Patents
Literature
397results about "Semiconductor laser excitation apparatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
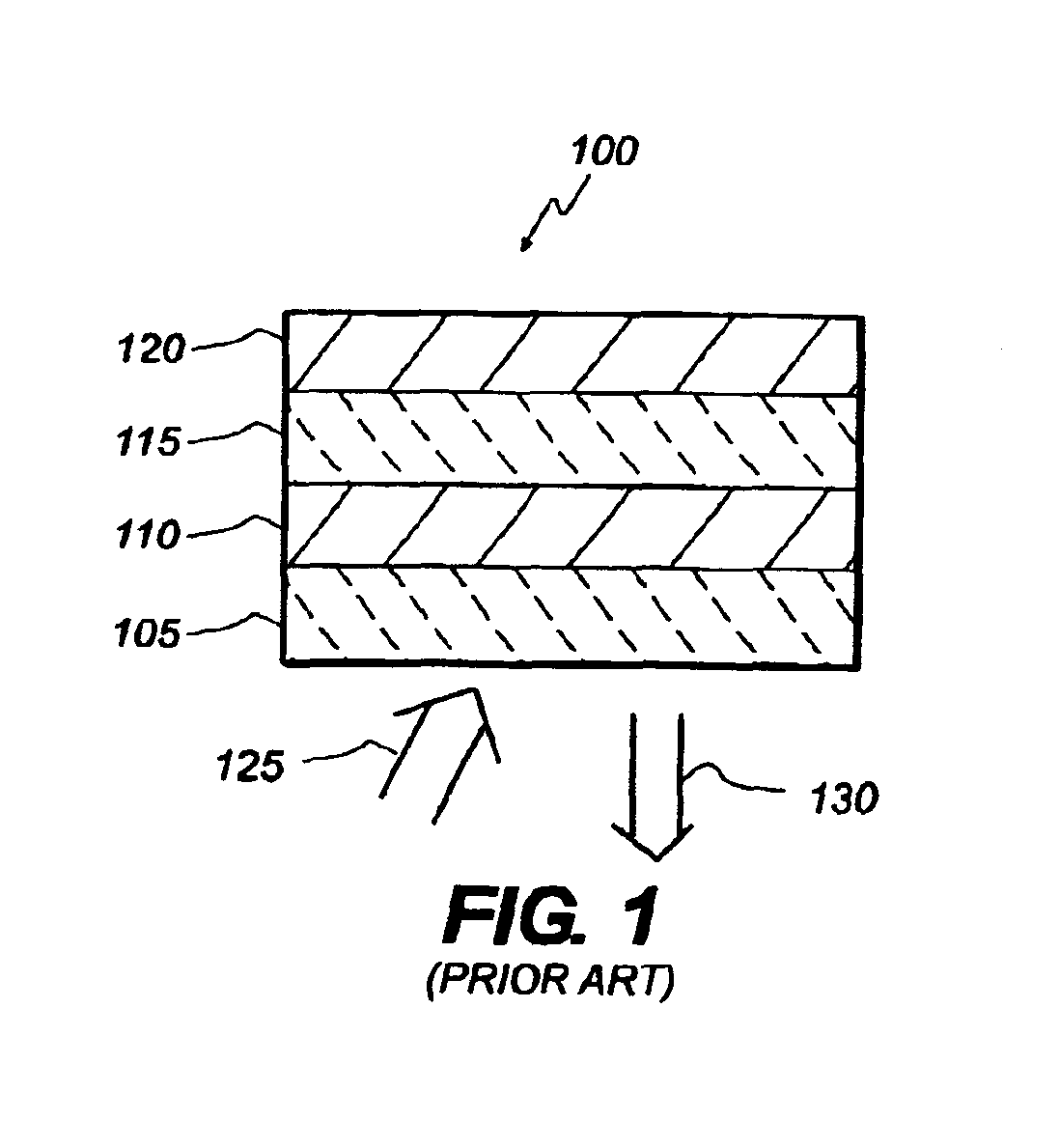
Organic vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
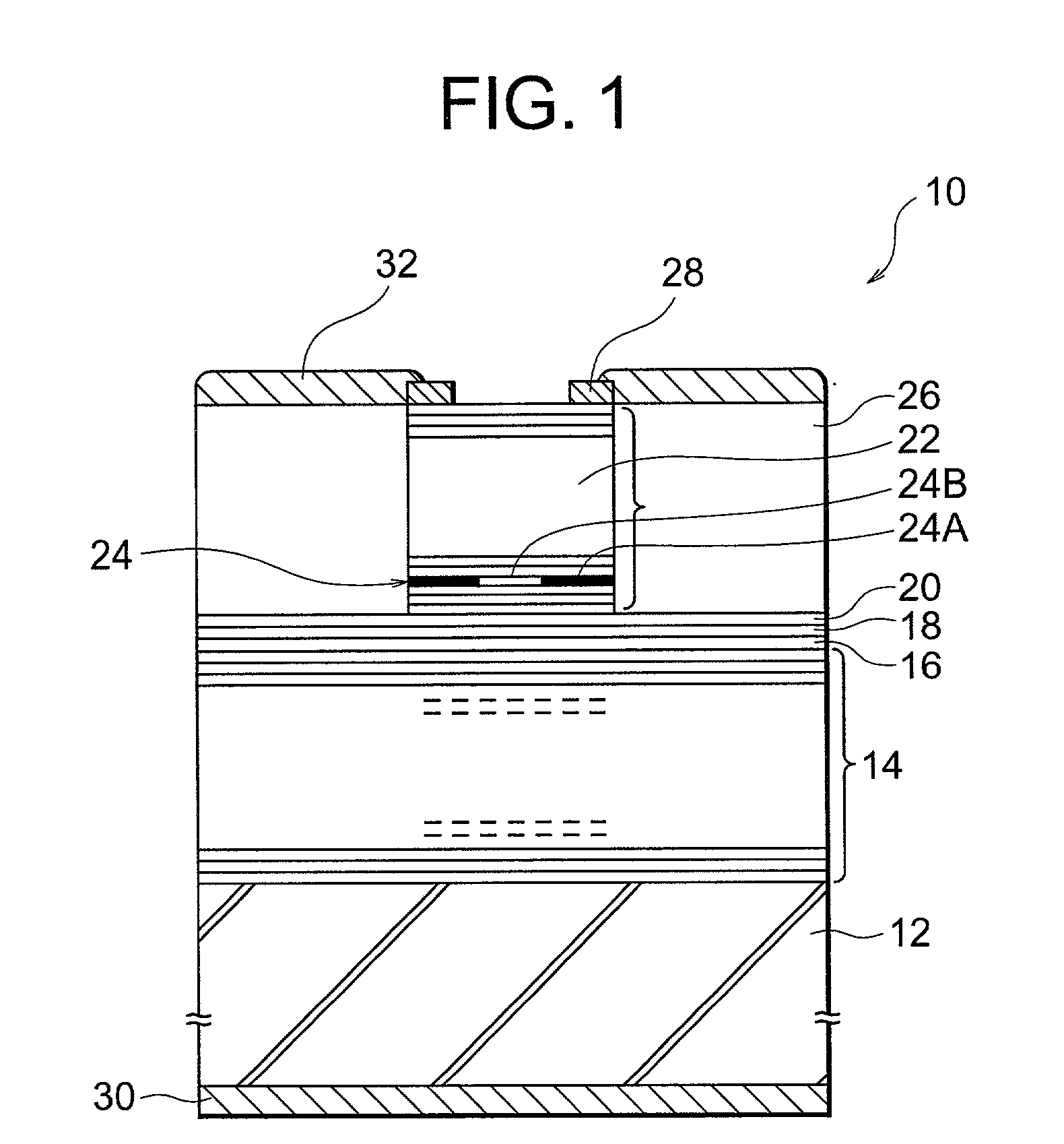
InactiveUS6160828ALaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserThin layer
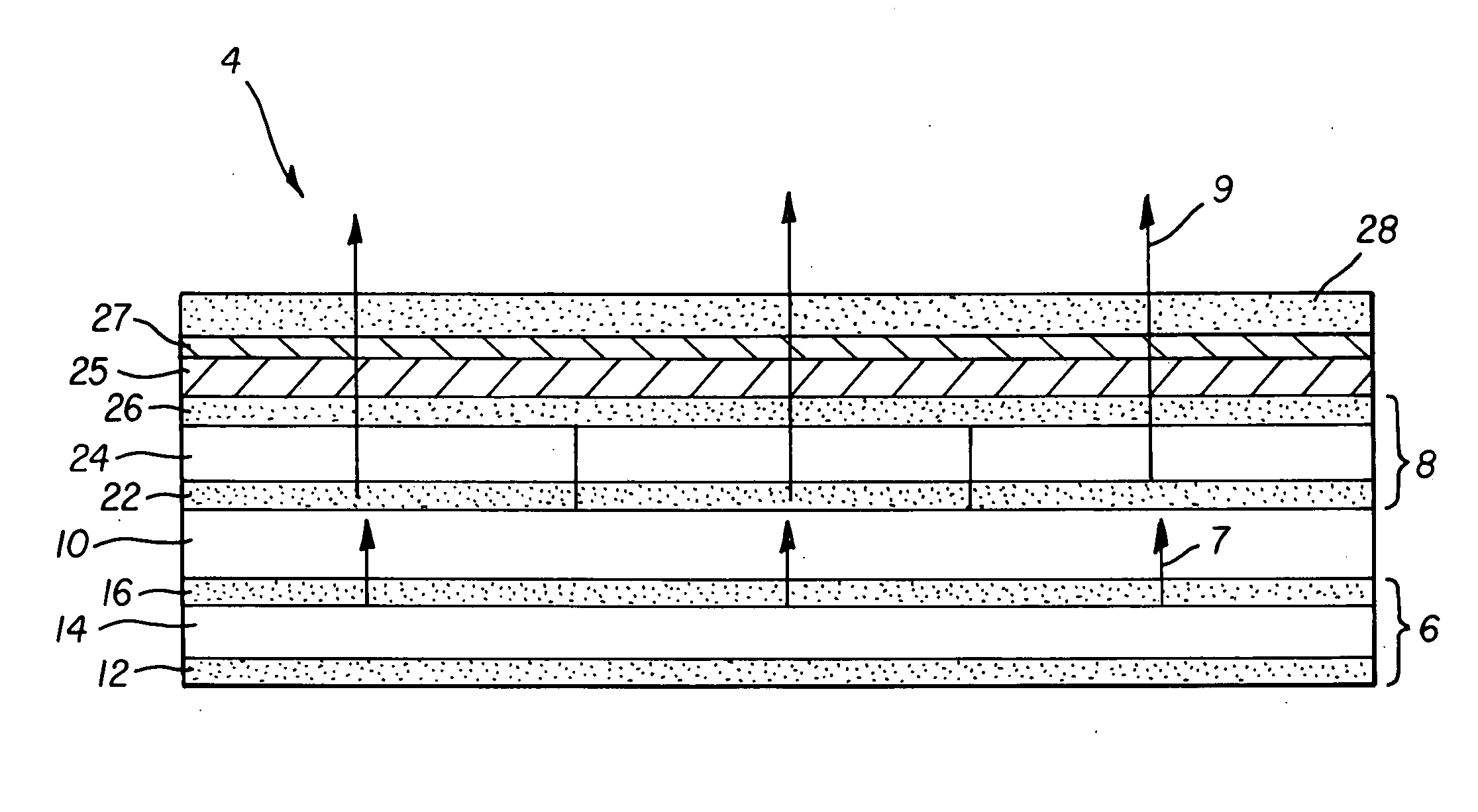
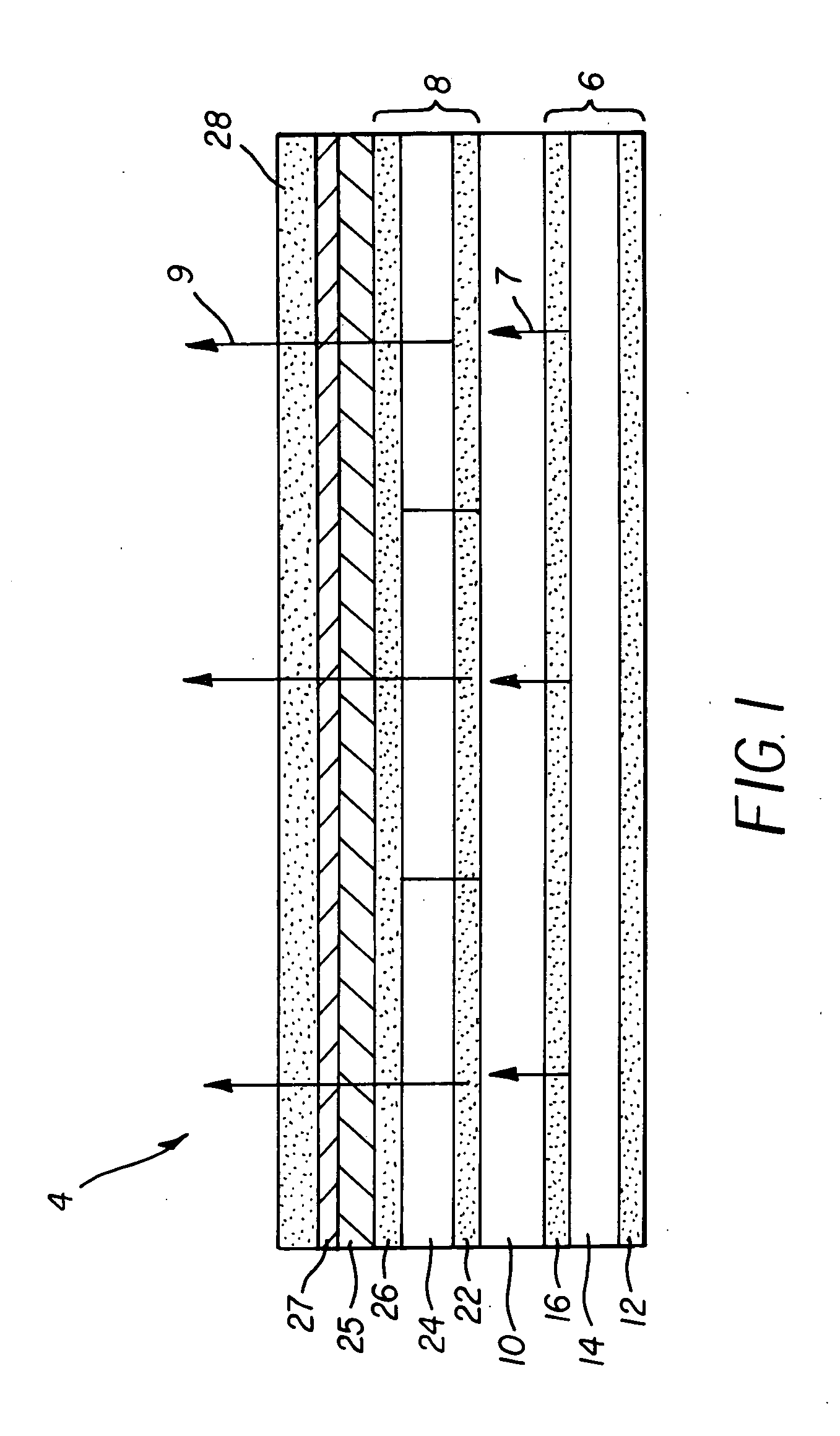
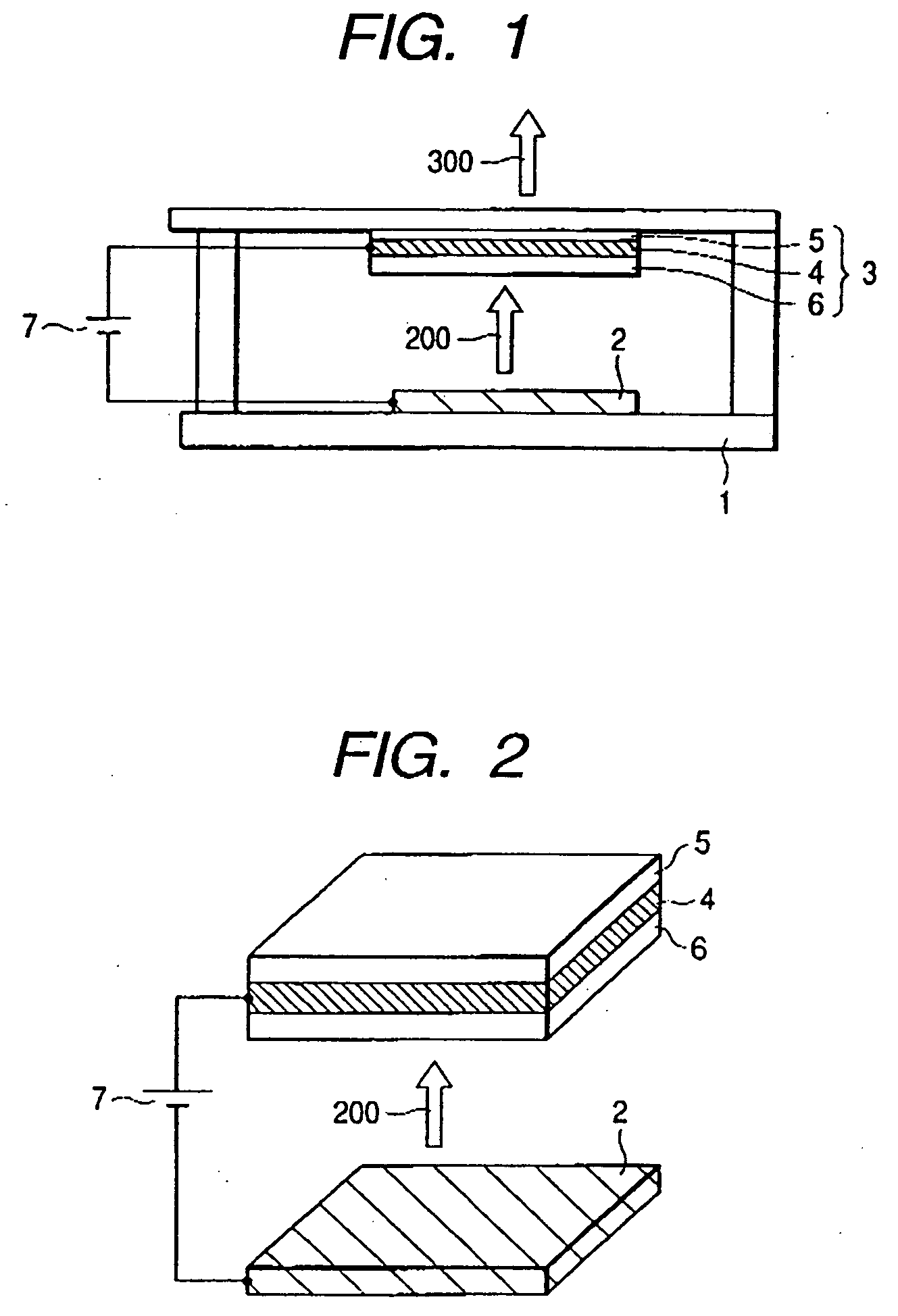
Organic vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers ("OVCSELs"), in which a thin layer of organic material is disposed between highly reflective mirrors to thereby form a vertical cavity within a stacked arrangement. The lasers of the present invention each comprise a first mirror layer; a layer of active organic material over the first mirror layer; and a second mirror layer over the layer of first active organic material. The active organic material lases when pumped to thereby produce laser light. The present invention provides for optical semiconductor lasers with desired properties such as narrow bandwidth emission, the minimal use of active organic materials, and the facilitation of wavelength tuning and electrical pumping.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV THE TRUSTEES OF
Ii-vi mqw vscel on a heat sink optically pumped by a GAN ld
InactiveUS20110150020A1Improved light emissionSuppress luminescenceLaser optical resonator constructionNanoopticsVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserOptical cavity
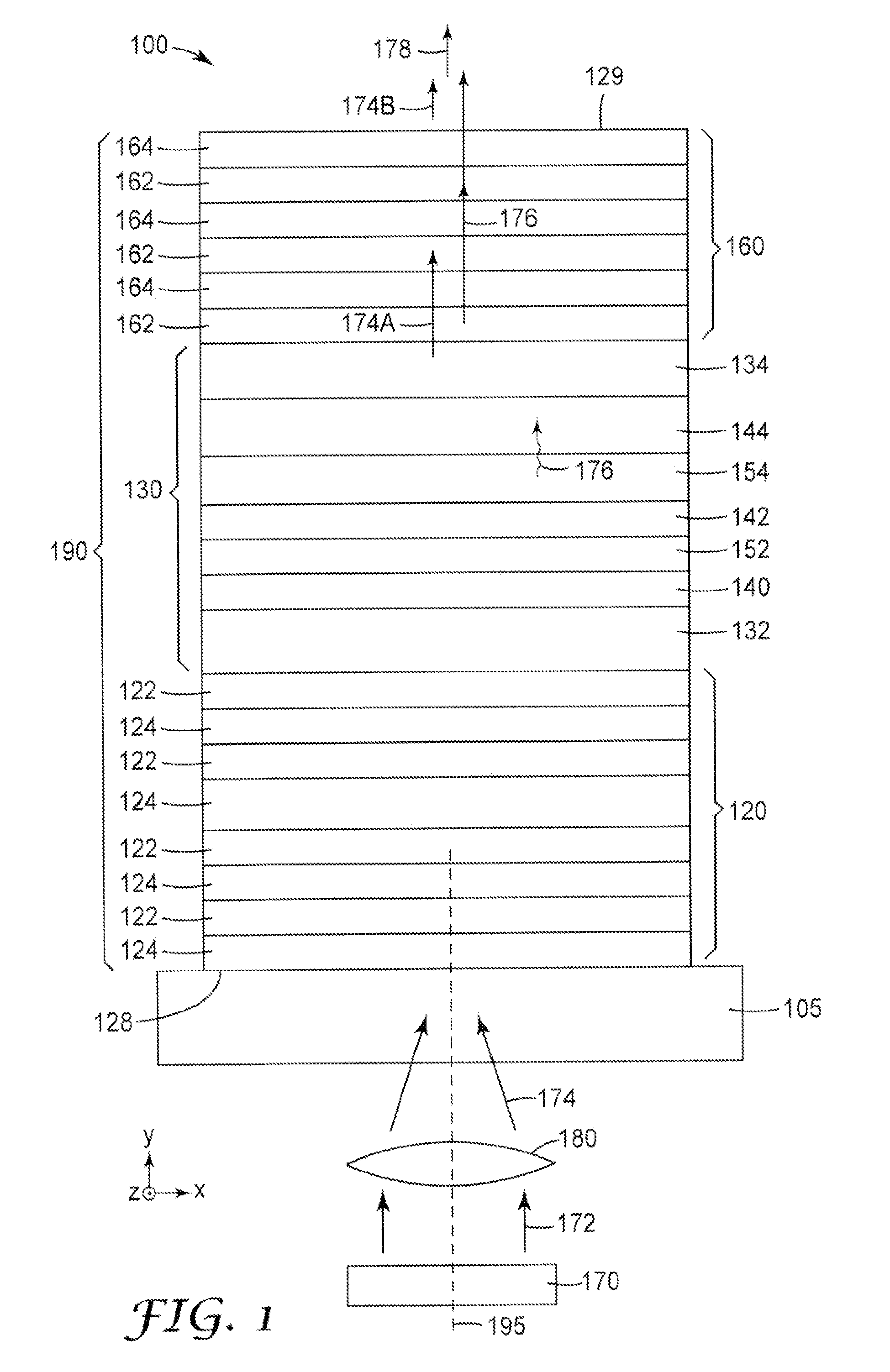
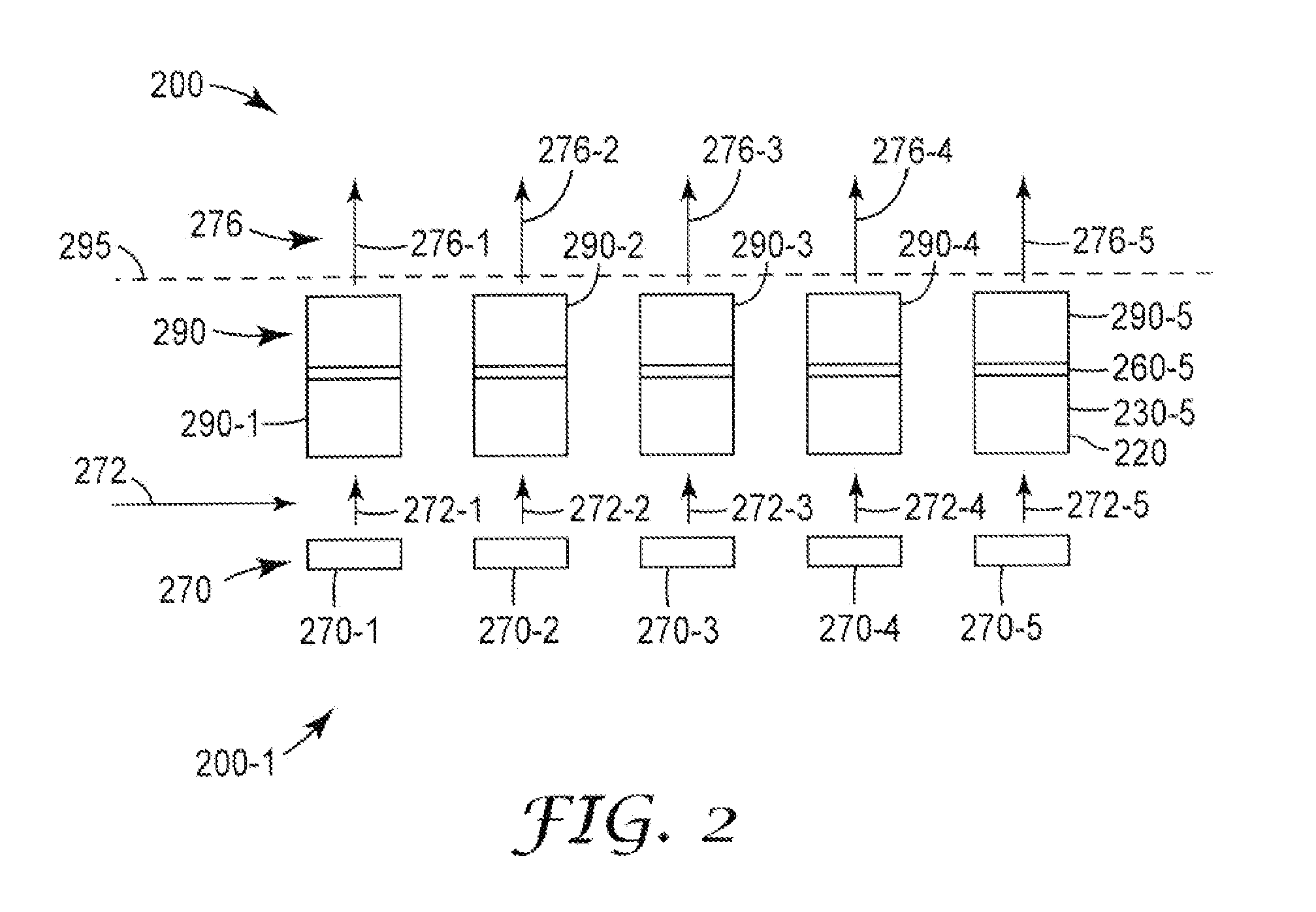
Light sources are disclosed. A disclosed light source includes a III-V based pump light source (170) that includes nitrogen and emits light at a first wavelength. The light source further includes a vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) that converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light (174) emitted by the pump light source (170) to at least a partially coherent light at a second wavelength (176). The VCSEL includes first and second mirrors (120, 160) that form an optical cavity for light at the second wavelength. The first mirror (120) is substantially reflective at the second wavelength and includes a first multilayer stack. The second mirror (160) is substantially transmissive at the first wavelength and partially reflective and partially transmissive and the second wavelength. The second mirror includes a second multilayer stack. The VCSEL further includes a semiconductor multilayer stack (130) that is disposed between the first and second mirrors and converts at least a portion of the first wavelength light to the second wavelength light. The semiconductor multilayer stack (130) includes a quantum well that includes a Cd(Mg)ZnSe alloy.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Electrically pumped semiconductor evanescent laser
InactiveUS20080002929A1Laser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor materialsCoupling
