Patents
Literature
83 results about "Quantum structure" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quantum structure definition, quantum structure meaning | English dictionary. quantum. n (Physics) one of a set of integers or half-integers characterizing the energy states of a particle or system of particles. n (Physics) a state of a system characterized by a set of quantum numbers and represented by an eigenfunction.
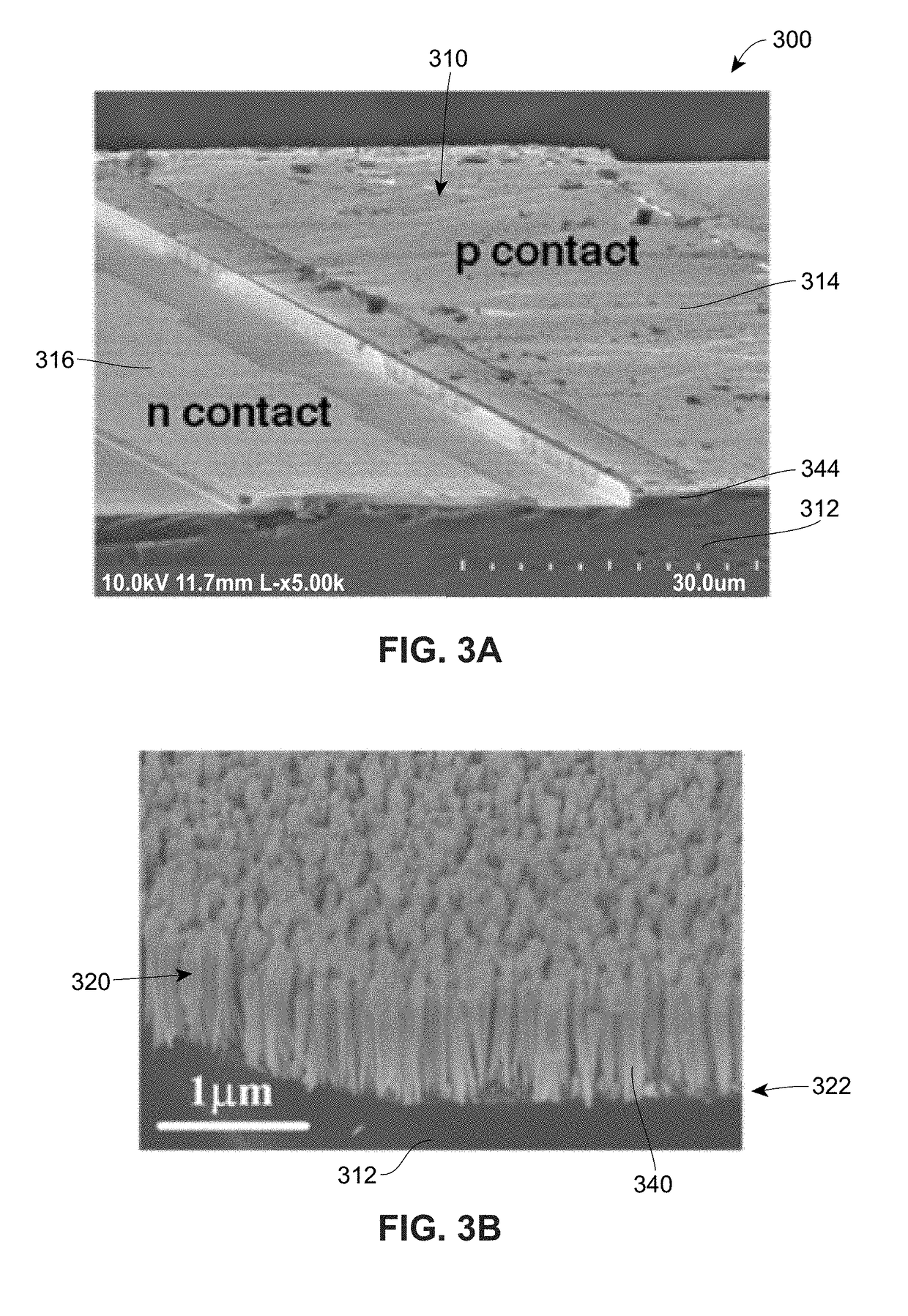
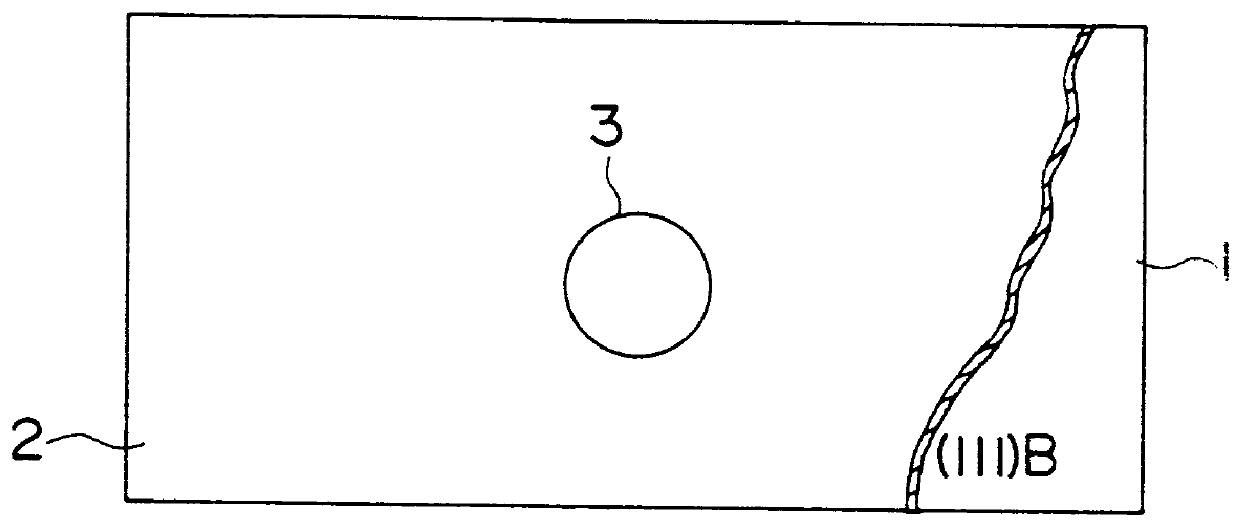
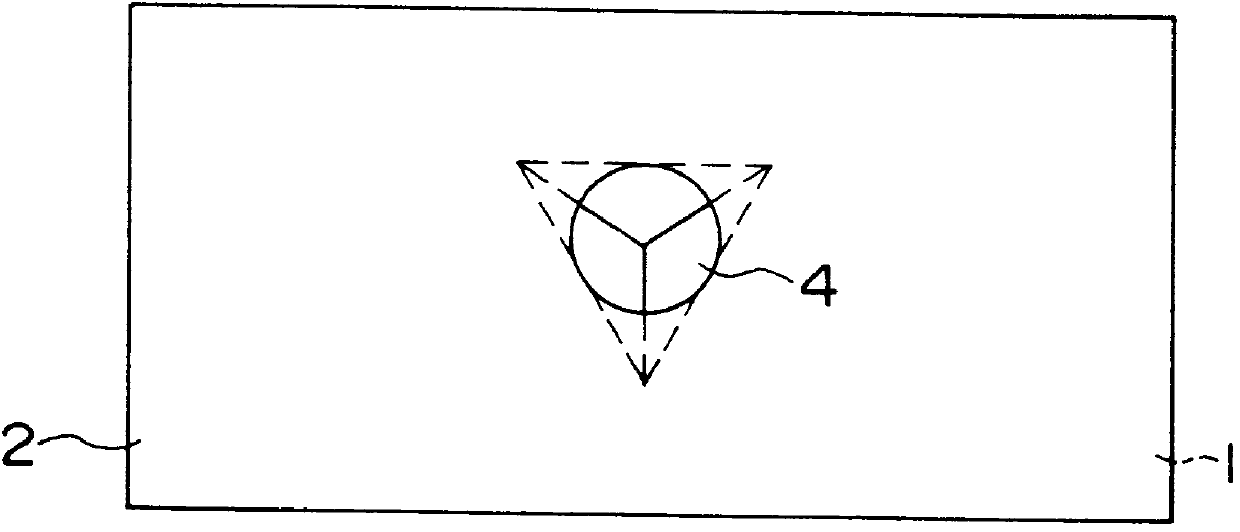
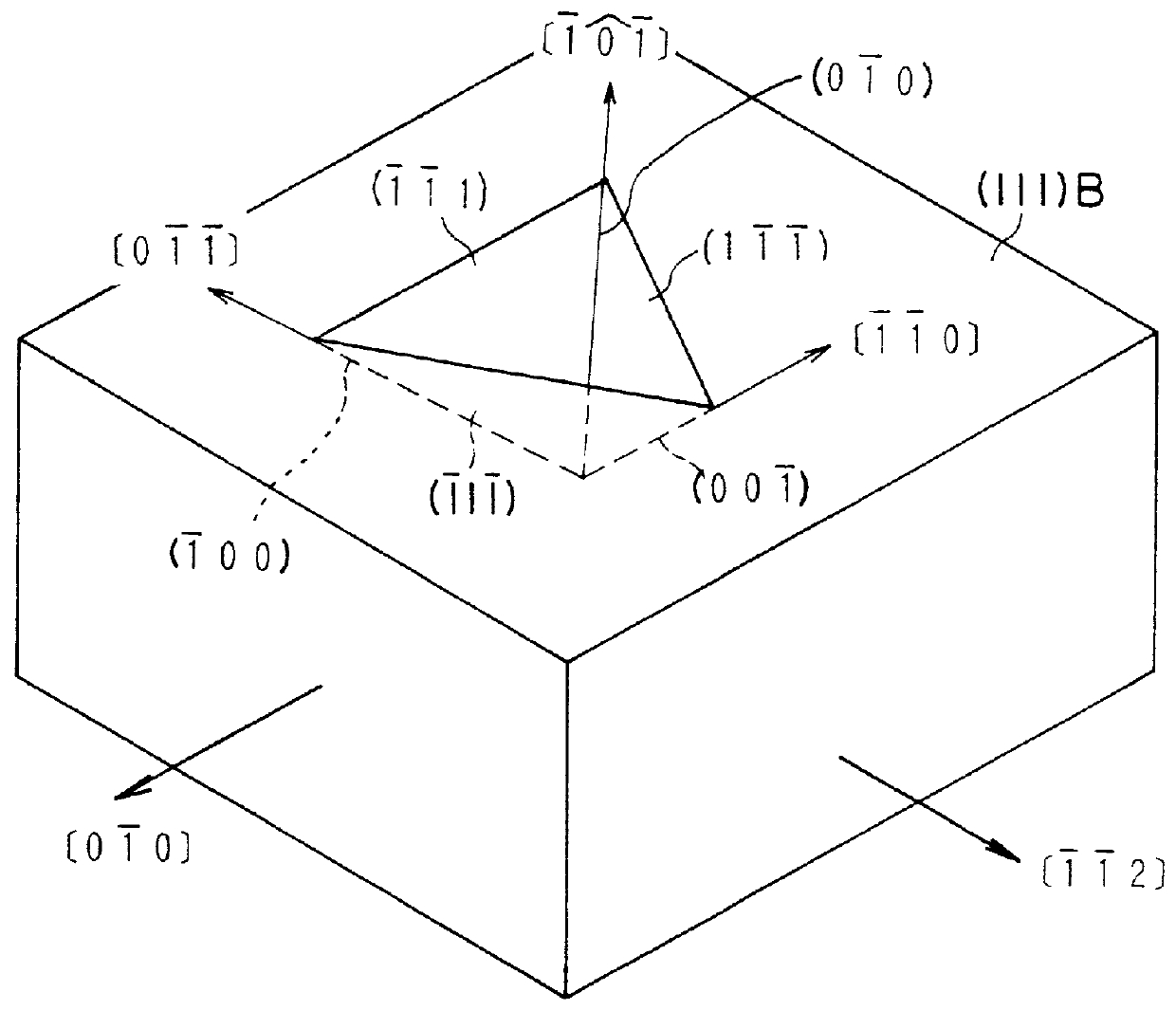
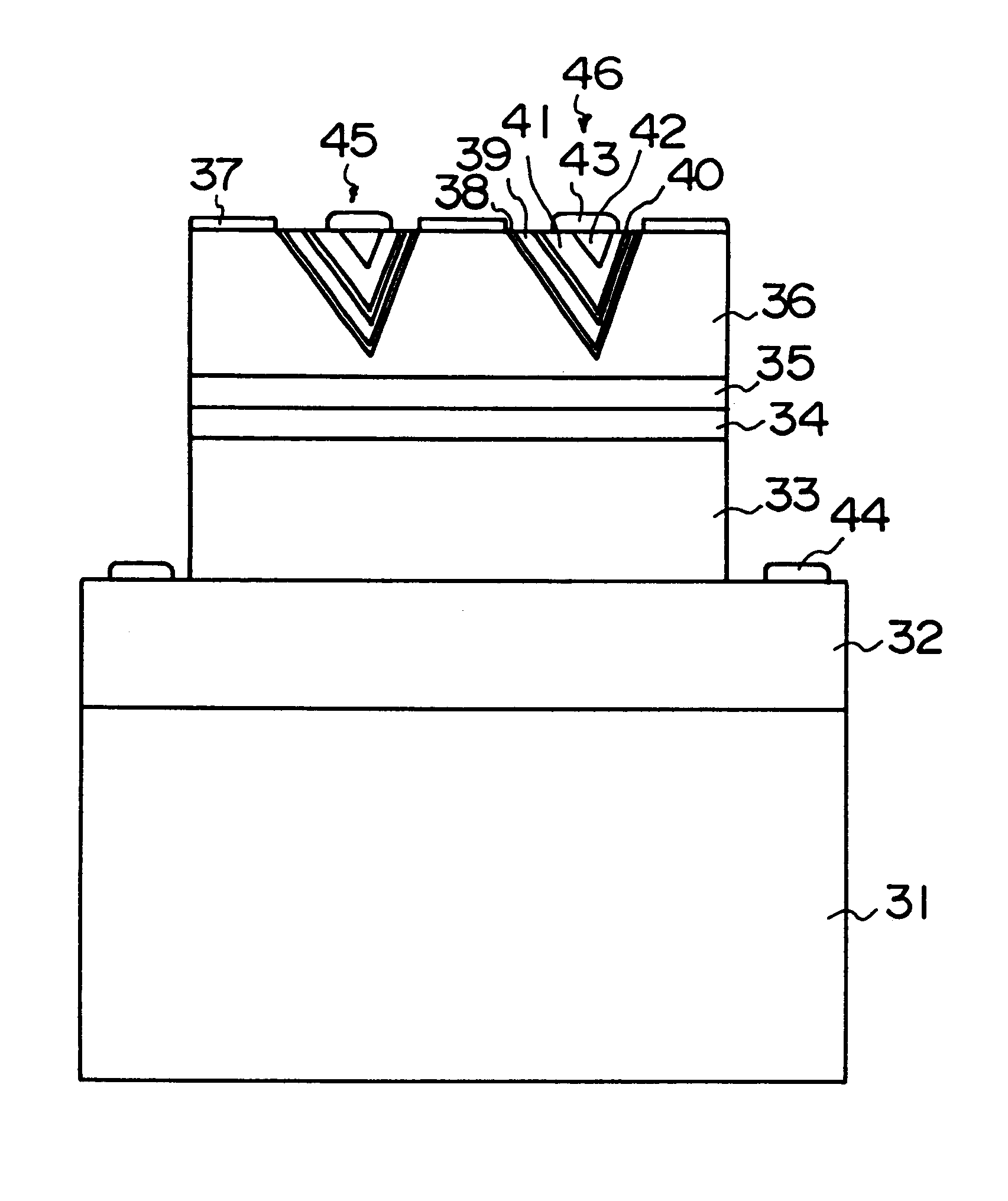
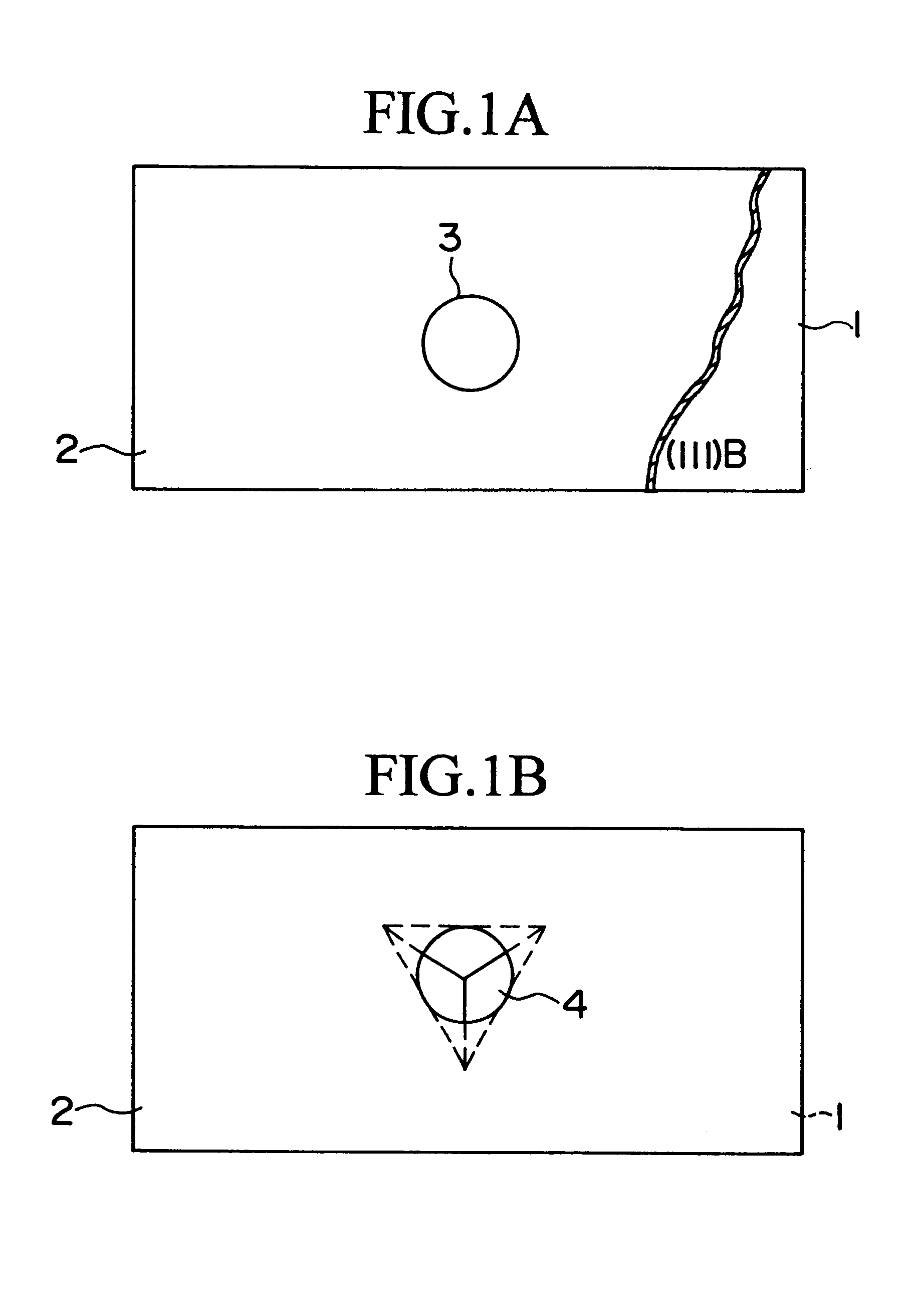
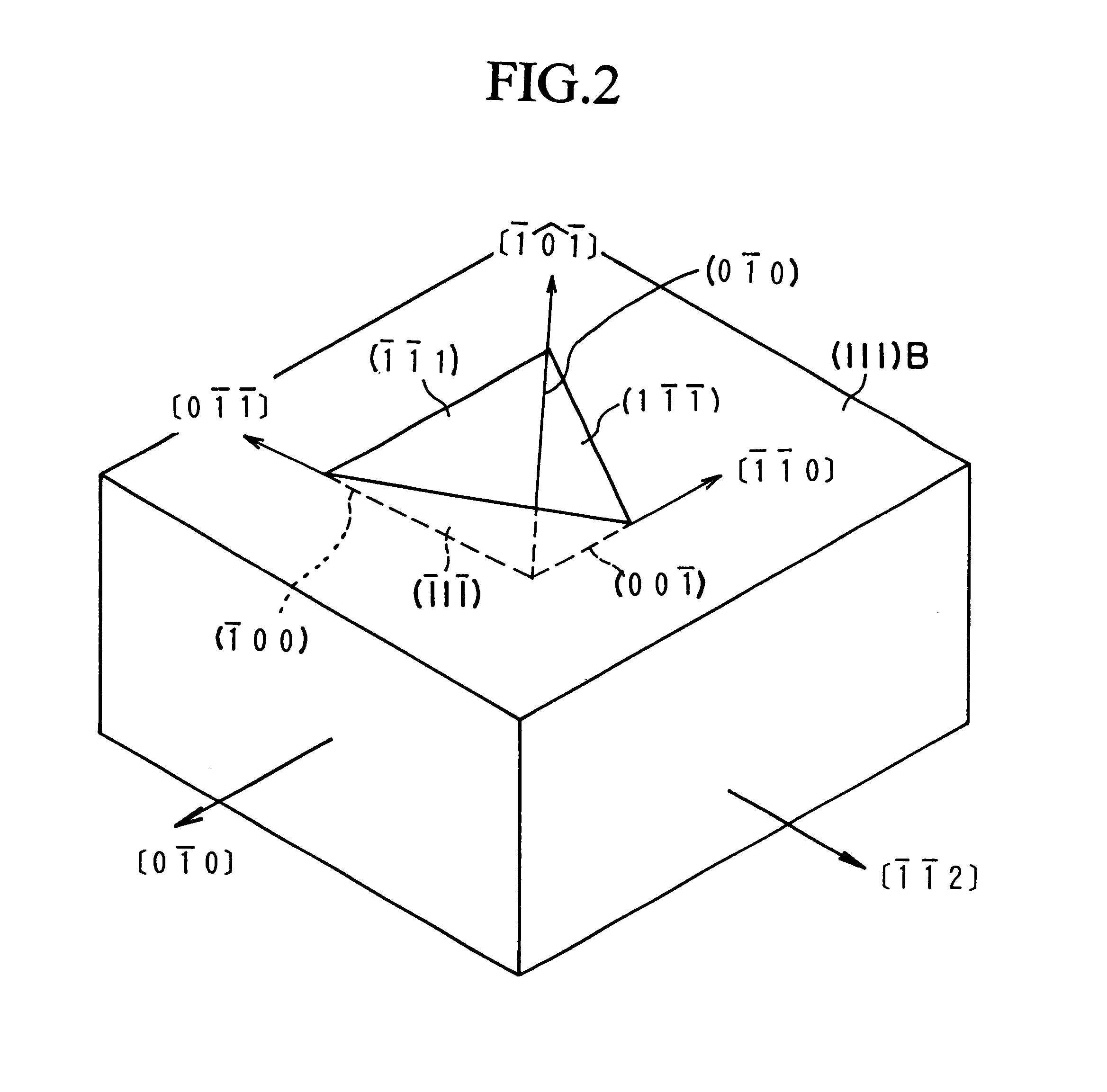
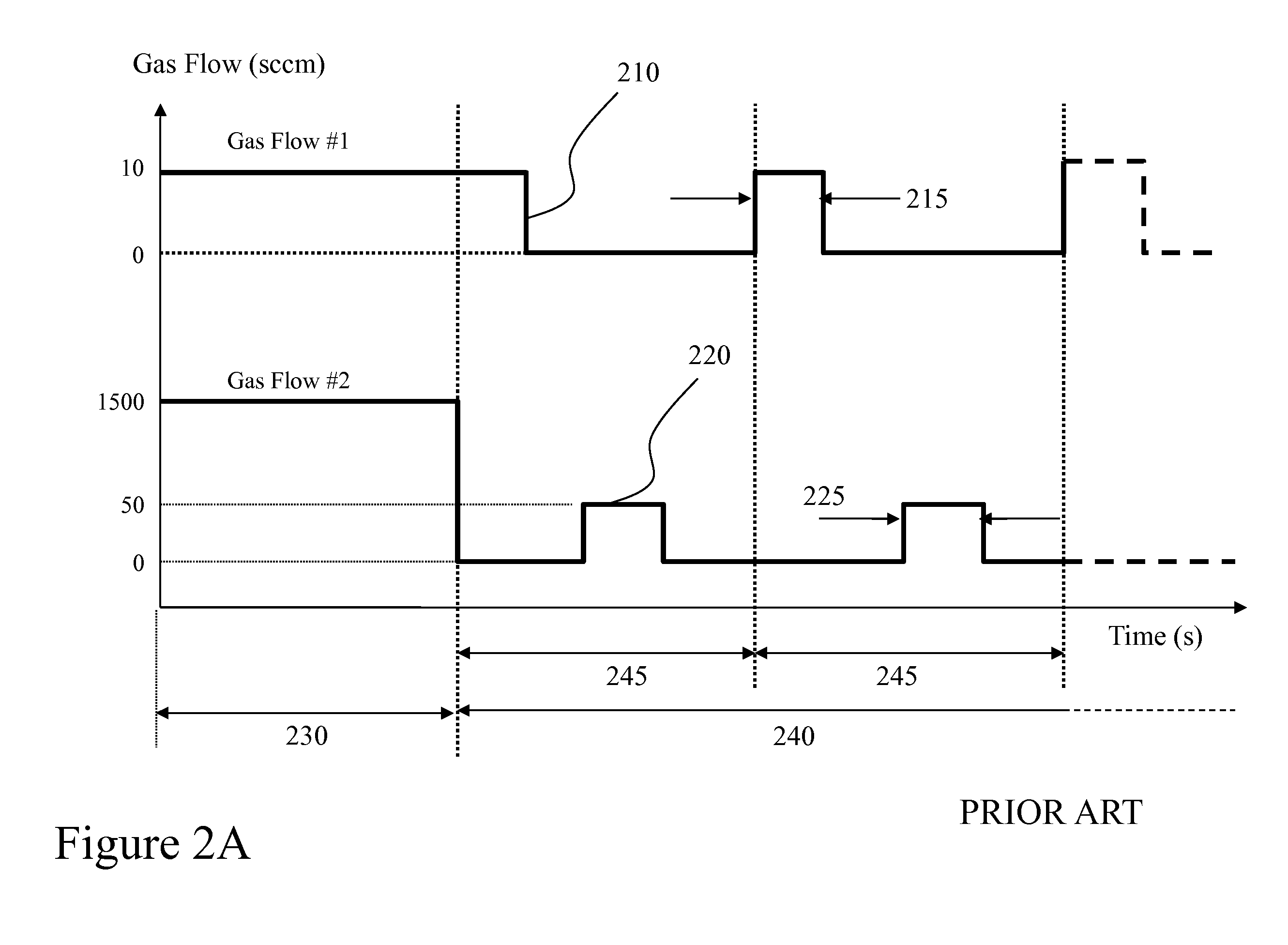
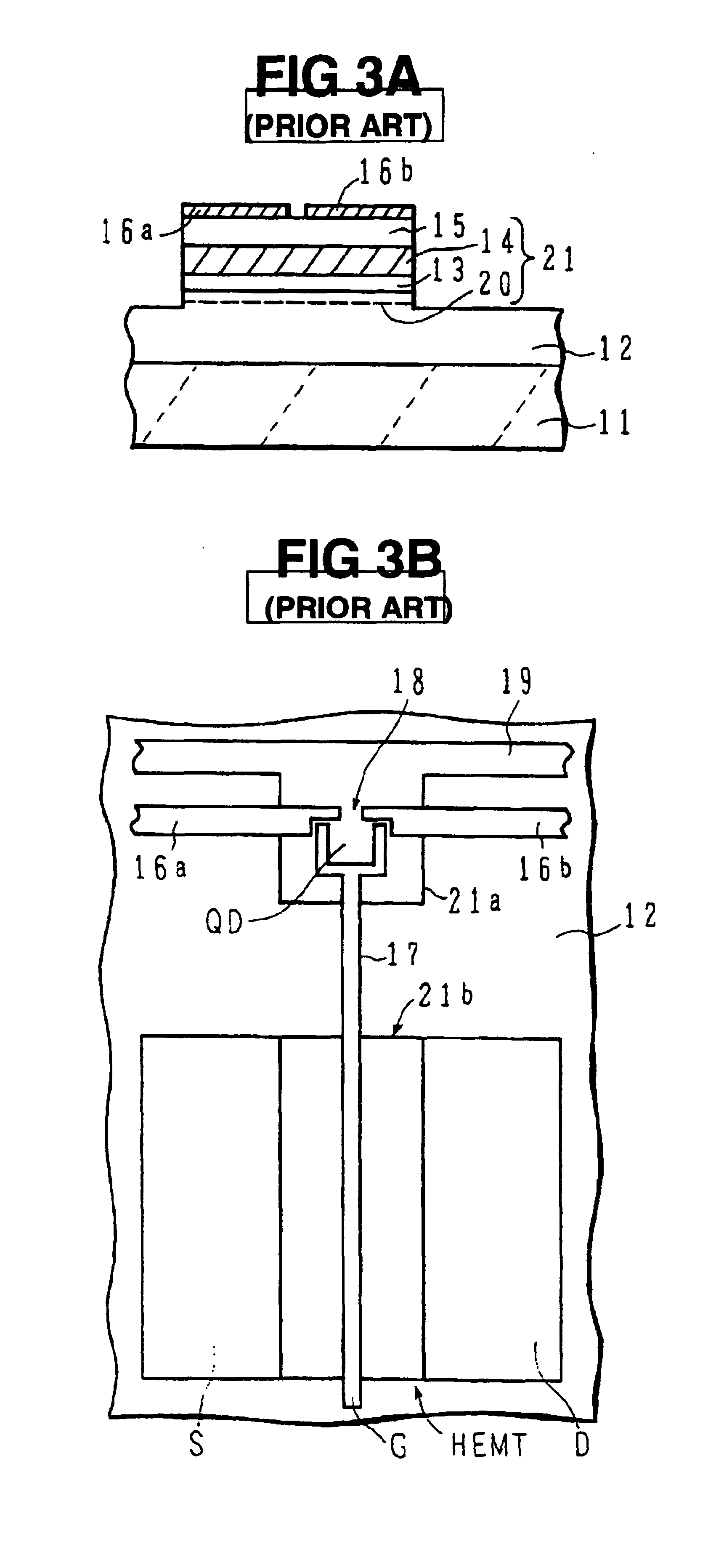
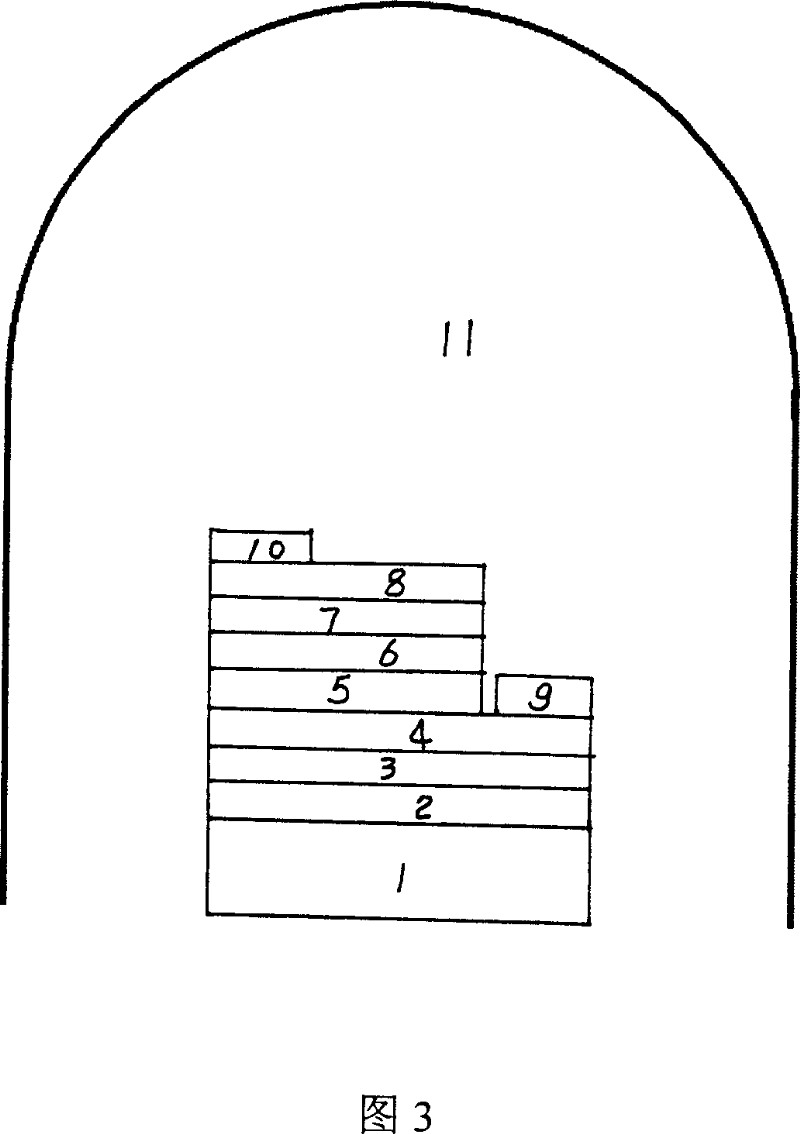
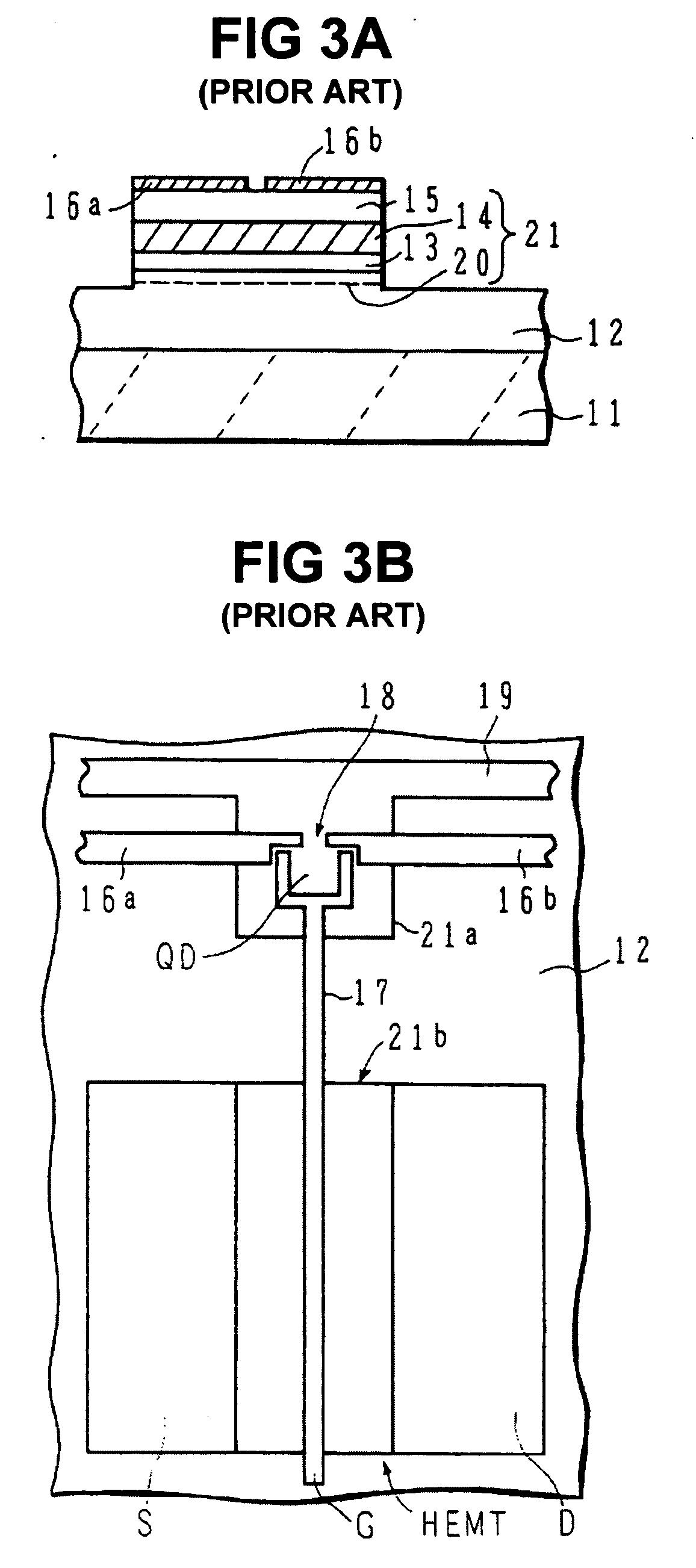
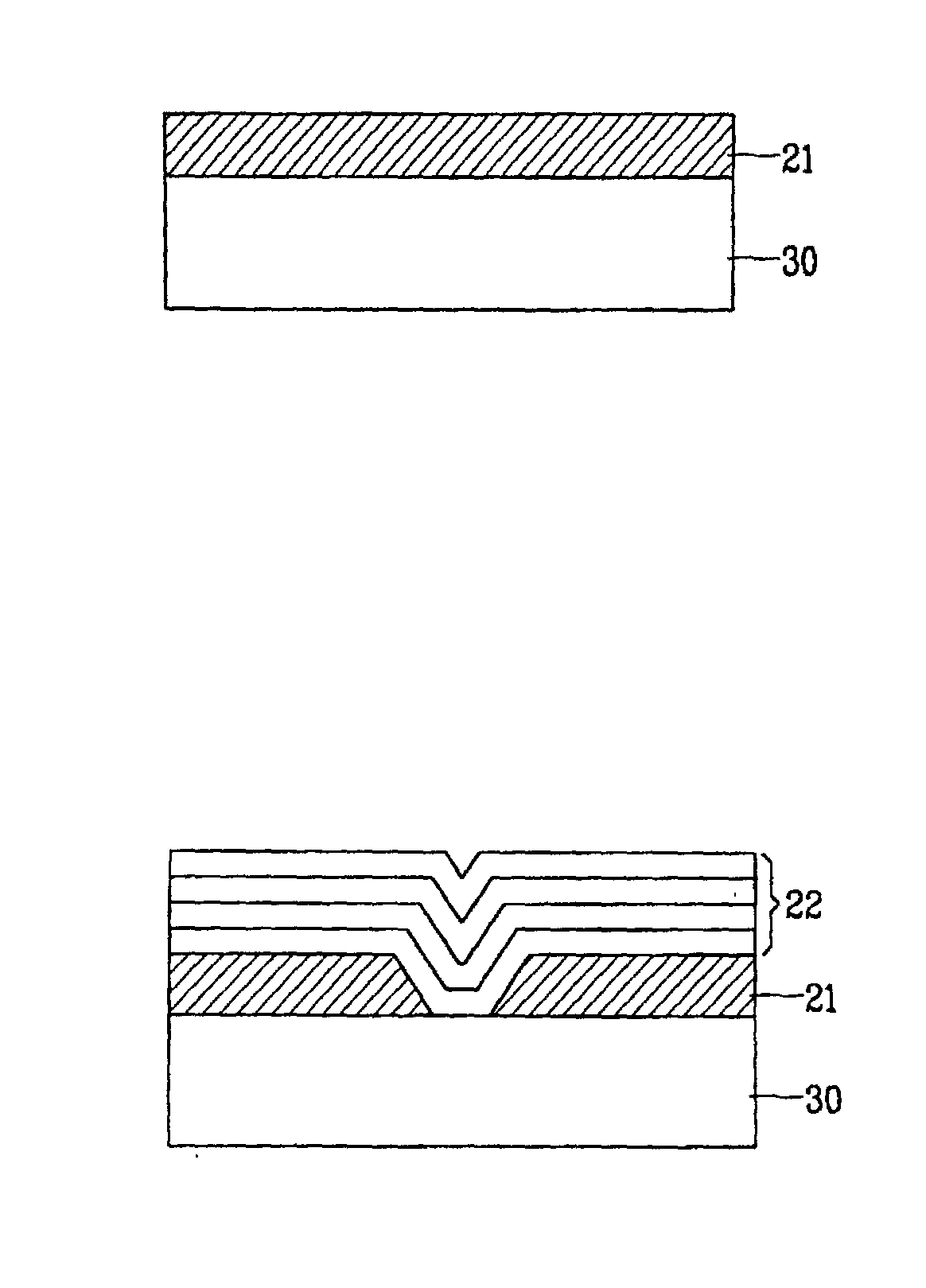
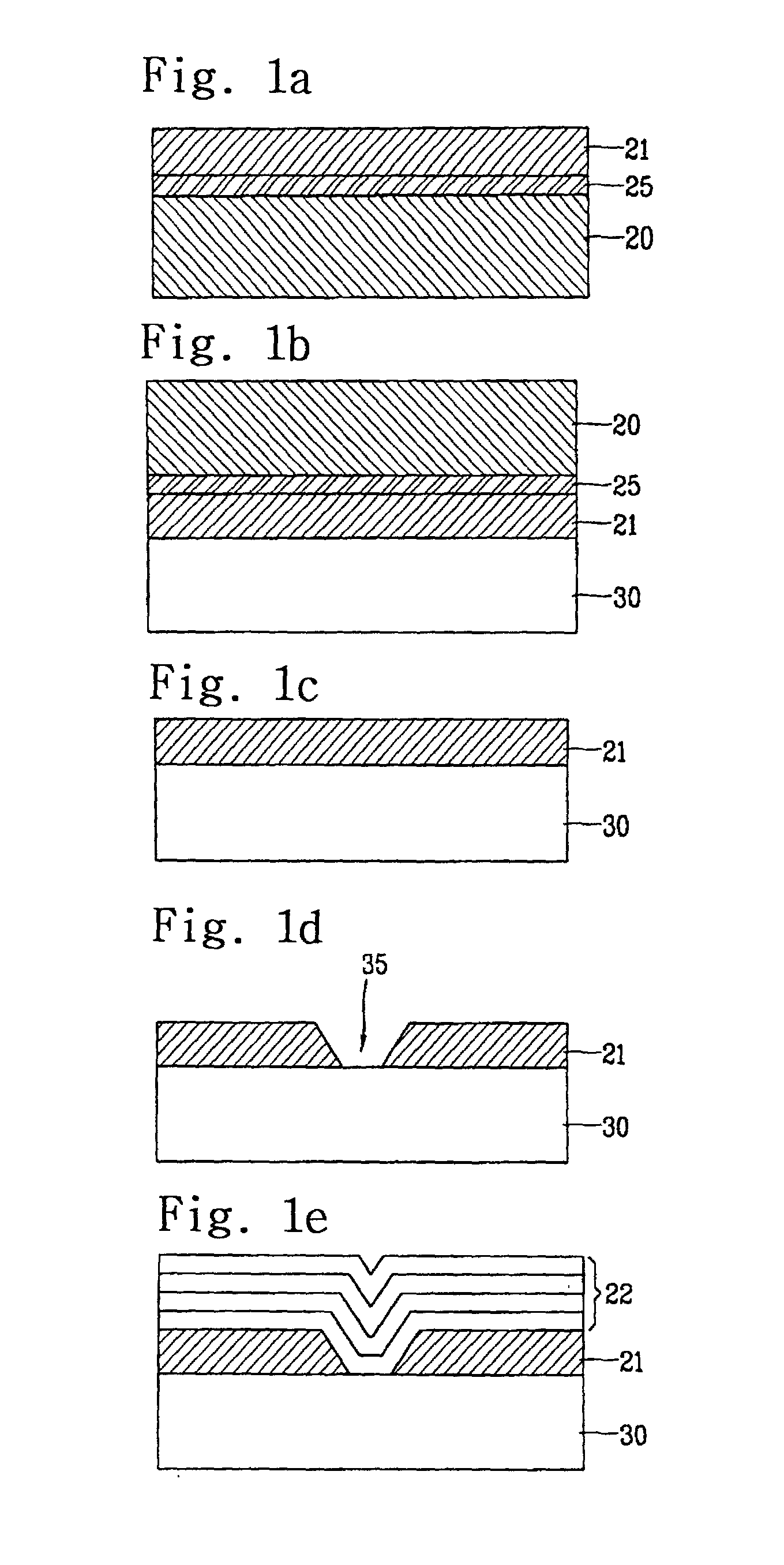
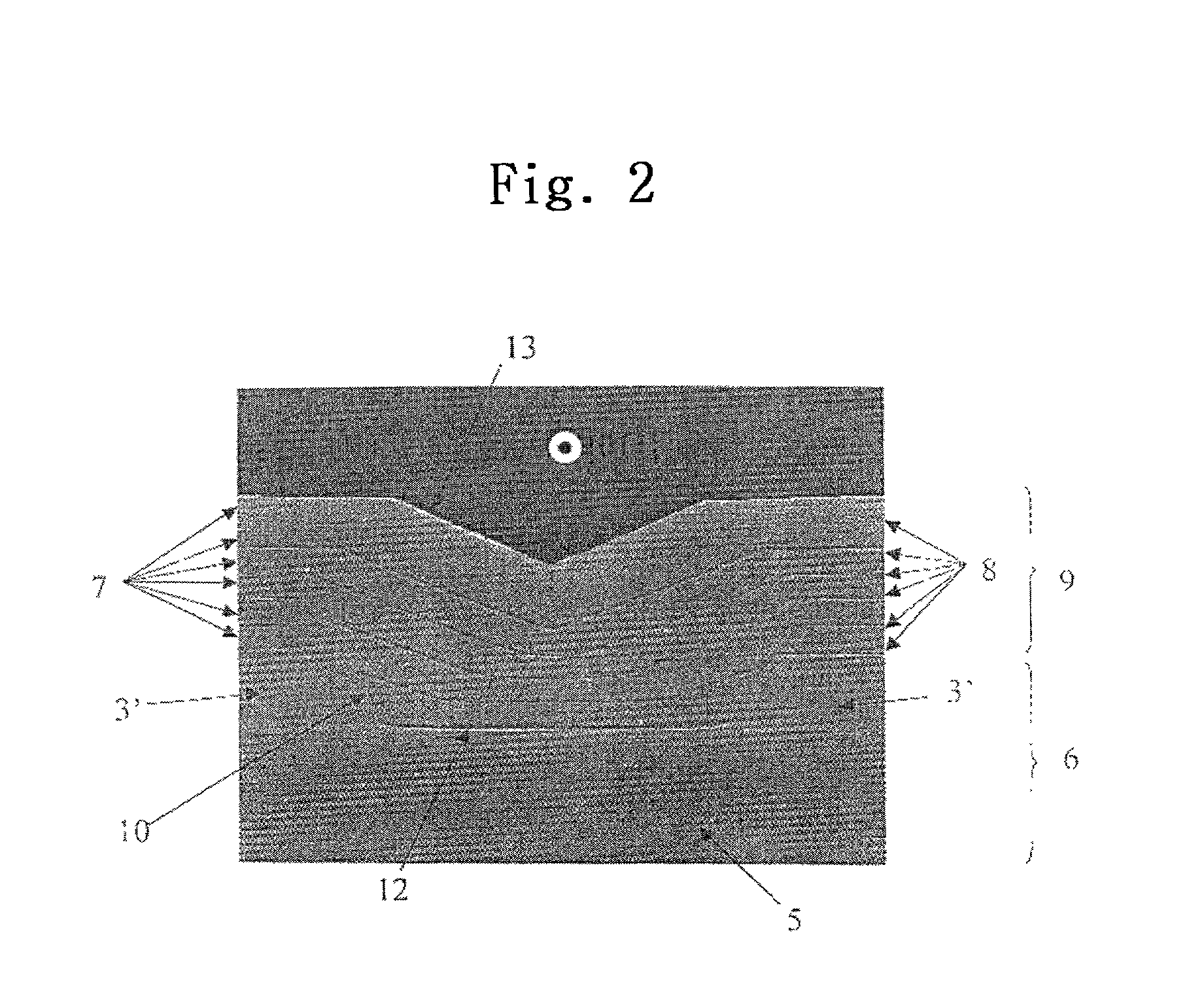
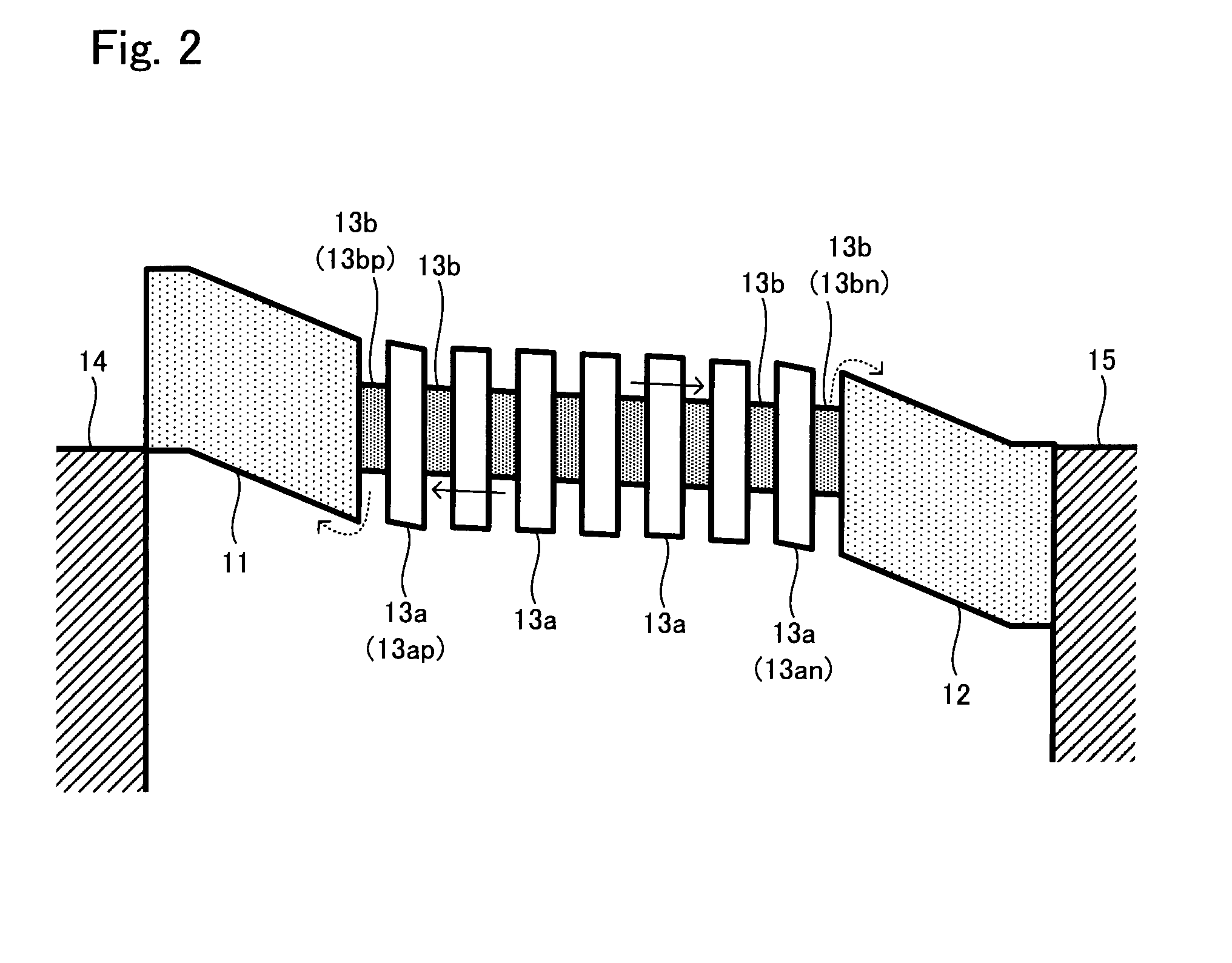
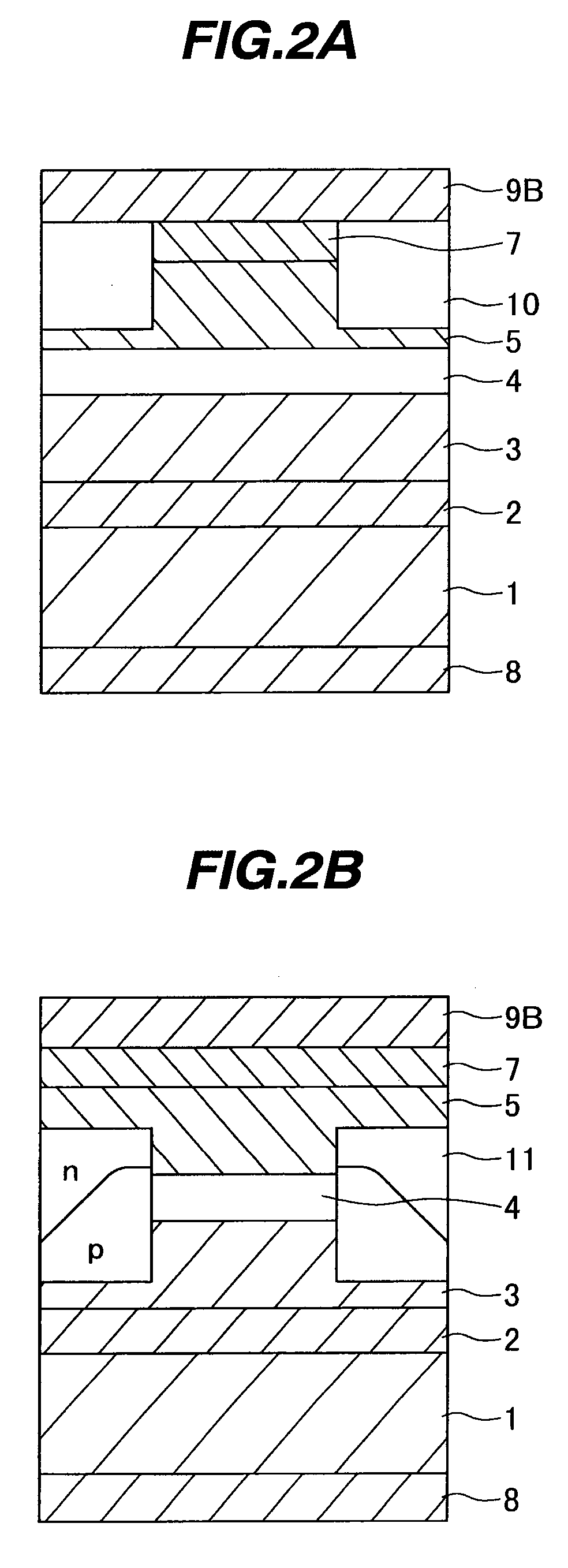
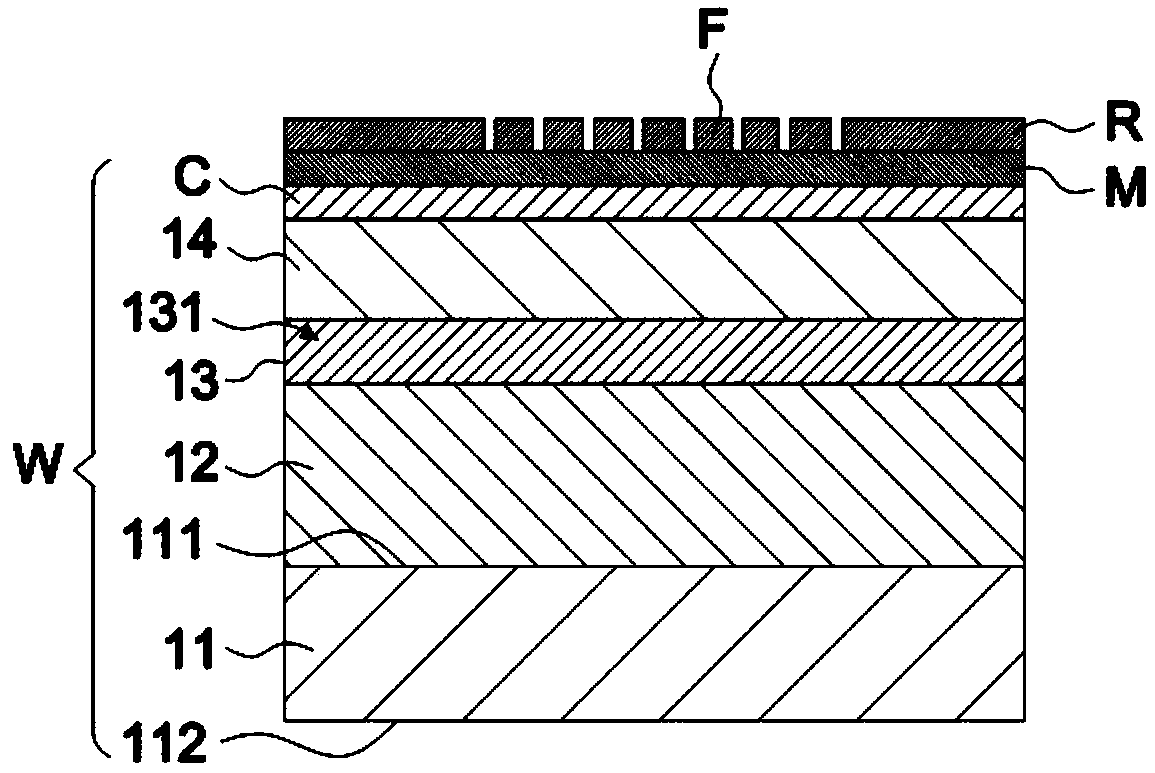
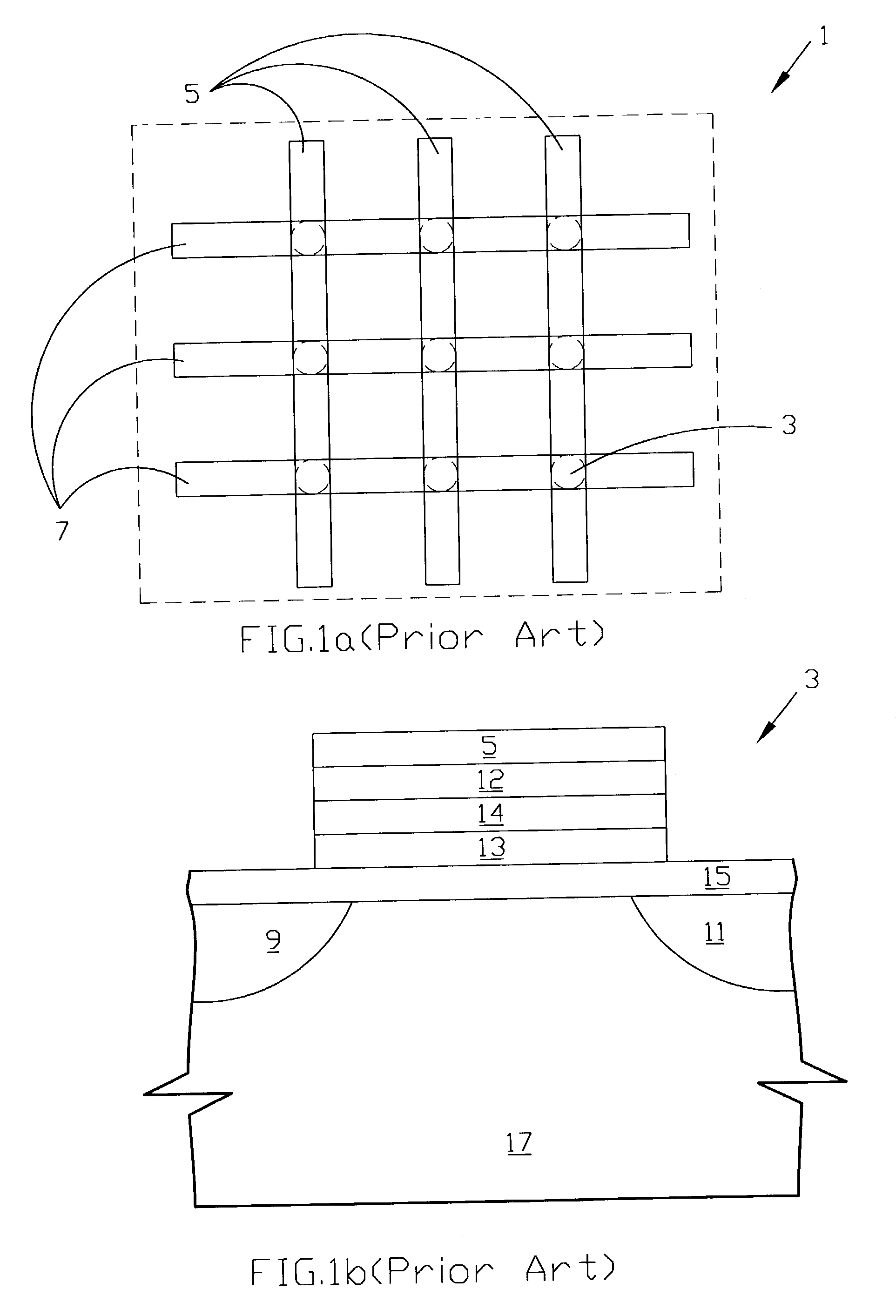
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
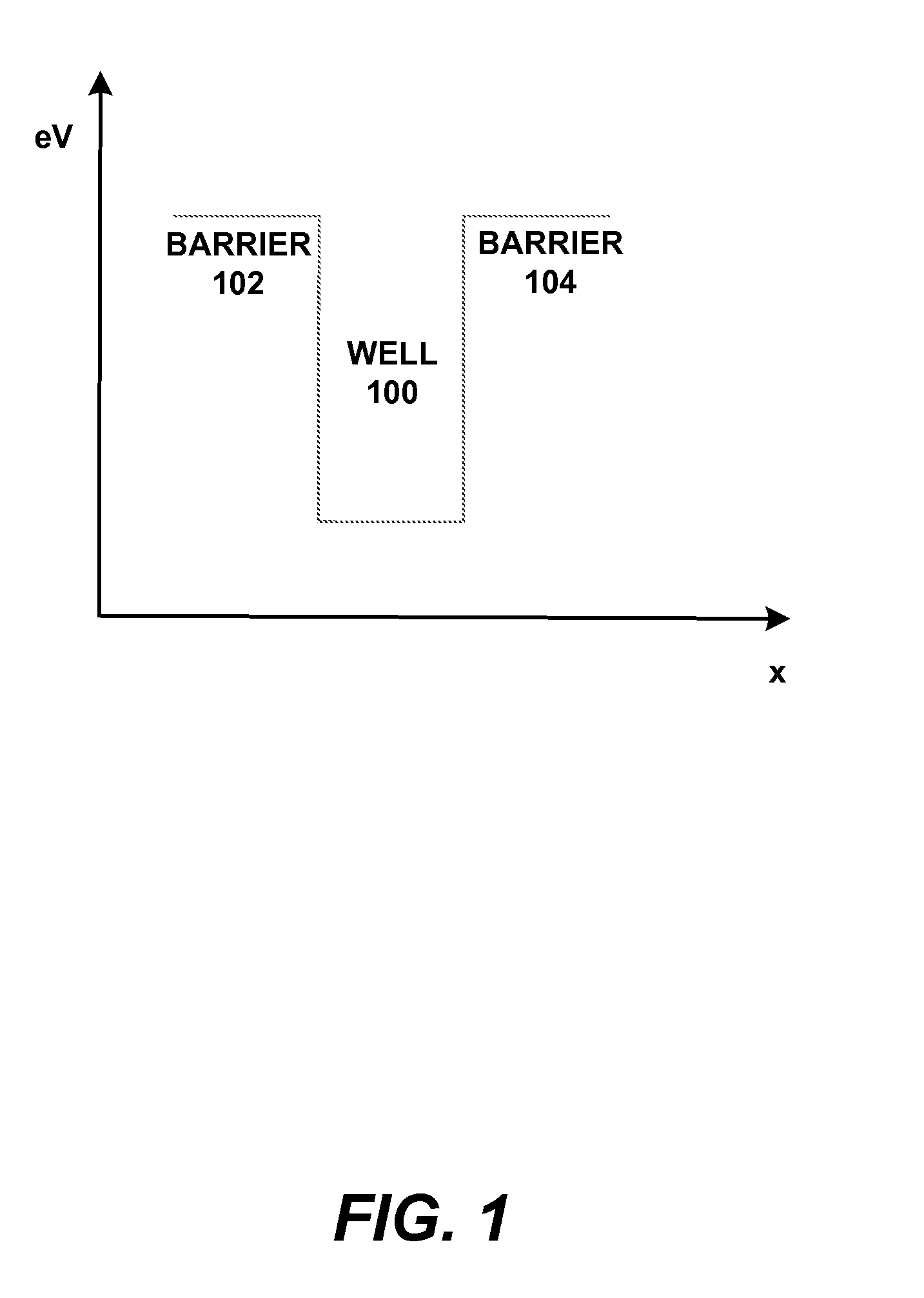
In a semiconductor device, concave sections in which an opening area becomes small in proportion as a depth becomes deep are formed in a crystal layer, and a quantum structure is formed on at least one crystal face of a bottom section of the concave section and a border formed between plural sidewalls thereof. In case the quantum structure is formed in the bottom section, a quantum box is formed therein. If the quantum structure is formed in the border between the sidewalls of the concave section, a quantum wire is formed therein. In case the quantum structure is formed in the sidewall of the concave section, a two-dimensional quantum well is formed therein.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
High Efficiency Broadband Semiconductor Nanowire Devices
Amongst the candidates for very high efficiency electronics, solid state light sources, photovoltaics, and photoelectrochemical devices, and photobiological devices are those based upon metal-nitride nanowires. Enhanced nanowire performance typically require heterostructures, quantum dots, etc which requirement that these structures are grown with relatively few defects and in a controllable reproducible manner. Additionally flexibility according to the device design requires that the nanowire at the substrate may be either InN or GaN. Methods of growing relatively defect free nanowires and associated structures for group IIIA-nitrides are presented without the requirement for foreign metal catalysts, overcoming the non-uniform growth of prior art techniques and allowing self-organizing quantum dot, quantum well and quantum dot-in-a-dot structures to be formed. Such metal-nitride nanowires and quantum structure embedded nanowires support a variety of devices including but not limited to very high efficiency electronics, solid state light sources, photovoltaics, and photoelectrochemical devices, and photobiological devices.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
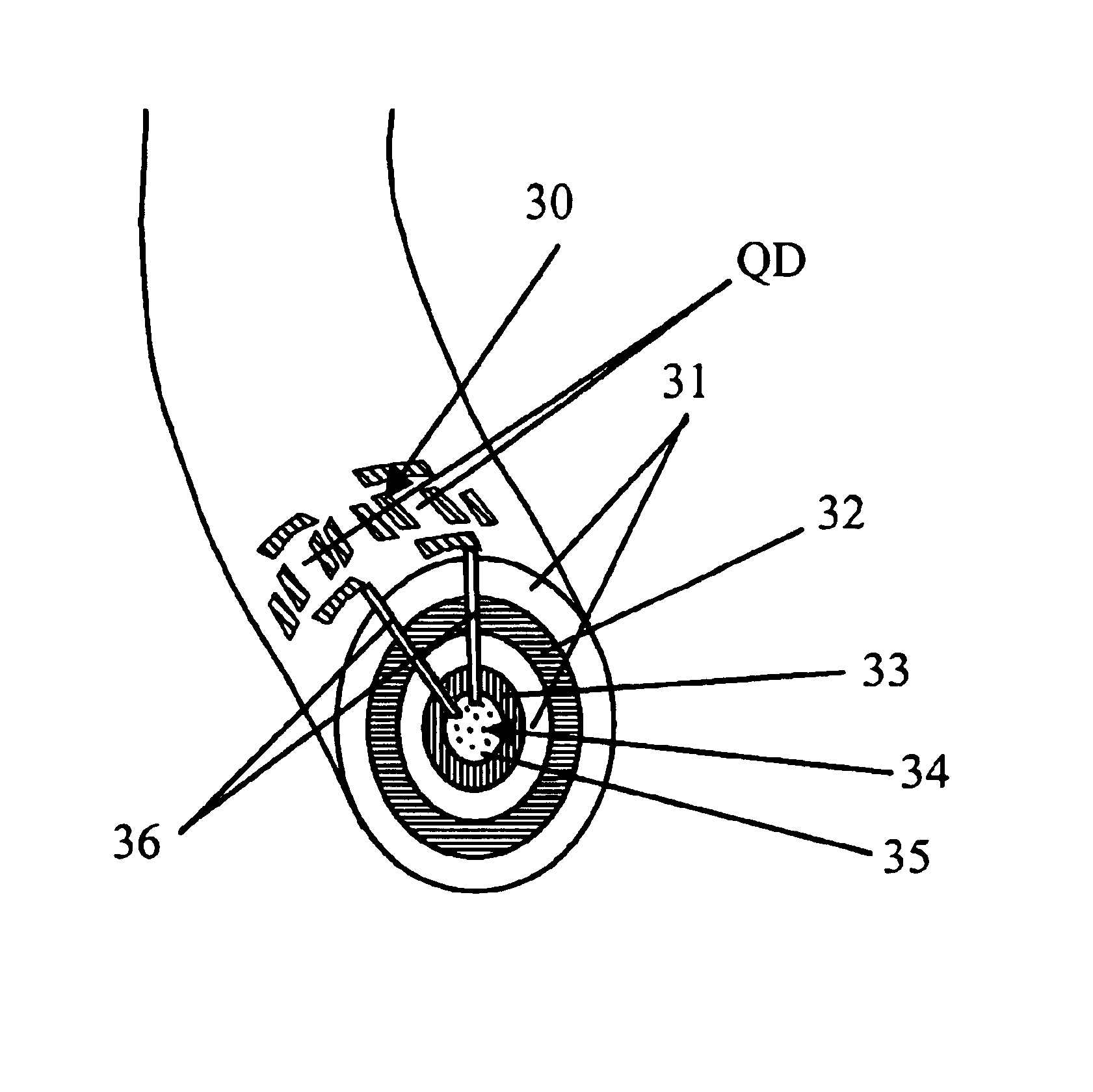
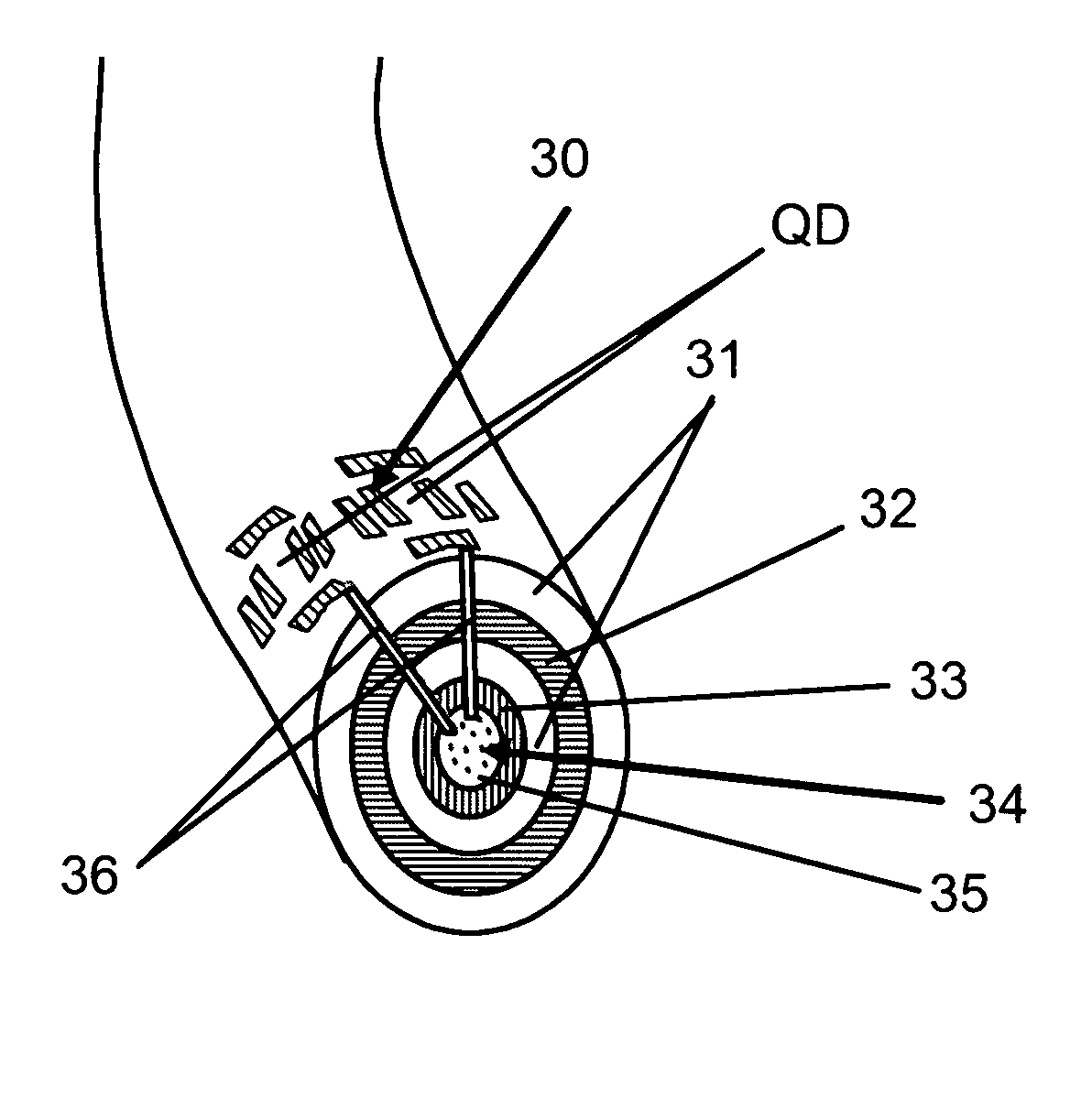
Fiber incorporating quantum dots as programmable dopants
InactiveUS6978070B1Control distortionAltering their doping characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreFiberArtificial atom
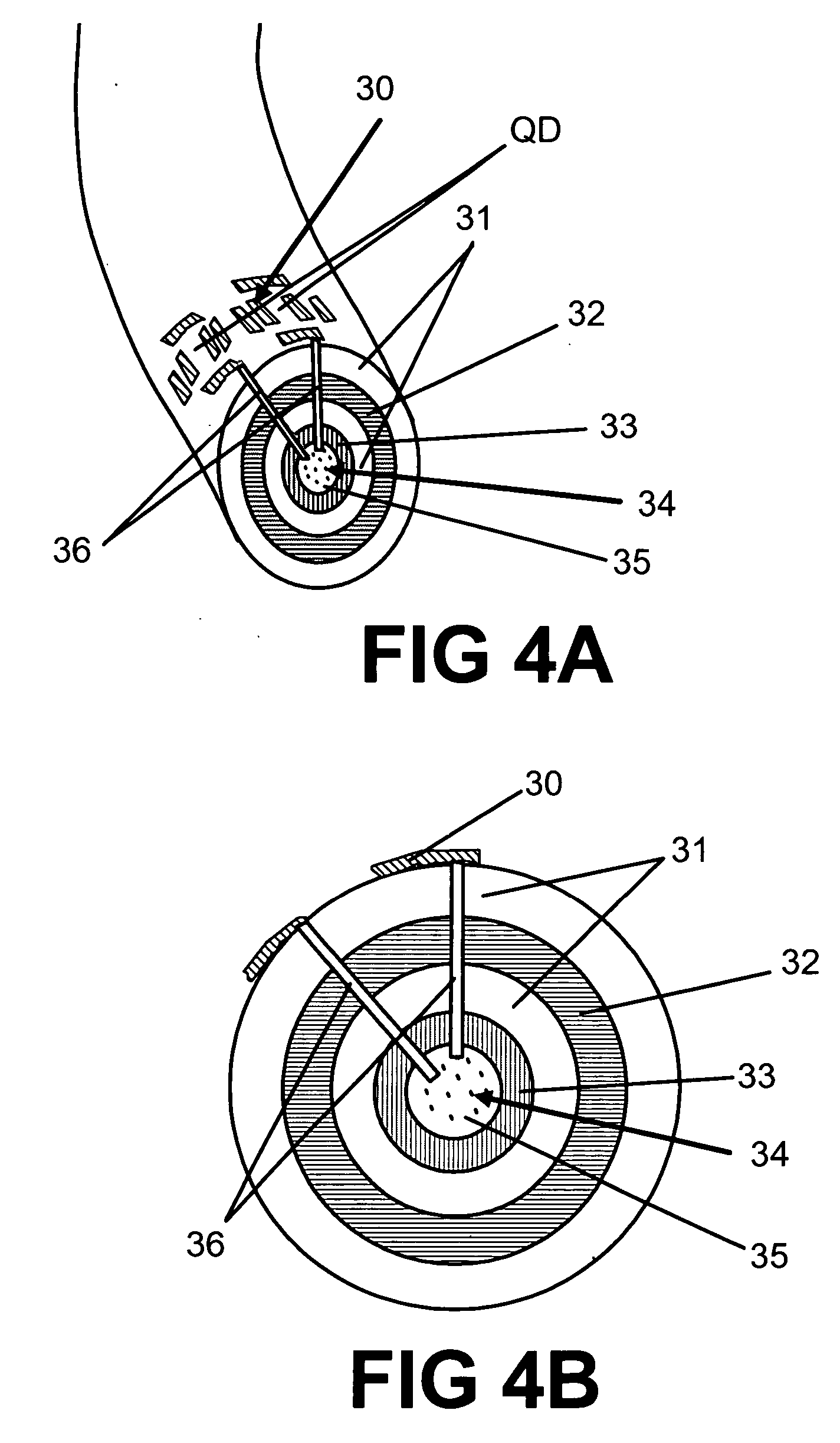
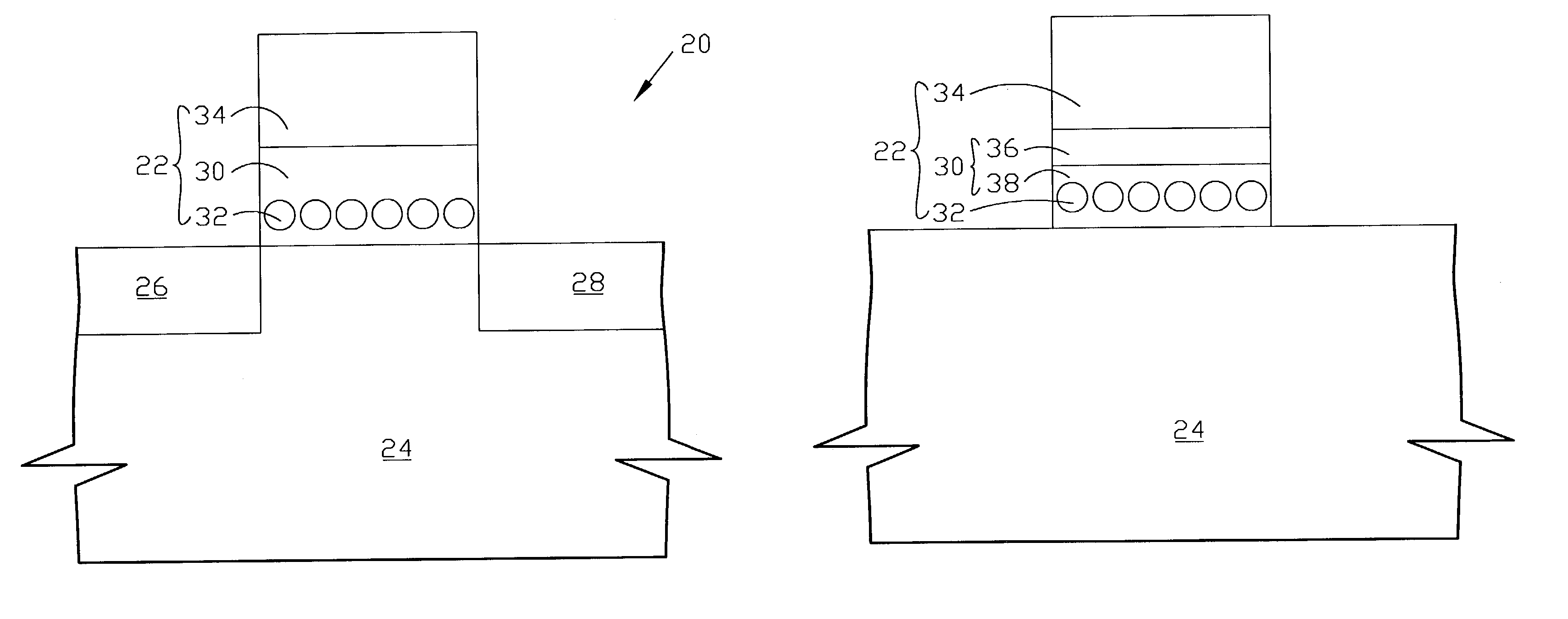
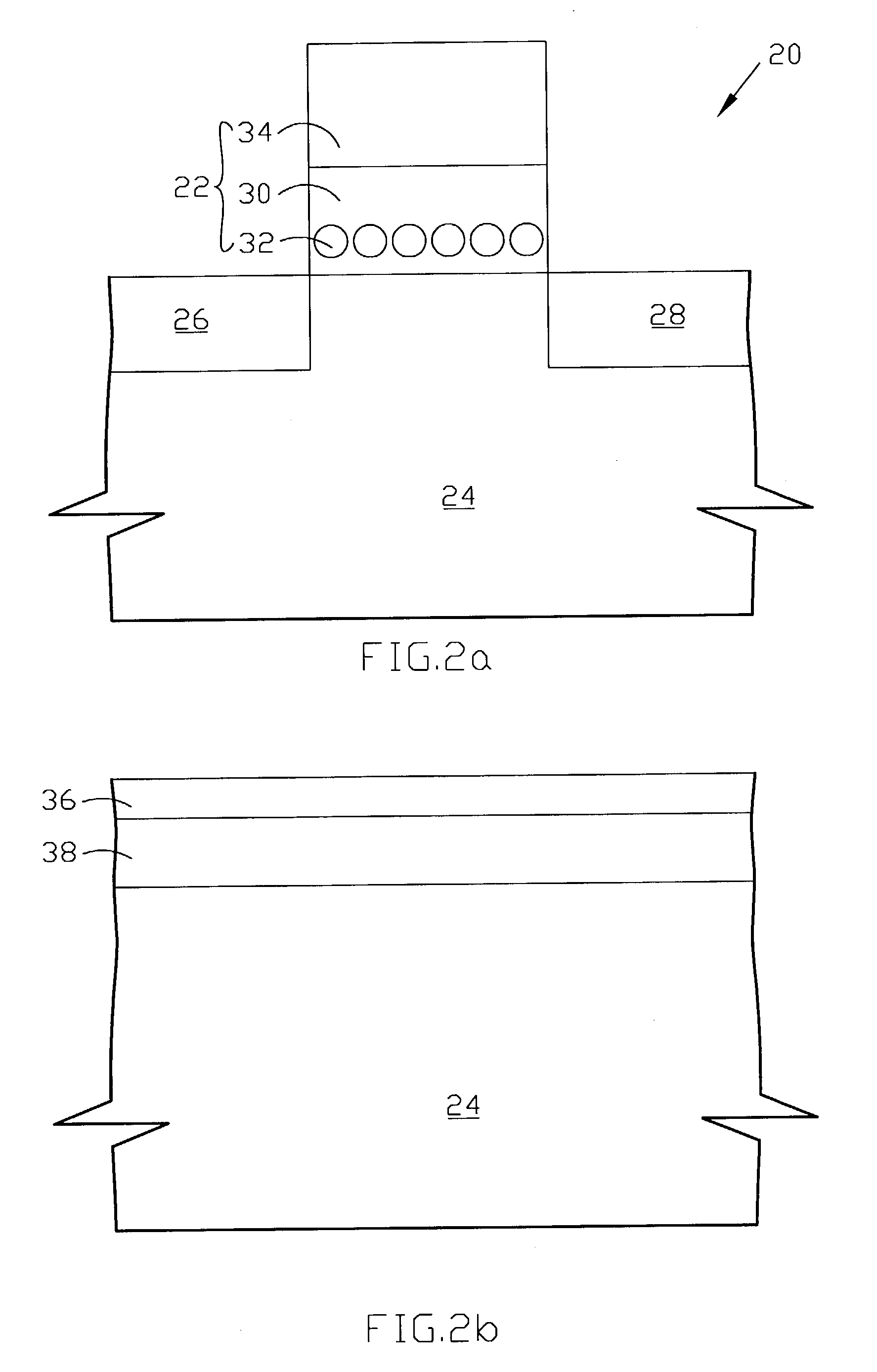
