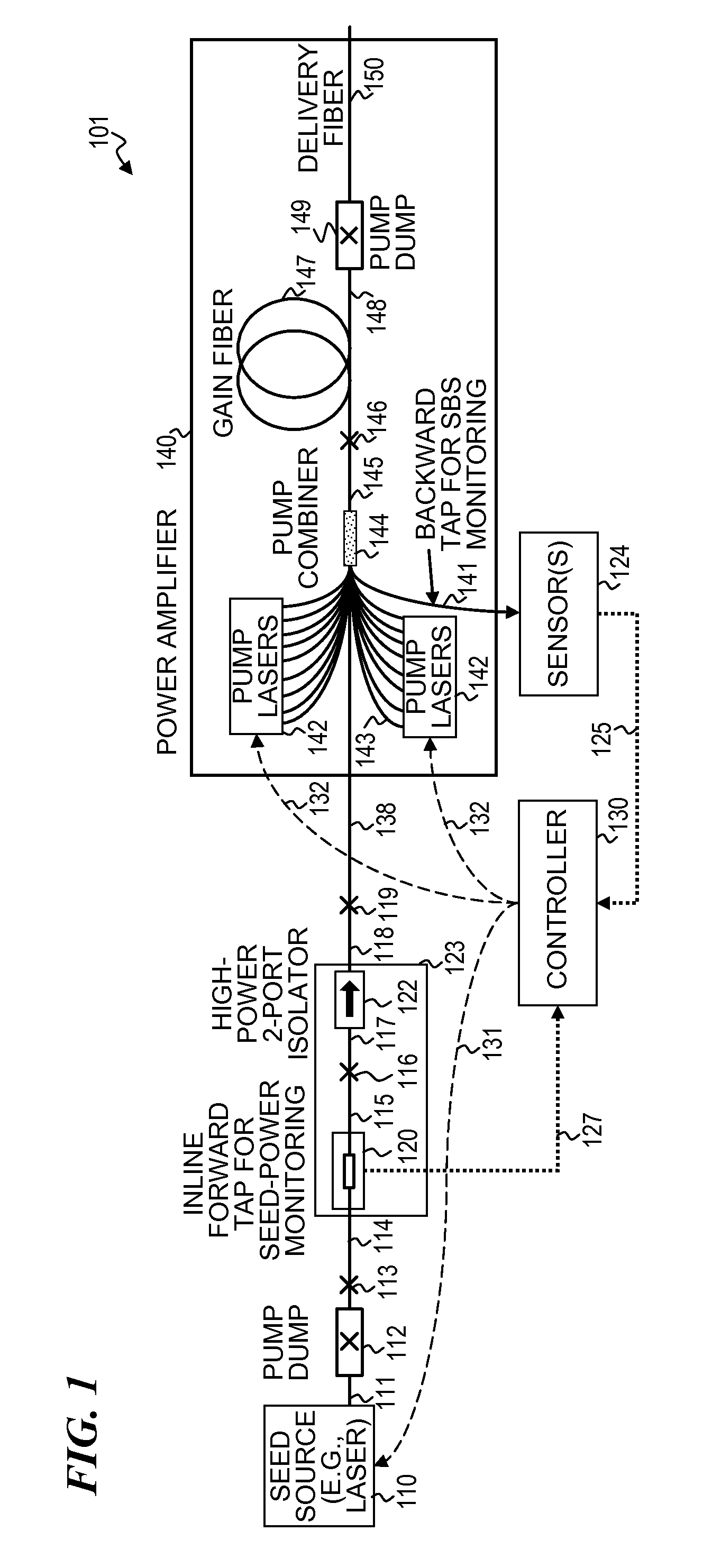
Apparatus and method for generating controlled-linewidth laser-seed-signals for high-powered fiber-laser amplifier systems
Apparatus and method for generating controlled-linewidth laser-seed-signals for high-powered fiber-laser amplifier systems. In some embodiments, the natural chirp (frequency change of laser light over a short start-up time) of a DBR laser diode when driven by pulsed current is used to broaden the linewidth of the laser output, while adjusting the peak current and / or the pulse duration to obtain the desired linewidth.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
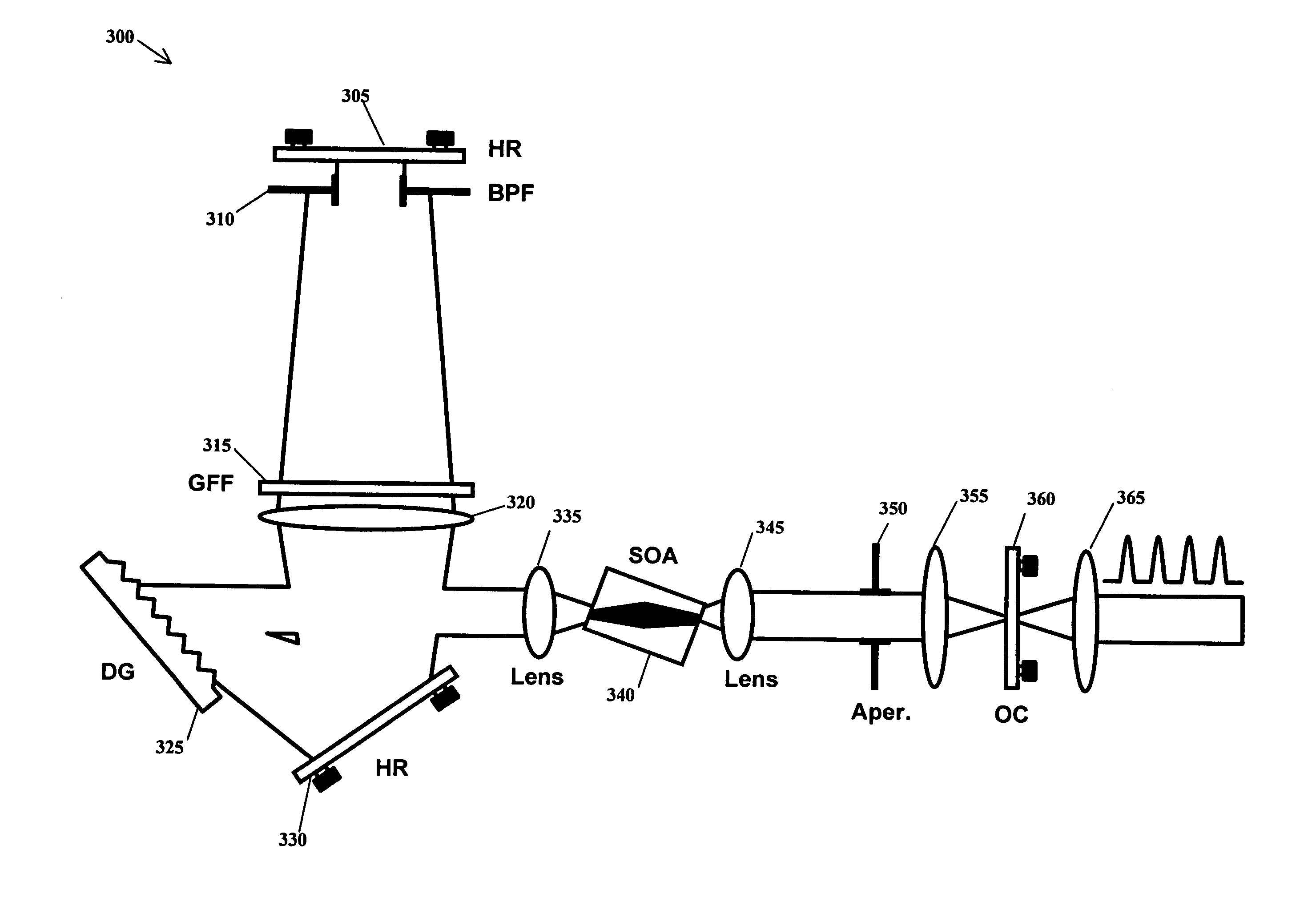
Extreme chirped/stretched pulsed amplification and laser
InactiveUS7095772B1Efficiently externally compressedIncrease powerExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor amplifier structureChirped pulse amplificationFiber Bragg grating
Methods, devices and systems for generating ultrashort optical linear chirped pulses with very high power by amplifying the pulses so that their temporal duration is longer than the storage time of the amplifying medium. The additional gain factor is related to the ratio of the storage time to the stretched pulse. A preferred embodiment connects a mode locked laser source that generates optical pulses whose duration is stretched with a chirped fiber Bragg grating. Embodiments include methods, devices and systems causing an extreme chirped pulse amplifier (XCPA) effect in an oscillator.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Method and apparatus for reliably laser marking articles
InactiveUS20110193928A1Desirable appearanceMarking is durableRecording apparatusDuplicating/marking methodsPulse parameterOptoelectronics
Disclosed is a method for creating a mark desired properties on an anodized specimen and the mark itself. The method includes providing a laser marking system having a controllable laser pulse parameters, determining the laser pulse parameters associated with the desired properties and directing the laser marking system to mark the article using the selected laser pulse parameters. Laser marks so made have optical density that ranges from transparent to opaque, white color, texture indistinguishable from the surrounding article and durable, substantially intact anodization. The anodization may also be dyed and optionally bleached to create other colors.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
Diode laser arrangement with a plurality of diode laser arrays
InactiveUS6898222B2Promote homogenizationSemiconductor laser arrangementsExcitation process/apparatusLaser arrayRadiation field
