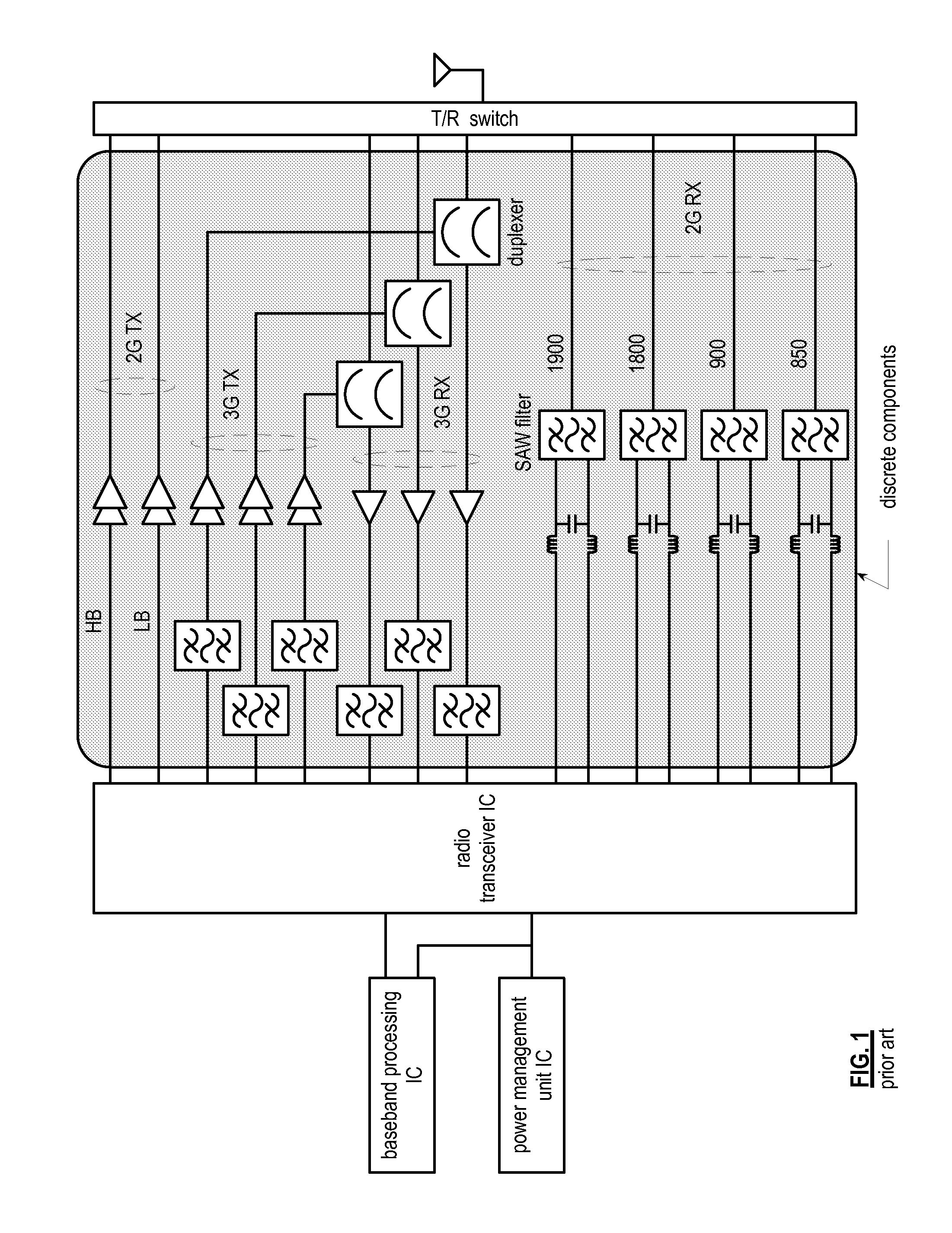
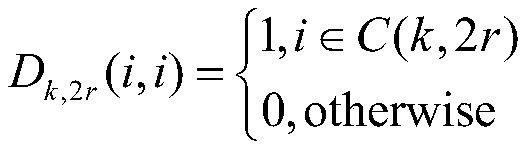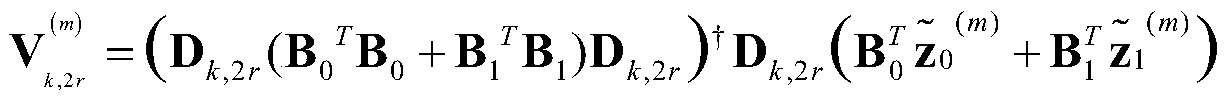Patents
Literature
61results about "N-path filters" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
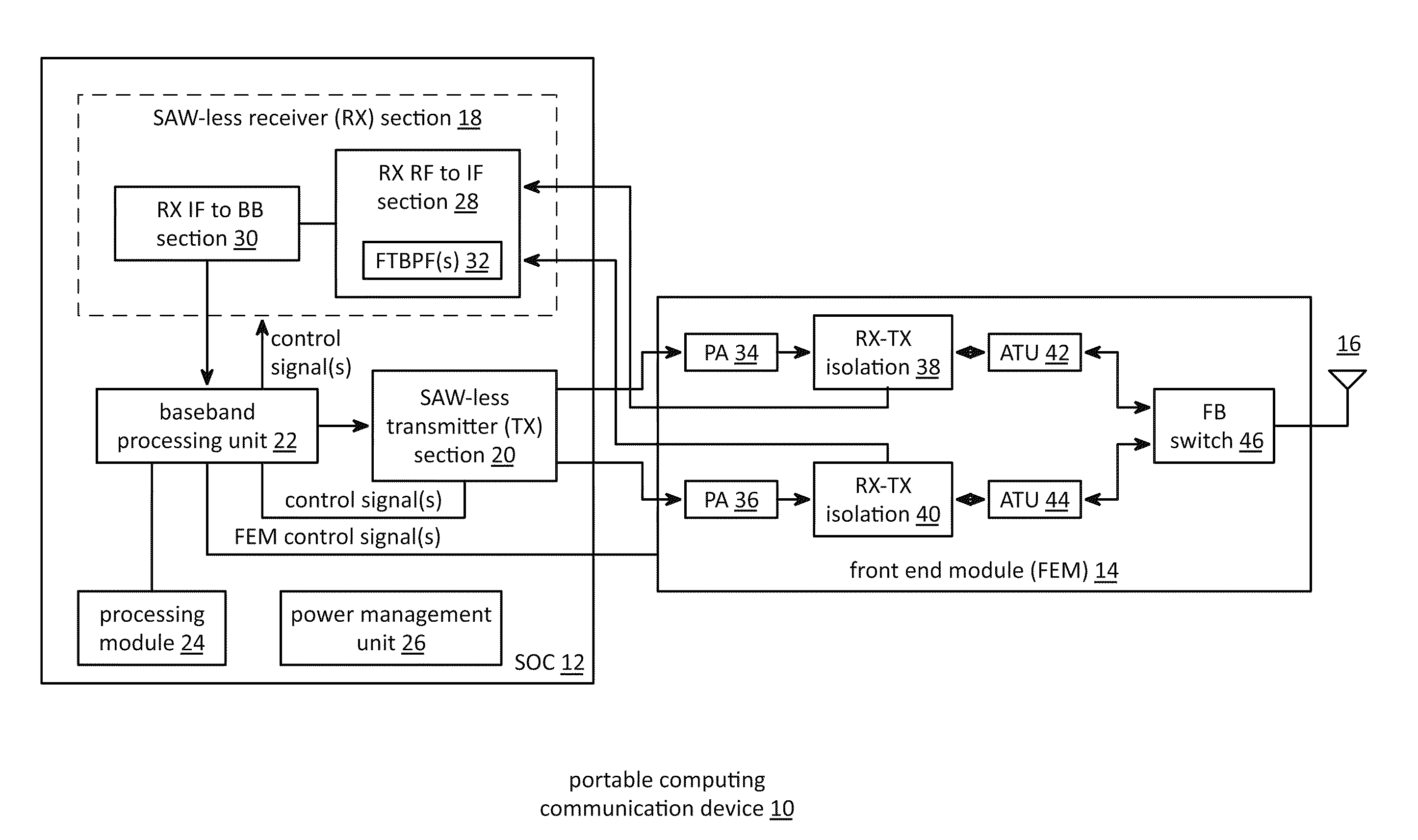
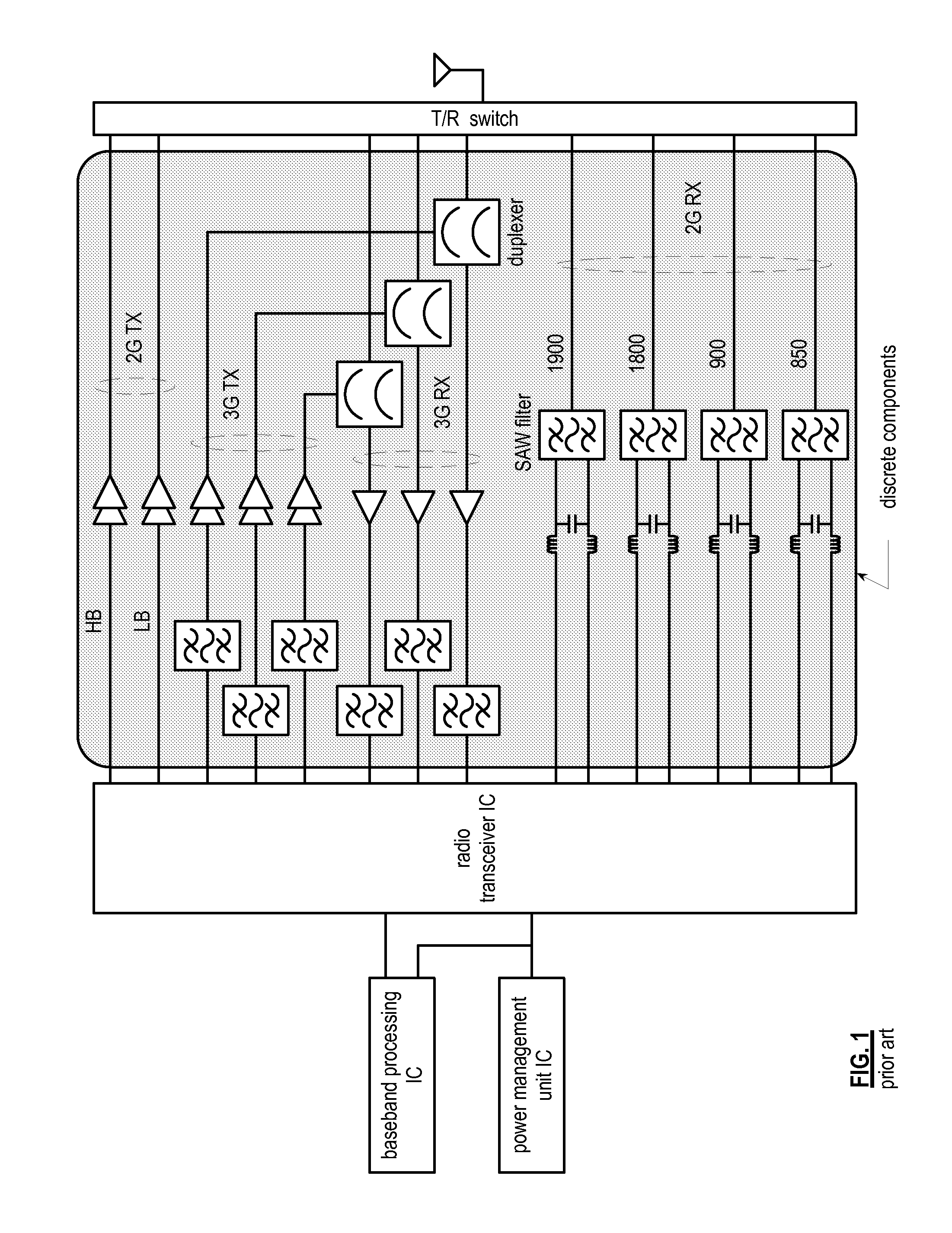
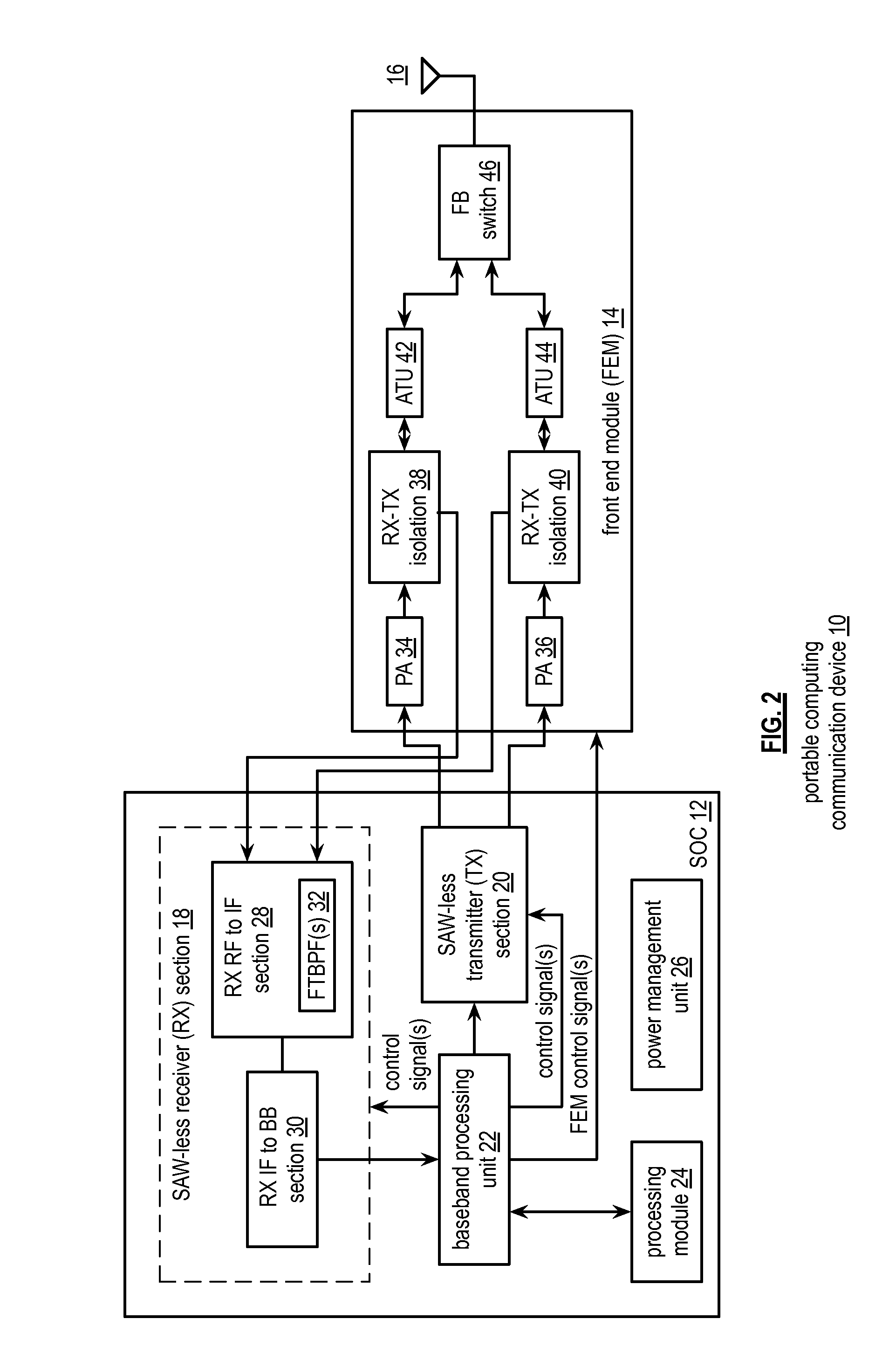
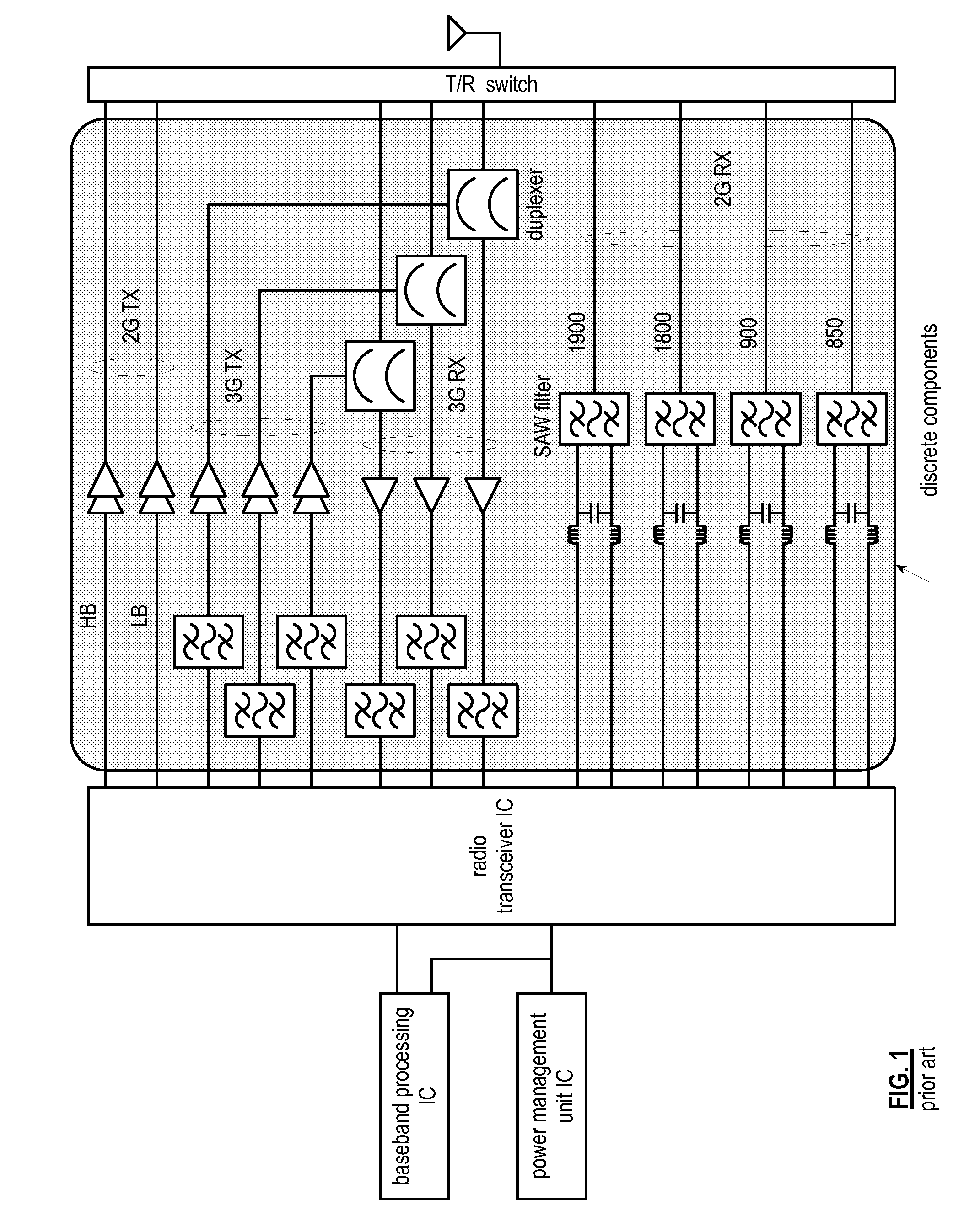
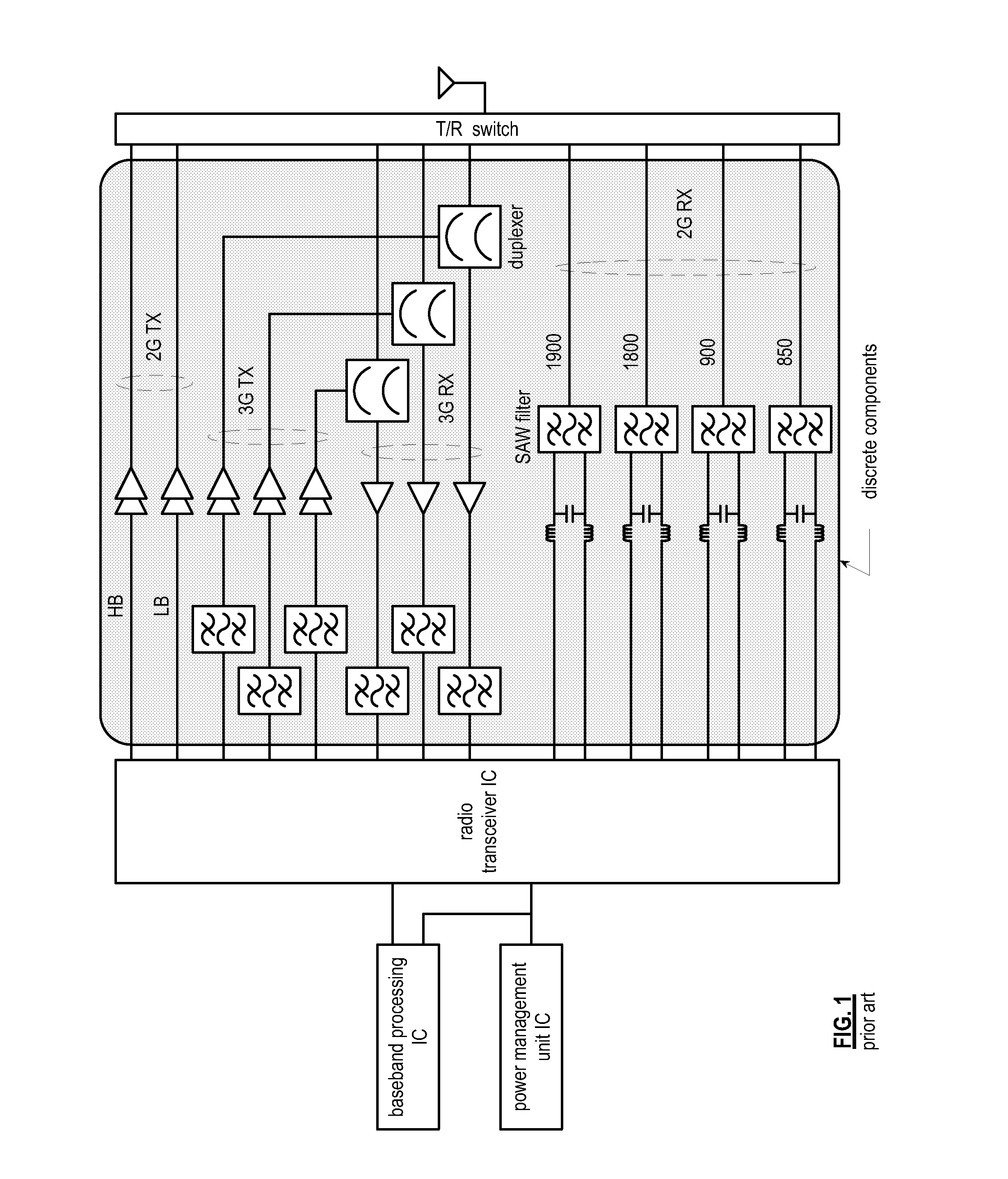
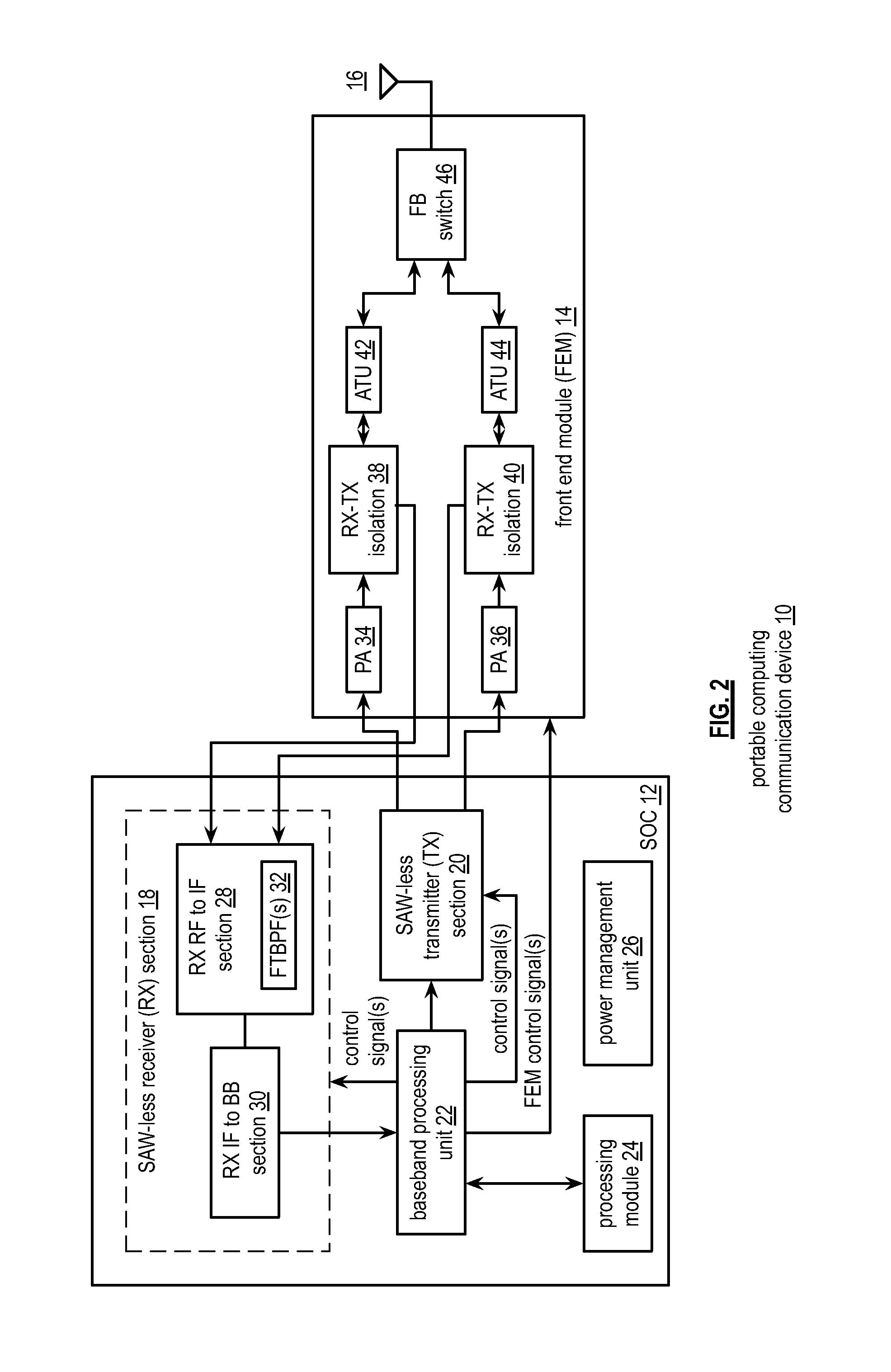
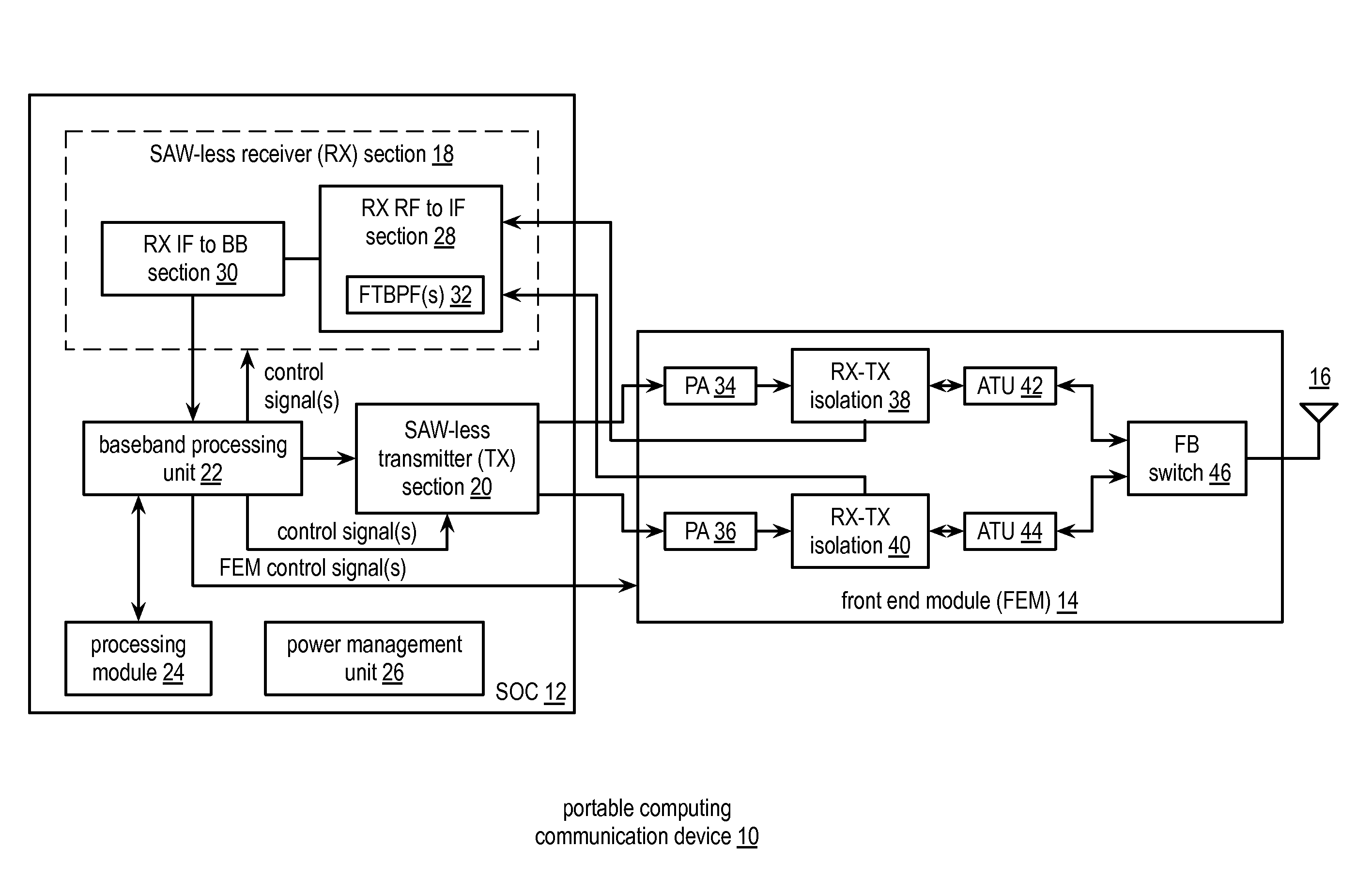
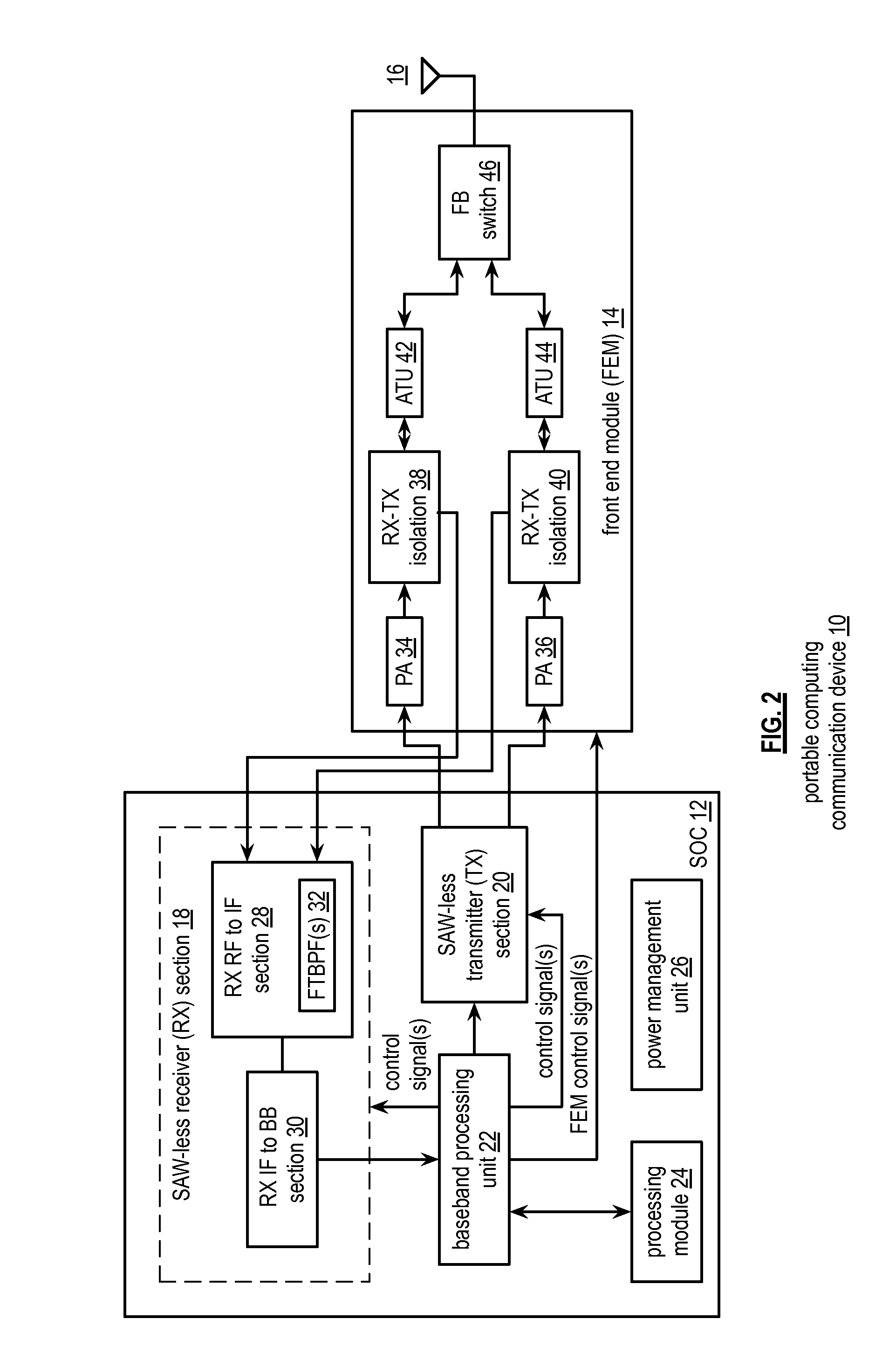
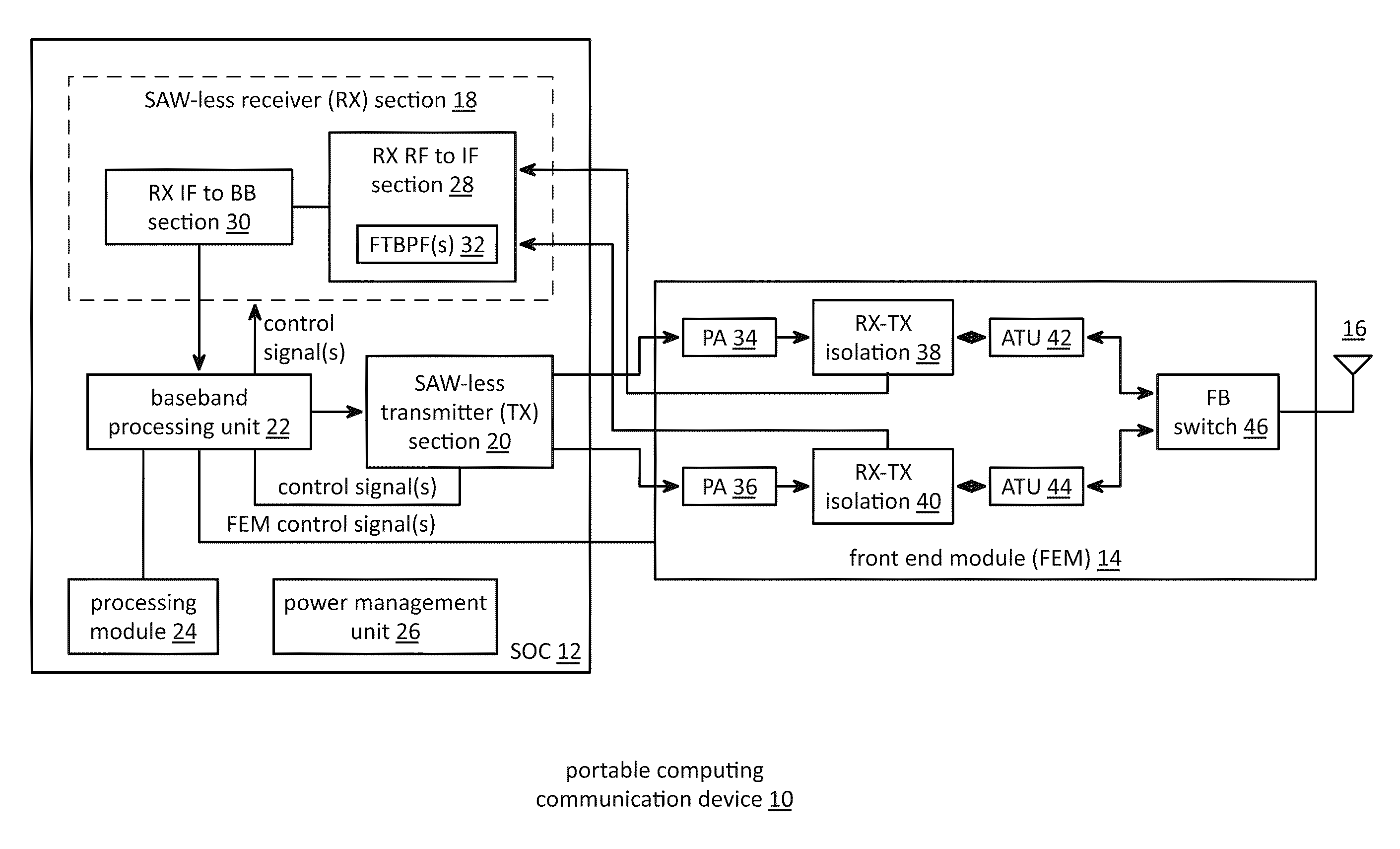
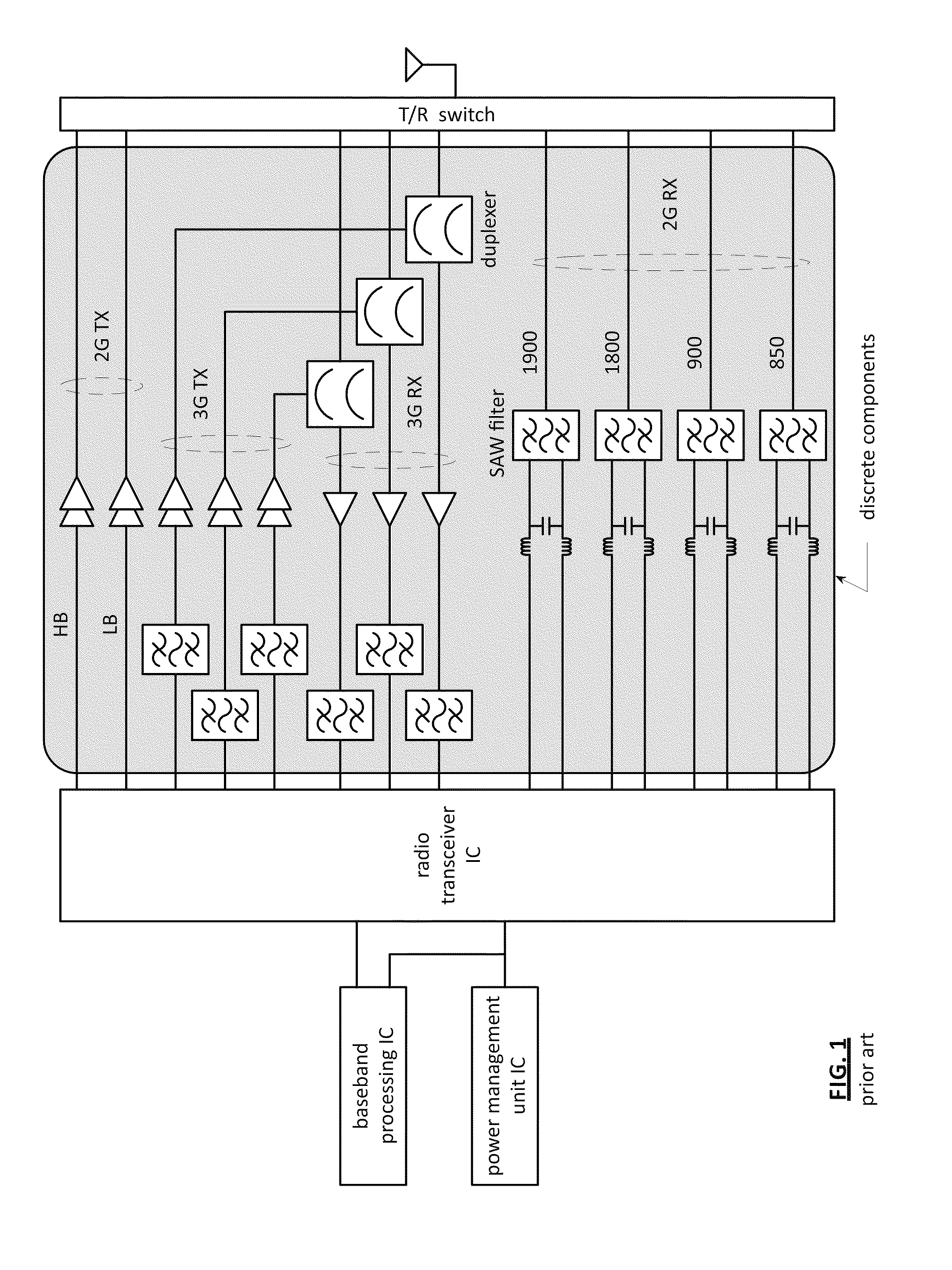
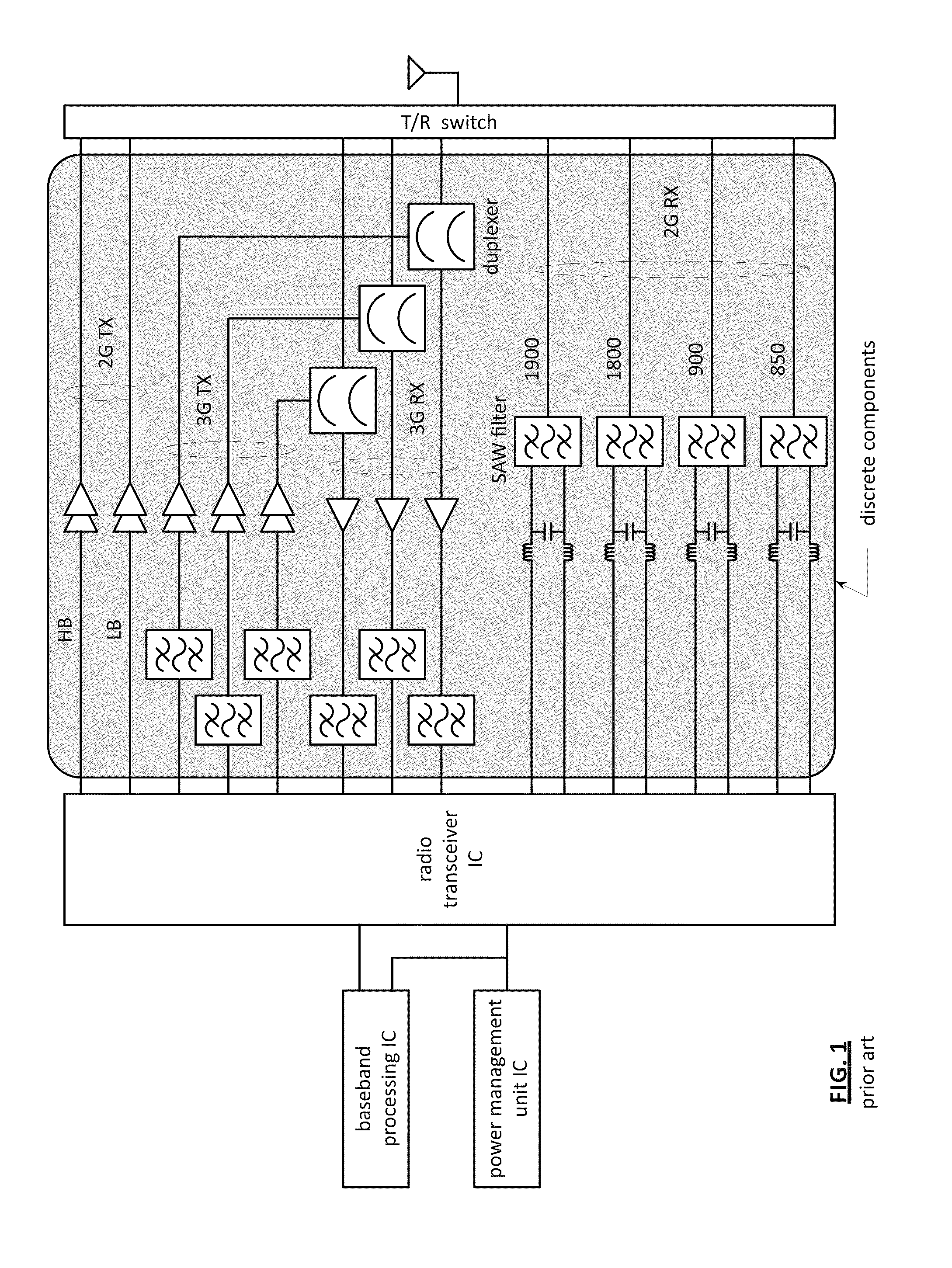
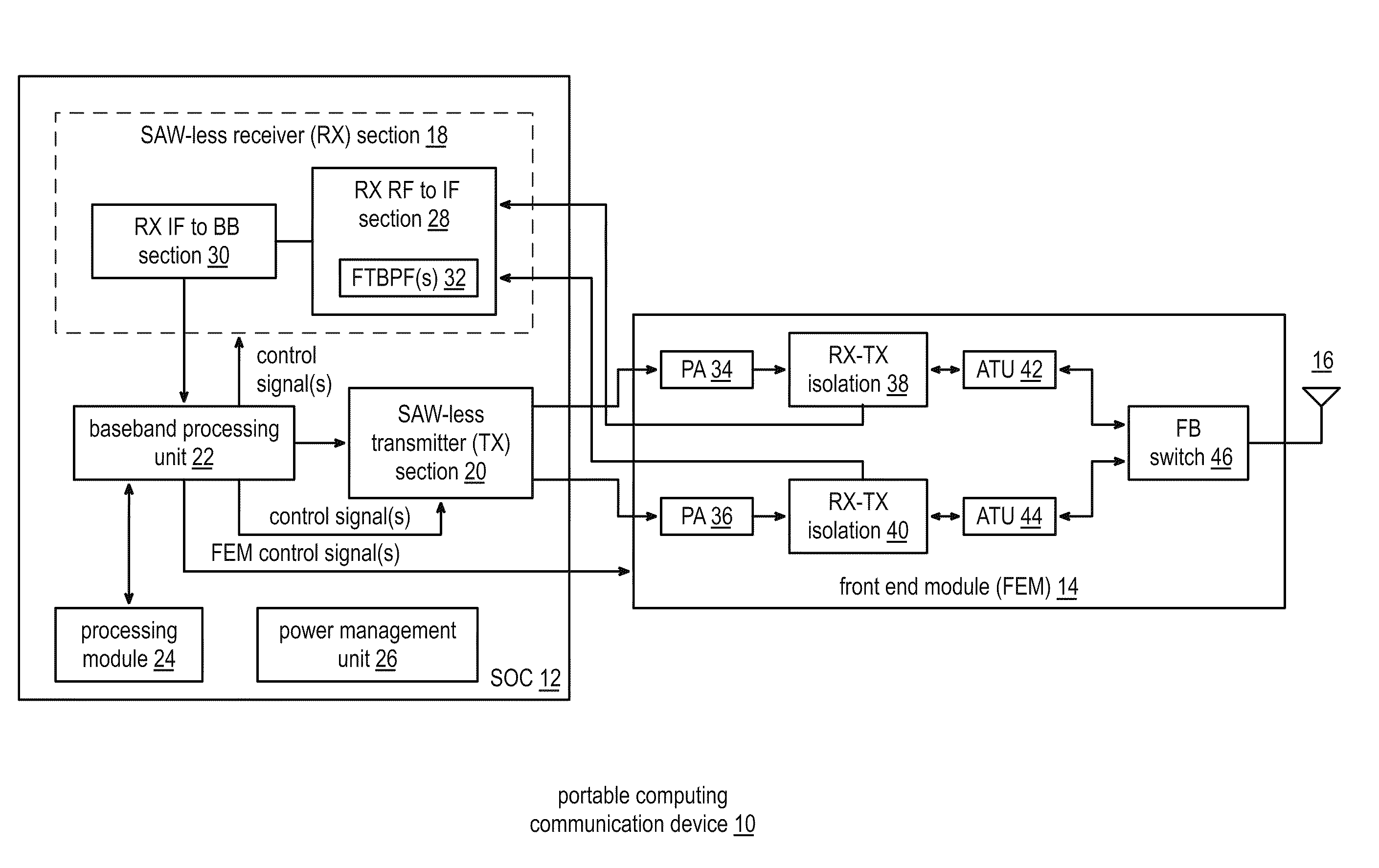
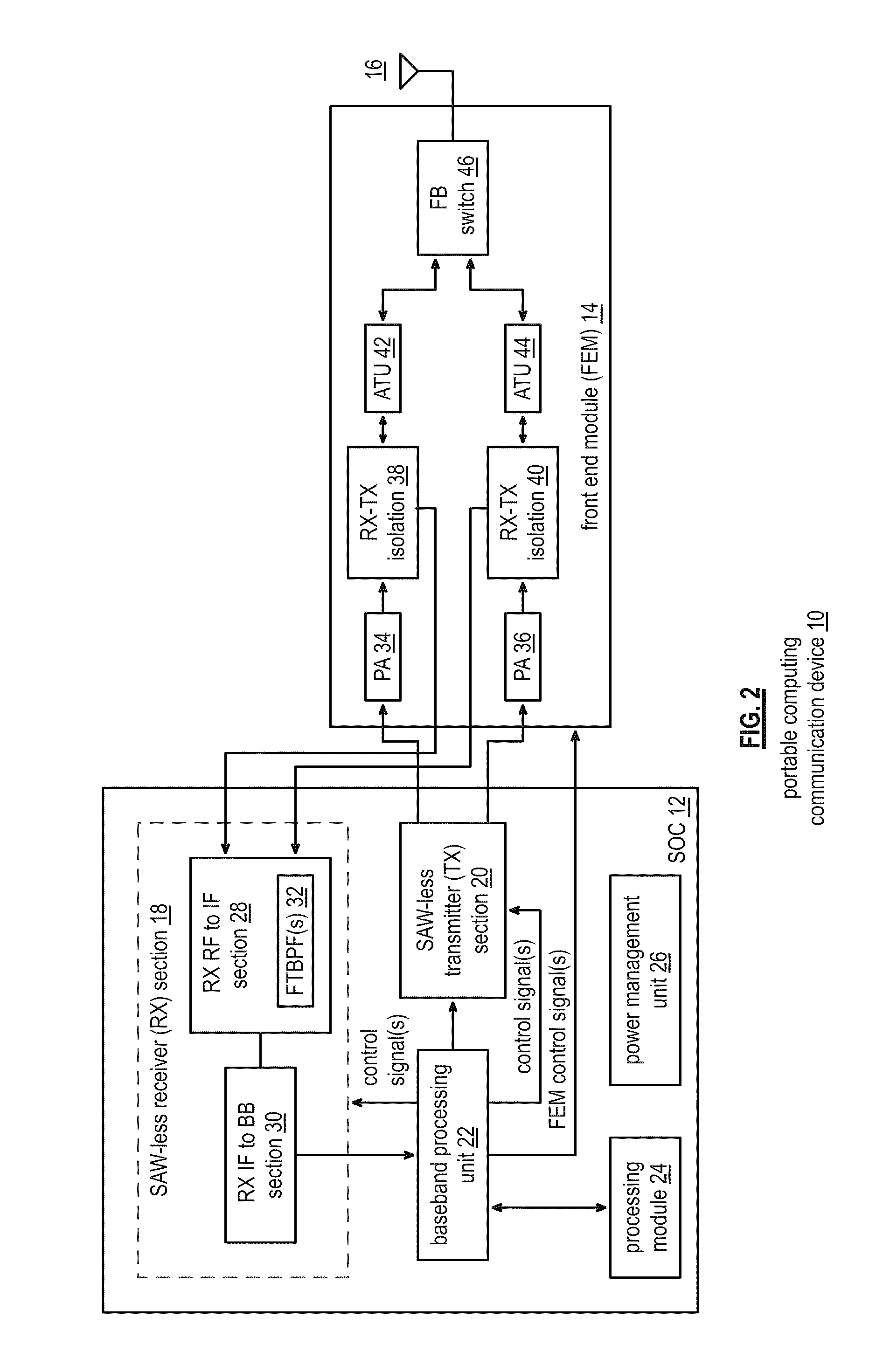
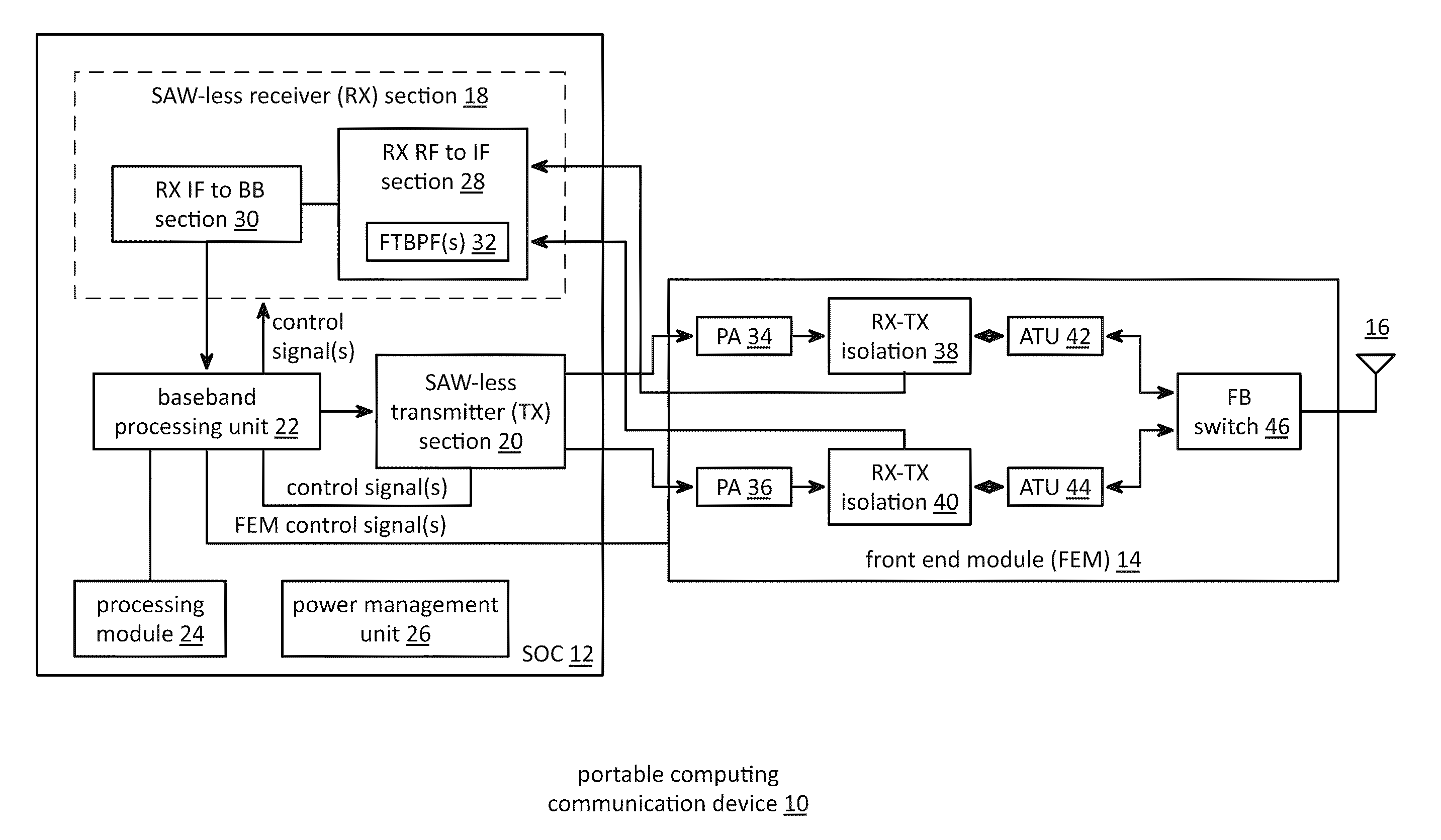
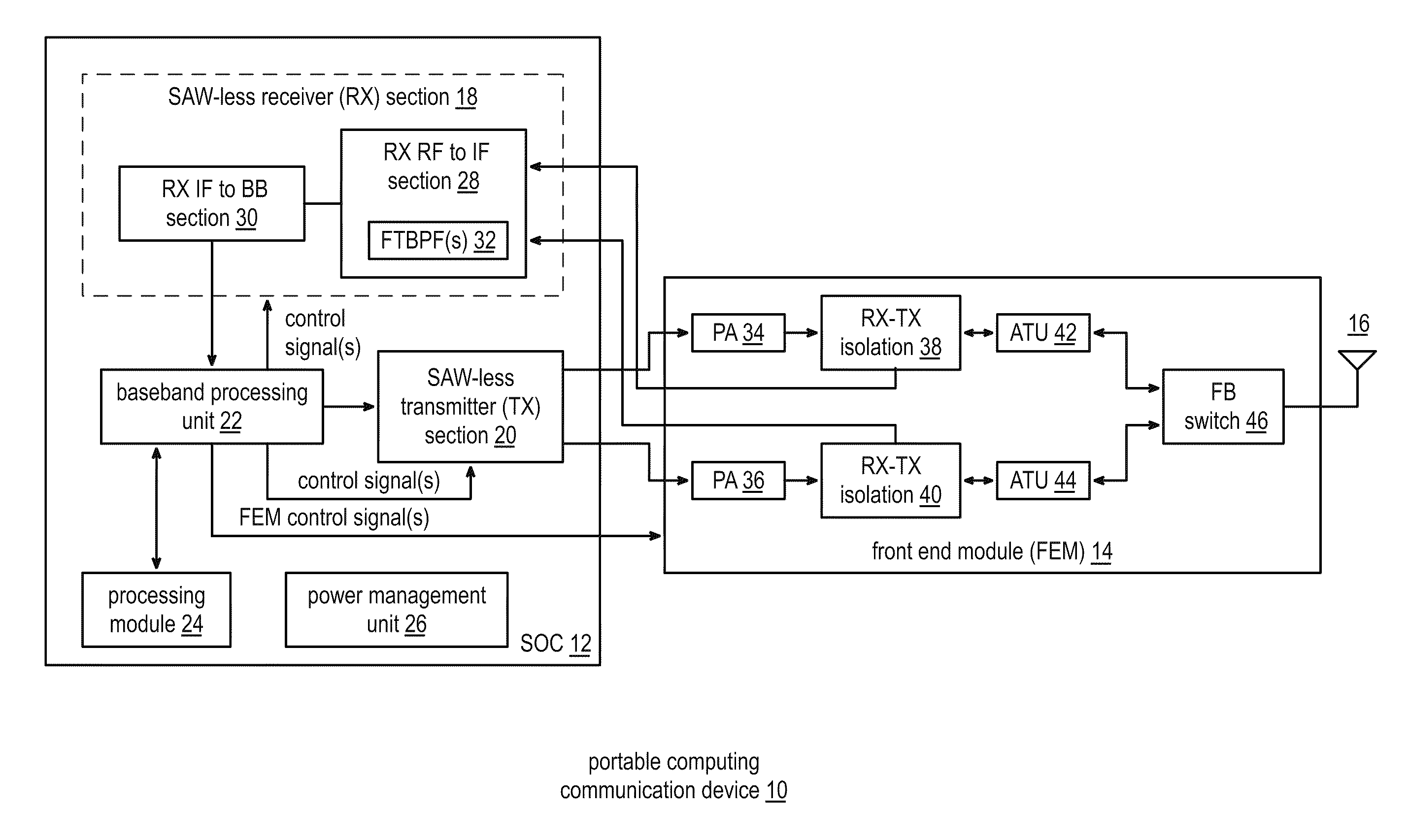
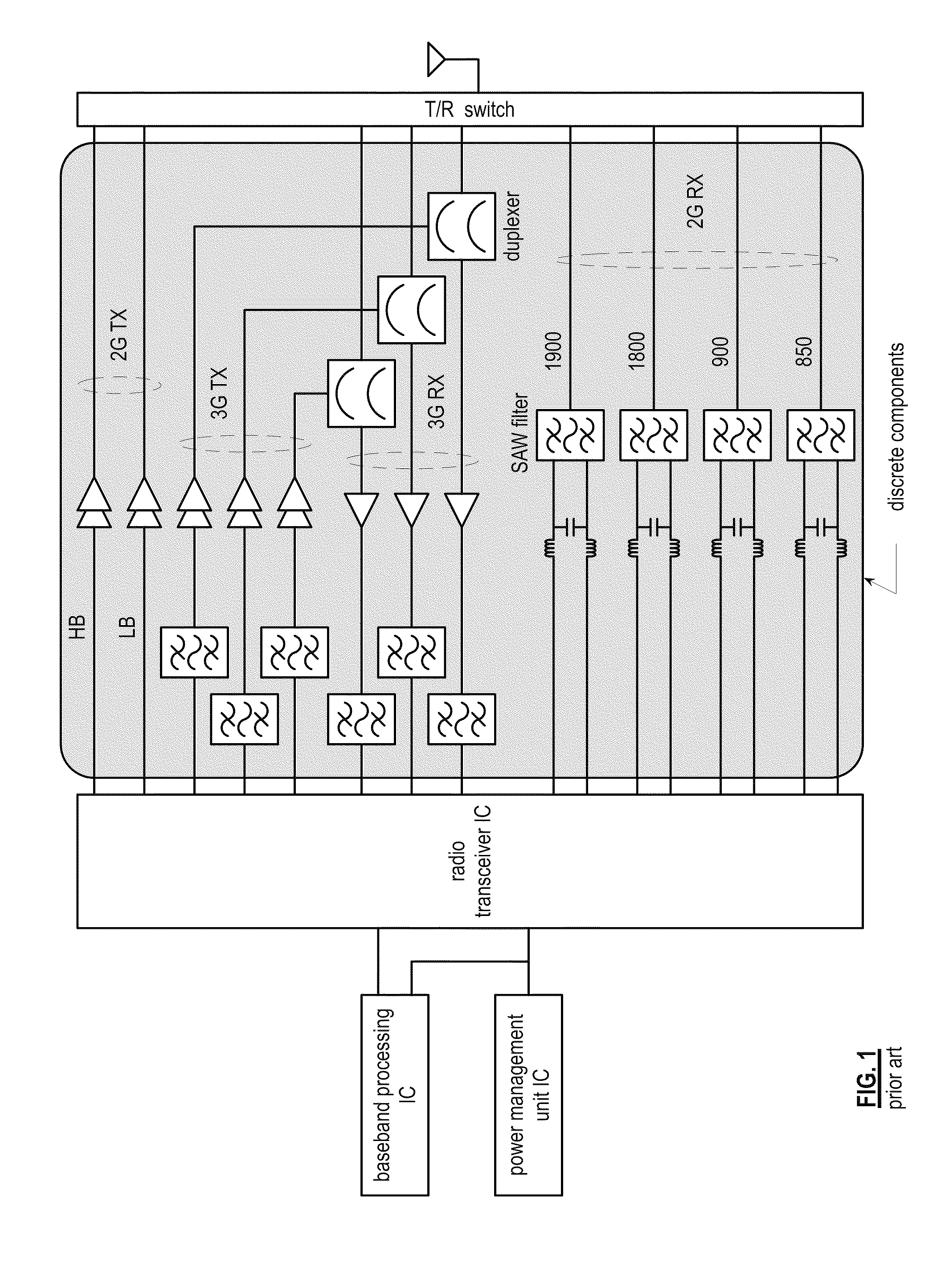
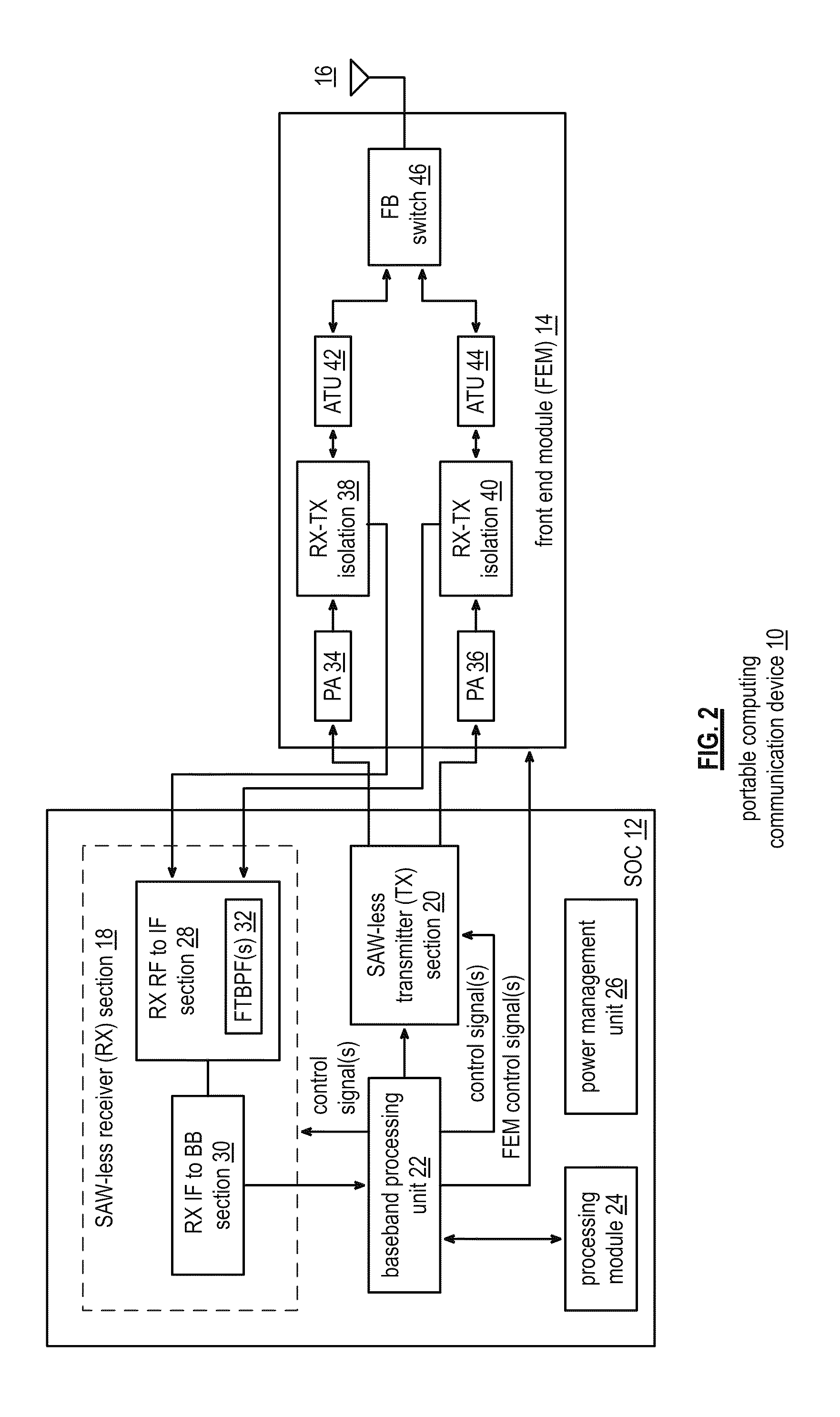
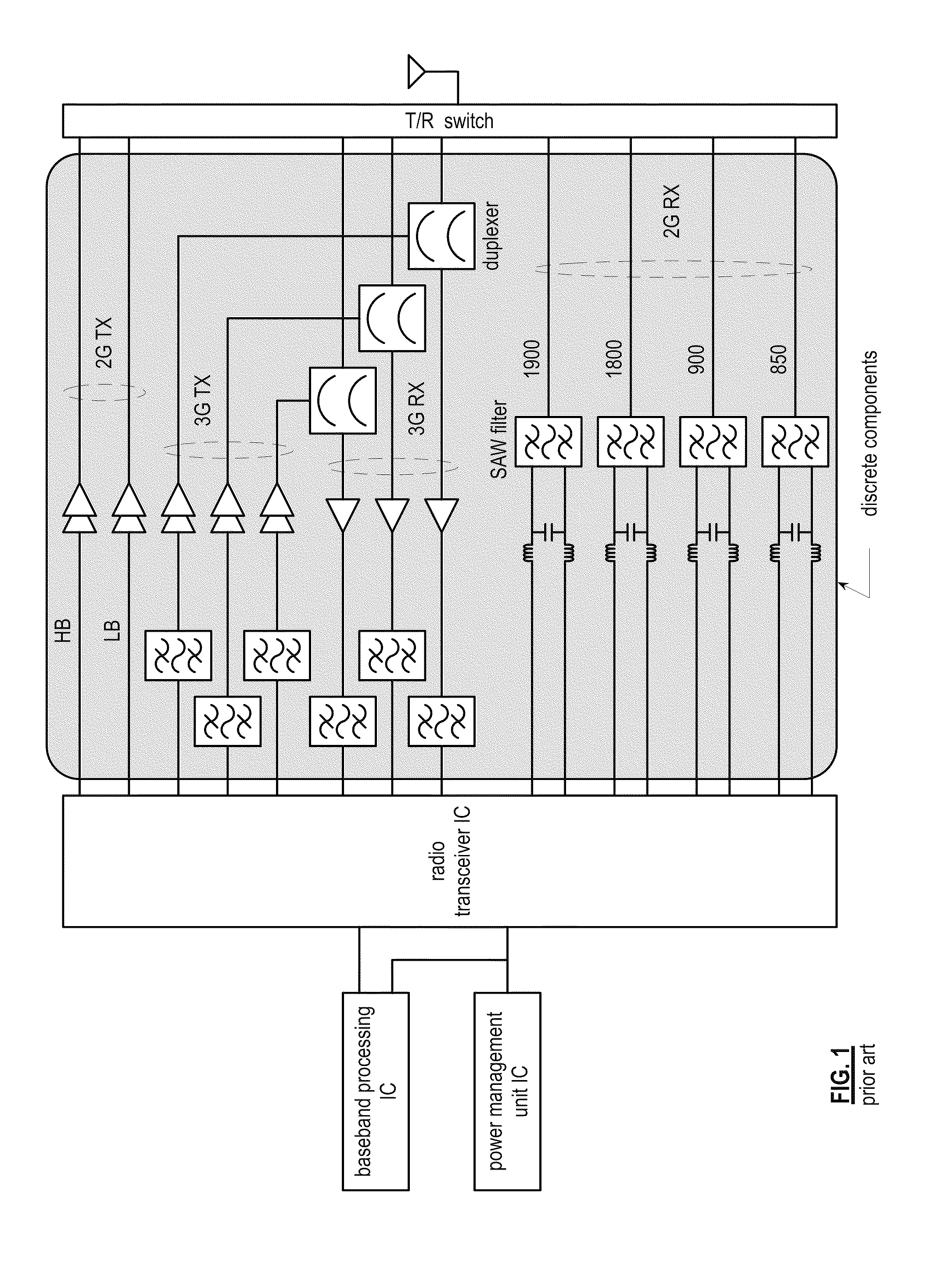
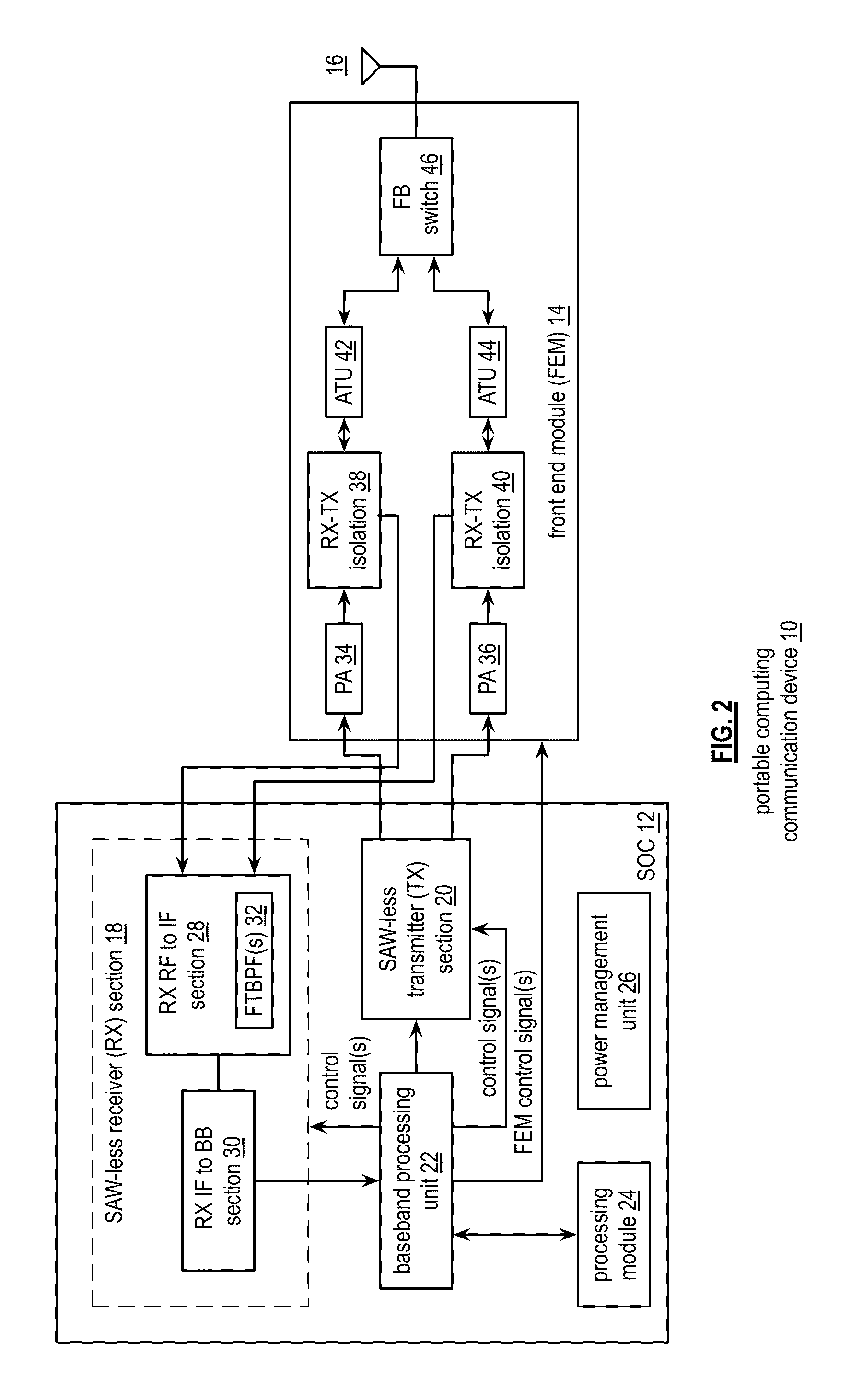
Front end module with a tunable balancing network
ActiveUS20110299431A1Multiple-port networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceBalancing network
A radio front module includes a power amplifier, a duplexer, and a tunable balancing network. The power amplifier is operably coupled to amplify an up-converted signal into an outbound wireless signal. The duplexer is operably coupled to an antenna and operable to provide electrical isolation between the outbound wireless signal and an inbound wireless signal. The tunable balancing network is operable to establish an impedance that substantially matches an impedance of the antenna. The tunable balancing network includes a plurality of capacitive elements, a plurality of resistive elements, and a plurality of low-voltage switching elements operable to, and in accordance with a tuning signal, couple one or more of the plurality of capacitive elements and one or more of the plurality of resistive elements to the duplexer as an impedance balancing load.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
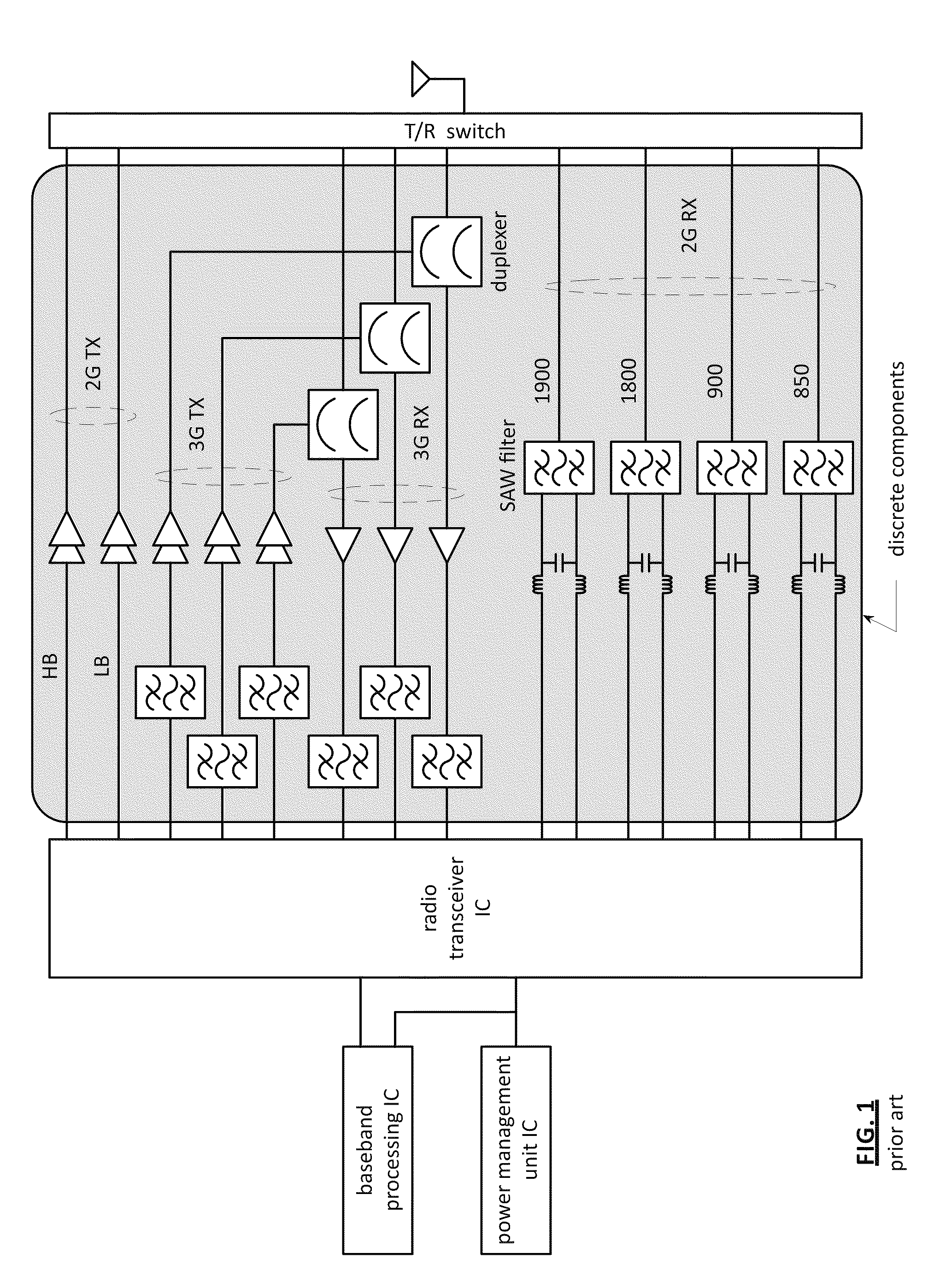
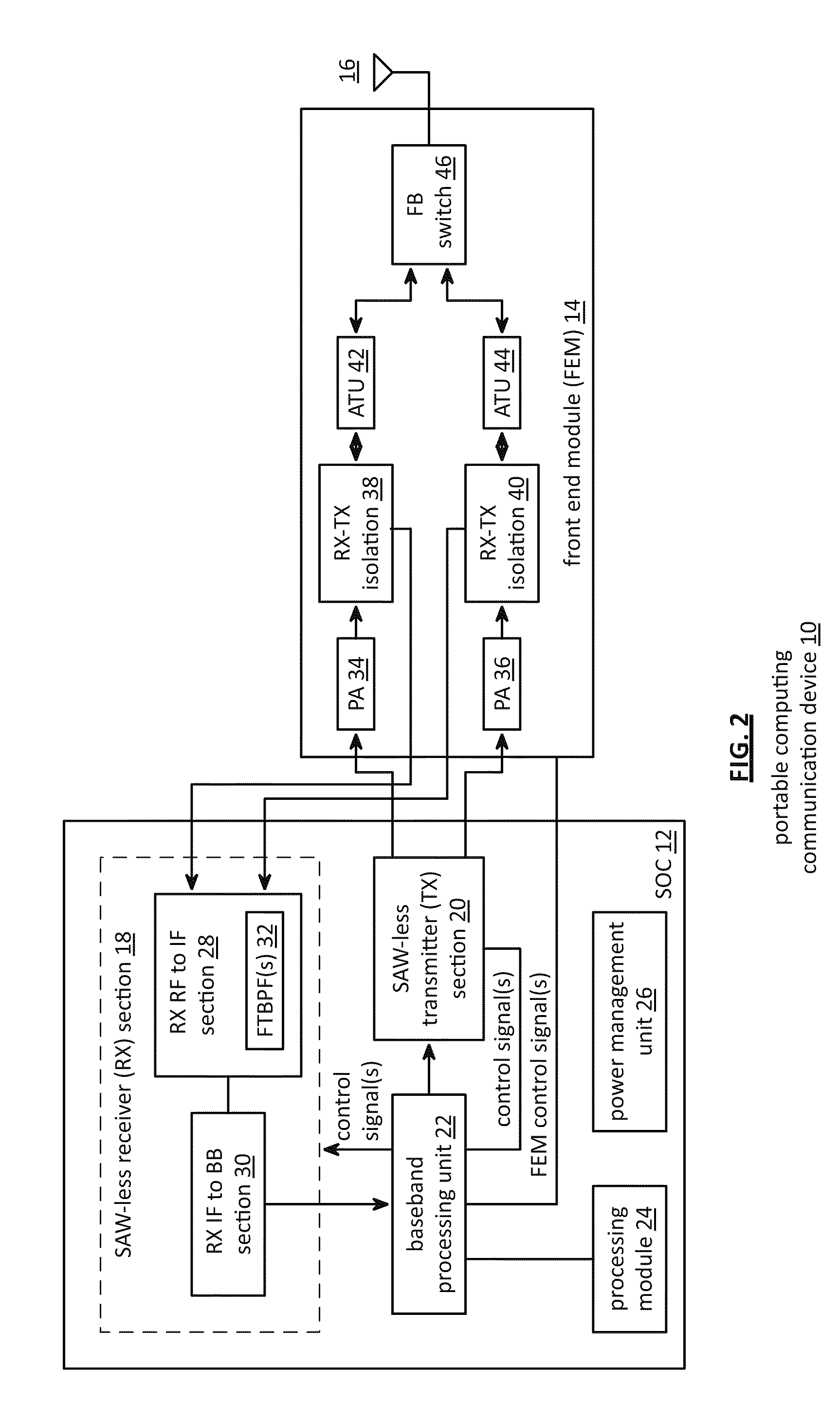
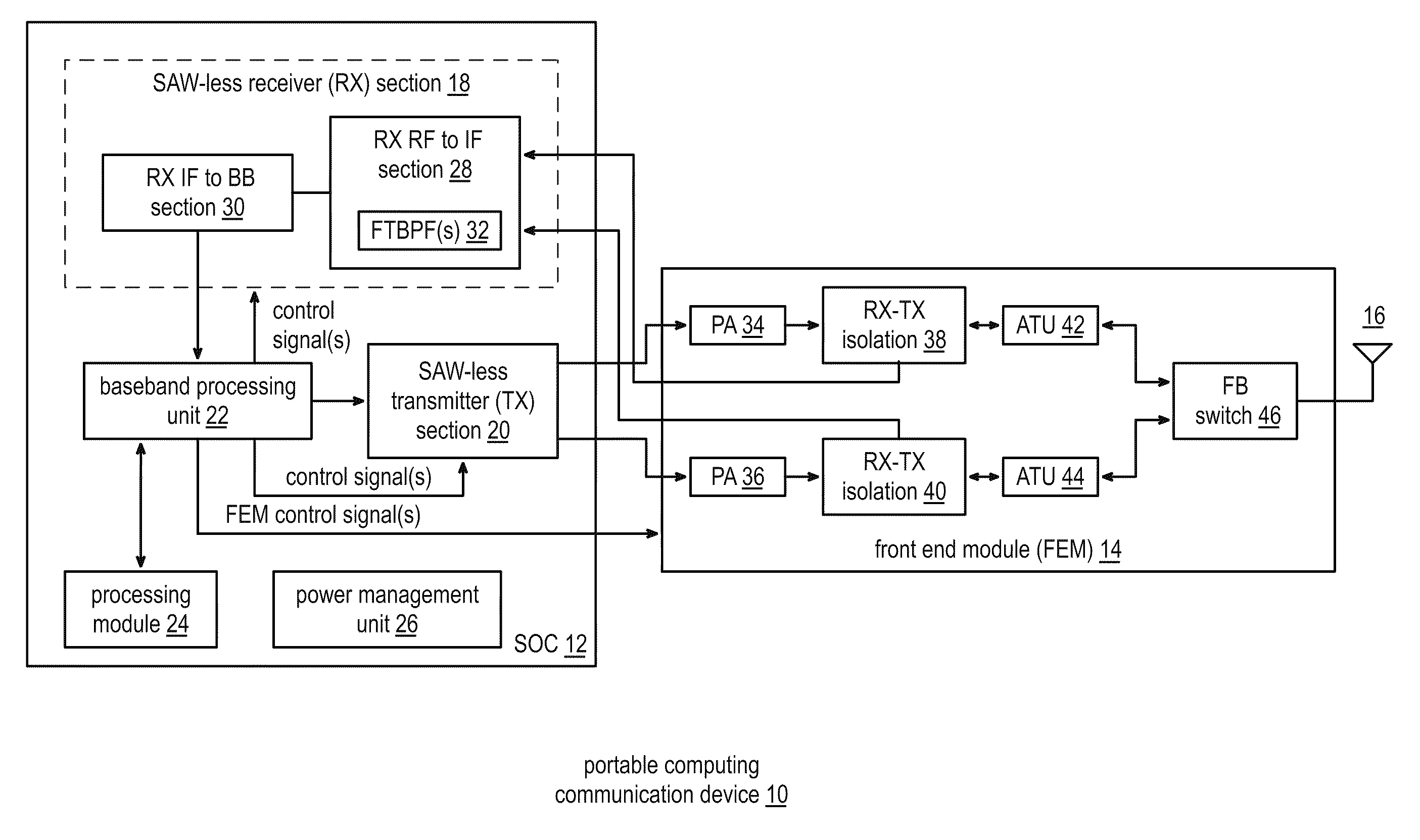
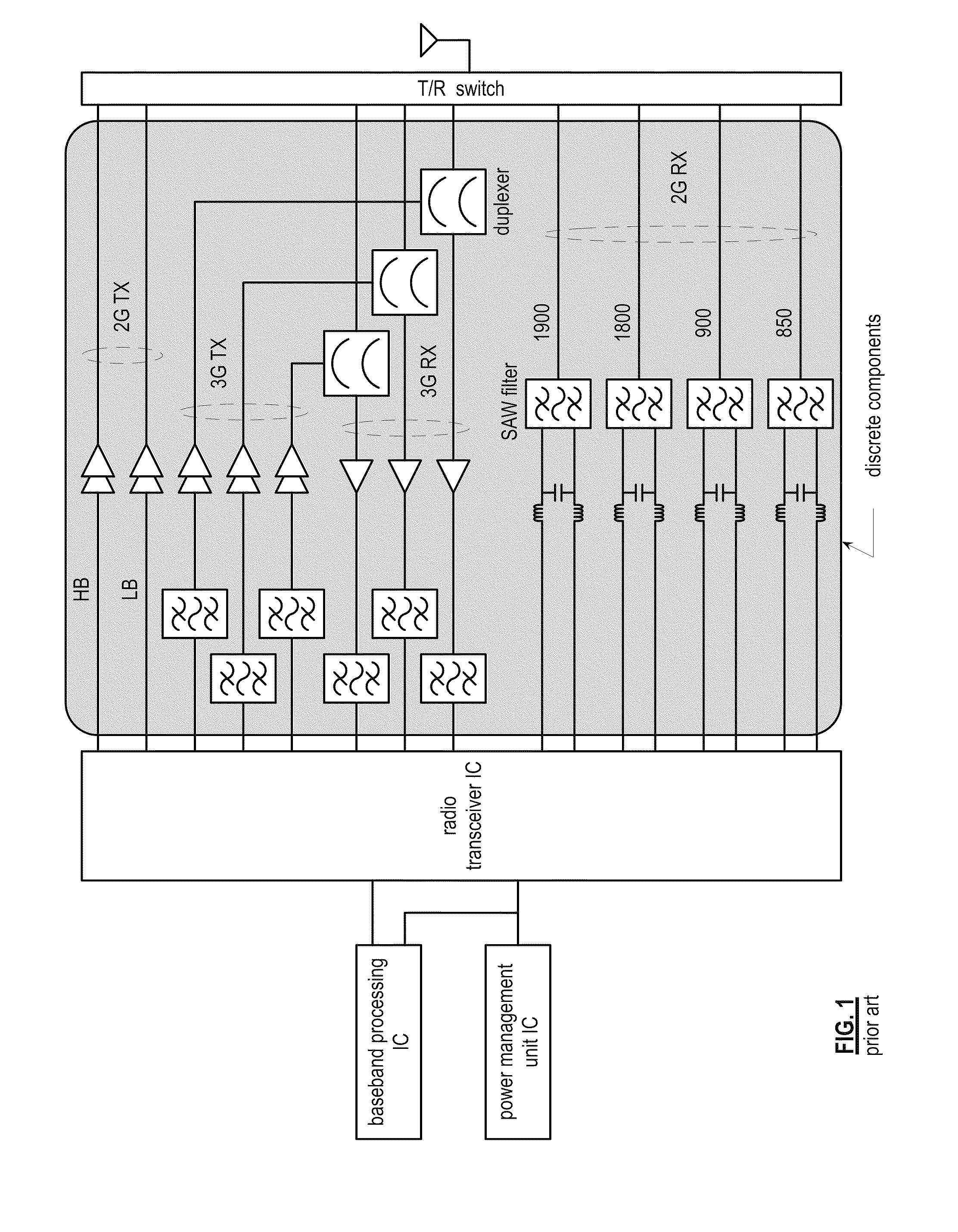
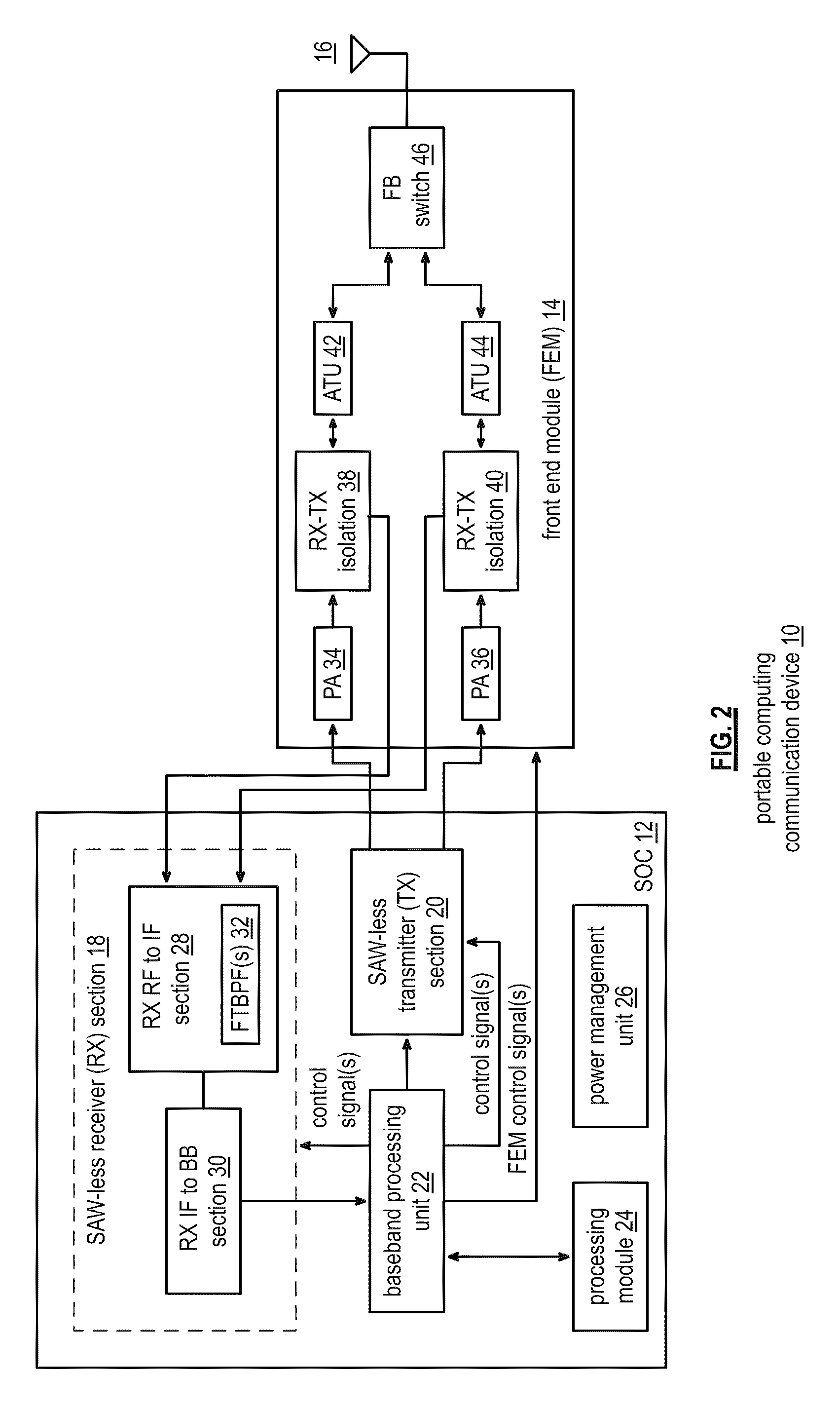
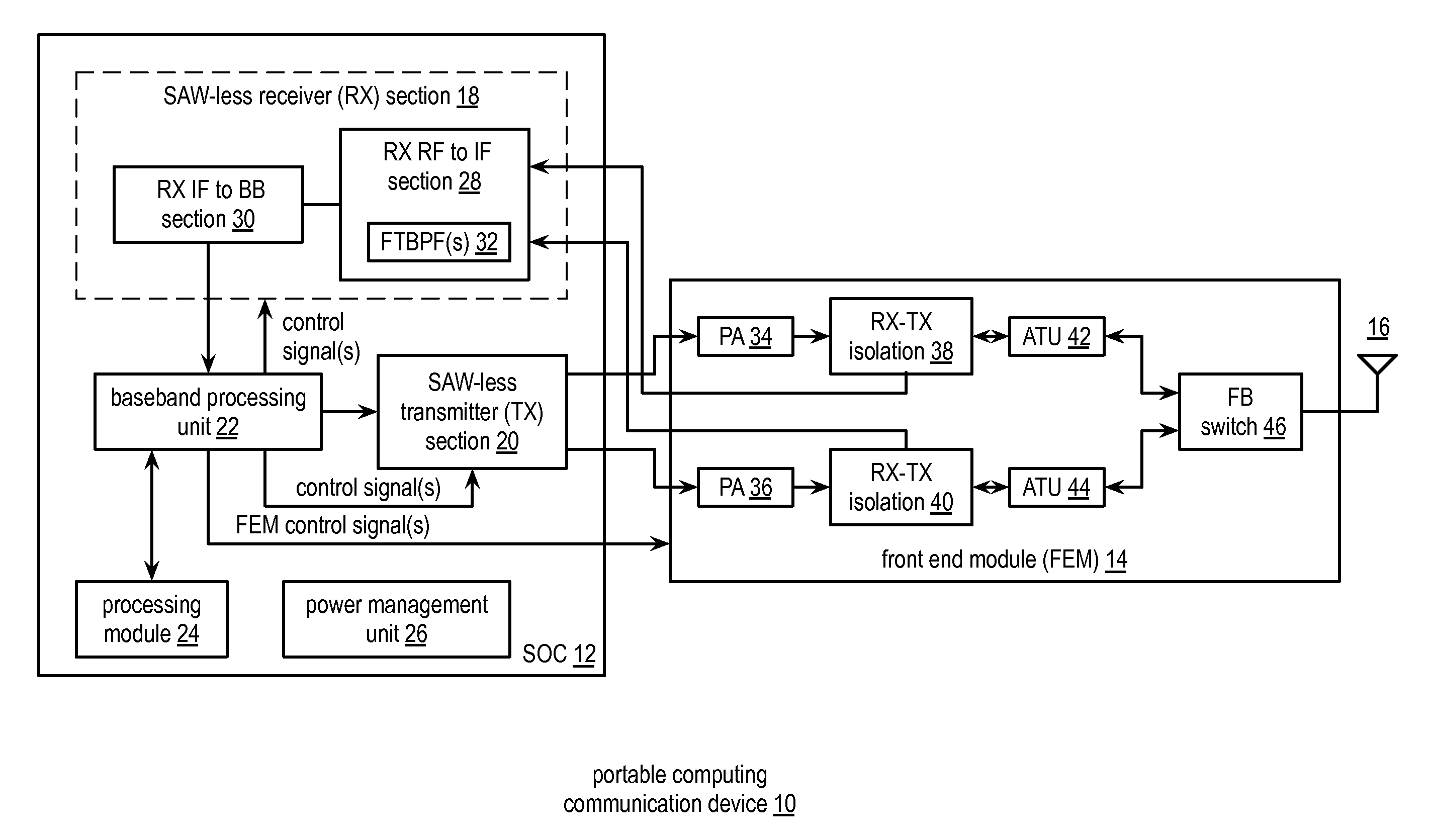
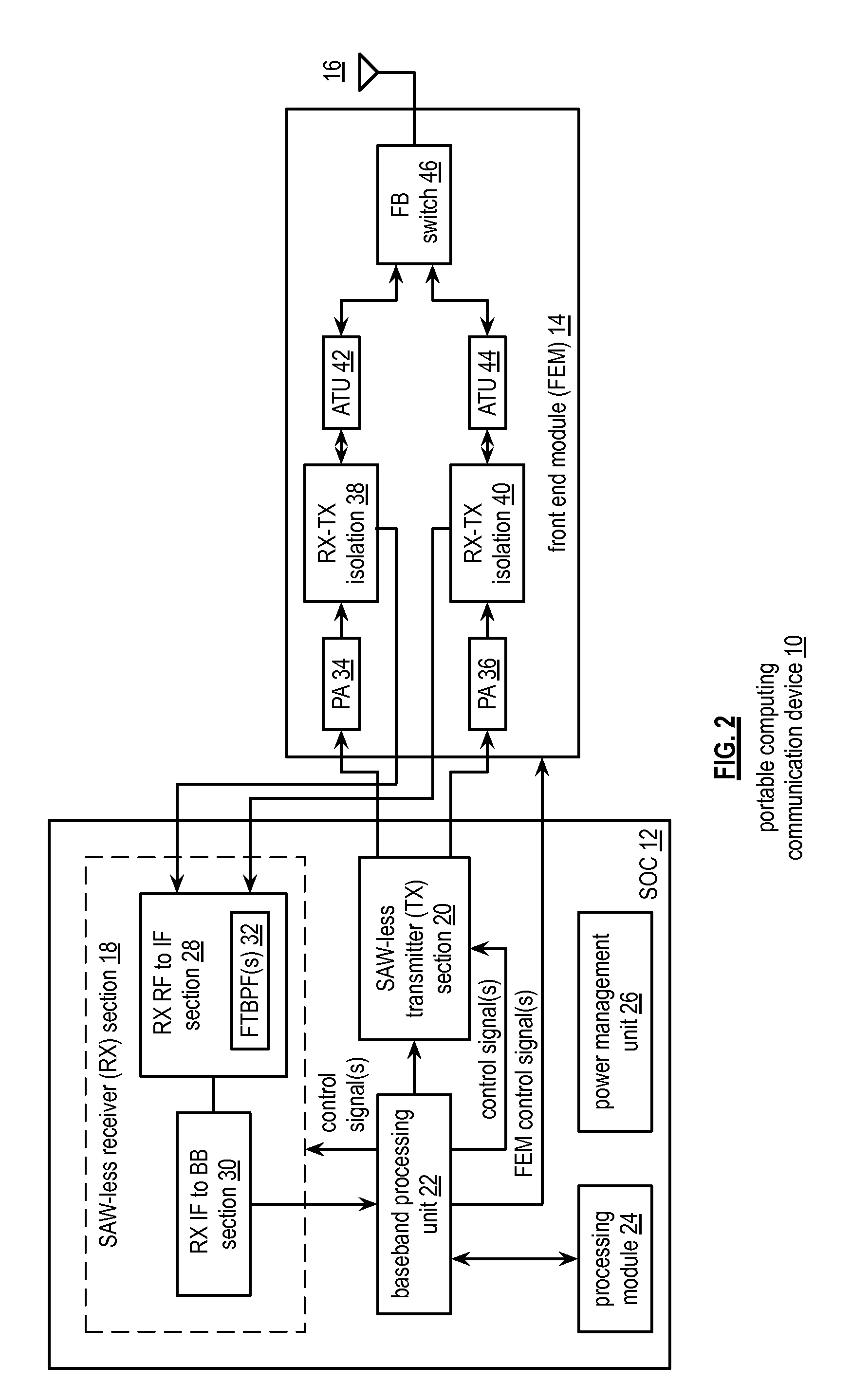
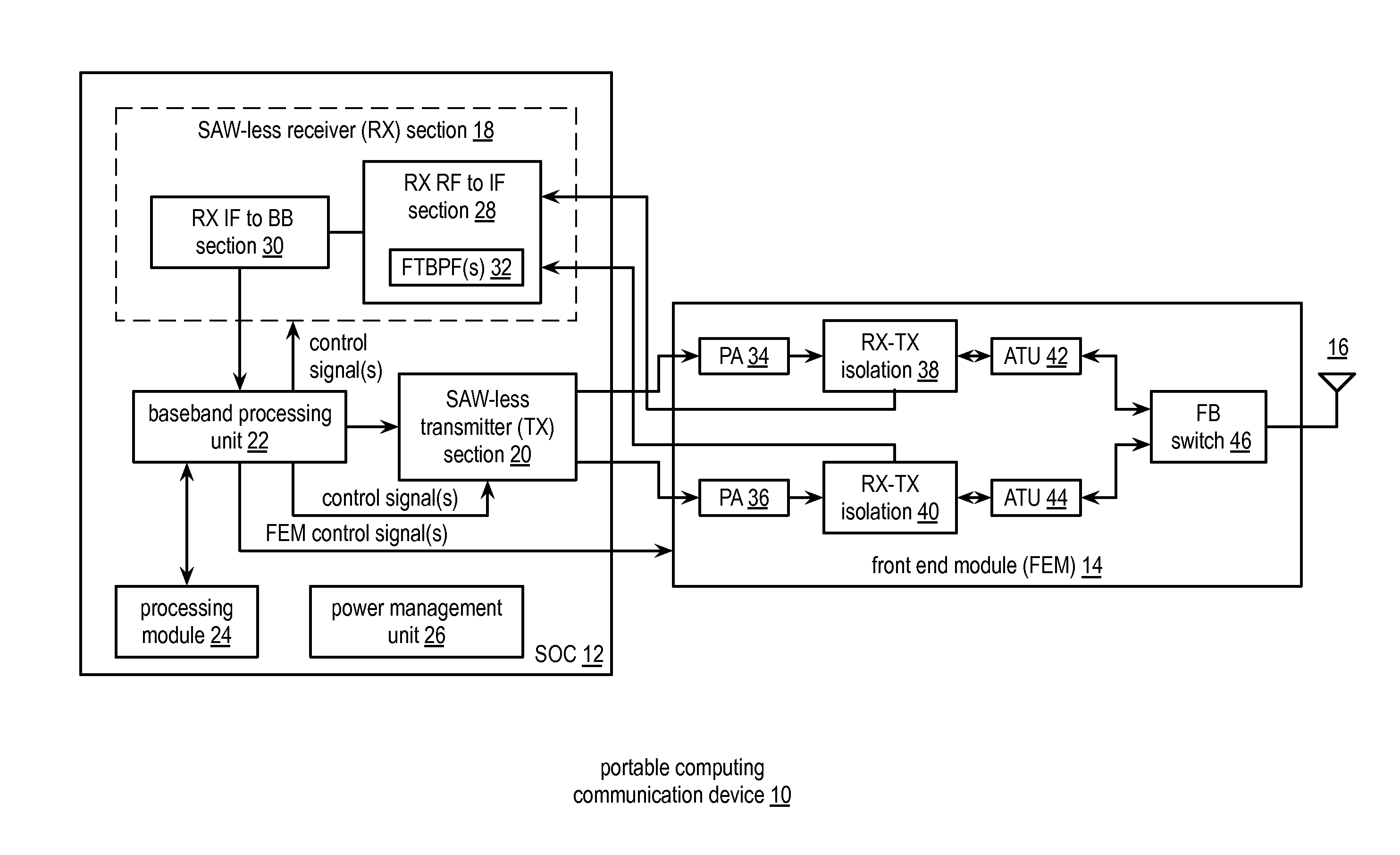
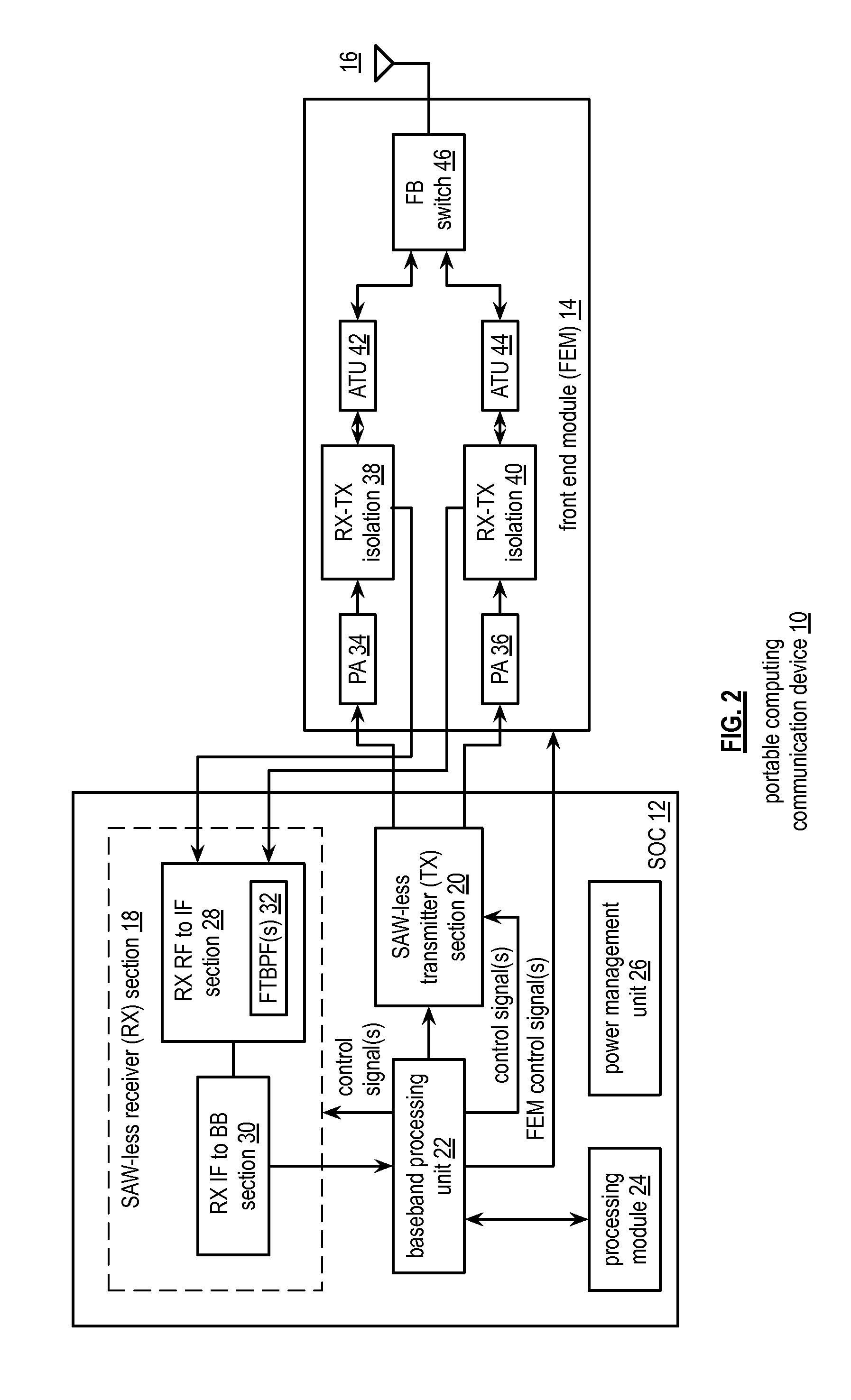
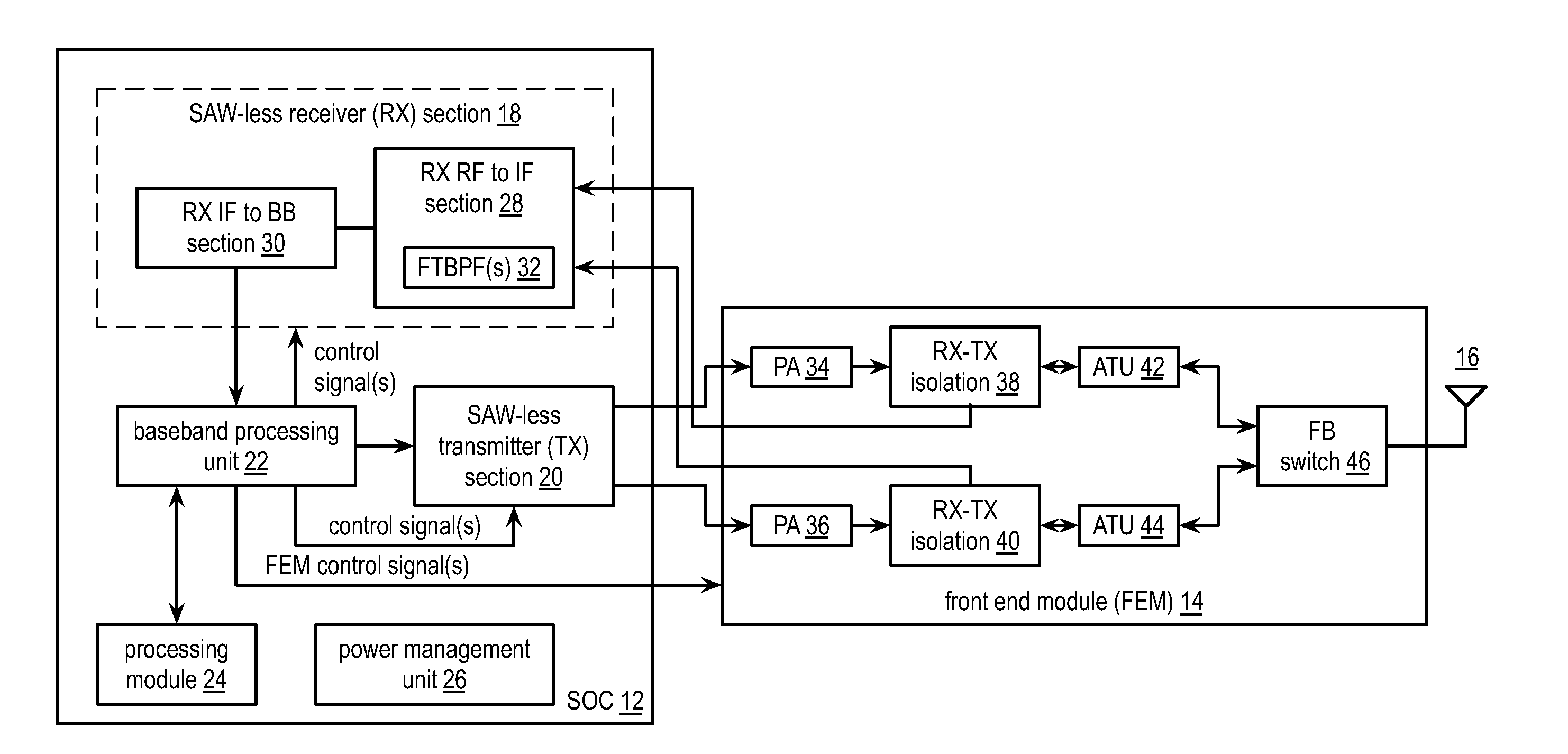
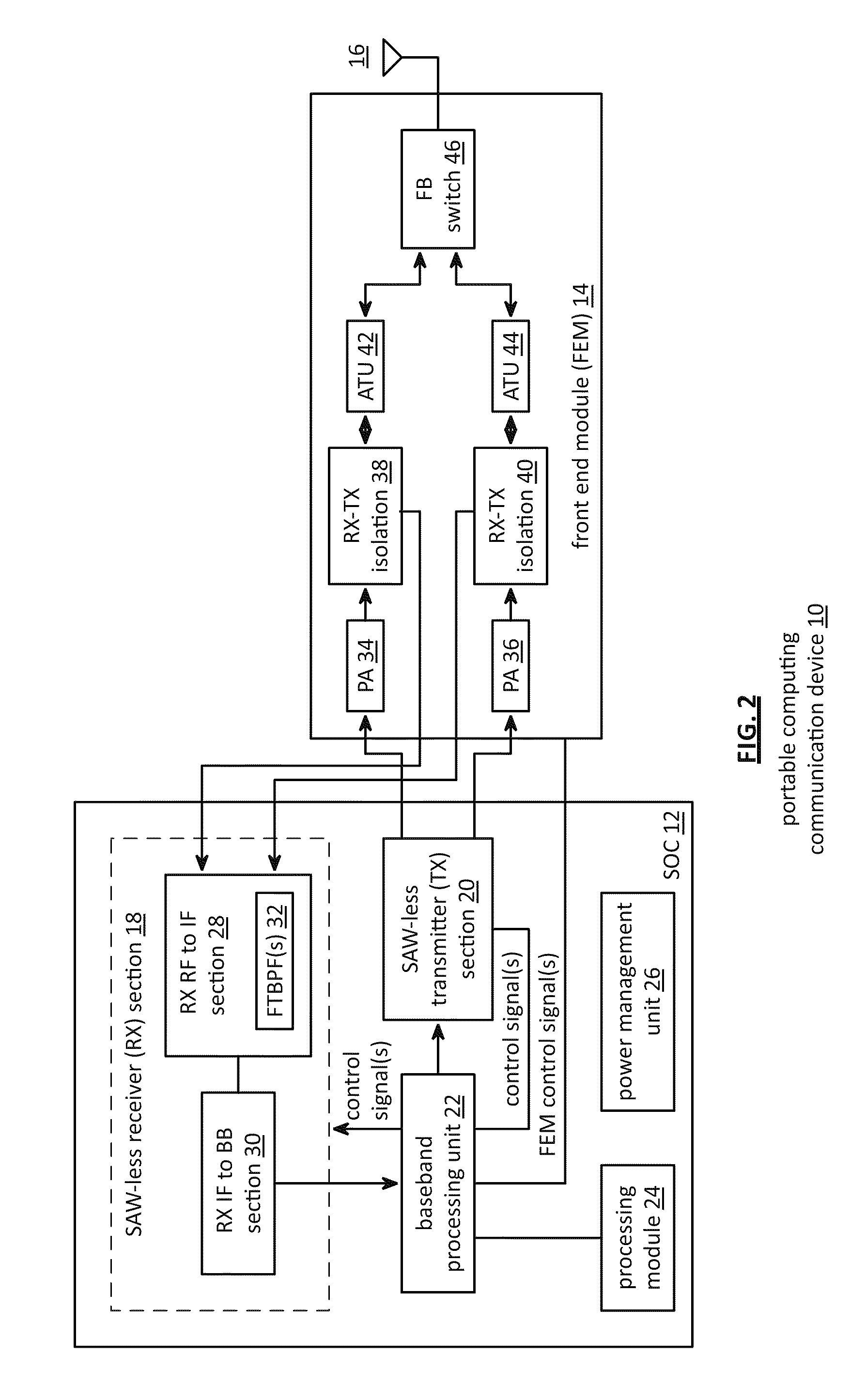
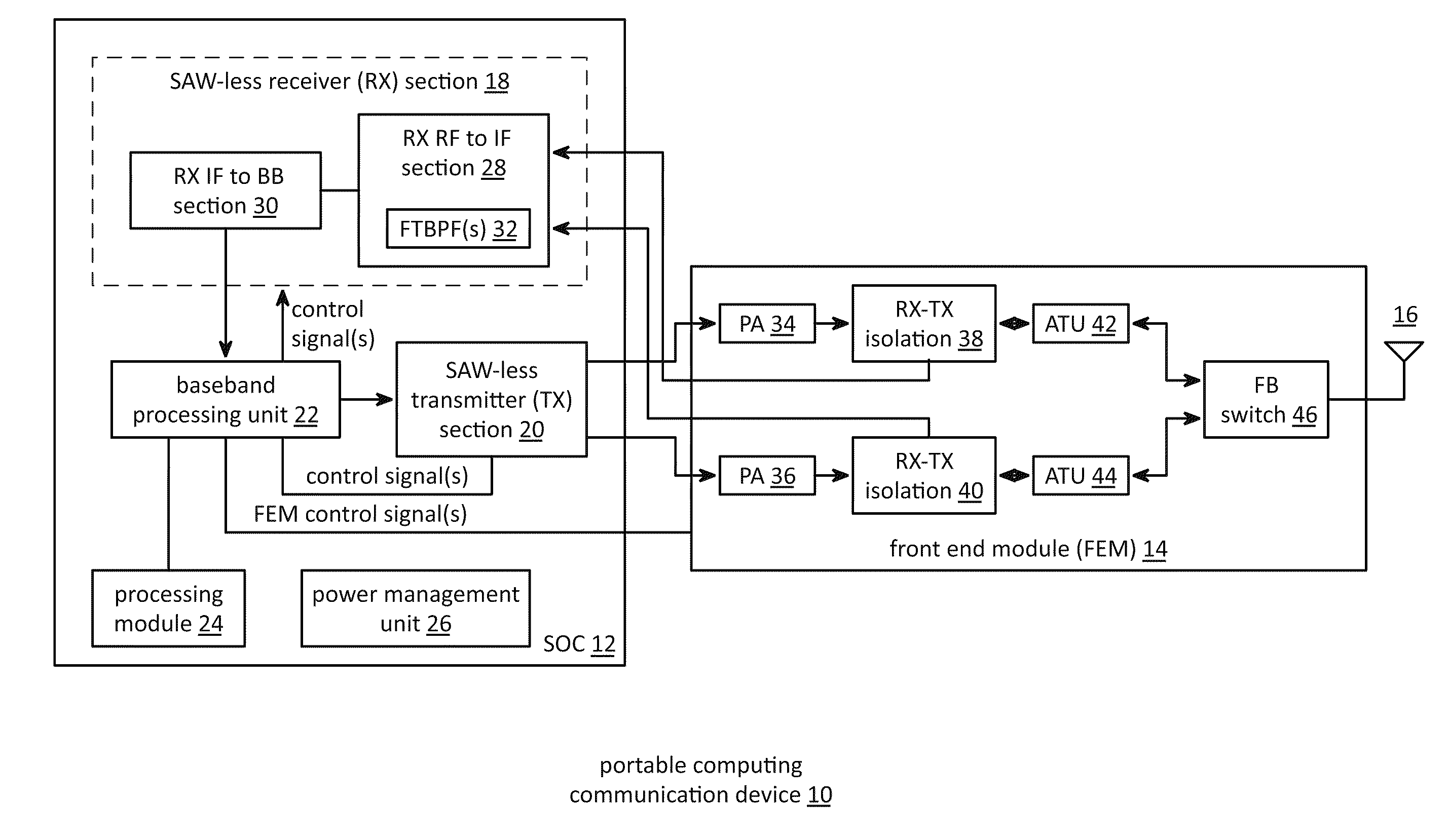
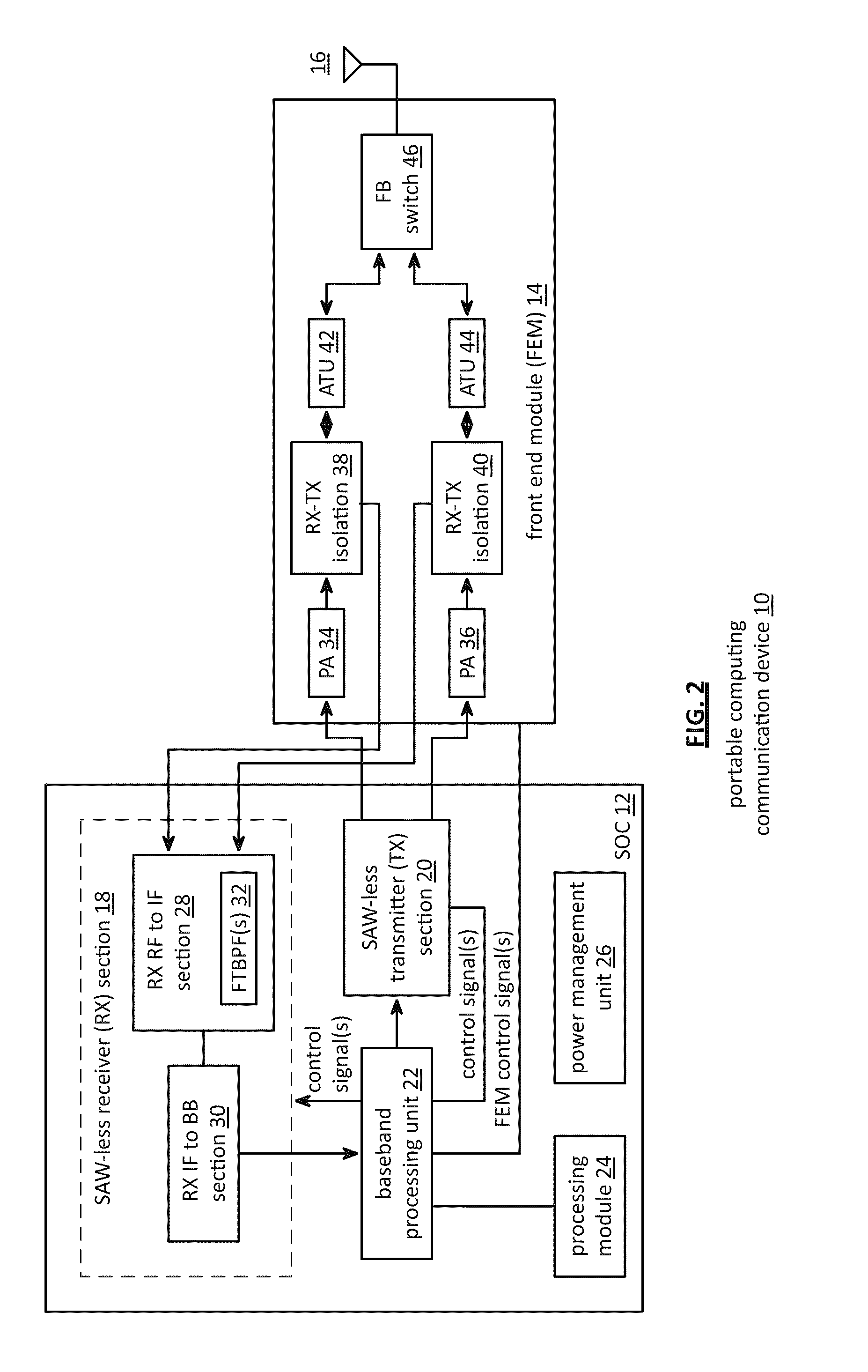
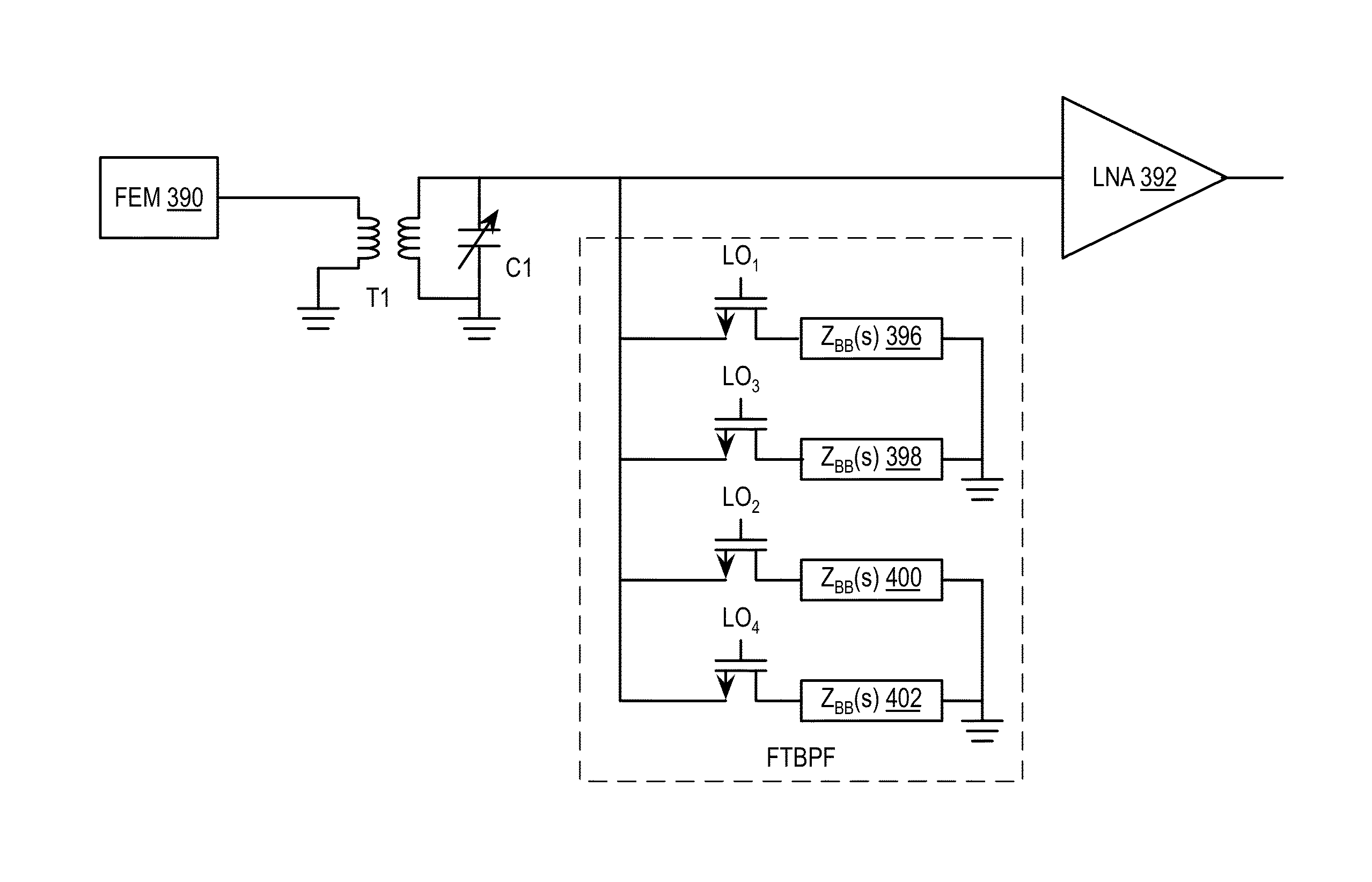
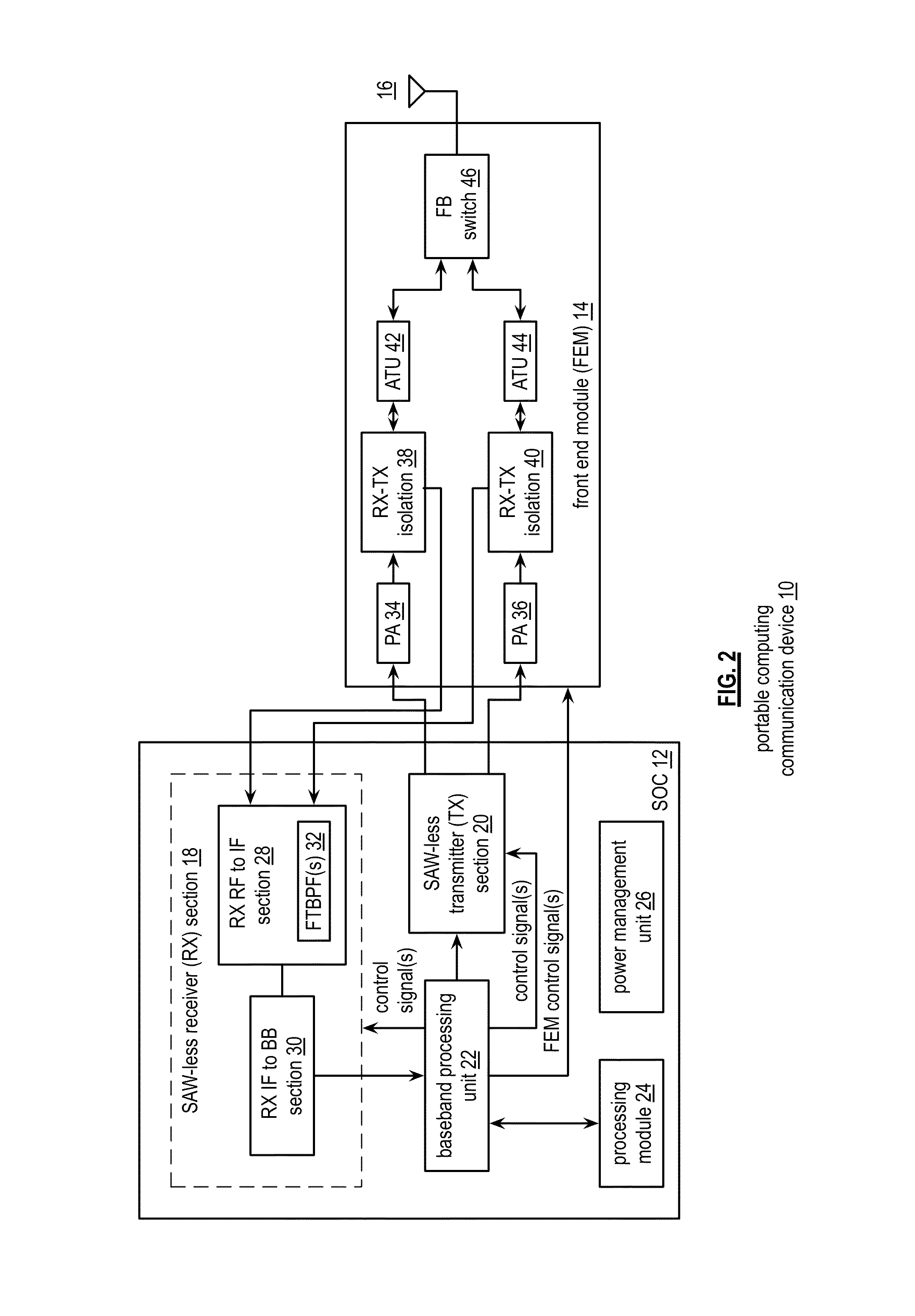
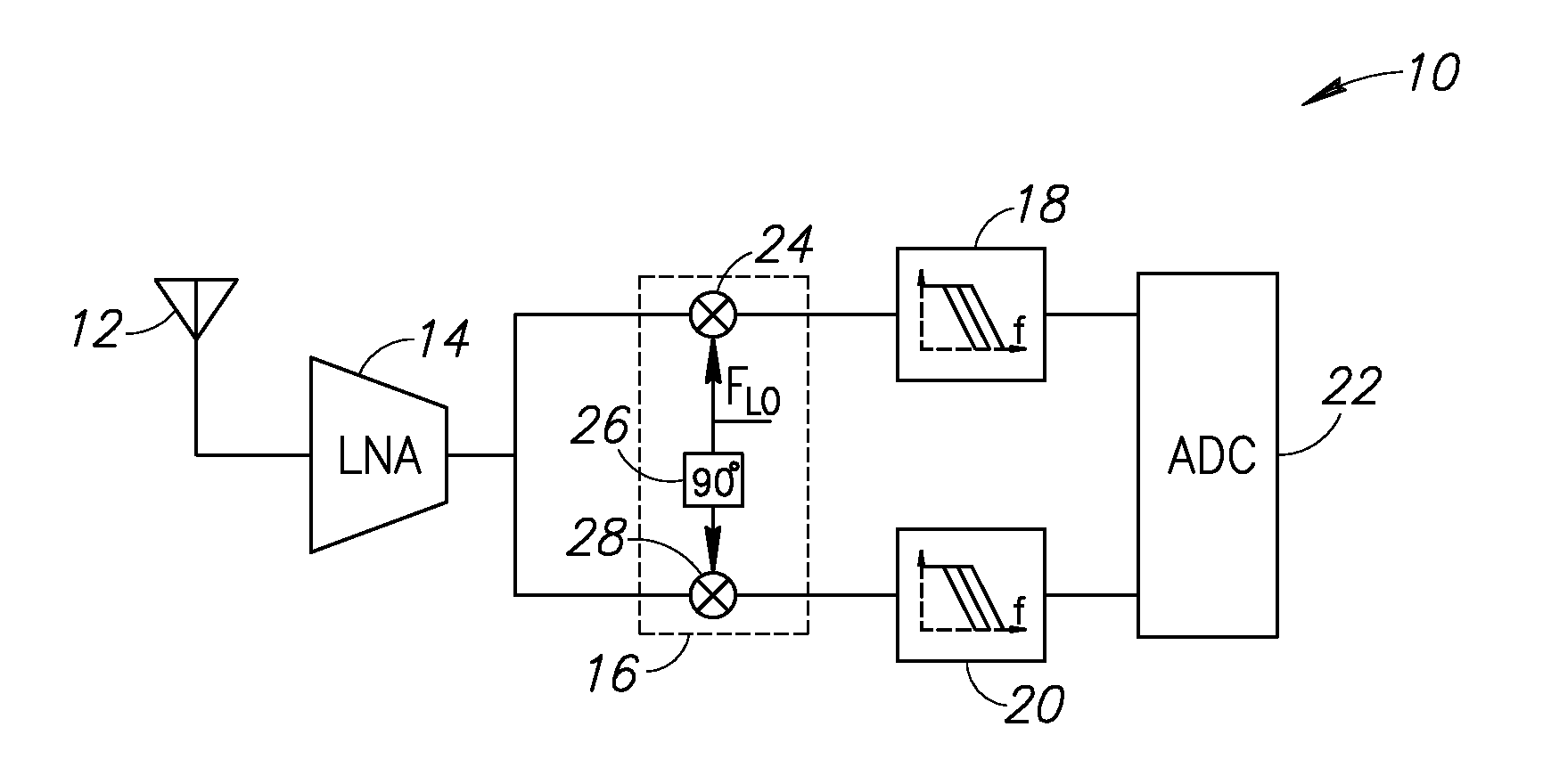
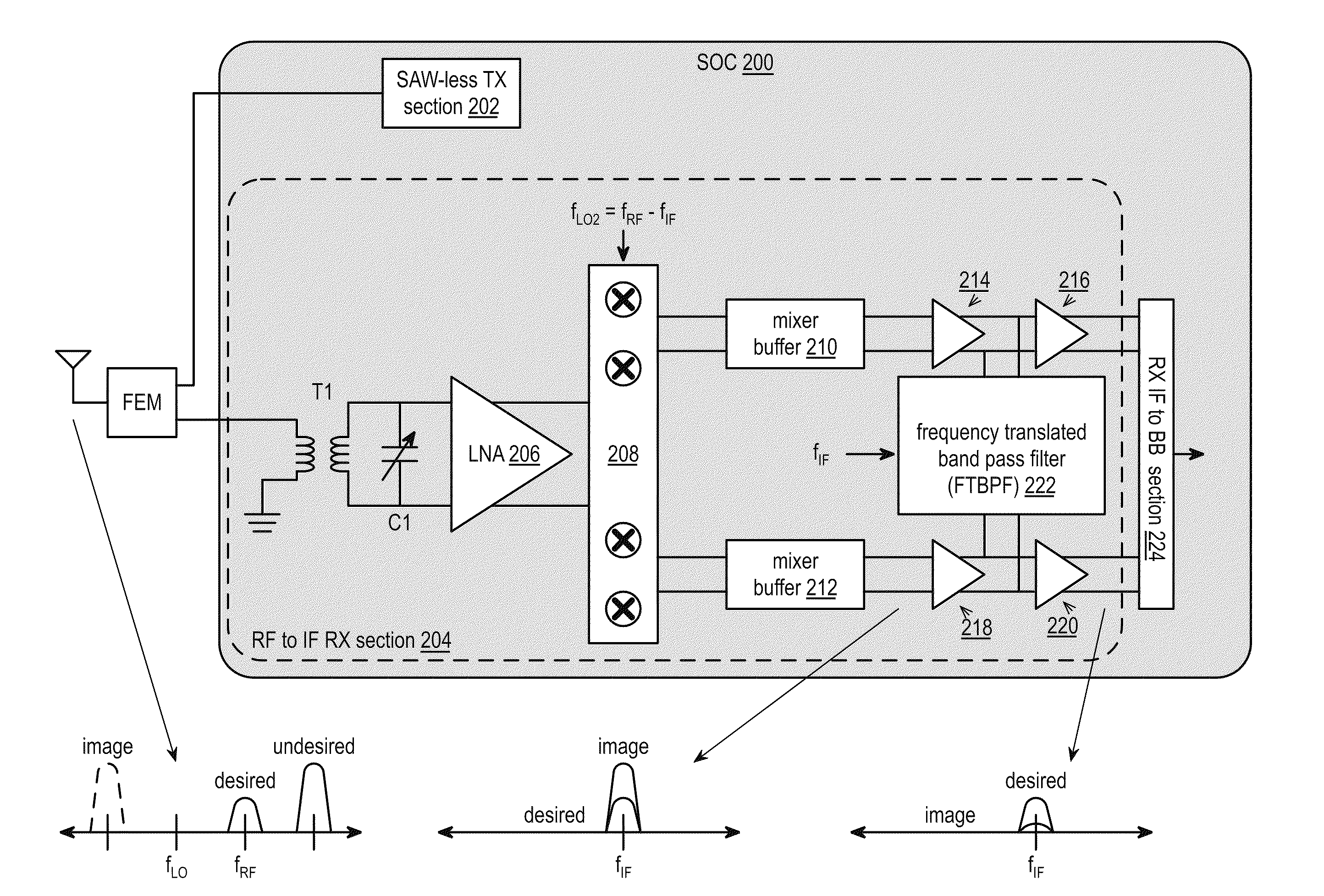
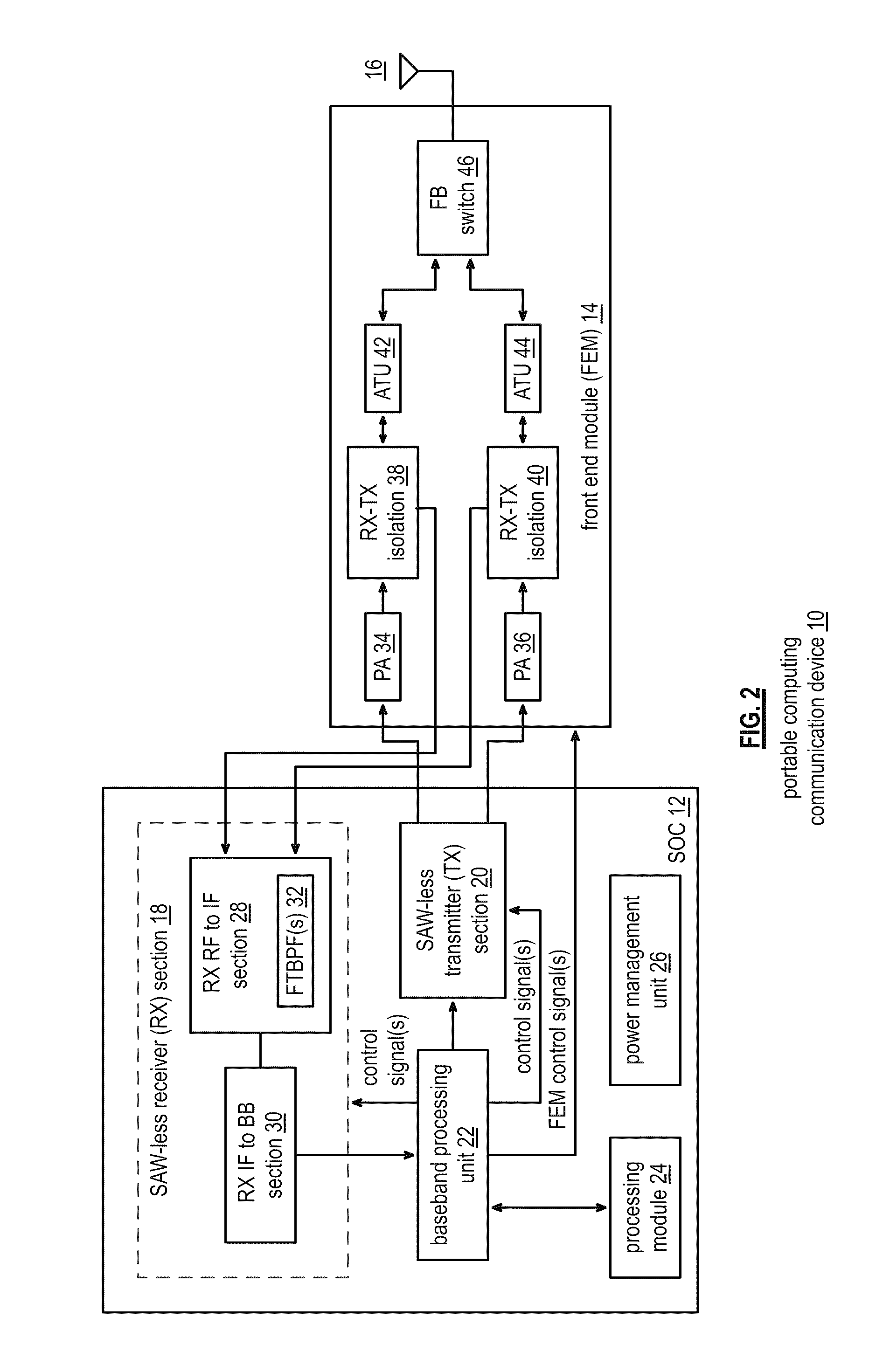
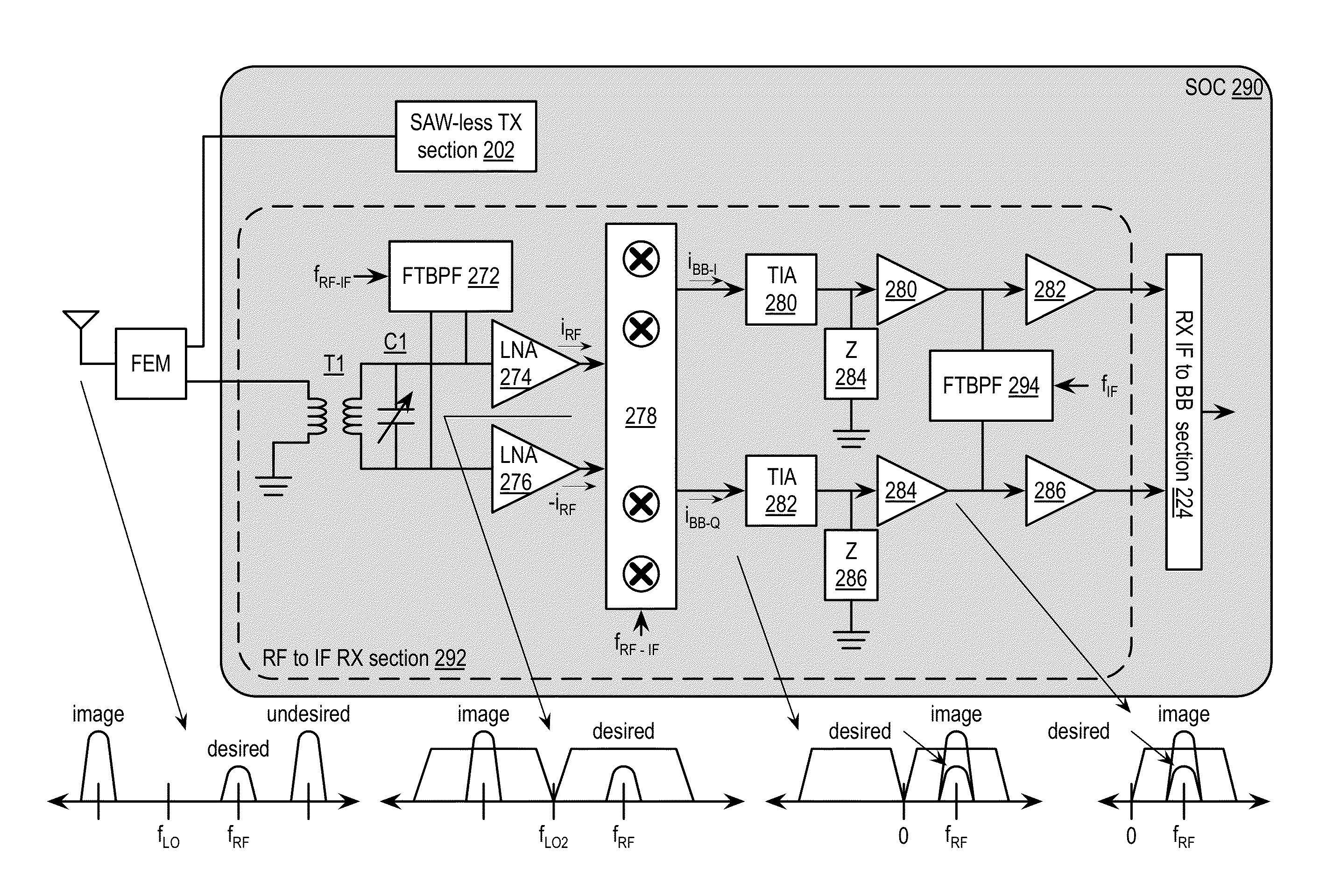
Saw-less receiver with RF frequency translated bpf
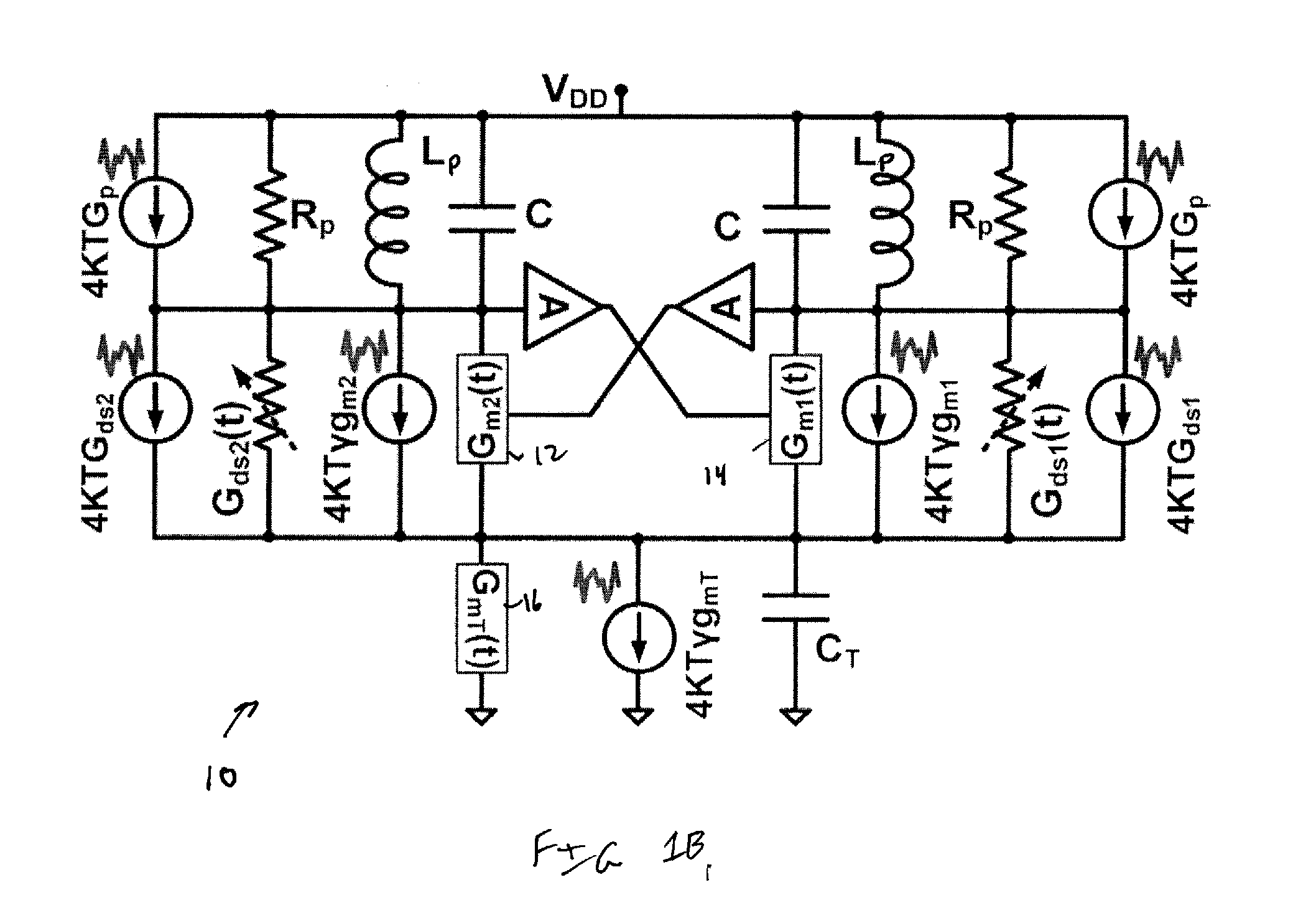
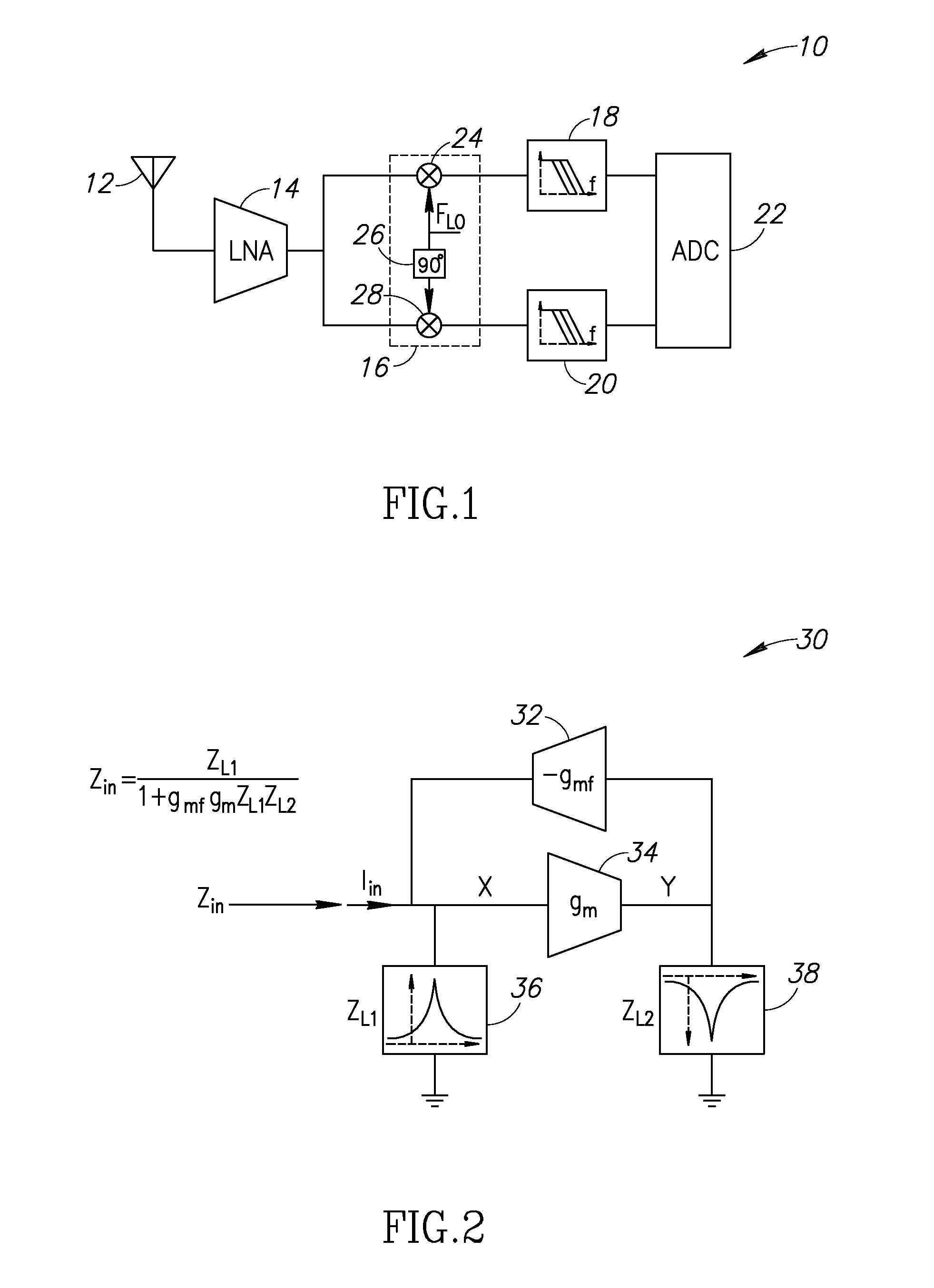
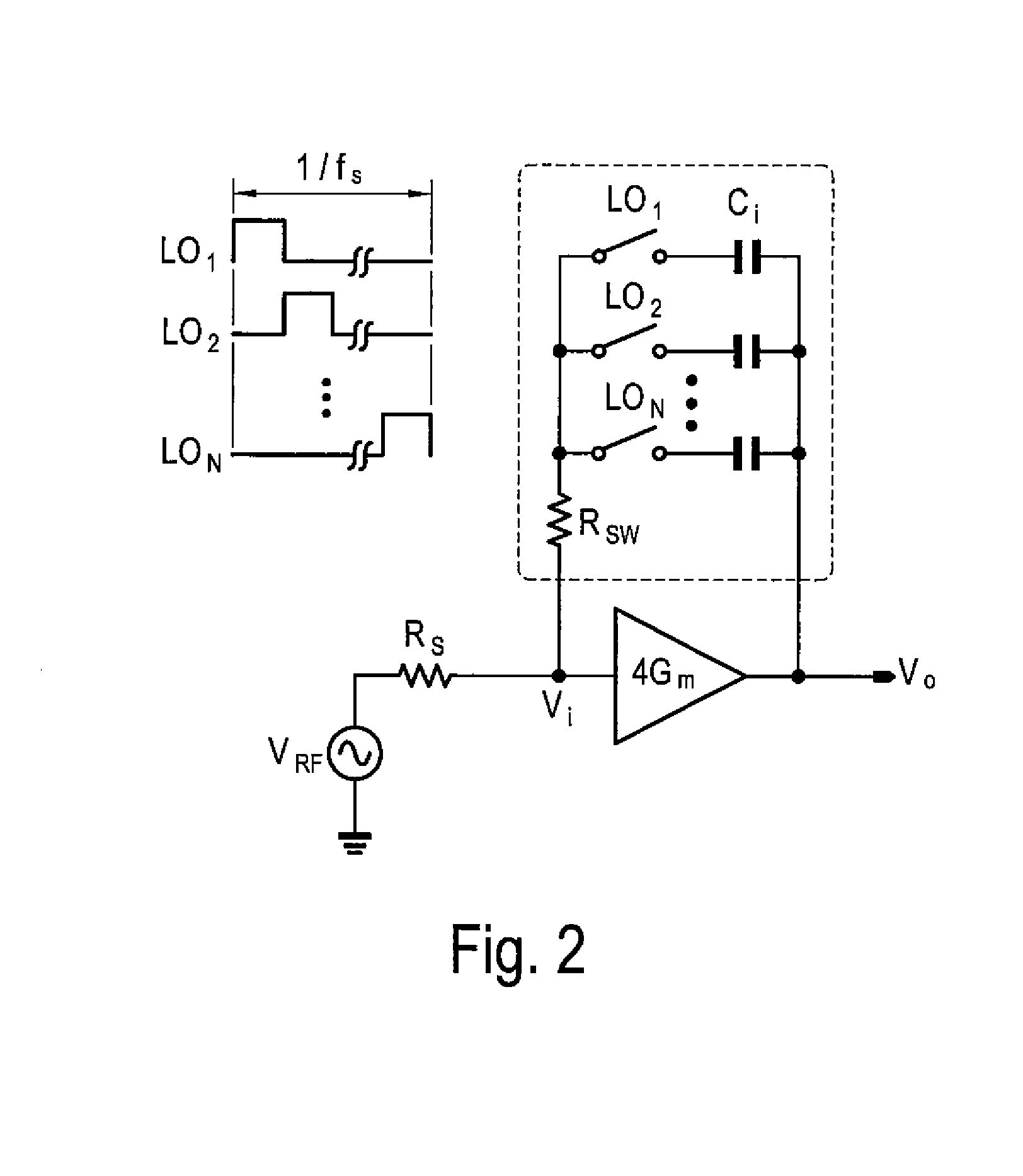
ActiveUS20110299632A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesN-path filtersBandpass filteringEngineering
A SAW-less receiver includes an FEM interface module, an RF to IF receiver section, and a receiver IF to baseband section. The RF to IF receiver section includes a frequency translated bandpass filter (FTBPF), an LNA, and a mixing section. The FTBPF includes a switching network and a plurality of baseband impedances. The switching network is operable to couple the plurality of baseband impedances to the FEM interface in accordance with a plurality of phase-offset RF clock signals to RF bandpass filter the inbound RF signal. The LNA amplifies the filtered inbound RF signal and the mixing section mixes the amplified inbound RF signal with a local oscillation to produce an inbound IF signal. The receiver IF to baseband section converts the inbound IF signal into one or more inbound symbol streams.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
