Patents
Literature
340 results about "Mo element" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High-temperature titanium alloy with high heat resistance and high thermal stabilization
The invention provides a novel high-temperature Ti alloy with high heat resistance and high heat stability. The alloy contains eutectic Nb, Ta and Mo elements. Based on the appropriate proportion of these three elements, the alloy is superior in high resistance and stability to heat and good antioxidant effect. The alloy contains (by weight) Al 5.0-6.3 percent, Sn 3.0-5.0 percent, Zr 2.5-7.0 percent, Mo 0.2-1.5 percent, Si 0.20-0.55 percent, Nb 0.2-1.0 percent, Ta 0.2-3.0 percent, C 0.01-0.09 percent, and Ti and other inevitable impurities in balance. The alloy is an ideal alternative material for high-temperature parts of aircraft engine, such as wheel disk, drum barrel, barrel shaft and blade.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
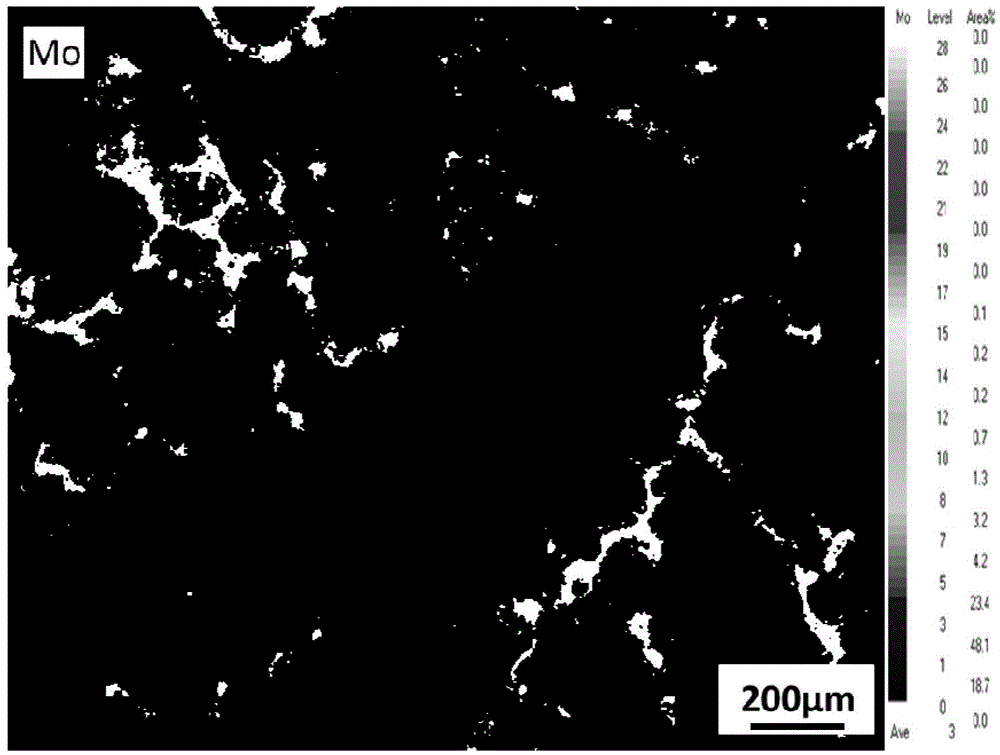
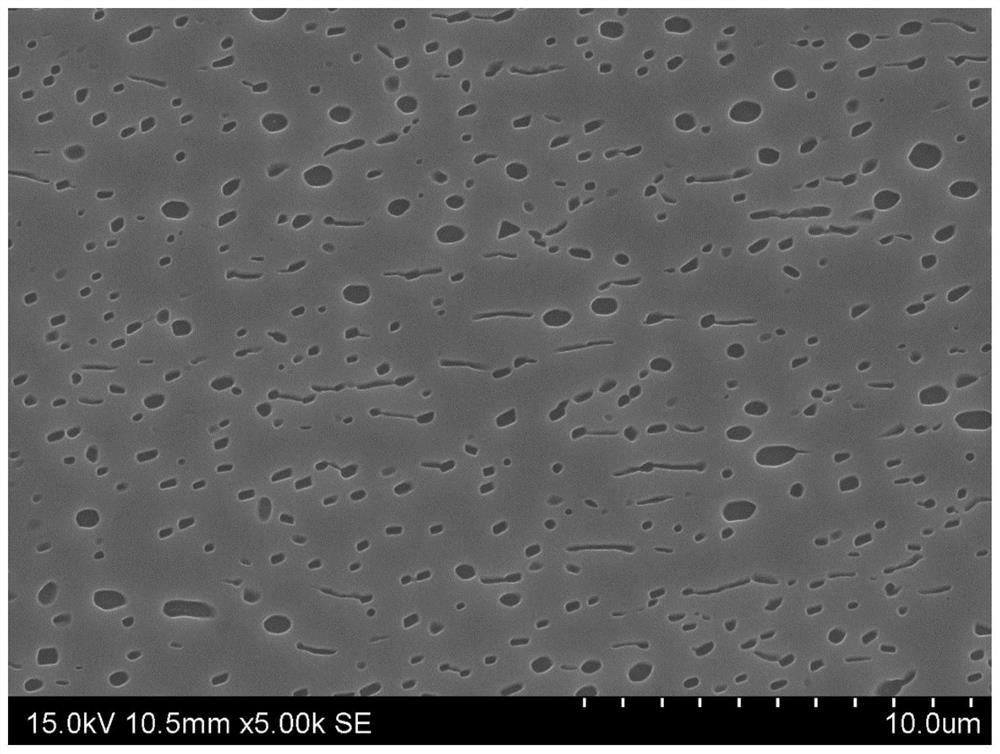
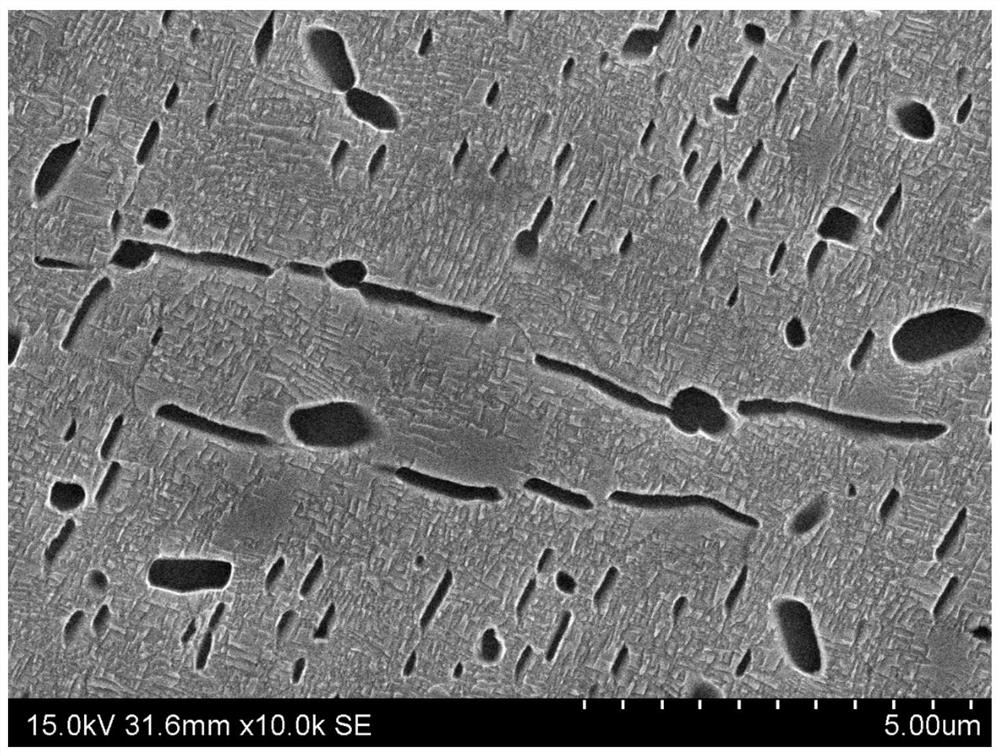
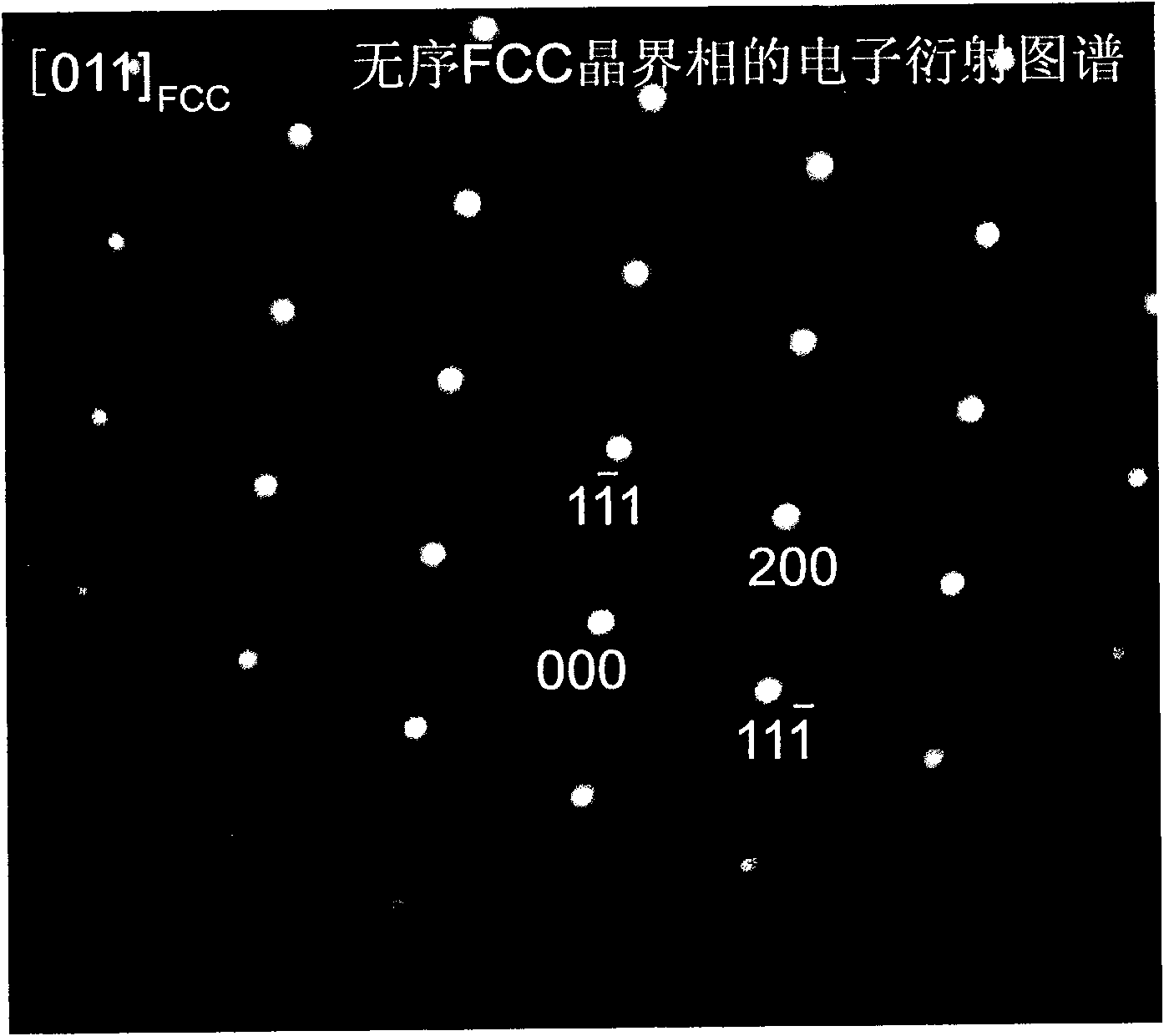
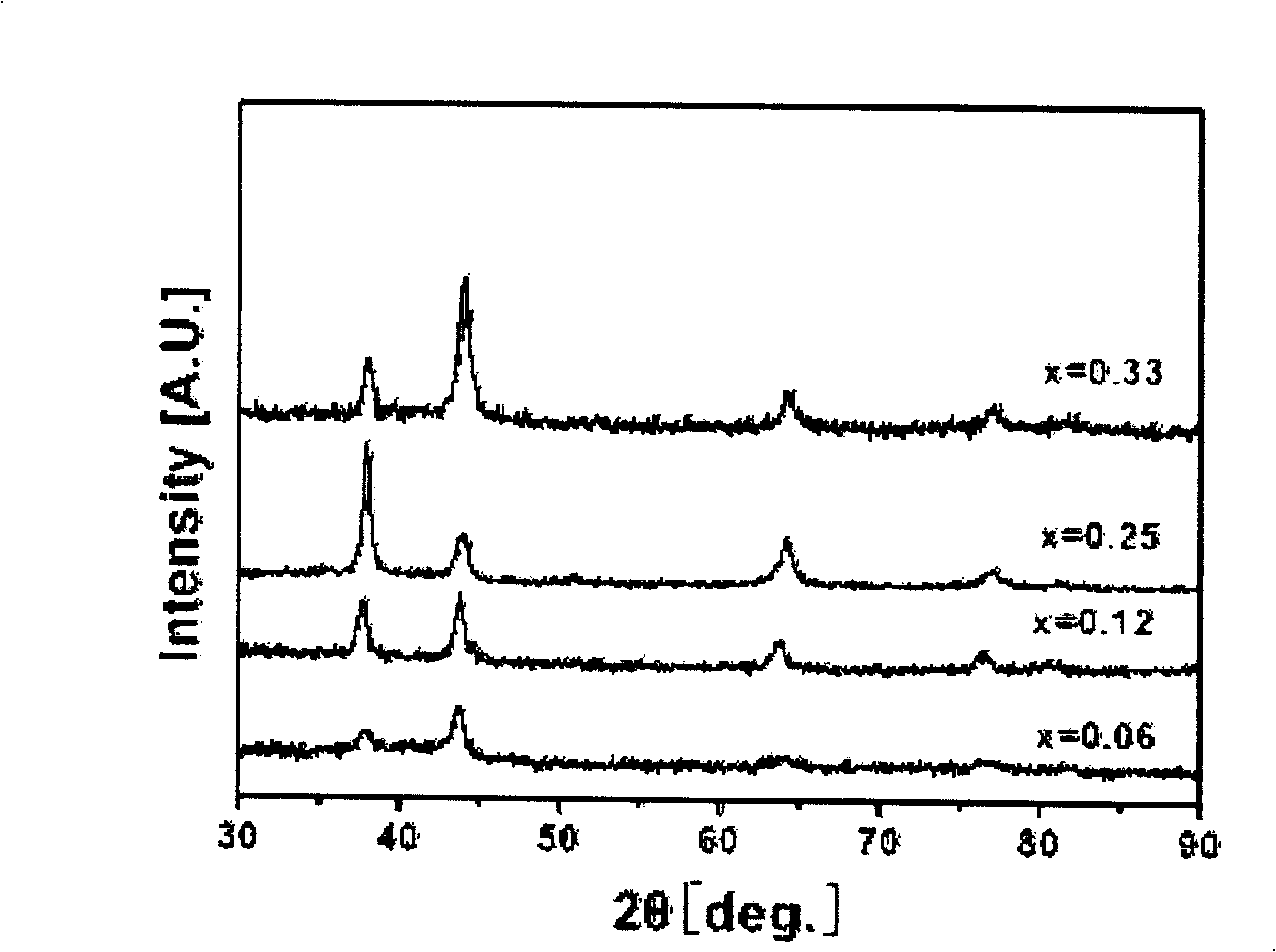
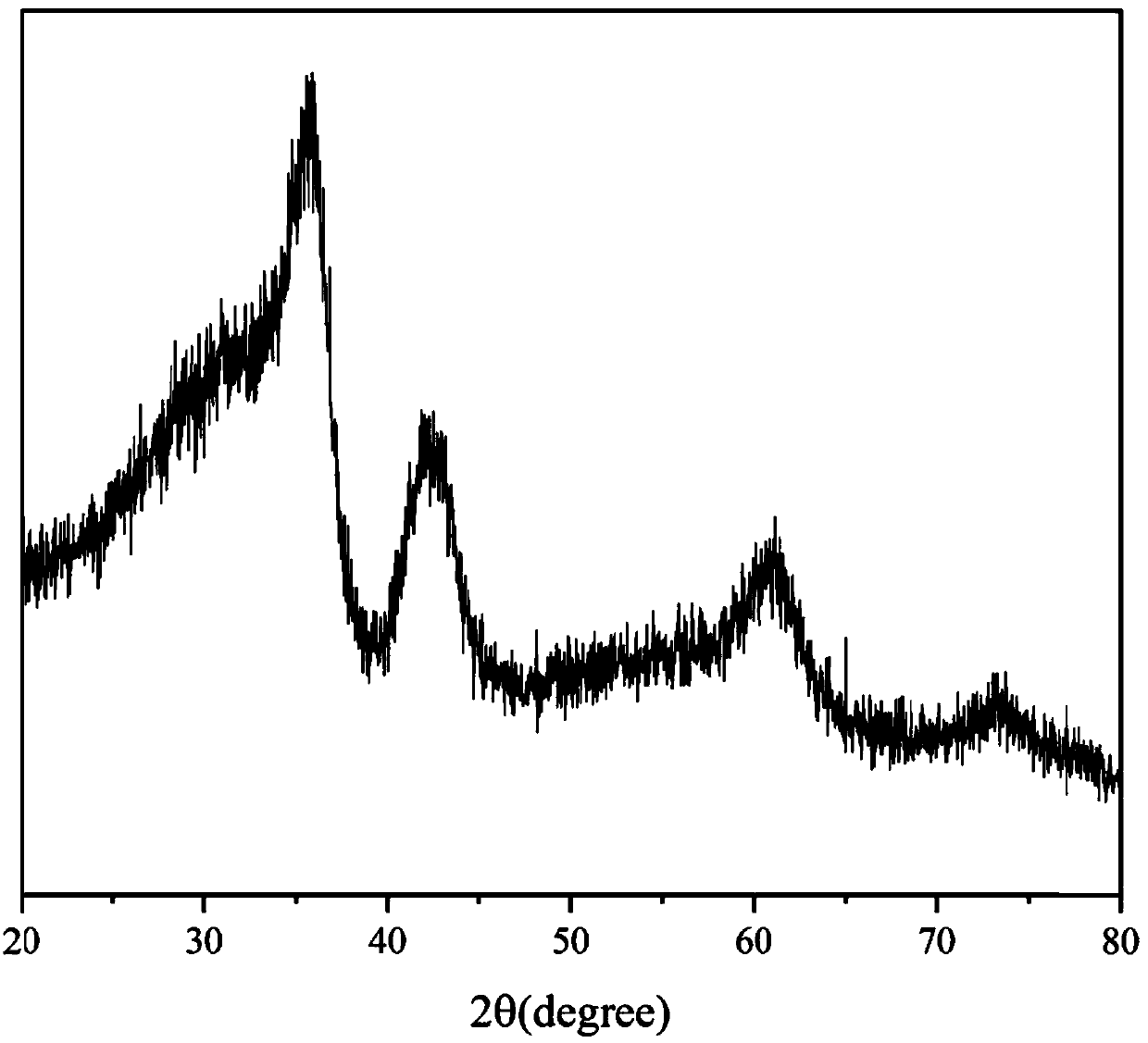
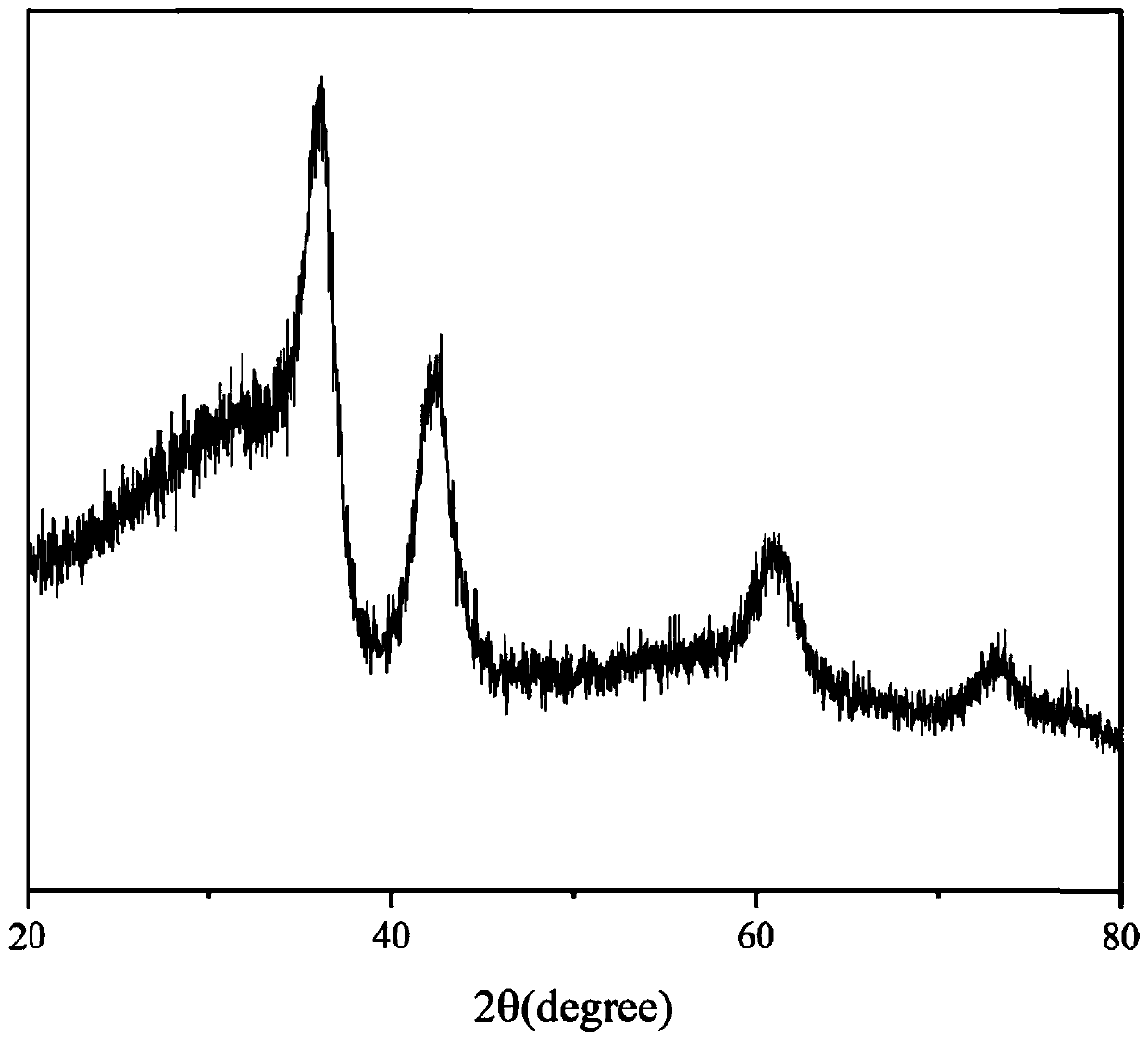
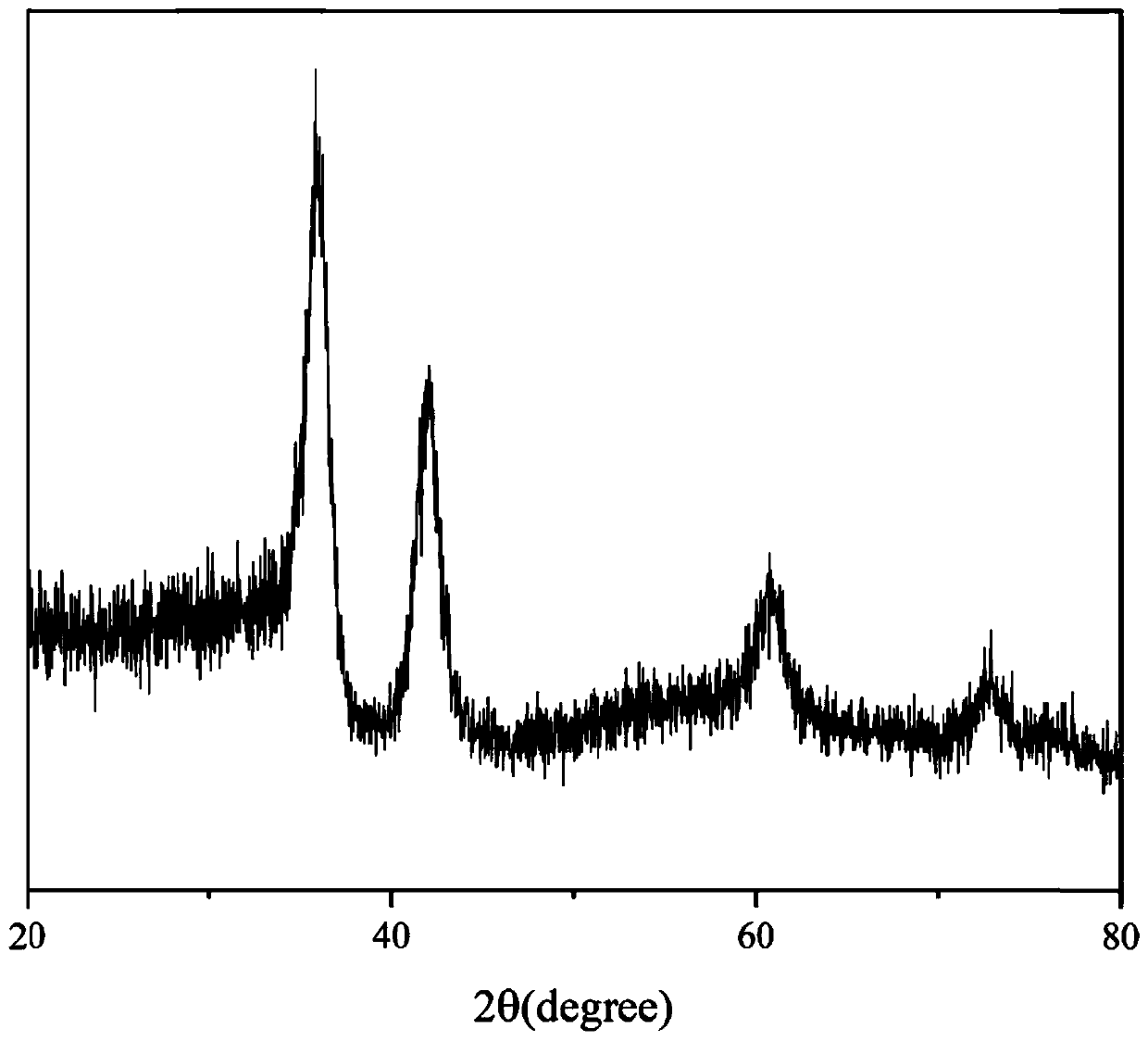
TiZrNbVMo[x] high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
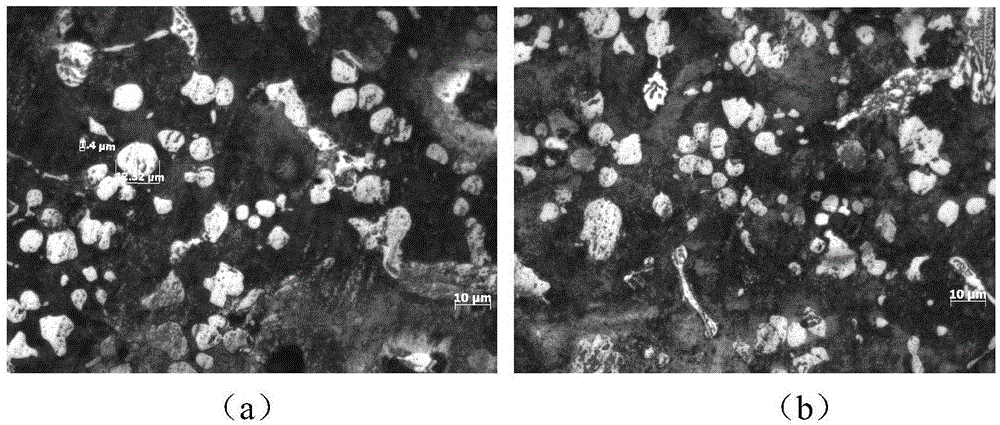
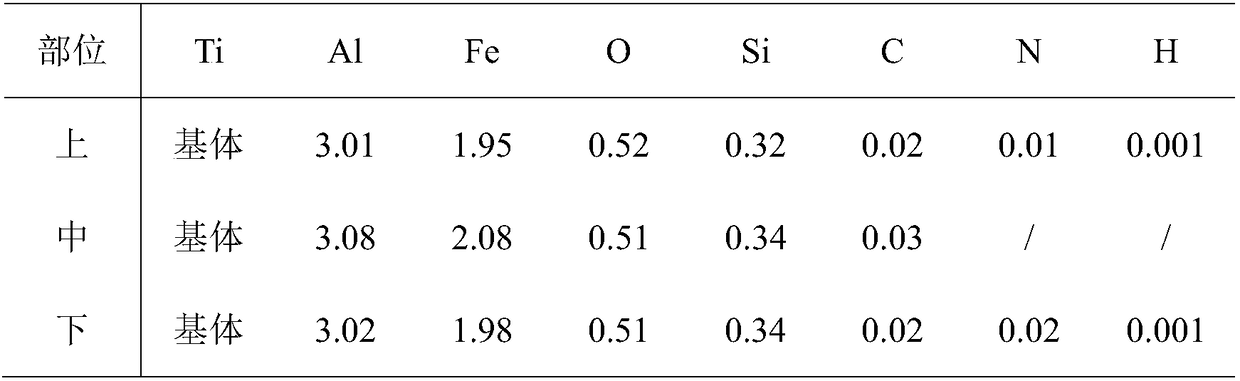
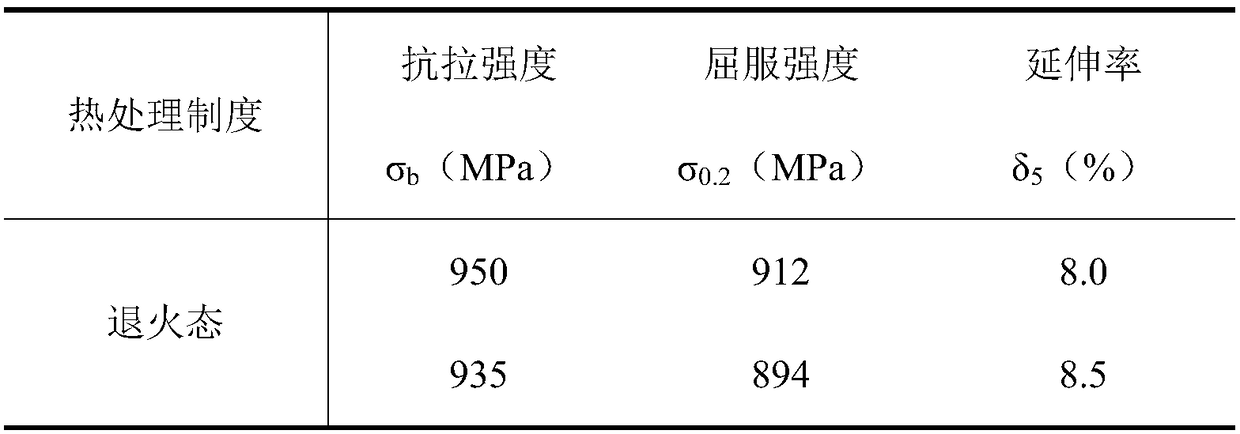
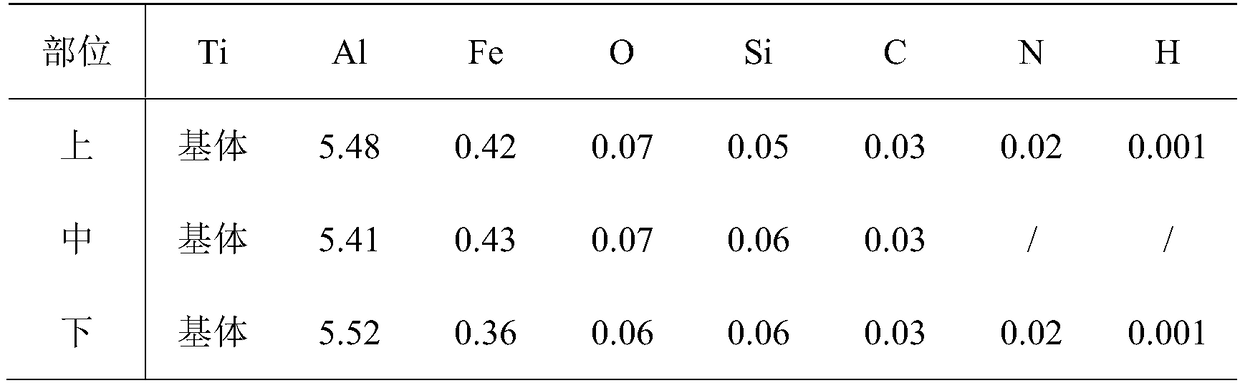
The invention relates to a high entropy alloy material and a preparation method thereof, the high entropy alloy composition is TiZrNbVMo[x], wherein x is the molar ratio with a value range of x = 0 ~ 1.0. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using a mechanical method to remove oxide skin of metallurgical raw materials of Ti, Zr, Nb, V and Mo elements, then accurately weighing according to the molar ratio; respectively melting intermediate alloys of MoTi and TiZrNbV in a non self-consumable vacuum electric-arc furnace or a cold crucible suspension furnace, finally putting the intermediate alloys together to melt into target alloys, melting each alloy for more than 3 times to ensure uniformity of the composition; taking a specific mass of a master alloy to preparing a rod or plate sample by use of vacuum suction casting or pouring equipment. Compared with traditional crystal materials, the high entropy alloy disclosed by the invention exhibits high hardness, yield strength and fracture strength, and compared with other high-strength body-core-structure high entropy alloys, the high entropy alloy disclosed by the invention has better plastic deformation ability.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Electronic packaging material
InactiveCN103103403AIncrease stiffnessHigh hardnessSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesMo elementLow density
