Low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel and production method of low-alloy high-intensity high-toughness steel
A production method and low-alloy technology, applied in the field of metal materials, can solve problems affecting performance, plastic toughness, wear resistance, etc., and achieve the effect of simple manufacturing and processing technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
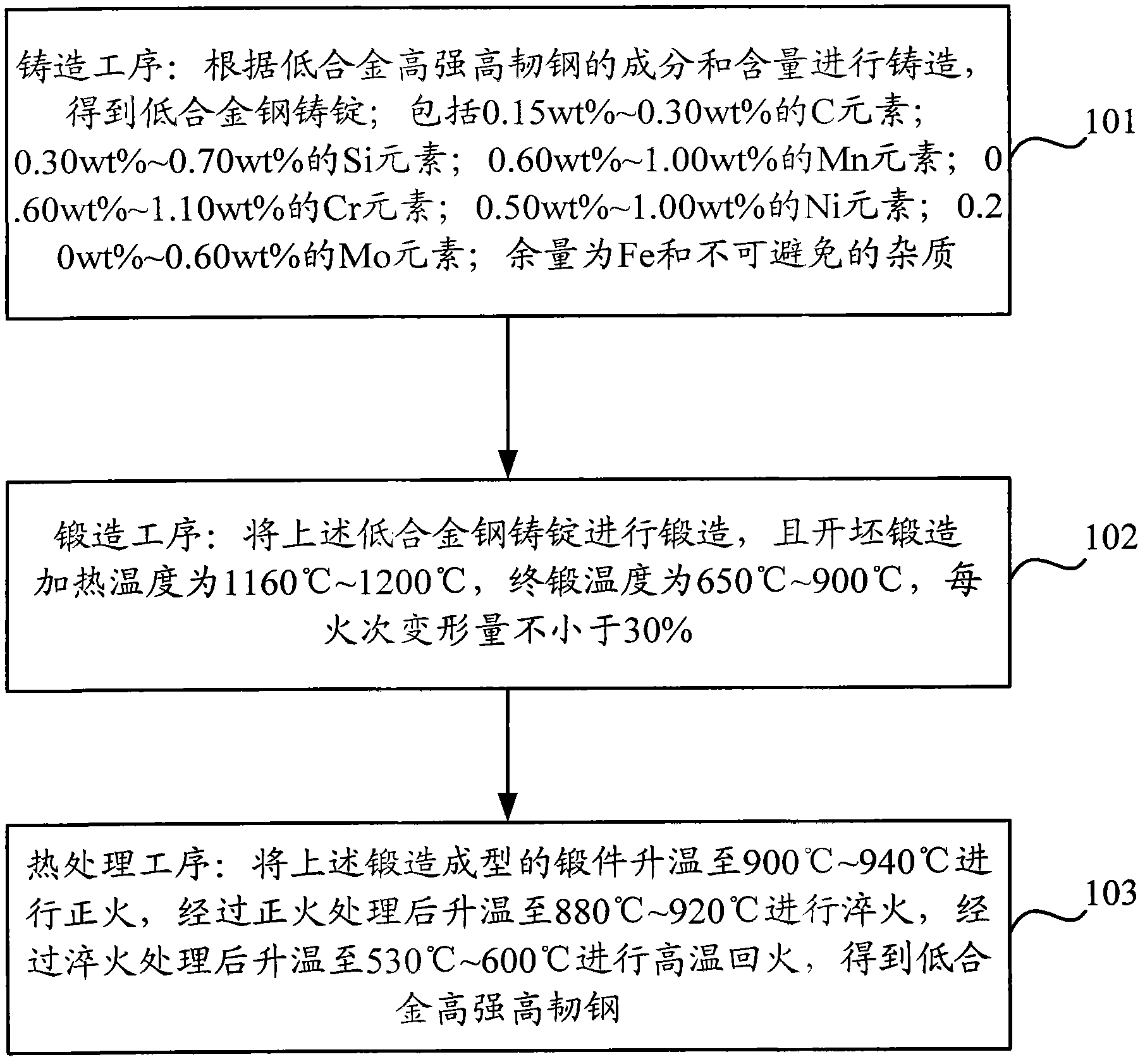
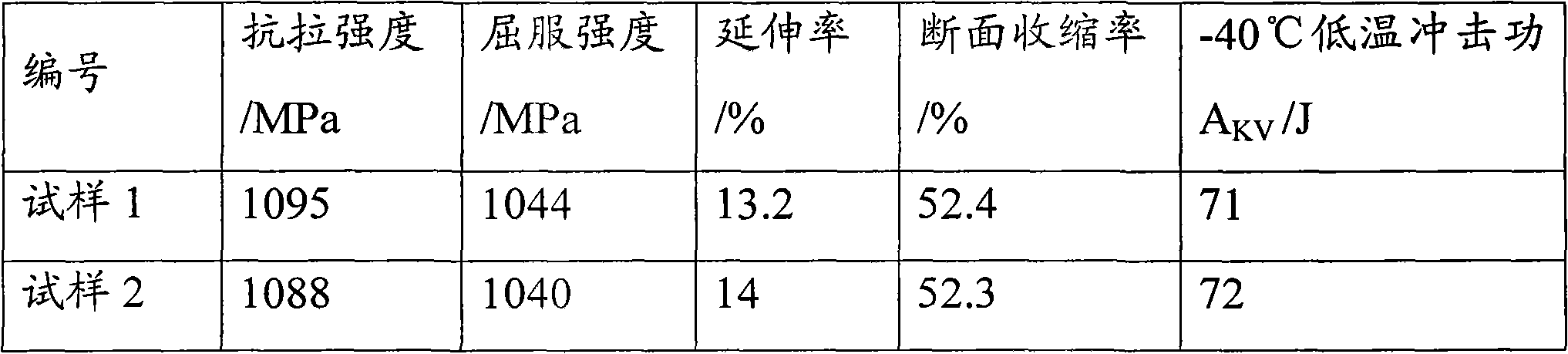
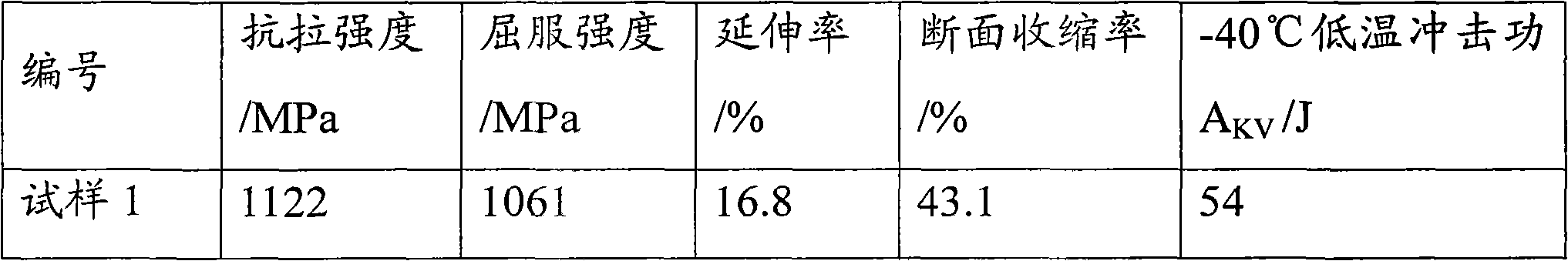
[0059]Based on the composition and content of the above-mentioned low-alloy high-strength high-toughness steel, Embodiment 1 of the present invention provides a production method of low-alloy high-strength high-toughness steel to realize low-alloy high-strength high-toughness steel with a yield strength of 1000 MPa; and the low-alloy high-strength steel High-toughness steel can solve problems such as alloy chemical element content, material forming process, and increase strength level; this method performs large deformation forging on the as-cast material, and forging can break the as-cast structure, refine the grain, and increase the dislocation density. , improve strength, and at the same time heal some defects formed by casting to prevent the reduction of plasticity and toughness; after forging, quenching + high temperature tempering heat treatment is carried out to obtain tempered sorbite structure, which can obtain high toughness while maintaining high strength.
[0060] ...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Step 1. Cast a low-alloy high-strength high-toughness steel ingot with the composition shown in Table 1, and the specification of the ingot is Φ100×110mm, and control the process of melting and pouring.