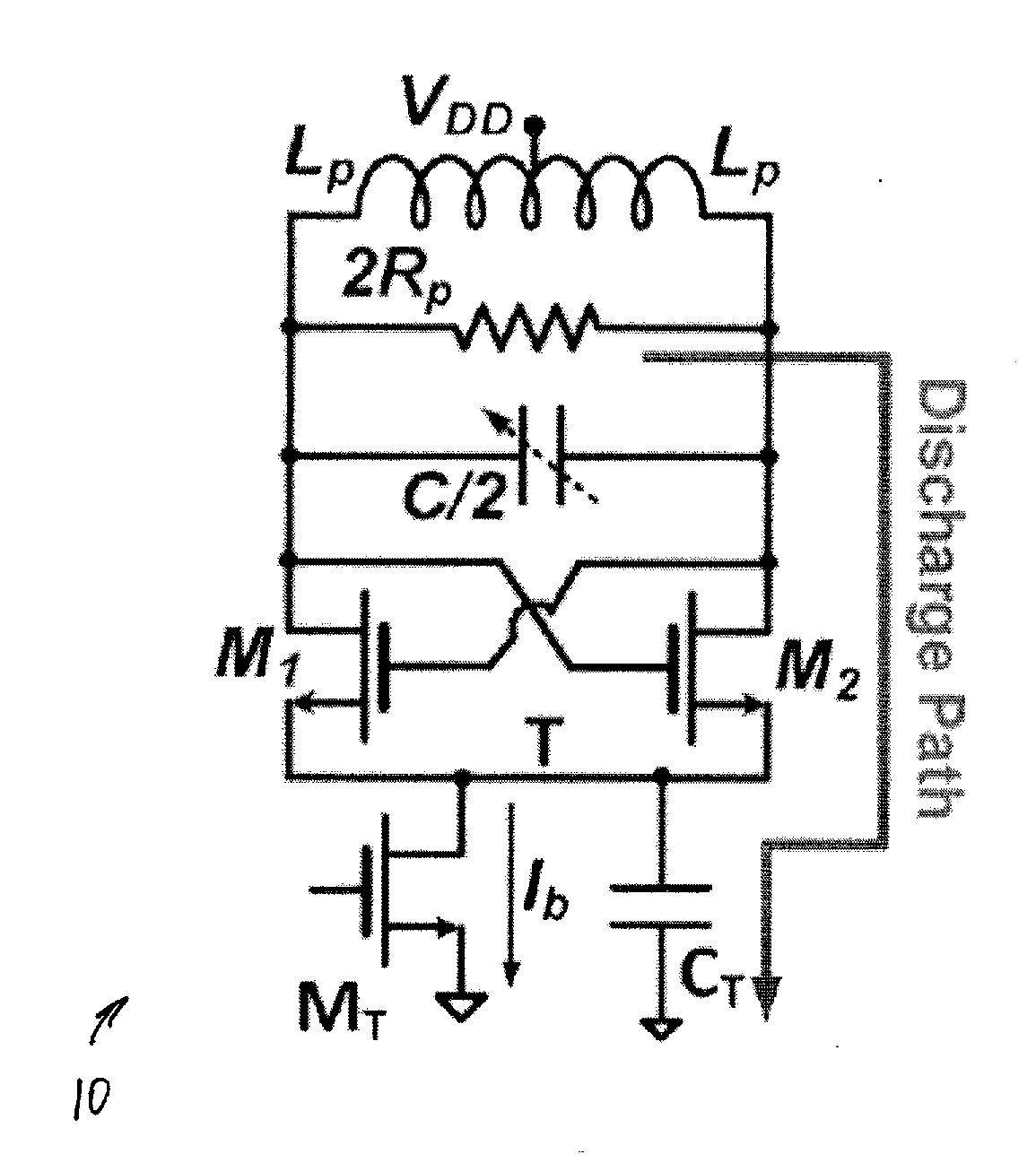
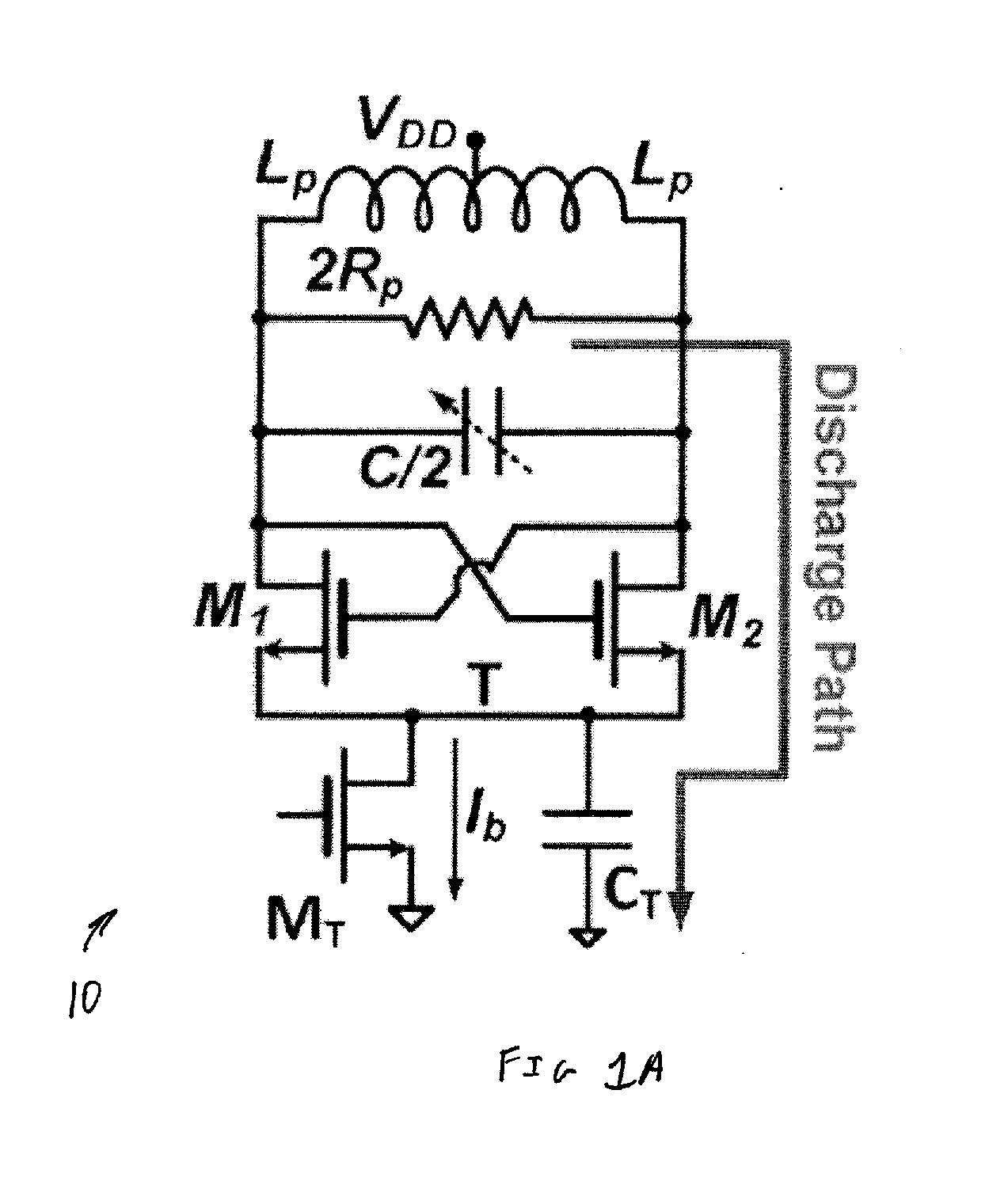
Class-f CMOS oscillator
InactiveUS20140077890A1Improve Phase Noise PerformanceReducing oscillator 's effective noise factorPulse automatic controlN-path filtersTransformerThird harmonic
A novel and useful oscillator topology demonstrating an improved phase noise performance that exploits the time-variant phase noise model with insights into the phase noise conversion mechanisms. The oscillator is based on enforcing a pseudo-square voltage waveform around an LC tank by increasing the third-harmonic of the fundamental oscillation voltage through an additional impedance peak. Alternatively, the oscillator is based on enforcing clipped oscillation waveform by increasing the second harmonic of the fundamental oscillation voltage through an additional impedance peak. This auxiliary impedance peak is realized by a transformer with moderately coupled resonating windings. As a result, the effective impulse sensitivity function (ISF) decreases thus reducing the oscillator's effective noise factor such that a significant improvement in the oscillator phase noise and power efficiency are achieved.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
Polar-based RF receiver
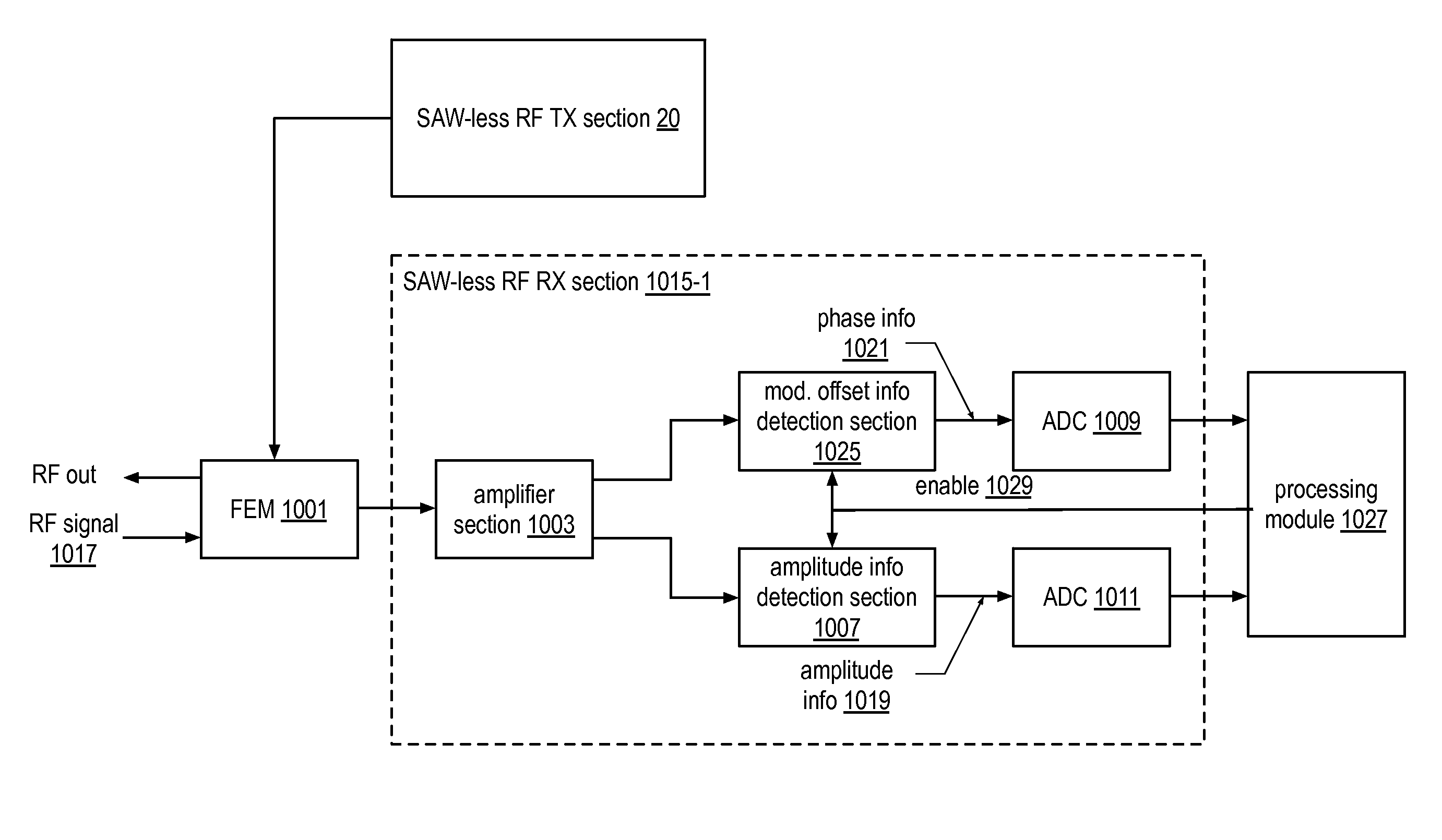
ActiveUS8369807B2Amplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationBandpass filteringAudio power amplifier
A receiver includes a frequency translation bandpass filter (FTBPF) and an RF receiver section. The RF receiver section includes an amplifier section, a phase information detection module, an amplitude information detection module, and analog to digital conversion (ADC) modules. The FTBPF is operable to filter an inbound radio frequency (RF) signal to produce a filtered inbound RF signal. The amplifier section is operable to amplify the filtered inbound RF signal to produce an amplified inbound RF signal. The phase information detection module, when enabled, is operable to determine phase information from the amplified inbound RF signal. The amplitude information detection module, when enabled, is operable to determine amplitude information from the amplified inbound RF signal. A first one of the ADCs is operable to convert the phase information into digital phase information and a second one of the ADCs is operable to convert the amplitude information into digital amplitude information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Transceiver including a weaved connection
A transceiver includes a local oscillation module, a transmitter section, and a receiver section. The local oscillation module is operable to generate a transmit local oscillation and a receive oscillation. The transmitter section includes a transmit mixing module and a transmit weaved connection that is operable to high frequency filter the transmit location oscillation. The transmit mixing module mixes the filtered transmit location oscillation with a transmit signal to produce an up-converted signal. The receiver section includes a receive mixing module and a receive weaved connection that is operable to high frequency filter the receive location oscillation. The receive mixing module mixes the filtered receive location oscillation with an RF received signal to produce a down-converted signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
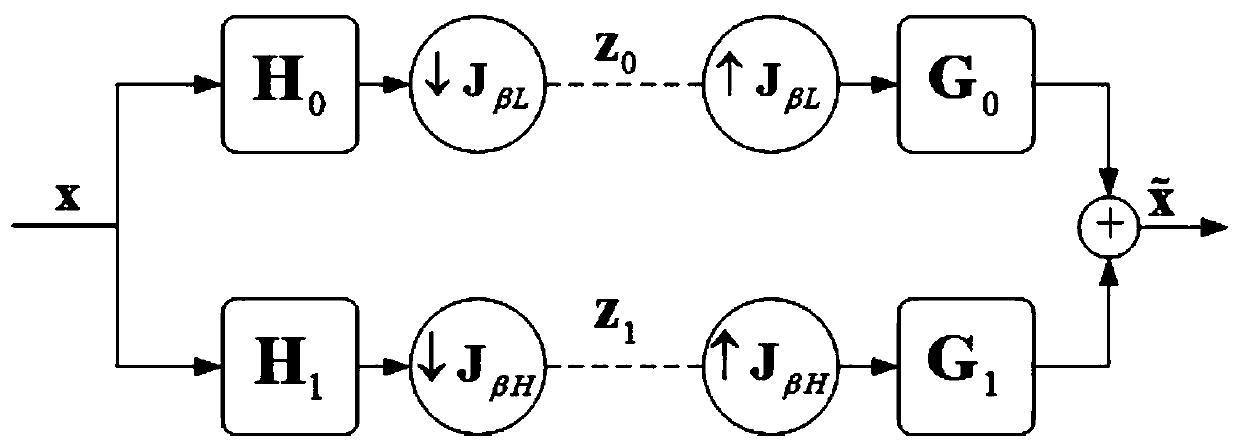
Multiple-phase frequency translated filter
A frequency translation filter includes a baseband filter circuit, a clock generator, and a switching circuit. The baseband filter circuit is operable to provide a baseband filter response. The clock generator is operable to generate multiple-phase clock signals at a desired frequency. The switching circuit is operable to frequency translate the baseband filter response of the baseband filter circuit to a high frequency filter response in accordance with the multiple-phase clock signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Saw-less receiver with RF frequency translated bpf