The invention discloses an electronic packaging material. The electronic packaging material is characterized by comprising a matrix and a reinforcement, wherein the matrix is made of aluminum, copper, aluminum alloy or copper alloy, the reinforcement is of graphene accounting for 0.5-30% of total mass percentage, and the graphene has 1-20 layers of tiny plates the area of each which is 1-5000 mu m<2> or plates the area of each which is more than 1mm<2>; and the aluminum or copper metal comprises Cr, Fe, Ti, W, B or Mo element, the content of the Cr, Fe, Ti, W, B or Mo element is 0.05-1%. The electronic packaging material has the advantages of being high-heat conductivity, high-strength, low-density, environment-friendly and good in machineable property; and as the electronic packaging material, the composite has excellent property and good application prospects.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Technology for steel making by directly alloying molybdenum oxide
The invention relates to a technology for steel making by directly alloying molybdenum oxide. The technology is characterized in that the smelting process comprises the following steps of a. adding a molybdenum oxide raw material to a container or a smelting furnace which is unfilled with or partially filled with molten steel or iron liquid, then continuously filling the molten steel or iron liquid, and mixing the molybdenum oxide raw material in the molten steel or iron liquid for certain time; b. after the molten steel or iron liquid stands still in the container or the smelting furnace, adding a certain amount of reducing agent to the surface of the molten steel or iron liquid and a slag surface; and c. after the content of a molybdenum element in the molten steel or iron liquid stabilizes in a smelting later period, adding molybdenum-containing alloy so as to adjust the components of the molten steel or iron liquid. The technology has the characteristics that the molybdenum alloying smelting process is simple to operate, the yield of the molybdenum alloy element is high, the alloying smelting time is short, the consumption of smelting energy sources is low and the smelting cost is low; and equipment has wide adaptation and can be applied to the smelting of steel with the molybdenum content of 0.001-15%.
Owner:JIANGYIN XINGCHENG SPECIAL STEEL WORKS CO LTD
3Cr seamless steel pipe and production method thereof
ActiveCN101899621ASolve the problem of water quenching and easy crackingImprove performanceFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesForeign matterChemical composition
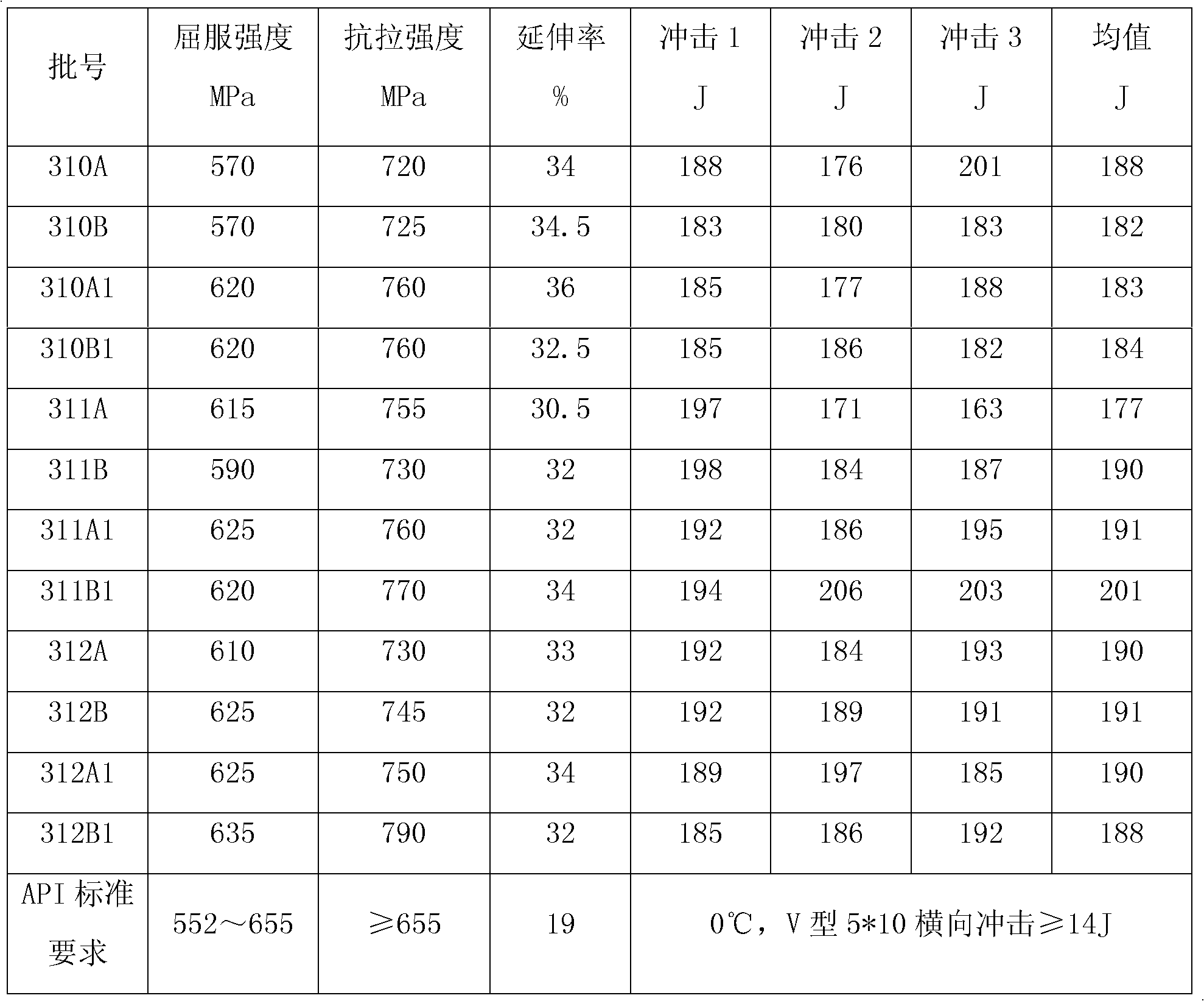
The invention belongs to the technical field of metallurgy, in particular to a 3Cr seamless steel pipe and a production method thereof. The invention solves the first technical problem by providing a 3Cr seamless steel pipe with high hardenability and refined grains, wherein the 3Cr seamless steel pipe comprises chemical components in percentage by weight: 0.1-0.2% of C, 0.1-0.5% of Si, 0.3-0.8% of Mn, 2-4% of Cr, 0.3-0.6% of Mo, 0.0024-0.024% of Ti, 0.01-0.04% of Al, 0-0.03% of P, 0-0.03% of S and the balance of Fe and unavoidable foreign matters. The 3Cr seamless steel pipe has the component design of lower C content, which can prevent cracking in hardening, Mo element can increase the hardenability, and Ti element can refine grains and ensure that the mechanical property satisfies the API standard.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP VANADIUM TITANIUM & RESOURCES +1
