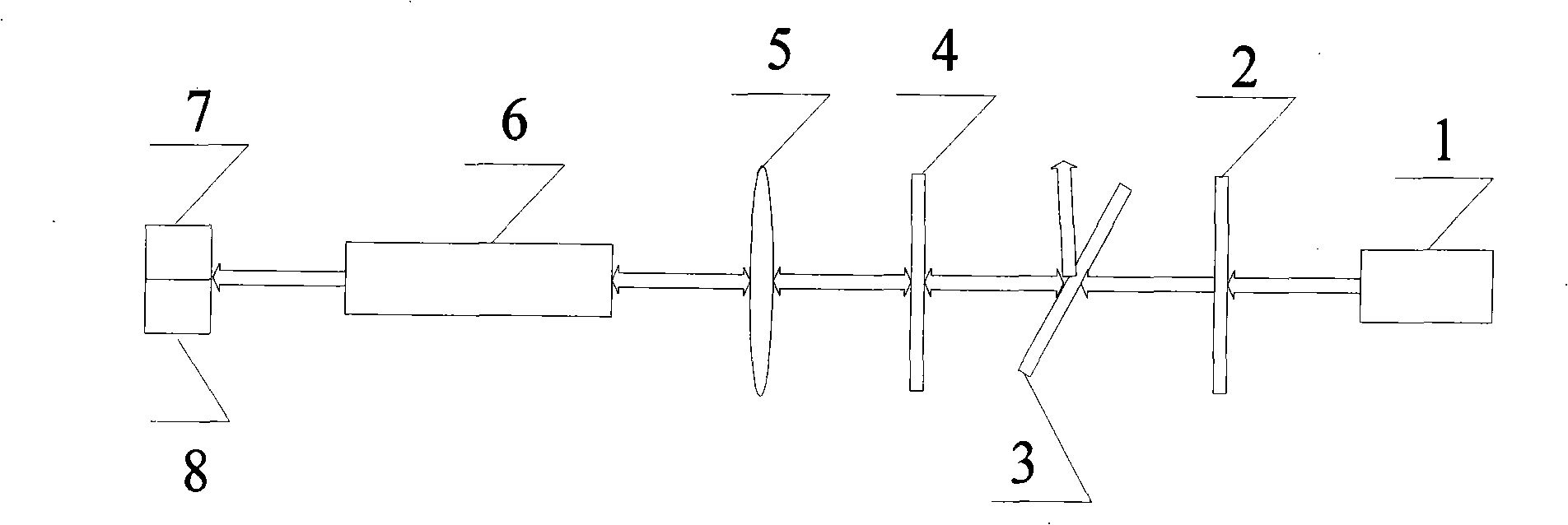Patents
Literature
32 results about "Acoustic Phonons" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
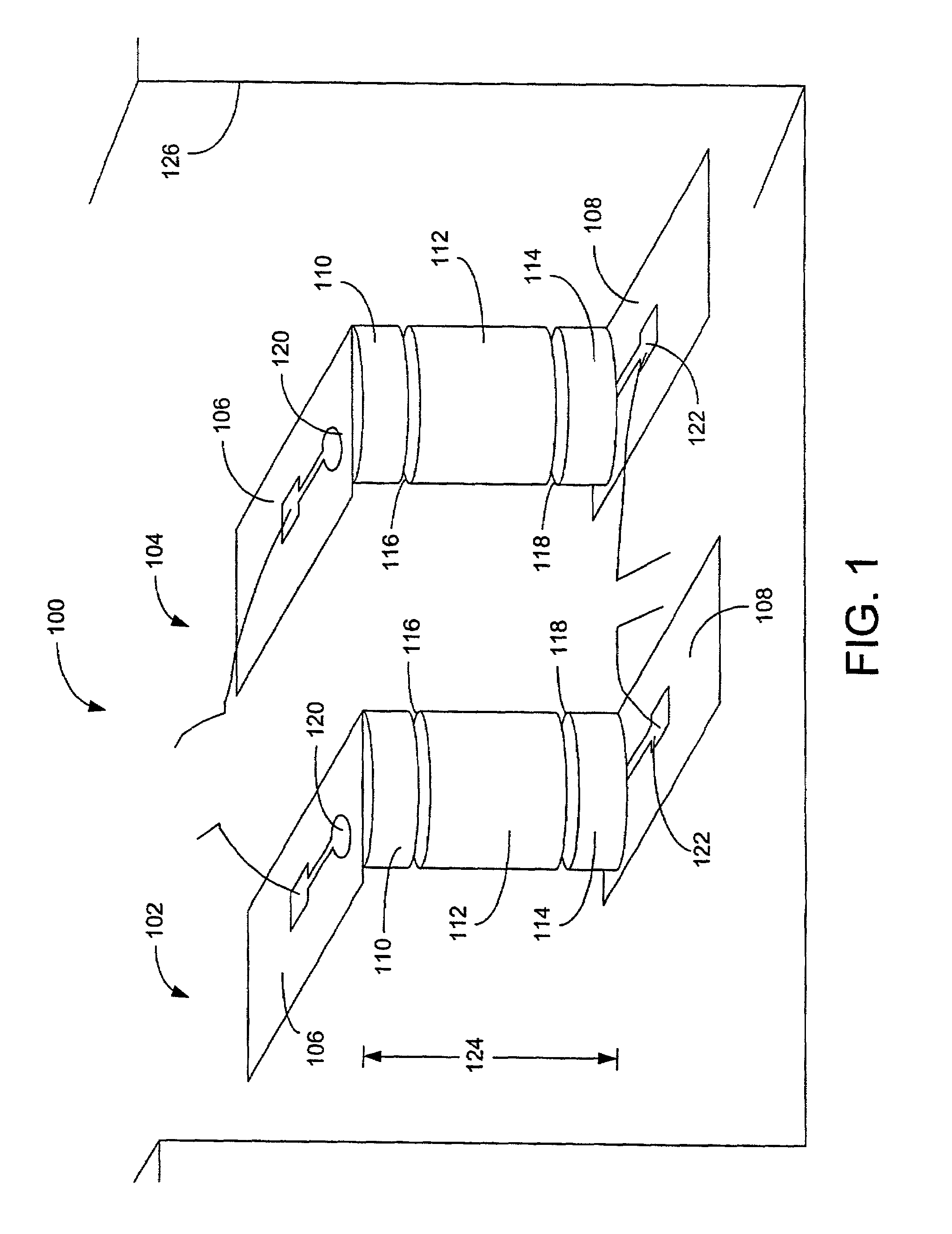
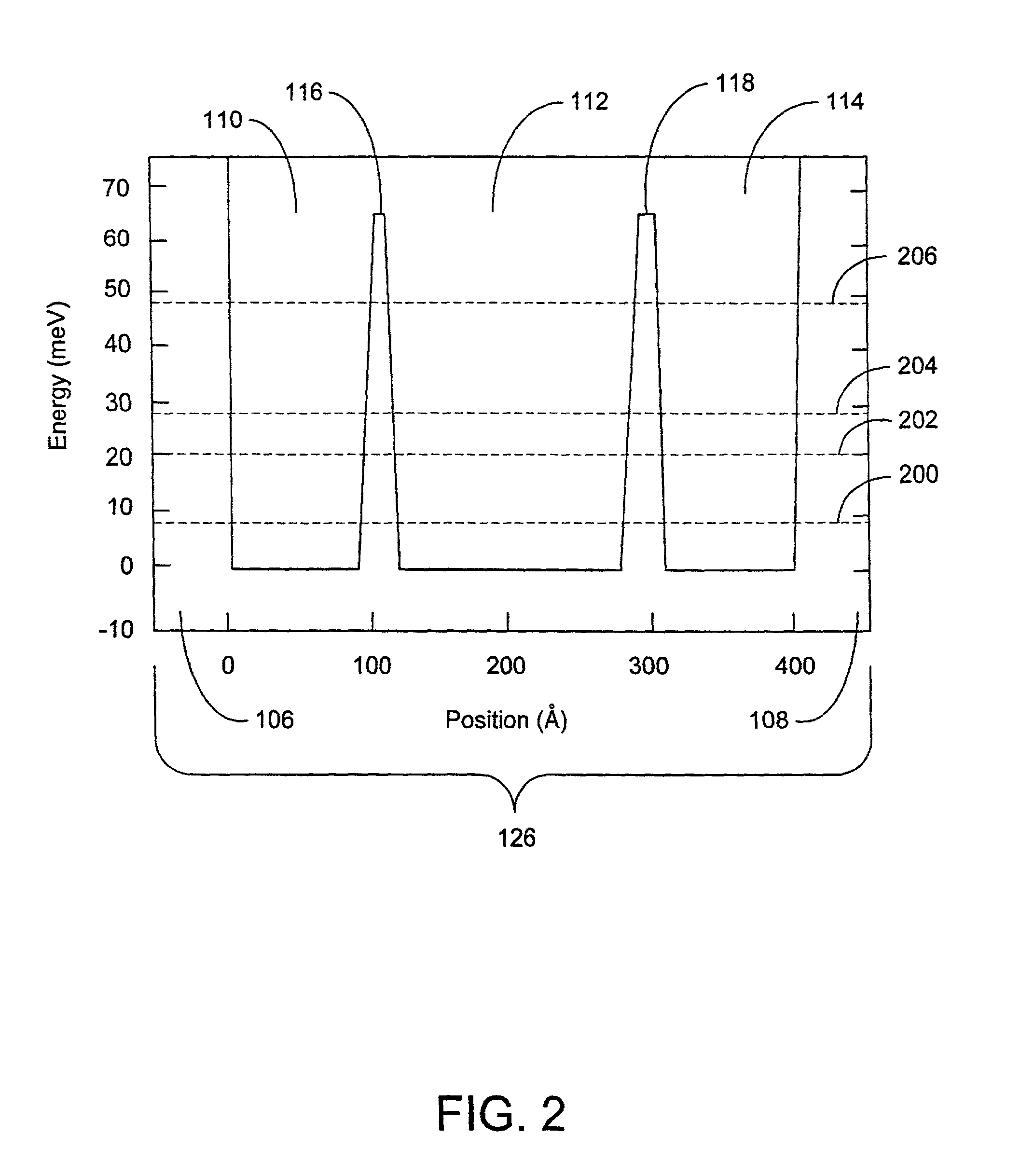
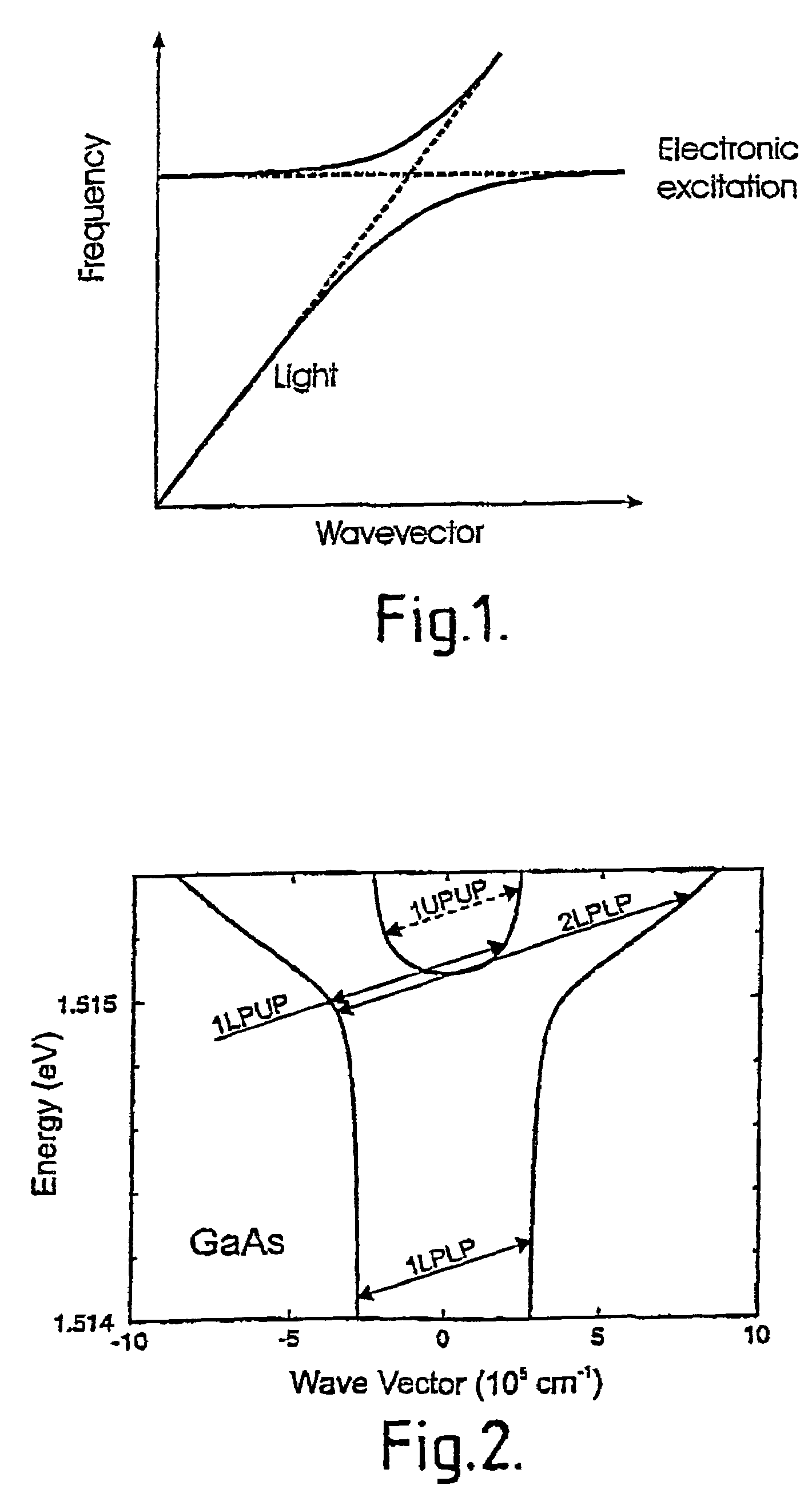
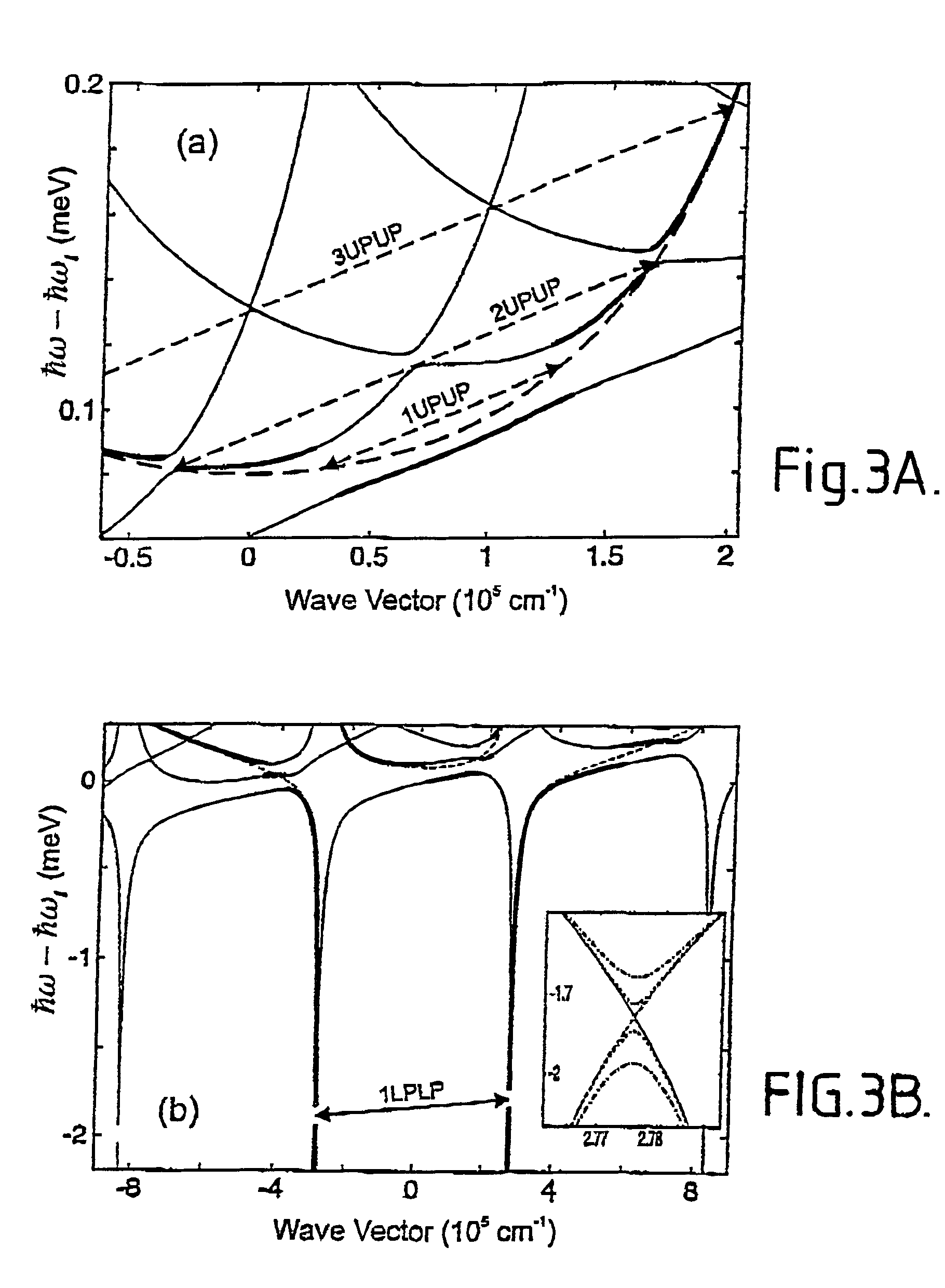
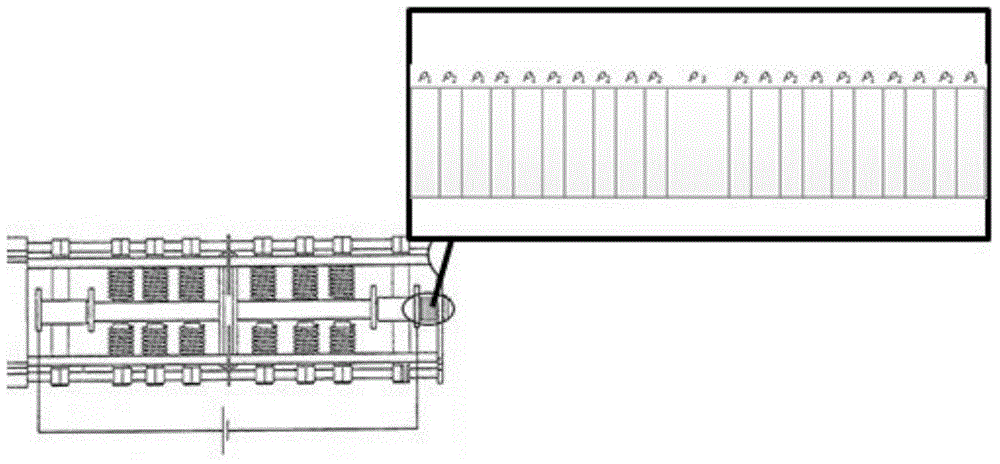
Acoustic phonons exhibit a linear relationship between frequency and phonon wavevector for long wavelengths. The frequencies of acoustic phonons tend to zero with longer wavelength. Longitudinal and transverse acoustic phonons are often abbreviated as LA and TA phonons, respectively.
