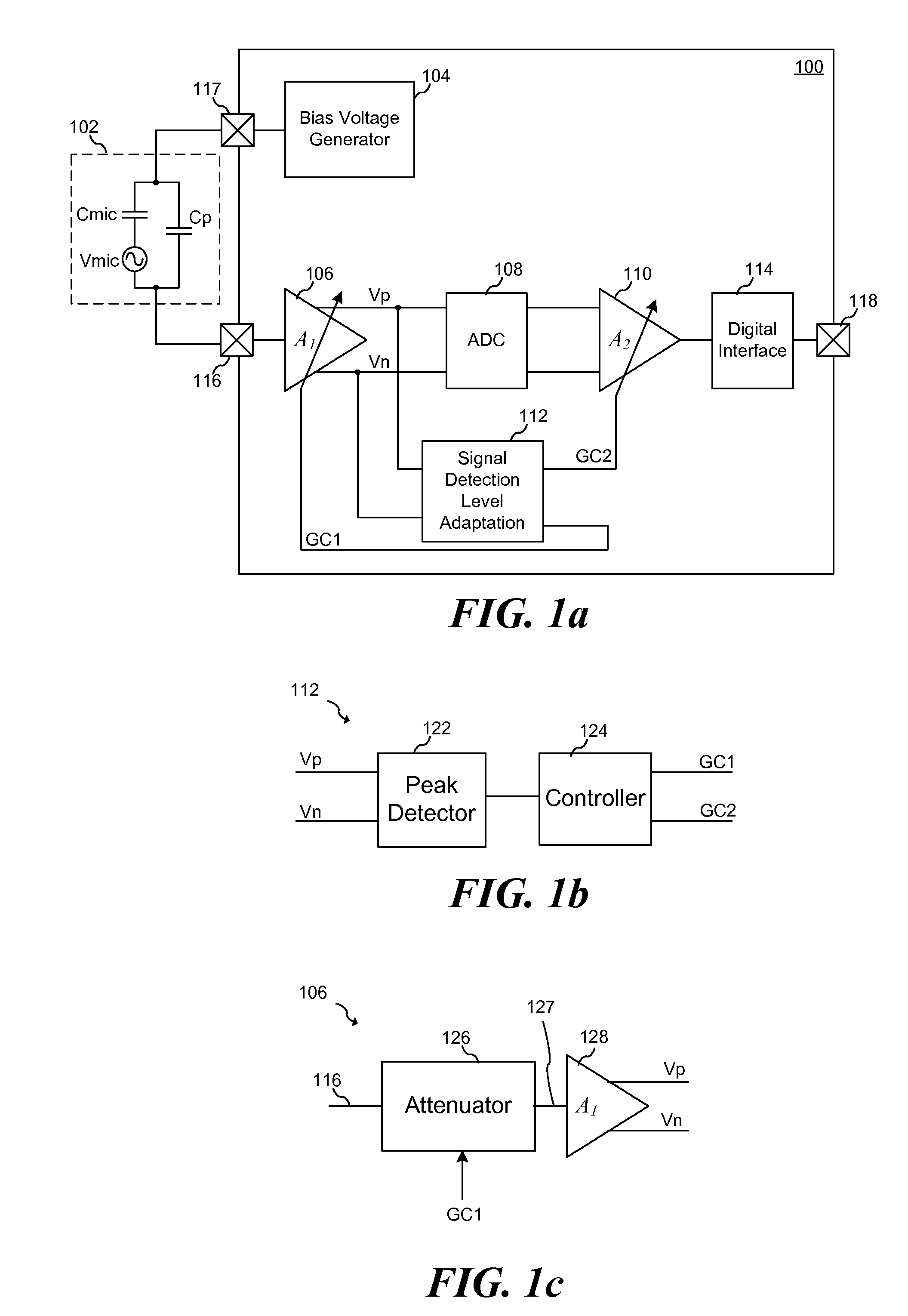
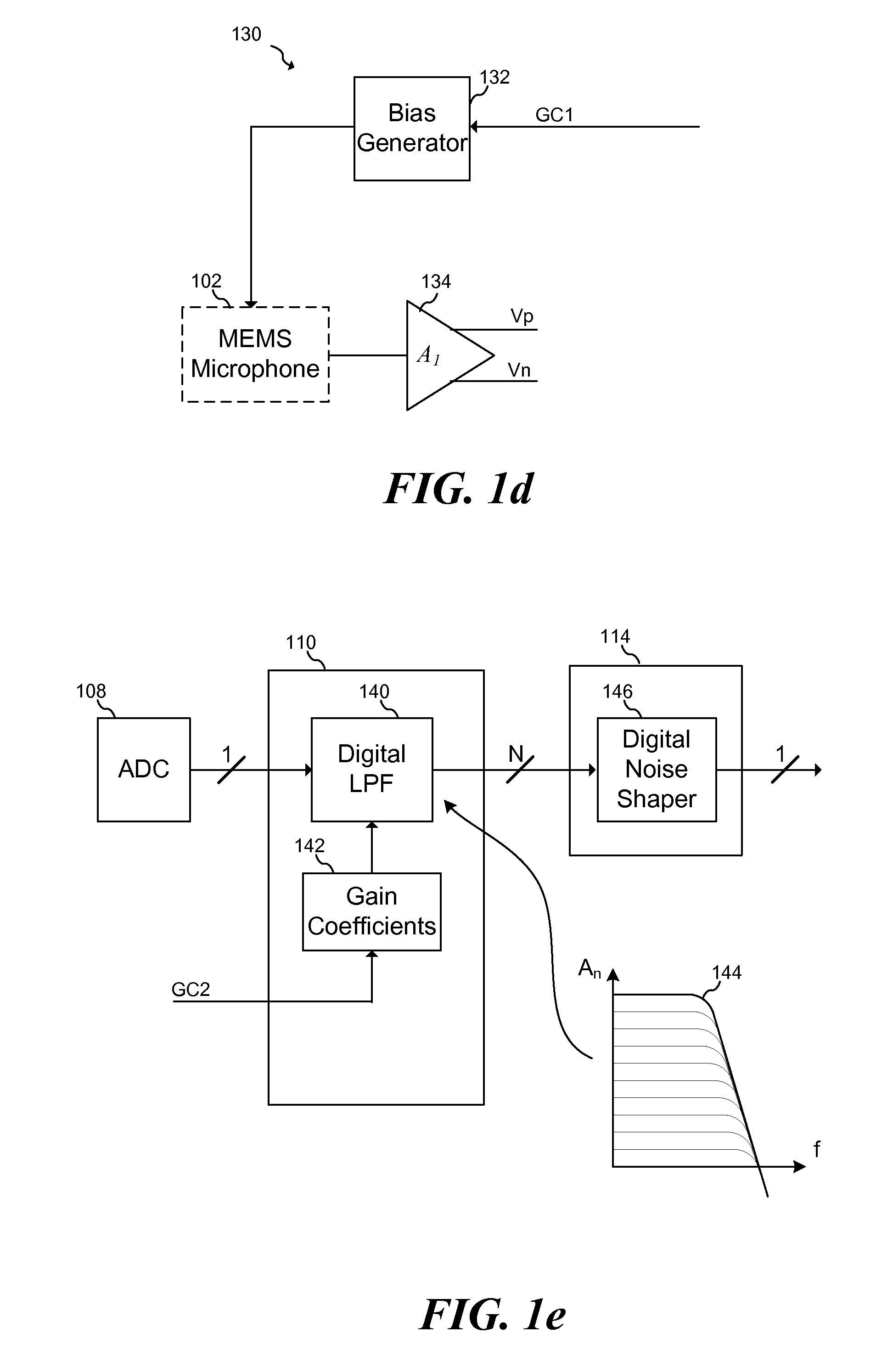
Patents
Literature
2794results about "Amplifier input/output impedence modification" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
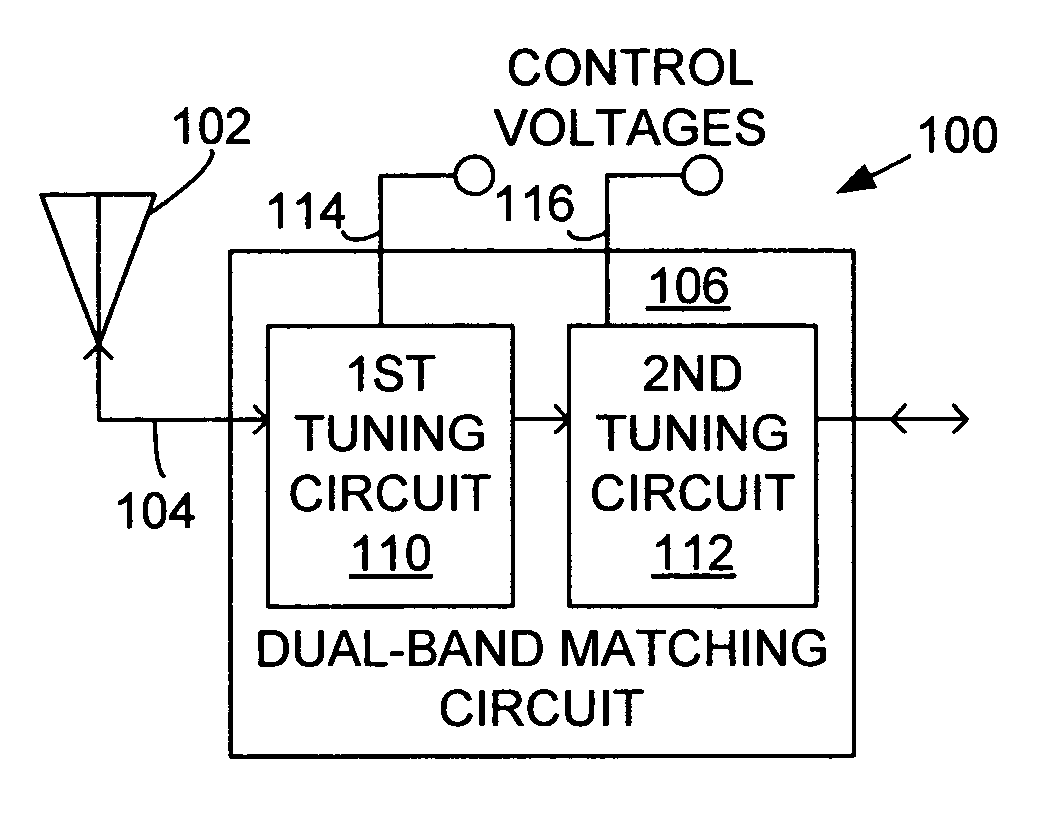
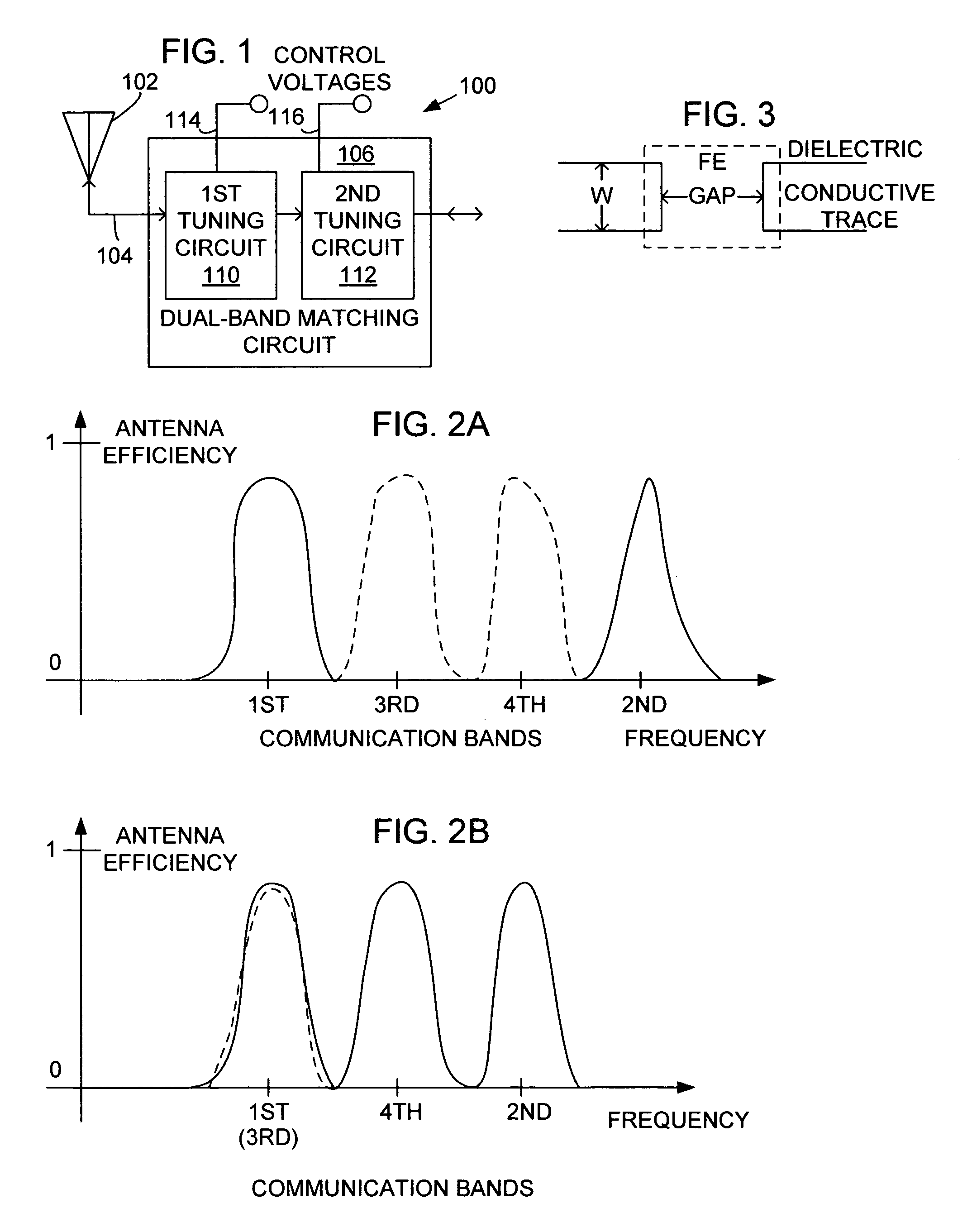
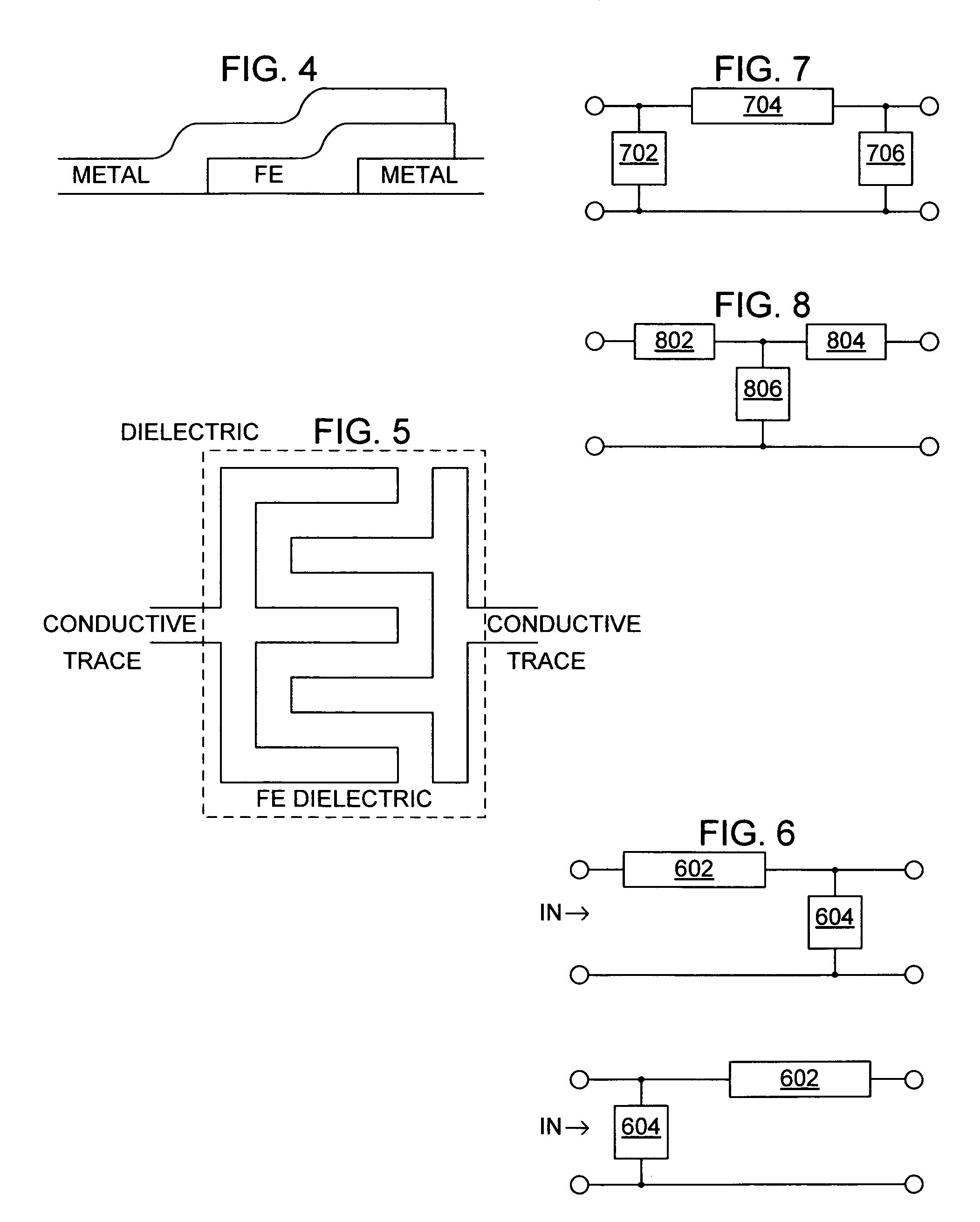
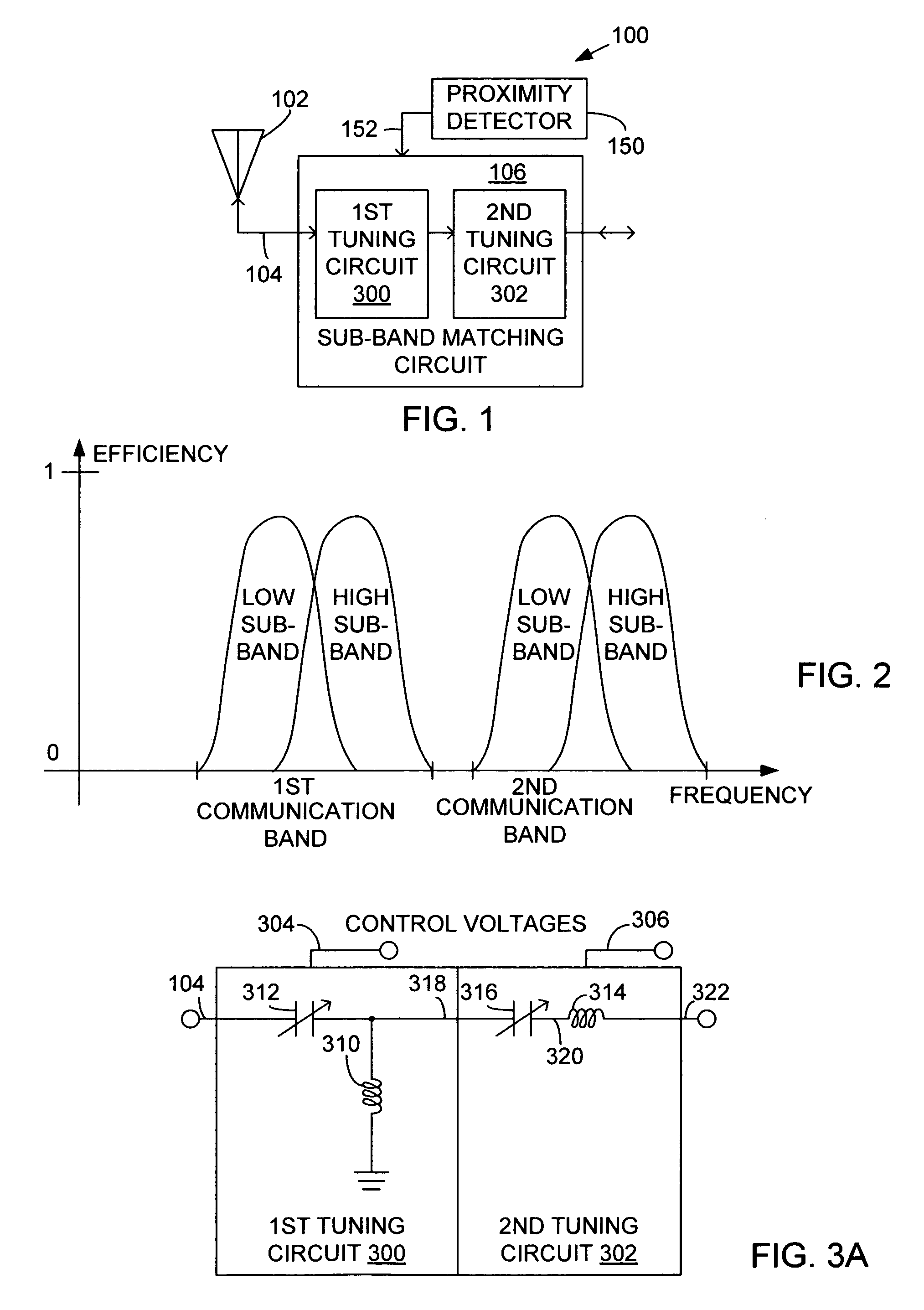
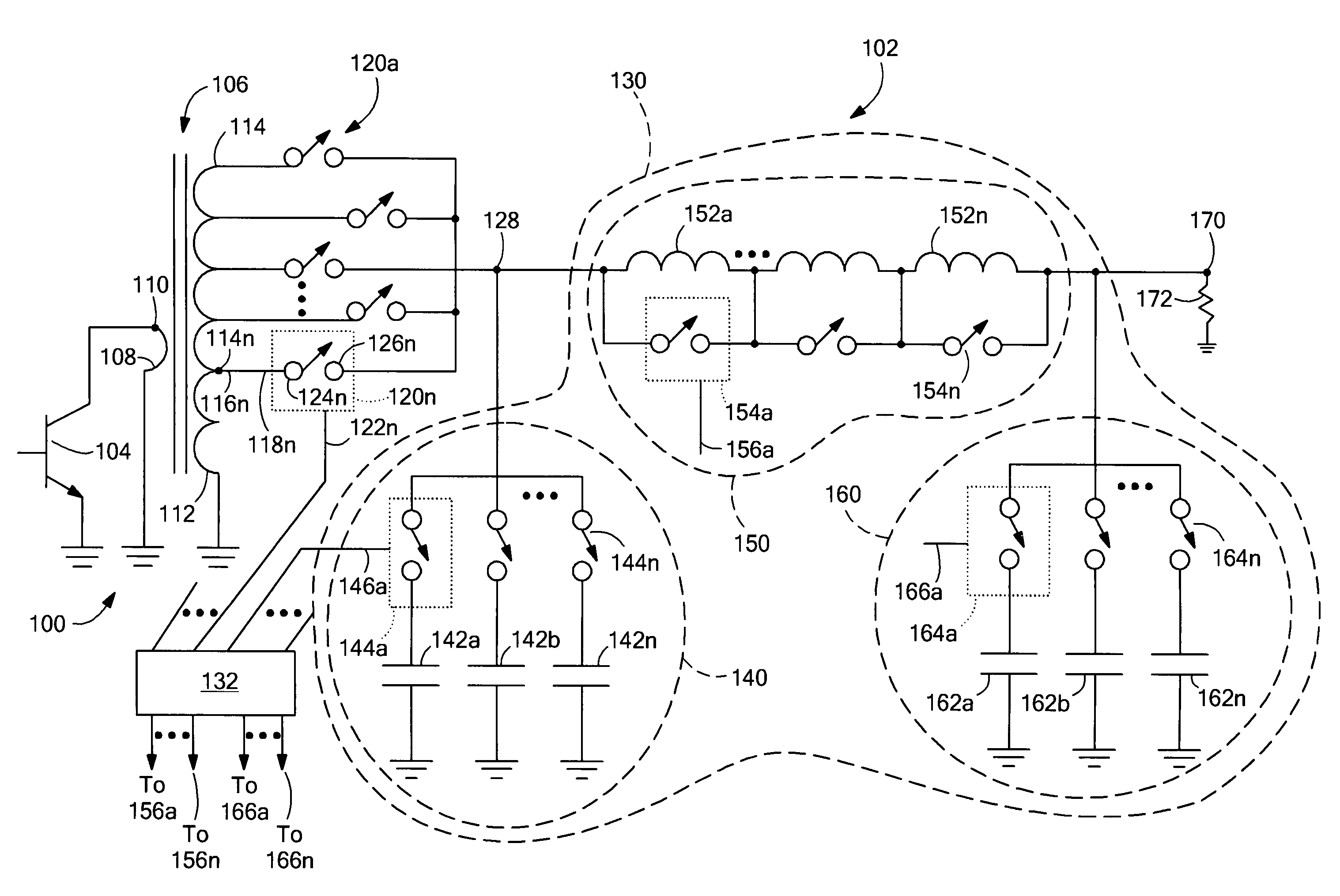
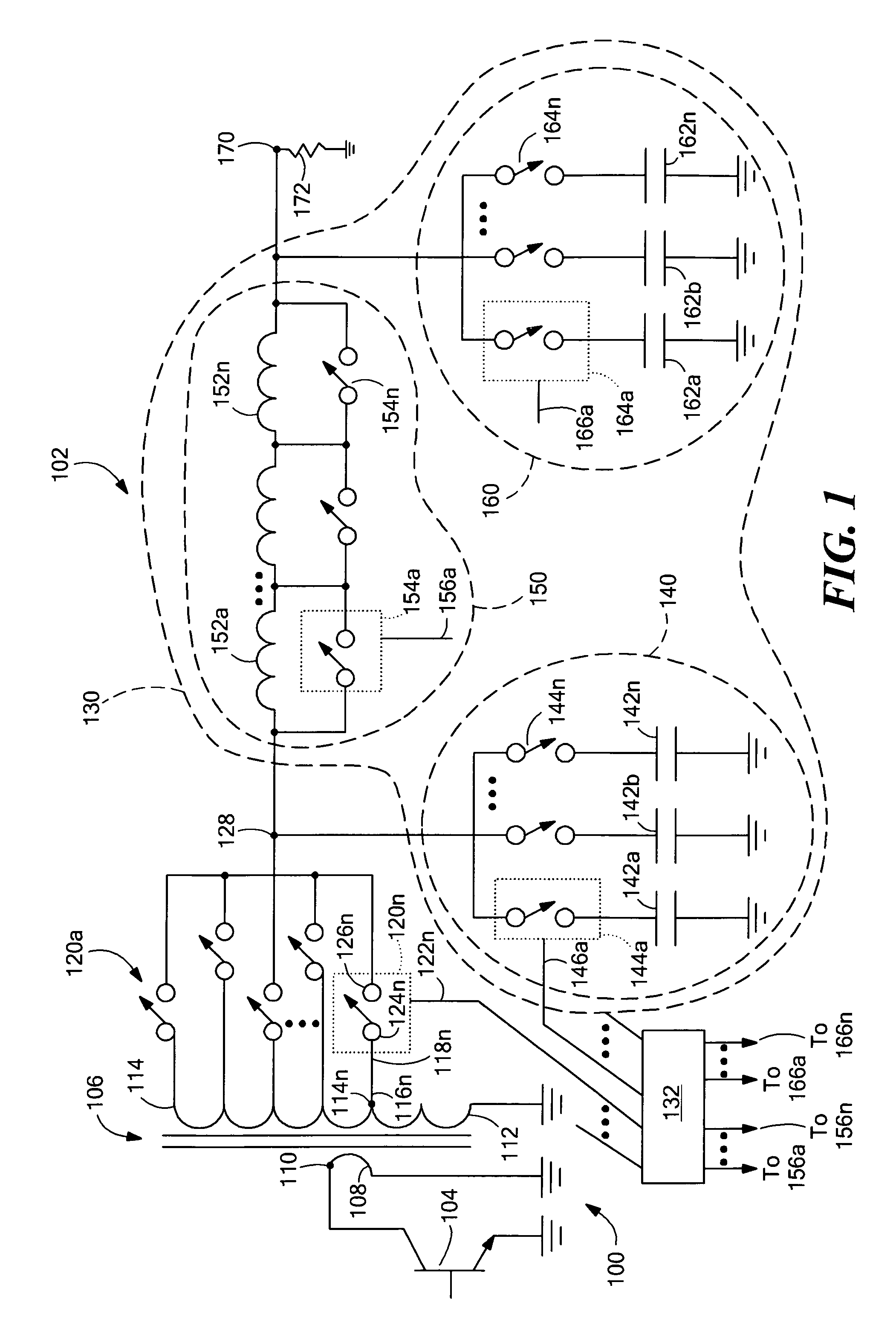
System and method for dual-band antenna matching
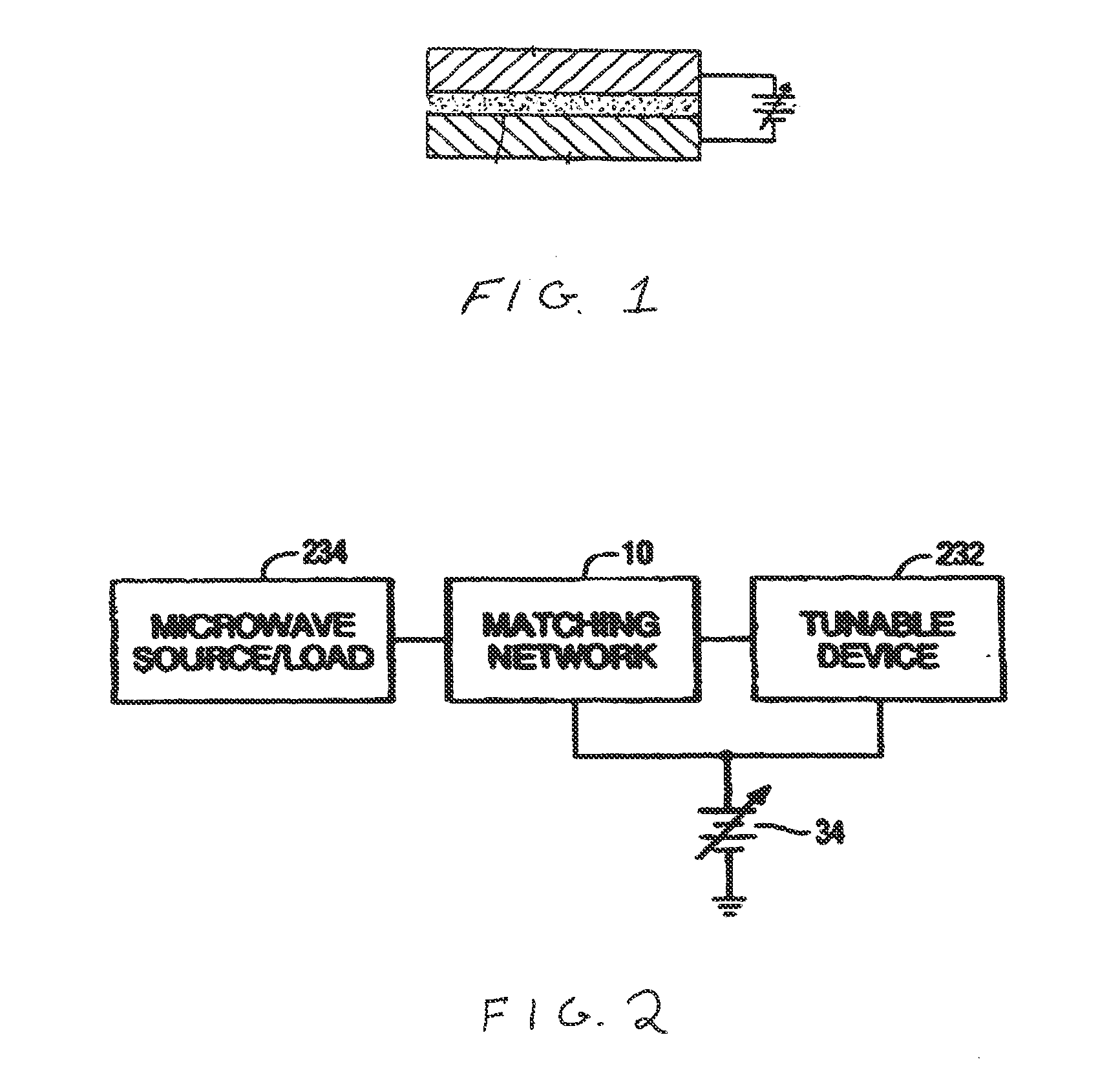
A dual-band antenna matching system and a method for dual-band impedance matching are provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at either a first and a second communication band, or a third and a fourth communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; and, simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency. In response, a conjugate match is supplied to the antenna in the first communication band in response to the first frequency. Simultaneously, the antenna is matched in the second communication band in response to the second frequency. When the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency, and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency, then conjugate matches are supplied for the third and fourth communication bands, responsive to the third and fourth frequencies, respectively.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Tunable microwave devices with auto-adjusting matching circuit
ActiveUS20060160501A1Realize automatic adjustmentMultiple-port networksResonant long antennasEngineeringHigh pressure
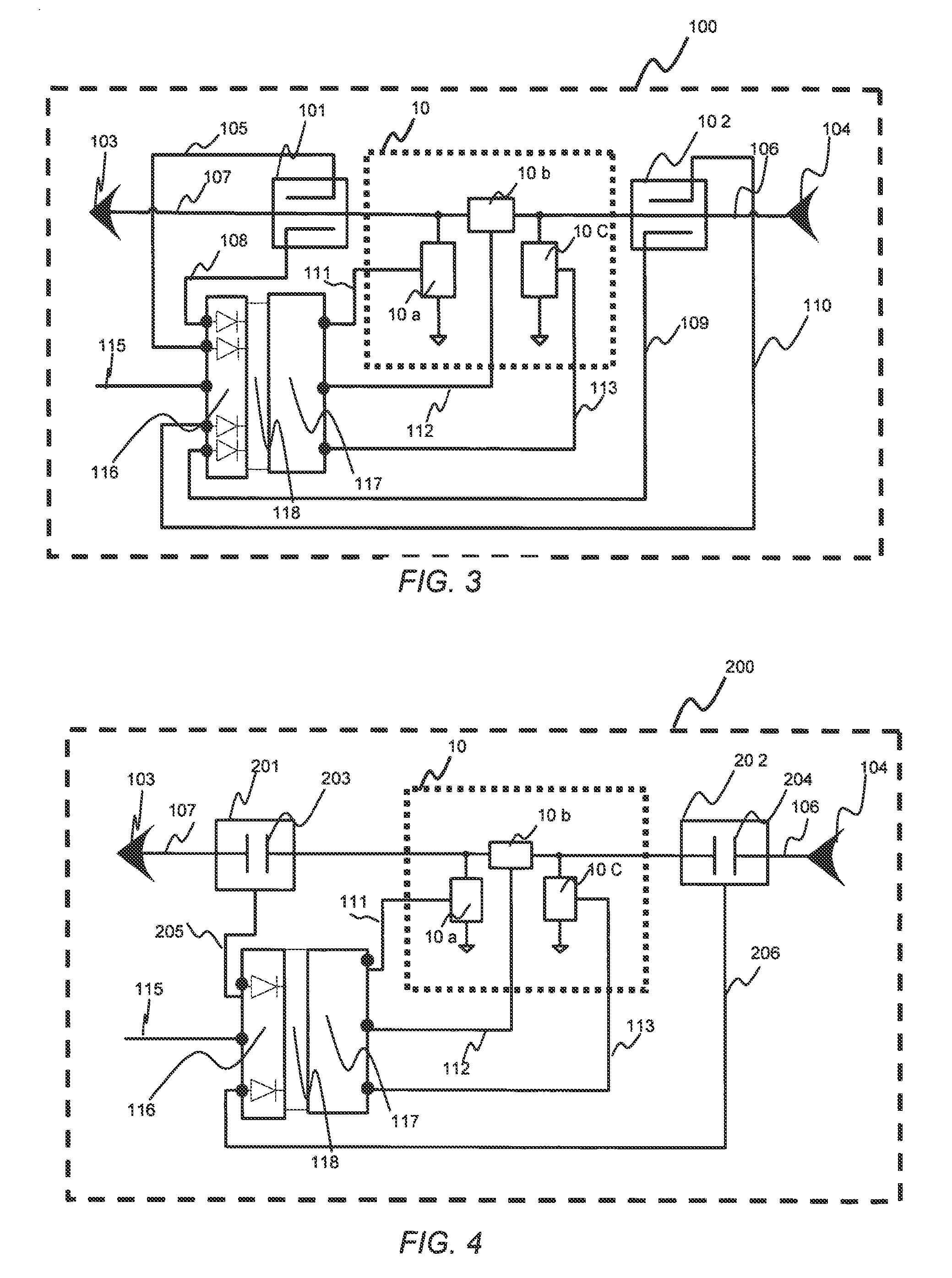
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an input port and a dynamic impedance matching network capable of determining a mismatch at the input port and dynamically changing the RF match by using at least one matching element that includes at least one voltage tunable dielectric capacitor. The matching network may be a “Pi”, a “T”, or “ladder” type network and the apparatus may further comprise at least one directional coupler capable of signal collection by sampling a portion of an incident signal, a reflected signal or