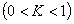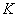Patents
Literature
501 results about "Holographic grating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
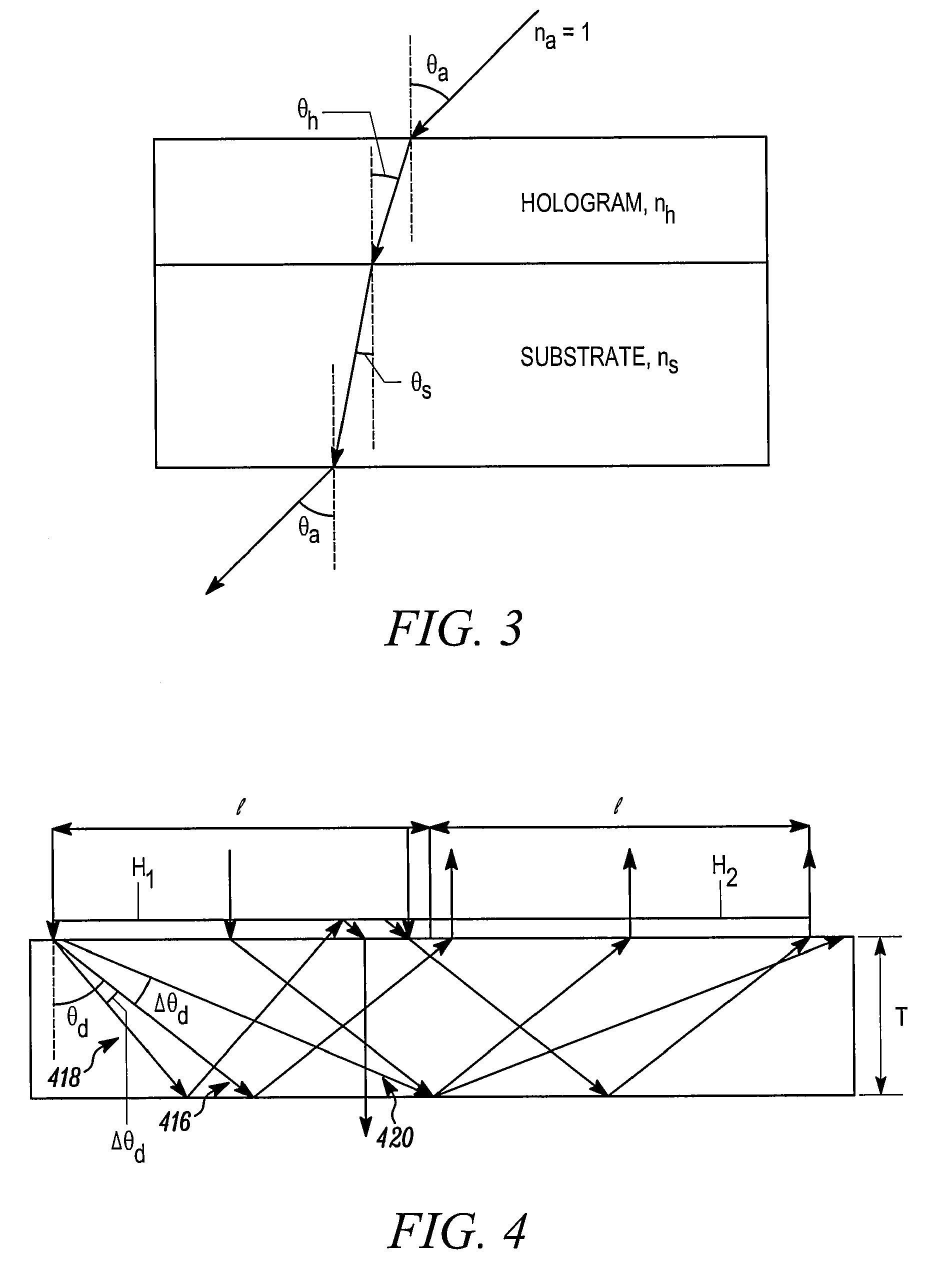
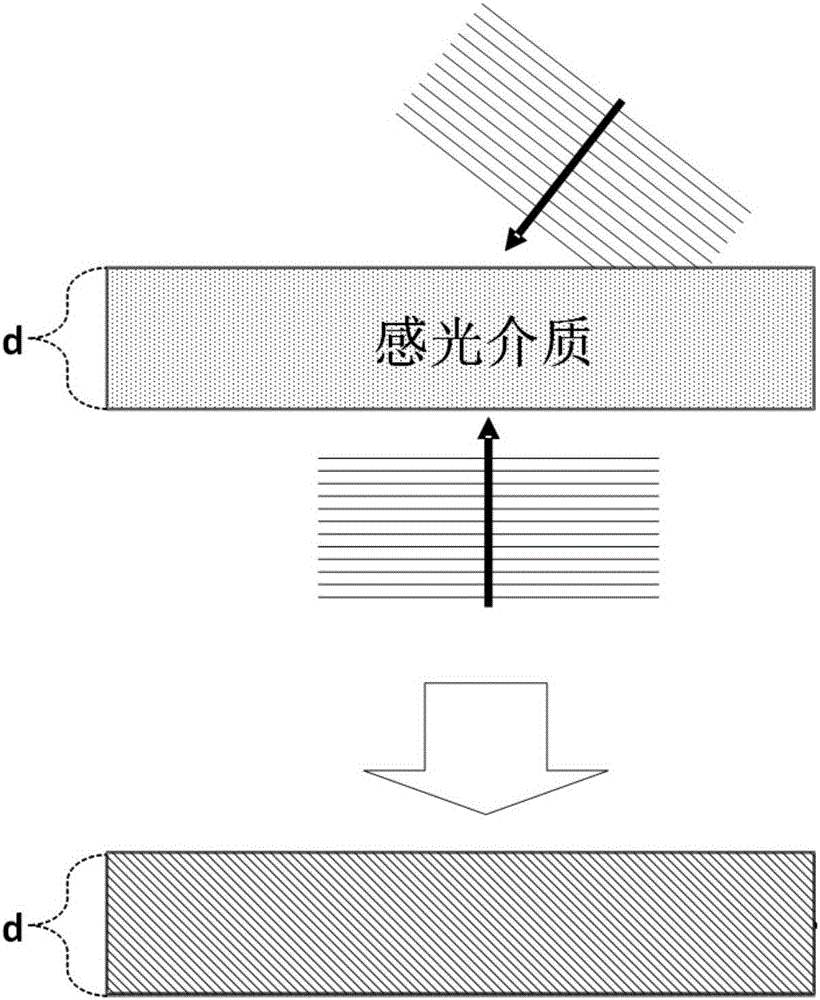
A holographic grating is a type of diffraction grating formed by an interference-fringe field of two laser beams whose standing-wave pattern is exposed to a polished substrate coated with photoresist. Processing of the exposed medium results in a pattern of straight lines with a sinusoidal cross section.
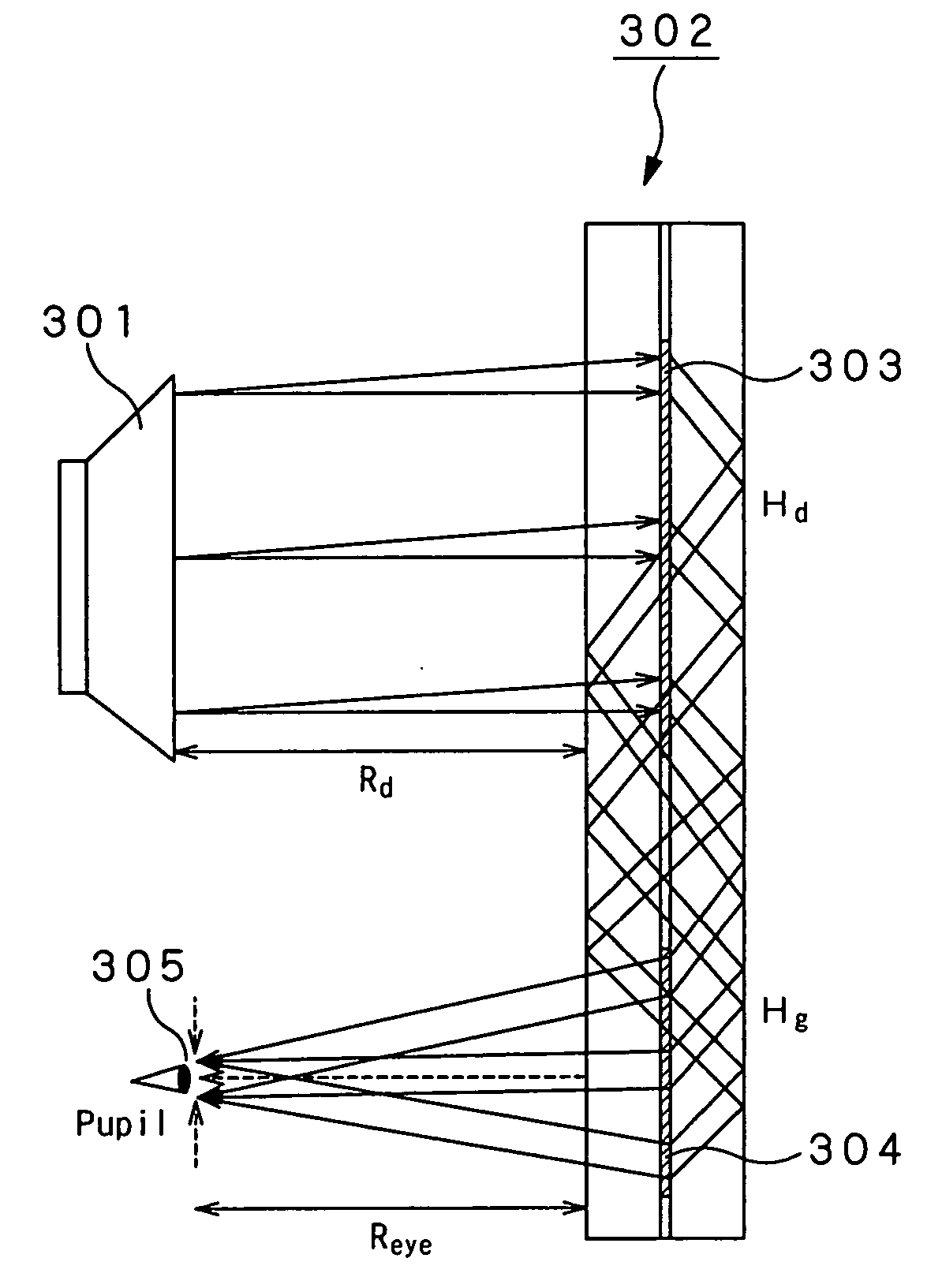
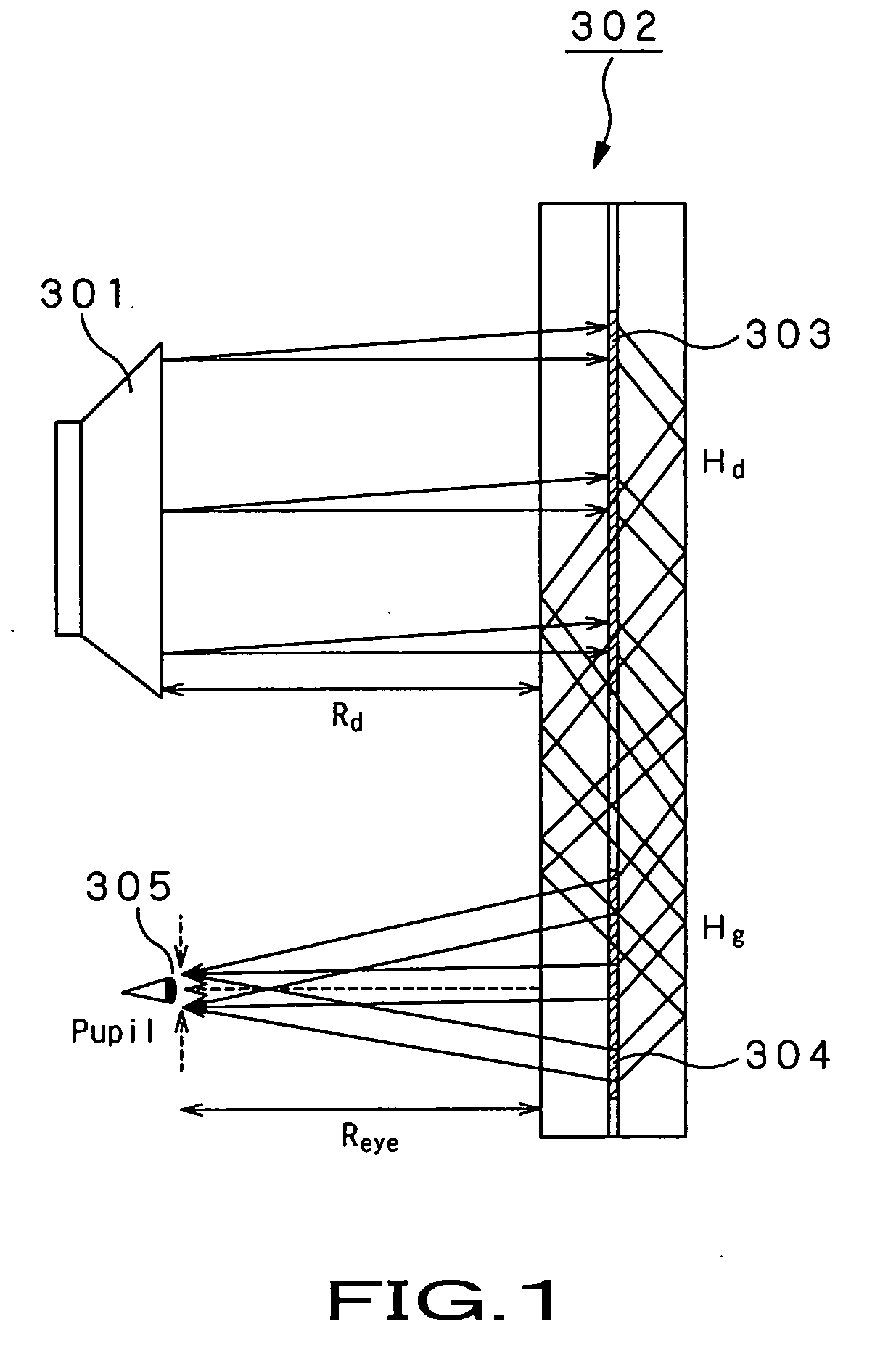
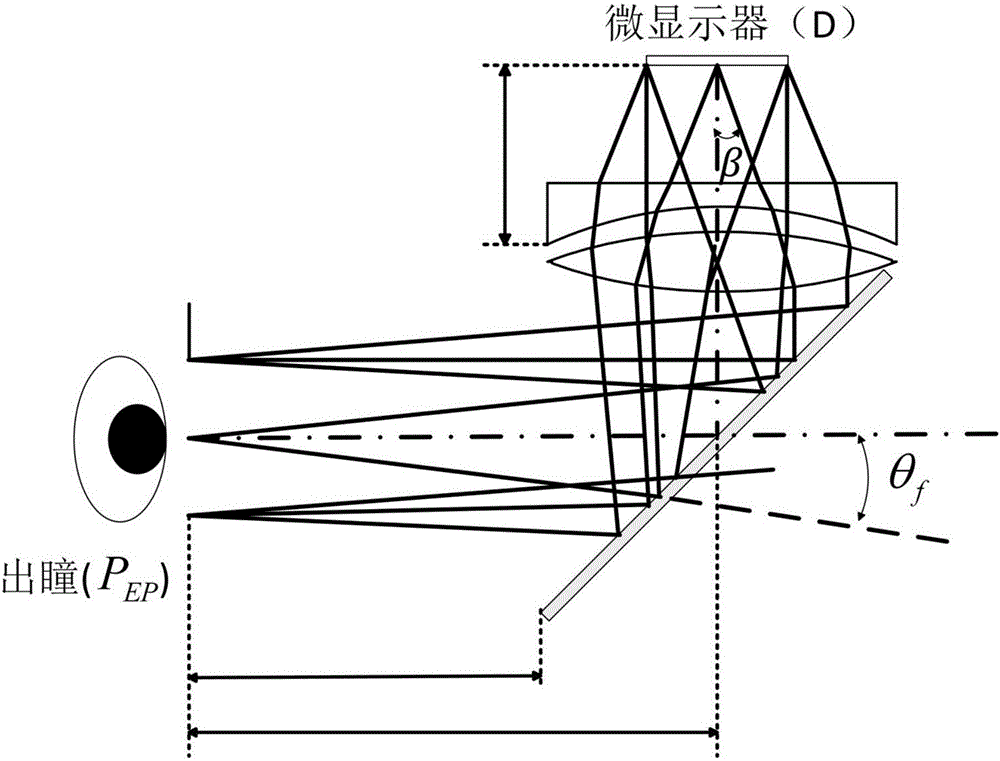
Optical device and virtual image display device
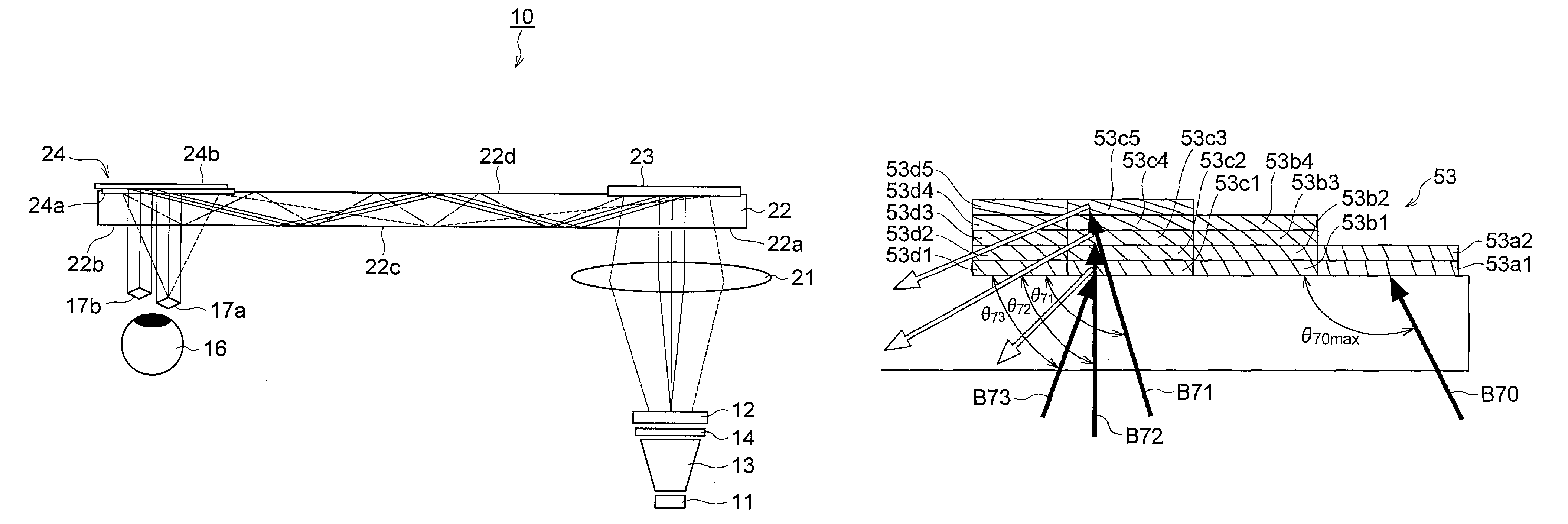
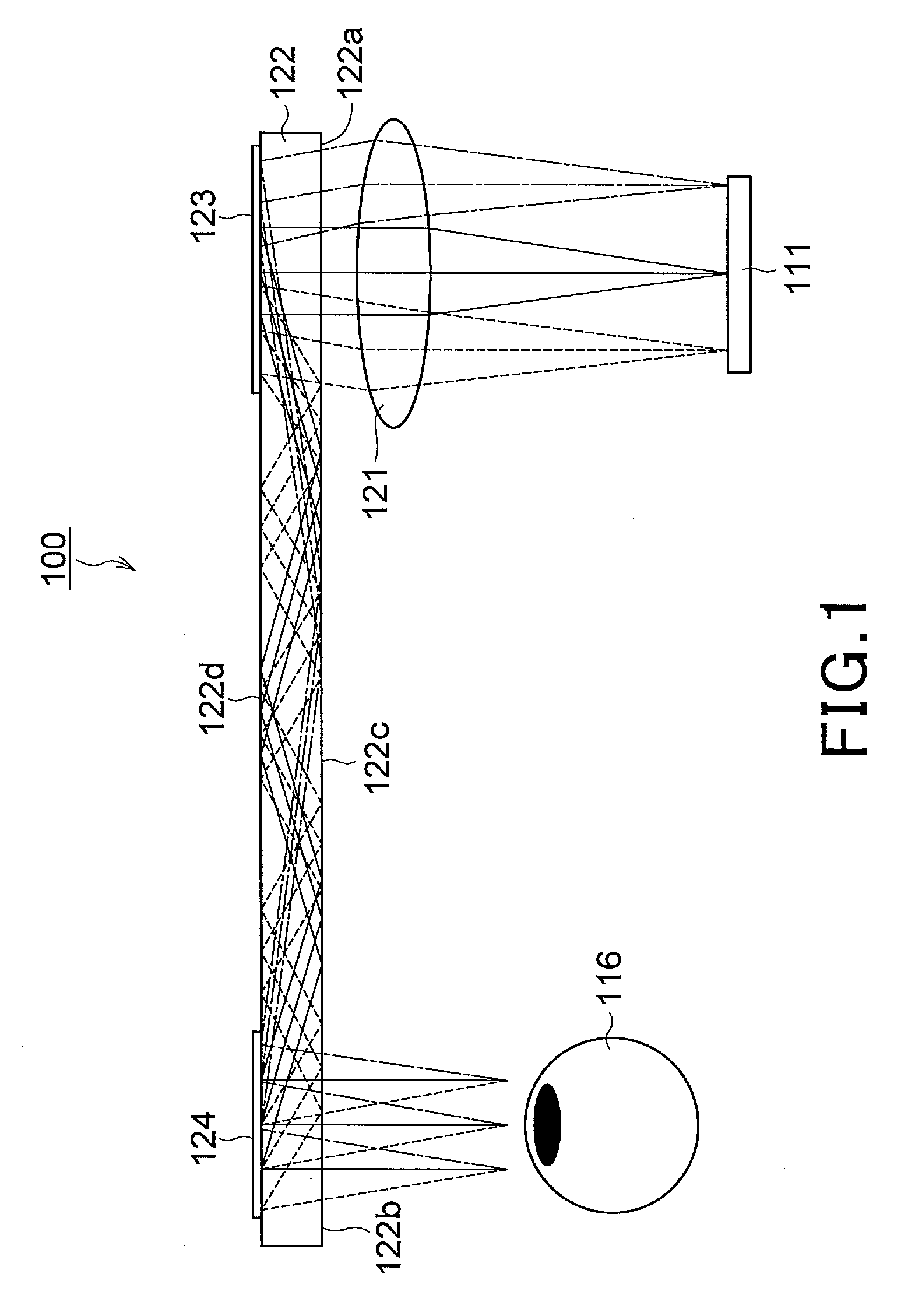
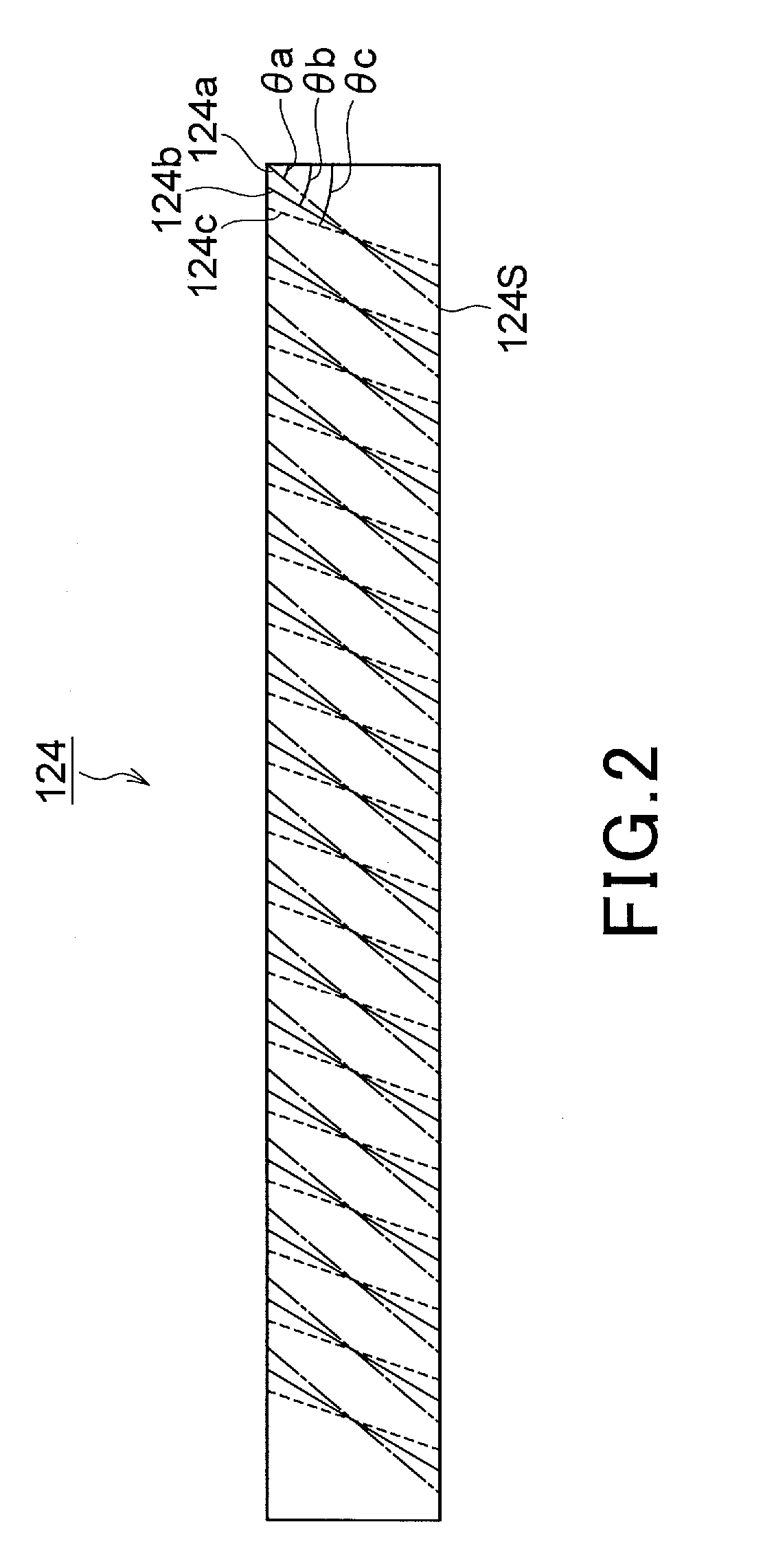
ActiveUS20060228073A1Improve imaging resolutionReduce aberrationDiffraction gratingsPlanar/plate-like light guidesGratingDisplay device
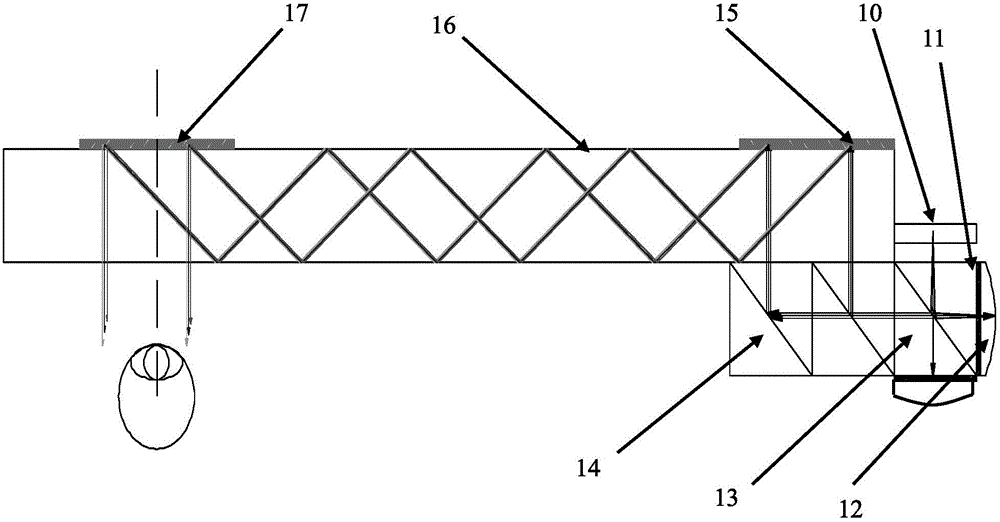
A virtual image display device is provided which displays a two-dimensional image for viewing a virtual image in a magnified form by a virtual optical system. The virtual image display device includes an optical waveguide (13) to guide, by internal total reflection, parallel pencil groups meeting a condition of internal total reflection, a first reflection volume hologram grating (14) to diffract and reflect the parallel pencil groups incident upon the optical waveguide from outside and traveling in different directions as they are so as to meet the condition of internal total reflection inside the optical waveguide and a second reflection volume hologram grating (15) to project the parallel pencil groups guided by internal total reflection inside the optical waveguide as they are from the optical waveguide by diffraction and reflection thereof so as to depart from the condition of internal total reflection inside the optical waveguide. Some of the parallel pencil groups guided through the optical waveguide being totally reflected different numbers of times for a period from external incidence upon the optical waveguide until outgoing from the optical waveguide.
