Patents
Literature
206 results about "Flux method" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flux method is a method of crystal growth where the components of the desired substance are dissolved in a solvent (flux). The method is particularly suitable for crystals needing to be free from thermal strain. It takes place in a crucible made of highly stable, non-reactive material. For production of oxide crystals, metals such as platinum, tantalum, and niobium are common. Production of metallic crystals generally uses crucibles made from ceramics such as alumina, zirconia, and boron nitride. The crucibles and their contents are often isolated from the air for reaction, either by sealing them in a quartz ampoule or by using a furnace with atmosphere control. A saturated solution is prepared by keeping the constituents of the desired crystal and the flux at a temperature slightly above the saturation temperature long enough to form a complete solution. Then the crucible is cooled in order to allow the desired material to precipitate. Crystal formation can begin by spontaneous nucleation or may be encouraged by the use of a seed. As material precipitates out of the solution, the amount of solute in the flux decreases and the temperature at which the solution is saturated lowers. This process repeats itself as the furnace continues to cool until the solution reaches its melting point or the reaction is stopped artificially.
Laser metalworking of reflective metals using flux
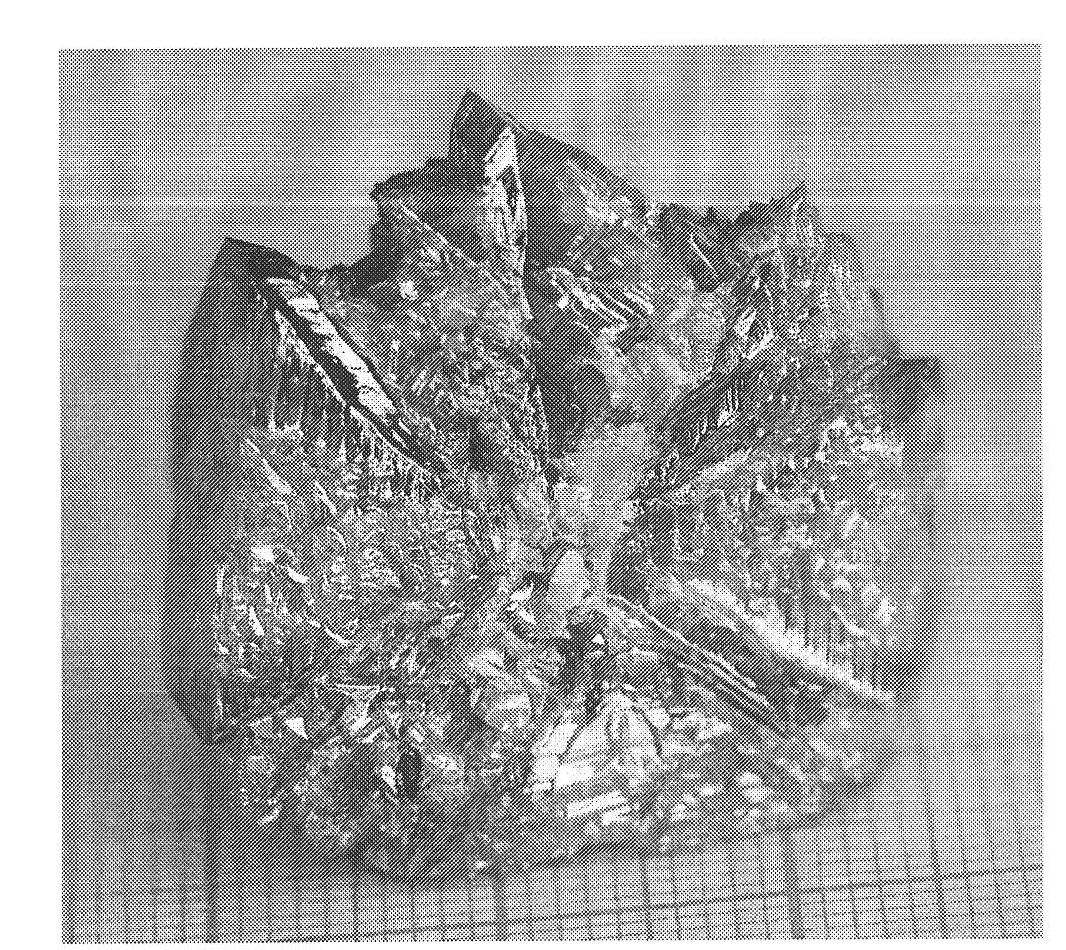
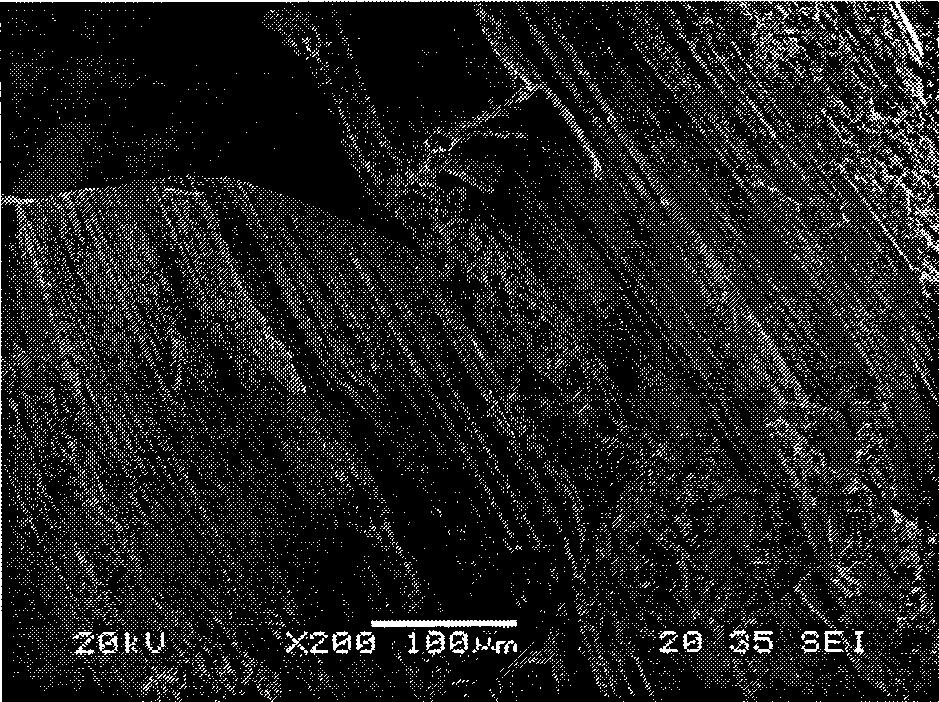
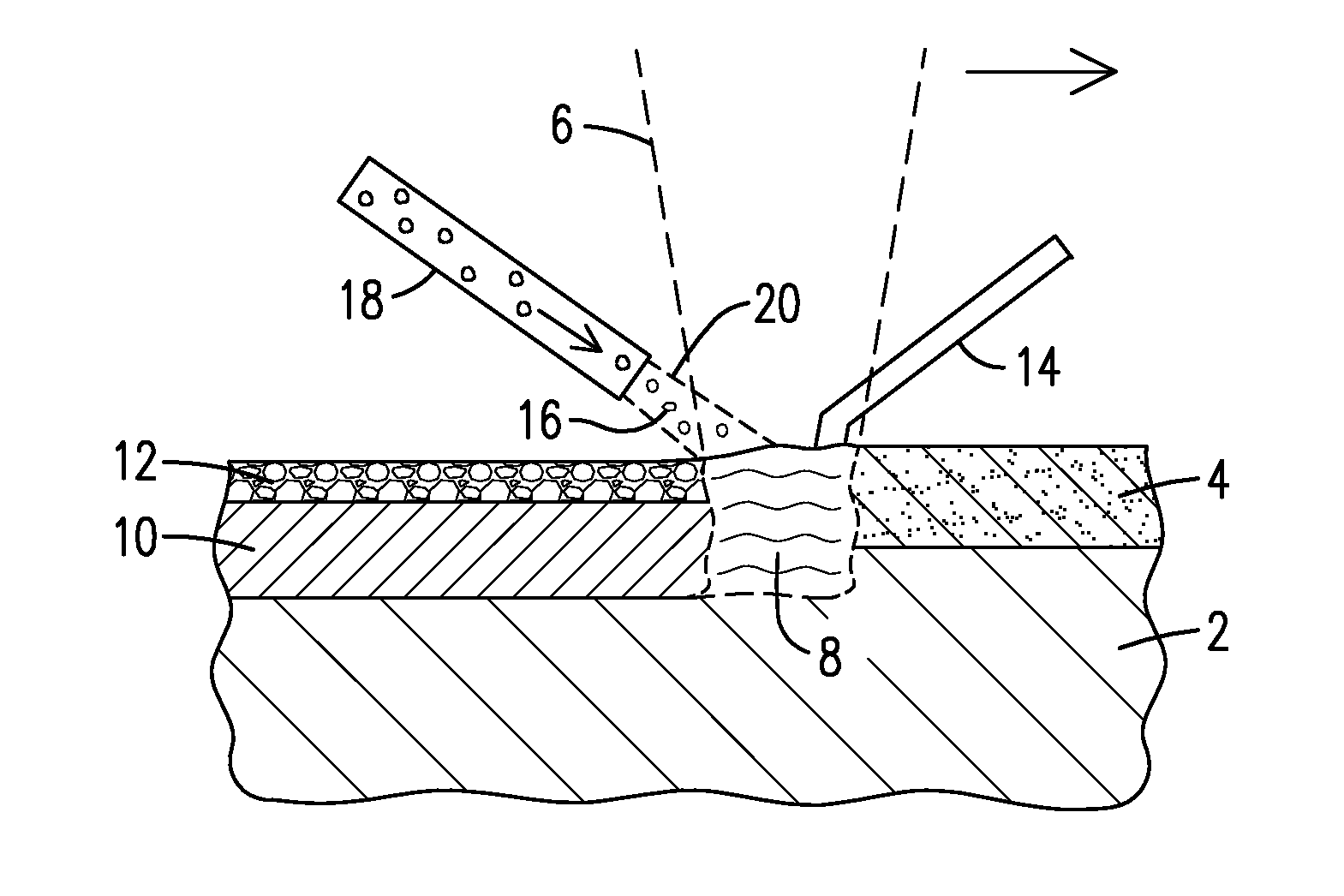
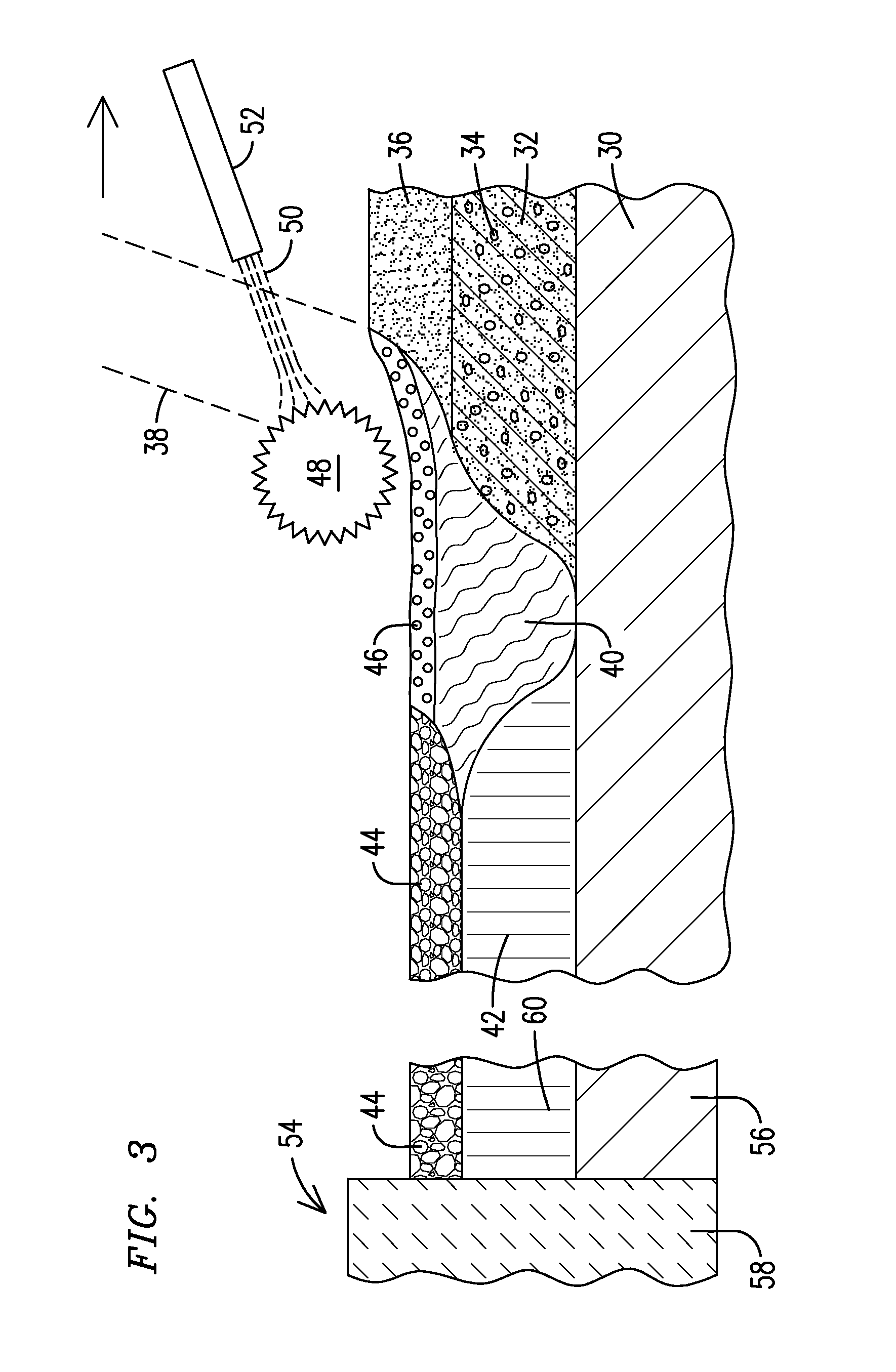
Methods for laser processing of reflective metals. A reflective metal (2) is heated by applying a laser beam (6) to a layer of flux (4) in contact with the reflective metal, in which the flux is a powdered flux composition. The laser beam (38) may be applied to a powdered flux composition (36) such that thermal energy absorbed from the laser beam is transferred to a reflective-metal filler material (32) situated on a support material (30), and the powdered flux composition and the reflective-metal filler material melt to form a melt pool (40) which solidifies to form a metal layer (42) covered by a slag layer (44).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