Cf/C-SiC composite material as well as preparation method and application thereof
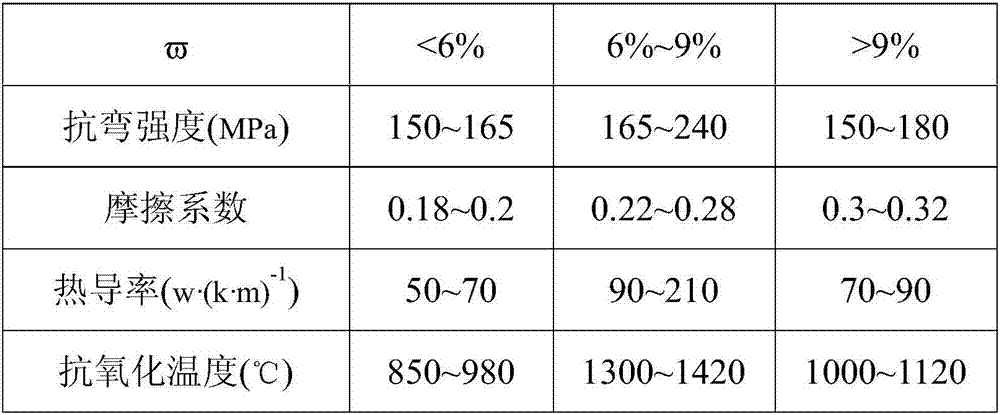
The invention designs a composite material. The composite material comprises carbon-fiber perform, matrix carbon, filler and diamond-like carbon, wherein the matrix carbon is uniformly adhered on the carbon fiber of the perform to form the carbon-fiber perform with the matrix carbon; the filler fills the inside of the carbon-fiber perform with the matrix carbon and coats the outside of the carbon-fiber perform with the matrix carbon to form a semifinished product; the diamond-like carbon comprises a diamond-like carbon layer coated on the semifinished product; and the filler contains a Ti element, a Si element, a C element and a Mo element. The composite material has the advantages that a method of combining four processes of CVI, SI, RMI and PECVD to prepare a finished product with the advantages of high compactness, low thermal expansion coefficient and friction coefficient, high self-lubricating property, high thermal conductivity, oxidation resistance, thermal shock resistance, ablation resistance, wear resistance, high strength and toughness and the like; and simultaneously, the process is simple, the preparation period is short, the equipment requirement is low, the cost is low, net shaping can be realized and convenience is brought for large-scale industrial application.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Powder metallurgy method for preparing high-density complicated shape titanium alloy product
A powder metallurgy method for producing titanium alloy products with high density and a complicated shape by using Ti powder and additive powder containing Al, V, Fe, and Mo elements as raw materials, comprising mixing the Ti powder with a certain granularity proportion and the additive powder with a certain component range evenly, preparing powder green bodies by using a cold press forming method, using a multi-stage heating technique giving priority to middle-low temperature quick heating and high temperature slow heating during sinter process, performing quenching immediately after the heating process is completed, thereby prepares the Ti alloy sintering blank, and the titanium alloy products with high density and a complicated shape are finally produced by forge work and subsequent anneal process. Since the powder metallurgy technique has the characteristics of near net shape and easily control components, alloying is realized easily. At the same time, the high-usage of raw material is provided, the raw material cost and processing cost are saved, and the production energy consumption is reduced greatly. The method is suitable for producing titanium alloy products with high density and a complicated shape.