both. In an embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus may also include a control and power control & logic unit (PC LU) to convert input analog signals into digital signals and sensing VSWR phase and magnitude and processing the digital signals using an algorithm to give it a voltage value and wherein the voltage values may be compared to values coming from the coupler and once compared and matched, the values may be passed to a Hi Voltage Application Specific Integrated Circuit (HV ASIC) to transfer and distribute compensatory voltages to the matching network elements.
Owner:NXP USA INC
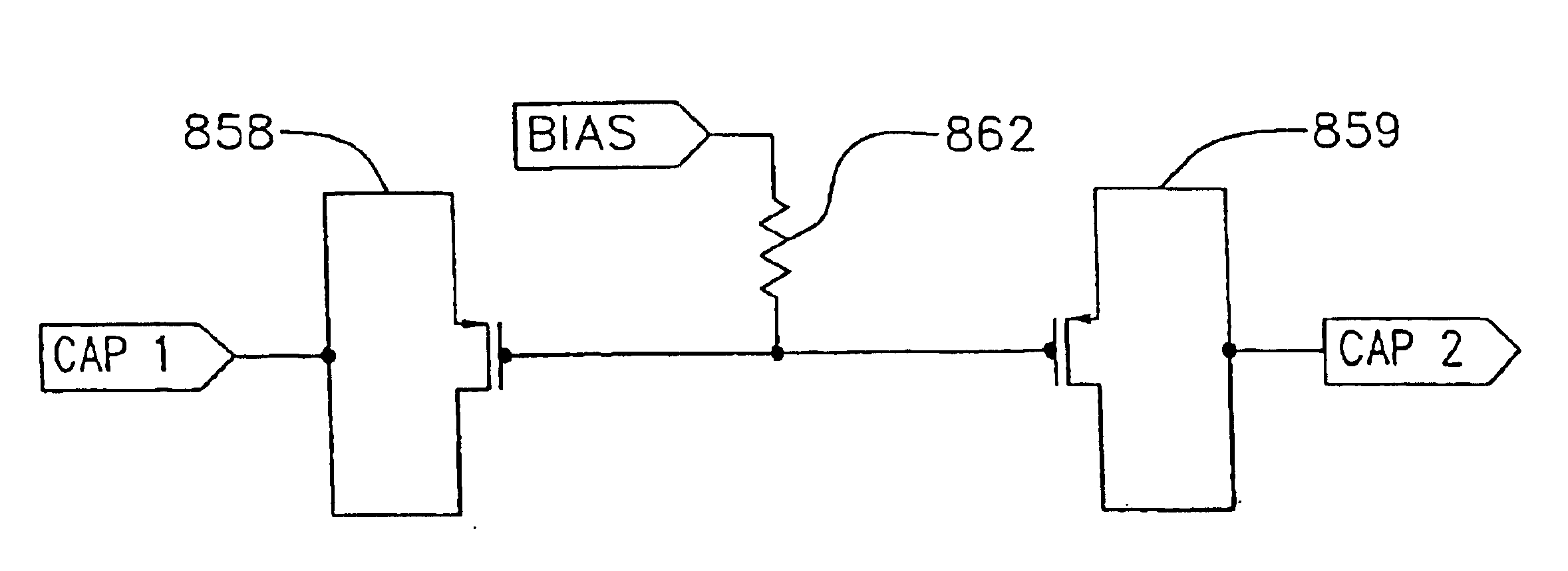
Bias Control for Stacked Transistor Configuration
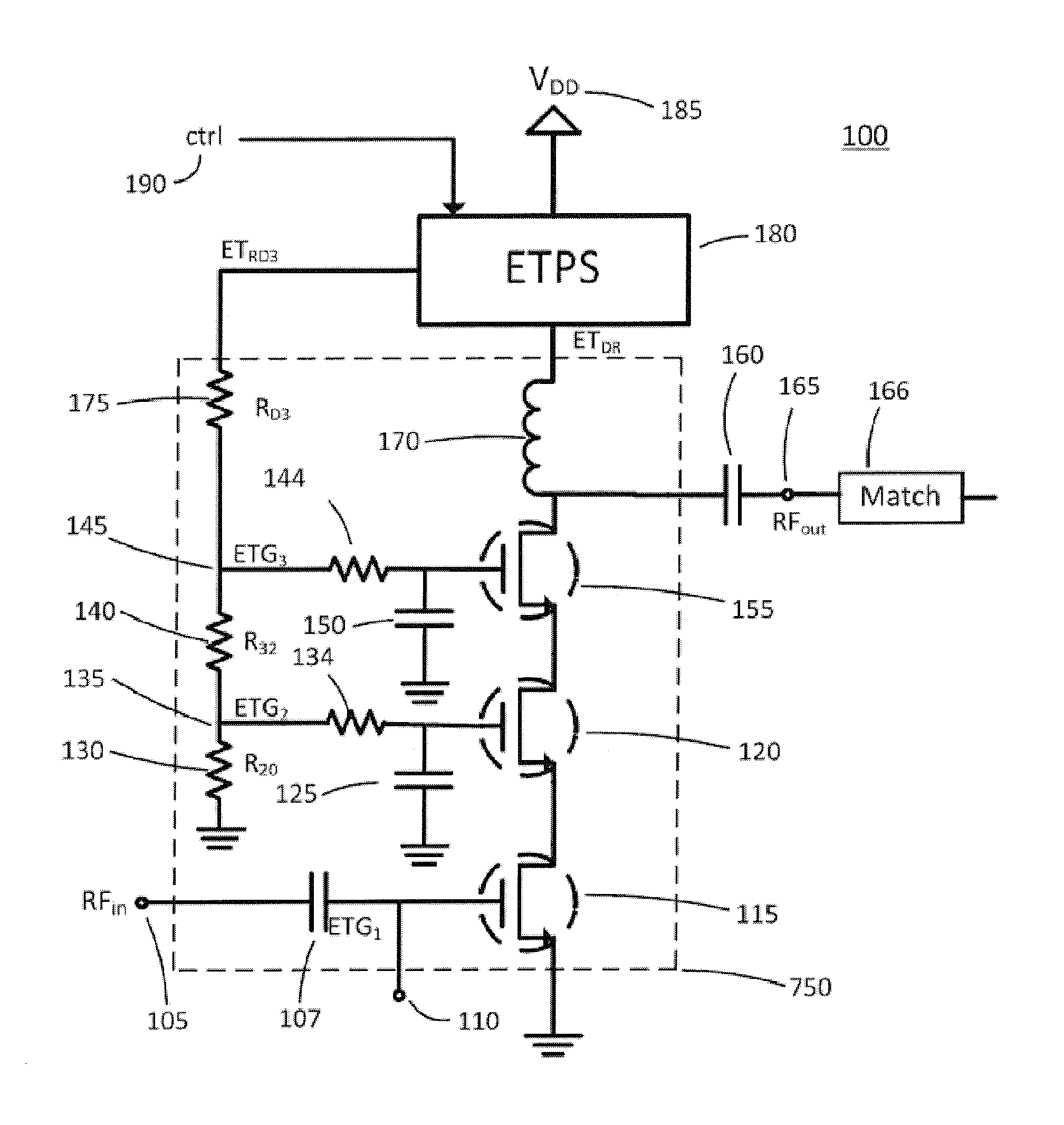
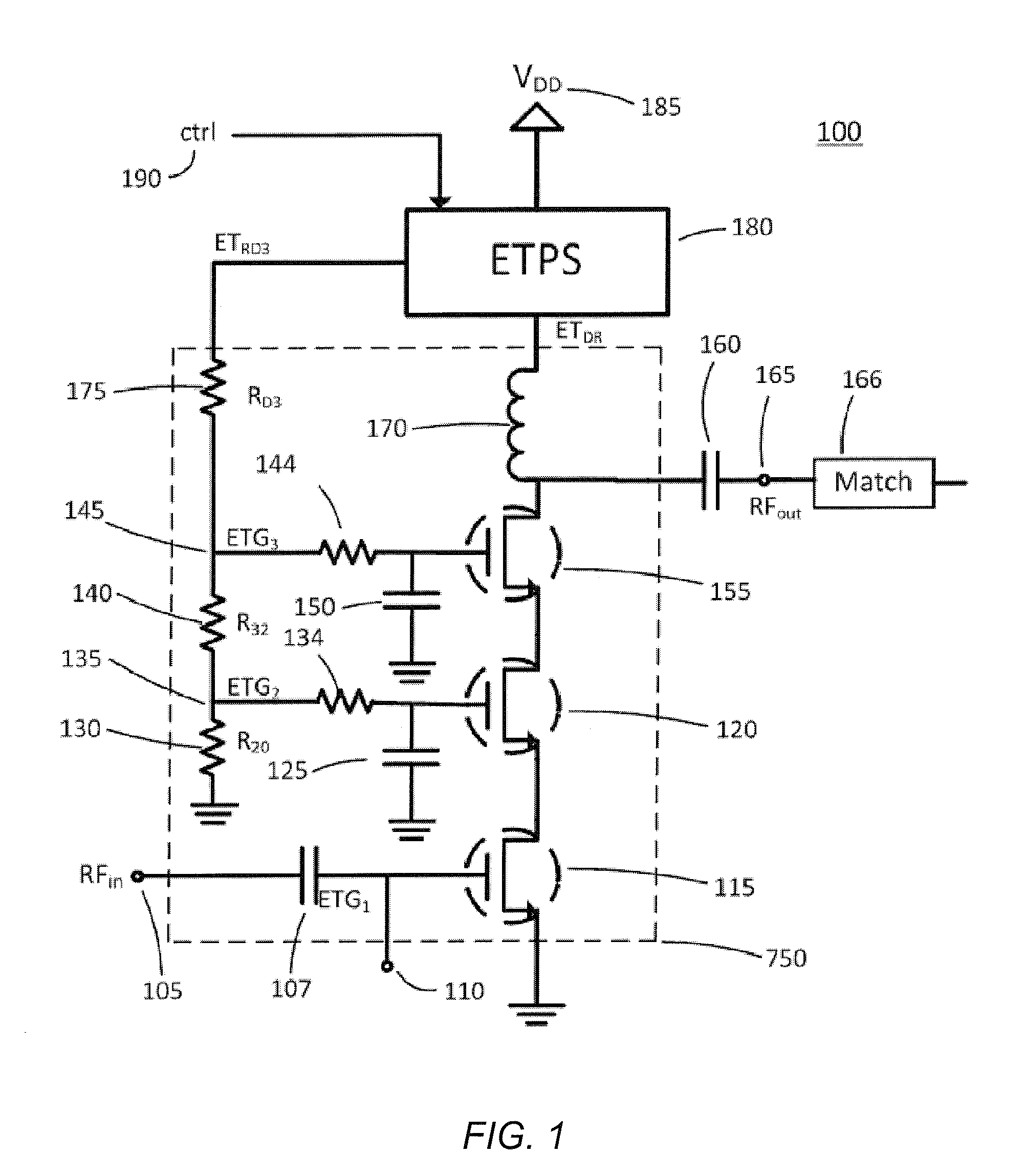
Various methods and circuital arrangements for biasing one or more gates of stacked transistors of an amplifier are presented, where the amplifier can be an envelope tracking amplifier. Circuital arrangements to generate reference gate-to-source voltages for biasing of the gates of the transistors of the stack are also presented. Particular biasing for a case of an input transistor of the stack is also presented.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Amplifiers Operating in Envelope Tracking Mode or Non-Envelope Tracking Mode
ActiveUS20140184335A1Power amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
Various envelope tracking amplifiers are presented that can be switched between an ET (envelope tracking) mode and a non-ET mode. Switches and / or tunable components are utilized in constructing the envelope tracking amplifiers that can be switched between the ET mode and the non-ET mode.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
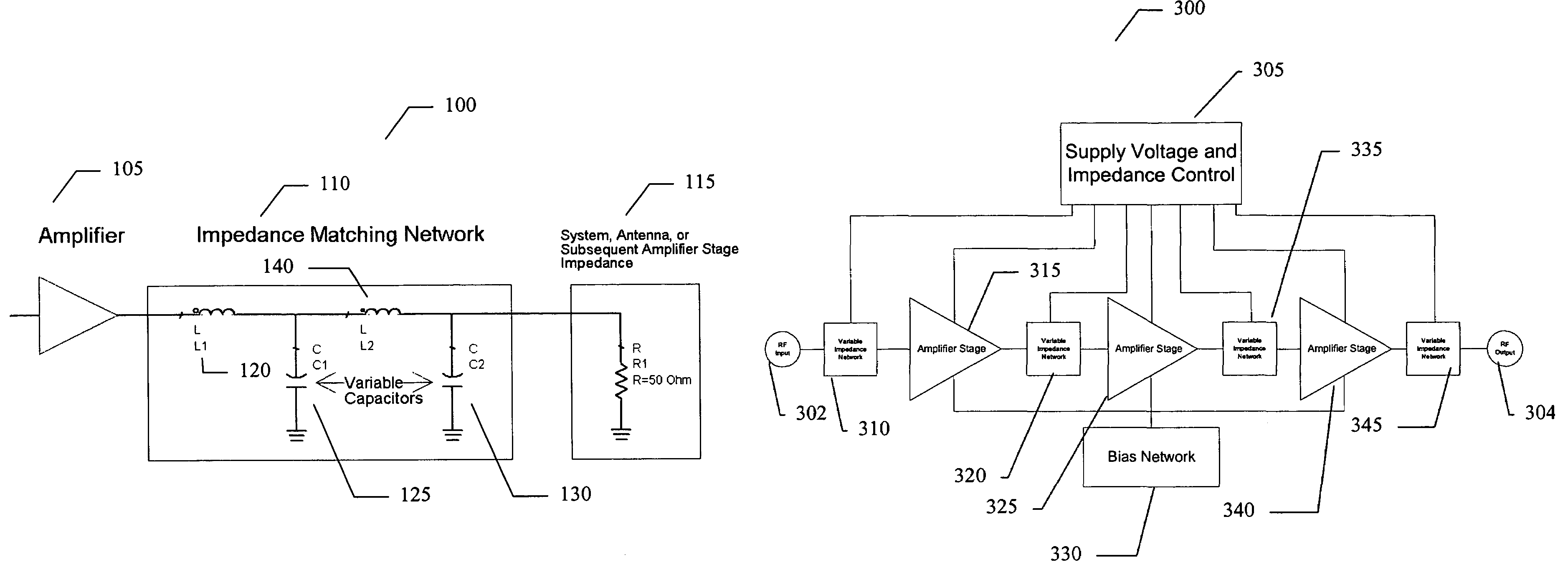
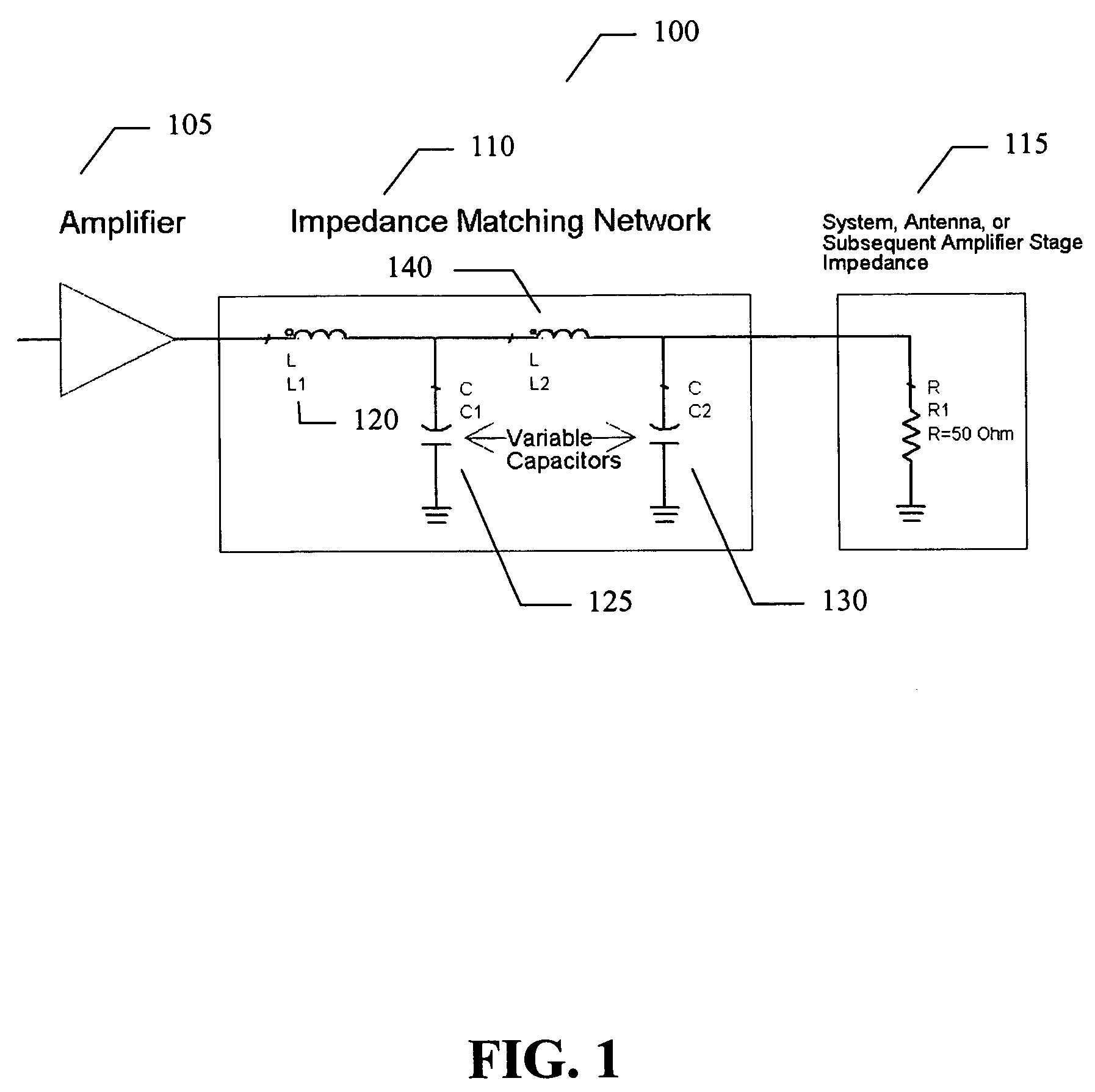
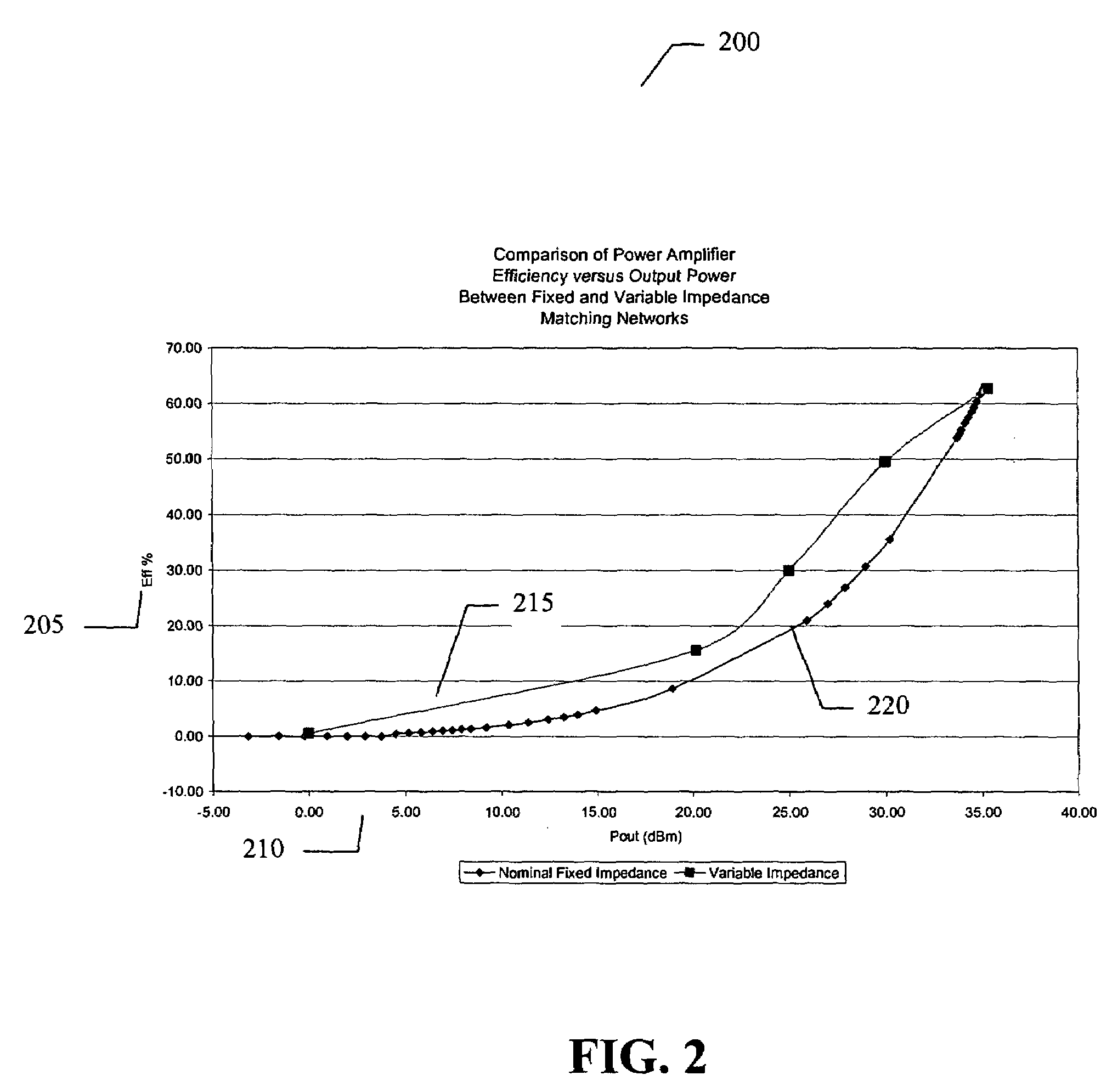
Amplifier system and method
ActiveUS7151411B2High frequency amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierImpedance matching
