High-temperature titanium alloy with high heat resistance and high thermal stabilization
A high thermal stability, high temperature titanium alloy technology, applied in the field of titanium-based alloys
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
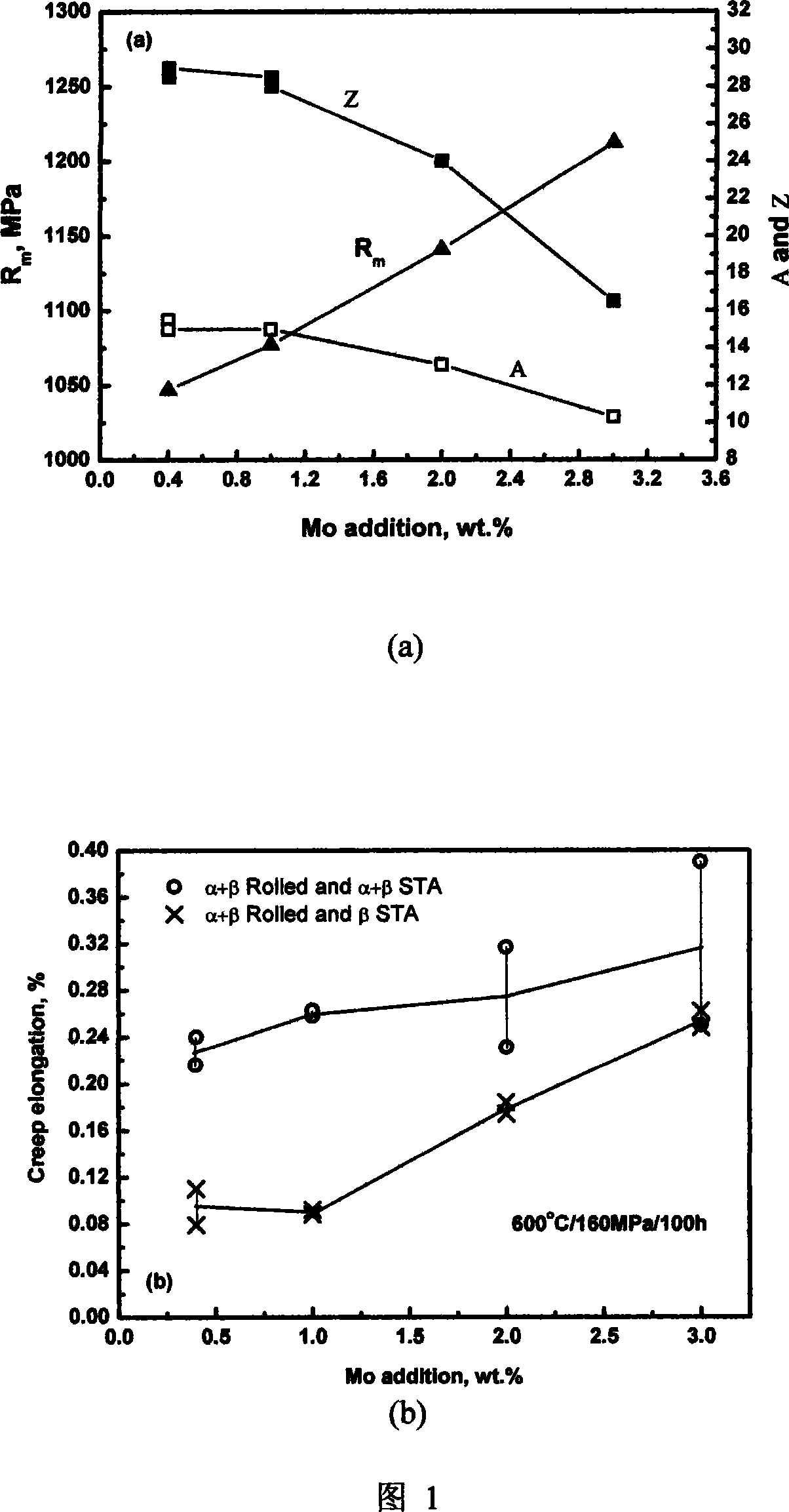
[0050] According to the following formula: Al5.3wt-%; Sn5.0wt-%; Zr7.0wt-%; Si0.55wt-%; Nb0.4wt-%; Ta3.0wt-%; Ti is mixed with sponge titanium, pure aluminum, sponge zirconium and master alloy and then pressed into an electrode. The amount of Mo added is (wt-%): 0.4; 1.0; 2.0; 3.0. Put it into a vacuum consumable electrode electric arc furnace for vacuum melting. Obtain four ingots with different compositions, and then carry out thermal processing and heat treatment according to the following process conditions: Ф45 precision forging is made by a precision forging machine under the condition of 1150 ° C billet opening and 40 ° C heating at the α + β / β transformation point The rod is heated to 1000°C and rolled into a Φ21.5 rod with a rolling mill. The heat treatment system is solid solution at α+β / β transformation point at 30°C / 2h, air cooling, and aging at 700°C / 2h. After heat treatment, the four groups of samples were processed to test their tensile properties at room te...
