Patents
Literature
479 results about "Near net shape" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Near net shape is an industrial manufacturing technique. The name implies that the initial production of the item is very close to the final (net) shape, reducing the need for surface finishing. Reducing traditional finishing such as machining or grinding eliminates more than two-thirds of the production costs in some industries.
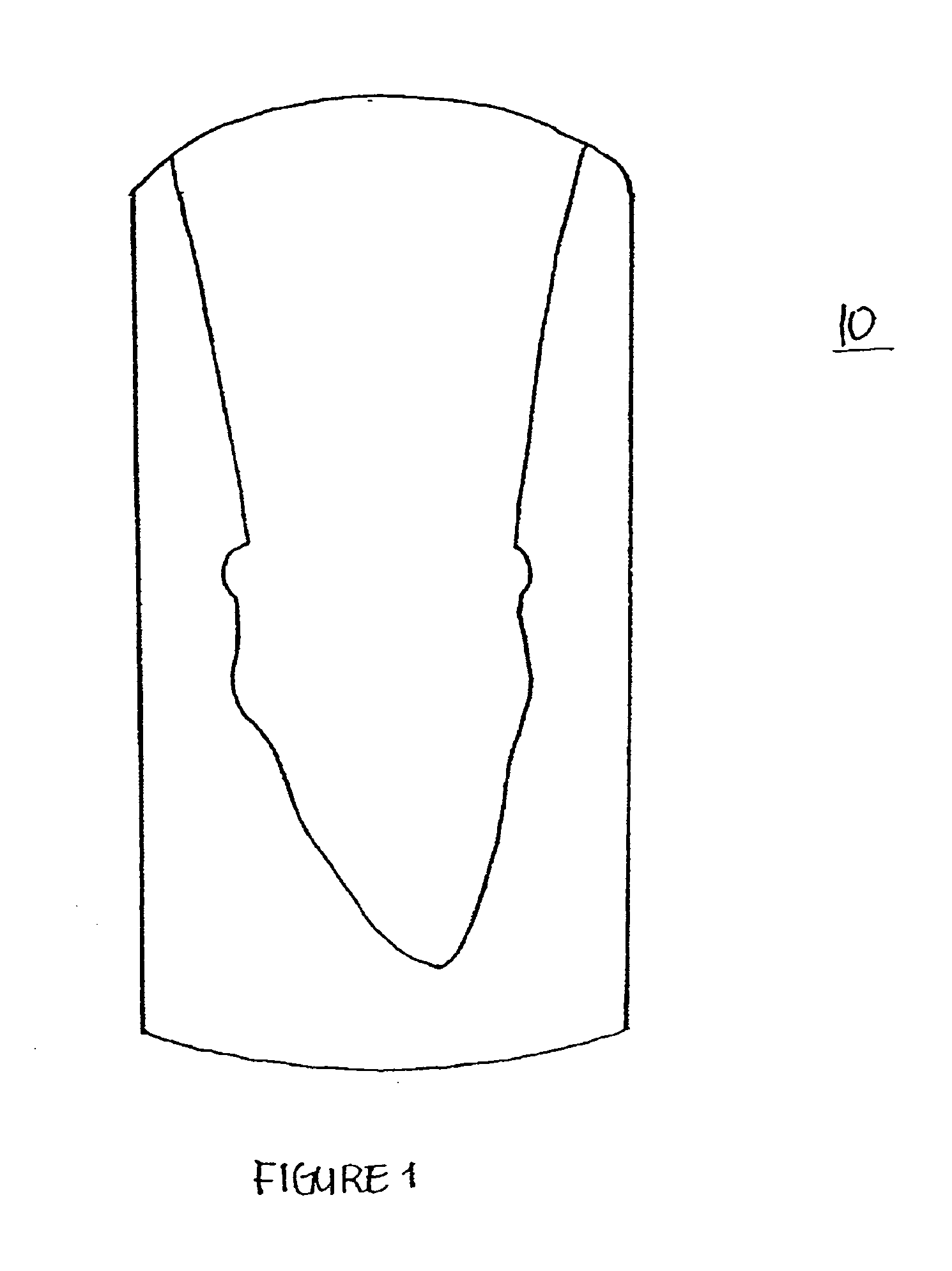
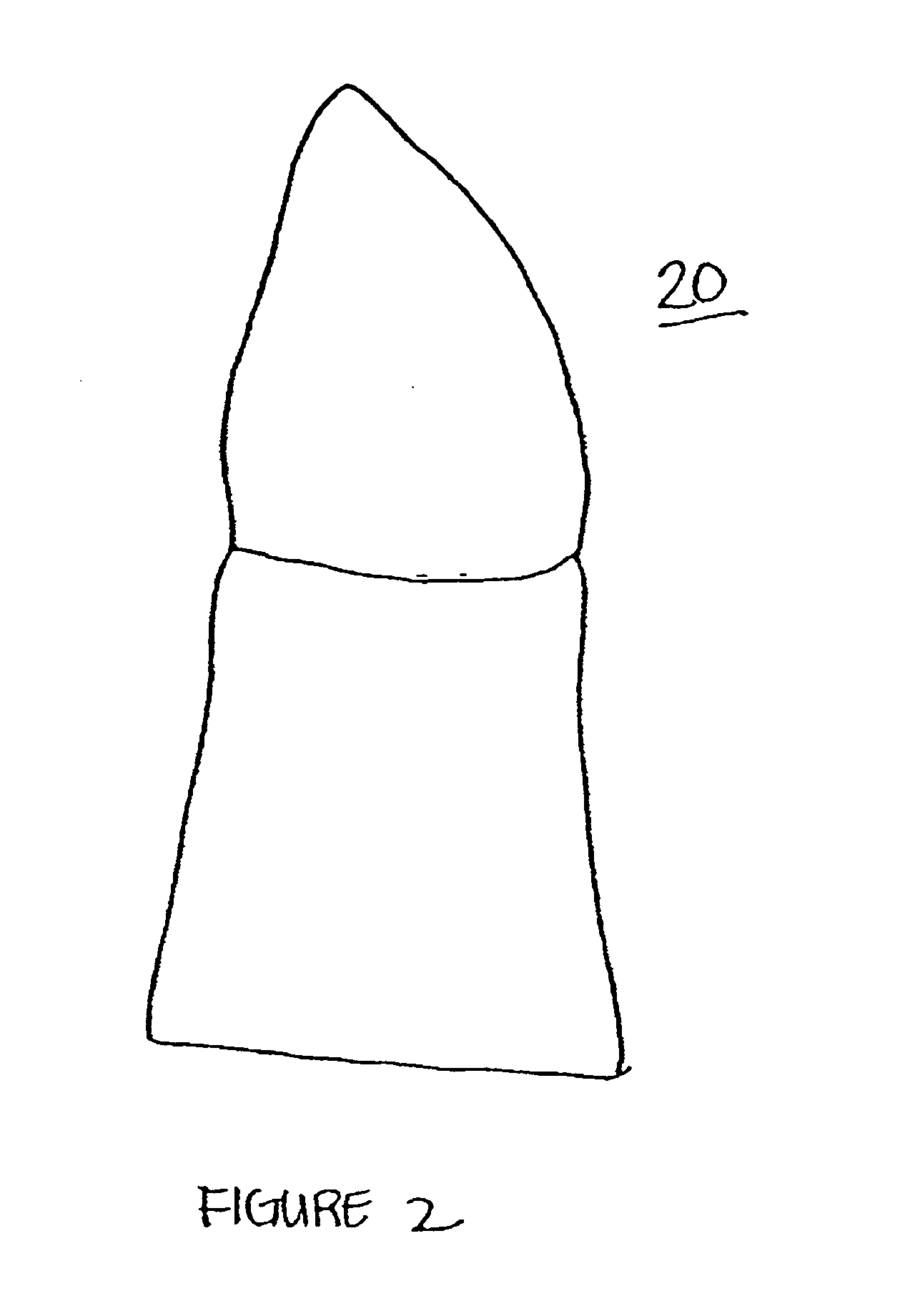
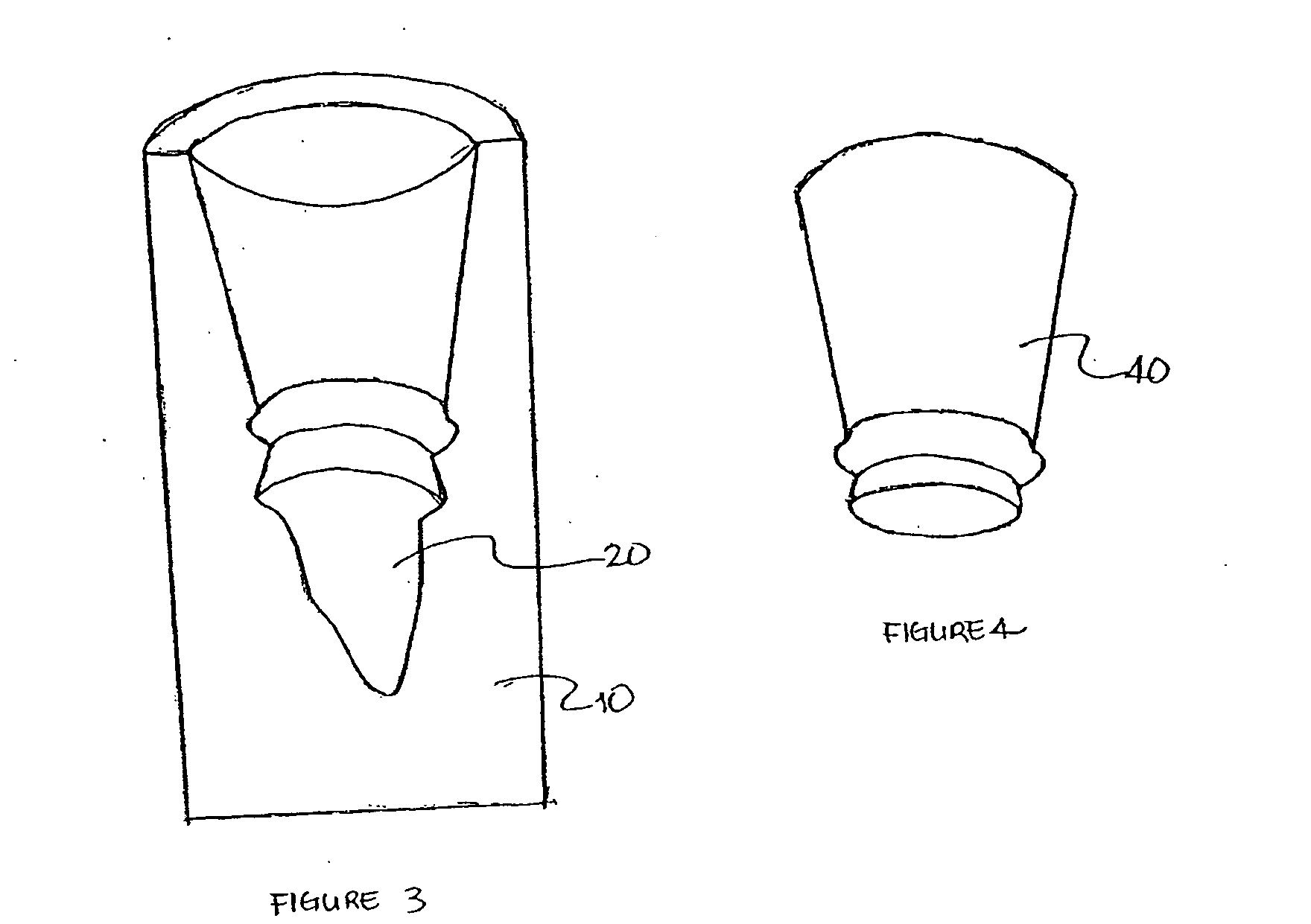
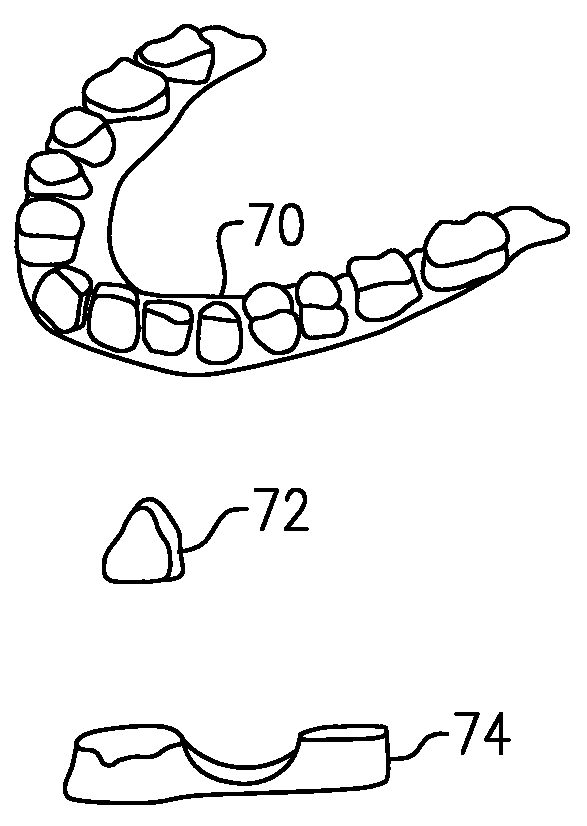
Solid free-form fabrication methods for the production of dental restorations
InactiveUS20050023710A1Improve bindingImpression capsCeramic shaping apparatusPolymer scienceFree form
Solid free form fabrication techniques can be utilized indirectly to manufacture substrates, dies, models, near-net shapes, shells, and wax-ups that are then used in the manufacture of dental articles. Digital light processing is the most preferred indirect method for the production of substrates. After the substrates are produced, various coating or deposition techniques such as gel casting, slip casting, slurry casting, pressure infiltration, dipping, colloidal spray deposition or electrophoretic deposition are used to manufacture the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
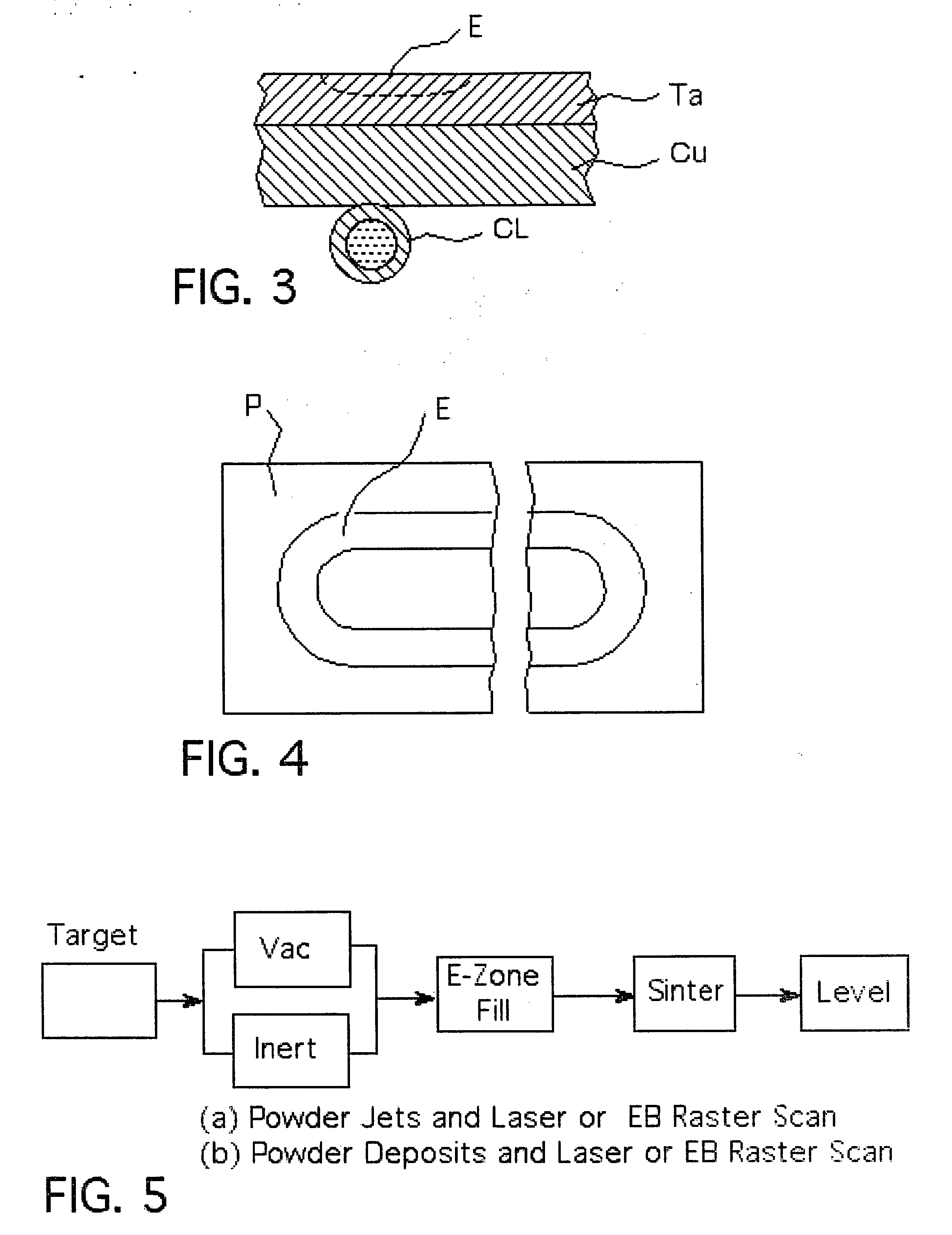
Method for manufacturing a near net-shape mold
A method for manufacturing a near net-shape mold from a weldable material, including creating a computer model of a mold portion (30,32), analytically sectioning the computer model of the mold portion into a plurality of mold zones (22), generating mold zone cutting paths for a cutting machine to follow, cutting the weldable material into plurality of mold zones, generating surface profile cutting paths for a cutting machine to follow, machining surface profiles into the mold zones, assembling the mold zones by placing the mold zones side-by-side, generating welding paths for an electron beam welding a machine to follow, and welding the mold zones together.