An apparatus and method electrically pumping a hybrid evanescent laser. For one example, an apparatus includes an optical waveguide disposed in silicon. An active semiconductor material is disposed over the optical waveguide defining an evanescent coupling interface between the optical waveguide and the active semiconductor material such that an optical mode to be guided by the optical waveguide overlaps both the optical waveguide and the active semiconductor material. A current injection path is defined through the active semiconductor material and at least partially overlapping the optical mode such that light is generated in response to electrical pumping of the active semiconductor material in response to current injection along the current injection path at least partially overlapping the optical mode.
Owner:INTEL CORP +1
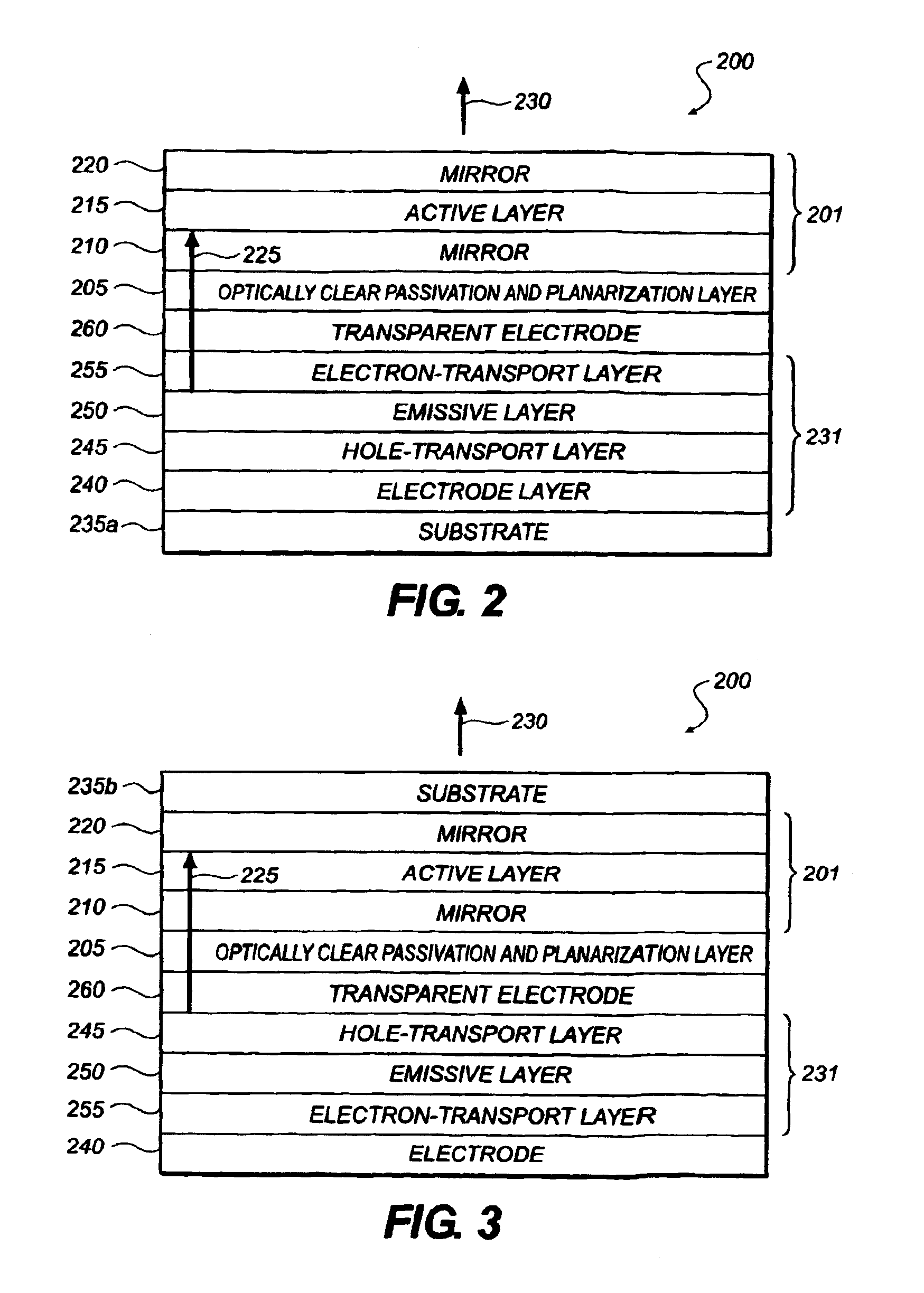
Organic vertical cavity laser and imaging system
InactiveUS6947459B2Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser light
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Organic laser and liquid crystal display
InactiveUS20050062903A1Improve efficiencySimple structureSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLiquid-crystal displayOrganic laser
An asymmetric light emitting structure for producing polarized light that includes a light emitting layer having a plurality of light emitting species, wherein orientation of the light emitting species is uncontrolled. Receipt of the emitted light from the light emitting layer is accomplished via an asymmetric geometric element that also produces polarized light. Additionally, the asymmetric light emitting structure includes a means for excitation of the light emitting layer.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
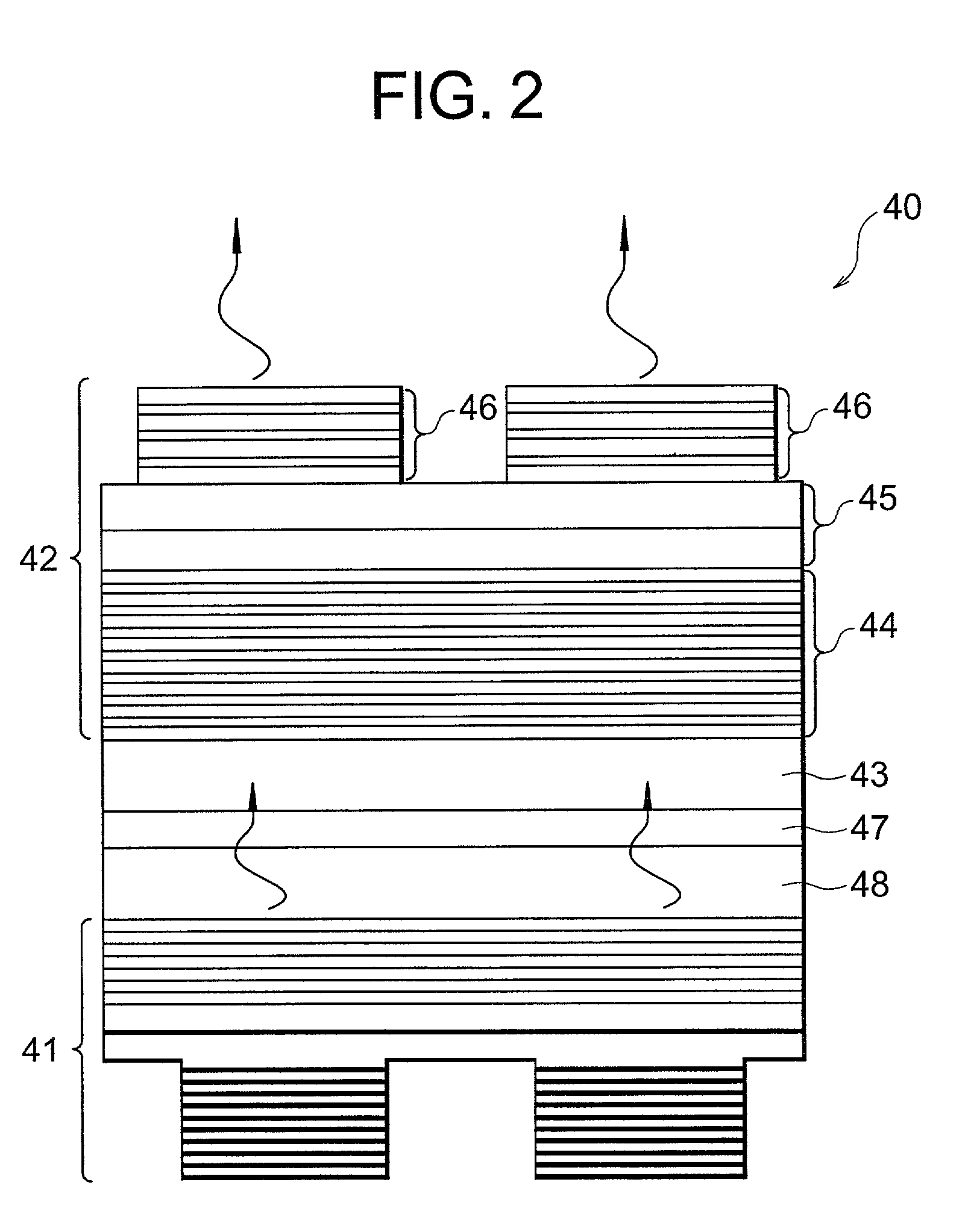
Multi-spectral laser array and optical system
InactiveUS20050147135A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser array
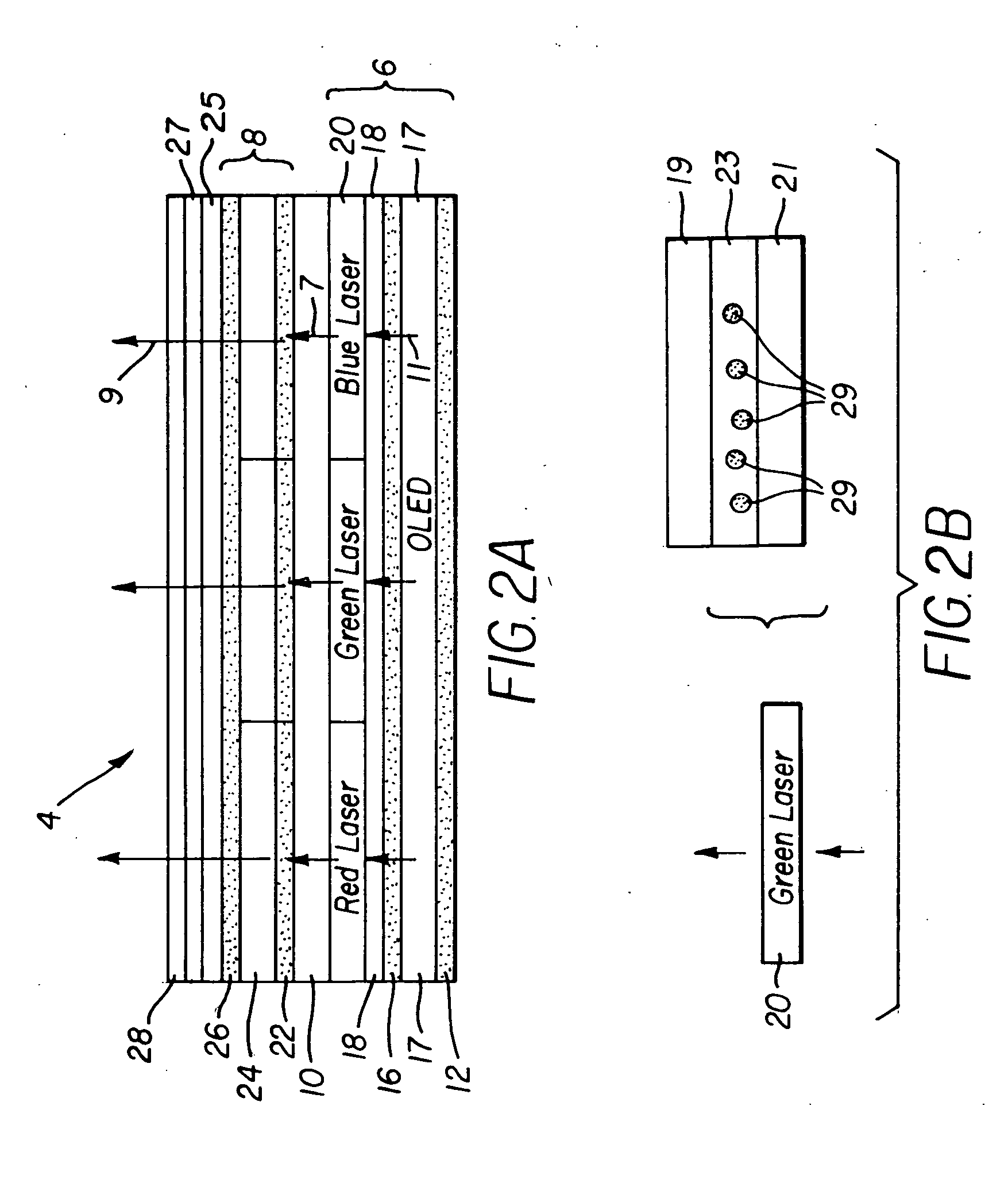
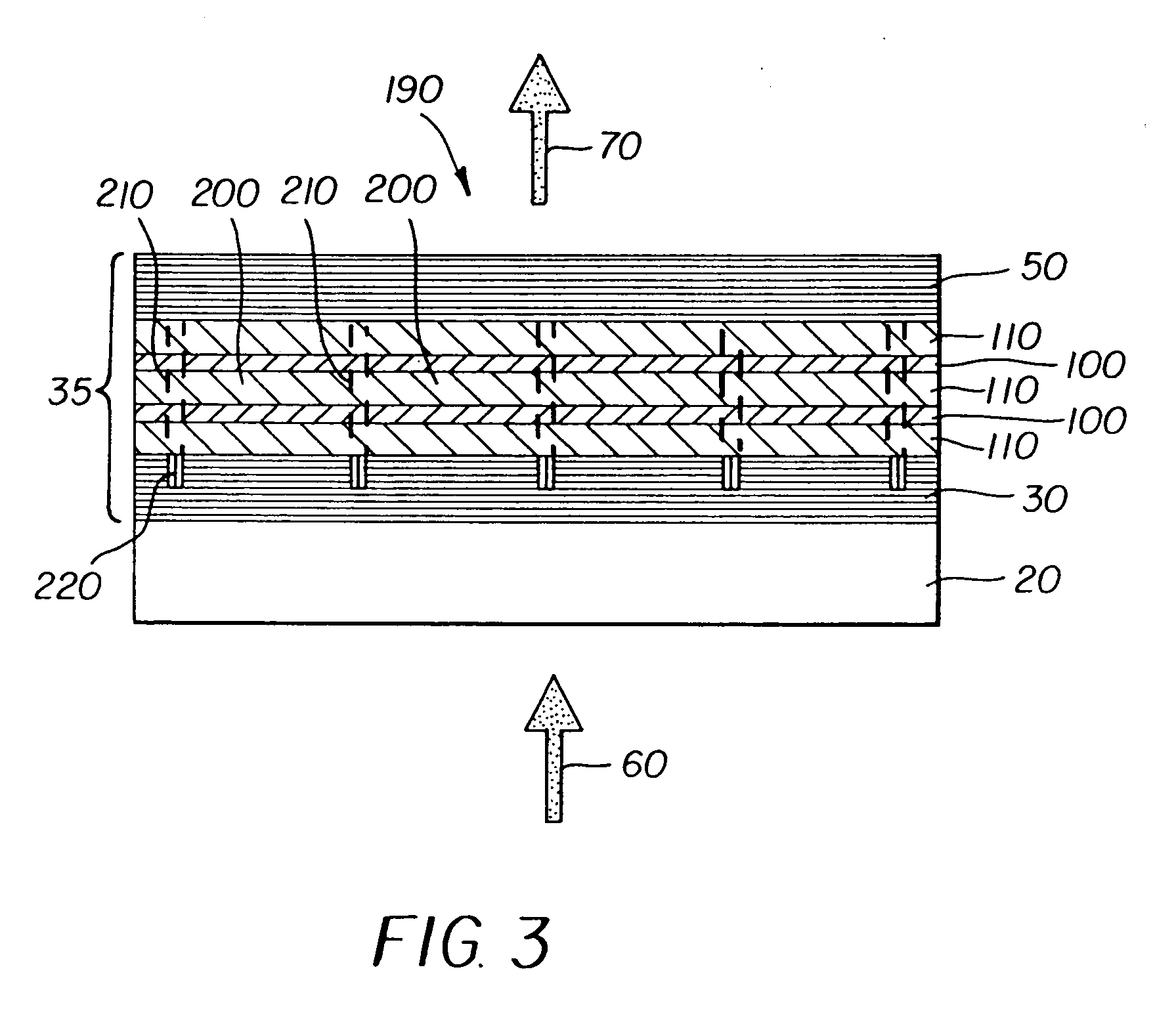
An organic vertical cavity laser light producing device (10) comprises a substrate (20). A plurality of laser emitters (200) emits laser light in a direction orthogonal to the substrate. Each laser emitter within the plurality of laser emitters has a first lateral mode structure in a first axis orthogonal to the laser light direction and has a second lateral mode structure in a second axis orthogonal to both the laser light direction and the first axis. Each laser emitter comprises a first mirror provided on a top surface of the substrate (20) and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. An organic active region (40) produces laser light (350). A second mirror is provided above the organic active region and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. A pumping means excites the plurality of laser emitters.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Optical semiconductor device
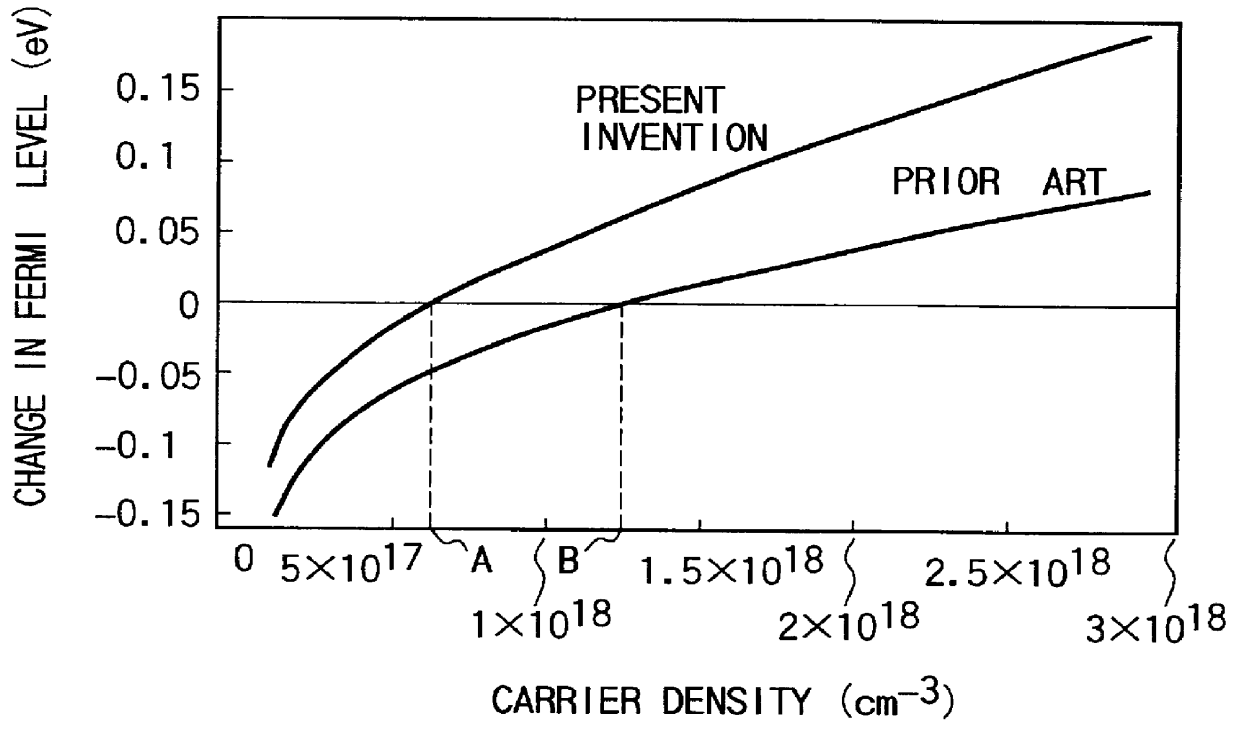
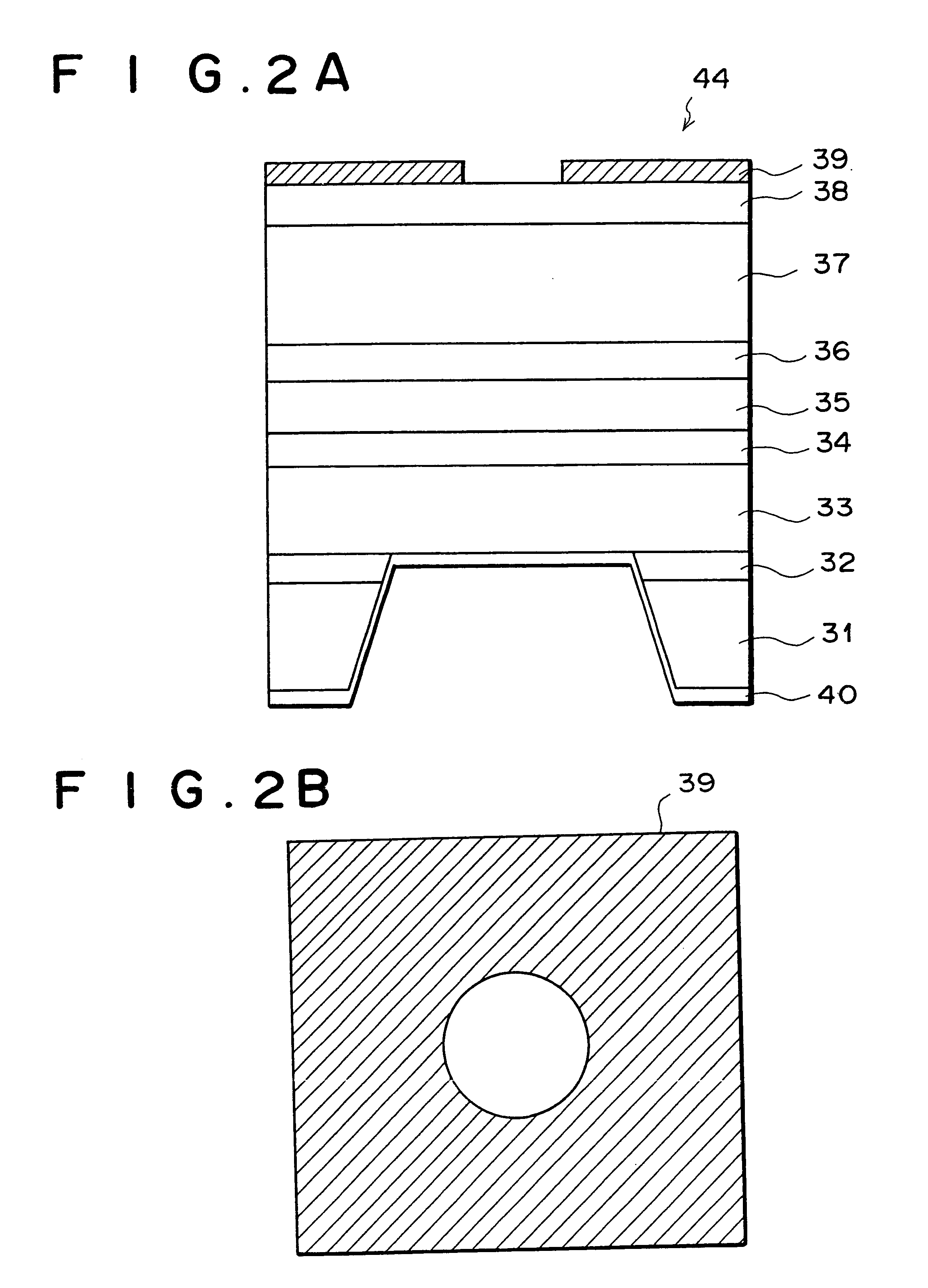
InactiveUS6043515AEasy population inversionImprove featuresExcitation process/apparatusSolid-state devicesMagnetizationContact layer
