Patents
Literature
326 results about "Selective filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
What is Frequency Selective Filters. 1. Digital filters which pass desired frequency components in a signal without distortion and attenuate other frequency components.
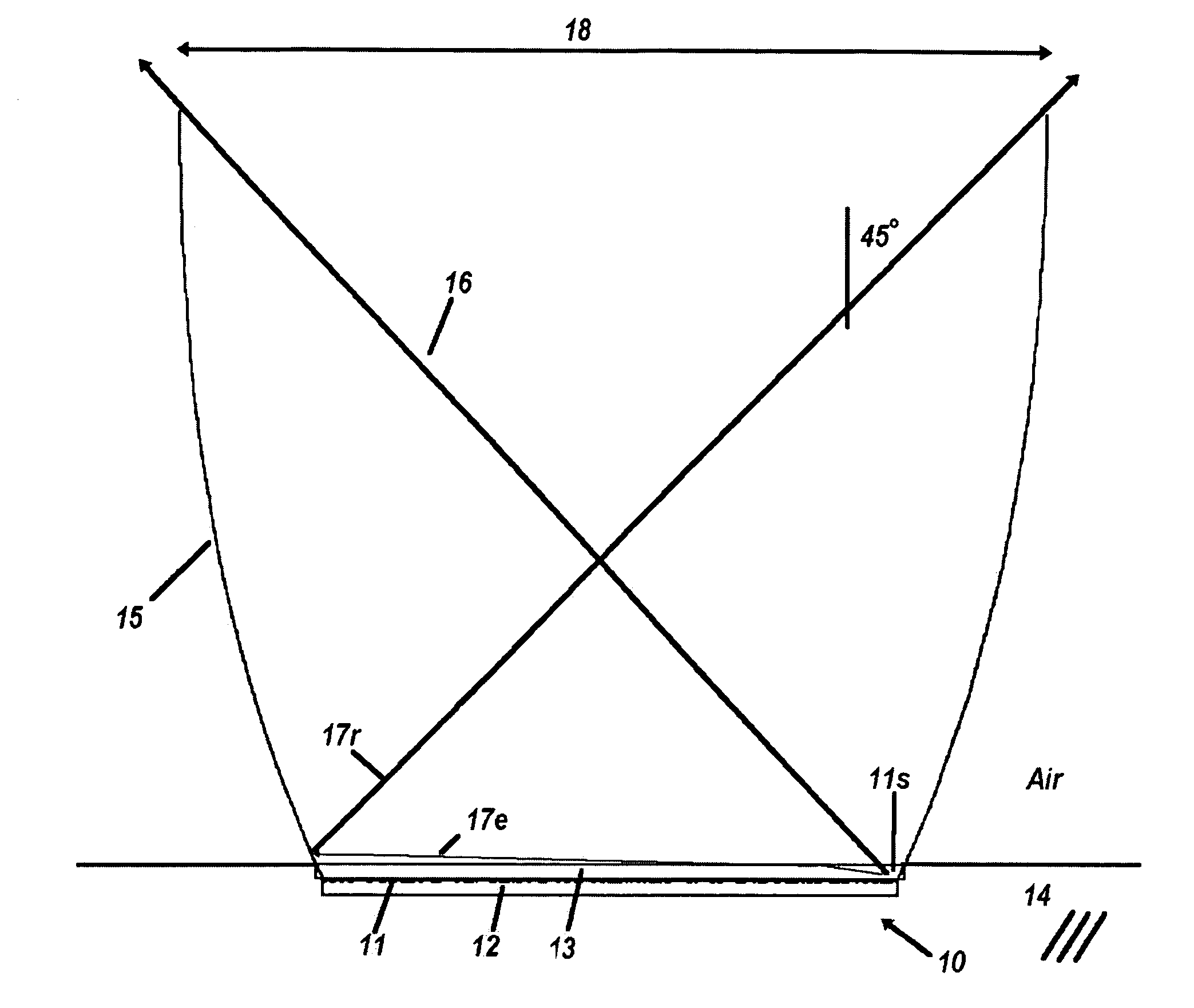
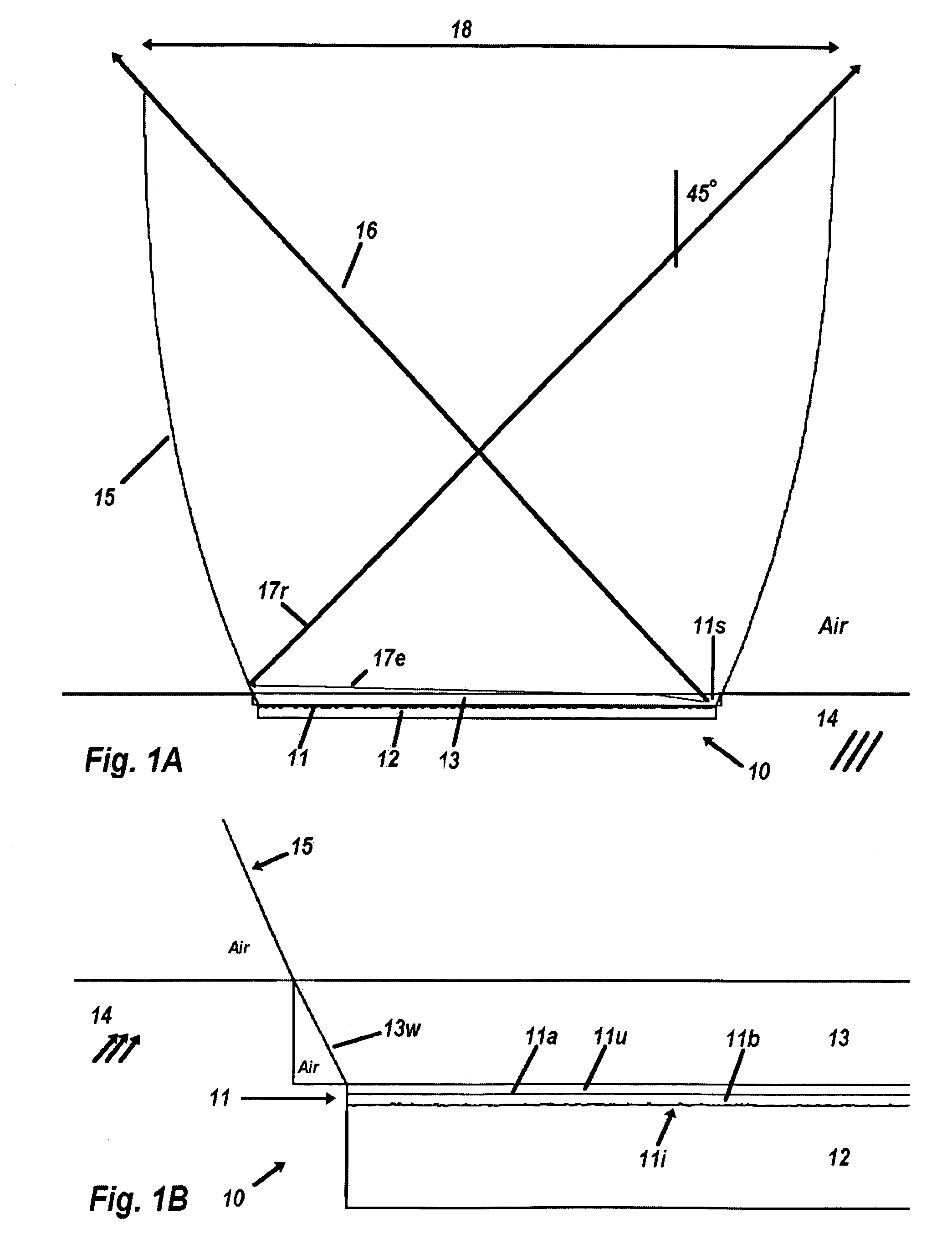
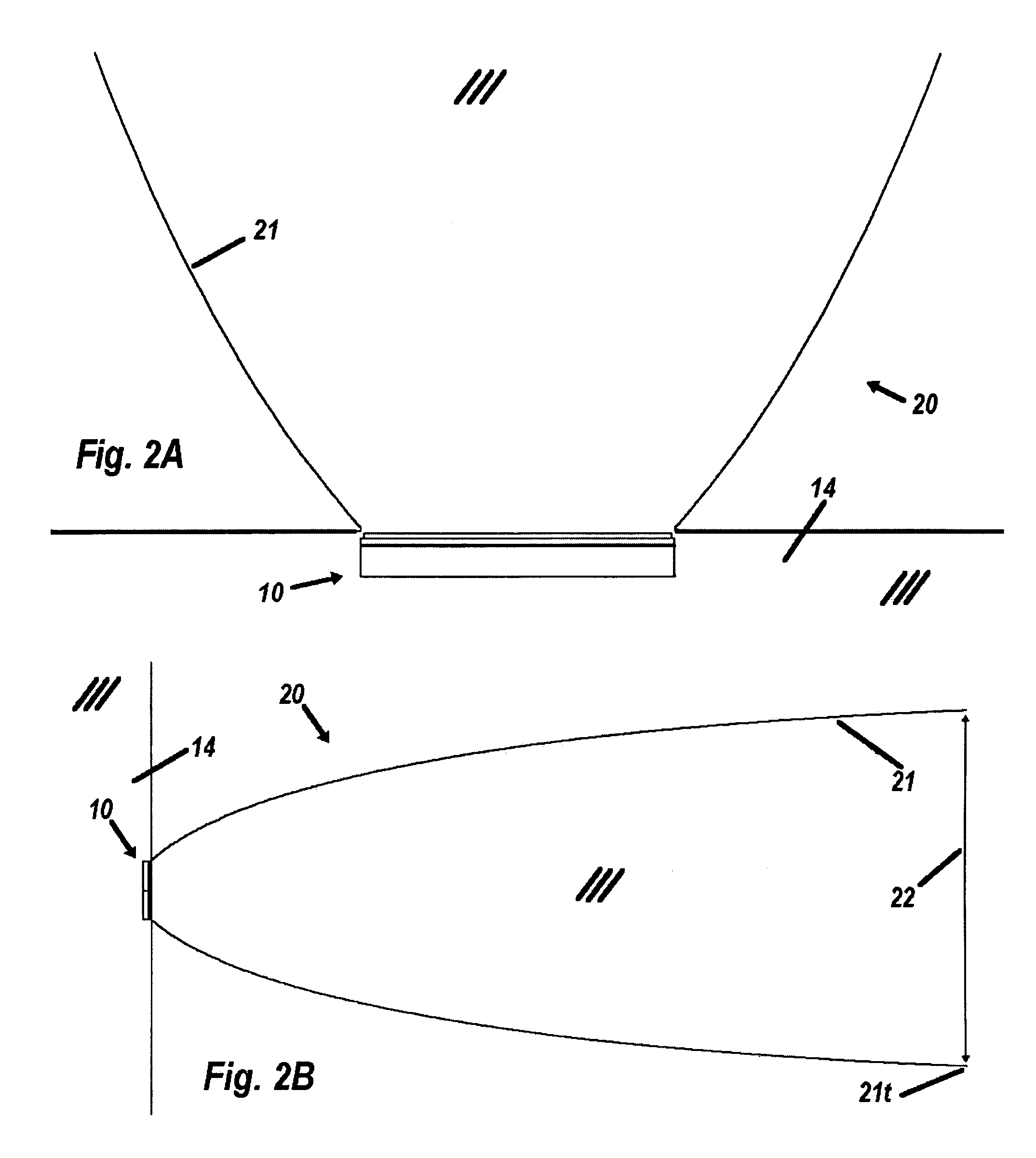
High performance selective light wavelength filtering providing improved contrast sensitivity
Owner:HIGH PERFORMANCE OPTICS
Method for representing real-time motion
InactiveUS6707487B1Accurate game reconstructionReduce data flowImage enhancementTelevision system detailsGraphicsContinuation
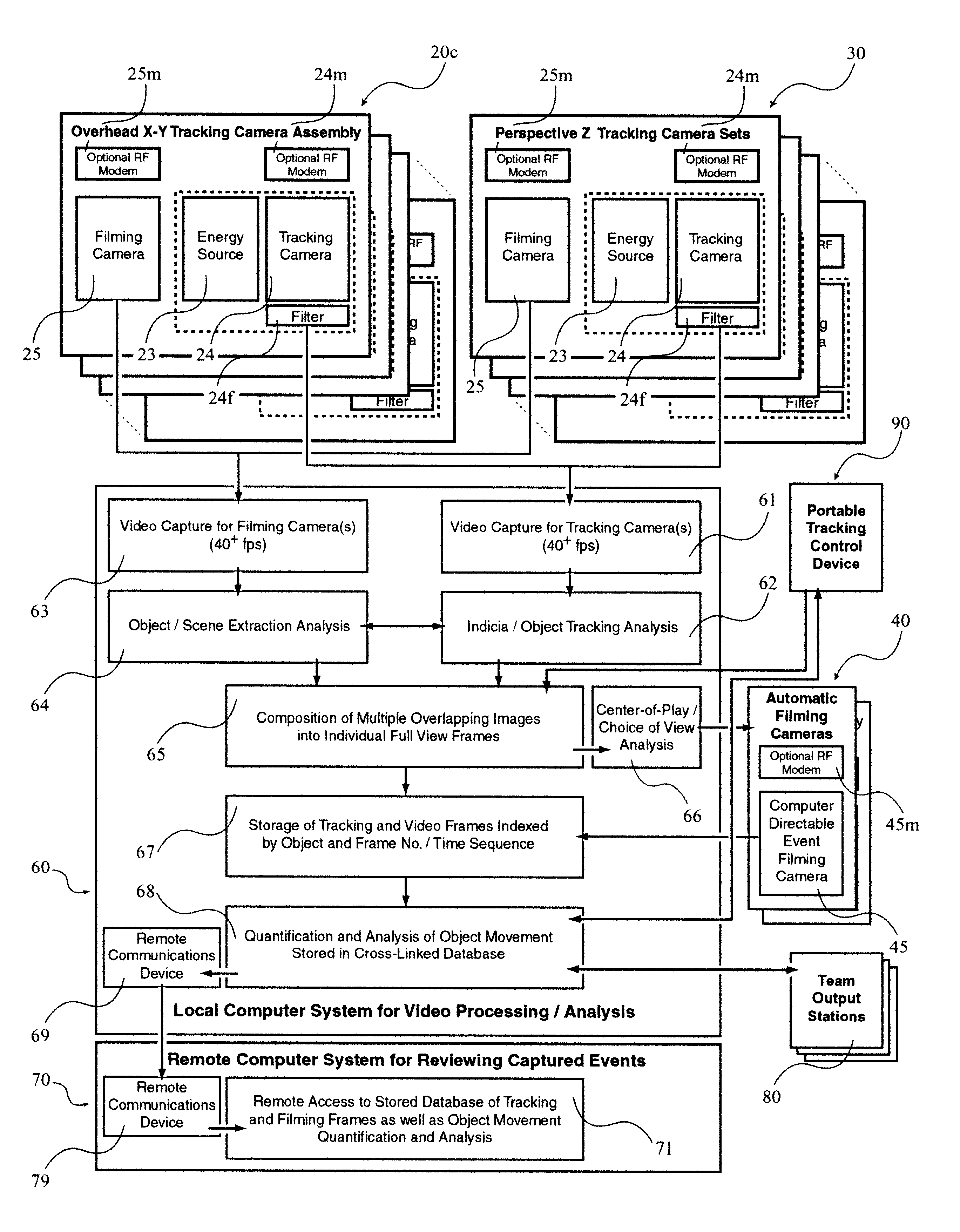
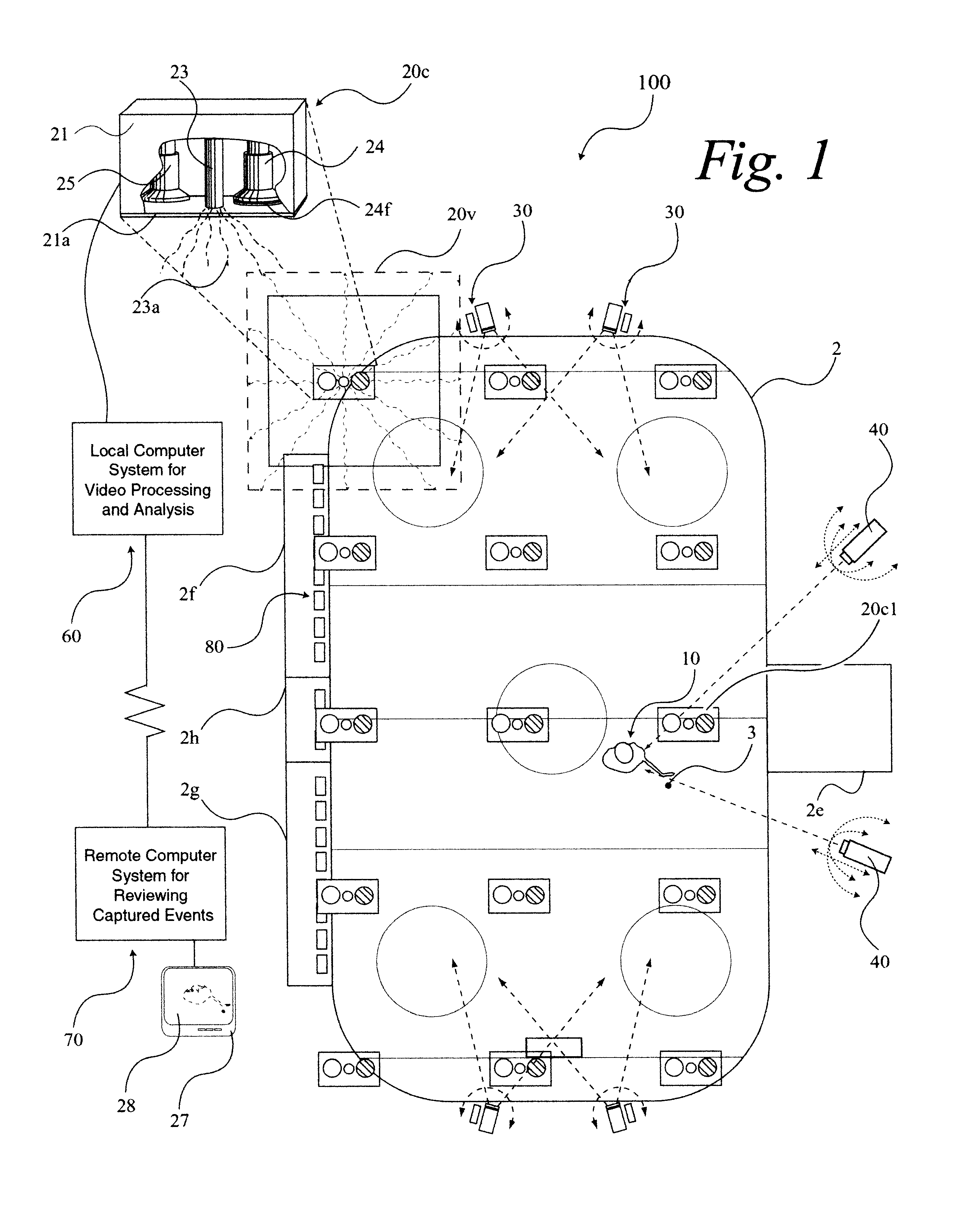
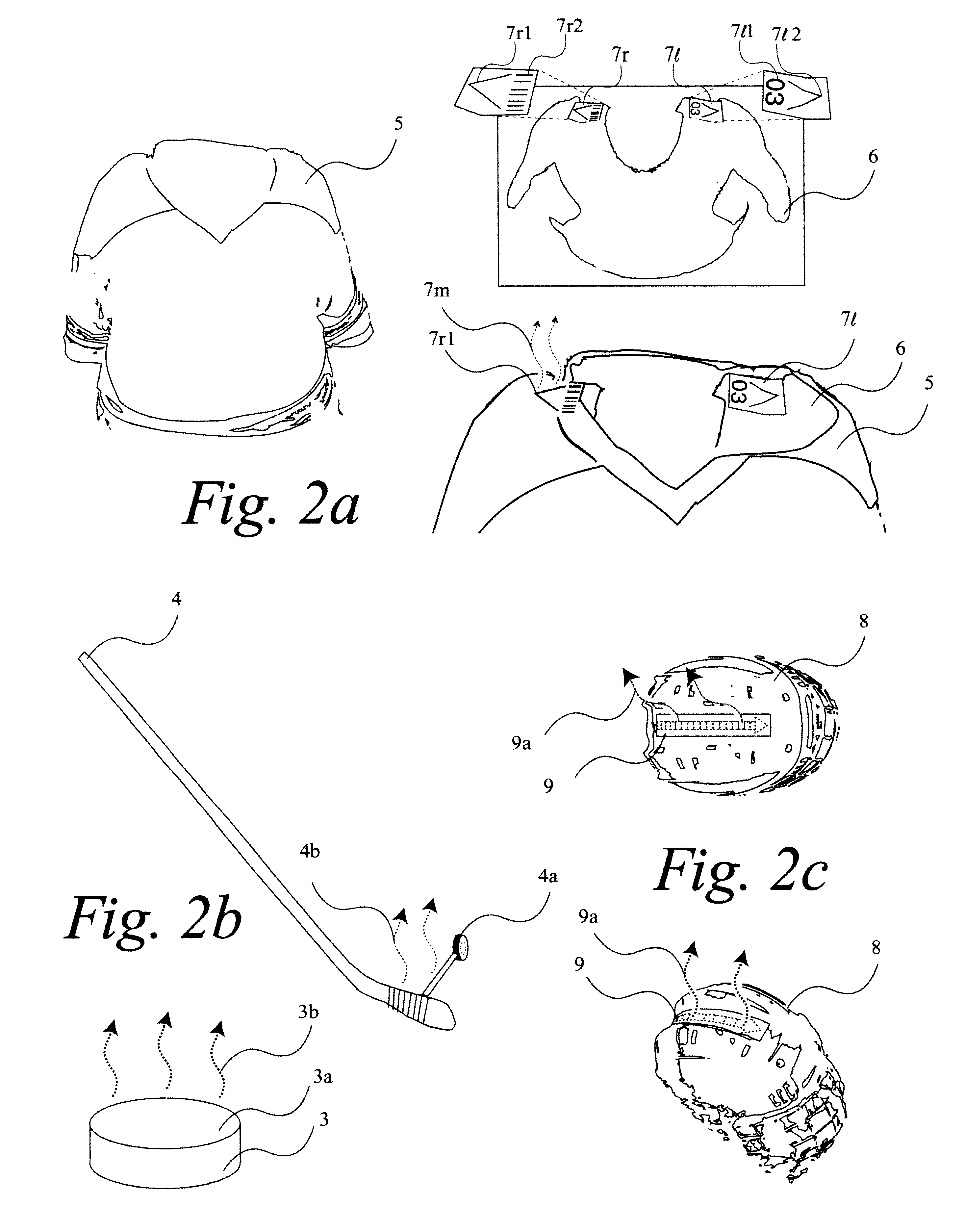
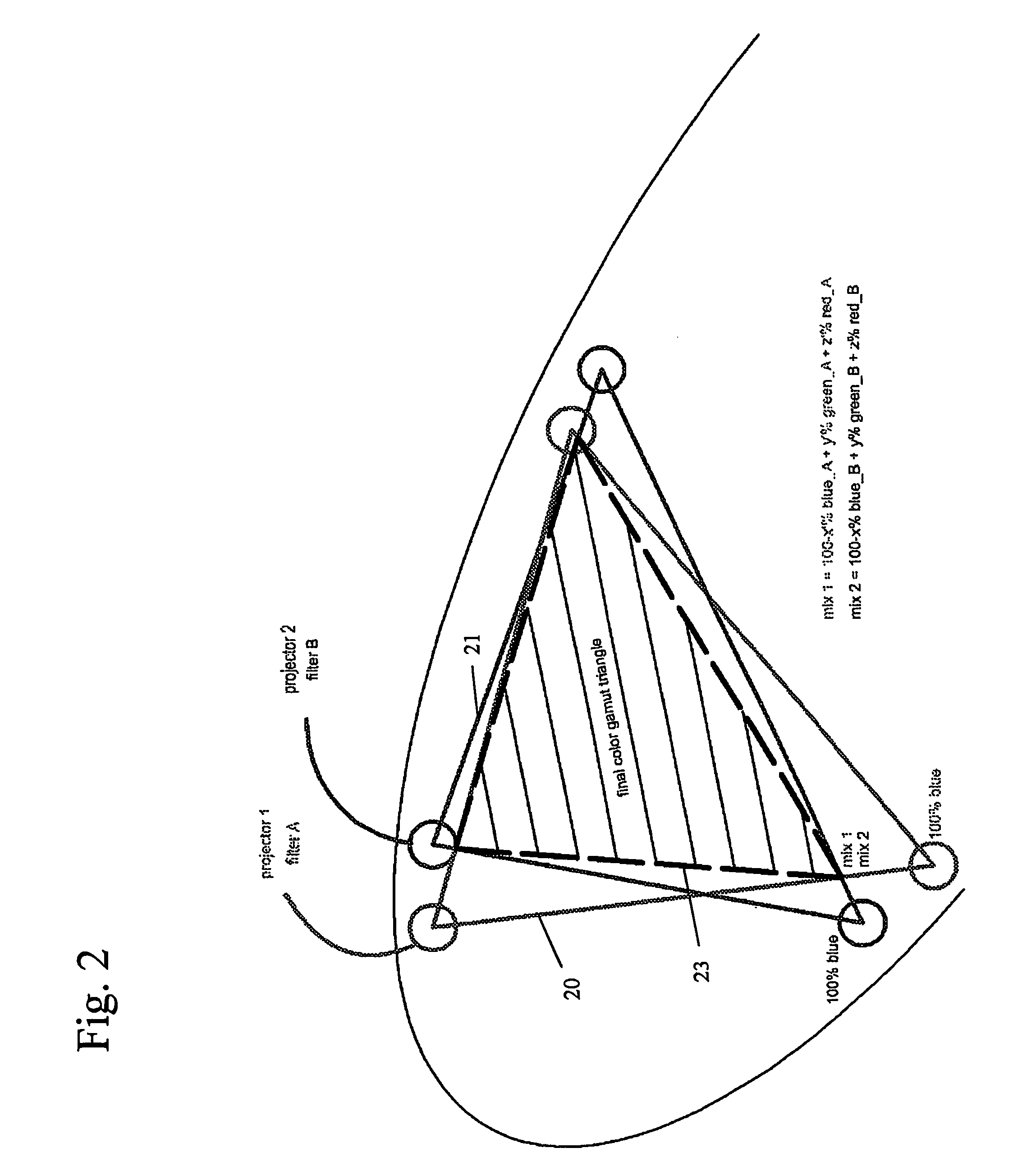
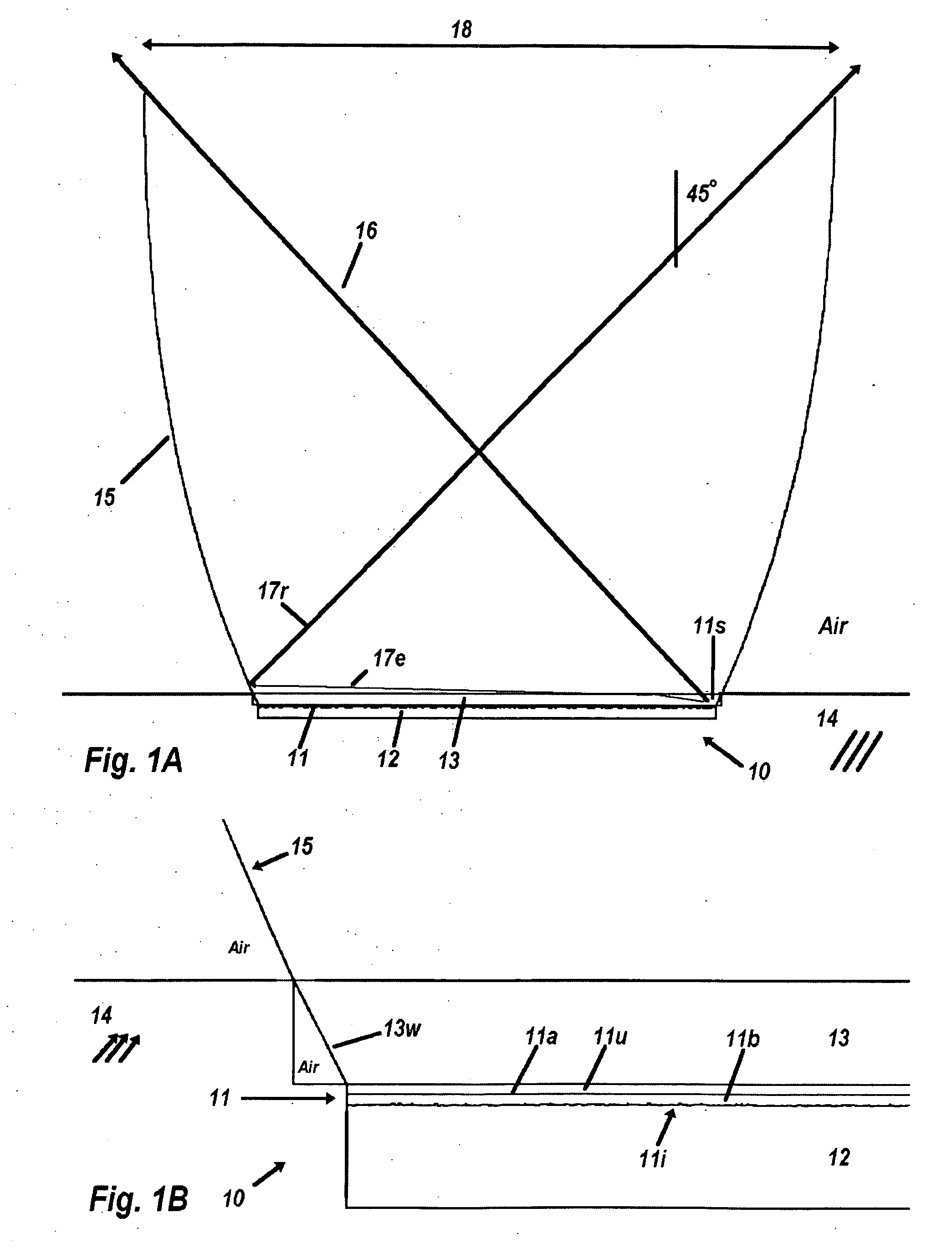
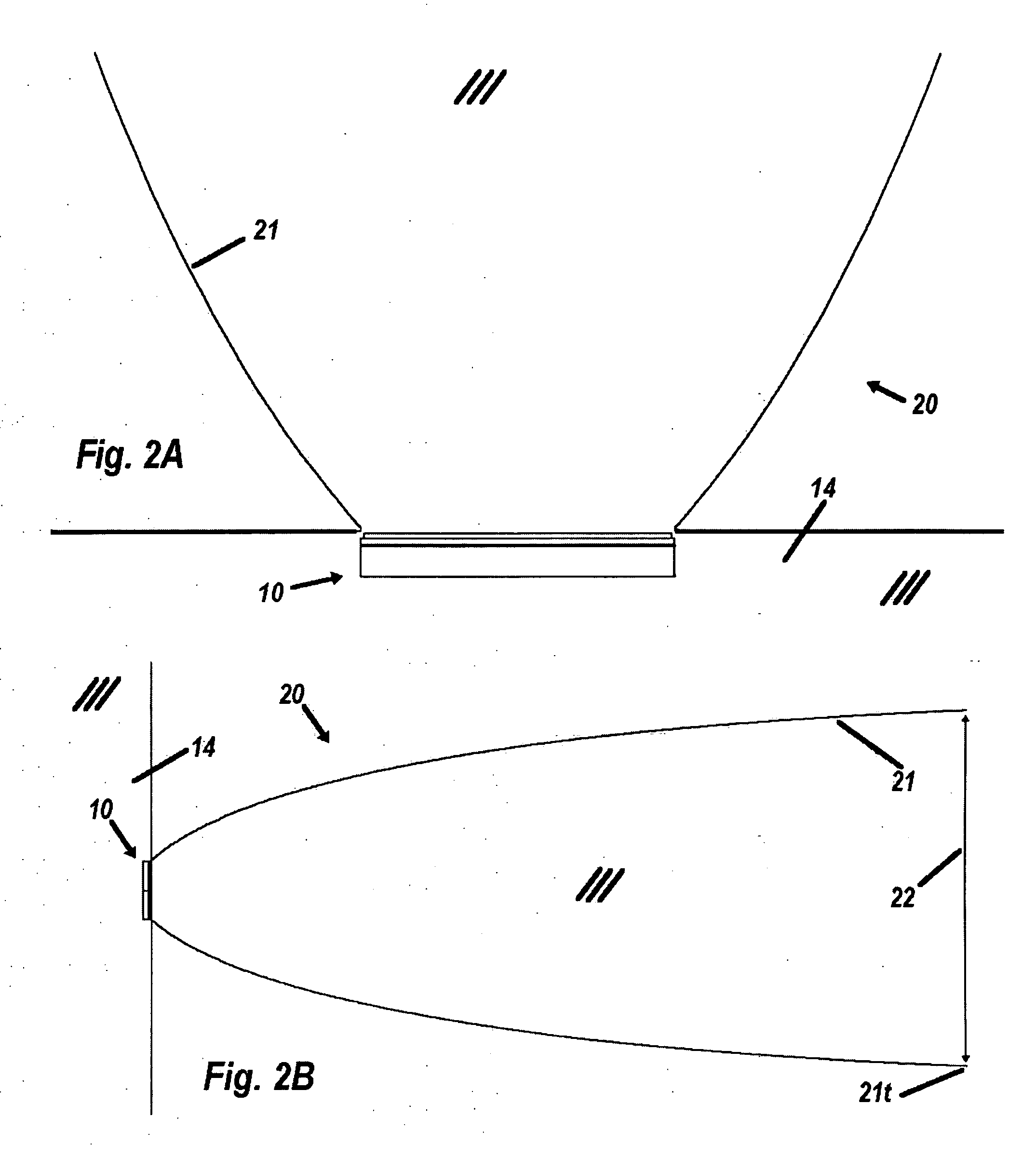
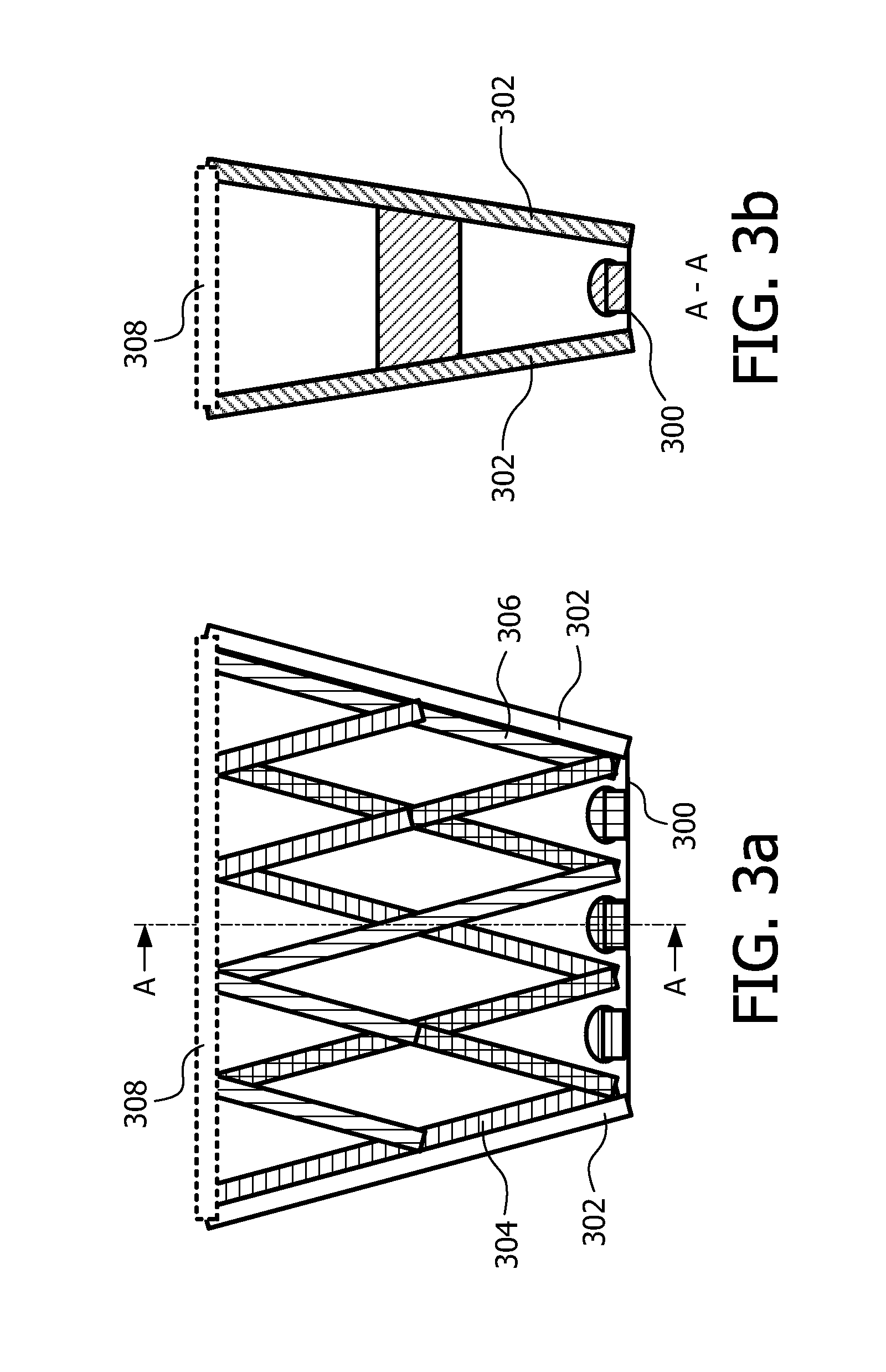
A system 100 for tracking the movement of multiple objects within a predefined area using a continuation of overhead X-Y tracking cameras 24 with attached frequency selective filter 24f. Also employed are perspective Z filming cameras sets 30. Objects to be tracked, such as player 17, have been marked to include some form of frequency selective reflective material such as an ink. Typical markers include patches 7r and 7l, sticker 9 and tape 4a as well as additional body joint markers 17af through 17l. System 100 radiates selected energy 23a throughout the predefined area of tracking that is specifically chosen to reflect off said reflective materials used to mark for instance player 17. The reflected energy is then received by tracking cameras 24 while all other ambient light is blocked by filter 24f. Local Computer System 60 continuously captures images from said tracking cameras 24 which include only the minimum information created by said reflected energy. System 60 efficiently locates said markings on said multiple objects and uses this location information to determine for each marking its angle of rotation, angle of azimuth and distance from a designated origin 17o local to player 17. Local origin 17o is then expressed as a three-dimensional coordinate with respect to the origin of the playing venue 2a. The continuous stream of tracked three-dimensional coordinates, defining the body joints on players such as 17, is then transmitted to a remote computer where it can be used to drive a graphic re-animation of the object movement. Along with this re-animation, additional performance measurements may be derived from the continuous stream and automatically made available in real-time.