A programmable dopant fiber includes a plurality of quantum structures formed on a fiber-shaped substrate, wherein the substrate includes one or more energy-carrying control paths (34), possibly surrounded by an insulator (35), which pass energy to quantum structures. Quantum structures may include quantum dot particles (37) on the surface of the fiber or electrodes (30) on top of barrier layers (31) and transport layer (32) which form quantum dot devices (QD). The energy passing through the control paths (34) drives charge carriers into the quantum dots (QD), leading to the formation of “artificial atoms” with real-time tunable properties. These artificial atoms then serve as programmable dopants, which alter the behavior of surrounding materials. The fiber can be used as a programmable dopant inside bulk materials, as a building block for new materials with unique properties, or as a substitute for quantum dots or quantum wires in certain applications.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
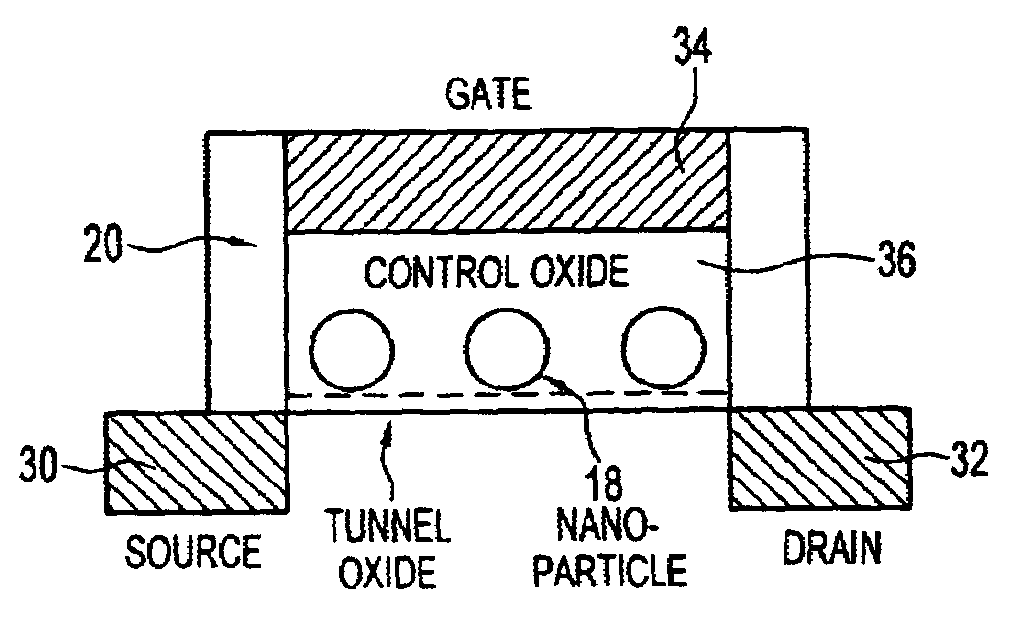
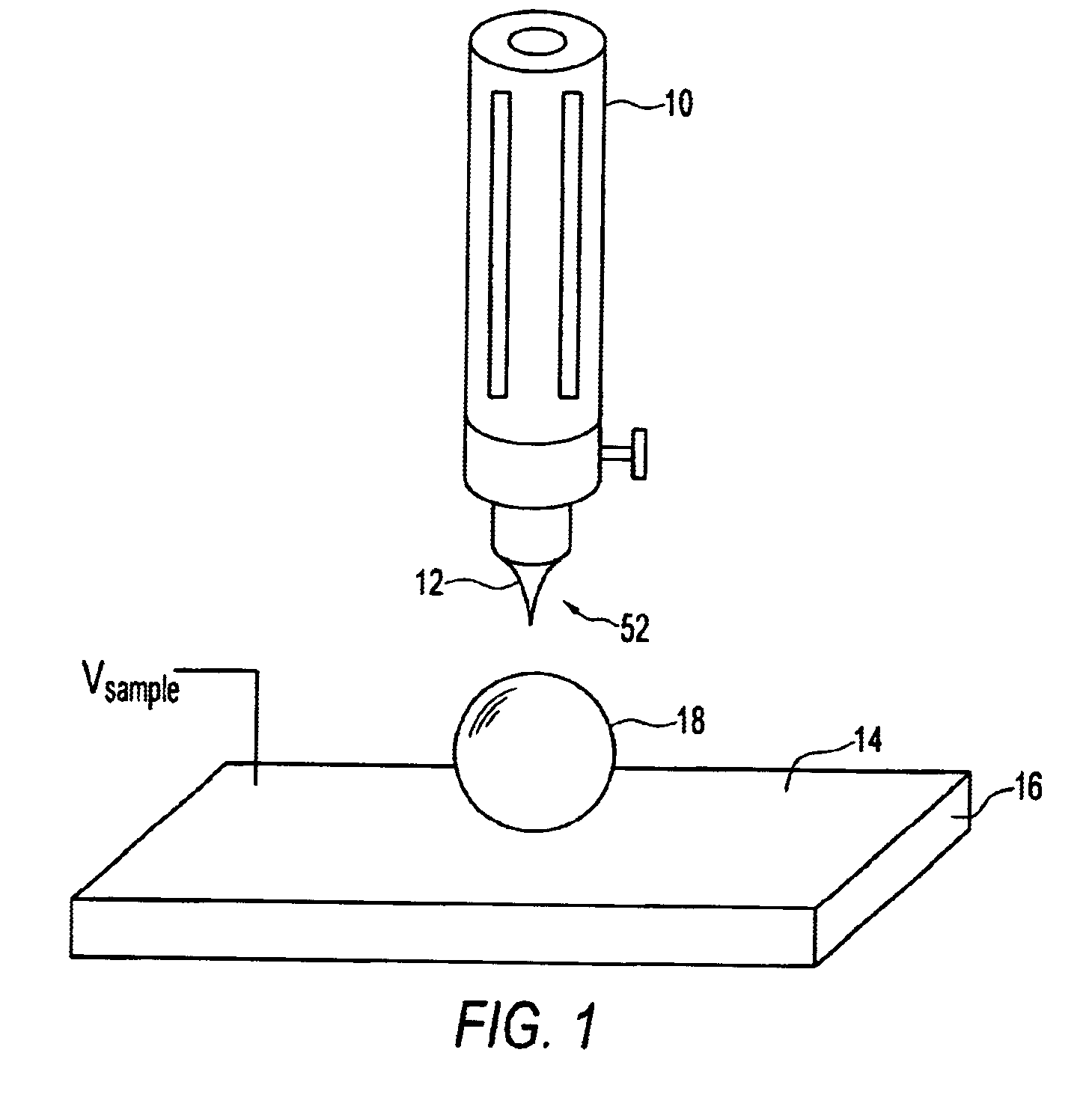
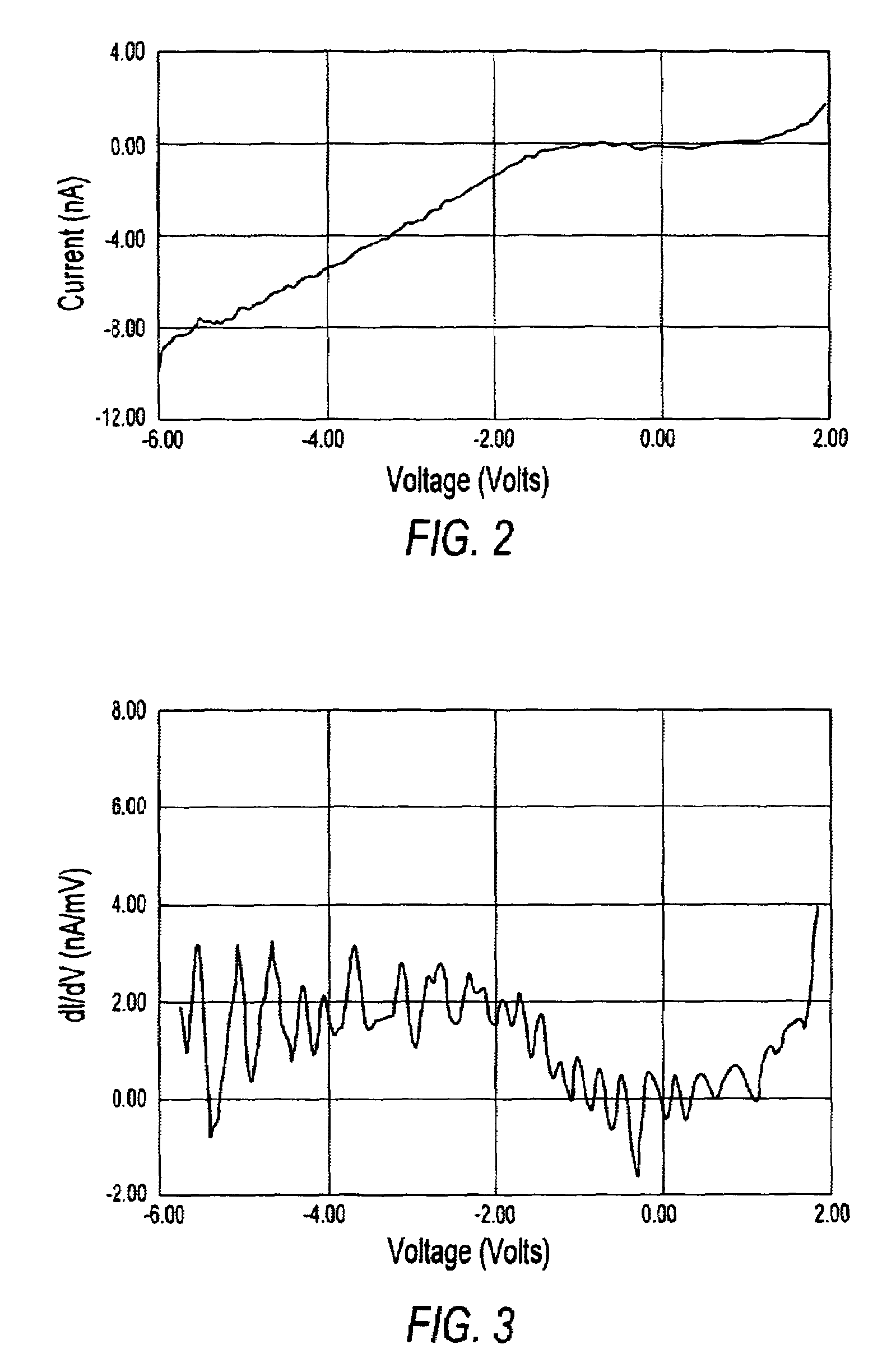
Silicon nanoparticle field effect transistor and transistor memory device
A silicon nanoparticle transistor and transistor memory device. The transistor of the invention has silicon nanoparticles, dimensioned on the order of 1 nm, in a gate area of a field effect transistor. The resulting transistor is a transistor in which single electron flow controls operation of the transistor. Room temperature operation is possible with the novel transistor structure by radiation assistance, with radiation being directed toward the silicon nanoparticles to create necessary holes in the quantum structure for the flow of an electron. The transistor of the invention also forms the basis for a memory device. The device is a flash memory device which will store electrical charge instead of magnetic effects.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Preparation method for small silicon-based nano hollow array with orderly heights
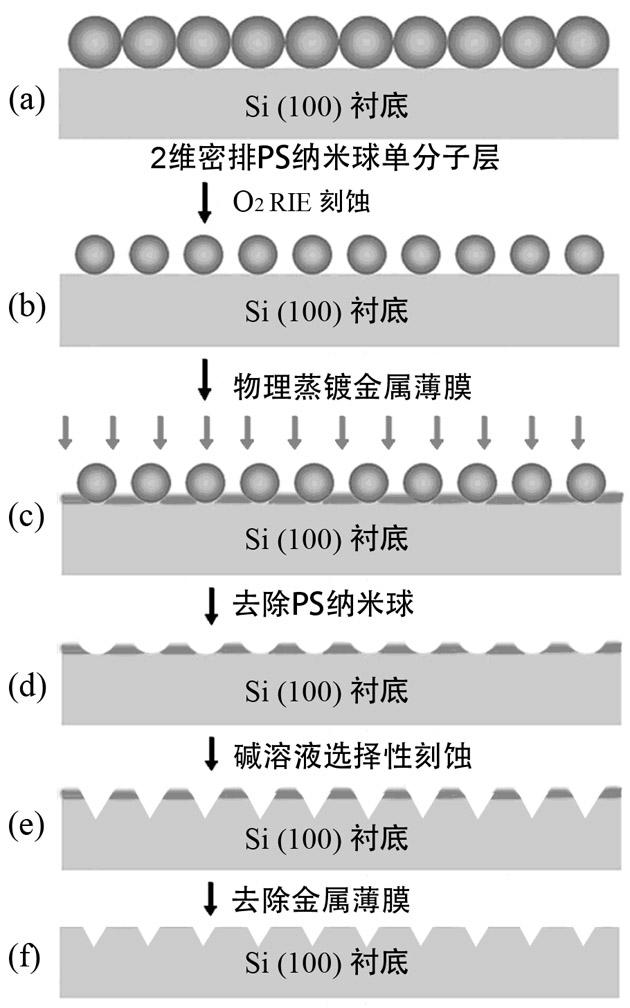
InactiveCN102173376ASmall sizeCycle controllableDecorative surface effectsChemical vapor deposition coatingMagnetic storagePolystyrene
The invention relates to a preparation method for a small silicon-based nano hollow array with orderly heights, belonging to the technical field of nano-structure preparation. The preparation method employs large-diameter polystyrene nano-spheres which are self-mounted into a single-layer nano-sphere film serving as masks on a Si substrate. After going through multiple technical procedures such as reaction ion lithography, direct current sputtering metal films, selective corrosion and the like, the mask is converted into a small inverted-pyramidal nano-hollow array, which is a two-dimensionalhexagonal dot array. The cycle of the nano-hollow arrays is determined by the diameters initially selected for the polystyrene nano-spheres. The invention is likely to be used in fields of growth of controllable quantum structures, photonic crystal manufacturing, quantum logic operation, magnetic storage media, etc.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
White light GaN LED epitaxial material without fluorescent powder conversion and method for making the same
InactiveCN101038947AThe production process is simpleLow costSemiconductor devicesPhosphorQuantum dot
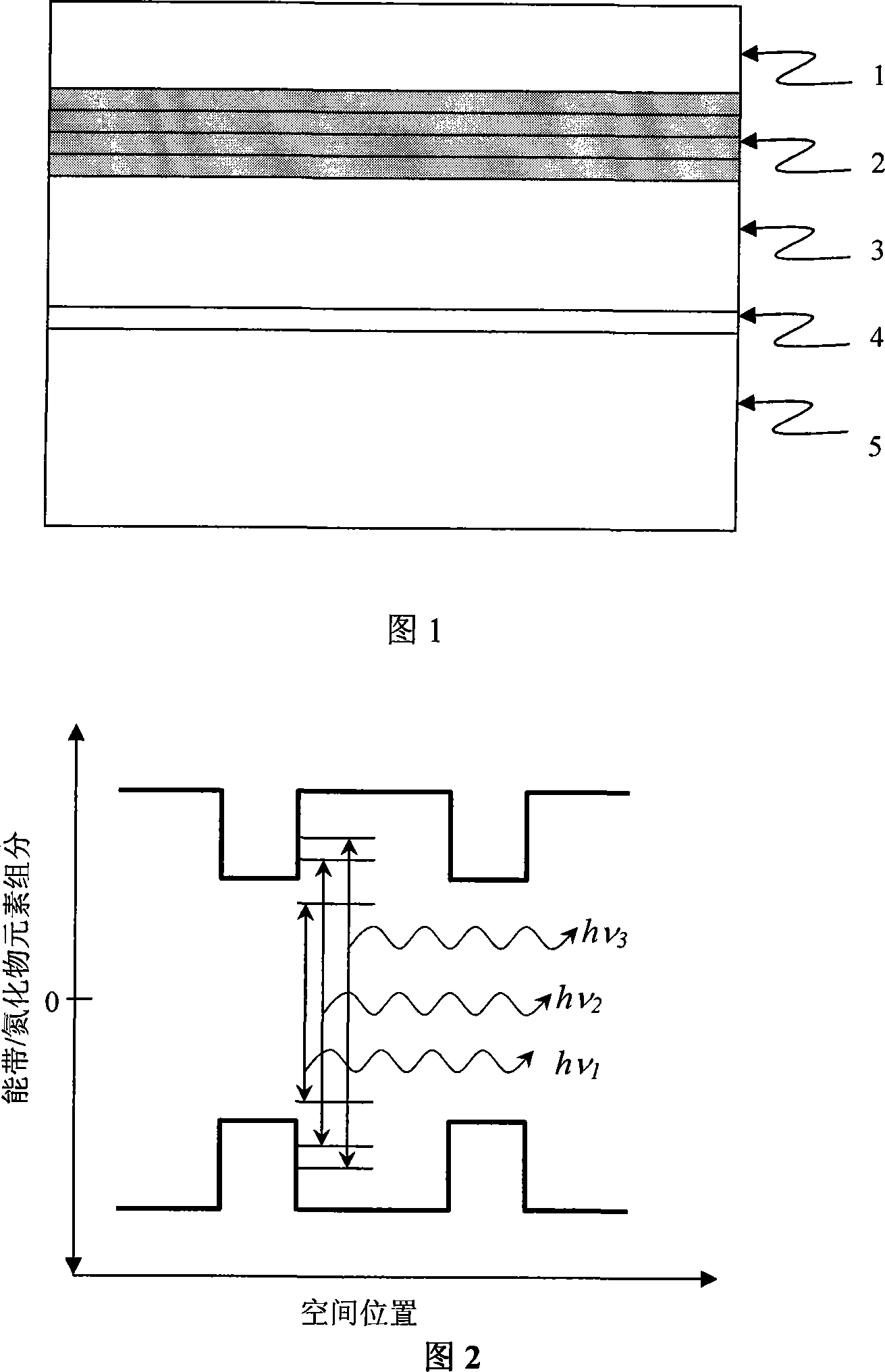
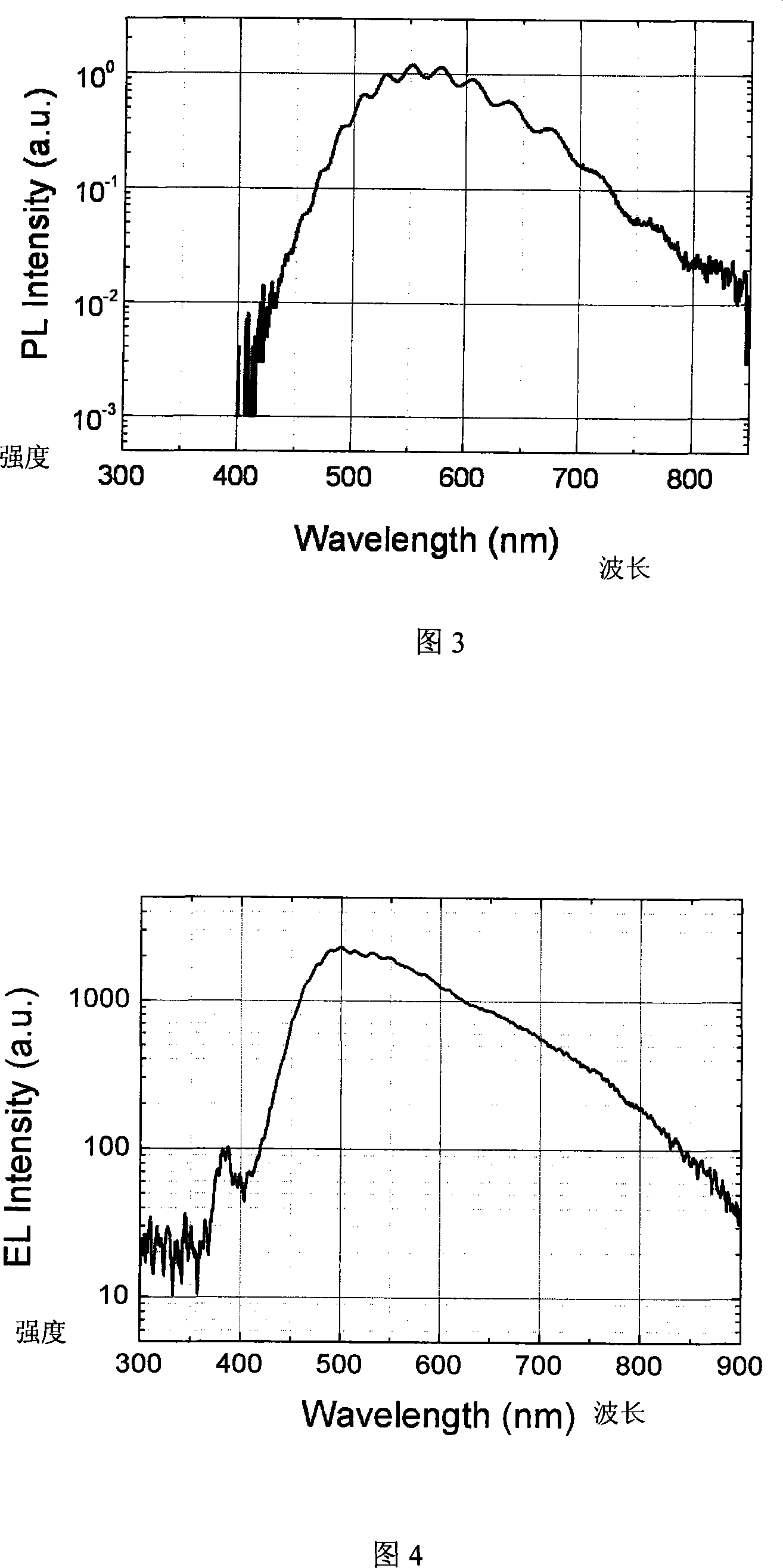
