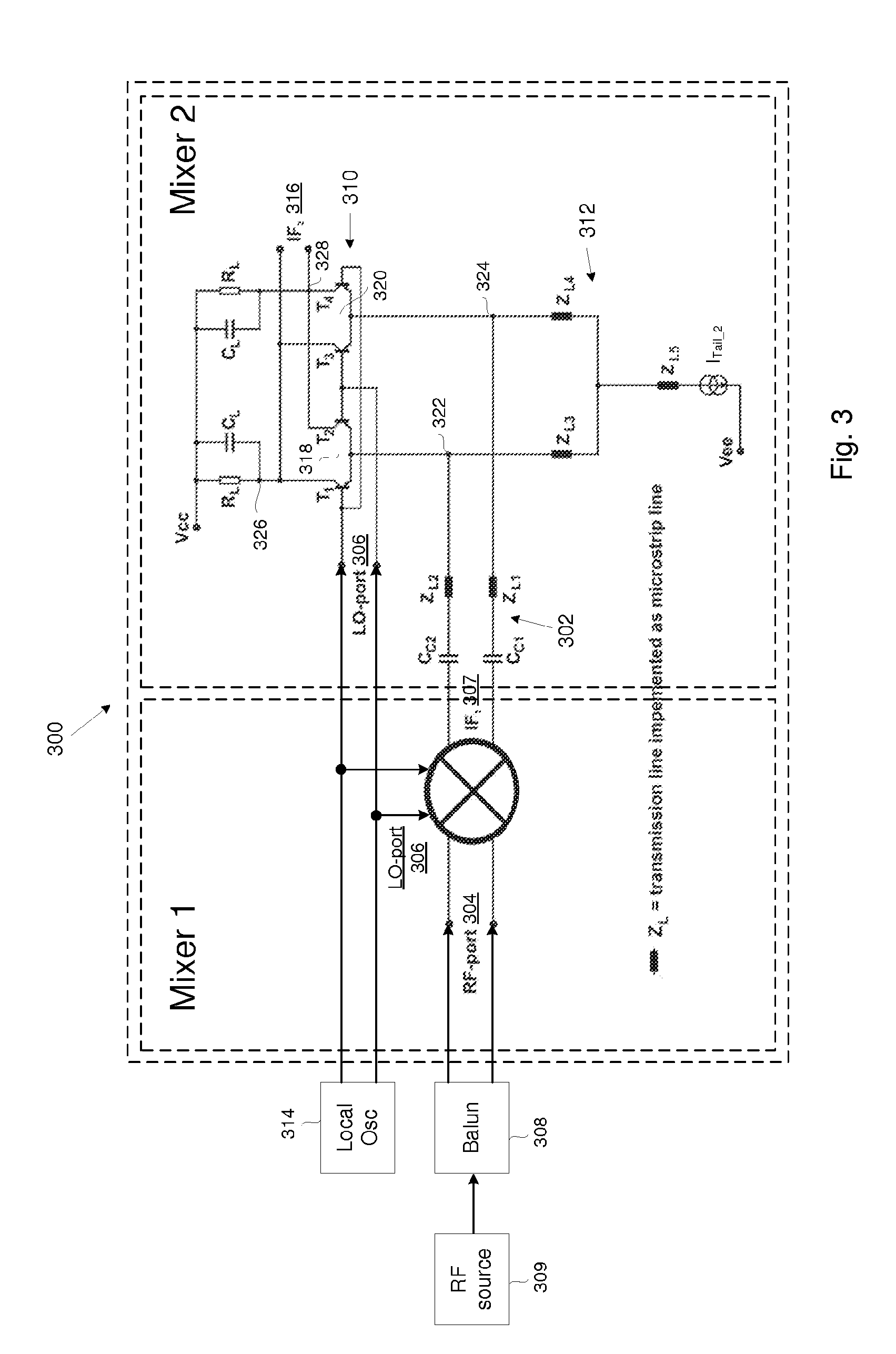
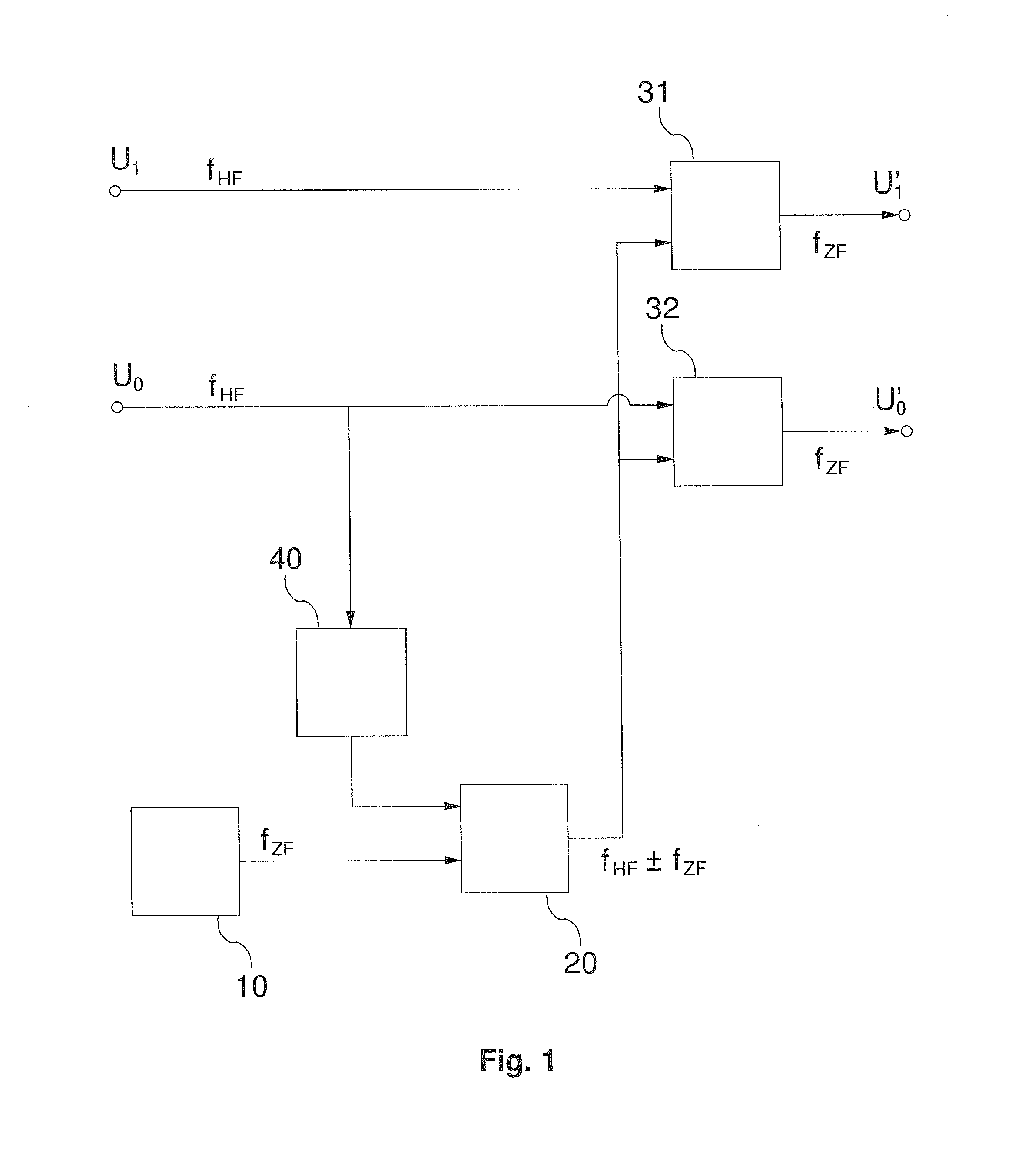
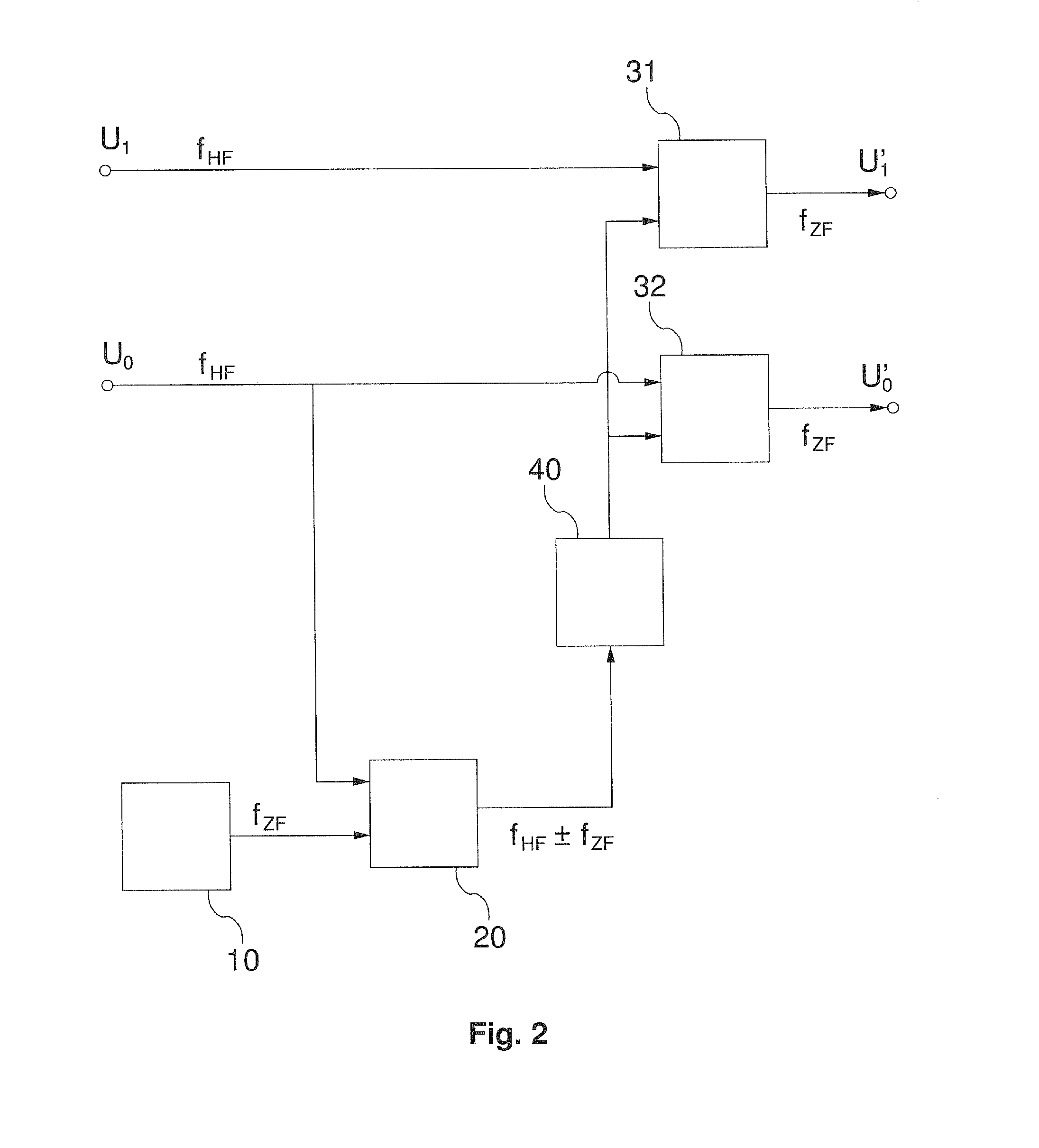
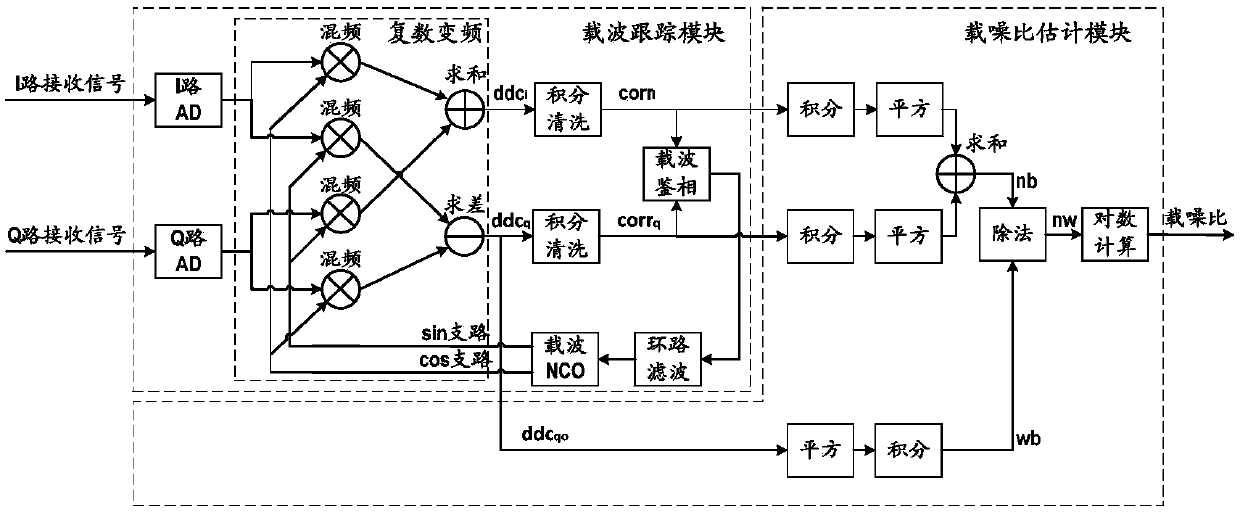
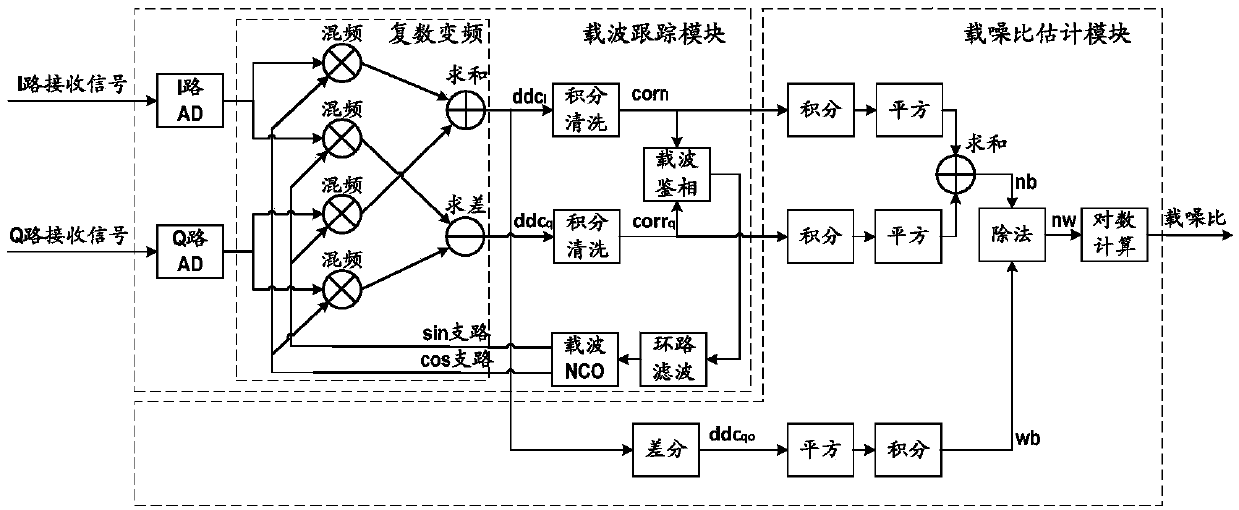
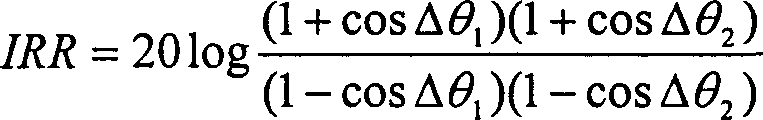Patents
Literature
75 results about "Superheterodyne receiver" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
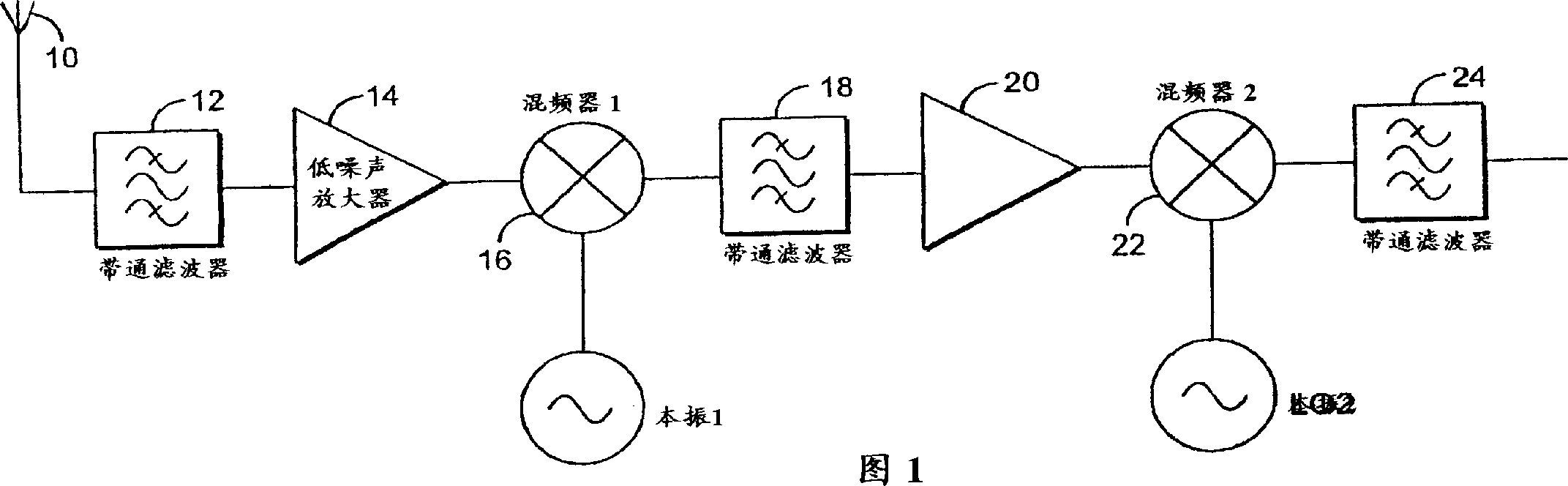
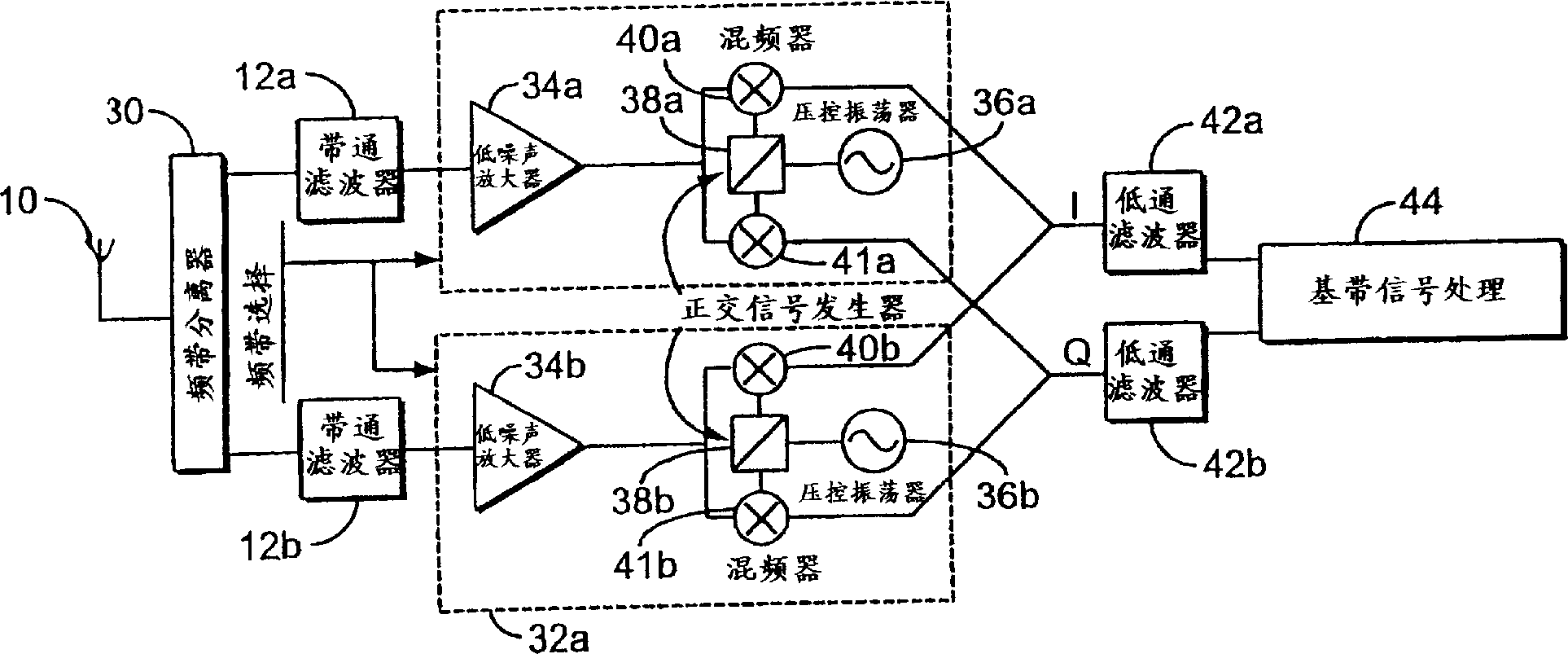
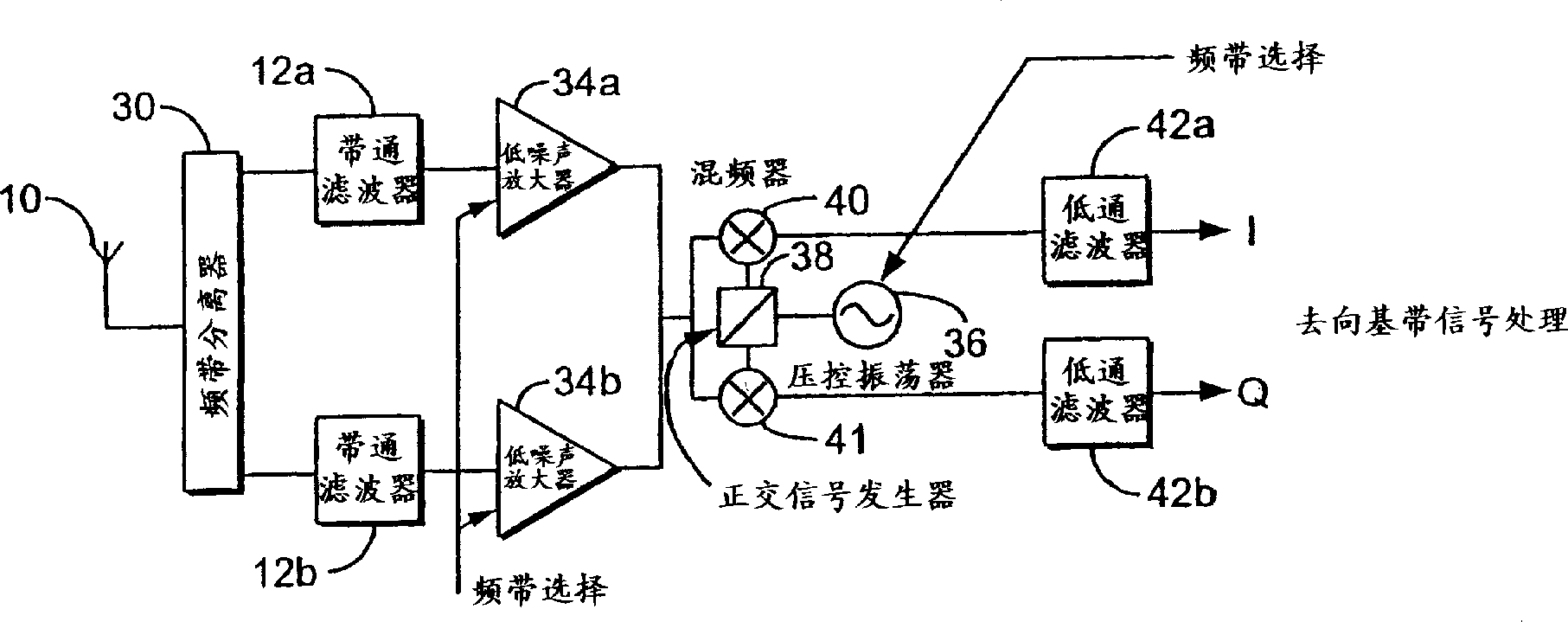
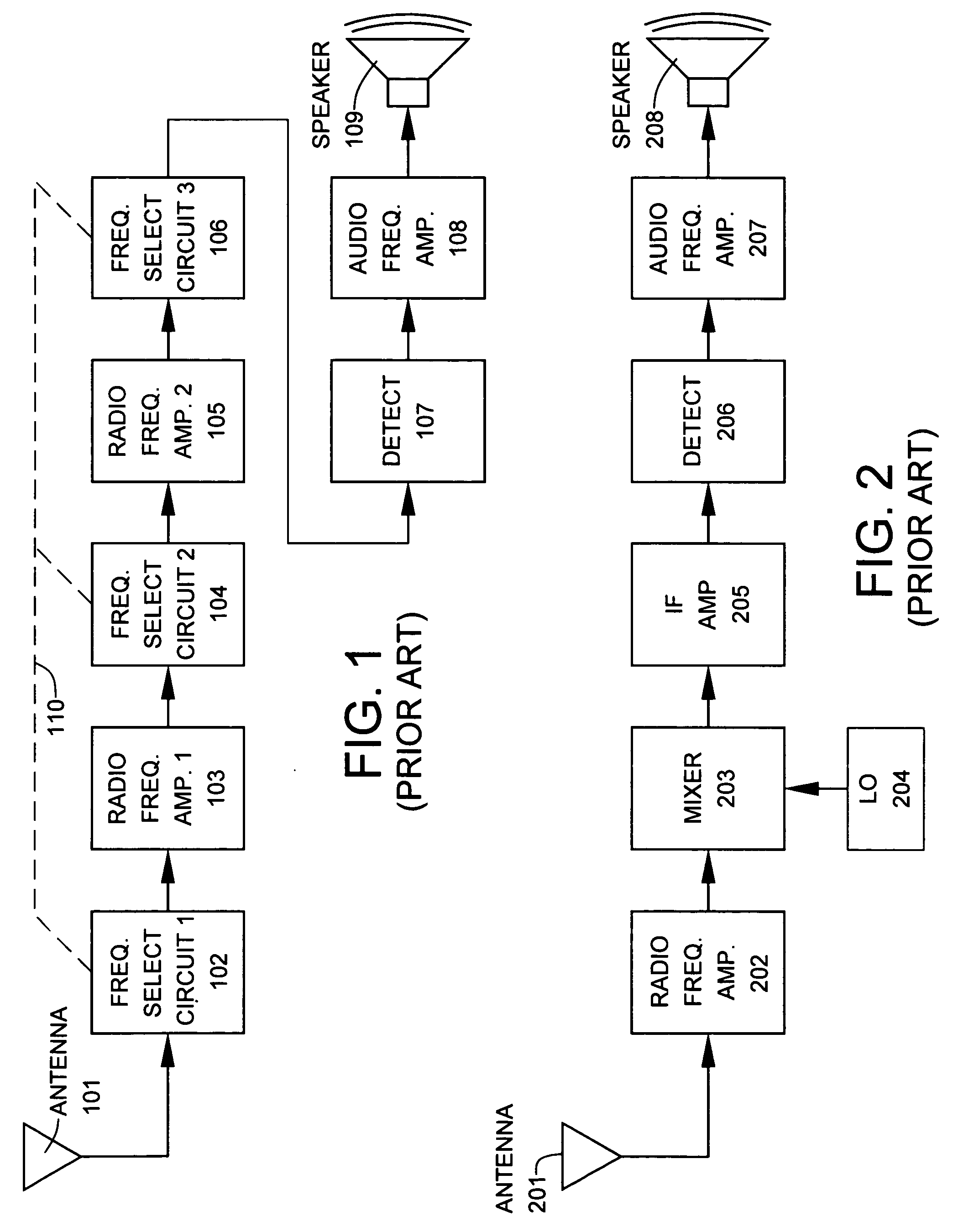
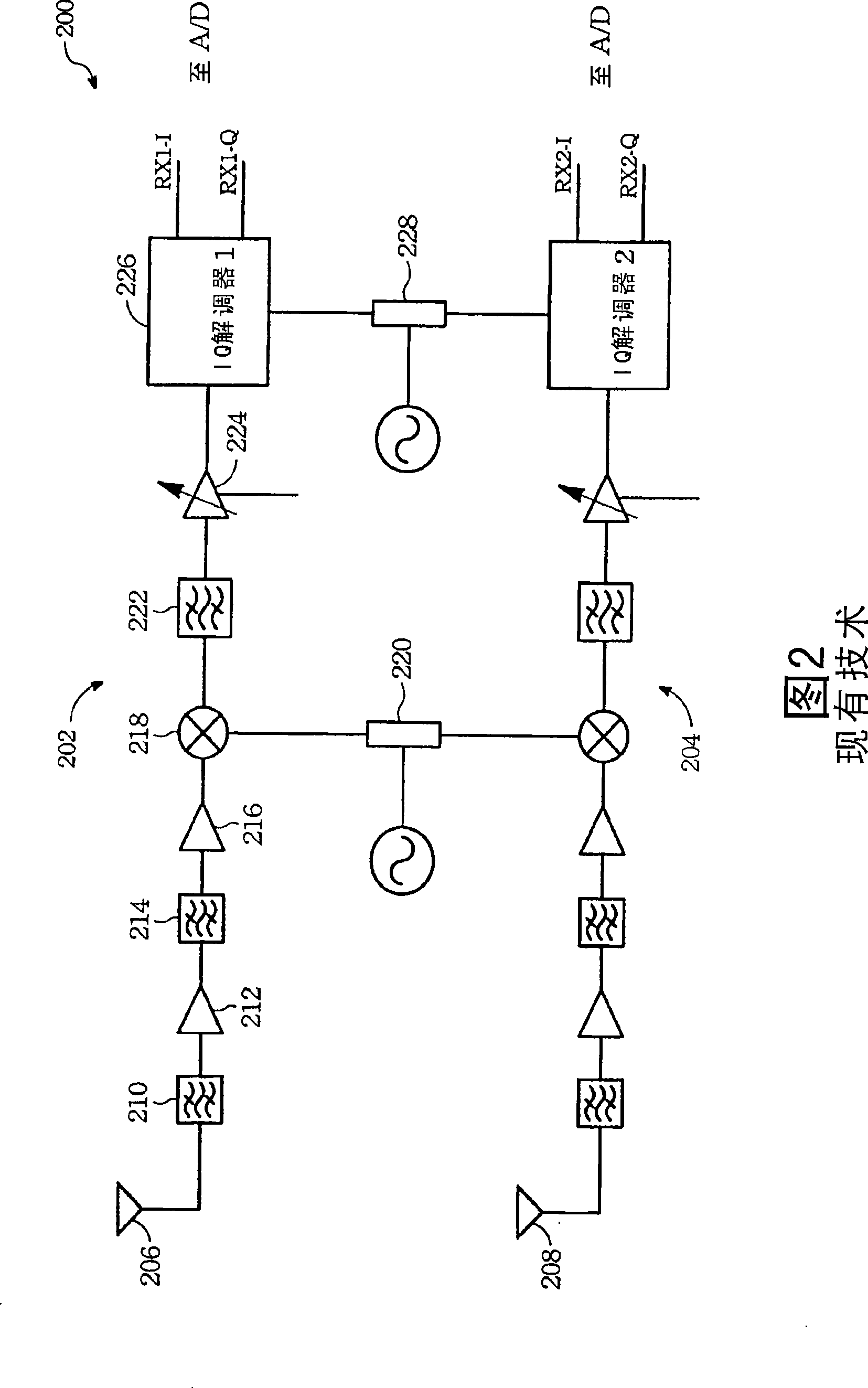
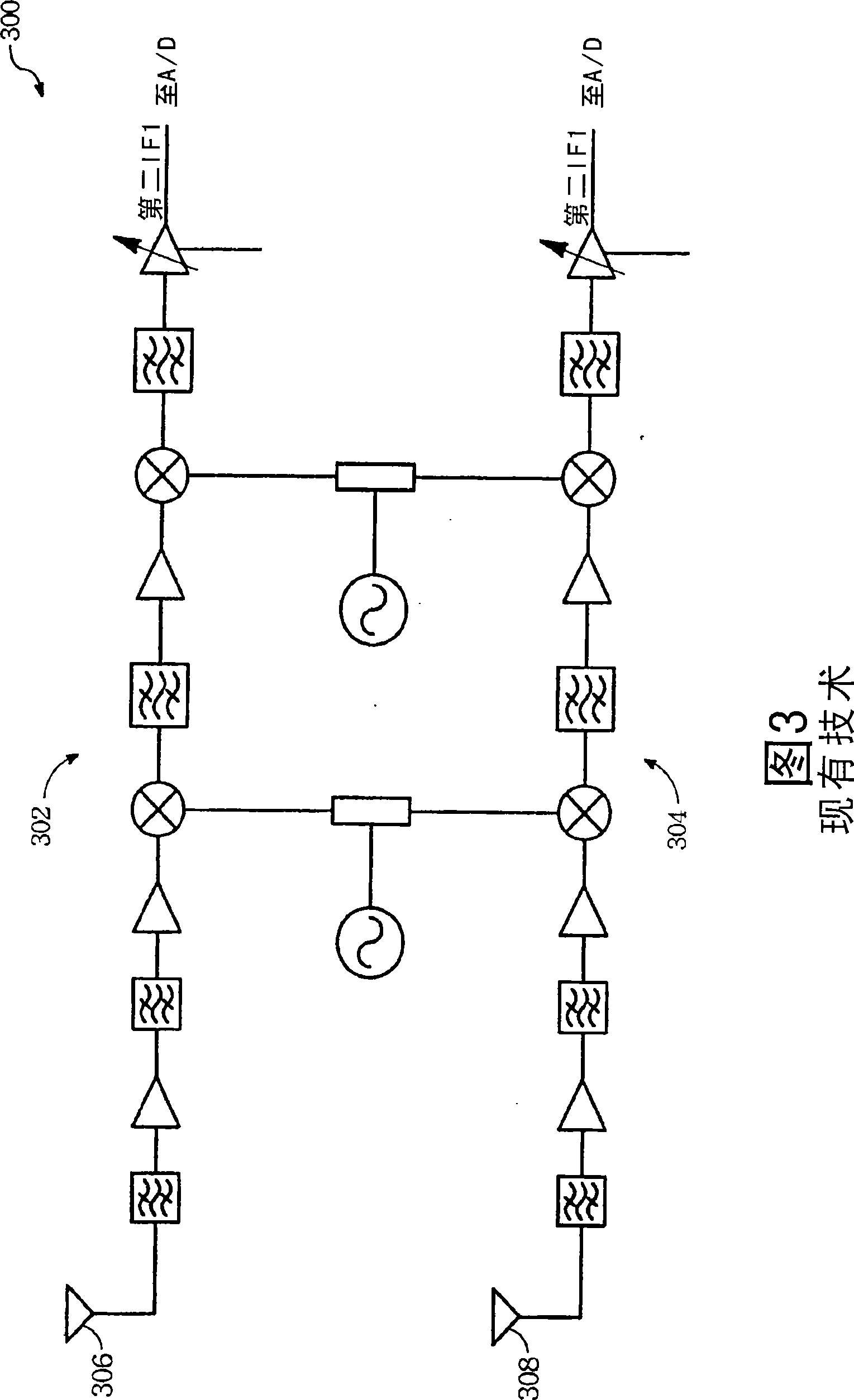
A superheterodyne receiver, often shortened to superhet, is a type of radio receiver that uses frequency mixing to convert a received signal to a fixed intermediate frequency (IF) which can be more conveniently processed than the original carrier frequency. It was invented by US engineer Edwin Armstrong in 1918 during World War I. Virtually all modern radio receivers use the superheterodyne principle.
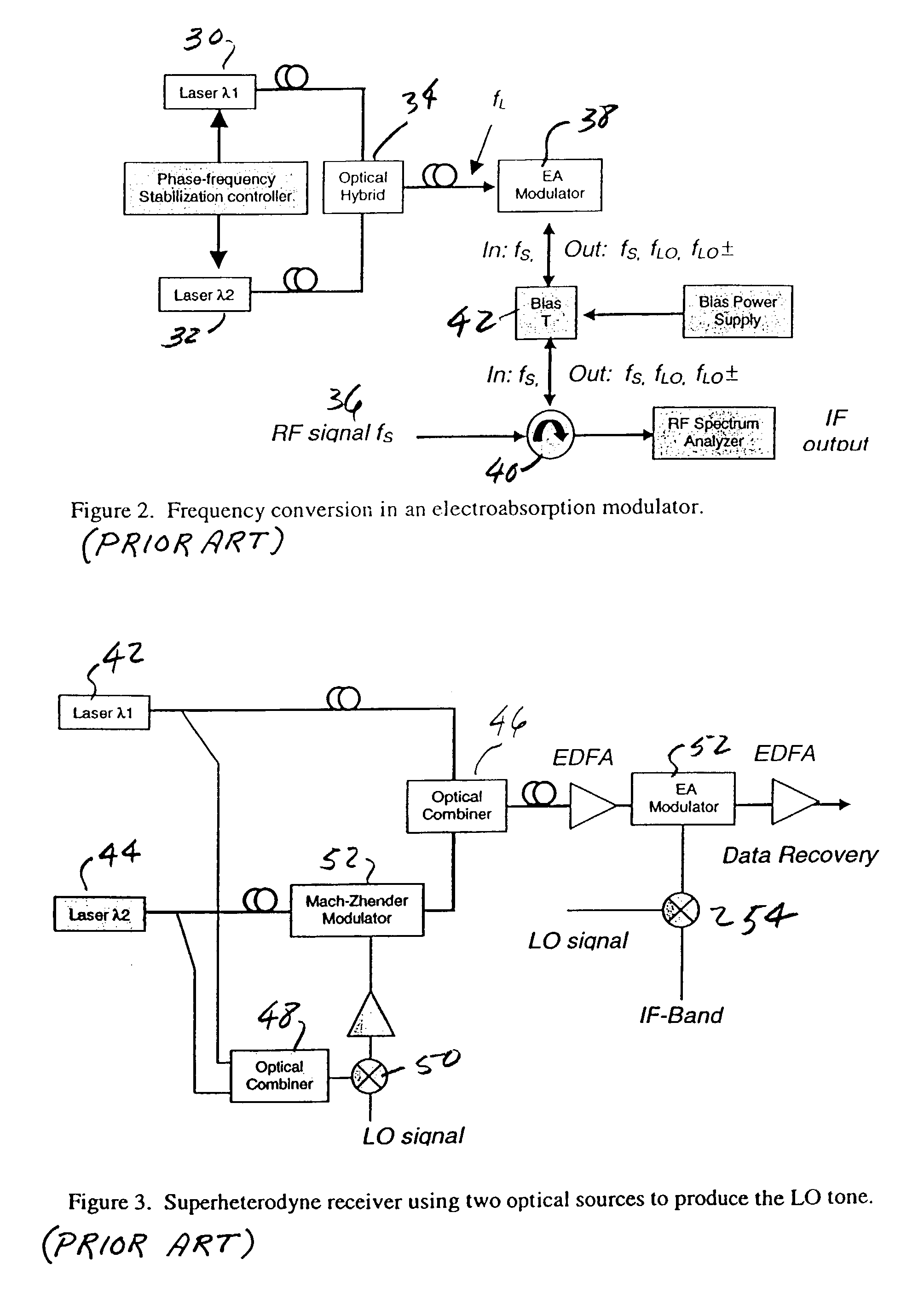
Optical communications using heterodyne detection