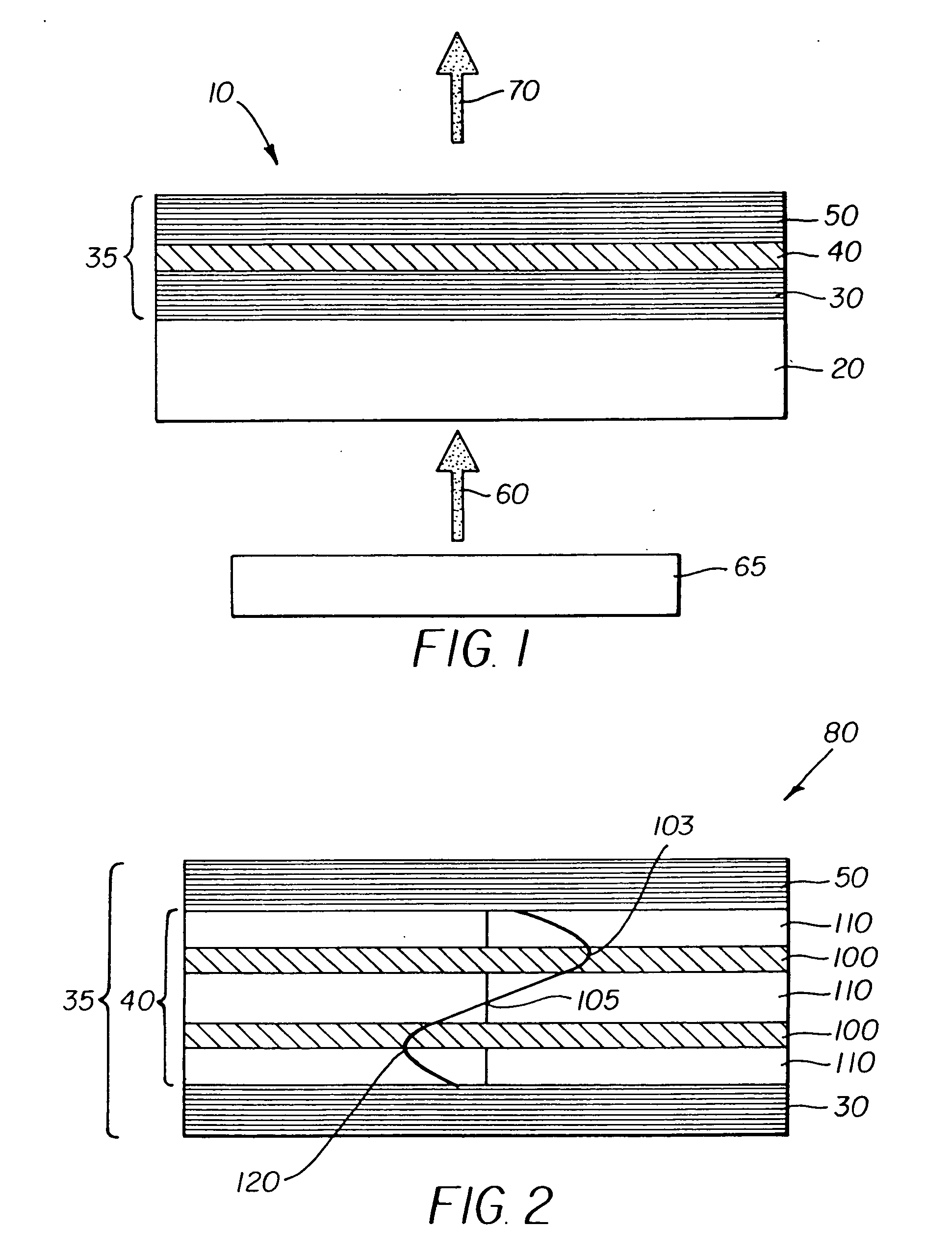
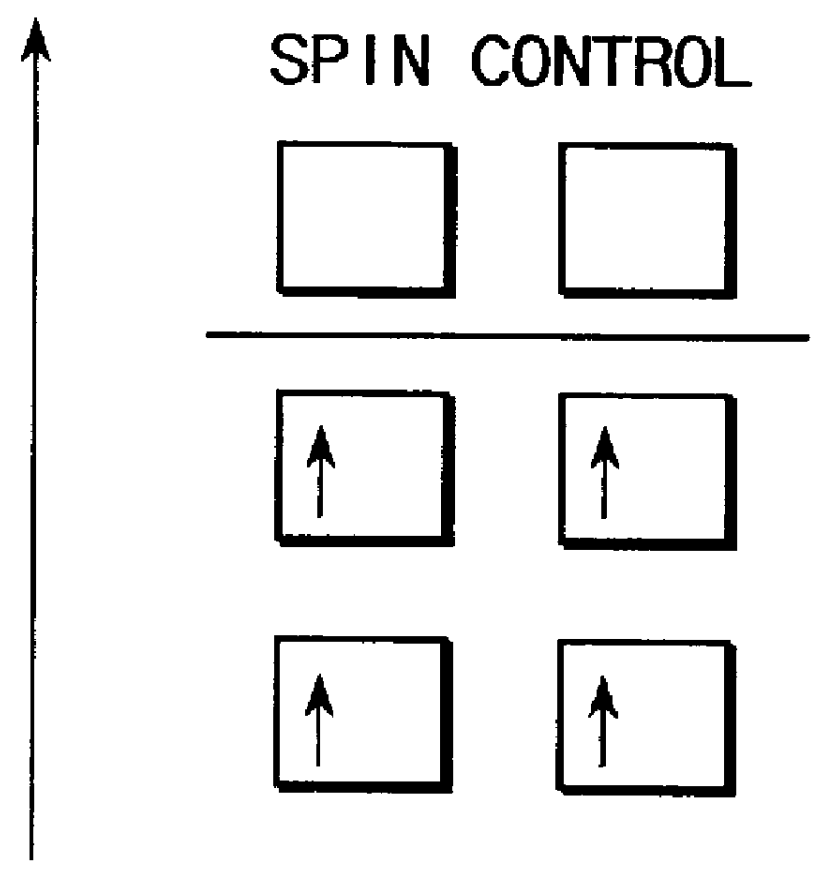
An optical semiconductor device has a structure in which a semiconductor active layer is sandwiched by a p-type semiconductor cladding layer and an n-type semiconductor cladding layer and a p-type contact layer is formed on the p-type semiconductor cladding layer side and an n-type contact layer is formed on the n-type semiconductor cladding layer side, wherein two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the n-type contact layer and two ferromagnetic layers are formed on the p-type contact layer. Magnetization directions of a pair of ferromagnetic layers vertically opposed to each other are set to be parallel to each other, and the magnetization directions of adjacent ferromagnetic layers are inverted to each other.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Short-wavelength optoelectronic device including field emission device and optical device and its fabricating method
InactiveUS6139760AEfficient productionHigh energyExcitation process/apparatusOptical articlesField emission deviceOpto electronic
Provided with a method of fabricating a 200-250 nm short-wavelength optoelectronic device, which has a combination of an optical device with a plurality of acceleration electrodes and a field emission device with a plurality of acceleration electrodes, from a semiconductor having a 5-6 eV energe band gap, based on a principle that an electron-hole pair is produced using a highly energetic electron which is injected from a field emission device, and short-wavelength photons are emitted when the electron recombines with the hole and confined in a quantum well to emit a light corresponding to the energy level of the quantum well, thereby eliminating the need of using dopants for forming n-p junctions in the semiconductor and achieving high efficiency in terms of energy because highly energetic electrons result in one or more electron-hole pairs.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
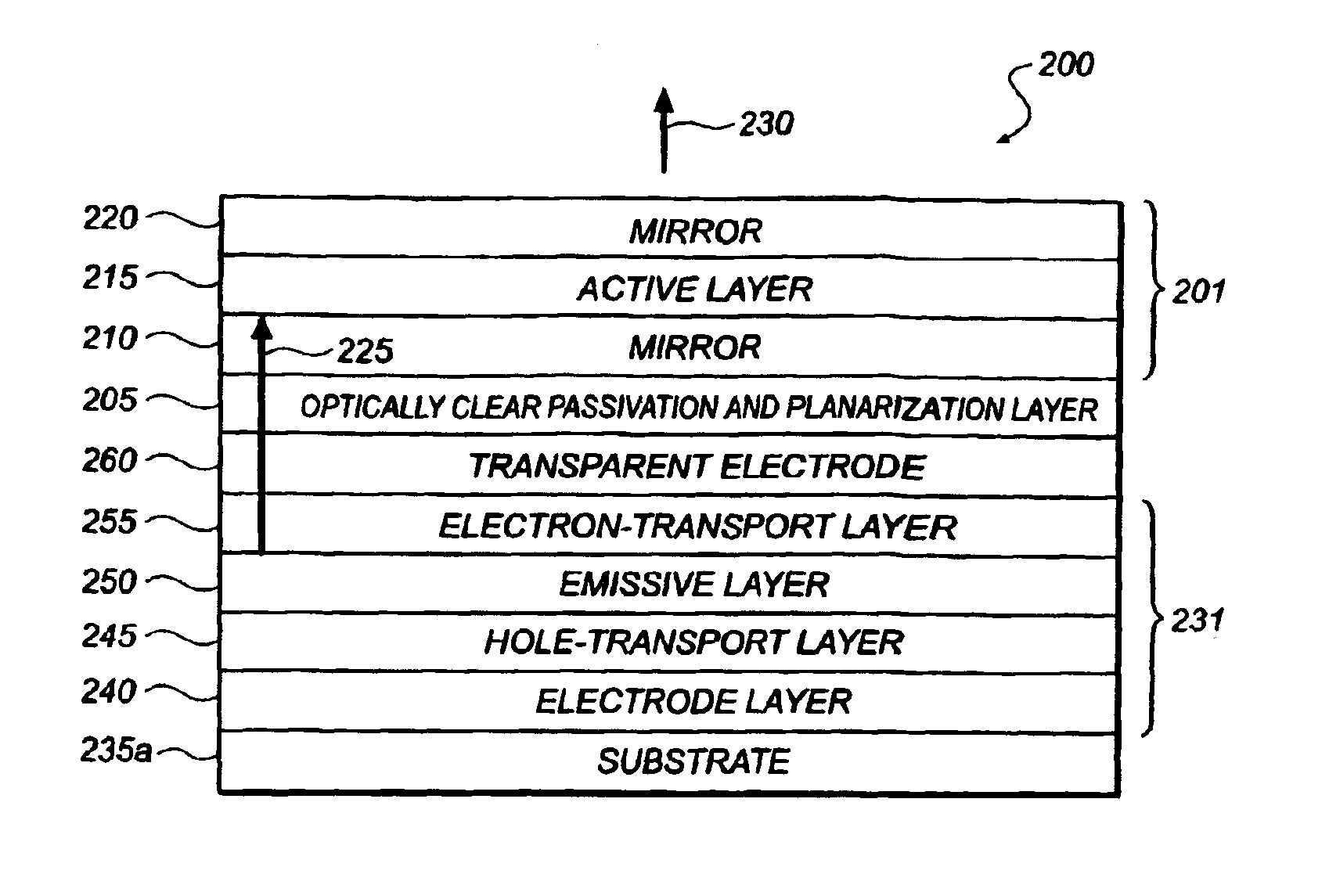
Light emitting device and method for making same
InactiveUS7112829B2Excitation process/apparatusSolid-state devicesLight emitting deviceLight emission
A light emission device and method for producing the device. The device includes, on a substrate, a stack including an etching stop layer, a first barrier layer, an emitting layer, and a second barrier layer. The stop layer is of the same nature as the emitting layer. One may form a mirror on the stack, eliminate the substrate by etching, and form another mirror on the stop layer to obtain a micro-cavity. The device may be applied in particular to the detection of gas.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Electron-beam excitation laser
InactiveUS20040218651A1Laser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusDielectricElectron source
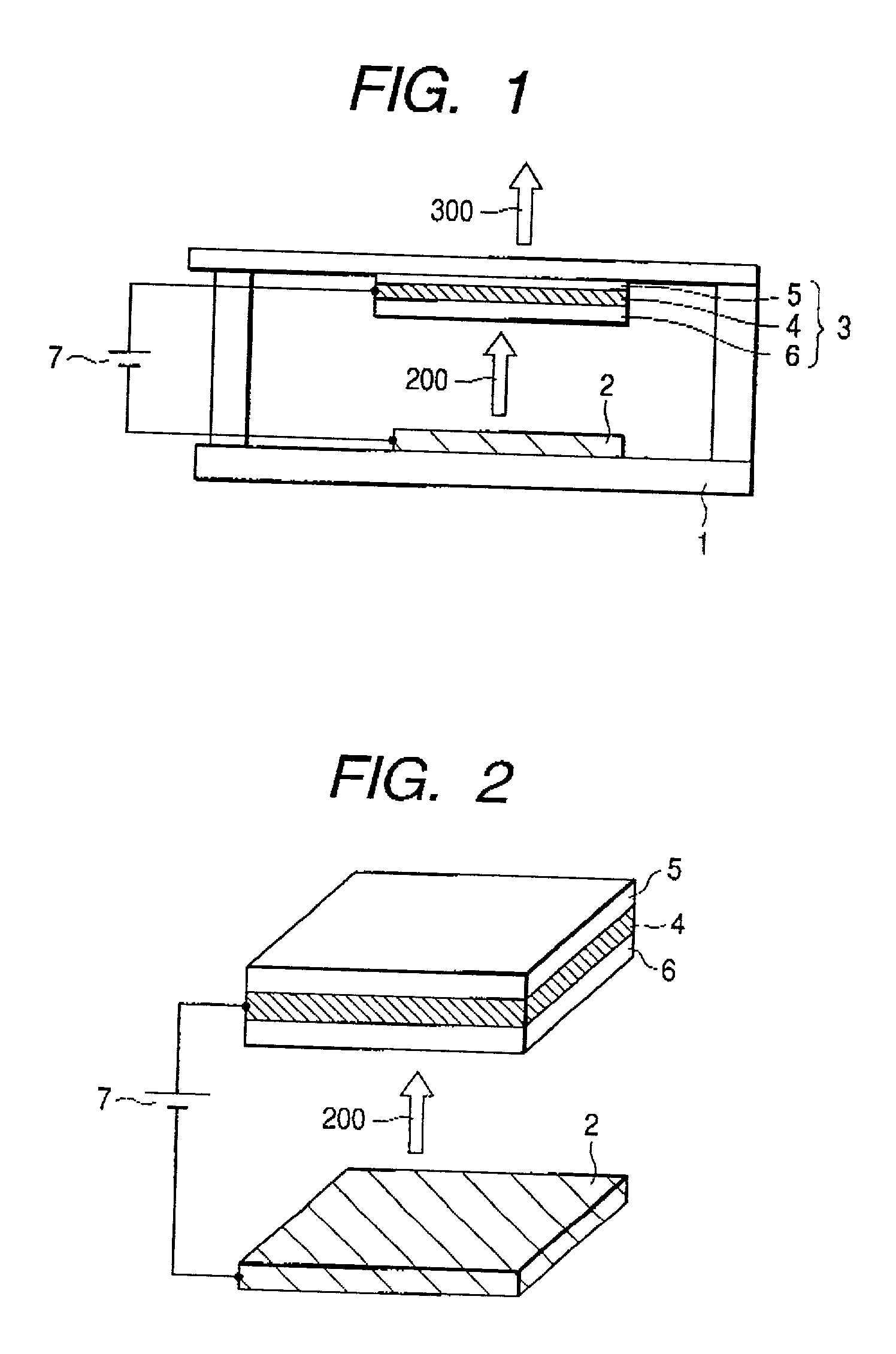
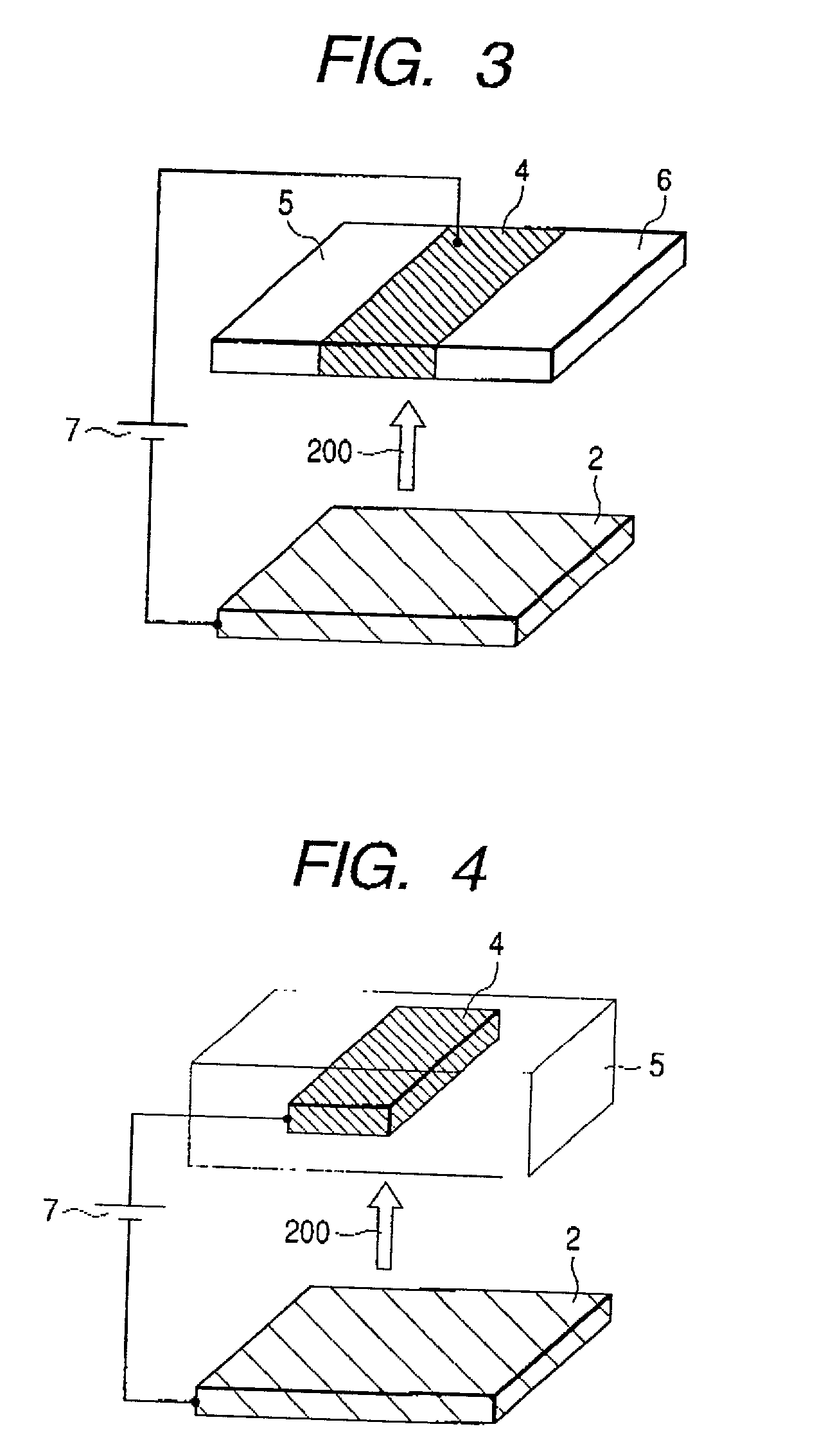
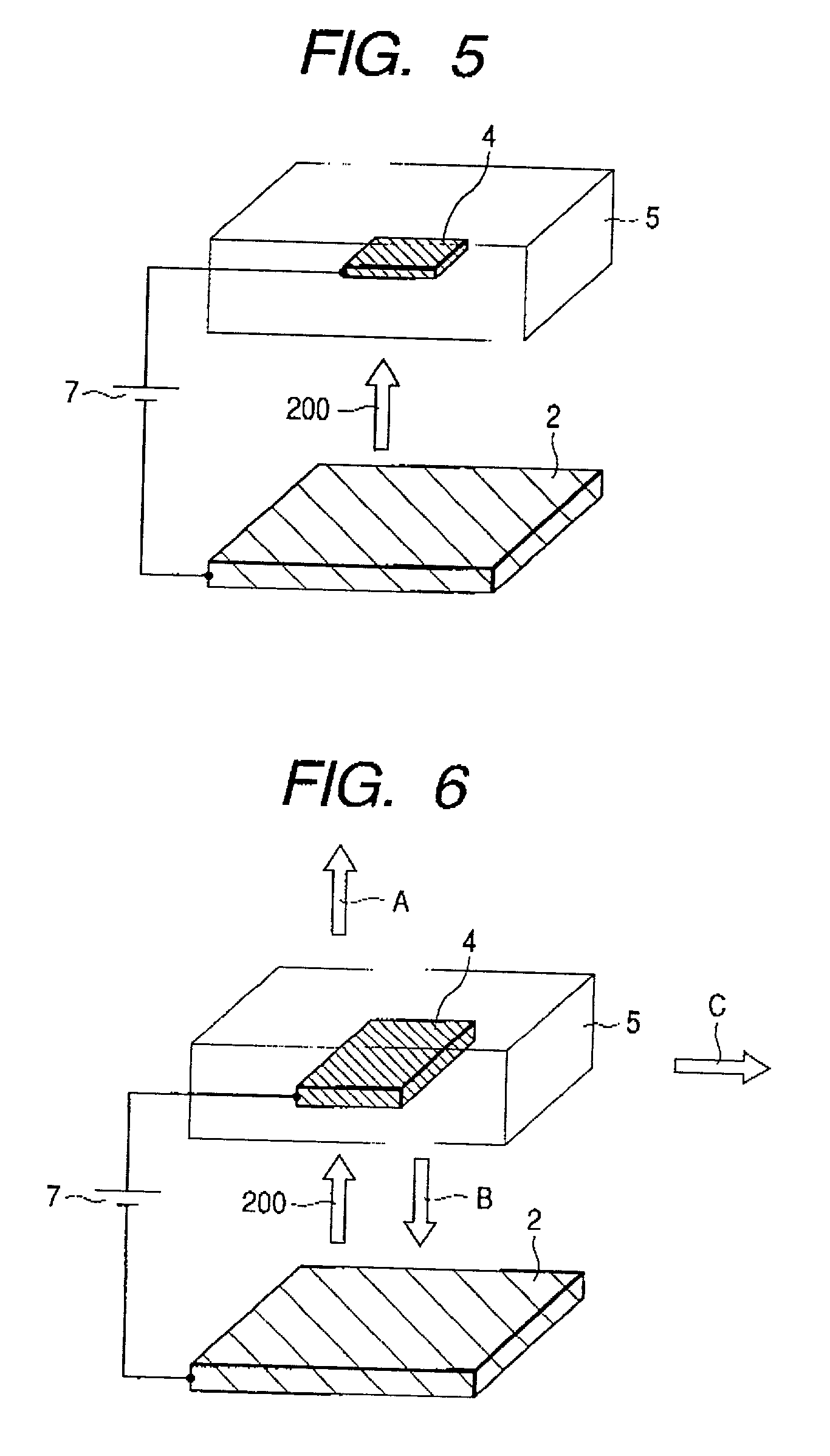
