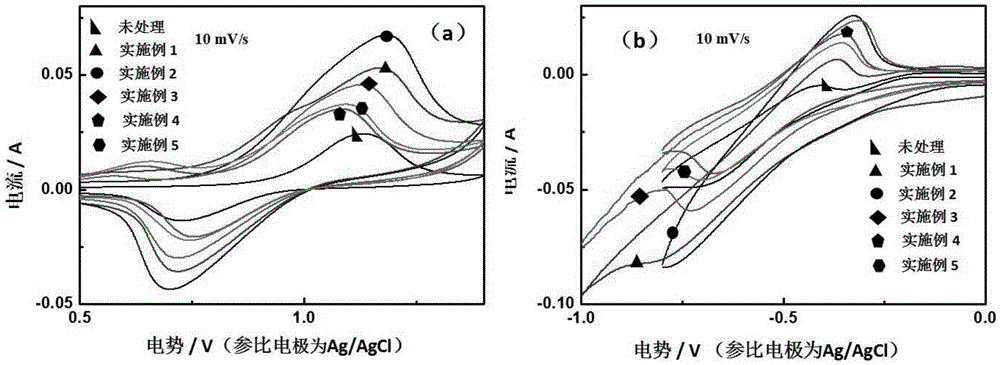
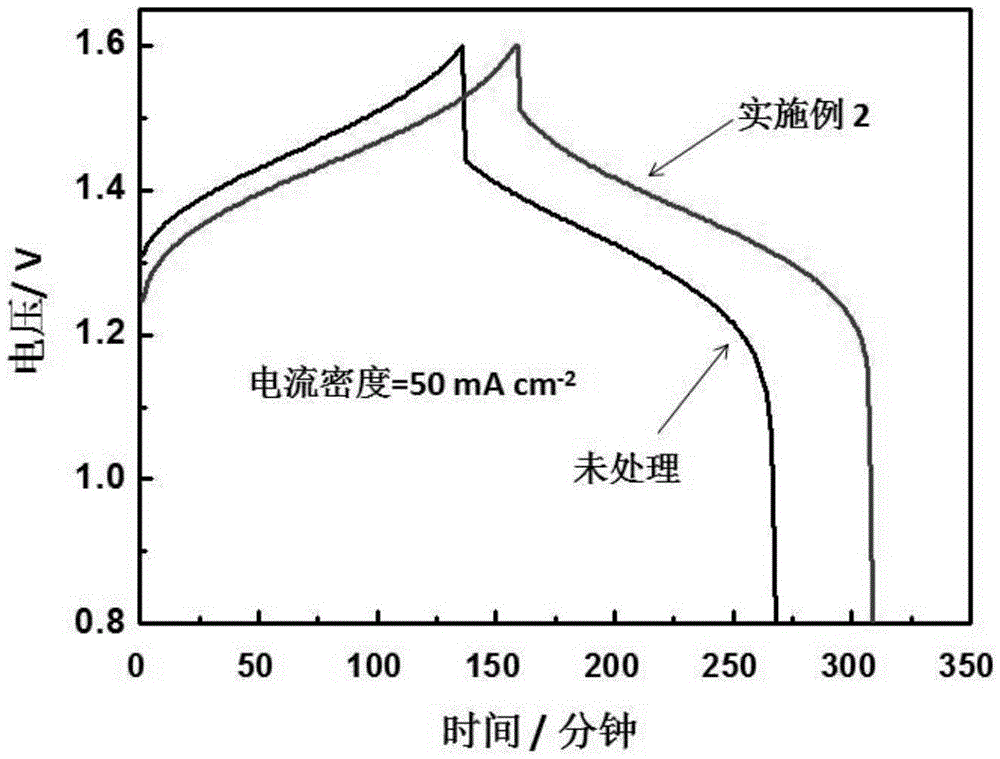
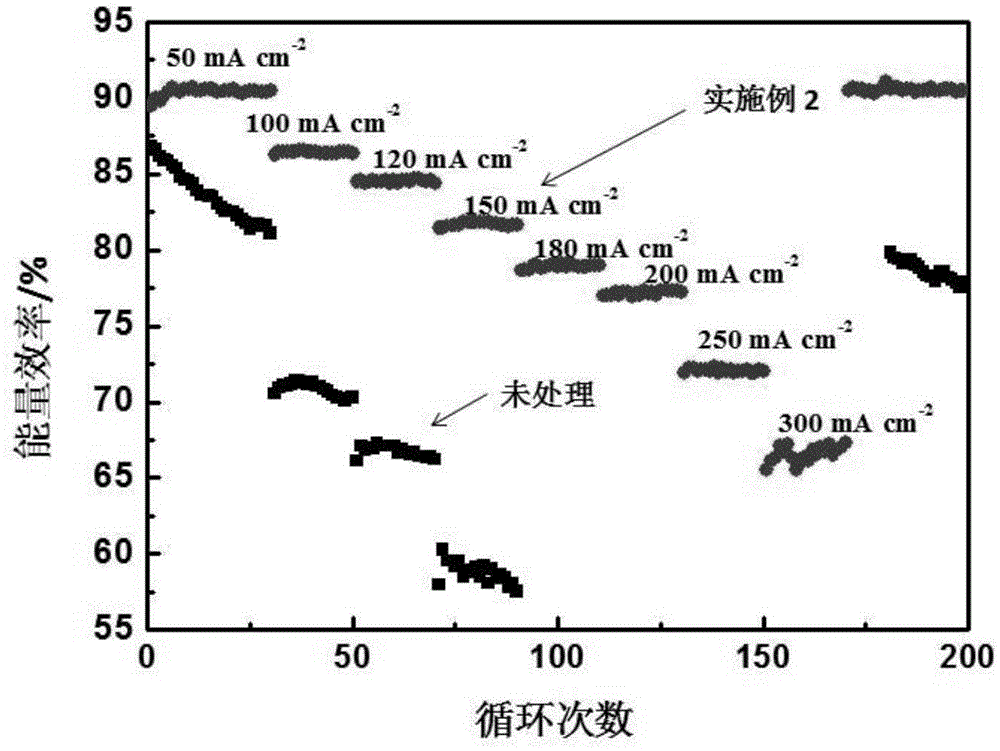
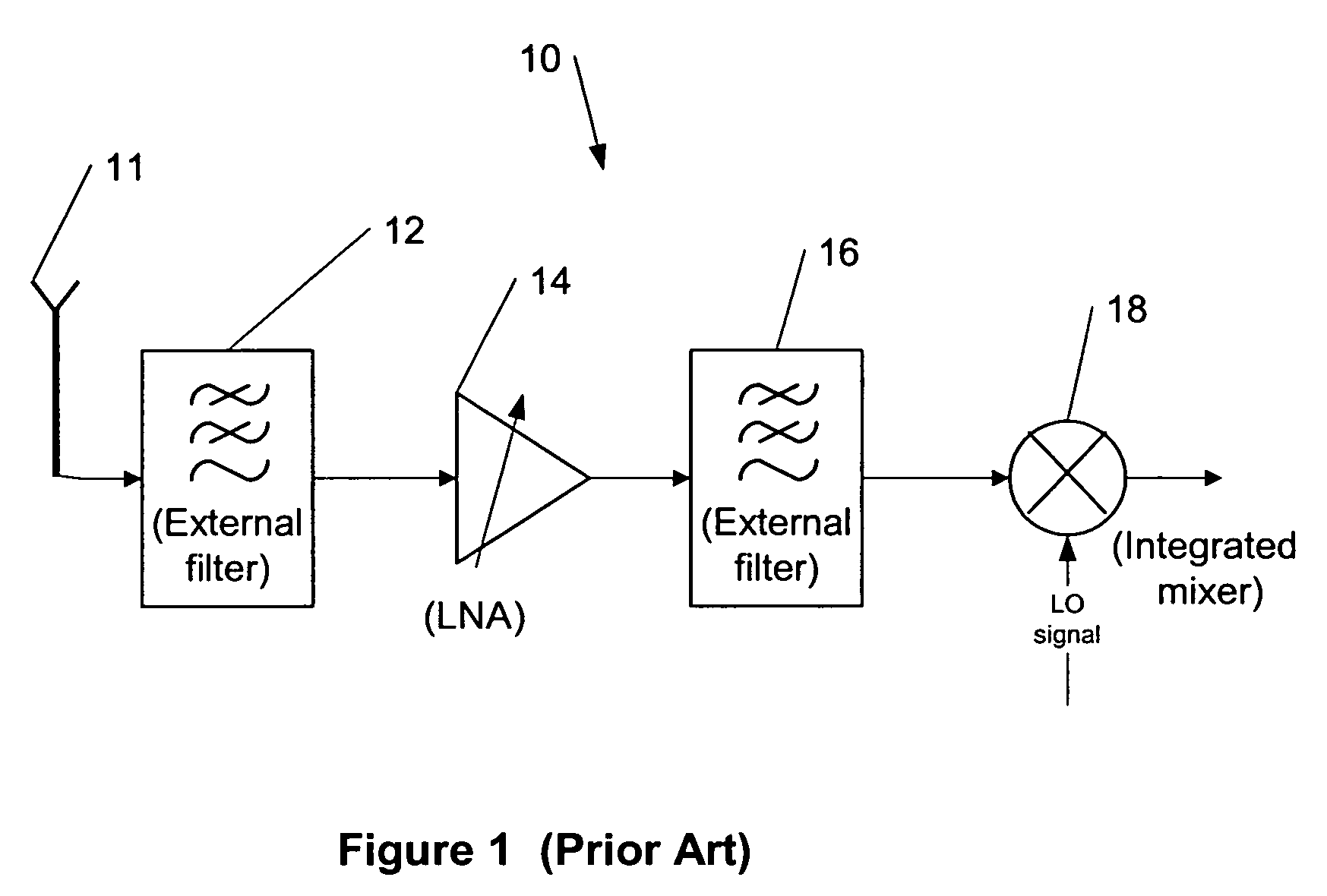
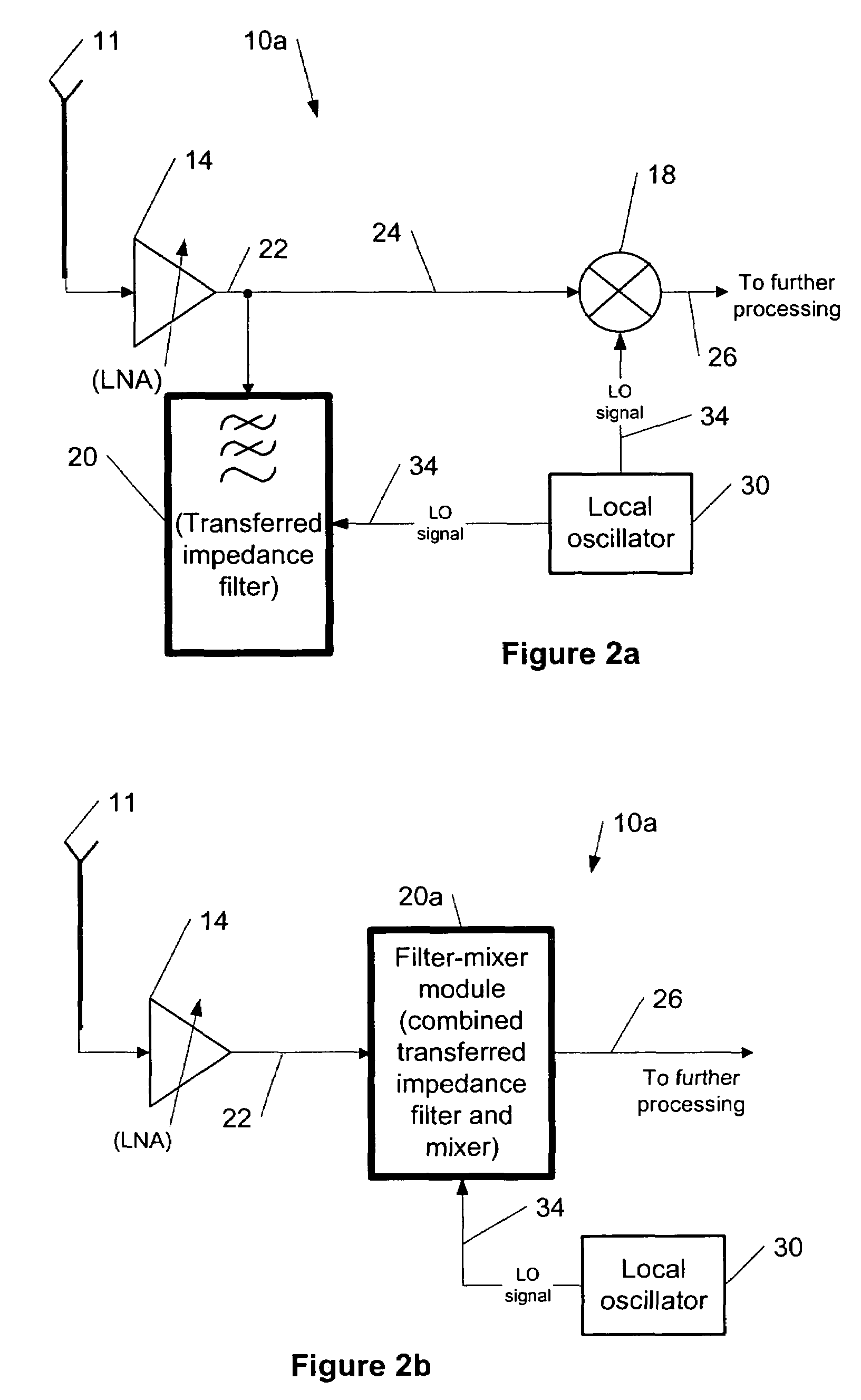
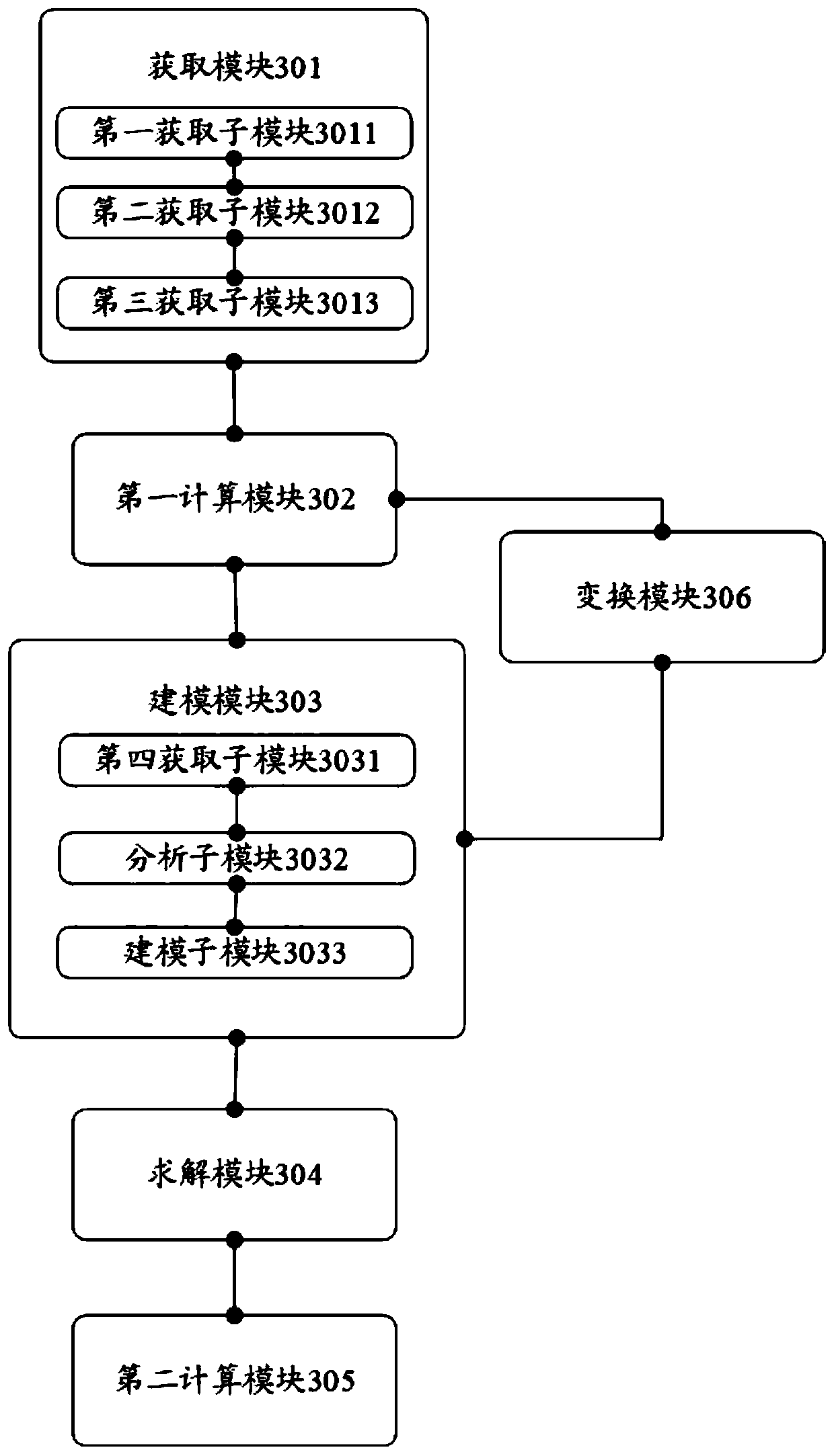
Patents
Literature
132 results about "Transfer impedance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
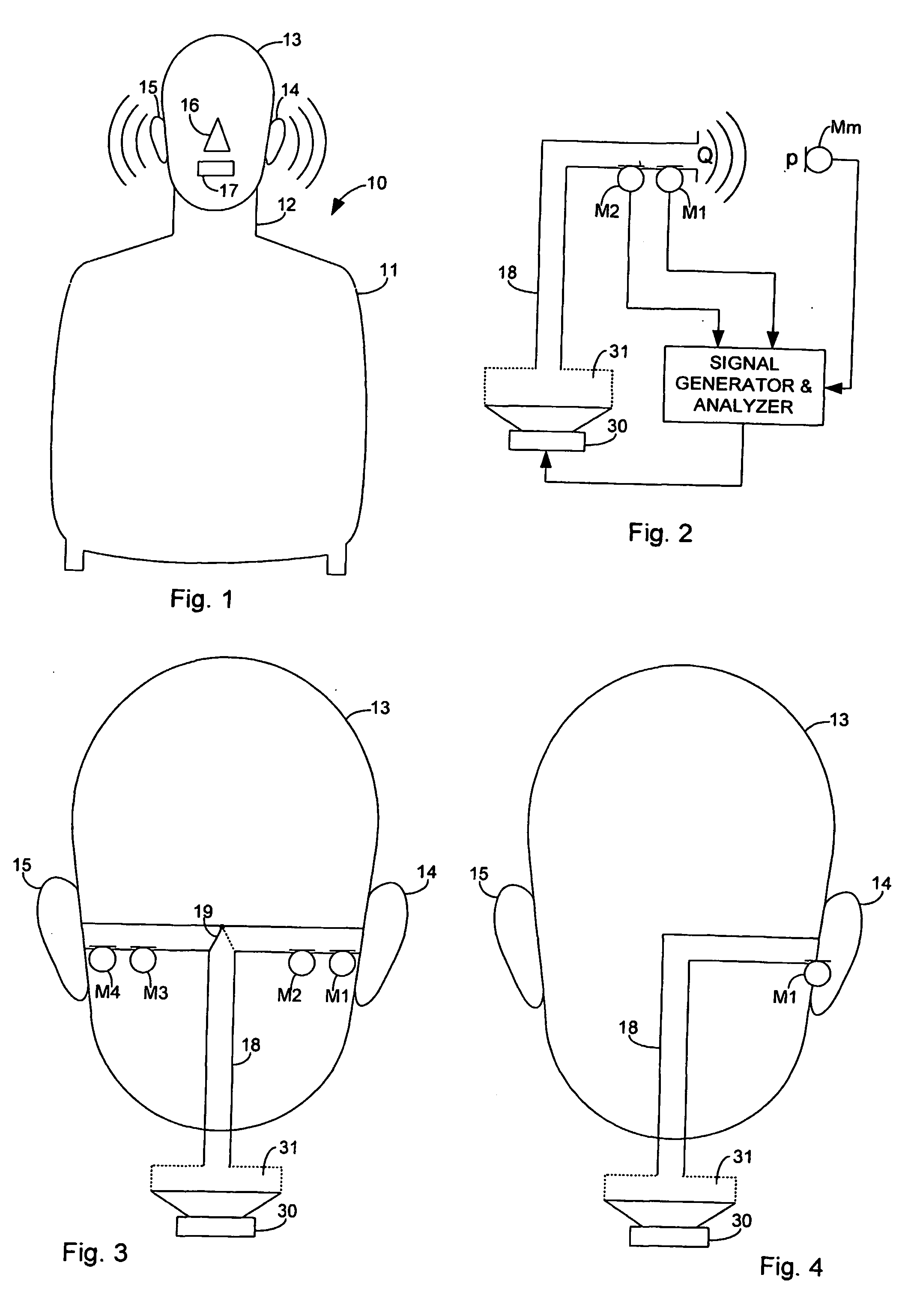
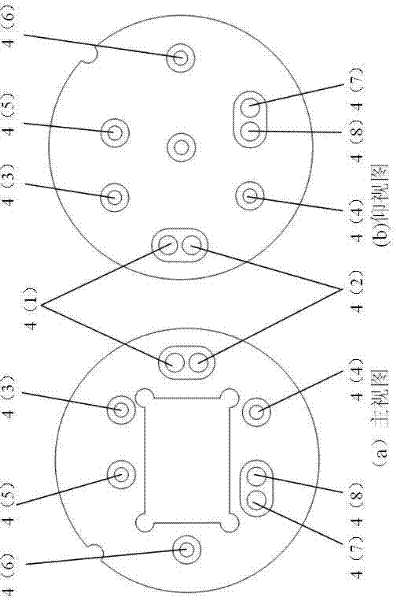
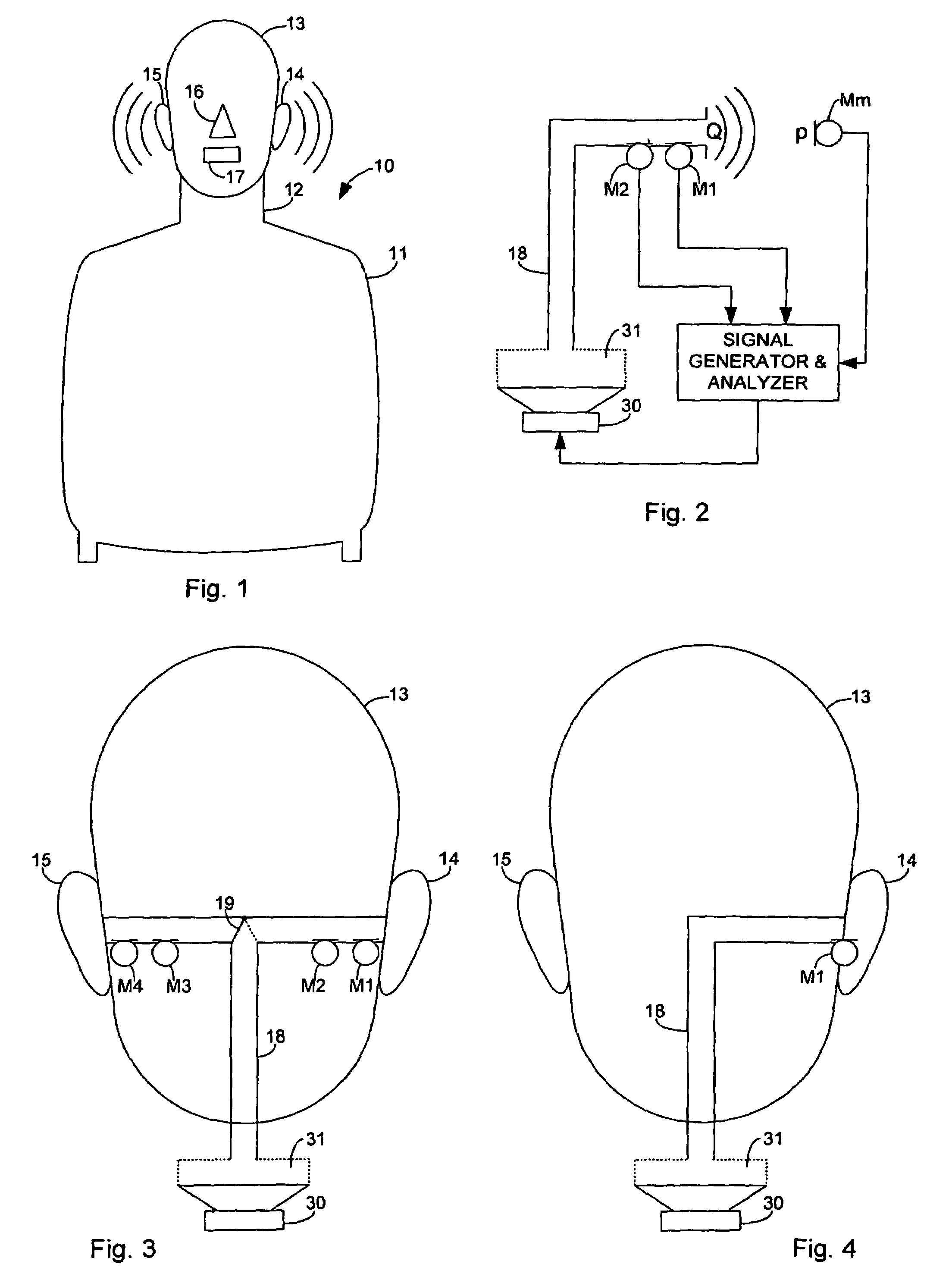
Transfer impedance measurement instrument system
InactiveUS6230105B1Electric cable installationsMeasuring interference from external sourcesMeasuring instrumentEngineering
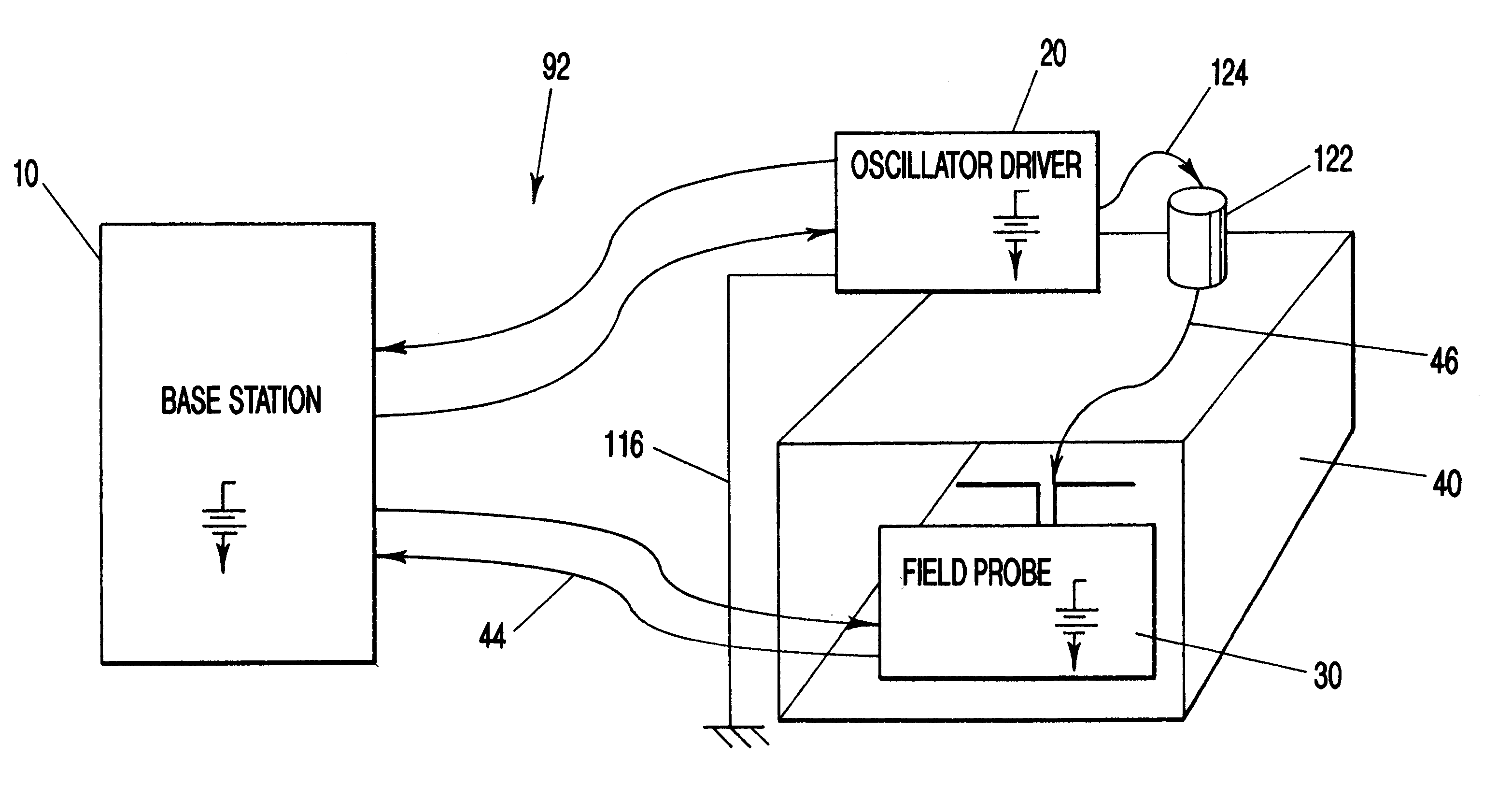
