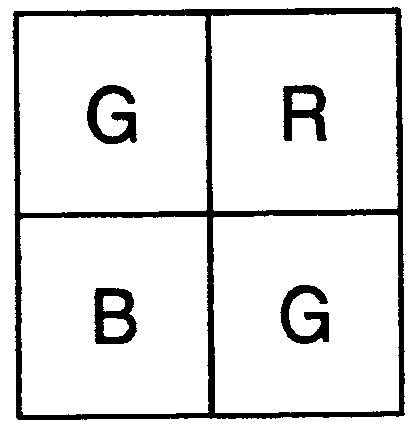Patents
Literature
53results about How to "Increase spectral bandwidth" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
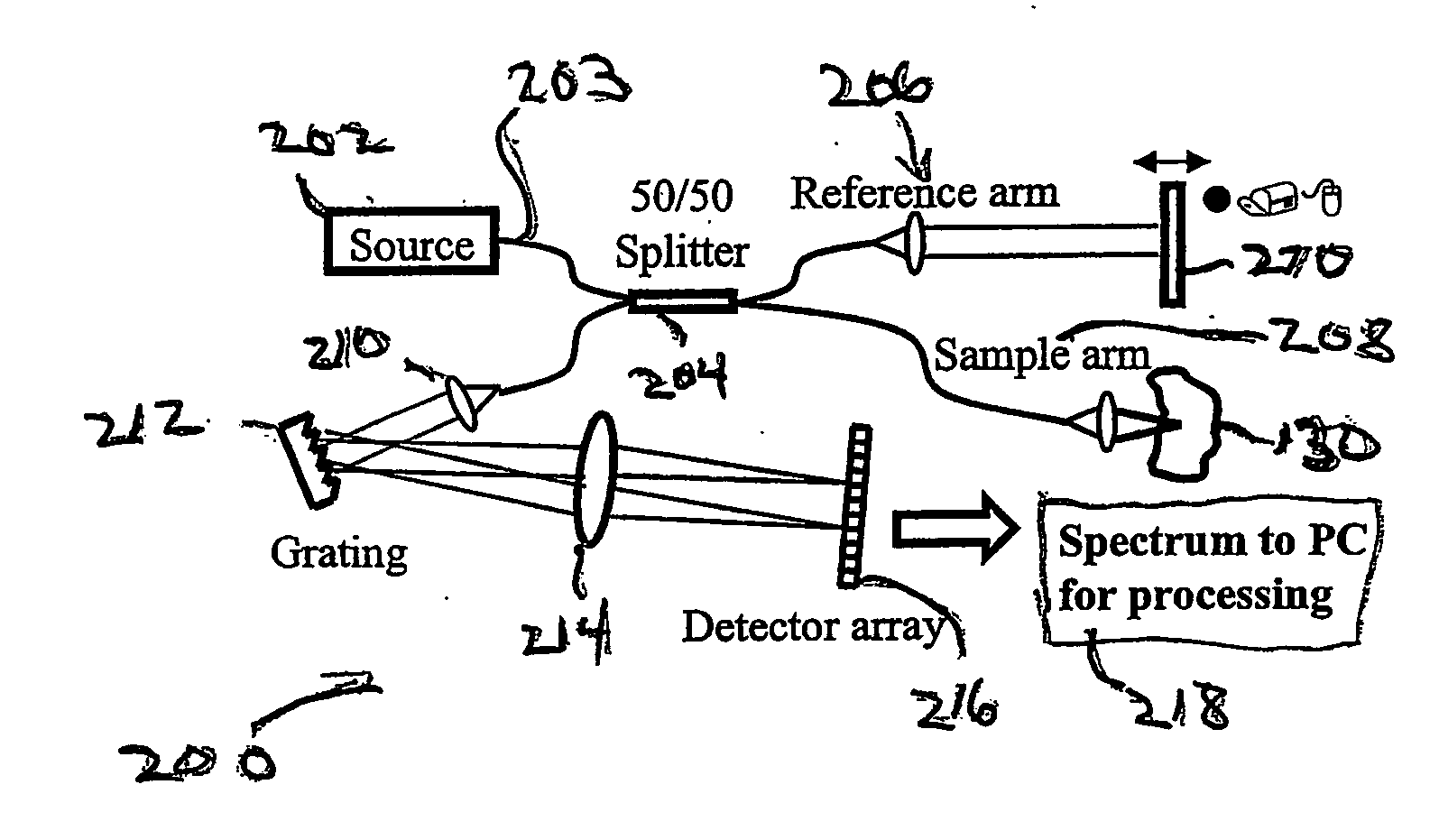
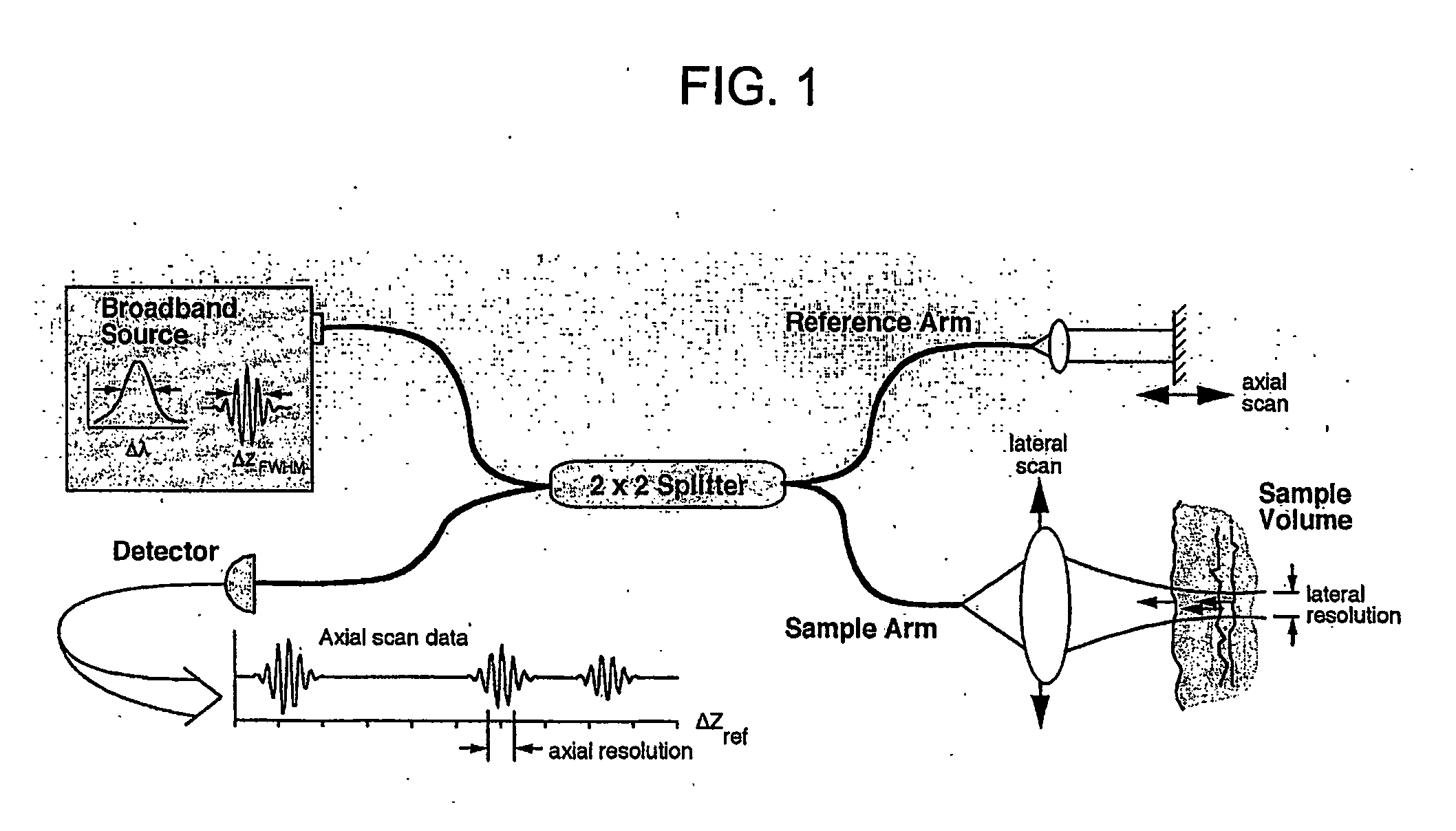
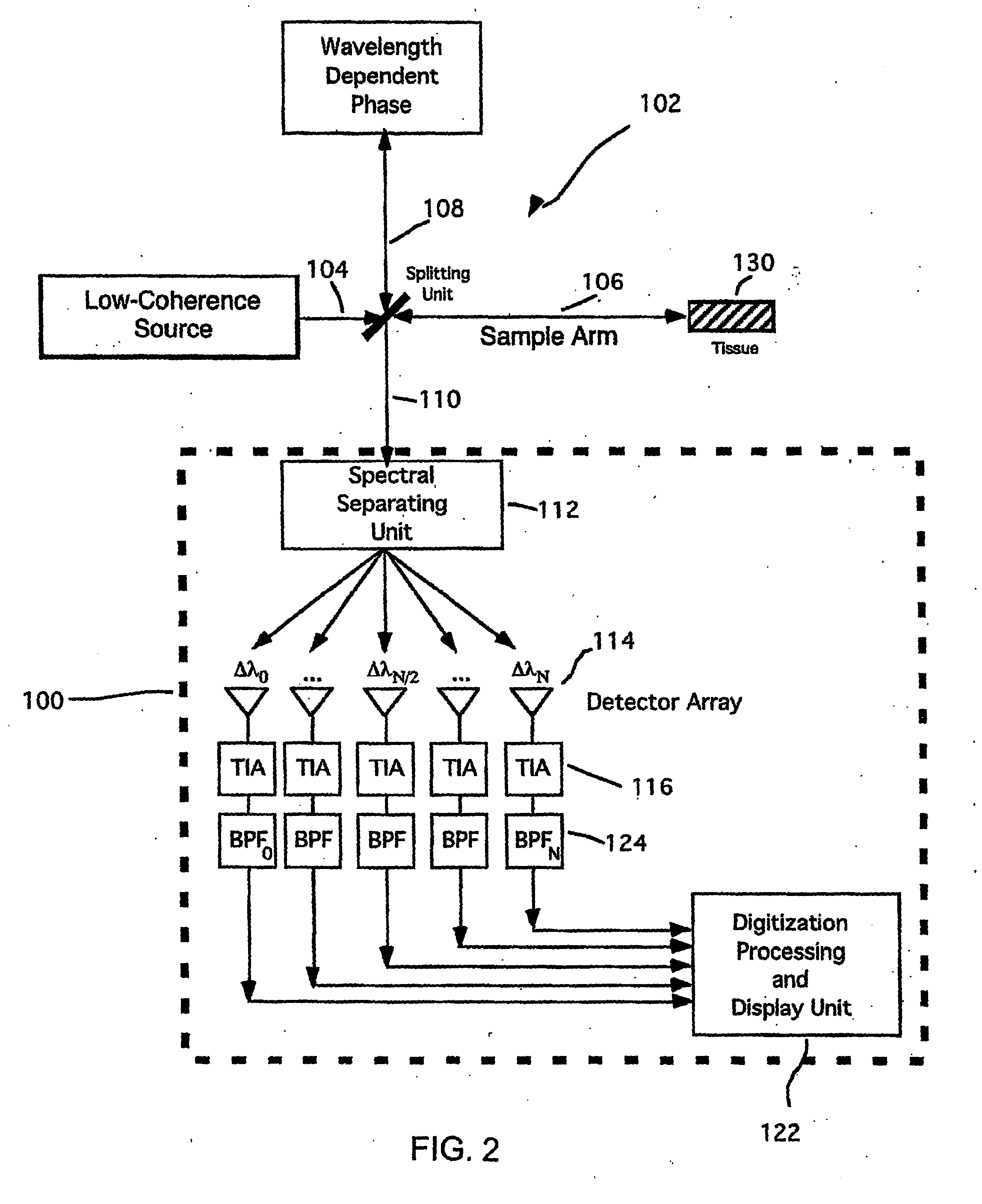
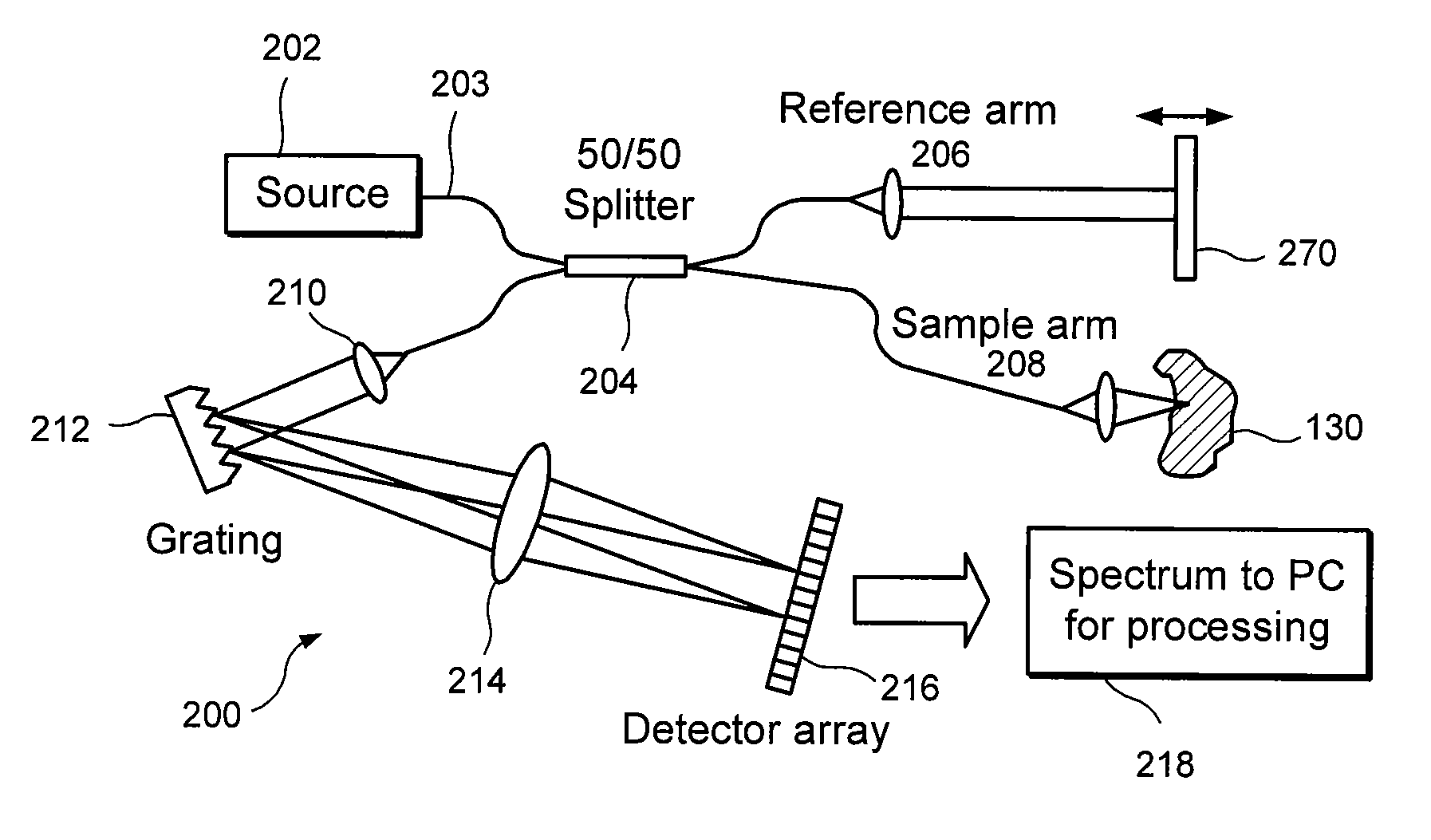
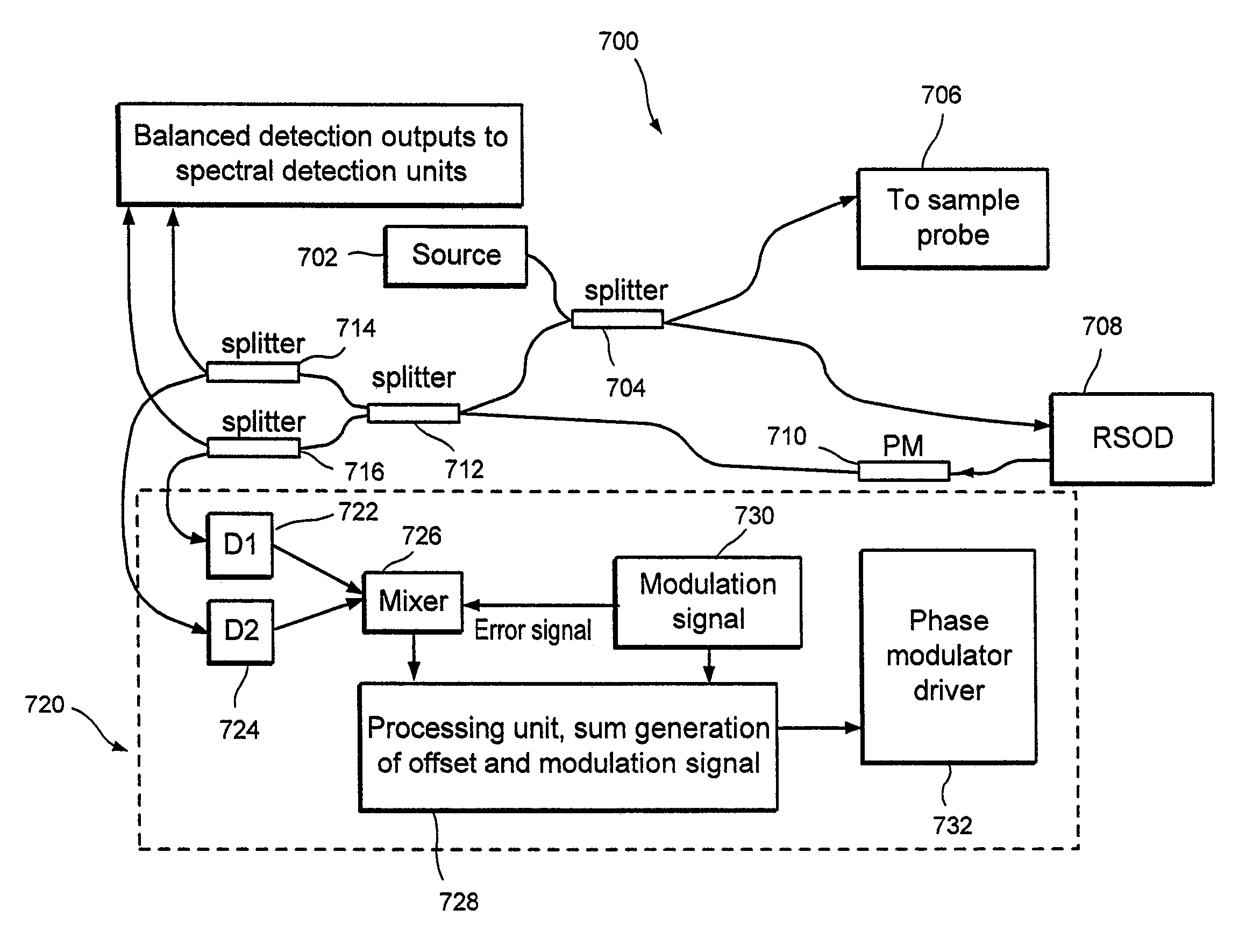
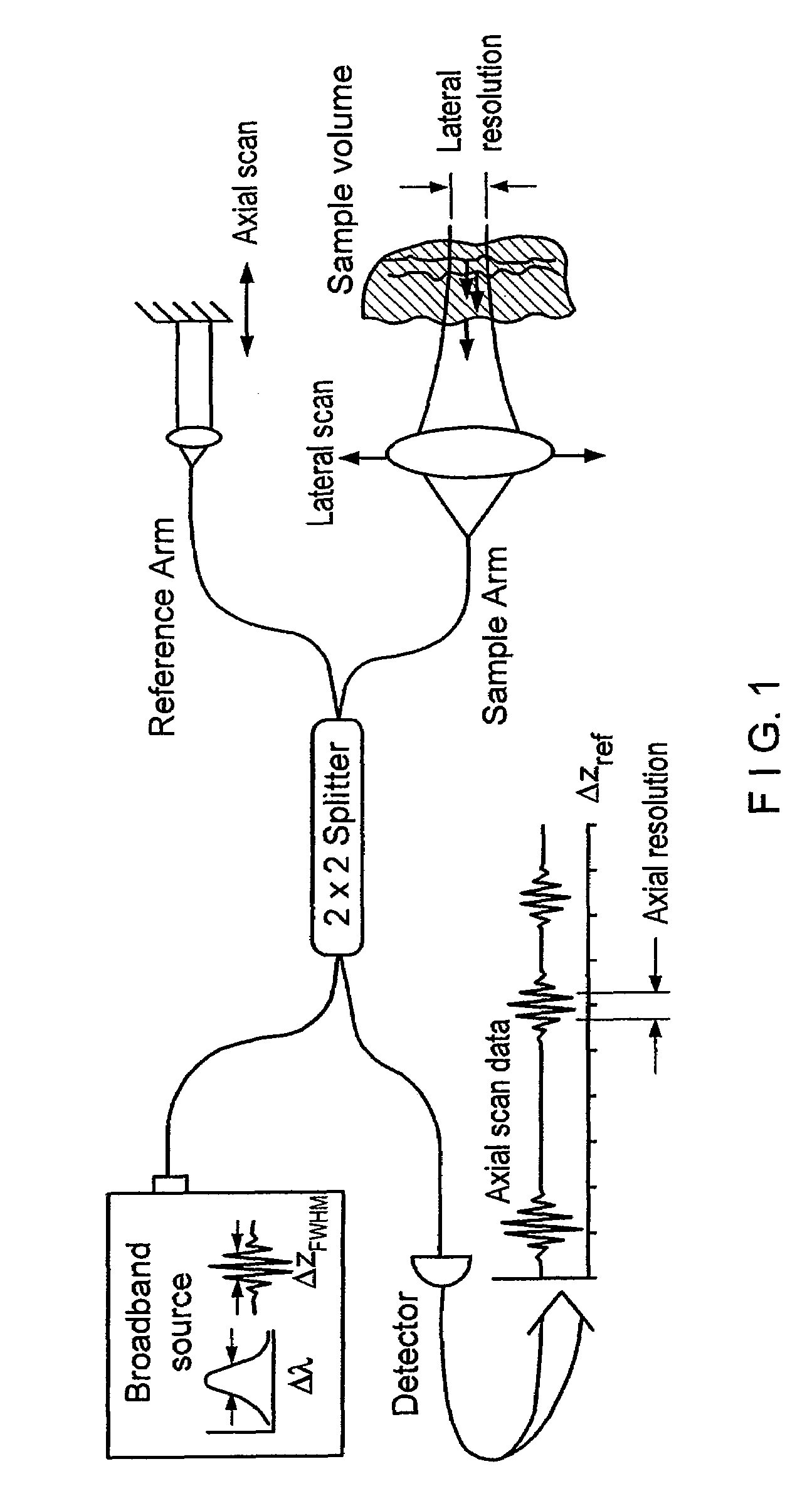
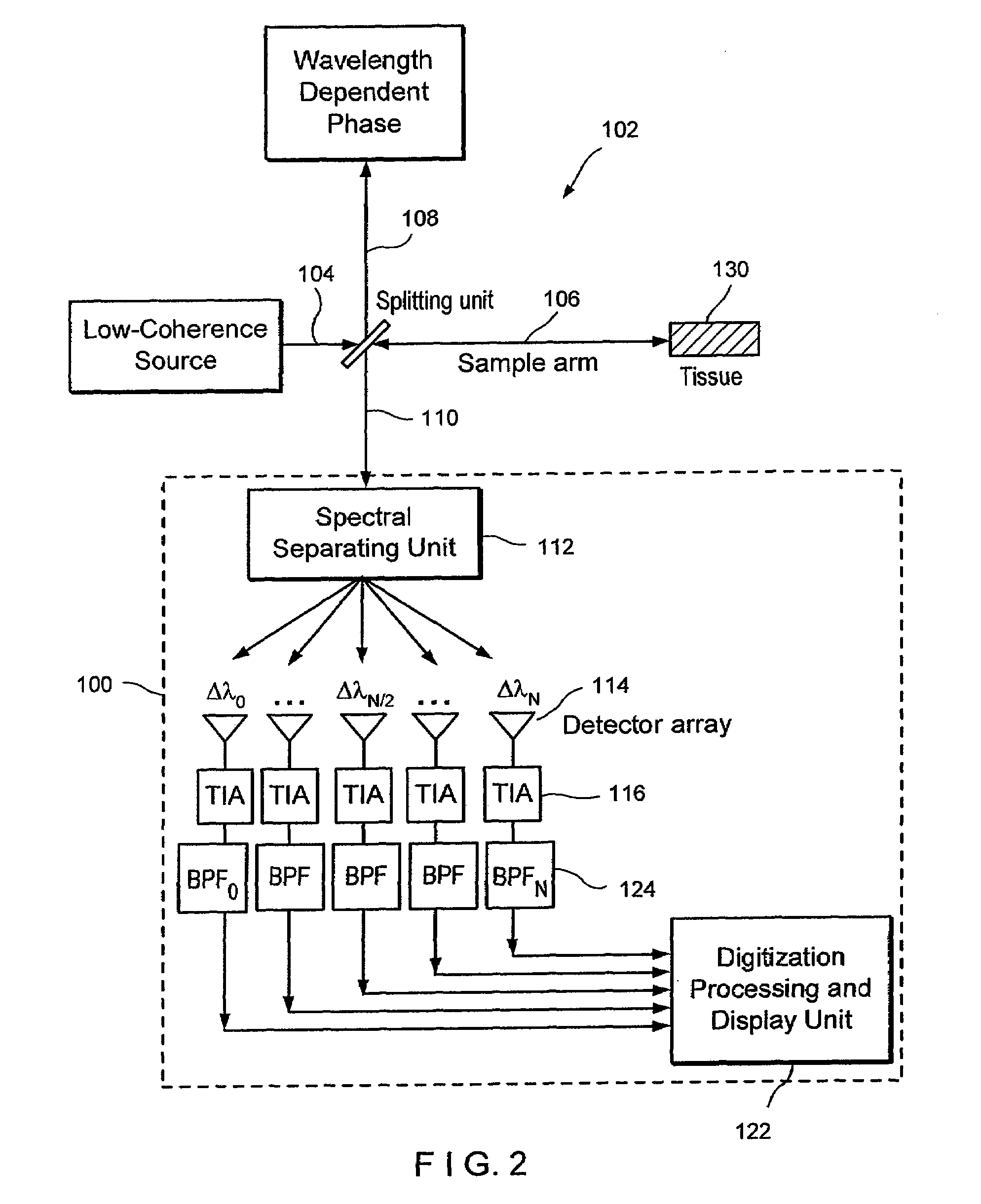
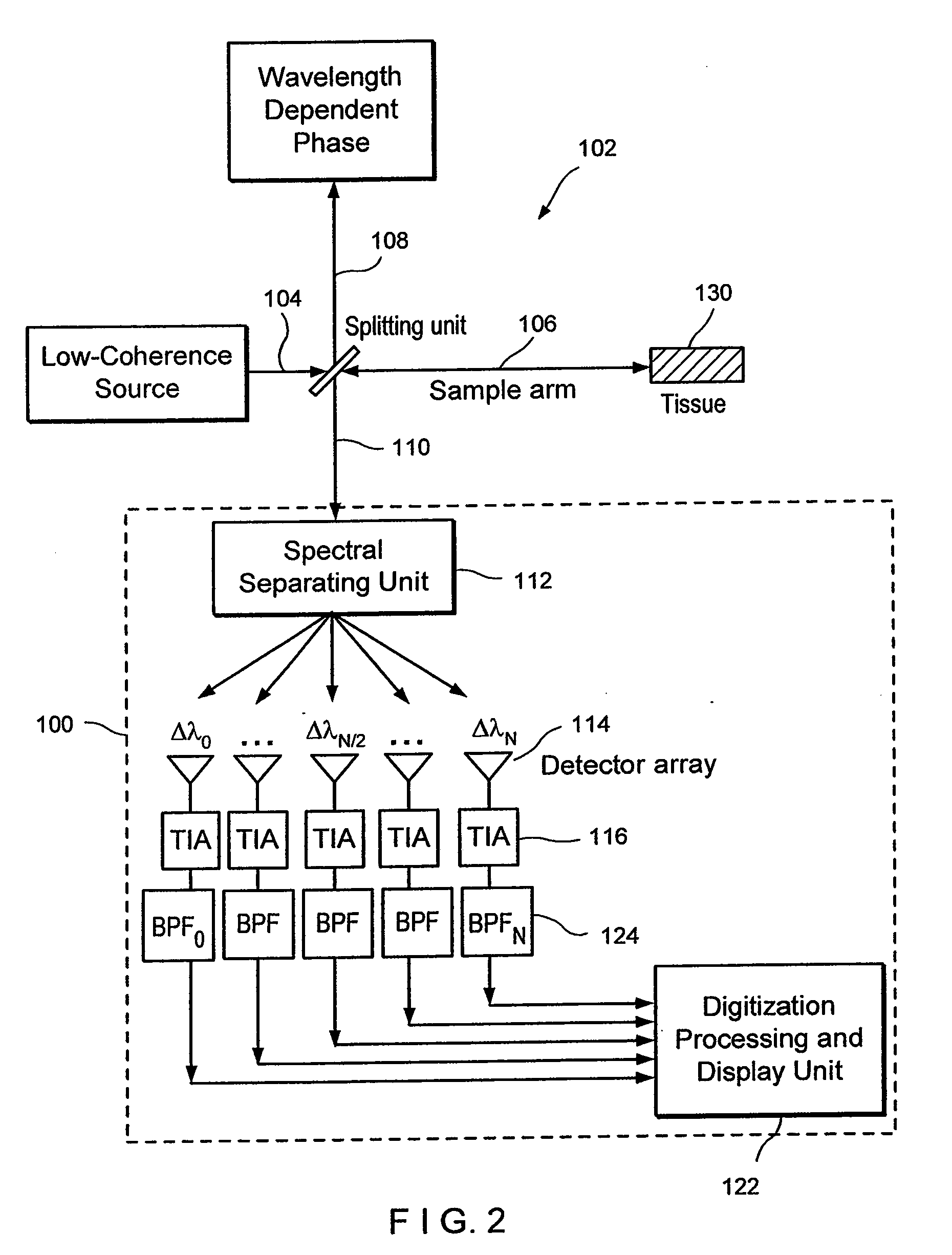
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
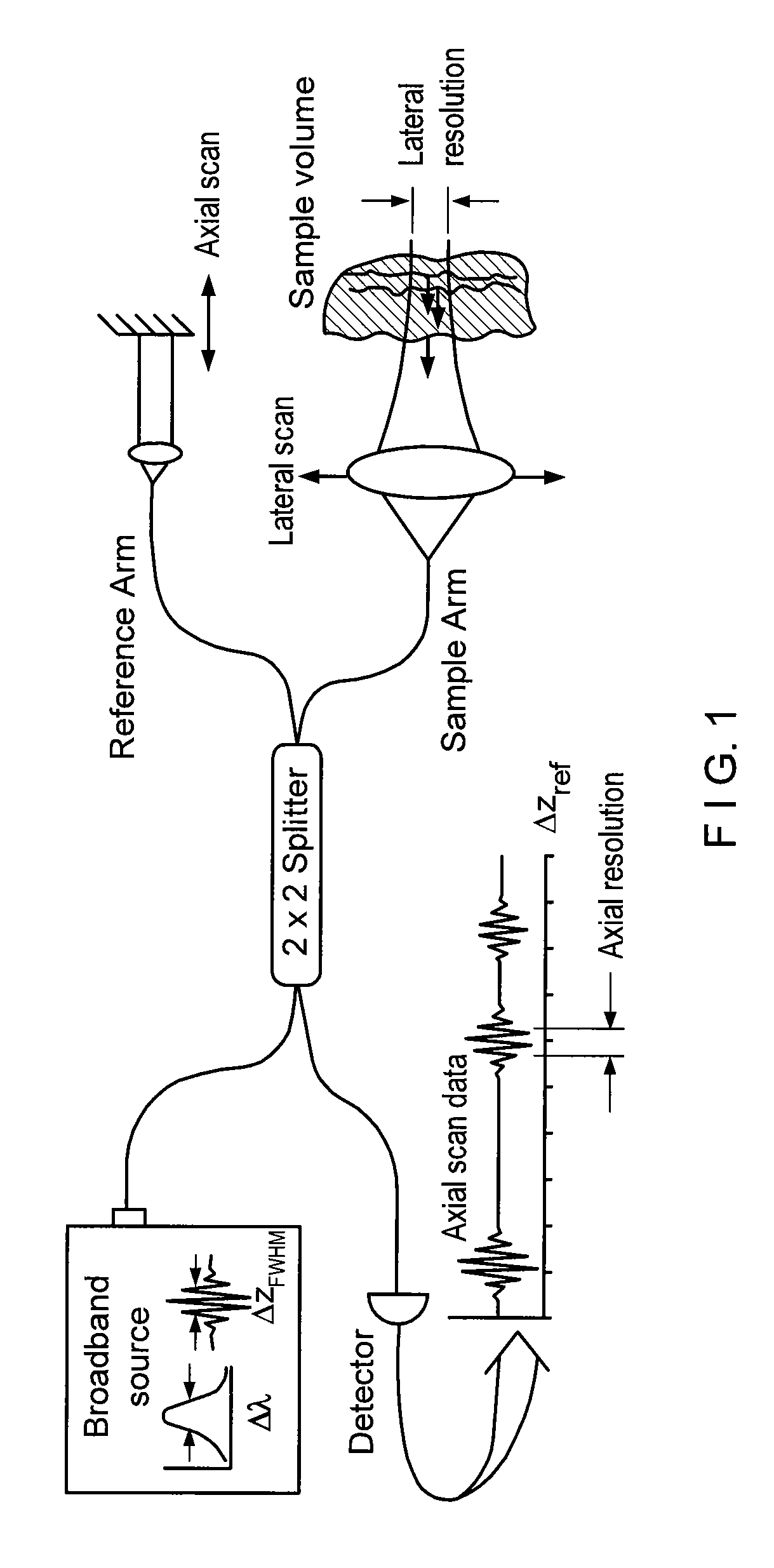
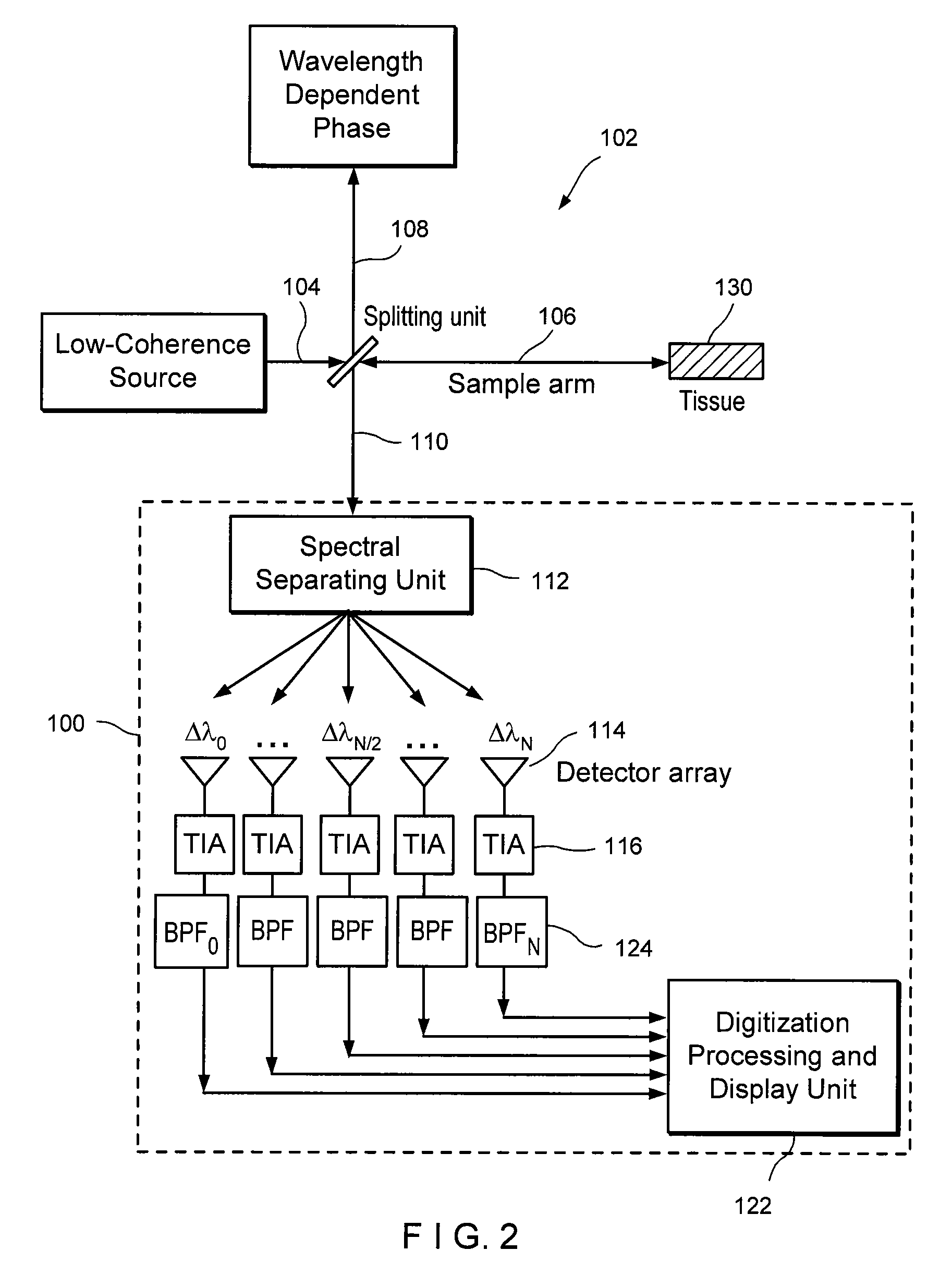
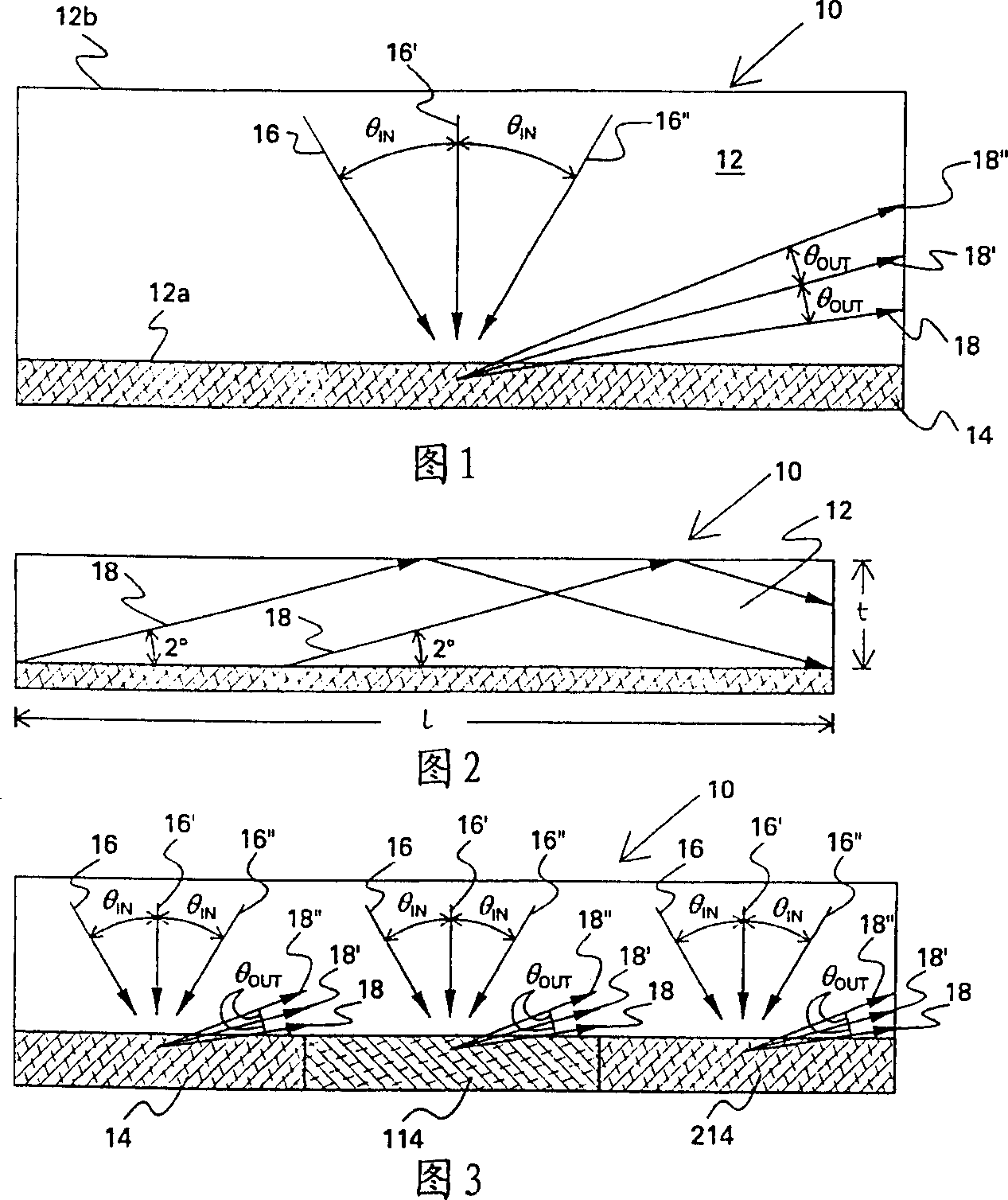
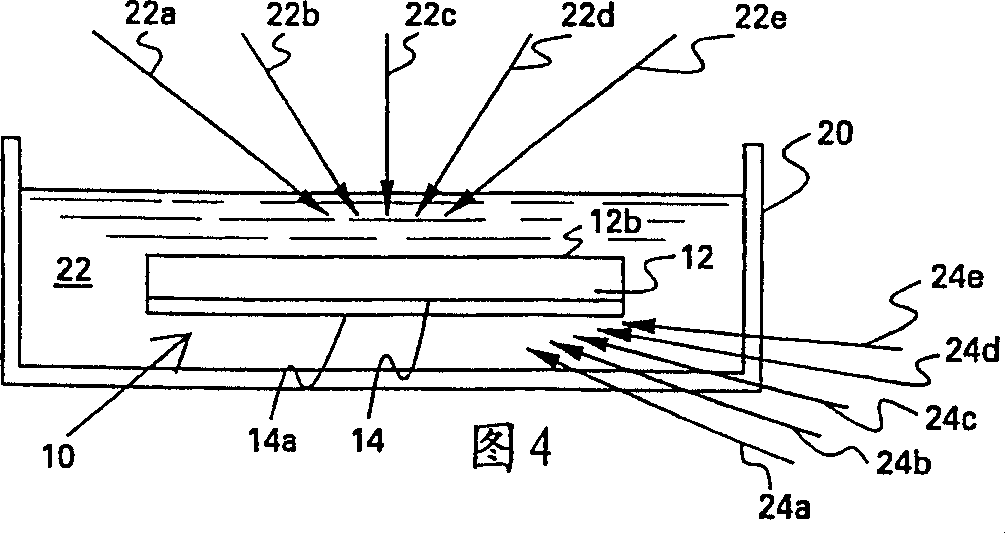
InactiveUS20050018201A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
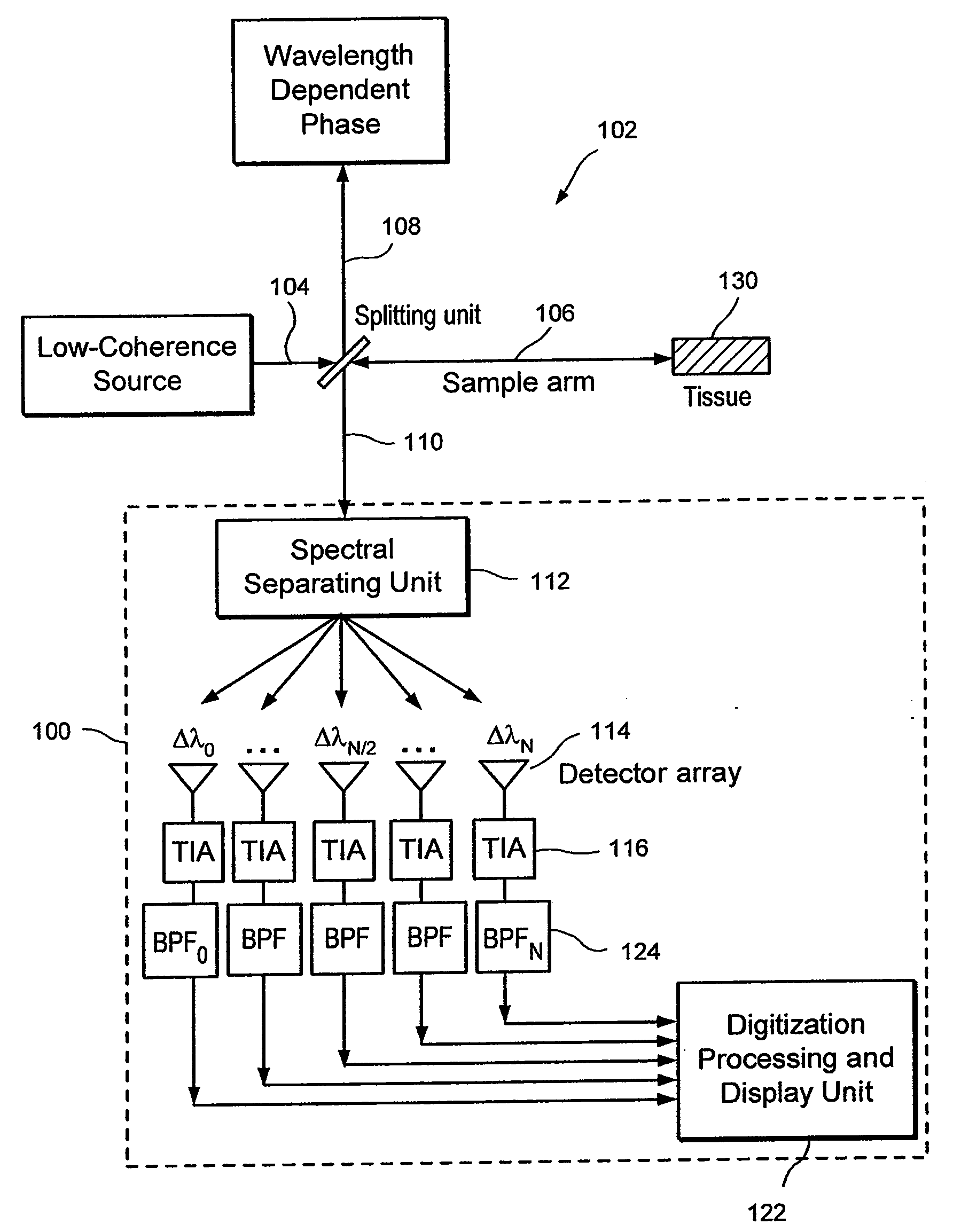
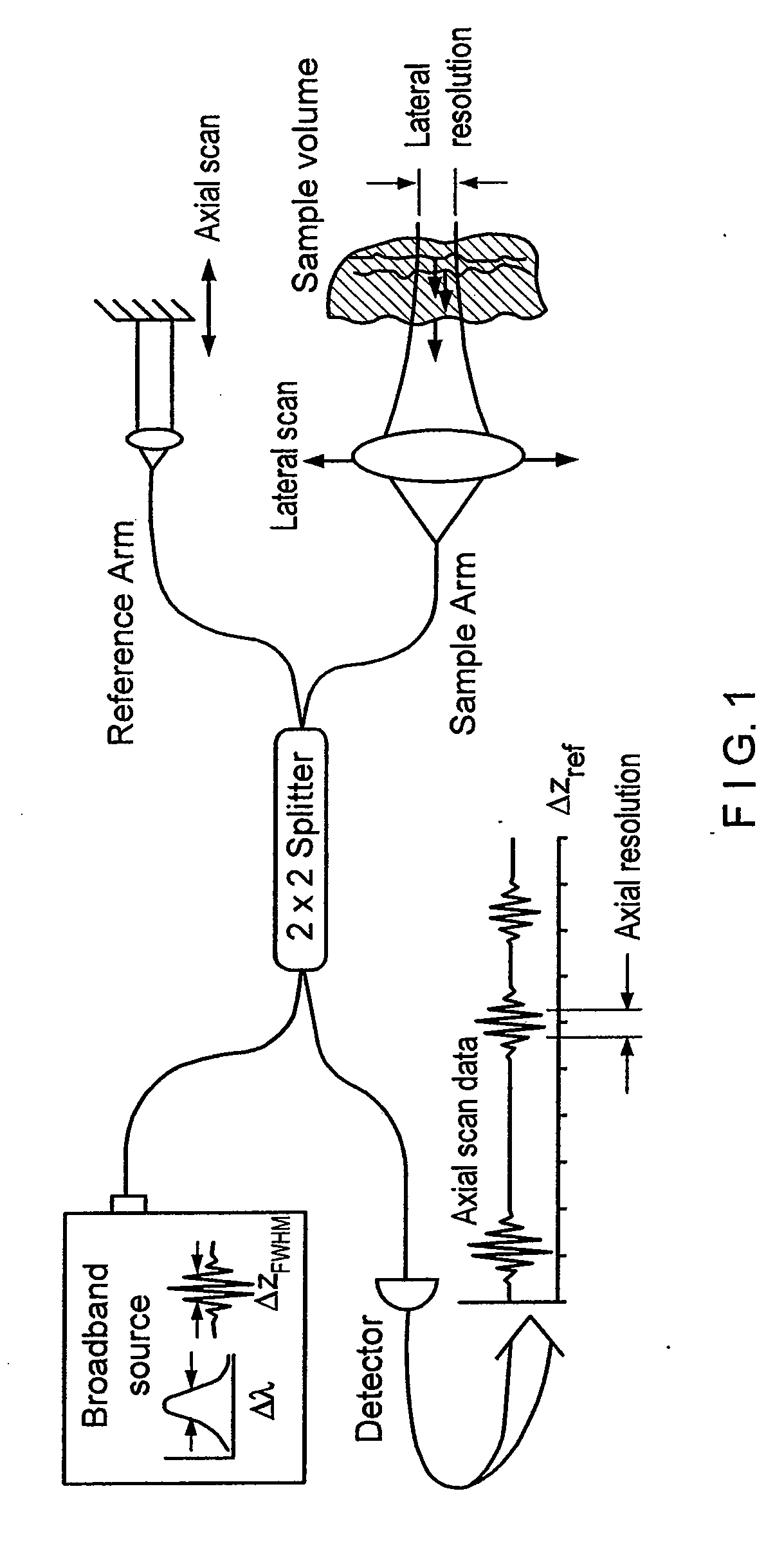
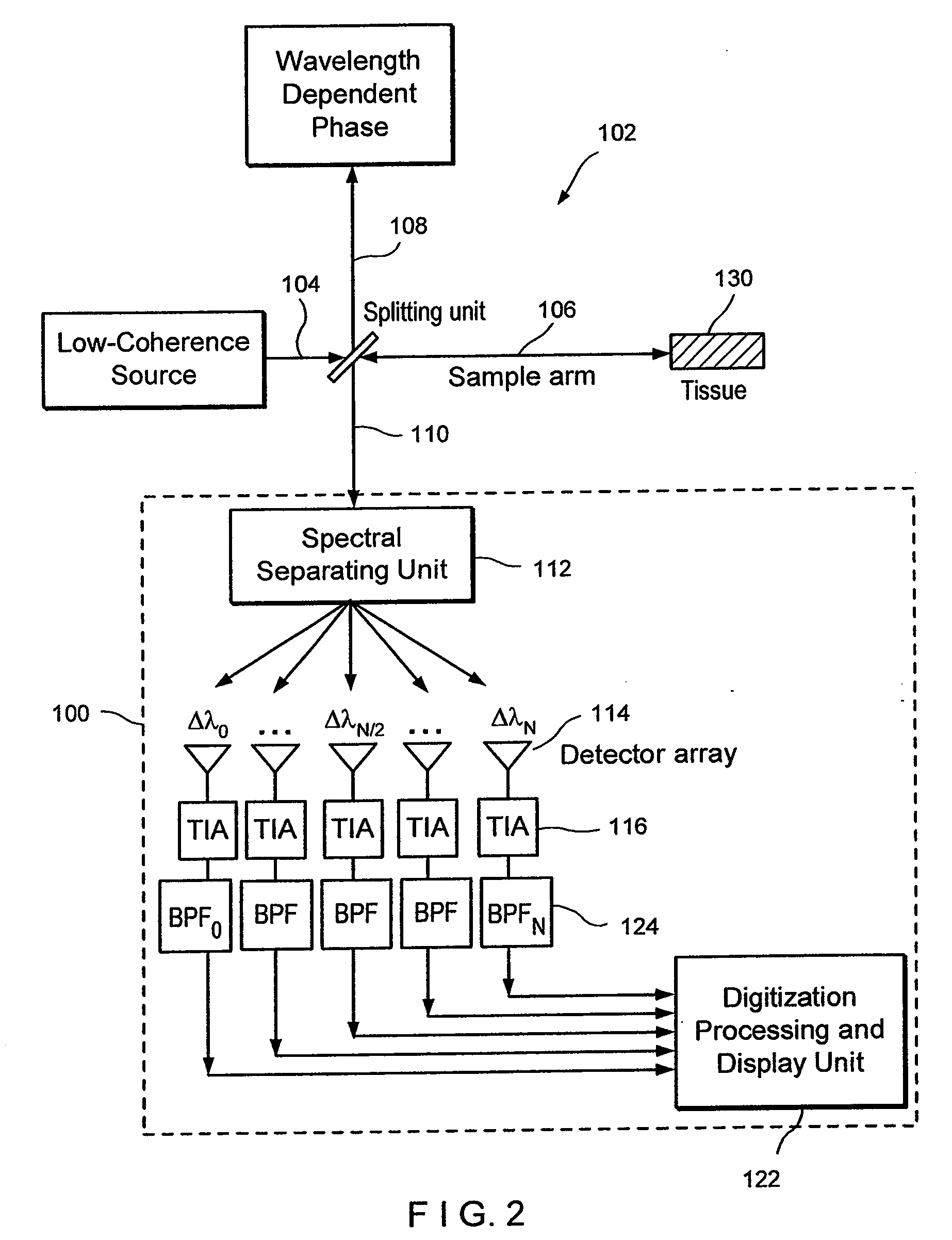
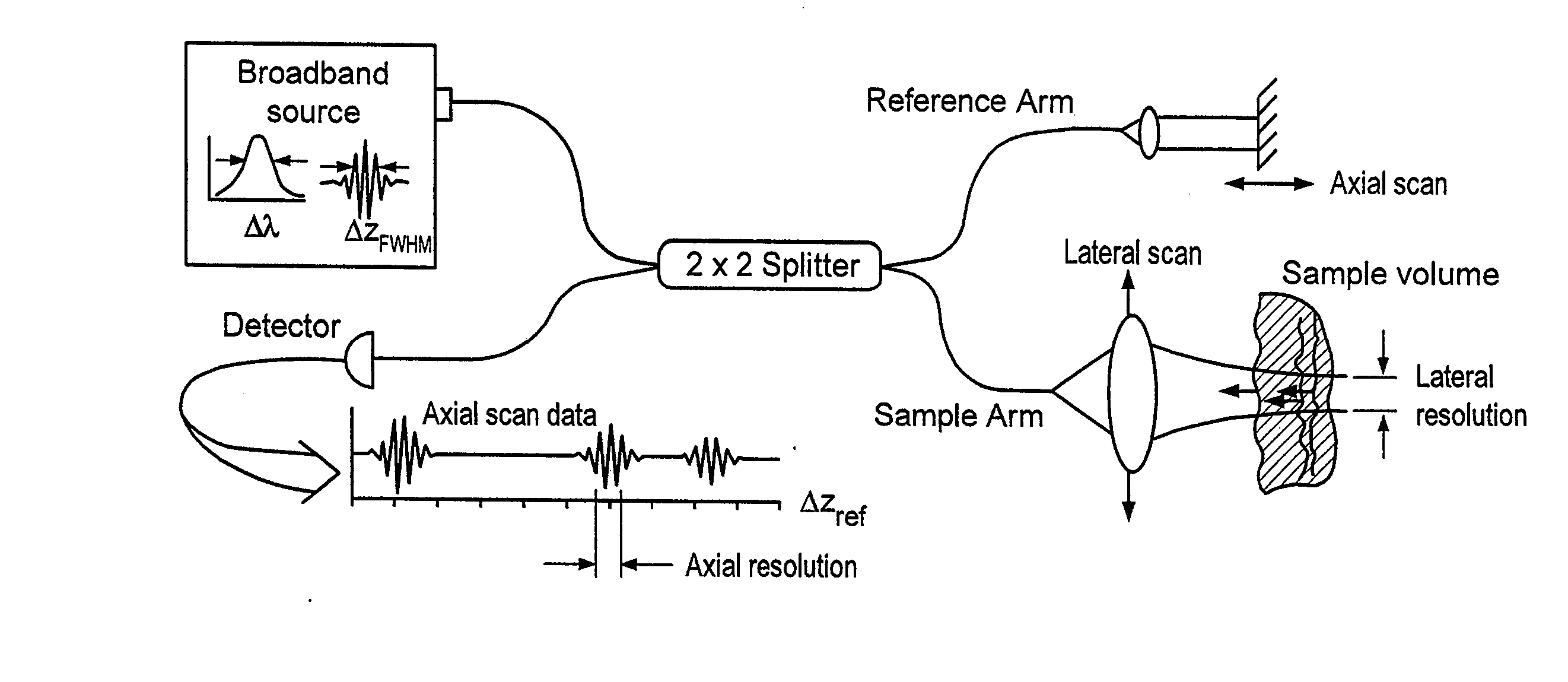
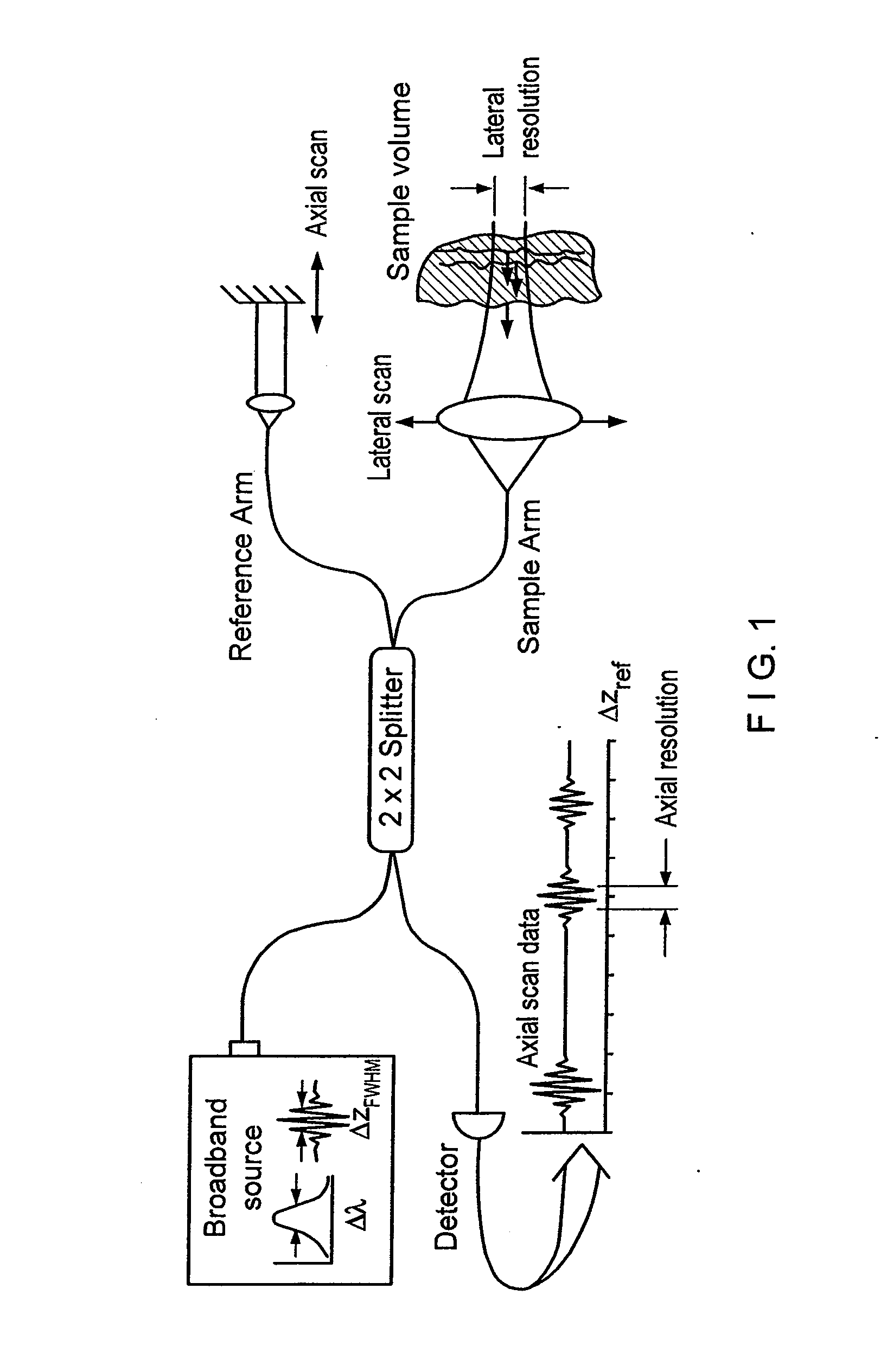
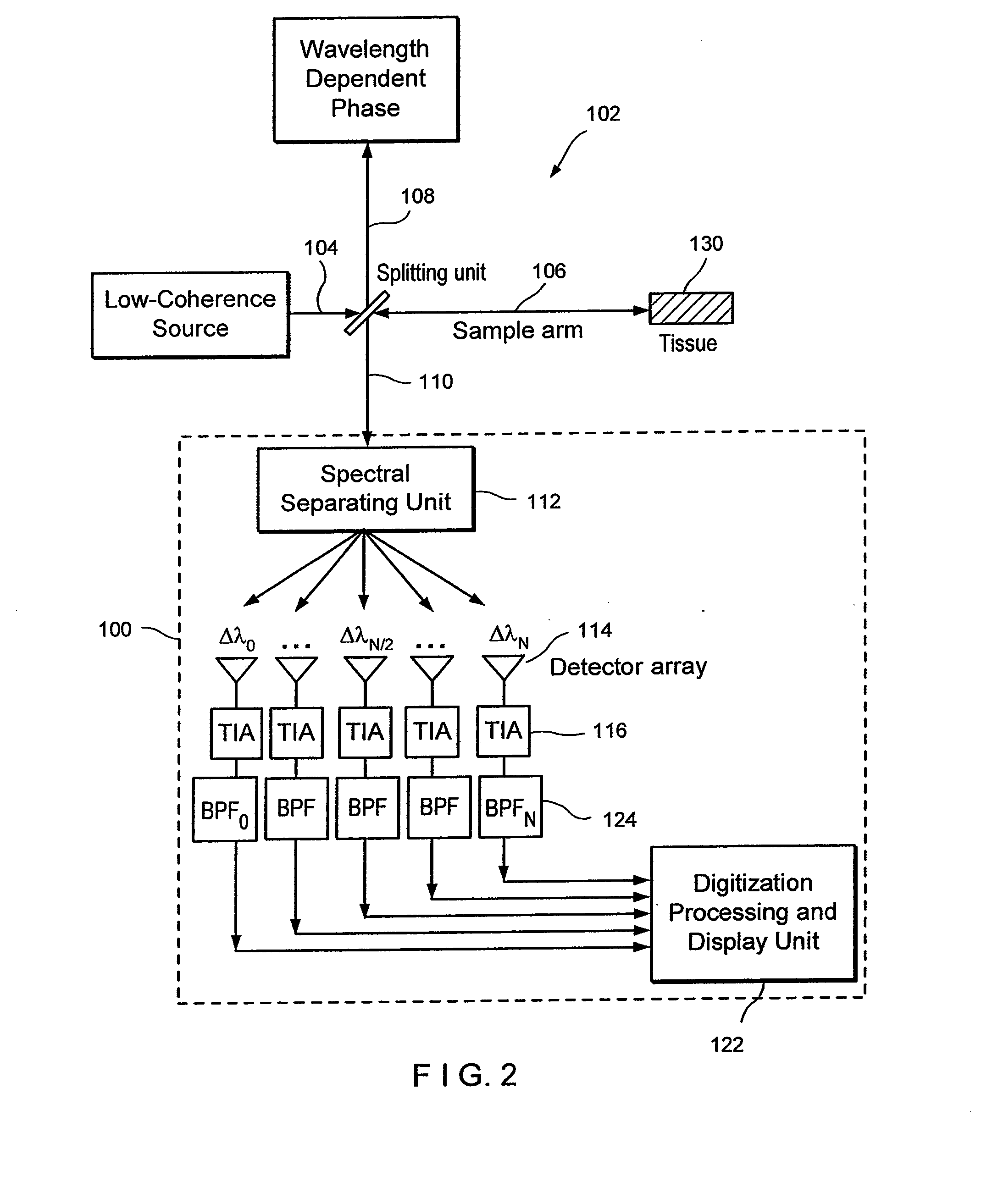
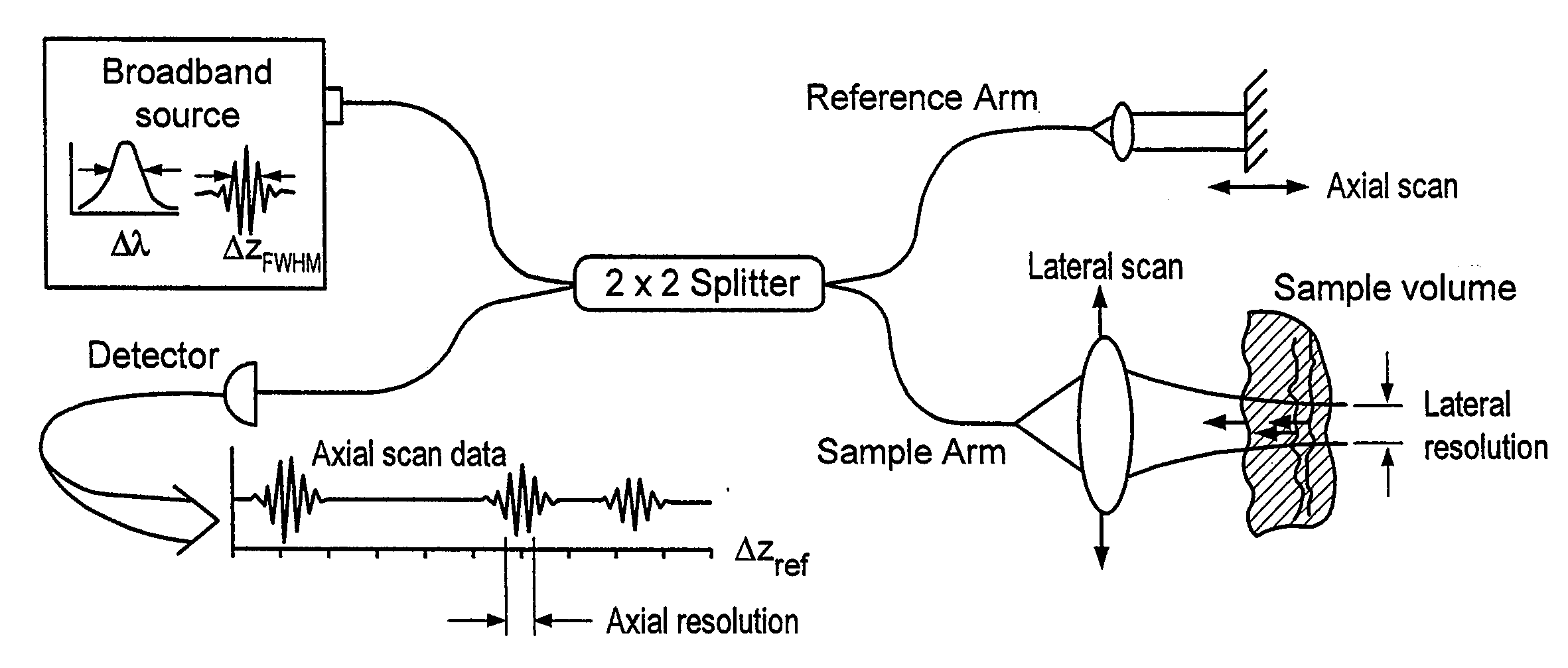
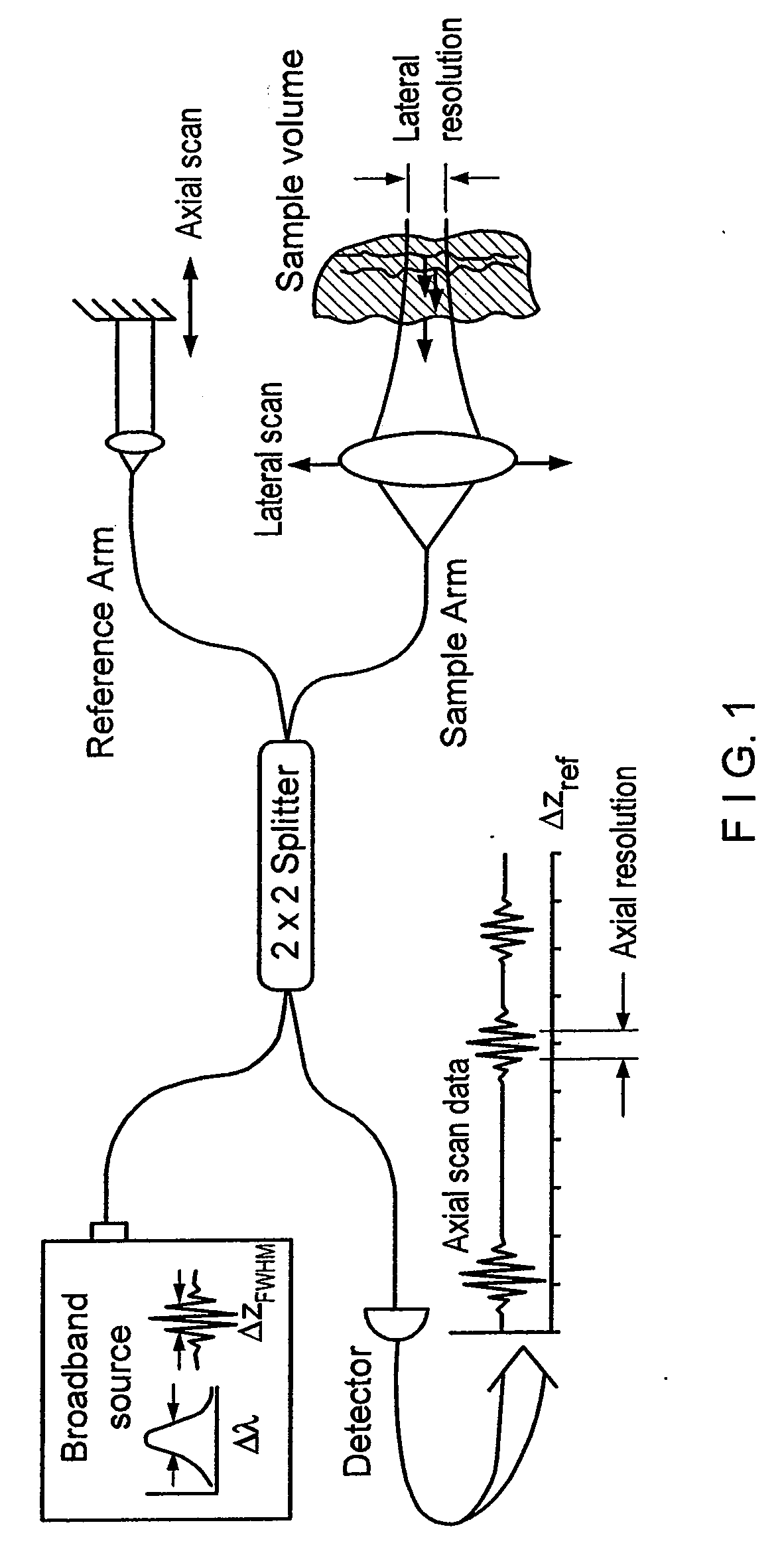
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7355716B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus, method, logic arrangement and storage medium are provided for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source can be split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands can be individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band may be detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band, the signal can be band p3 filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is likely reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands, while the signal amplitude can remain the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
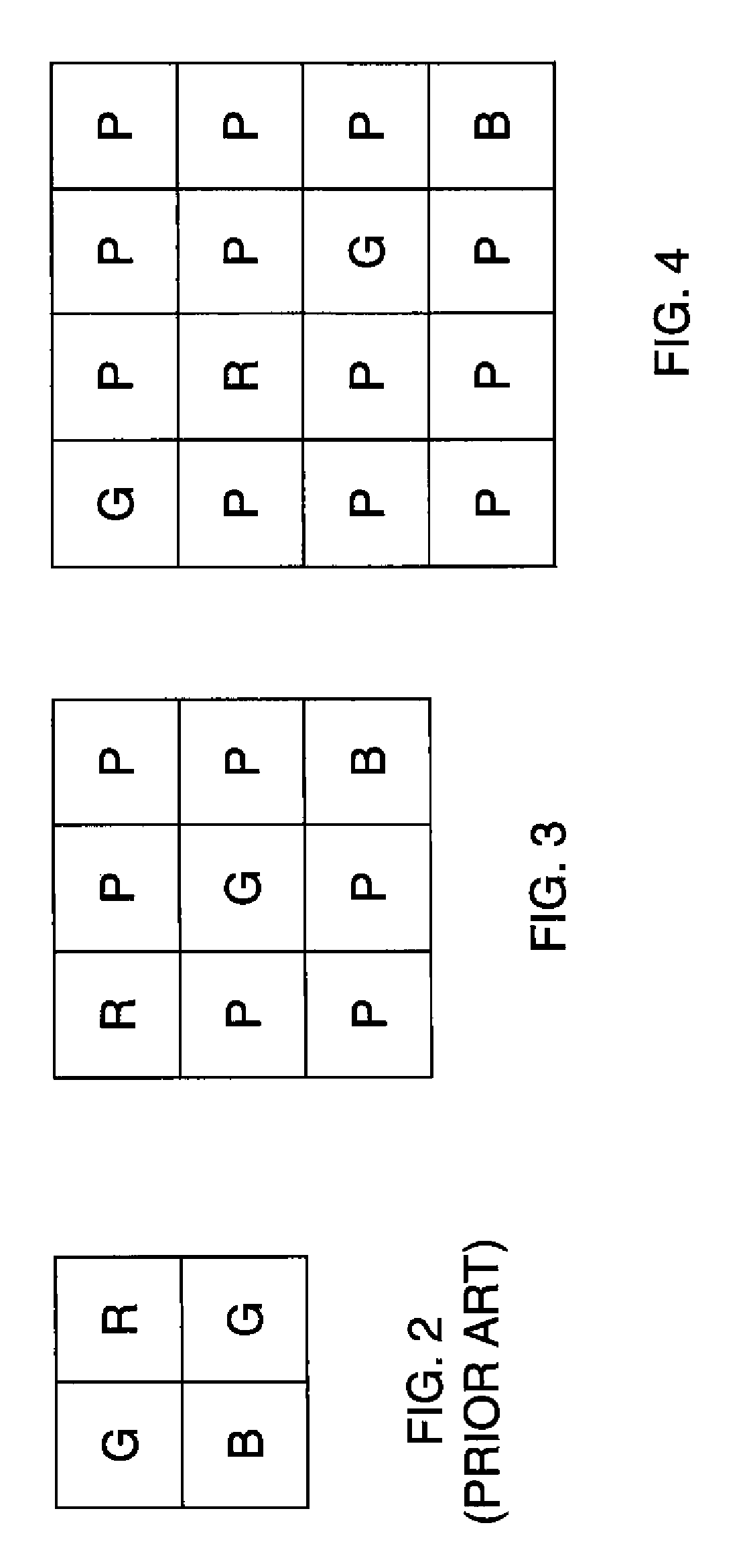
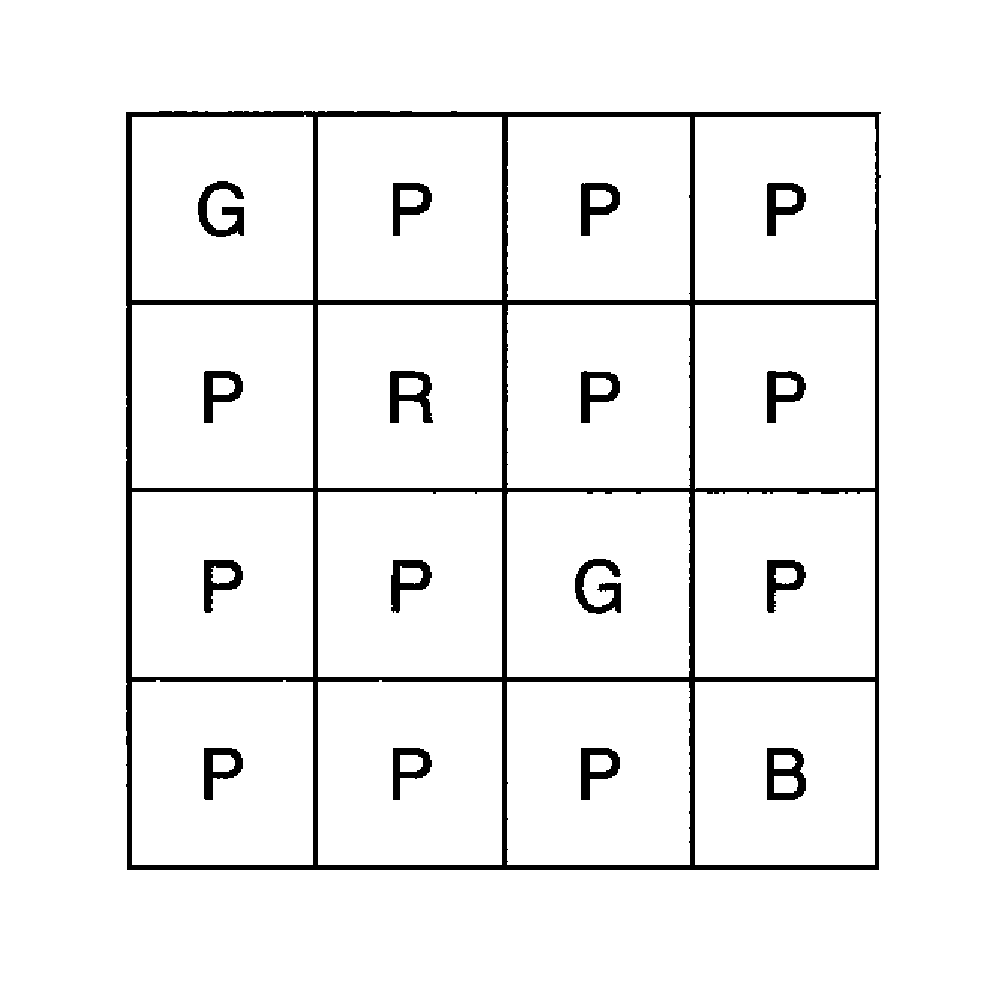