Optical phase conjugation laser diode
A phase-conjugating resonator that includes a semiconductor laser diode apparatus that comprises a phase-conjugating array of retro-reflecting hexagon apertured hexahedral shaped corner-cube prisms, an electrically and / or optically pumped gain-region, a distributed bragg reflecting mirror-stack, a gaussian mode providing hemispherical shaped laser-emission-output metalized mirror. Wherein, optical phase conjugation is used to neutralize the phase perturbating contribution of spontaneous-emission, acoustic phonons, quantum-noise, gain-saturation, diffraction, and other intracavity aberrations and distortions that typically destabilize any stimulated-emission made to undergo amplifying oscillation within the inventions phase-conjugating resonator. Resulting in stablized high-power laser-emission-output into a single low-order fundamental transverse cavity mode and reversal of intra-cavity chirp that provides for high-speed internal modulation capable of transmitting data at around 20-Gigabits / ps.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
Quantum computation with quantum dots and terahertz cavity quantum electrodynamics
InactiveUS6988058B1Without significant qubit overheadQuantum computersNanoinformaticsCavity quantum electrodynamicsGate voltage
A quantum computer is proposed in which information is stored in the two lowest electronic states of doped quantum dots. Multiple quantum dots are located in a microcavity, and a pair of gates controls the energy levels in each quantum dot. A controlled NOT (CNOT) operations involving any pair of quantum dots can be effected by a sequence of gate voltage pulses which tune the quantum dot energy levels into resonance with frequencies of the cavity or a laser. The duration of a CNOT operation is estimated to be much shorter than the time for an electron to decohere by emitting an acoustic phonon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
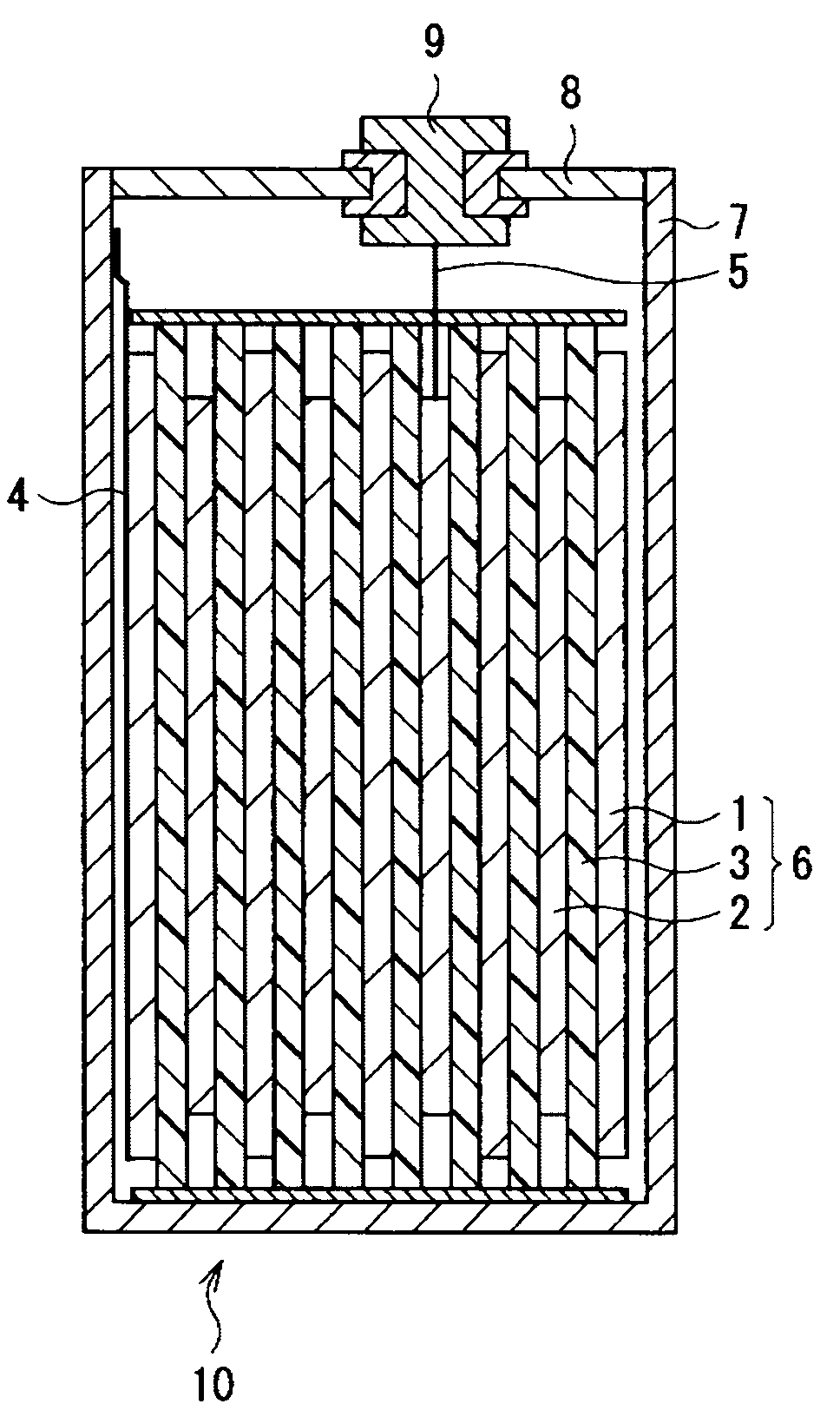
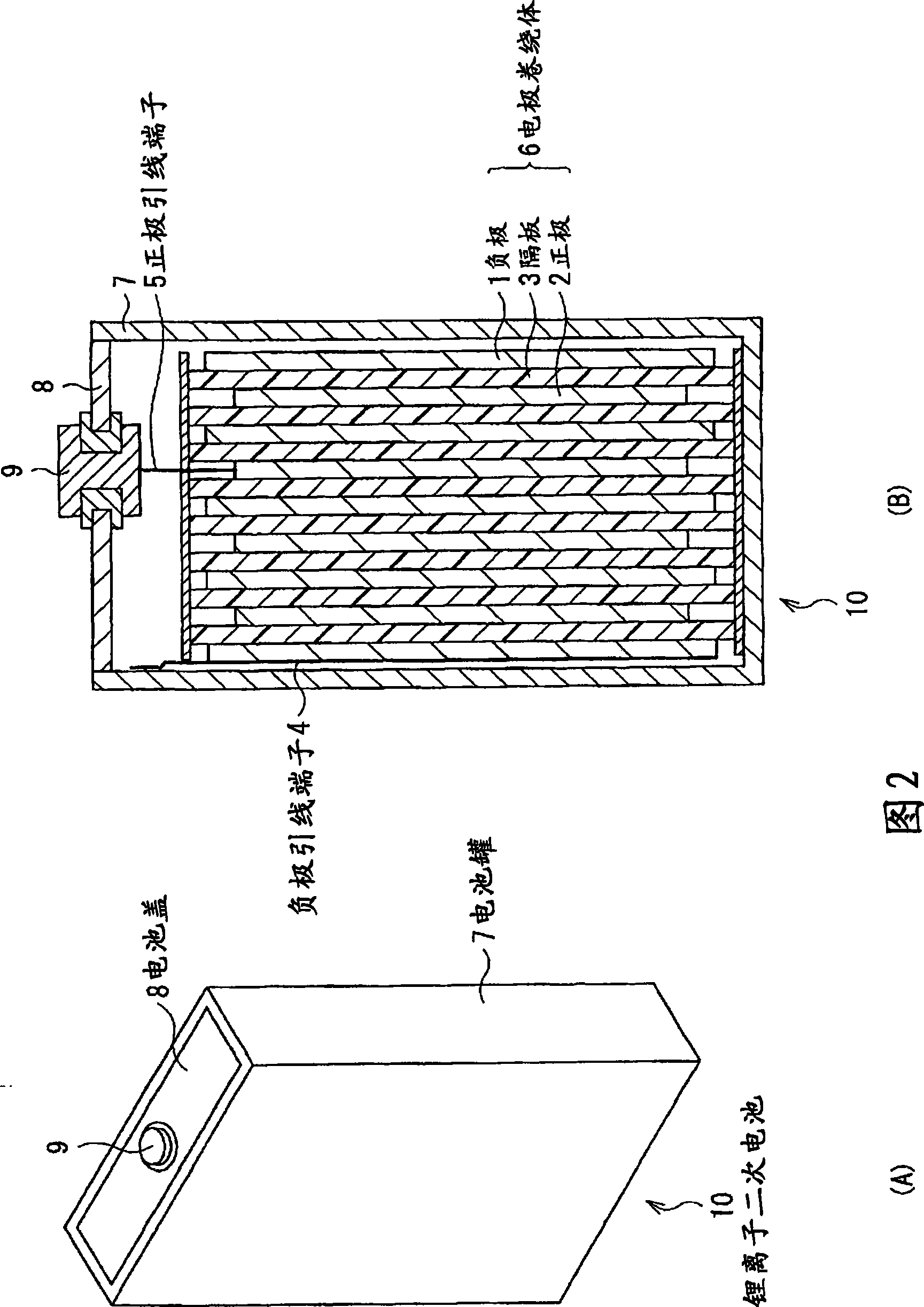
Anode for secondary battery, method of manufacturing it, and secondary battery
InactiveUS20090068567A1Different degreeLow degreeAlkaline accumulatorsElectrode manufacturing processesAcoustic PhononsSilicon
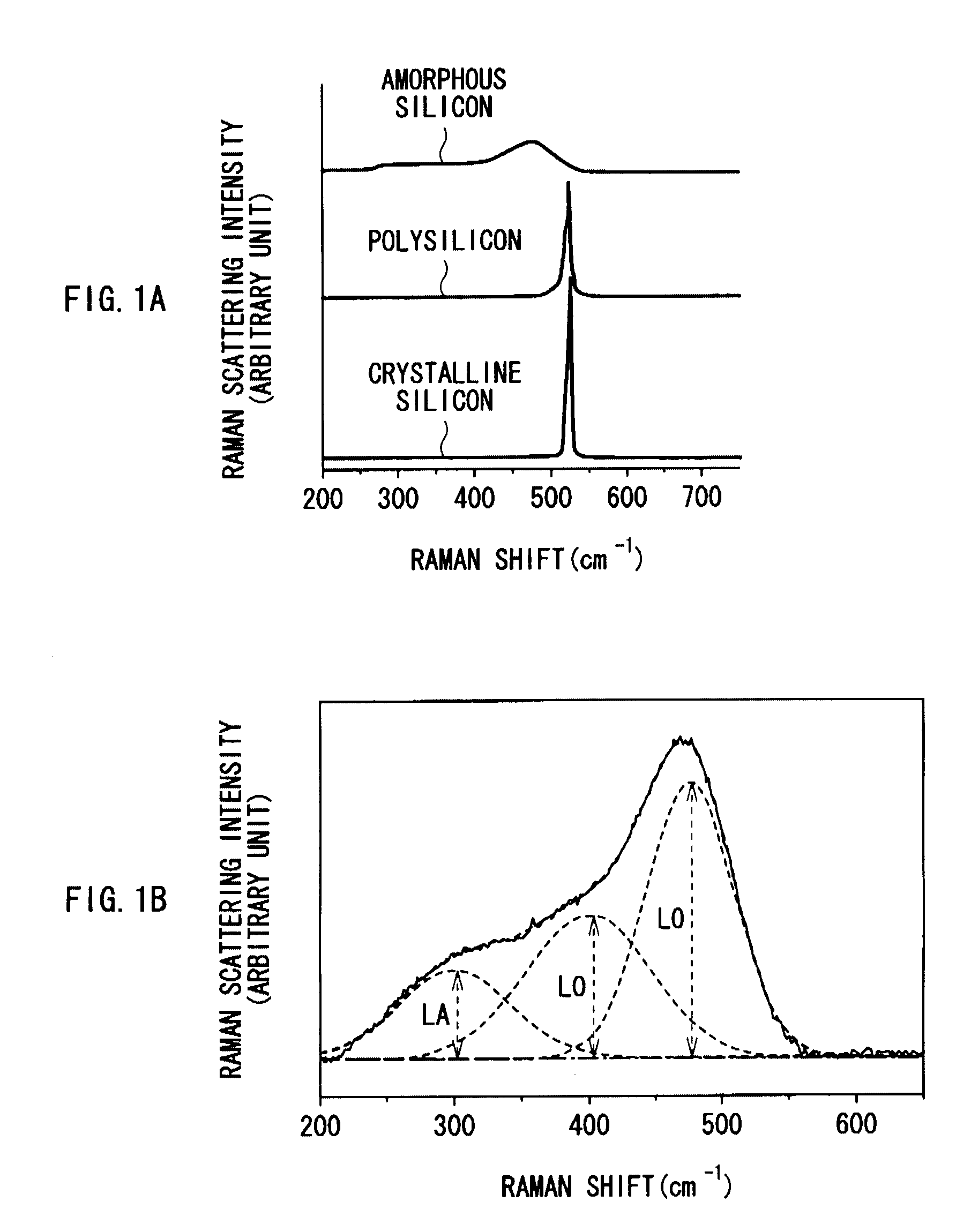
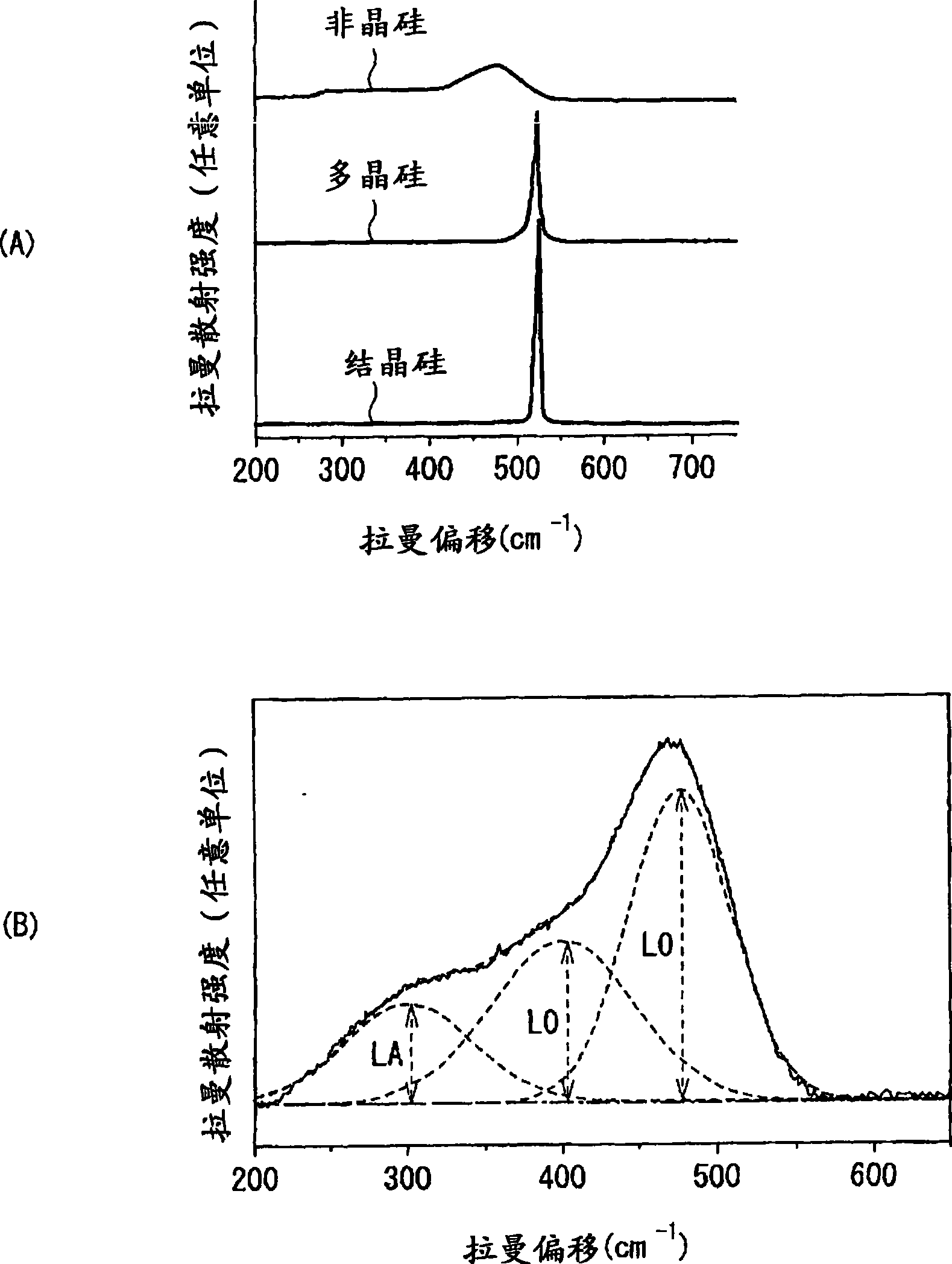
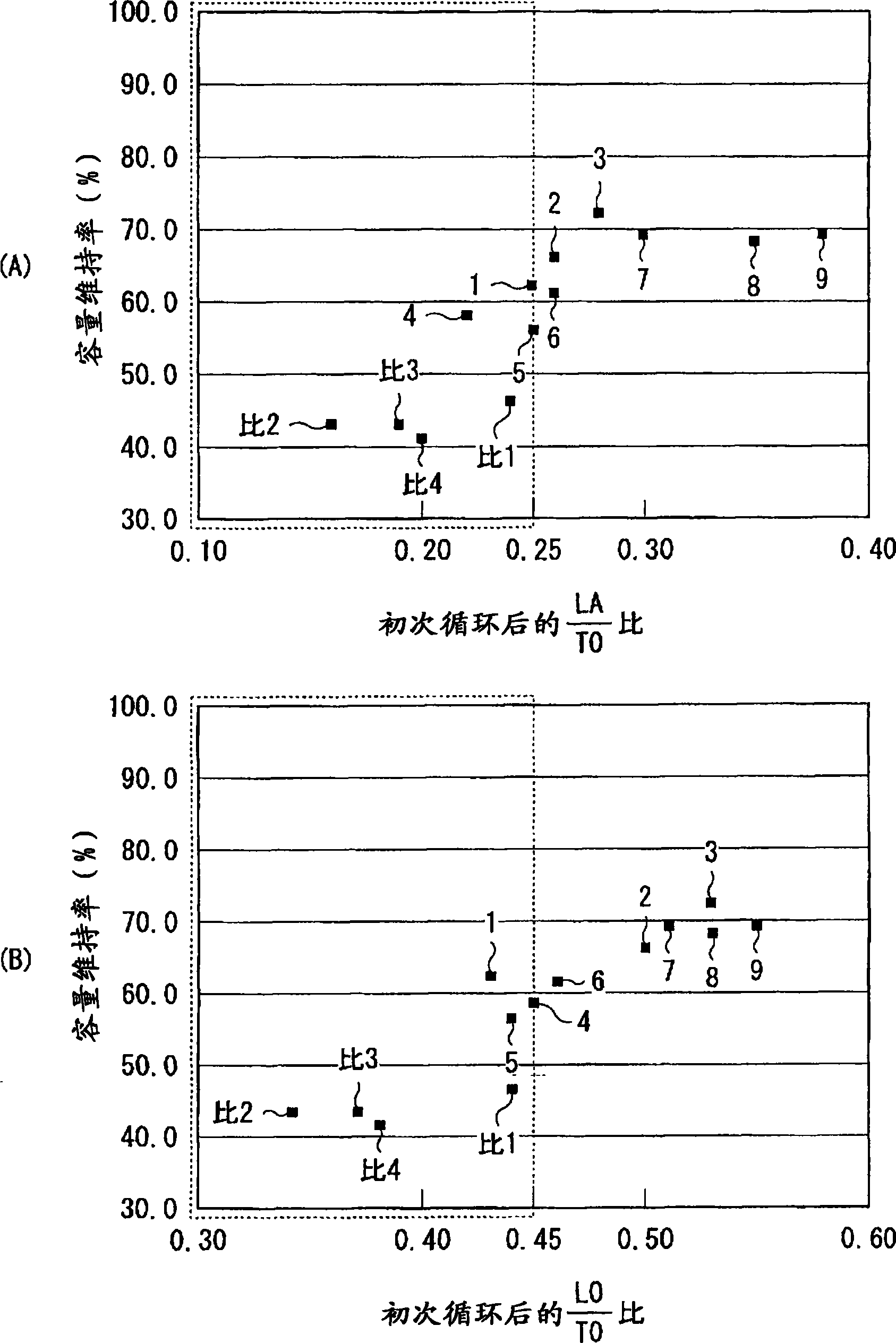
An anode for secondary battery is provided with an anode active material layer containing silicon on an anode current collector. Silicon in the anode active material has an amorphous structure. In a Raman spectrum of silicon having the amorphous structure after an initial charge and discharge, 0.25≦LA / TO and / or 45≦LO / TO is satisfied, where an intensity of a scattering peak occurred in the vicinity of shift position 480 cm−1 based on scattering due to transverse optical phonon is TO, an intensity of a scattering peak occurred in the vicinity of shift position 300 cm−1 based on scattering due to longitudinal acoustic phonon is LA, and an intensity of a scattering peak occurred in the vicinity of shift position 400 cm−1 based on scattering due to longitudinal optical phonon is LO.