An embodiment of the present invention provides an amplifier system, comprising at least one variable impedance matching network, the output of which provides the input to at least one amplifier stage or provides an output of the power amplifier itself, and a bias network associated with the at least one amplifier stage. The amplifier system may further comprise a controller enabling impedance control to the at least one variable impedance matching network and a supply voltage provided to the at least one variable impedance network and / or the at least one amplifier stage and wherein the at least one variable impedance network and the at least one amplifier stage may be a plurality of impedance networks connected to a plurality of amplifier stages. The at least one variable impedance network may include at least one variable capacitor and the at least one variable capacitor may be a voltage tunable dielectric capacitor which may include Parascan® voltage tunable dielectric material.
Owner:NXP USA INC
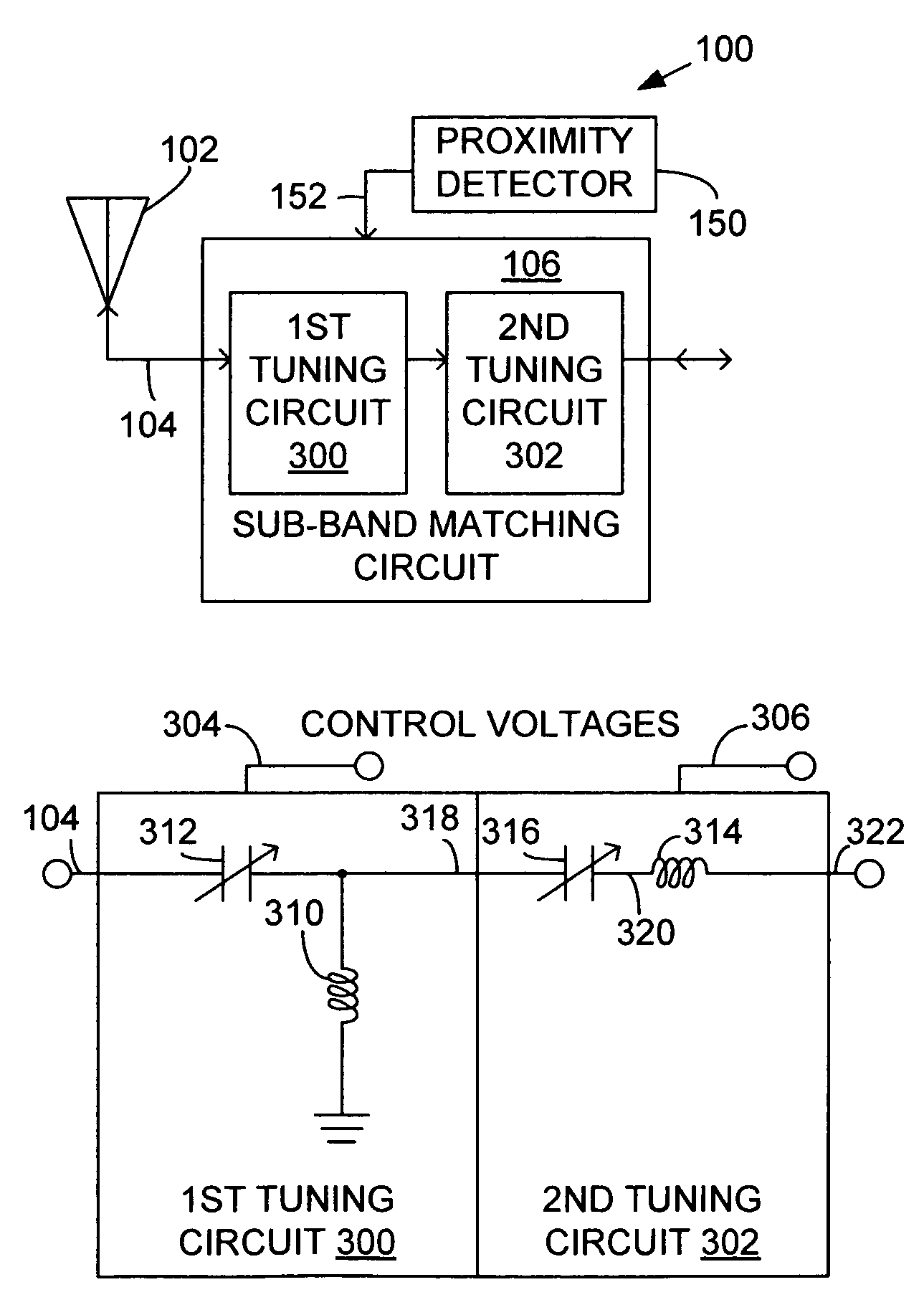
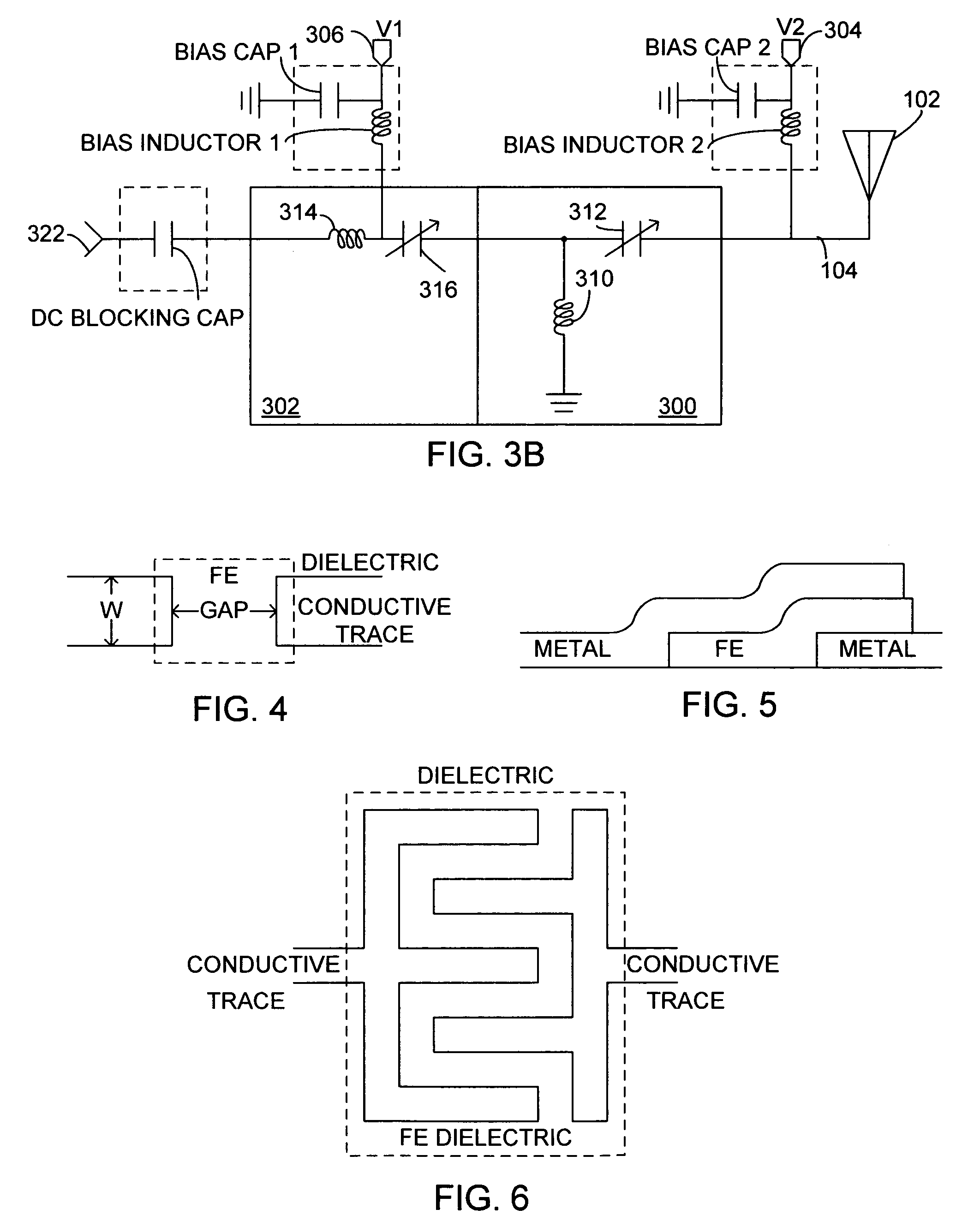
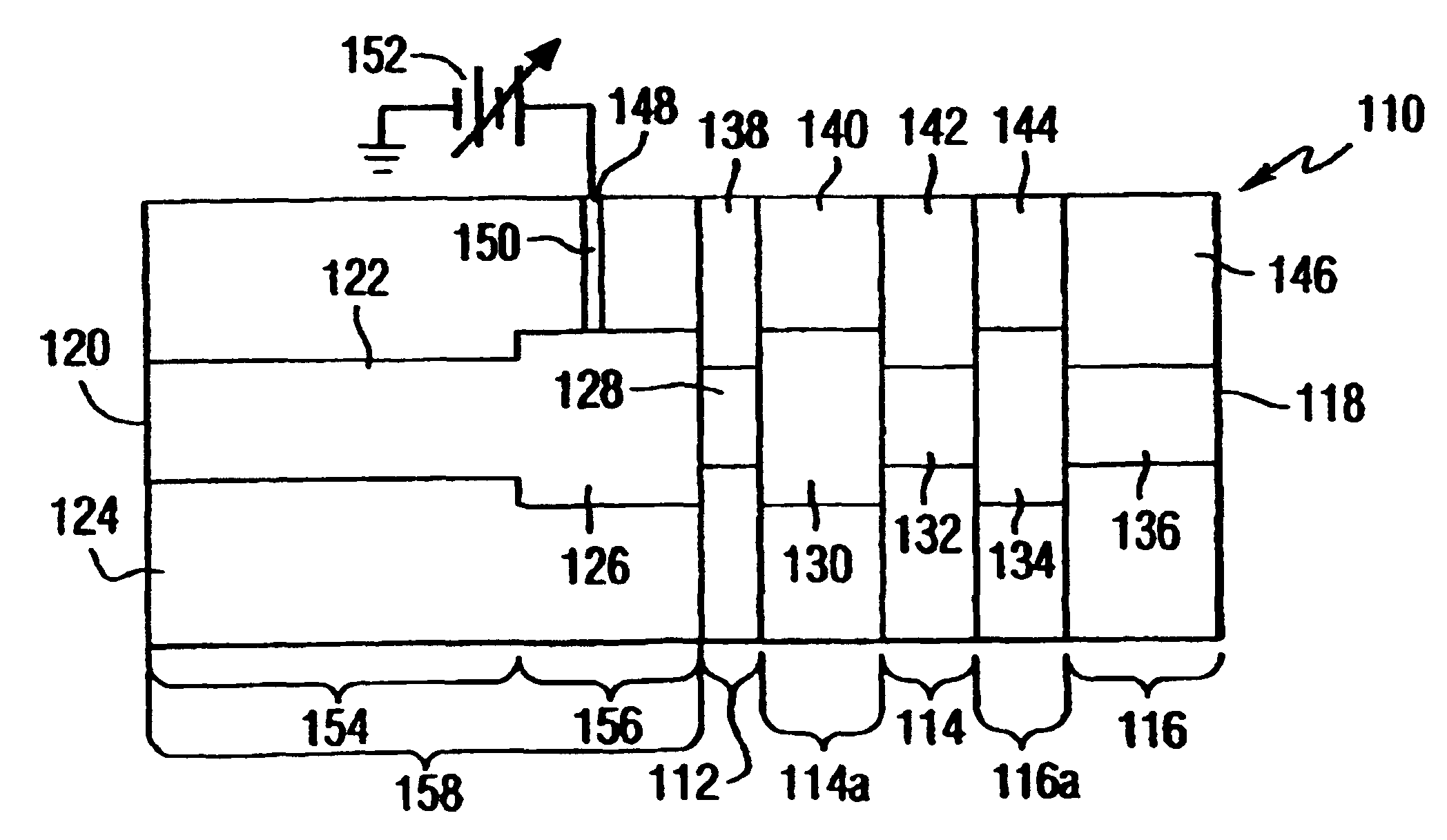
System and method for impedance matching an antenna to sub-bands in a communication band
InactiveUS7176845B2Improve efficiencyReduce noiseMultiple-port networksAntenna supports/mountingsAntenna impedanceMethod selection
A sub-band antenna matching method and an antenna matching system for selectively matching a communication bandwidth segment impedance have been provided. The method comprises: accepting a frequency-dependent impedance from an antenna; and, selectively supplying a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a first communication band. In some aspects, the method selectively supplies a conjugate impedance match for the antenna at a sub-band of a second communication band. More specifically, the method comprises: tuning a first tuning circuit to a first frequency; simultaneously tuning a second tuning circuit to a second frequency to match the antenna at a low end of the first communication band. Likewise, the first tuning circuit is tuned to a third frequency and the second tuning circuit is tuned to a fourth frequency to match the antenna at a high end of the first communication band in response to the third and fourth frequencies.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
Tunable microwave devices with auto-adjusting matching circuit
