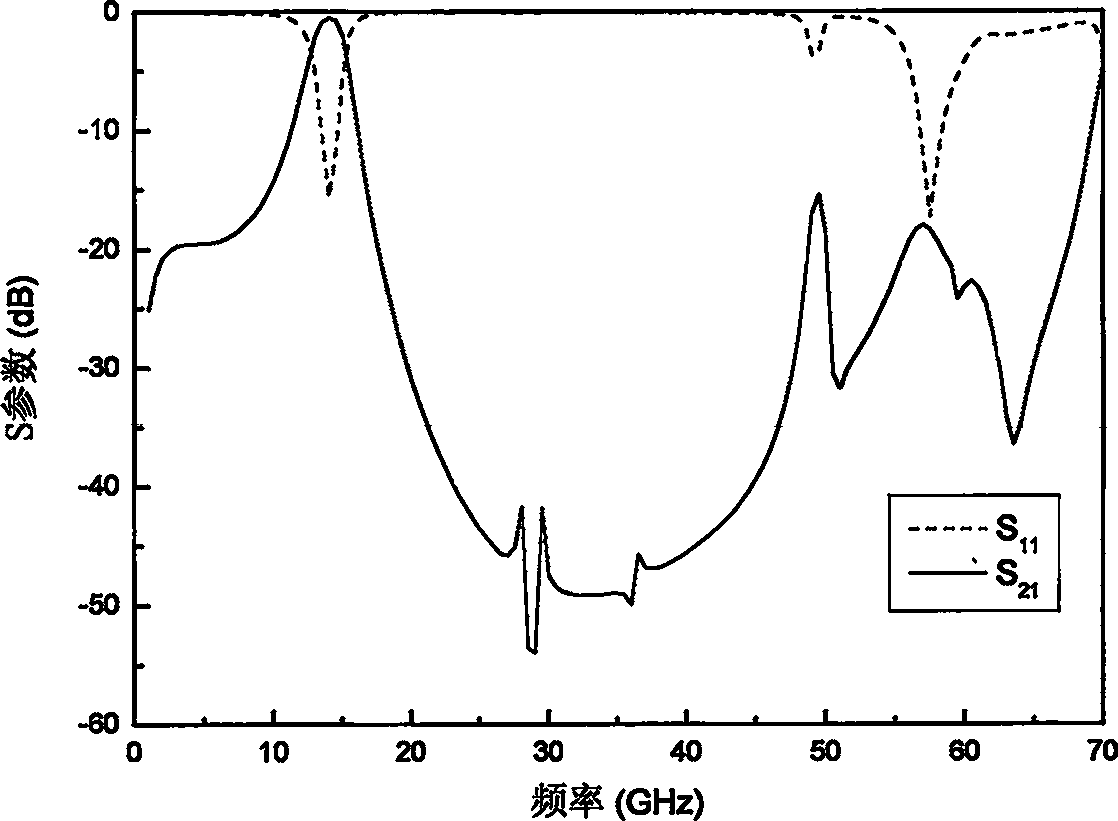
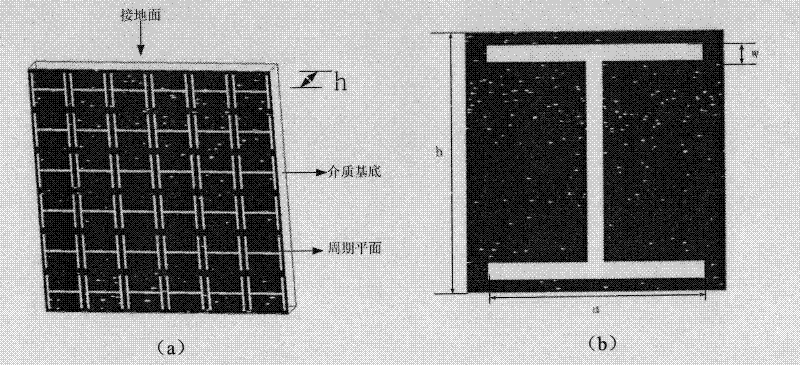
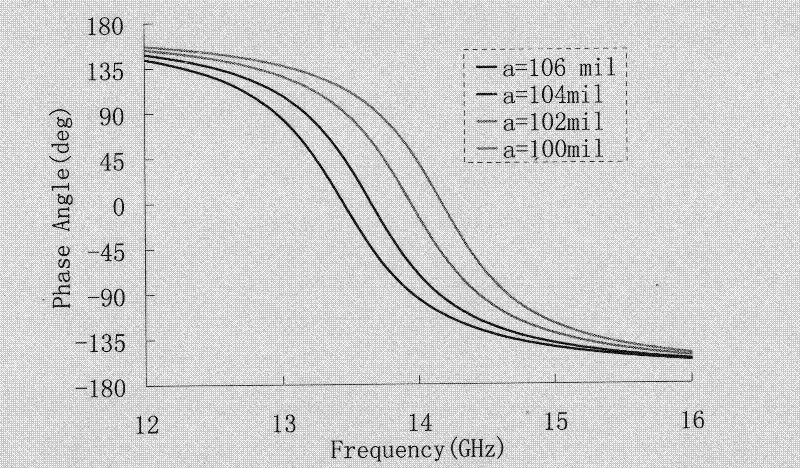
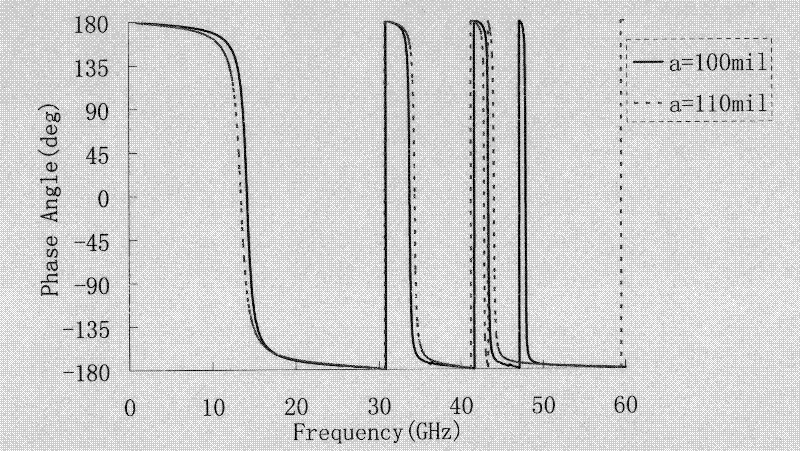
Patents
Literature
362 results about "Electromagnetic band gap" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
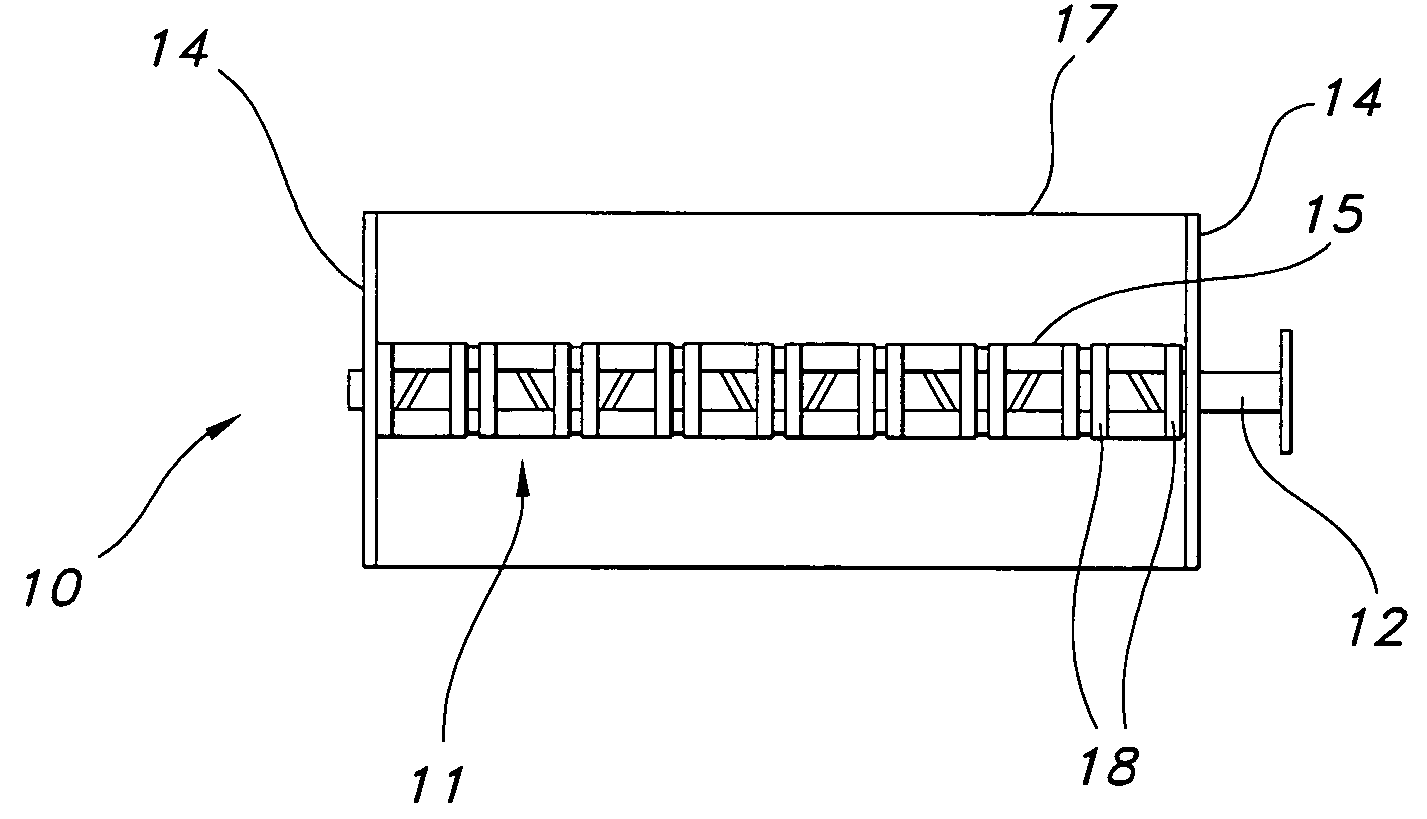
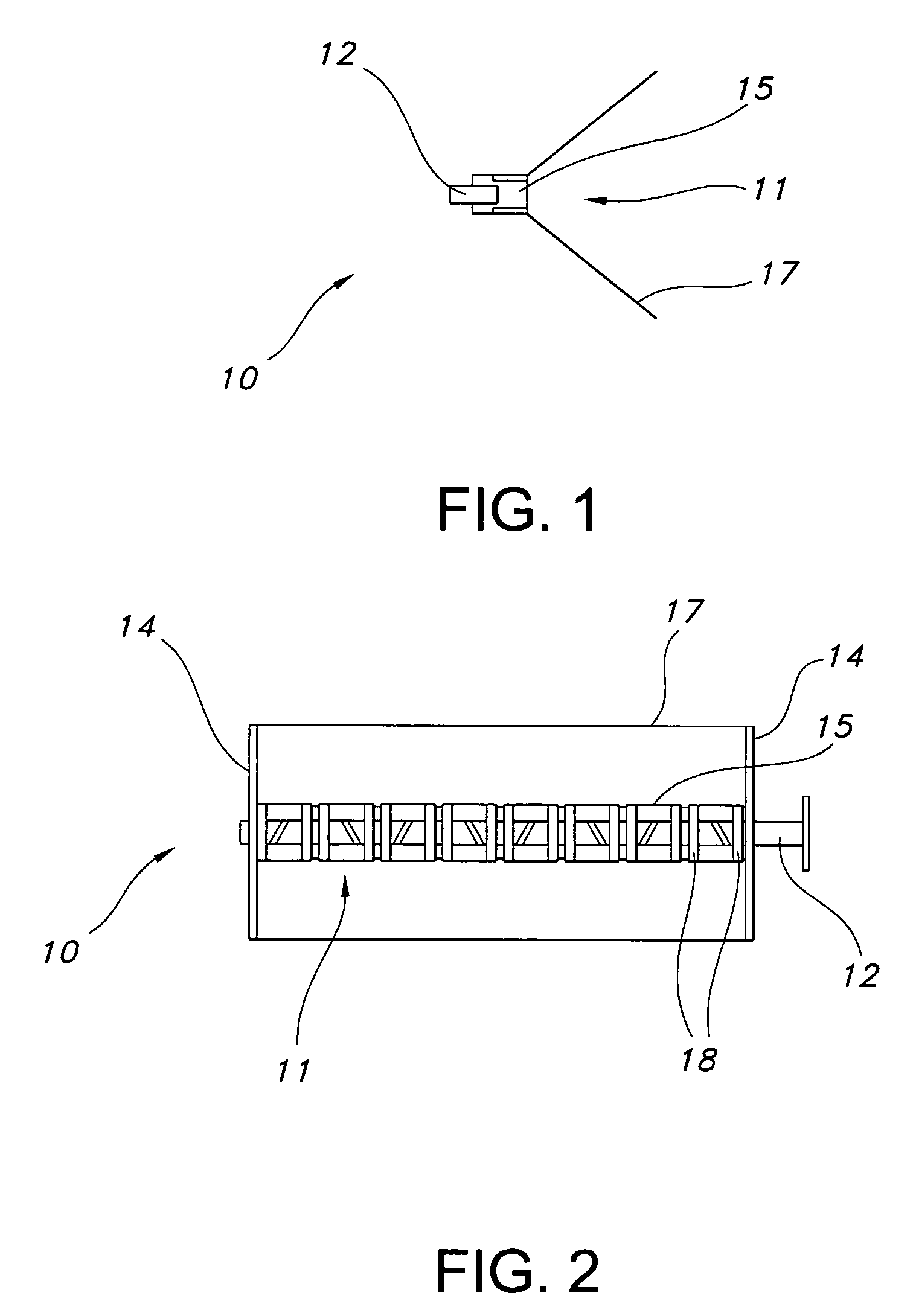
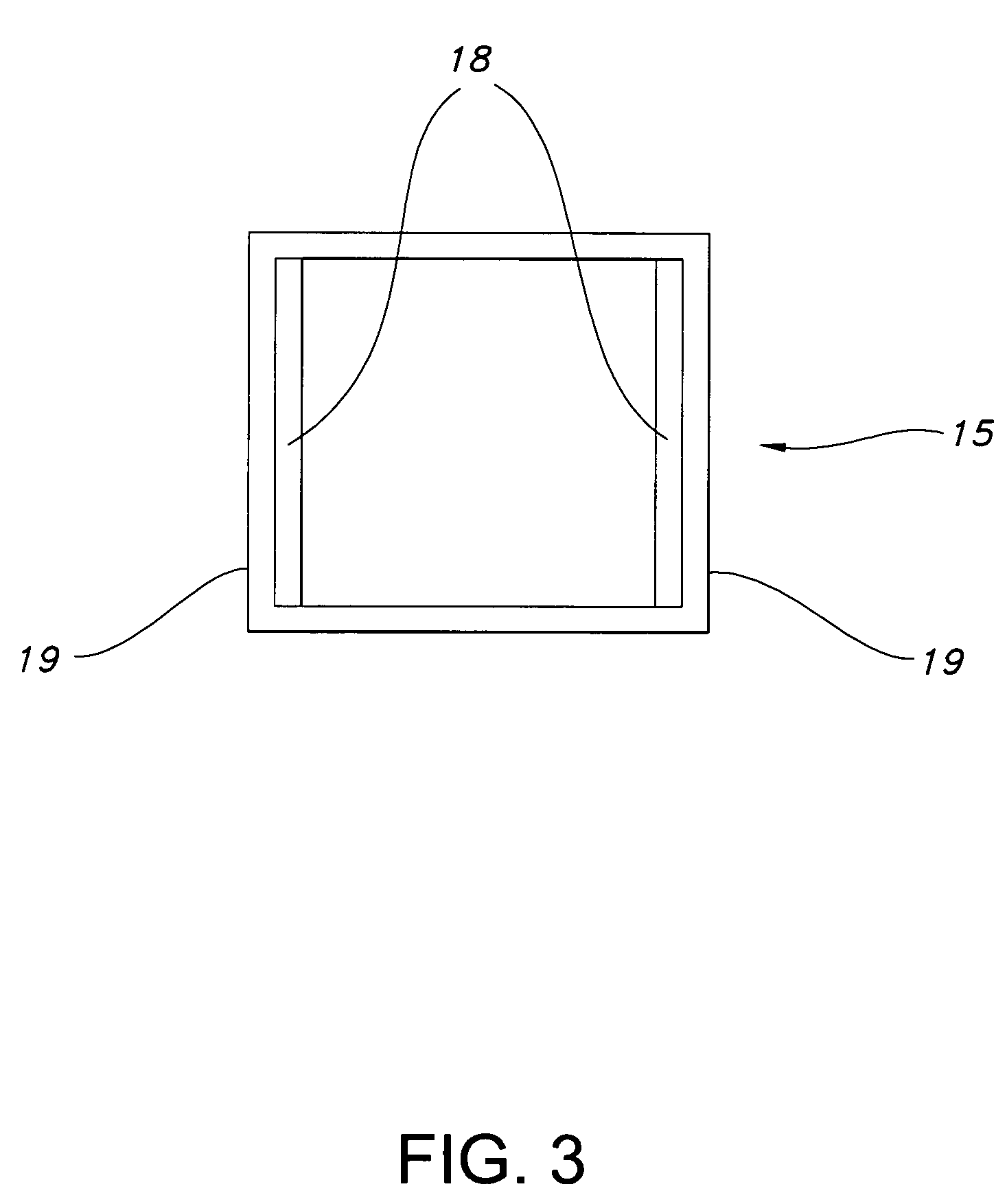
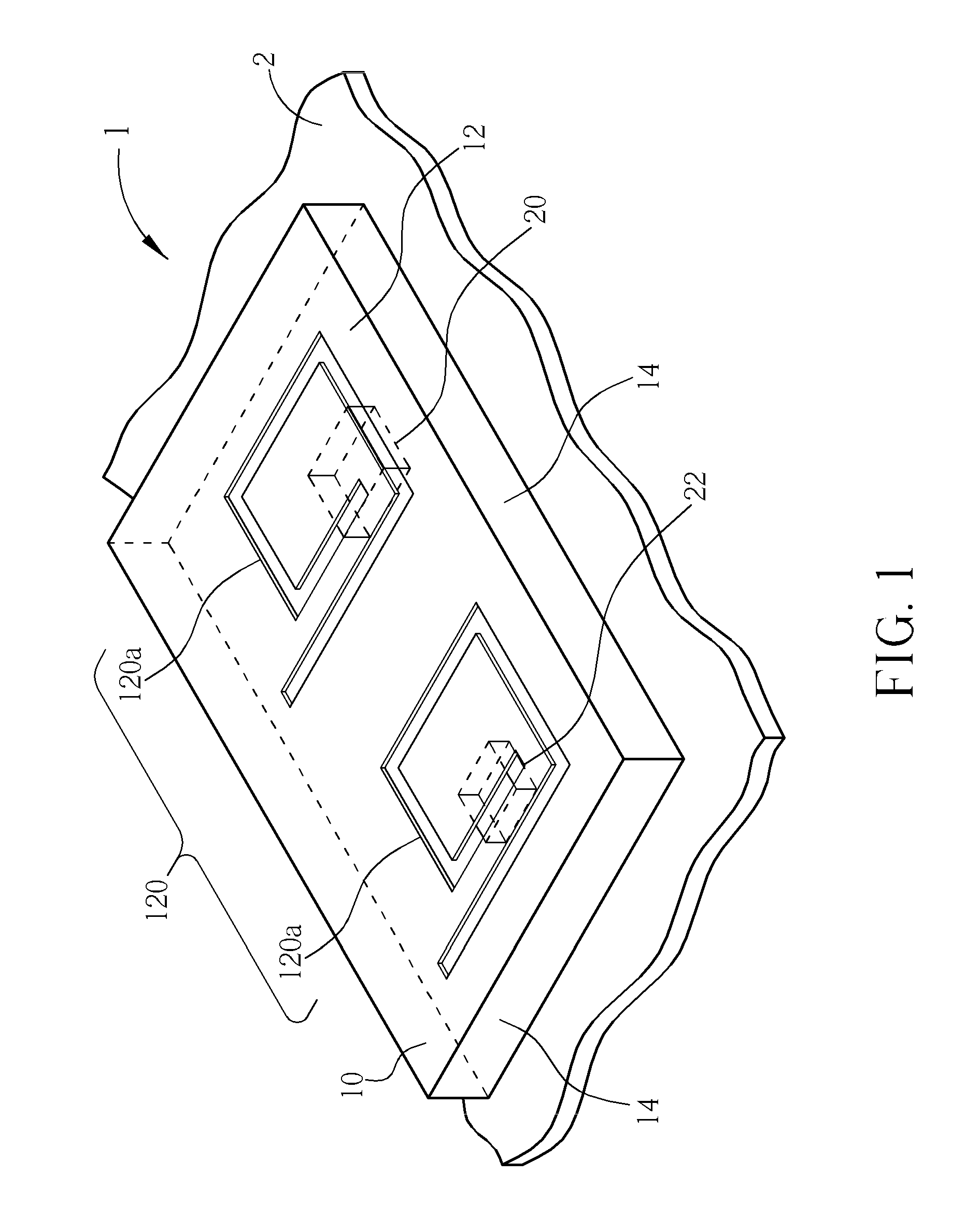
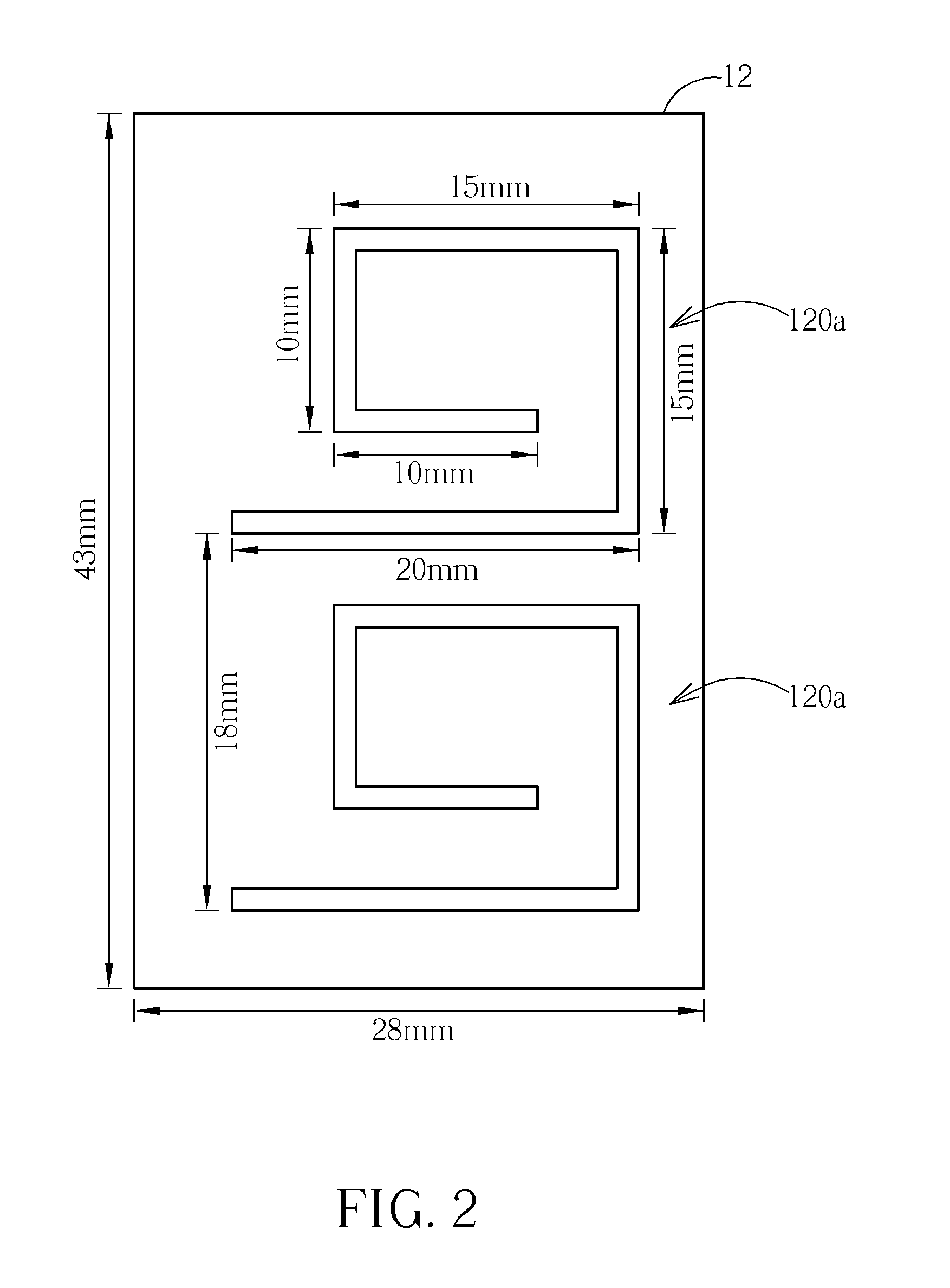
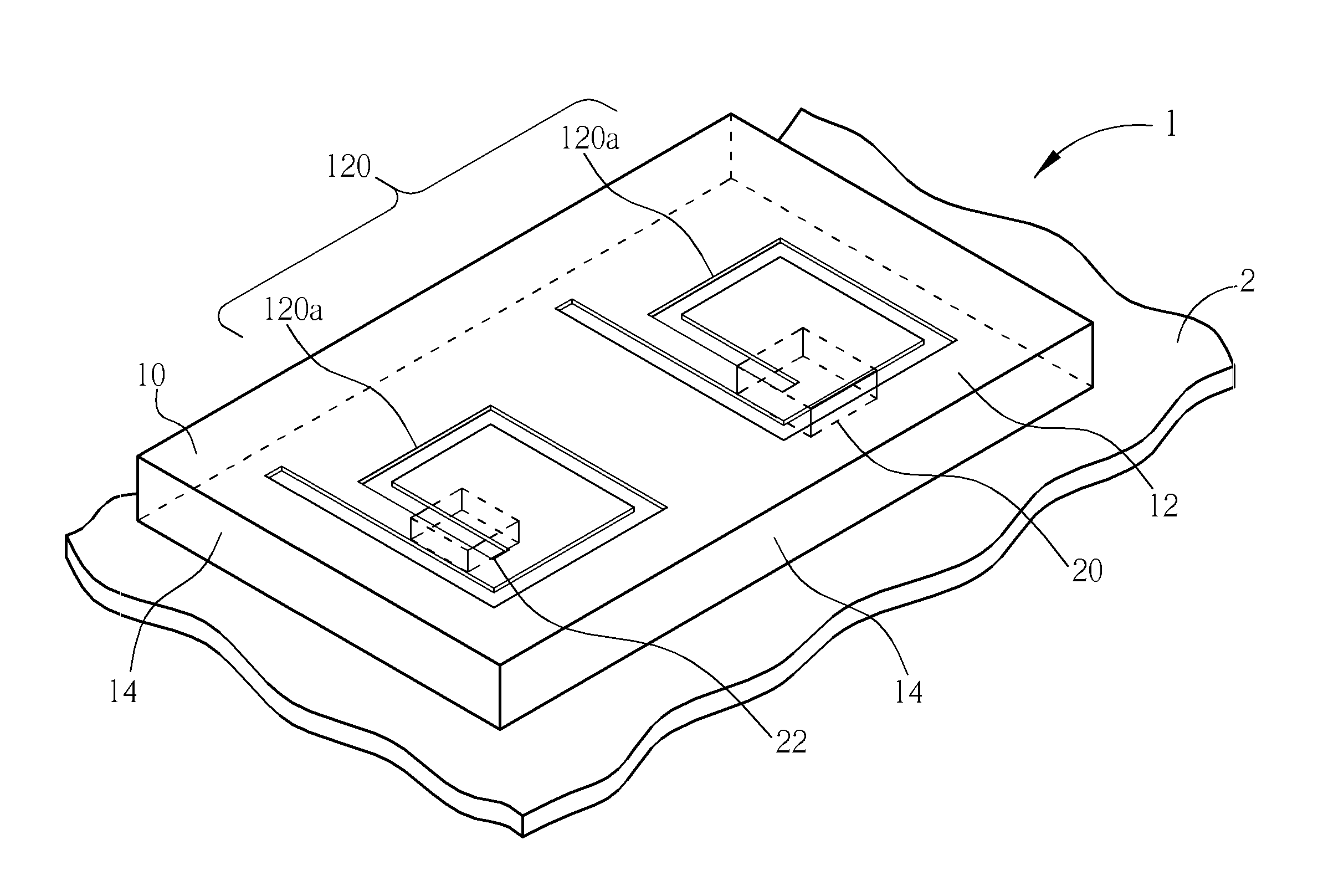
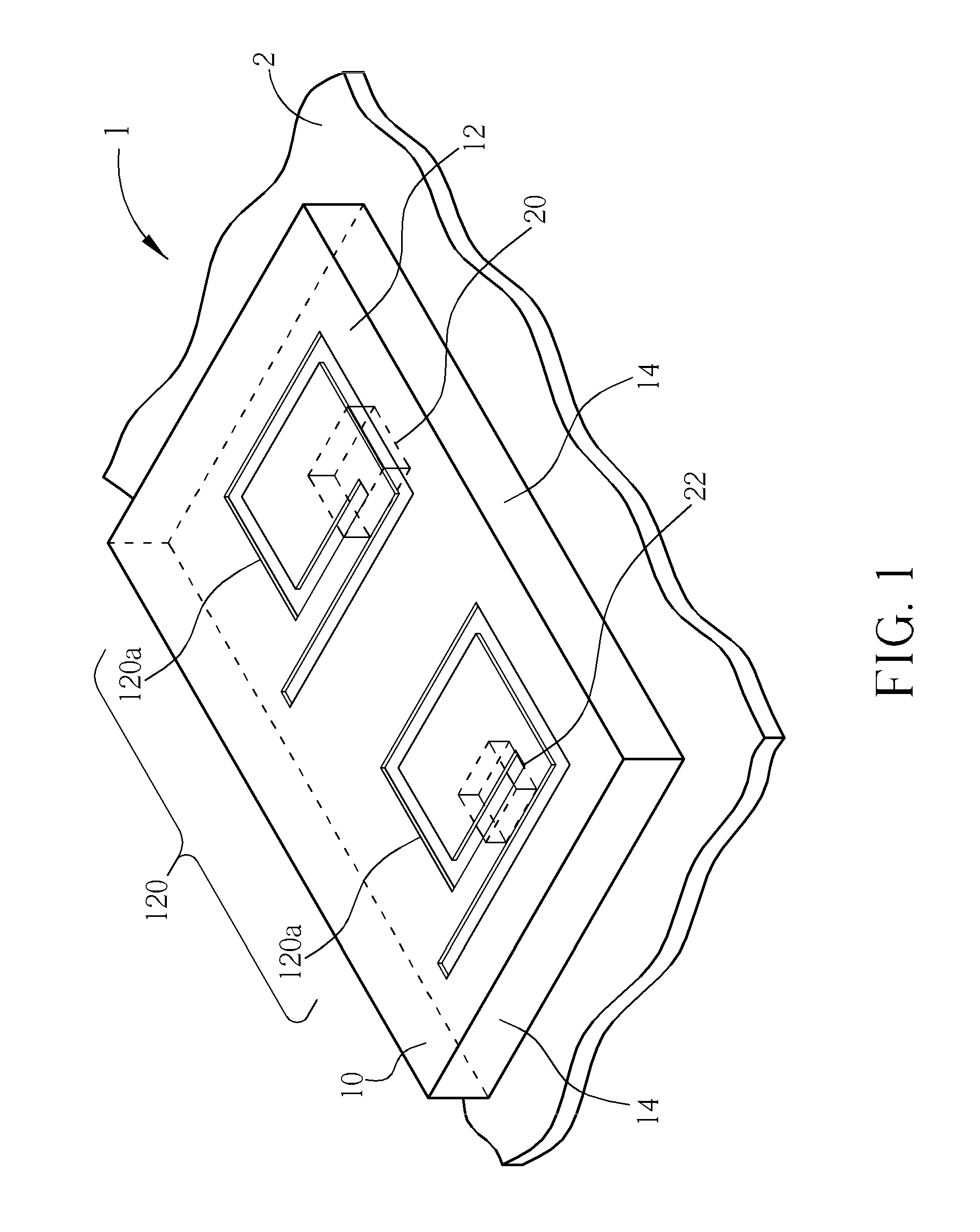
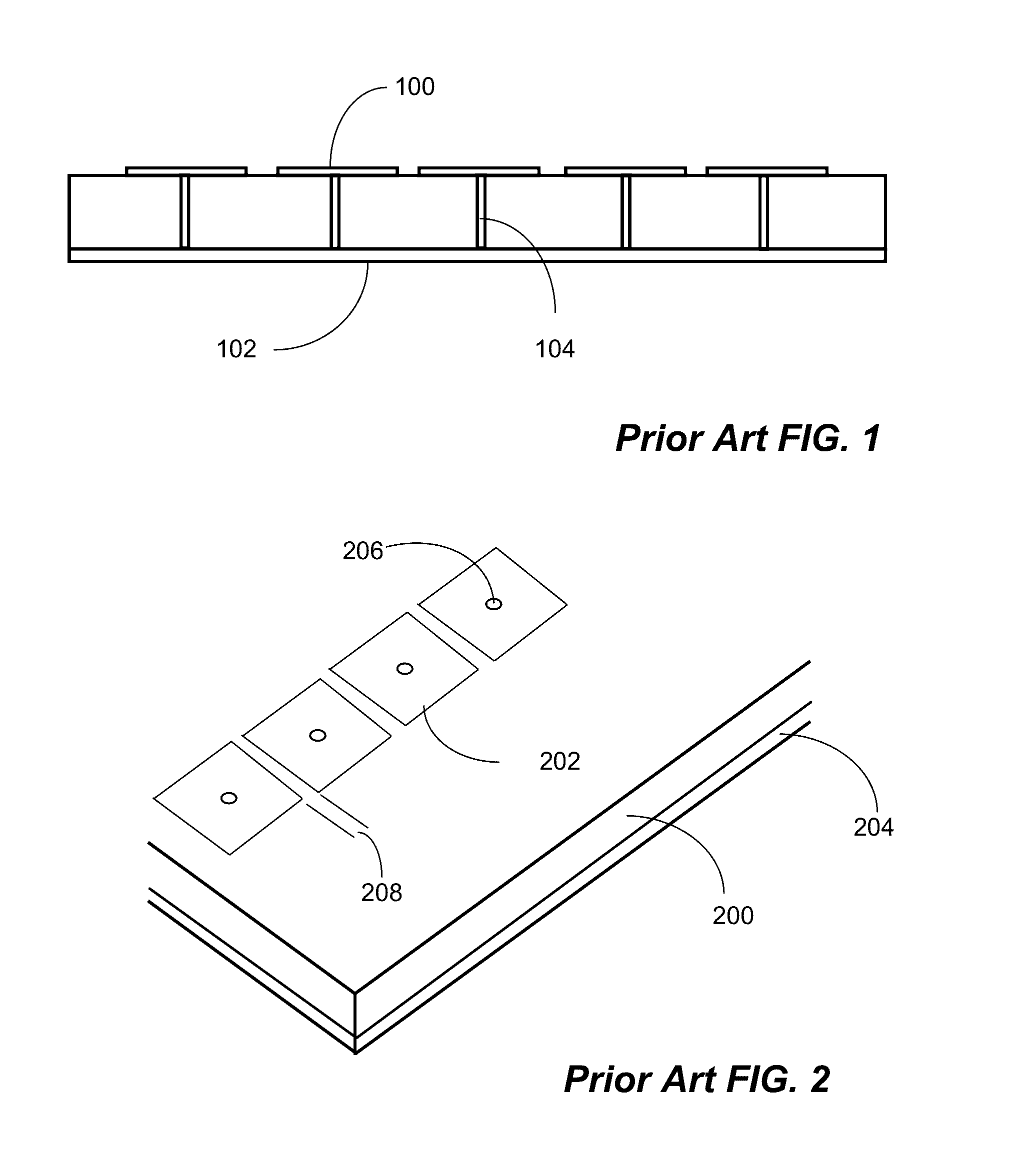
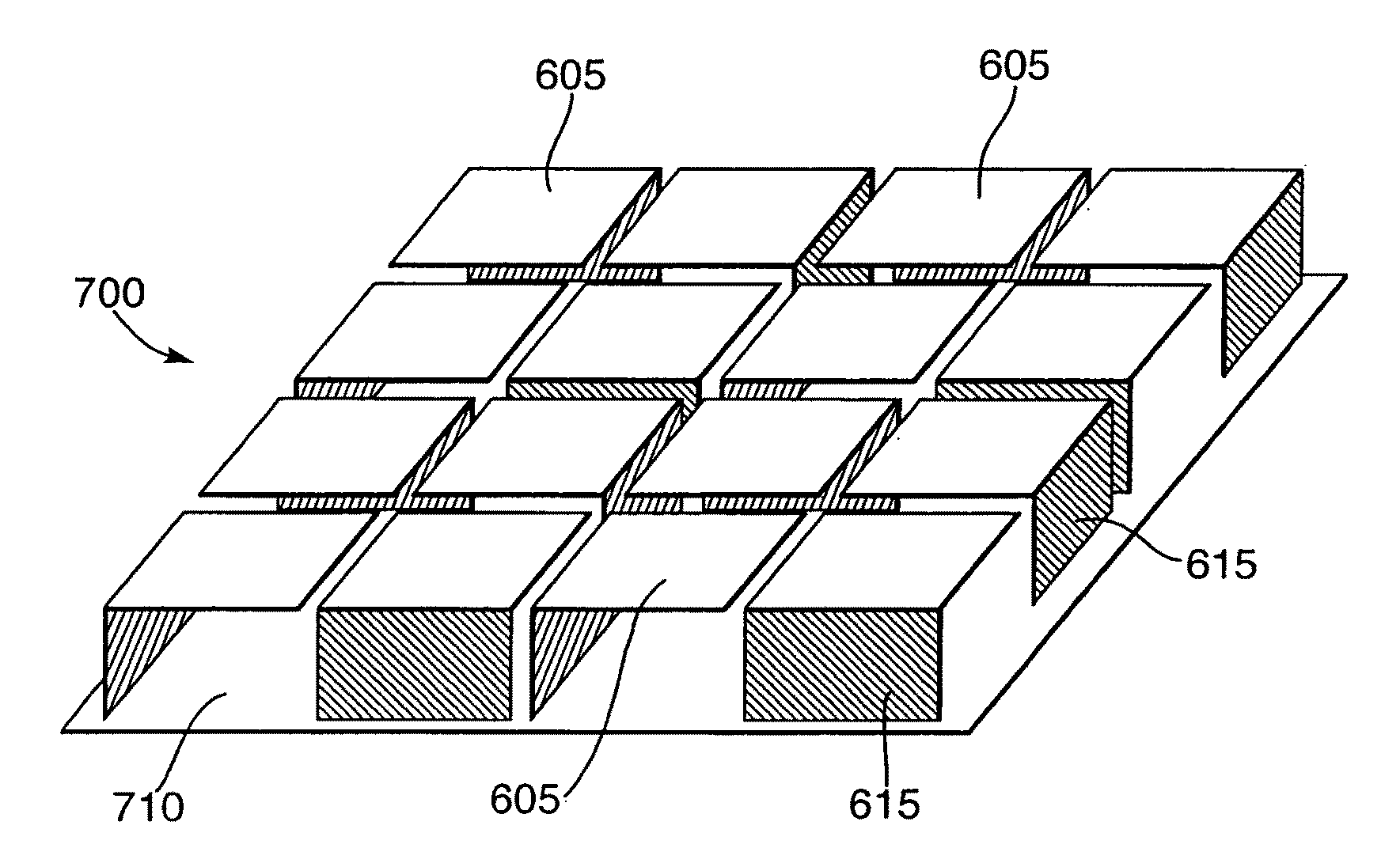
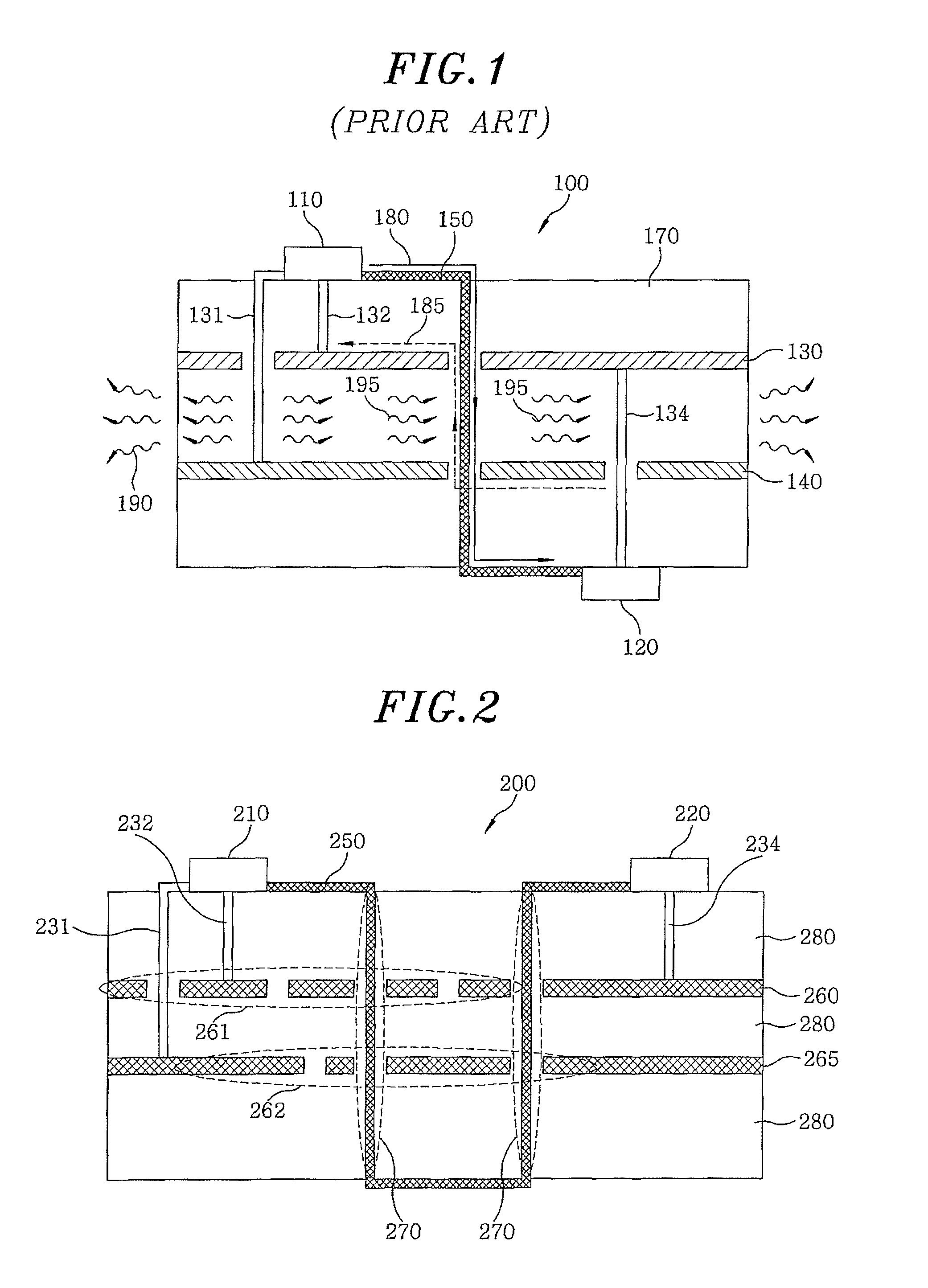
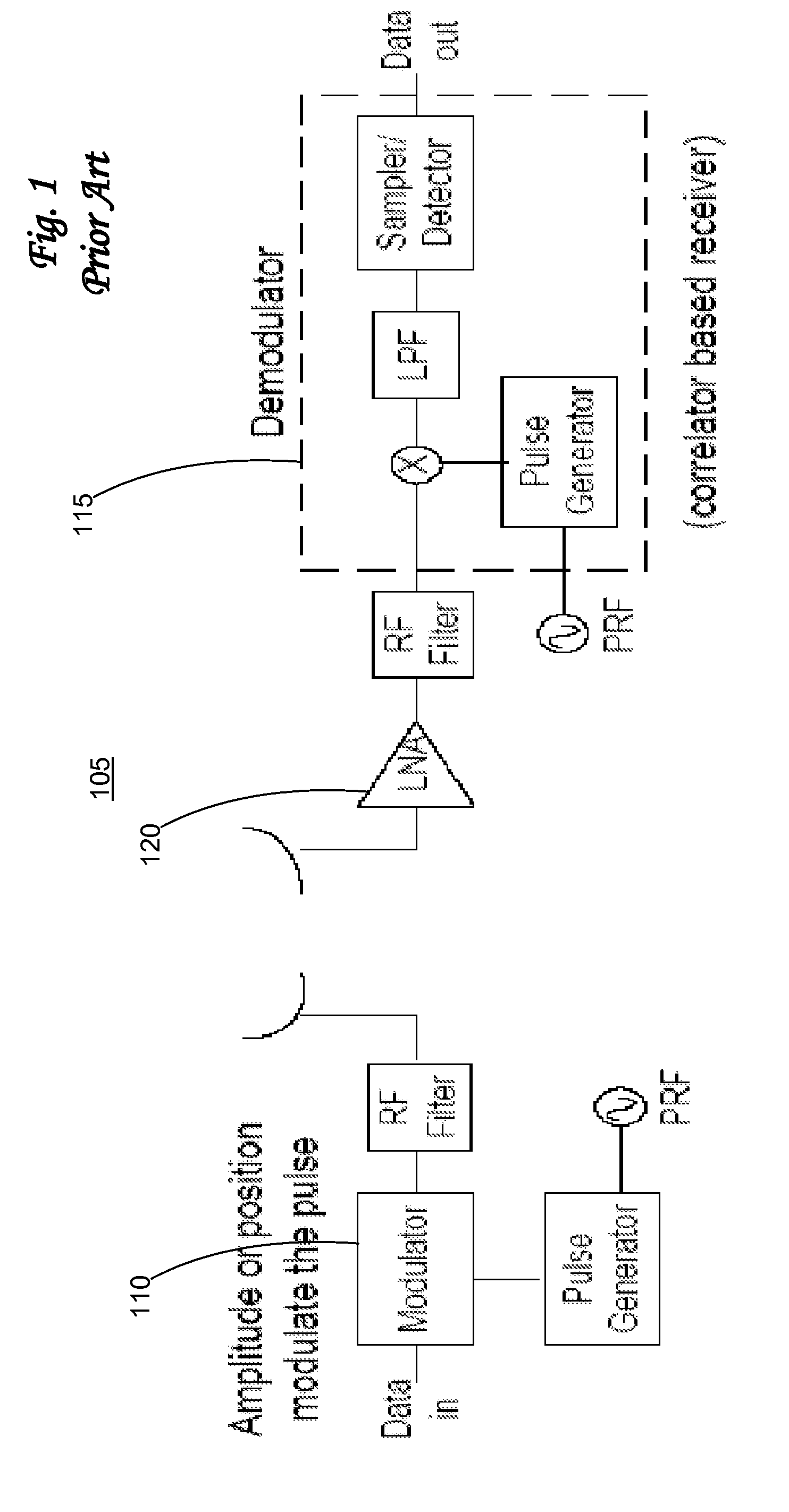
Low-cost one-dimensional electromagnetic band gap waveguide phase shifter based ESA horn antenna
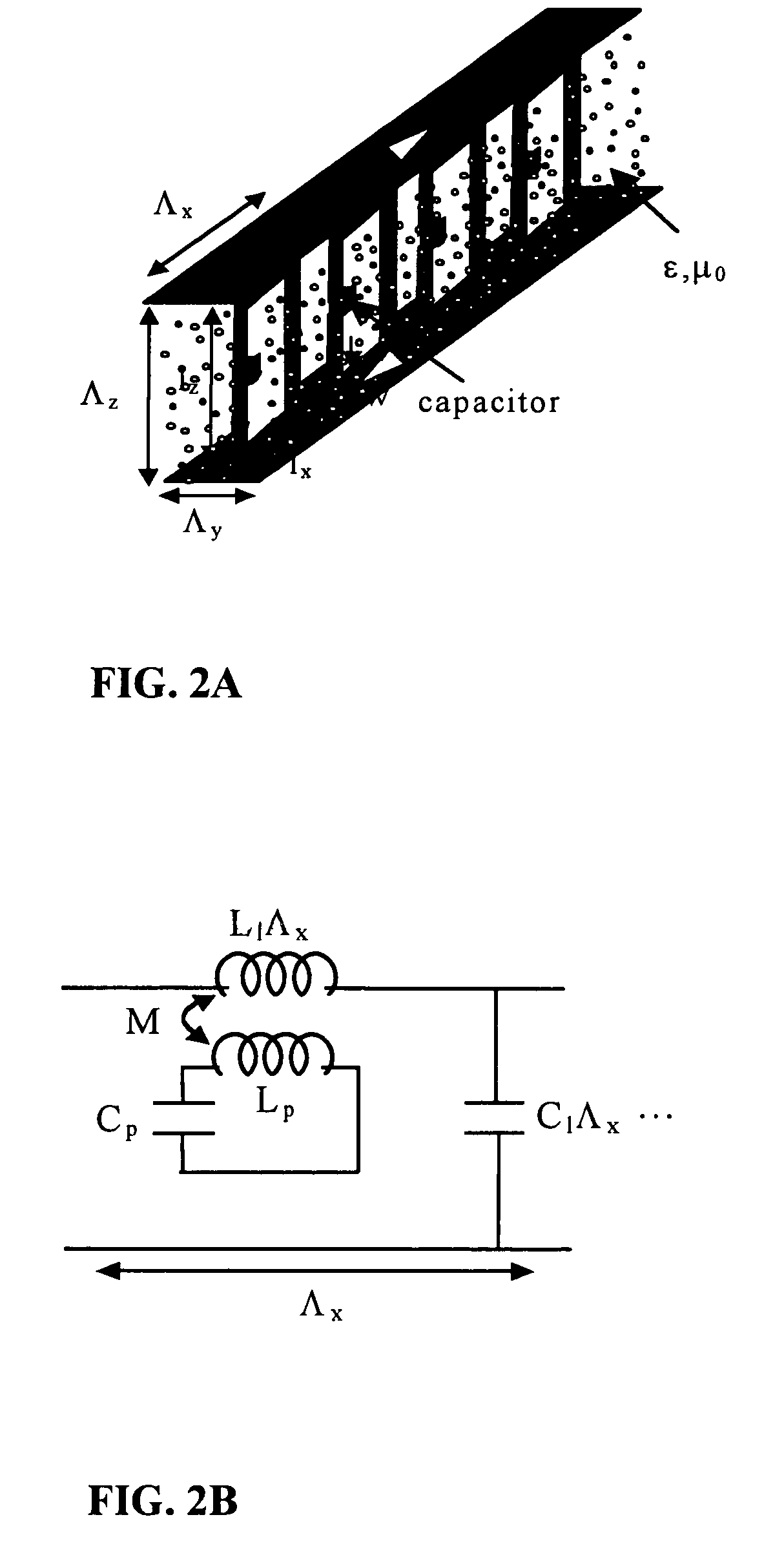
A one-dimensional electromagnetic band gap (EBG) waveguide phase shifter electronically scanned array (ESA) horn antenna utilizes a linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters for scanning and radiating a beam. A linear array feed feeds the linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters. A horn directs radiation from the linear array of EBG waveguide phase shifters. Each of the EBG waveguide phase shifters is a waveguide with vertical and horizontal sidewalls. EBG devices are located on the vertical waveguide walls to shift phase to scan the beam.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
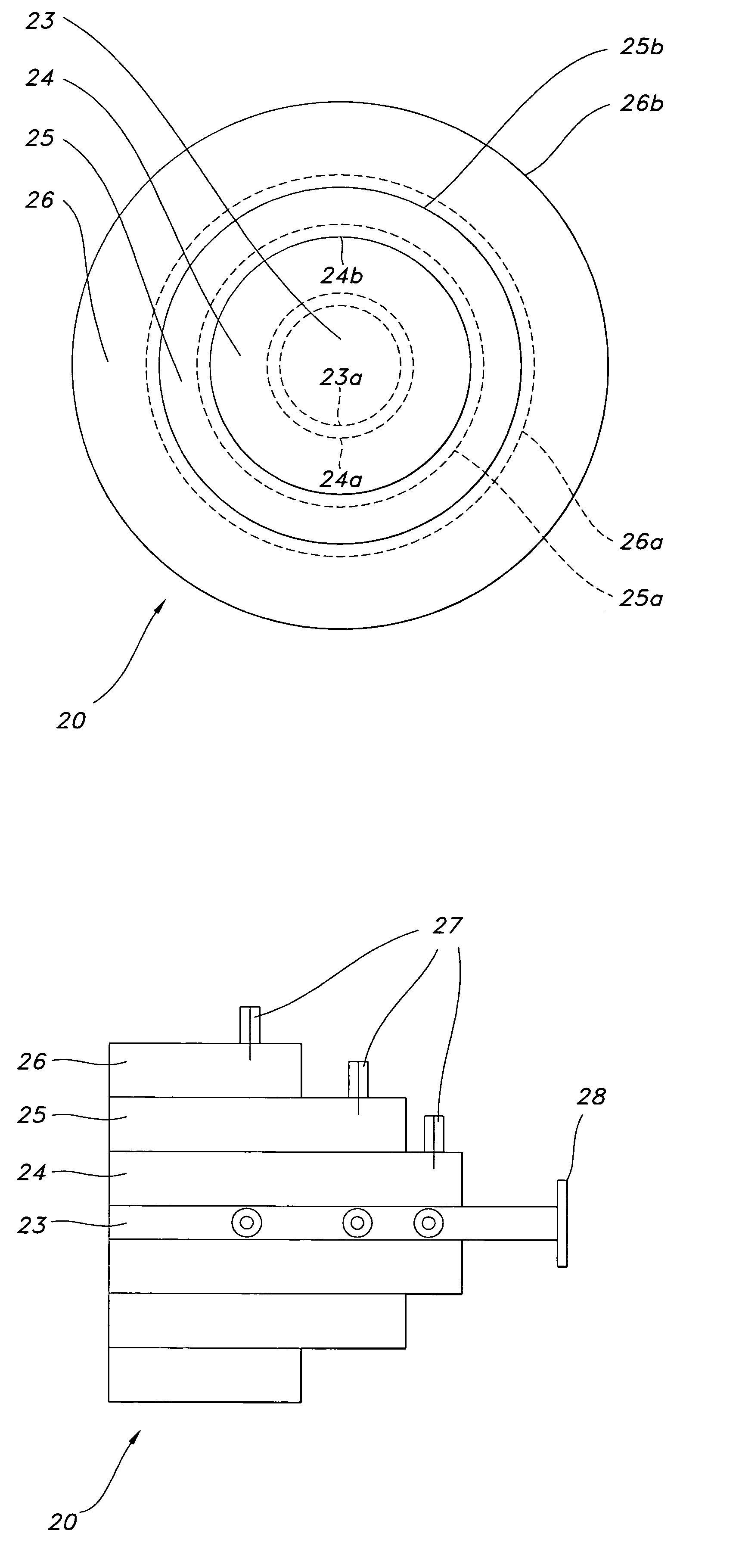
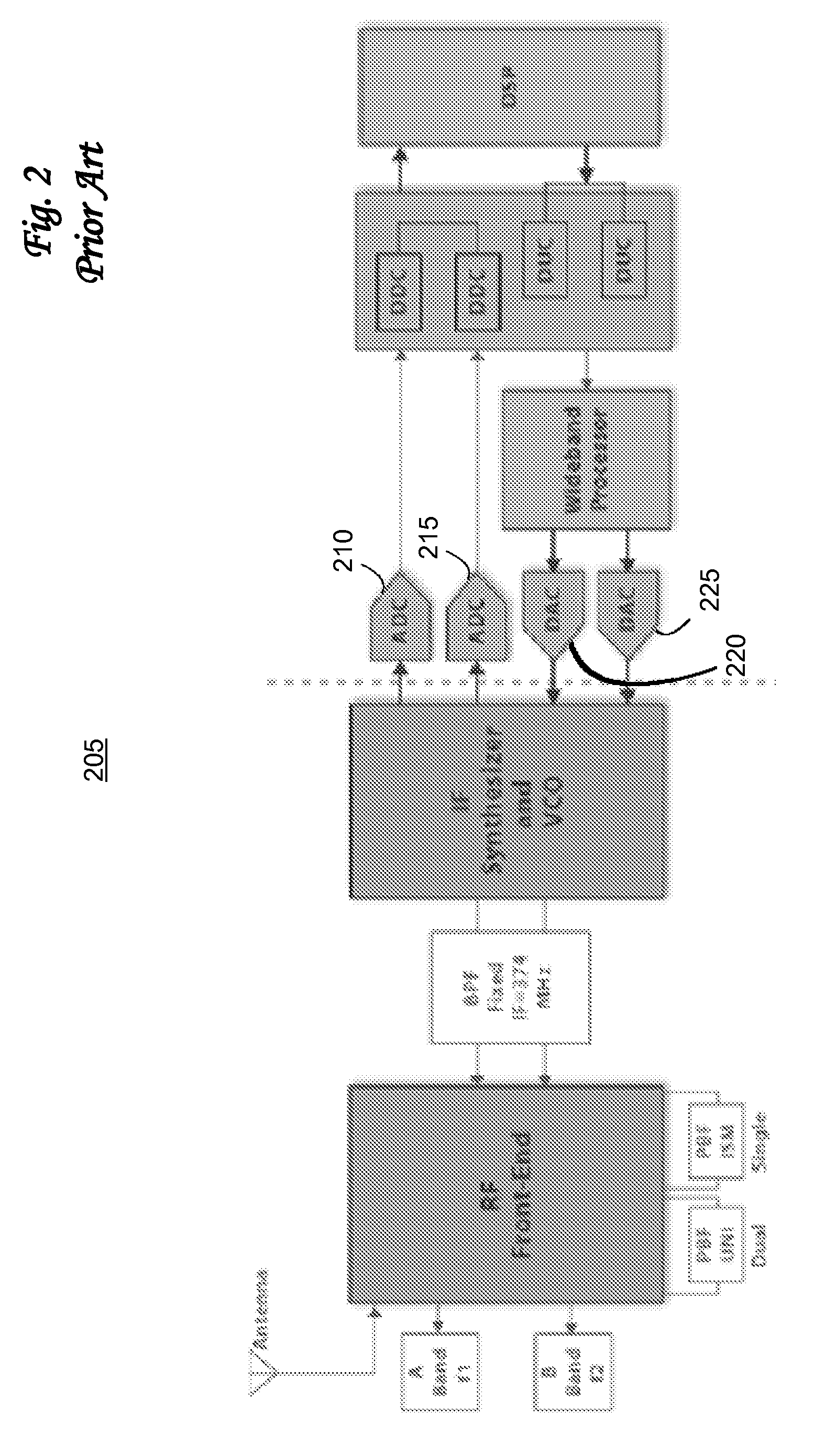
Multiband waveguide reflector antenna feed