Owner:STEWART DAVID H
Solid freeform fabrication system and method
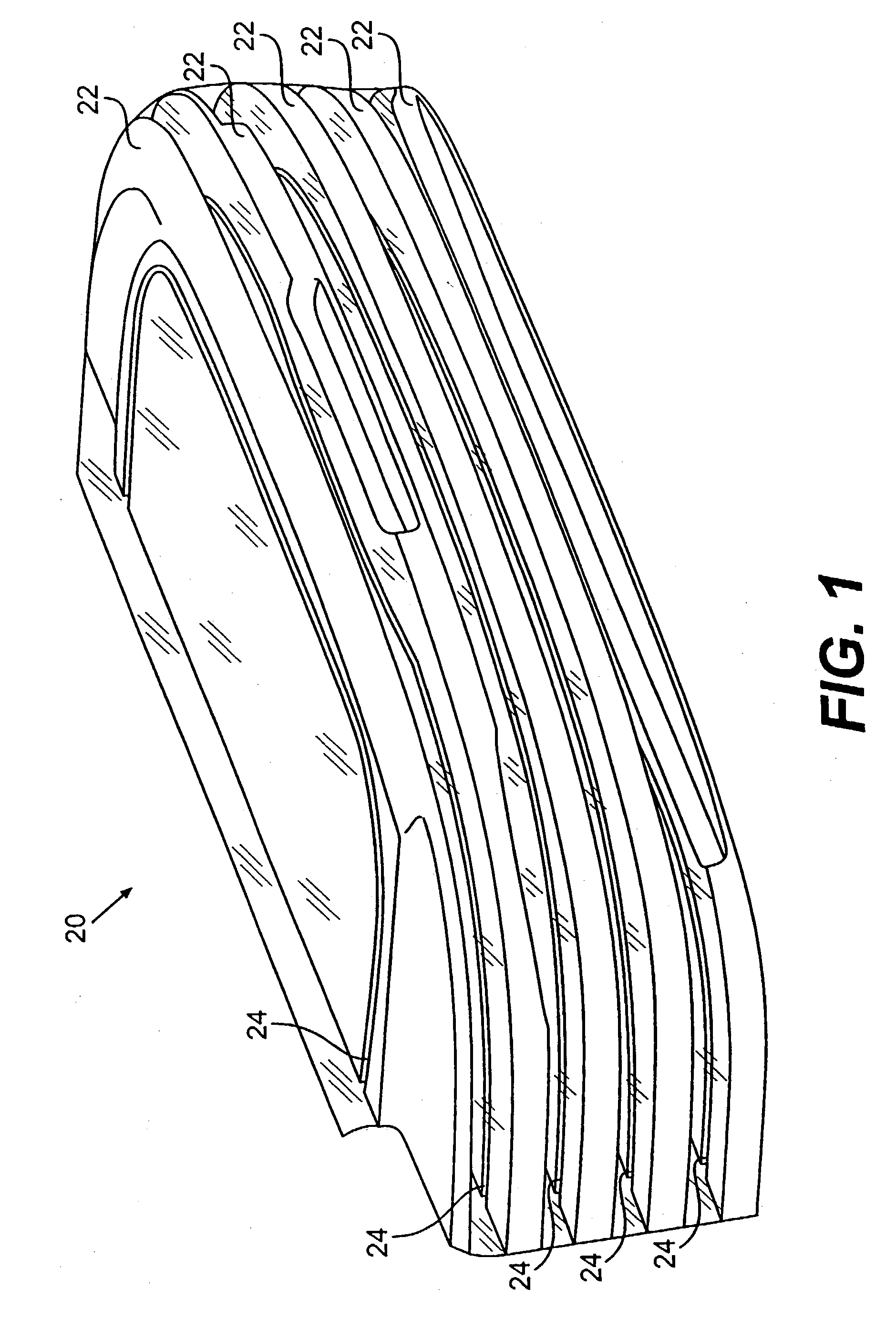
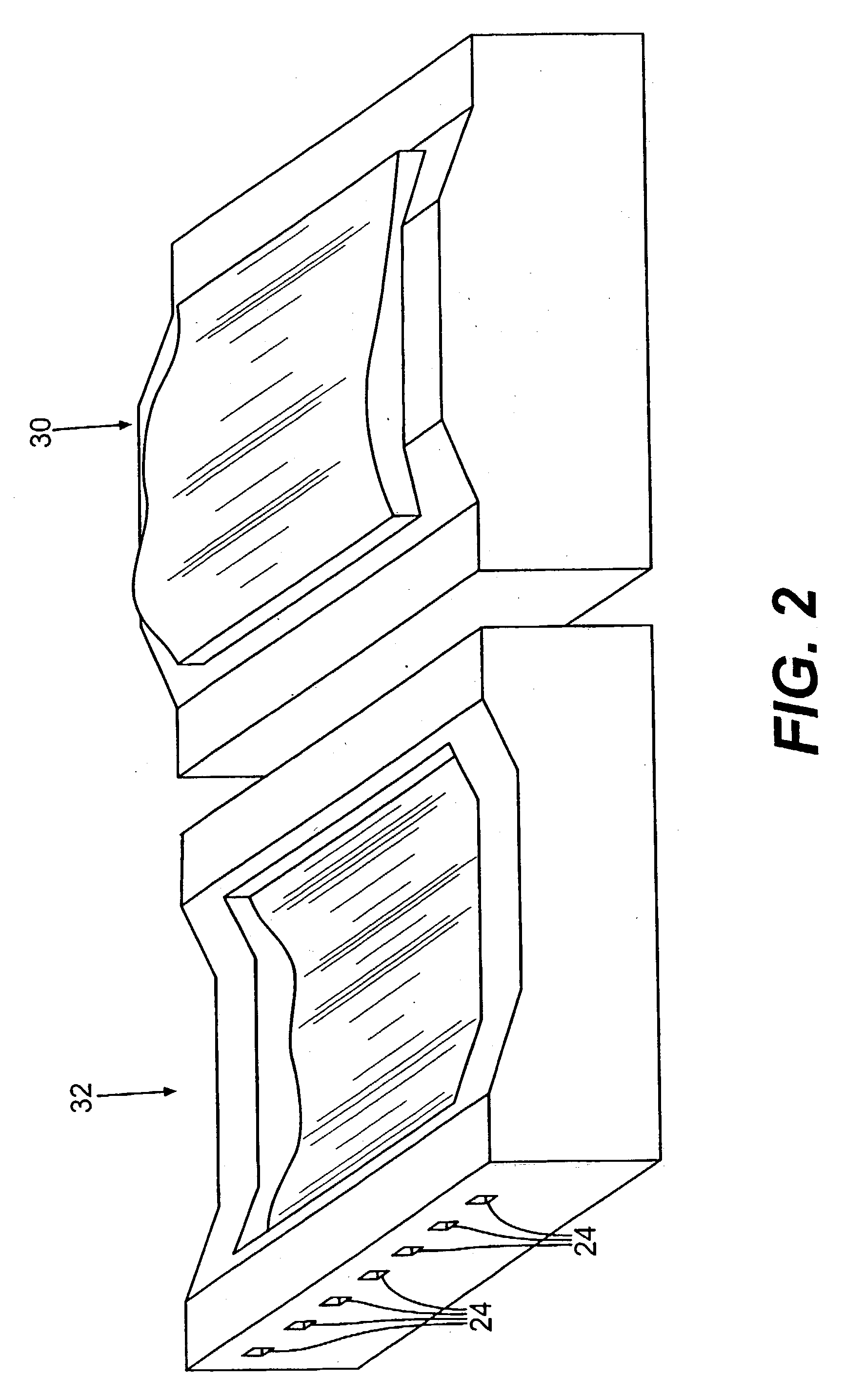
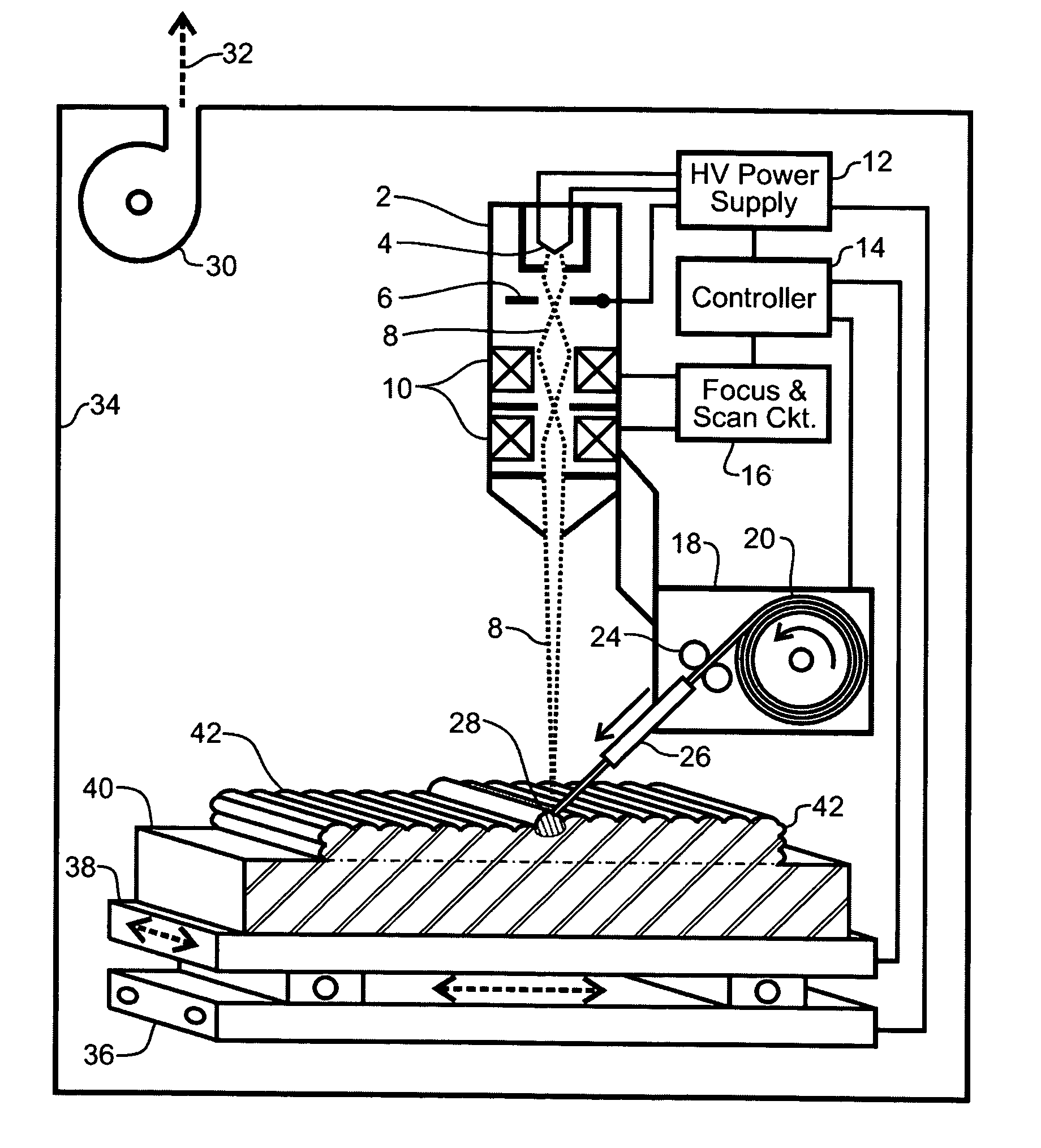
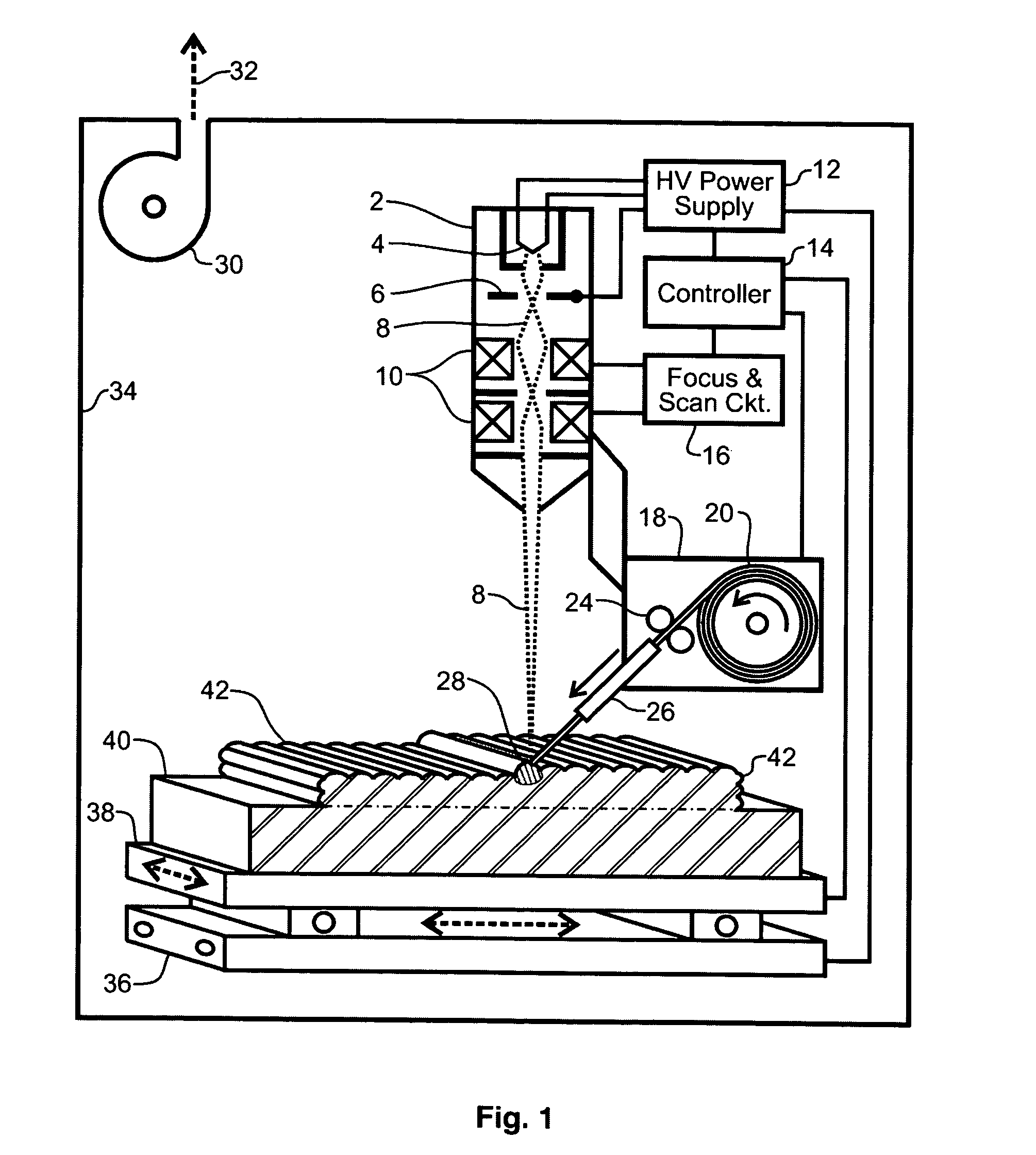
A system and method of solid freeform work piece fabrication through layered deposition of feedstock material on a mold structure. An energy beam and feedstock are fed to a feed point adjacent to a mold structure, thereby forming a molten puddle. The feed point is moved relative to the mold structure, thereby advancing the molten puddle of presently fed feedstock and rapidly solidifying previously fed feedstock. The feed point is sequentially advanced within a predetermined geometric volume containing at least a portion of the mold structure, thereby sequentially fusing the feedstock, by action of the advancing molten puddle, into a near net shape work piece built-up upon the mold structure.
Owner:HENN DAVID S
Method for producing 700Mpa V-N microalloyed high-strength air corrosion-resistant steel based on sheet bar continuous casting tandem rolling process
InactiveCN1884608AHigh strengthGood formabilityTemperature control deviceMetal rolling arrangementsSheet steelChemical composition
This invention exposed the producing method of V-N microalloyed high strength weathering steel which produced with near net shape con-casting technology. It is smelted in electric furnace or converter, refined, con-casted, casted, then directly sent into roller hearth furnace or soaking pit, hot-rolled, laminar cooled, coiled. The liquid steel's chemical elements are (Wt.%): C: <=0.08%, Si: 0.25- 0.75%, Mn: 0.8-2.0%, P: 0.070-0.150%, S: <=0.040%, Cu: 0.25-0.60 %, Cr: 0.30-1.25 wt%, Ni: <=0.65%, V: 0.05-0.20%, N: 0.015-0.030%. This invention can get the high intensity, formation, weathering, joining character stably. The alloying cost is relatively low. So it can be used to produce container, carriage, and other industry facility.
Owner:GUANGZHOU PEARL RIVER STEEL & IRON
Low cost process for the manufacture of near net shape titanium bodies
InactiveUS20060185473A1Low costAdditive manufacturing apparatusArc welding apparatusHigh energyTitanium
Owner:ATS MER LLC
3-D Printing of near net shape products
InactiveUS20100279007A1Easy to handleHigh porosityAdditive manufacturingCeramic shaping apparatusPorosityCeramic metal
The disclosed method relates to manufacture of a near net-shaped products such as ceramic containing products such as ceramic-metal composites. The method entails forming a mixture of a build material and a binder and depositing that mixture onto a surface to produce a layer of the mixture. An activator fluid then is applied to at least one selected region of the layer to bond the binder to the build material to yield a shaped pattern. These steps may be repeated to produce a porous whitebody that is heat treated to yield a porous greenbody preform having a porosity of about 30% to about 70%. The greenbody then is impregnated with a molten material such as molten metal. Where the build material is SiC, the molten metal employed is Si to generate a SiC—Si composite.