Owner:MAXX HLDG
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS20050243570A1Cost-effectiveImprove throughputMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourcePhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of LED outputs into a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. The optical manifolds can be used to combine multiple LEDs of the same color and provide a high intensity output aperture with very high uniformity and sharp borders, or they can be used to generate a multiwavelength output, such as red, green, and blue LEDs that are combined to generate white light. Embodiments are also disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. The optical manifolds are designed to alleviate substantial luminance inhomogeneities inherent to LEDs. The optical manifold utilizes principles of non-imaging optics to transform light and provide directed, substantially uniform light sources.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
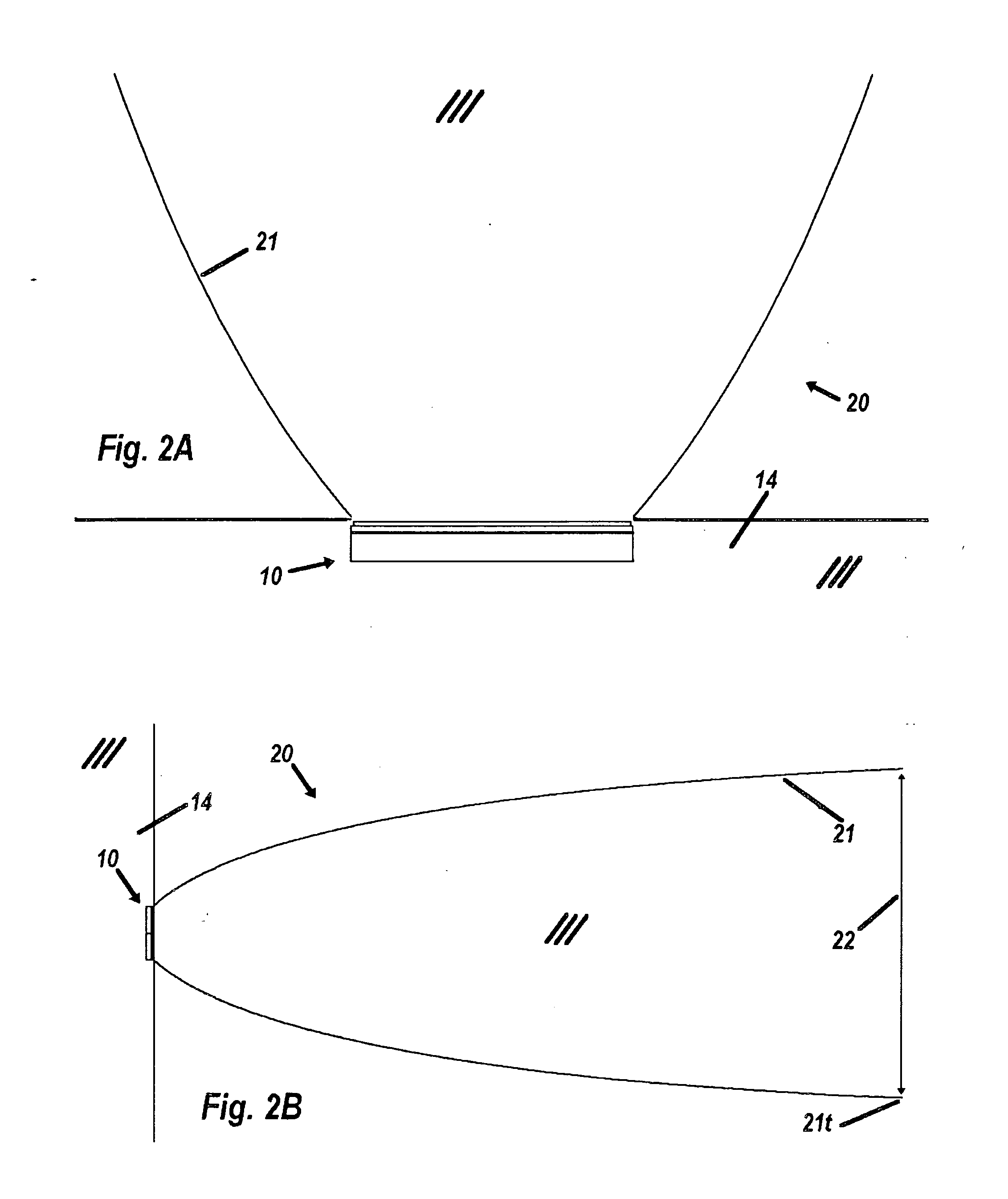
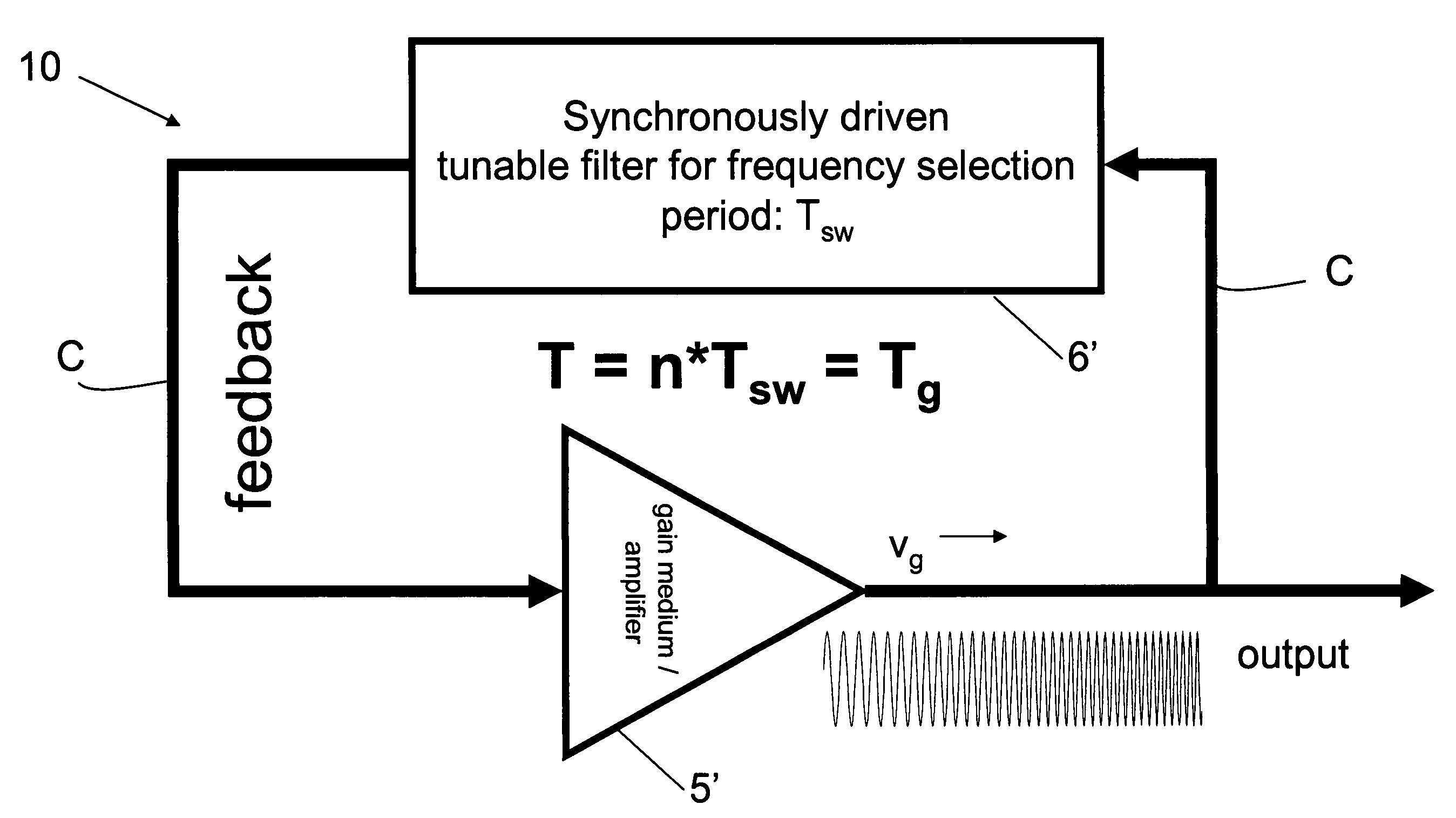
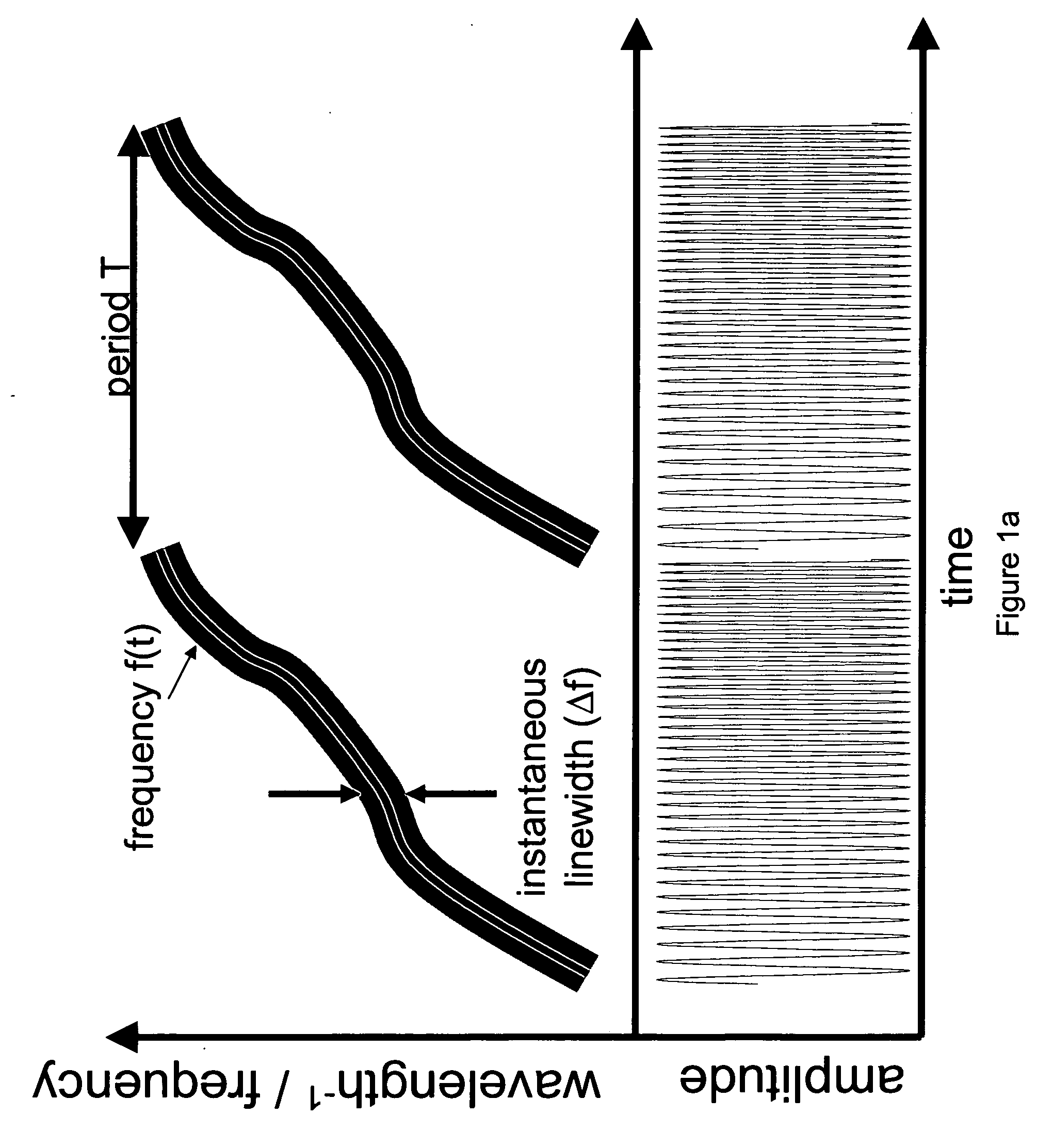
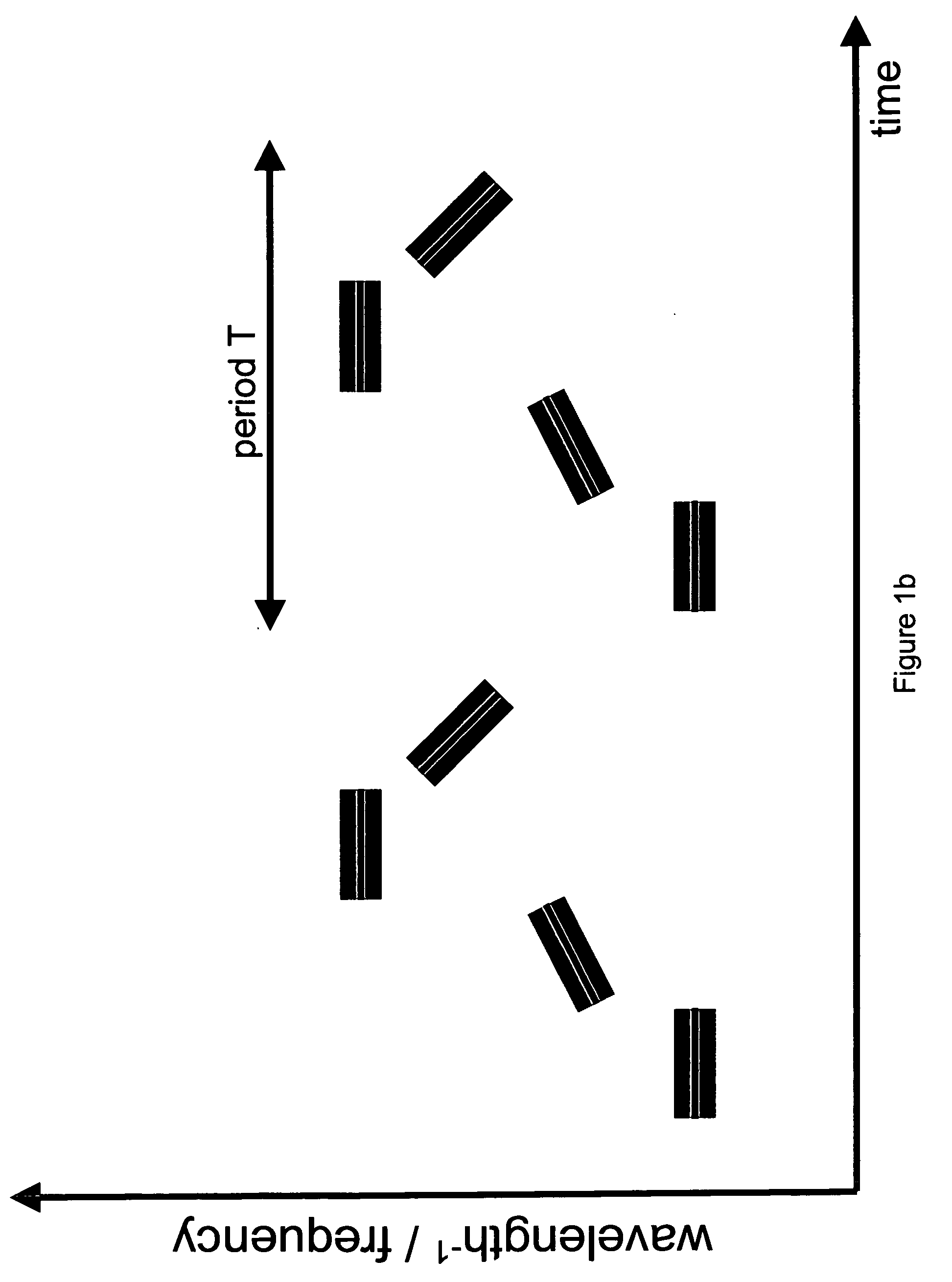
Mode locking methods and apparatus
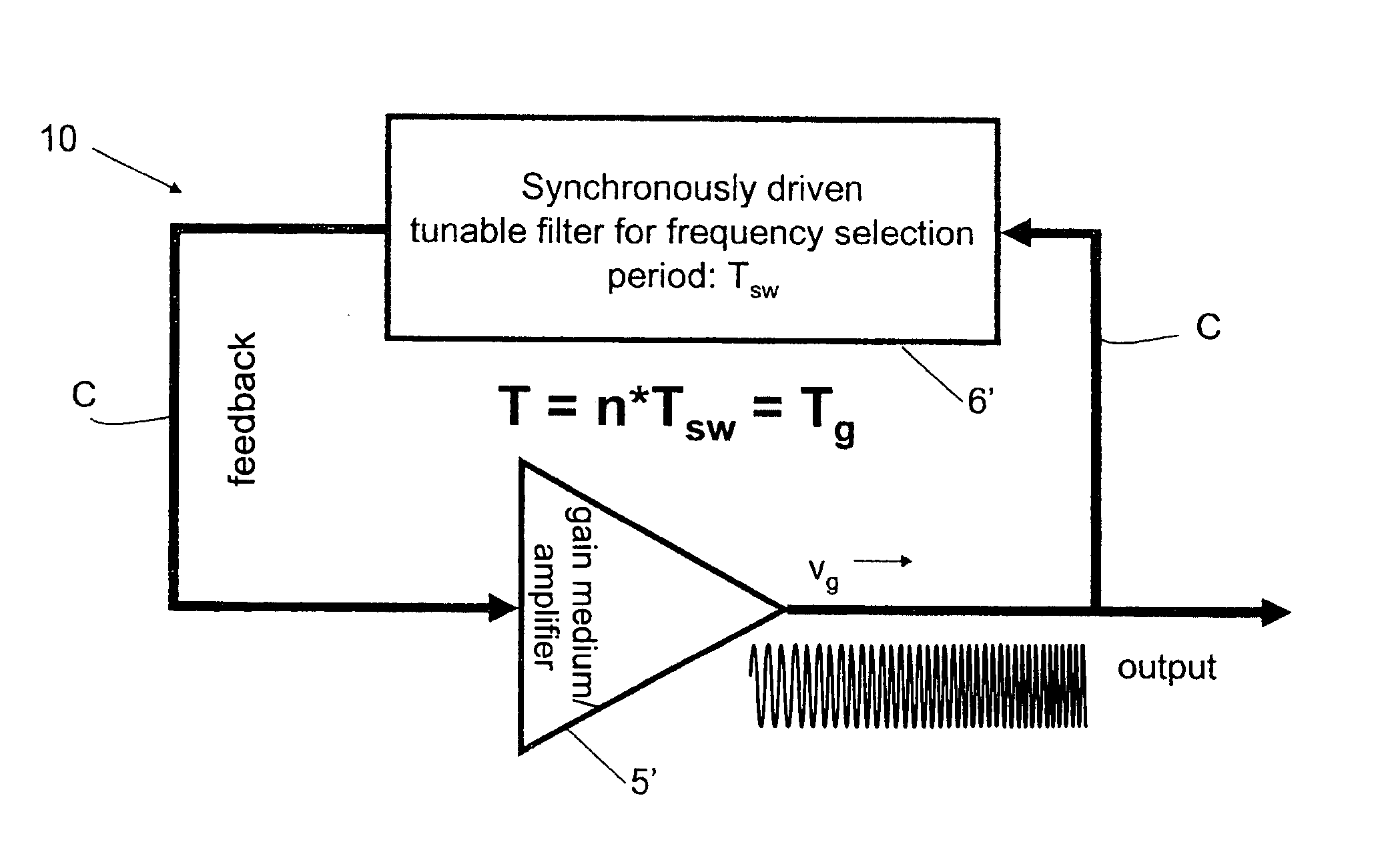
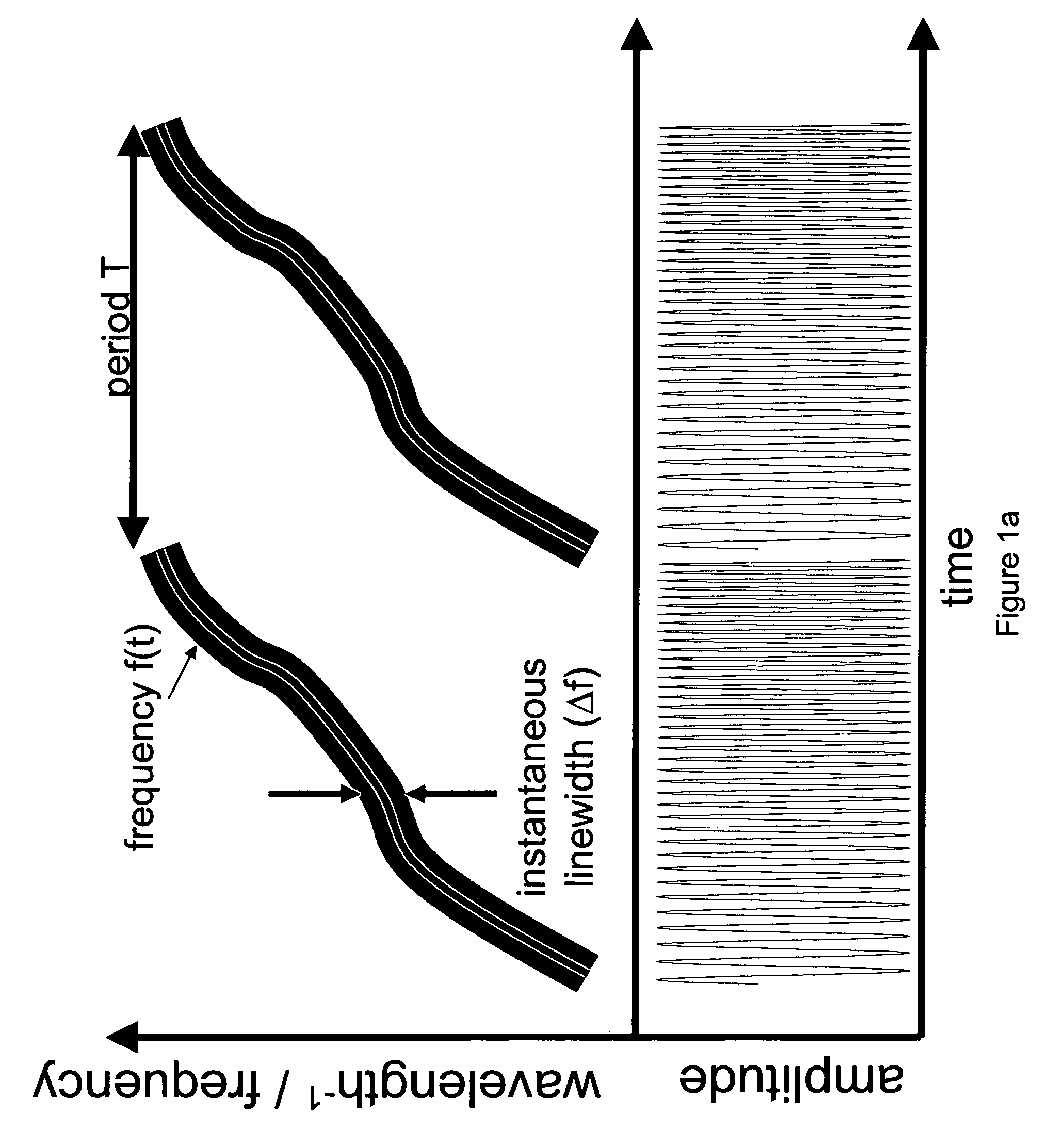
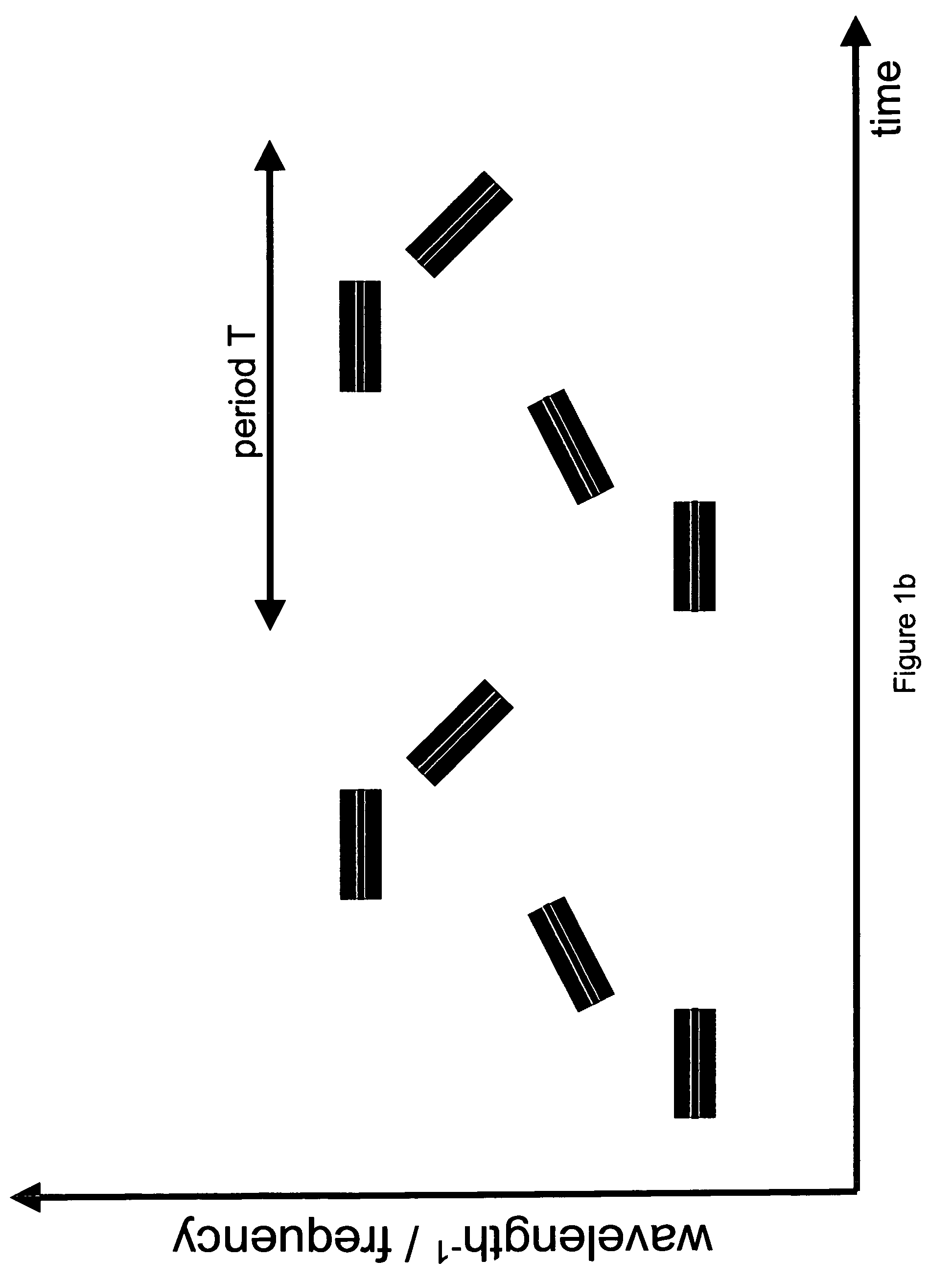
In one aspect the invention relates to a frequency varying wave generator. The generator includes a gain element adapted to amplify a wave having a wavelength; a time varying tunable wavelength selective filter element in communication with the gain element, the tunable filter element adapted to selectively filter waves during a period T; and a feedback element in communication with the tunable filter element and the gain element, wherein the tunable wavelength selective filter element, the gain element and the feedback element define a circuit such that the roundtrip time for the wave to propagate through the circuit is substantially equal to a non-zero integer multiple of the period T.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS7286296B2Cost-effectiveImprove throughputMechanical apparatusPoint-like light sourcePhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of LED outputs into a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. The optical manifolds can be used to combine multiple LEDs of the same color and provide a high intensity output aperture with very high uniformity and sharp borders, or they can be used to generate a multiwavelength output, such as red, green, and blue LEDs that are combined to generate white light. Embodiments are also disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. The optical manifolds are designed to alleviate substantial luminance inhomogeneities inherent to LEDs. The optical manifold utilizes principles of non-imaging optics to transform light and provide directed, substantially uniform light sources.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Mode locking methods and apparatus