InactiveUS20140140455A1Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesN-path filtersBandpass filteringAudio power amplifier
A SAW-less receiver includes an interface, an RF to IF receiver section, and a receiver IF to baseband section. The RF to IF receiver section includes a frequency translated bandpass filter (FTBPF), a Low Noise Amplifier (LNA), and a mixing section. The FTBPF includes a switching network and a plurality of baseband impedances. The switching network is operable to couple the plurality of baseband impedances to the interface in accordance with a plurality of phase-offset RF clock signals to RF bandpass filter the inbound RF signal. The LNA amplifies the filtered inbound RF signal and the mixing section mixes the amplified inbound RF signal with a local oscillation to produce an inbound IF signal. The receiver IF to baseband section converts the inbound IF signal into one or more inbound symbol streams. Filtering may be prior or after amplification by the LNA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
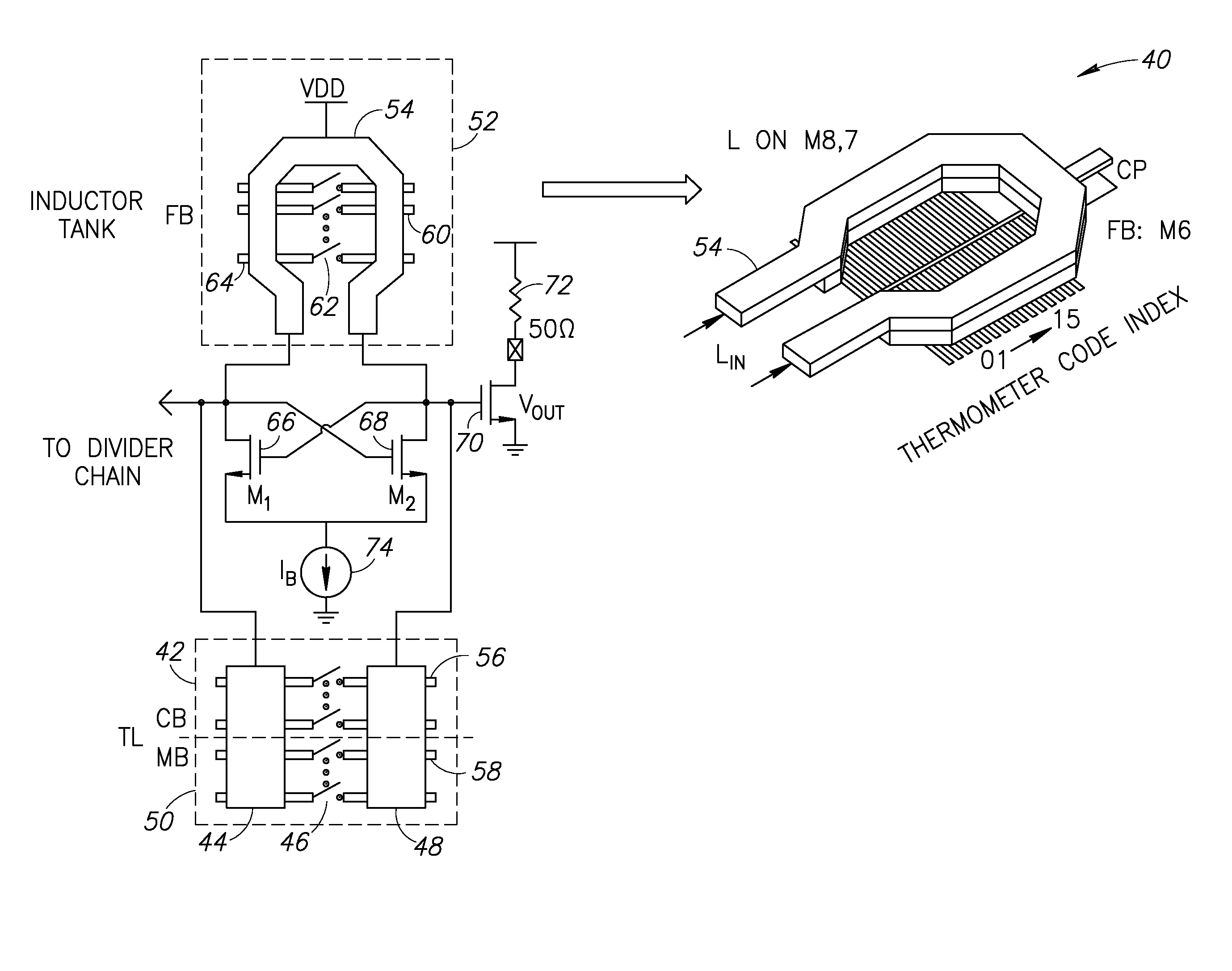
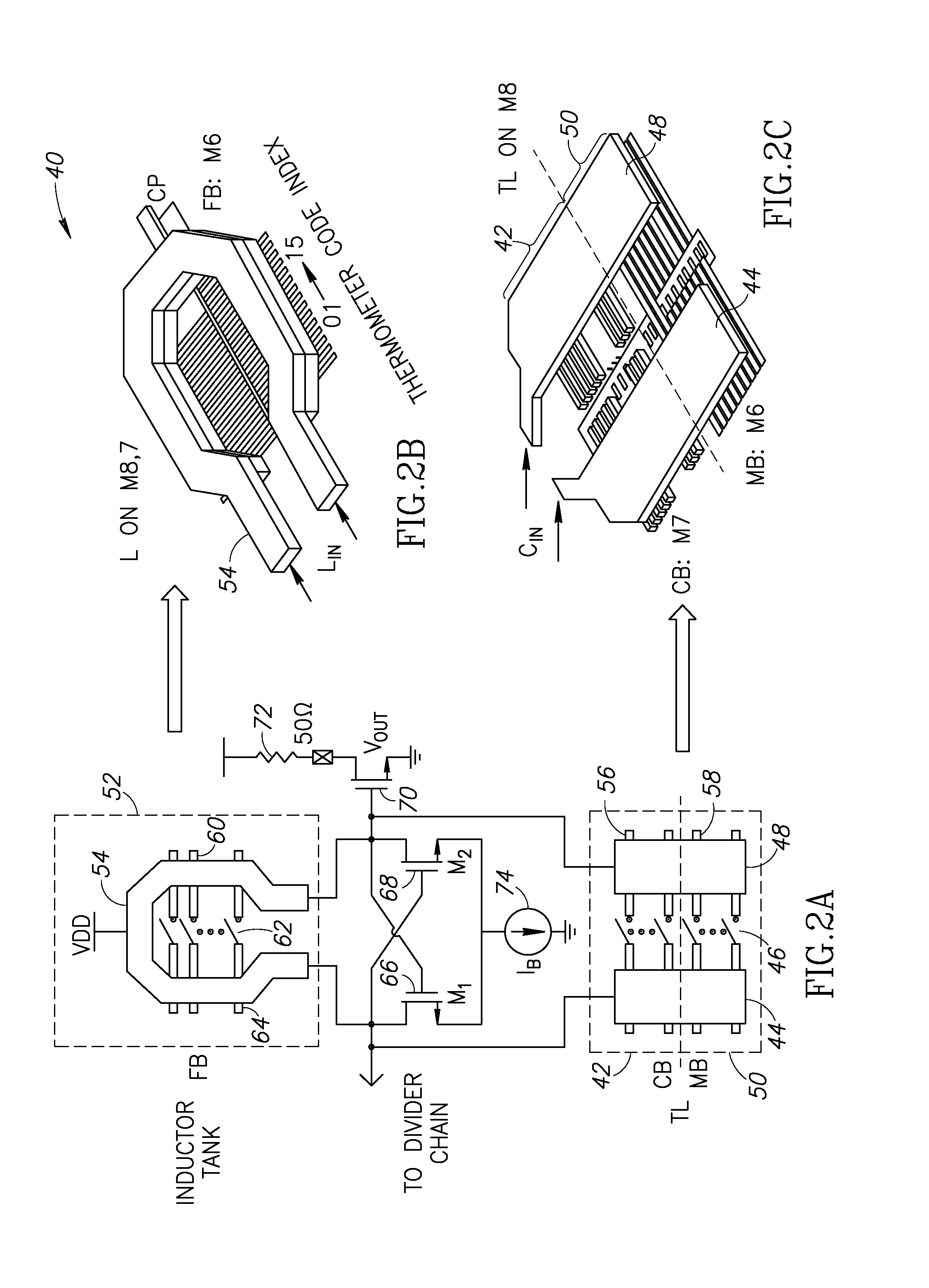
High resolution millimeter wave digitally controlled oscillator with reconfigurable distributed metal capacitor passive resonators
A novel and useful millimeter-wave digitally controlled oscillator (DCO) that achieve a tuning range greater than 10% and fine frequency resolution less than 1 MHz. Switched metal capacitors are distributed across a passive resonator for tuning the oscillation frequency. To obtain sub-MHz frequency resolution, tuning step attenuation techniques are used that exploit an inductor and a transformer. A 60-GHz fine-resolution inductor-based DCO (L-DCO) and a 60 GHz transformer-coupled DCO (T-DCO), both fabricated in 90 nm CMOS, are disclosed. The phase noise of both DCOs is lower than −90.5 dBc / Hz at 1 MHz offset across 56 to 62 GHz frequency range. The T-DCO achieves a fine frequency tuning step of 2.5 MHz, whereas the L-DCO tuning step is over one order of magnitude finer at 160 kHz.
Owner:TECH UNIV DELFT
Polar-based RF receiver
A receiver includes a frequency translation bandpass filter (FTBPF) and an RF receiver section. The RF receiver section includes an amplifier section, a phase information detection module, an amplitude information detection module, and analog to digital conversion (ADC) modules. The FTBPF is operable to filter an inbound radio frequency (RF) signal to produce a filtered inbound RF signal. The amplifier section is operable to amplify the filtered inbound RF signal to produce an amplified inbound RF signal. The phase information detection module, when enabled, is operable to determine phase information from the amplified inbound RF signal. The amplitude information detection module, when enabled, is operable to determine amplitude information from the amplified inbound RF signal. A first one of the ADCs is operable to convert the phase information into digital phase information and a second one of the ADCs is operable to convert the amplitude information into digital amplitude information.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Front end module with tone injection
InactiveUS20110300814A1Multiple-port networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesBalancing networkAudio power amplifier