A diode laser arrangement is disclosed wherein a radiation source is designed which can be scaled with respect to power such that different types of cooling can be applied and the configuration of the radiation field is suitable for adapting to different tasks in a simple manner. For this purpose, every diode laser is connected to a thermal contact surface of a separate, heat-spreading carrier which is fastened to a cooling surface of a common cooling element so as to be electrically insulated. The carriers are arranged adjacently in such a way that the line-shaped emission regions of the diode lasers are adjacent in series and the p-n junction planes extend parallel to the thermal contact surfaces. The diode laser arrangement is particularly suitable as a pump light source.
Owner:JENOPTIK LASERDIODE
Organic laser and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20050062903A1Improve efficiencySimple structureSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLiquid-crystal displayOrganic laser
An asymmetric light emitting structure for producing polarized light that includes a light emitting layer having a plurality of light emitting species, wherein orientation of the light emitting species is uncontrolled. Receipt of the emitted light from the light emitting layer is accomplished via an asymmetric geometric element that also produces polarized light. Additionally, the asymmetric light emitting structure includes a means for excitation of the light emitting layer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
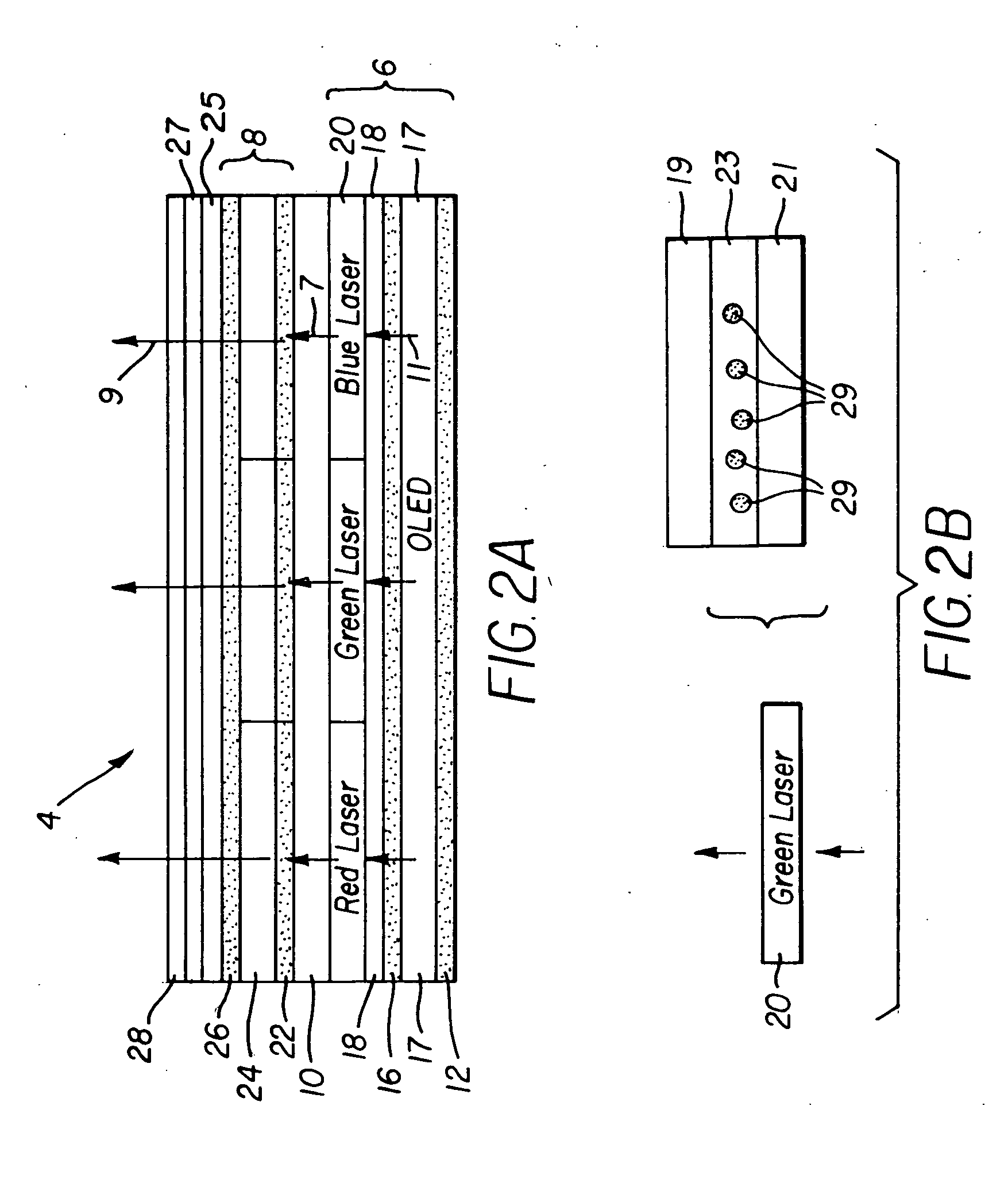
Multi-spectral laser array and optical system
InactiveUS20050147135A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser array
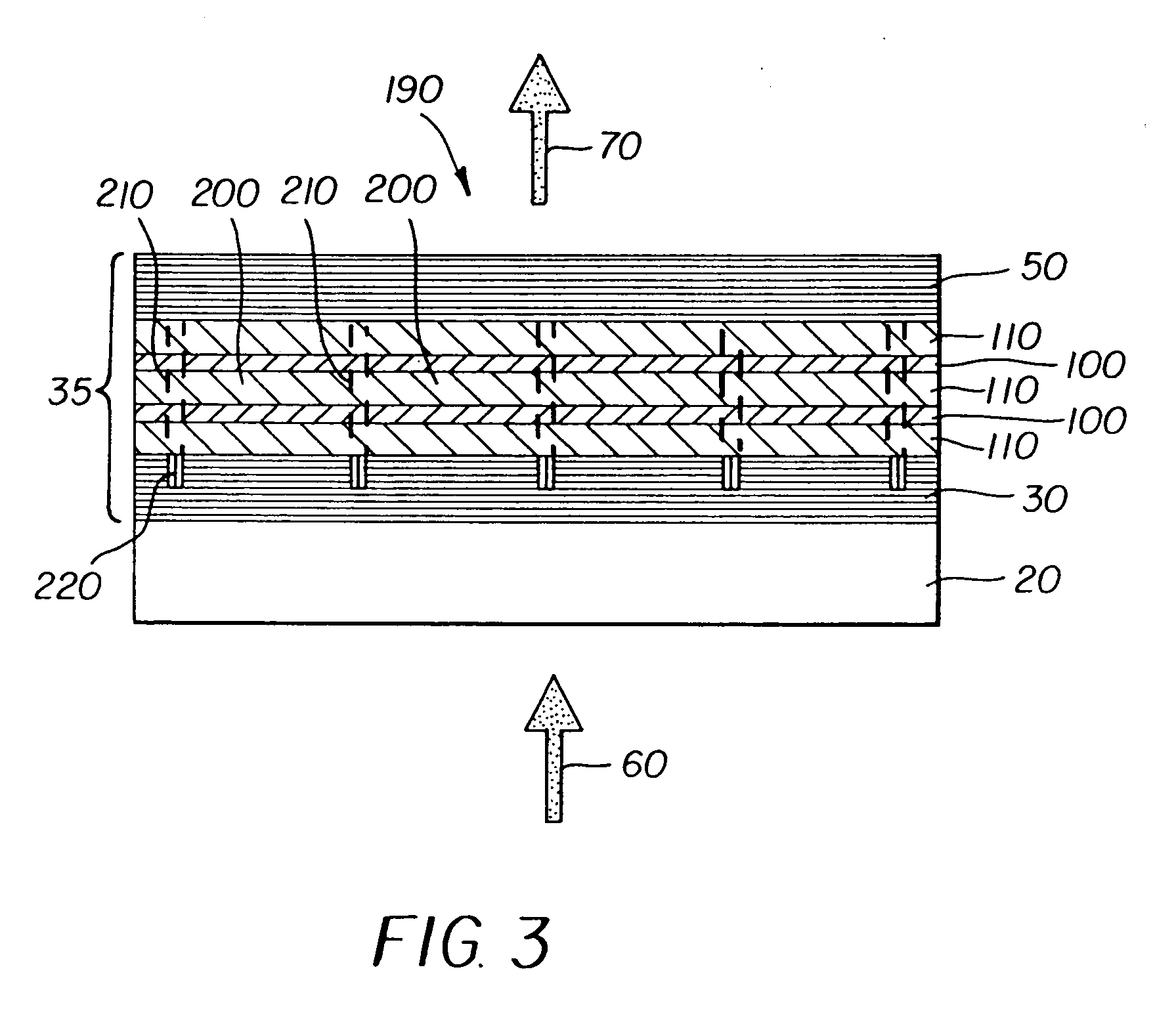
An organic vertical cavity laser light producing device (10) comprises a substrate (20). A plurality of laser emitters (200) emits laser light in a direction orthogonal to the substrate. Each laser emitter within the plurality of laser emitters has a first lateral mode structure in a first axis orthogonal to the laser light direction and has a second lateral mode structure in a second axis orthogonal to both the laser light direction and the first axis. Each laser emitter comprises a first mirror provided on a top surface of the substrate (20) and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. An organic active region (40) produces laser light (350). A second mirror is provided above the organic active region and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. A pumping means excites the plurality of laser emitters.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Optical semiconductor device
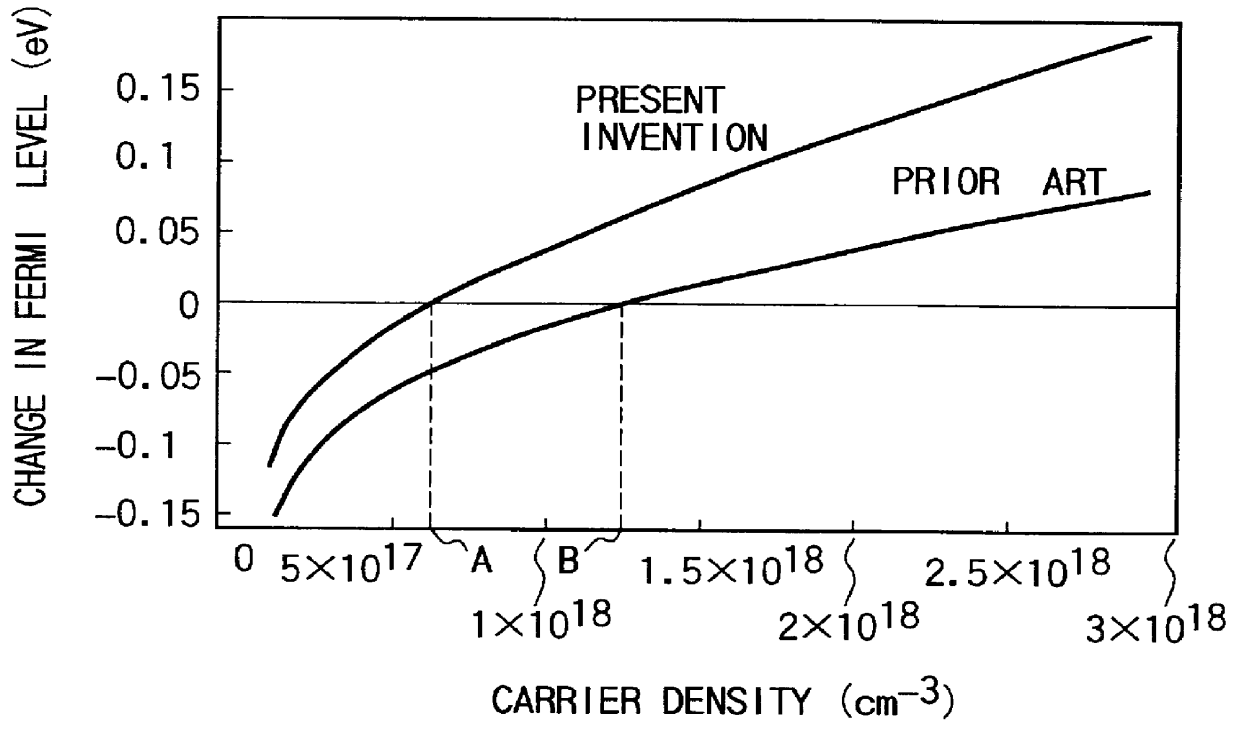