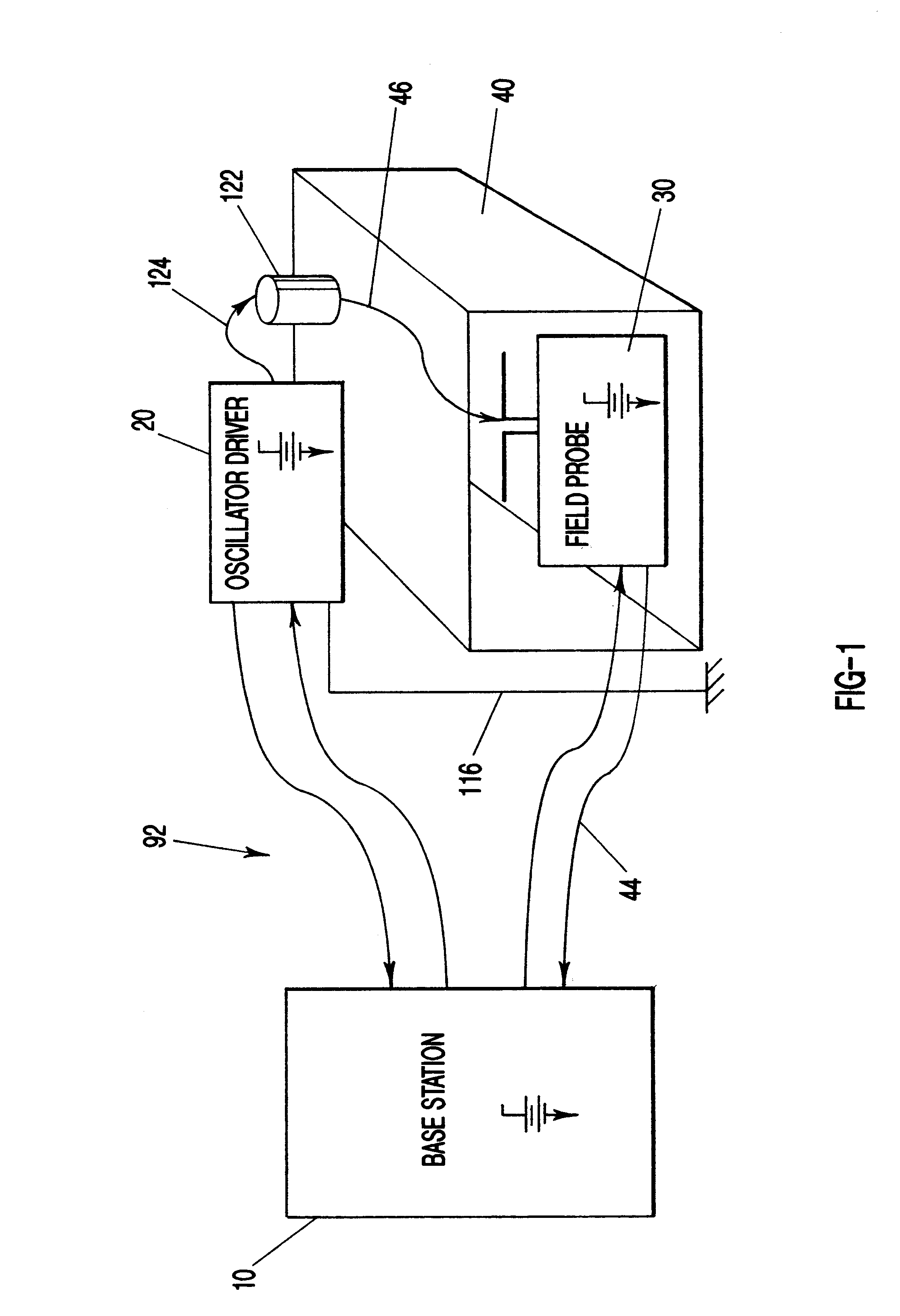
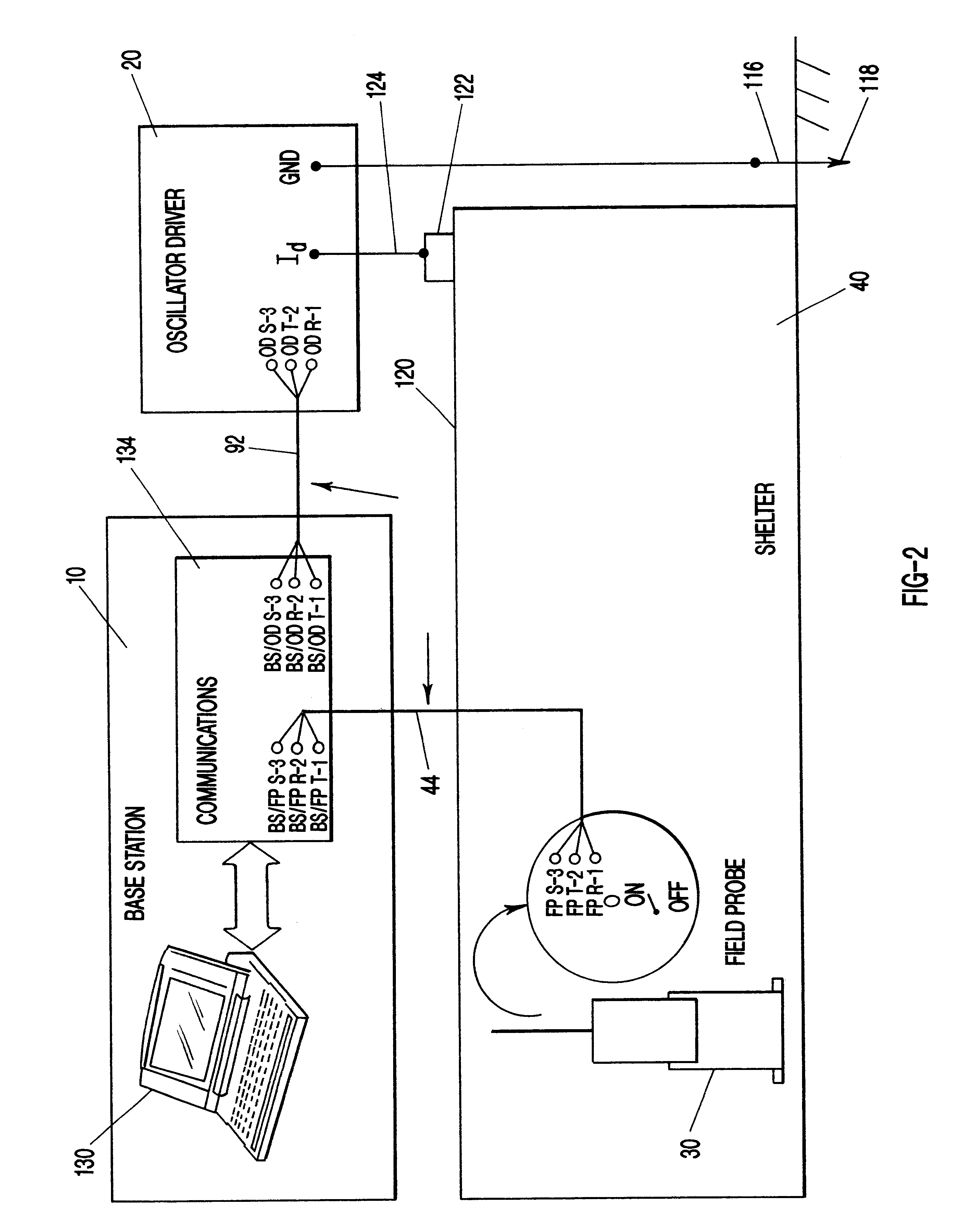
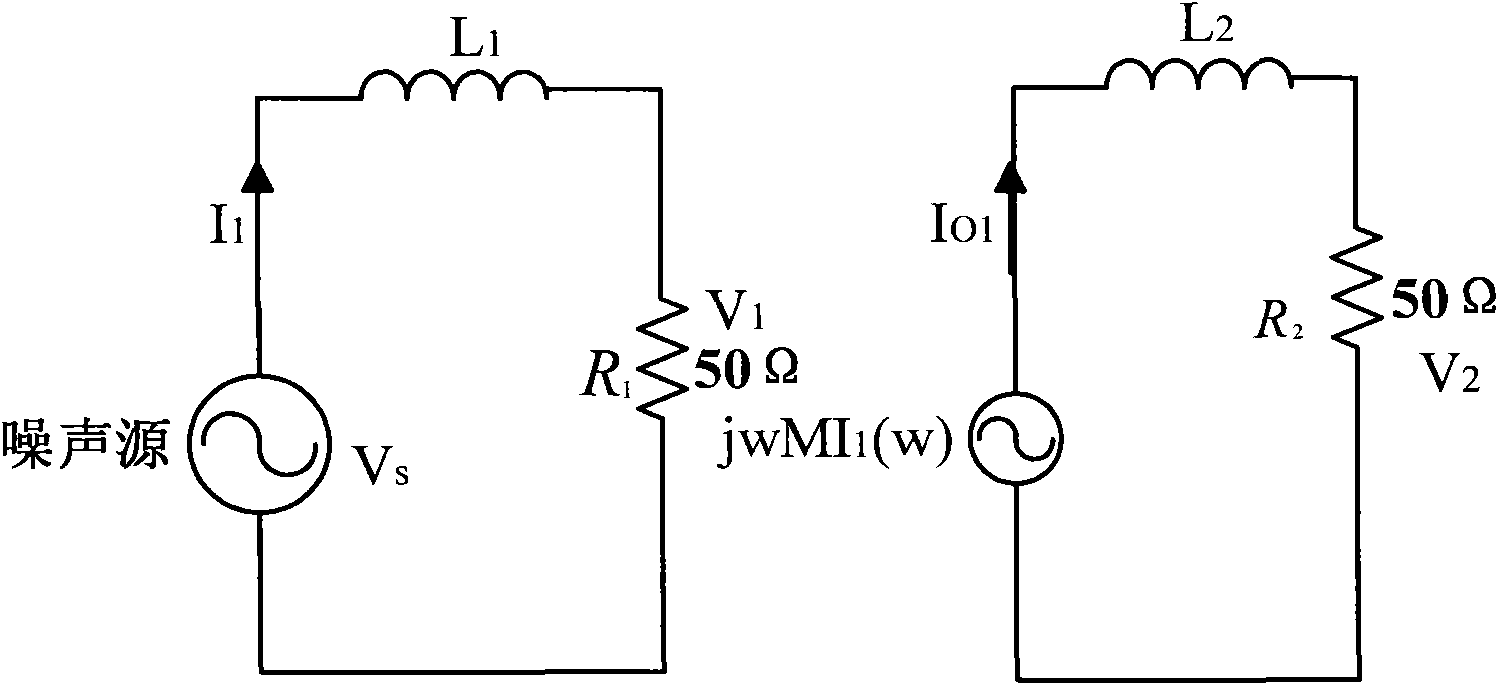
An apparatus and method for measuring the transfer impedance of a structure. Oscillator driver 20 produces a small electrical drive signal into structure 40. Field probe 30 detects the electric field produced by the drive signal and is comprised of a skinny half-dipole and fat half-dipole antenna. Fat half-dipole 34 encloses synchronous detection circuitry. Power supplies are isolated for all components. Base station 10 communicates with oscillator driver 20 and field probe 30 via wireless links 92 and 44 to control the drive signal, the synchronous detection, and to determine the transfer impedance.