A multiband waveguide reflector antenna feed comprises waveguide feeds in a concentric architecture. A waveguide feed is located in the center and coaxial waveguide feeds are disposed around the center feed. The waveguide feeds may be all-metallic with the center feed operating in a TE11 mode and the coaxial feeds operating in a coaxial TE11 mode. The waveguide feeds may have electromagnetic band gap (EBG) surfaces on waveguide surfaces. The center waveguide feed may have an EBG outer conductor surface and operate in a circular waveguide TEM mode. The coaxial waveguide feeds may have EBG inner and outer conductors and operate in a circular waveguide TEM mode. The coaxial feeds may have EBG inner conductors and near perfect electrical conductor (PEC) outer conductors and operate in a circular waveguide-like TE11 mode or may comprise EBG outer conductors and PEC inner conductors and operate in a quasi-TEM waveguide mode.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Electro-ferromagnetic, tunable electromagnetic band-gap, and bi-anisotropic composite media using wire configurations
InactiveUS6933812B2High bandwidthImprove the effective dielectric constantRadiating elements structural formsResonatorsDielectricElectricity
An artificial electro-ferromagnetic meta-material demonstrates the design of tunable band-gap and tunable bi-anisotropic materials. The medium is obtained using a composite mixture of dielectric, ferro-electric, and metallic materials arranged in a periodic fashion. By changing the intensity of an applied DC field the permeability of the artificial electro-ferromagnetic can be properly varied over a particular range of frequency. The structure shows excellent Electromagnetic Band-Gap (EBG) behavior with a band-gap frequency that can be tuned by