InactiveUS6864757B2Reduce signal reflectionReduce reflectionMultiple-port networksAmplifiers wit coupling networksElectrical conductorCoplanar waveguide
Owner:NXP USA INC
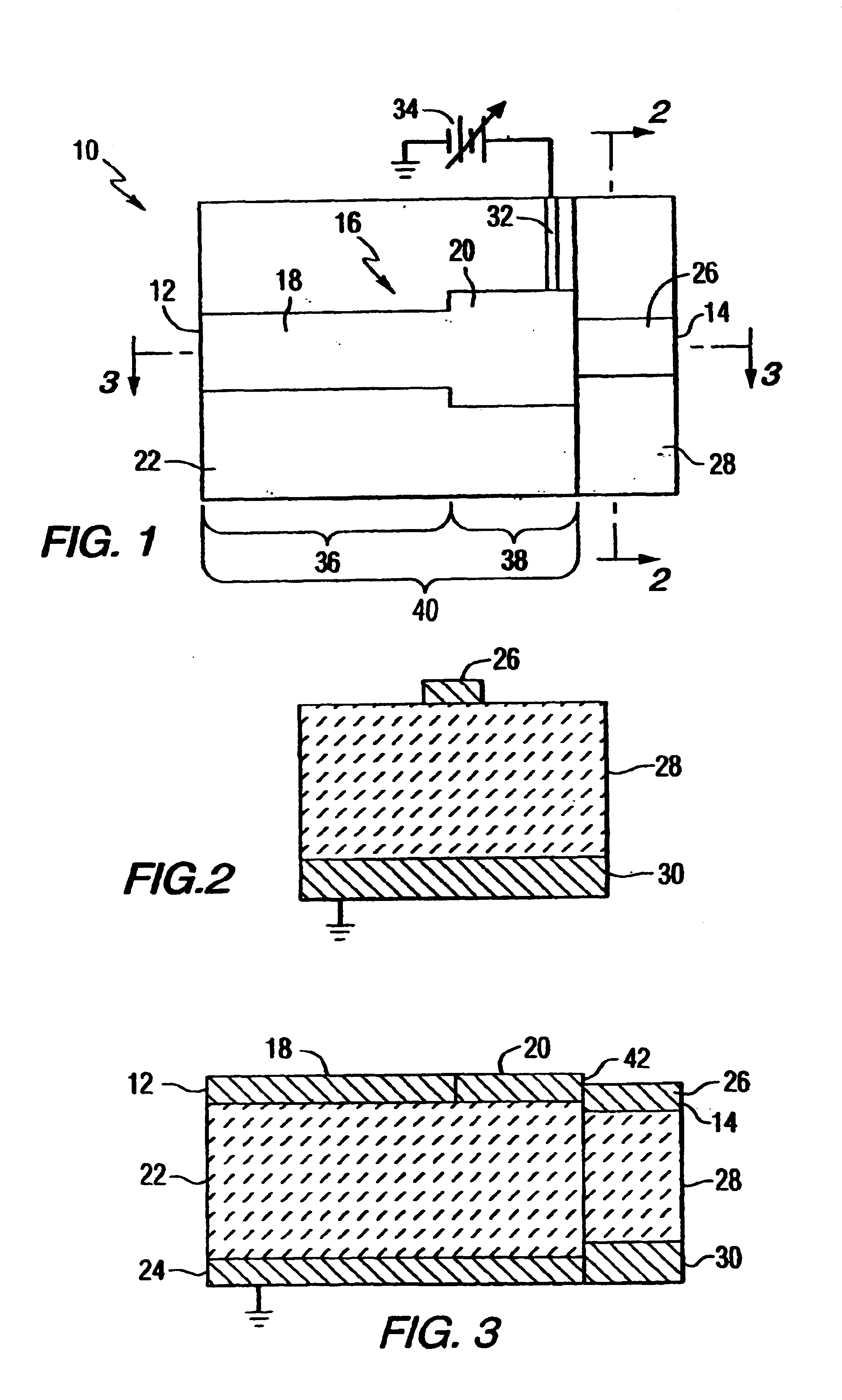
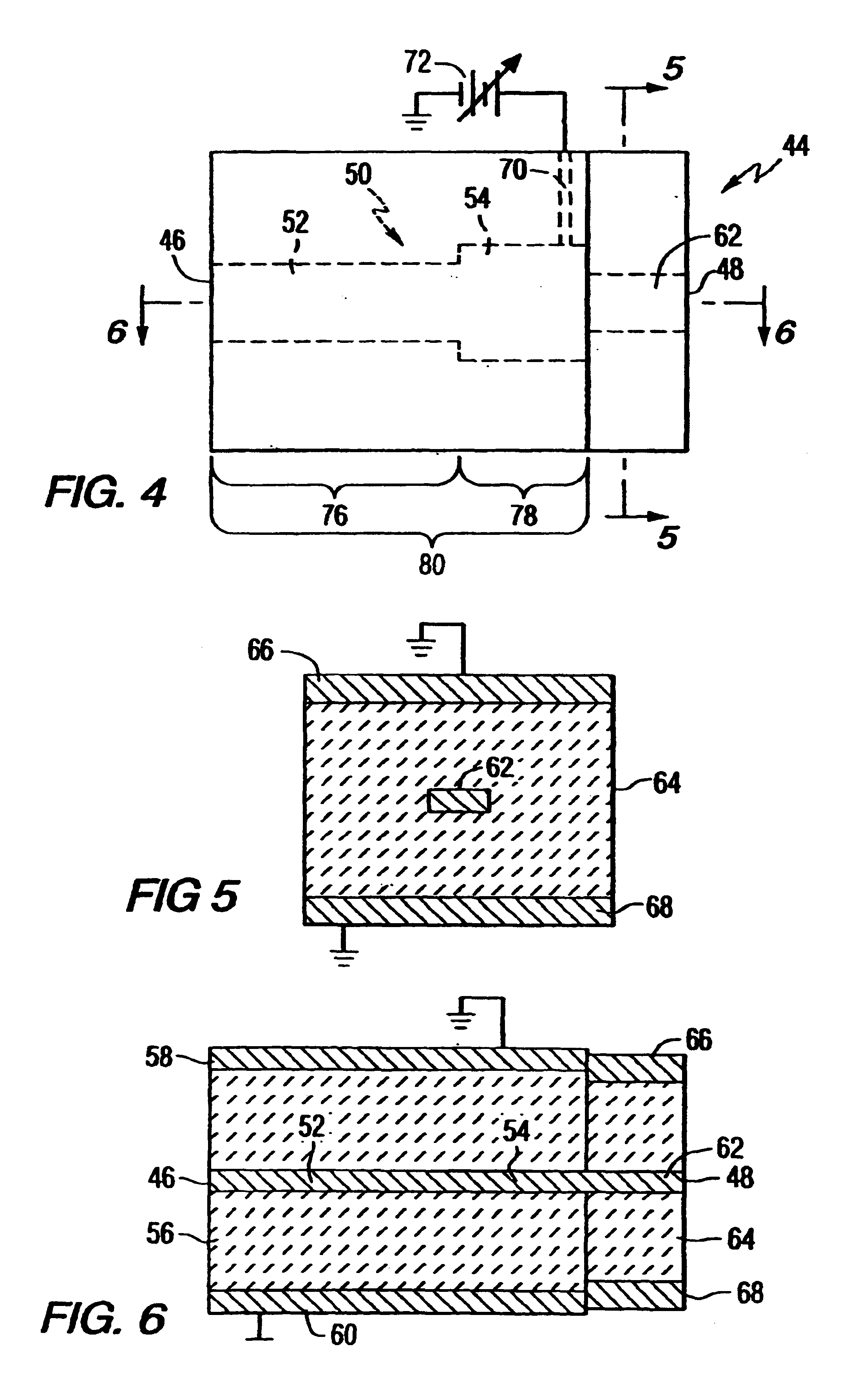
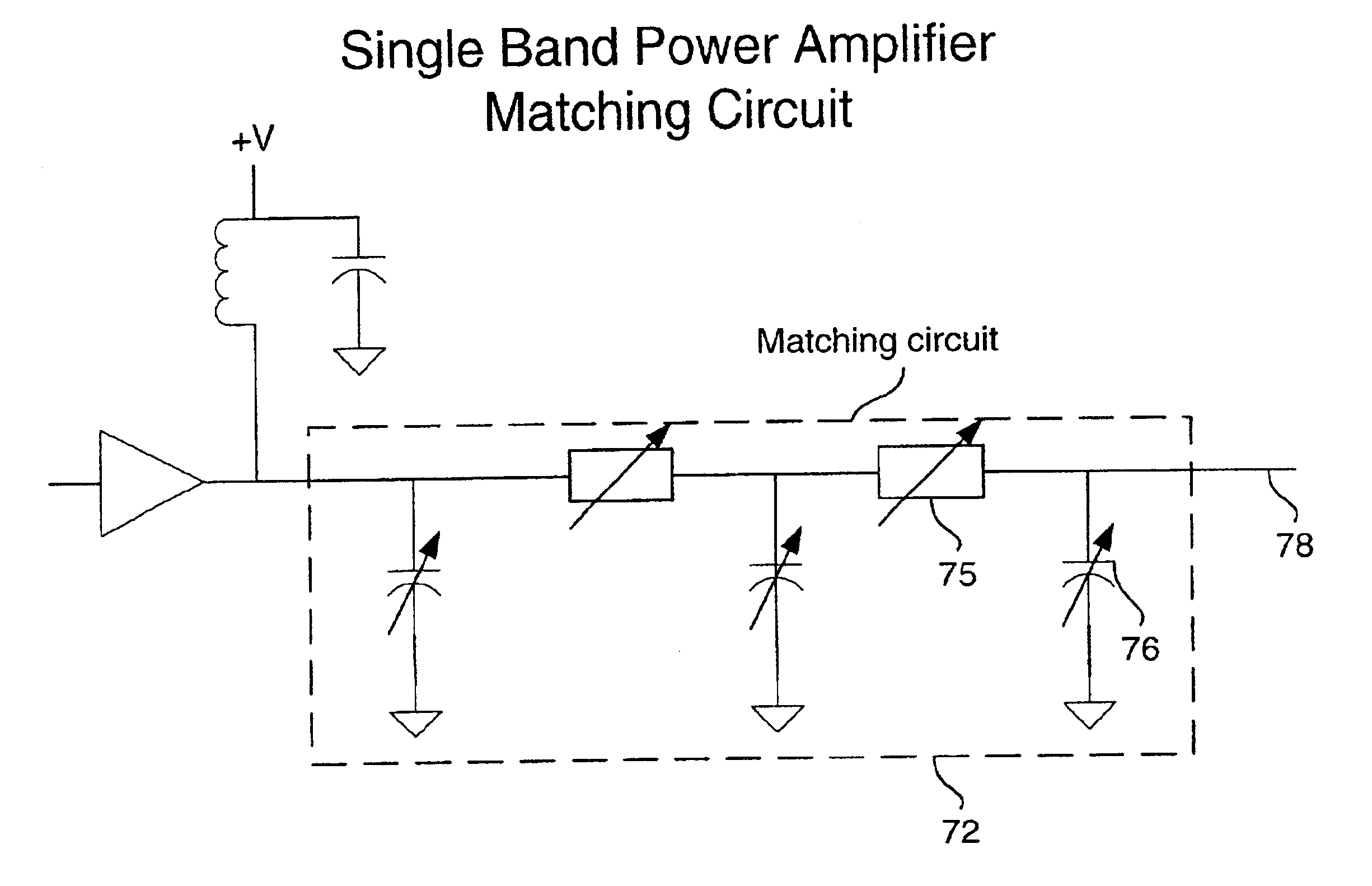
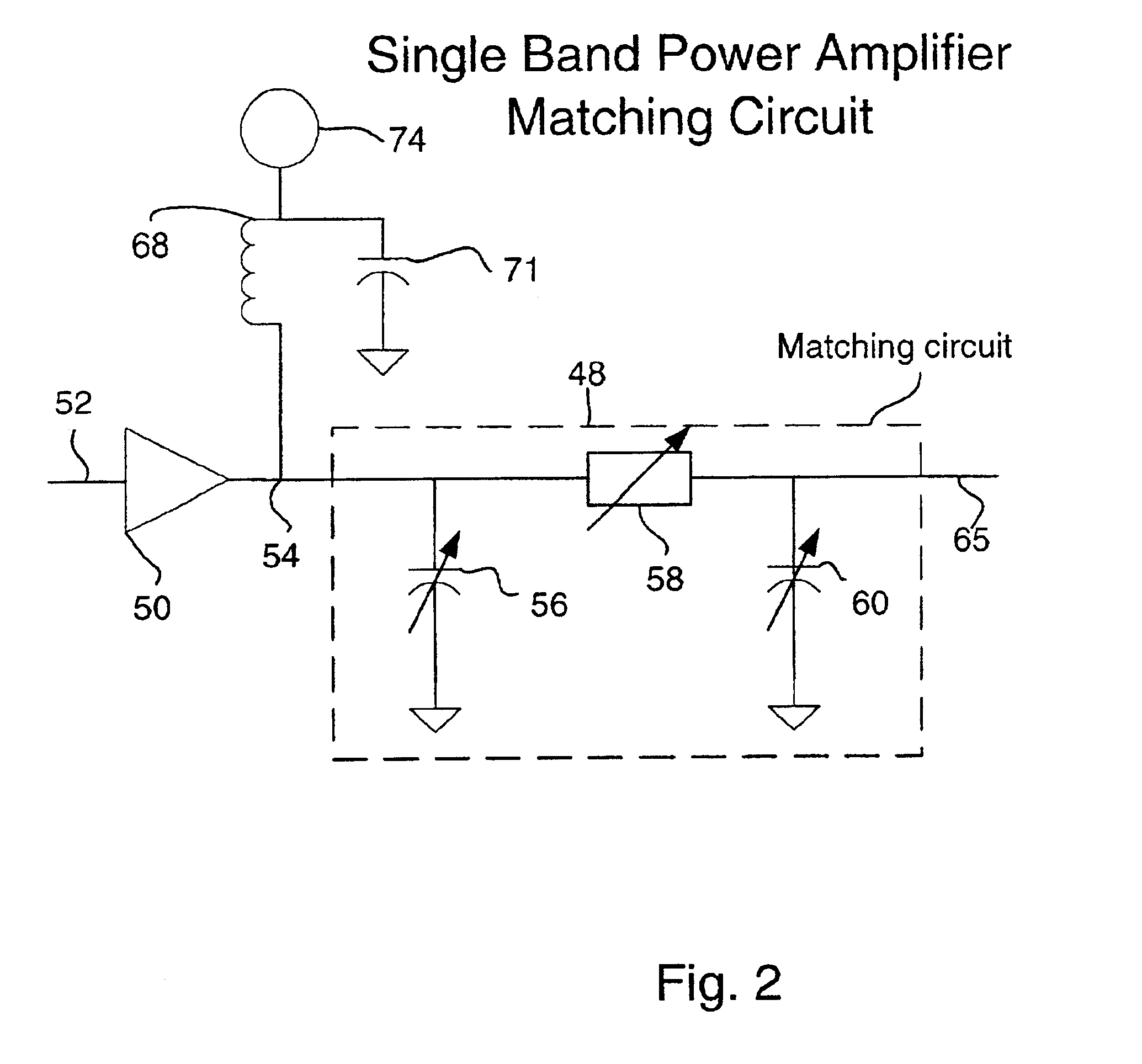
Tunable power amplifier matching circuit
InactiveUS6859104B2Reduce cost and size and power consumptionMultiple-port networksHigh frequency amplifiersAudio power amplifierControl signal
A power amplifier matching circuit is provided. The matching circuit includes a ferro-electric tunable component. A control signal is applied to the tunable component, changing the component's impedance. This changes the impedance of the matching circuit.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
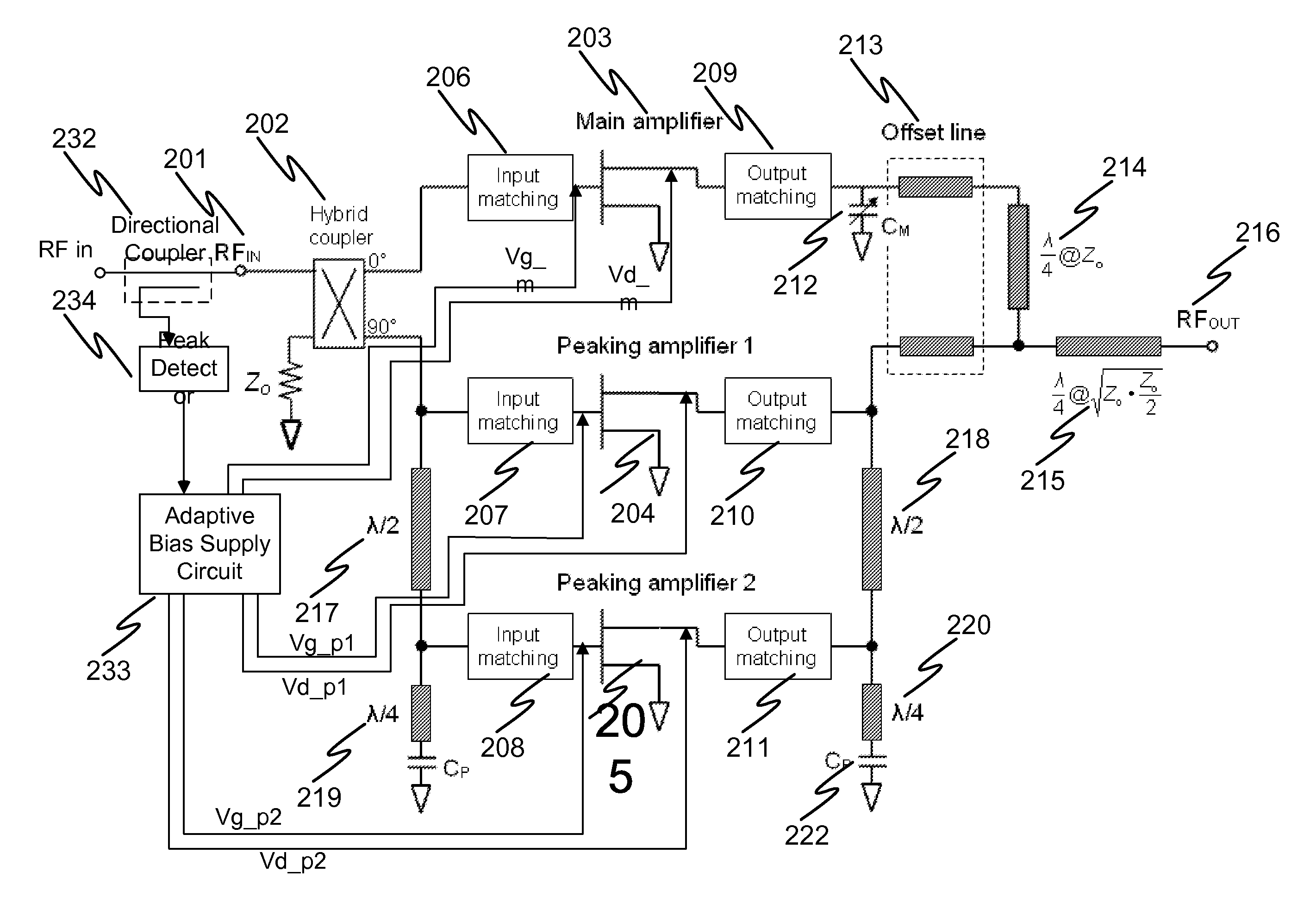
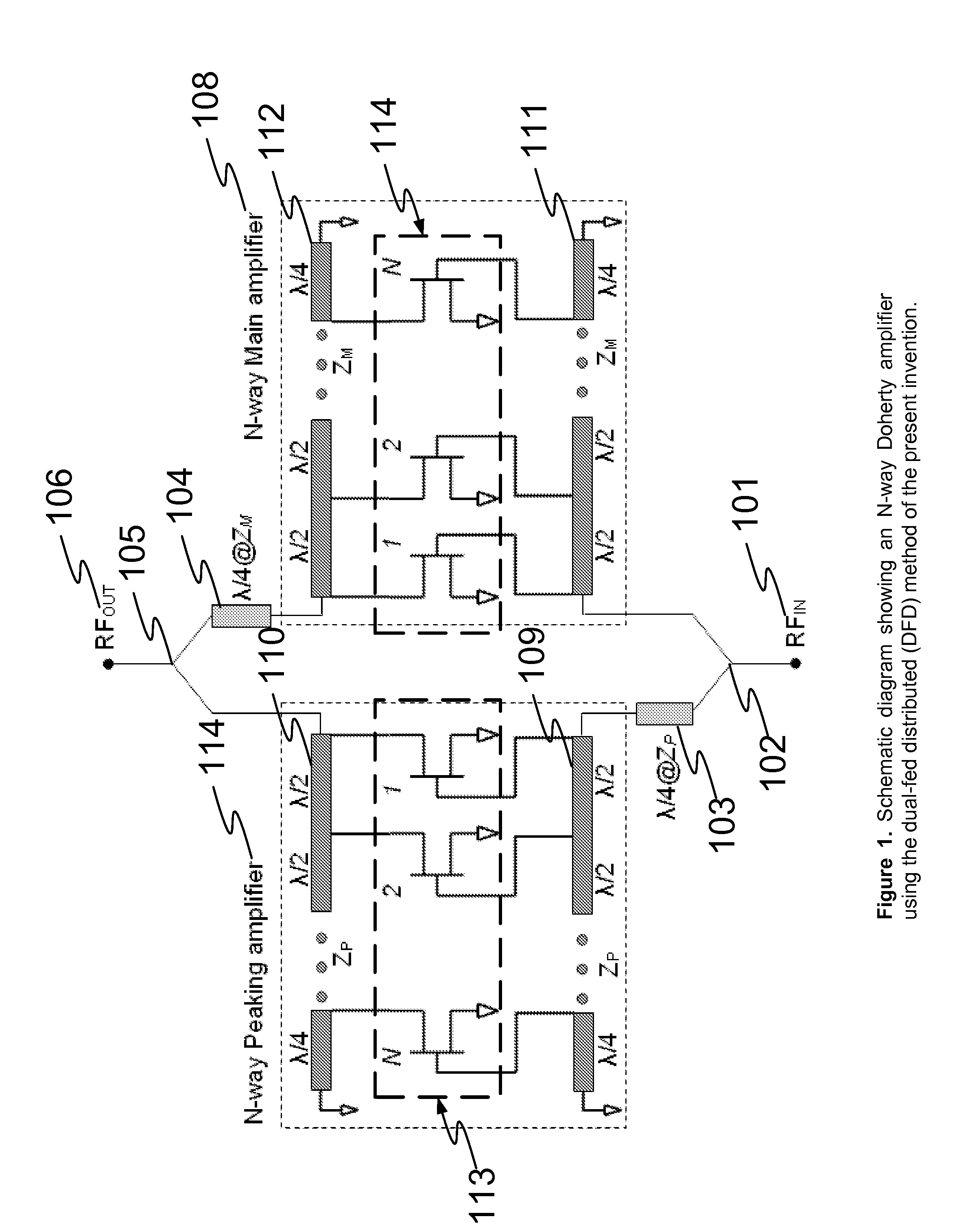
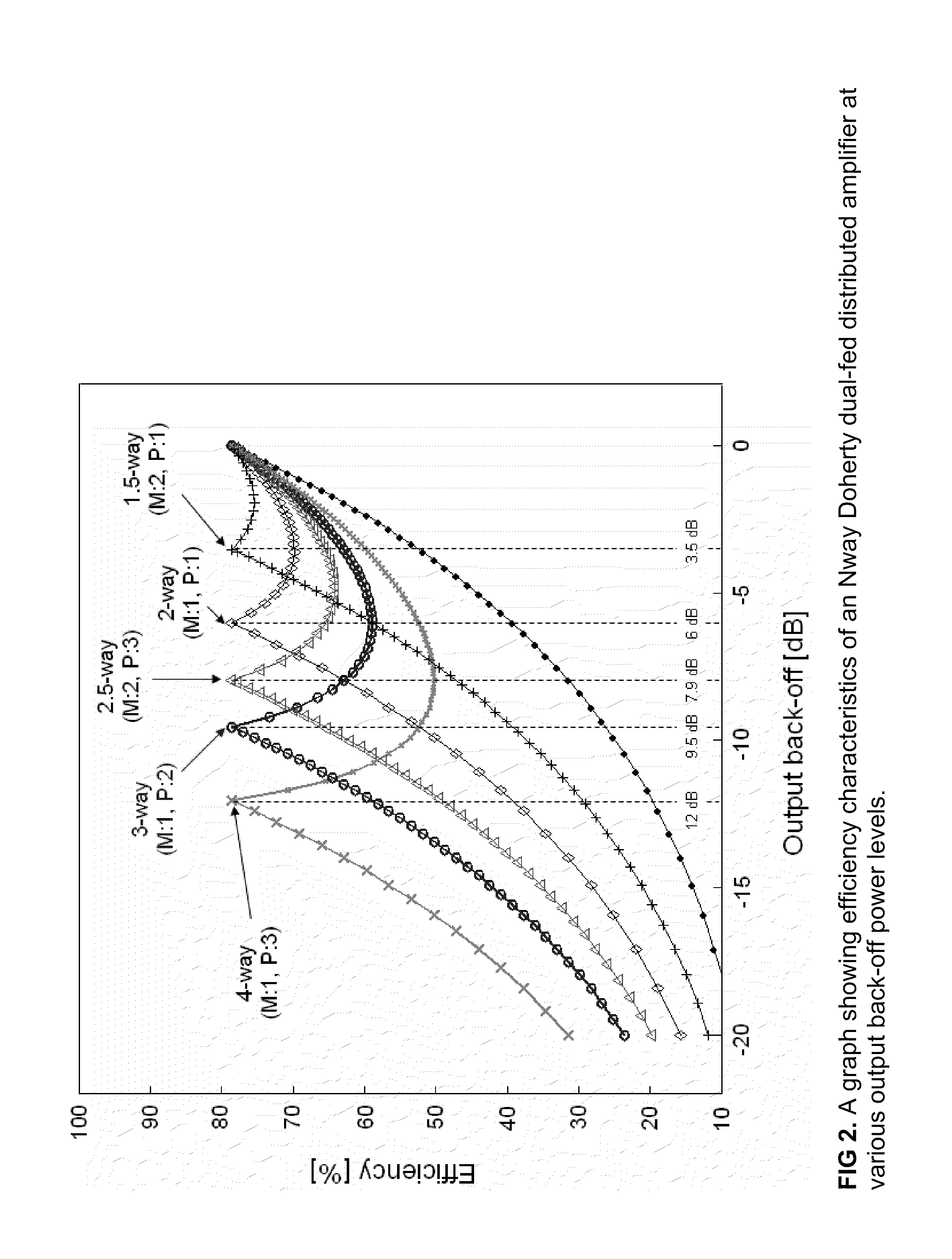
N-way Doherty distributed power amplifier with power tracking
ActiveUS8274332B2Improve performanceIncrease productionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAdaptive biasMultiplexing
Owner:DALI SYST LTD
Full-duplex antenna system and method
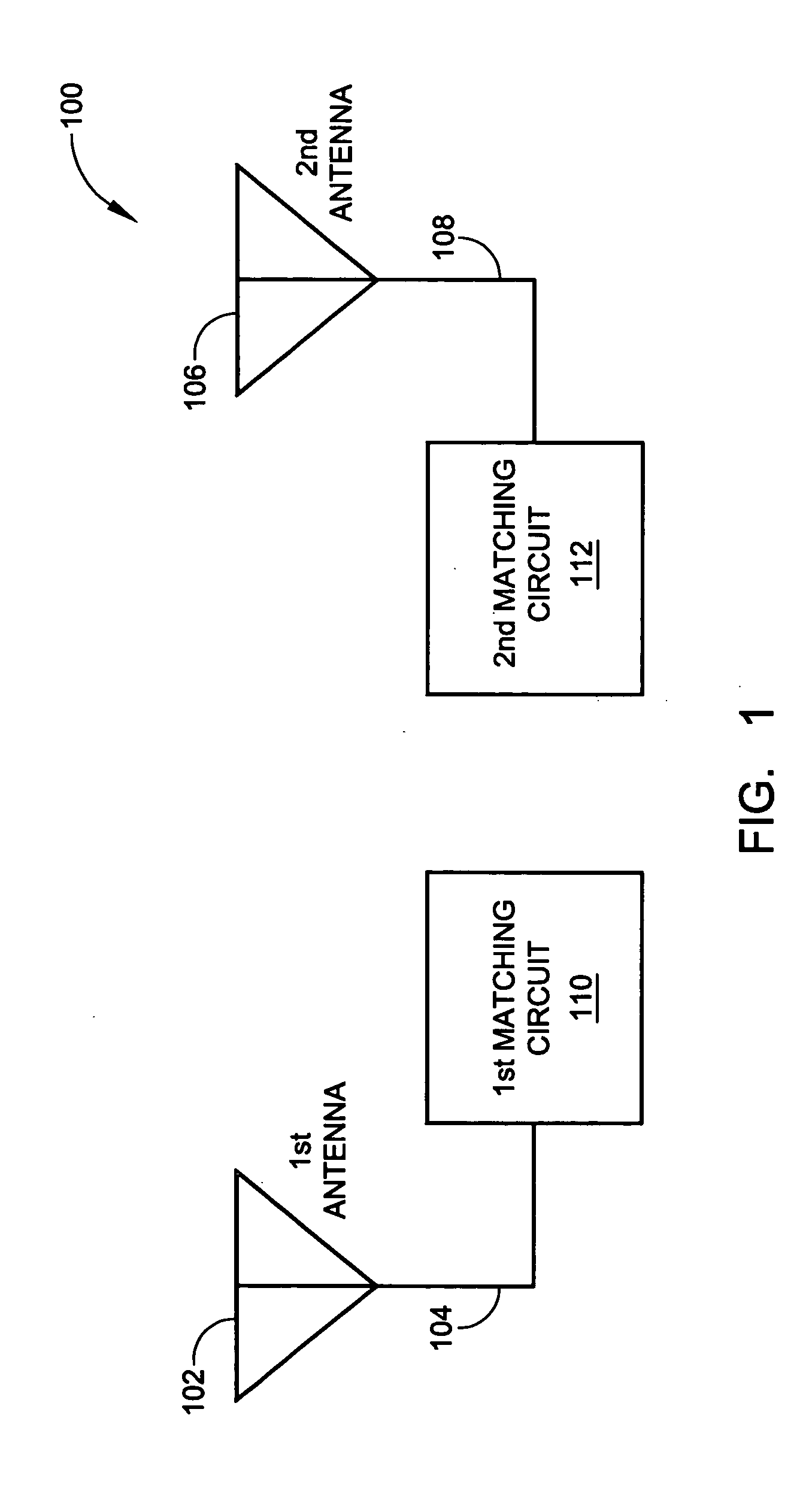
A system and method is provided for full-duplex antenna impedance matching. The method comprises: effectively resonating a first antenna at a frequency selectable first channel in a first frequency band; generating a first antenna impedance at the first channel frequency; effectively resonating a second antenna at a frequency selectable second channel in the first frequency band; generating a second antenna impedance at the second channel frequency; supplying a first conjugate impedance match at the first channel frequency; and, supplying a second conjugate impedance match at the second channel frequency. For example, the first antenna may be used for transmission, while the second antenna is used for received communications. The antennas effectively resonant in response to: supplying frequency selectable conjugate impedance matches to the antennas; generating frequency selectable antenna impedances; and / or selecting the frequency of antenna resonance.