InactiveUS6043515AEasy population inversionImprove featuresExcitation process/apparatusSolid-state devicesMagnetizationContact layer
An optical semiconductor device has a structure in which a semiconductor active layer is sandwiched by a p-type semiconductor cladding layer and an n-type semiconductor cladding layer and a p-type contact layer is formed on the p-type semiconductor cladding layer side and an n-type contact layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor cladding layer side, wherein two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the n-type contact layer and two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the p-type contact layer. Magnetization directions of a pair of ferromagnetic layers vertically opposed to each other are set to be parallel to each other, and the magnetization directions of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are inverted to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
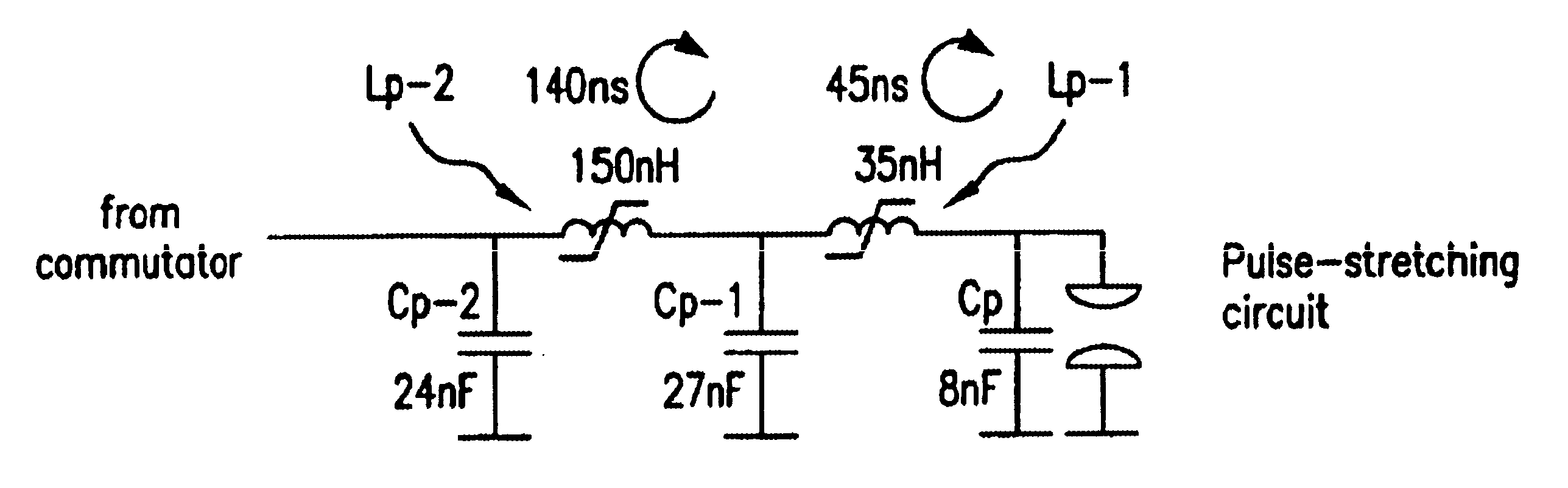
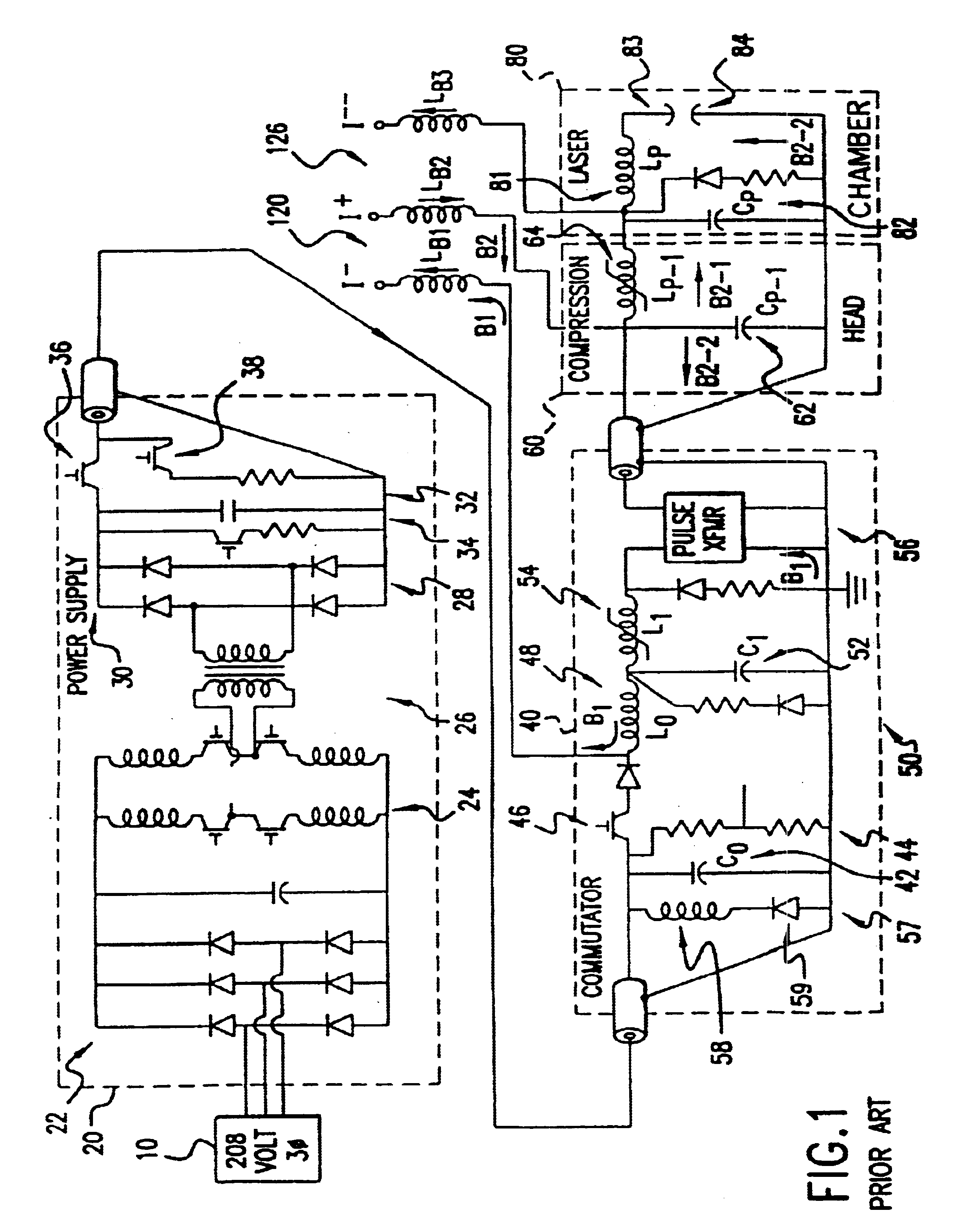
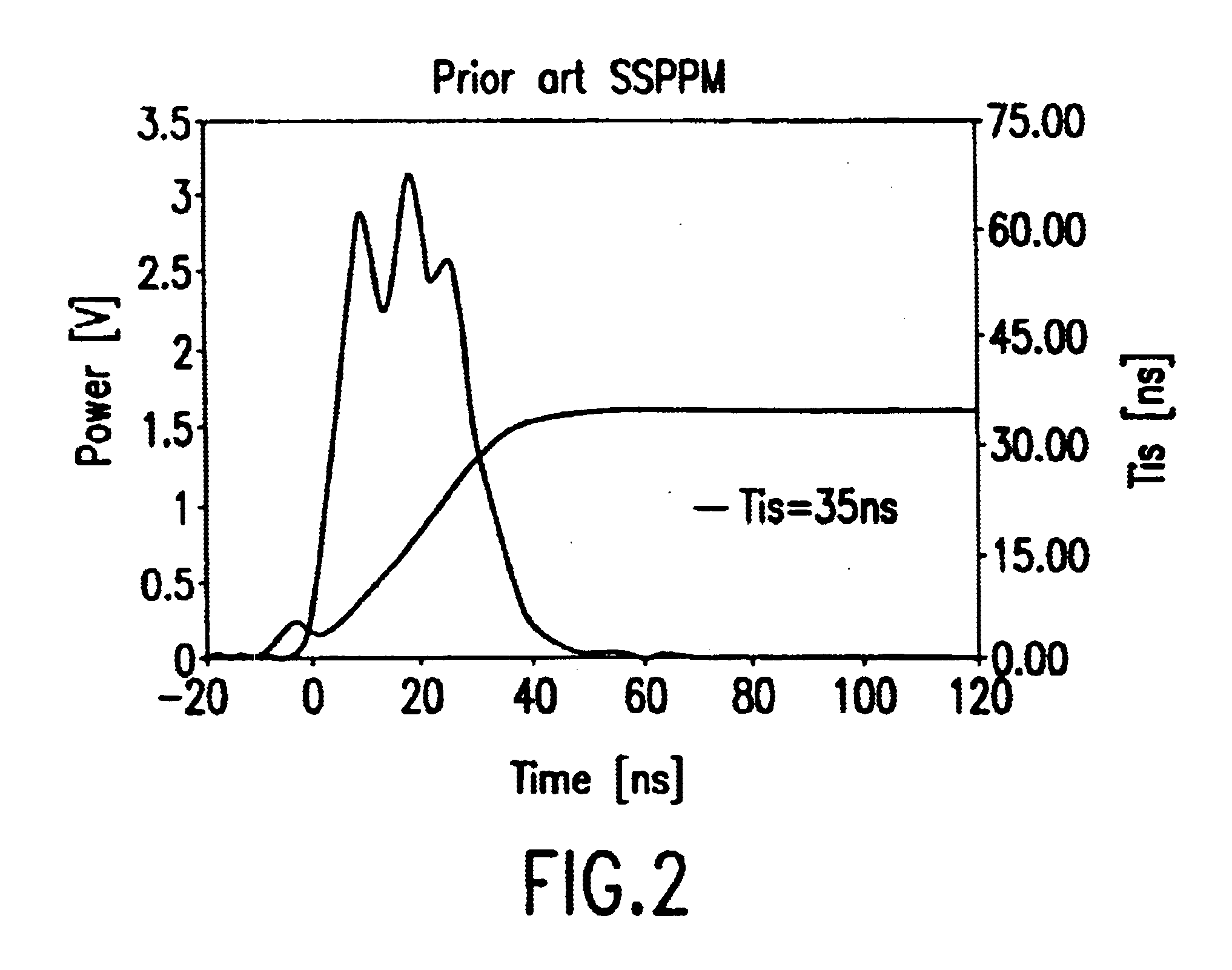
Long-pulse pulse power system for gas discharge laser
A long pulse power system for gas discharge lasers. The system includes a sustainer capacitor for accepting a charge from a high voltage pulse power source. A peaking capacitor with a capacitance value of less than half the sustainer capacitance provides the high voltage for the laser discharge.
Owner:CYMER INC
Short-wavelength optoelectronic device including field emission device and optical device and its fabricating method
InactiveUS6139760AEfficient productionHigh energyExcitation process/apparatusOptical articlesField emission deviceOpto electronic
Provided with a method of fabricating a 200-250 nm short-wavelength optoelectronic device, which has a combination of an optical device with a plurality of acceleration electrodes and a field emission device with a plurality of acceleration electrodes, from a semiconductor having a 5-6 eV energe band gap, based on a principle that an electron-hole pair is produced using a highly energetic electron which is injected from a field emission device, and short-wavelength photons are emitted when the electron recombines with the hole and confined in a quantum well to emit a light corresponding to the energy level of the quantum well, thereby eliminating the need of using dopants for forming n-p junctions in the semiconductor and achieving high efficiency in terms of energy because highly energetic electrons result in one or more electron-hole pairs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
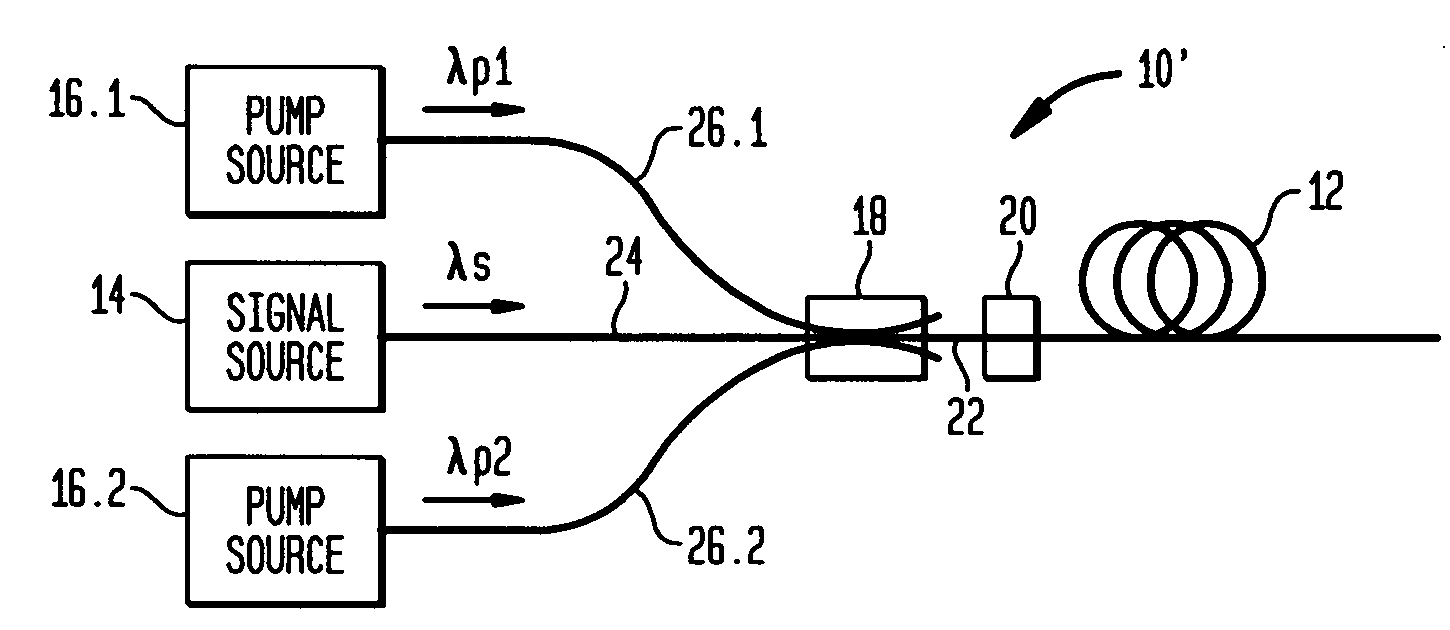
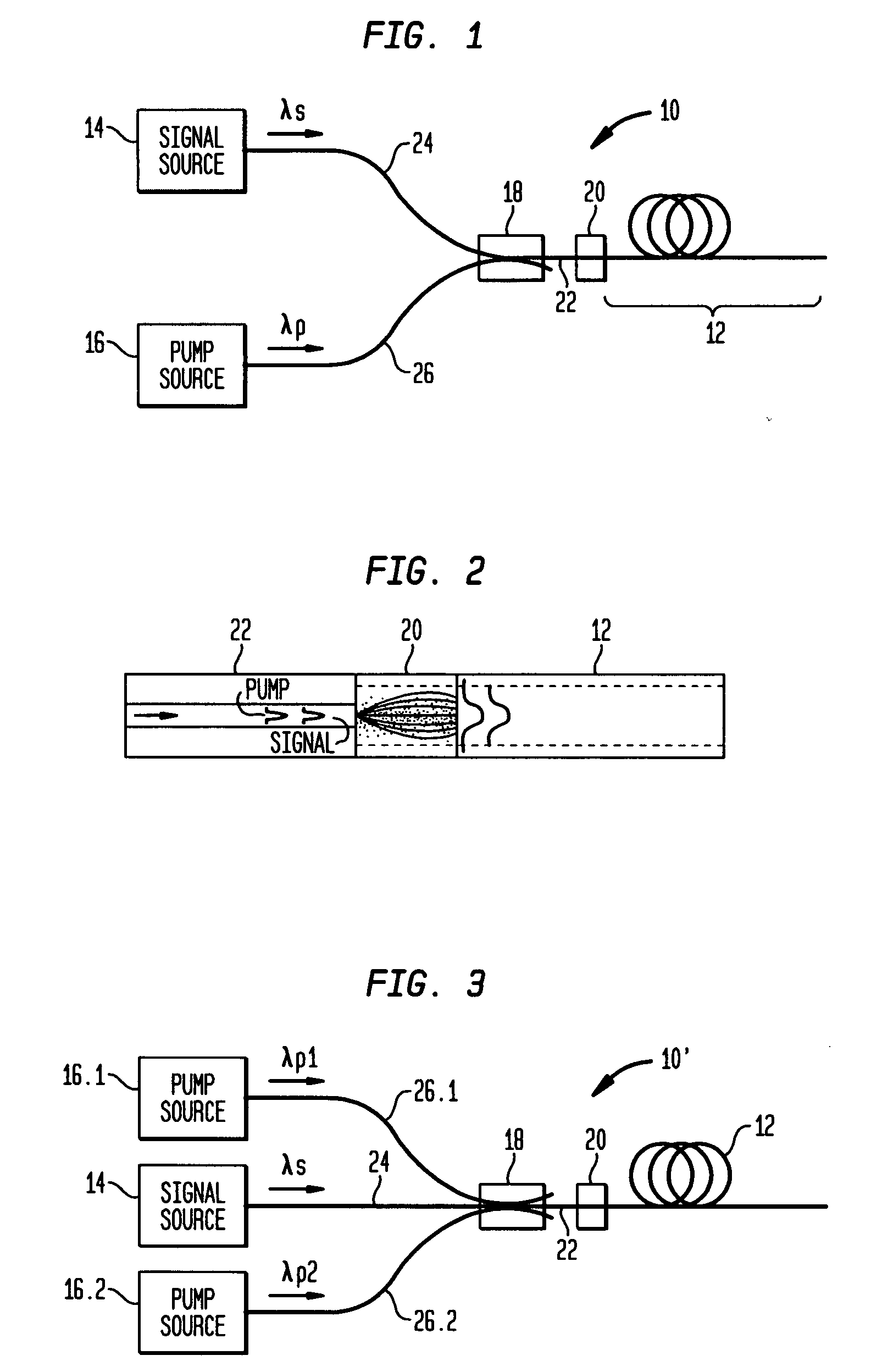
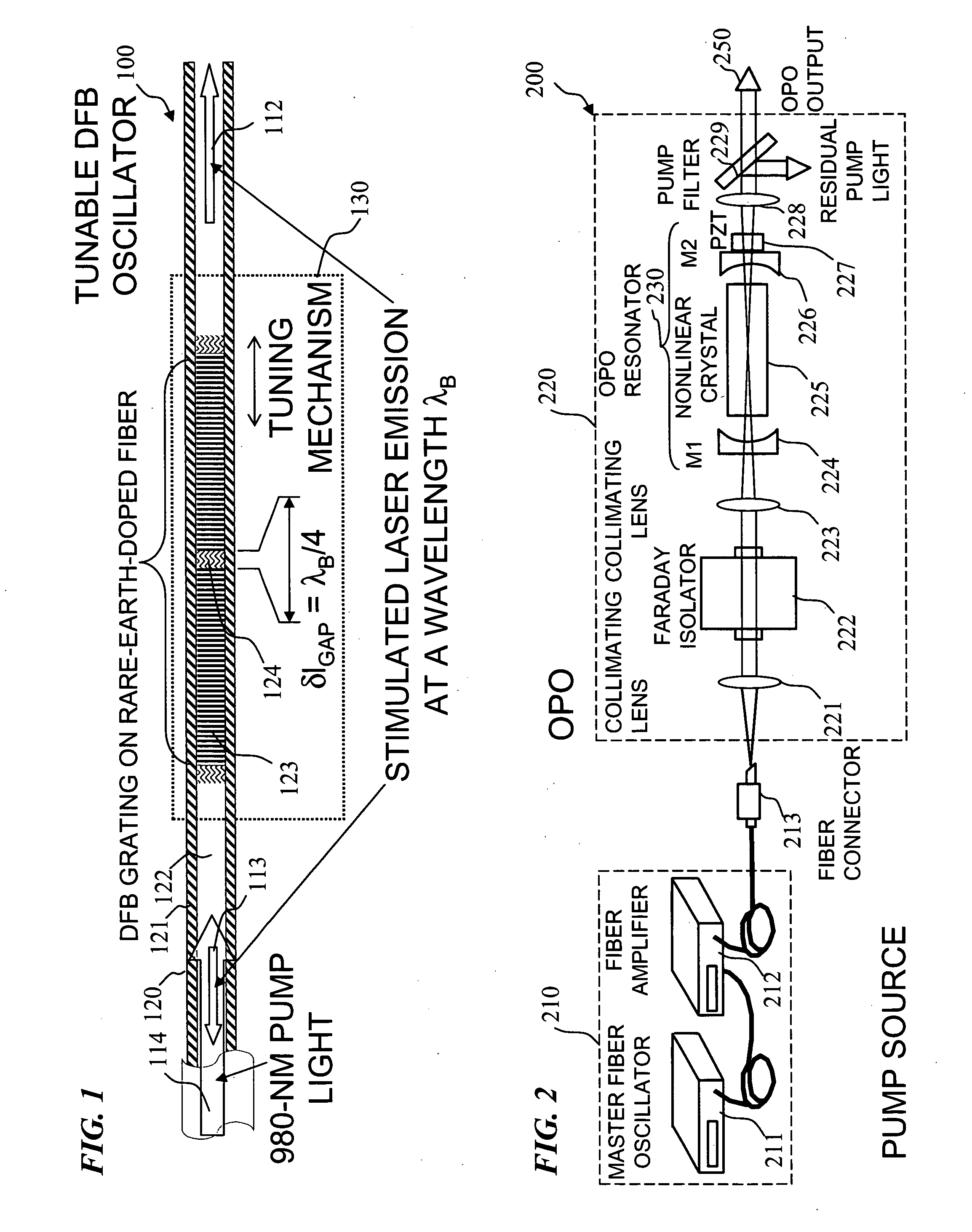