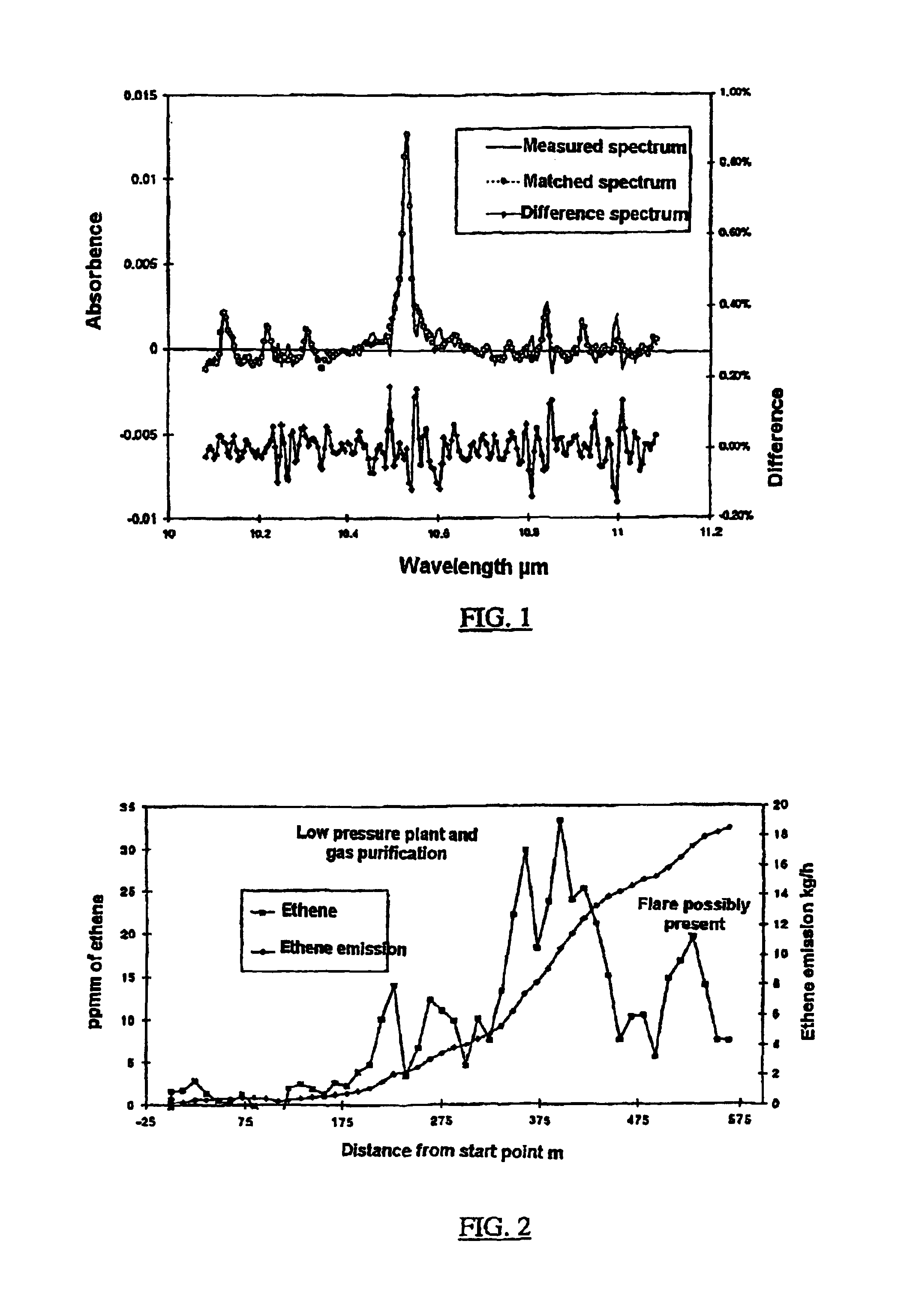
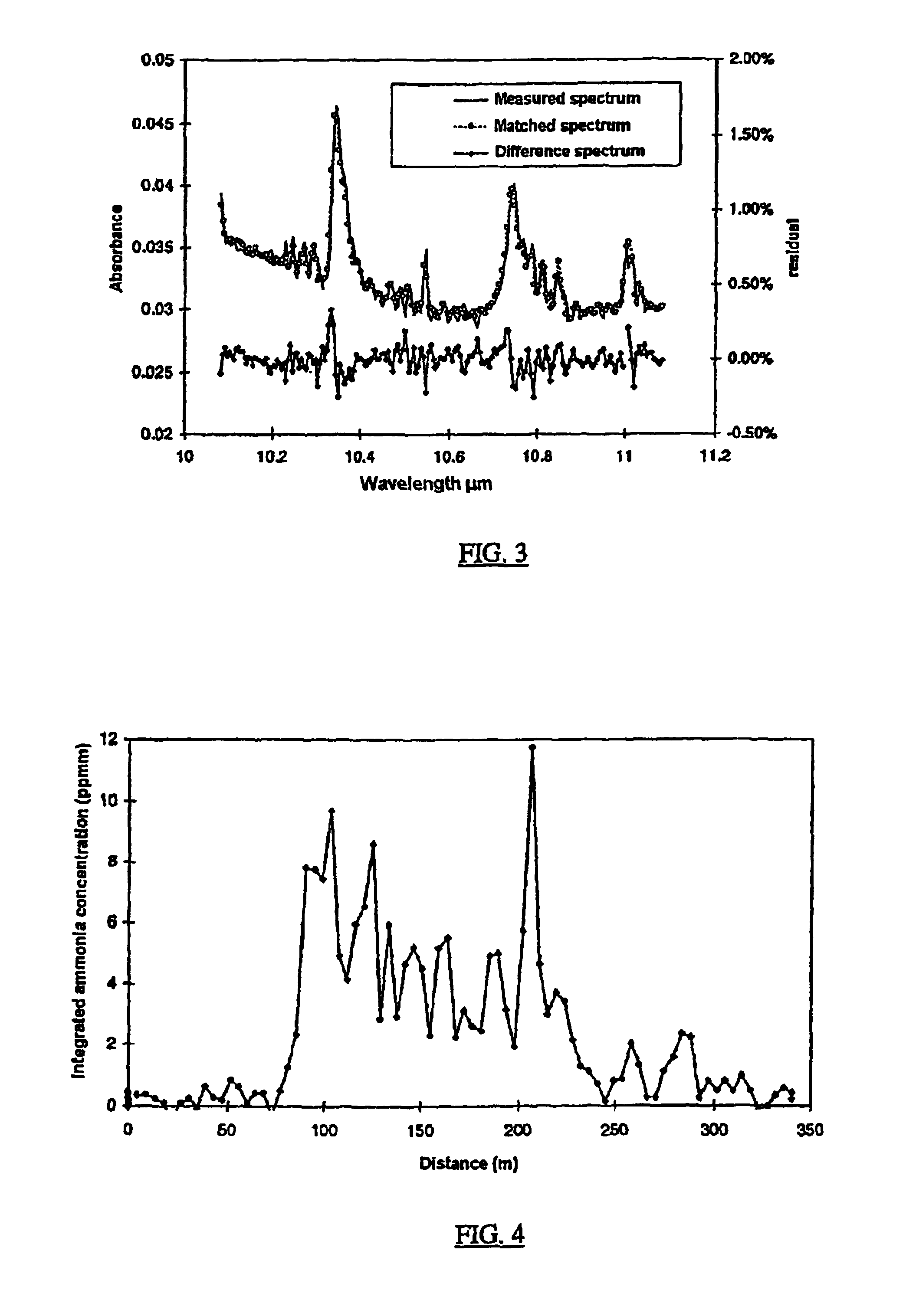
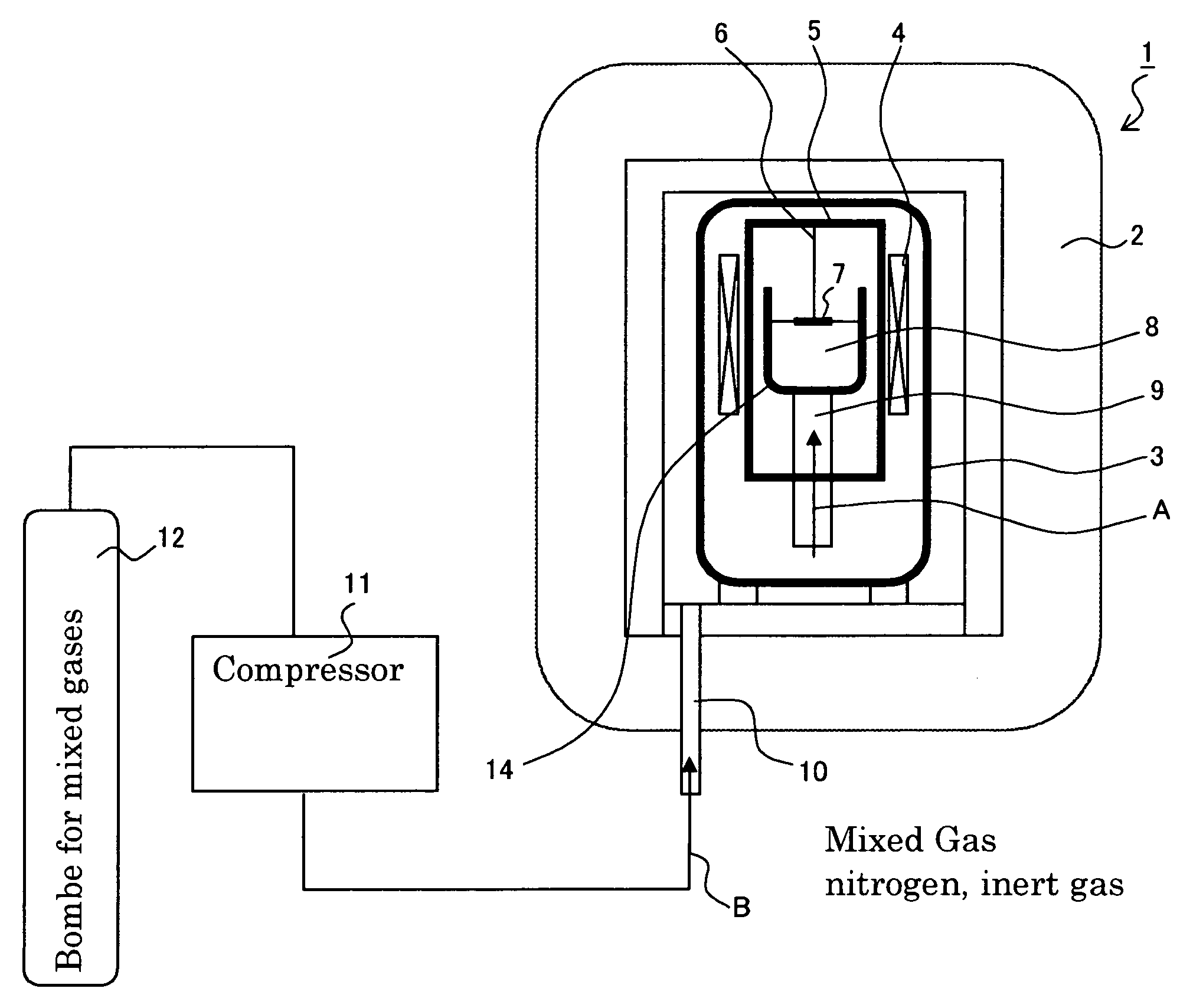
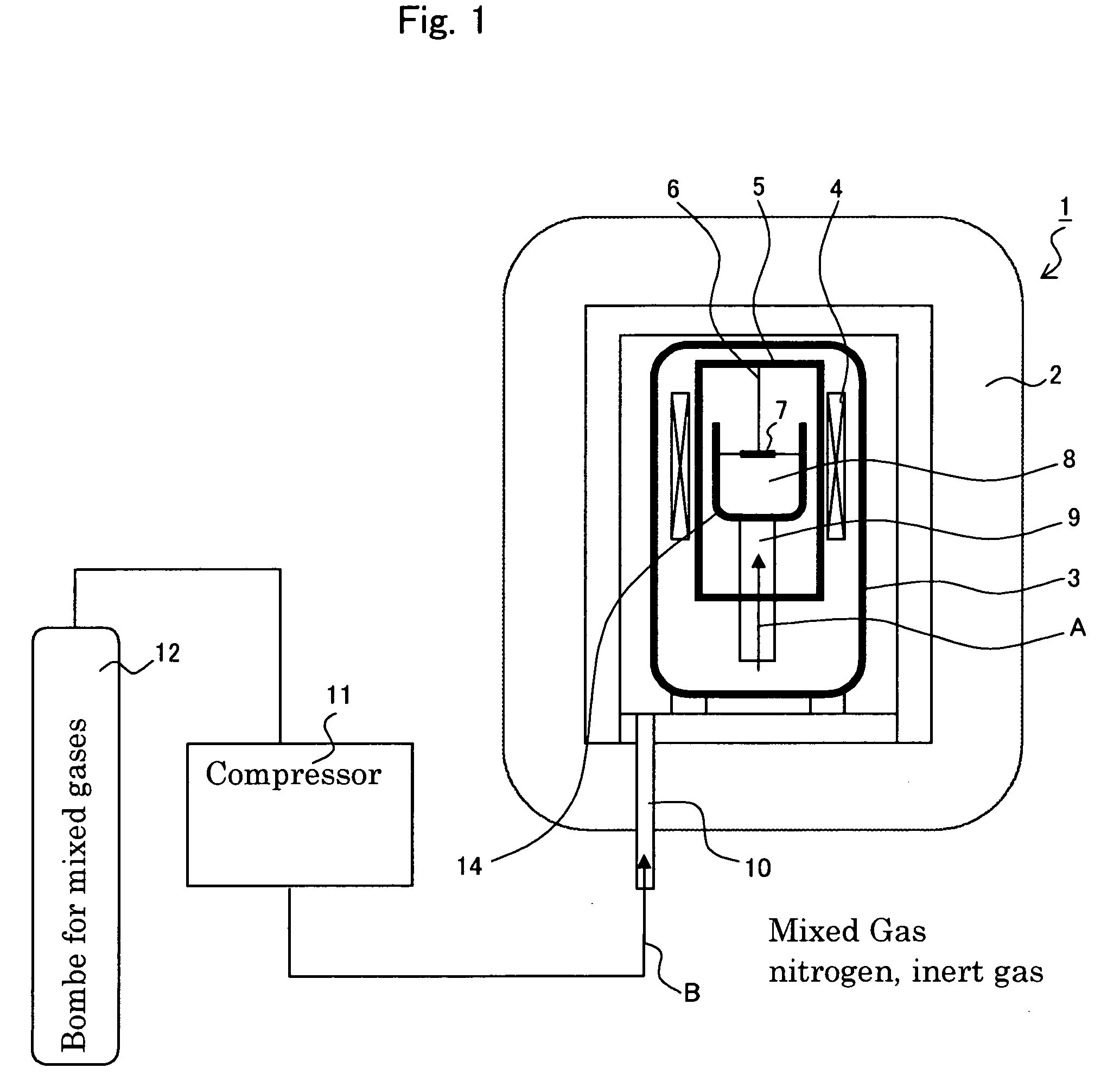
Method for measuring of gaseous emissions and/or flux
InactiveUS6864983B2Transmissivity measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLength waveElectromagnetic radiation
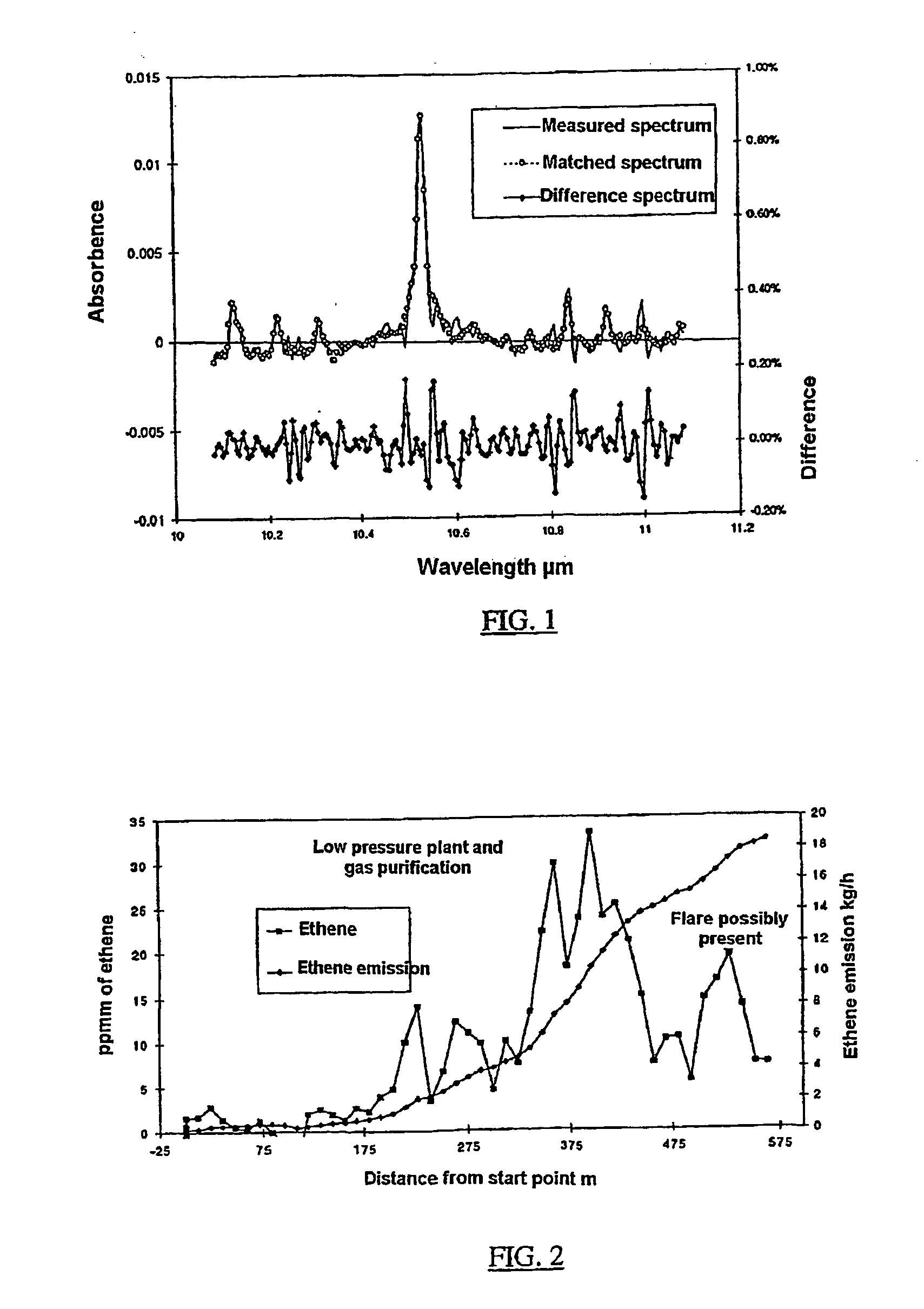
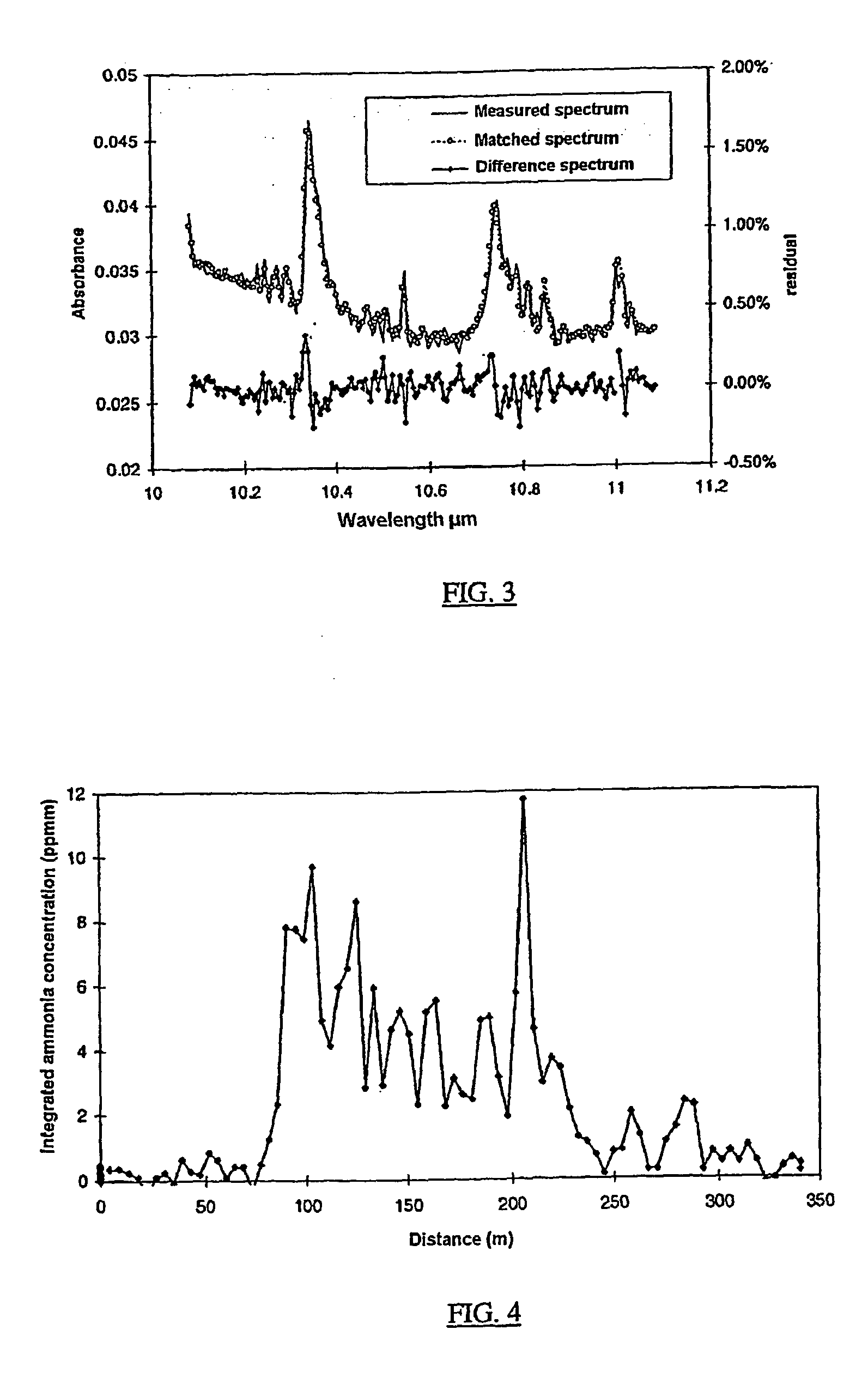
Method for measuring gaseous emissions and / or flux based on using a spectrometer instrument for receiving absorption spectra to detect and record, in a wavelength-resolved manner, the electromagnetic radiation which is coming directly from the sun. The instrument is arranged in such a way that the connecting line between the instrument and the sun transects a gas volume which constitutes all or part of the gas flow emitted from a source. The electromagnetic radiation which is recorded is used for calculating the gas concentration along the optical connecting line in the gas volume. The concentration which is obtained in this way, and which is integrated over the cross-sectional area traversed by the connecting line, is used, together with information on the speeds of the wind, the instrument and the gas-emitting source, to calculate the gas flow through the cross-sectional area which is traversed.
Owner:GALLE BO +1
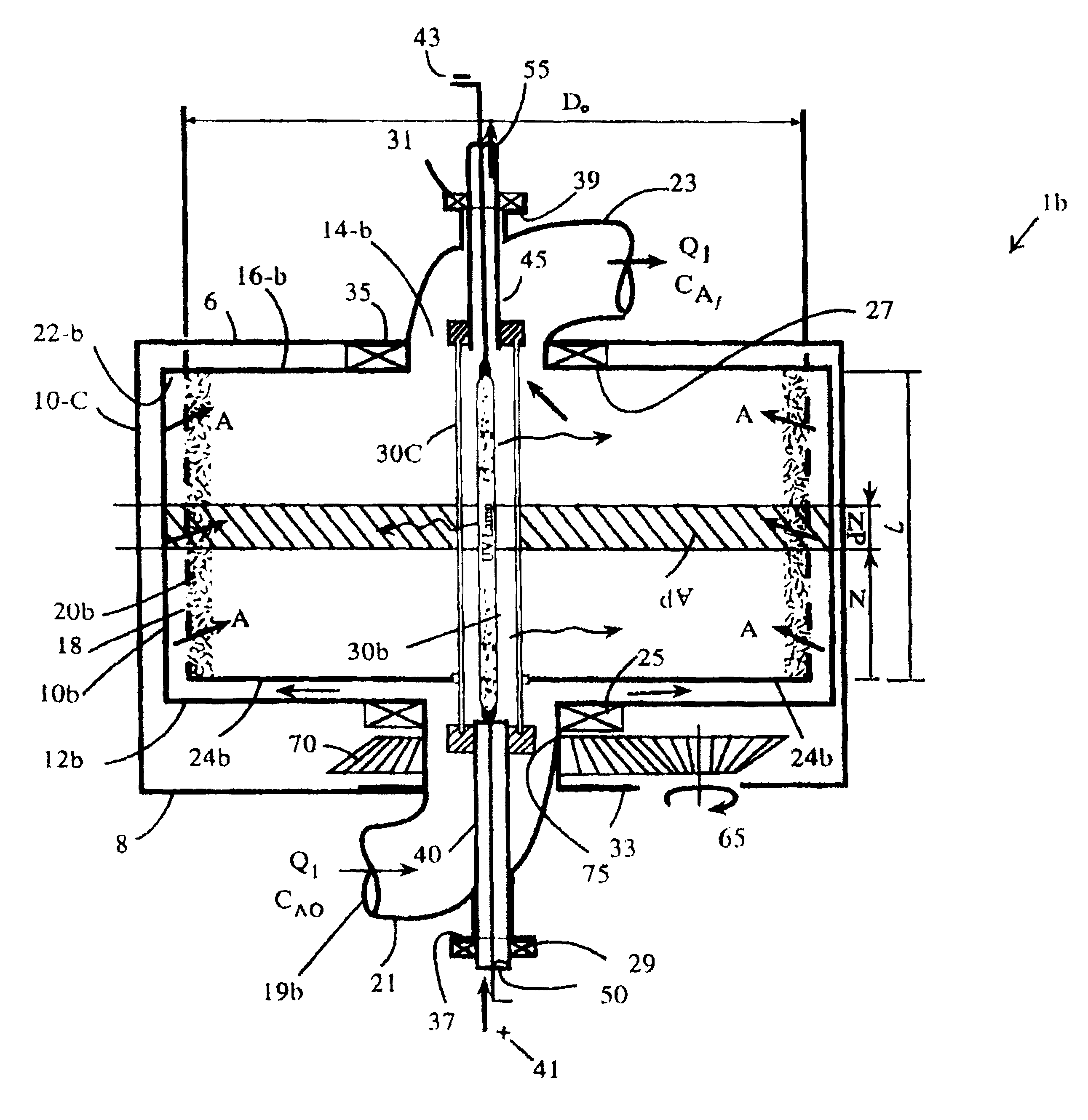
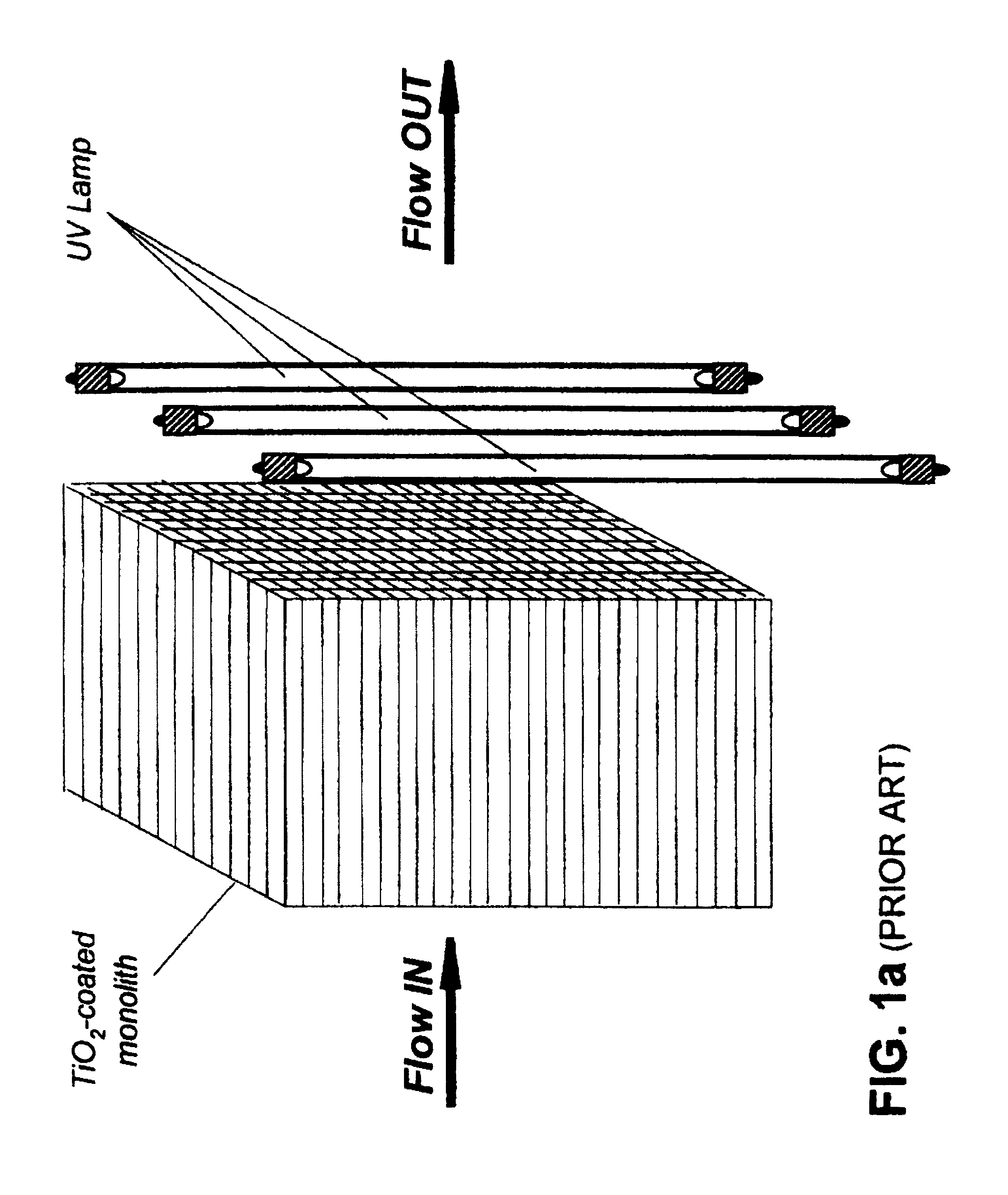
Method for high flux photocatalytic pollution control
InactiveUS6315870B1Efficient retentionMinimizes mass transfer intrusionNitrogen compoundsEnergy based wastewater treatmentEnergeticsPollution
A new method for design and scale-up of photocatalytic and thermocatalytic processes is disclosed. The method is based on optimizing photoprocess energetics by decoupling of the process energy efficiency from the DRE for target contaminants. The technique is applicable to both low- and high-flux photoreactor design and scale-up. The low-flux method is based on the implementation of natural biopolymeric and other low-pressure drop media support for titanium dioxide and other band-gap photocatalysts. The high-flux method is based on the implementation of multifunctional metal oxide aerogels and other media in conjunction with a novel rotating fluidized particle bed reactor.
