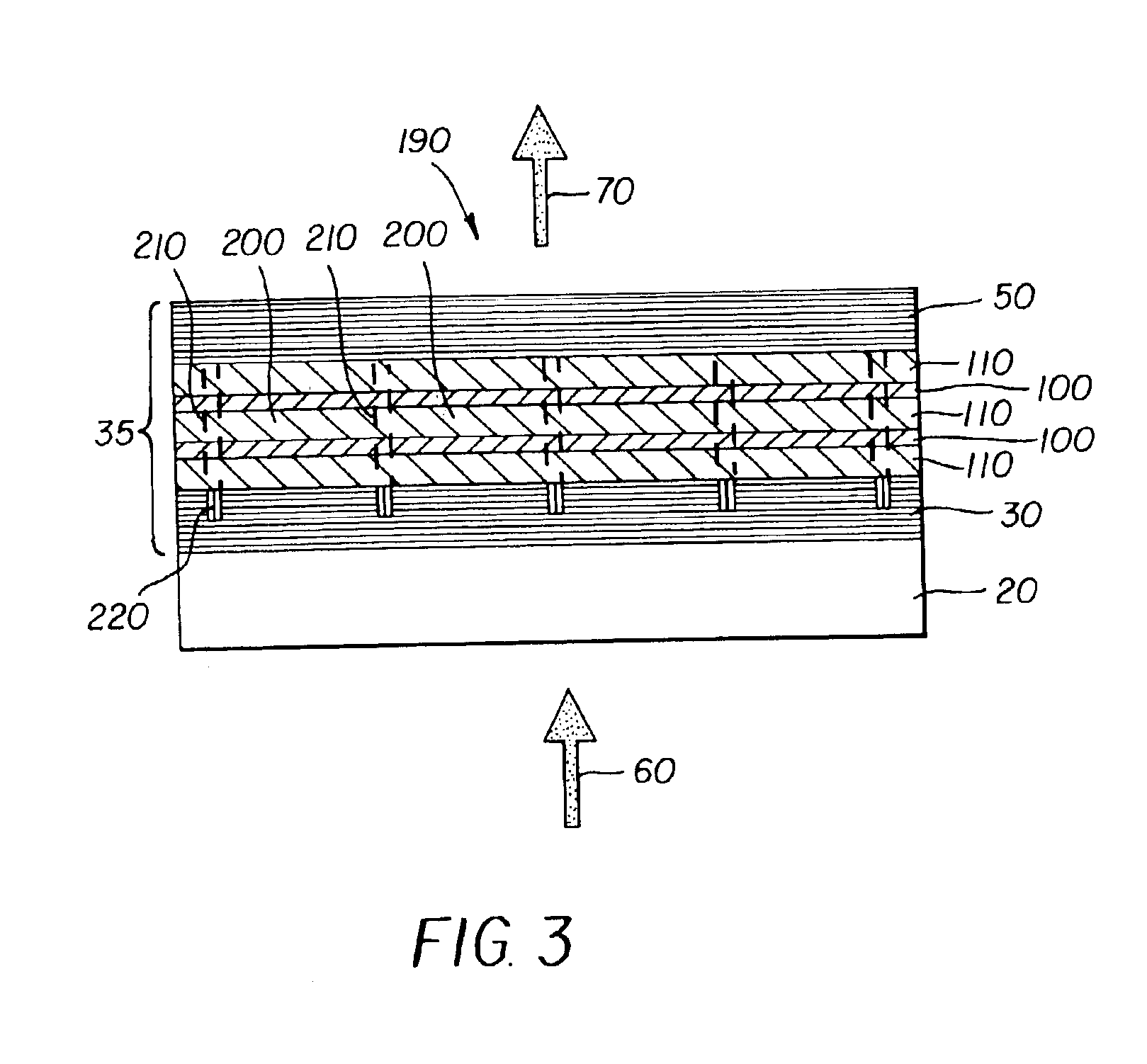
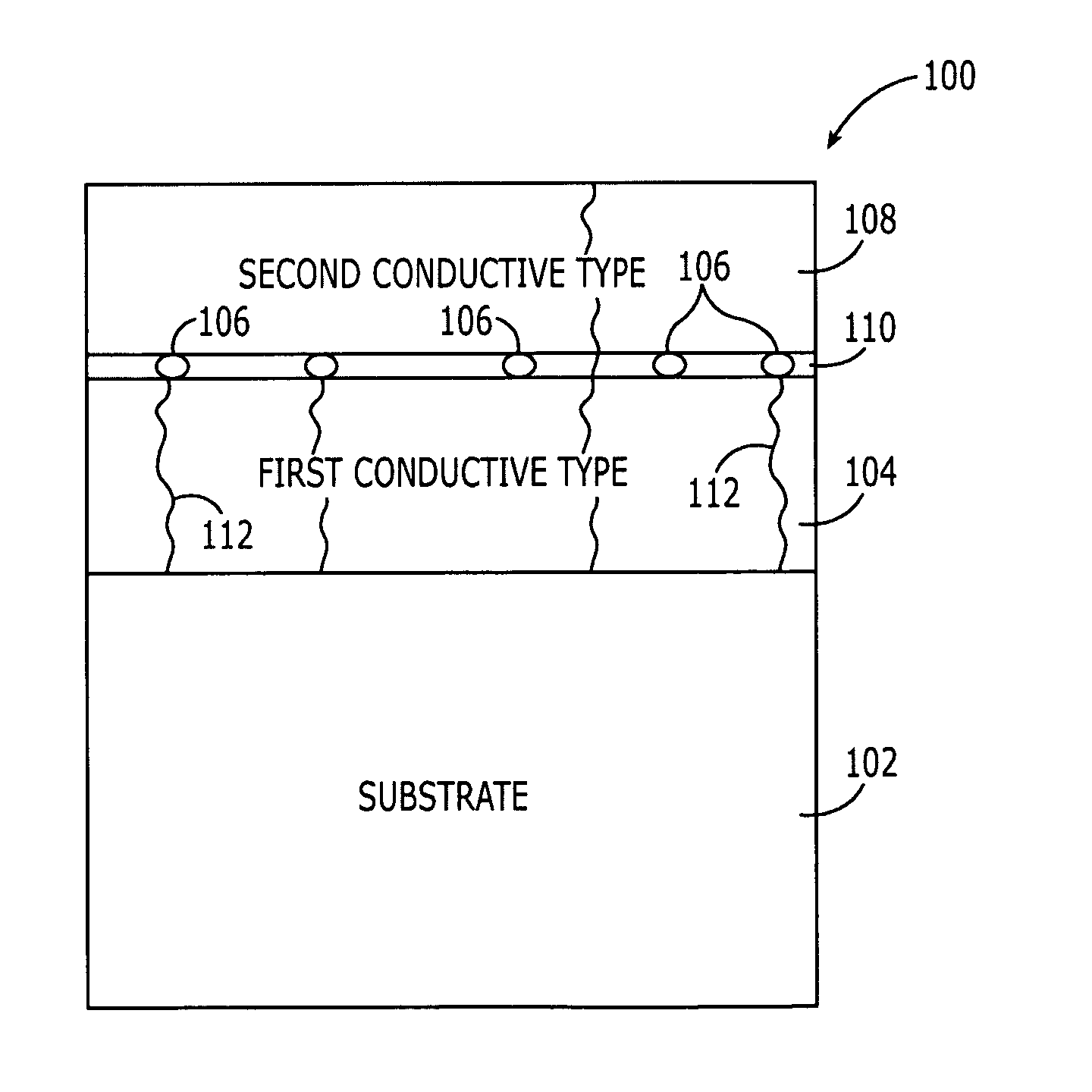
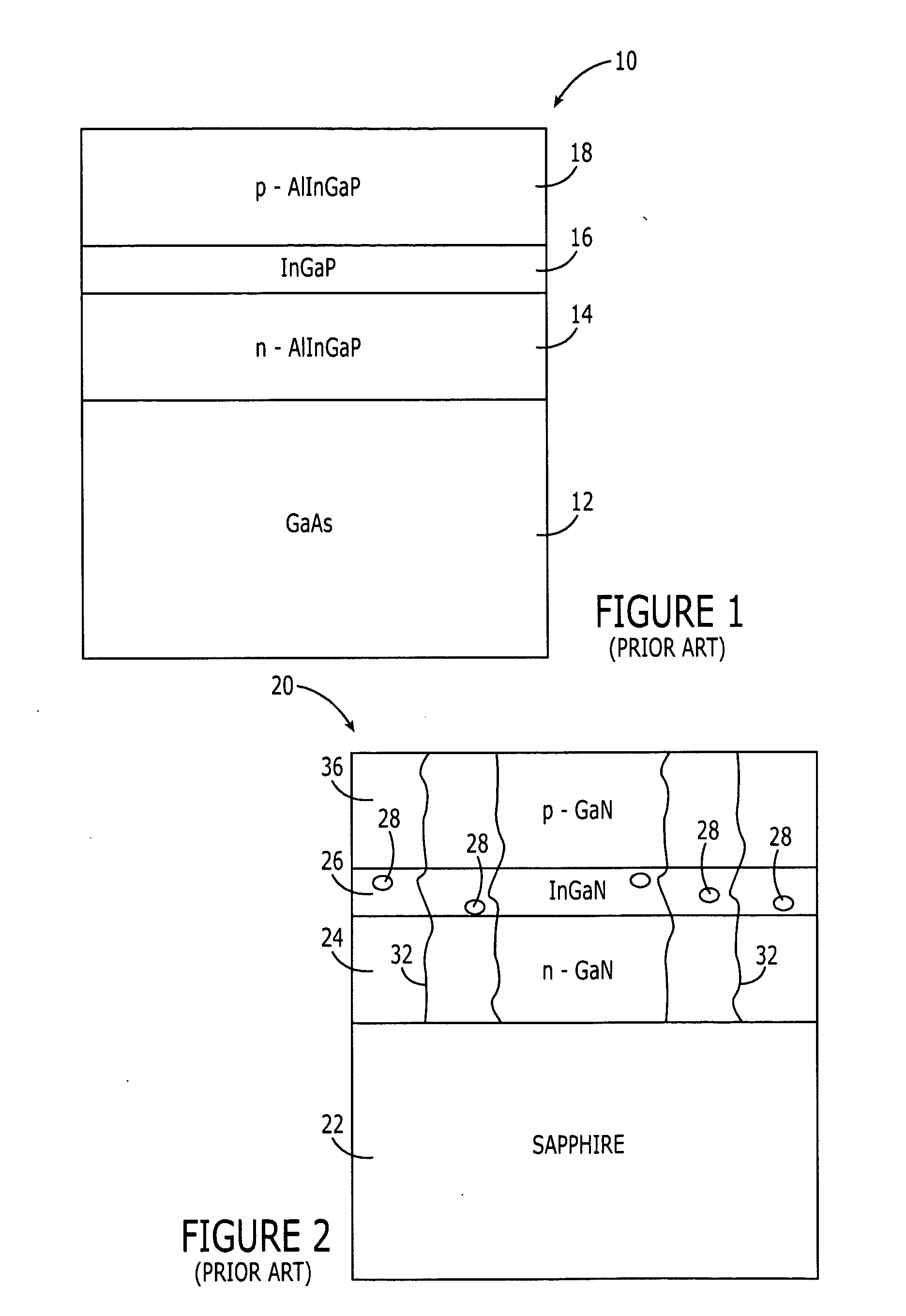
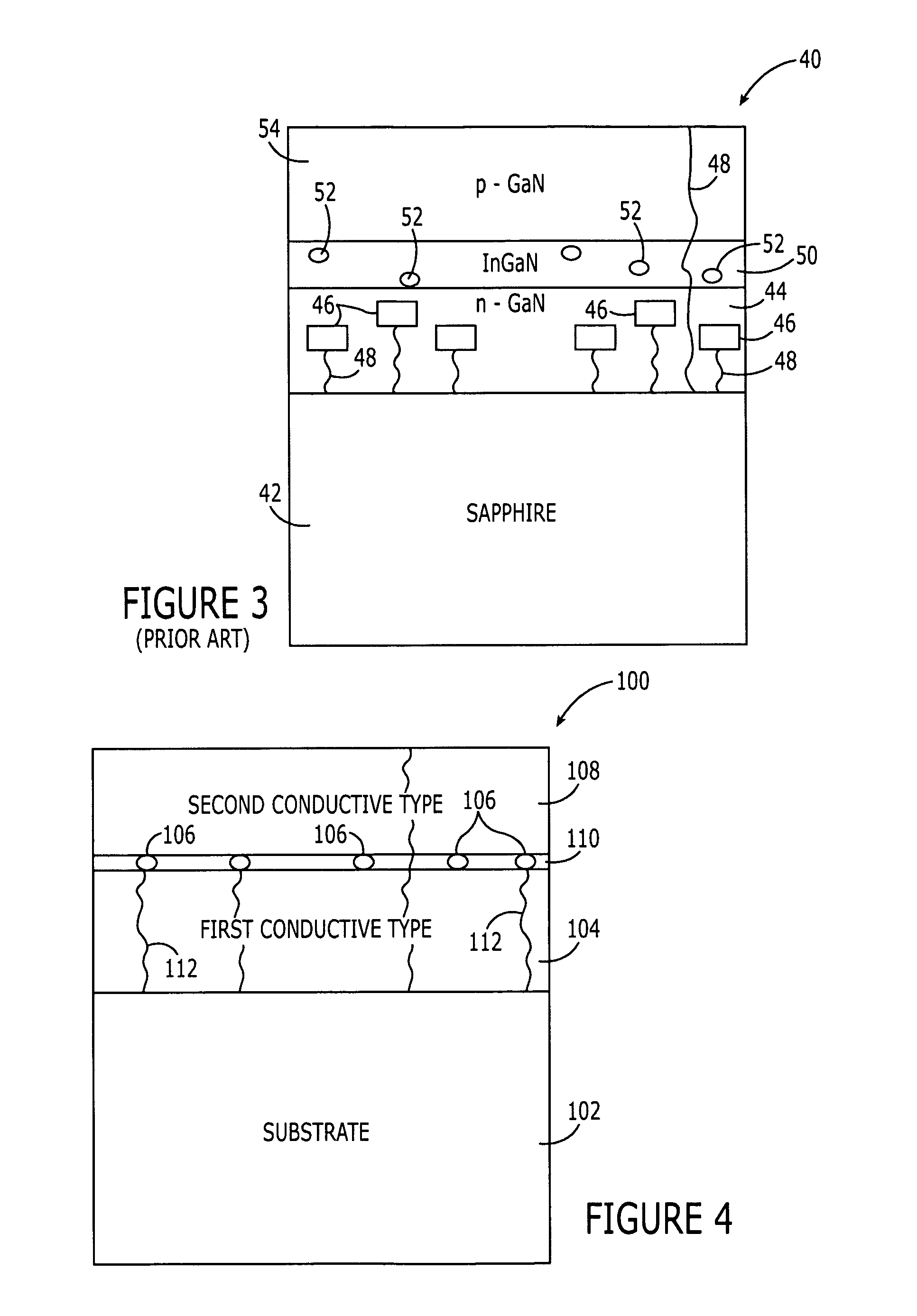
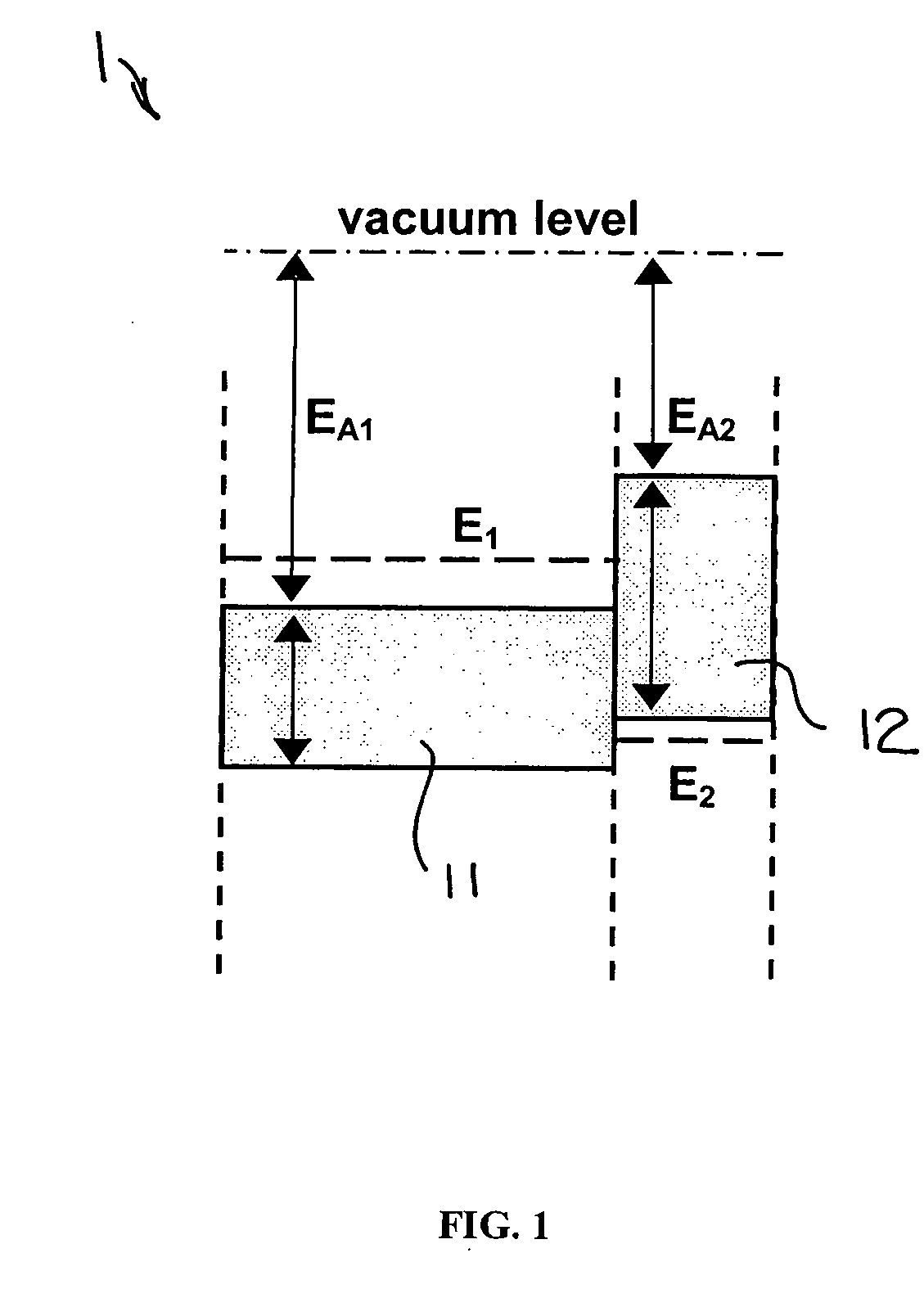
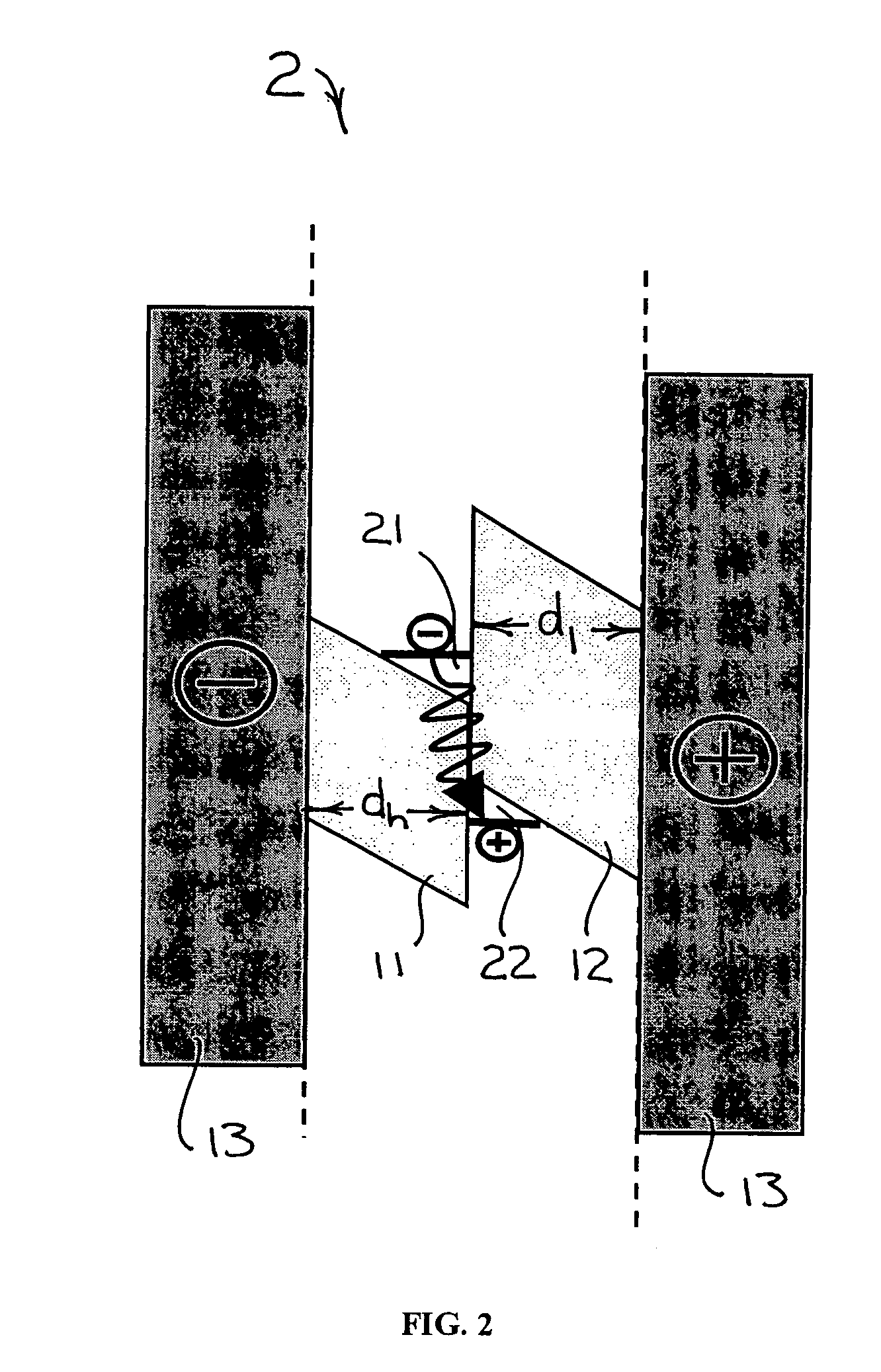
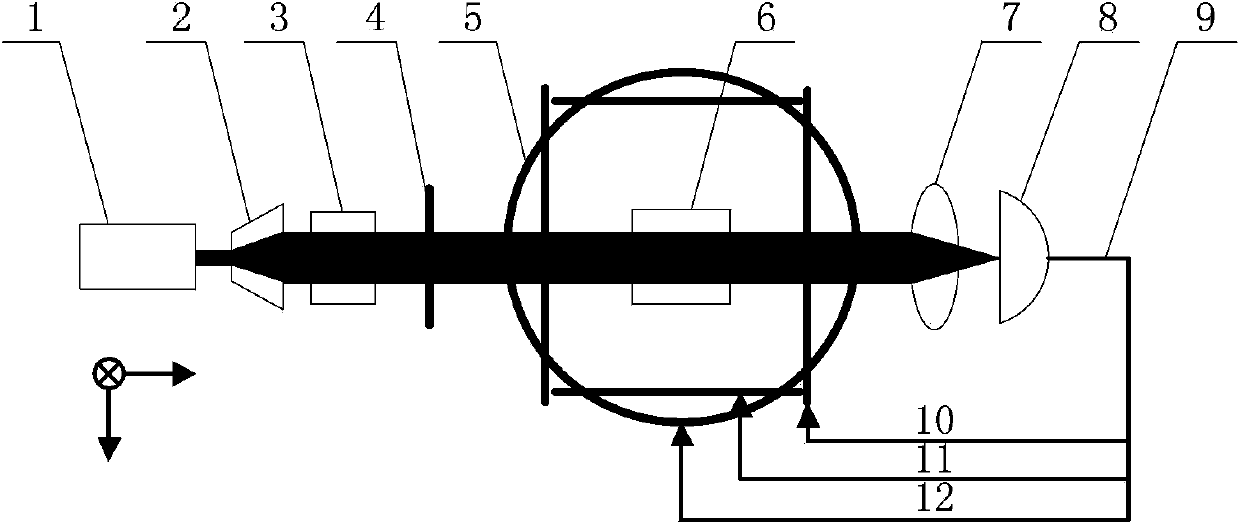
Patents
Literature
693 results about "Optical pumping" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
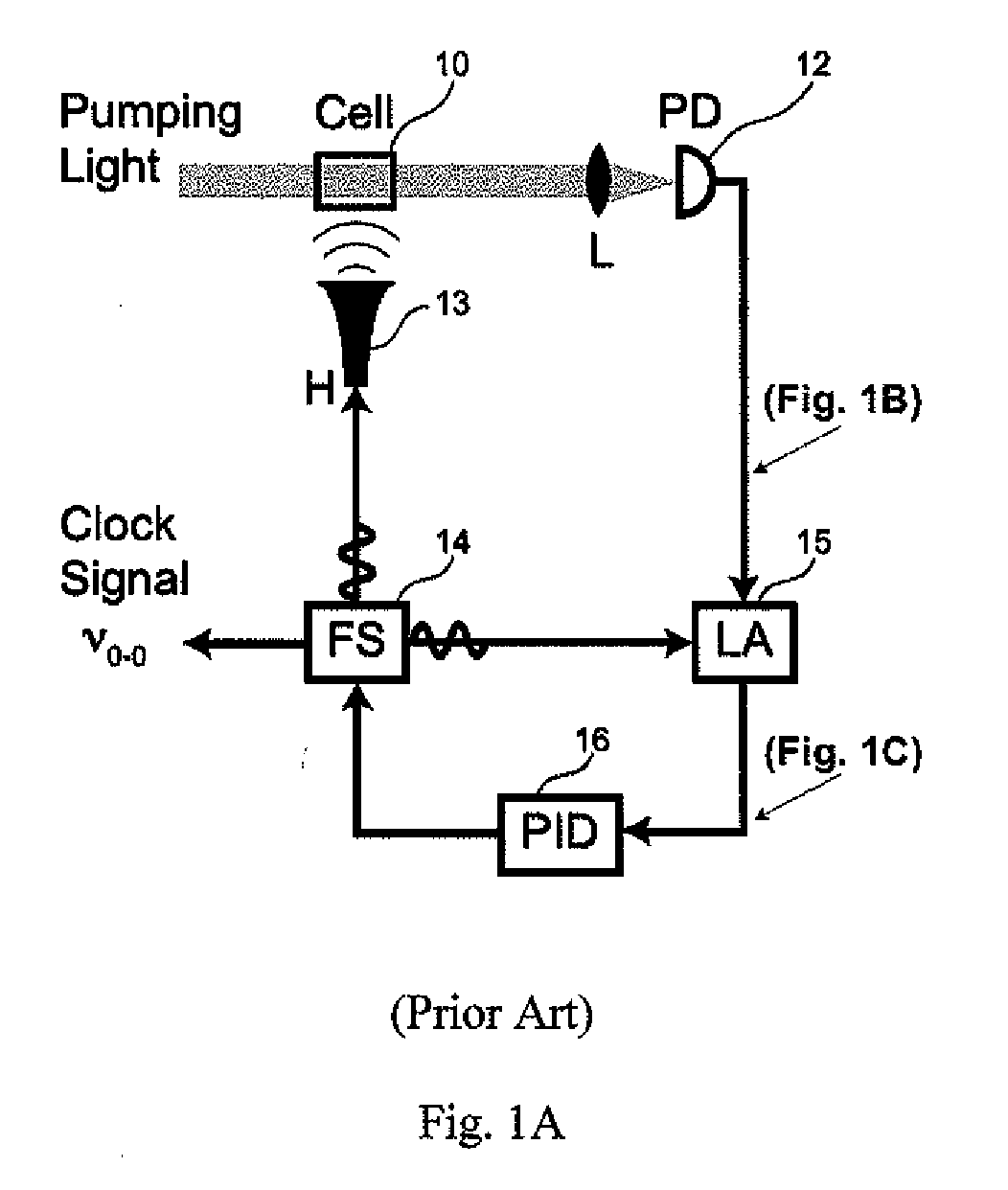
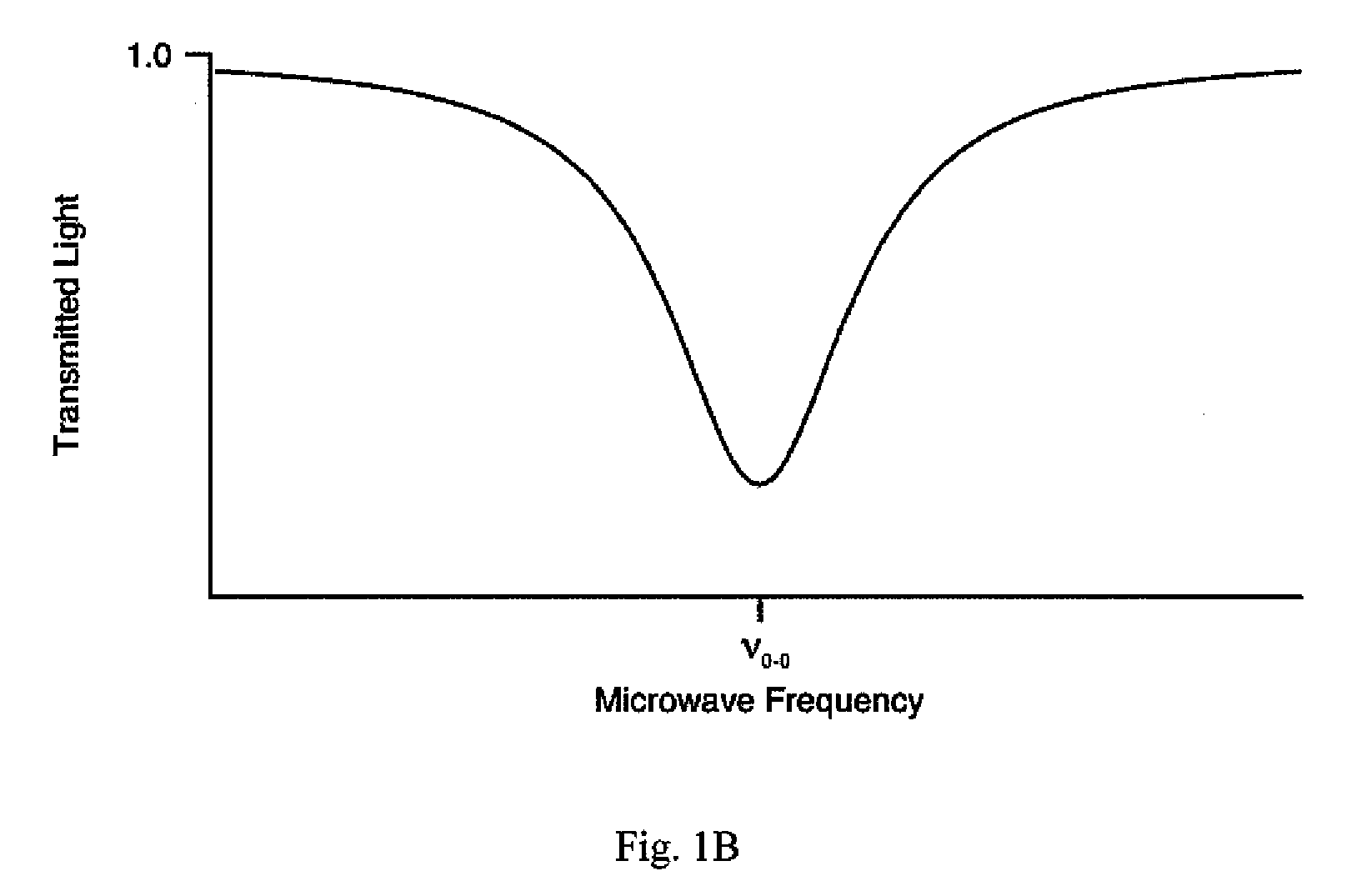
Optical pumping is a process in which light is used to raise (or "pump") electrons from a lower energy level in an atom or molecule to a higher one. It is commonly used in laser construction, to pump the active laser medium so as to achieve population inversion. The technique was developed by 1966 Nobel Prize winner Alfred Kastler in the early 1950s. Optical pumping is also used to cyclically pump electrons bound within an atom or molecule to a well-defined quantum state.