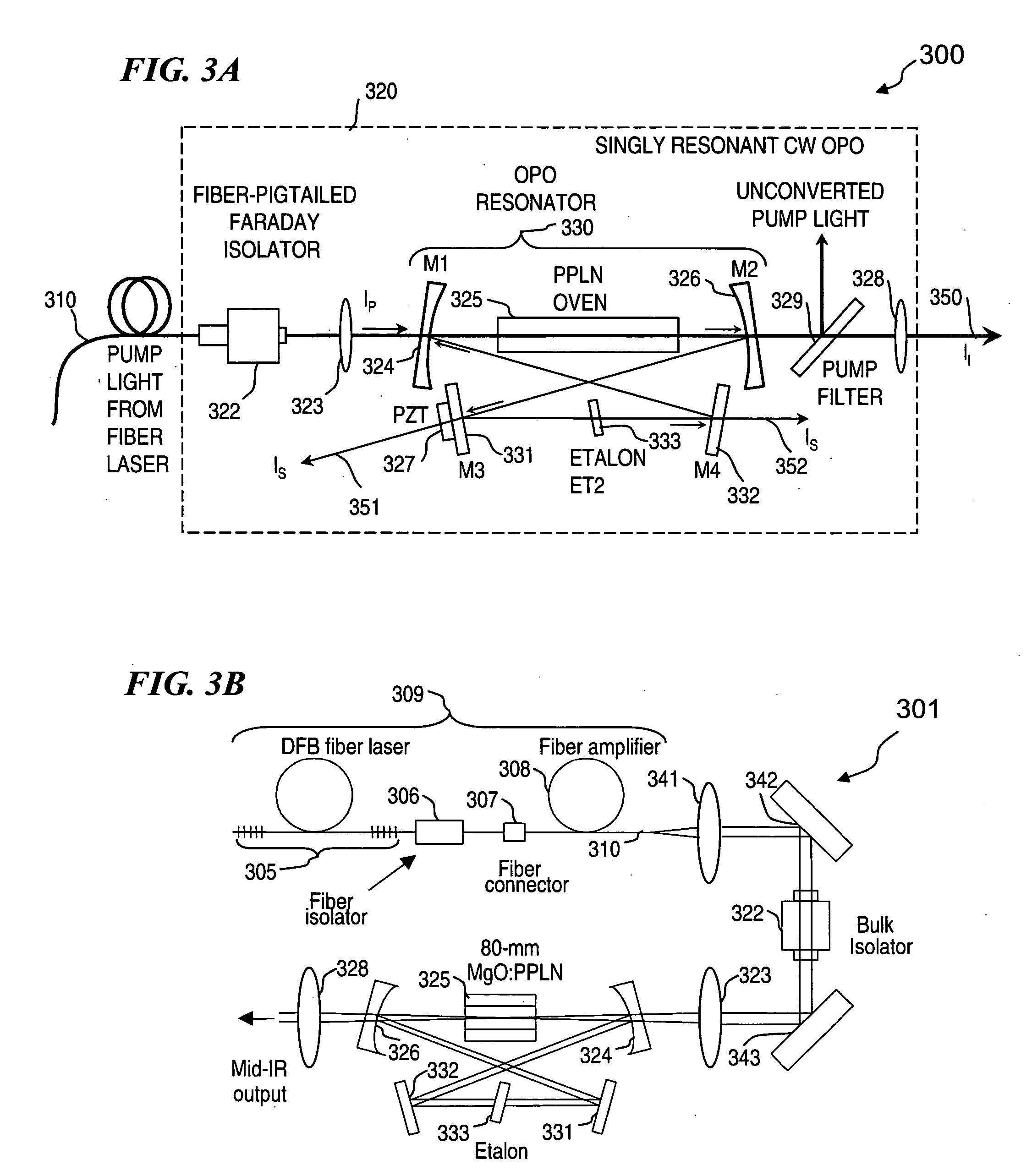
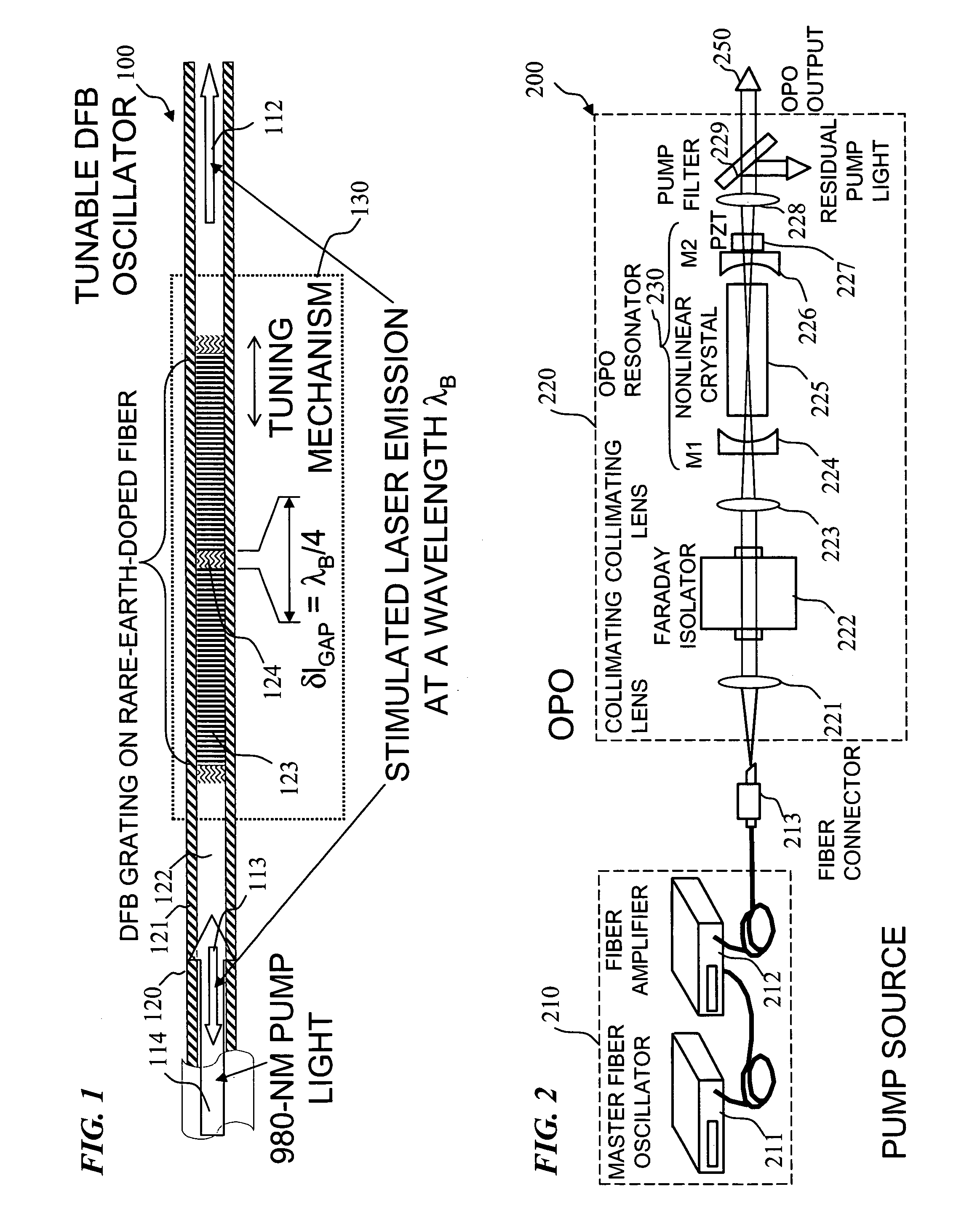
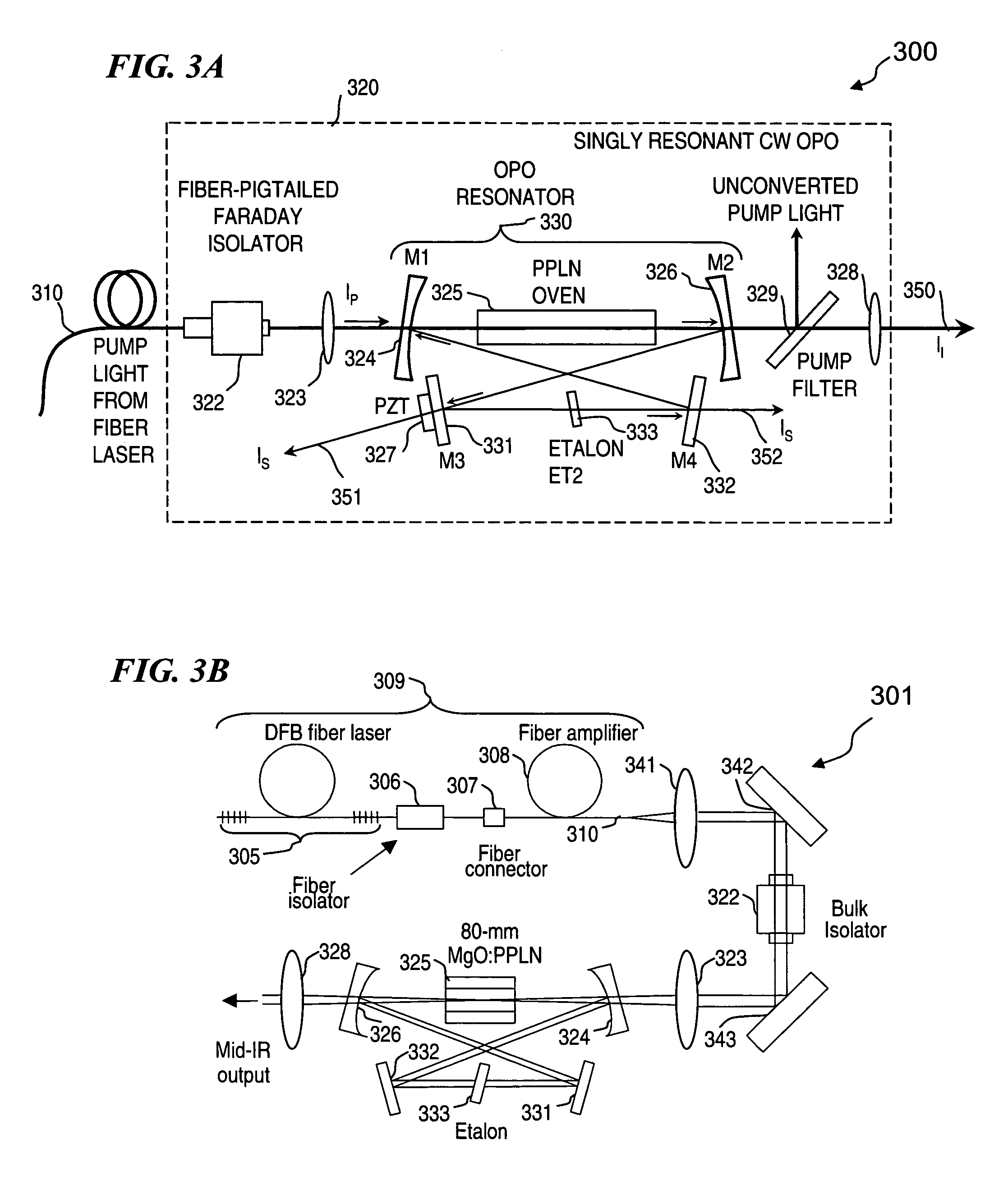
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS20070035810A1Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
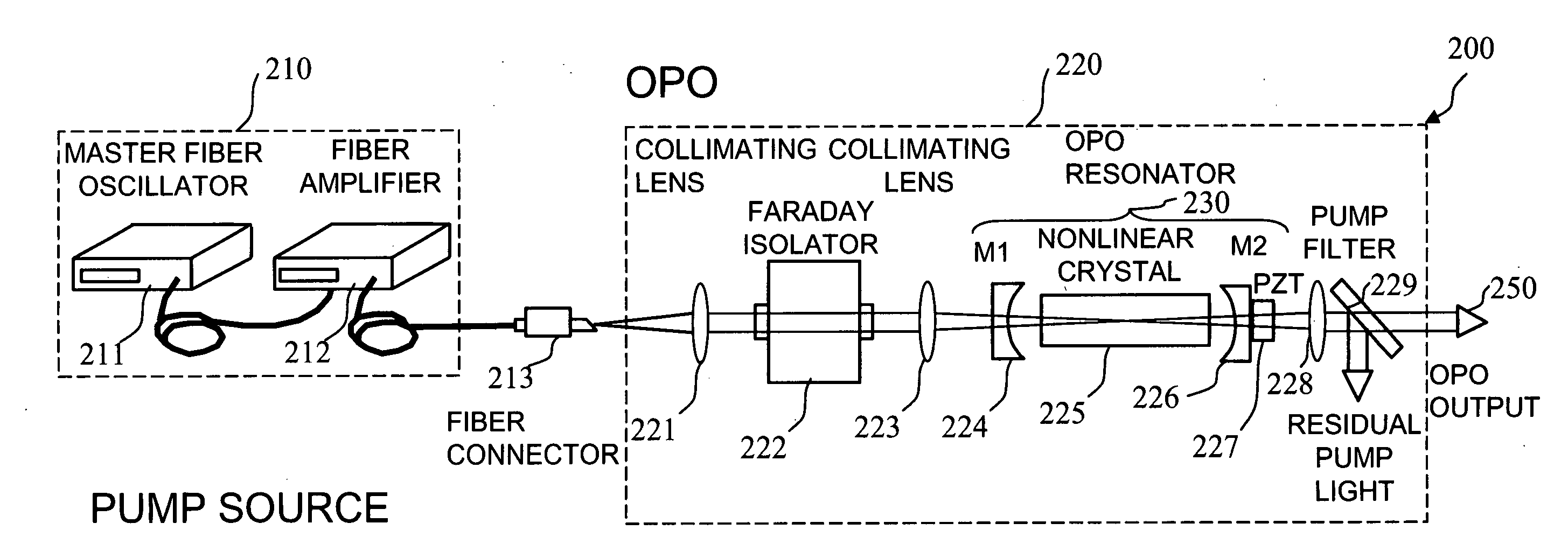
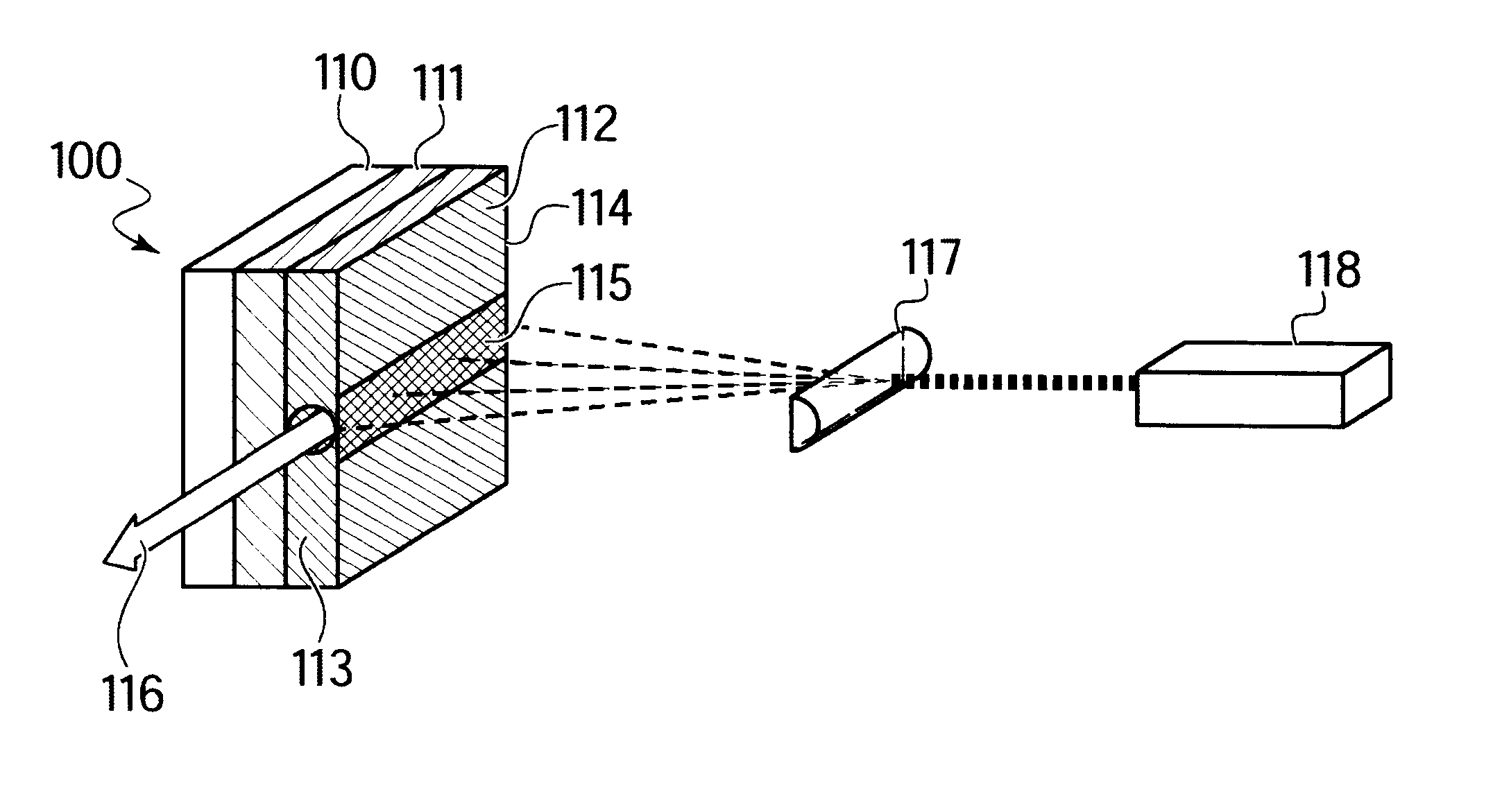
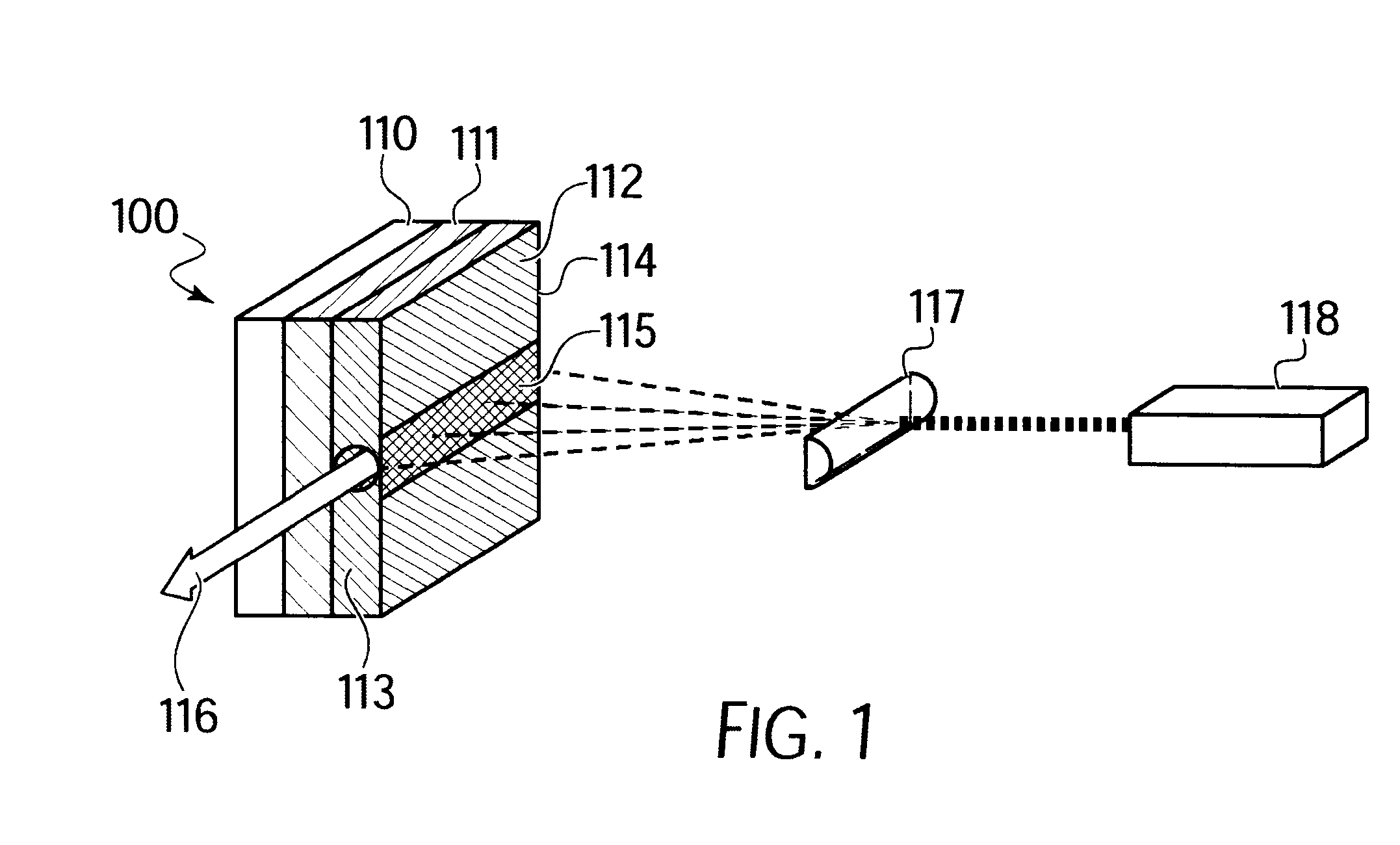
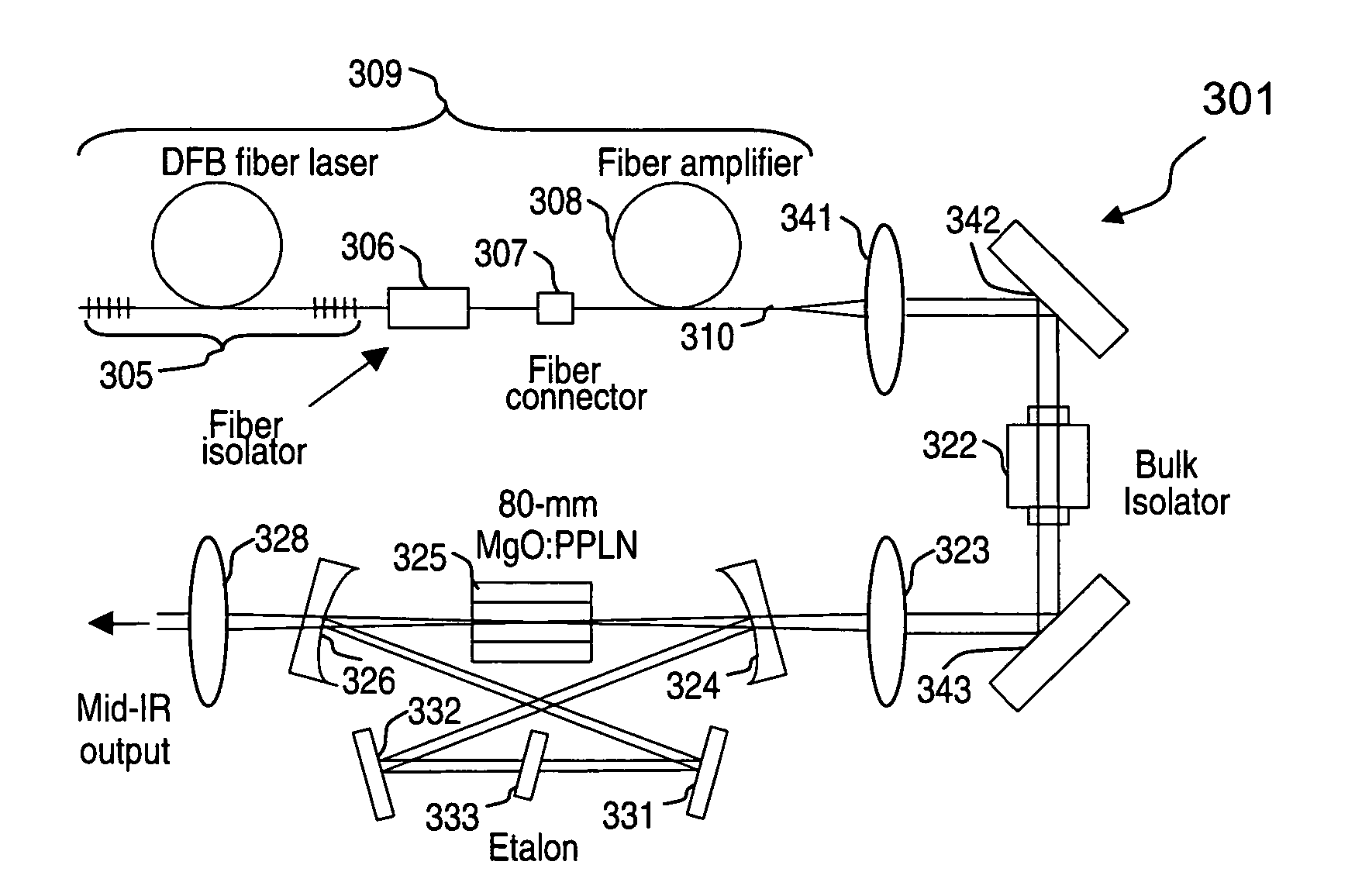
An optical parametric oscillator (OPO) is described that efficiently converts a near-infrared laser beam to tunable mid-infrared wavelength output. In some embodiments, the OPO includes an optical resonator containing a nonlinear crystal, such as periodically-poled lithium niobate. The OPO is pumped by a continuous-wave fiber-laser source having a low-power oscillator and a high-power amplifier, or using just a power oscillator). The fiber oscillator produces a single-frequency output defined by a distributed-feedback (DFB) structure of the fiber. The DFB-fiber-laser output is amplified to a pump level consistent with exceeding an oscillation threshold in the OPO in which only one of two generated waves (“signal” and “idler”) is resonant within the optical cavity. This pump source provides the capability to tune the DFB fiber laser by straining the fiber (using an attached piezoelectric element or by other means) that allows the OPO to be continuously tuned over substantial ranges, enabling rapid, wide continuous tuning of the OPO output frequency or frequencies.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
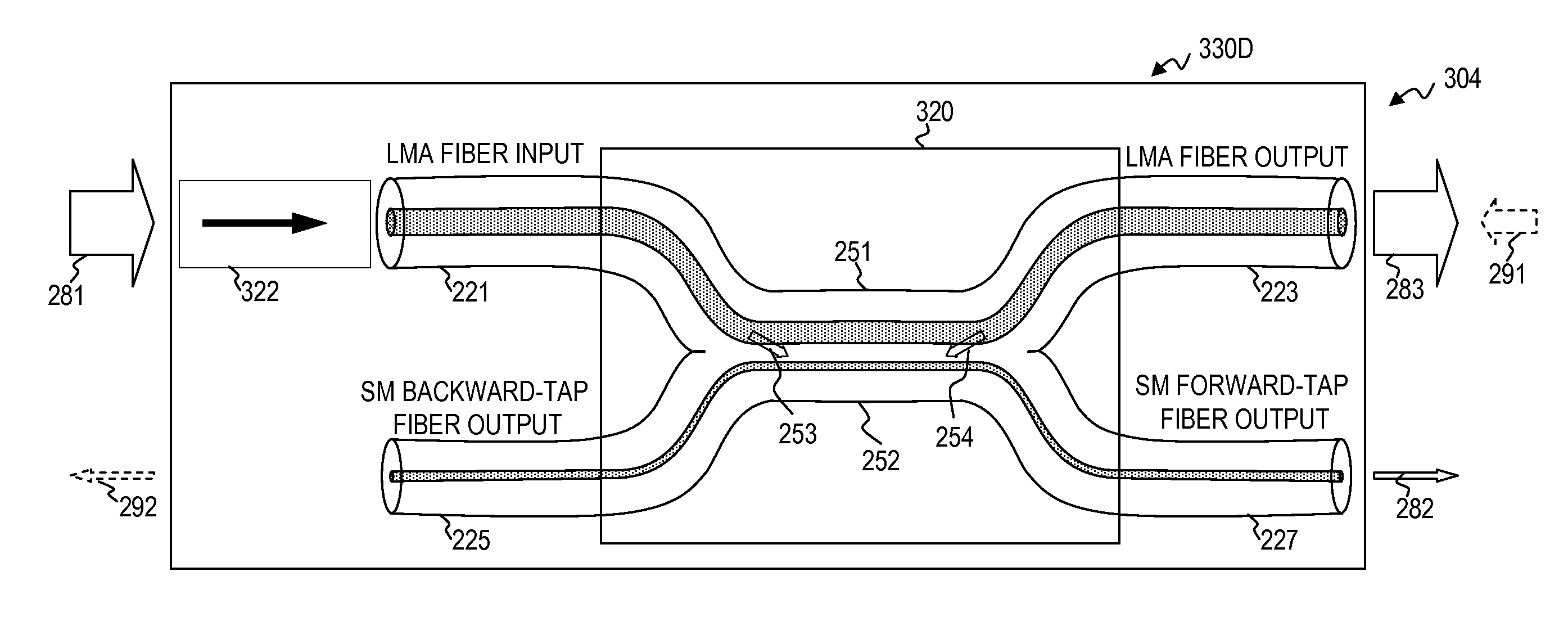
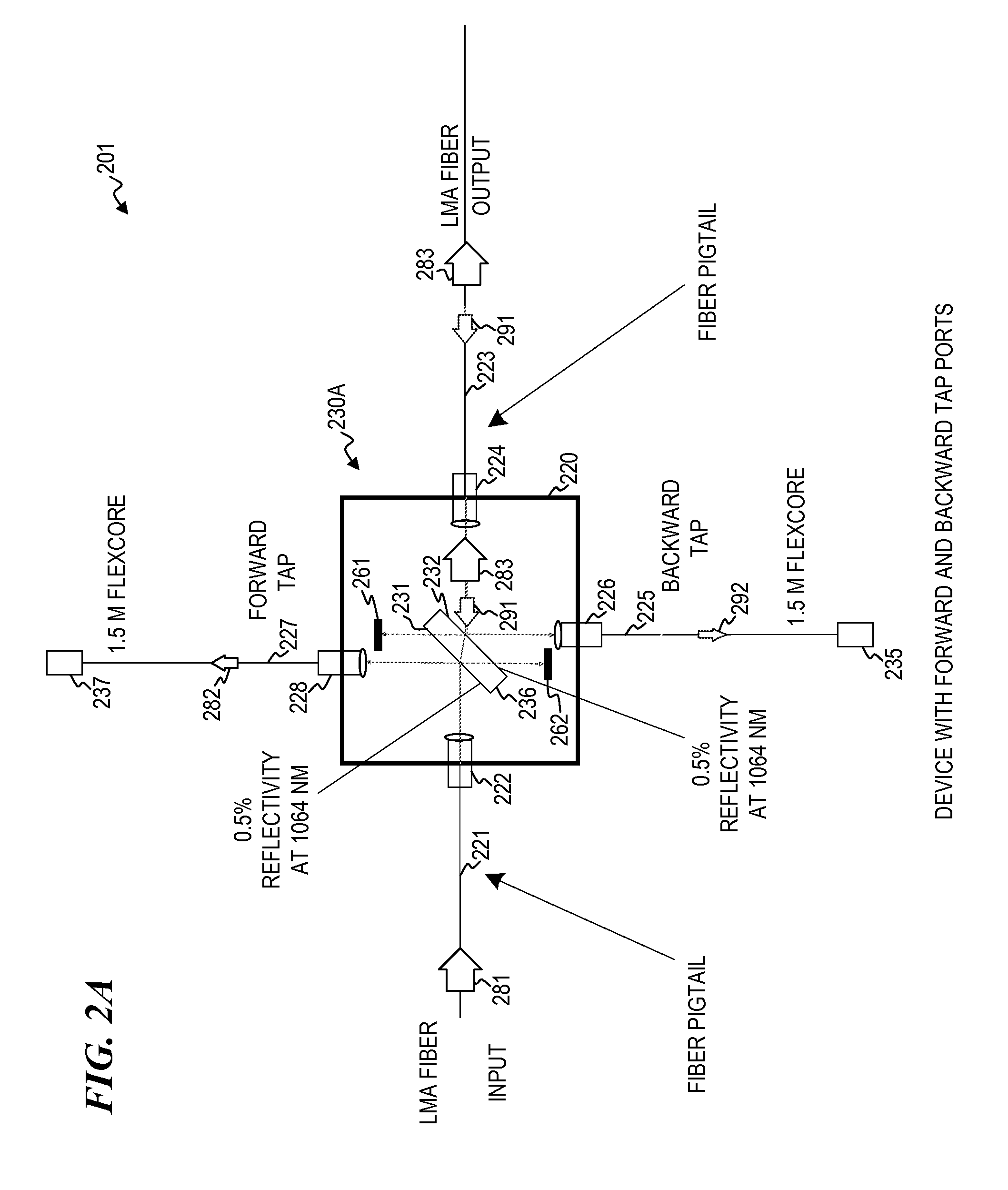
In-line forward/backward fiber-optic signal analyzer
ActiveUS20110091155A1Reduce catastrophic damageAvoid damageExcitation process/apparatusFibre transmissionAudio power amplifierSignal analyzer
An optical connector having a plurality of directional taps and connecting between a plurality of optical waveguides (e.g., such as a connector between a waveguide that is part of, or leads from, a seed laser and / or an initial optical-gain-fiber power amplifier, and a waveguide that is part of, or leads to, an output optical-gain-fiber power amplifier and / or a delivery fiber), wherein one of the directional taps extracts a small amount of the forward-traveling optical output signal from the seed laser or initial power amplifier (wherein this forward-tapped signal is optionally monitored using a sensor for the forward-tapped signal), and wherein another of the directional taps extracts at least some of any backward-traveling optical signal that may have been reflected (wherein this backward-tapped signal is optionally monitored using a sensor for the backward-tapped signal).