The invention relates to epitaxial material of white light GaN light emitting diode which requires no phosphor for conversion and manufacturing method thereof, i.e. employing conventional semiconductor device deposition technique to orderly deposit an initial growth layer, an intrinsic GaN buffer layer, a n-type GaN layer, a InGaN relaxation layer, an InGaN luminescent layer of multi quantum structure, a p-type AlGaN interlayer and a p-type GaN layer; and employing the epitaxial material to make single chip white light light emitting diode; the method preserves the manufacturing techniques for making current normal monochromatic light light emitting diode device, and only improves the growth process of the GaN based luminescent material, thus, the In component achieves the level to form In quantum dot, and a stress releasing layer is added. In this manner, in the precondition of not increasing the complexity of the device, the production cost for making white light light emitting diode can be basically reduced, and the light emitting efficiency and utilization can be increased, and the weakness of the white light light emitting diode which employs phosphor for conversion can be overcome, and the whole performance of white light light emitting diode can be improved.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fiber incorporating quantum dots as programmable dopants
InactiveUS20050157996A1Control distortionAltering their doping characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreFiberArtificial atom
A programmable dopant fiber includes a plurality of quantum structures formed on a fiber-shaped substrate, wherein the substrate includes one or more energy-carrying control paths, which pass energy to quantum structures. Quantum structures may include quantum dot particles on the surface of the fiber or electrodes on top of barrier layers and a transport layer, which form quantum dot devices. The energy passing through the control paths drives charge carriers into the quantum dots, leading to the formation of “artificial atoms” with real-time, tunable properties. These artificial atoms then serve as programmable dopants, which alter the behavior of surrounding materials. The fiber can be used as a programmable dopant inside bulk materials, as a building block for new materials with unique properties, or as a substitute for quantum dots or quantum wires in certain applications.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
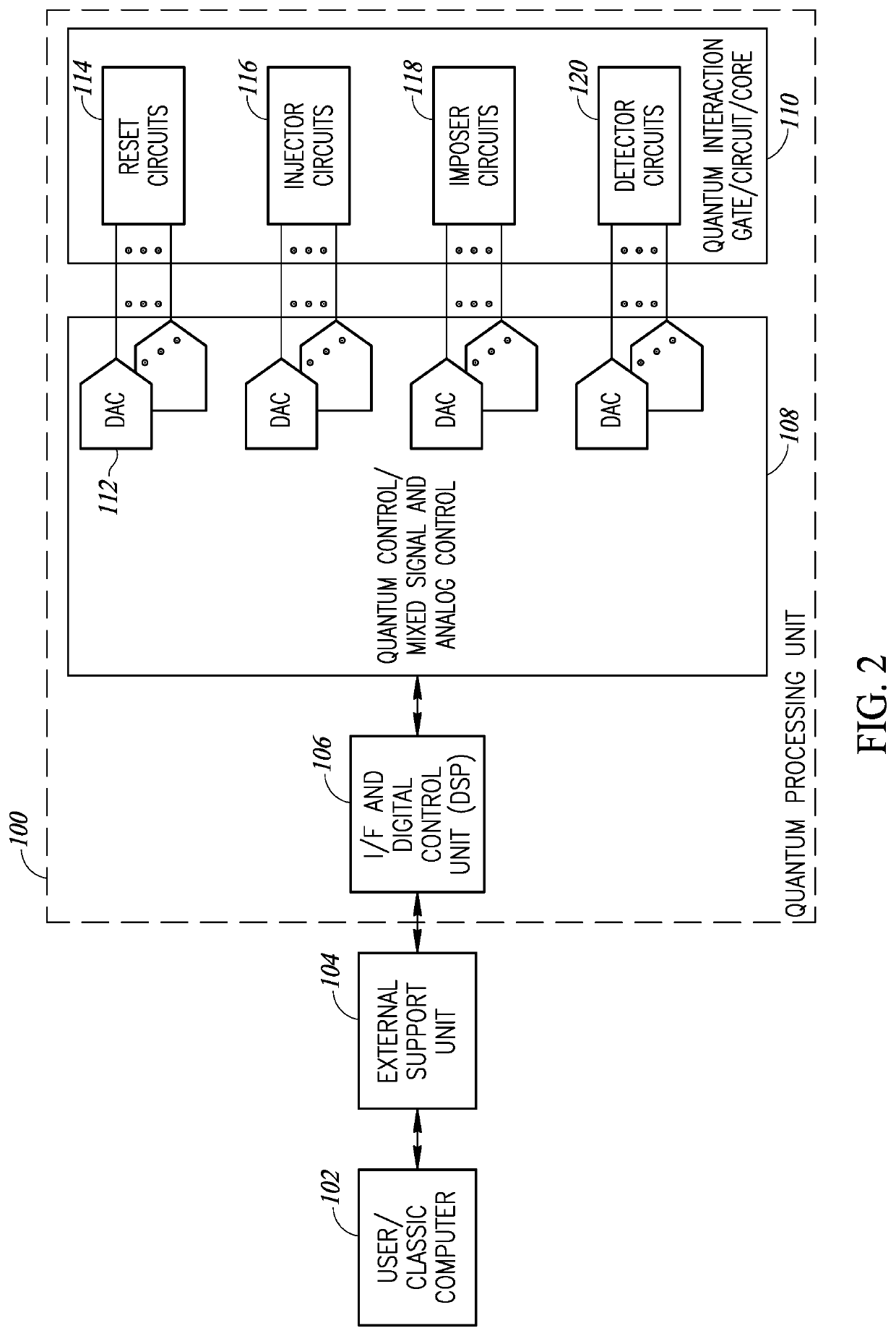
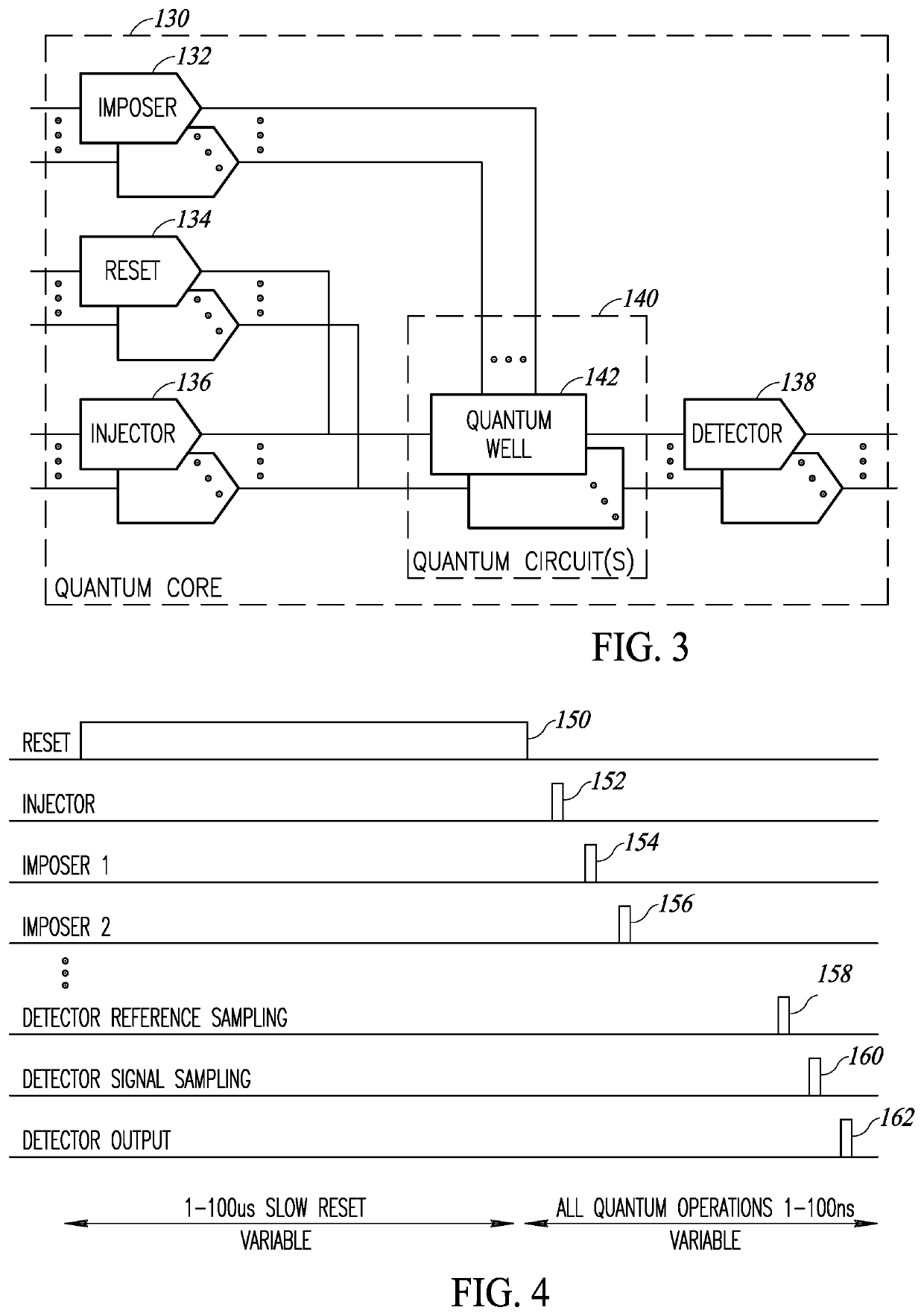
Quantum shift register based ancillary quantum interaction gates
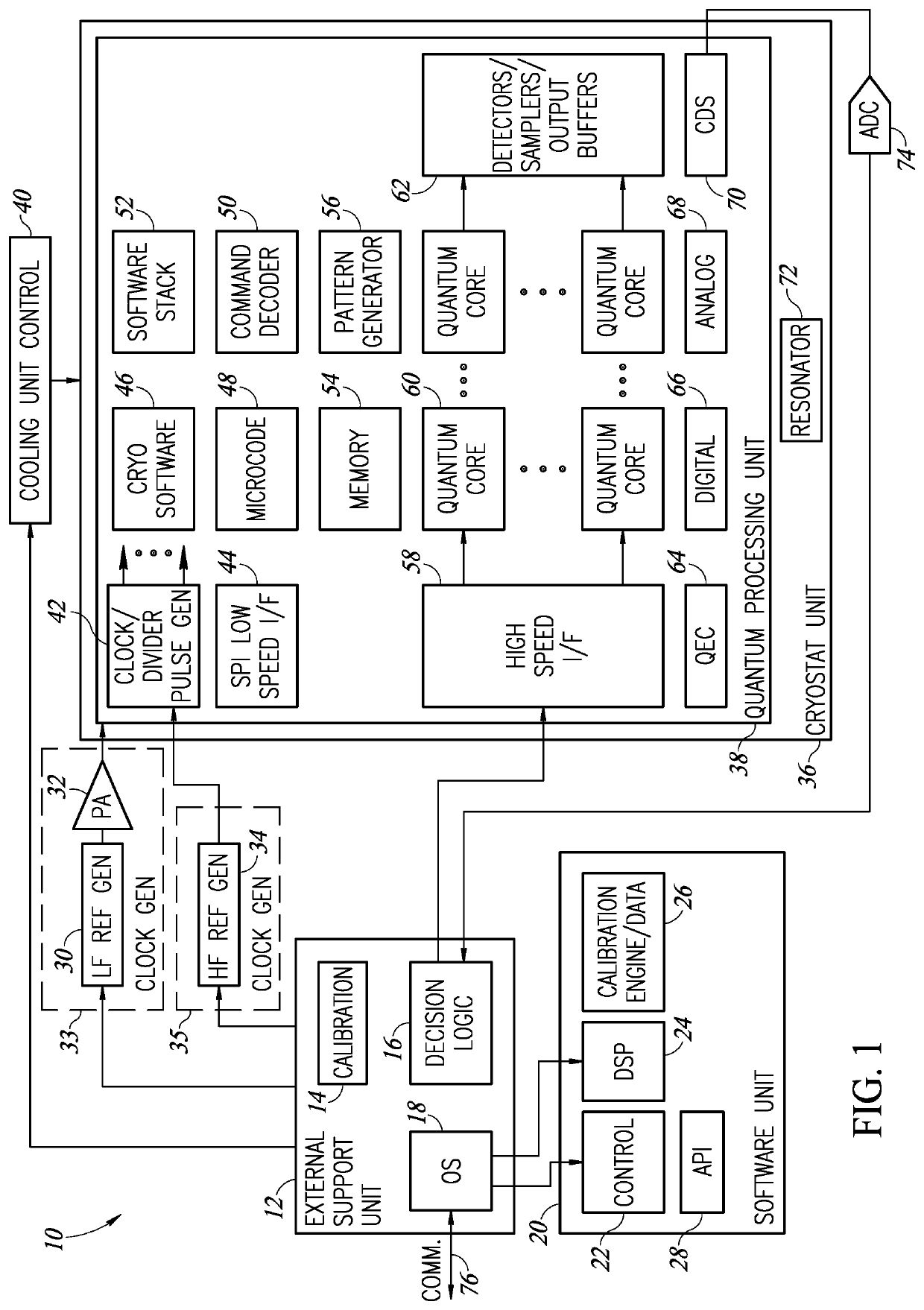
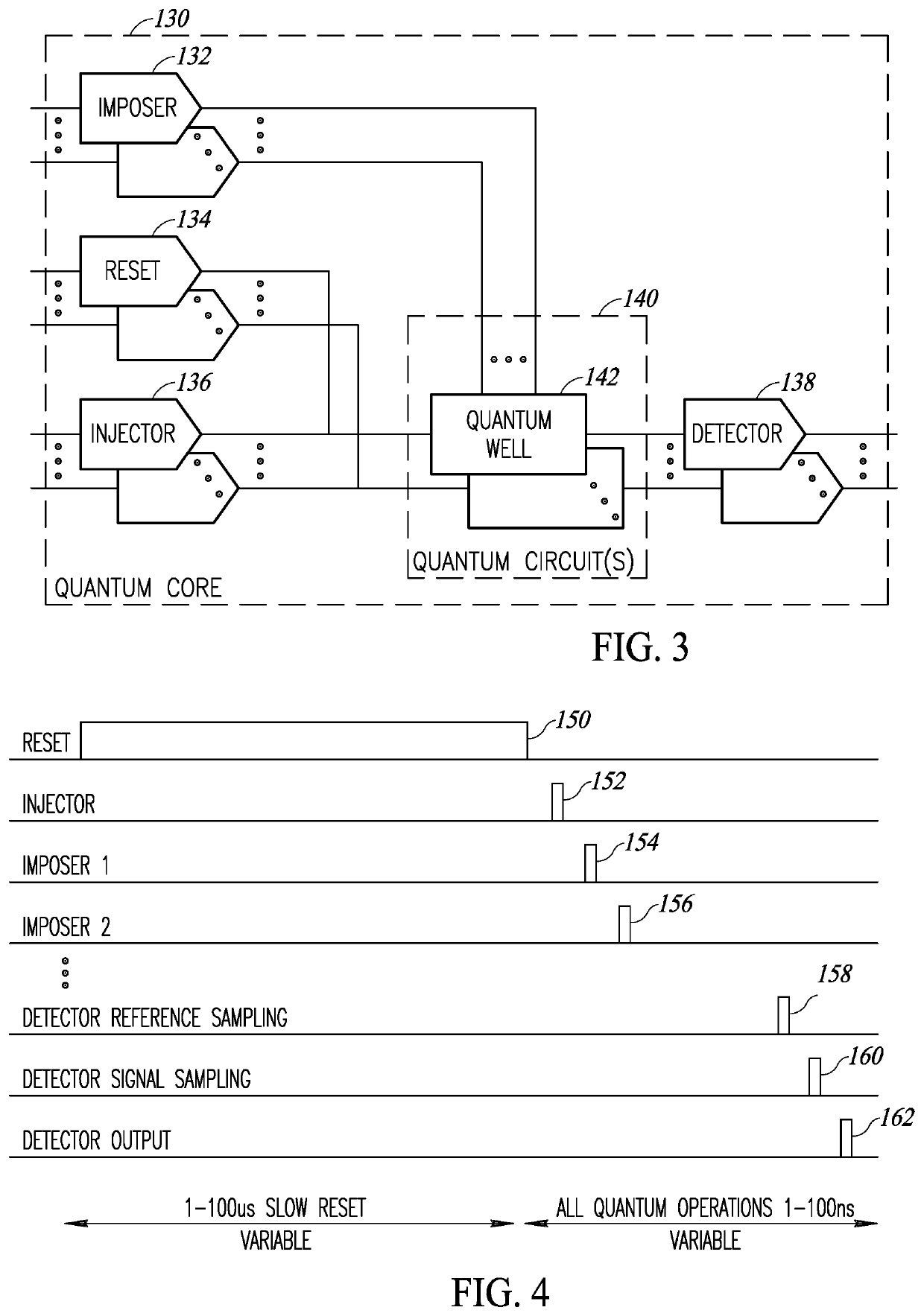
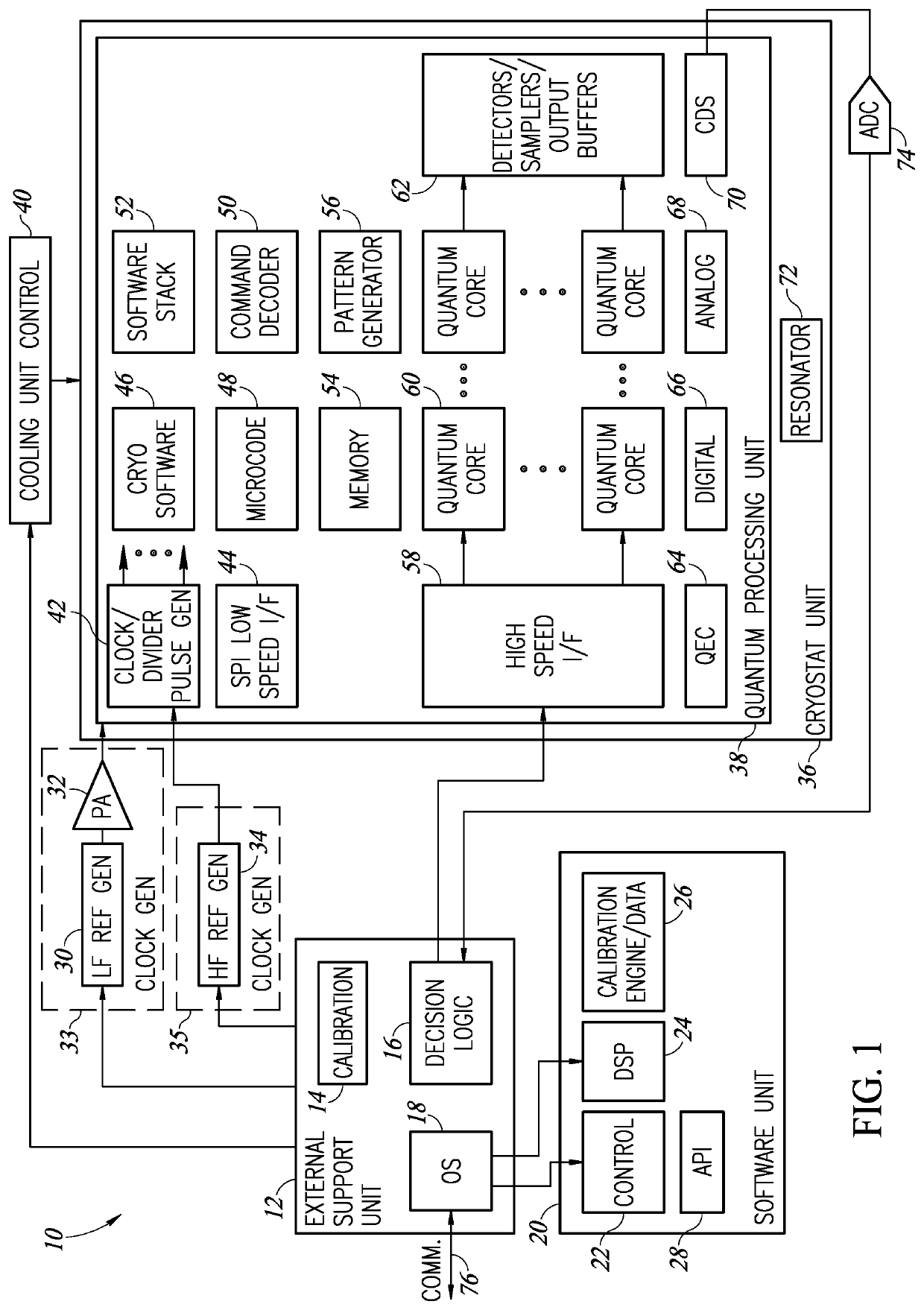
A novel and useful controlled quantum shift register for transporting particles from one quantum dot to another in a quantum structure. The shift register incorporates a succession of qdots with tunneling paths and control gates. Applying appropriate control signals to the control gates, a particle or a split quantum state is made to travel along the shift register. The shift register also includes ancillary double interaction where two pairs of quantum dots provide an ancillary function where the quantum state of one pair is replicated in the second pair. The shift register also provides bifurcation where an access path is split into two or more paths. Depending on the control pulse signals applied, quantum dots are extended into multiple paths. Control of the shift register is provided by electric control pulses. An optional auxiliary magnetic field provides additional control of the shift register.
Owner:EQUAL1 LABS INC
Quantum shift register incorporating bifurcation
A novel and useful controlled quantum shift register for transporting particles from one quantum dot to another in a quantum structure. The shift register incorporates a succession of qdots with tunneling paths and control gates. Applying appropriate control signals to the control gates, a particle or a split quantum state is made to travel along the shift register. The shift register also includes ancillary double interaction where two pairs of quantum dots provide an ancillary function where the quantum state of one pair is replicated in the second pair. The shift register also provides bifurcation where an access path is split into two or more paths. Depending on the control pulse signals applied, quantum dots are extended into multiple paths. Control of the shift register is provided by electric control pulses. An optional auxiliary magnetic field provides additional control of the shift register.