changing the applied DC field intensity. The building block of the electro-ferromagnetic material is composed of miniaturized high Q resonant circuits embedded in a low-loss dielectric background. The resonant circuits are constructed from metallic loops terminated with a printed capacitor loaded with a ferro-electric material. Modifying the topology of the embedded-circuit, a bi-anisotropic material (tunable) is examined. The embedded-circuit meta-material is treated theoretically using a transmission line analogy of a medium supporting TEM waves.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
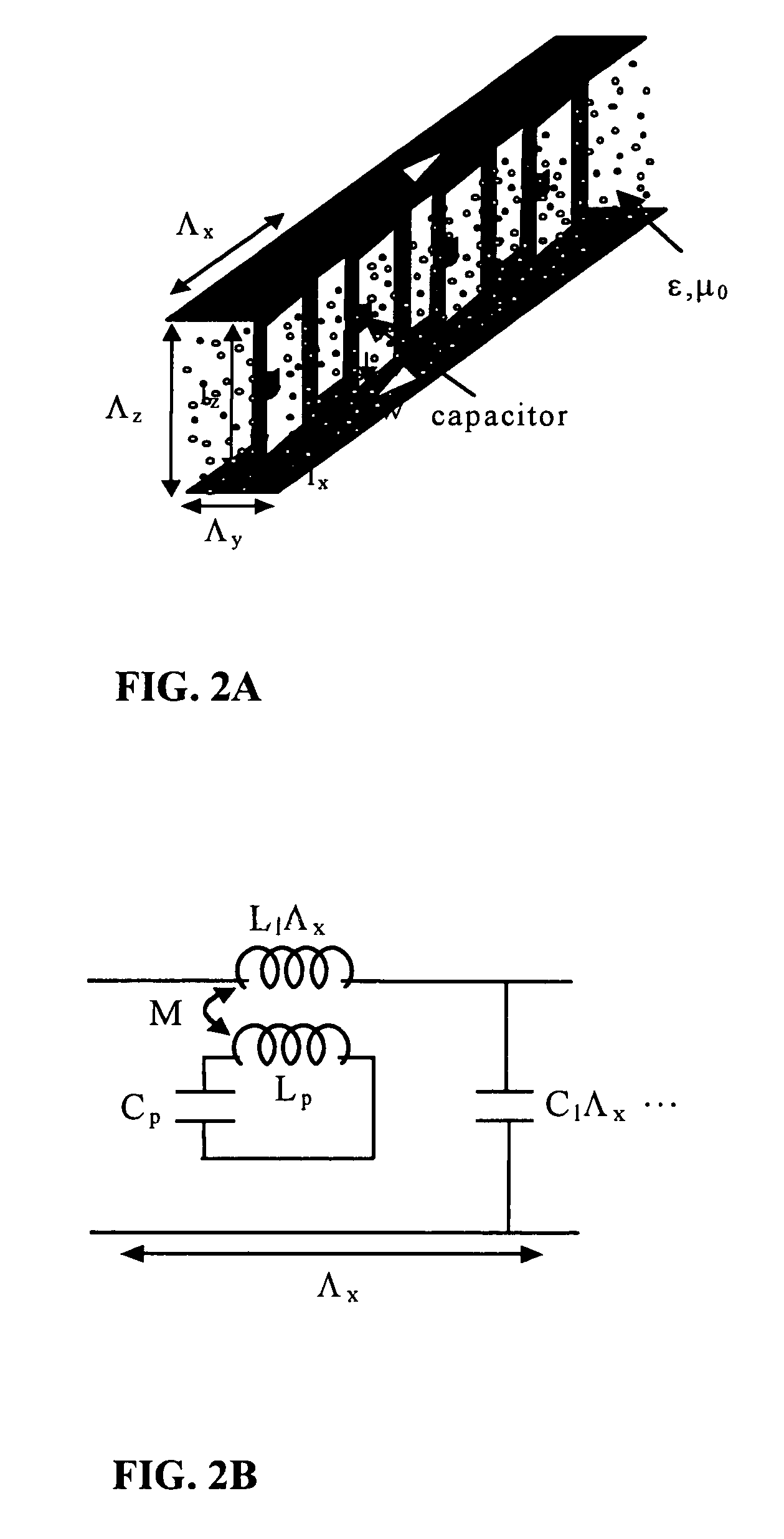
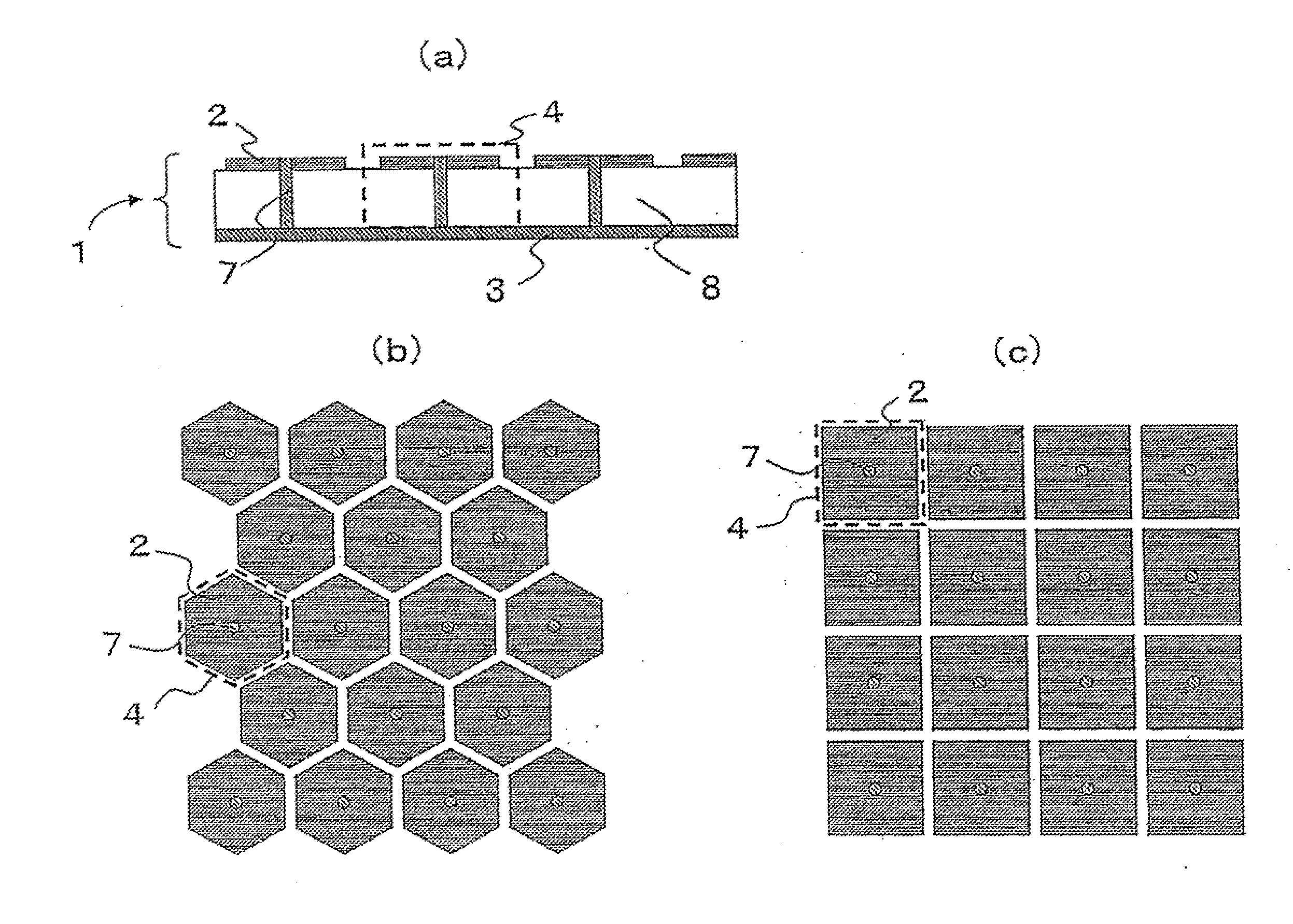
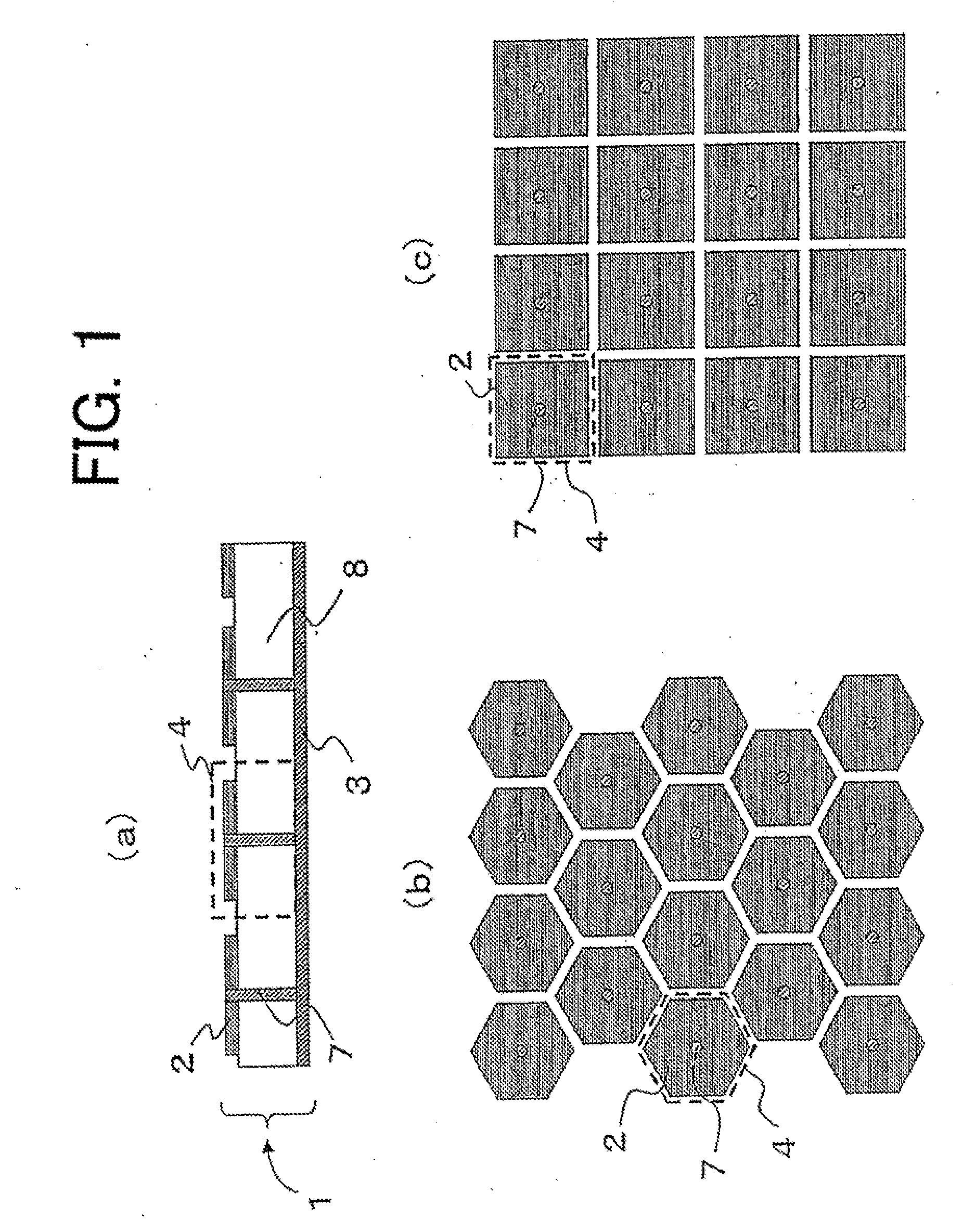
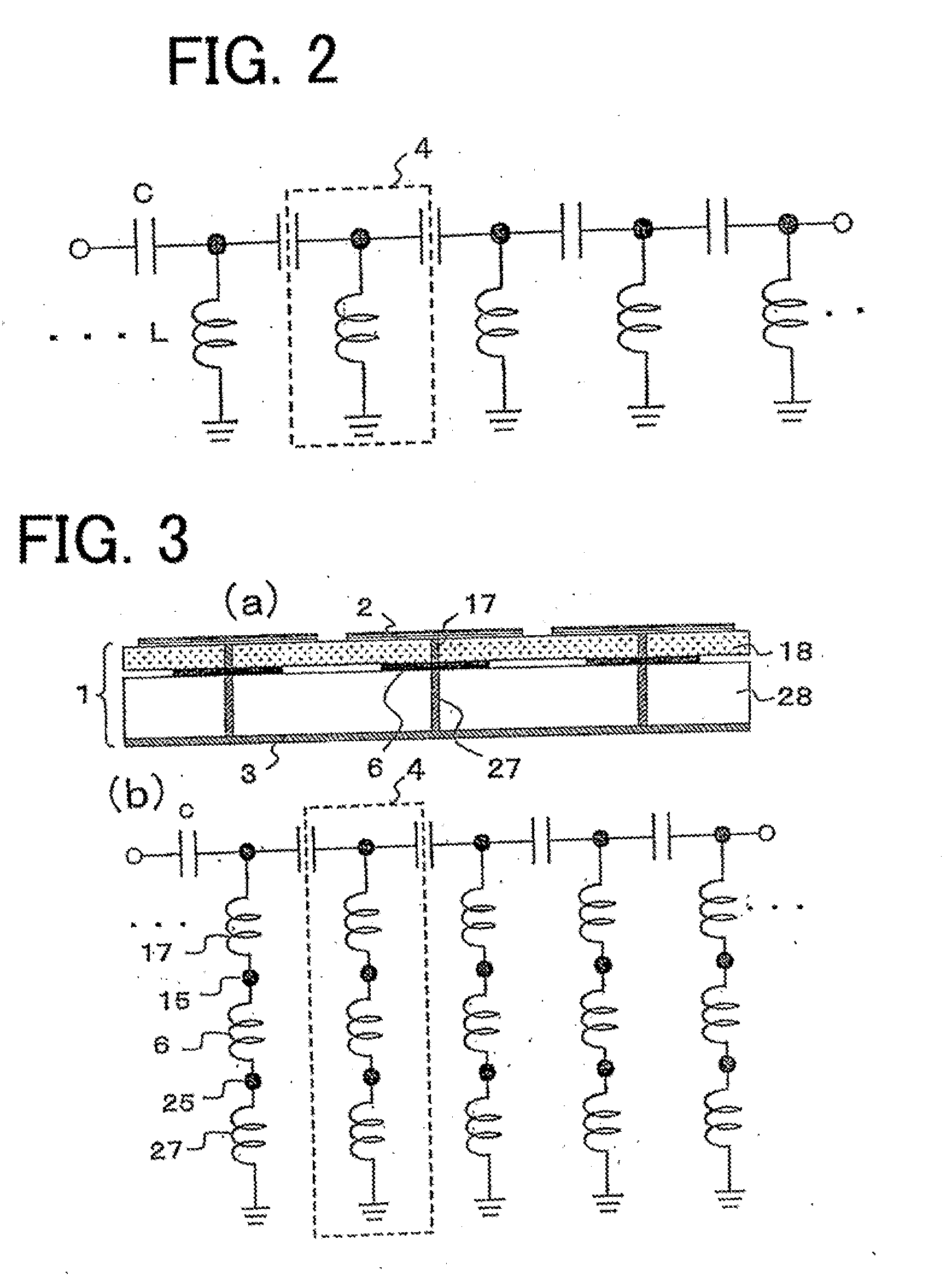
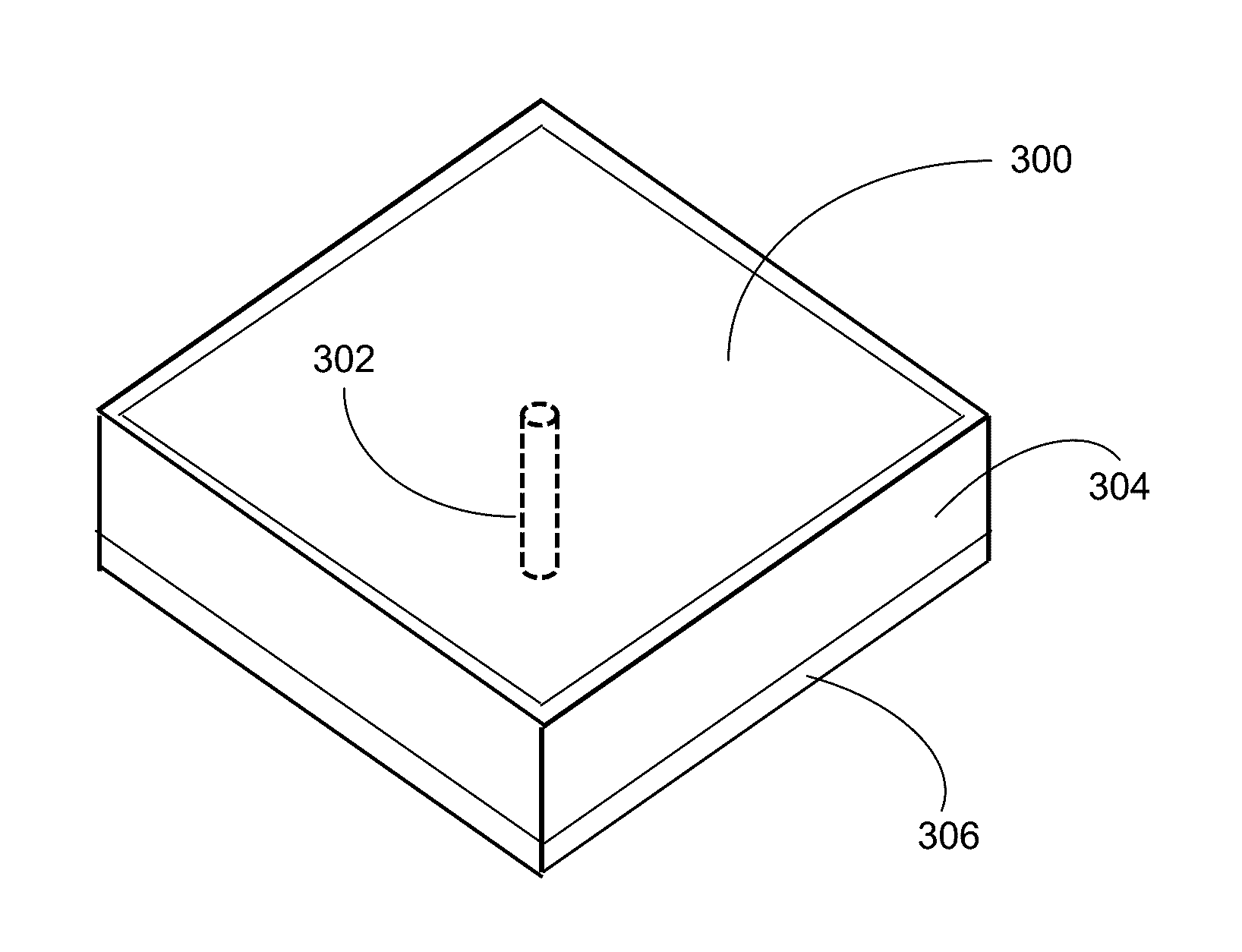
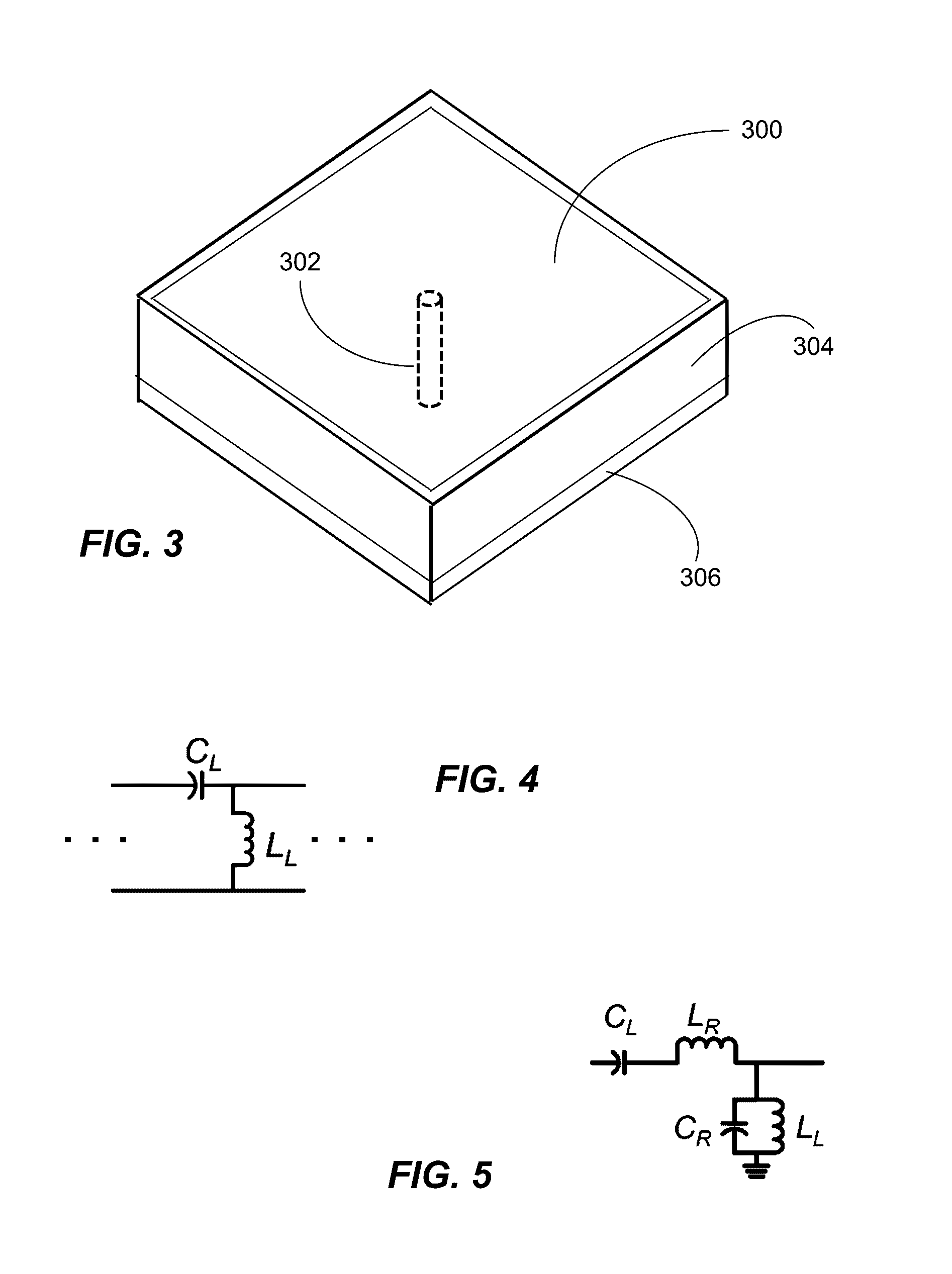
Electromagnetic band gap element, and antenna and filter using the same
ActiveUS20100265159A1Small sizeReduce thicknessMagnetic/electric field screeningCross-talk/noise/interference reductionDielectricElectrical conductor
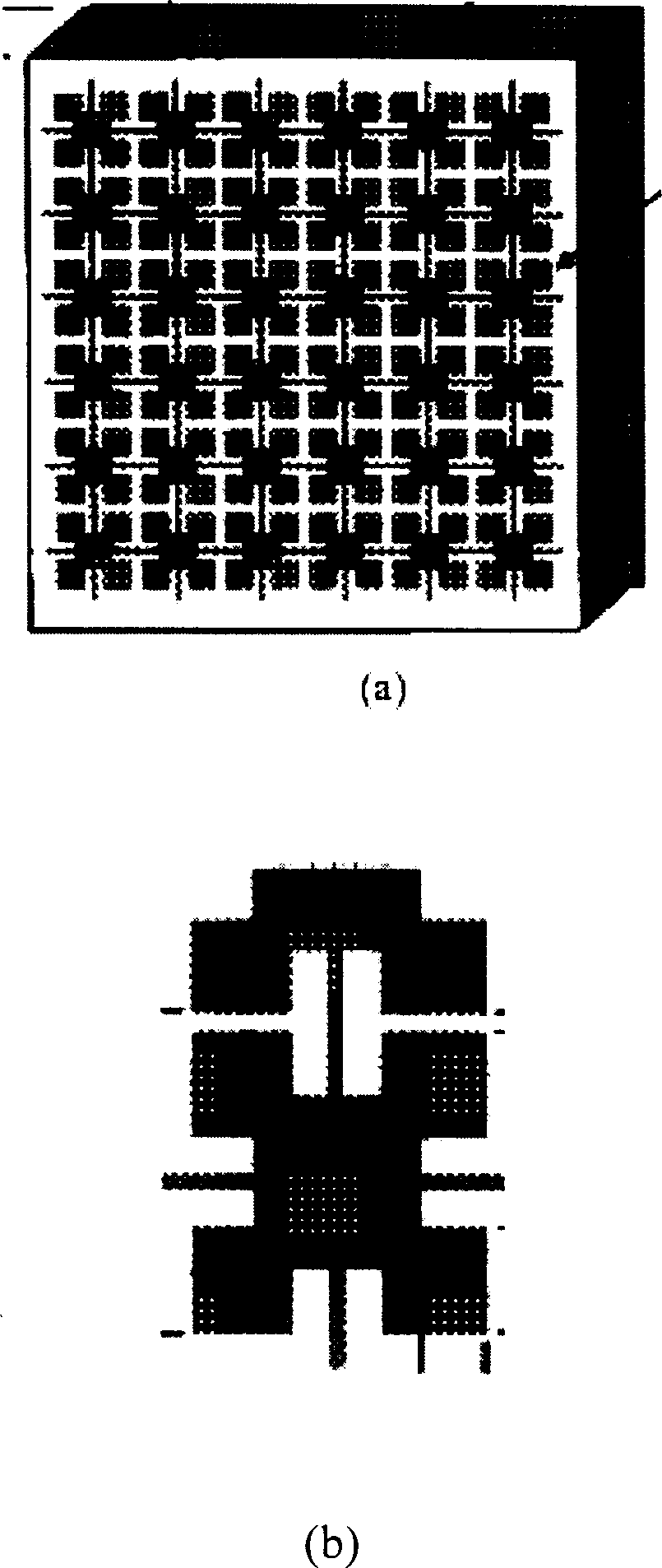
Conductor pieces 102 that are periodically arrayed, a conductor plane 103 that has openings 104 periodically arrayed so as to correspond to the conductor pieces 102, and a dielectric 108 that is arranged between the conductor pieces 102 and the conductor plane 103, are included. Island electrodes 105 and planar inductance elements 106 are arranged in the openings 104 of the conductor plane 103. The island electrodes 105 and the conductor pieces 102 are connected by conductor posts 107. The island electrodes 105 and the conductor plane 103 are connected through the planar inductance elements 106.