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Light emitting device and method for making same
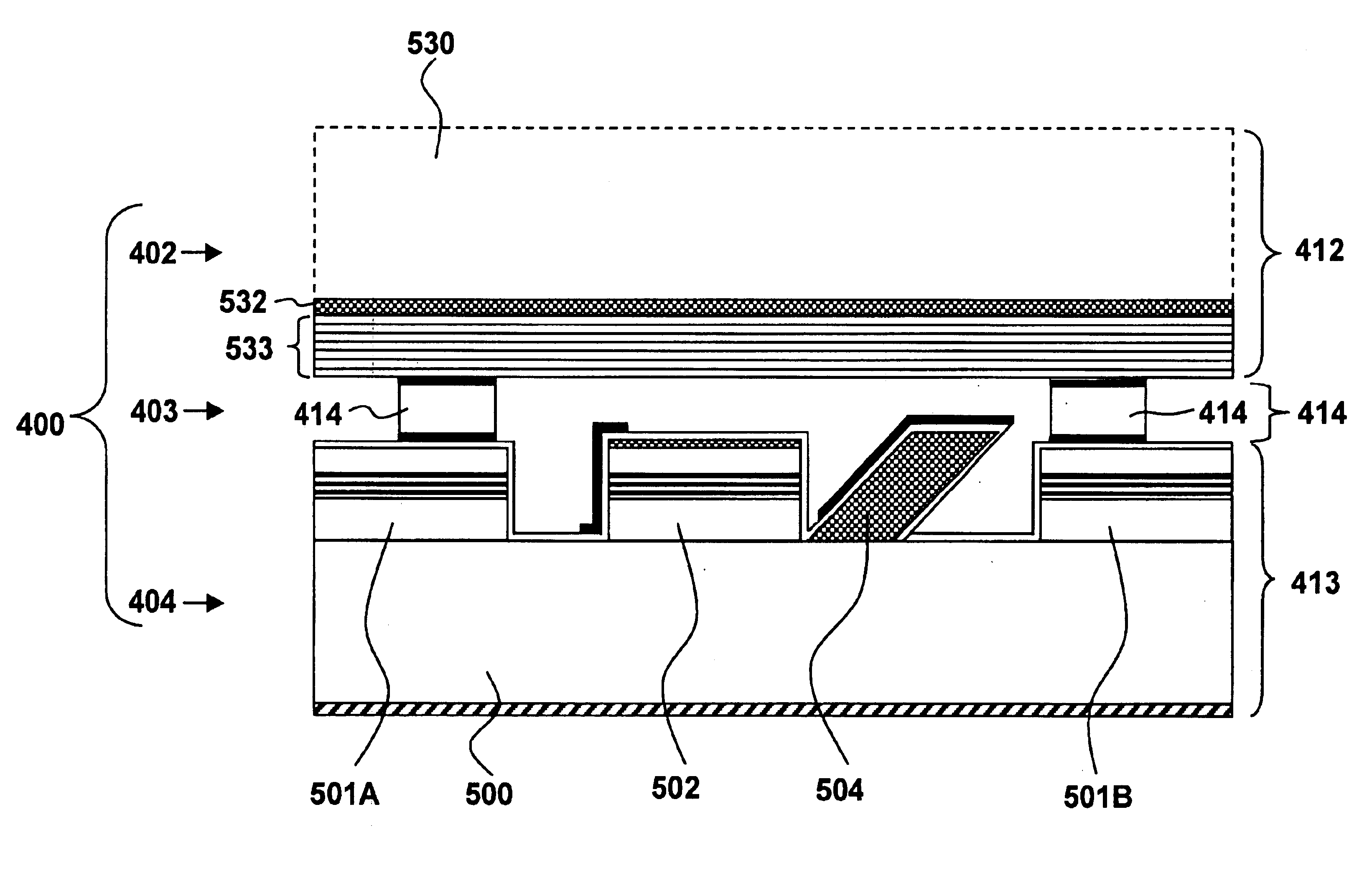
InactiveUS7112829B2Excitation process/apparatusSolid-state devicesLight emitting deviceLight emission
A light emission device and method for producing the device. The device includes, on a substrate, a stack including an etching stop layer, a first barrier layer, an emitting layer, and a second barrier layer. The stop layer is of the same nature as the emitting layer. One may form a mirror on the stack, eliminate the substrate by etching, and form another mirror on the stop layer to obtain a micro-cavity. The device may be applied in particular to the detection of gas.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
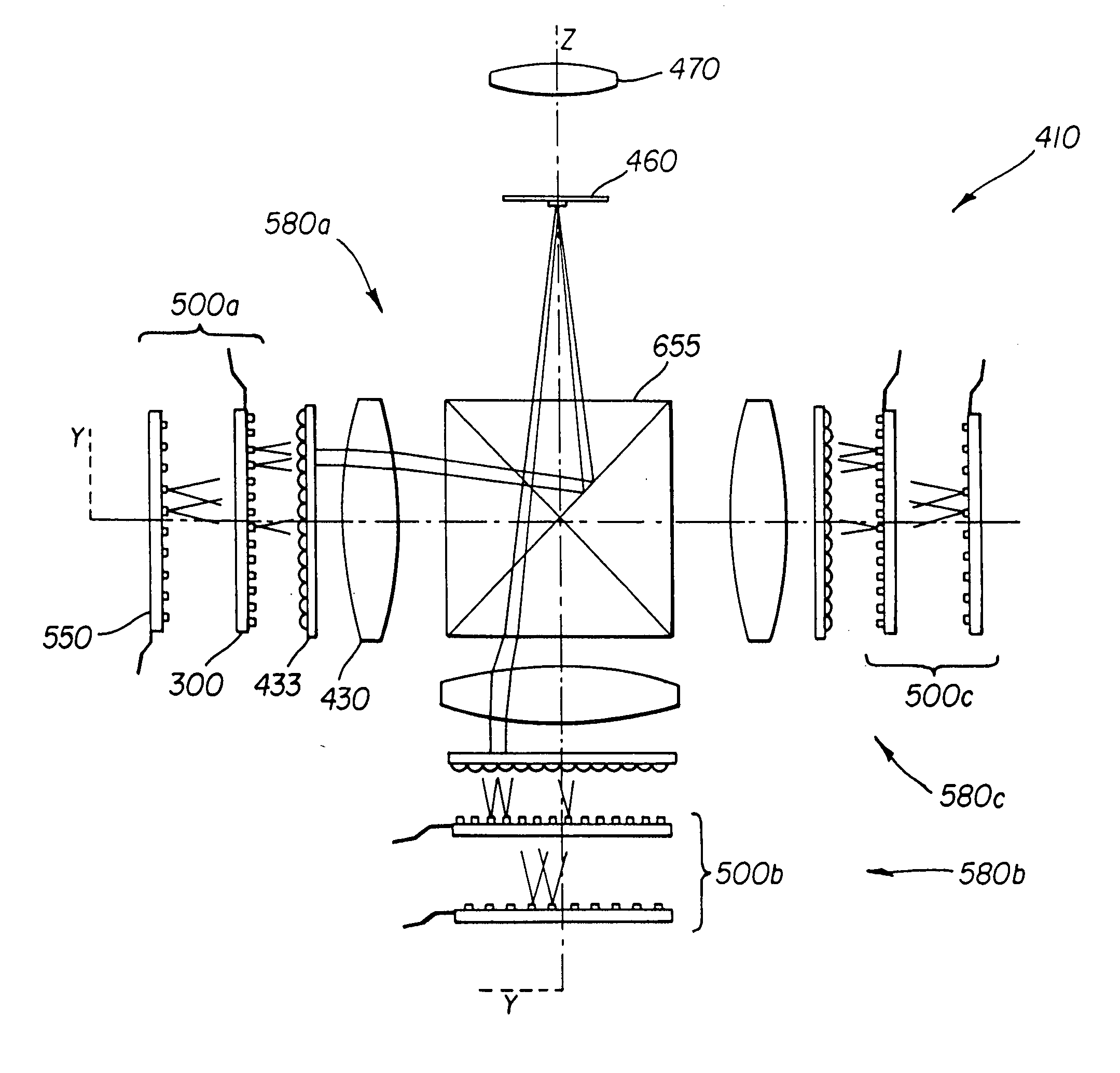
VCSEL and VCSEL array having integrated microlenses for use in a semiconductor laser pumped solid state laser system
InactiveUS6888871B1Reduce disagreementHigh power outputSemiconductor laser structural detailsExcitation process/apparatusVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserLight beam
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) device with improved power and beam characteristics. The VCSEL device contains one VCSEL or an array of VCSELs. Each VCSEL has a corresponding integrated microlens, and a heat sink is attached to the device side of the VCSEL device. The heat sink allows improved heat dissipation, and therefore provides improved power characteristics of the VCSEL device output laser beam. The microlens or microlens array allows easier and more compact focussing of the VCSEL device output laser beam. The VCSEL device can be used in a variety of optical systems, and its improved power and focusing characteristics provide a compact, low power, low cost laser system.
Owner:PRINCETON OPTRONICS
Electron-beam excitation laser
InactiveUS20040218651A1Laser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusDielectricElectron source
An electron-beam excitation laser has a laser structure with a light emitter and reflectors on one hand and an electron source on the other hand, wherein at least part of the light emitter or reflectors has a multidimensional photonic crystal structure. An electron-beam excitation laser includes an electron source emitting electrons and a laser structure consisting of a light emitter and reflectors, accelerates electrons from the electron source, and irradiates the electrons to the laser structure to emit a laser beam from the laser structure, wherein the reflectors and / or the light emitter in the laser structure are formed with multidimensional photonic crystals in which dielectrics with different dielectric constants are arrayed in a plurality of directions at periodic intervals, and one of the dielectrics with different dielectric constants may be formed with a light-emitting material.
Owner:CANON KK
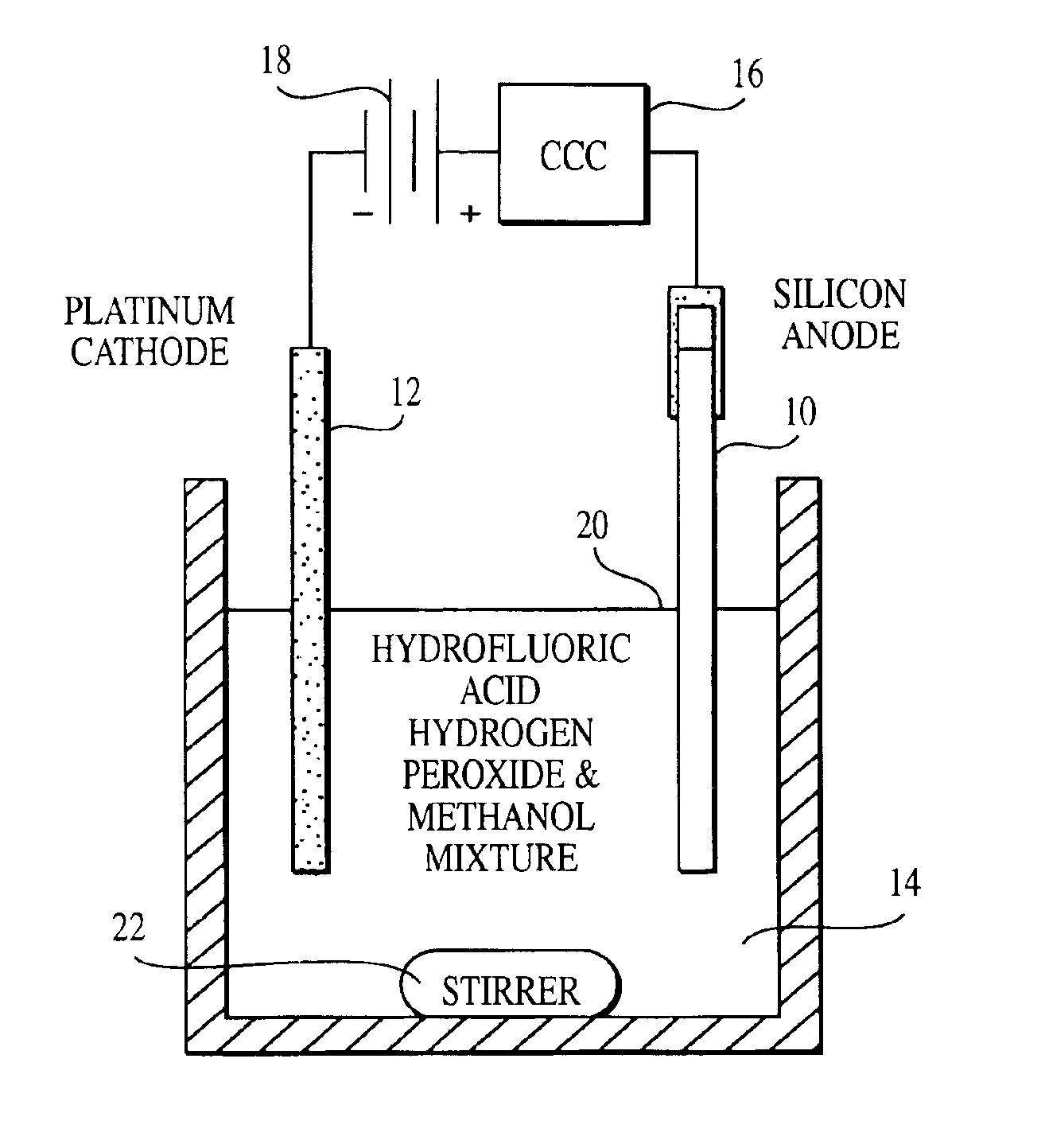
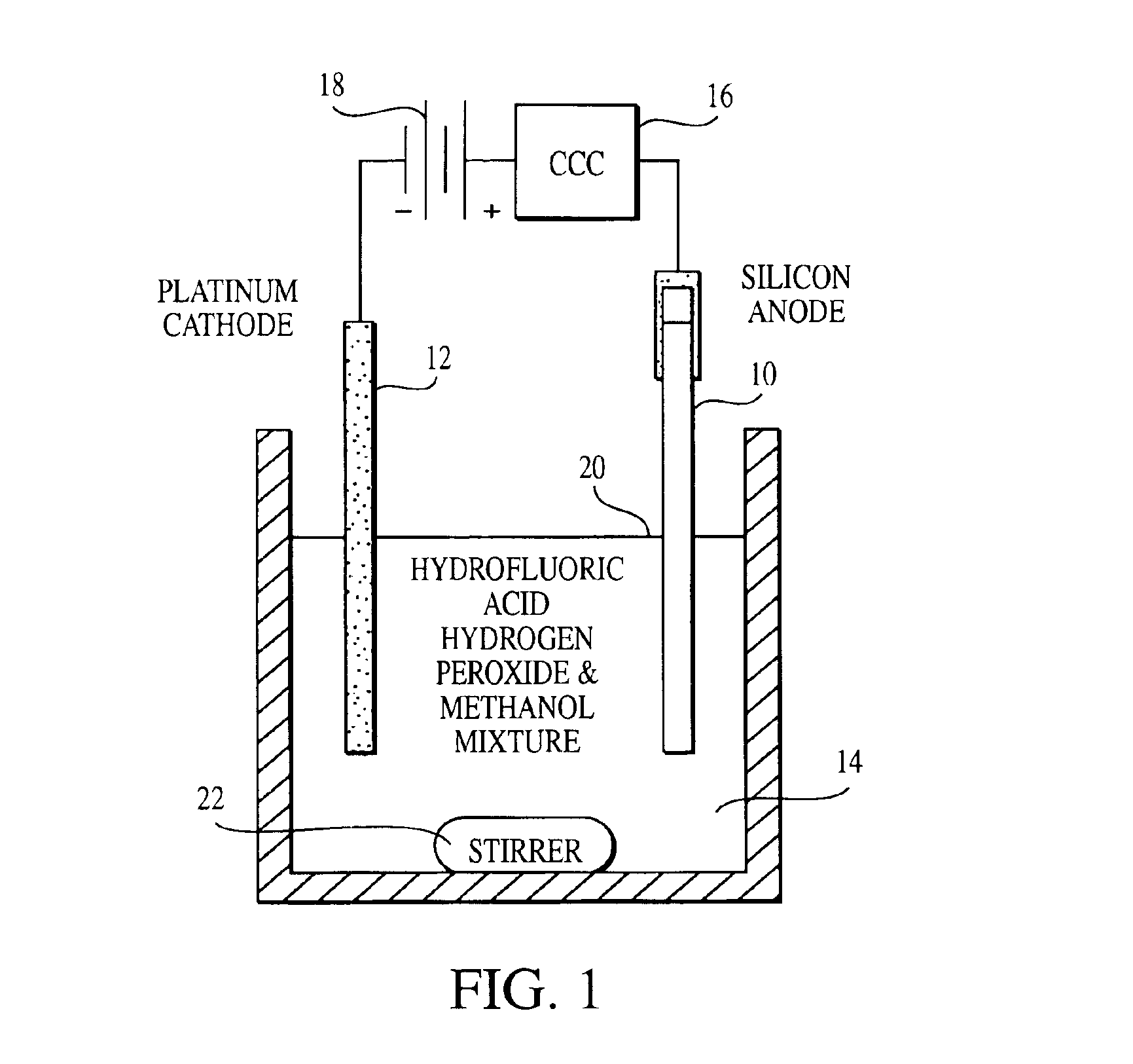
Silicon nanoparticle and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6846474B2Highly uniform in sizeEasily filtered outMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleColloid
Highly uniform 1 nm silicon nanoparticles are provided by the invention. The nanoparticles exhibit beneficial properties. They are a source of stimulated emissions. They may be suspended in liquids, and solids. They can be formed into crystals, colloids and films. The nanoparticles of the invention are about 1 nm having about only one part in one thousand greater than 1 nm. A method for producing the silicon nanoparticle of the invention is a gradual advancing electrochemical etch of bulk silicon. Separation of nanoparticles from the surface of the silicon may also be conducted. Once separated, various methods may be employed to form plural nanoparticles into colloids, crystals, films and other desirable forms. The particles may also be coated or doped.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Optically Surface-Pumped Edge-Emitting Devices and Systems and Methods of Making Same
InactiveUS20150288129A1Laser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusPhosphorPhotoluminescence
Optical resonator devices and systems enhanced with photoluminescent phosphors and designed and configured to output working light in an edge-emitting fashion at one or more wavelengths based on input / pump light, and systems and devices made with such resonators. The edge-emitting functionality is enabled by providing one or more waveguides that direct light luminesced from the phosphors to one or more edges of the device. In some embodiments, the resonators contain multiple optical resonator cavities in combination with one or more photoluminescent phosphor layers or other structures. In other embodiments, the resonators are designed to simultaneously resonate at the input / pump and output wavelengths. The photoluminescent phosphors can be any suitable photoluminescent material, including semiconductor and other materials in quantum-confining structures, such as quantum wells and quantum dots, among others.