InactiveUS7209660B1High sensitivityGood wavelength selectivityFrequency-division multiplex detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsCommunications systemLocal oscillator
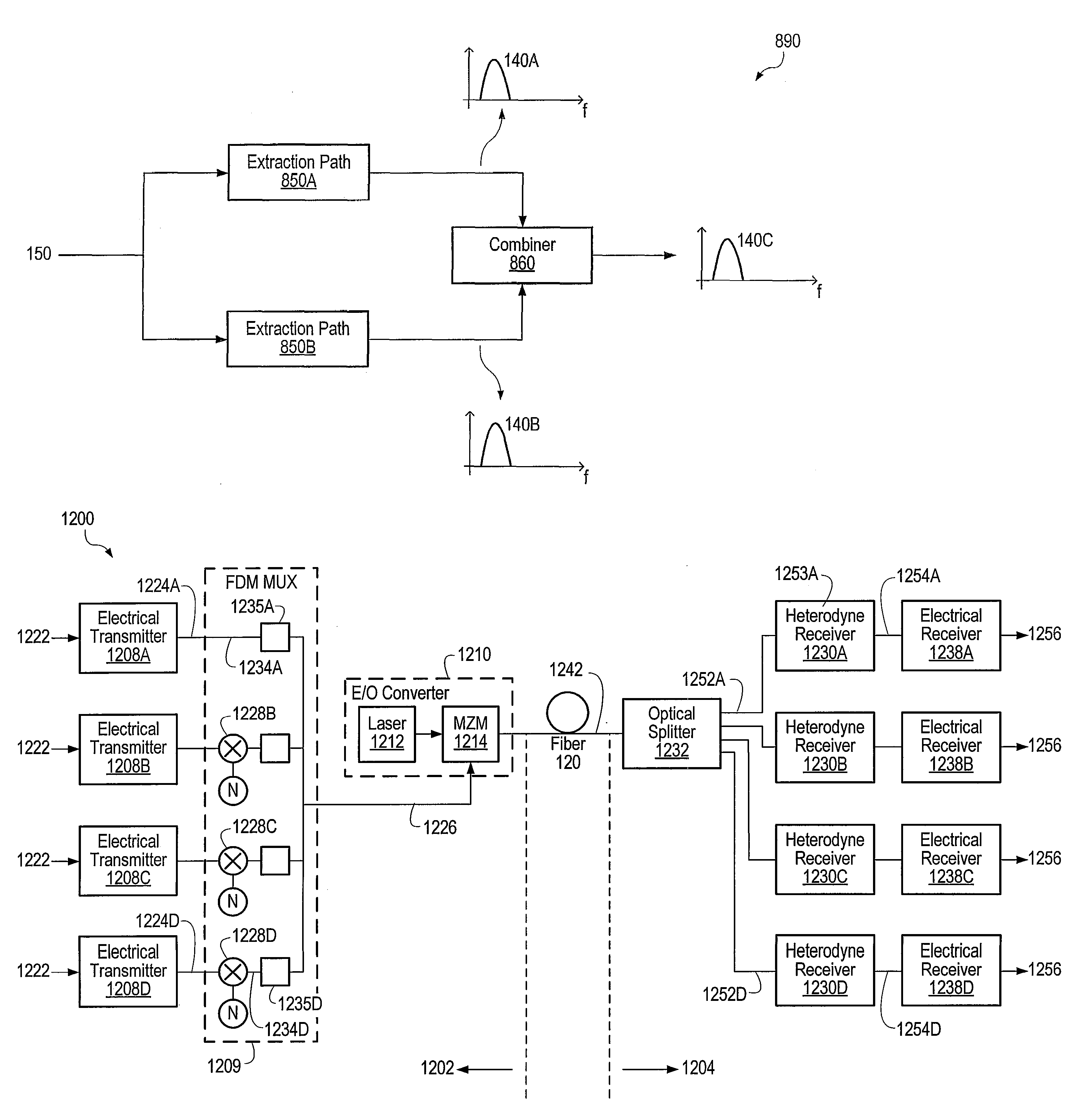
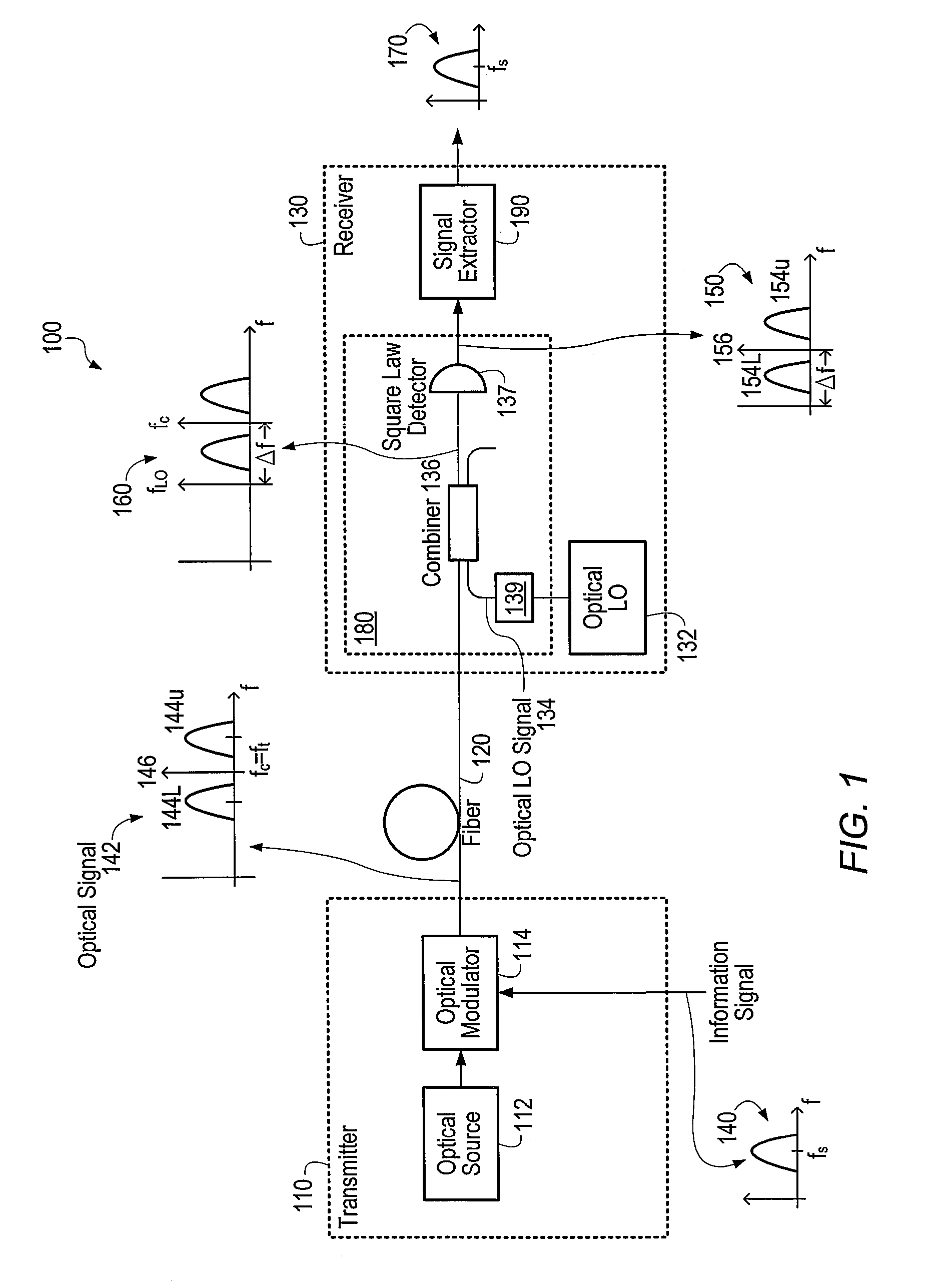
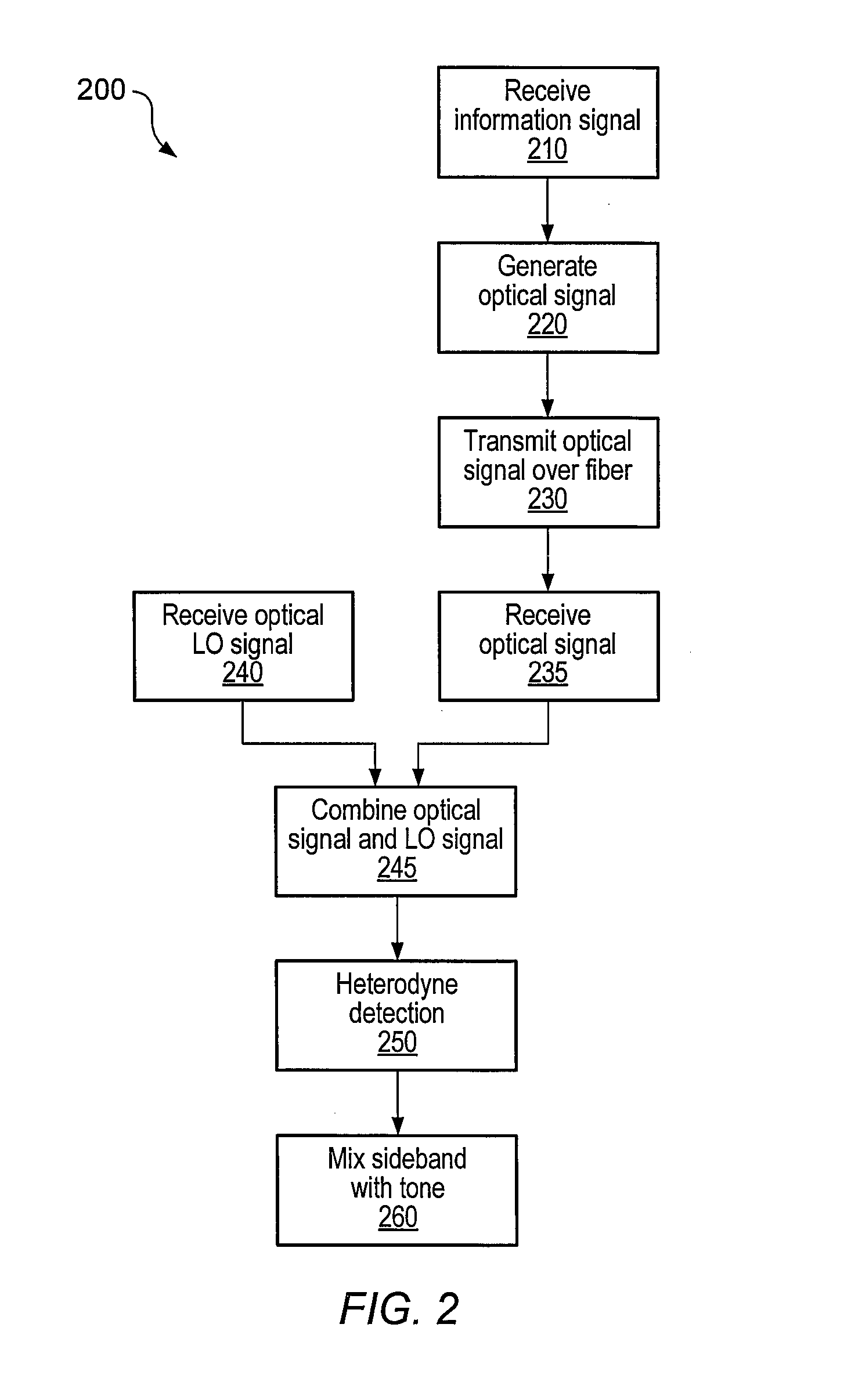
An optical communications system includes a receiver subsystem with at least two heterodyne receivers. The receiver subsystem receives a composite optical signal having two or more subbands of information and corresponding tones. An optical splitter splits the composite optical signal into optical signals. Each optical signal includes a subband(s) and corresponding tone. Each heterodyne receiver receives an optical signal. The receiver includes a heterodyne detector coupled to a signal extractor. The heterodyne detector mixes the optical signal with an optical local oscillator to produce an electrical signal which includes a frequency down-shifted version of the subband and the tone of the optical signal. The signal extractor mixes the frequency down-shifted subband with the frequency down-shifted tone to produce a frequency component containing the information.