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and device for performing stereoscopic image display based on color selective filters
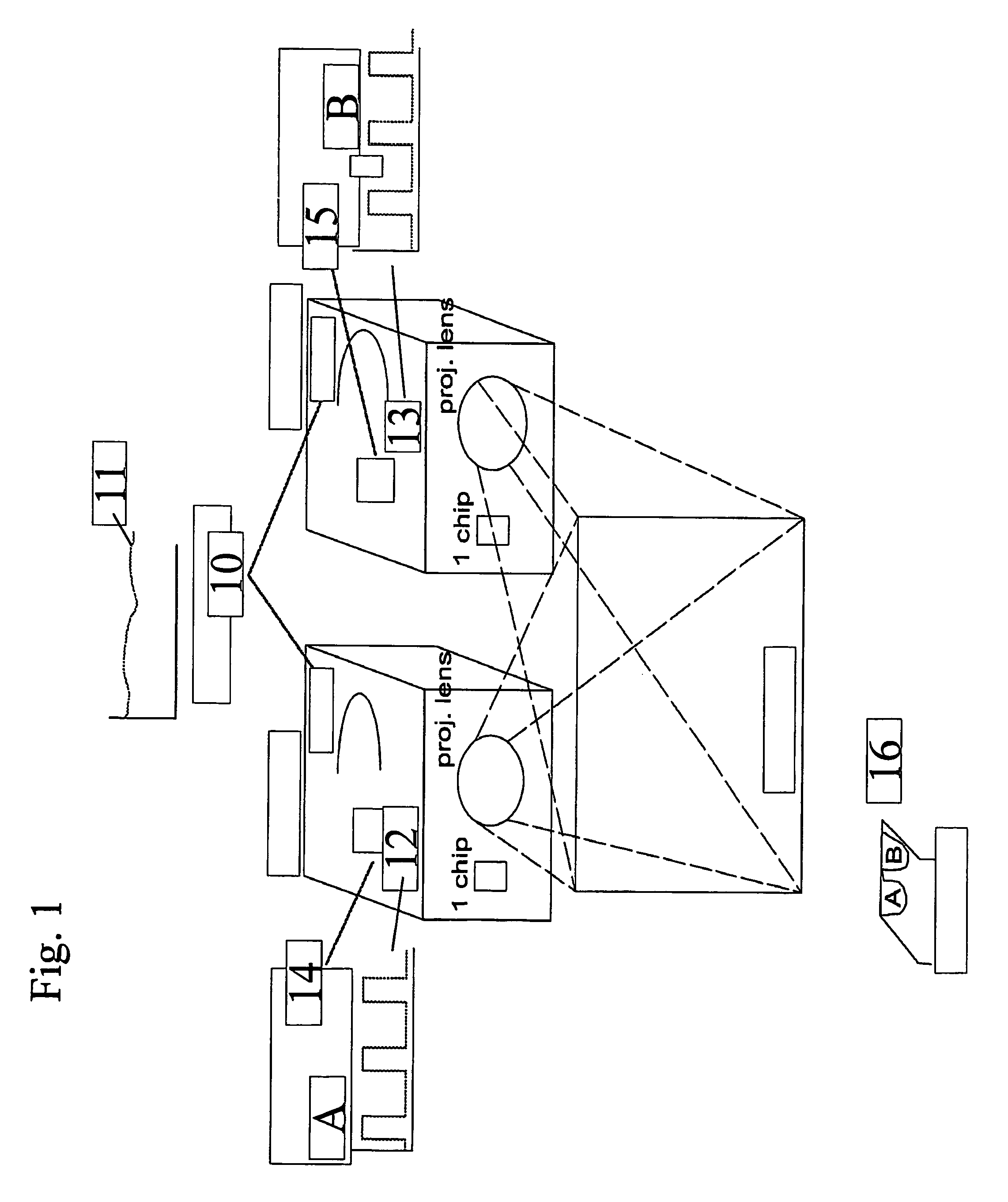
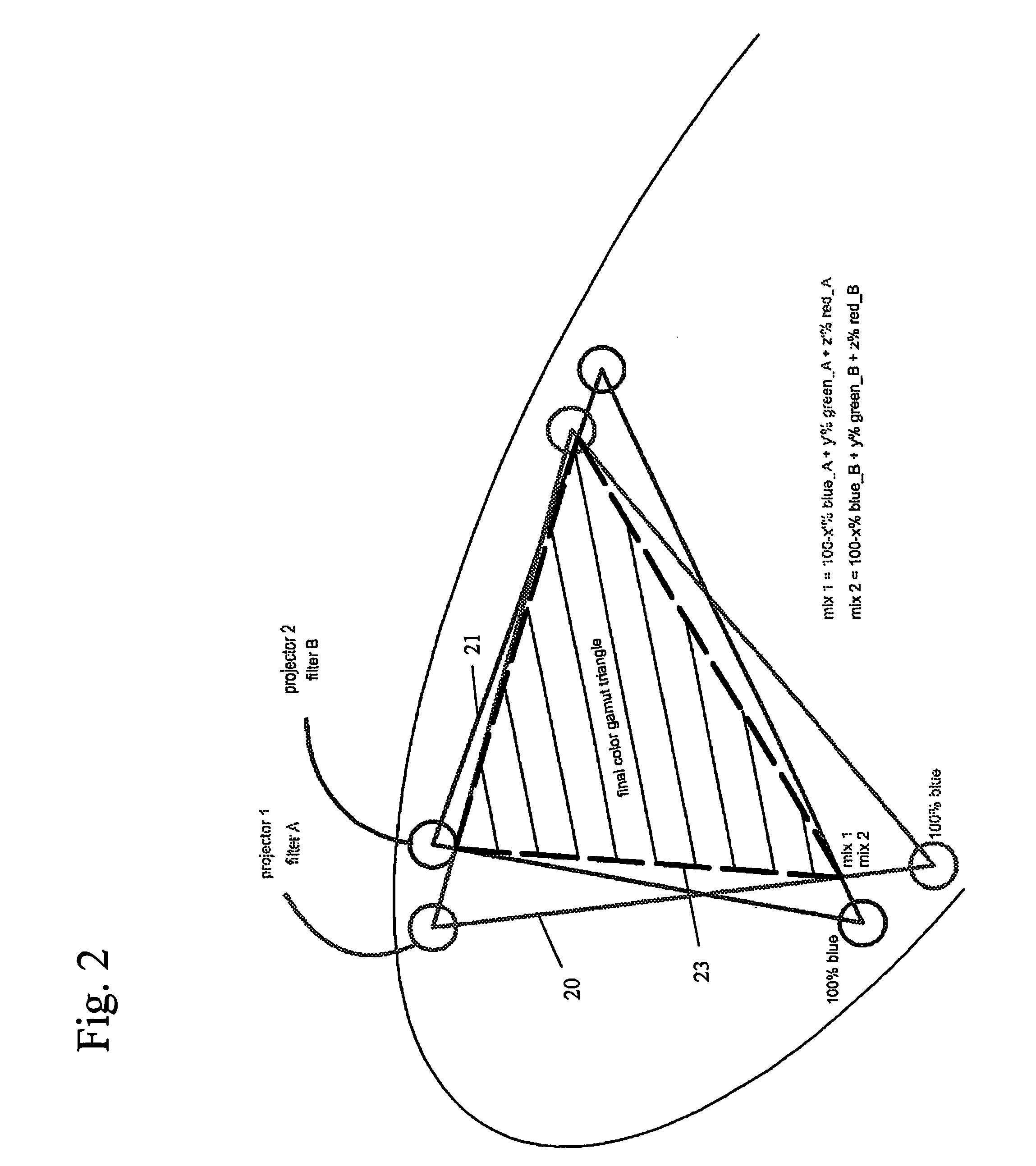
InactiveUS20070127121A1Lower requirementFast synchronized switchingStereoscopic photographySteroscopic systemsPolarizerProjection system
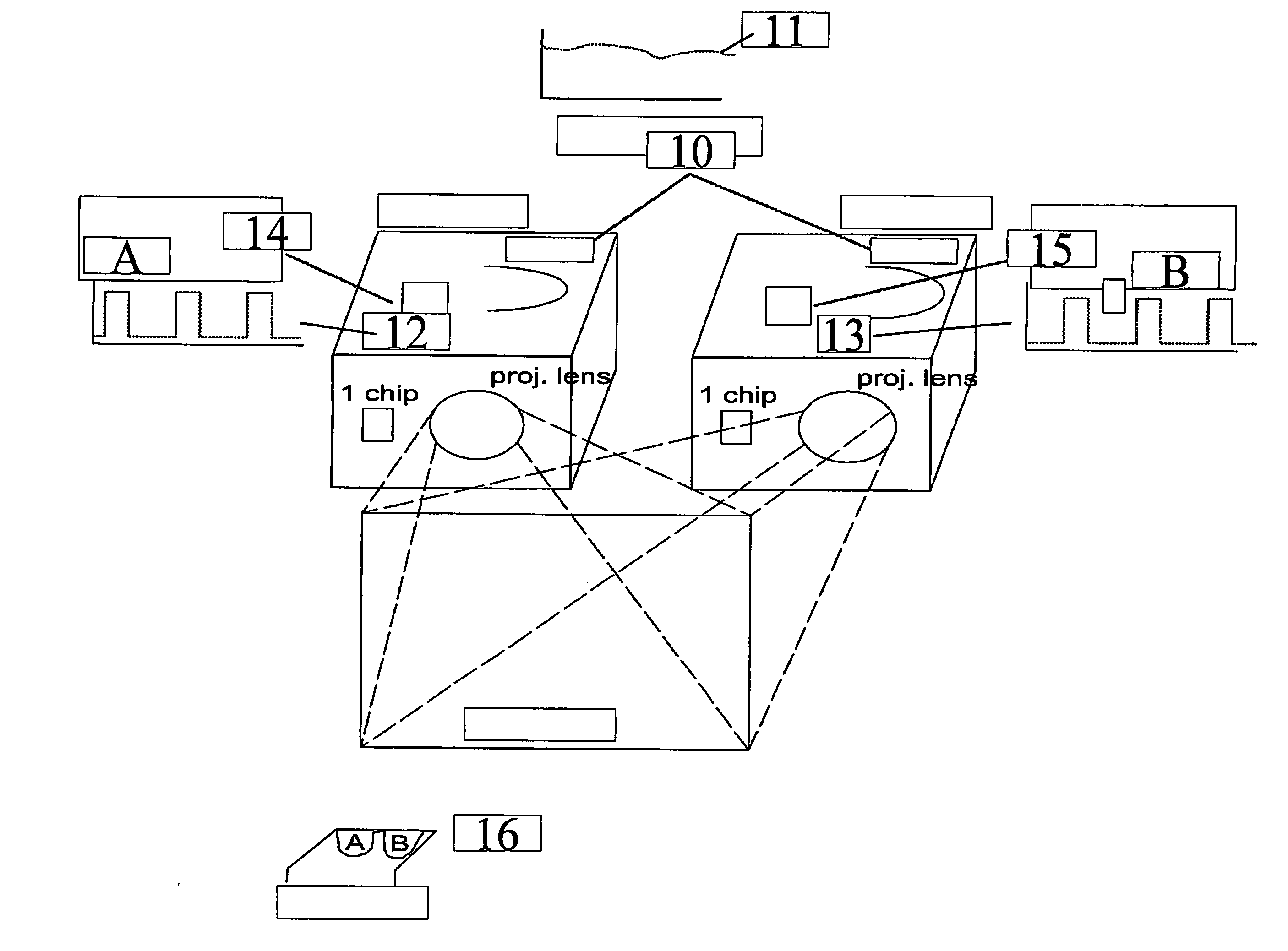
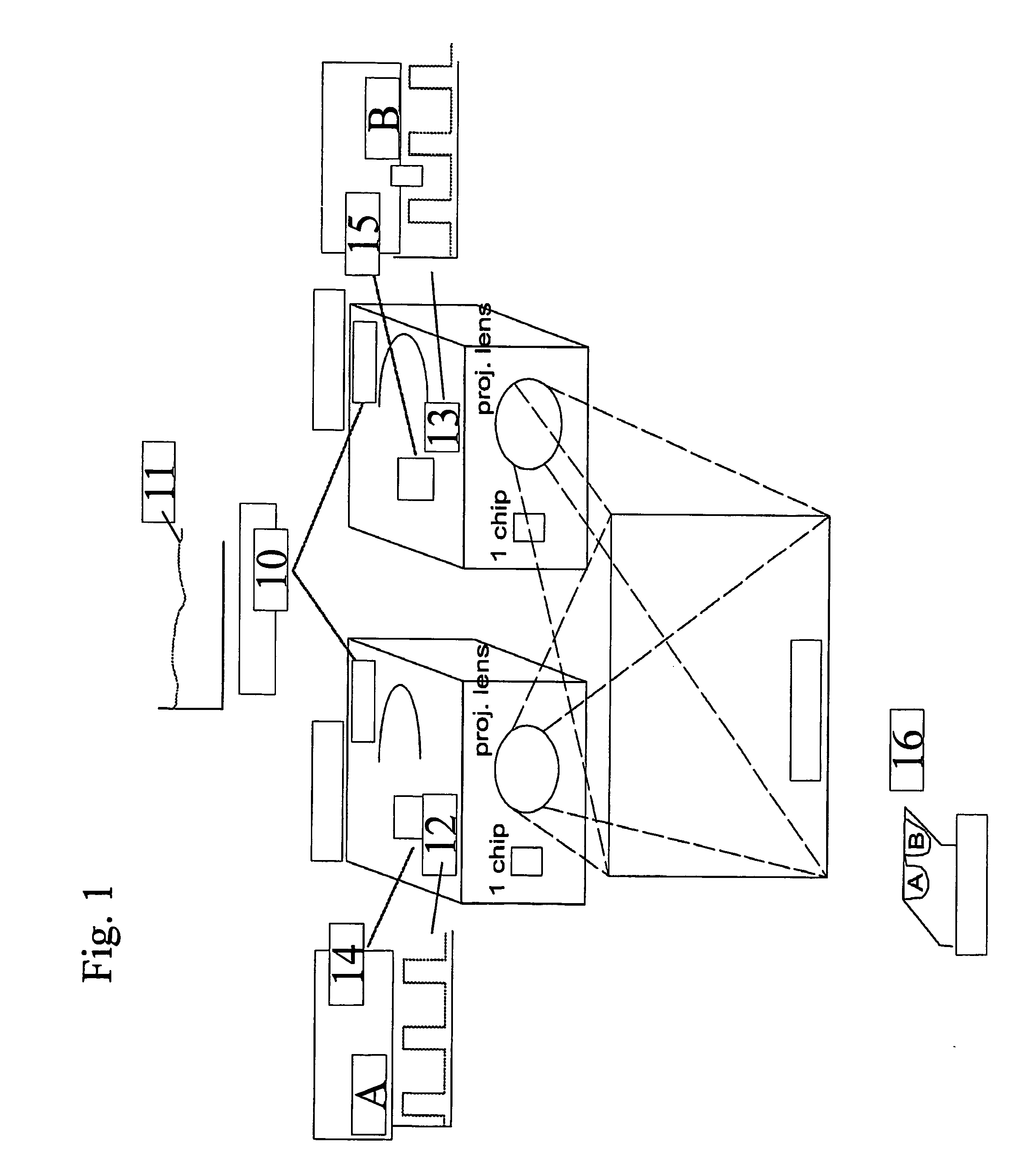
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a stereoscopic projection system including a projection device with at least one filter which filters a parameter of the light in a color selective manner. The at least one filter which filters a parameter of the light in a color selective manner has a spectral characteristic for transmitting light in a first wavelength band or set of wavelength bands and for reflecting light in a second wavelength band or set of wavelength bands. The projection device includes a device, such as e.g. a rotating wheel or a sliding filter, for fast synchronized switching between light in different wavelength bands or sets of wavelength bands. In a further aspect, a stereoscopic projection system is provided in which a combination of a first and a second filter mechanism are used, the first filter mechanism being a filter which filters a parameter of the light in a color selective manner, such as a color selective filter or a color selective retarder, and the second filter mechanism preferably being a polarizer or a shutter.
Owner:INFITEC
Photoluminescence color display
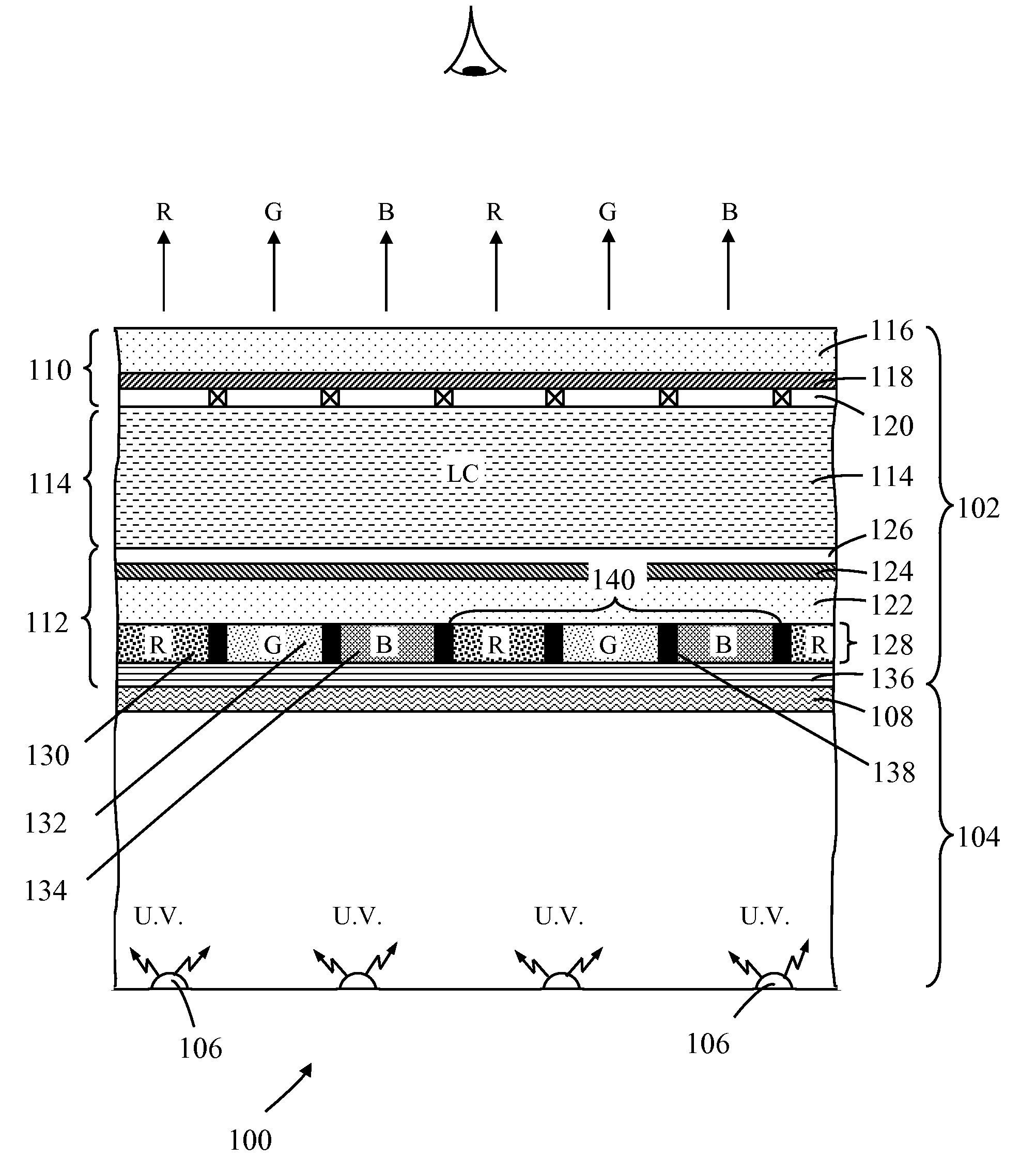
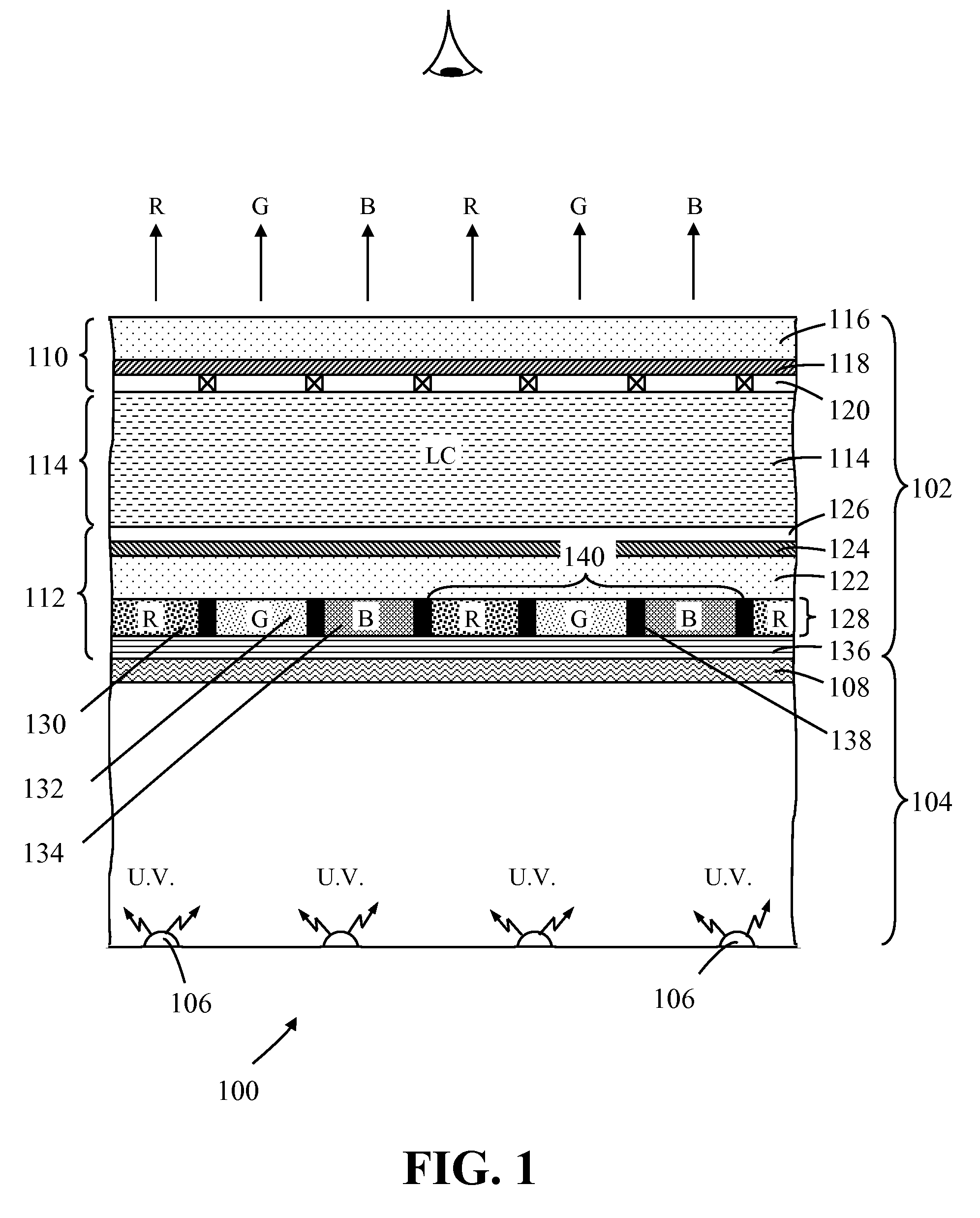
A photoluminescence color display comprises a display panel that displays red, green and blue pixel areas, an excitation source operable to generate excitation radiation for operating the display, and a photoluminescence color-element plate. The color-element plate comprises at least one photoluminescence material, such as a phosphor material or quantum dots, that is operable to emit light corresponding to red, green and blue pixel areas of the display in response to said excitation radiation. Additionally, the photo-luminescence color display comprises a wavelength selective filter that is provided between the color-element plate and the excitation source. The filter has a transmission characteristic that allows the passage of excitation radiation from the excitation source to excite the at least one photoluminescence material whilst preventing the passage of photoluminescence light back to the excitation source thereby prevent cross contamination of light among the different pixel areas of the display.
