Patents
Literature
1023 results about "Third harmonic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Harmonics are multiple of fundamental frequency. So 3rd multiple of fundamental frequency is known as 3rd harmonic. Generally depending on the country fundamental frequency is 50hz or 60 hz. Non linear loads like electronics, some large induction motor with improper winding, generators etc generate this third harmonics.
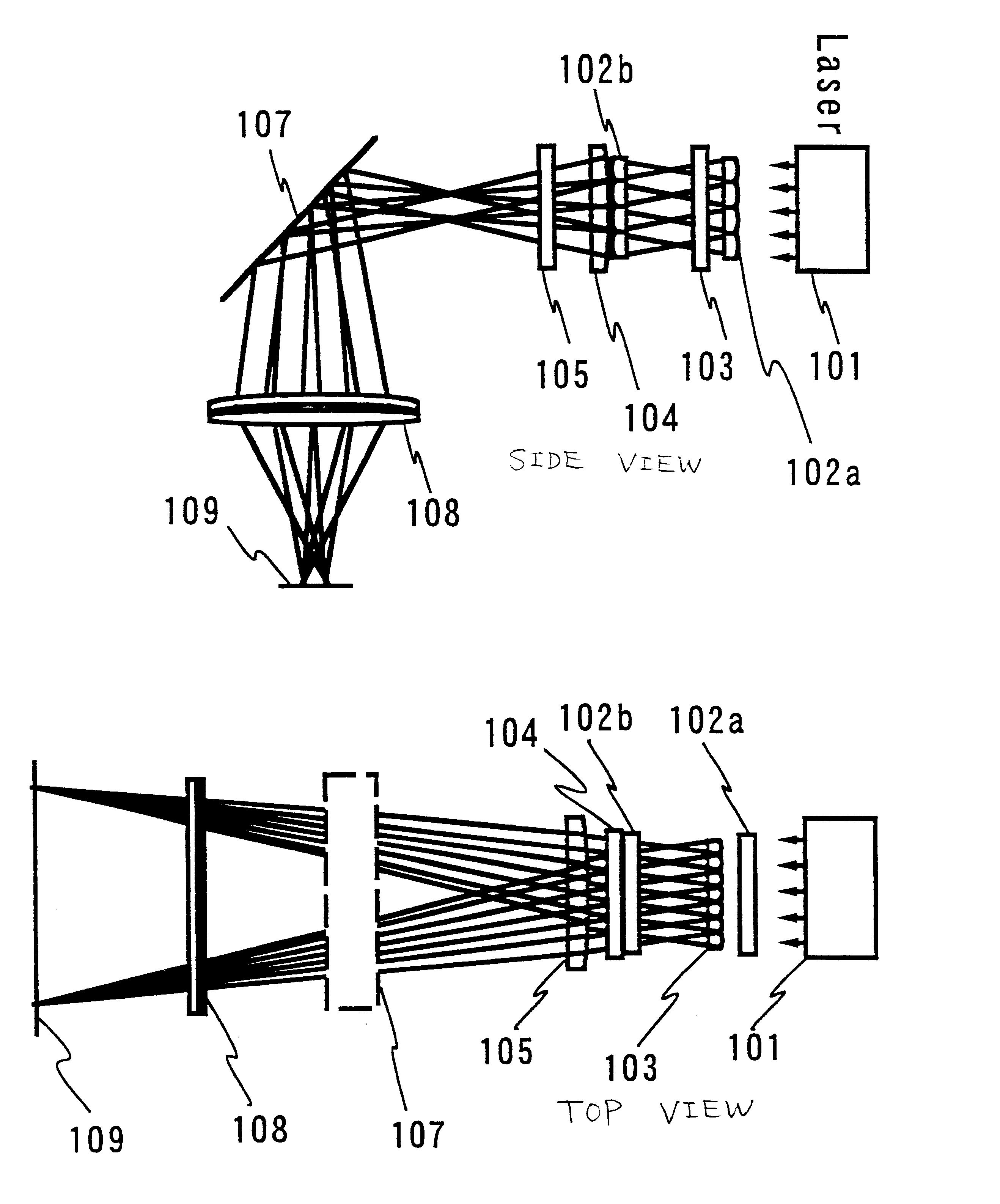
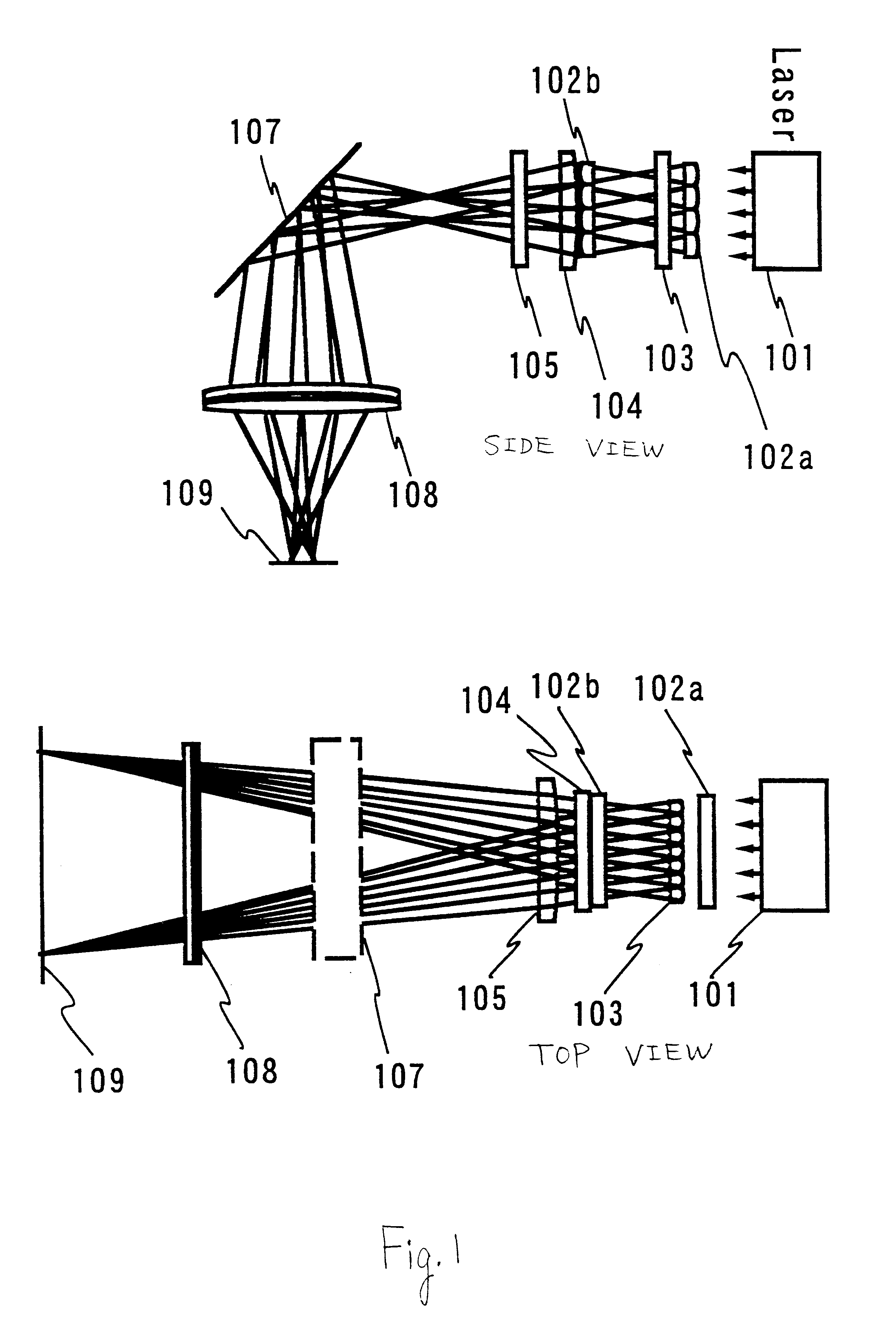
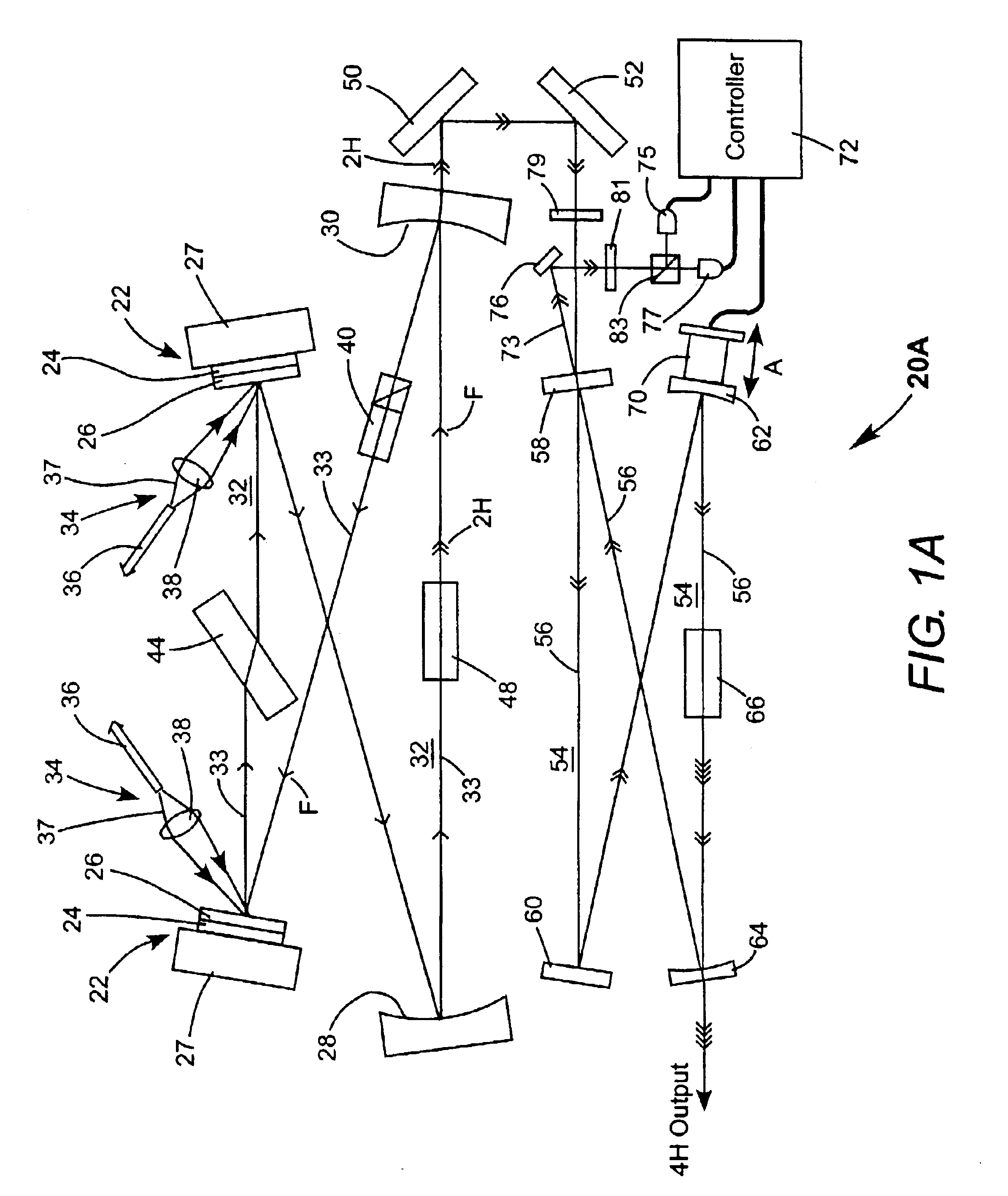
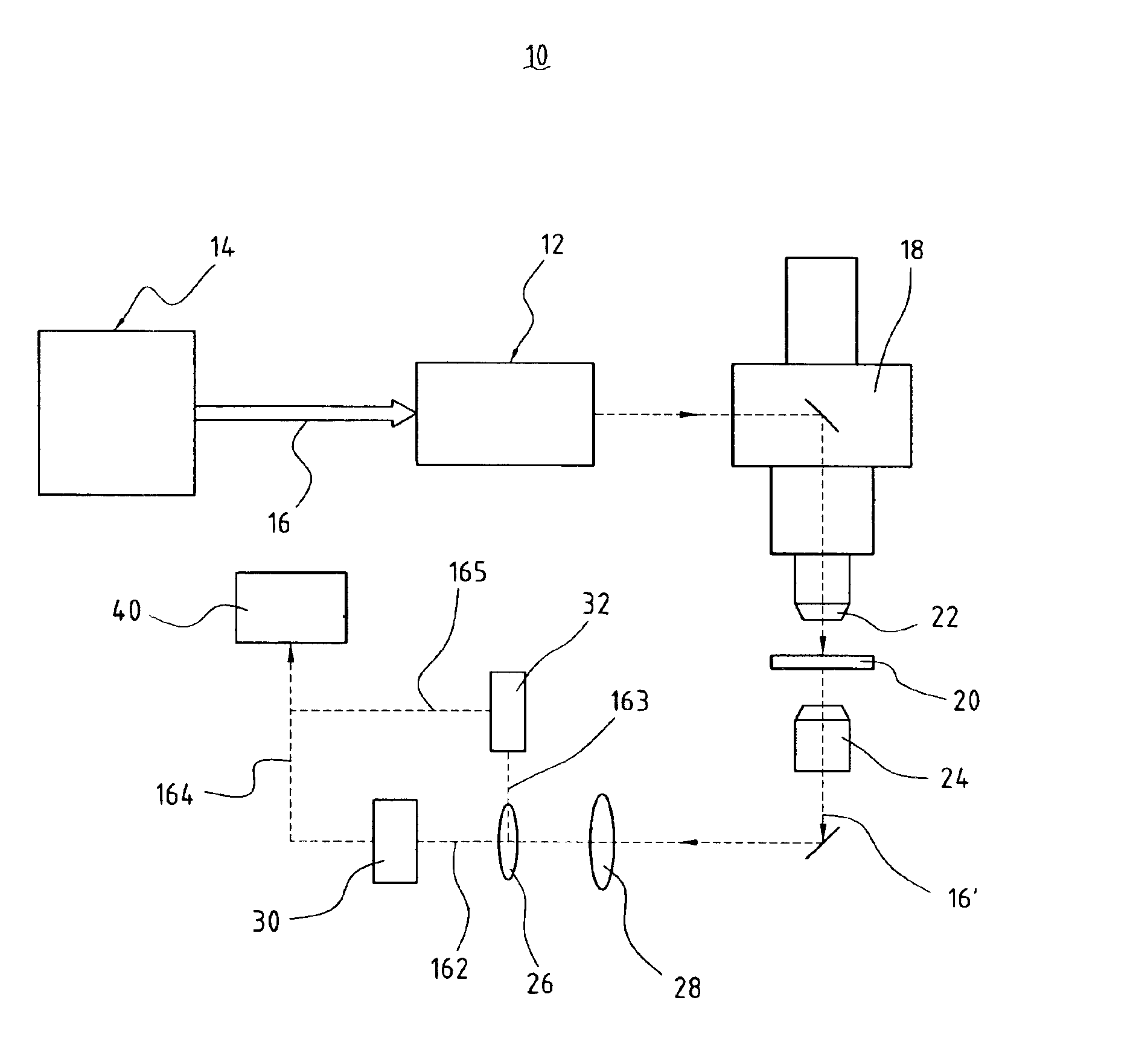
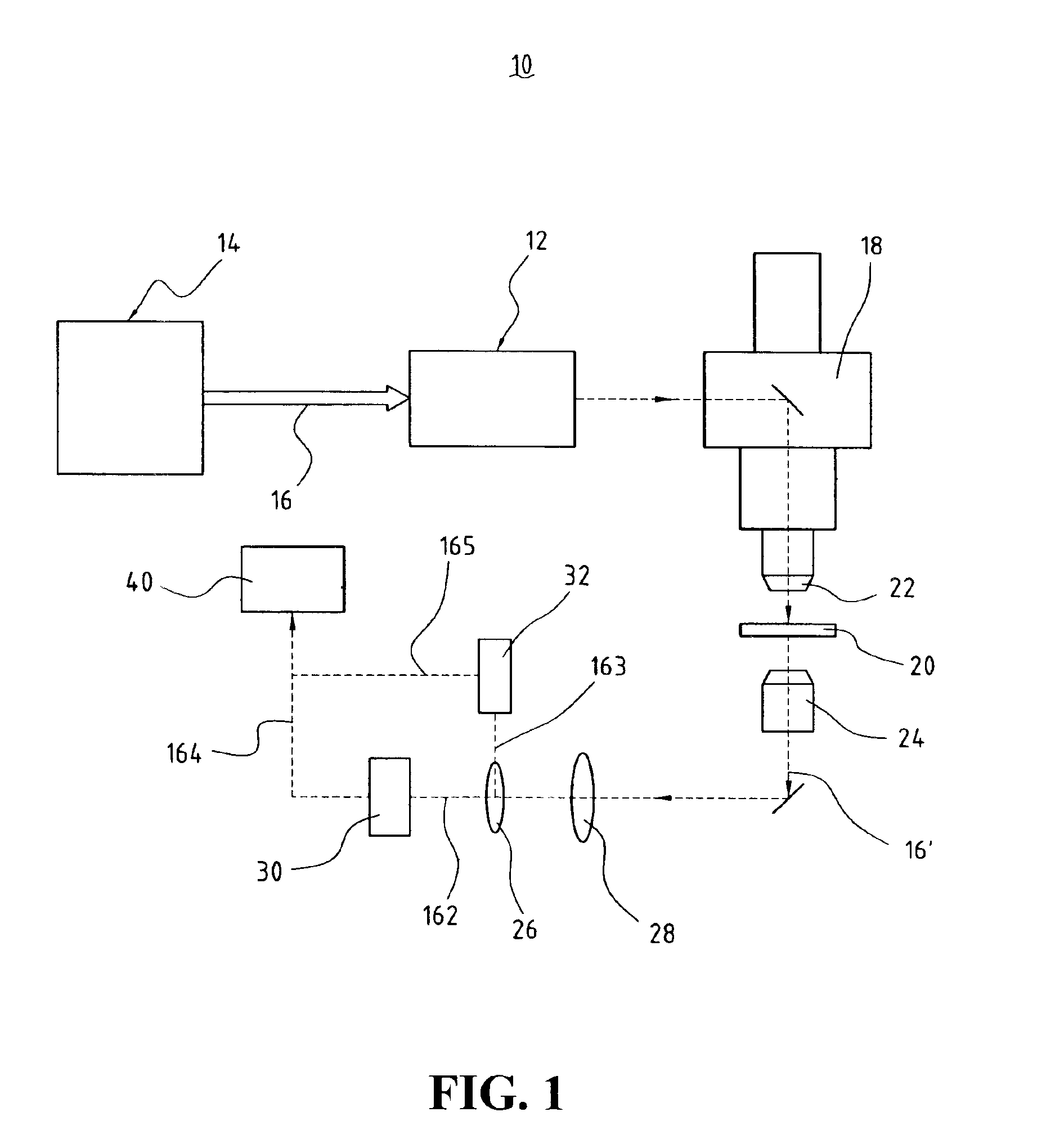
Laser irradiation apparatus, laser irradiation method, and method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
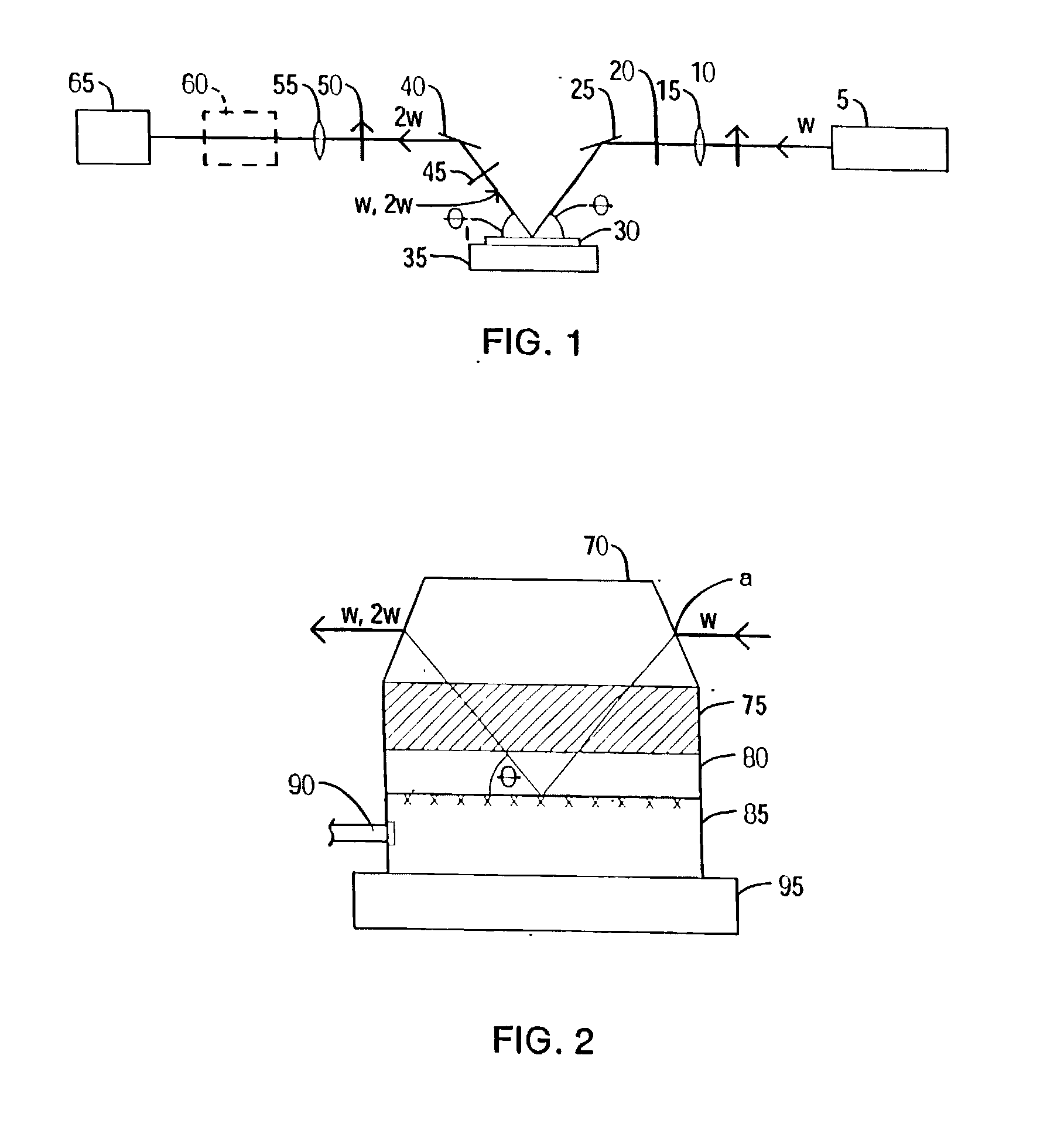
YAG laser can simultaneously emit a plurality of laser beams having different wavelengths from each other. By simultaneously irradiating the laser beams having different wavelengths from each other to a same region of a non-single crystal semiconductor film, an interference influence is suppressed to obtain a more uniform laser beam. For example, by simultaneously generating second and third harmonics of YAG laser to irradiate the same region through suitable optical system, a laser beam having higher uniformity and having an energy in which interference is highly suppressed is obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20030148391A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyFrequency generationThird harmonic
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
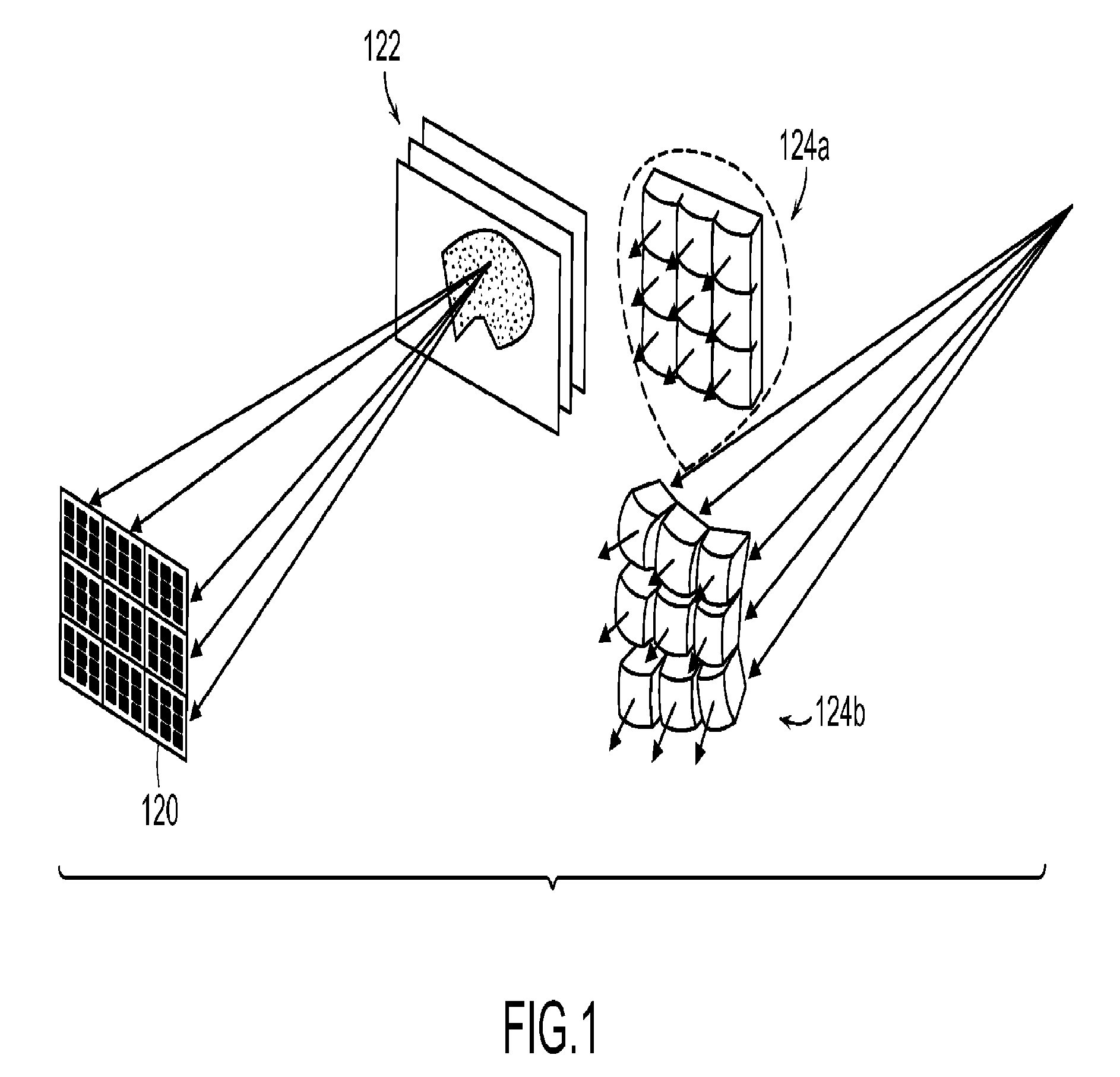
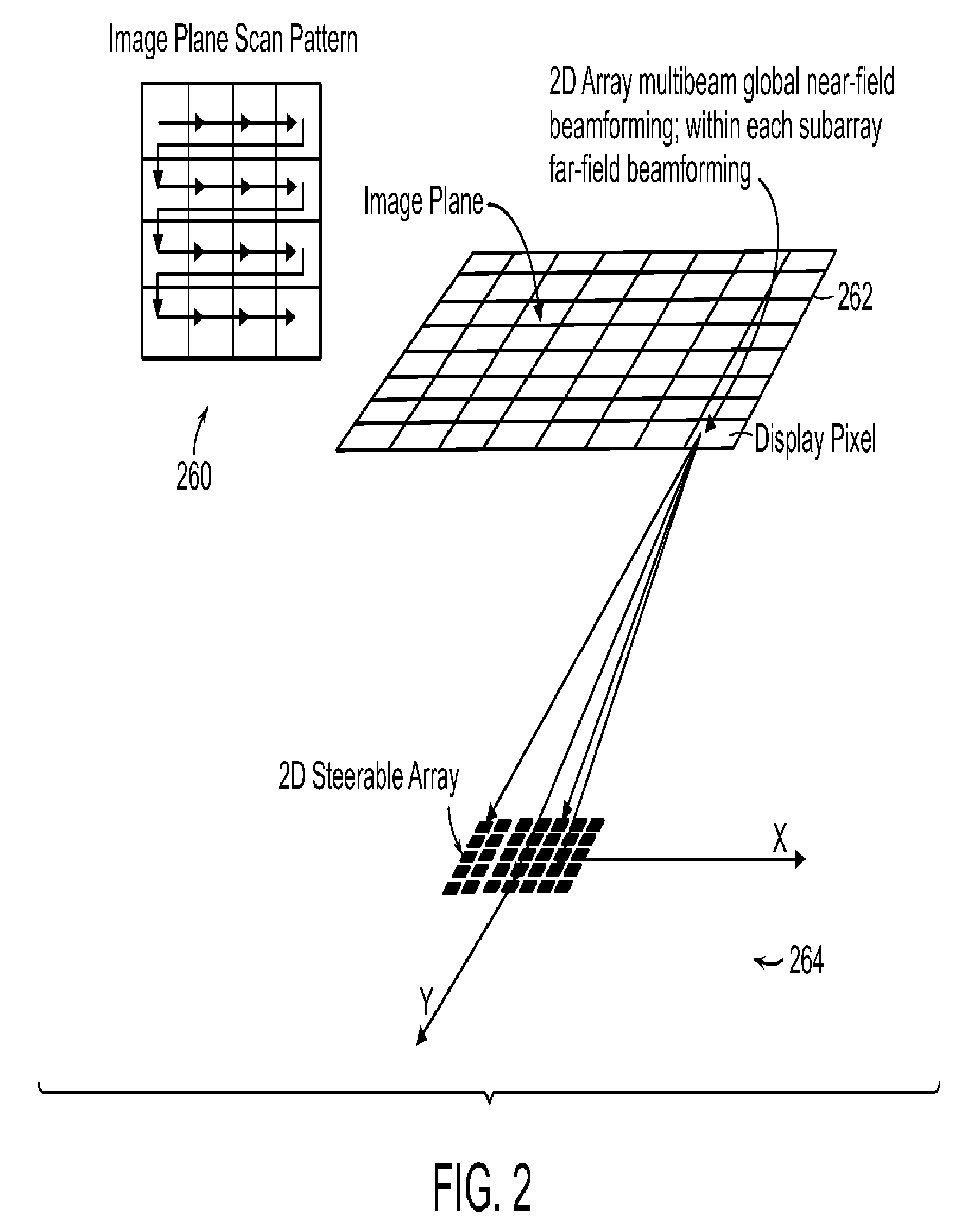
Ultrasound 3D imaging system
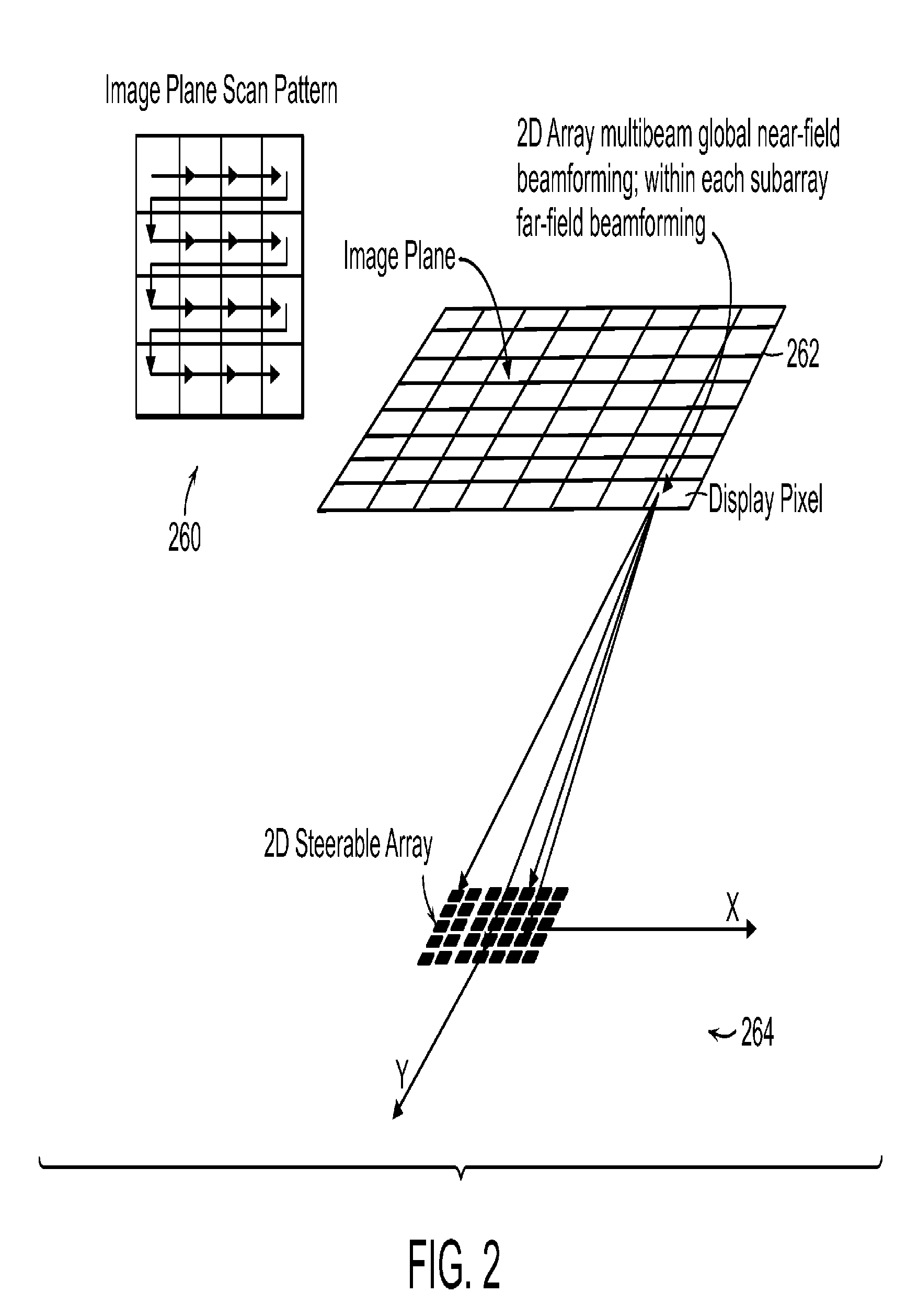
InactiveUS20120179044A1Reduce the amount requiredImproved harmonic imagingOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationEngineering
The present invention relates to an ultrasound imaging system in which the scan head includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field subarray beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. When using a hierarchical two-stage or three-stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images can be generated in real-time. The invention further relates to flexible printed circuit boards in the probe head. The invention furthermore relates to the use of coded or spread spectrum signalling in ultrasound imaging systems. Matched filters based on pulse compression using Golay code pairs improve the signal-to-noise ratio thus enabling third harmonic imaging with suppressed sidelobes. The system is suitable for 3D full volume cardiac imaging.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
Method using a nonlinear optical technique for detection of interactions involving a conformational change
InactiveUS20060228725A1No need for labor and time-consuming washing stepLow backgroundCompound screeningMaterial nanotechnologyThird harmonicFrequency generation
A nonlinear optical technique, such as second or third harmonic or sum or difference frequency generation, is used to detect binding interactions, or the degree or extent of binding, that comprise a conformational change. In one aspect of the present invention, the nonlinear optical technique detects a conformational change in a probe due to target binding. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate probes by detecting a conformational change due to a probe-target interaction. In another aspect of the invention, the nonlinear optical technique screens candidate modulators of a probe-target interaction by detecting a conformational change in the presence of the modulator.