A radio front end includes a power amplifier, a tone injection module, a duplexer, a balancing network, and a processing module. The tone injection module is operable, in a first mode, to produce a tone having a carrier frequency that is substantially similar to a carrier frequency of an inbound wireless signal. The duplexer is operable, in the first mode, to provide electrical isolation between the outbound wireless signal and a combination signal of the tone and inbound wireless signal and is operable, in a second mode, to provide electrical isolation between the outbound wireless signal and the inbound wireless signal. The processing module is operable to determine an amplitude of a tone component of the combination signal; correlate the amplitude of the tone component to an inbound frequency band isolation; and adjust baseband processing of a down converted representation of the combination signal based on the inbound frequency band isolation.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Front end module with active tuning of a balancing network
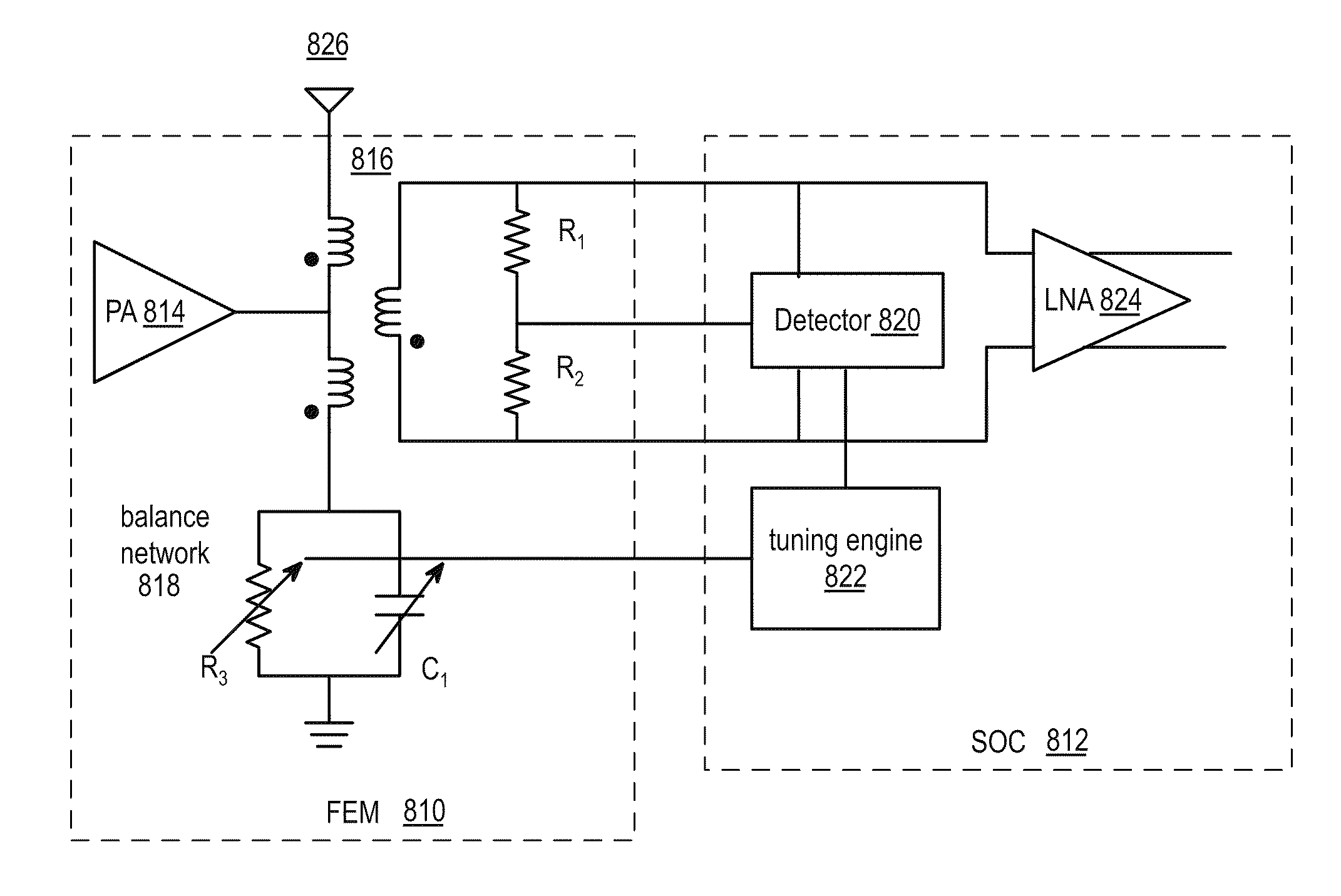
ActiveUS20110299435A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equalisingElectricityBalancing network
A radio front end includes a duplexer, a tunable balancing network, a detector module, and a processing module. The duplexer is operably coupled to an antenna and is operable to provide electrical isolation between an outbound wireless signal and an inbound wireless signal. The tunable balancing network is operably coupled to the duplexer and operable to establish an impedance that substantially matches an impedance of the antenna based on a tuning signal. The detector module is operable to generate an error signal based on an electrical performance characteristic of the duplexer. The processing module is operable to generate the tuning signal based on the error signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Tunable RF channel select filter
Methods and apparatus, including computer program products, are provided for RF filtering. Related apparatus, systems, methods, and articles are also described.
Owner:RPX CORP
Saw-less receiver with RF frequency translated BPF
ActiveUS8655299B2Amplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringElectrical impedance
A SAW-less receiver includes an FEM interface module, an RF to IF receiver section, and a receiver IF to baseband section. The RF to IF receiver section includes a frequency translated bandpass filter (FTBPF), an LNA, and a mixing section. The FTBPF includes a switching network and a plurality of baseband impedances. The switching network is operable to couple the plurality of baseband impedances to the FEM interface in accordance with a plurality of phase-offset RF clock signals to RF bandpass filter the inbound RF signal. The LNA amplifies the filtered inbound RF signal and the mixing section mixes the amplified inbound RF signal with a local oscillation to produce an inbound IF signal. The receiver IF to baseband section converts the inbound IF signal into one or more inbound symbol streams.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Design method of time-varying separable non-downsampled filter bank based on iterative calculation
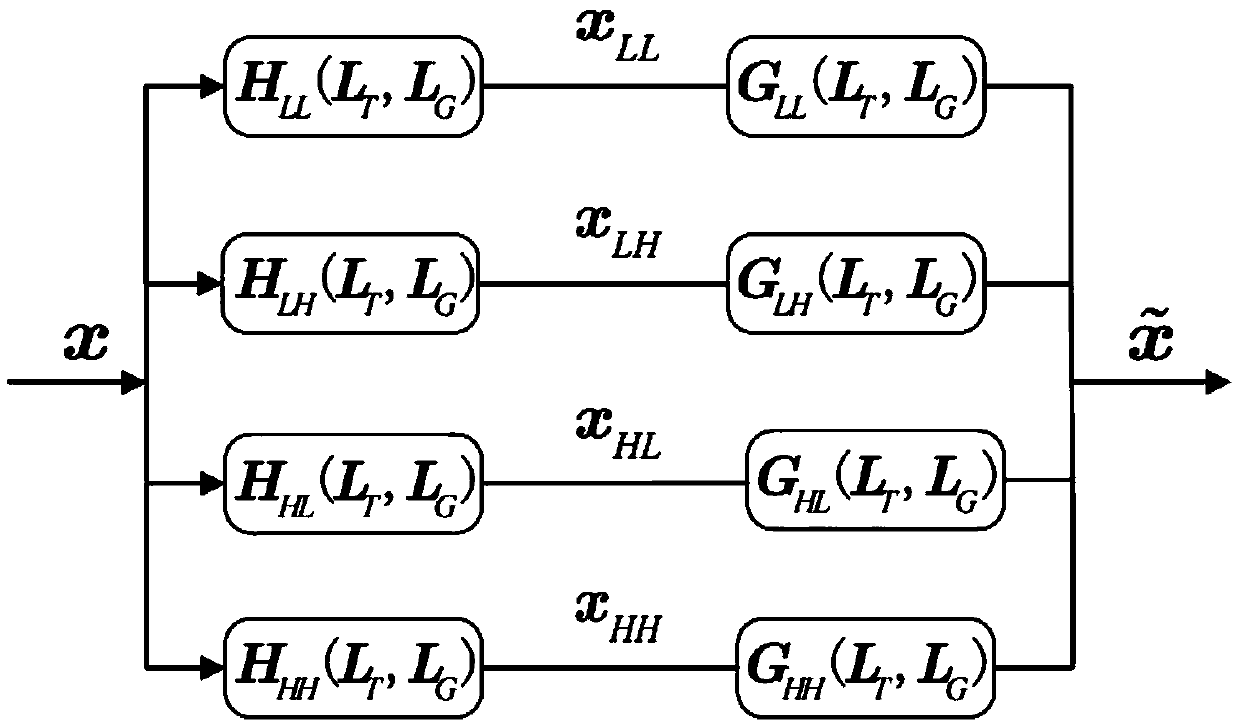
ActiveCN109586688AWith frequency responseFully refactorableNetworks with variable switch closing timeN-path filtersSeparable filterReconstruction problem
The invention discloses a design method of a time-varying separable non-downsampled filter bank based on iterative calculation. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, based on the properties of atwo-dimensional separable filter, designing an analysis filter bank with a frequency response; and finally, converting the reconstruction problem of the output signal of an integrated filter bank toa global least squares problem, converting the global least squares problem into a local least squares problem, and performing solution through an iteration mode. The iteration calculation method is low in iteration times, the designed time-varying separable non-downsampled filter bank has the complete reconstruction feature and the better denoising performance, and the analysis filter has frequency response.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
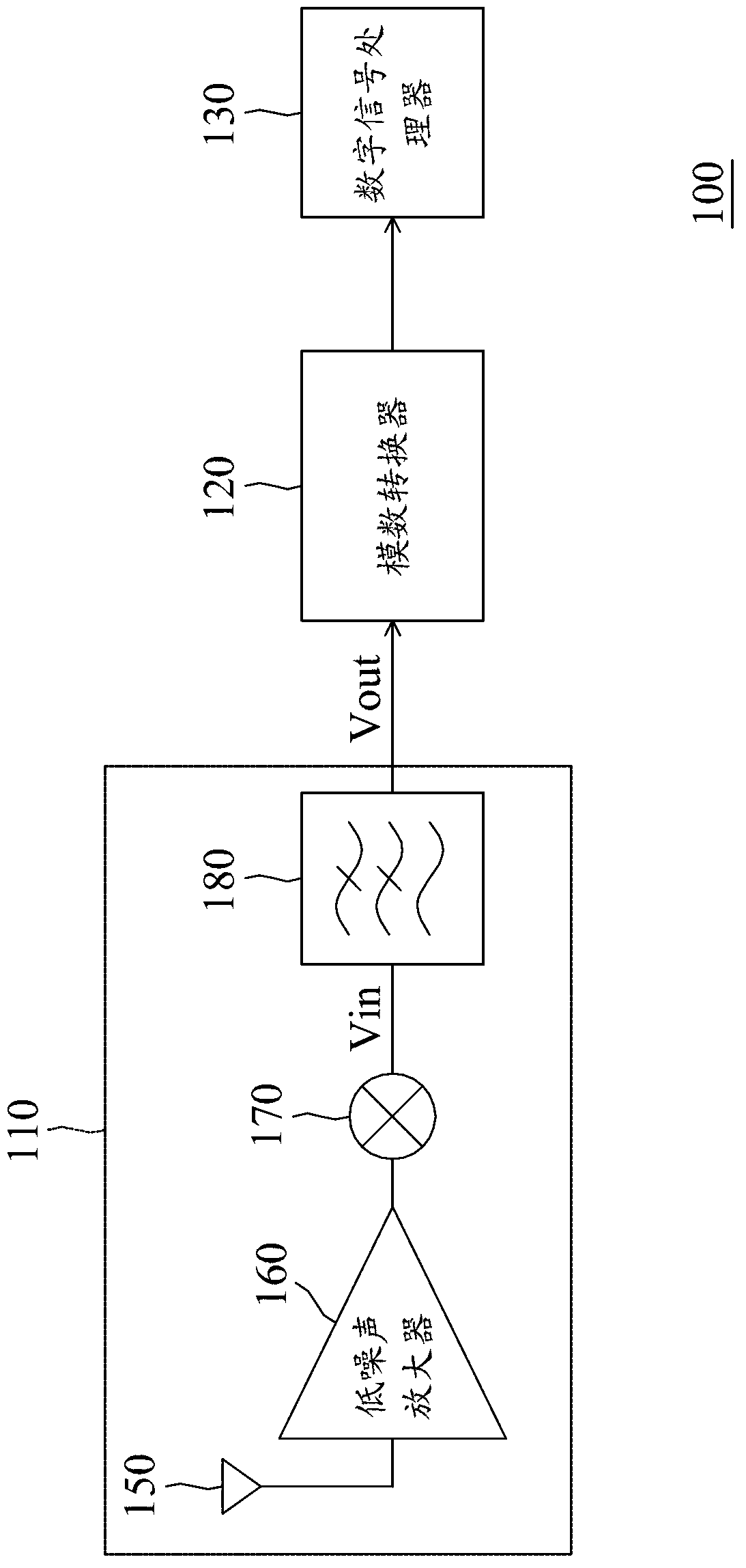