Owner:EQUAL1 LABS INC
Fiber incorporating quantum dots as programmable dopants
InactiveUS20050157997A1Control distortionAltering their doping characteristicsMaterial nanotechnologyCladded optical fibreFiberArtificial atom
A programmable dopant fiber includes a plurality of quantum structures formed on a fiber-shaped substrate, wherein the substrate includes one or more energy-carrying control paths, which pass energy to quantum structures. Quantum structures may include quantum dot particles on the surface of the fiber or electrodes on top of barrier layers and a transport layer, which form quantum dot devices. The energy passing through the control paths drives charge carriers into the quantum dots, leading to the formation of “artificial atoms” with real-time, tunable properties. These artificial atoms then serve as programmable dopants, which alter the behavior of surrounding materials. The fiber can be used as a programmable dopant inside bulk materials, as a building block for new materials with unique properties, or as a substitute for quantum dots or quantum wires in certain applications.
Owner:RAVENBRICK
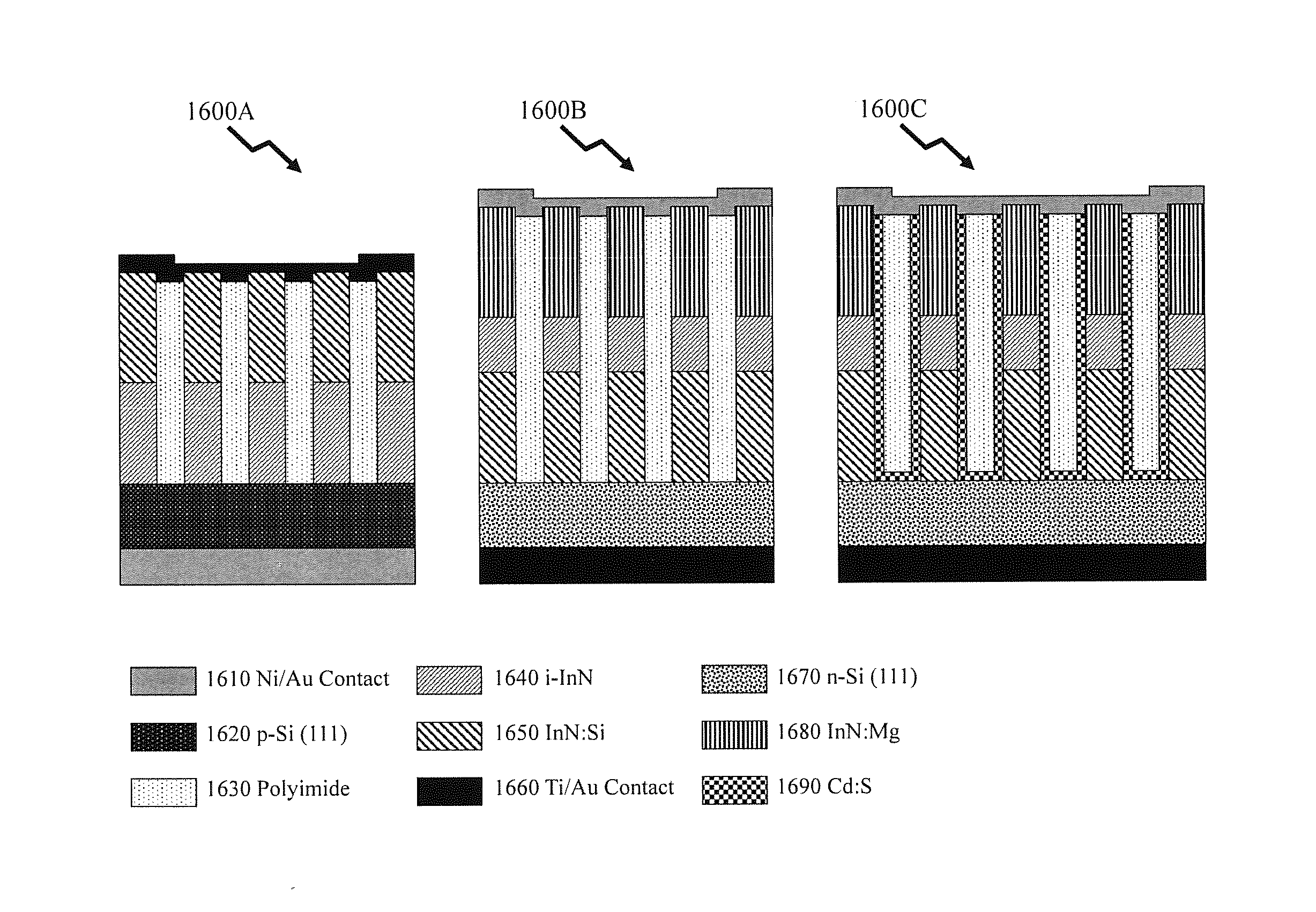
High efficiency broadband semiconductor nanowire devices
Amongst the candidates for very high efficiency electronics, solid state light sources, photovoltaics, and photoelectrochemical devices, and photobiological devices are those based upon metal-nitride nanowires. Enhanced nanowire performance typically require heterostructures, quantum dots, etc which requirement that these structures are grown with relatively few defects and in a controllable reproducible manner. Additionally flexibility according to the device design requires that the nanowire at the substrate may be either InN or GaN. Methods of growing relatively defect free nanowires and associated structures for group IIIA-nitrides are presented without the requirement for foreign metal catalysts, overcoming the non-uniform growth of prior art techniques and allowing self-organizing quantum dot, quantum well and quantum dot-in-a-dot structures to be formed. Such metal-nitride nanowires and quantum structure embedded nanowires support a variety of devices including but not limited to very high efficiency electronics, solid state light sources, photovoltaics, and photoelectrochemical devices, and photobiological devices.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Iii-nitride nanowire array monolithic photonic integrated circuit on (001)silicon operating at near-infrared wavelengths
ActiveUS20190067900A1Relieve pressureImprove performanceSemiconductor laser arrangementsLaser active region structurePhotodetectorInfrared wavelength
Photonic devices such as semiconductor lasers and photodetectors of various operating wavelengths are grown monolithically on a Silicon substrate, and formed of nanowire structures with quantum structures as active regions. A reduction of strain during fabrication results from the use of these nanowire structures, thereby allowing devices to operate for extended periods of time at elevated temperatures. Monolithic photonic devices and monolithic photonic integrated circuits formed on Silicon substrates are thus provided.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
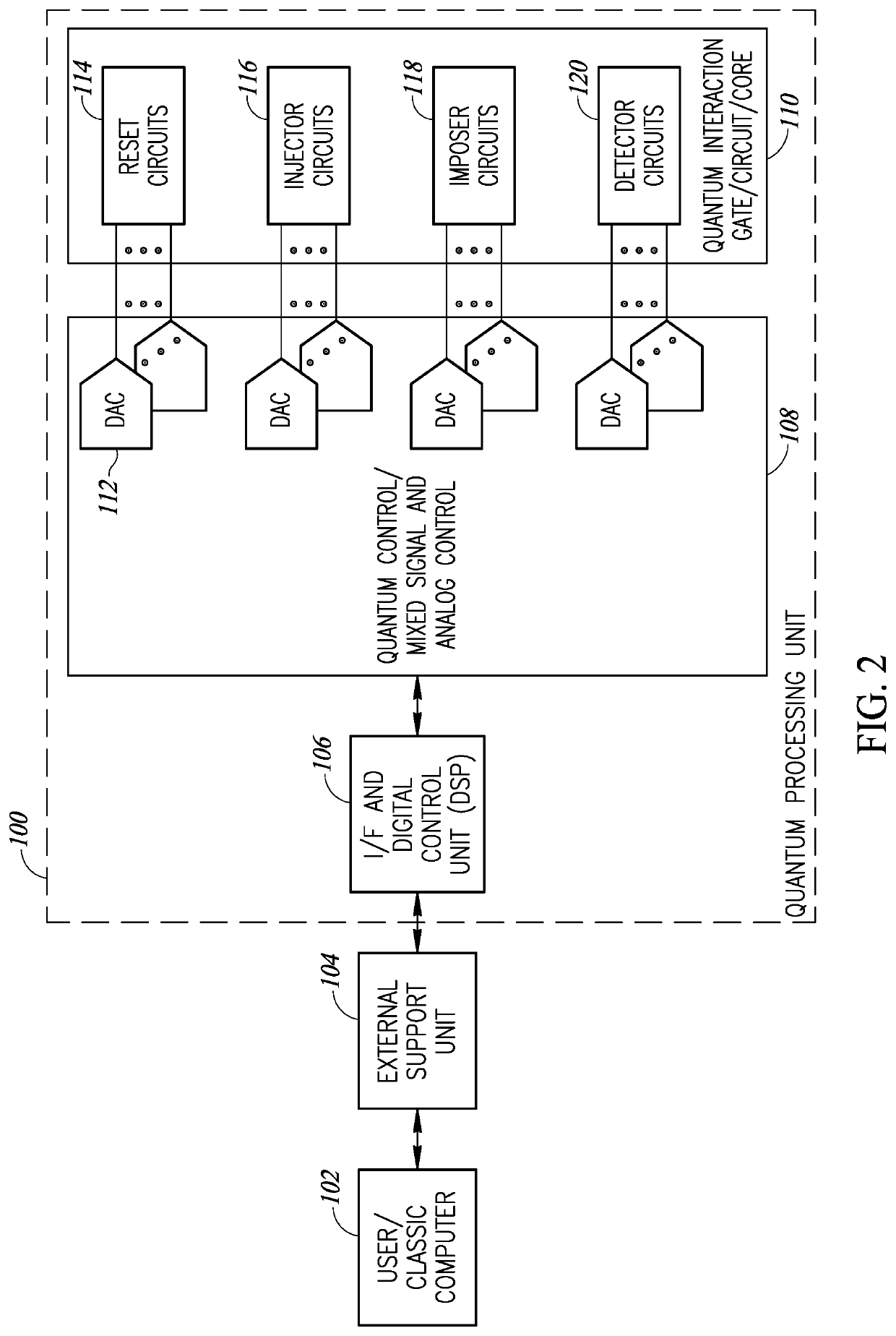
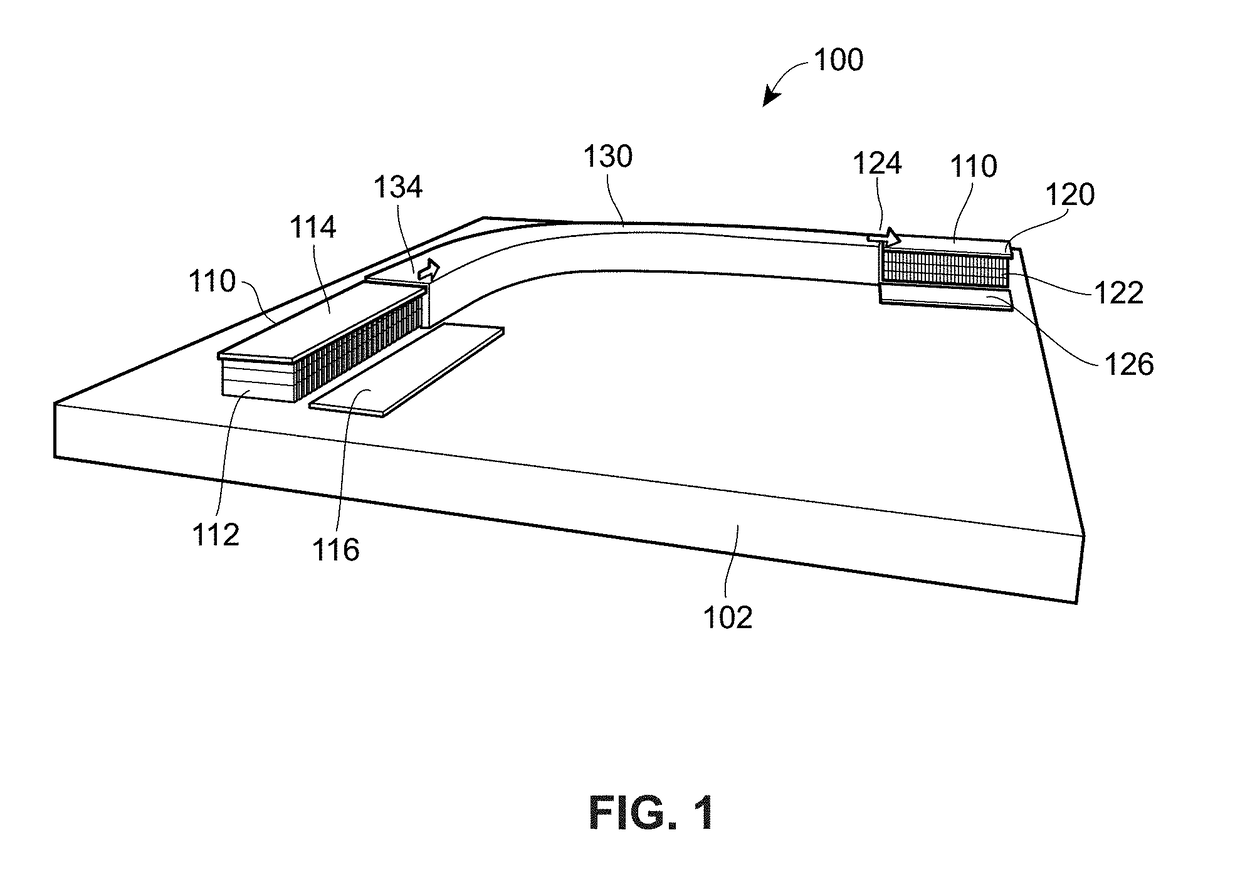