An electron-beam excitation laser has a laser structure with a light emitter and reflectors on one hand and an electron source on the other hand, wherein at least part of the light emitter or reflectors has a multidimensional photonic crystal structure. An electron-beam excitation laser includes an electron source emitting electrons and a laser structure consisting of a light emitter and reflectors, accelerates electrons from the electron source, and irradiates the electrons to the laser structure to emit a laser beam from the laser structure, wherein the reflectors and / or the light emitter in the laser structure are formed with multidimensional photonic crystals in which dielectrics with different dielectric constants are arrayed in a plurality of directions at periodic intervals, and one of the dielectrics with different dielectric constants may be formed with a light-emitting material.
Owner:CANON KK
Silicon nanoparticle and method for producing the same
InactiveUS6846474B2Highly uniform in sizeEasily filtered outMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureNanoparticleColloid
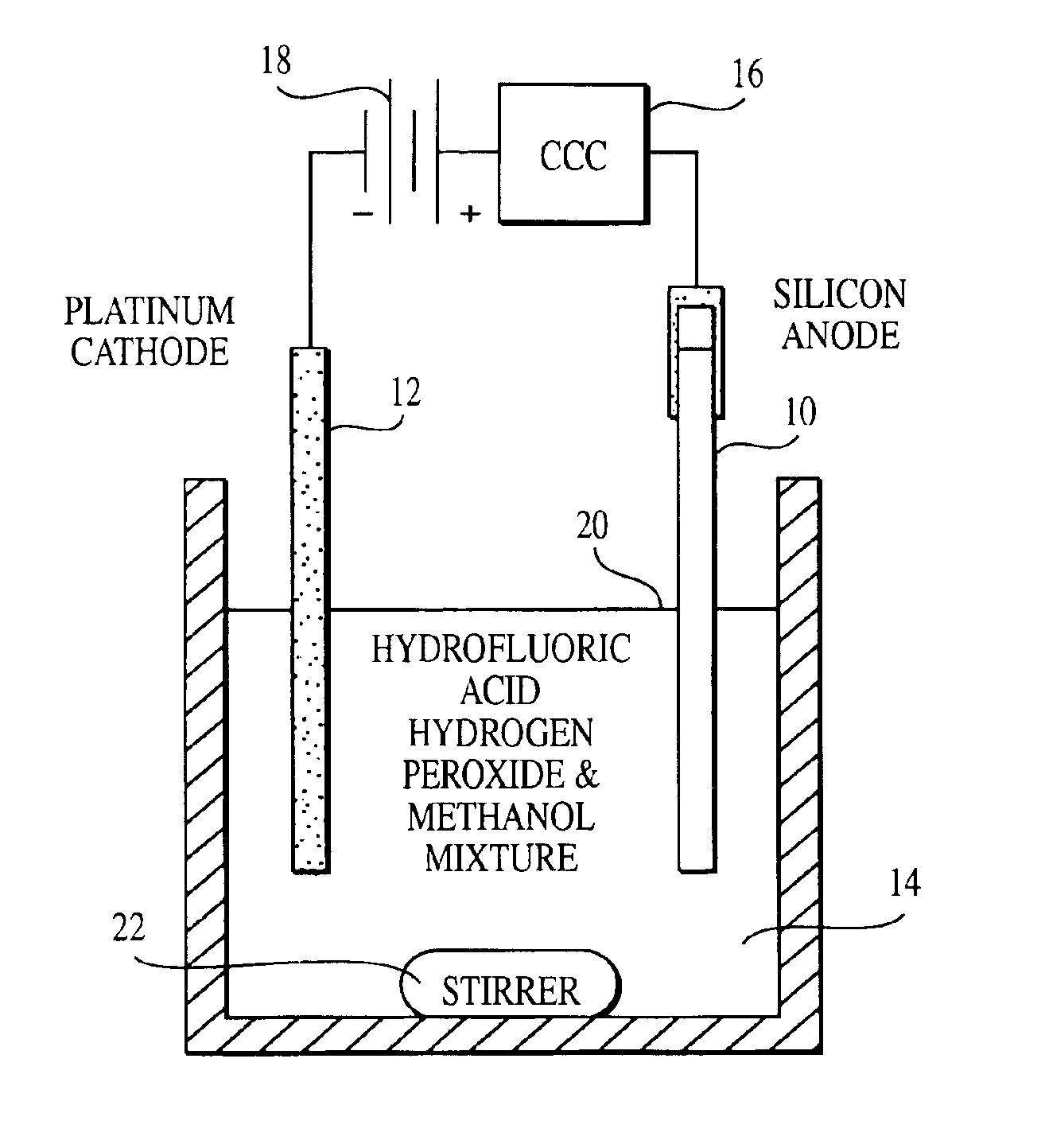
Highly uniform 1 nm silicon nanoparticles are provided by the invention. The nanoparticles exhibit beneficial properties. They are a source of stimulated emissions. They may be suspended in liquids, and solids. They can be formed into crystals, colloids and films. The nanoparticles of the invention are about 1 nm having about only one part in one thousand greater than 1 nm. A method for producing the silicon nanoparticle of the invention is a gradual advancing electrochemical etch of bulk silicon. Separation of nanoparticles from the surface of the silicon may also be conducted. Once separated, various methods may be employed to form plural nanoparticles into colloids, crystals, films and other desirable forms. The particles may also be coated or doped.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Optically Surface-Pumped Edge-Emitting Devices and Systems and Methods of Making Same
InactiveUS20150288129A1Laser using scattering effectsExcitation process/apparatusPhosphorPhotoluminescence
Optical resonator devices and systems enhanced with photoluminescent phosphors and designed and configured to output working light in an edge-emitting fashion at one or more wavelengths based on input / pump light, and systems and devices made with such resonators. The edge-emitting functionality is enabled by providing one or more waveguides that direct light luminesced from the phosphors to one or more edges of the device. In some embodiments, the resonators contain multiple optical resonator cavities in combination with one or more photoluminescent phosphor layers or other structures. In other embodiments, the resonators are designed to simultaneously resonate at the input / pump and output wavelengths. The photoluminescent phosphors can be any suitable photoluminescent material, including semiconductor and other materials in quantum-confining structures, such as quantum wells and quantum dots, among others.