Owner:SONY CORP
Terahertz lasers and amplifiers based on resonant optical phonon scattering to achieve population inversion
ActiveUS7158545B2Promote generationHigh selectivityOptical wave guidanceLaser using scattering effectsAudio power amplifierOptical frequencies
The present invention provides quantum cascade lasers and amplifier that operate in a frequency range of about 1 Terahertz to about 10 Terahertz. In one aspect, a quantum cascade laser of the invention includes a semiconductor heterostructure that provides a plurality of lasing modules connected in series. Each lasing module includes a plurality of quantum well structure that collectively generate at least an upper lasing state, a lower lasing state, and a relaxation state such that the upper and the lower lasing states are separated by an energy corresponding to an optical frequency in a range of about 1 to about 10 Terahertz. The lower lasing state is selectively depopulated via resonant LO-phonon scattering of electrons into the relaxation state.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for enhancing plasmon polariton and phonon polariton resonance
ActiveUS20070273959A1Laser detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPicosecond laser pulsePhoton emission
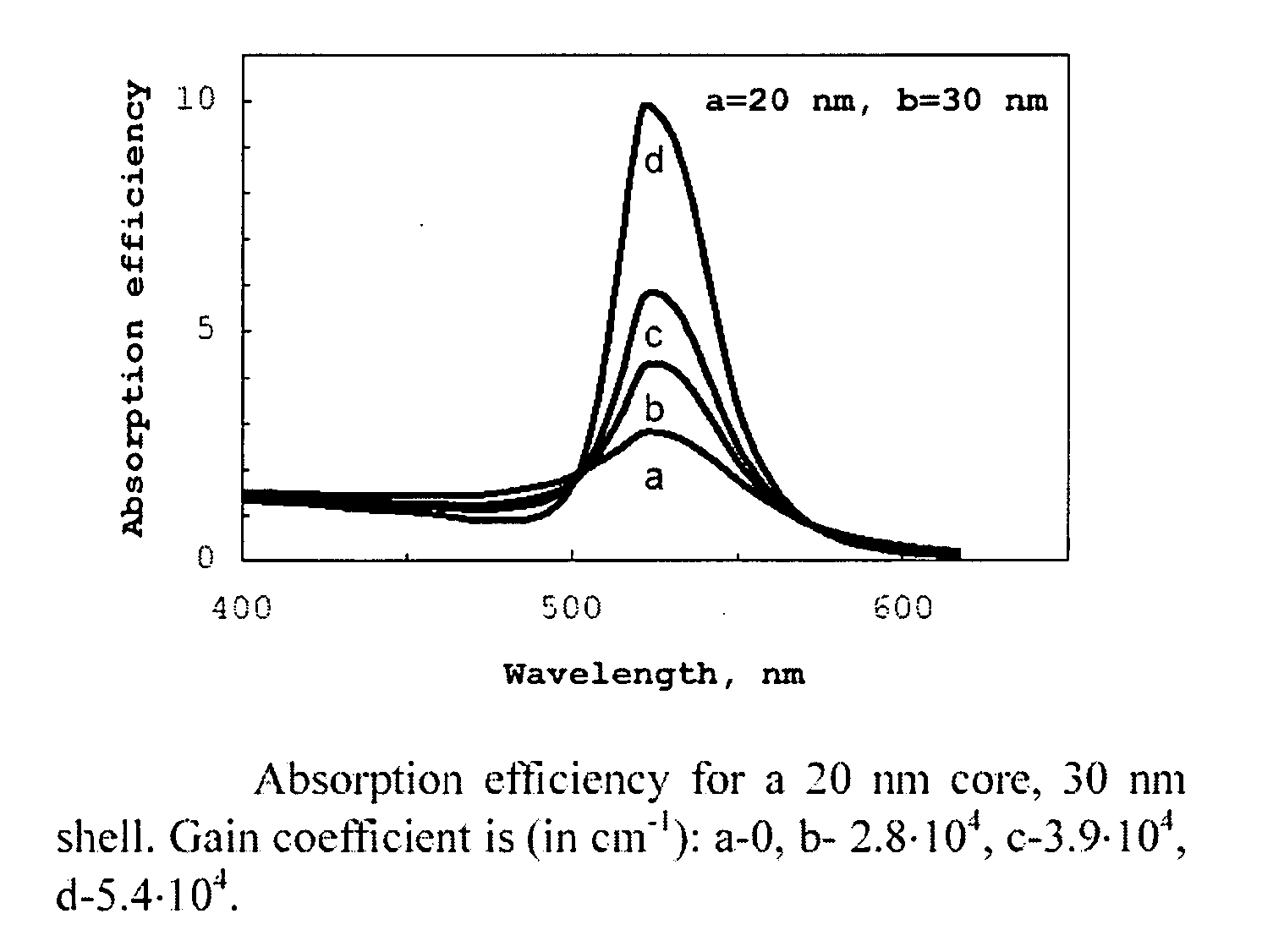
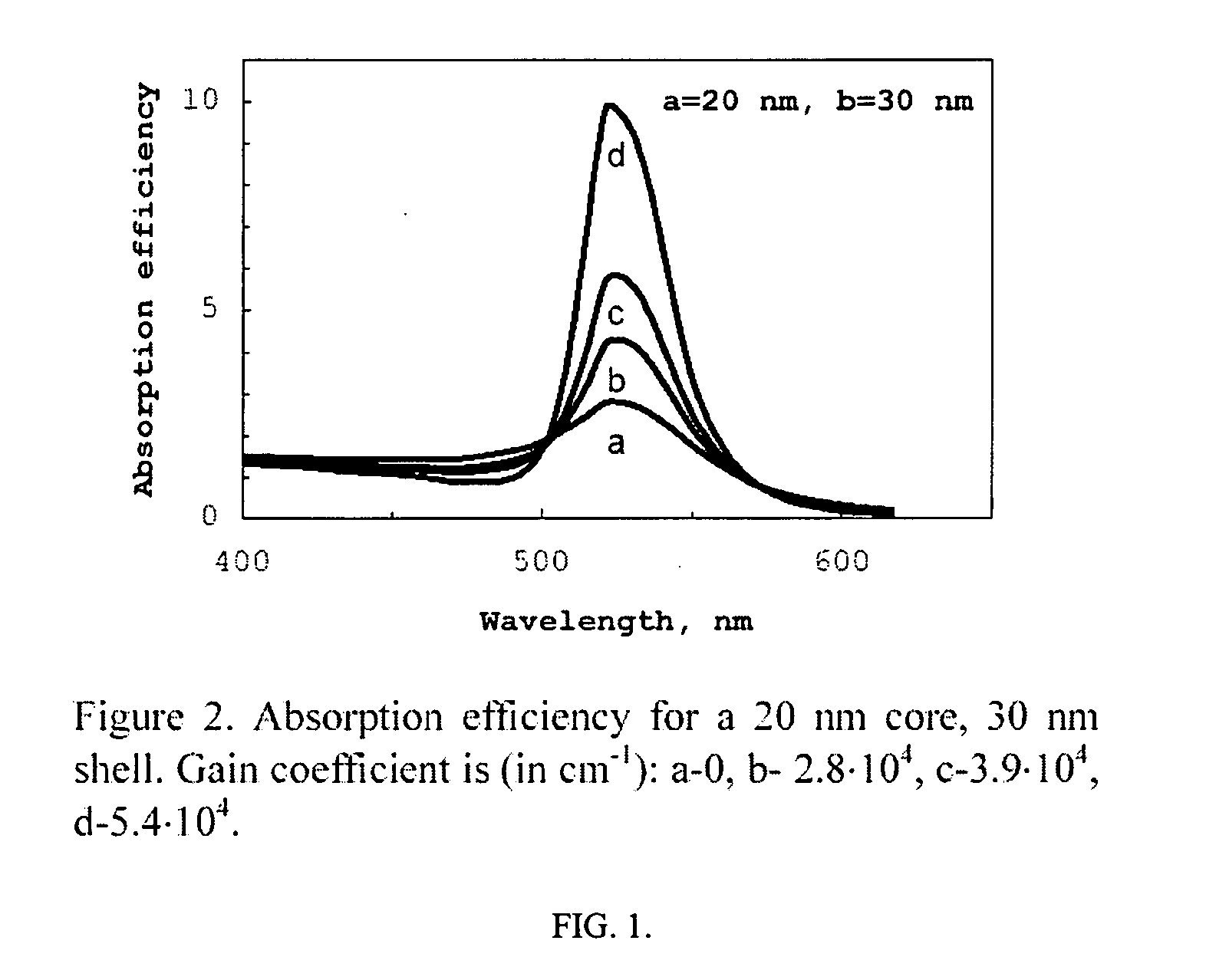
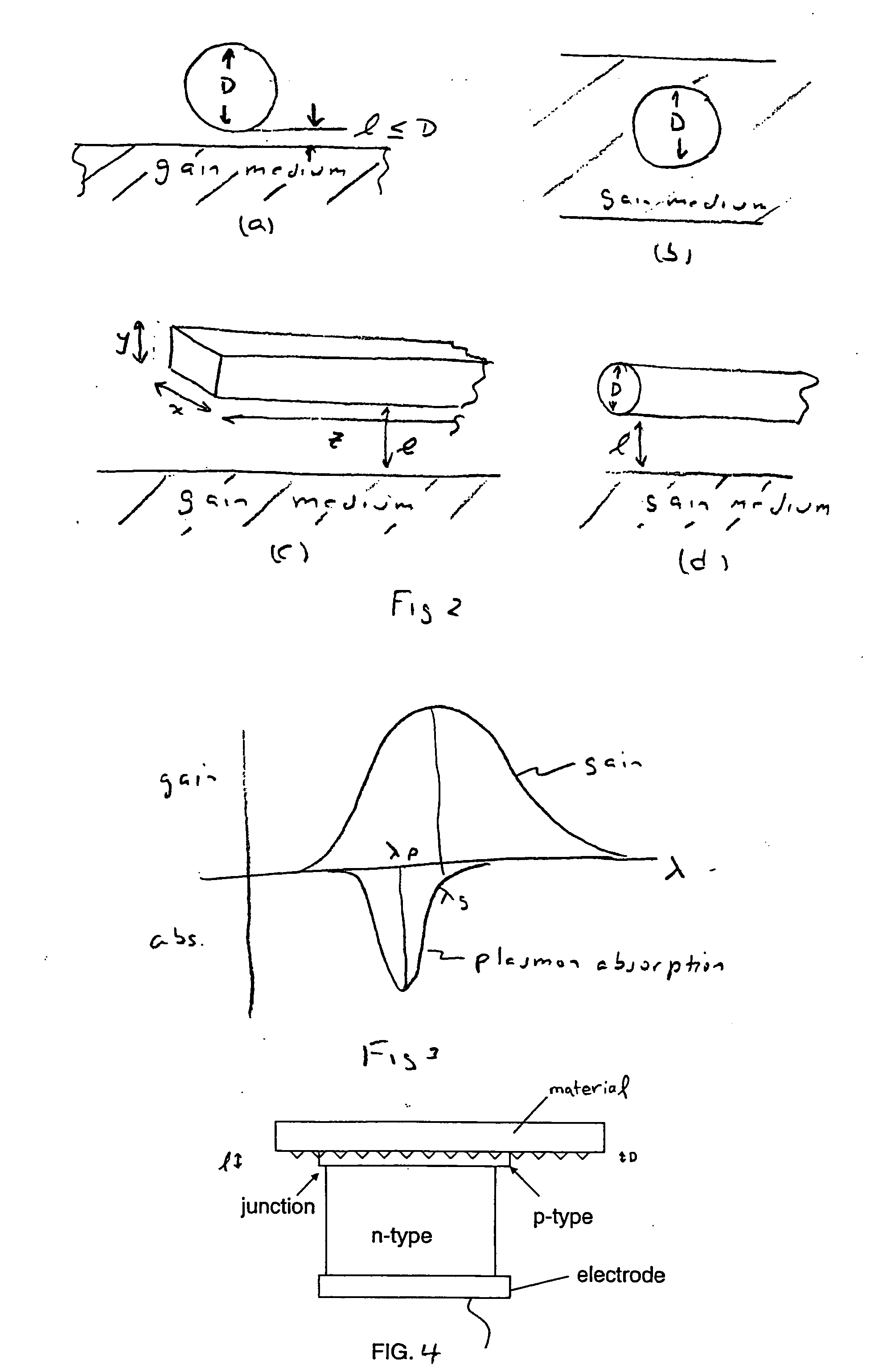
A metallic nano-particle surrounded by an amplifying medium results in a boundary condition that creates a singularity in the particle's dynamic polarizability at the localized surface plasmon resonance and at a critical value of the gain is disclosed. The boundary condition may be time dependent due to excitation by a sub-picosecond laser pulse and couples to the electromagnetic vacuum resulting in photon emission in an analogue of the Unruh Effect. The vacuum emission from 2-D nanostructures embedded in high gain laser dyes predicts energies nearly two orders of magnitude larger than the spontaneous emission background. The vacuum radiation is may have a unique dependence on the excitation.
Owner:SOLARIS NANOSCI
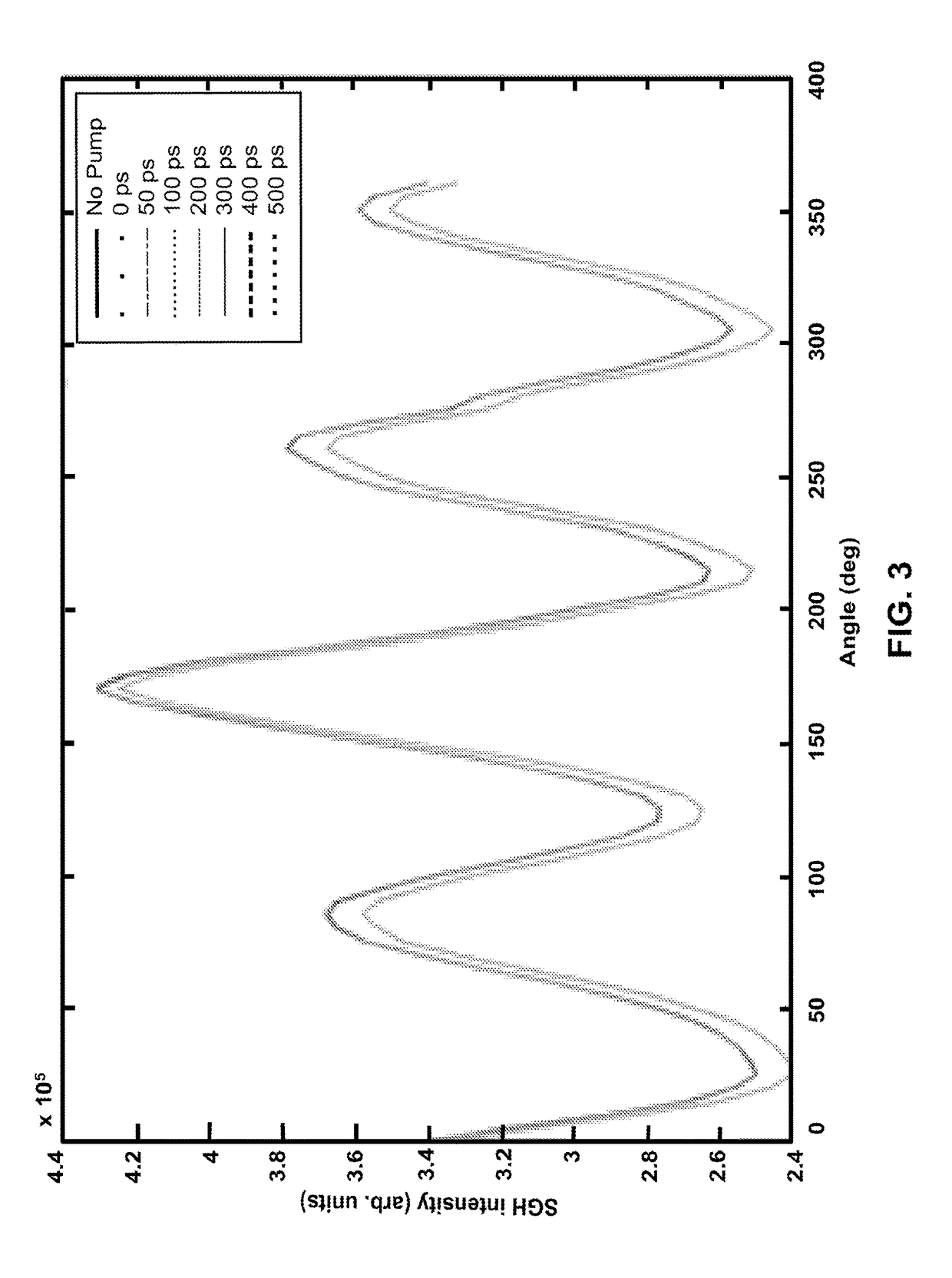
Apparatus and methods for probing a material as a function of depth using depth-dependent second harmonic generation
ActiveUS10371668B2Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInvestigating crystalsHarmonicDepth dependent
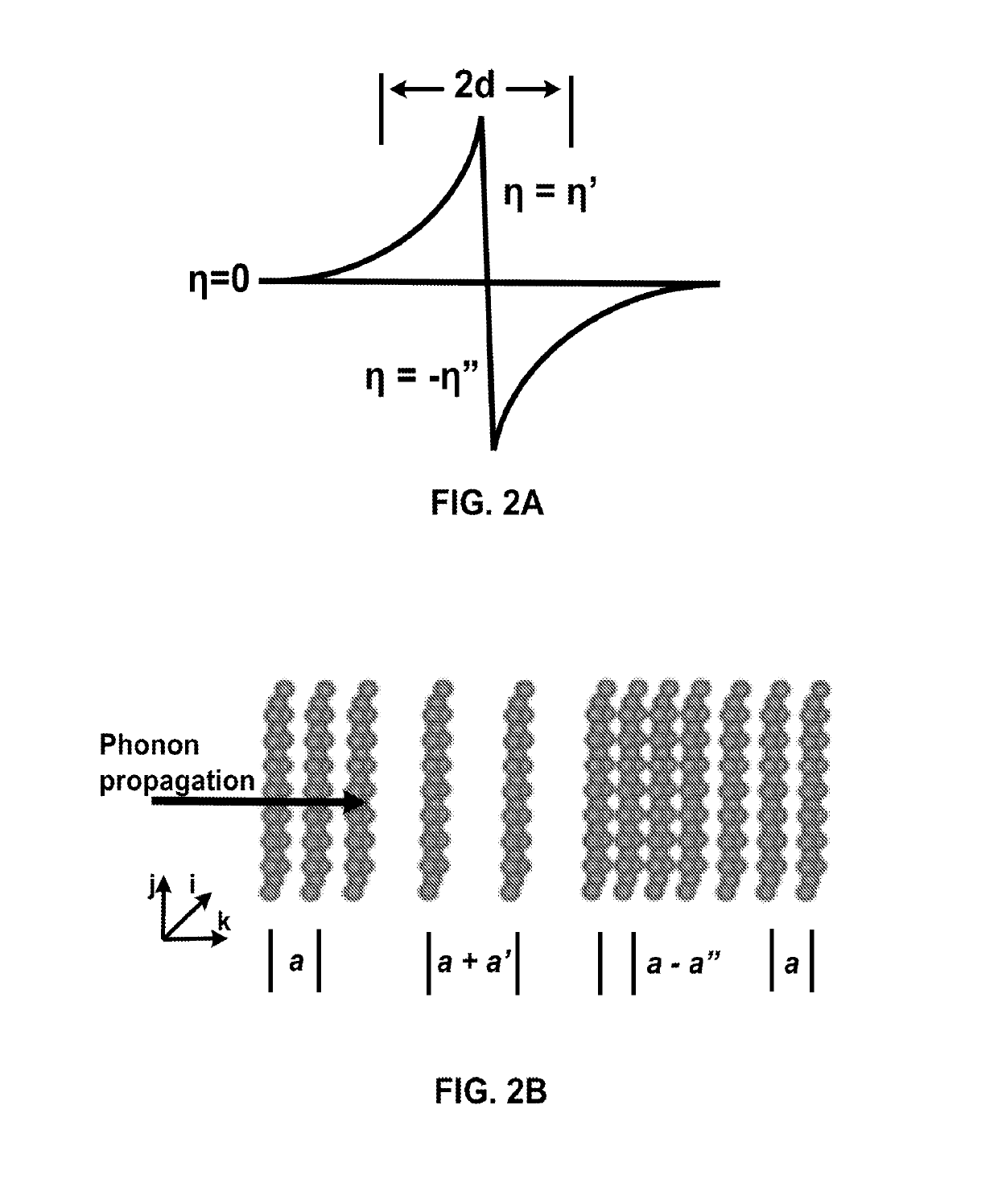
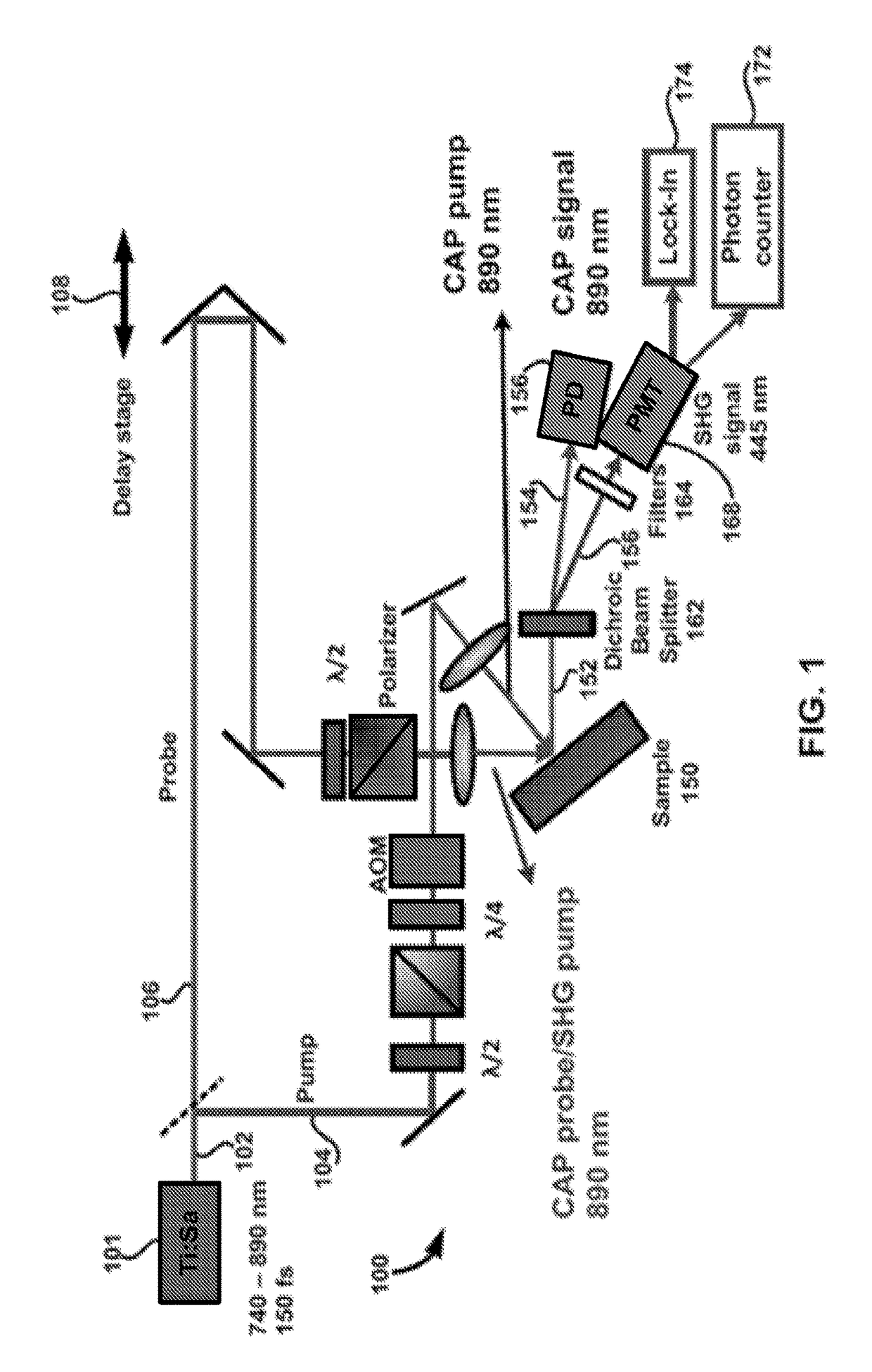
A method for non-invasively probing at least one physics property of a solid material. In one embodiment, the method has the steps of splitting a photon beam into a first photon beam and a second photon beam, exposing the solid material to the first photon beam to generate a coherent acoustic phonon wave in the solid material at time t, and exposing the solid material to the second photon beam at a time t+Δt, where t+Δt≥t, to generate corresponding second harmonic generation signals, where from the corresponding second harmonic generation signals, the at least one physics property of the solid material is determinable.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Apparatus and methods for probing a material as a function of depth using depth-dependent second harmonic generation
ActiveUS20170205377A1Analysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInvestigating crystalsHarmonicDepth dependent
A method for non-invasively probing at least one physics property of a solid material. In one embodiment, the method has the steps of splitting a photon beam into a first photon beam and a second photon beam, exposing the solid material to the first photon beam to generate a coherent acoustic phonon wave in the solid material at time t, and exposing the solid material to the second photon beam at a time t+Δt, where t+Δt≧t, to generate corresponding second harmonic generation signals, where from the corresponding second harmonic generation signals, the at least one physics property of the solid material is determinable.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
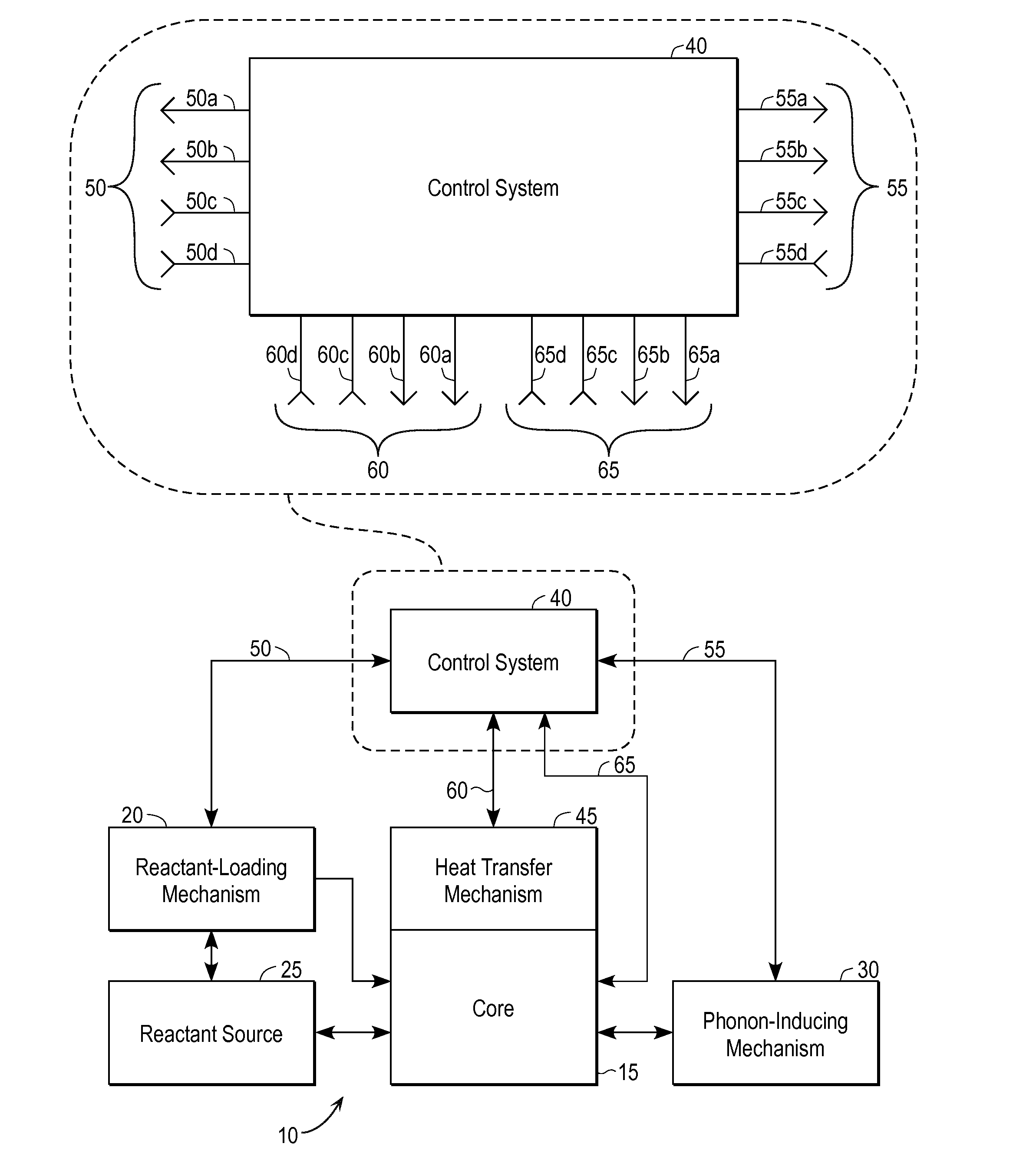
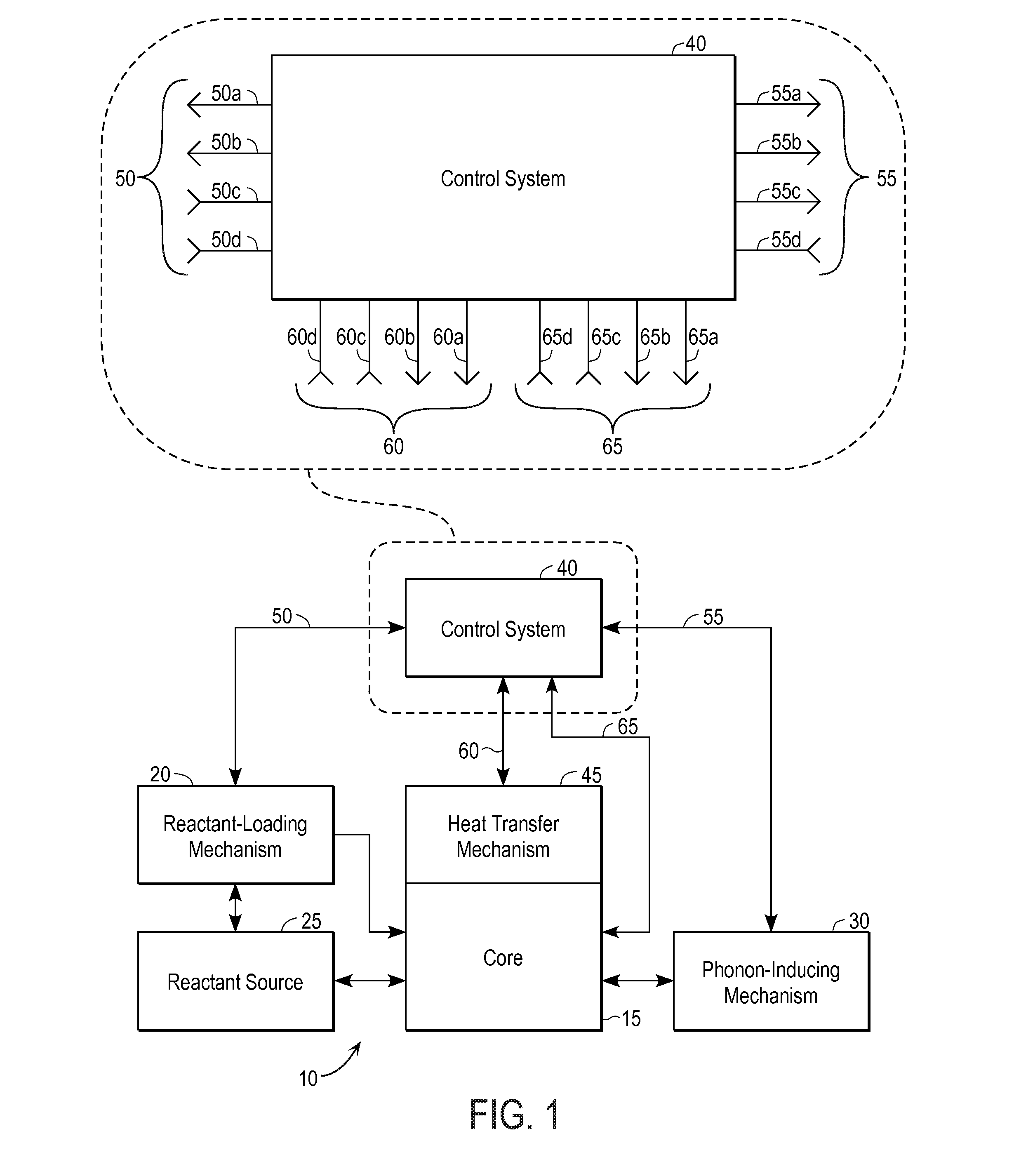
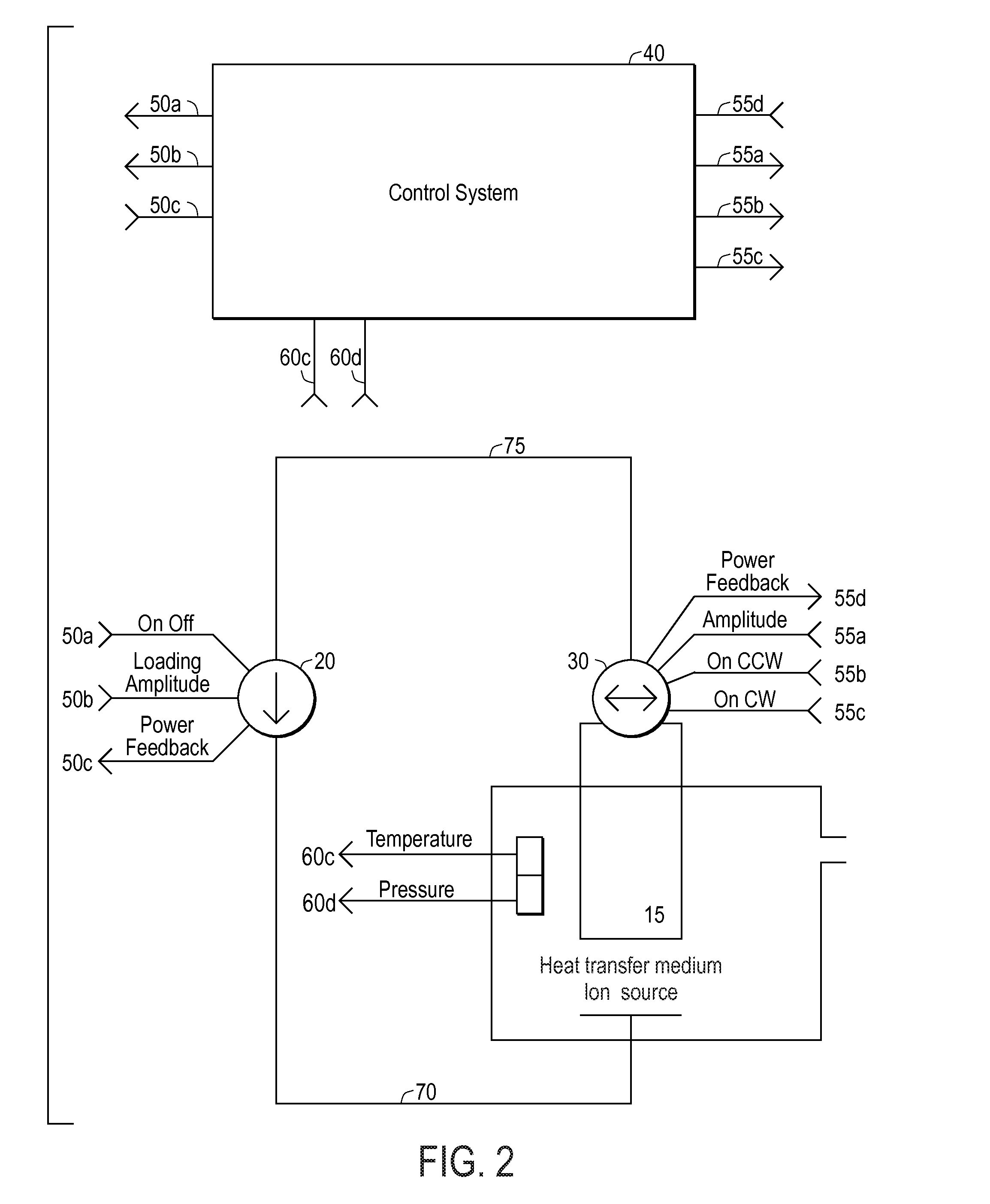
Energy generation apparatus and method
InactiveUS20110122984A1Avoid destructionViable source of energyNuclear energy generationLow temperature fusion reactorEngineeringAcoustic Phonons
A practical technique for inducing and controlling the fusion of nuclei within a solid lattice. A reactor includes a loading source to provide the light nuclei which are to be fused, a lattice which can absorb the light nuclei, a source of phonon energy, and a control mechanism to start and stop stimulation of phonon energy and / or the loading of reactants. The lattice transmits phonon energy sufficient to affect electron-nucleus collapse. By controlling the stimulation of phonon energy and controlling the loading of light nuclei into the lattice, energy released by the fusion reactions is allowed to dissipate before it builds to the point that it causes destruction of the reaction lattice.
Owner:BRILLOUIN ENERGY CORP
Nanoparticle doping for lasers and amplifiers operating at eye-safer wavelengths, and/or exhibiting reduced stimulated brillouin scattering
ActiveUS20180109063A1Improve solubilityReduced Stimulated Brillouin ScatteringMaterial nanotechnologyNanoopticsFiberSolubility
Methods for synthesizing fibers having nanoparticles therein are provided, as well as preforms and fibers incorporating nanoparticles. The nanoparticles may include one or more rare earth ions selected based on fluorescence at eye-safer wavelengths, surrounded by a low-phonon energy host. Nanoparticles that are not doped with rare earth ions may also be included as a co-dopant to help increase solubility of nanoparticles doped with rare earth ions in the silica matrix. The nanoparticles may be incorporated into a preform, which is then drawn to form fiber. The fibers may beneficially be incorporated into lasers and amplifiers that operate at eye safer wavelengths. Lasers and amplifiers incorporating the fibers may also beneficially exhibit reduced Stimulated Brillouin Scattering.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Anode for secondary battery, its manufacturing method and secondary battery
ActiveCN101388450AGood charge and discharge cycle performanceReliable manufacturingElectrode manufacturing processesElectrode carriers/collectorsLithiumLongitudinal wave
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Sound energy collector by adopting phonon crystal and electromechanical Helmholtz resonator
InactiveCN105281599AEasy to collectEfficient collectionPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMachines/enginesResonant cavityElectricity
A sound energy collector by adopting a phonon crystal and an electromechanical Helmholtz resonator, which comprises an electromechanical Helmholtz resonator, a phonon crystal resonant cavity (1), a support column (4) and a base (5), wherein the electromechanical Helmholtz resonator comprises a composite piezoelectric transducer (3) and a Helmholtz resonant cavity (2); the electromechanical Helmholtz resonator is located in the middle position of the phonon crystal resonant cavity and the electromechanical Helmholtz resonator is fixed on the base through the support column; and a phonon crystal resonant cavity body is fixed on the base through bonding. After incident sound waves sequentially go through the gather amplification effects of the phonon crystal resonant cavity and the Helmholtz resonant cavity, the composite piezoelectric transducer is driven to vibrate, so the composite piezoelectric transducer is deformed to transmit electric signals for realizing sound-mechanism-electricity conversion; and the sound energy collector can be applied to sound energy collectors with the characteristics of multi-directions and lower energy density under complex environment, thereby providing electricity for various wireless sensors and micro electro mechanical systems.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO +1
Method for obtaining time domain flat-top beam by once stimulated Brillouin scattering light limiting amplitude