Owner:INTEMATIX
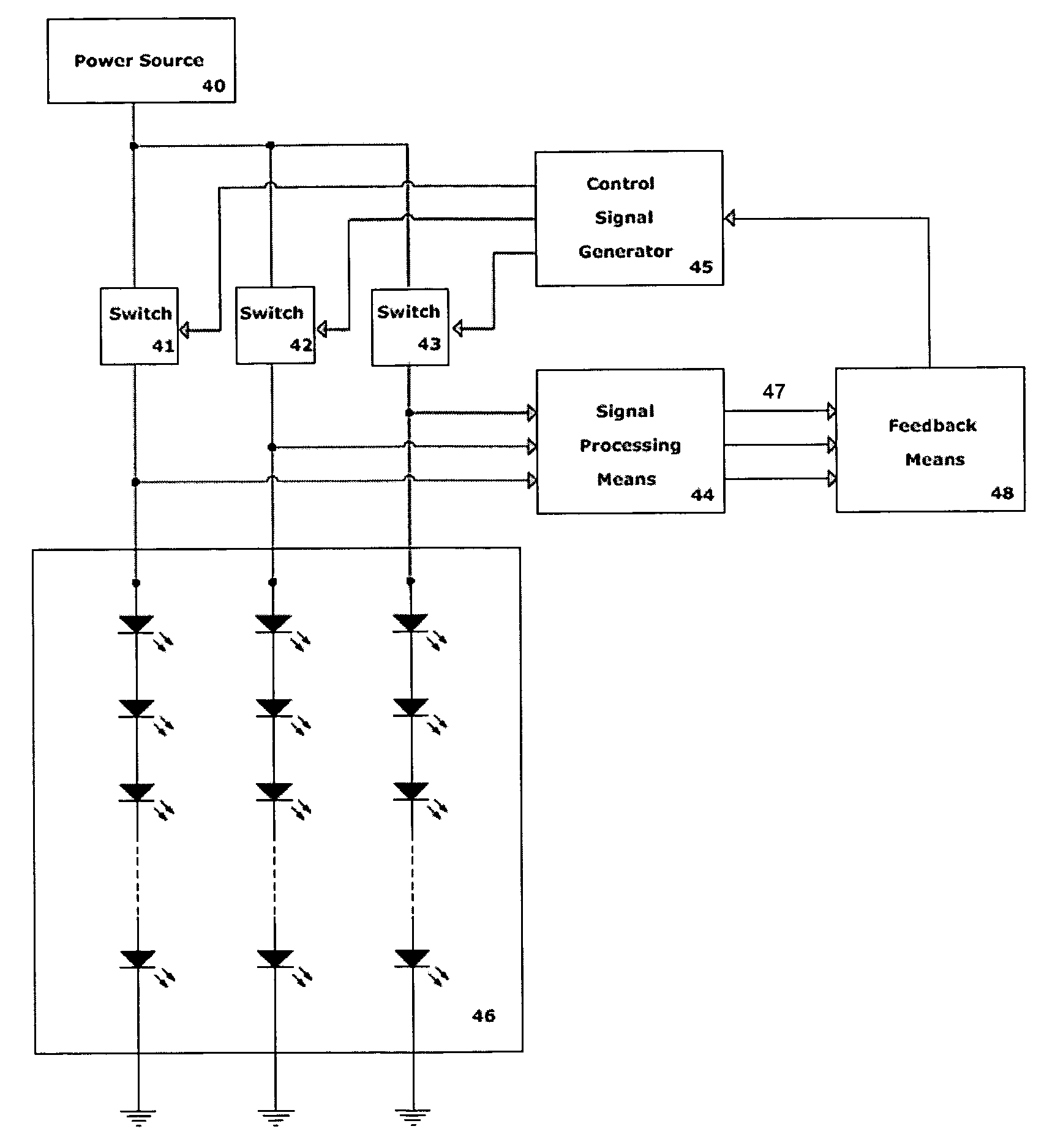
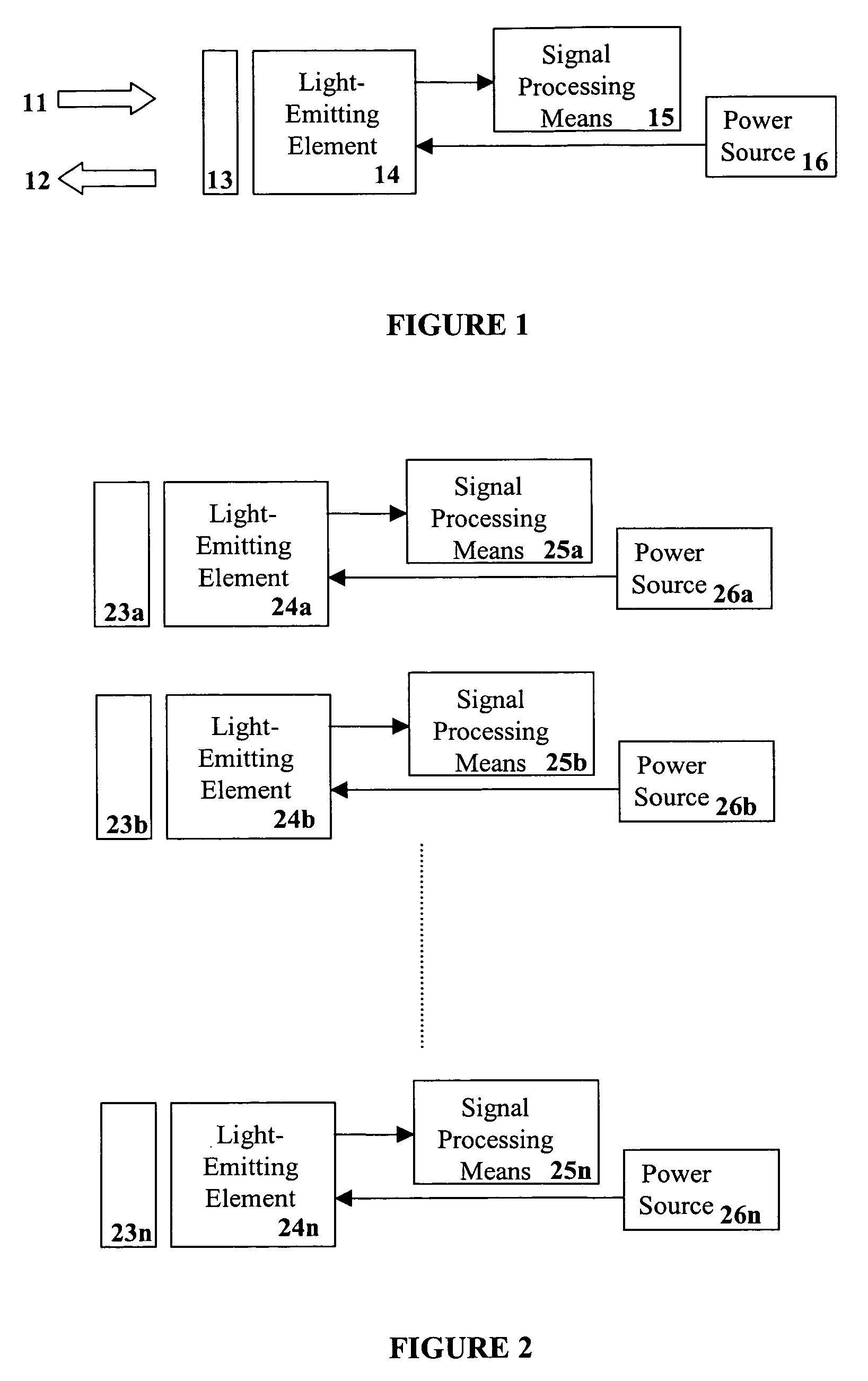
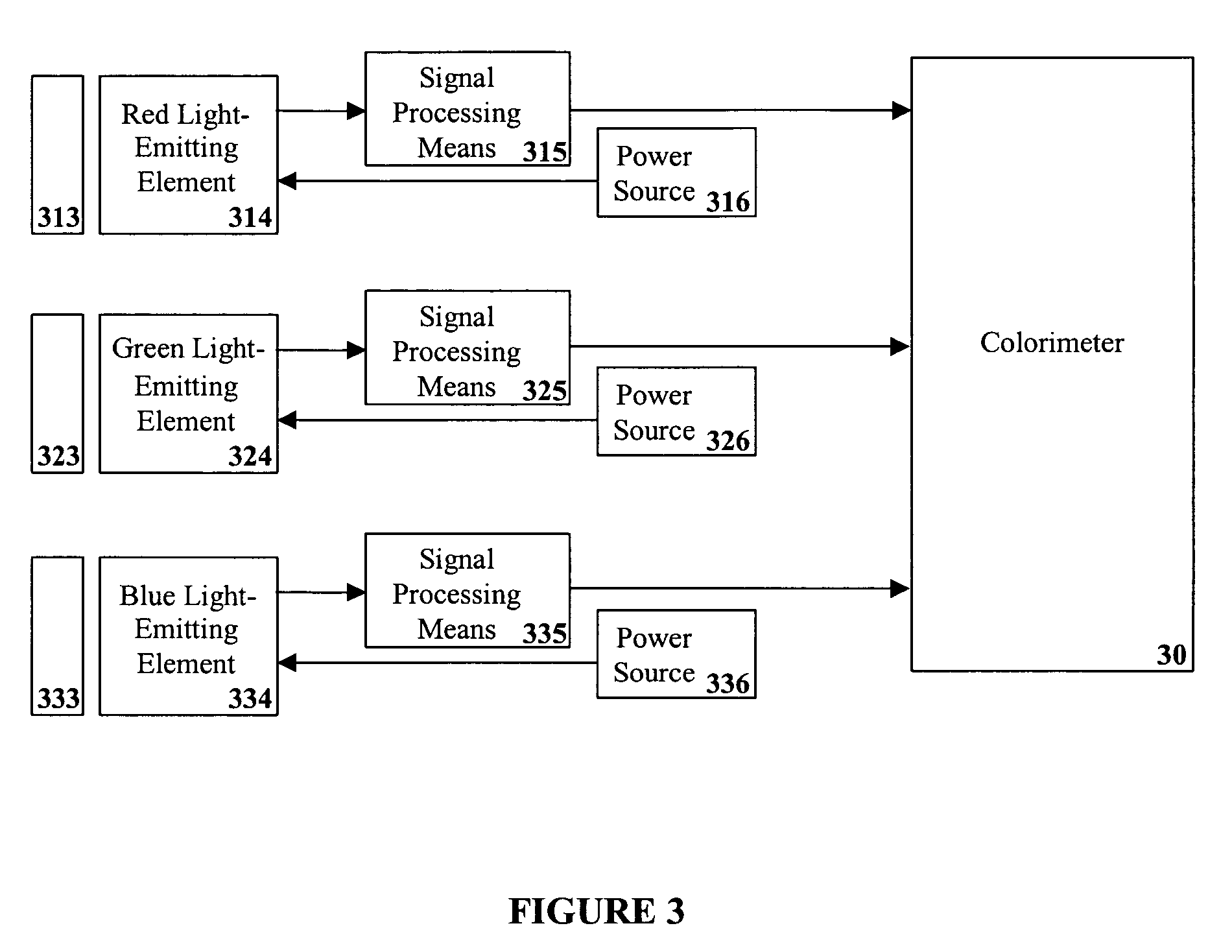
Lighting system including photonic emission and detection using light-emitting elements
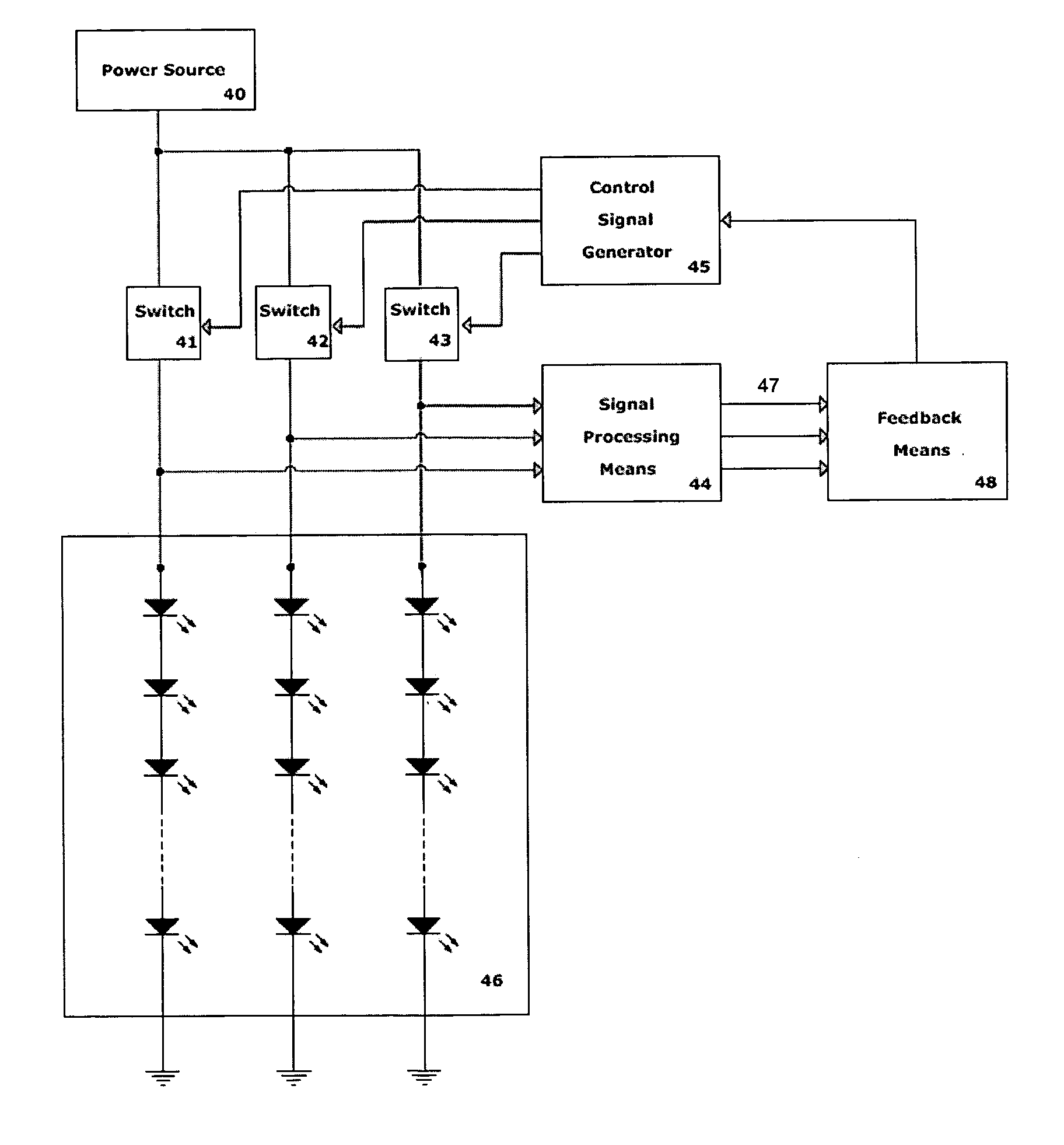
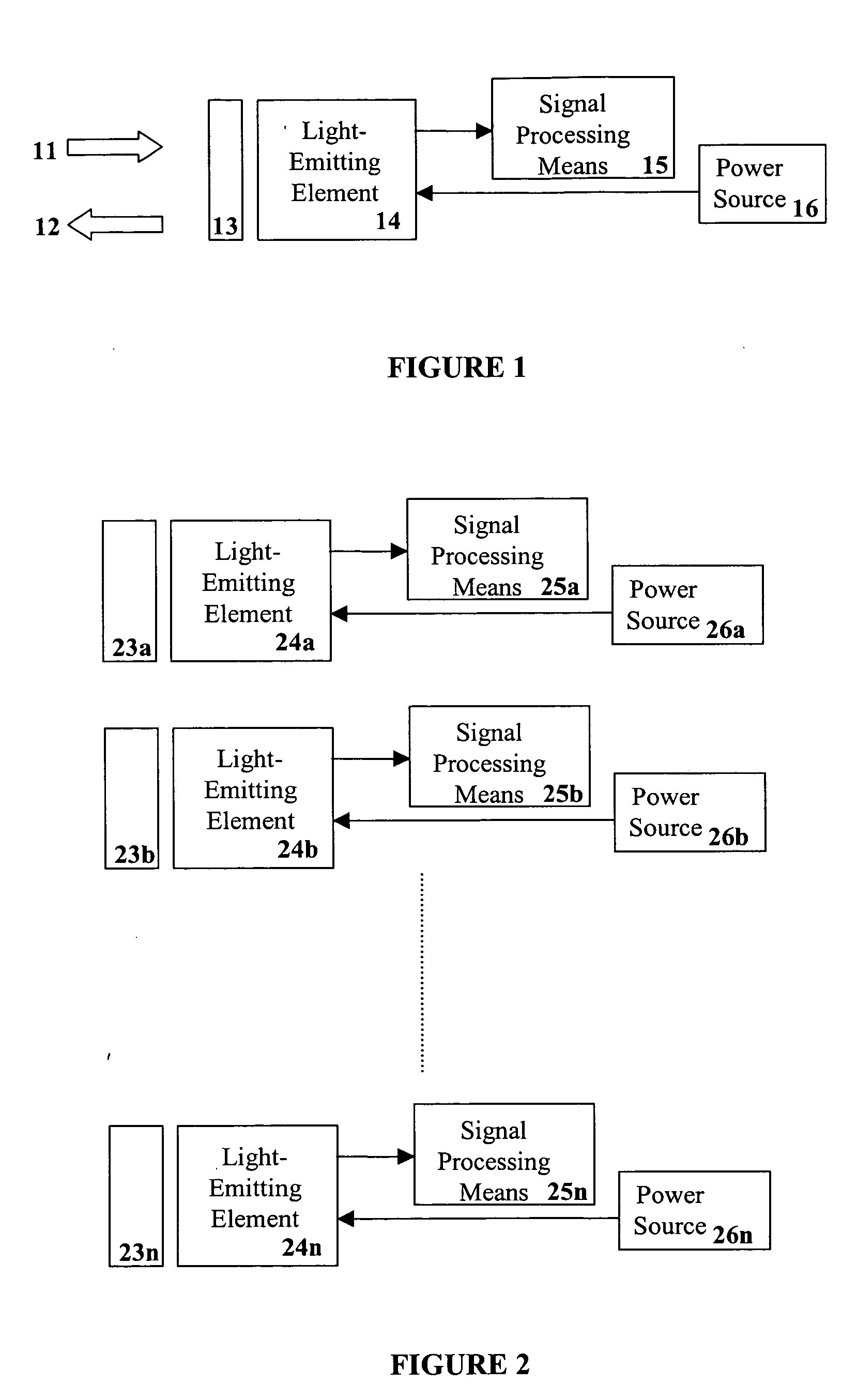
The present invention provides a system and method for generating light using light-emitting elements and detecting the intensity and spectral power distribution of light using the same light-emitting elements as spectrally sensitive photodetectors. The light-emitting elements function in two modes, an ON mode and an OFF mode, wherein in the ON mode the light-emitting elements are activated and emit light of a particular frequency or range of frequencies. When in the OFF mode, the light-emitting elements are deactivated, wherein they do not emit light but serve to detect photons incident upon them thus generating an electrical signal representative of the intensity and spectral power distribution of the incident photons. The detected signal from the deactivated light-emitting elements can be used to provide photonic feedback to a lighting system, and thereby may be used to control the brightness and color balance of the lighting system. In addition, the light-emitting elements may be arranged such that no spectrally selective filters or optics are necessary to block or focus light onto the light-emitting elements when in the detection or OFF mode.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS20060239006A1Easy to useImprove color uniformityMechanical apparatusLight source combinationsPhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of blue LED outputs to illuminate a phosphor for a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. Embodiments are disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor, and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. A further aperture mask is used to boost phosphor luminance with only modest loss of luminosity. Alternative non-recycling embodiments provide blue and yellow light in collimated beams, either separately or combined into white.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
Lighting system including photonic emission and detection using light-emitting elements
ActiveUS20060028156A1Electrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPhoton emissionPhotodetector
The present invention provides a system and method for generating light using light-emitting elements and detecting the intensity and spectral power distribution of light using the same light-emitting elements as spectrally sensitive photodetectors. The light-emitting elements function in two modes, an ON mode and an OFF mode, wherein in the ON mode the light-emitting elements are activated and emit light of a particular frequency or range of frequencies. When in the OFF mode, the light-emitting elements are deactivated, wherein they do not emit light but serve to detect photons incident upon them thus generating an electrical signal representative of the intensity and spectral power distribution of the incident photons. The detected signal from the deactivated light-emitting elements can be used to provide photonic feedback to a lighting system, and thereby may be used to control the brightness and colour balance of the lighting system. In addition, the light-emitting elements may be arranged such that no spectrally selective filters or optics are necessary to block or focus light onto the light-emitting elements when in the detection or OFF mode.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Chopped Hall effect sensor
ActiveUS7425821B2Fast response timeEliminating the significant low pass filtering requirementsCounting mechanisms/objectsVoltage/current isolationLow noiseAudio power amplifier
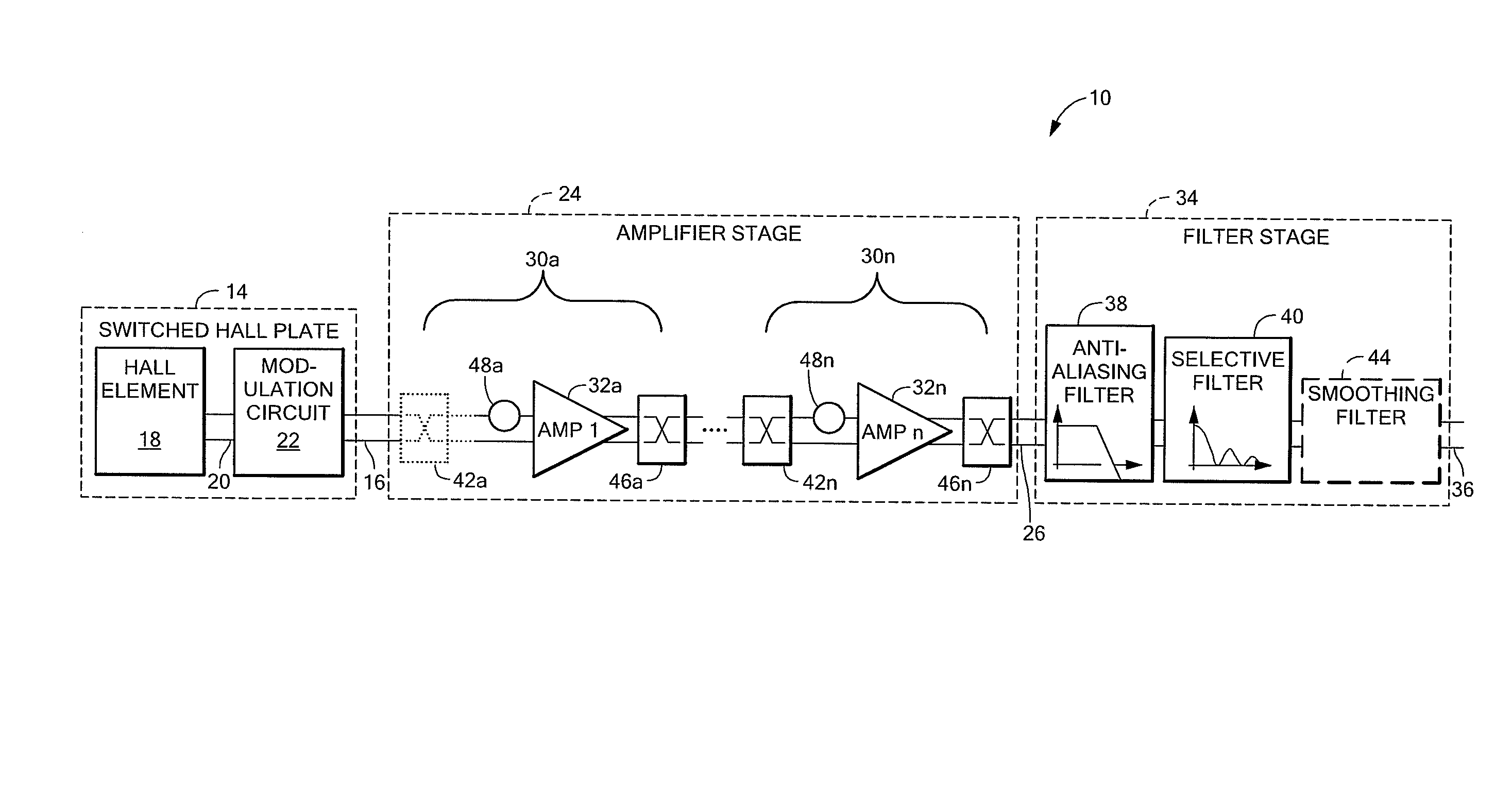
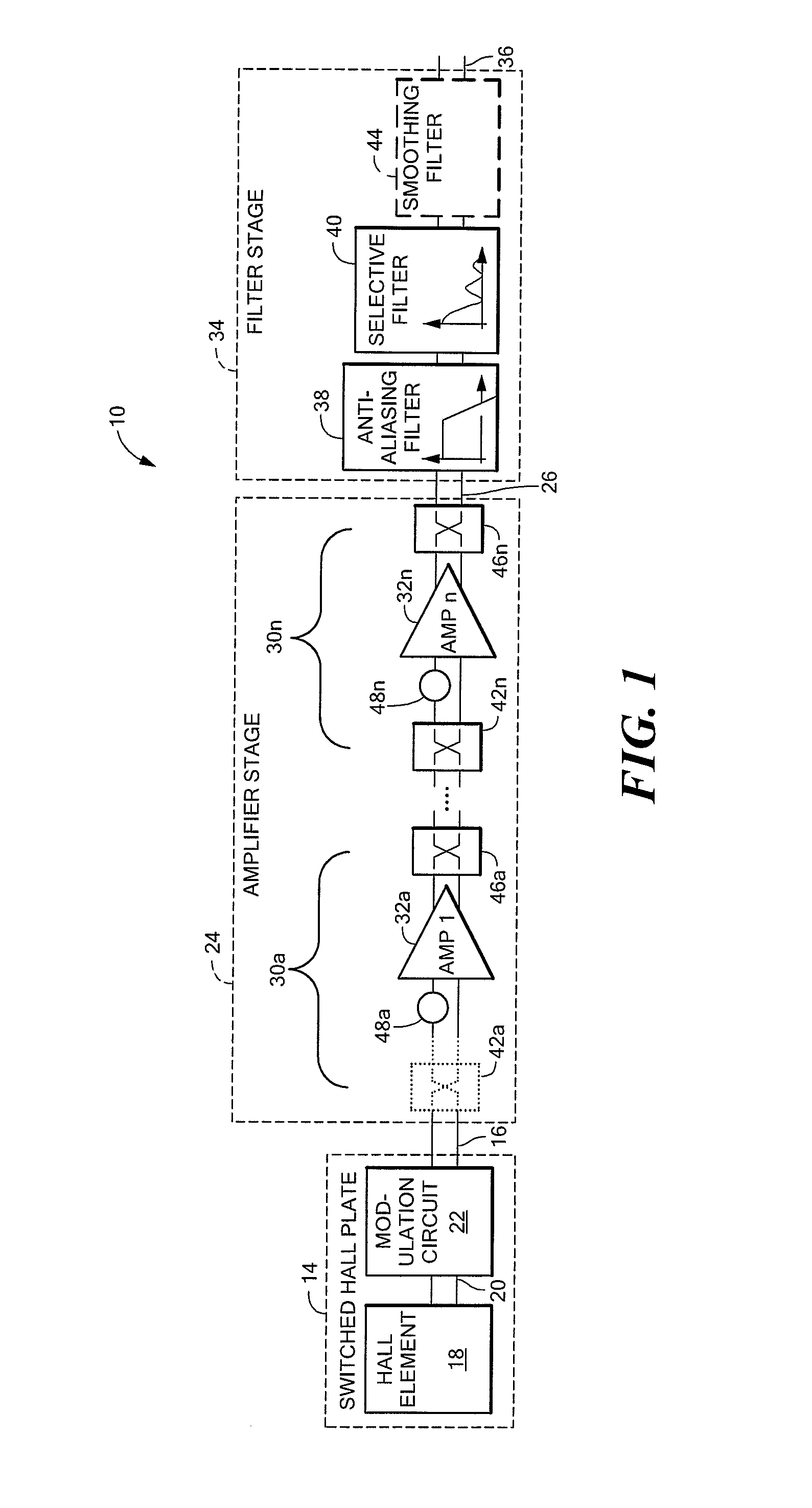
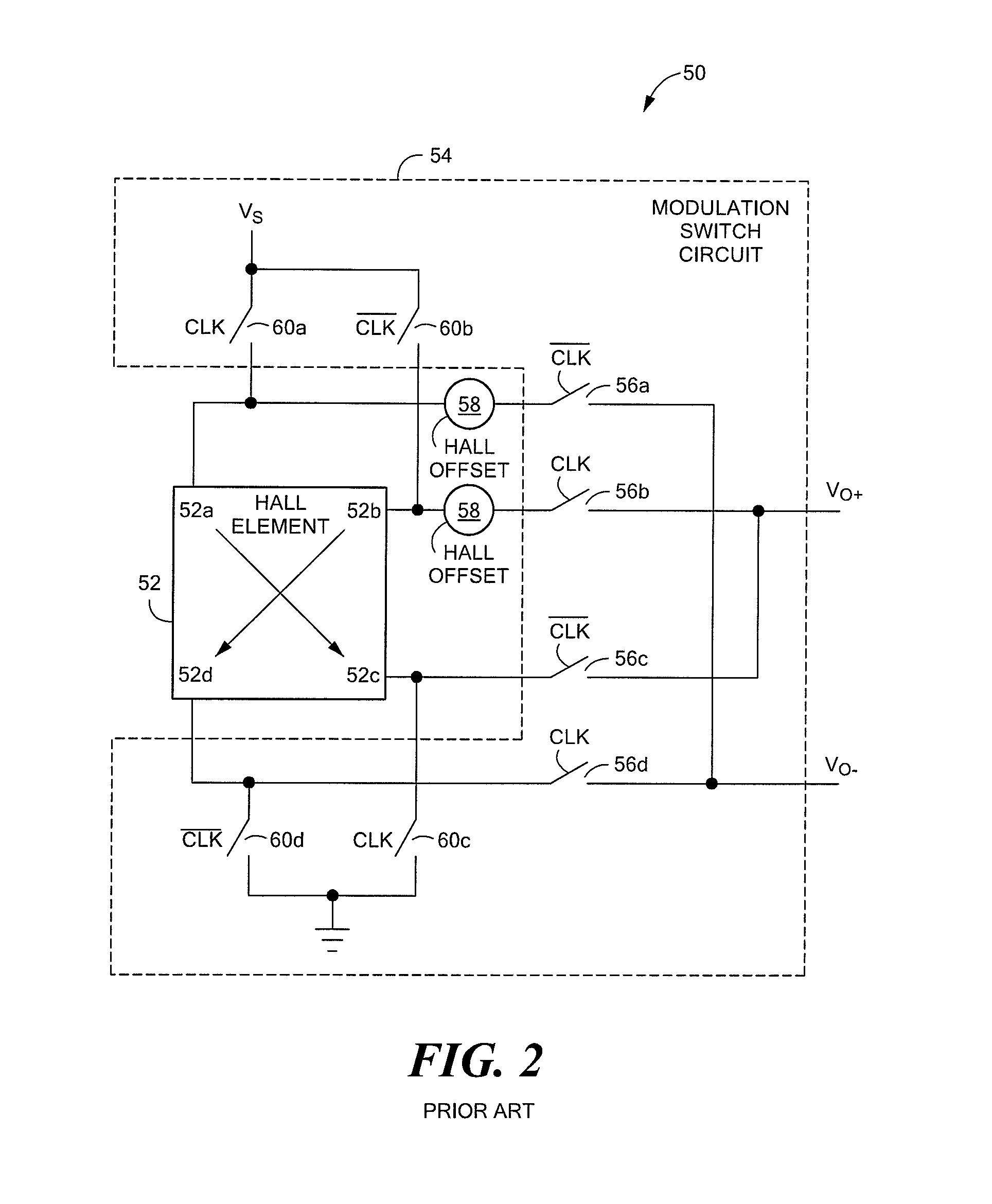
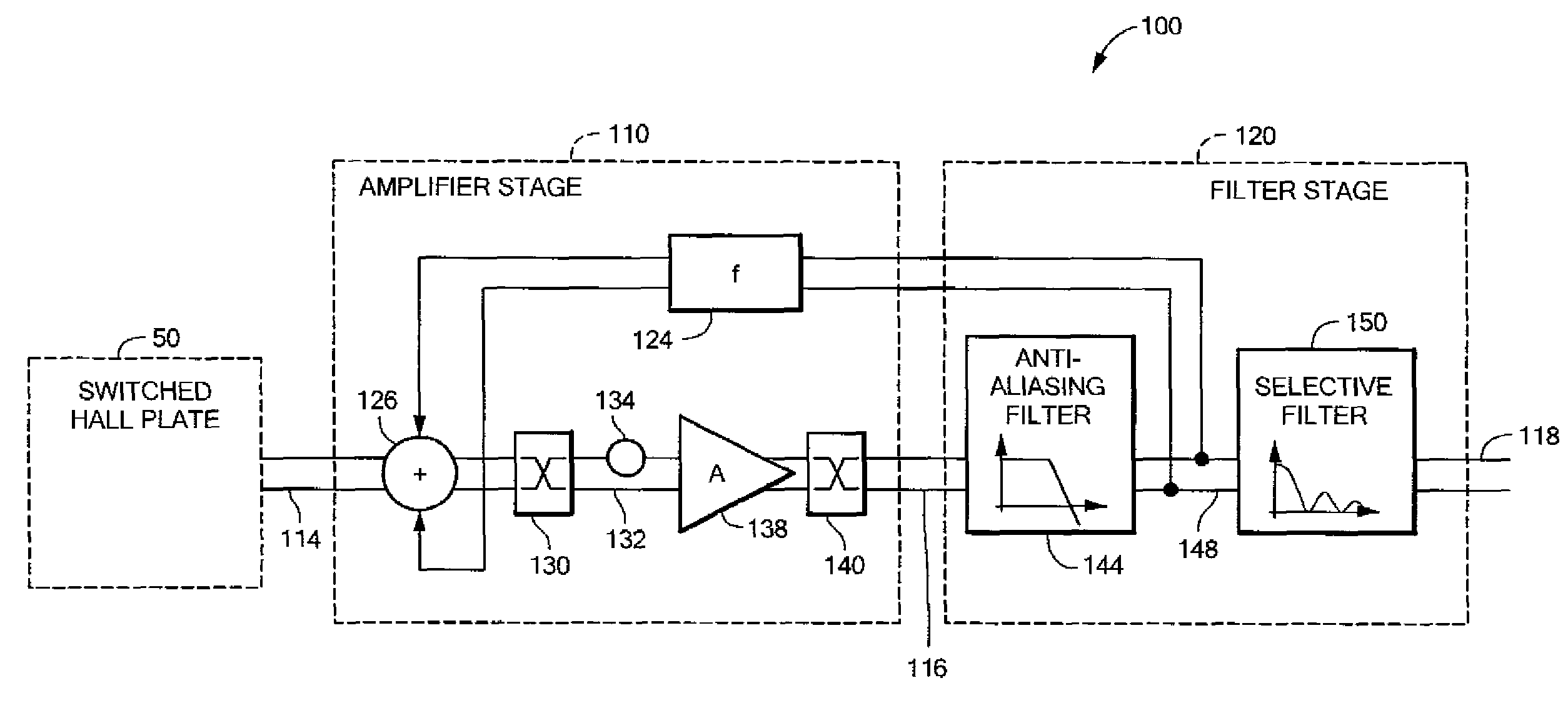
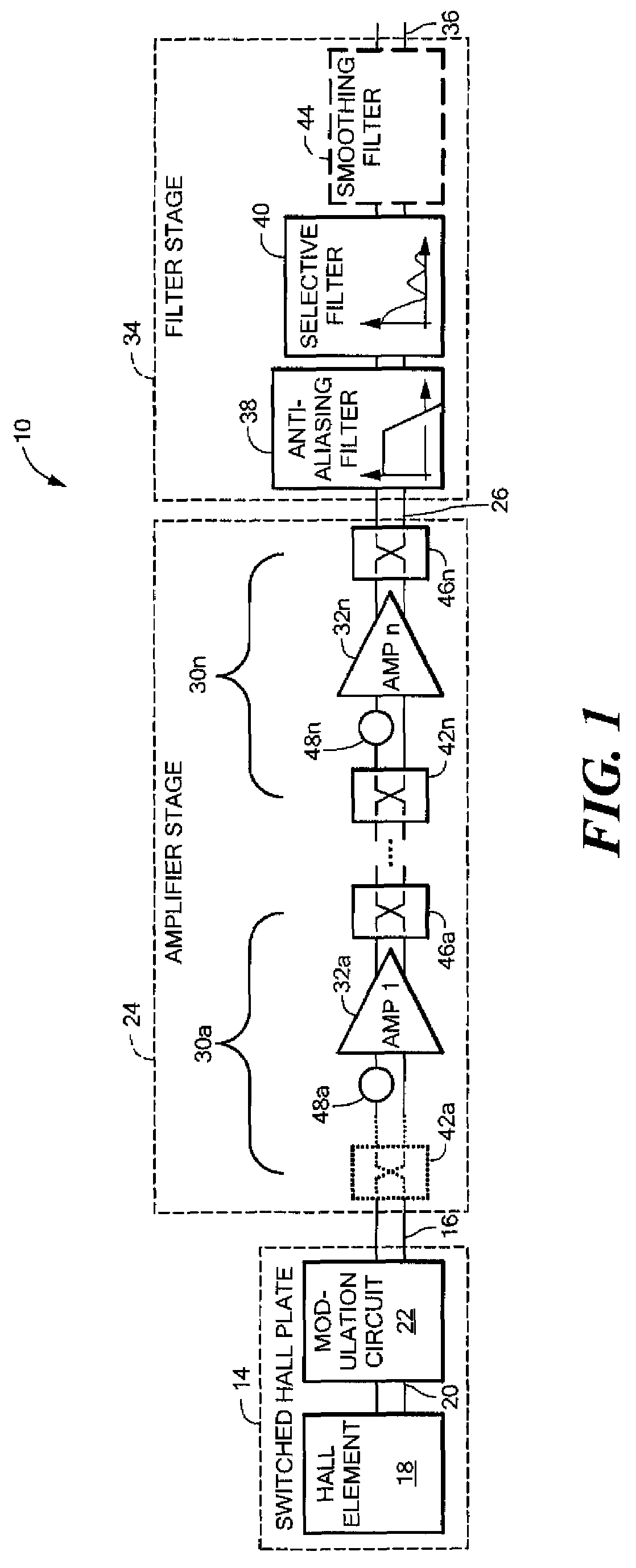
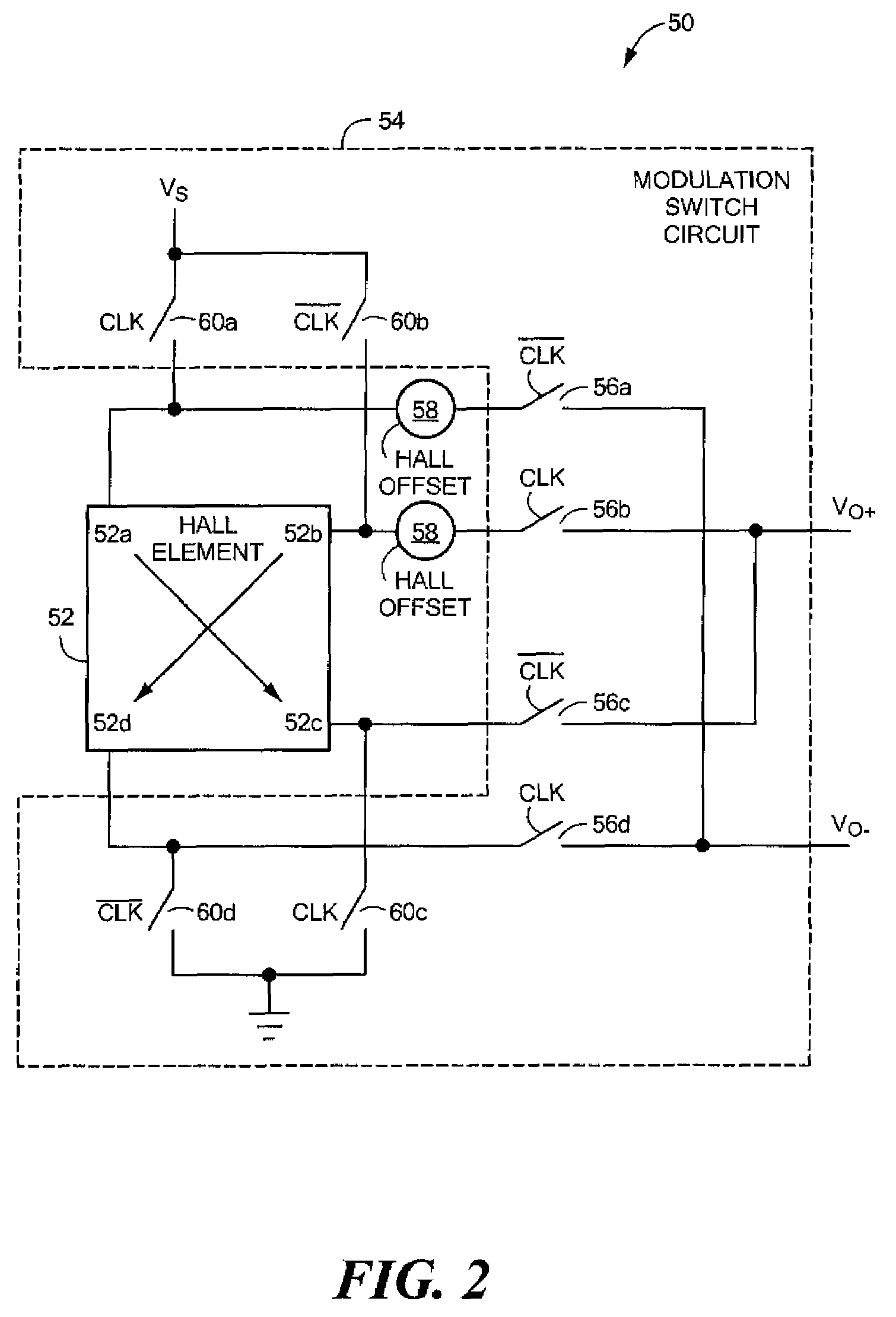
A chopped Hall effect sensor topology includes a switched Hall plate, an amplifier responsive to an output of the switched Hall plate and a filter stage responsive to the output of the amplifier and including an anti-aliasing filter and a selective filter that is tuned to the modulation frequency. The switched Hall plate includes a Hall element and a Hall plate modulation circuit that modulates the Hall offset signal component or the magnetic signal component. In embodiments in which the Hall offset signal component is modulated by the switched Hall plate, the amplifier, if chopped, includes an even number of additional modulation circuits. In embodiments in which the magnetic signal component is modulated by the switched Hall plate, the amplifier contains an odd number of modulation circuits. The described topology provides a low noise, fast response time Hall effect sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Chopped hall effect sensor
ActiveUS20080094055A1Fast response timeEliminating the significant low pass filtering requirementsVoltage/current isolationCounting mechanisms/objectsLow noiseAudio power amplifier
A chopped Hall effect sensor topology includes a switched Hall plate, an amplifier responsive to an output of the switched Hall plate and a filter stage responsive to the output of the amplifier and including an anti-aliasing filter and a selective filter that is tuned to the modulation frequency. The switched Hall plate includes a Hall element and a Hall plate modulation circuit that modulates the Hall offset signal component or the magnetic signal component. In embodiments in which the Hall offset signal component is modulated by the switched Hall plate, the amplifier, if chopped, includes an even number of additional modulation circuits. In embodiments in which the magnetic signal component is modulated by the switched Hall plate, the amplifier contains an odd number of modulation circuits. The described topology provides a low noise, fast response time Hall effect sensor.