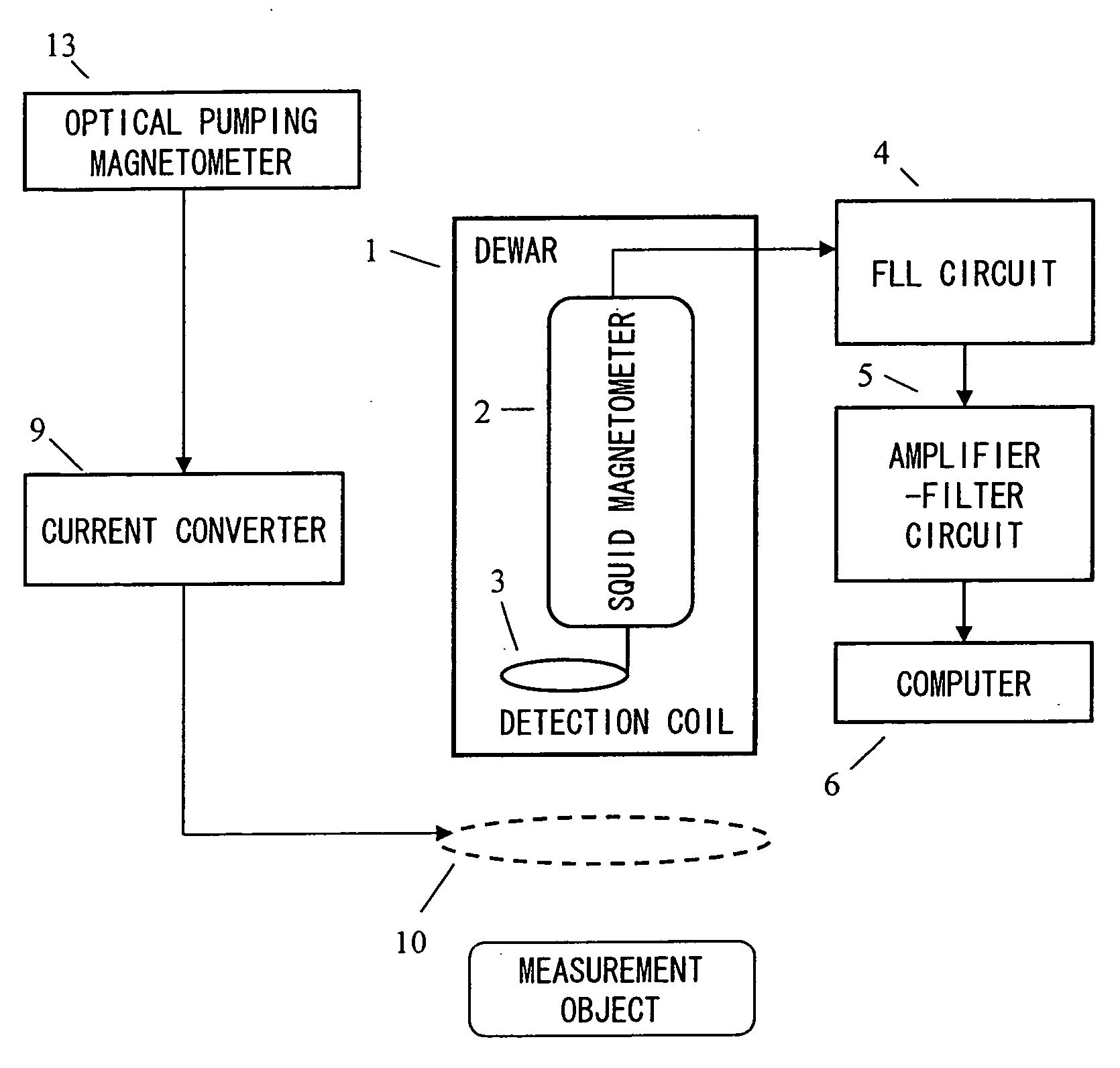
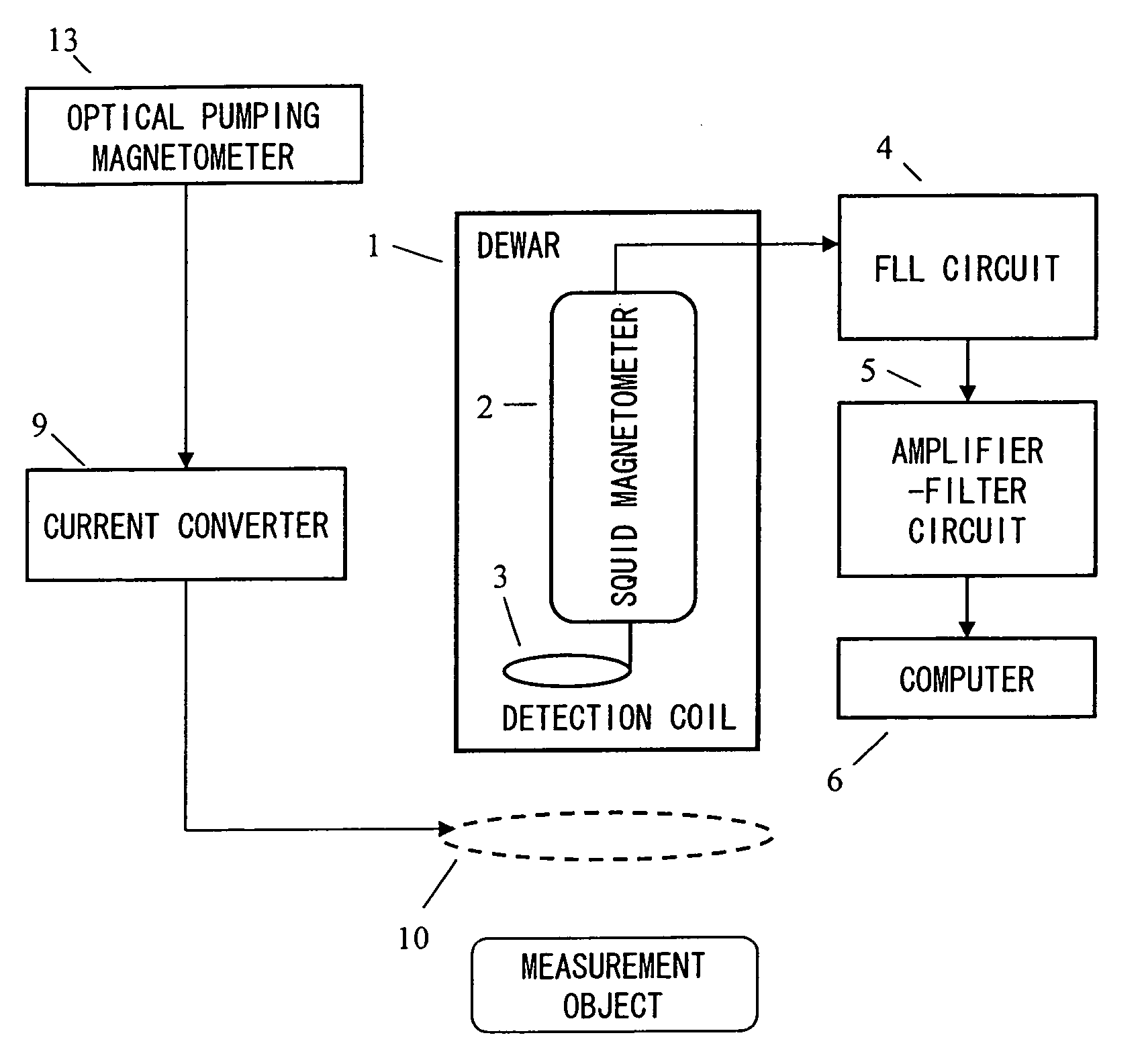
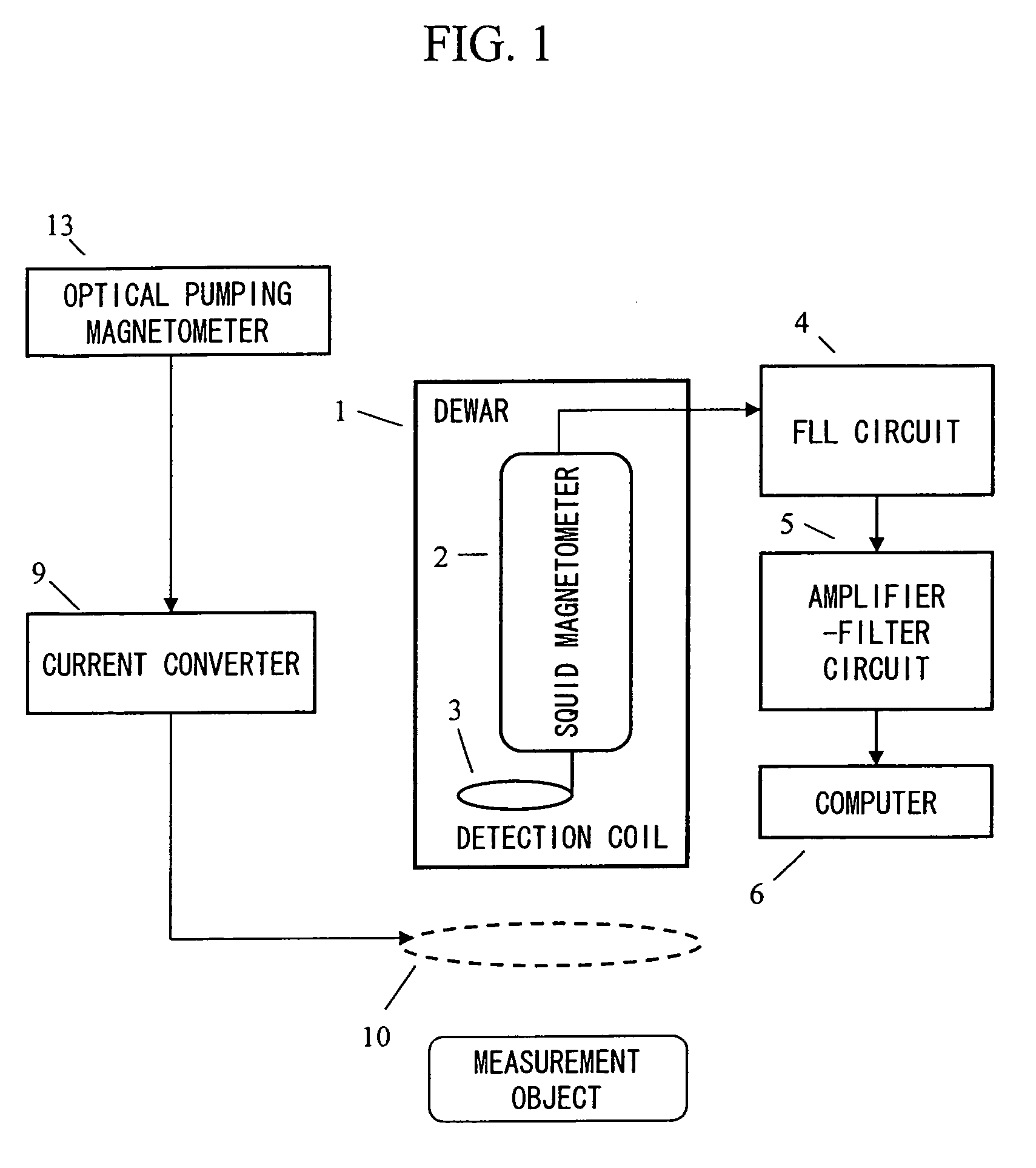
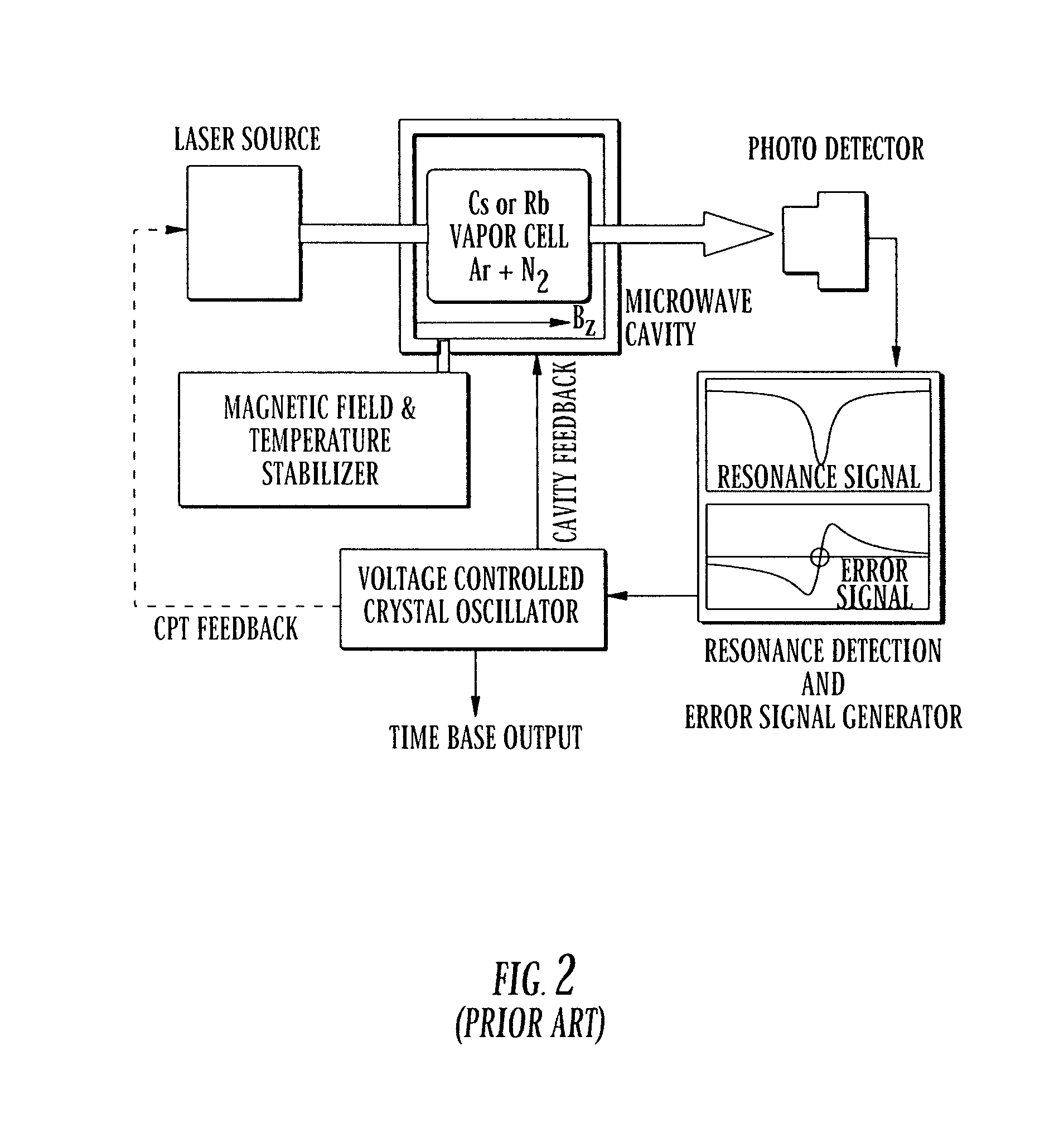
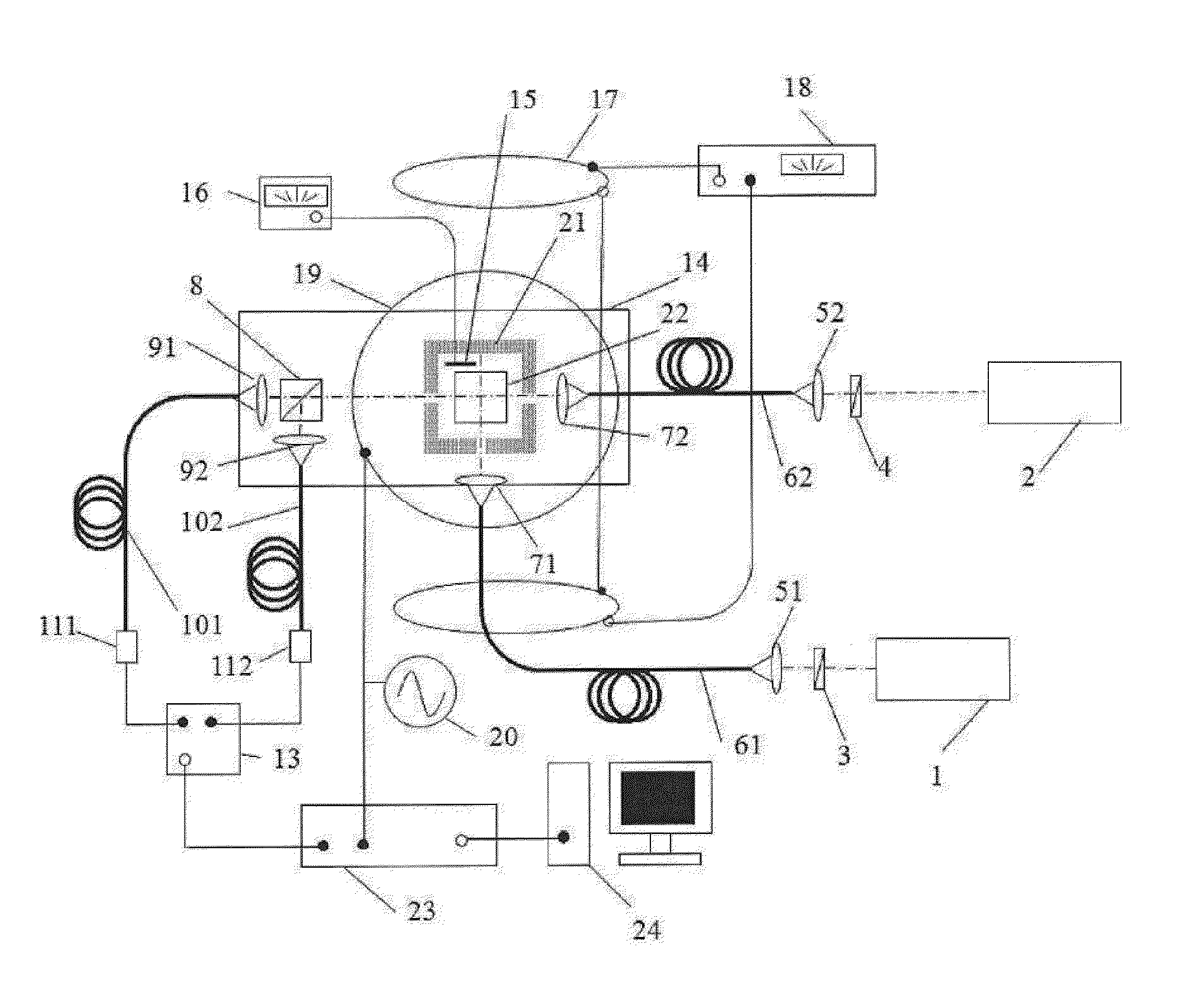
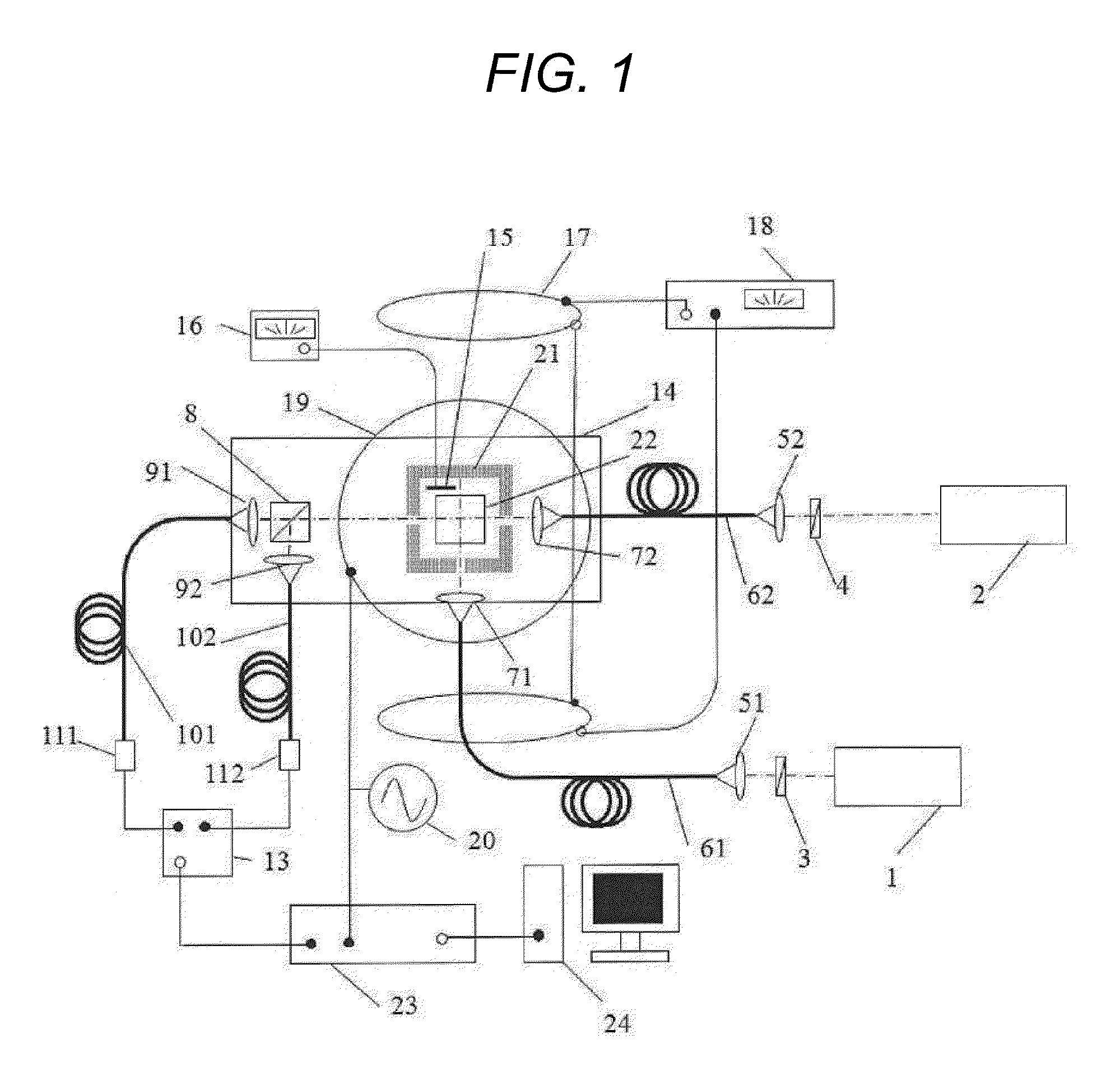
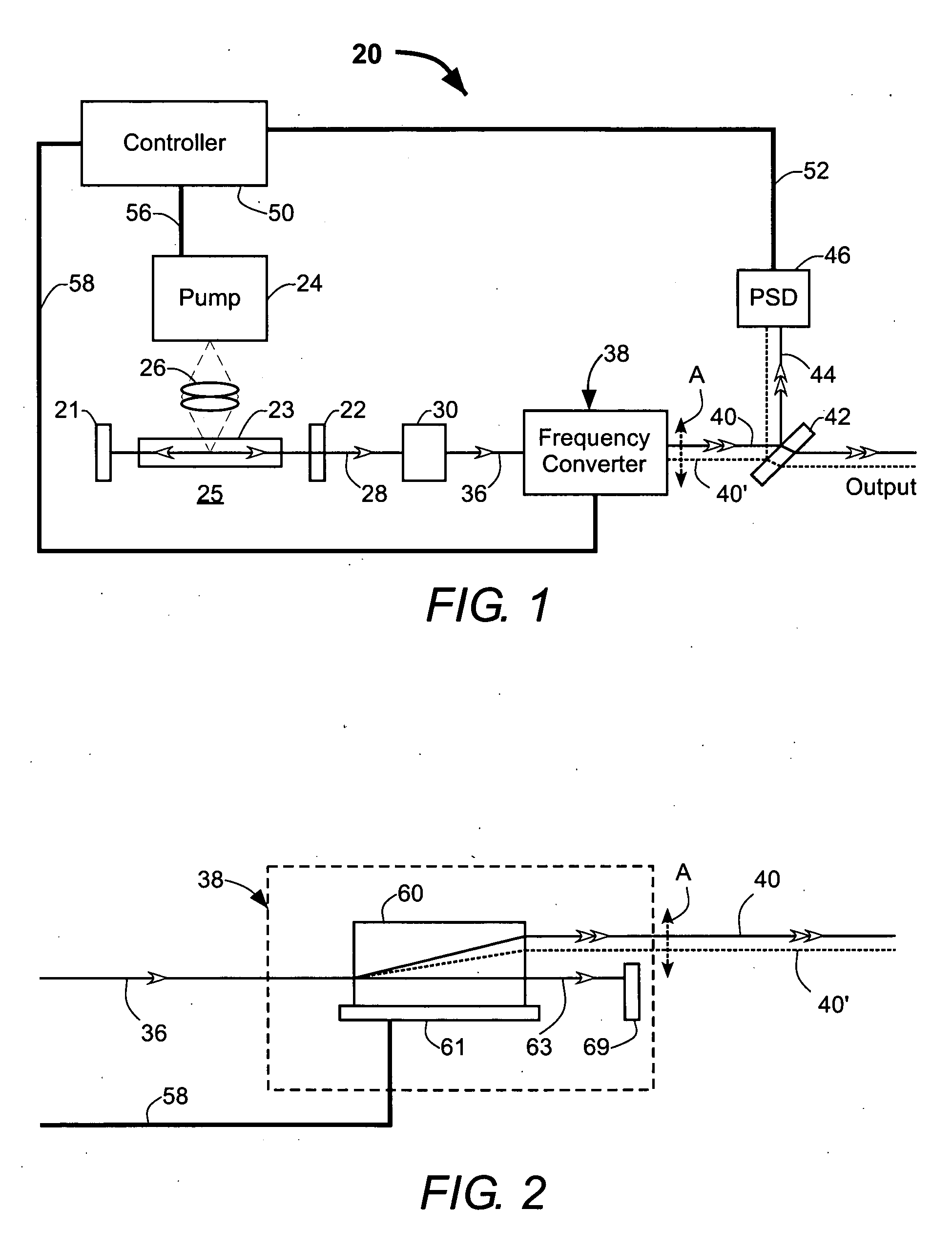
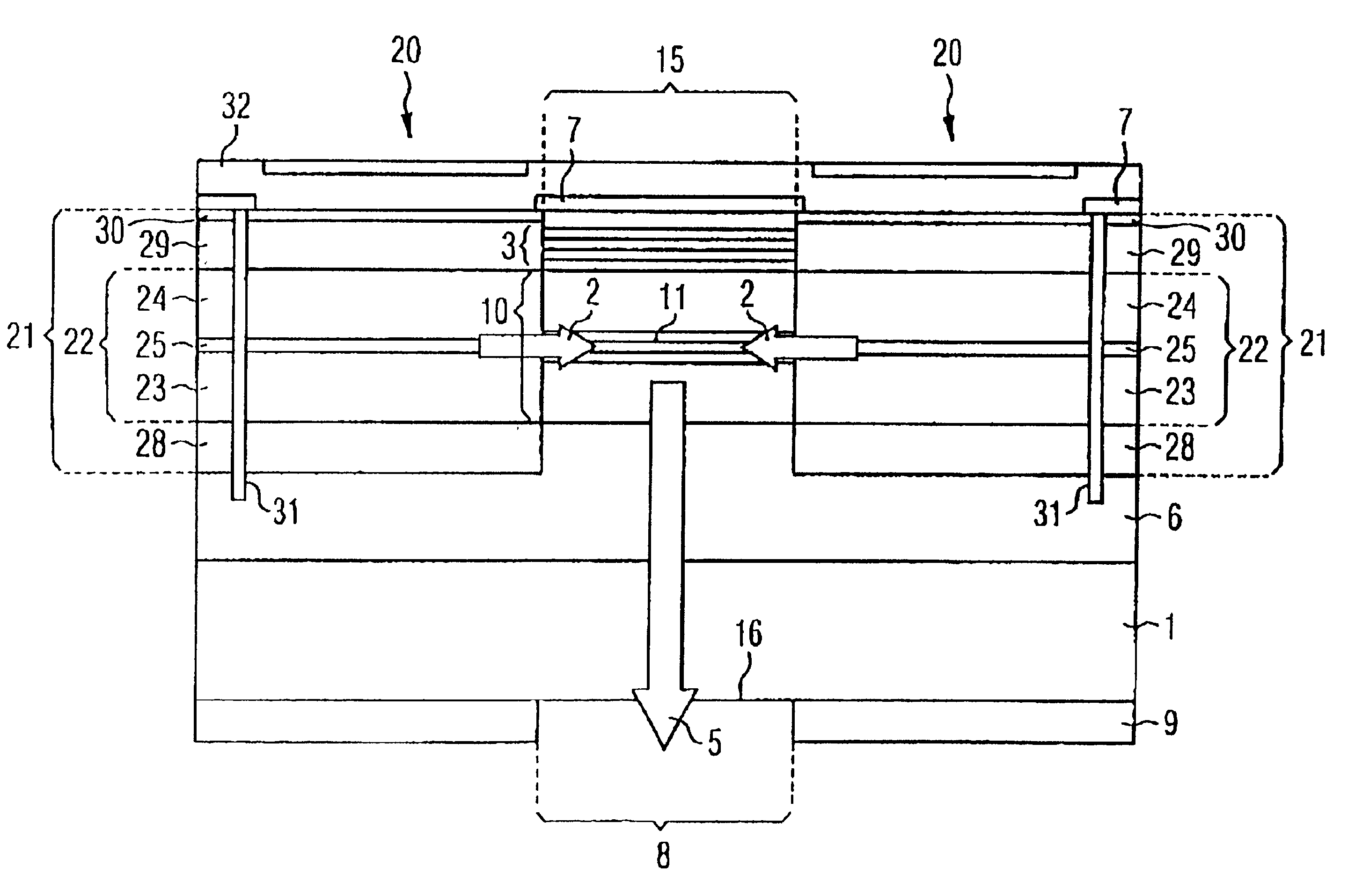
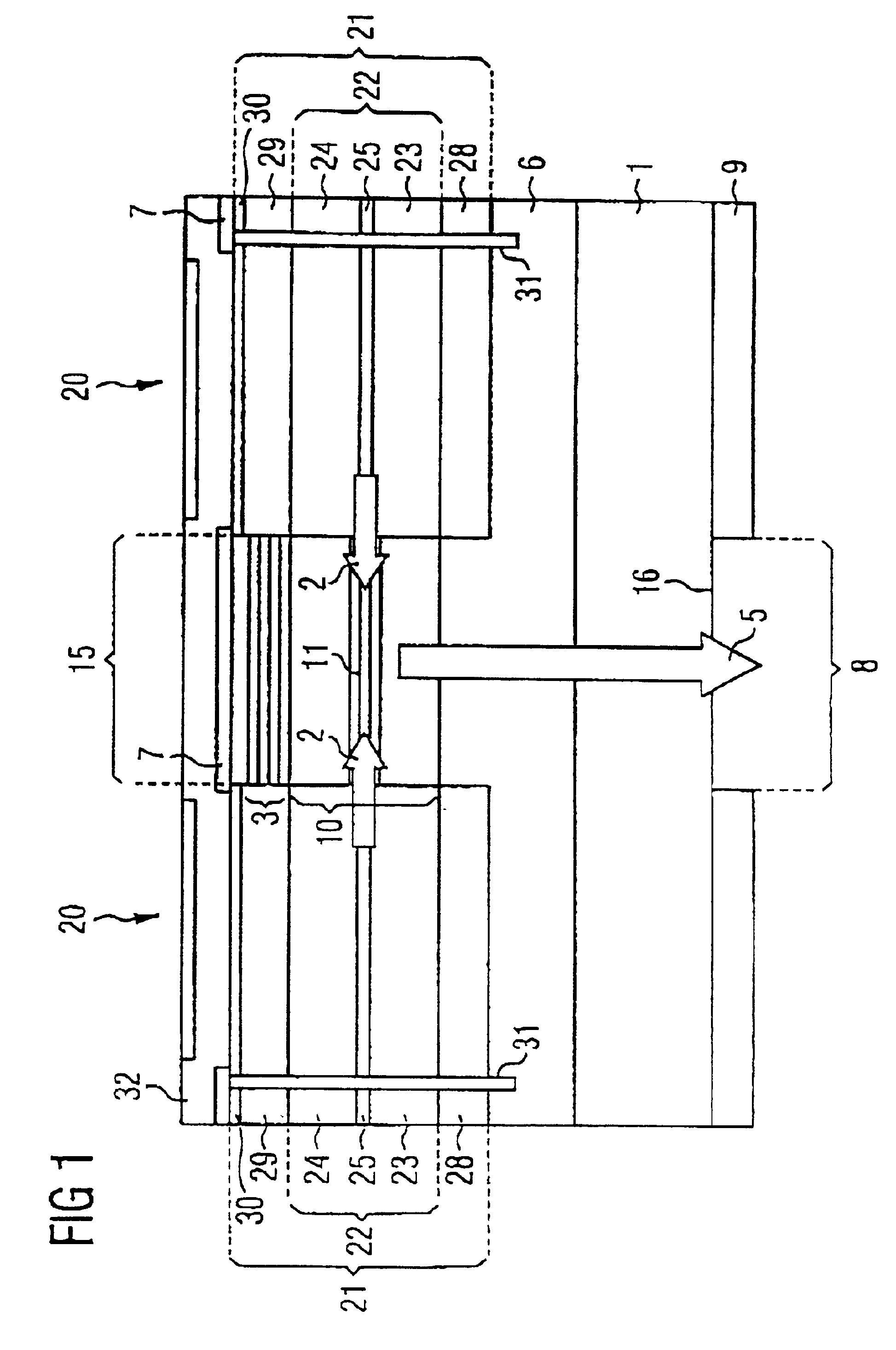
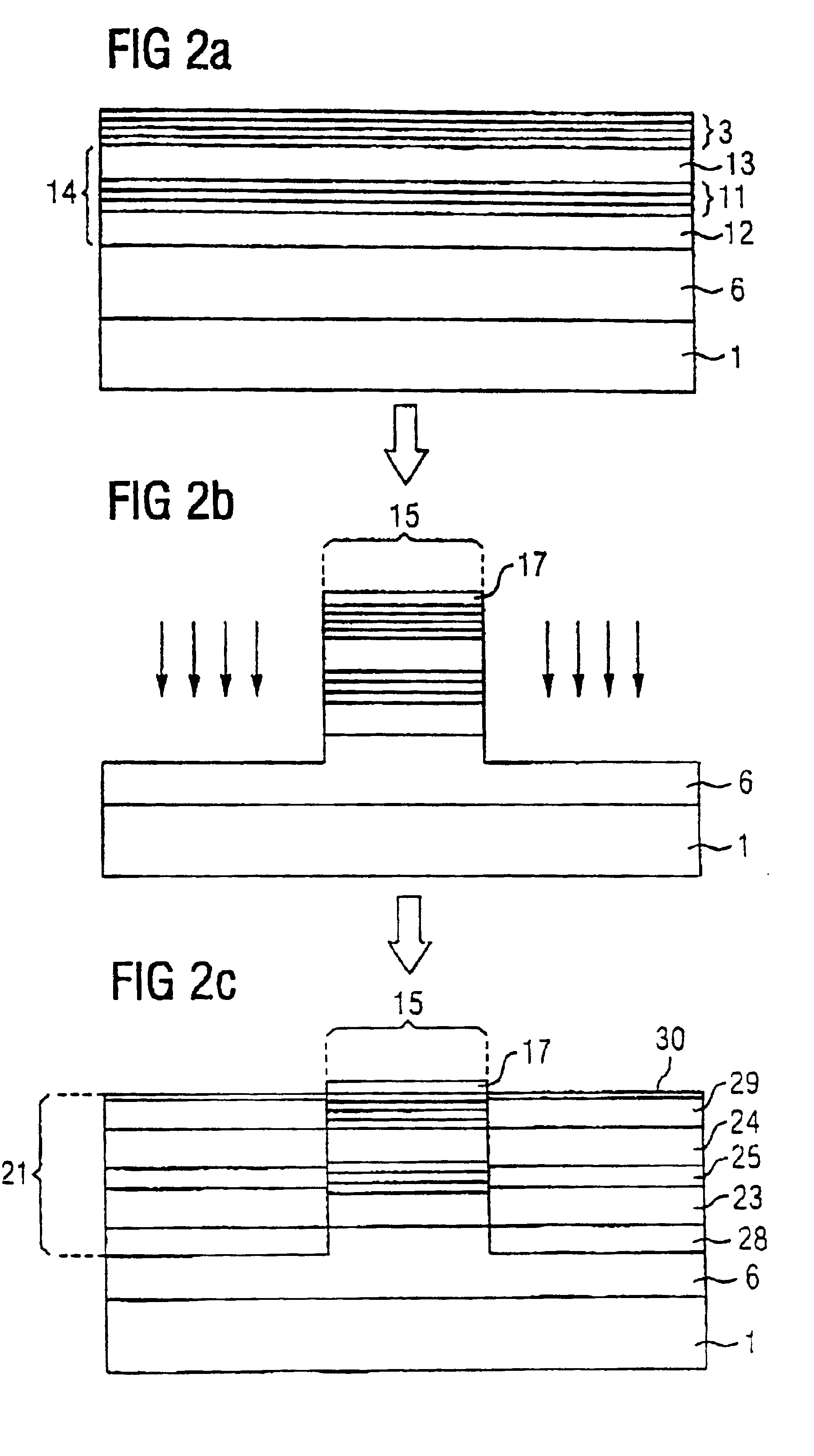
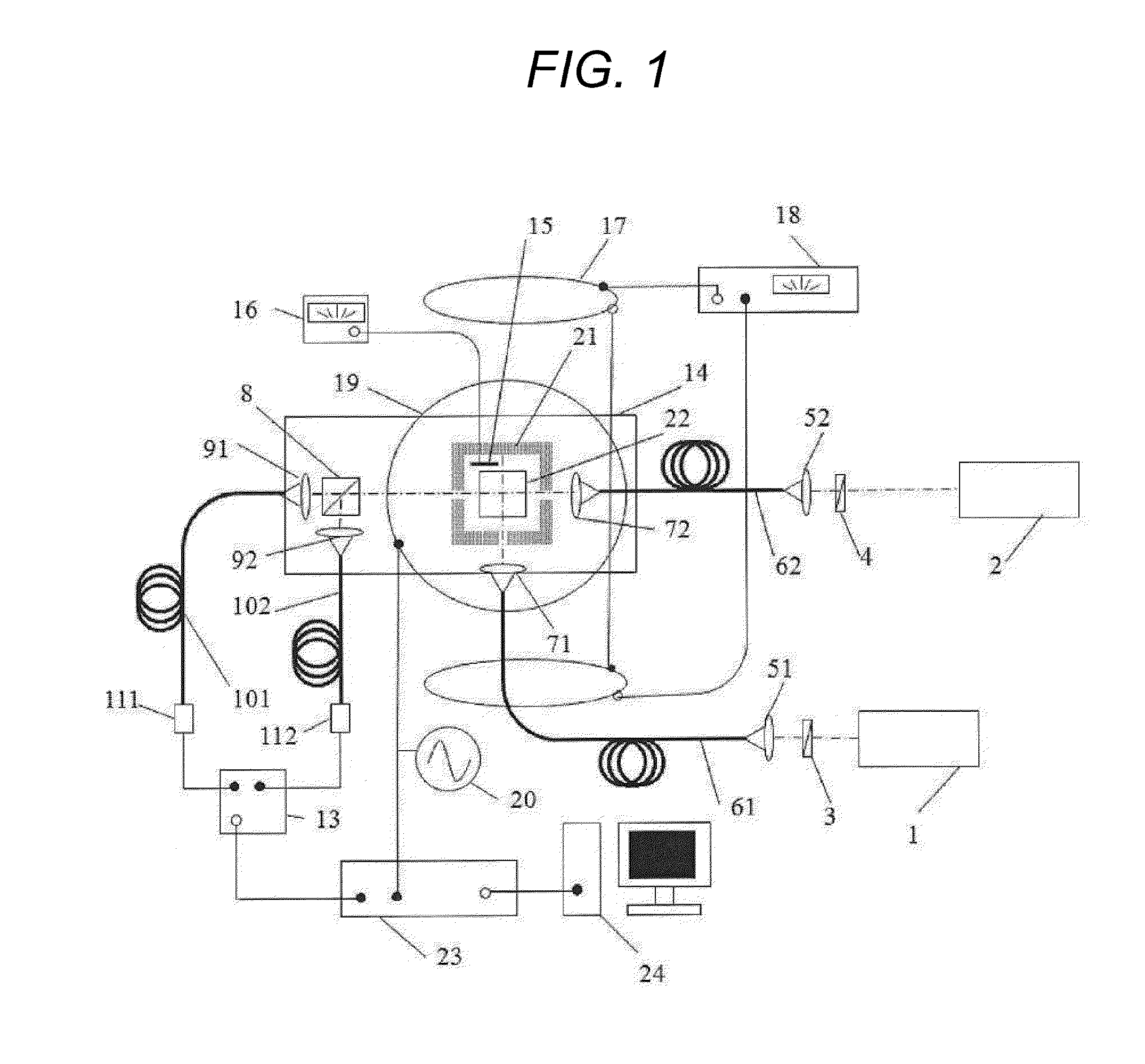
Magnetic field measurement system and optical pumping magnetometer
ActiveUS20070120563A1Reduce magnetic noiseAffect operationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityComing out
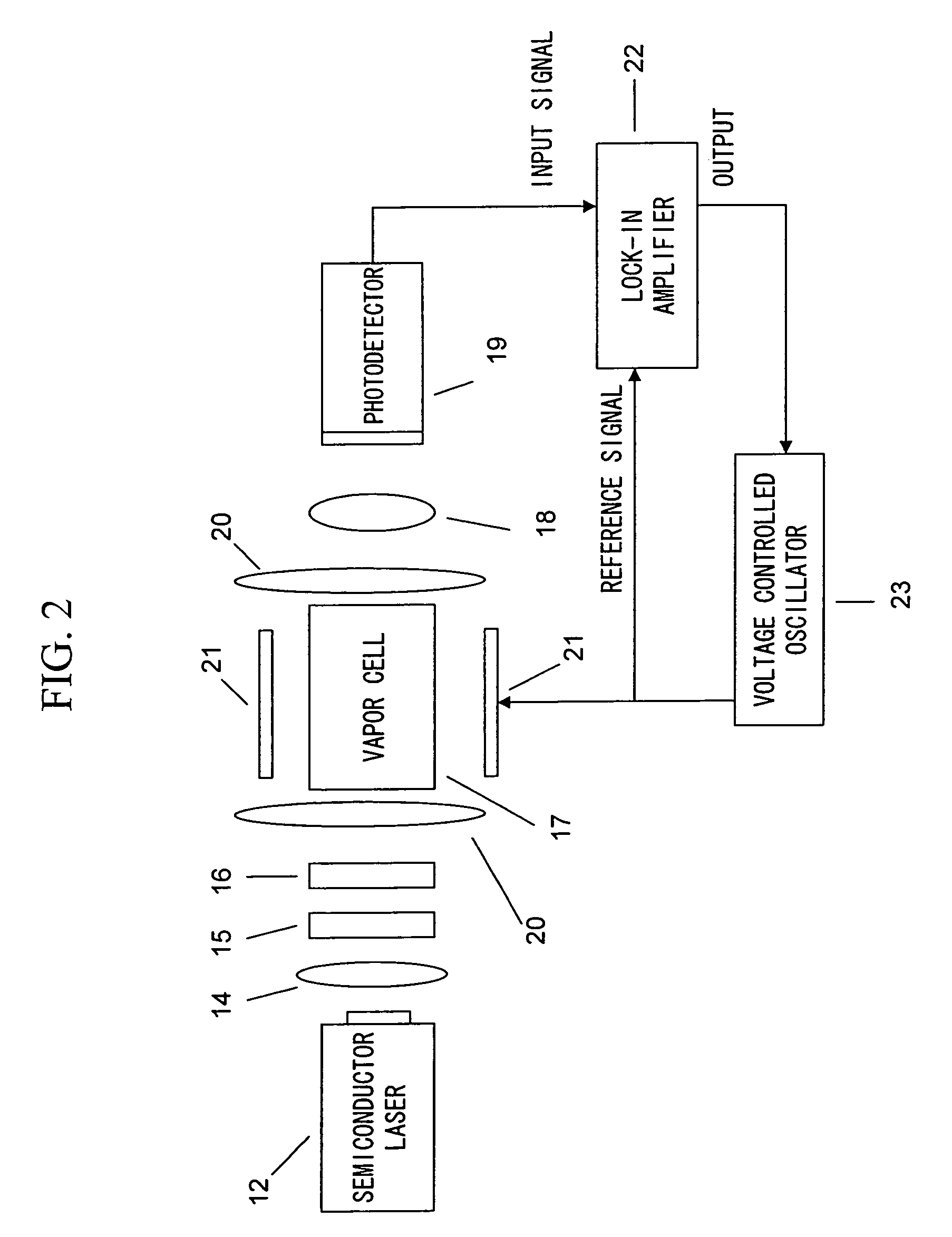
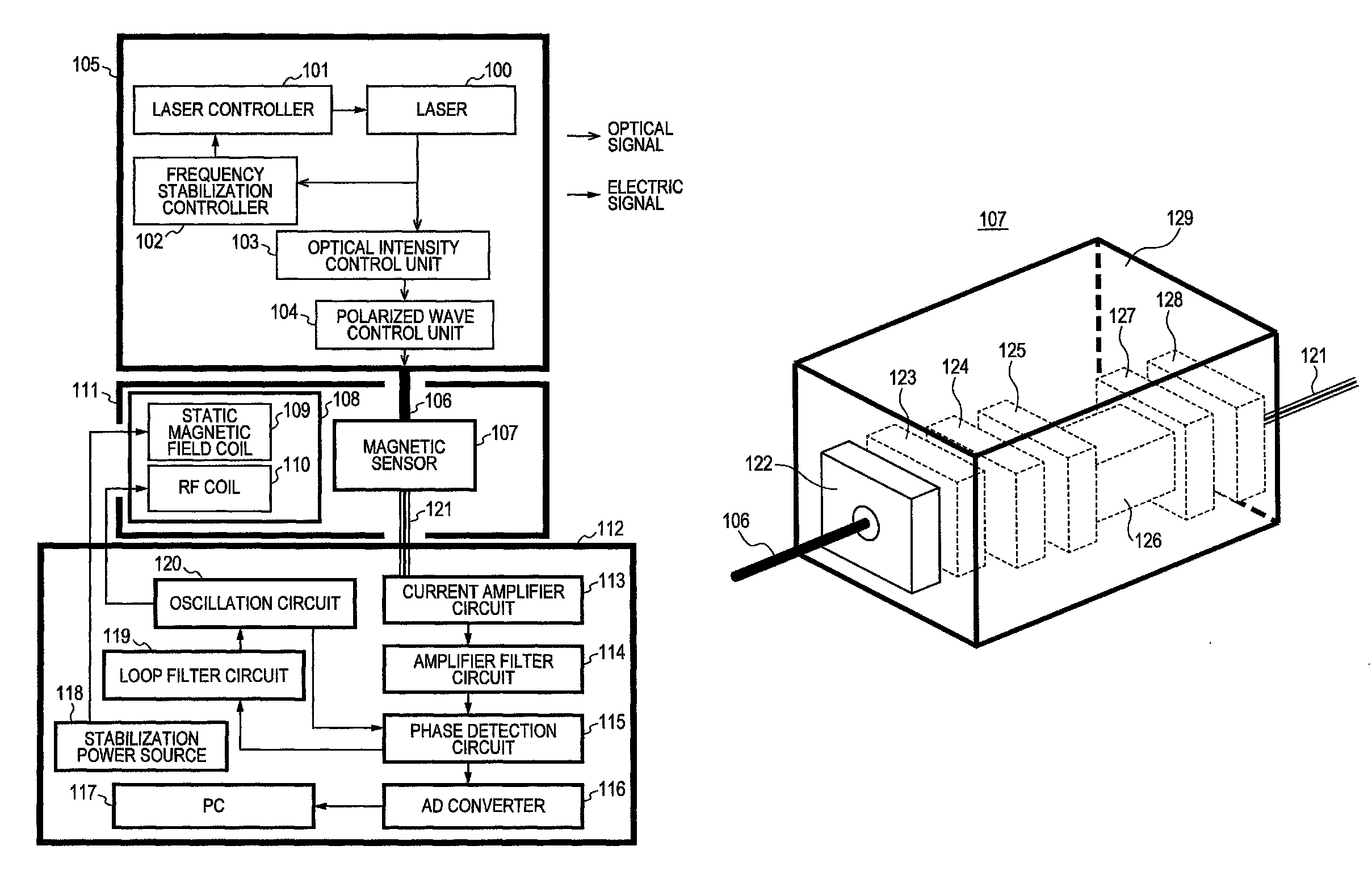
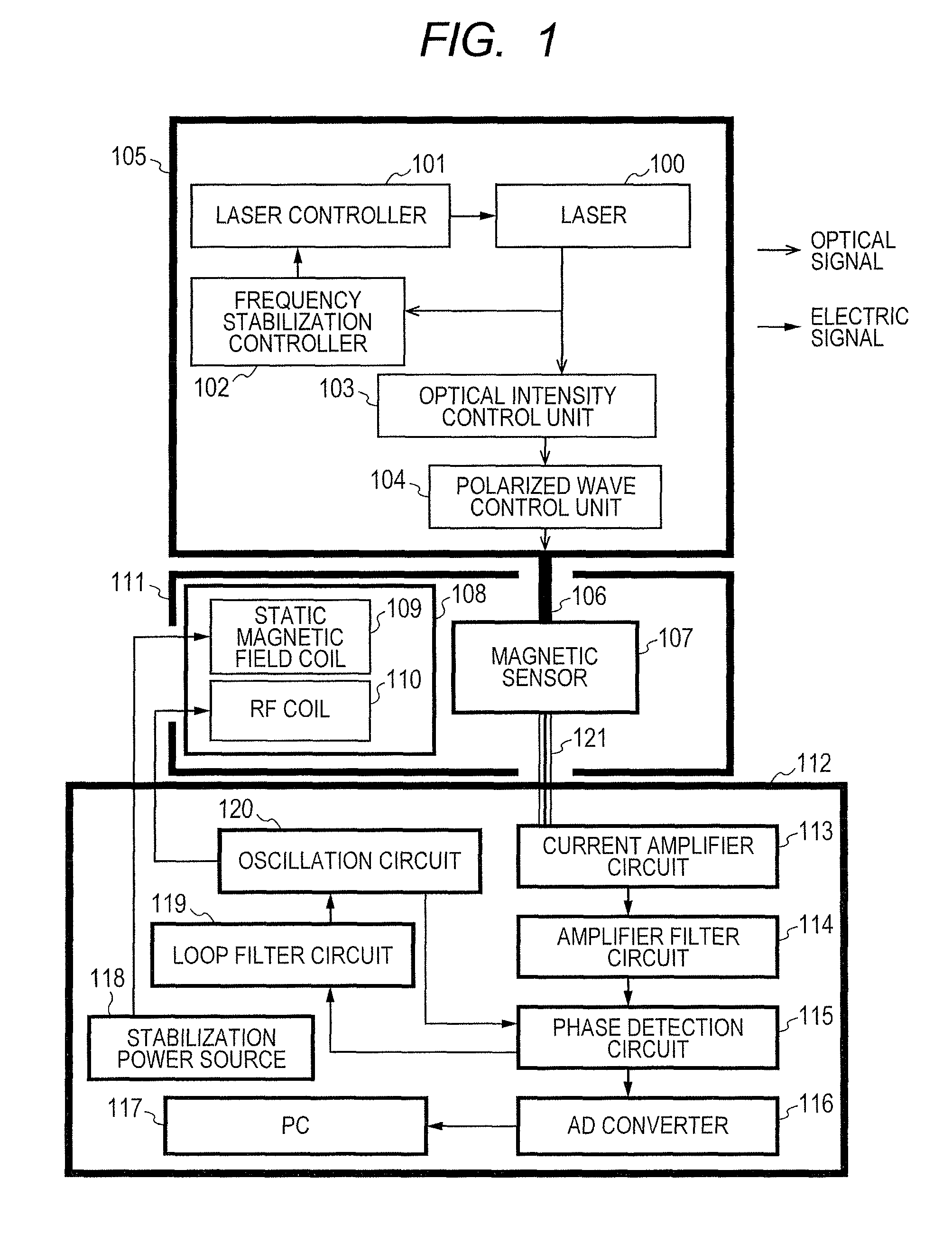
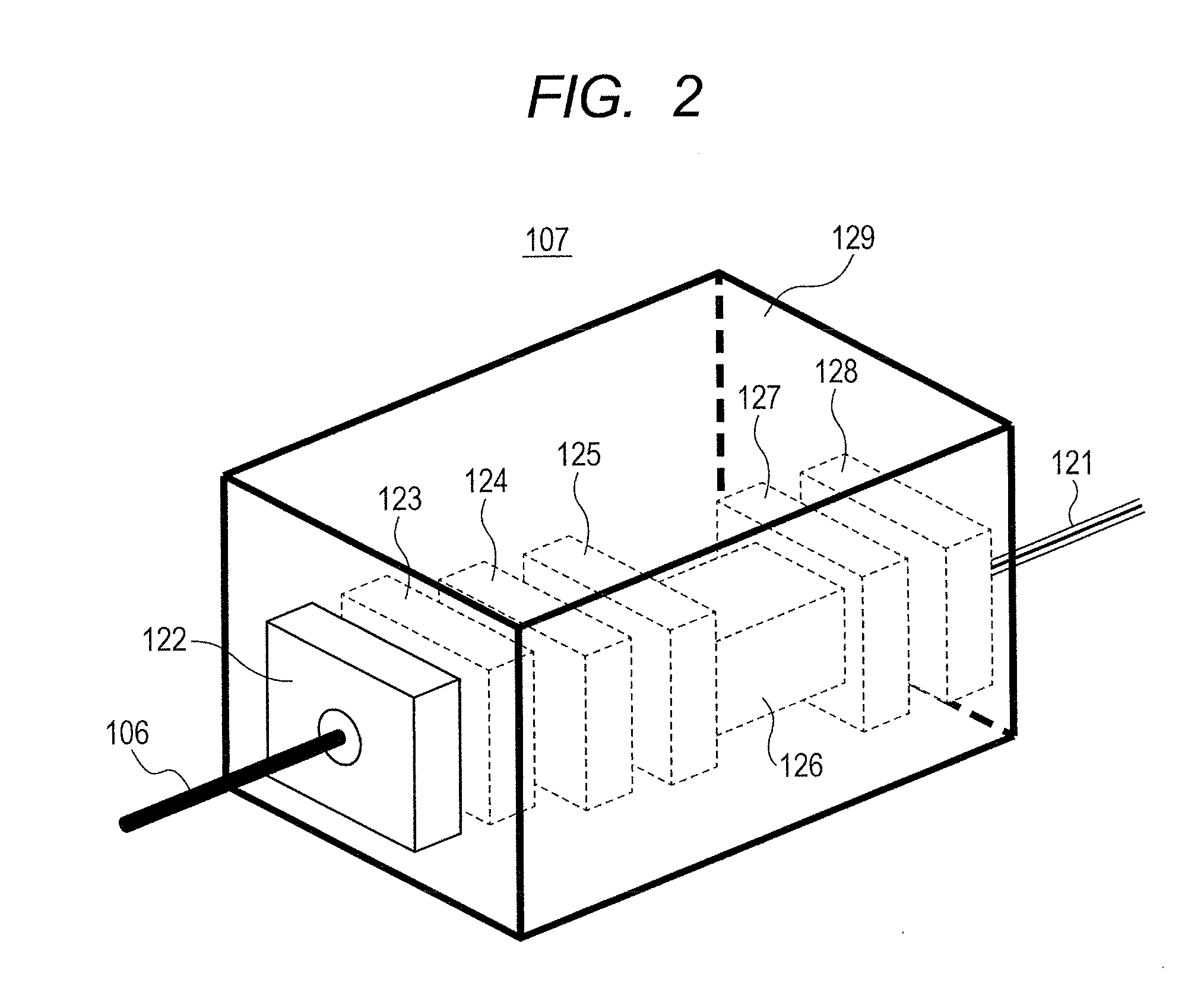
Provided is a highly accurate optical pumping magnetometer, in which a static magnetic field and an oscillating field to be applied to a vapor cell are stabilized. To this end, the optical pumping magnetometer includes: Helmholtz coils for applying a constant static magnetic field to a vapor cell serving as a magnetic field detector; fluxgate magnetometers for detecting environmental magnetic noise in two directions of X-axis direction and Y-axis direction other than Z-axis direction which is a direction for detecting a magnetic field coming out of a measurement object while locating the vapor cell in the center thereof; magnetometer drive circuits for driving the fluxgate magneotometers; current converters for converting outputs of the magnetometer drive circuits into amount of currents; and magnetic field generating coils for generating a magnetic field in a phase opposite to the environmental magnetic noise in the two directions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
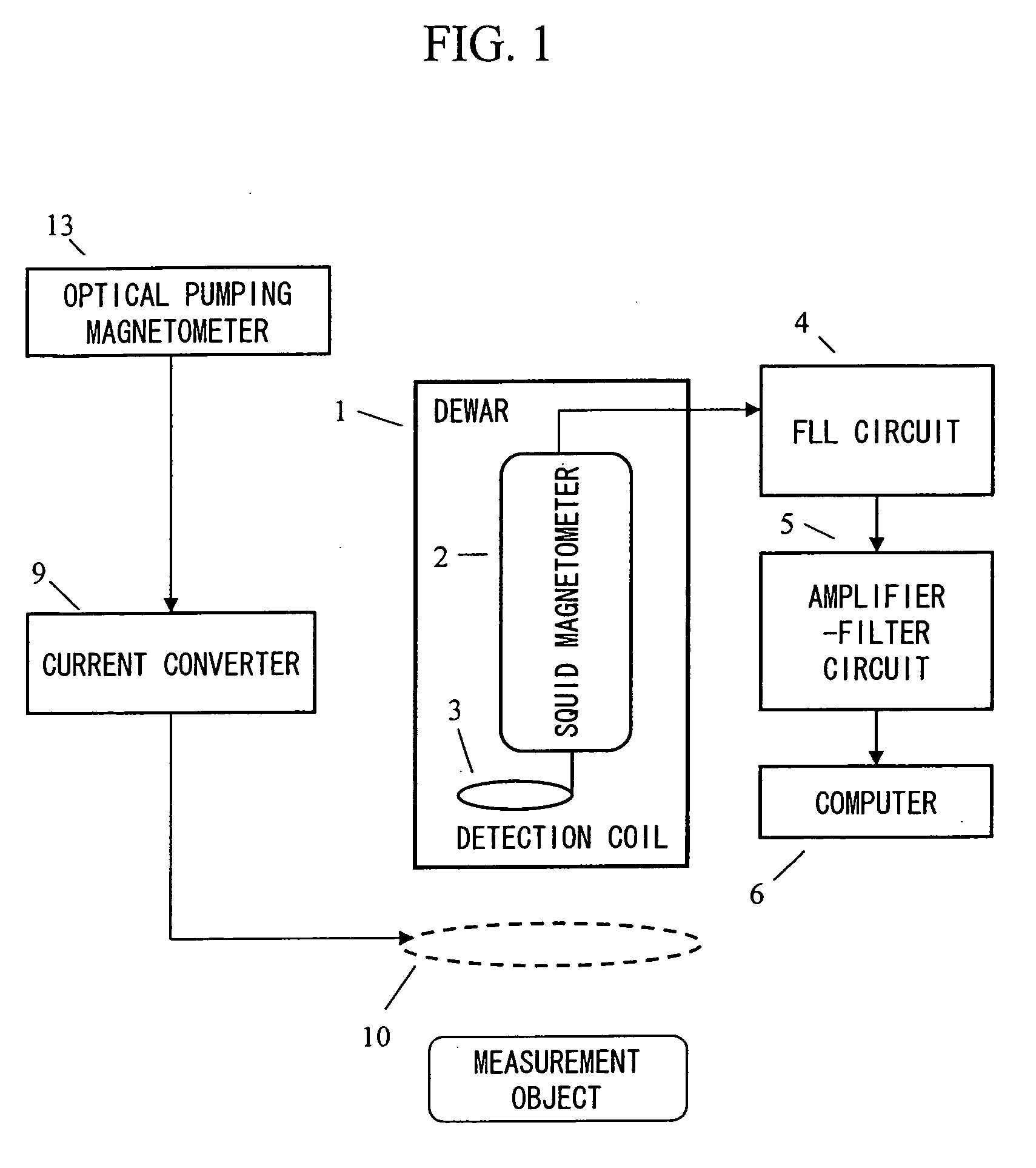
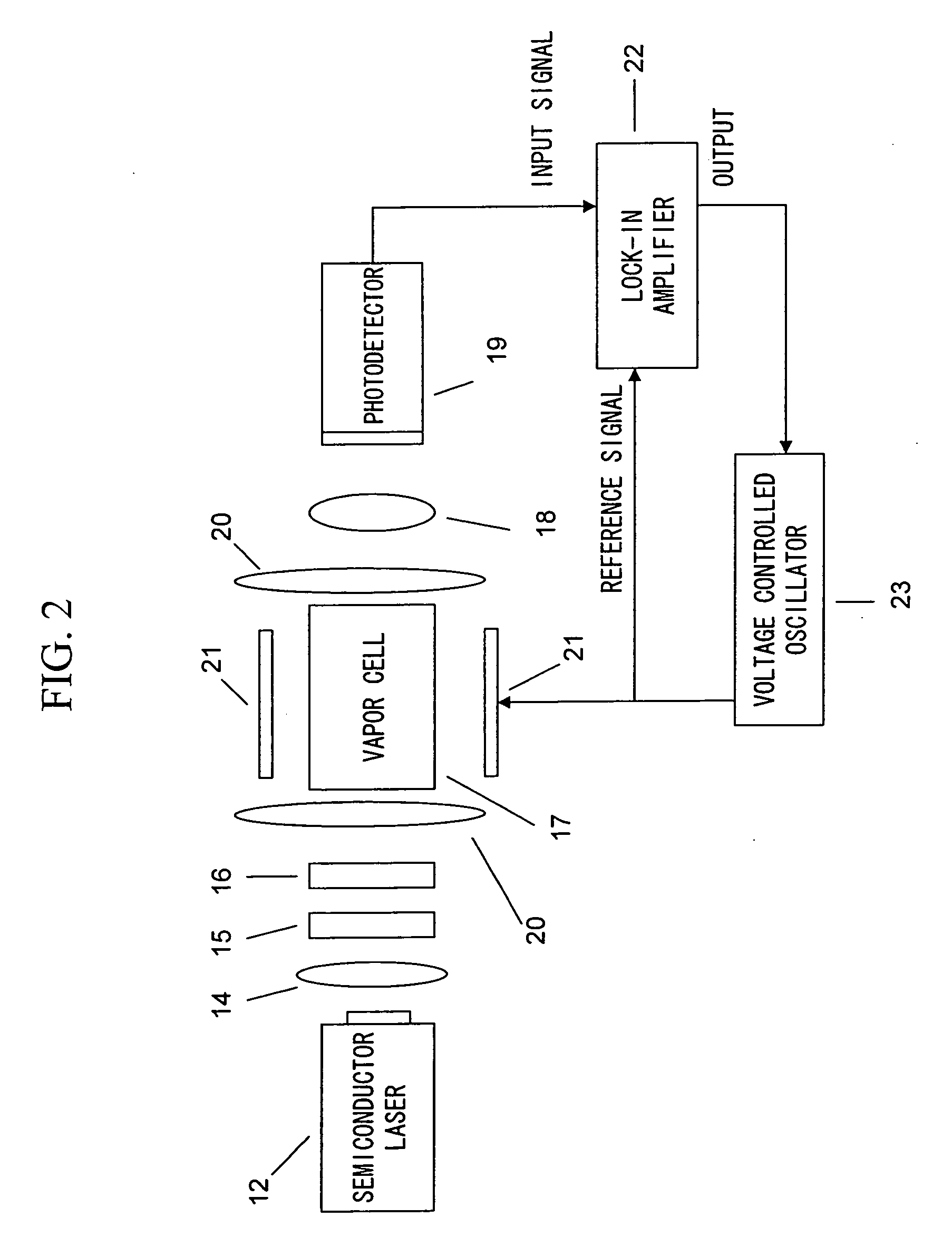
Optical Pumping Magnetometer
ActiveUS20130265042A1Easy to controlGuaranteed uptimeElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceFrequency stabilizationPhotodetector