InactiveCN101324736ASimple to useApplicable to a wide range of wavelengthsLaser detailsNon-linear opticsNonlinear opticsHigh power lasers
The invention provides a method for obtaining time domain flat top beams by using one-time stimulated brillouin scattering light limiting, which relates to the field of nonlinear optics. The method solves the problems that the prior non-linear limiting mechanism can not be applied to protection of a high-power laser system, the device used in the prior method for obtaining flat top beams is complicated, and large output energy from the stimulated brillouin scattering light limiting is lost. The method provided by the invention is that s polarized pump light is input to the system; the light is transmitted to a lens (5) after passing through a 1 / 2 wave plate (2), a Polaroid (3), and a 1 / 4 wave plate (4); the light is focused on an oscillating pond (6), and shows the stimulated brillouin scattering effect with a brillouin medium in the oscillating pond (6); the transmitted light resulting from the scattering effect is the time domain flat top beam output from the system; and the phonon lifetime of the brillouin medium ranges from 0ns to 0.3ns. The method for obtaining time domain flat top beams by using one-time stimulated brillouin scattering light limiting has the advantages of simple devices used, wide application scope of wavelengths, high efficiency, etc.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Acoustic wave resonator adopting multiple layers of coupled phononic crystals
PendingCN107091686AEfficient detectionEfficient captureSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementImpedence networksVacancy defectAcoustic wave
The invention belongs to the field of acoustic functional devices, and discloses an acoustic wave resonator adopting multiple layers of coupled phononic crystals. The acoustic wave resonator is formed by a plurality of two-dimensional phononic crystals with different scattering body sizes and different crystal lattice coefficients in a nested manner. From the inside out, the first layer of phononic crystals is formed by a 3*3 scattering body array with the center being a single-point vacancy defect, the second layer of phononic crystals is formed by a 2*2 scattering body array, the third layer of phononic crystals is formed by a 3*3 scattering body array with the center being a single-point vacancy defect, and the fourth layer of phononic crystals is formed by a 5*5 scattering body array with the center being a multi-point vacancy defect. The acoustic wave resonator can realize efficient detection and capture for weak acoustic waves; compared with a single phononic crystal with the same volume, the multiple layers of coupled phononic crystals have a stronger acoustic wave localization effect and a higher acoustic pressure amplification factor.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGXI ELECTRIC POWER CO LTD RES INST +1
Method for Generating Terahertz Electromagnetic Waves by Using Coherent Phonons
InactiveUS20080279227A1Generate efficientlyLaser using scattering effectsLaser active region structureHigh densityQuantum well
In a method for generating a terahertz electromagnetic wave by using coherent phonons in a quantum structure, high density of coherent phonons acting as a radiation source of the terahertz electromagnetic wave are obtained by exciting the inter-band transitions in a quantum structure under the condition that the energy difference between two inter-band transitions in the quantum structure is resonated with the energy of the coherent phonons, and the terahertz electromagnetic wave is generated by the oscillatory polarizations of the coherent phonons. High density of coherent phonons may be created through the elementary excitation generated by using instantaneous laser pulses. A quantum well structure is effective as the quantum structure, and a scattering process of coherent phonon may be suppressed by confining coherent LO phonons in a well layer. Under the condition that the difference of energies between the heavy-hole and light-hole exitons in a quantum well structure agrees with the energy of LO phonons and both the exitons are created simultaneously, high density of coherent phonons may be generated. With this method, a terahertz electromagnetic wave can be effectively and strongly emitted from the coherent phonons.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
Yb and Er -codoped gadolinium silicate laser crystal and preparation method therefor
InactiveCN1865538APromote growthImprove energy transferPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsFluorescenceGadolinium
The invention discloses an ytterbium-erbium doping gadolinium silicate crystal and preparing method, which is characterized by the following: the laser single-crystal structure formula is Ybx, Ery:Gd2SiO5, wherein x is 0.01-0.5; y is 0.001-0.15; the crystal adopts flux method growth; the Yb,Er:Gd2SiO5 crystal possesses high-sound acoustic phonon energy (1000cm-1) with large crystal field splitting, 0.86*10-20cm-1 transmitting cross-section of 1.55 mum band and 7ms fluorescent lifetime, which improves Er3+ luminous efficiency.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
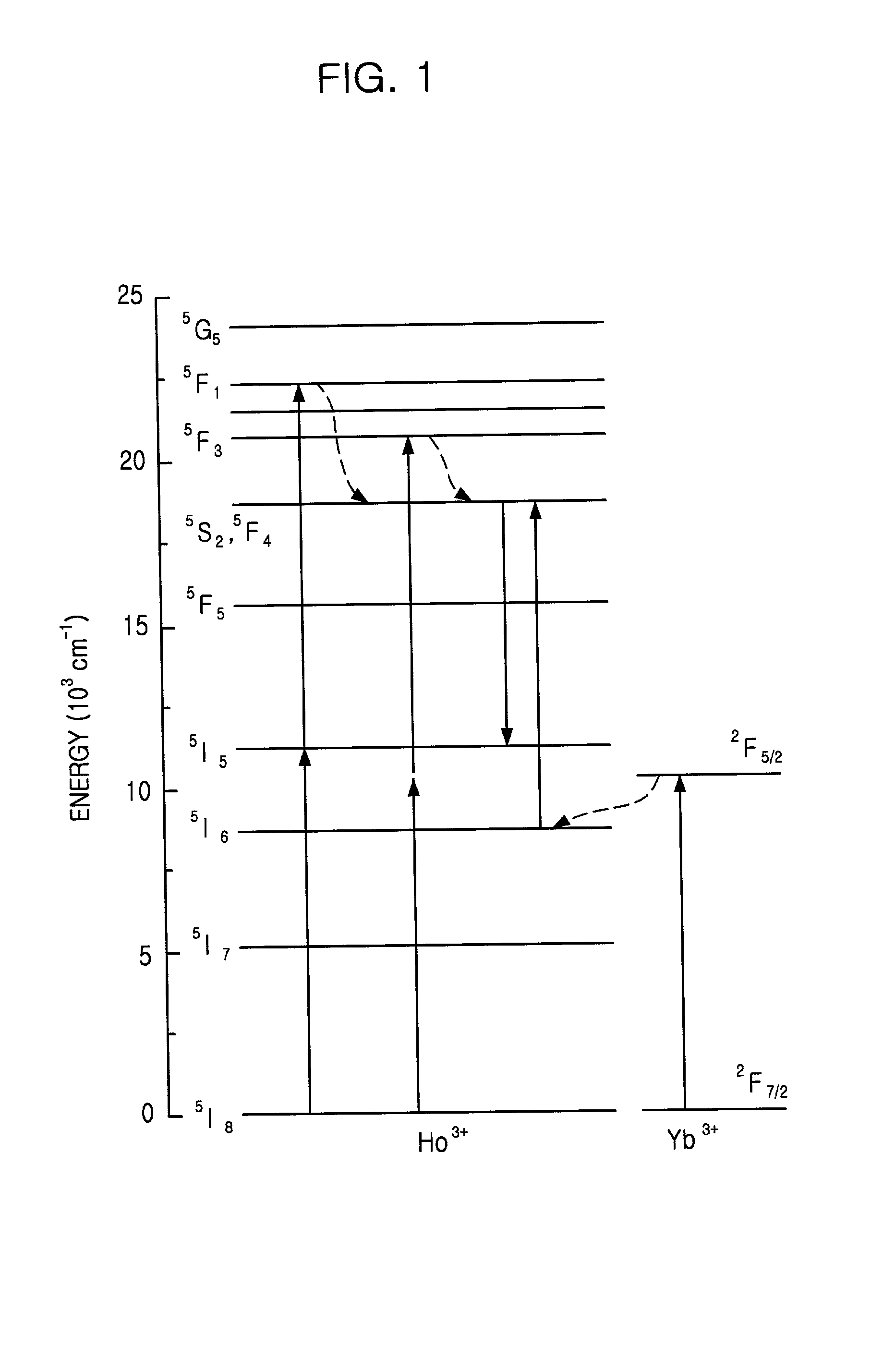
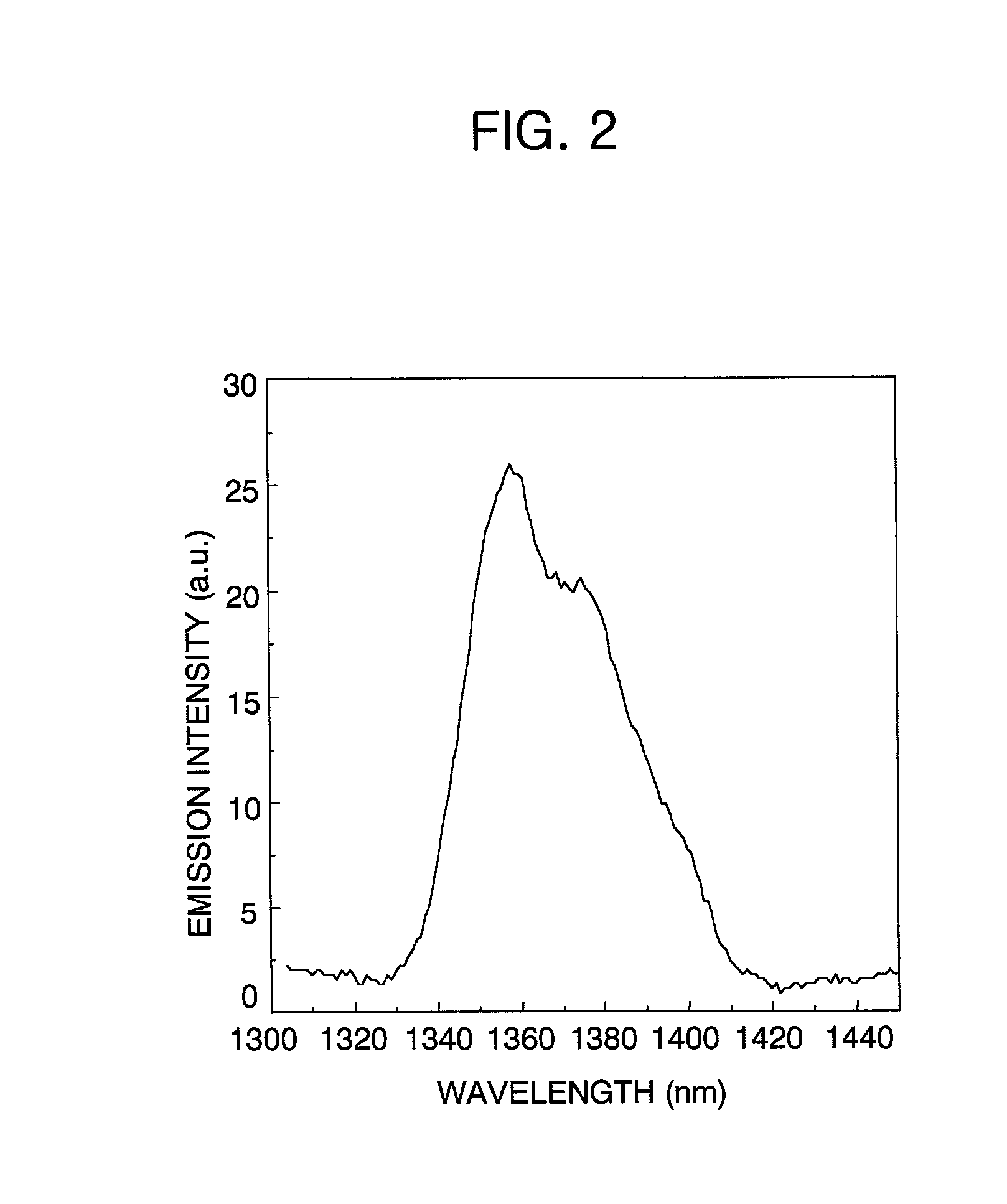
Optical amplifier incorporating therein holmium-doped optical fiber
An optical amplifier of the present invention includes a pump source for generating a pumping light, a wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) coupler for multiplexing an inputted optical signal and the pumping light and an optical fiber including a core and a clad, wherein the core has holmium ions less than 0.5 mole % and the clad has ions selected from the group consisting of transition metal ions, rare earth ions and a combination thereof. In addition, the phonon energy of a host material is less than 600 cm-1 and an absorption band at short-wavelength side is shorter than 530 nm.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL DISCOVERY CO LTD
Method for preparing nano-micrometer lacunaris SiGe thermoelectric material
InactiveCN100364126CSimple processLow costThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentGas phaseSilicon alloy
The invention discloses a method for making a nano-micro meter multi holes germanium-silicon alloy pyroelectric material. The invention involve the preparation of nano-micro meter multi holes germanium-silicon alloy chips that contain silicon of nanometer size, In, InSb or Sb quantum wire or points. The silicon of nanometer and germanium-silicon quantum wires can be prepared by exploiting electrochemical corrosion, physical vapor phase deposition and secondary chemical corrosion. The multi holes germanium-silicon alloy metal chip comprises In, InSb or Sb and the general weight percentage of them is less than 2%; it has quantized structure of real-hollow combination for separating the actions of electrons and acoustic phonon and improving pyroelectricity property.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Broadband air medium ultrasonic transducer with phononic crystal matching and radiation composite structure
ActiveCN108543689AImprove sound radiationHigh resolutionMechanical vibrations separationAuditory radiationSonification
The invention relates to a broadband air medium ultrasonic transducer with a phononic crystal matching and radiation composite structure. According to the structure of the broadband air medium ultrasonic transducer, a perforated matching plate capable of changing a vibration mode and acoustic matching is arranged on the radiation end surface of a shell, the perforated matching plate is provided with a piezoelectric element capable of generating a plane radial vibration mode in a stacking mode, and the piezoelectric element is used as an excitation source to excite the perforated matching plateto generate bending vibration and to radiate ultrasonic waves. The broadband air medium ultrasonic transducer improves acoustic matching of a conventional air medium ultrasonic transducer, can increase the bandwidth, improves the acoustic radiation of the transducer, and improves the resolution and range of action of the transducer.