Owner:XYLON LLC
Superheterodyne receiver apparatus and reception method, and semiconductor integrated circuit for receiver apparatus
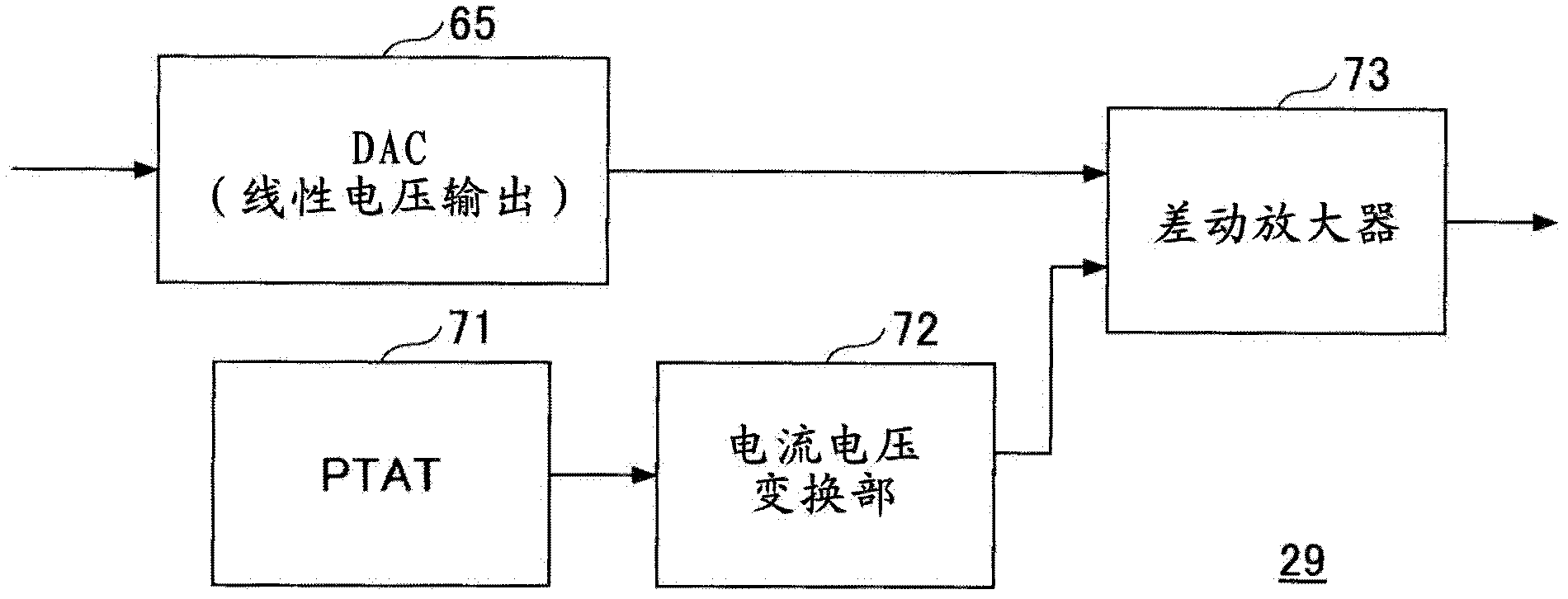
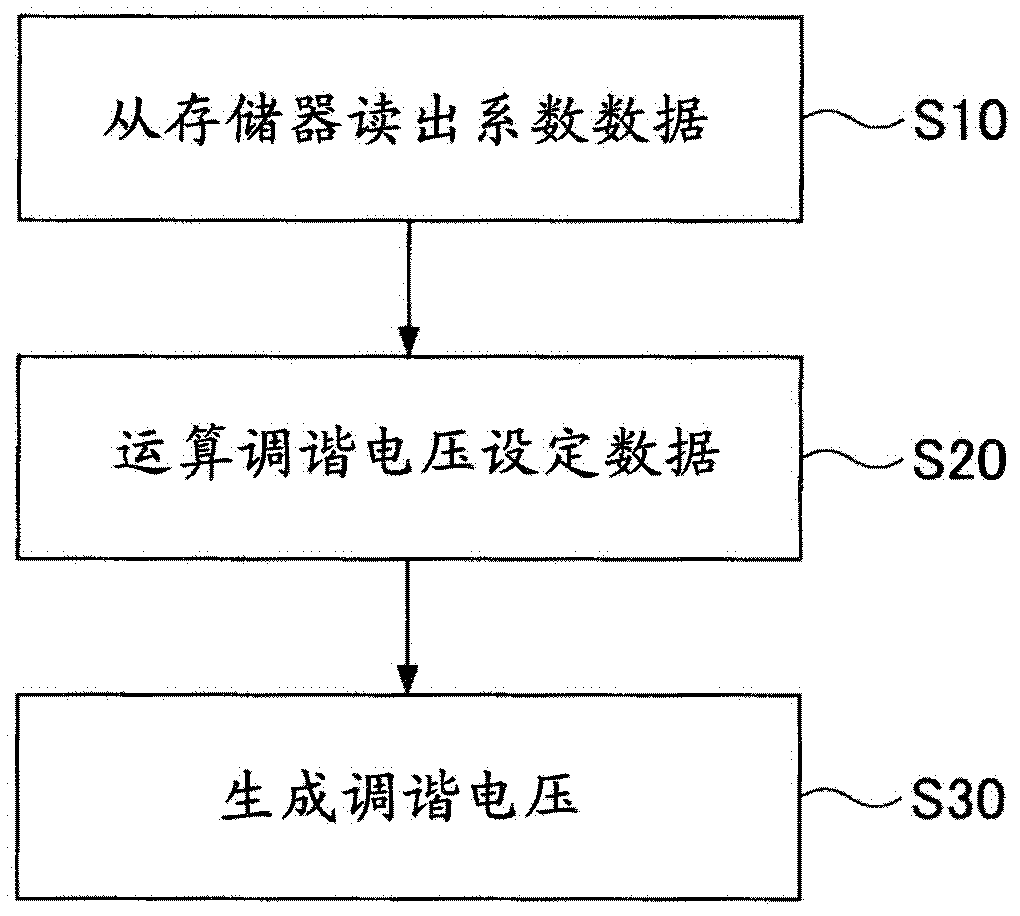
InactiveCN102484492AEasy to tuneContinuous tuning detailsResonant circuit detailsCapacitanceIntermediate frequency
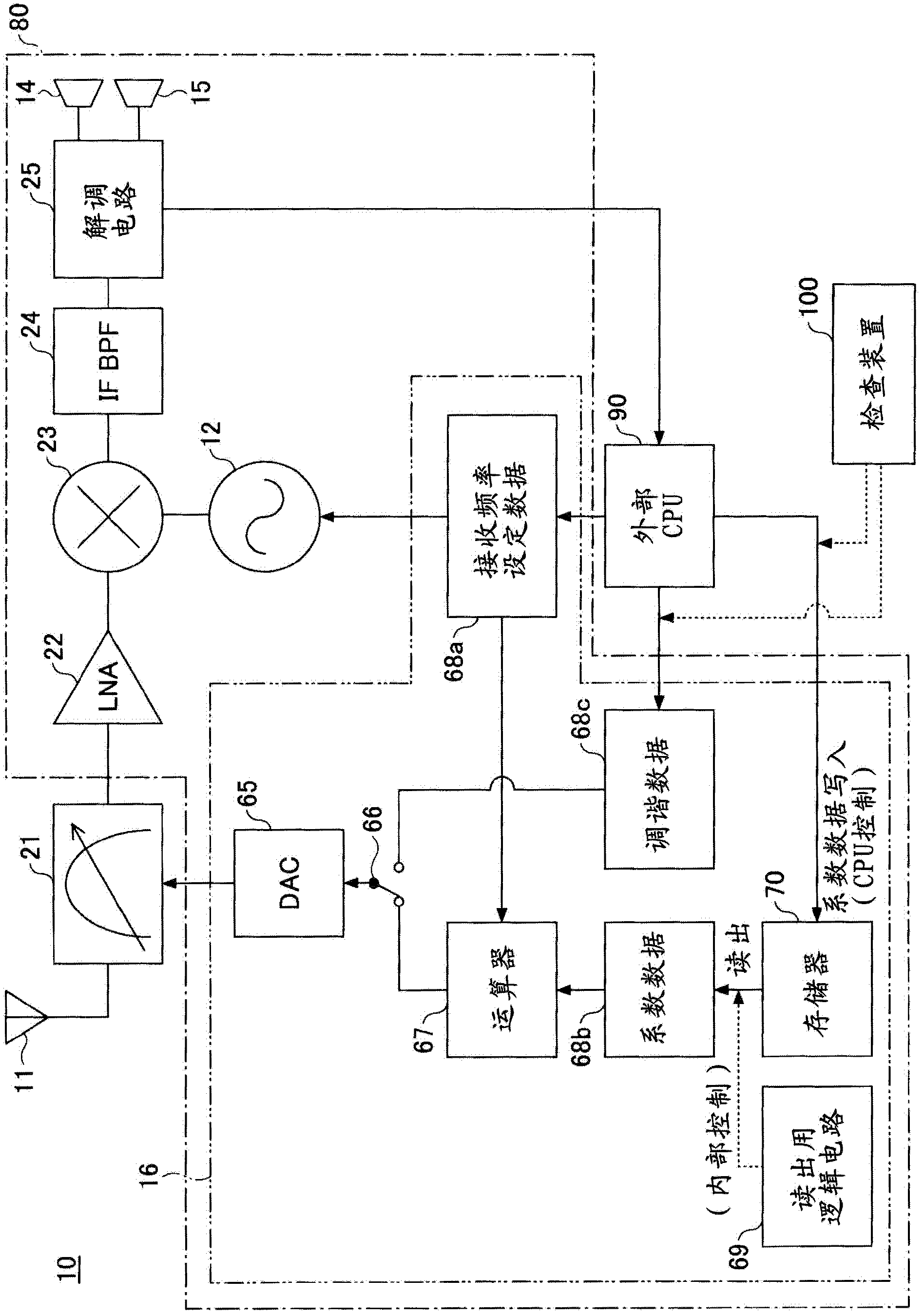
A superheterodyne receiver apparatus comprises: a tuning circuit for selecting and receiving a high frequency signal, said circuit being composed of a voltage-variable capacitance element and an inductance element; and a frequency converting unit for frequency converting the high frequency signal to an intermediate frequency signal. The superheterodyne receiver apparatus further comprises: an electrically rewritable read only memory; a calculation unit for calculating tuning voltage setting data, which used to set the tuning circuit to a tuning voltage corresponding to a desired reception frequency, in accordance with a mathematical expression that uses the data stored in the memory as coefficients; and a D / A conversion unit for D / A converting the tuning voltage setting data to the tuning voltage.
Owner:MITSUMI ELECTRIC CO LTD
Laser light detector with reflection rejection algorithm
ActiveUS7838808B1Improved signal-to-noise ratioPeak AccurateAngle measurementBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLaser transmitterSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A modulated laser light detector that converts laser light energy into electrical signals which exhibit a frequency that is substantially the same as the laser light modulation frequency, in which these signals allow the detector unit to determine a position where the laser light is impacting upon a photodiode array. A superheterodyne receiver circuit is used to provide high gain at an improved signal-to-noise ratio to improve the range at which the modulated laser light signal can be reliably detected. Various types of signal detection circuits are available. Various processing algorithms are disclosed, including one which rejects laser light strikes that are due to reflections, rather than due to a direct strike from the laser transmitter.
Owner:TRIMBLE NAVIGATION LTD
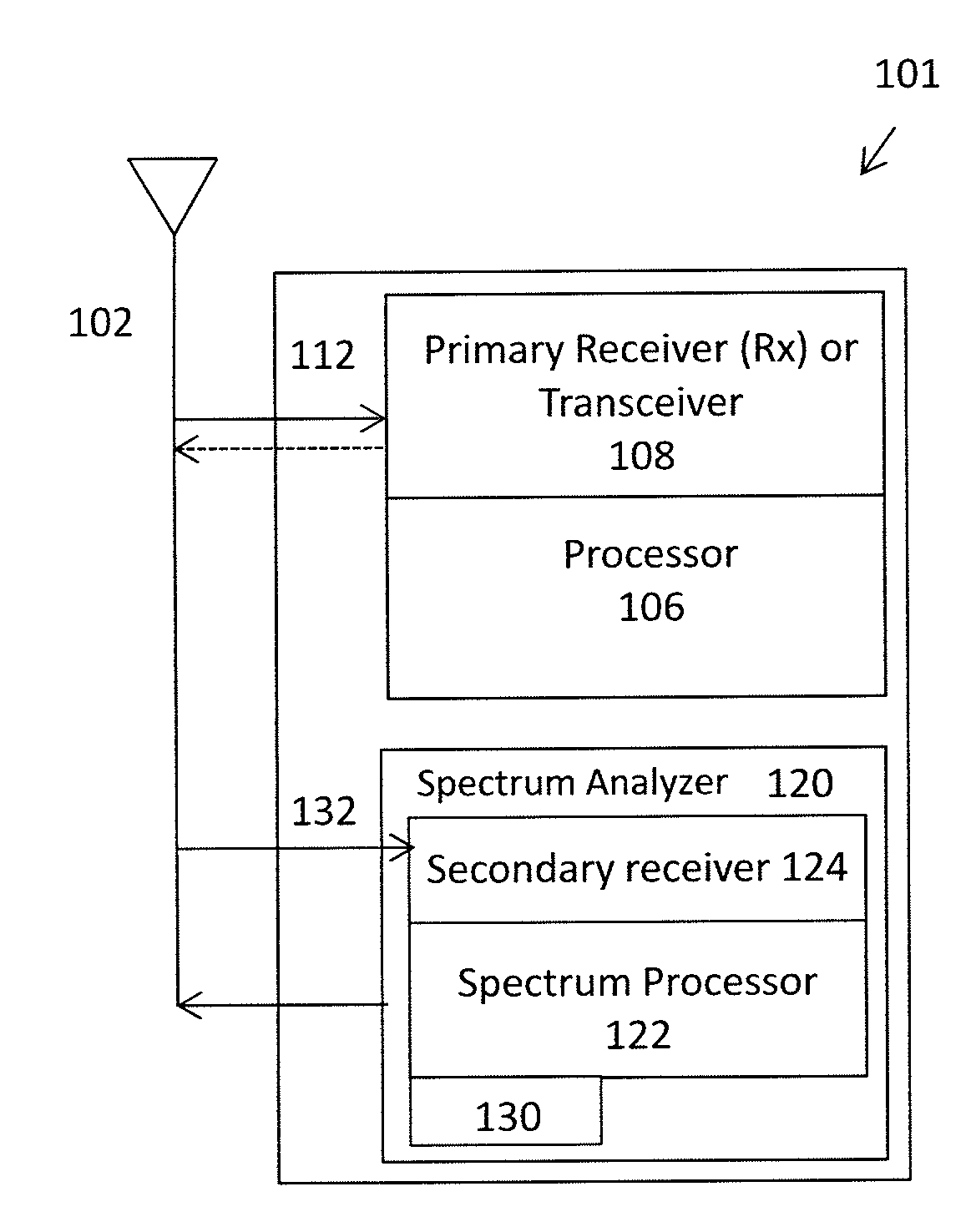
Wireless radio system optimization by persistent spectrum analysis
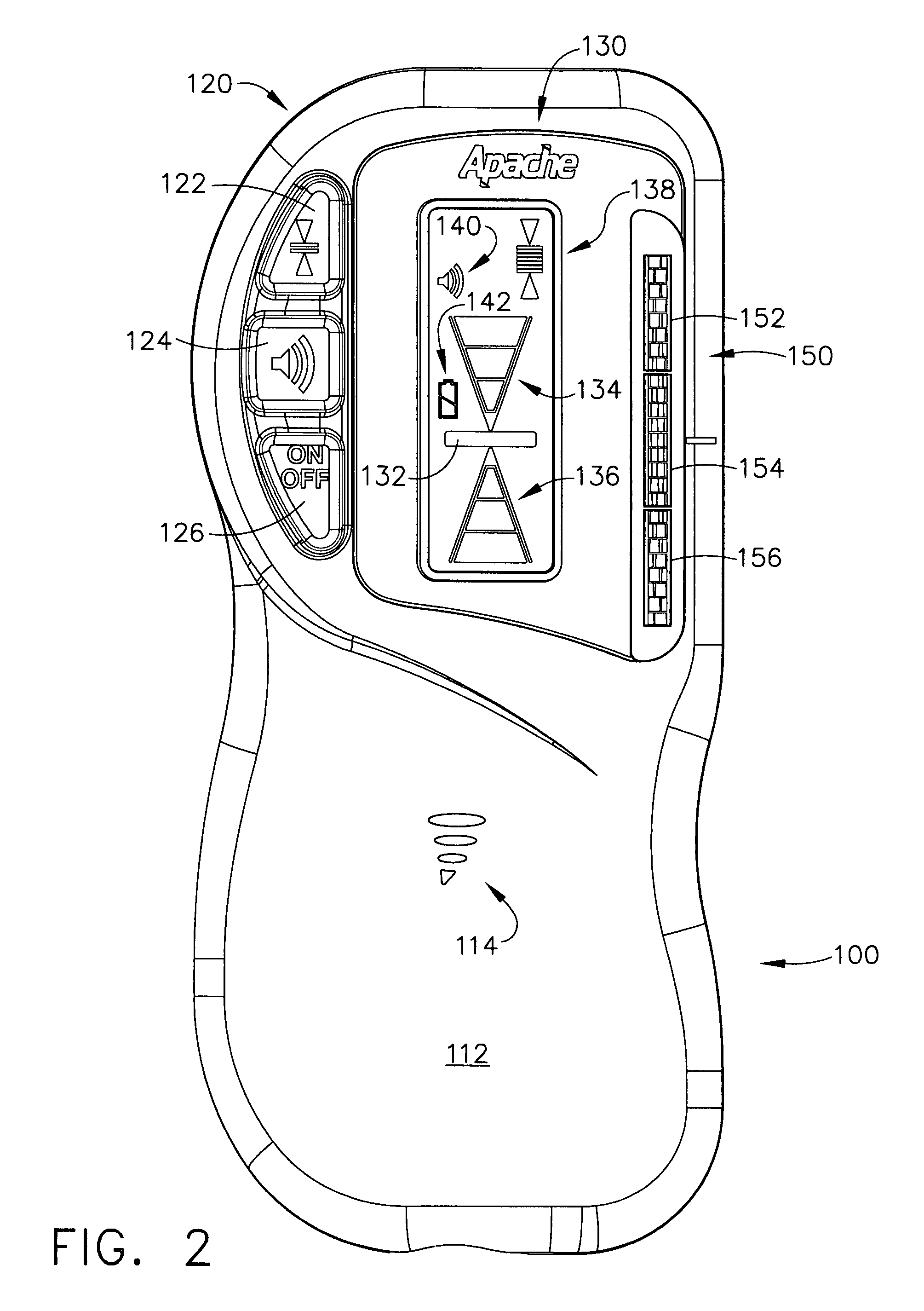
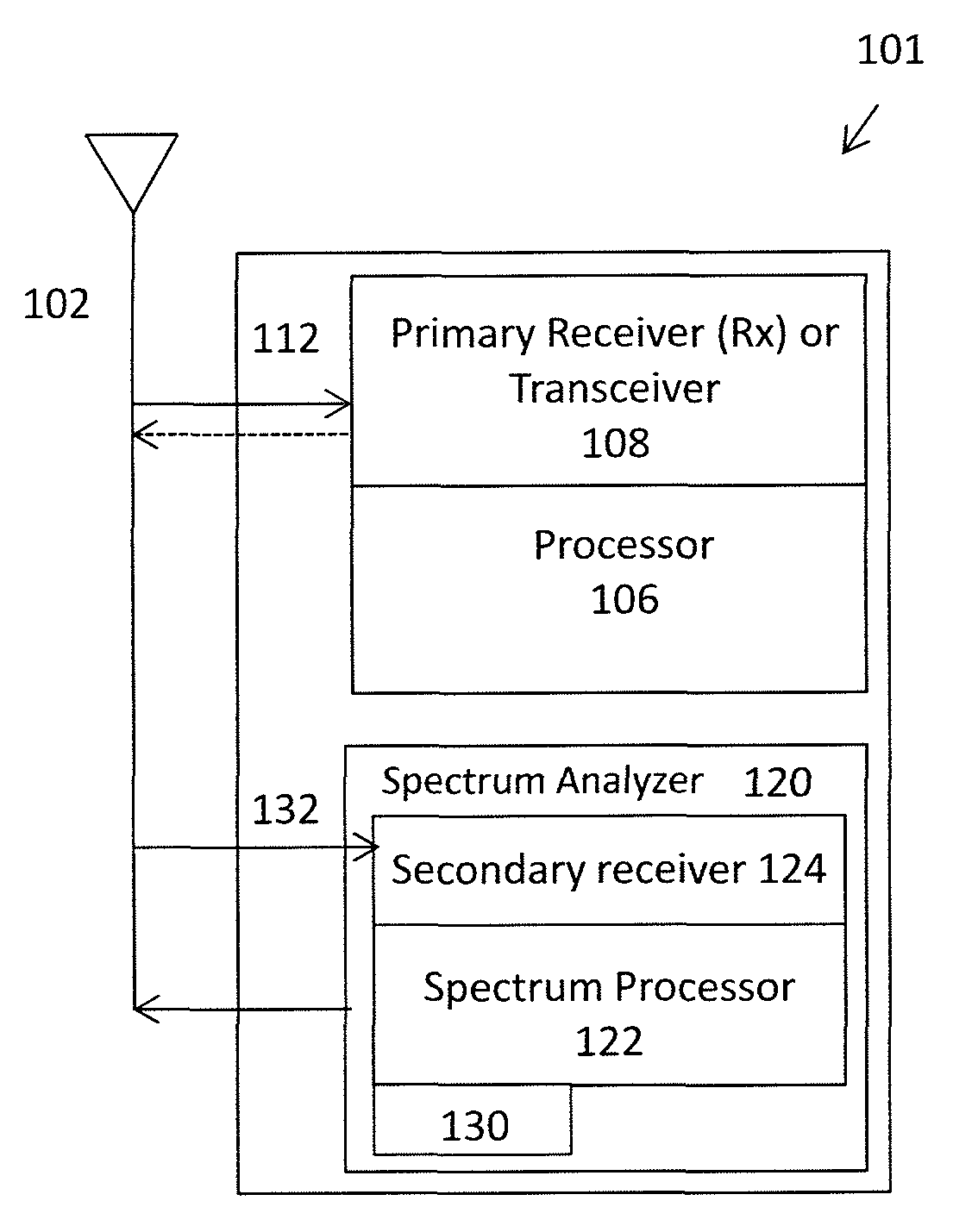
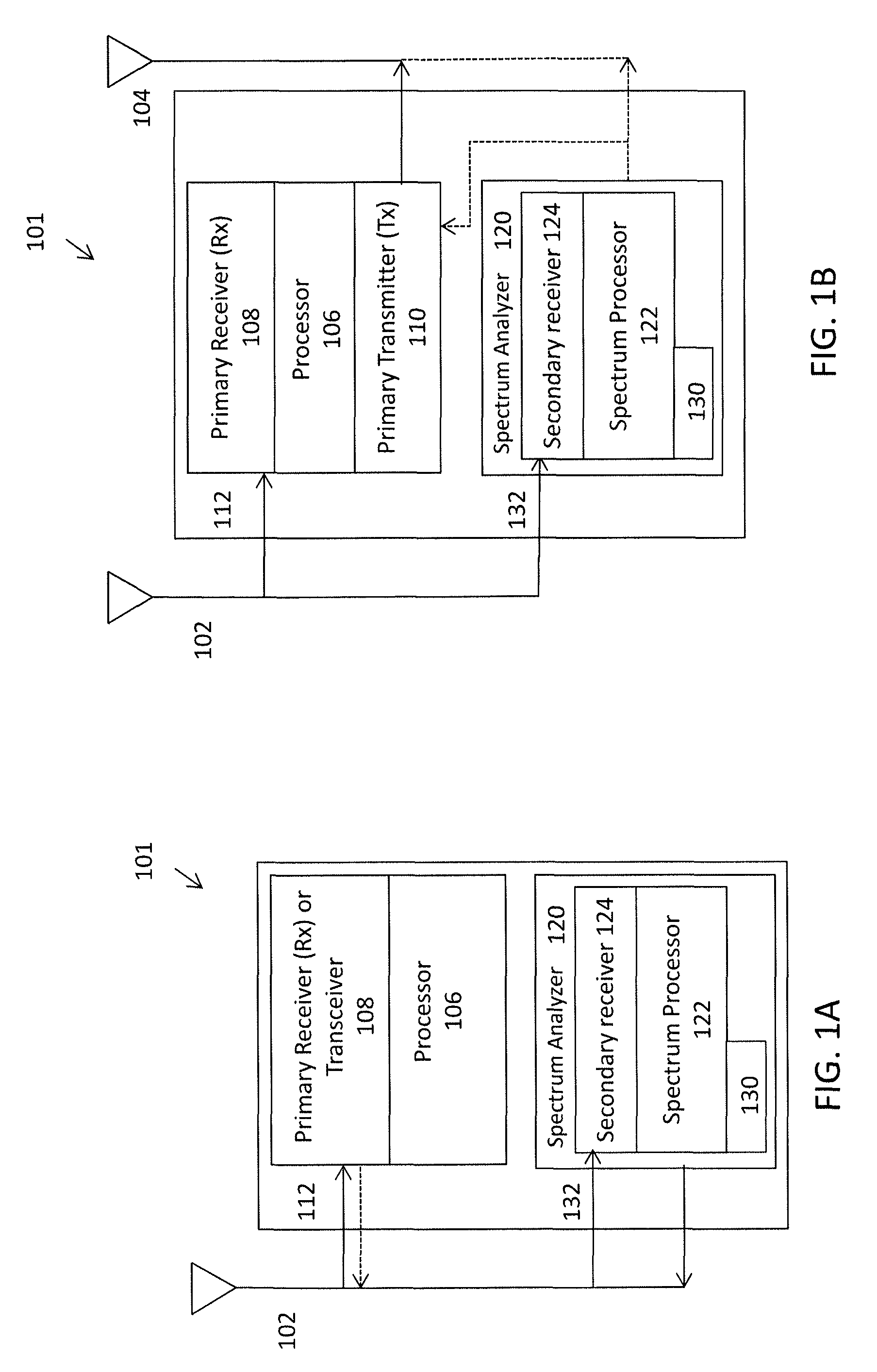
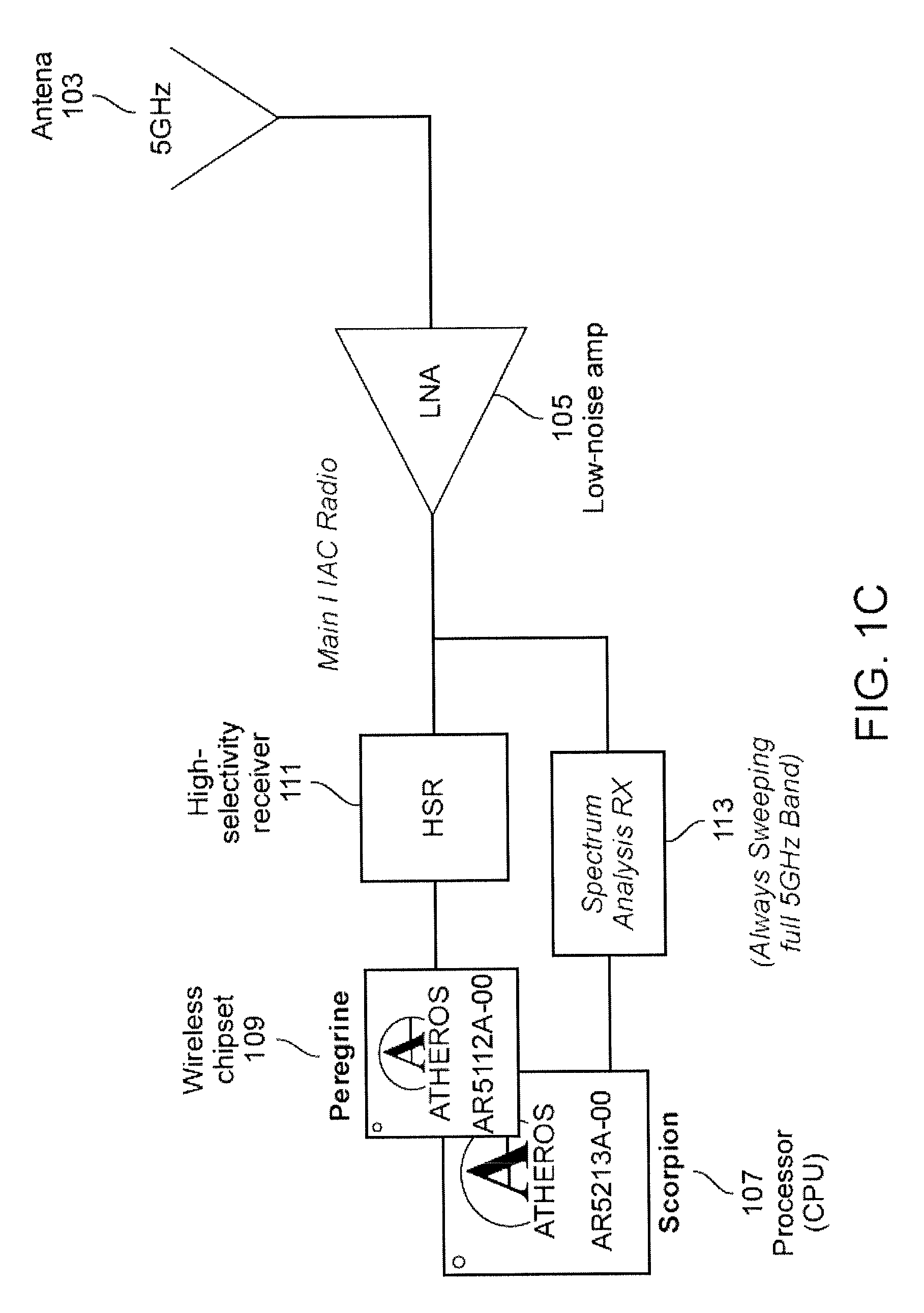
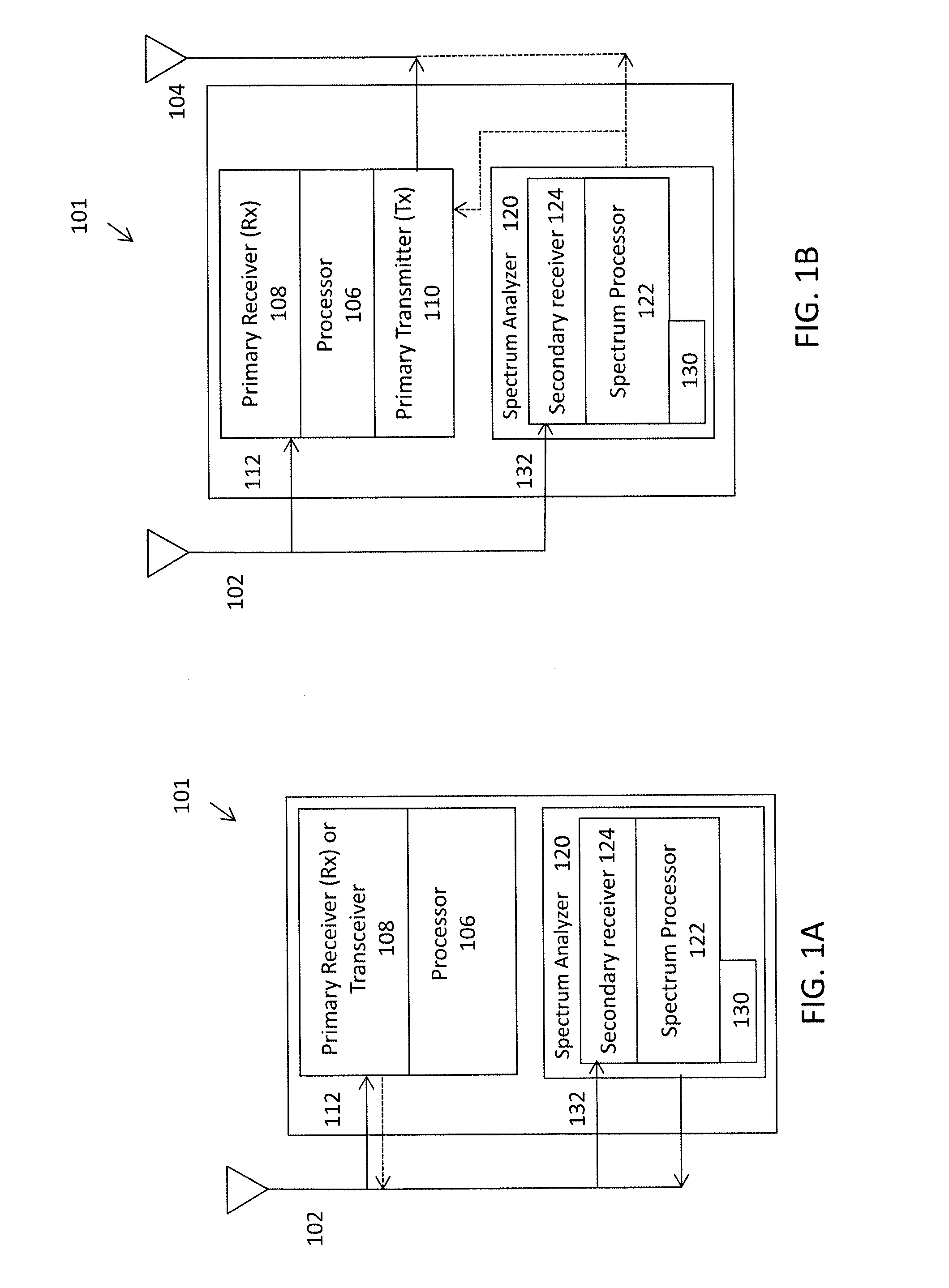
Apparatuses and methods for simultaneously operating as a wireless radio and monitoring the local frequency spectrum. For example, described herein are wireless radio devices that use a secondary receiver to monitor frequencies within the operating band and prevent or avoid interferers, including in particular half-IF interferers. The systems, devices, and methods described herein may adjust the intermediate frequency in a superheterodyne receiver to select an intermediate frequency that minimizes interference. In particular, described herein are apparatuses and methods that use a second receiver which is independent of the first receiver and may be connected to the same receiving antenna to monitor the geographically local frequency spectrum and may detect spurious interferers, allowing the primary receiver to adjust the intermediate frequency and avoid spurious interferes.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
Multiple mode direct conversion receiver
InactiveCN1261996AFrequency-division multiplex detailsDiscontinuous tuning for band selectionAudio power amplifierIntermediate frequency
A multiple-mode receiver incorporating direct conversion (processing received signals using intermediate frequencies within the same frequency range as the received signal bandwidth) rather than superheterodyne circuitry, allowing receiver hardware components to be re-used rather than replicated for each band. Various embodiments are disclosed in which low pass filters, mixers, quadrature generators, oscillators, and amplifiers are re-used.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Configurable homodyne/heterodyne radio receiver and RFID reader employing same
InactiveUS7529533B2Facilitate listen-before-talk functionEnhance the imageNear-field transmissionAutomatic scanning with simultaneous frequency displayReceiver functionRadio receiver