Owner:VERLASE TECH
Long-distance quantum communication
InactiveUS20080212186A1Good compensationEasy to takeExcitation process/apparatusPhotomechanical apparatusBeam splitterNoise level
The invention provides systems and methods enabling high fidelity quantum communication over long communication channels even in the presence of significant loss in the channels. The invention involves laser manipulation of quantum correlated atomic ensembles using linear optic components (110, 120), optical sources of low intensity pulses (10), interferers in the form of beam splitters (150), and single-photon detectors (180, 190) requiring only moderate efficiencies. The invention provides fault-tolerant entanglement generation and connection using a sequence of steps that each provide built-in entanglement purification and that are each resilient to realistic noise levels. The invention relies upon collective rather single particle excitations in atomic ensembles and results in communication efficiency scaling polynomially with the total length of the communication channel.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE +1
Apparatuses and methods for generating coherent electromagnetic laser radiation
The present disclosure is directed to laser apparatuses for generating coherent electromagnetic laser radiation having an electron beam generator, a diffraction grating element oriented such that a beam of electrons from the electron beam generator is directed over the diffraction grating element, and at least one wing element coupled to the diffraction grating element. In some embodiments, the wing element(s) can be coupled to a top portion of the diffraction grating element. While in others, the wing element(s) can be coupled to a side portion of the diffraction grating element. The present disclosure is also directed to methods of manufacturing diffraction grating elements involving placing at least one secondary conducting sheet having a first height on at least one primary conductive sheet having a different second height, and securing the primary and secondary conductive sheets together. The primary and secondary conductive sheets can be alternating and their thicknesses may also be different. Additionally, the primary and secondary conductive sheets may be secured via a clamping device.
Owner:VERMONT PHOTONICS
Laser pulse picking employing controlled AOM loading
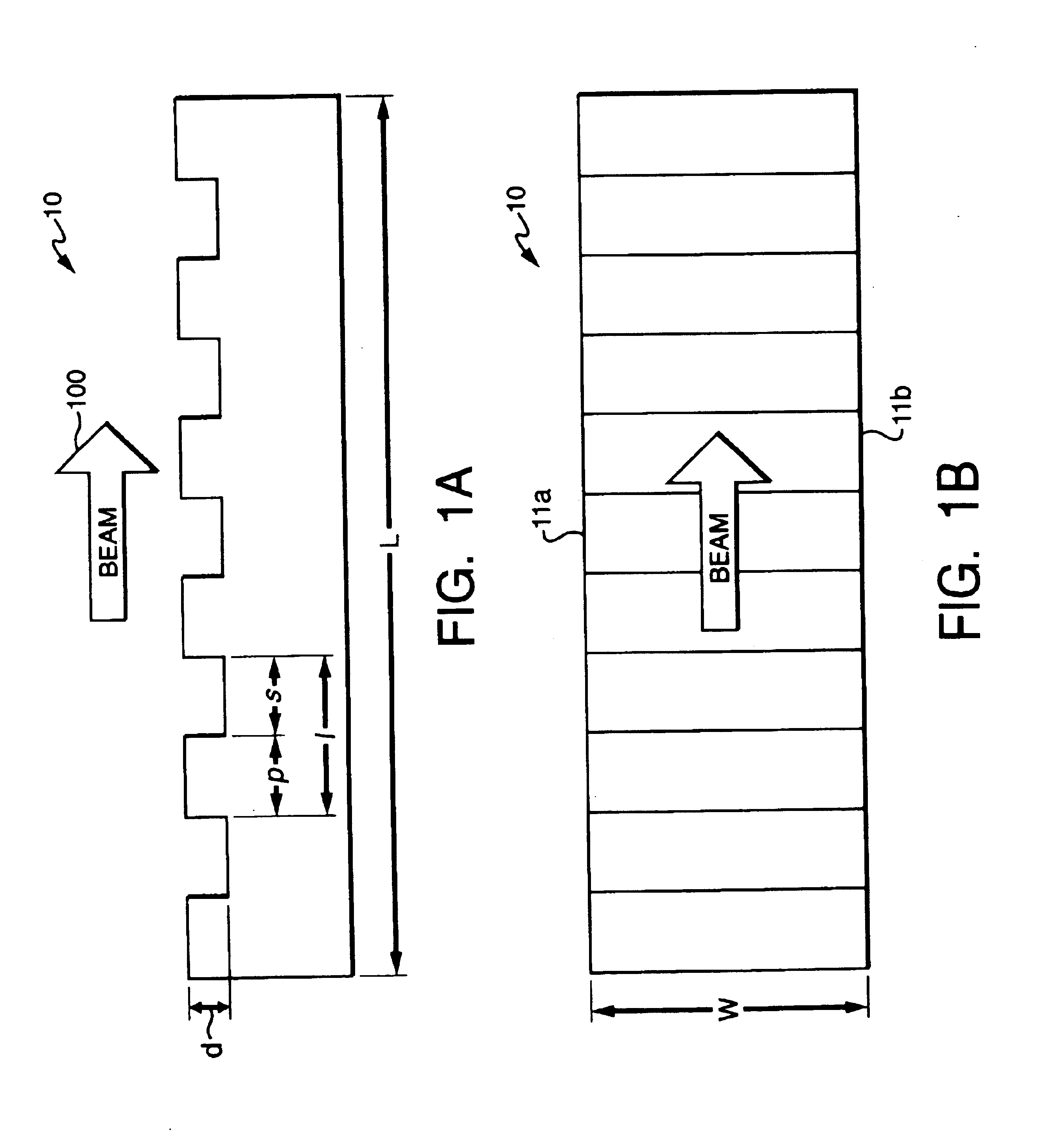
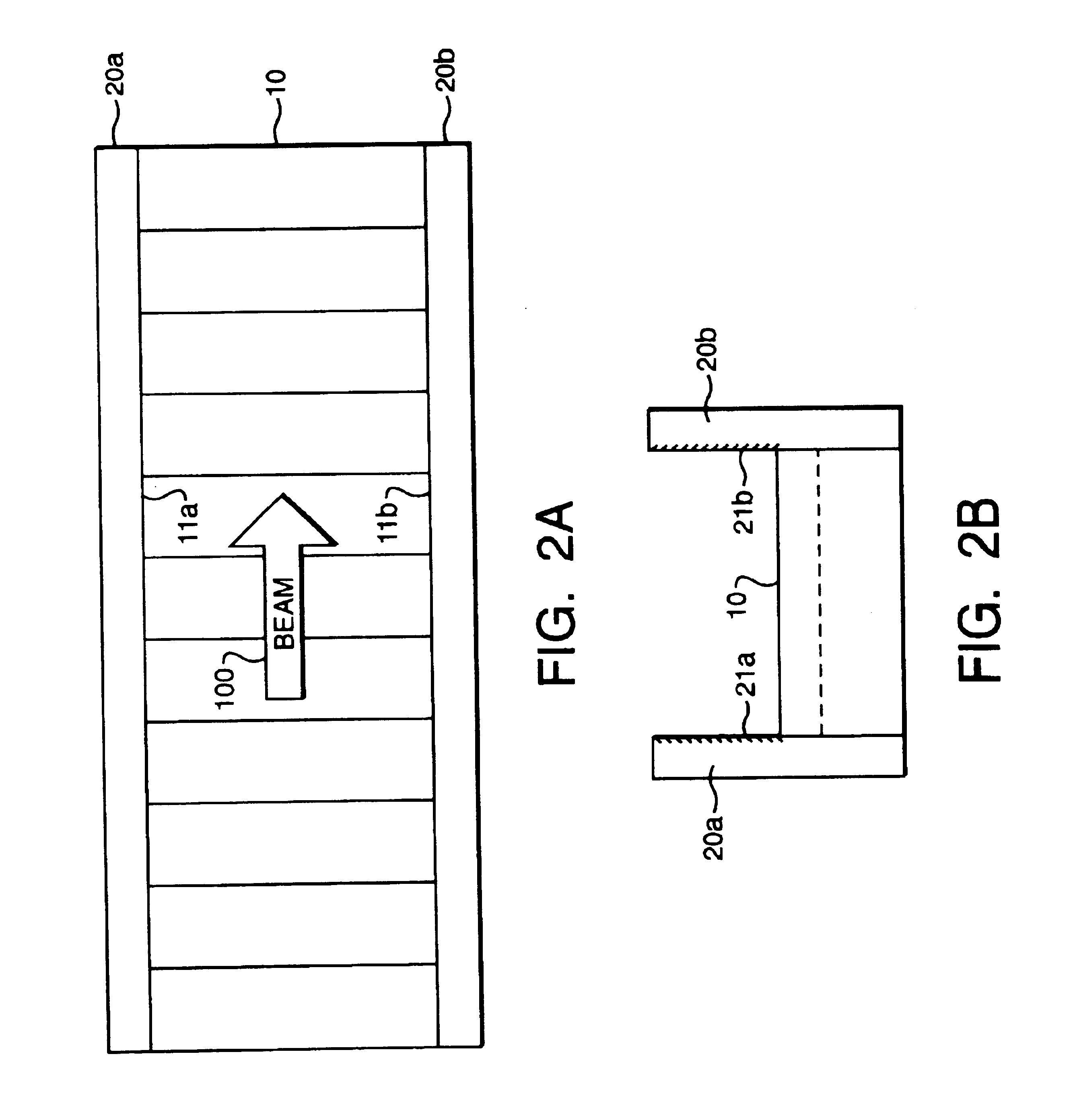
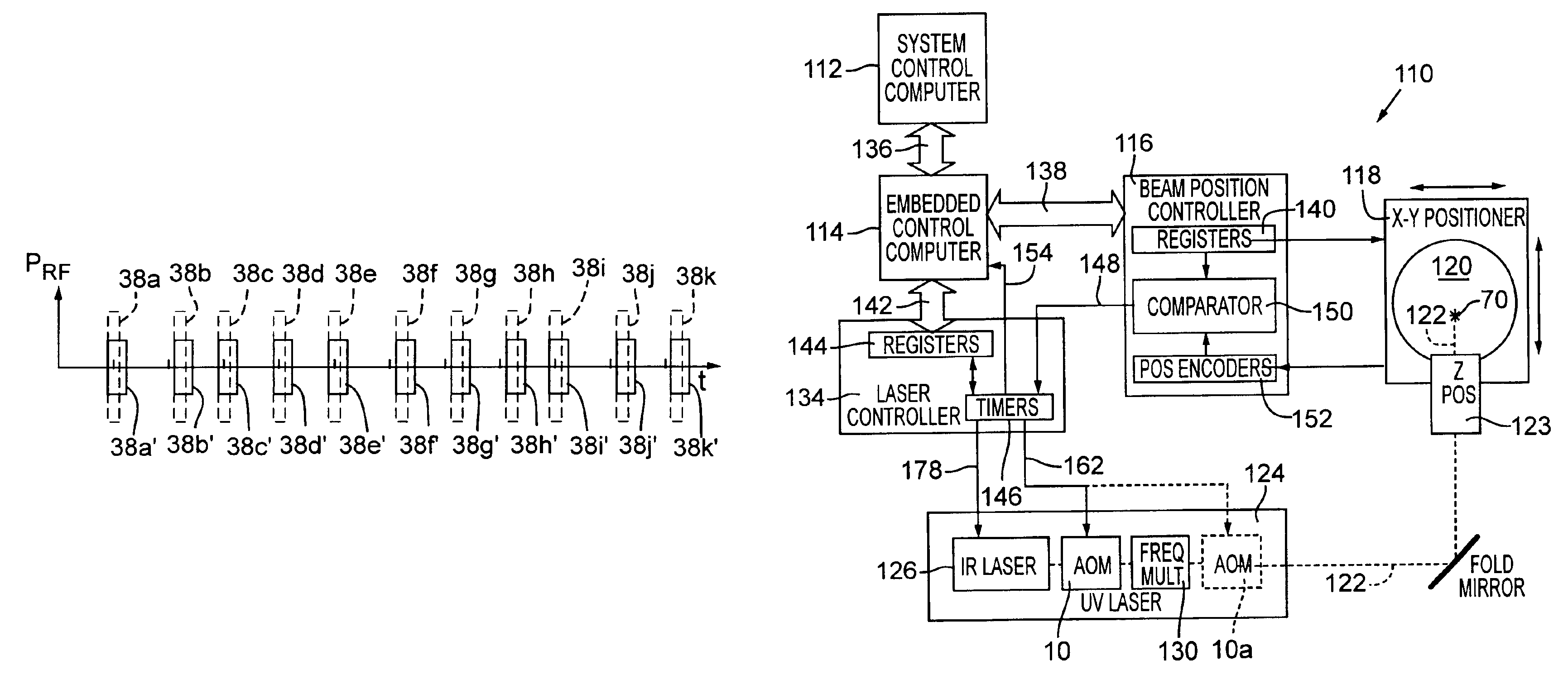
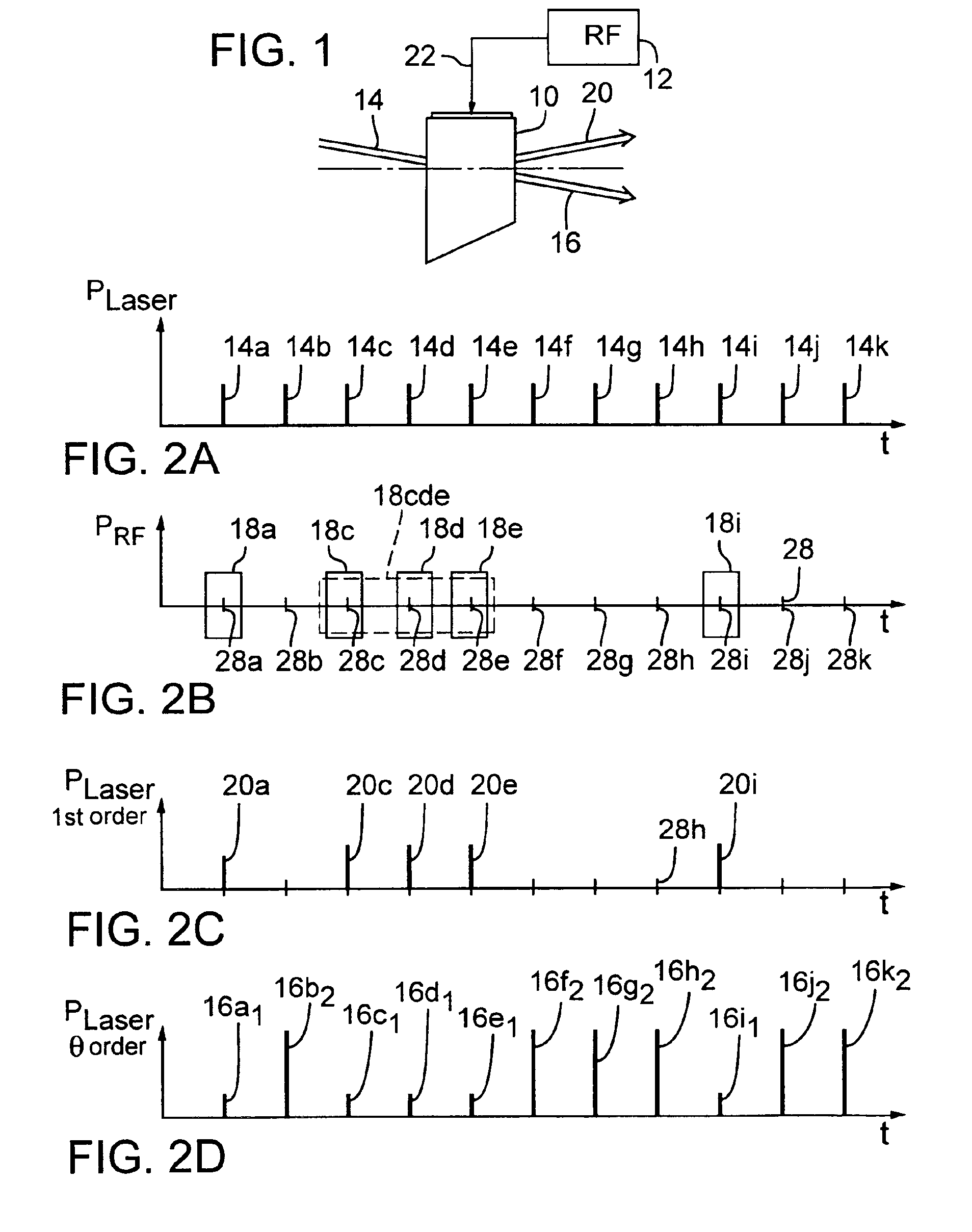
ActiveUS6947454B2Constant RF powerConstant thermal loadingExcitation process/apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPulse energyOptoelectronics
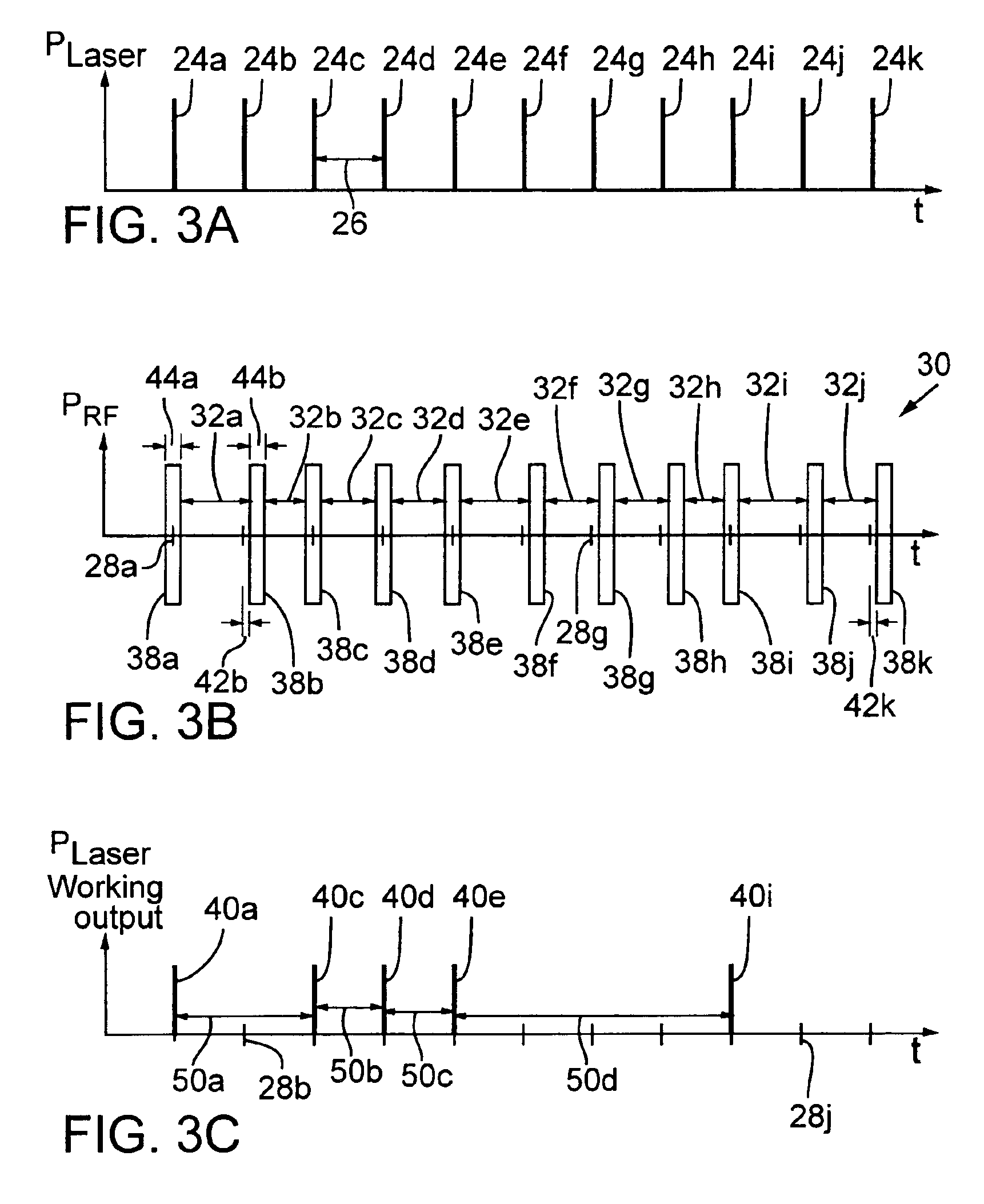
A laser (126) and an AOM (10) are pulsed at substantially regular and substantially similar constant high repetition rates to provide working laser outputs (40) with variable nonimpingement intervals (50) without sacrificing laser pulse-to-pulse energy stability. When a working laser output (40) is demanded, an RF pulse (38) is applied to the AOM (10) in coincidence with the laser output (24) to transmit it to a target. When no working laser output (40) is demanded, an RF pulse (38) is applied to the AOM (10) in noncoincidence with the laser output (24) so it gets blocked. So the average thermal loading on the AOM (10) remains substantially constant regardless of how randomly the working laser outputs (40) are demanded. The AOM (10) can also be used to control the energy of the working laser output (40) by controlling the power of the RF pulse (38) applied. When the RF power is changed, the RF duration (44) of the RF pulse (38) is modified to maintain the constant average RF power. Consistent loading on the AOM (10) eliminates deterioration of laser beam quality and laser beam pointing accuracy associated with thermal loading variation on the AOM (10) and is advantageous for applications such as IC chip link processing where stable working laser outputs (40) with variable output intervals (50) are needed.