Owner:KYOCERA CORP
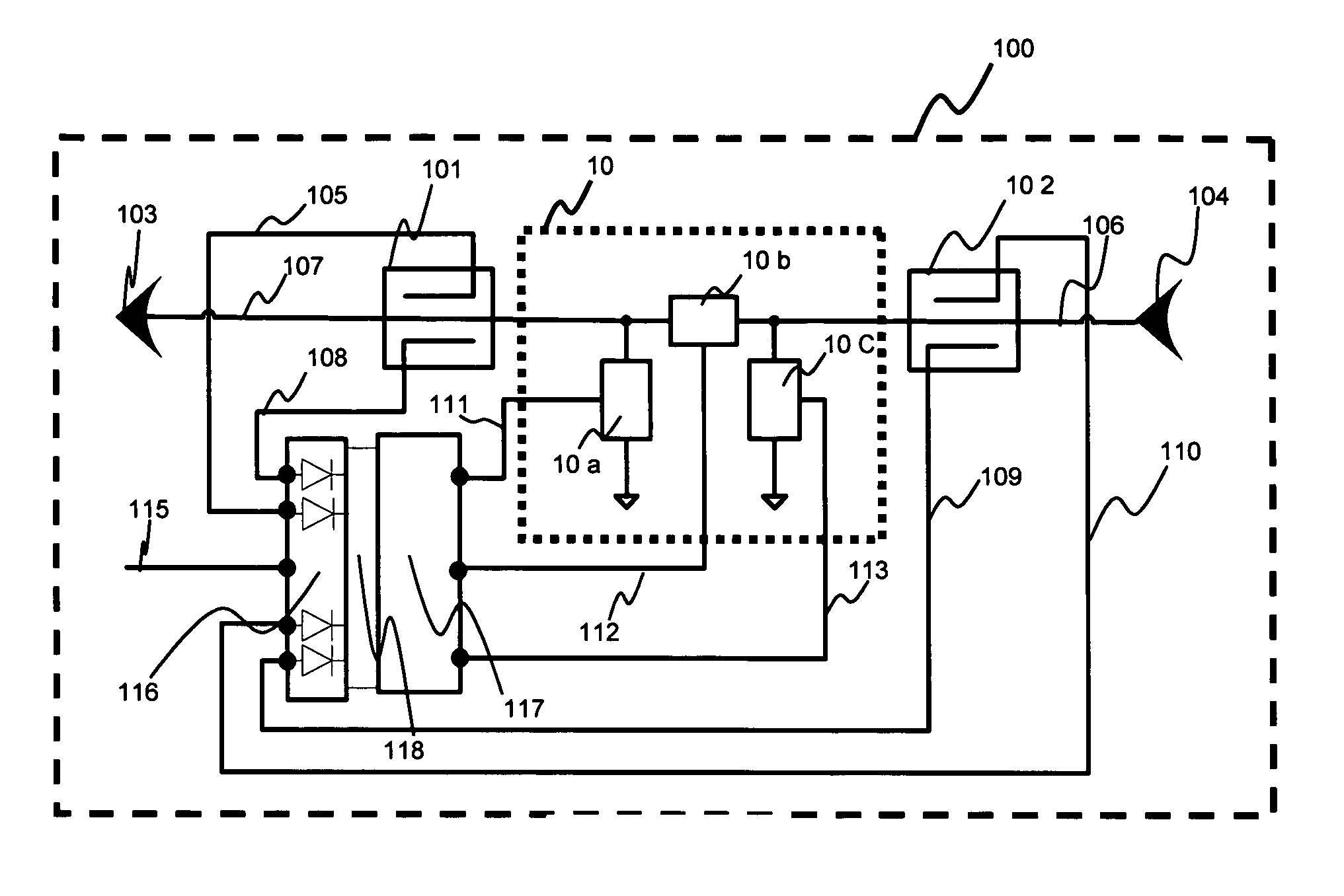
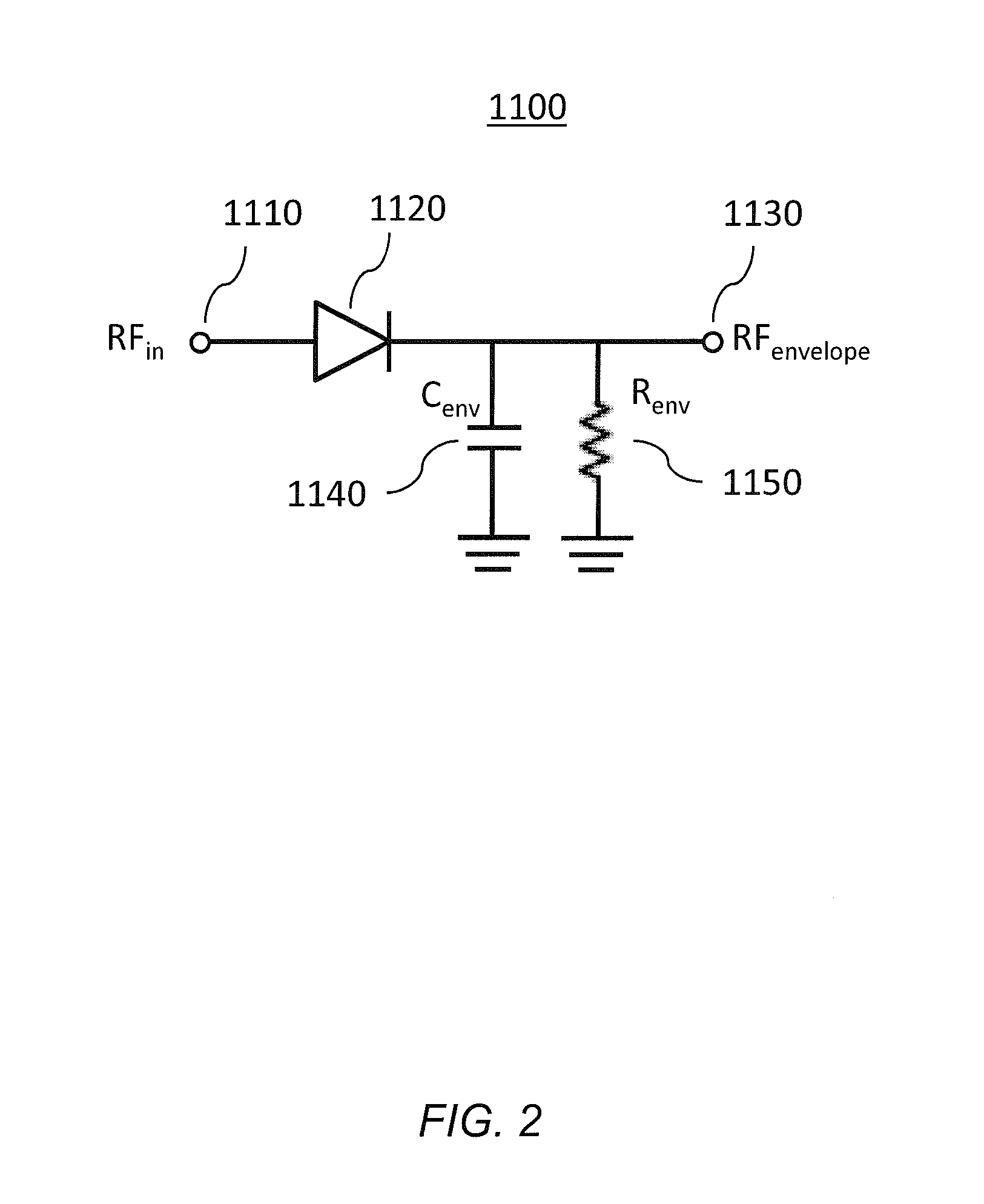
Method and arrangement for detecting load mismatch, and a radio device utilizing the same
ActiveUS6965837B2Reduce lossesAccurate and reliable detectionResonant long antennasResistance/reactance/impedenceRadio equipmentEngineering
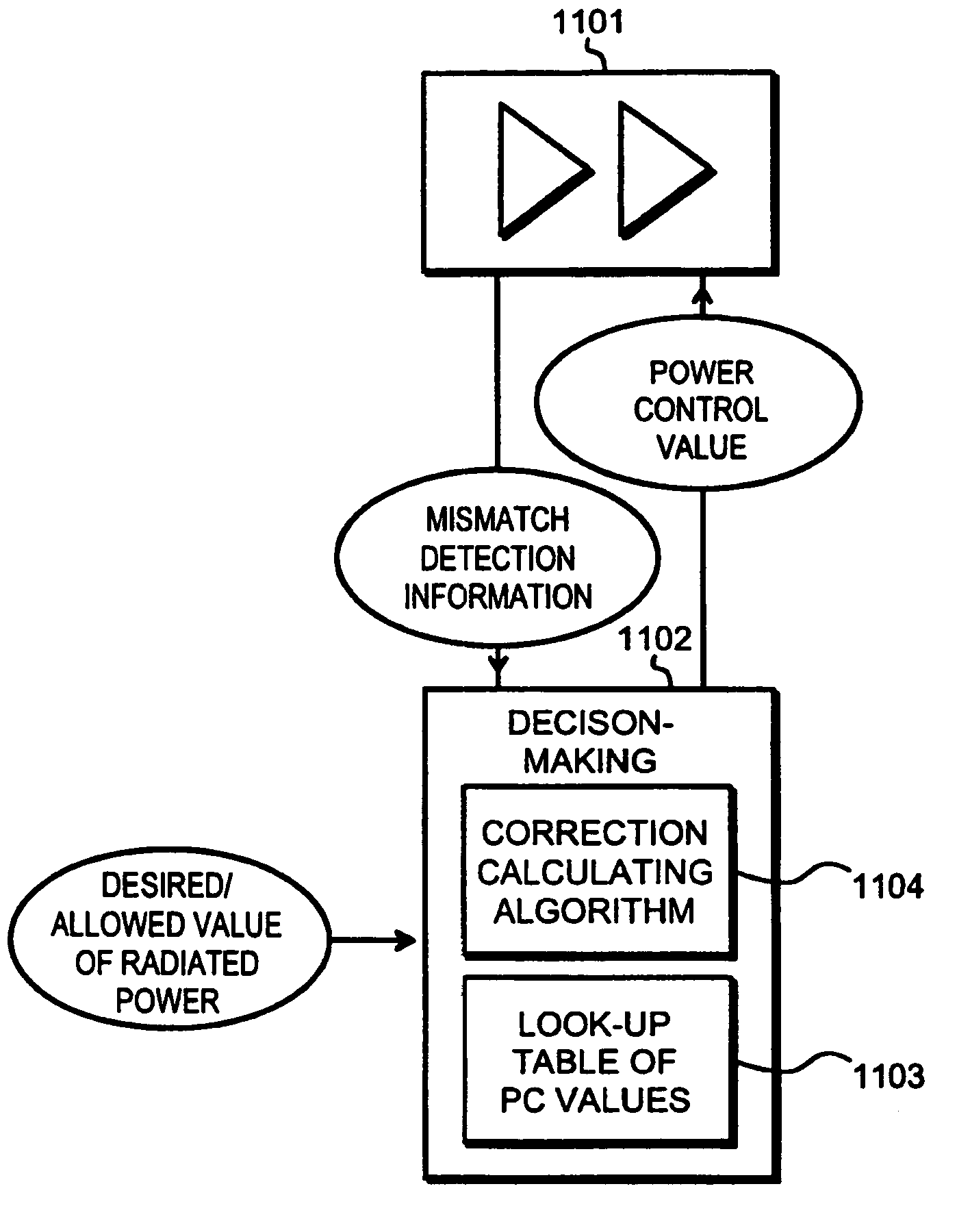
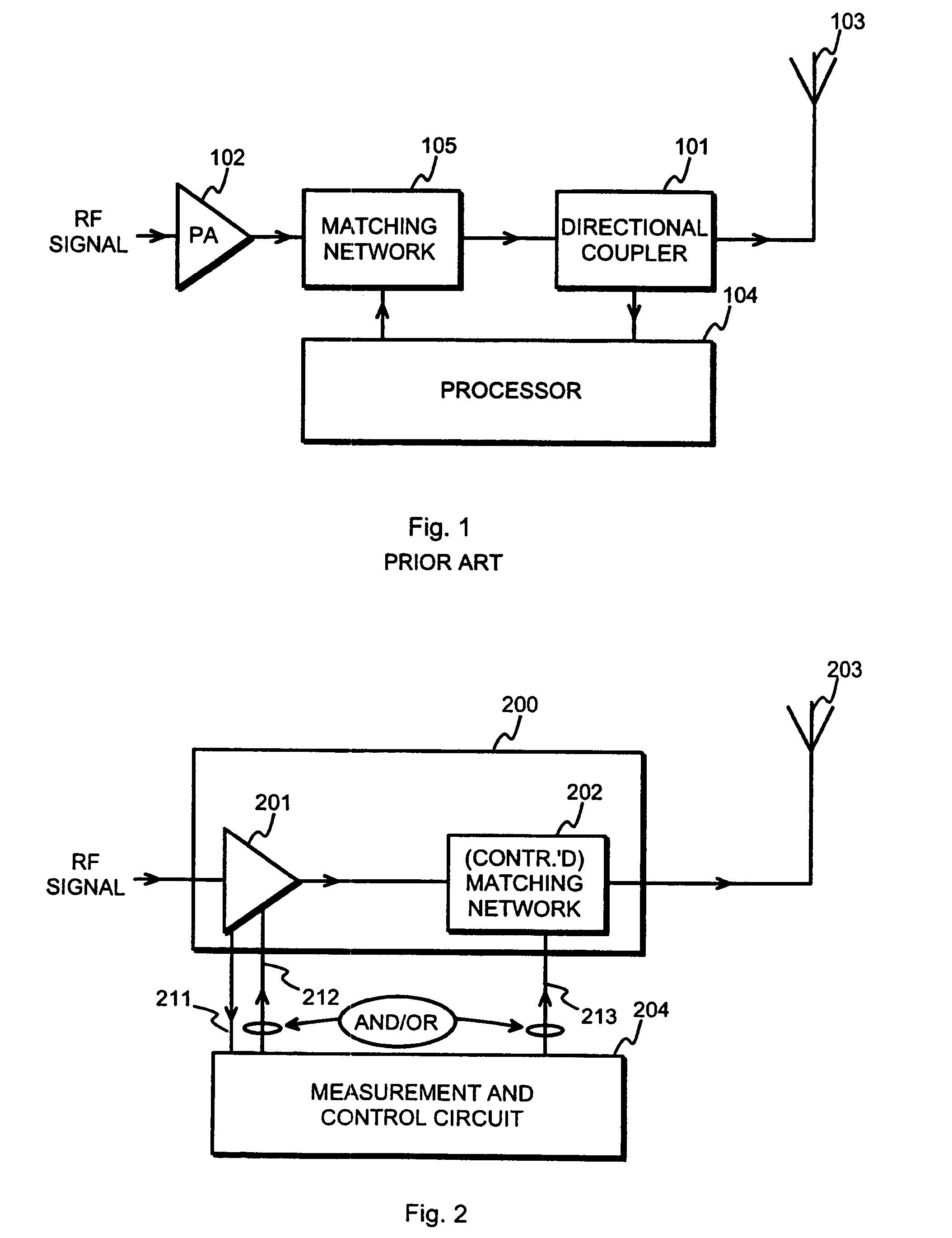
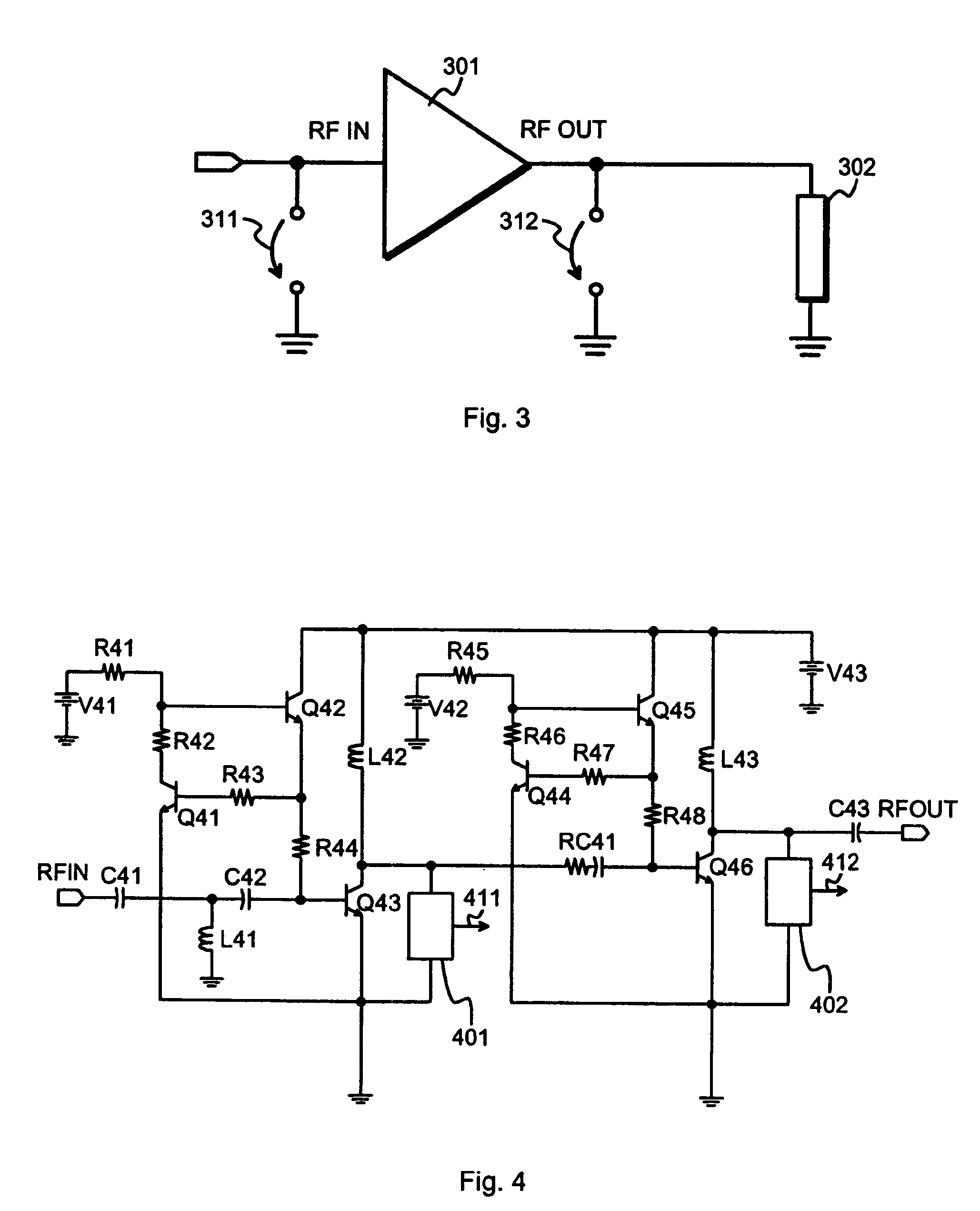
A method and an arrangement for detecting impedance mismatch between an output of a radio frequency amplifier (200, 901, 911, 921, 1101) which has an amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) and an input of a load (203, 302) coupled to the output of the radio frequency amplifier having: first monitoring means (401) to monitor a measurable electric effect (311) at a side of the amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) other than the load (203, 302) and to produce a first measurement signal (411). Second monitoring means (402) monitor a measurable electric effect (312) between the amplifying component (201, 301, Q46, 701, 801) and the load (203, 302) and produce a second measurement signal (412). Decision-making means (204, 902, 912, 923, 1102) receive said first (411) and second (412) measurement signals and decide, whether said first and second measurement signals together indicate impedance mismatch.
Owner:III HLDG 3
Mems-tuned high power, high efficiency, wide bandwidth power amplifier
InactiveUS6992543B2High output power levelAdvantage in sizeMultiple-port networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesTransformerControl signal
A circuit for matching the impedance of an output load to an active device includes a transformer including a first winding having a terminal for coupling to the output of the active device and a second winding electromagnetically coupled to the first winding, and a plurality of taps, each of the plurality of taps having a first end coupled to a position on the second winding corresponding to a ratio of the second winding to first winding differing from other ones of the plurality of taps, and a second end. The matching circuit further includes a plurality of MEMS switches each having a control input for receiving a corresponding control signal, a first terminal coupled to the second end of a corresponding one of the plurality of taps, and a switched output selectively coupled to a matching junction in response to the corresponding control signal.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Tunable microwave devices with auto-adjusting matching circuit
Owner:NXP USA INC
Scalable Periphery Tunable Matching Power Amplifier
A scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier is presented. Varying power levels can be accommodated by selectively activating or deactivating unit cells of which the scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier is comprised. Tunable matching allows individual unit cells to see a constant output impedance, reducing need for transforming a low impedance up to a system impedance and attendant power loss. The scalable periphery tunable matching power amplifier can also be tuned for different operating conditions such as different frequencies of operation or different modes.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Optimization Methods for Amplifier with Variable Supply Power
ActiveUS20140184334A1Affecting responseAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierLinear region
Optimization methods via various circuital arrangements for amplifier with variable supply power are presented. In one embodiment, a switch can be controlled to include or exclude a feedback network in a feedback path to the amplifier to adjust a response of the amplifier dependent on a region of operation of the amplifier arrangement (e.g. linear region or compression region).