Owner:CENT FLORIDA UNIV OF
Air-lift-type circulation photobioreactor
ActiveCN103374511AReduce shading effectEasy to trainBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsPhotobioreactorEngineering
The invention relates to an air-lift-type circulation photobioreactor. According to the photobioreactor, light sources are respectively installed at the wall surfaces of an outer cylinder and an inner flow guide cylinder of the reactor; air enters the reactor from an air distributor at the bottom of the circulation reactor, and drives a microalgae solution in the reactor to circulate, so that light generated by the light sources can irradiate an area between the inner sleeve cylinder and the outer sleeve cylinder, and the microalgae blink effect is fully utilized to promote the microalgae culture. According to the invention, the radial distance of inner and outer dual-surface irradiation reactor descending sections is determined by a dual-flux method, thereby designing and amplifying the air-lift-type circulation photobioreactor for irradiating the descending sections synchronously by the light sources inside and outside.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102031563AEasy to implementEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthPolarising elementsNonlinear optical crystalCrystal system
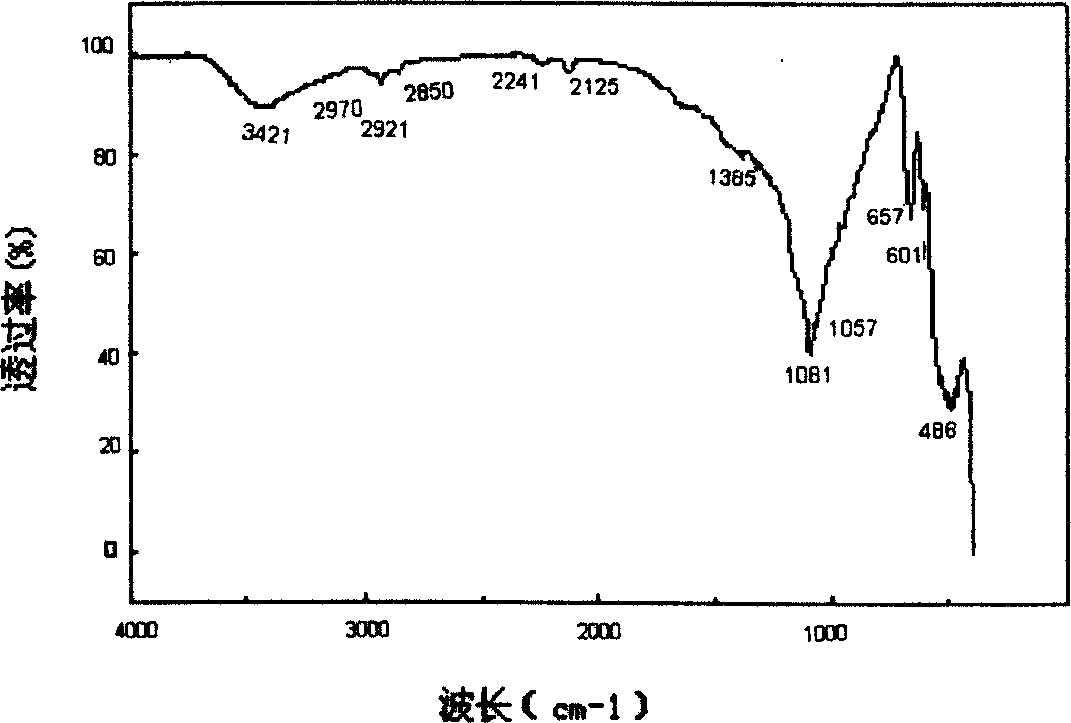
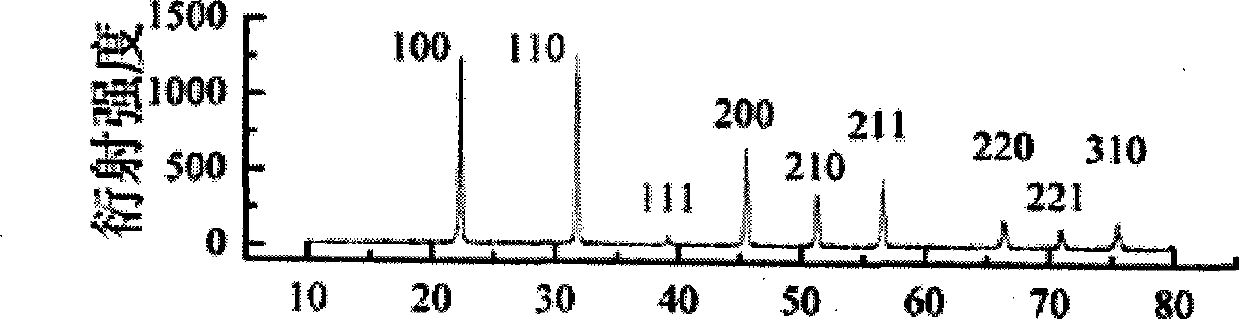
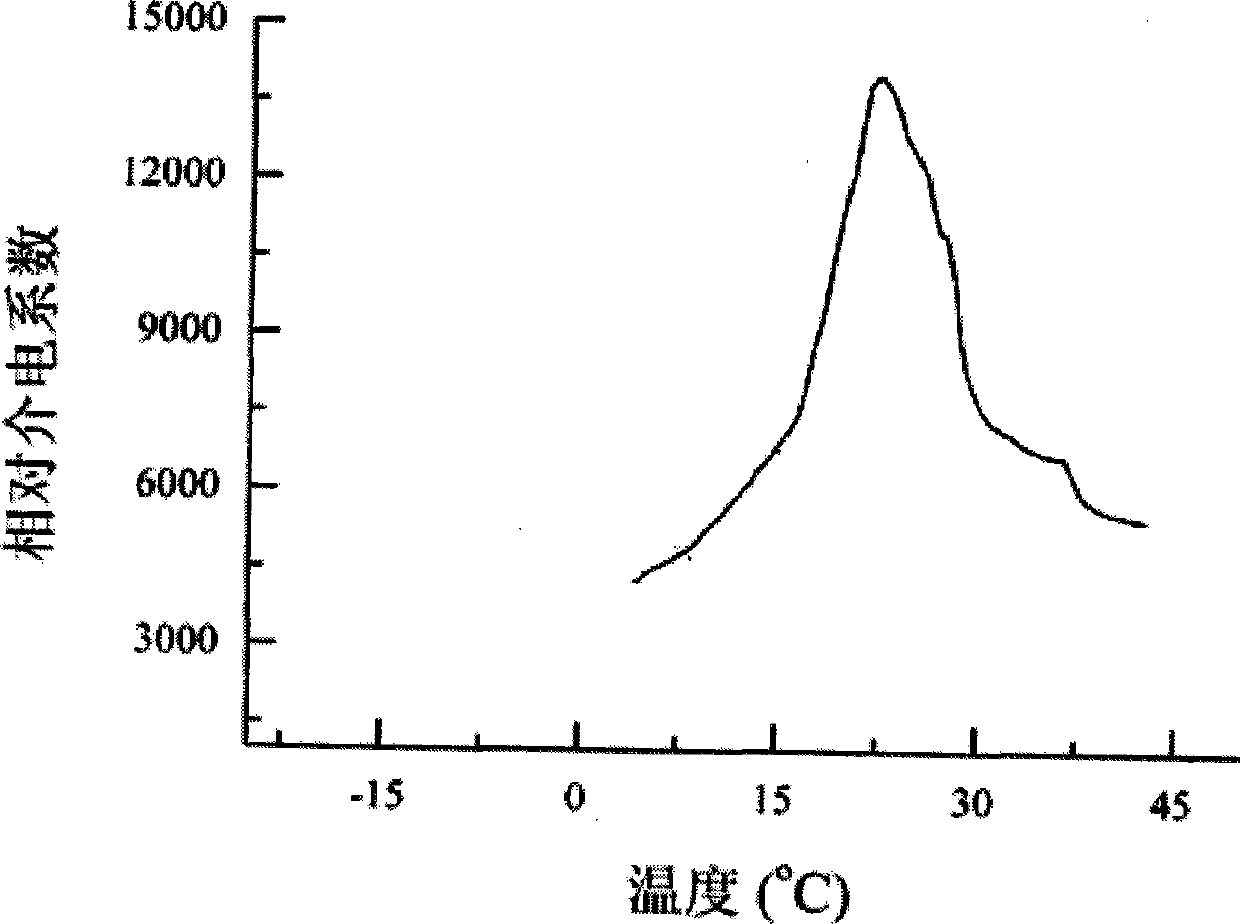
The invention relates to a high-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal as well as a preparation method and the applications thereof. The high-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal belongs to an orthorhombic system, a space group is Pca21, a=14.8683 (2), b=5.66360 (10), c=17.6849 (3), ultraviolet-visible-near-infrared light is displayed through a light spectrum, intermediate infrared light is displayed through the light spectrum, the crystal permeates the wavelength range of 380-5530 nm, and infrared laser of 1064 nm is incident into the crystal at a room temperature to generate green light with the wavelength of 532 nm. A fluxing agent method is adopted for growth. The invention also provides the applications of the high-temperature-phase tellurium barium molybdate crystal as a nonlinear optical crystal, a birefringent crystal, a piezoelectric crystal, a ferroelectric crystal, a pyroelectric crystal or a laser substrate material.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Fluoborate and crystal containing rare earth ions, growing method and application of crystal
The invention relates to fluoborate and a crystal containing rare earth ions, and preparation method thereof. The chemical formula of the fluoborate is (Ca1-xRex)5(BO3)3F1-5xO5x, wherein x is more than 0 and less than 0.2; Re is Sc, Y or the rare earth ions; and the rare earth ions are La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm , Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Yb, or Lu, or mixture of the rare earth ions. A flux method is adopted to grow a fluoborate crystal with high quality and large size; the crystal meets the requirement of blue green light wave-band laser frequency conversion, and can be used for manufacturing nonlinear optical devices; a monocrystal doped with rare-earth laser activated ions can manufacture laser-nonlinear multi-functional optical devices; and lasers manufactured by the crystal can be used in the fields such as spectroscopy, biomedicine, military, and the like.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Group 3B nitride crystal substrate
ActiveUS20110274609A1Quality improvementGood colorPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthNitrideSeed crystal
A group 13 nitride crystal substrate according to the present invention is produced by growing a group 13 nitride crystal on a seed-crystal substrate by a flux method, wherein a content of inclusions in the group 13 nitride crystal grown in a region of the seed-crystal substrate except for a circumferential portion of the seed-crystal substrate, the region having an area fraction of 70% relative to an entire area of the seed-crystal substrate, is 10% or less, preferably 2% or less.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method for developing potassium fluoroboric beryllium acid / sodium crystal through hydrothermal method
InactiveCN101050547AIncrease growth rateQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsPotassiumDistilled water
This invention relates to a hydrothermal method for growing KBBF / Na single crystal from crushed crystal. The method comprises: (1) placing crushed crystal of KBBF / Na as the nitrition medium at the bottom of a gold bushing, adding 0-2.0 mol / L deionized water or distilled water solution of mineralizer 60-80% of the gold bushing, and adjusting the pH value to 2.0-10.0; (2) hanging KBBF / Na seed crystal along c direction at the top of the gold bushing; (3) heating so that the average temperatures of the growth region and the dissolution region reach 300-450 deg.C and 400-500 deg.C, respectively, and the pressure less than or equal to 200 MPa; (4) growing for 10-90 days to obtain KBBF / Na single crystal. The method has such advantages as simple process, and better crustal quality than flux method. The length of the obtained KBBF / Na single crystal at C direction can reach cm level or higher.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Gallium Nitride Single Crystal Growing Method and Gallium Nitride Single Crystal
InactiveUS20070209575A1Improve productivityQuality improvementPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsProduction rateNitrogen partial pressure
It is provided a method of growing gallium nitride single crystal of good quality with a high productivity, in the growth of gallium nitride single crystal by Na-flux method. Gallium nitride single crystal is grown using flux 8 containing at least sodium metal. Gallium nitride single crystal is grown in atmosphere composed of gases mixture “B” containing nitrogen gas at a pressure of 300 atms or higher and 2000 atms or lower. Preferably, the nitrogen partial pressure in the atmosphere is 100 atms or higher and 2000 atms or lower. Preferably, the growth temperature is 1000° C. or higher and 1500° C. or lower.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Method for measuring of gaseous emissions and/or flux