Owner:TRIQUINT SEMICONDUCTOR
Multicasting optical switch fabric and method of detection based on novel heterodyne receiver
InactiveUS7373091B2Time-consume wavelength fine tuningQuick selectionGain controlMultiplier circuit arrangementsLocal oscillatorEngineering
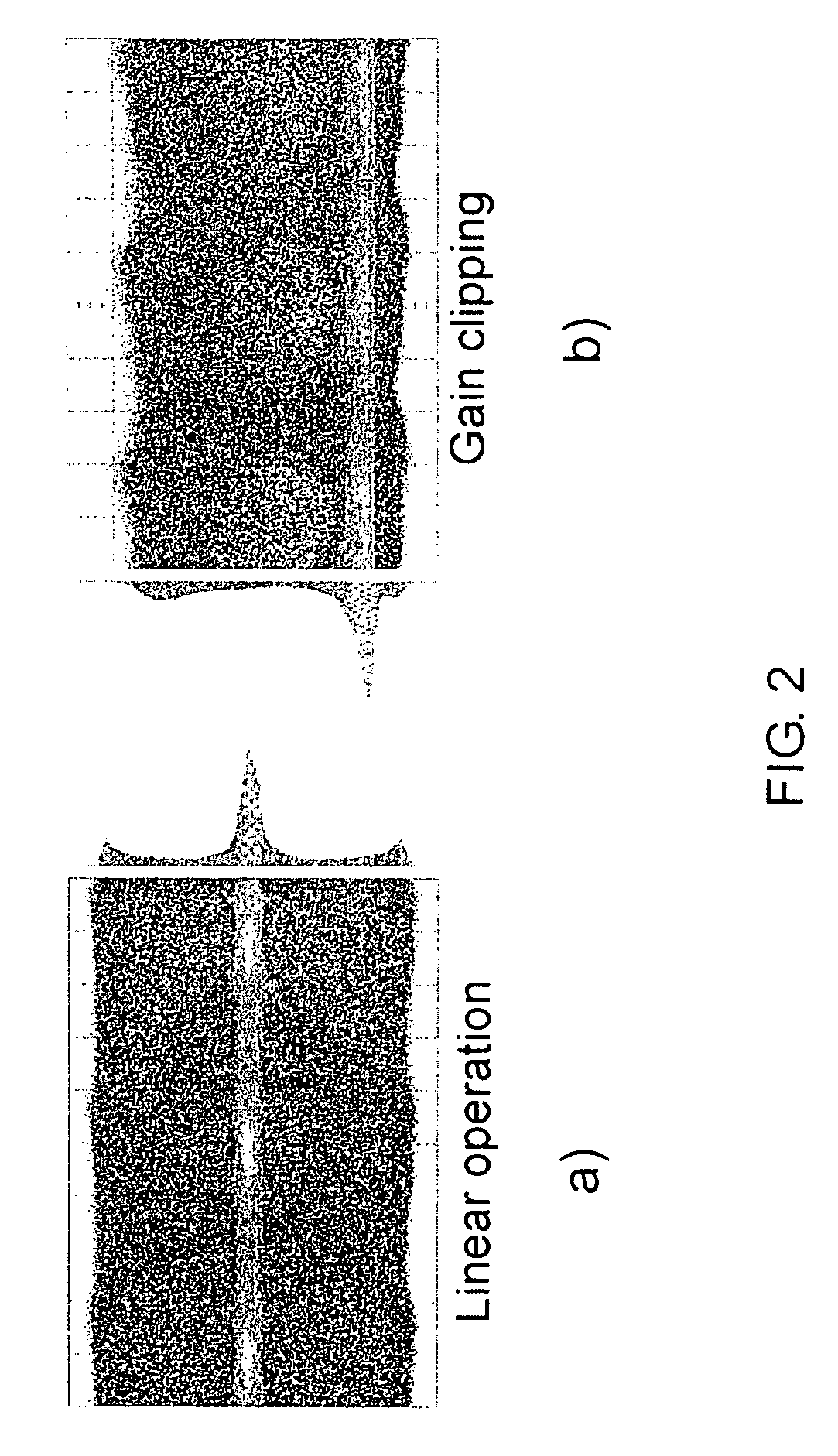
The inventors propose herein a switch fabric architecture that allows broadcasting and fast channel access in the ns-range. In various embodiments of the present invention, 10 Gb / s receiver modules are based on a novel heterodyne receiver and detection technique, which is tolerant to moderate wavelength drifts of a local oscillator. A gain clipped electrical amplifier is used in the novel receiver as a rectifier for bandpass signal recovery.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Front-ene circuit of two-step double-orthogonal zero medium frequency structure receiver of global digital broadcasting
InactiveCN1794594AImprove image rejection ratioAmplitude demodulation by homodyne/synchrodyne circuitsTransmissionIntermediate frequencyRadio frequency signal
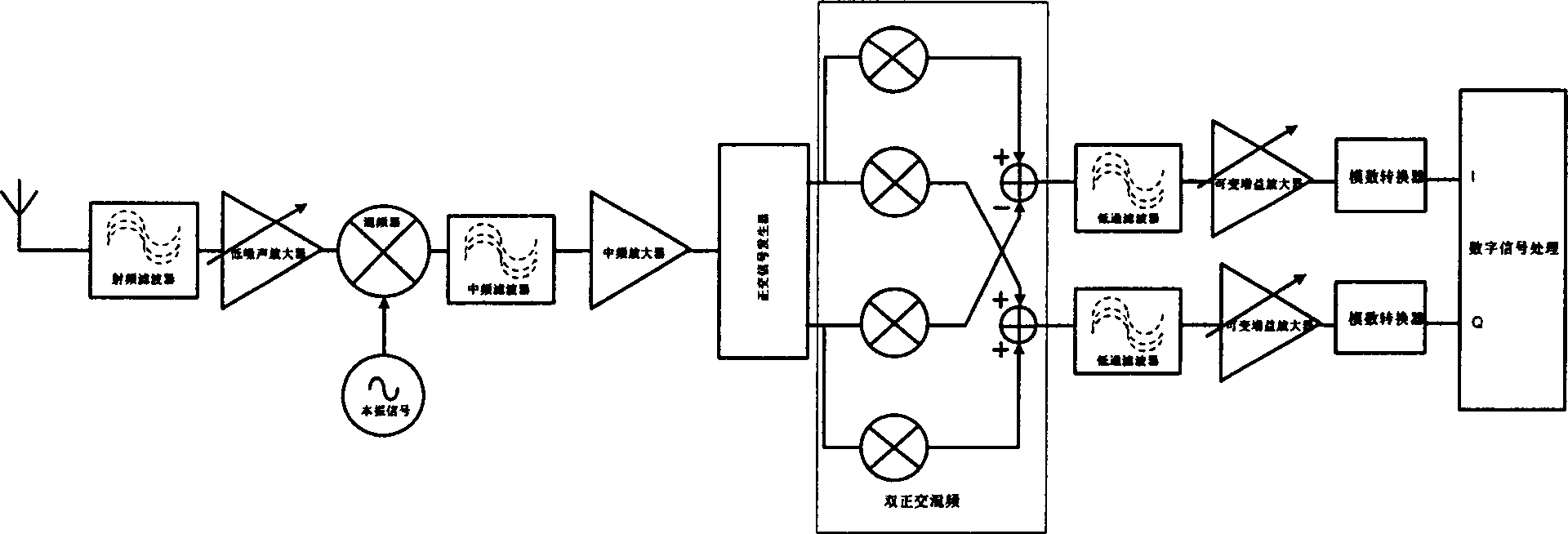
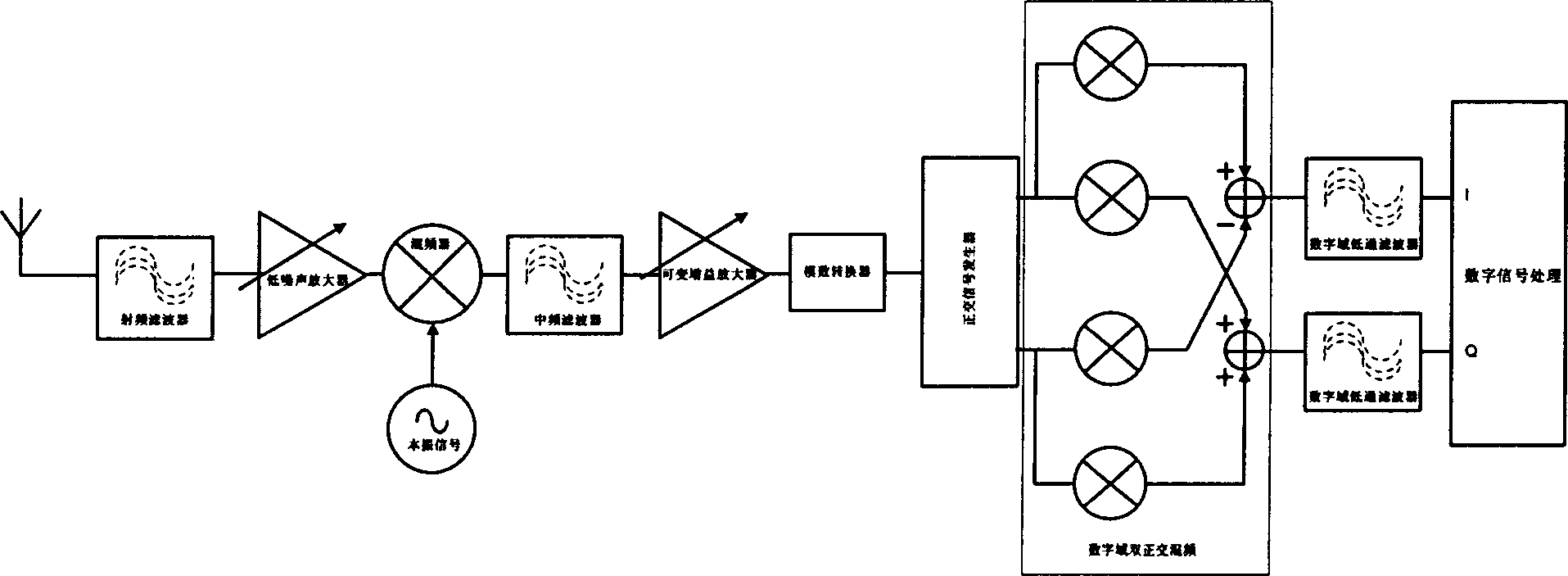
This invention relates to a global digital broadcast technology characterizing in applying two step double orthogonal zero IF including the following steps: transforming a RF signal to a high IF then to be switched to a base band directly via a double orthogonal mixed frequency structure. In practice, two different modes can be applied according to the different places set for the A / D converter by digitalizing after the first time of mixing the frequency then carrying out a second time orthogonal mixing and digitalization after that, which overcomes the shortcoming of converting frequencies for many times of the traditional superheterodyne receivers used at present in the global digital broadcast system
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
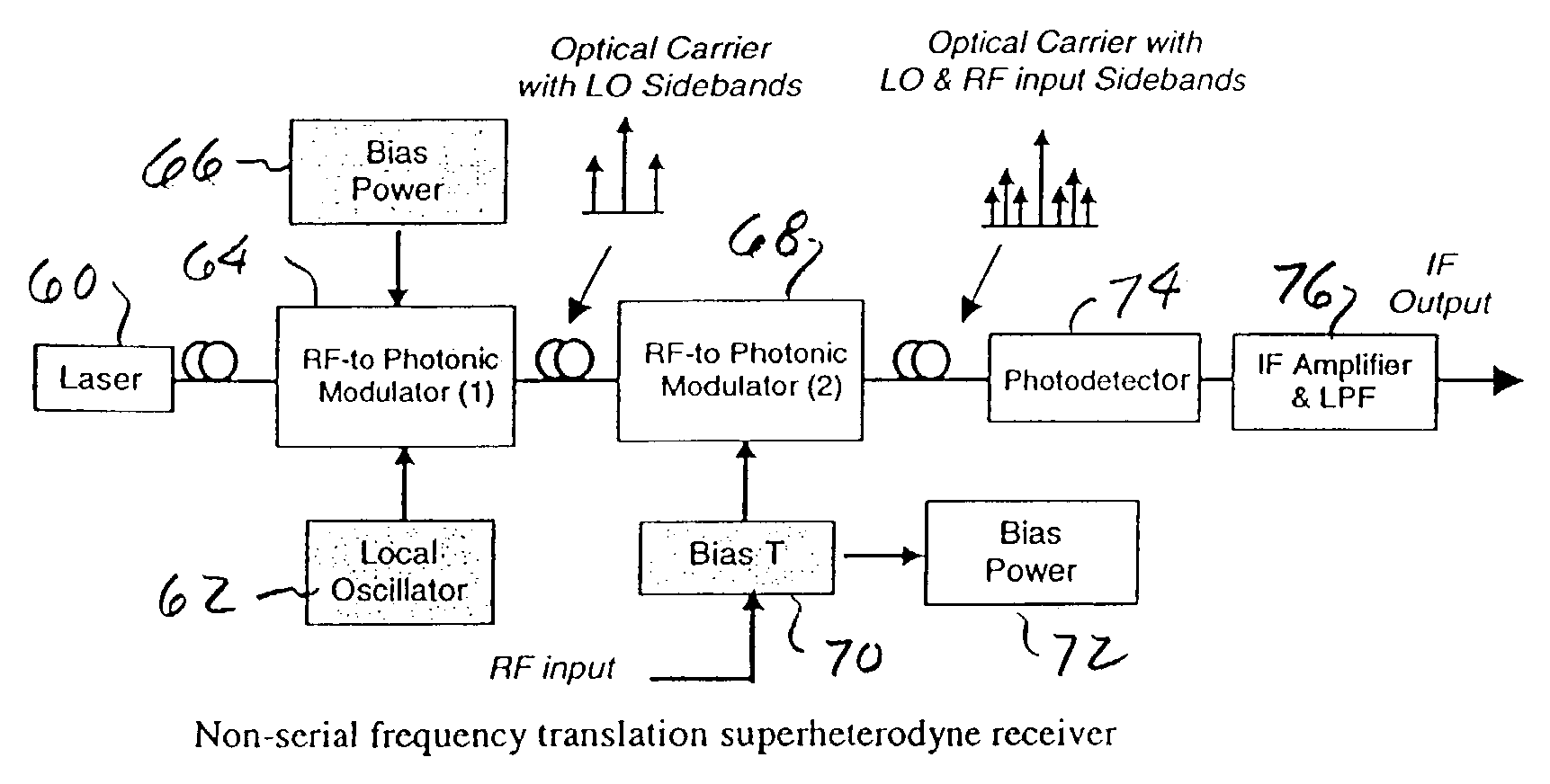
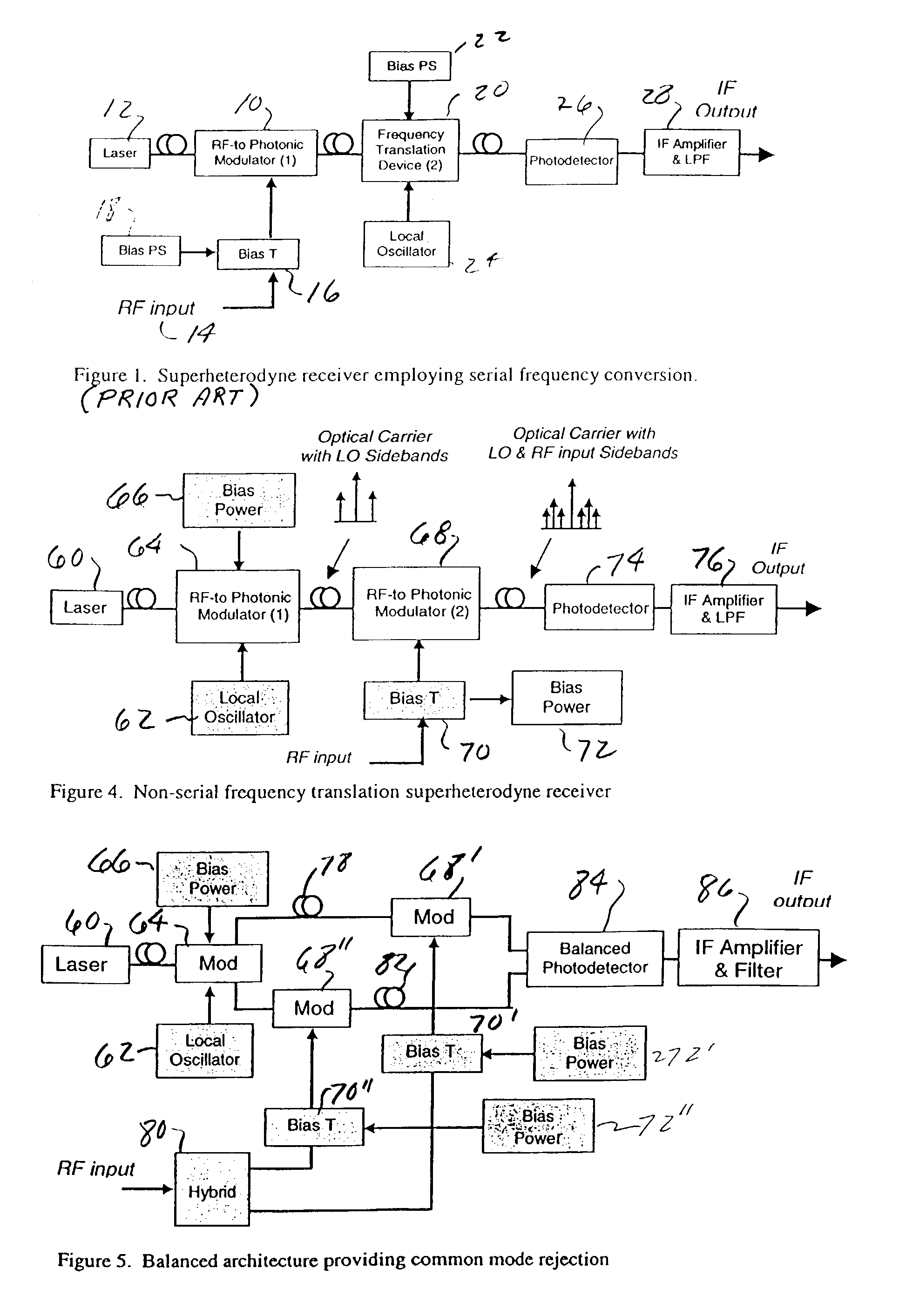
Superheterodyne photonic receiver using non-serial frequency translation
ActiveUS7269354B1Reduce signal lossFrequency is eliminatedOptical transmission for RF signal generation/processingRadio-over-fibreCarrier signalPhotonics
An optoelectronic RF signal receiver utilizes a first RF to photonic modulator for receiving an optical carrier signal and an electrical signal from a local oscillator and producing an optical carrier signal with first optical sidebands offset from the carrier signal by the local oscillator frequency. A second RF to photonic modulator receives an electrical RF signal and the signals from the first modulator and produces second sidebands to each of the first optical sidebands from the first modulator with each of the second sidebands being offset from the first sidebands by the RF signal frequency. A detector then receives signals produced by the second modulator and produces an electrical IF signal for further processing. The receiver does not utilize a frequency translation device in the RF signal path and thereby eliminates RF loss, noise, and limited dynamic range characteristic of prior art electro-optical receivers. The two modulators can be biased for optimum linearity and for optimum rejection of in-band spurious signal products.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Wireless radio system optimization by persistent spectrum analysis
Apparatuses and methods for simultaneously operating as a wireless radio and monitoring the local frequency spectrum. For example, described herein are wireless radio devices that use a secondary receiver to monitor frequencies within the operating band and prevent or avoid interferers, including in particular half-IF interferers. The systems, devices, and methods described herein may adjust the intermediate frequency in a superheterodyne receiver to select an intermediate frequency that minimizes interference. In particular, described herein are apparatuses and methods that use a second receiver which is independent of the first receiver and may be connected to the same receiving antenna to monitor the geographically local frequency spectrum and may detect spurious interferers, allowing the primary receiver to adjust the intermediate frequency and avoid spurious interferes.