Owner:ALLEGRO MICROSYSTEMS INC
Method and device for performing stereoscopic image display based on color selective filters
InactiveUS7832869B2Fast synchronized switchingLower requirementProjectorsColor television detailsPolarizerLength wave
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a stereoscopic projection system including a projection device with at least one filter which filters a parameter of the light in a color selective manner. The at least one filter which filters a parameter of the light in a color selective manner has a spectral characteristic for transmitting light in a first wavelength band or set of wavelength bands and for reflecting light in a second wavelength band or set of wavelength bands. The projection device includes a device, such as e.g. a rotating wheel or a sliding filter, for fast synchronized switching between light in different wavelength bands or sets of wavelength bands. In a further aspect, a stereoscopic projection system is provided in which a combination of a first and a second filter mechanism are used, the first filter mechanism being a filter which filters a parameter of the light in a color selective manner, such as a color selective filter or a color selective retarder, and the second filter mechanism preferably being a polarizer or a shutter.
Owner:INFITEC
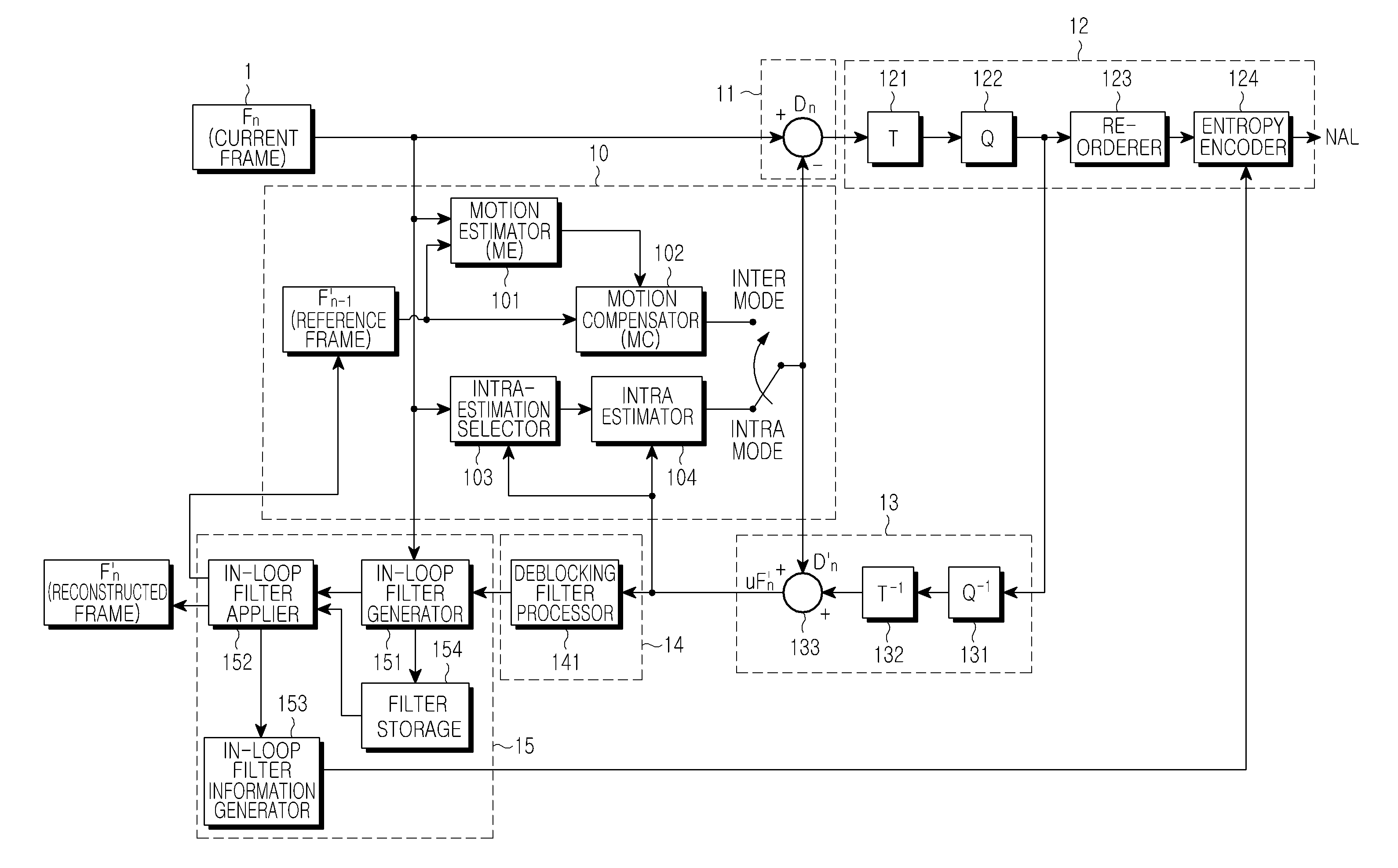
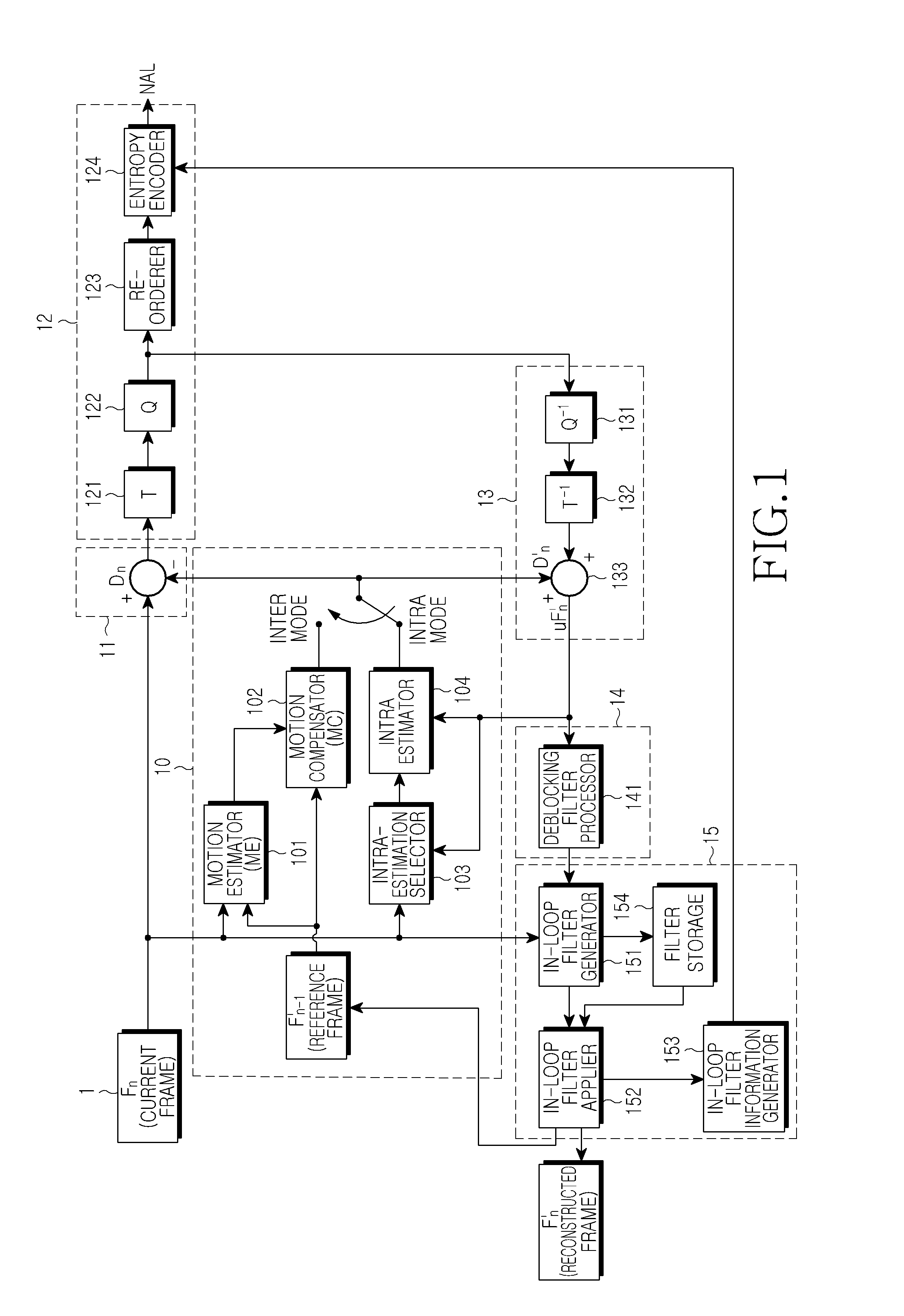
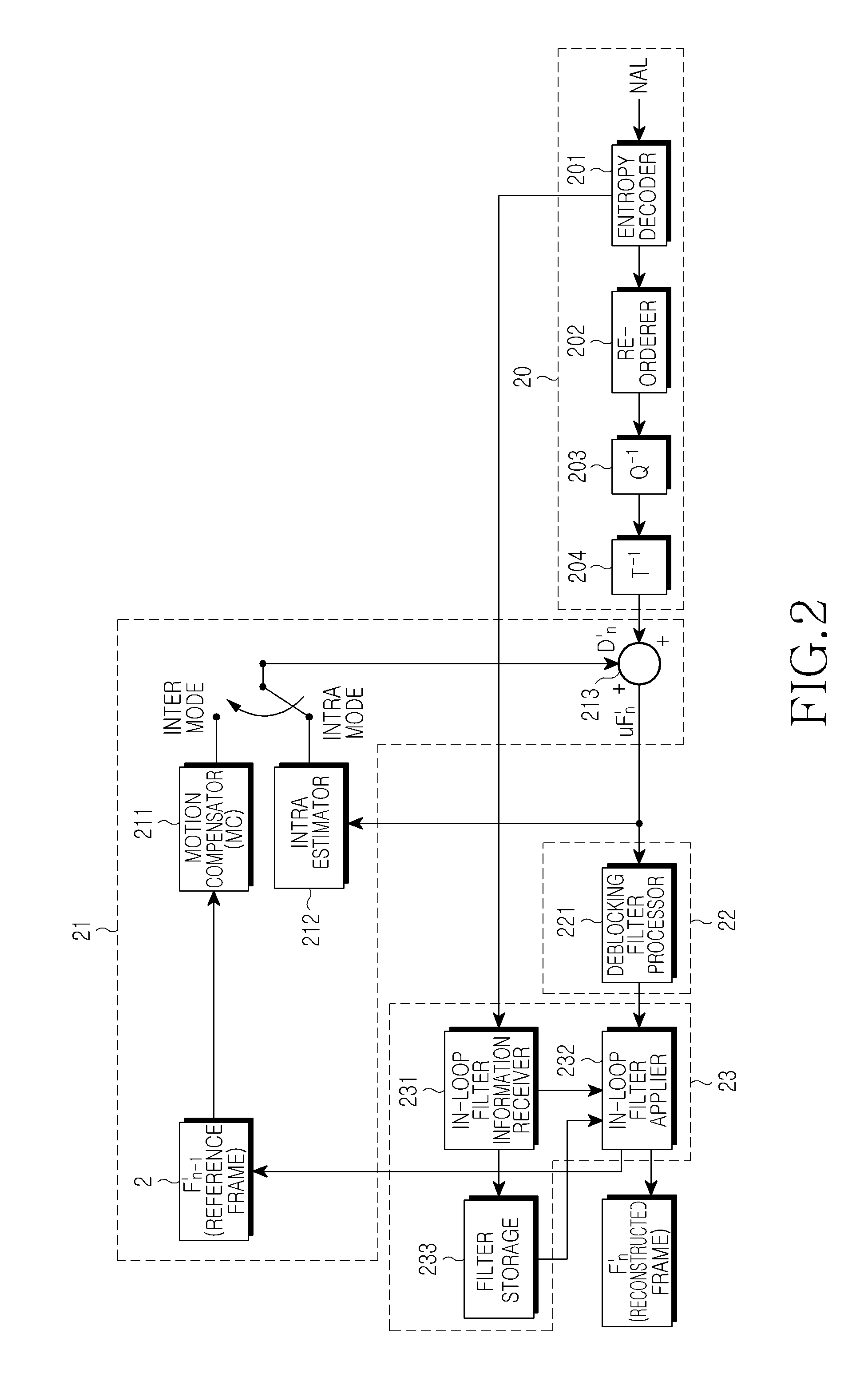
Apparatus and method for in-loop filtering of image data and apparatus for encoding/decoding image data using the same
InactiveUS20100329361A1Eliminate errorsColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputational scienceLoop filter
An in-loop filtering apparatus for eliminating an error of deblocking-filtered image data in an encoder of image data, the apparatus including: an in-loop filter generator which generates in-loop filters using different filter coefficients for a block boundary and a block inside of the deblocking-filtered image; an in-loop filter applier which performs selective filtering on at least one of the block boundary and the block inside using the generated in-loop filters; and an in-loop filter information generator which generates in-loop filter information including at least one of coefficients of the generated in-loop filters, information indicating an area to which in-loop filtering is applied between the block boundary and the block inside, a size of a block to which in-loop filtering is applied, and a flag indicating whether to use an in-loop filter generated for a current frame or an in-loop filter generated for a previous frame.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Optical manifold for light-emitting diodes
ActiveUS7380962B2Cost-effectiveImprove throughputMechanical apparatusVehicle headlampsPhotoluminescencePhosphor
An optical manifold for efficiently combining a plurality of blue LED outputs to illuminate a phosphor for a single, substantially homogeneous output, in a small, cost-effective package. Embodiments are disclosed that use a single or multiple LEDs and a remote phosphor, and an intermediate wavelength-selective filter arranged so that backscattered photoluminescence is recycled to boost the luminance and flux of the output aperture. A further aperture mask is used to boost phosphor luminance with only modest loss of luminosity. Alternative non-recycling embodiments provide blue and yellow light in collimated beams, either separately or combined into white.
Owner:SEOUL SEMICONDUCTOR
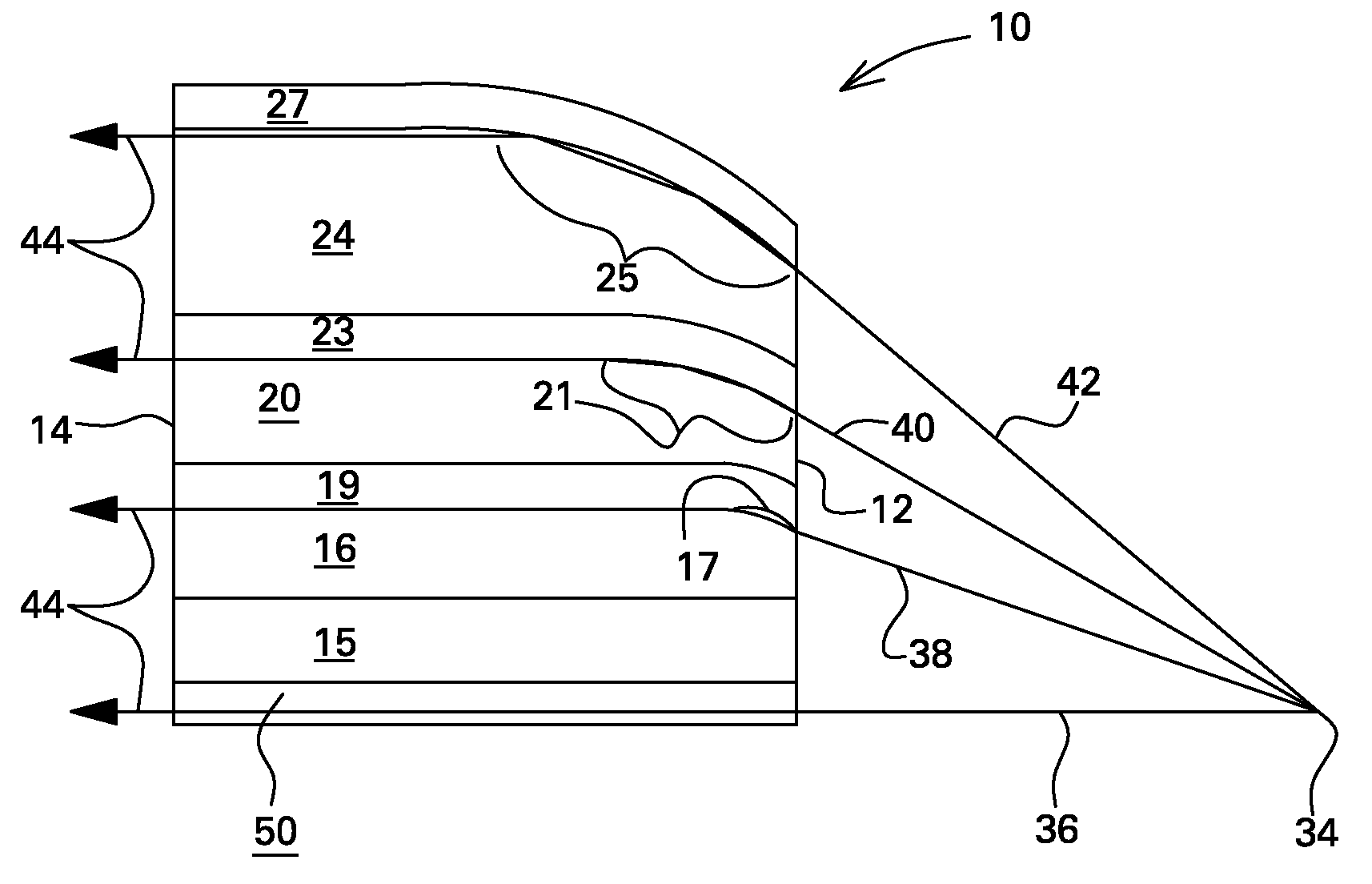
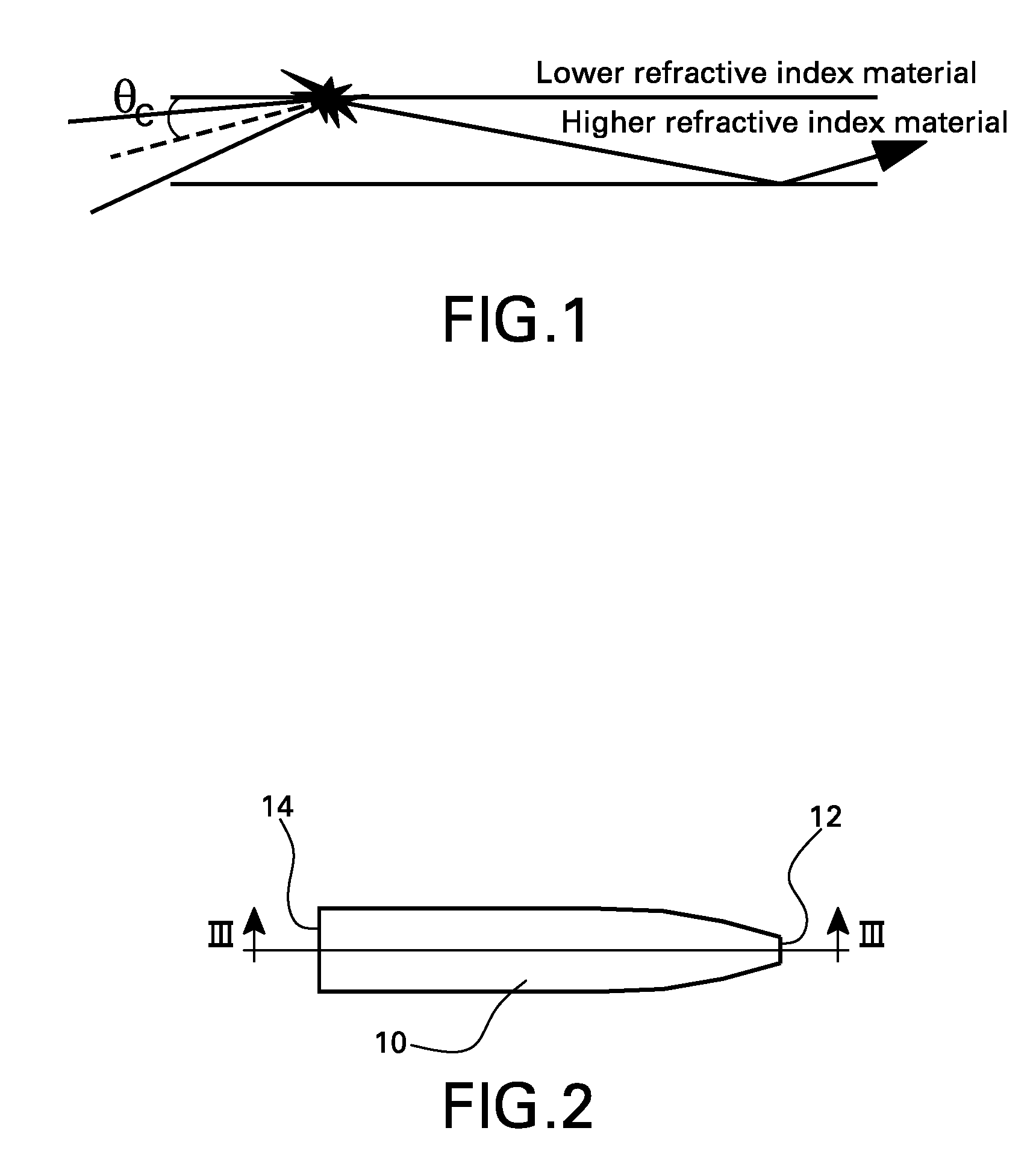
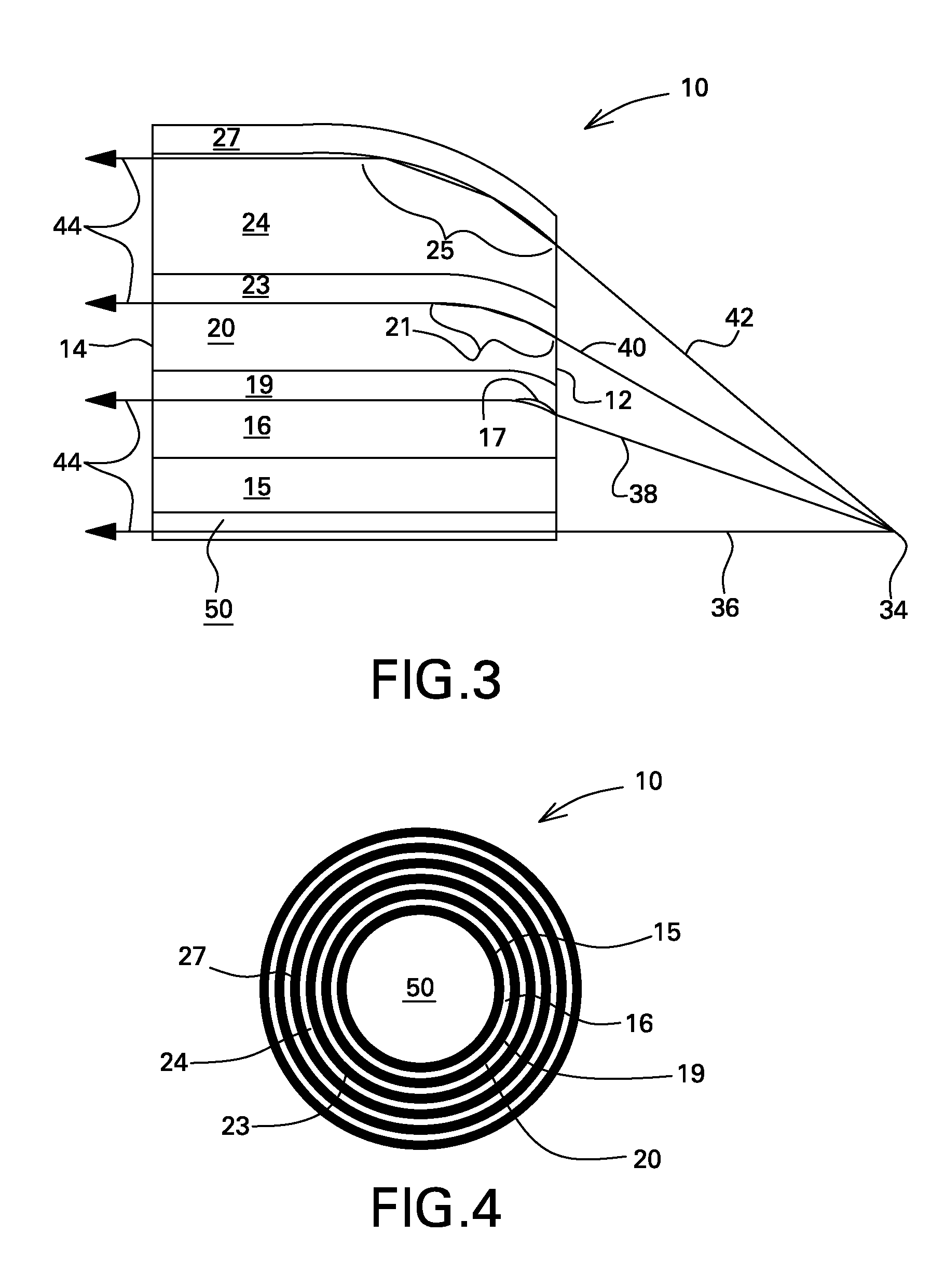
High performance selective light wavelength filtering providing improved contrast sensitivity
InactiveUS20120075577A1Improved contrast sensitivityHigh sensitivitySpectales/gogglesIntraocular lensWavelength filterLength wave
The present invention relates to ophthalmic systems and coatings comprising a selective light wavelength filter, wherein said selective filter provides improved contrast sensitivity.
Owner:ISHAK ANDREW W +7
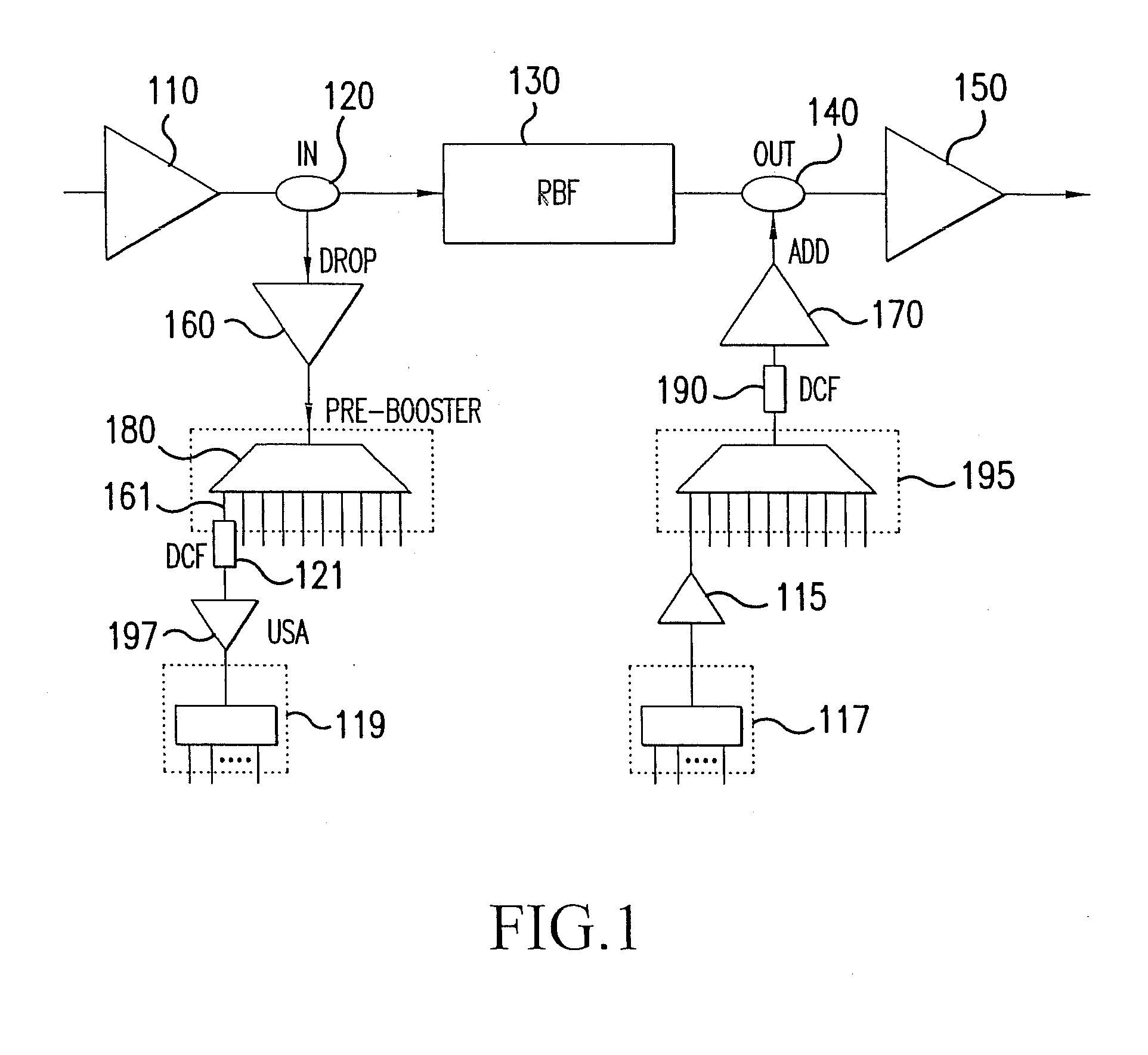
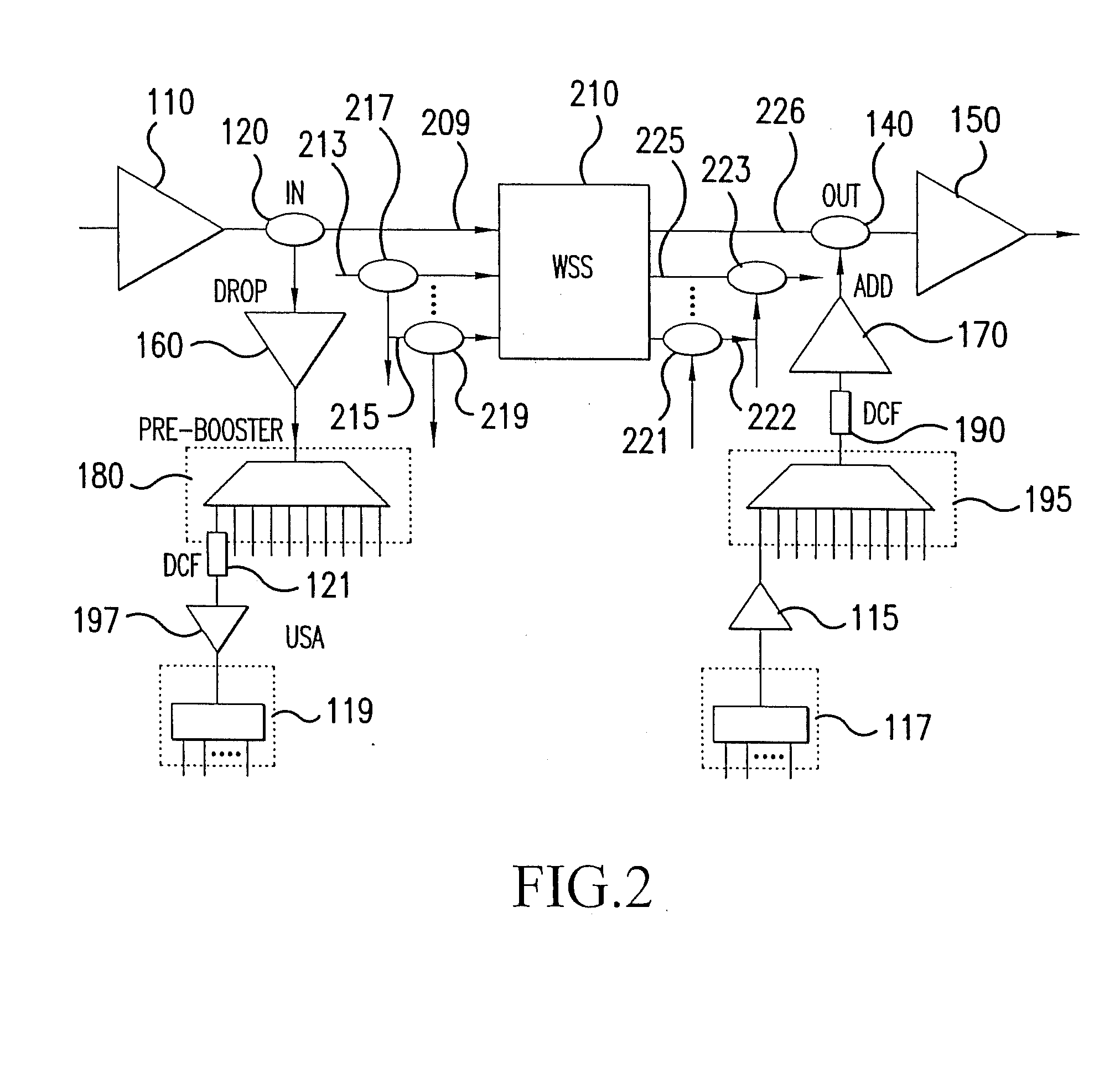
Optimized directionless optical add/drop module systems and methods
ActiveUS20100129082A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesAudio power amplifierOptical add-drop multiplexer
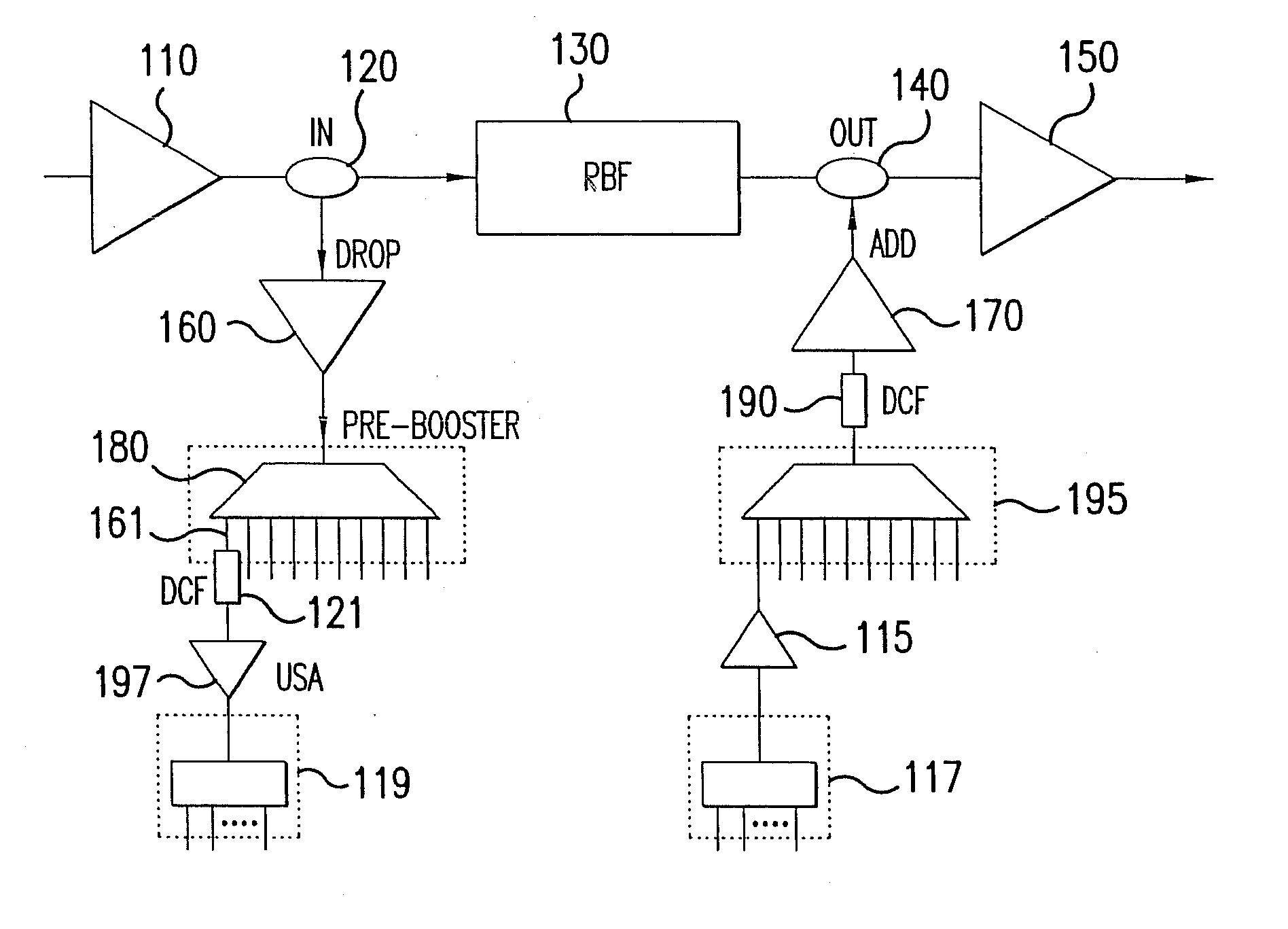
The present disclosure provides optimized configurations for a directionless reconfigurable optical add / drop multiplexer application. The present invention includes an add module with improved optical signal-to-noise through placing amplifiers prior to a multi-cast optical switch. The present invention includes various drop module configurations utilizing distributed gain, channel selective filters, and bi-directional configurations to reduce power consumption and complexity. Additionally, the present invention includes an integrated broadcast and select architecture.