Owner:BIODESY
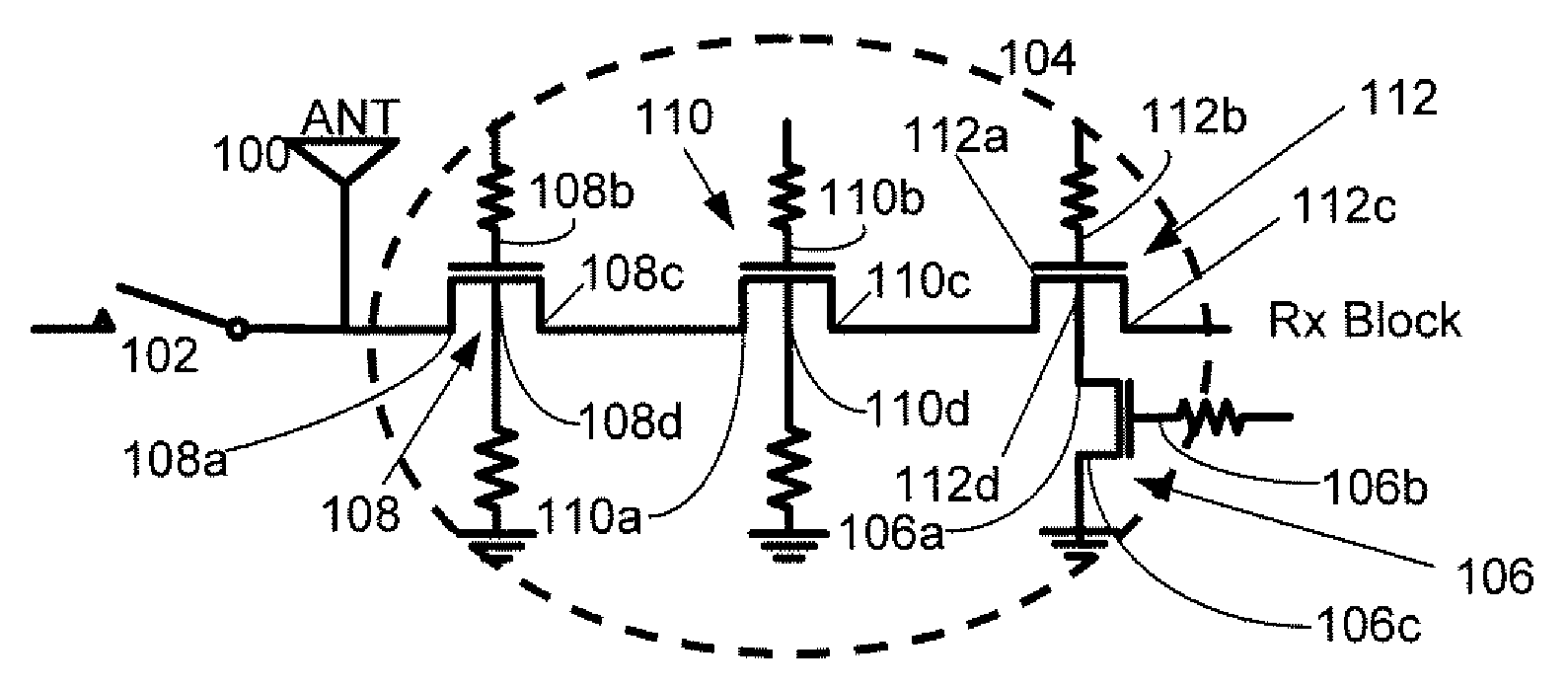
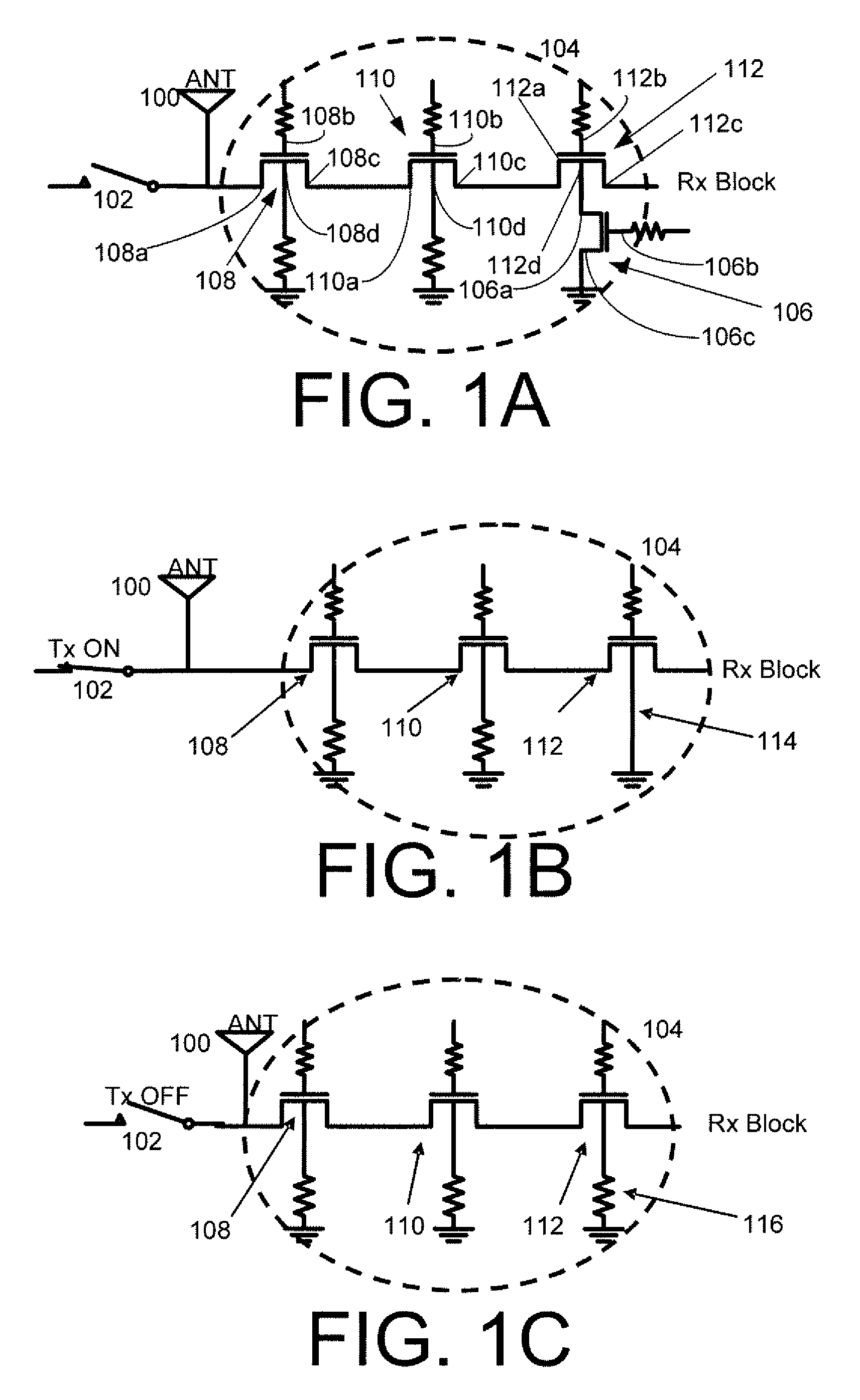
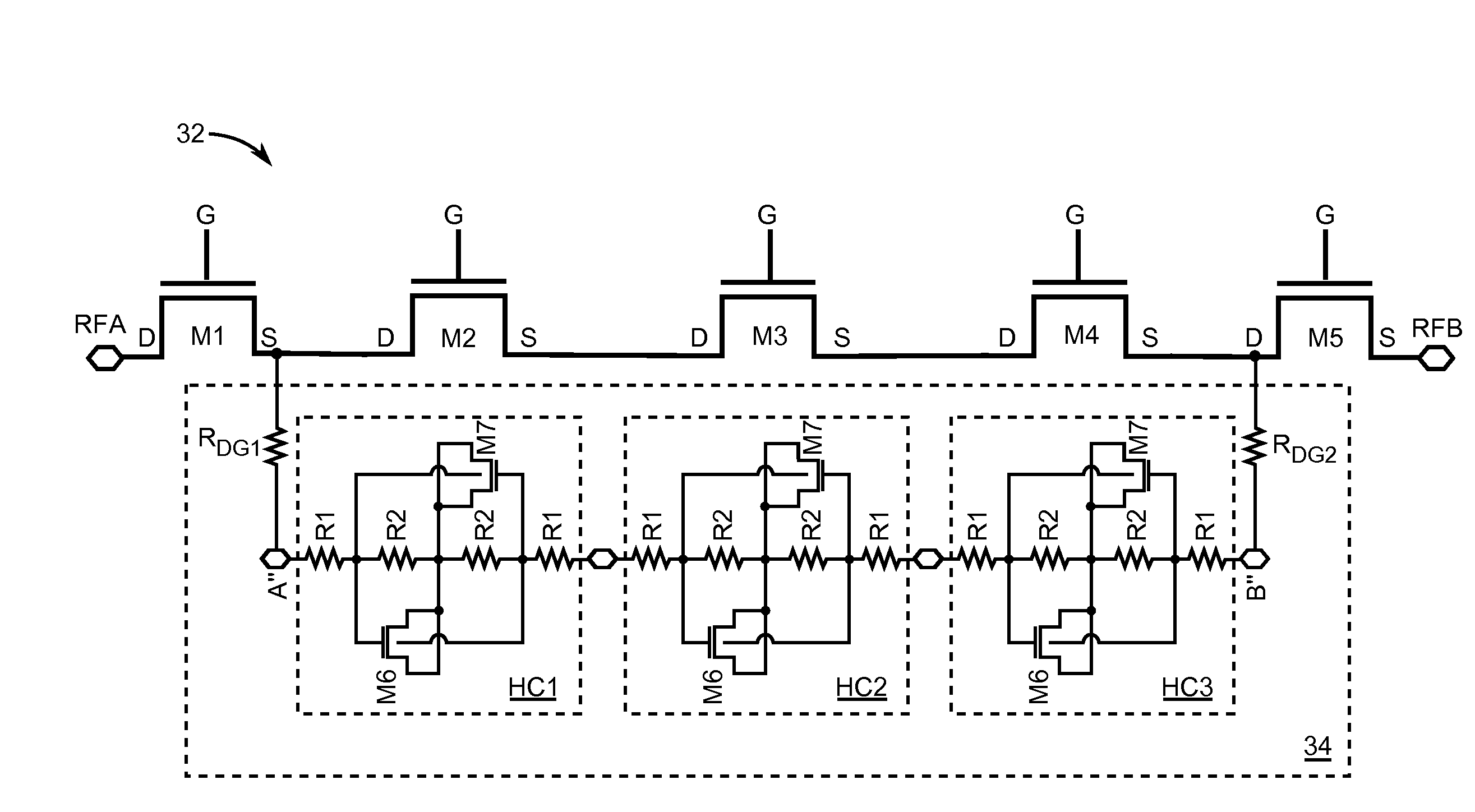
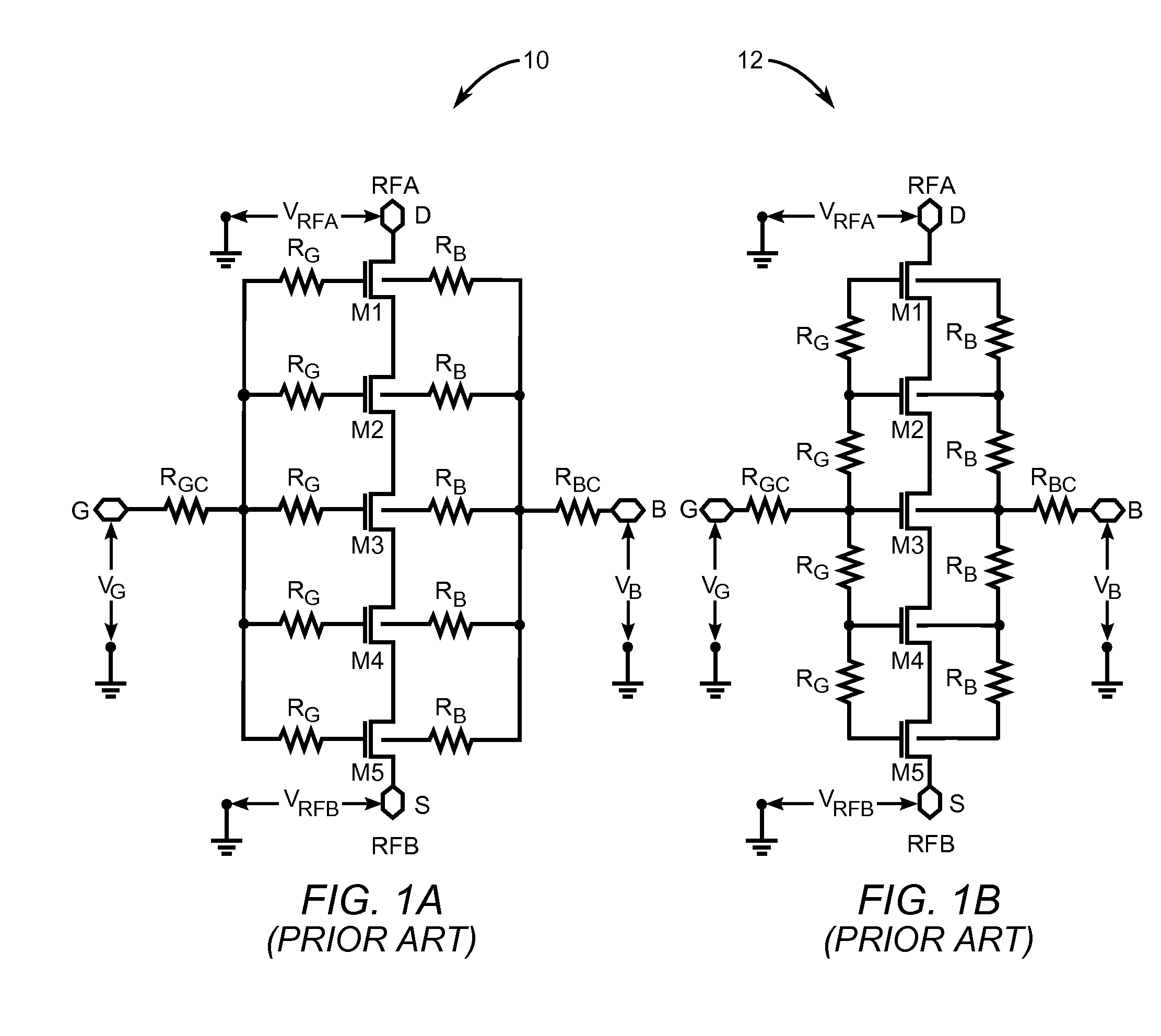
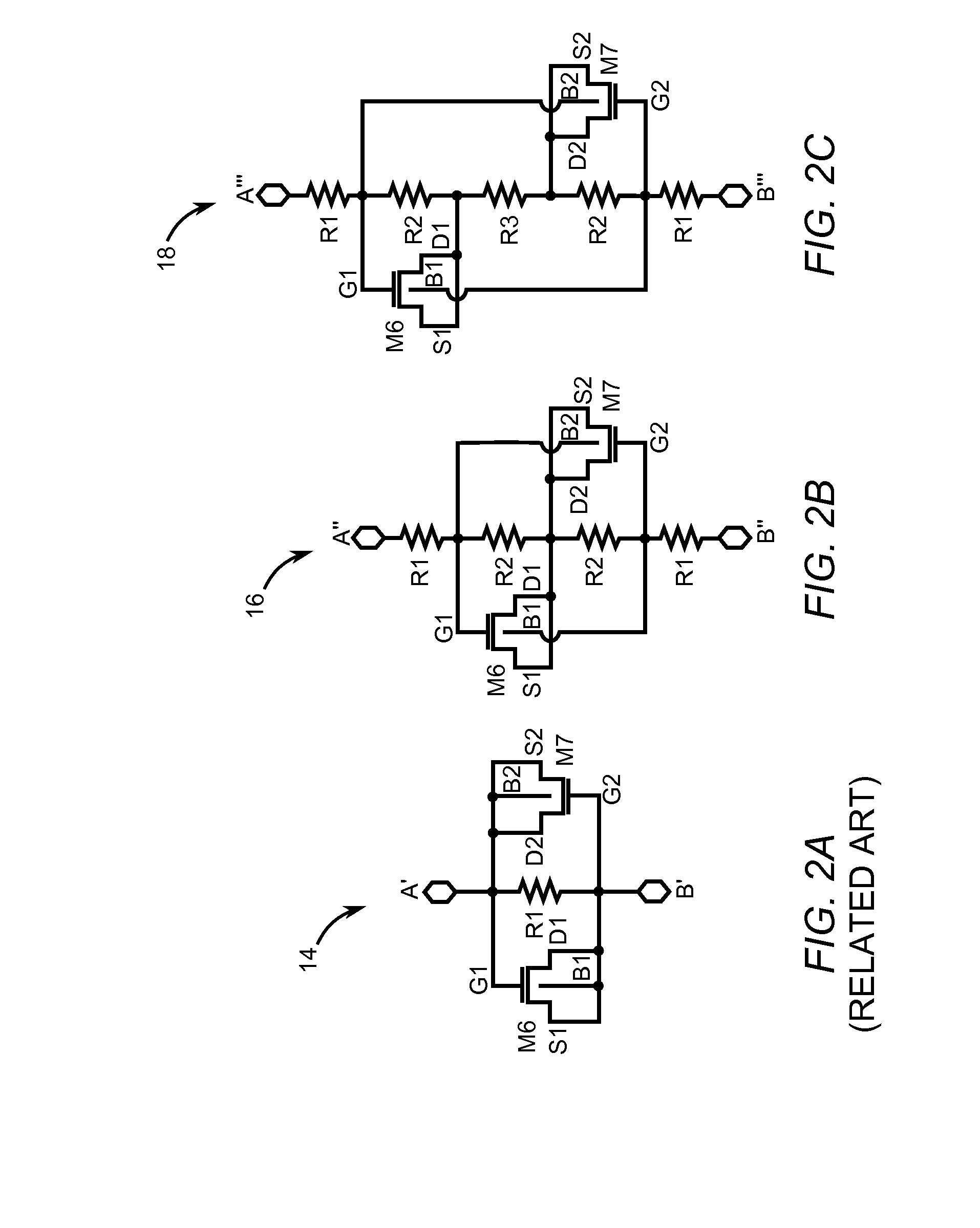
Systems, Methods and Apparatuses for High Power Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) Antenna Switches Using Body Switching and External Component in Multi-Stacking Structure
ActiveUS20090073078A1High Power Handling CapabilityHigh power blocking capabilityTransistorElectronic switchingMulti bandCMOS
Embodiments of the invention may provide for a CMOS antenna switch, which may be referred to as a CMOS SPDT switch. The CMOS antenna switch may operate at a plurality of frequencies, perhaps around 900 MHz, 1.9 GHz and 2.1 GHz according to an embodiment of the invention. The CMOS antenna switch may include both a receiver switch and a transmit switch. The receiver switch may utilize a multi-stack transistor with body substrate switching and attachment of external capacitor between drain and gate to block high power signals from the transmit path as well as to maintain low insertion loss at the receiver path. Exemplary embodiments of the CMOS antenna switch may provide for 38 dBm P 0.1 dB at multi bands (e.g., 900 MHz, 1.8 GHz, and 2.1 GHz). In addition, −60 dBc second and third harmonic performance up to 30 dBm input, may be obtained according to example embodiments of the invention.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
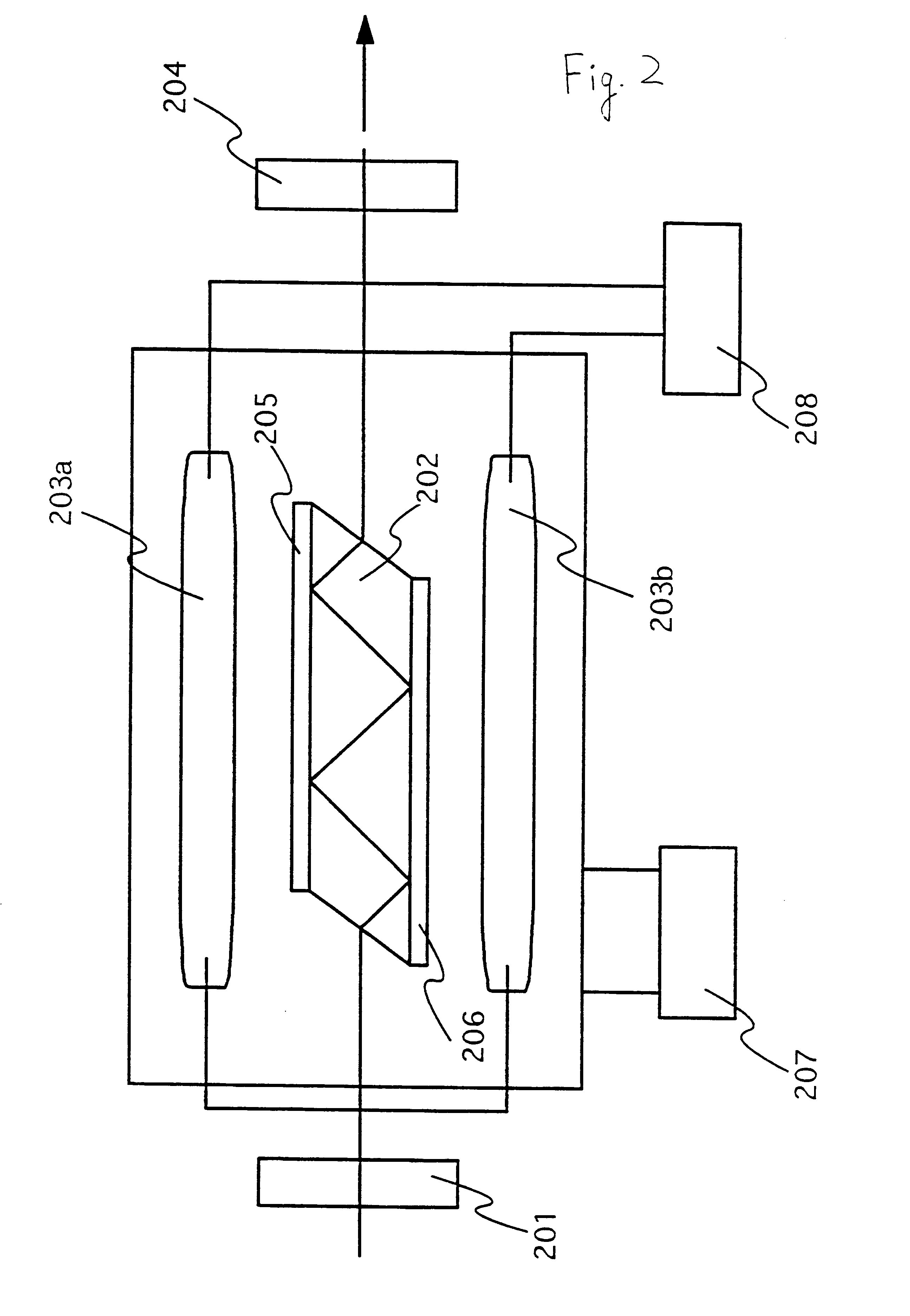
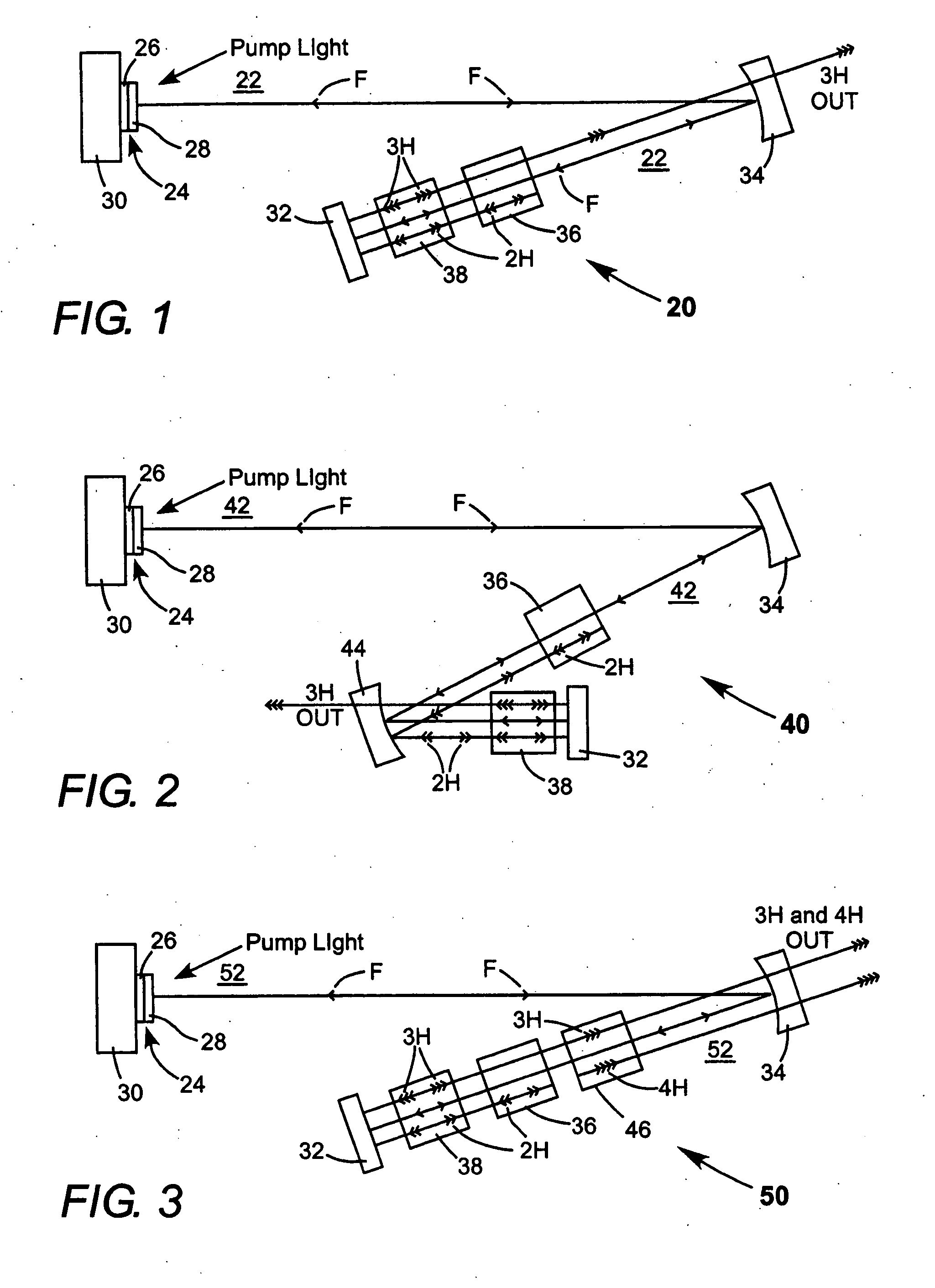
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser
InactiveUS20050078718A1High frequencyImprove efficiencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusNonlinear crystalsPhysics
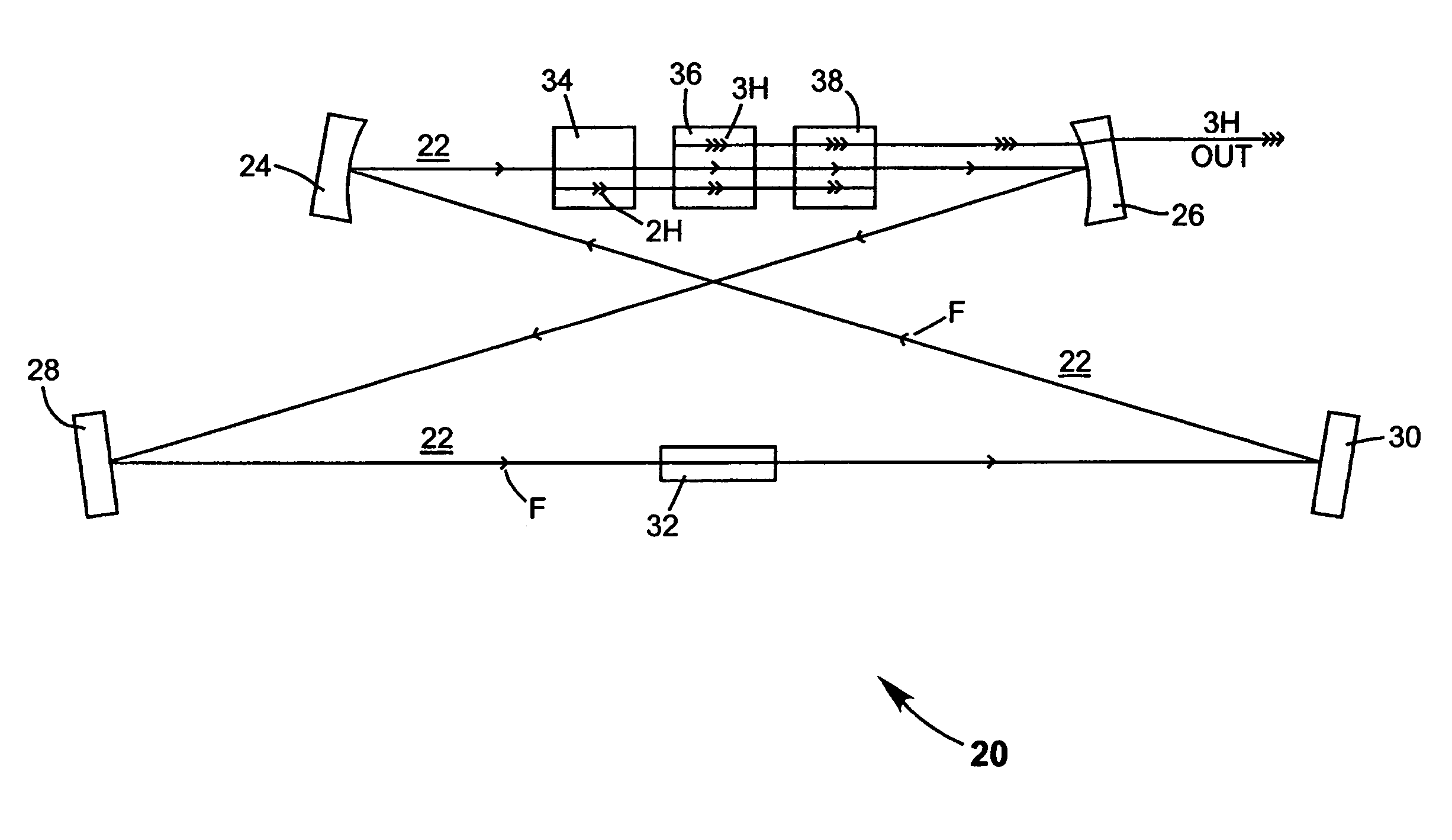
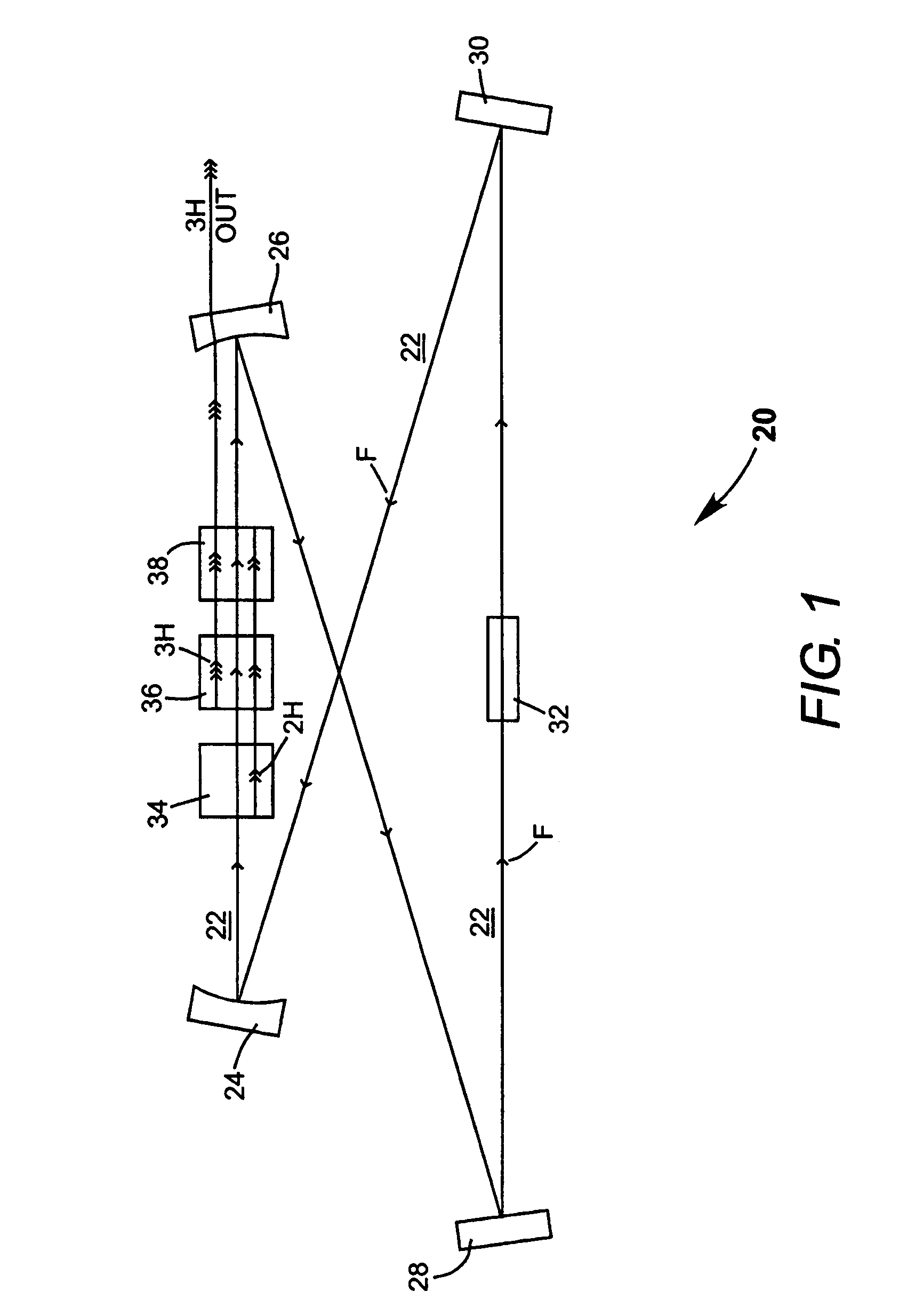
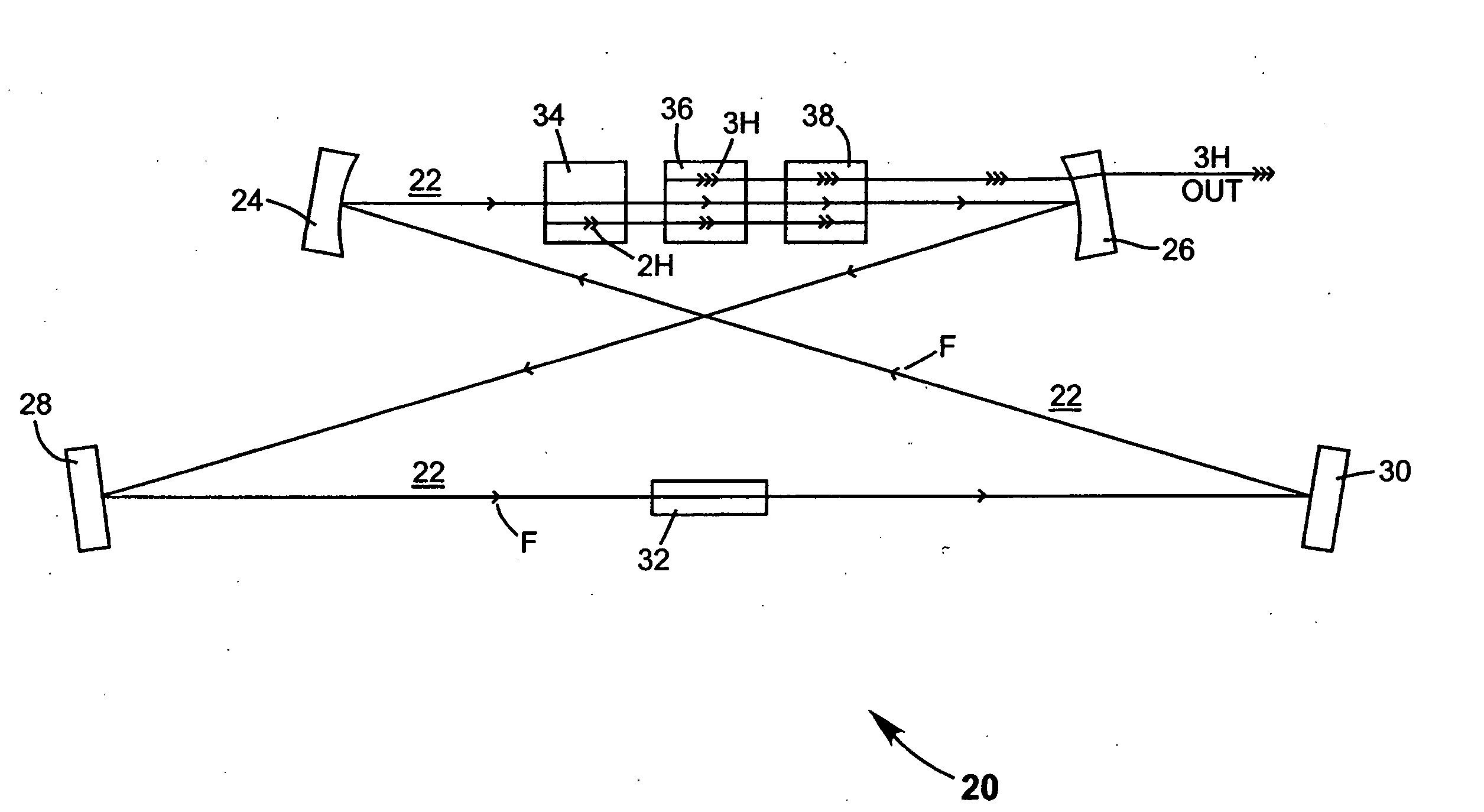
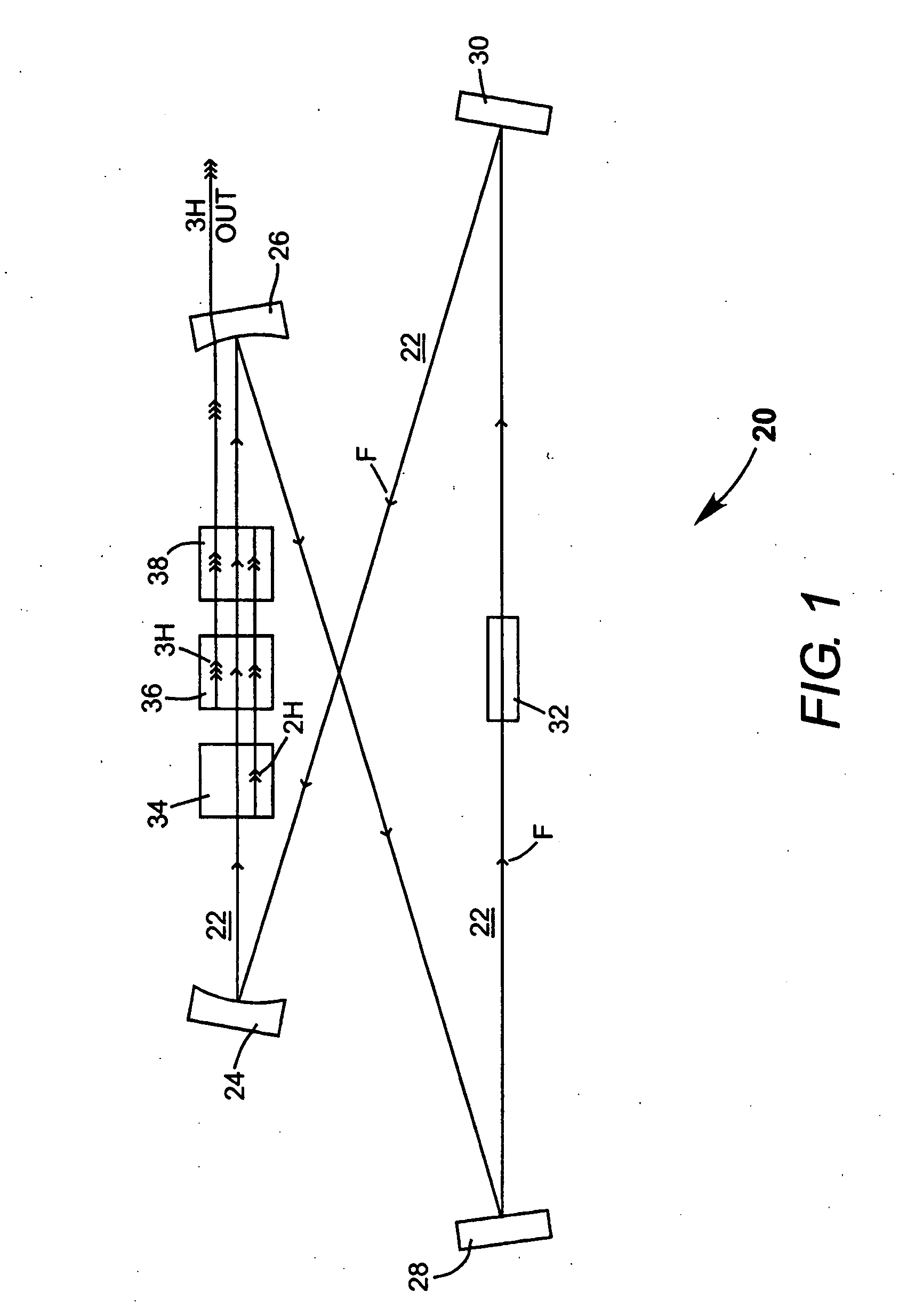
A method of intracavity frequency conversion in a CW laser includes causing fundamental radiation to circulate in a laser resonator. The fundamental radiation makes a first pass through an optically nonlinear crystal where a fraction of the fundamental radiation generates second-harmonic radiation in a forward pass through the crystal. The residual fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation are then sum-frequency mixed in forward and reverse passes through an optically nonlinear crystal such that a fraction of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. The residual second-harmonic radiation and fundamental radiation from the sum-frequency mixing then make a reverse pass through the second-harmonic generating crystal where the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation, or can be used to pump another optically nonlinear crystal in an optical parametric oscillator. Second-harmonic radiation can also be used to pump an optical parametric oscillator.
Owner:COHERENT INC
Optically pumped semiconductor ring laser
InactiveUS6940880B2Doubling frequencyLaser optical resonator constructionExcitation process/apparatusFourth harmonicOptical pumping
An optically pumped semiconductor laser includes an active ring-resonator having two or more optically pumped semiconductor (OPS) structures each including a mirror-structure and a multilayer gain-structure. The mirror-structures serve as fold mirrors for the resonator axis. An optically nonlinear crystal may be included in the ring-resonator for generating second-harmonic radiation from fundamental radiation generated in the resonator. Another optically nonlinear crystal may be provided for generating third-harmonic or fourth-harmonic radiation from the second-harmonic radiation. In one example, including a third-harmonic generating crystal, a passive ring-resonator partially coaxial with the active ring-resonator is provided for circulating second-harmonic radiation to provide resonant amplification of the second-harmonic radiation for enhancing third-harmonic conversion. Apparatus for automatically maintaining the passive ring-resonator in a resonant condition for the second-harmonic radiation is disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
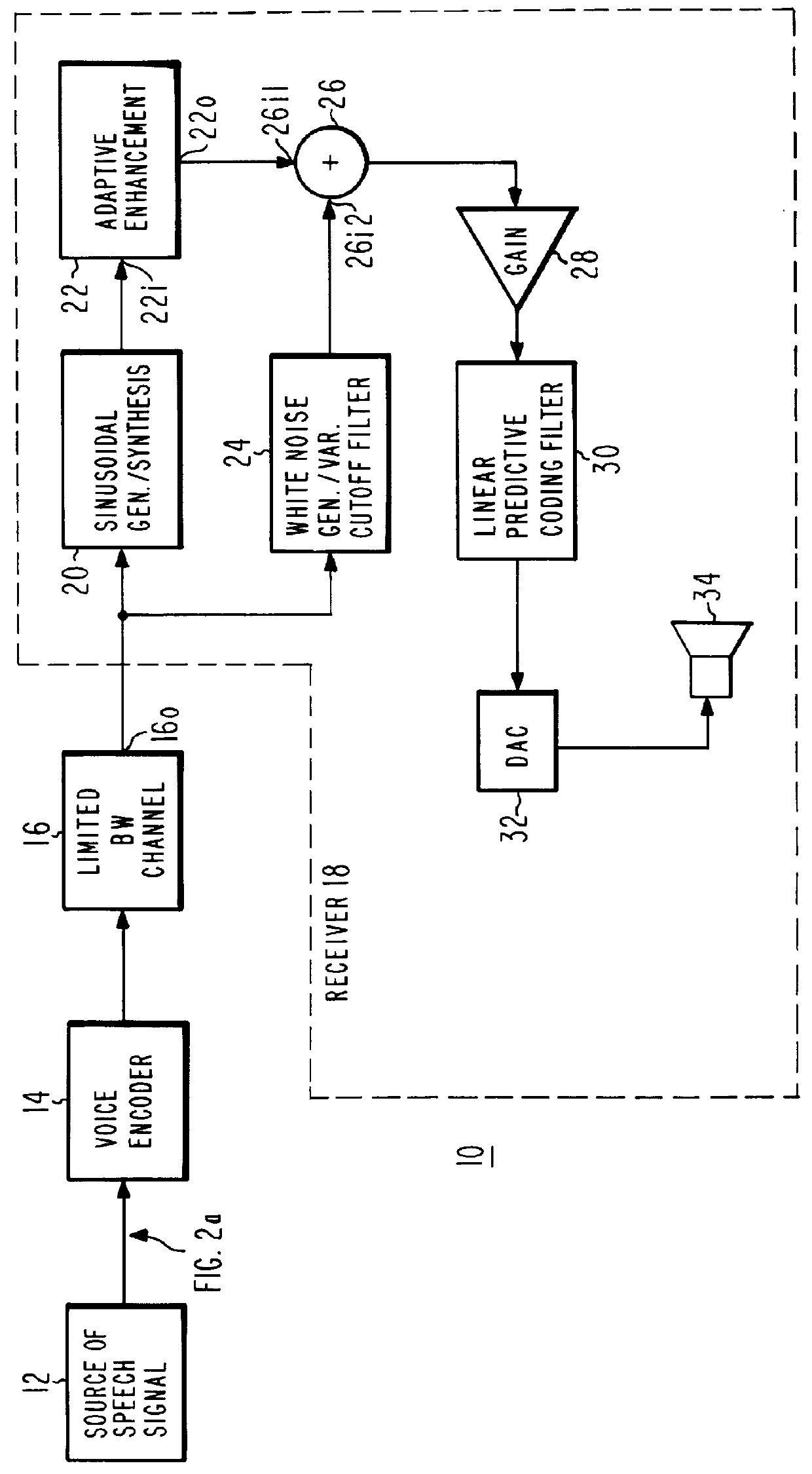
Enhancement of speech signals transmitted over a vocoder channel