Owner:BOLT
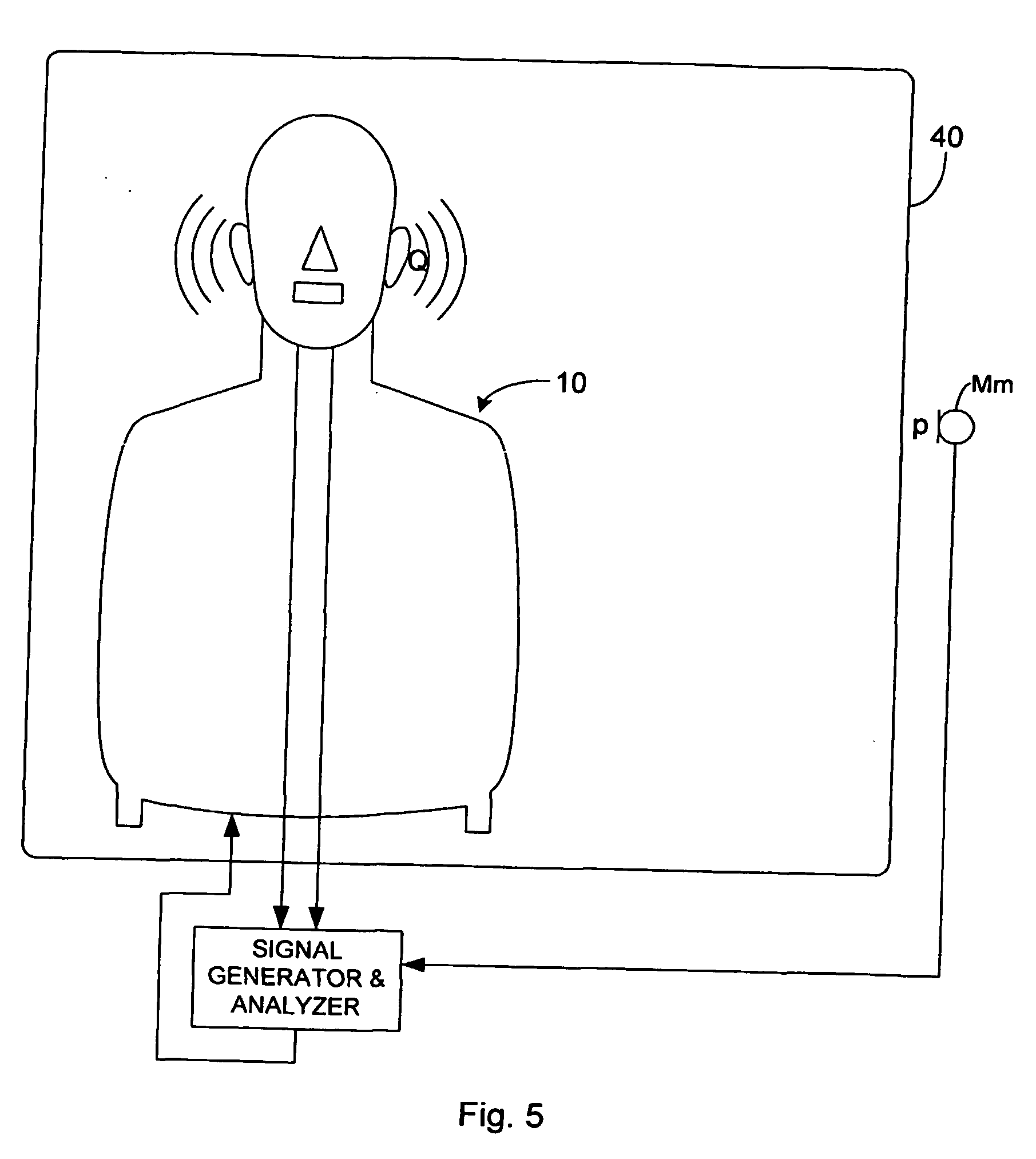
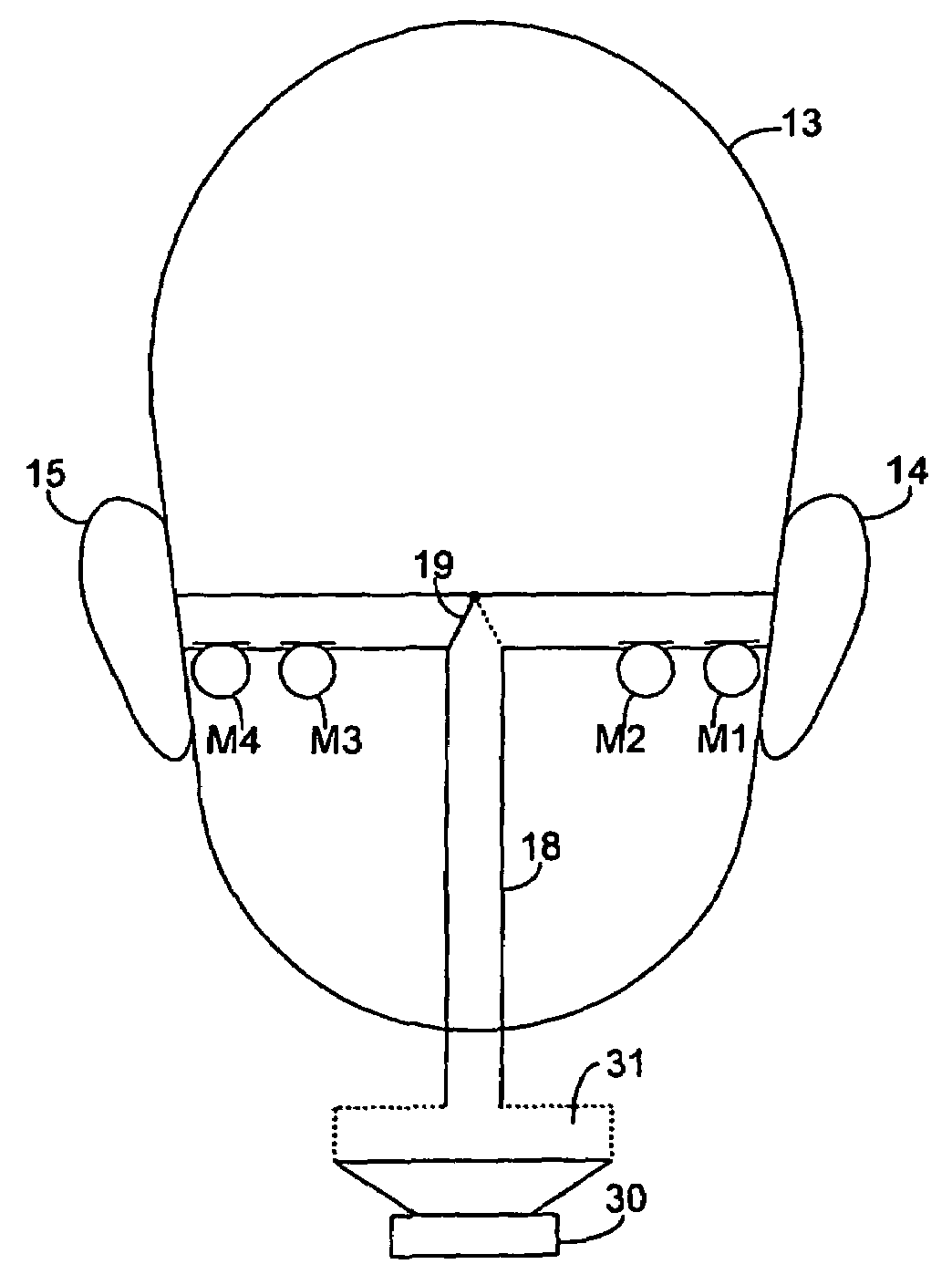
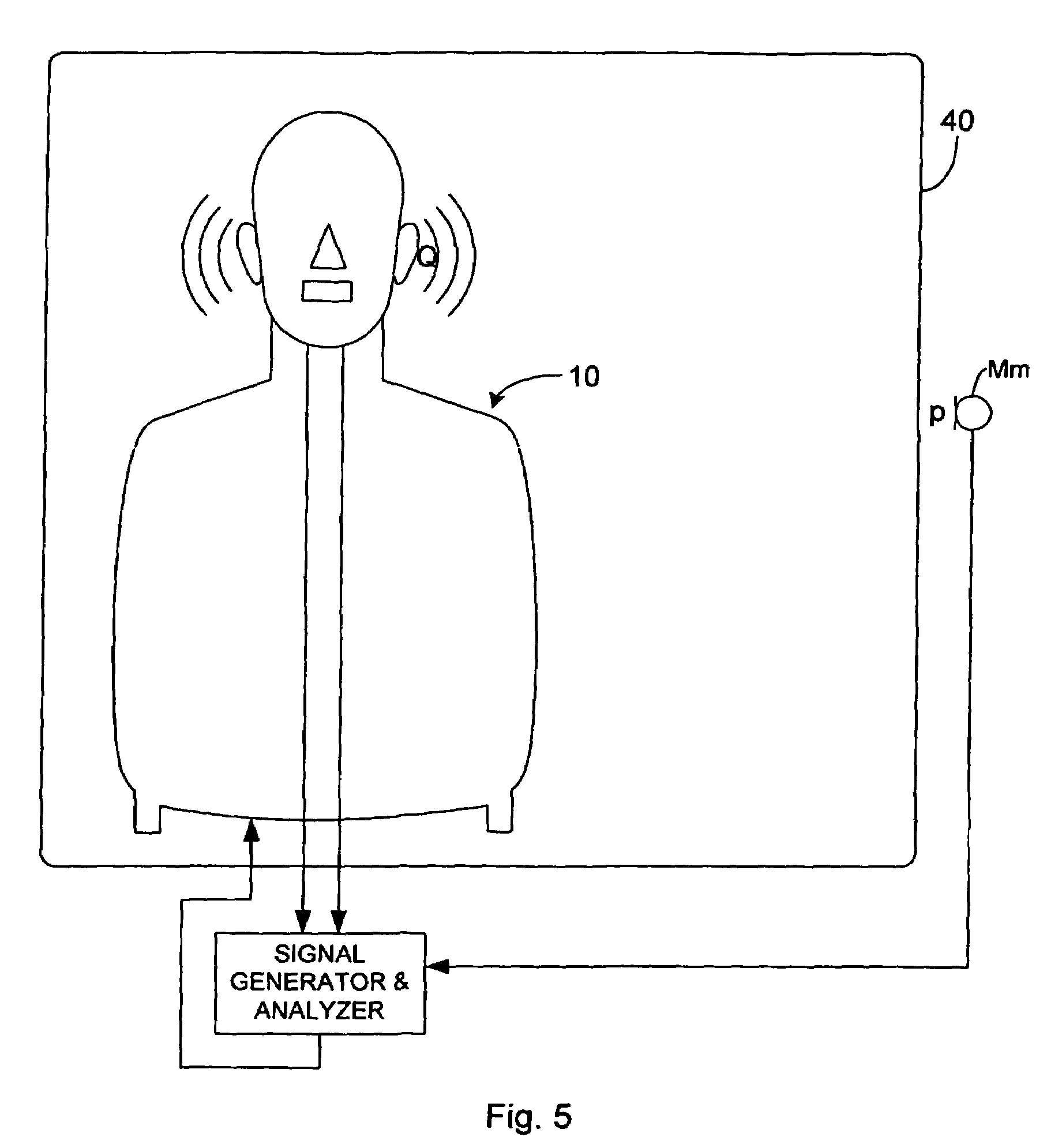
Method and device for determining acoustical transfer impedance
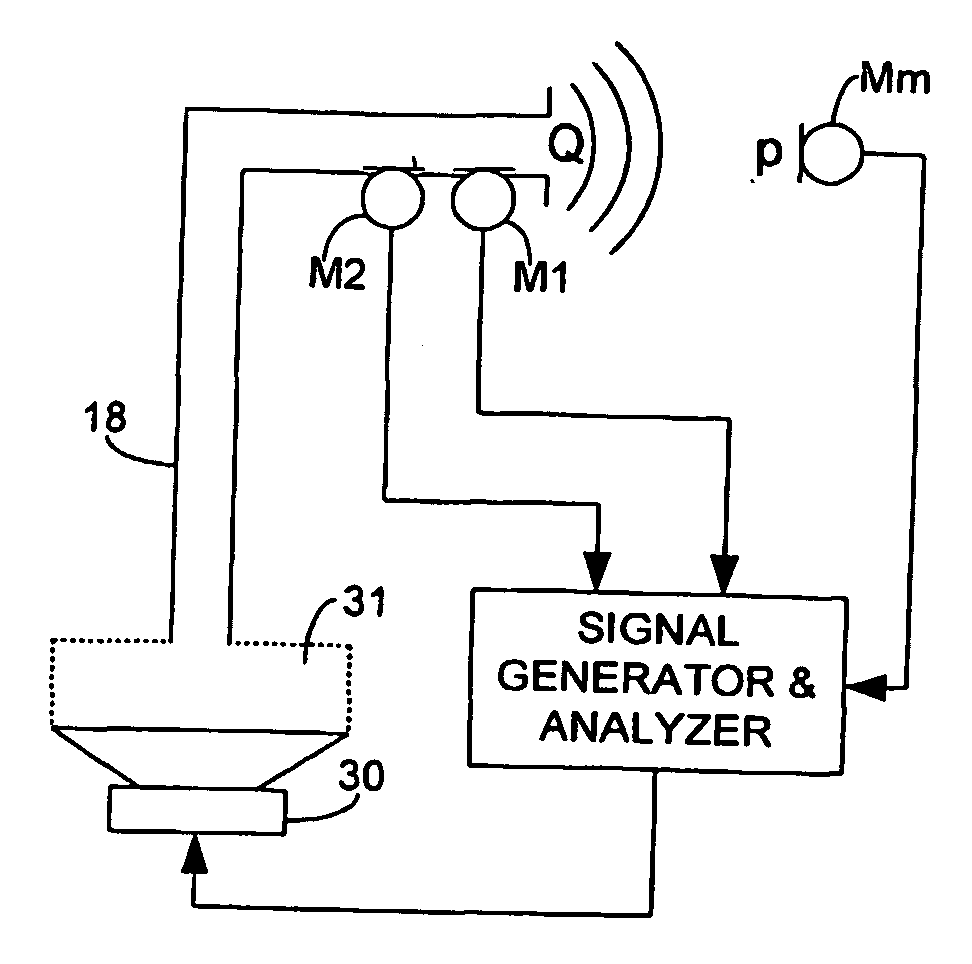
A method and device for determining acoustical transfer impedance The method comprises generating an acoustical volume velocity Q in the listening position, measuring a response quantity p, such as sound or vibration, at a suspected source position resulting from the volume velocity Q, and determining the acoustical transfer impedance Zt as the response quantity p divided by the acoustical volume velocity Q, Zt=p / Q. According to the invention the acoustical volume velocity Q is generated using a simulator (10) simulating acoustic properties of at least a head of a human being, the simulator comprising a simulated human ear (14, 15) with an orifice in the simulated head and a sound source (30) for outputting the acoustical volume velocity Q through the orifice. The output volume velocity Q from the orifice of an ear is estimated from measurements with two microphones inside the corresponding ear canal.
Owner:BRUEL & KJAER SOUND & MEASUREMENT
APD-TIA (Avalanche Photodiode-Transfer-Impedance Amplifier) coaxial photoelectric module with temperature control function and fabrication method thereof
InactiveCN102412240APrecise and controllable temperatureStable temperatureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCapacitanceTemperature control
The invention discloses an Avalanche Photodiode-Transfer-Impedance Amplifier (APD-TIA) coaxial photoelectric module with a temperature control function and a fabrication method thereof. The APD-TIA coaxial photoelectric module mainly comprises a TO56 base with eight pins plus one pin, a thermoelectric cooler (TEC), an AIN (aluminium nitride) ceramic circuit substrate, an APD, a TIA, a RC (resistor-capacitor) filter module, a thermistor, a first filter capacitor and a second filter capacitor, wherein the TEC as a first layer is attached on the upper surface of the coaxial TO56 base, the AIN ceramic circuit substrate as a second layer is attached on the upper surface of the TEC, and the ADP, the TIA, the thermistor, the RC filter module, the first filter capacitor and the second filter capacitor are arranged on the surface of the AIN ceramic circuit substrate to form a third layer. The coaxial photoelectric module has the advantages of small size, good temperature characteristic, stable photoelectric properties and high reliability.