Owner:SHAANXI NORMAL UNIV
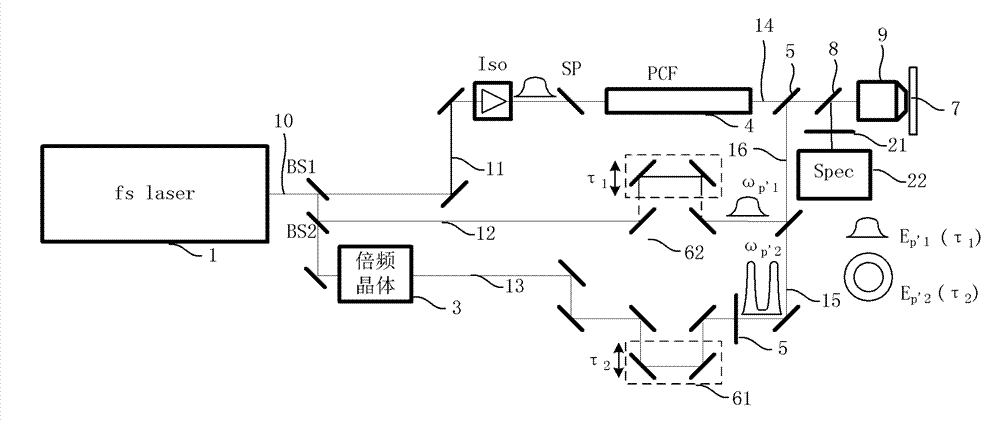
Acoustic resonance spectrometry system and method
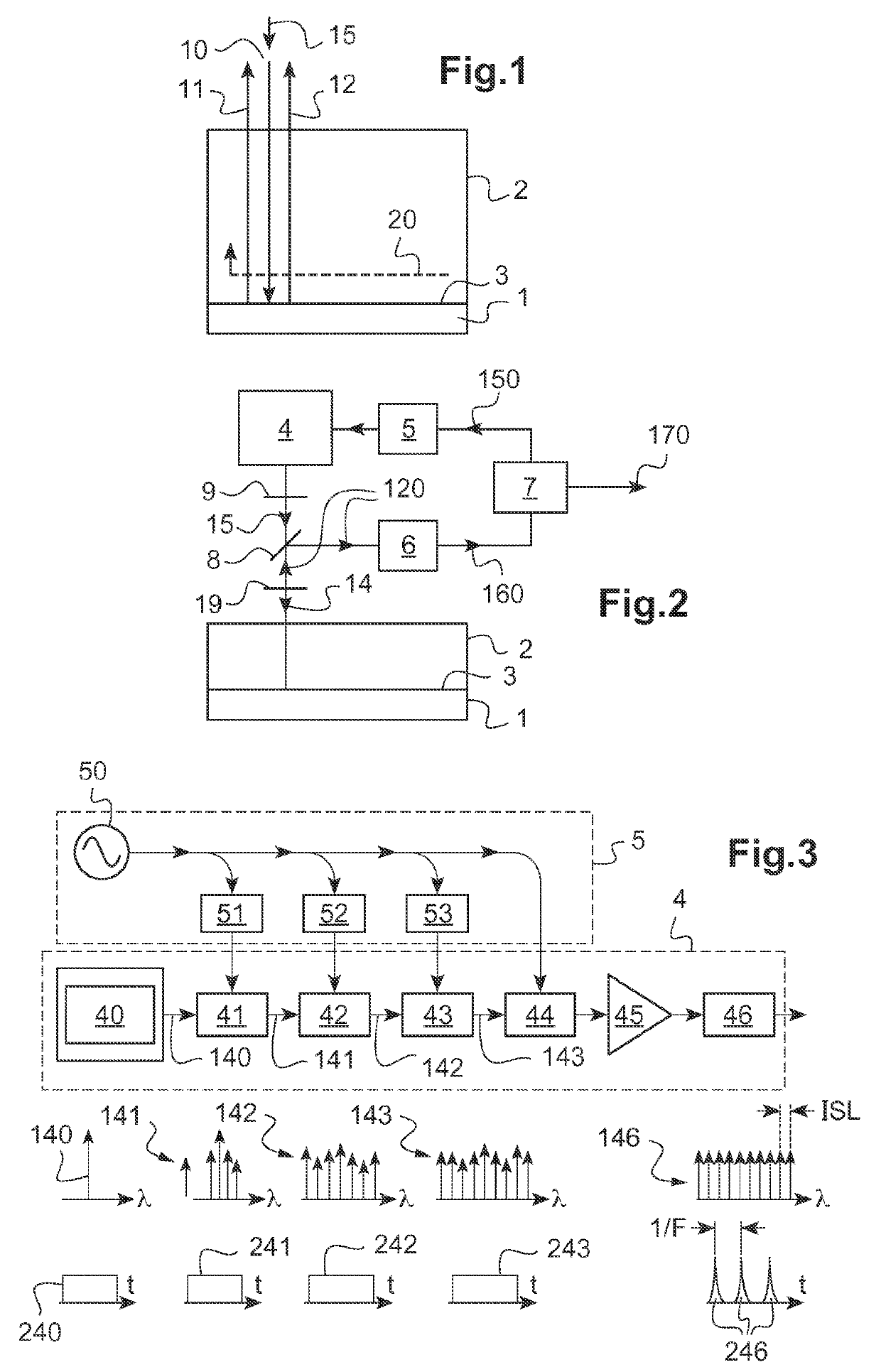
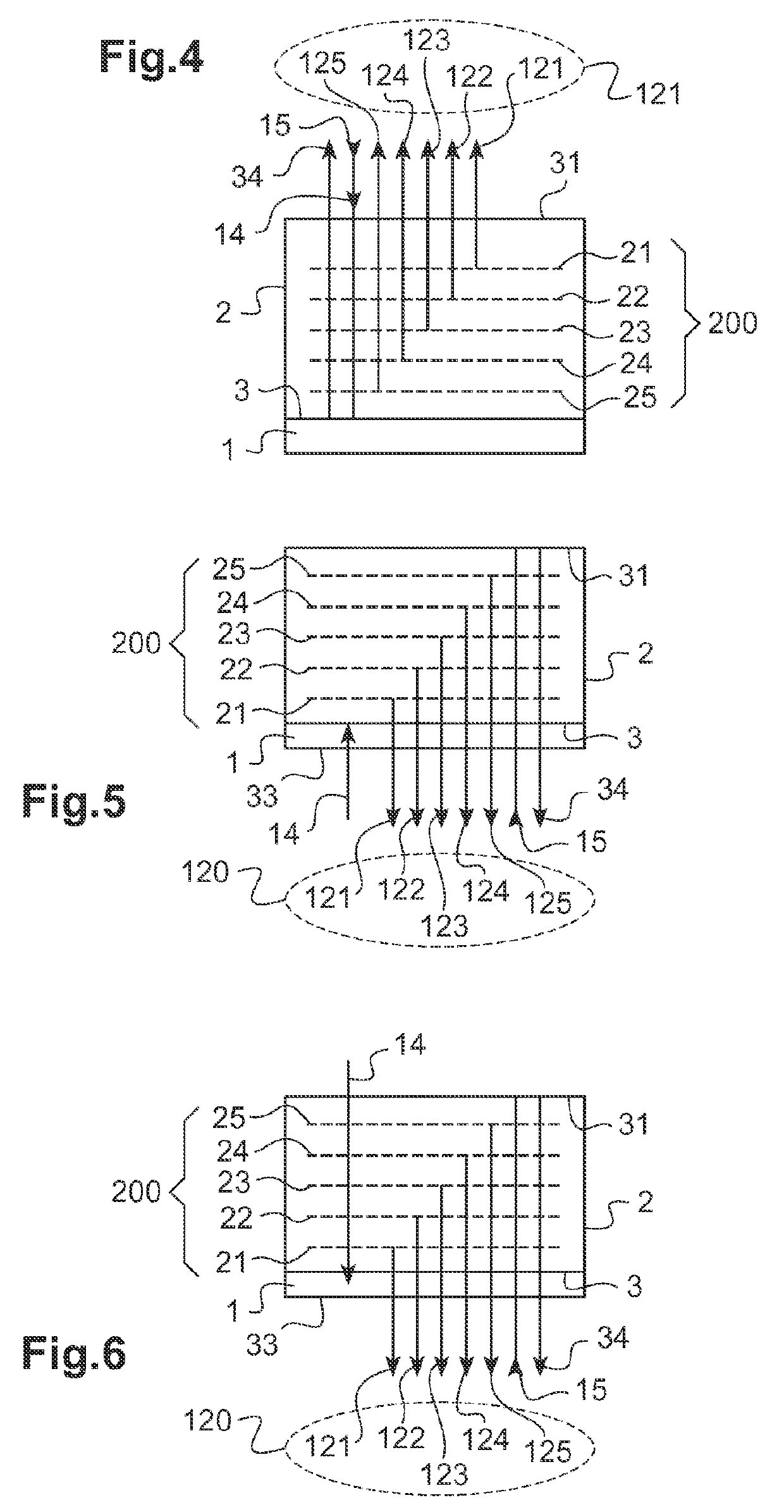
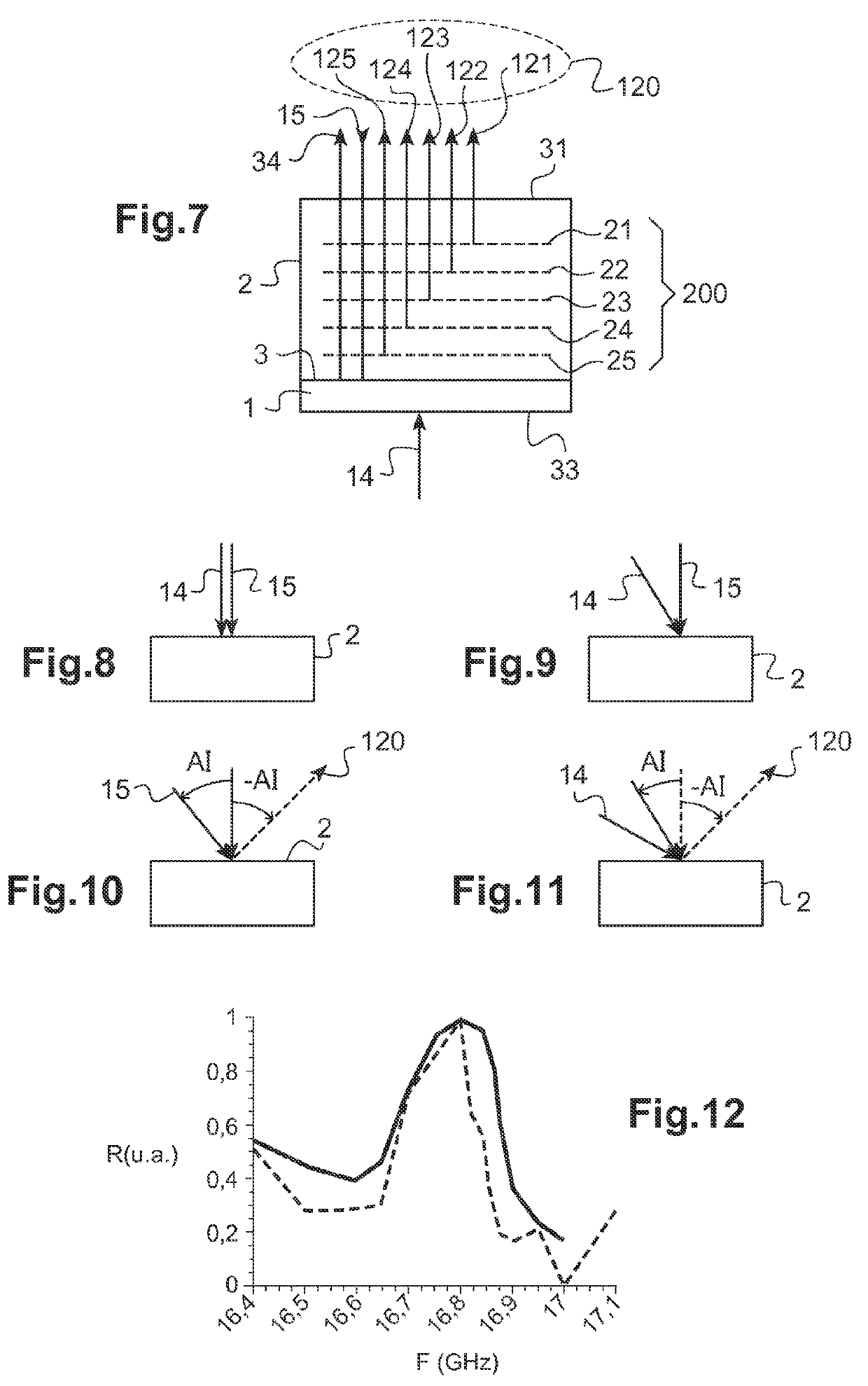
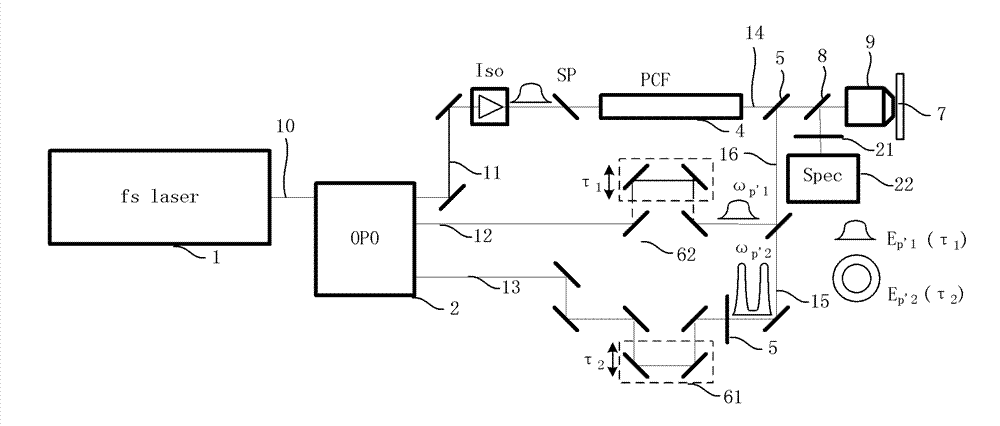
Disclosed is an acoustic resonance spectrometry system for analysing a sample, which includes an optical pump-probe device adapted to generate a pump beam and a probe beam, the pump beam being consisted of a series of ultra-short pump light pulses having a repetition frequency in the spectral domain of the gigahertz, the pump beam being directed towards an optoacoustic transducer to generate a periodic grating of coherent acoustic phonons in the sample, the probe beam being directed towards the sample to form a scattering beam of the probe beam on the grating of phonons, a frequency variation device being adapted to vary the repetition frequency of the pump beam in a spectral range and a photo-detection system configured to measure a scattering signal as a function of the repetition frequency in the spectral range.
Owner:UNIV DE BORDEAUX +5
Acoustic resonance spectrometry system and method
Disclosed is an acoustic resonance spectrometry system for analysing a sample, which includes an optical pump-probe device adapted to generate a pump beam and a probe beam, the pump beam being consisted of a series of ultra-short pump light pulses having a repetition frequency in the spectral domain of the gigahertz, the pump beam being directed towards an optoacoustic transducer to generate a periodic grating of coherent acoustic phonons in the sample, the probe beam being directed towards the sample to form a scattering beam of the probe beam on the grating of phonons, a frequency variation device being adapted to vary the repetition frequency of the pump beam in a spectral range and a photo-detection system configured to measure a scattering signal as a function of the repetition frequency in the spectral range.