Owner:NEC CORP
Multilayer Broadband Microstrip Antenna
InactiveCN102299418ADirectionalHigh bandwidthRadiating elements structural formsBroadband microstrip antennaAntenna gain
The invention discloses a multilayer broadband microstrip antenna, comprising an upper dielectric baseplate, a middle dielectric baseplate, a lower dielectric baseplate, an upper low dielectric constant insulating dielectric layer, a lower low dielectric constant insulating dielectric layer, a reflection plate and a feed probe, wherein rectangle radiators of metallic copper pasters are arranged on the lower surface of the upper dielectric baseplate and the upper surface of the middle dielectric baseplate and provided with U-shaped slot structures with different sizes respectively. Due to a special double-layer inverted U-shaped slot coupling feed way, the symmetry of directional diagrams on an E surface or H surface of the antenna is good, thus ensuring that the antenna has more consistent performances in more directions, and having more actual meanings as an exploration antenna and a communication antenna. The reflection plate with an EBG (electromagnetic band gap) structure can preferably restrain backward radiation in the specified frequency relative to a traditional metal reflection plate, thus improving the directivity of the antenna, thereby further improving the gain of theantenna.
Owner:JIMEI UNIV
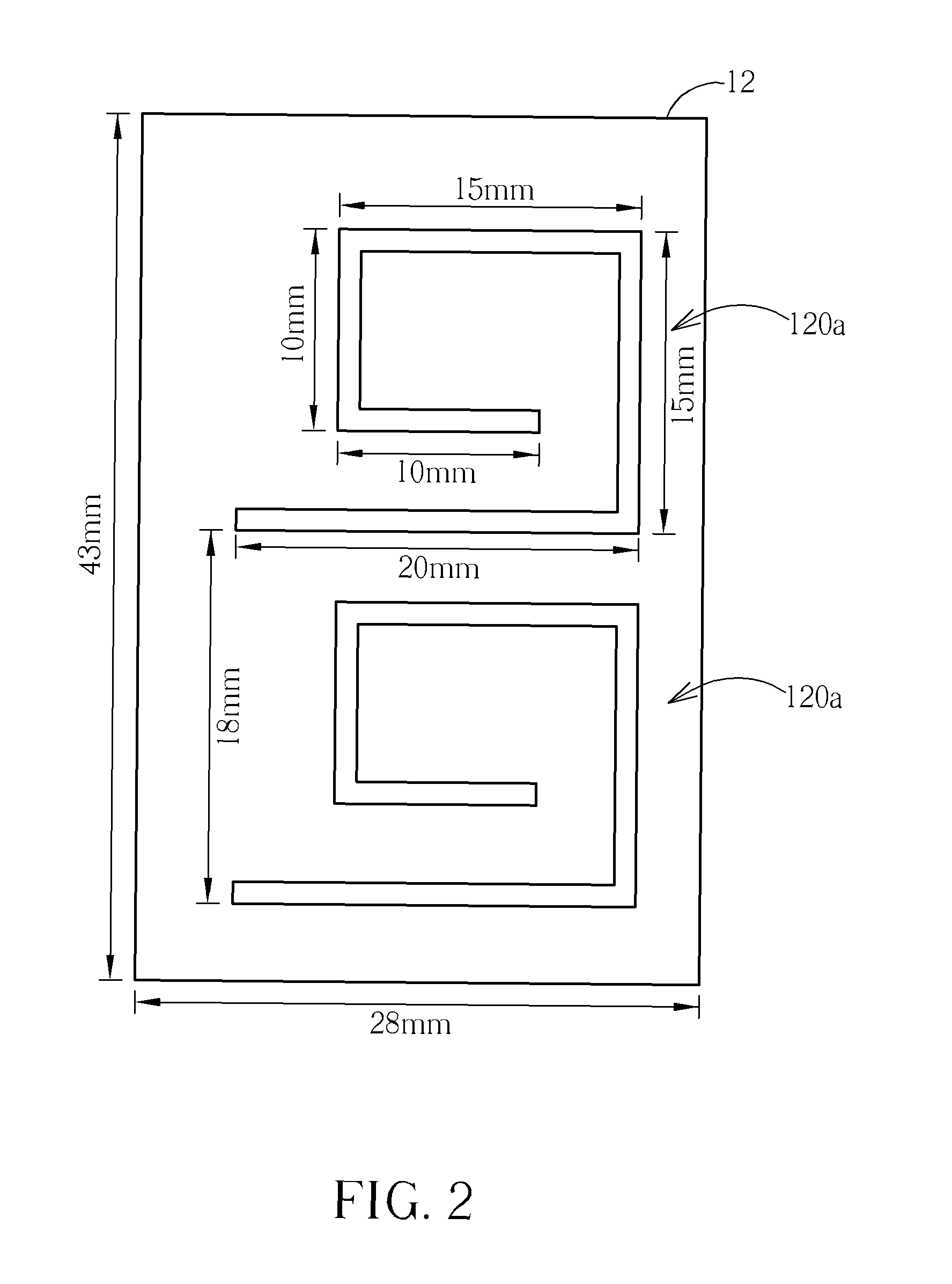
RFID tag and antenna
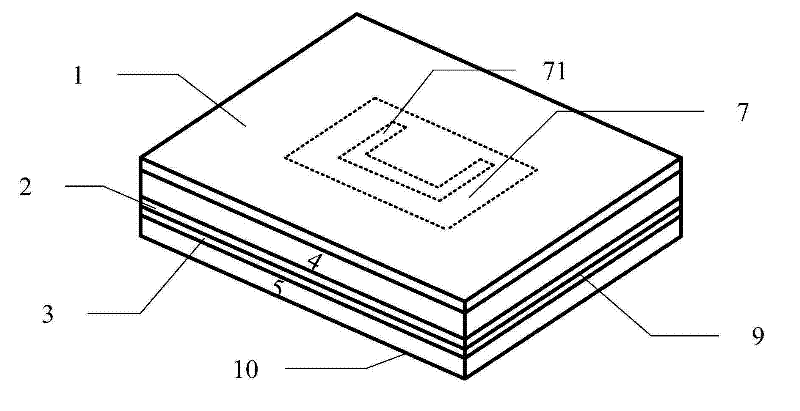
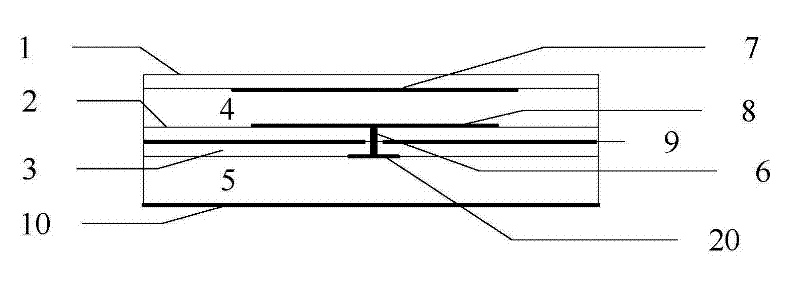
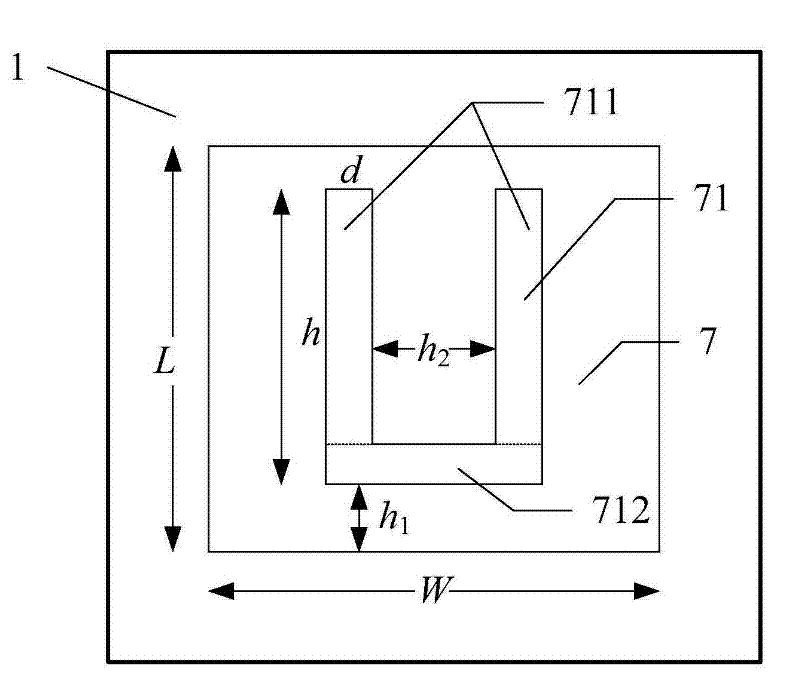
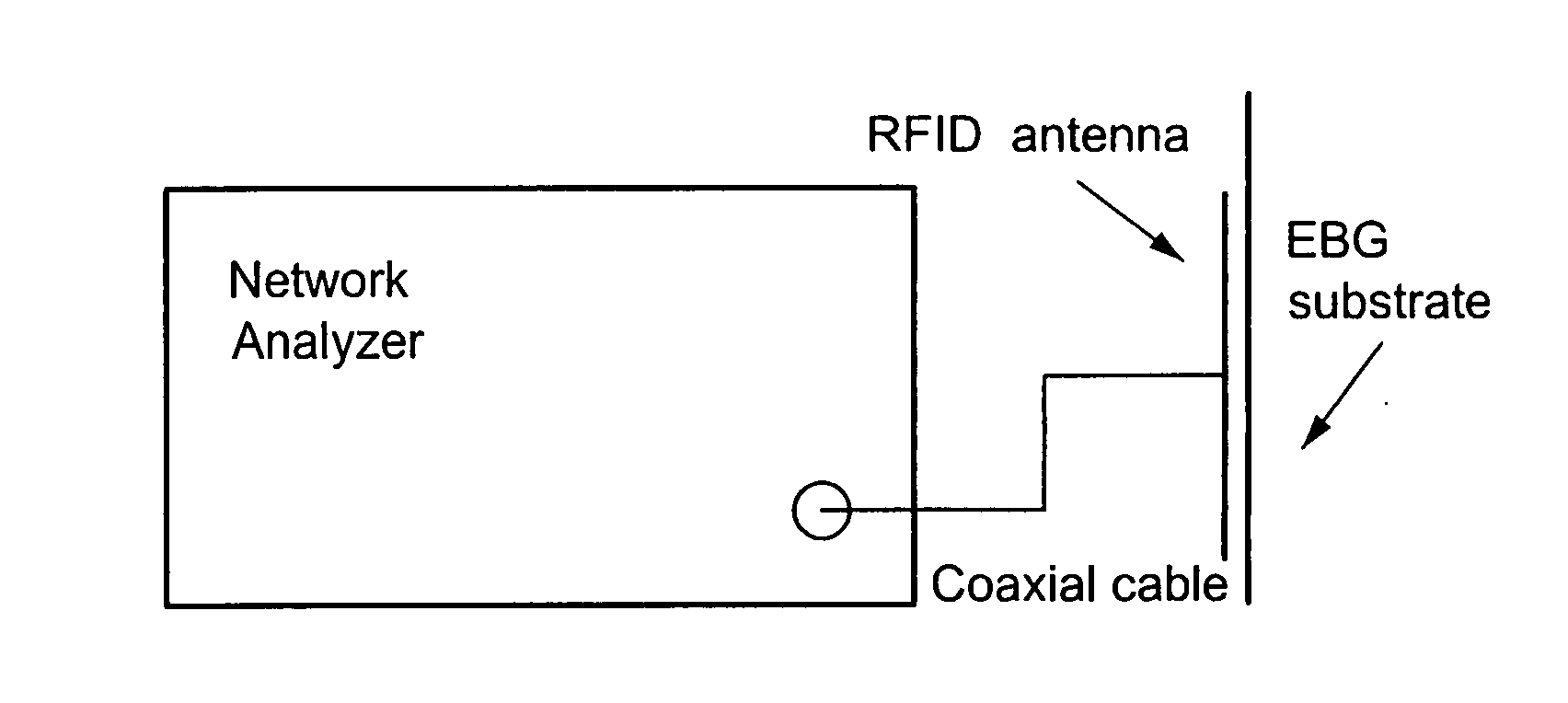
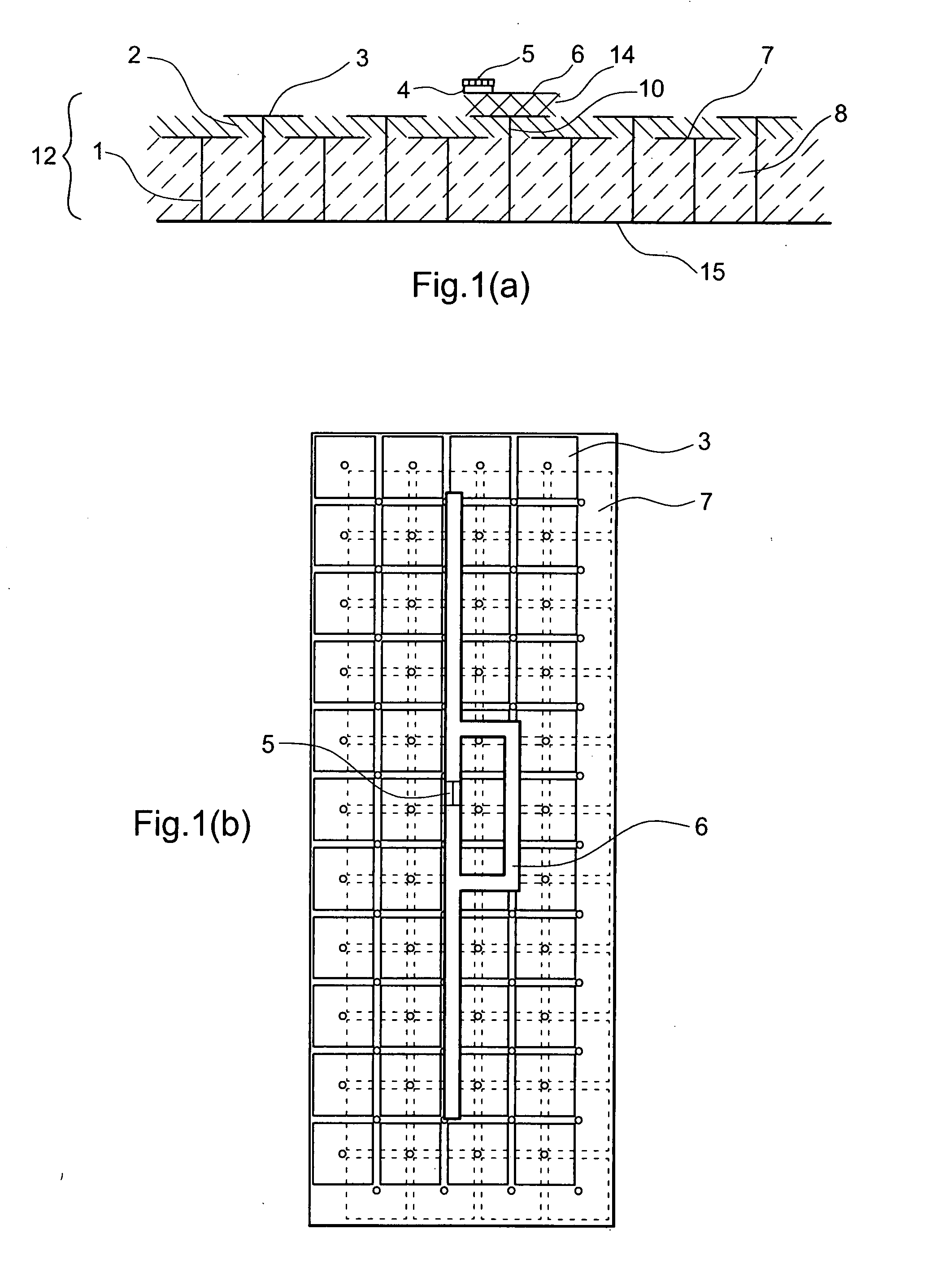
ActiveUS20080129511A1Improve performanceLess sensitiveRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalDielectricElectromagnetic band gap
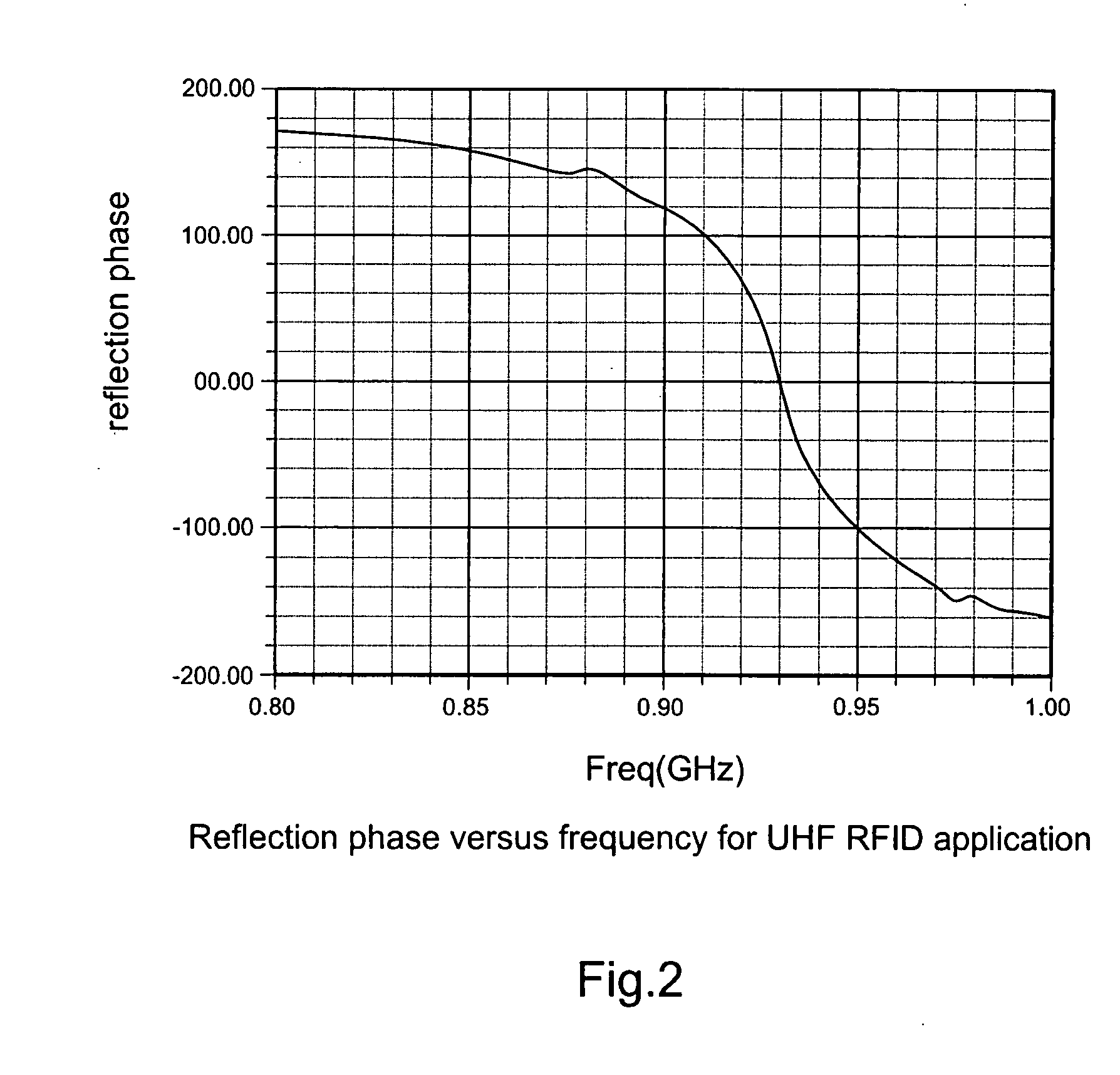
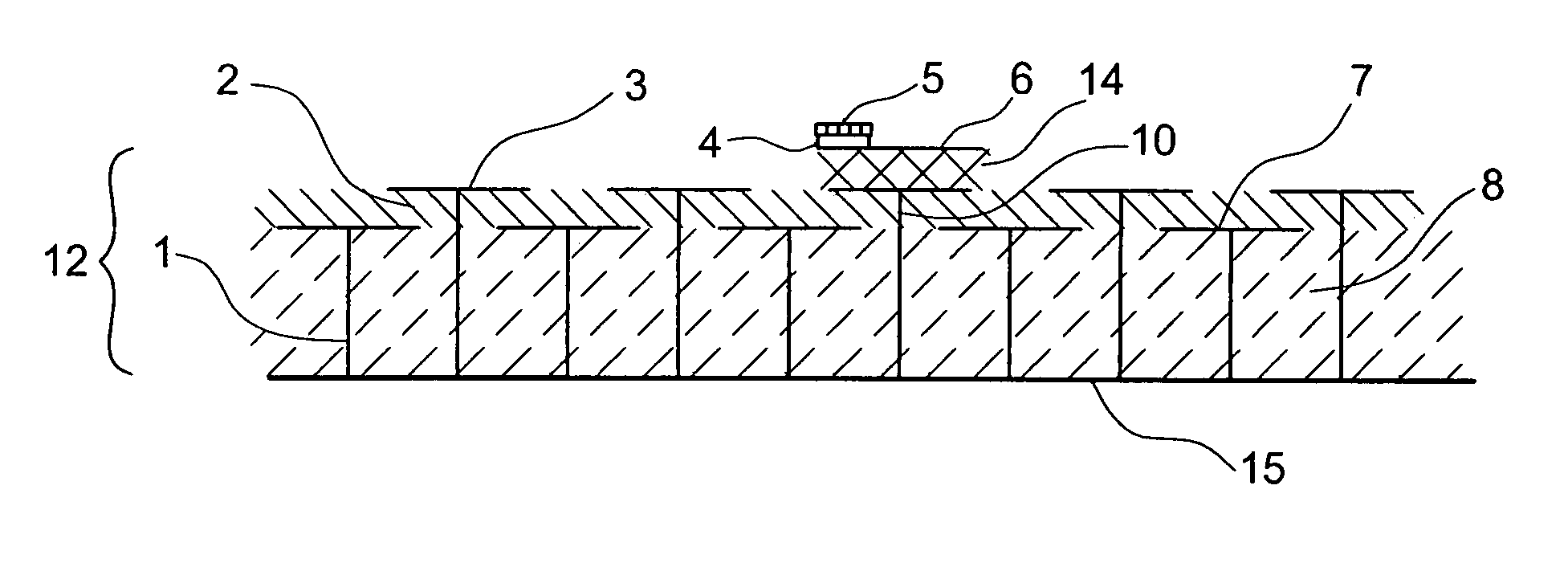
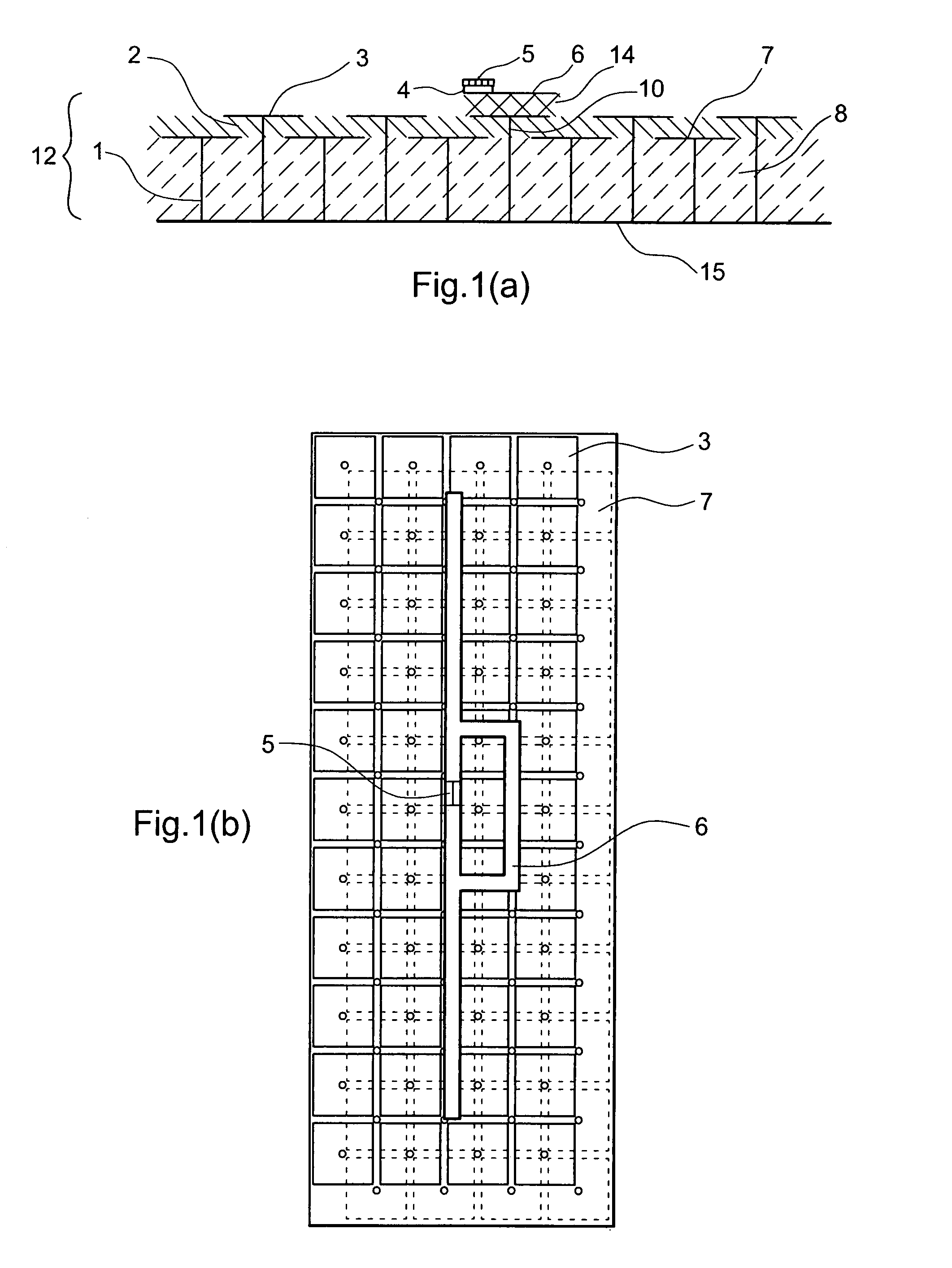
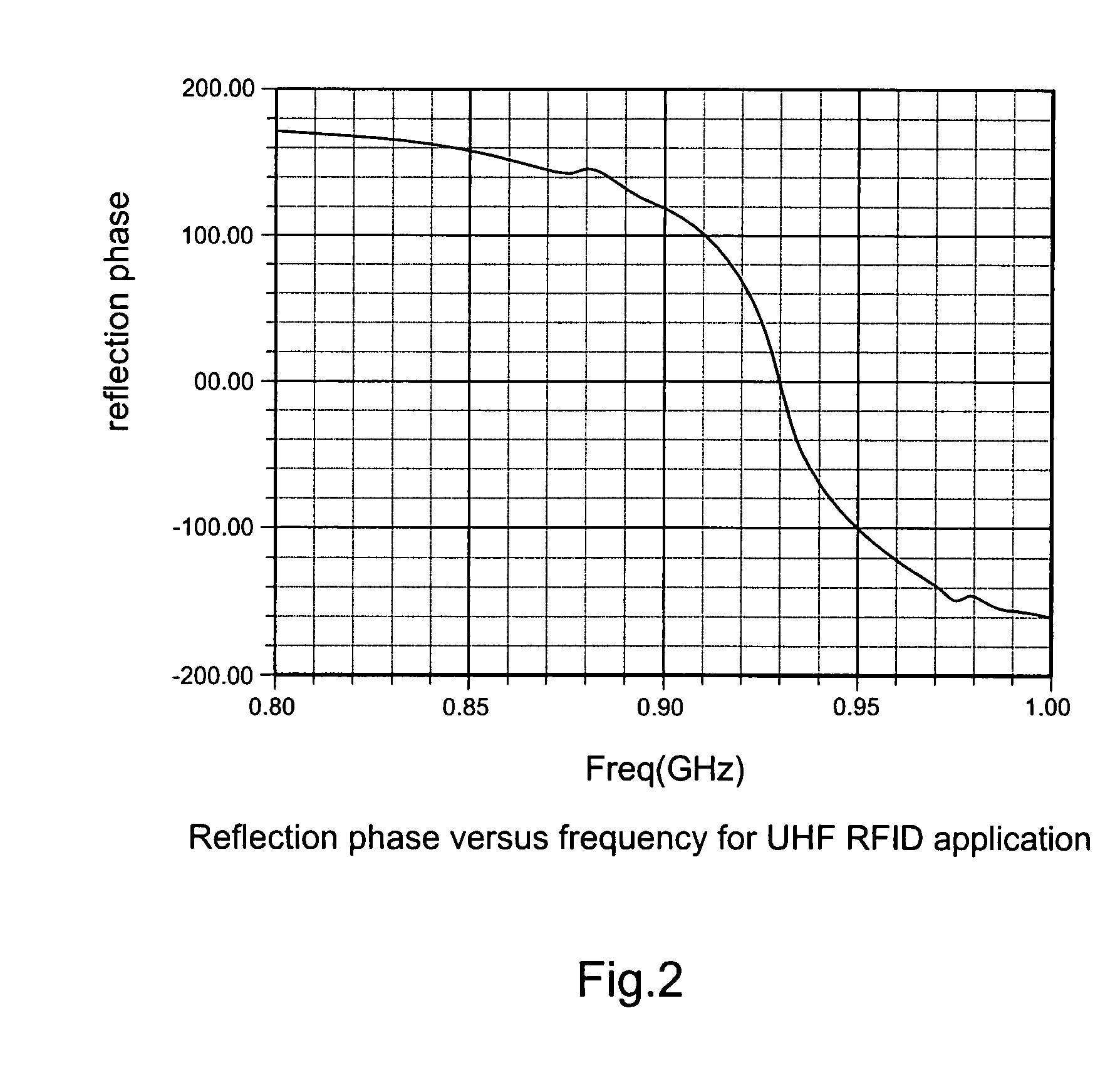
The present invention relates to an RFID Tag and Antenna for use with an RFID tag and a method of radio frequency identification (RFID). The RFID Tag comprises a RFID chip 5 for storing data, an antenna 6 and an electromagnetic band gap substrate 12. The RFID chip 5 and the antenna 6 are mounted above the electromagnetic band gap substrate 12. The electromagnetic band gap substrate has a reflection phase which is different from 180° at the operation frequency of the antenna. The electromagnetic band gap substrate enables the RFID to operate even if it is mounted on a conductive object, as the reflection phase is not 180° so it does not destructively interfere with the radiation from the antenna at the operating frequency. Preferably the reflection phase is between 340° and 115° or −95° and 145°. The preferred embodiment uses a band gap substrate having two mushroom-like conductive layers 3, 7 with a dielectric in between.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electro-ferromagnetic, tunable electromagnetic band-gap, and bi-anisotropic composite media using wire configurations
InactiveUS20050146402A1High bandwidthSmall sizeRadiating elements structural formsResonatorsDielectricElectricity
An artificial electro-ferromagnetic meta-material demonstrates the design of tunable band-gap and tunable bi-anisotropic materials. The medium is obtained using a composite mixture of dielectric, ferro-electric, and metallic materials arranged in a periodic fashion. By changing the intensity of an applied DC field the permeability of the artificial electro-ferromagnetic can be properly varied over a particular range of frequency. The structure shows excellent Electromagnetic Band-Gap (EBG) behavior with a band-gap frequency that can be tuned by changing the applied DC field intensity. The building block of the electro-ferromagnetic material is composed of miniaturized high Q resonant circuits embedded in a low-loss dielectric background. The resonant circuits are constructed from metallic loops terminated with a printed capacitor loaded with a ferro-electric material. Modifying the topology of the embedded-circuit, a bi-anisotropic material (tunable) is examined. The embedded-circuit meta-material is treated theoretically using a transmission line analogy of a medium supporting TEM waves.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MICHIGAN
Electromagnetic band gap microwave filter
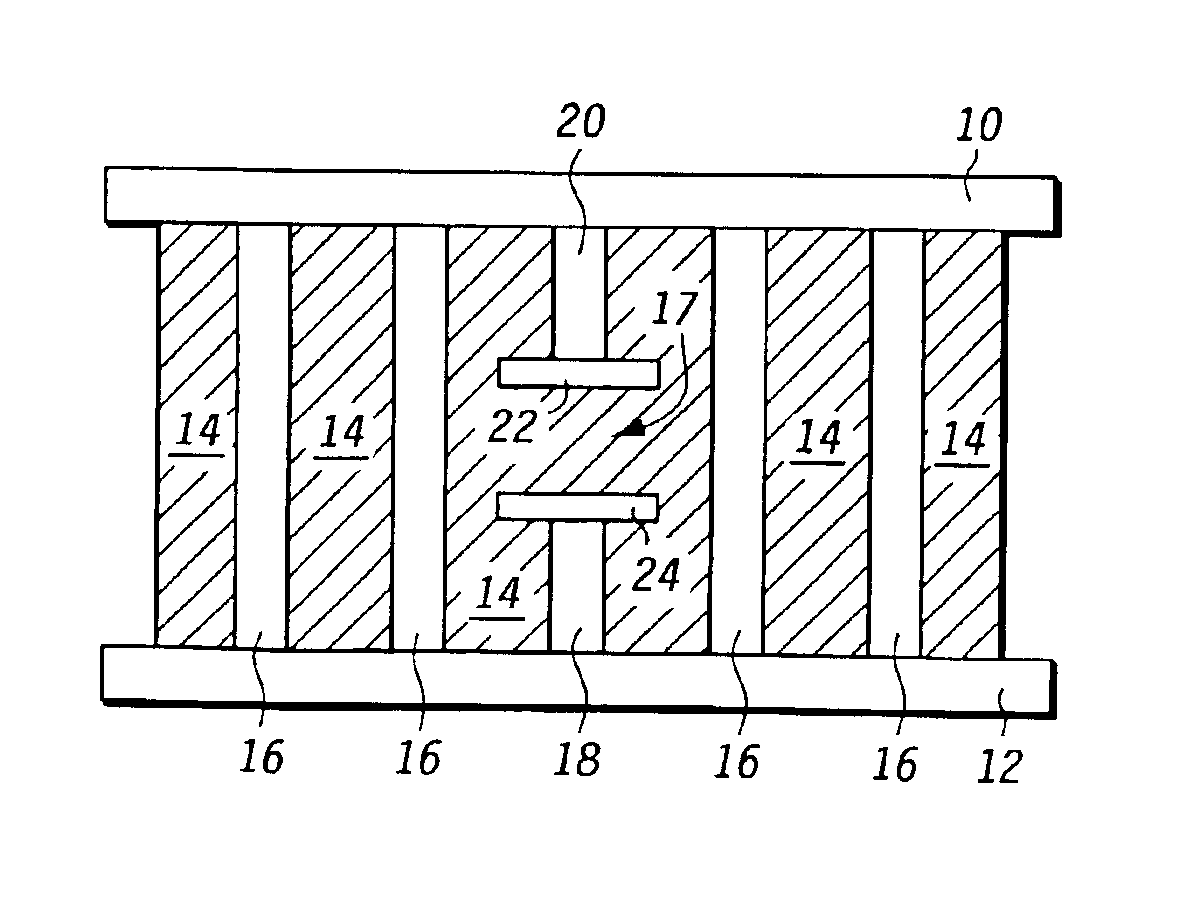
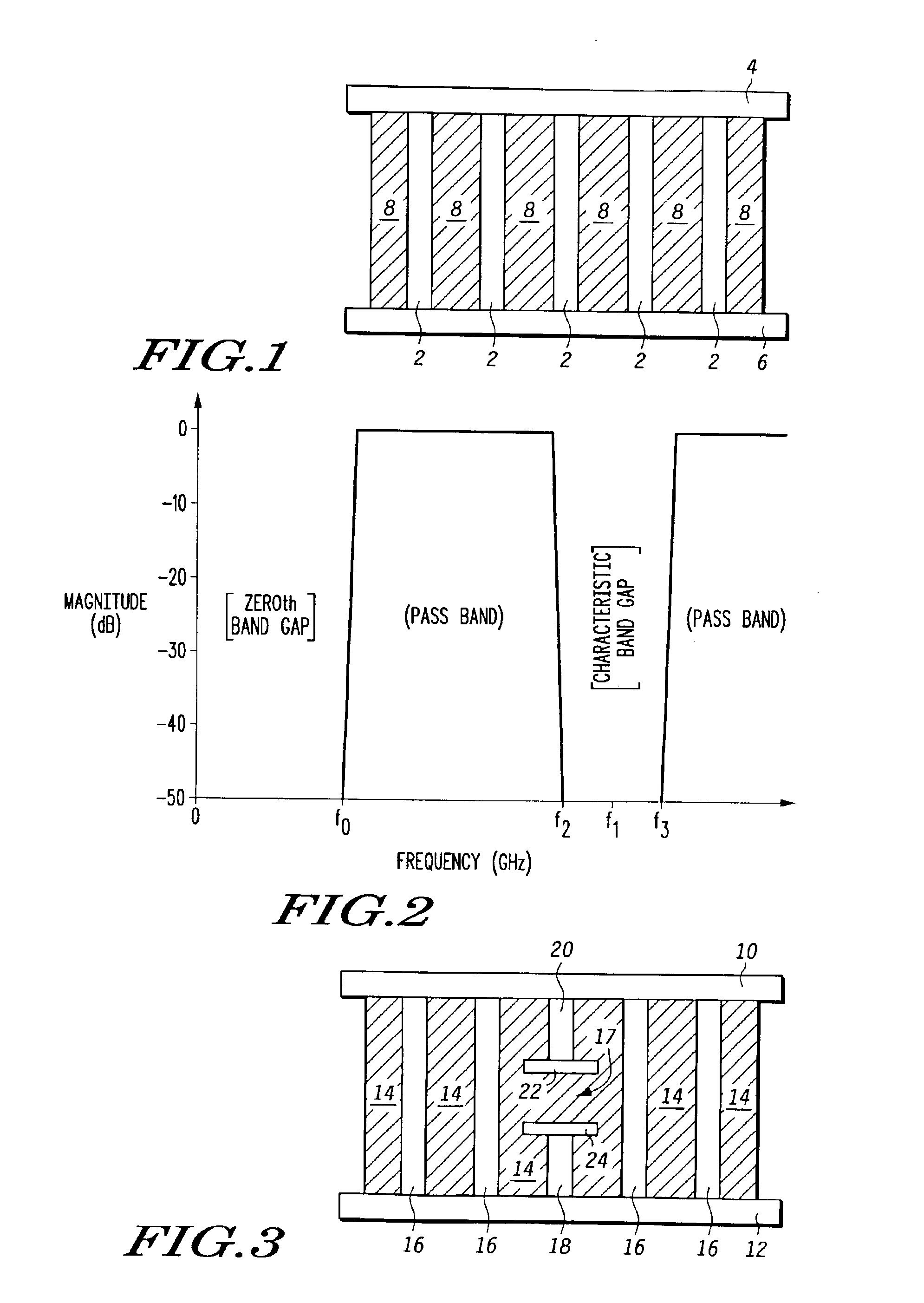
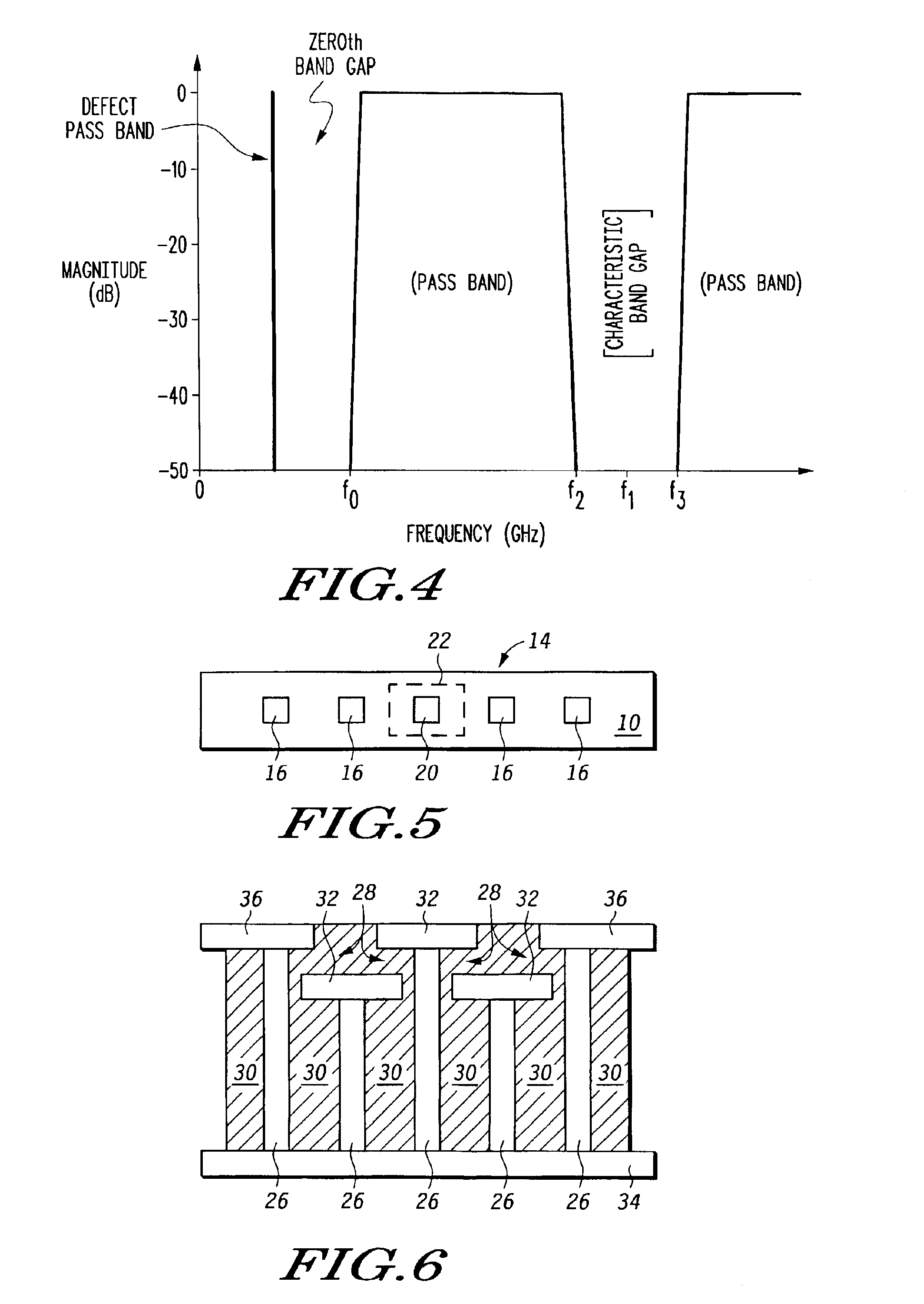
A microwave filter is formed from an electromagnetic band gap structure. The electromagnetic band gap structure includes a periodic array of metal features (16, 42, 44, 50) formed within a dielectric matrix (14, 52). A defect feature (17, 48) is formed within the periodic array of metal features (16, 42, 44, 50) in order to create a pass band within a stop band region.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Low-loss, dual-band electromagnetic band gap electronically scanned antenna utilizing frequency selective surfaces
A dual-band electromagnetic band gap (EBG) electronically scanned antenna utilizing frequency selective surfaces (FSS) uses FSS waveguide phase shifters. Each FSS waveguide phase shifter has a low-frequency phase shifter with low-frequency EBG devices on vertical waveguide walls, horizontal waveguide broadwalls that are substantially twice the width of the vertical waveguide walls and an FSS located at the center of the horizontal waveguide broadwalls. Two high-frequency phase shifters are formed within the low-frequency phase shifter. Each high-frequency phase shifter comprises a vertical waveguide wall, the FSS, half of the horizontal waveguide broadwalls, and high-frequency EBG devices located on each half of the horizontal waveguide broadwalls, The FSS is transparent at a low frequency and opaque at a high frequency.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
Shielding device
ActiveUS20090308653A1Hinders its propagationEliminate the effects ofMagnetic/electric field screeningCross-talk/noise/interference reductionEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Shielding device