Owner:SONY CORP
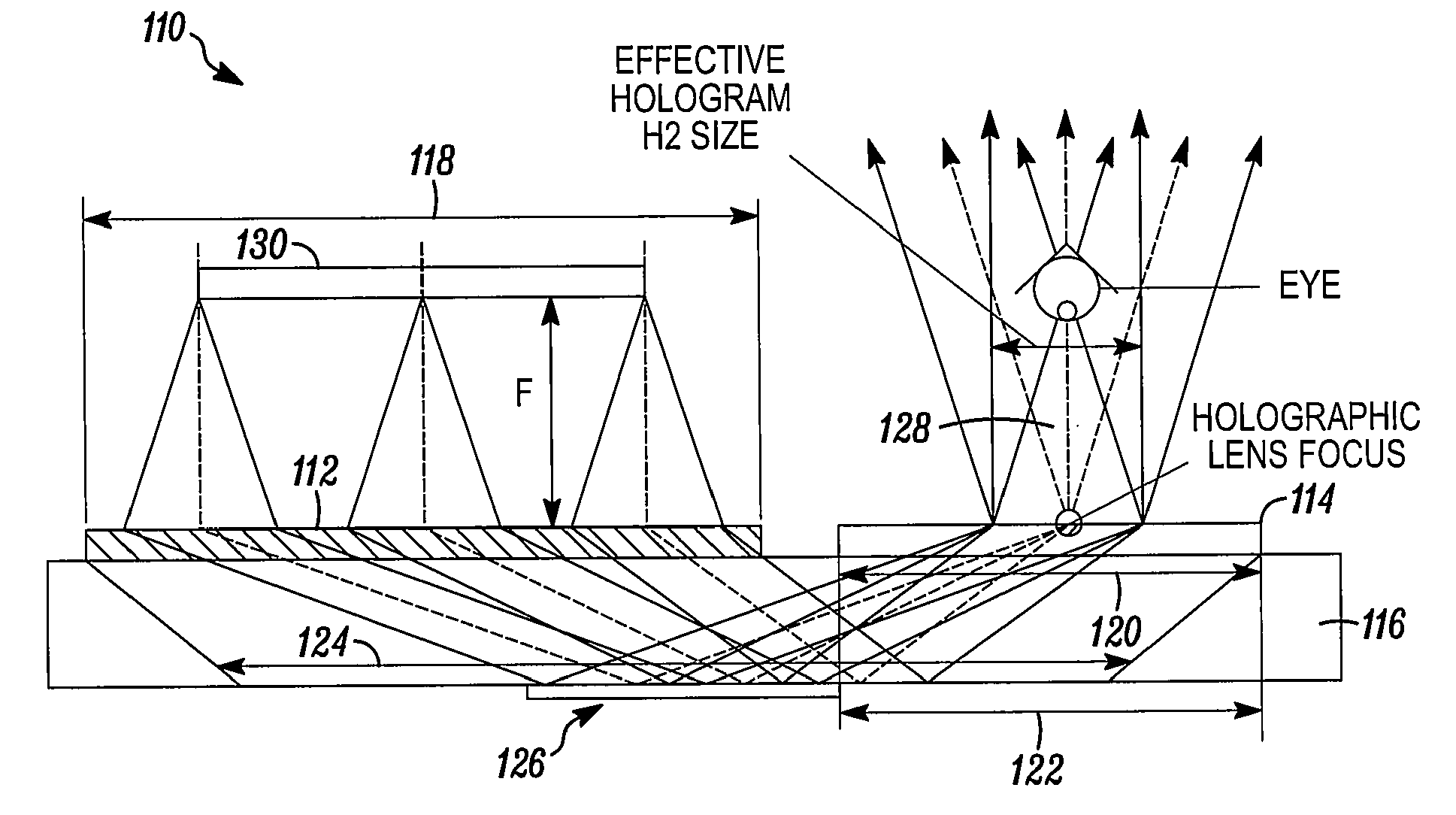
Holographic Substrate-Guided Wave-Based See-Through Display
ActiveUS20100157400A1Increase viewing area and qualityHolographic object characteristicsCoupling light guidesTotal internal reflectionGrating
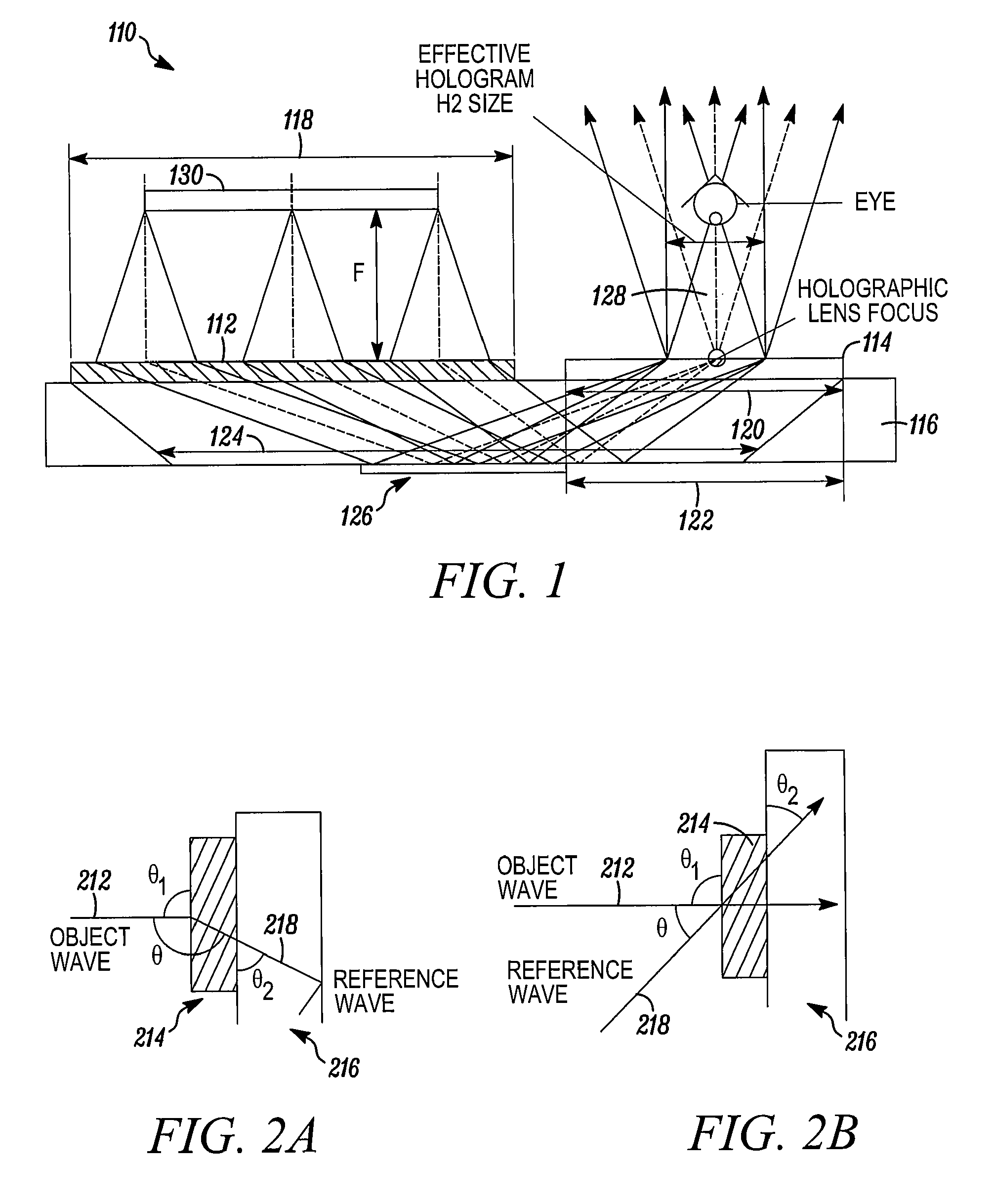
A holographic substrate-guided wave-based see-through display can has a microdisplay, capable of emitting light in the form of an image. The microdisplay directs its output to a holographic lens, capable of accepting the light in the form of an image from the microdisplay, and capable of transmitting the accepted light in the form of an image. The holographic lens couples its output to an elongate transparent substrate, capable of accepting the light in the form of an image from the holographic lens at a first location, and transmitting the light in the form of an image along a length of the substrate by total internal reflection to a second location spaced from the first location, the elongate substrate being capable of transmitting the accepted light in the form of an image at the second location. The substrate couples out what it receives to a transparent holographic grating, capable of accepting the light transmitted from the elongate substrate and transmitting it to a location outside of the holographic grating as a viewable image.
Owner:LUMINIT
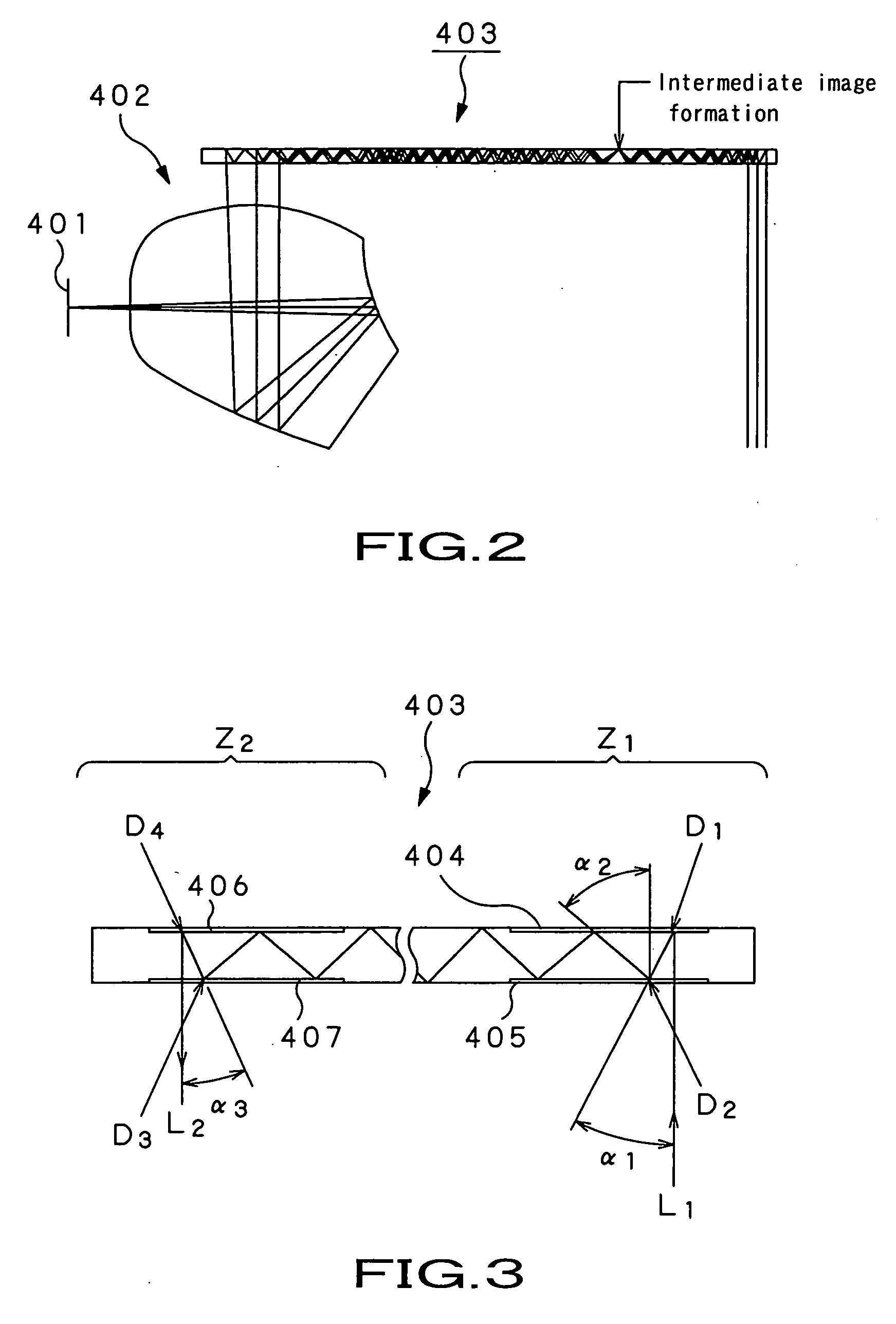
Optical device, and virtual image display
ActiveUS20060291021A1Reduce color unevennessReduce unevennessDiffraction gratingsOptical light guidesGratingLight beam
There is provided an optical device including an optical waveguide upon which a group of parallel light beams different in traveling direction from each other are incident and from which the group of parallel light beams go out after propagated by repeated total reflection through it. The optical waveguide includes a first reflection-type volume hologram grating, and a second reflection-type volume hologram grating. The pitches of interference fringes on the hologram surfaces of the first and second reflection-type volume hologram gratings are equal to each other. In at least the second reflection-type volume hologram grating, the angle formed between the interference fringes and hologram surfaces are varied continuously or stepwise within the hologram in relation to the main incident light beam so as to meet the Bragg condition. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the unevenness of color and brightness due to angles of view.
Owner:SONY CORP
Holographic recording medium and holographic recording/reproducing apparatus using the same
InactiveUS6856433B2High sensitivityMitigating optical damageRecord carriers used with machinesRecording/reproducing/erasing using optical interference patternsDopantReduction treatment
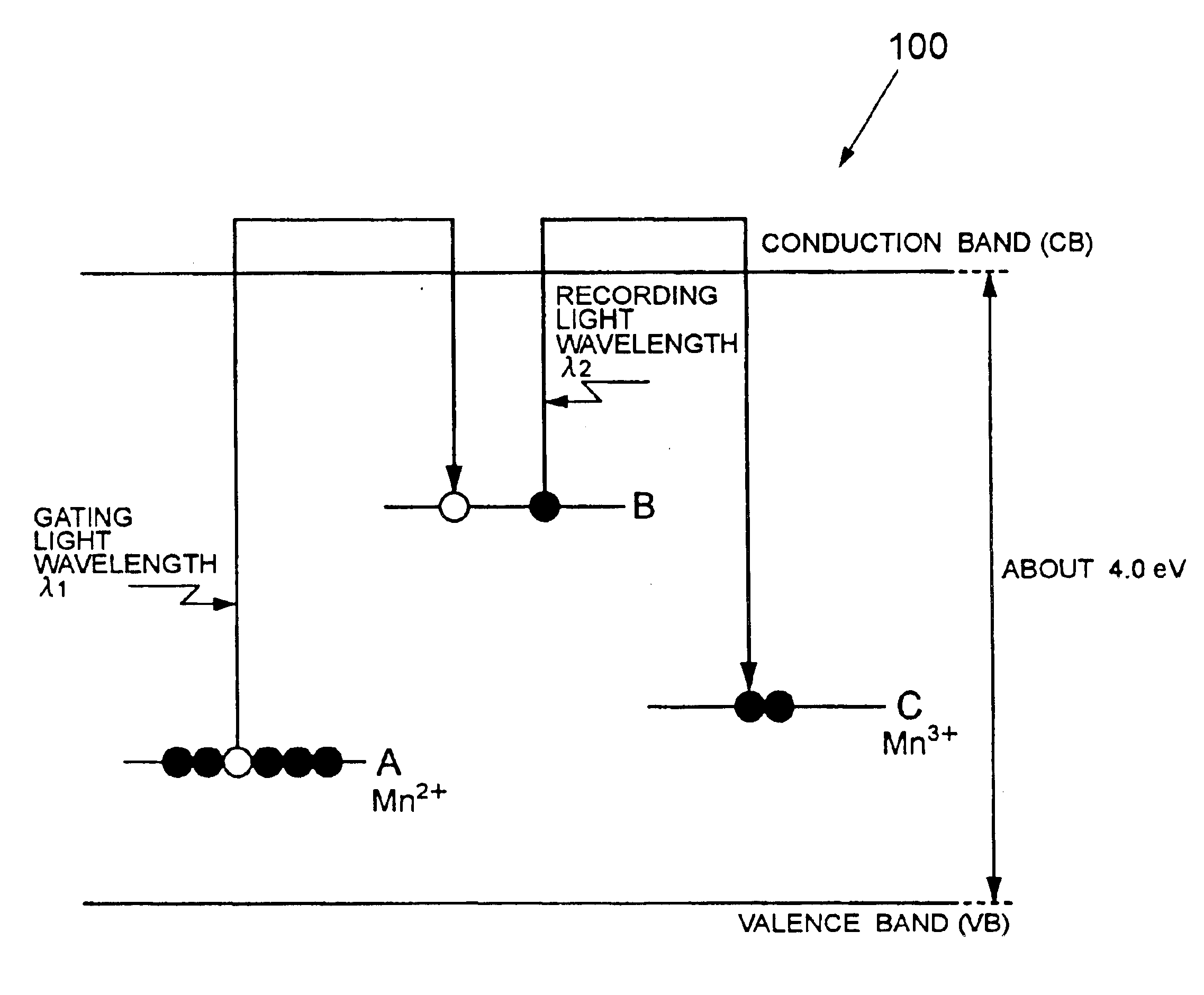
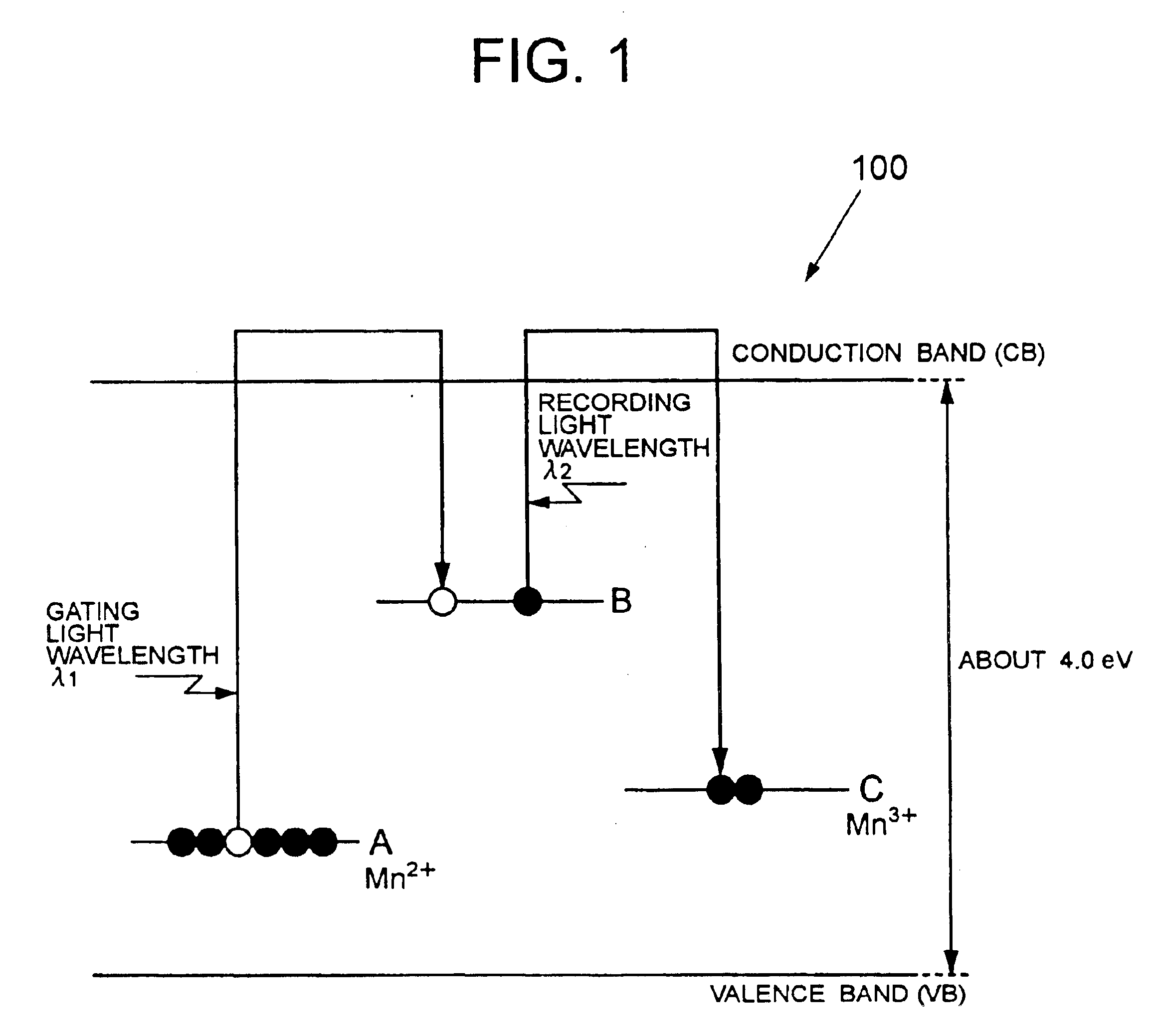
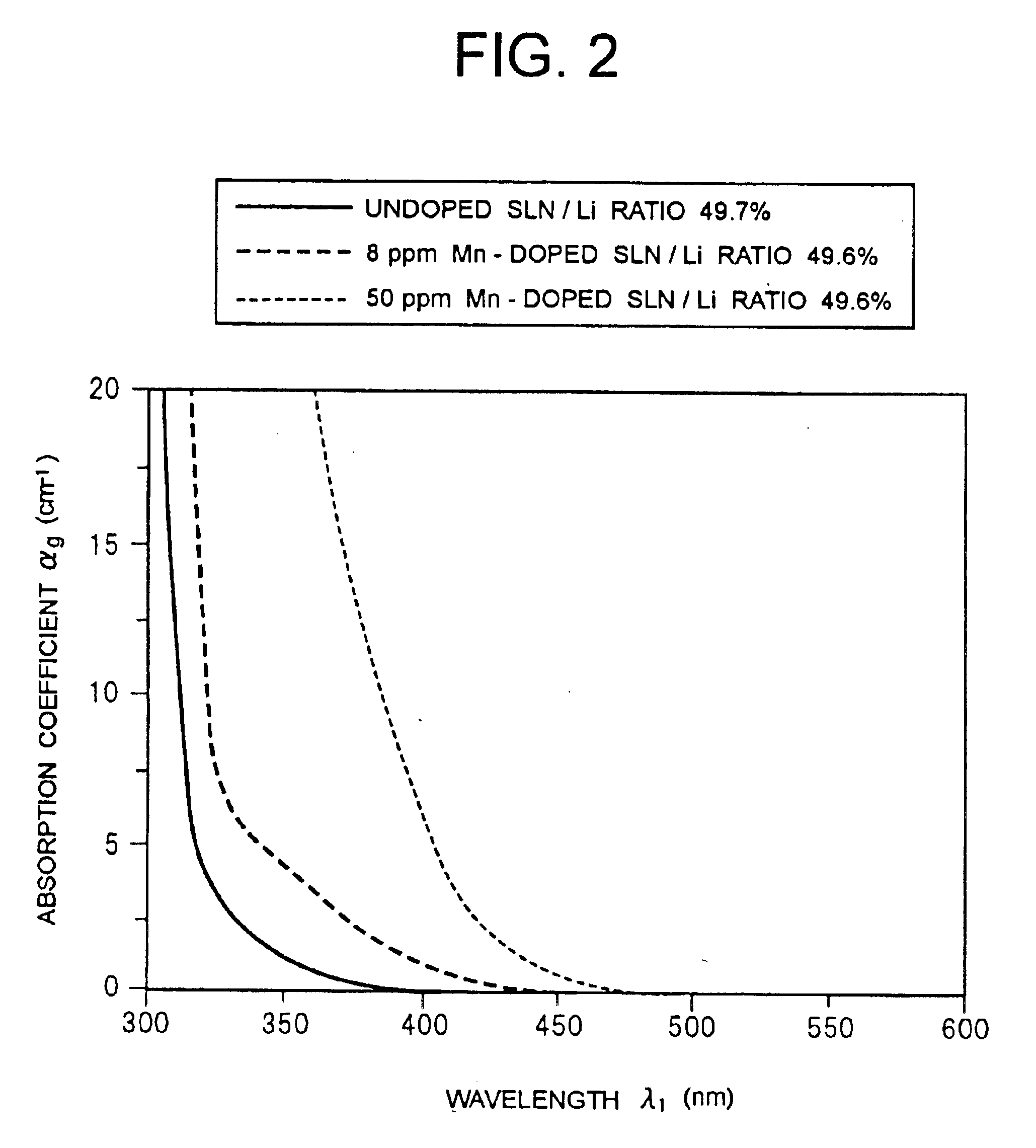
A holographic recording medium exhibiting a high recording sensitivity without execution of reduction treatment. A system records information on the holographic recording medium by using a gating light within a wavelength band causing less optical damage to the holographic recording medium. The holographic recording medium includes a single crystal of lithium niobate (LiNbO3) or lithium tantalate (LiTaO3) containing Mn as a dopant.