Owner:UNIV DE BORDEAUX +5
Opto-acoustic signal processing
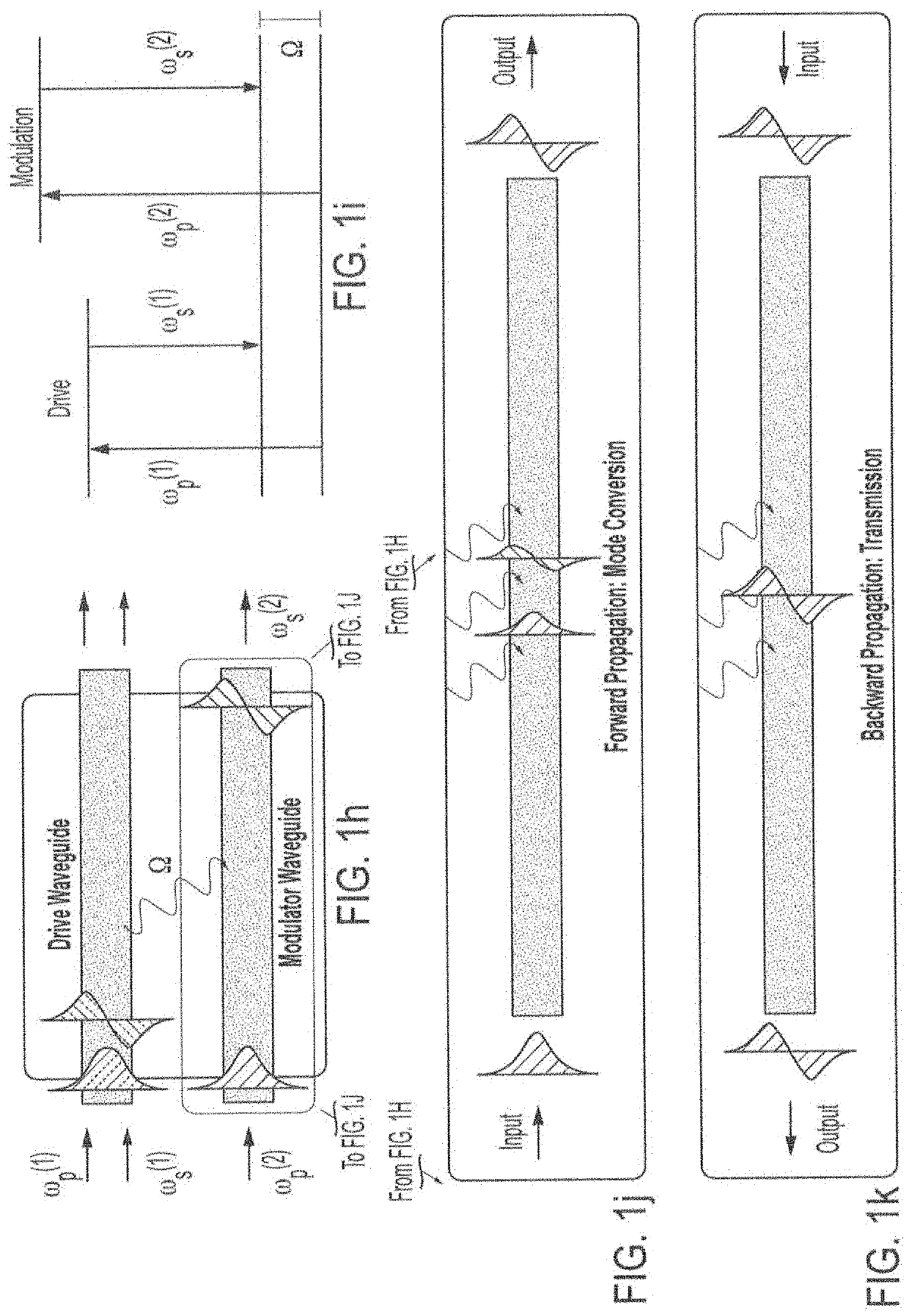
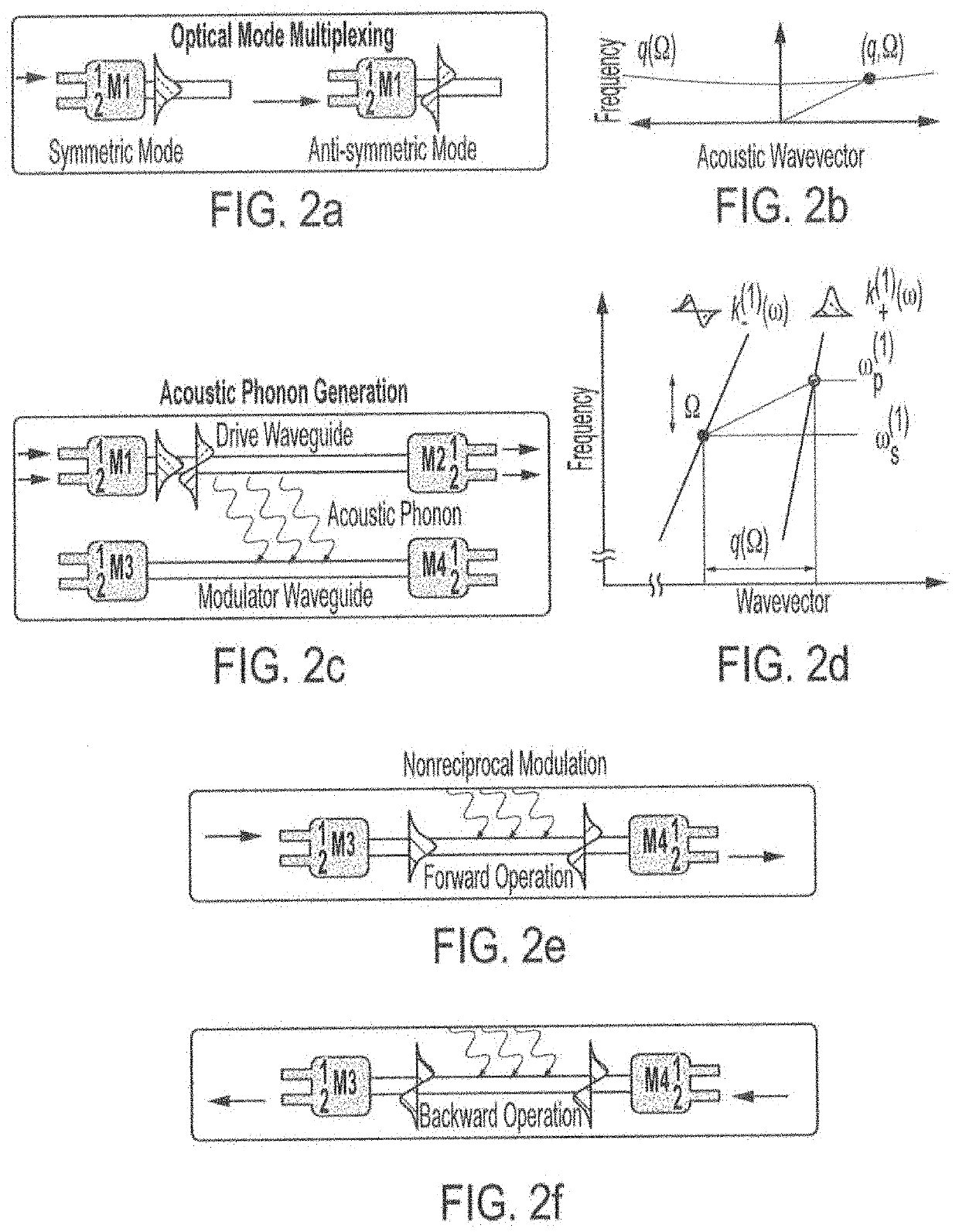
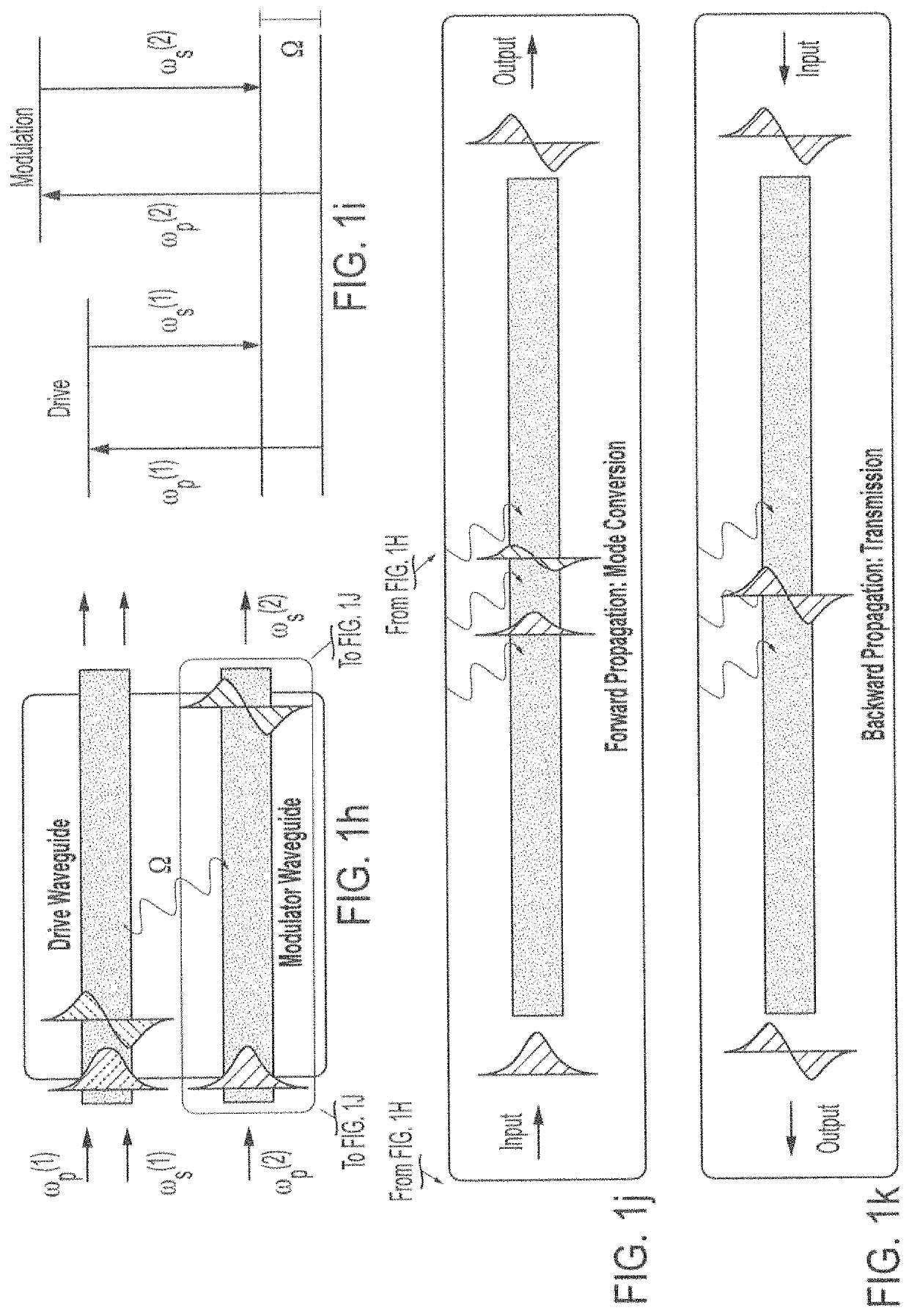
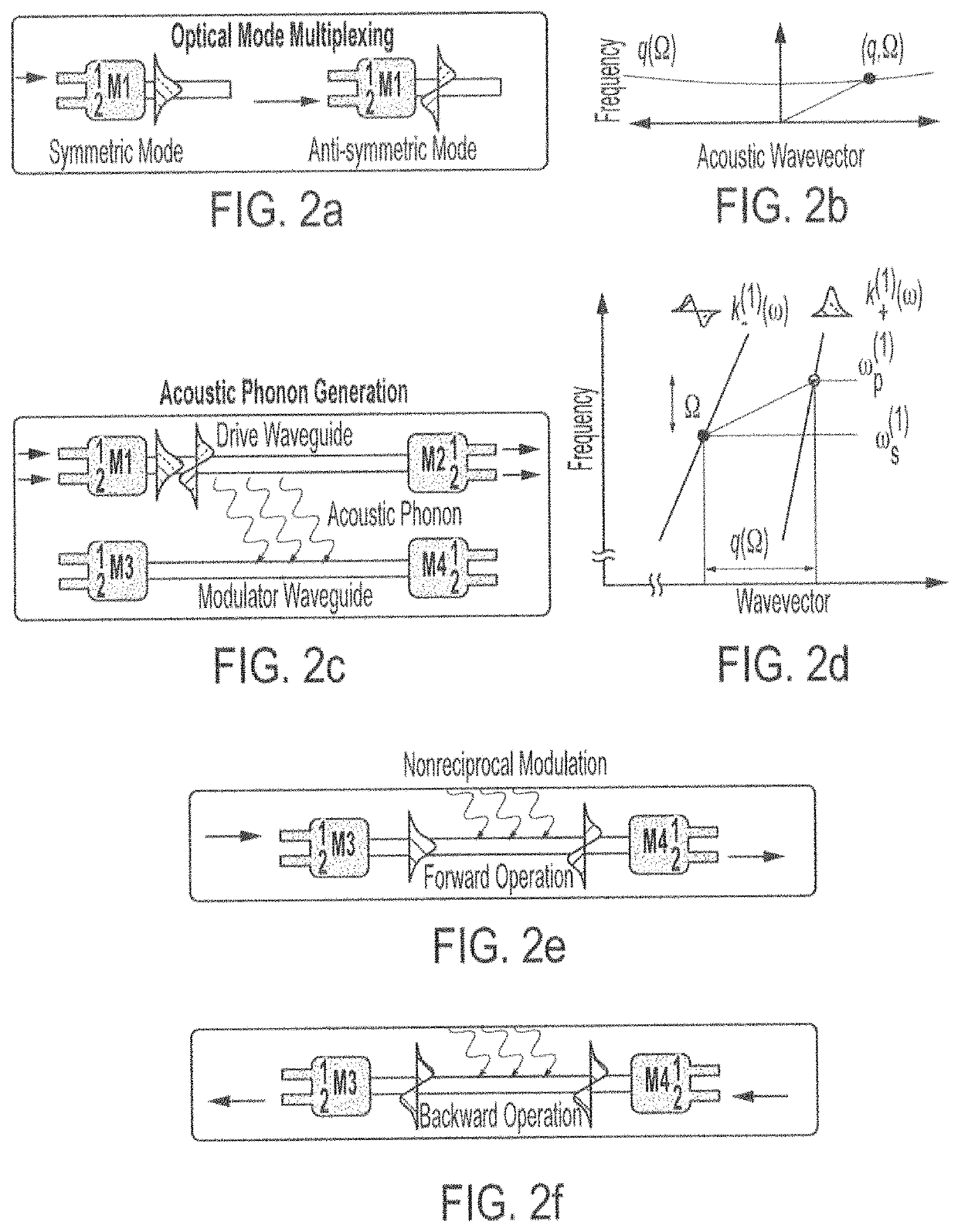
Devices and systems for opto-acoustic signal processing are described herein. In one embodiment, the device may include a structure configured to laterally confine travelling acoustic phonons (hypersound) throughout, a first multimode optical waveguide embedded within the structure, and an acoustic phonon emitter within the structure, where the first multimode optical waveguide is selected to couple to the acoustic phonons (hypersound) confined within the structure. In one embodiment, the system may include a first light source optically coupled to a proximal end of the first multimode optical waveguide, the first light source emitting a probe wave having a frequency ωp(1), and a driver configured to drive the acoustic phonon emitter to emit acoustic phonons (hypersound).
Owner:YALE UNIV
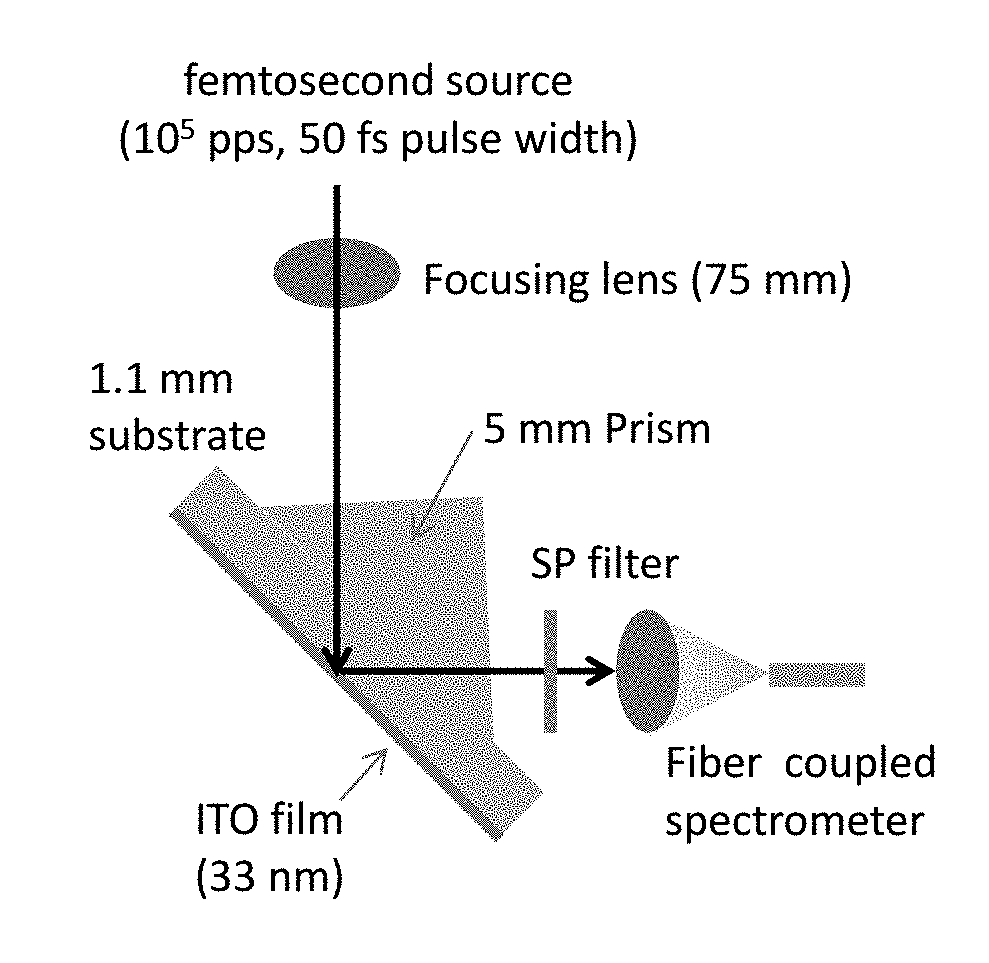
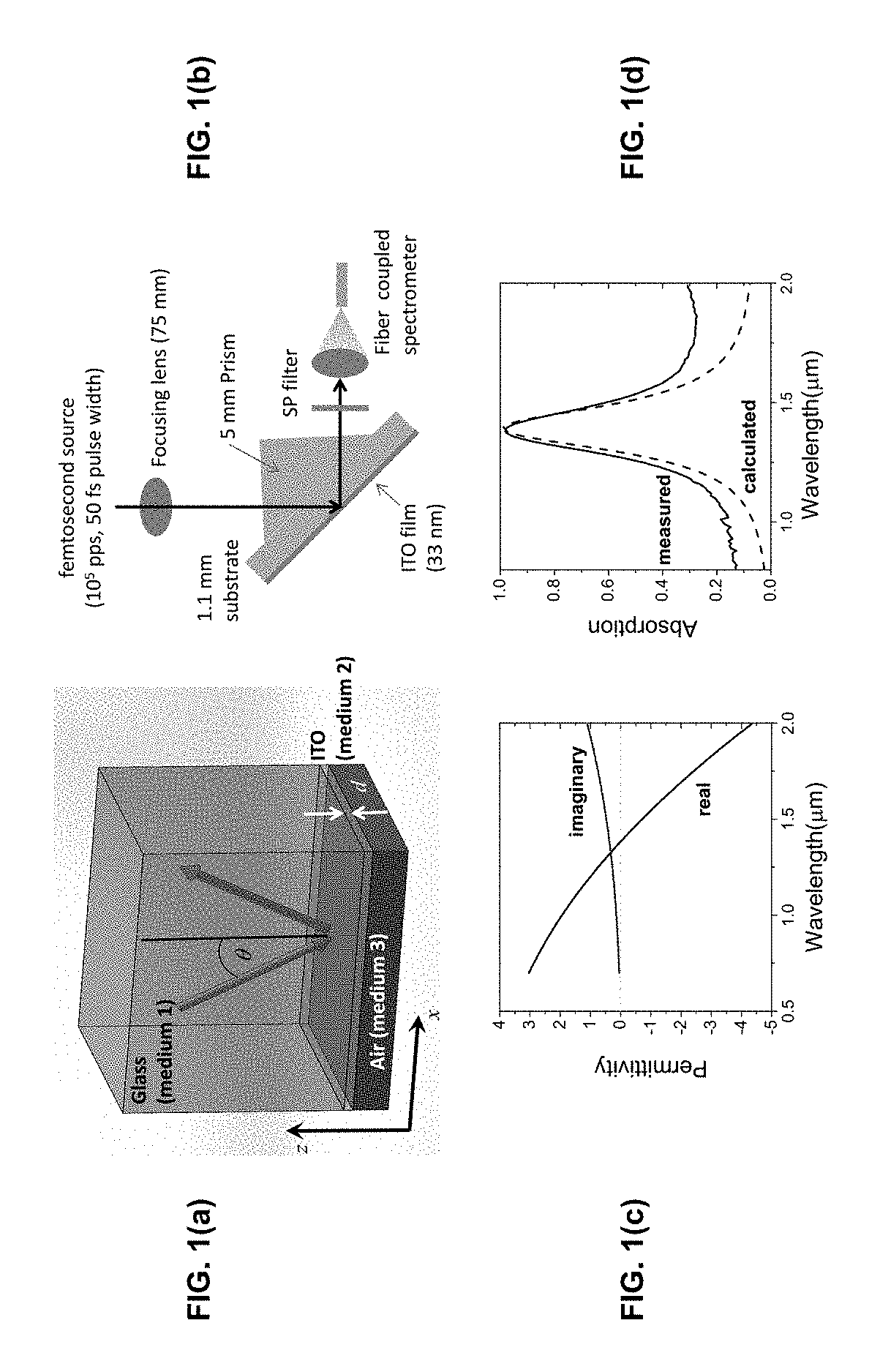
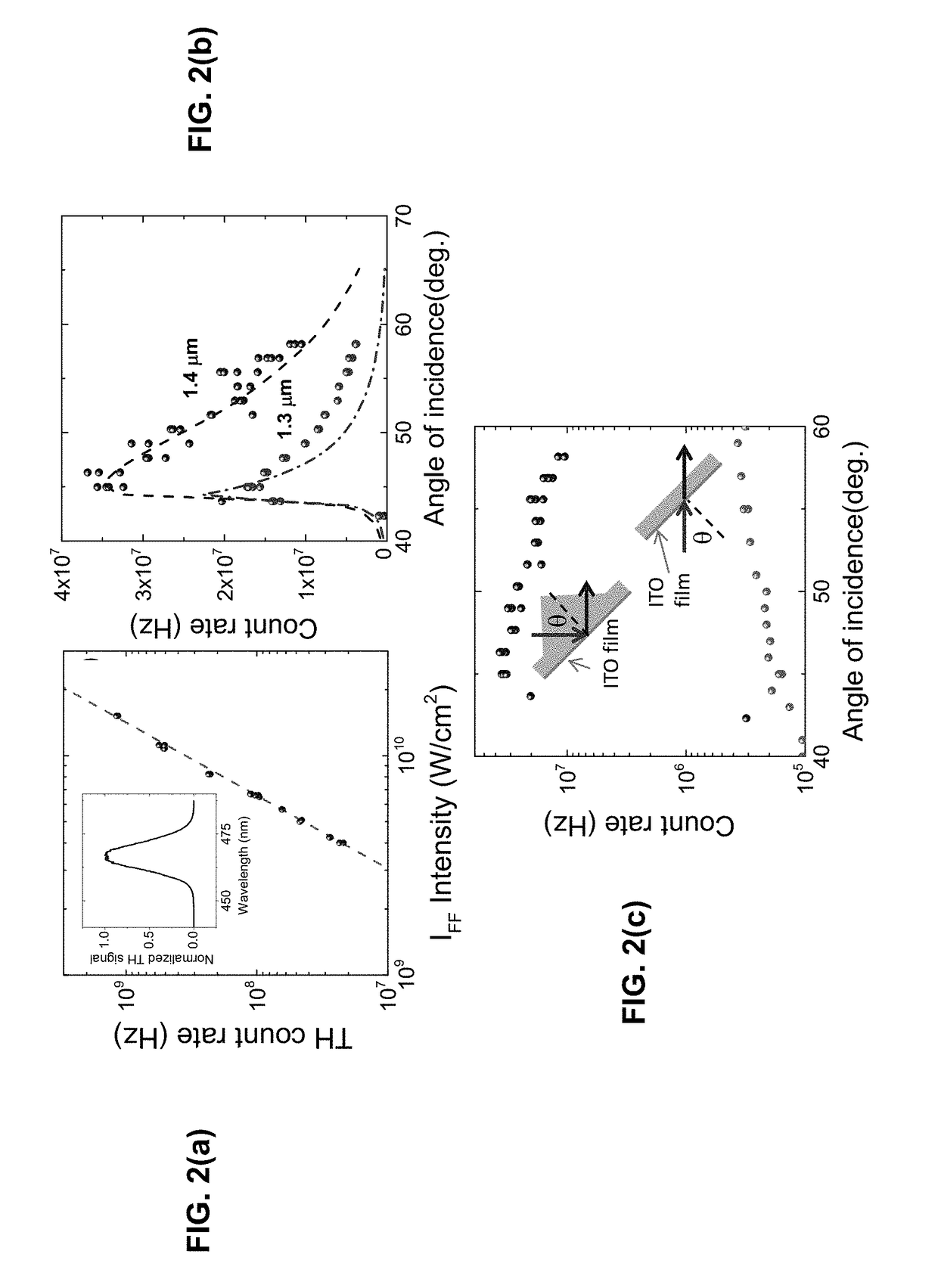
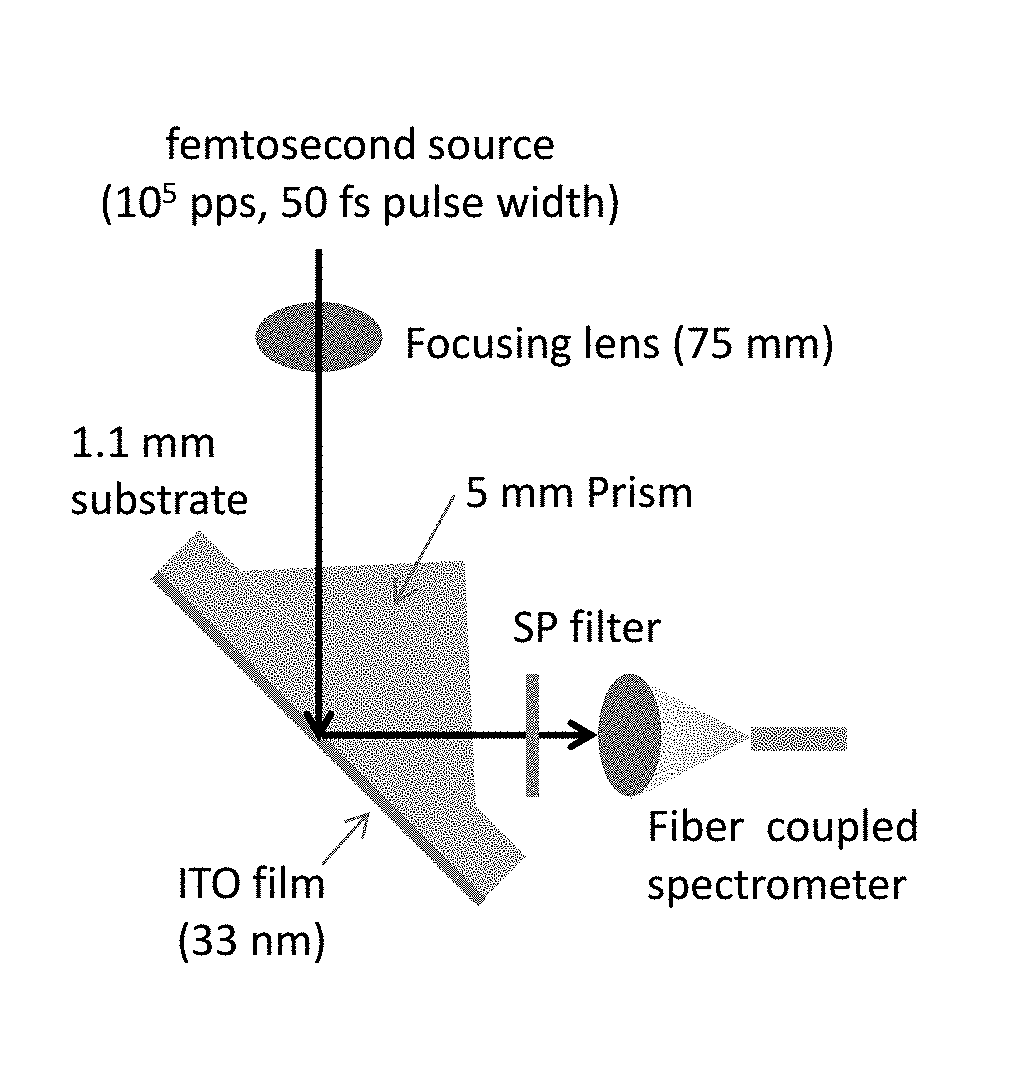
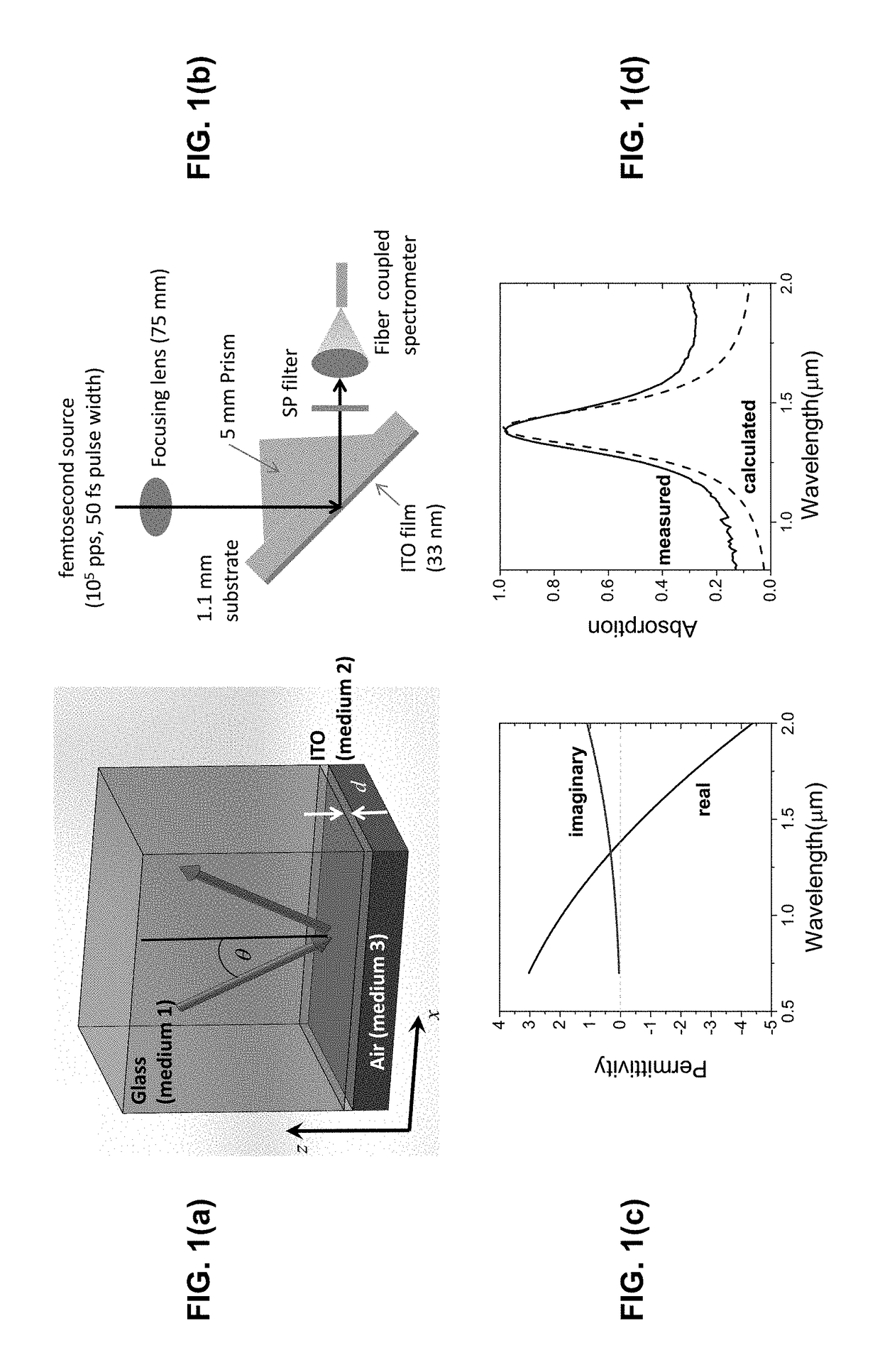
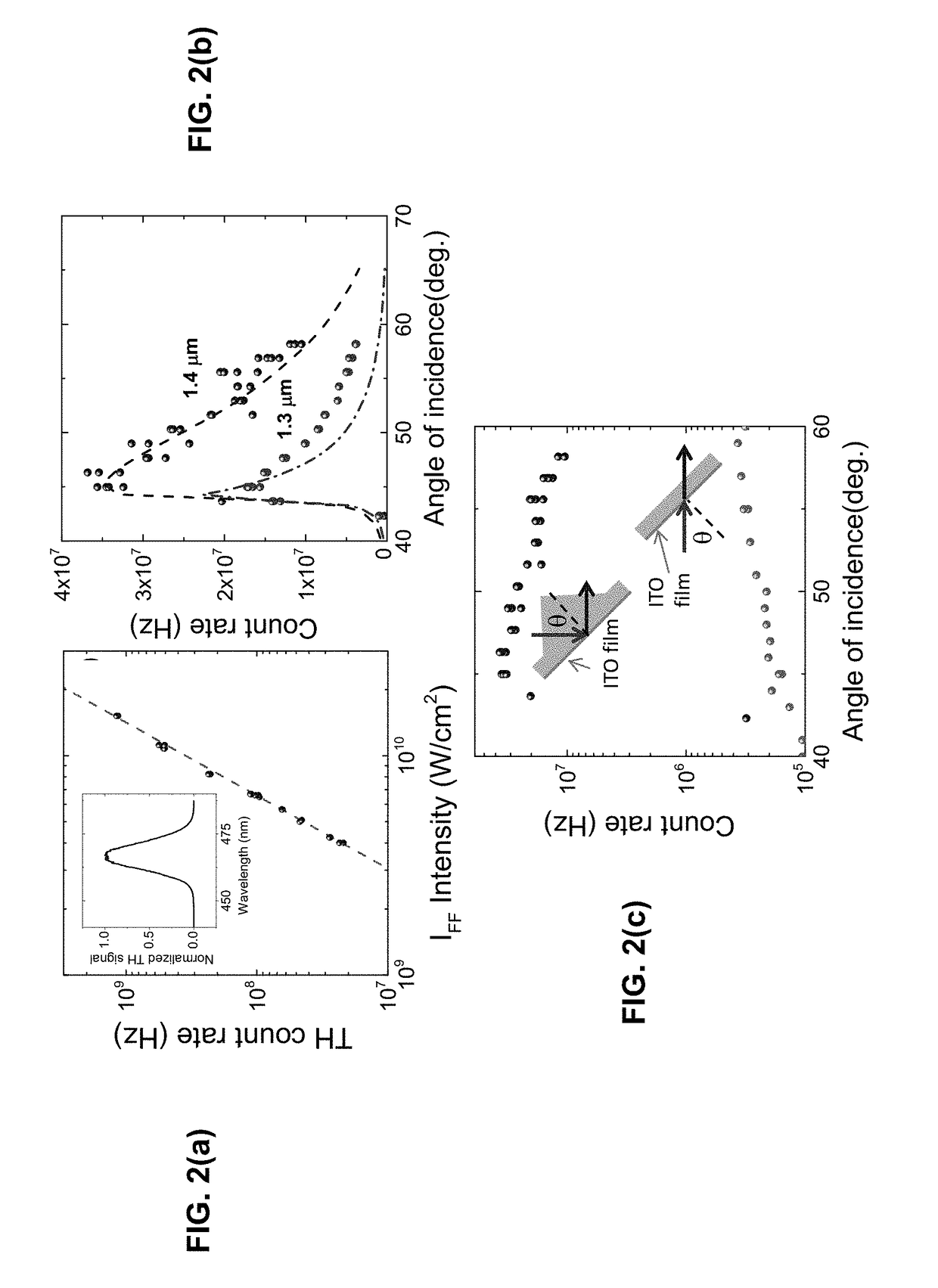
Photon energy conversion by near-zero permittivity nonlinear materials
Efficient harmonic light generation can be achieved with ultrathin films by coupling an incident pump wave to an epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) mode of the thin film. As an example, efficient third harmonic generation from an indium tin oxide nanofilm (λ / 42 thick) on a glass substrate for a pump wavelength of 1.4 μm was demonstrated. A conversion efficiency of 3.3×10−6 was achieved by exploiting the field enhancement properties of the ENZ mode with an enhancement factor of 200. This nanoscale frequency conversion method is applicable to other plasmonic materials and reststrahlen materials in proximity of the longitudinal optical phonon frequencies.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Photon energy conversion by near-zero permittivity nonlinear materials
Efficient harmonic light generation can be achieved with ultrathin films by coupling an incident pump wave to an epsilon-near-zero (ENZ) mode of the thin film. As an example, efficient third harmonic generation from an indium tin oxide nanofilm (λ / 42 thick) on a glass substrate for a pump wavelength of 1.4 μm was demonstrated. A conversion efficiency of 3.3×10−6 was achieved by exploiting the field enhancement properties of the ENZ mode with an enhancement factor of 200. This nanoscale frequency conversion method is applicable to other plasmonic materials and reststrahlen materials in proximity of the longitudinal optical phonon frequencies.