ActiveUS8013258B2Eliminate the effects ofReduce in quantityMagnetic/electric field screeningCross-talk/noise/interference reductionEngineeringElectromagnetic shielding
Owner:XUESHAN TECH INC
Electromagnetic forbidden band structure material
InactiveCN1787280AImprove performanceCorrectly designedAntenna arraysRadiating elements structural formsMicrowaveEngineering
The invention provides a new, small-size, wide-band gap electromagnetic band gap structural material, and the manufacturing method prints special metal pattern on microwave medium material plate by PCB process, where the size of the pattern is determined according to the applied frequency range. The electromagnetic band gap structural material can be used in antennas, filters, resonators, and other microwave devices, to improve their performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI FANGSHENG INFORMATION TECH +1
Metamaterial Substrate For Circuit Design
ActiveUS20170033468A1Improve electrical characteristicsSolid-state devicesRadiating elements structural formsEngineeringSystem in package
This invention enables Frequency Selective Surface (“FSS”) and Artificial Magnetic Conductor (“AMC”) which exhibits Electromagnetic Band Gap (“EBG”) in any of the substrate's layer from a small and thin systems and sub-systems in package to a large-format PCBs. The metamaterial substrate may be integrated with electronic circuit components or buried in PCBs for circuit designs capable of transmitting, receiving and reflecting electromagnetic energy, altering electromagnetic properties of natural circuit materials, enhancing electrical characteristics of electrical components (such as filters, antennas, baluns, power dividers, transmission lines, amplifiers, power regulators, and printed circuits elements) in systems and sub-systems circuit designs. The metamaterial substrate creates new electrical characteristics, properties and systems, sub-systems or component's specification not readily available with conventional circuit materials, substrates, and PCBs. The metamaterial substrate can be less than 70 μm thick and buried into any PCB layer.
Owner:TRANSSIP
Electromagnetic band gap structure based dual-frequency microstrip array antenna with high isolation
InactiveCN105633574AImprove isolationSimultaneous aerial operationsIndividually energised antenna arraysMicrostrip array antennaDielectric substrate
The invention discloses an electromagnetic band gap structure based dual-frequency microstrip array antenna with high isolation. The dual-frequency microstrip array antenna comprises two oscillators of the array antenna and an L-shaped electromagnetic band gap unit organized array, wherein the L-shaped electromagnetic band gap unit organized array is loaded between the two oscillators, the two oscillators and the L-shaped electromagnetic band gap unit organized array are all supported on a FR4 dielectric substrate, each oscillator comprises a high-frequency monopole, a low-frequency monopole, a microstrip feeder line and metal ground, the high-frequency monopole and the lower-frequency monopole are connected with the microstrip feeder line, the microstrip feeder line is inserted into the metal ground, the L-shaped electromagnetic band gap unit organized array comprises a plurality of L-shaped electromagnetic bang gap units arranged in an array, each L-shaped electromagnetic band gap unit comprises an electromagnetic band gap metal patch, and the electromagnetic band gap metal patch is connected with a ground floor on other side via a conductive via hole in the middle. In the dual-frequency microstrip array antenna, the working frequency band is 2.27-2.67GHz and 5.29-7.09GHz, and the frequency band range of WLAN is completely covered; and the electromagnetic band gap structure with dual-band gap characteristic is loaded between oscillator units, and thus, the antenna has relatively high isolation in dual frequency bands.
Owner:张晓燕
Multi-layer electromagnetic band gap decoupling structure for microstrip antenna array
ActiveCN106910999AReduce couplingImprove isolationParticular array feeding systemsAntennas earthing switches associationAntenna designMicrostrip antenna array
The invention provides a multi-layer electromagnetic band gap decoupling structure for a microstrip antenna array. The multi-layer electromagnetic band gap decoupling structure is used for reducing coupling between antenna array elements of the array by adding three four-layer electromagnetic band gap structures with completely identical structures between array elements of the antenna array. Therefore, coupling between antenna array elements can be reduced and the isolation of the antenna array can be improved. The antenna array includes a common ground plate arranged at the lower surface of a dielectric plate, a rectangular radiation paster arranged at the upper surface of the dielectric plate, two coaxial feed ports, four electromagnetic band gap structure units, and respective short-circuit probes. According to the designed multi-layer electromagnetic band gap decoupling structure, coupling between antenna array elements can be reduced effectively; the isolation of the antenna array can be improved; and the high-performance array antenna design can be realized.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Application method of high dielectric microwave composite material on antenna made
InactiveCN1866612AImprove performanceSolve technical problems that cannot be used in antennasRadiating elements structural formsWaveguide type devicesDielectricMicrowave
The invention discloses an antenna of high-dielectric microwave composite function, which is characterized by the following: the material adopts Sr1-xBaxTiO3(X=0.05-0.95) high-dielectric microwave ceramic material with surface containing periodical electromagnetic band-gap structure, which can be antenna base material as well as radiation dielectrics; this new method minimizes the bulk, which guarantees radiation efficiency and benefit for GPS(f=1.575GHz),2G PCS(f=1.8GHz),3G PCS(f=1.7-2.1GHz),802.11Blue Tooth communication (f=2.4-2.5GHz) and 802.16 WIMAX(f=3.4-3.53GHz) wireless communication domain.