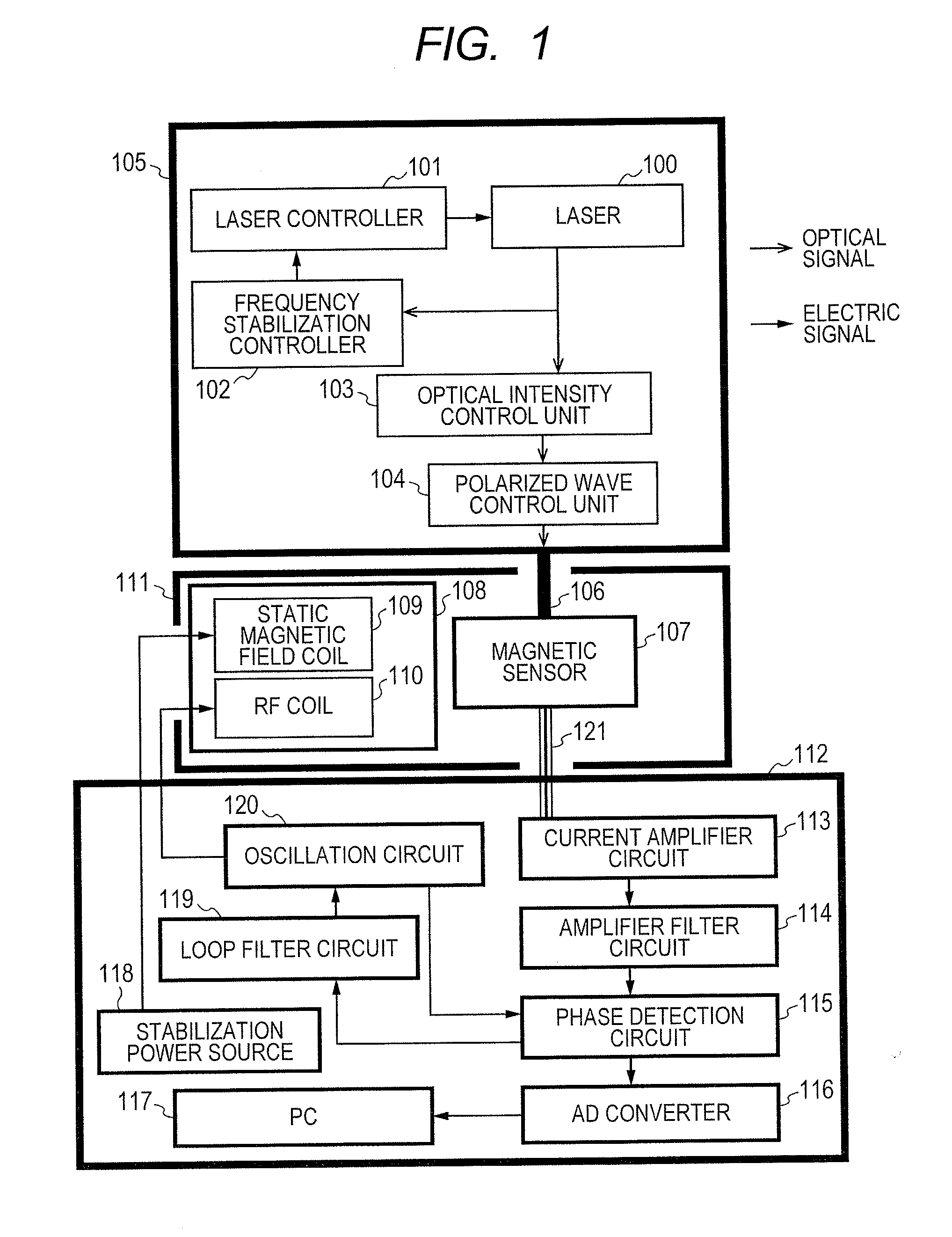
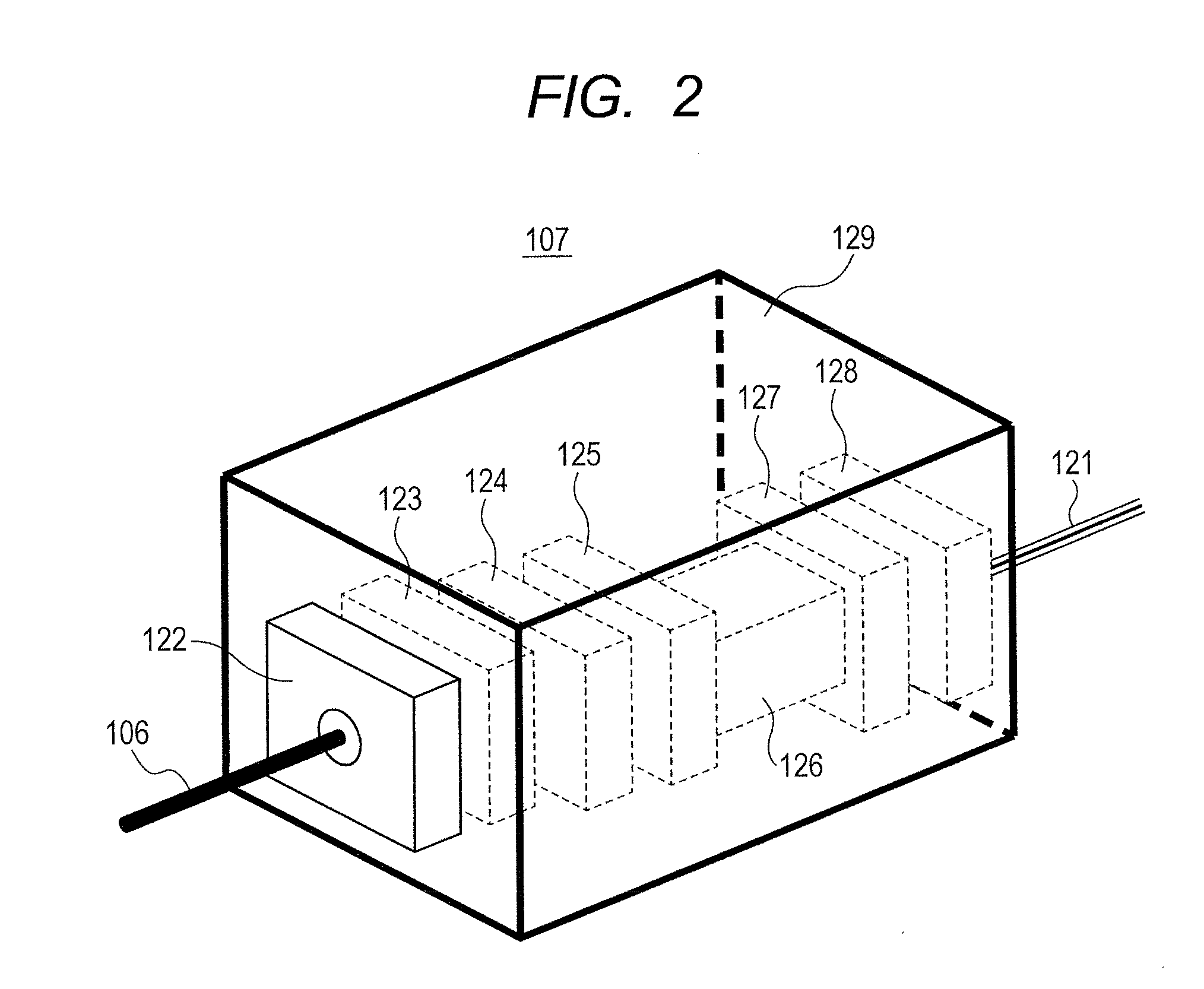
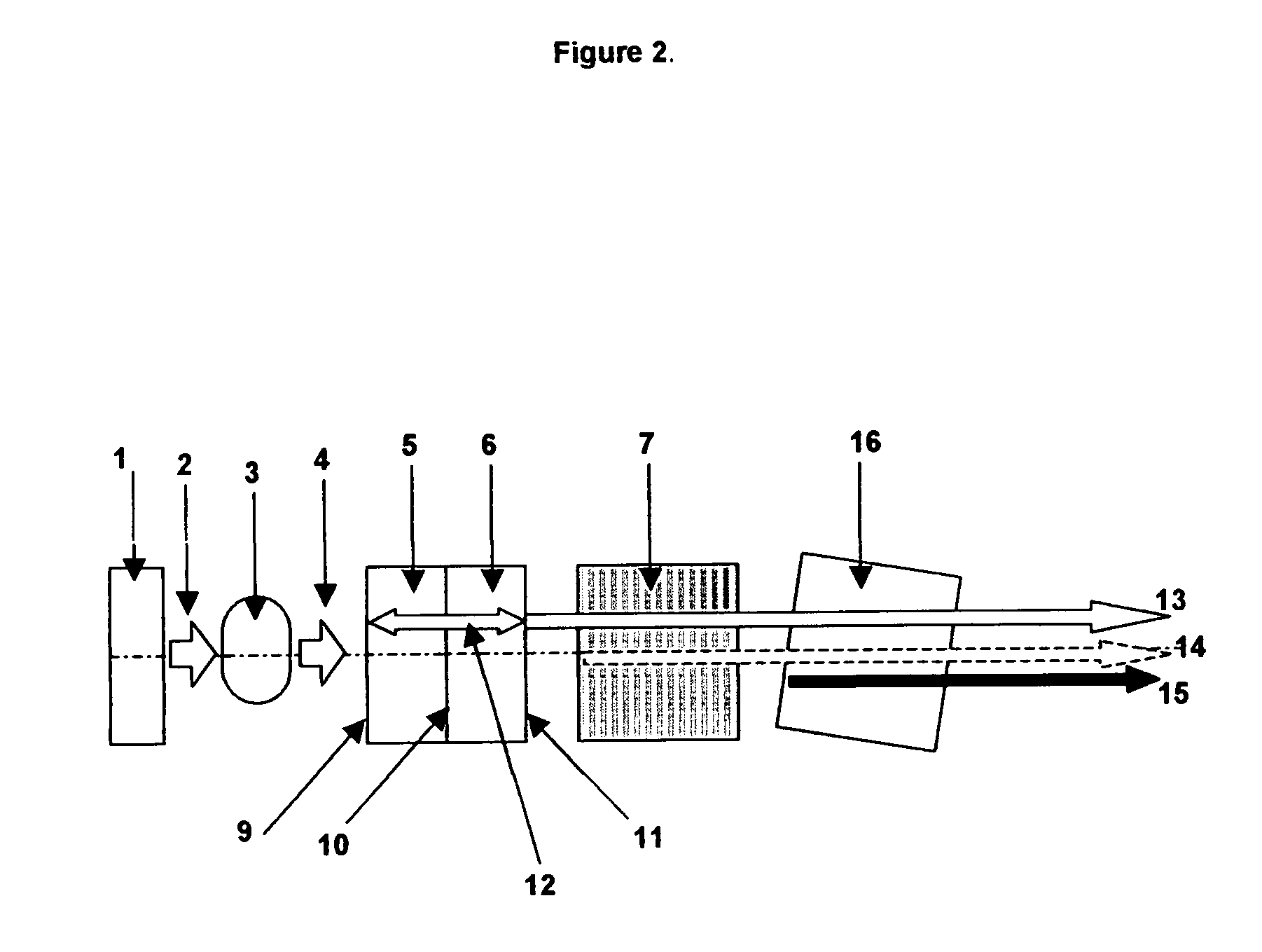
Stable magnetic field measurement is enabled without collapse of polarization or fluctuation of intensity of a laser beam incident on a glass cell of an optical pumping magnetic sensor. Excitation light generated with a light source, having optimized light intensity and polarized wave, through frequency stabilization, intensity control and polarized-wave control, is introduced via a polarized wave holding optical fiber to a magnetic sensor provided in a magnetic shield, and magnetic field measurement is performed by optical pumping using magneto-optical properties of spin-polarized alkali metal. The magnetic sensor has a structure where a lens, a polarization optical device, the glass cell and a photodetector, are integrally accommodated in a non-magnetic case.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Organic vertical cavity laser and imaging system
InactiveUS6947459B2Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser light
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Quantum dot optoelectronic devices with nanoscale epitaxial lateral overgrowth and methods of manufacture
InactiveUS20050051766A1Improve efficiencyHigh efficiency entitlementLaser detailsLaser active region structurePhotoluminescenceOptical pumping
Optoelectronic devices are provided that incorporate quantum dots as the electroluminescent layer in an inorganic wide-bandgap heterostructure. The quantum dots serve as the optically active component of the device and, in multilayer quantum dot embodiments, facilitate nanoscale epitaxial lateral overgrowth (NELOG) in heterostructures having non-lattice matched substrates. The quantum dots in such devices will be electrically pumped and exhibit electroluminescence, as opposed to being optically pumped and exhibiting photoluminescence. There is no inherent “Stokes loss” in electroluminescence thus the