In a vocoder system, the receiver is arranged to emphasize at least the fundamental or lowest-frequency sinusoidal signal in response to the pitch, in a manner which provides more emphasis at lower pitch values, corresponding to larger pitch intervals. The emphasis provides a subjectively improved speech synthesis. In a preferred embodiment, the enhancement takes place at fundamental component frequencies below 400 Hz. According to another aspect of the invention, the second and third harmonics are also emphasized, but generally not as much as the fundamental component. Below certain frequencies, the enhancement is limited for the fundamental and the harmonics.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Rotating induction apparatus
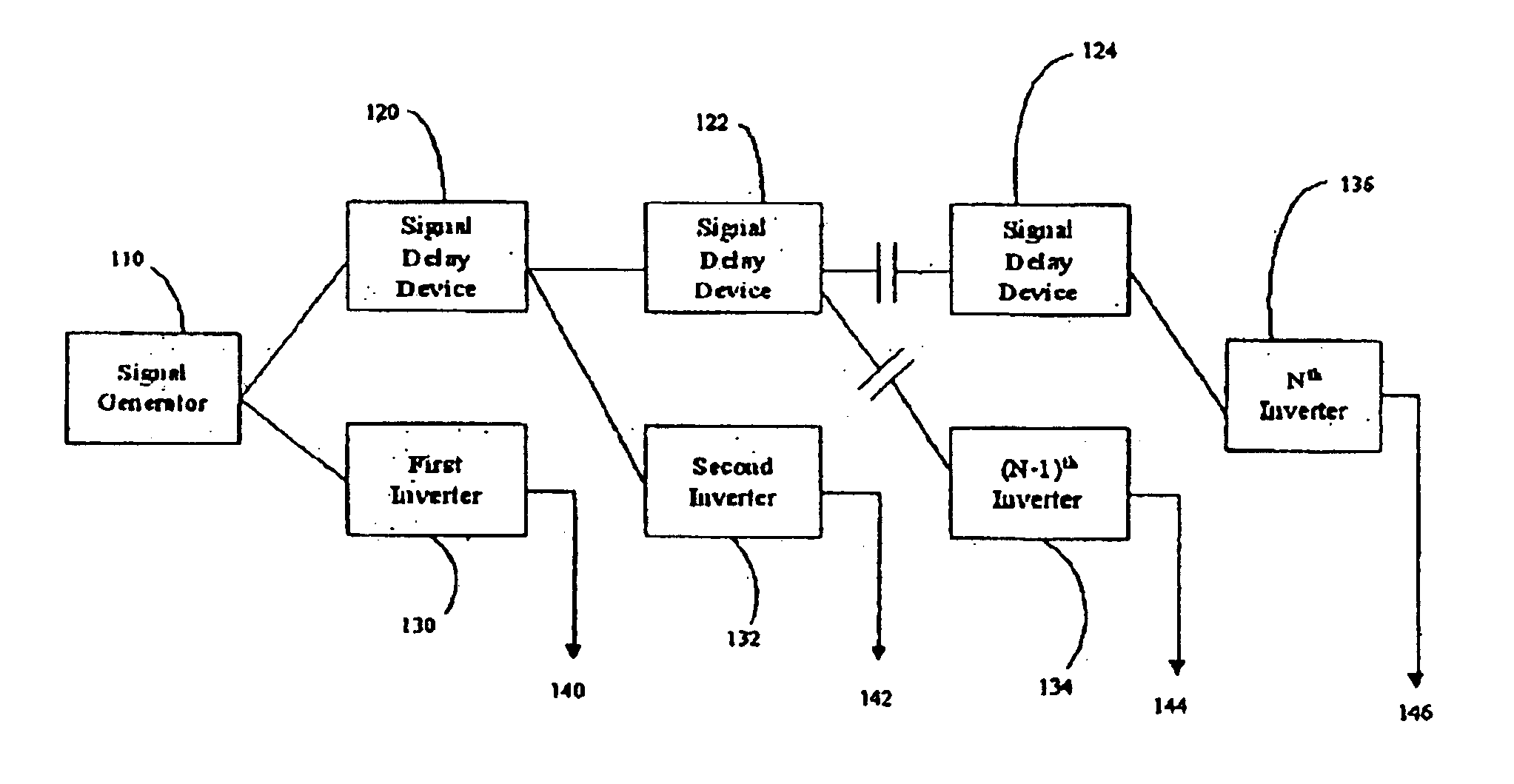
InactiveUS6922037B2Reduce decreaseImprove performanceAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlWave shapeThird harmonic
An electrical rotating apparatus comprises an inverter system that outputs more than three phases. The apparatus further includes a stator electrically coupled to the inverter system, and a rotor electromagnetically coupled to a magnetic field generated by the stator. A signal generator generates a pulse modulated drive waveform signal, that has a frequency synchronized with the rotational frequency of the rotor, and the pulse modulated drive waveform signal drives the inverter system. The pulse modulated drive waveform signal has a pulsing frequency. Additionally, the inverter system may be fed by a pulse modulated drive waveform signal that is fed through at least one signal delay device. Alternatively, the system may also be fed selected harmonic components, such as the third harmonic, up until the number of phases in the apparatus.
Owner:BOREALIS TECH LTD
Ultrasound 3D imaging system
ActiveUS20130261463A1Minimizing energyEliminate periodicityOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnosticsSonificationEngineering
The present invention related to an ultrasound imaging system win which the scan head includes a beamformer circuit that performs far field subarray beamforming or includes a sparse array selecting circuit that actuates selected elements. When using a hierarchical two-stage or three-stage beamforming system, three dimensional ultrasound images can be generated in real-time. The invention further relates to flexible printed circuit boards in the probe head. The invention furthermore related to the use. of coded or spread spectrum signaling in ultrasound imagining systems. Matched filters based on pulse compression using Golay code pairs improve the signal-to-noise ratio thus enabling third harmonic imaging with suppressed sidelobes. The system is suitable for 3D full volume cardiac imaging.
Owner:TERATECH CORP
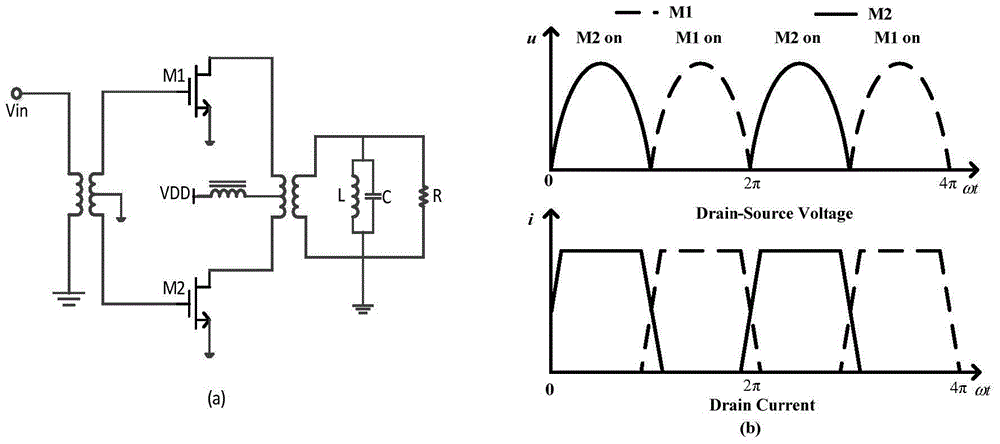
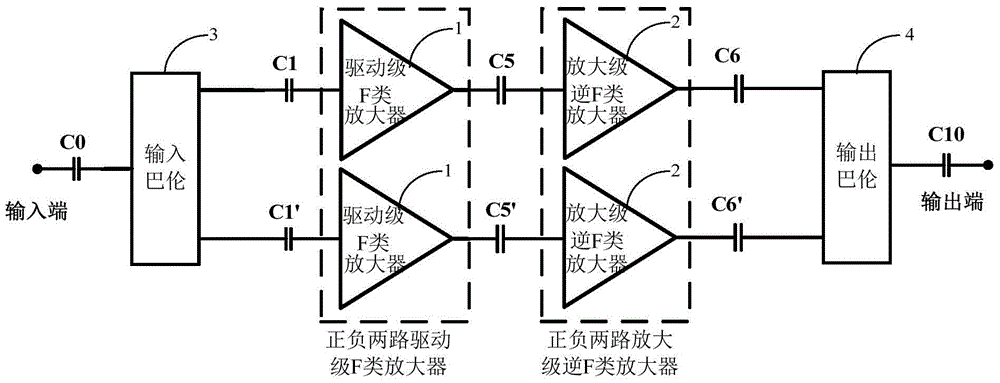
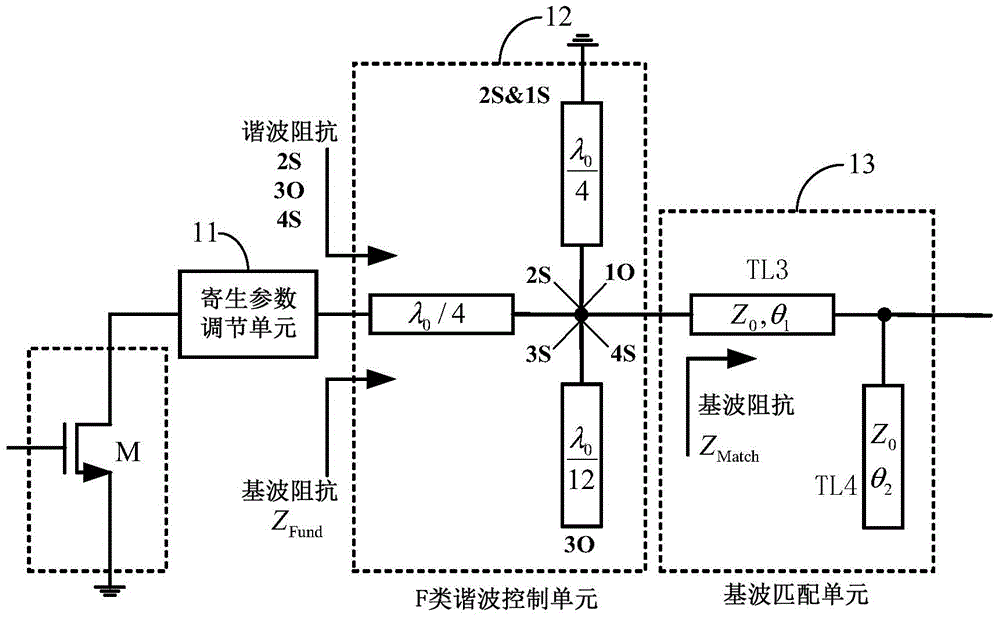
Double-stage inversing D-class power amplifying circuit and radio frequency power amplifier
ActiveCN104953961AImprove efficiencyReduce energy lossHigh frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
The invention is suitable for the field of radio frequency communication, and provides a double-stage inversing D-class power amplifying circuit and a radio frequency power amplifier. The circuit comprises an input passive component connected with a block condenser, a positive and negative double-way driving-stage F-class amplifier, a positive and negative double-way amplifying-stage inversing F-class amplifier and an output passive component, wherein the two input ends of the positive and negative double-way driving-stage F-class amplifier are connected with the two output ends of the input passive component through two block coupling condensers, the two input ends of the positive and negative double-way amplifying-stage inversing F-class amplifier are connected with the two output ends of the positive and negative double-way driving-stage F-class amplifier through two condensers, and the two input ends of the output passive component are connected with the two output ends of the positive and negative double-way amplifying-stage inversing F-class amplifier through the two condensers. By utilizing an F-class driving inversing F-class push-pull structure, according to the harmonic shaping technology, the efficiency, the power and the gain of the power amplifier are improved, the independent control from a fundamental wave to a triple frequency harmonic impedance is achieved, the design difficulty is lowered, and the tedious debugging work in the later period is lowered. In addition, due to the positive and negative double-way structural design, the power and the gain are further improved.