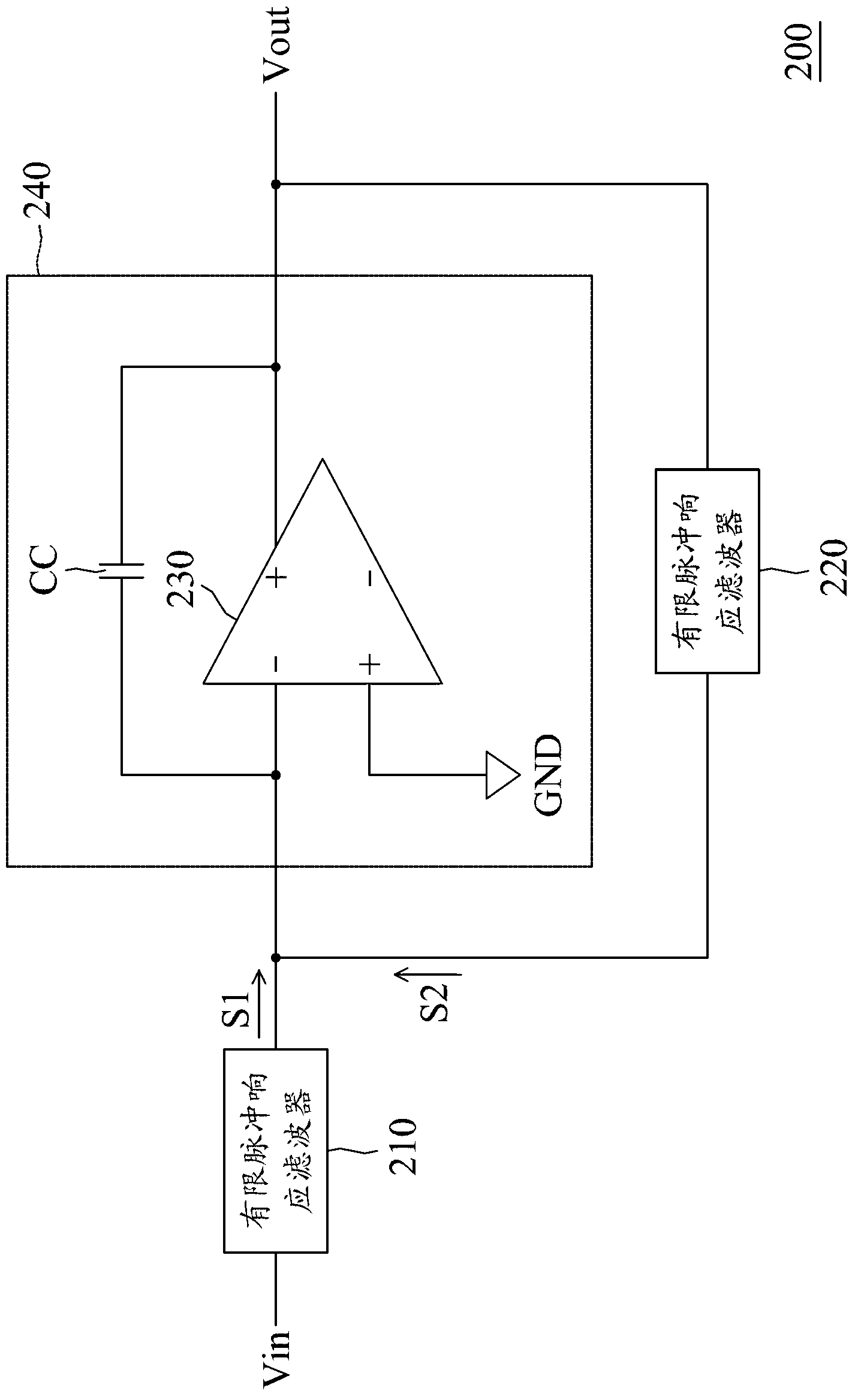
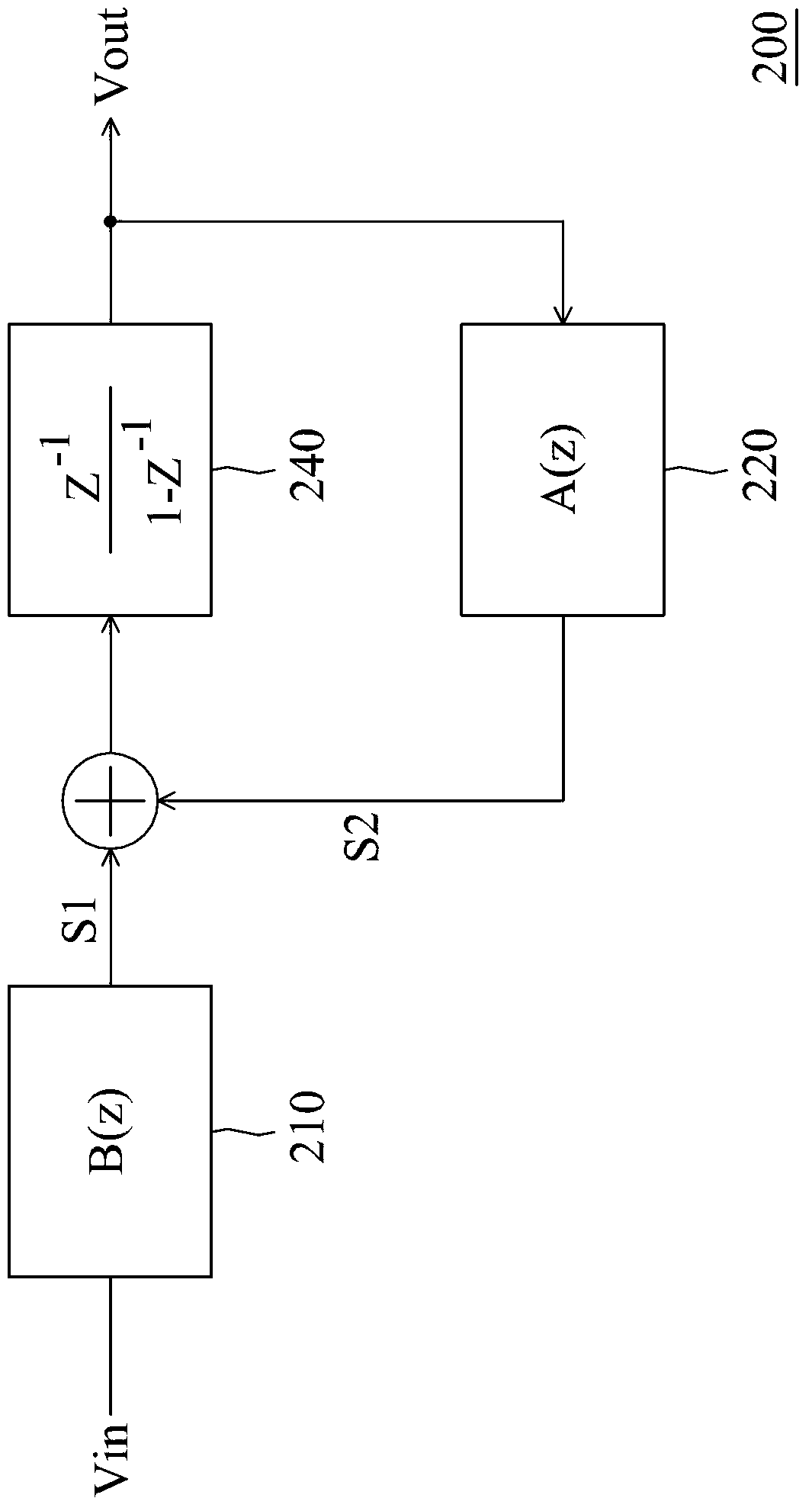
Infinite impulse response (IIR) filter and filtering method
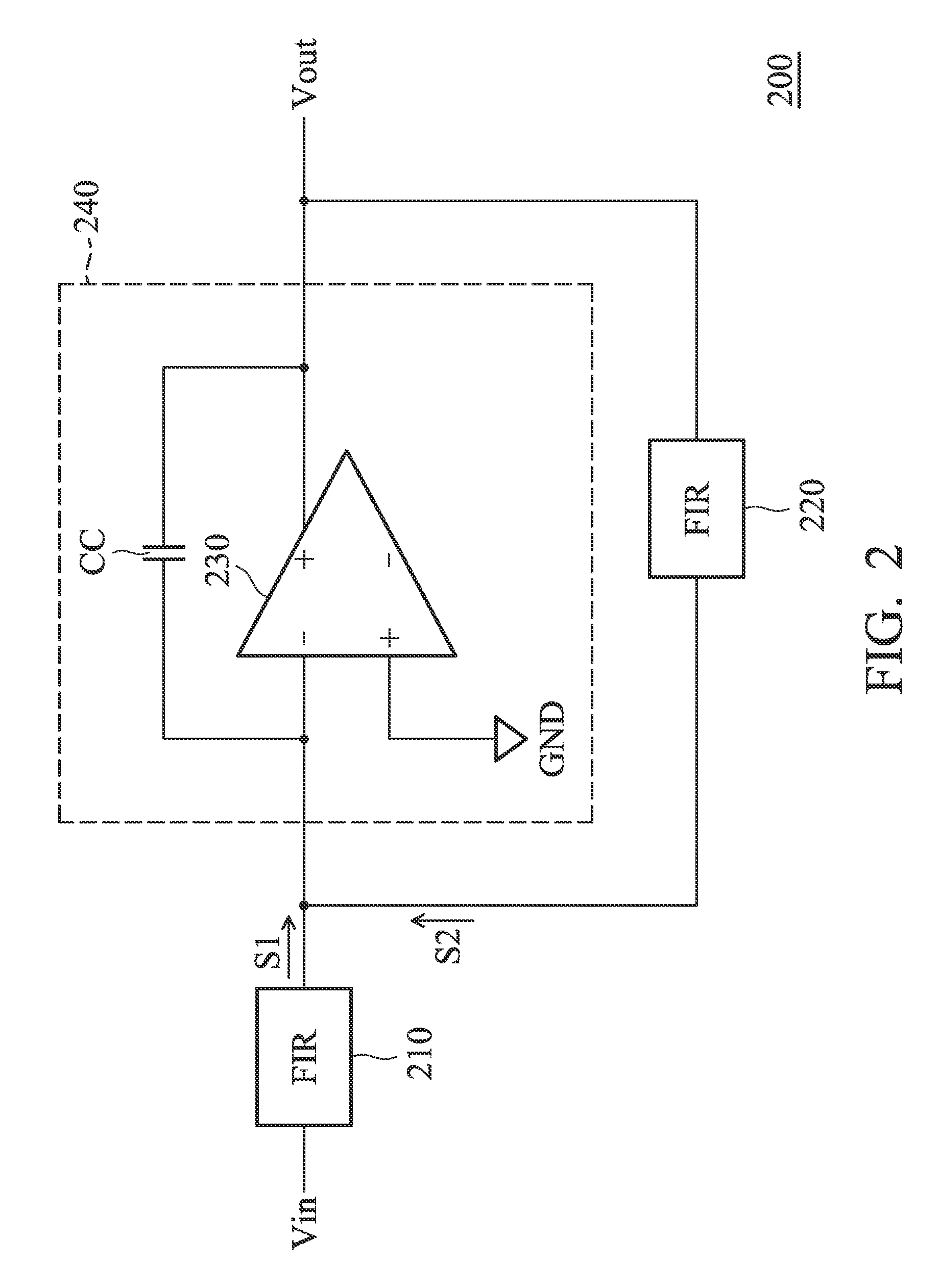
An infinite impulse response (IIR) filter is provided. The IIR filter includes an amplifier and a filter coupled in a feedback path of the amplifier. The amplifier generates an output signal according to an input signal. The filter filters the output signal according to a first transfer function and provides the filtered output signal to an input of the amplifier. The IIR filter and the first filter have the same order larger than one.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
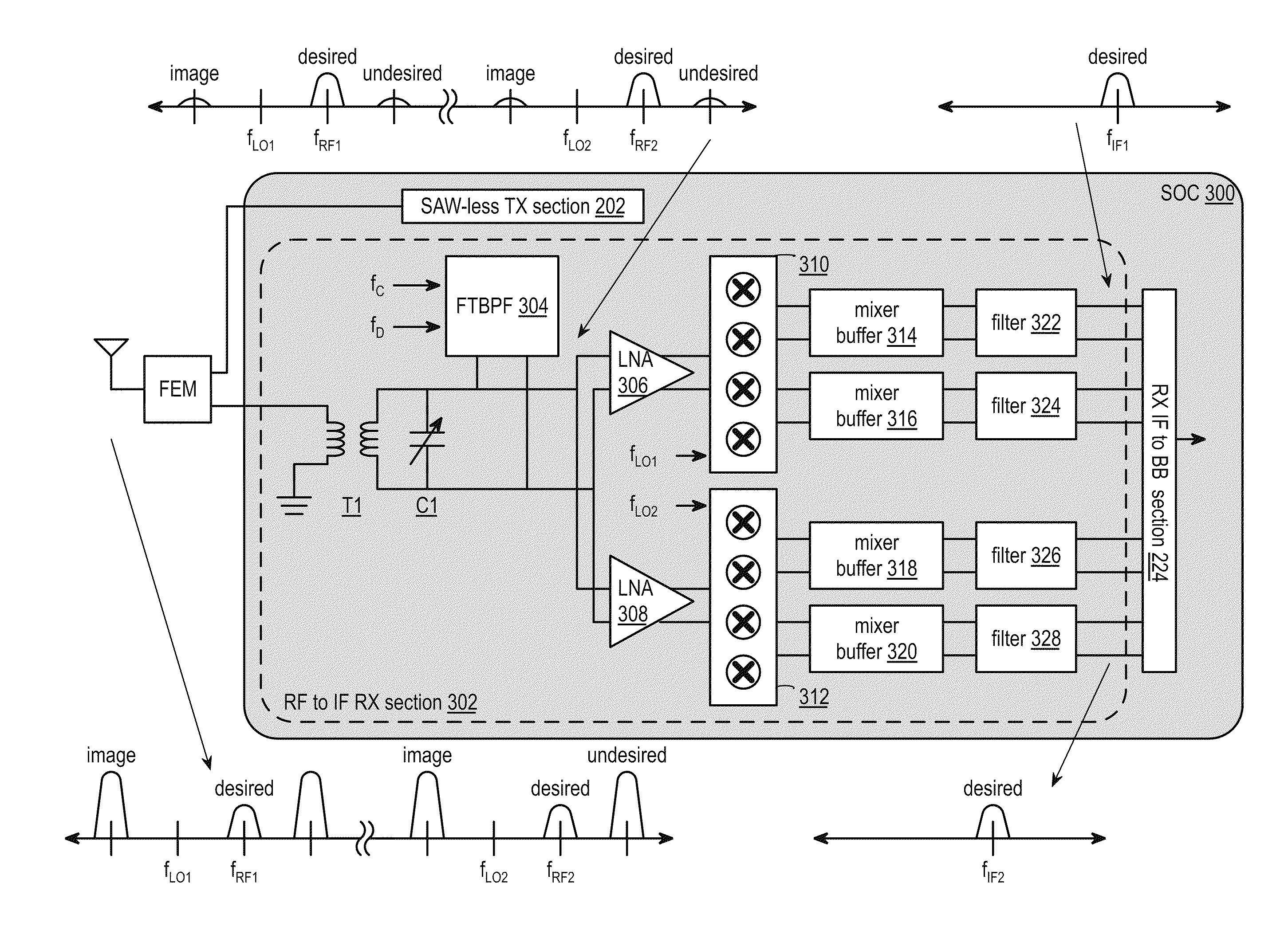
Saw-less receiver with offset RF frequency translated bpf
ActiveUS20110299459A1Multiple-port networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesBandpass filteringResponse Frequency
A SAW-less receiver includes a front end module (FEM) interface module, an RF to IF section, and an IF to baseband section. The RF to IF section includes a frequency translated bandpass filter (FTBPF), an LNA, and a mixing section. The FTBPF includes a switching network and a complex baseband filter having an offset baseband filter response. The switching network is operable to frequency translate the offset baseband filter response to an RF frequency response such that the FTBPF filters the inbound RF signal by passing, substantially unattenuated, a desired RF signal component and by attenuating an image signal component and / or an undesired signal component. The LNA amplifies the filtered inbound RF signal and the mixing section mixes the amplified inbound RF signal with a local oscillation to produce an inbound IF signal. The IF to baseband section converts the inbound IF signal into an inbound symbol stream(s).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
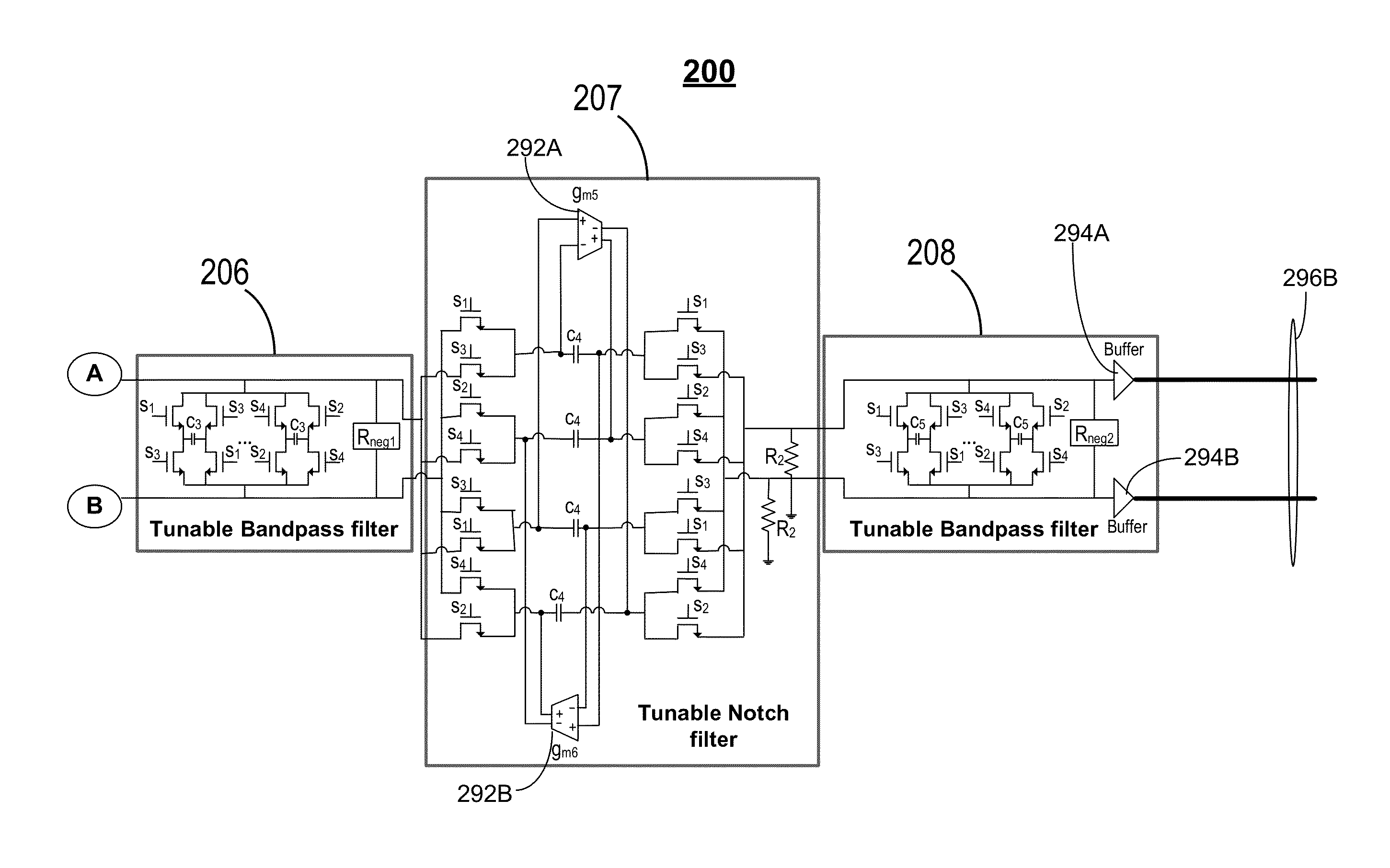
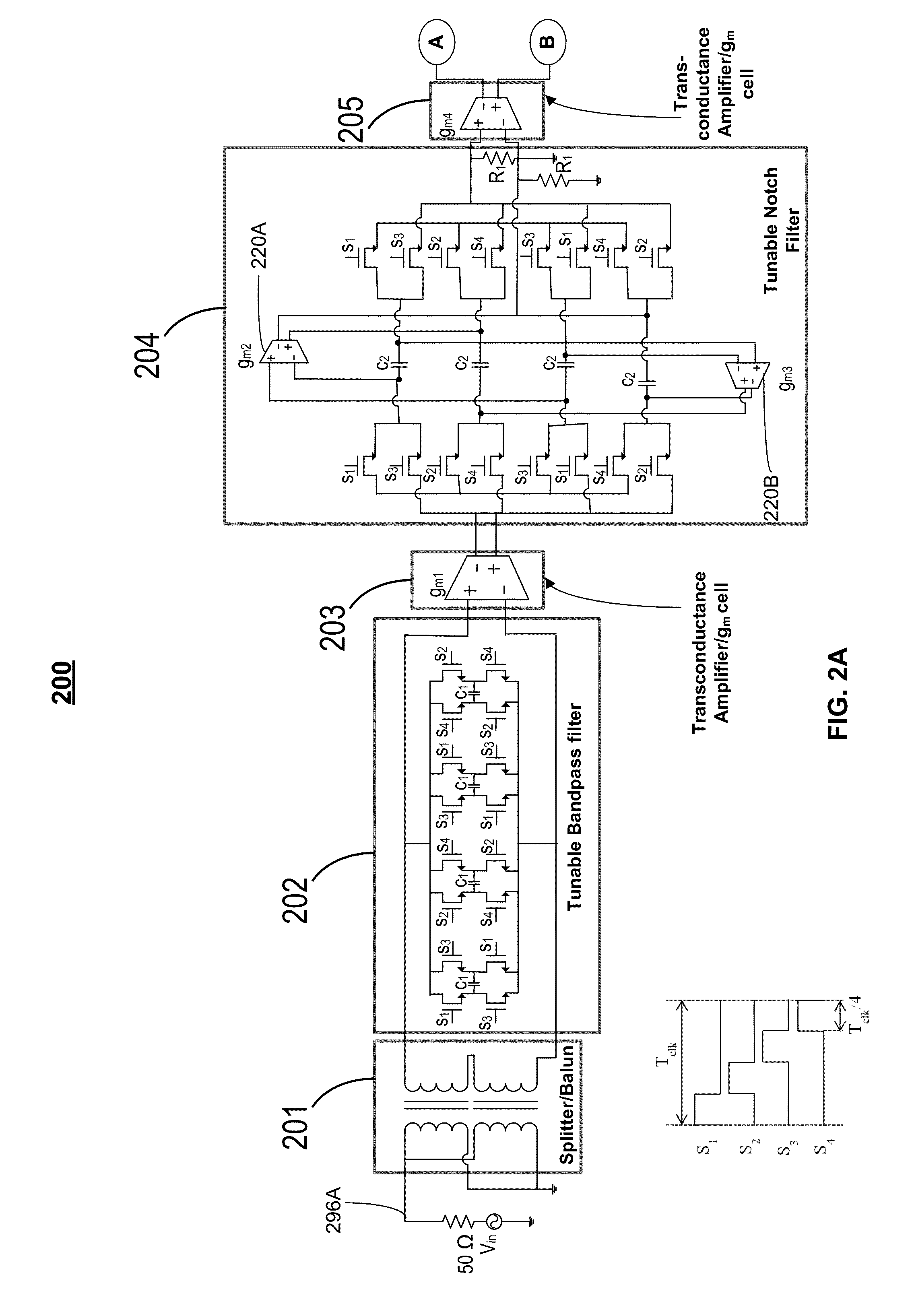
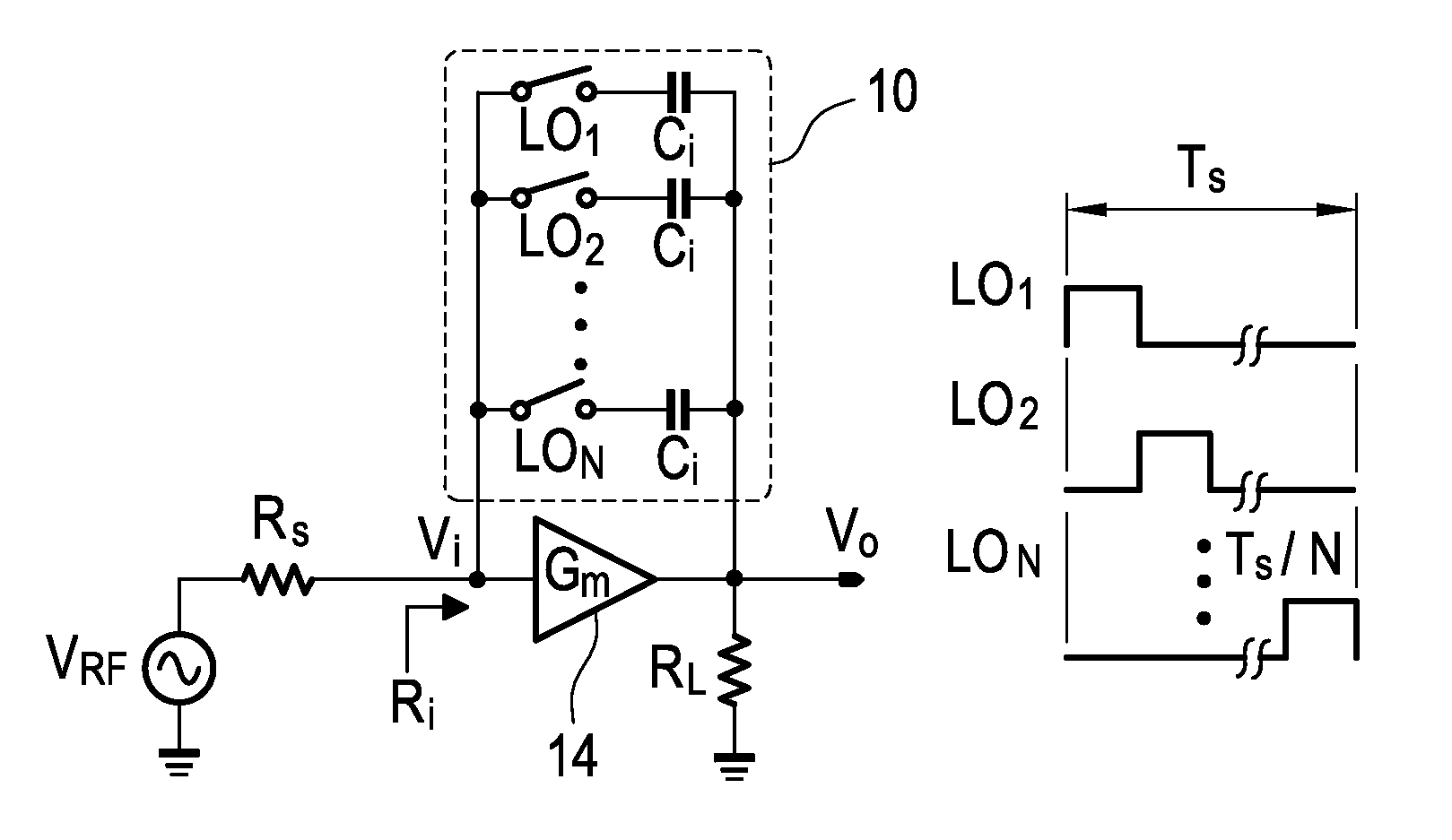
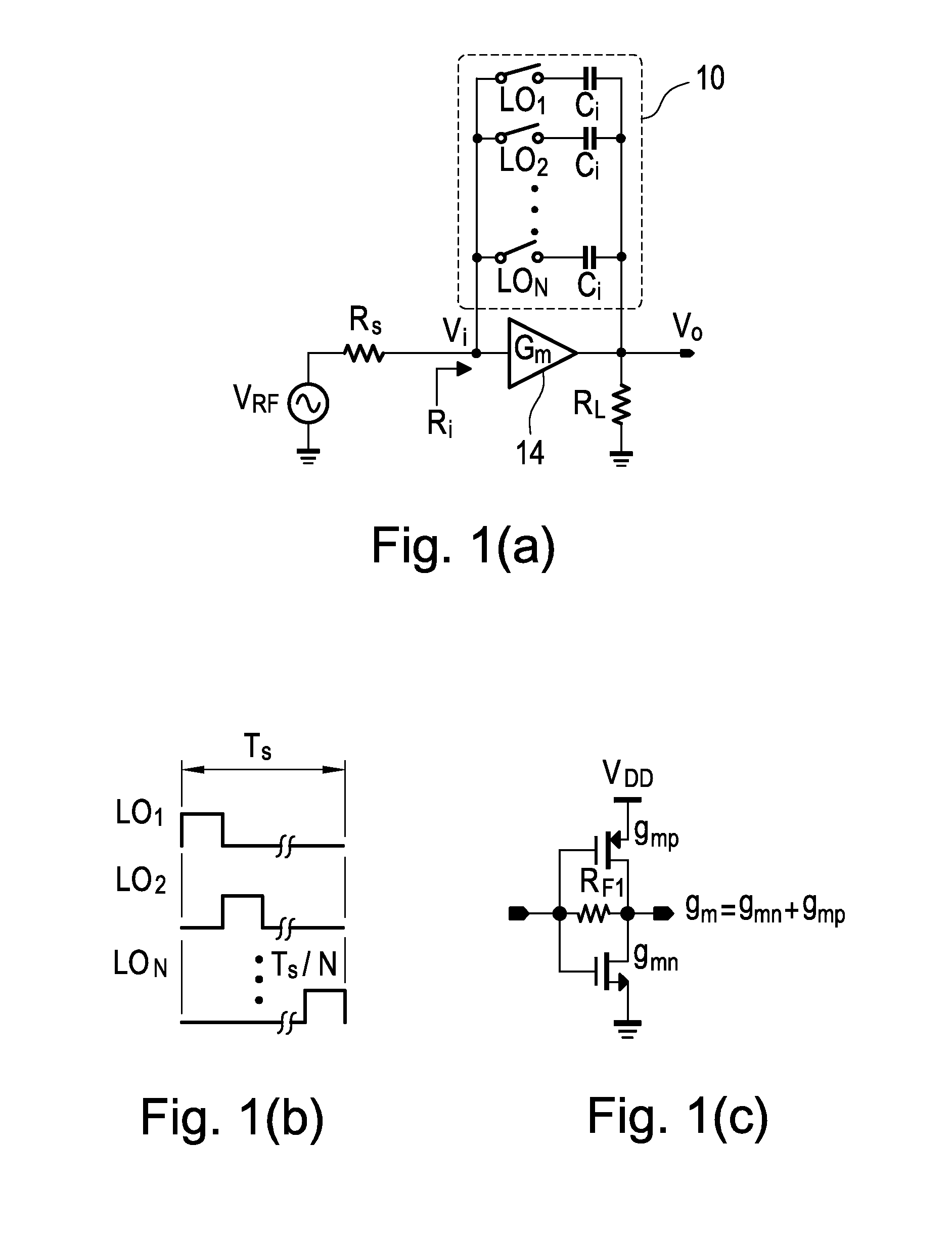
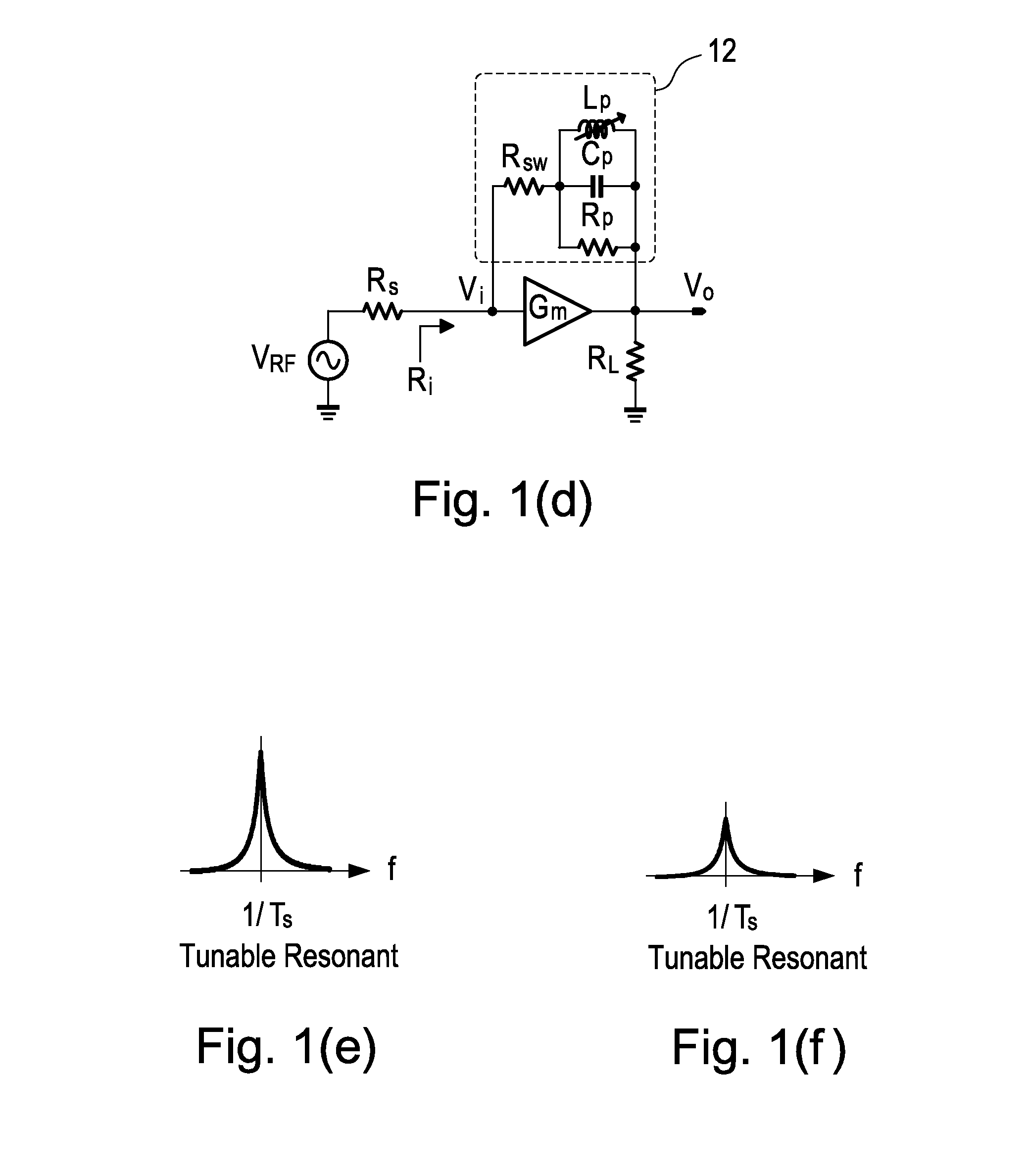
Gain-boosted N-path bandpass filter
ActiveUS9374063B1SmallHigh bandwidthHigh frequency amplifiersSwitched capacitor networksBandpass filteringCapacitance
The present invention discloses a gain-boosted N-path SC bandpass filter (GB-BPF) with a number of sought features. It is based on a transconductance amplifier (Gm) with an N-path SC branch as its feedback network, offering 1) double RF filtering at the input and output of the Gm in one step; 2) customized passband gain and bandwidth with input-impedance match, and 3) reduced physical capacitance thanks to the loop gain offered by Gm. All have been examined using a RLC model of the SC branch before applying the linear periodically time-variant (LPTV) analysis to derive the R, L and C expressions and analytically study the harmonic selectivity, harmonic folding and noise. The latter reveals that: 1) the noise due to the switches is notched at the output, allowing smaller switches to save the LO power; and 2) the noises due to the source resistance and Gm are narrowband at the output, reducing the folded noise during harmonic mixing.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
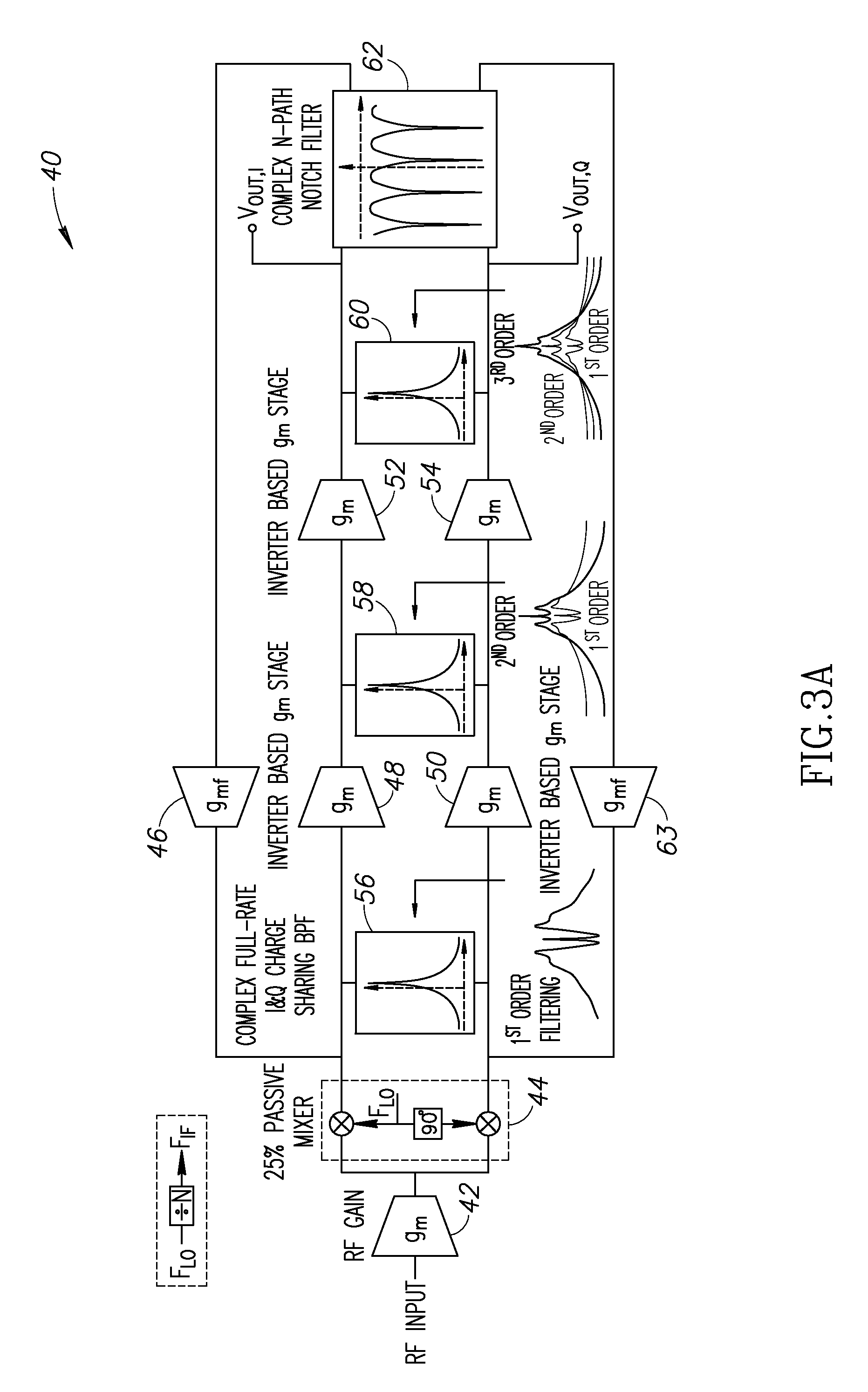
High-if superheterodyne receiver incorporating high-q complex band pass filter
A novel and useful reconfigurable superheterodyne receiver that employs a 3rd order complex IQ charge-sharing band-pass filter (BPF) for image rejection and 1st order feedback based RF BPF for channel selection filtering. The operating RF input frequency of the receiver is 500 MHz to 1.2 GHz with varying high IF range of 33 to 80 MHz. The gain stages are inverter based gm stages and the total gain of the receiver is 35 dB and in-band IIP3 at mid gain is +10 dBm. The NF of the receiver is 6.7 dB which is acceptable for the receiver without an LNA. The architecture is highly reconfigurable and follows the technology scaling.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Multiple band saw-less receiver including a frequency translated bpf