InactiveUS20040012787A1Simpler and cheapStrong specificityColor/spectral properties measurementsLength waveElectromagnetic radiation
Method for measuring gaseous emissions and / or flux based on using a spectrometer instrument for receiving absorption spectra to detect and record, in a wavelength-resolved manner, the electromagnetic radiation which is coming directly from the sun. The instrument is arranged in such a way that the connecting line between the instrument and the sun transects a gas volume which constitutes all or part of the gas flow emitted from a source. The electromagnetic radiation which is recorded is used for calculating the gas concentration along the optical connecting line in the gas volume. The concentration which is obtained in this way, and which is integrated over the cross-sectional area traversed by the connecting line, is used, together with information on the speeds of the wind, the instrument and the gas-emitting source, to calculate the gas flow through the cross-sectional area which is traversed.
Owner:GALLE BO +1
Method for producing group III Nitride-based compound semiconductor
ActiveUS20080271665A1Increase crystal growth rateHigh crystallinityPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltCrucibleNitrogen
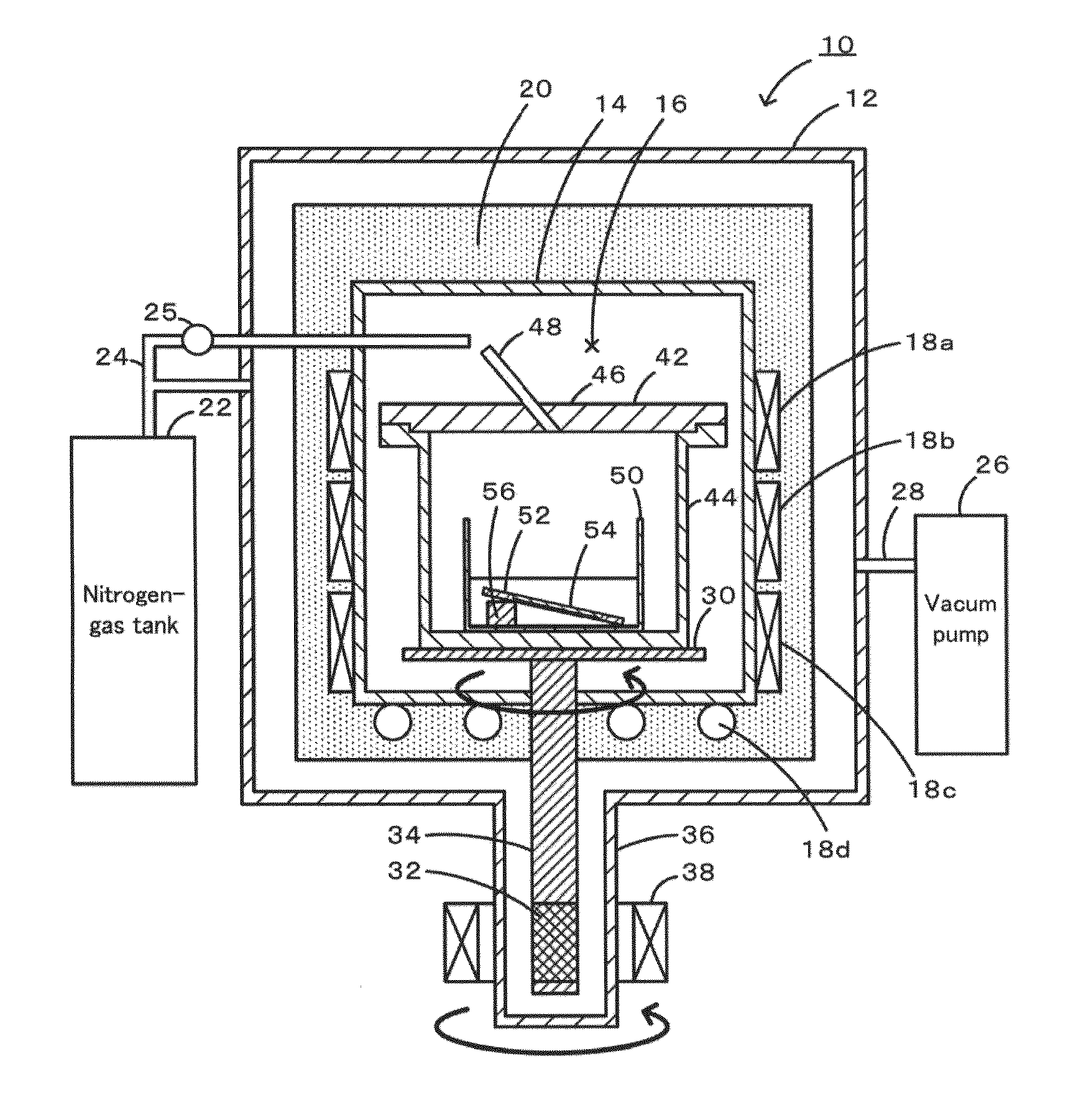
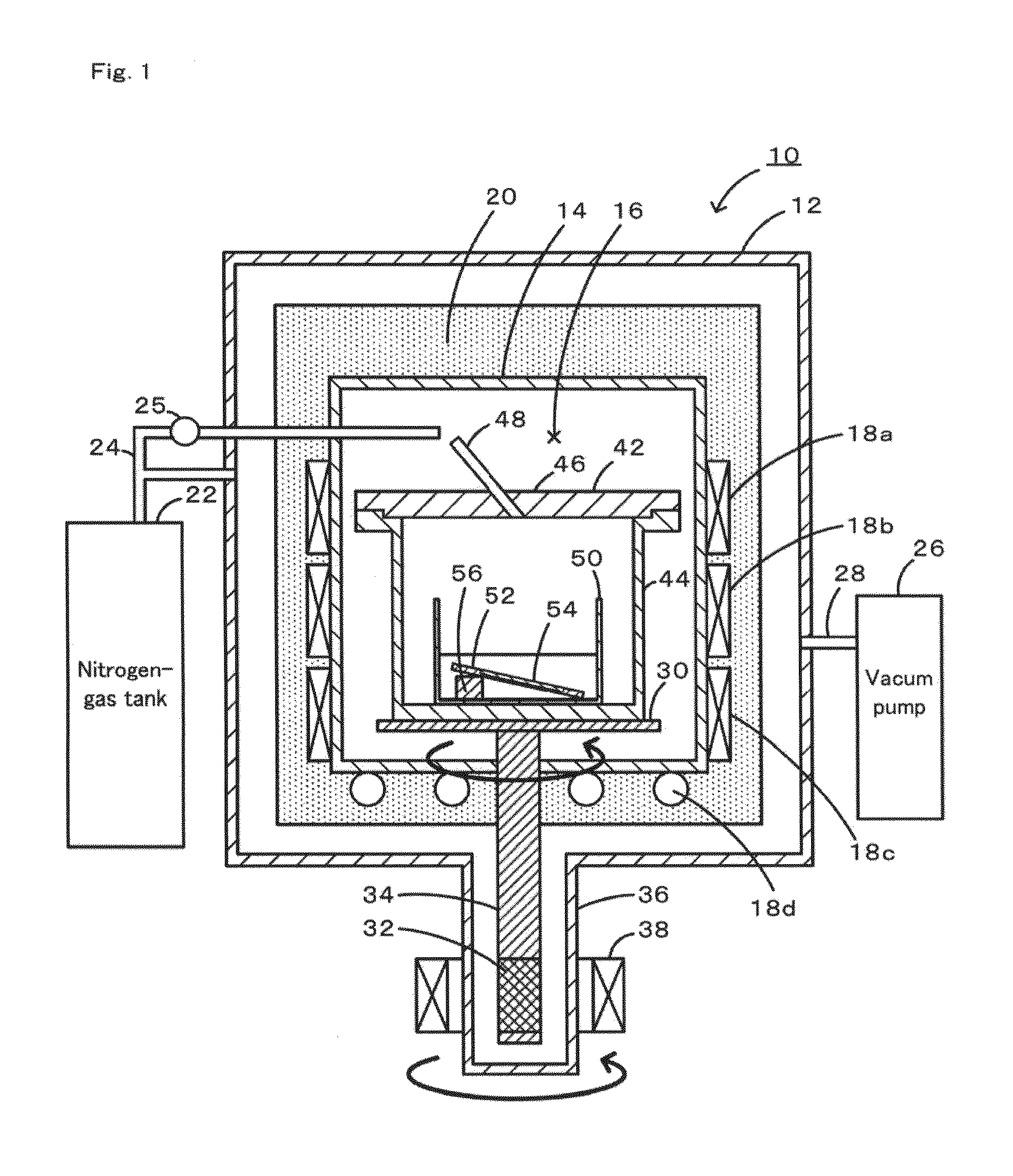
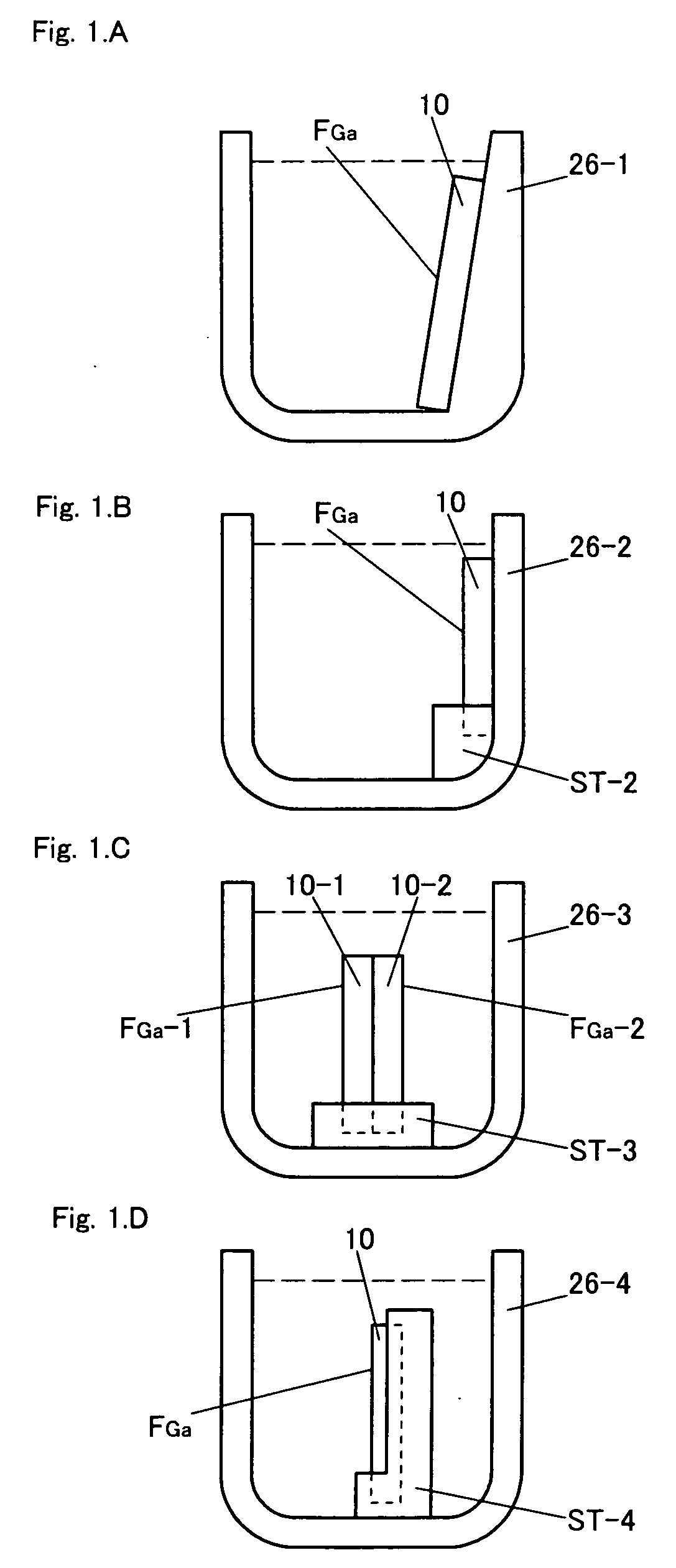
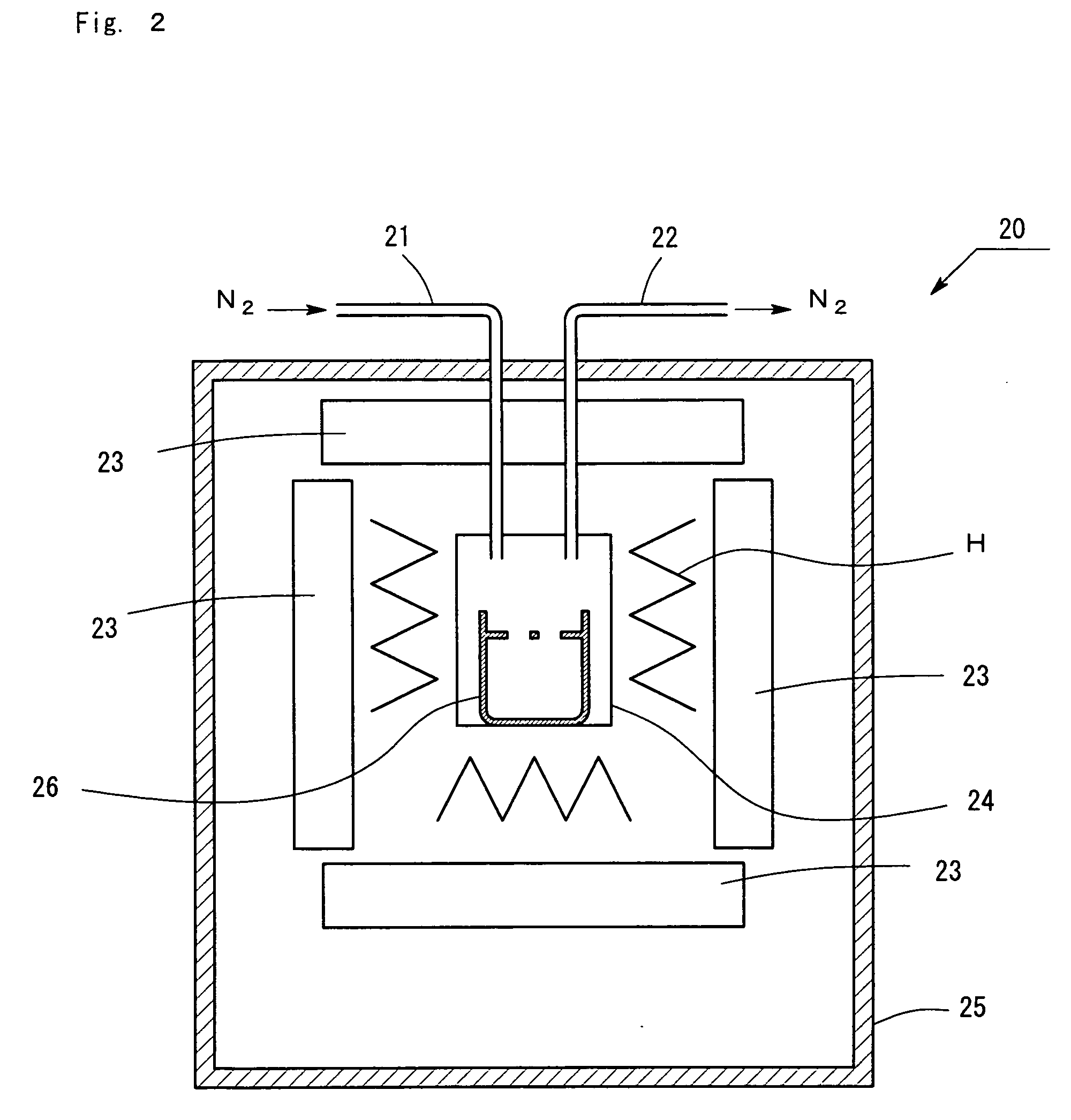
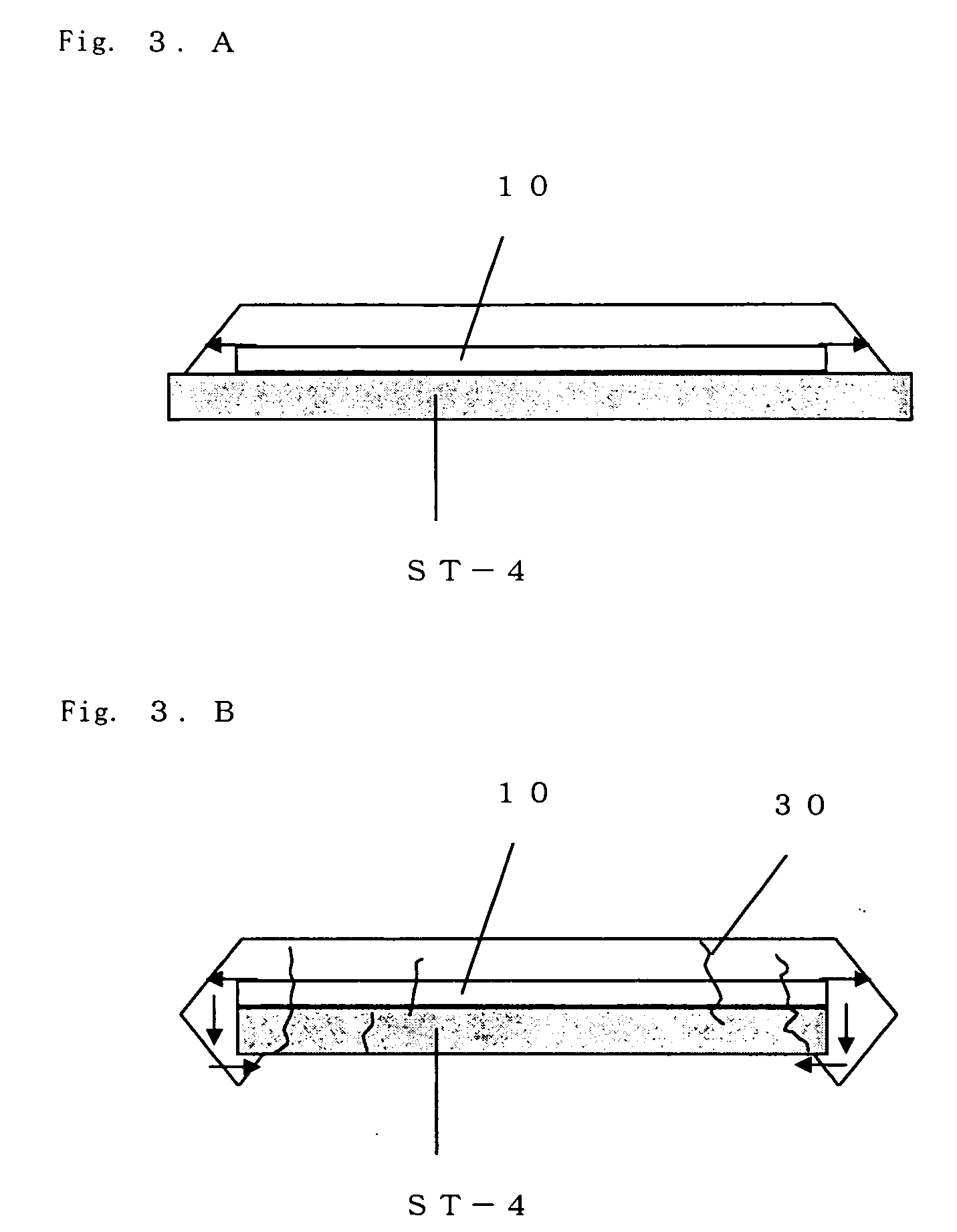
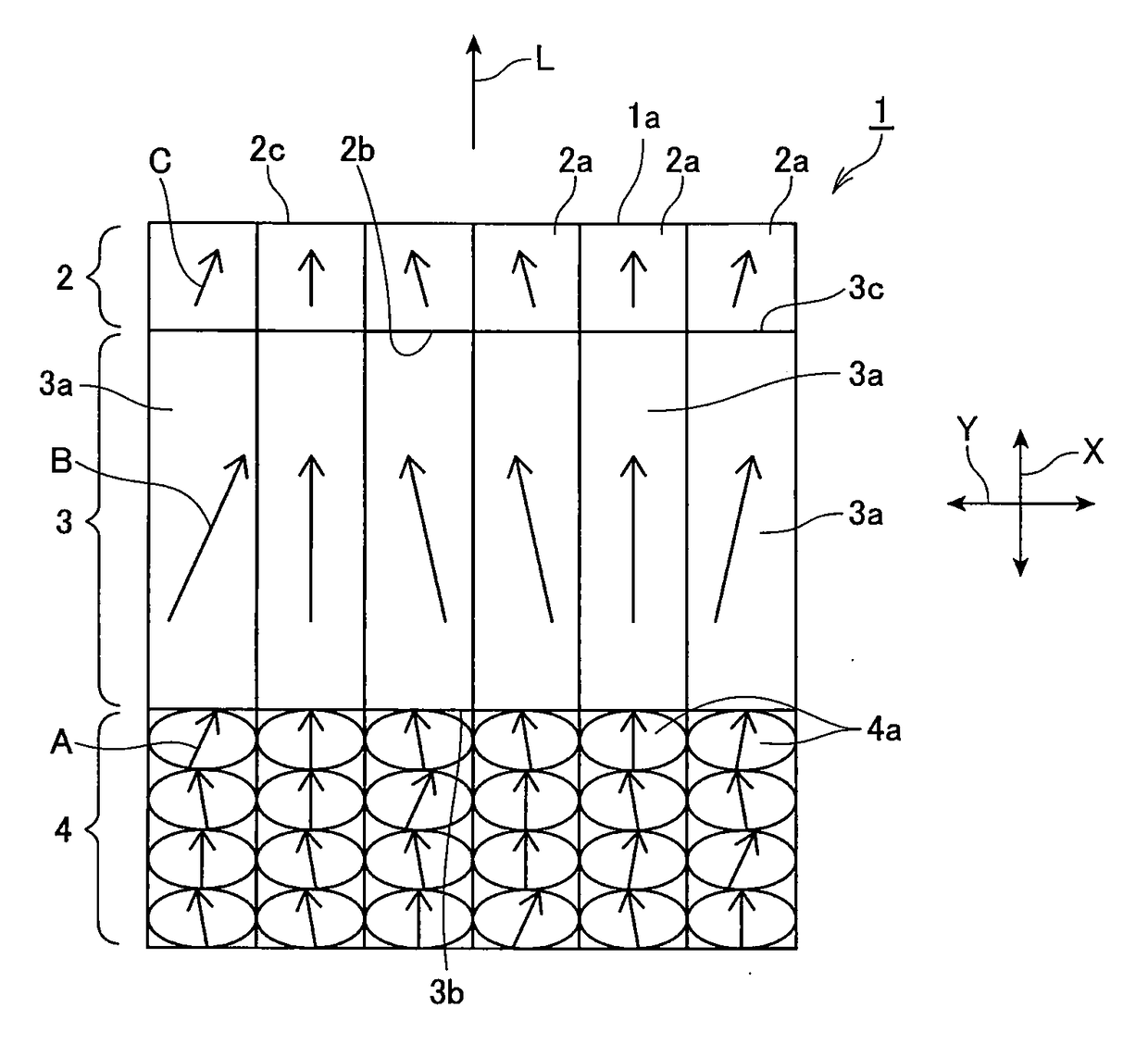
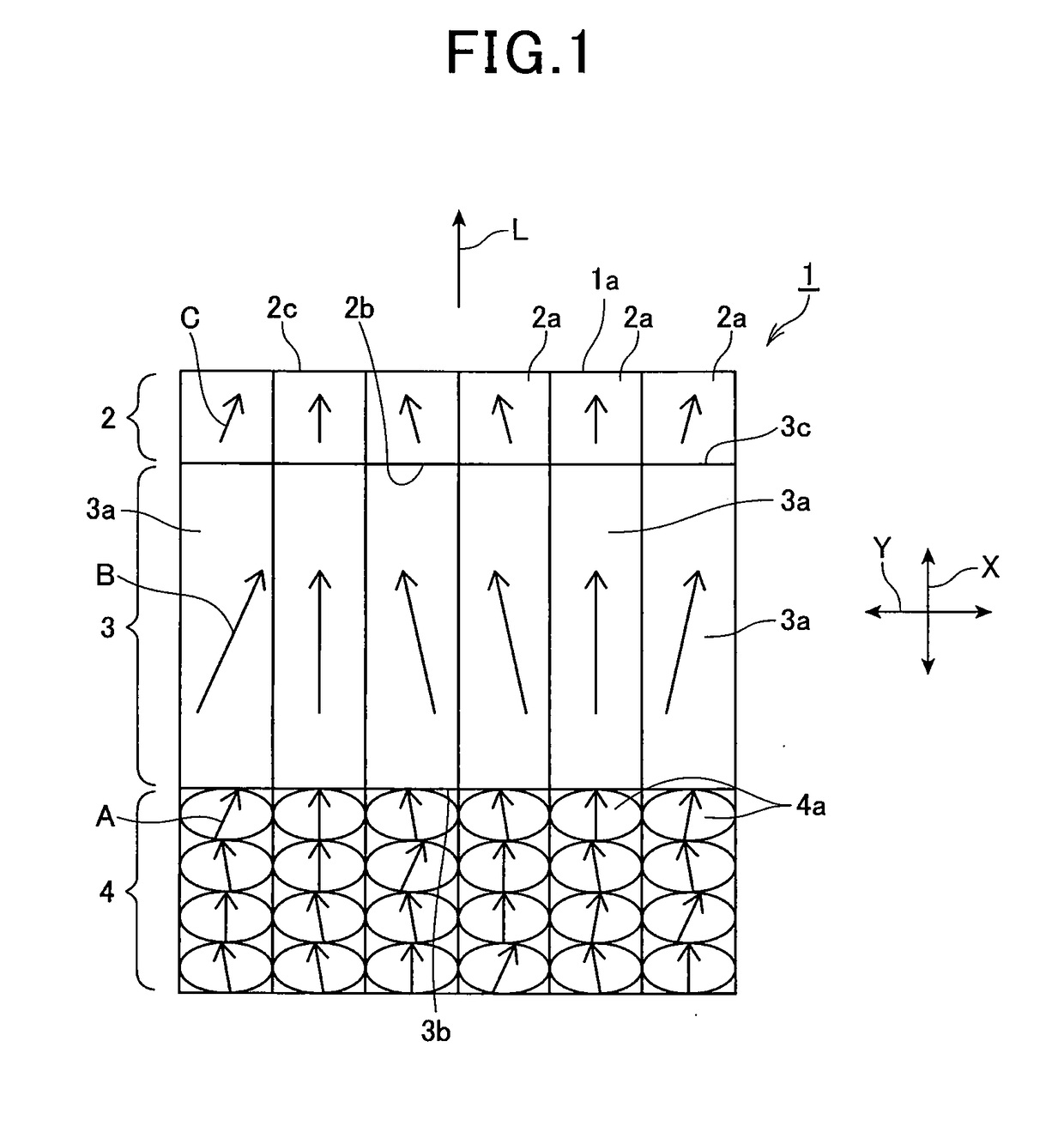
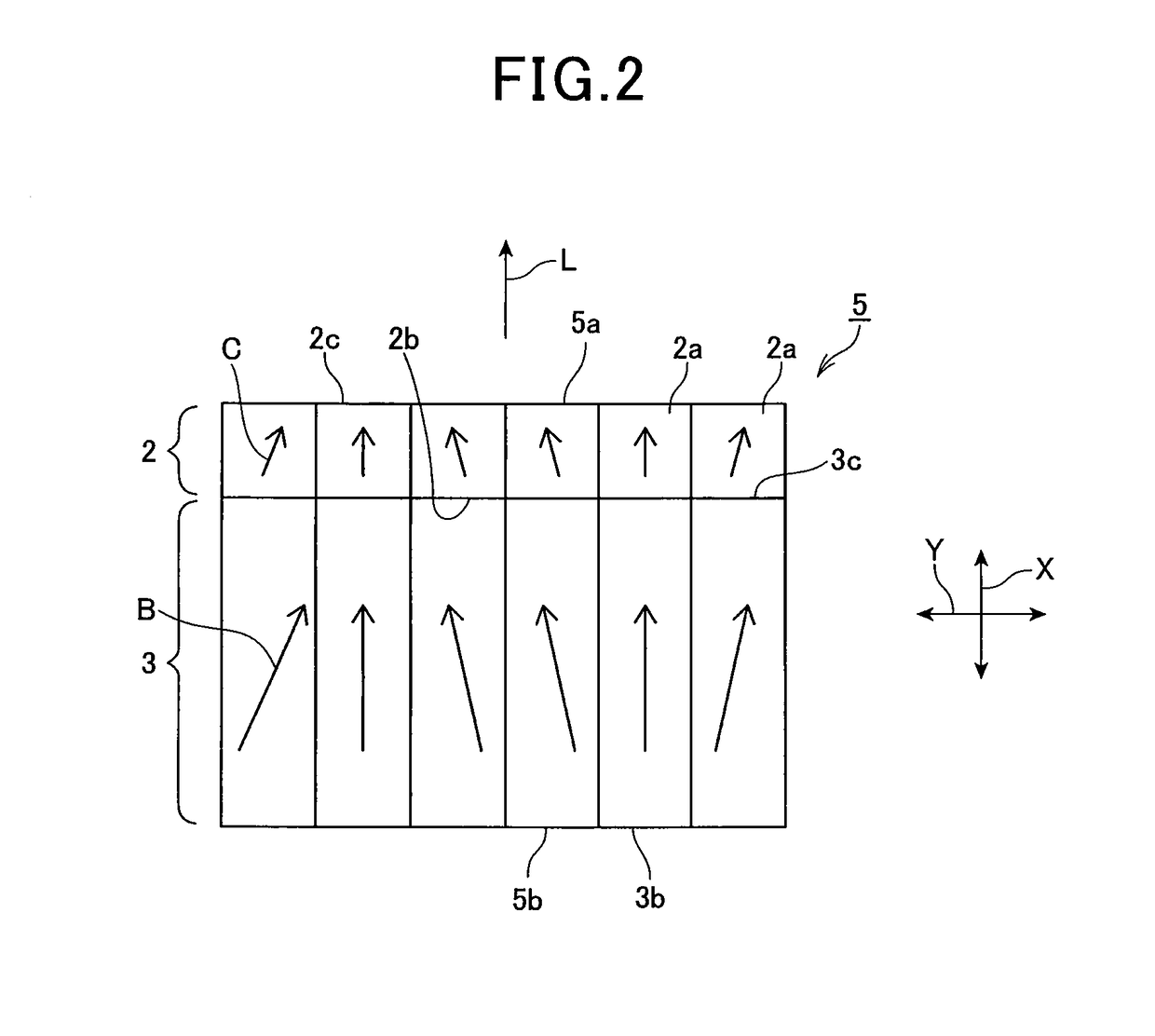
In the production of GaN through the flux method, deposition of miscellaneous crystals on the nitrogen-face of a GaN self-standing substrate and waste of raw materials are prevented. Four arrangements of crucibles and a GaN self-standing substrate are exemplified. In FIG. 1A, a nitrogen-face of a self-standing substrate comes into close contact with a sloped flat inner wall of a crucible. In FIG. 1B, a nitrogen-face of a self-standing substrate comes into close contact with a horizontally facing flat inner wall of a crucible, and the substrate is fixed by means of a jig. In FIG. 1C, a jig is provided on a flat bottom of a crucible, and two GaN self-standing substrates are fixed by means of the jig so that the nitrogen-faces of the substrates come into close contact with each other. In FIG. 1D, a jig is provided on a flat bottom of a crucible, and a GaN self-standing substrate is fixed on the jig so that the nitrogen-face of the substrate is covered with the jig. A flux mixture of molten gallium and sodium is charged into each crucible, and a GaN single crystal is grown on a gallium-face under pressurized nitrogen.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD +1
Tellurium-caesium molybdate crystal, growth of tellurium-caesium molybdate crystal by flux method and application
ActiveCN102011189AEasy to implementEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsNonlinear optical crystalHexagonal crystal system
The invention relates to a tellurium-caesium molybdate crystal, growth of tellurium-caesium molybdate crystal by a flux method and application. The tellurium-caesium molybdate crystal belongs to a hexagonal crystal system, the space group is P63, and the crystal has penetrability within the wavelength range of 430-5380nm; the piezoelectric coefficient at room temperature is as follows: d33=20.5pC / N; and infrared laser with the wavelength of 1064nm generated by a Nd:YAG laser irradiates the crystal to generate strong green light. In the invention, crystal growth is realized by the flux method to finally obtain the large-sized monocrystal; and the obtained crystal is used for manufacturing a piezoelectric device and can be also taken as a nonlinear optical crystal, a ferroelectric crystal, a pyroelectric crystal and a laser host crystal.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Method for growth of sulfide crystal containing alkali metal, gallium or indium
InactiveCN1952222AAvoid difficultiesEasy to getPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsIndiumAlkaline earth metal
Growing method of alkali metals, chalcogene compounds crystal of gallium or indium, involves synthesis and crystal growth of a type alkali metals, chalcogene compounds crystal of gallium or indium ATrQ2(A=Li,Na,K,Rb,Cs;Tr=Ga,In;Q=S,Se,Te)the synthesis and crystal growth. The purpose of this invention is to combine the synthesis of alkali metals, chalcogene compounds crystal of gallium or indium ATrQ2 and growth technology of flux crystal. Choose alkaline earth metal chalcogene compounds, chalcogene compounds of gallium or indium and proper alkaline metal halide flux for raw materials, through reaction flux method to prepare and grow alkali metals, gallium or indium sulfur compounds ATrQ2 crystal.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Flux method for growth of gallium phosphate crystal
InactiveCN1763264AImprove piezoelectric performanceElimination contentPolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsLithium carbonateSeed crystal
The present invention is fluxing agent growth process of gallium phosphate crystal. Through using lithium carbonate and molybdenum oxide as flux, gallium oxide and ammonium dihydrogen phosphate as main material, mixing ammonium dihydrogen phosphate, gallium oxide, lithium carbonate and molybdenum oxide in the weight ratio of 1 to 1.23 to 1.12 to 6.57, setting the mixture in platinum crucible, heating to melt inside growth furnace and cooling to the temperature of 10-20 deg.c over the solution saturation point to obtain the mixed melt of gallium phosphate and the flux, introducing seed crystal into the growth furnace, lowering the temperature to 1-2 deg.c over the solution saturation point when the seed crystal begins to melt and rotating the seed crystal in 30 rpm for 24 hr, gallium phosphate crystal is grown. After lowering the temperature, the crystal is taken out of the solution. The process can eliminate water from the crystal and raise the piezoelectric performance of the crystal.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Cubic phase sodium potassium tantalateniobate crystal and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101372361AUniform compositionImprove optical qualityTantalum compoundsOptical propertyTantalum