Owner:CHINA COMM MICROELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD +1
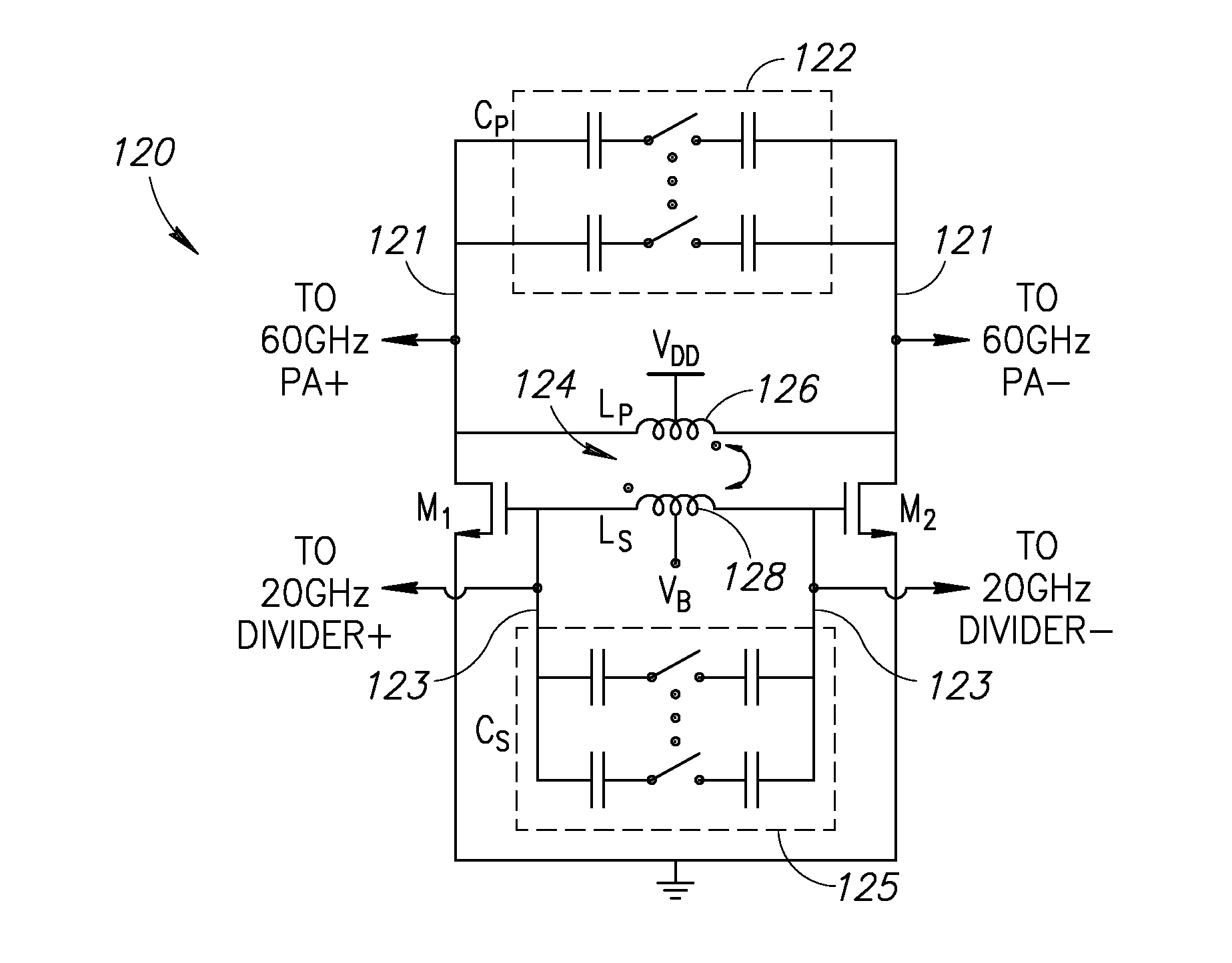
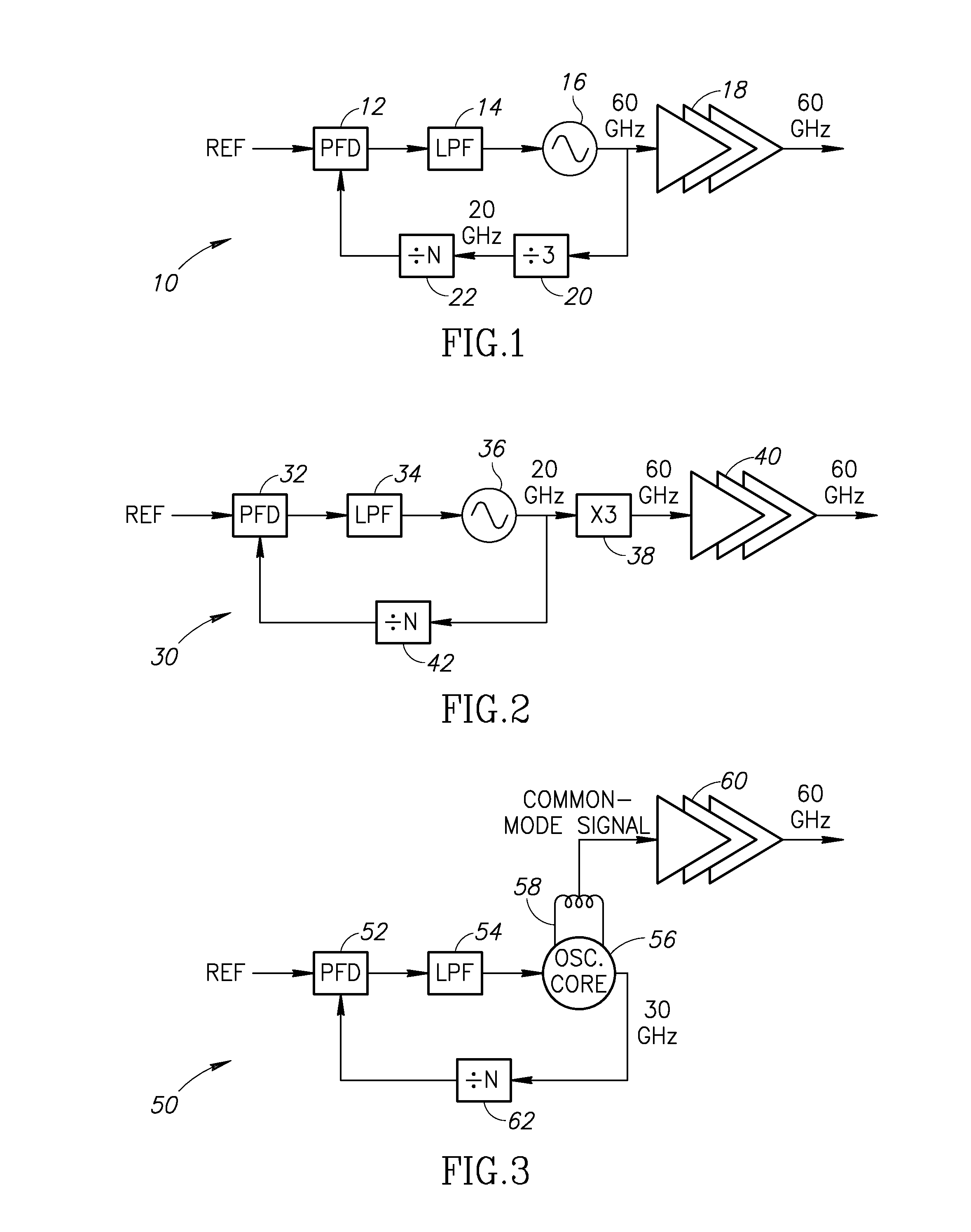
60 GHz Frequency Generator Incorporating Third Harmonic Boost And Extraction
ActiveUS20160099681A1Improve efficiencyImprove noiseResonant circuit tuningPulse automatic controlCMOSDBc
A novel and useful 60 GHz frequency generator based on a third harmonic extraction technique which improves system level efficiency and performance. The frequency generator employs a third harmonic boosting technique to increase the third harmonic at the output of the oscillator. The oscillator generates both ˜20 GHz fundamental and a significant amount of the third harmonic at ˜60 GHz and avoids the need for a frequency divider operating at 60 GHz. The undesired fundamental harmonic at ˜20 GHz is rejected by the good fundamental HRR inherent in the oscillator buffer stage while the ˜60 GHz component is amplified to the output. The fundamental harmonic is further suppressed by an active cancellation by properly combining the two outputs. The oscillator fabricated in 40 nm CMOS exhibits a phase noise of −100 dBc / Hz at 1 MHz offset from a 60 GHz carrier and have a tuning range of 25%.
Owner:SHORT CIRCUIT TECH LLC
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
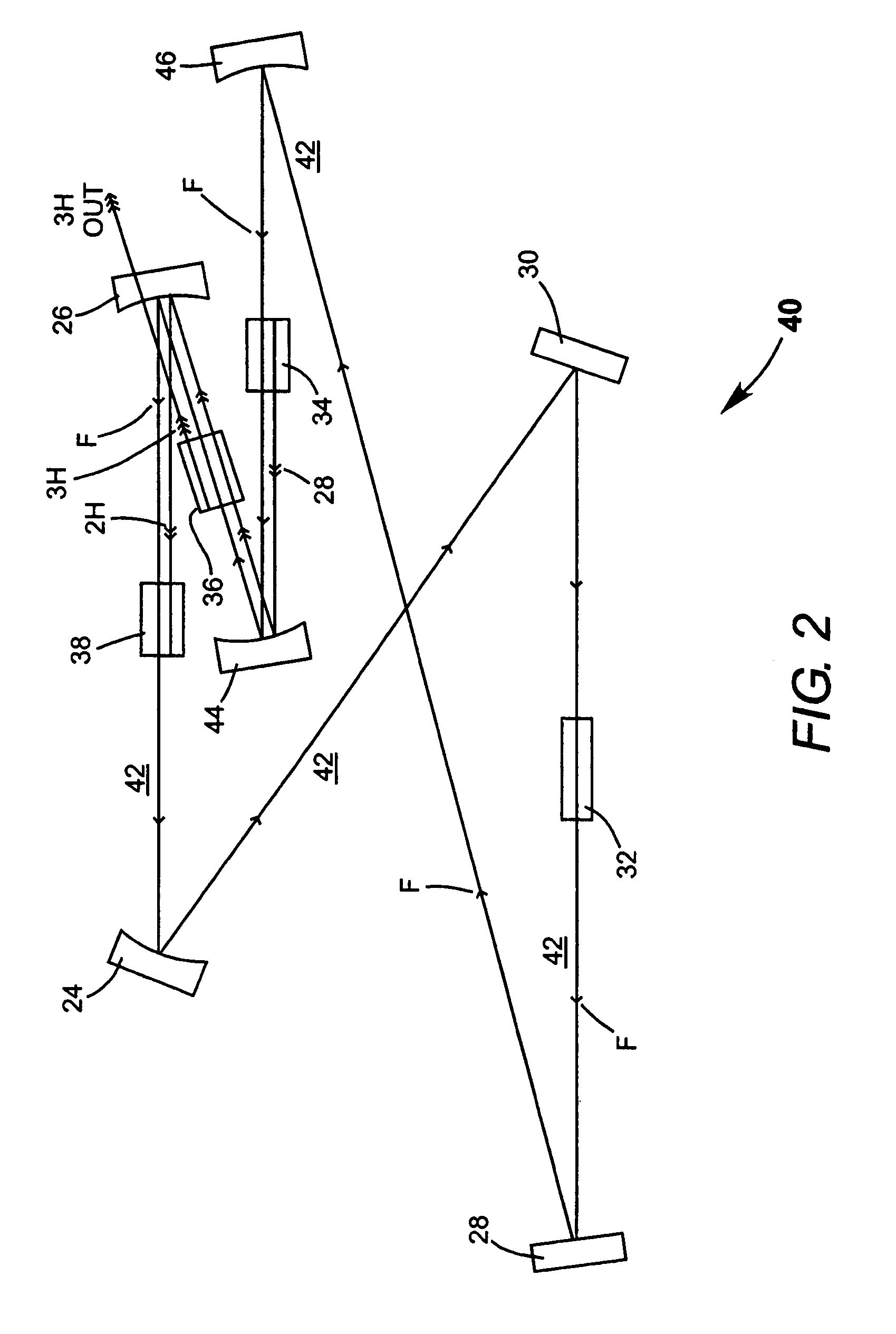
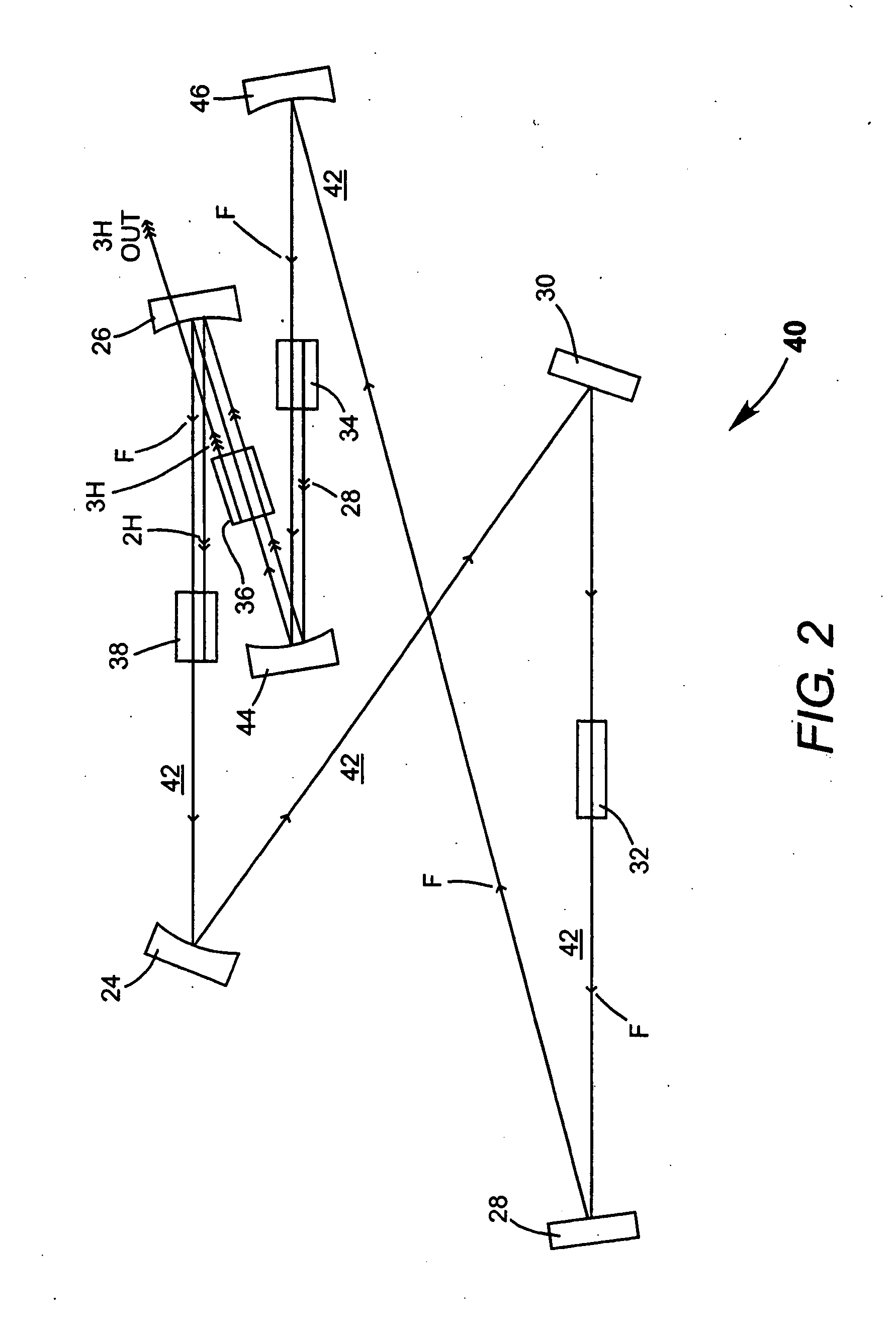
InactiveUS7130321B2Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
Owner:COHERENT INC
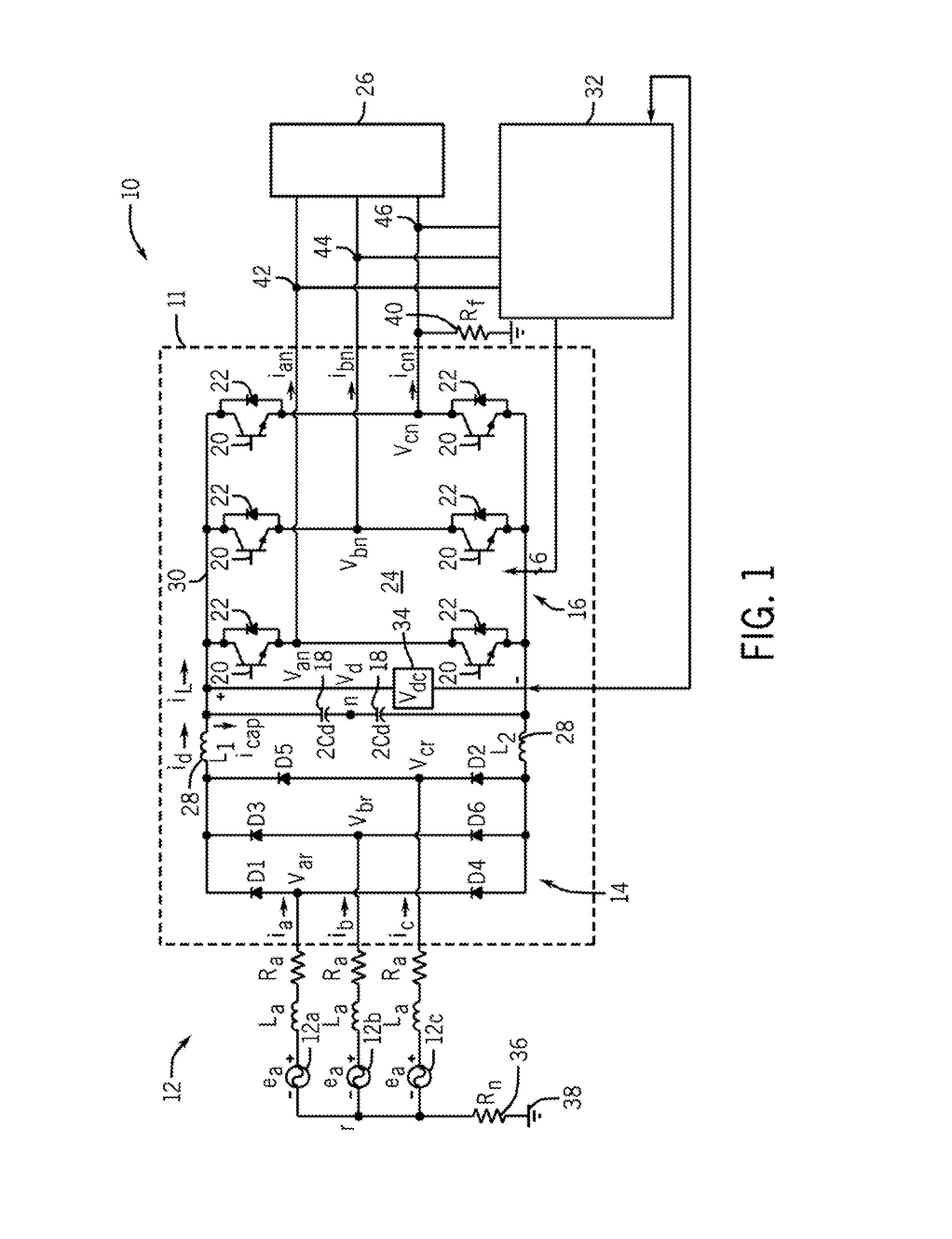
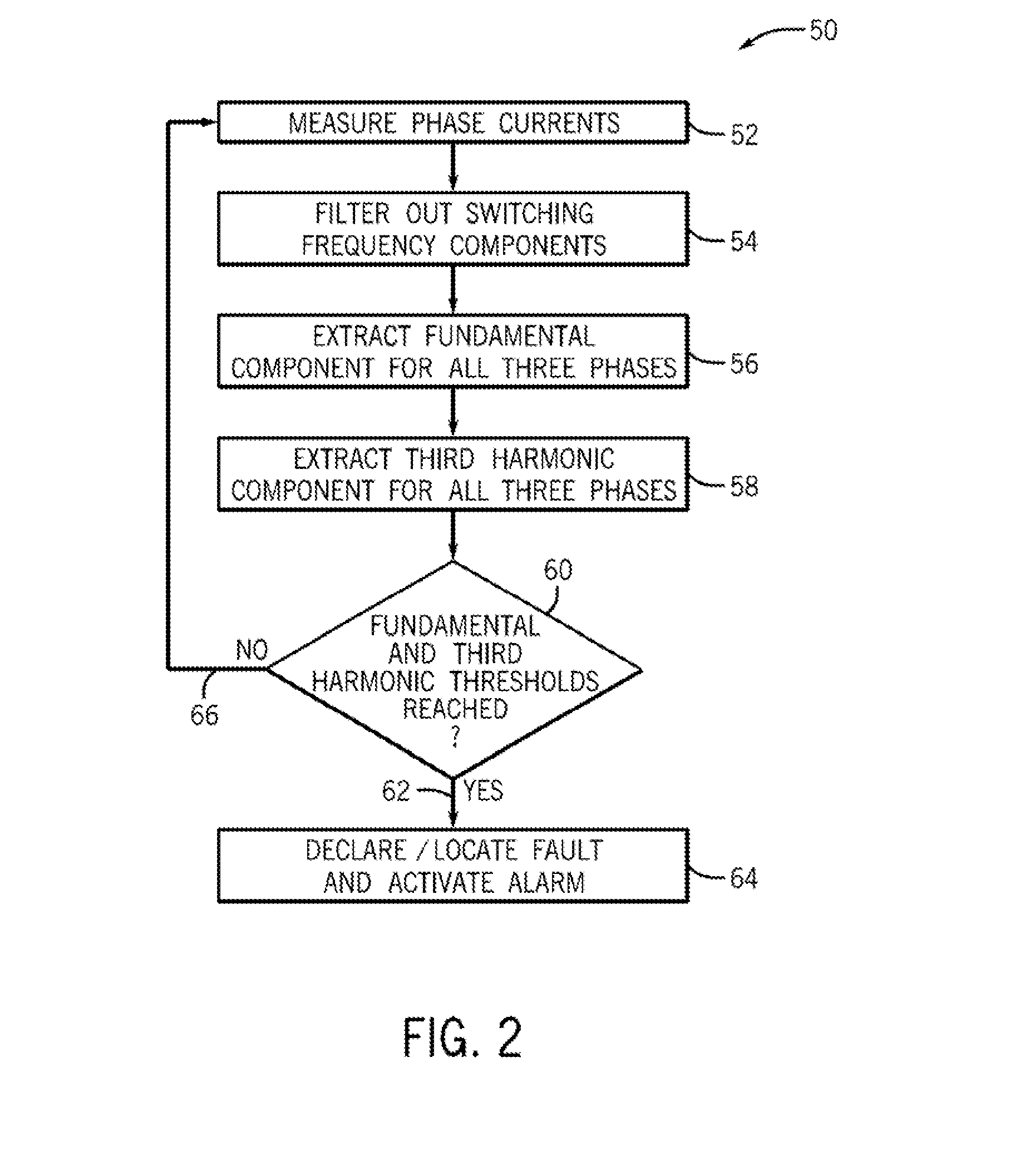
System and method for high resistance ground fault detection and protection in power distribution systems
ActiveUS20130322133A1Current/voltage measurementShort-circuit testingHigh resistanceElectrical resistance and conductance
A system and method for detecting high resistance ground faults in a power distribution system is disclosed. A fault detection and protection system is provided that includes a plurality of current sensors to measure current on the three phase output of the converter-inverter arrangement of the power distribution system and a controller configured to measure the three phase current on the three phase output, extract a fundamental current component for each phase of the three phase output, extract a third harmonic component for each phase of the three phase output, compare the fundamental current component and the third harmonic component extracted from each phase to a first threshold and a second threshold, respectively, and detect a ground fault on a phase of the three phase output based on the comparisons of the fundamental current component and the third harmonic component to the first and second thresholds.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
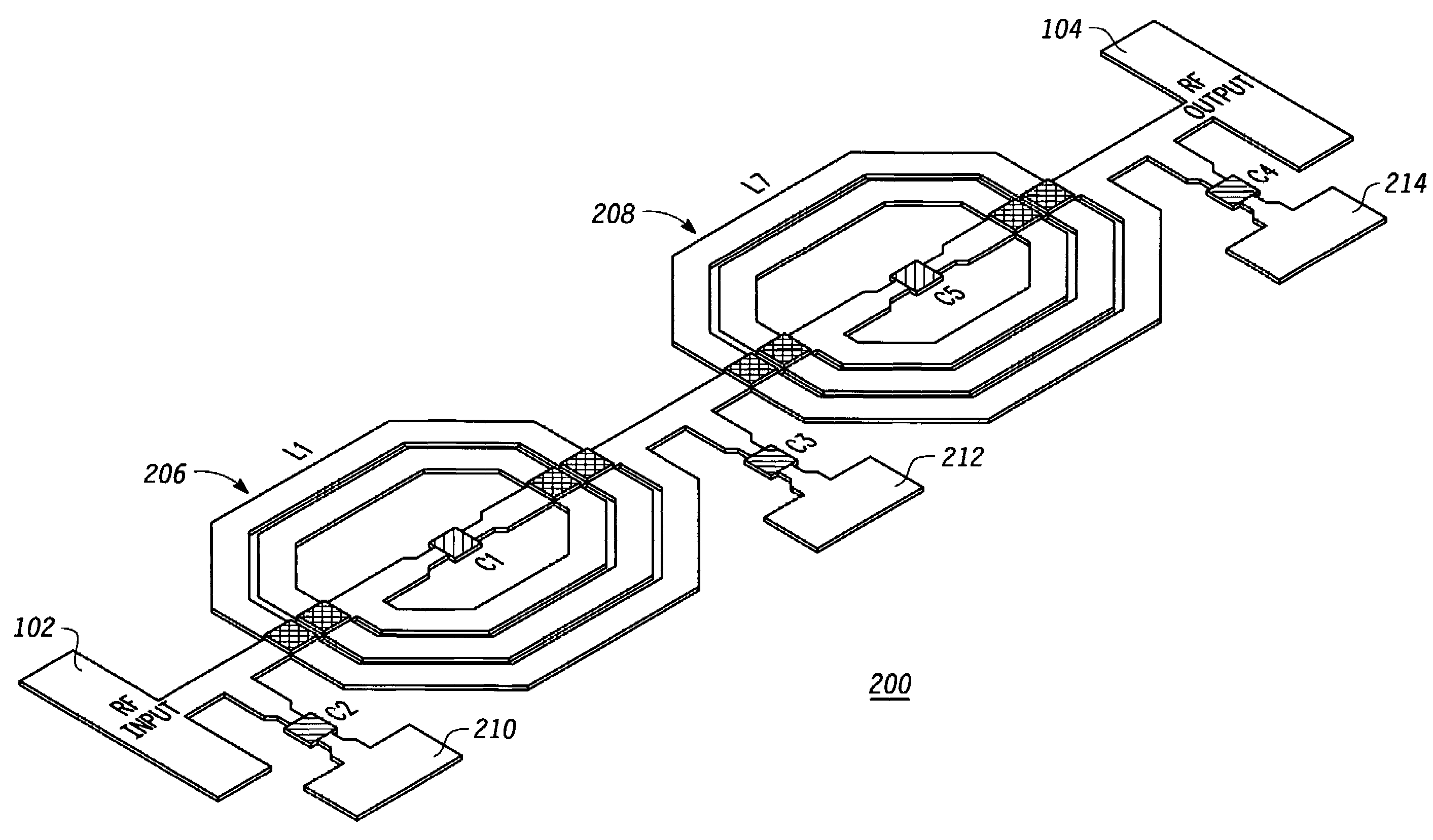
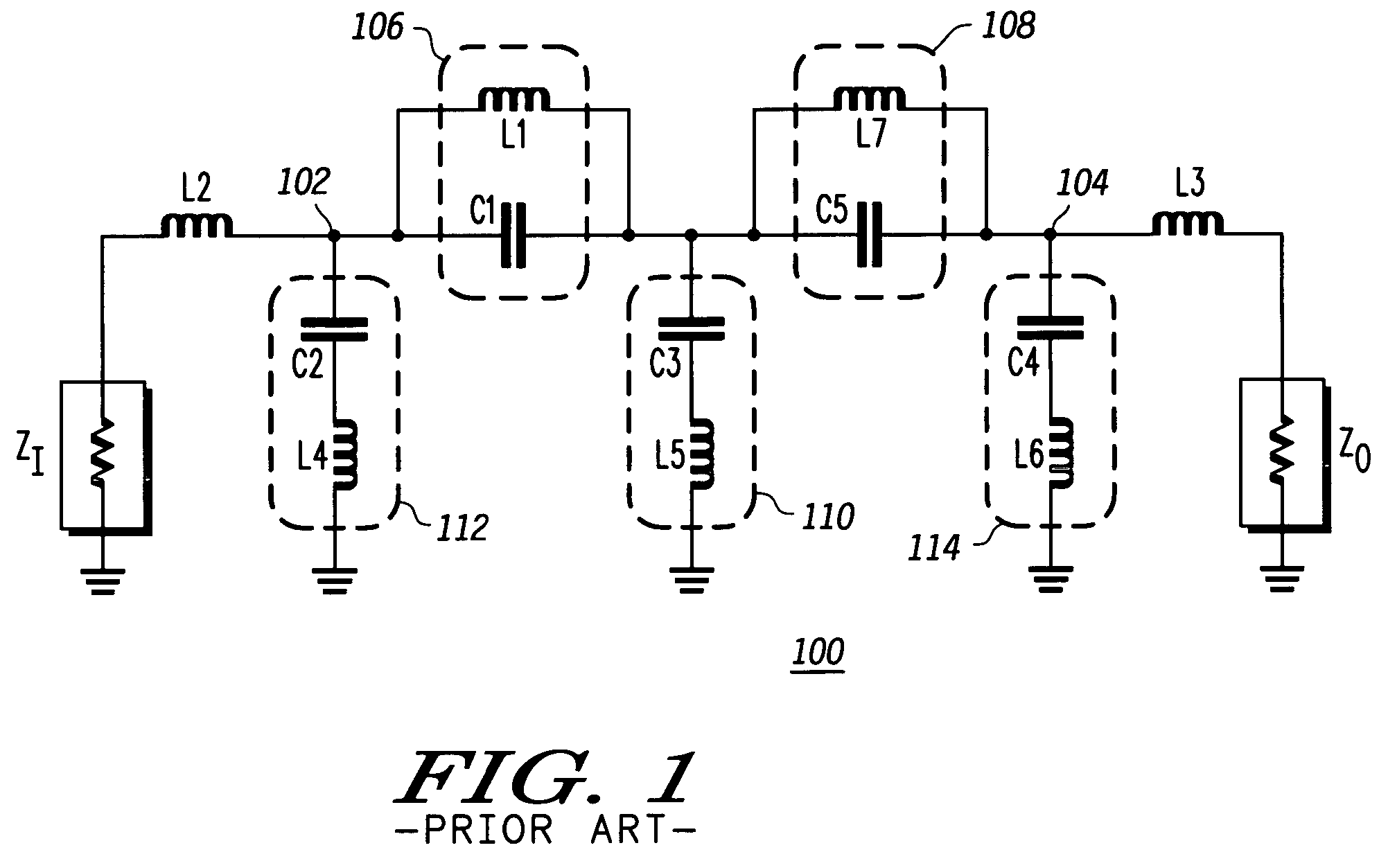
Compact radio frequency harmonic filter using integrated passive device technology
ActiveUS7418251B2Reducing overall size and packaging requirementReduce equipment footprintMultiple-port networksTransmissionFourth harmonicThird harmonic
A radio frequency (“RF”) harmonic filter circuit as disclosed herein is fabricated using integrated passive device (“IPD”) technology. The RF harmonic filter circuit is configured to provide second, third, and fourth harmonic rejection while providing good input and output impedance matching. The RF harmonic filter circuit employs only one IPD loop inductance (preferably used for a second harmonic resonance circuit), which results in a significant die / package size reduction. The RF harmonic filter circuit also employs a combined circuit that performs input and / or output impedance matching and third harmonic rejection.