ActiveUS20110299633A1Modulation transferenceAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsBandpass filteringBaseband
A SAW-less receiver includes an FEM interface module, an RF to IF receiver section, and a receiver IF to baseband section. The RF to IF receiver section includes a frequency translated bandpass filter (FTBPF), an LNA, and a mixing section. The FTBPF includes a switching network and baseband impedances. The switching network is operable to frequency translate a baseband filter response to a first RF band frequency response and / or to a second RF frequency band response. The FTBPF filters the inbound RF signal to pass, substantially unattenuated, the first and / or second RF band signal components. The LNA amplifies the first and / or second filtered inbound RF signals and the mixing section mixes the first and / or second amplified inbound RF signals with a corresponding first and / or second local oscillation. The IF to baseband section converts the first and / or second inbound IF signals into first inbound symbol stream(s) and / or second inbound symbol stream(s).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Infinite impulse response (IIR) filter and filtering method
InactiveCN102916677AReduce power consumptionReduce noiseTransversal filtersDigital technique networkIir filteringAudio power amplifier
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Filter
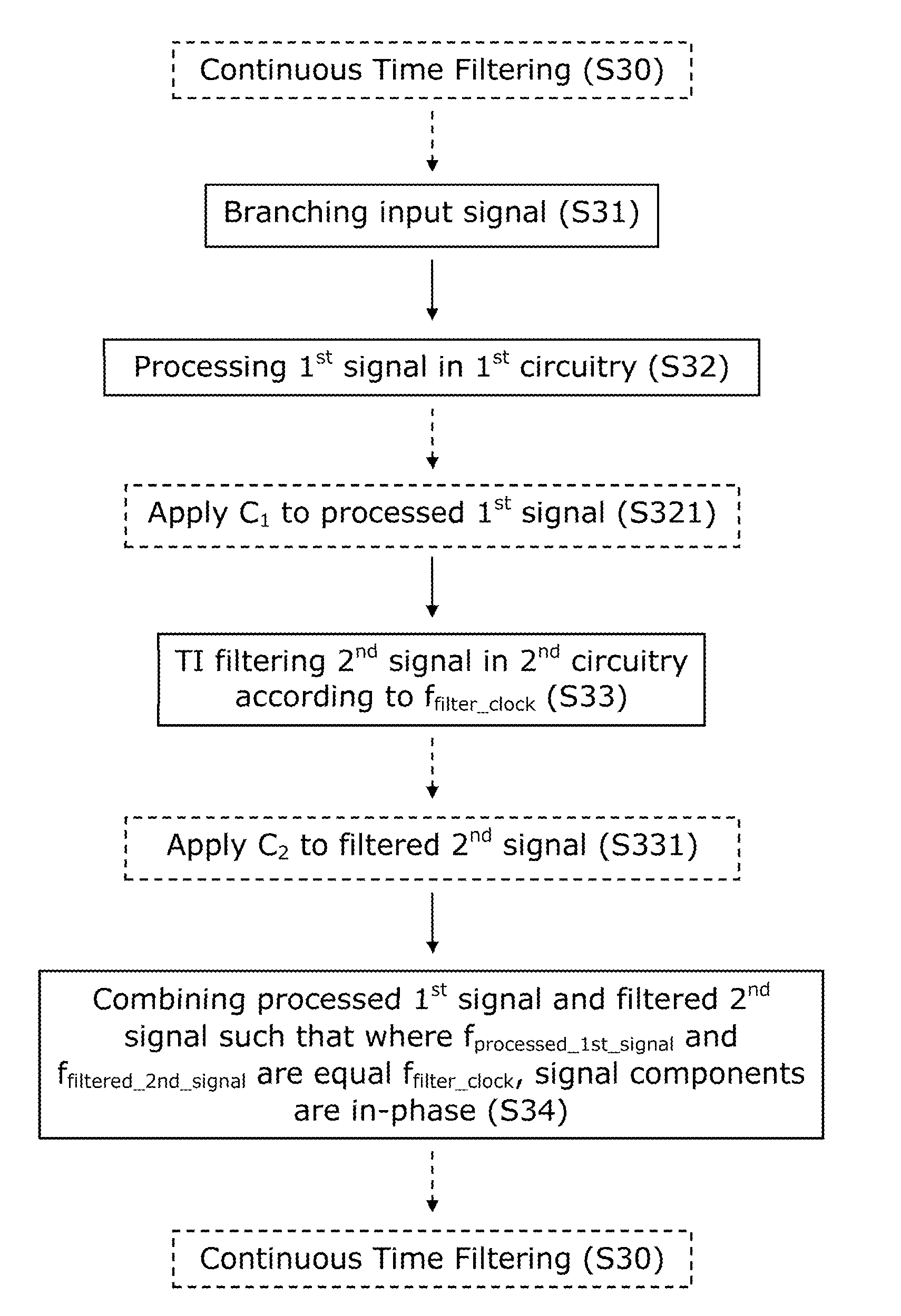
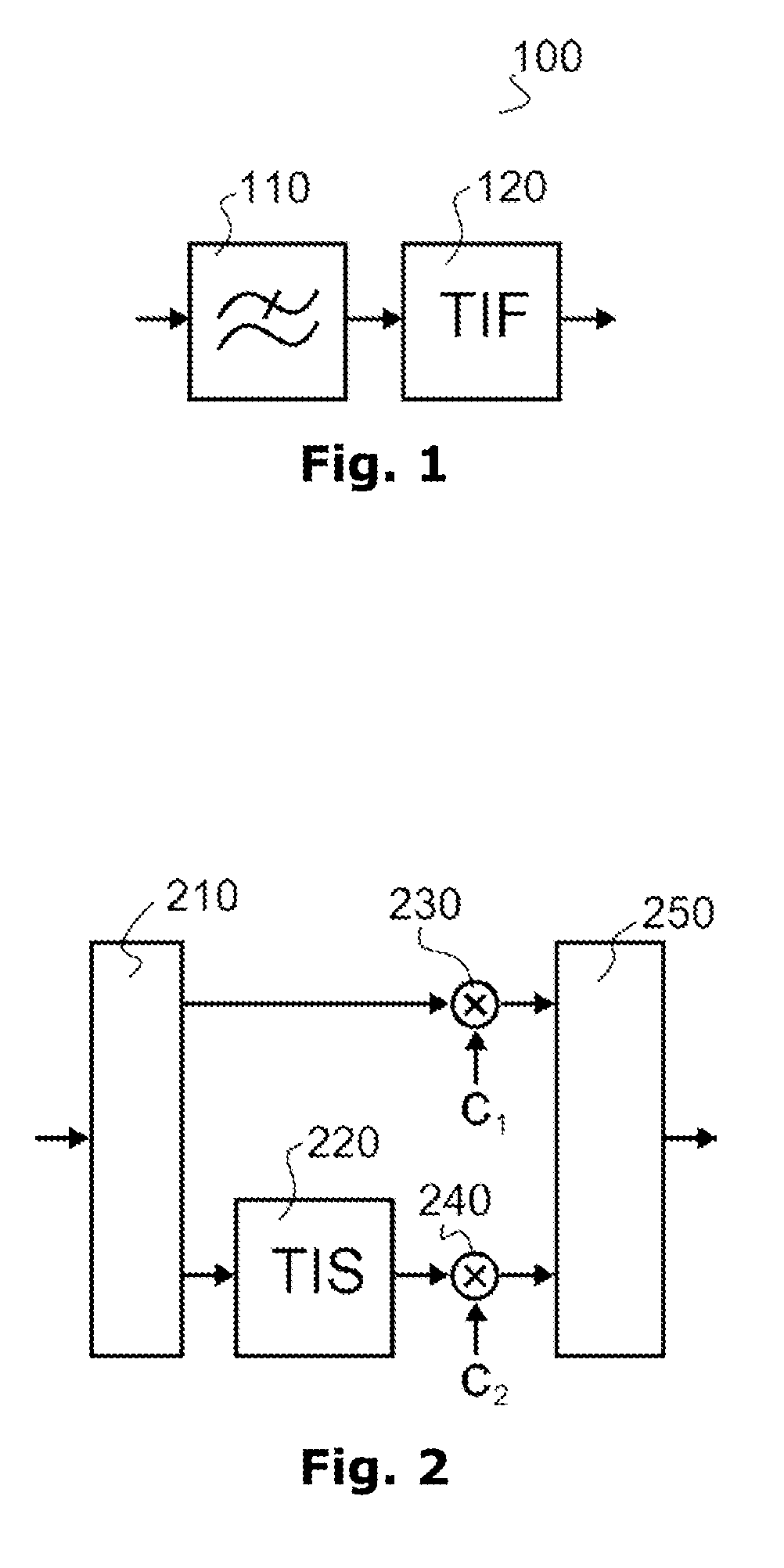
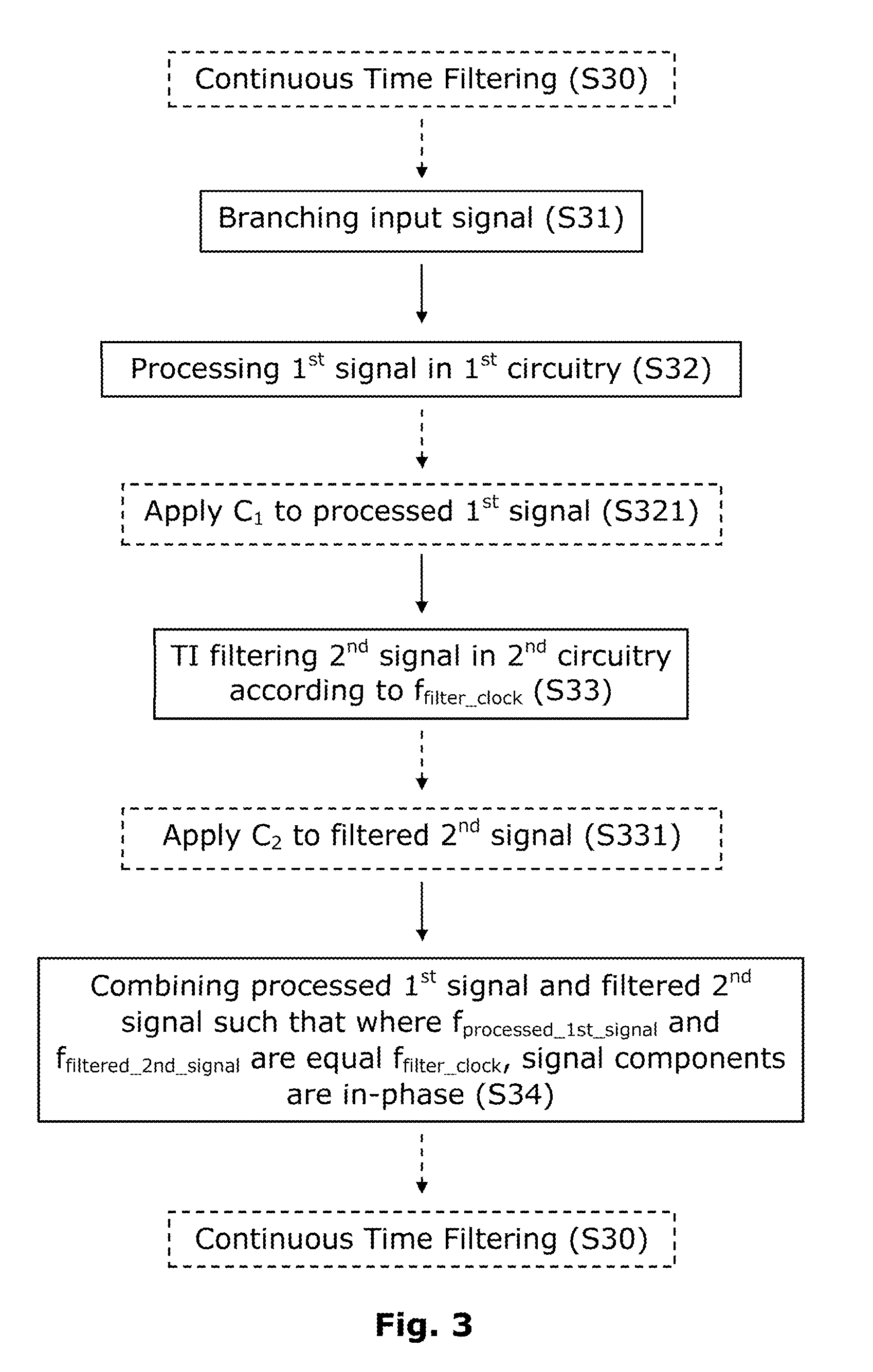
InactiveUS20130235959A1Suppressing signal component in signalUniform gainNetworks with variable switch closing timeN-path filtersEngineeringTransfer impedance
An apparatus and method suppress unwanted signal components in receiving signals during wireless communication. A first circuitry is arranged to process a first signal, a second circuitry is arranged to apply transferred impedance filtering on a second signal according to a filter clock frequency, a signal branching circuitry is arranged to branch an input signal into the first circuitry and the second circuitry, and a signal combining circuitry is arranged to combine the processed first signal and the filtered second signal such that signal components of the first signal processed in the first circuitry and the filtered second signal are in-phase for signal frequencies equal to the filter clock frequency.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Front end module with scalable impedance balancing
InactiveUS20110299436A1Multiple-port networksTransmission control/equalisingBalancing networkAudio power amplifier
A radio front end includes a power amplifier, a duplexer, a detection module, a processing module, and a tunable balancing network. The duplexer is operable to provide electrical isolation between the outbound wireless signal and an inbound wireless signal. The detection module is operable to detect non-linear function of the power amplifier to produce a detected non-linearity and to detect transmit leakage of the duplexer to produce detected transmit leakage. The processing module is operable to generate a coarse tuning signal based on the detected non-linearity and to generate a fine tuning signal based on the detected transmit leakage. The tunable balancing network is operably coupled to the duplexer and operable to establish an impedance based on the coarse and fine tuning signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Radio-frequency-to-baseband function-reuse receiver with shared amplifiers for common-mode and differential-mode amplification
ActiveUS20160233908A1High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierRadio frequency