Owner:WUHAN HUAGONG GENUINE OPTICS TECH
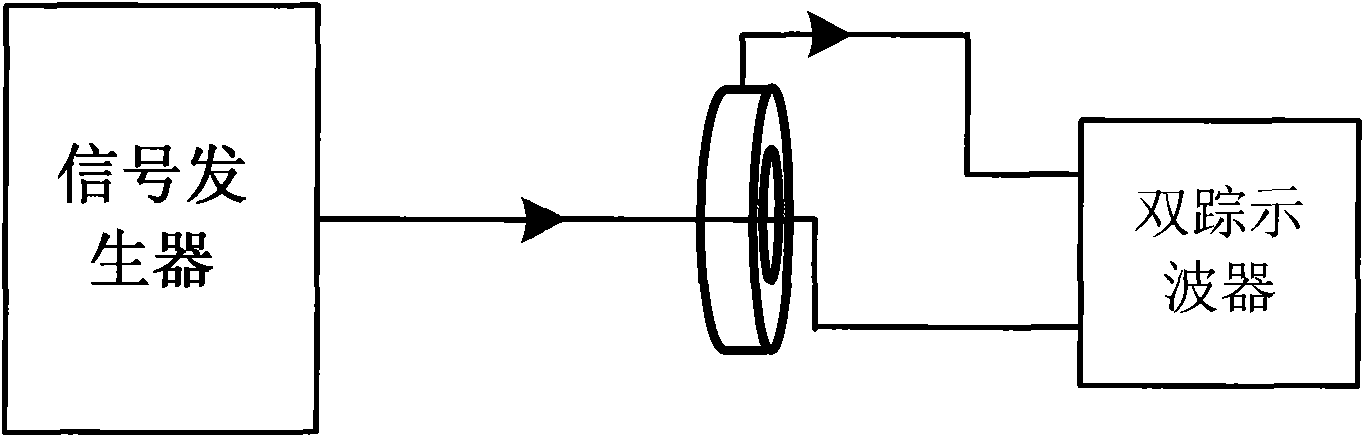
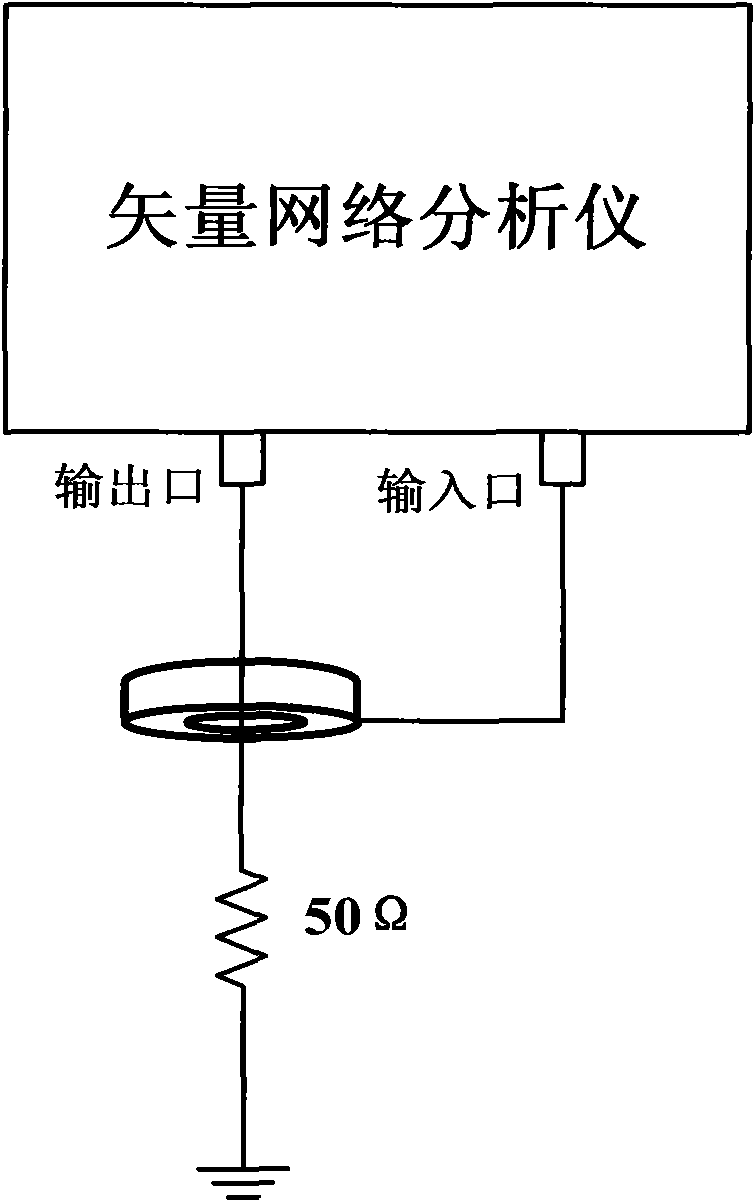
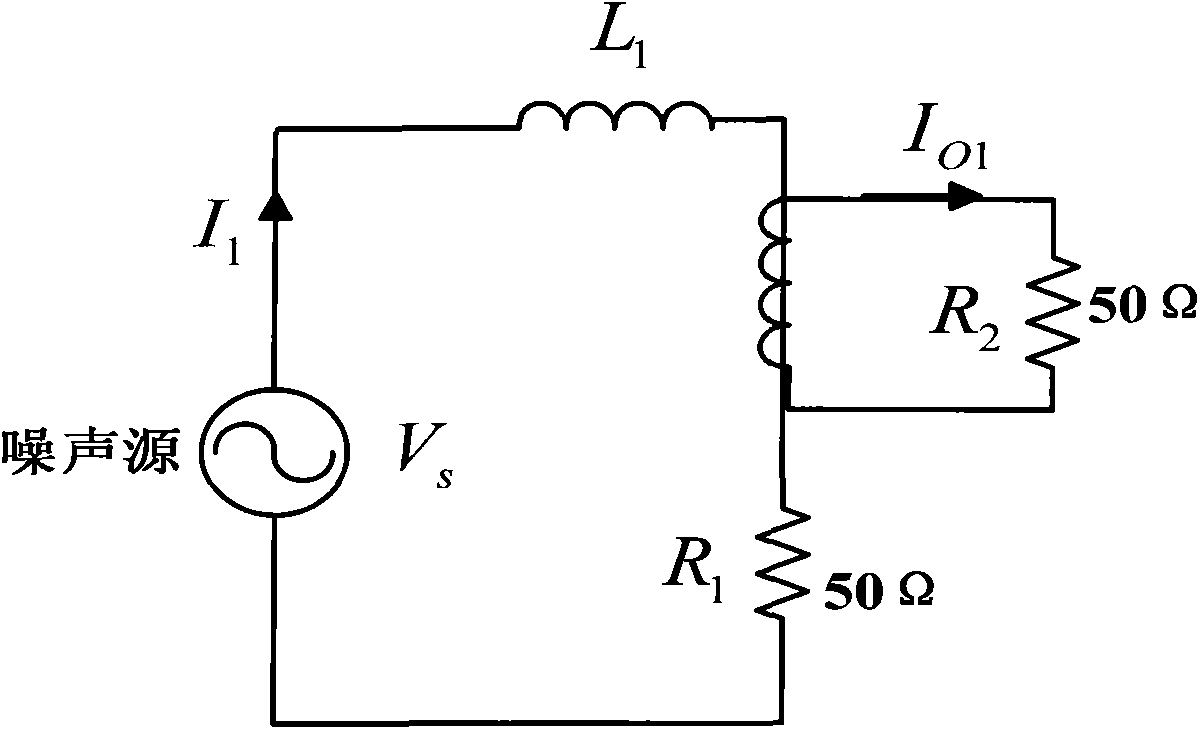
Radio frequency current probe characteristic calibrating method based on electromagnetic compatibility analysis and application
InactiveCN101782637AMastering Measurement Conversion FactorsEasy to operateResistance/reactance/impedenceConversion coefficientsRadio frequency
The invention discloses a radio frequency current probe characteristic calibrating method based on electromagnetic compatibility analysis and application and belongs to the field of electromagnetic compatibility analysis and application and electromagnetic interference noise measurement. According to a frequency section needing to be measured, in the method, the transfer impedance of a current probe is tested in a time domain by utilizing a dual-trace oscilloscope and then tested in a frequency domain by utilizing a vector network analyzer and adopting a scattering parameter method; and finally, a measurement conversion coefficient of the current probe can be more accurately obtained. The method has simple operation and accurate test, enables a result of electromagnetic interference noisemeasured by the current probe to be more accurate, and provides a theoretical basis for conducting the electromagnetic interference noise.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
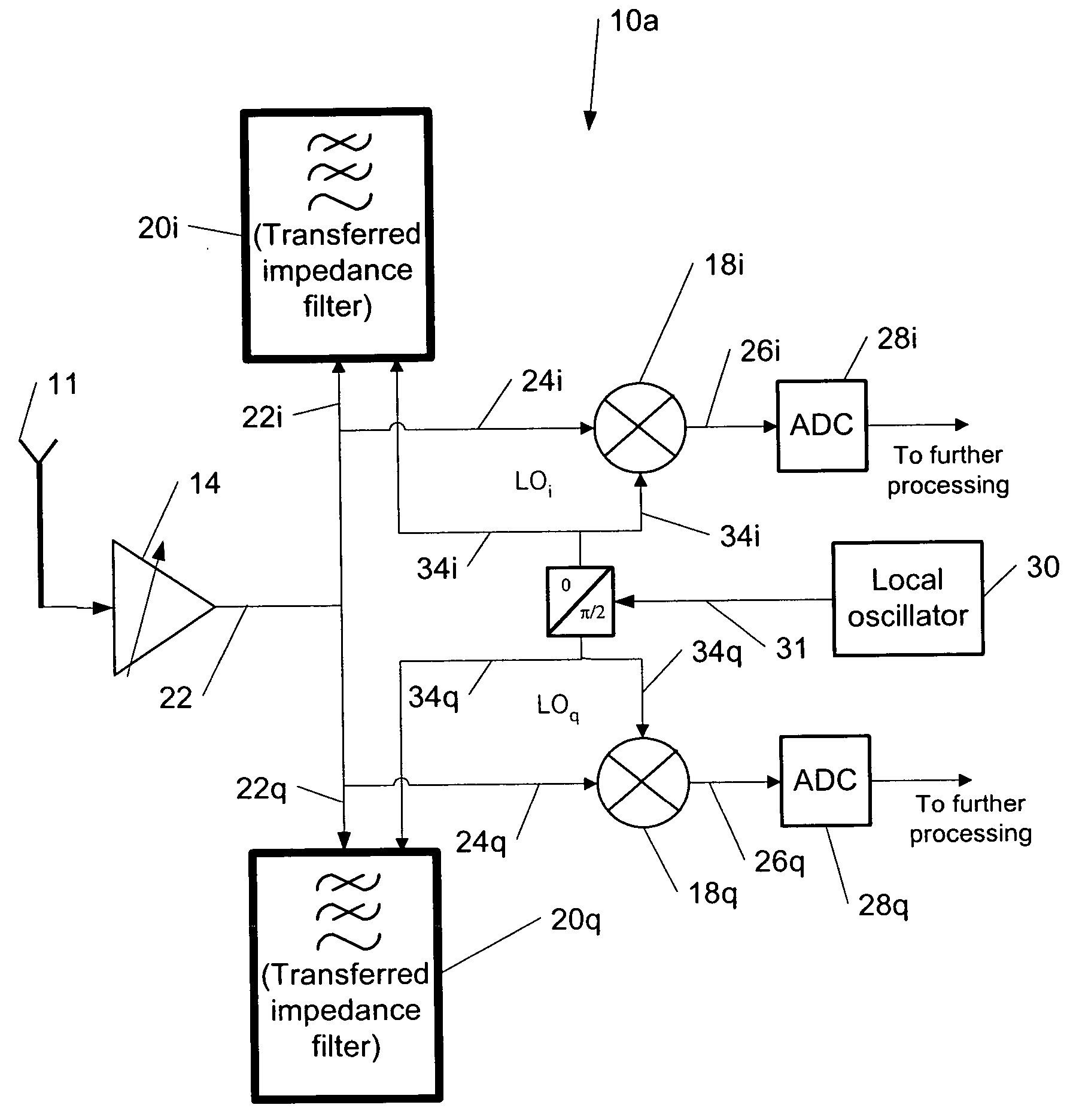
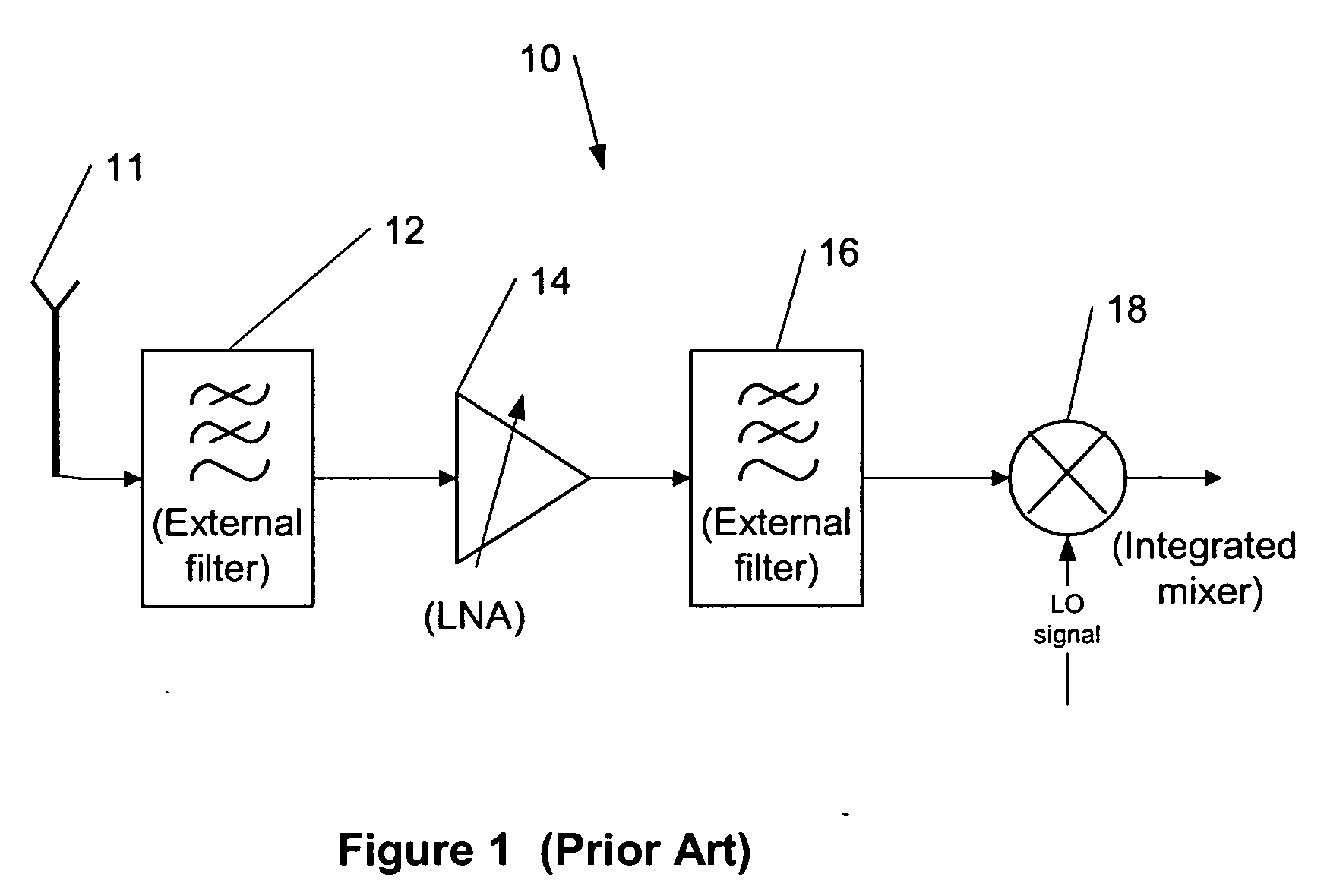
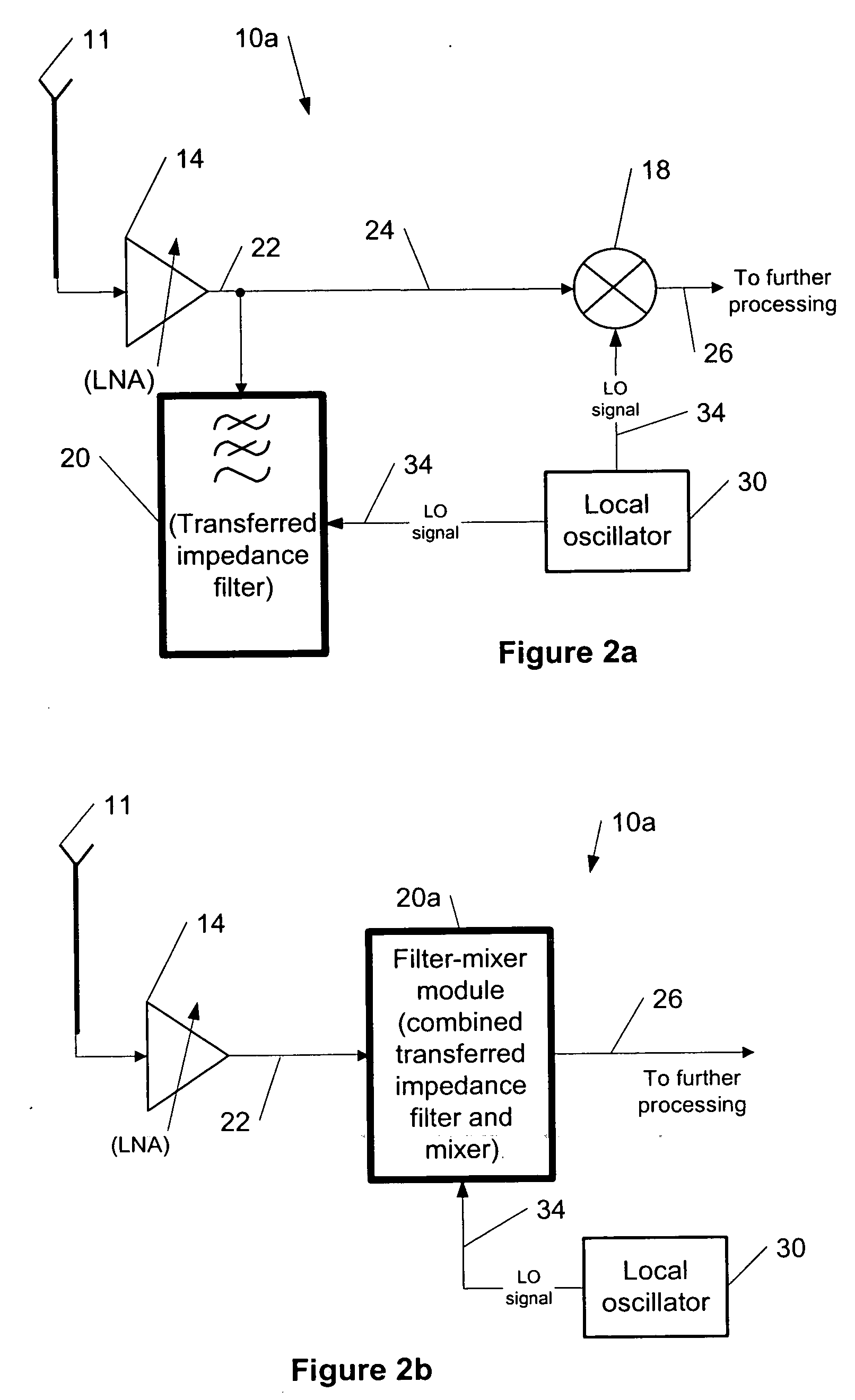
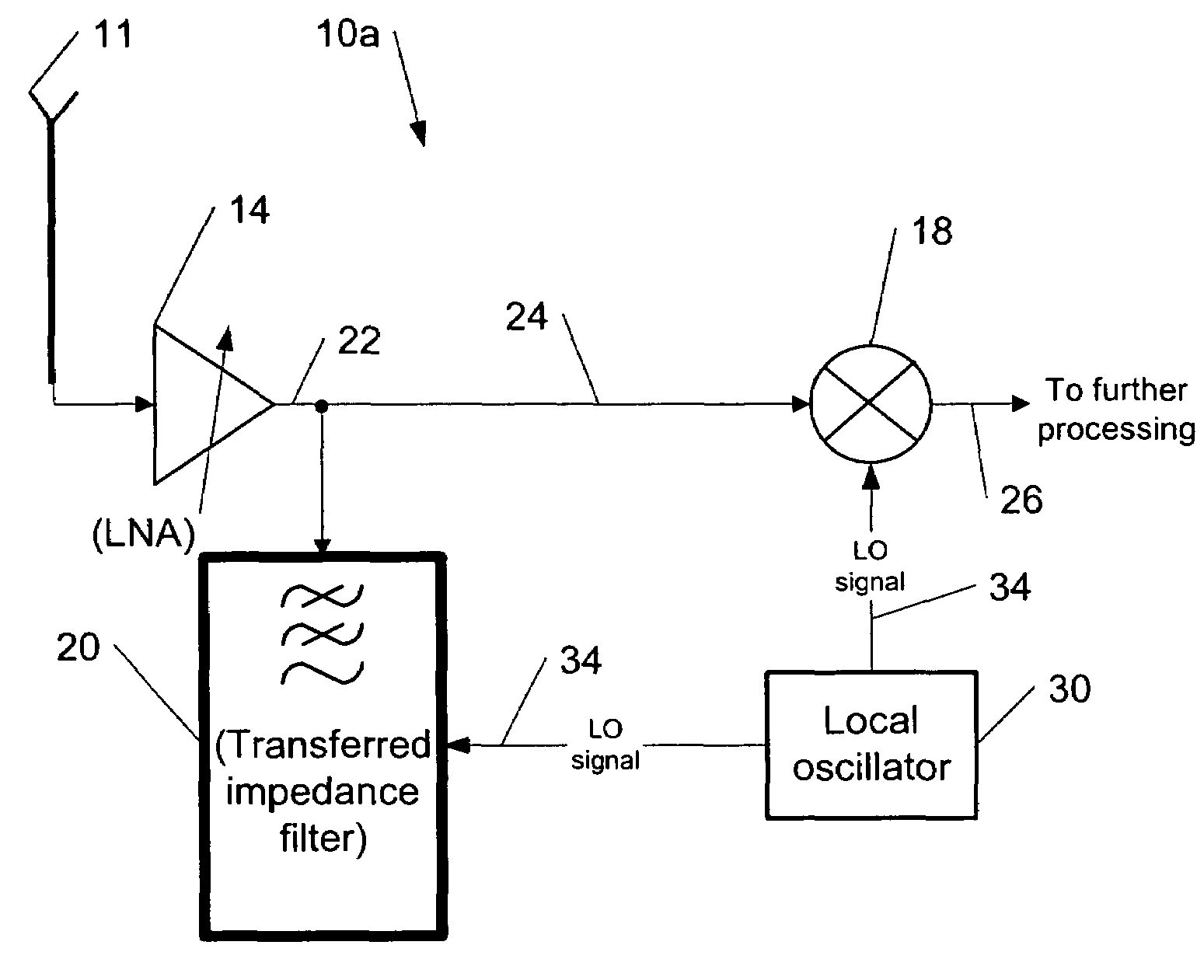
Transferred-impedance filtering in RF receivers
ActiveUS20060208791A1Easy accessNetworks with variable switch closing timeOscillations generatorsRFICFrequency filtering
The present invention provides a method for using transferred-impedance filtering in RF (radio frequency) receivers (e.g., inside of a mobile communication device), wherein said filtering can be done with MOS-switches transferring impedance of a regular RC or RCL circuit to RF frequency filtering inside an RFIC (radio frequency integrated circuit).