Owner:NXP USA INC
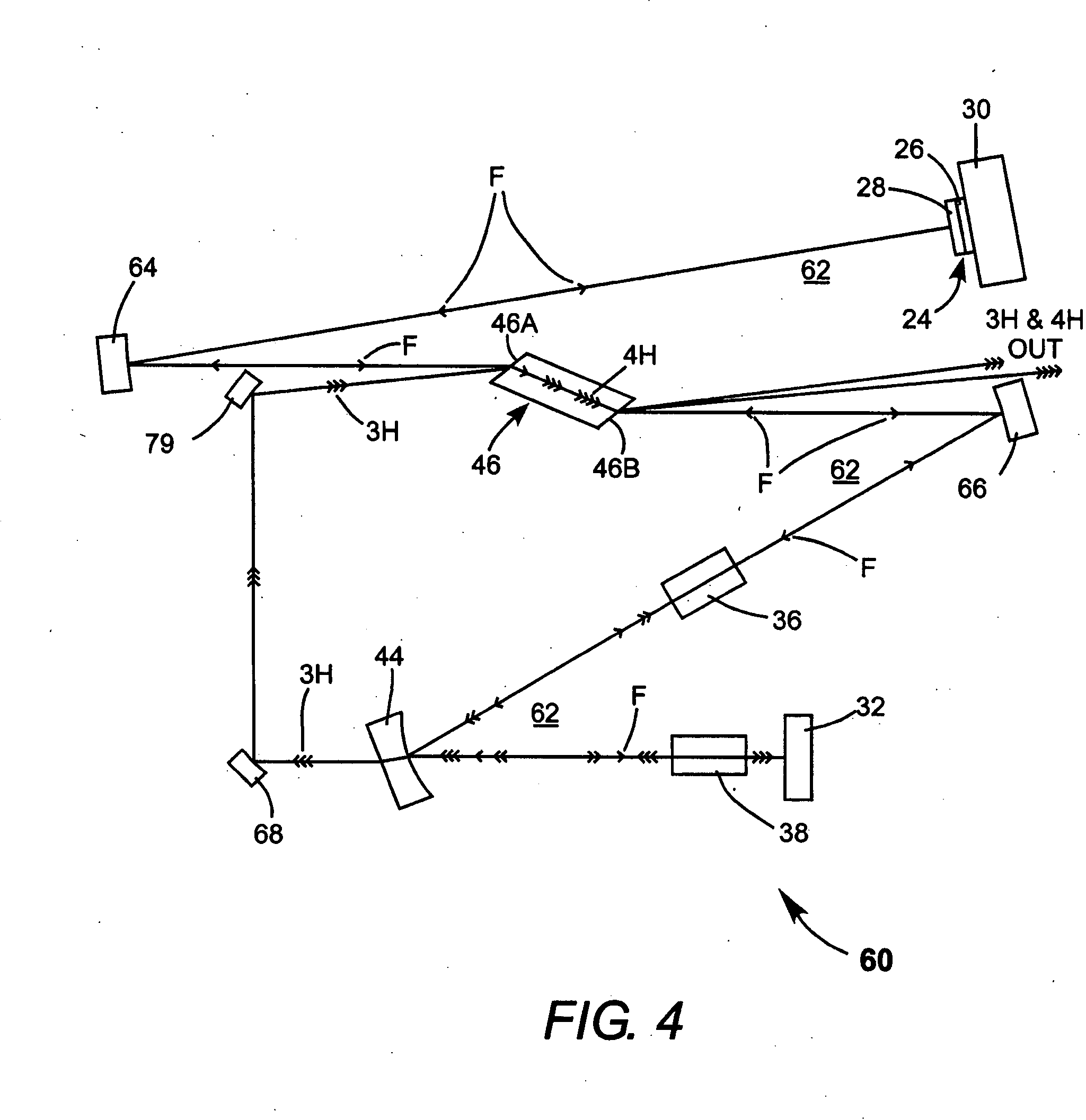
Intracavity frequency-tripled CW laser with traveling-wave ring-resonator
InactiveUS20050163187A1Improve efficiencyIncrease volumeLaser optical resonator constructionLaser output parameters controlFourth harmonicThird harmonic
A traveling-wave ring laser resonator includes one or more gain-elements for generating fundamental radiation and three optically nonlinear crystals. A portion of the fundamental radiation is converted to second-harmonic radiation in a first of the crystals. Remaining fundamental radiation and the second-harmonic radiation traverse a second of the optically nonlinear crystals where a portion of each is converted to third-harmonic radiation. Fundamental and second-harmonic radiation pass through the third of the optically nonlinear crystals where most of the second-harmonic radiation is converted back to fundamental radiation. The third-harmonic radiation can be delivered from the resonator as output radiation or mixed with the fundamental radiation in a fourth optically nonlinear crystal to generate fourth harmonic radiation. An optical parametric oscillator arrangement is also disclosed.
Owner:COHERENT INC
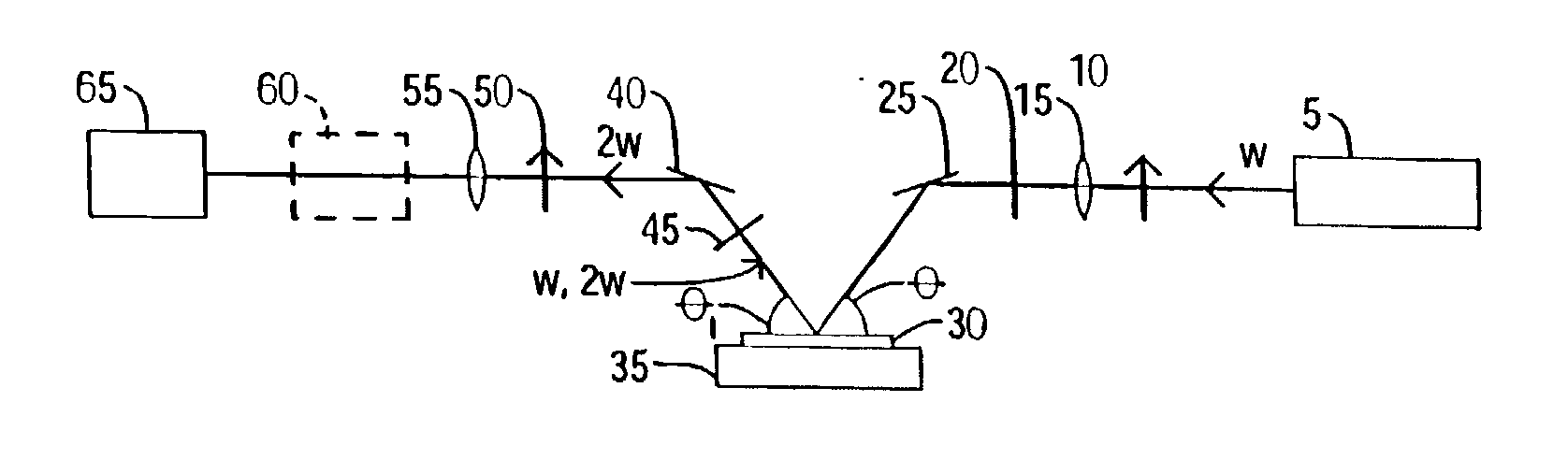
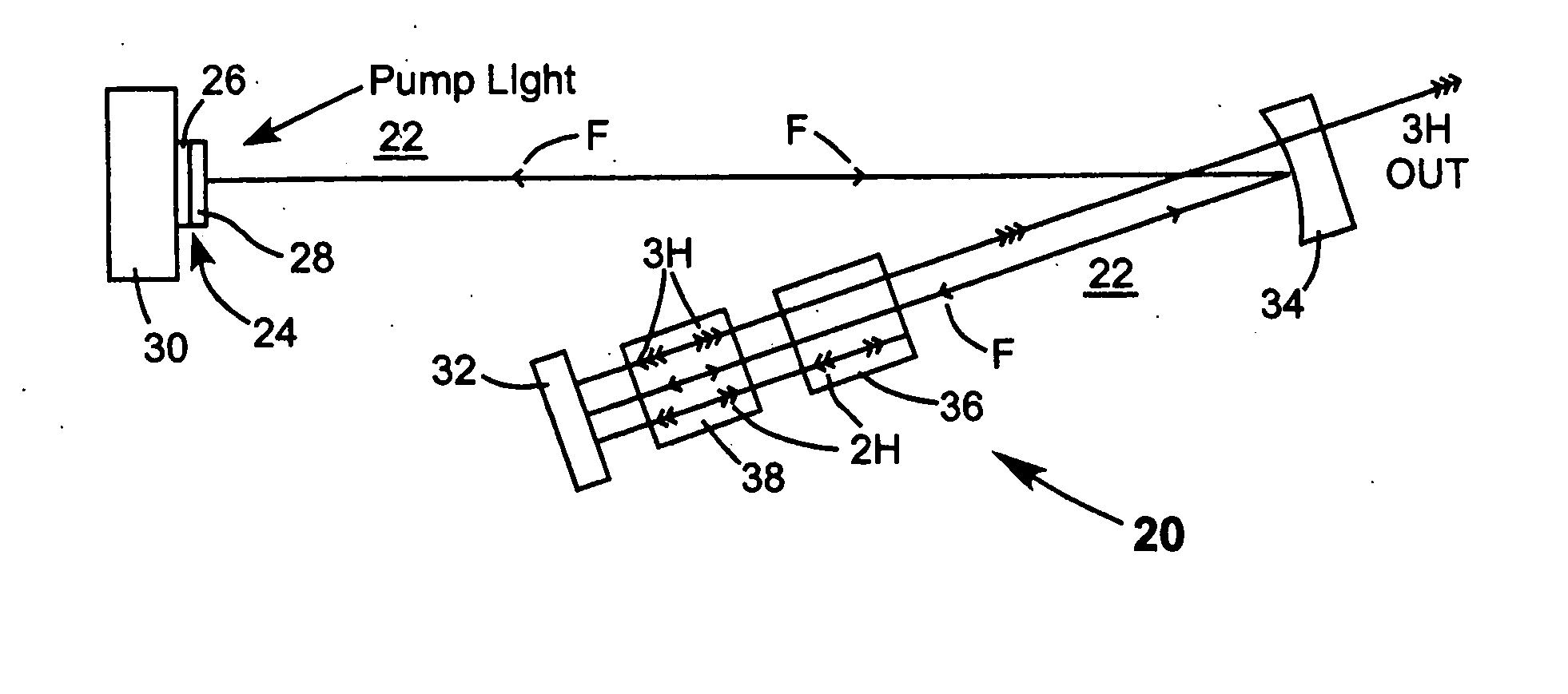
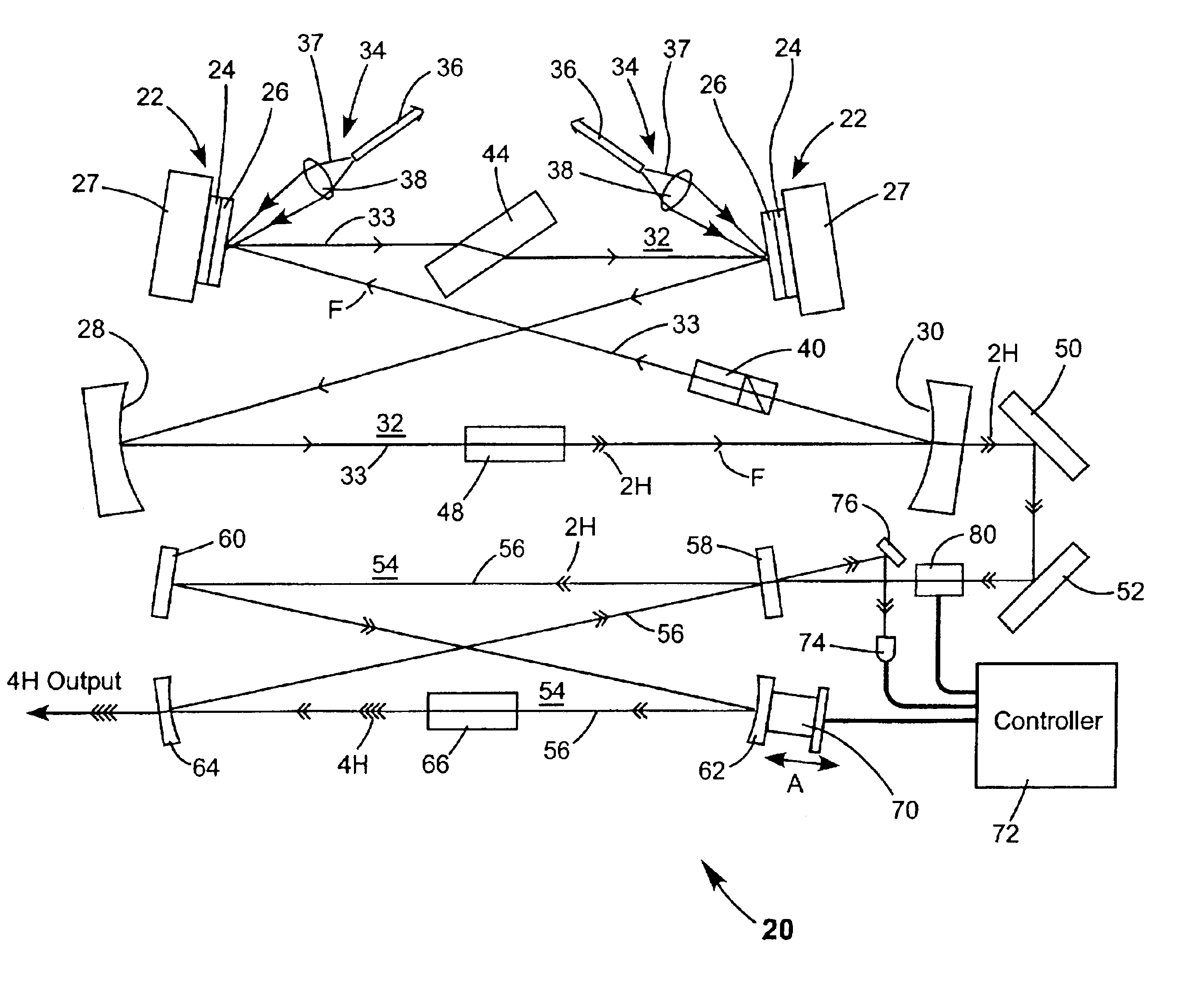
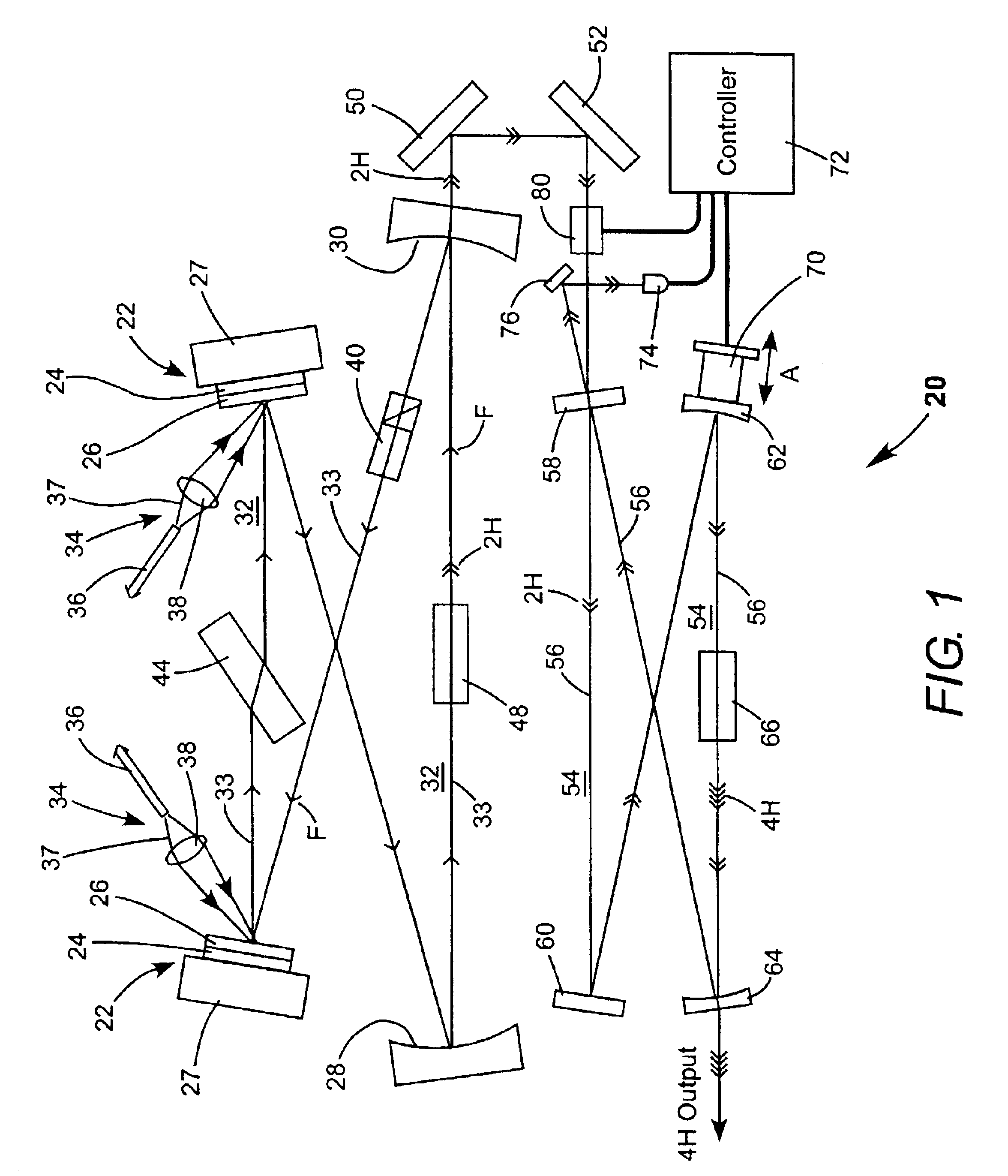
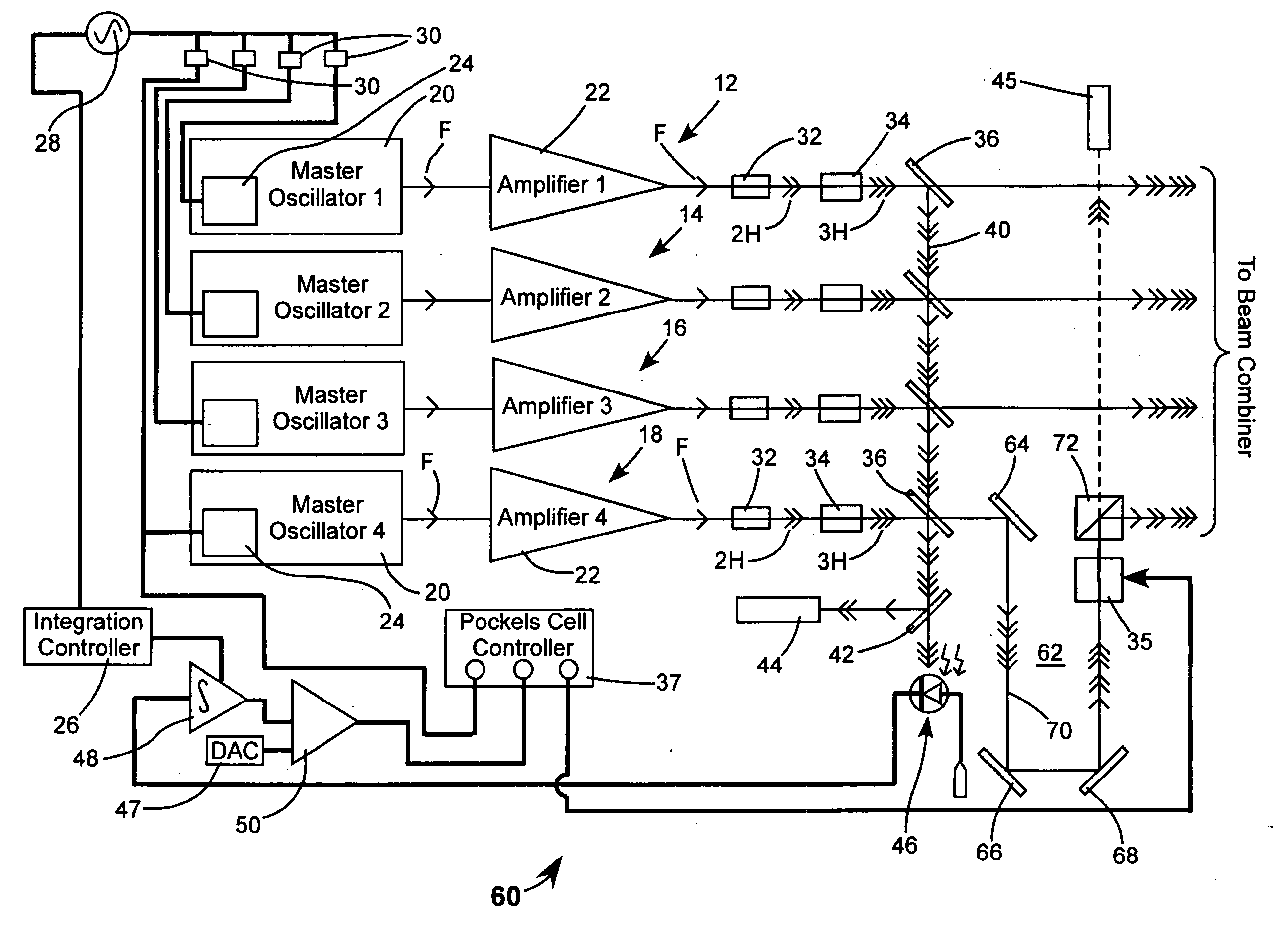
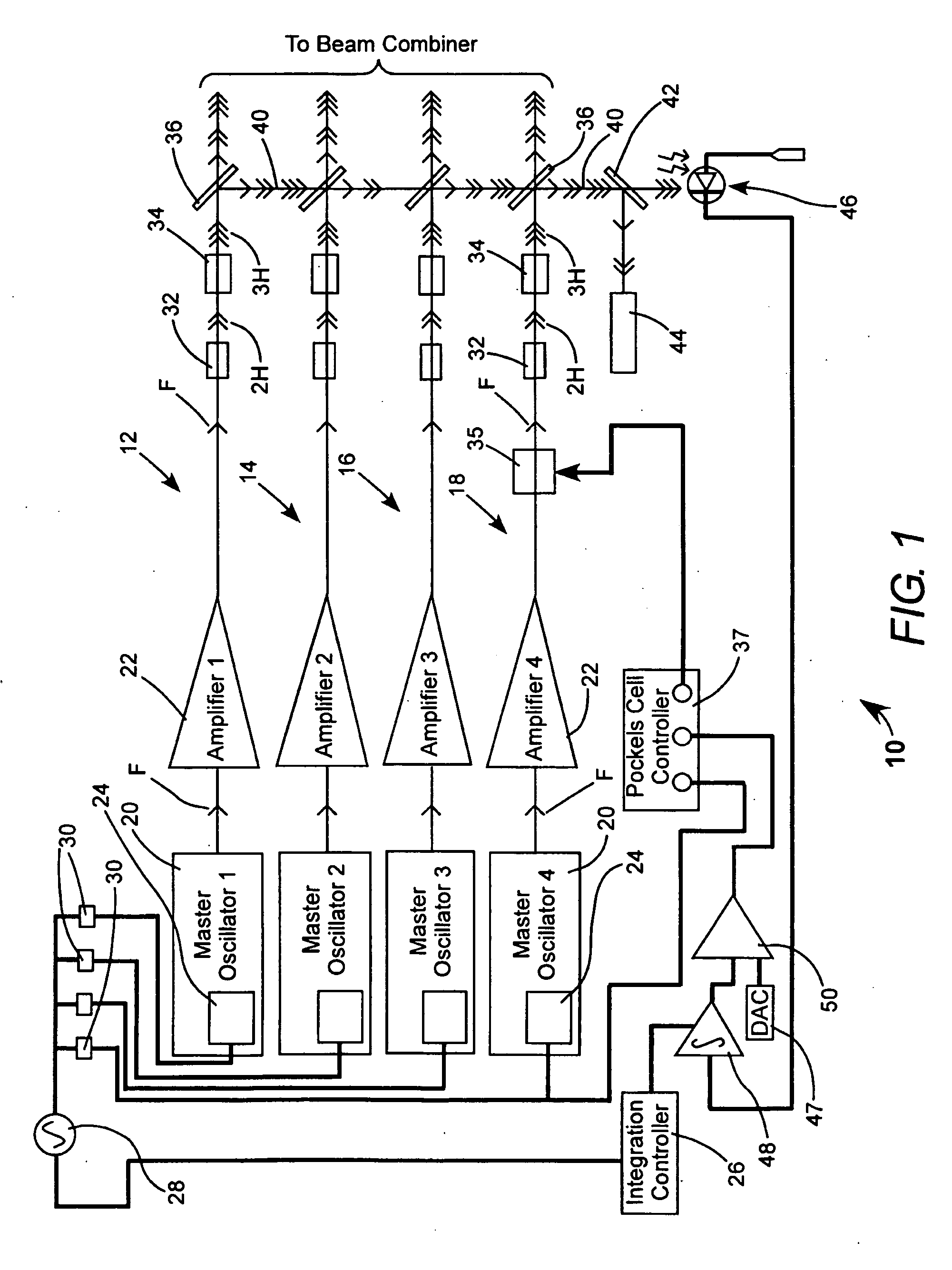
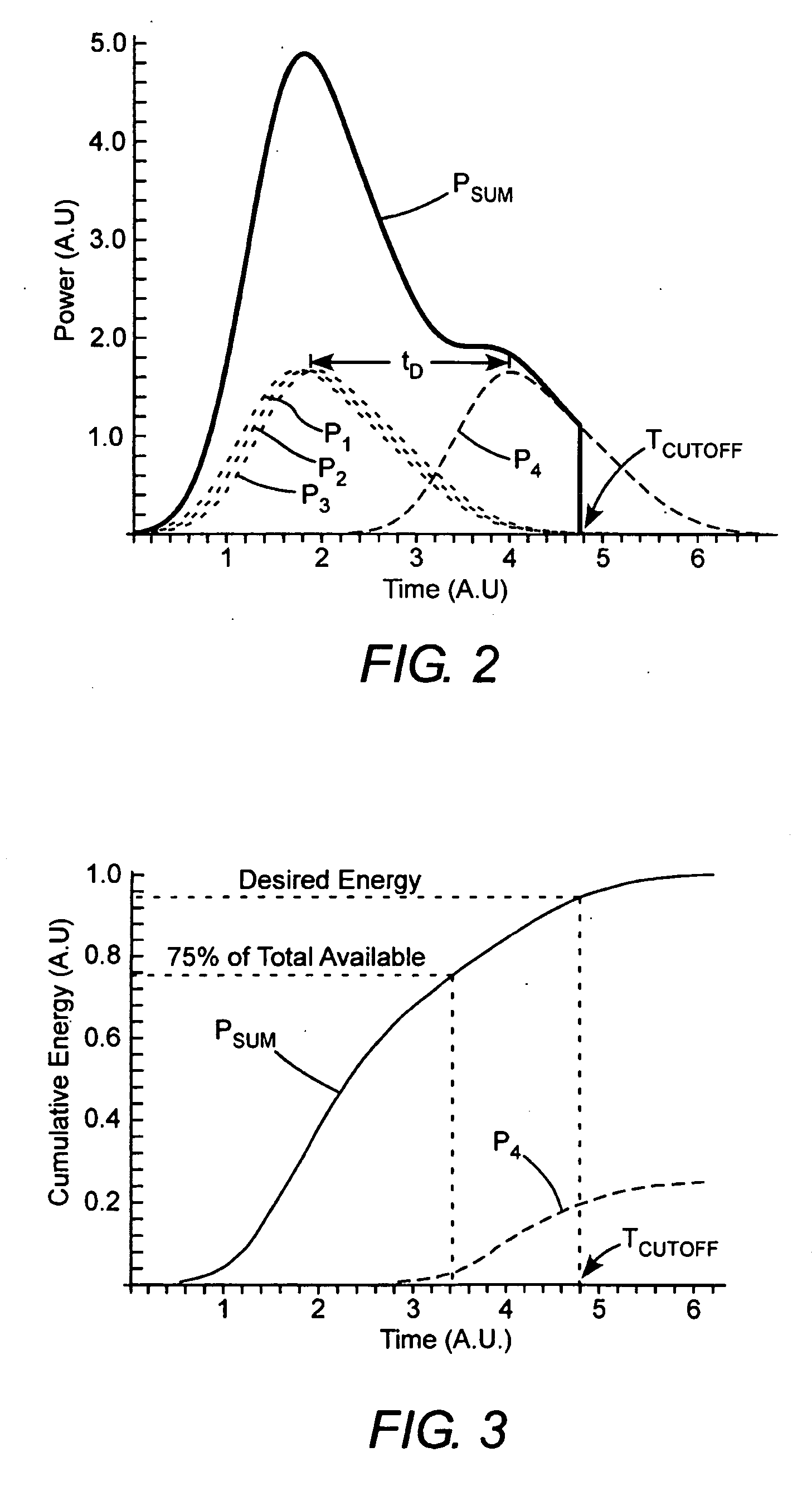
Energy stabilization of combined pulses from multiple lasers
A combined radiation pulse of a predetermined energy is provided by temporally and spatially overlapping four pulses from four extra-cavity, frequency-tripled lasers. Frequency tripling is effected in each laser by a second-harmonic generating crystal followed by a third-harmonic generating crystal. One of the lasers includes a Pockels cell preceding the second-harmonic generating crystal. The third harmonic pulse from this laser is the fourth and last delivered in the sequence. The total available energy in three of the pulses is less than the predetermined energy. The cumulative integrated energy of the pulses is determined while the pulses are being delivered. When the energy is determined to have reached the predetermined value, the Pockels cell is activated to rotate the polarization plane of fundamental radiation entering the second-harmonic generating crystal, thereby terminating generation of the fourth pulse and delivering the combined radiation pulse at the predetermined energy.