[0077] Table 1 Low alloy steel chemical composition (wt%)
[0078] C
S
P
mn
Si
Cr
Ni
Mo
Al
La
0.25
0.003
0.012
0.72
0.32
1.04
0.83
0.31
0.039
0.0009
[0079] Step 2, forging the ingot obtained in Step 1.
[0080] In the embodiment of the present invention, the heating temperature for blank forging is 1160-1200°C, the final forging temperature is 700°C, the deformation per firing is not less than 30%, and the cross-sectional specification of the forging is 16×80mm.
[0081] Step 3. Heating the forging obtained in step 2 to 930° C., keeping it warm for 3 hours, and cooling to room temperature in the air; this process is a normalizing process.
[...
Embodiment 3
[0089] Step 1. Cast a low-alloy high-strength high-toughness steel ingot with the composition shown in Table 3, and the specification of the ingot is Φ100×110mm, and control the melting and pouring process.
[0090] Table 3 Chemical Composition of Low Alloy Steel (wt%)
[0091] C
S
P
mn
Si
Cr
Ni
Mo
Al
La
0.29
0.004
0.017
0.62
0.40
0.85
0.82
0.25
0.046
0.0005
[0092] Step 2, forging the ingot obtained in Step 1.
[0093] In the embodiment of the present invention, the heating temperature for blank forging is 1160-1200°C, the final forging temperature is 750°C, the deformation per firing is not less than 30%, and the cross-sectional specification of the forging is 16×80mm.
[0094] Step 3. Heating the forging obtained in step 2 to 930° C., keeping it warm for 3 hours, and cooling to room temperature in the air; this process is a normalizing process.
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Yield strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com