Owner:PSEMI CORP
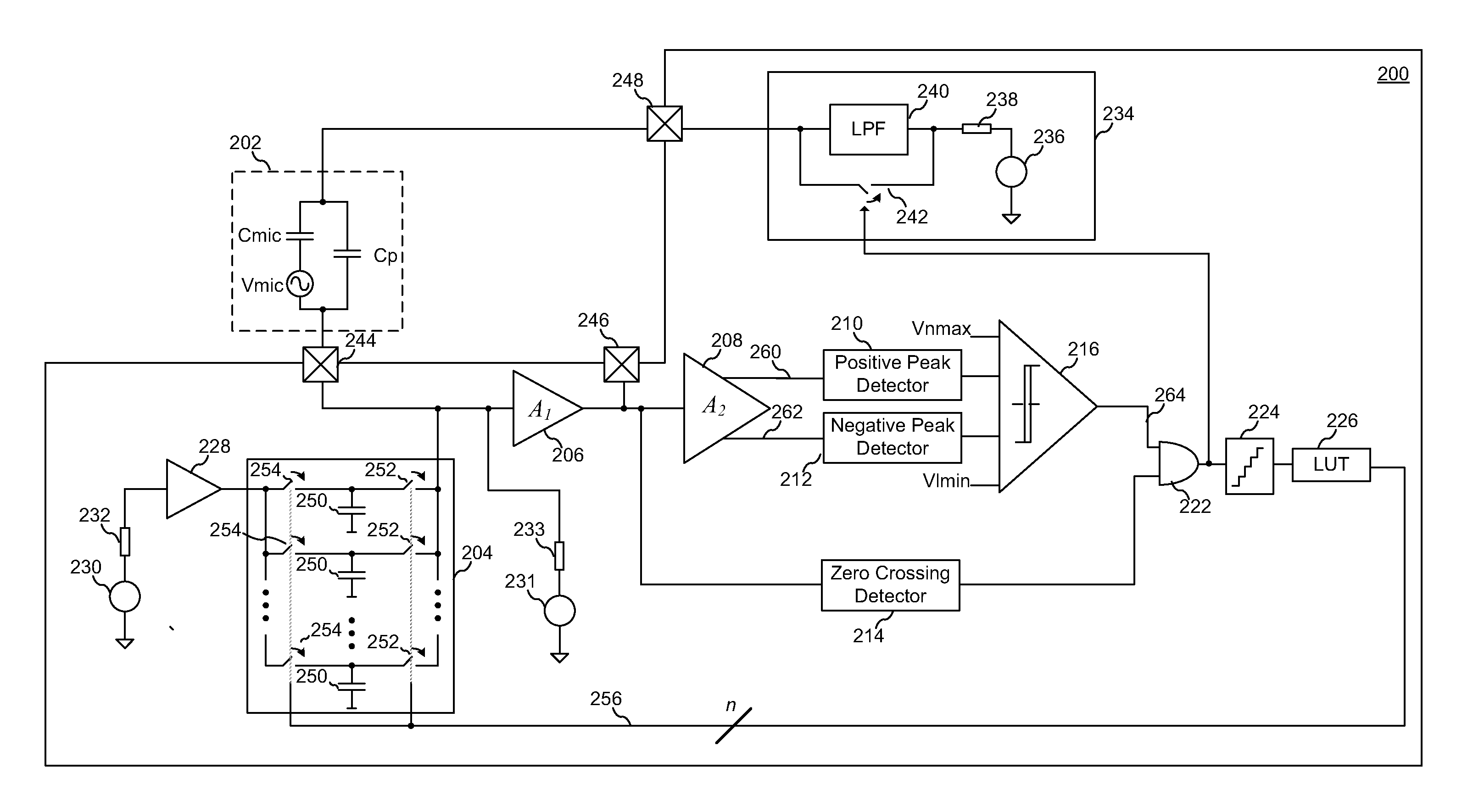
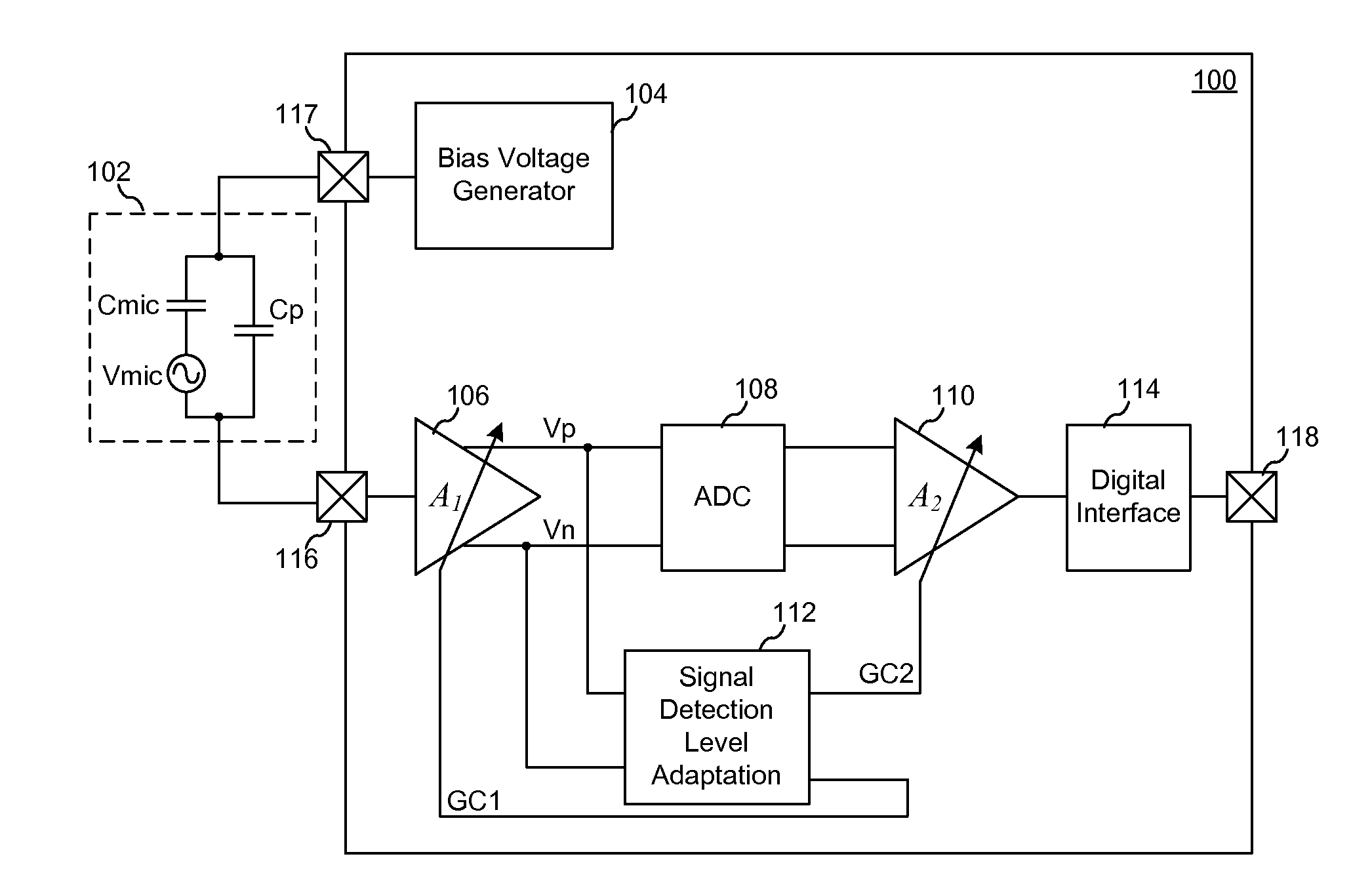
System and Method for Low Distortion Capacitive Signal Source Amplifier
ActiveUS20130051582A1Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationCapacitanceLow distortion
According to an embodiment, a method includes amplifying a signal provided by a capacitive signal source to form an amplified signal, detecting a peak voltage of the amplified signal, and adjusting a controllable impedance coupled to an output of the capacitive signal source in response to detecting the peak voltage. The controllable impedance is adjusted to a value inversely proportional to the detected peak voltage.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
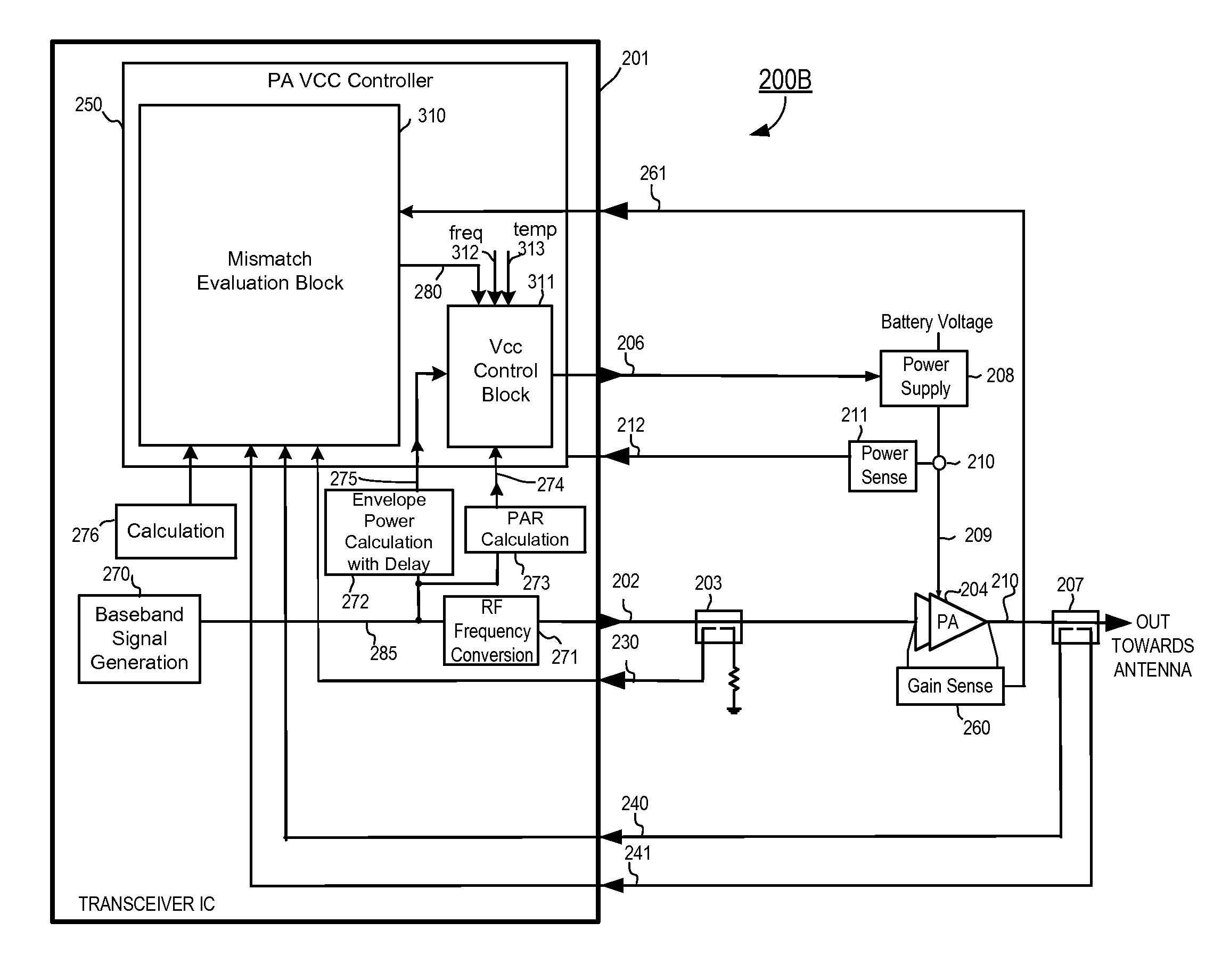
RF power amplifier circuit with mismatch tolerance
ActiveUS8183917B2Improve efficiencyReduce phase distortionHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
Owner:QUANTANCE
Switched-mode power amplifier using lumped element impedance inverter for parallel combining
InactiveUS20050007194A1Effective compensationAmplifier combinationsAmplifier input/output impedence modificationAudio power amplifierParasitic capacitance
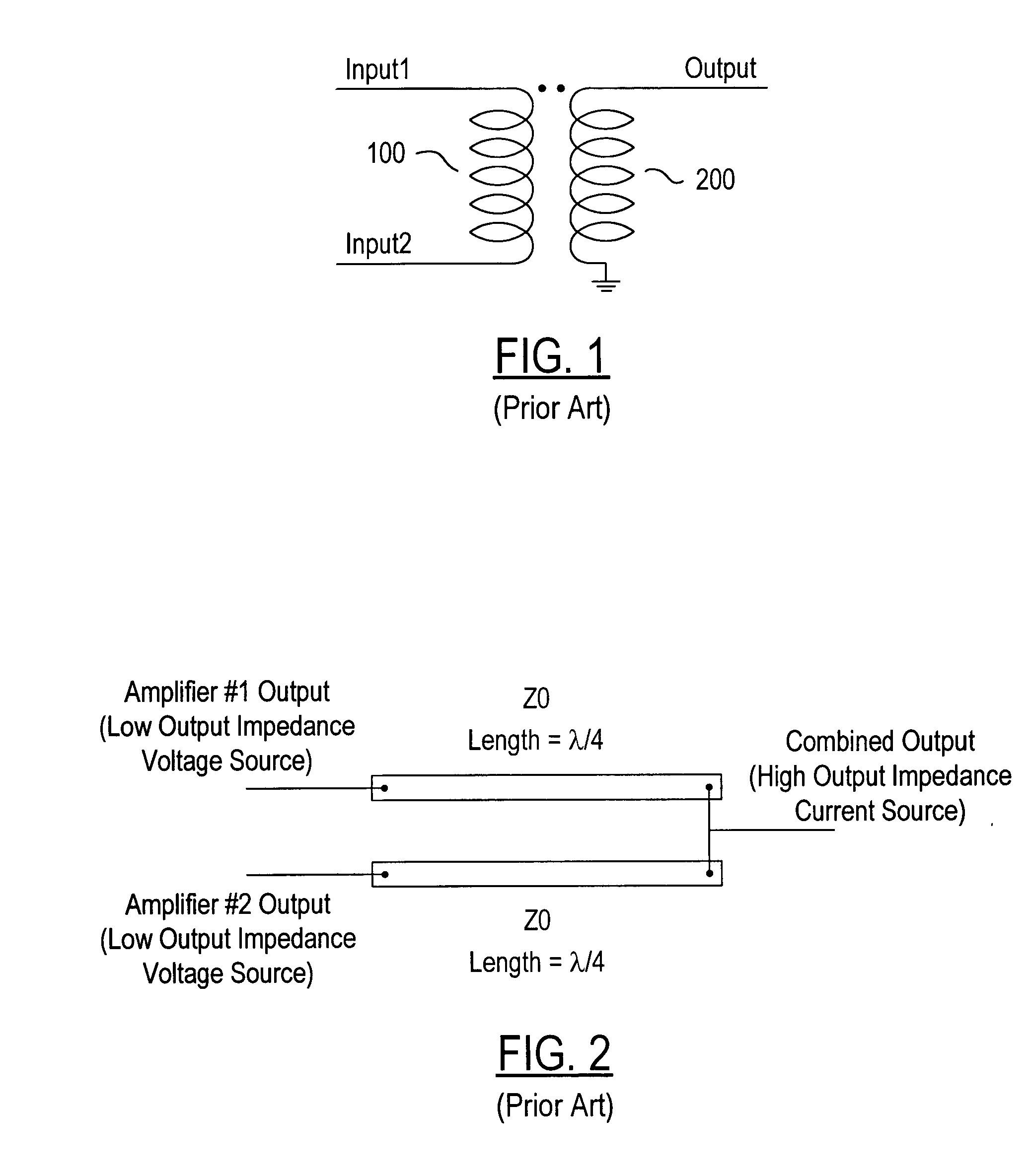
A switched-mode Class F power amplifier is provided for parallel connection with at least one other like amplifier, within a Chireix architecture, for combining the signals output therefrom. An input component includes at least one active device configured to be alternately switched by a signal input thereto to present an amplified signal corresponding to the input signal and constituting a low output impedance voltage source. A lumped element impedance inverter is provided between the input component and an output resonator component, the impedance inverter being configured for transforming the low output impedance voltage source to instead constitute a high output impedance current source configured for said parallel connection. In accordance with the invention, the negative reactive component values required by the impedance inverter are eliminated and effectively provided by incorporating those values into pre-selected reactive components of the input and output components. Further, a source-drain parasitic capacitance across the active device is eliminated by one or more pre-selected reactive components of the input component, the value(s) of which effectively compensate for the parasitic capacitance.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND
Optimization methods for amplifier with variable supply power
ActiveUS9219445B2Amplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionGain controlLinear regionAudio power amplifier
Owner:PSEMI CORP
Low power consumption adaptive power amplifier
ActiveUS7170341B2Gain controlAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierEngineering
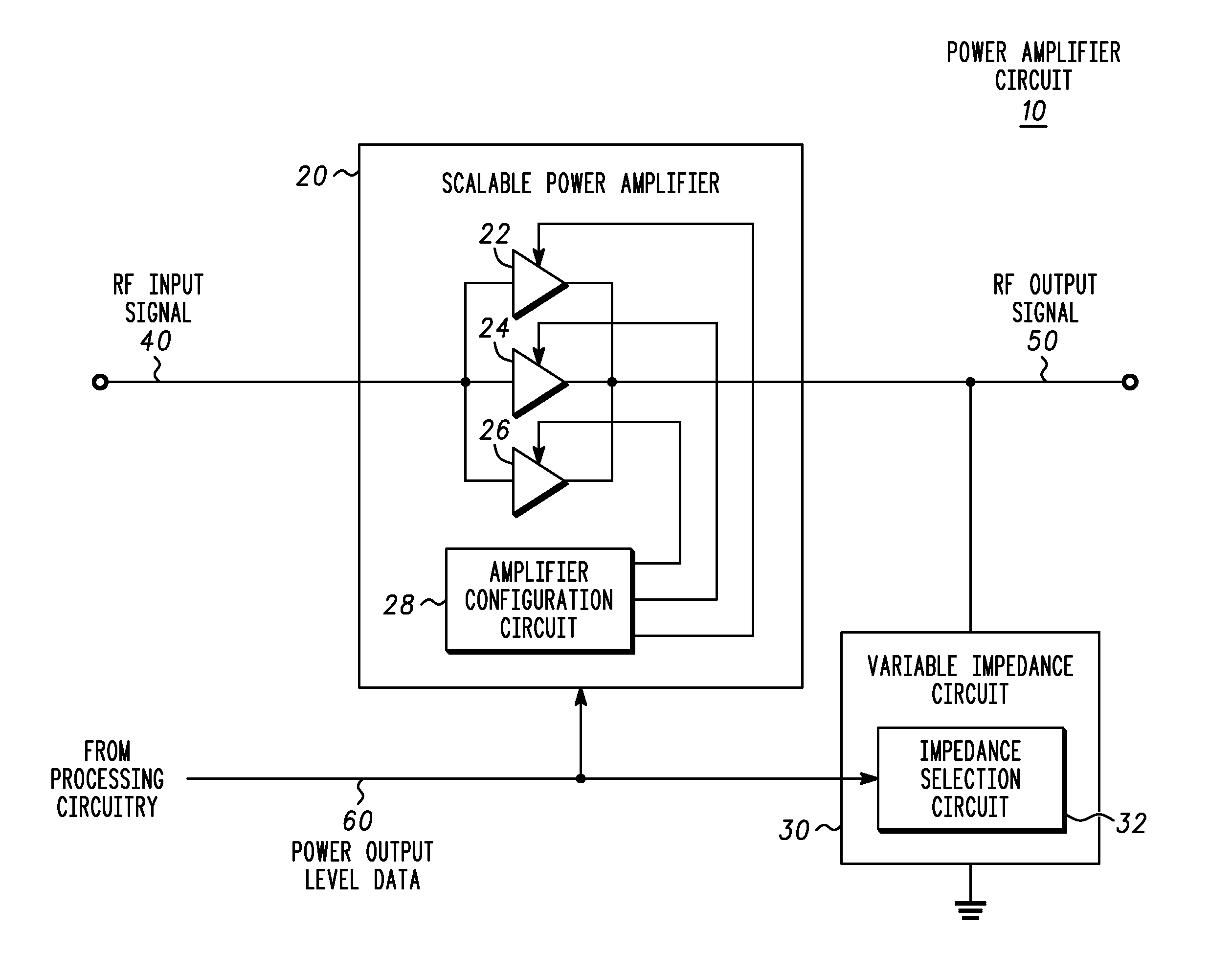
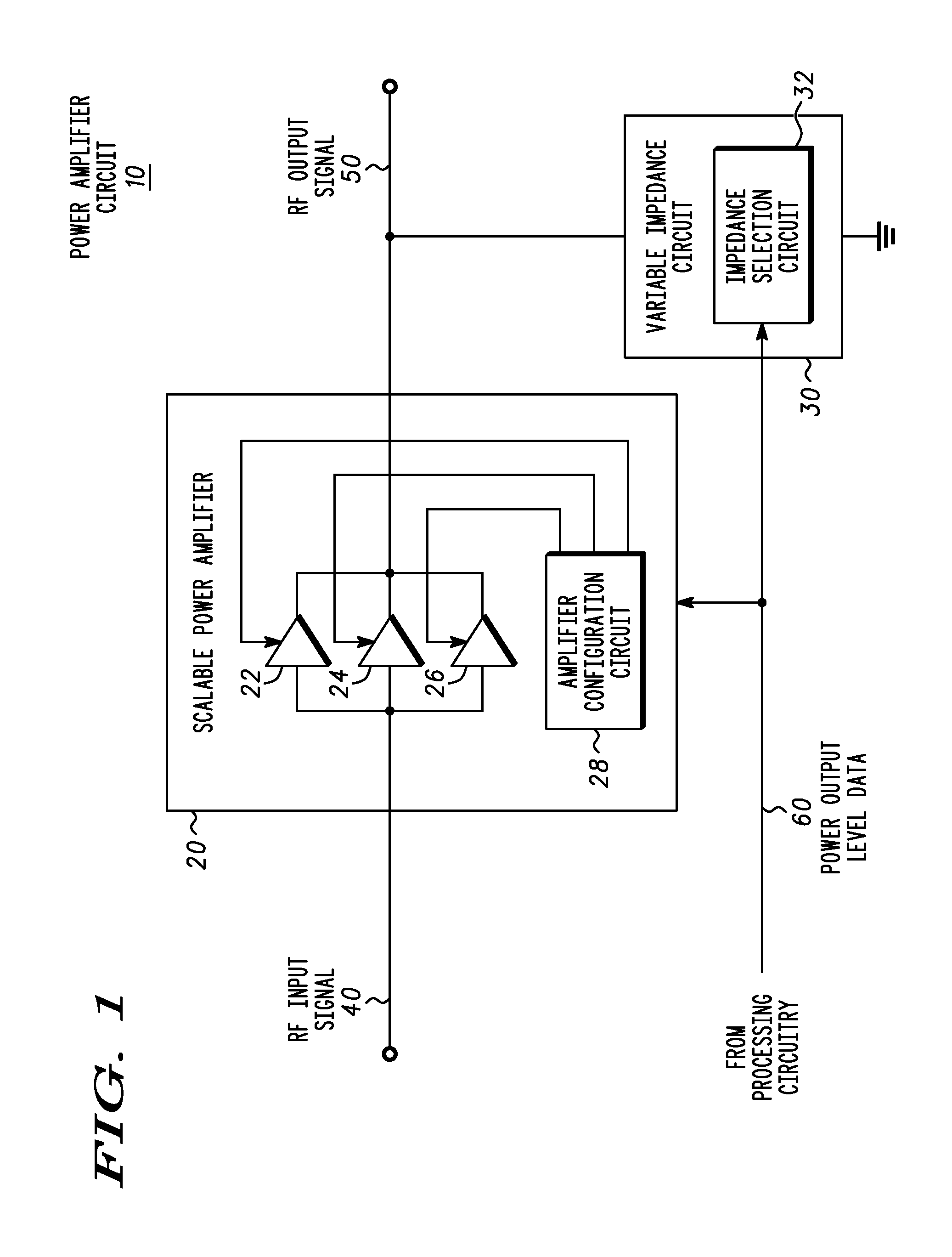
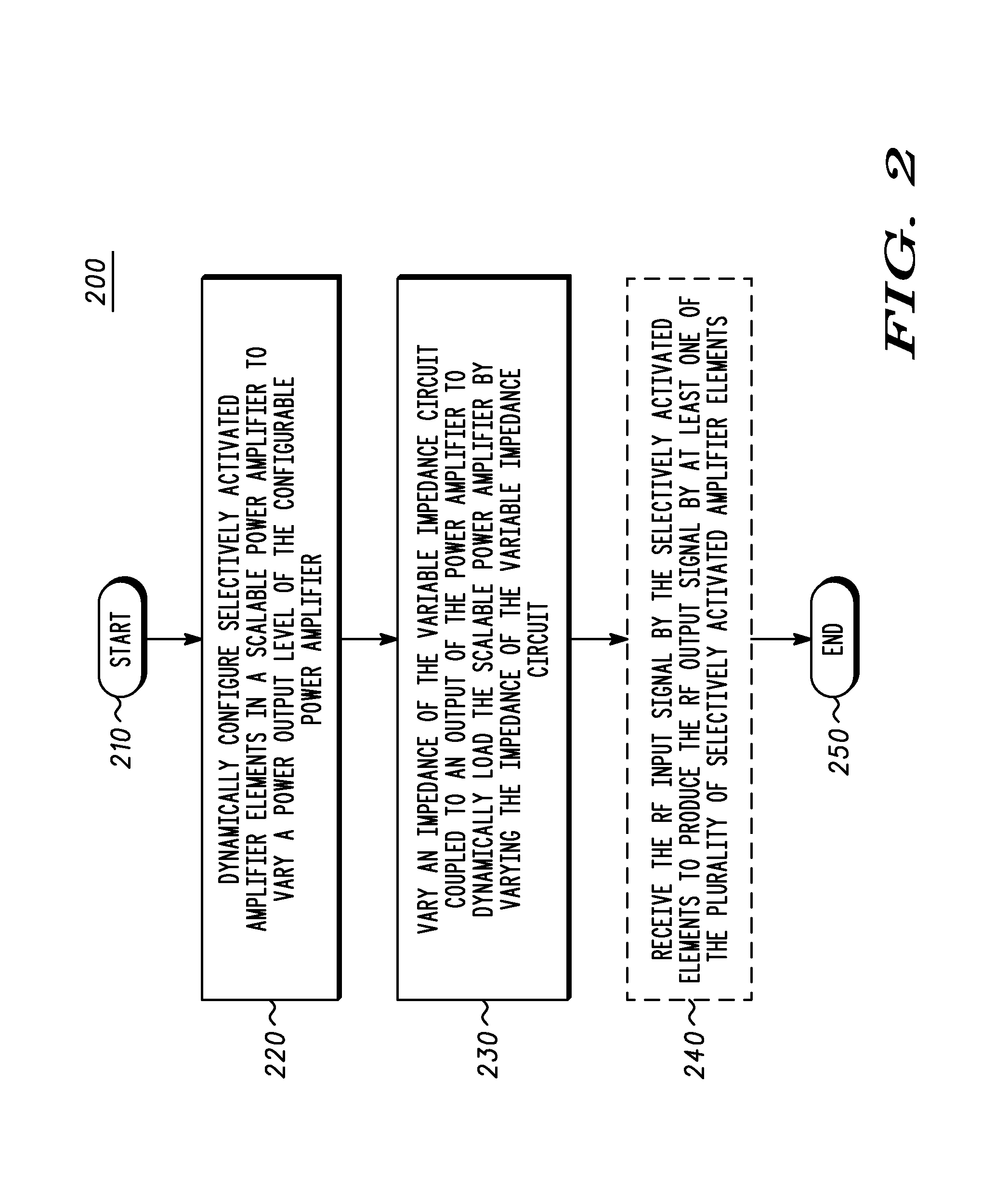
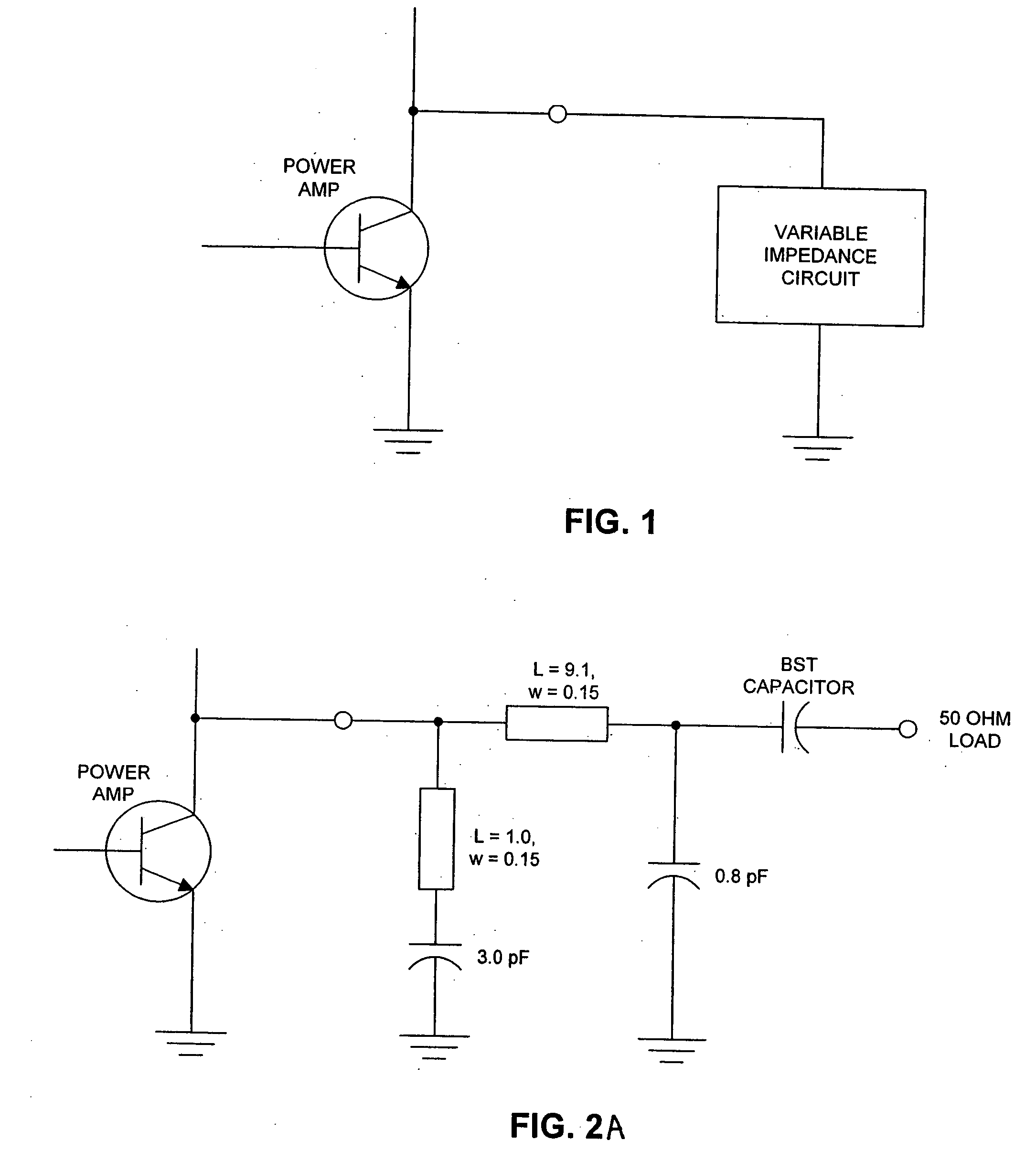
A power amplification circuit (10) includes a scalable power amplifier (20) to produce an RF output signal (50) at an output of the power amplification circuit (10), and a variable impedance circuit (30) coupled to the output of the power amplification circuit (10). The scalable power amplifier (20) includes a plurality of selectively activated amplifier elements (22), (24), (26) to produce the RF output signal (50) in accordance with a desired RF output signal power level. The power amplification circuit (10) selectively activates individual amplifier elements by, for example reducing power or increasing power to at least one amplifier element. The variable impedance circuit (30) varies an impedance of the variable impedance circuit (30) to dynamically load the output of the scalable power amplifier (20).