Owner:STORM DEV LLC +1
Ply, method for manufacturing ply, and method for manufacturing article with ply
ActiveUS20170030207A1Additive manufacturing apparatusContinuous combustion chamberNear net shapeMaterials science
A method for manufacturing a ply is disclosed. The method includes printing the ply, the ply including a near net shape and a ceramic matrix composite nonwoven material. A ply is disclosed wherein the near net shape is a predetermined layer of an article. A method for manufacturing an article is also disclosed. The method includes printing a first ply and a second ply. The first ply includes a first near net shape and a first ceramic matrix composite nonwoven material, and the second ply includes a second near net shape and a second ceramic matrix composite nonwoven material. The method further includes applying the second ply to the first ply, and consolidating the first ply and the second ply.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
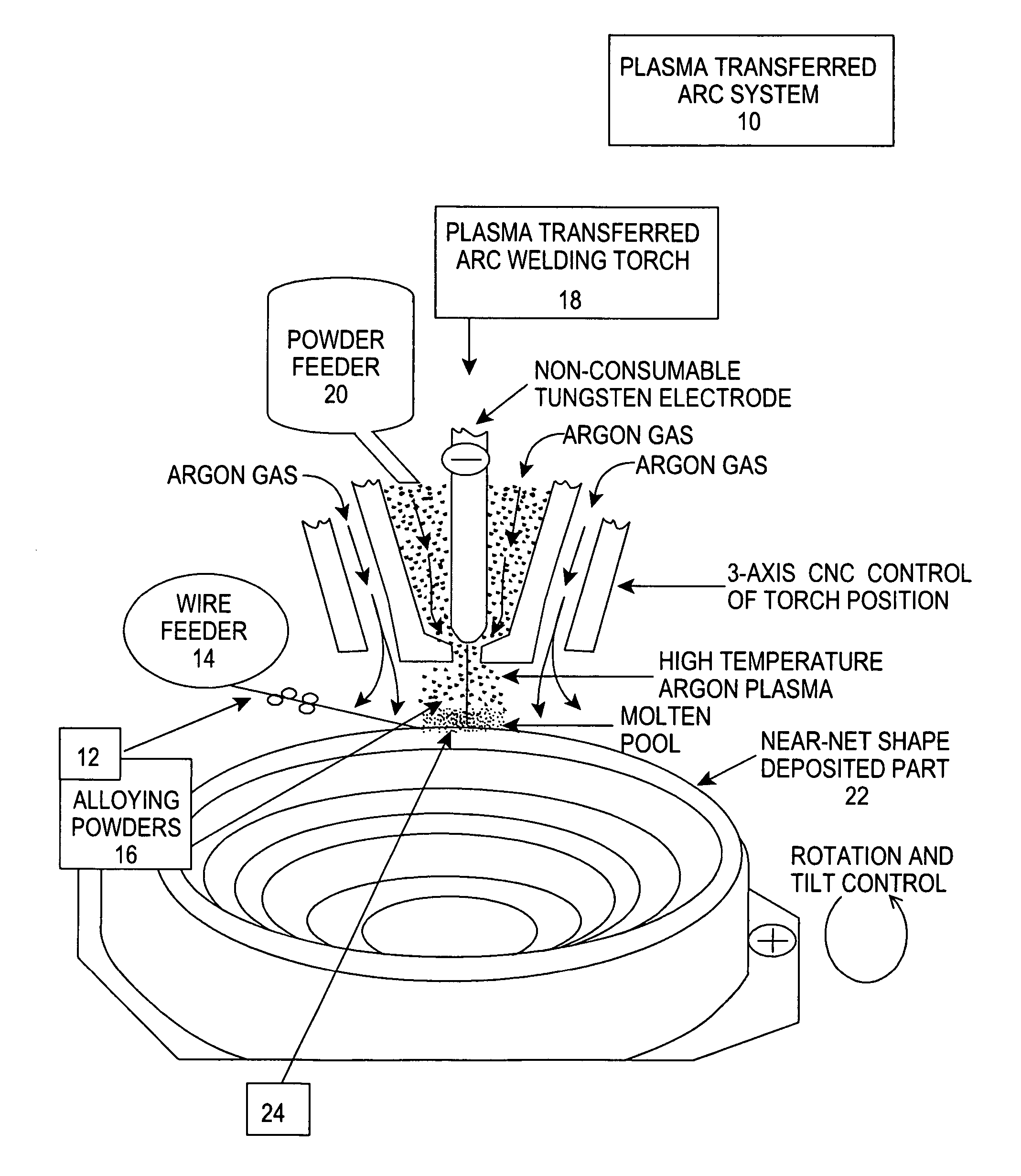
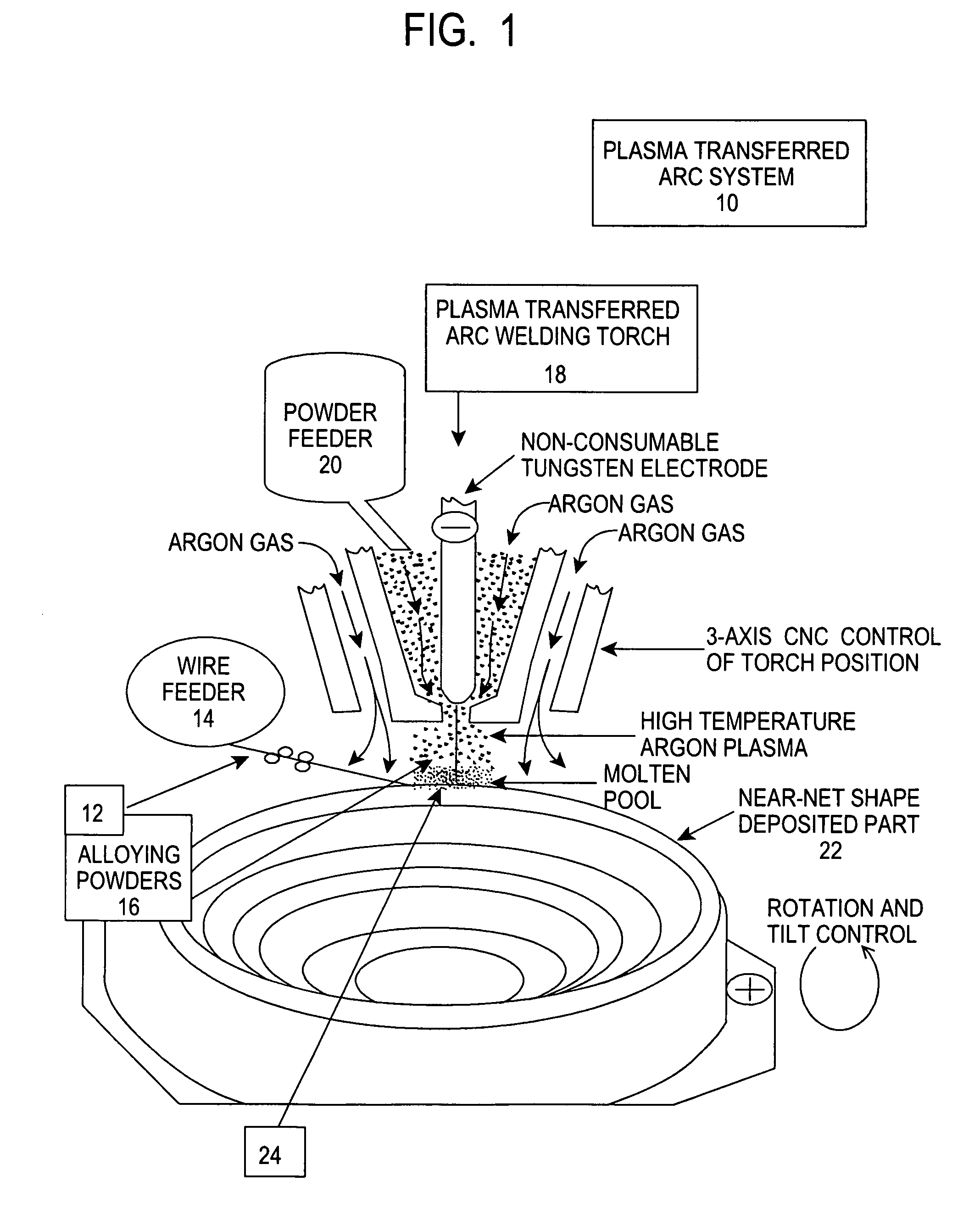
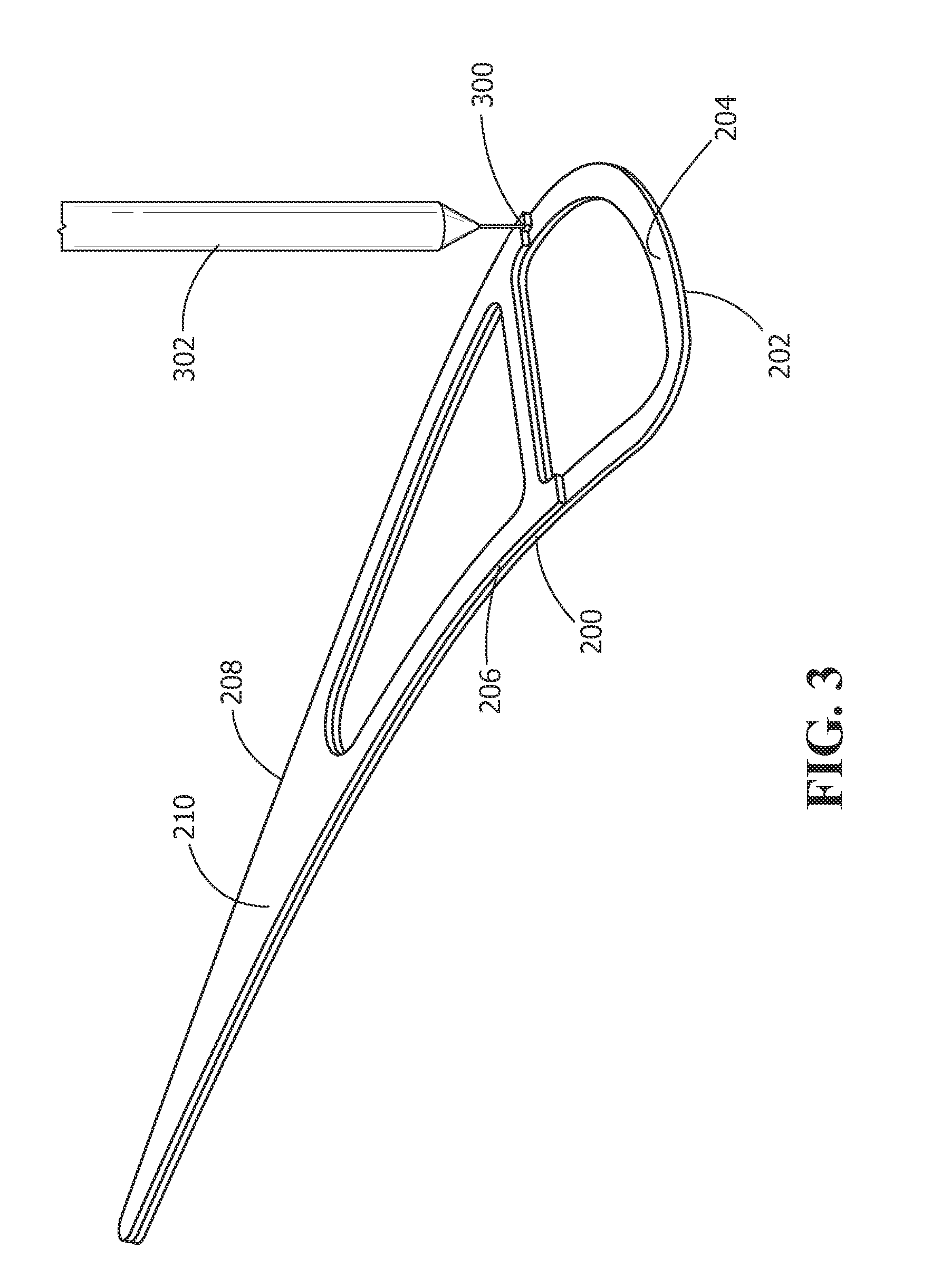
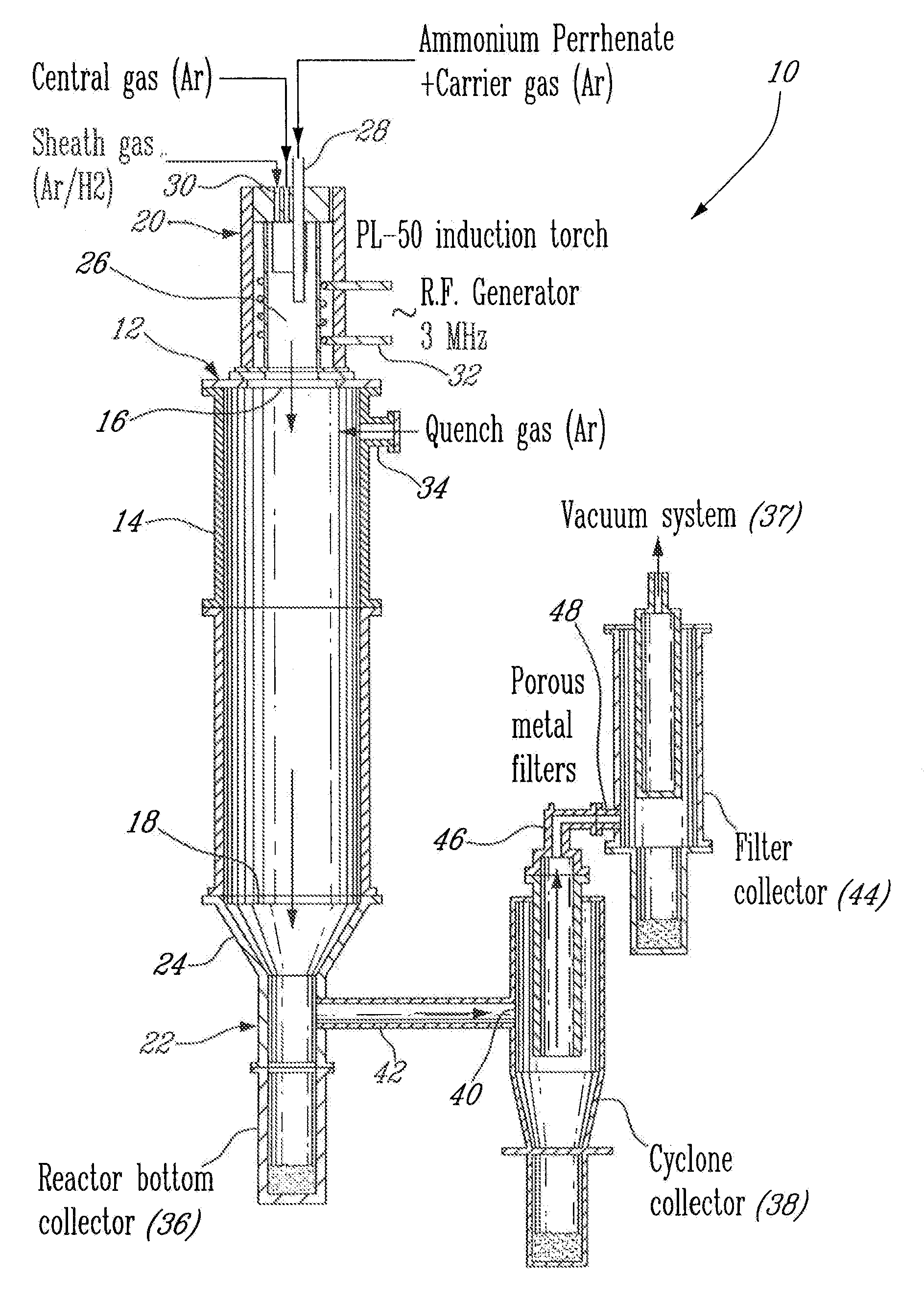
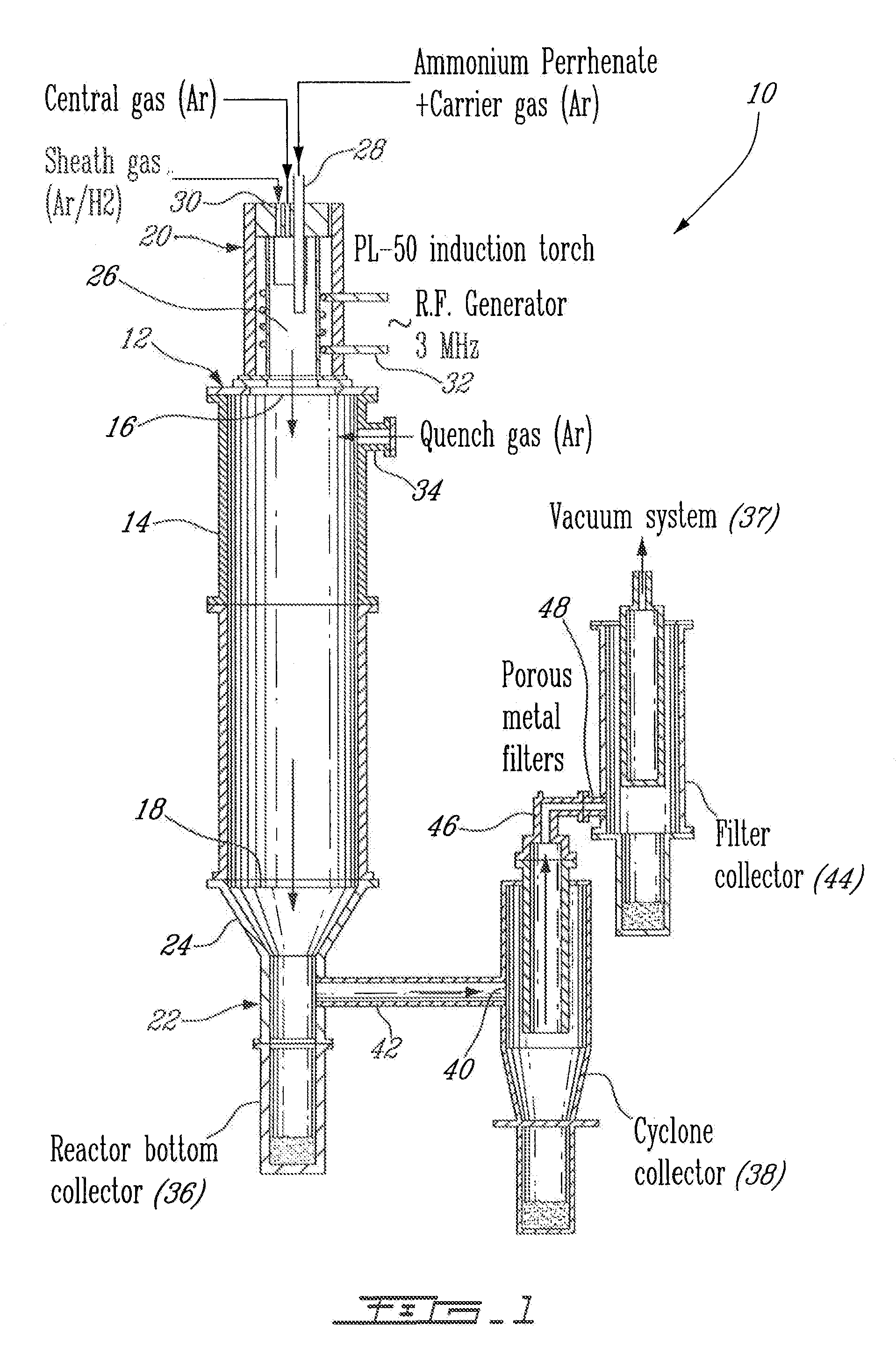
Process for plasma synthesis of rhenium nano and micro powders, and for coatings and near net shape deposits thereof and apparatus therefor
Owner:TEKNA PLASMA SYST INC
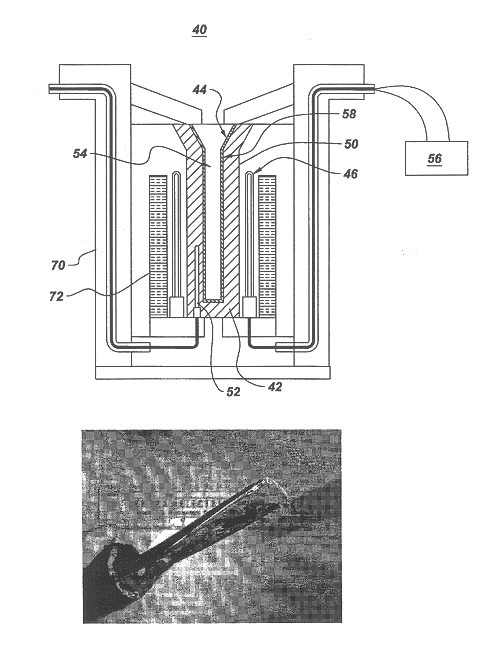
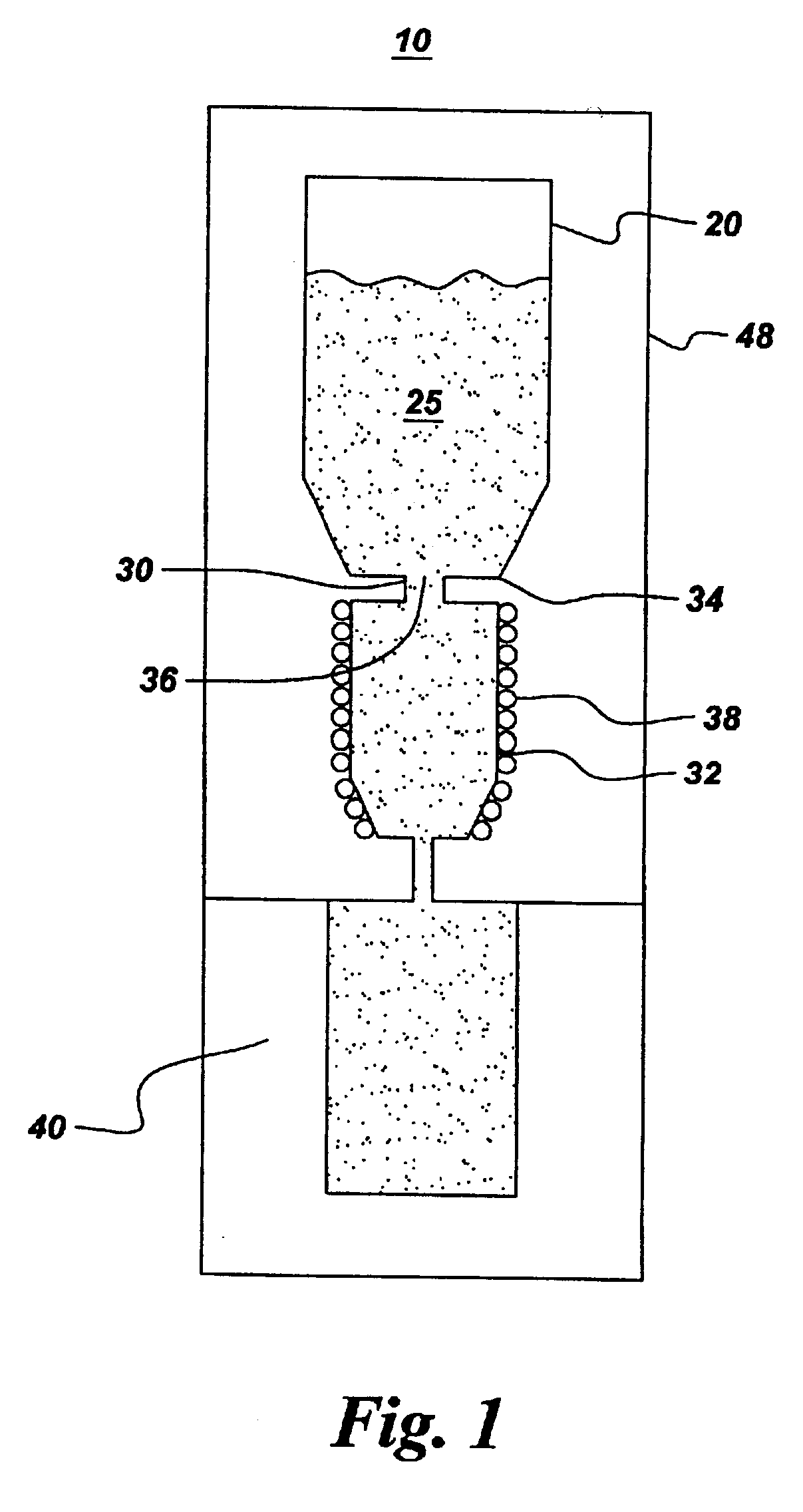
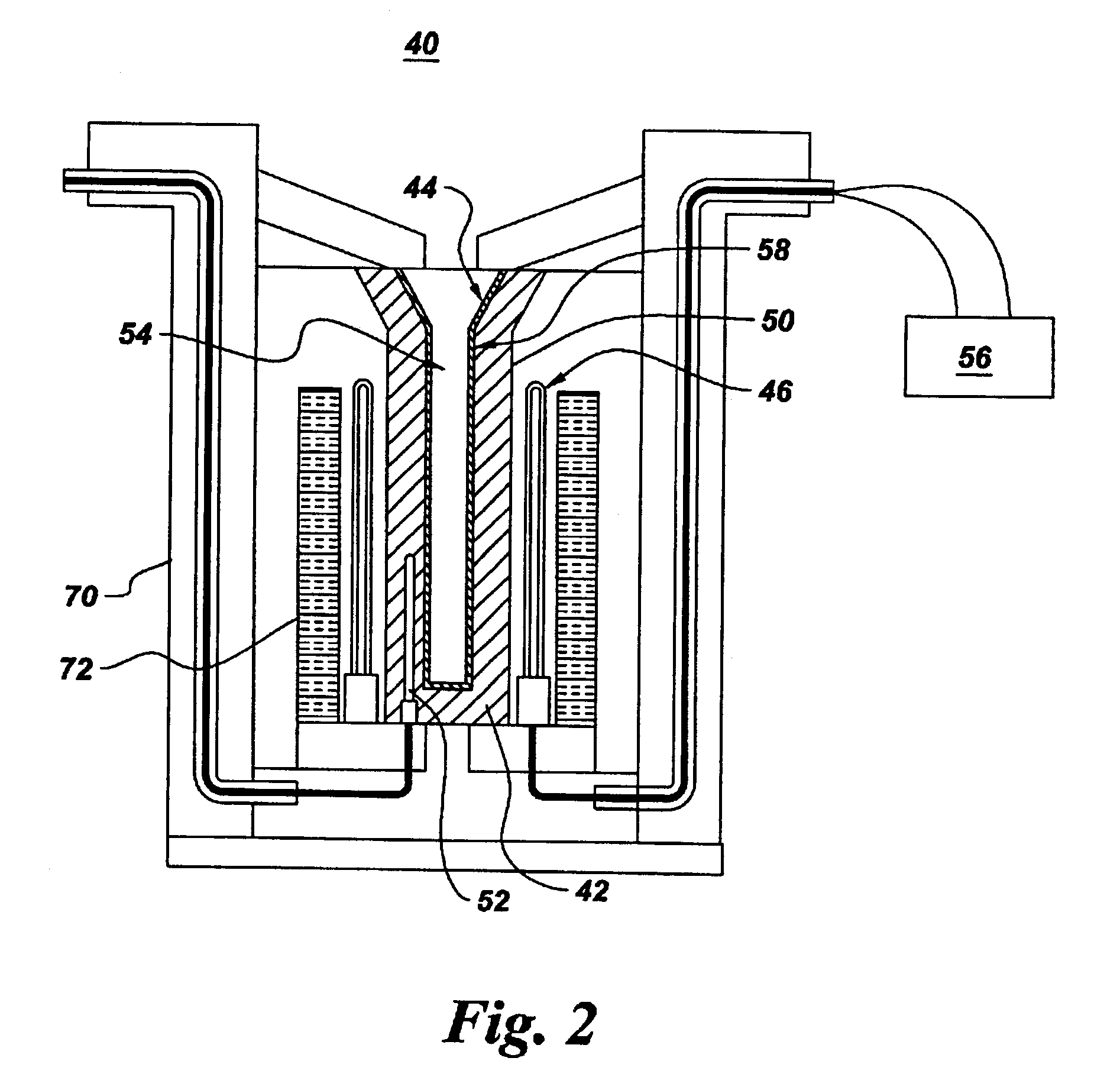
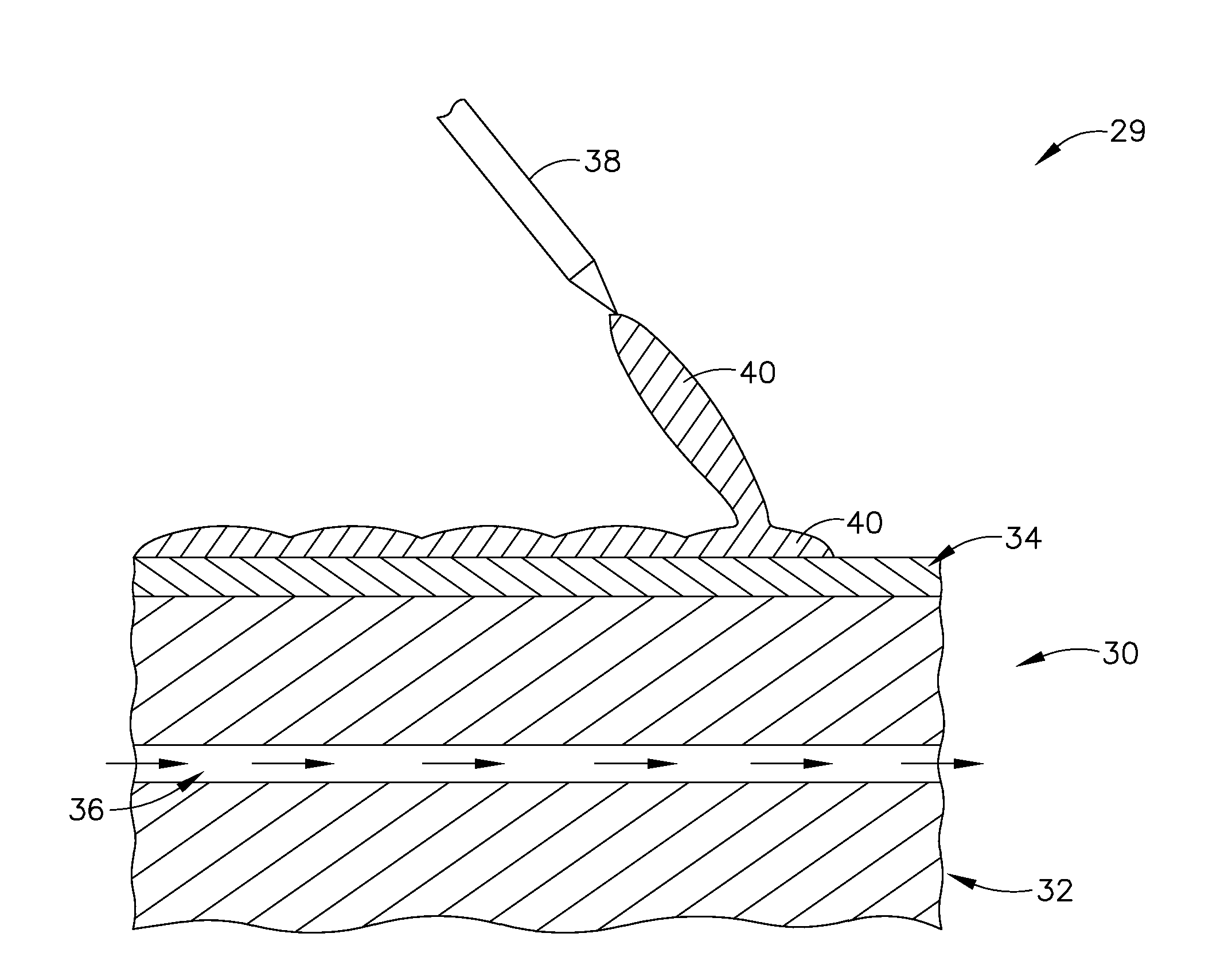
Method and apparatus for casting near-net shape articles
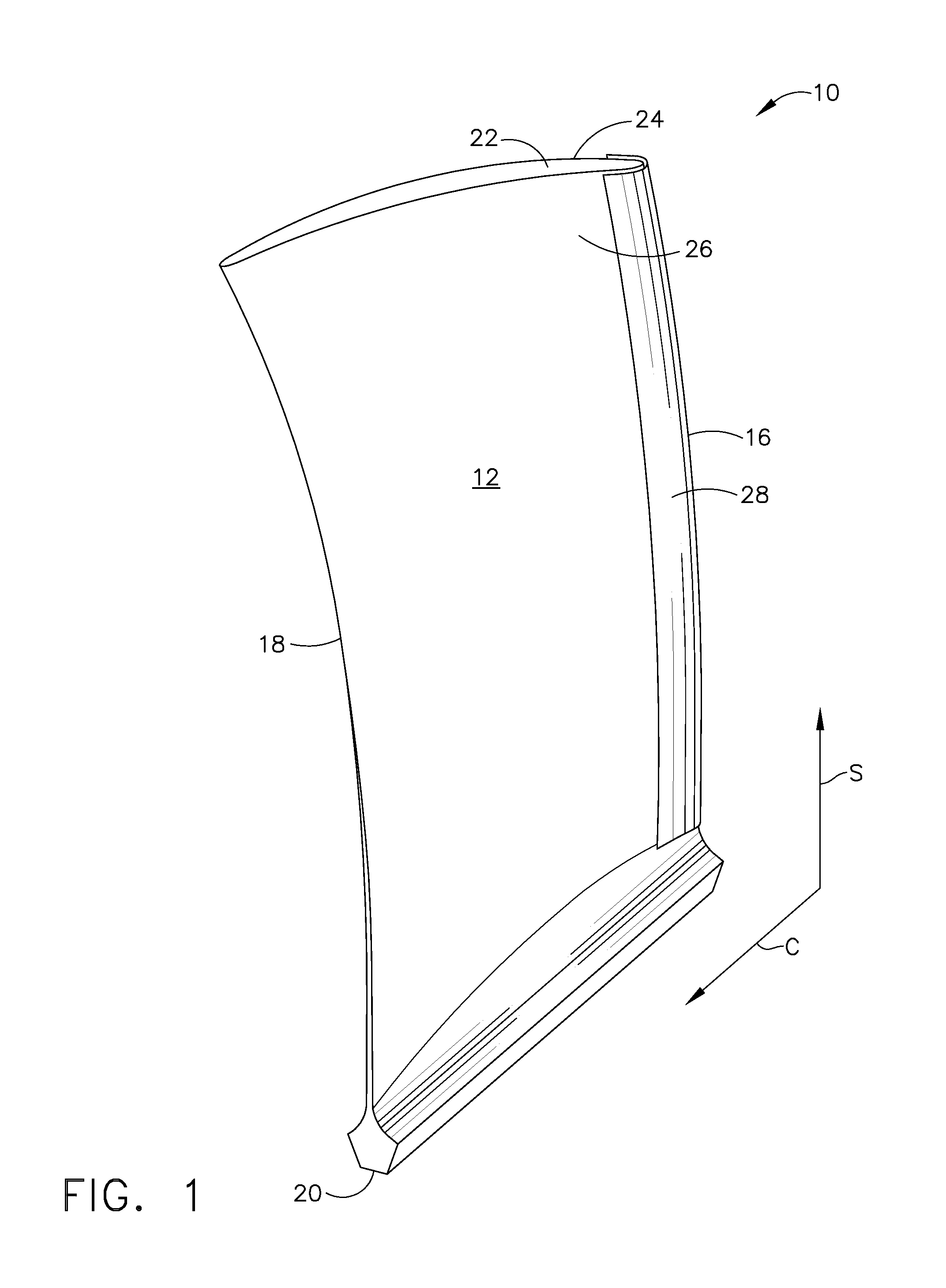
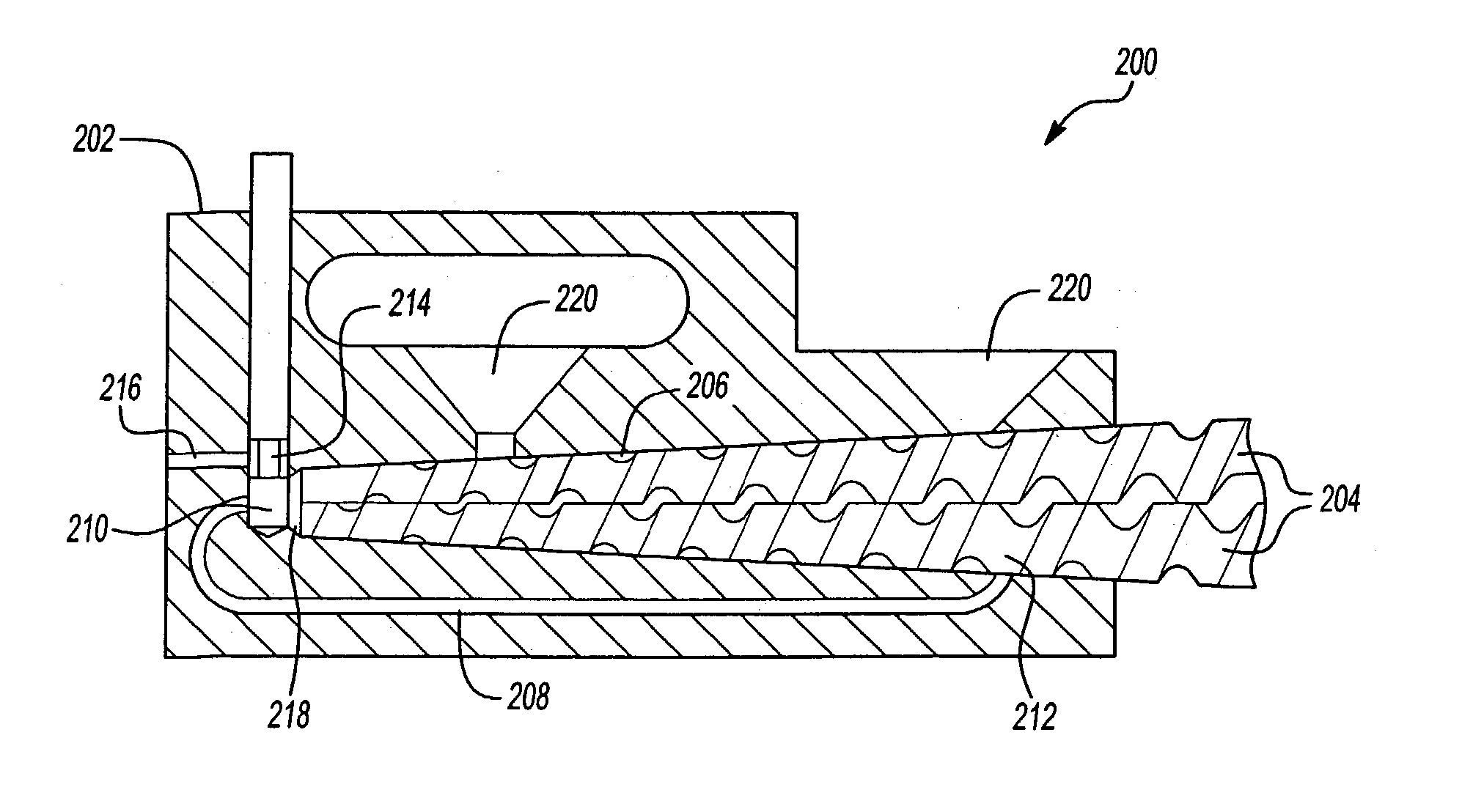
A method and apparatus for casting a near-net-shape article from a high temperature material, such as a refractory metal intermetallic composite material. The apparatus includes: a means for forming a molten material comprising at least one of a metal and an alloy; a means for pouring the molten material; a mold assembly comprising a solid shell having a face coat