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Random walk magnetic dielectric antenna to generate brillouin and sommerfeld precursors
ActiveUS20190058528A1Loop antennas with ferromagnetic coreSimultaneous aerial operationsDielectricAcoustic Phonons
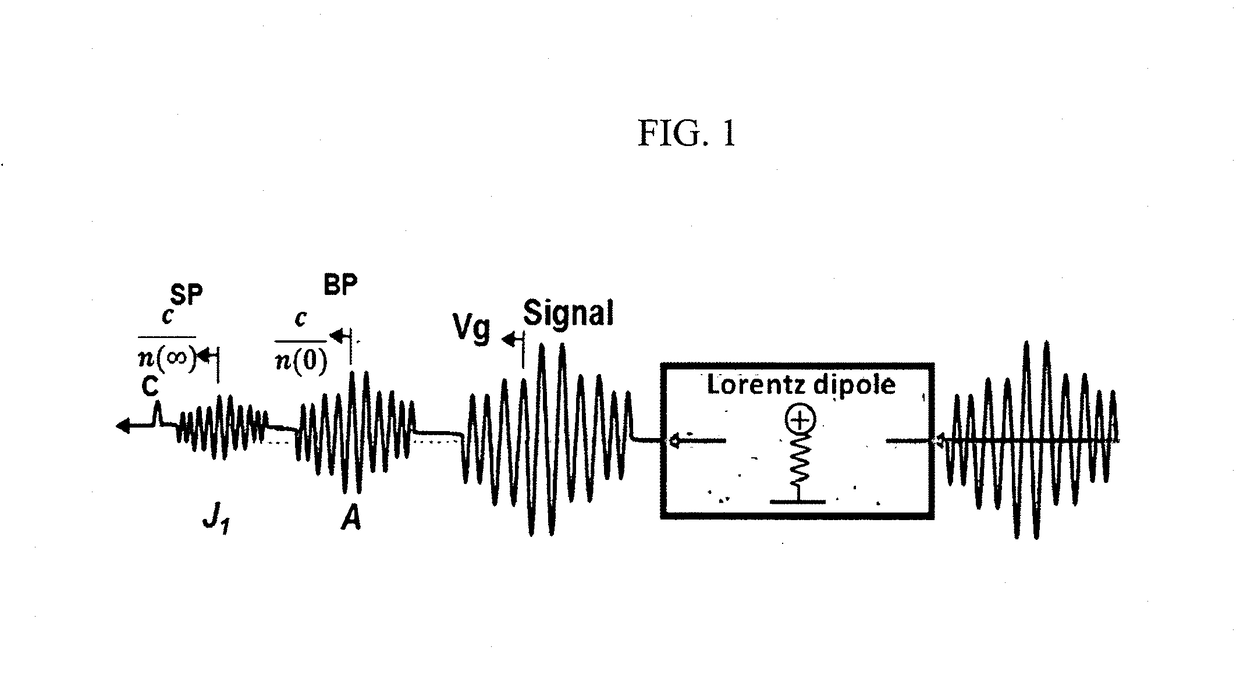
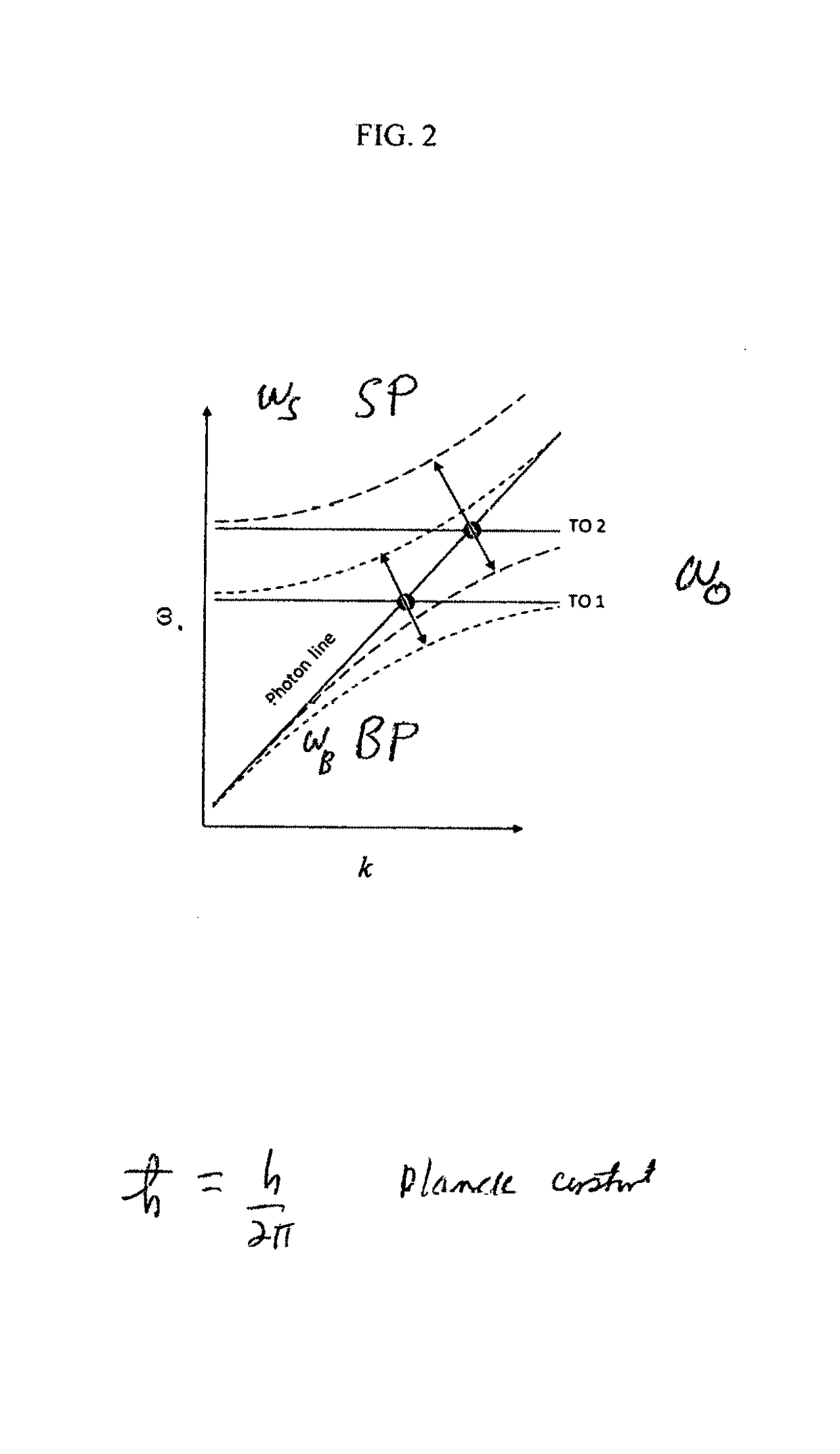
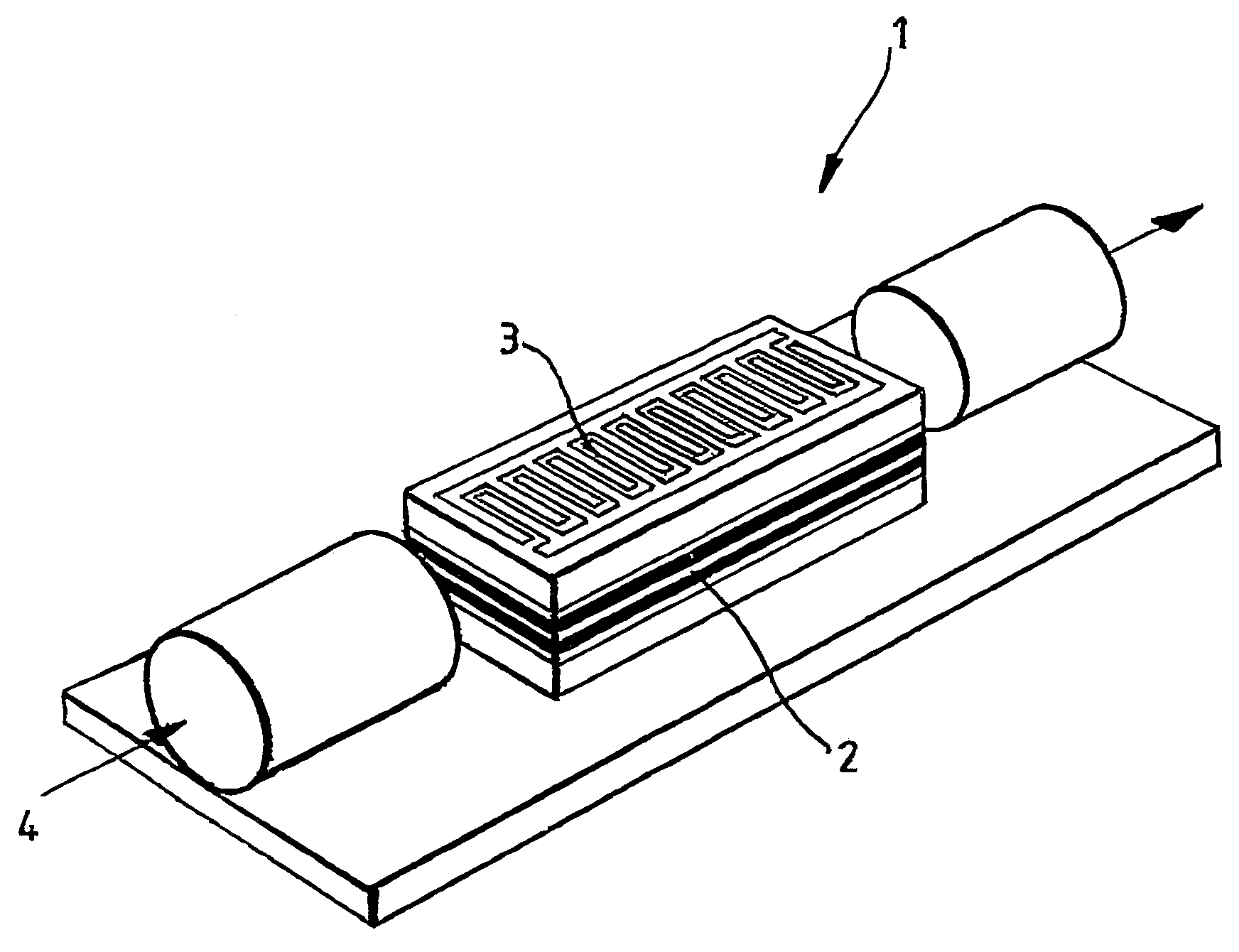
A Random Walk Antenna (RWA) generates VLF, ULF, RF, MHz and GHz waves by dispersion of a driving signal through a ferriomagnetic ferrite nano and micron composite in compact ultra-small antenna. When oscillator frequency spans several resonances of ferrite magnetic dielectric media consisting of resonances from optical phonons and magnon high frequency and lower frequency are produced from Sommerfeld Polaritons Precursor (SP) and Brillouin Polariton Precursors (BP), respectively. The ferrite nano and micron size particle in antenna resultant electromagnetic waves from RWA contain Sommerfeld and Brillouin polariton precursors. High and low-frequency waves propagate with an algebraic attenuation making them ideal for deep use in highly conductive or highly attenuating media such as in seawater, buildings, underground and or free space on the Earth. Warfighters can use the RAW ferrite nano and micron size antenna system.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT
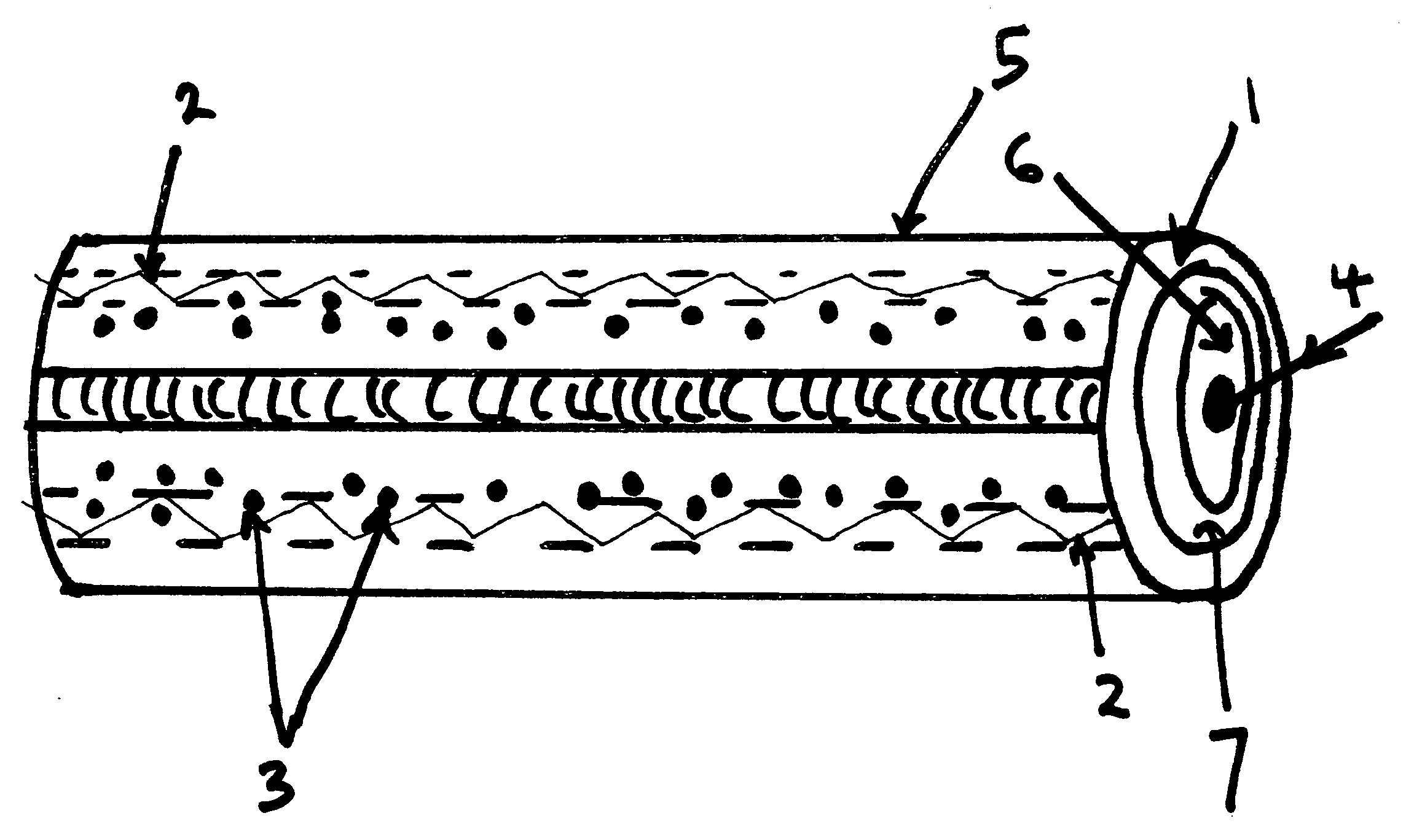
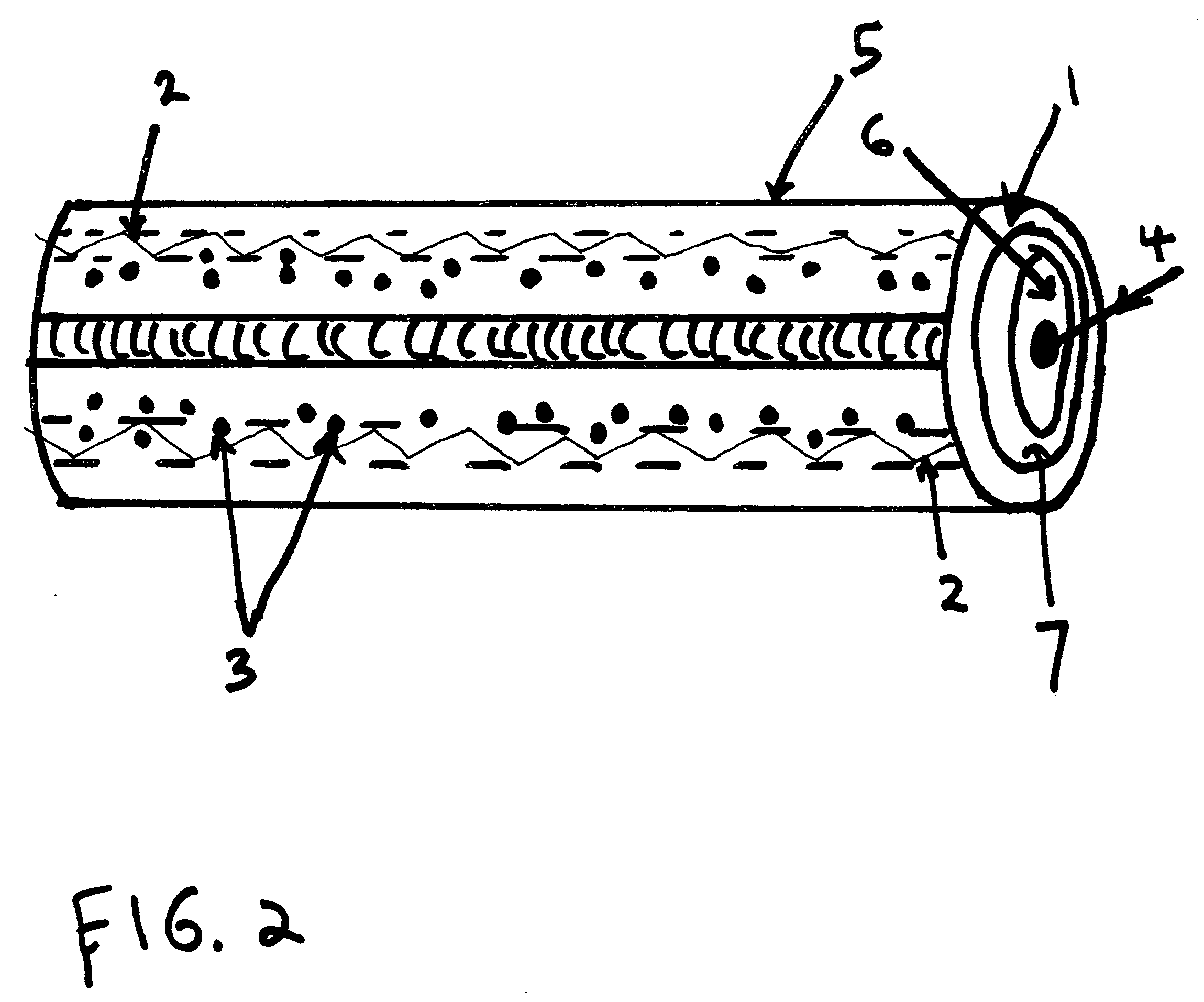
Acousto-optical device based on phonon-induced polaritonic band gaps
InactiveUS7209603B2Extensive interactionRealize switchingLaser detailsNanoopticsPolaronAcoustic wave
The device comprises an optical waveguide and an acoustic wave generating device. The waveguide has an optical band gap and a sharp electronic transition (e.g. an excitonic transition) in the band gap, and the acoustic wave generating device generates acoustic waves within the waveguide. Light passing through the waveguide is of a frequency within the band gap of the waveguide and is nearly resonant with the sharp electronic transition. The wave generating device is arranged to generate acoustic waves so as to induce optical band gas in the polariton spectrum, thereby affecting the transmission of the light passing through the waveguide, the transmission of which is thereby affected.
