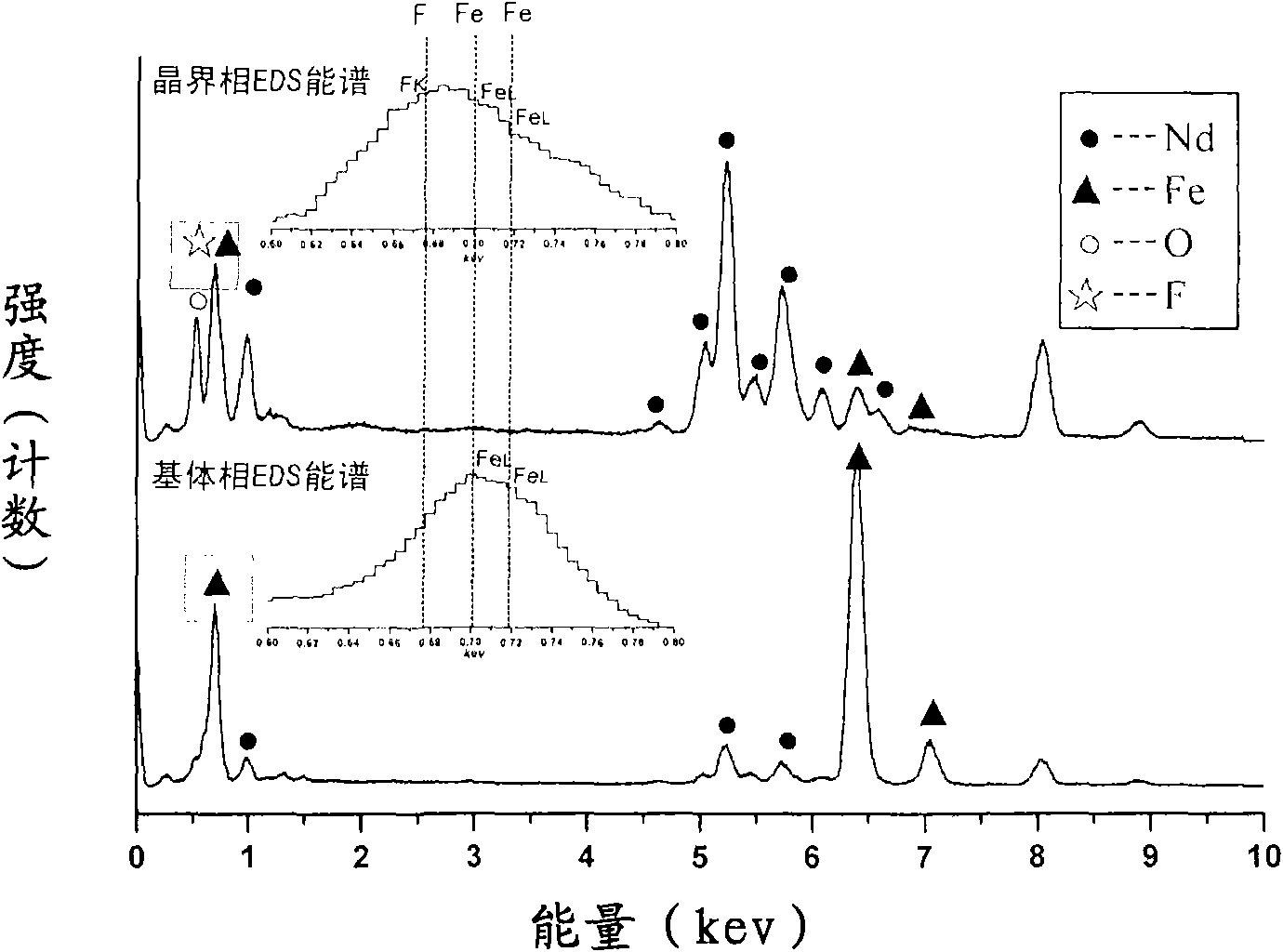
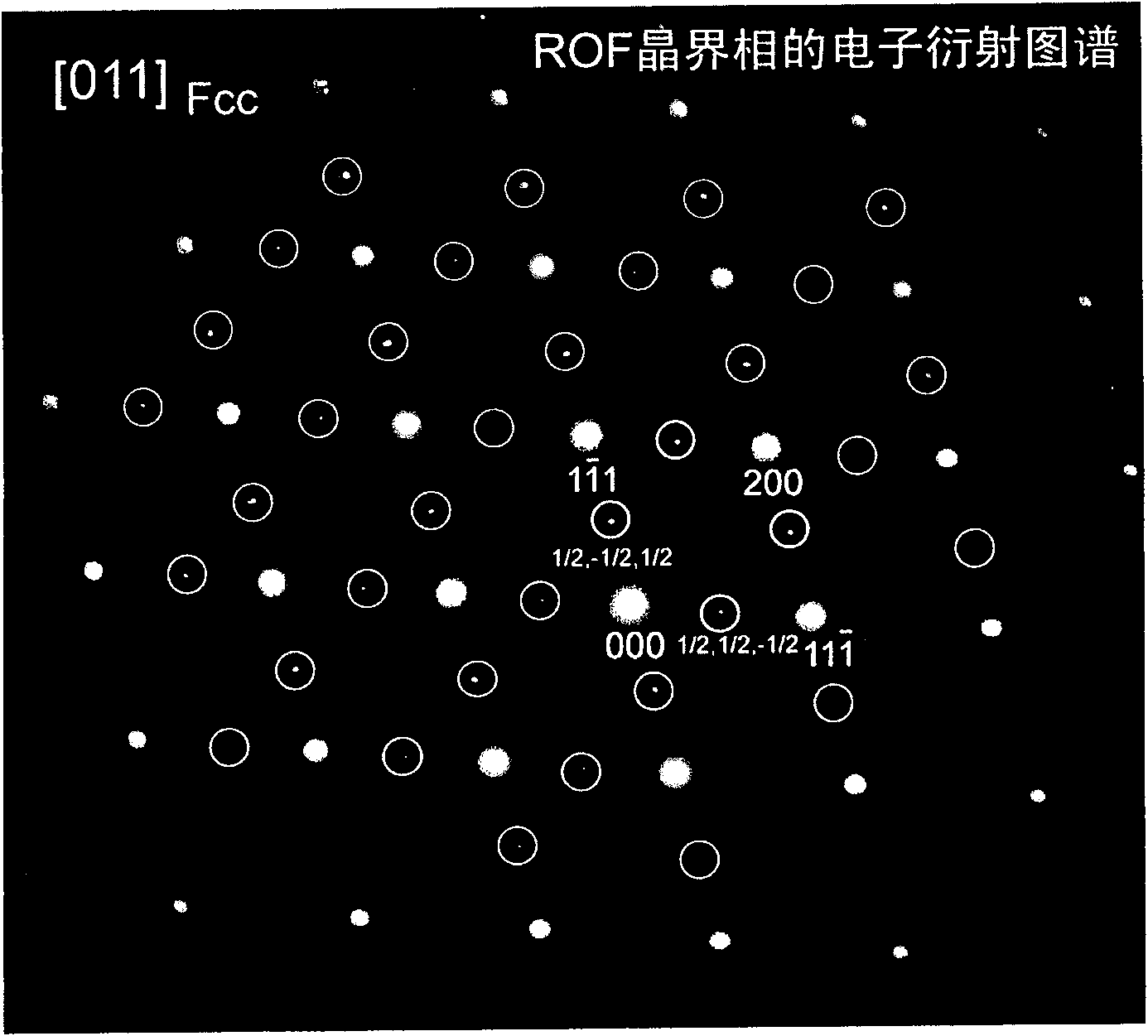
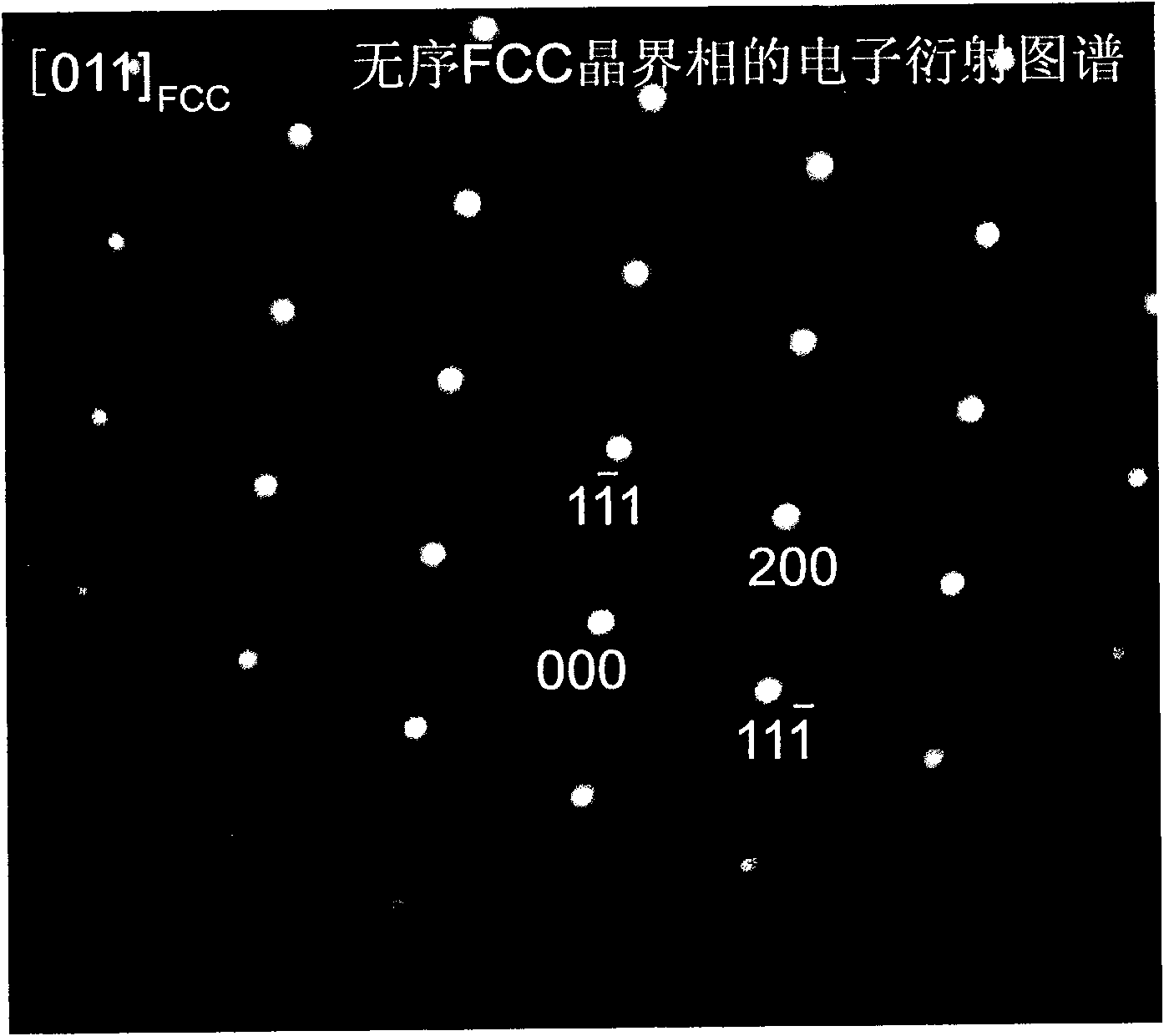
Sintered NdFeB rare-earth permanent magnet material with modified grain boundary phase and preparation method thereof
A rare earth permanent magnet and grain boundary phase technology, applied in the direction of magnetic materials, inorganic material magnetism, magnetic objects, etc., can solve the problem of increasing the coercive force of NdFeB permanent magnets, high addition of rare earth fluoride, remanence and magnetic energy product Reduce and other problems to achieve the effect of reducing magnetic coupling, facilitating sintering, and improving magnetic properties and resistivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0045] The original materials are Nd metal, Dy metal, electrolytic pure iron, iron-boron alloy and Al, according to the pre-designed composition Nd 15 Dy 1.2 Fe 余 al 0.8 B 6 (at.%) for proportioning, using ingot casting process to make R-Fe-M-B NdFeB alloy. The alloy is first coarsely crushed in a jaw crusher, then crushed to 60-80 mesh by a secondary crusher, and then jet-milled in high-purity nitrogen to produce magnetic powder with an average particle size of 3-6 μm. 1 ~ 1000nm NdF 3 The micropowder is fully dispersed in