Embodiment 2
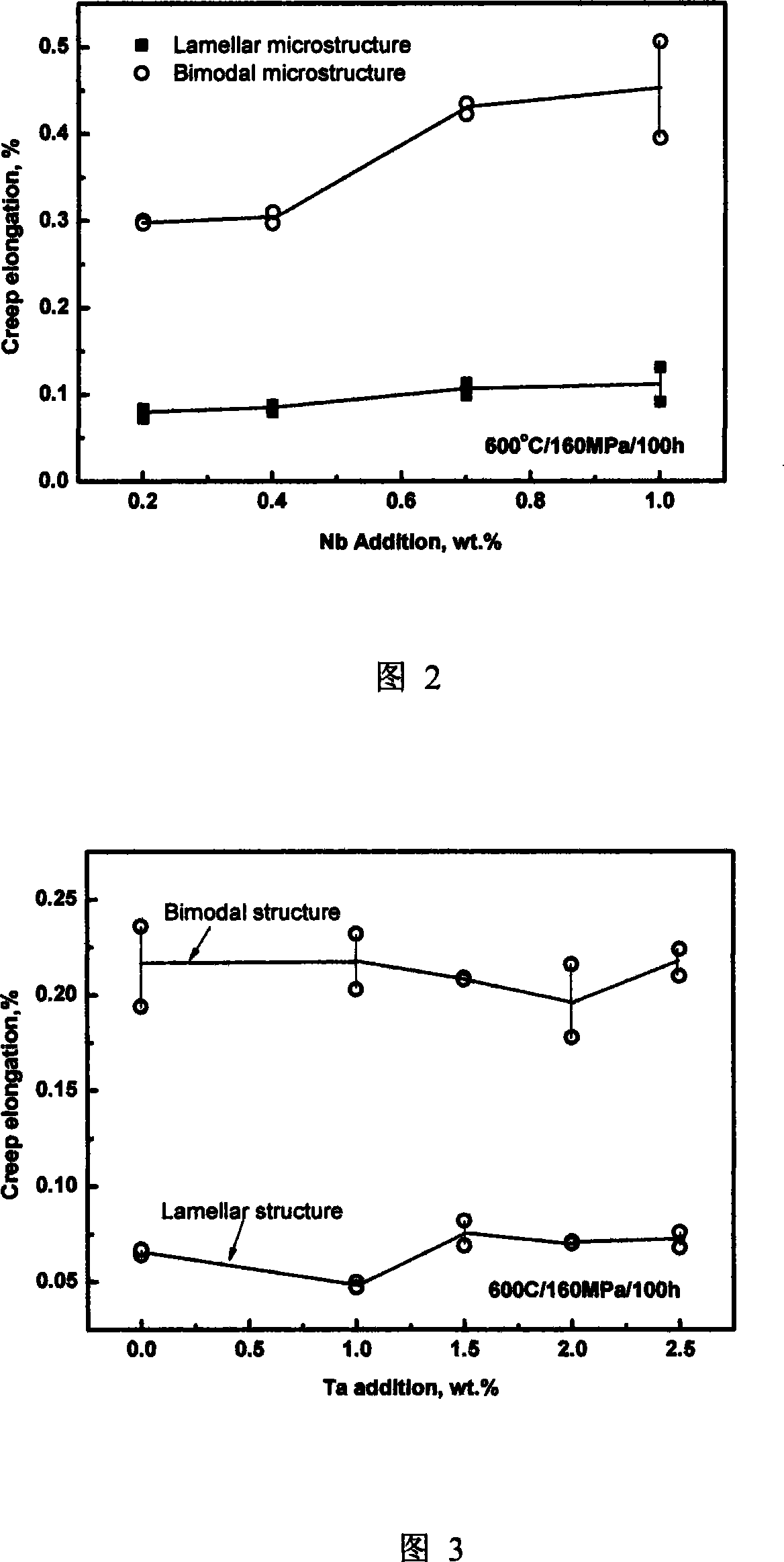
[0052] According to the following formula: Al 6.1wt-%; Sn 3.0wt-%; Zr 2.5wt-%; Mo 0.2wt-%; Si0.25wt-%; Ta 0.3wt-%; Ti is uniformly mixed in the form of sponge titanium and master alloy, and then pressed to make square bars and welded to form electrodes. The addition of Nb is (wt-%): 0.2; 0.4; 0.7; 1.0. The above four electrodes with different compositions were put into a vacuum consumable electrode electric arc furnace and smelted three times, and smelted into four ingots with different Nb compositions. Carry out thermal processing and heat treatment by the processing condition of embodiment 1 again. Finally, four groups of samples were made to test their creep elongation after 100 hours at 600°C / 160MPa, and the curves shown in Figure 2 were obtained. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the creep resistance of the alloy begins to decrease when the Nb content in the titanium alloy increases above 0.4wt-%.