interposed between the solid shell and molten material; and a heater assembly for maintaining the solid shell at a temperature. The molten material solidifies within the solid shell to form a near-net shape of the article. The near-net shape article may be a turbine assembly component, such as, but not limited to, a vane or airfoil.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High temperature additive manufacturing systems for making near net shape airfoils leading edge protection, and tooling systems therewith
InactiveUS20100242843A1Reduce pollutionMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingLeading edgeNear net shape
Tooling systems including a mandrel for receiving, and providing shape to, a metallic deposit applied using a high temperature additive manufacturing device; a metallic cladding applied to the mandrel for reducing contamination of the metallic deposit; and at least one cooling channel associated with the mandrel for removing heat from the system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Refractory metal and alloy refining by laser forming and melting
ActiveUS20050142021A1Shorten cycle timeRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingNiobiumLinearity
Owner:MATERION NEWTON INC
Crack free metallic articles
InactiveUS6103402AReduce material stressReduce solidificationTurbinesBy zone-melting liquidsCrazingClosed loop
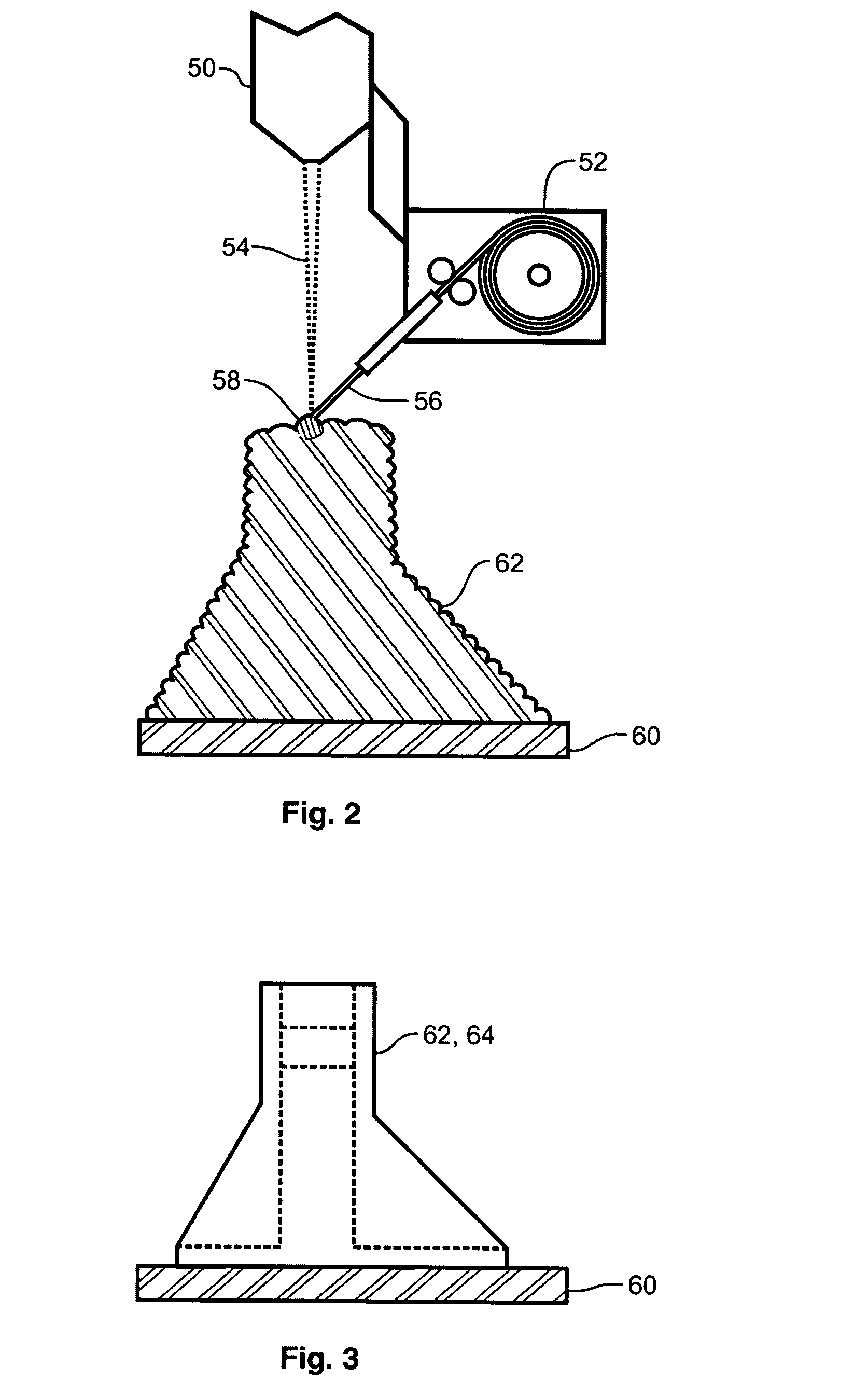
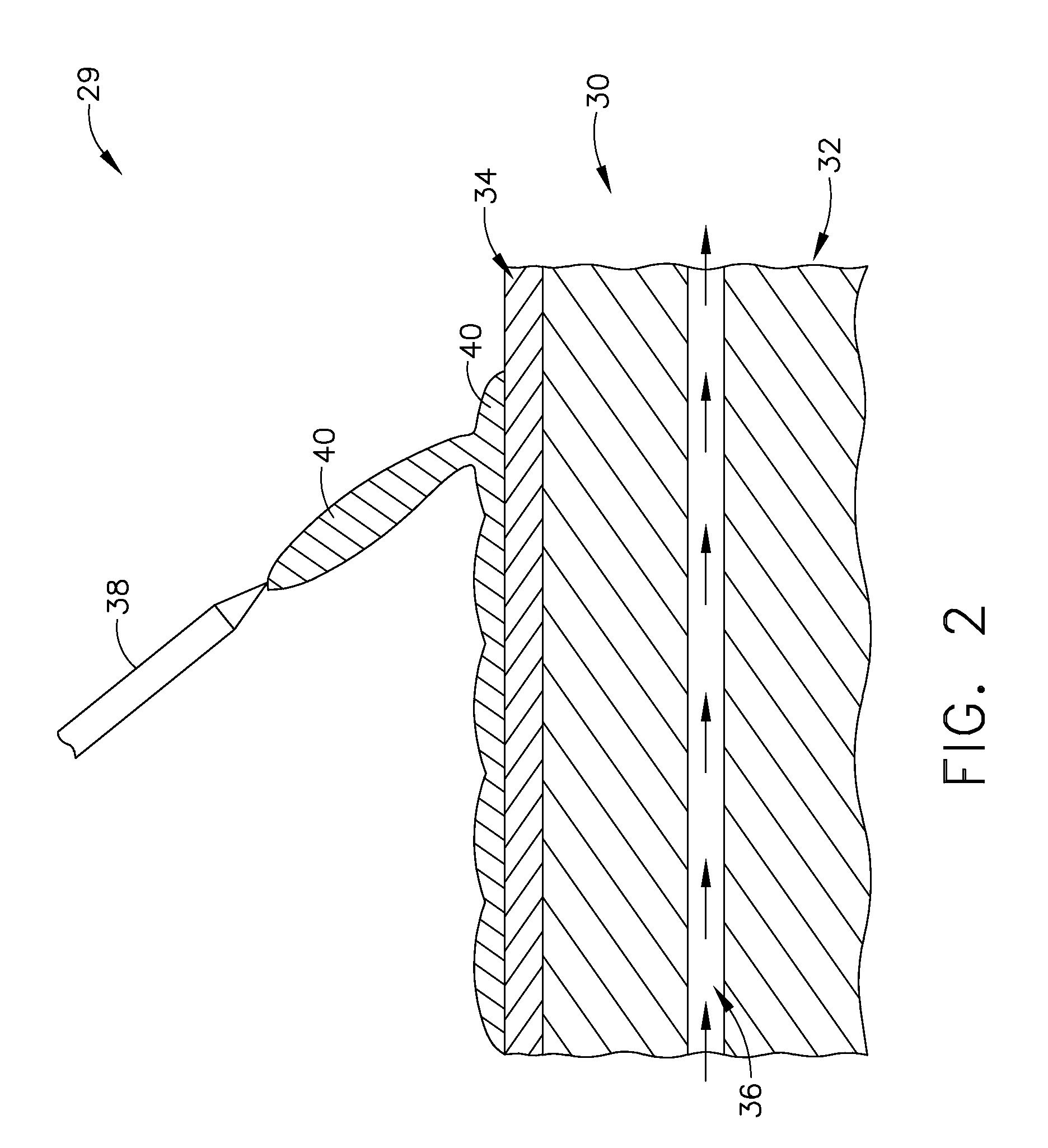
A containerless method of producing a crack free metallic article of near-net shape includes melting a filler material into a metallic substrate or seed under conditions chosen to preclude cracking. In a preferred embodiment of the invention, a laser beam is operated at a relatively low power density and at a relatively large beam diameter at the substrate surface for an extended length of time to produce a molten pool with a low aspect ratio. Near-net shape is achieved by applying the process in a closed-loop, multi-axis material deposition system.