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
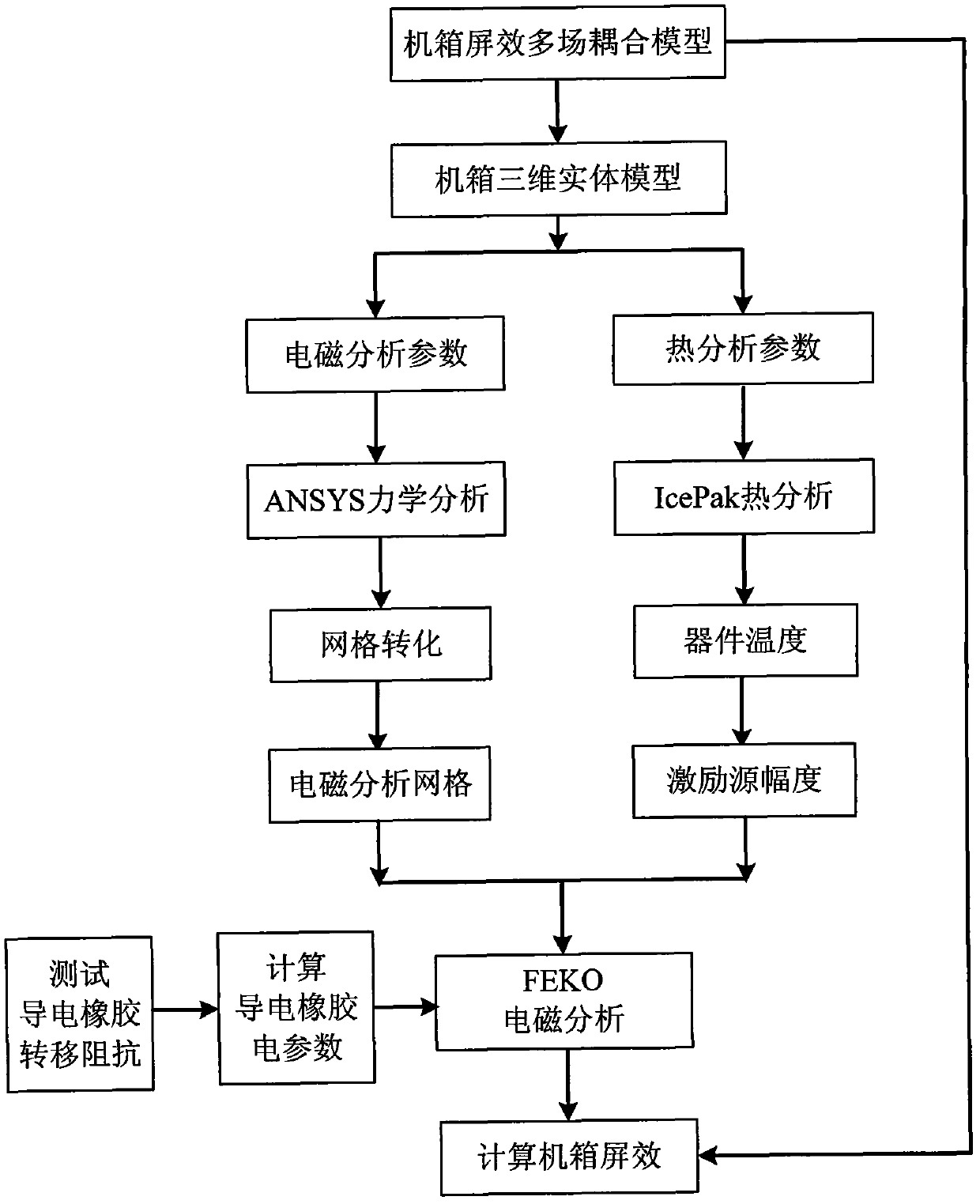
Electromagnetic shielding effect multi-field coupling simulation method for electronic device chassis with conductive rubber
InactiveCN102004810ASolve difficult problems that are difficult to model and simulateAnalyzing electromagnetic screen effectsMagnetic/electric field screeningSpecial data processing applicationsMulti fieldEngineering
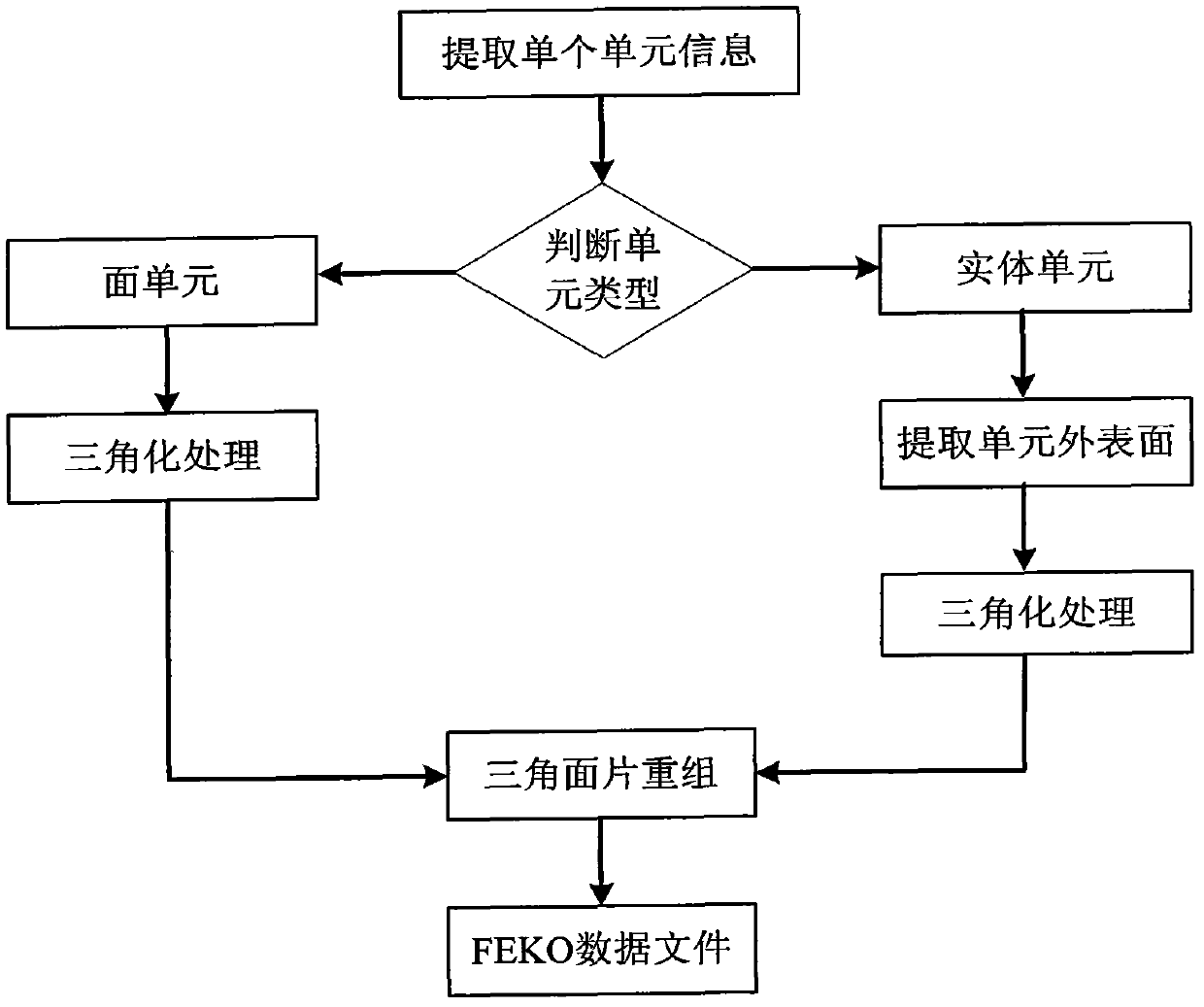
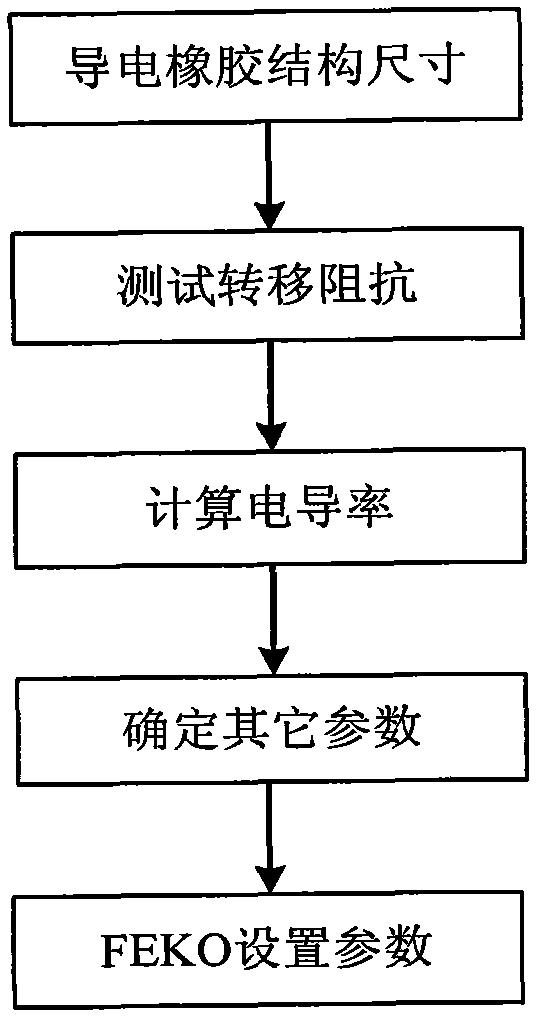
The invention discloses an electromagnetic shielding effect simulation method for an electronic device chassis with conductive rubber, which is mainly used for solving the problem that the conductive rubber can not be simulated during shielding effect simulation in the prior art. The steps are as follows: establishing a multi-field coupling theoretical model for shielding effect of the chassis; introducing a chassis solid model established by Pro / E (pro / engineer) into Ansys for calculating structural displacement; transforming structural grids to electromagnetic grids and introducing into Feko software; measuring the transfer impedance of the conductive rubber, calculating the electrical conductivity and determining other electrical parameters; introducing the solid model into IcePak, and calculating the temperature of all devices in the chassis; determining the magnitude of a driving source through a curve of a device radiation electric field along with the temperature change according to the temperature; setting the parameters of the conductive rubber and the magnitude of the driving source in the FEKO and calculating the electric field value of an observation point outside the chassis; and putting the electric field value into the multi-field coupling theoretical model and obtaining the shielding effect of the chassis. The electromagnetic shielding effect simulation method can simulate the electromagnetic shielding effect of the electronic device chassis with the conductive rubber, and be used for guiding the design of electromagnetic compatibility of the structure of the chassis.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
CoSx nanomaterial used as super capacitor electrode and preparation method of CoSx nanomaterial
ActiveCN104876282ALarge specific surface areaIncrease contact spaceMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitanceNanowire
The invention discloses a CoSx nanomaterial used as super capacitor electrode and preparation method of the CoSx nanomaterial. The nanomaterial is composed of two parts, namely a CoSx core of a nanowire structure and CoSx nanosheets distributed on the surface of the nanowire in a leaf form. The CoSx nanomaterial is prepared by use of a two-step hydrothermal synthesis method, and the method comprises the following steps: preparing a precursor Co(CO3)0.35Cl0.20(OH)1.10 nanowire by use of a hydrothermal reaction method, and then performing sulfidizing treatment on the precursor by use of a hydrothermal reaction method, thereby obtaining the CoSx nanomaterial. The nanomaterial is tested by use of a triple-electrode system, and the nano-electrode material shows high specific capacity of 2383F / g under the current density of 10A / g and still has the specific capacity of 1488F / g after 1000 charge-discharge cycles, and the charge transfer impedance of the nano-electrode material is 1.11omega / cm<2>. The CoSx nano-electrode material prepared by use of the method has the advantages of high specific capacity, good cycle performance, simple preparation method and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nitrogen and phosphor-doped biomass carbon material synthetic method and application of biomass carbon material in microbiological fuel cell cathode
InactiveCN107394217AFacilitate the reduction reactionLower transfer resistanceCell electrodesBiochemical fuel cellsOxygenElectron
The invention discloses a nitrogen and phosphor-doped biomass carbon material synthetic method and an application of the biomass carbon material in a microbiological fuel cell cathode. The method comprises the following steps: taking cellular biomass as a substrate, after pretreatment, respectively sintering the cellular biomass to a carbon material under inert atmosphere at the temperatures of 600 DEG C, 700 DEG C and 800 DEG C, taking cellular as a carbon source, respectively taking melamine and 1,2-vinyl diphosphate as a nitrogen source and a phosphorus source, mixing the raw materials according to a certain proportion for doping, performing a hydrothermal reaction for 5 h in a reaction vessel at the temperature of 100 DEG C, and successfully preparing a nitrogen and phosphor-doped carbon N / P-C semispherical porous microbe cathode material. The method has the advantages that the microbe cathode oxygen reduction catalytic activity is increased, the biomass carbon material has more excellent cycle stability, catalysis electrode charge transfer impedance is reduced, the electron transfer rate is accelerated, a cathode oxygen reduction reaction is promoted, and the provided electric energy can supplies the requirements of other fields.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Molybdenum carbide material and molybdenum carbide@molybdenum sulfide composite material, and preparation methods and applications thereof
ActiveCN109019602AIncrease the active siteImprove conductivityMaterial nanotechnologyTungsten/molybdenum carbideMolybdenum carbideElectrolysis of water
The invention discloses a molybdenum carbide material and a molybdenum carbide@molybdenum sulfide composite material, and preparation methods and applications thereof. The preparation method of the molybdenum carbide material comprises the following steps: adding a carbon source and a molybdenum source to a dispersion liquid, performing stirring for 6-12 h, drying the obtained mixture at 80-120 DEG C, grinding the dried mixture, and collecting the ground mixture to form a molybdenum carbide precursor; and performing temperature programming on the molybdenum carbide precursor to 400-900 DEG C from room temperature in an inert atmosphere, calcining the precursor at 400-900 DEG C for 1-3 h, grinding the calcined precursor, and collecting the ground calcined precursor to obtain molybdenum carbide. The molybdenum carbide is vulcanized at 160-400 DEG C by using a vulcanizing agent to obtain molybdenum carbide@molybdenum sulfide. The molybdenum carbide and the molybdenum carbide@molybdenum sulfide respectively have the morphology of a porous nanosheet structure, and the microstructure facilitates storage of an electrolyte and reduction of the charge transfer impedance and provides a lot of electrocatalytic activity sites; and the material and the composite material can be used as an HER electrocatalyst, have a high catalytic activity and a good stability, and are expected to replace aPt-based catalyst for electrolysis of water to produce hydrogen.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
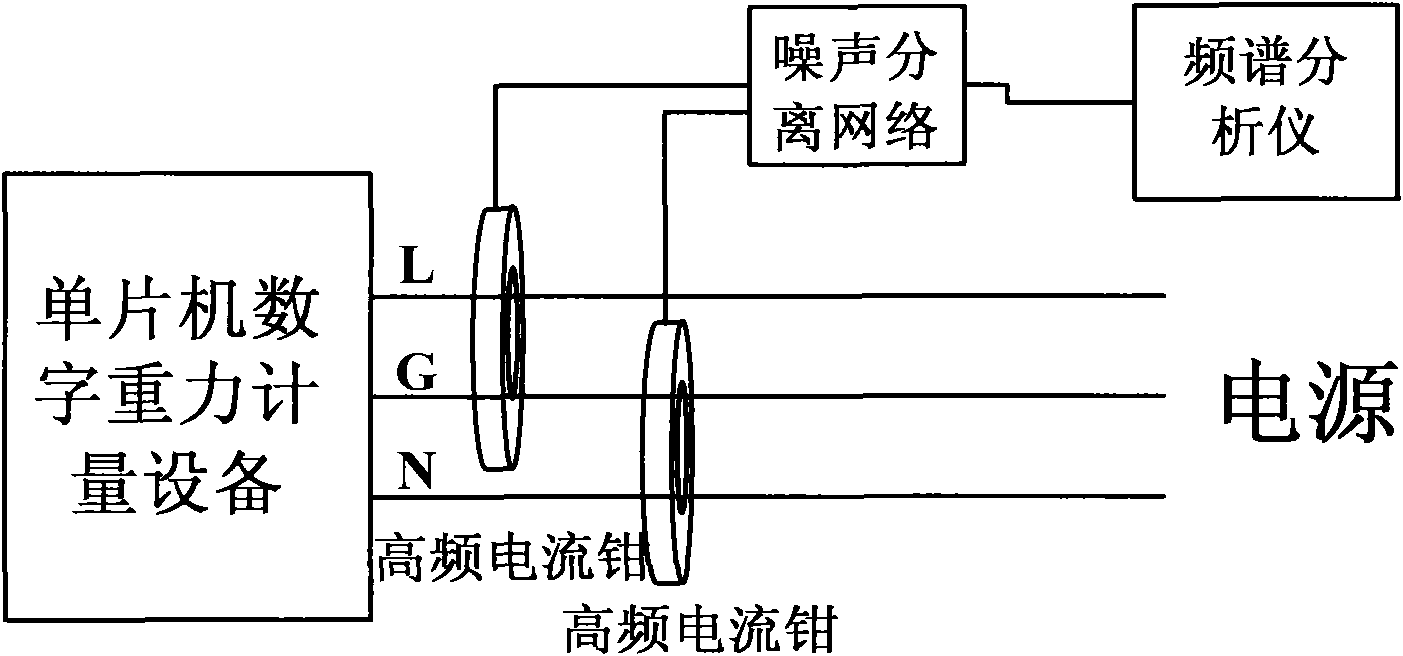
Method for testing radiated noises of digital gravity metering device
ActiveCN101887095ALow cost of measurementSuppress radiated noiseNoise figure or signal-to-noise ratio measurementElectrical testingEngineeringCurrent clamp
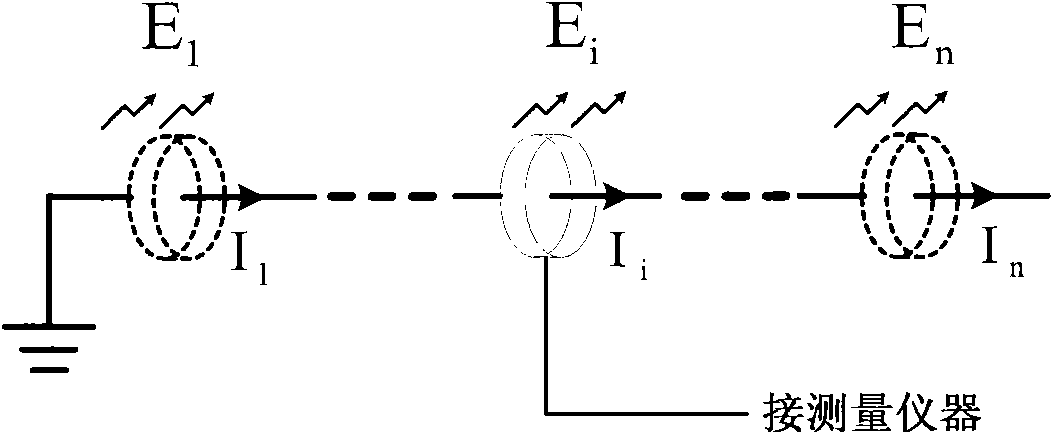
The invention discloses a method for testing radiated noises of a digital gravity metering device, which comprises the following steps of: calculating corresponding transfer impedance according to a high-frequency current clamp structure; putting a measuring loop in the high-frequency current clamp on a power cord of the digital gravity metering device so as to extract a first noise voltage and a second noise voltage in the power cord; performing a vector operation and a vector difference operation on the first noise voltage and the second noise voltage by using a noise separation network so as to obtain a difference mode conducted noise voltage and a common mode conducted noise voltage; performing operation on the difference mode conducted noise voltage, the common mode conducted noise voltage and the transfer impedance of the high-frequency current clamp to obtain a difference mode conducted noise current and a common mode conducted noise current; and acquiring an electric field which emits the radiation noises in a free space according to a common mode noise current formula. In the method, the common mode noise current of a single-chip digital gravity metering device is measured by using the high-frequency current clamp and the noise separation network, and the radiated noises are predicted through the common mode noise current.