Owner:GUIZHOU TAIYI TECH DEV
Low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel and production method of low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel
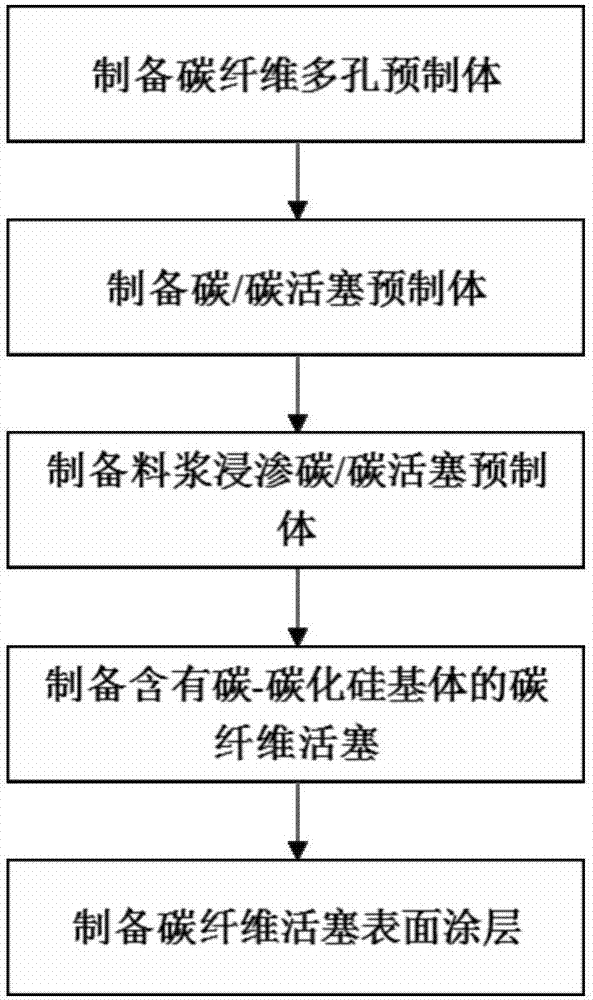
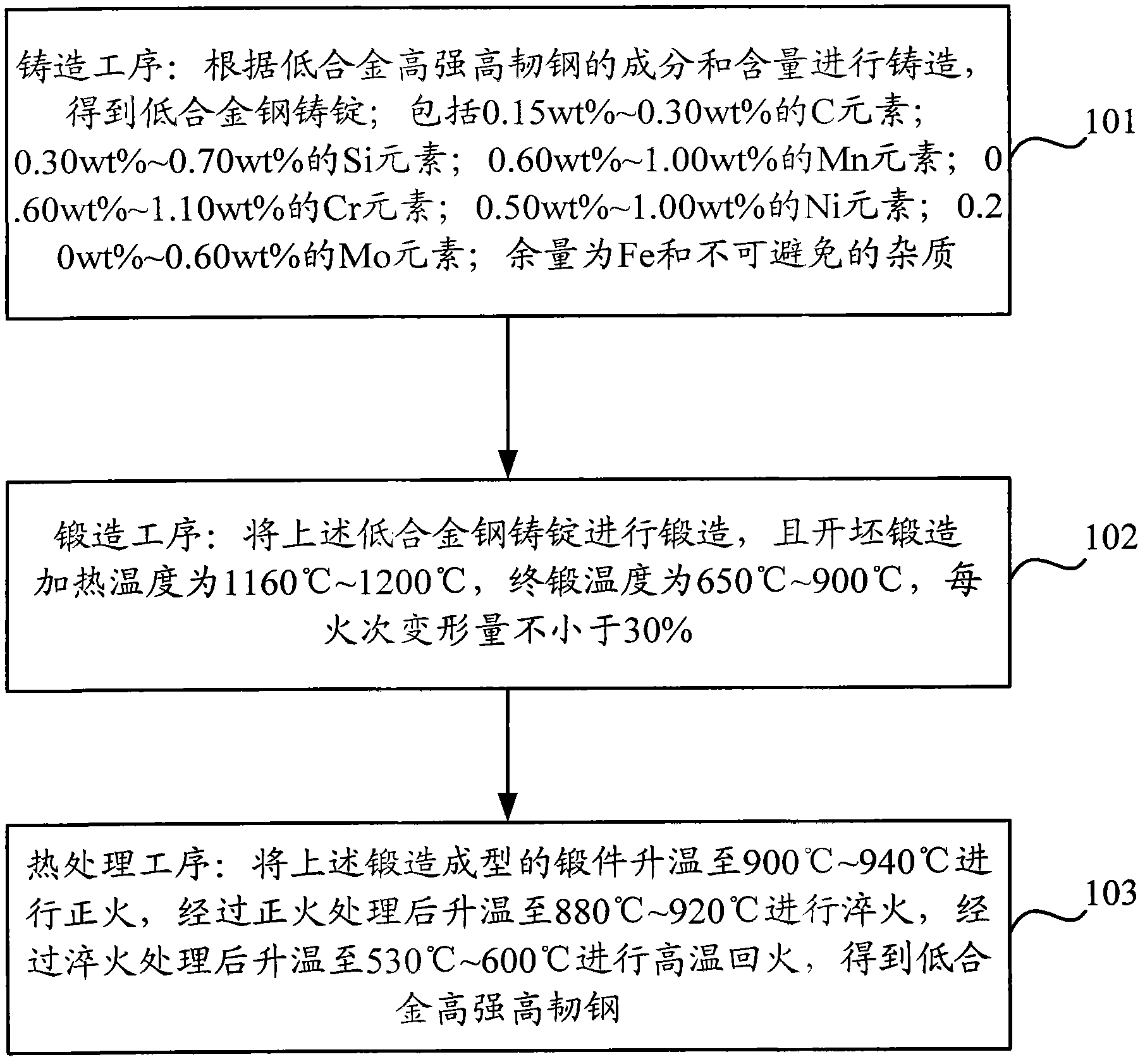
The invention discloses low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel and a production method of low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel. The method comprises the following work procedures of: the casting work procedure: the casting is carried out according to the following ingredients and contents to obtain low-alloy steel cast ingots: 0.15 to 0.30 weight percent of C elements, 0.30 to 0.70 weight percent of Si elements, 0.60 to 1.00 weight percent of Mn elements, 0.60 to 1.10 weight percent of Cr elements, 0.50 to 1.00 weight percent of Ni elements, 0.20 to 0.60 weight percent of Mo elements and the balance Fe and unavoidable impurities; the forging work procedure: the low-alloy steel cast ingots are forged, in addition, the blank opening forging heating temperature is 1160 DEG C to 1200 DEG C, the final forging temperature is 650 DEG C to 900 DEG C, and the deformation in each firing time is not smaller than 30 percent; and the heat treatment work procedure: the temperature of the forged and formed forgings is raised to 900 to 940 DEG C to be subjected to normalizing, the temperature is raised to 880 to 920 DEG C for carrying out quenching after the normalizing treatment, the temperature is raised to 530 to 600 DEG C for carrying out high-temperature tempering after the quenching treatment, and the low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel is obtained. In the embodiment of the invention, the low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel has high intensity and high toughness.
Owner:SANY GRP
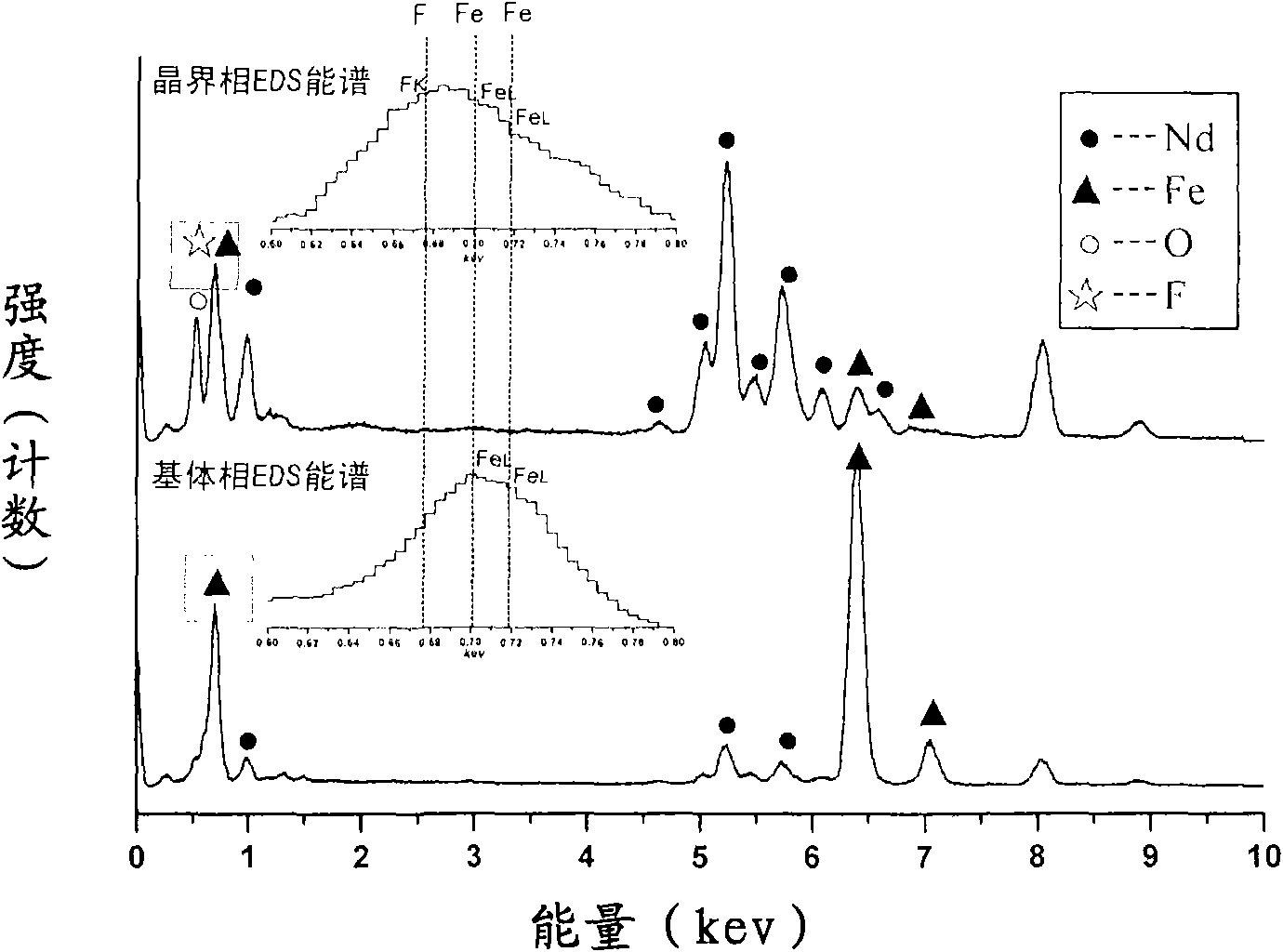
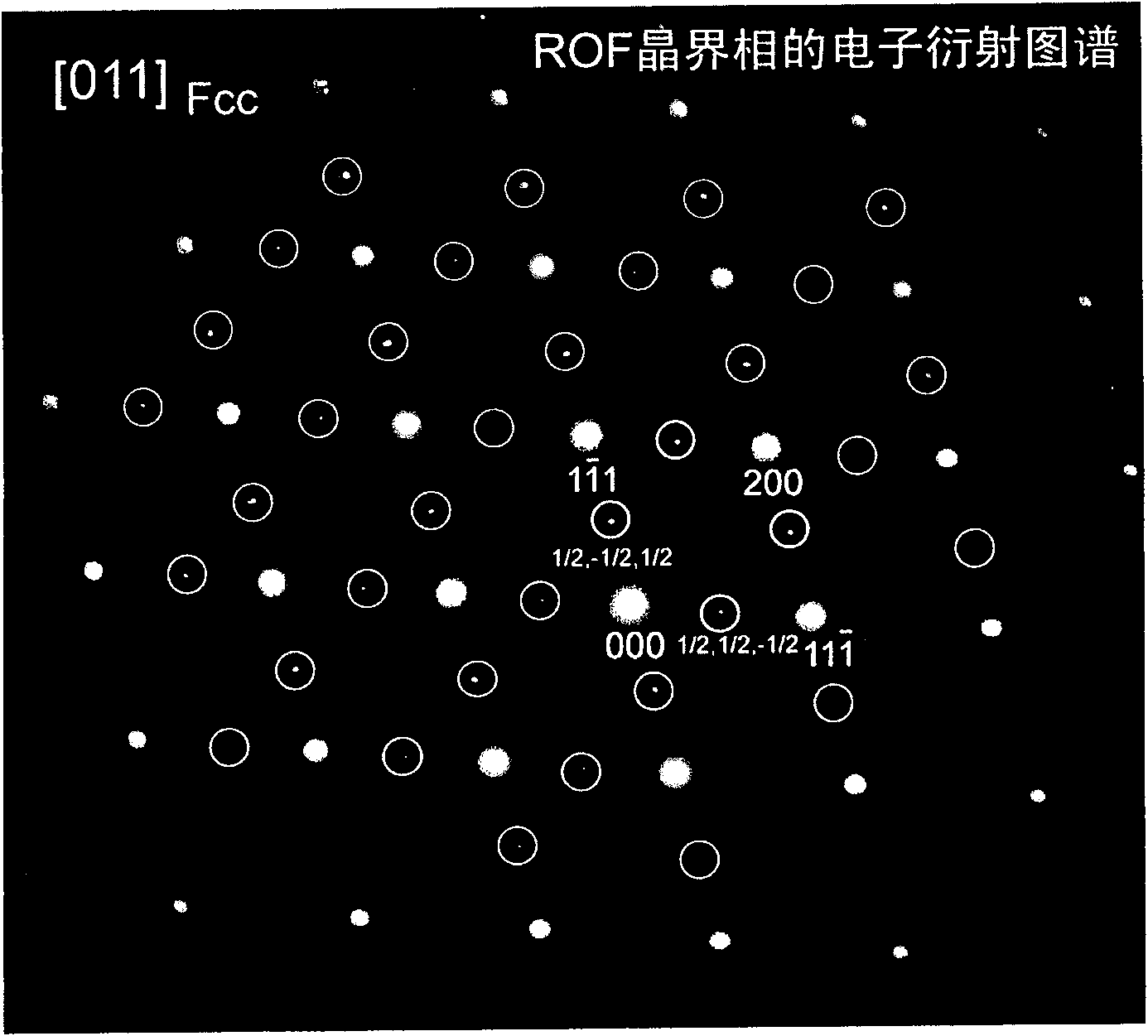
Sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnet material with modified grain boundary phase and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnet material with modified grain boundary phase and a preparation method thereof. The material refers to the R-Fe-M-B-based rare-earth permanent magnet of ROF compound with ordered fcc structure in the grain boundary phase, wherein R is one or more of rare earth element Nd, Pr, Dy, Tb and Y, and M is one or more of Al, Cu, Ga, Nb, Mg, Si and Mo elements. The major elements of the grain boundary phase are R, O and F elements, and the ratio of R to O and F is approximately equal to 1:1:1 (atomic percent). The preparation method is that the temperatures and cooling rates of sintering and second tempering are controlled to ensure that the F atoms in the added fluoride which can fuse with the grain boundary rich-R phase of the NdFeB magnet and the O atoms in the grain boundary phase can be in ordered arrangement to form an ordered fcc grain boundary phase. The ordered fcc grain boundary phase has better demagnetizing and coupling functions, thus facilitating to increase the coercive force of the magnet and furthest reducing the dosages of Dy and Tb.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
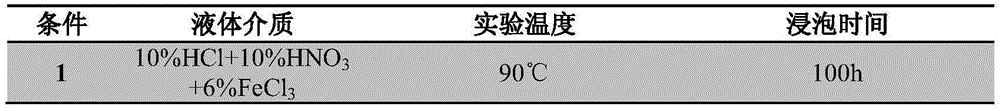
Cast-rolling method for restraining Cr element and Mo element of super-austenitic stainless steel from center segregation
The invention discloses a cast-rolling method for restraining a Cr element and a Mo element of super-austenitic stainless steel from center segregation and belongs to the technical field of manufacturing of the super-austenitic stainless steel. The method includes the steps that (1) raw materials are weighed according to the composition proportion of the super-austenitic stainless steel, and the raw materials are subjected to heat preservation at the temperature ranging from 150 DEG C to 250 DEG C for 100 minutes to 150 minutes; (2) the raw materials are sorted and placed into a vacuum induction melting furnace step by step to obtain molten steel by being smelted; and (3) the molten steel is poured into a dual-roll thin strip cast-rolling machine for cast rolling under shielding of high-purity nitrogen, and a thin super-austenitic stainless steel strip 2.0-3.0 mm thick is obtained, wherein the pouring temperature ranges from 1450 DEG C to 1550 DEG C, the cast-rolling speed ranges from 10 m / min to 40 m / min, and the cast-rolling force ranges from 30 kN to 70 kN. According to the manufactured thin super-austenitic stainless steel strip, center segregation of the Cr element and the Mo element is restrained, and on the premise of maintaining the plasticity, the yield strength is improved by 5%-10% compared with that of traditional strip steel of the same specification as the thin super-austenitic stainless steel strip. Meanwhile, the cast-rolling method reduces energy consumption and production cost, improves the utilization rate of materials and reduces environmental pollution.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