Owner:UBIQUITI INC
System for achieving transient signal capture and spectral analysis
ActiveCN103763051AIncrease flexibilityImprove good performanceTransmission monitoringFrequency spectrumSpecific time
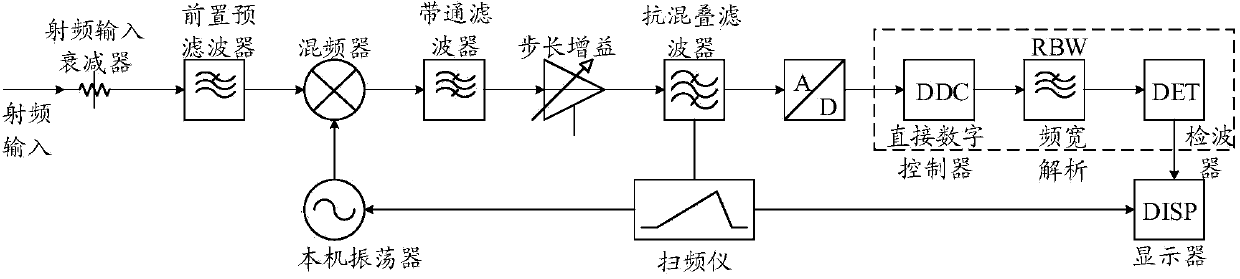
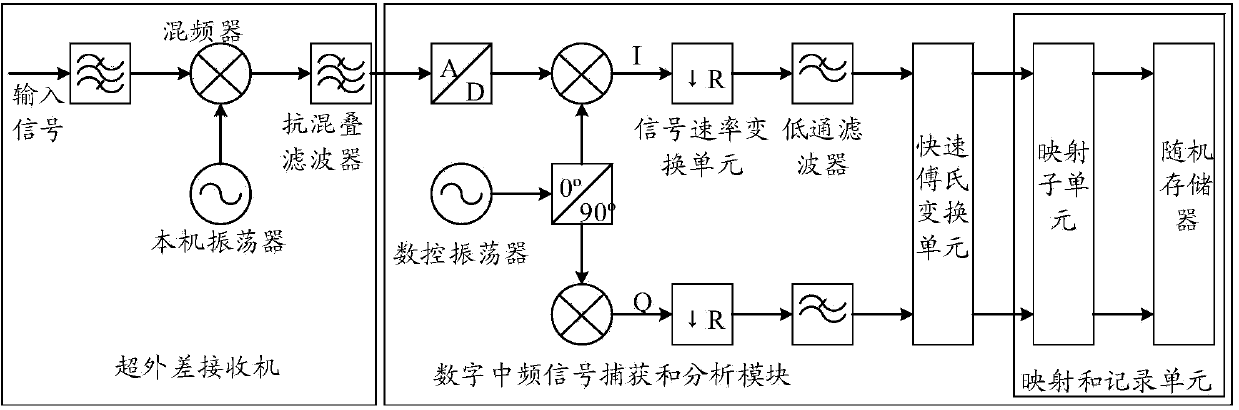
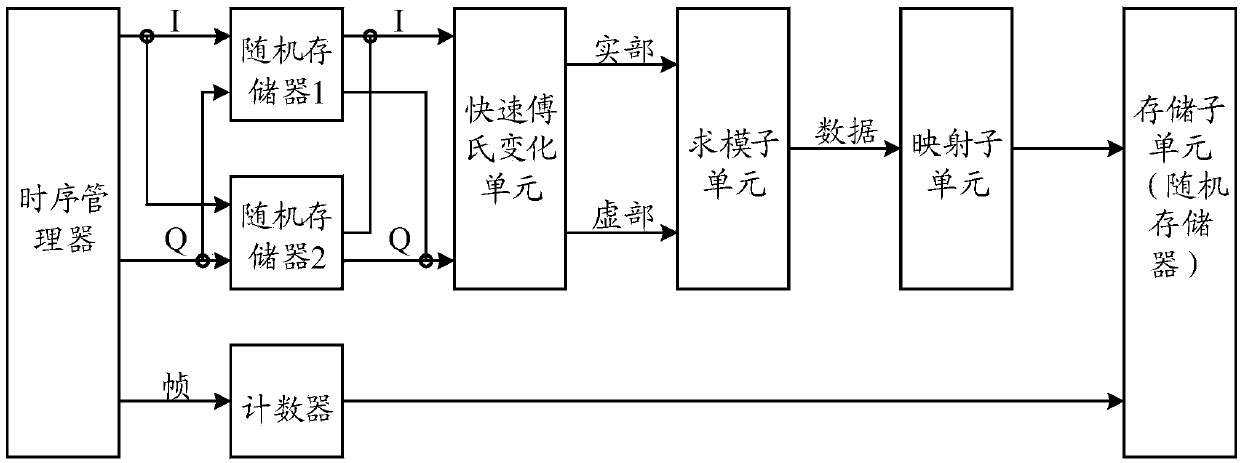
The invention relates to a system for achieving transient signal capture and spectral analysis. The system comprises a superheterodyne receiver and a digital intermediate frequency capture and analysis module. The digital intermediate frequency capture and analysis module comprises an analog-digital conversion unit, an IQ modulation unit, a rapid Fourier transform unit and a mapping and recording unit. The mapping and recording unit is used for calculating the signal amplitude of each frequency component output by the rapid Fourier transform unit, conducting probability mapping on the signal amplitudes and recording the appearing frequency of frequency points. According to the system for achieving transient signal capture and spectral analysis, by the adoption of the structure, the information of the frequency, amplitude and occurrence probability and time of signals can be analyzed and recorded at the same time, the method for comprehensively analyzing suddenly-burst signals is provided, the occurrence probability and the specific time of the signals are analyzed from the perspective of the frequency domain, four-dimensional analysis can be carried out on the signals, and the system is widely applied in the actual signal analysis, has good flexibility and expandability and is applicable to large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:TRANSCOM INSTR
Dual mode radio frequency receivers for wideband signal processing
ActiveUS20140378079A1Requires minimizationIncrease spectral bandwidthRadio transmissionTuned radio frequency receiverFrequency spectrum
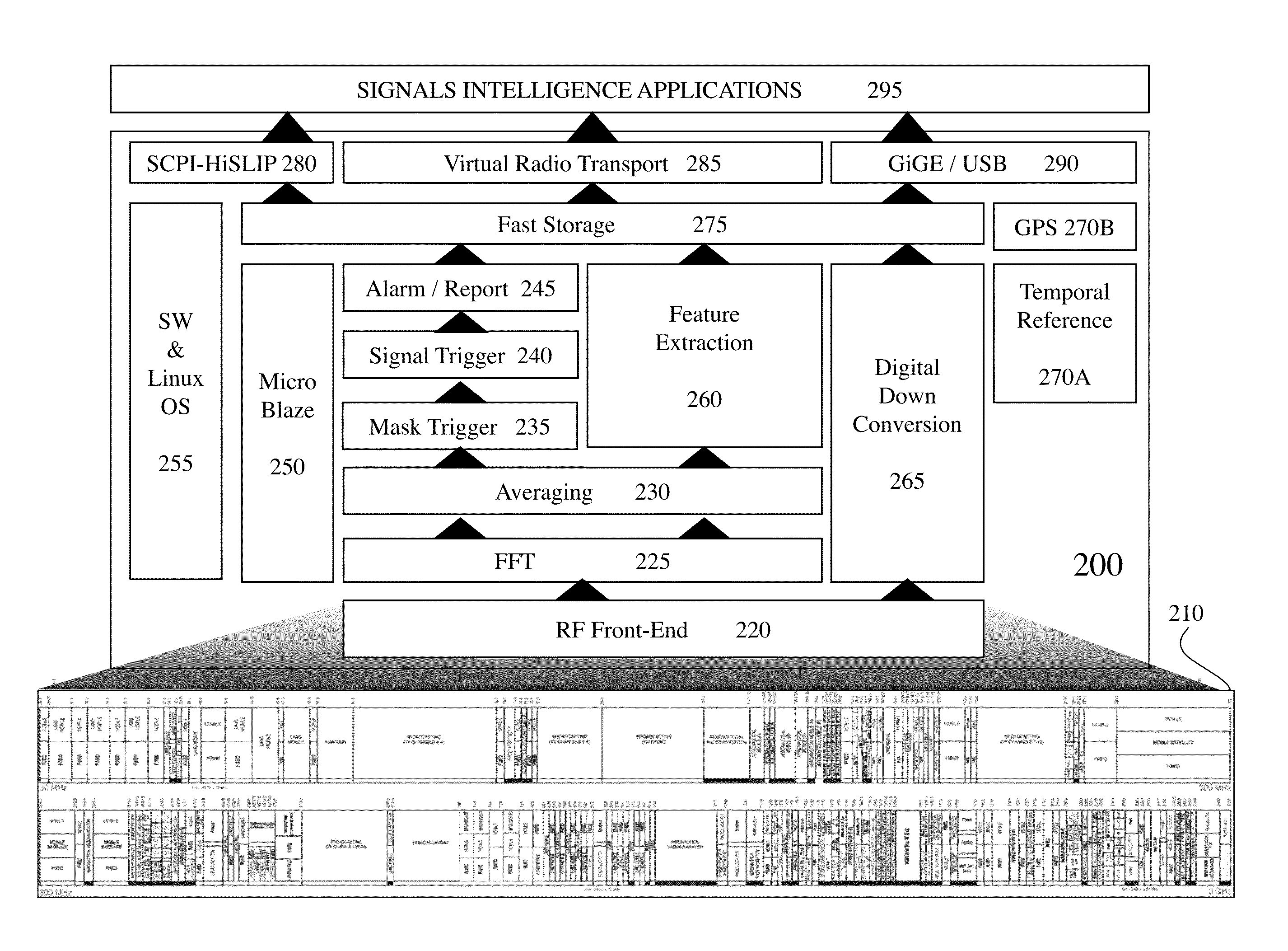
Wireless communication is ubiquitous today with increasing deployments leading to increased interference, increasing conflicts, etc. Monitoring the wireless environment is therefore important for regulators, service providers, Government agencies, enterprises etc. Such monitoring should be flexible both in networks monitored within the wireless environment as well as detecting unauthorized transmitters, allowing dynamic network management, etc. However, such real time spectral / signal analysis in the prior art requires both a wideband direct conversion receiver (DCR), for high performance, wideband, fast, programmable spectral analysis, and a super heterodyne receiver for fast, narrowband, programmable demodulation for signal analysis. According to embodiments of the invention a single receiver design methodology exploiting a single RF circuit to provide superheterodyne and direct conversion receiver functionalities.
Owner:THINKRF
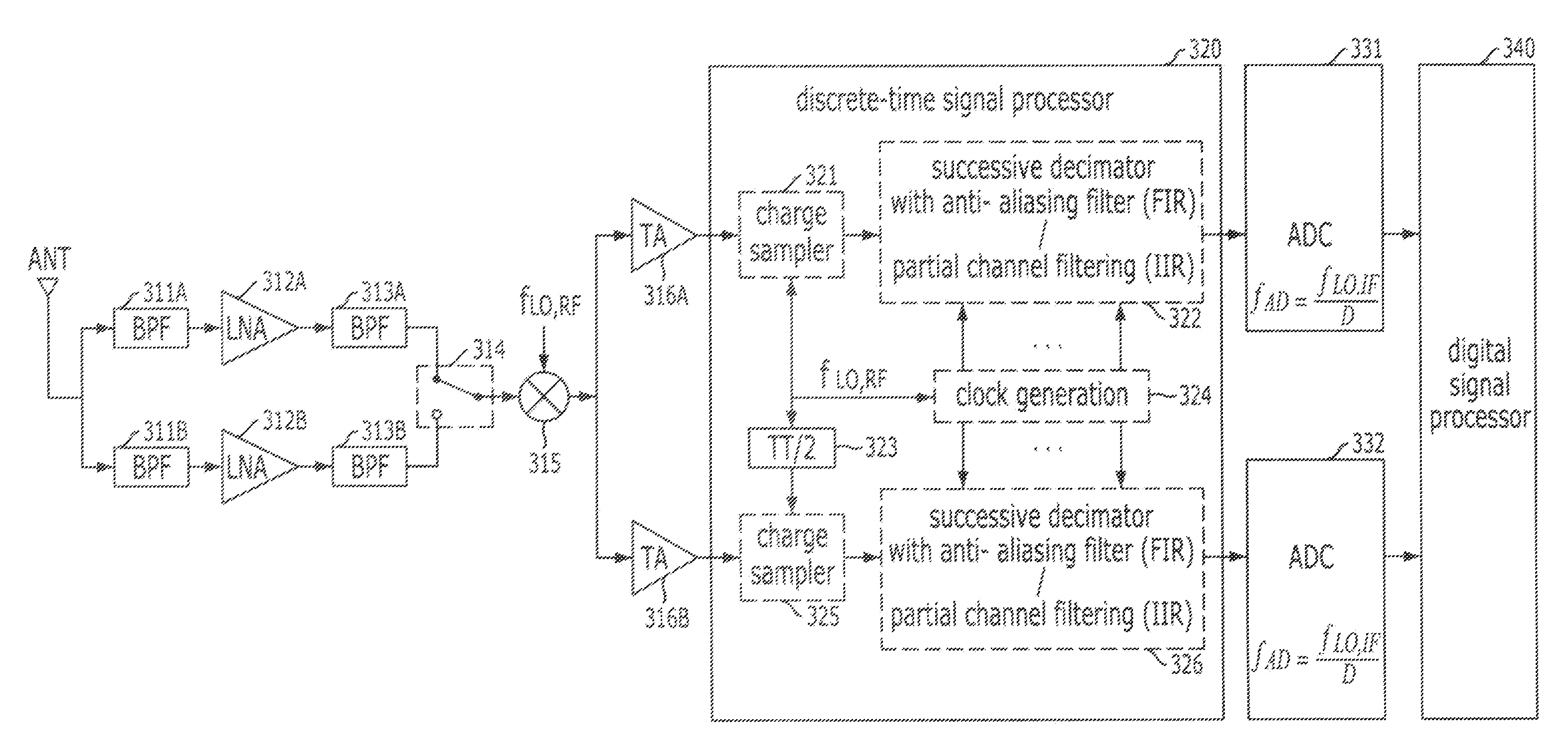
Heterodyne receiver using analog discrete-time signal processing and signal receiving method thereof
InactiveUS20100093301A1Easy to integrateTransmission noise suppressionAnti-aliasingIntermediate frequency
A heterodyne receiver of a wireless communication system using an analog discrete-time signal processing is provided. The heterodyne receiver includes: a radio signal processing unit configured to extract a signal of a desired band from a received radio signal and convert the extracted signal into an intermediate frequency (IF) signal that is an integer multiple of a sample rate specified in a specification of the wireless communication system; a discrete-time signal processing unit configured to charge-sample the IF signal in unit of a predetermined time and perform an anti-aliasing filtering and a successive decimation on the charge-sampled signal, a final output rate according to the decimation being an integer multiple of the specified sample rate; and an analog-to-digital conversion unit configured to convert the successively-decimated analog signal into a digital signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
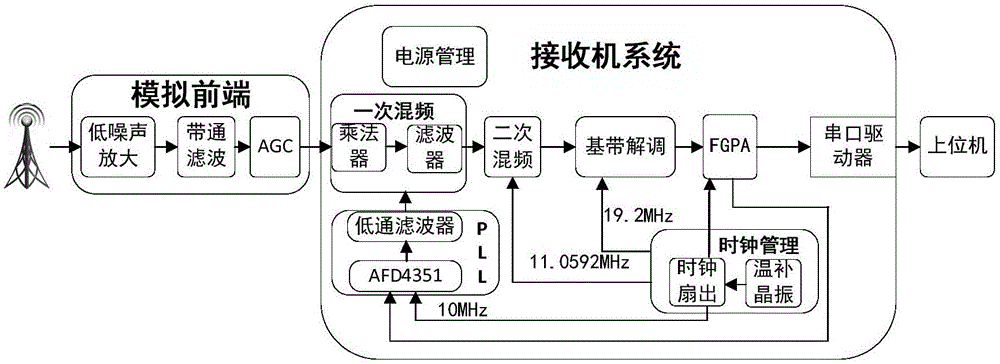
AIS receiver based on superheterodyne principle
ActiveCN106487401AGuaranteed SNRImprove demodulation sensitivityTransmissionFrequency stabilizationSystems design
The invention relates to an AIS receiver based on the superheterodyne principle. The AIS receiver taking the FPGA as a control core comprises a simulation front-end module, a primary frequency mixing module, a secondary frequency mixing module, a base band demodulation module, a PLL module, a clock management module, a power supply management module, an FPGA controller module and a serial port driver module. According to the invention, by use of a low-noise amplifier and an AGG circuit, the dynamic range is wide, weaker signals can be captured, and ships in the longer distance can be detected; by use of an intermediate frequency signal processing chip with quite high demodulation sensitivity, the sensitivity of the receiver is further improved; by use of the CMX7042, demodulation, decoding and verification of base band signals are achieved, system design is simplified, and cost is controlled; and temperature-compensation crystal oscillators are used for supplementing the system clock, and a clock fan-out chip is used for carrying out unified distribution, synchronization of the system is achieved, output frequency stability of a phase-locked loop is improved and precision of the system is further improved.
Owner:南京欢涛仪器有限公司
Heterodyne receiver
ActiveUS20110124309A1Computations using contact-making devicesComputing operations for multiplication/divisionCross connectionAudio power amplifier
Owner:NXP USA INC
Passive radar system for switching among multiple antenna arrays
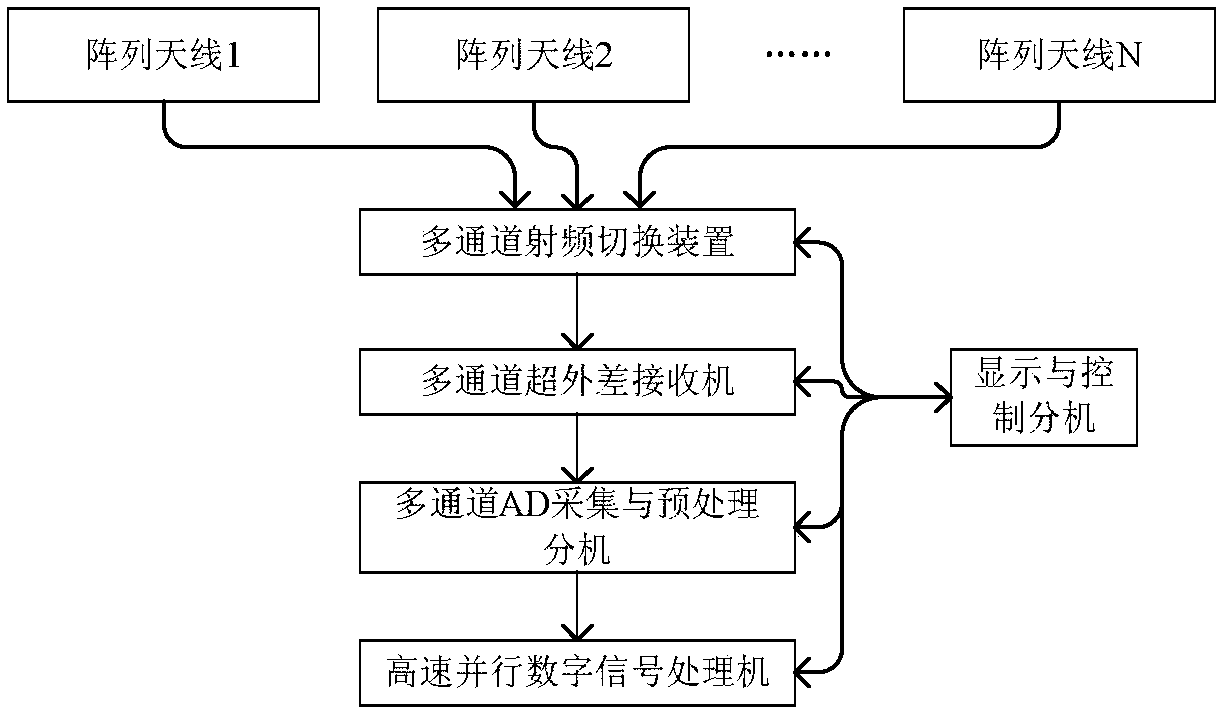
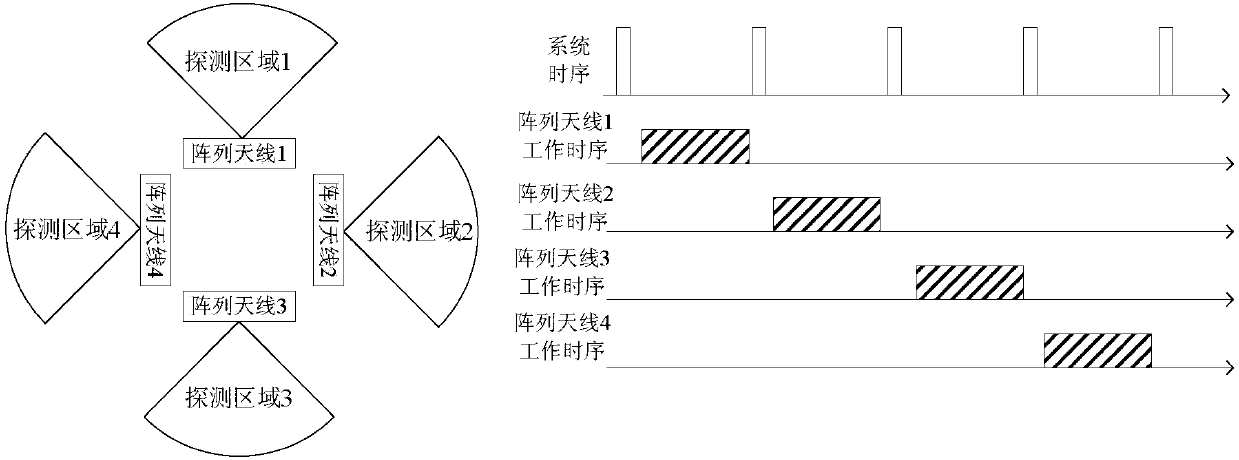
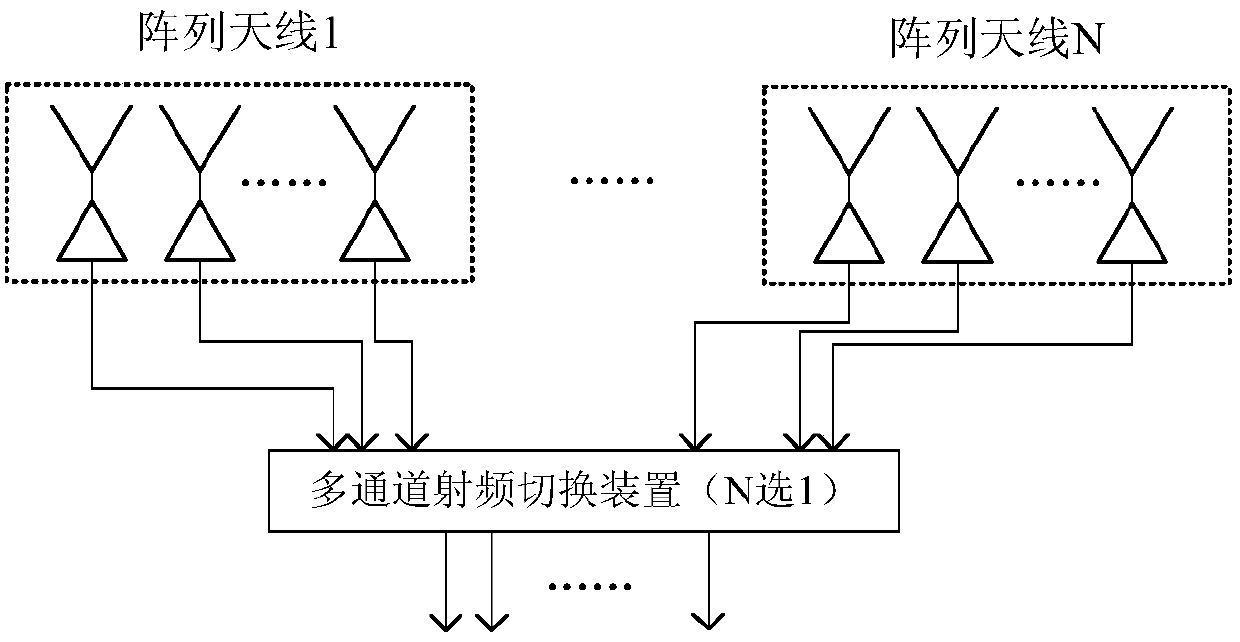
ActiveCN107728137AMeet airspace coverage requirementsLow costRadio wave reradiation/reflectionDigital signal processingPassive radar
The invention discloses a passive radar system for the switching among multiple antenna arrays. The system comprises a plurality of array antennas, and the combined airspace coverage orientation of the array antennas is 360 degrees. A multi-channel radio frequency switching device selects one array antenna in a fixed time period according to the time sequence, and sends signals received by the array antenna to a multi-channel superheterodyne receiver. In this way, multiple channels of radio-frequency signals are converted to fixed intermediate-frequency signals. After that, the intermediate-frequency signals are sent to a multi-channel AD acquisition and preprocessing sub-machine, so that the AD acquisition and the digital down-conversion of the intermediate-frequency analog signals are completed. After that, the clutter suppression, the target detection, the positioning and the tracking are conducted by a high-speed parallel digital signal processing machine. By adopting the system, aplurality of antenna arrays are switched to take turn and run according to a certain time sequence, so that the orientation360-degree airspace coverage of the passive radar system is realized. Compared with a traditional circular array antenna, the antenna side lobe is low, and the clutter suppression capability is high. Meanwhile, the low-altitude target detection capability is high, and the cost of the system can be effectively controlled.
Owner:芜湖华创光电科技有限公司
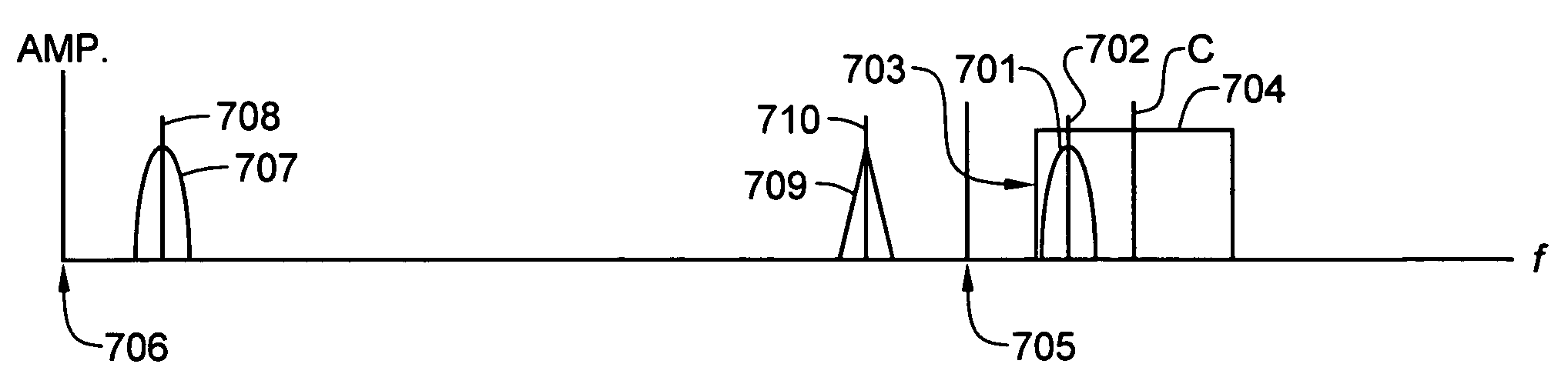
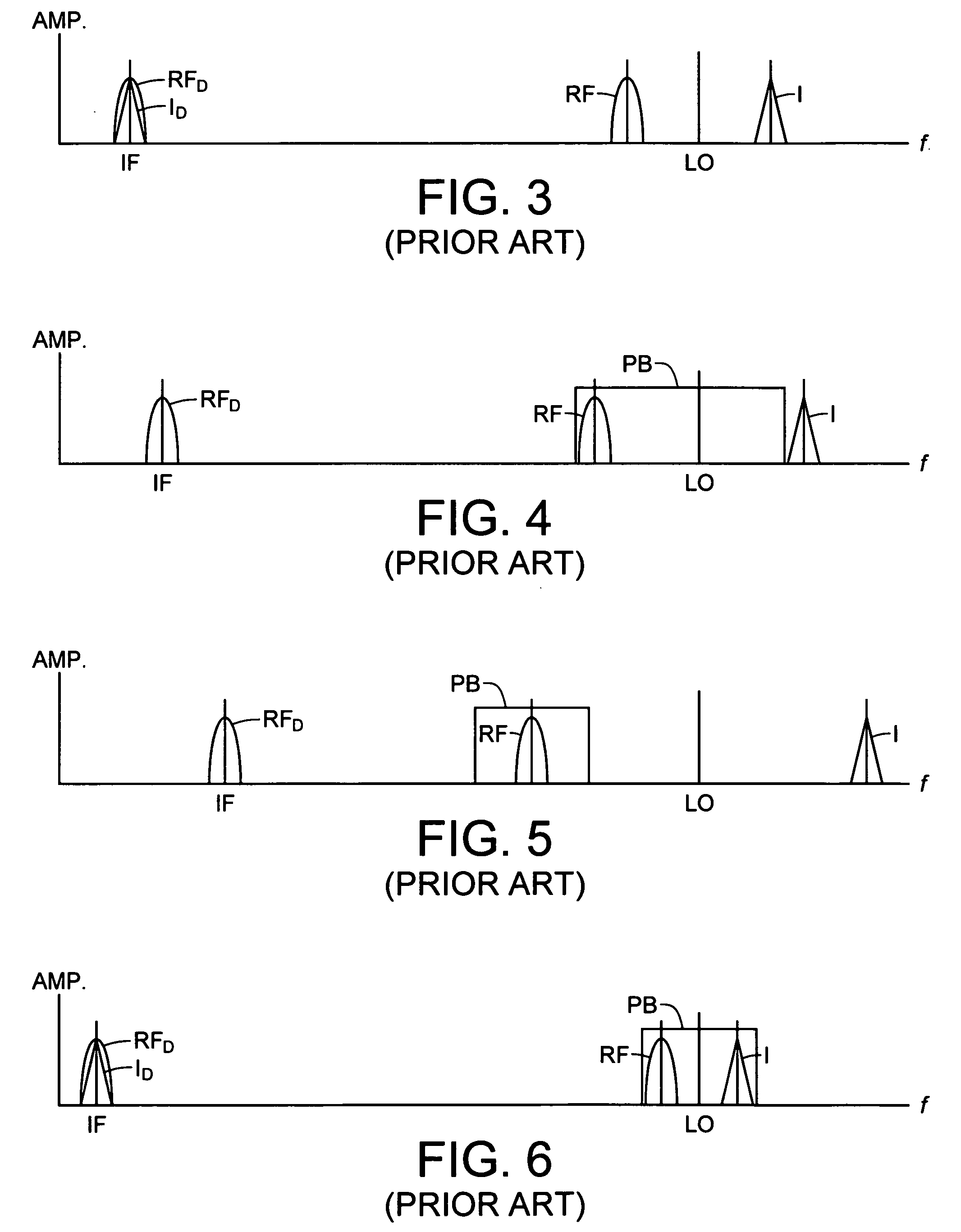
Superheterodyne receiver having at least one downconversion stage empolying a single image reject filter stage and both low-side injection and high-side injection of a local oscillator signal
ActiveUS20070037546A1Maximize filter bandwidthSimplified receiver designMultiplex communicationTransmissionLocal oscillator signalIntermediate frequency
A multi-channel superheterodyne receiver employs a low intermediate frequency (IF) and both high-side injection and low-side injection of a selected local oscillator (LO) signal into the mixer in order to position image frequencies outside the passband of a single image reject filter. Any channel that falls within a used portion of the image reject filter passband can be downconverted with image rejection if the utilized bandwidth portion is no greater than about 4 times the IF minus the bandwidth of a channel in the filter passband. Low side injection is used for channels falling within the lower half of the passband of the image reject filter, while high-side injection is used for channels falling within the upper half thereof. The image always remains outside the passband and the receiver can accommodate a greatly increased number of channels.