Four-channel color filter array pattern
ActiveUS20100302423A1Good colorReduce colorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageDiagonal
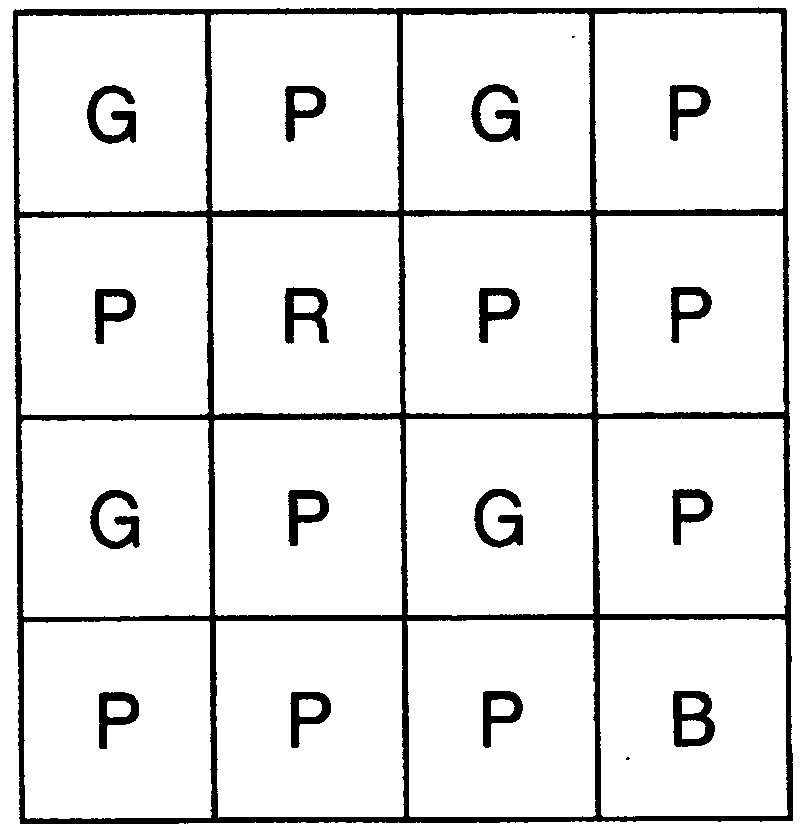
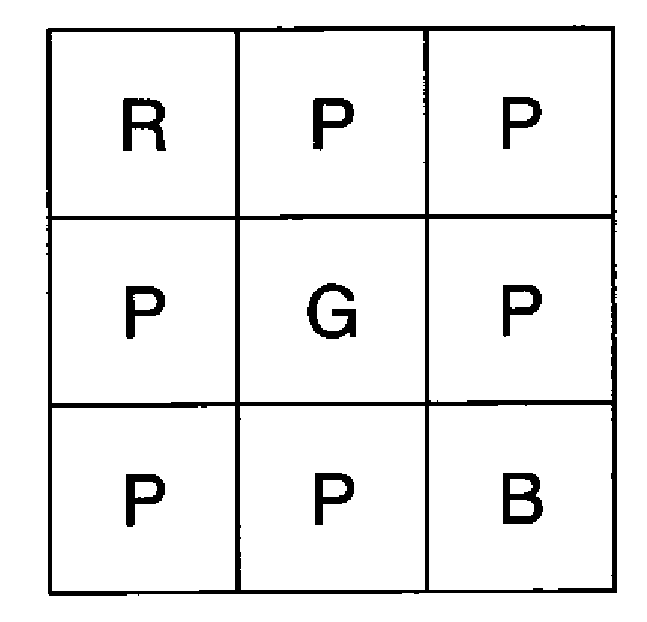
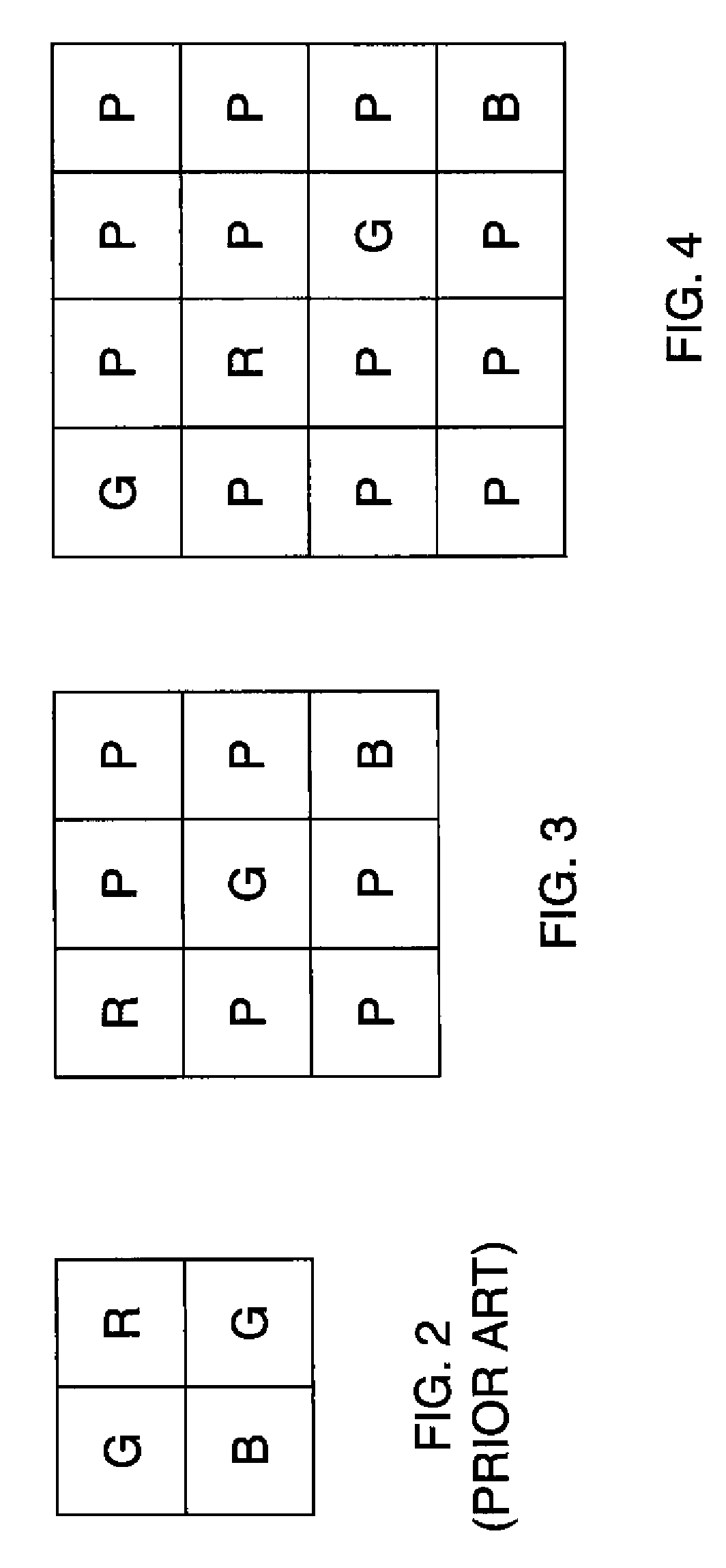
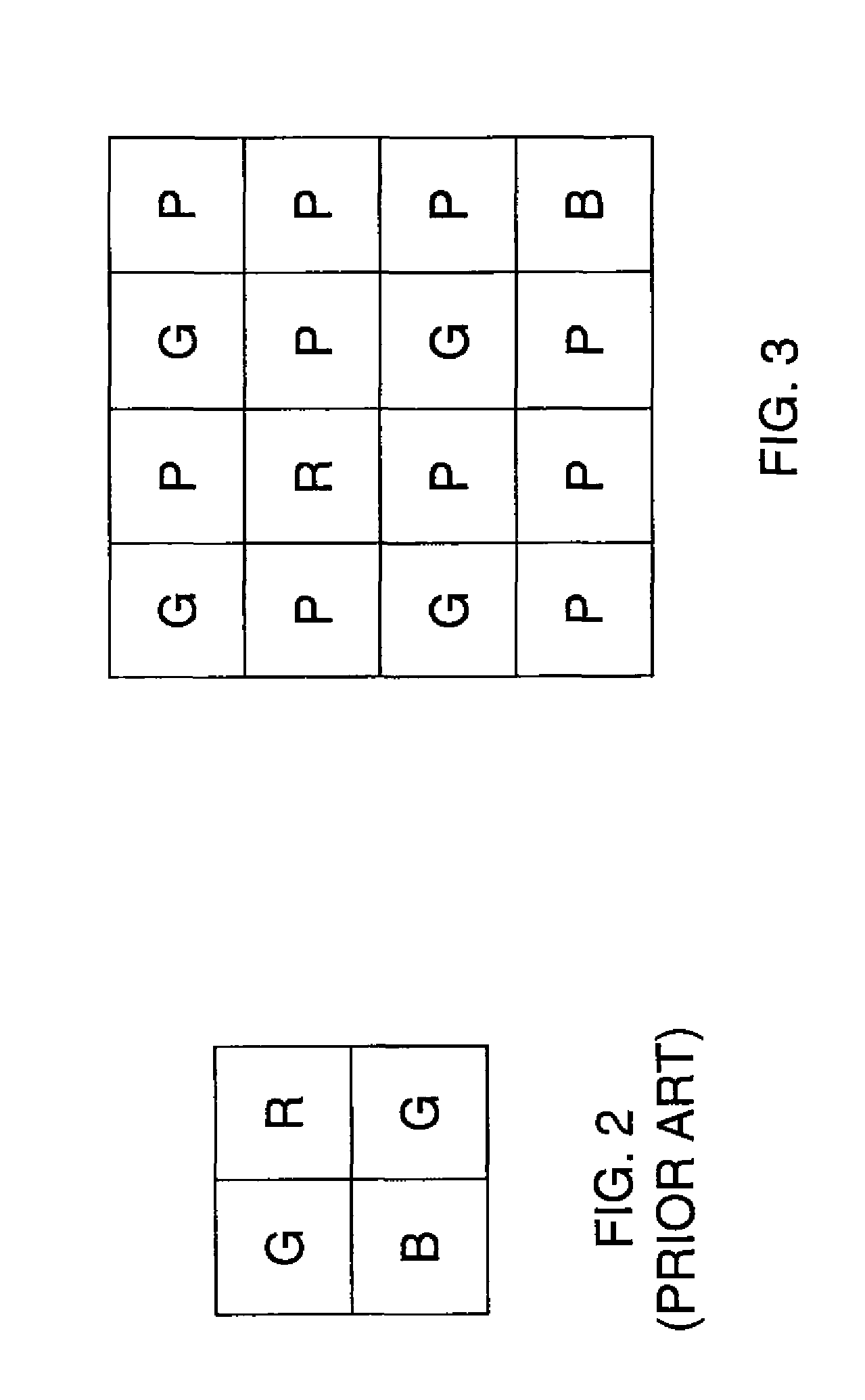
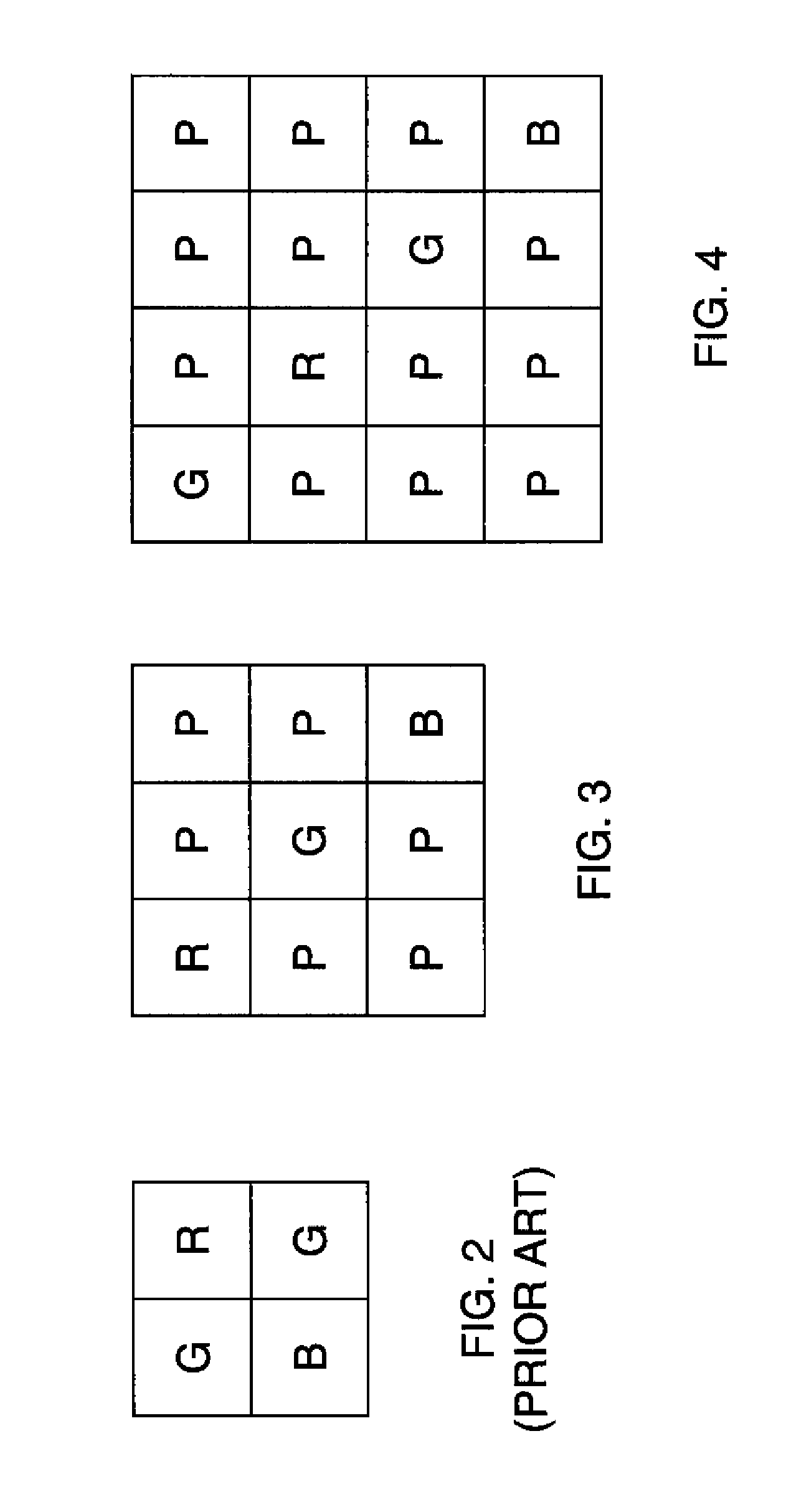
An image sensor for capturing a color image comprising a two dimensional array of light-sensitive pixels including panchromatic pixels and color pixels having at least two different color responses, the pixels being arranged in a repeating pattern having a square minimal repeating unit having at least three rows and three columns, the color pixels being arranged along one of the diagonals of the minimal repeating unit, and all other pixels being panchromatic pixels.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography OCT signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS7643153B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioImproves current data acquisition speed and availabilityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
ActiveUS20080094613A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityRadiation pyrometryDiagnostics using lightBandpass filteringSpectral bands
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for ranging and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry LCI and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080094637A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightInterferometersBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and method for rangings and noise reduction of low coherence interferometry lci and optical coherence tomography oct signals by parallel detection of spectral bands
InactiveUS20080097709A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioHigh sensitivityDiagnostics using lightNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementBandpass filteringFrequency spectrum