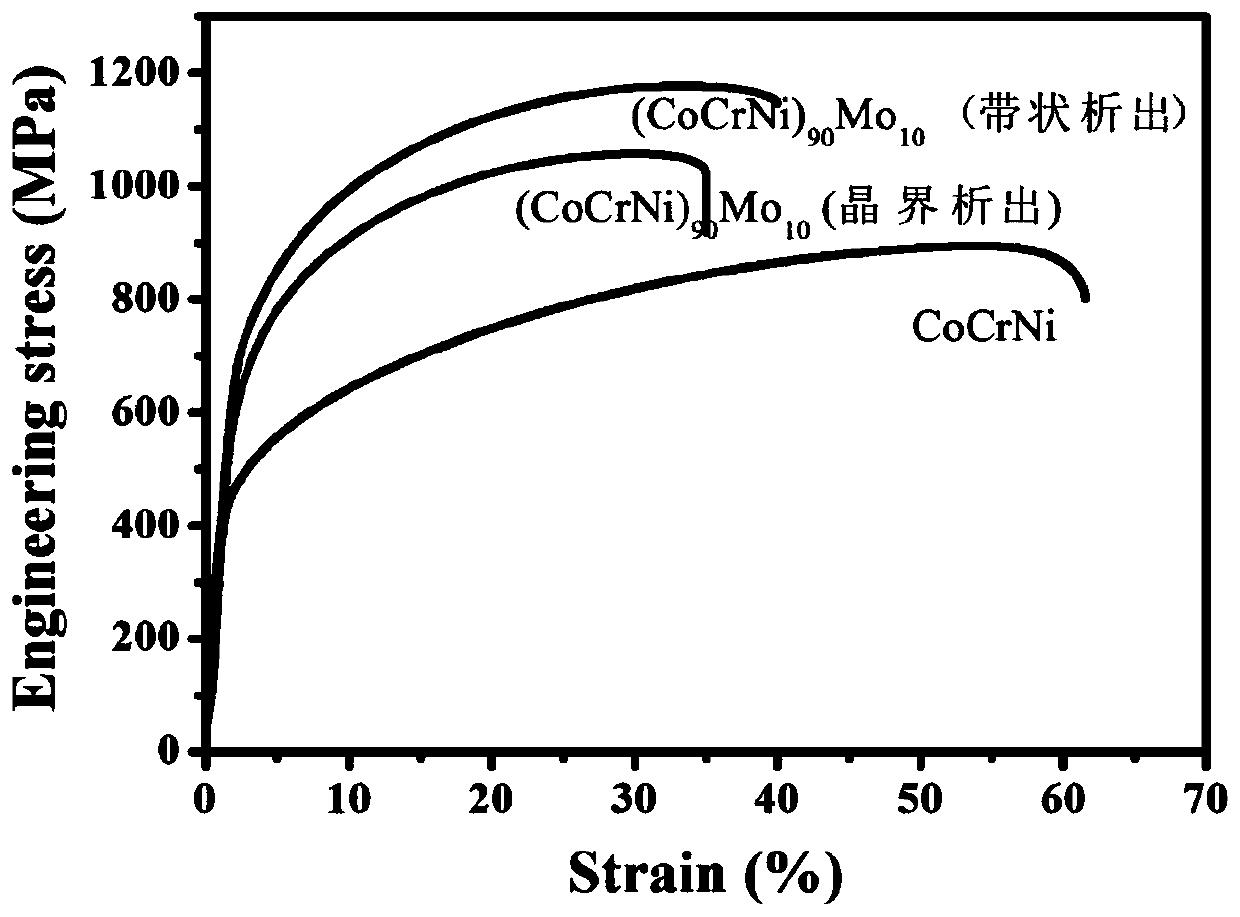
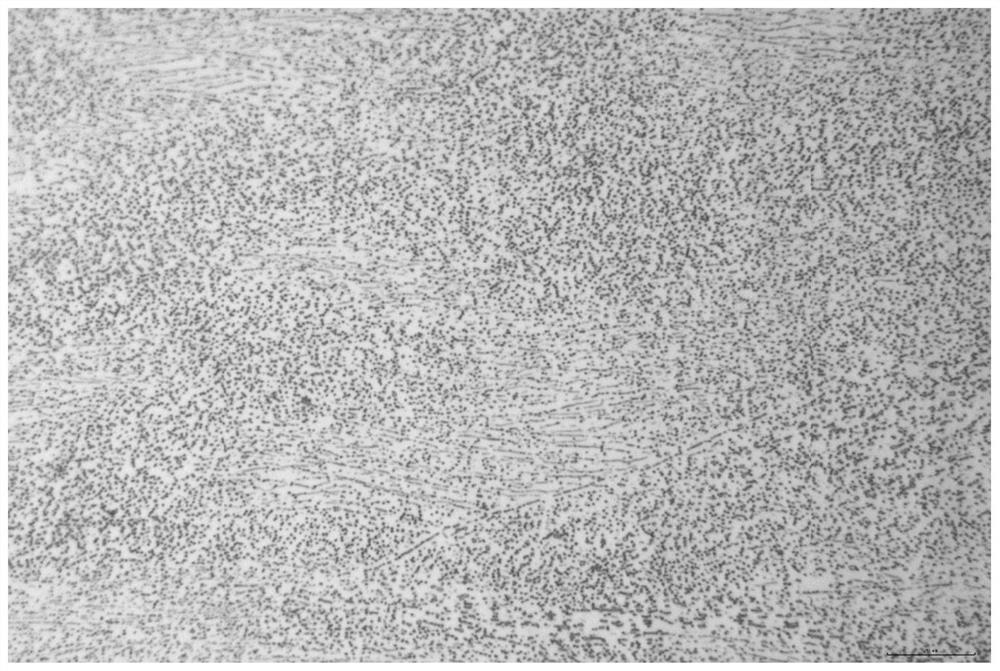
High-entropy alloy with banded precipitated phase and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110106428AGood room temperature tensile propertiesImprove solid solution strengtheningHigh entropy alloysMo element
The invention discloses a high-entropy alloy with a banded precipitated phase. The high-entropy alloy consists of Co, Cr, Ni and Mo elements, wherein the atomic percent of Co is 25-35%, the atomic percent of Cr is 25-35%, the atomic percent of Ni is 25-35%, the atomic percent of Mo is 5-15%, and the sum of atomic percents of the components is 100%. The phase composition of the high-entropy alloy with the banded precipitated phase comprises a face-centered cubic phase and a sigma precipitated phase, wherein the sigma precipitated phase accounts for 40-60%. In the preparation method, the non-uniform precipitation of the Mo-rich phase is achieved through the combination of hot processing, solid solution processing, cold processing and annealing process, and the high-entropy alloy with the banded precipitated phase is obtained. The alloy can ensure excellent strength and toughness matching, and has application prospects in the fields of cutter materials, aerospace materials and the like.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Contact fatigue-highly resistant cold-rolling intermediate roller and manufacture method thereof
ActiveCN104294168AReduce contentIncrease contentFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesMo elementMatrix strength
The invention discloses a contact fatigue-highly resistant cold-rolling intermediate roller and a manufacture method thereof, the roller comprises the following components by weight percentage: 0.70-0.85% of C, 0.40-1.00 of Si, 0.20-0.60% of Mn, 2.80-3.50% of Cr, 0.25-0.60% of Ni, 0.30-0.50% of Mo, 0.10-0.30% of V, less than or equal to 0.02 of P; less than or equal to 0.015 of S, and the balance of Fe and inevitable impurities. The manufacture method comprises the following steps: smelting in an electric furnace, refining outside the electric furnace, degassing under vacuum, casting an electrode bar, remelting electroslag, forging, annealing and performing heat treatment, roughly machining, tempering and performing heat treatment, semifinishing, performing heat treatment on the roller body, finely tempering, and acquiring the finished product roller. By reducing the content of an element C and increasing the content of Si, Ni and Mo elements, strength and toughness performance as well as the matrix strength of the intermediate roller can be increased, and tissue can be refined, and the cold-rolling intermediate roller has high contact fatigue resistance through heat treatment.
Owner:YIXING YONGCHANG ROLL
Laser-cladding cobalt-base alloy powder and repairing method for repairing damaged expander blade
ActiveCN105349995AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove hardenabilityMetallic material coating processesMo elementLaser scanning
The invention discloses laser-cladding cobalt-base alloy powder and a repairing method for repairing a damaged expander blade. The laser-cladding cobalt-base alloy powder comprises the following raw materials in percentage by mass: 20.0% to 50% of Co, 1.0% to 3.0% of W, 2.0% to 5.0% of Mo, 20.0% to 26.0% of Cr, 19.0% to 45.0% of Fe, 0 to 9% of Ni and the balance of Si. The repairing method comprises the following steps: pre-treating the damaged expander blade before laser cladding; performing reverse modeling by three-dimensional laser scanning; determining the to-be-repaired position and size of the blade; performing multi-track lapped laser cladding repair on the damaged expander blade by using the laser-cladding cobalt-base alloy powder. The laser-cladding cobalt-base alloy powder disclosed by the invention adopts austenite as a main phase; Co and Ni elements are used for stabilizing the main phase; W and Mo elements are added, and meanwhile, the content of Si and B elements is reduced, so the toughness and corrosion resistance are improved, and the phenomenon of cracking generated during multi-track lapping of a laser cladding layer is reduced. The alloy powder component has the effects of lowering the cost and improving the stability of a cladding technique, and the laser repair quality and the effective service life of the blade of an energy recycling turbo expander are guaranteed.