Owner:苏州泰思特电子科技有限公司
Signal filtering
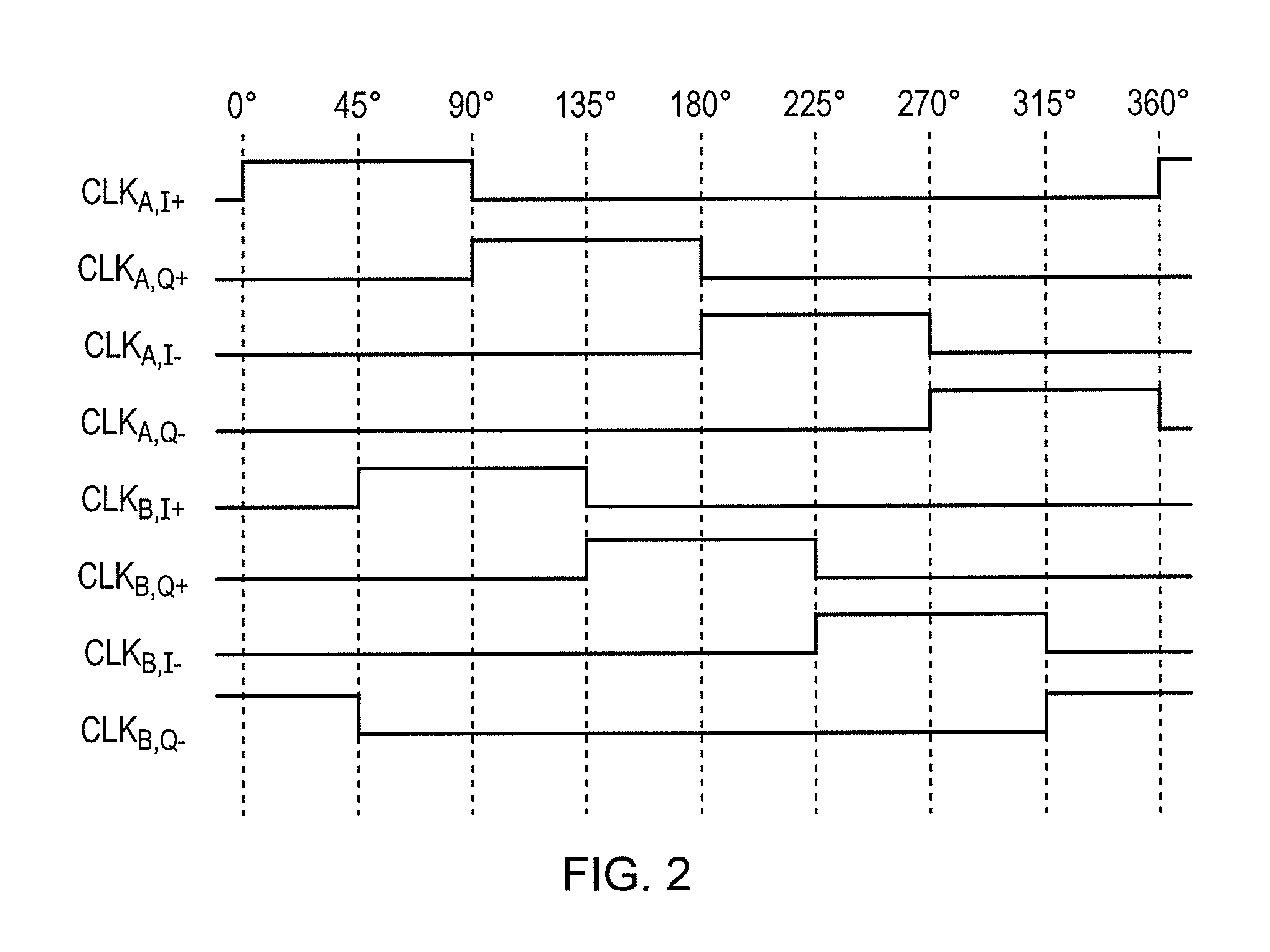
ActiveUS9191127B2Reduced harmonic foldingSpeed up the descentNetwork topologiesNetworks with variable switch closing timeEngineeringClock generator
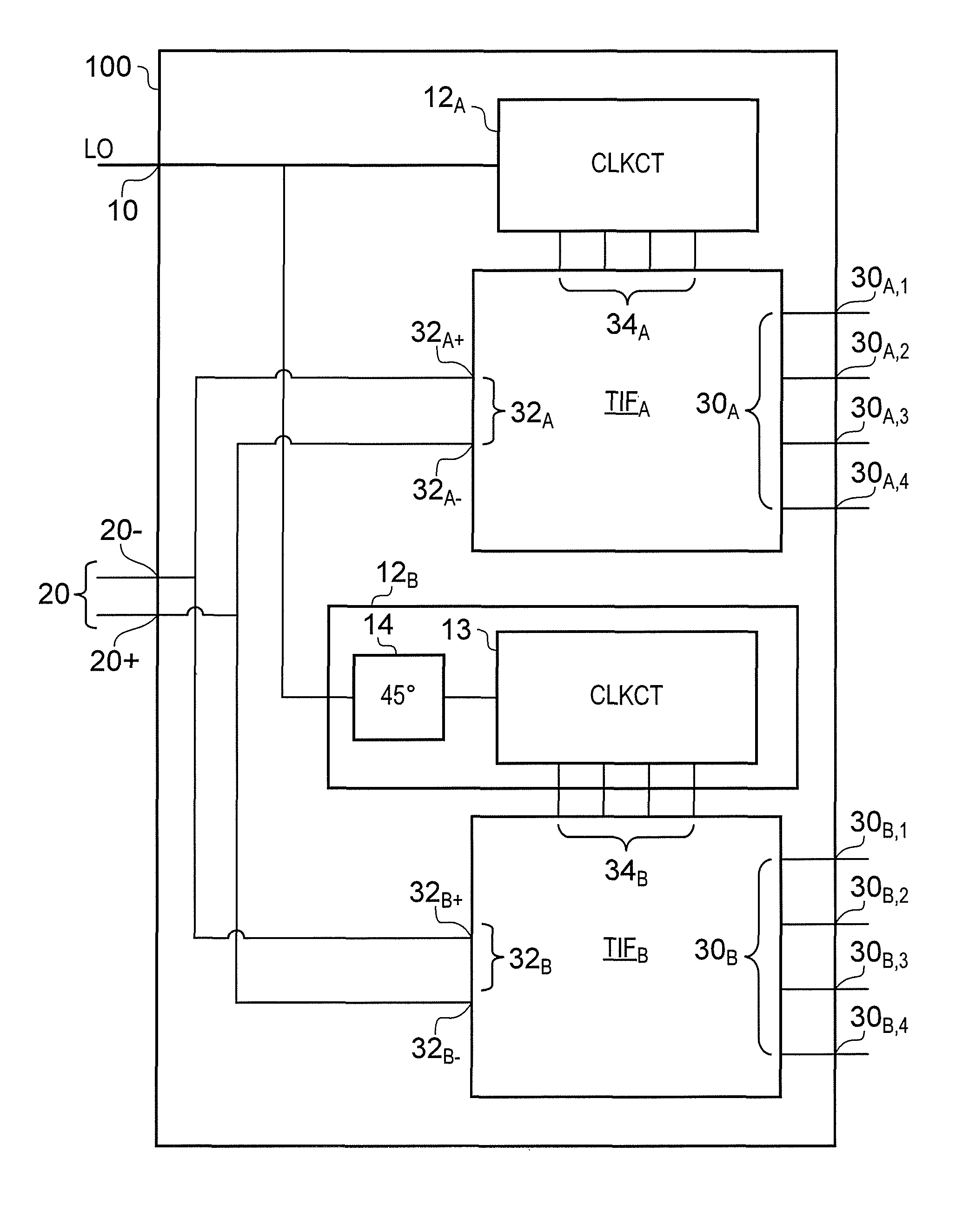
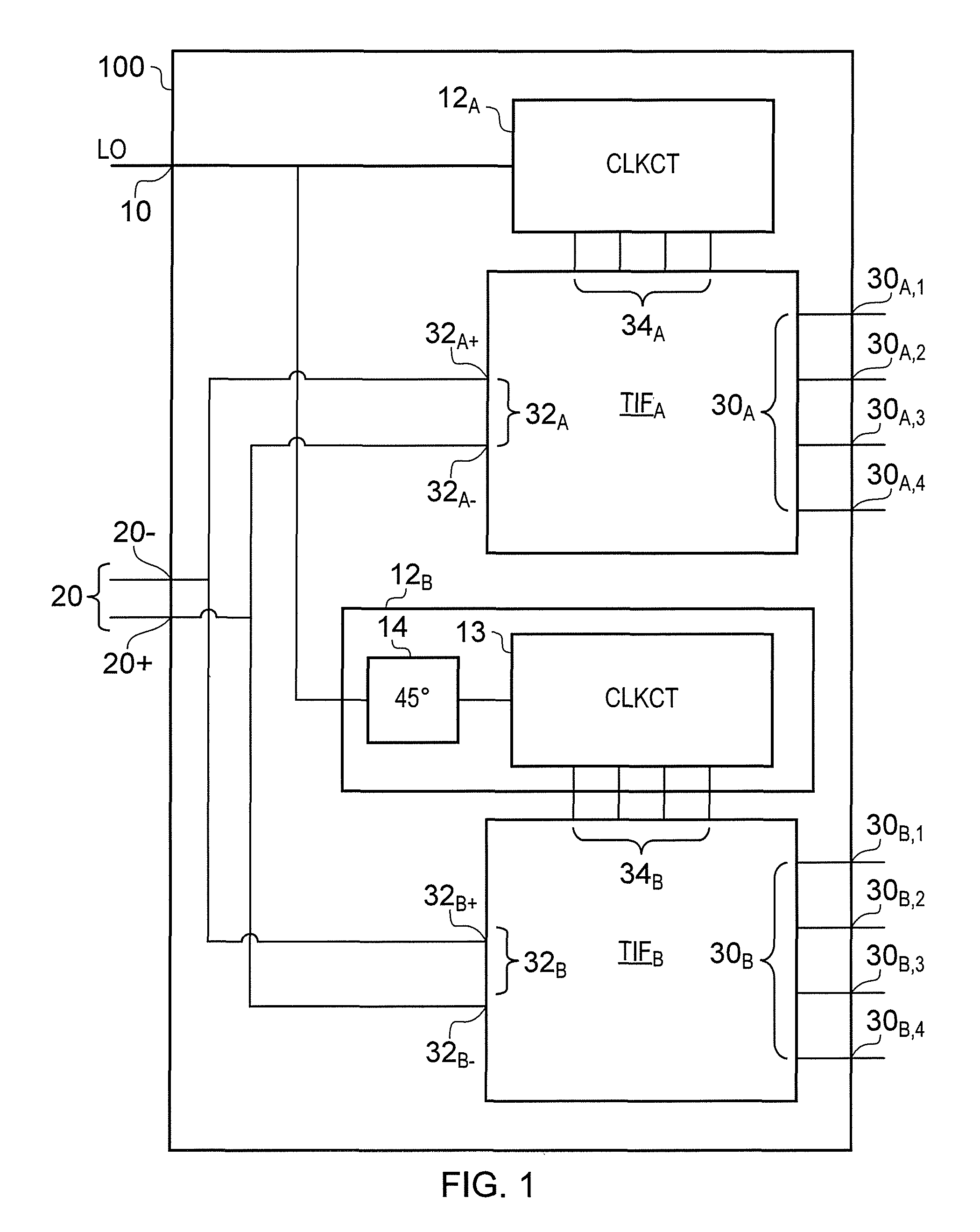
A signal filter (100) comprises a first transferred impedance filter, TIF, (TIFA) having four differential signal paths (PA,1, PA,2, PA,3, PA,4) and a second TIF (TIFB) having four differential signal paths (PB,1, PB,2, PB,3, PB,4)- A first differential signal port of the first TIF (32A) is coupled to a first differential signal port of the second TIF (32B). A first clock generator (12A) is arranged to provide first-TIF clock signals (CLKA,I+, CLKA,Q+, CLKA,I−, CLKA,Q−) having four non-overlapping phases for selecting the respective first-TIF differential signal paths (PA,1, PA,2, PA,3, PA,4), and a second clock generator (12B) is arranged to provide second-TIF clock signals (CLKB,I+, CLKB,Q+, CLKB,J−, CLKB,Q−) having four non-overlapping phases for selecting the respective second-TIF differential signal paths (PB,1, PB,2, PB,3, PB,4). The phases of the second-TIF clock signals (CLKB,I+, CLKB,Q+, CLKB,I−, CLKB,Q−) are equal to the phases of the first-TIF clock signals (CLKA,I+, CLKA,Q+, CLKA,I−, CLKA,Q−) delayed by 45 degrees. The first-TIF first, second, third and fourth clock signals (CLKA,I+, CLKA,Q+, CLKA,I−, CLKAQ−) and the second-TIF first, second, third and fourth clock signals (CLKB,I+, CLKB,Q+, CLKB,I−, CLKB,Q−) have a duty cycle in the range 16.75% to 25%.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
System and method for determining the required decoupling capacitors for a power distribution system using an improved capacitor model
InactiveUS6850878B2Accurate predictionEasy to manageAnalogue computers for nuclear physicsComputation using non-denominational number representationMathematical modelElectric power distribution
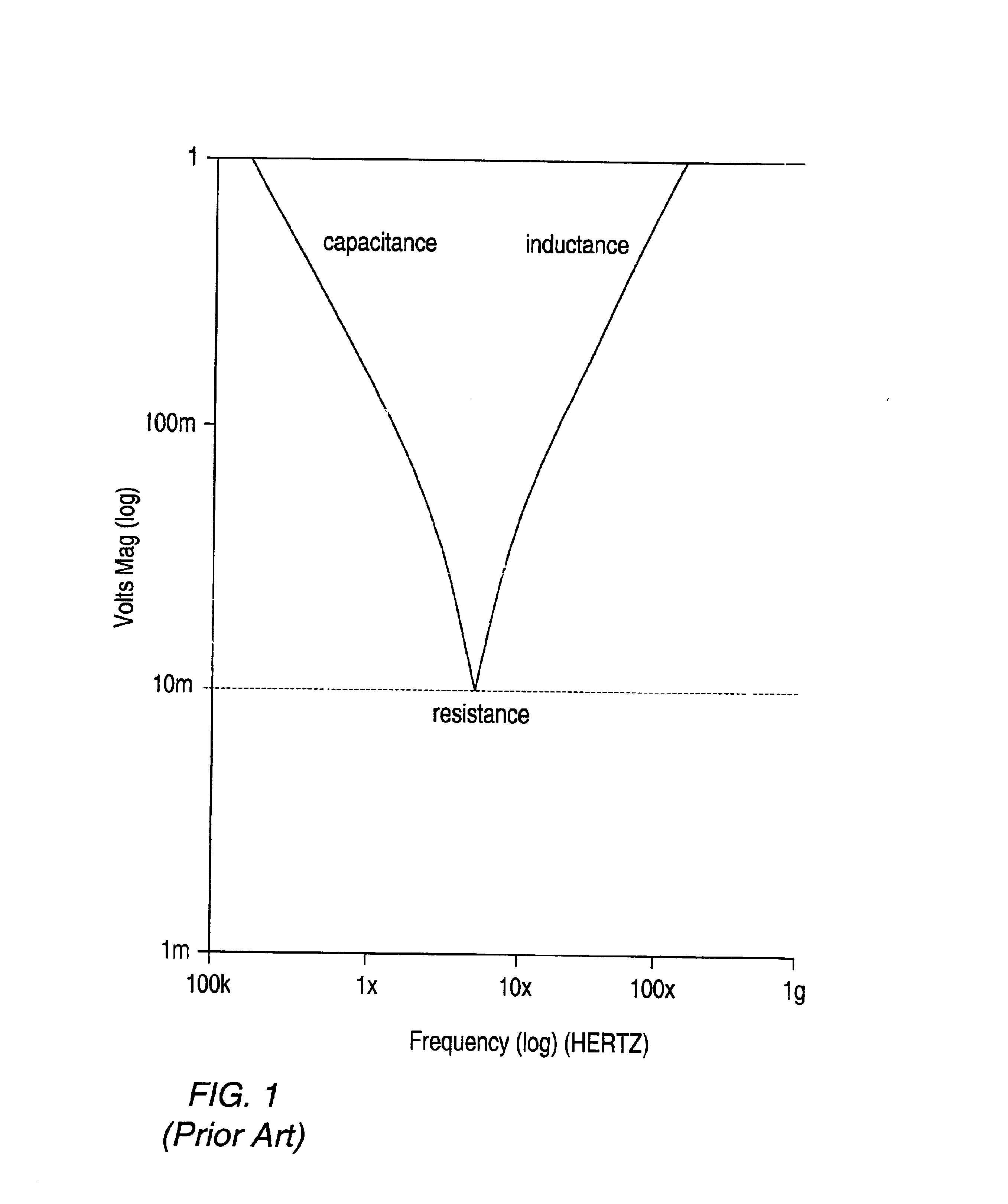
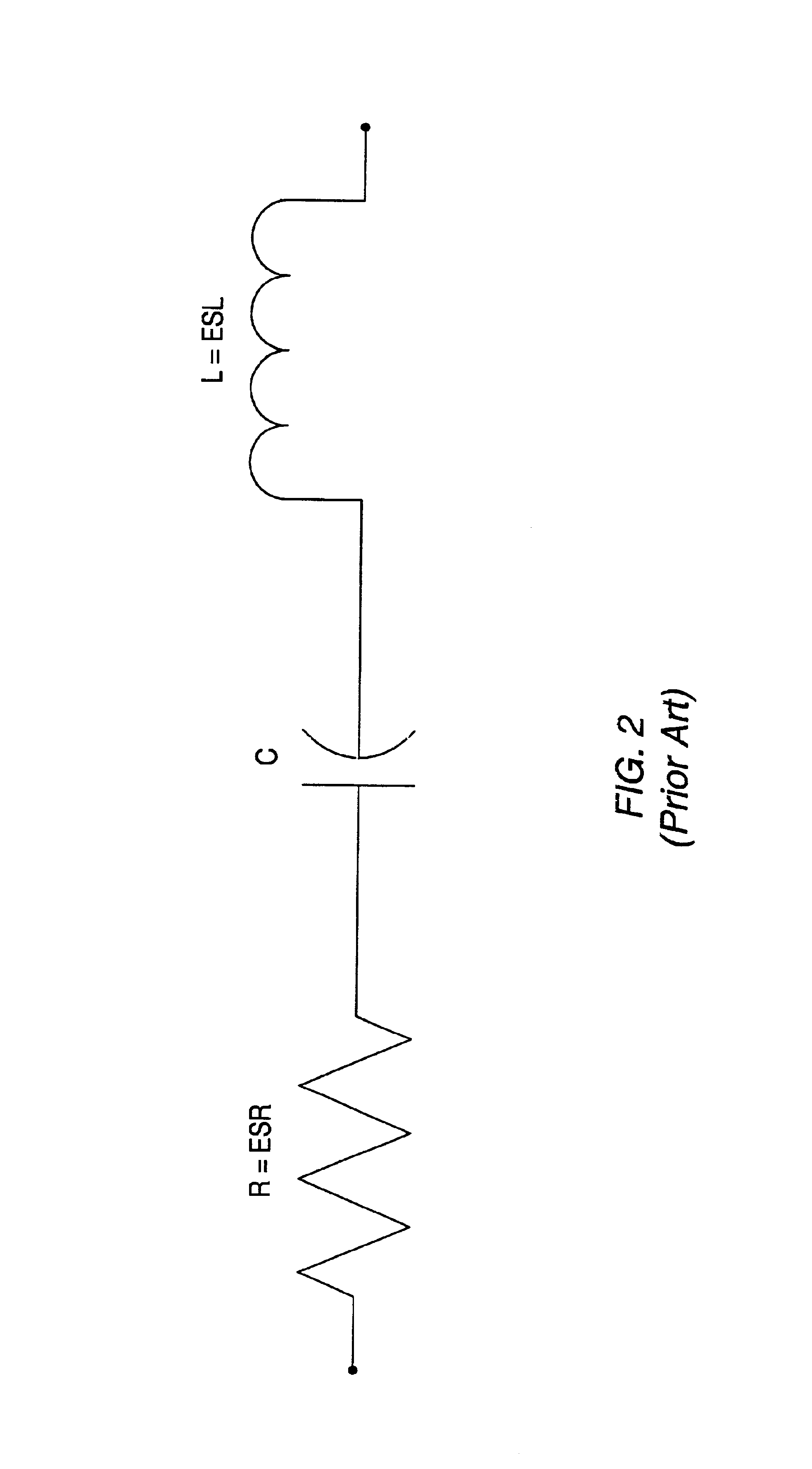
A system and method for determining the required decoupling capacitors for a power distribution system using an improved capacitor model. In one embodiment, a method for determining the decoupling capacitors for a power distribution system includes creating a model of the power distribution system using circuit simulation software, such as SPICE. The power distribution system model includes a plurality of cells interconnected at predetermined nodes. The method then selects one or more decoupling capacitors for the power distribution system. The decoupling capacitors are represented in the power distribution system model by a capacitor model, which is a mathematical model of an electrical circuit. The electrical circuit upon which the capacitor model is based is a ladder circuit. Following the selecting of the decoupling capacitors, the power distribution system model is update based on the selections, and operation of the power distribution system is then simulated. During the simulation, transfer impedance values are determined for each of the nodes, and compared to target impedance. The method is then repeated until each of the transfer impedance values is at or below the target impedance.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Treatment method for all-vanadium redox flow battery electrode
InactiveCN105529471AOptimize process flowEasy to operateCell electrodesRegenerative fuel cellsHigh current densityCharge discharge
The invention provides a treatment method for an all-vanadium redox flow battery electrode. The method comprises the following steps: with carbon electrode materials of a graphite felt, a carbon felt and the like as raw materials, drying the raw materials after fully soaking in an alkali liquor; carrying out high-temperature activation under protection of an inert gas; and washing and drying the product to prepare the activated carbon electrode materials. The treatment method has the advantages of being simple, simple and convenient to operate and low in cost; the surfaces of the treated carbon electrode materials are etched; the effective reaction area of vanadium ion electron pairs on the electrode surface is increased; the charge transfer impedance of an all-vanadium redox flow battery in a charge-discharge process is greatly reduced, so that the voltage efficiency and the energy efficiency of the all-vanadium redox flow battery under high current density are greatly improved.