Owner:上海联能科技有限公司 +2
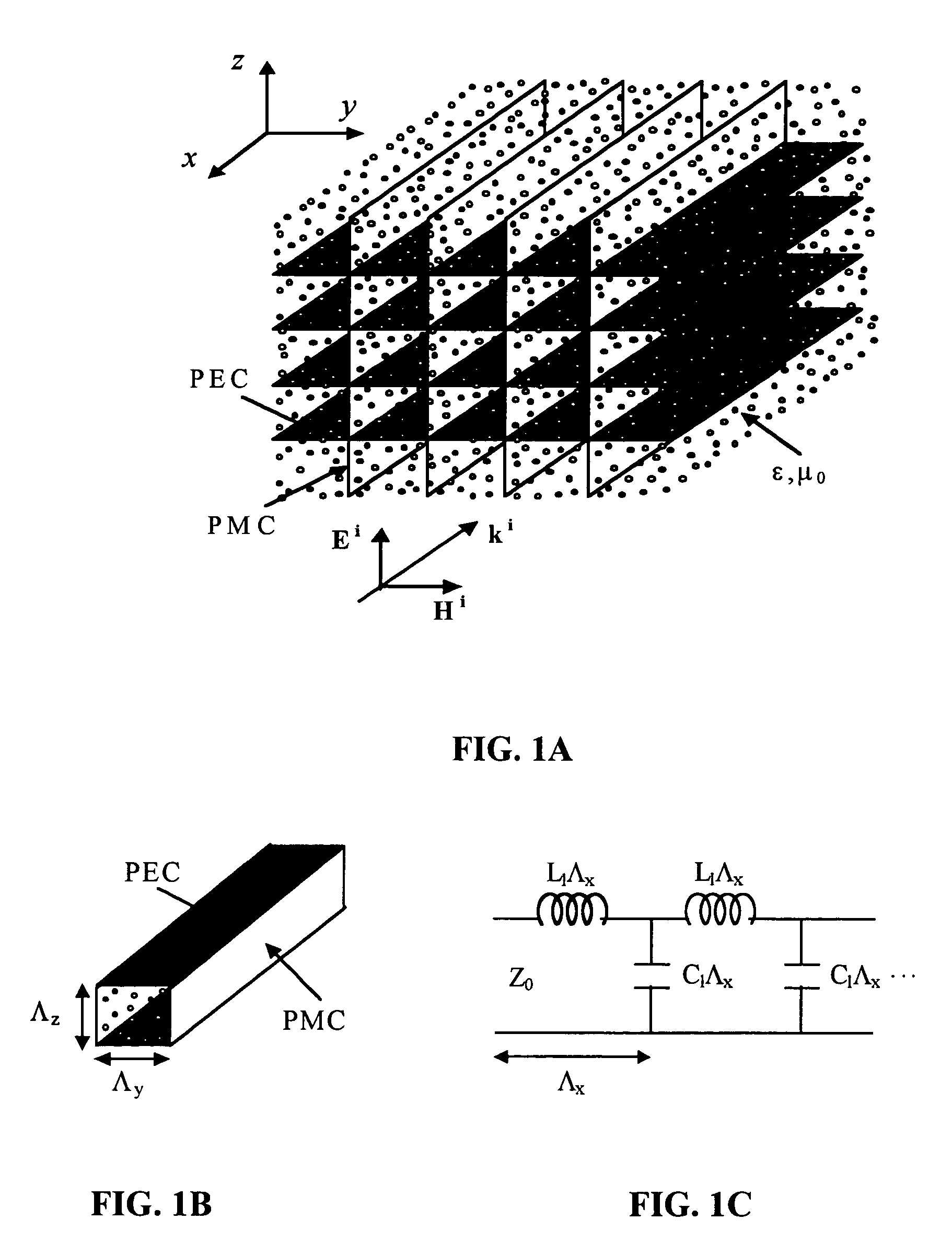
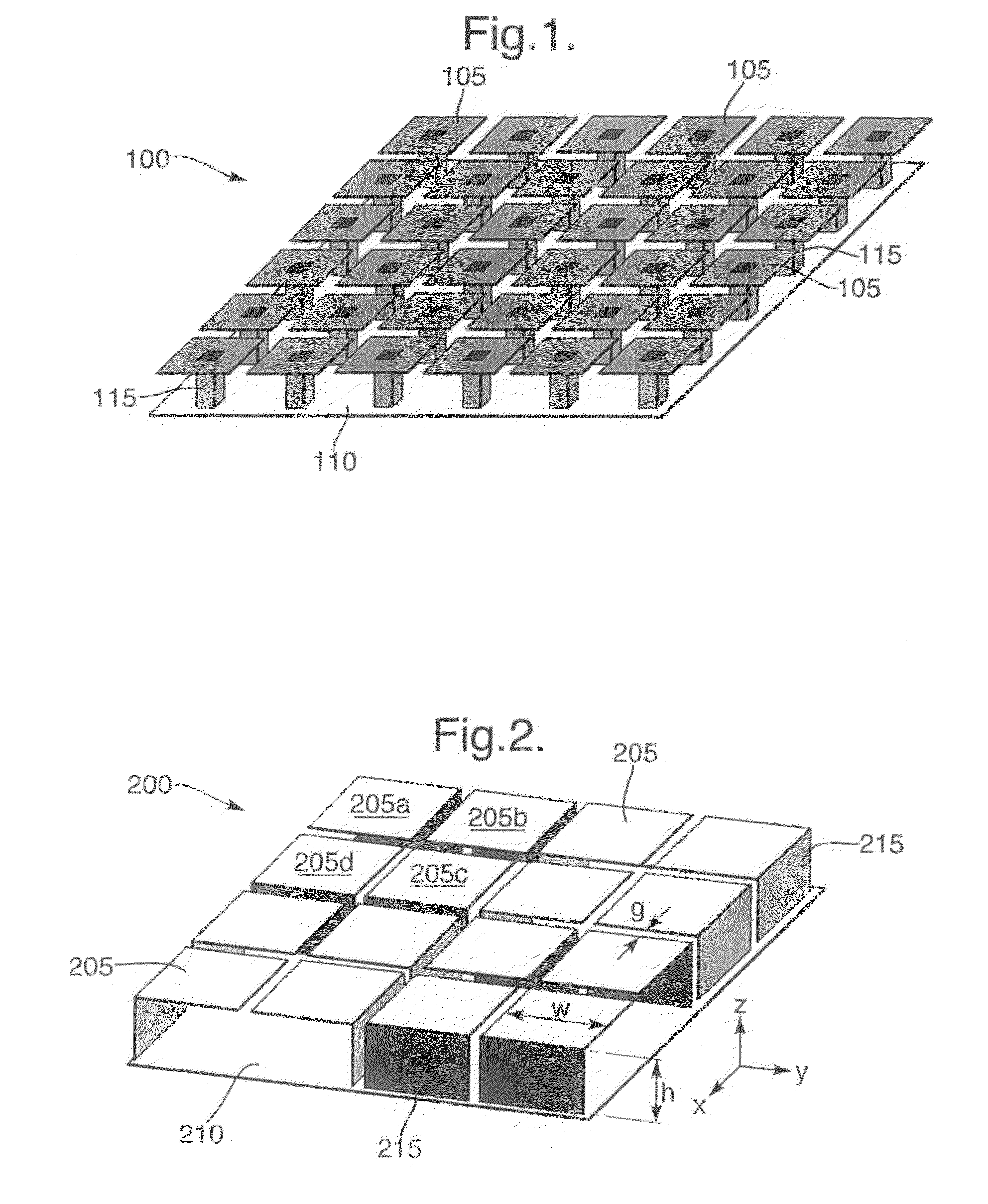
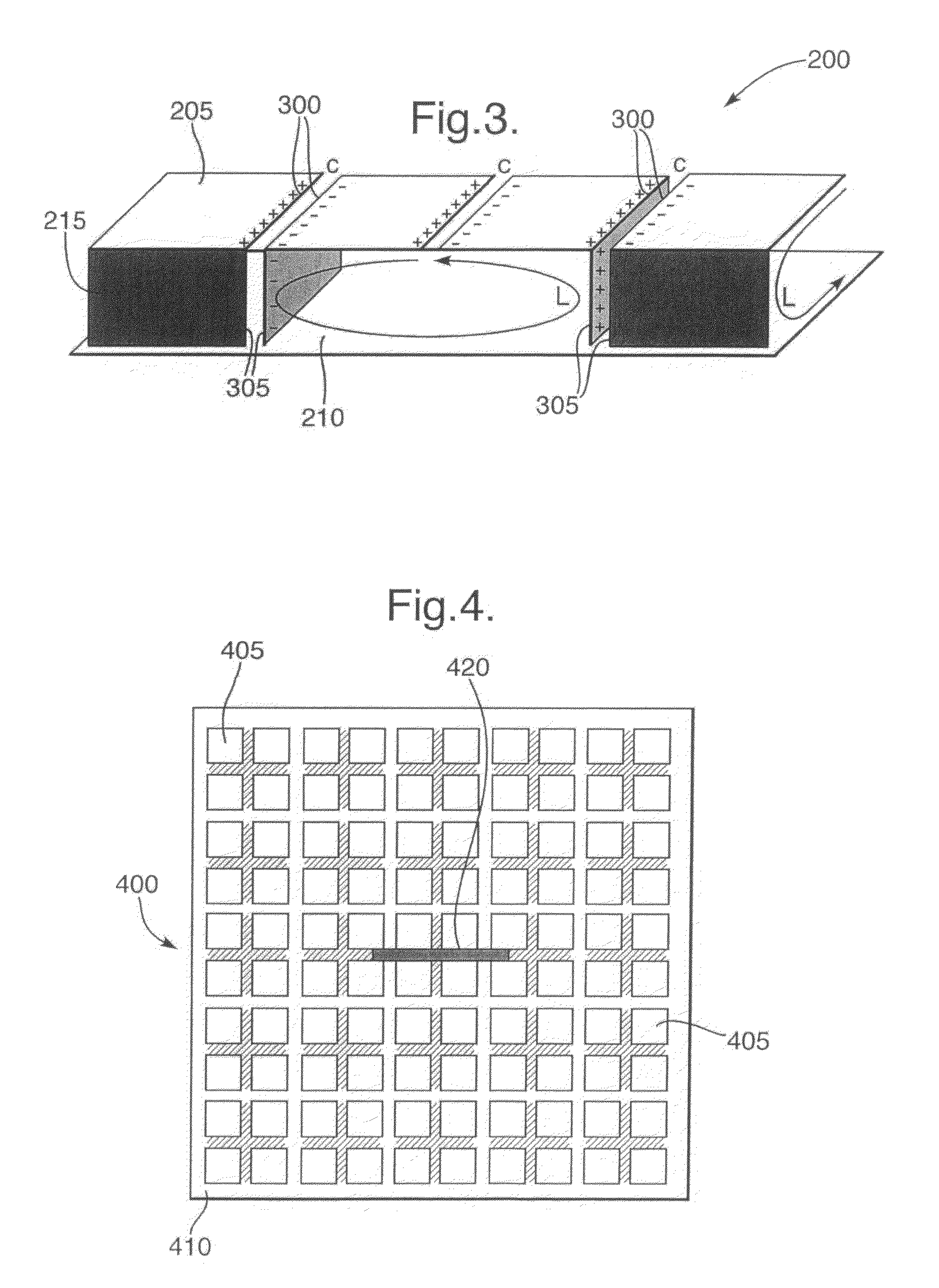
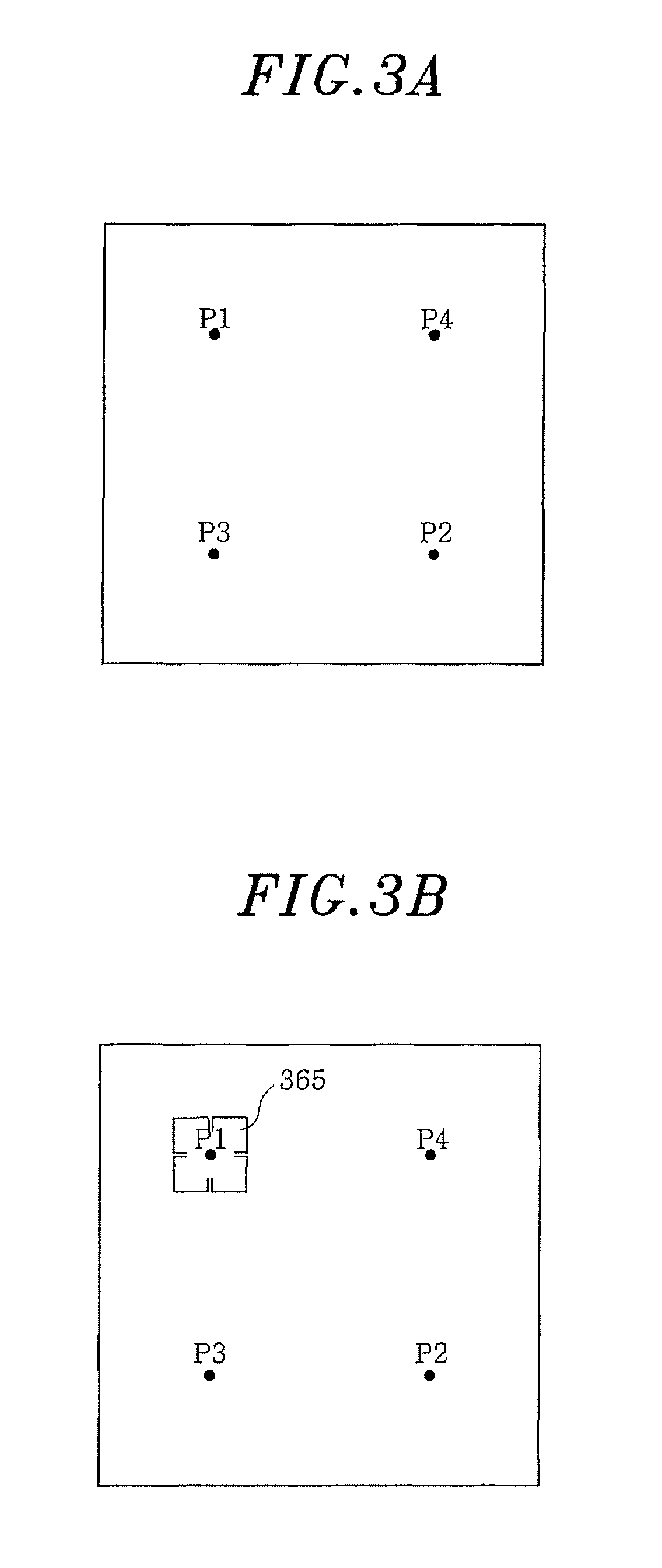
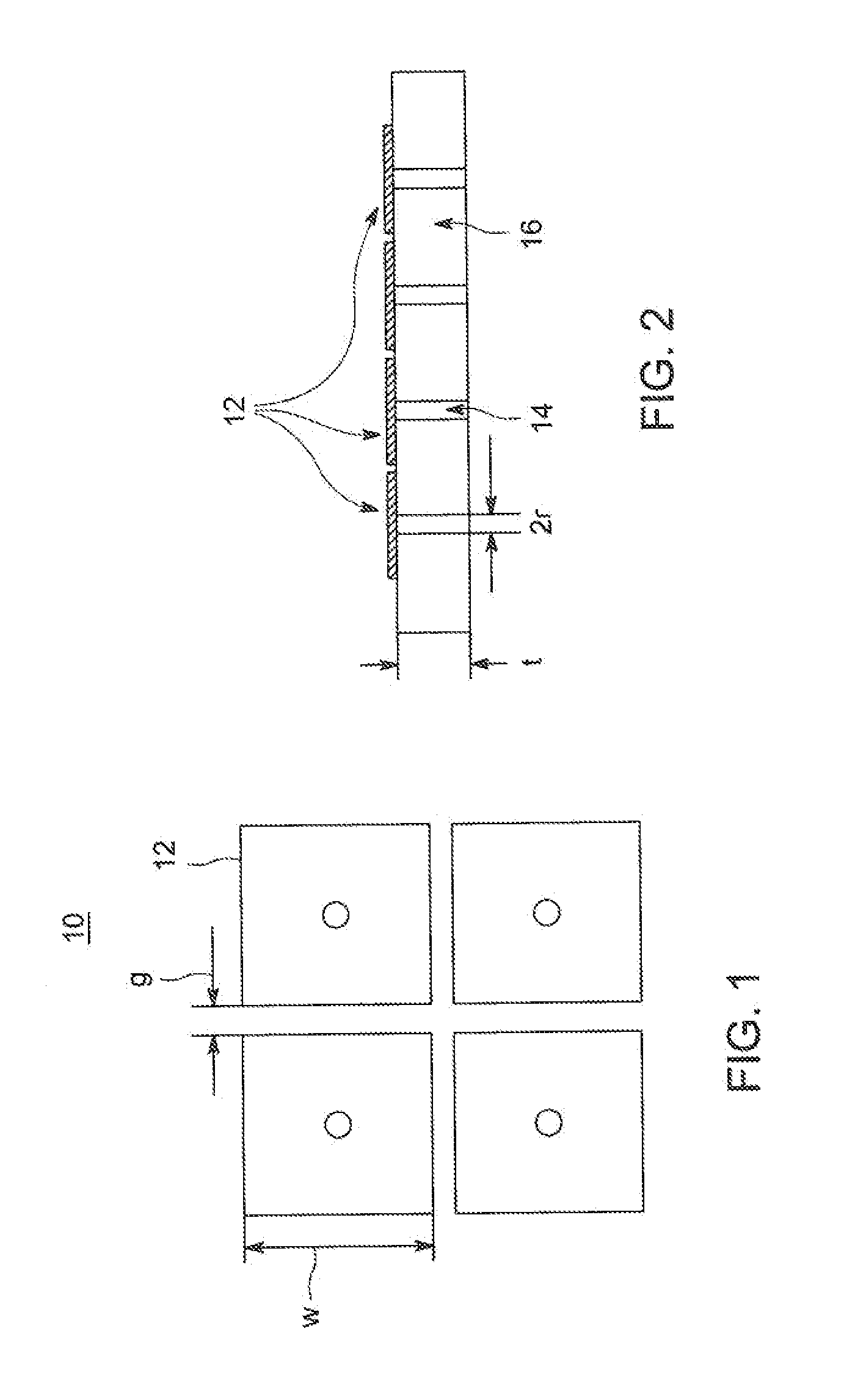
Electromagnetic band-gap structure
InactiveUS7982673B2High impedanceLess expenseSimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsGround planeAntenna element
An electromagnetic band gap structure is provided including a ground plane and a periodic planar arrangement of surface elements mounted parallel to and at a predetermined distance from the ground plane. Each of the surface elements is supported in the planar arrangement by at least one conducting support element extending from an edge of the surface element to the ground plane, avoiding back-to-back parallel support elements. This arrangement allows for the surface elements and their respective support elements to be folded from flat metal templates to greatly simplify manufacture. An antenna is also provided in which an antenna element is mounted in such a way as to use the electromagnetic band-gap structure as a ground plane. This allows for a low-profile antenna to be made as the antenna element may be mounted close to the plane of surface elements in the structure.
Owner:BAE SYSTEMS PLC
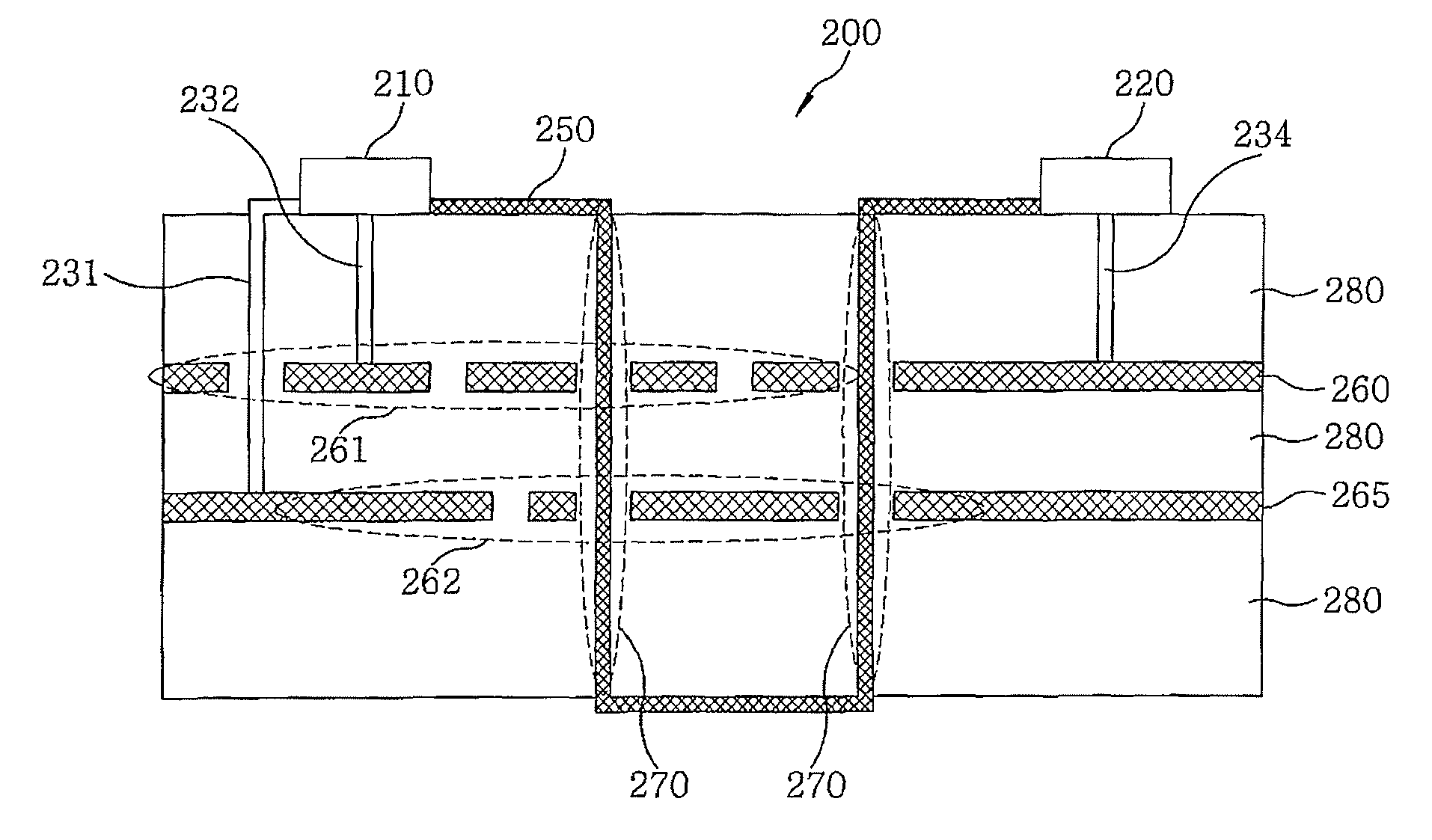
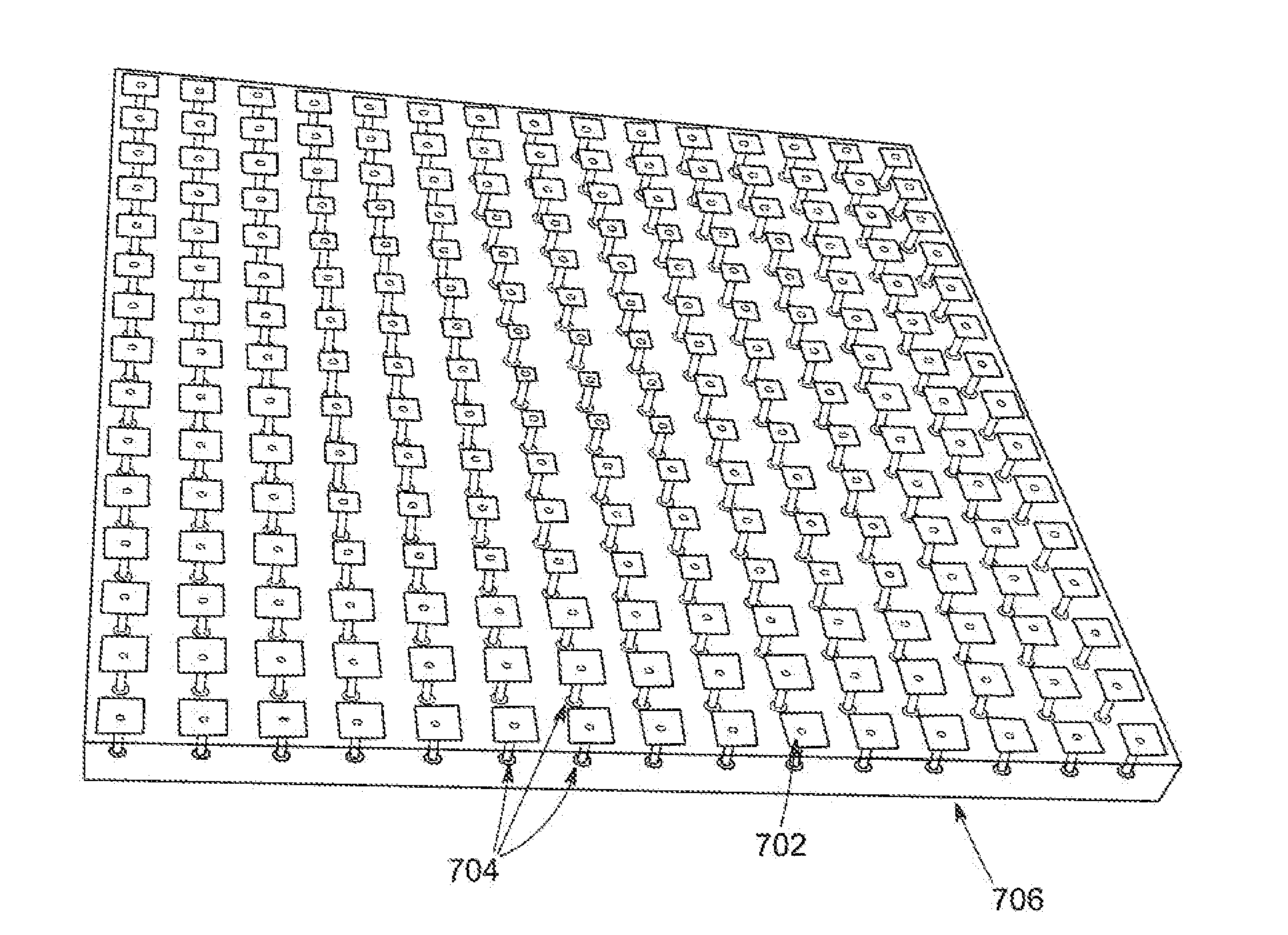
Arrangement structure of electromagnetic band-gap for suppressing noise and improving signal integrity
ActiveUS8004369B2Inhibition is effectiveImprove featuresMultiple-port networksMagnetic/electric field screeningEngineeringElectromagnetic band gap
An electromagnetic-wave suppression structure in a multilayer PCB or package structure is supplied with a power to be used therein by a power distribution network including a power plane and a ground plane. The multilayer PCB and package includes: an electromagnetic-wave suppression structure including an electromagnetic band-gap; and the electromagnetic-wave suppression structure is formed at a specific portion(s) of the power plane and / or the ground plane to suppress noises.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
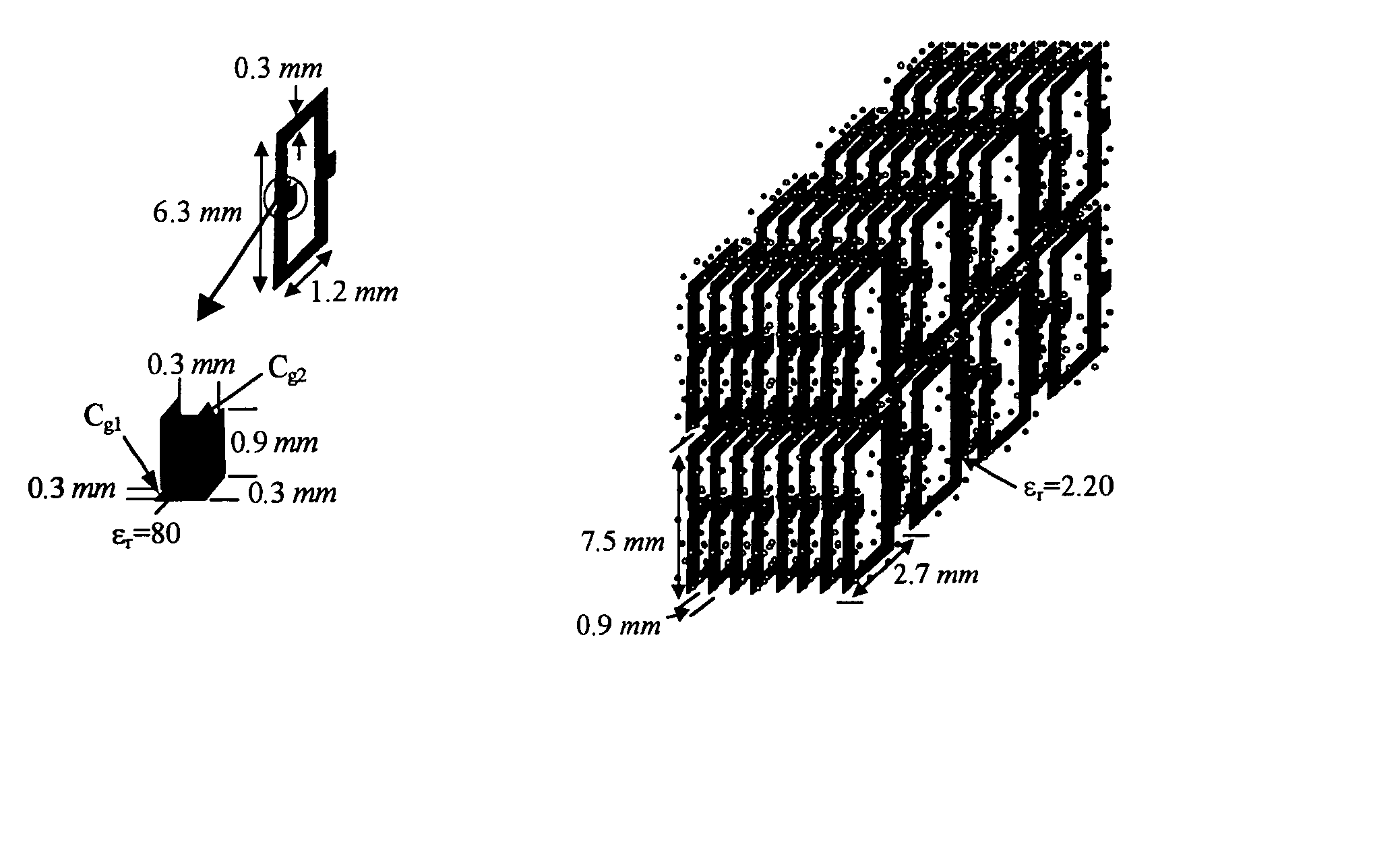
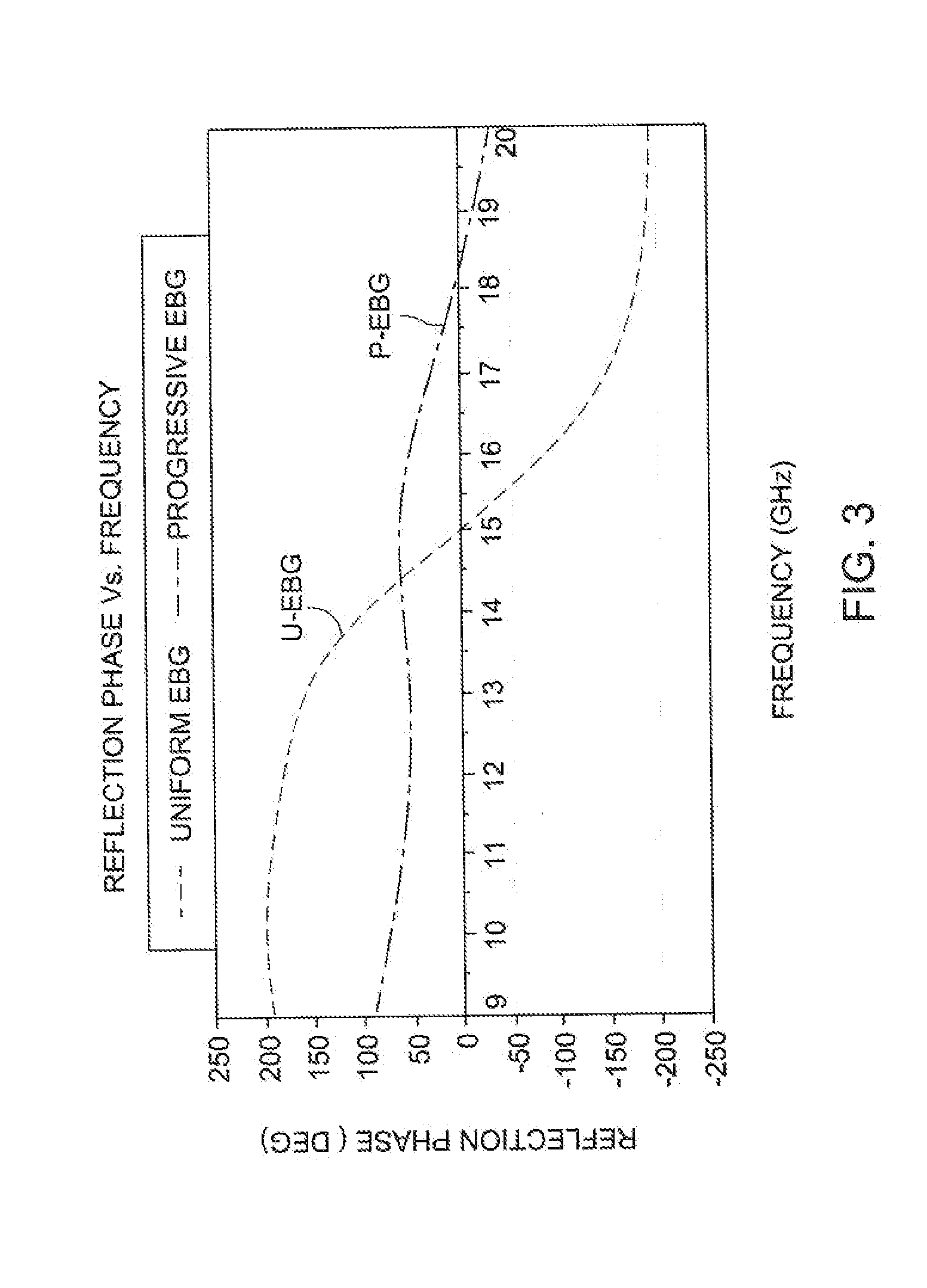
Broadband electromagnetic band-gap (EBG) structure
An electromagnetic bandgap structure comprising a progressive cascade of a plurality of patterns of cells. The cells of each pattern are dimensioned so that each pattern has a reflection phase response centered at a different, but closely-spaced, frequency compared with the reflection phase response of an adjacently positioned pattern, so that the combined reflection phase response of the plurality of patterns provides a continuous wideband operational range.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Antenna apparatus having patch antenna
ActiveUS20160028161A1Beam width can be retainedDirectivity can be suppressedAntenna arraysSimultaneous aerial operationsElectrical conductorDielectric substrate
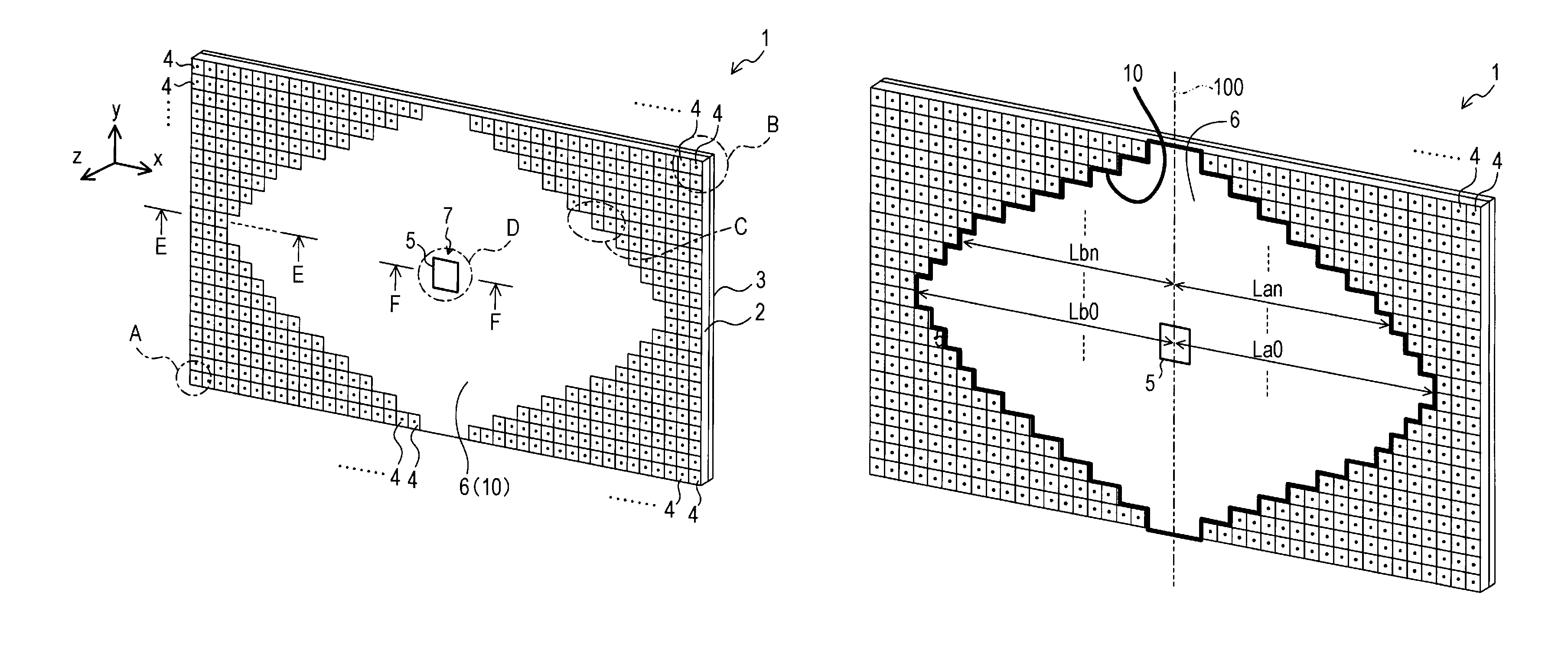
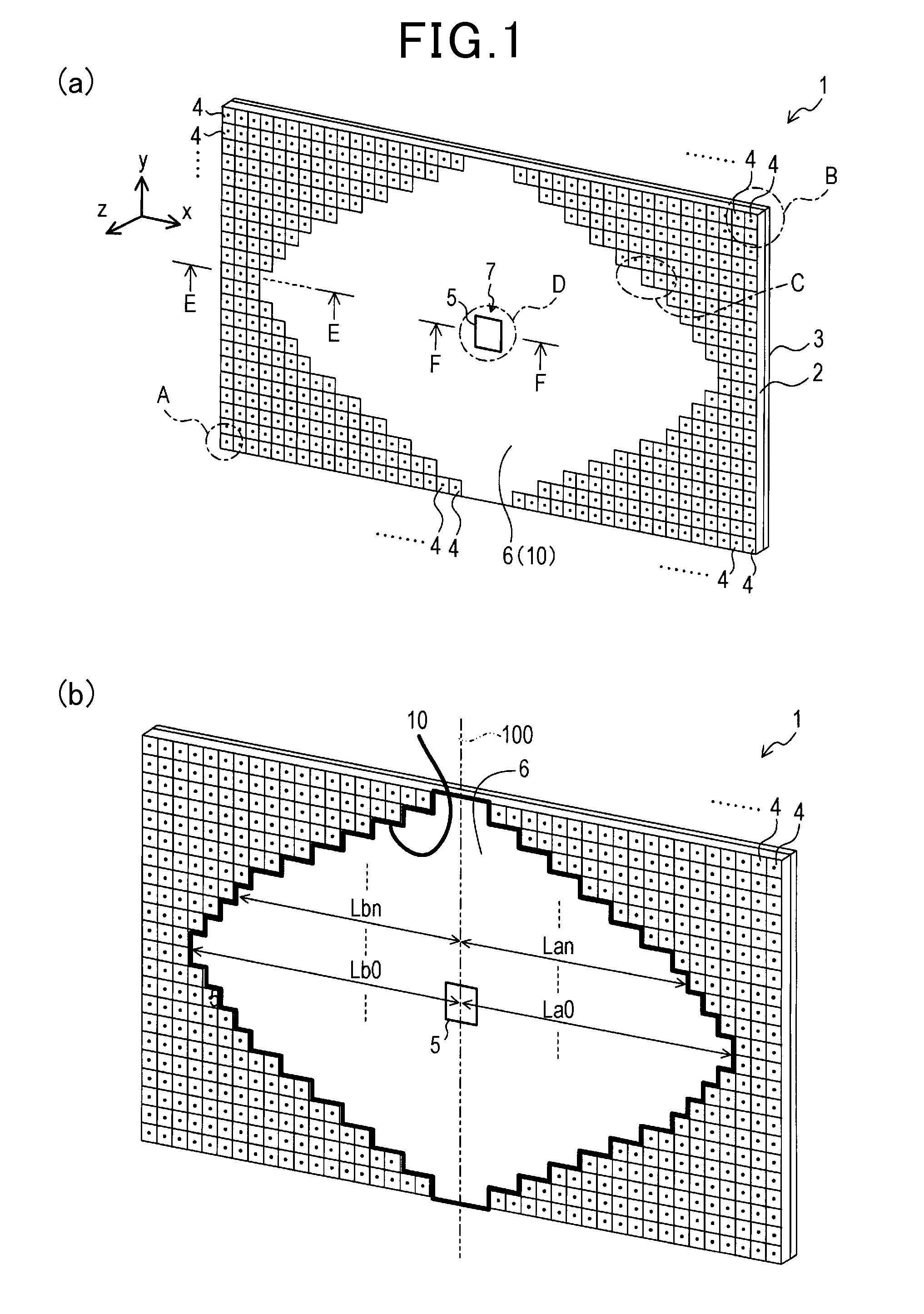
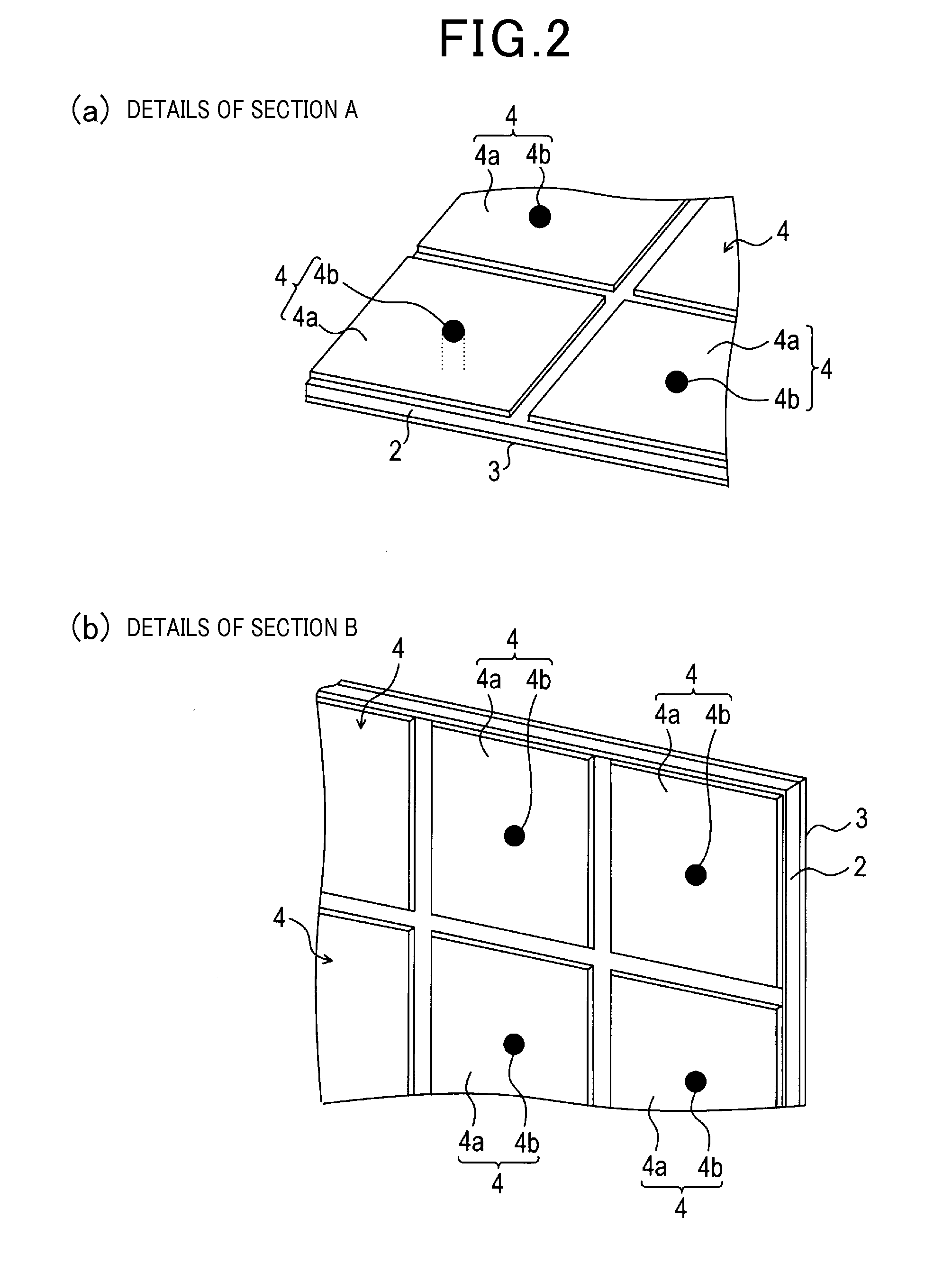
An antenna apparatus includes a dielectric substrate, a ground plate, a patch antenna provided with a patch radiating element, and a plurality of EBGs (Electromagnetic Band Gaps). The EBGs are composed of patch-shaped patterns formed on a surface of the substrate and connecting conductors electrically connecting the patch-shaped patterns and the ground plate. Each EBG is arranged to provide an EBG absent region having no EBG on the surface of the substrate. The patch radiating element is arranged within the EBG absent region. The EBG absent region is formed such that distances (absent distances) in a dominant polarized wave direction changes into a plurality of types depending on the position on a vertical patch line, where the distances range, to the boundary of the region, from an arbitrary position on the virtual patch line which is perpendicular to the dominant polarized wave direction of the patch antenna.
Owner:DENSO CORP
A substrate integrated ridge gap waveguide and a broadband circularly polarized leaky wave antenna
InactiveCN109037925AOptimum Axial Ratio PerformanceImproved Gain FlatnessParticular array feeding systemsRadiating elements structural formsDielectric plateWide band
The invention discloses a substrate integrated ridge gap waveguide and a broadband circularly polarized leaky wave antenna. The substrate integrated ridge gap waveguide comprises an upper layer dielectric plate, upper layer peripheral metallized vias, an upper layer rectangular metal patch, two rectangular annular metal patches, a lower layer dielectric plate, lower layer peripheral metallized vias, a metal ridge, an electromagnetic band gap EBG structure, a metal ground, a feeding probe and a matching probe; the substrate integrate metal ridge is formed by two rows of metallized vias in the center of the low layer and a dumbbell-shaped metal patch; the electromagnetic band gap EBG structure is composed of periodic mushroom-shaped structural units arranged on both sides of a rectangular strip in the middle of the dumbbell-shaped metal patch, and is used for limiting electromagnetic wave leakage to two sides. The upper layer and lower layer dielectric plates are tightly bonded. The wideband circularly polarized leaky wave antenna is a slot array arranged on the upper surface of the upper rectangular metal patch, and circularly polarized radiation is realized. The invention maintainsthe wide band and frequency scanning characteristics of the leaky wave antenna, and realizes the characteristics of circular polarization and high gain flatness.