According to another aspect of the present disclosure, a radio-frequency-to-baseband-function-reuse receiver with shared amplifiers for common-mode and differential-mode amplification is provided. The receiver includes two set networks connected in parallel. The set networks includes a first and a second input capacitors, a first and a second output capacitors, a first transconductance amplifier having an input terminal, a second transconductance amplifier having an input terminal, a first switch, and a second switch. The first and the second input capacitors connect to a first node. The first and the second output capacitors connect to a second node. The first transconductance amplifier connects between the first input capacitor and the first output capacitor. The second transconductance amplifier connects between the second input capacitor and the second output capacitor. The first switch connects between the input terminal of the first transconductance amplifier and the second node. The second switch connects between the input terminal of the second transconductance amplifier and the second node.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
Saw-less receiver including an if frequency translated bpf
A SAW-less receiver includes an FEM interface module, an RF to IF receiver section, and a receiver IF to baseband section. The RF to IF receiver section includes a mixing module, a mixed buffer section, and a frequency translated BPF (FTBPF) circuit module. The mixing module converts an inbound RF signal into an in-phase (I) mixed signal and a quadrature (Q) mixed signal. The mixed buffer section filters and buffers the I mixed signal and filter and buffer the Q mixed signal. The FTBPF circuit module frequency translates a baseband filter response to an IF filter response such that the FTBPF circuit module filters undesired signal components of the IF I signal and the IF Q signal to produce an inbound IF signal. The receiver IF to baseband section converts the inbound IF signal into one or more inbound symbol streams.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
SAW-less receiver including an IF frequency translated BPF
A SAW-less receiver includes an FEM interface module, an RF to IF receiver section, and a receiver IF to baseband section. The RF to IF receiver section includes a mixing module, a mixed buffer section, and a frequency translated BPF (FTBPF) circuit module. The mixing module converts an inbound RF signal into an in-phase (I) mixed signal and a quadrature (Q) mixed signal. The mixed buffer section filters and buffers the I mixed signal and filter and buffer the Q mixed signal. The FTBPF circuit module frequency translates a baseband filter response to an IF filter response such that the FTBPF circuit module filters undesired signal components of the IF I signal and the IF Q signal to produce an inbound IF signal. The receiver IF to baseband section converts the inbound IF signal into one or more inbound symbol streams.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Multiple band saw-less receiver including a frequency translated BPF
A SAW-less receiver includes an FEM interface module, an RF to IF receiver section, and a receiver IF to baseband section. The RF to IF receiver section includes a frequency translated bandpass filter (FTBPF), an LNA, and a mixing section. The FTBPF includes a switching network and baseband impedances. The switching network is operable to frequency translate a baseband filter response to a first RF band frequency response and / or to a second RF frequency band response. The FTBPF filters the inbound RF signal to pass, substantially unattenuated, the first and / or second RF band signal components. The LNA amplifies the first and / or second filtered inbound RF signals and the mixing section mixes the first and / or second amplified inbound RF signals with a corresponding first and / or second local oscillation. The IF to baseband section converts the first and / or second inbound IF signals into first inbound symbol stream(s) and / or second inbound symbol stream(s).