Owner:NAT INST FOR MATERIALS SCI +1
Optical device, and virtual image display
ActiveUS7453612B2Reduce color unevennessReduce unevennessDiffraction gratingsOptical light guidesGratingWaveguide
An optical device including an optical waveguide upon which a group of parallel light beams different in traveling direction from each other are incident and from which the group of parallel light beams go out after propagated by repeated total reflection through it. The optical waveguide includes a first reflection-type volume hologram grating, and a second reflection-type volume hologram grating. The pitches of interference fringes on the hologram surfaces of the first and second reflection-type volume hologram gratings are equal to each other. In at least the second reflection-type volume hologram grating, the angle formed between the interference fringes and hologram surfaces are varied continuously or stepwise within the hologram in relation to the main incident light beam so as to meet the Bragg condition. Therefore, it is possible to reduce the unevenness of color and brightness due to angles of view.
Owner:SONY CORP
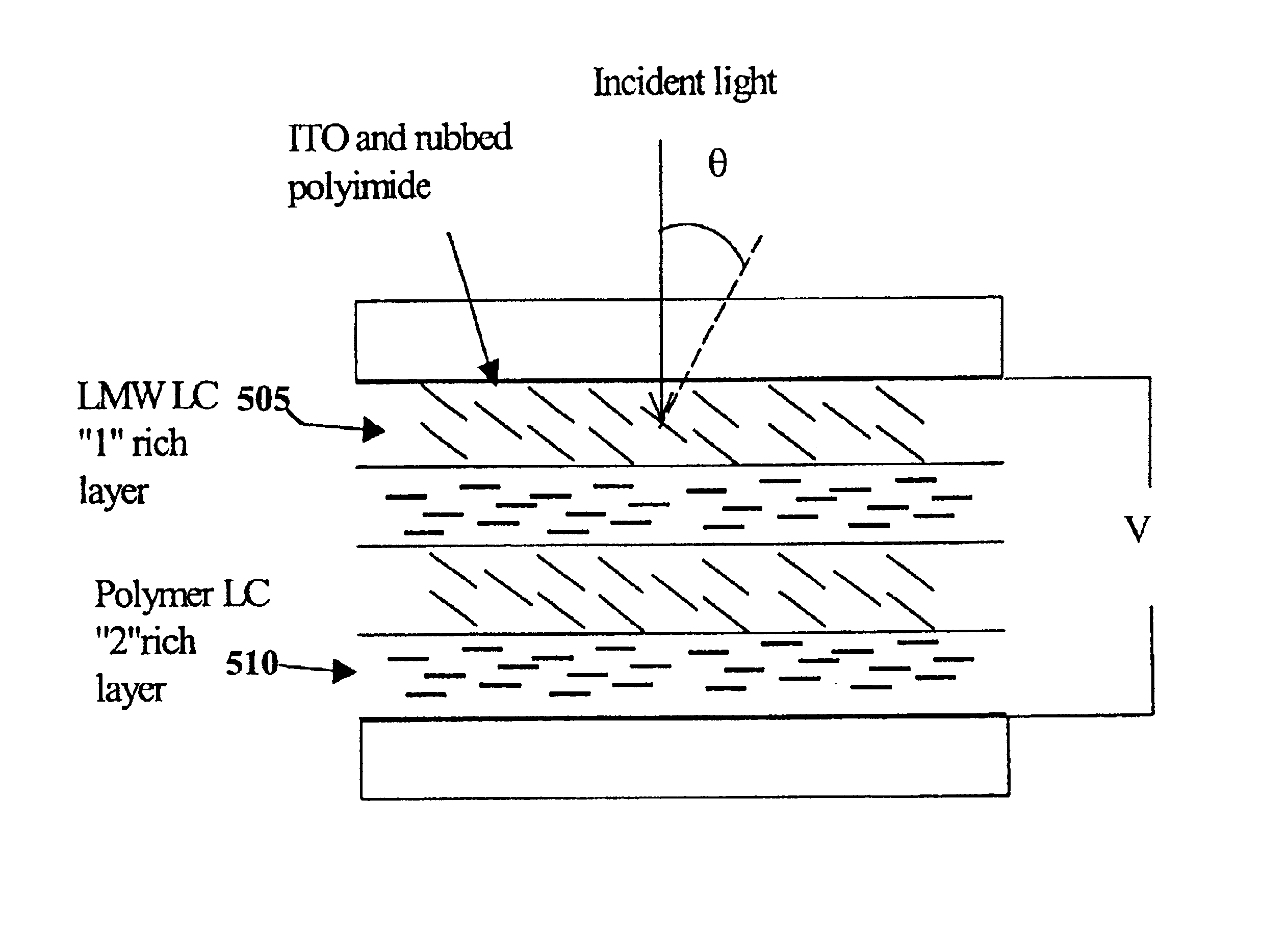
Electrically switchable polymer dispersed liquid crystal materials including transmissive holographic gratings
InactiveUS6667134B1Fast curingImprove clarityLiquid crystal compositionsPhotomechanical apparatusElectricityCrystallography
A new photopolymerizable material allows single-step, fast recording of volume holograms with properties that can be electrically controlled. Polymer-dispersed liquid crystals (PDLCs) in accordance with the invention preferably comprise a homogeneous mixture of a nematic liquid crystal and a multifunctional pentaacrylate monomer, in combination with photoinitiator, coinitiator and cross-linking agent. Optionally, a surfactant such as octanoic acid may also be added. The PDLC material is exposed to coherent light to produce an interference pattern inside, the material. Photopolymerization of the new PDLC material produces a hologram of clearly separated liquid crystal domains and cured polymer domains. Volume transmission gratings made with the new PDLC material can be electrically switched between nearly 100% diffraction efficiency and nearly 0% diffraction efficiency. By increasing the frequency of the switching voltage, switching voltages in the range of 50 Vrms can be achieved.
Owner:LEIDOS
Conjugated narrow-band tri-phosphor staggered volume holographic grating waveguide near-to-eye optical display device
The invention provides a conjugated narrow-band tri-phosphor staggered volume holographic grating waveguide near-to-eye optical display device. The device comprises an image display light source which is used for providing image information to be viewed, a P&S photo-conversion component which is used for converting P light and S light, a collimating lens group which is used for collimating light wave, a PBS component which is used for the polarizing beam-splitting of light wave, a beam-splitting selecting component which is used for uniformly spreading the light wave on a coupling input surface; a conjugated tri-phosphor staggered coupling input volume holographic grating which is used for dispersing incident ray and totally reflecting and transmitting the ray inside the substrate, a light-guide transmitting substrate which is used for totally reflecting and transmitting the light wave, and a conjugated tri-phosphor staggered coupling output volume holographic grating which is used for coupling the dispersed incident ray in sequence and outputting the ray to the outside of the substrate. The device has the advantages of full color, ultra-thinness, large field angle and simplicity in process and implementation, and can be applied to the damage-free display of a mobile screen, the display of a terminal, the scene teaching instruction for a doctor, the real-time information positioning for fire fighting, 3D game and other fields.
Owner:SHANGHAI RAYPAI PHOTONIC CRYSTAL LTD
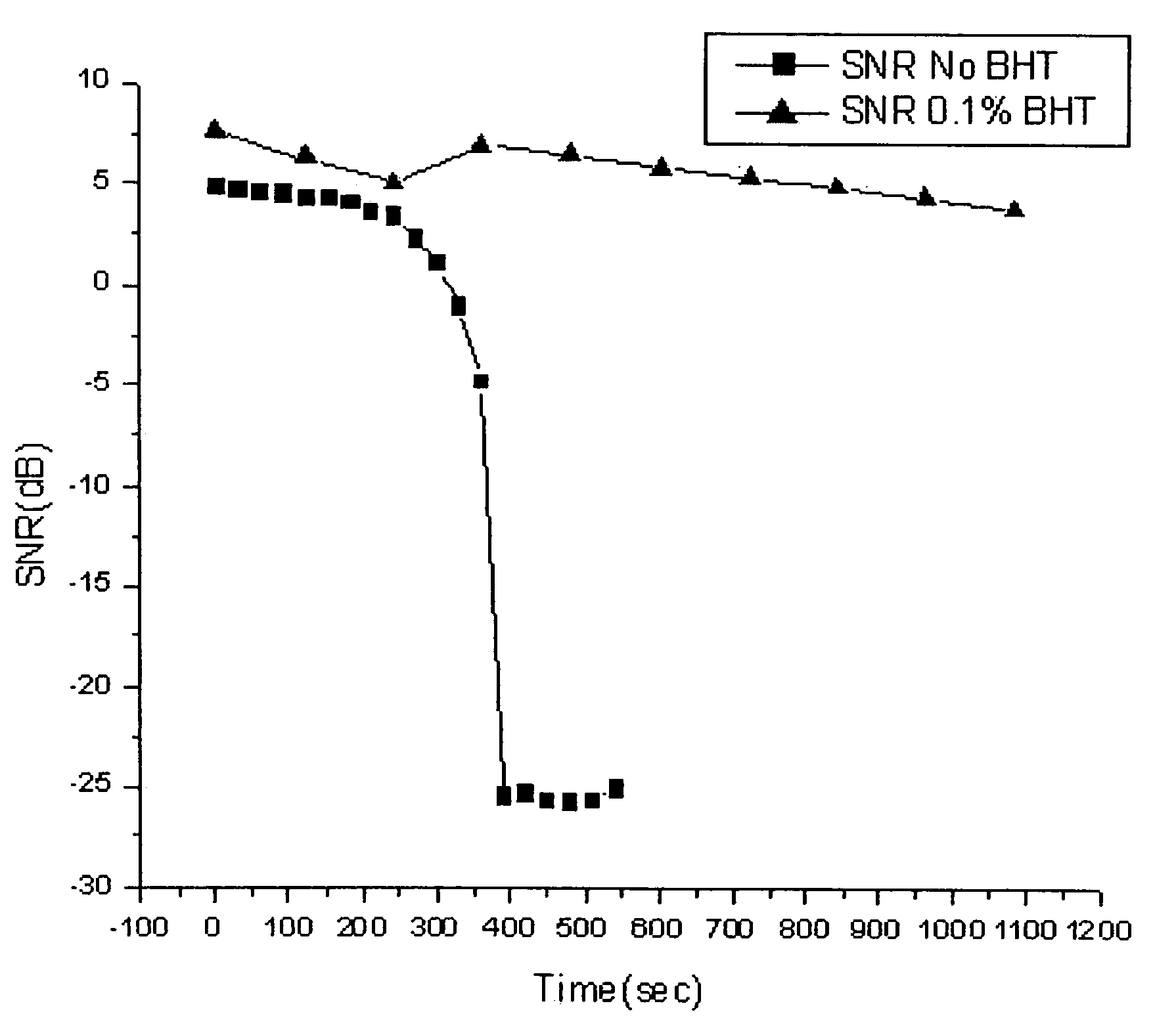
Holographic recording medium with control of photopolymerization and dark reactions