devices of the present invention have potentially higher efficiency than optically pumped quantum dot devices. Devices resulting from the present invention are capable of providing deep green visible light, as well as, any other color in the visible spectrum, including white light by blending different sizes and compositions of the dots and controlling manufacturing processes.
Owner:NORTH CAROLINA AT CHARLOTTE THE UNIV OF +1
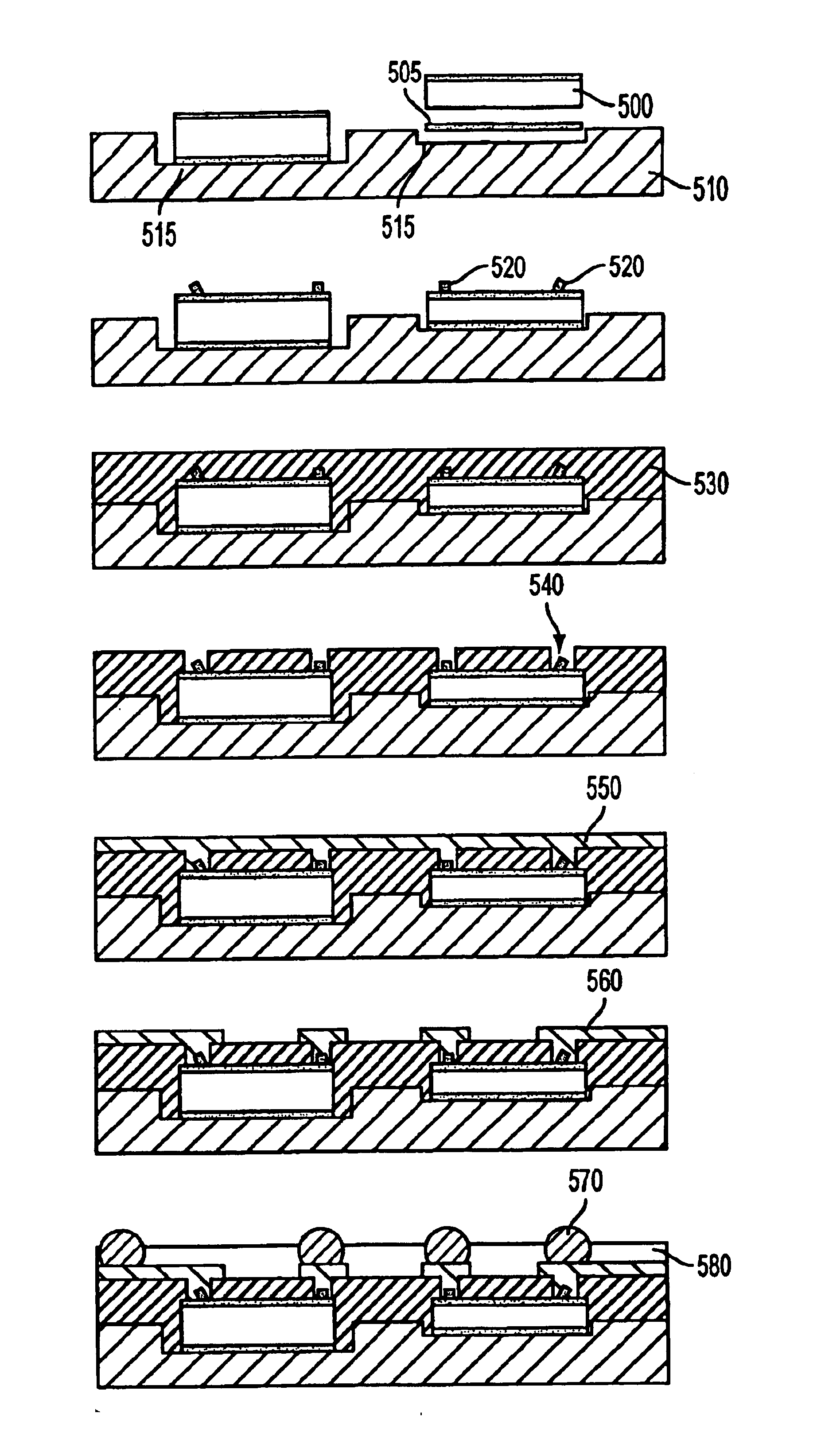
Build-up structures with multi-angle vias for chip to chip interconnects and optical bussing
InactiveUS6919508B2Improve performanceIncrease speedTelevision system detailsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesAnisotropic conductive filmCopper interconnect
A build-up structure for chip to chip interconnects and System-In-Package utilizing multi-angle vias for electrical and optical routing or bussing of electronic information and controlled CTE dielectrics including mesocomposites to achieve optimum electrical and optical performance of monolithic structures. Die, multiple die, Microelectromechanical Machines (MEMs) and / or other active or passive components such as transducers or capacitors can be accurately positioned on a substrate such as a copper heatsink and multi-angle stud bumps can be placed on the active sites of the components. A first dielectric layer is preferably placed on the components, thereby embedding the components in the structure. Through various processes of photolithography, laser machining, soft lithography or anisotropic conductive film bonding, escape routing and circuitry is formed on the first metal layer. Additional dielectric layers and metal circuitry are formed utilizing multi-angle vias to form escape routing from tight pitch bond pads on the die to other active and passive components. Multi-angle vias can carry electrical or optical information in the form of digital or analog electromagnetic current, or in the form of visible or non-visible optical bussing and interconnections.