Owner:UNITED TECH CORP
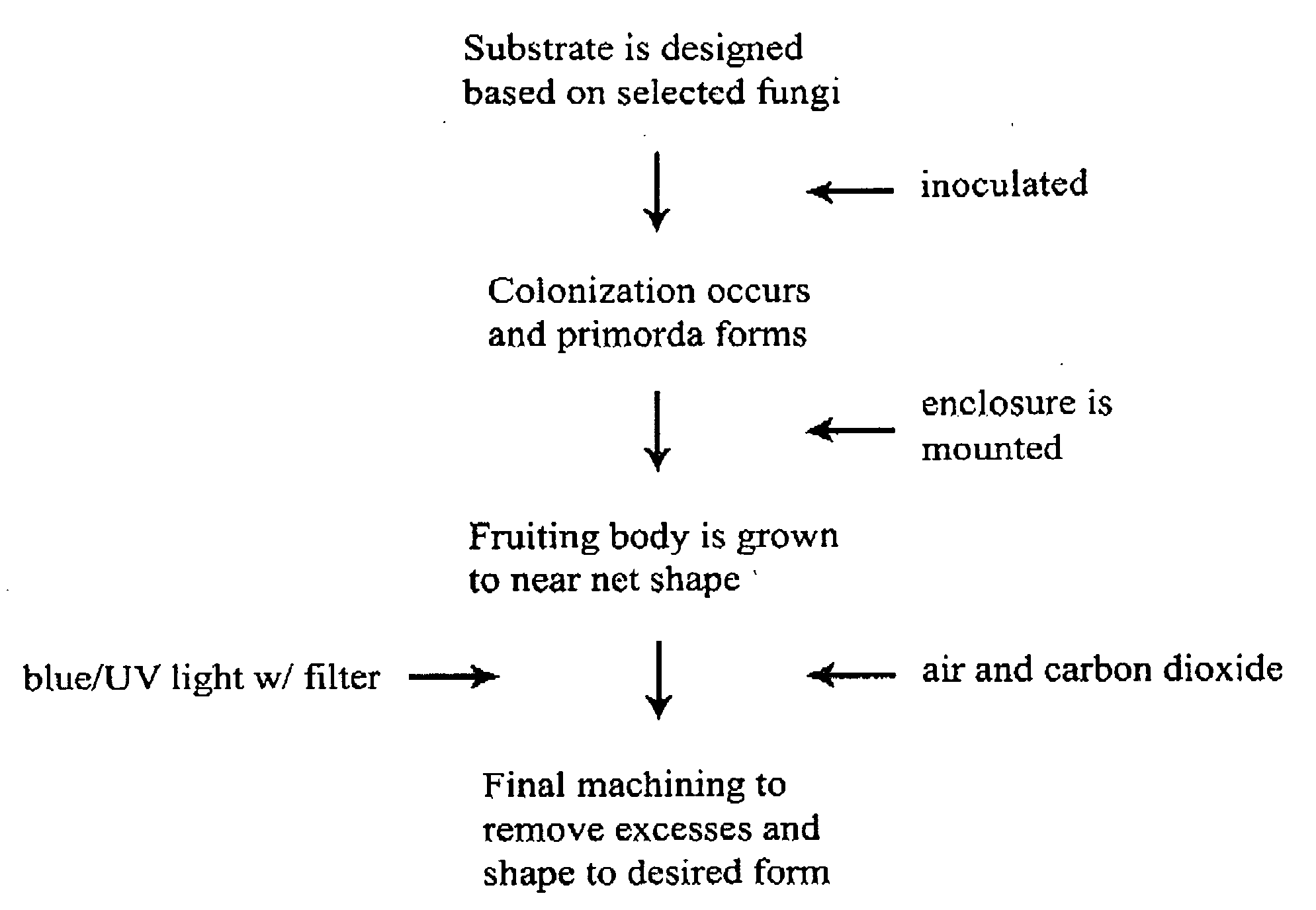
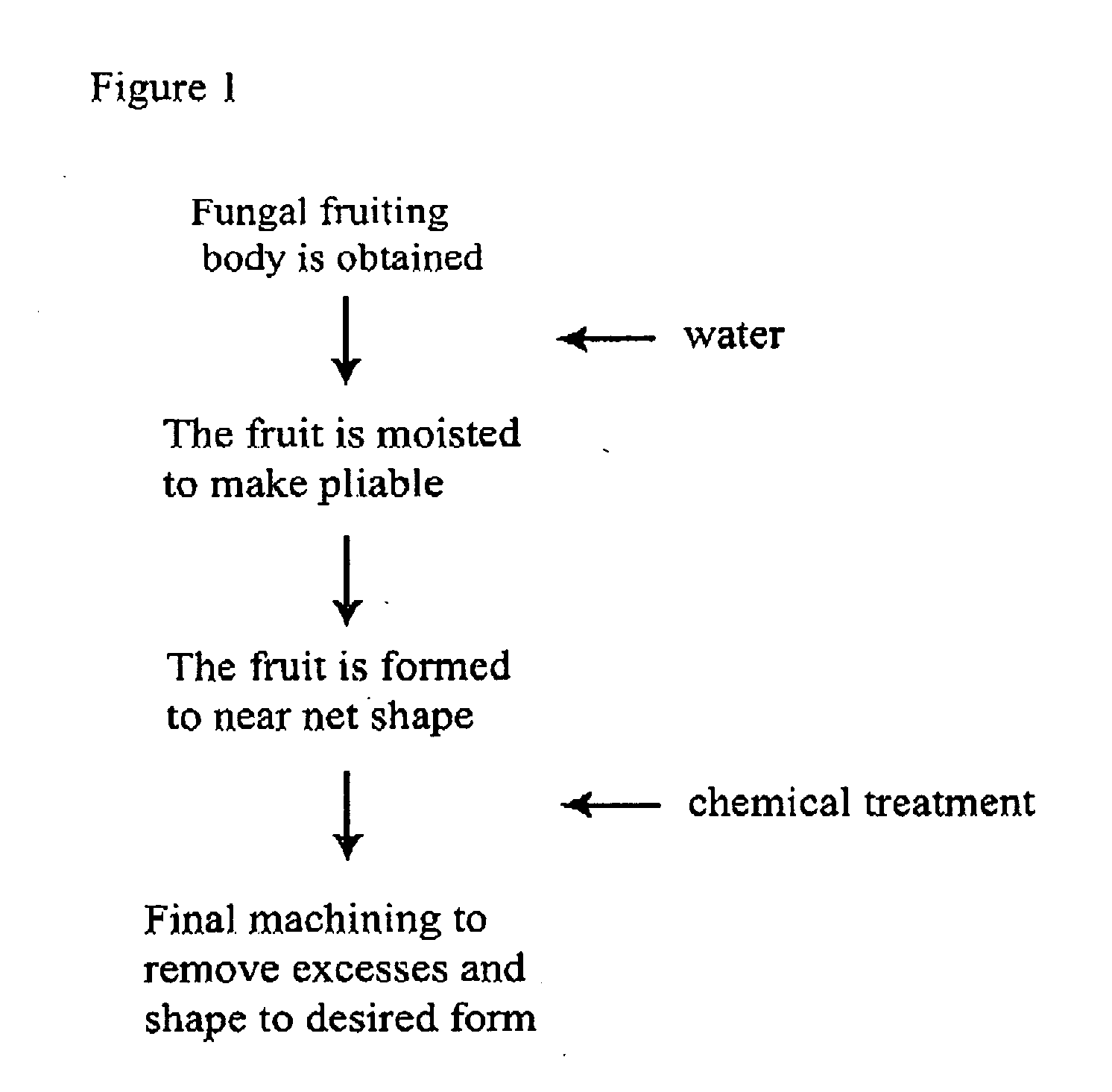
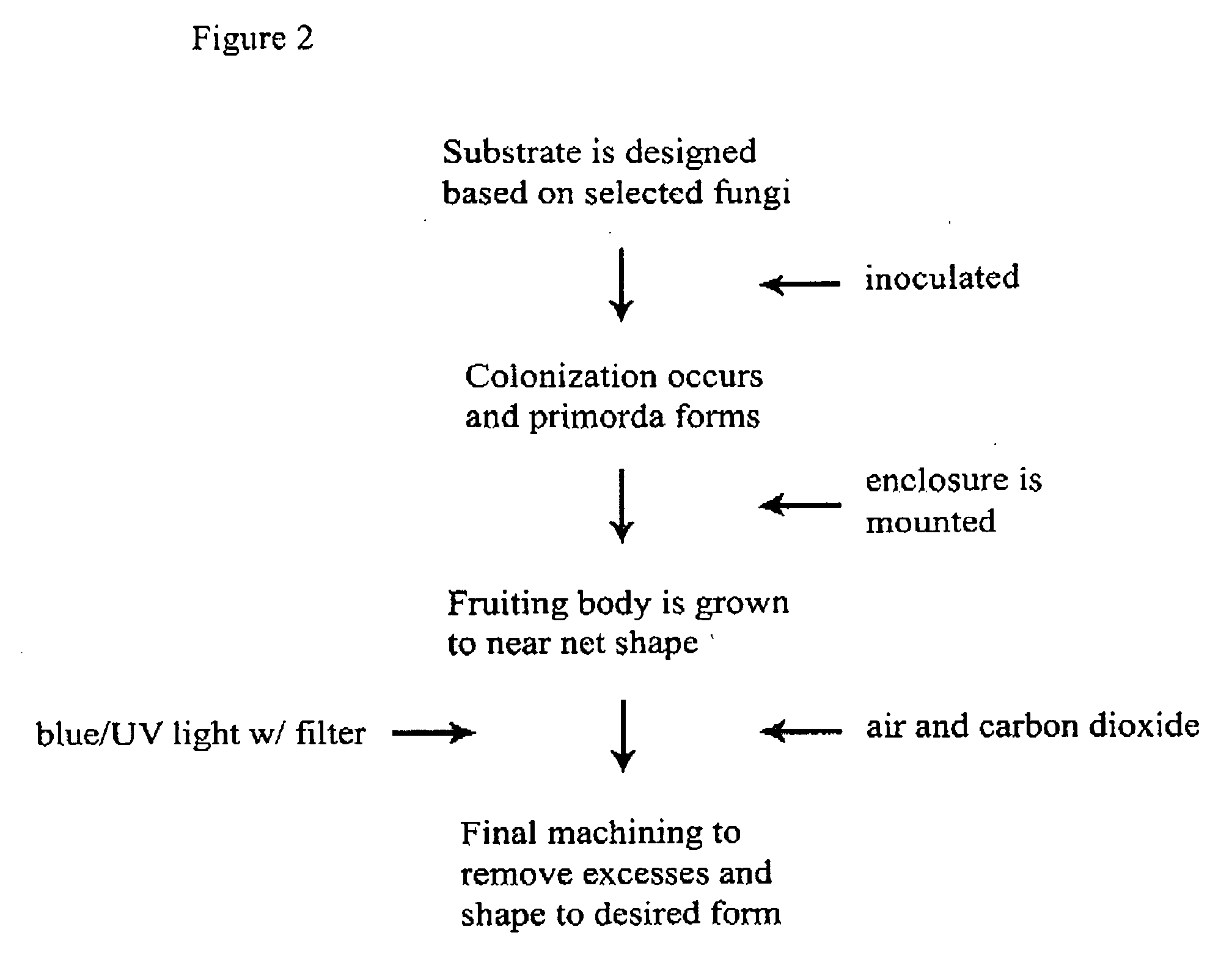
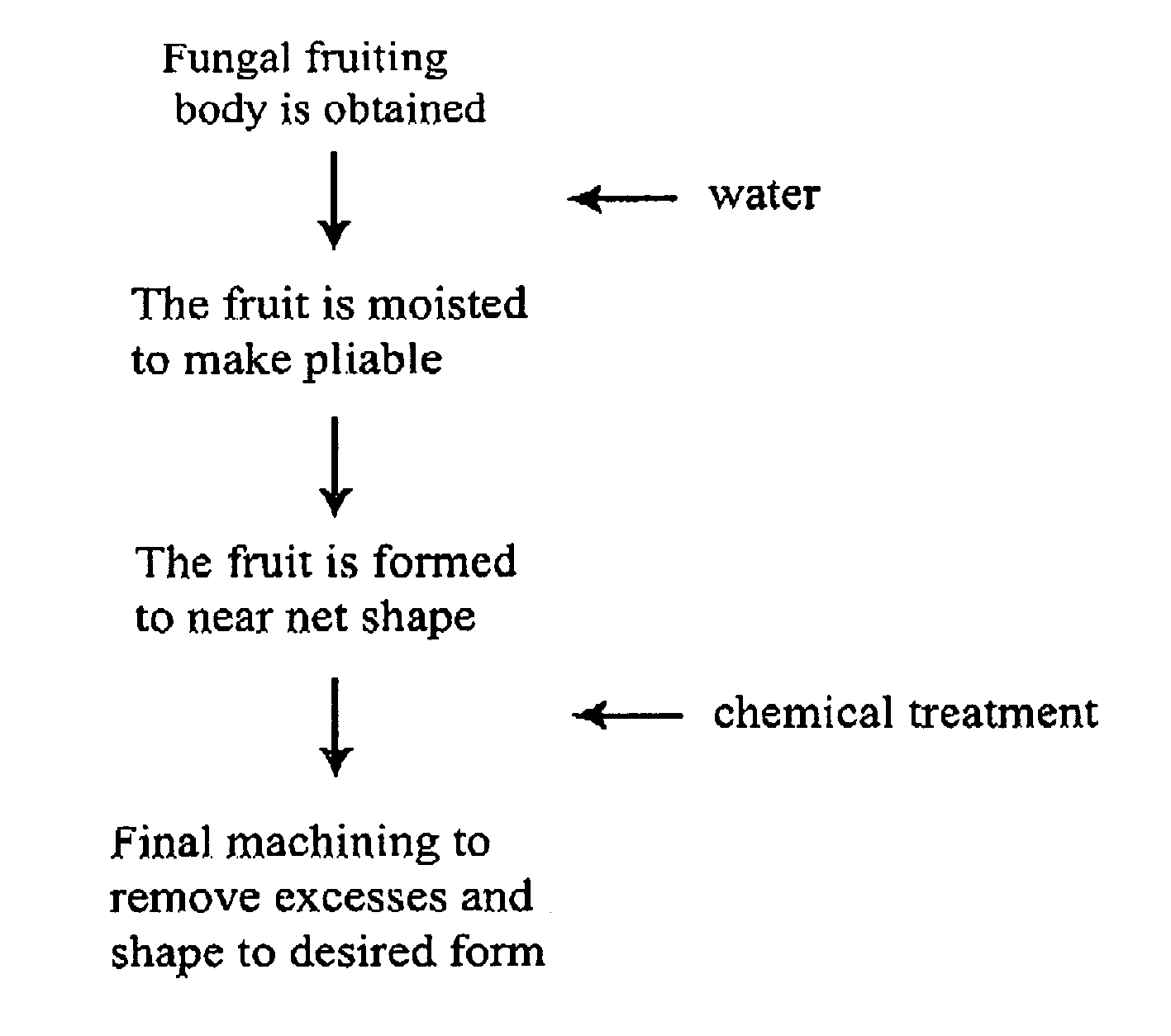
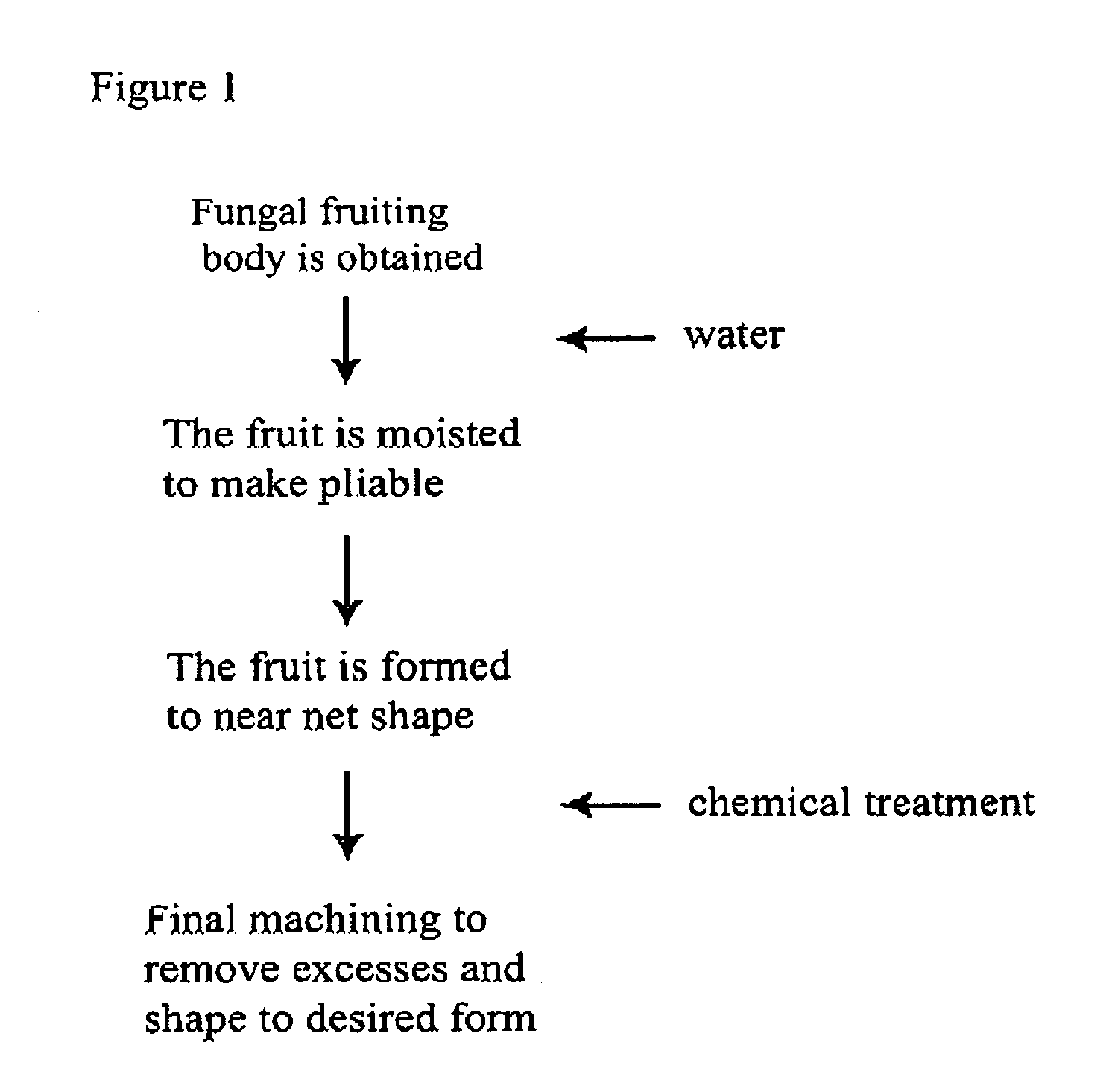
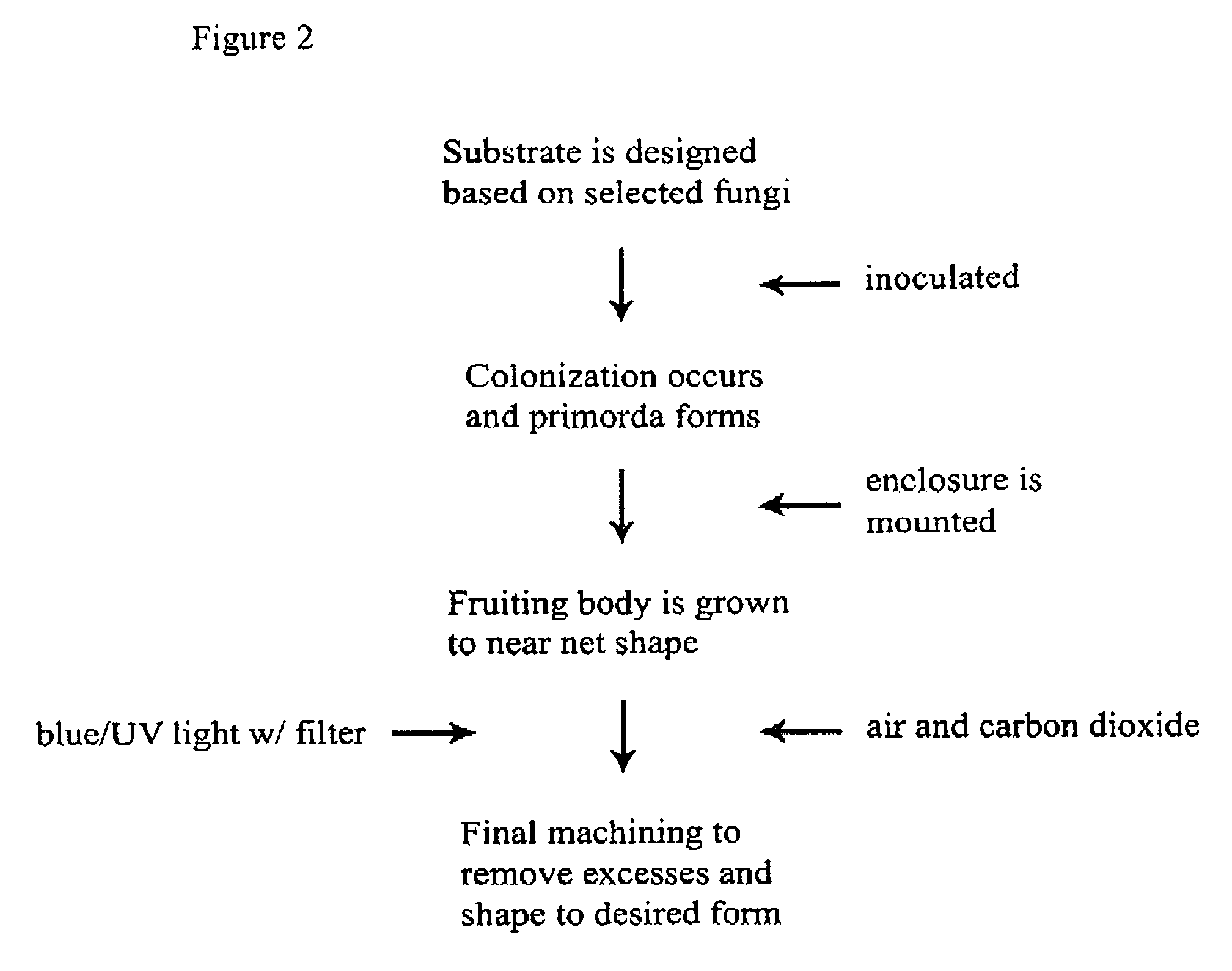
Method for producing rapidly renewable chitinous material using fungal fruiting bodies and product made thereby
ActiveUS20090307969A1Influence growth speedInfluence spore dispersionCultivating equipmentsMushroom cultivationBiotechnologyBiological body
The method of growing a fungal fruiting body requires exposing a mycelium of a desired organism type to environmental conditions sufficient to induce fruiting of fungal primordium in the organism type followed by enclosing the fungal primordium within a mold of a designated shape representing a near net shape volume of a desired final product. The fungal primordium is allowed to grow and fill the mold to form a mass of fungal tissue equivalent in shape to the designated shape of the mold after which the mass of fungal tissue is removed from the mold and dried.