Owner:汉中艾斯达特新材料科技有限公司
High-strength and high-toughness metastable beta titanium alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN112251632AHigh yield strengthLow costTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsMo elementSolid solution strengthening
The invention discloses a high-strength and high-toughness metastable beta titanium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The Ti-Al-Mo-V-Cr-Zr metastable beta titanium alloy comprises the componentsof, in percentage by weight, 4.5%-5.5% of Al, 6.5%-9.0% of Mo, 1%-4% of V, 1.5%-4% of Cr, 1%-2.5% of Zr and the balance Ti and other inevitable impurities. According to the high-strength and high-toughness metastable beta titanium alloy and the preparation method thereof, after an alloy is subjected to smelting, hot rolling and heat treatment, good matching of strength and plasticity can be obtained; according to the high-strength and high-toughness metastable beta titanium alloy and the preparation method thereof, the content of the V element is further reduced to about 3.5%, and the cheap Cr element is added so that the cost can be reduced to a certain extent; meanwhile, a certain amount of the Cr and Mo elements are added to reinforce a beta matrix, so that the solid solution strengthening effect of the multi-component alloy is improved; and according to the high-strength and high-toughness metastable beta titanium alloy and the preparation method thereof, the yield strength of thealloy is improved to 1518 MPa, meanwhile, and the alloy also has the total elongation at break of 5.3%, so that the requirements of a new generation of high-strength and high-toughness titanium alloyare met.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
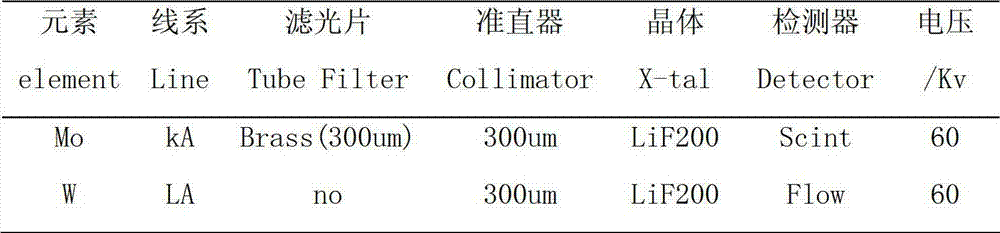
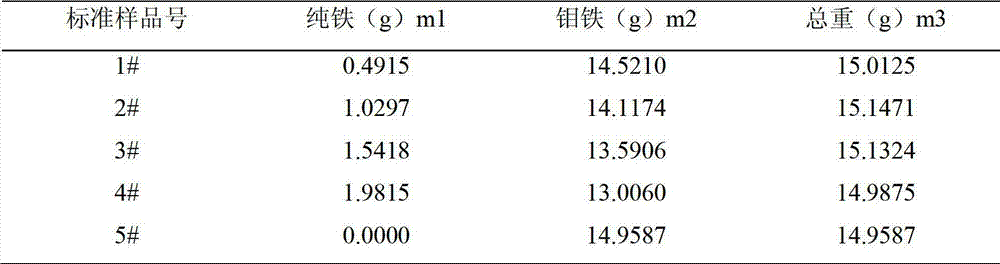
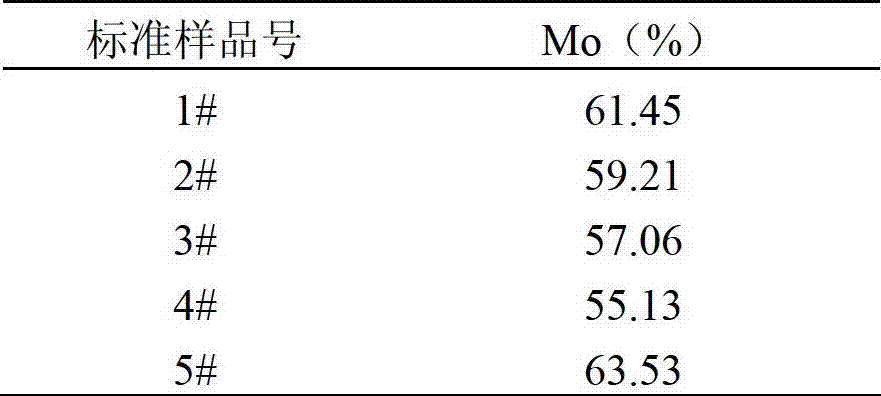
Method for measuring Mo element in tungstenic ferro-molybdenum alloy through X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis
ActiveCN103076351AFast and accurate determinationSatisfy the rapidityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMo elementX-ray
The invention provides a method for measuring a Mo element in a tungstenic ferro-molybdenum alloy through X-ray fluorescence spectrum analysis. The method comprises the following steps: preparing instrument measurement conditions and samples, selecting standard samples, drawing a working curve, and measuring accuracy and precision. According to the invention, the method has the effects that the arrangement of the series of standard samples to draw the working curve in combination with the calibration of the Mo element and W element can realize the accurate and quick measurement of the Mo element in the tungstenic ferro-molybdenum alloy. According to the former measurement result, the Mo element content in practical production samples is 56.32 percent and is different with 62.31 percent obtained from a chemical humid analysis, with 6 percent deviation, so the analysis result is inaccurate. The method provided by the invention has an accurate and reliable analysis result and meets the enterprises' requirements of being quick and accurate for detection and assay data. Moreover, the method is simple in operation, and good in repeatability, and can accurately and quickly measure the content of the Mo element in the tungstenic ferro-molybdenum alloy. Compared with a chemical analysis which is classical, but is long in period and large in chemical reagent consumption, the method provided by the invention saves the period and the chemical reagent consumption.
Owner:TIANJIN PIPE GROUP CORP
Molybdenum base nitride composite ganoine thin film and preparation thereof
InactiveCN101244644AReduce the temperatureNo holesLayered productsVacuum evaporation coatingMo elementArea ratio
The invention discloses a Mo-based nitride composite hard film and a preparation method, wherein the substrate is coated with nanometer composite hard film that is made of Mo-based metal nitride or nonmetal nitride, the crystallized size of the film is 5-40nm, the thickness of the film is 1-5Mum, the molar percentage between the Mo element and the substitution element in the film is 50 to 94% : 6 to 50%; the preparation method is that: (a) the target material (made of Mo and the substitution) and the substrate are respectively arranged on the cathode and sample table in vacuum room of magnetic control sputtering equipment, the area ratio of the Mo and the substitution in the target material is 1 to 8 : 8 to 1, the distance between the target material and the substrate is 40-80mm; (b) after the vacuum degree in the vacuum room is less than or equal to 8 x 10-4pa and substrate temperature reaches 300 to 500 DEG C, the vacuum room is made to be in the atmosphere of argon and nitrogen mixed gas and 30-130 minutes sputtering is made so as to prepare the Mo-based nitride composite hard film. The invention can widely be used for material protection and can improve abradability and durability of material obviously.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Grade-90 chain steel
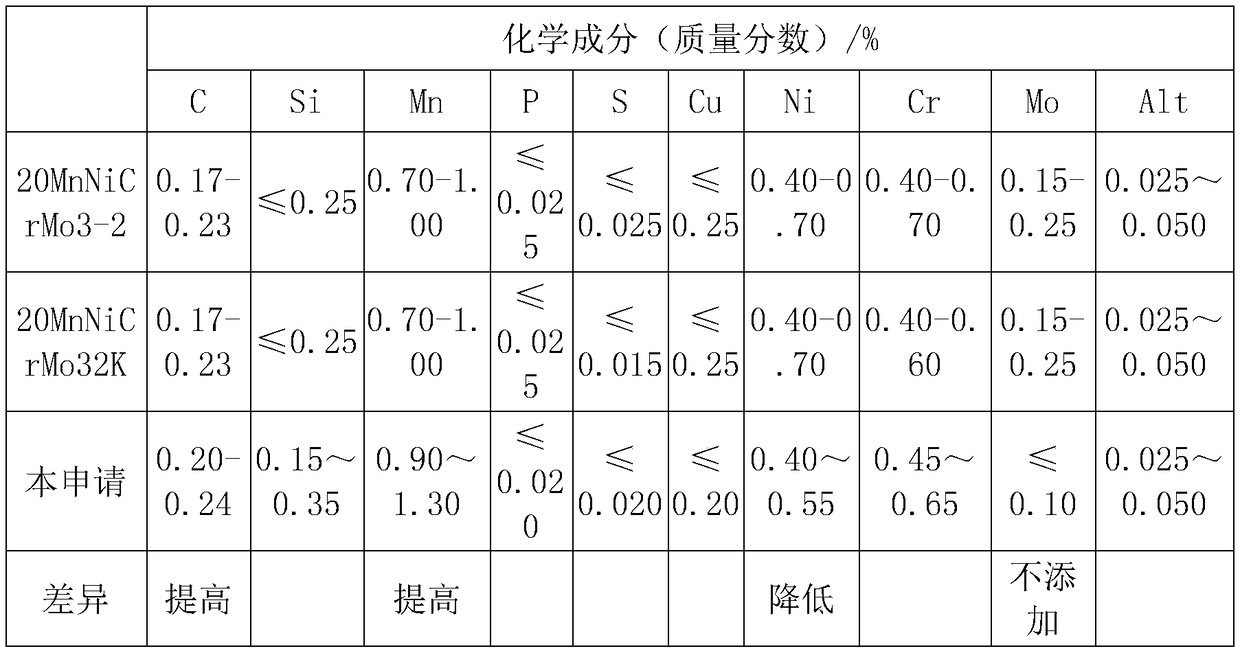
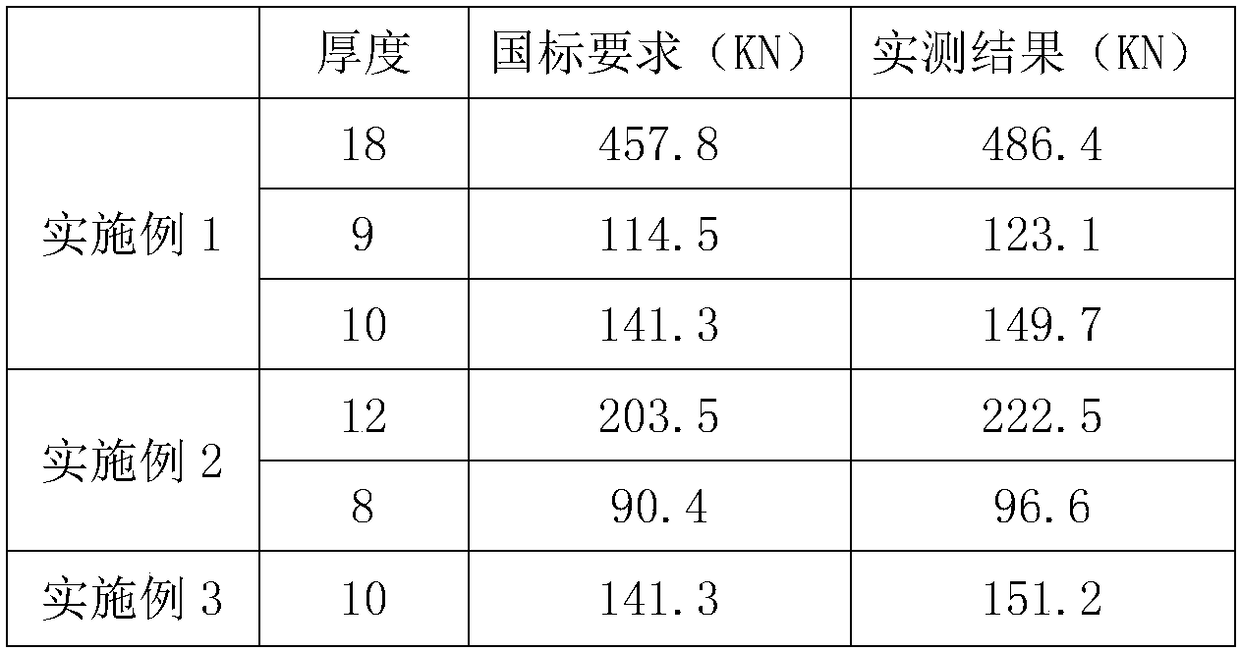
The invention relates to grade-90 chain steel. The grade-90 chain steel is prepared from the following chemical components by weight percent: 0.20 to 0.24 percent of C, 0.15 to 0.35 percent of Si, 0.90 to 1.30 percent of Mn, less than or equal to 0.020 percent of P, less than or equal to 0.020 percent of S, less than or equal to 0.20 percent of Cu, 0.40 to 0.55 percent of Ni, 0.45 to 0.65 percentof Cr, less than or equal to 0.10 percent of Mo, 0.025 to 0.050 percent of Alt, and the balance of Fe and unavoidable impurities. Compared with the brand number corresponding to the national standardand European standard, the grade-90 chain steel disclosed by the invention ahs the following advantages: (1) the contents of C and Mn are increased, the cost is slightly increased, and the strength and hardness of the material are greatly improved; (2) the content of Ni is reduced, no Mo element is added, and the cost is greatly reduced; and (3) by reasonably optimizing the alloy elements, on thepremise of ensuring the qualification of breaking strength of the material, the welding performance of the material is also considered, and the cost of raw materials are greatly reduced.
Owner:NANJING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
High-vanadium wear-resistant alloy material and production technique thereof
InactiveCN104946964AIncrease the amount of participationIncrease in the number of particlesWear resistantMaterials science
The invention relates to the field of wear-resistant materials, particularly a high-vanadium wear-resistant alloy material and a production technique thereof. The high-vanadium wear-resistant alloy material is composed of the following components in percentage by mass: 2.7-3.5% of C, 7.5-8.5% of V, 0.5-1.5% of Si, 0.8-1.5% of Mn, 2.0-3.5% of Cr, 1.0-2.5% of Mo, 1.0-2.0% of Ti, at most 0.04% of S, at most 0.04% of P and the balance of iron. The V is used instead of the Cr element in the high-chromium cast iron to generate the high-hardness VC carbide particles in the iron base. 1.0-2.0% of Ti element is added into the iron to generate a (V,Ti)C eutectic carbide in the iron. Since the workpiece generally has a certain thickness, certain amounts of chromium (Cr) element and molybdenum (Mo) element are added as hardenability-enhancing elements. The Ti element can be easily combined with the sulfur element to generate the hazardous compound Ti2S, and therefore, the sulfur and phosphorus elements are respectively strictly controlled to at most 0.04% according to the requirements.
Owner:曾松盛
Manufacturing method for nodular cast iron used for crankshaft
The invention discloses a manufacturing method for nodular cast iron used for a crankshaft. Waste steel, pig iron, coke, melted-down waste iron, tin slag and iron-ore slag are selected as raw materials. The manufacturing method includes the five steps of raw material melting, spheroidizing, primary inoculation, secondary inoculation and pouring. Compared with the prior art, the manufacturing method has the beneficial effects that the silicon content is reduced, the recovery rate can be increased, and the production cost can be reduced; as Sb elements and Re elements are additionally arranged in the nodular cast iron, the abrasion resistance, the corrosion resistance and the tensile strength of the nodular cast iron are improved on the original basis; timely slag raking is carried out after spheroidizing to remove impurities in molten iron, slag raking is carried out again after two times of inoculation are carried out under the corresponding conditions, impurities are reduced, the quality of materials is improved accordingly, and the tenacity of the nodular cast iron is guaranteed; and the content of Nb elements and the content of Mo elements are increased, and as the thermal expansion coefficient of the Nb elements and the thermal expansion coefficient of the Mo elements are small, the heat resistance and the abrasion resistance of the nodular cast iron are improved.
Owner:HEFEI CITY TENVER PRECISION CASTING
Low-cost medium-strength titanium alloy material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109182840ALower phase transition temperatureReduce manufacturing costElectric arc furnaceSilicon alloy
The invention relates to a low-cost medium-strength titanium alloy material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps that sponge titanium, Fe chips, Al shots, titanium dioxide and titanium-silicon alloy are weighed and mixed, and the mixture is pressed into electrode blocks; ion welding or vacuum electron beam welding is adopted, and the pressed electrode blocks are welded into strip-shaped electrodes; the prepared strip-shaped electrodes are used as a consumable electrode to be smelted in a vacuum self-consuming electric arc furnace, and a primary ingot is obtained; the primary ingot is inverted and serves as a consumable electrode, then secondary smelting is carried out in a vacuum self-consuming electric arc furnace, and a secondary ingot is obtained; after the secondary ingot is cooled, the secondary ingot is heated, and cogging forging is carried out to obtain a blank; and after the blank is heated, rod materials or plate blanks are obtained through multiple forging. According to the preparation method, the low-cost Fe element is adopted to replace the high-cost V element and Mo element and is used as an alloy reinforcing agent, the manufacturing cost of the alloy can be reduced by 12% to 20%, and the tensile strength of the prepared titanium alloy material, rod materials, plate materials and forged parts ranges from 700 MPa to 950 MPa, and the elongation percentage is 8% to 25%.