Owner:VERLASE TECH
Systems, methods, and apparatuses for optically pumped vertical cavity surface emitting laser devices
InactiveUS6940885B1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser structural detailsResonant cavityVertical-cavity surface-emitting laser
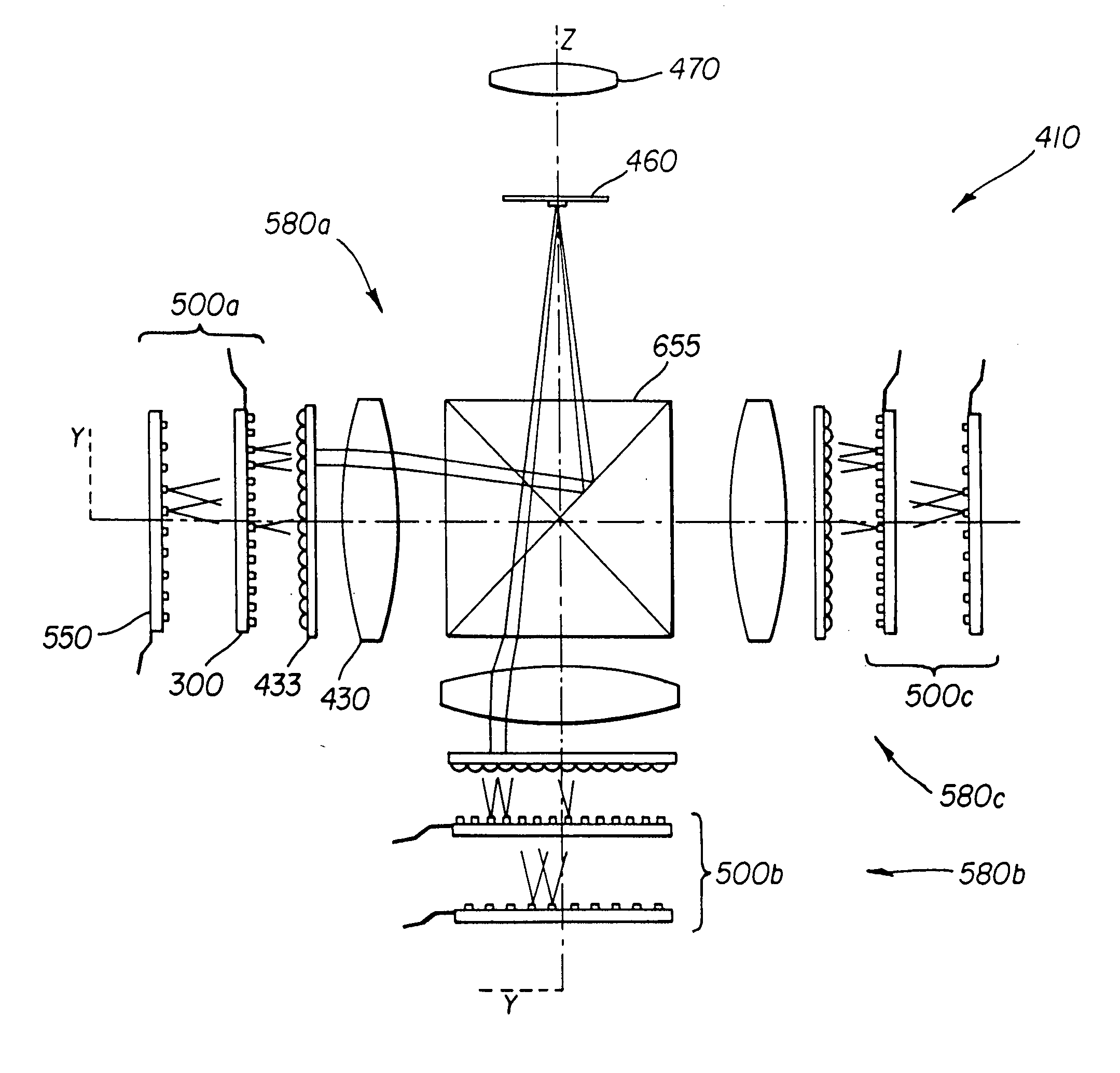
Monolithic integrated vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser devices are disclosed including an edge-emitting semiconductor pump laser (PL), an optically-pumped vertical-cavity surface-emitting laser (VCSEL), and a means for deflecting and shaping the output beam of the pump laser to optically excite the VCSEL. The optically-pumped VCSEL structure may be adapted to include a resonant cavity with multiple fixed wavelengths, or a resonance cavity whose wavelength is continuously tunable. Wafer level manufacturing techniques are also disclosed.
Owner:JDS UNIPHASE CORP
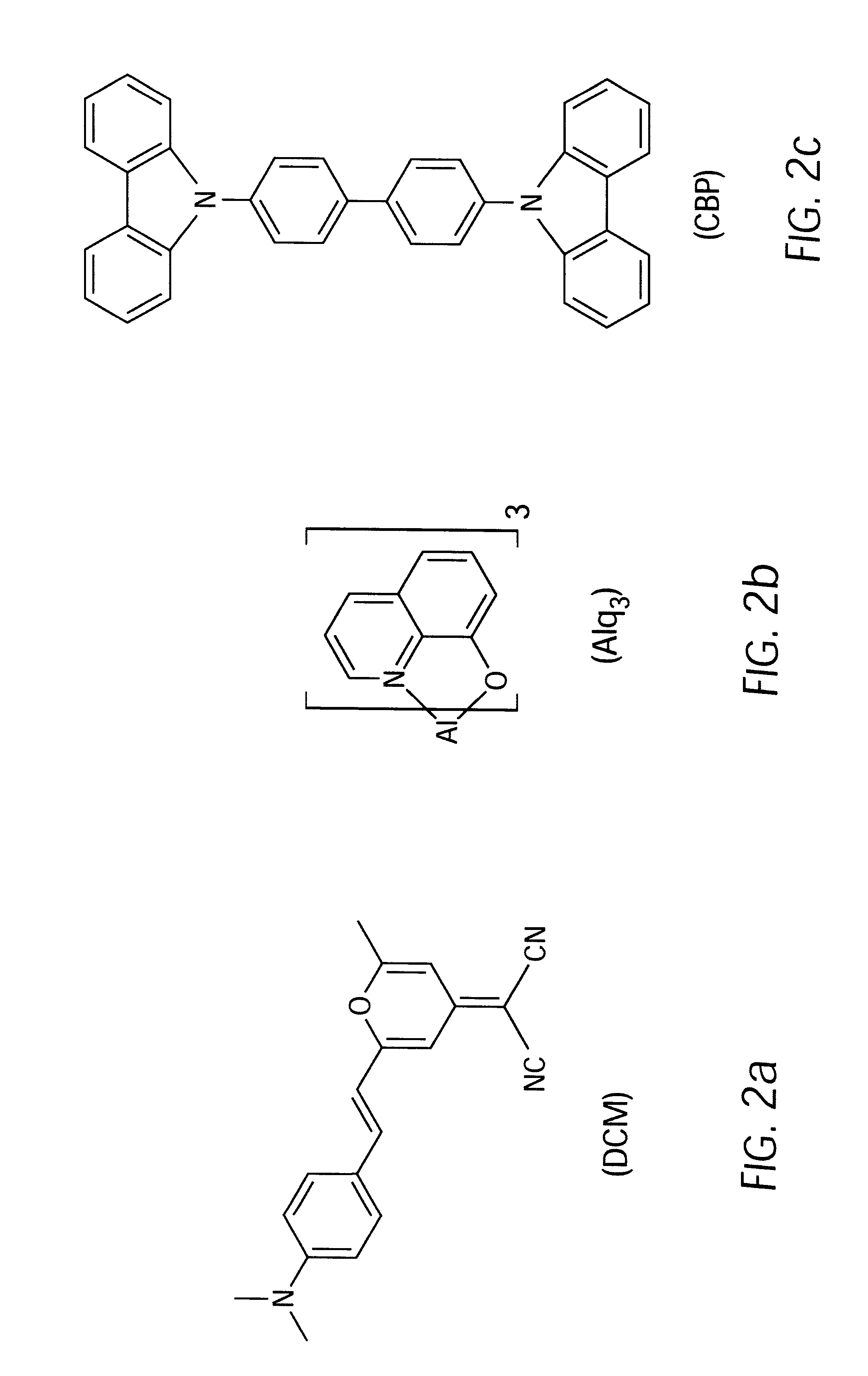
Organic semiconductor lasers
Lasers comprising a substrate and a layer of organic material over the substrate. The organic material includes host and dopant materials that result in the laser emission of a desired color when pumped by optical pump energy. Host materials include CBP and tris-(8-hydroxyquinoline) aluminum, which when combined with dopant materials such as coumarin-47, coumarin-30, perylene, rhodamine-6G, DCM, DCM2, and pyrromethane-546 result in the efficient lasing of colors such as blue, green and yellow.
Owner:SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA UNIV OF THE +2
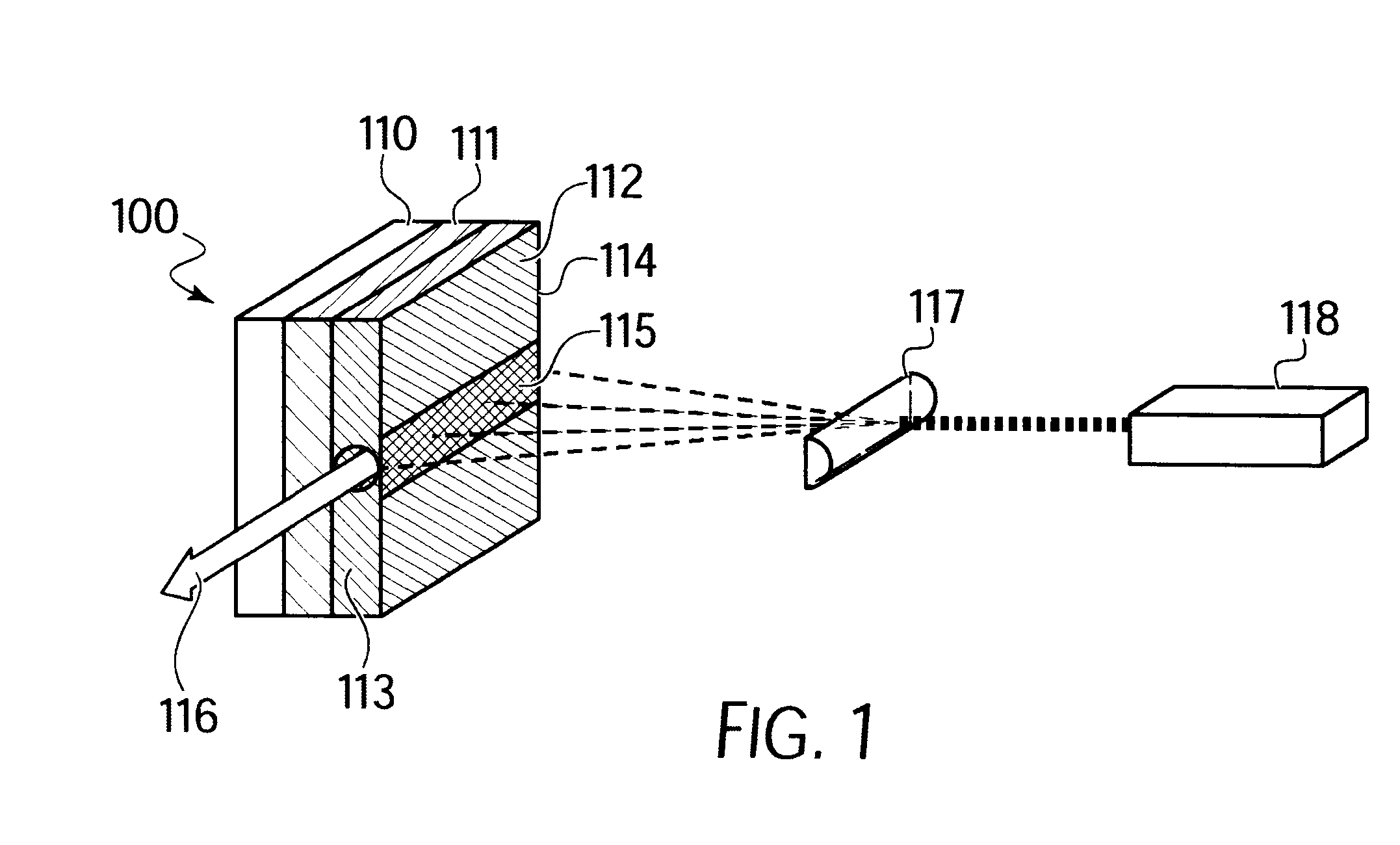
Surface emitting laser with an integrated absorber
InactiveUS20060029112A1Laser using scattering effectsLaser optical resonator constructionOutput couplerOptoelectronics
A surface emitting laser (SEL) with an integrated absorber. A lower mirror and an output coupler define a laser cavity of the SEL. A monolithic gain structure positioned in the laser cavity includes a gain region and an absorber, wherein a saturation fluence of the absorber is less than a saturation fluence of the gain region.
Owner:TAHOE RES LTD
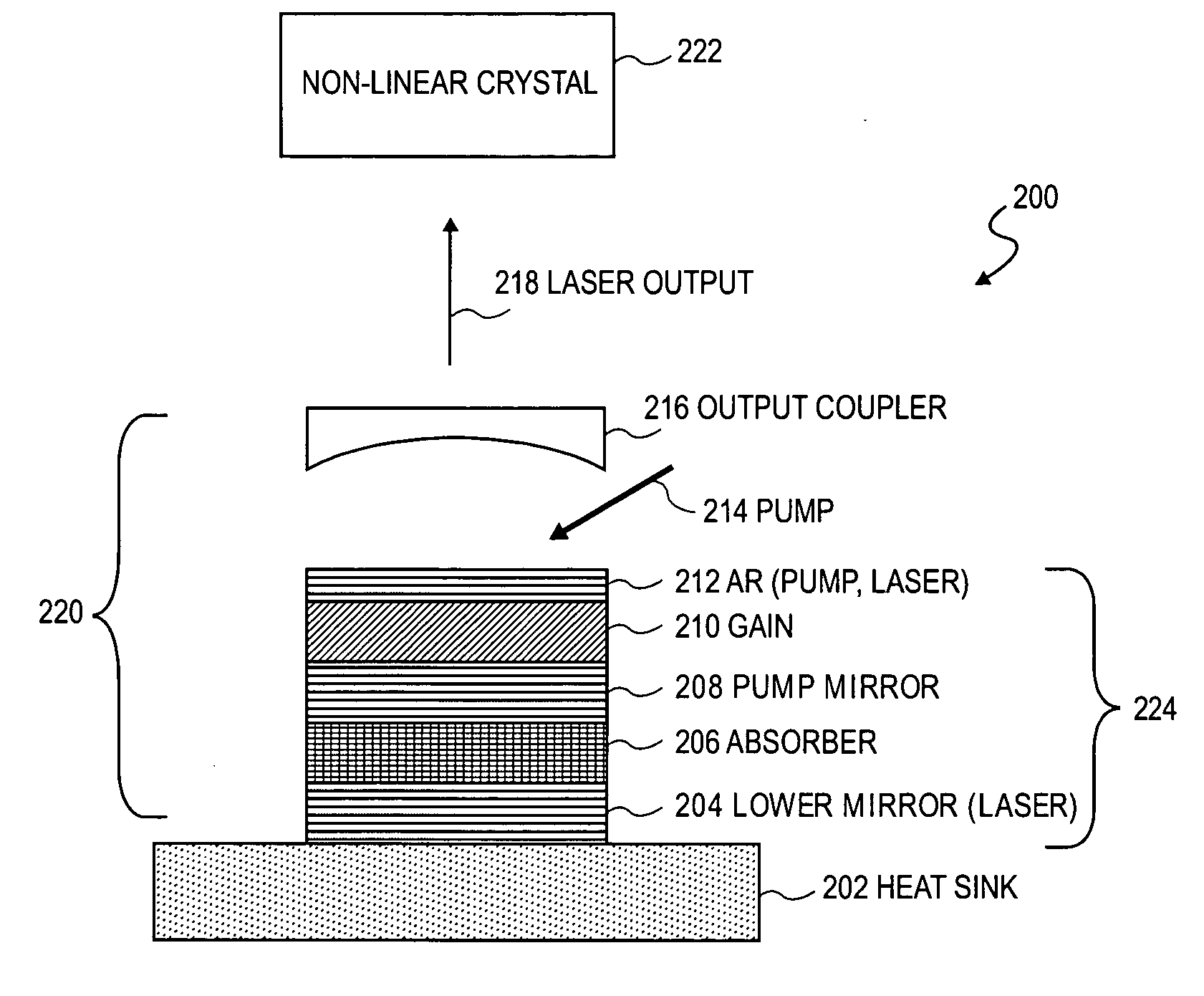
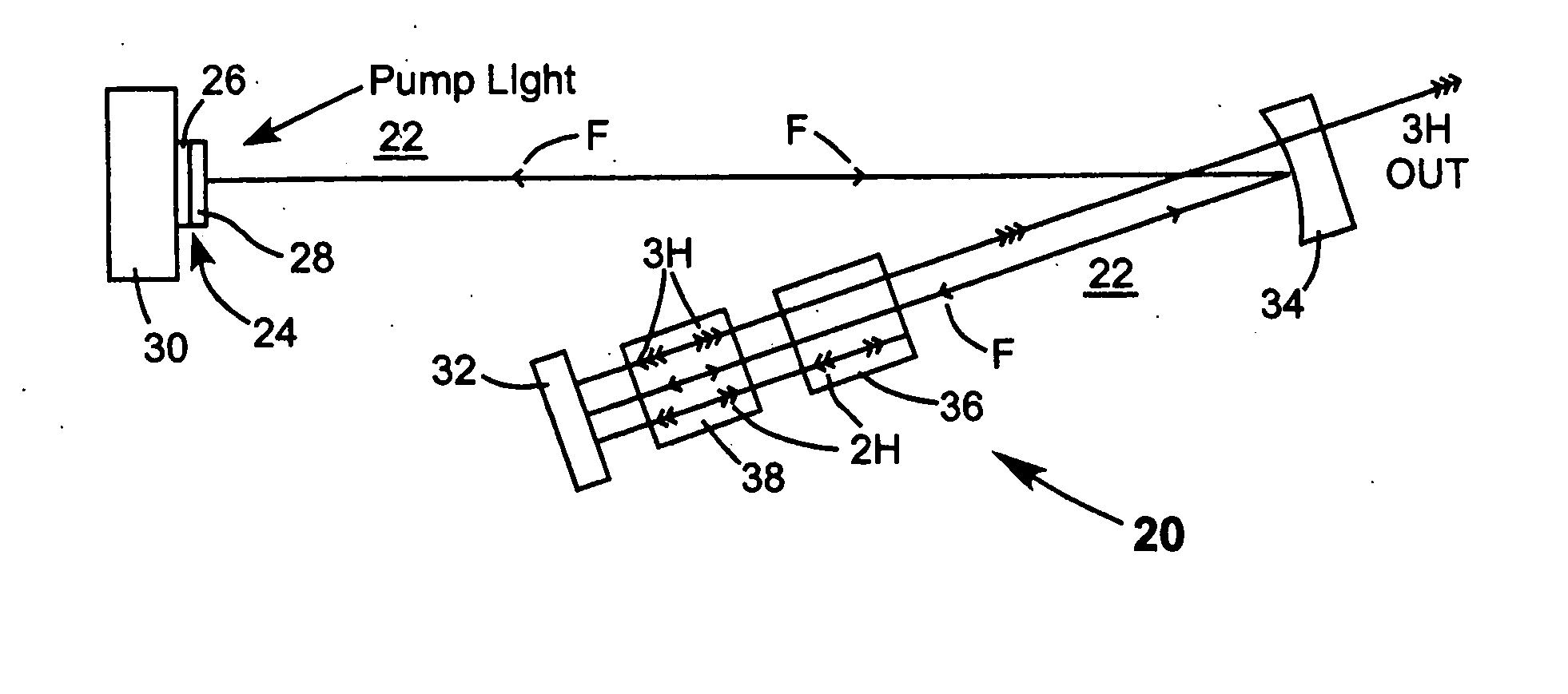
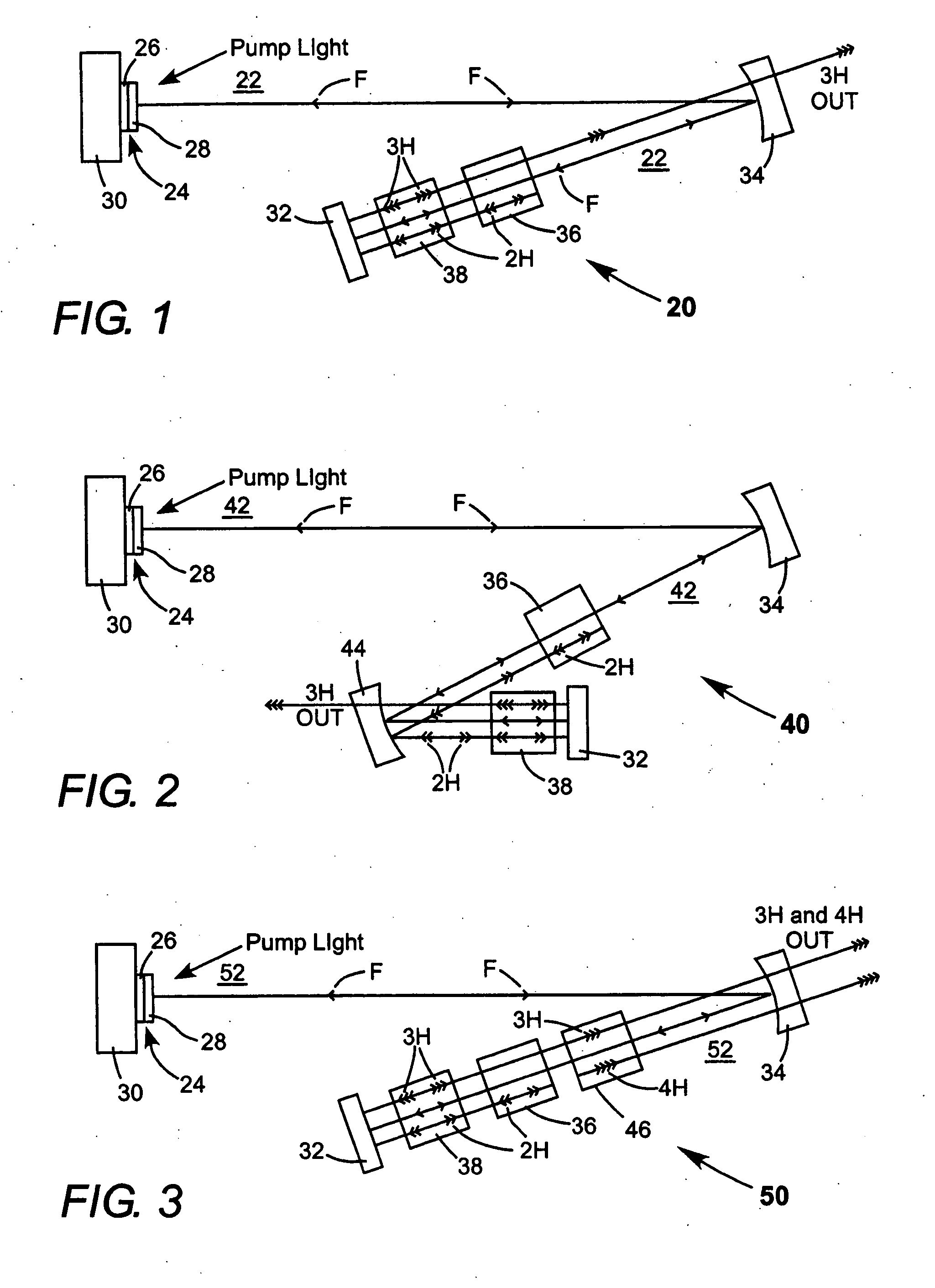
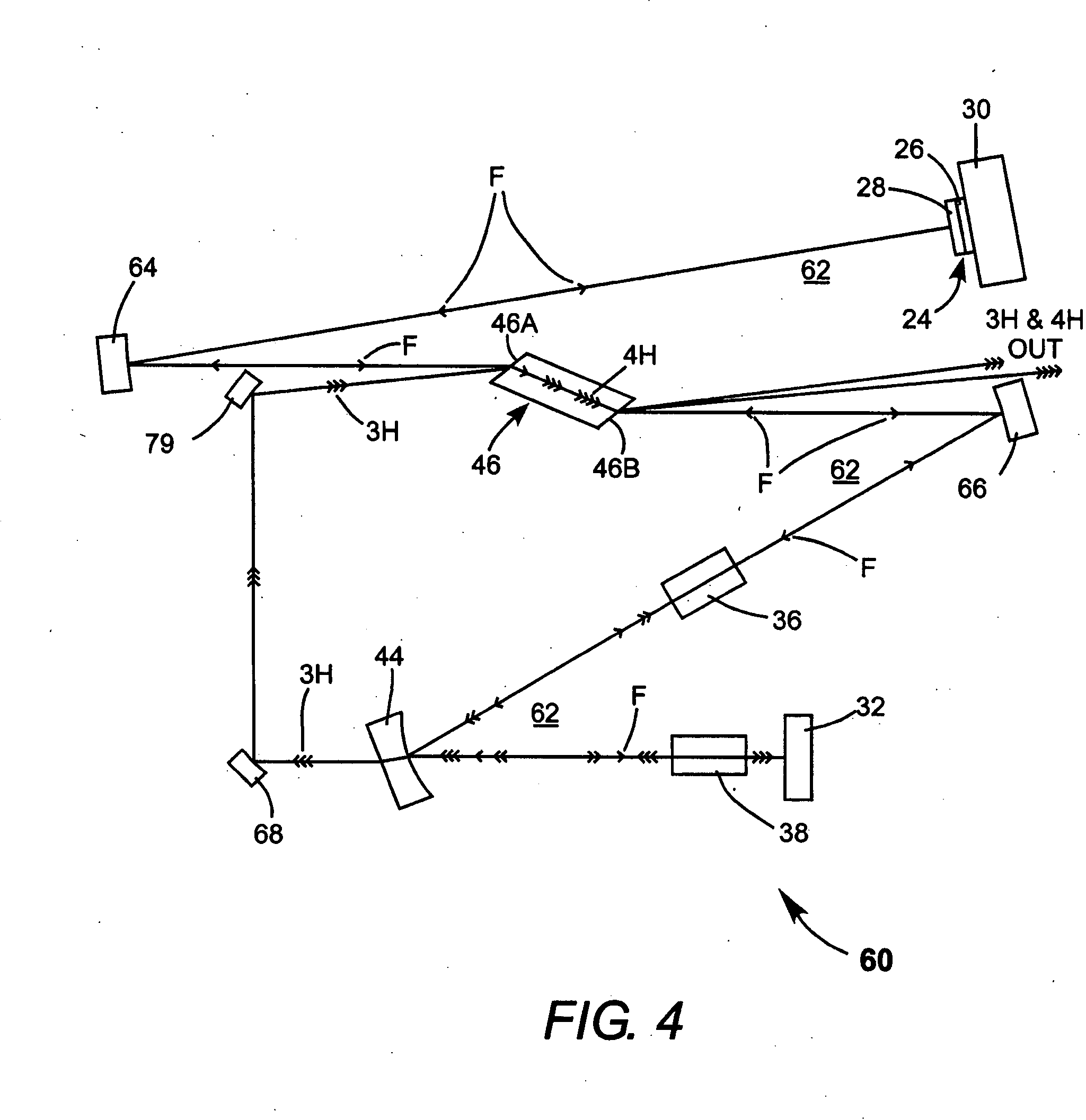
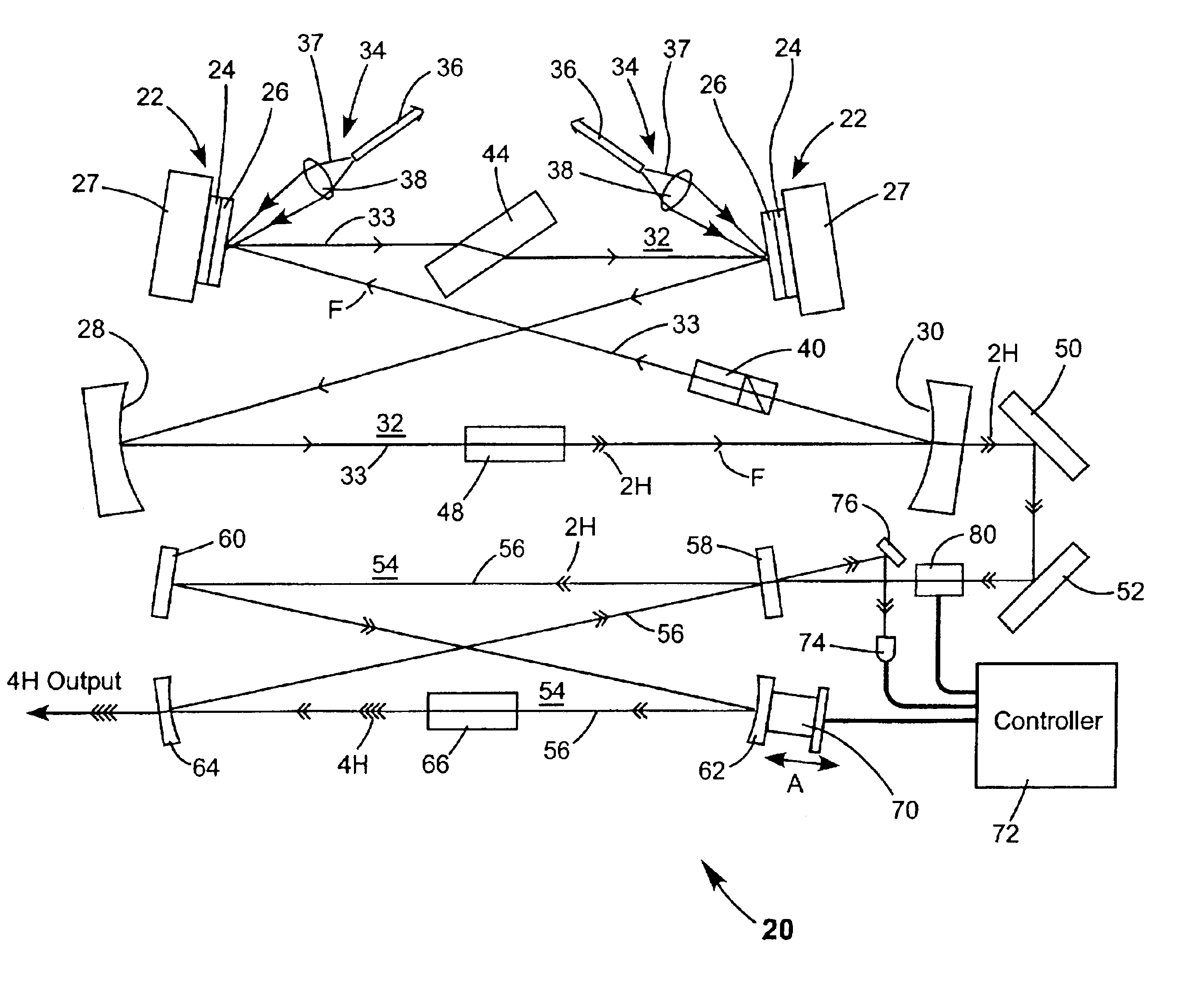
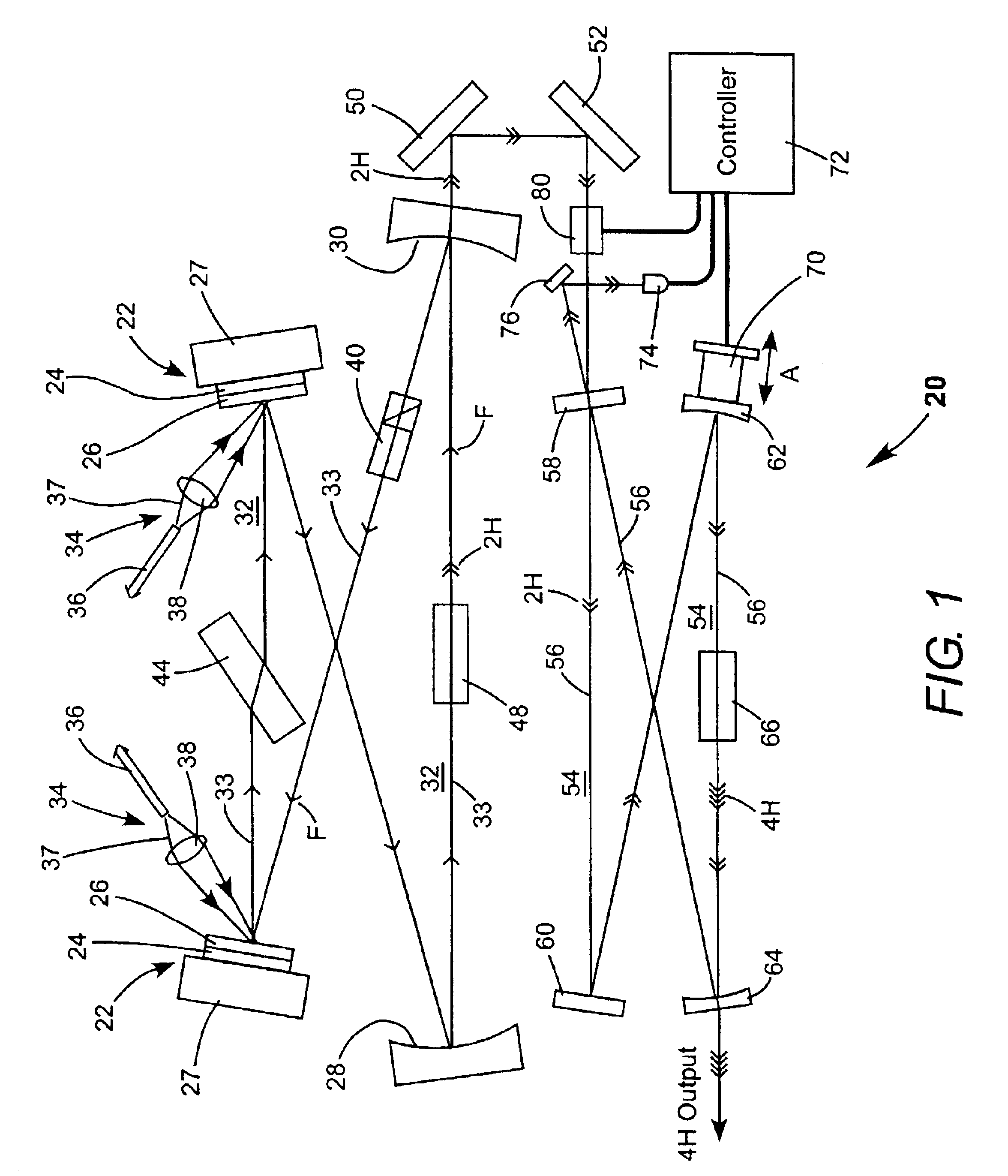
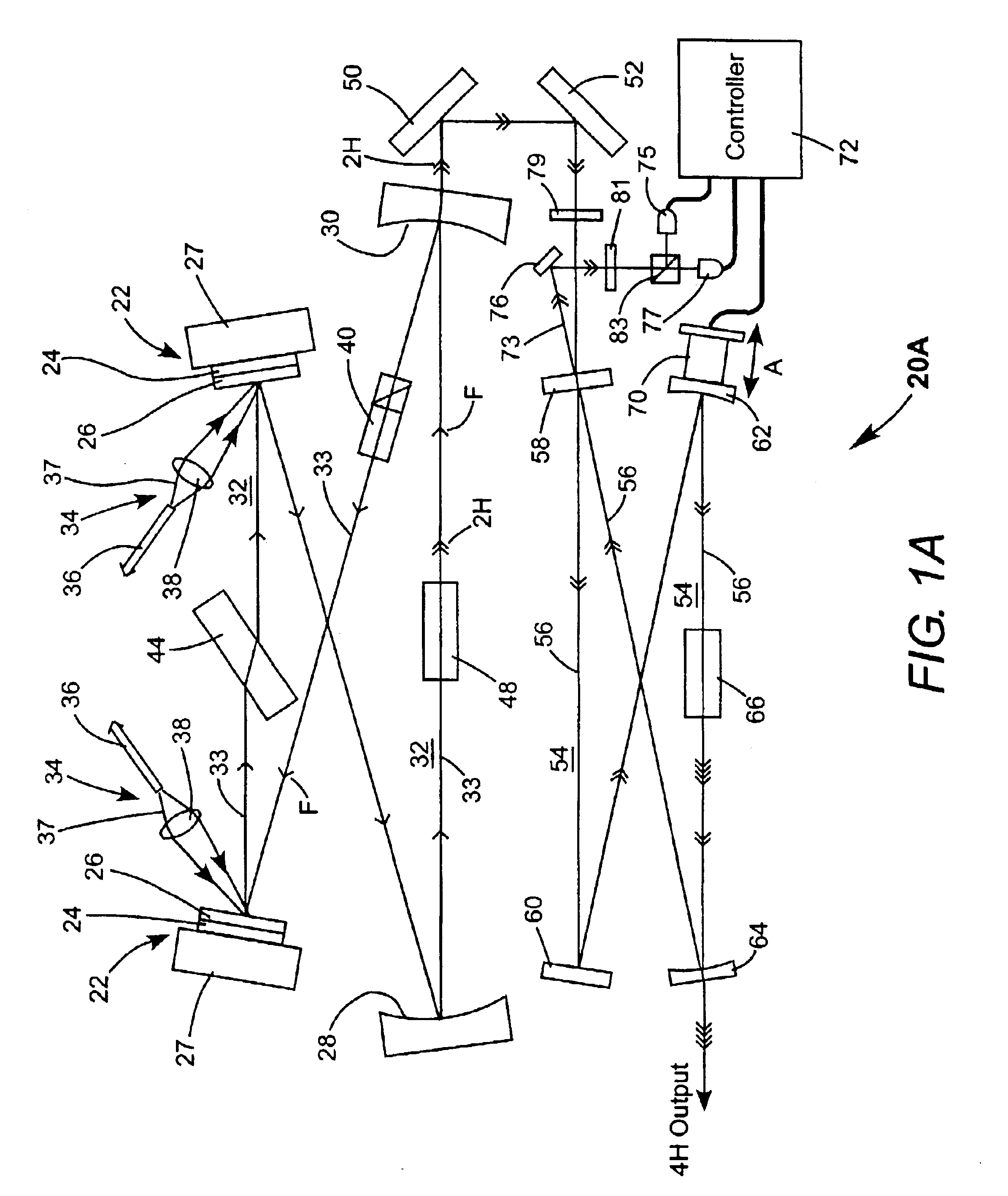
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser
InactiveUS20050078718A1High frequencyImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusNonlinear crystalsPhysics
A method of intracavity frequency conversion in a CW laser includes causing fundamental radiation to circulate in a laser resonator. The fundamental radiation makes a first pass through an optically nonlinear crystal where a fraction of the fundamental radiation generates second-harmonic radiation in a forward pass through the crystal. The residual fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation are then sum-frequency mixed in forward and reverse passes