The present invention relates to a system, as well as articles and holographic recording medium comprising the system, where the system comprises: a polymerizable component comprising at least one photoactive polymerizable material; and a photoinitiator component comprising at least one photoinitiator for causing the polymerizable component to polymerize to thereby form a plurality of holographic gratings when activated by exposure to a photoinitiating light source; wherein when a portion of the polymerizable component has been polymerized to form at least one holographic grating, the unpolymerized portion of the polymerizable component is resistant to further polymerization when not exposed to the photoinitiating light source. The present invention also provides methods for forming at least one holographic grating in a holographic recording medium having such a photopolymerizable system.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
System and methods for spectral beam combining of lasers using volume holograms
Volume holographic gratings are used to spectrally combine the emissions from multiple sources into a single output beam. Transmission or reflection gratings are utilized with either laser diode bars, fiber lasers, or fiber collimated light sources. The volume holographic spectral combiner can also be used to feedback and stabilize the wavelength of the sources in an external cavity configuration.
Owner:ONDAX
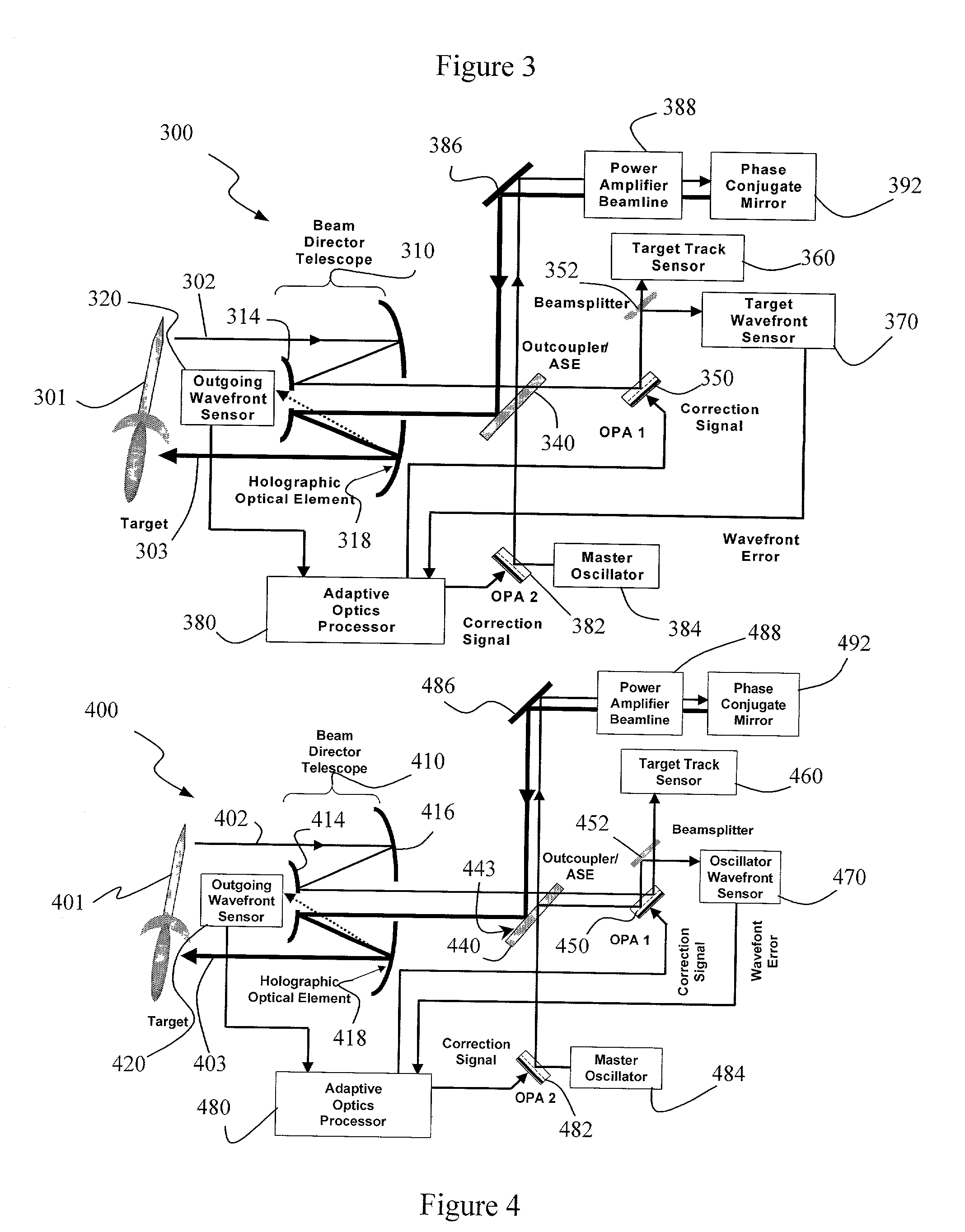
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with outgoing wavefront correction utilizing holographic sampling at primary mirror, phase conjugation, and adaptive optics in low power beam path
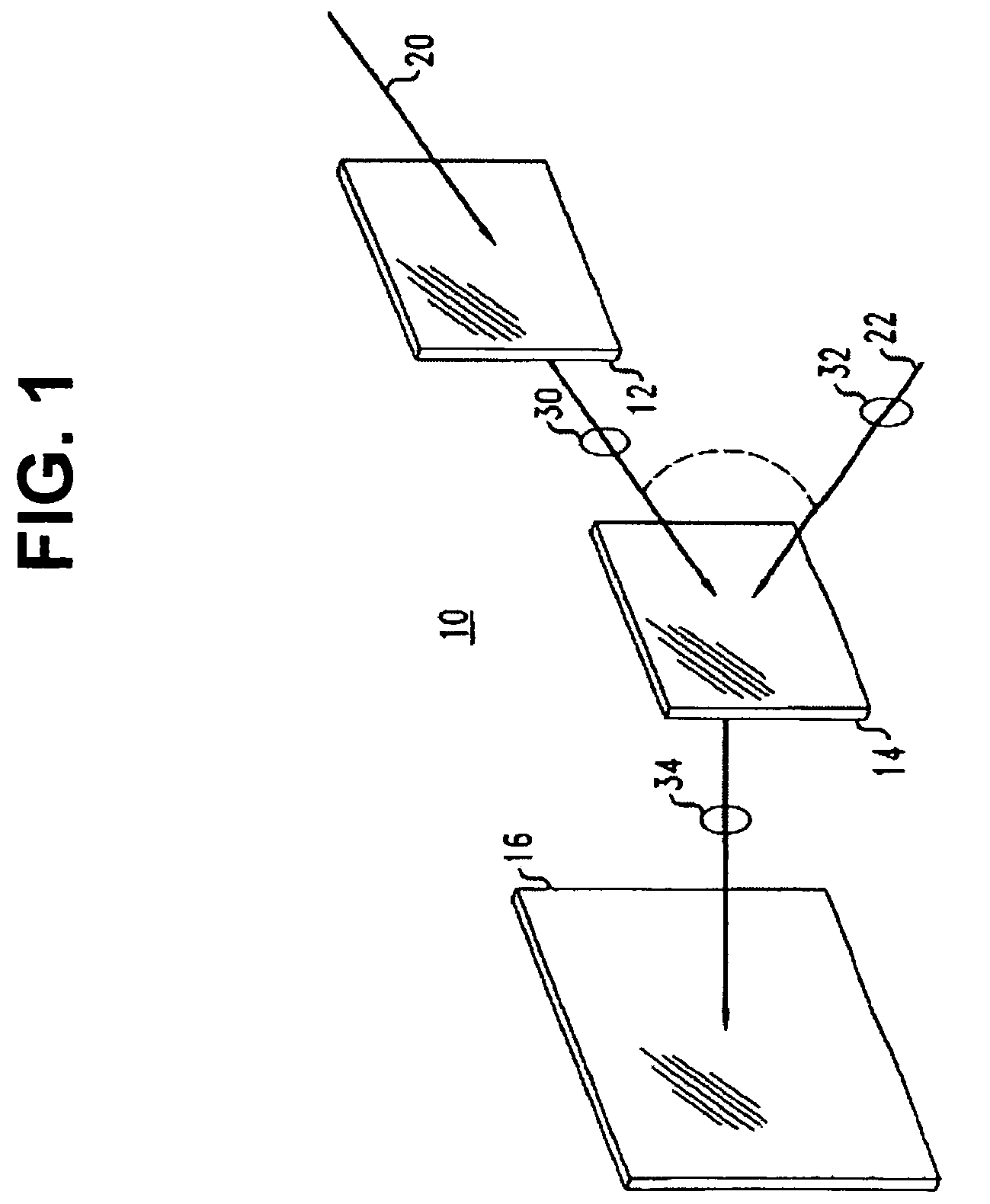
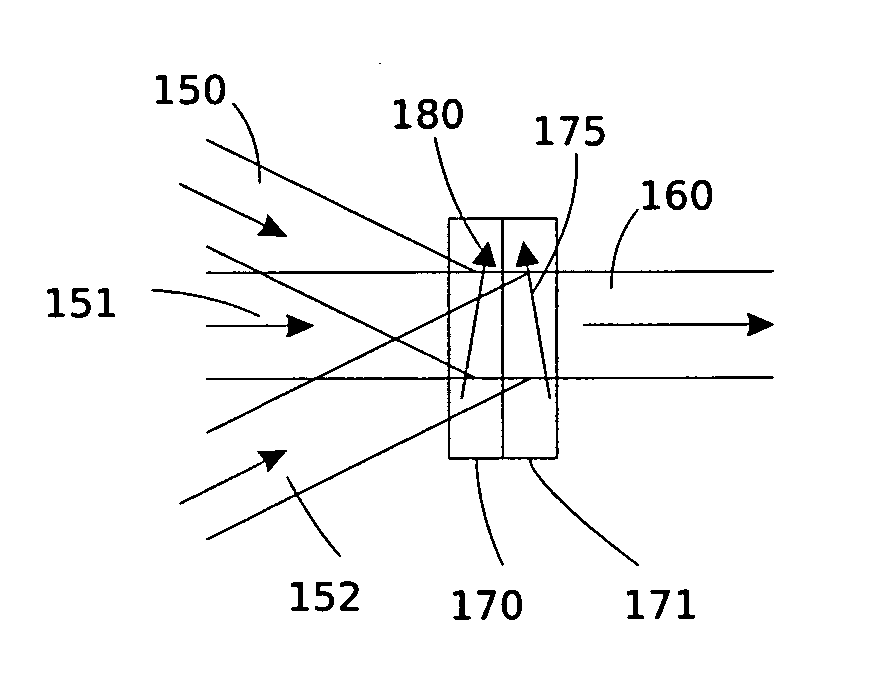
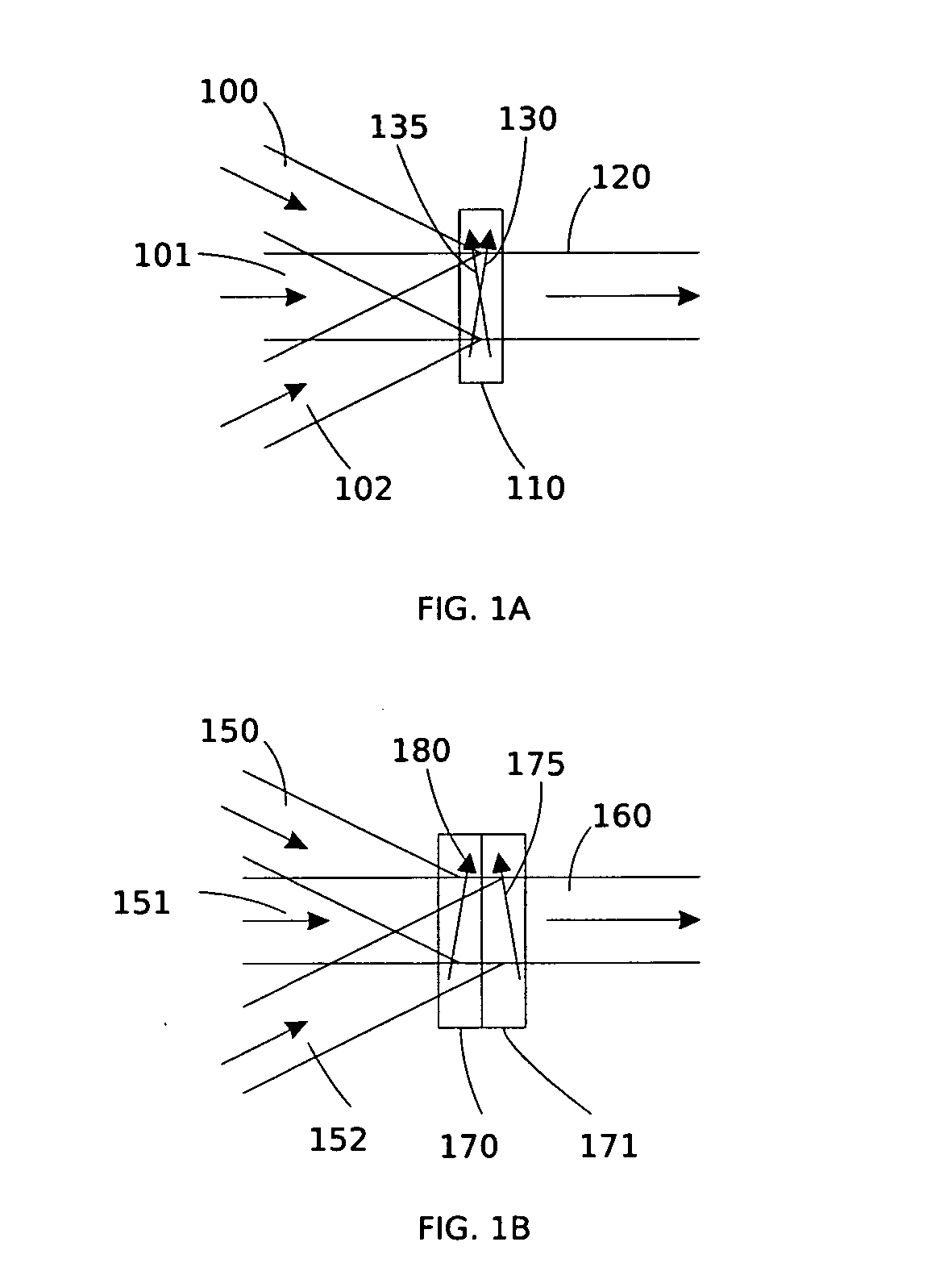
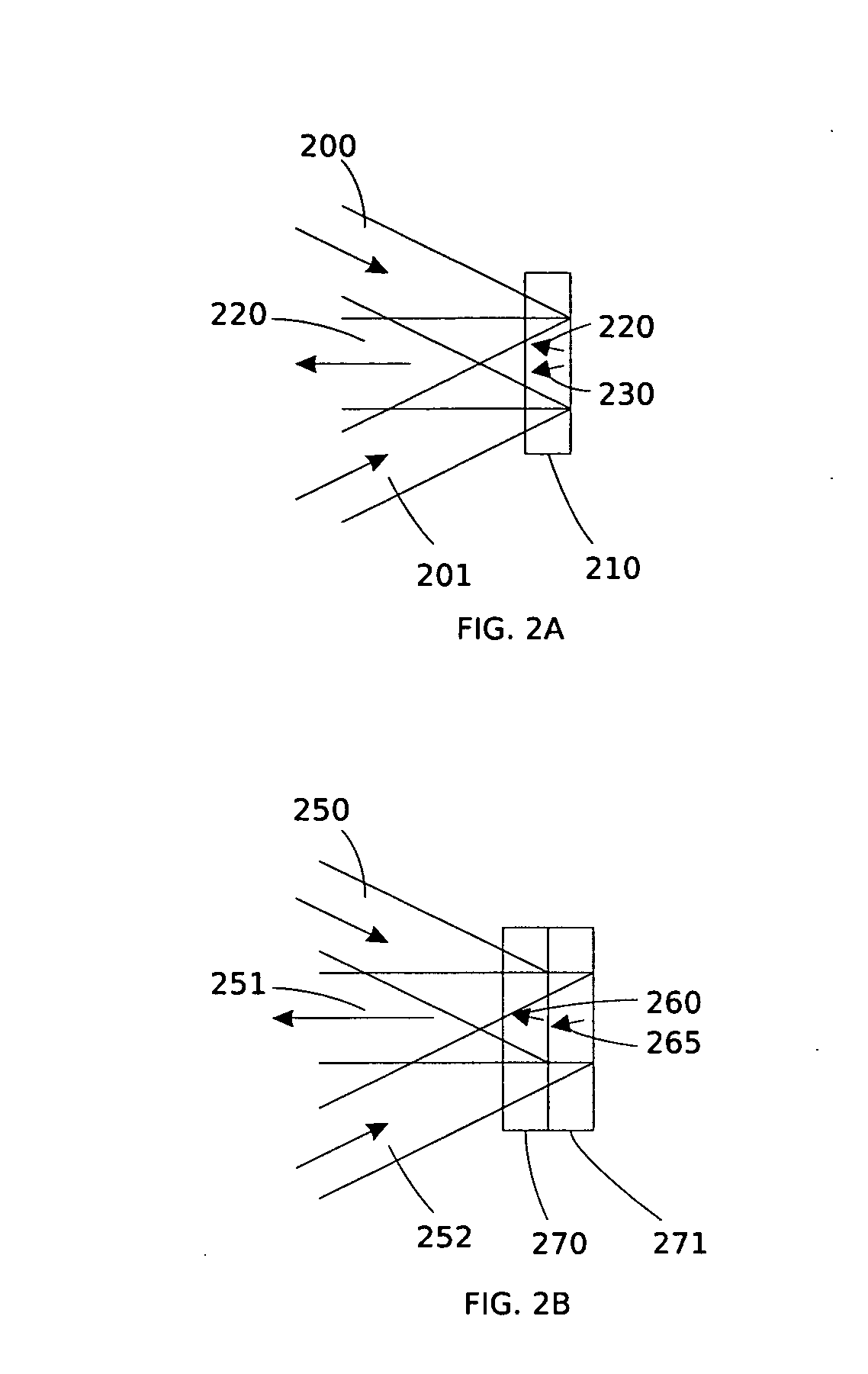
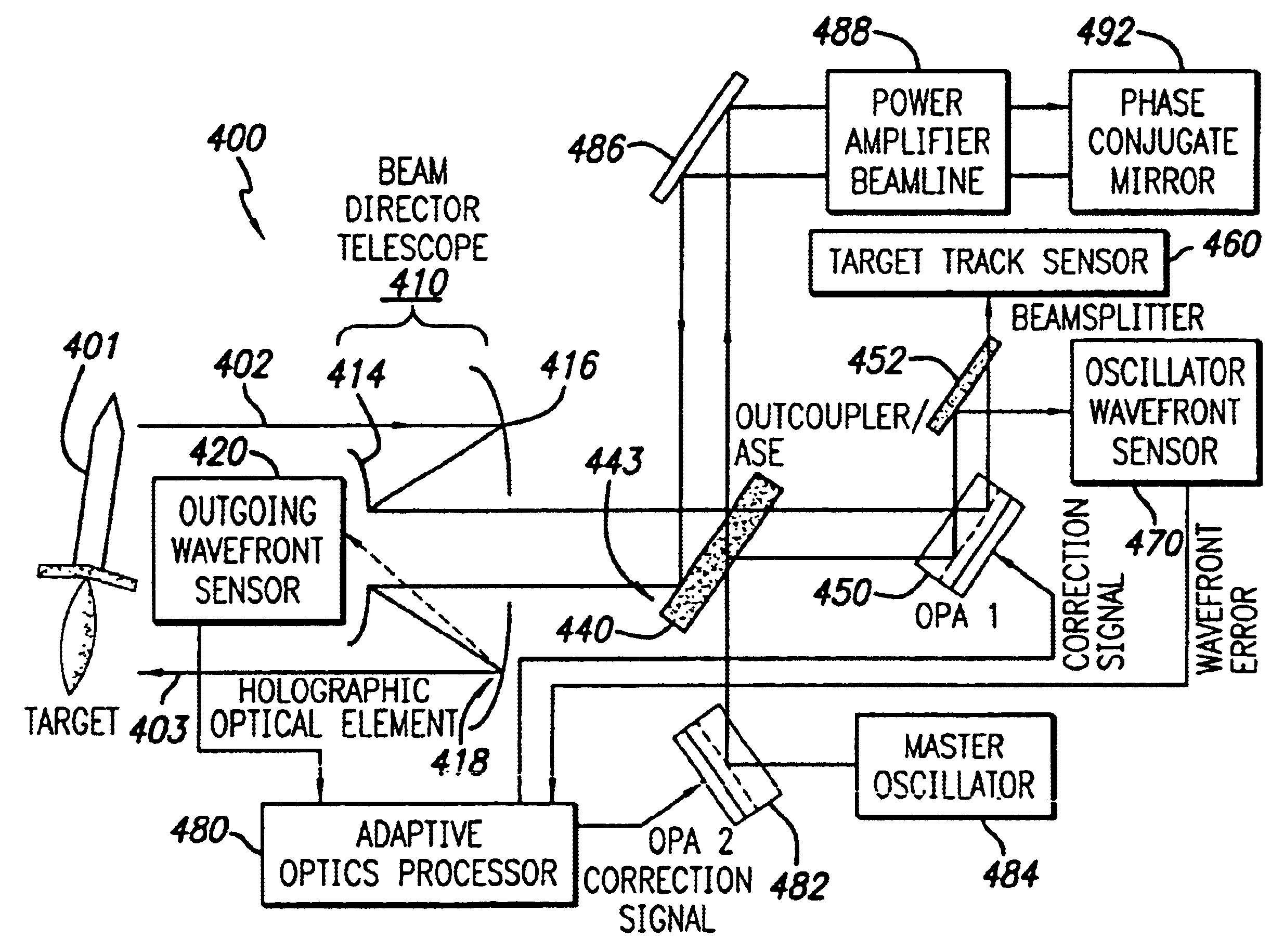
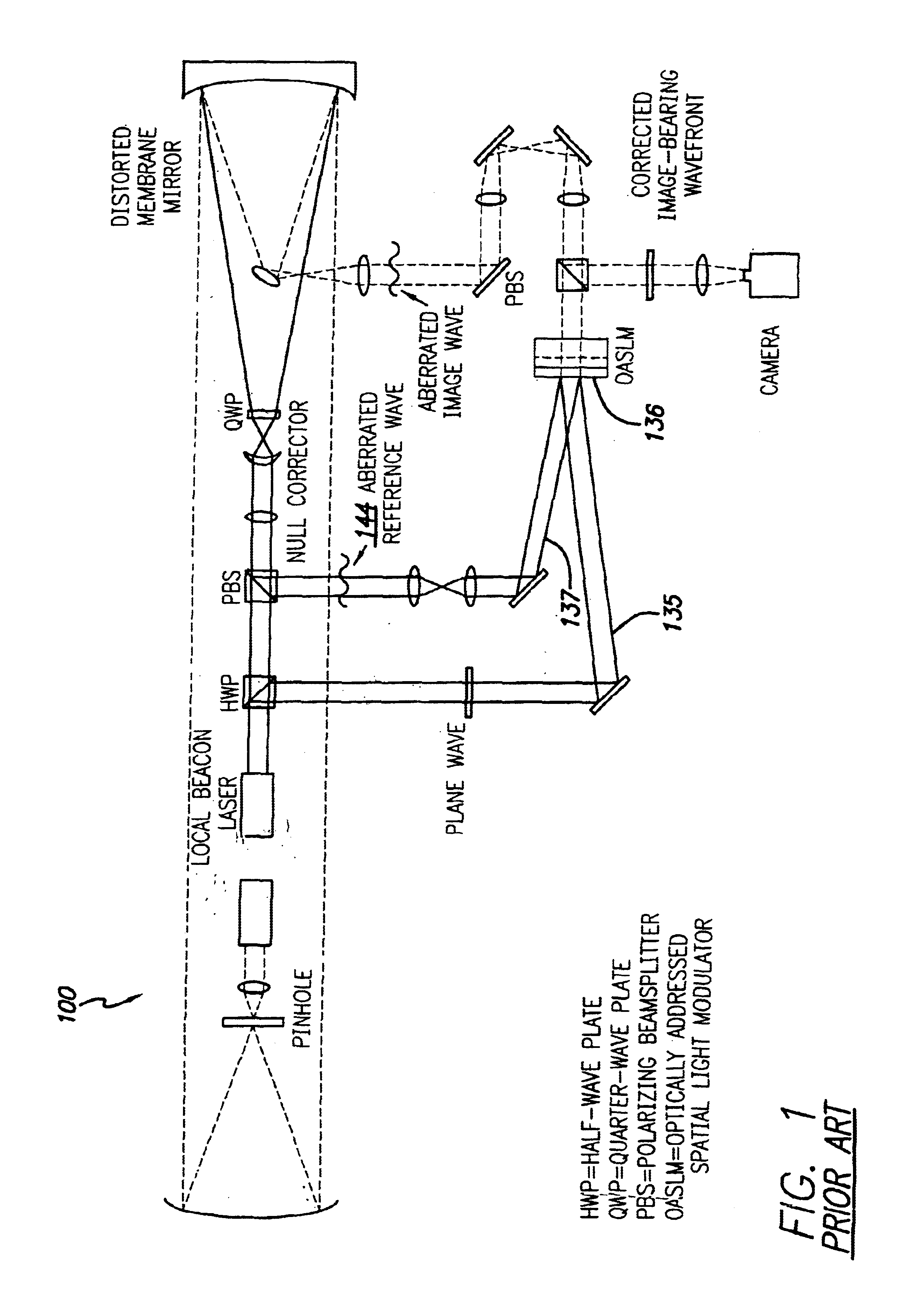
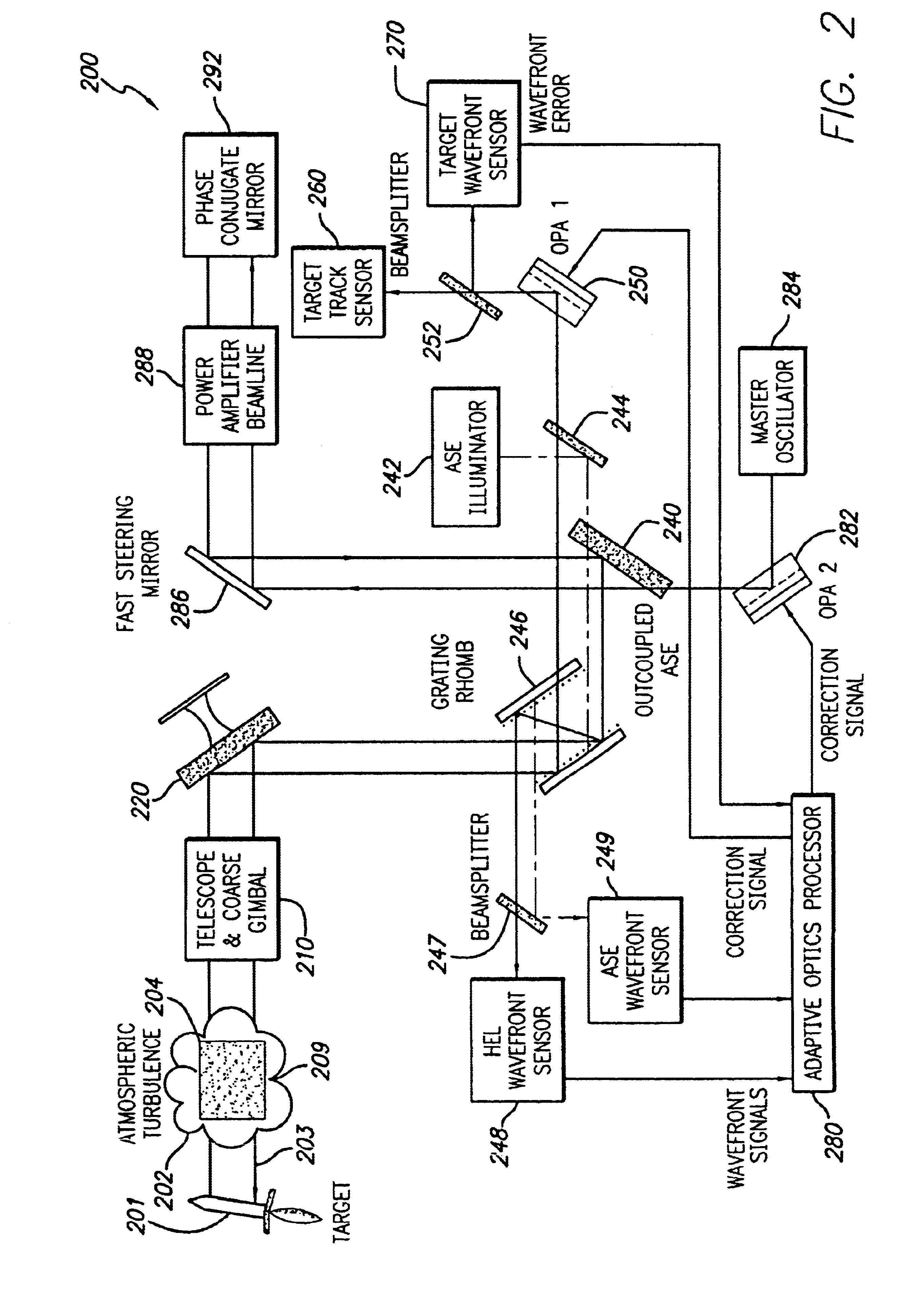
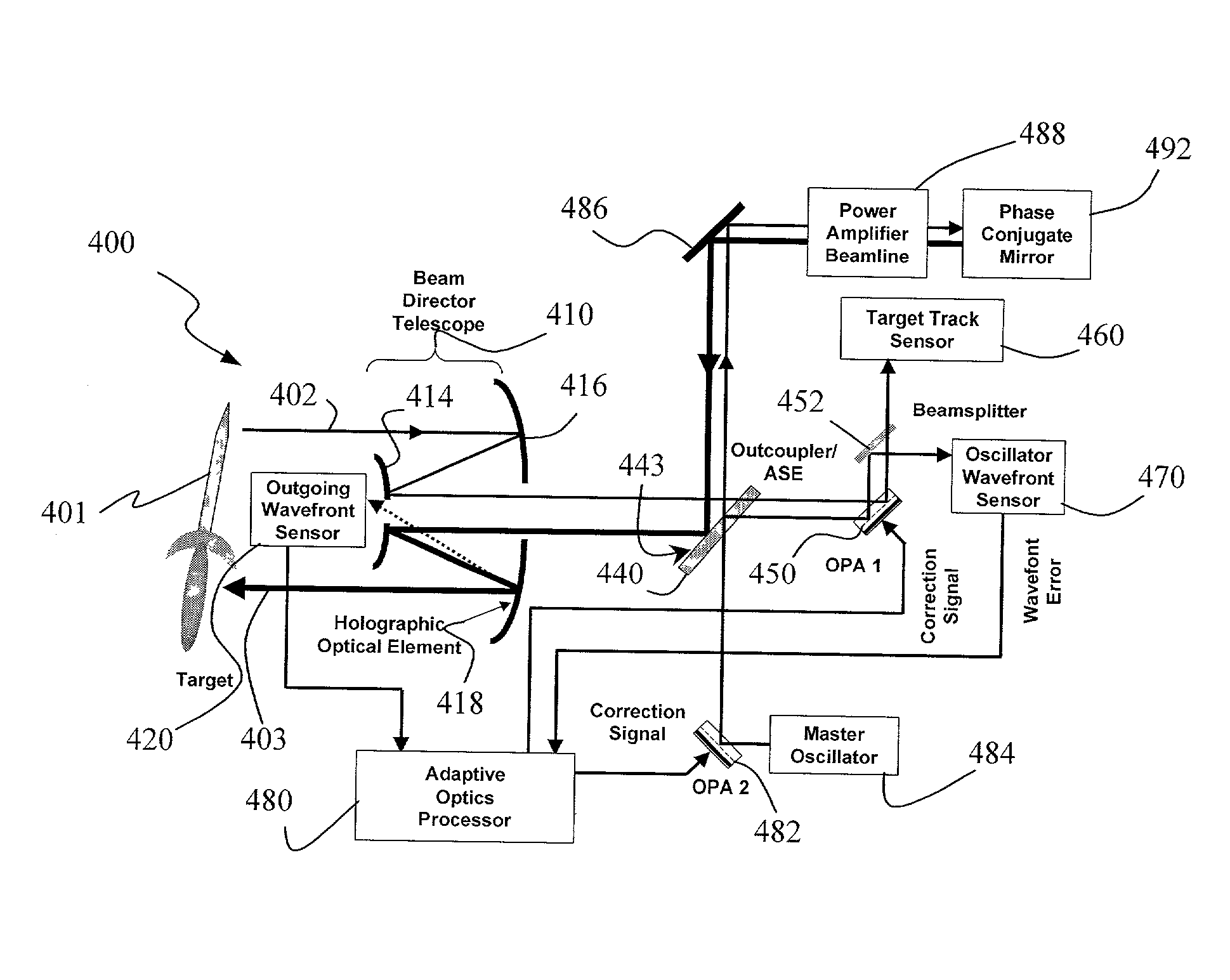
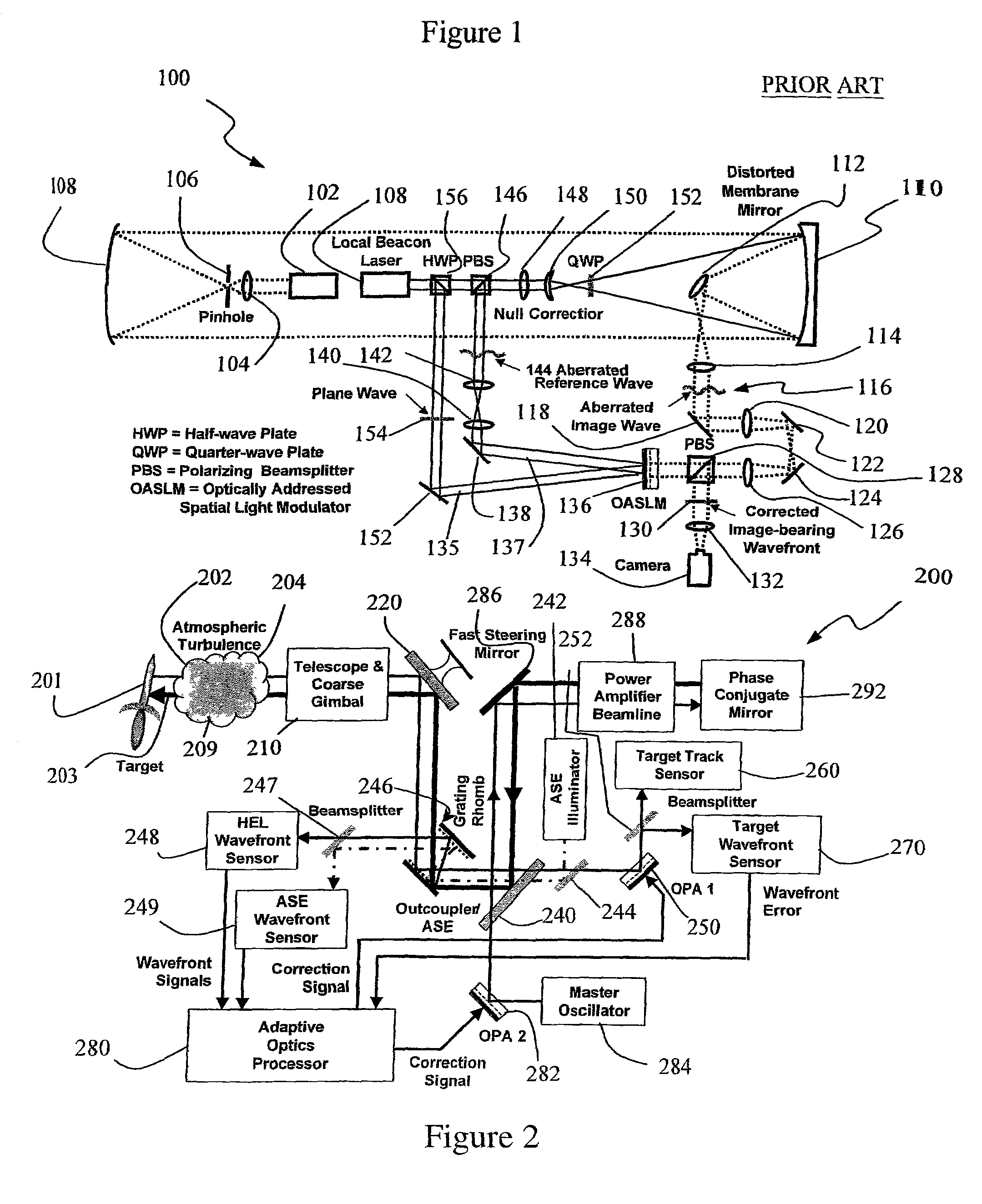
InactiveUS6849841B2Cancellation effectPhotometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorPhased array
A beam control system and method. In an illustrative embodiment, the inventive system (500) provides a first beam of electromagnetic energy (503); samples the first beam (503) and provides a second beam (505) in response thereto; detects aberrations in the second beam (505); and corrects aberrations in the first beam (503) in response to the detected aberrations. In a specific implementation, the invention (500) includes a beam director telescope (510) having a primary mirror (516) on which a holographic optical element (518) is disposed. The holographic optical element (518) samples the output high-power beam and provides a sampled beam to a wavefront sensor (520). The wavefront sensor (520) provides signals to an adaptive optics processor (580). The adaptive optics processor (580) analyzes the sampled wavefront, detects aberrations therein and provides a correction signal to an optical phased array (550).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Holographic recording medium with control of photopolymerization and dark reactions
The present invention relates to a system, as well as articles and holographic recording medium comprising the system, where the system comprises: a polymerizable component comprising at least one photoactive polymerizable material; and a photoinitiator component comprising at least one photoinitiator for causing the polymerizable component to polymerize to thereby form a plurality of holographic gratings when activated by exposure to a photoinitiating light source; wherein when a portion of the polymerizable component has been polymerized to form at least one holographic grating, the unpolymerized portion of the polymerizable component is resistant to further polymerization when not exposed to the photoinitiating light source. The present invention also provides methods for forming at least one holographic grating in a holographic recording medium having such a photopolymerizable system.