A cubic phase potassium sodium tantalum niobate crystal and a preparation method thereof relate to the potassium sodium tantalum niobate crystal and the preparation method thereof, which solve the problems that the existing potassium sodium tantalum niobate crystal products crack easily, and the paraelectric (cubic) phase potassium sodium tantalum niobate crystal has low optical quality, high sintering temperature, long time consumption, low yield and high cost. The chemical formula of the cubic phase potassium sodium tantalum niobate crystal is K1-yNayTa1-xNbxO3 or M:K1-yNayTa1-xNbxO3. The method comprises the following steps: (1) raw materials are weighed; (2) a potassium sodium tantalum niobate polycrystal is prepared; (3) the potassium sodium tantalum niobate polycrystal is cooled and seeded; (4) the cubic phase potassium sodium tantalum niobate crystal is obtained by a top seeded crystal flux method. The top seeded crystal flux method is utilized to realize the preparation of the cubic phase potassium sodium tantalum niobate crystal for the first time. The obtained product has the advantages of no crack, no stripe growth, high optical quality, even crystal components, and that the crystal has good optical property and good mechanical property. The preparation method has the advantages of simple process, short time consumption, low sintering temperature and low cost.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for producing group III nitride semiconductor
ActiveUS20110155046A1Easy to separatePromote generationPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthNitrogen pressureNitrogen gas
In the Na flux method, a target semiconductor layer is separated from a sapphire substrate of a template substrate. The template substrate formed of the sapphire substrate and a GaN layer is placed in a Ga—Na molten mixture. The temperature the molten mixture and the nitrogen pressure are adjusted to 850° C. and 2.5 MPa, respectively. Under the conditions, a part of the GaN layer is melted back until the surface of the sapphire substrate is exposed, so that the remaining portion of the GaN layer is left in the form of a plurality of upright columns. Then, the pressure is elevated to 3 MPa, whereby a target GaN layer is grown on the processed GaN layer. Through lowering temperature, stress due to the difference in linear expansion coefficient and lattice constant between sapphire and GaN is generated, to thereby generate cracks in the processed GaN layer. By virtue of the cracking, the target GaN layer is separated from the sapphire substrate.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Production method of Zintl phase monocrystal
InactiveCN101429676AReduce energy consumptionLow costPolycrystalline material growthFrom frozen solutionsThermoelectric materialsReaction temperature
The invention relates to a Zintl phase single crystal thermoelectric material and a preparation method thereof. The single crystal thermoelectric material comprises the following components: BaMn2Sb2, Ba1-xSrxMn2Sb2, Ba1-xYbxMn2Sb2, BaMn2-yZnySb2 and BaMn2Sb2-zGez (x is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 1,y is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 2, and z is more than or equal to 0 and less than or equal to 0.5) Ba0.75Sr0.25Mn2Sb2, Ba0.7Yb0.3Mn2Sb2, BaMn1.5Zn0.5Sb2 and BaMn2Sb1.5Ge0.5. The preparation method adopts a flux method. The method comprises the following steps: firstly weighing tin, manganese, antimony, barium and strontium, Yttrium, zinc or germanium for doping in a glove box, and adding the raw materials into a corundum crucible; then putting an inverted corundum crucible onto the corundum crucible containing the raw materials, filling a small amount of quartz wool between the two corundum crucibles, and putting the two corundum crucibles into a quartz tube; sealing the quartz tube through a preservative film and taking the quartz tube out of the glove box; carrying out vacuum pumping and repeatedly flushing the quartz tube with argon gas; and then sealing and welding the quartz tube and finally adopting a program temperature control furnace to prepare the single crystal. As the reaction temperature of the method is lower than that of a simple substance fusion method, the method is simpler and has less power consumption and lower cost.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
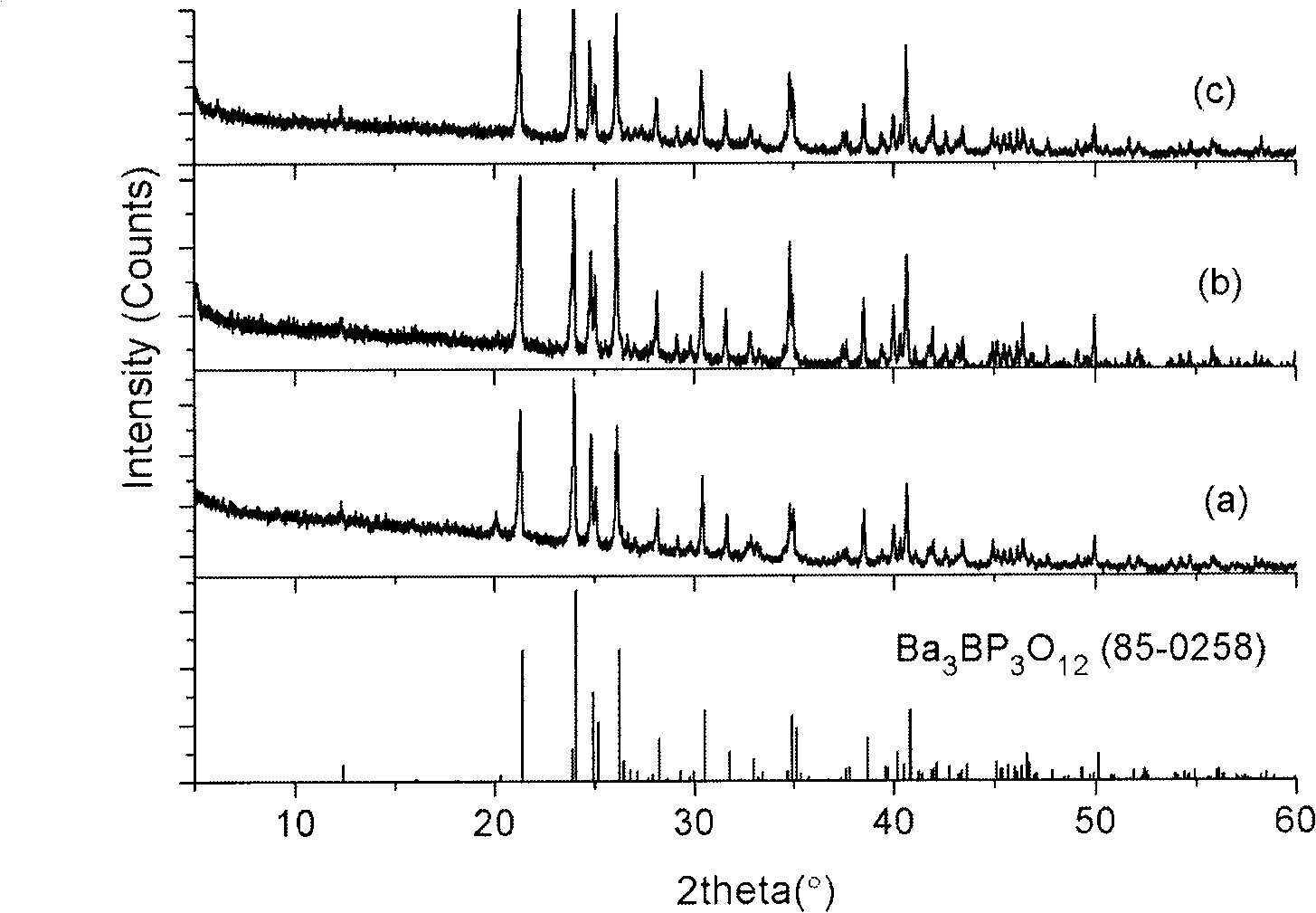
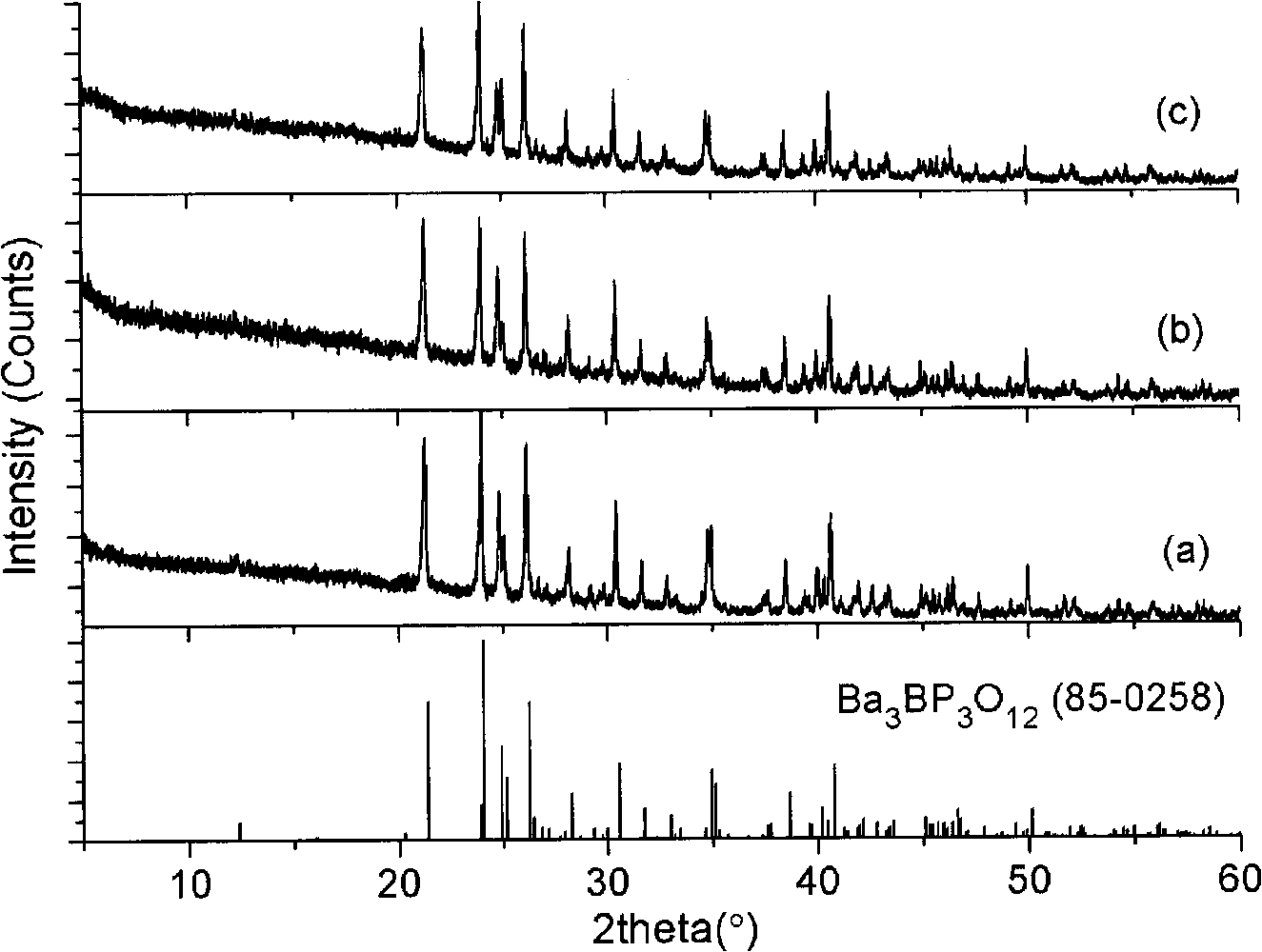
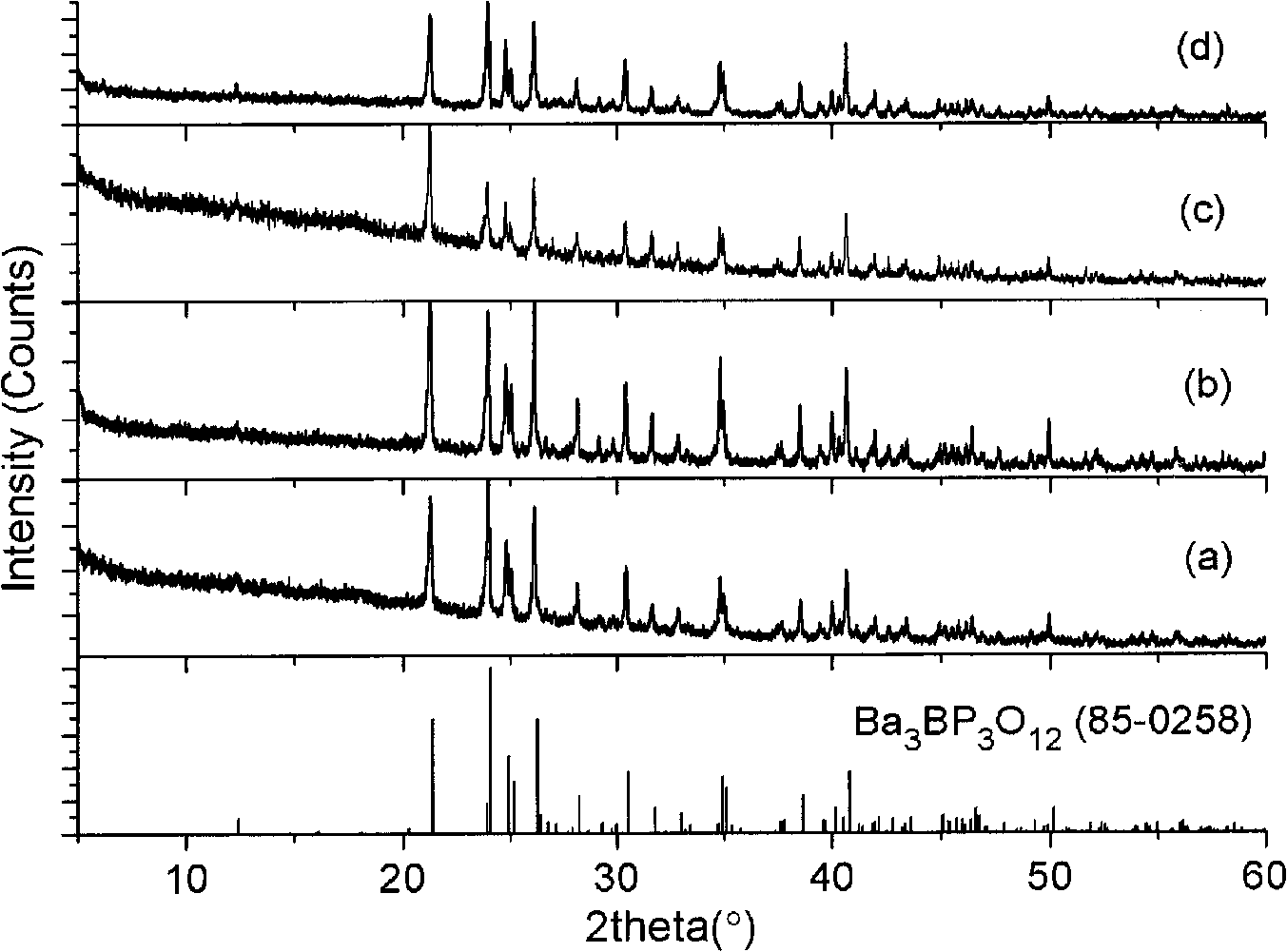
Ba3BP3O12 crystalloid, growing method and application thereof
InactiveCN101514491AHigh hardnessImprove mechanical propertiesPolycrystalline material growthBy pulling from meltFlux growthPhotonic crystal
The invention relates to a Ba3BP3O12 crystalloid, a growing method and the application thereof, belonging to the field of crystalloid growth. The Ba3BP3O12 crystalloid of the invention has the chemical formula composition of Ba (1-x-2y-2z) M (X) M (y)A (y) M (Z) 3 BP3O12, wherein, x, y and z are less than or equal to 0.35 and more than or equal to 0; M is one ion or a plurality of ions in Sr, Ca, Mg, Be, Zn, Eu, Mn and Yb which have +2 valent state; the M is one ion or a plurality of ions in Cr, Bi, Ti, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm and Yb which have +3 valent state; A is one ion or a plurality of ions in Li, Na, K, Rb and Cs; and M is one ion or a plurality of ions in Cr, Ti, Zr and Hf which have +4 valent state. The crystalloid produced by a flux growth method has the advantages of great hardness, good mechanical property, difficult cracking and deliquescence, easy processing and storing and the like, so as to be applied to the fields such as laser crystal, acousto-optic crystal, photorefractive crystal or photonic crystal.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
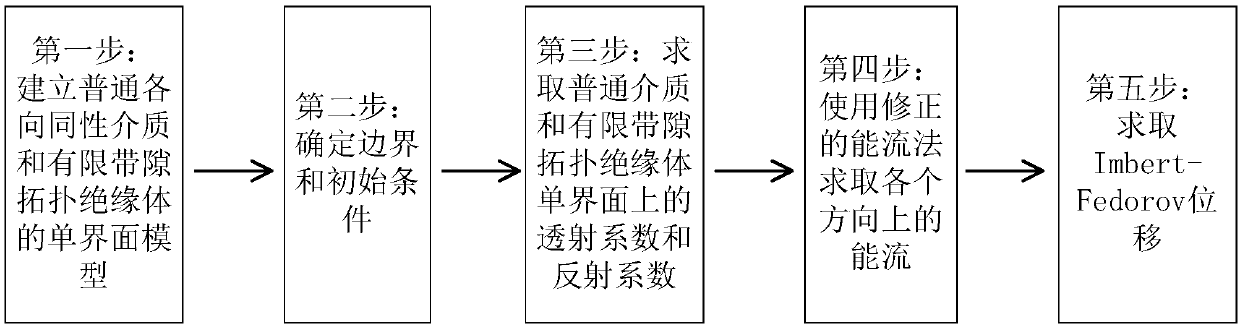
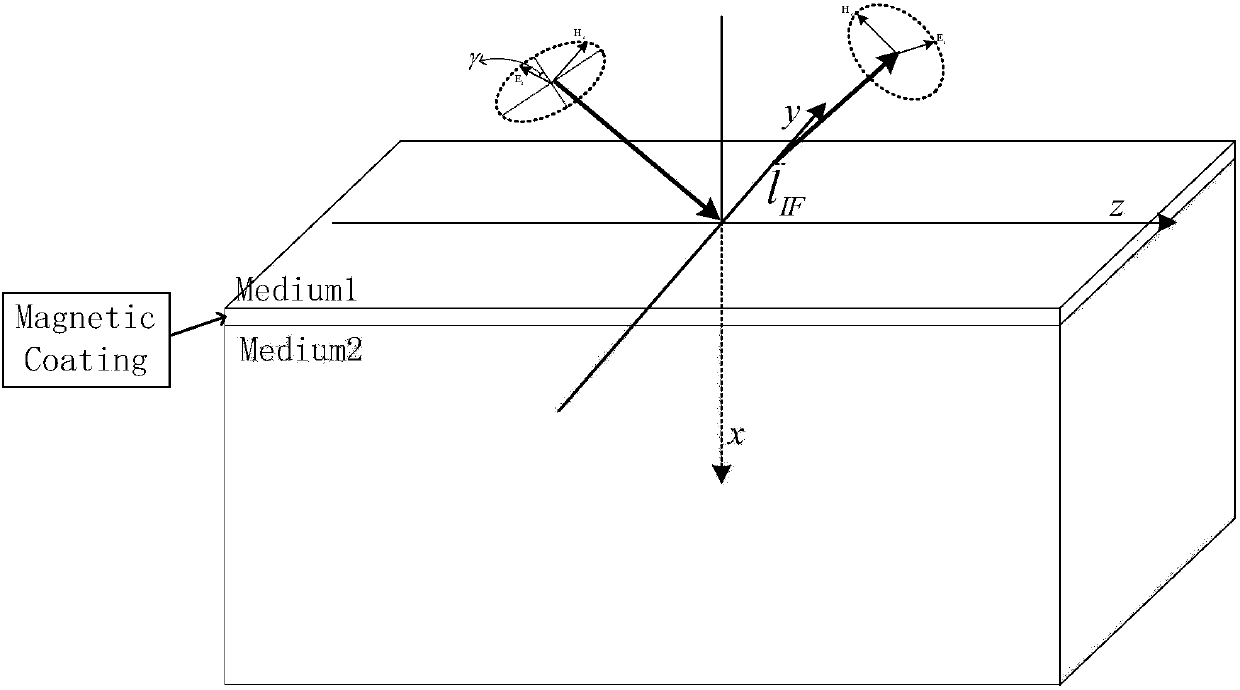
Finite surface band gap topologic insulator-based material interface light beam IF displacement system
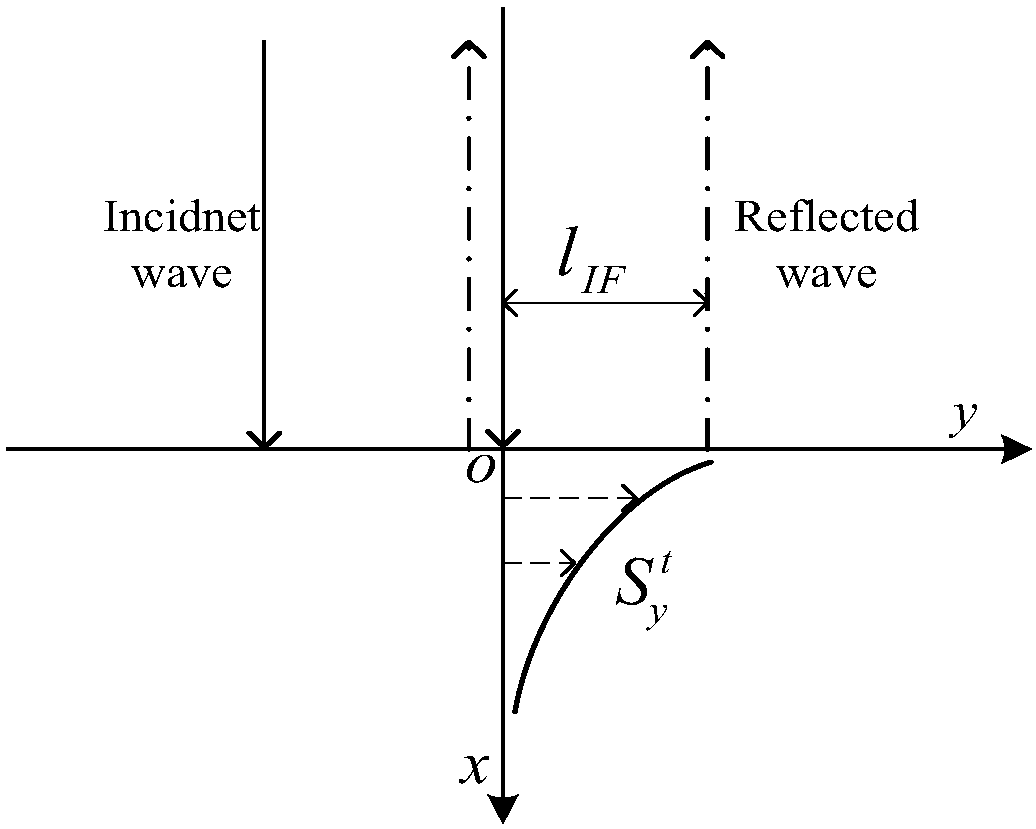
ActiveCN108614911AAccurate analysisDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsEnergy fluxDisplacement control