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
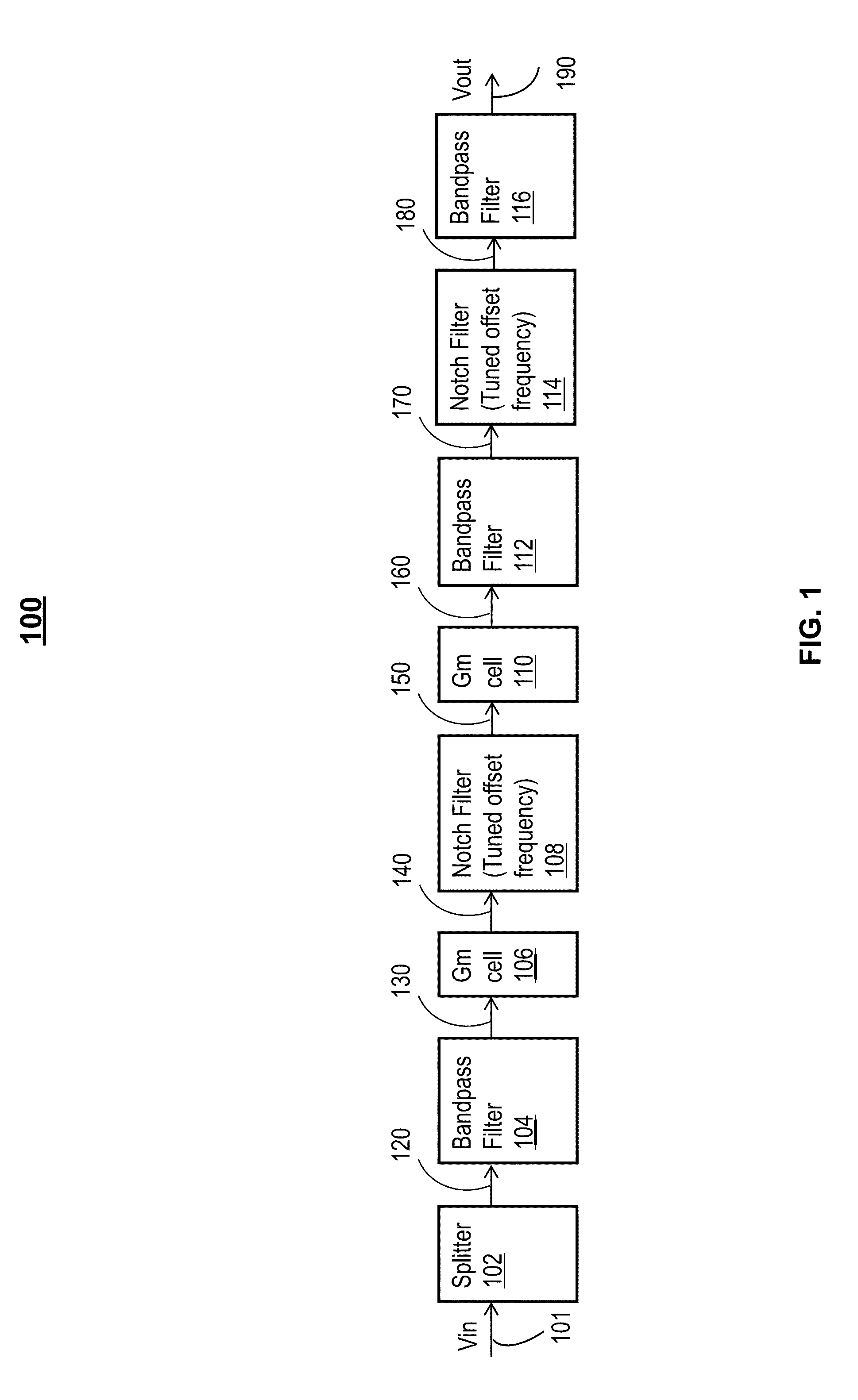
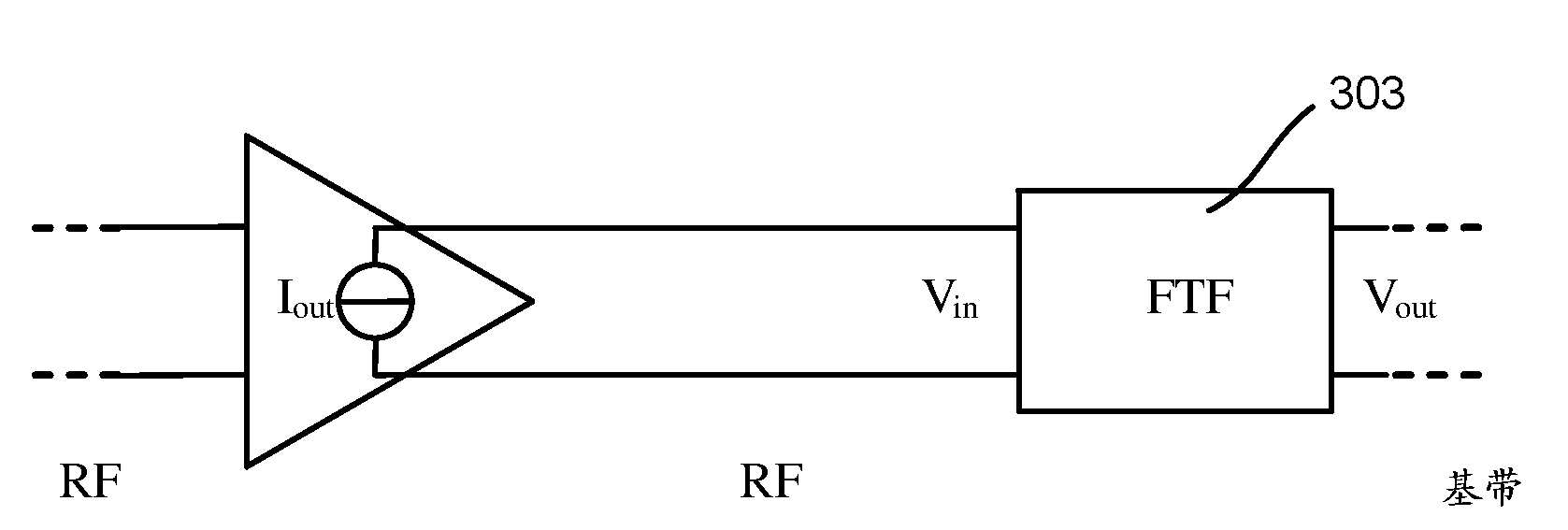
Frequency translation filter apparatus and method
ActiveCN103348589AN-path filtersMulti-frequency-changing modulation transferenceFrequency mixerLocal oscillator
A frequency translation filter 500 is configured to receive a radio frequency (RF) signal 501 comprising first and second non-contiguous carriers or non-contiguous frequency ranges. The frequency translation filter comprises a mixer 503 configured to mix the RF signal 501 received on a first input with a local oscillator (LO) signal 505 received on a second input. A filter 507 has band-pass characteristics which, when frequency translated using the mixer 503, contain first and second pass-bands corresponding to the first and second non-contiguous carriers or non-contiguous frequency ranges. The first and second pass-bands are centered about the local oscillator frequency.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multiple-phase frequency translated filter
A frequency translation filter includes a baseband filter circuit, a clock generator, and a switching circuit. The baseband filter circuit is operable to provide a baseband filter response. The clock generator is operable to generate multiple-phase clock signals at a desired frequency. The switching circuit is operable to frequency translate the baseband filter response of the baseband filter circuit to a high frequency filter response in accordance with the multiple-phase clock signals.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Distributed reconstruction method of two-channel critical sampling graph filter bank
ActiveCN111444470AReduce the number of iterationsEliminate errorsN-path filtersHigh level techniquesSample graphTheoretical computer science
The invention discloses a distributed reconstruction method for a two-channel critical sampling graph filter bank. The method comprises the steps: firstly converting a total optimization problem intoa series of local optimization problems through a truncation operator, and enabling the truncation operator to be related to the related characteristics of a graph; solving the local optimization problem to obtain a result, and performing fusion averaging on the result; and performing iterative updating on a result obtained by fusion, and eliminating an error to obtain an optimal solution. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that compared with the prior art, the complexity is lower, the number of iterations of the algorithm is smaller, and consumed time is shorter.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
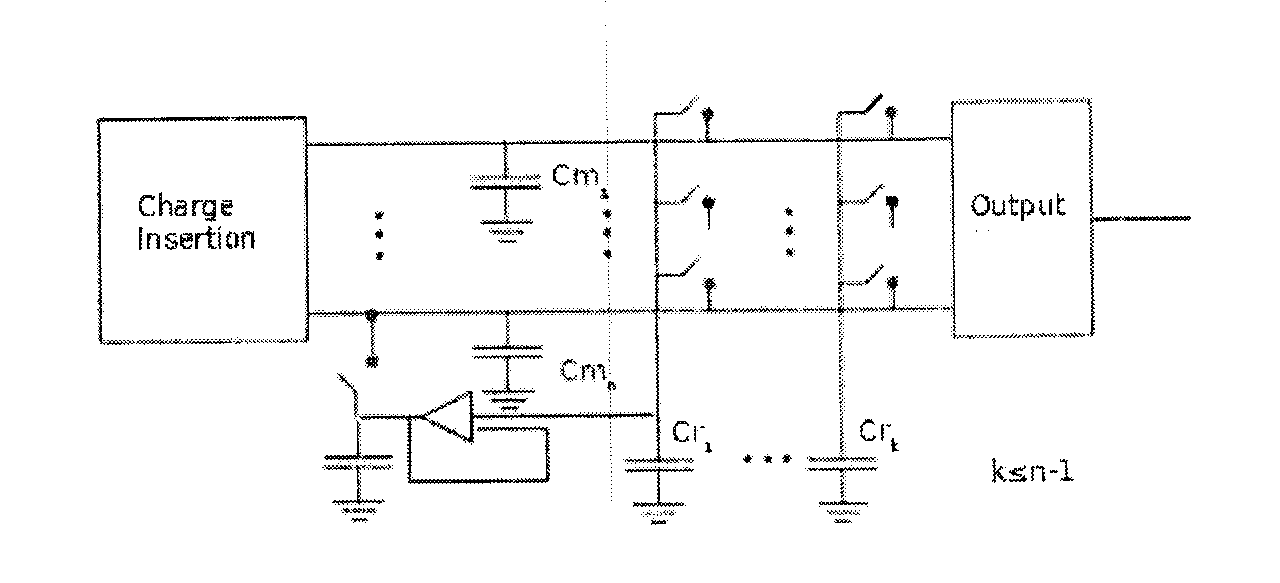
N-path filter with coupling between paths
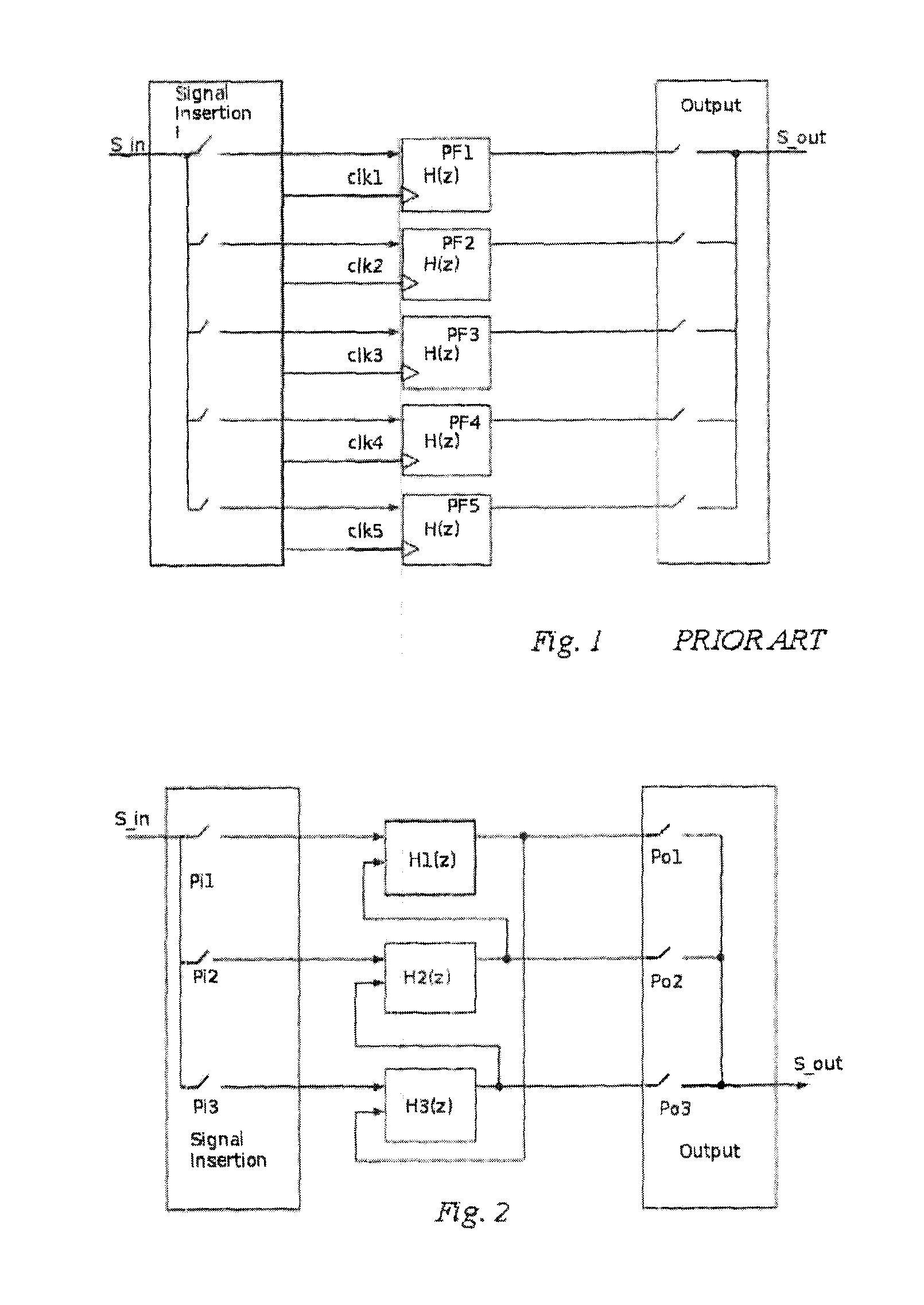
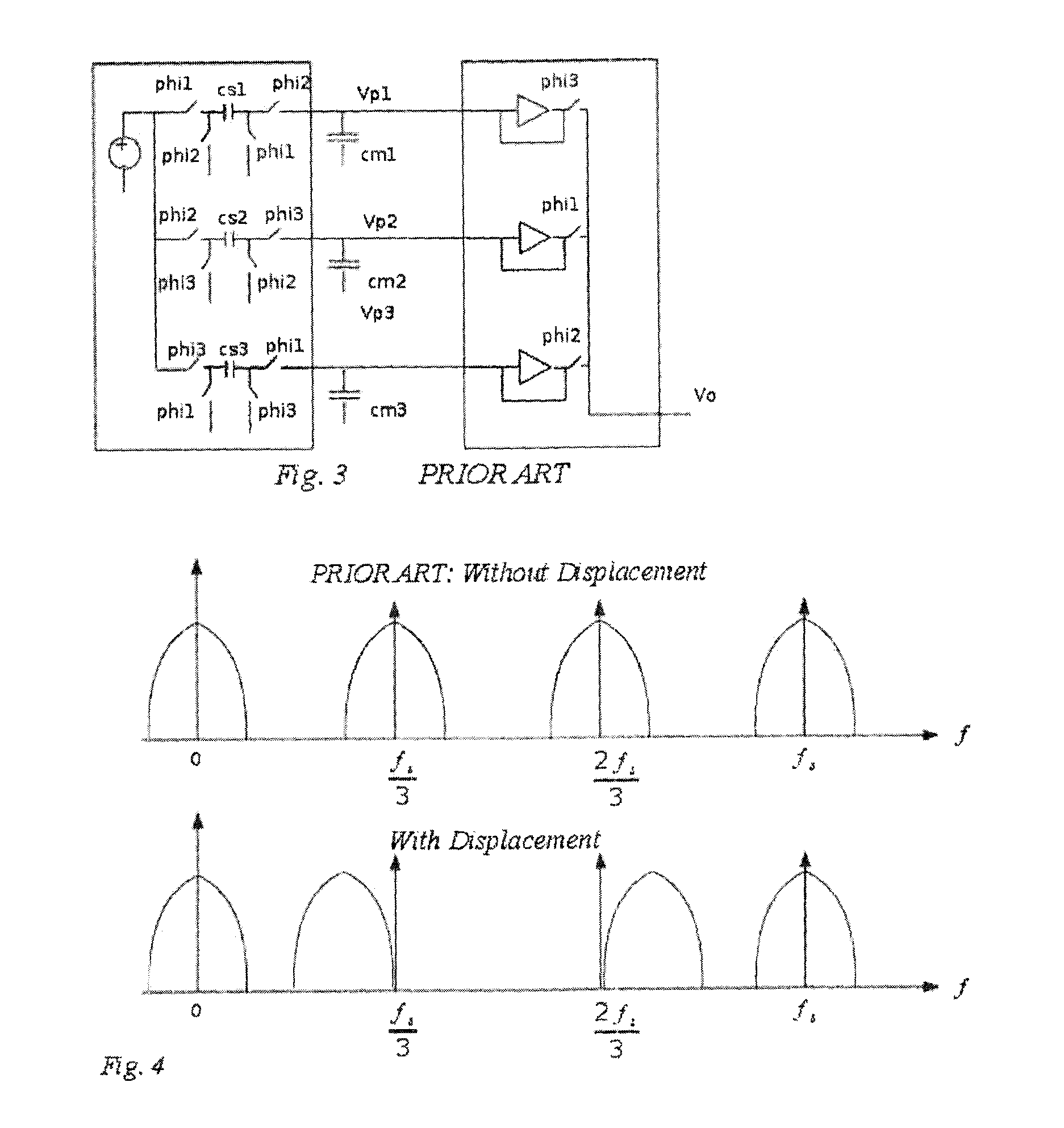
InactiveUS20130271210A1Minimal numberReduce in quantityMultiple-port networksN-path filtersCouplingEngineering
An N-path filter with each path forming a different filter. A signal insertion block is provided at the start of the circuit and, in one embodiment, multiple memory capacitors are coupled to the signal insertion block. A bank of sequential rotating capacitors are provided along with a bank of switches. By activating selected switches, any of the memory capacitors can be coupled to selected rotating capacitors. A different filter subcircuit is formed by coupling each memory capacitor to different rotating capacitors as this creates a different signal path. By timing the switching of the rotating capacitors, signals from previous outputs can be inserted into the circuit. At the output end of the circuit, the output of the different filter subcircuits is put together into an output for the whole circuit.
Owner:KABEN WIRELESS SILICON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com