Owner:XIAN SUPERCRYSYAL SCI TECH DEV CO LTD
6-8mm high-strength structural steel plate and manufacture method thereof
The invention provides a 6-8mm high-strength structural steel plate and a manufacture method thereof, aiming at meeting the market requirement for the technology of utilizing thinner steel plates for a concrete pump truck, an aerial ladder and a special vehicle for high-level rescue, and overcoming the shortcomings in the aspect ofdue to the strength, service life and the likeothers of low-level steel. The manufacture method is characterized in that low carbon and manganese contents are is designed; 0.0012% of boron and 0.08% of molybdenum element are added; a converter is utilized for realizing quick smelting; the external refining and degassing refining are performed to improve the purity of molten steel; and rolling, quenching and tempering technologies are carried out to improve the strength and toughness of the steel as well as improve the straightness of the steel plate, in order to obtain a tempered sorbite metallographic structure. The method is short in process, high in efficiency, easy to operate and weld, and low in cost; and the shape and straightness of the plate are controlled to meet the requirements on manufacturing and using of modern pump trucks, high-level aerial ladders, rescue work facilities and other telescopic arm structures.
Owner:JIGANG GRP
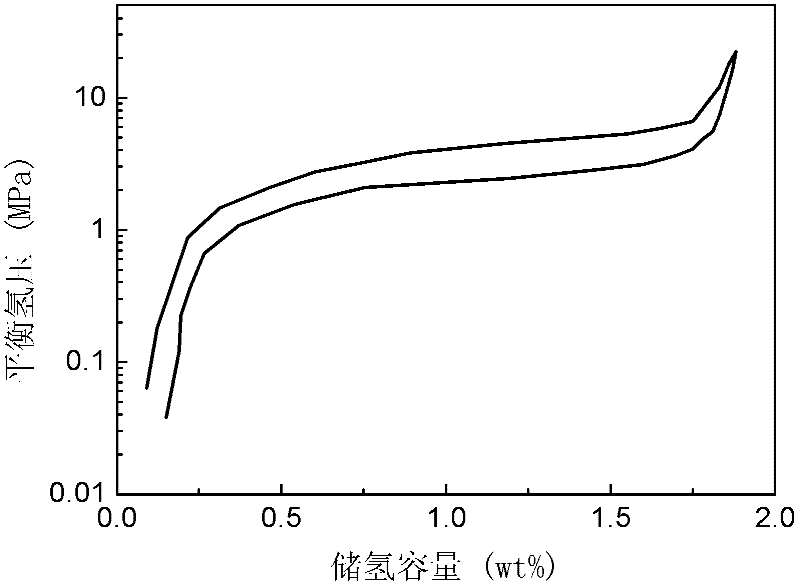
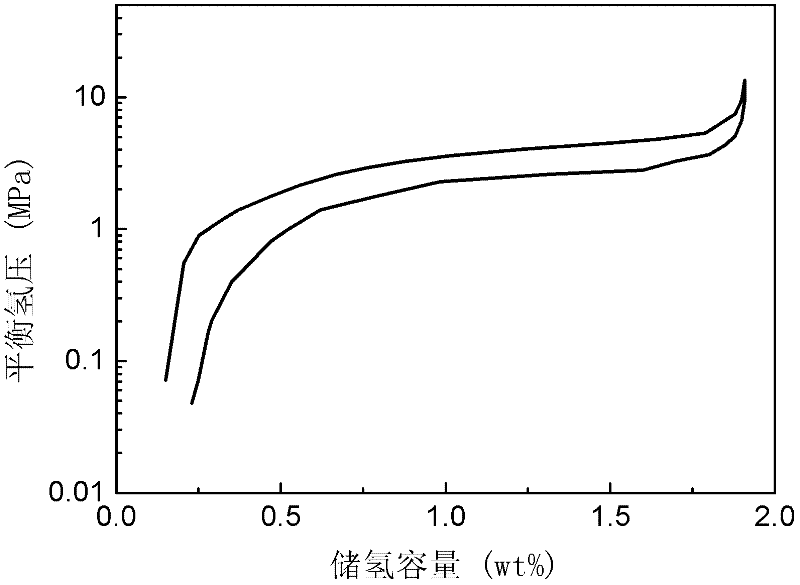
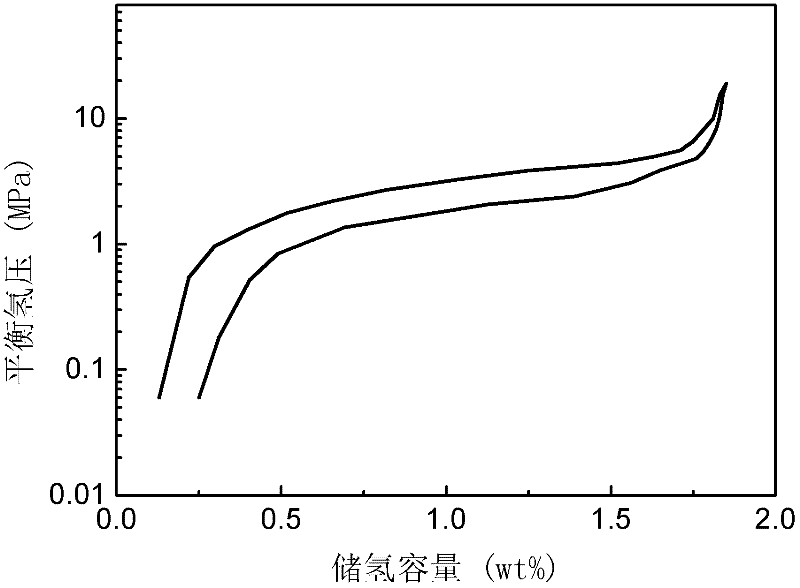
Hydrogen-storage alloy producing high-pressure hydrogen
The invention discloses hydrogen-storage alloy producing high-pressure hydrogen. The alloy has a chemical general formula of Ti(1-a)ZraRbCrxFeyMz, wherein R is one or more selected from rare earth metal La, rare earth metal Ce, and mixed rare earth metal Mm; M is one or two selected from V and Mo elements; 1-a, a, b, x, y, and z are atomic ratios of Ti, Zr, R, Cr, and Fe to M; a is greater than 0 and no greater than 0.3; b is greater than 0 and no greater than 0.1; x is no smaller than 0.5 and no greater than 1.3; y is no smaller than 0.8 and no greater than 1.25; and z is greater than 0 and no greater than 0.3. The hydrogen-storage alloy can produce high-pressure hydrogen with a pressure of 40MPa under a temperature below 150 DEG C, and can produce high-pressure hydrogen with a pressure of 70MPa under a temperature below 180 DEG C. The temperatures are far lower than the temperatures required by corresponding hydrogen-emission pressures of common alloys such as TiFe and LaNi5. The alloy is easy to activate, and a maximal hydrogen storage amount of the alloy is higher than 1.8wt%, which is higher than that of the common alloy LaNi5.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
NCM ternary cathode material doped with Mo element in surface layer and bulk phase, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN108878868AStable structureImprove electrochemical performanceSecondary cellsPositive electrodesMo elementManganese
The invention relates to an NCM ternary cathode material doped with a Mo element in a surface layer and a bulk phase, and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the field of chemical energy storage batteries. In total mass of 100% material, Mo element doped in the surface layer and the bulk phase accounts for 0.5-2%, and the other is NCM ternary cathode material. The method comprises the stepsof adding alcohol to a mixture of nickel-cobalt-manganese hydroxide precursor, ammonium molybdate and LiOH.H2O and grinding and mixing uniformly, so as to obtain dry grinded material; calcining the dry grinded material, precalcining the material for 300-400 minutes at 500-550DEG C, then calcining for 800-900 minutes at 700-750DEG C so as to obtain the material. The doped Mo element can stabilizethe material structure, lower charge transfer impedance, and improve electrochemical performance of the material. The method is easy to perform and the process technology are easy to realize.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Ti-Mo-Ni alloy ingot preparation method
A Ti-Mo-Ni alloy ingot preparation method is characterized in that Ni-Mo intermediate alloy (the mass proportion content of Mo element is 20-35%) is added, the production steps of the Ti-Mo-Ni alloy ingot include that: titanium sponge, Ni-Mo intermediate alloy or Ti-Mo intermediate alloy are mixed uniformly and pressed into electrode blocks, the electrode blocks are welded into consumable electrodes through welding modes such as plasma arc, and the Ti-Mo-Ni alloy ingot is prepared through twice vacuum consumable electric arc smelting. The Ti-Mo-Ni alloy ingot produced by the preparation method has uniform and stable chemical compositions, has the chemical composition deviation of being less than 0.15%, is segregation free and overcomes the defect of high density metallurgical inclusion. The invention is applicable to producing the Ti-Mo-Ni alloy ingot with high metallurgical quality requirement.
Owner:BAOJI TITANIUM IND CO LTD
Powder for laser-cladding aluminum bronze alloy gradient coating layer and preparation method
ActiveCN108315733AImprove mechanical propertiesHigh environmental resistanceMetallic material coating processesManganeseMechanical equipment
The invention relates to a powder for a laser-cladding aluminum bronze alloy gradient coating layer and a preparation technology method. The alloy powder is prepared from nine elements, such as Al (aluminum), Cu (copper), Fe (iron), Ni (nickel), Mn (manganese), Si (silicon), Cr (cobalt), B (boron) and Mo (molybdenum),wherein the amount of Al element is 6 to 7%; the amount of Fe element is equal tothe amount of Ni element; the total amount of Fe element and Ni element is 1 to 12wt%; the total amount of Mn element, Si element, Cr element, B element and Mo element is 0.5 to 2wt%; the balance element is Cu. The novel aluminum bronze alloy gradient coating layer prepared by a laser cladding technique has the advantages that the hardness is high, the corrosion-resistant property, abrasion-resistant property and high temperature oxidizing-resistance property are excellent, and the like; the novel aluminum bronze alloy gradient coating layer can be widely applied to the repair and re-manufacturing of mechanical equipment in the fields of metallurgy, power, ocean transportation and the like, and the obvious economic benefits and social benefits are realized.
Owner:SHENYANG POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Nitride high-entropy ceramic fiber and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111592361AUniform diameterWell formedNitrogen compoundsCarboxylic acid esters preparationFiberSpinning
The invention discloses a nitride high-entropy ceramic fiber and a preparation method and application thereof. The high-entropy ceramic fiber contains Ti, Hf, Ta, Nb and Mo elements, the nitride high-entropy ceramic fiber is in a single crystalline phase, and all the elements are uniformly distributed in a molecular level. The preparation method of the high-entropy ceramic fiber comprises the following steps: uniformly mixing a carbide high-entropy ceramic precursor containing a target metal element, a spinning aid and a solvent to prepare a precursor spinning solution, and then carrying out spinning, degumming and nitriding processes to prepare the nitride high-entropy ceramic fiber. The nitride high-entropy ceramic fiber can be applied to a process for preparing methane by photocatalysisof carbon dioxide.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