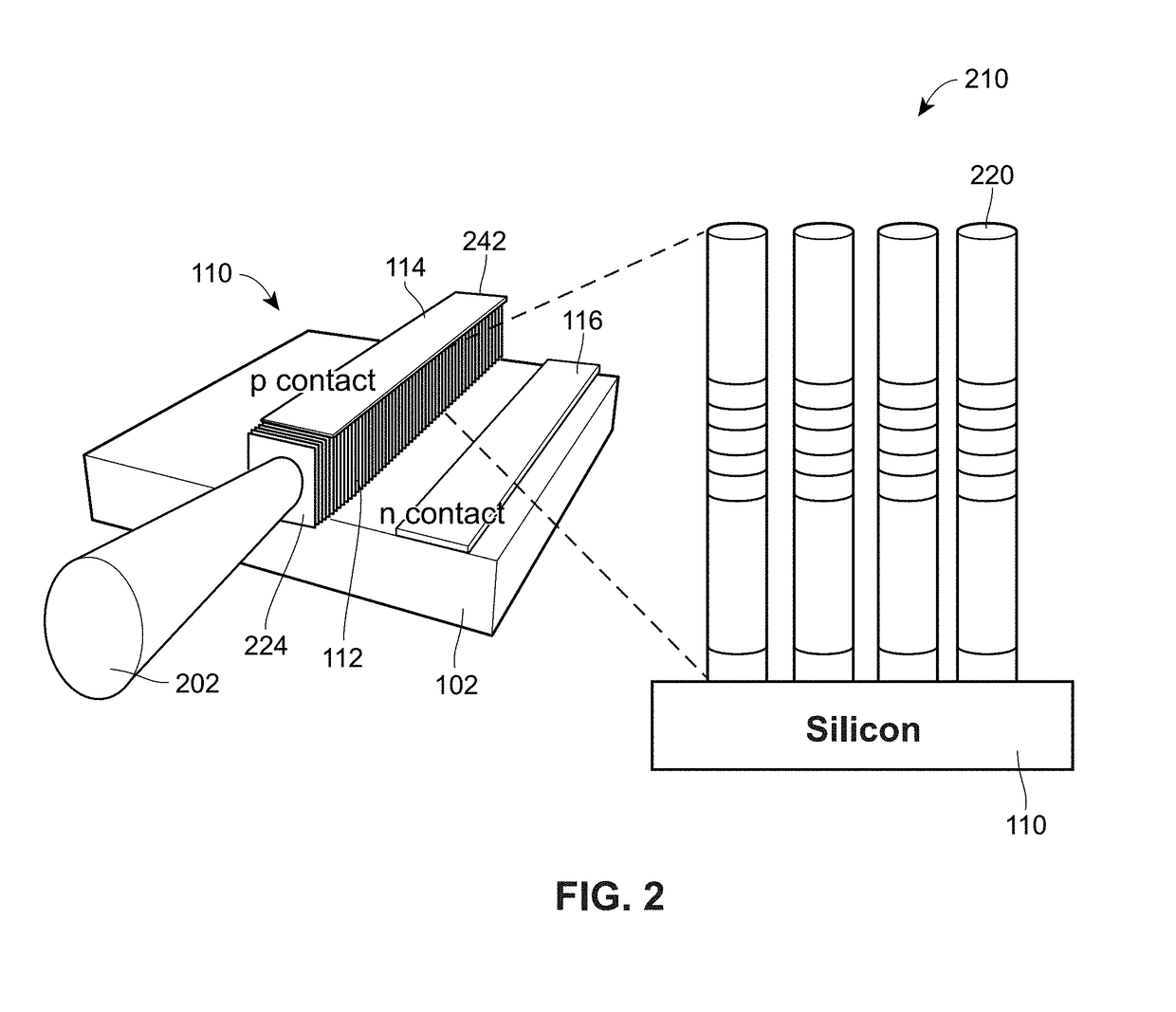
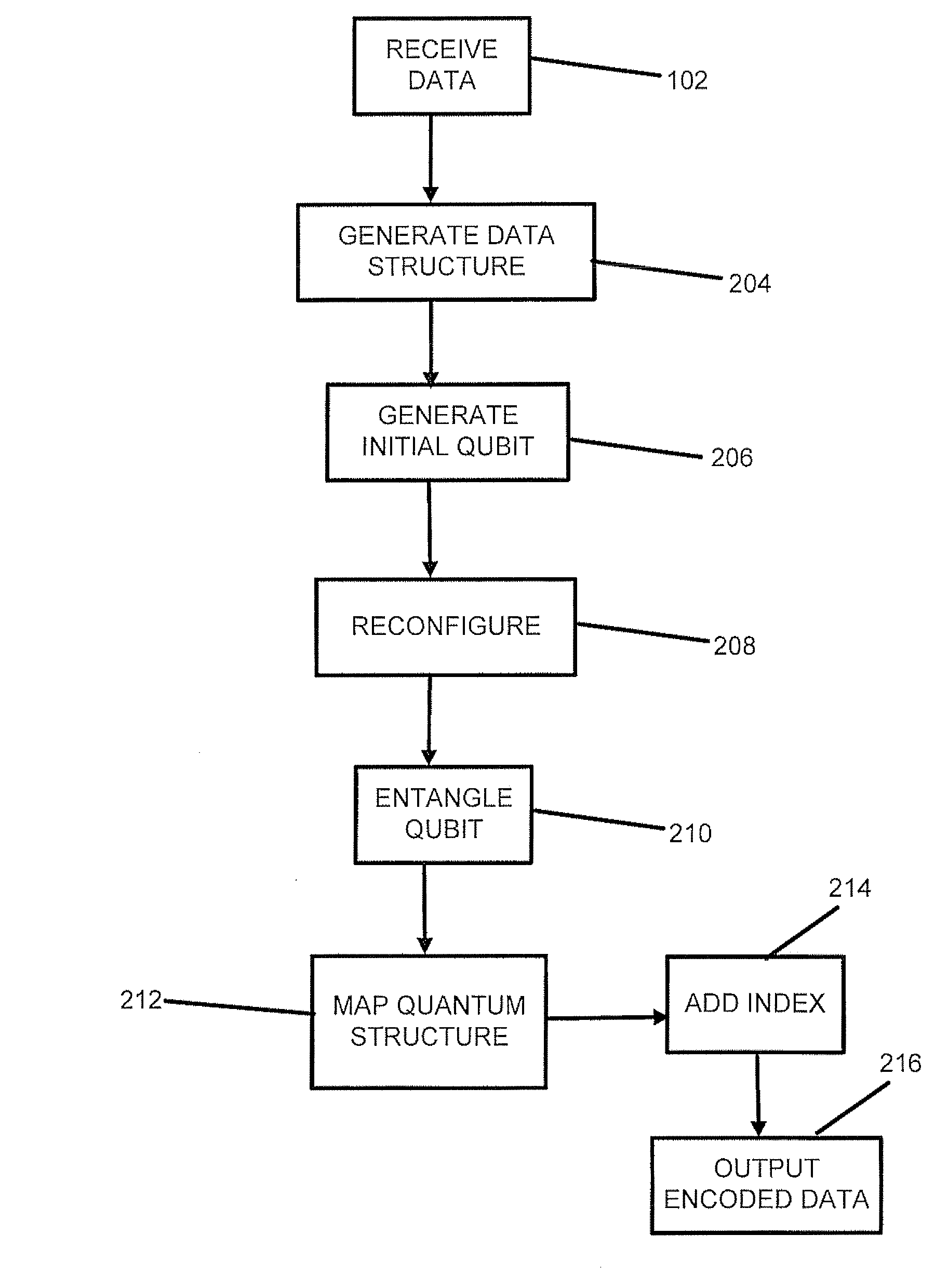
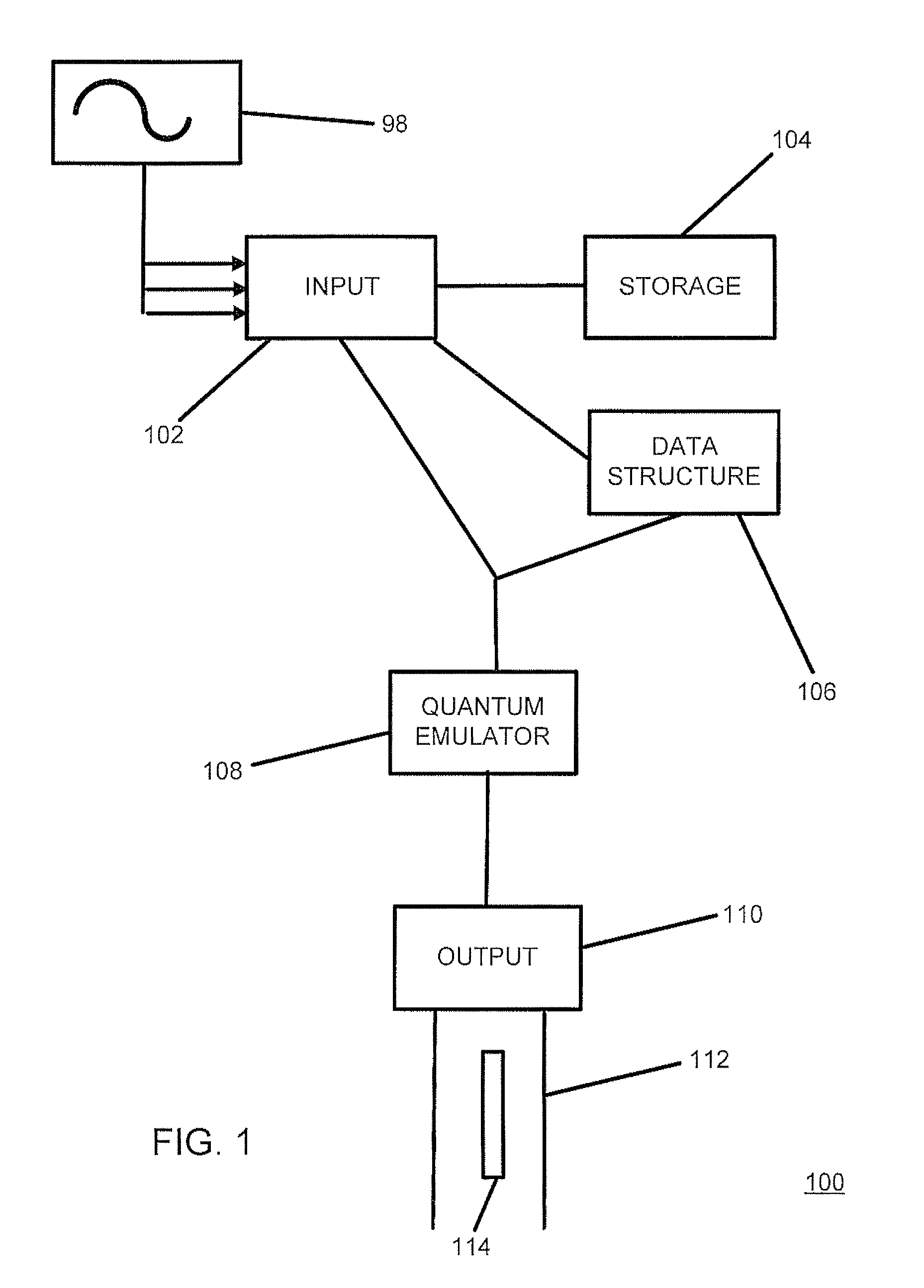
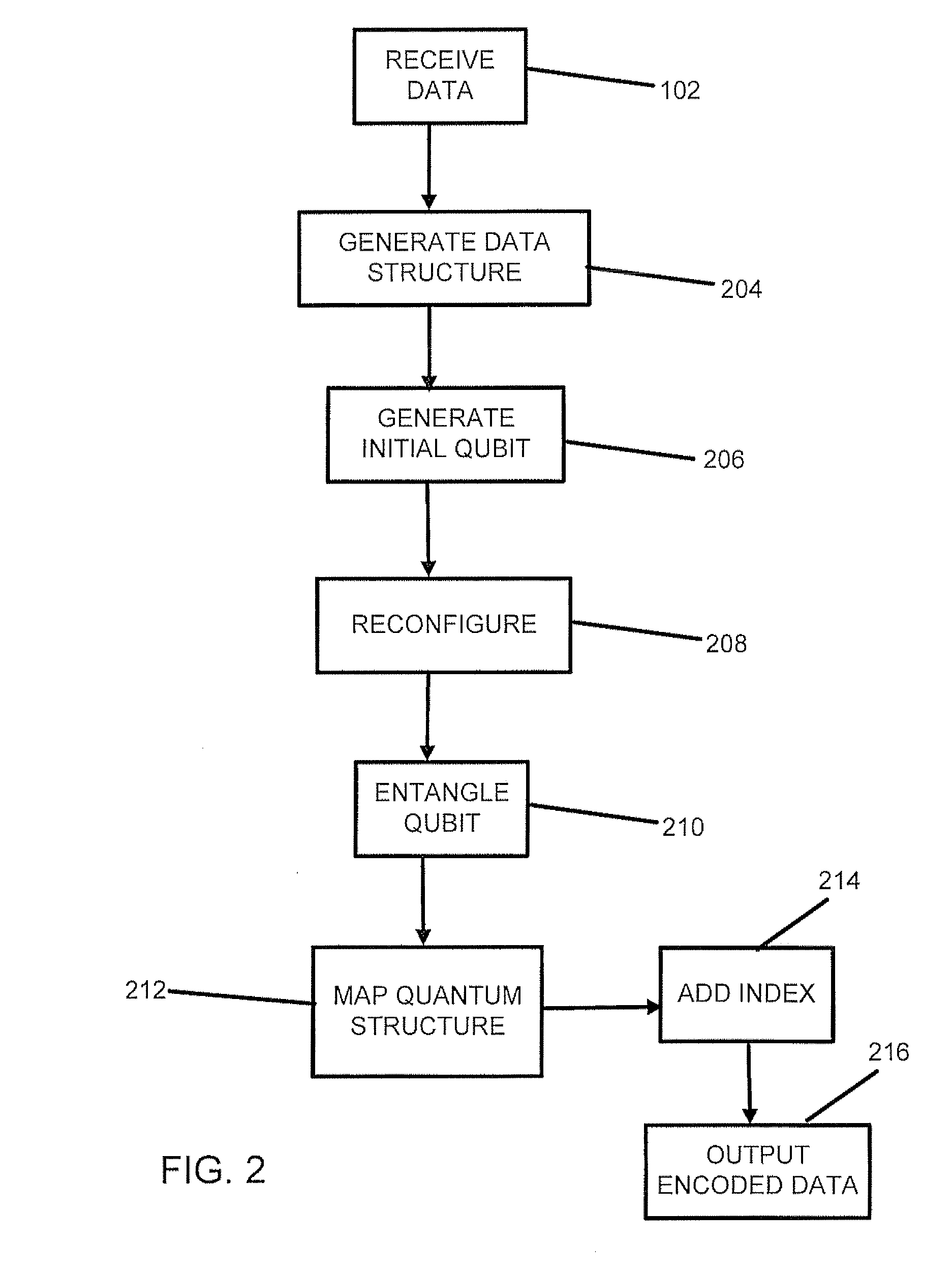
Method for processing data using quantum system
A method and system for encoding or processing data is provided. Data is represented by a qubit. The qubit is generated by an emulator within an encoding system. The qubit is entangled with another qubit to create encoded data. The encoded data is useable for a non-quantum environment. The qubit and the another qubit are entangled by reconfiguring a quantum structure that is mapped onto the encoded data.
Owner:PIXSPAN
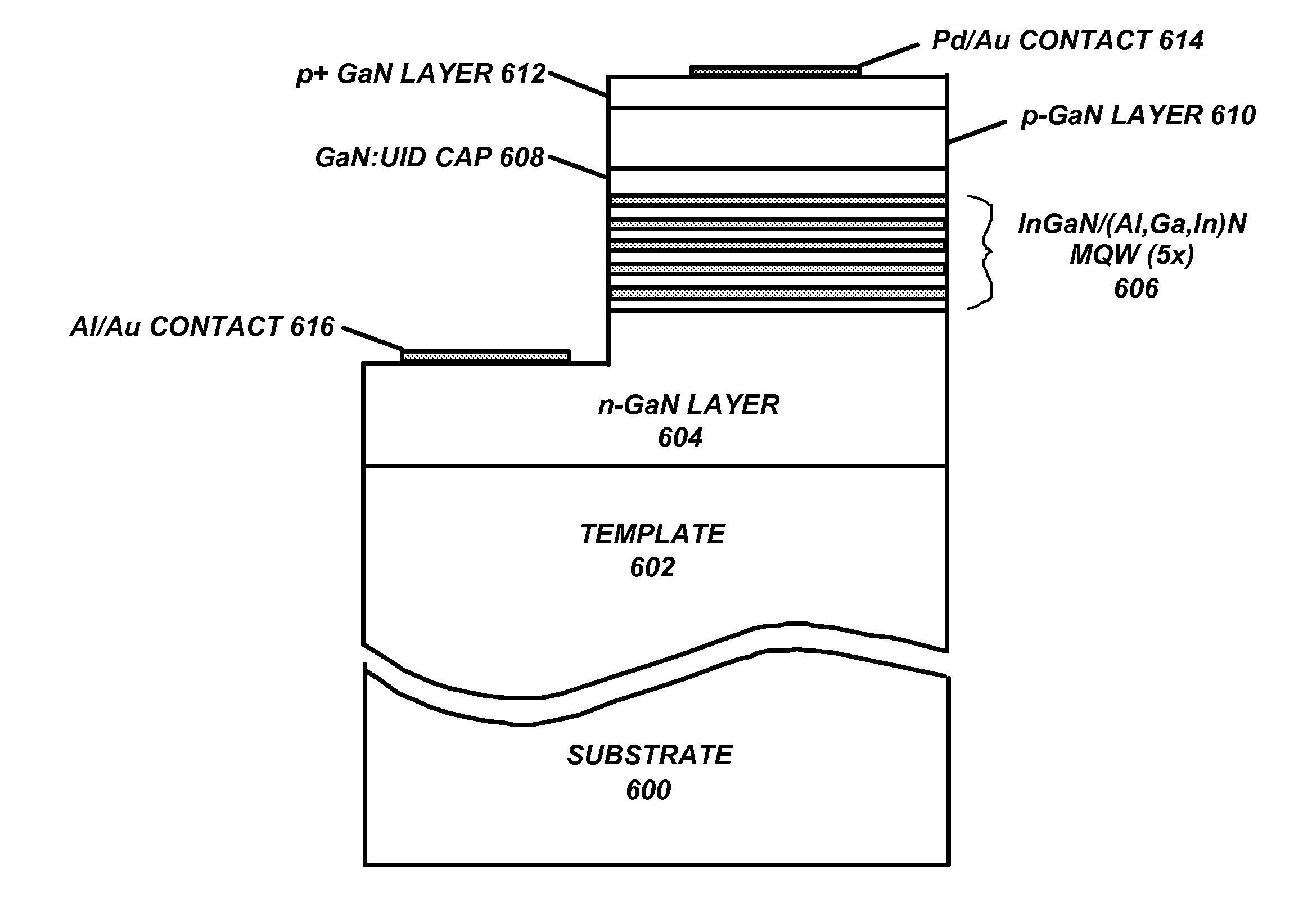
Light emitting device with a stair quantum well structure
InactiveUS20110089399A1Improve radiation efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellRadiative efficiency
A light emitting device with a stair quantum well structure in an active region. The stair quantum well structure may include a primary well and a single step or multiple steps. The light emitting device may be a nonpolar, semipolar or polar (Al,Ga,In)N based light emitting device. The stair quantum structure improves the radiative efficiency of the light emitting device.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
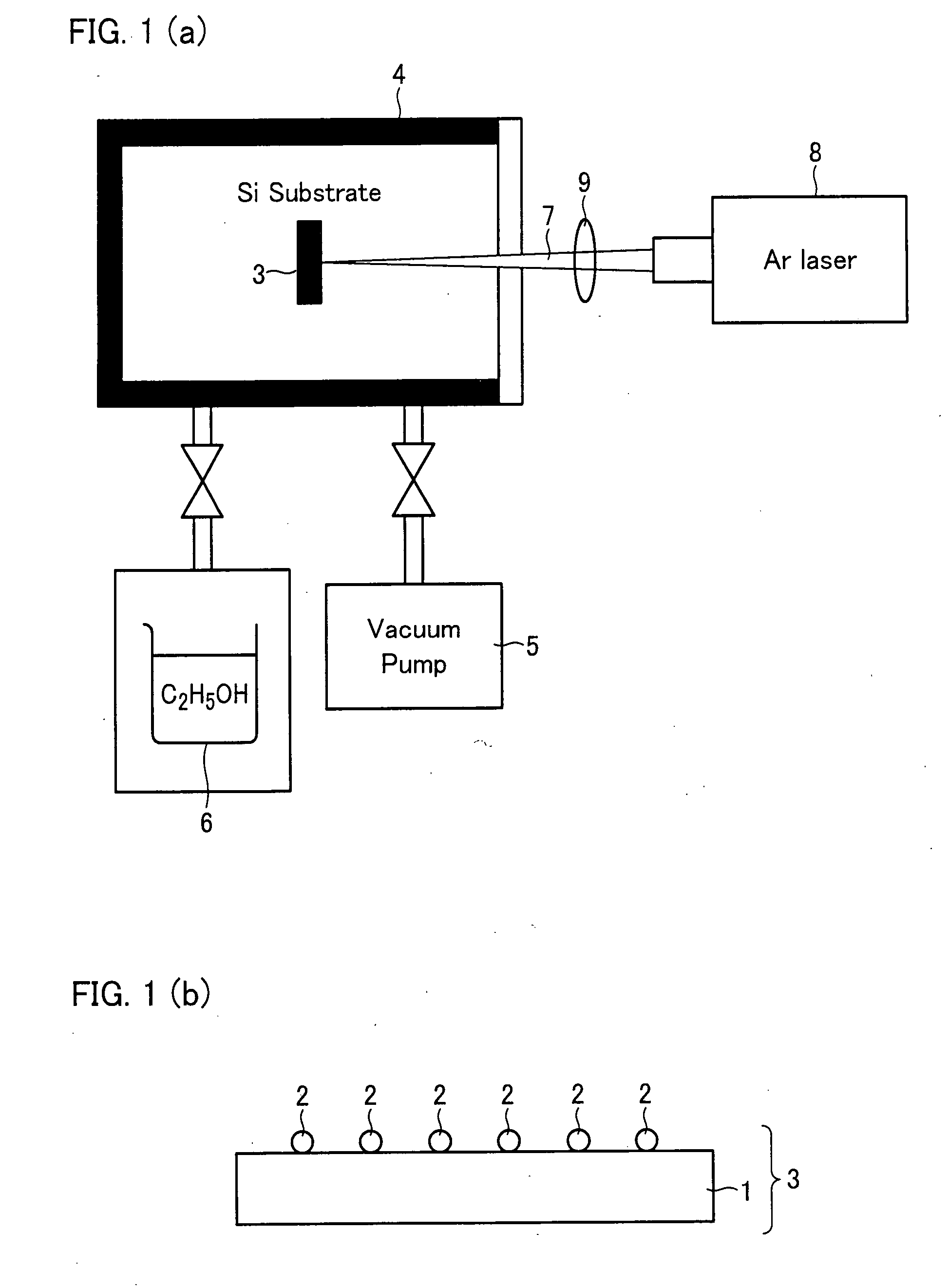
Method for Producing Nano-Scale Low-Dimensional Quantum Structure, and Method for Producing Integrated Circuit Using the Method for Producing the Structure
InactiveUS20070287202A1Increase temperatureImprove availabilityMaterial nanotechnologyCarbon compoundsCarbon nanotubeCarbon source
A method of an embodiment of the present of the present application is for producing a nano-scale low dimensional quantum structure. The method includes: bringing a catalyst on a substrate into contact with vaporized carbon source, and emitting an electromagnetic wave to the catalyst so as to form single-walled carbon nano-tubes on the catalyst. As a result, it is possible to form the nano-scale low-dimensional quantum structure on a target area.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
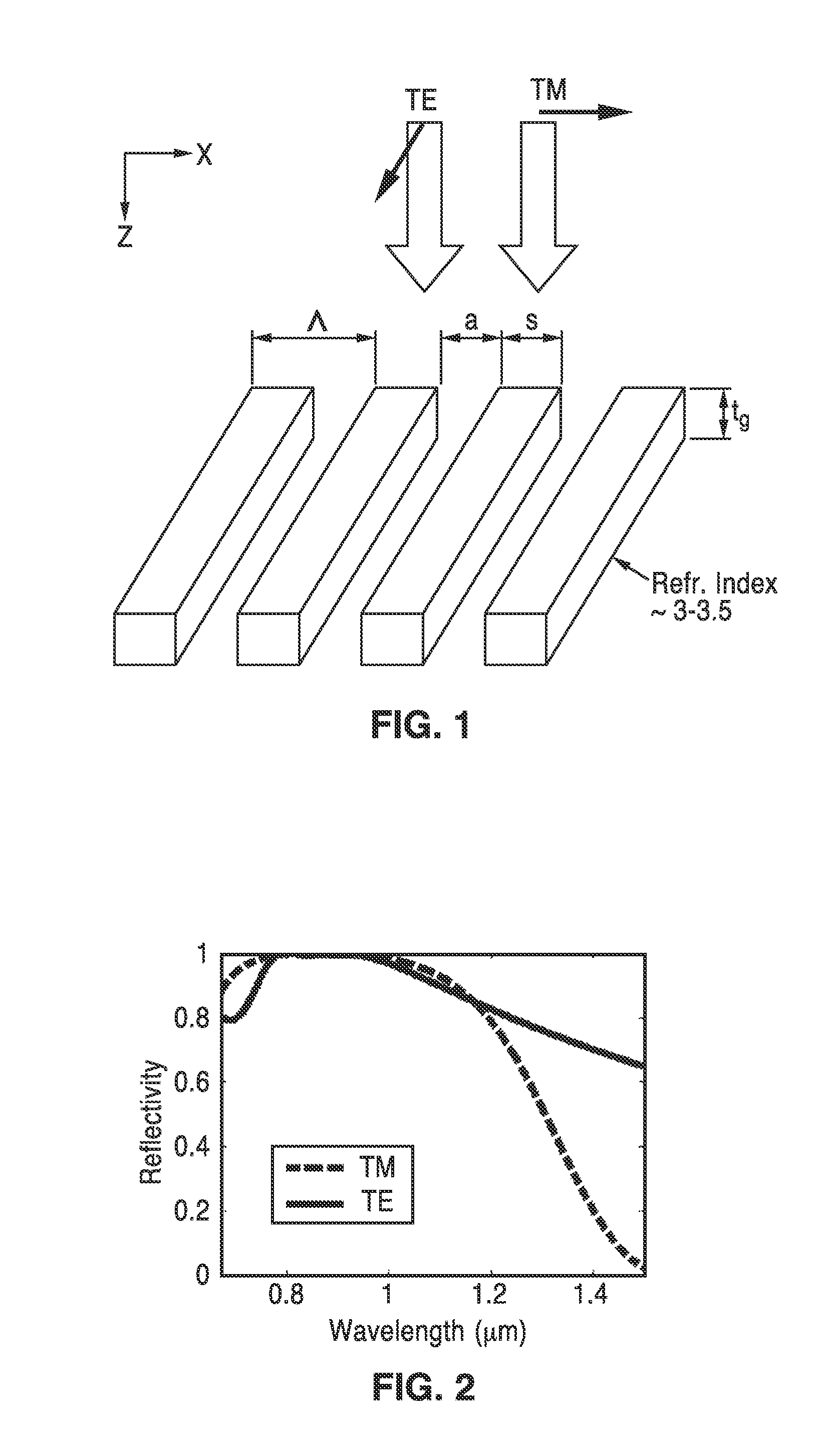
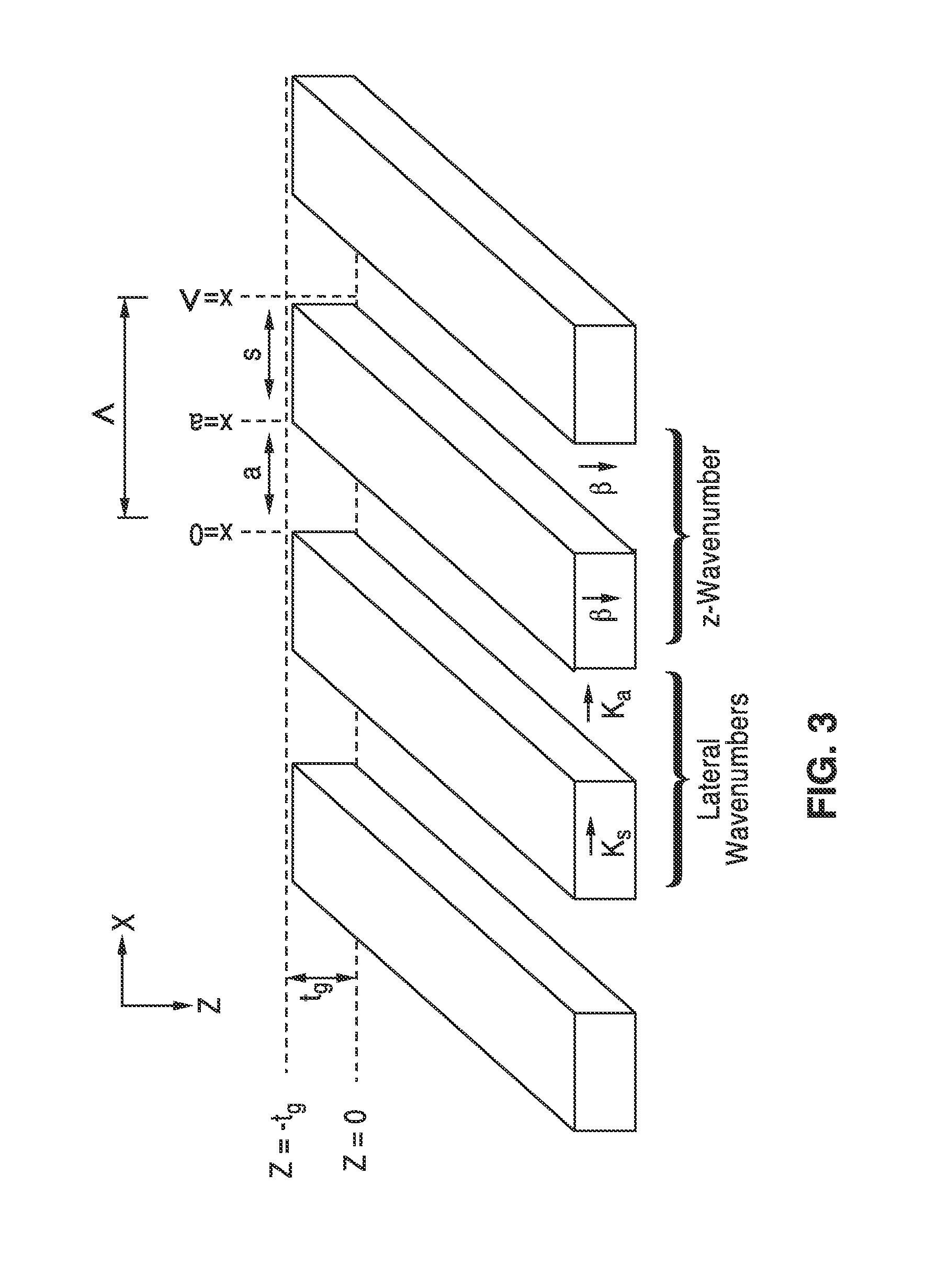
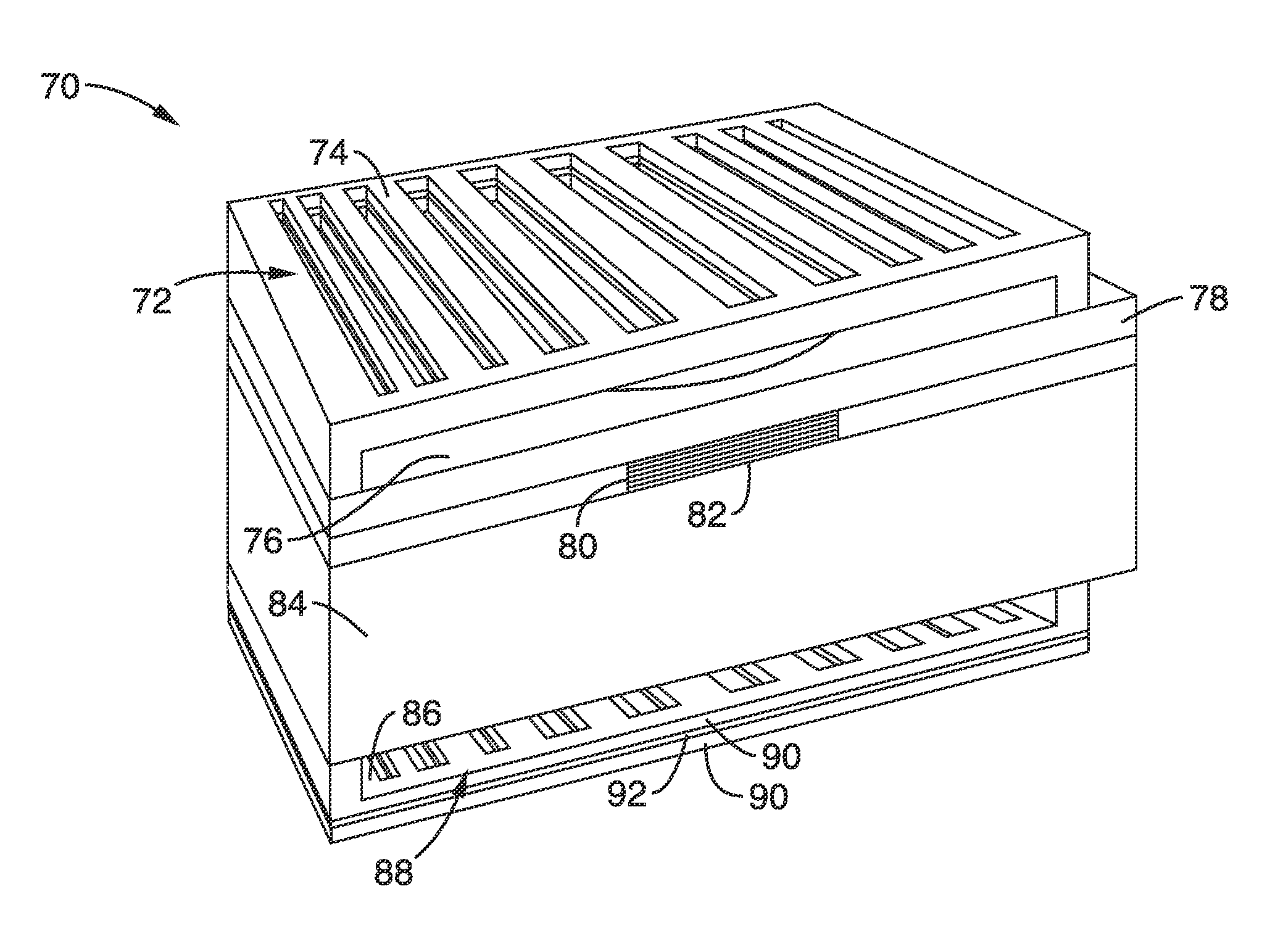
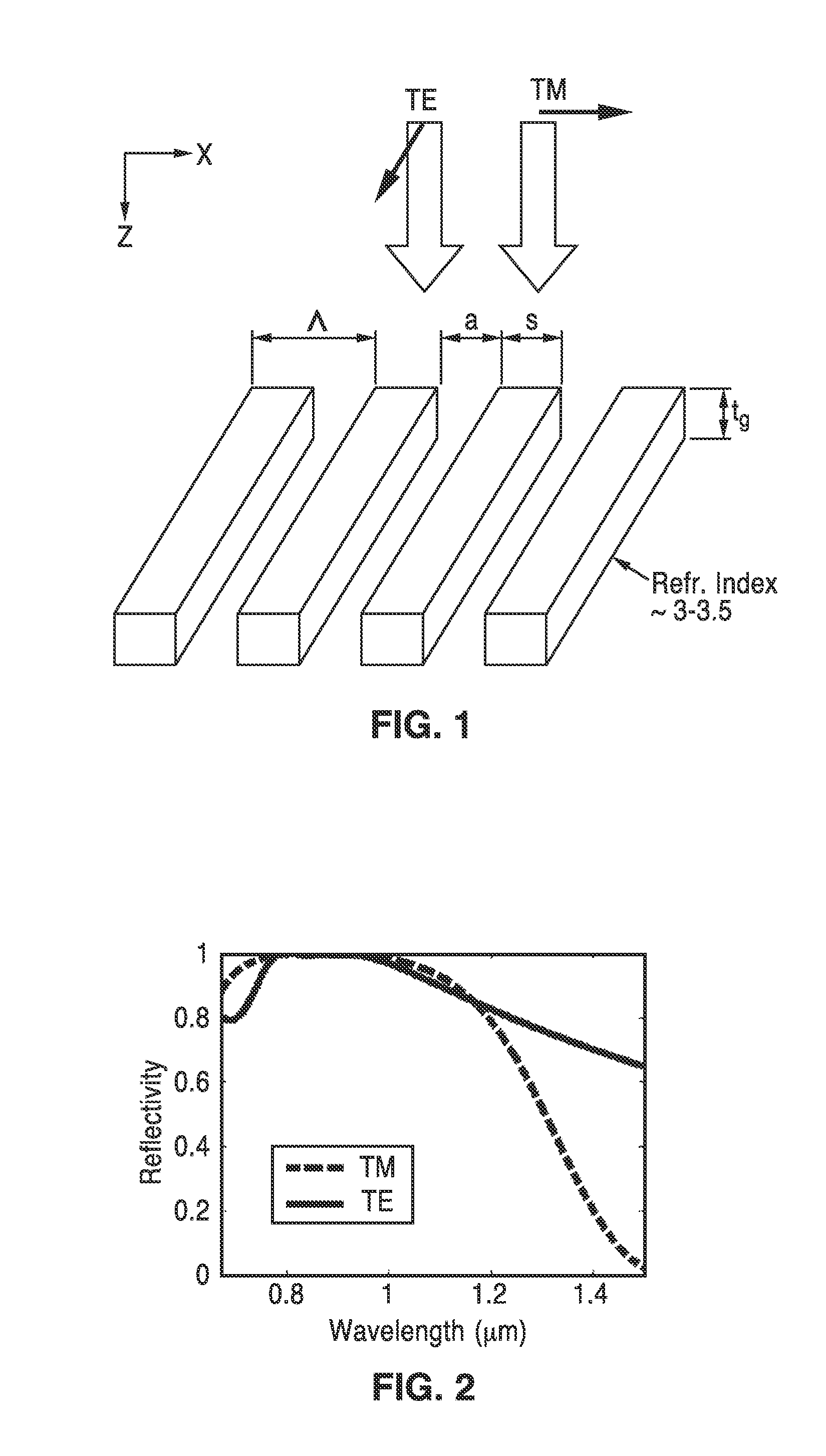
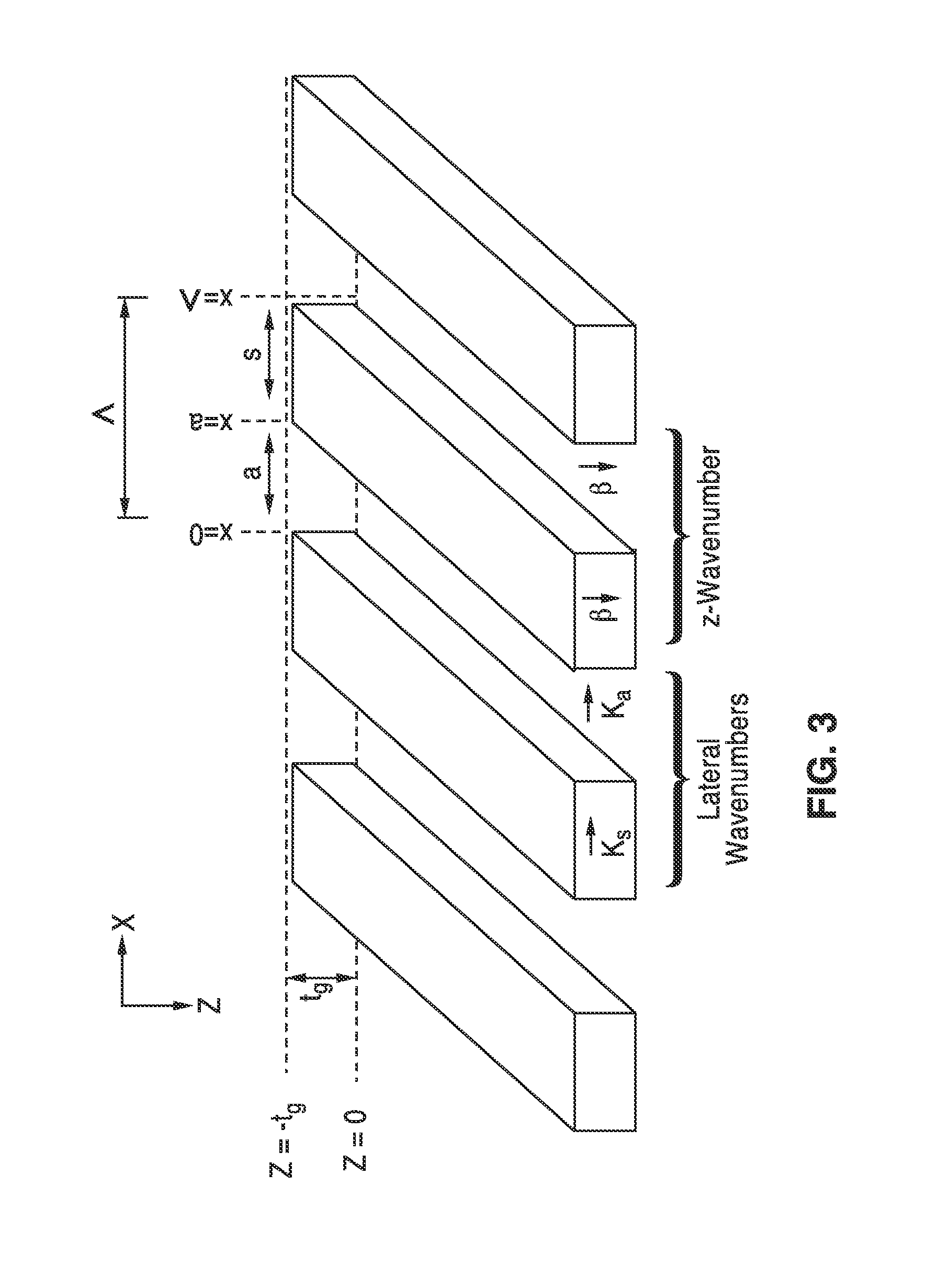
High contrast grating based saturable absorber for mode-locked lasers and its applications in passively mode-locked vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
ActiveUS20130051410A1Low fluenceMaximum flexibilityLaser detailsDiffraction gratingsGratingPhase relationship
A saturable absorber (SA) based on a high-contrast grating (HCG) having a buried layer of quantum structures for absorption, and which is particularly well suited for use in a mode-locked application. The HCG-SA provides three times the bandwidth compared with traditional DBR structures, while exhibiting a lower saturation fluence due to the field enhancement inside the grating. Varying grating bar width over one or two axis provides lensing effects on the optical output, while chirping of the period and duty cycle changes optical phase relationships. Novel VCSEL embodiments with external or internal cavities are described using the HCG-SA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of fusion for heteroepitaxial layers and overgrowth thereon
InactiveUS20020086494A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor materialsVertical growth
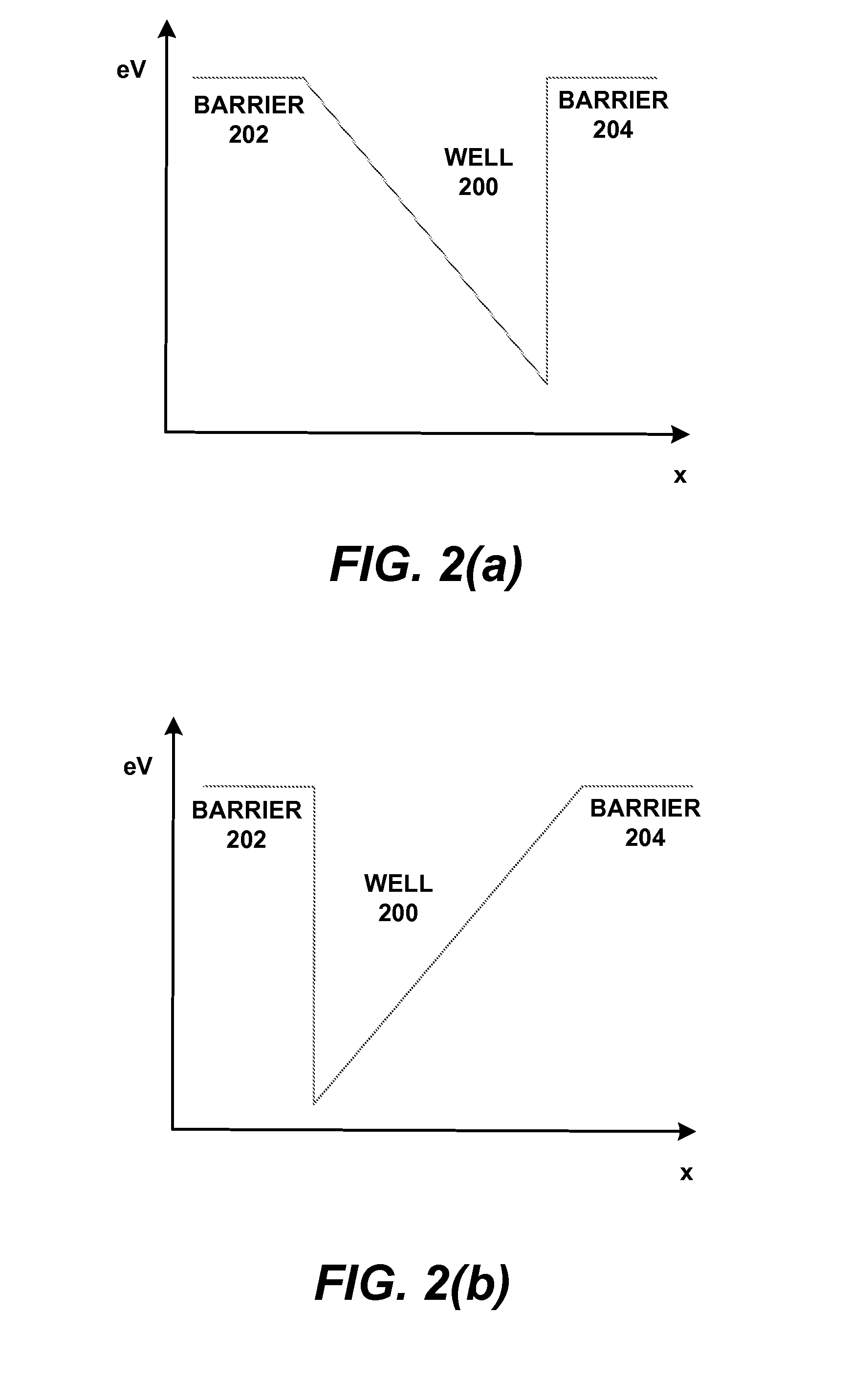