Owner:CAPITALSOURCE FINANCE
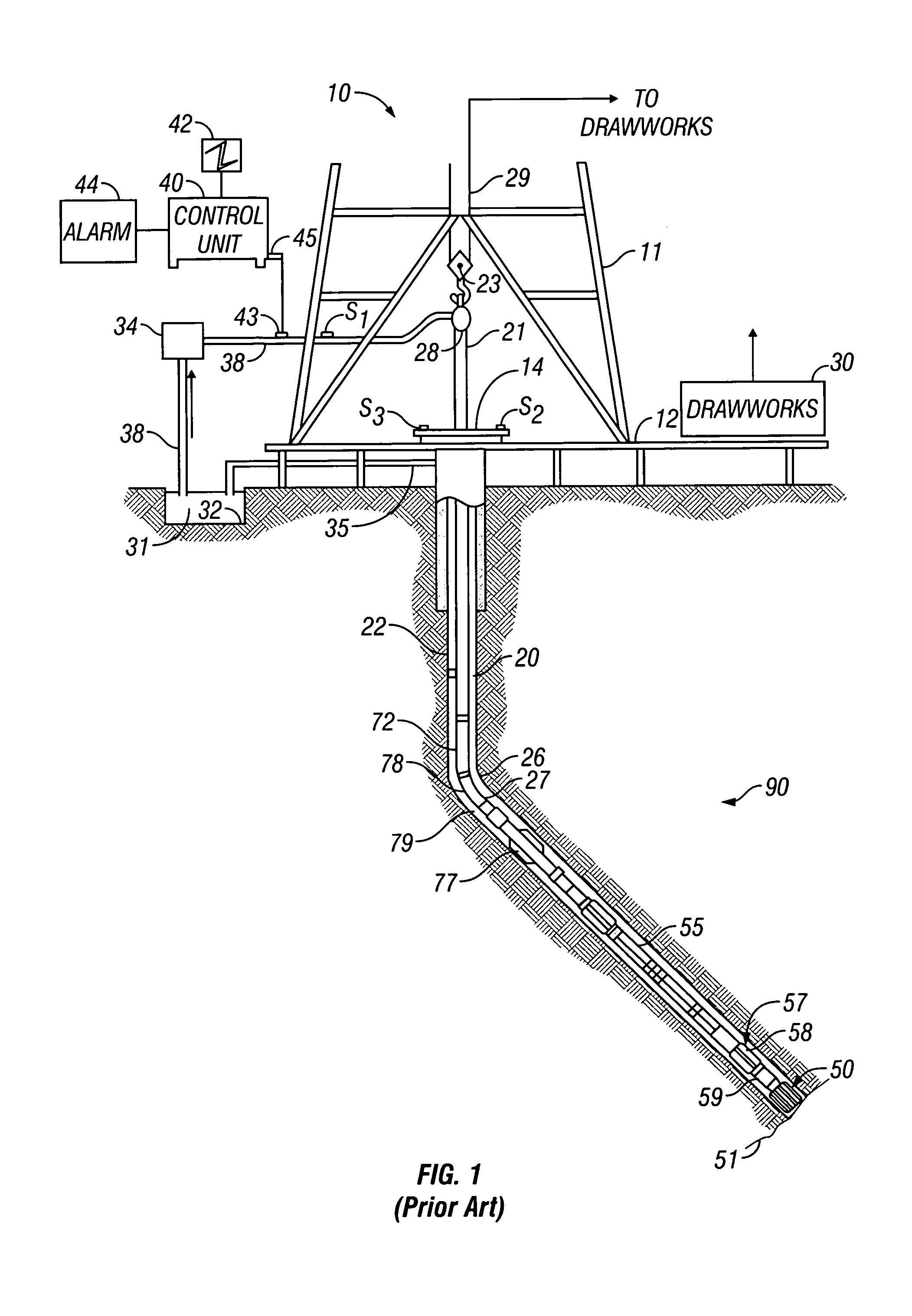
Downhole high resolution NMR spectroscopy with polarization enhancement
InactiveUS7126332B2Increase amplitudeElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingMeasurements using double resonanceSignal onProton NMR
An apparatus and method is discussed for characterizing a fluid sample downhole of aliphatic hydrocarbon compounds, aromatic hydrocarbon compound, or connate mud filtrates containing carbon-13 isotopes using an enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) signal on a measurement-while-drilling device. To enhance the carbon-13 NMR signal these nuclei are being hyperpolarized. Either the Overhauser Effect (OE) or the Nuclear Overhauser Effect or optical pumping and the Spin Polarization Induced Nuclear Overhauser Effect (SPINOE) can serve as a mechanism for hyperpolarization of the carbon-13 nuclei.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES HLDG LLC
Magnetic field measurement system and optical pumping magnetometer
ActiveUS7656154B2Reduce magnetic noiseAffect operationSuperconductors/hyperconductorsMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityComing out
Provided is a highly accurate optical pumping magnetometer, in which a static magnetic field and an oscillating field to be applied to a vapor cell are stabilized. To this end, the optical pumping magnetometer includes: Helmholtz coils for applying a constant static magnetic field to a vapor cell serving as a magnetic field detector; fluxgate magnetometers for detecting environmental magnetic noise in two directions of X-axis direction and Y-axis direction other than Z-axis direction which is a direction for detecting a magnetic field coming out of a measurement object while locating the vapor cell in the center thereof; magnetometer drive circuits for driving the fluxgate magneotometers; current converters for converting outputs of the magnetometer drive circuits into amount of currents; and magnetic field generating coils for generating a magnetic field in a phase opposite to the environmental magnetic noise in the two directions.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Multi-spectral laser array and optical system
InactiveUS20050147135A1Semiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structureLaser transmitterLaser array
An organic vertical cavity laser light producing device (10) comprises a substrate (20). A plurality of laser emitters (200) emits laser light in a direction orthogonal to the substrate. Each laser emitter within the plurality of laser emitters has a first lateral mode structure in a first axis orthogonal to the laser light direction and has a second lateral mode structure in a second axis orthogonal to both the laser light direction and the first axis. Each laser emitter comprises a first mirror provided on a top surface of the substrate (20) and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. An organic active region (40) produces laser light (350). A second mirror is provided above the organic active region and is reflective to light over a predetermined range of wavelengths. A pumping means excites the plurality of laser emitters.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
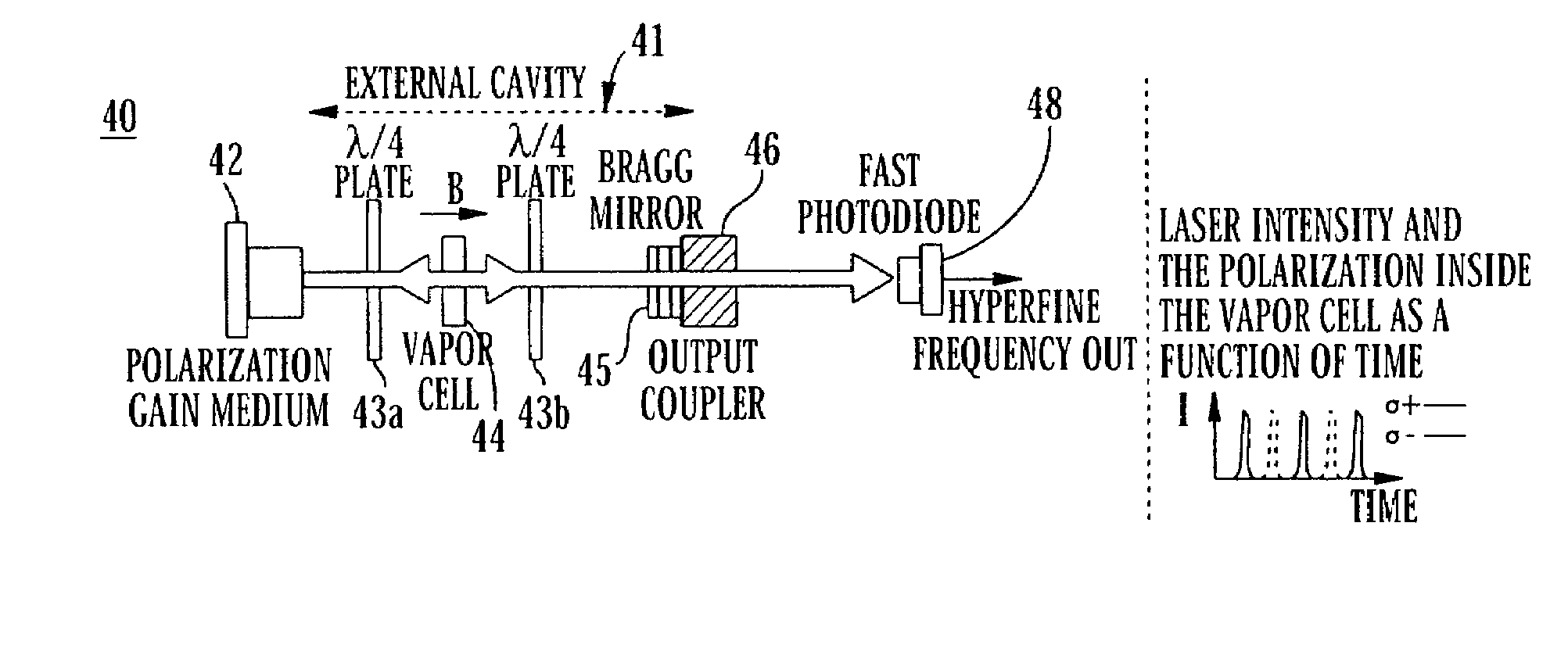
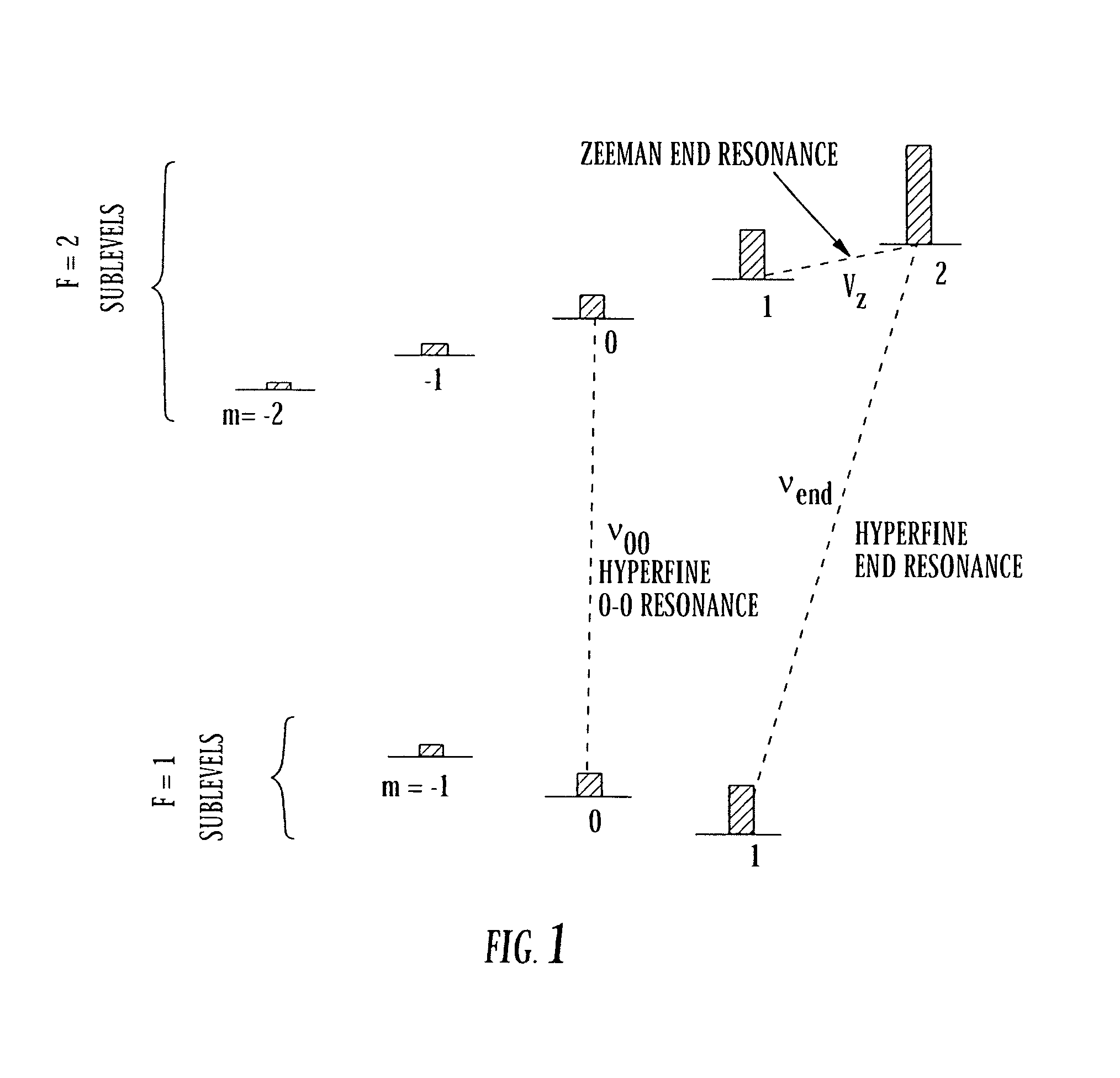
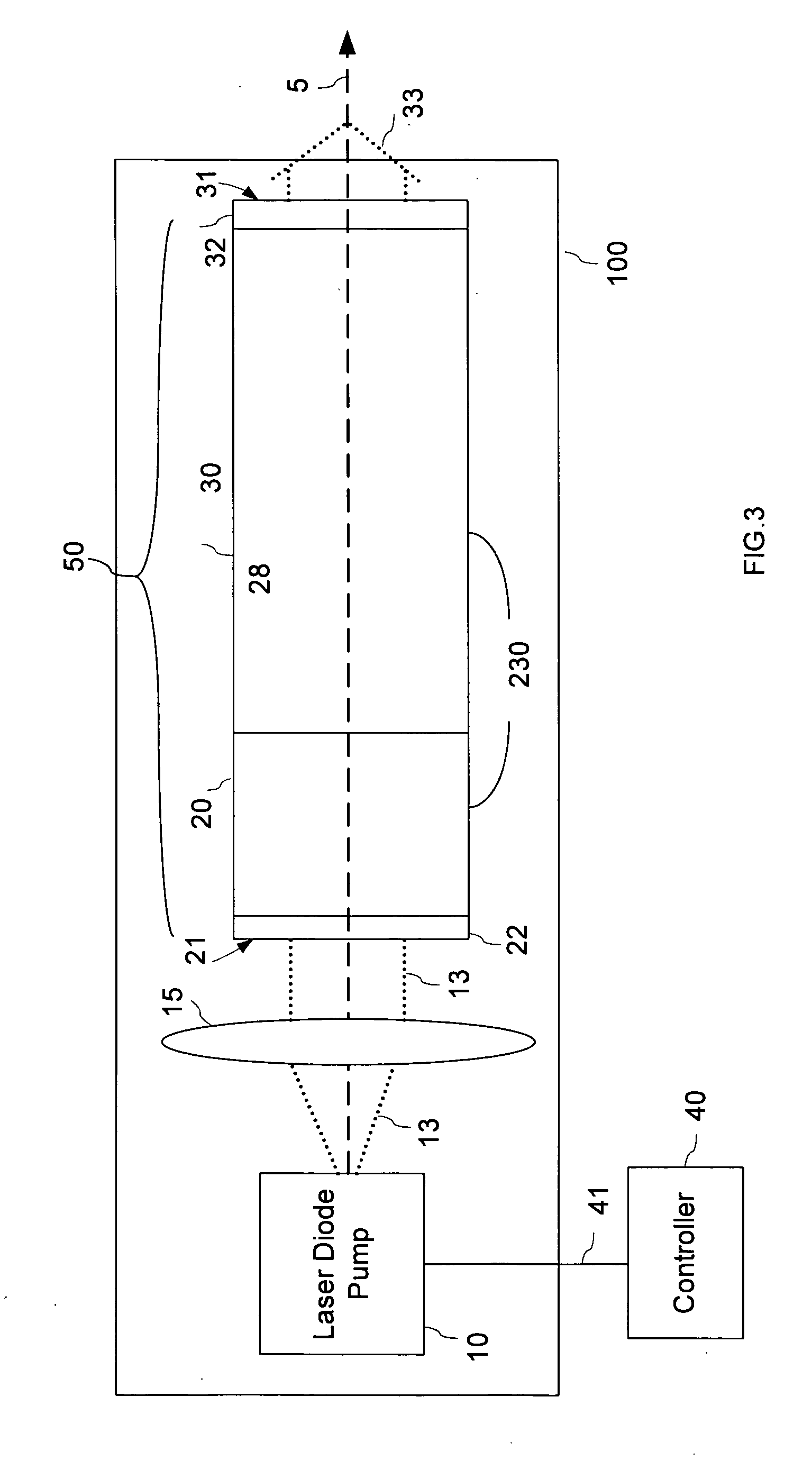
Method and system for operating a laser self-modulated at alkali-metal atom hyperfine frequency
InactiveUS7323941B1Boost up CPT signalImprove performancePulse automatic controlGaseous masersPhotodetectorPush pull
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for making atomic clocks or atomic magnetometers as self-modulated laser systems based on the physics of push-pull optical pumping. An atomic vapor cell is required to be in the laser cavity. With proper conditions, spontaneous push-pull optical pumping can occur inside the laser cavity. This causes the laser beam to be modulated at hyperfine-resonance frequency. With a fast photodetector, the modulated laser signal can be converted into the electrical signal, which serves as the atomic clock ticking signal or magnetometer signal. The self-modulated laser system does not use any local oscillator and the microwave circuit to lock the oscillator frequency to the hyperfine-resonance frequency, and therefore can consume less power and become more compact than conventional systems. This invention will benefit applications of time measurements and magnetic-field measurements.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV
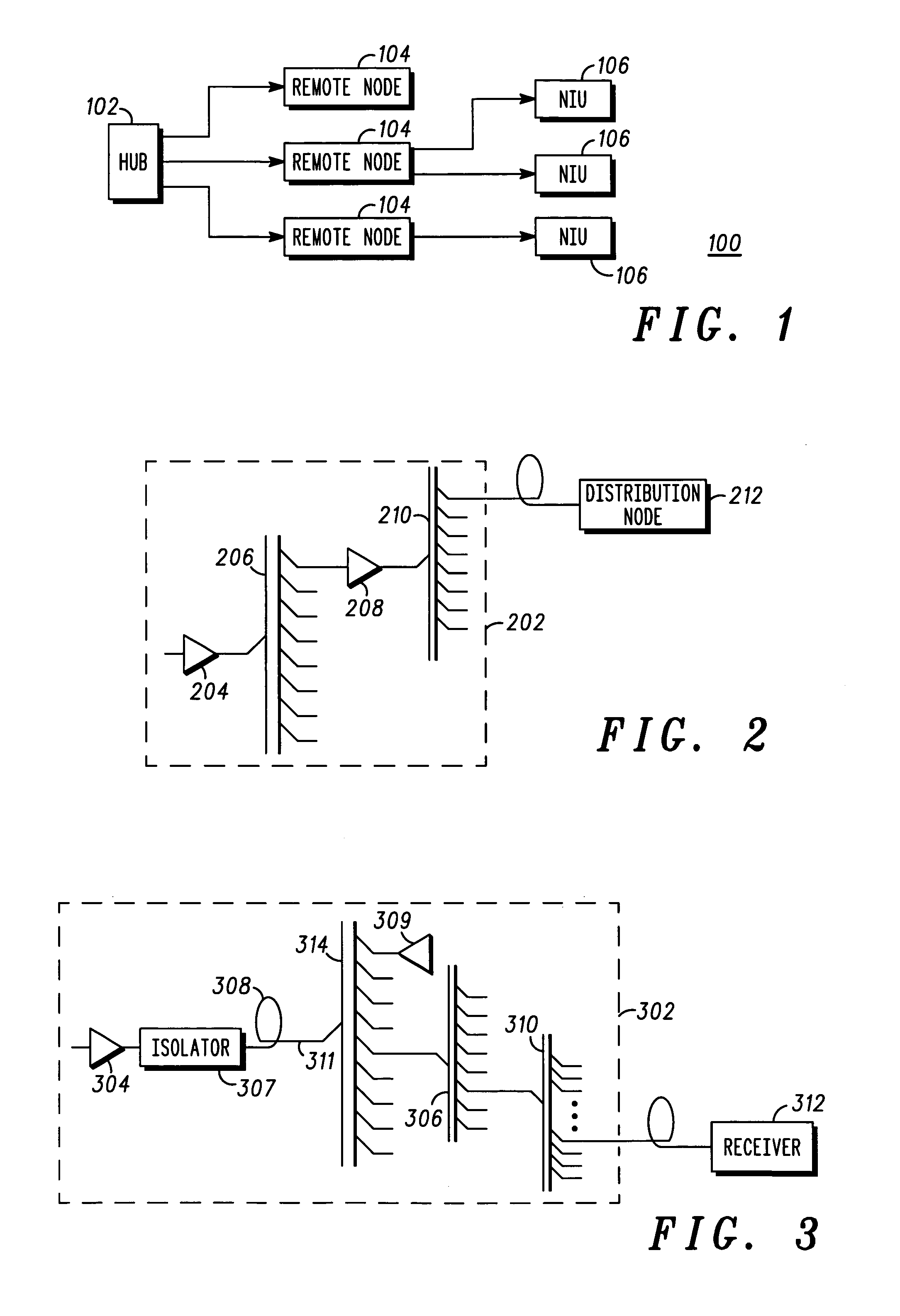
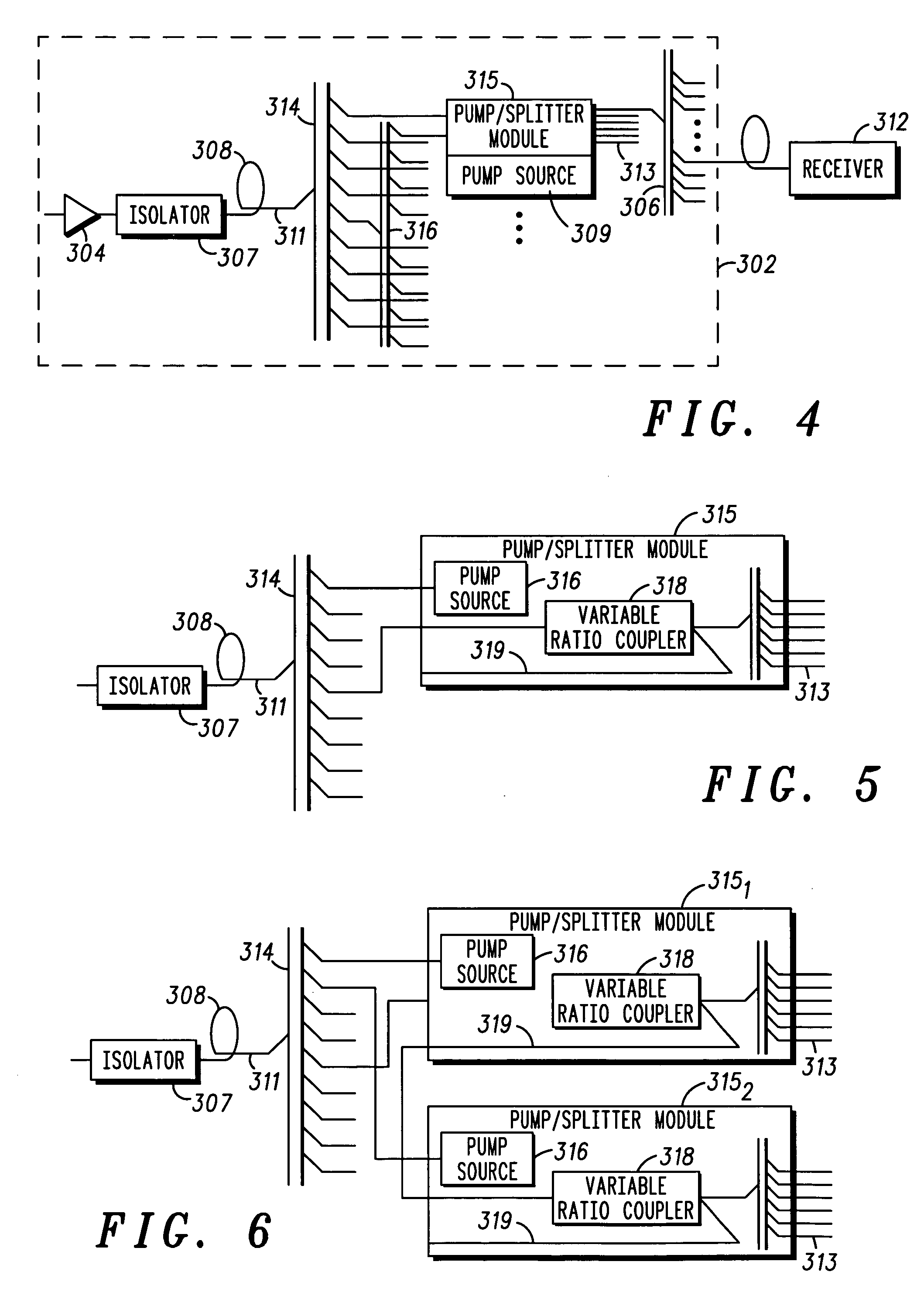
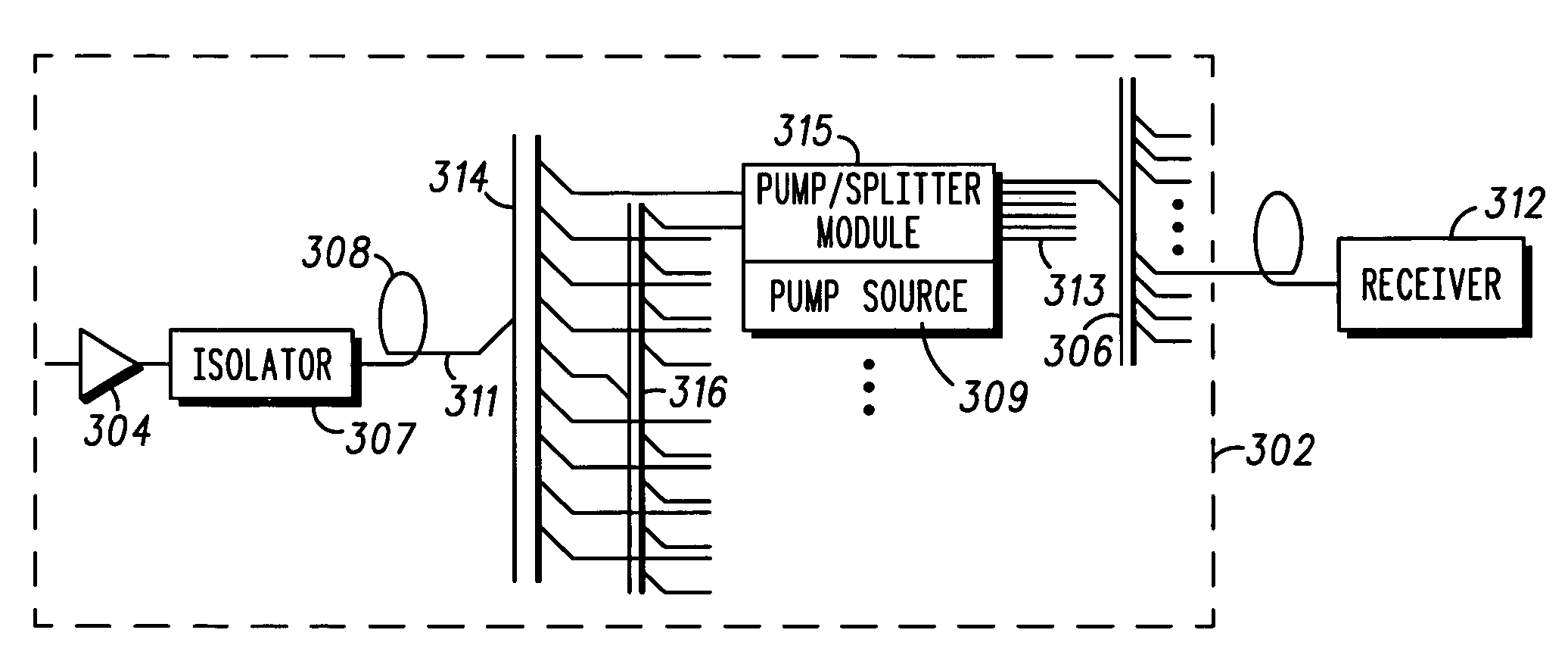
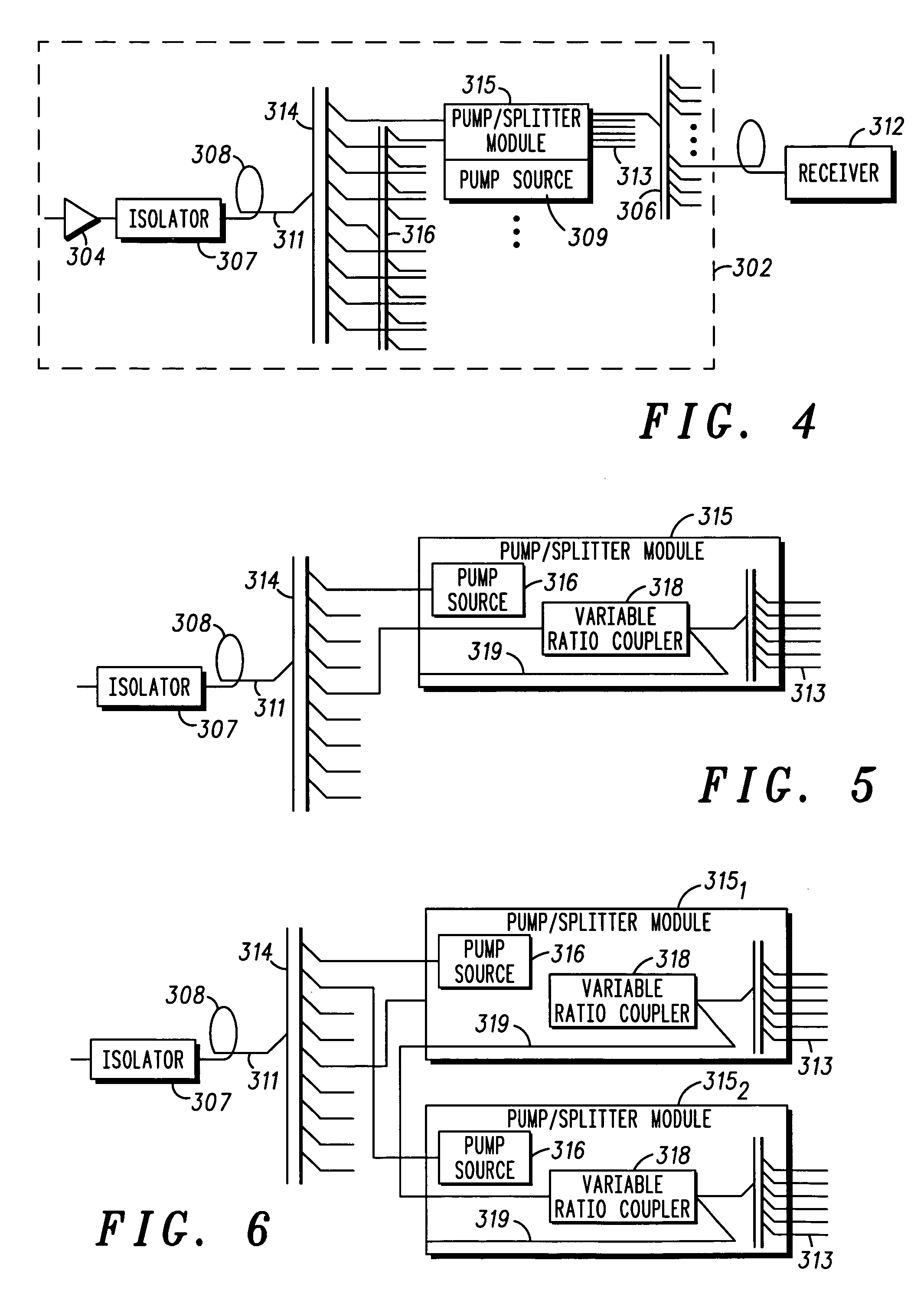
Hub for a passive optical network hub
ActiveUS20050036786A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical pumpingRare earth
A hub for use in a passive optical network (PON) includes a transmission fiber on which an information-bearing optical signal is received, a double-cladded, rare-earth doped fiber located along the transmission fiber for imparting gain to the information-bearing optical signal, and a combiner having an output coupled to the transmission fiber and a plurality of inputs. The output is coupled to the transmission fiber such that optical energy at pump energy wavelengths but not signal wavelengths are communicated therebetween. At least one pump source is optically coupled to one of the inputs of the combiner for providing optical pump energy to the double-cladded, rare-earth doped fiber. An optical splitter is also provided. The optical splitter has an input coupled to the transmission fiber for receiving an amplified, information-bearing optical signal and a plurality of outputs for directing portions of the amplified, information-bearing optical signal to remote nodes in the PON.