Owner:CIENA
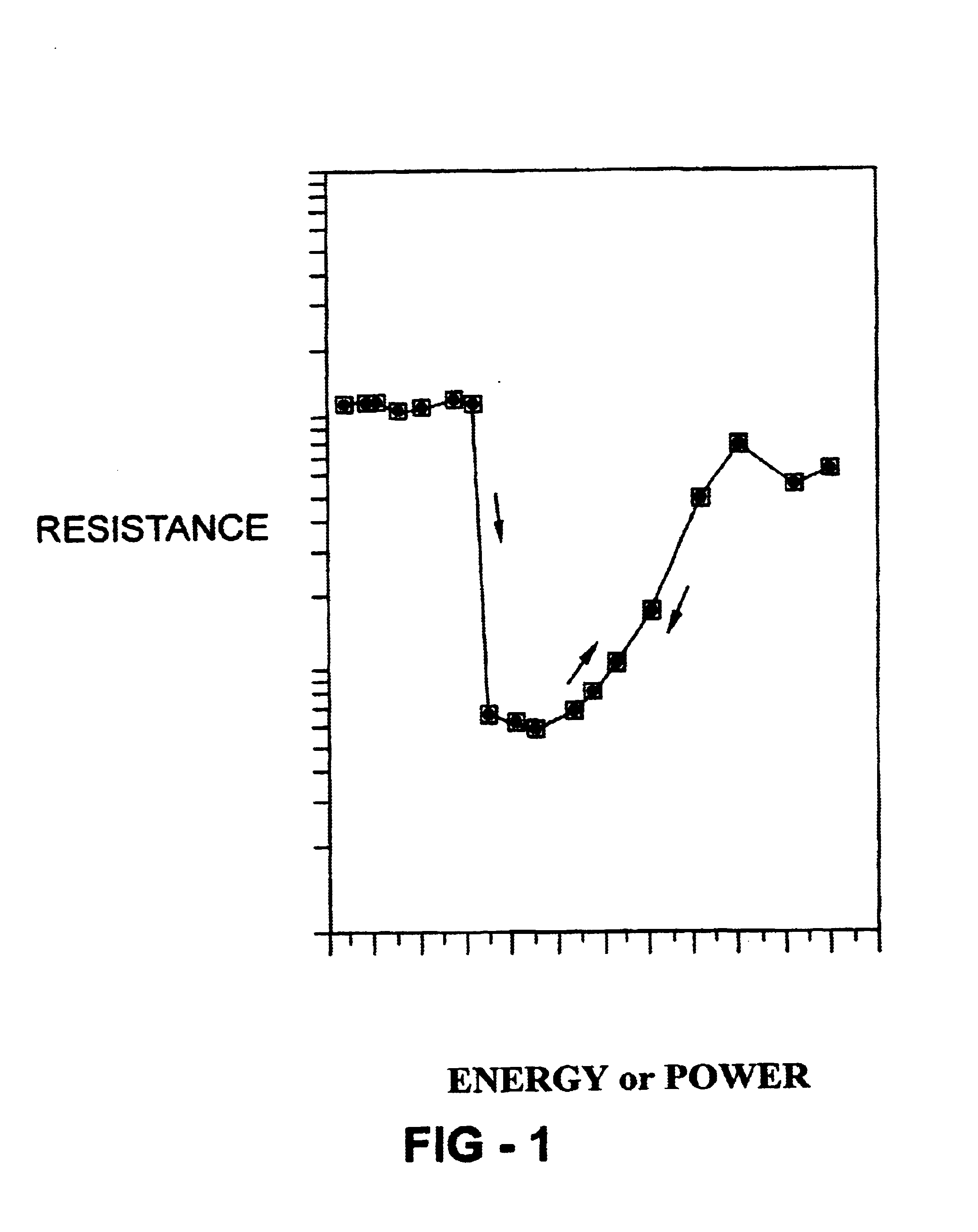
Photonic crystals and devices having tunability and switchability
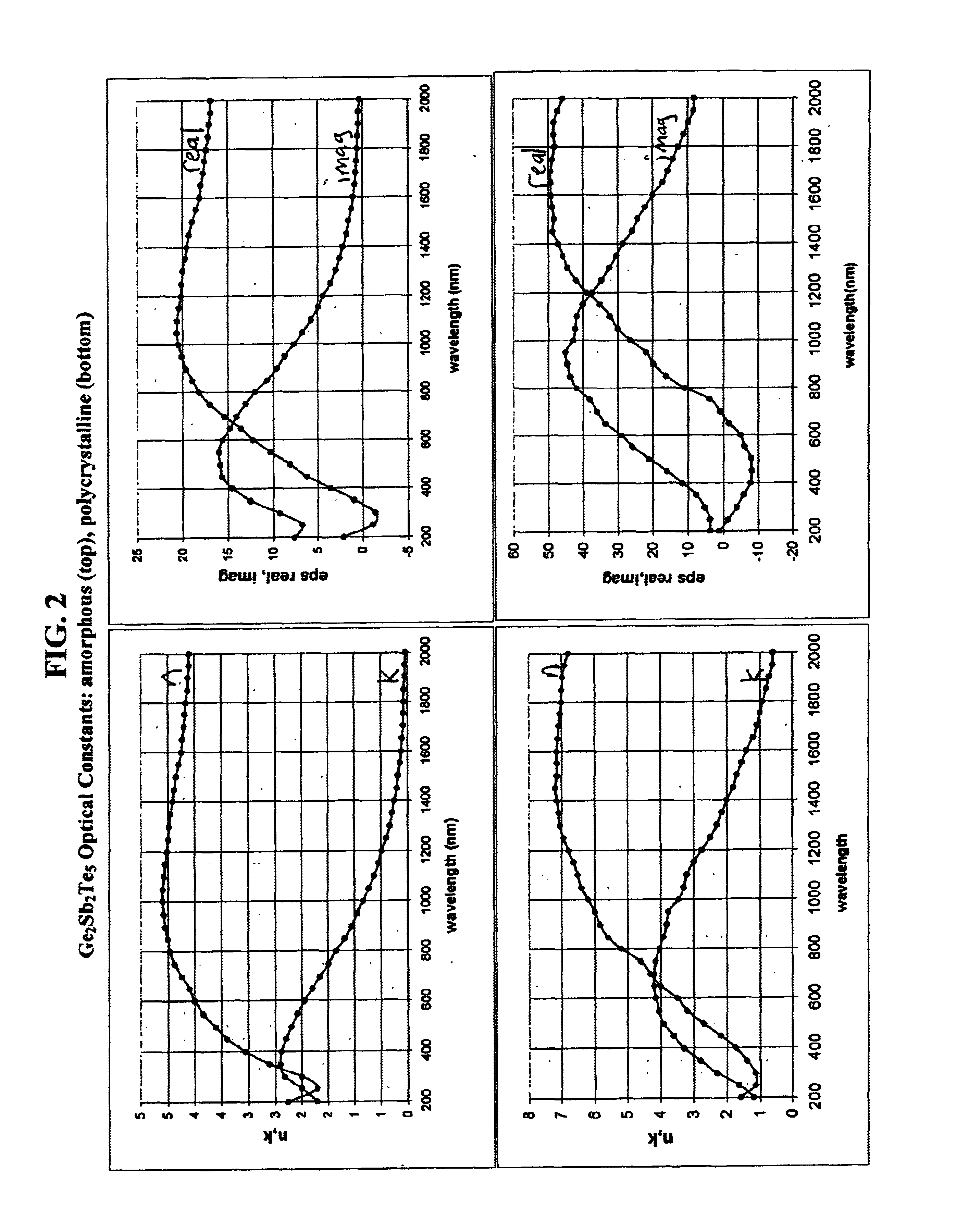
A photonic crystal having reversibly tunable photonic properties. The photonic crystal includes a phase change material having a plurality of structural states that vary with respect to fractional crystallinity. Optical constants including refractive index, extinction coefficient and permittivity vary as the fractional crystallinity of the phase change material is varied thereby providing tunability of photonic crystal properties. Variations among the structural states of the phase change material are reversibly effected through the addition of energy in forms including optical or electrical energy. The photonic crystals may include defects that provide photonic states within the photonic band gap. The position of these states is tunable through the control of the fractional crystallinity of the phase change material included in the photonic crystal. Electromagnetic radiation resonators including photonic crystals having photonic states in the photonic band gap are further provided. These resonators may be used for frequency selective filtering or routing of electromagnetic radiation and permit tunable variation in the frequency and decay rates of resonant modes through control of the structural state of the phase change material. These resonators are further coupled to waveguides to provide tunable channel drop filters and narrowband reflectors.
Owner:ENERGY CONVERSION DEVICES INC
Optical transceiver with a plurality of optical subassemblies electrically connected by integrated FPC board with a substrate
ActiveUS20090052898A1Improve reliabilityReduce manufacturing costLaser detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsTransceiverEngineering
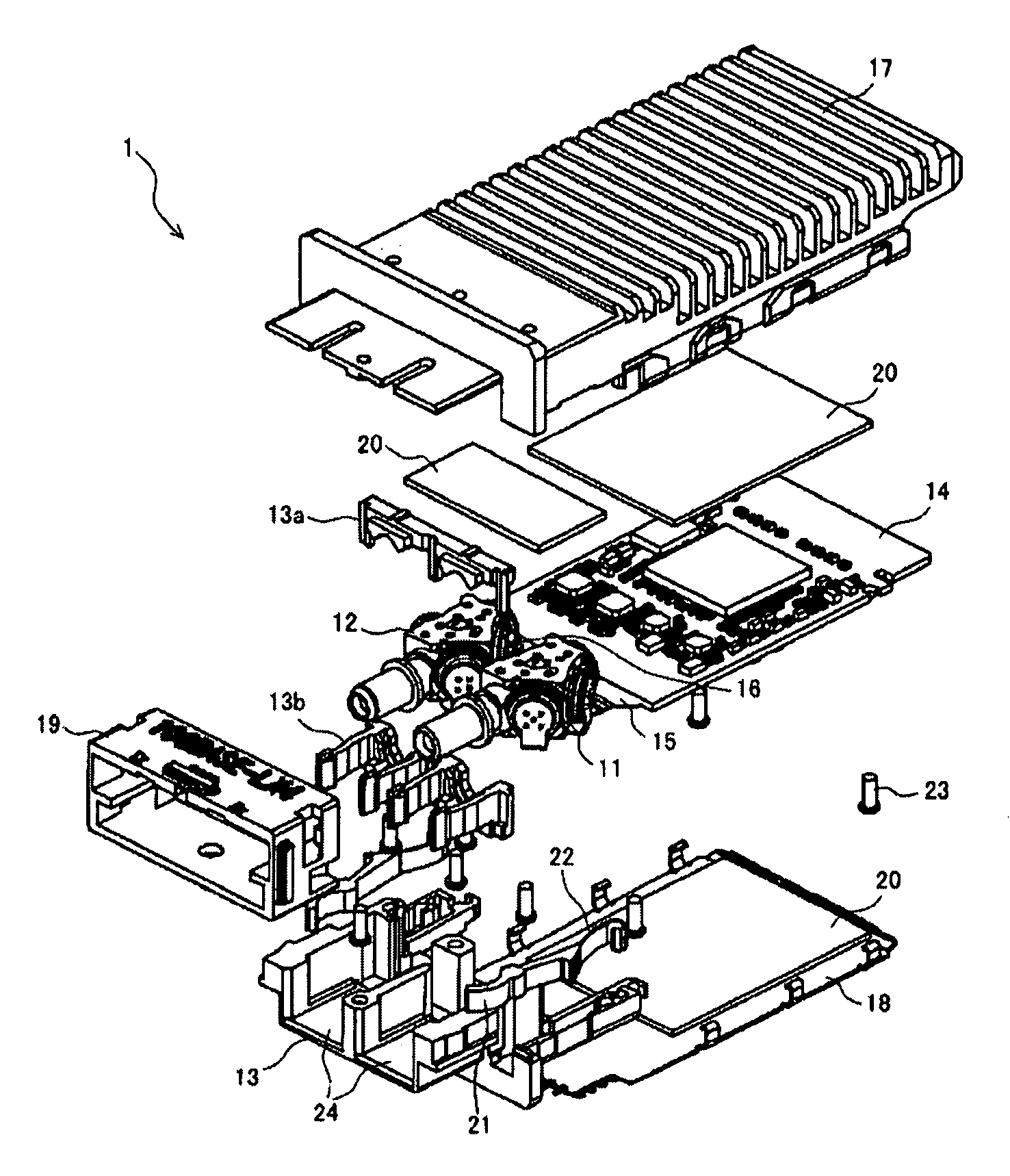
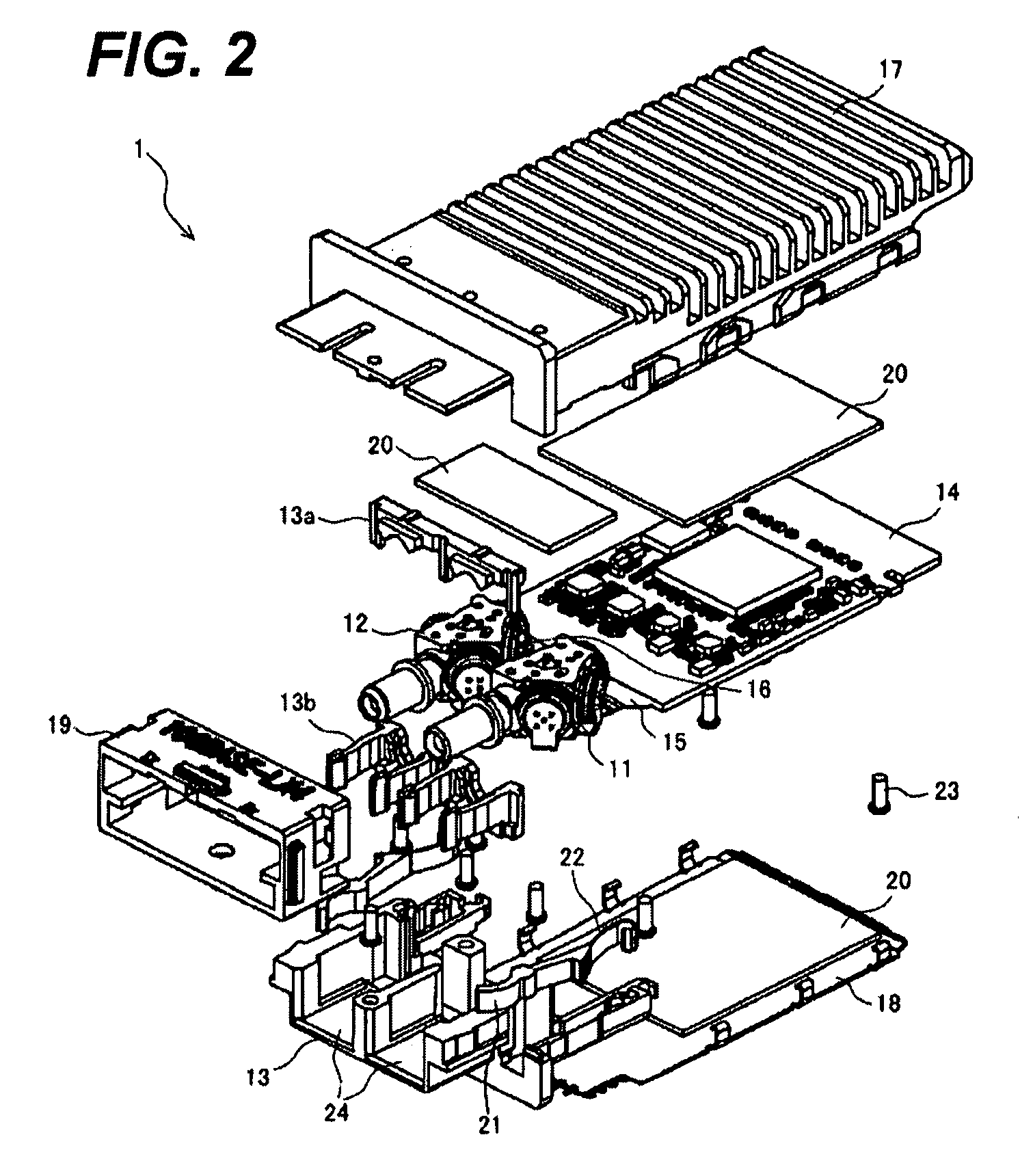
The present invention provides an optical transceiver with a function of the wavelength division multiplexing. The transceiver includes a receiver optical unit, a transmitter optical units and a substrate. Both optical unit includes a plurality of receiver optical subassemblies (ROSAs) or a plurality of transmitter optical subassemblies (TOSAs) and a plurality of wavelength selective filters. The ROSAs or the TOSAs in respective optical units is electrically connected with the circuit on the substrate by the flexible printed circuit (FPC) board with a plurality of branches, each connected to the ROSAs or the TOSAs, and a connecting portion fixed to the substrate.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Multi-energy imaging system and method using optic devices
InactiveUS20090147922A1NanoinformaticsElectrode and associated part arrangementsPhoton transmissionX-ray
A multi-energy imaging system and method for selectively generating high-energy X-rays and low-energy X-ray beams are described. A pair of optic devices are used, one optic device being formed to emit high X-ray energies and the other optic device being formed to emit low X-ray energies. A selective filtering mechanism is used to filter the high X-ray energies from the low X-ray energies. The optic devices have at least a first solid phase layer having a first index of refraction with a first photon transmission property and a second solid phase layer having a second index of refraction with a second photon transmission property. The first and second layers are conformal to each other.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Systems and methods for wavelength selective measurement of properties of small volume liquid samples
InactiveUS7277175B2Color/spectral properties measurementsSpectrum generationLength waveSelectivity filter
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
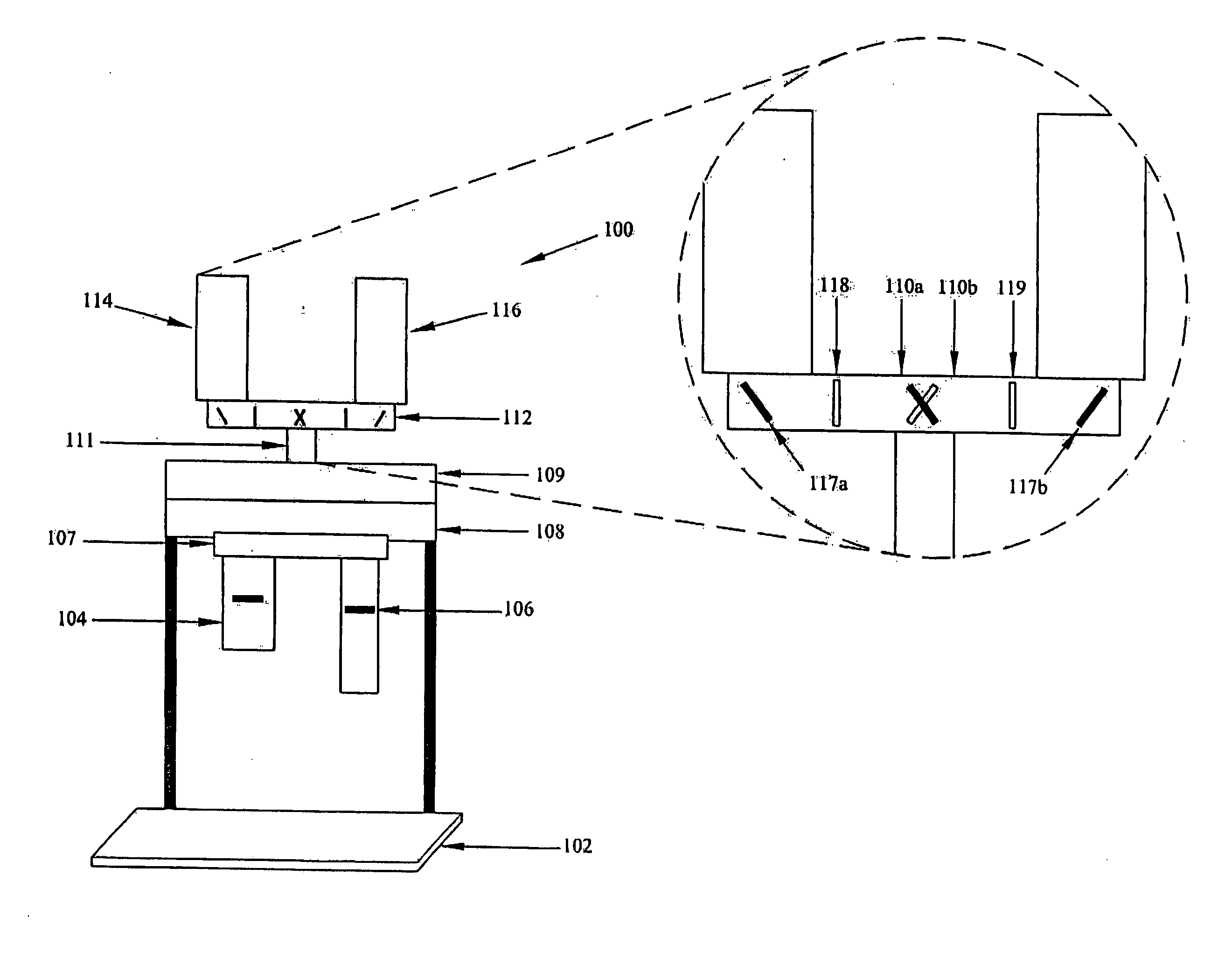
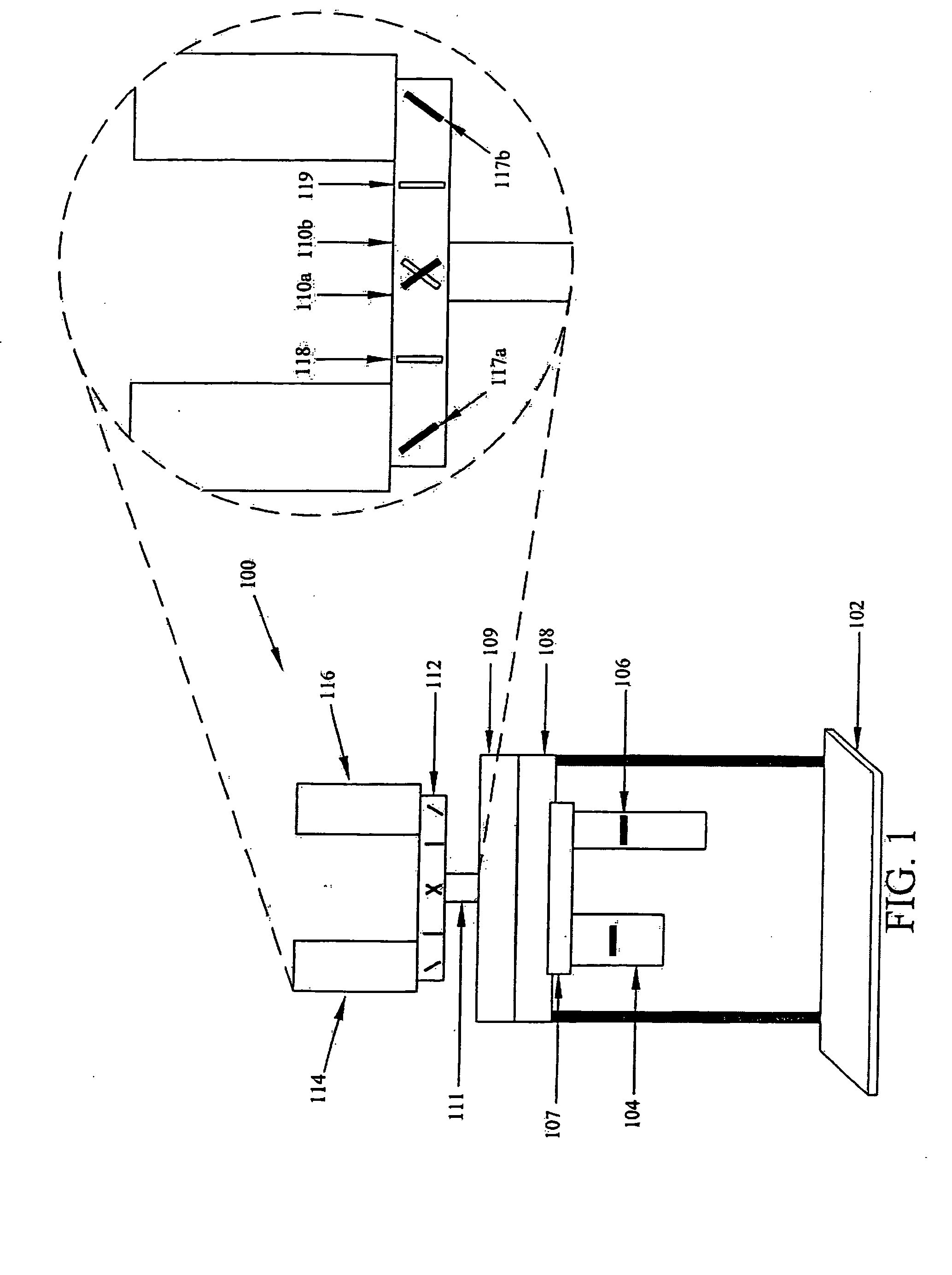
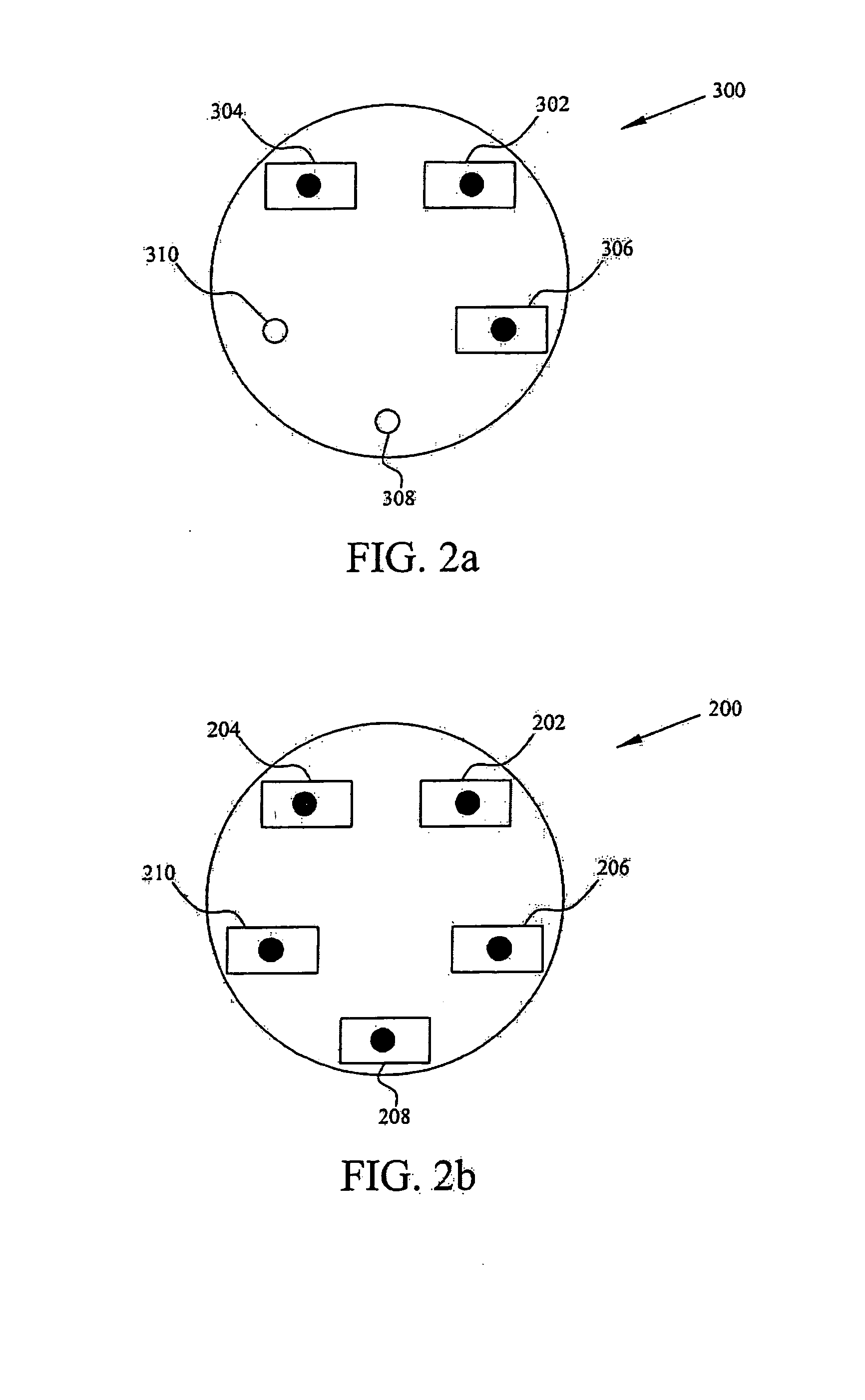
Lighting device
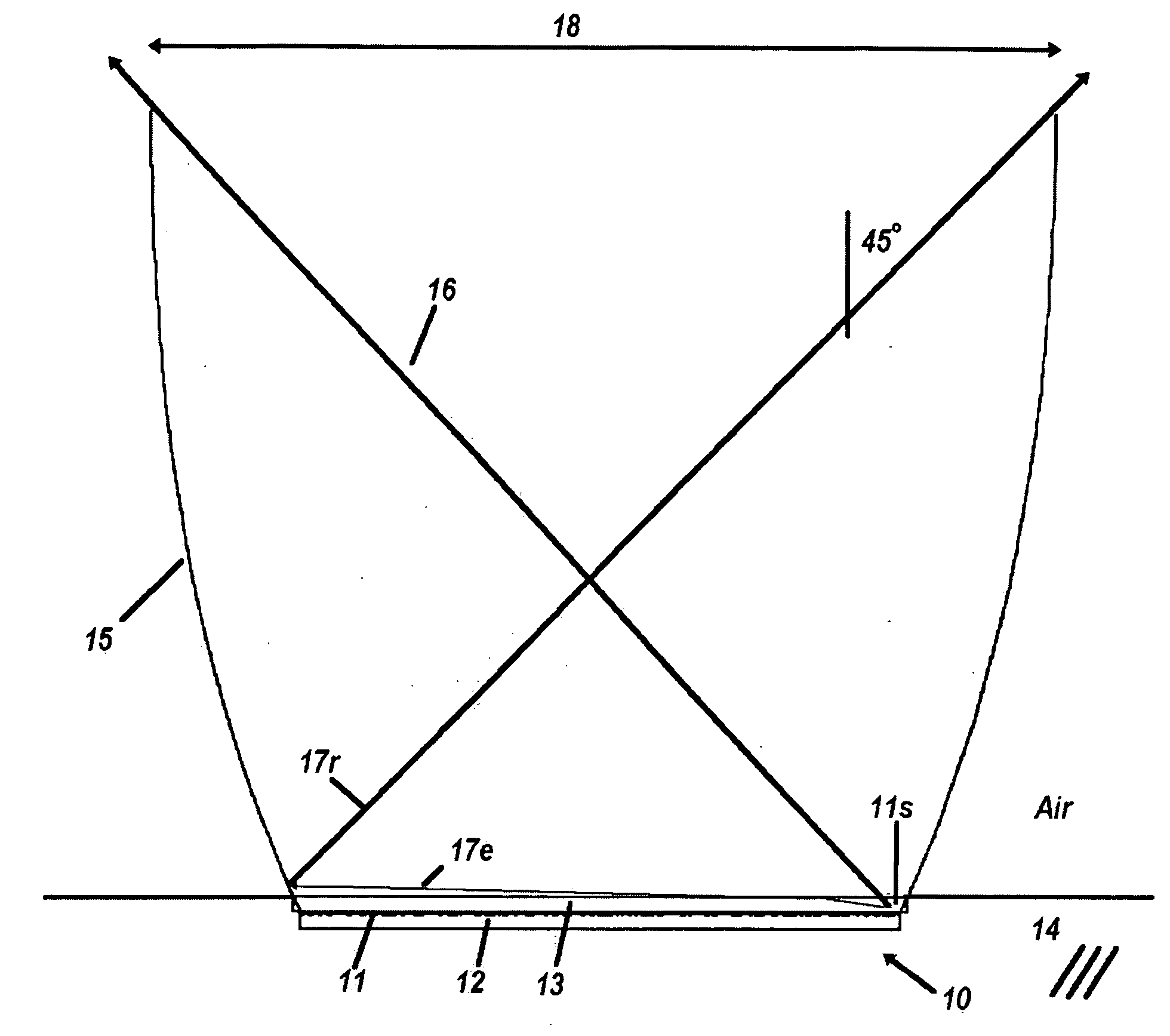
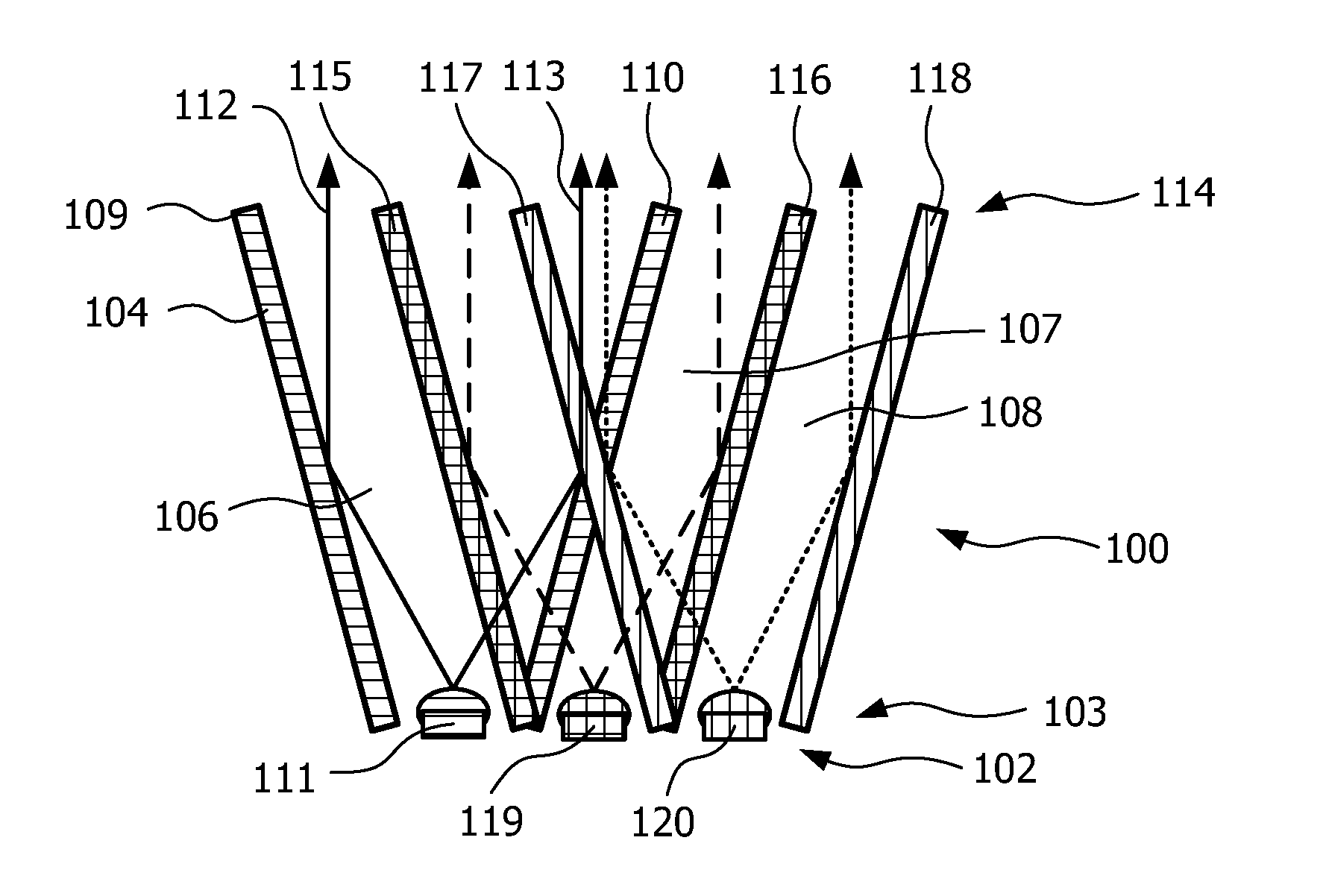
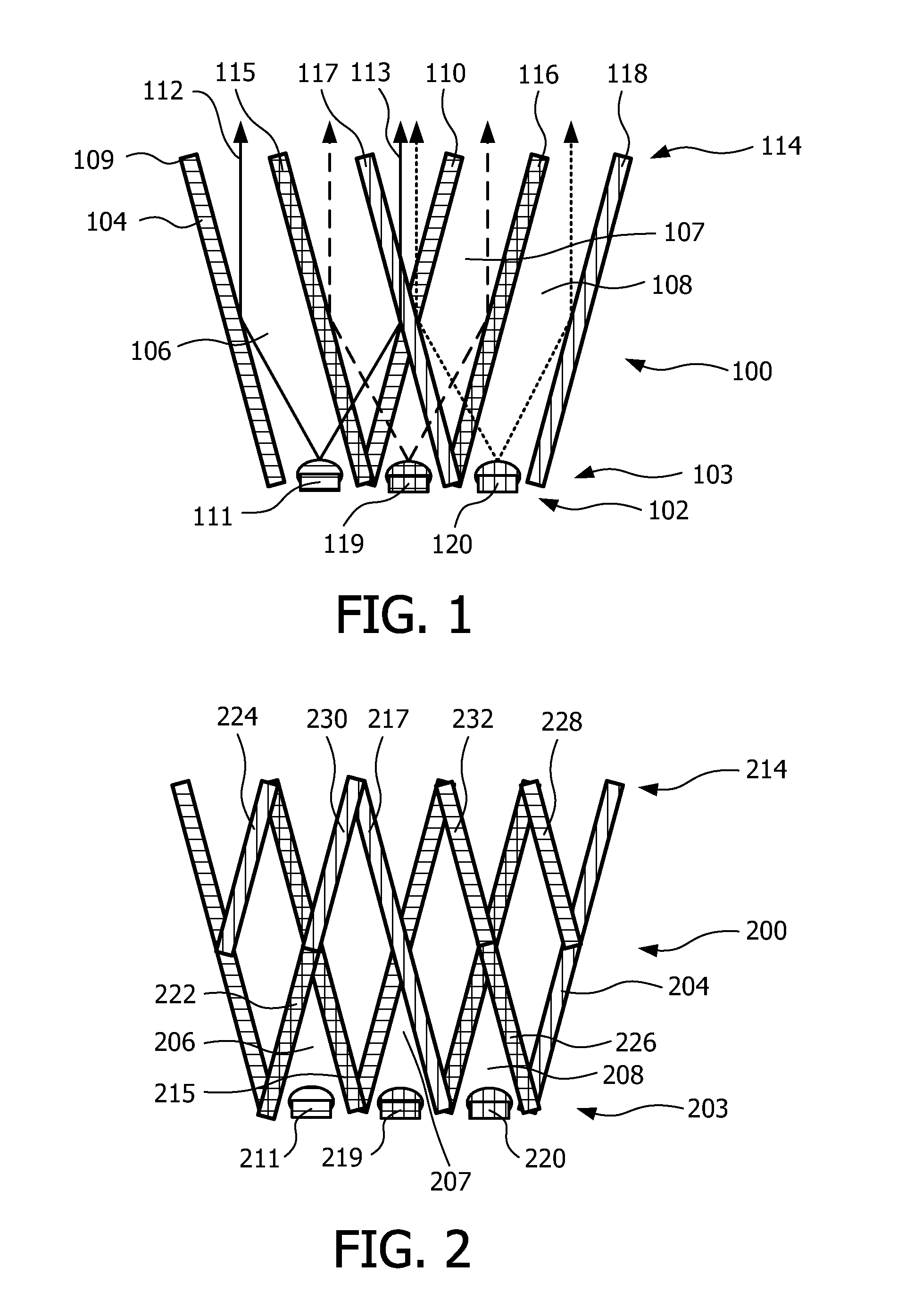
InactiveUS20110228527A1Reduce discolorationAccurate filtering propertyGlobesCondensersLow-pass filterLength wave
A lighting device (100, 200, 300, 400) is disclosed. The device comprises a plurality of light sources (111, 119, 120, 211, 219, 220) providing light in different wavelengths, a collimating means (104, 204) having a receiving end (103, 203, 407) and an output end (114, 214, 409), wherein said light sources are arranged at said receiving end. The collimating means comprises a set of wavelength selective filters (109, 110, 115, 116, 117, 118, 215, 217) arranged as sub-collimators (106, 107, 108, 206, 207, 208) to each of said plurality of light sources such that, for each light source, said sub-collimator collimates the light from its light source, and said wavelength selective filter of said each light source is translucent for light from adjacent light sources of different wavelength, wherein said wavelength selective filters are high pass or low pass filters.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Displays including addressible trace structures