Owner:AKONIA HOLOGRAPHICS
Multiplexed volume holographic grating
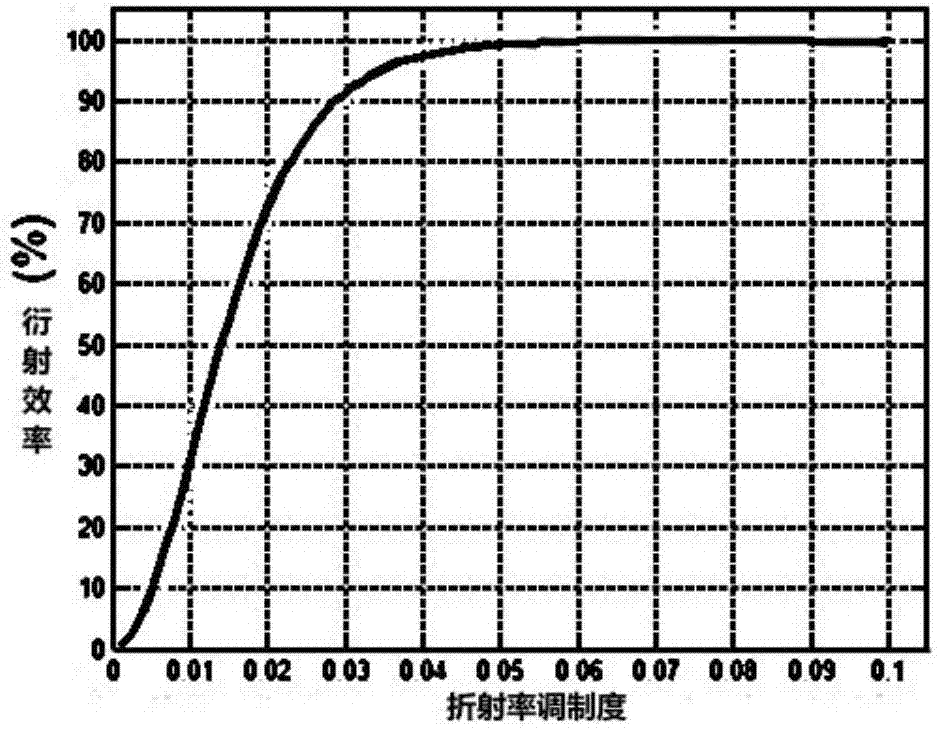
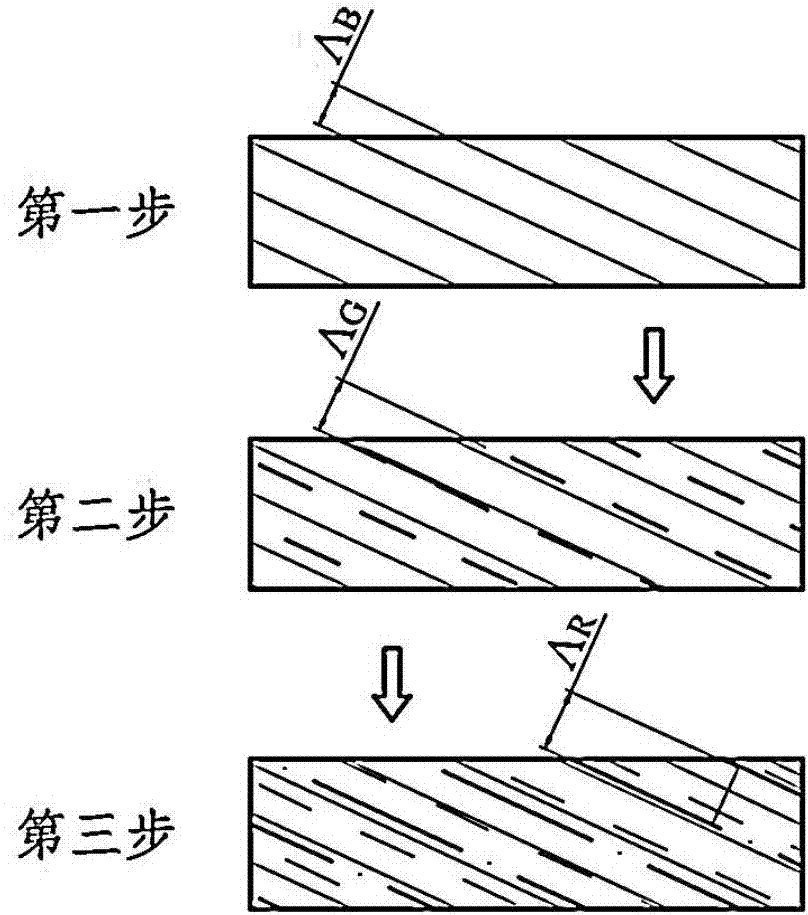
The invention discloses a multiplexed volume holographic grating. The multiplexed volume holographic grating respectively records red, green and blue three holograms on the same dielectric layer by exposing for three times; volume holographic gratings formed by exposure of different wavelengths are the same in inclination angle and are different in period; by controlling exposure time, refractive index modulation depths corresponding to red, green and blue light after exposure accords with the relation that delta n red light is greater than delta n green light, and delta n green light is greater than delta n blue light, and peak diffraction efficiencies corresponding to the red, green and blue light after exposure are similar. The multiplexed volume holographic grating can effectively balance irradiating energy of red, green and blue light waves and avoid color offset.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
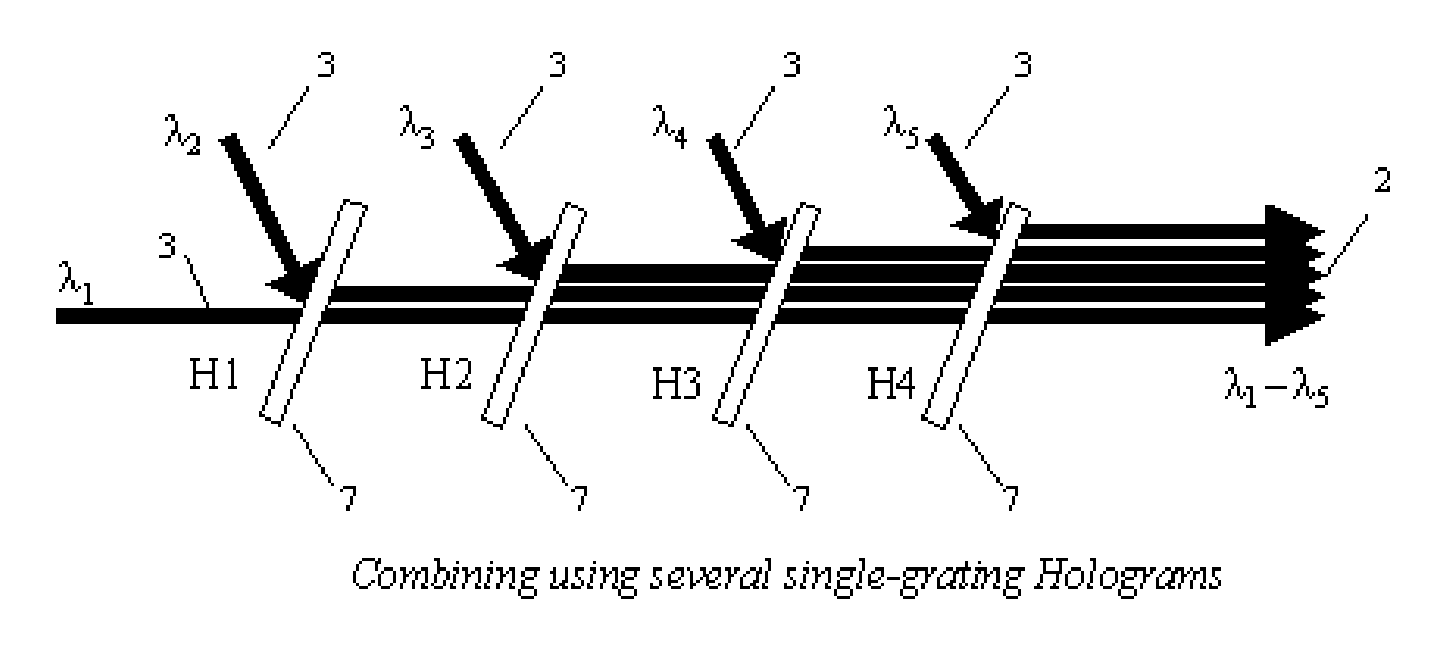
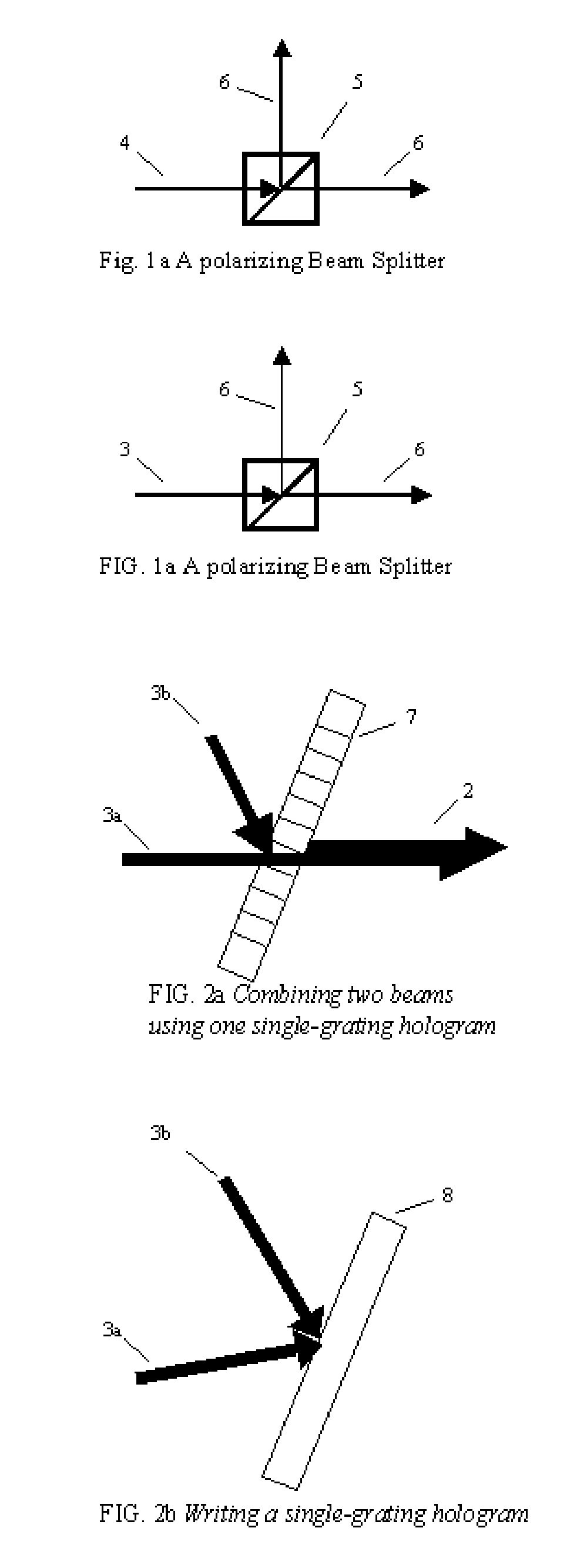
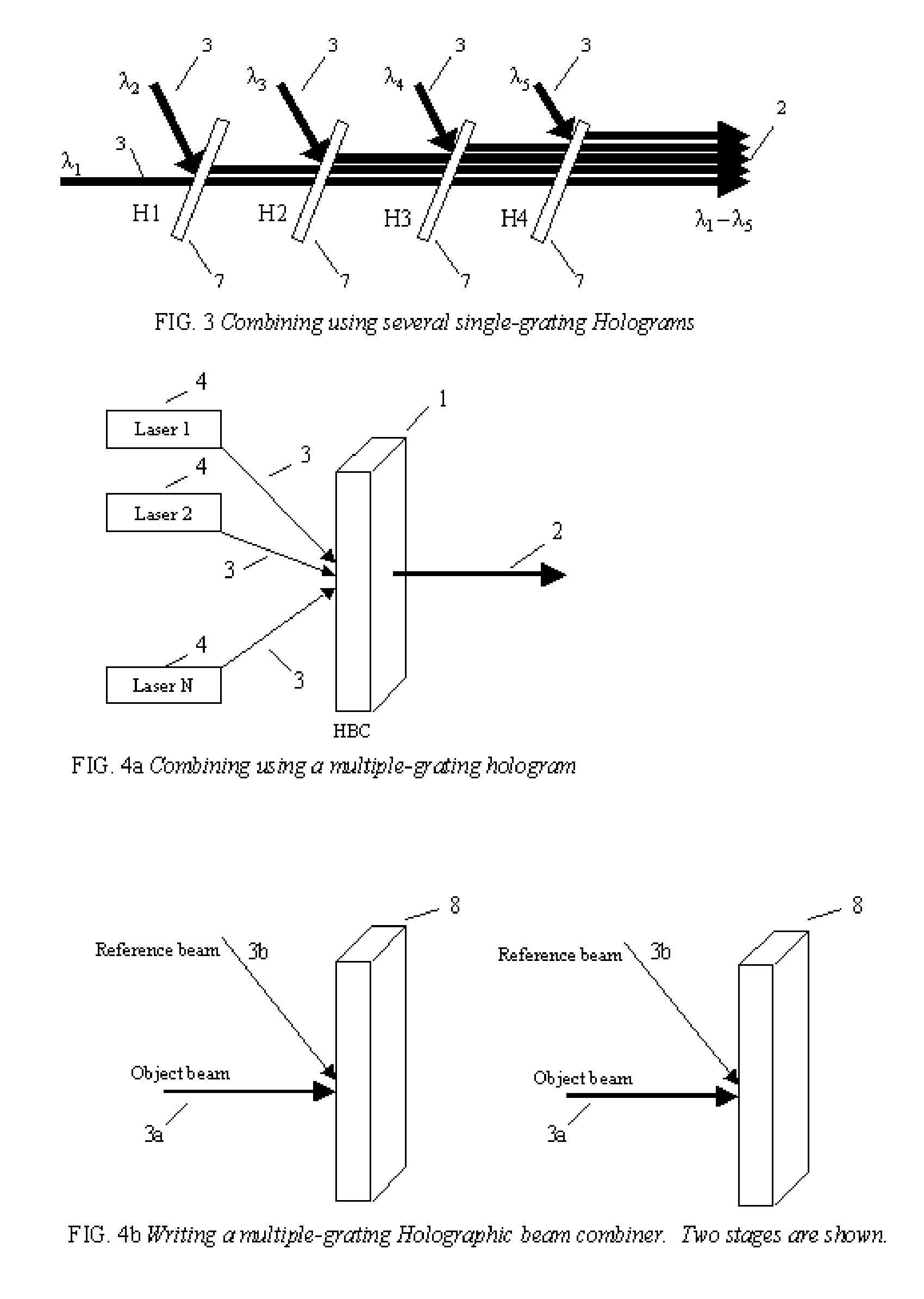
Method and system for combining multiple laser beams using transmission holographic methodologies
InactiveUS20060109876A1Low costGood techniqueOptical resonator shape and constructionCondensersQuinonePhotopolymer
The Holographic Beam Combiner, (HBC), is used to combine the output from many lasers into a single-aperture, diffraction-limited beam. The HBC is based on the storage of multiple holographic gratings in the same spatial location. By using a photopolymer material such as quinone-doped polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) that uses a novel principle of “polymer with diffusion amplification” (PDA), it is possible to combine a large number (N) of diode lasers, with an output intensity and brightness 0.9 N times as much as those of the combined outputs of individual N lasers. The HBC will be a small, inexpensive to manufacture, and lightweight optical element. The basic idea of the HBC is to construct multiple holograms onto a recording material, with each hologram using a reference beam incident at a different angle, but keeping the object beam at a fixed position. When illuminated by a single read beam at an angle matching one of the reference beams, a diffracted beam is produced in the fixed direction of the object beam. When multiple read beams, matching the multiple reference beams are used simultaneously, all the beams can be made to diffract in the same direction, under certain conditions that depend on the degree of mutual coherence between the input beams.
Owner:SHAHRIAR SELIMM
Optical router switch array and method for manufacture
InactiveUS6885414B1Simple configurationLow insertion lossLiquid crystal compositionsTelescopesElectricityGrating
An optical router switch array includes a plurality of switchable mirror elements having holographic liquid crystal arranged in stack cells. Each of the mirror elements is isolated electrically from the other switchable mirror elements by a plurality of substrates alternative arranged between the switchable mirror elements. Holographic gratings are formed on the holographic liquid crystal by exposure to holography at predetermined incident angles. A single switchable mirror element can also be provided in cases where an array is not required. The switchable mirror elements are polarization insensitive, stable within the operational spectral region, and stable versus temperature. The invention also includes methods for manufacturing a single switchable mirror element and the optical arrray.
Owner:KENT OPTRONICS
Holographic optical waveguide and holographic optical waveguide display device
InactiveCN105487170ASolving Off-Axis Transmission IssuesSolve the problems of large thickness, uncompact structure and large volumeOptical light guidesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
The invention discloses a holographic optical waveguide, and belongs to the technical field of augmented reality and virtual reality. The holographic optical waveguide comprises a planar optical waveguide, and an optical coupling in end and an optical coupling out end which are respectively arranged at the two ends of the planar optical waveguide. The optical coupling in end reflects received light rays so that the reflected light rays are enabled to meet the total reflection conditions to be transmitted to the optical coupling out end through multiple times of total reflection between the two reflecting surfaces of the planar optical waveguide. The received light rays are diffractively emergent out of the optical coupling out end. The optical coupling out end is a holographic grating. The holographic grating is a polarization holographic liquid crystal grating comprising a transparent substrate, a light orientation layer and a liquid crystal layer which are arranged in turn, wherein polarization holographic patterns having periodic structures are recorded on the light orientation layer. The invention also discloses a holographic optical waveguide display device. The polarization holographic liquid crystal grating is used as the optical coupling out end of the holographic optical waveguide so that 100% of diffraction efficiency can be achieved theoretically, and zero order waves can be suppressed and conjugate images can be eliminated.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for holographic mastering and replication
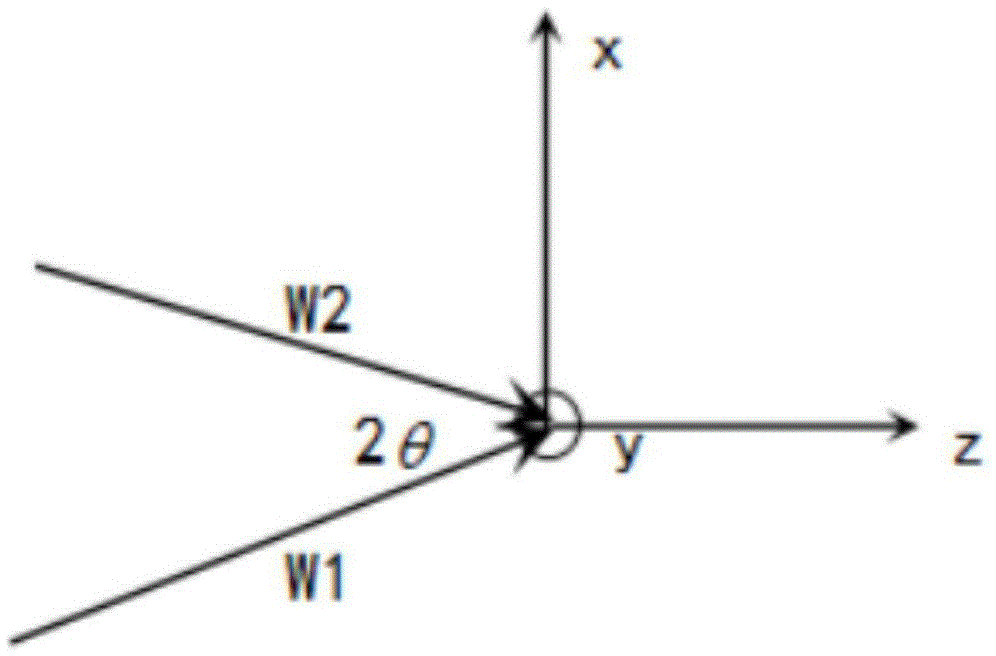
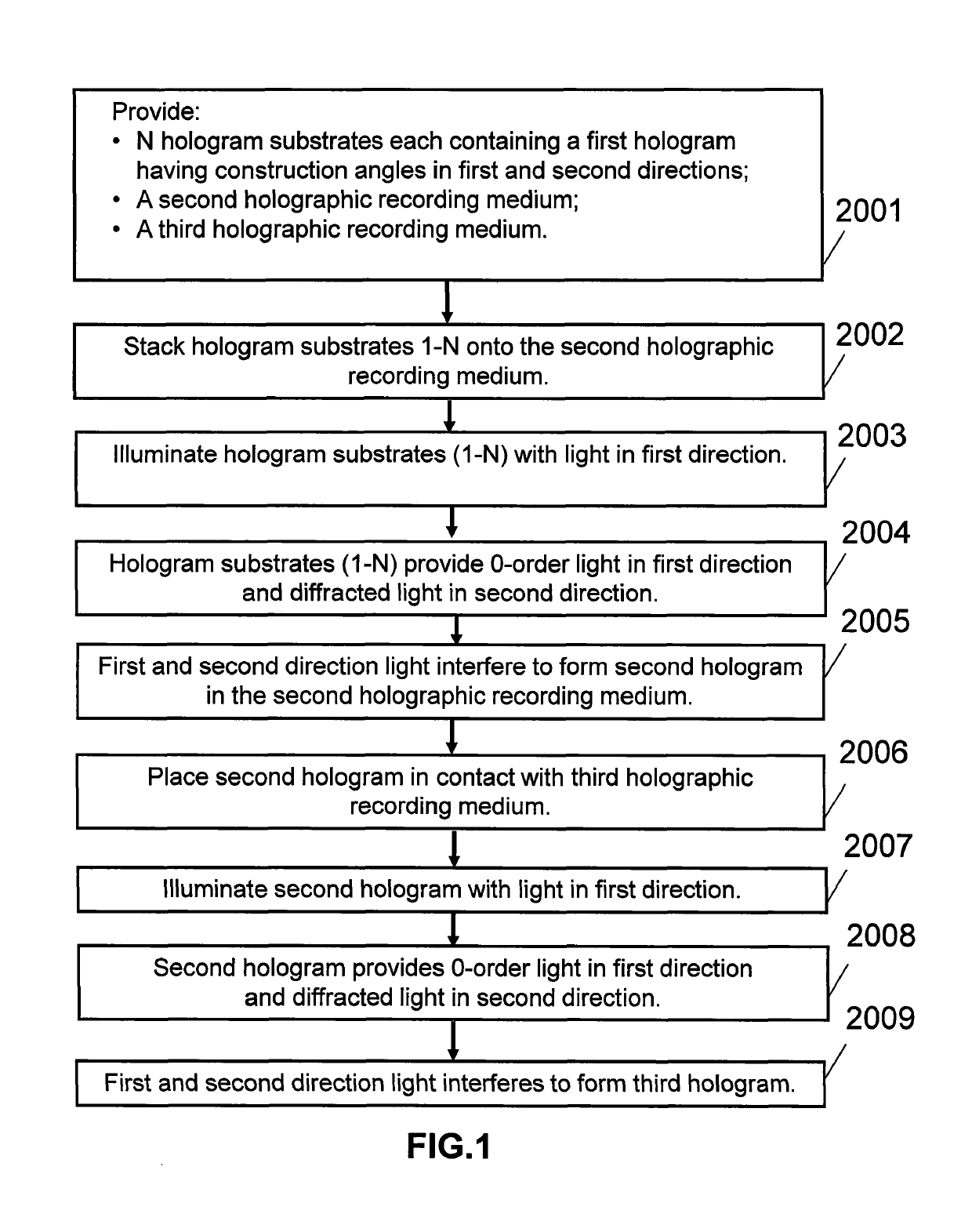
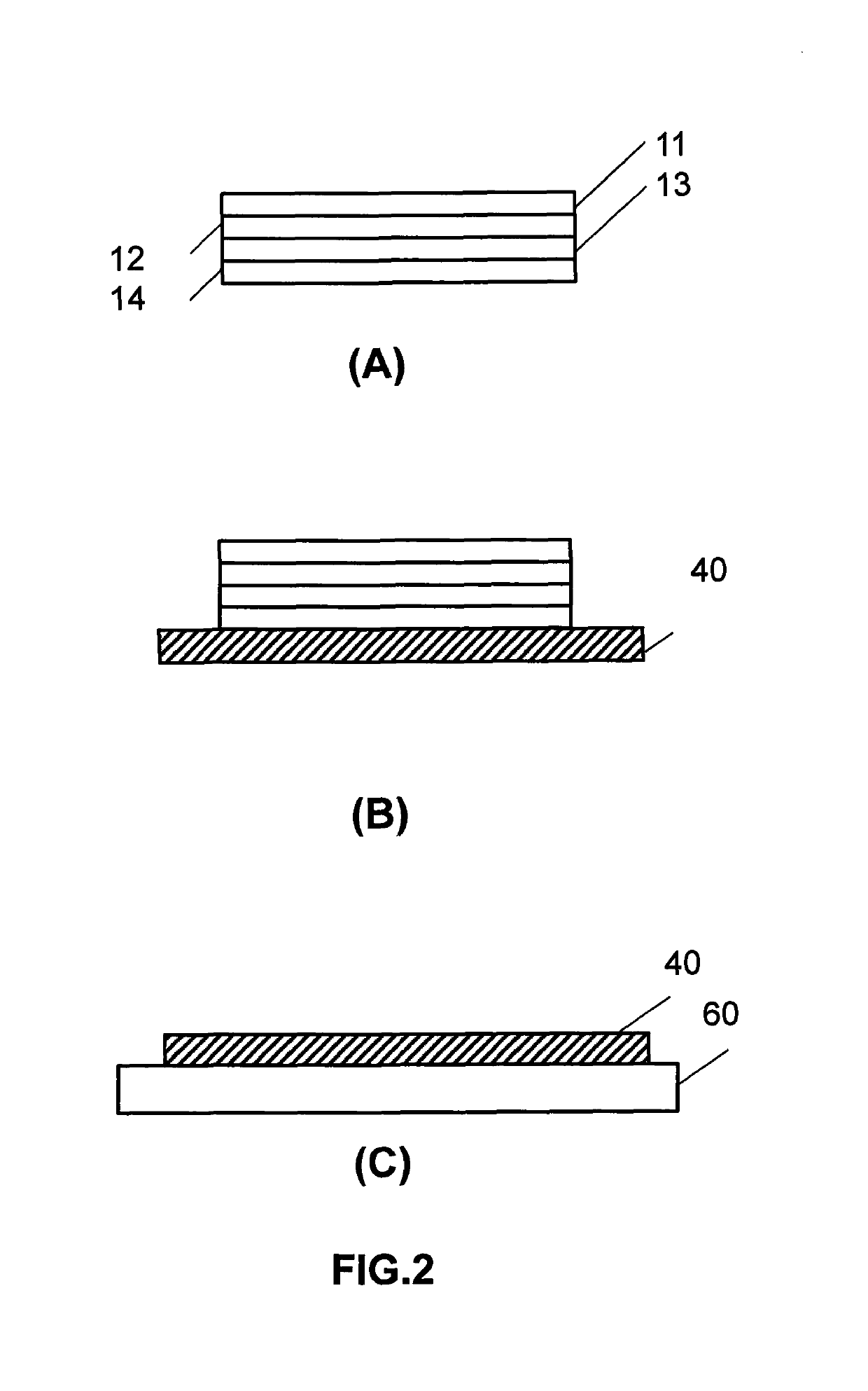
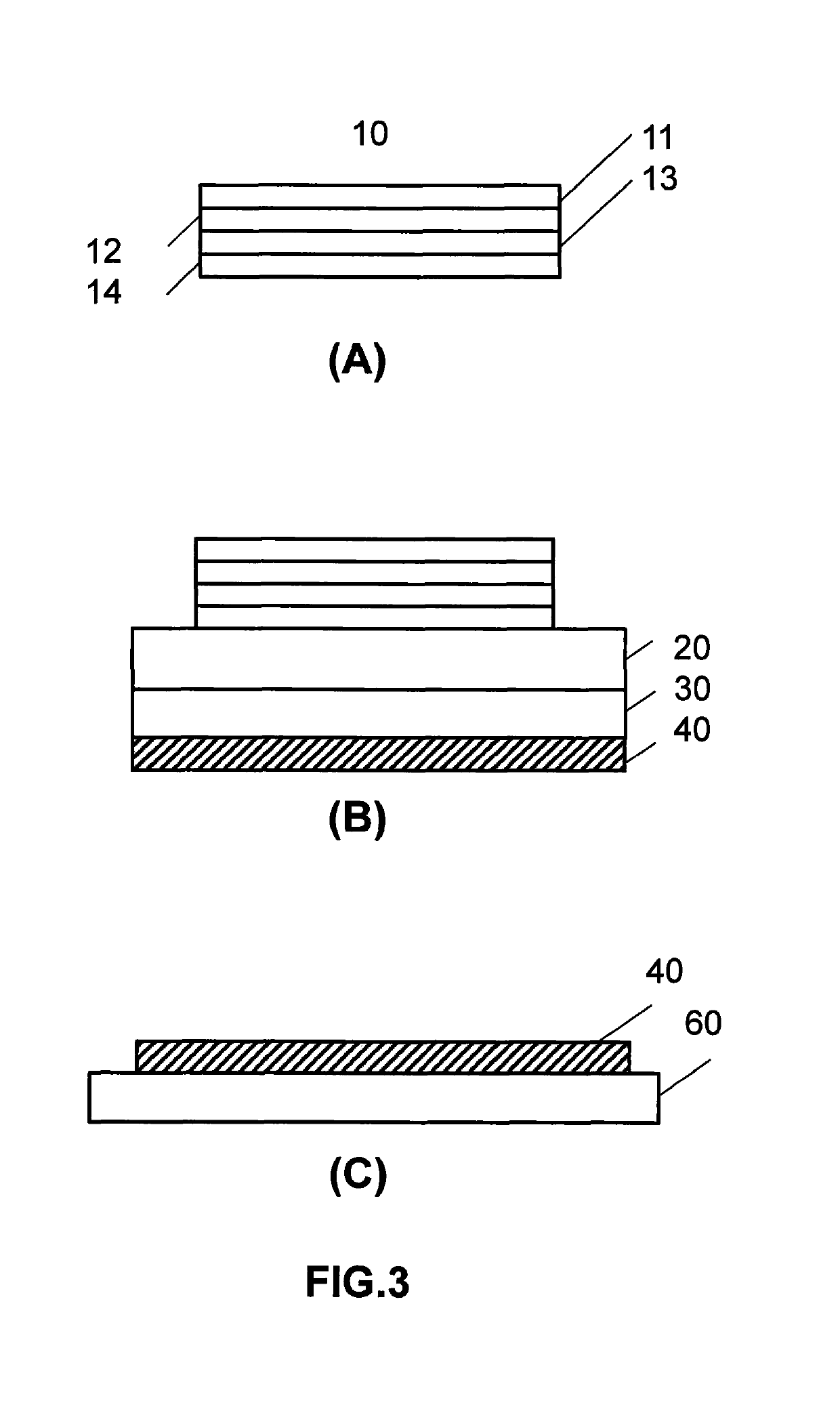
ActiveUS10359736B2Efficient and cost-effectiveHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsHolographic recordingRecording media
A method for producing holograms with a multiplicity of holographic prescriptions from a single master is provided. A multiplicity of holographic substrates each having a first hologram is stacked on a second holographic recording medium substrate. The first hologram is designed to diffract light from a first direction into a second direction. When expose to illumination from the first direction zero order and diffracted light from each first hologram interfere in the second holographic recording medium substrate forming a second hologram. The second hologram is then copied into a third holographic recording medium substrate to provide the final copy hologram.