Owner:HUNAN YINFENG NEW ENERGY
Transferred-impedance filtering in RF receivers
ActiveUS7187230B2Networks with variable switch closing timeOscillations generatorsRFICFrequency filtering
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
W-doped and modified high-nickel ternary positive electrode material
InactiveCN109904432AHigh capacity retentionExcellent rate performanceCell electrodesSynthesis methodsManganese
The invention relates to a W-doped and modified high-nickel ternary positive electrode material, and belongs to the field of a chemical energy storage battery. The material is obtained by grinding anduniformly mixing a mixture of a nickel-cobalt manganese hydroxide, a tungsten source and LiOH.H2O to obtain solid powder, calcining the solid powder under an oxygen atmosphere and then cooling. By Wdoping, the material structure can be stabilized, charger transfer impedance is reduced, so that the electrochemical performance of the material is improved, and the material capacity retention rate and the rate performance of the material are improved. The synthesis method is simple, the process and the technology are easy to implement, and large-scale commercial application can be achieved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Hybrid mesh partition method with design of integrity of system-level packaging power supply
InactiveCN101976287AReduce the number of nodesMeet modeling needsSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringGrid partition
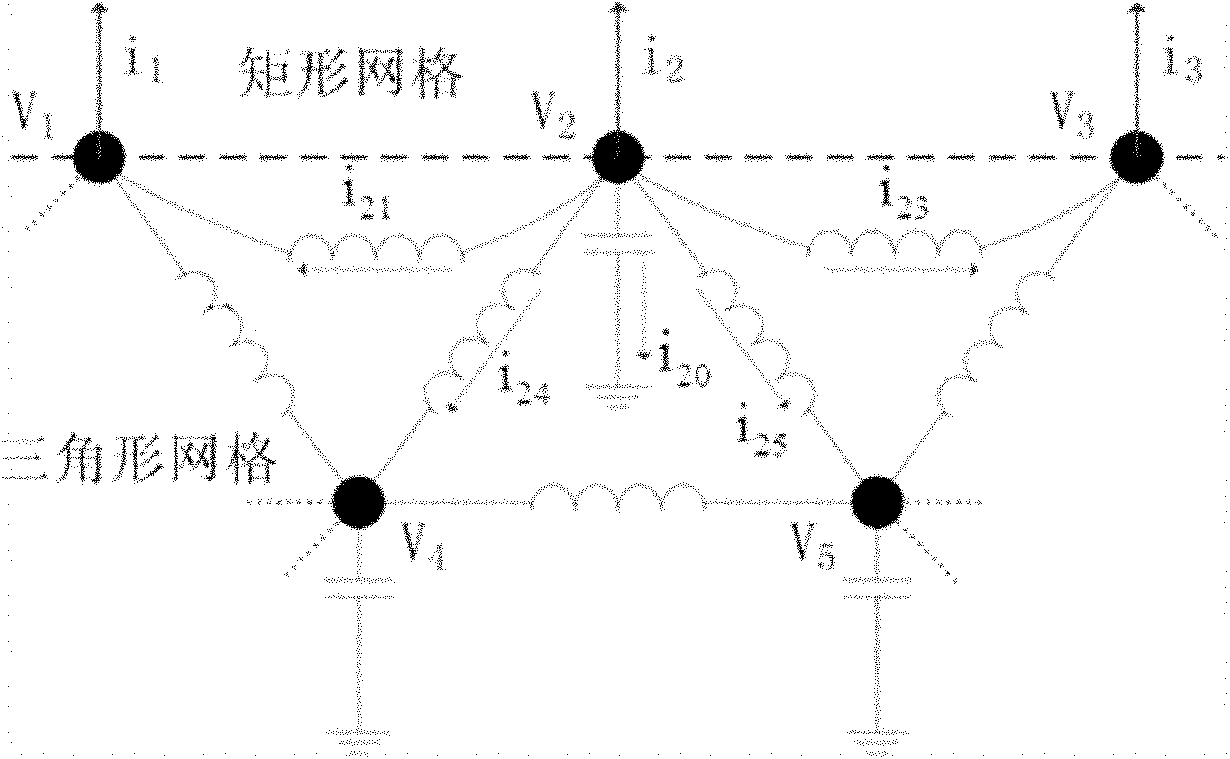
The invention relates to a hybrid mesh partition method in the field of electronic technologies, in particular to the hybrid mesh partition method with the design of integrity of a system-level packaging power supply. The hybrid mesh partition method comprises the following steps: (1) decomposing an irregular power supply / ground plane into a series of convex polygons by utilizing convex partition treatment; (2) obtaining an optimal rectangular mesh based on the recursive partitioning technology of the rectangular mesh, setting auxiliary ports on sides of the rectangular mesh, and establishing the transfer impedance relationship among the ports; (3) adopting a triangular mesh to fill the remaining structure, and carrying out modeling of an equivalent circuit for the triangular mesh; (4) establishing the electrical relationship among the ports at an interface of the rectangular mesh and the triangular mesh; and (5) solving simultaneous overall equations. The hybrid mesh partition method has the advantages of a wide range of applications, few internal nodes, high analysis precision and efficiency and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
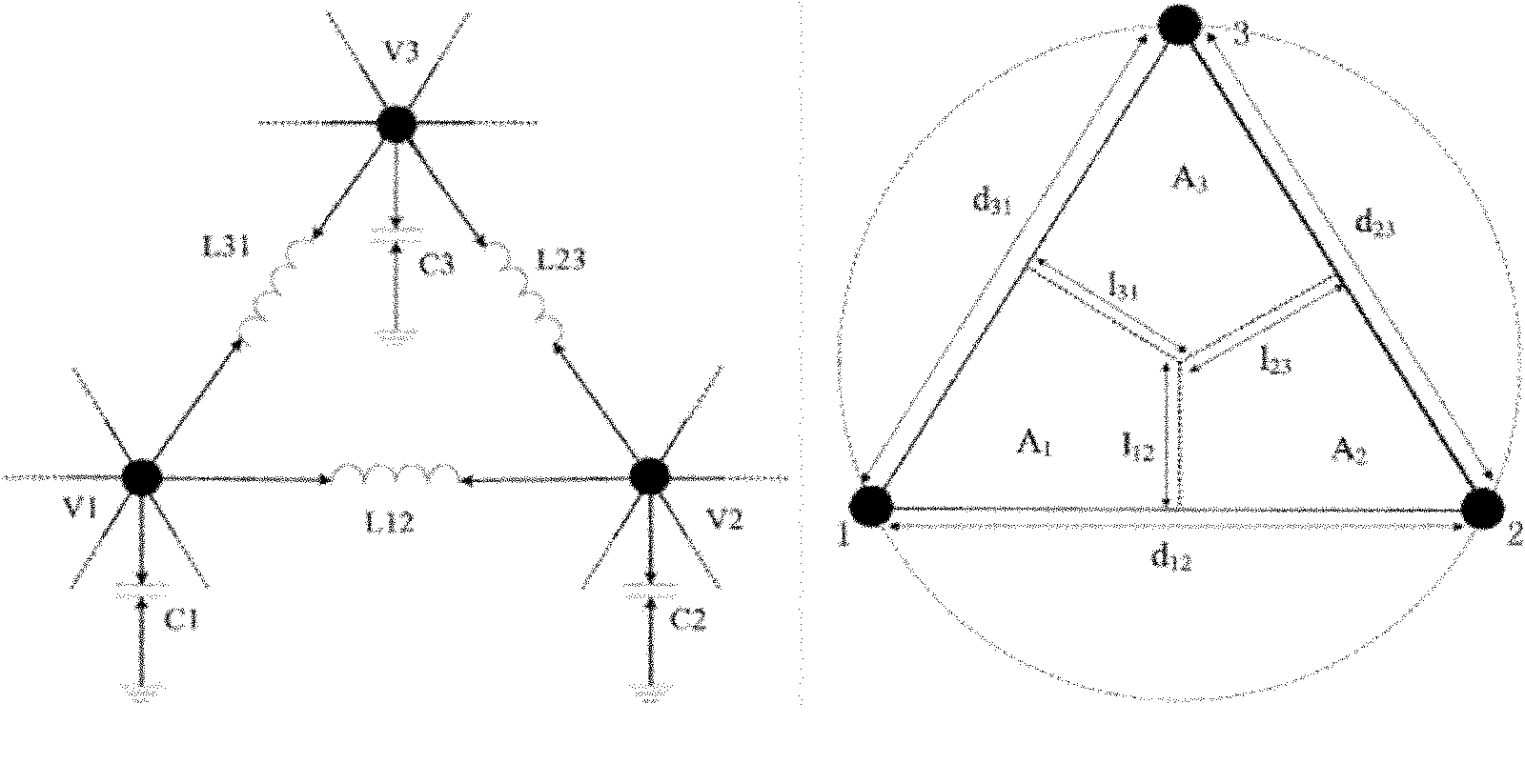
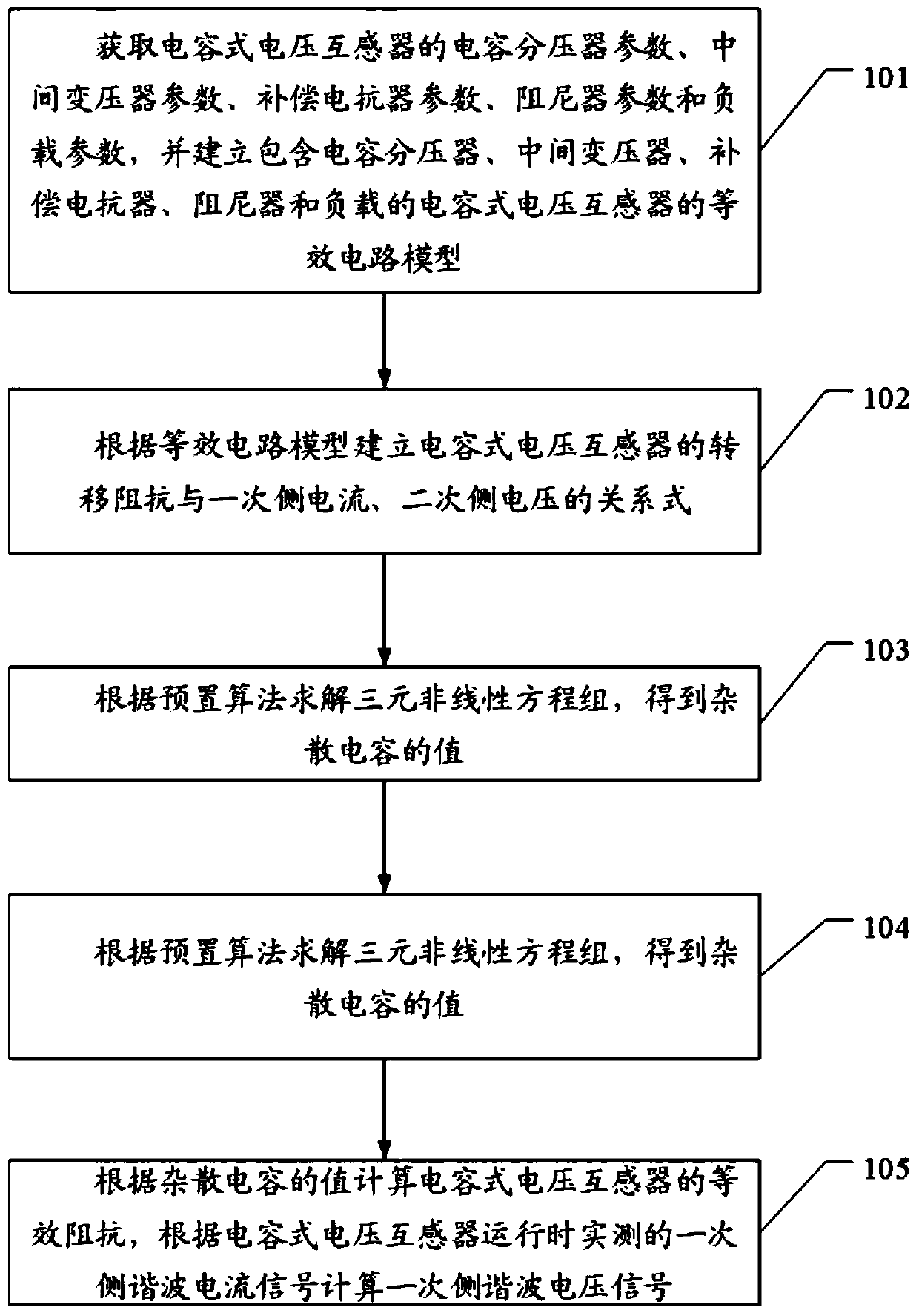
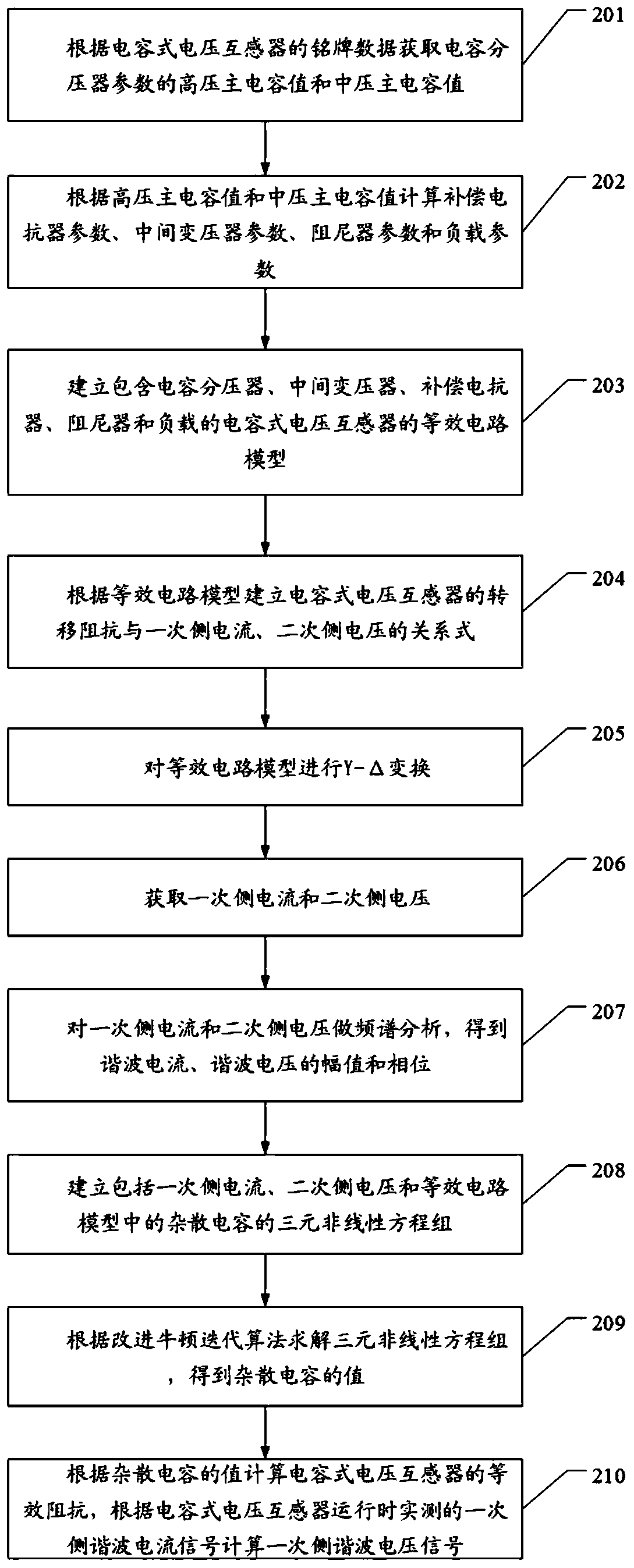
Capacitance type voltage transformer harmonic voltage measurement method and device
InactiveCN110221237AAddressing the Effects of Harmonic Voltage MeasurementsVoltage measurements onlyCapacitanceNonlinear systems of equations
The invention discloses a capacitance type voltage transformer harmonic voltage measurement method and device. The method comprises the following steps that: establishing the equivalent circuit modelof a capacitance type voltage transformer; according to the equivalent circuit model, establishing a relational expression between the transfer impedance of the capacitance type voltage transformer and primary side current and a relational expression between the transfer impedance of the capacitance type voltage transformer and secondary side voltage; establishing a ternary nonlinear equation setcontaining the primary side current, the secondary side voltage and stray capacitance in the equivalent circuit model; and solving the ternary nonlinear equation set, according to the solved value ofthe stray capacitance, calculating the equivalent impendence of the capacitance type voltage transformer, and according to a primary side harmonic current signal which is actually measured when the capacitance type voltage transformer operates, calculating a primary side harmonic voltage signal. By use of the method, the technical problems in an existing capacitance type voltage transformer harmonic voltage measurement method that a structure is complex, cost is high, reliability is difficult in prediction and the method is not suitable for field measurement since the capacitance type voltagetransformer needs to be transformed or depends on a high-voltage harmonic source can be solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Calculation method of direct-current components of short circuit current of power supply system
ActiveCN106990326AThe calculation result is accurateFault location by conductor typesUltrasound attenuationPower flow
The invention relates to a calculation method of direct-current components of short circuit current of a power supply system. A key problem of calculation of direct current components of short circuit current is researched; a frequency domain equivalent theory of the direct-current component calculation is provided; based on the principle, the method for calculating direct current of the short circuit current and attenuation features by use of a transfer impedance is provided. In the method, effects on short circuit current and direct current component calculation imposed by frequency are considered, and features of mathematical models of a complex electric power system network are combined, so the calculation results are quire precise, and the method is simple to operate, and usable for routine calculation of engineering.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
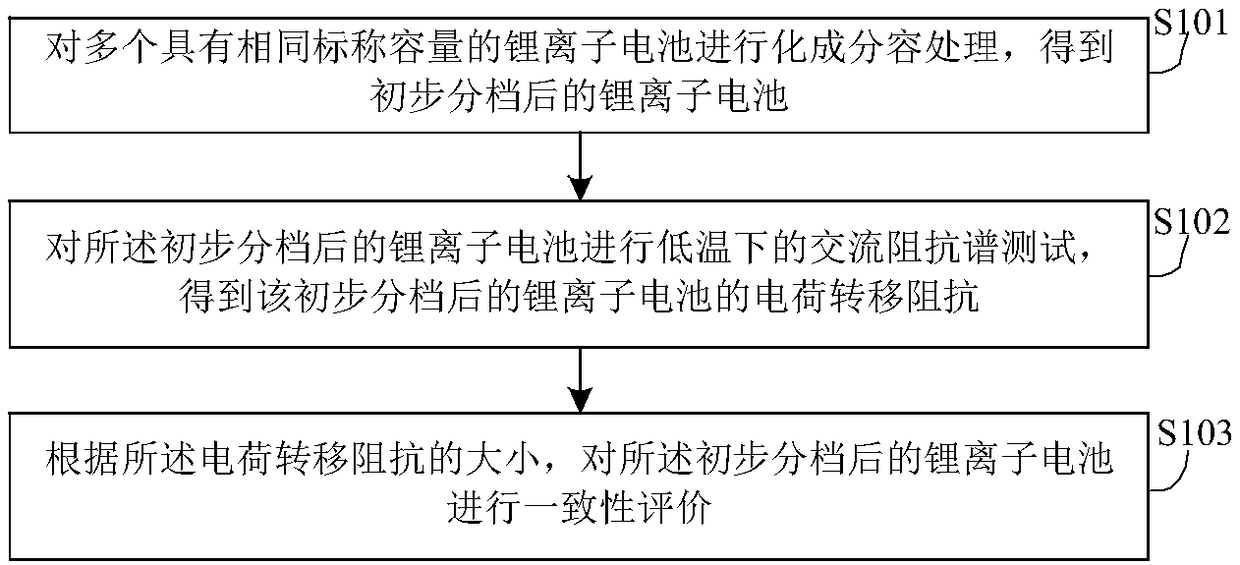
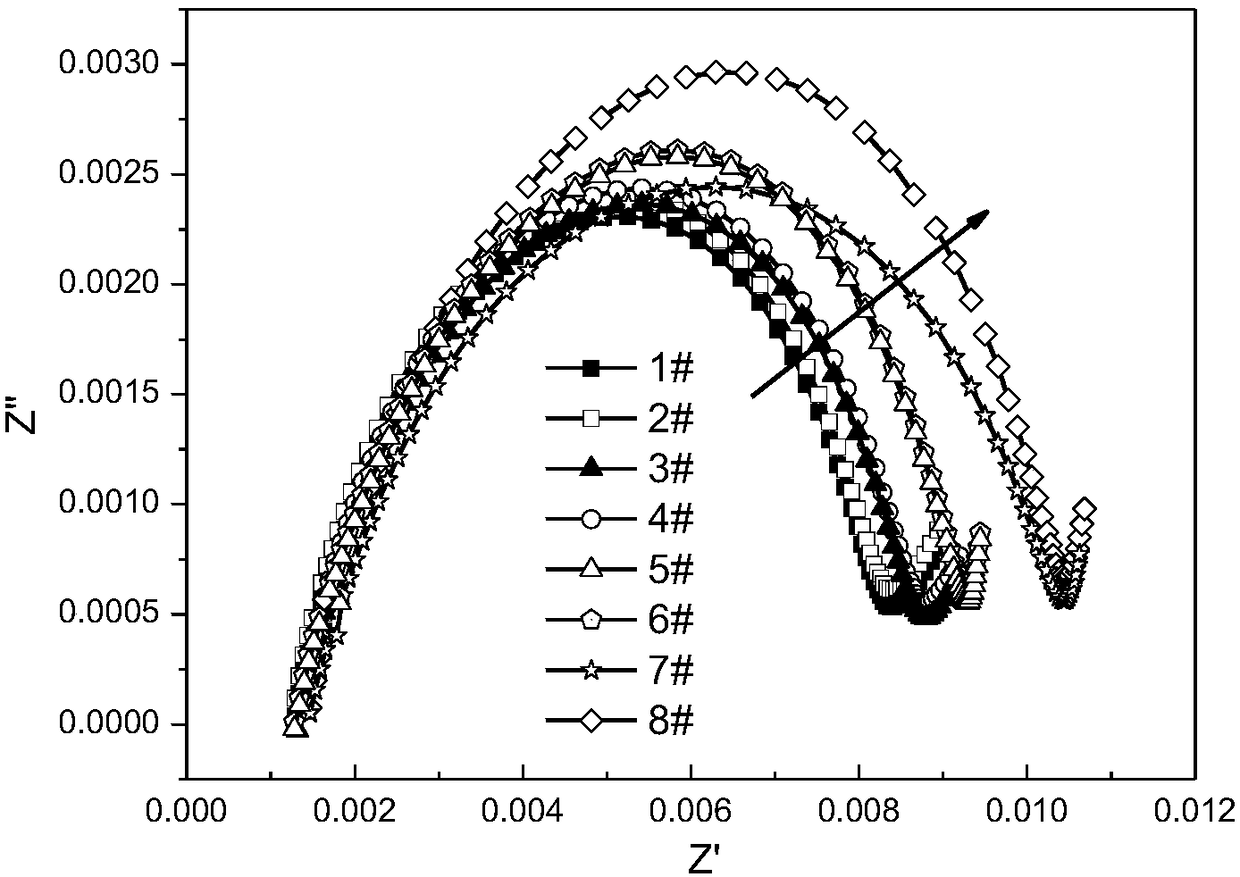
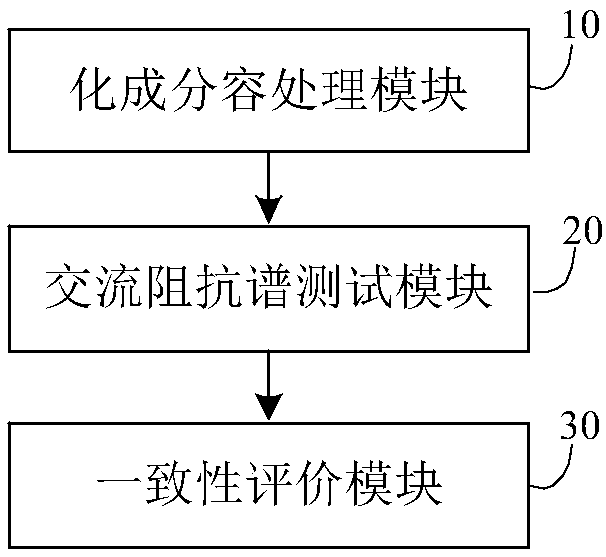
Method and system for evaluating consistency of lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN108511815AAdd AC impedance testGood electrical performance consistencyElectrical testingSecondary cells servicing/maintenanceElectrical batteryAlternating current
Owner:HEFEI GUOXUAN HIGH TECH POWER ENERGY
Layout design of multilayer printed circuit board
InactiveUS20080072204A1Reducing self-impedanceReduce transferCross-talk/noise/interference reductionPrinted circuit aspectsEngineeringElectromagnetic band gap
A layout design of a multilayer printed circuit board (PCB) is provided, which makes use of partial electromagnetic band gap (EBG) structure to constitute a power layer or a ground layer. The EBG structure is mainly used on the linear transmission path from the port of the first integrated circuit to the port of the second integrated circuit on the power layer or the ground layer, so as to overcome the problems concerning self-impedance and transfer-impedance easily occurred in the conventional complete EBG structure.