InactiveUS20090051863A1Discharge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsDisplay deviceMicroelectromechanical systems
The present invention relates to displays including resonant trace structures. Displays are disclosed that include a first array of first electrically conductive traces configured to conduct alternating current, each of the first electrically conductive traces can be coupled to a first microelectromechanical system (MEM) surface acoustic wave (SAW) frequency selective filter. The displays further include a second array of second electrically conductive traces configured to conduct alternating current, each of the second electrically conductive traces can be coupled to a second microelectromechanical system (MEM) surface acoustic wave (SAW) frequency selective filter. The displays further include a material located between at least a portion of the first array and the second array, the material having a property that changes to cause illumination at points of intersection between the first array and the second array in response to current conducted in one or more of the first electrically conductive traces and current conducted in one or more of the second electrically conductive traces.
Owner:MEISNER CONSULTING
Optical transceiver module
InactiveUS8303195B2Reduce in quantitySacrificing low-loss optical characteristic and high reliabilitySemiconductor laser optical deviceCoupling light guidesTransceiverPhotodetector
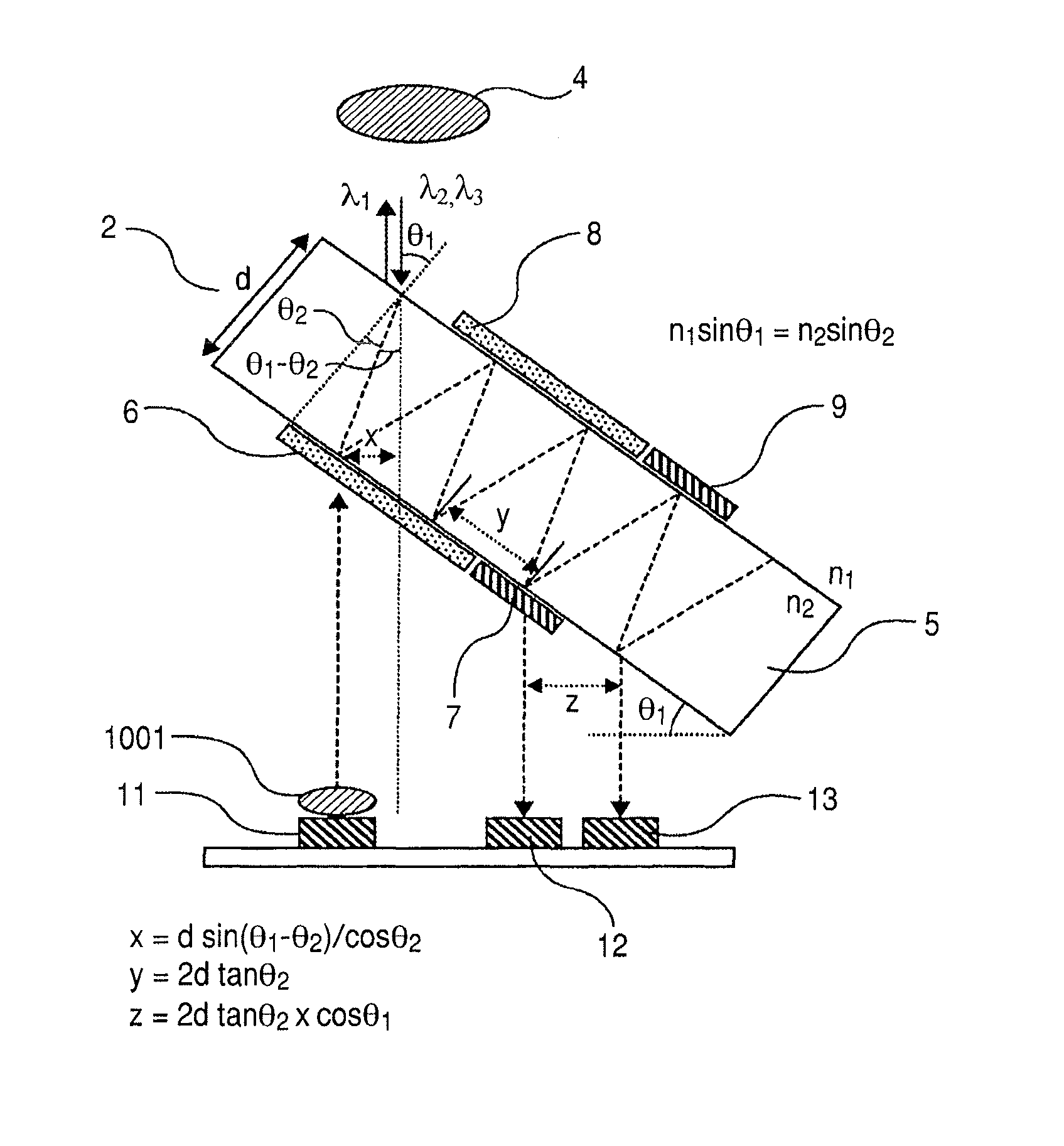
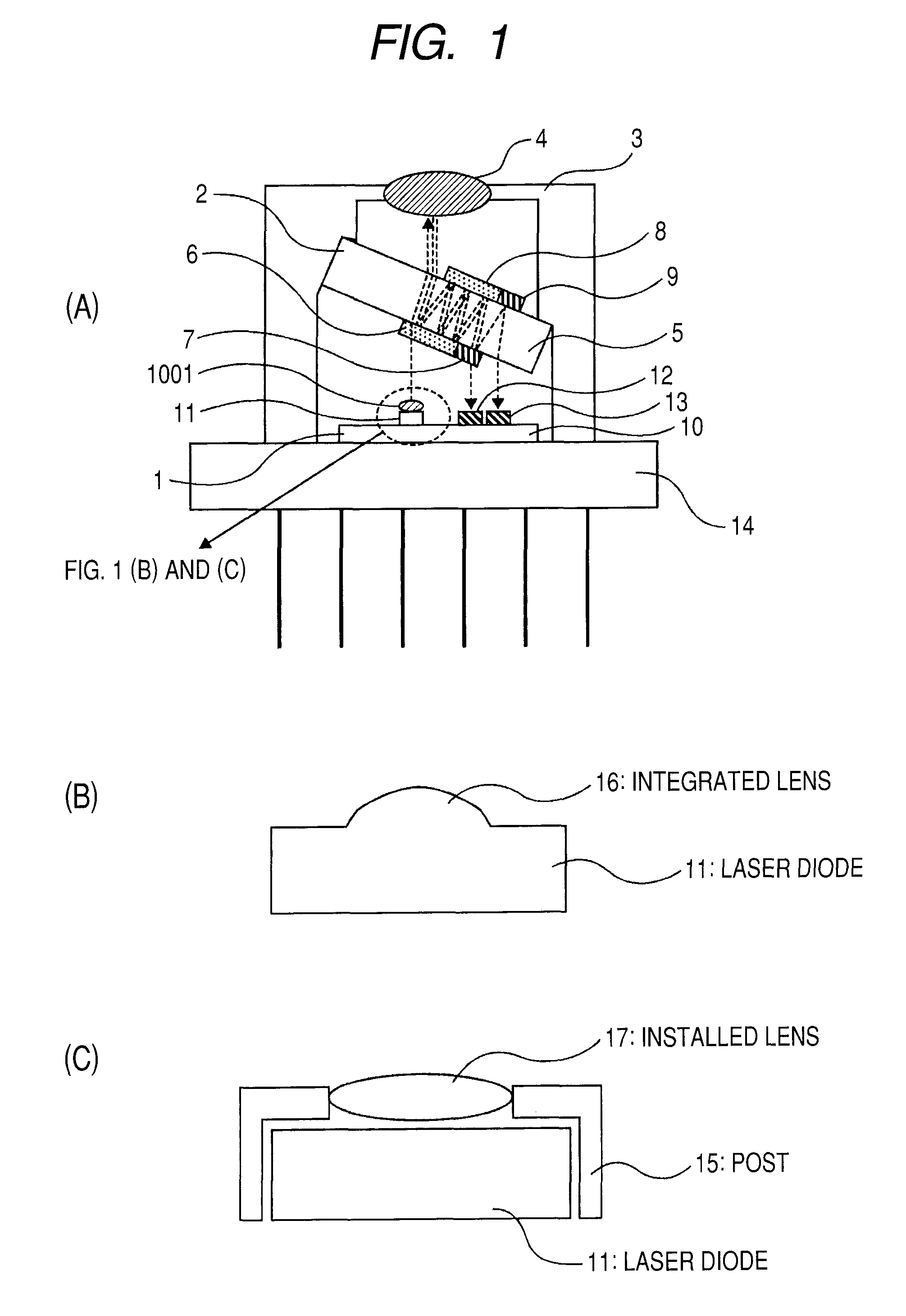
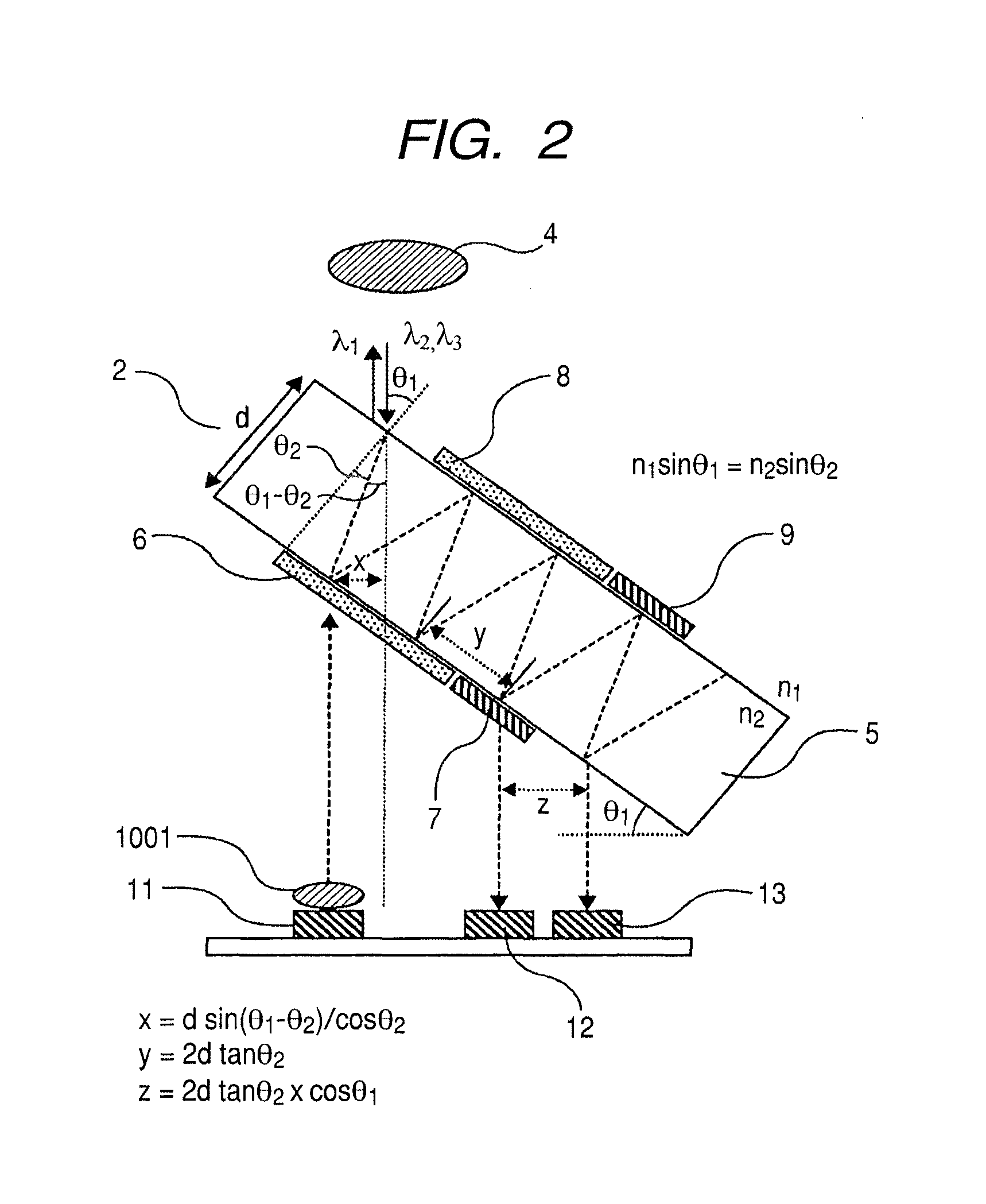
The optical module includes an optical device mounting substrate 1 and an optical multiplexer / demultiplexer 2. One laser diode and at least one photodetector, which are positioned in the same plane, are mounted on the optical device mounting substrate 1. The optical multiplexer / demultiplexer is prepared by mounting a wavelength-selective filter and a mirror on the front and back surfaces of a transparent substrate. The optical device mounting substrate and the optical multiplexer / demultiplexer are mounted in a package 3 in such a manner that the optical device mounting surface and the filter surface are not parallel to each other. The optical module also includes a first lens, which is positioned near the laser diode or monolithically integrated with the laser diode, and a second lens, which converges light coming out of the optical multiplexer / demultiplexer toward an optical fiber.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
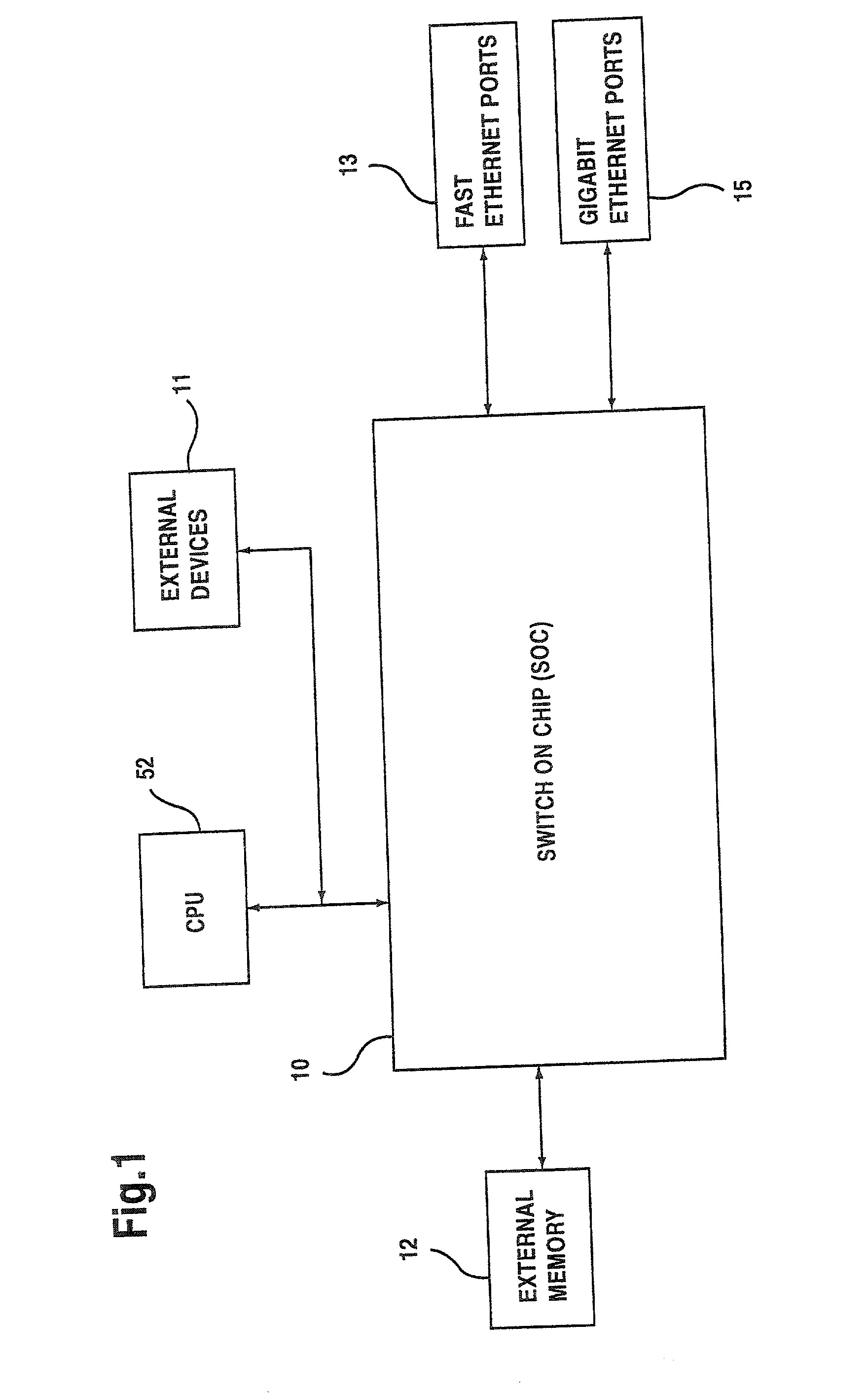
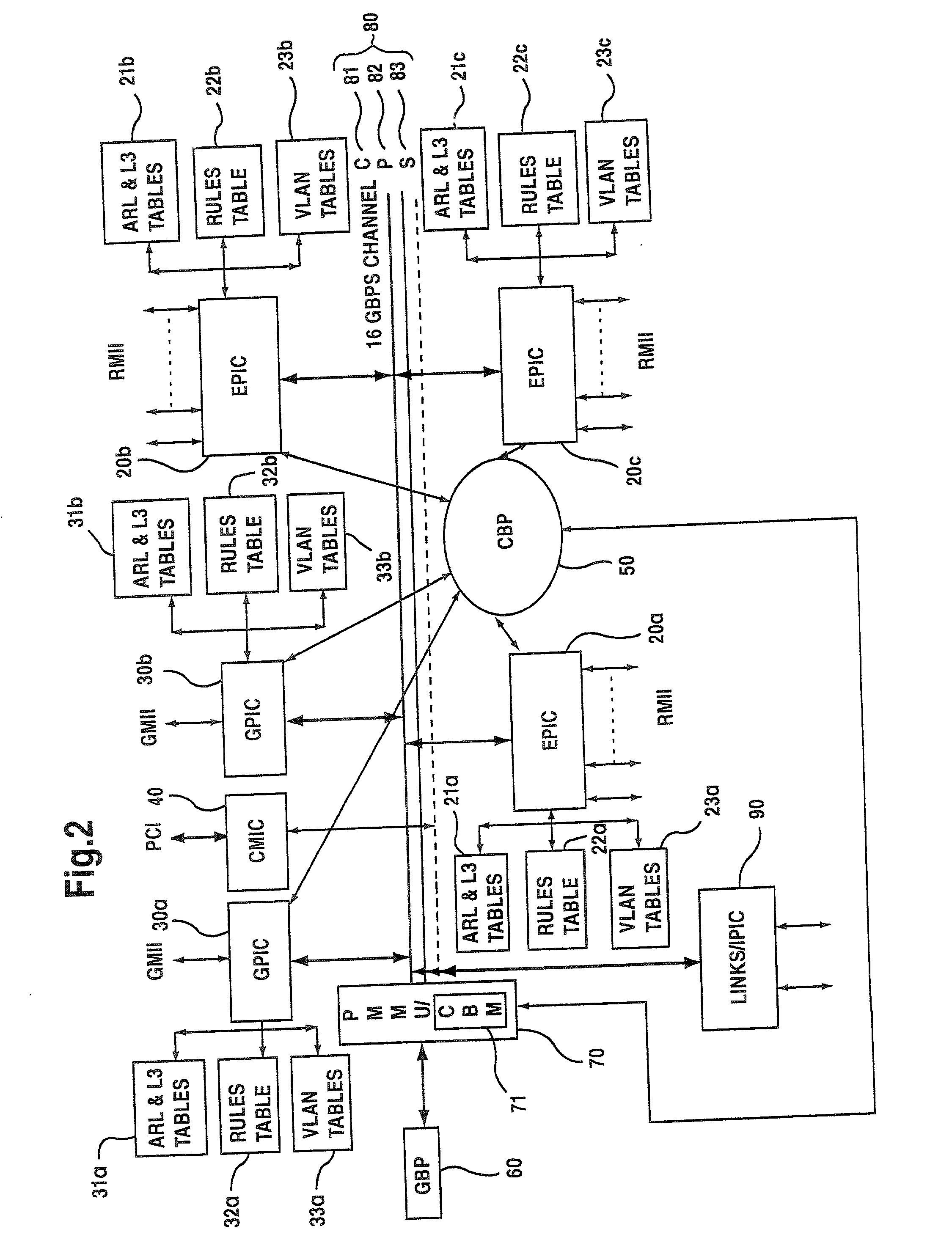
Network switching architecture with fast filtering processor
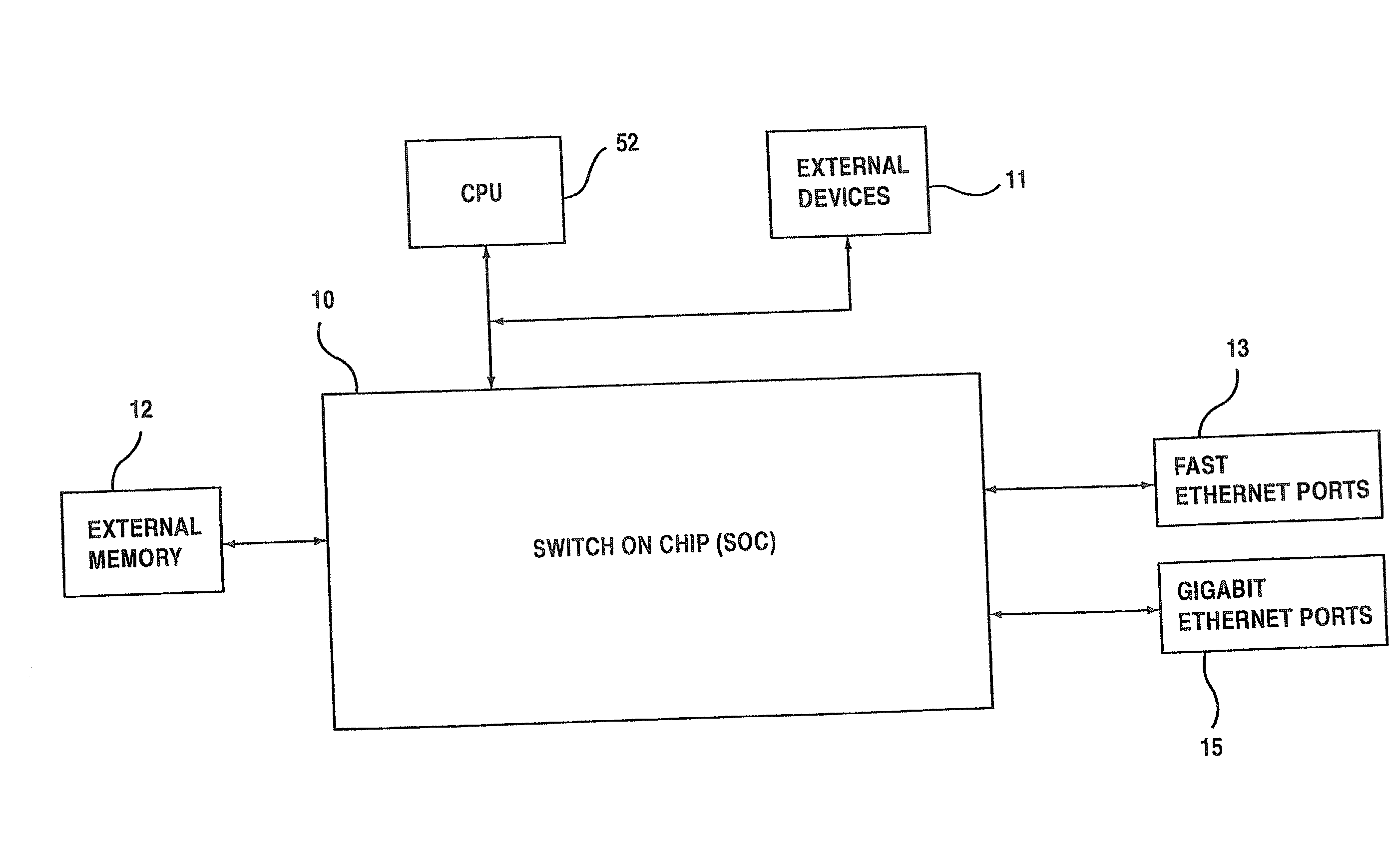
InactiveUS20020054604A1Special service provision for substationEnergy efficient ICTInternal memoryManagement unit
A network switch for network communications includes a first data port interface supporting a plurality of data ports transmitting and receiving data at a first data rate. A second data port interface supports a plurality of data ports transmitting and receiving data at a second data rate. A CPU interface is configured to communicate with a CPU, and an internal memory communicates with the first data port interface and the second data port interface. A memory management unit is provided, including an external memory interface, for communicating data from at least one of the first data port interface and the second data port interface and an external memory. A communication channel is provided, for communicating data and messaging information between the first data port interface, the second data port interface, the internal memory, and the memory management unit. One data port interface of the first data port interface and the second data port interface includes a fast filtering process, with the fast filtering processor filtering packets coming into the one data port interface. Selective filter action is taken based upon a filtering result.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method and apparatus for extended hyperspectral imaging
ActiveUS20060050278A1Attenuate laser lightRadiation pyrometryColor/spectral properties measurementsLength waveSpectral analysis
The disclosure relates to method and apparatus for obtaining a multimodal hyperspectral image of a sample for widefield spectral analysis. An apparatus according to one embodiment may include a plurality of optical lenses configured to interchangeably receive photons and focus the photons; a plurality of tunable filters positioned in a filter housing, each tunable filter selectively receiving the focused dispersed photons from one of the plurality of optical lenses, each tunable filter providing wavelength-selective filtered photons; a first optical camera and a second optical cameras for selectively receiving the wavelength-selective filtered photons from each of the plurality of tunable filters and combining said filtered photons to form a hyperspectral spatially accurate, wavelength-resolved image of the sample.