The present invention relates to a method of fusion for heteroepitaxial layers and overgrowth thereon. According to the present invention, a high quality heteroepilayer can be formed by patterning a fused semiconductor layer, overgrowing it with a persistent patterned character, and fusing other semiconductors having different lattice constants by means of utilizing the rate difference between the lateral growth rate and the vertical growth rate exhibited, on the above process. Further, according to the present invention, the lattice constant difference of the two semiconductors can be overcome and a high quality quantum structure can be formed. According to the present invention, the junction of two semiconductor materials having different lattice constants, as well as a good overgrowth on heteroepitaxial layers can be carried out. Accordingly to the present invention, the base material from which the new, as yet on realized, conceptive optoelectronic device can be made.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Electronically pumped surface-emitting photonic crystal laser
ActiveUS10340659B1Reduce lossesOptical wave guidanceLaser detailsDivergence anglePhotonic crystal structure
An electrically pumped surface-emitting photonic crystal laser includes an electric currents confinement structure arranged on a photonic crystal structure and an active layer with an opening, a transparent conducting layer arranged on the electric currents confinement structure and covering the photonic crystal structure, a metal anode arranged on the transparent conducting layer with an aperture. The photonic crystal laser has its epitaxy structure etched from above to fabricate the photonic crystal to allow laser beams to pass through with conductivity for the purpose of electrically pumping a quantum structure without complex technologies of wafer fusion bonding or epitaxial regrowth. Thereby the laser beams can be emitted from a front surface of the epitaxy structure with a narrow divergence angle.
Owner:PHOSERTEK CORP
A structure of semiconductor luminous device with wide spectrum photo-emission function
InactiveCN101217175AEliminate separationQuality improvementSemiconductor devicesQuantum wellLight emitting device
The invention relates to a semiconductor light-emitting device with wide spectrum light emission function and the preparation method, including a substrate material, a transition layer which directly grows on the substrate and a GaN or n-GaN which is arranged on the transition layer, a plurality of layers of quantum well active regions: a nitride quantum structure luminous layer with the wide spectrum light emission function is a quantum well structure, which is composed of an InxGa1-xN well layer and an InyGa1-yN barrier layer, wherein, 1 is more than x which is more than y which is not less than 0, the x and y in the quantum well structure is spacially even in the layers; the well / barrier double layers of the quantum well structure repeat 1 to 10 periods; a top layer nitride, GaN or p-GaN, the thickness of the top layer nitride is 0.02 to 2 microns; the invention further comprises multiple luminous centers which can emit light which contains the continuous spectrum with the nano-scope of 360 to 900. The nitride semiconductor material is obtained by the epitaxial growth of a metal-organic chemical vapor deposition (MOCVD) epitaxial growth system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
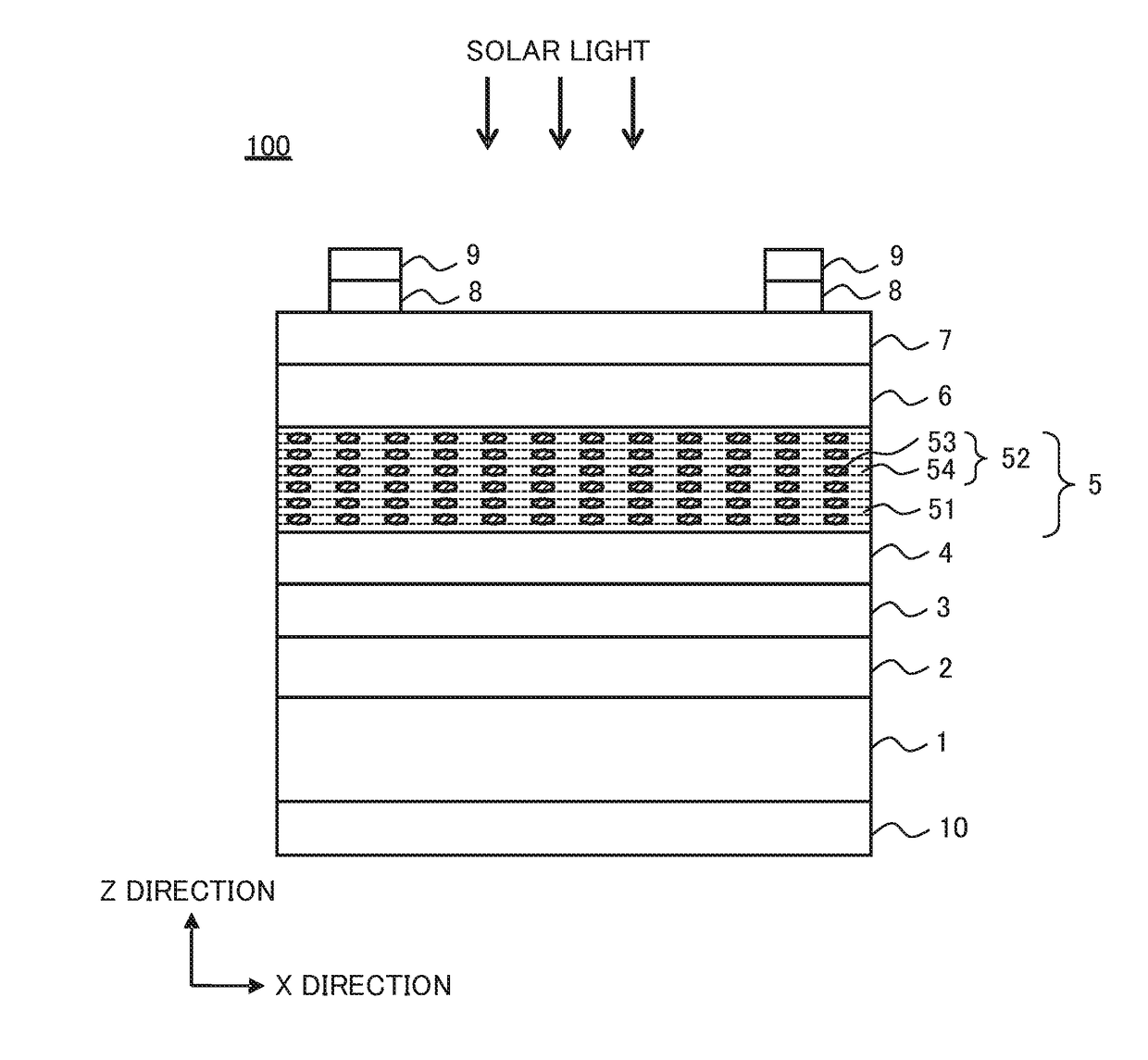
Photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20120111398A1Easy transferImprove photoelectric conversion efficiencyNanotechPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotoelectric conversionSemiconductor