Owner:GOOGLE TECHNOLOGY HOLDINGS LLC
Tunable microwave devices with auto-adjusting matching circuit
InactiveUS20110063042A1Realize automatic adjustmentMultiple-port networksAmplifiers wit coupling networksHigh pressureDigital signal
An embodiment of the present invention provides an apparatus, comprising an input port and a dynamic impedance matching network capable of determining a mismatch at the input port and dynamically changing the RF match by using at least one matching element that includes at least one voltage tunable dielectric capacitor. The matching network may be a “Pi”, a “T”, or “ladder” type network and the apparatus may further comprise at least one directional coupler capable of signal collection by sampling a portion of an incident signal, a reflected signal or both. In an embodiment of the present invention, the apparatus may also include a control and power control & logic unit (PC LU) to convert input analog signals into digital signals and sensing VSWR phase and magnitude and processing the digital signals using an algorithm to give it a voltage value and wherein the voltage values may be compared to values coming from the coupler and once compared and matched, the values may be passed to a Hi Voltage Application Specific Integrated Circuit (HV ASIC) to transfer and distribute compensatory voltages to the matching network elements. Additional embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Self-tuning variable impedance circuit for impedance matching of power amplifiers
ActiveUS20050130608A1Improve power efficiencyImprove matchResonant long antennasAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationAudio power amplifierSelf-tuning
A self-tuning variable impedance circuit provides improved performance. A variation in the power applied to the variable impedance circuit causes a corresponding change in the impedance of the circuit, resulting in improved performance. For example, the variable impedance circuit may be a matching circuit that “follows” the output power of a power amplifier, thereby increasing the power efficiency of the power amplifier.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Dynamic stability, gain, efficiency and impedance control in a linear/non-linear CMOS power amplifier
A power amplifier (PA) provides dynamic stability and gain control for linear and non-linear operation. The PA operates with a baseband processor and a transmitter, in which the PA receives a signal from the transmitter for power amplification prior to transmission of the signal. The PA is configured to select between the linear mode of operation and the non-linear mode of operation, in which device scaling within the PA is achieved by changing a device sizing of at least one stage of the PA. Further to changing the device size, the PA changes biasing resistance and impedance of a matching network in response to the changing of the device size to control power output and stability for the PA.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Control Systems and Methods for Power Amplifiers Operating in Envelope Tracking Mode
ActiveUS20140184337A1Improve stabilityReduce oscillationPower amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierControl system
Control systems and methods for power amplifiers operating in envelope tracking mode are presented. A set of corresponding functions and modules are described and various possible system configurations using such functions and modules are presented.
Owner:PSEMI CORP
RF power amplifier circuit with mismatch tolerance
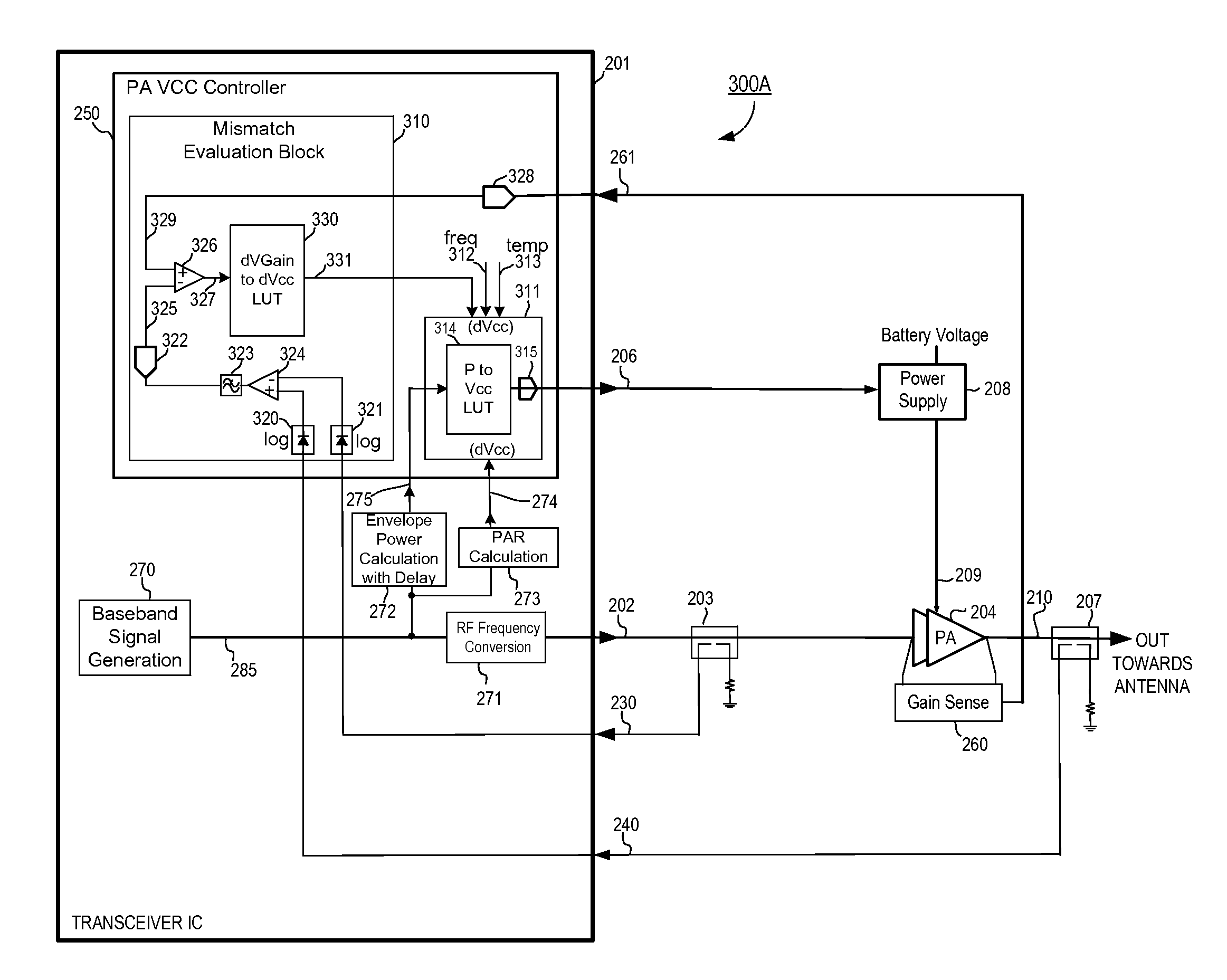
ActiveUS20110298539A1Efficiency of PA is improvedImprove efficiencyHigh frequency amplifiersGain controlAudio power amplifierControl signal
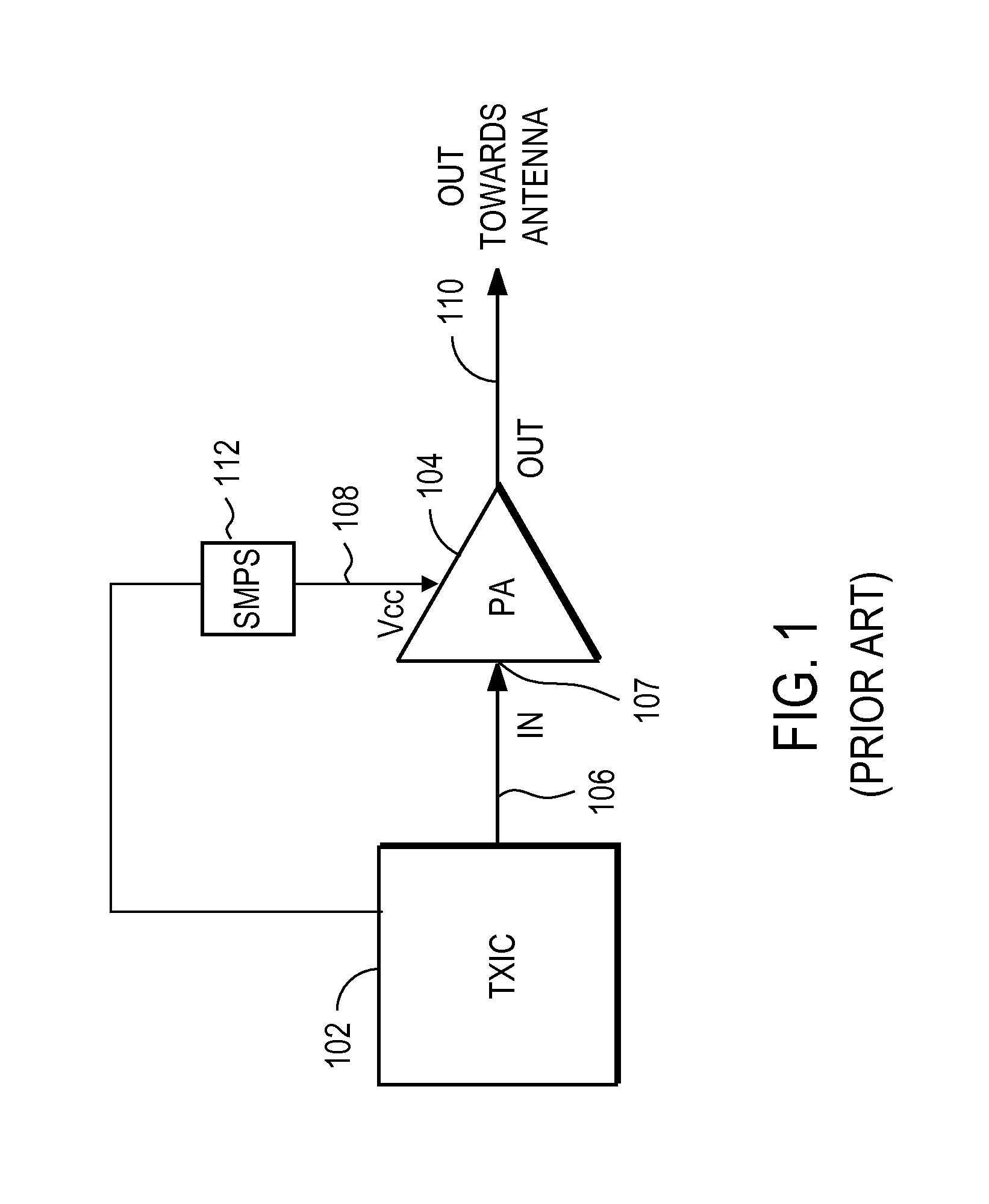
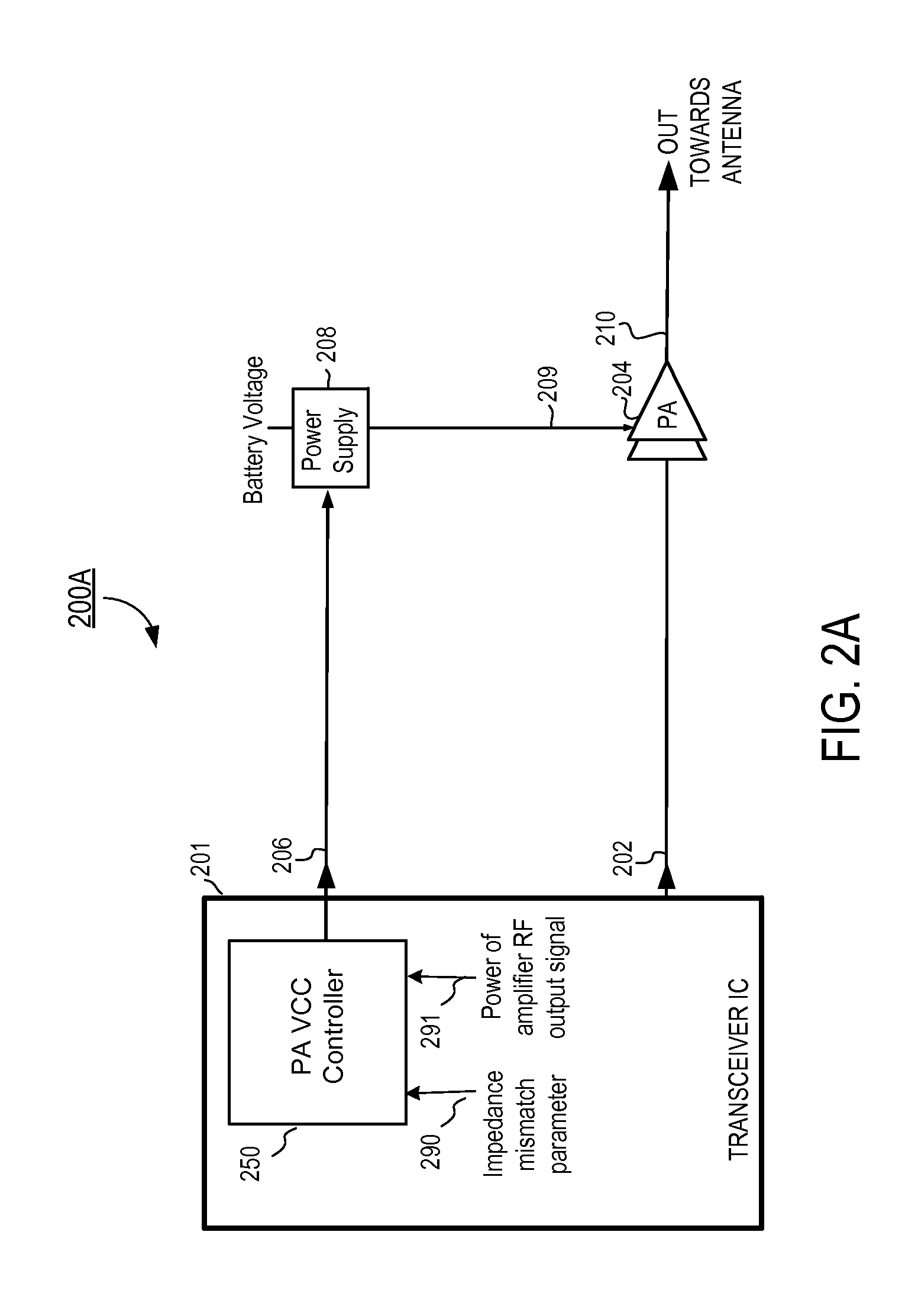
A radio frequency (RF) power amplifier system adjusts the supply voltage provided to a power amplifier (PA) adaptively, responsive to the measured or estimated power of the RF output signal of the PA. The RF PA system includes a power amplifier (PA) which receives and amplifies an RF input signal to generate an RF output signal at a level suitable for transmission to an antenna. A PA supply voltage controller generates a supply voltage control signal, which is used to control the supply voltage to the final stage of the PA. The supply voltage control signal is generated responsive to the measured or estimated power of the PA RF output signal, and also may be responsive to a parameter indicative of impedance mismatch experienced at the PA output. By controlling this supply voltage to the RF PA, the efficiency of the PA is improved.
Owner:QUANTANCE
Wireless electric field power transmission system and method
ActiveUS20130147427A1Prevent electromagnetic field (EMF) leakageIncrease the electric field strengthNear-field transmissionElectromagnetic wave systemElectrical conductorTransfer system
A wireless electric field power transmission system comprises: a transmitter comprising a transmitter antenna, the transmitter antenna comprising at least two conductors defining a volume therebetween; and at least one receiver, wherein the transmitter antenna transfers power wirelessly via electric field coupling when the at least one receiver is within the volume.
Owner:SOLACE POWER INC
Using degeneration in an active tunable low-noise radio frequency bandpass filter
ActiveUS8314653B1Easy to FeedbackReduce gainSwitched capacitor networksAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesLow noiseBandpass filtering
The present disclosure relates to a first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter that includes at least a first transistor element and a tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit coupled to a first non-inverting output of the first transistor element. The first active tunable low-noise RF bandpass filter combines low noise amplifier (LNA) and tunable bandpass filter functionalities into a single active RF bandpass filter. The tunable frequency selective degeneration circuit uses degeneration at frequencies outside of a passband of the active RF bandpass filter to increase feedback, thereby decreasing gain of the active RF bandpass filter. By decreasing the gain, linearity of the active RF bandpass filter may be improved in the presence of strong interfering RF signals, thereby enabling elimination of passive bandpass filter elements, such as surface acoustic wave (SAW) and bulk acoustic wave (BAW) filters, without degrading reception of in-band RF signals.