Owner:DIGI INTERNATIONAL
Multiple input multiple output signal receiving apparatus with optimized performance
A MIMO signal receiving apparatus includes a first antenna (402 in chart 4) for receiving a first RF signal; a second antenna (404) for receiving a second RF signal; a superheterodyne receiver for receiving one or all of the first and second RF signals into at least one first analog signal; a direct conversion receiver (410) for converting one or all of the first and second RF signals into at least one second signal; and an antenna switching module coupling the first and second antennas to the superheterodyne receiver (408) and the direct conversion receiver for electively directing the first and second RF signals to the superheterodyne receiver and / or the direct conversion receiver, depending on an antenna switch control signal indicating a signal quality derived from the first and second analog signals.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Wideband integrated reconnaissance receiver and working method thereof
ActiveCN106788506AImprove quick response abilityImprove adaptabilityTransmissionBandpass filteringMicrowave
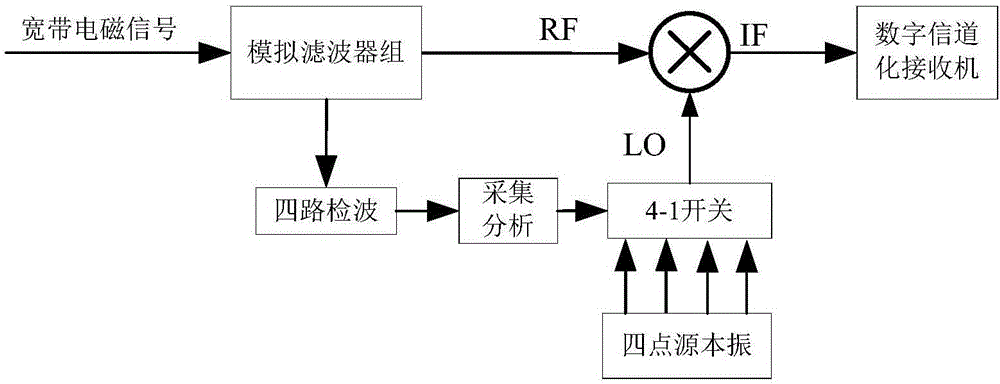
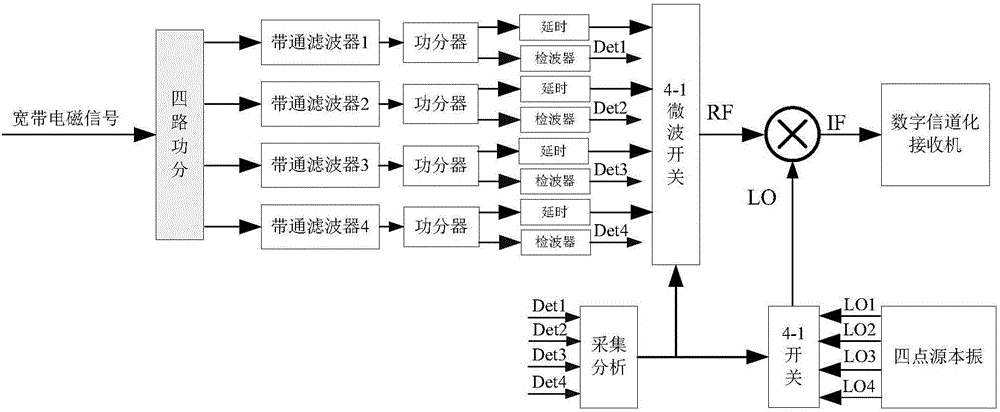
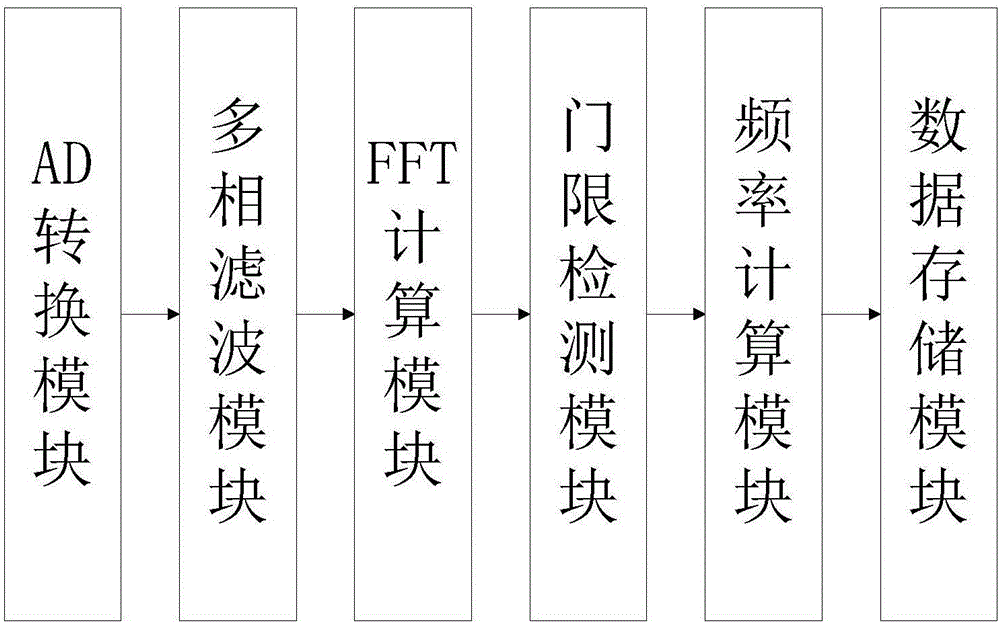
The invention relates to a wideband integrated reconnaissance receiver, which comprises an analog channelized module and a digital channelized module, wherein the analog channelized module further comprises a four-way power divider, bandpass filters from a first to a fourth, two-way power dividers from a first to a fourth, detectors from a first to a fourth, delay modules from a first to a fourth, an acquisition analysis module, a four-point source module, a 4-1 microwave switch module and a mixing module; and the digital channelized module further comprises an AD conversion module, a multi-phase filter module, an FFT calculation module, a threshold detection module, a frequency calculation module and a data storage module. The reconnaissance receiver thoroughly merges features of a direct detection-type receiver, a superheterodyne receiver and a digital channelized receiver, the quick response ability of the receiver and the adaptability to a complex electromagnetic environment are increased, and the adaptability to the complex electromagnetic environment and the reconnaissance real-time performance are met.
Owner:BEIJING ZHENXING METROLOGY & TEST INST
High-if superheterodyne receiver incorporating high-q complex band pass filter
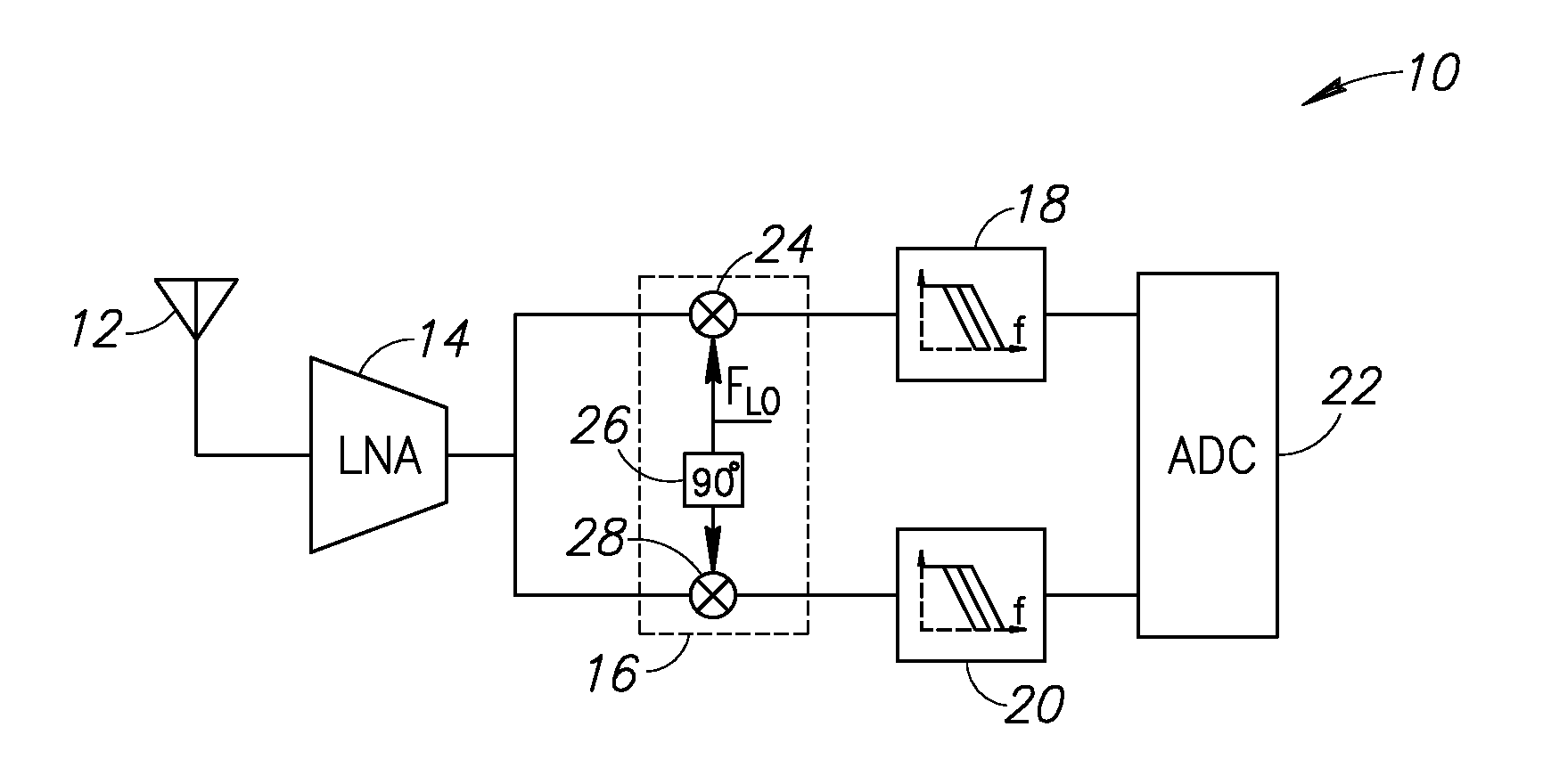
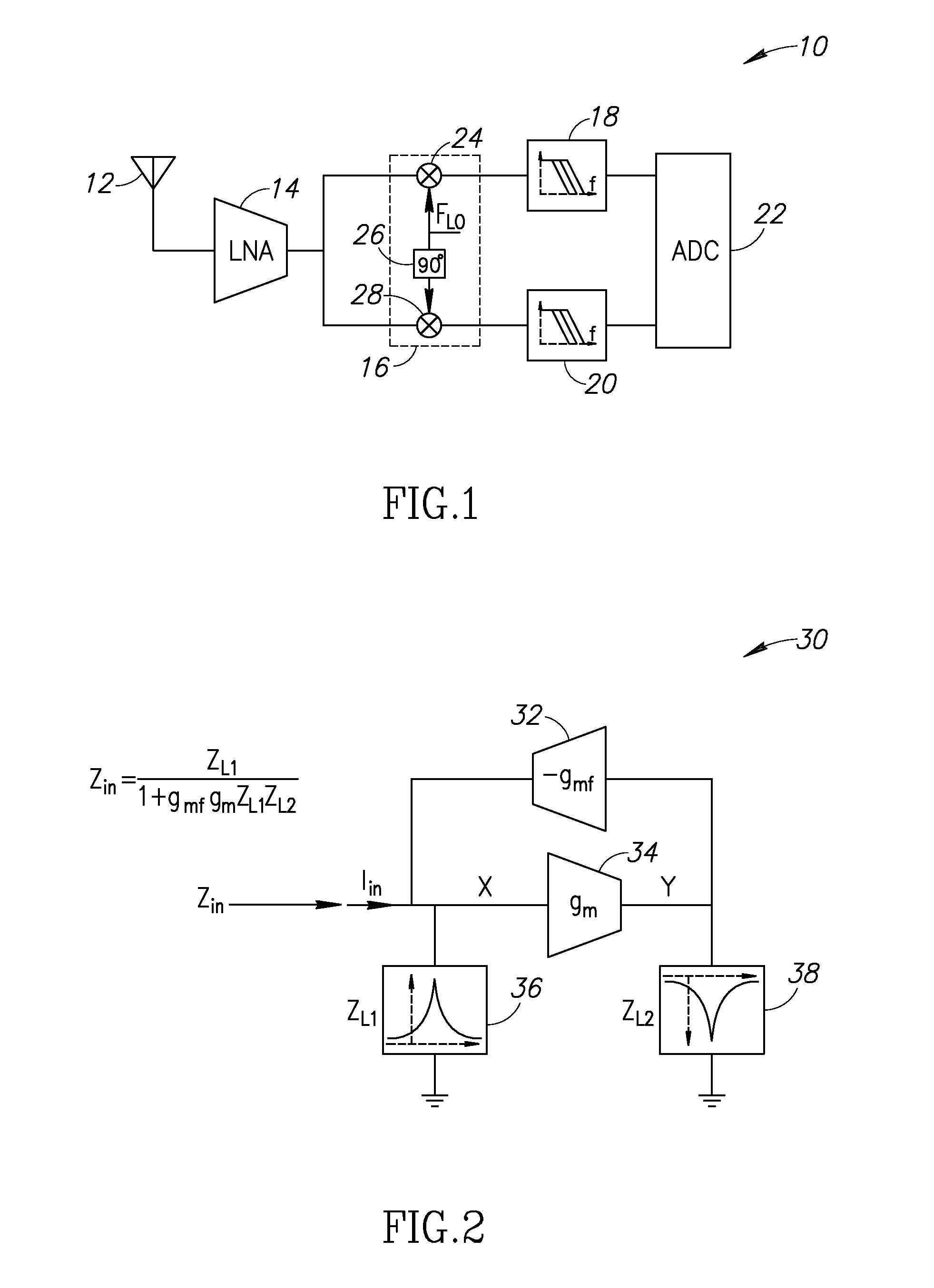
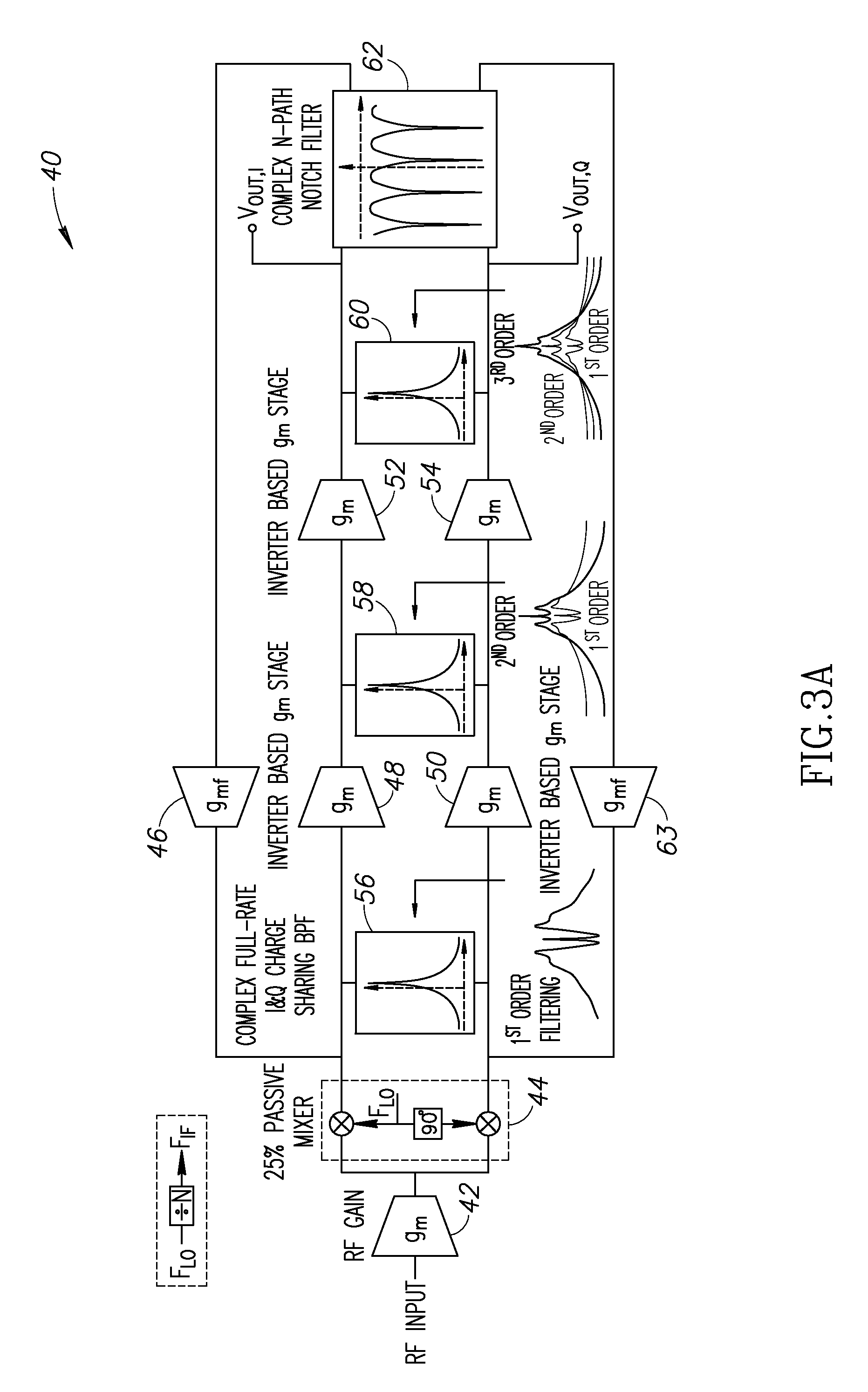
A novel and useful reconfigurable superheterodyne receiver that employs a 3rd order complex IQ charge-sharing band-pass filter (BPF) for image rejection and 1st order feedback based RF BPF for channel selection filtering. The operating RF input frequency of the receiver is 500 MHz to 1.2 GHz with varying high IF range of 33 to 80 MHz. The gain stages are inverter based gm stages and the total gain of the receiver is 35 dB and in-band IIP3 at mid gain is +10 dBm. The NF of the receiver is 6.7 dB which is acceptable for the receiver without an LNA. The architecture is highly reconfigurable and follows the technology scaling.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Height measurement method for continuous wave search radar
InactiveCN102323579AReduce difficultyImprove caliber utilizationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFiltrationIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a height measurement method for a continuous wave search radar. In the method, a multi-port network is adopted to receive a pair of wave beams in mirror image distribution generated by a pitching surface of an antenna array; a slot waveguide and two output ports are distributed on the multi-port network; the two output ports of the multi-port network are connected to input ends of two paths of symmetric microwave receivers respectively; the used microwave receivers are superheterodyne receivers; the two paths of microwave receivers change the received echo to be intermediate frequency through amplification, frequency mixing and filtration and generate I and Q-baseband signals through amplification of an amplification filter and orthogonal demodulation; the I and Q-baseband signals are converted into digital quantity through A / D (Analog to Digital) conversion; modulo operation is performed through a signal processing module; a directional value is solved by using a sum-difference device; and a numerical value of an elevation angle is obtained from a pulse-out meter or through polynomial fitting by taking the directional value as an address. The method is easy to implement, has high data rate and is suitable for a small-sized three-coordinate search radar.