through an optically nonlinear crystal such that a fraction of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. The residual second-harmonic radiation and fundamental radiation from the sum-frequency mixing then make a reverse pass through the second-harmonic generating crystal where the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation, or can be used to pump another optically nonlinear crystal in an optical parametric oscillator. Second-harmonic radiation can also be used to pump an optical parametric oscillator.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Optically pumped semiconductor ring laser
InactiveUS6940880B2Doubling frequencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusFourth harmonicOptical pumping
An optically pumped semiconductor laser includes an active ring-resonator having two or more optically pumped semiconductor (OPS) structures each including a mirror-structure and a multilayer gain-structure. The mirror-structures serve as fold mirrors for the resonator axis. An optically nonlinear crystal may be included in the ring-resonator for generating second-harmonic radiation from fundamental radiation generated in the resonator. Another optically nonlinear crystal may be provided for generating third-harmonic or fourth-harmonic radiation from the second-harmonic radiation. In one example, including a third-harmonic generating crystal, a passive ring-resonator partially coaxial with the active ring-resonator is provided for circulating second-harmonic radiation to provide resonant amplification of the second-harmonic radiation for enhancing third-harmonic conversion. Apparatus for automatically maintaining the passive ring-resonator in a resonant condition for the second-harmonic radiation is disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Incoherent light-emitting device apparatus for driving vertical laser cavity
InactiveUS6879618B2Low thresholdImprove quantum efficiencyLaser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusLaser lightLight emitting device
A laser emitting apparatus includes a substrate having on one side an incoherent light-emitting device having a light-emitting layer wherein an electric field is applied across the light-emitting layer to produce light which is transmitted out of the incoherent light-emitting device through an optically transparent layer into a vertical laser cavity structure disposed to receive light transmitted from the incoherent light-emitting device and produce laser light.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
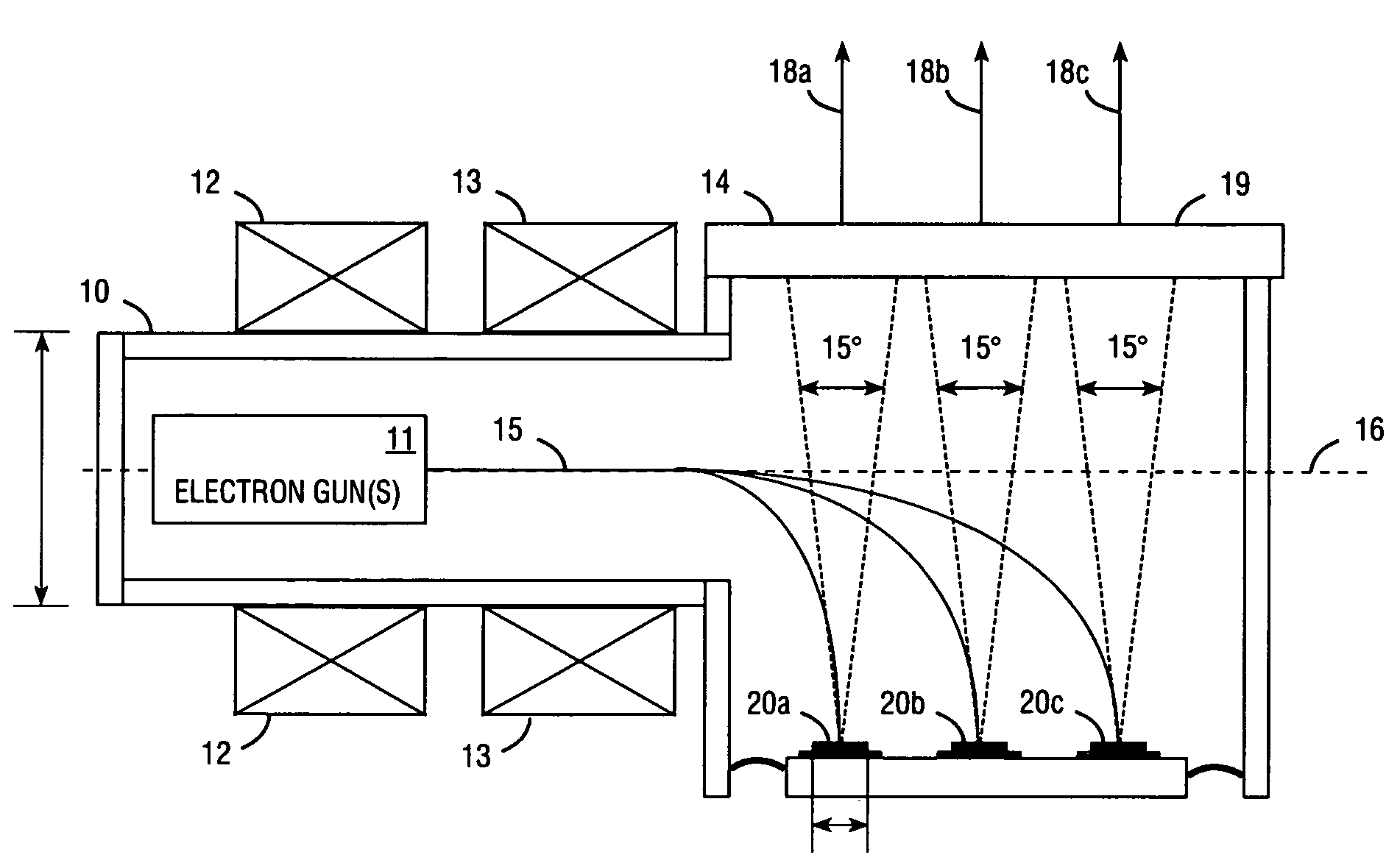
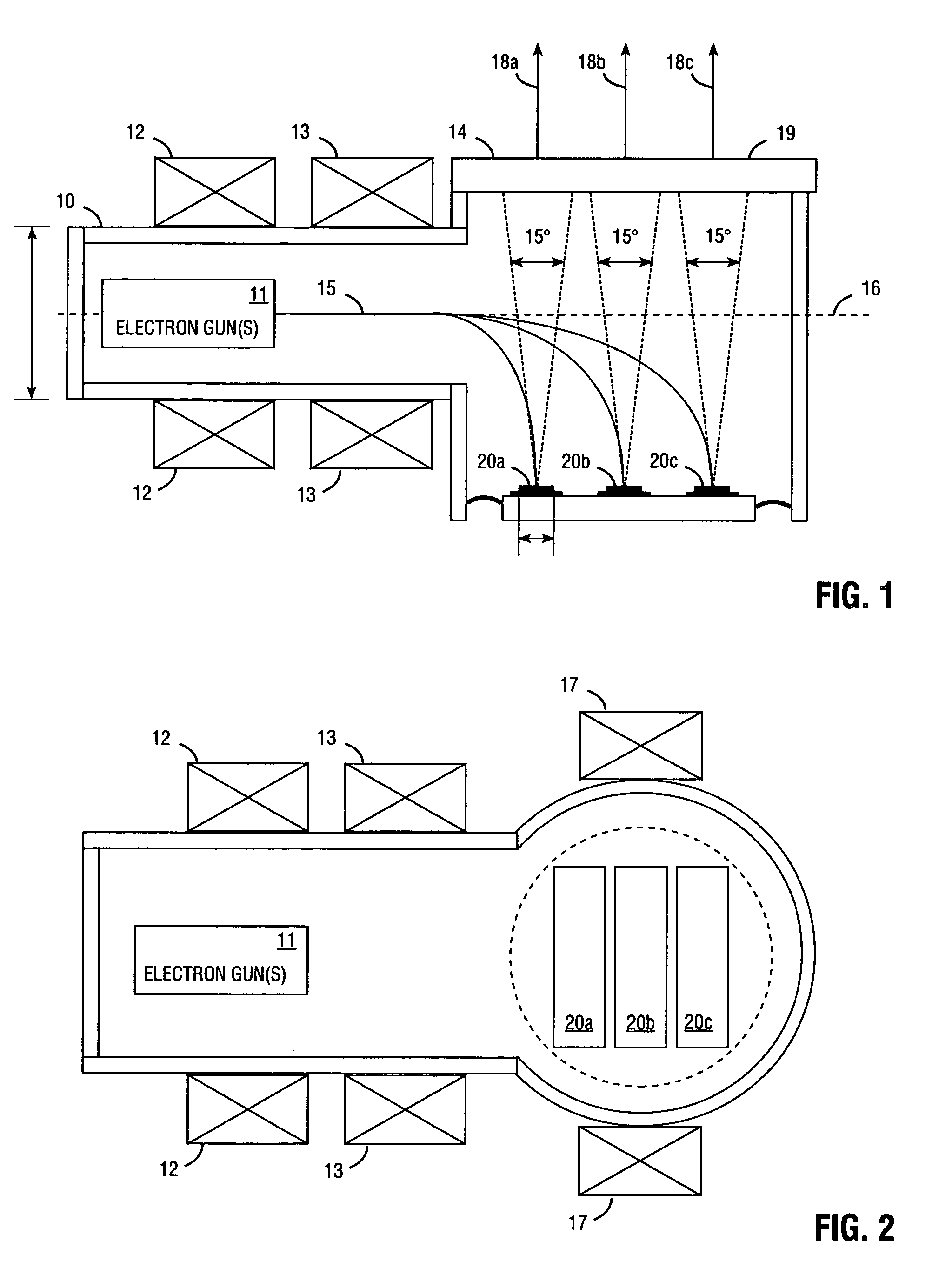
Electron beam pumped laser light source for projection television
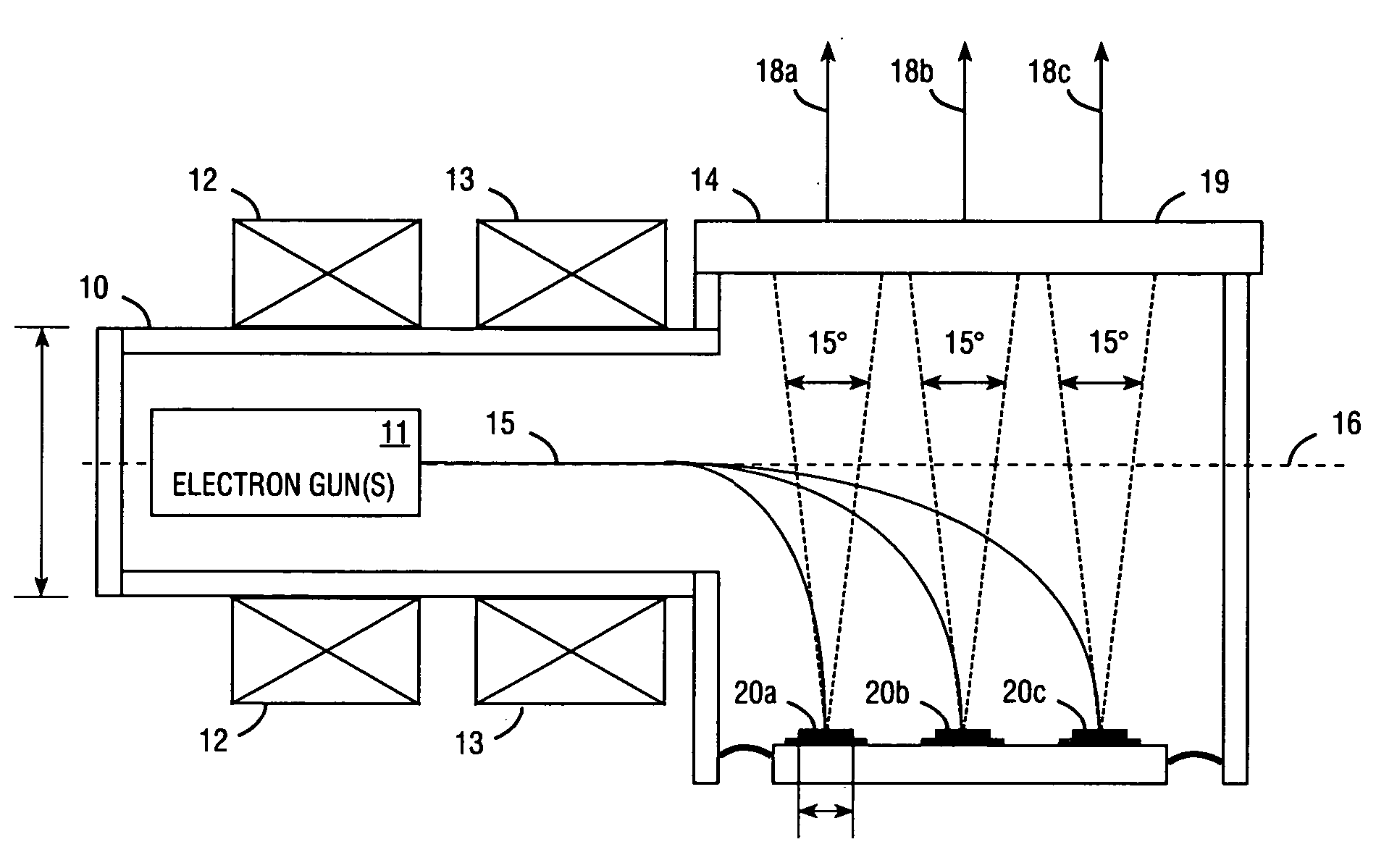
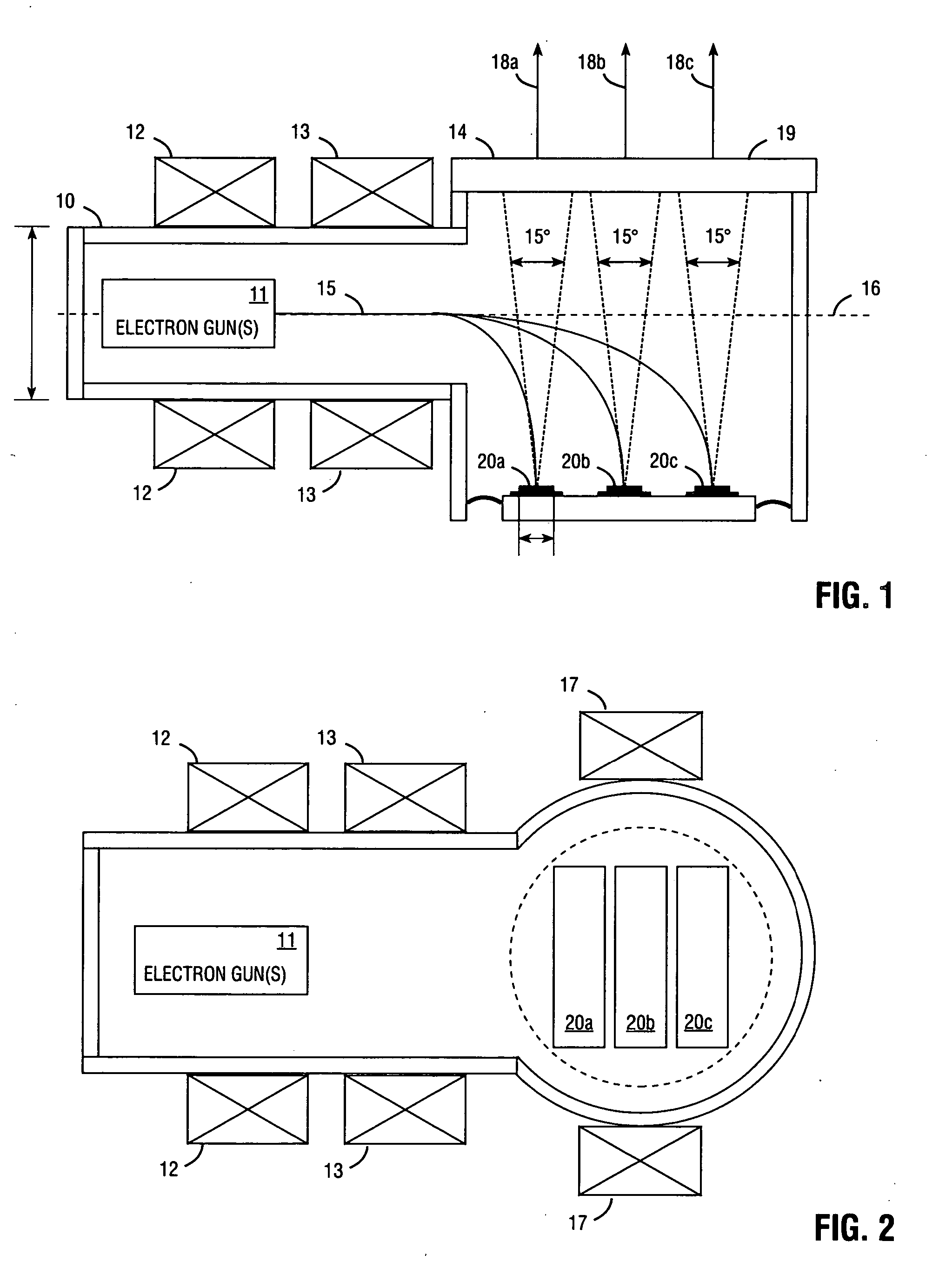
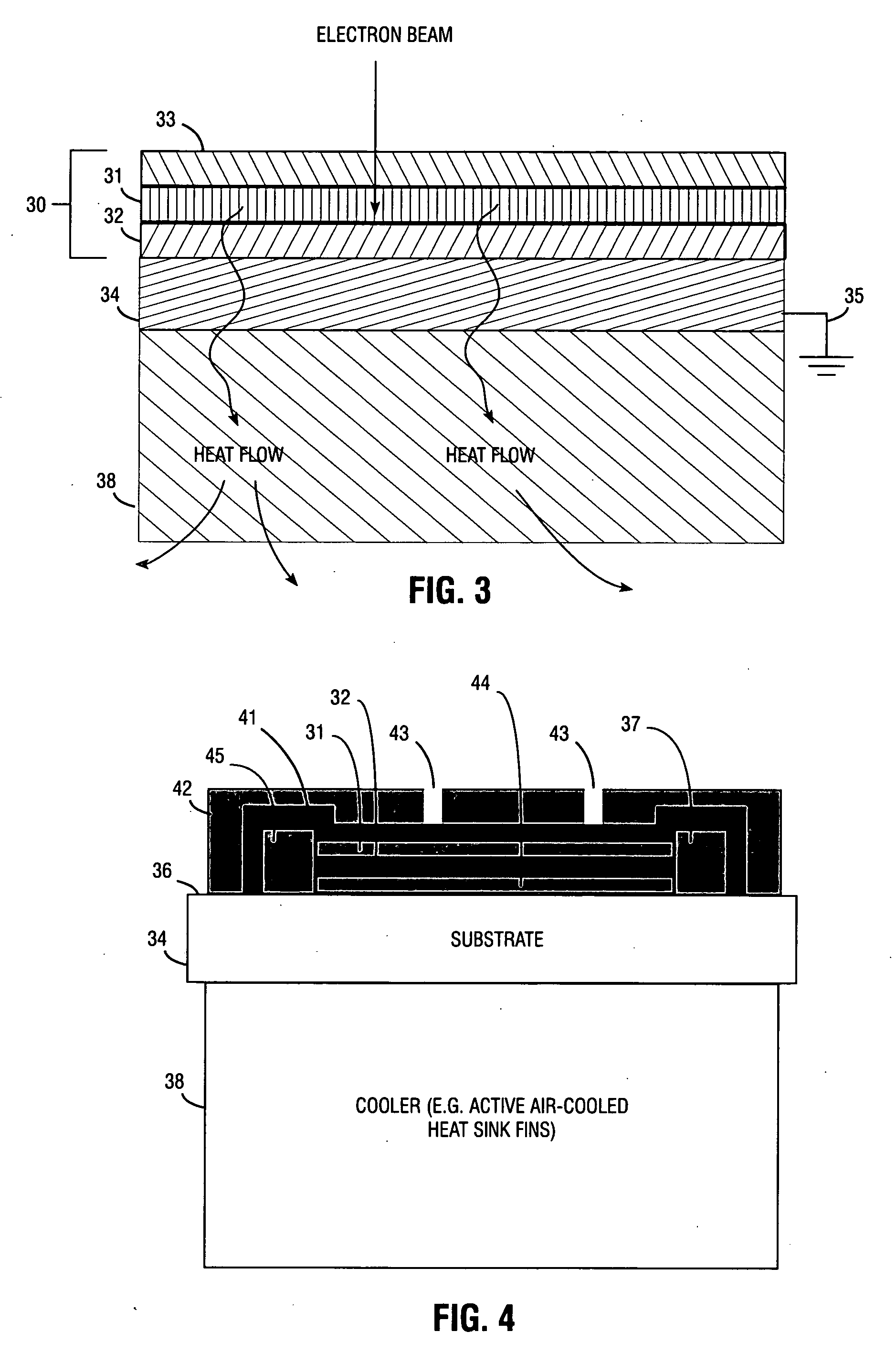
InactiveUS7309953B2Improve heat transfer performanceHigh strengthCathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionIncadescent screens/filtersContinuous lightDirect path