Embodiment 3
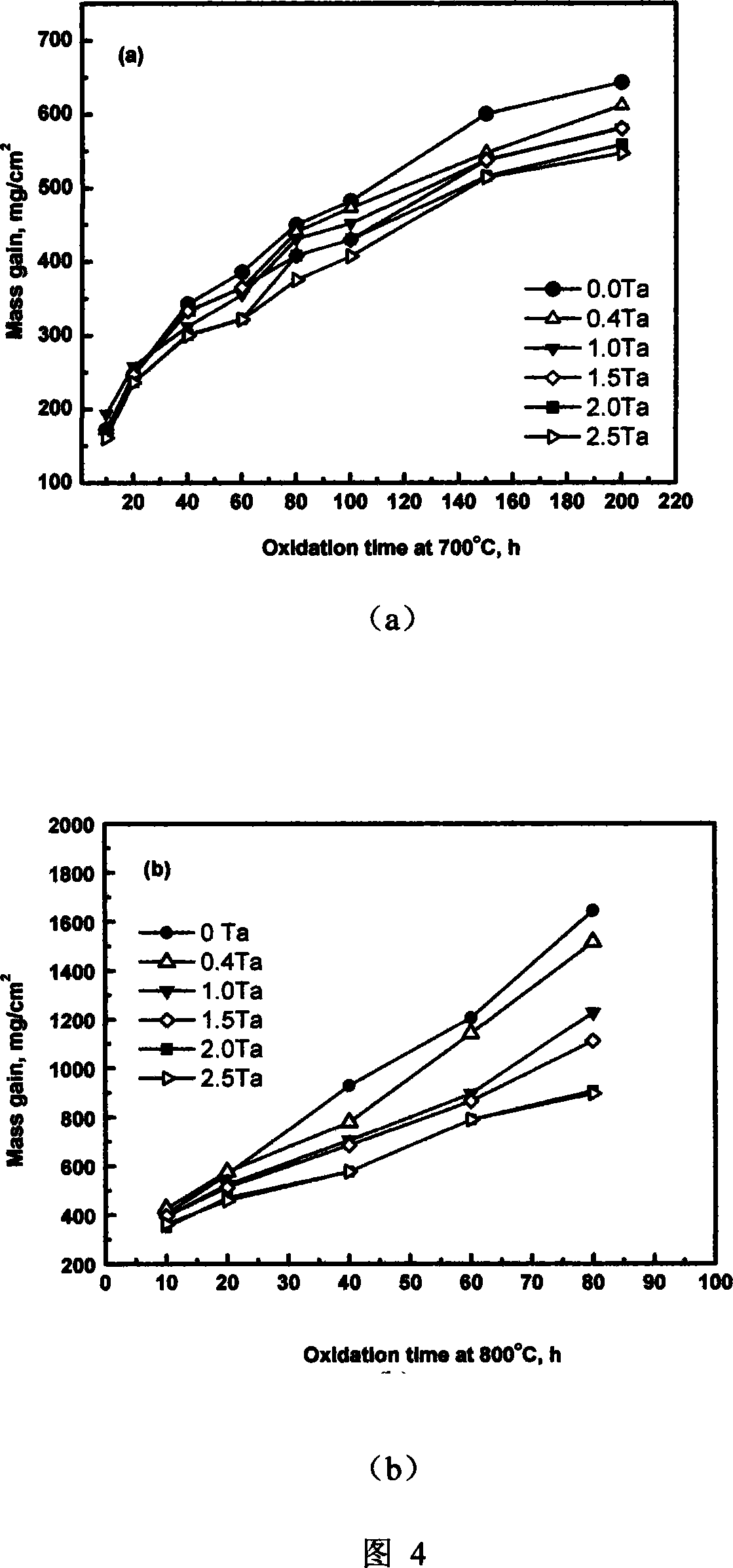
[0054] According to the following formula: Al 5.8wt-%; Sn 4.0wt-%; Zr 3.5wt-%; Mo 0.4wt-%; Si 0.35wt-%; Nb 0.4wt-%; The added amounts are (wt-%): 0; 0.4; 1.0; 1.5; 2.0; 2.5, and the balance is titanium and unavoidable impurities. Smelting, processing and heat treatment with the process of Example 1, and finally made six groups of samples to carry out the creep test as in Example 2, the results are shown in Figure 3; Next, measure the curve of oxidative gain over time within 200 hours, and the results are shown in Fig. 4(a) and (b) respectively. It can be seen from Figure 3 that Ta has a limited effect on the creep resistance of the alloy in a relatively wide range, but it is reflected in Figure 4 that its effect on improving the oxidation resistance of the alloy is obvious.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com