Owner:ARMY ENG UNIV OF PLA
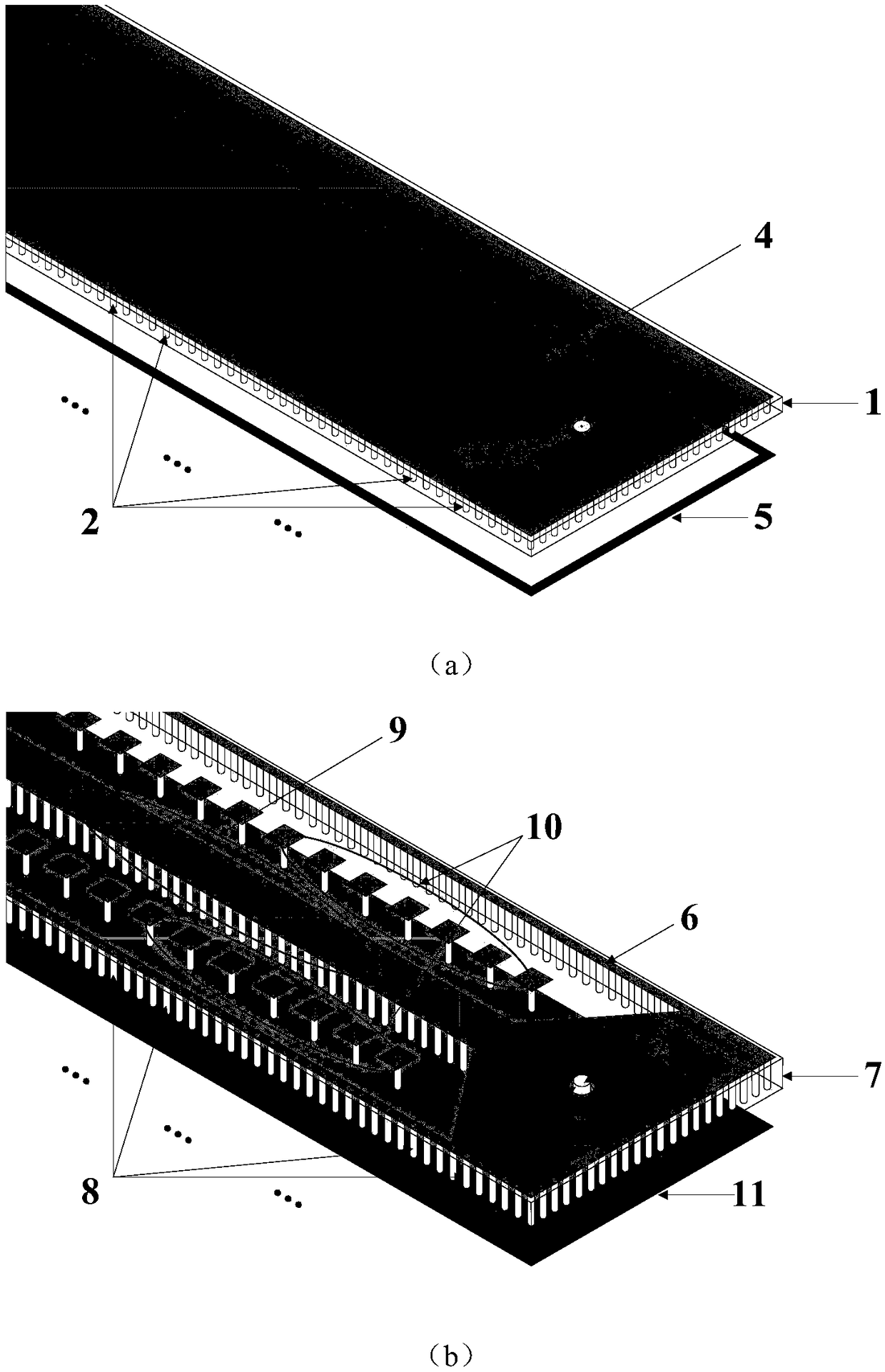
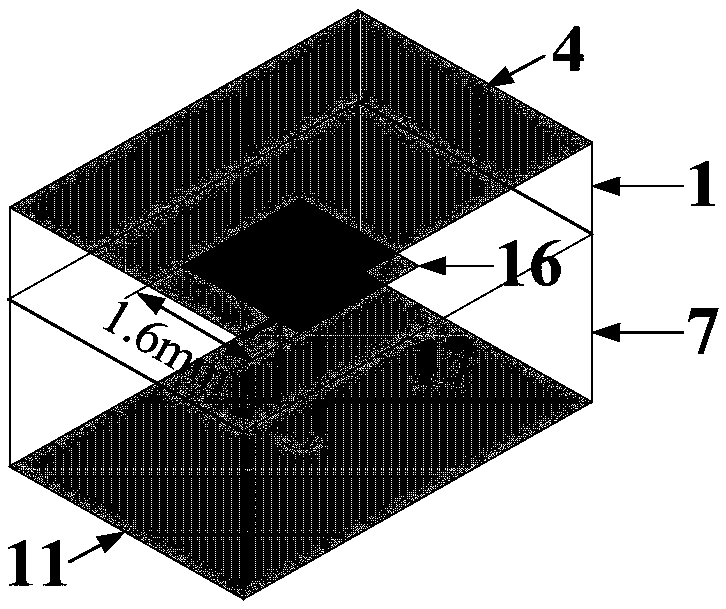
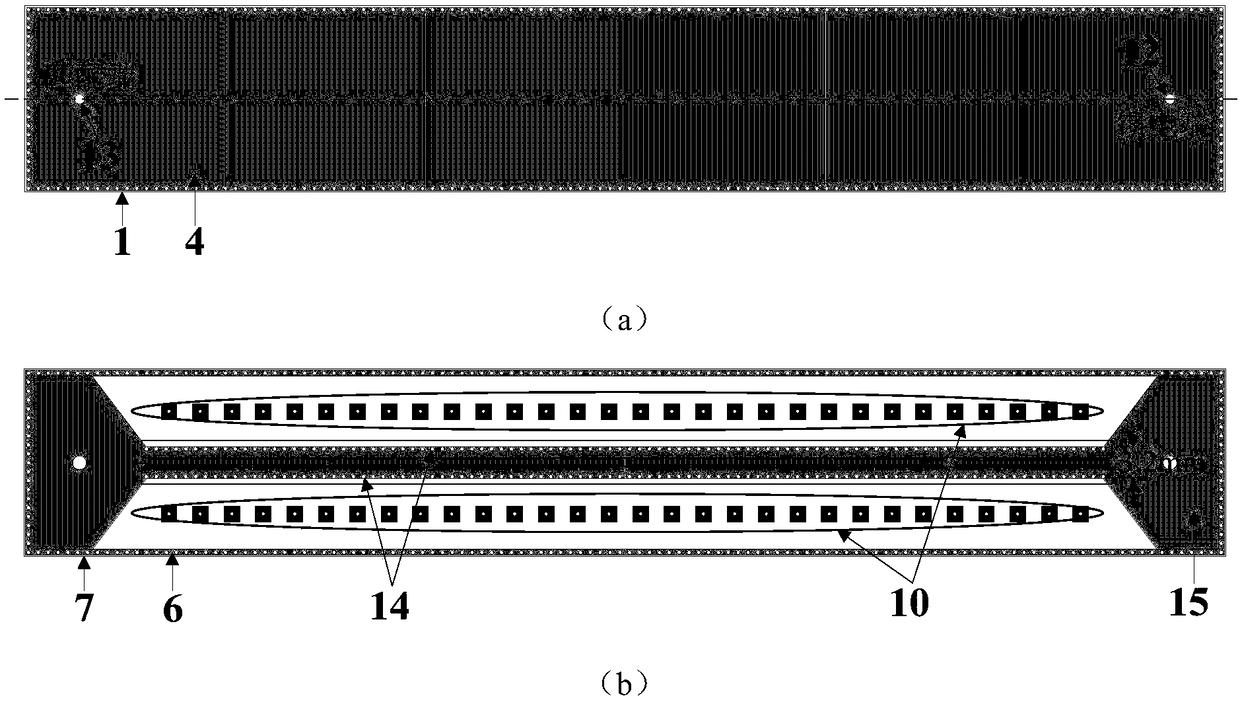
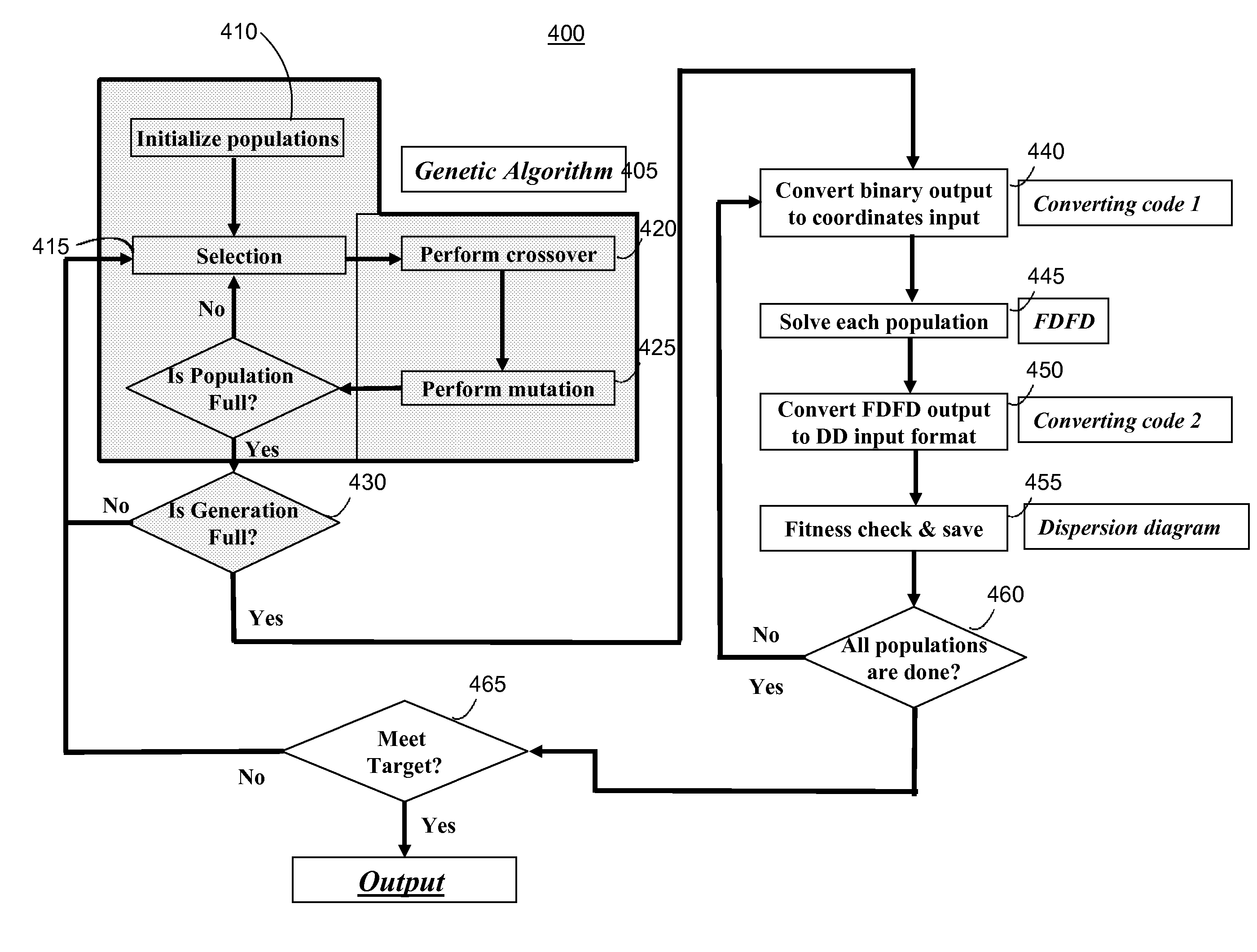
Systems and methods for electromagnetic band gap structure synthesis
The present invention describes methods and apparatus for electromagnetic band gap structure synthesis. An exemplary embodiment of the present invention provides a method of electromagnetic band gap structure synthesis, which includes the step of providing a set of desired characteristics for an electromagnetic band gap structure. Furthermore, the method includes generating populations of patch shape members with a genetic algorithm routine and solving one or more of patch shape members of the populations with an electrodynamics modeling technique. Thereafter, the method includes the step of converting the output of the electrodynamics modeling technique into a set of response data for one or more of the patch shape members and calculating a fitness level for one or more of the sets of response data in comparison to the set of desired characteristics for the electromagnetic band gap structure. Next, the method includes the step of determining whether the fitness level of one of the patch shape members is within a predetermined tolerance. Subsequently, if none of the patch shape members provides a fitness level within the predetermined tolerance, then the steps of generating, solving, converting, calculating, and determining are repeated.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
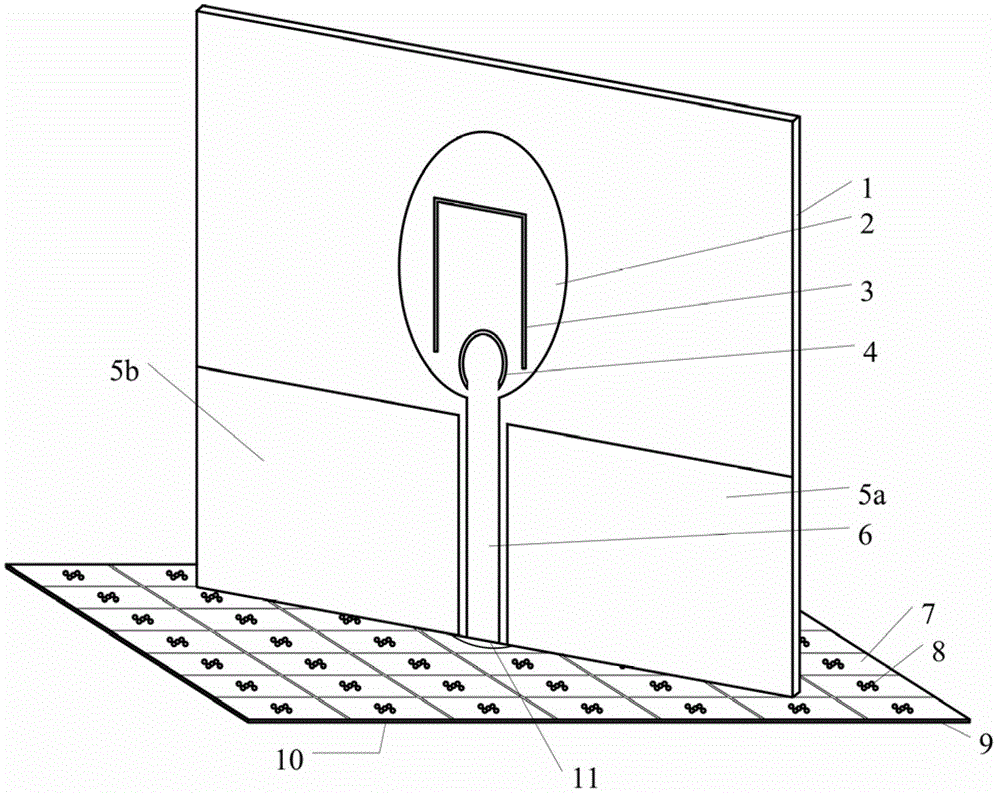
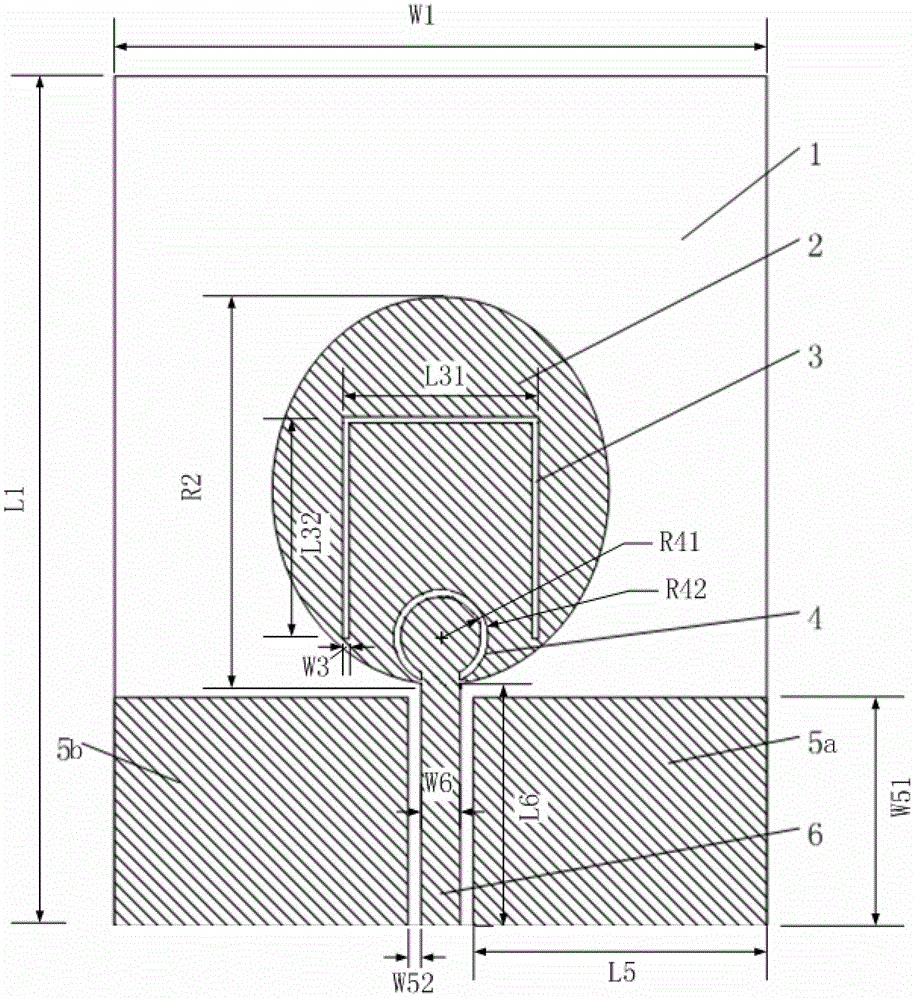
Ultra-wide-band dual-notch paster antenna adopting wide-attenuation-band electromagnetic band gap structure
ActiveCN102723601AReduce volumeReduce weightRadiating elements structural formsAntenna earthingsUltrasound attenuationCoaxial line
The invention relates to an ultra-wide-band dual-notch paster antenna adopting a wide-attenuation-band electromagnetic band gap structure. The antenna comprises a wide-attenuation-band electromagnetic band gap structure and an ultra-wide-band dual-notch paster antenna, wherein the wide-attenuation-band electromagnetic band gap structure is formed in the way that multiple hole-penetrating electromagnetic band gap units are periodically arranged, and comprises a square metal paster, metalized penetrating holes, a central round through hole, a square medium substrate and a metal floor; the ultra-wide-band dual-notch paster antenna comprises an oval metal paster provided with a combined slot liner of a reversed-U-shaped slot liner and an opened ring-shaped slot liner, a microstrip line, an antenna grounding part, a rectangular medium substrate and a coaxial line; the oval metal paster provided with the combined slot liner of the reversed-U-shaped slot liner and the opened ring-shaped slot liner, the microstrip line and the antenna grounding part are located on the same plane and manufactured on the rectangular substrate to achieve the ultra-wide-band dual-notch performance. According to the invention, the forward and backward radiation of the antenna is reduced by the performance of the wide attenuation band of the porous electromagnetic band gap structure, and the omnidirectional radiation performance of the antenna is improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
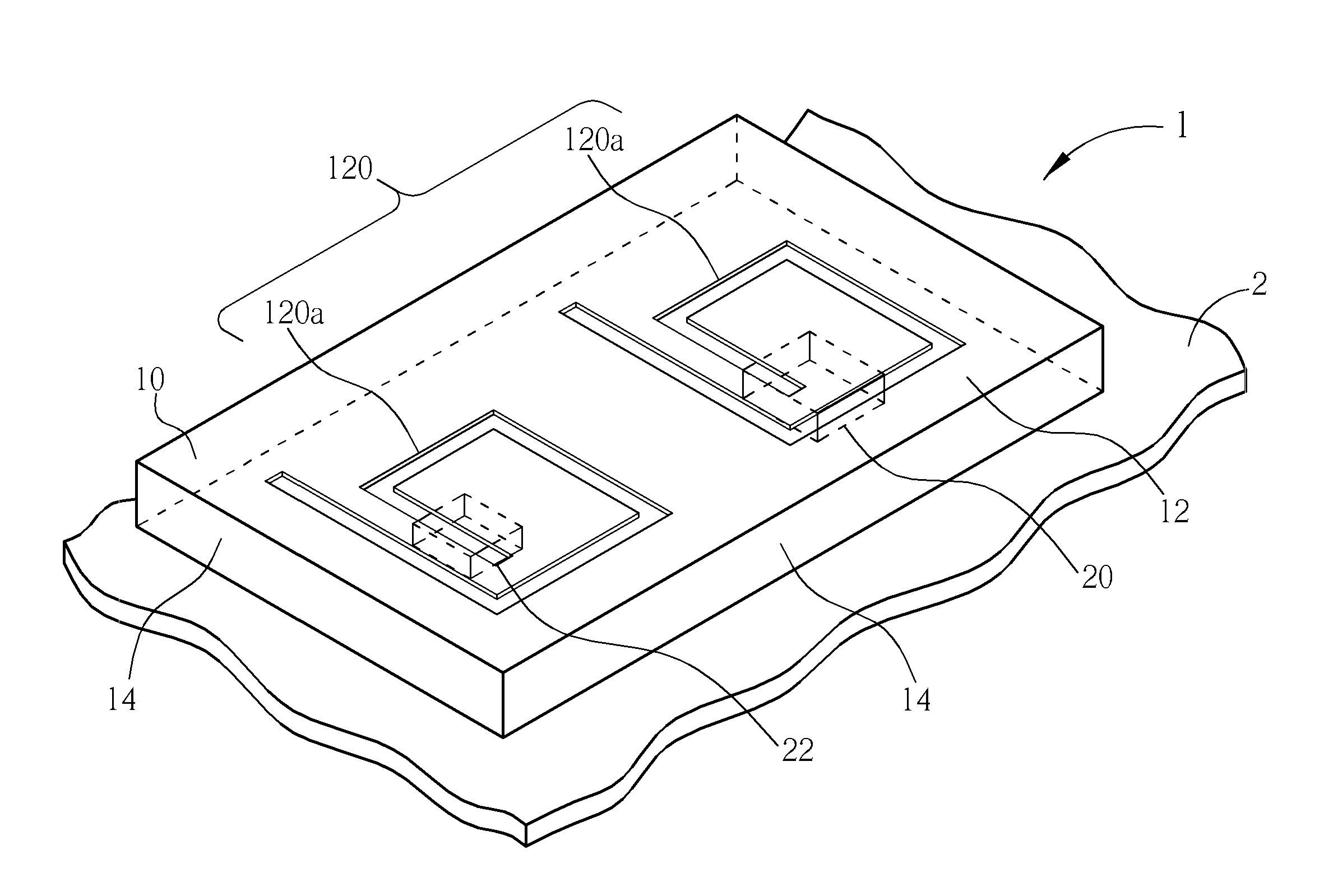
Substrate for semiconductor package
InactiveUS20070285188A1Current interference reductionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSemiconductor packageDielectric substrate
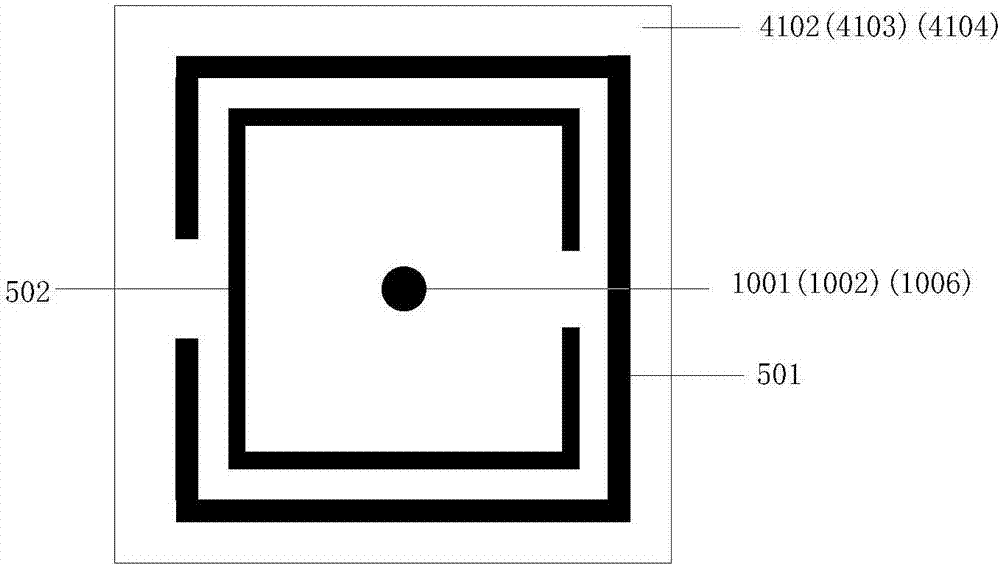
A substrate for a semiconductor package comprises a dielectric substrate, a circuit pattern, and an electromagnetic band gap (EBG) pattern. The circuit pattern is formed on a first surface of the dielectric substrate and is connected to ground via a ground connection. The electromagnetic band gap (EBG) pattern comprises a plurality of zigzag unit structures formed on a second surface of the dielectric substrate, wherein the second surface is formed on an opposite side of the dielectric substrate from the first surface; the zigzag unit structures are electrically connected to each other; and at least one of the zigzag unit structures is electrically connected to the ground connection.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
RFID tag and antenna
ActiveUS7612676B2Improve performanceLess sensitiveRecord carriers used with machinesBurglar alarm by hand-portable articles removalDielectricElectromagnetic band gap
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Power supply distribution network based on local electromagnetic band gap structure
InactiveCN102957310AImprove signal integrityReduce distractionsPower conversion systemsElectromagnetic interferenceEngineering
The invention discloses a power supply distribution network based on a local electromagnetic band gap structure. The electromagnetic band gap structure is locally etched on a power supply plane, and a ground plane is kept intact. Basic units of the electromagnetic band gap structure are formed by complementary split ring resonators, and the adjacent basic units of the electromagnetic band gap structure are connected by a Z-shaped bridge. The problems that the inhibiting degree of synchronous switching on and off noise in a hybrid circuit system is not high enough and the inhibiting frequency band is not wide enough are effectively solved, and the problem that the destructiveness of the traditional global electromagnetic band gap structure to the power supply plane is large can be solved. The power supply distribution network disclosed by the invention has excellent power supply integrity, and the influence of electromagnetic interference can be lowered.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Miniaturized band-pass filter with harmonic suppression for loading fan-shaped offset of microstrip