Owner:GOOGLE TECH HLDG LLC
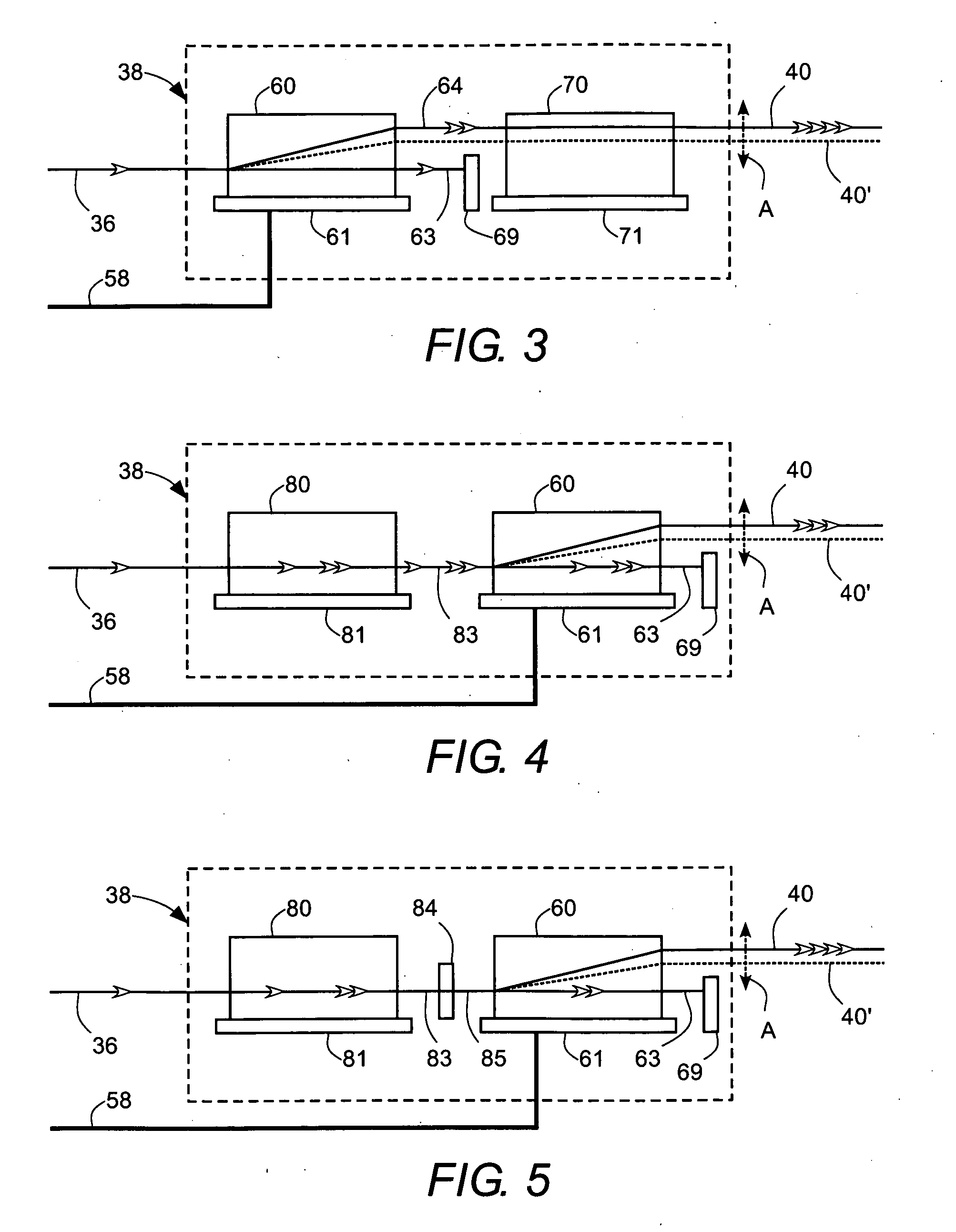
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet solid-state laser sources based on nonlinear frequency conversion in periodically poled materials
InactiveUS7570676B2Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsNonlinear crystalsLight source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
System and method for active protection of a resource
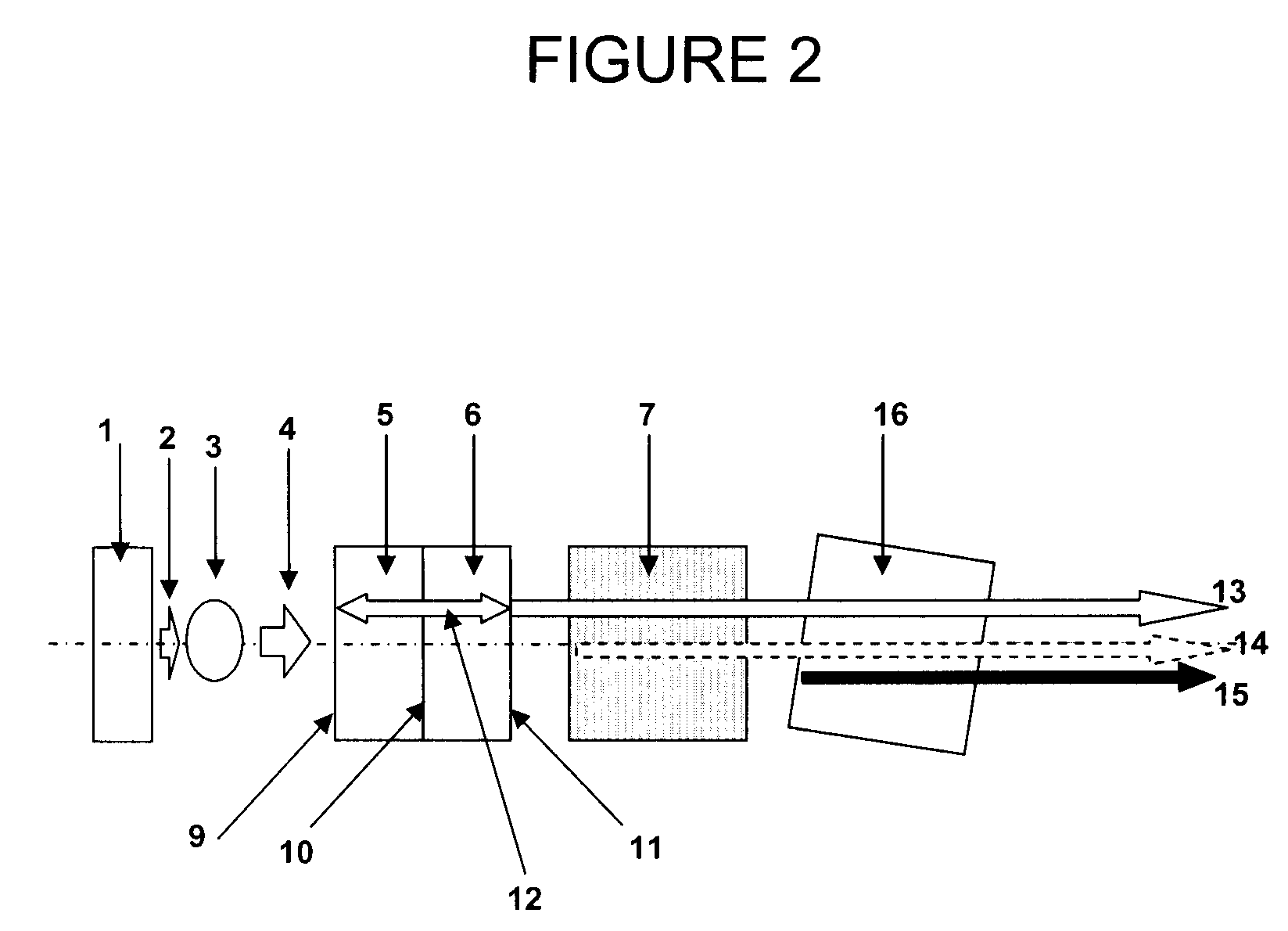
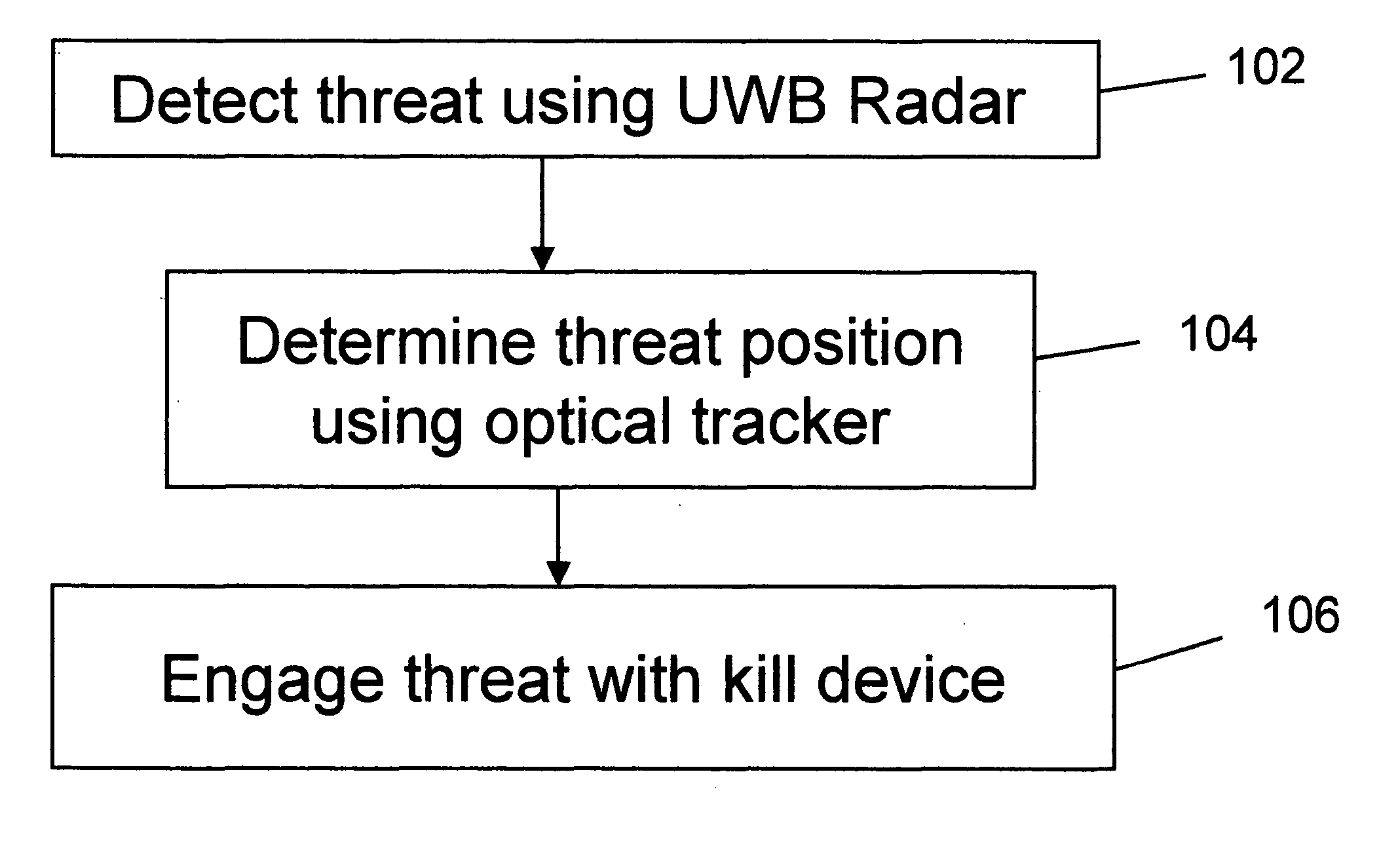
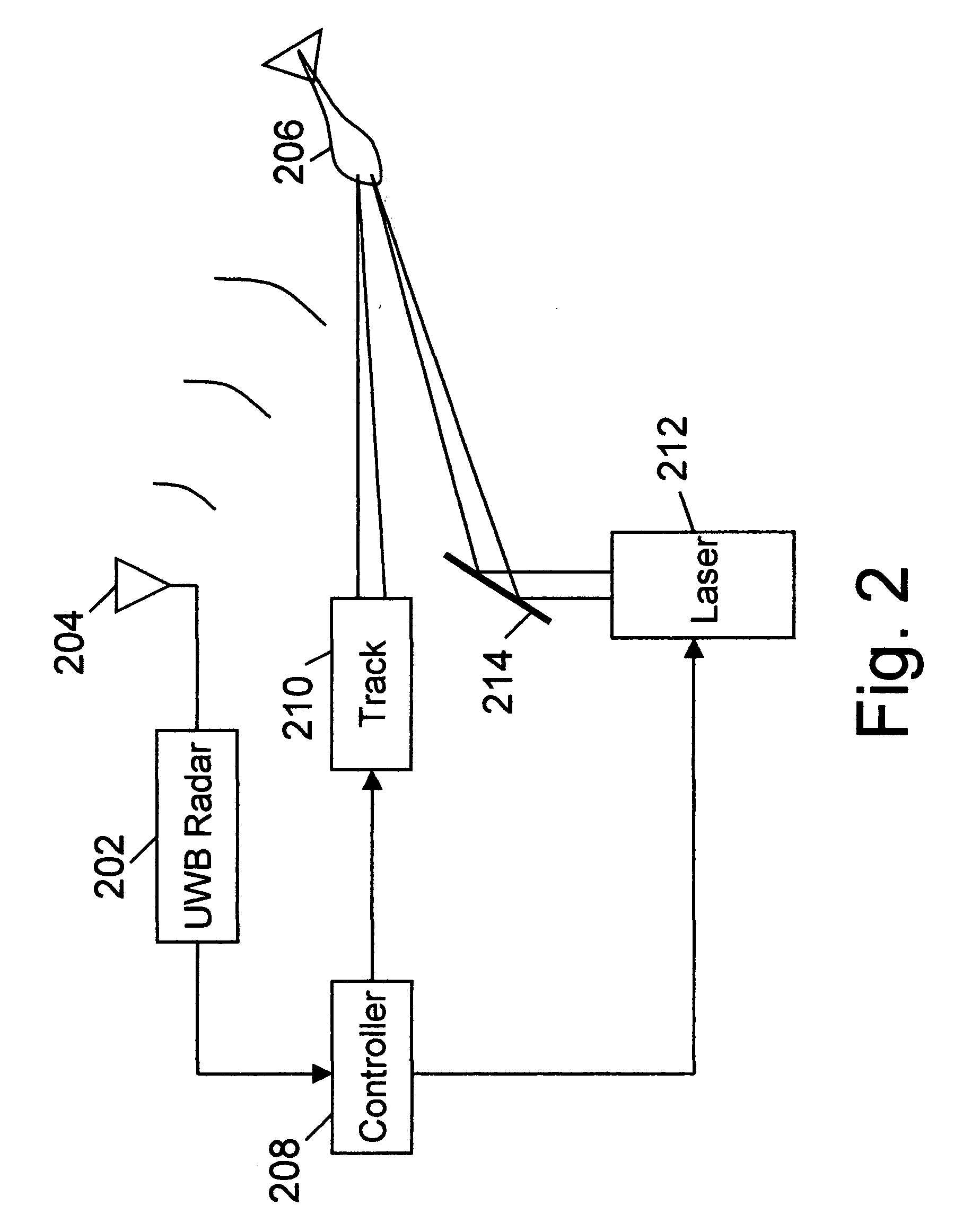
An active protection system comprising an ultrawideband radar for threat detection, an optical tracker for precision threat position measurement, and a high powered laser for threat kill or mitigation. The uwb radar may use a sparse array antenna and may also utilize Doppler radar information. The high powered laser may be of the optically pumped solid state type and in one embodiment may share optics with the optical tracker. In one embodiment, the UWB radar is used to focus the high power laser. Alternative interceptor type kill mechanisms are disclosed. In a further embodiment, the kill mechanism may be directed to the source of the threat.
Owner:HUMATICS CORP
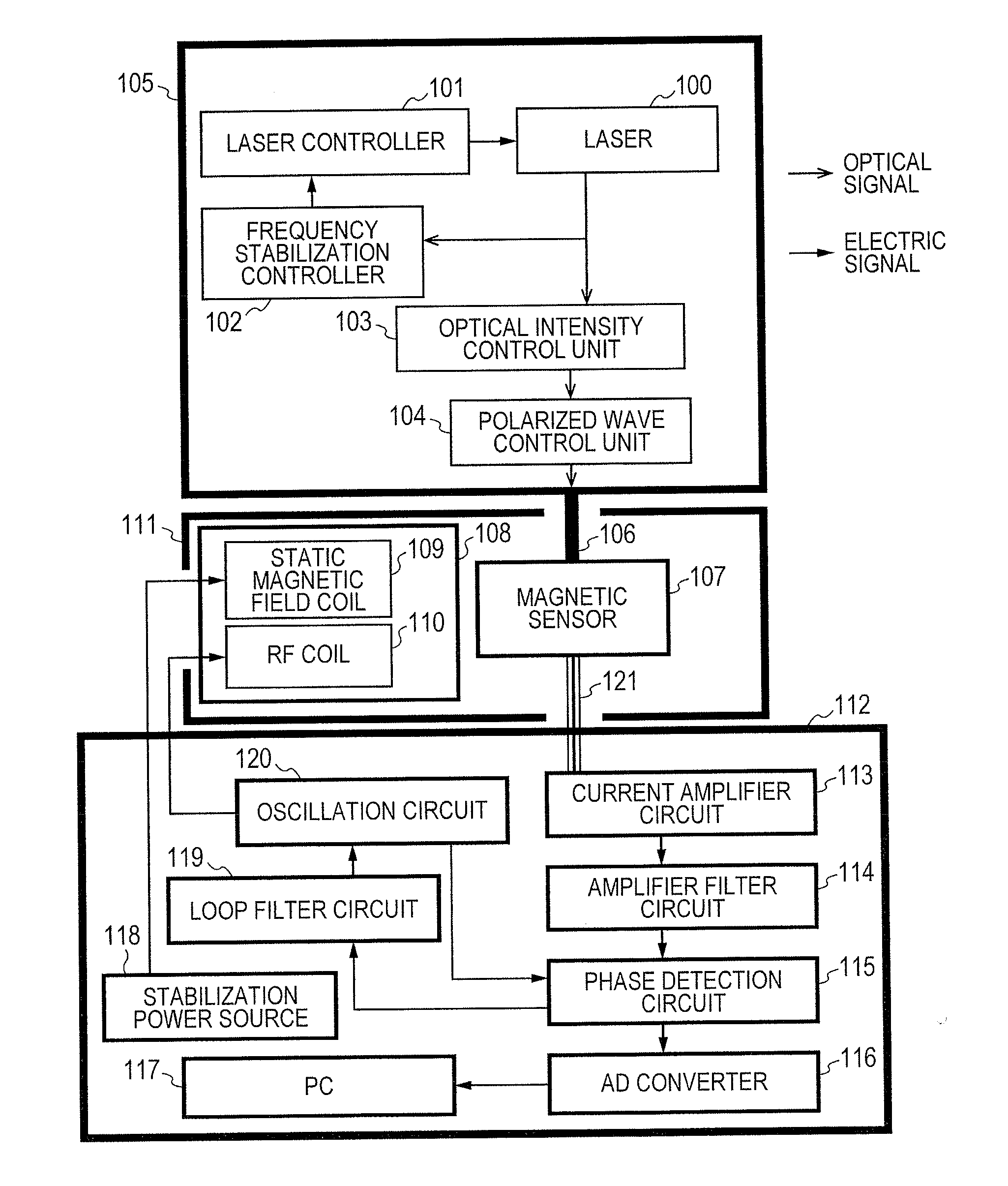
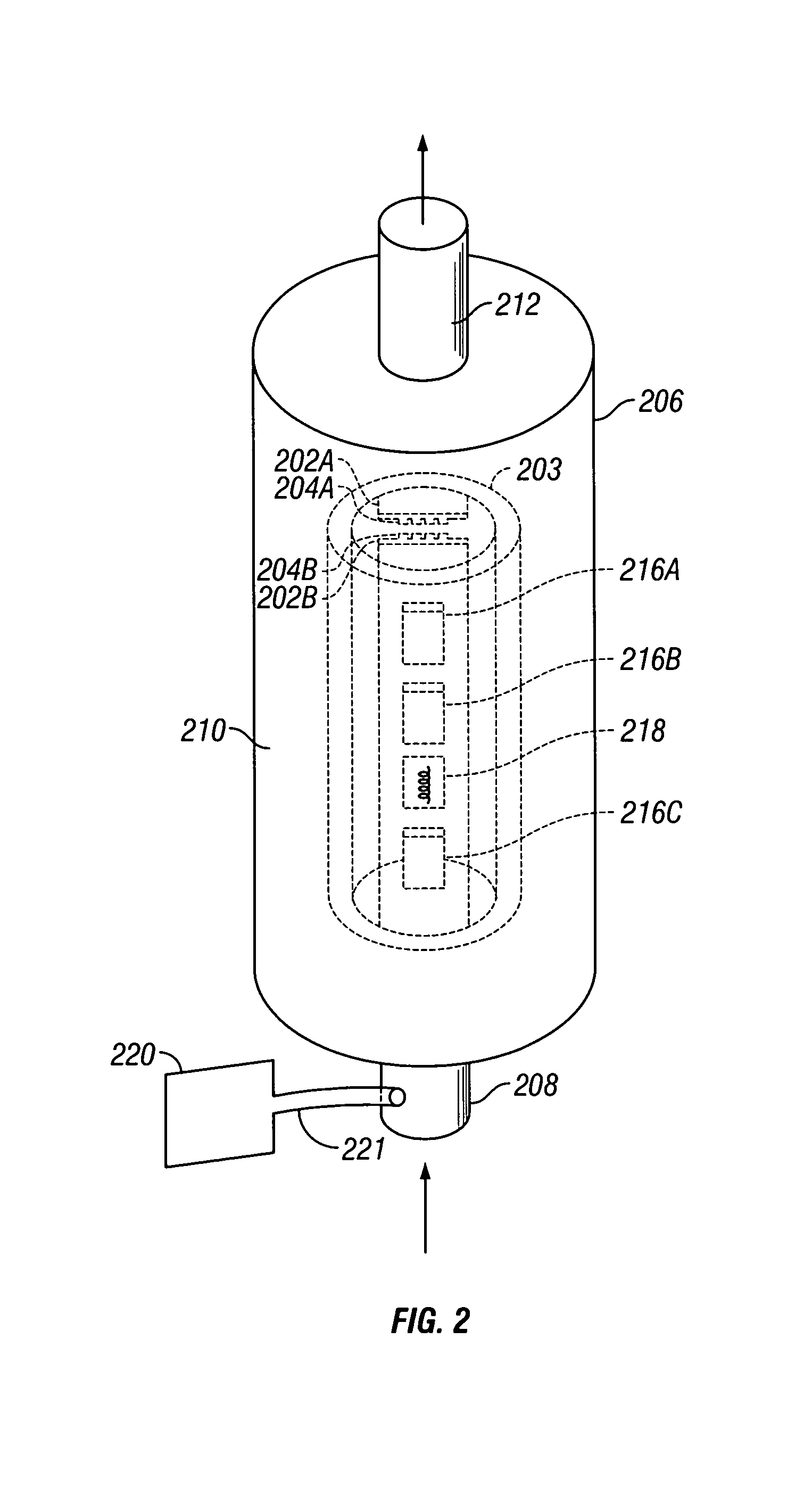
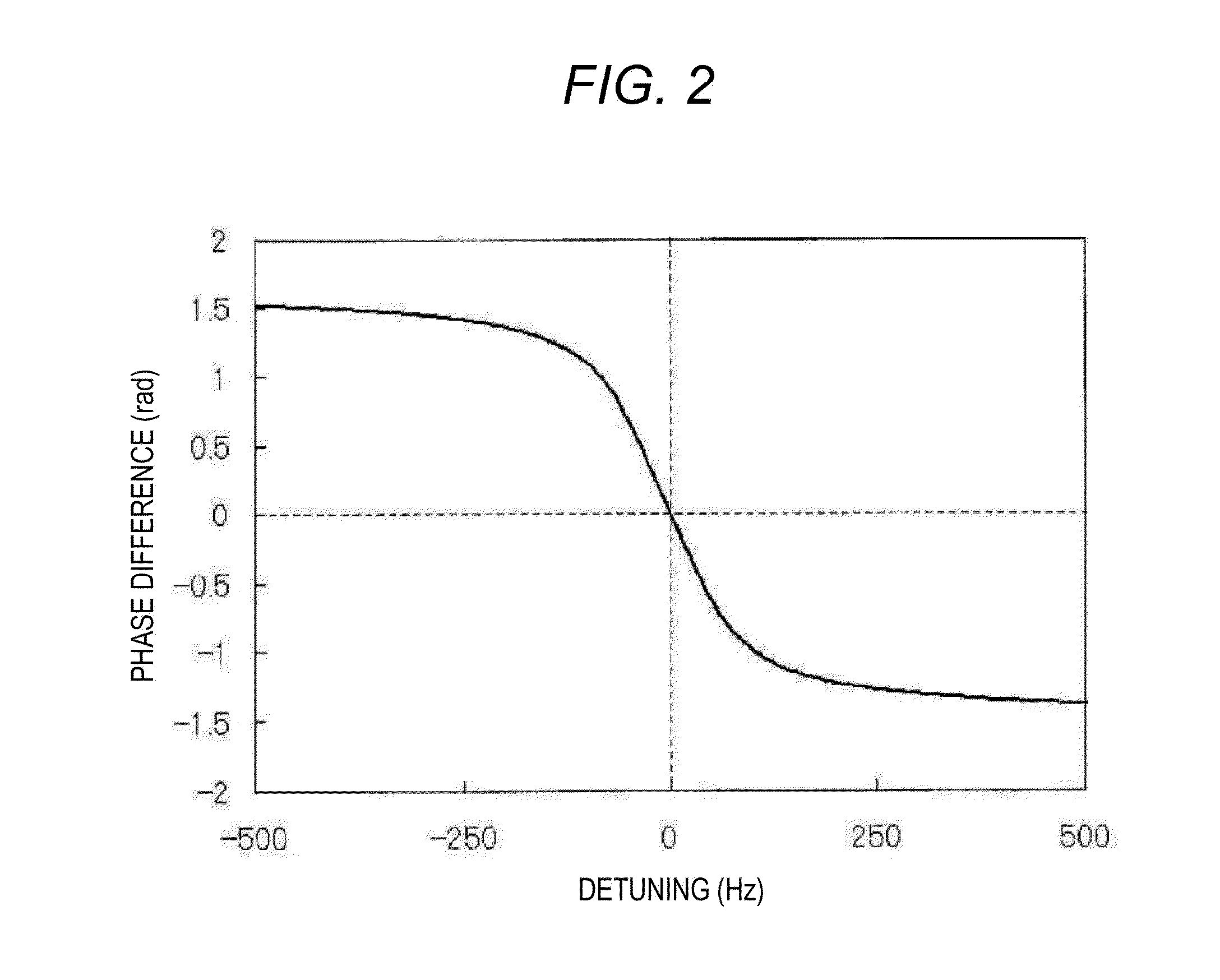
Magnetic Field Measuring Apparatus
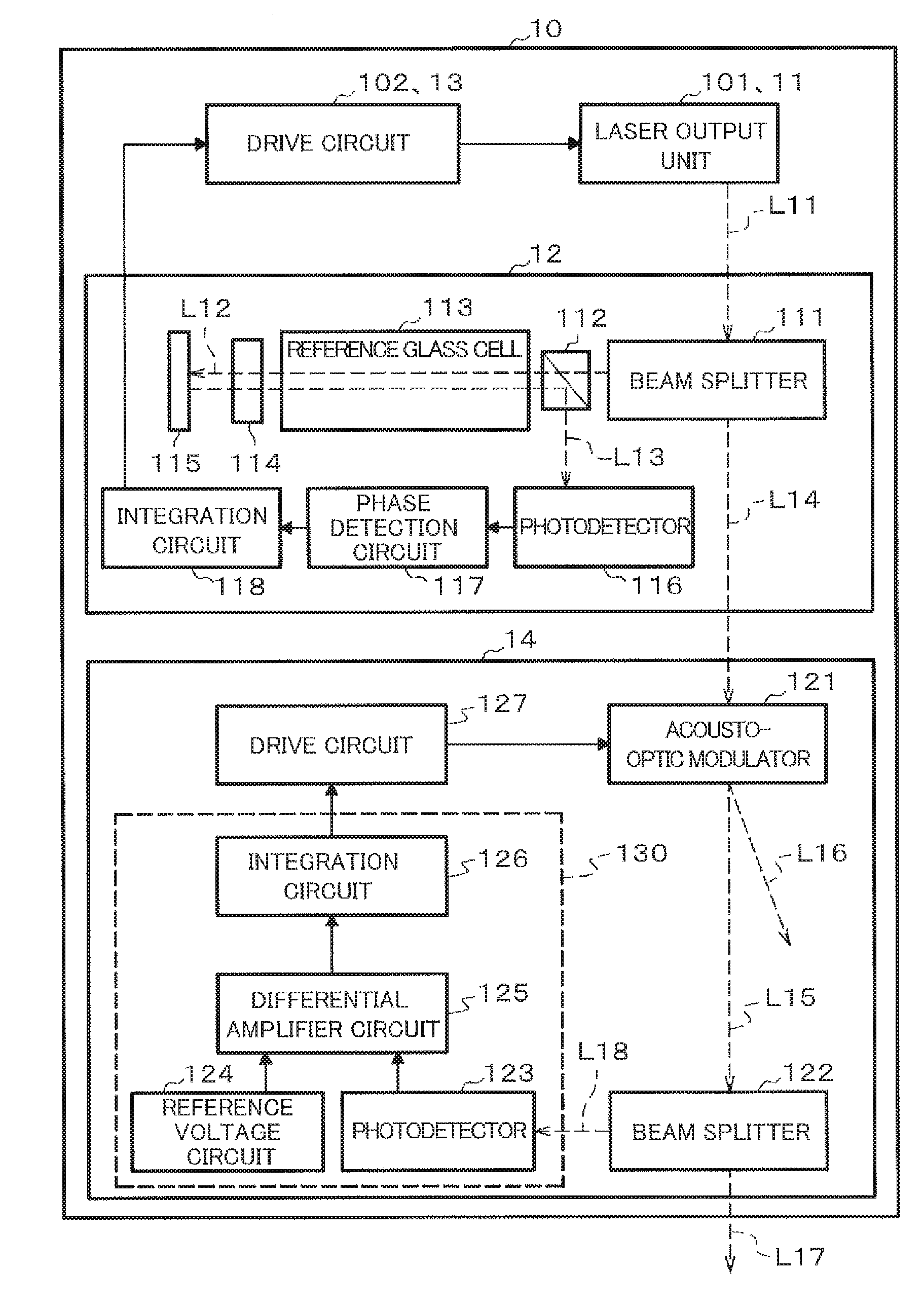
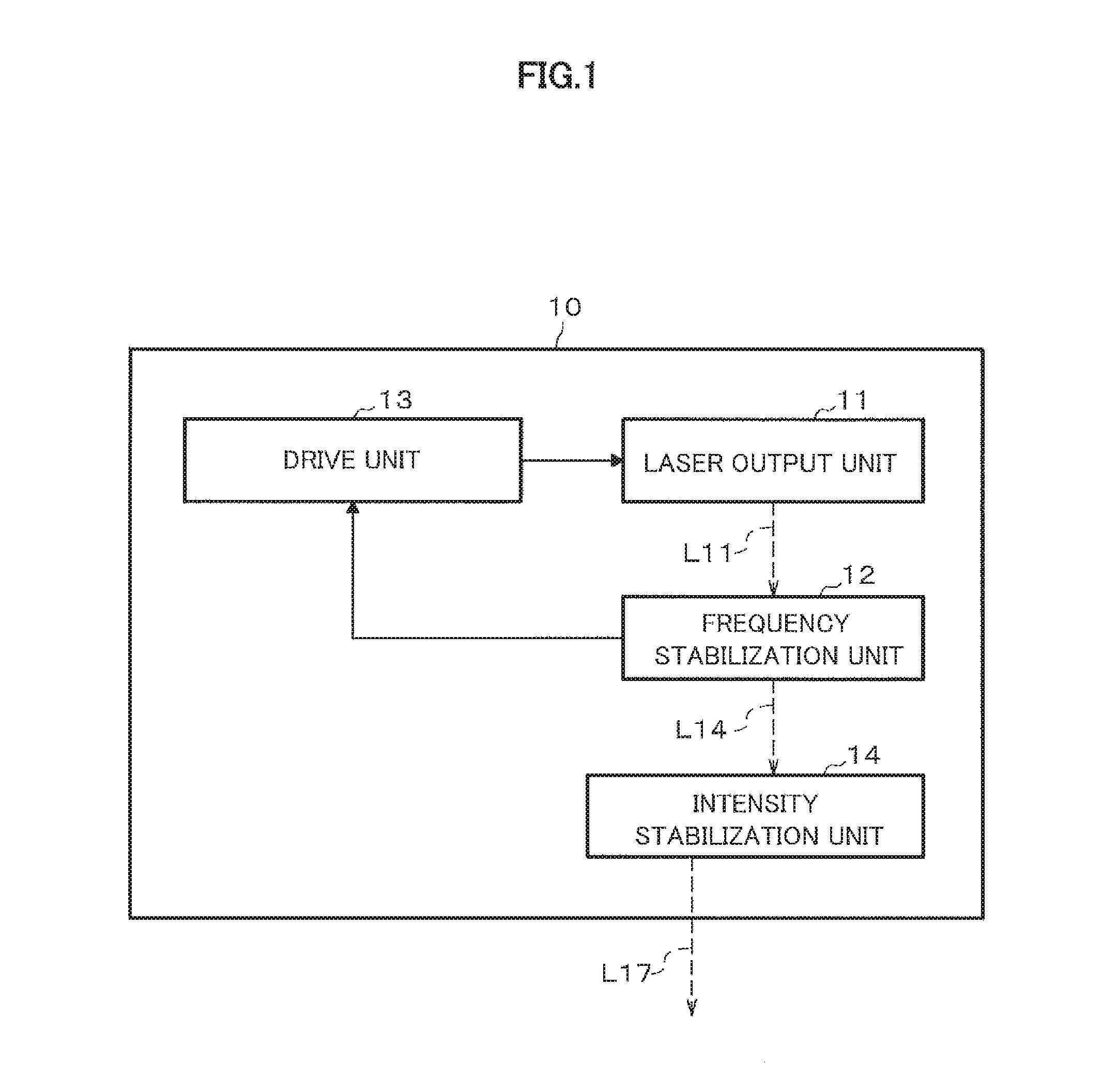
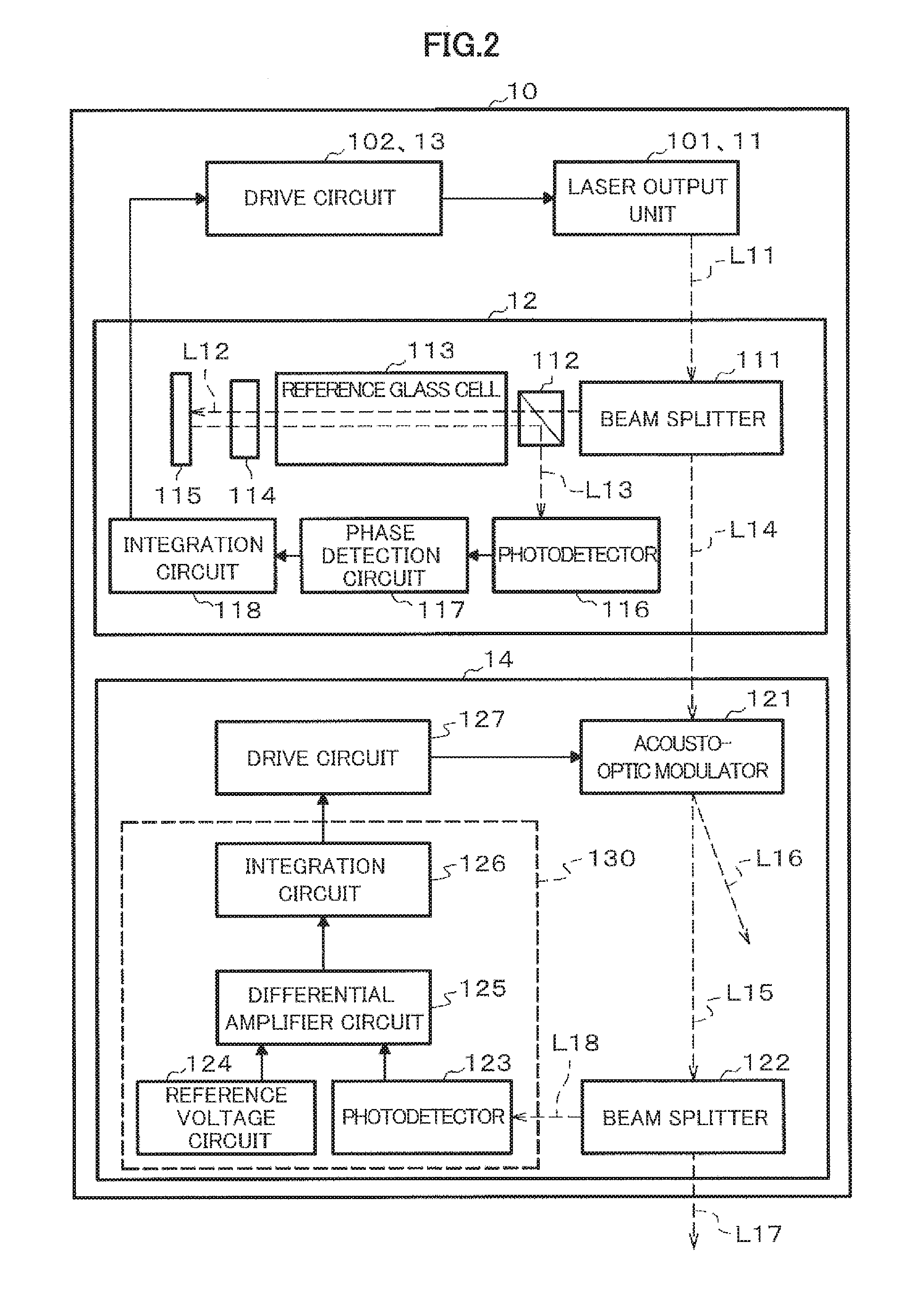
ActiveUS20160313417A1Stable signalLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionOptical pumpingAcousto-optics
The present invention addresses the problem of stabilizing signals in magnetic field measurement using optical pumping. In order to solve the problem, disclosed is a light source apparatus (10) that is characterized in having: a light intensity fluctuation detection circuit (130) that detects intensity fluctuation of light outputted from a laser output unit (11); and an acousto-optic modulator (121) that corrects light intensity on the basis of light intensity fluctuation detected by means of the light intensity fluctuation detection circuit (130) such that the light intensity is constant Furthermore, a magnetic field measuring apparatus of the present invention is characterized in having: one sensor unit that passes therethrough light outputted from a light source unit: and a signal control processor that eliminates the light intensity fluctuation on the basis of two lights passed through the sensor unit.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Semiconductor light source with electrically tunable emission wavelength
A semiconductor light source is disclosed comprising a substrate, lower and upper claddings, a waveguide region with imbedded active area, and electrical contacts to provide voltage necessary for the wavelength tuning. The active region includes single or several heterojunction periods sandwiched between charge accumulation layers. Each of the active region periods comprises higher and lower affinity semiconductor layers with type-II band alignment. The charge carrier accumulation in the charge accumulation layers results in electric field build-up and leads to the formation of generally triangular electron and hole potential wells in the higher and lower affinity layers. Nonequillibrium carriers can be created in the active region by means of electrical injection or optical pumping. Radiative recombination occurs between the electrons and holes, accumulated in the ground states of the triangular potential wells formed in the high- and low-affinity layers of each active region periods. The ground state energy in the triangular wells and the radiation wavelength can be tuned by changing the voltage drop across the active region.
Owner:MAXION TECH +1
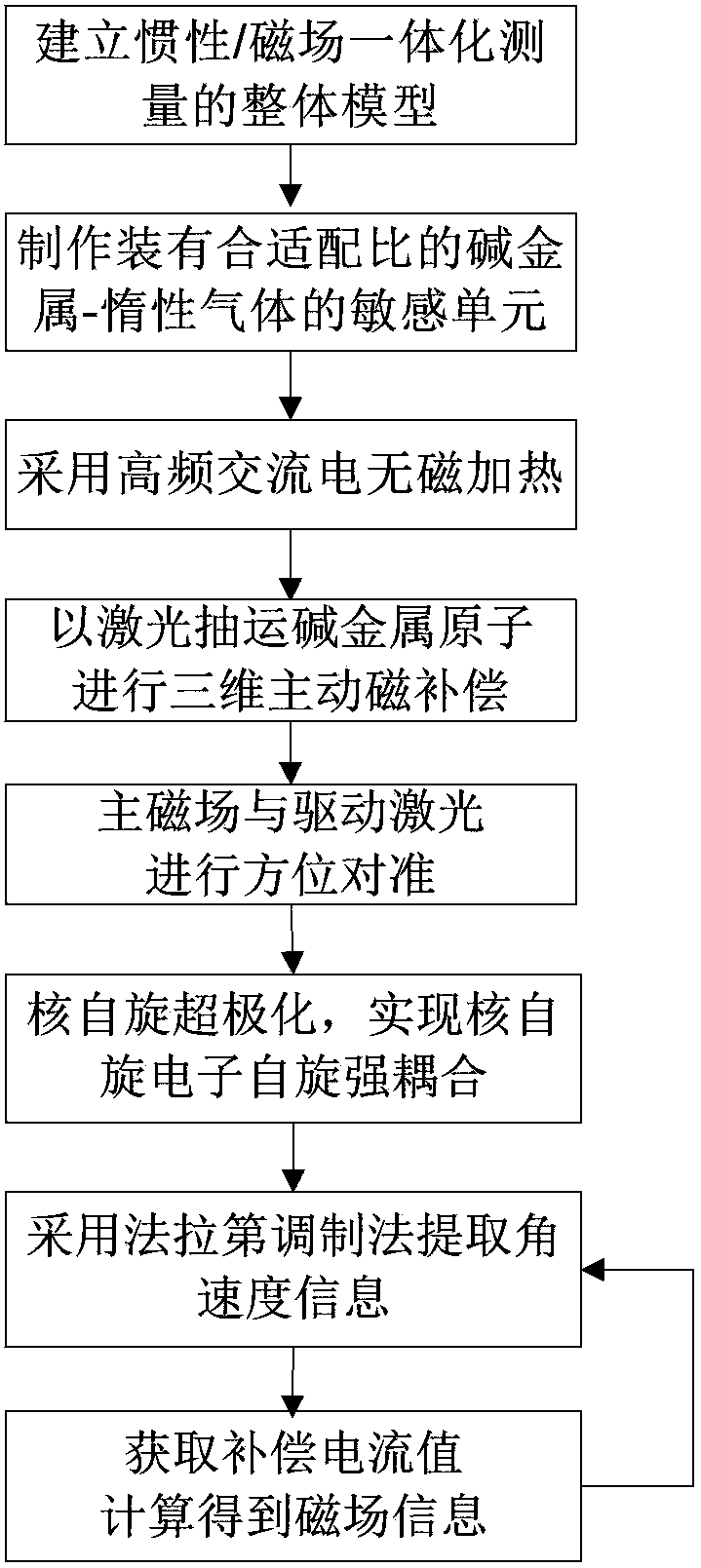
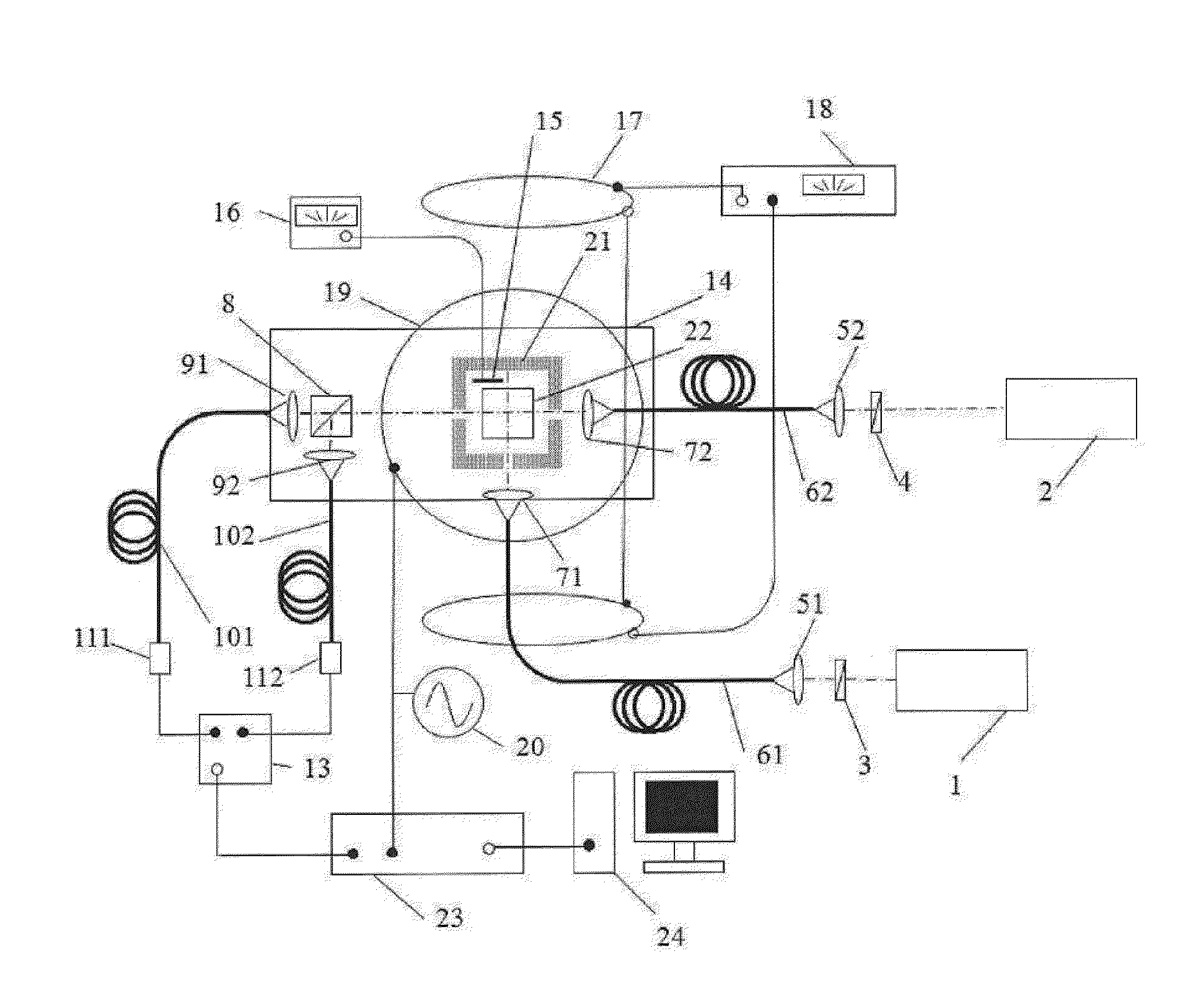
Inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on SERF (spin-exchange-relaxation-free) atomic spin effect
ActiveCN103438877AHigh measurement accuracyStrong autonomyRotary gyroscopesMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsSpin effectClosed loop