Owner:INVENTEC CORP
NCM ternary cathode material doped with Mo element in surface layer and bulk phase, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108878868AStable structureImprove electrochemical performanceSecondary cellsPositive electrodesMo elementManganese
The invention relates to an NCM ternary cathode material doped with a Mo element in a surface layer and a bulk phase, and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of chemical energy storage batteries. In total mass of 100% material, Mo element doped in the surface layer and the bulk phase accounts for 0.5-2%, and the other is NCM ternary cathode material. The method comprises the stepsof adding alcohol to a mixture of nickel-cobalt-manganese hydroxide precursor, ammonium molybdate and LiOH.H2O and grinding and mixing uniformly, so as to obtain dry grinded material; calcining the dry grinded material, precalcining the material for 300-400 minutes at 500-550DEG C, then calcining for 800-900 minutes at 700-750DEG C so as to obtain the material. The doped Mo element can stabilizethe material structure, lower charge transfer impedance, and improve electrochemical performance of the material. The method is easy to perform and the process technology are easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Modified nickel oxide negative material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105514421AIncrease the number ofIncrease potential energyCell electrodesSecondary cellsLithiumNitrate
The invention discloses a modified nickel oxide negative material. Nickel oxide with a hollow structure is taken as a matrix and is doped with metal elements (including one or more of lithium, sodium and potassium). A preparation method of the modified nickel oxide negative material comprises the following steps: dissolving metal element nitrate and nickel nitrate in water for mixing uniformly to obtain a mixed liquor, and then performing spray pyrolysis treatment on the obtained mixed liquor, thereby obtaining the modified nickel oxide negative material, wherein a metal element is one or more of lithium, sodium and potassium, and the molar concentration ratio of metal ions and nickel ions in the mixed liquor is equal to (1:100)-(10:100). The nickel oxide negative material has a hollow spherical feature, so that diffusion paths of lithium ions are reduced, and the volume change in a circulating process is alleviated to a certain degree. As nickel oxide is doped with the metal elements including lithium, sodium and potassium, the conductivity of the material is improved, the charge transfer impedance is lowered, and the electrochemical performance of a battery is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
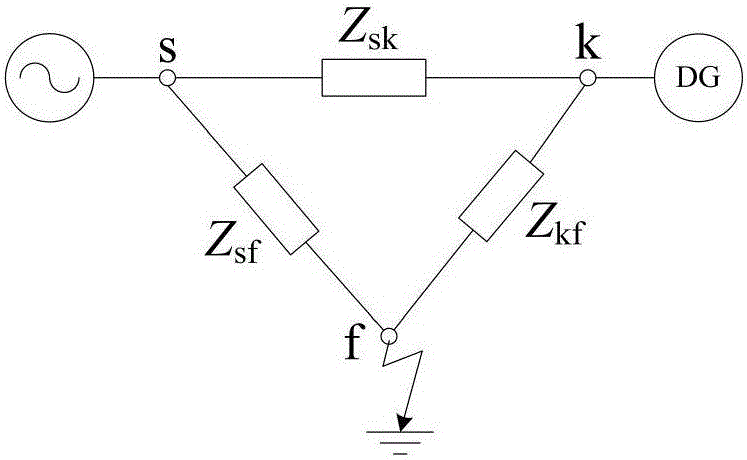
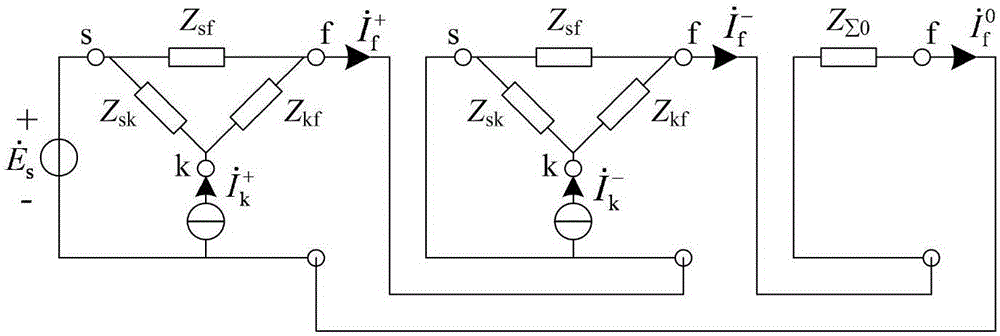
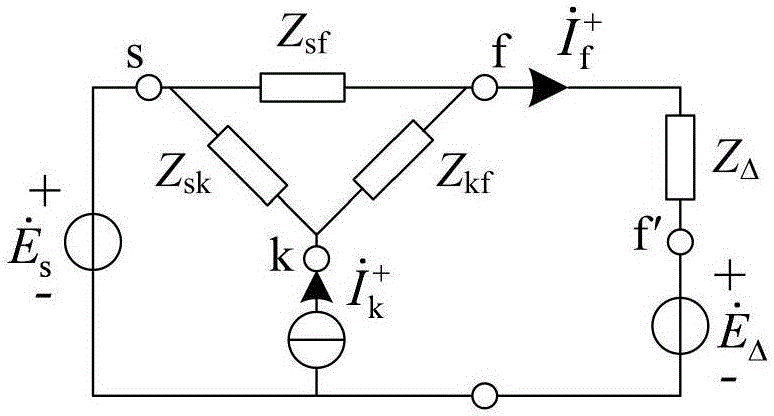
Operational curved surface method for determining asymmetric short-circuit current of distributed generation access power grid
ActiveCN105162099AEmergency protective circuit arrangementsSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPoint boundaryPower grid
The invention discloses an operational curved surface method for determining asymmetric short-circuit current of a distributed generation access power grid. The method comprises steps of acquiring a three-node simplified network and transfer impedance between different nodes by using network simplification when multiple DGs and conventional generators have access to the power grid; in view of different types of asymmetric short-circuit faults, ignoring the influence of DG zero-sequence current injection, obtaining a short-circuit calculation compound sequence network and positive and negative sequence augmented networks according to a fault point boundary condition, and calculating the additional voltage and additional impedance in the augmented networks; performing Thevenin equivalent on systems except the DG access points in the positive and negative sequence networks, and deriving short-circuit impedance and open-circuit voltage open-circuit voltage computational formulas when DC injection current is zero; establishing a operational curved surface of a DG short-circuit current negative-sequence component, computing impedance, and positive and negative sequence open-circuit voltage in order to obtain a DG short-circuit current negative-sequence component; calculating a DG asymmetric short-circuit current positive-sequence component in combination with a three-phase short-circuit operational curved surface according to a DG access positive-sequence augmented network access point equivalent open-circuit voltage computing method.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Preparation method of phosphate-coated metal-doped ternary cathode active material and preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN110400929AImprove cycle stabilityImproved magnification performanceSecondary cellsPositive electrodesPhosphatePhosphoric acid
The invention belongs to the technical field of cathode materials, and specifically discloses a preparation method of a phosphate-coated metal-doped ternary cathode active material. A ternary cathodematerial uniformly coated with nanometer oxide is obtained through sintering after simple liquid phase ultrasonic treatment, the ternary cathode material is uniformly coated with the metal phosphate after high temperature treatment with a phosphoric acid source to obtain a metal ion-doped ternary cathode material. The ion surface diffusion and internal transfer impedance can be reduced through physical coating and cation doping, the side reaction between the electrolyte and the cathode material is reduced, and the layered structure of the material is stabilized, so that the cycle stability andthe rate performance of the ternary cathode material are greatly improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Cobalt selenide nanometer material serving as electrode material of supercapacitor and preparation method of cobalt selenide nanometer material
InactiveCN106098393ALarge specific surface areaImprove space utilizationHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureCapacitanceNanowire
The invention discloses a Co<0.85>Se nanometer material serving as an electrode material of a supercapacitor and a preparation method of the Co<0.85>Se nanometer material. The nanometer material adopts a fibrous nanometer structure. The Co<0.85>Se nanometer material adopts a two-step hydrothermal synthesis method, and the two-step hydrothermal synthesis method comprises the steps of firstly, preparing a precursor Co(OH)(CO<3>)<0.5> nanowire by a hydrothermal reaction method; and secondly, carrying out selenization processing on the precursor by the hydrothermal reaction method to obtain the Co<0.85>Se nanometer material. When placed in a three-electrode system for test, the nanometer electrode material is endowed with high specific capacity of 1,249F / g under current density of 2A / g, the specific volume over 80% still can be maintained after 3,000 cycles of charging and discharging under 100mA current, and the charge transfer impedance is 0.32 ohm / cm<2>. The Co<0.85>Se nanometer electrode material prepared according to the method has the advantages of high specific capacitance, good cycle performance, simplicity in preparation method and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide modified graphite felt electrode and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108598498AImprove hydrophilicityHigh adsorption rateCell electrodesFreeze-dryingNitrogen doped
The invention discloses a nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide modified graphite felt electrode and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly dispersing a mixed solution of a nitrogen-containing compound and graphene oxide into a hydrophilically treated graphite felt electrode, freeze-drying to obtain a graphite felt composite electrode preform, and thenplacing the graphite felt composite electrode preform in the tube furnace for heat treatment, so as to obtain the graphite felt electrode. Another preparation method comprises the steps of: firstly dispersing a mixed solution of graphene oxide into a hydrophilically treated graphite felt electrode, freeze-drying to obtain a graphite felt composite electrode preform, and then separately performingheat treatment with independent control of the temperature on the graphite felt composite electrode perform and nitrogen-containing compound under N2 atmosphere protection, so as to obtain the graphite felt electrode. The nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide-modified graphite felt electrode prepared by the above two methods is capable of improving the anode reaction redox current, enhancing theelectrochemical reversibility and reducing the charge transfer impedance, and has the potential to improve the performance of the all-vanadium flow battery.
Owner:SHENYANG JIANZHU UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of shape-controllable ordered layer porous chromium carbide skeleton carbon material for supercapacitor
ActiveCN103771392AShape controllable and diverseFast transferMaterial nanotechnologyHybrid capacitor electrodesCapacitanceChromium carbide
The invention discloses a preparation method of a shape-controllable ordered layer porous chromium carbide skeleton carbon material for a supercapacitor. In a preparation process, a chromium carbide precursor with a special shape is synthesized through template control, a chromium atom is removed by using an etching agent in situ to obtain a micropore, then orderly arranged meso pores with regular pore passages are obtained by removing a mesopore template to form porous carbon hierarchically combined by meso pore and micropores, wherein the shape of the chromium carbide framework carbon can be controlled through a template process, the relative content of the micropores and the meso pores can be adjusted through controlling a synthesis reaction condition and a raw material ratio, and thus the ordered layer porous chromium carbide skeleton carbon the pore structure and the pore diameter distribution of which are accurate and adjustable in atom-scale level and controllable in shape is obtained. According to the preparation method, a shape-controlled porous electrode material for a novel supercapacitor, which is high in specific capacitance, small in ion diffusion and transfer impedance, better in rate capability, excellent in cycle performance and controllable in shape can be obtained.
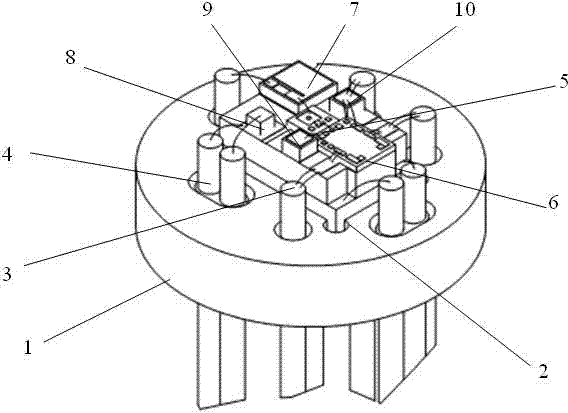
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Method and device for determining acoustical transfer impedance
The method comprises generating an acoustical volume velocity Q in the listening position, measuring a response quantity p, such as sound or vibration, at a suspected source position resulting from the volume velocity Q, and determining the acoustical transfer impedance Zt as the response quantity p divided by the acoustical volume velocity Q, Zt=p / Q. According to the invention the acoustical volume velocity Q is generated using a simulator (10) simulating acoustic properties of at least a head of a human being, the simulator comprising a simulated human ear (14, 15) with an orifice in the simulated head and a sound source (30) for outputting the acoustical volume velocity Q through the orifice. The output volume velocity Q from the orifice of an ear is estimated from measurements with two microphones inside the corresponding ear canal.
Owner:BRUEL & KJAER SOUND & MEASUREMENT
Method for recycling retired battery
InactiveCN110021796AAchieve recyclabilityPerformance fixesWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingElectrical batteryLithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a method for recycling a retired battery, and relates to the technical field of recycling of lithium ion batteries. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, selecting single retired batteries with actual capacity which is 60-80% of the nominal capacity, and performing grading on the batteries based on battery capacity; next, according to the different grades, injecting the batteries with electrolytes of different weights and sealing the batteries; and finally, carrying out grading and grouping again according to the battery capacity and the charge transfer impedance after the batteries are activated. By adopting the method disclosed by the invention, the capacity of the batteries repaired by the method can be recovered to the level of an in-service powerbattery, and the recycling performance is high.
Owner:SHENZHEN PANDPOWER CO LTD
Nanomaterial used as supercapacitor electrode material, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106006576AHigh specific capacitanceIncrease contact spaceHybrid capacitor electrodesMetal selenides/telluridesCapacitanceInternal resistance
The invention discloses a Co0.85Se nanomaterial used as a supercapacitor electrode material, and a preparation method thereof. The nanometerial is a connected space hole-containing three-dimensional porous nanostructure formed through interlacing nanosheets. The Co0.85Se nanomaterial is synthesized through a one-step hydrothermal technology without using an organic template or a surfactant, so the method has the advantages of simple preparation, energy saving, and suitableness for industrial production. A Co0.85Se nanomaterial electrode containing the synthesized nanosheet structure is tested in a three-electrode system, a KOH solution is adopted as an electrolyte, the electrode nanomaterial has a high specific capacity of 1528F / g at a current density of 1A / g and still keeps 90% or above of the initial capacitance after 5000 frequency cycle charge and discharge at a high current of 10A / g, the internal resistance of the electrode nanomaterial is 1.4omega / cm<2>, and the charge transfer impedance is 0.73omega / cm<2>. The Co0.85Se electrode nanomaterial has the advantages of large specific surface area, high specific capacitance, good cycle performances, simple preparation cost and low cost.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com