Owner:DIGILENS
Device for manufacturing microstructure through focal field trajectory based on dynamic control
InactiveCN105259666AAchieve preparationRealize the processing effectOptical elementsGratingSpatial light modulator
A device for manufacturing a microstructure through a focal field trajectory based on dynamic control. The device comprises a femtosecond laser, a dynamic femtosecond vector light field array generation and control system and a tightly-focused micromachining system. According to the working principle, a holographic grating is loaded on a spatial light modulator for generating a vector light field array, and a tightly-focused field with the specific light intensity distribution is obtained through focusing of a microscope objective. The dynamic-changing vector light field array is obtained by designing dynamic-changing holographic grating, and a focal field trajectory in the special shape such as a quadrangle, an octagon, a fan blade shape and the like and changing along with time can be generated after tight focusing is performed. On the basis of the generated focal field trajectory, the microstructure corresponding to the focal field trajectory can be obtained on the basis of the generated focal field trajectory. Compared with other methods for manufacturing micro nanometer structures, the device has the unique advantage that samples or light sources do not need to move, the manufactured microstructure is close to the wavelength magnitude, the two-dimensional / three-dimensional structure of any design can be machined, and the advantages of being efficient, high in repeatability, good in stability and the like are achieved when the microstructure is manufactured.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
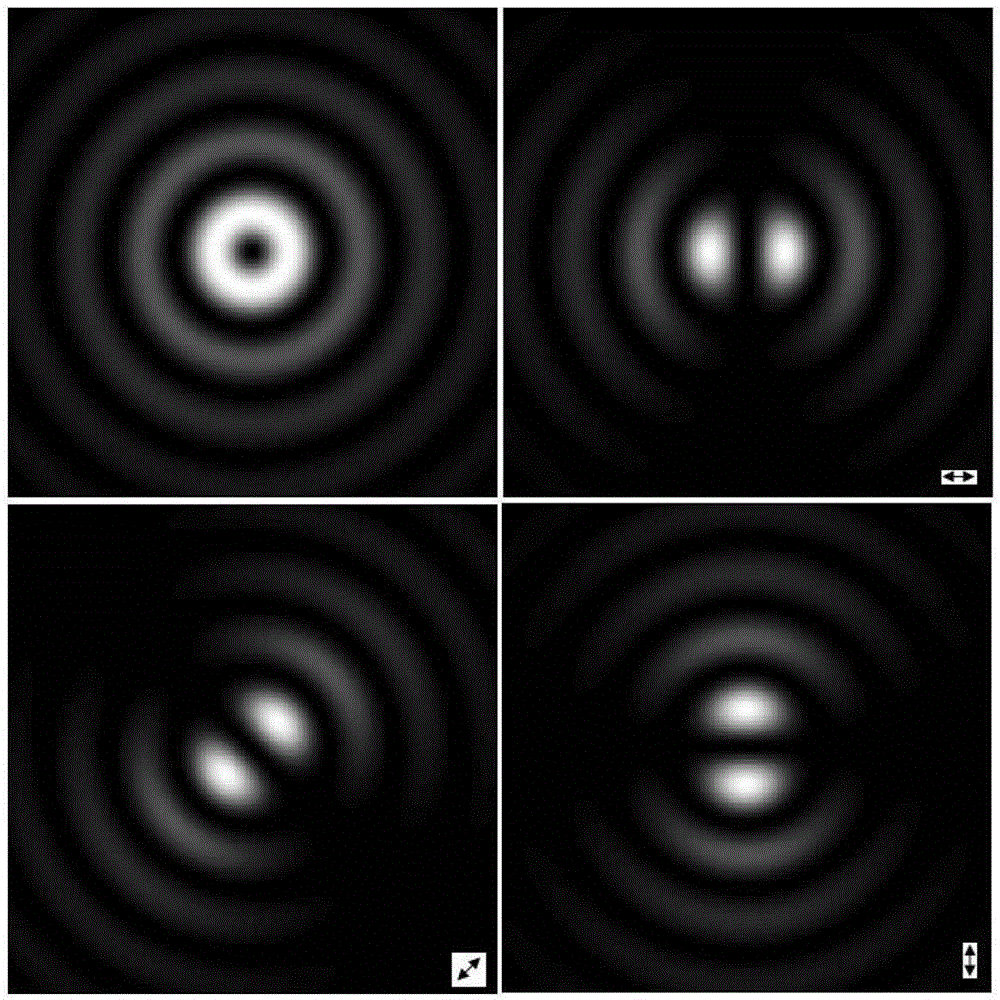
System and method for generating radial Bessel-Gaussian beam
The invention discloses a system for generating a radial Bessel-Gaussian beam. The system comprises a beam expander, a computer-controlled spatial light modulator, a vortex phase plate and a radial polarization convertor that are sequentially arranged in a light direction of a light source generating linearly polarized light, wherein a topological charge of the vortex phase plate is 1; and a calculation hologram generated by a computer is loaded to the spatial light modulator to form a calculation holographic grating, so that a first order Bessel-Gaussian beam is generated. The vortex phase plate is rotated to ensure that phase structure distribution of the vortex phase plate is right opposite to the phase structure distribution of the Bessel-Gaussian beam coming out of the spatial light modulator, and a vortex phase of the Bessel-Gaussian beam is eliminated. Then, the Bessel-Gaussian beam with the vortex phase being eliminated passes through the radial polarization convertor. Radial polarization Bessel-Gaussian beams with different ring numbers can be generated by generating different holograms due to the flexibility of the holograms of the computer, and have self-restorability.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Method for holographic mastering and replication
ActiveUS20180210396A1Efficient and cost-effective methodEfficient and cost-effectiveHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsHolographic recordingRecording media
A method for producing holograms with a multiplicity of holographic prescriptions from a single master is provided. A multiplicity of holographic substrates each having a first hologram is stacked on a second holographic recording medium substrate. The first hologram is designed to diffract light from a first direction into a second direction. When expose to illumination from the first direction zero order and diffracted light from each first hologram interfere in the second holographic recording medium substrate forming a second hologram. The second hologram is then copied into a third holographic recording medium substrate to provide the final copy hologram.
Owner:DIGILENS
Waveguide display based on diffractive optical element
ActiveCN104035157ASolve the problem of limited field of viewOptical light guidesOutput couplerWaveguide
The invention discloses a waveguide display based on a diffractive optical element. The waveguide display comprises an image source, an input coupler, an output coupler and a planar optical waveguide, wherein the output coupler is a multiplexed volume holographic grating. By adopting the structure, the problem of limitation on the field angle of the conventional waveguide display based on the diffractive optical element is solved. The waveguide display can be widely applied to the field of waveguide displays.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Semiconductor Bragg reflector and a method of fabricating said reflector
InactiveUS6023354ASmall sizeImprove the overall coefficientOptical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionGratingSemiconductor
A semiconductor Bragg reflector and to a method of fabricating it. The reflector comprises a plurality of stacked layers on a substrate of a III-V type material, one of the stacked layers forming a holographic grating. The layer forming the grating comprises an alternating succession of air pockets and of III-V type material. Such a reflector is particularly suitable for use in laser devices.
Owner:OCLARO NORTH AMERICA
Nano-brick array holographic sheet applied to holographic anti-counterfeiting and design method for nano-brick array holographic sheet
The invention relates to a nano-brick array holographic sheet applied to holographic anti-counterfeiting and a design method for the nano-brick array holographic sheet. Nano-brick array units in periodical arrangement are etched in the working surface of a substrate, a resonance-based reflective type working pattern is adopted, and the diffraction distance is 1-10[mu]m; the substrate can be divided into multiple unit structures corresponding to the nano bricks; all the unit structures are the same in lengths, widths and heights, the working surface of a single unit structure is square, and the length of side can be obtained by electromagnetic simulation optimization; in the nano-brick array units, the number of the nano bricks and the number of pixels in target images are equal; and the lengths, widths and heights of all the nano bricks are equal, and the orientation angles are designed according to phase distribution. According to the nano-brick array holographic sheet, redundant diffraction levels are omitted, good imaging quality and high efficiency are realized, and the energy is completely refracted basically; and compared with the conventional surface embossment type and refractive index type phase hologram, the nano-brick array holographic sheet has the advantages of small size, high integration, light weight, batch copying and the like, and can be widely applied to the aspects of laser trademarks, holographic anti-counterfeiting and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
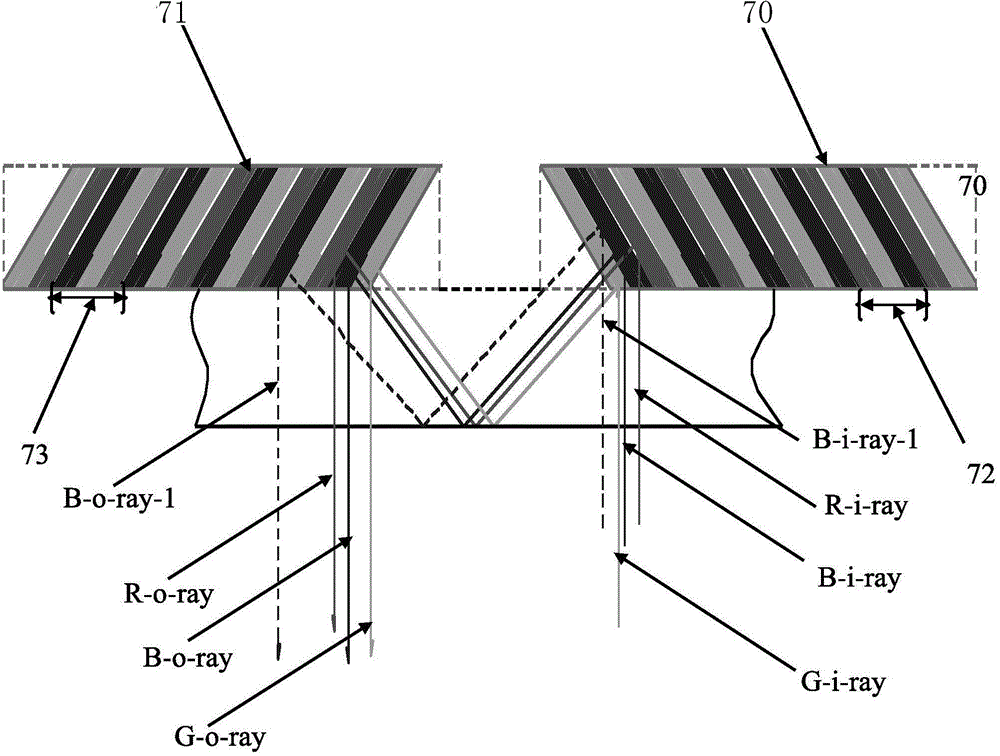
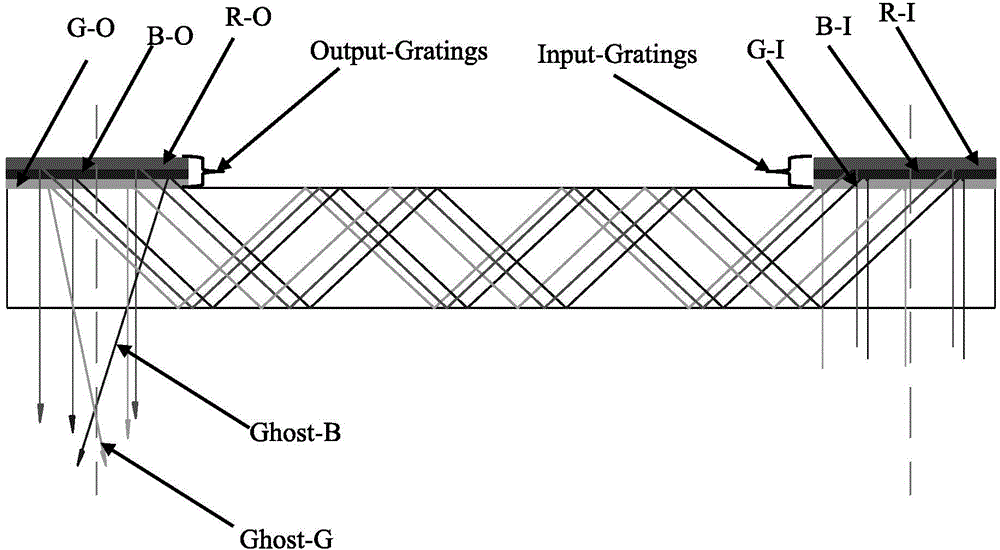
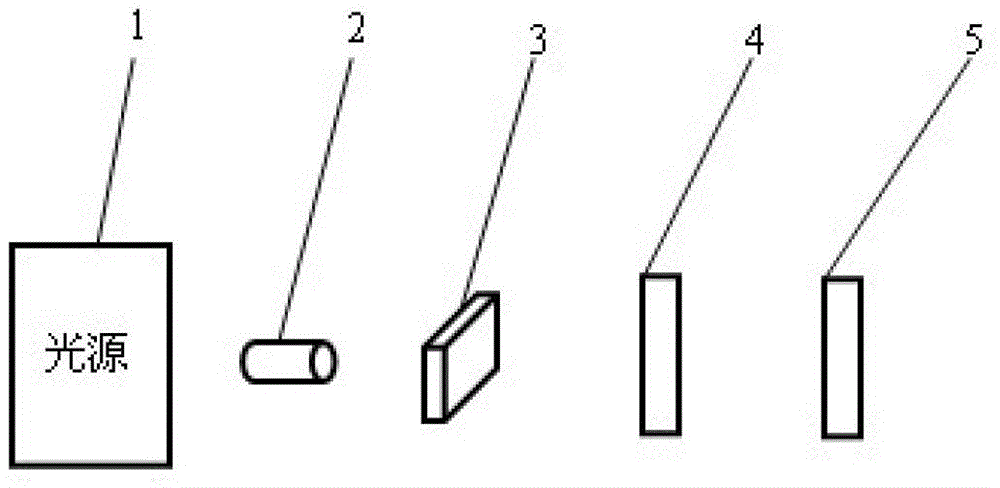
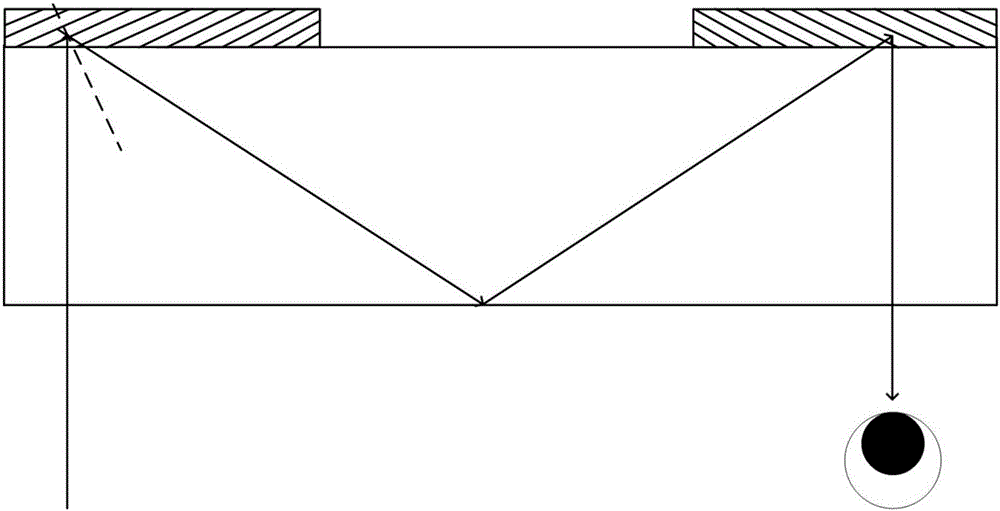
Reflection volume holographic grating waveguiding structure
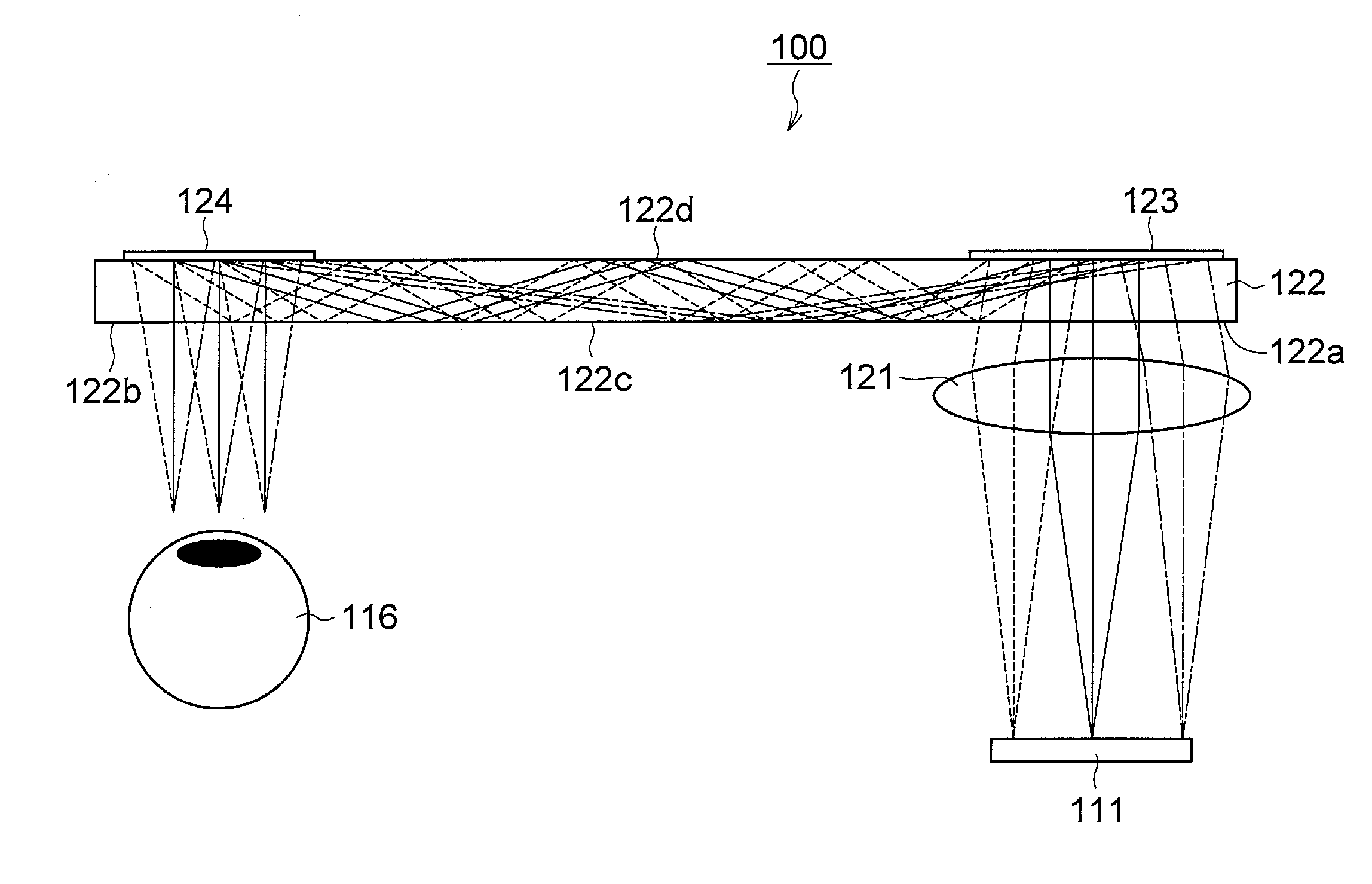
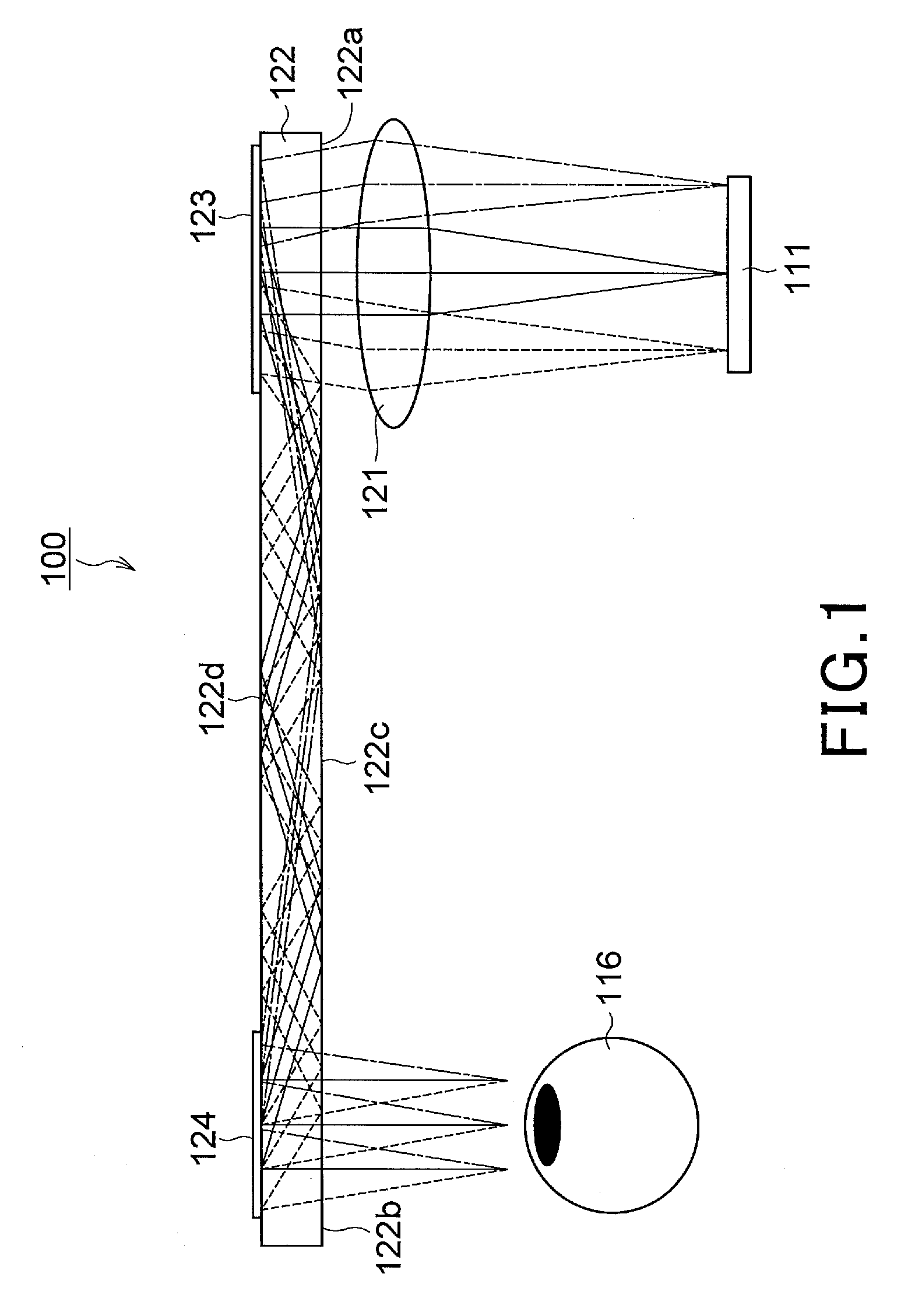
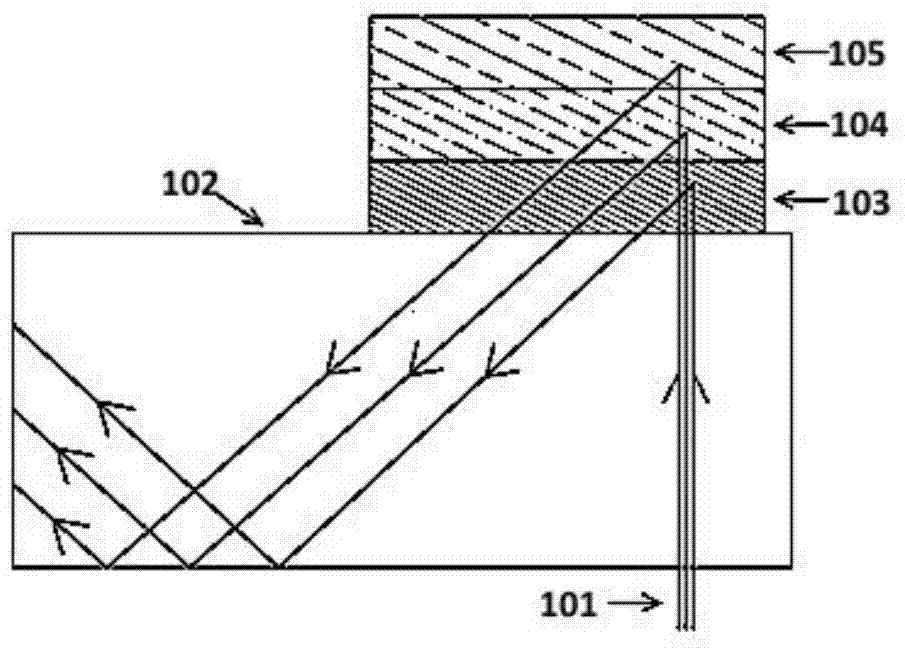
The invention discloses a reflection volume holographic grating waveguiding structure.The reflection volume holographic grating waveguiding structure comprises a plane light source (1), a flat panel wave guide(4), an incidence end grating and an emergence end grating, and the incidence end grating and the emergence end grating are arranged on the flat panel wave guide(4) and are in a mirror-image relation; the incidence end grating comprises a first reflection volume holographic grating (2) and a second first reflection volume holographic grating (3), while the emergence end grating comprises a third reflection volume holographic grating (5) and a fourth reflection volume holographic grating (6), incident light beams are subjected to bragg diffraction through the first reflection volume holographic grating (2) and the second first reflection volume holographic grating (3), emergent light beams are subjected to bragg diffraction through the third reflection volume holographic grating (5) and the fourth reflection volume holographic grating (6), and the light beams are emitted into human eyes (7).By means of the reflection volume holographic grating waveguiding structure, the range of an incidence angle can be enlarged, meanwhile, dispersion can be reduced, the view field can be enlarged, continuity of exit pupils is guaranteed, and thereby display quality is improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Holographic anti-counterfeiting algorithm based on shape of screen dot
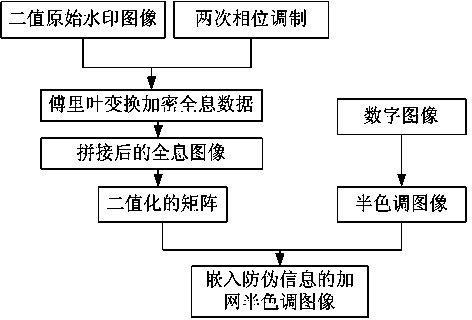
InactiveCN103996166AImprove robustnessEnsure safetyImage data processing detailsComputer visionDigital image
The invention relates to a holographic anti-counterfeiting algorithm based on the shape of a screen dot. The holographic anti-counterfeiting algorithm based on the shape of the screen dot comprises the steps of processing an original digital image through the minimum threshold screening technology to generate a halftone image; transforming a two-value original watermark image to generate Fourier transform encrypted holographic data, splicing the data and performing binaryzation on the data to generate a new data matrix; embedding watermarks into the generated halftone image according to the generated data matrix to obtain an screening image containing anti-counterfeiting information; performing printing, collecting the screening image, judging and extracting anti-counterfeiting information according to the shape of the screen dot, multiplying the extracted information with a randomly-encrypted phase mask hologram image, and performing inverse Fourier transform to obtain original anti-counterfeiting information. By means of the screen dot carrying the anti-counterfeiting information, special information is given to the screen dot by means of the holographic technology, and anti-counterfeiting authentication information can be extracted in a distortionless mode when any one of printing images is cropped. The holographic anti-counterfeiting algorithm based on the shape of the screen dot has strong robustness and can ensure anti-counterfeiting security and stability.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
Perspective laser holography anti-fake film with reflecting effect and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN103354059AAvoid coveringGuaranteed service lifeStampsSynthetic resin layered productsInformation layerPolyester
The invention relates to the technical field of physic anti-fake parts of legal certificates, in particular to a perspective laser holography anti-fake film with a reflecting effect and a preparing method thereof. The anti-fake film comprises a base material layer, an information layer, a reflecting layer, a protection layer, a blocking layer and a bonding layer which are combined together in sequence form top to bottom, wherein a sequestration layer is arranged between the base material layer and the information layer, the base material layer is a PET polyester film, the information layer is an acrylic resin layer, and the base material layer and the information layer are integrated through the sequestration layer. The prepared method of the anti-fake film comprises the steps of (1) copying of a laser holography working version, (2) treating of the surface of the PET base material, (3) coating of the sequestration layer, (4) key opening treatment, (5) coating of the information layer, (6) transferring and copying of a holographic grating, (7) manufacturing of the reflecting layer, (8) protecting of the reflecting layer, (9) curing, (10) fine chemical etching, (11) coating of the blocking layer, (12) corona, and (13) coating of the bonding layer. According to the perspective laser holography anti-fake film with the reflecting effect and the preparing method thereof, a major breakthrough is made in respects of certificate binding force, hologram image diffraction efficiency and visual identification of certificate information.