Owner:ELECTRO SCI IND INC
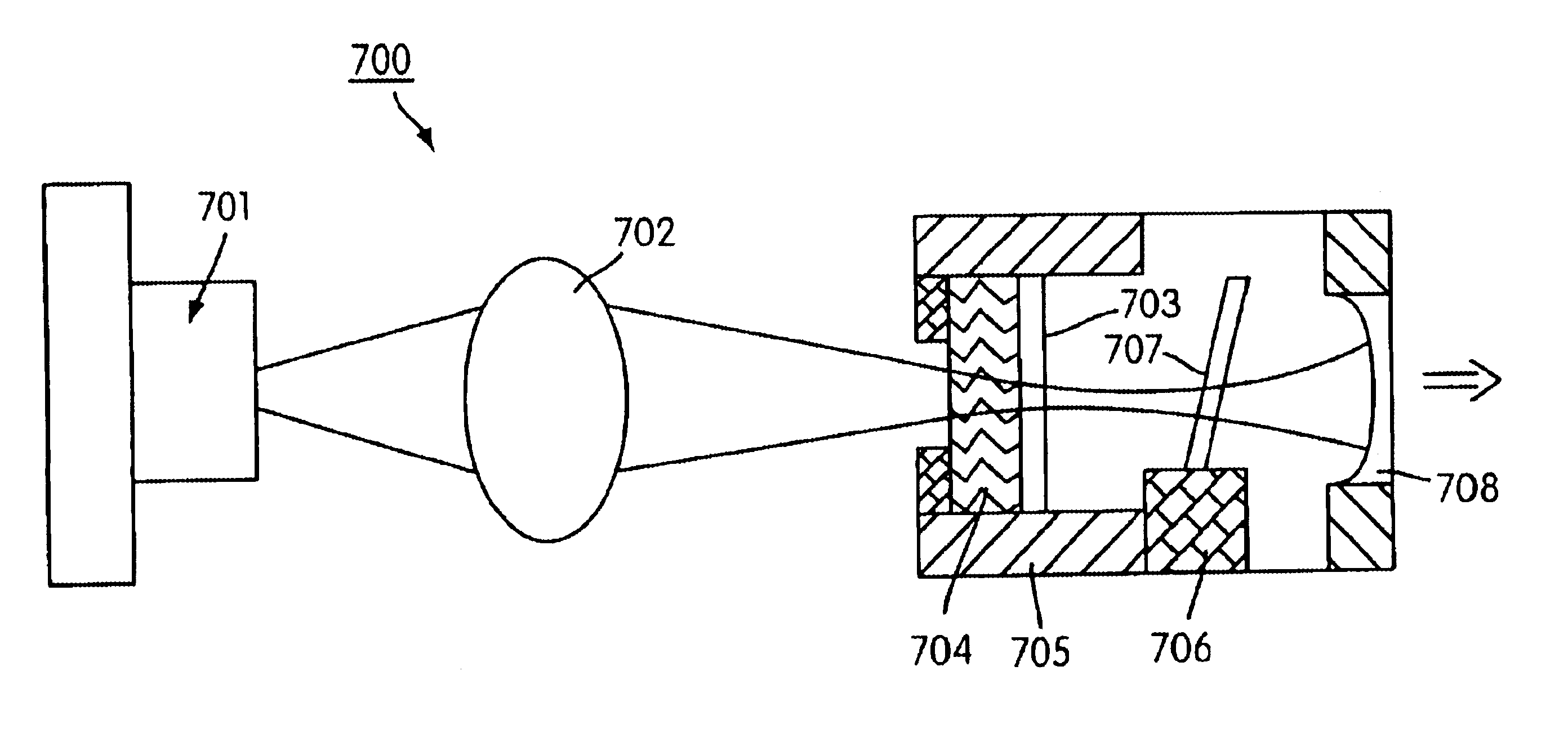
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for optically pumped vertical cavity surface emitting laser devices
InactiveUS6940885B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsResonant cavityVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
Monolithic integrated vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser devices are disclosed including an edge-emitting semiconductor pump laser (PL), an optically-pumped vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL), and a means for deflecting and shaping the output beam of the pump laser to optically excite the VCSEL. The optically-pumped VCSEL structure may be adapted to include a resonant cavity with multiple fixed wavelengths, or a resonance cavity whose wavelength is continuously tunable. Wafer level manufacturing techniques are also disclosed.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
Organic semiconductor lasers
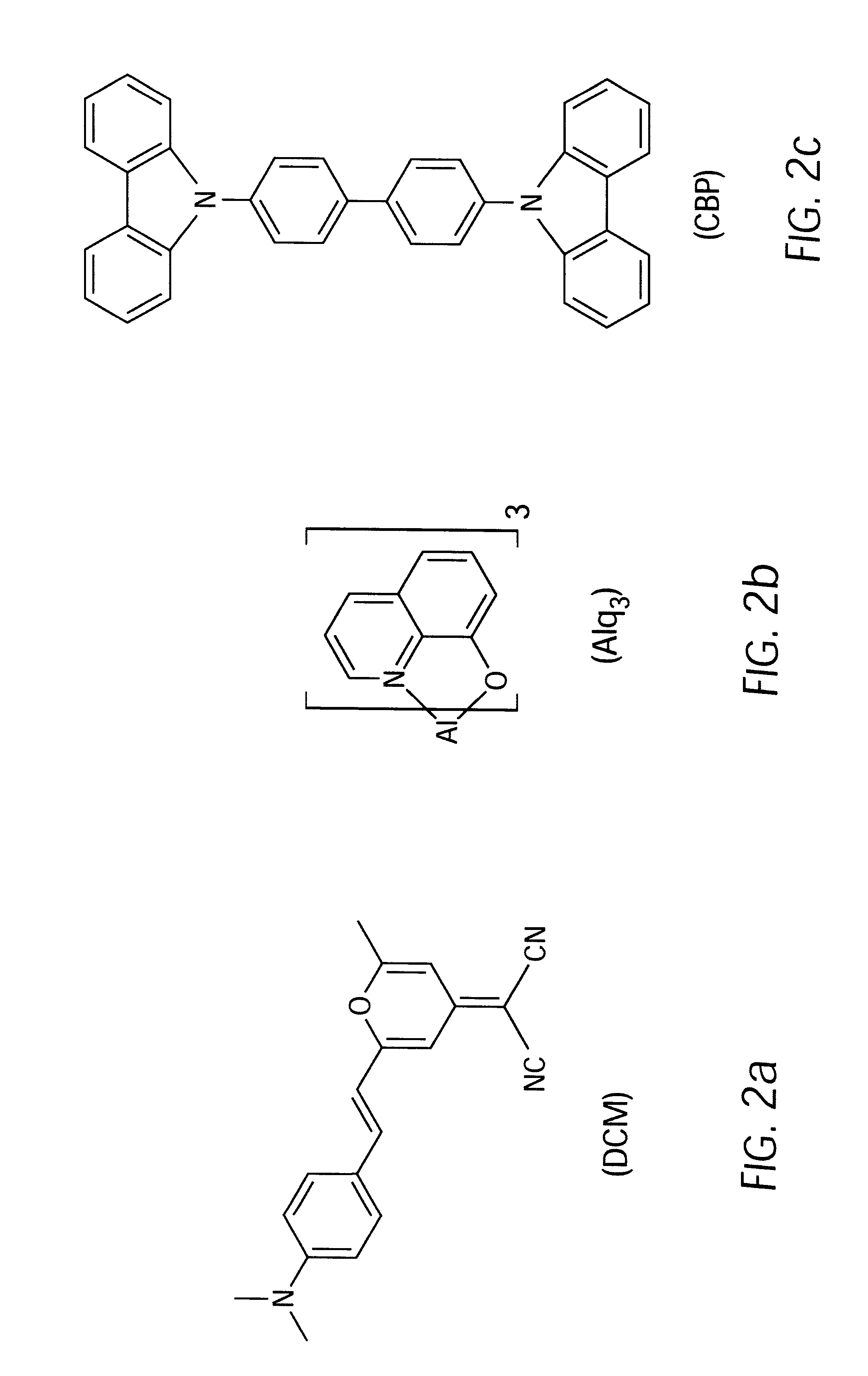
Lasers comprising a substrate and a layer of organic material over the substrate. The organic material includes host and dopant materials that result in the laser emission of a desired color when pumped by optical pump energy. Host materials include CBP and tris-(8-hydroxyquinoline) aluminum, which when combined with dopant materials such as coumarin-47, coumarin-30, perylene, rhodamine-6G, DCM, DCM2, and pyrromethane-546 result in the efficient lasing of colors such as blue, green and yellow.
Owner:SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA UNIV OF THE +2
Apparatus and method for pumping and operating optical parametric oscillators using DFB fiber lasers
ActiveUS7620077B2Reduce pump powerLarge and undesirable buildupLaser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusInfrared laser beamLithium niobate
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
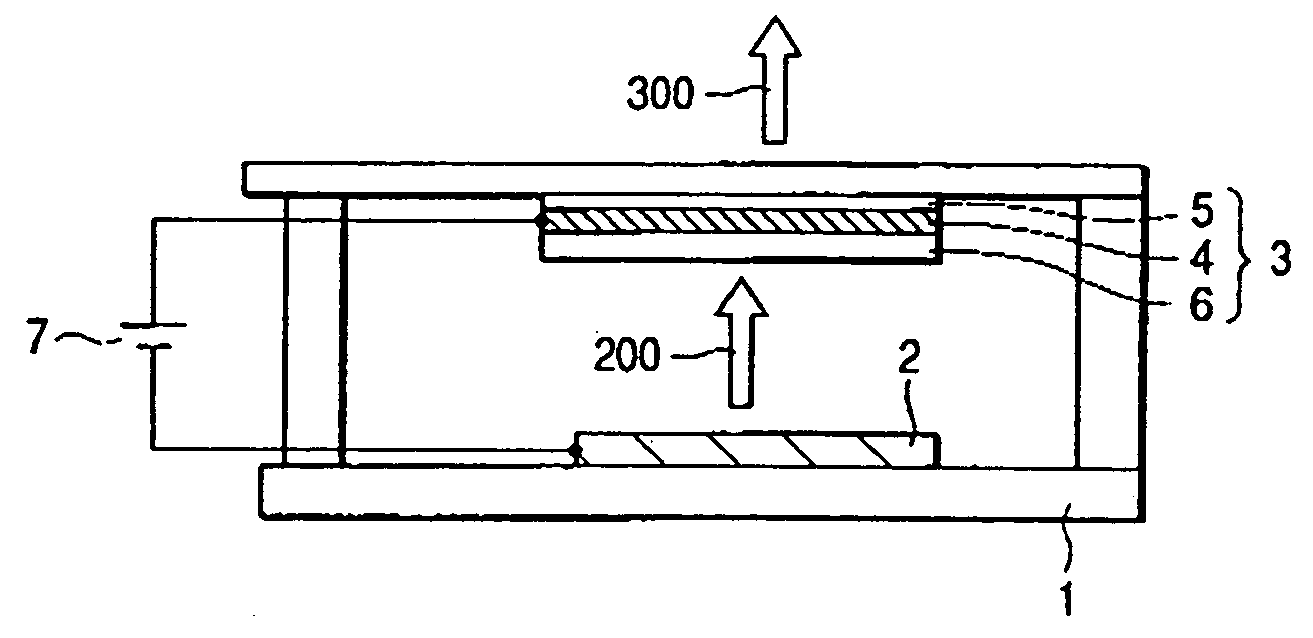
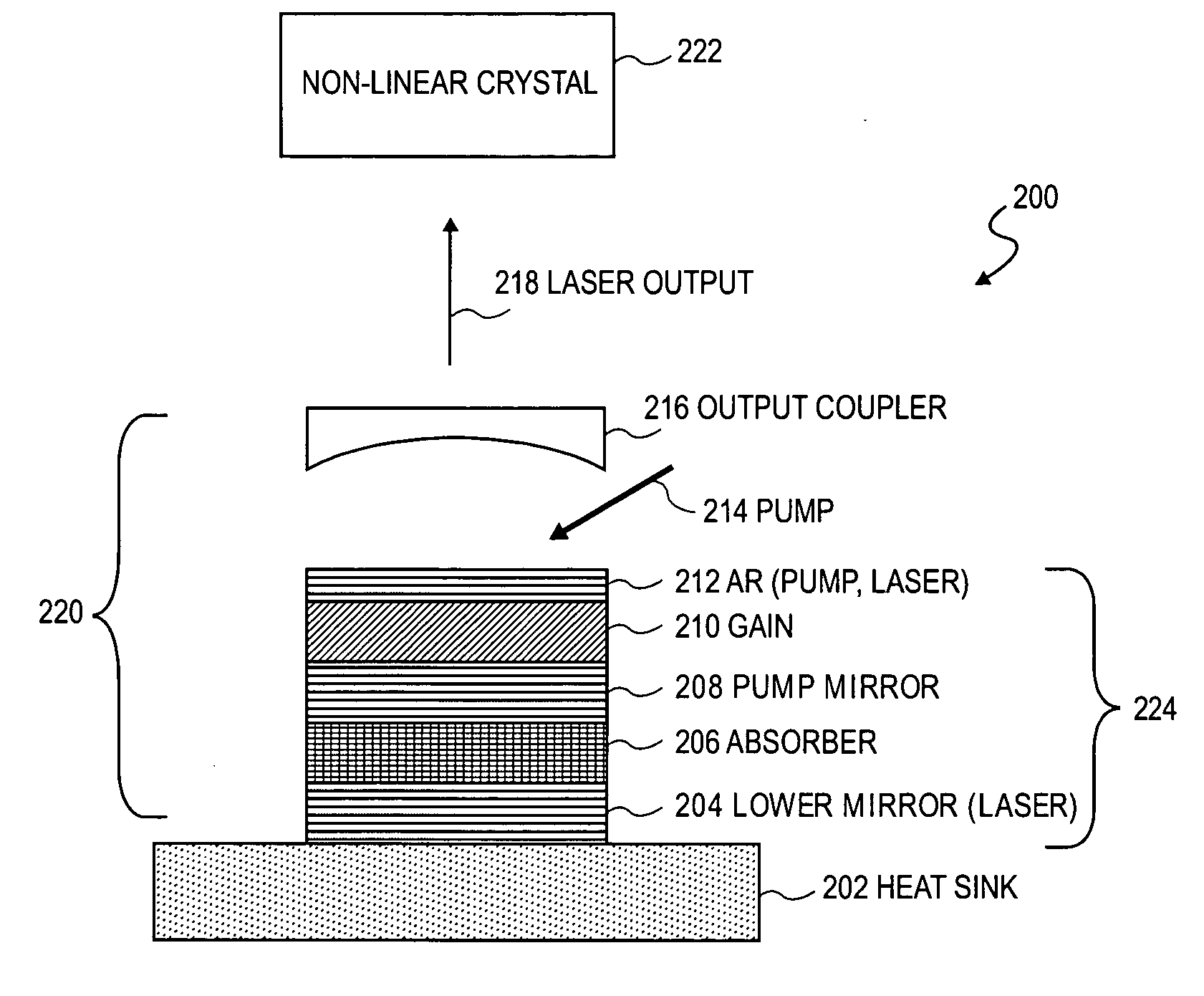
Surface emitting laser with an integrated absorber
InactiveUS20060029112A1Laser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionOutput couplerOptoelectronics
A surface emitting laser (SEL) with an integrated absorber. A lower mirror and an output coupler define a laser cavity of the SEL. A monolithic gain structure positioned in the laser cavity includes a gain region and an absorber, wherein a saturation fluence of the absorber is less than a saturation fluence of the gain region.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
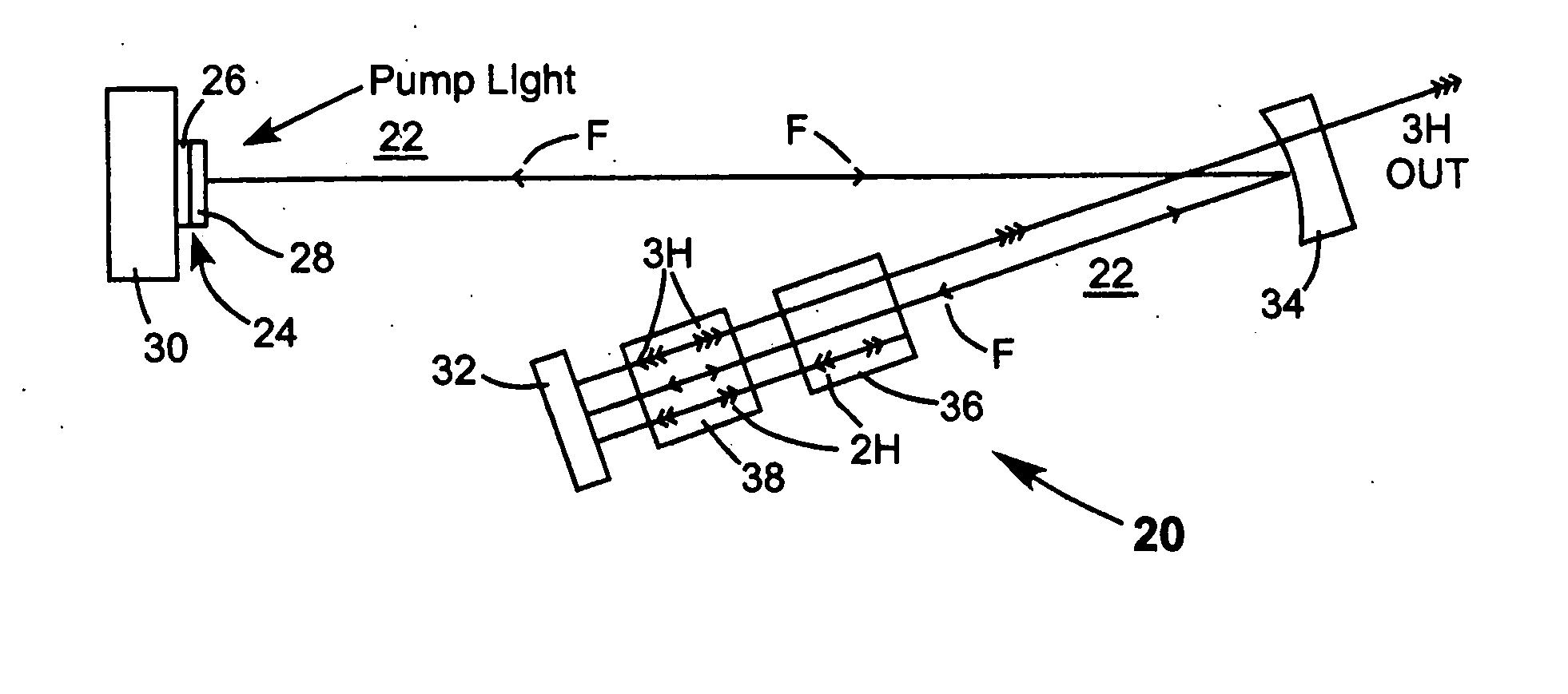
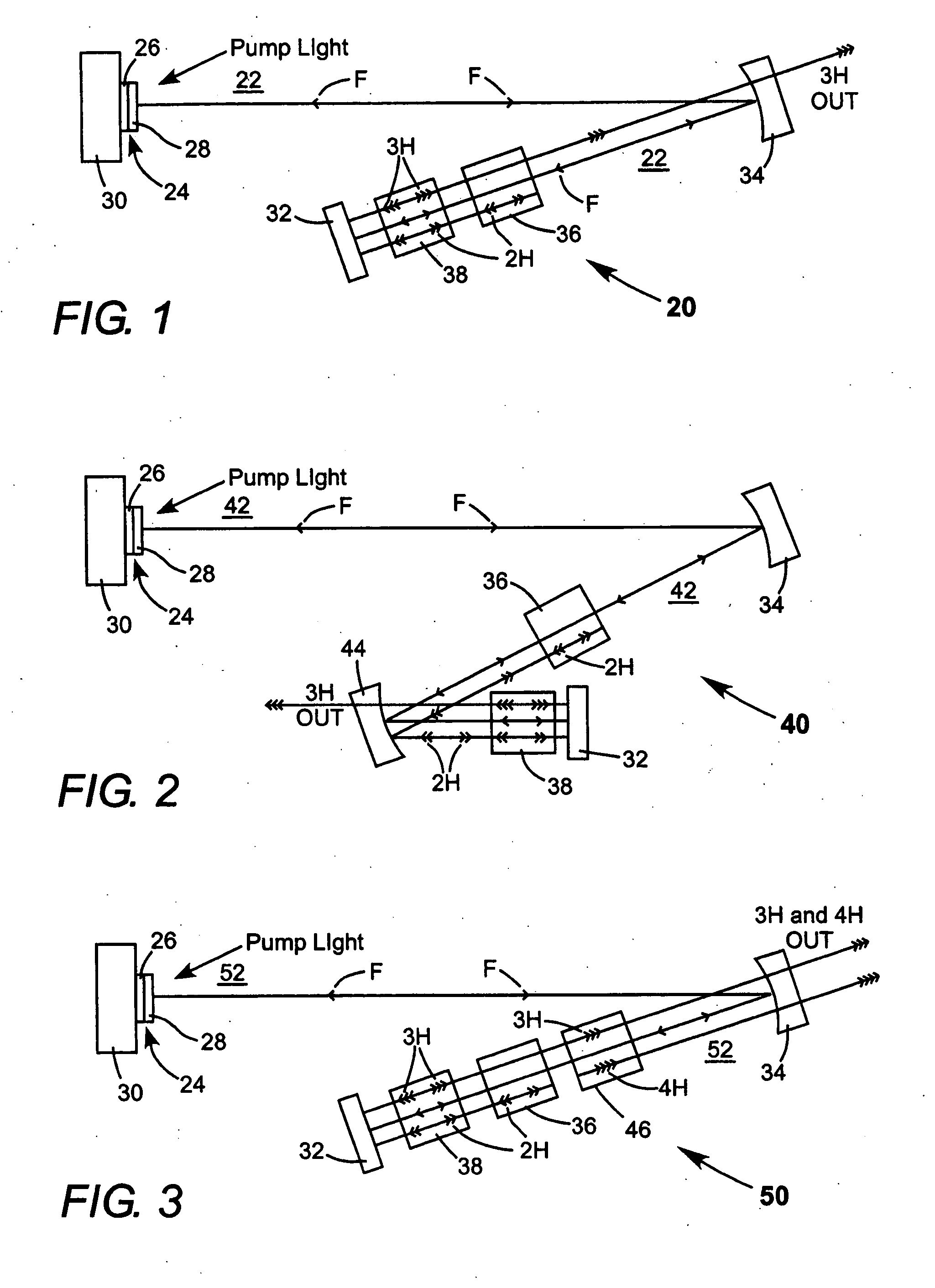
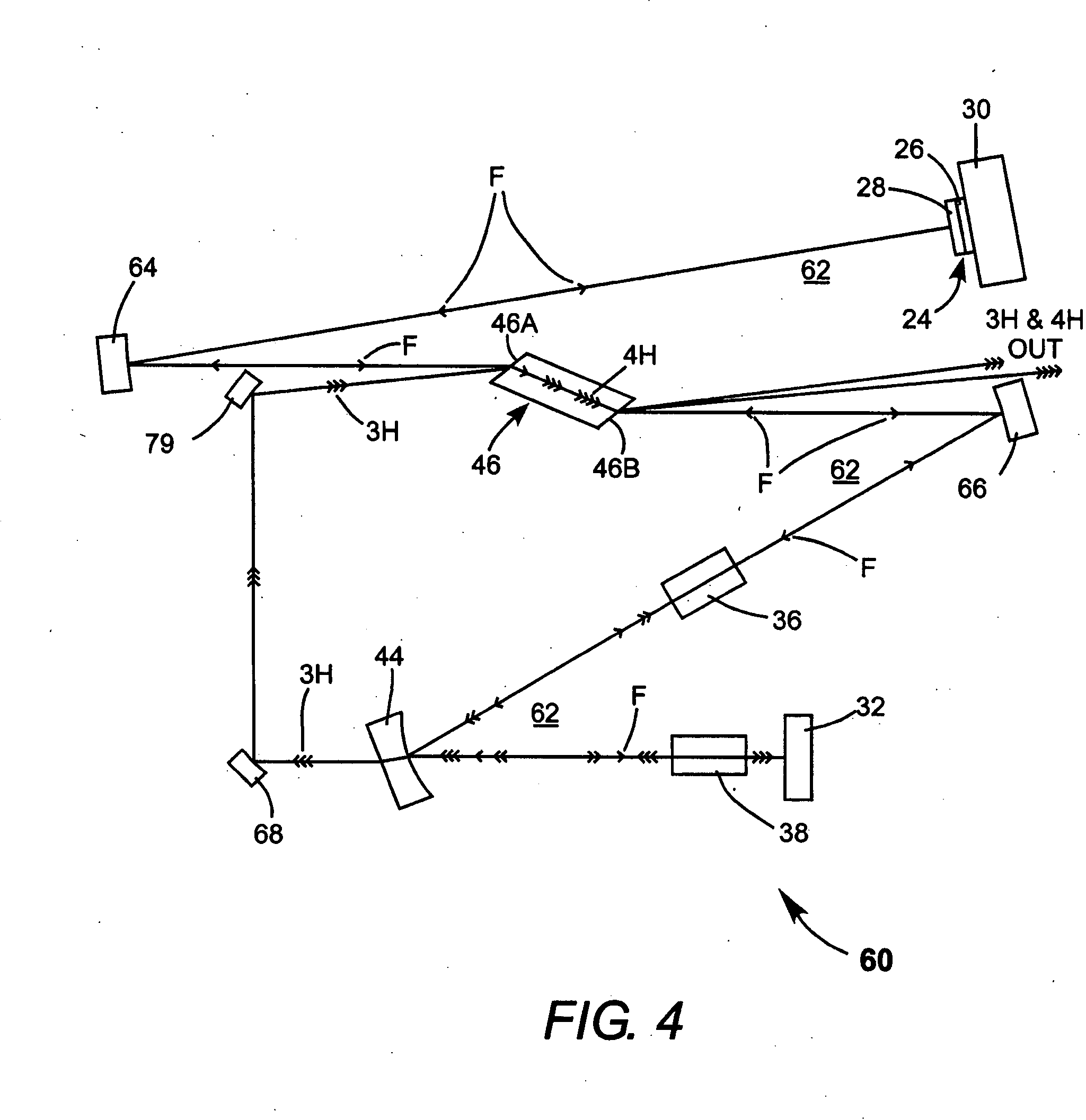
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser
InactiveUS20050078718A1High frequencyImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusNonlinear crystalsPhysics