Owner:ECOVATIVE DESIGN LLC
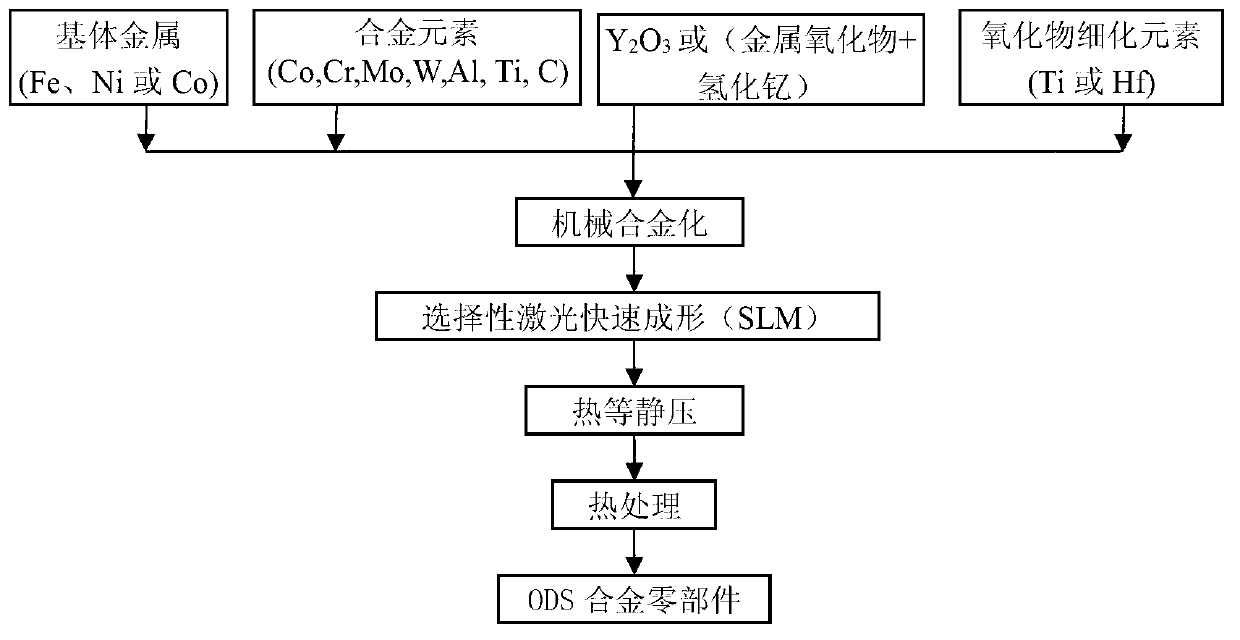
Method for preparing oxide dispersion strengthened alloy by rapid forming
InactiveCN103008657AHigh densitySmall particle sizeAdditive manufacturingIncreasing energy efficiencyOxide dispersion-strengthened alloySoftware design
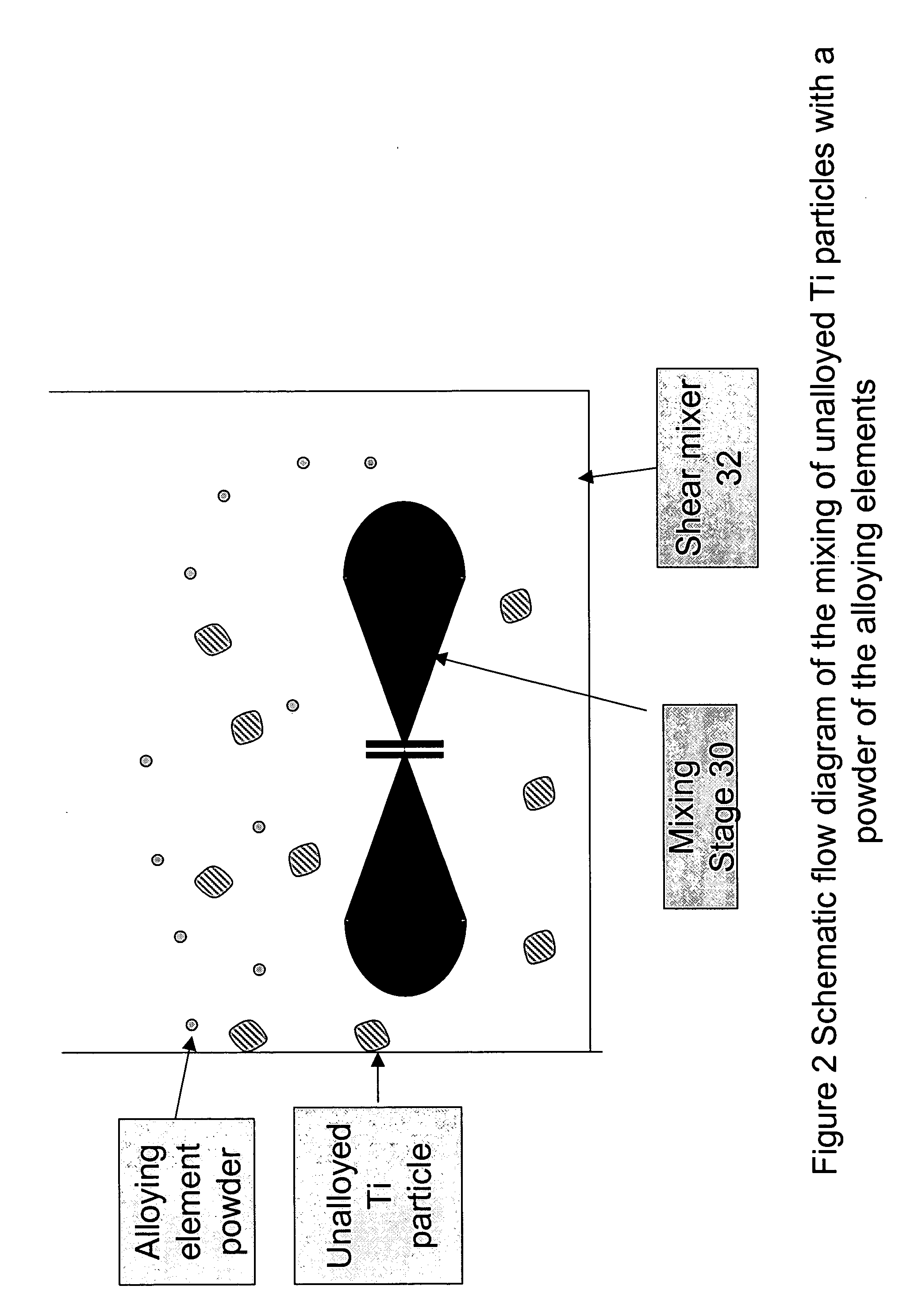
The invention belongs to the technical field of high-temperature alloy near net shape forming and discloses a method for preparing oxide dispersion strengthened alloy by rapid forming. The method includes: using the mechanical alloying process to obtain oxide dispersion strengthened alloy powder, using CAD (computer-aided design) software to design a three-dimensional solid model of an ODS (oxide dispersion strengthened) alloy part, subjecting the three-dimensional model to layering and slicing to disperse the three-dimensional model into a series of two-dimensional layers, smelting the ODS alloy powder layer by layer according to slicing information to obtain a laser rapidly formed blank in a needed shape, eliminating residue pores in the laser rapidly formed blank by means of hot isostatic pressing, and optimizing structure property by means of subsequent annealing or solid solution and aging heat treatment to obtain an ODS alloy part in a complex shape. Wrap packaging or fixture moulds are not needed, the complexity of shapes of parts is unlimited, and alloy components and structures are easy to control. The prepared ODS alloy is small in oxide dispersed phase, and products are high in compactness and excellent in comprehensive mechanical property.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
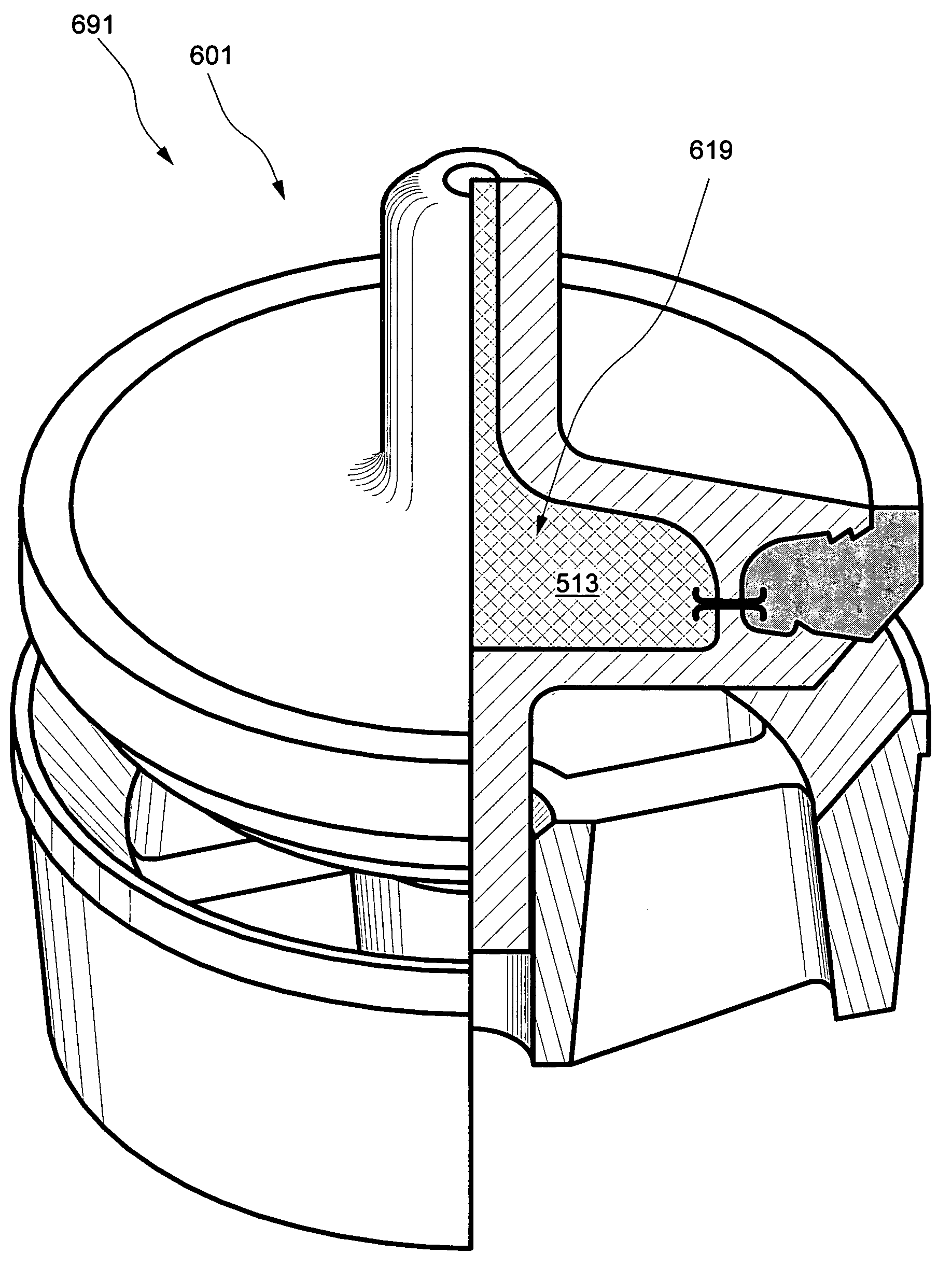
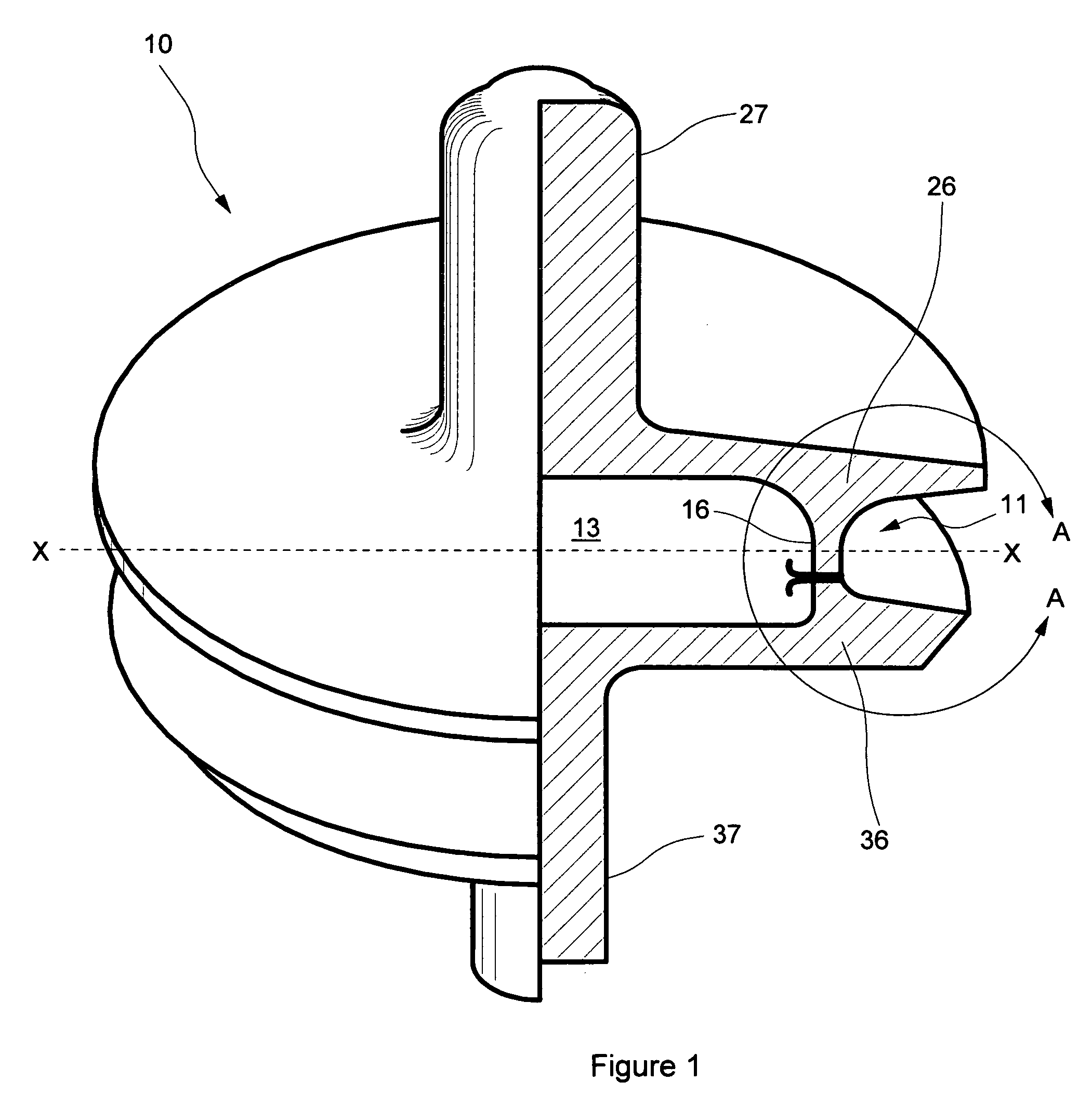
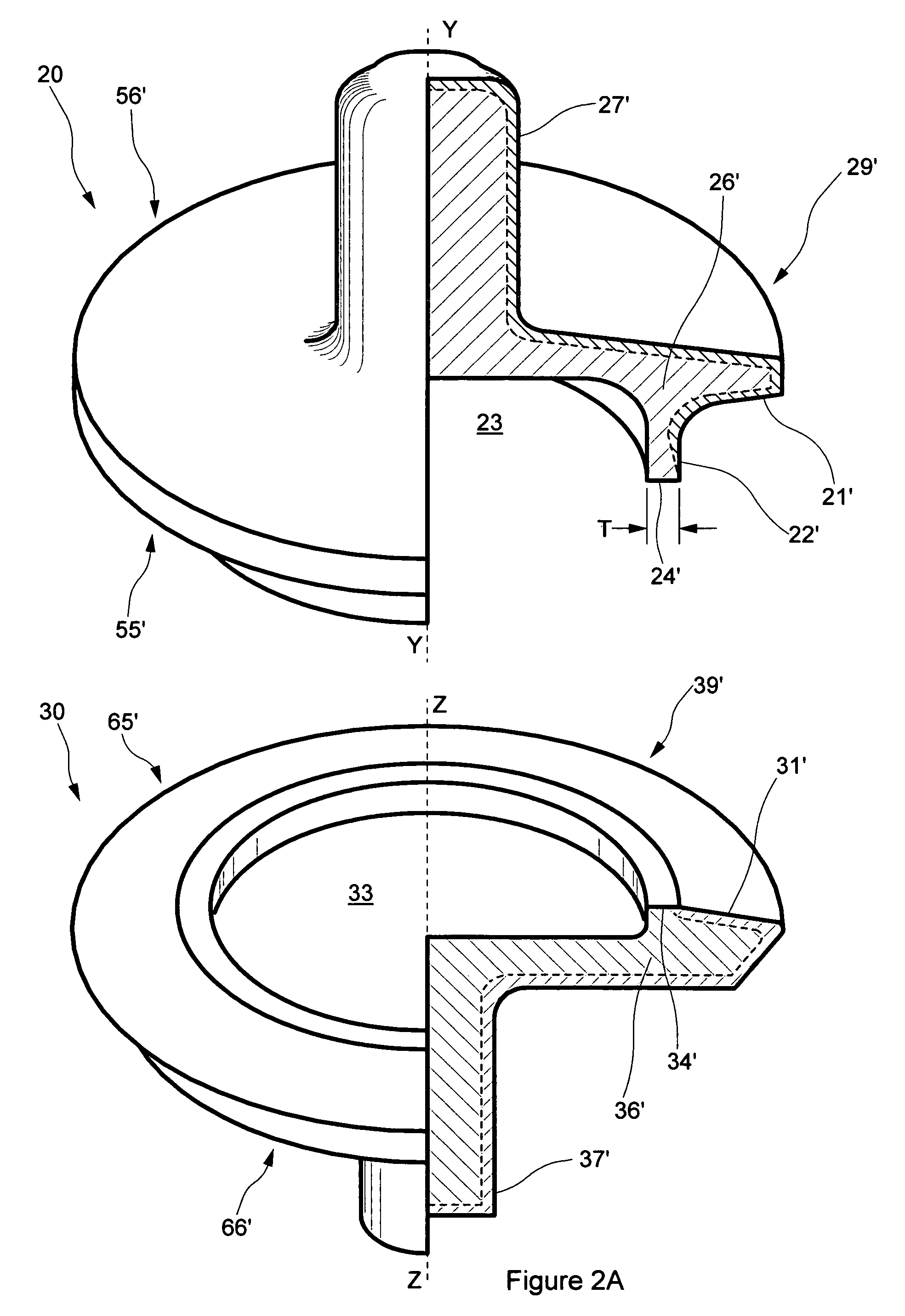
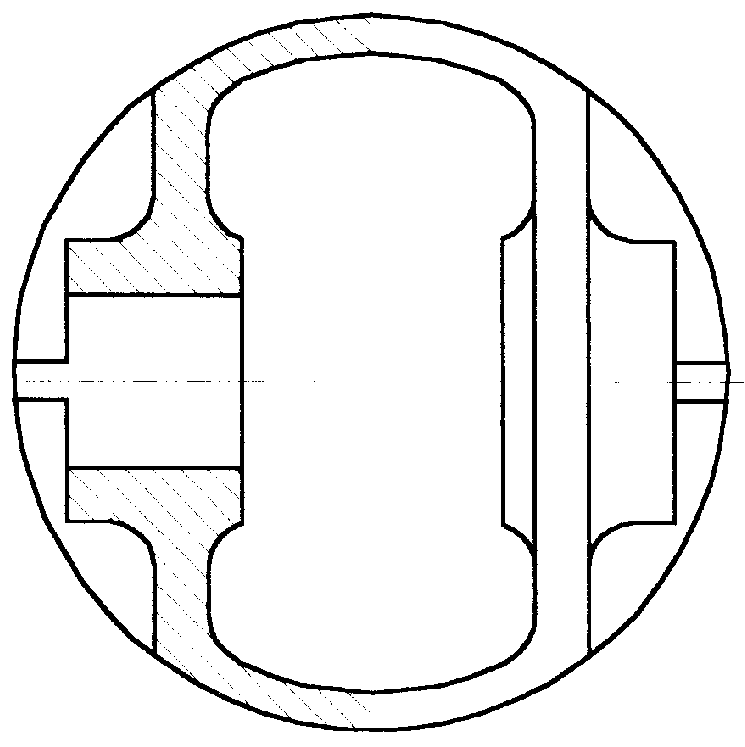
Valve body with integral seal retention groove
InactiveUS7222837B1Easy to makeLittle finish machiningCheck valvesEqualizing valvesInterior spaceEngineering
A valve body having at least one internal hollow or space comprises two separately formed portions joined by at least one cylindrical web. Internal space may communicate with space outside the valve body via a fluid passage, and internal space may be filled with a substantially incompressible flowable substance to facilitate pressure equalization across the valve body. Forging or casting valve body portions to near-net-shape prior to joining minimizes machining necessary to achieve a final desired shape. Increased valve durability and reduced metal wear arise from the reduced valve body weight and correspondingly reduced impact loading as the valve body moves to seal against a valve seat. A single-durometer or dual-durometer elastomeric seal may be cast and cured in place in a peripheral integral seal retention groove, coupled thereto in part through welding flash protruding into the groove and / or through at least one serration in the groove.