Owner:TIANWEI ELECTRONICS SYST ENG
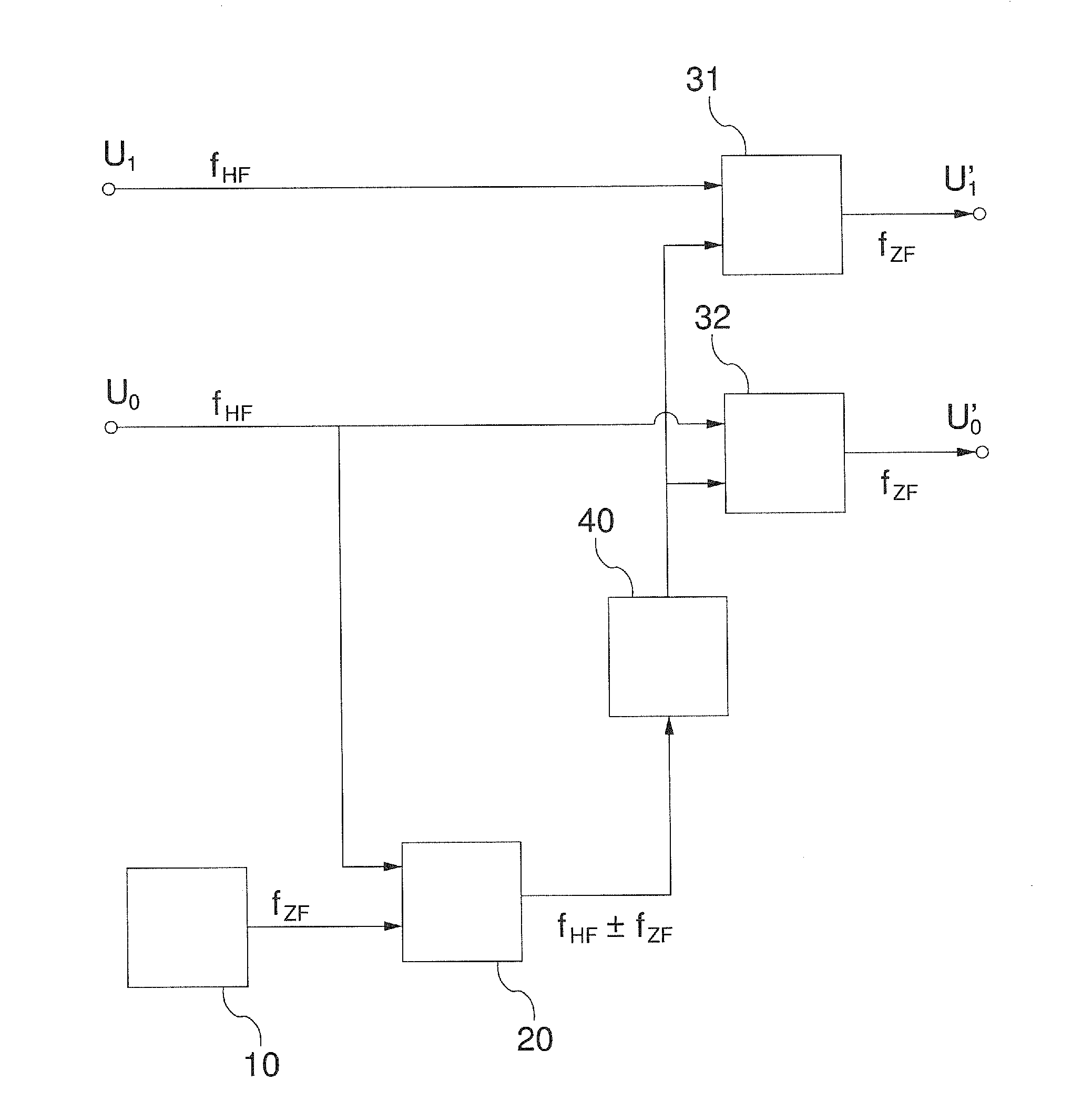
Superheterodyne receiver
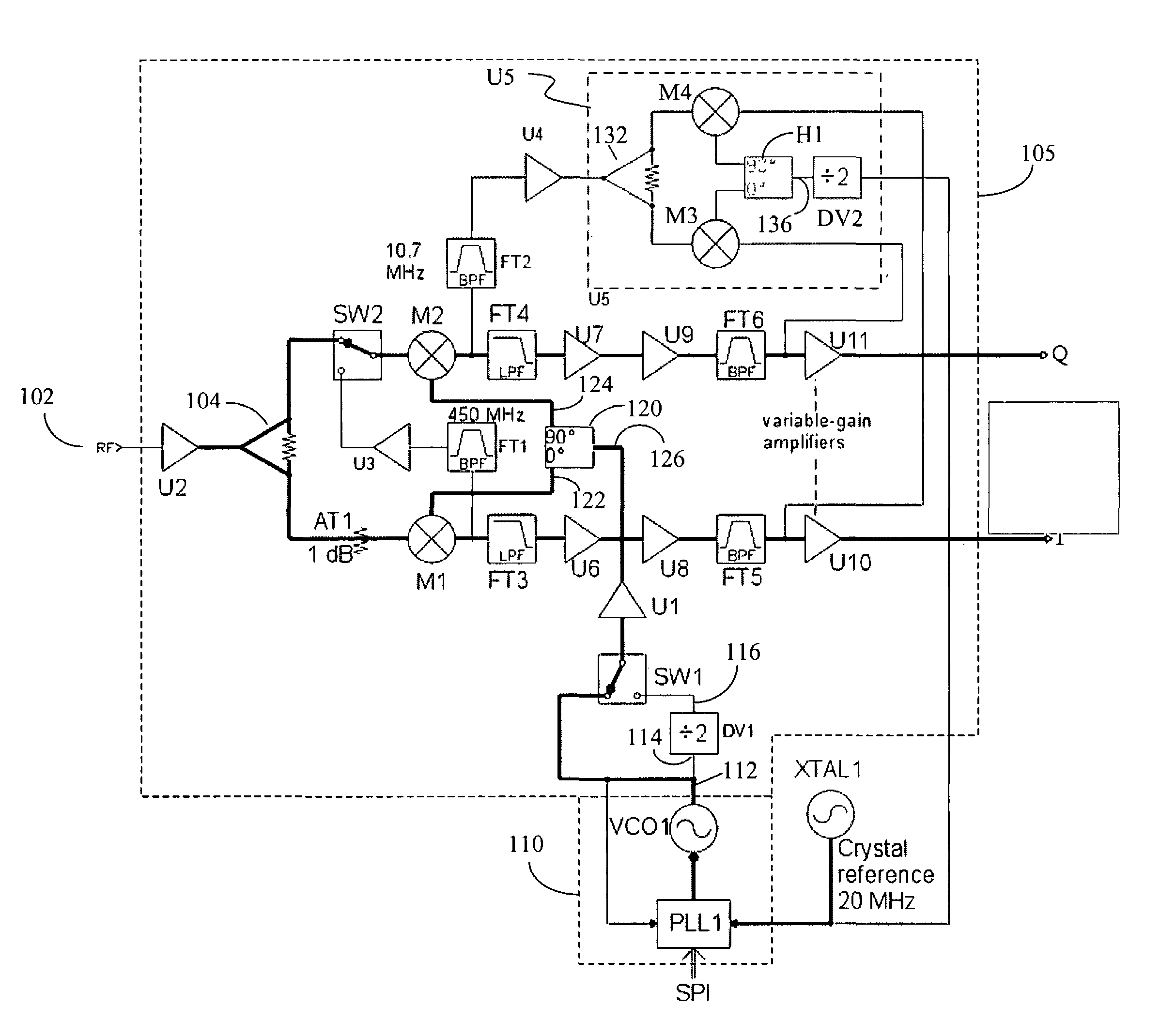
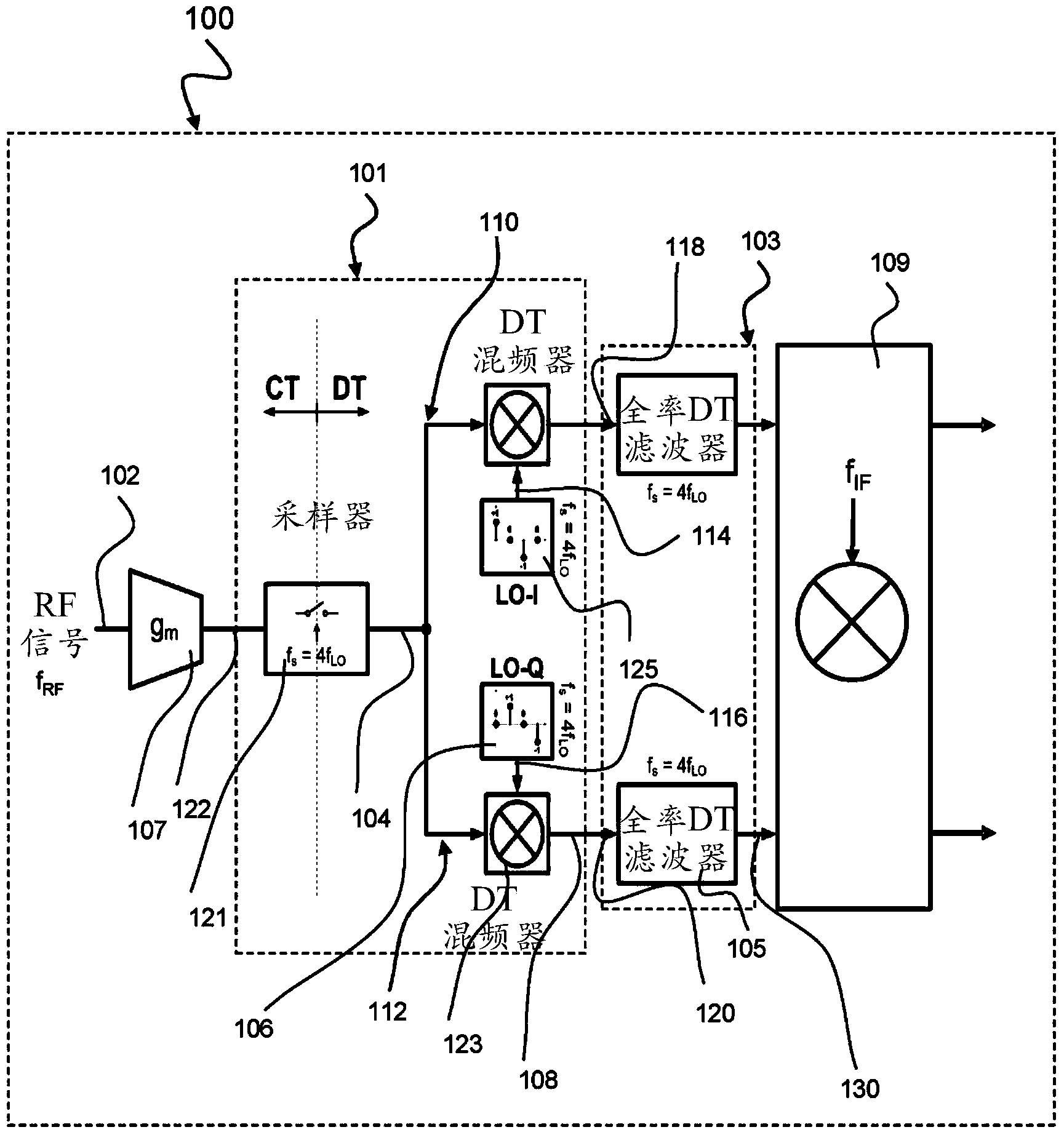
ActiveCN103828244AReduce sensitivitySolving the time-varying DC offset problemTransmissionDiscrete time filteringIntermediate frequency
The invention relates to a superheterodyne receiver (100), comprising: a sampling mixer (101) being configured to sample an analogue radio frequency signal (102) using a predetermined sampling rate (fs) to obtain a discrete-time sampled signal (104), and to shift the discrete-time sampled signal (104) towards a first intermediate frequency (|fRF-fLO|) to obtain an intermediate discrete-time signal (108) sampled at the predetermined sampling rate (fs); a discrete-time filter (103) being configured to filter the intermediate discrete-time signal (108) at the predetermined sampling rate (fs) to obtain a filtered signal (130); and a discrete-time mixer (109) being configured to shift the filtered signal (130) towards a second intermediate frequency (fIF).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Antenna tuned circuit for a superheterodyne receiver
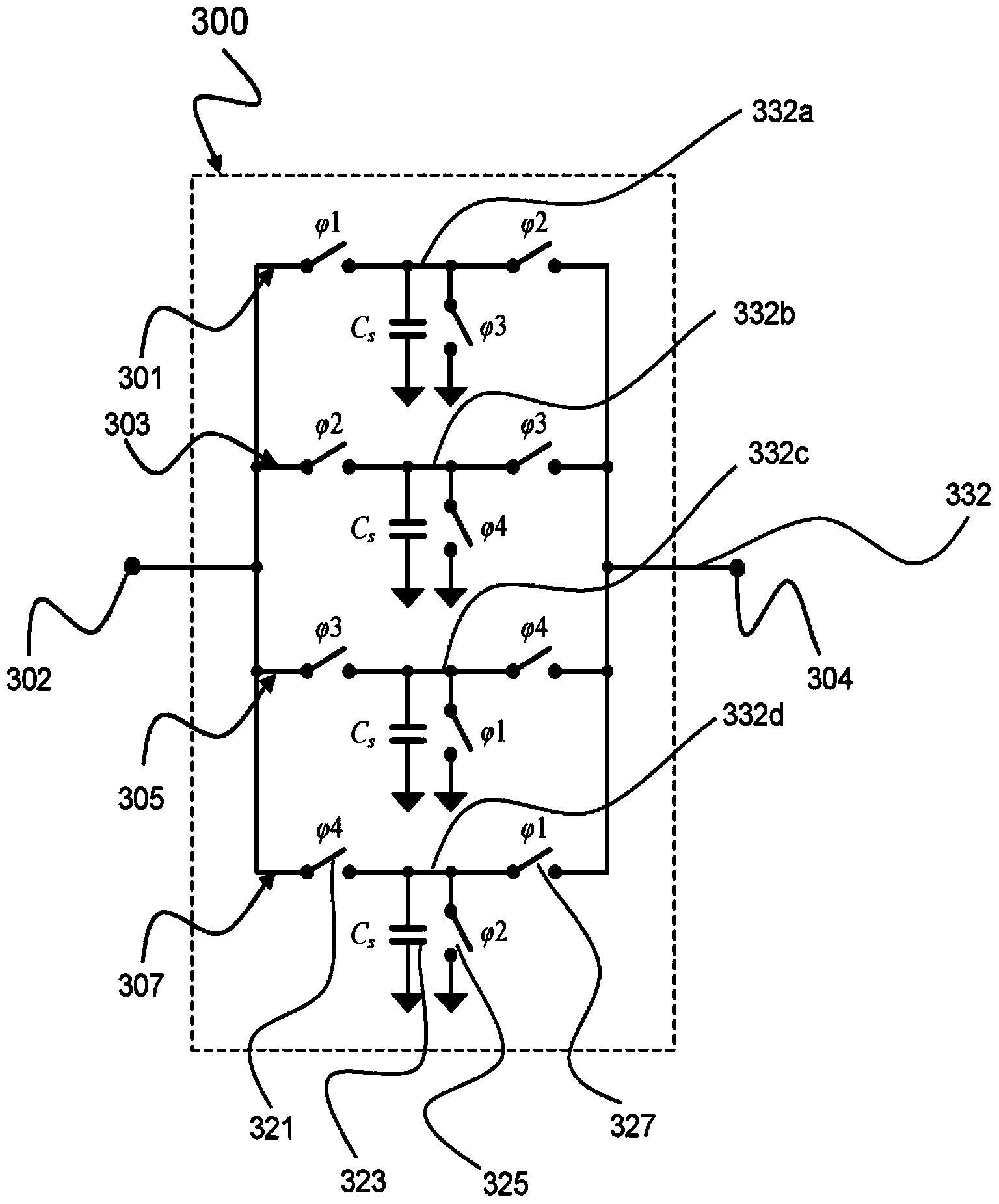
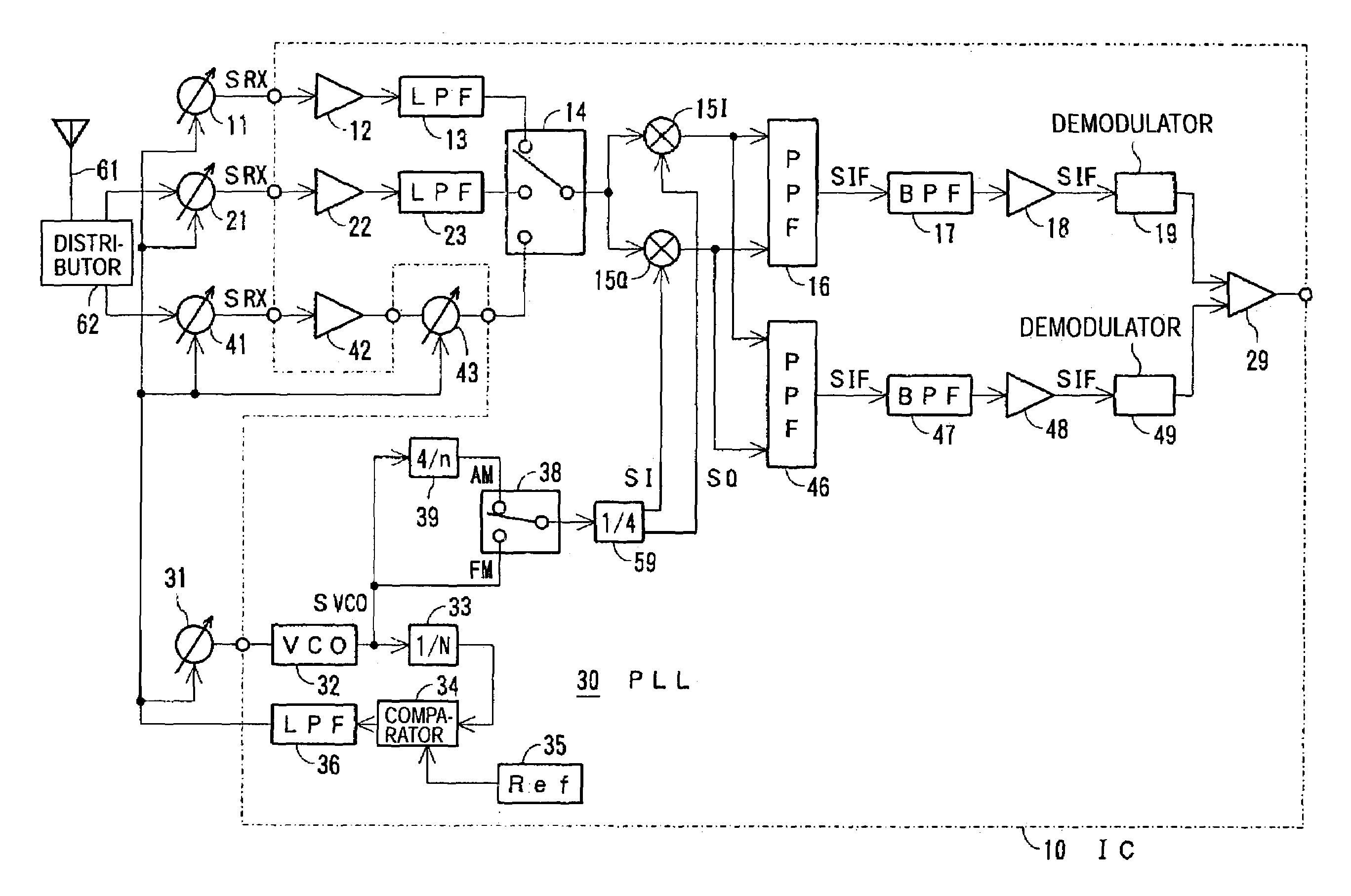
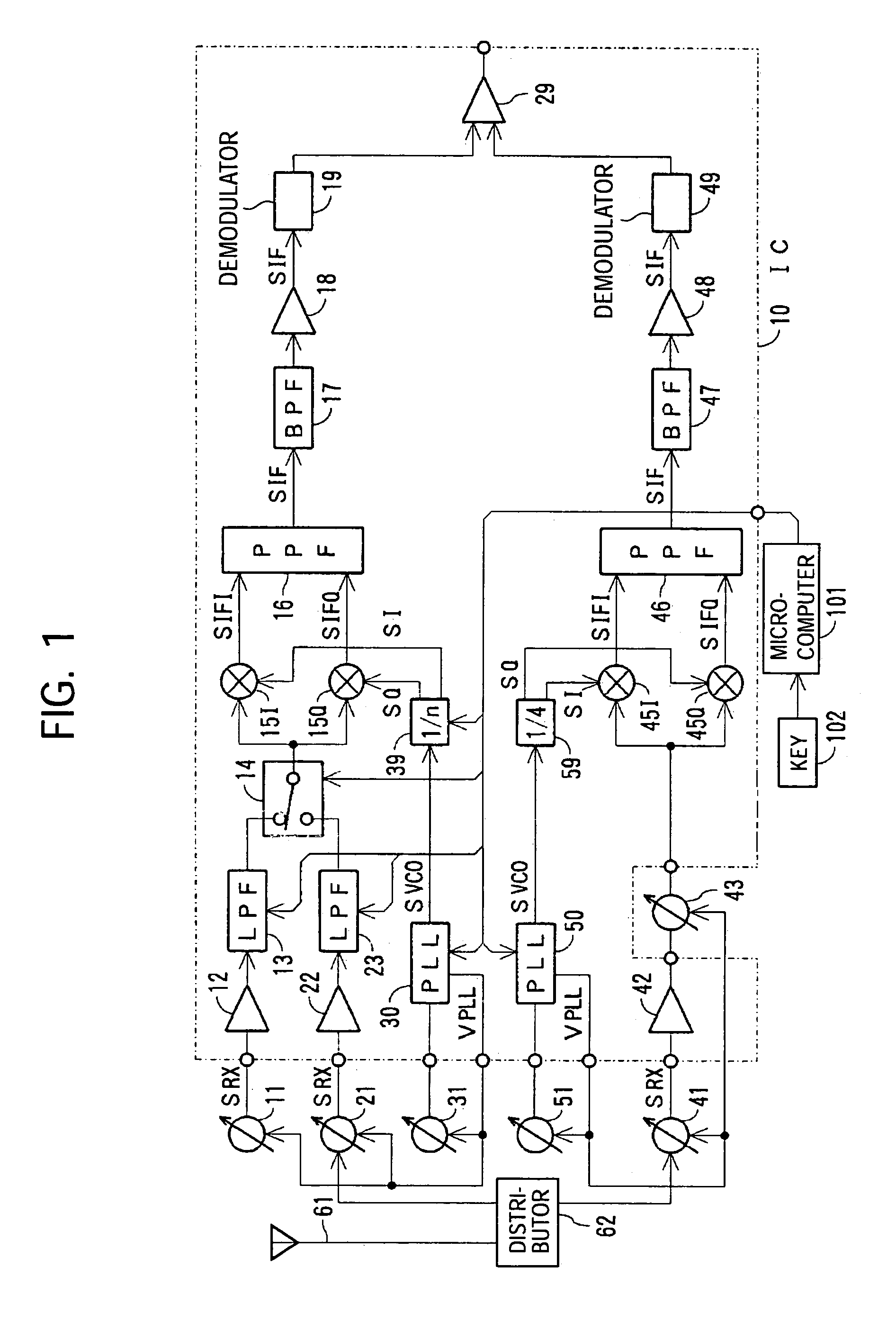
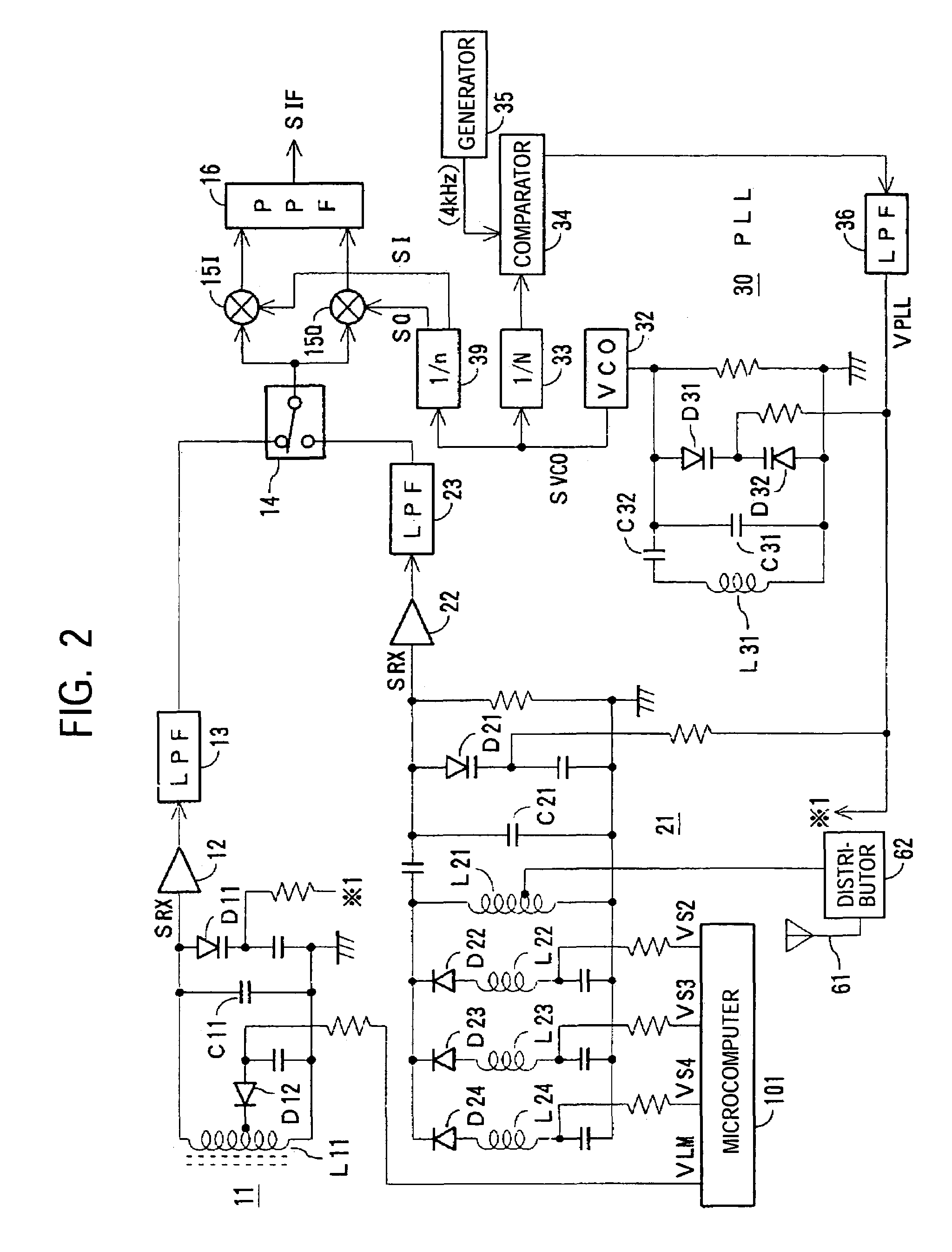
InactiveUS7164895B2Suitable receiverWaste of laborPulse automatic controlAngle demodulation by phase difference detectionMulti bandIntermediate frequency
A multi-band receiver in which characteristics including a tracking error are improved is provided with a variable frequency oscillator circuit, a variable divider circuit (39) for dividing an oscillation signal (SVCO) of the variable frequency oscillator circuit, and mixer circuits (15I) and (15Q) for subjecting a received signal SRX to frequency conversion into an intermediate frequency signal (SIF) by a local oscillation signal (SLO). A divided output of the variable divider circuit (39) is supplied as the local oscillation signal (SLO) to each of the mixer circuits (15I) and (15Q). When a signal in a first frequency band is received, the division ratio n of the variable divider circuit (39) and the oscillation frequency of the variable frequency oscillator are changed to change the reception frequency in the first frequency band. When a signal in a second frequency band is received, at least the oscillation frequency of the variable frequency oscillator circuit is changed to change the reception frequency in the second frequency band.
Owner:SONY CORP
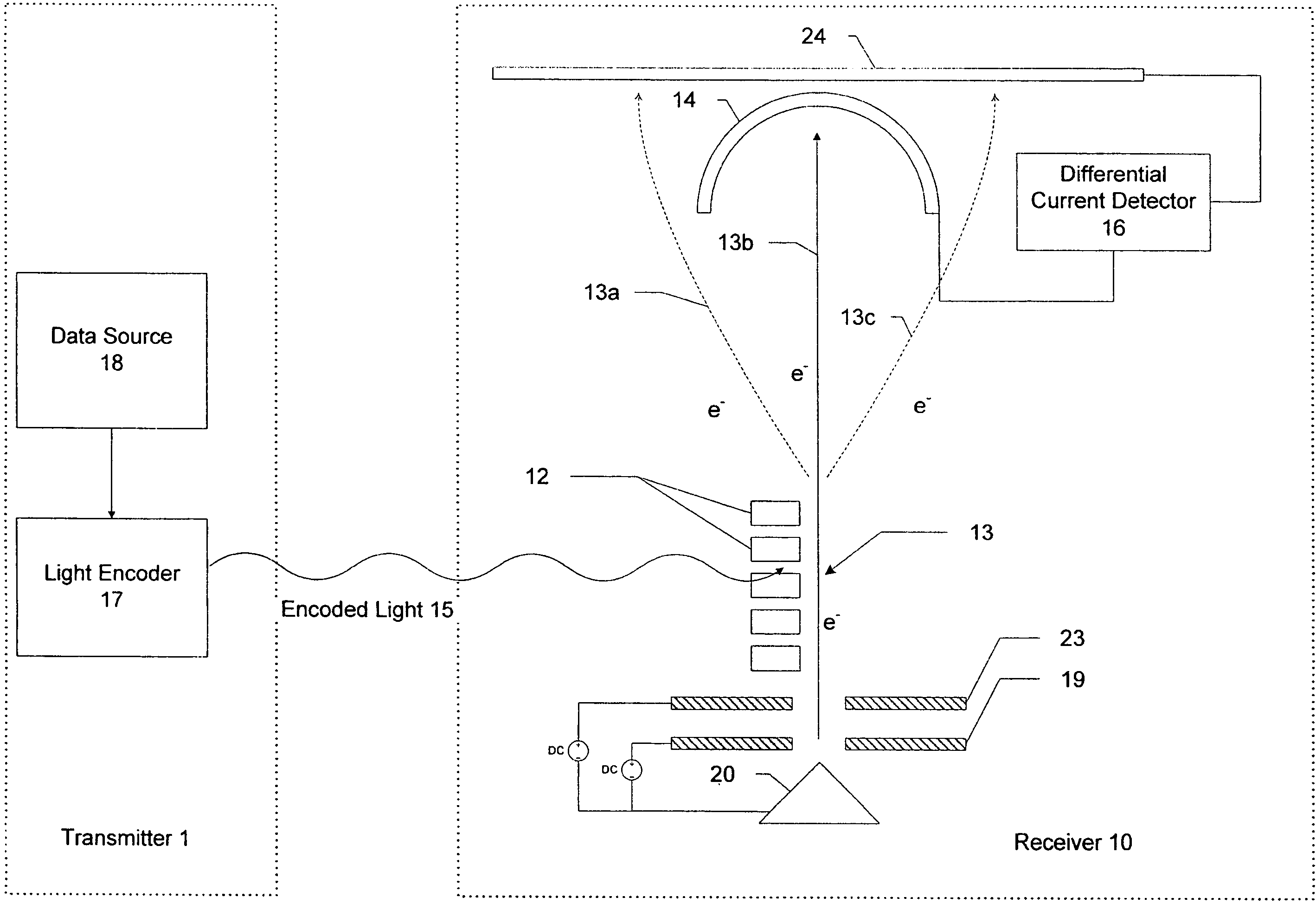
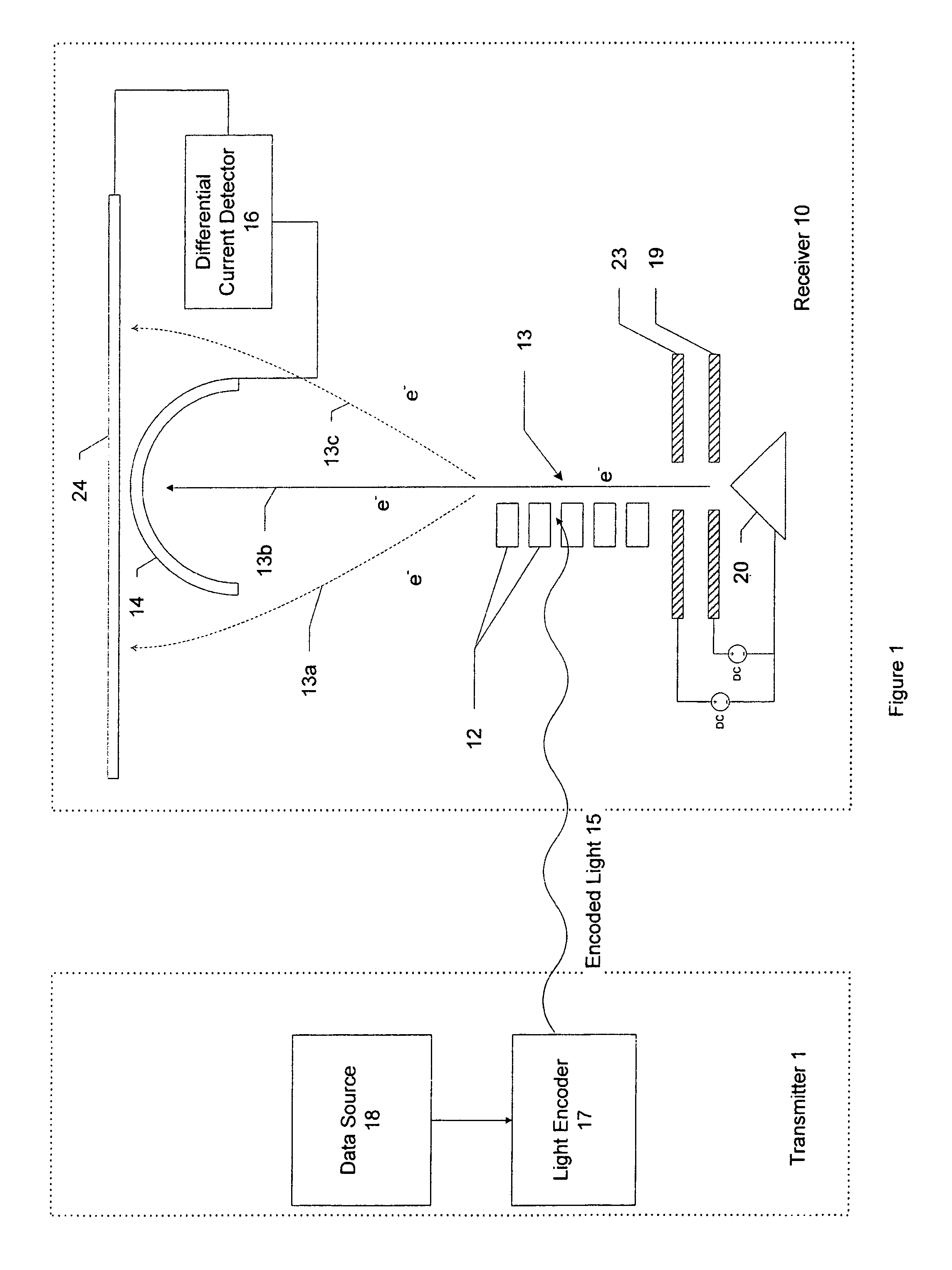
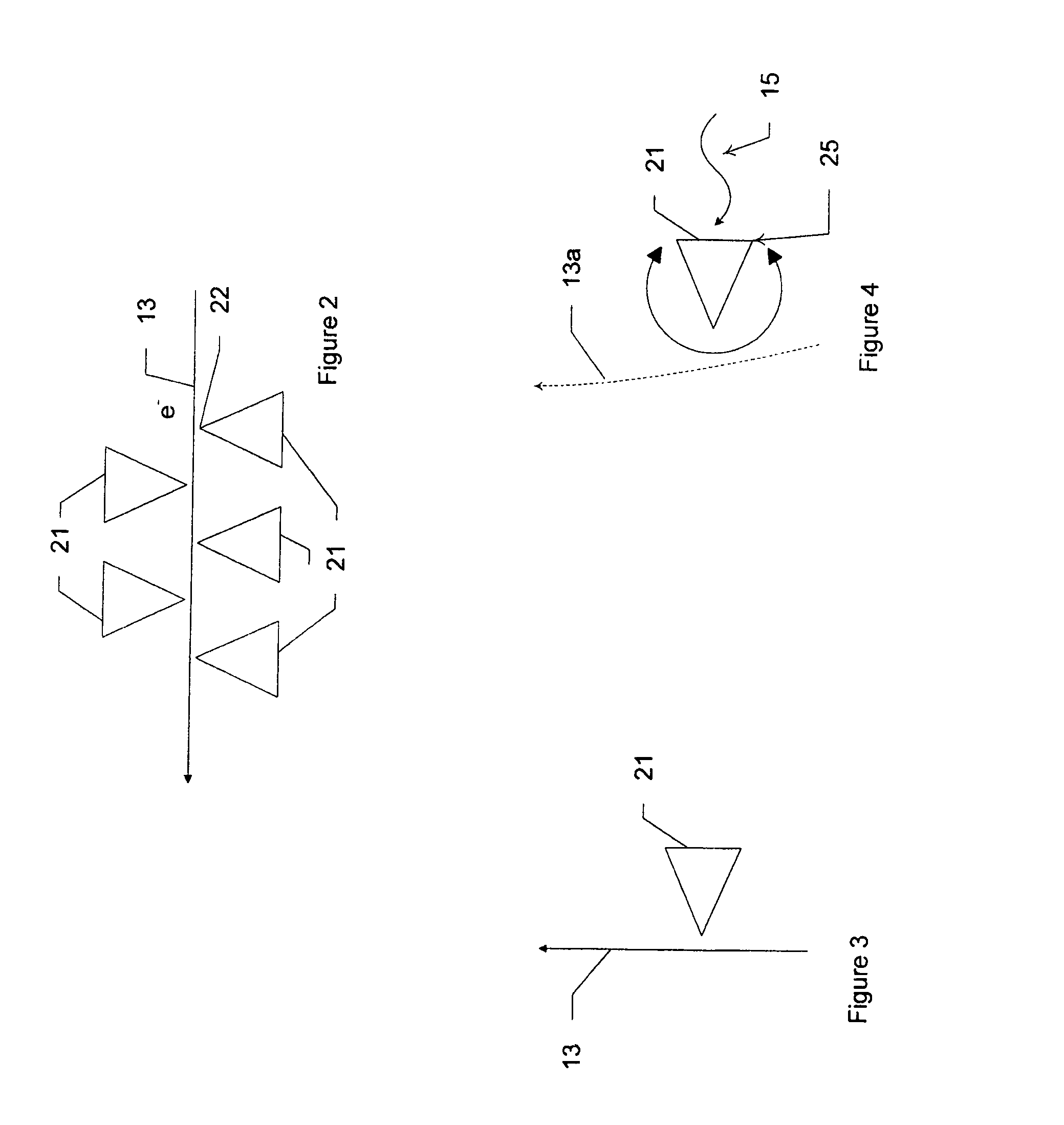
Heterodyne receiver using resonant structures
An electronic receiver for decoding data encoded into electromagnetic radiation (e.g., light) is described. The light is received at an ultra-small resonant structure. The resonant structure generates an electric field in response to the incident light and light received from a local oscillator. An electron beam passing near the resonant structure is altered on at least one characteristic as a result of the electric field. Data is encoded into the light by a characteristic that is seen in the electric field during resonance and therefore in the electron beam as it passes the electric field. Alterations in the electron beam are thus correlated to data values encoded into the light.