The invention discloses a method for calculating Imbert-Fedorov displacement of reflected light beam on a topologic insulator of a finite surface band gap based on an energy flux method. The method comprises the following steps of 1: building single interface models of a general isotropic medium and the isotropic finite band gap topologic insulator; 2: determining boundary and initial conditions;3: calculating transmission coefficients and reflection coefficients on single interfaces of the general medium and a chiral medium; 4: calculating energy fluxes in all directions by using a correctedenergy flux method; and 5, calculating the Imbert-Fedorov (IF) displacement. The transverse displacement characteristics of the single interface models of the general medium and the finite band gap topologic insulator can be accurately analyzed; the topologic insulator of the finite surface band gap is relatively close to a theoretical model of an actual topologic insulator material, and has relatively high application values as a test model; a new way is provided for IF displacement control; and an optical method is provided for measuring topologic magnetoelectric polarization properties.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Compound cesium lithium borate (CLBO) nonlinear optical crystal, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101974783AFast preparationEasy to operatePolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsChemical compoundNonlinear optical
The invention relates to a compound cesium lithium borate (CLBO) nonlinear optical crystal, which belongs to a trigonal system, and the chemical formula is Li4Cs3B7O14, the molecular weight is 726.14, the space group is P3121, the lattice parameters is as follows: a = 6.9313 (6), b = 6.9312 (6), c = 26.799 (4), Z = 3 and V = 1115.01 (19), and the mohs scale is 2 to 3; the compound grows crystals by using a flux growth method, and the CLBO nonlinear optical crystal prepared by using the method is used for preparing nonlinear optical devices. The compound is a melting compound prepared from different ingredients; and the prepared crystal is at least in a cm-level size, and has the advantages of quick preparation speed, simple operation, low cost, large size, wide nonopaque waveband, good mechanical performance, small possibility of crazing, stable physicochemical property, easy processing, and the like.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Neodymium-doped potassium gadolinium phosphate laser crystal, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102534777AQuality improvementDifficult to cleavagePolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsSpectroscopyMechanical property
The invention relates to a neodymium-doped potassium gadolinium phosphate laser crystal of which the molecular formula is Nd:KGdP4O12, belonging to monoclinic systems. The neodymium-doped potassium gadolinium phosphate laser crystal has C2 / c space group structure, wherein neodymium ions are used as doping ion to substitute the lattice position of gadolinium ions, and the doping content of the neodymium is 1-20at / %.The preparation method is implemented in a way that: a mixture of Gd2O3, Nd2O3, K2CO3 and NH4H2PO4 is used as a raw material, potassium metaphosphate obtained by reacting K2CO3 and NH4H2PO4 is used as a fluxing agent, and a self-flux method is utilized to prepare the neodymium-doped potassium gadolinium phosphate laser crystal.The laser crystal preparation technique is simple and easy to operate; the prepared crystal can not be easily cloven, has the advantages of of moderate hardness, favorable mechanical properties, favorable thermal properties and favorable optical spectral characteristics, and is used as a working substance in a solid laser; a flash lamp or LD is used as a pumping source to activate the laser output of which the wavelength is 1.06 mu m; and thus, the invention can be widely used in the fields of spectroscopy, biomedicine and military affairs.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
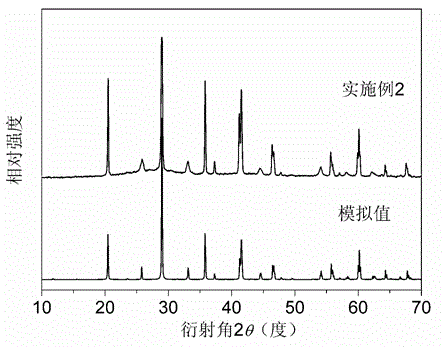
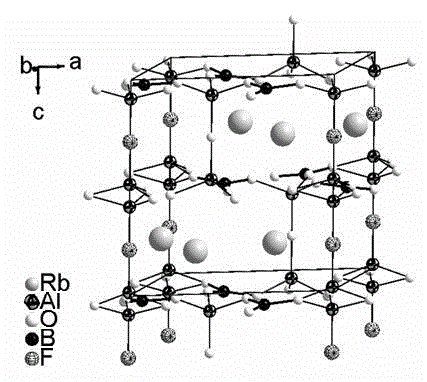
Rb3Al3B3O10F compound, Rb3Al3B3O10F nonlinear optical crystals as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN104556084ALarge nonlinear optical effectPhysicochemically stablePolycrystalline material growthFrom melt solutionsNonlinear optical crystalUv absorbance
The invention provides an Rb3Al3B3O10F compound, Rb3Al3B3O10F nonlinear optical crystals as well as a preparation method and use thereof and relates to the field of non-linear optical crystal materials. The frequency-doubling conversion efficiency of the Rb3Al3B3O10F nonlinear optical crystals at 1064nm is about 1.2 times of that of the KH2PO4 (KDP) crystal, ultraviolet absorption cutoff edges of the Rb3Al3B3O10F nonlinear optical crystals are shorter than 200nm and the Rb3Al3B3O10F nonlinear optical crystals do not absorb moisture; the large-size transparent Rb3Al3B3O10F nonlinear optical crystals can separately grow by a fluxing agent method and adopting RbF-B2O3 as a fluxing agent; and the Rb3Al3B3O10F crystals have stable physical and chemical properties and moderate hardness and are easy to cut, process, store and use and can be used for preparing non-linear optical devices so as to explore nonlinear optical applications of ultraviolet and deep-ultraviolet bands.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
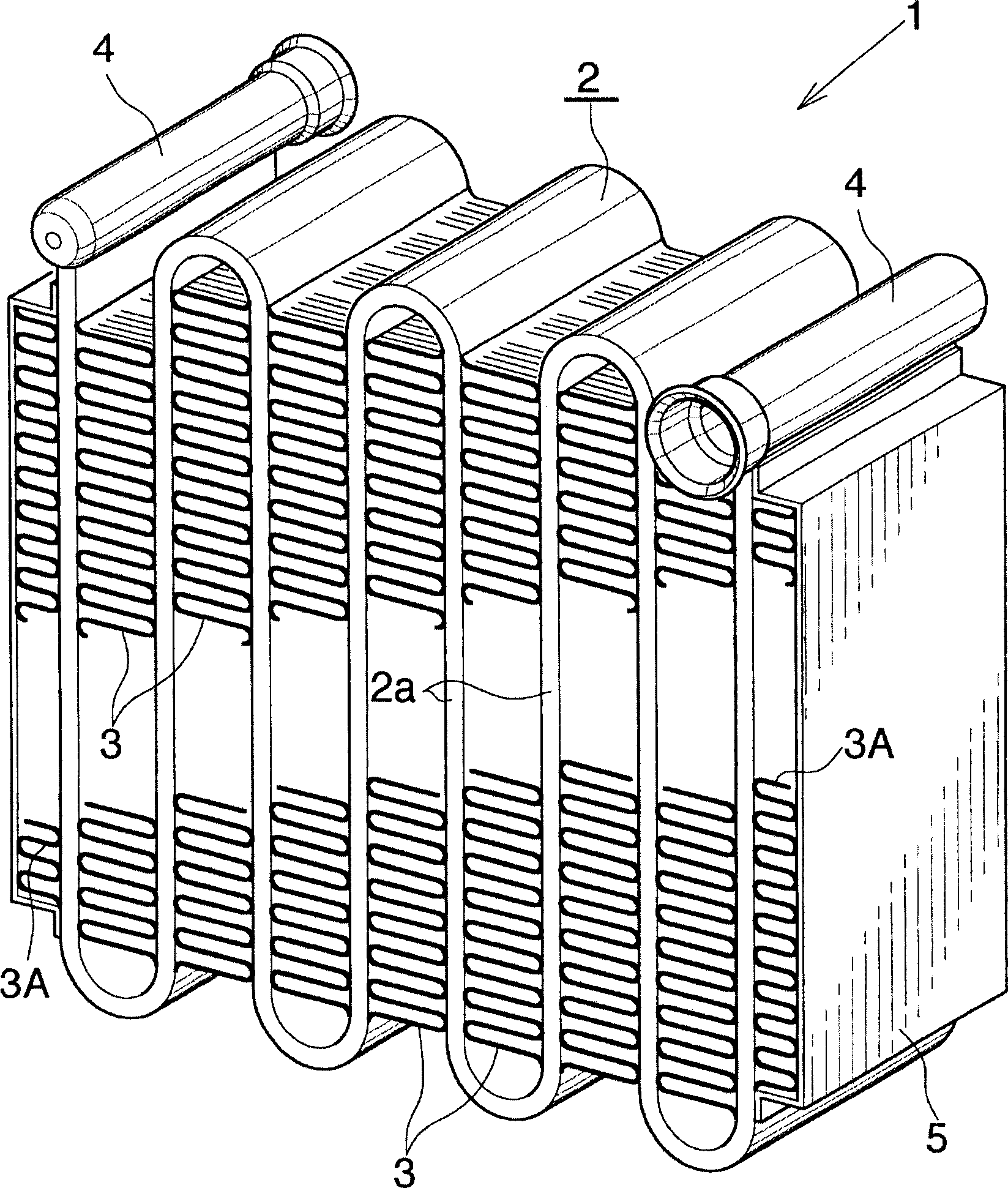
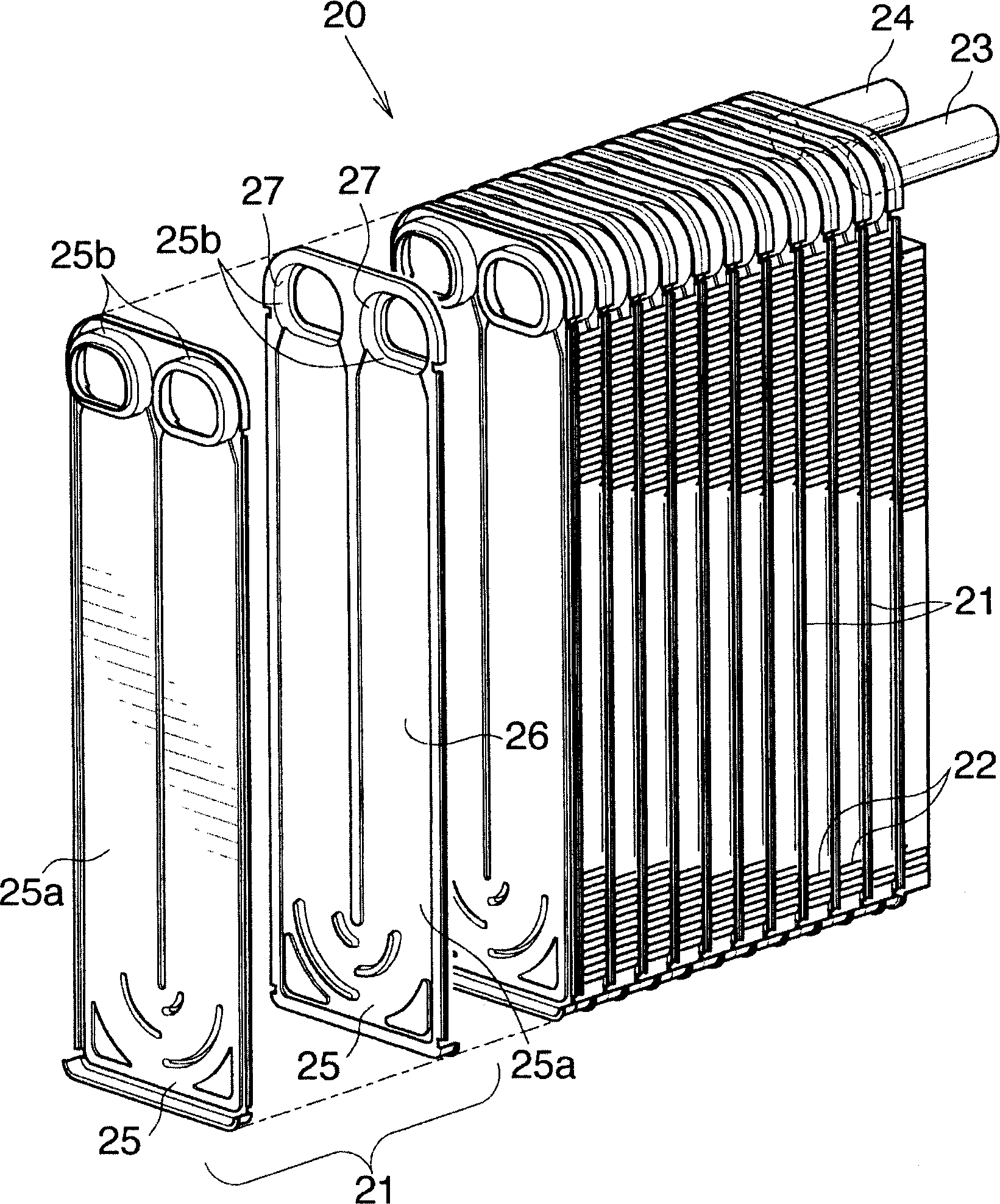
Evaporator and its manufacturing method
InactiveCN1781009AAvoid emissionsAvoid Defective Brazed ConnectionsTubular elementsStraight tubeEngineering
The invention discloses an evaporator (1), which comprises a zigzag flat tube (2) arranged between each pair of adjacent straight tube parts (2a) of the flat tube (2) and brazed by flux corrugated fins (3) brazed thereon. The amount of flux remaining on the surface of the portion of the corrugated fin (3) that is not brazed to the straight pipe portion (2a) is 0.03-1 g / m2. The evaporator (1) is manufactured by applying 0.05-2.8g / m2 flux on the outer surface of the Z-shaped flat tube (2), and setting the corrugated fins (3) on the flat tube (2) ) between each pair of adjacent straight tube parts (2a), and the fins (3) are brazed on the flat tubes (2). The evaporator (1) can effectively suppress the emission of odor.