The invention provides an inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on an SERF (spin-exchange-relaxation-free) atomic spin effect. The inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on the SERF atomic spin effect comprises the following steps: firstly establishing an overall model for the inertia and magnetic field integration measurement; secondly, manufacturing a measurement sensing unit, and carrying out high-frequency alternating current non-magnetic electric heating; starting a driving laser (z-axis) for carrying out optical pumping on the sensing unit; and emitting a detection laser (x-axis) in a direction vertical to the z-axis; thirdly, carrying out driving magnetic compensation through a three-dimensional magnetic compensation coil so as to counteract a magnetic field of the outside world; fourthly, carrying out azimuth alignment on a main magnetic field and the driving laser and hyperpolarization nucleon self-spin so as to realize the nuclear spin-electron spin strong coupling; fifthly, extracting the information of the atomic spin precession movement in the detection laser by adopting a closed-loop faraday modulation detection method, and obtaining inertia angular speed information; and finally, obtaining the current value of a compensation signal of the magnetic field, and calculating to obtain the information of the current magnetic field. The inertia and magnetic field integration measuring method based on the SERF atomic spin effect has the characteristics of high measurement accuracy and strong autonomy.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Laser rod thermalization
InactiveUS6414980B1Additive manufacturing apparatusOptical resonator shape and constructionLaser processingOptical pumping
A method for operating an extracavity frequency-converted solid-state laser for performing a laser processing operation is disclosed. The laser has a laser-resonator including an optically-pumped gain-medium. The resonator is configured to compensate for a predetermined range of thermal lensing in the gain-medium. An optically-nonlinear crystal located outside the resonator converts fundamental laser radiation delivered by the resonator into frequency converted radiation. The laser processing operation is performed by a train of pulses of the frequency-converted radiation having sufficient power to perform the processing operation. The power of frequency-converted radiation is dependent on delivery parameters of the laser radiation from the laser-resonator. The laser is operated in a manner which provides that the resonator delivers effectively the same average power of fundamental laser radiation before and during the laser processing operation. This provides that thermal-lensing in the gain-medium is within the predetermined range before and during a laser processing operation. Delivery parameters of the laser radiation before and during the processing operation are varied such that power of frequency-converted radiation generated before the processing operating is insufficient to perform a laser processing operation.
Owner:COHERENT INC
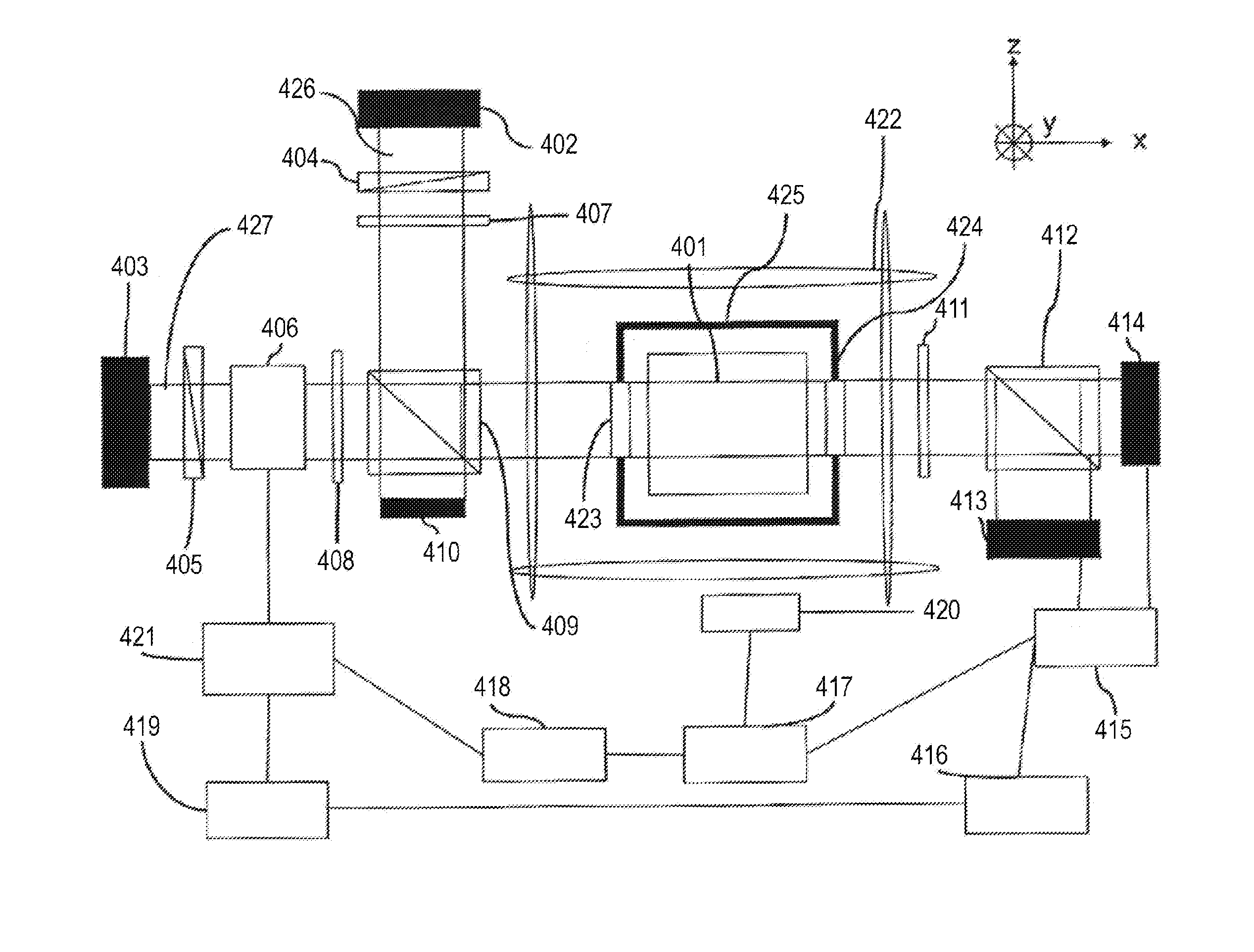
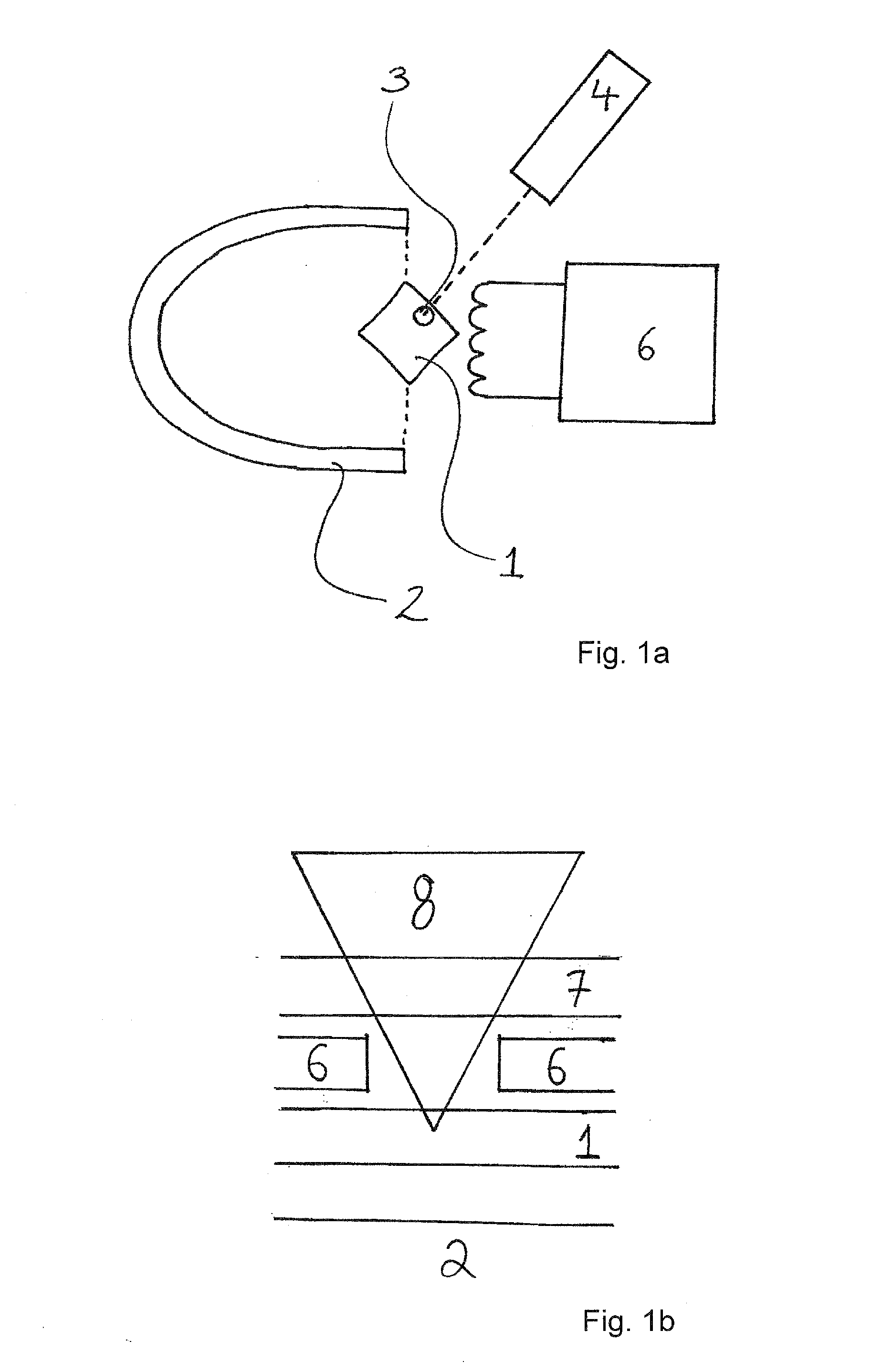
Optically pumped magnetometer and optical pumping magnetic force measuring method
InactiveUS20150022200A1Reduce noiseSuppressing the influence by the fluctuation of the spin polarizationElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceOptical axisOptical pumping
An optically pumped magnetometer having a single optical axis using atomic electron spin or nuclear spin includes a detection unit configured to detect an angle of a polarization plane of probe light having components of linear polarization and a modulation unit configured to apply a modulation to the angle of the polarization plane of the probe light having the components of linear polarization. The modulation unit is configured to control an offset in applying the modulation to the angle of the polarization plane of the probe light having the components of linear polarization according to the angle of the polarization plane of the probe light detected by the detection unit.