Owner:COHERENT INC
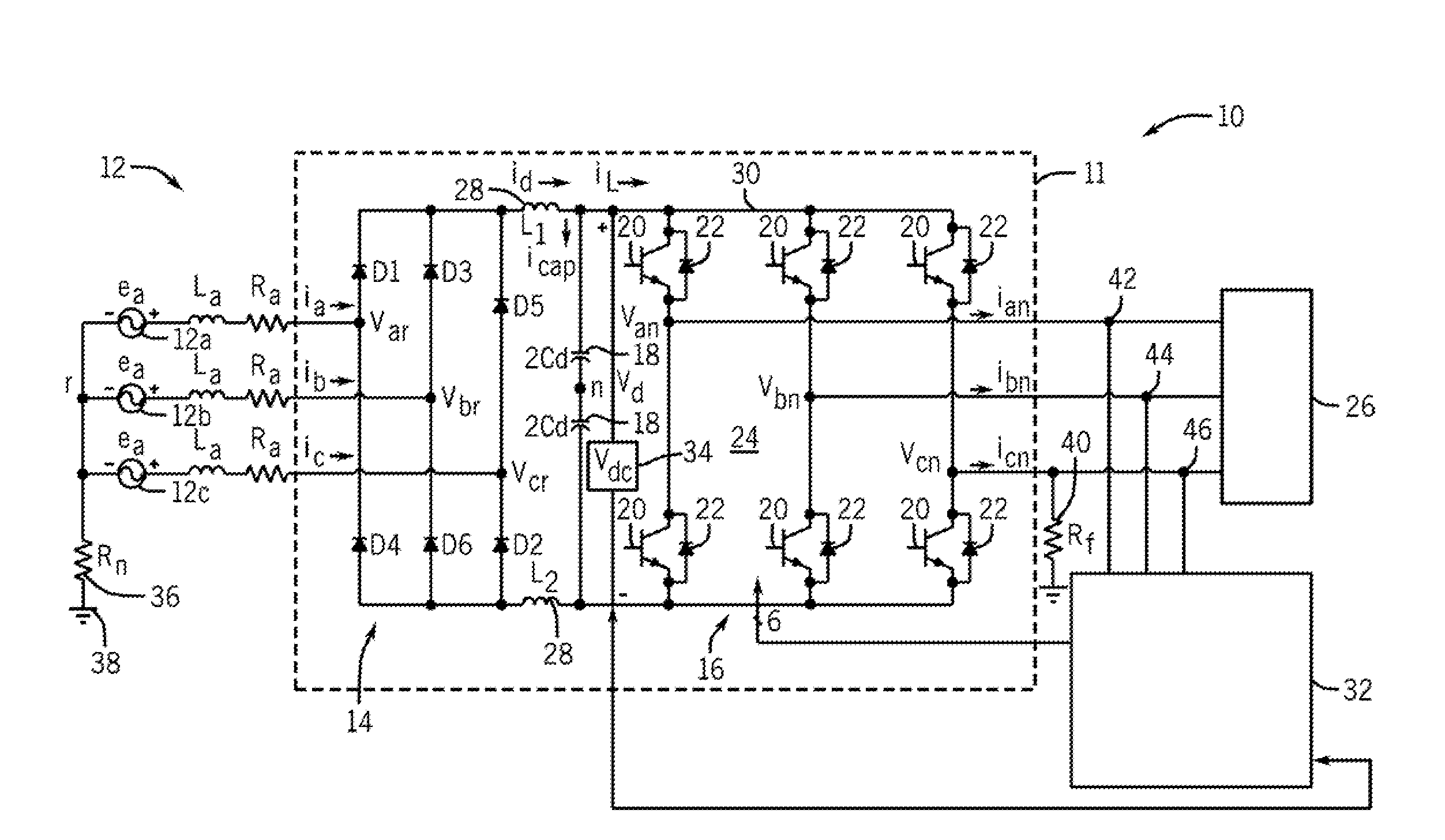
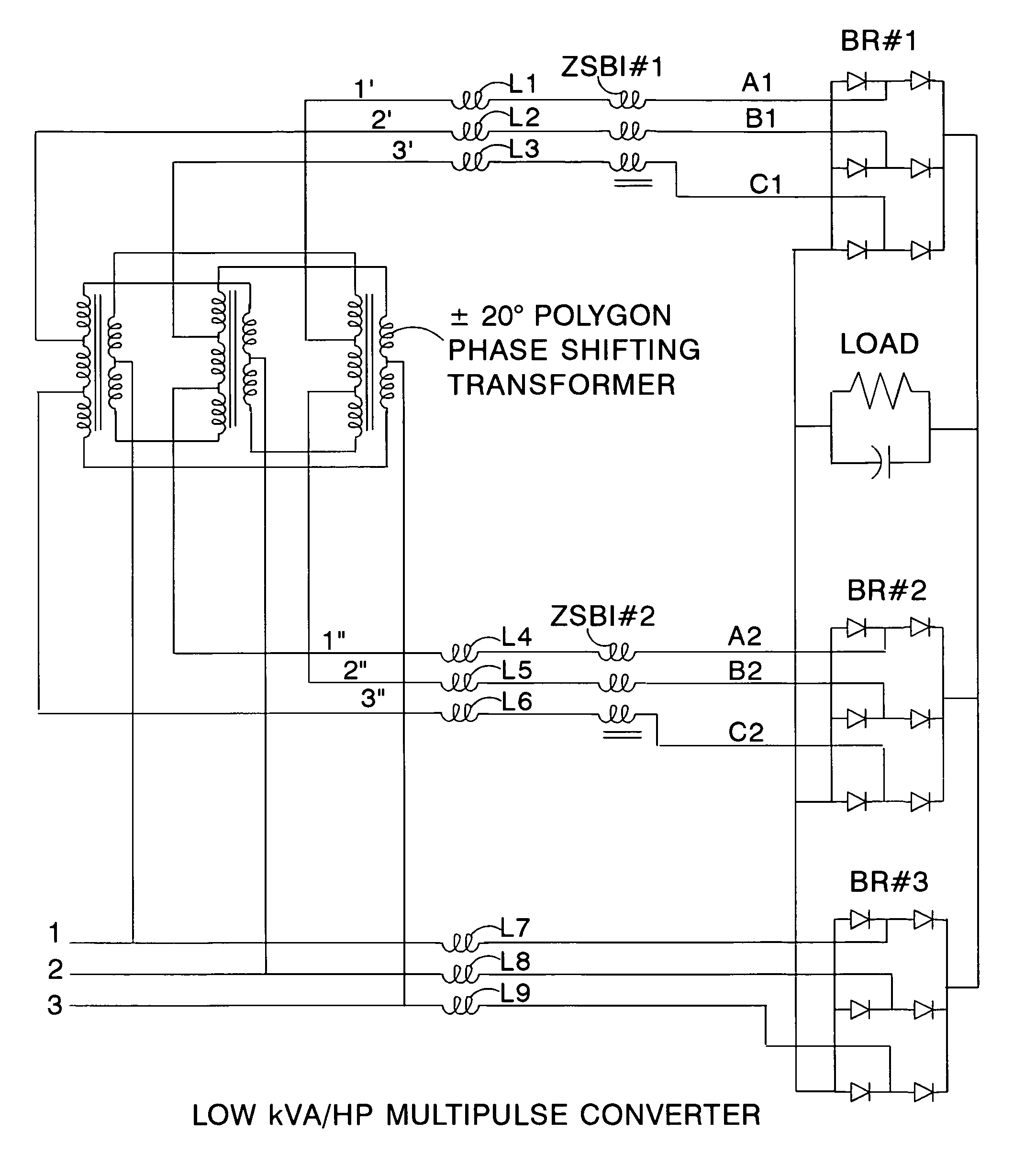
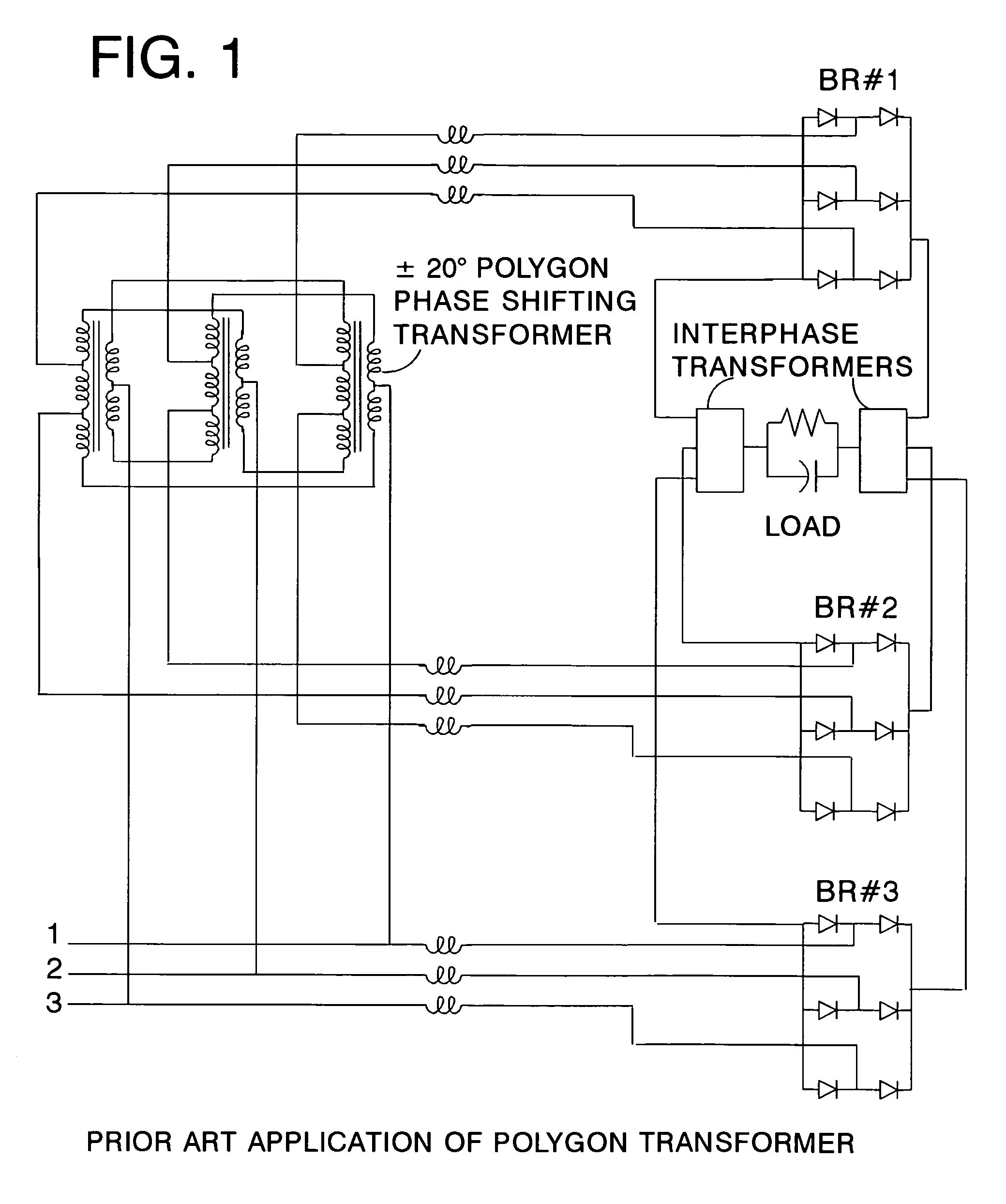
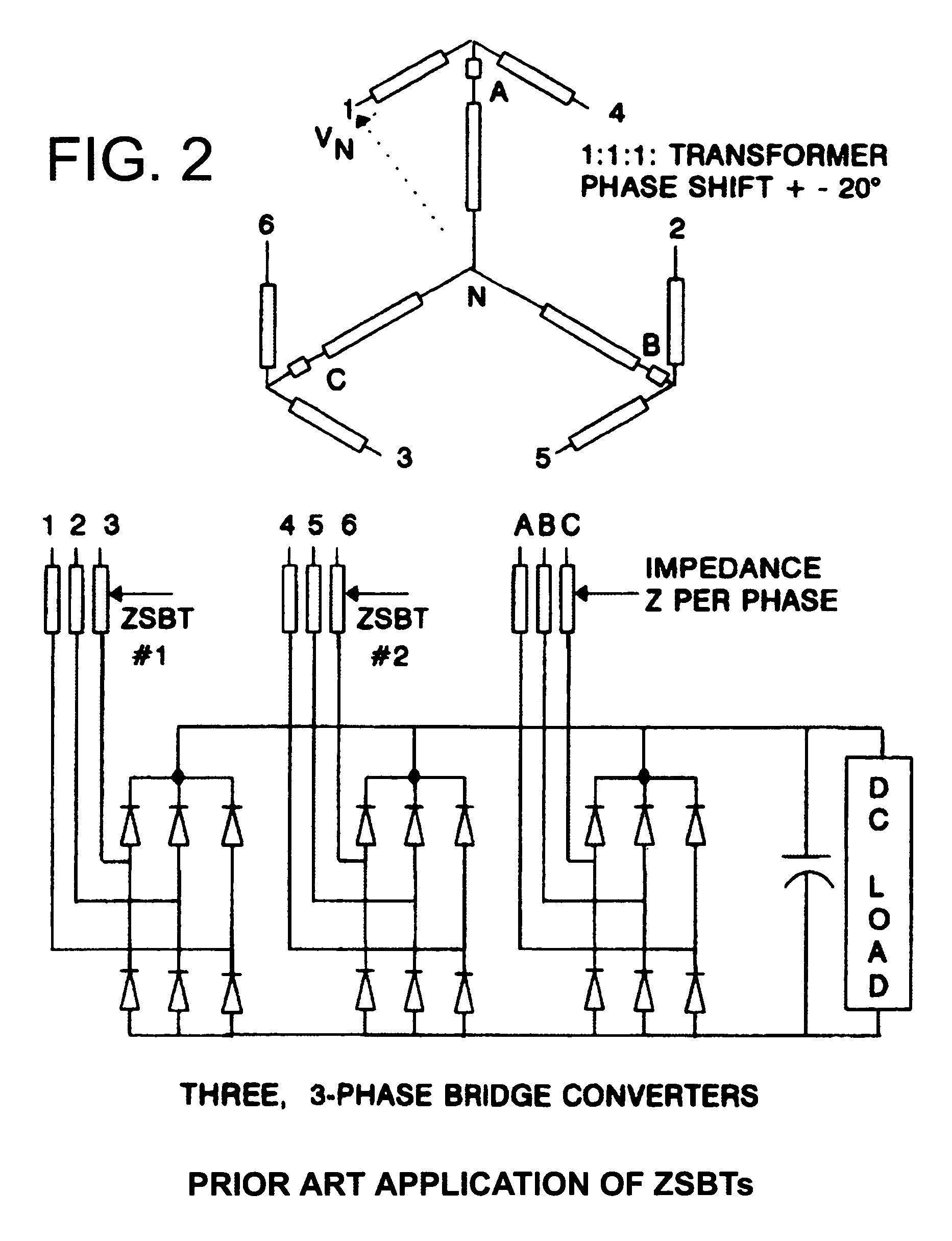
Low kVA/kW transformers for AC to DC multipulse converters
A polygon connected autotransformer in conjunction with zero sequence blocking inductor(s) enables multipulse AC to DC converters to use lower kVA parts rating by using appropriate phase-shifted voltage sets in conjunction with inductors that extend the conduction period and reduce rms current. Also, lower harmonic voltages in the transformer facilitate use of lower performance magnetic steel. Designs for 12, 18, and 24-pulse use the same conceptual approach. Very efficient high power ratings are feasible. Means are given to limit the maximum no-load DC output voltage. A technique is disclosed that reduces the size of polygon transformers supplying loads with substantial third harmonic.
Owner:SCHAFFNER MTC LLC
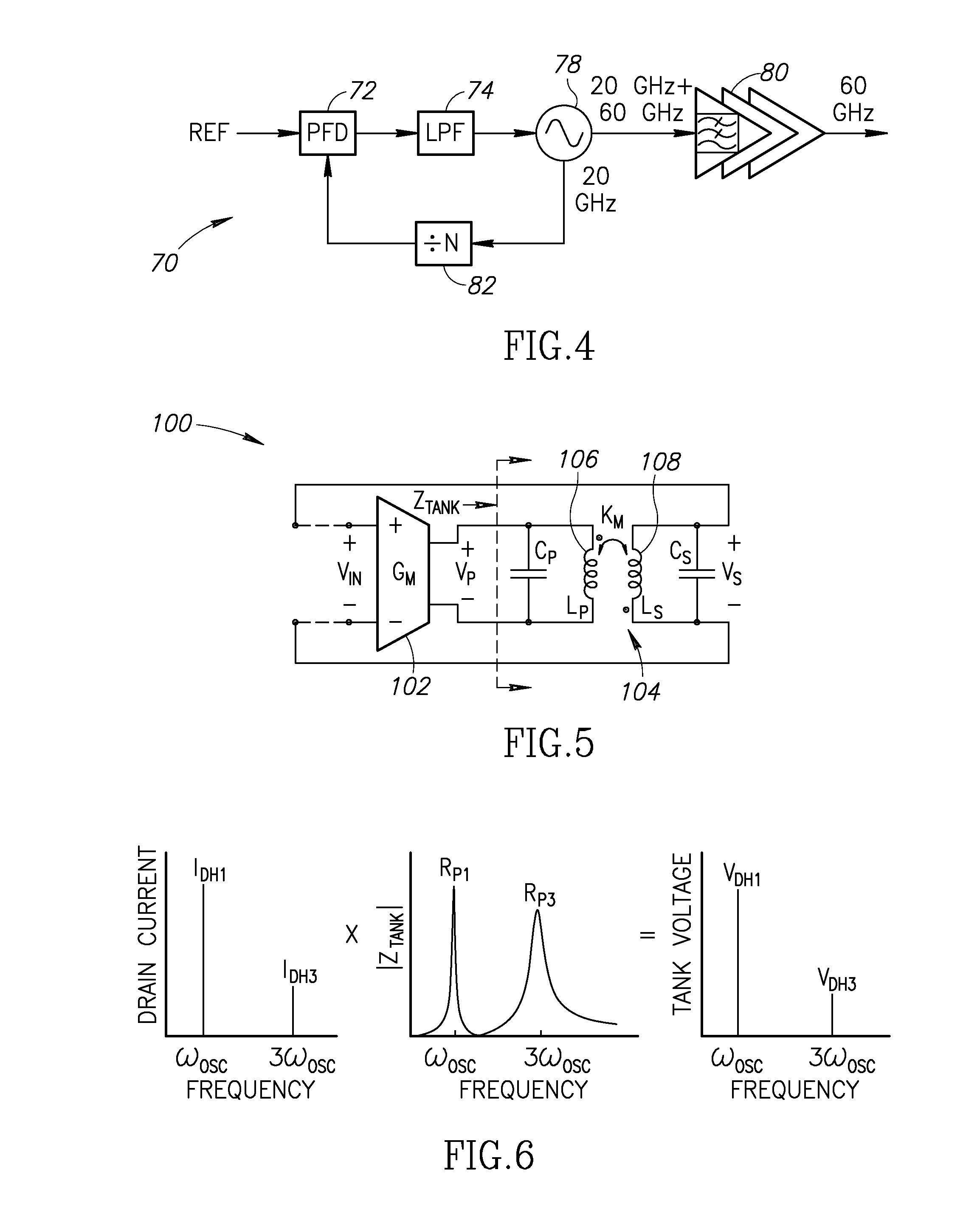
Class-f CMOS oscillator
InactiveUS20140077890A1Improve Phase Noise PerformanceReducing oscillator 's effective noise factorPulse automatic controlN-path filtersTransformerThird harmonic
A novel and useful oscillator topology demonstrating an improved phase noise performance that exploits the time-variant phase noise model with insights into the phase noise conversion mechanisms. The oscillator is based on enforcing a pseudo-square voltage waveform around an LC tank by increasing the third-harmonic of the fundamental oscillation voltage through an additional impedance peak. Alternatively, the oscillator is based on enforcing clipped oscillation waveform by increasing the second harmonic of the fundamental oscillation voltage through an additional impedance peak. This auxiliary impedance peak is realized by a transformer with moderately coupled resonating windings. As a result, the effective impulse sensitivity function (ISF) decreases thus reducing the oscillator's effective noise factor such that a significant improvement in the oscillator phase noise and power efficiency are achieved.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
Encoder output signal correction apparatus and method
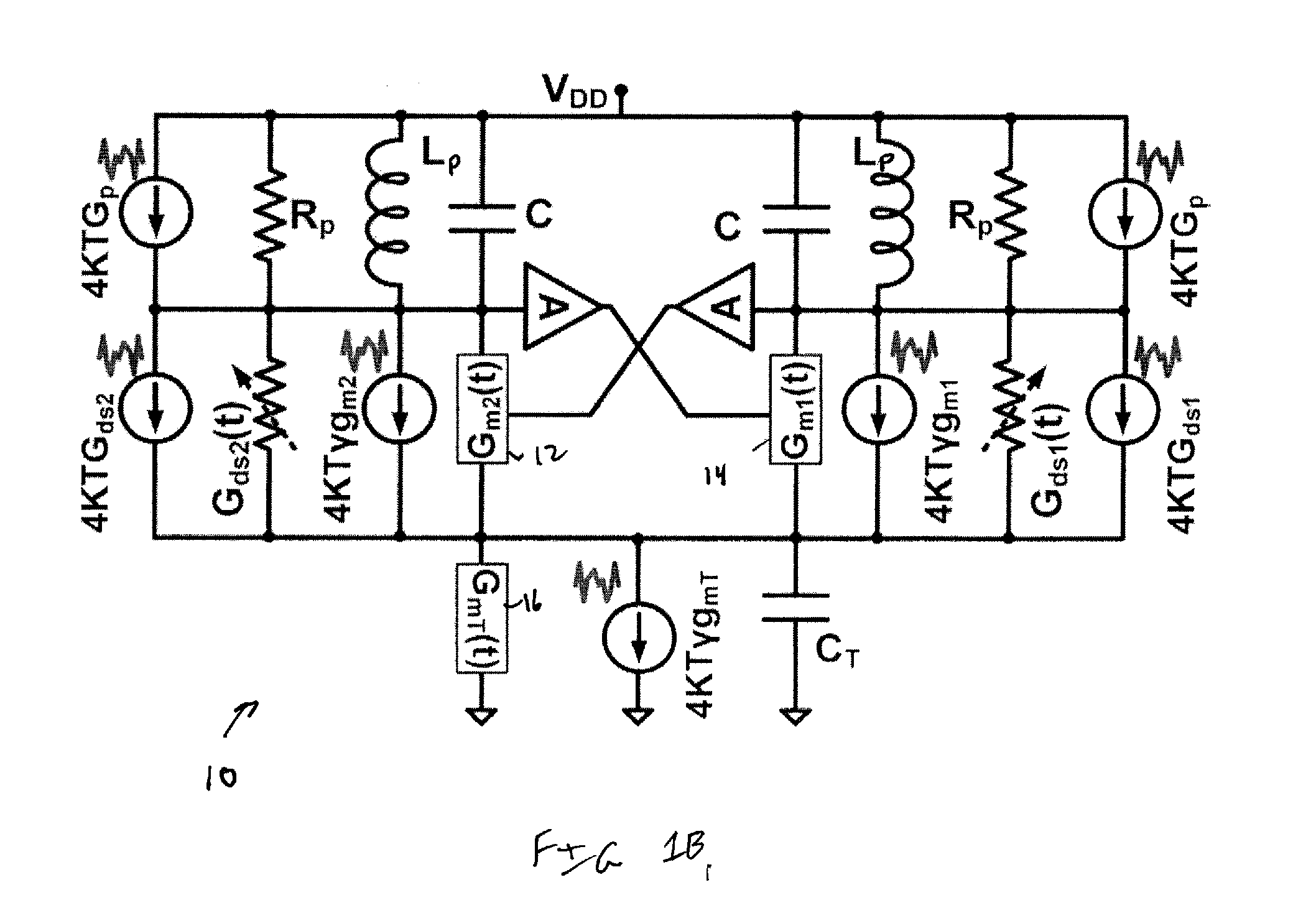
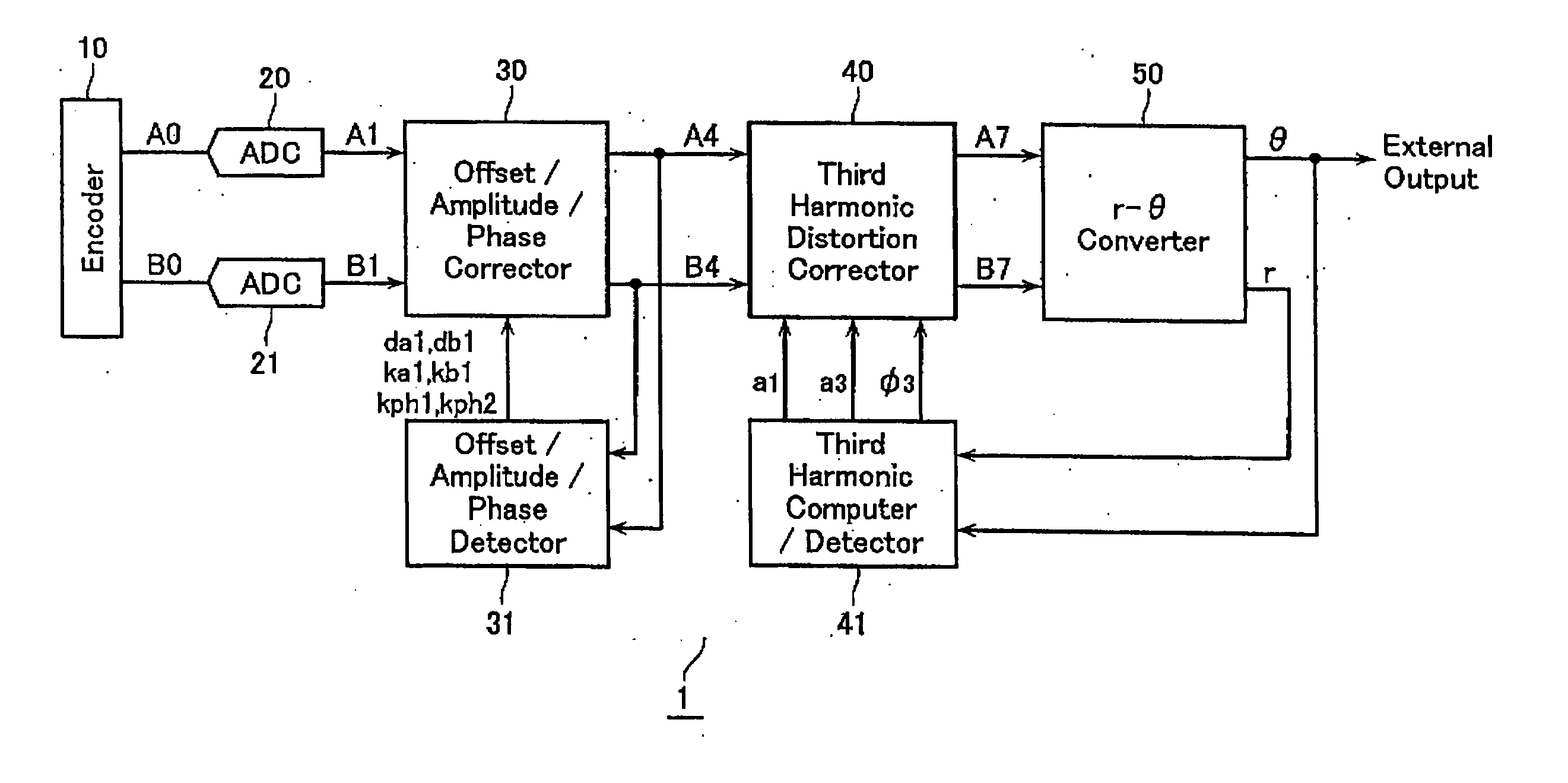
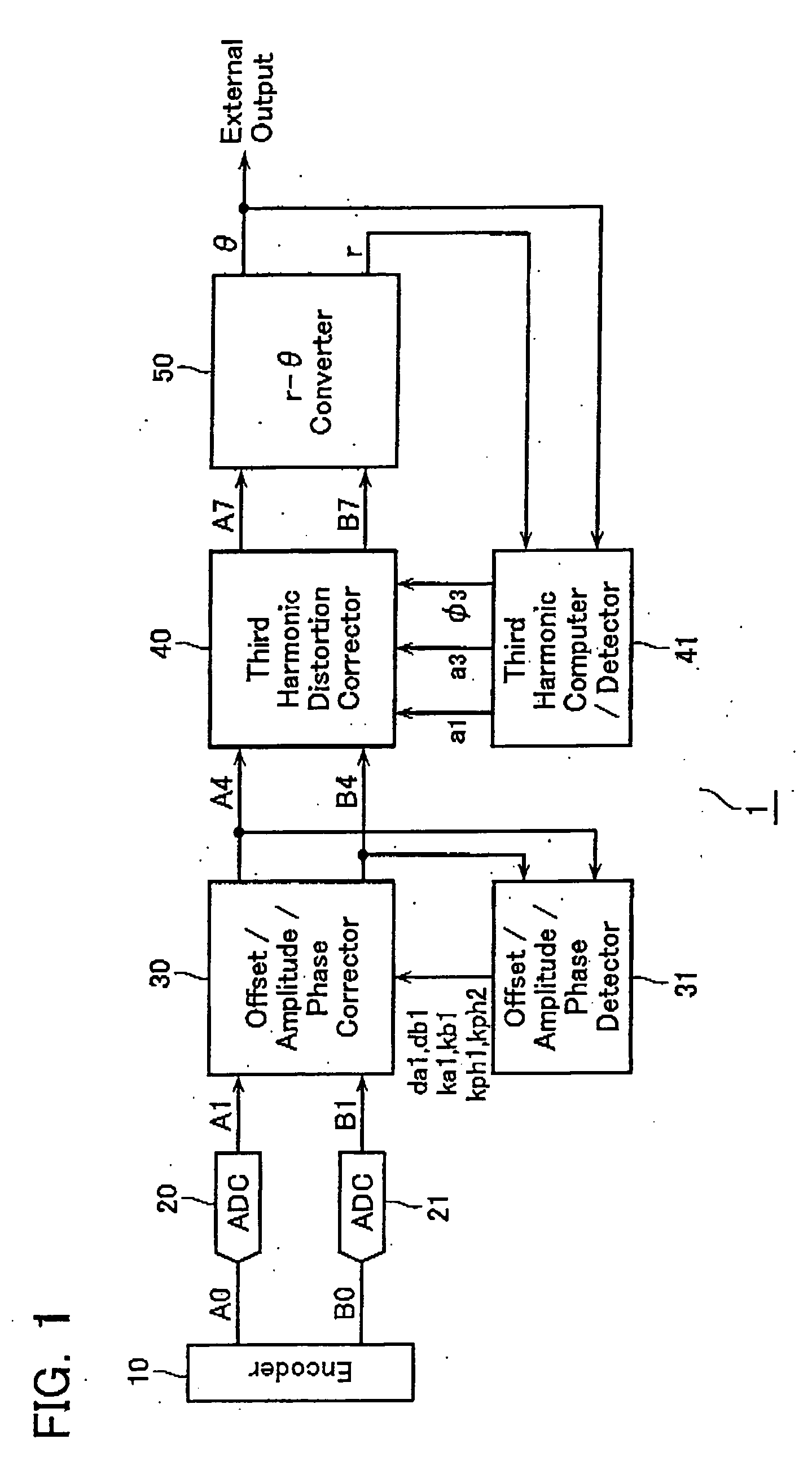
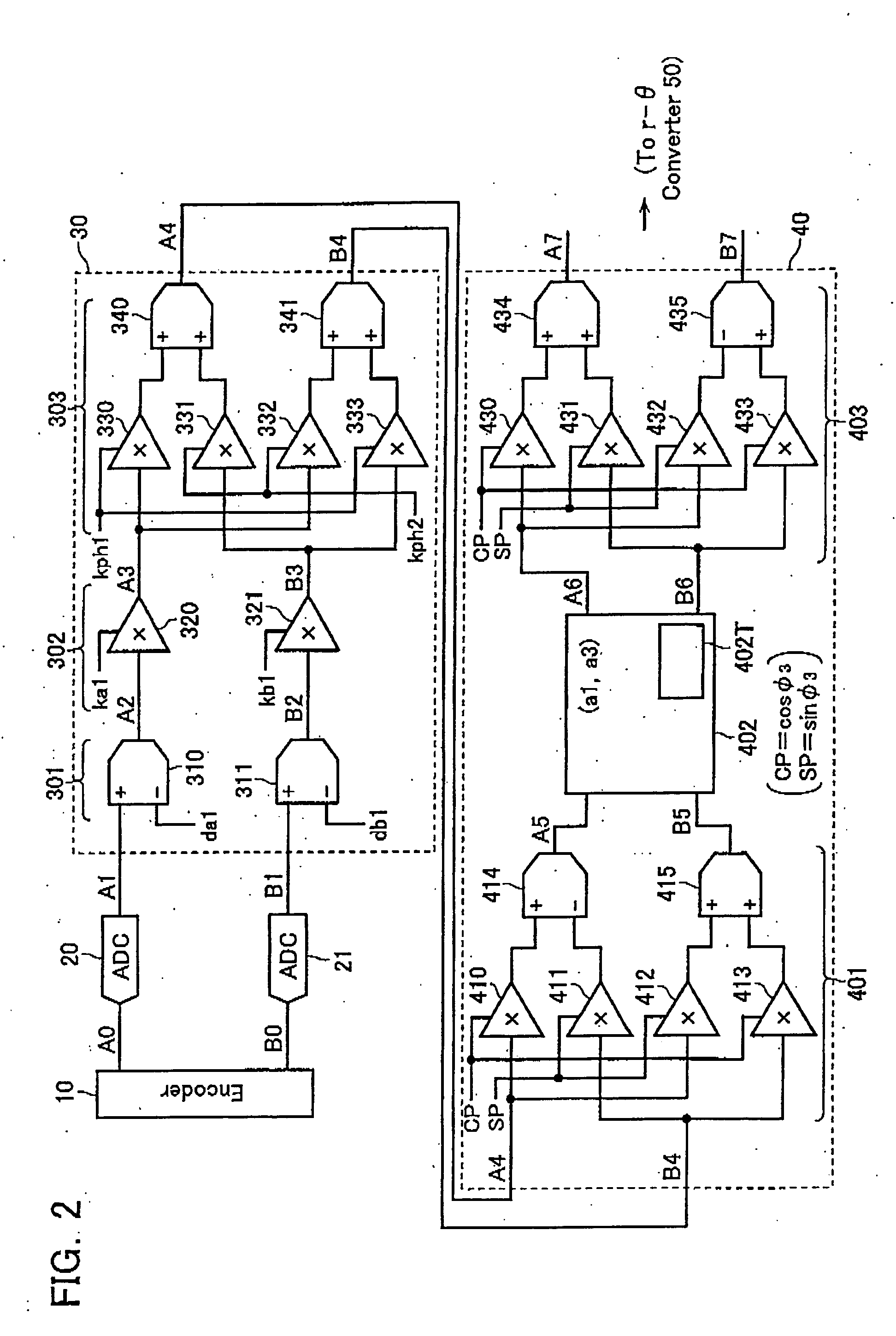
ActiveUS20060077083A1Improve interpolation accuracyComponent with highElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersSignal correctionThird harmonic
A third harmonic distortion corrector is equipped for correcting a third harmonic distortion contained in a two-phase sinusoidal signals with different phases output from an encoder. A third harmonic calculator / detector calculates the amplitude a3 and the phase φ3 of the third harmonic using Fourier analysis, based on change in radius r of the Lissajous waveform output from a r-θ converter. The third harmonic distortion corrector corrects the third harmonic distortion of the two-phase sinusoidal signal A4, B4 based on the amplitude a3 and the phase φ3 of the third harmonic calculated.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Harmonic cancellation circuit for an RF switch branch
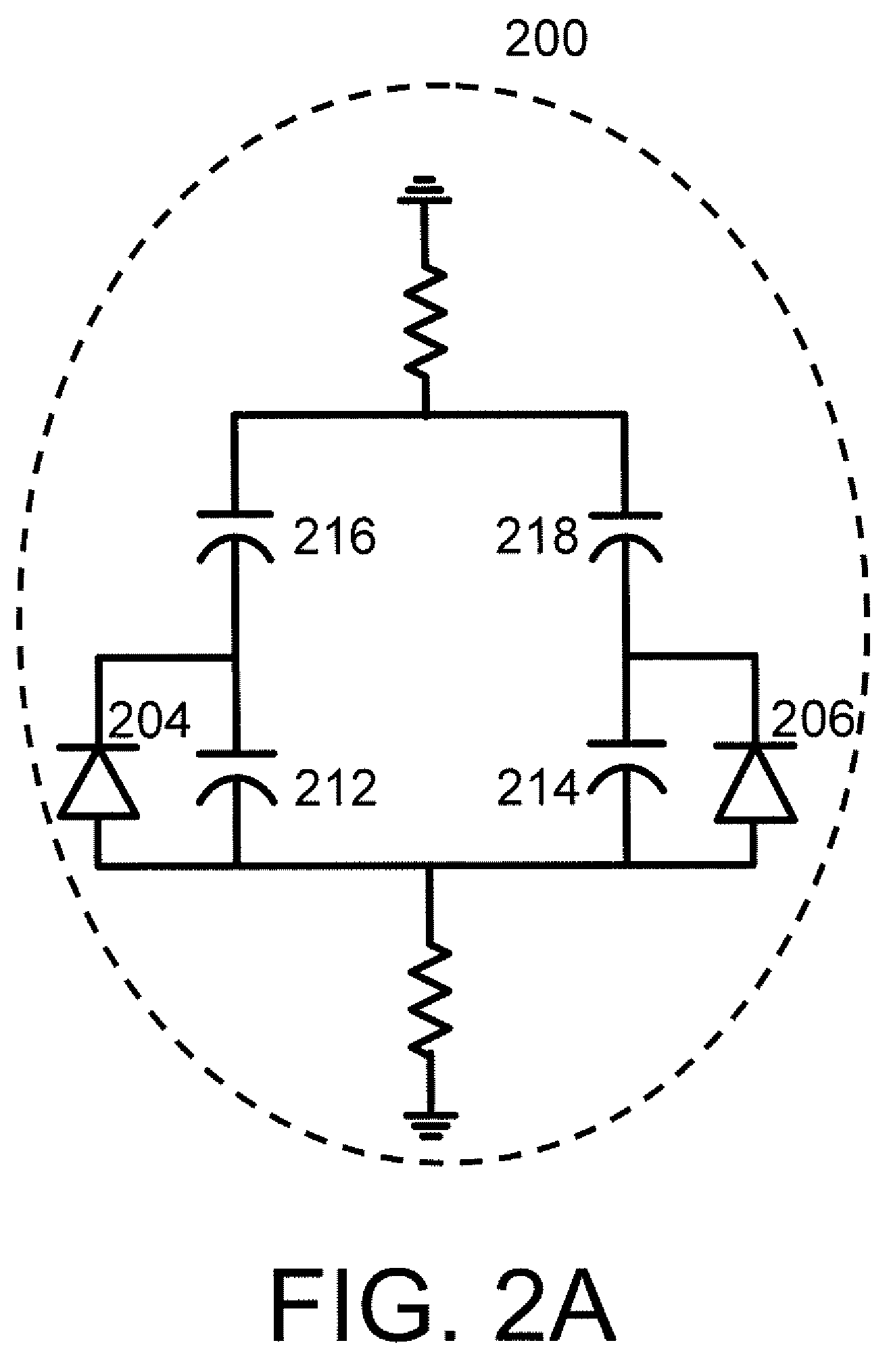
ActiveUS20140266415A1Reduce third harmonic signalReduce signalingElectronic switchingOscillations generatorsCouplingThird harmonic
Disclosed is a harmonic cancellation circuit for an RF switch branch having a first transistor with a first gate terminal and a first body terminal, a second transistor having a second gate terminal coupled to the first body terminal, and having a second body terminal coupled to the first gate terminal. Also included is a first resistor coupled between a first coupling node and the second body terminal, and a second resistor coupled between a second coupling node and the first body terminal, wherein the first transistor and second transistor are adapted to generate an inverse phase third harmonic signal relative to a third harmonic signal generated by the RF switch branch, such that the inverse phase third harmonic signal is output through the first resistor and the second resistor to the RF switch branch to reduce the third harmonic signal.