Owner:SHANGHAI HONGDUN ANTI COUNTERFEIT MATERIAL
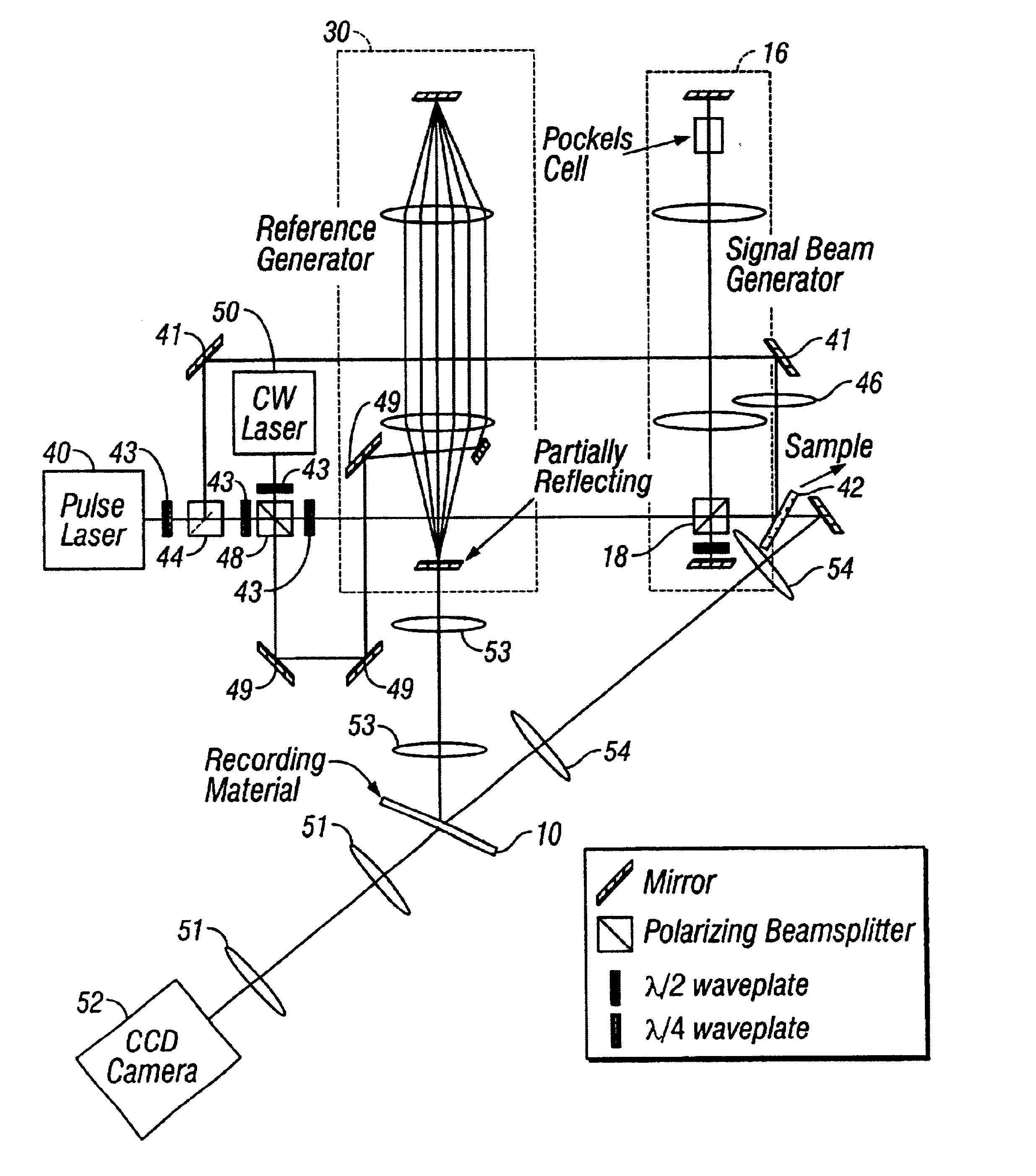
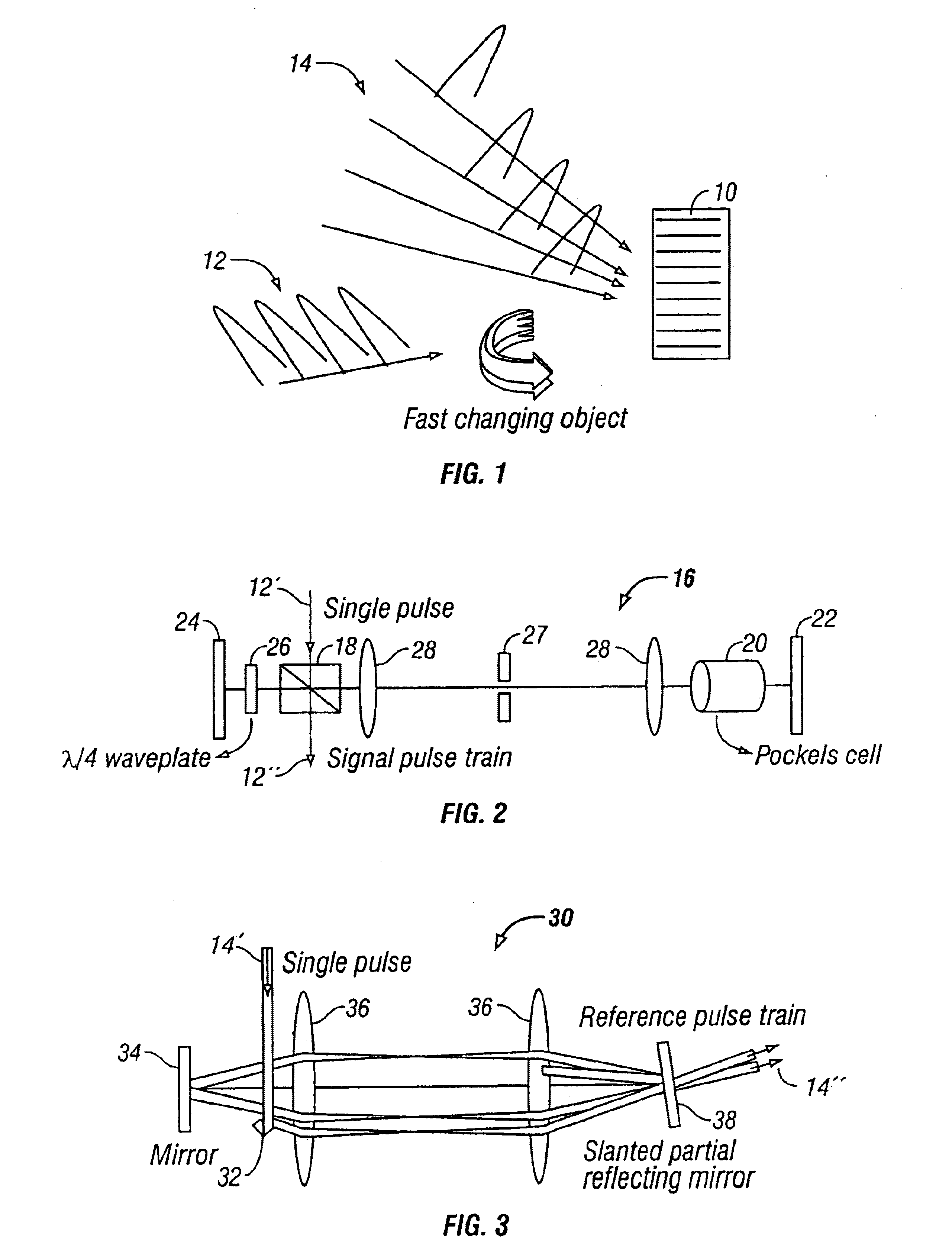
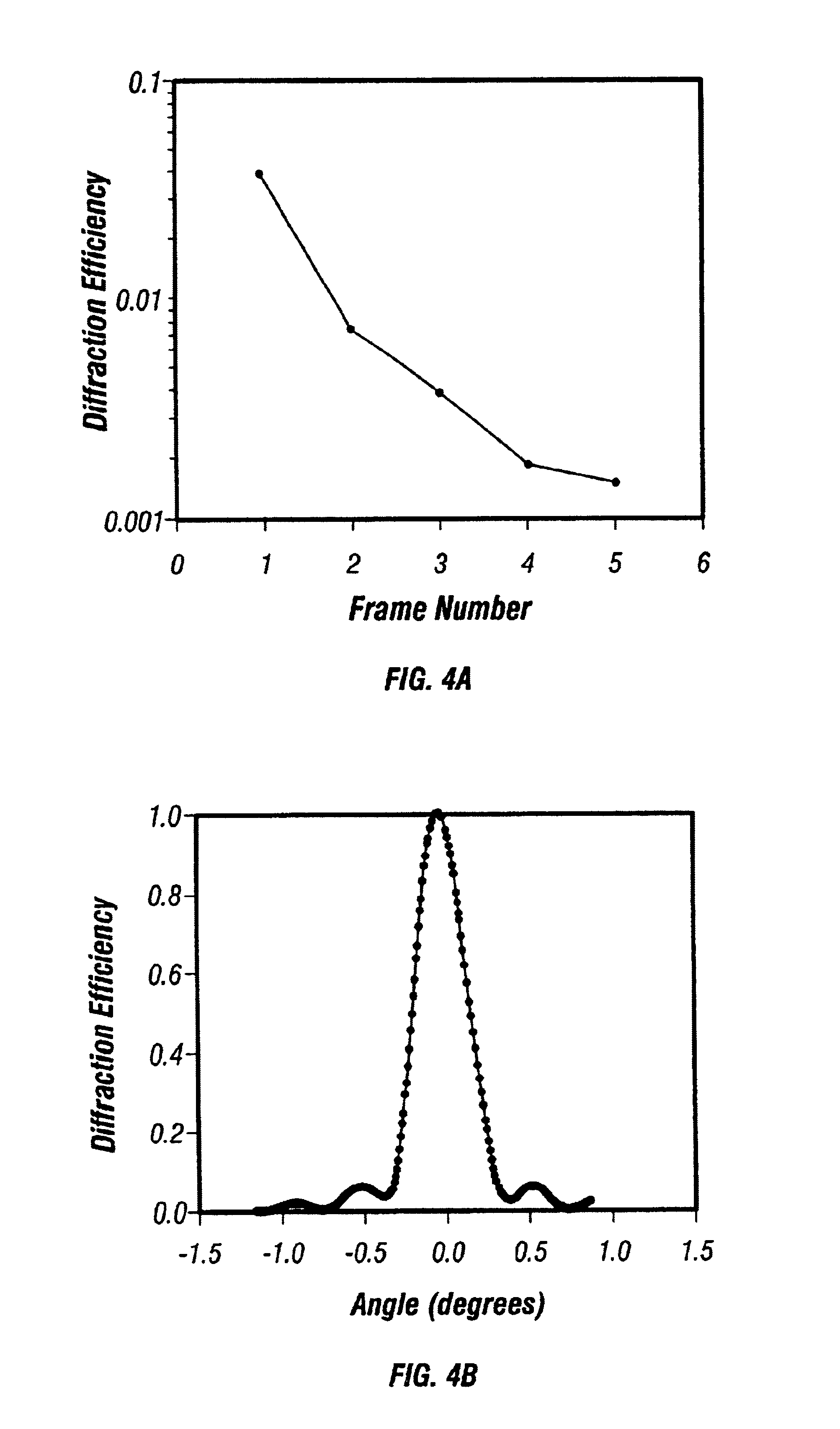
Method and apparatus for holographic recording of fast phenomena
InactiveUS6862121B2Television system detailsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesShock waveMultiplexing
Holographic methods for recording fast movies whose speed is limited by the laser pulse duration if the recording material has sufficient sensitivity to reliably record a frame of the fast event with a single pulse. The method we describe uses the selectivity of multiplexed holograms to resolve frames that are recorded with adjacent pulses. Specially designed pulse generators are used to generate the signal and reference pulse trains. We experimentally demonstrate the system by making movies of laser induced shock waves with a temporal resolution of 5.9 ns, limited by the pulse width of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser used in the experiments.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
System and method for effecting high-power beam control with outgoing wavefront correction utilizing holographic sampling at primary mirror, phase conjugation, and adaptive optics in low power beam path
InactiveUS20030062464A1Photometry using reference valueMaterial analysis by optical meansWavefront sensorPhased array
A beam control system and method. In an illustrative embodiment, the inventive system (500) provides a first beam of electromagnetic energy (503); samples the first beam (503) and provides a second beam (505) in response thereto; detects aberrations in the second beam (505); and corrects aberrations in the first beam (503) in response to the detected aberrations. In a specific implementation, the invention (500) includes a beam director telescope (510) having a primary mirror (516) on which a holographic optical element (518) is disposed. The holographic optical element (518) samples the output high-power beam and provides a sampled beam to a wavefront sensor (520). The wavefront sensor (520) provides signals to an adaptive optics processor (580). The adaptive optics processor (580) analyzes the sampled wavefront, detects aberrations therein and provides a correction signal to an optical phased array (550). A master oscillator (552) provides a reference beam, which reads the optical phased array (550) and is back reflected off a front surface of an aperture sharing element (540). The resulting beamfront is conjugated by a first phase conjugate mirror (546) and then again by a second phase conjugate mirror (556). The output of the second phase conjugate mirror (556) is amplified and reflected off the front surface of the aperture sharing element (540). The aperture sharing element (540) outputs the high power beam via the telescope (510) which is corrected for the optical distortions in the telescope and beam path.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
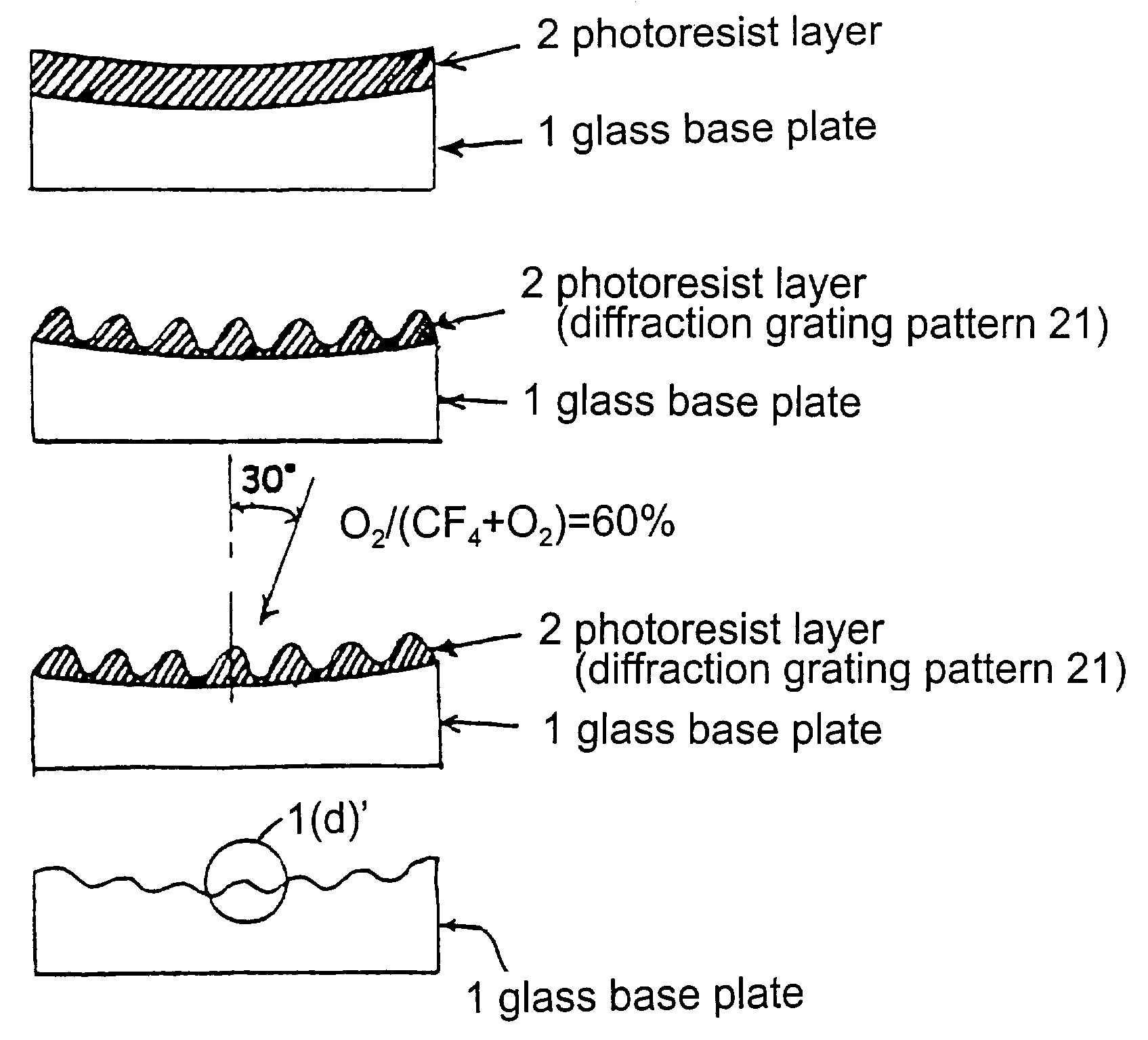
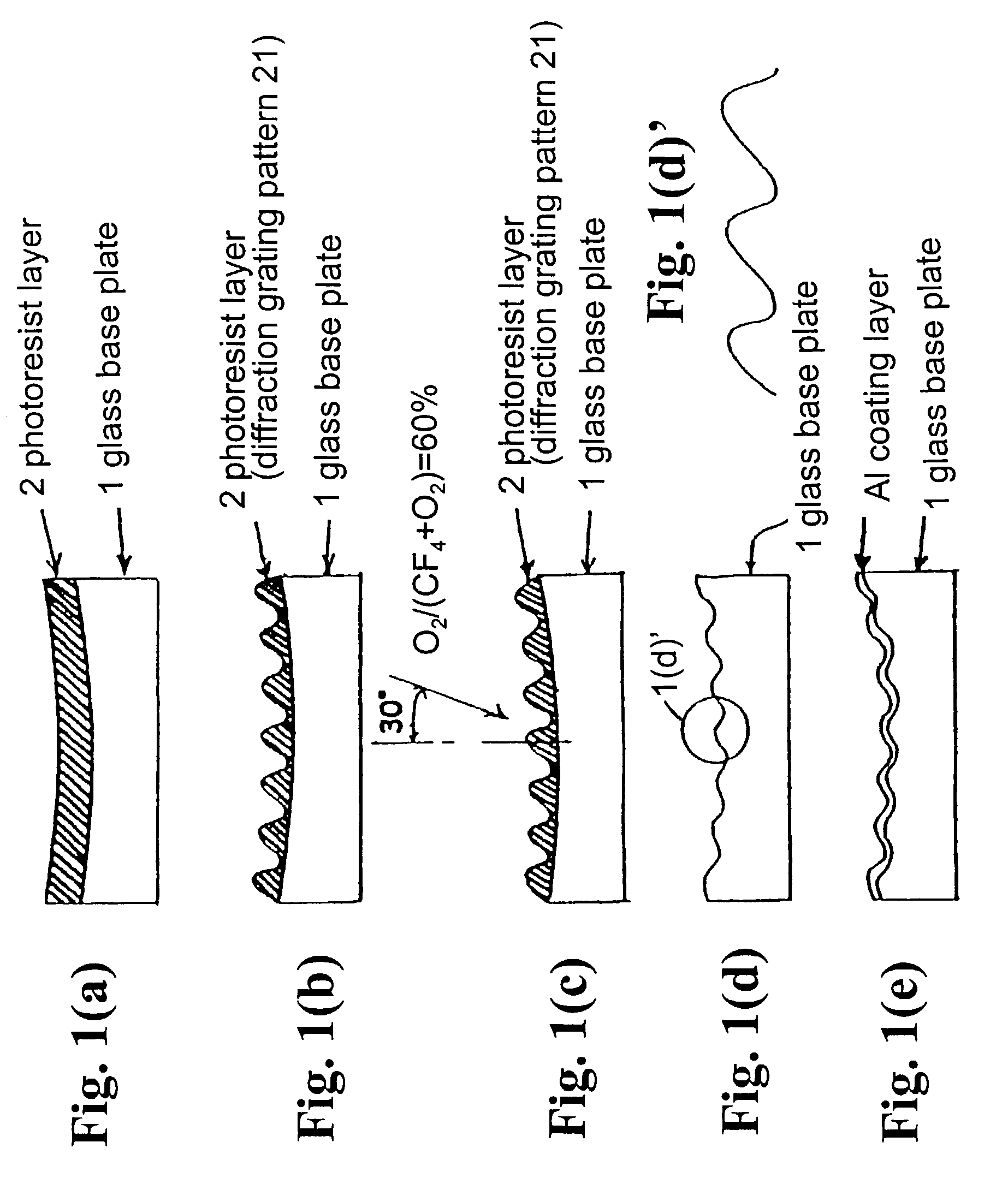
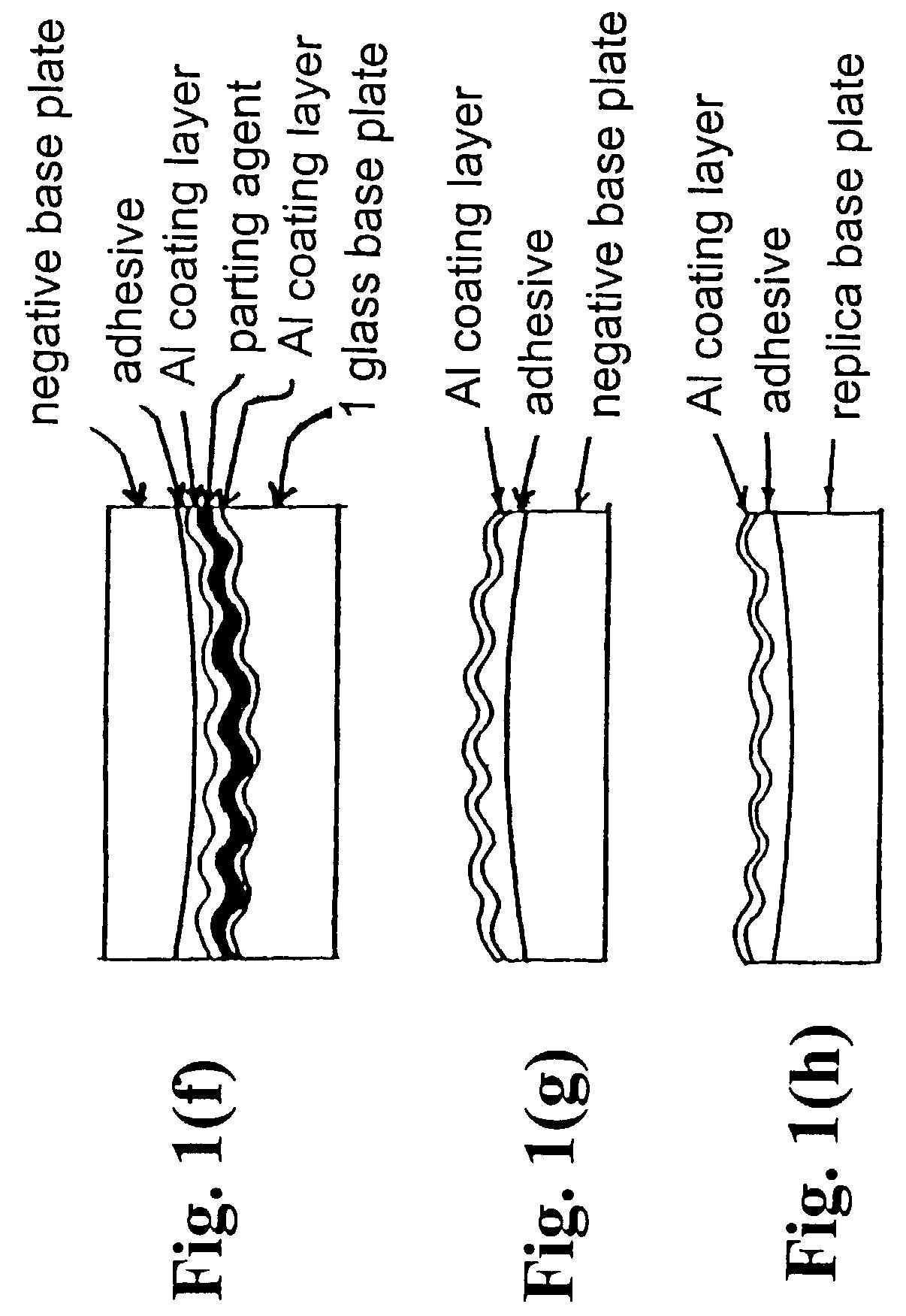
Method of forming holographic grating
InactiveUS7129028B2Avoid turbidityAvoid etchingDecorative surface effectsSpectrum generation using diffraction elementsResistOxygen