ethanol by ultrasonic waves to form a uniform dispersion liquid with a concentration of about 1.5 mg / mL. There is no particle settlement at the bottom of the dispersion liquid. The ultrasonic time is controlled at 15-30 min. 3 In the dispersion system, ultrasonic again to make it fully mixed, the ultrasonic time is 10min. NdF 3 The amount corresponding to the addition of NdFeB magnetic powder is 0~0.5wt.%, where 0 means that no NdF is added by the sa...
Embodiment 2
[0055] The original materials are Nd-Pr alloy (80at.% is Nd), electrolytic pure iron, iron-boron alloy, according to the pre-designed composition (Nd 0.8 PR 0.2 ) 16 Fe 78 B 6 (at.%) for proportioning, using ingot casting process to make R-Fe-M-B NdFeB alloy. The technology of preparing green body is the same as embodiment 1, NdF 3 The added amount of is 0~0.8wt.%, 0 represents the reference magnet without adding fluoride by the same method. The green body is subjected to cold isostatic pressing to increase the density of the green body, and the isostatic pressure is 220MPa. Put the green body into a high-vacuum sintering furnace, sinter at 1080°C for 2 hours under vacuum, blow it with argon, and cool it at a cooling rate of about 5°C / min. After two atmosphere tempering at 900°C and 545°C, the cooling rate is 10°C / min after tempering at 900°C, and the cooling rate is about 50°C / min after tempering at 545°C, and the tempering time is 2h. The sintered NdFeB rare earth per...
Embodiment 3
[0062] The original materials are Nd-Pr alloy (80at.% is Nd), electrolytic pure iron, iron-boron alloy, according to the pre-designed composition (Nd 0.8 PR 0.2 ) 16 Fe 78 B 6 (at.%) for proportioning, using ingot casting process to make R-Fe-M-B NdFeB alloy. The technology of preparing green body is the same as embodiment 2, NdF 3 The added amount of is 0~1.5wt.%, 0 means the reference magnet without adding fluoride by the same method. The green body is subjected to cold isostatic pressing to increase the density of the green body, and the isostatic pressure is 220MPa. Put the green body into a high-vacuum sintering furnace, sinter at 1100°C for 2 hours under vacuum, and blow it with argon to cool at a cooling rate of about 10°C / min. After tempering twice at 900°C and 525°C, the tempering time is 2 hours, the cooling rate is 10°C / min after tempering at 900°C, and the cooling rate is about 50°C / min after tempering at 525°C. The sintered NdFeB rare earth permanent magnet...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Average particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com