Apparatus and method for increasing the sensitivity in the detection of optical coherence tomography and low coherence interferometry (“LCI”) signals by detecting a parallel set of spectral bands, each band being a unique combination of optical frequencies. The LCI broad bandwidth source is split into N spectral bands. The N spectral bands are individually detected and processed to provide an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio by a factor of N. Each spectral band is detected by a separate photo detector and amplified. For each spectral band the signal is band pass filtered around the signal band by analog electronics and digitized, or, alternatively, the signal may be digitized and band pass filtered in software. As a consequence, the shot noise contribution to the signal is reduced by a factor equal to the number of spectral bands. The signal remains the same. The reduction of the shot noise increases the dynamic range and sensitivity of the system.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
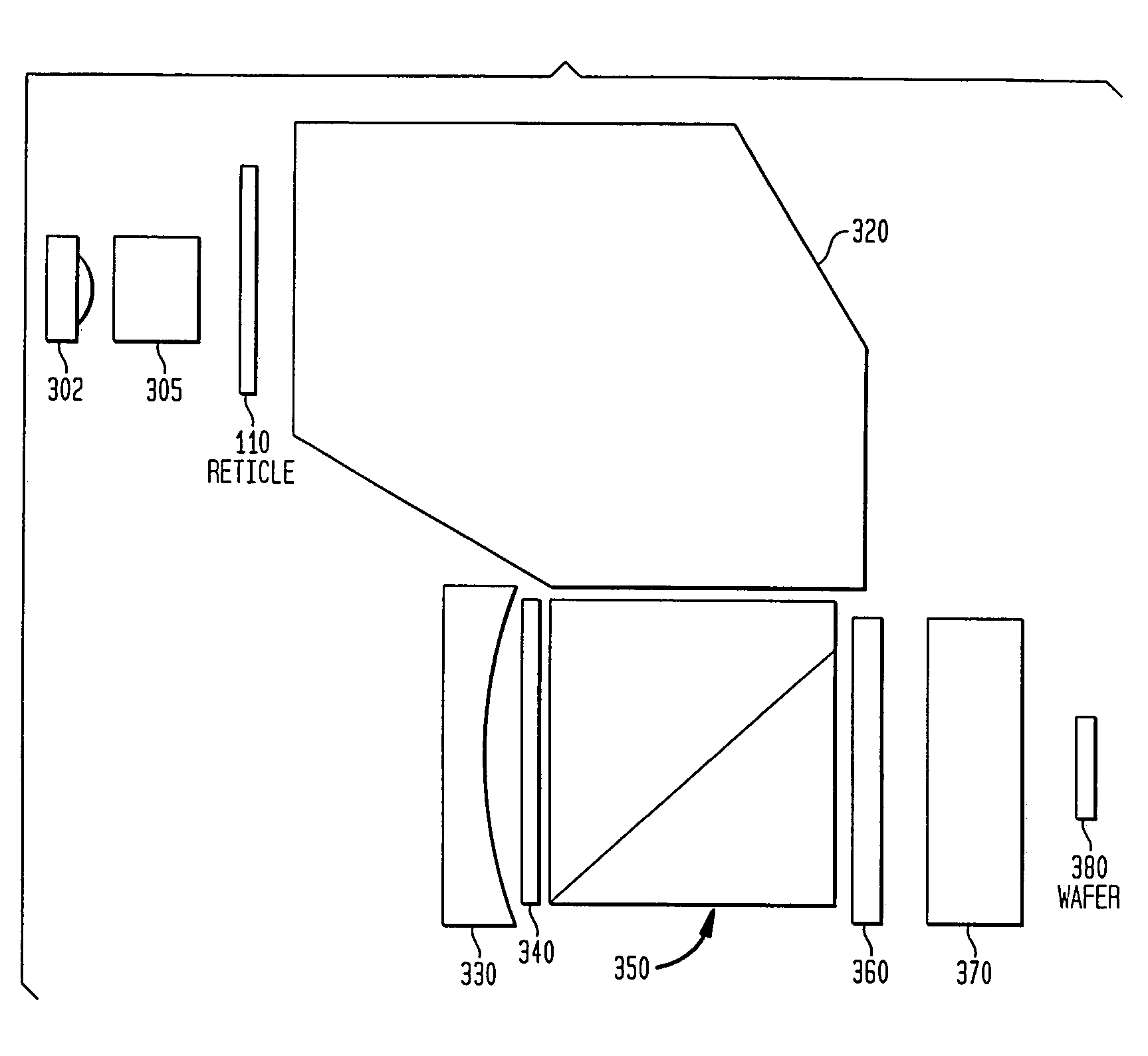
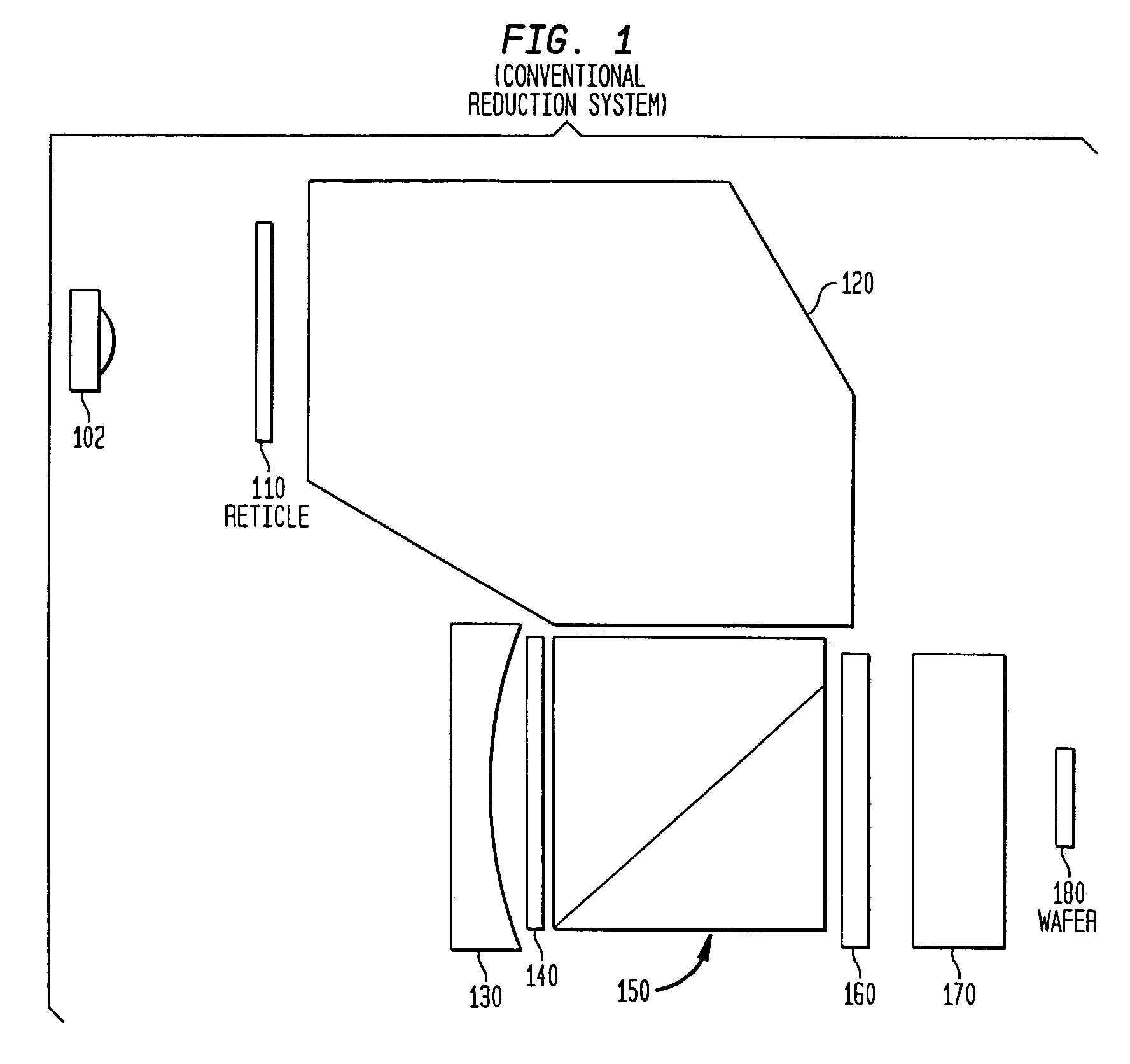
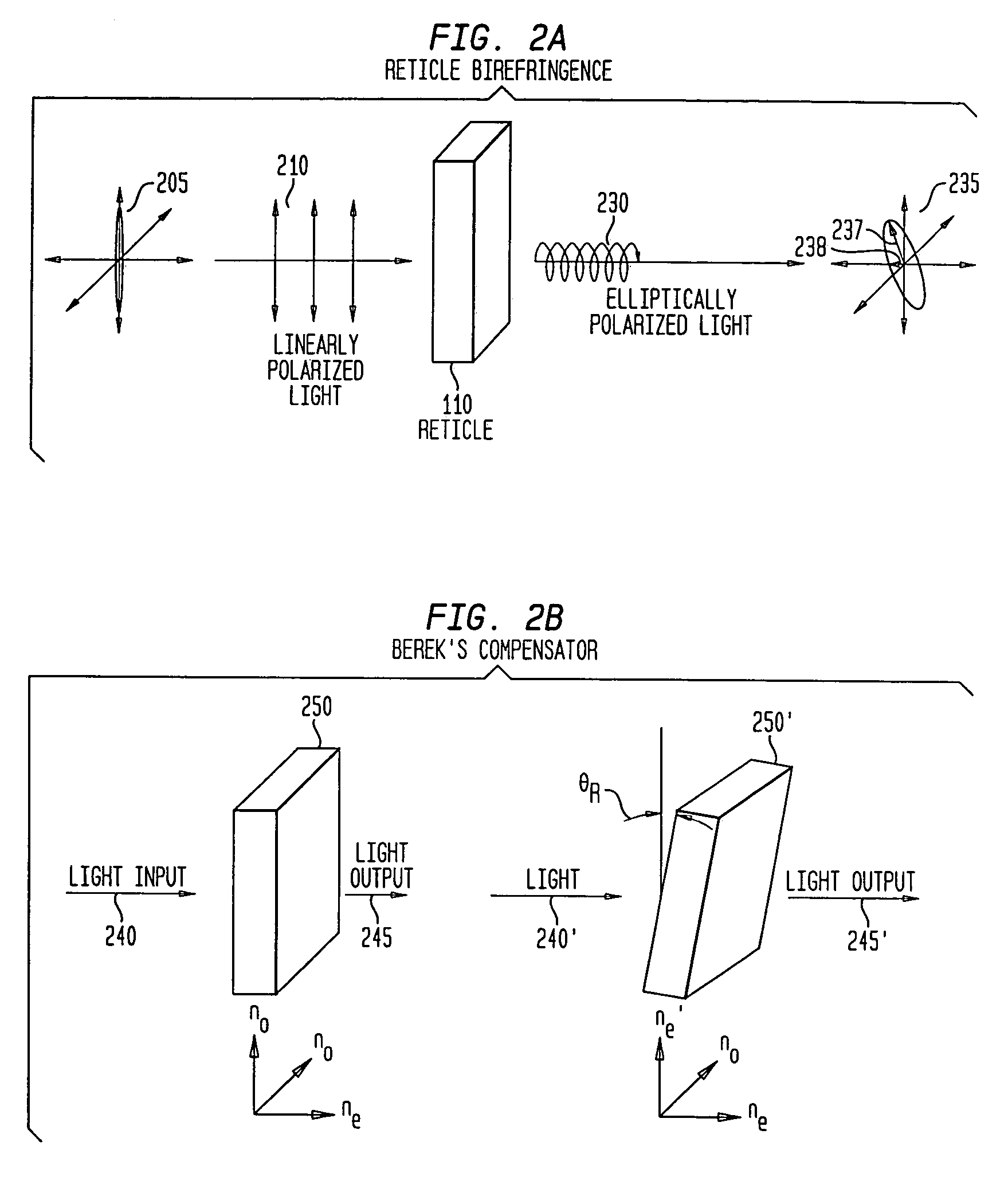
Optical reduction system with control of illumination polarization
InactiveUS7239446B2Improve system performanceMinimize impactSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPolarising elementsHigh numerical apertureEngineering
An optical reduction system with polarization dose sensitive output for use in the photolithographic manufacture of semiconductor devices having variable compensation for reticle retardation before the long conjugate end. The variable compensation component(s) before the reticle provides accurate adjustment of the polarization state at or near the reticle. The variable compensation