In a method of forming a holographic grating, a photoresist layer is formed on an optical substrate, and a resist pattern is formed in the photoresist layer to have grooves depth deeper than a predetermined depth of diffraction grating grooves to be formed. Then, the photoresist layer with the resist pattern is etched by an ion beam generated by a mixed gas containing a fluorine based gas and oxygen until the resist pattern is substantially completely disappears. Thus, the diffraction grating grooves having the predetermined depth are directly engraved on the optical glass plate.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Method for producing large area holographic grating based on second exposure of reference grating
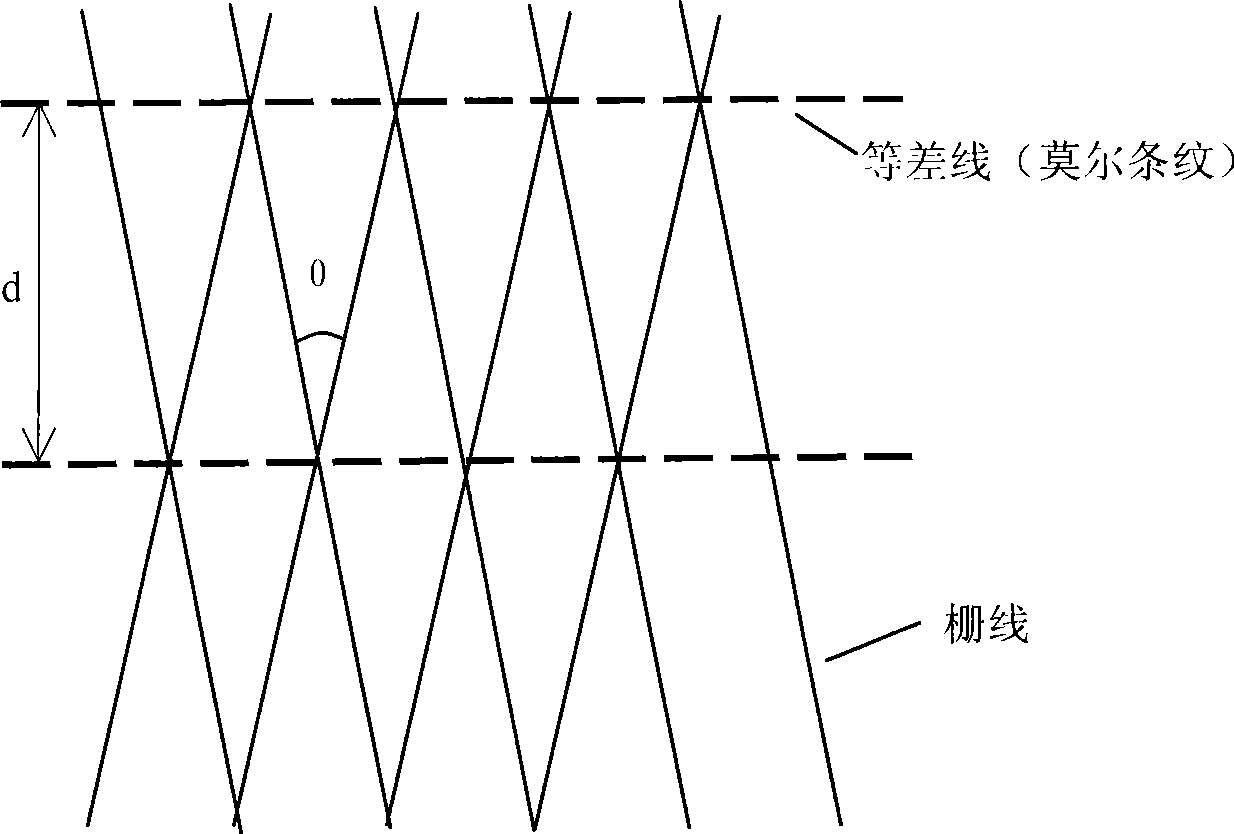
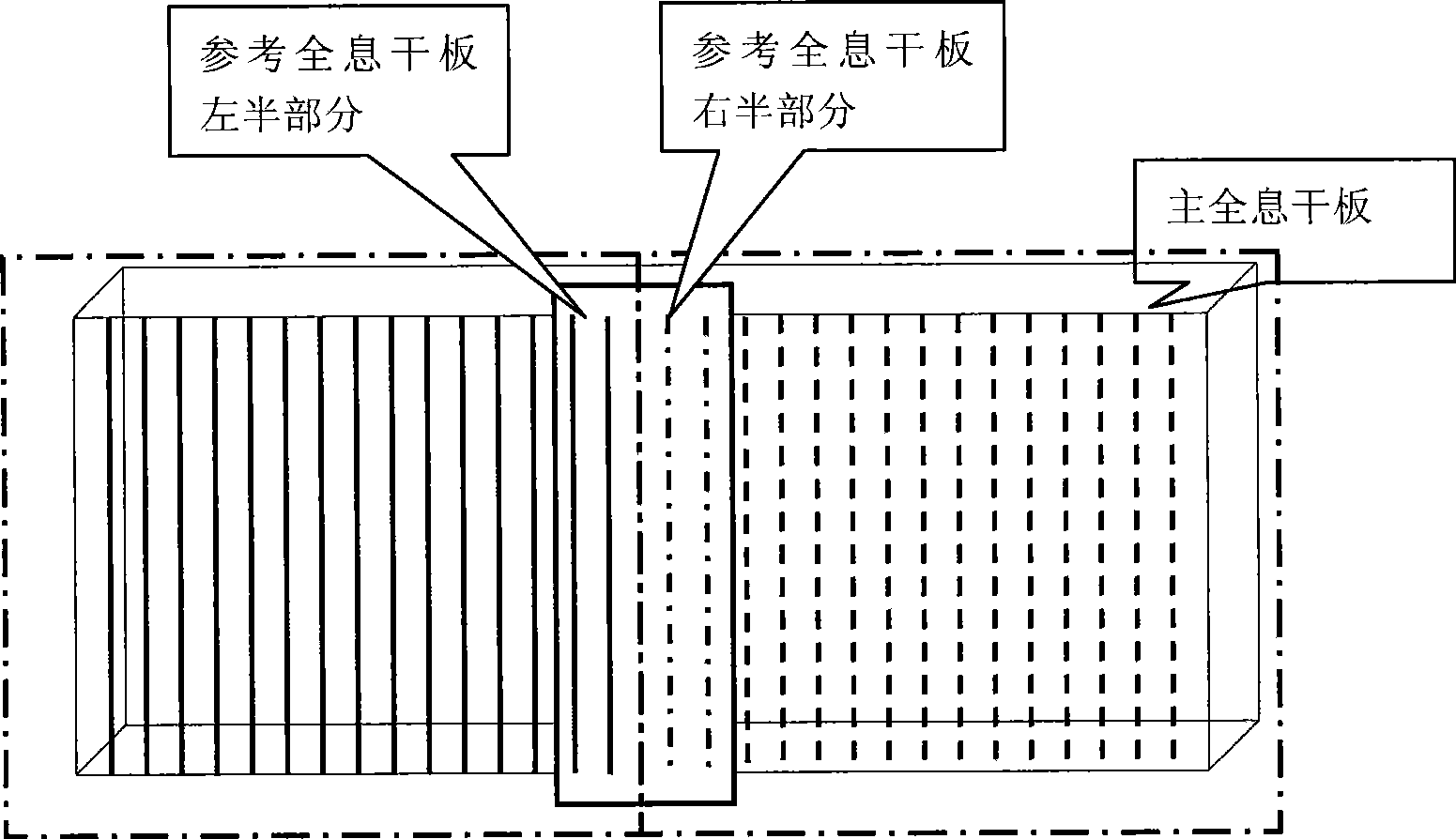
ActiveCN101382611AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed Phase RelationshipPhotomechanical apparatusDiffraction gratingsPhase relationshipGrafting
The invention discloses a preparation method of a large area holographic grating based on reference grating double exposure to prepare diffraction grating; the method comprises the following steps: (1) a reference holographic plate is fixed; (2) a main holographic plate is shielded, the holographic grating recording optical field is used for preparing reference grafting; (3) more non-dense Moire fringe is formed by the reference grafting and the recording grafting, the direction of the Moire fringe is vertical to the line direction of the reference grafting, and the Moire fringe information is recorded; (4) the first part of the main holographic plate is exposed and developed; (5) the main holographic plate and the reference holographic plate are moved simultaneously, the relative position of the reference grafting and the recording optical field is adjusted to lead the reappeared Moire fringe information to be the same as the Moire fringe information in the step (3); and (6) the second part of the main holographic plate is exposed and developed, and the production of holographic exposure splicing grating is finished. The preparation method realizes splicing of adjacent sections in the preparation process of diffraction grating guarantees the parallelism precision and the phase relationship and can be used for preparing the large area diffraction grating.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
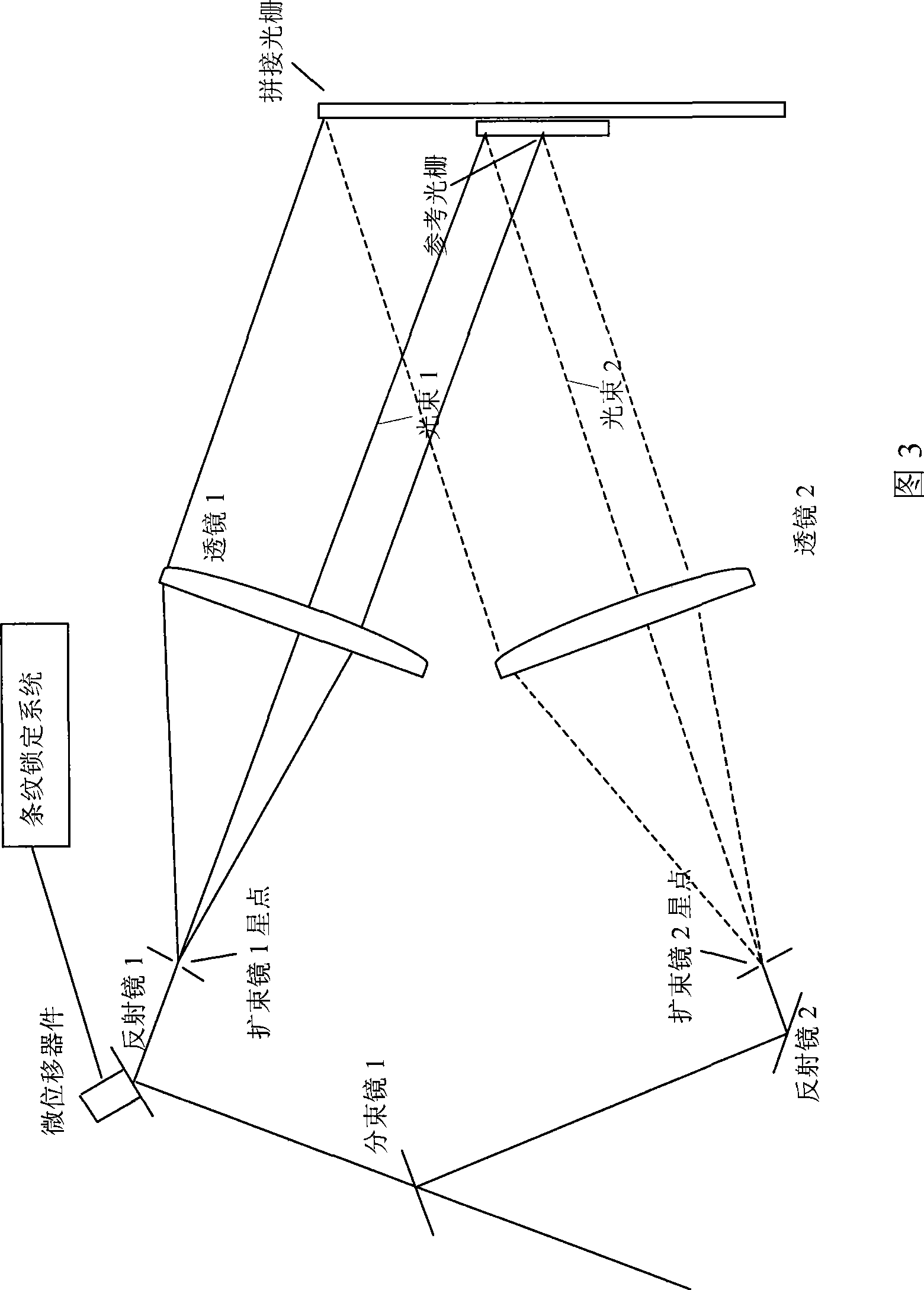
Method and apparatus for stabilizing holographic interference fringes by control apparatus
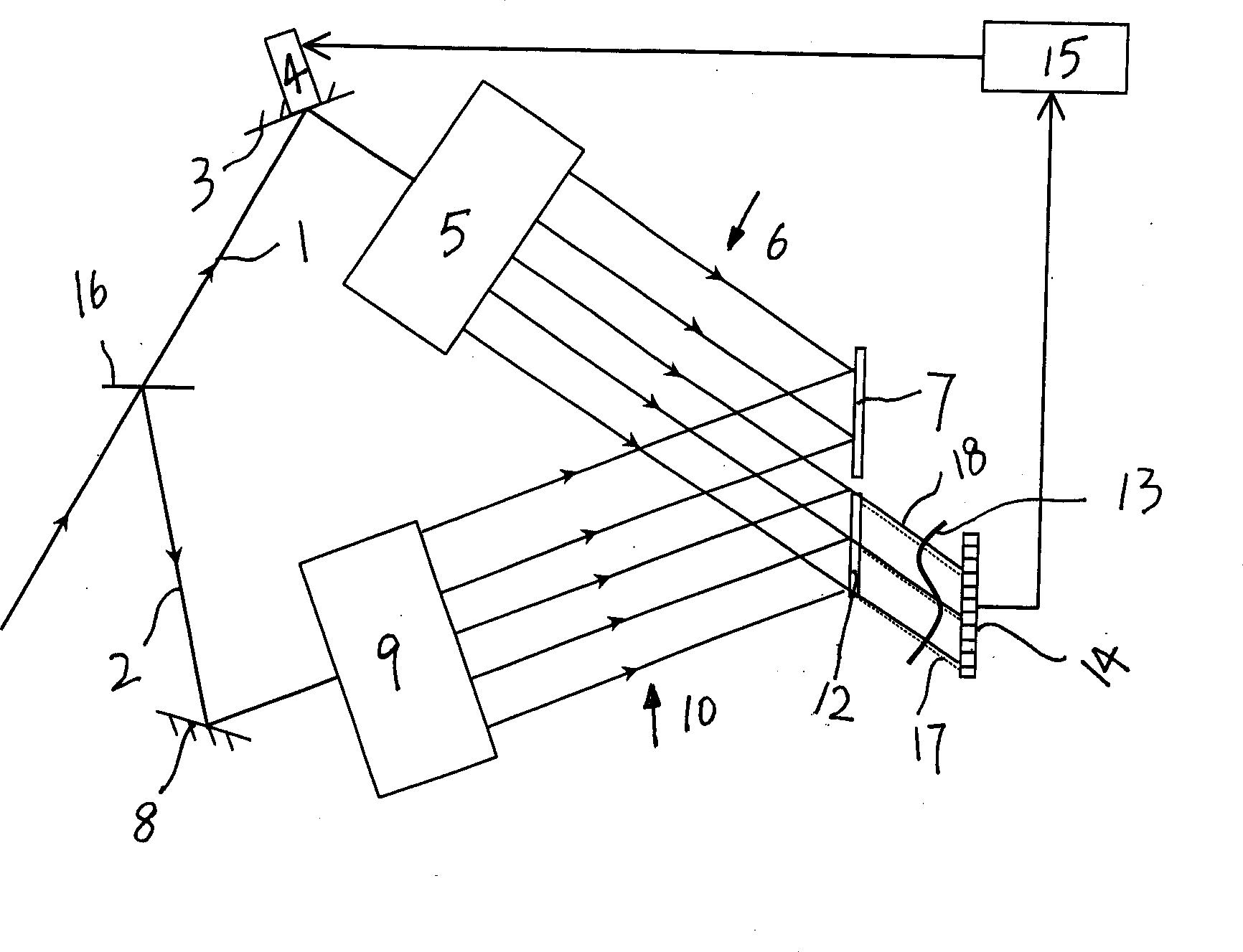
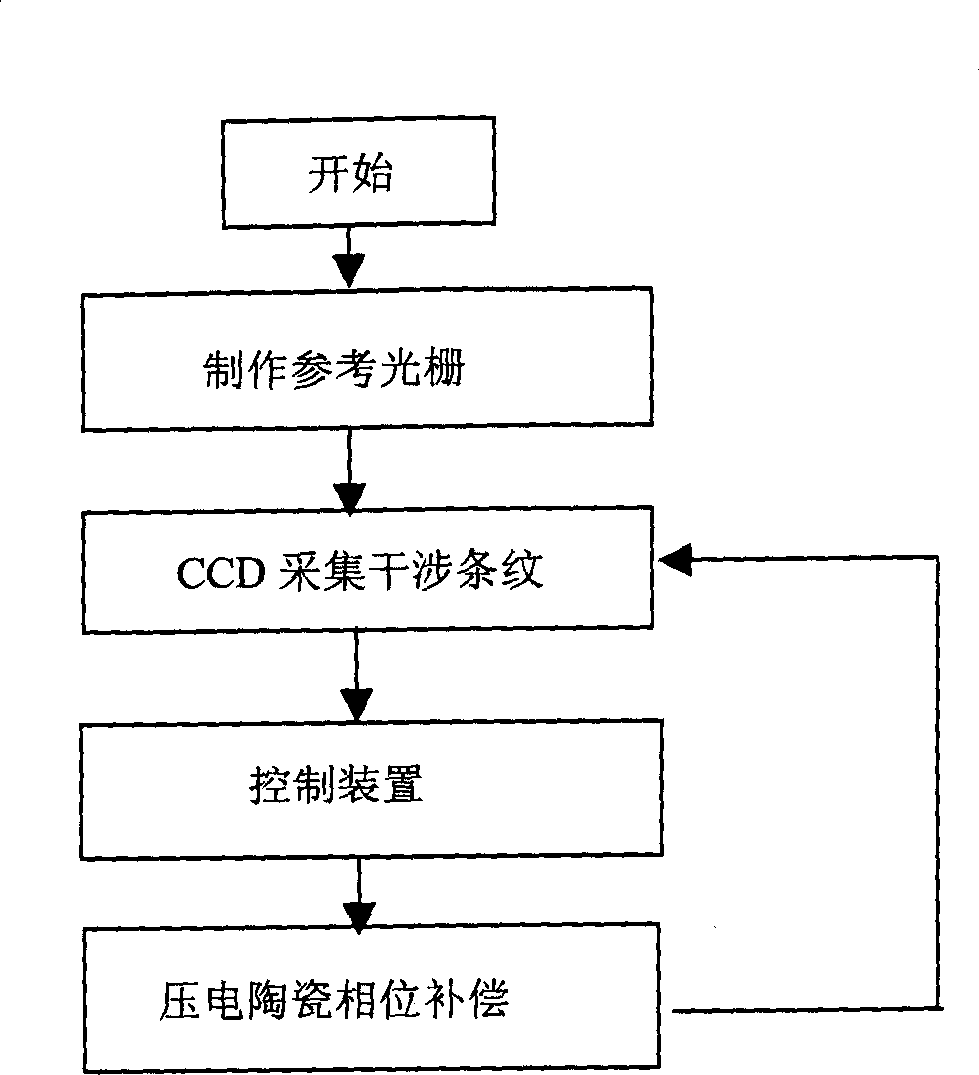
The invention relates to a method for using one controller to stabilizing the holographic interference pattern, and relative device. The external disturbance will cause the random excursion of holographic interference pattern, to reduce the quality of shot holographic grating. The invention uses linear CCD to collect the interference pattern information to the controller; the controller calculates the stripe excursion and control the piezoelectric ceramic that connected to the reflector to move and process phase compensation, to reduce the excursion of interference strip, and stabilize the interference strip in exposal area, therefore, the exposal time can be prolonged significantly.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com