Owner:SHOWA DENKO KK
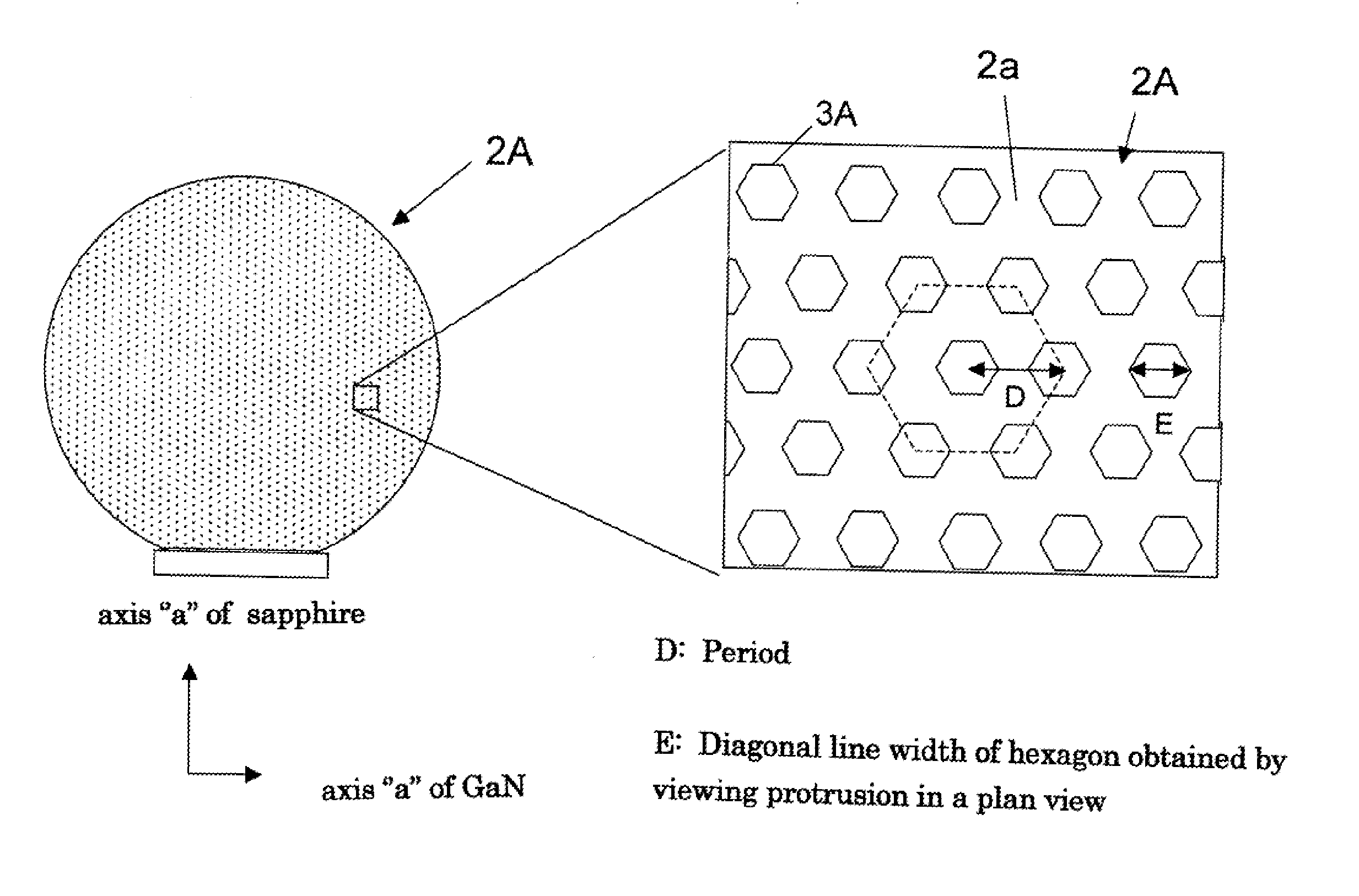
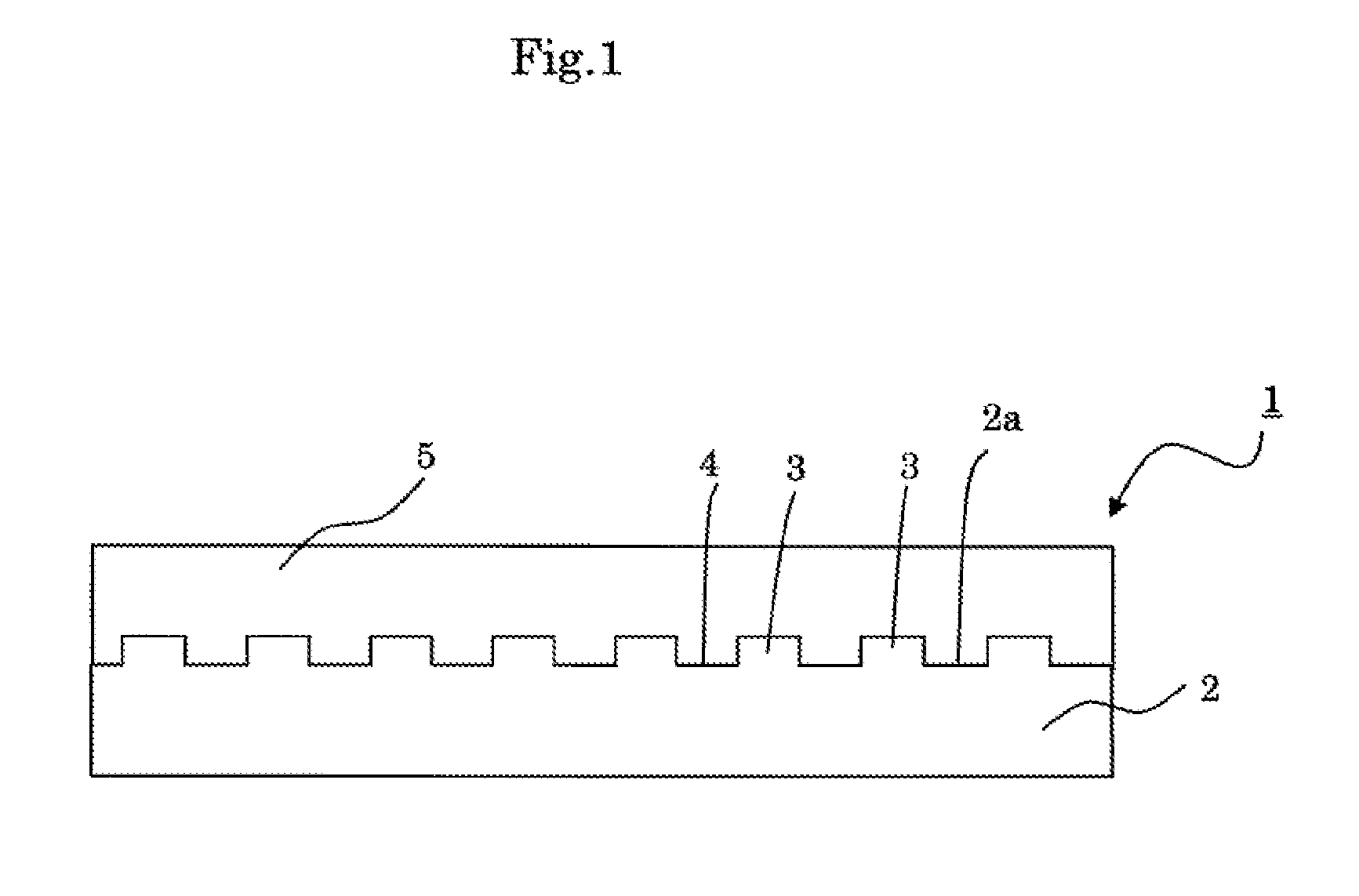
Composite Substrates, Light Emitting Devices and a Method of Producing Composite Substrates
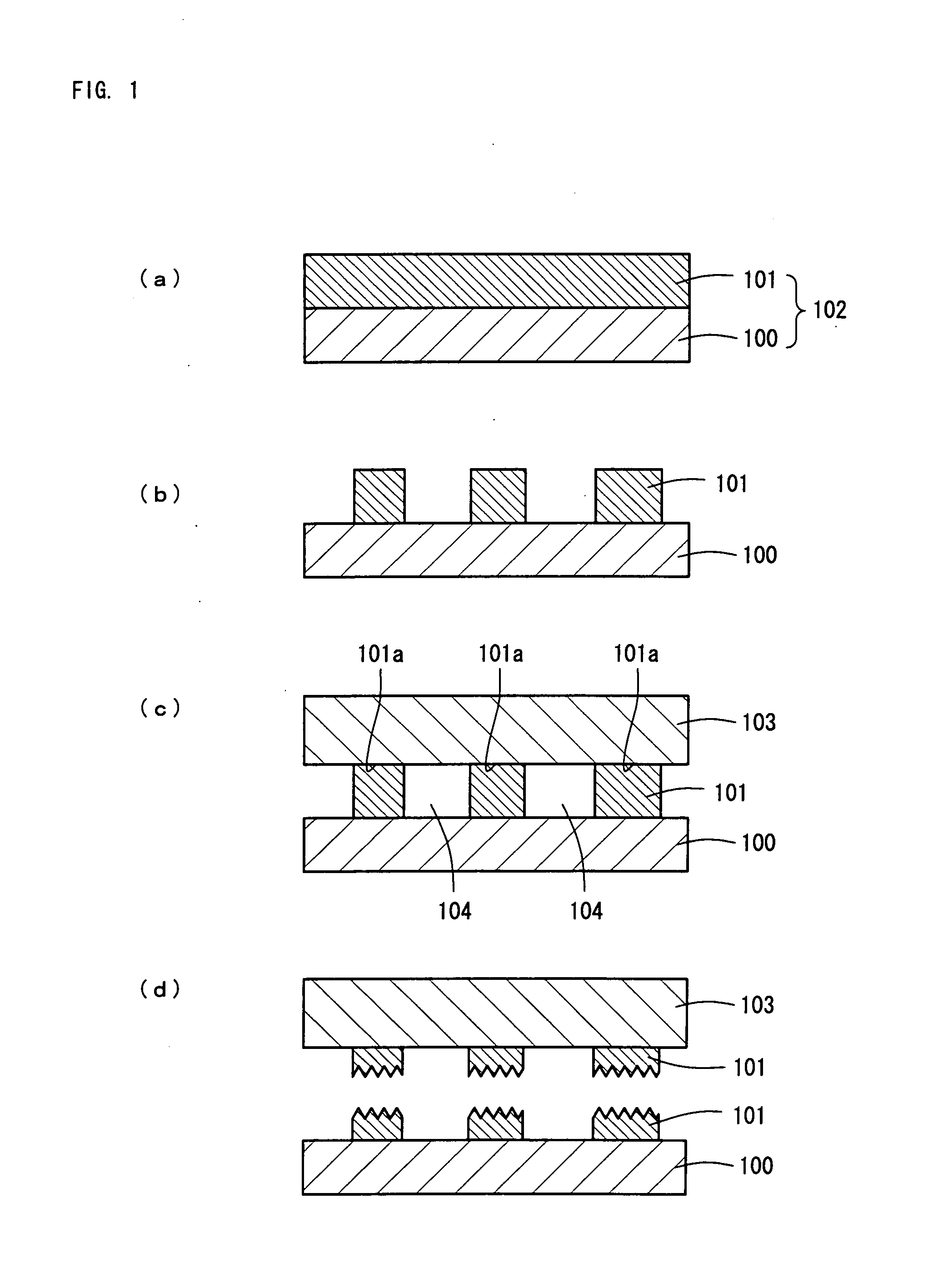
InactiveUS20140054605A1Small warping amountRelieve pressurePolycrystalline material growthSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseComposite substrate
A plurality of protrusions 3 are provided on a c-face 2a of a sapphire body 2. An underlying layer 5 made of gallium nitride is then grown by vapor phase epitaxy process on the c-face 2a. A gallium nitride crystal layer 6 is then provided by flux method on the underlying layer 5. Each of the protrusions 3 has a shape of a hexagonal prism or a six-sided pyramid. Differences of growth rates of the gallium nitride crystal around the protrusions 3 are utilized to relax a stress between the sapphire body and gallium nitride crystal and to reduce cracks or fractures due to the stress.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Free-standing substrate, function element and method for producing same
ActiveUS20170330749A1Reduce biasReduce gapPolycrystalline material growthFrom normal temperature solutionsIndiumNitride
A self-supporting substrate includes a first nitride layer grown by hydride vapor deposition method or ammonothermal method and comprising a nitride of one or more element selected from the group consisting of gallium, aluminum and indium; and a second nitride layer grown by a sodium flux method on the first nitride layer and comprising a nitride of one or more element selected from the group consisting of gallium, aluminum and indium. The first nitride layer includes a plurality of single crystal grains arranged therein and being extended between a pair of main faces of the first nitride layer. The second nitride layer includes a plurality of single crystal grains arranged therein and being extended between a pair of main faces of the second nitride layer. The first nitride layer has a thickness larger than a thickness of the second nitride layer.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
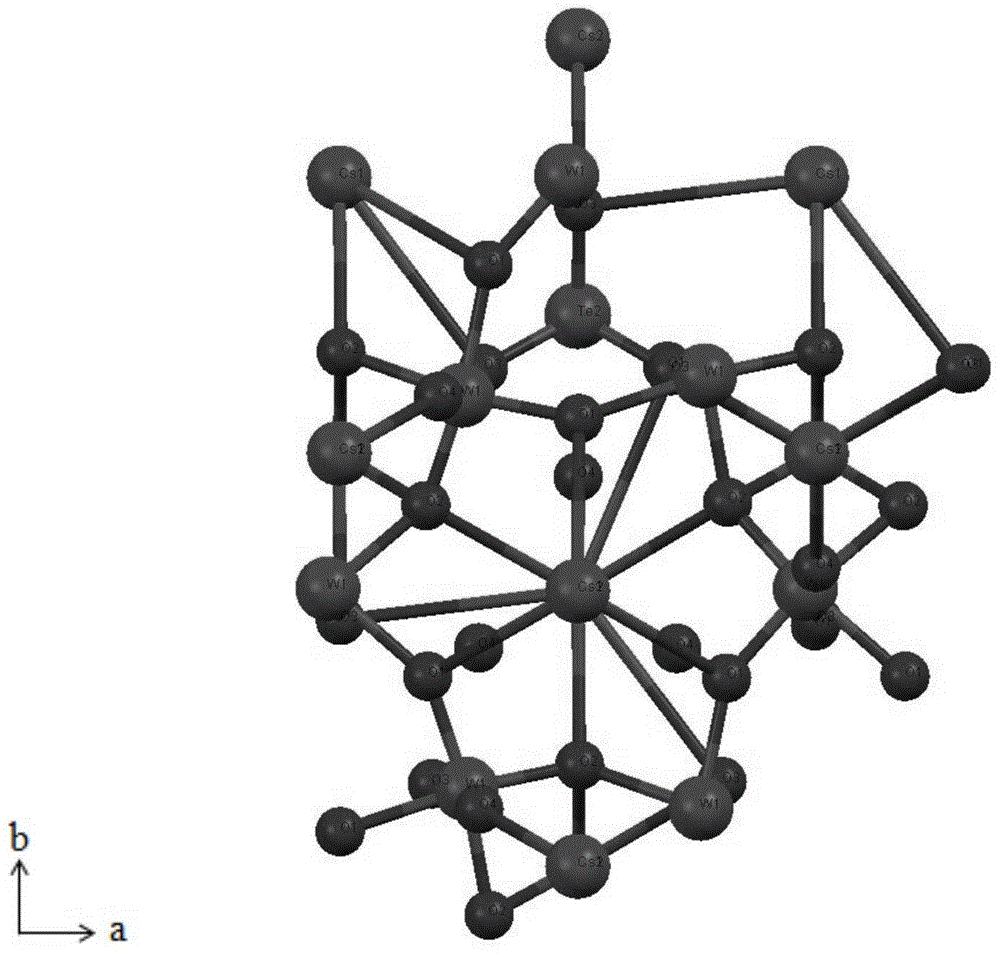
Cesium tungsten-tellurite crystal as well as flux growth method and application thereof
The invention relates to a flux growth method and an application of a cesium tungsten-tellurite crystal. The cesium tungsten-tellurite crystal has a chemical formula of Cs2TeW3O12 and belongs to a hexagonal system, the space group refers to P63, the ultraviolet-visible-near infrared transmission spectrum and intermediate infrared transmission spectrum show that the crystal can penetrate through a wavelength range of 430-5350nm, and the transmittance can be over 80 percent under the uncoated condition; an infrared laser incidence crystal with the wavelength of 1064nm generated by using an Nd:YAG laser generates strong green light. Compared with the Cs2TeW3O12 polycrystalline synthetic technology reported in the existing literature, a flux growth method for growing high-quality Cs2TeW3O12 single crystals is provided at first internationally, the crystal structure is successfully analyzed, and the Cs2TeW3O12 single crystal of which the size is enough to meet the application is obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
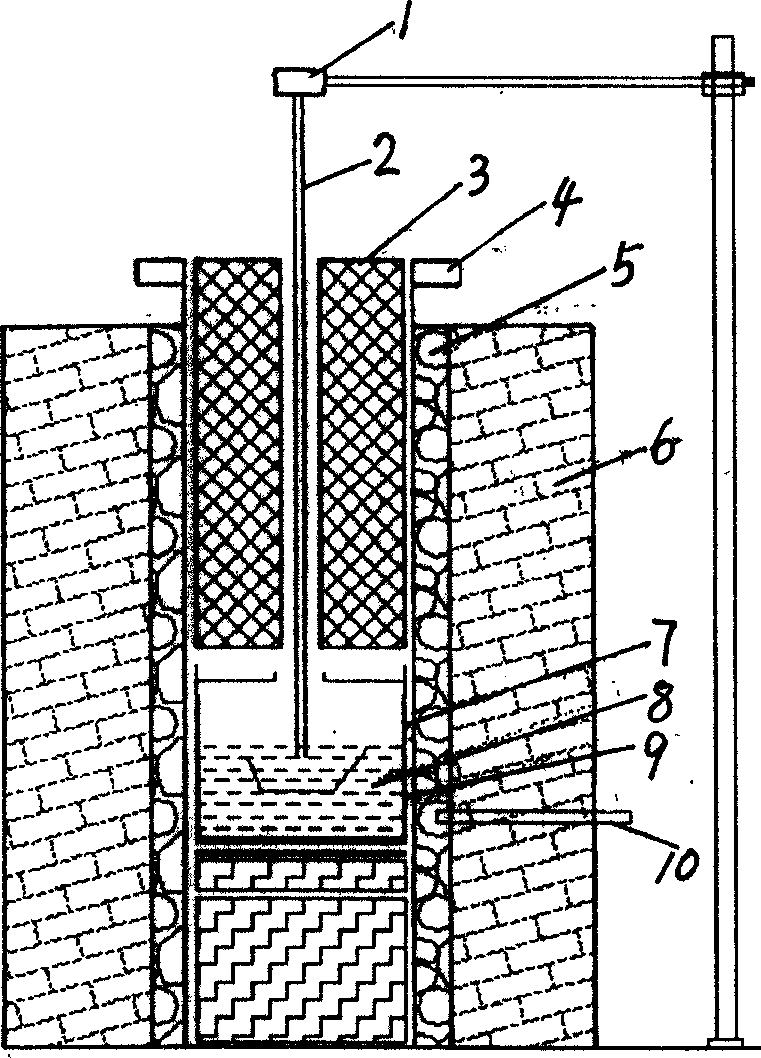
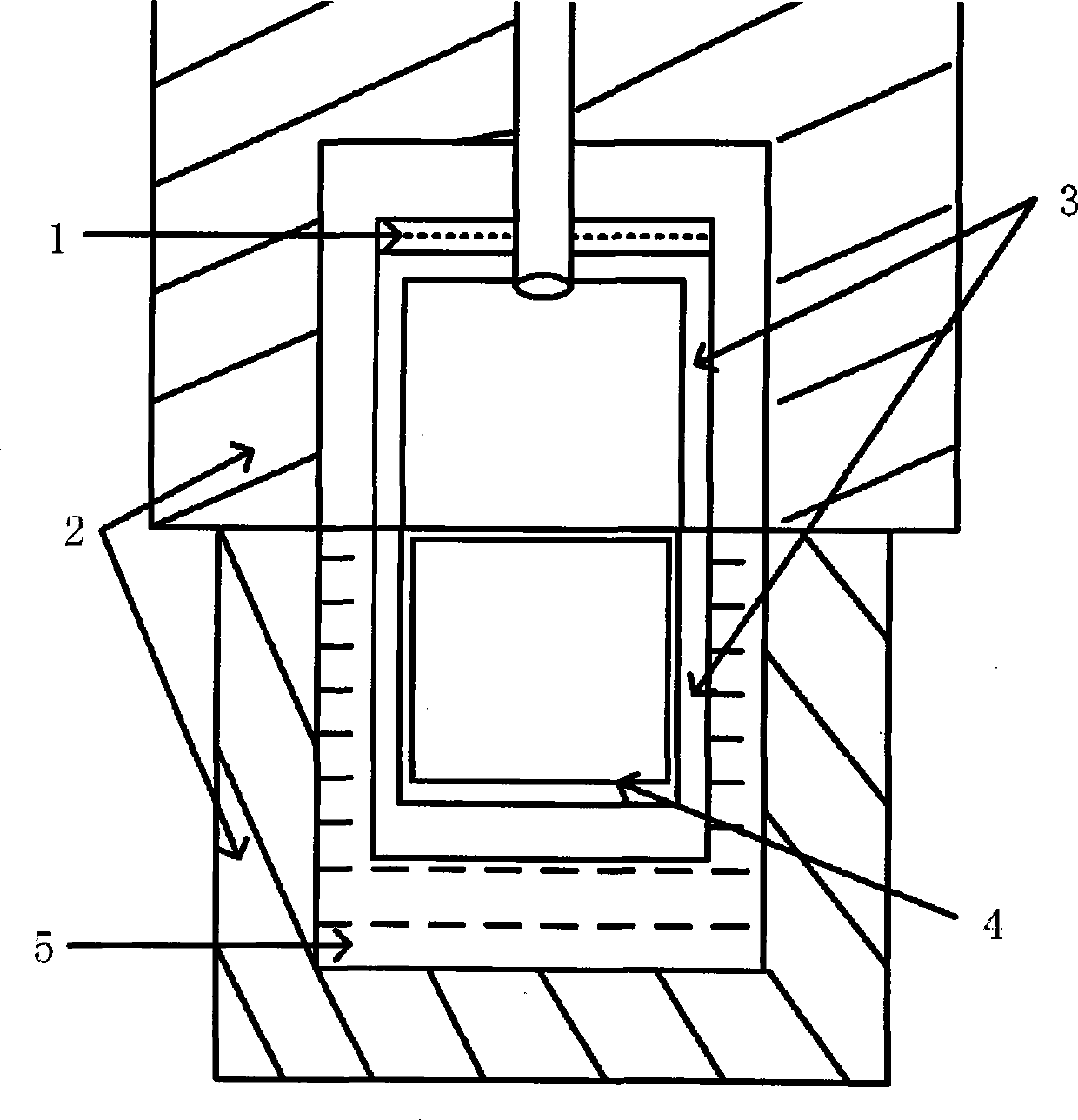
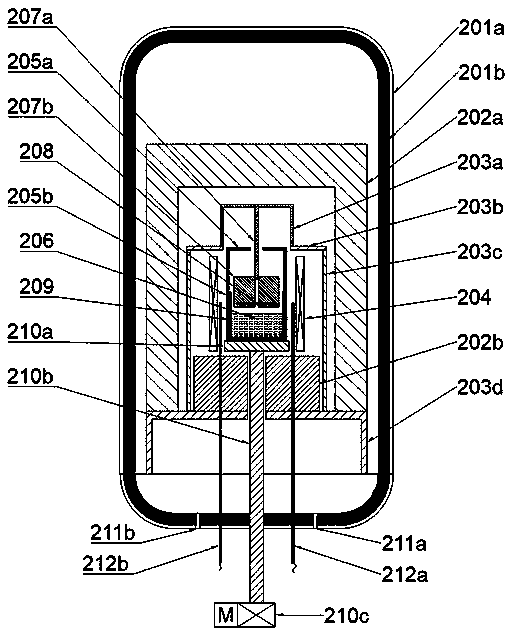
Growth device for sodium flux method gallium nitride single crystal
InactiveCN109680334AReduce escapeAvoid introducingPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthDecompositionGallium nitride
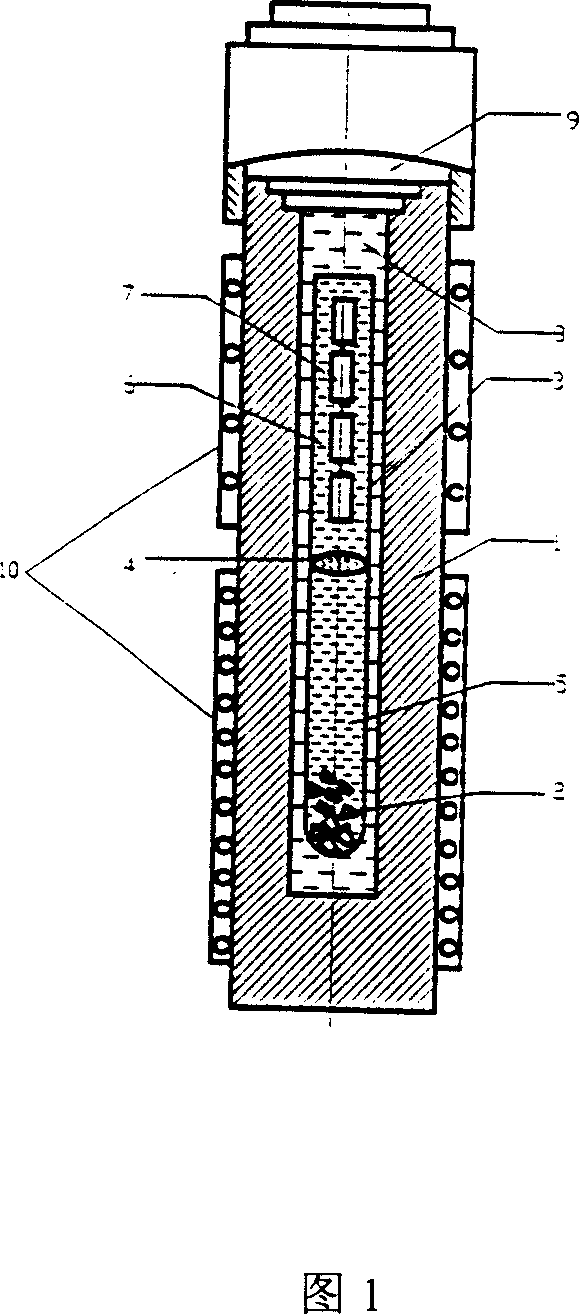
The invention discloses a growth device for a sodium flux method gallium nitride single crystal. Structures such as a seed crystal clamp, a reaction container and a carrying platform are designed inside the device; in epitaxial growth of a single crystal, the seed crystal can be prevented from contacting a molten metal liquid with an over-saturated nitrogen atom concentration by reducing the height of the carrying platform, so that seed crystal decomposition is avoided, and surface quality degradation is prevented; a reaction cavity tray is driven by a motor connected with a transmission rod to rotate, so that the reaction container and a crucible inside are rotated relative to the seed crystal clamp, the molten metal liquid can be then stirred by a seed crystal clamping rod, the nitrogenatom concentration uniformity inside can be improved, the purpose of increasing the concentration of nitrogen atoms around the seed crystal can be achieved, and crystal nitrogen insufficiency can be avoided; due to adoption of a semi-sealed reaction container structure, escape of sodium steam in the crystal growth process can be reduced, external impurity atmospheres can be baffled, so that the metal sodium can play a role of a fluxing agent continuously, and a stable and pure growth condition can be provided for epitaxy of the gallium nitride single crystal.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP NO 46 RES INST
Lithium ion battery electrode and method for manufacture of same
InactiveUS20090117471A1Excellent cation orderingMaximum flexibilityIron compoundsCobalt compoundsNanostructureLithium-ion battery
Disclosed is a method for synthesizing a lithium transition metal oxide nanostructure for the cathode material LiCoO2, by using a molten salts / hydroxides flux method, and a device thereof.