A main object of the present invention is to provide a photoelectric conversion device which is capable of improving the photoelectric conversion efficiency. The invention comprises: a p-layer; an n-layer; an i-layer disposed between the p-layer and the n-layer; a first electrode connected to the p-layer; and a second electrode connected to the n-layer, wherein the i-layer comprises a wall layer constituted by a first semiconductor, and a quantum structure portion constituted by a second semiconductor disposed in the wall layer; a band gap of the first semiconductor is wider than that of the second semiconductor; when a concentration of the n-type impurity that may be contained in the middle of the i-layer in a thickness direction thereof is defined as Cn1, a concentration of the n-type impurity that may be contained in the region on the p-layer side of the i-layer is defined as Cn2, a concentration of the p-type impurity that may be contained in the middle of the i-layer in a thickness direction thereof is defined as Cp1, and a concentration of the p-type impurity that may be contained in the region on the n-layer side of the i-layer is defined as Cp2, the relations Cn1<Cn2 and / or Cp1<Cp2 are satisfied.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
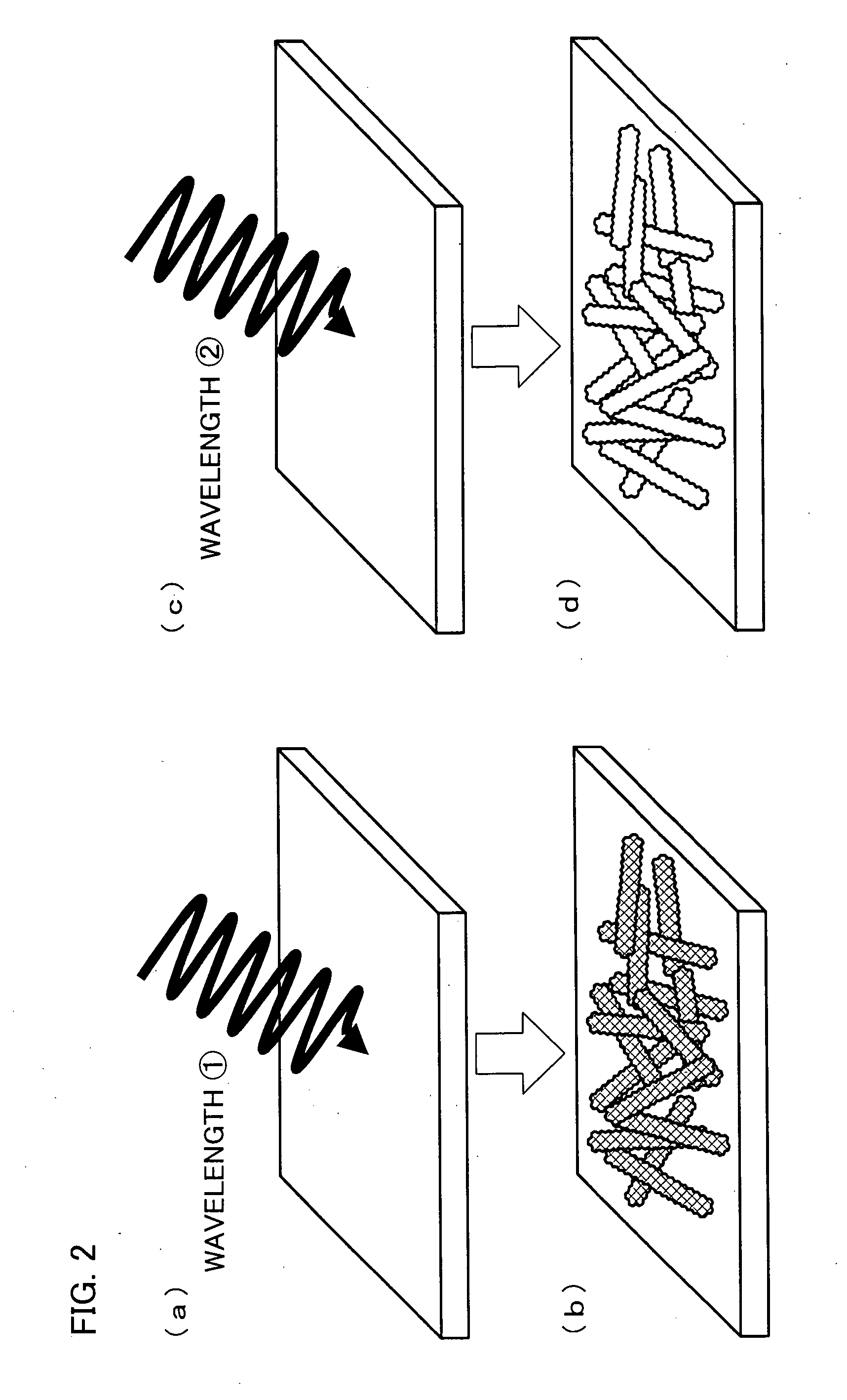
Method for controlling structure of nano-scale substance, and method for preparing low dimensional quantum structure having nano-scale using the method for controlling structure
InactiveUS20070004231A1High strengthMaterial nanotechnologyNanostructure manufactureVolumetric Mass DensityIrradiation
A method for controlling a structure of a nano-scale substance, which comprises irradiating a mixture of low-dimensional quantum structures having a nano-scale with an electromagnetic wave in an oxygen atmosphere, to thereby selectively oxidize a low-dimensional quantum structure having a density of states resonating with the electromagnetic wave used for the irradiation. The method allows a low-dimensional quantum structure having a specific structure to be selectively disappeared from the mixture of low-dimensional quantum structures having a nano-scale.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
High contrast grating based saturable absorber for mode-locked lasers and its applications in passively mode-locked vertical-cavity surface-emitting lasers
ActiveUS8526471B2Low fluenceMaximum flexibilityLaser detailsDiffraction gratingsGratingPhase relationship
A saturable absorber (SA) based on a high-contrast grating (HCG) having a buried layer of quantum structures for absorption, and which is particularly well suited for use in a mode-locked application. The HCG-SA provides three times the bandwidth compared with traditional DBR structures, while exhibiting a lower saturation fluence due to the field enhancement inside the grating. Varying grating bar width over one or two axis provides lensing effects on the optical output, while chirping of the period and duty cycle changes optical phase relationships. Novel VCSEL embodiments with external or internal cavities are described using the HCG-SA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Photoelectric conversion element having quantum structure using indirect transition conductor material
InactiveUS20170200841A1Reduce extraction efficiencyHigh sensitivityPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesNano structuringElectrical conductor
A photoelectric conversion element includes a photoelectric conversion layer having the quantum structure and utilizes intersubband transition in a conduction band. The photoelectric conversion element includes a superlattice semiconductor layer in which a barrier layer and a quantum dot layer as a quantum layer are alternately and repeatedly stacked. The barrier layer includes an indirect transition semiconductor material, and the quantum dot layer has a nano-structure including a direct transition semiconductor material. The indirect transition semiconductor material constituting the barrier layer has a bandgap of more than 1.42 eV at room temperature.