An electron beam pumped laser including a surface-emitting laser faceplate oriented at a non-perpendicular angle. Embodiments are described in which a bending coil bends the electron beam, or in which the faceplate is situated in the direct path of the e-beam emission but with a non-zero orientation angle. The faceplate may include a substantially opaque substrate, and an opaque heat-removing structure may be attached to the substrate to provide high heat transfer, thereby allowing high electron-beam pumping intensity and providing more light emission from a smaller package. In some embodiments the partially reflective mirror comprises a metal layer that has a plurality of openings. Multiple laser faceplates (e.g., red, green, and blue) may be placed in the same tube, to provide a continuous light source for projection television. The substrate may be connected to ground to provide an exit path for electrons from the laser gain layer.
Owner:PRINCIPIA LIGHTWORKS
Optically pumped, surface-emitting semiconductor laser device and method for the manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6954479B2High positioning accuracyLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor structureOptical pumping
The invention is directed to an optically pumped surface-emitting semiconductor laser device having at least one radiation-generating quantum well structure and at least one pump radiation source for optically pumping the quantum well structure, whereby the pump radiation source comprises an edge-emitting semiconductor structure. The radiation-generating quantum well structure and the edge-emitting semiconductor structure are epitaxially grown on a common substrate. A very efficient and uniform optical pumping of the radiation-generating quantum well structure is advantageously possible with this monolithically produced semiconductor laser device. Methods for manufacturing inventive semiconductor laser devices are also specified.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Electron-beam excitation laser
InactiveUS20010019565A1Laser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusDielectricElectron source
An electron-beam excitation laser has a laser structure with a light emitter and reflectors on one hand and an electron source on the other hand, wherein at least part of the light emitter or reflectors has a multidimensional photonic crystal structure. An electron-beam excitation laser includes an electron source emitting electrons and a laser structure consisting of a light emitter and reflectors, accelerates electrons from the electron source, and irradiates the electrons to the laser structure to emit a laser beam from the laser structure, wherein the reflectors and / or the light emitter in the laser structure are formed with multidimensional photonic crystals in which dielectrics with different dielectric constants are arrayed in a plurality of directions at periodic intervals, and one of the dielectrics with different dielectric constants may be formed with a light-emitting material.