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK
Method for producing gallium nitride layer and seed crystal substrate used in same
InactiveUS8795431B2Facilitate spontaneous peelingReduce dislocation densityPolycrystalline material growthLiquid-phase epitaxial-layer growthGallium nitrideSeed crystal
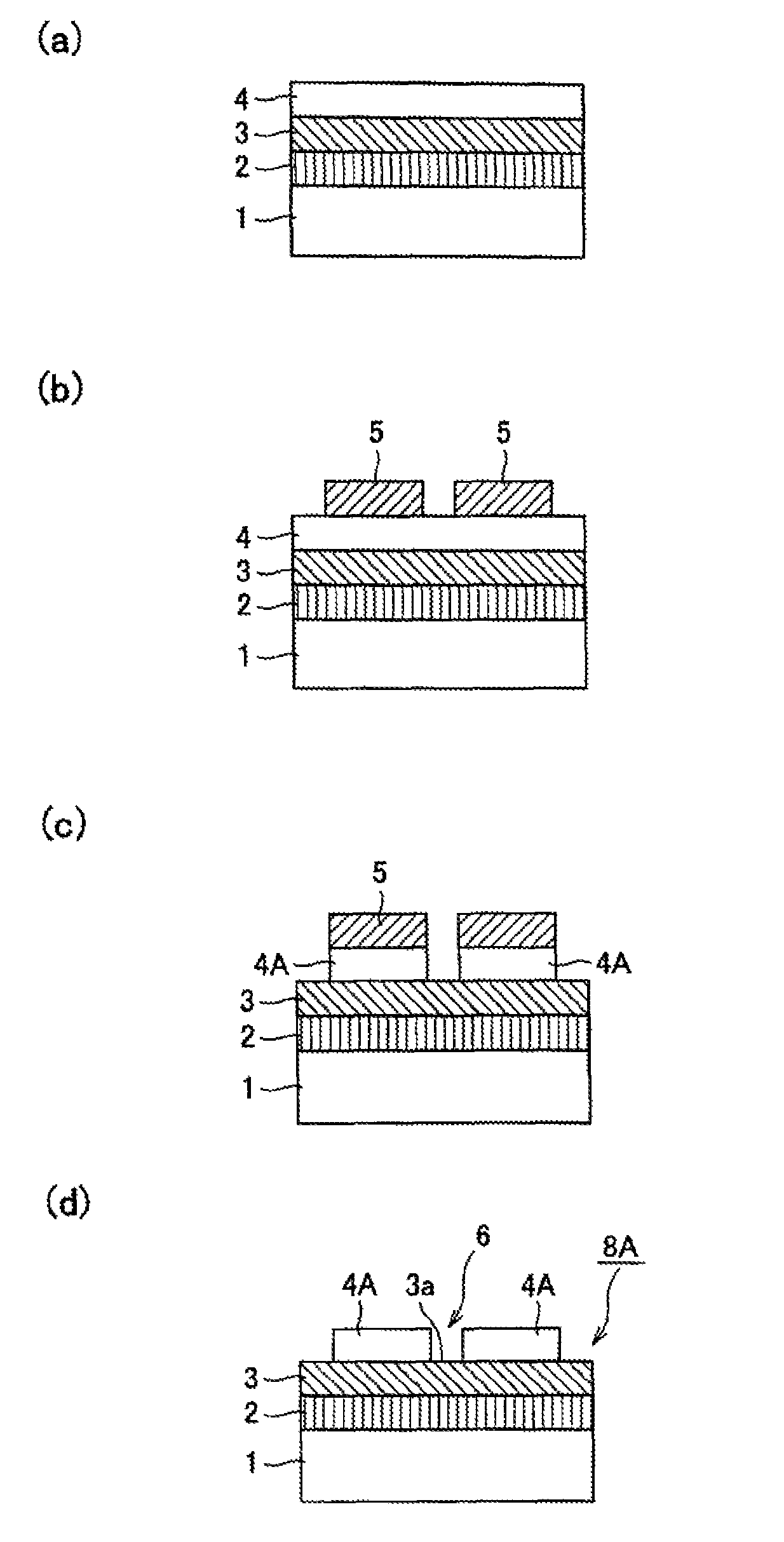
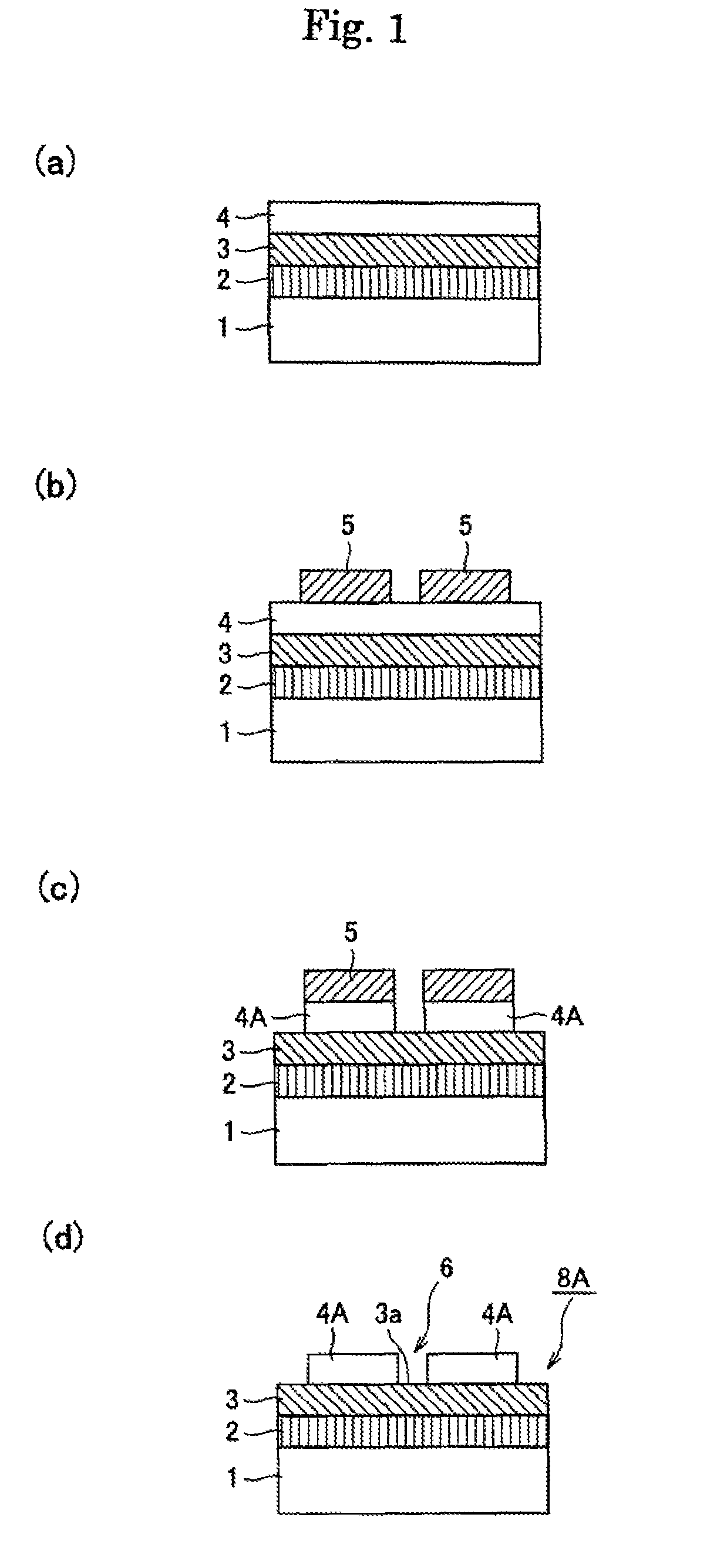
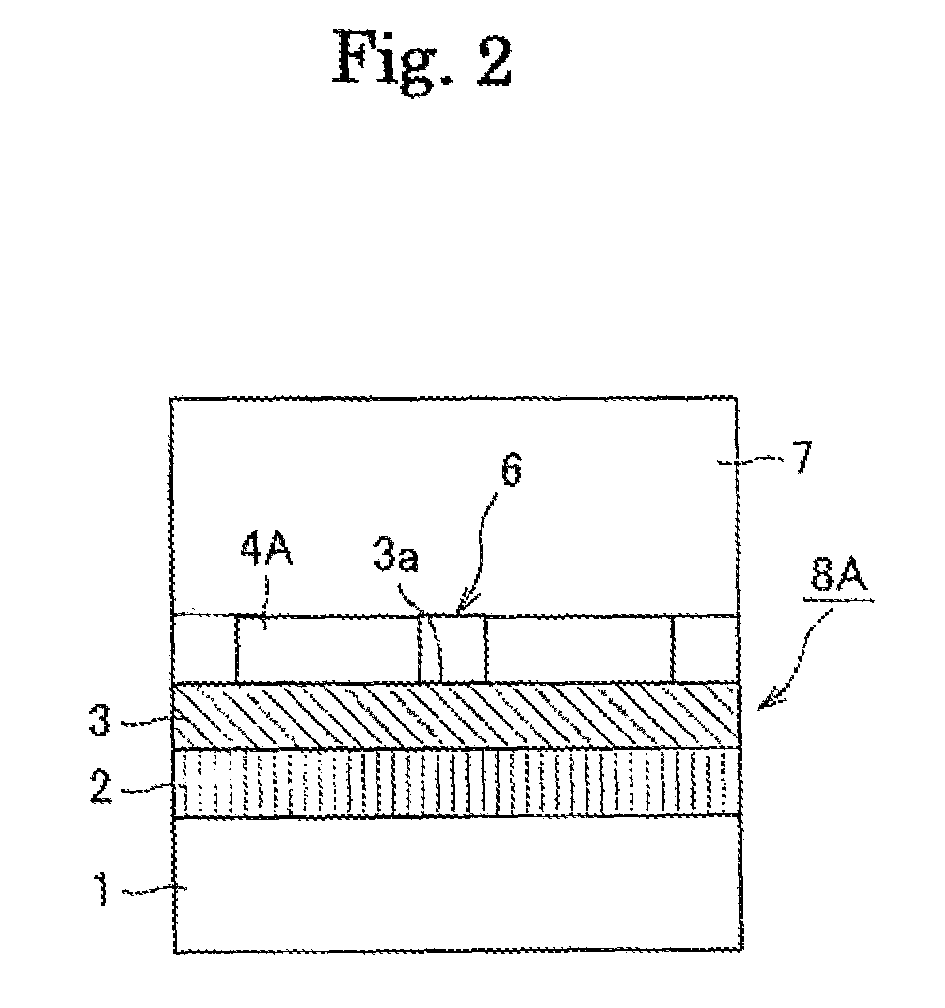
A gallium nitride layer is produced using a seed crystal substrate by flux method. The seed crystal substrate 8A includes a supporting body 1, a plurality of seed crystal layers 4A each comprising gallium nitride single crystal and separated from one another, a low temperature buffer layer 2 provided between the seed crystal layers 4A and the supporting body and made of a nitride of a group III metal element, and an exposed layer 3 exposed to spaces between the adjacent seed crystal layers 4A and made of aluminum nitride single crystal or aluminum gallium nitride single crystal. The gallium nitride layer is grown on the seed crystal layers by flux method.
Owner:NGK INSULATORS LTD
Methods and compositions for forming solder bumps on a substrate with radiation curable or thermal curable solder flux
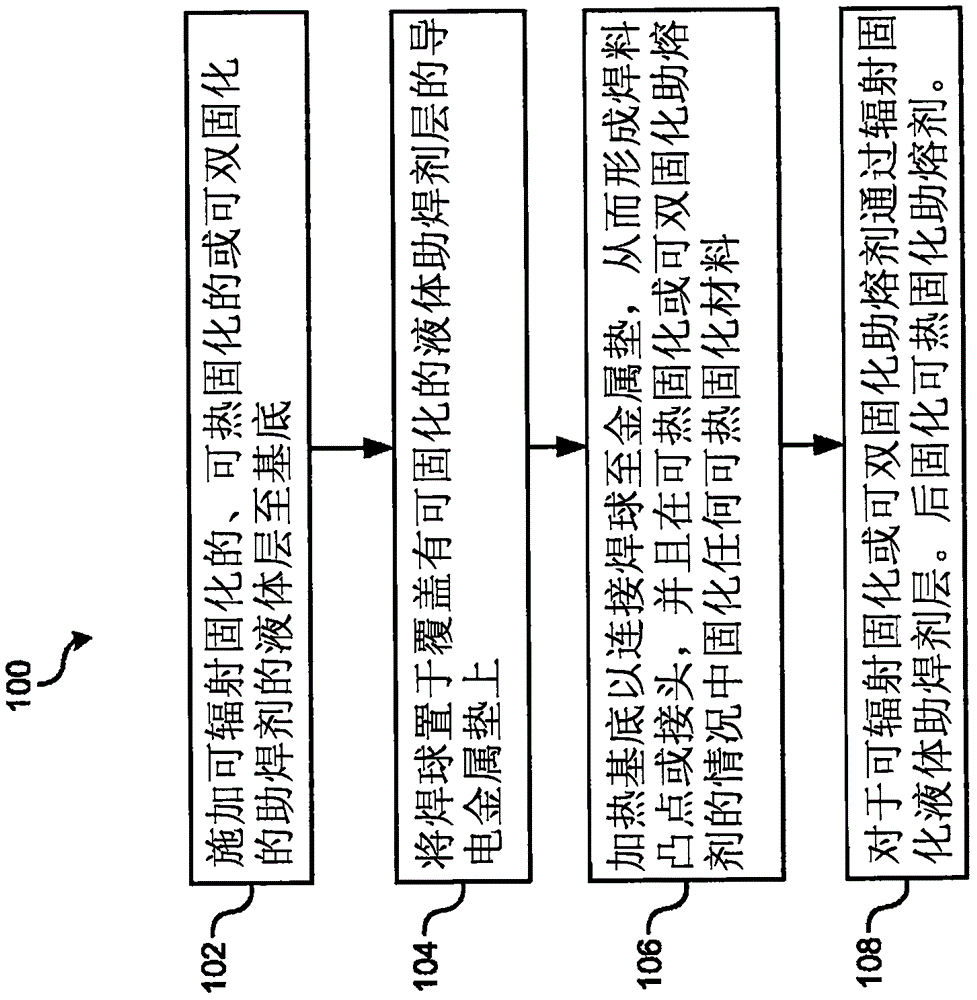
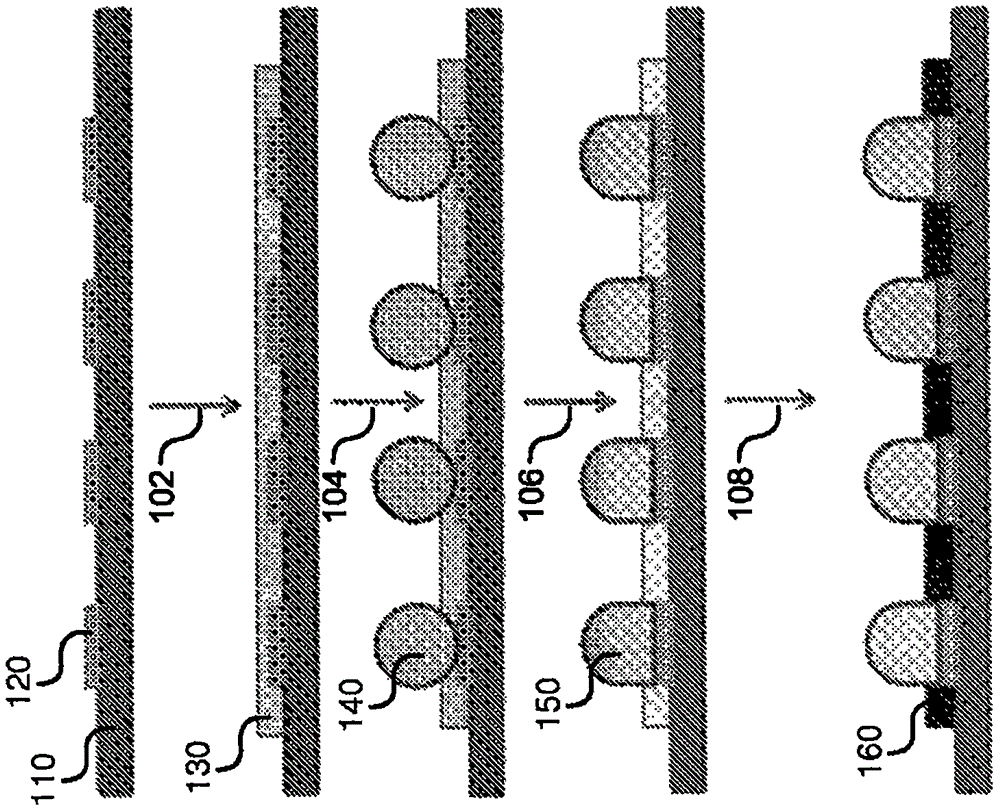
InactiveCN106134300APrinted circuit assemblingSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsContact padMetallurgy
Methods of forming solder bumps or joints using a radiation curable, thermal curable solder flux, or dual curable solder fluXare disclosed. The method includes applying a liquid solder fluX130 that is radiation curable or thermal curable to a substrate 110 such that the solder fluXcovers contact padsl20 on the substrate; placing solder balls 140 on the contacts pads covered with the radiation curable or thermal curable solder flux; heating the substrate to join the solder balls to the contact pads, thereby forming solder bumps or solder joints 150; and curing the liquid solder fluXby applying radiation or heat to the substrate, thereby forming a solid film 160. The solder fluXincludes radiation curable, thermally curable, or dual curable materials that aid formation of solder bumps or joints before the solder fluXis cured; and are curable to form a solid material by the application of radiation or heat.
Owner:INDIUM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com