components can be variable wave plates, layered wave plates, opposing mirrors, a Berek's compensator and / or a Soleil-Babinet compensator. The catadioptric optical reduction system provides a relatively high numerical aperture of 0.7 capable of patterning features smaller than 0.25 microns over a 26 mm×5 mm field. The optical reduction system is thereby well adapted to a step and scan microlithographic exposure tool as used in semiconductor manufacturing. Several other embodiments combine elements of different refracting power to widen the spectral bandwidth which can be achieved.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
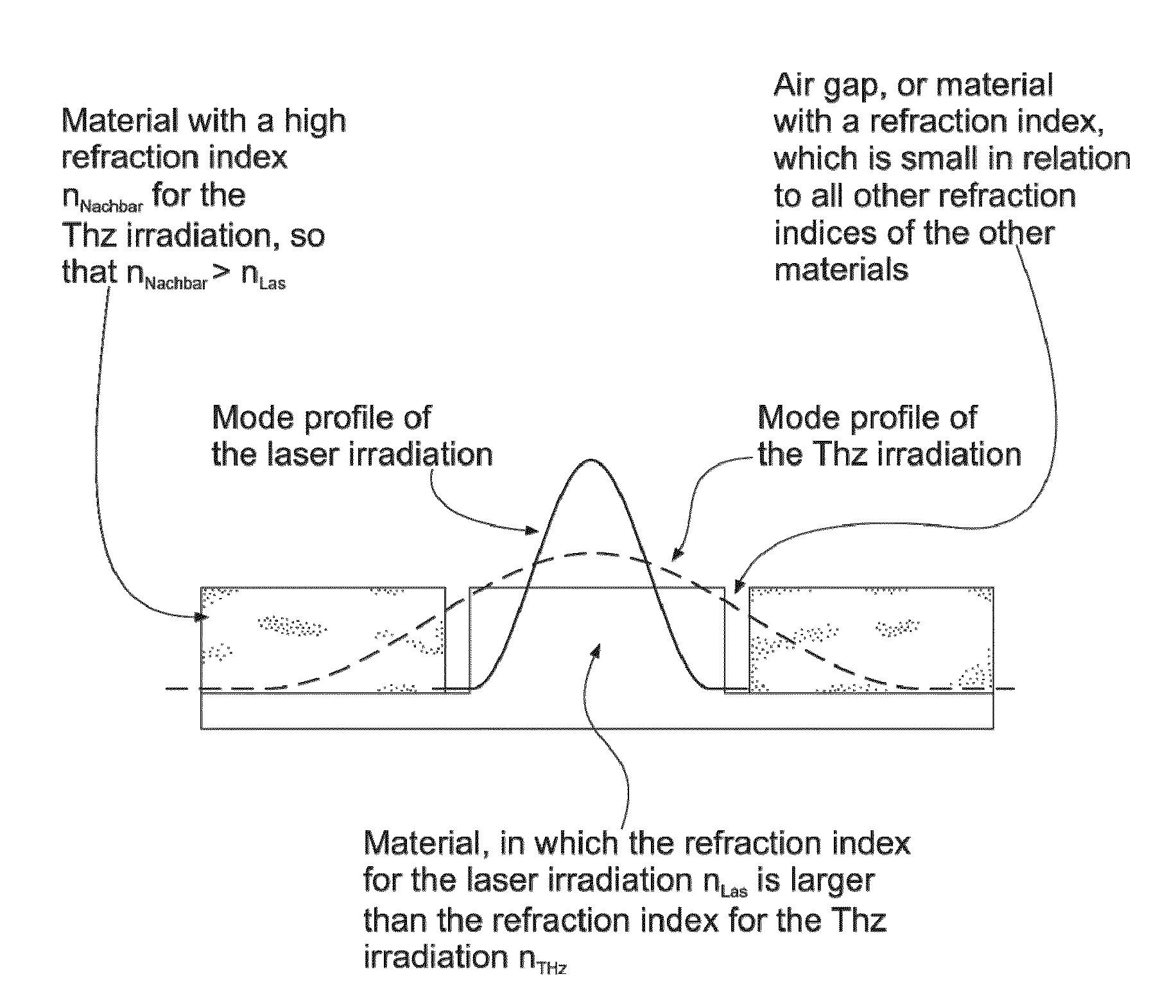
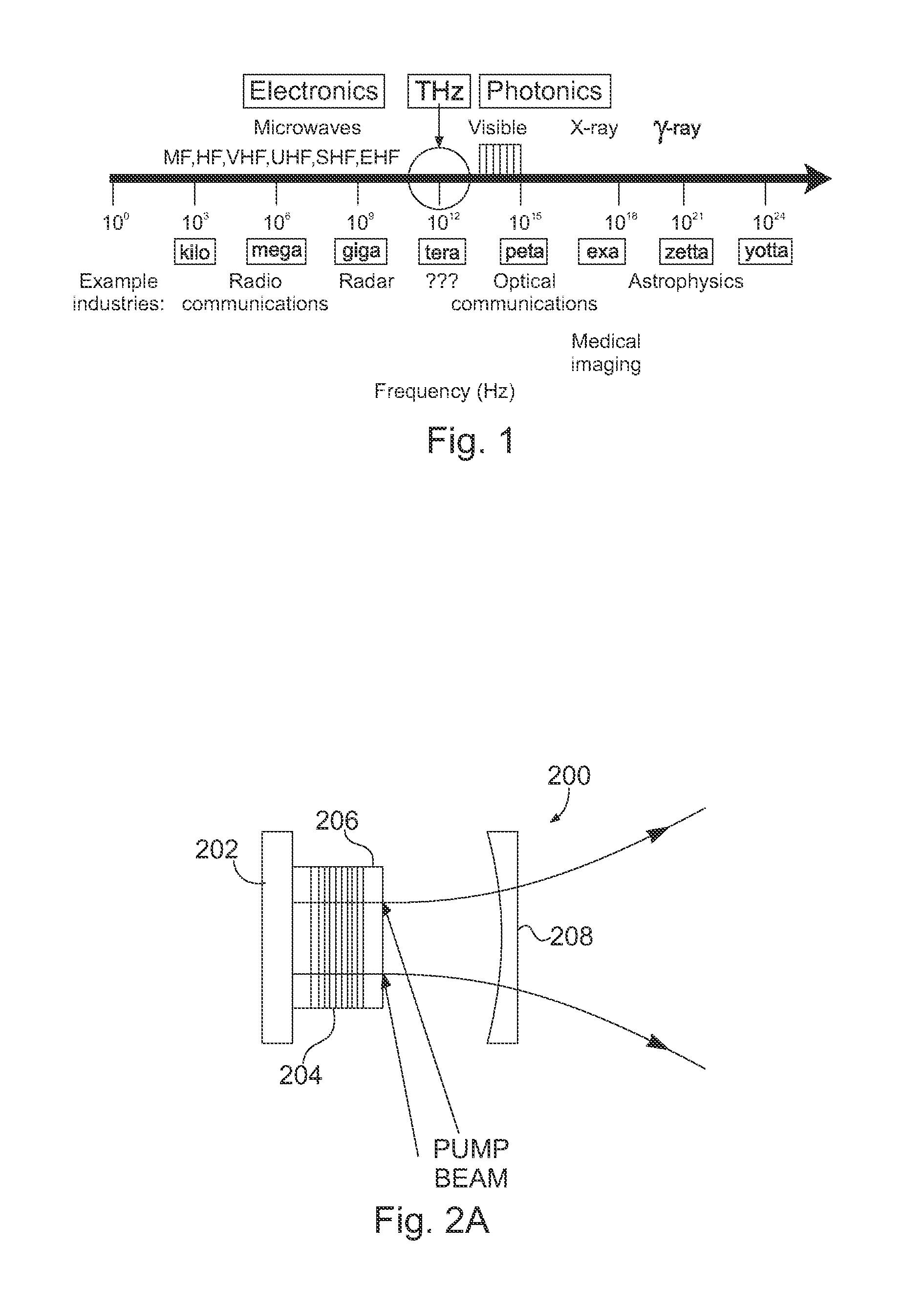
Terahertz and millimeter wave source
InactiveUS20100195675A1Avoid disadvantagesSuitable spectral positionLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsClassical mechanicsMillimeter
The present invention relates generally to a terahertz and millimeter wave source, and more particularly, but not exclusively, to structures for coupling the terahertz electromagnetic waves out of the source.
Owner:MOLONEY JEROME V +6
Laser-based source for terahertz and millimeter waves
InactiveUS20130294467A1Minimize reflection lossAvoid reflectionsLaser optical resonator constructionActive medium shape and constructionSemiconductor quantum wellsLength wave
A multi-wavelength VECSEL includes an active region comprising a plurality of semiconductor quantum wells having an intrinsically broadened gain with a wavelength selective filter disposed within the cavity to provide a laser output that oscillates at two or more separated wavelengths simultaneously. A non-linear crystal may be provided in the cavity to emit radiation at a frequency in the THz range that is the difference of the frequencies associated with two of the separated wavelengths.