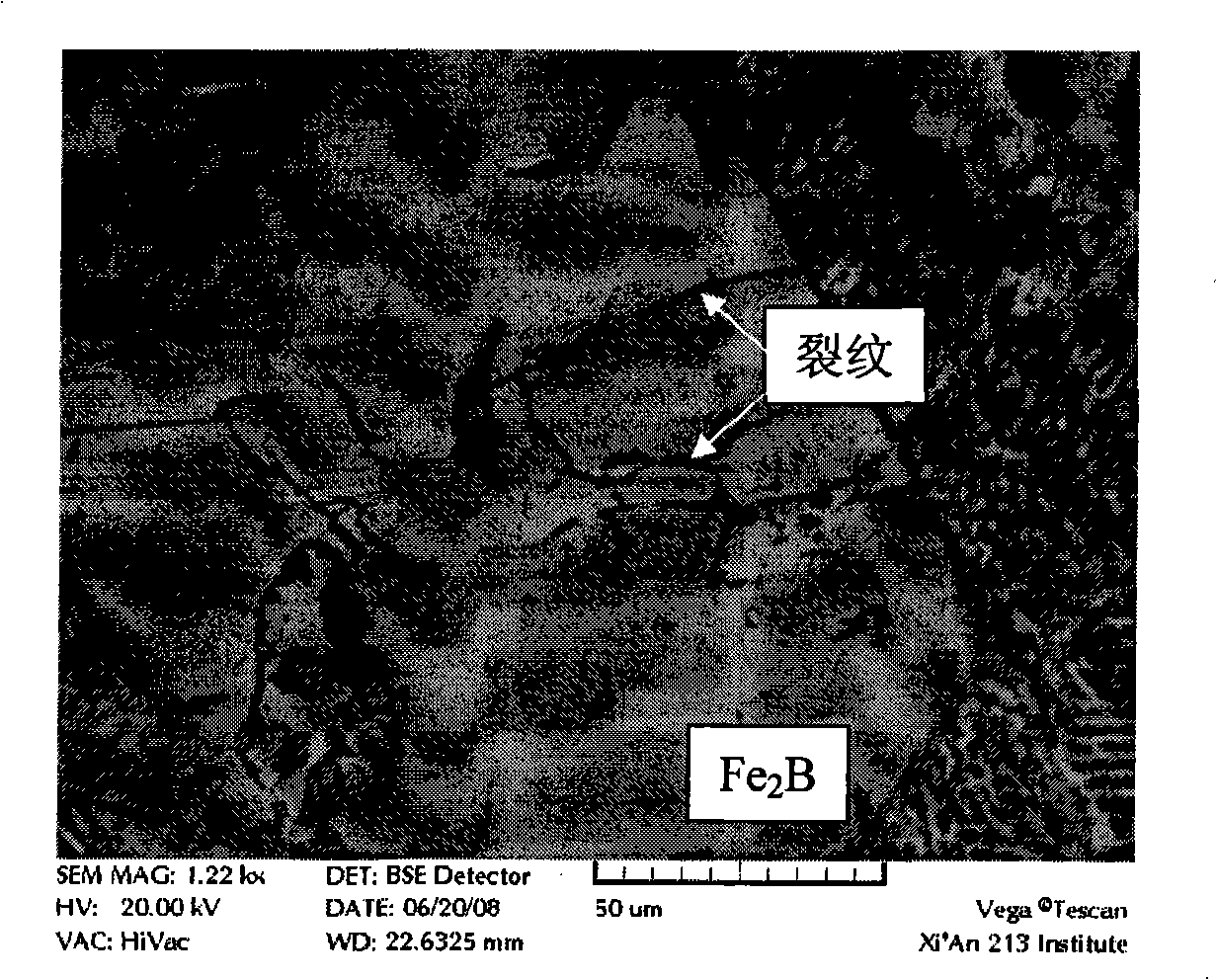
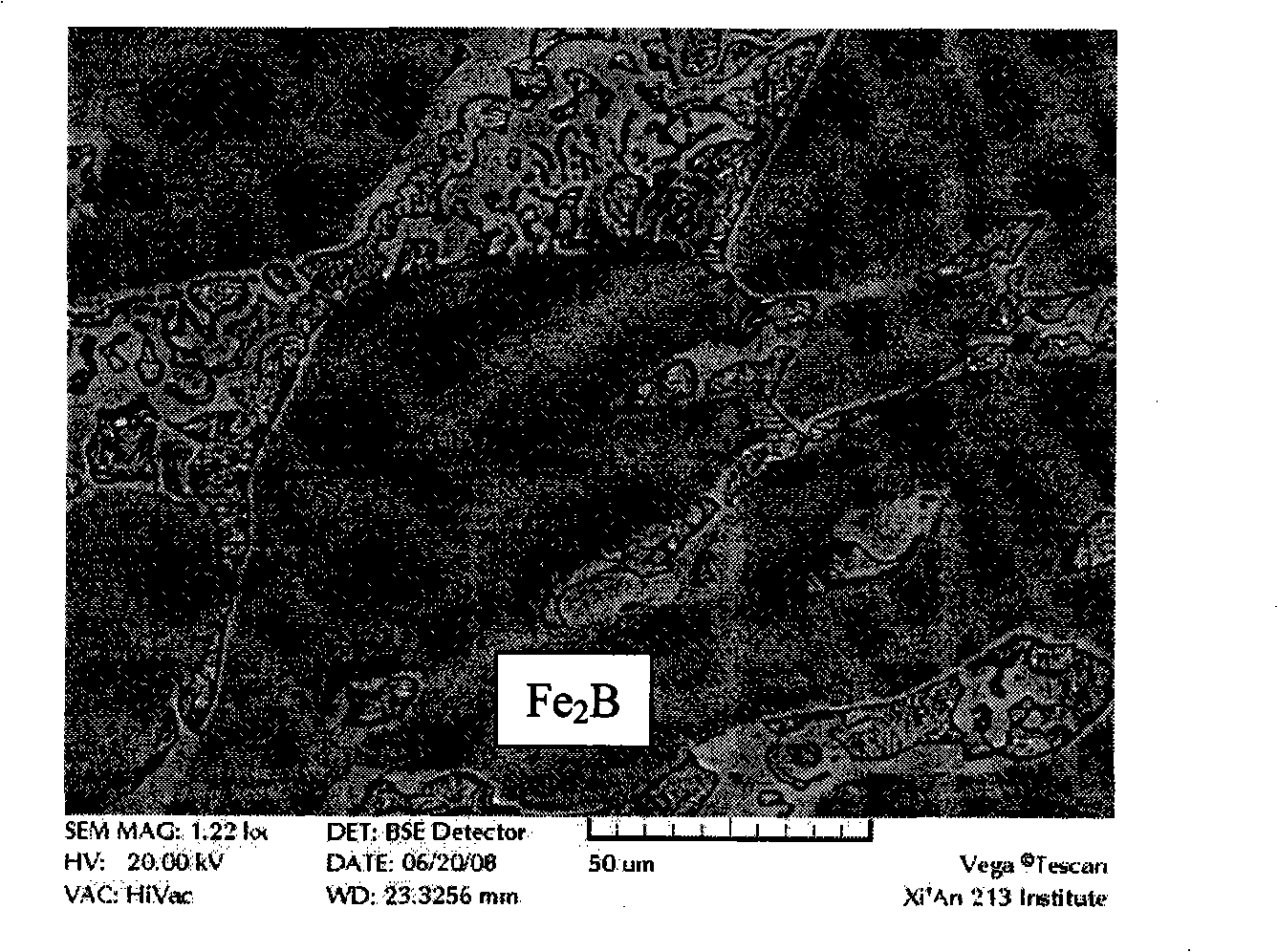
Toughening processing method of hard phase Fe2B in iron boron wear-resistant alloy
The invention relates to the ferroboron wearproof cast alloy field and discloses a method for toughening a hard phase Fe2B in the ferroboron cast wearproof alloy. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, the ingredients of the ferroboron cast wearproof alloy are determined and comprises scrap steel, silicoferrite, ferromanganese and ferroboron; based on the total weight of the ingredients of the ferroboron cast wearproof alloy, ferrochromium, ferromolybdenum and the ingredients of the ferroboron cast wearproof alloy are respectively calculated and weighed according to 0.5 to 10 percent of Cr element and 0 to 4.0 percent of Mo element; then the ferroboron is taken out for standby; the other ingredients of the ferroboron cast wearproof alloy are added into a furnace for smelting in turn; after the ingredients are melted down, aluminum wire which accounts for 0.01 percent of the molten iron weight is adopted for deoxidation; the ferrochromium and ferromolybdenum are added into the furnace and melted down; finally, a ferroboron block is added into the furnace and melted down; after the molten iron is melted down and kept stand, slag are removed and the mixed materials are molded, thereby completing the toughening.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
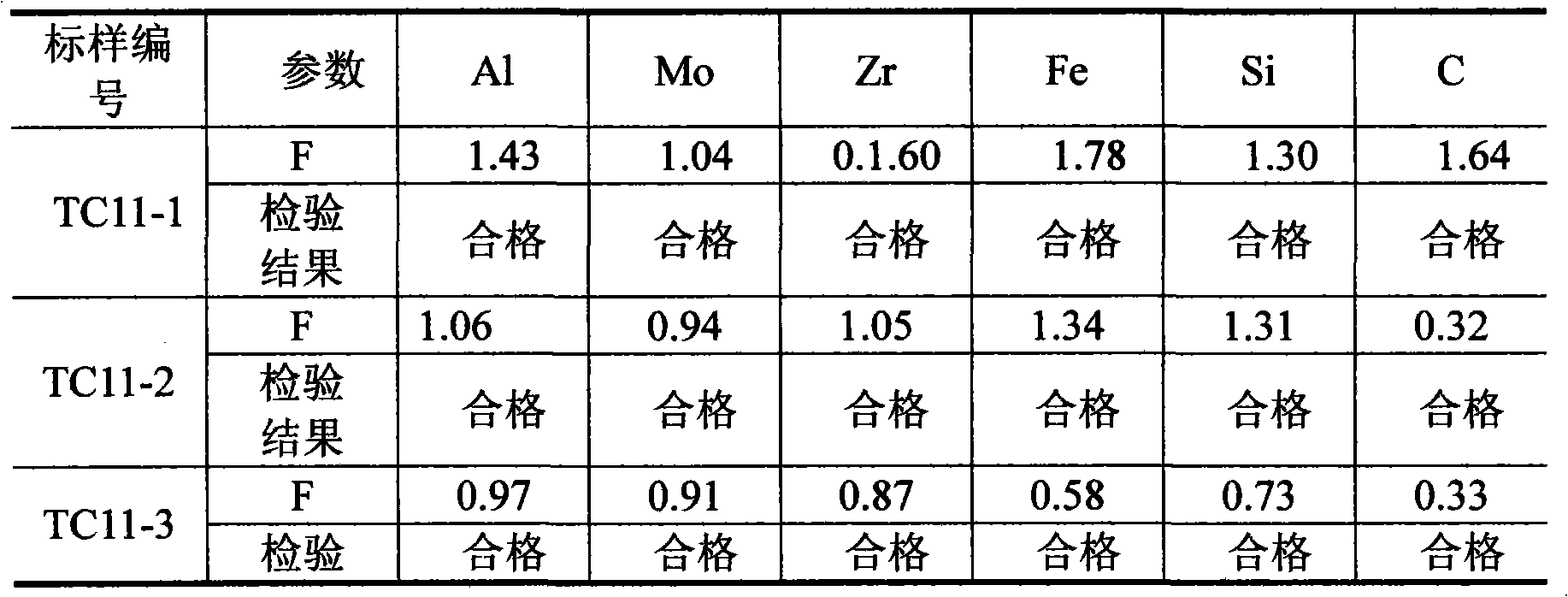
Standard substance for TC11 titanium alloy photoelectric spectral analysis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101975750AGood composition uniformityLarge coverageColor/spectral properties measurementsElectric arc furnaceHydrogen
The invention discloses a standard substance for TC11 titanium alloy photoelectric spectral analysis, which comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 4.53% to 7.51% of Al, 2.2% to 4.65% of Mo, 0.59% to 2.41% of Zr, 0.15% to 0.46% of Si, 0.15% to 0.35% of Fe, 0.021% to 0.12% of C and the balance of titanium, wherein the weight percentage sum of the components is 100%. The preparation method of the standard substance comprises the following steps: dosing; suppressing electrodes by utilizing a vertical lateral pressure machine; welding the electrodes in a vacuum argon charging tank; smelting primary cast ingots by utilizing a vacuum consumable electrode arc furnace; casting secondary cast ingots by utilizing a vacuum consumable electrode arc skull furnace; smelting tertiarycast ingots by utilizing the vacuum consumable electrode arc furnace; homogenizing and carrying out transform processing; and carrying out hot hydrogen processing to prepare the standard substance for the titanium alloy photoelectric spectral analysis. The standard substance and the preparation method of the invention have the advantages that the homogenization of the components is good; the problem that alloy elements cannot be effectively detected because the Zr element has no effective distribution point in the content section of 0.6 to 2.6% and the Mo element has no effective distributionpoint in the content section of 2.2 to 4.6% in the existing standard substance is solved.
Owner:CSIC NO 12 RES INST
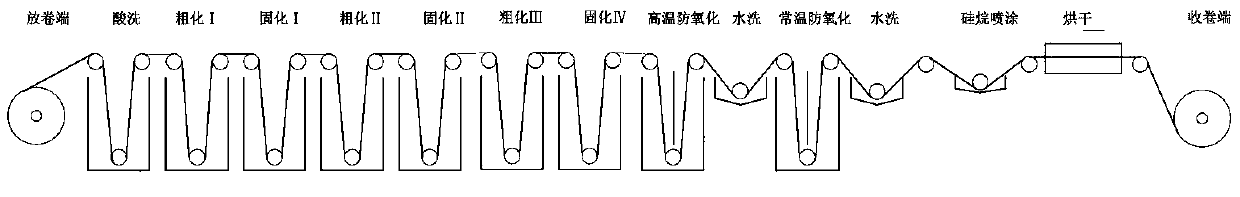
Production process of electrodeposited copper foil with shiny surface subjected to roughening
The invention discloses a production process of electrodeposited copper foil with a shiny surface subjected to roughening. The copper foil is subjected to acid pickling, roughening I, curing I, roughening II, curing II, curing III, curing IV, high-temperature anti-oxidation, water washing I, normal-temperature anti-oxidation, water washing II, silane spraying and drying in sequence; and the process conditions of the roughening I and the roughening II are that the current densities is 28 A / dm<2>-33 A / dm<2>, the temperature is 25 DEG C-35 DEG C, the sulfuric acid concentration is 160 g / l-180 g / l, the copper ion concentration is 7 g / l-13 g / l, the chloride ion concentration is 15 mg / l-30 mg / l, the sodium tungstate concentration is 0 mg / l-90 mg / l, the sodium molybdate concentration is 0 mg / l-70mg / l, and the cobalt sulfate concentration is 0 g / l-45 g / l. According to the process, tungsten, cobalt and molybdenum elements are added in the roughening procedures, so that the surface morphology of the copper foil is improved, and the anti-stripping strength of the electrodeposited copper foil is improved; and elements such as lanthanum or cerium are added in the high-temperature anti-oxidation process to form a special plating layer, and the structural morphology of the plating layer is changed, so that the anti-stripping strength and the corrosion resistance of the electrodeposited copper foil are improved.
Owner:JIANGDONG ELECTRONIC MATERIALS CO LTD
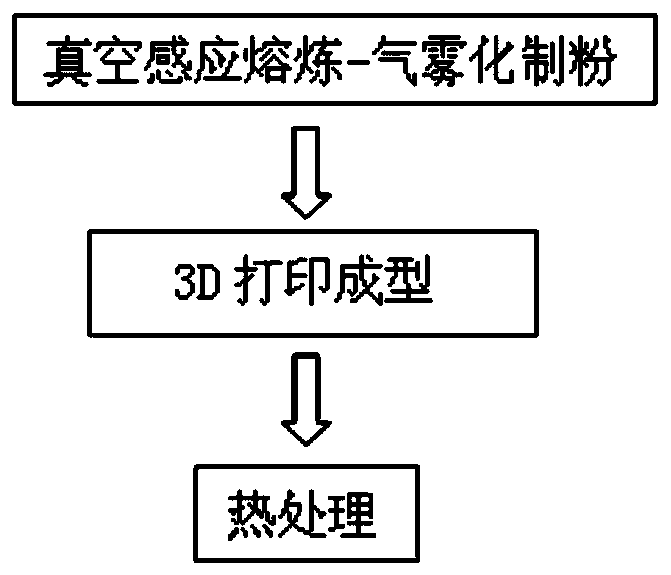
3D printing high-wear-resistance stainless steel material, preparation method and application of material
InactiveCN111304552AImprove wear resistanceImprove corrosion resistanceAdditive manufacturing apparatus3d printManganese
The invention discloses a 3D printing high-wear-resistance stainless steel material, a preparation method and application of the material in manufacture of a 3D printing mold. The 3D printing high-wear-resistance stainless steel material comprises, by mass, 10.0-14.0% of a chrome element, 6.0-9.0% of a nickel element, 1.0-3.0% of a molybdenum element, 0.5-1.5% of an aluminum element, 0-0.5% of a silicon element, 0-0.5% of a manganese element, 0-1.0% of a niobium element, 0-0.5% of a vanadium element, 0-1.0% of a titanium element, 0-0.08% of a nitrogen element, 0.1-0.3% of a carbon element andthe balance iron element. A vacuum smelting gas atomization method is adopted for mixing all the materials to prepare 3D printing stainless steel metal powder, namely the 3D printing high-wear-resistance stainless steel material. The 3D printing high-wear-resistance stainless steel material is good in wear resistance and corrosion resistance and high in rigidity, and deforms less and does not crack in the 3D printing formation process.
Owner:上海镭镆科技有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![TiZrNbVMo[x] high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof TiZrNbVMo[x] high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2902361d-51ee-4238-b4c1-5d60d73103a3/HDA0000405578970000011.PNG)
![TiZrNbVMo[x] high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof TiZrNbVMo[x] high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2902361d-51ee-4238-b4c1-5d60d73103a3/HDA0000405578970000021.PNG)
![TiZrNbVMo[x] high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof TiZrNbVMo[x] high entropy alloy and preparation method thereof](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/2902361d-51ee-4238-b4c1-5d60d73103a3/HDA0000405578970000031.PNG)