Owner:NOVATECH HLDG CORP
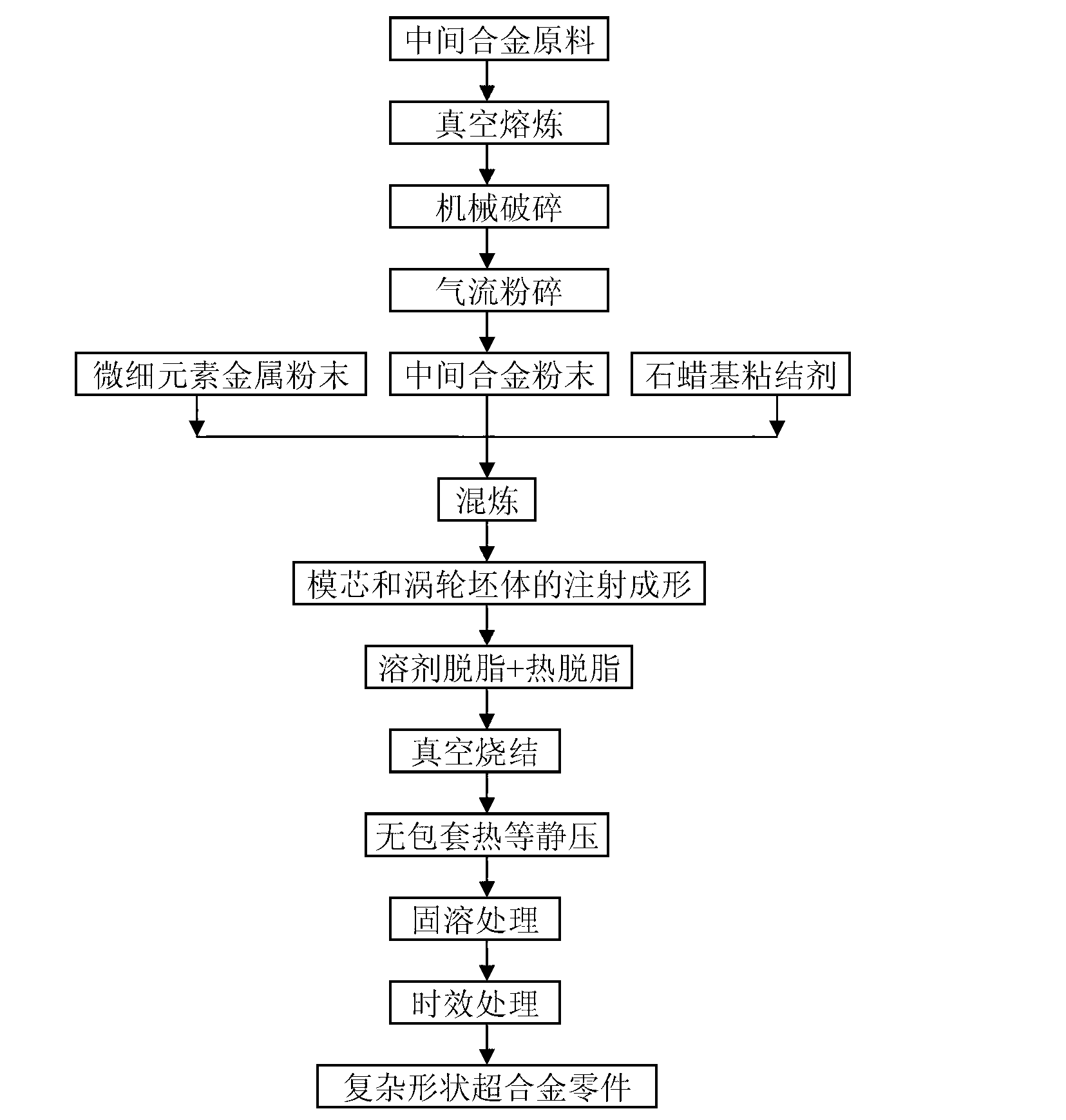
Method for preparing powder super-alloy by near net shape
Disclosed is a method for preparing powder super-alloy by a near net shape. Firstly, high-purity intermediate alloy powder is prepared by the aid of vacuum melting and air jet pulverization technology. Secondly, the intermediate alloy powder and fine particle diameter metal powder (such as carbonyl nickel powder, carbonyl iron powder, reduction tungsten powder and reduction molybdenum powder) are mixed in a high-energy ball mill with protective atmosphere to obtain mixed powder. The mixed powder and paraffin base binders are uniformly premixed, feedstock with a uniform rheological performance is obtained by mixing and is formed on an injection forming machine to obtain a blank in a complicated shape. The binders are removed from the blank in the complicated shape by the aid of solvent degreasing and hot degreasing technologies, the degreased blank is sintered in the vacuum atmosphere, the sintered blank is further compacted by the aid of unjacketed hot isostatic pressure, and finally, a super-alloy part in the complicated shape is obtained by the aid of solid solution and aging treatment. Raw material powder cost and technological energy consumption are remarkably reduced, and prepared super-alloy is almost fully compact, uniform in structure and excellent in comprehensive mechanical property.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
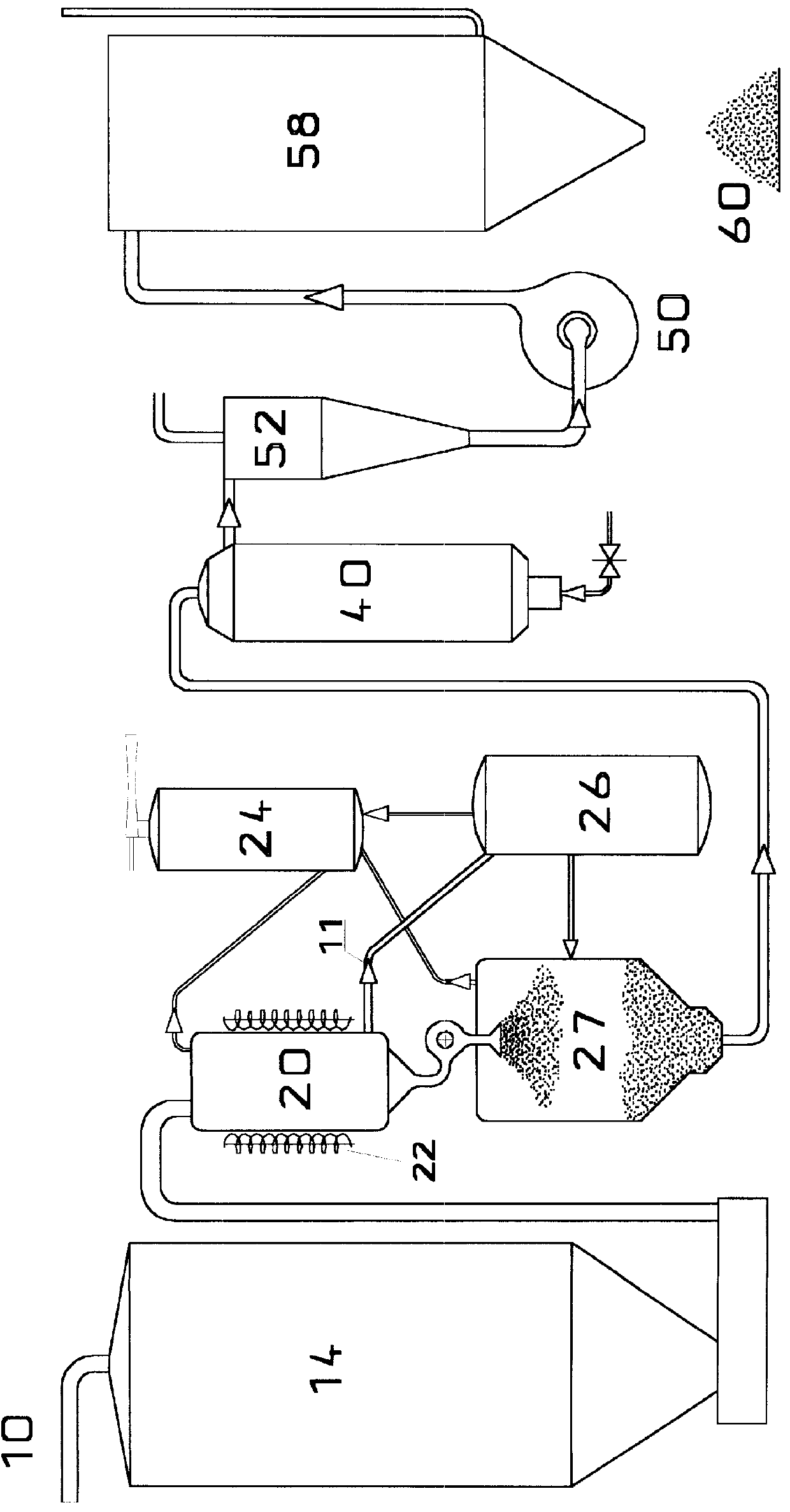
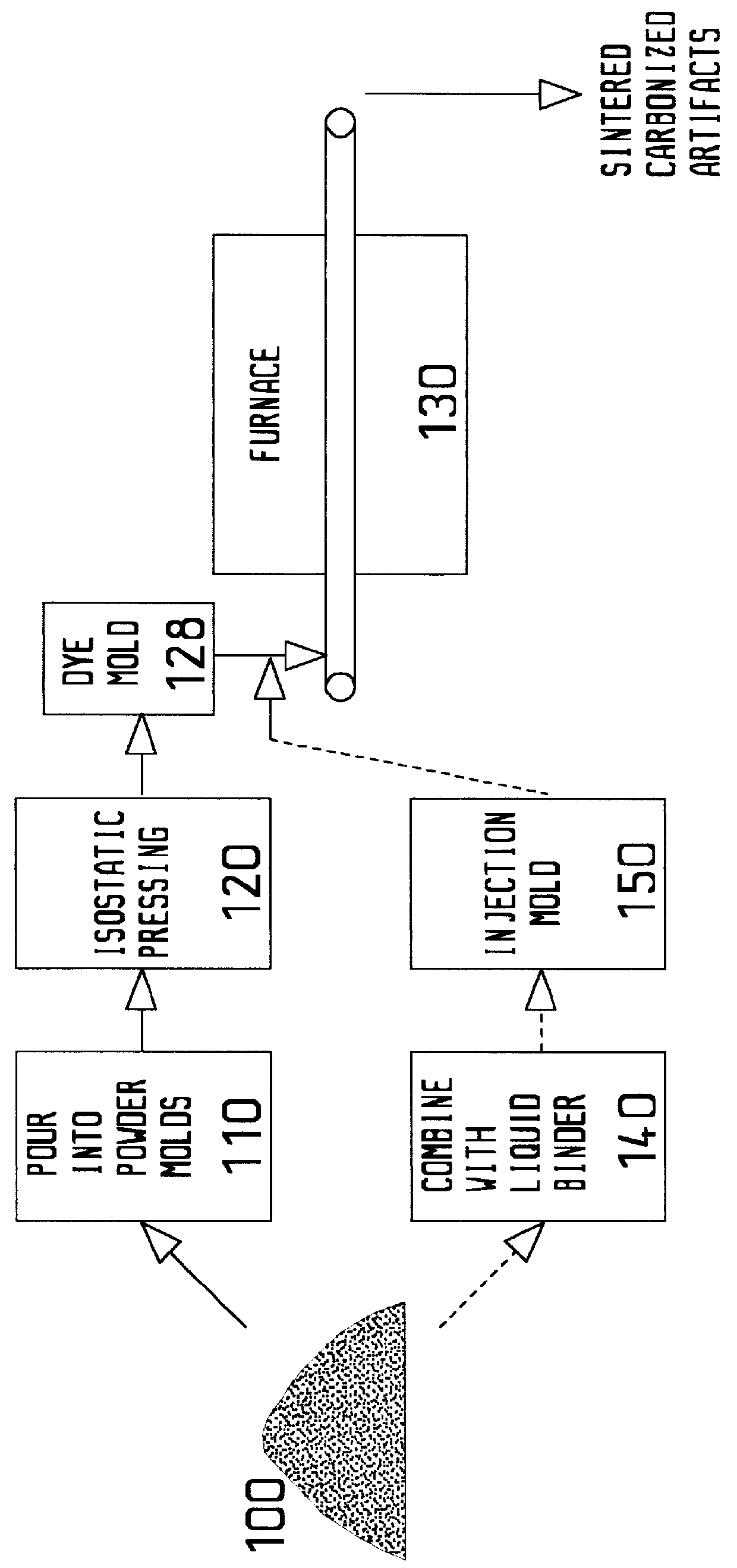
Carbon artifacts and compositions and processes for their manufacture
InactiveUS6013371ASaving evaporation requirementSimple processCasingsLayered productsFiberCarbon composites
Producing of near net shape carbon (optionally carbon-carbon composite) pistons and other artifacts by sintering (with or without carbon fibers, preferably pitch-based carbon fibers and most preferably blends of vapor grown carbon fibers(VGCF)) homogeneous powders derived from petroleum pitch. The powders preferably exhibit properties equal to or exceeding those of POCO AXF-5Q. Preferred specific technical steps are substantially as follows: 1. Individually prepare, by evaporation, heat treating and / or oxidizing of carbon-containing pitches, followed by oxidizing, comminuting and / or spray drying, to produce sinterable pitch powders (and optionally create uniform dryblends of pitch powder with various fractions of vapor-grown or other carbon fiber.) 2. Produce near net shape carbon-carbon artifacts, such as cup shapes which are convertible to internal-combustion (i-c) pistons with minimal machining, by pressing or injecting into molds, then sintering and carbonizing. Both uniaxially (e.g. injection molded) and isostatically compacted powder blends, can be employed. Related apparatus, compositions and artifacts are also taught.
Owner:MOTORCARBON
Petroleum pitch-based carbon foam
InactiveUS6833012B2Useful and reliableImprove efficiencyPigmenting treatmentHarvestersLow densityNet shape
Petroleum or coal tar pitch-based cellular or porous products having a density of preferably between about 0.1 g / cm<3 >and about 0.8 g / cm<3 >are produced by the controlled heating of mesophase carbon materials derived from coal tar or petroleum pitch having a softening point in excess of about 300° C. and preferably between about 300 and about 400° C. in a "mold" and under a non-oxidizing atmosphere. The porous product thereby produced, preferably as a net shape or near net shape, can be machined, adhered and otherwise fabricated to produce a wide variety of low cost, low density products.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE RES LAB
Solid Free-Form Fabrication Methods For The Production of Dental Restorations
Solid free form fabrication techniques can be utilized indirectly to manufacture substrates, dies, models, near-net shapes, shells, and wax-ups that are then used in the manufacture of dental articles. Digital light processing is the most preferred indirect method for the production of substrates. After the substrates are produced, various coating or deposition techniques such as gel casting, slip casting, slurry casting, pressure infiltration, dipping, colloidal spray deposition or electrophoretic deposition are used to manufacture the dental article.