Owner:UNIV COLLEGE CARDIFF CONSULTANTS LTD +1
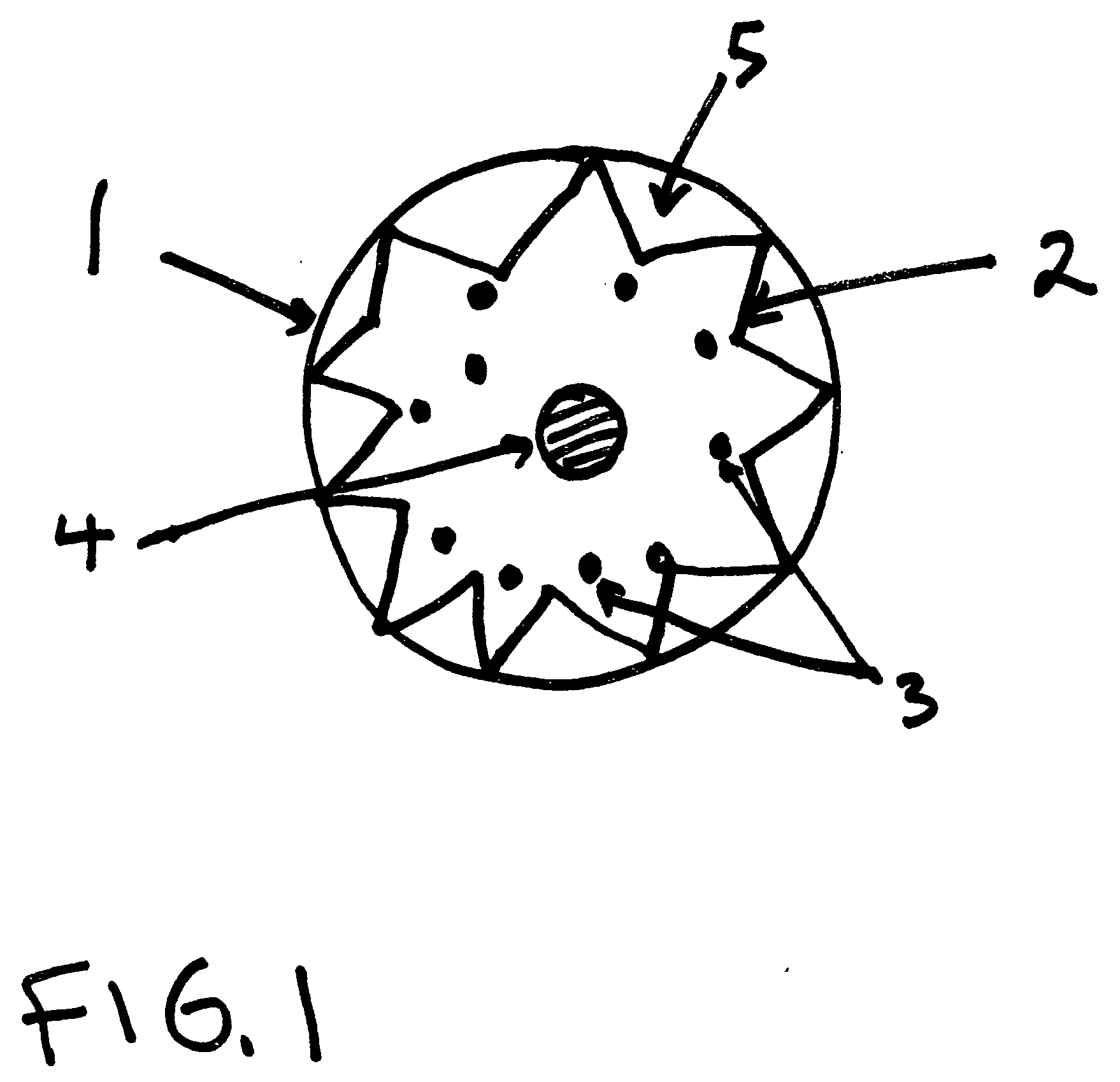
Phonon optical grating used for superconductivity dielectric resonant cavity phonon laser device
Provided is a phonon optical grating used for a superconductivity dielectric resonant cavity phonon laser device. The phonon optical grating comprises a buffer layer (1), a dielectric layer (2), an impurity layer (3), another dielectric layer (4) and another buffer layer (5), wherein the buffer layer (1) and the buffer layer (5) are arranged to enable the phonon optical grating to be matched with the size of a gap of the phonon laser device when the phonon optical grating is embedded in the emitting end of the superconductivity dielectric resonant cavity phonon laser device and to prevent the dielectric layer (2) and the dielectric layer (4) from being abraded, the dielectric layer (2) and the dielectric layer (4) are composed of two different materials in an alternately repeated mode, the impurity layer (3) is arranged between the dielectric layer (2) and the dielectric layer (4), and the dielectric layer (2), the impurity layer (3) and the dielectric layer (4) are in axial symmetry on the whole.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Confocal microscopic device capable of accurately measuring transverse and longitudinal acoustic phonon velocities of medium
PendingCN114371147AQuick measurementGuaranteed in situSubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementScattering properties measurementsConfocalPolarizer
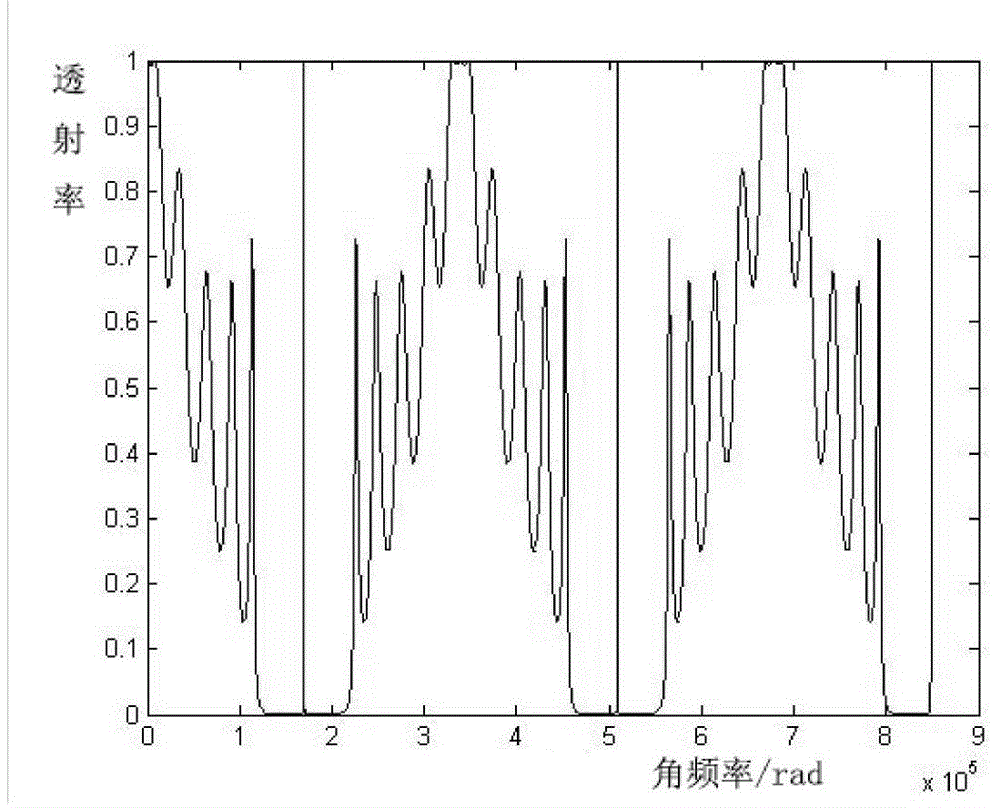
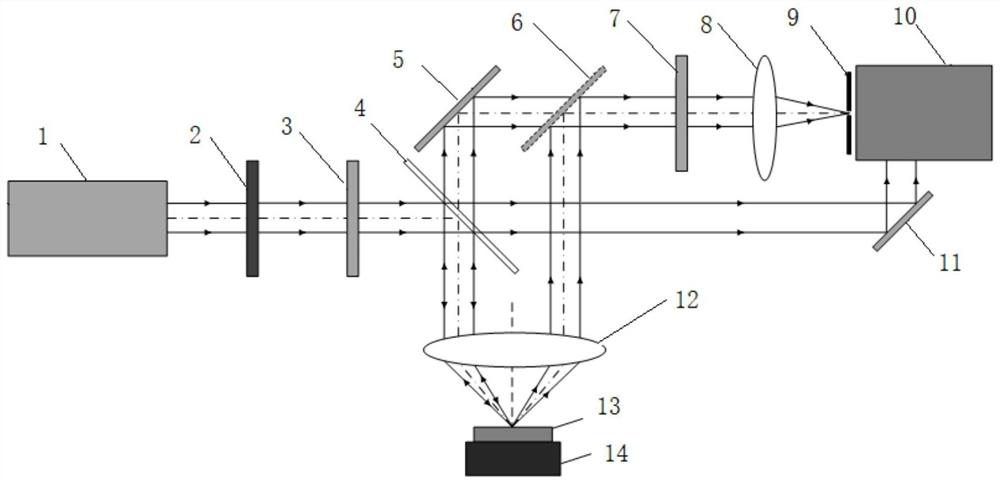
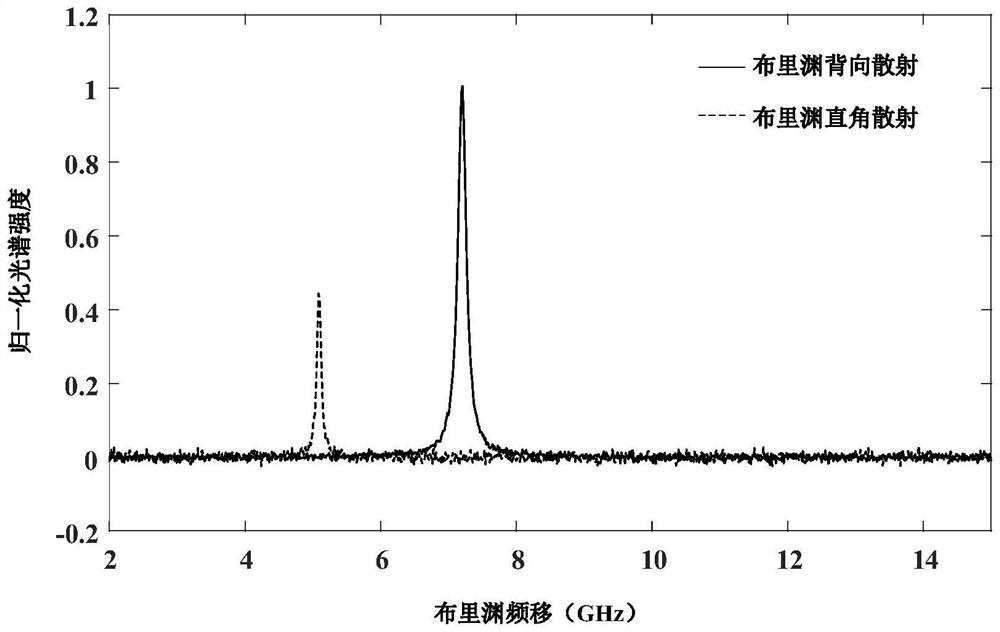
The confocal microscopic device capable of accurately measuring the transverse and longitudinal acoustic phonon velocities of the medium comprises a continuous laser, a three-dimensional translation stage and an F-P interferometer, a to-be-measured sample is placed on the upper side of the three-dimensional translation stage, and a measuring objective lens is arranged right above the to-be-measured sample; a lambda / 2 wave plate, a polarizer, a light splitting plain film and a first reflecting mirror are sequentially arranged on one side of the continuous laser; and a confocal pinhole, a convergent lens, an analyzer, a rotary reflector and a second reflector are sequentially arranged on one side of the F-P interferometer. According to the invention, the angle between the incident light path and the scattered light path does not need to be changed in the measurement process, the acoustic phonon speed of the measured material is rapidly measured by dynamically switching the collected light paths, the in-situ property and accuracy of the measurement result are ensured, and the measurement efficiency is improved. The method has remarkable advantages in the aspects of measuring speed, measuring precision, measuring mode complexity and the like.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF RADIO METROLOGY & MEASUREMENT
Opto-acoustic signal processing
Owner:YALE UNIV
Coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopic method and system of super-diffraction limit
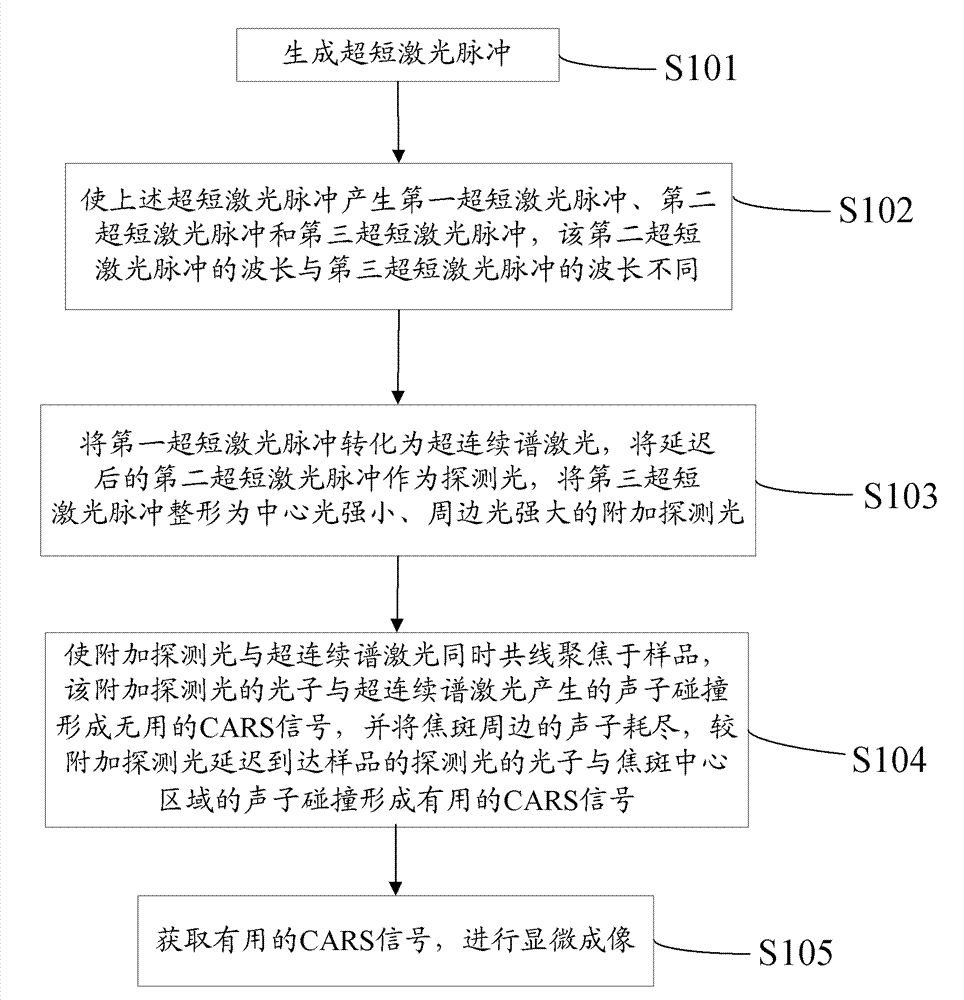
The invention is applicable to the field of laser detection and provides a coherent anti-Stokes Raman scattering microscopic method and system of a super-diffraction limit. In the method, a spatial resolution of the super-diffraction limit can be obtained through increasing an additional detecting light which is collinearly focused on a sample together with a pump light and a Stokes light at the same time, enabling the additional detecting light to exhaust phonons generated by the pump light and the Stokes light on a periphery of a focal spot so as to form useless CARS (Coherent Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering) signals, enabling photons in accordance with a phase matching condition in the delayed detecting light to hit phonons at a central area of the focal spot so as to form useful CARS signals, and separating the useless CARS signals. Because supercontinuum laser with a broad band is adopted as the pump light and the Stokes light, a complete CARS spectrum signal of a molecule is obtained to image the whole molecule.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Total internal reflection energy/heat source
InactiveUS20120052610A1Improve permeabilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical waveguide light guideElectricityMicroparticle
The Total Internal Reflection Energy / Heat Source includes an object that allows electromagnetic radiation or phonons to be in total internal reflection within the object. The object, such as a microparticle or optical fiber, is doped with atoms or molecules that convert the electromagnetic radiation or phonons to heat, where the heat is transferred out of the object or converted to electricity. A second embodiment of the Total Internal Reflection Energy / Heat Source includes an object that allows electromagnetic radiation or phonons to be in total internal reflection within the object. The object, such as a microparticle, contains P-type and N-type materials beneath the surface, where the electromagnetic radiation or phonons in total internal reflection strikes the P-N junction of the P-type and N-type materials creating electricity.
Owner:TAMBUNGA GABRIEL JAMES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com