Owner:QORVO US INC
Adaptive radio transceiver with floating MOSFET capacitors
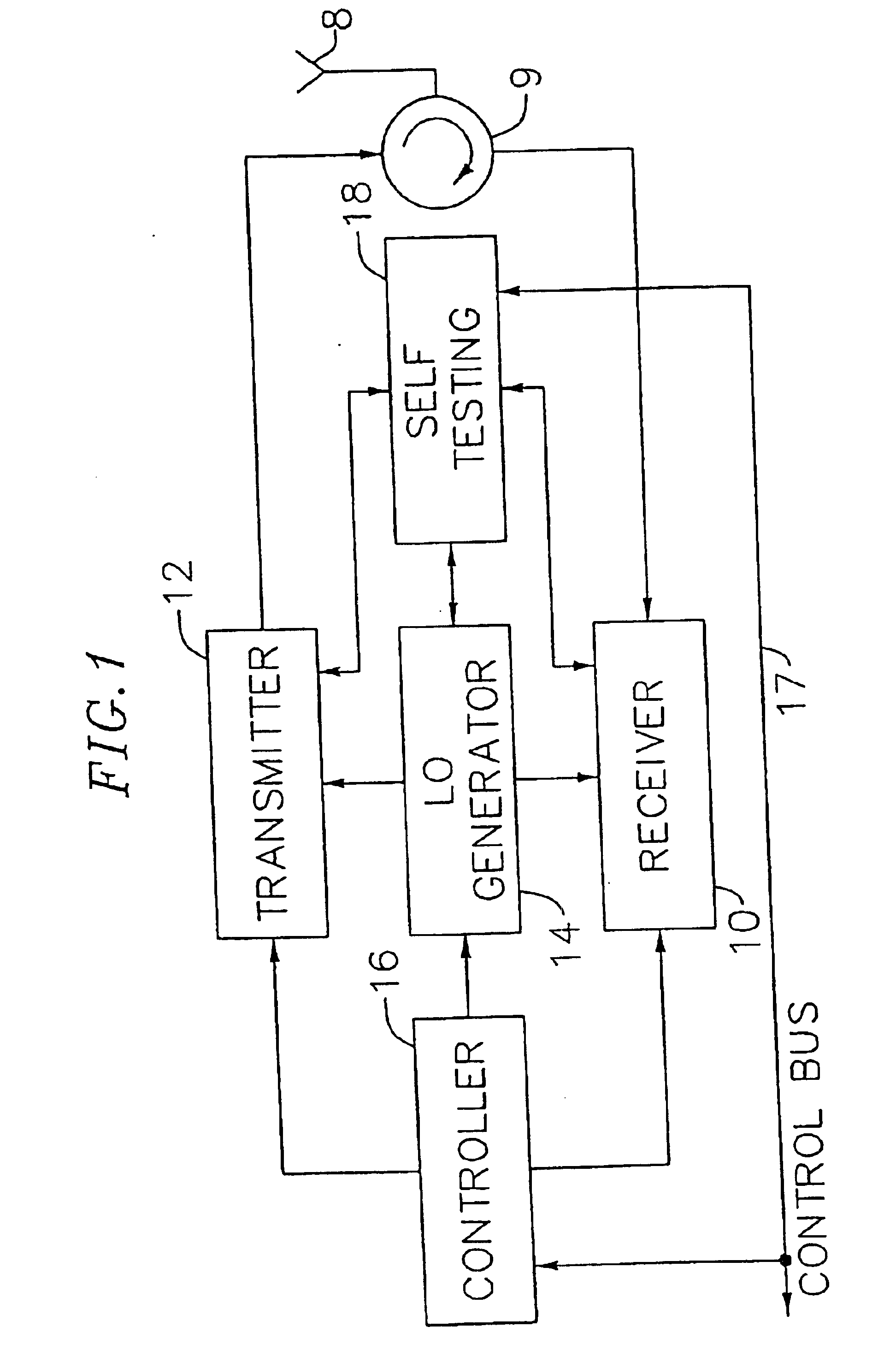
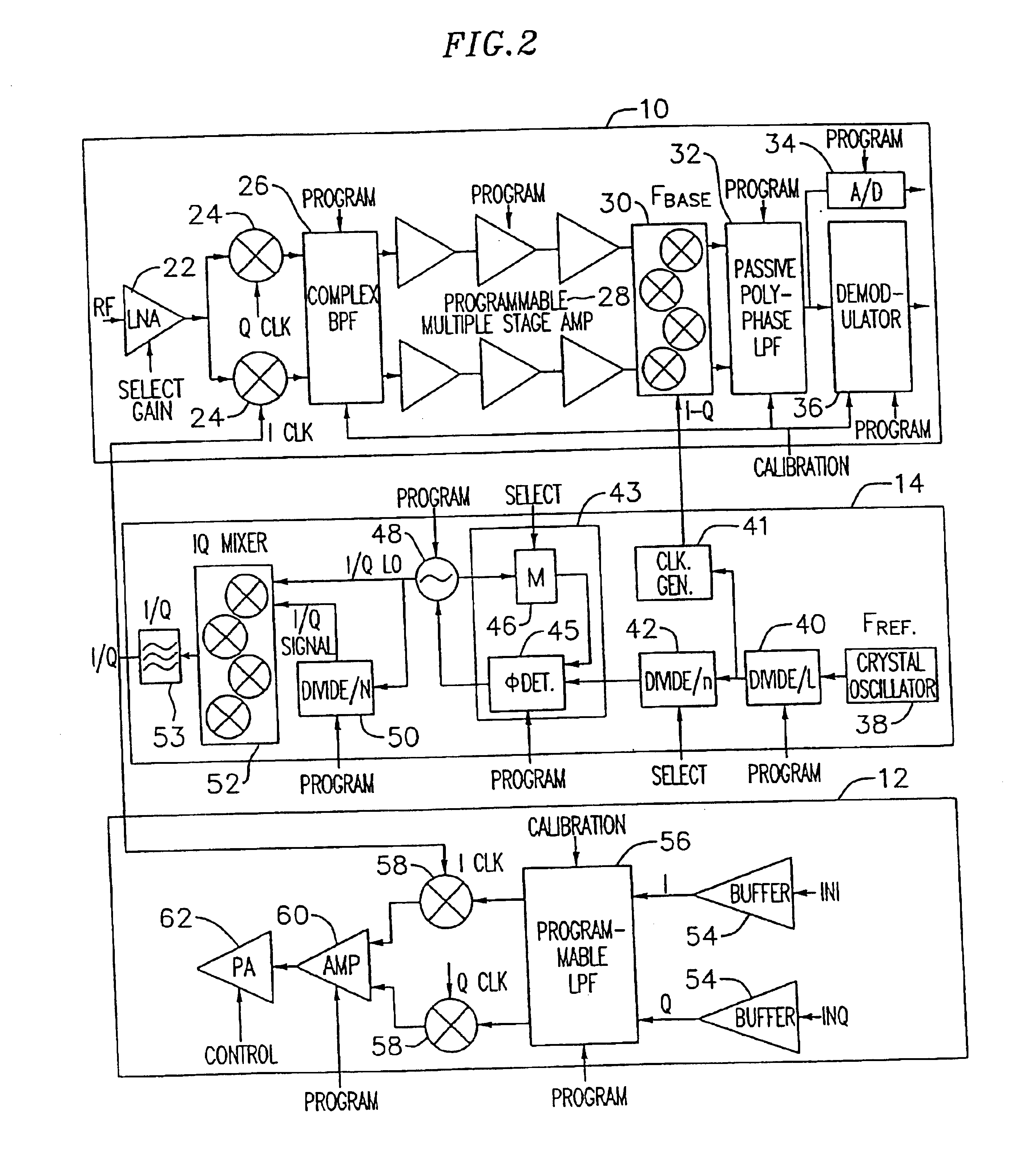
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention described and shown in the specification and drawings is a transceiver with a receiver, a transmitter, a local oscillator (LO) generator, a controller, and a self-testing unit. All of these components can be packaged for integration into a single IC including components such as filters and inductors. The controller for adaptive programming and calibration of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. The self-testing unit generates is used to determine the gain, frequency characteristics, selectivity, noise floor, and distortion behavior of the receiver, transmitter and LO generator. It is emphasized that this abstract is provided to comply with the rules requiring an abstract which will allow a searcher or other reader to quickly ascertain the subject matter of the technical disclosure. It is submitted with the understanding that it will not be used to interpret or limit the scope or the meaning of the claims.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
System and Method for High Input Capacitive Signal Amplifier
ActiveUS20130271307A1Electric signal transmission systemsVolume compression/expansion having semiconductor devicesCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
In accordance with an embodiment, a method includes determining an amplitude of an input signal provided by a capacitive signal source, compressing the input signal in an analog domain to form a compressed analog signal based on the determined amplitude, converting the compressed analog signal to a compressed digital signal, and decompressing the digital signal in a digital domain to form a decompressed digital signal. In an embodiment, compressing the analog signal includes adjusting a first gain of an amplifier coupled to the capacitive signal source, and decompressing the digital signal comprises adjusting a second gain of a digital processing block.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
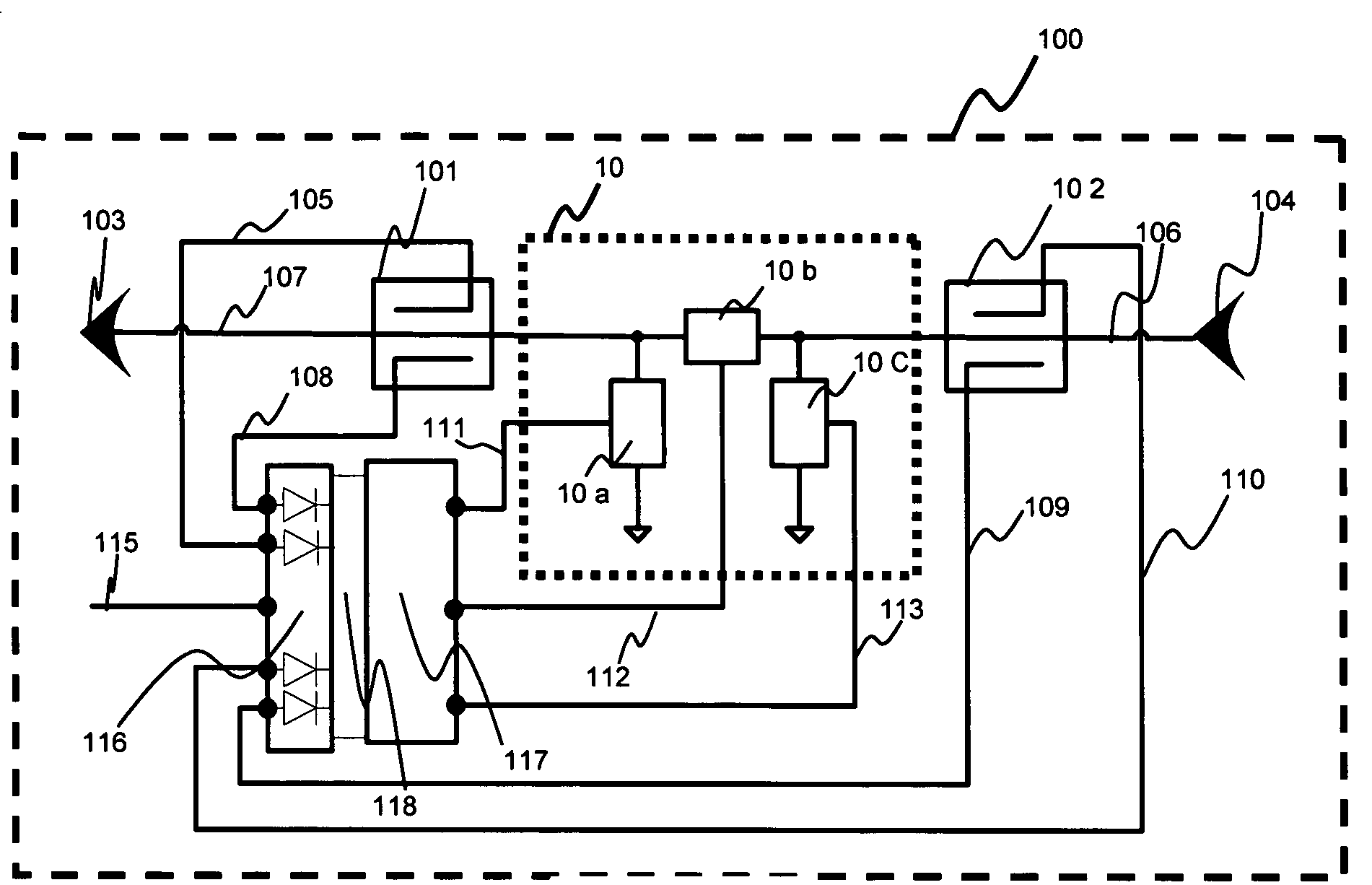
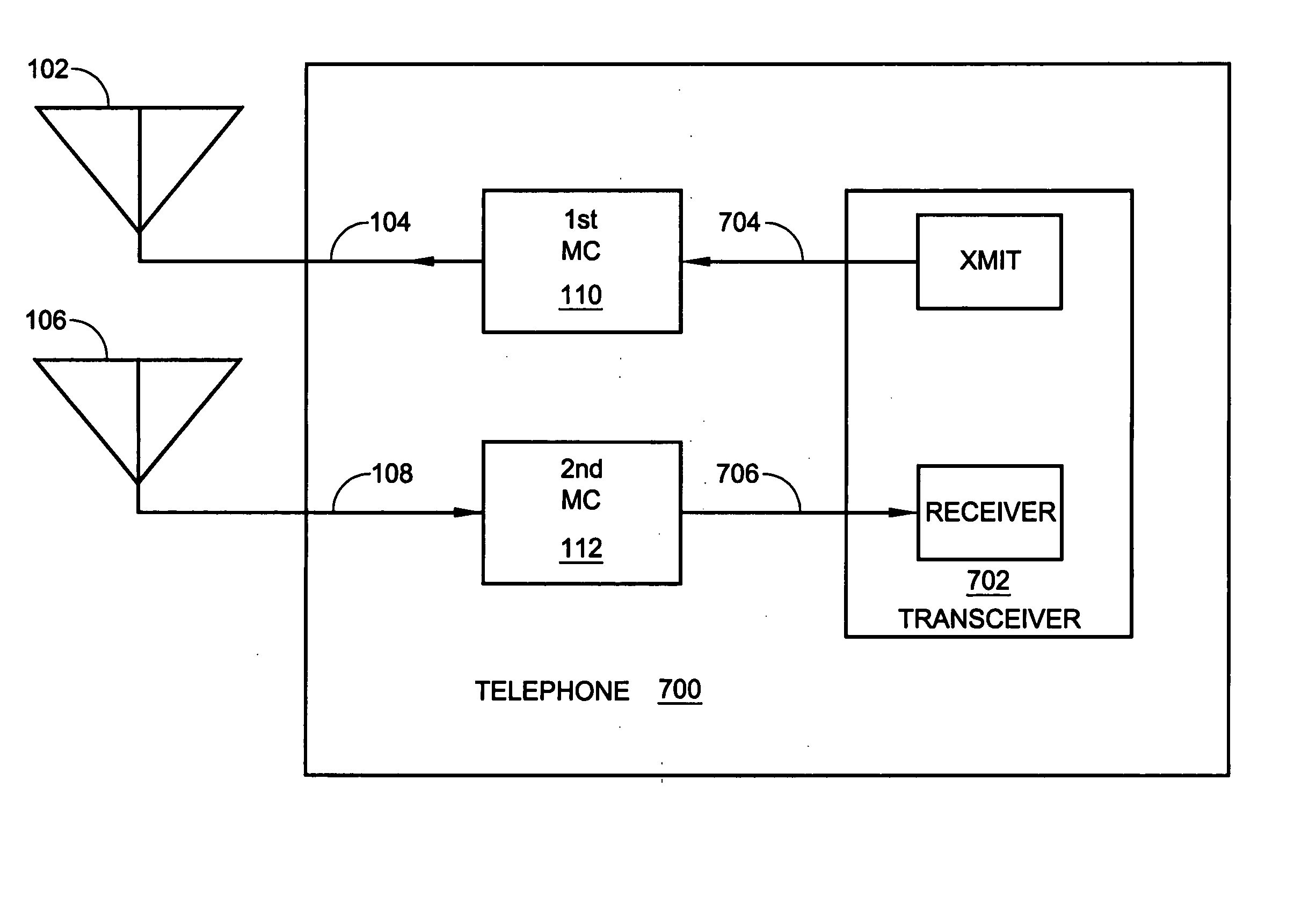
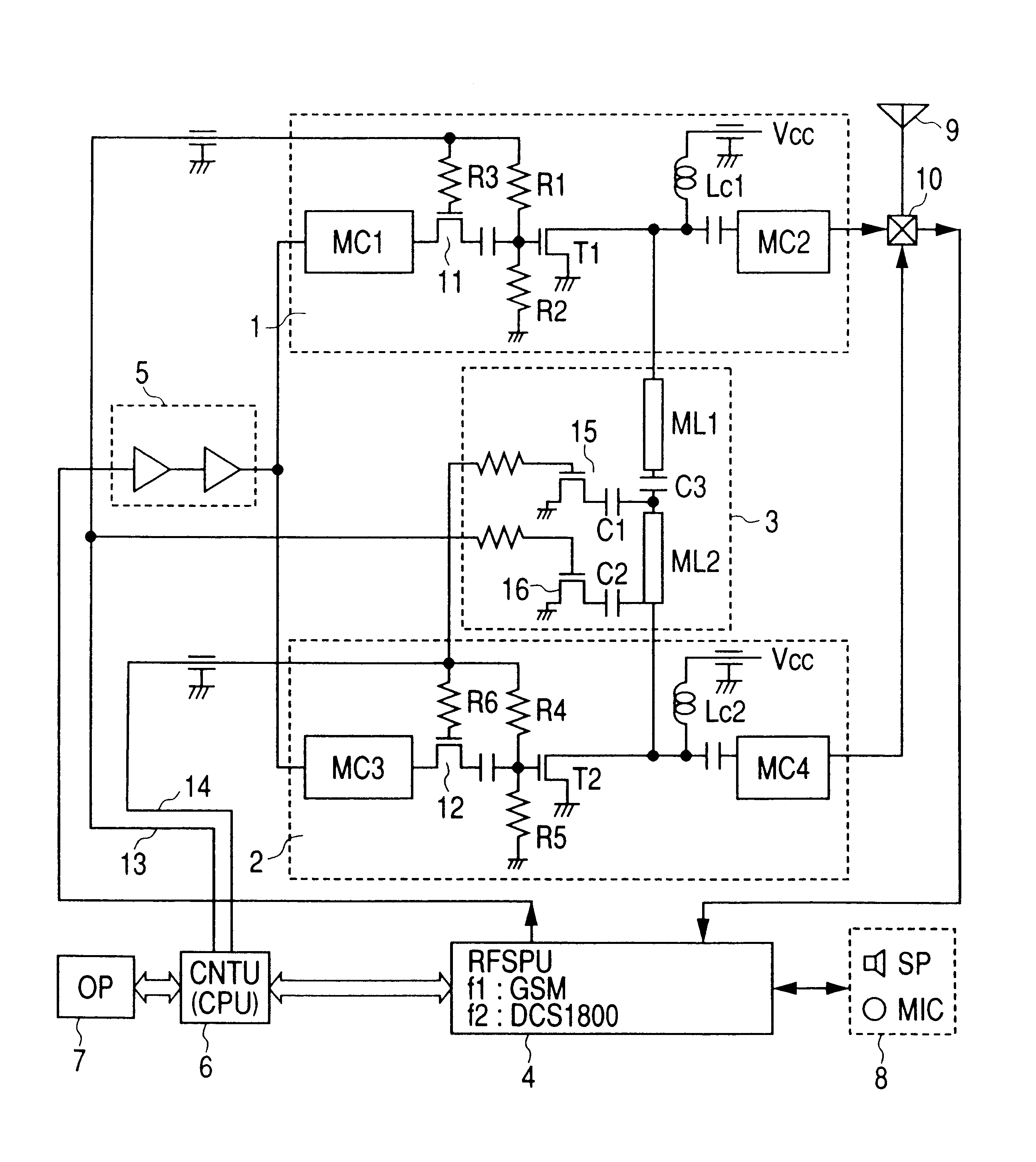
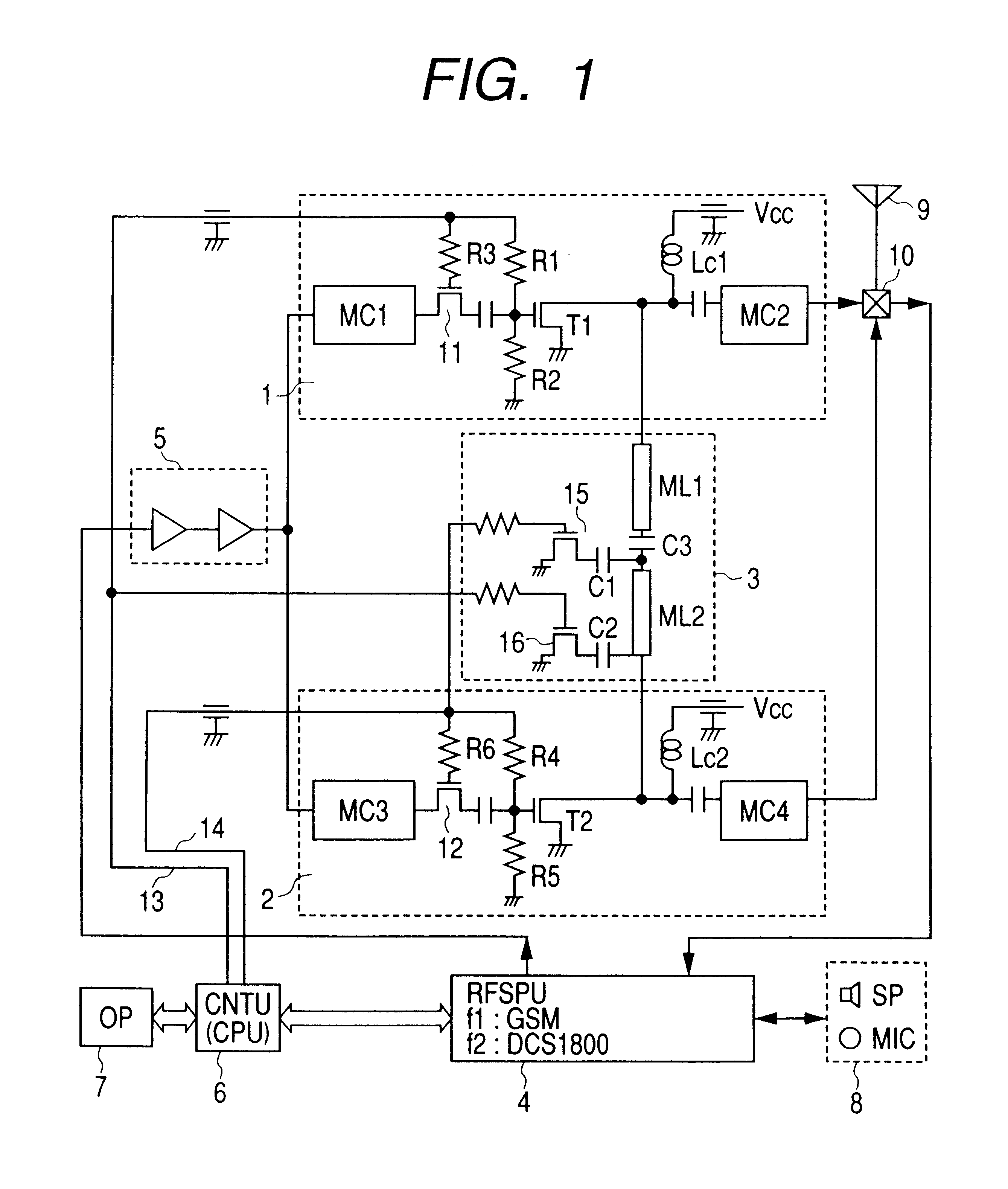
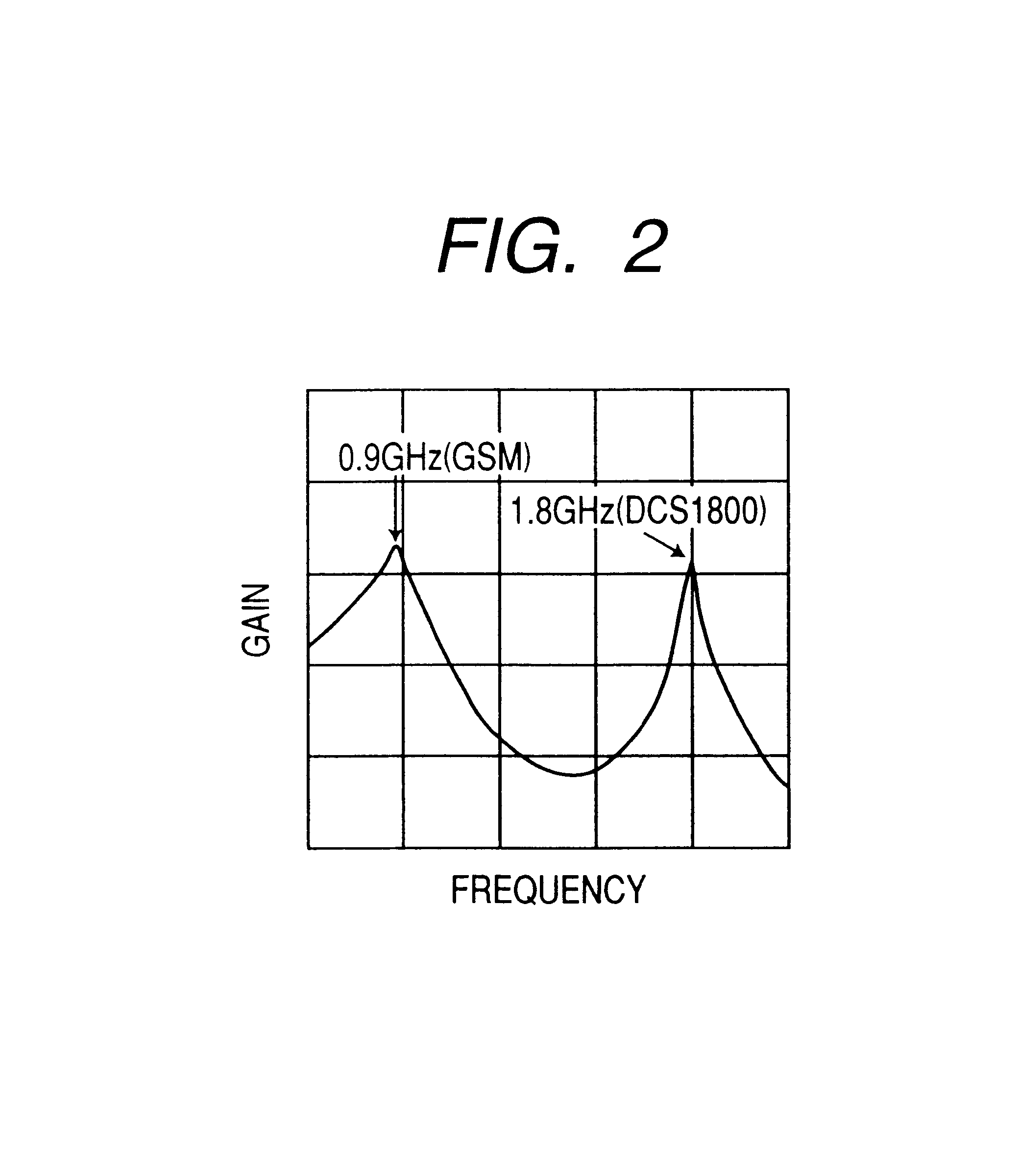
Mobile telephone apparatus
InactiveUS6865399B2Efficient outputMost efficientResonant long antennasGated amplifiersCommunications systemControl signal
In a mobile telephone apparatus corresponding to dual-band provided with an RF power module to operate in two kinds of different frequencies, a common harmonics control circuit is provided to the output circuit of such RF power module to realize higher efficiency in view of controlling respective harmonics power for both band frequencies. Moreover, a means for selectively setting the bias is also provided so that the maximum efficiency can be attained depending on the output power required with respective communication systems with the bias control signal output from the CPU of the control unit interlocking with selection of frequency of the mobile telephone apparatus body.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com