Owner:QORVO US INC
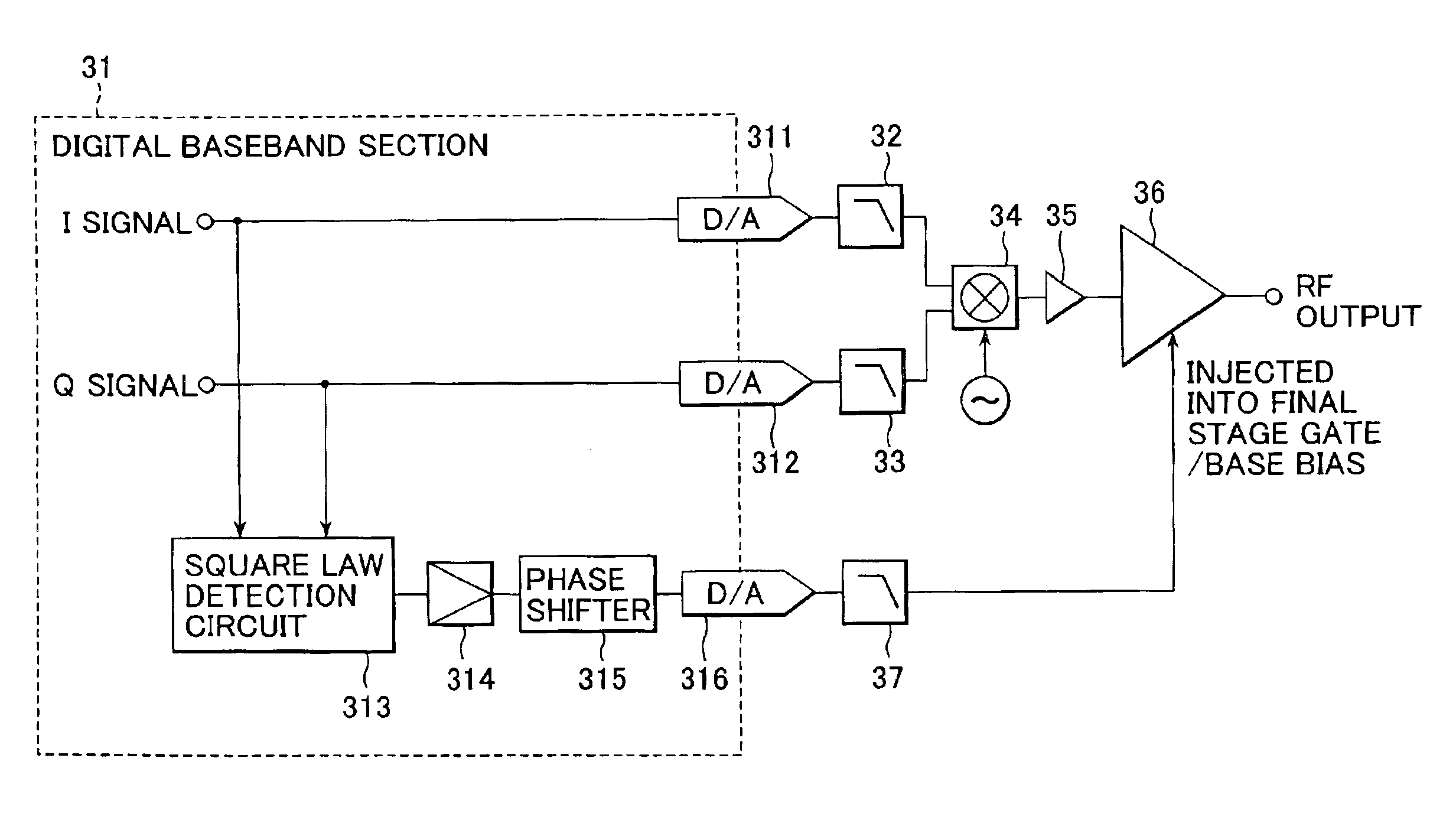
Power amplifying apparatus and radio communications apparatus using same
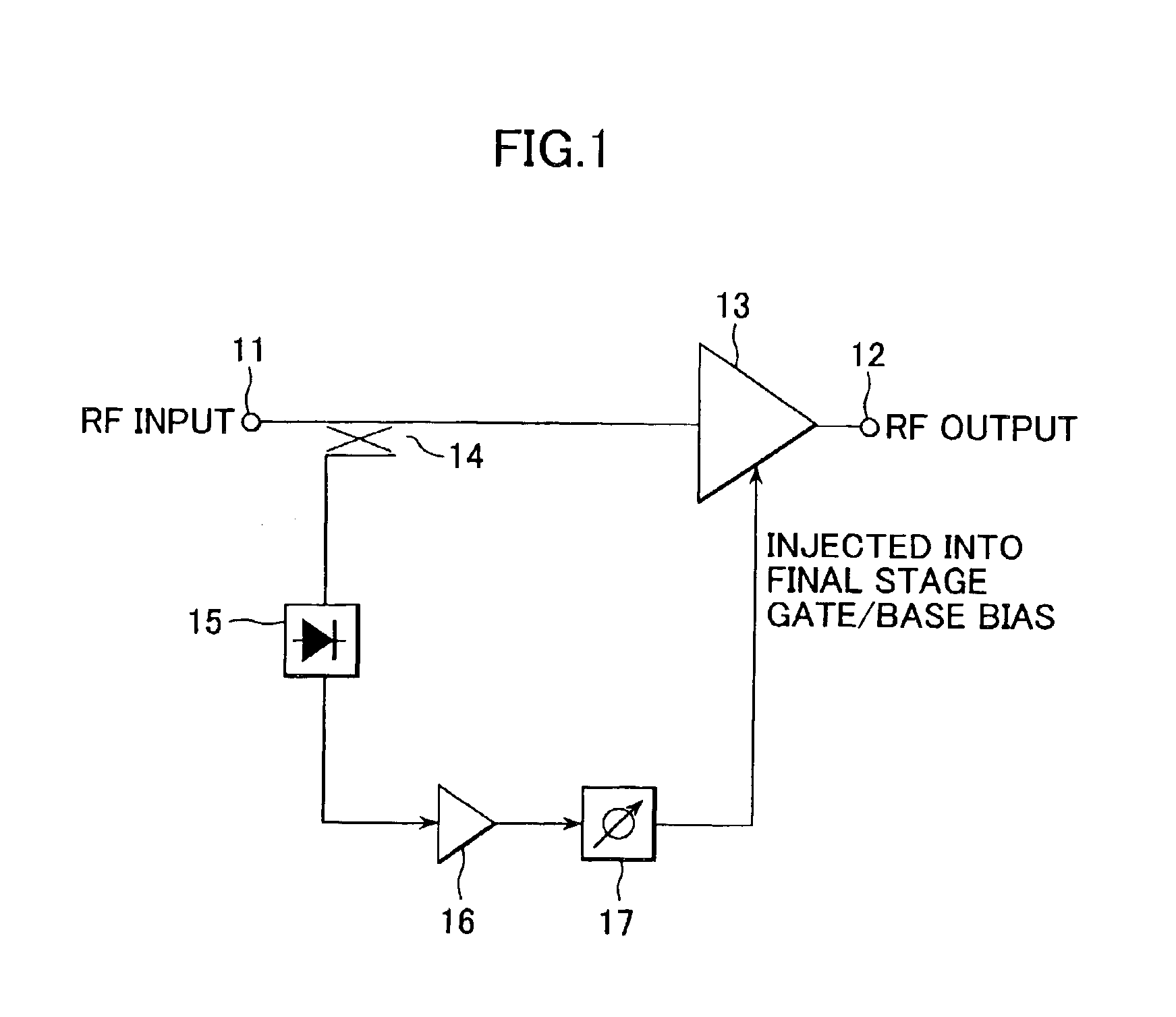
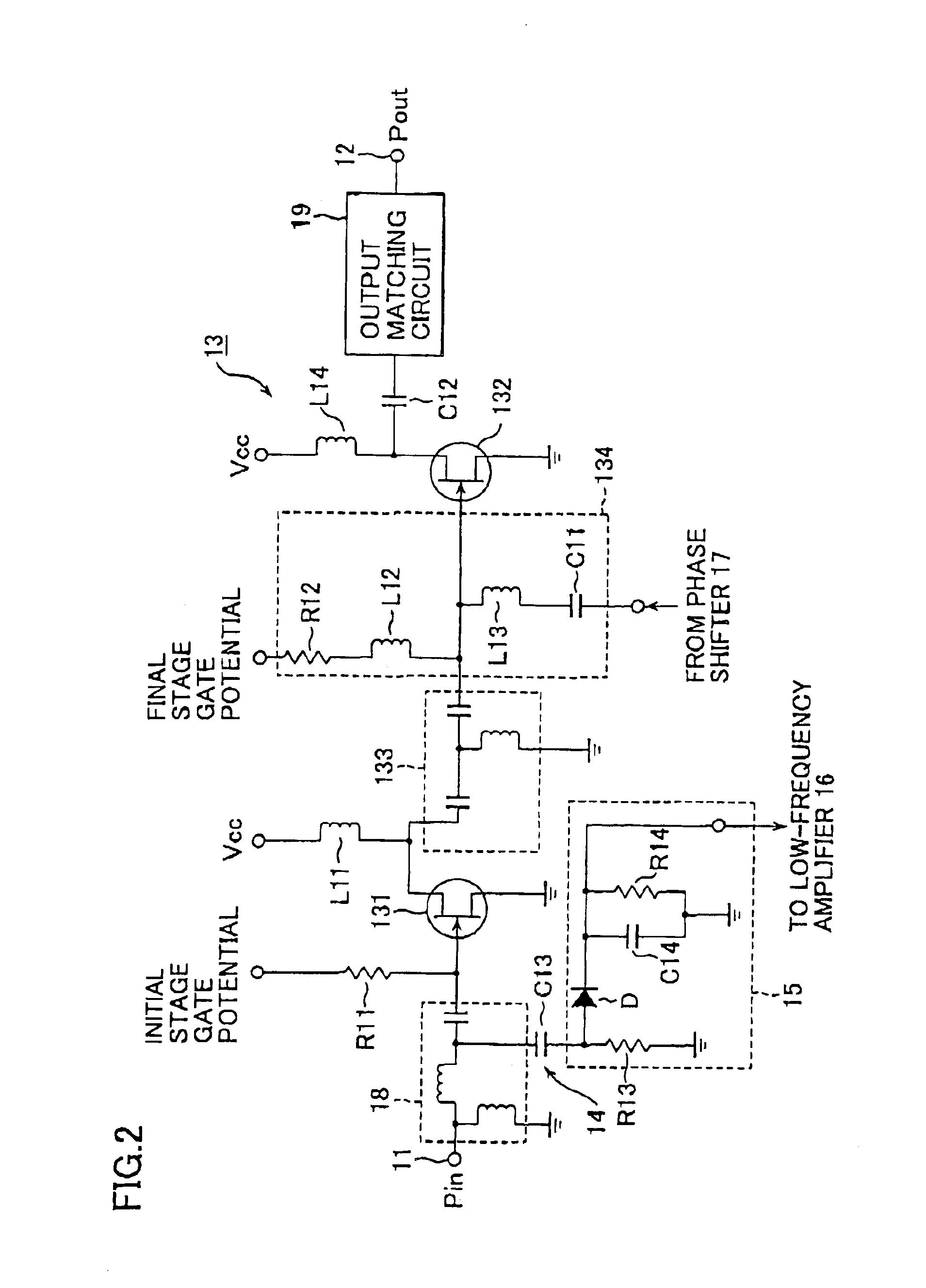
InactiveUS6900693B2Sufficient powerLow costAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlAudio power amplifierThird harmonic
By extracting a portion of RF signals from an input side of a multistage RF amplifier with a detector, and converting extracted signals into envelope signals, low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are efficiently extracted. Then, the extracted low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are amplified with a low-frequency amplifier, and phase adjusted with a phase shifter, after which they are injected into a gate or base bias of the final stage of the multistage RF amplifier. As a result, the low-frequency second-harmonic distortion components are converted into third-harmonic distortion due to the non-linearity of transistors, and the third-harmonic distortion thus obtained cancels out the third-harmonic distortion originally present in the multistage RF amplifier.
Owner:SONY CORP
Method and system of thermographic non-destructive inspection for detecting and measuring volumetric defects in composite material structures
A thermographic non-destructive inspection method of a structure, comprising the steps of: generating a modulated thermal wave in the direction of the structure; generating a temperature signal identifying a phase shift between the modulated thermal wave and a return thermal wave emitted from the structure; processing the temperature signal to obtain a first sub-signal related to the phase of the first harmonic of the temperature signal; identifying a first dimension of said defect as a function of the phase of the first harmonic of the temperature signal; calculating a first and a second intermediate parameter, ΔΦ1 for the first harmonic and ΔΦ2 for the third harmonic of the temperature signal, by calculating the difference, in degrees, between the phase value inside the zone with a defect and the phase value, absolute or mean of a plurality of points, of the undamaged zone close to the defect; and identifying a second dimension of the defect as a function of the first dimension and of the intermediate parameters ΔΦ1 and ΔΦ2.
Owner:LEONARDO SPA
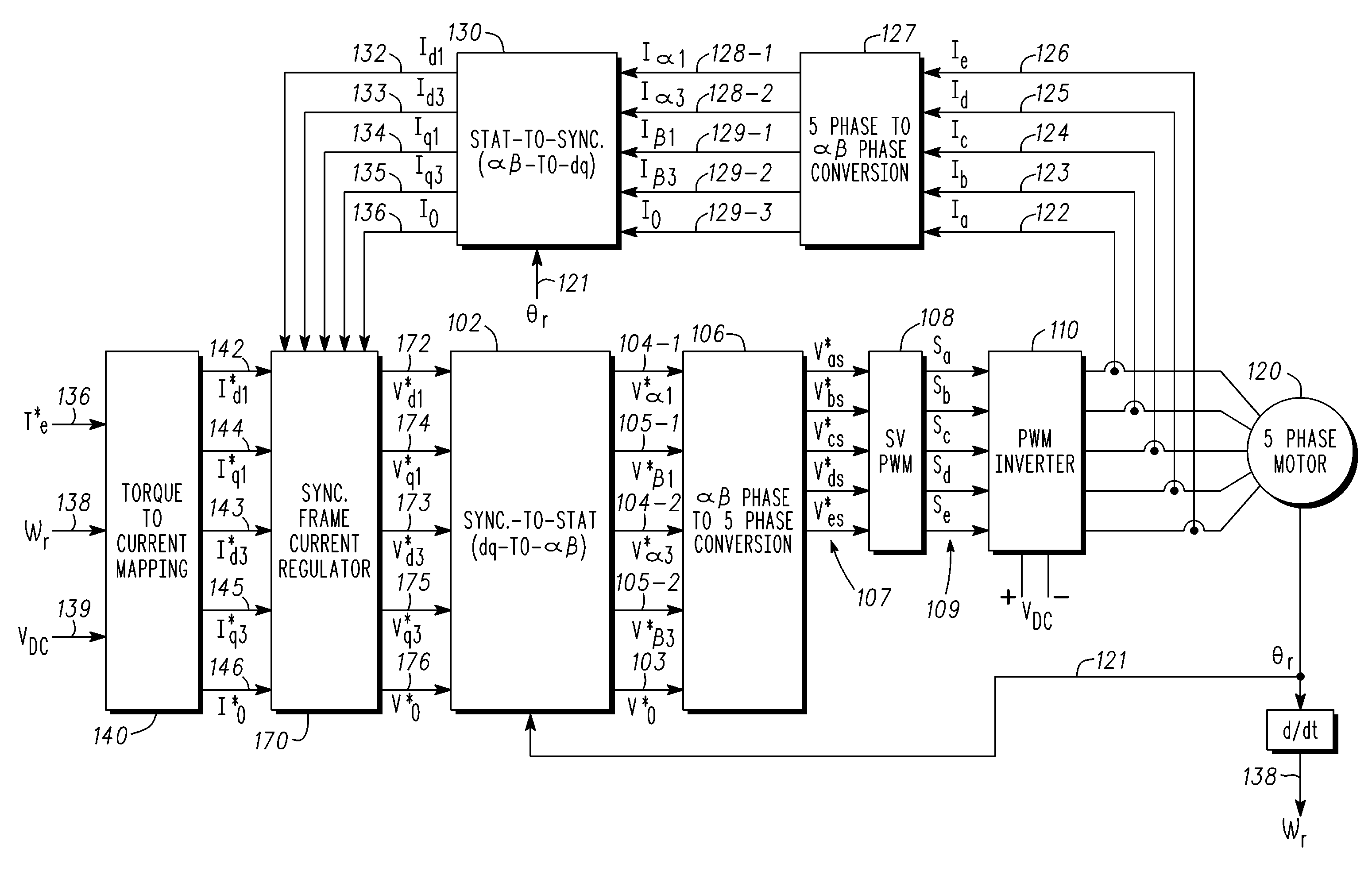
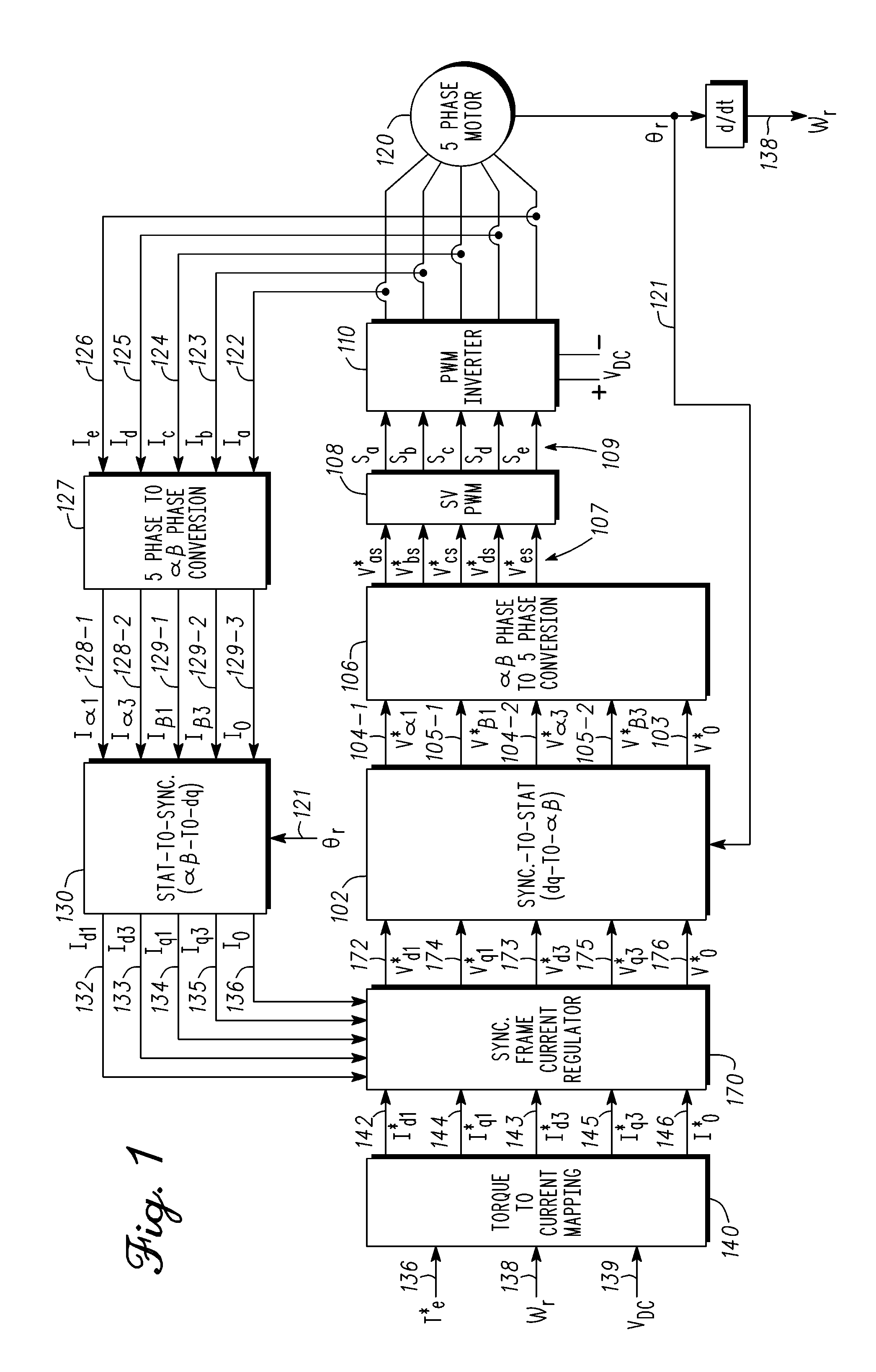
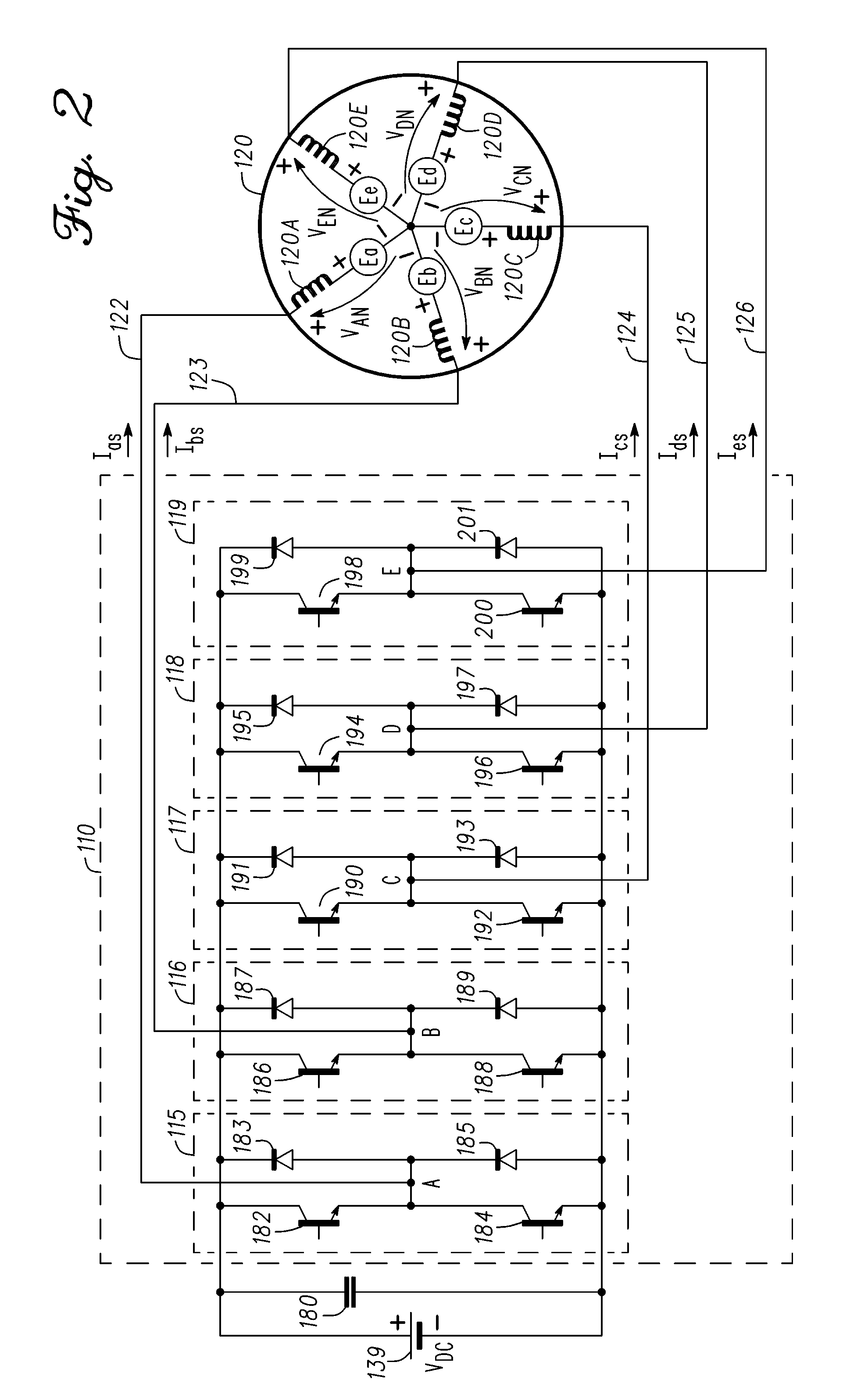
Methods, systems and apparatus for optimization of third harmonic current injection in a multi-phase machine
InactiveUS20110221365A1Improves phase voltage utilizationSynchronous motors startersAC motor controlControl vectorOperating point
Methods, system and apparatus are provided for increasing voltage utilization in a five-phase vector controlled machine drive system that employs third harmonic current injection to increase torque and power output by a five-phase machine. To do so, a fundamental current angle of a fundamental current vector is optimized for each particular torque-speed of operating point of the five-phase machine.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
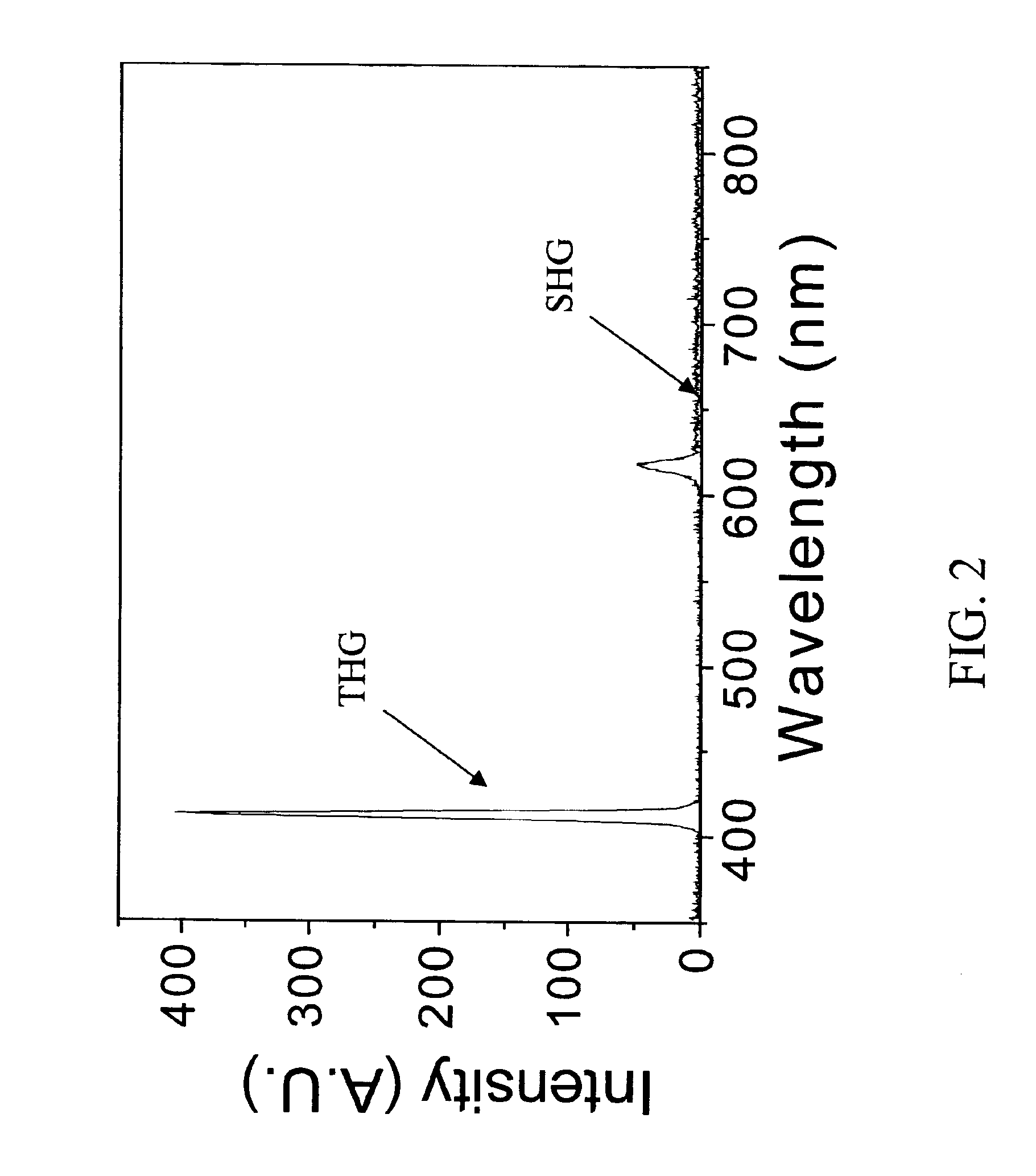
Harmonic generation microscopy
A harmonic generation microscopy employs a laser device that emits a laser beam having a predetermined wavelength that causes no autofluorescence in a biological sample and that, after excited, induces both the second and third harmonic waves. The laser beam is projected onto a sample and an observation beam from the sample is received. The observation beam is directed through a splitter to separate the second harmonic wave and the third harmonic wave both of which are then converted into corresponding electrical signals. The electrical signals are fed to a computer-based image processing equipment to form an image of the sample on the basis of the second and third harmonic waves.