Owner:THE ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ON BEHALF OF THE UNIV OF ARIZONA
High-brightness holographic waveguide display device
ActiveCN107167920AIncrease spectral bandwidthIncrease display brightnessOptical light guidesCouplingDisplay device
The invention discloses a high-brightness holographic waveguide display device which comprises a micro display device, a collimating mirror, a waveguide, an incident coupler and an outgoing coupling member holographic grating. The incident coupler comprises a top-layer holographic grating and a bottom-layer holographic grating. The top-layer holographic grating and the outgoing coupling member holographic grating are tightly connected with two ends of the first surface of the waveguide. The bottom-layer holographic grating is closely connected with the second surface of the waveguide and is arranged below the top-layer holographic grating. The top-layer holographic grating and the bottom-layer holographic grating realize Bragg diffraction on an incident light beam and the incident light beam enters the waveguide. The incident light beam is transmitted in a total reflection manner until the light beam is diffused and output by the outgoing holographic grating. Compared with the prior art, the high-brightness holographic waveguide display device increases spectral bandwidth and improves display brightness of the holographic waveguide display device under a precondition that the peak diffraction efficiency of the holographic grating does not reduce.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and device for monitoring optical layer of passive optical network based on two-dimensional optical orthogonal code
ActiveCN102223176APerformance monitoringDoes not affect workMultiplex system selection arrangementsElectromagnetic transmissionOptical powerMonitoring system
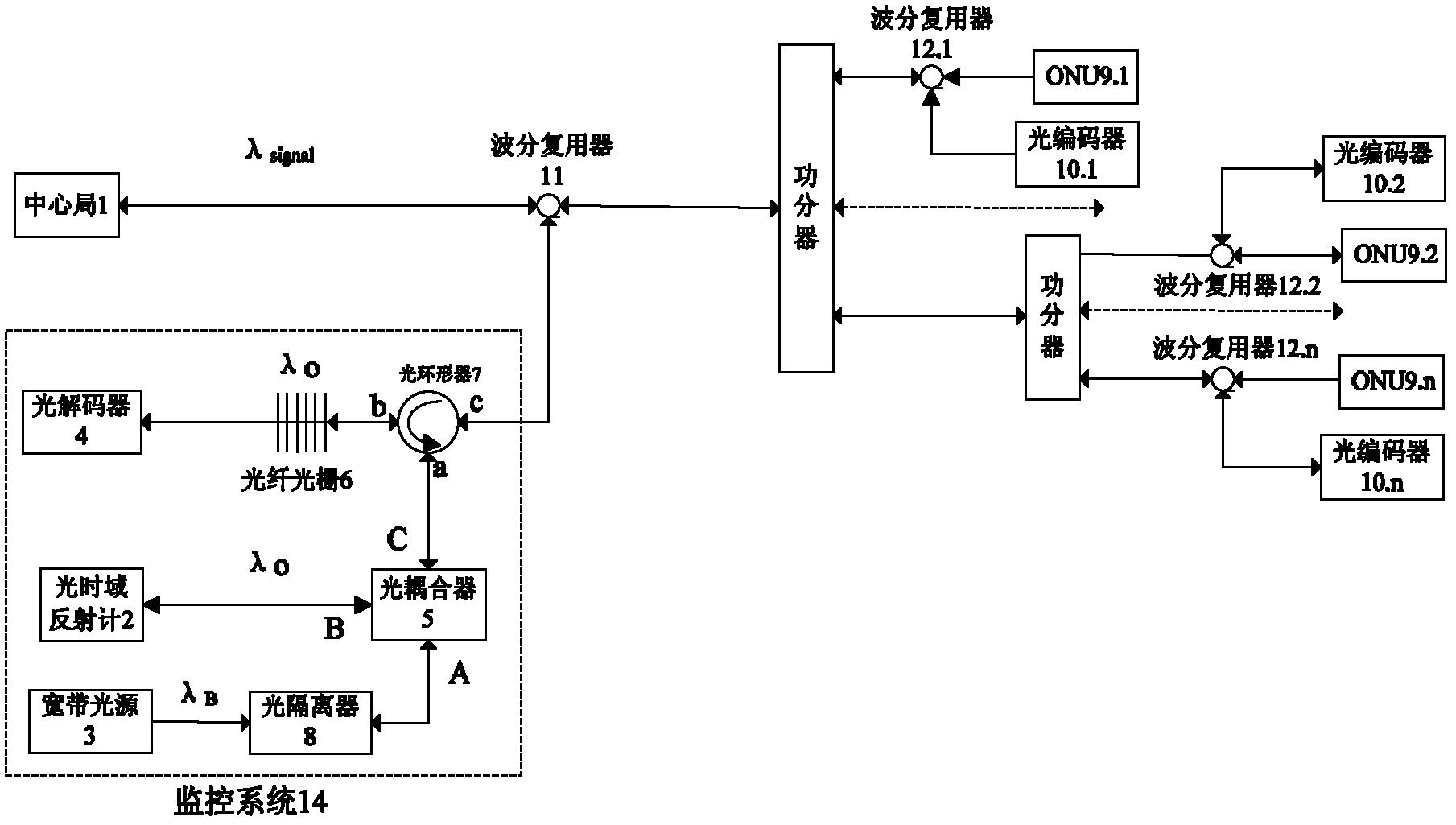
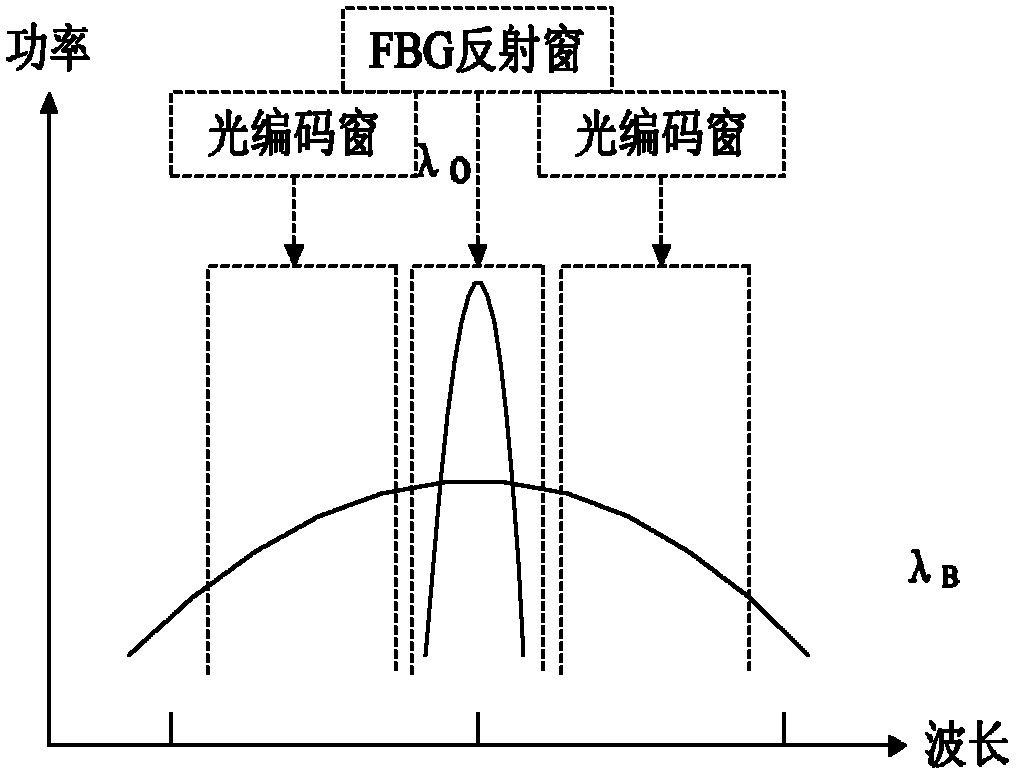
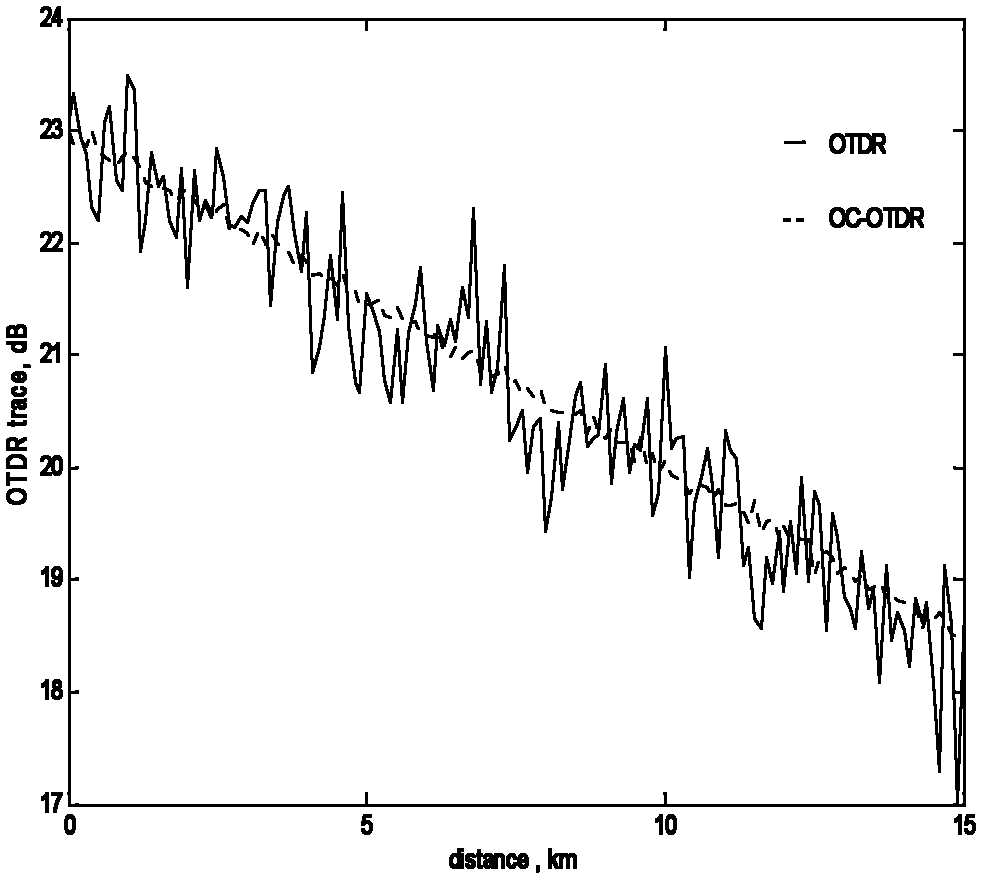
The invention provides a method and device for monitoring an optical layer of a passive optical network based on a two-dimensional optical orthogonal code. Each user is identified by using the two-dimensional optical orthogonal code. An optical encoder is added in the front of user equipment. The optical encoder performs optical encoding on a detected optical pulse and reflects an encoded optical signal to a monitoring system. The reflected optical signal is decoded in the monitoring system. The health state of each branch optical fibre is judged through the decoded signal. An optical power detection part in the monitoring system performs fault location and analysis functions simultaneously. In the invention, the link state of an optical network is monitored by adopting the passive optical device without limitation of a network topological structure and branch length. The device disclosed by the invention can identify that a fault is in the user equipment or an optical fibre link, judge the branch in which a fault is and position the specific position of the fault, and support the monitoring of the optical fibre link of the high-user-capacity passive optical network.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Modulation format with low sensitivity to fiber nonlinearity
InactiveUS6606176B1Solve narrow bandwidthImprove performanceElectromagnetic transmittersReturn-to-zeroFrequency spectrum
A method for modulating fiber optic transmissions with a low sensitivity to fiber non-linearity utilizes short pulses (typically shorter than 20 ps), and bit rates of 10 Gb / s and higher, to improve performance relative to heretofore known nonlinear transmission with Return-to-Zero (RZ) format implementations. At a base bit rate of 40 Gb / s, a distance determination for achieving 100% cumulative dispersion compensation is made, and a predetermined amount of pre-dispersion compensation is applied based on a determined distance using lower duty cycles for transmission. Higher bit rates (i.e., higher than 40 Gb / s) broaden the spectral bandwidth of the transmission and can result in no pre-dispersion compensation or negative distance pre-dispersion compensation of the same sign as the transmission fiber.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
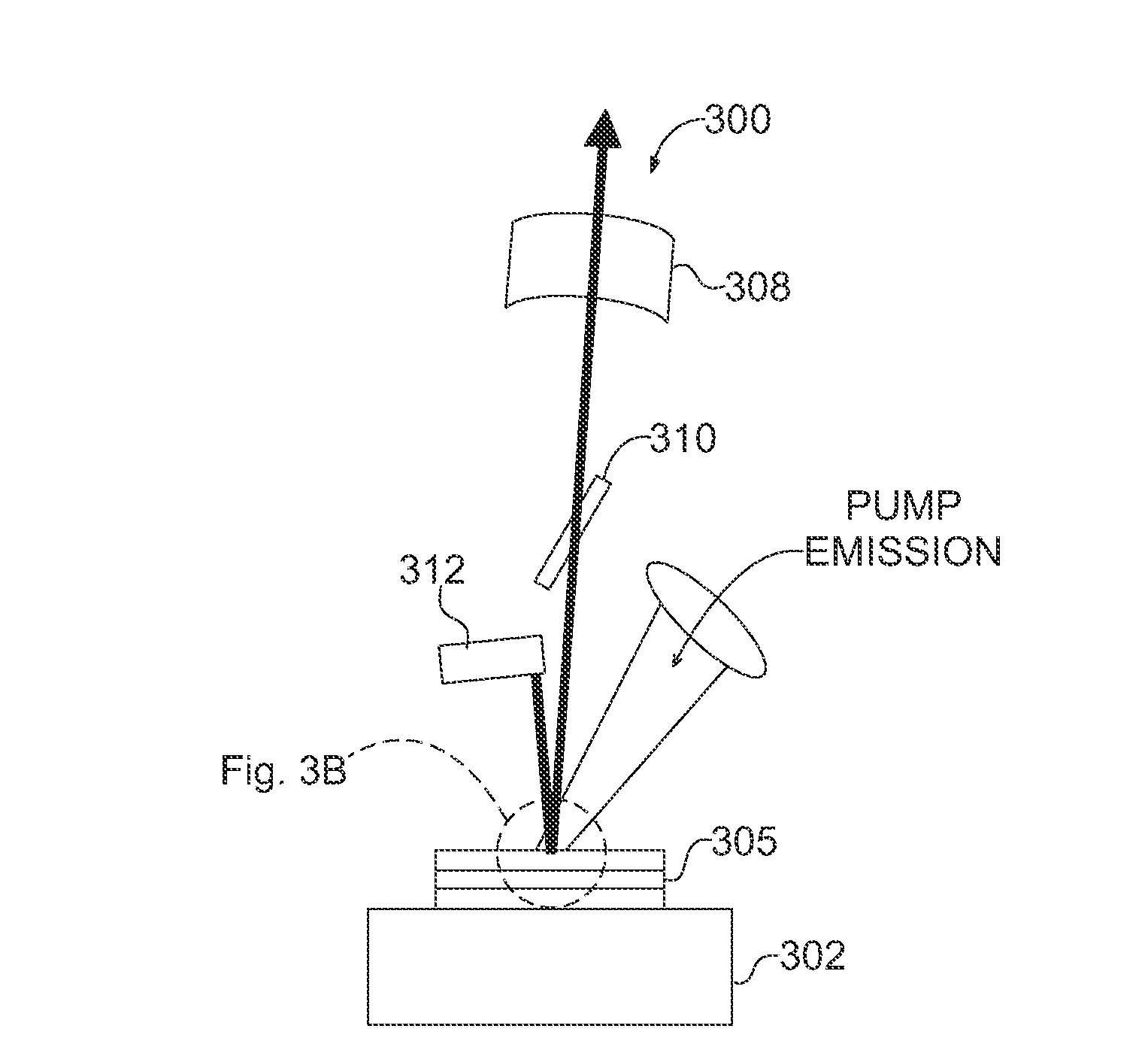
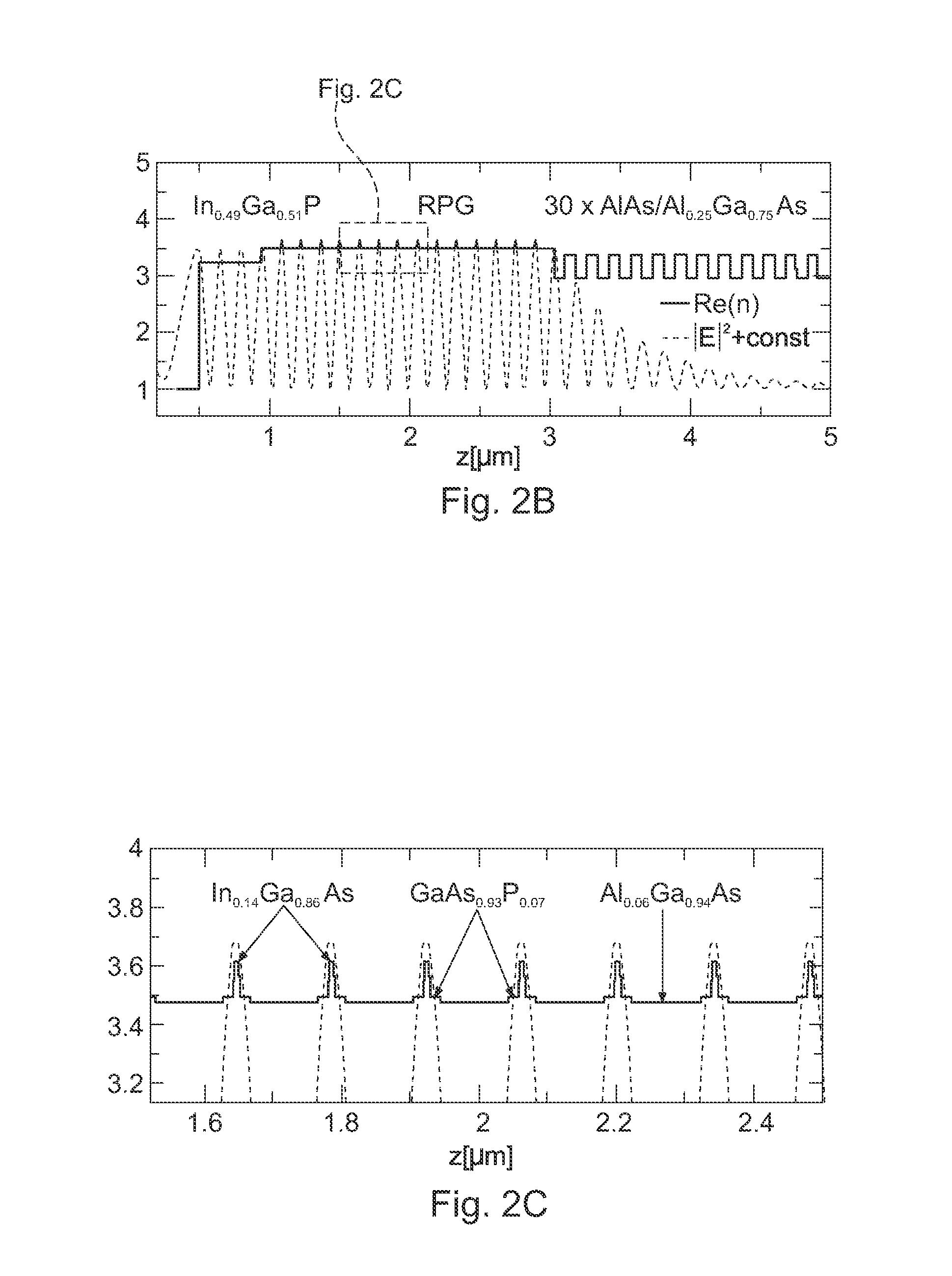
Compact coherent high brightness light source for the mid-IR and far IR