Owner:CANON KK
Photonic crystal laser sources for chemical detection
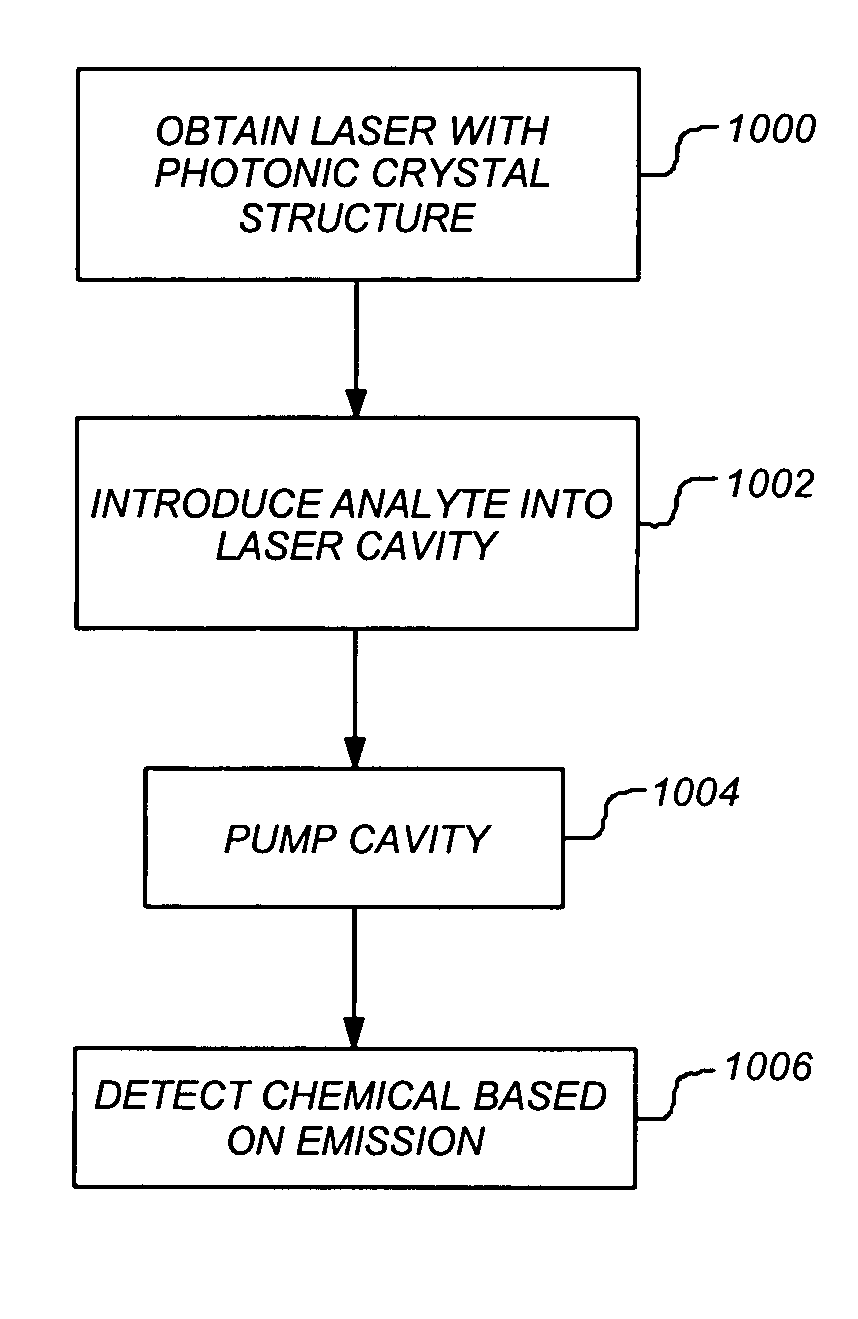
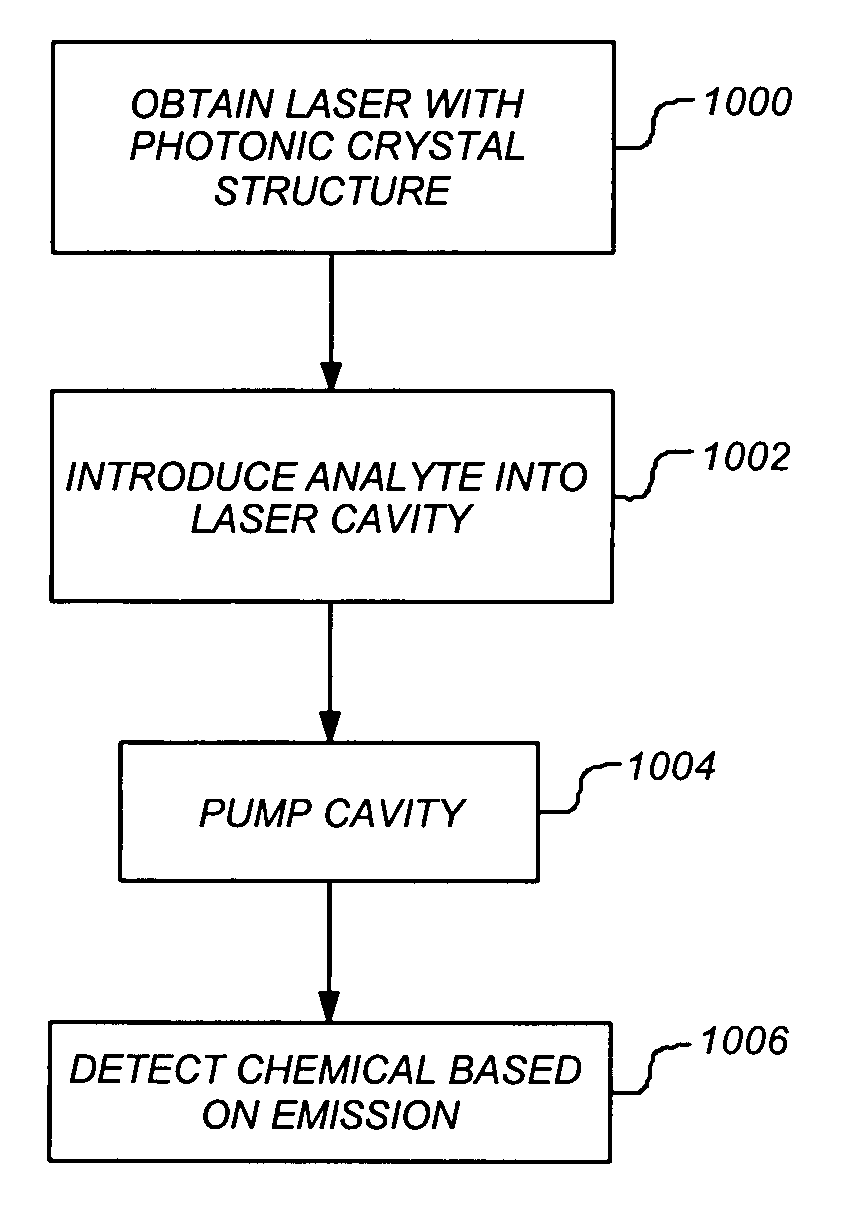
ActiveUS20050110992A1Single-molecule sensitivityRadiation pyrometryLaser optical resonator constructionPhotonic crystalAnalyte
A system, method and apparatus provide the ability to detect a chemical in an analyte. To detect the chemical, the invention utilizes a laser having an open cavity. A photonic crystal lattice structure having a defect defines a suitable geometry for such a cavity. The analyte is introduced directly into a high optical field of the cavity. Thereafter, the cavity is pumped and an emission from the laser is used to detect the presence of the chemical in the analyte.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
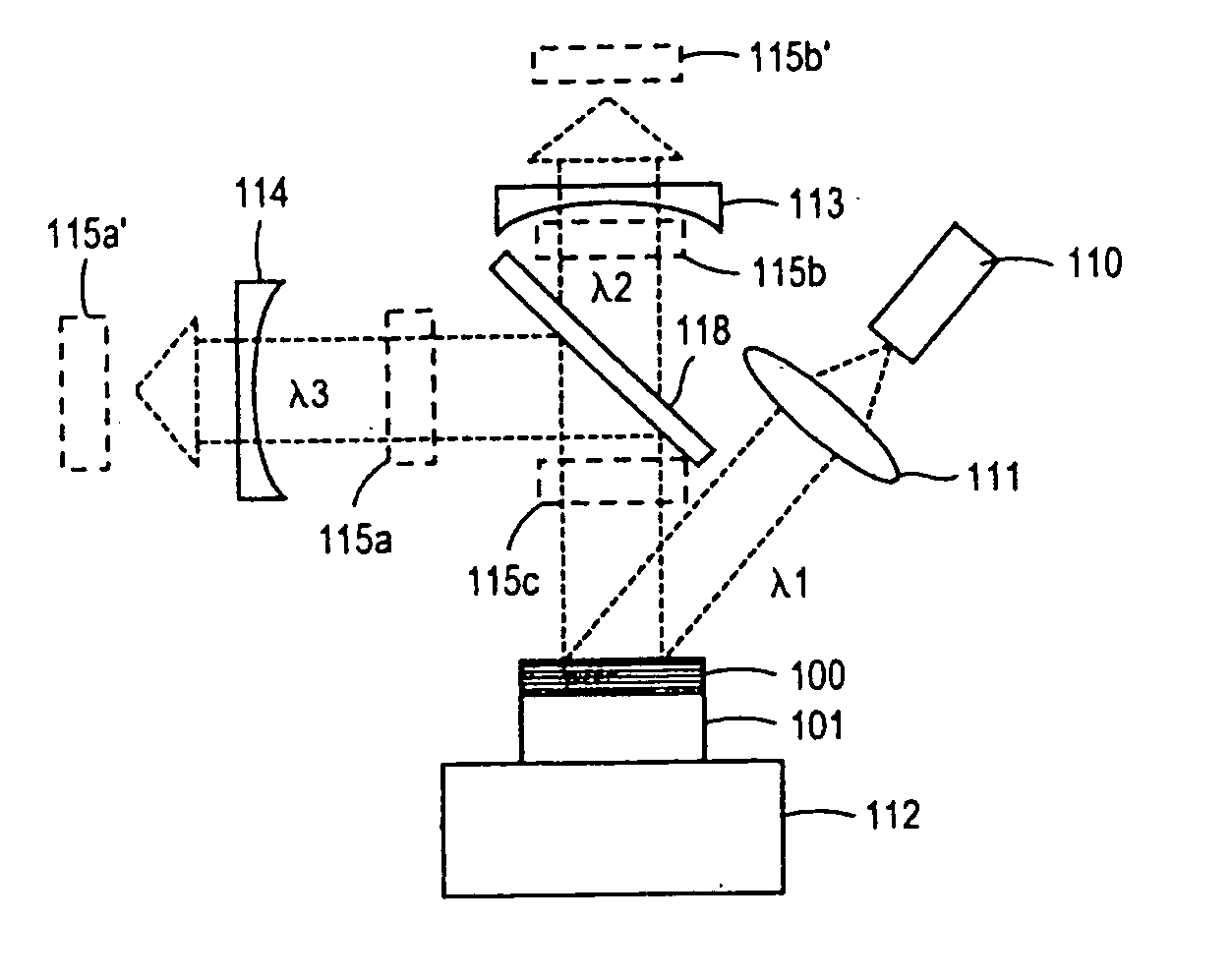
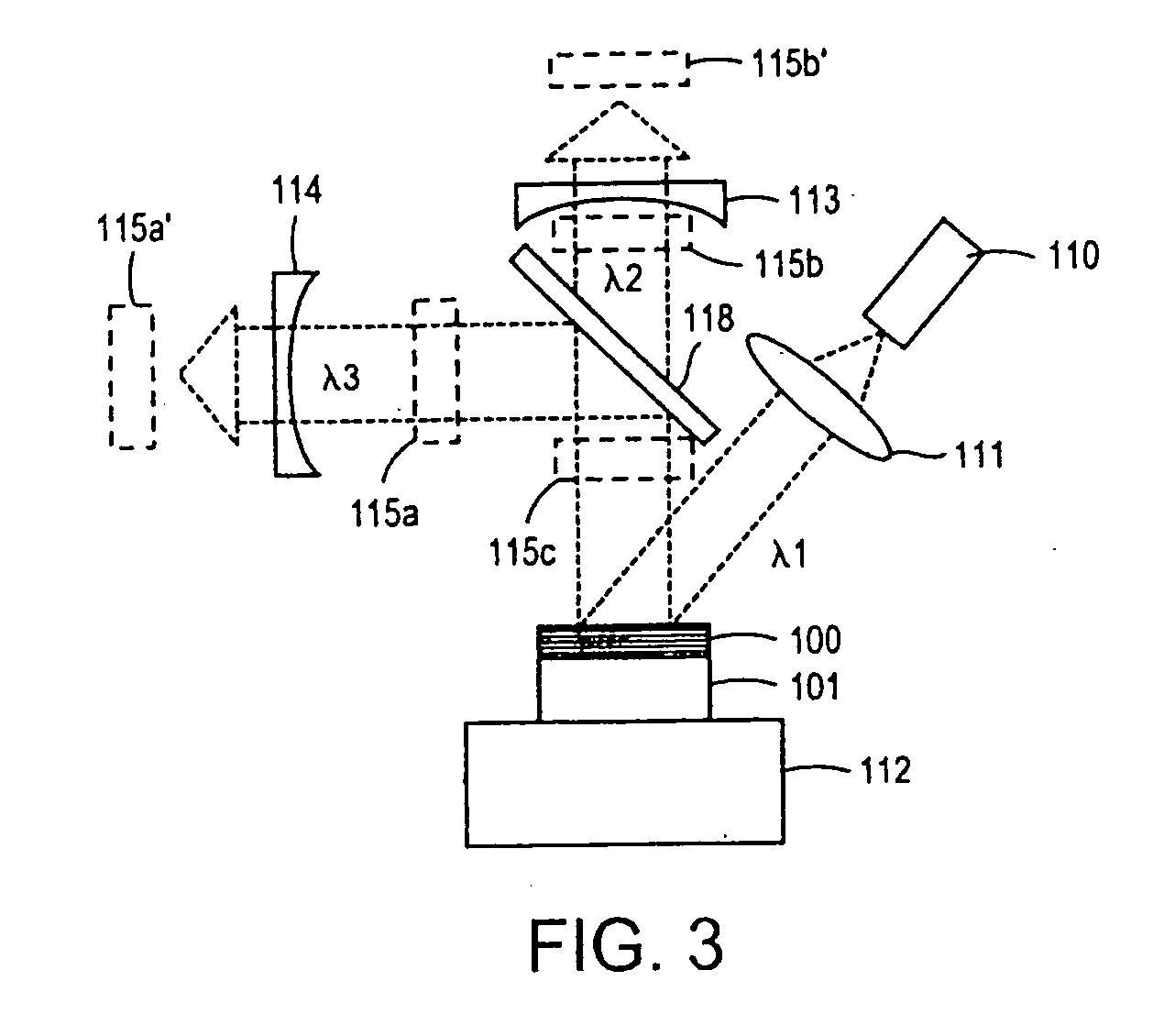
Laser apparatus in which surface-emitting semiconductor is excited with semiconduct laser element and high-order oscillation modes are suppressed
InactiveUS6594297B1Eliminate the effects ofMaintain relatively stableLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusLaser lightLength wave
A laser apparatus includes a semiconductor laser element, a surface-emitting semiconductor element including a first mirror, and a second mirror. The semiconductor laser element emits first laser light having a first wavelength. The surface-emitting semiconductor element is excited with the first laser light, and emits second laser light having a second wavelength which is longer than the first wavelength. The first mirror in the surface-emitting semiconductor element is arranged on one side of the first active layer. The second mirror is arranged outside the surface-emitting semiconductor element so that the first and second mirrors form a resonator in which the second laser light resonates. The surface-emitting semiconductor element includes a structure for controlling a spatial mode of the second laser light.
Owner:NICHIA CORP +1
External cavity dual wavelength laser system
ActiveUS20050281308A1Increasing cost of manufacture and cost of operationRelative power of the laser light output can be balancedLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusQuantum wellLength wave
The number and type of quantum wells in a multi-layer gain structure of an external cavity surface emitting laser (VECSEL) are controlled to provide output light of more than one coherent wavelength. The number and type of layers in a multiplayer mirror provides a dual wavelength reflector.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Photonic crystal laser sources for chemical detection
A system, method and apparatus provide the ability to detect a chemical in an analyte. To detect the chemical, the invention utilizes a laser having an open cavity. A photonic crystal lattice structure having a defect defines a suitable geometry for such a cavity. The analyte is introduced directly into a high optical field of the cavity. Thereafter, the cavity is pumped and an emission from the laser is used to detect the presence of the chemical in the analyte.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Surface emitting semiconductor laser device
A surface emitting semiconductor laser device includes a GaAs substrate, and first and second laser sections consecutively and monolithically formed on the GaAs substrate. The second laser section has an active layer structure having a bandgap wavelength longer than the bandgap wavelength of the active layer structure of the first laser section. The second laser section is pumped by a first laser emitted by the first laser section to emit second laser.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Crystalline color-conversion device
ActiveUS9871345B2Improve optical efficiencyAvoid low lightSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureElectricityUltraviolet
According to an embodiment, a crystalline color-conversion device includes an electrically driven first light emitter, for example a blue or ultraviolet LED, for emitting light having a first energy in response to an electrical signal. An inorganic solid single-crystal direct-bandgap second light emitter having a bandgap of a second energy less than the first energy is provided in association with the first light emitter. The second light emitter is electrically isolated from, located in optical association with, and physically connected to the first light emitter so that in response to the electrical signal the first light emitter emits first light that is absorbed by the second light emitter and the second light emitter emits second light having a lower energy than the first energy.
Owner:X DISPLAY CO TECH LTD
Semiconductor device with vertical electron injection and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20070093009A1Less costlyLaser optical resonator constructionCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesElectronic accessElectron injection
A method for making a semiconductor device with vertical electron injection, including: transferring a monocrystalline thin film onto a first face of a support substrate; producing at least one electronic component from the monocrystalline thin film; forming at least one recess in a second face of the substrate to enable electric or electronic access to the electronic component through the monocrystalline thin film; and producing a vertical electron injector configured to inject electrons into the electronic component.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Electron beam pumped laser light source for projection television
InactiveUS20060163998A1Simple processImprove performanceCathode-ray/electron-beam tube electrical connectionIncadescent screens/filtersContinuous lightLaser light
An electron beam pumped laser including a surface-emitting laser faceplate oriented at a non-perpendicular angle. Embodiments are described in which a bending coil bends the electron beam, or in which the faceplate is situated in the direct path of the e-beam emission but with a non-zero orientation angle. The faceplate may include a substantially opaque substrate, and an opaque heat-removing structure may be attached to the substrate to provide high heat transfer, thereby allowing high electron-beam pumping intensity and providing more light emission from a smaller package. In some embodiments the partially reflective mirror comprises a metal layer that has a plurality of openings. Multiple laser faceplates (e.g., red, green, and blue) may be placed in the same tube, to provide a continuous light source for projection television. The substrate may be connected to ground to provide an exit path for electrons from the laser gain layer.
Owner:PRINCIPIA LIGHTWORKS
Photonic circuit device with on-chip optical gain measurement structures
ActiveUS20160252692A1Laser active region structureExcitation process/apparatusPhotonicsGain measurement
The present invention is directed to a photonic circuit device for optical gain measurement, including: a substrate with a photonic circuit; an active gain section; at least two light couplers arranged such that at least a part of the active gain section is between the light couplers; and a partial reflector arranged to reflect light propagating along the same direction back to a center of the gain section, and wherein the device does not include any other reflector opposite to the partial reflector with respect to the active gain section and configured to reflect light back to the center of the gain section. The present invention is further directed to related gain measurement methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
Popular searches
Optical resonator shape and construction Active medium material Semiconductor laser excitation apparatus Active medium shape and construction Semiconductor devices Coupling light guides Optical waveguide light guide Semiconductor laser optical device Picture reproducers using projection devices Laser arrangements
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com