Owner:NARIONAL TAIWAN UNIV
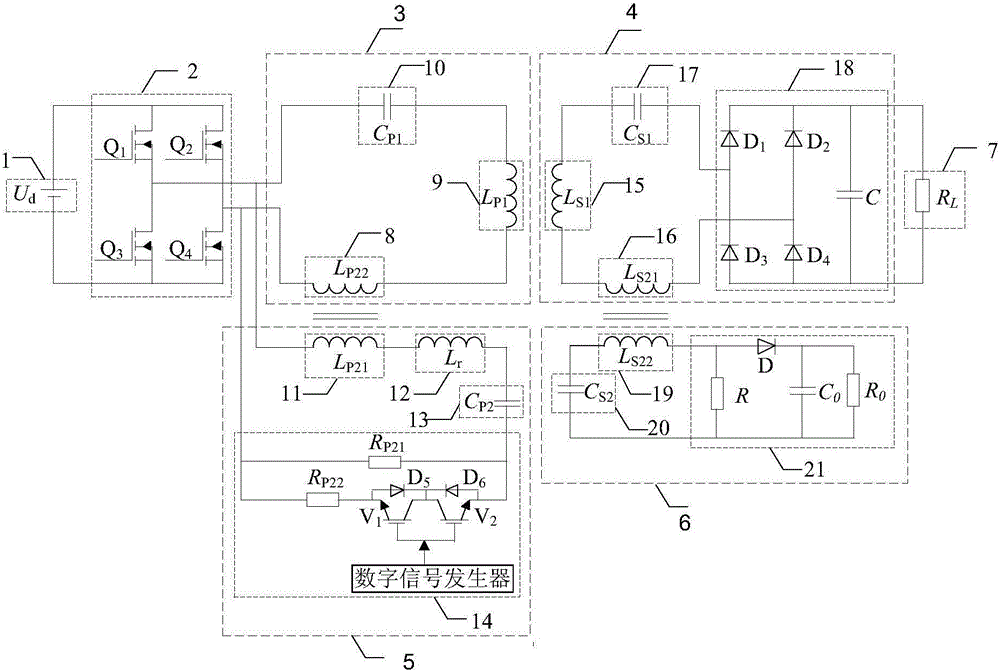
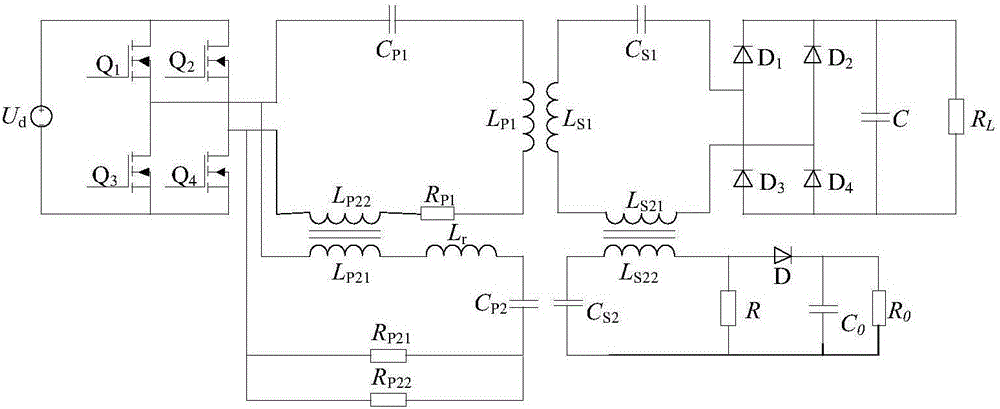
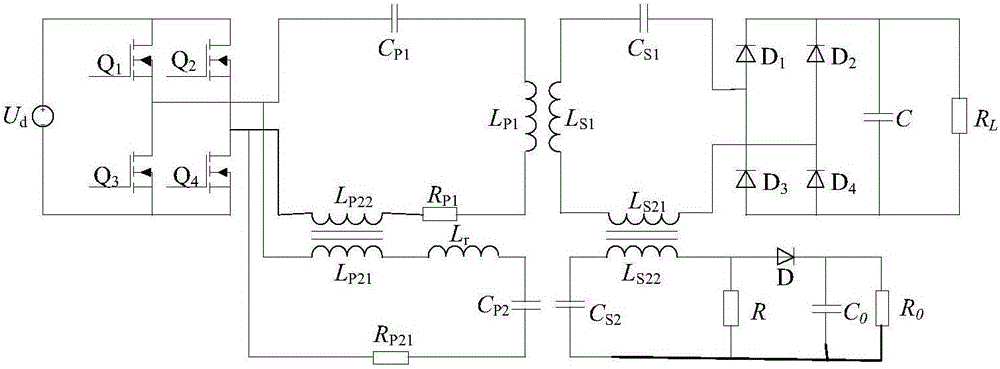
Noncontact electric energy and signal synchronous transmission system and control method thereof
InactiveCN105846684AReduce volumeImprove efficiencyDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationLoose couplingEnergy conversion efficiency
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
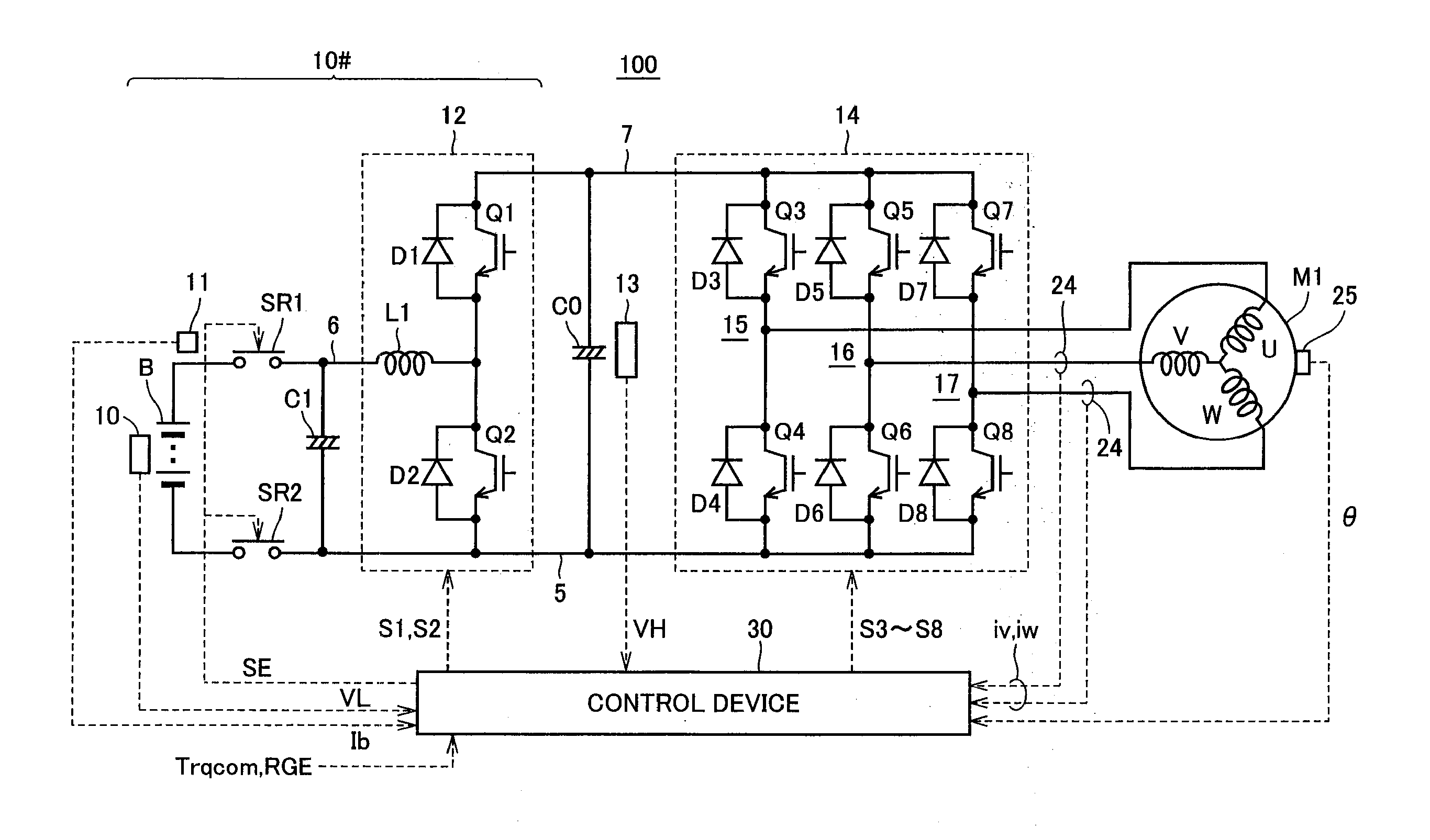
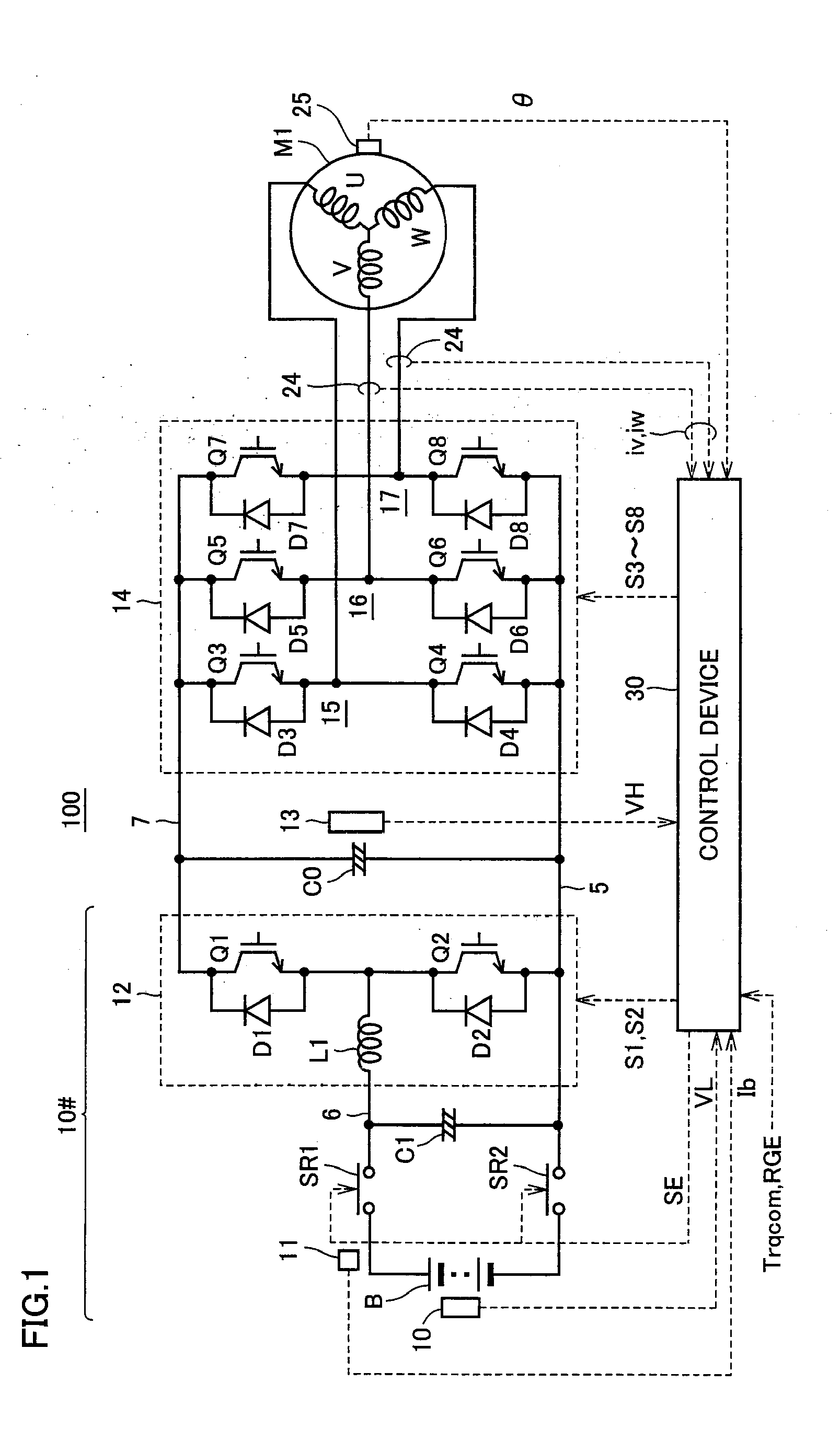
Control device for ac motor
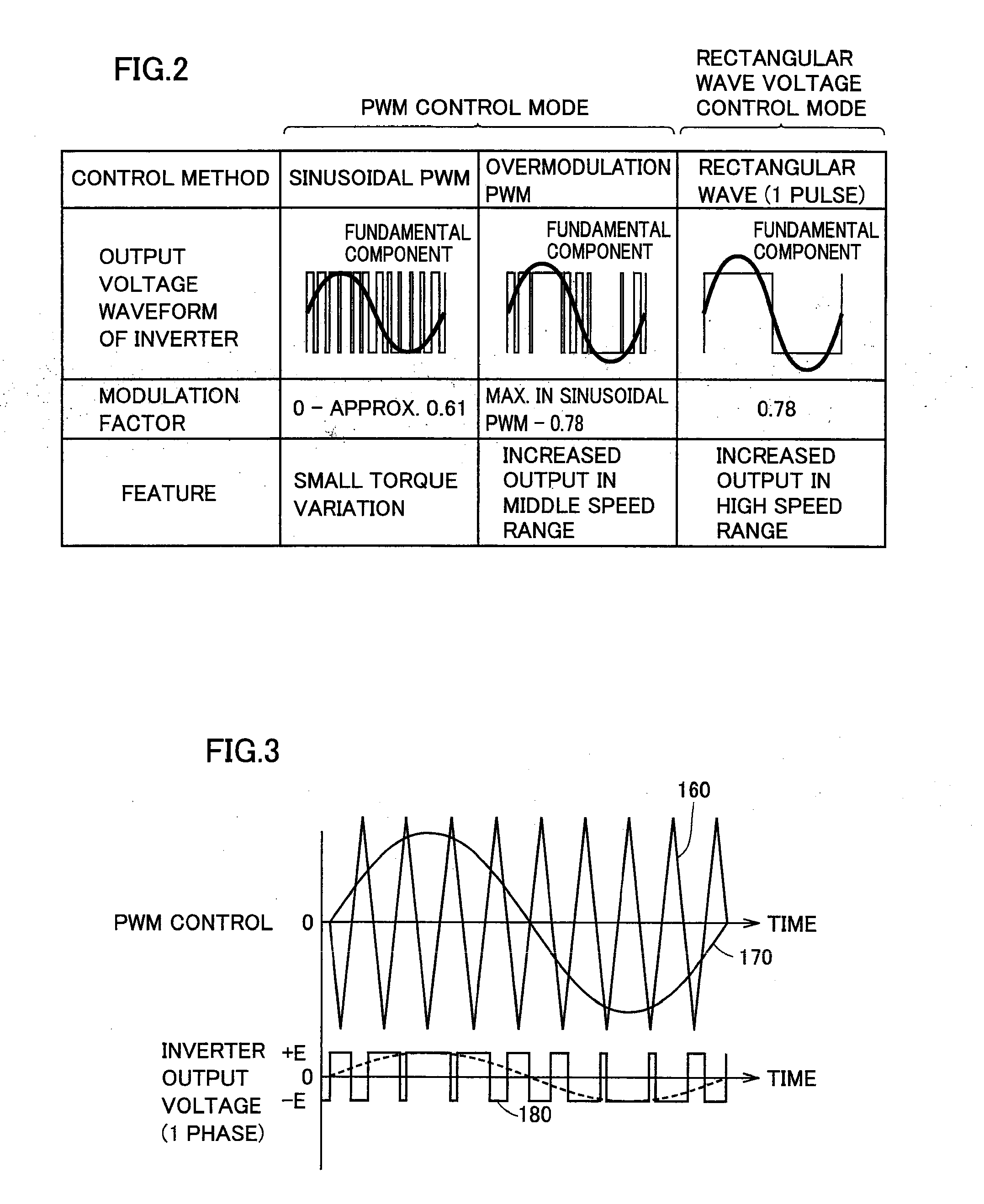
ActiveUS20110279071A1Process stabilityMotor/generator/converter stoppersAC motor controlVoltage amplitudeSuperimposition
An overmodulation PWM control unit includes a voltage amplitude calculating unit for calculating a voltage command amplitude of an original voltage command based on current feedback control, a voltage amplitude correcting unit performing linear compensation on the voltage command amplitude so that a fundamental amplitude of a pulse width modulation voltage provided from an inverter may match the original voltage command amplitude, and a harmonic determining unit for determining presence or absence of superimposition of a three-order harmonic component on a phase voltage command. The harmonic determining unit performs switching between presence and absence of the three-order harmonic component based on transition of the original voltage command amplitude to avoid passing through a change point where discontinuity occurs in the voltage amplitude characteristics representing a relationship between a fundamental amplitude obtained in advance for each of the cases of presence and absence of the superimposition of the three-order harmonic component and the voltage command amplitude required for achieving the fundamental amplitude.
Owner:DENSO CORP
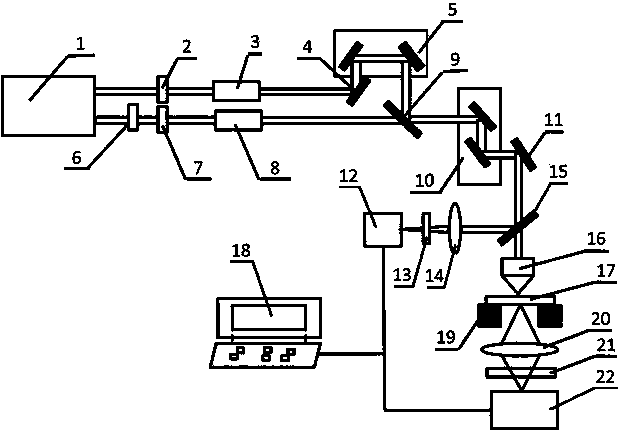
Wavelength converting optical system, laser light source, exposure apparatus, mask examining apparatus, and macromolecular crystal lens machining device
ActiveUS7623557B2Eliminate needSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusThird harmonicWave form
A fifth harmonic wave is formed from a fundamental wave of p-polarized light via a second harmonic wave forming optical element 3, a third harmonic wave forming optical element 4, and a fifth harmonic wave forming optical element 6 and a second harmonic wave of p-polarized light is formed from a fundamental wave of s-polarized light by a second harmonic wave forming optical element 9. The fifth harmonic wave of p-polarized light that is subjected to beam shaping by cylindrical lenses 7 and 8, the fundamental wave of s-polarized light, and the second harmonic wave of p-polarized light are combined by a dichroic mirror 10, and are incident on a seventh harmonic wave forming optical element 11. Furthermore, a seventh harmonic wave of s-polarized light is formed from the second harmonic wave and fifth harmonic wave of p-polarized light, and this seventh harmonic wave is mixed with the fundamental wave of s-polarized light in an eighth harmonic wave forming optical element 12, so that an eighth harmonic wave of p-polarized light is formed. As a result, an eighth harmonic wave can be formed in a simpler optical system than a conventional optical system.
Owner:NIKON CORP
Laser process to produce drug delivery channel in metal stents
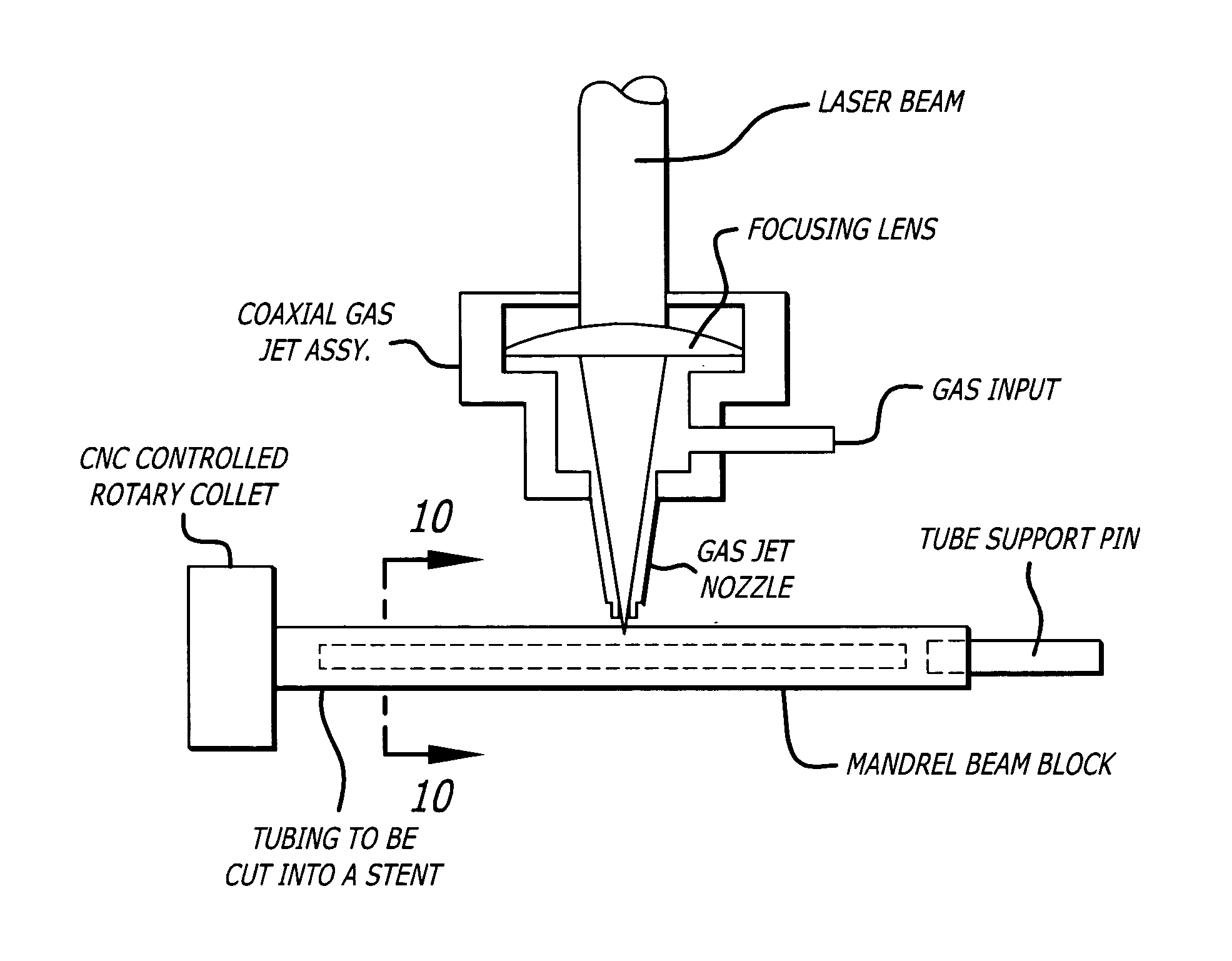
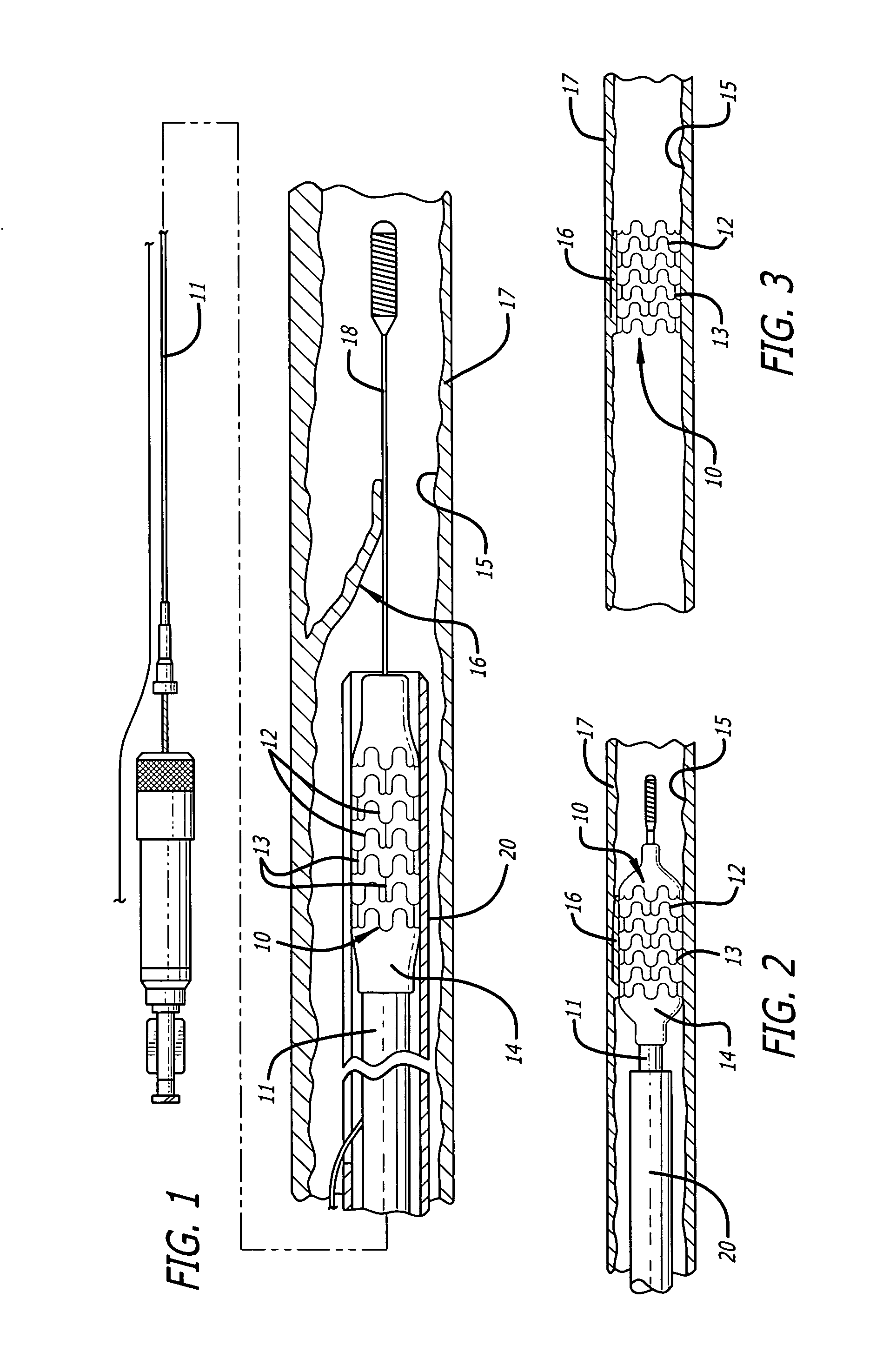
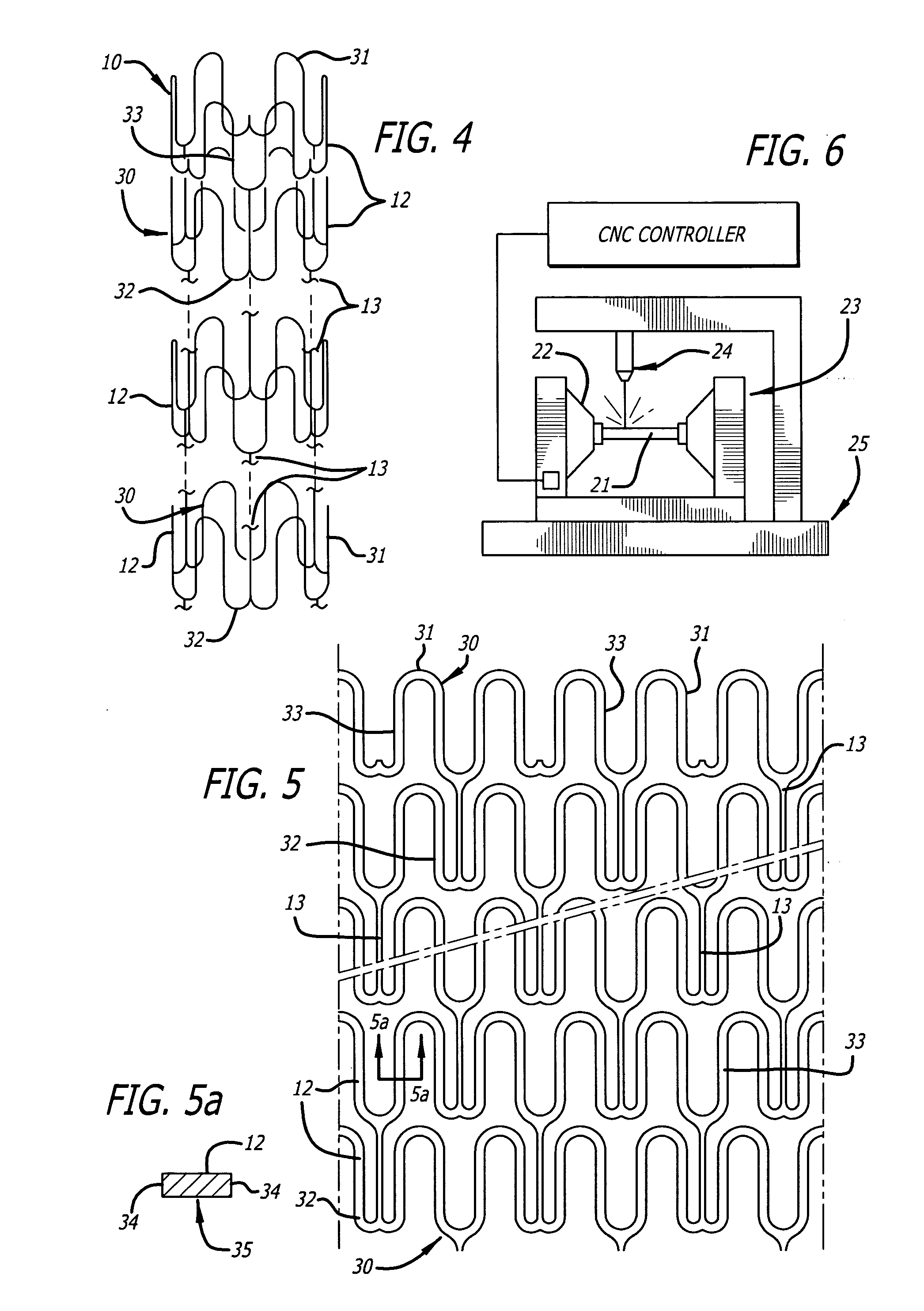
A method for forming a stent and for also forming channels in the outer surface of selected regions of the stent structure. The method includes impinging a laser beam generated by a diode pumped Q-switched pulsed Nd / YAG laser operating at the third harmonic on an outer surface of a stent and controllably machining channels in the outer surface of the stent. The depth of the channels may be controlled by adjusting the power and pulse rate of the laser, and also by adjusting the rate at which the stent moves relative to the laser beam.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
Multi-mode non-linear optical microscopy imaging method and device
The invention relates to a multi-mode non-linear optical microscopy imaging method and device. The multi-mode non-linear optical microscopy imaging device mainly comprises a laser system, an optical scanning microscope and a non-linear optical signal detecting and acquiring system. The multi-mode non-linear optical microscopy imaging device can work in a single-laser-beam mode and a dual-laser-beam mode and can realize multi-mode non-linear optical microscopy imaging such as two-photon excited Fluorescence (TPEF) imaging, multiphoton high-order harmonic (such as second harmonic generation SHG, and third harmonic generation THG) scattering imaging, coherent Raman scattering (such as anti-Stokes CARS) microscopy imaging) on isolated biological tissues and living cells, so that various non-linear specific optical signals of biological tissue samples can be obtained in situ, so that the important basis is provided for the optical diagnosis and deep analysis of the samples. Besides, a reflection measurement manner disclosed by the invention can be further directly applied to the acquiring of various non-linear specific optical signals of live animals and the microscopy imaging.
Owner:FUJIAN NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com