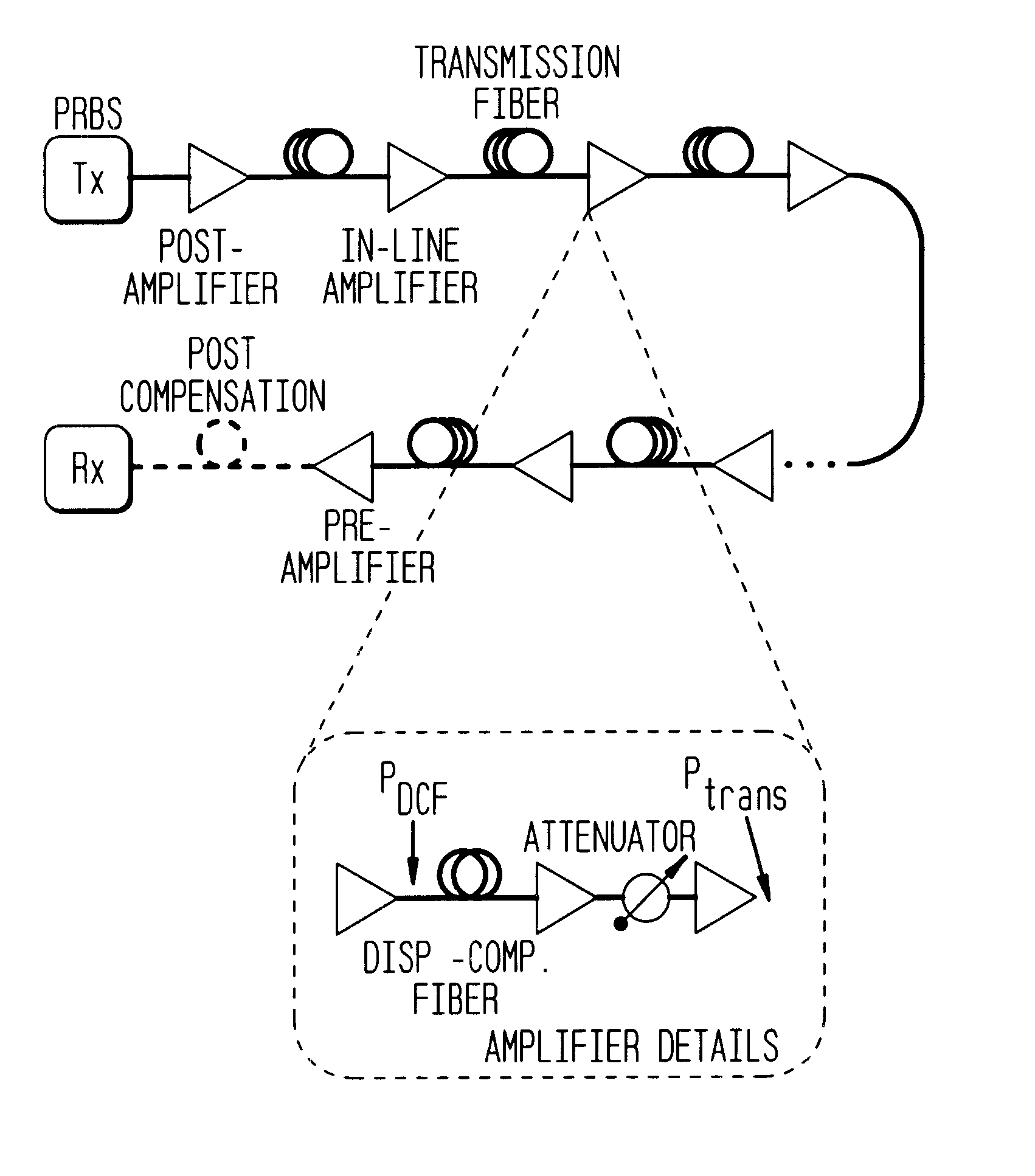
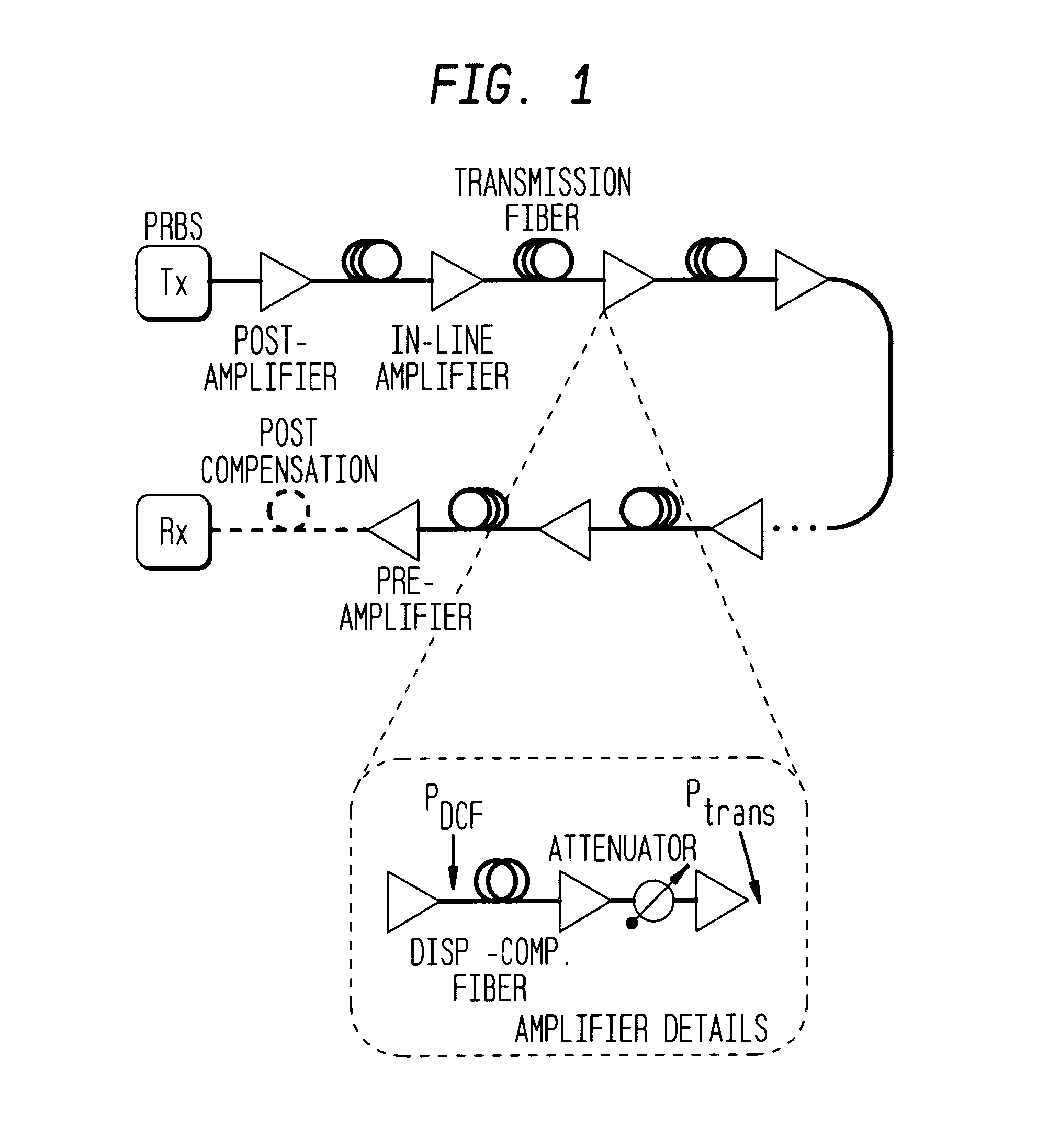
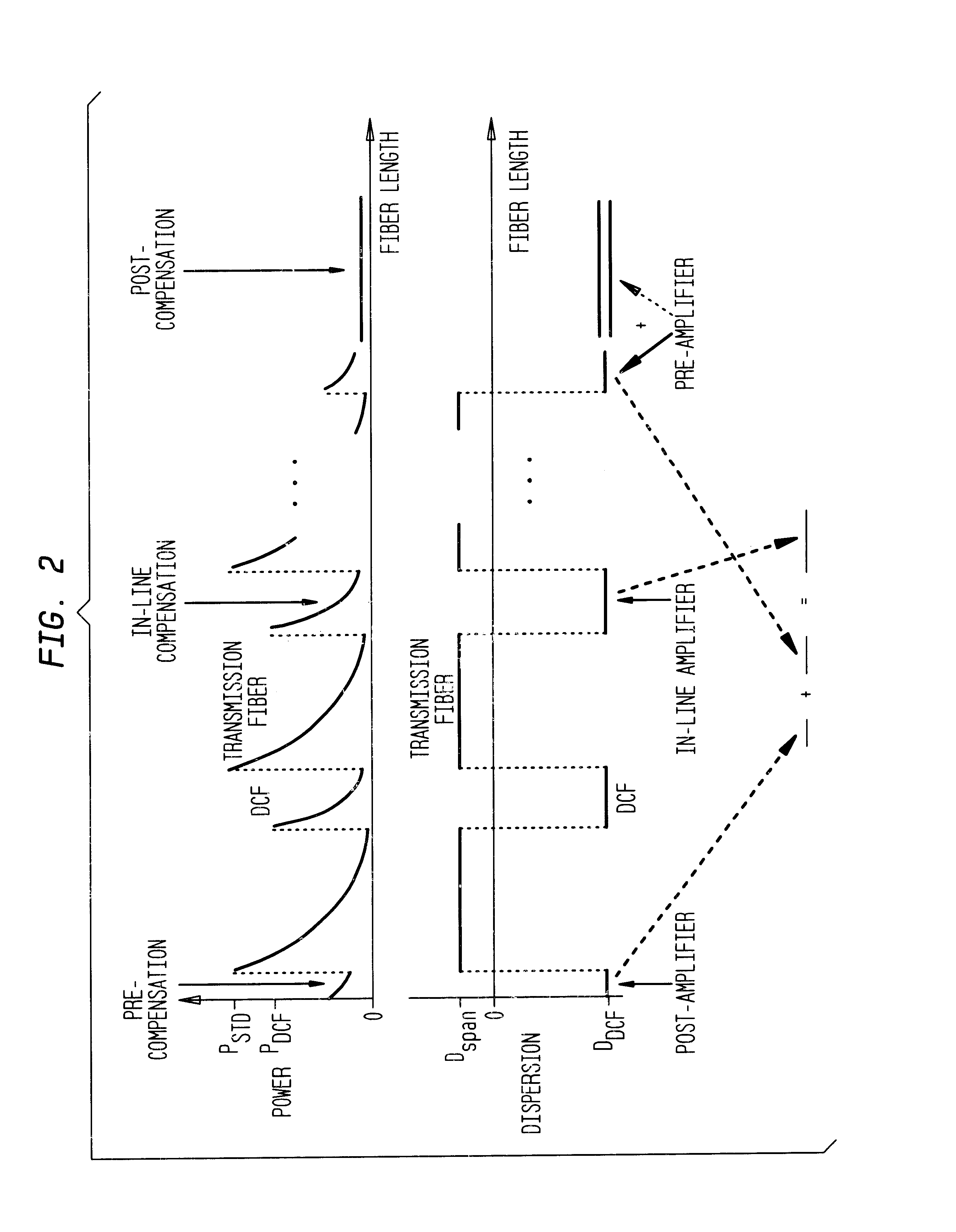
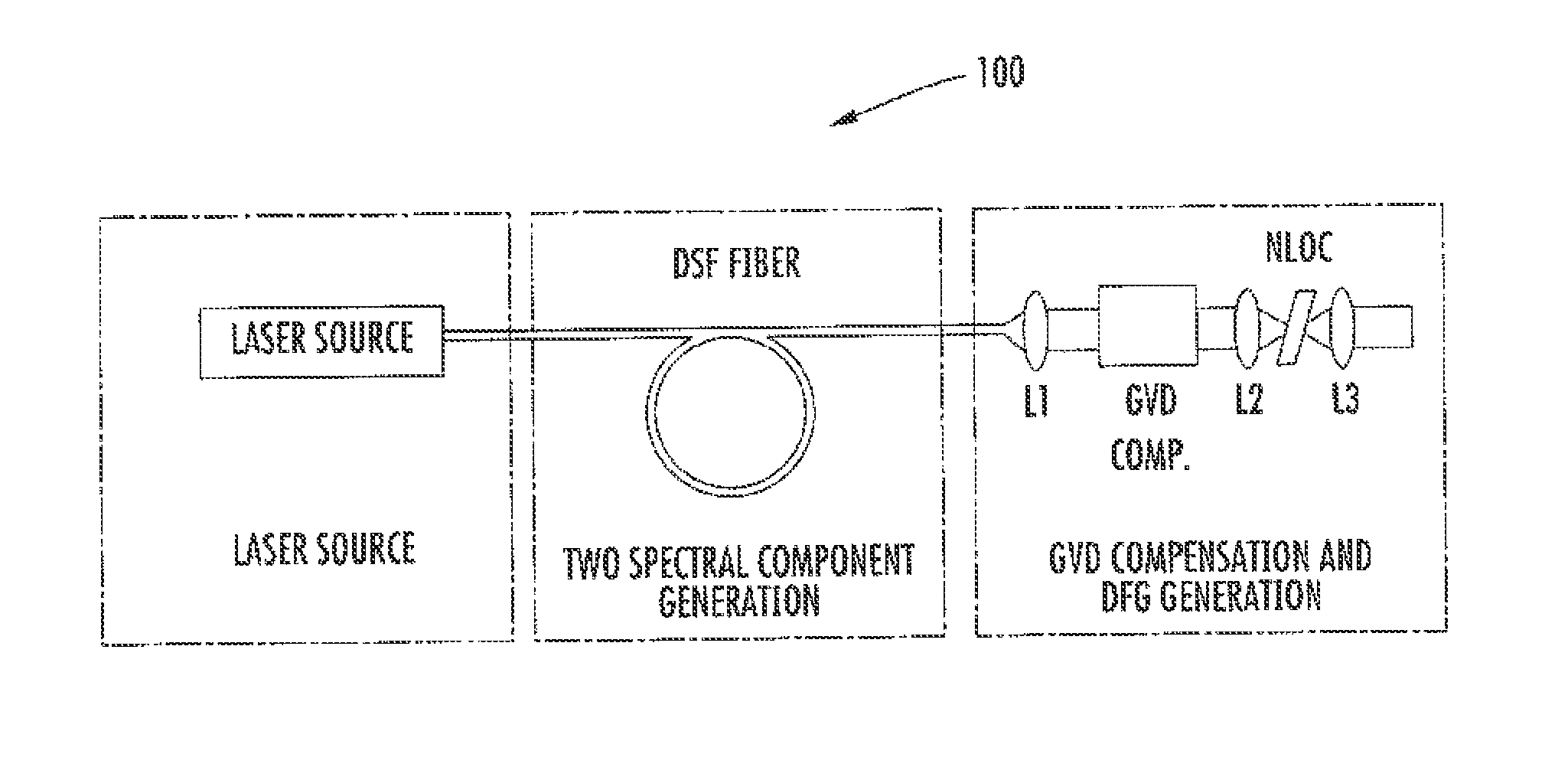
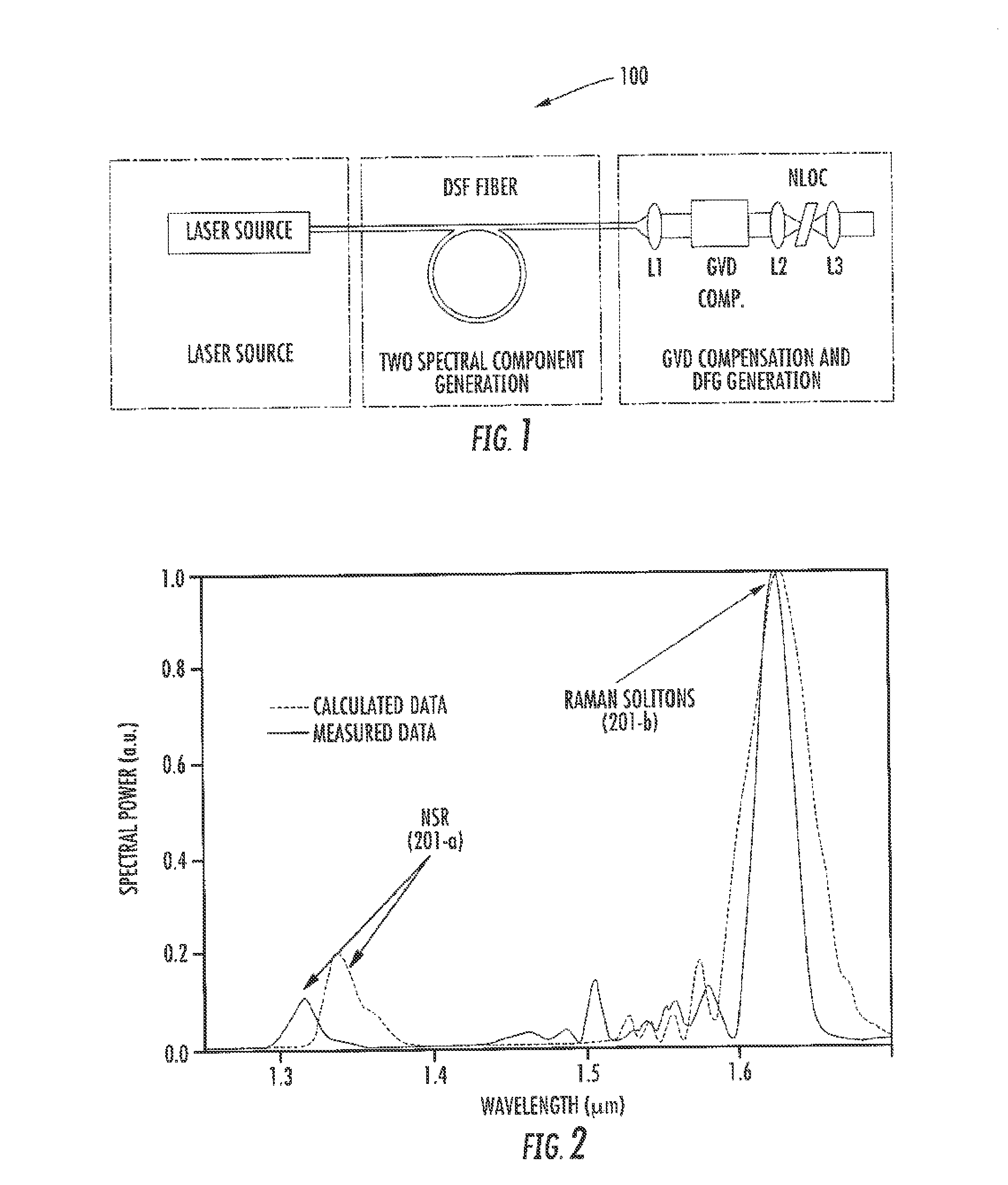
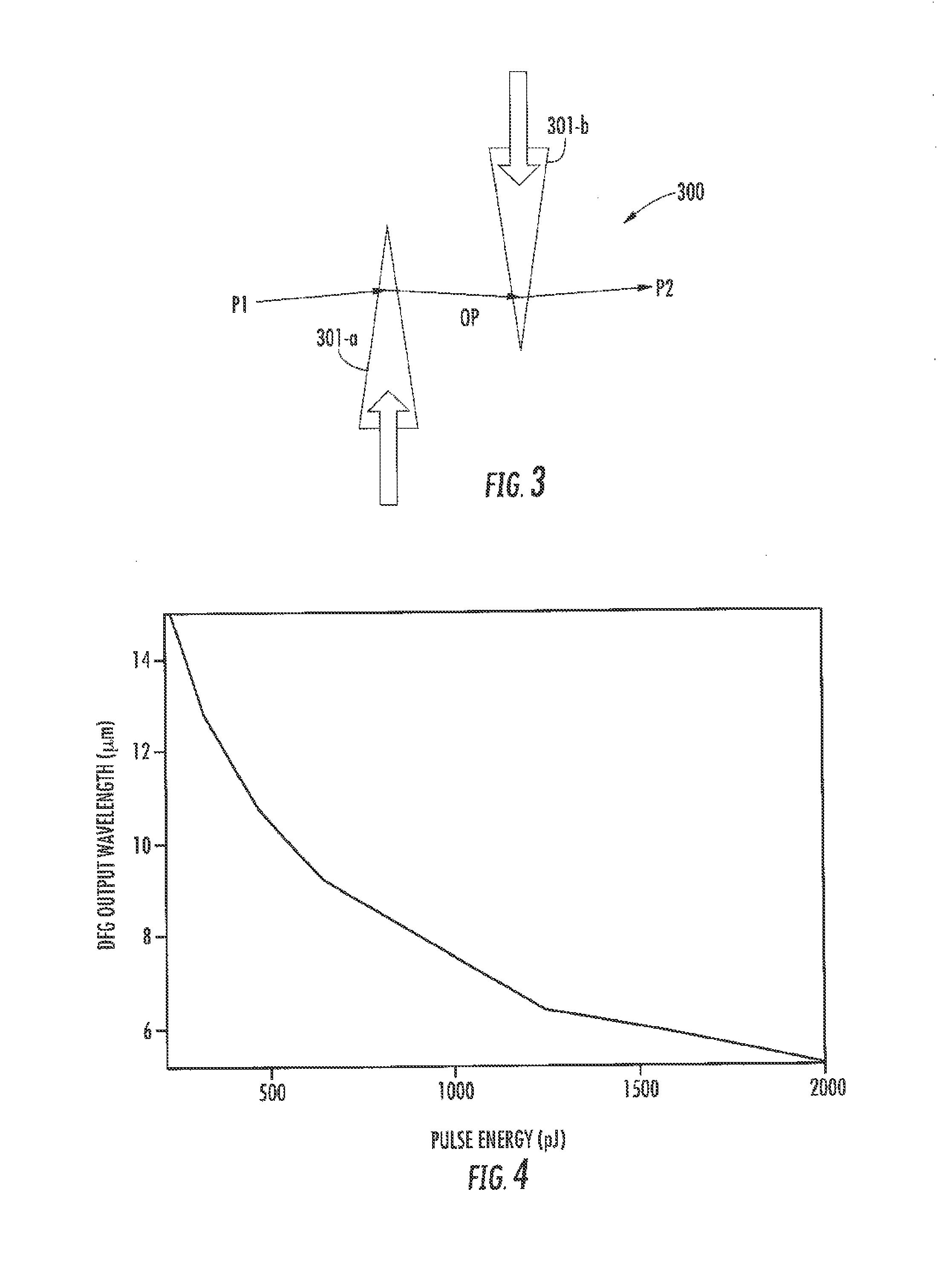
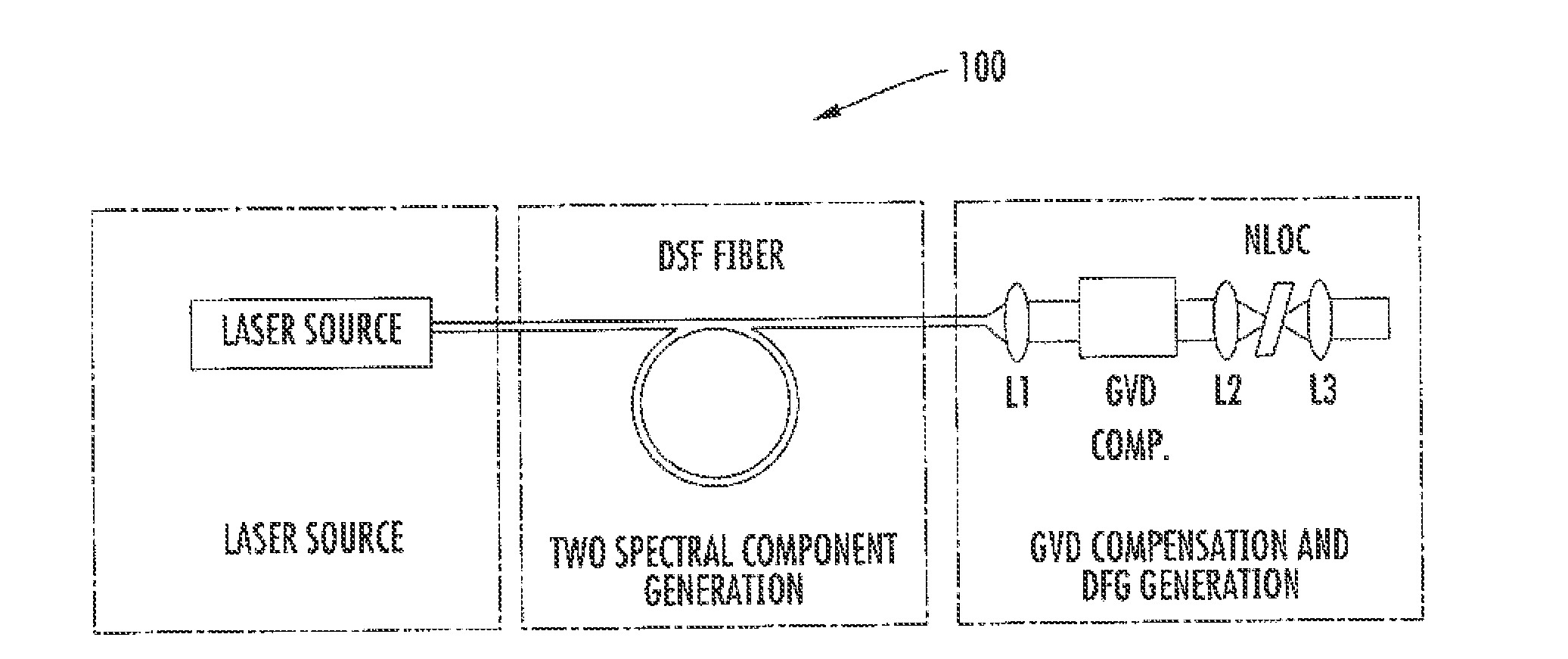
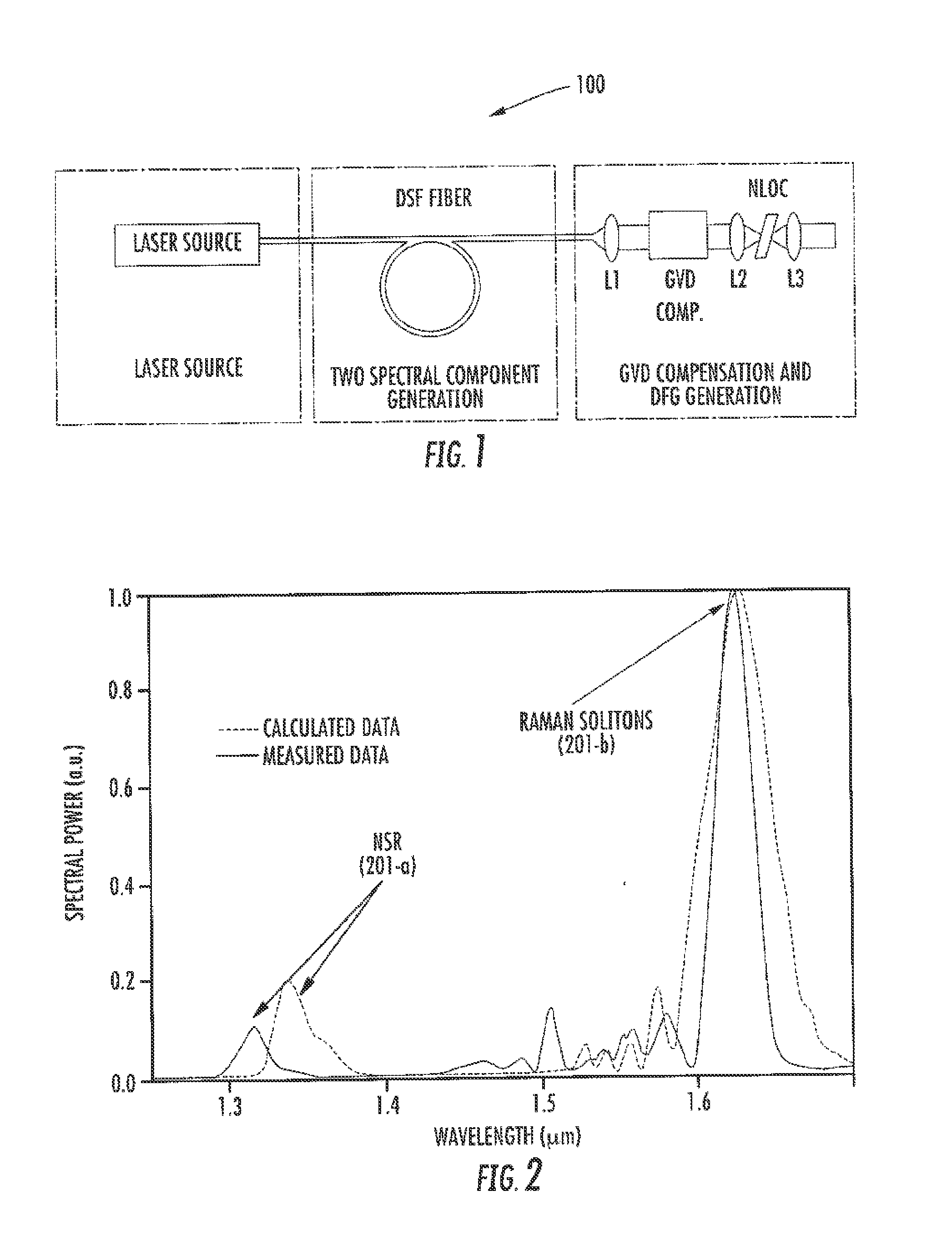
ActiveUS8861555B2Increase spectral bandwidthImprove fluencyLaser using scattering effectsCladded optical fibreMode locked fiber laserMetrology
Compact laser systems are disclosed which include ultrafast laser sources in combination with nonlinear crystals or waveguides. In some implementations fiber based mid-IR sources producing very short pulses and / or mid-IR sources based on a mode locked fiber lasers are utilized. A difference frequency generator receives outputs from the ultrafast sources, and generates an output including a difference frequency. The output power from the difference frequency generator can further be enhanced via the implementation of large core dispersion shifted fibers. Exemplary applications of the compact, high brightness mid-IR light sources include medical applications, spectroscopy, ranging, sensing and metrology.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Interpolation for four-channel color filter array
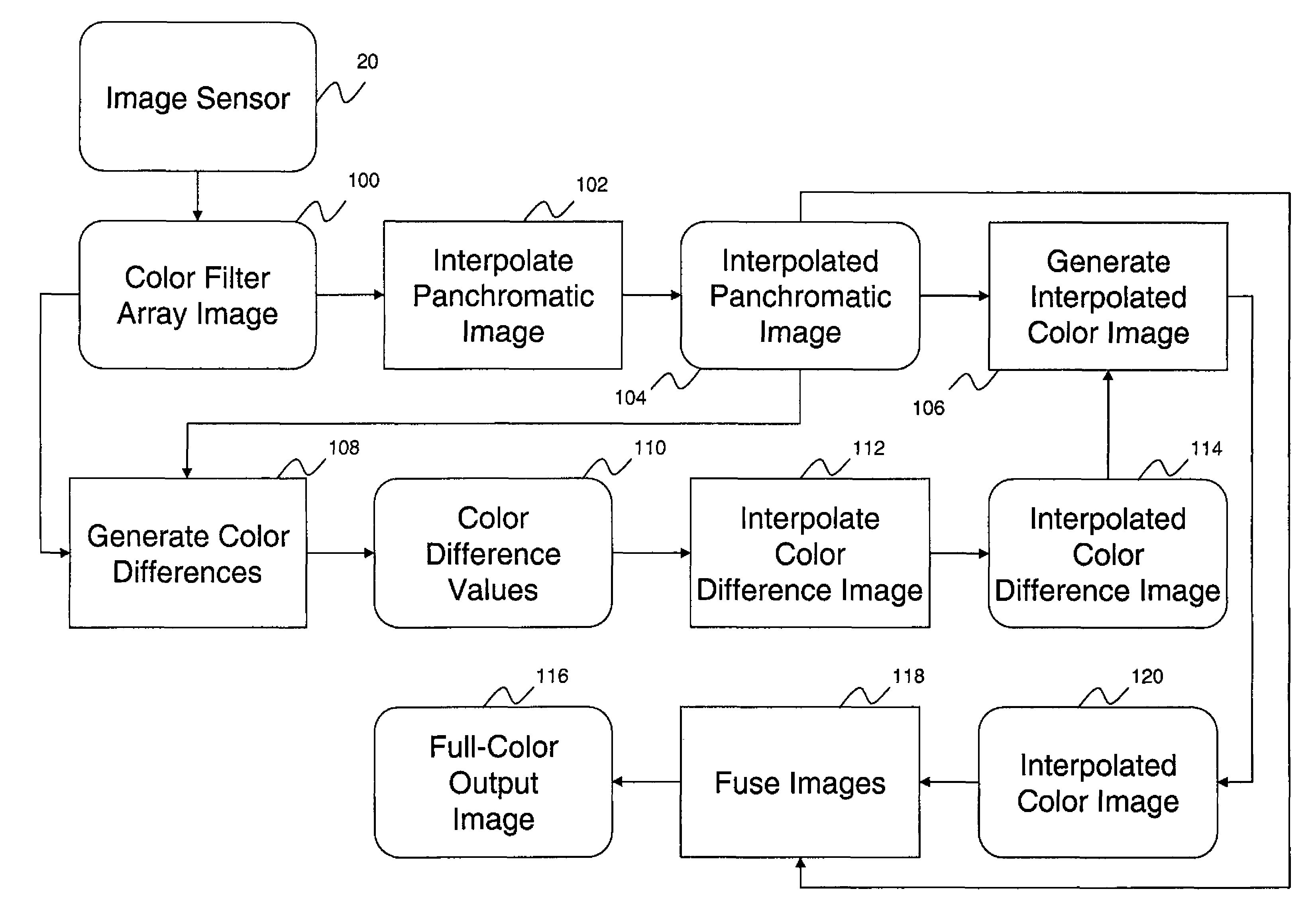
ActiveCN102461175AColor space resolution improvementsNo need to increase the percentageGeometric image transformationSolid-state device signal generatorsColor imageColor filter array
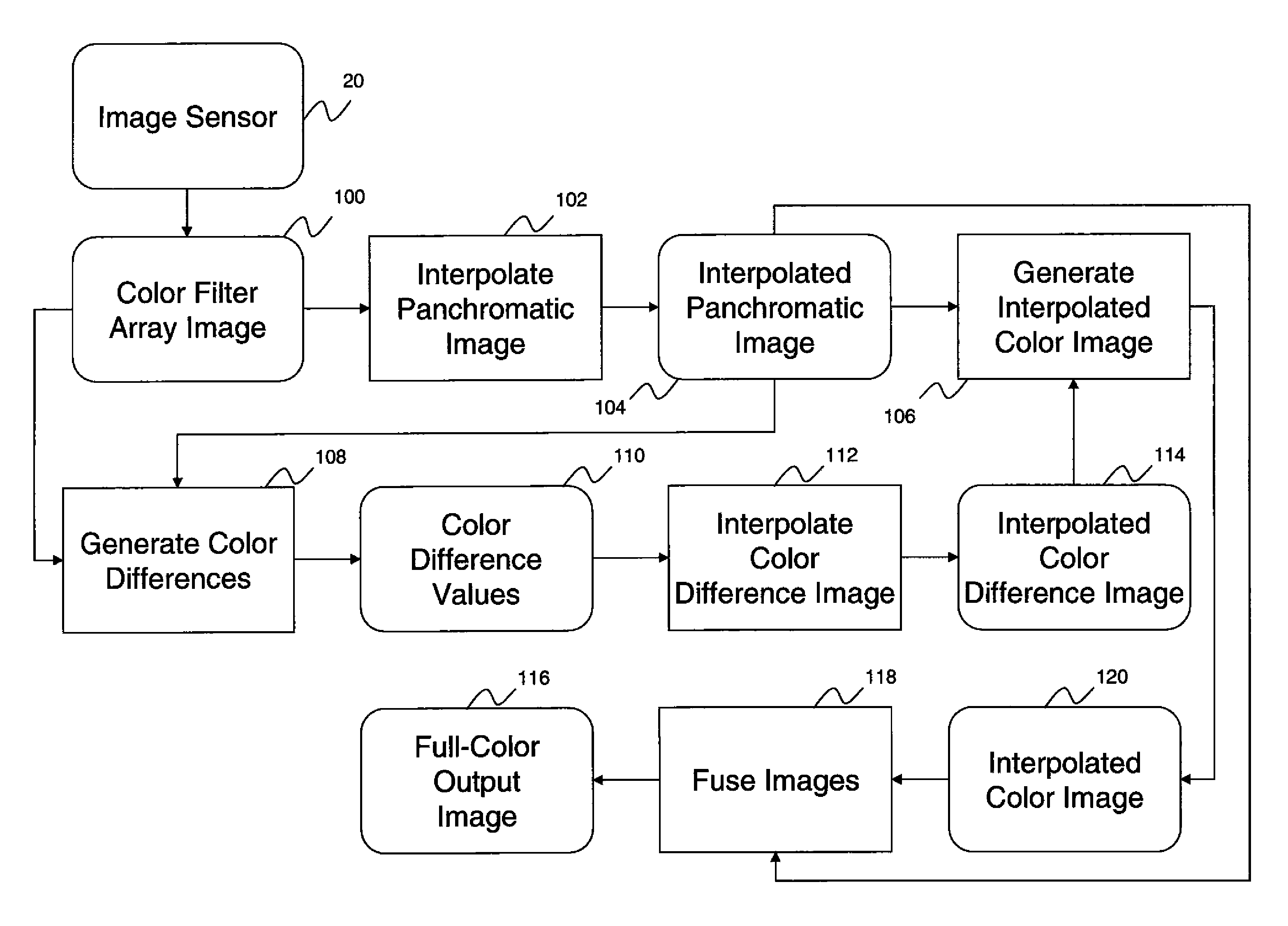
A method is described for forming a full-color output image from a color filter array image comprising capturing an image using an image sensor including panchromatic pixels and color pixels having at least two different color responses, the pixels being arranged in a rectangular minimal repeating unit wherein for a first color response, the color pixels having the first color response alternate with panchromatic pixels in at least two directions, and for each of the other color responses there is at least one row, column or diagonal of the repeating pattern that only has color pixels of the given color response and panchromatic pixels. The method further comprising, computing an interpolated panchromatic image from the color filter array image; computing an interpolated color image from the color filter array image; and forming the full color output image from the interpolated panchromatic image and the interpolated color image.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Four-channel color filter array pattern
ActiveUS8203633B2Good colorReduce colorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageDiagonal
An image sensor for capturing a color image comprising a two dimensional array of light-sensitive pixels including panchromatic pixels and color pixels having at least two different color responses, the pixels being arranged in a repeating pattern having a square minimal repeating unit having at least three rows and three columns, the color pixels being arranged along one of the diagonals of the minimal repeating unit, and all other pixels being panchromatic pixels.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Dual mode radio frequency receivers for wideband signal processing
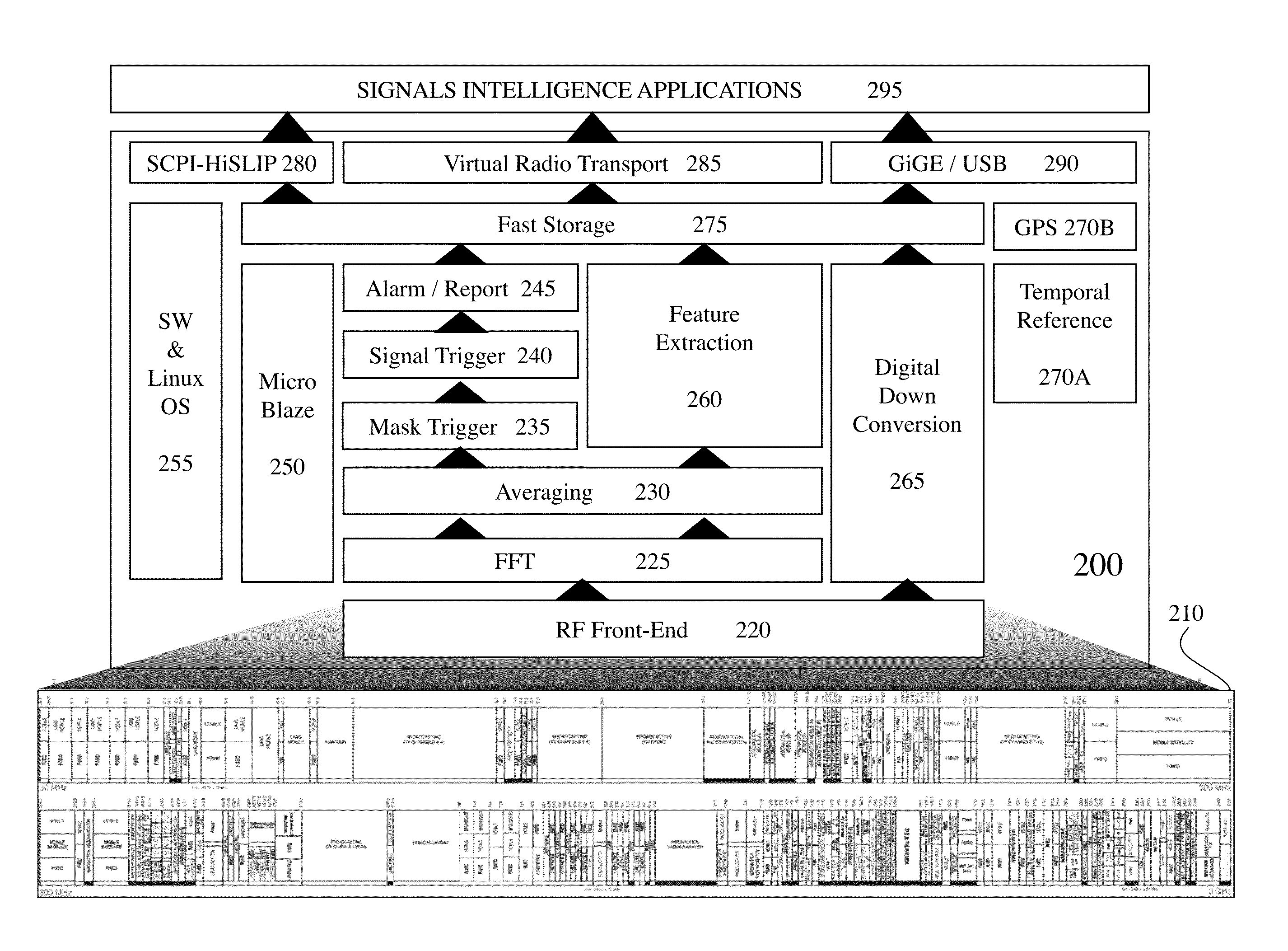
ActiveUS20140378079A1Requires minimizationIncrease spectral bandwidthRadio transmissionTuned radio frequency receiverFrequency spectrum
Wireless communication is ubiquitous today with increasing deployments leading to increased interference, increasing conflicts, etc. Monitoring the wireless environment is therefore important for regulators, service providers, Government agencies, enterprises etc. Such monitoring should be flexible both in networks monitored within the wireless environment as well as detecting unauthorized transmitters, allowing dynamic network management, etc. However, such real time spectral / signal analysis in the prior art requires both a wideband direct conversion receiver (DCR), for high performance, wideband, fast, programmable spectral analysis, and a super heterodyne receiver for fast, narrowband, programmable demodulation for signal analysis. According to embodiments of the invention a single receiver design methodology exploiting a single RF circuit to provide superheterodyne and direct conversion receiver functionalities.