Owner:SHARP KK +1
Semiconductor optical amplifier suitable for coarse WDM communications and light amplification method
InactiveUS7167301B2Reduce gain differenceConstant gainLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGain coefficientLength wave
An active layer contains quantum structures. The active layer amplifies light propagating therein while current is injected therein. Electrodes are provided for sections of the active layer sectionalized along a light propagation direction. The electrodes inject different currents into the sections. Current is supplied to the electrodes in such a manner that a first current density is set to one section of the active layer and a second current density is set to another section. The first current density is lower than that at a cross point and the second current density is higher than that at the cross point. The cross point is a cross point between gain coefficient curves at least two different transition wavelengths of the quantum structures. The curves are drawn in a graph showing a relation between a density of current injected into the active layer and a gain coefficient of the active layer.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Quantum shift register structures
A novel and useful controlled quantum shift register for transporting particles from one quantum dot to another in a quantum structure. The shift register incorporates a succession of qdots with tunneling paths and control gates. Applying appropriate control signals to the control gates, a particle or a split quantum state is made to travel along the shift register. The shift register also includes ancillary double interaction where two pairs of quantum dots provide an ancillary function where the quantum state of one pair is replicated in the second pair. The shift register also provides bifurcation where an access path is split into two or more paths. Depending on the control pulse signals applied, quantum dots are extended into multiple paths. Control of the shift register is provided by electric control pulses. An optional auxiliary magnetic field provides additional control of the shift register.
Owner:EQUAL1 LABS INC
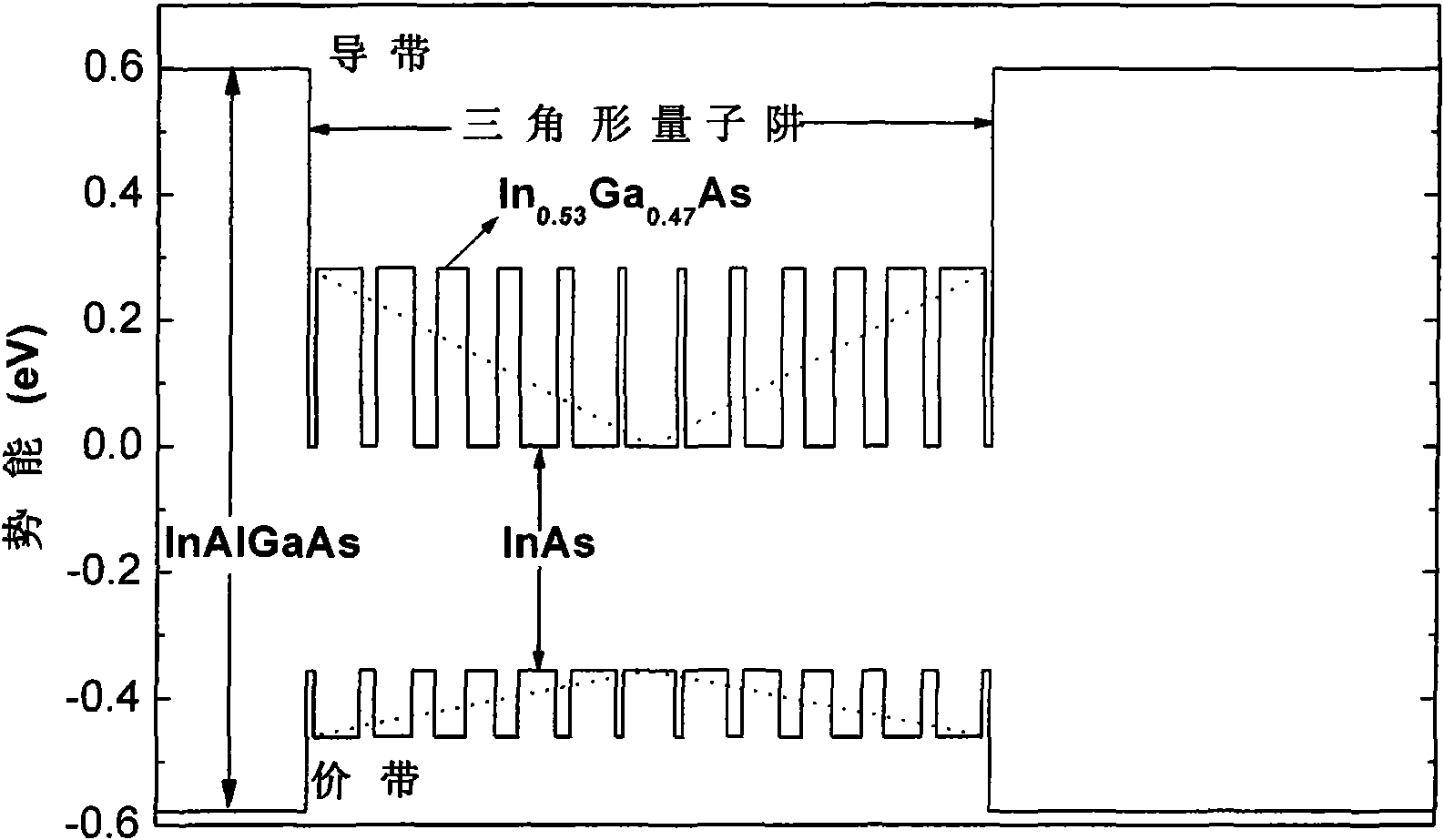
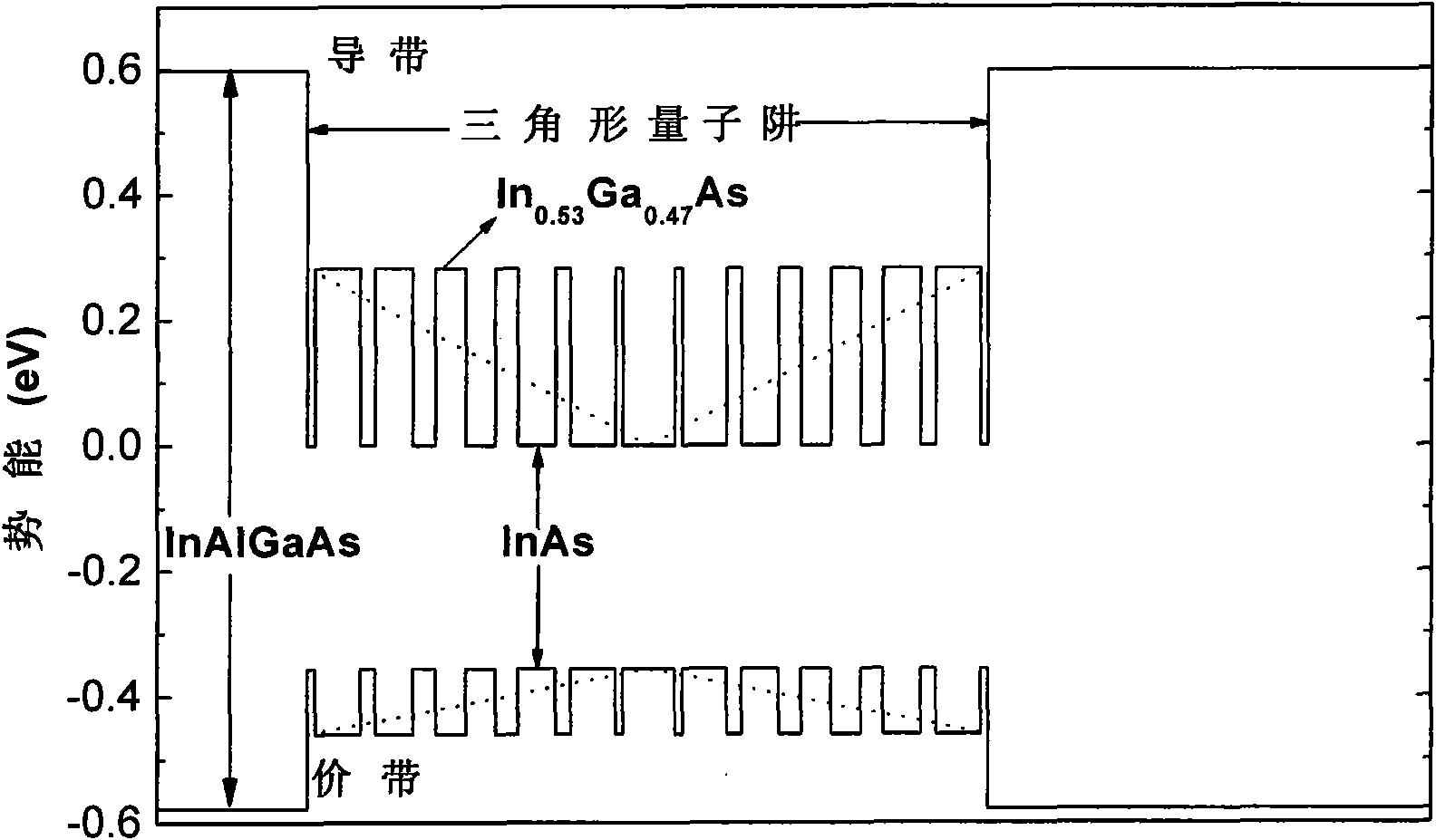
Non-rectangular quantum structure based on digital alloy and implementation method thereof
InactiveCN101811659ASolve the singularityIncrease freedomIndividual molecule manipulationQuantum wellEpitaxial material
The invention relates to a non-rectangular quantum structure based on a digital alloy and an implementation method. The non-rectangular quantum structure is characterized in that the non-rectangular quantum structure is implemented by selecting a hetero-epitaxial material system and combinatorial design and adopting a method of the digital alloy; and the digital alloy is formed by two binary or multi-component alloy materials. The implementation method can effectively control the components of the material to precisely vary according to the design requirement on the quantum scale, thereby overcoming the single problem that the rectangular quantum structures with components mutated are only suitable to be grown by the conventional growth method, bringing in higher degree of freedom for design and implementation of the quantum structure and functions and bringing benefits to strain and interface control of the quantum structure. The invention is not only suitable for the special semiconductor lasers needing to adopt non-rectangular quantum wells but also suitable for other novel electronic or photoelectronic devices and has good universality.
Owner:弦海(上海)量子科技有限公司
Electrically excited photonic crystal surface emitting type laser element
ActiveCN110535033AConductiveSuitable for surface-firing laserLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionCurrent limitingDivergence angle
An electrically excited photonic crystal surface emitting type laser element comprises: a current limiting structure which is located on a photonic crystal structure and an active layer and is provided with an aperture; a transparent conducting layer positioned on the current limiting structure and covering the photonic crystal structure; and positive electrode metal positioned on the transparentconductive layer and provided with a metal hole. According to the invention, the photonic crystal is manufactured by directly etching from the uppermost part of the epitaxial structure to the inside;a complex technology of wafer fusion or epitaxial growth is not needed, laser light can penetrate the photonic crystal structure and has conductivity, the quantum structure is electrically excited, light can be emitted from the front face of the epitaxial structure through the photonic crystal structure, and the photonic crystal structure has the excellent characteristics of being small in far-field divergence angle and the like.
Owner:PHOSERTEK CORP
Quantum structure and forming method of the same
InactiveUS7022571B2Improve disadvantagesConveniently formedNanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectric layerImpurity
A quantum structure and the forming method based on the difference in characteristic of two matters is provided. The forming method includes several steps. At first, providing a first dielectric layer for forming a second dielectric layer thereon. The second dielectric layer has major elements and impurities contained. Treating the second dielectric layer to drive the impurities to form the quantum structure. For example, oxidizing the major elements to drive the impurities in the first dielectric layer to form the quantum structure in said first dielectric layer because the oxidizing capability of the major elements is stronger than that of the impurities.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
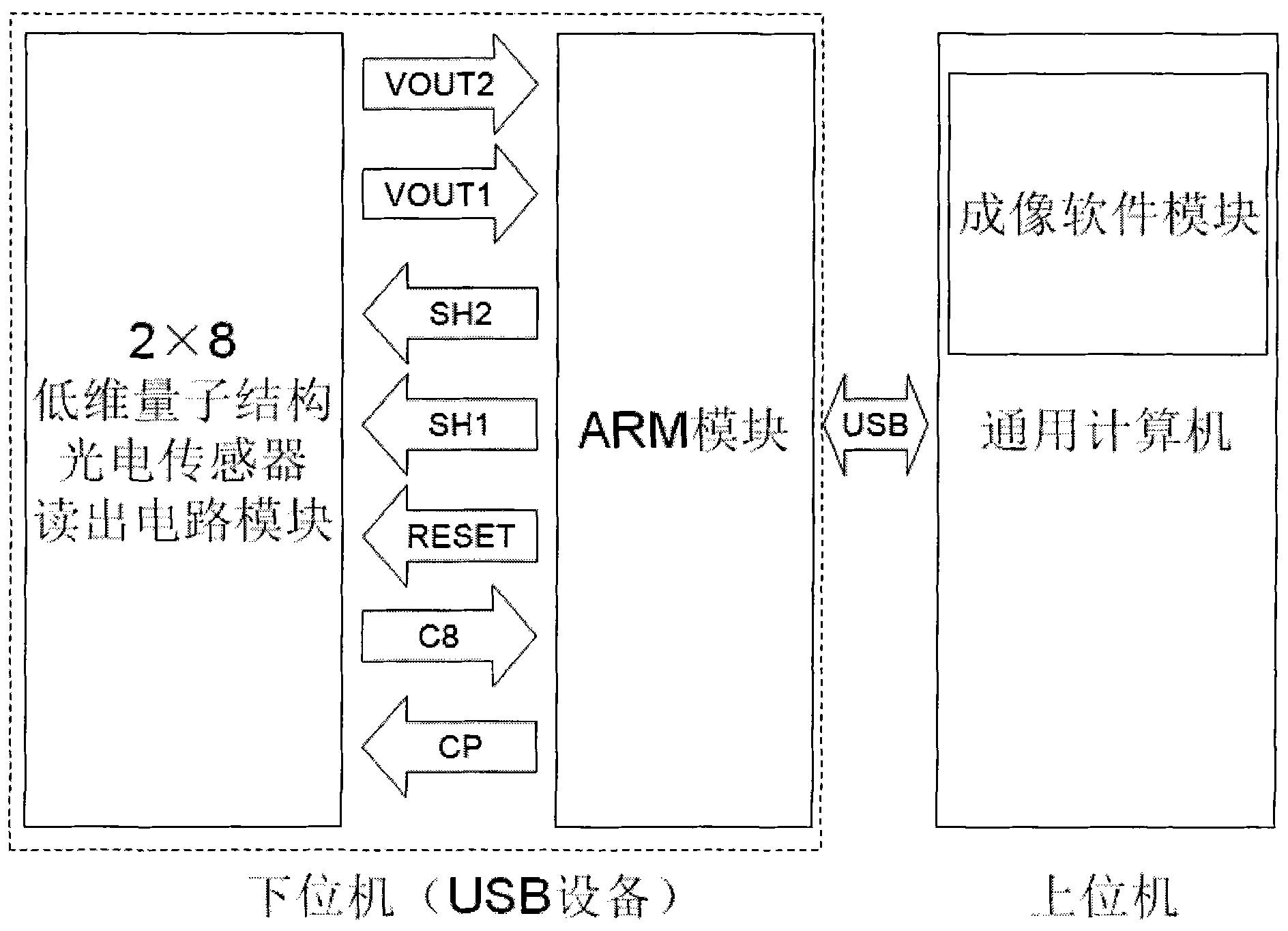
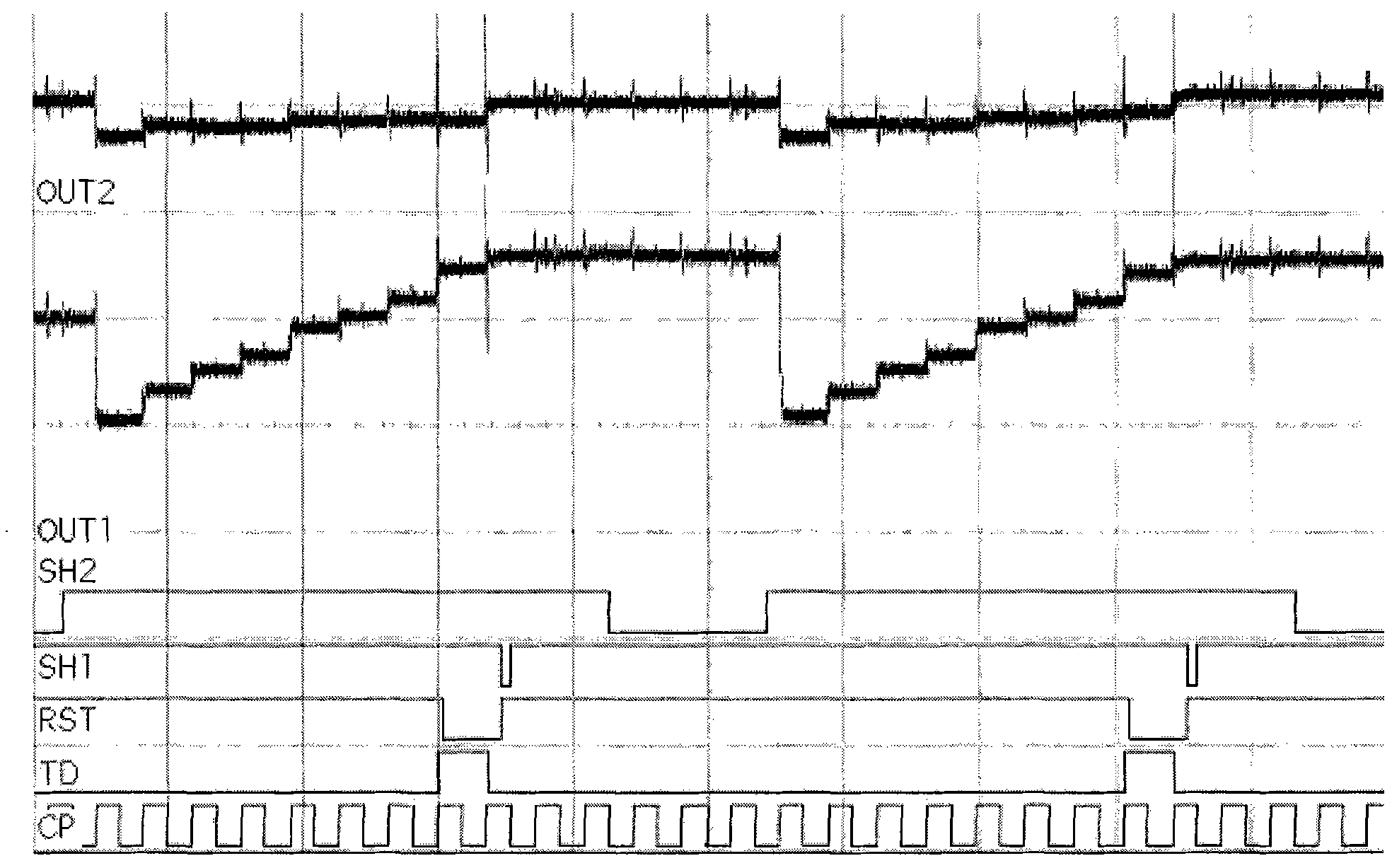
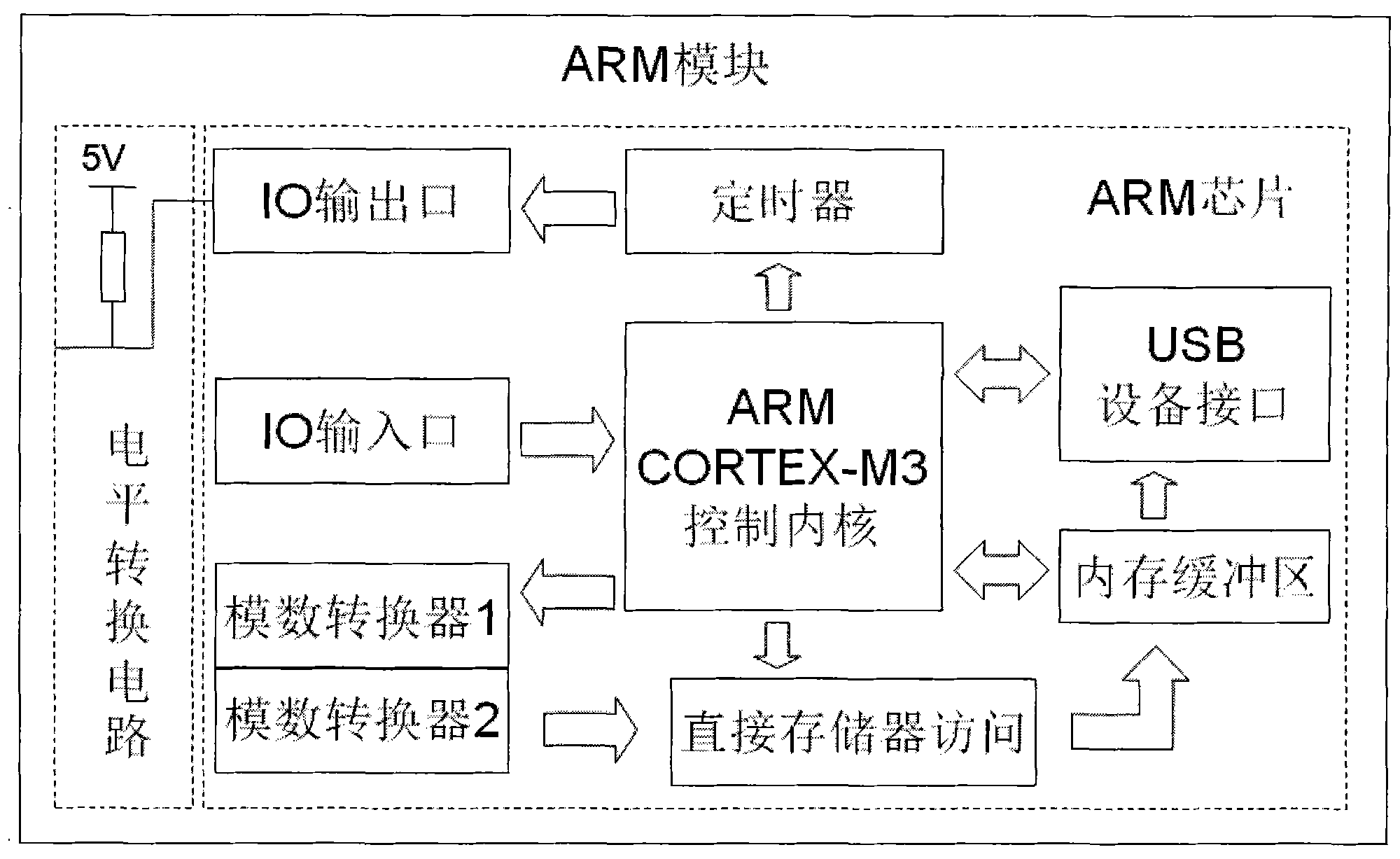
Photoelectric imaging system based on low-dimensional quantum structure photoelectricity sensor reading circuit
InactiveCN101841636ATelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsControl signalHardware modules
The invention discloses a photoelectric imaging system based on a low-dimensional quantum structure photoelectricity sensor reading circuit. The system comprises a low-dimensional quantum structure photoelectricity sensor reading circuit module, an ARM (Advanced RISC Machines) module and a general-purpose computer imaging software module. Hardware modules are connected in a bus mode, the ARM module outputs parallel control signals, receives status signals output by the reading circuit module and collects serial data, the ARM module communicates with a general-purpose computer in a universal serial bus (USB) mode, and the imaging software module runs in the general-purpose computer, obtains data through drivers, processes voltage value uploaded by lower computers of each pixel of a photoelectricity sensor and displays the corresponding gray value. The system presents gray images of vision corresponding to the photoelectricity sensor on the general-purpose computer, and provides convenience for measurement, adjustment, application and development of the photoelectricity sensor.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com