Owner:CANON KK
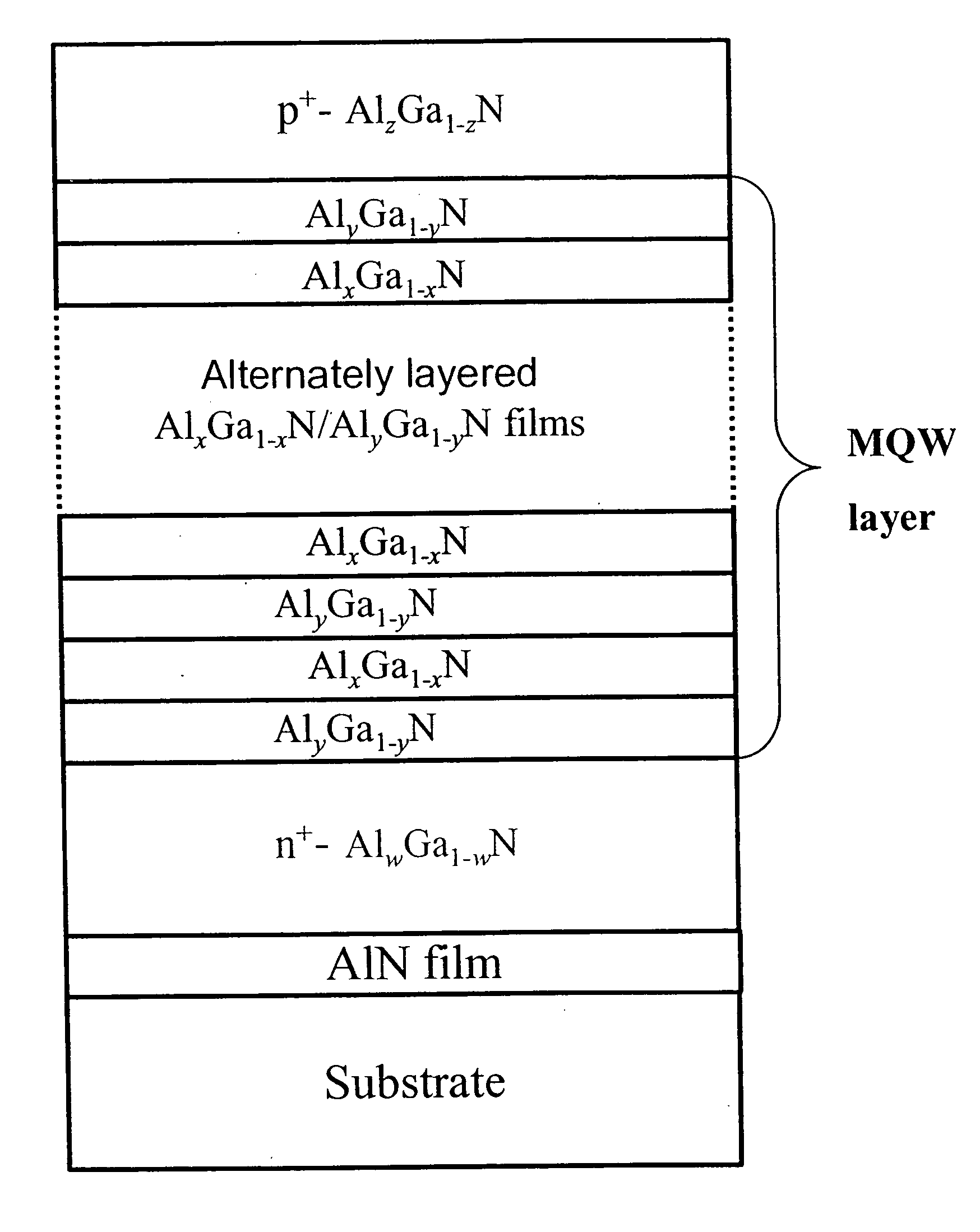
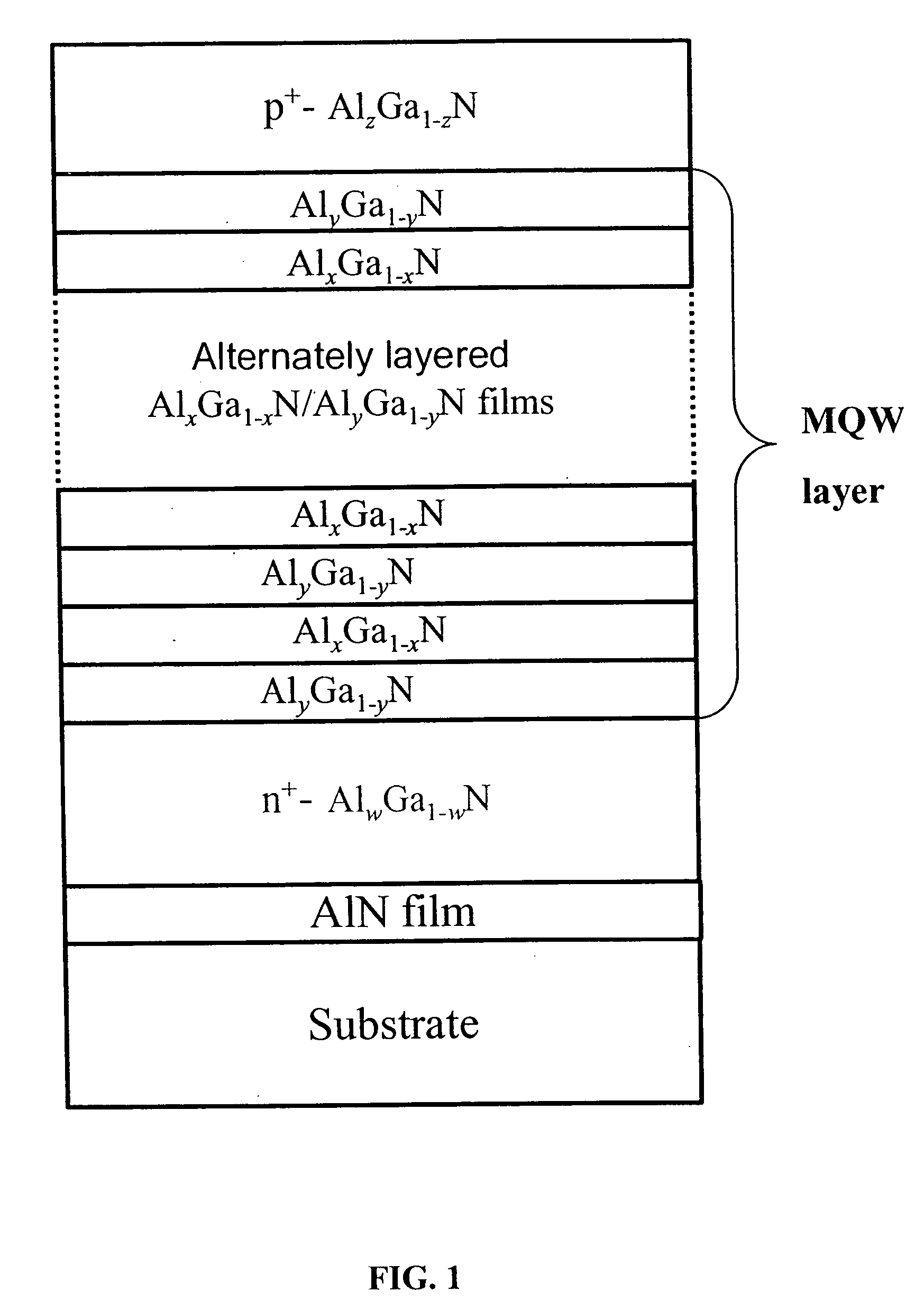
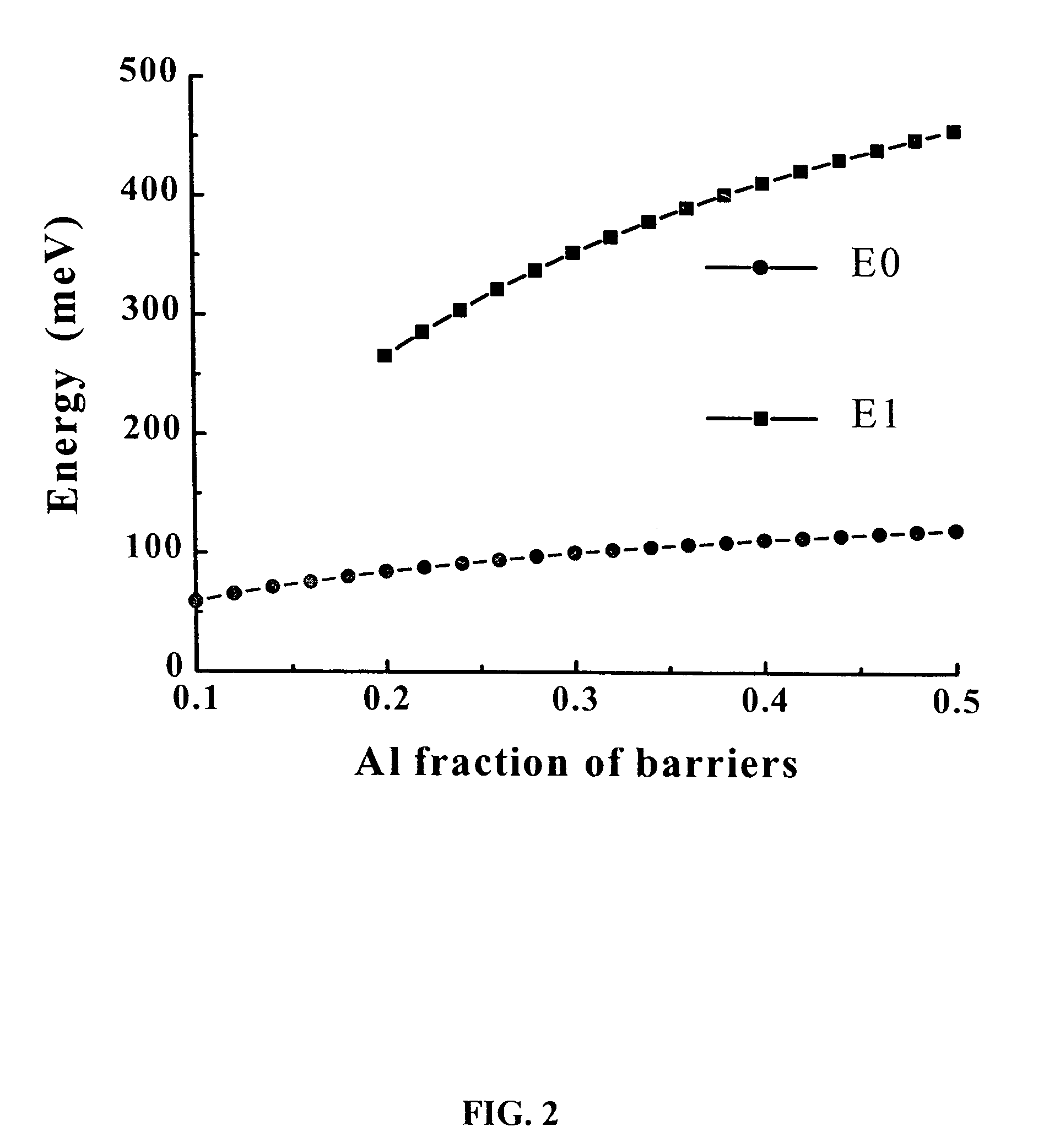
Photodetectors and optically pumped emitters based on III-nitride multiple-quantum-well structures
The design and operation of a p-i-n device, operating in a sequential resonant tunneling condition for use as a photodetector and an optically pumped emitter, is disclosed. The device contains III-nitride multiple-quantum-well (MQW) layers grown between a III-nitride p-n junction. Transparent ohmic contacts are made on both p and n sides. The device operates under a certain electrical bias that makes the energy level of the first excitation state in each well layer correspond with the energy level of the ground state in the adjoining well layer. The device works as a high-efficiency and high-speed photodetector with photo-generated carriers transported through the active MQW region by sequential resonant tunneling. In a sequential resonant tunneling condition, the device also works as an optically pumped infrared emitter that emits infrared photons with energy equal to the energy difference between the first excitation state and the ground state in the MQWs.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK
Compact efficient and robust ultraviolet
InactiveUS20070263693A1Low costHigh peak powerOptical devices for laserNon-linear opticsUltravioletLaser source
A compact and efficient ultraviolet laser source based on a optically-pumped solid-state or fiber laser that produces near-infrared output light suitable for nonlinear frequency conversion. The infrared laser output is frequency tripled or quadrupled to produce light in the ultraviolet wavelength range (200 nm to 400 nm). The novel technology is the use of highly efficient periodically poled nonlinear crystals, such as stoichiometric and MgO-doped lithium tantalate and lithium niobate. As opposed to conventional frequency-converted UV laser sources, which have high power consumption, high cost, and low efficiency, the laser sources of this invention utilize high efficiency nonlinear conversion provided by periodically poled materials and allow lower-cost architectures without additional focusing lenses, high power pump diodes, etc.
Owner:OOO SPECTRALUS
Optical pumping magnetometer
ActiveUS9366735B2Easy to controlGuaranteed uptimeElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceFrequency stabilizationPhotodetector
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Optically pumped semiconductor ring laser
InactiveUS6940880B2Doubling frequencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusFourth harmonicOptical pumping
An optically pumped semiconductor laser includes an active ring-resonator having two or more optically pumped semiconductor (OPS) structures each including a mirror-structure and a multilayer gain-structure. The mirror-structures serve as fold mirrors for the resonator axis. An optically nonlinear crystal may be included in the ring-resonator for generating second-harmonic radiation from fundamental radiation generated in the resonator. Another optically nonlinear crystal may be provided for generating third-harmonic or fourth-harmonic radiation from the second-harmonic radiation. In one example, including a third-harmonic generating crystal, a passive ring-resonator partially coaxial with the active ring-resonator is provided for circulating second-harmonic radiation to provide resonant amplification of the second-harmonic radiation for enhancing third-harmonic conversion. Apparatus for automatically maintaining the passive ring-resonator in a resonant condition for the second-harmonic radiation is disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Optical phase conjugation laser diode
A phase-conjugating resonator that includes a semiconductor laser diode apparatus that comprises a phase-conjugating array of retro-reflecting hexagon apertured hexahedral shaped corner-cube prisms, an electrically and / or optically pumped gain-region, a distributed bragg reflecting mirror-stack, a gaussian mode providing hemispherical shaped laser-emission-output metalized mirror. Wherein, optical phase conjugation is used to neutralize the phase perturbating contribution of spontaneous-emission, acoustic phonons, quantum-noise, gain-saturation, diffraction, and other intracavity aberrations and distortions that typically destabilize any stimulated-emission made to undergo amplifying oscillation within the inventions phase-conjugating resonator. Resulting in stablized high-power laser-emission-output into a single low-order fundamental transverse cavity mode and reversal of intra-cavity chirp that provides for high-speed internal modulation capable of transmitting data at around 20-Gigabits / ps.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
Passively Q-switched laser with adjustable pulse repetition rate
A method is disclosed for varying a pulse repetition rate of a passively q-switched laser while maintaining other characteristics of the laser radiation. The laser is optically pumped with a sequence of pump pulses which includes alterations between non-zero power levels and is characterized by two adjustable parameters. By simultaneously changing the adjustable parameters, the pulse repetition rate of the laser can be changed while maintaining the laser pulse energy, divergence of the pulsed laser radiation, and optical spectrum of the pulsed laser radiation at constant levels. In one embodiment, the sequence of pump pulses includes pump power offset which magnitude and / or duration is adjusted when the laser repetition rate is changed.
Owner:LUMENTUM OPERATIONS LLC
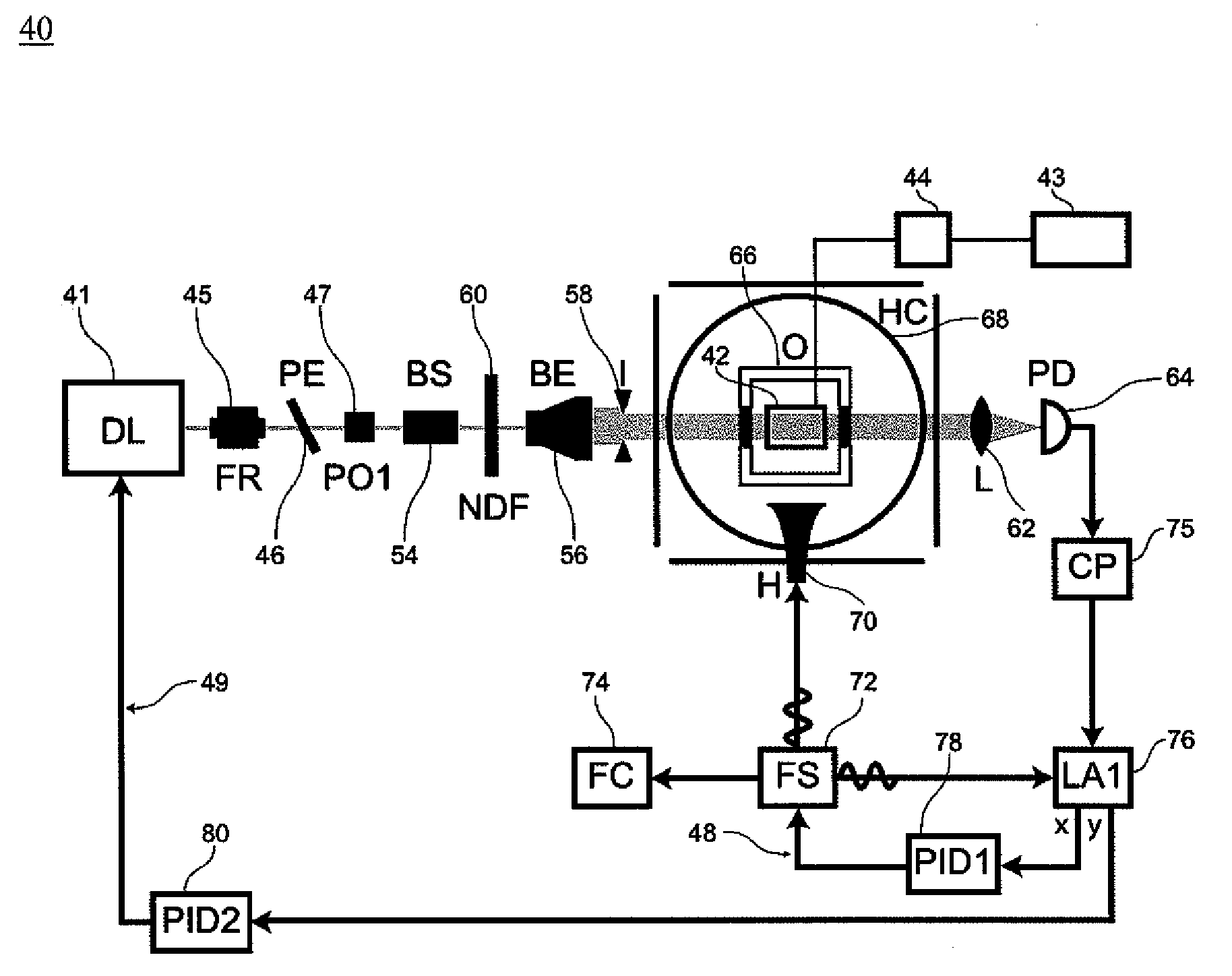
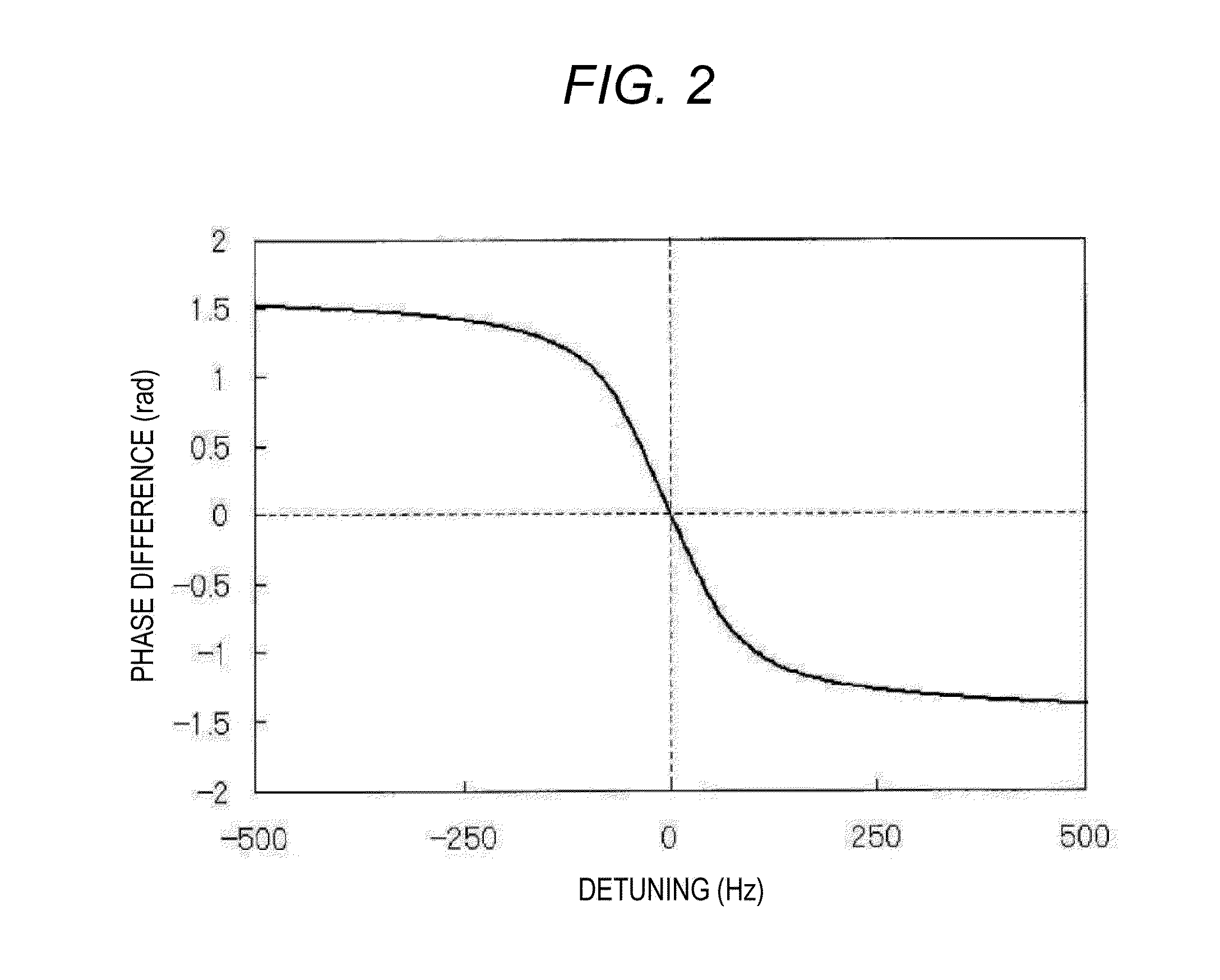
Method for suppressing light shift in optical pumping systems
InactiveUS20100156547A1Suppress and eliminate light shiftEasy to implementPulse automatic controlGaseous masersLight ShiftMicrowave
The present invention relates to a method and system to suppress or eliminate light shift in an optical pumping system, such as an atomic clock. The method uses modulation of a radiation source, such as a radio frequency or microwave source, to simultaneously lock the frequency of the radiation source to an atomic resonance and lock the frequency of the optical pumping source in order to suppress or eliminate light shift. In one embodiment, the method of the present invention directly utilizes the out-of-phase channel of a lock-in amplifier to additionally lock an optical pumping source to a zero-light-shift frequency, where the in-phase channel is used to lock the frequency of the radiation source to an atomic resonance.
Owner:PRINCETON UNIV +1
Optical pumping magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS9244137B2Improve responseHigh sensitivity measurementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic tension forceOptical pumping
An optical pumping magnetometer is provided that is capable of improving the response of the magnetometer with respect to a magnetic field that varies with a period shorter than the transverse relaxation time of electron spin of an alkali metal atom.
Owner:CANON KK
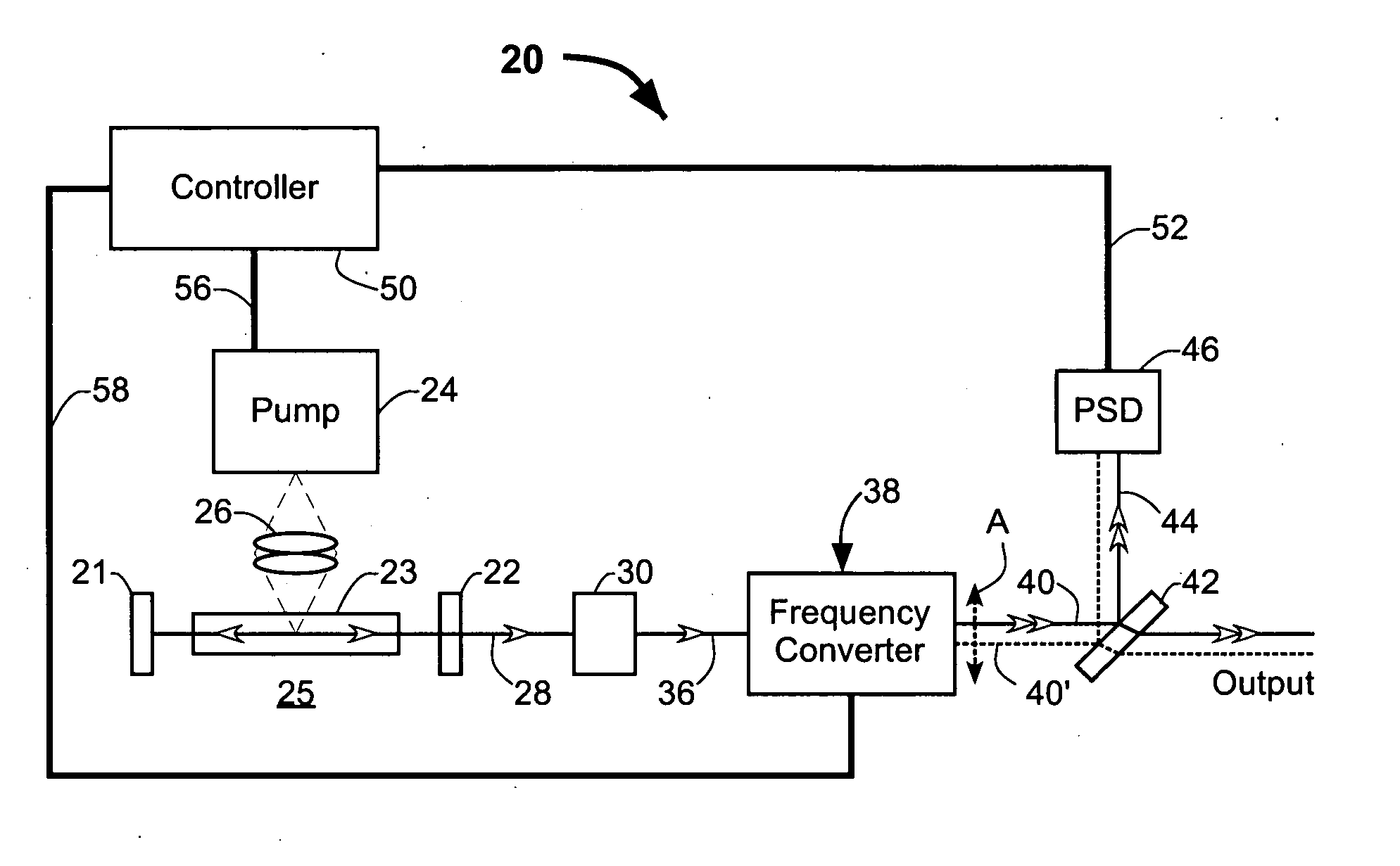
Stabilized frequency-converted laser system
A laser system includes an optically pumped laser resonator that produces a fundamental-wavelength beam. A temperature-tuned frequency converter outside the laser resonator converts a portion of the fundamental-wavelength beam to a frequency-converted beam. The frequency converter includes at least one temperature-tuned optically nonlinear crystal. The power and position of the frequency-converted beam are dependent on the temperature of the optically nonlinear crystal and the optical pumping power. The power and position of the frequency-converted beam are monitored. The temperature of the optically nonlinear crystal is adjusted to maintain the frequency-converted beam at a predetermined position. The optical pump power is adjusted to maintain the power of the frequency-converted beam at a predetermined level.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Method for the hyperpolarisation of nuclear spin in a diamond via a long-range interaction
ActiveUS20160061914A1Narrow line widthEfficient transferQuantum computersNanoinformaticsColour centreOptical pumping
The invention concerns a method for the hyperpolarisation of 13C nuclear spin in a diamond, comprising an optical pumping step, in which colour centre electron spins in the diamond are optically pumped. The method further comprises a transfer step in which the polarisation of a long-lived state of the colour centre electron spins is transferred to 13C nuclear spins in the diamond via a long-range interaction.
Owner:UNIV ULM
Optically pumped, surface-emitting semiconductor laser device and method for the manufacture thereof
InactiveUS6954479B2High positioning accuracyLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsSemiconductor structureOptical pumping
The invention is directed to an optically pumped surface-emitting semiconductor laser device having at least one radiation-generating quantum well structure and at least one pump radiation source for optically pumping the quantum well structure, whereby the pump radiation source comprises an edge-emitting semiconductor structure. The radiation-generating quantum well structure and the edge-emitting semiconductor structure are epitaxially grown on a common substrate. A very efficient and uniform optical pumping of the radiation-generating quantum well structure is advantageously possible with this monolithically produced semiconductor laser device. Methods for manufacturing inventive semiconductor laser devices are also specified.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Hub for a passive optical network hub
ActiveUS7366416B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesOptical pumpingRare earth
A hub for use in a passive optical network (PON) includes a transmission fiber on which an information-bearing optical signal is received, a double-cladded, rare-earth doped fiber located along the transmission fiber for imparting gain to the information-bearing optical signal, and a combiner having an output coupled to the transmission fiber and a plurality of inputs. The output is coupled to the transmission fiber such that optical energy at pump energy wavelengths but not signal wavelengths are communicated therebetween. At least one pump source is optically coupled to one of the inputs of the combiner for providing optical pump energy to the double-cladded, rare-earth doped fiber. An optical splitter is also provided. The optical splitter has an input coupled to the transmission fiber for receiving an amplified, information-bearing optical signal and a plurality of outputs for directing portions of the amplified, information-bearing optical signal to remote nodes in the PON.
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Optical pumping magnetometer and magnetic sensing method
ActiveUS20140320123A1Improve responseHigh sensitivity measurementMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMeasurements using magnetic resonanceOptical pumpingSpins
An optical pumping magnetometer is provided that is capable of improving the response of the magnetometer with respect to a magnetic field that varies with a period shorter than the transverse relaxation time of electron spin of an alkali metal atom.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com