Owner:THINKRF
Color filter array pattern having four-channels
ActiveUS8125546B2Good colorReduce colorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsColor imageDiagonal
An image sensor for capturing a color image comprising a two dimensional array of light-sensitive pixels including panchromatic pixels and color pixels having at least three different color responses, the pixels being arranged in a rectangular minimal repeating unit having at least eight pixels and having at least two rows and two columns, wherein for a first color response, the color pixels having the first color response alternate with panchromatic pixels in at least two directions, and for each of the other color responses there is at least one row, column or diagonal of the repeating pattern that only has color pixels of the given color response and panchromatic pixels.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Double chirped spectrum optical parametric amplifier and amplification method
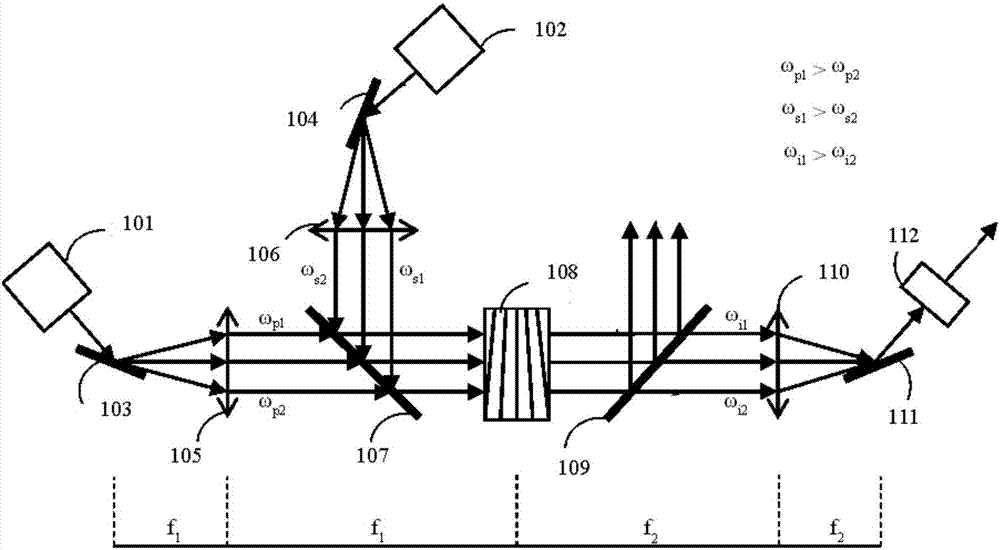
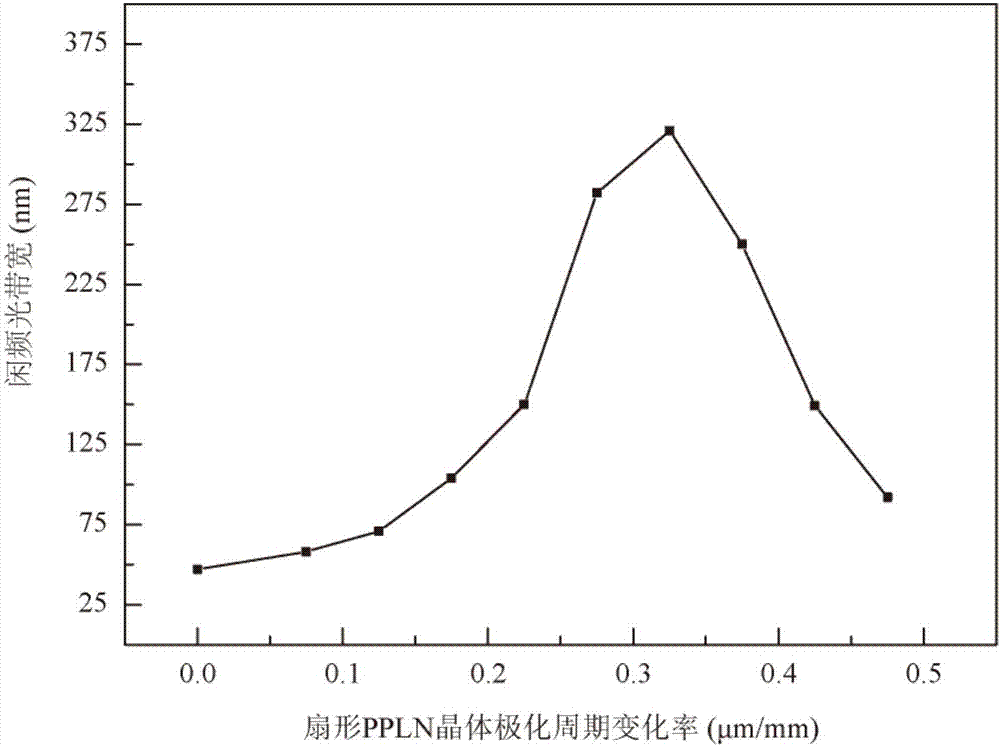
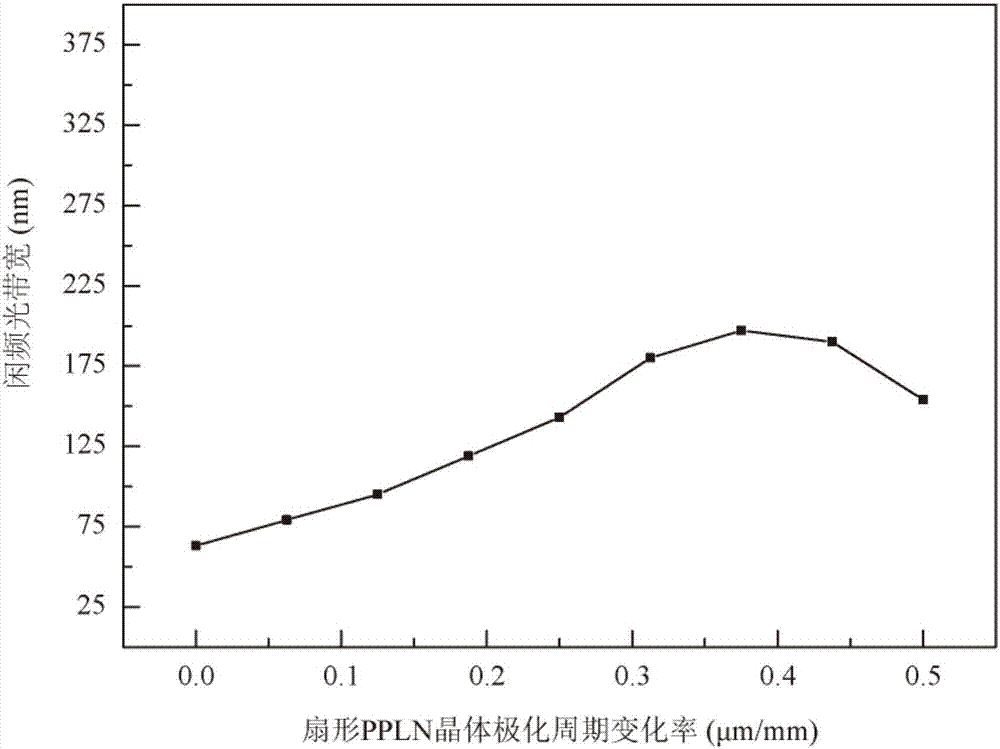
ActiveCN107247380AIncrease spectral bandwidthSatisfy the phase matching conditionNon-linear opticsChirp spectrumVIT signals
The invention is applicable to the technical field of laser and provides a double chirped spectrum optical parametric amplifier and an amplification method. The double chirped spectrum optical parametric amplifier is characterized in that pump light and signal light in time synchronization are generated by a femtosecond laser component and independently pass through an input grating and an input collimating lens to make different spectral components of the signal light and the pump light linearly dispersively focused on respective focal points to realize spatial chirps opposite in frequency change rate signs in focal planes; then on the basis of sector-shaped periodic polar crystal, efficient full-spectrum optical parametric amplification of the signal light is completed through the pump light, and broadband-spectrum idler-frequency light is generated; finally, a spectroscope is adopted for separating out the broadband-spectrum idler-frequency light, Fourier transformation from a spectral domain to a time domain is completed through an output collimating lens and an output grating, and necessary dispersion compensation is performed to obtain long-wavelength ultra-short pulse laser. The optical parametric amplifier is simple in structure, and the long-wavelength ultra-short pulse laser can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Fiber Optic Sensor Utilizing Broadband Sources
ActiveUS20110007313A1Increase spectral bandwidthEfficient use ofRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationCelluloseMoisture
Fiber optic sensors employ a high brightness light source such as a fiber optic supercontinuum source, multiplexed superluminescent light emitting diodes, or a broadband tunable laser diode. Light is delivered to the measurement location via fiber optics and sensor optics directs infrared radiation onto material the being monitored that is located in a hostile environment. A disperse element is positioned in the detection beam path in order to separate the wavelengths and to perform spectral analysis. A spectral analysis of the radiation that emerges from the sheet yields information on a plurality of parameters for the material. For papermaking applications, the moisture level, temperature and cellulose content in the paper can be obtained.
Owner:HONEYWELL ASCA INC
Device for concentrating optical radiation
InactiveCN1358333AReduce coolingFlexible designSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersOptical radiationTotal internal reflection
Owner:TERRASUN LLC
Reduction of pulse width by spectral broadening in amplification stage and after amplification stage
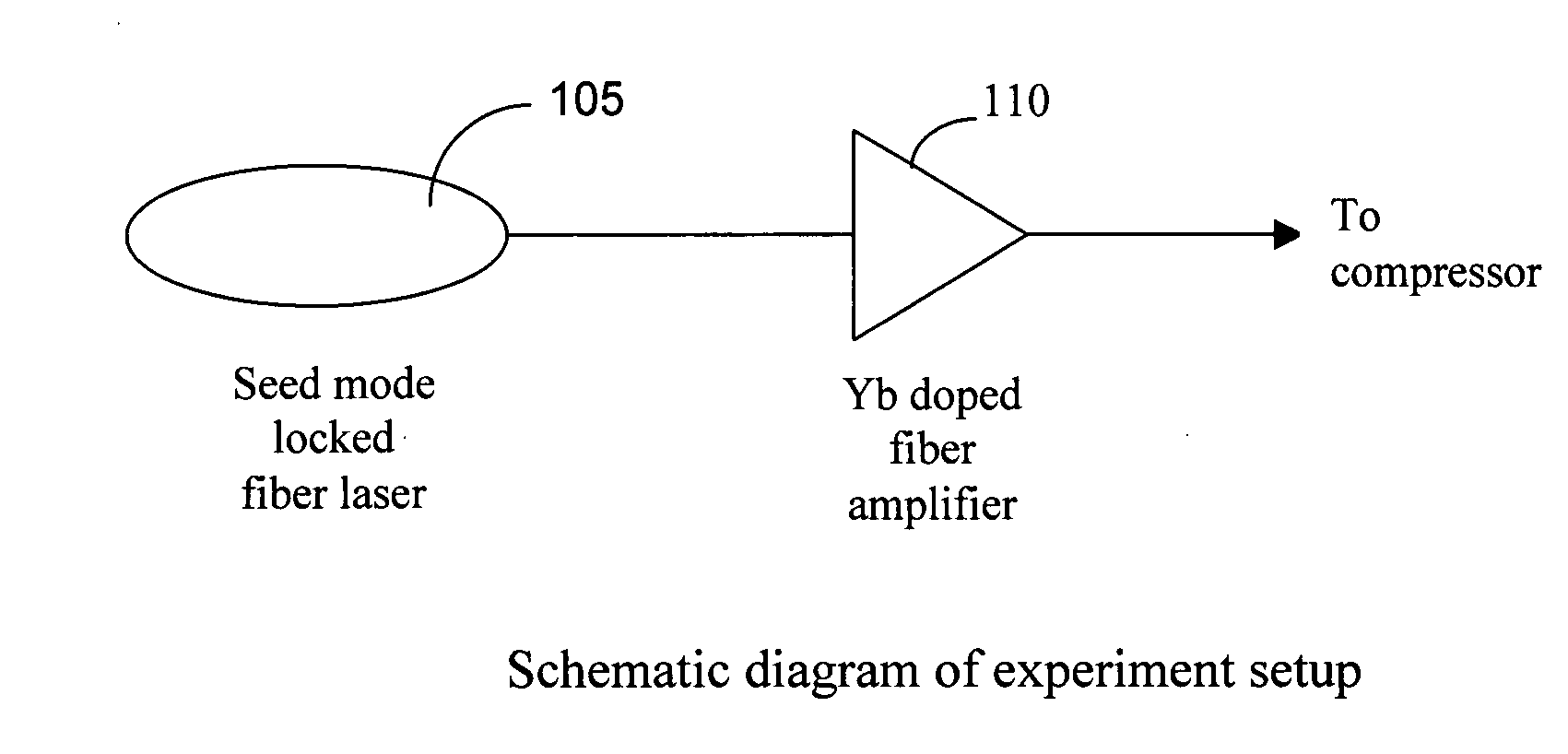
ActiveUS20070177643A1Reduce widthIncrease spectral bandwidthLaser using scattering effectsFiberAudio power amplifier
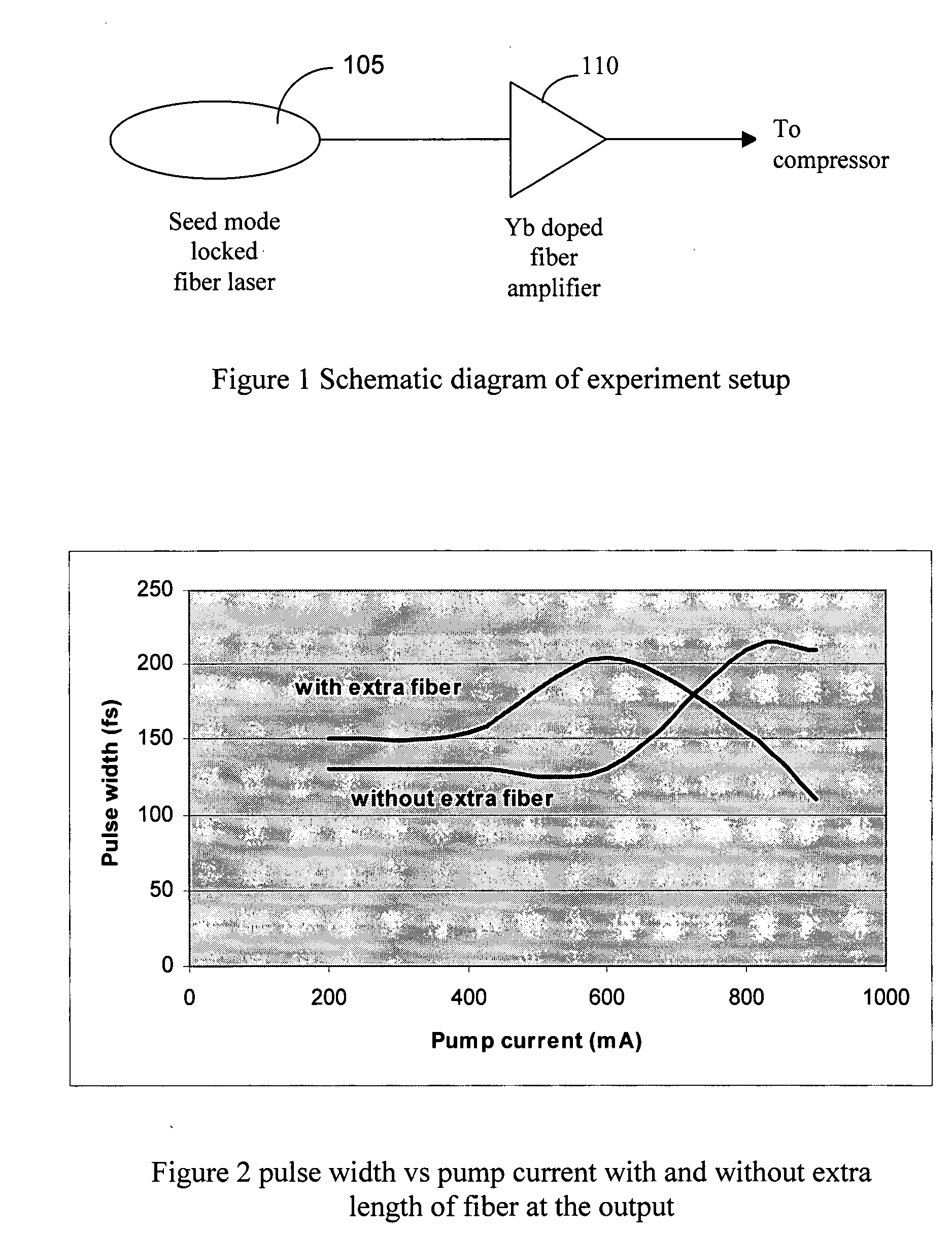
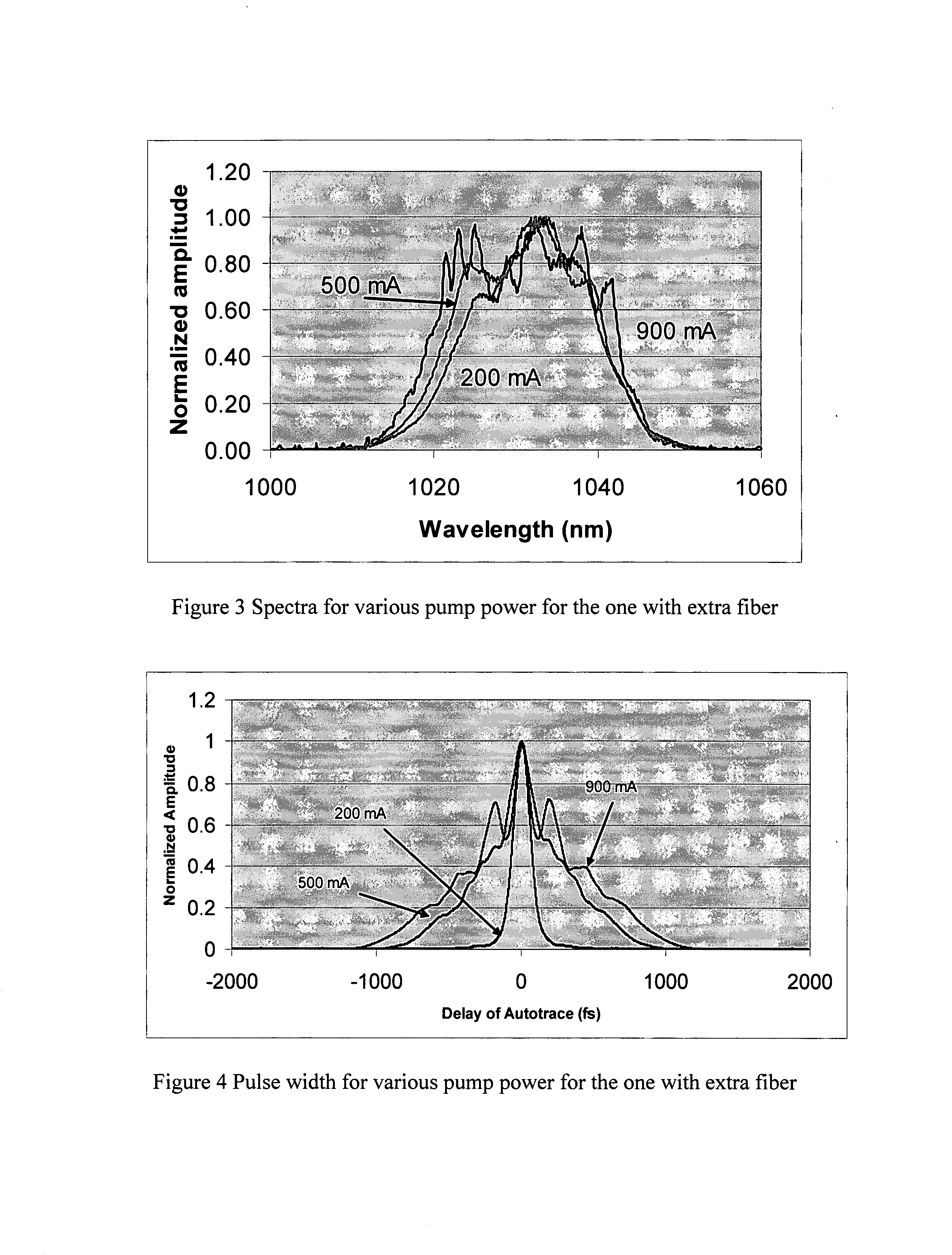
This invention discloses a fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) laser system. The system includes a fiber mode-locking oscillator for generating a seed laser. The laser system further includes a stretching stage for stretching the seed laser for projecting to an Yb doped amplifier. The Yb doped amplifier is implemented for taking advantage of a self phase modulation (SPM) to broaden a spectrum whereby an amplification of the laser pulse is without narrowing down the spectrum. The amplifier has a gain spectrum corresponding to a broaden spectrum by taking advantage of the SPM in the amplifier. The amplifier is further connected to an output fiber having a predefined length with a predefined level of SPM for broadening a spectrum.
Owner:POLARONYX
Chirp laser pulse frequency spectrum shaping system based on angular spectral dispersion
PendingCN108281877AHigh energyEnergy amplificationLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersEnergy transferFrequency spectrum
The invention provides a chirp laser pulse frequency spectrum shaping system based on angular spectral dispersion, and relates to the technical field of laser pulse amplification. The chirp laser pulse frequency spectrum shaping system based on angular spectral dispersion comprises a chromatic dispersion module, an optical parameter conversion module, an optical delay module and a reflection module. After chirp laser pulse with frequency spectra to be shaped passes the chromatic dispersion module, light with different frequencies is dispersed by the chromatic dispersion module and then entersthe optical parameter conversion module by different incident angles, pump light pulse sequentially passes the optical delay module and the reflection module and then enters the optical parameter conversion module by incident angles non-collinear with the chirp laser pulse, the chirp laser pulse and the pump light pulse are subjected to energy transfer in the optical parameter conversion module and transmitted by the optical parameter conversion module to shape the frequency spectra of the chirp laser pulse, and the technical problems of low use rate of signal light energy, poor relative use flexibility and the like of a chirp laser pulse frequency spectrum shaping system in the prior art are relieved.
Owner:CHENGDU NORMAL UNIV
System and method for extending spectral bandwidth of an audio signal
ActiveUS7756714B2Increase spectral bandwidthEnhanced signalSpeech analysisFrequency spectrumLimited speech
A system is provided for extending the spectral bandwidth of a bandwidth limited audio signal by applying a nonlinear function to the bandwidth limited speech signal to generate the low frequency audio signal components that were attenuated in the bandwidth limited audio signal.
Owner:CERENCE OPERATING CO
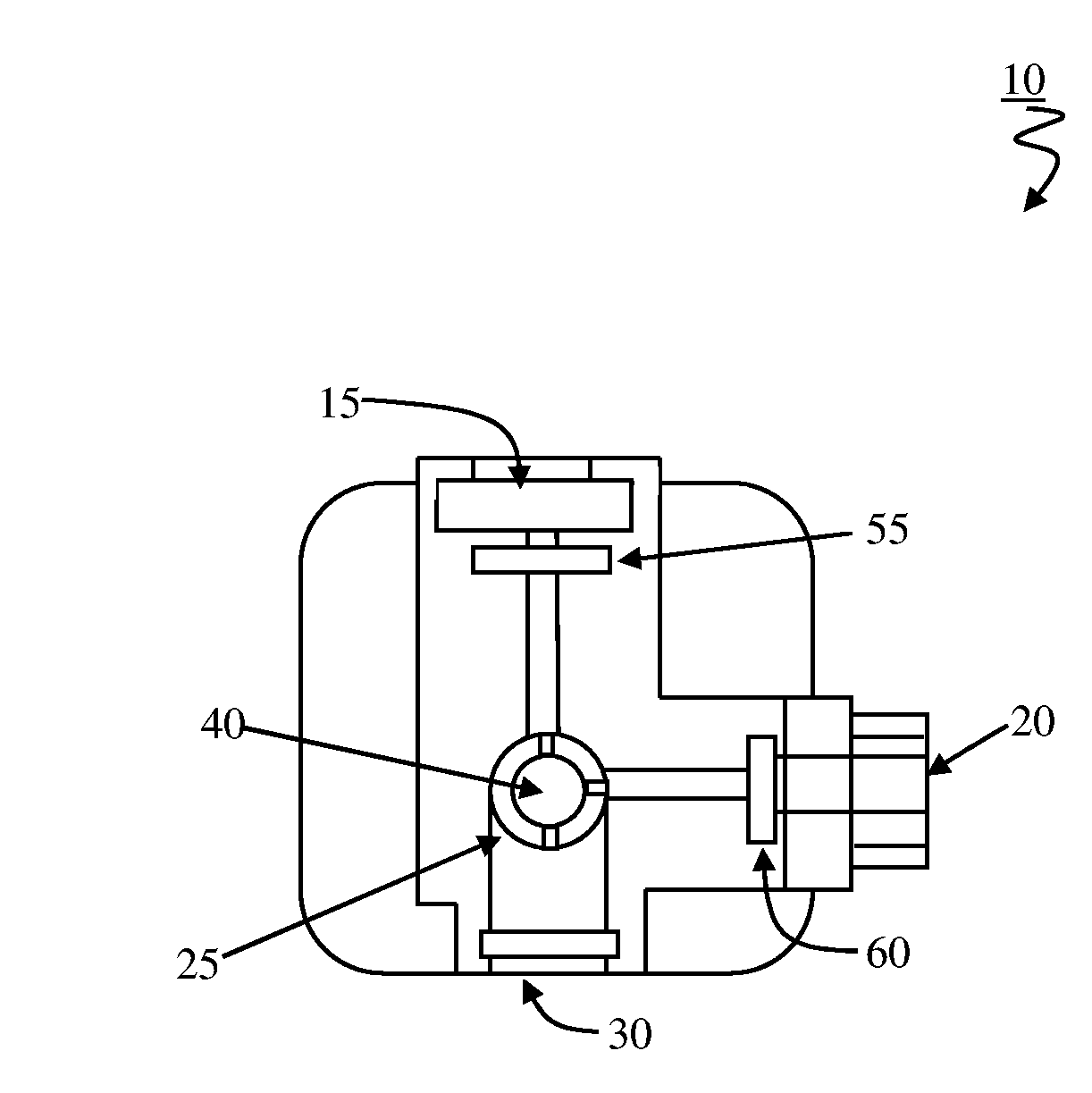
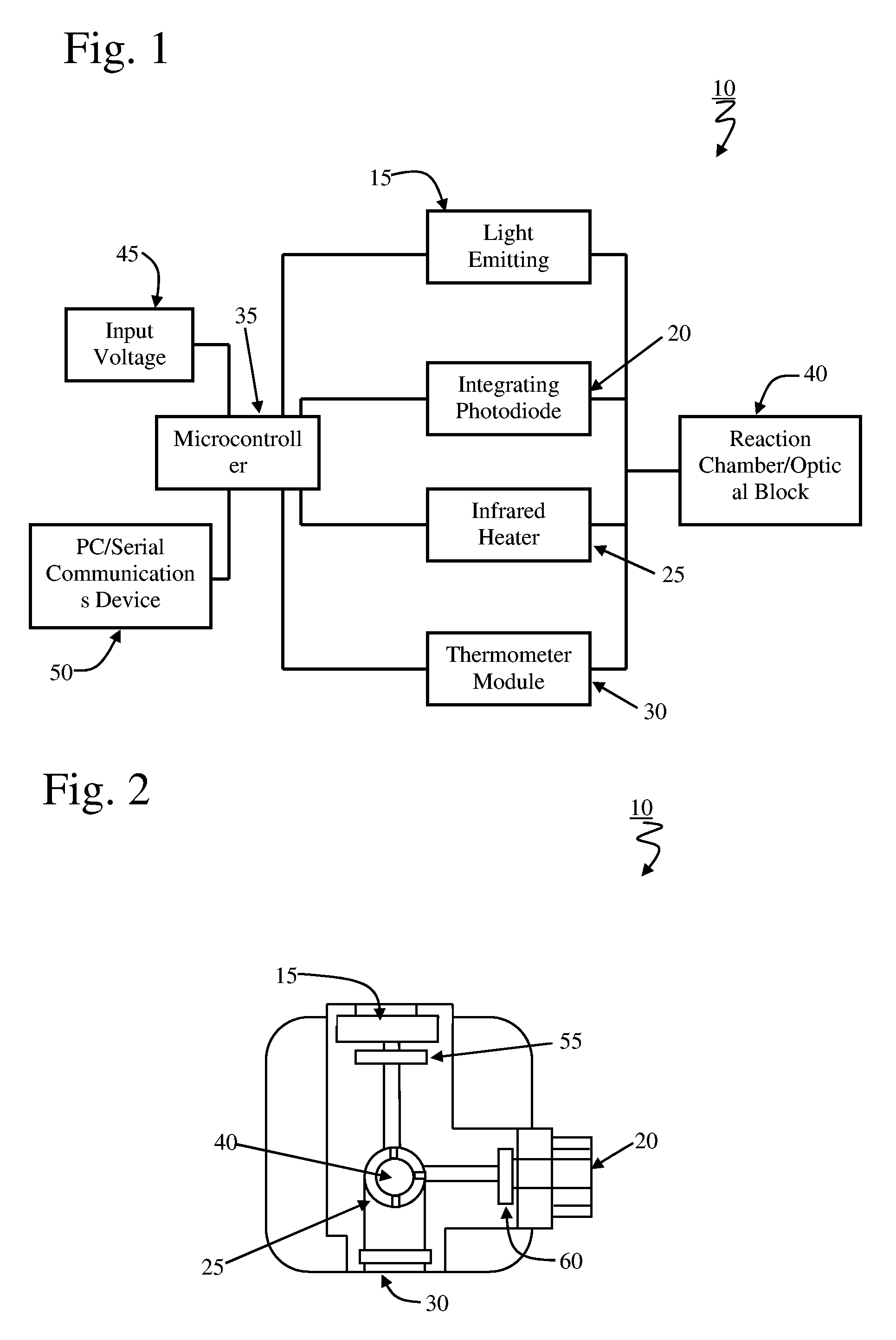
Low thermal mass fluorometer
InactiveUS7186989B2Low costImprove heat distributionPhotometryLuminescent dosimetersReal time analysisPhotodetector
The present invention provides core technologies necessary for a portable, low cost, thermal-regulating LED-based handheld fluorometer. The regulated fluorometer is based on a low thermal mass infrared heater, and an orthogonal geometry LED based filter fluorometer. Power is supplied through an external power supply and data is collected in real-time through standard serial interfaces of personal computers or personal digital assistants. Thermal regulation is automatically maintained using temperature sensor feedback control. Optical excitation relies on LED light source(s) and optical detection is through an adjustable integrating photodetector. Such a handheld system can allow applications requiring temperature sensitive photometric measurements for real time analyte detection to be performed in the field.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
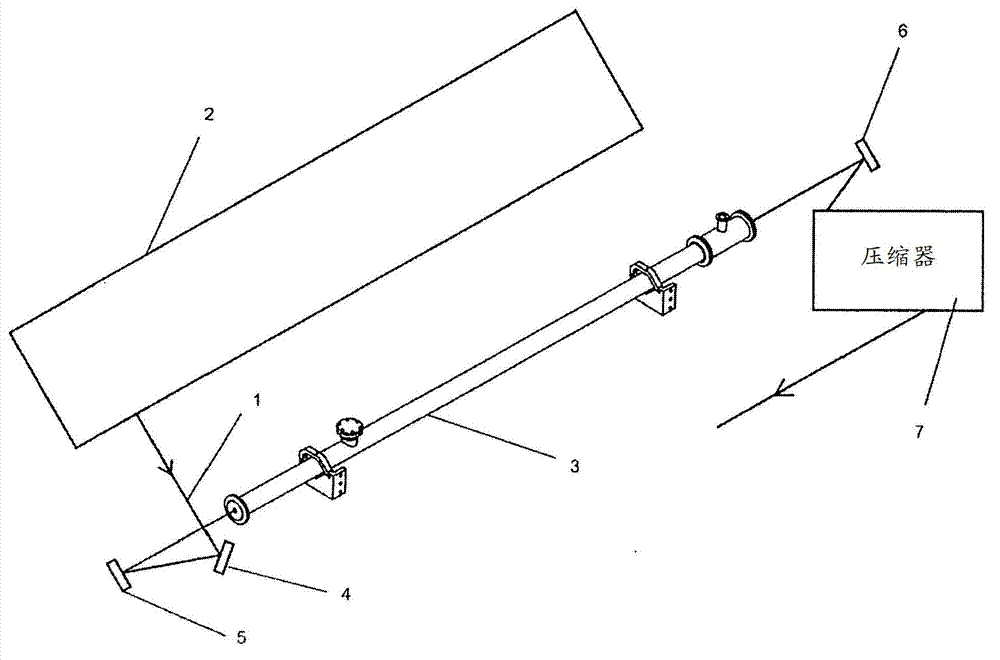
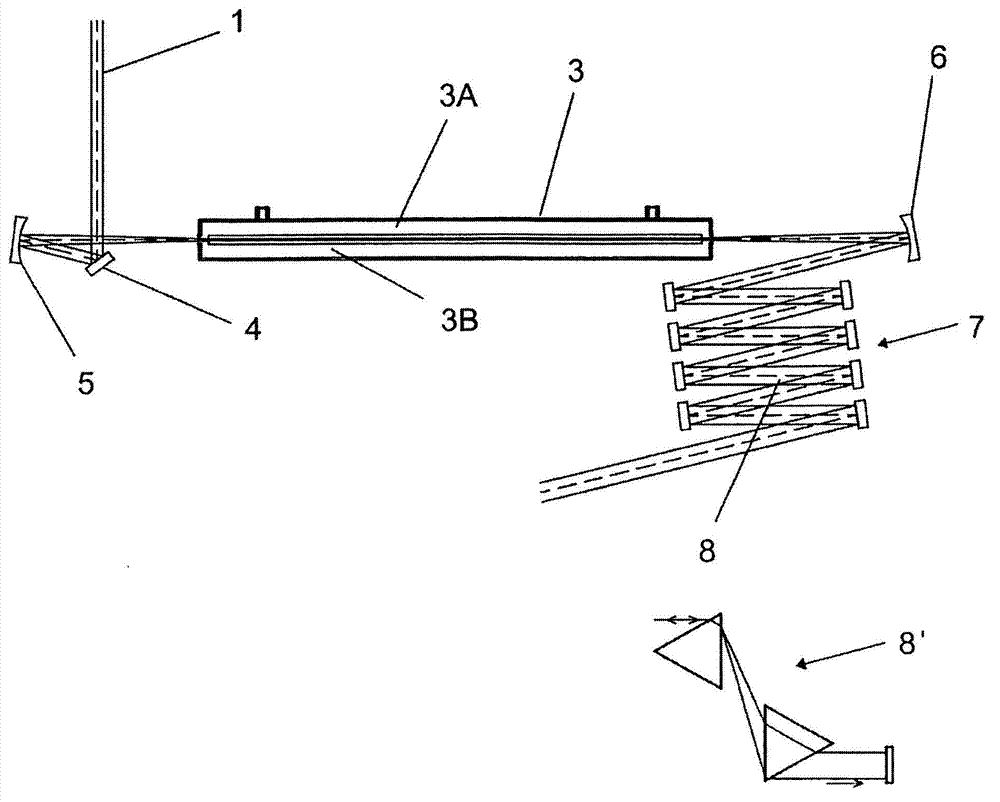
A device for increasing the spectral bandwidth of optical pulses as well as an arrangement and a method for reducing the duration of optical pulses with the use of such a device
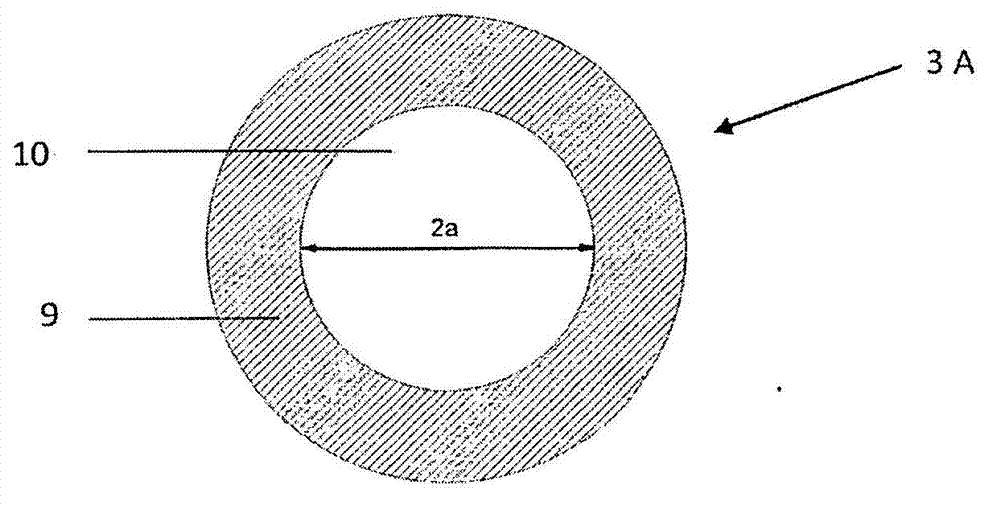
ActiveCN102959465AIncrease spectral bandwidthShort durationLaser detailsNon-linear opticsFiberLight beam
A device for increasing the spectral bandwidth of optical pulses, comprises a hollow fiber waveguide (3A), optical components (5; 6) for focusing the beam (1) into the hollow fiber waveguide (3A) and for recollimating the beam at the exit of the hollow fiber waveguide, the hollow fiber waveguide (3A) being contained in an air-tight chamber (3B) filled with a gas at a given pressure; the length of the hollow fiber (3A) is such that, for a given input pulse energy and gas pressure, the energy contained in a fundamental propagation mode of the optical pulses that has minimum propagation losses exhibits substantially periodic oscillations over the full length (Lf) of the hollow fiber waveguide (3A) and reaches a local maximum at the output end (13) of the said hollow fiber waveguide.