InactiveCN1874053ASuppresses higher harmonicsStrong shielding signal abilityWaveguide type devicesCapacitanceHigher order harmonics
Miniaturized harmonic suppression type band-pass filter includes symmetrical electromagnetic band gap structure of microstrip composed of odd pieces of band gap unit. Loading fan-shaped microstrip branched structure on two sides of microstrip line obtains symmetrical band gap unit symmetrical in up down, and left and right. Coupling slot is introduced in a band gap unit in center of the symmetrical band gap structure. Thus, the band gap unit is divided into total identical two parts in horizontal direction to form two parts with identical resonance frequencies symmetrical to slot so as to establish resonant-type band-pass filter, as well as its center frequency and stopband characteristic. The coupling slot is equivalent to coupling capacitance. The disclosed band-pass filter possesses selected ultra wide stop band, and makes high order harmonics be fallen on range of stop band. Moreover, since effect of slow wave, size of filter is reduced greatly.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Implementation method of H-type groove fractal UC-EBG (Uniplanar Compact Electromagnetic Band Gap) structure oriented to multifrequency antenna substrate
InactiveCN102510658AFractal structure is simpleEasy to processPrinted circuit detailsAntennasUnit sizeDielectric substrate
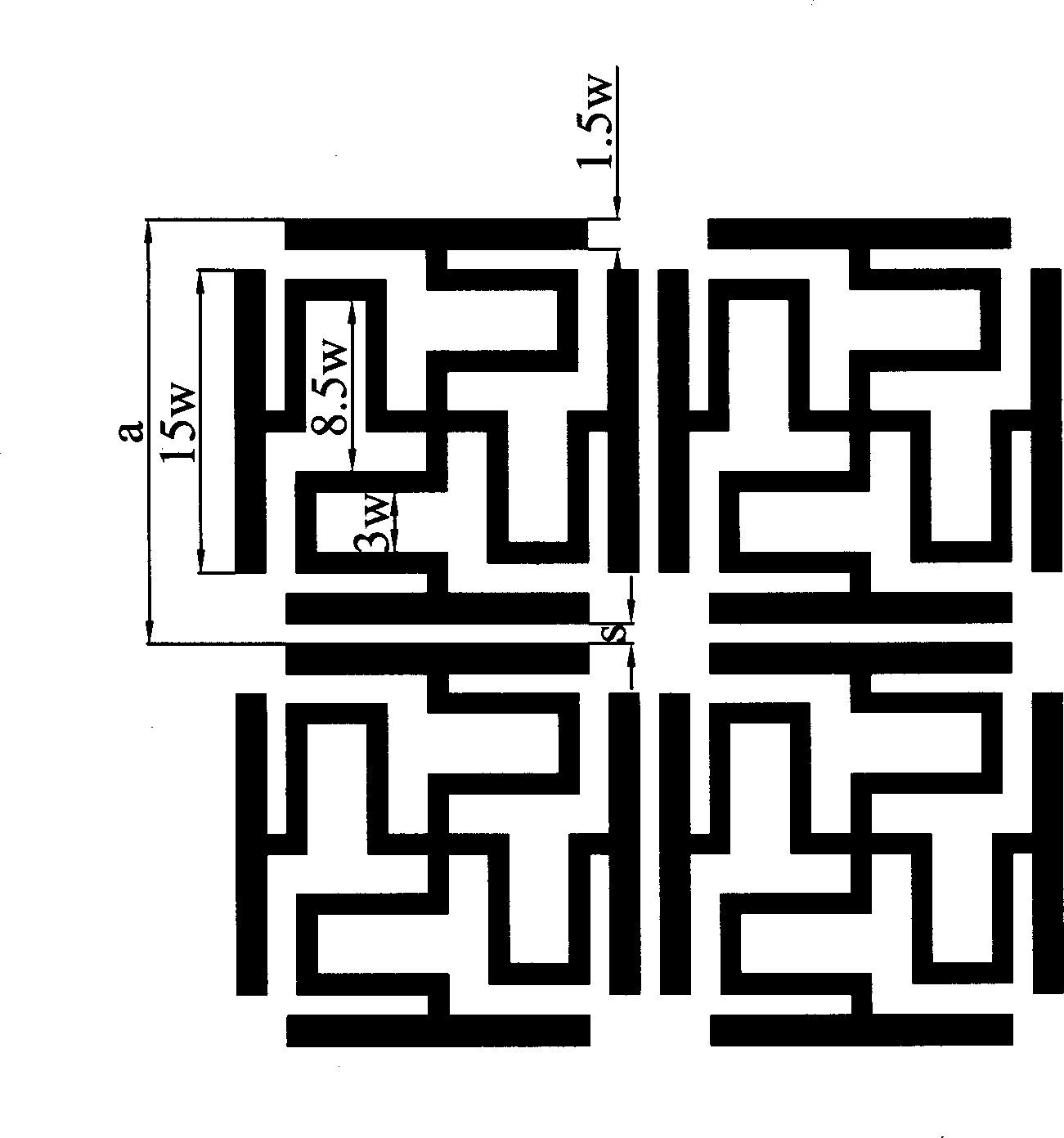
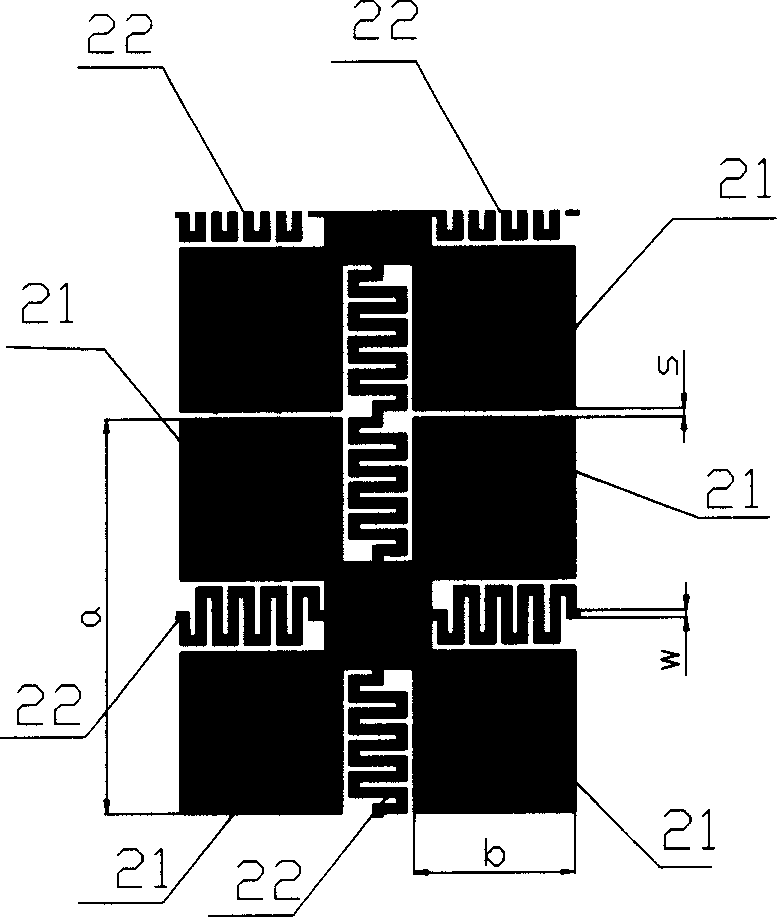
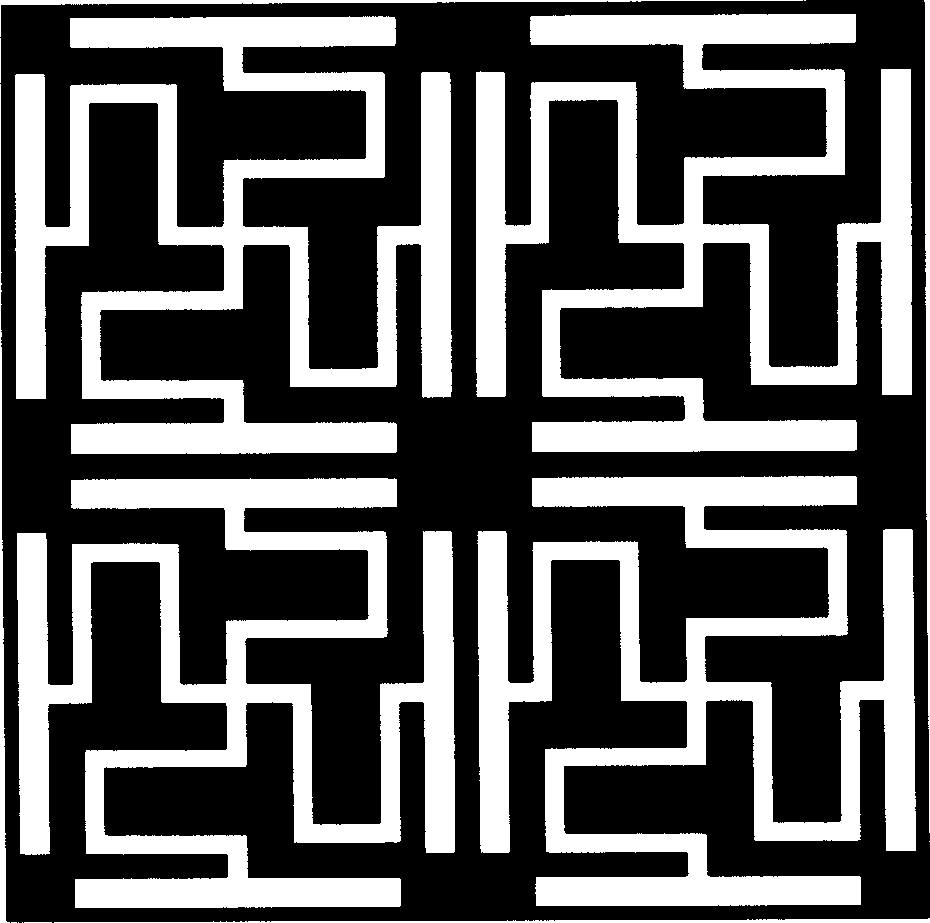
The invention relates to an implementation method of a multi-frequency-band UC-EBG (Uniplanar Compact Electromagnetic Band Gap) structure and belongs to the technical field of electromagnetic propagation and reception. According to the method provided by the invention, an H-type groove is arranged on a unit paster, so as to design a four-frequency-band H-type groove UC-EBG structure within a frequency range of less than 60GHz; the invention also provides a method for realizing the miniaturization of the structure by increasing the groove length w of the H-type groove, decreasing the groove width a and increasing the dielectric constant epsilon of a dielectric substrate and the like. In addition, the method provided by the invention can be used for further realizing the miniaturization of the EBG structure by introducing an H-type groove primary fractal structure, and designing the four-frequency-band H-type groove UC-EBG structure within a frequency range of less than 3 GHz by enlarging the structure through the period unit size SF (Scale Factor). The implementation method provided by the invention can be used for solving the problem that the EBG structure has less possibility of realizing multiple frequency bands in a lower frequency because of the size restriction and providing guidance for the specific design of a multi-frequency-band miniaturized electromagnetic band-gap structure.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Stacked dual-band electromagnetic band gap waveguide aperture for an electronically scanned array
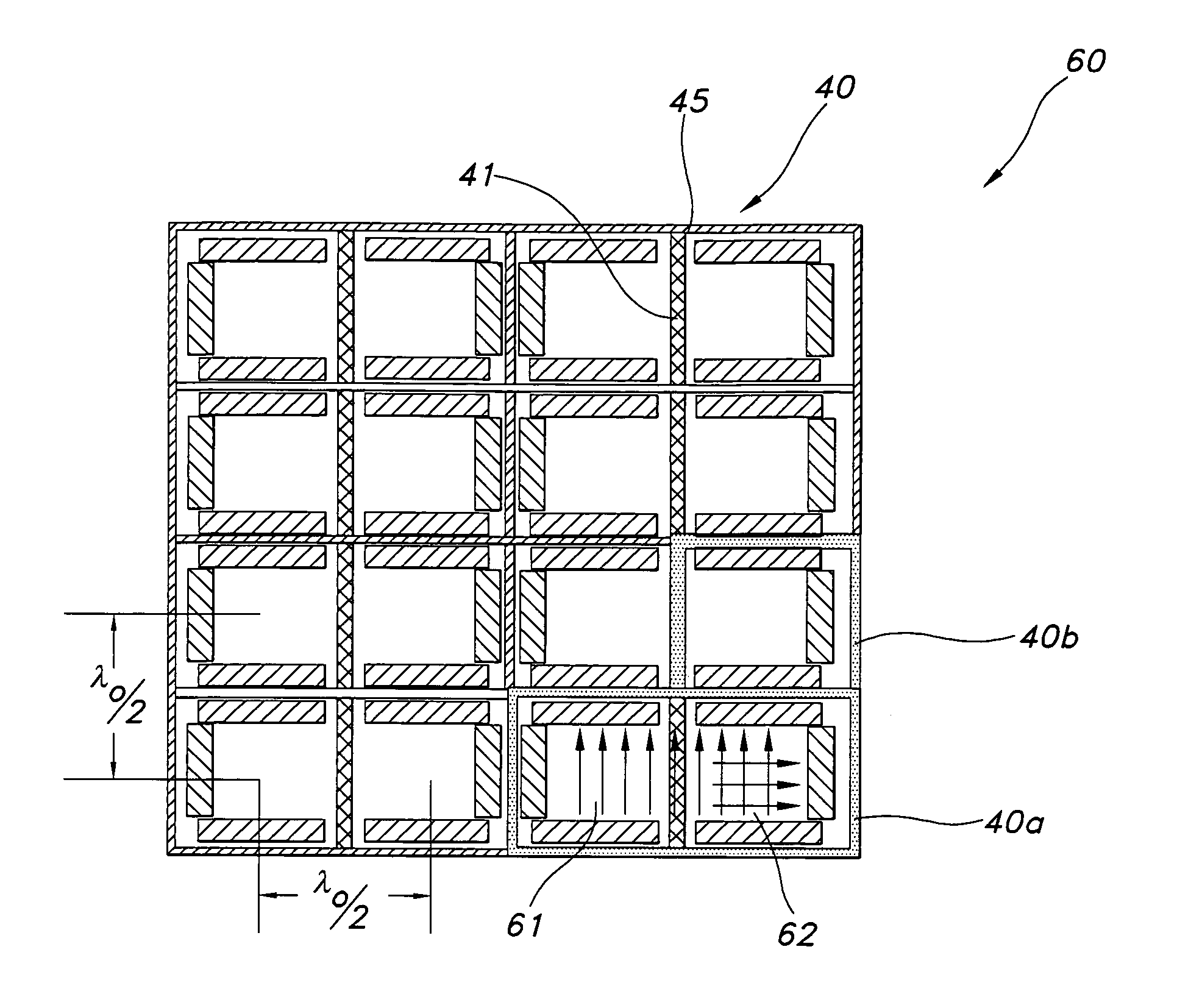
InactiveUS7639197B1Provide benefitsEasy constructionDelay linesWaveguidesPhase shiftedDouble frequency
A dual-band stacked electromagnetic band gap (EBG) electronically scanned array (ESA) has a first aperture with a waveguide element spacing of less than λ / 2 and a length to provide about 360° of upper frequency phase shift. A second aperture is stacked on the first aperture and has an element spacing of less than λ / 2 at a lower frequency and a length such that when summed with the first aperture length about 360° of lower-frequency phase shift is provided. The second aperture comprises metal slats perpendicular to EBG slats to form an equivalent waveguide element with a broadwall dimension to support a TE10 mode at the upper frequency. The second aperture may also comprise metal slats and alternating frequency selective surface (FSS) slats with perpendicular EBG slats lengthening the broadwall at the upper frequency. The EBG slats provide lower-frequency phase shifting in both embodiments.
Owner:ROCKWELL COLLINS INC
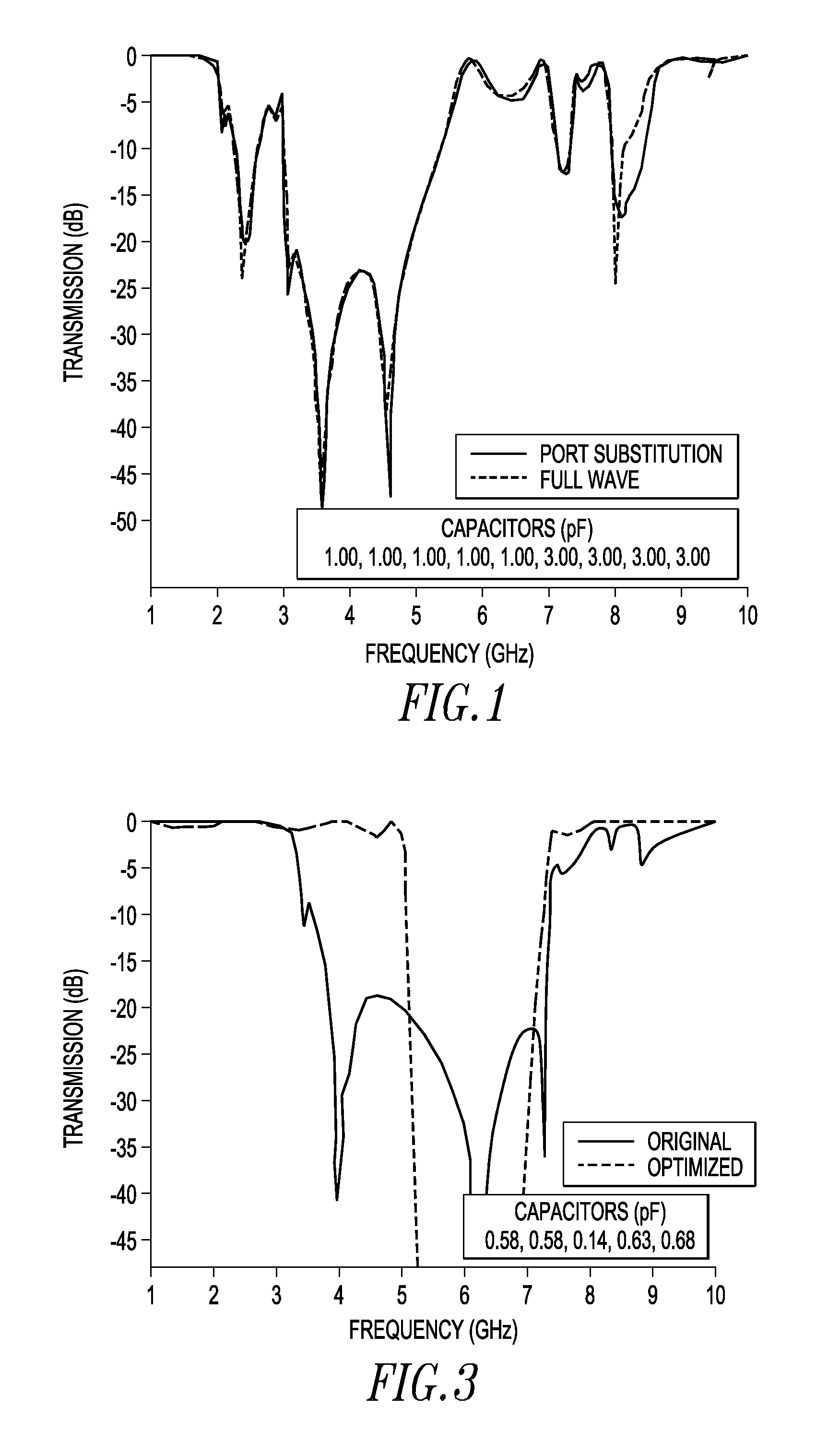
Electromagnetic Band Gap Structure and Method for Enhancing the Functionality of Electromagnetic Band Gap Structures
ActiveUS20130268250A1Improving S/N for transmission/receivingPrinted circuit aspectsFull waveEngineering
A method for making an electromagnetic band gap structure includes performing a single full wave simulation for the structure using a computer to perform the simulation, extracting a multiple port scattering matrix based on the single full wave simulation using a computer, and measuring or estimating a transmission of waves across the body between a first port and a second port of the body. The body has multiple ports between the first port and the second port that are defined by scattering elements using the computer. The matrix may be reduced to a two by two matrix recursively one dimension at a time using the computer.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com