A method of intracavity frequency conversion in a CW laser includes causing fundamental radiation to circulate in a laser resonator. The fundamental radiation makes a first pass through an optically nonlinear crystal where a fraction of the fundamental radiation generates second-harmonic radiation in a forward pass through the crystal. The residual fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation are then sum-frequency mixed in forward and reverse passes through an optically nonlinear crystal such that a fraction of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. The residual second-harmonic radiation and fundamental radiation from the sum-frequency mixing then make a reverse pass through the second-harmonic generating crystal where the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation, or can be used to pump another optically nonlinear crystal in an optical parametric oscillator. Second-harmonic radiation can also be used to pump an optical parametric oscillator.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Laser with optimized coupling of pump light to a gain medium in a side-pumped geometry
InactiveUS6157663AImprove the level ofEasy maintenanceExcitation process/apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavityHigh absorption
A solid-state laser includes a high-absorption coefficient solid-state gain medium such as Nd:YVO4 that is side pumped with a semiconductor laser diode array. The resonant cavity of the solid-state laser is positioned so that the TEM00 mode is spaced from the face of the laser through which the laser is pumped by a distance sufficient to reduce diffraction losses but sufficiently near to allow coupling of pump light into the gain mode. The gain medium, the doping level of the gain medium, and the operating temperature of the pump laser are selected to efficiently couple pump light into the gain mode. The pump laser is positioned to side pump the gain medium without collimating or focusing optics between the pump laser and the face of the gain medium. A gap between the pump laser and the gain medium is empirically selected to match the angular extent of the pump laser output light to the height of the gain mode at the position of the gain mode fixed to optimize coupling and diffraction losses.
Owner:3D SYST INC
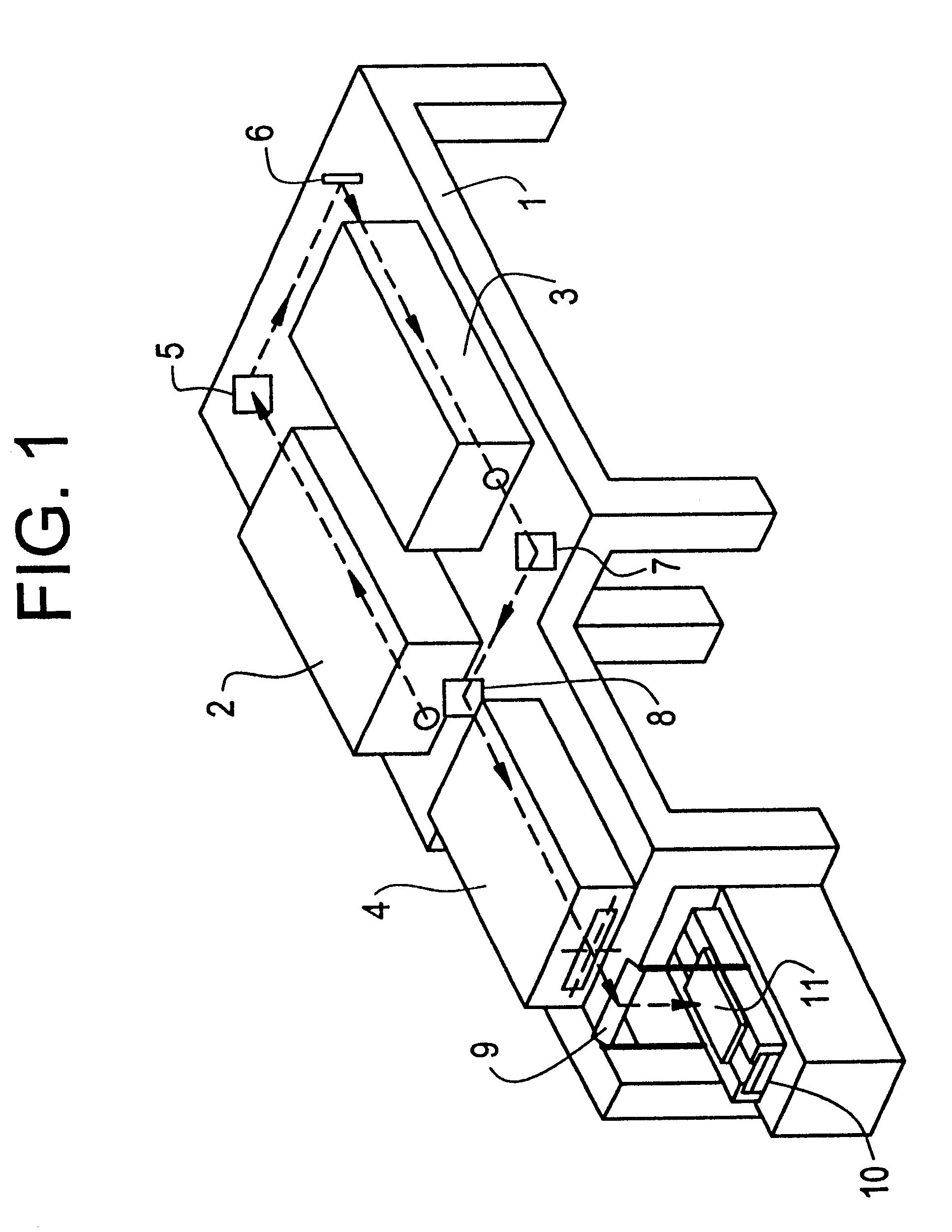
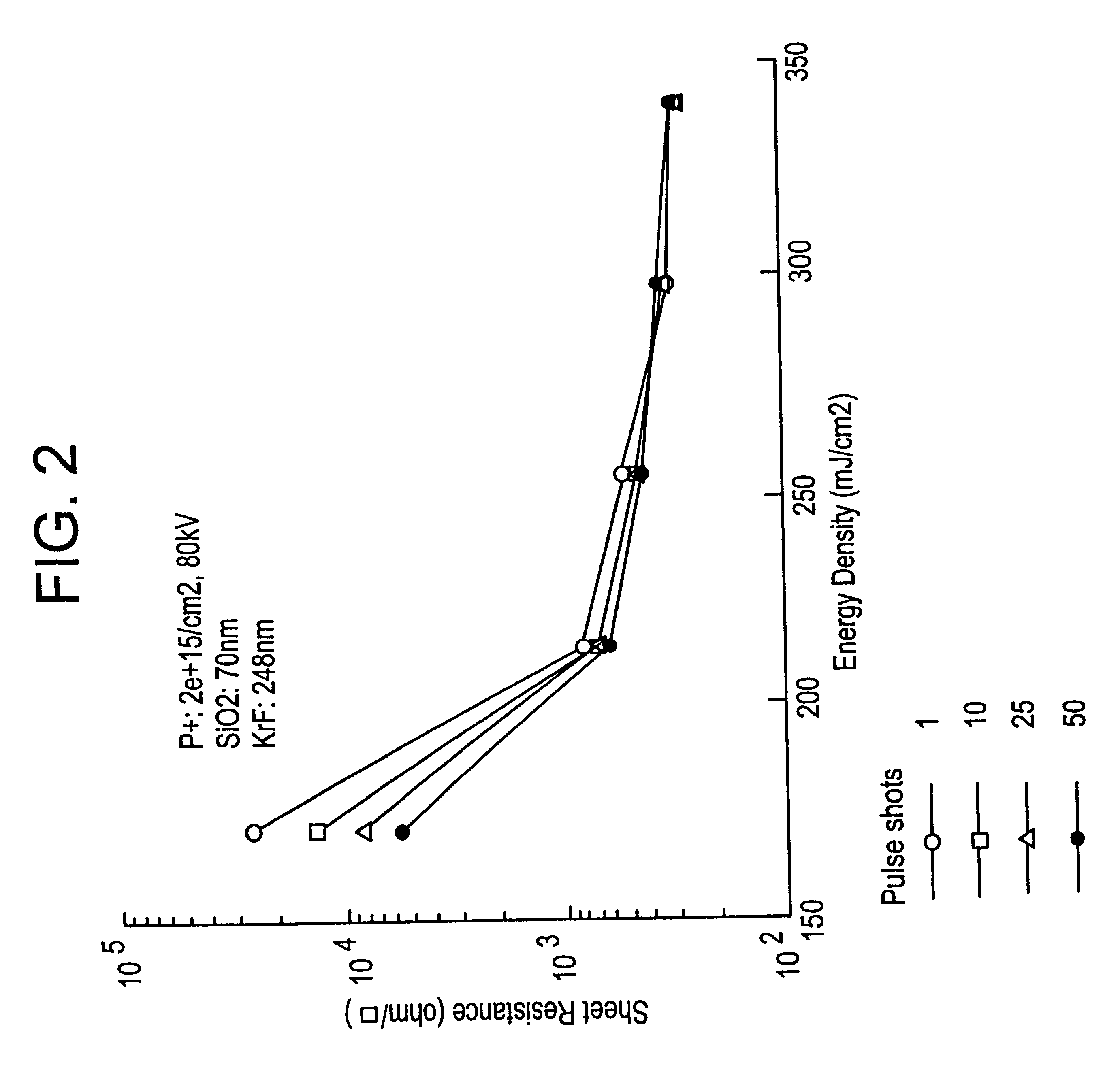
Method of manufacturing a semiconductor device utilizing a laser annealing process
A laser annealing process for recovering crystallinity of a deposited semiconductor film such as of silicon which had undergone morphological damage, said process comprising activating the semiconductor by irradiating a pulsed laser beam operating at a wavelength of 400 nm or less and at a pulse width of 50 nsec or less onto the surface of the film, wherein,said deposited film is coated with a transparent film such as a silicon oxide film at a thickness of from 3 to 300 nm, and the laser beam incident to said coating is applied at an energy density E (mJ / cm2) provided that it satisfies the relation:where N is the number of shots of the pulsed laser beam.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Popular searches
Active medium material Semiconductor laser excitation apparatus Active medium shape and construction Semiconductor laser optical device Picture reproducers using projection devices Laser arrangements Laser cooling arrangements Optical elements Surface reaction electrolytic coating Thin material handling
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com