Owner:HIGH Q LASER
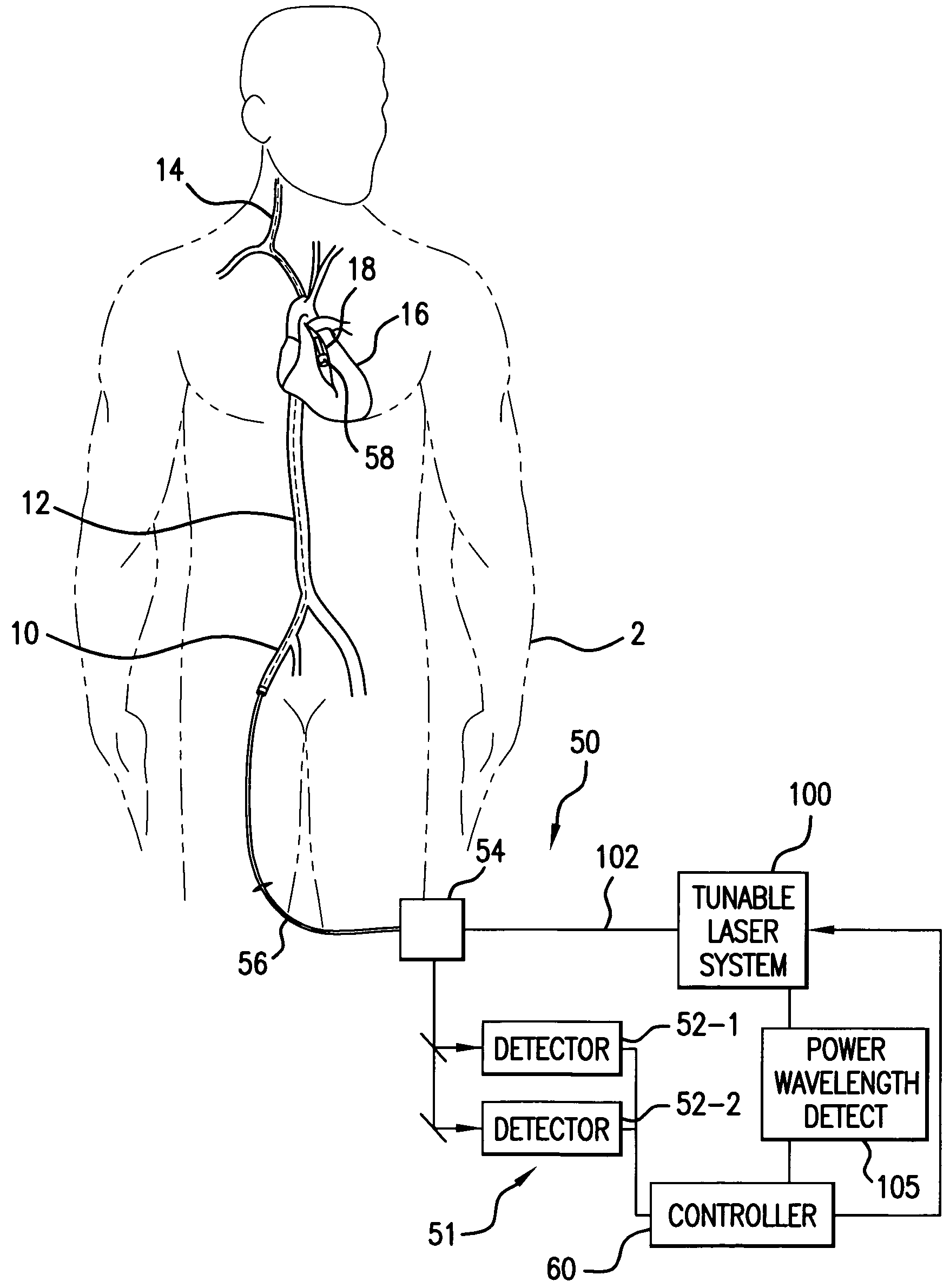
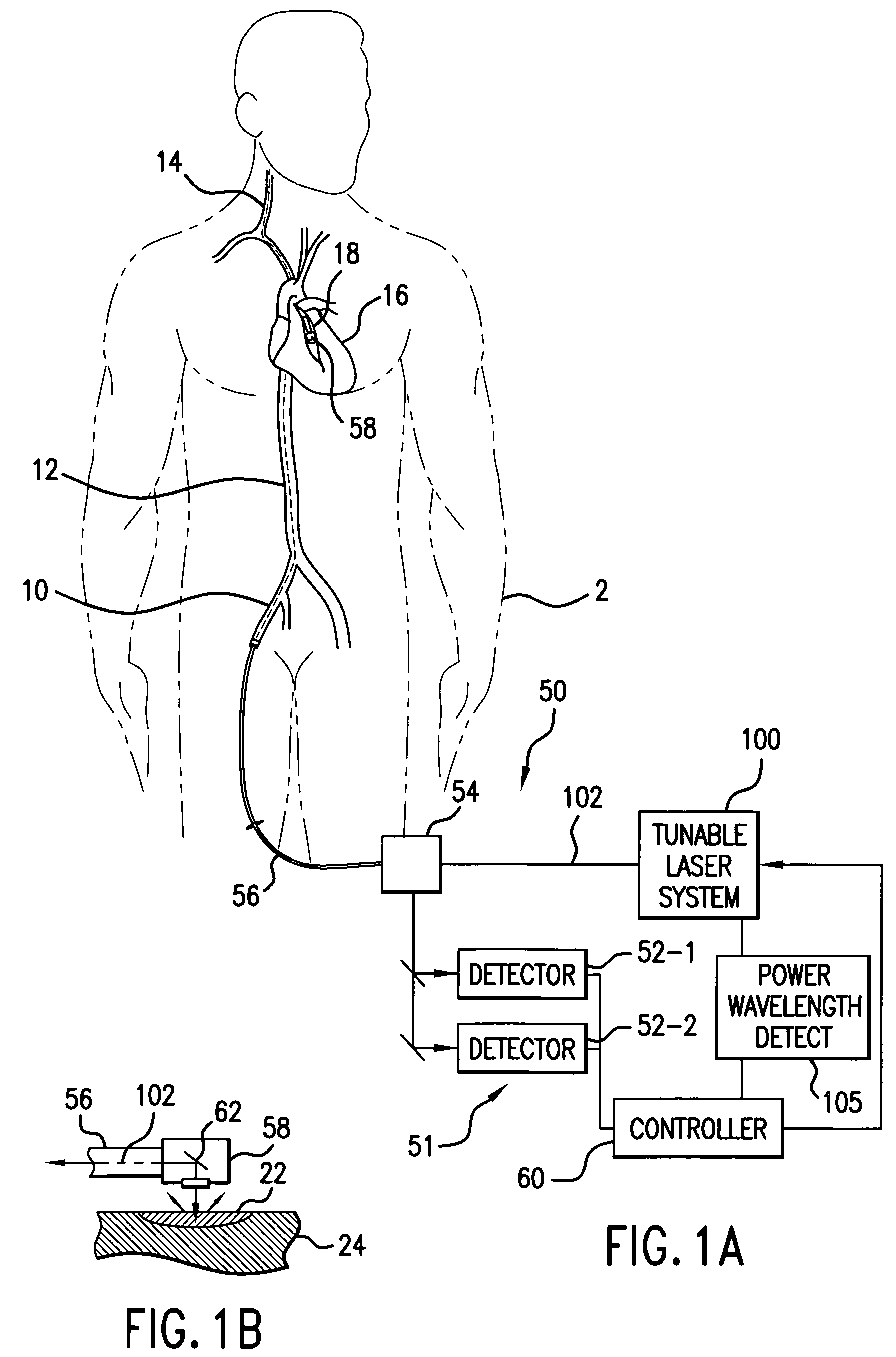
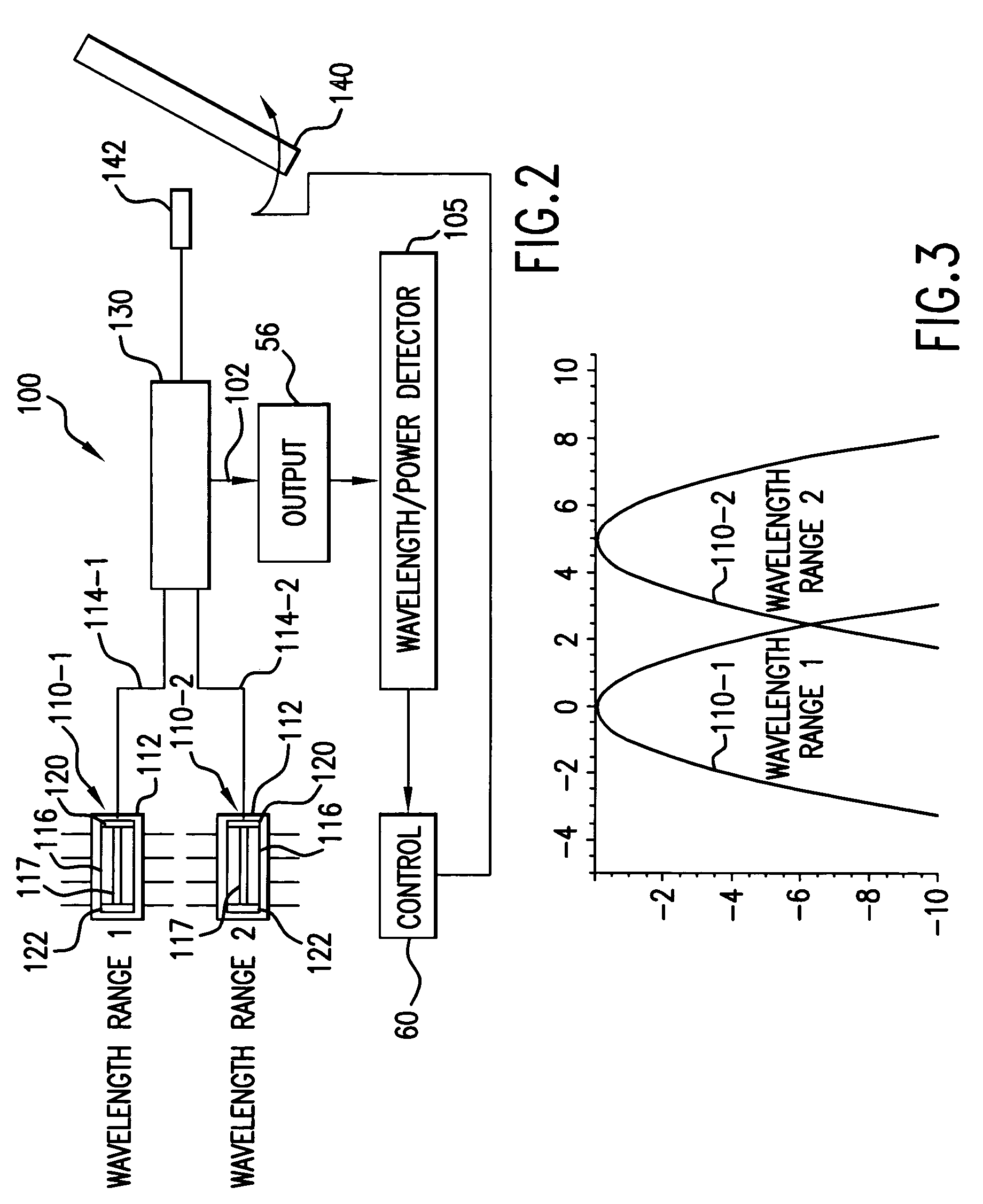
Spectroscopic catheter system with widely tunable source and method of operation
ActiveUS7535935B2Inexpensive and efficient and smallBroad spectral outputLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsFtir spectraPeak value
A laser system for a spectroscopic catheter system uses multiple semiconductor gain media having gain peaks at different wavelengths. The output from the gain media is preferably coupled into single-mode fiber using conventional opto-electronic packaging techniques. As a result, the laser oscillator source has a spectral output that is wider than the gain bandwidth of a single medium to enable it to access the entire spectrum of interest, which is presently in the near infrared. Moreover, the semiconductor gain media can be packaged in a stable and controlled environment for long-term performance.
Owner:INFRAREDX INC
System and Method for Resampling Optical Coherence Tomography Signals in Segments
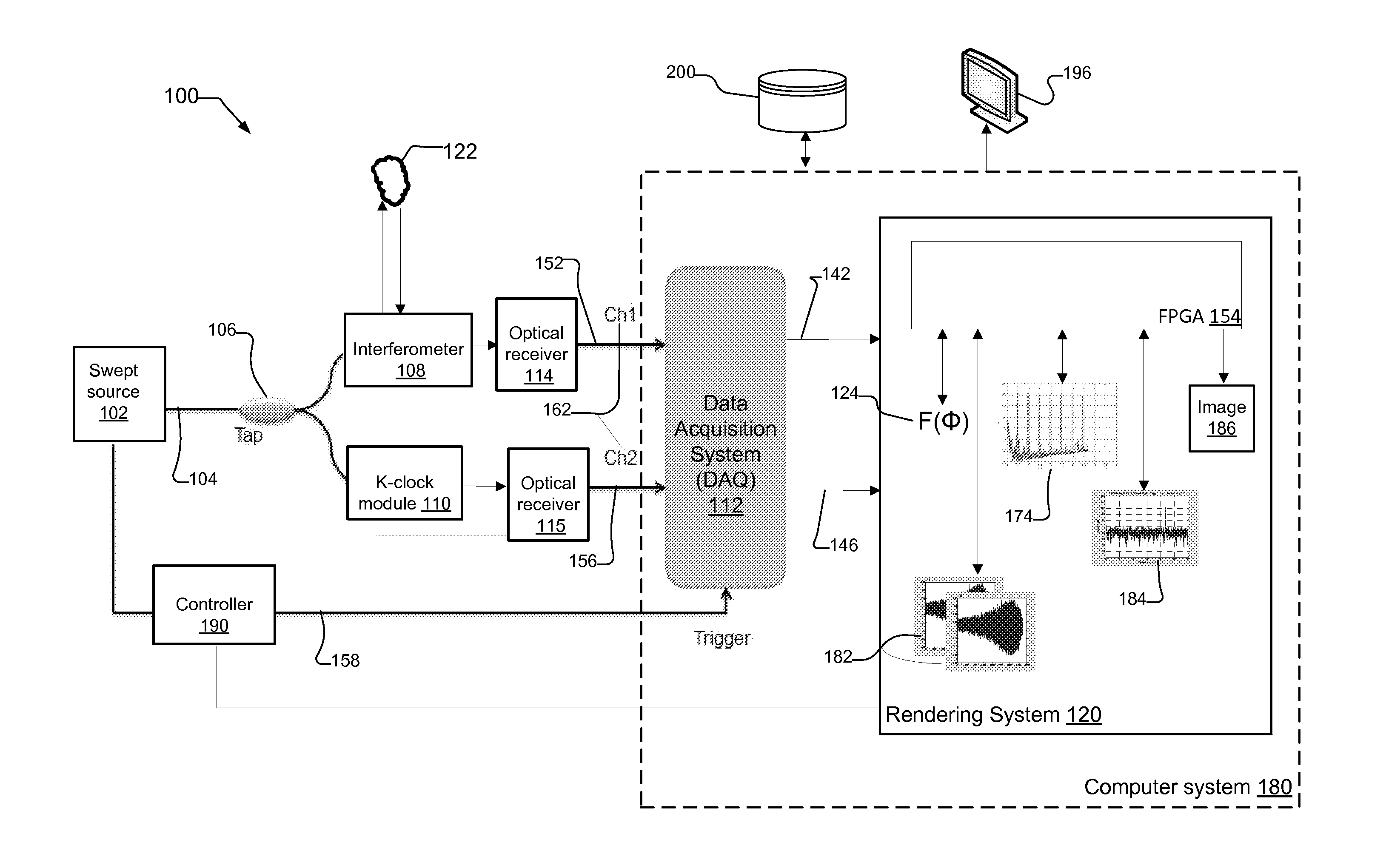
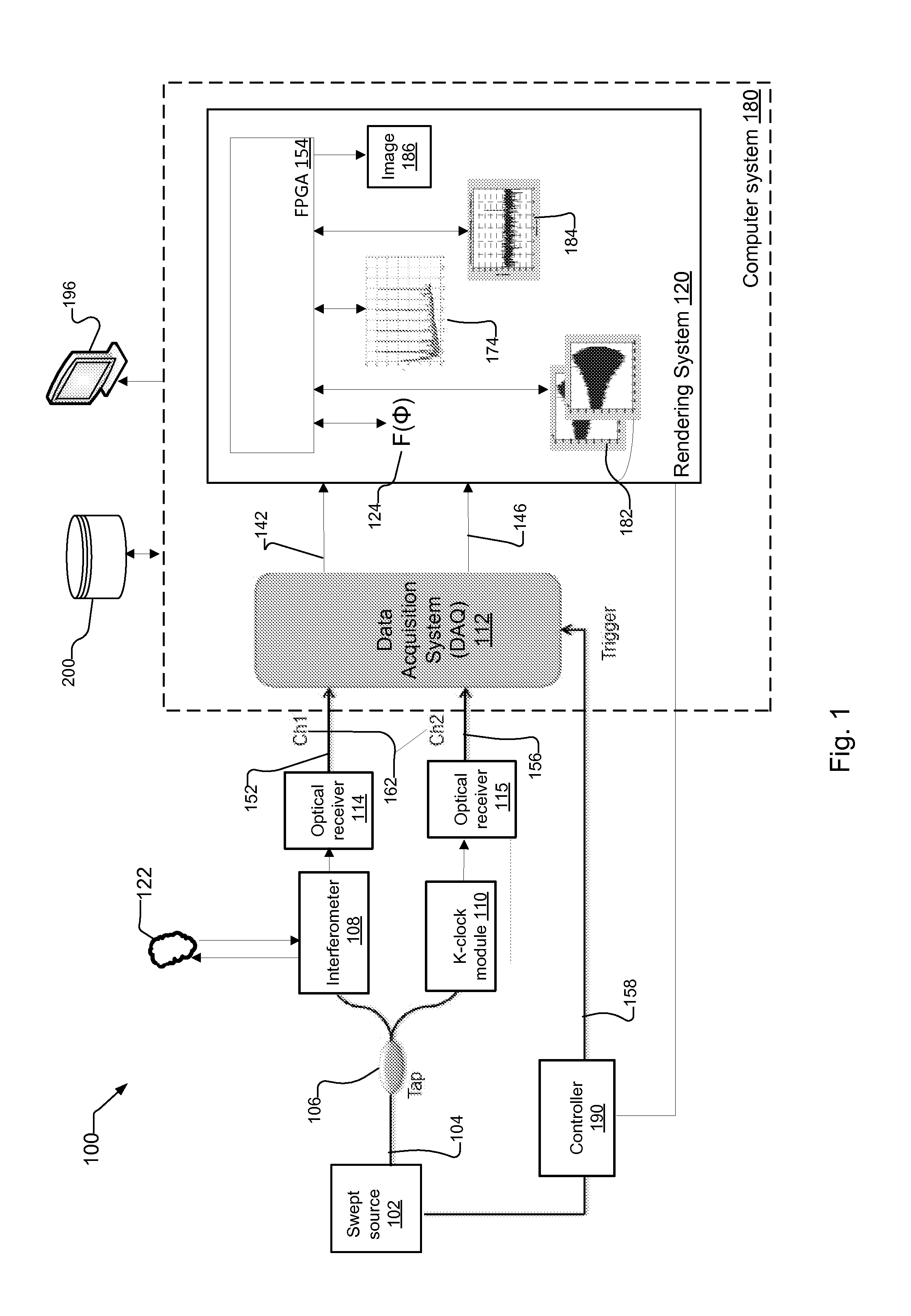
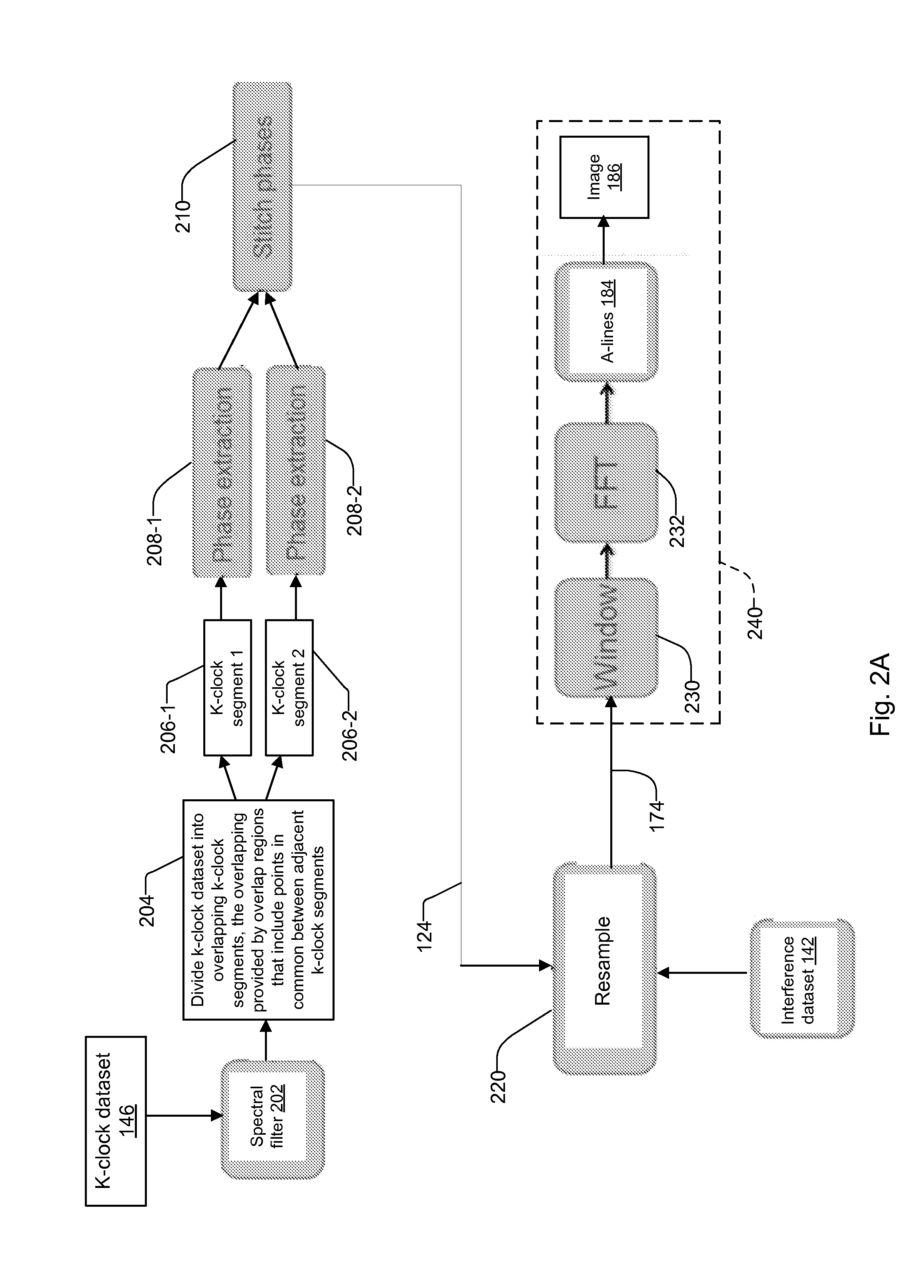
ActiveUS20150300806A1Lower component costsImprove processing speedUsing optical meansFast Fourier transformData set
A system and method for resampling interference datasets of samples in segments, in a swept-source based Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) system. The resampling is preferably performed within a Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) of the OCT system, the FPGA preferably having Fourier-transform based signal processing capabilities such as Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) cores. Resampling the interference datasets in segments provides a flexible approach to resampling that makes efficient use of system resources such as FFT cores. By resampling the interference datasets in segments, the system adjusts to an increased number of resampling points as the imaging depth upon the sample increases. The OCT system then combines the segments using overlapping values of the resampling points between adjacent resampling regions of the resampled segments, and performs Fourier Transform based post-processing on the combined segments to obtain axial profiles of the sample at desired imaging depths.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
Four-channel color filter array interpolation
ActiveUS8237831B2Good colorReduce colorTelevision system detailsRadiation pyrometryColor imageDiagonal
A method of forming a full-color output image from a color filter array image having a plurality of color pixels having at least two different color responses and panchromatic pixels, comprising capturing a color filter array image using an image sensor including panchromatic pixels and color pixels having at least two different color responses, the pixels being arranged in a repeating pattern having a square minimal repeating unit having at least three rows and three columns, the color pixels being arranged along one of the diagonals of the minimal repeating unit, and all other pixels being panchromatic pixels; computing an interpolated panchromatic image from the color filter array image; computing an interpolated color image from the color filter array image; and forming the full color output image from the interpolated panchromatic image and the interpolated color image.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Compact coherent high brightness light source for the mid-ir and far ir
ActiveUS20140219296A1Optimize temporal overlapTemporal overlapLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingDispersion-shifted fiberNonlinear crystals
Compact laser systems are disclosed which include ultrafast laser sources in combination with nonlinear crystals or waveguides. In some implementations fiber based mid-IR sources producing very short pulses and / or mid-IR sources based on a mode locked fiber lasers are utilized. A difference frequency generator receives outputs from the ultrafast sources, and generates an output including a difference frequency. The output power from the difference frequency generator can further be enhanced via the implementation of large core dispersion shifted fibers. Exemplary applications of the compact, high brightness mid-IR light sources include medical applications, spectroscopy, ranging, sensing and metrology.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com