Owner:ADVANCED PLASMONICS
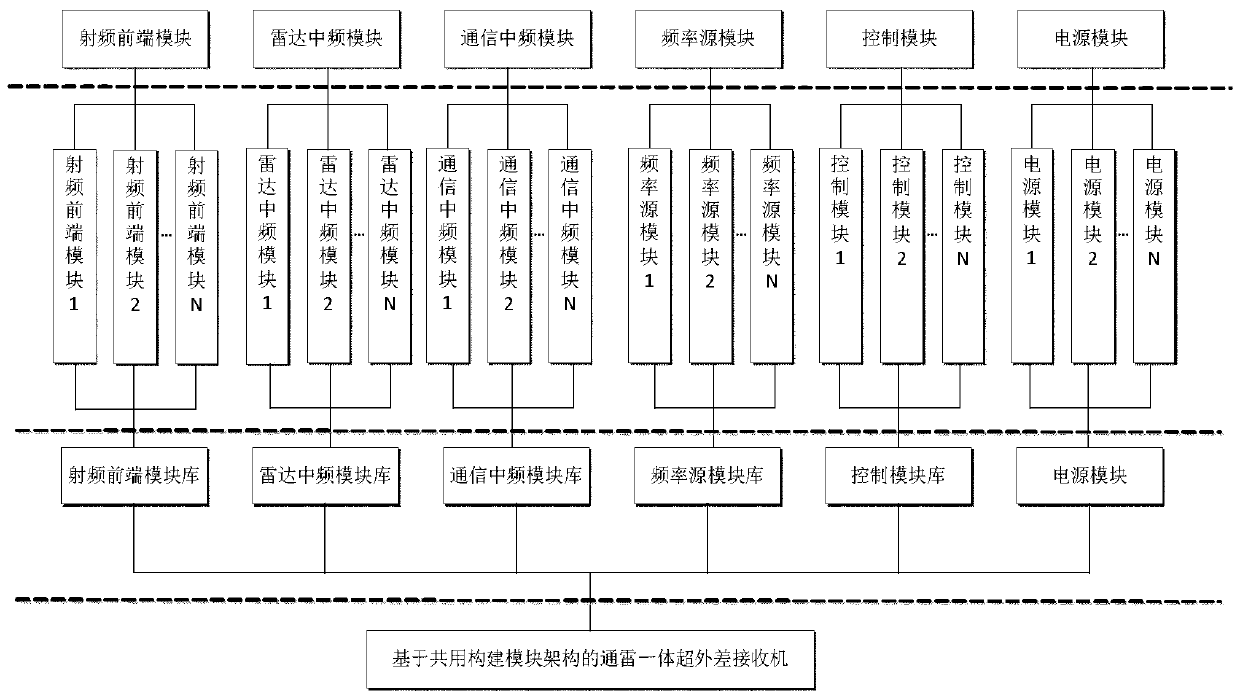
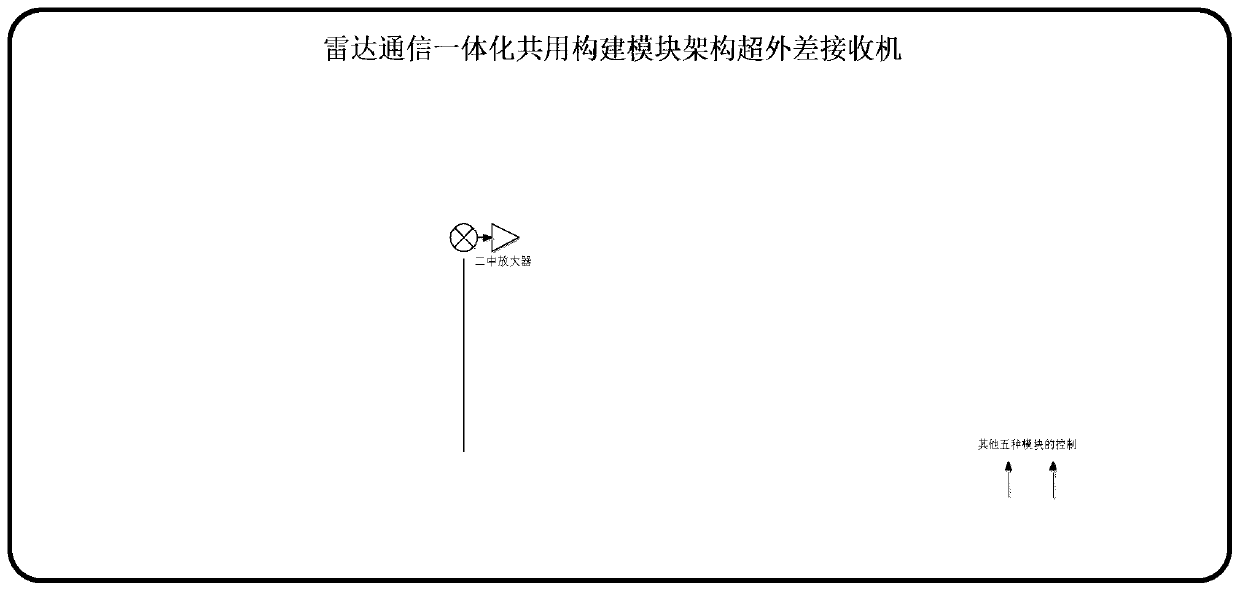
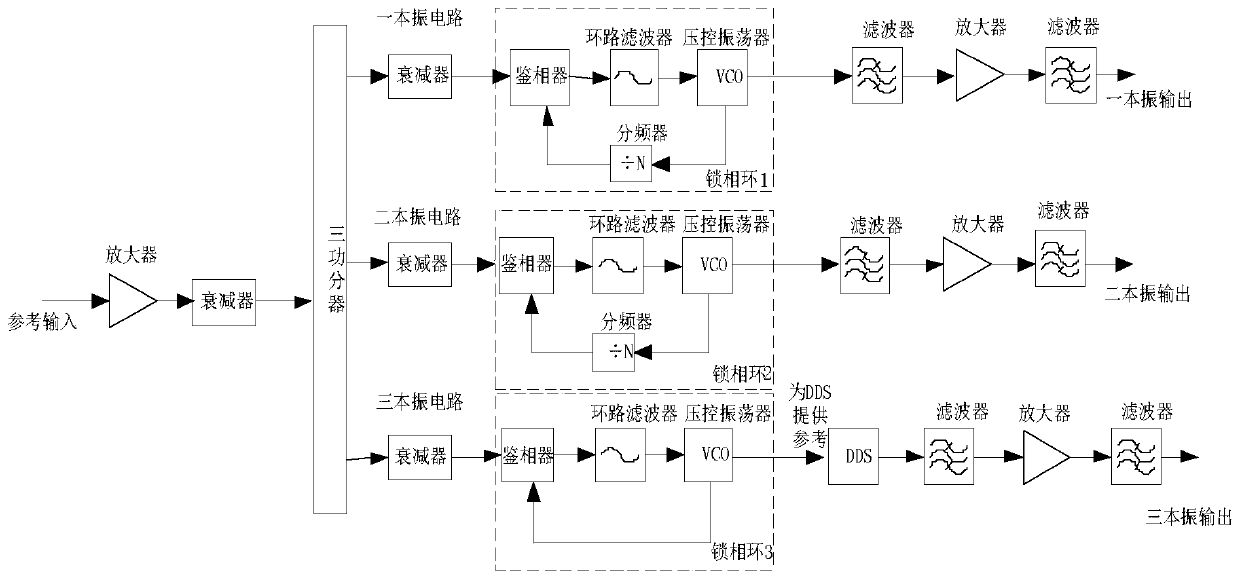
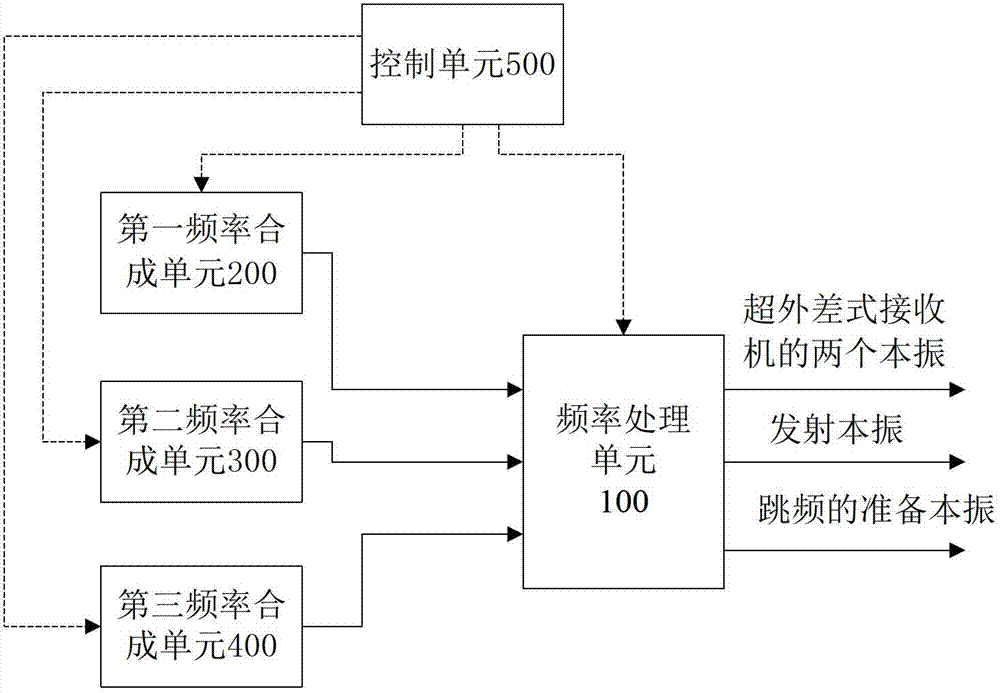
Design method of radar communication integrated shared construction module architecture superheterodyne receiver
The invention provides a design method of a radar communication integrated shared construction module architecture superheterodyne receiver, and aims to provide a rapid and efficient multi-purpose receiving complete machine design method. The method is realized through the following technical scheme of according to a superheterodyne system, firstly planning six common construction modules, namelya radio frequency front end module, a radar intermediate frequency module, a communication intermediate frequency module, a power supply module, a control module and a frequency source module; secondly, for the circuit principle of the six common construction modules, serializing a series of product libraries of the common construction modules; then designing a superheterodyne radar-communicationintegrated receiving complete machine, and respectively selecting the corresponding shared construction modules for combination according to an existing shared construction module product series in the design of the radar-communication integrated receiving superheterodyne receiver in combination with the technical index requirements to realize the radar-communication integrated receiving superheterodyne complete machine.
Owner:10TH RES INST OF CETC
Multi-slot transceiver
ActiveCN103209004AAvoid transmitting co-channel interference receptionEasy to filterSynchronising arrangementTransceiverIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a multi-slot transceiver. The multi-slot transceiver comprises a frequency generation unit. The frequency generation unit a control unit, a first frequency synthesis unit, a second frequency synthesis unit, a third frequency synthesis and a frequency processing unit, wherein the first frequency synthesis unit is used for outputting a first high frequency local oscillator; the second frequency synthesis unit is used for outputting a second high frequency local oscillator; the third frequency synthesis unit is used for outputting an intermediate frequency local oscillator; and the frequency processing unit is used for using the first high frequency local oscillator and the intermediate frequency local oscillator as two local oscillators of a superheterodyne receiver in a receiving timeslot respectively, processing the first high frequency local oscillator and the intermediate frequency local oscillator in a transmission timeslot, using a processed signal as a transmission local oscillator, and using the second high frequency local oscillator as a preparatory local oscillator of frequency hopping in the next receiving or transmission timeslot. According to the technical scheme, the multi-slot transceiver occupies a small space, and is low in cost and power consumption, a few serial peripheral interface (SPI) resources are occupied, the interference of transmission of a same-frequency signal with reception in a same-frequency reception-to-transmission working mode of adjacent timeslots can be avoided, and noise signals generated by the modulation of a modulator in a different-frequency transmission-to-transmission working mode of adjacent timeslots are easy to filter.
Owner:HYTERA COMM CORP
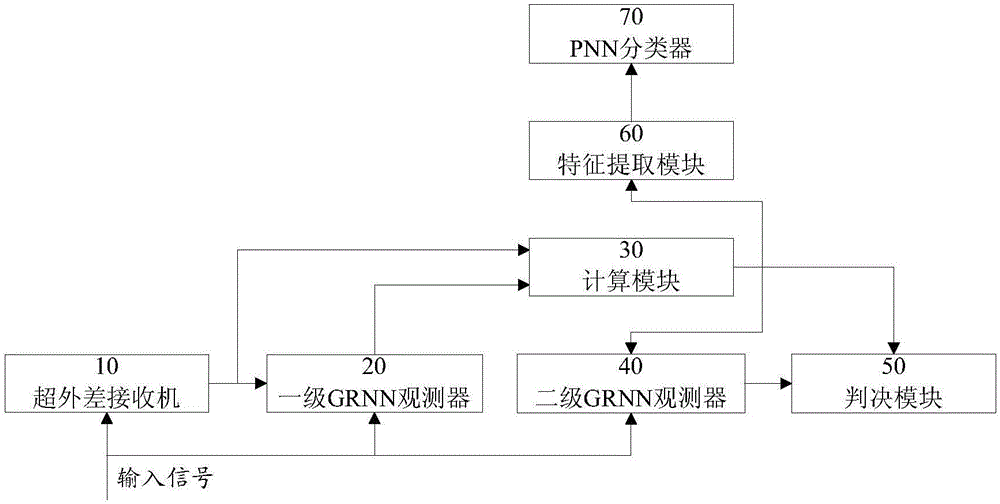
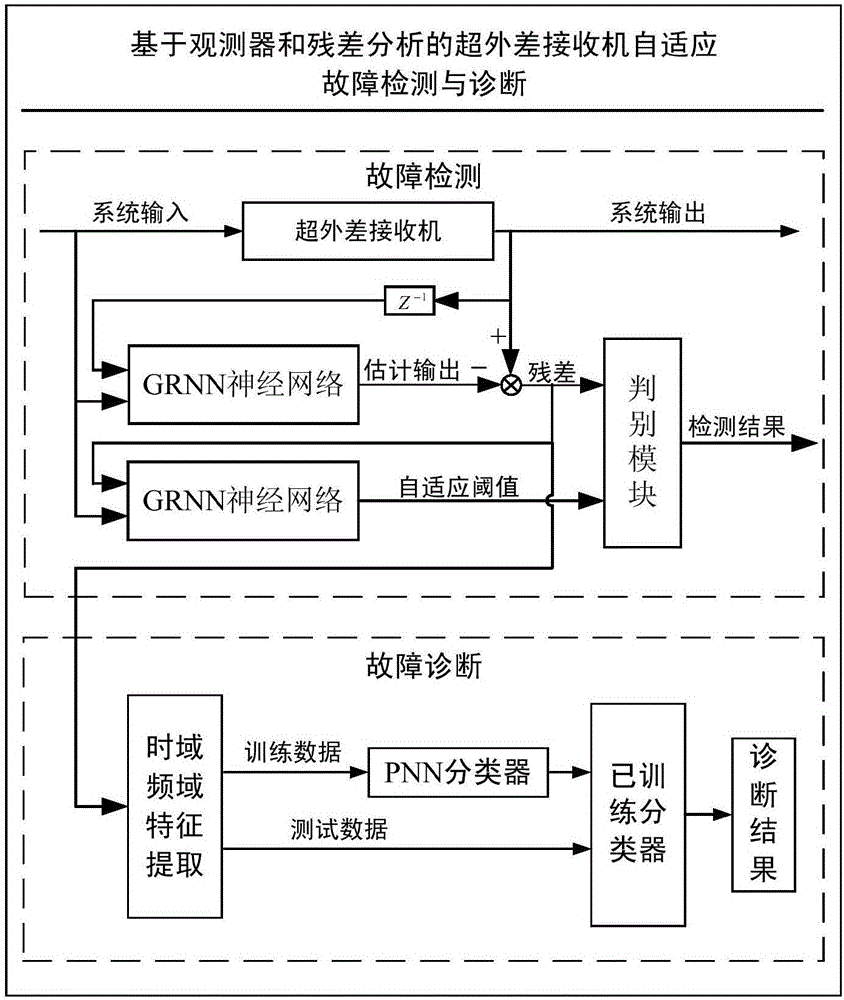
Self-adaptive fault detection and diagnosis method and device for superheterodyne receiver
InactiveCN106301610AFill detectionFill in the diagnostic gapReceivers monitoringDiagnosis methodsEngineering
The invention discloses a self-adaptive fault detection and diagnosis method and device for a superheterodyne receiver. The method comprises the steps of inputting an input signal in the superheterodyne receiver and processing the input signal by the superheterodyne receiver; processing the input signal and an output signal of the superheterodyne receiver in previous time by a trained first-level GRNN observer, thereby obtaining an estimated output signal; obtaining a residual error according to the estimated output signal and the output signal of the superheterodyne receiver in current time; processing the input signal and the residual error by employing a trained second-level GRNN observer, thereby obtaining a self-adaptive threshold value; and determining whether a fault occurs in the superheterodyne receiver or not according to the residual error and the self-adaptive threshold value. According to the method and the device, whether the fault occurs in the superheterodyne receiver or not can be detected, and a fault type can be diagnosed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV +1
Auto-heterodyne receiver
ActiveUS20140120855A1Reducing circuitry demandDesired accuracyReceivers monitoringDirection findersQuadrature modulatorFrequency mixer
A receiver with a local oscillator, a quadrature modulator, a first mixer and a second mixer, wherein a first input of the quadrature modulator is connected to a second signal input of the receiver circuit and a second input of the quadrature modulator is connected to the local oscillator. Further, a first input of the first mixer is connected to a first signal input of the receiver circuit, a second input of the first mixer is connected to an output of the quadrature modulator, and an output of the first mixer is connected to a first signal output of the receiver circuit. A first input of the second mixer is connected to the second signal input, a second input of the second mixer is connected to the output of the quadrature modulator, and an output of the second mixer is connected to a second signal output of the receiver circuit.
Owner:FORSCHUNGSVERBUND BERLIN EV
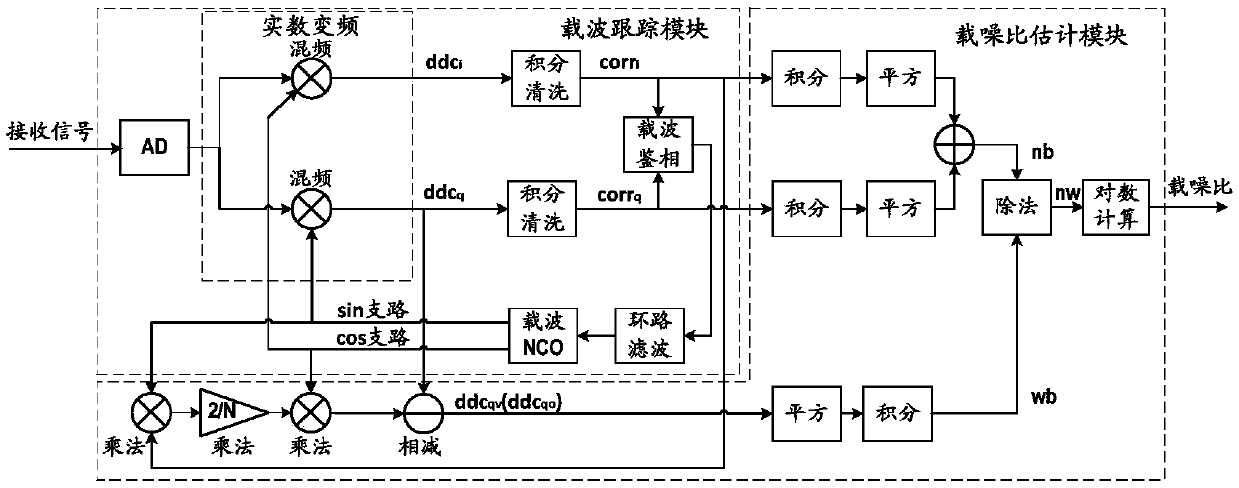
Estimation method and system of high-precision carrier-to-noise ratio
ActiveCN109541648AReduced influence of signal power fluctuationsAccurate noise powerNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementSatellite radio beaconingSignal qualityEstimation methods
The invention discloses an estimation method of a high-precision carrier-to-noise ratio. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring an observation value for a complex frequency conversionreceiver or a superheterodyne receiver; forming a power ratio of a narrowband signal to a wideband noise by respectively calculating a narrowband signal observation value and a wideband noise observation value of different kinds of receivers; and calculating through the power ratio to obtain the carrier-to-noise ratio in decibels. The estimation method and the system of the high-precision carrier-to-noise ratio overcomes the problem that various carrier-to-noise ratio estimation methods in the prior art is difficult to further improve the precision and cannot accurately reflect the slight fluctuation of the signal quality of the receiver by forming the wideband noise observation value through integrating a frequency conversion value or a virtual frequency conversion value before cleaning and calculating on the basis of the broadband frequency conversion value and the correlation value.
Owner:XIAN INSTITUE OF SPACE RADIO TECH
A non-radiative dielectric waveguide circuit positioned between two metal plates which are multi-layered for different seizes of spacers
InactiveCN1454401ADemodulation by distributed inductance and capacitanceResonatorsDielectricIntermediate frequency
A non-radiating dielectric waveguide circuit between two multilayer parallel metal plates. Due to the multiple layers, the circuit has spacers of different heights between the boards, so non-radiating dielectric waveguides of different sizes designed according to their frequency of use are all inserted into a single circuit. By utilizing the present invention, we are able to construct a superheterodyne receiver which has the property of being able to mix received waves by a local oscillator to produce an intermediate frequency. The amplitude can easily be increased by means of the intermediate frequency, thus improving the reception sensitivity.
Owner:NRDTECH +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com