Owner:CHEMIMAGE TECH
Magnification device and assembly
A magnification device including a housing having a distal open end and a proximal open end is disclosed. The housing includes an optical system including one or more objective lenses adjacent the distal open end, and one or more eye lenses adjacent the proximal open end, the optical system produced a desired level of magnification; and a filtering system having first filter selectively filtering a first group of wavelengths and a second filter selective filtering a second group of wavelengths. The first and second filters having an optical density selected based on a magnification level of the optical system. A vision enhancing assembly including a carrier device and one or more magnification devices coupled to the carrier device is also disclosed, wherein the magnification devices include filters that have optical densities based on a magnification level.
Owner:DESIGNS FOR VISION
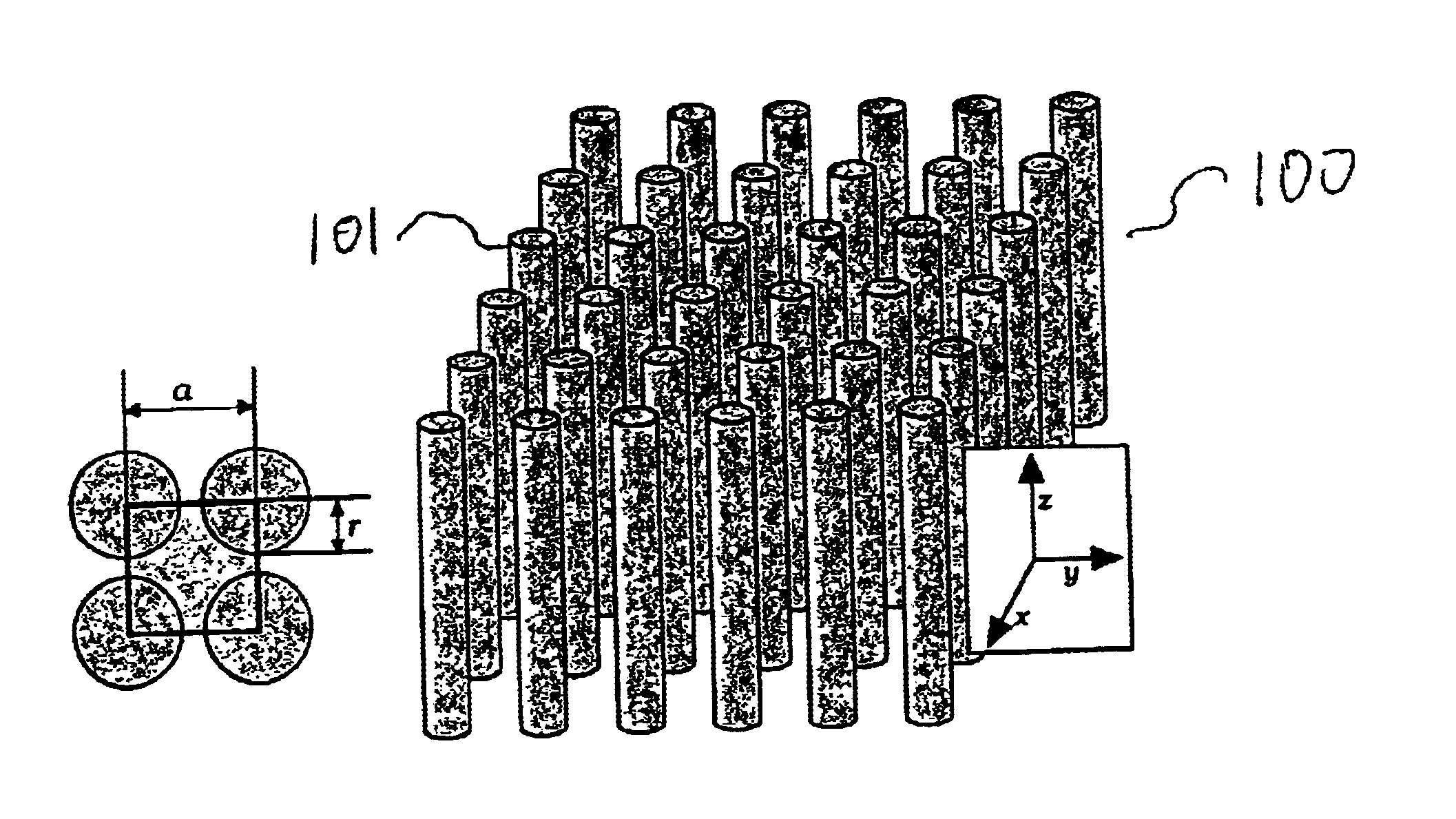
Active Optical Fibers With Wavelength-Selective Filtering Mechanism, Method of Production and Their Use
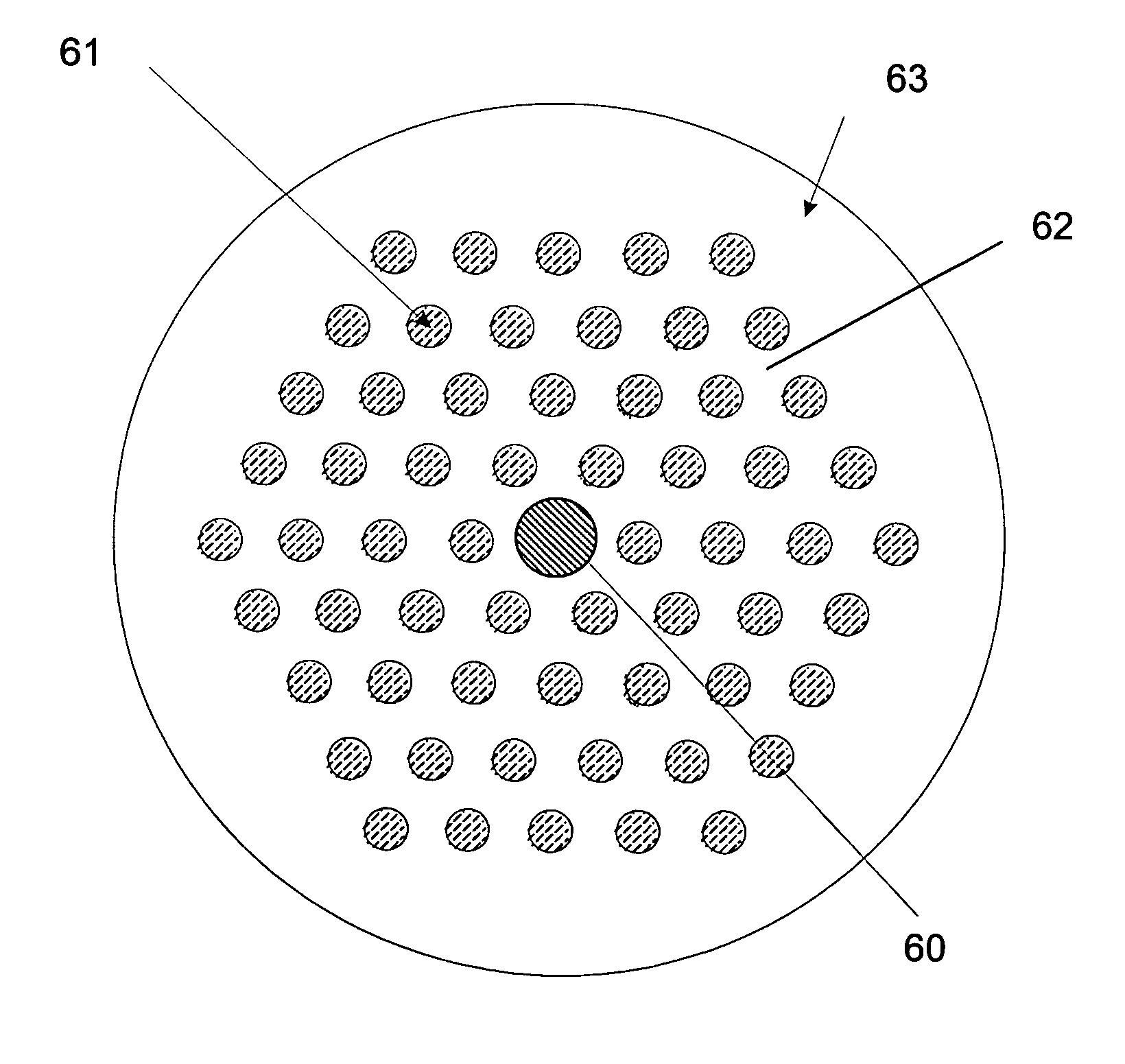
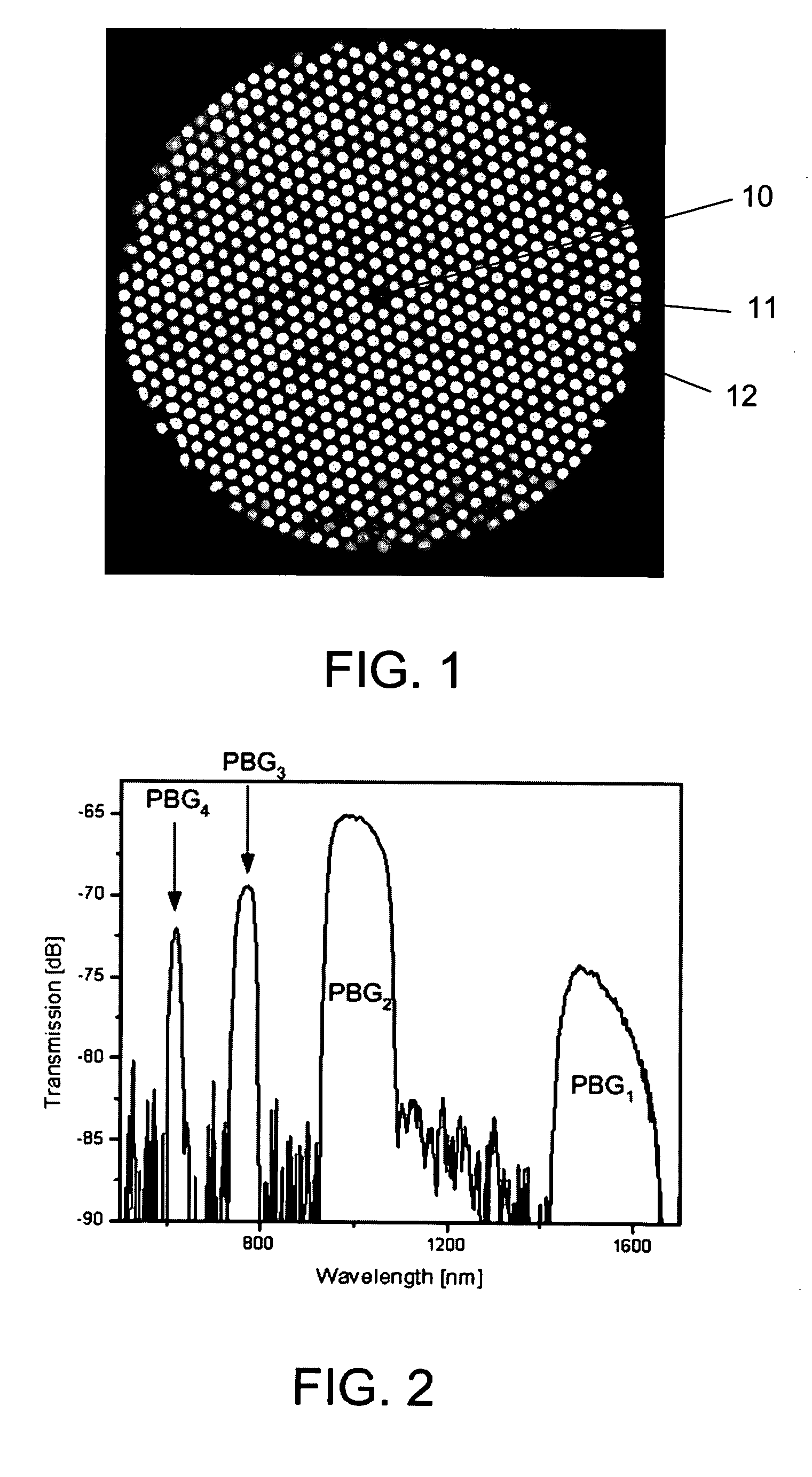
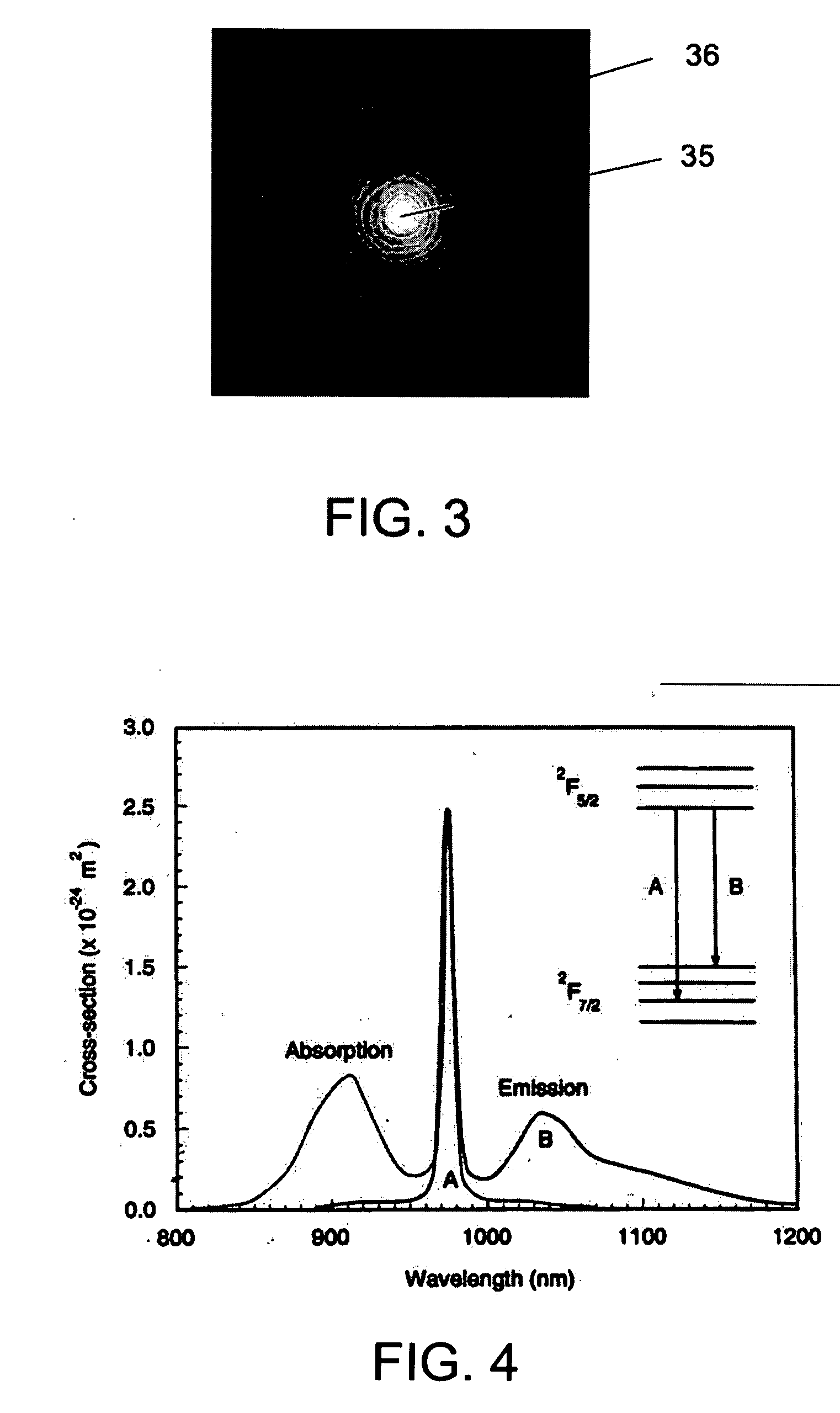
ActiveUS20090168149A1Efficient amplificationEnhanced spontaneous emissionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFibre transmissionPhotonic bandgapPhotonics
The invention relates to optical fibers for use in optical amplification of light, such as in optical fiber amplifiers and lasers and for use in delivery of high power light, in particular to a scheme for reducing amplified spontaneous emission at undesired wavelengths. The invention further relates to articles, methods and use. An object of the invention is achieved by a micro-structured optical fiber, which is adapted to guide light by the photonic bandgap effect and to have one or more pass bands and at least one stop-band over a wavelength range from λstop1 to λstop2. In an aspect of the invention, the at least one stop-band provides filter functions that suppress nonlinear effects. In another aspect, the core region is actively doped, and the active material has an emission spectrum with a higher value of the emission cross section σE at a wavelength λASE between λstop1 and λstop2 than outside said wavelength range such that amplified spontaneous emission and lasing within the wavelength range from λstop1 to λstop2 is reduced. In still another aspect, the optical fiber exhibits photonic bandgaps at different wavelength ranges in different radial directions of a cross section of the optical fiber.
Owner:NKT PHOTONICS
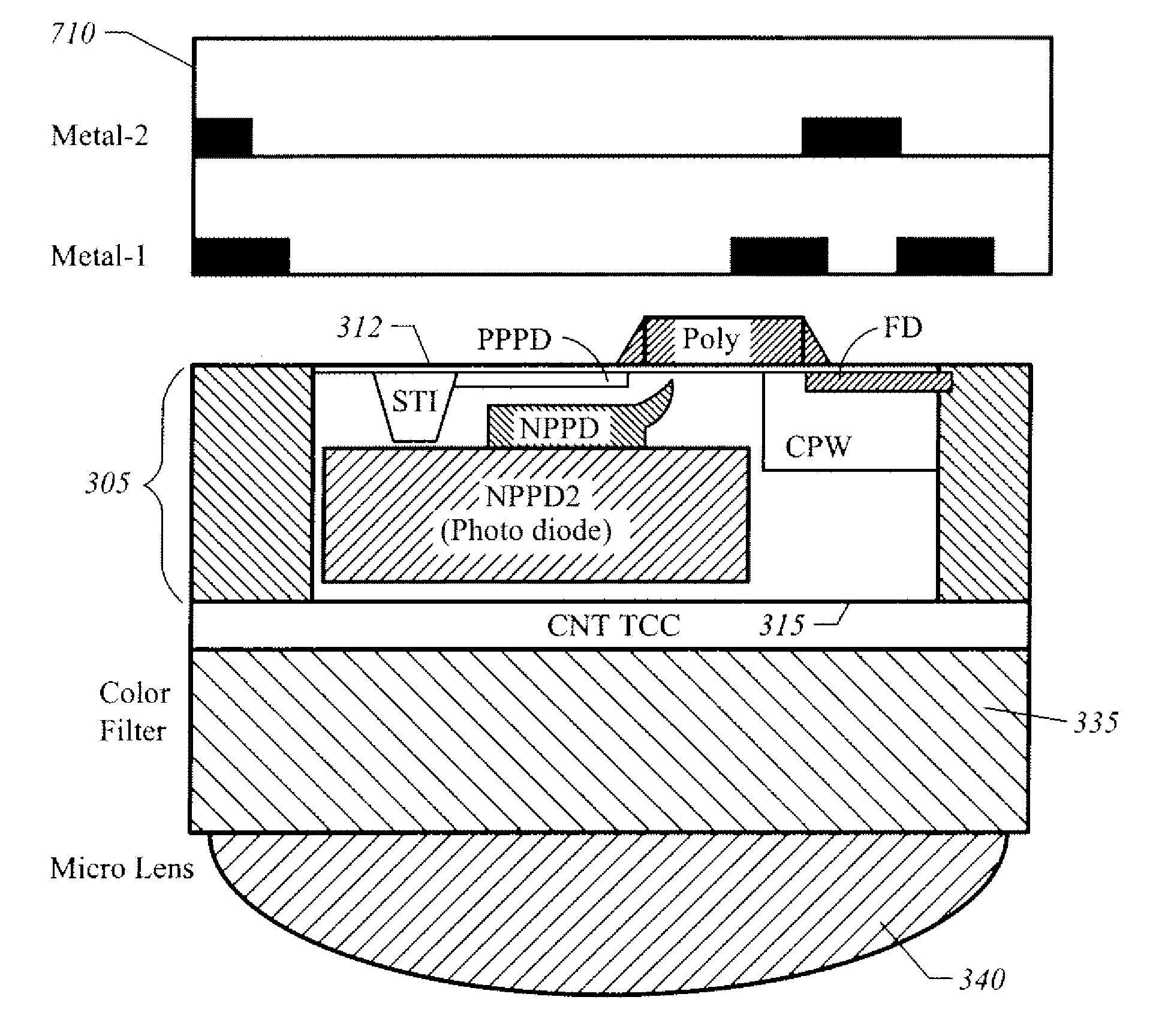
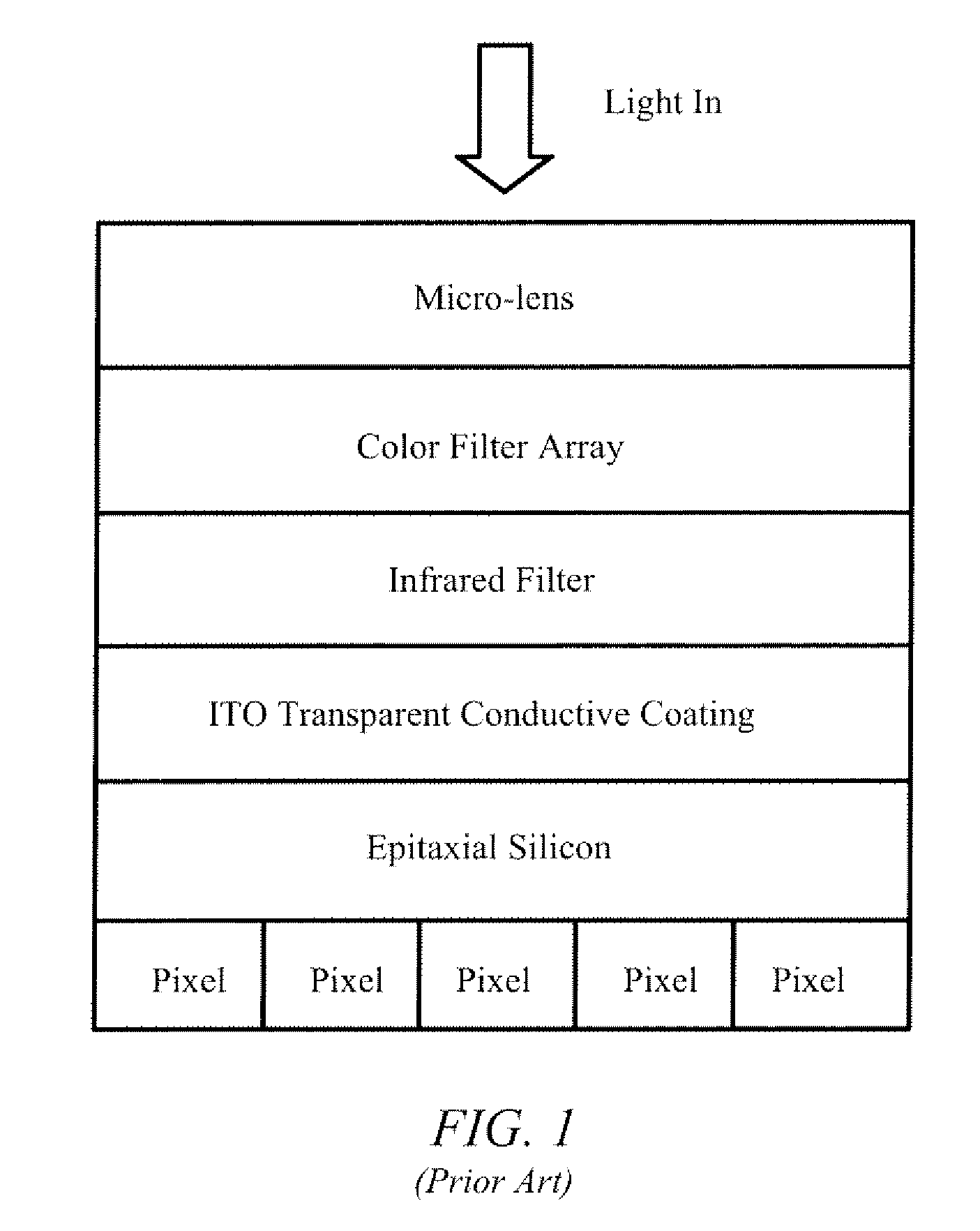
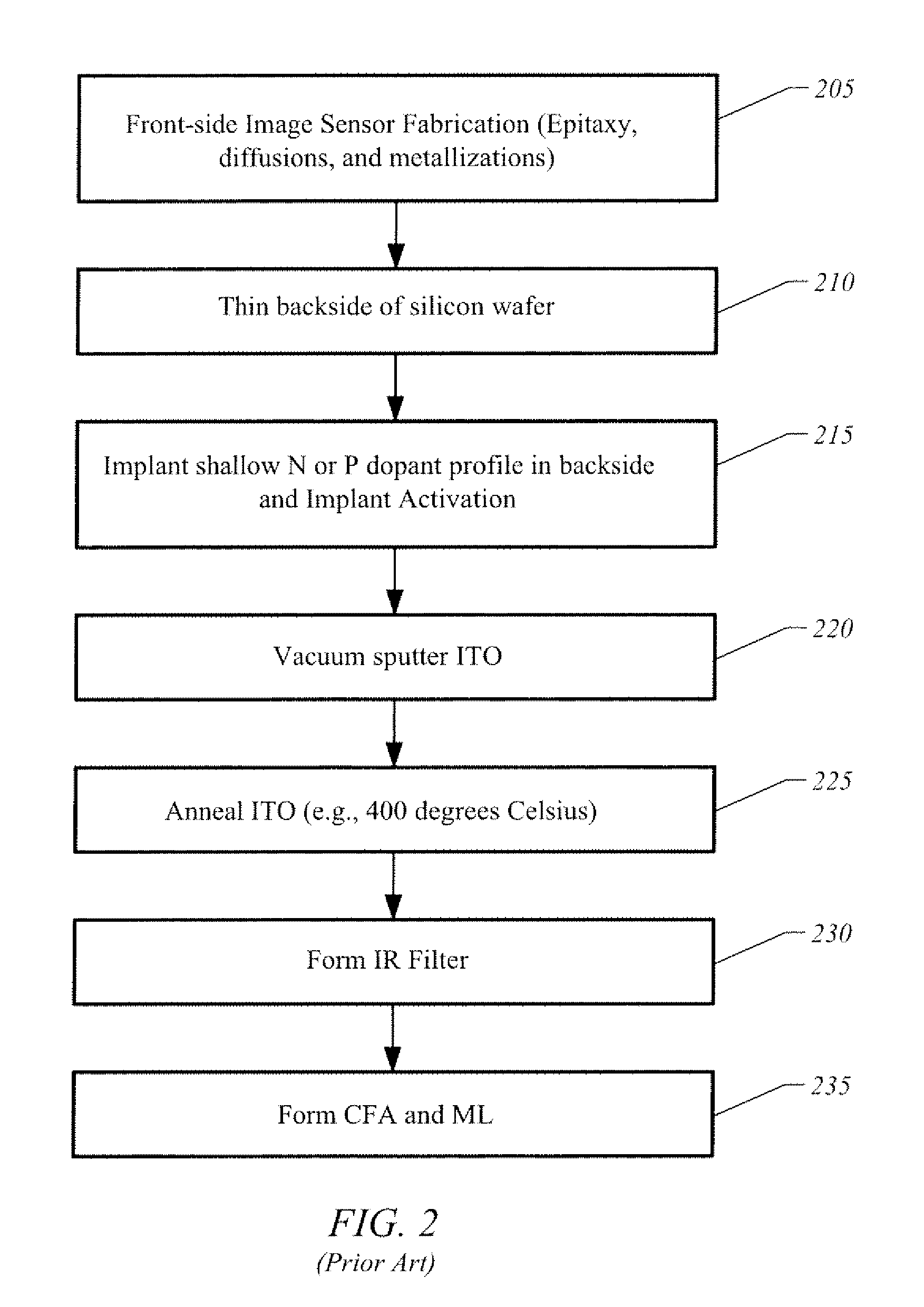
Apparatus And Method For Image Sensor With Carbon Nanotube Based Transparent Conductive Coating
A backside illuminated image sensor has a carbon nanotube transparent conductive coating formed on the backside of the image sensor. In one implementation the carbon nanotube transparent conductive coating acts as a wavelength selective filter to filter out infrared light. In one implementation the carbon nanotube transparent conductive coating has an optical transparency between 50% and 80% for blue and green color bands.
Owner:OMNIVISION TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com