Owner:IVOCLAR VIVADENT AG
Composite airfoils having leading edge protection made using high temperature additive manufacturing methods
Composite airfoils including a leading edge, and a near net shape metal leading edge protective strip operably connected to the leading edge, the protective strip made by providing a high temperature additive manufacturing device; providing a tooling system including a mandrel; a metallic cladding; and at least one cooling channel applying a metallic deposit to the mandrel having the metallic cladding using the high temperature additive manufacturing device; and concurrently removing heat from the mandrel using the at least one cooling channel.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
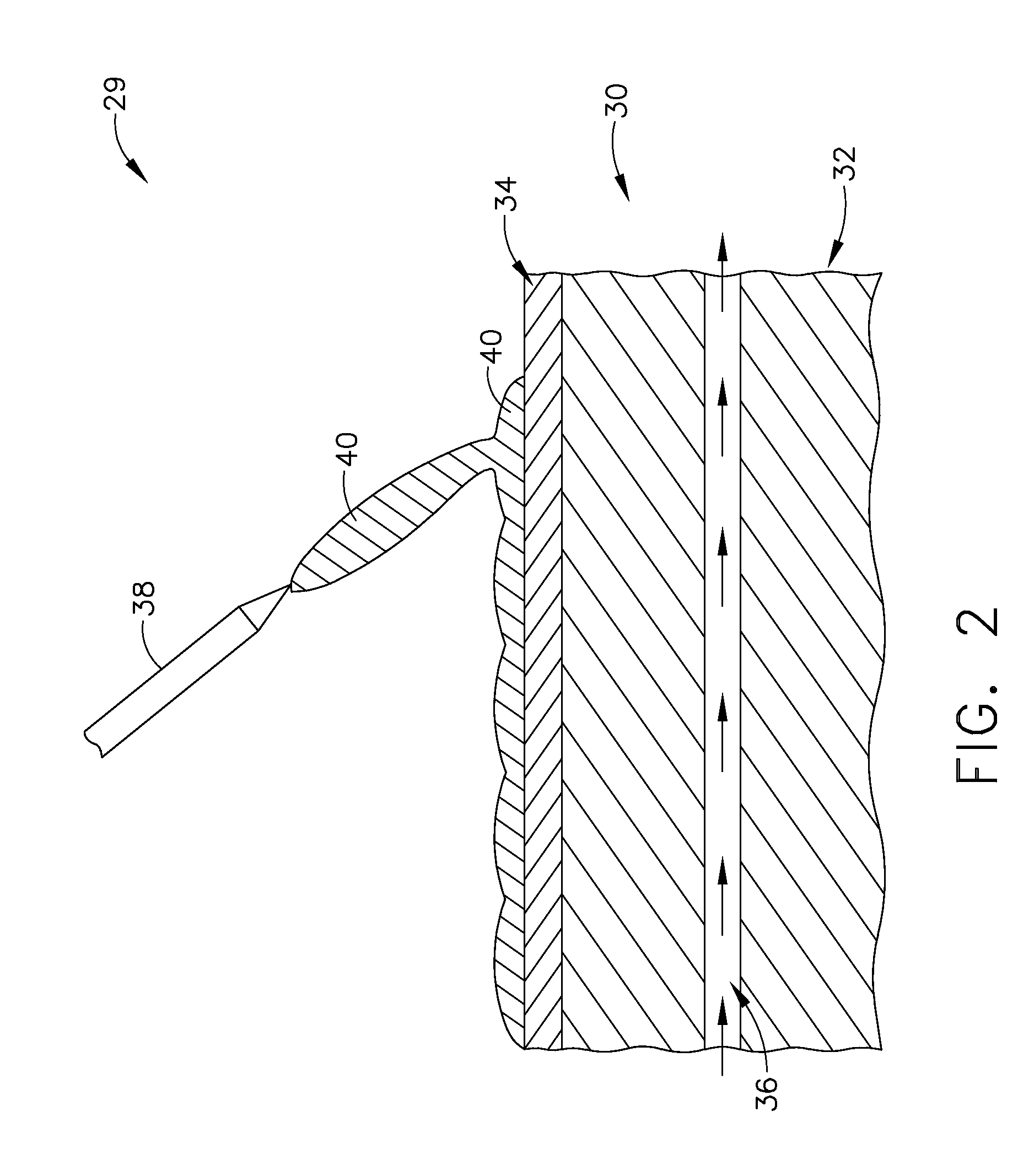
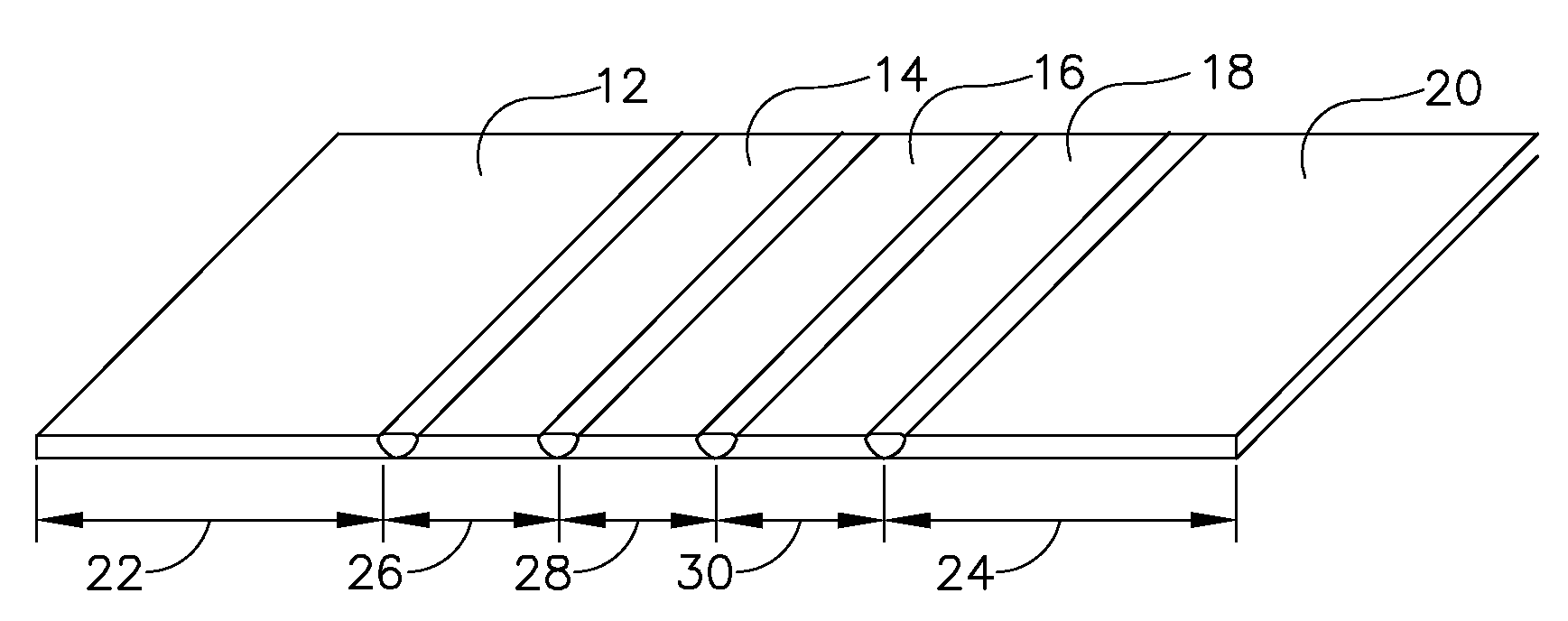
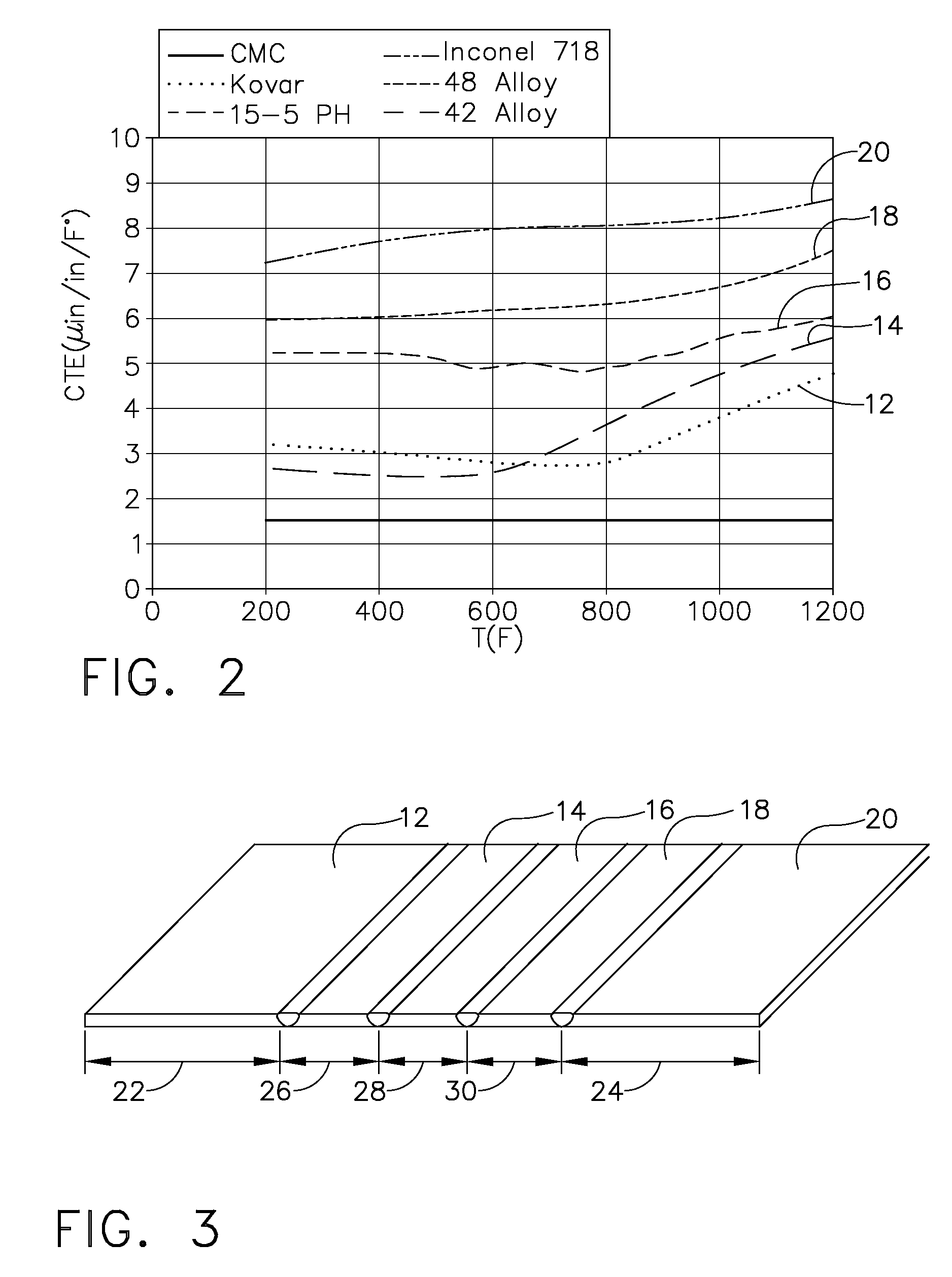
Joined composite structures with a graded coefficient of thermal expansion for extreme environment applications
An integrated composite structure with a graded coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is formed by selecting a plurality of layers of materials with a graded CTE and using joining approaches such as welding, brazing, or solid state bonding to produce a CTE-graded layered composite or near net shape. The integrated composite billet or near net shape is then processed to produce a first surface for attachment of a first structural member having a first CTE and to produce a second surface of for attachment of a second structural member having a second CTE.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
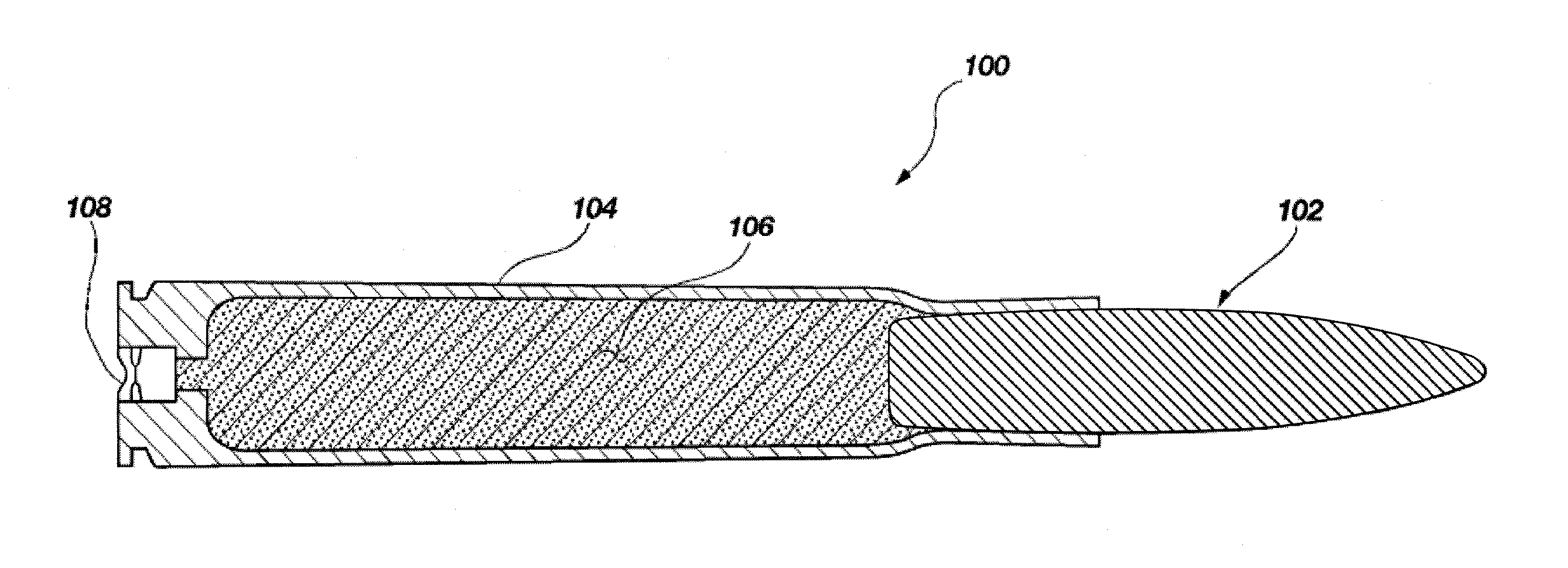
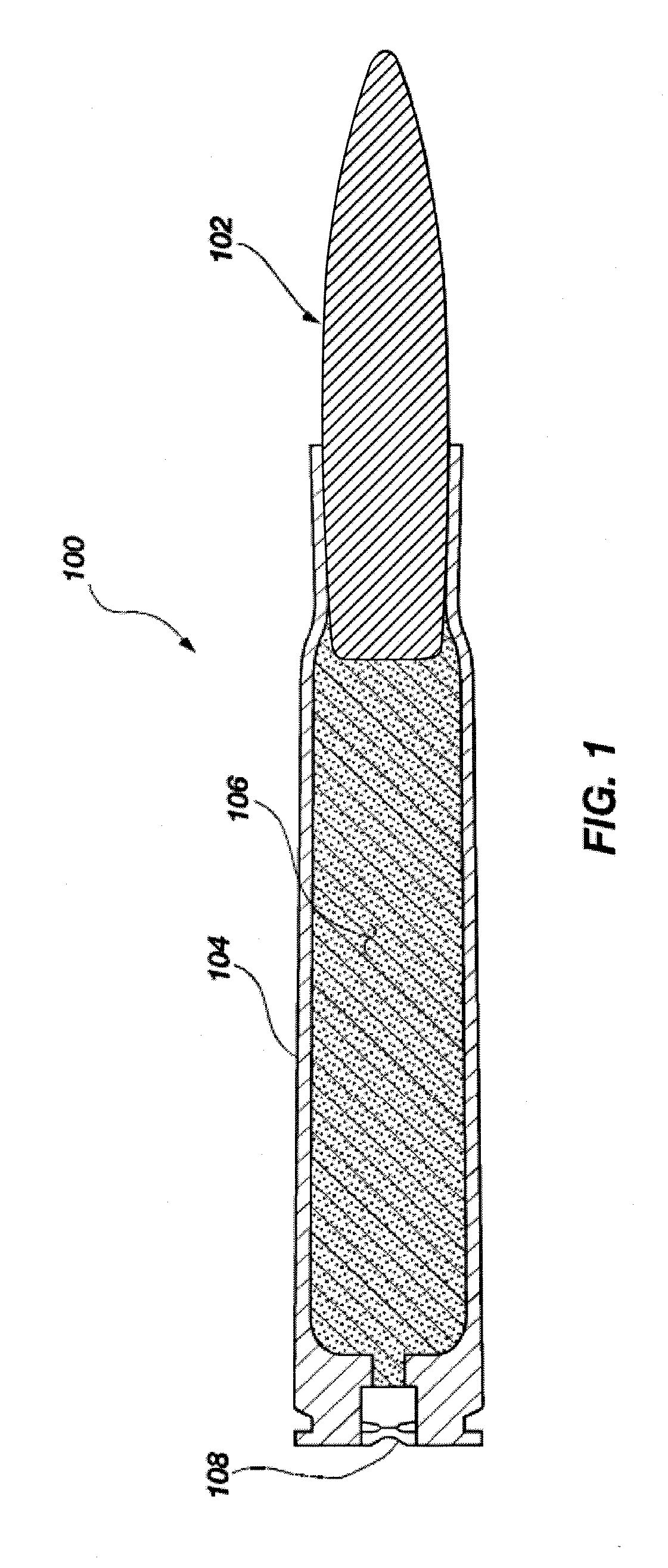
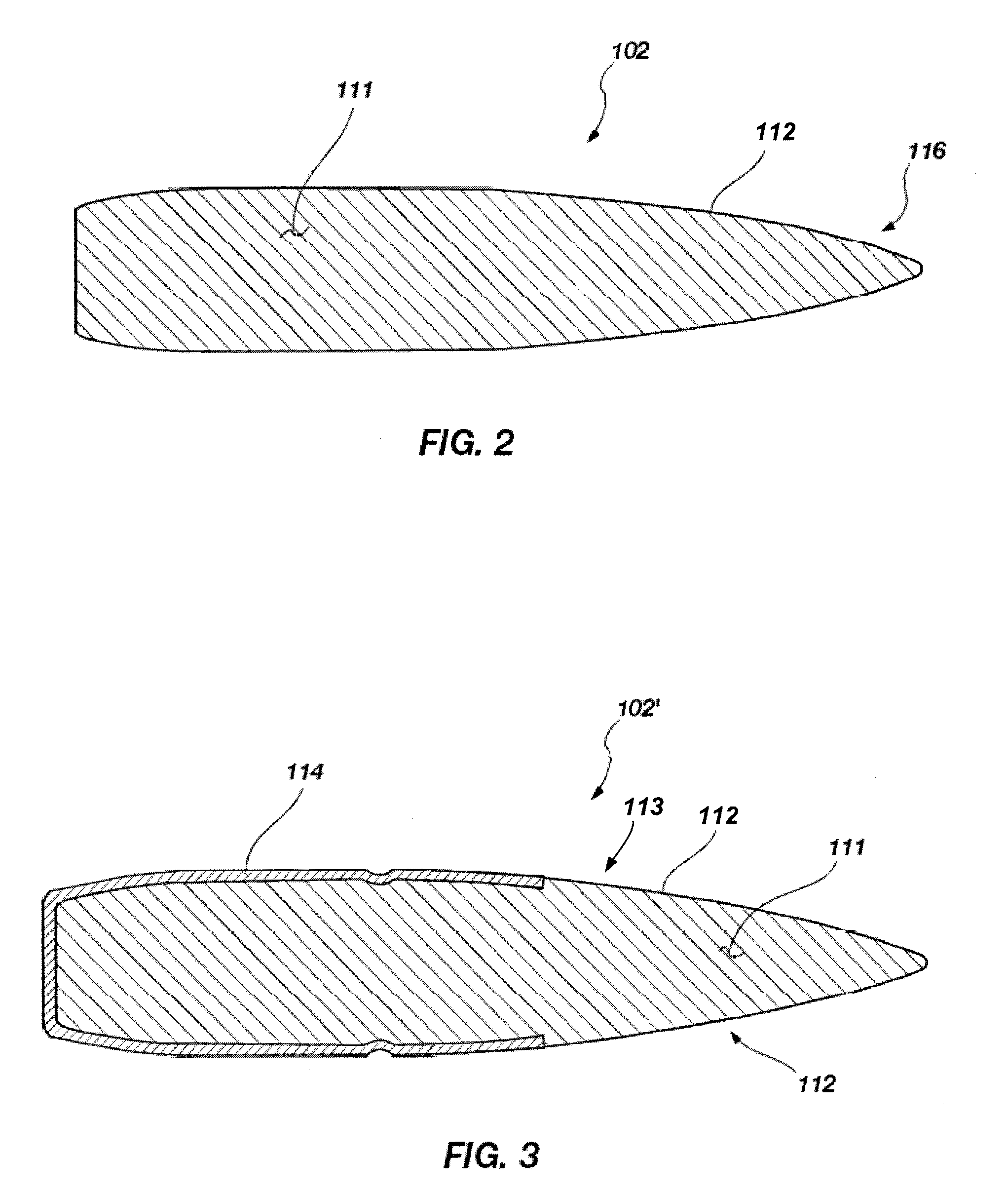
Reactive material enhanced projectiles and related methods
ActiveUS20080035007A1Simple and robustDesign economyAmmunition projectilesCartridge ammunitionEngineeringReactive material
A munition, such as a projectile formed of at least one reactive material, is provided. In one embodiment, the projectile includes a body portion formed of at least one reactive material composition wherein the at least one reactive material composition defines at least a portion of an exterior surface of the projectile. In other words, a portion of the reactive material may be left “unbuffered” or exposed to the barrel of a gun or weapon from which it is launched and similarly exposed to a target with which the projectile subsequently impacts. In one embodiment, the projectile may be formed with a jacket surrounding a portion of the reactive material to provide additional structural integrity. The projectile may be formed by casting or pressing the reactive material into a desired shape. In another embodiment of the invention, the reactive material may be extruded into a near-net shape and then machined into the desired shape.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
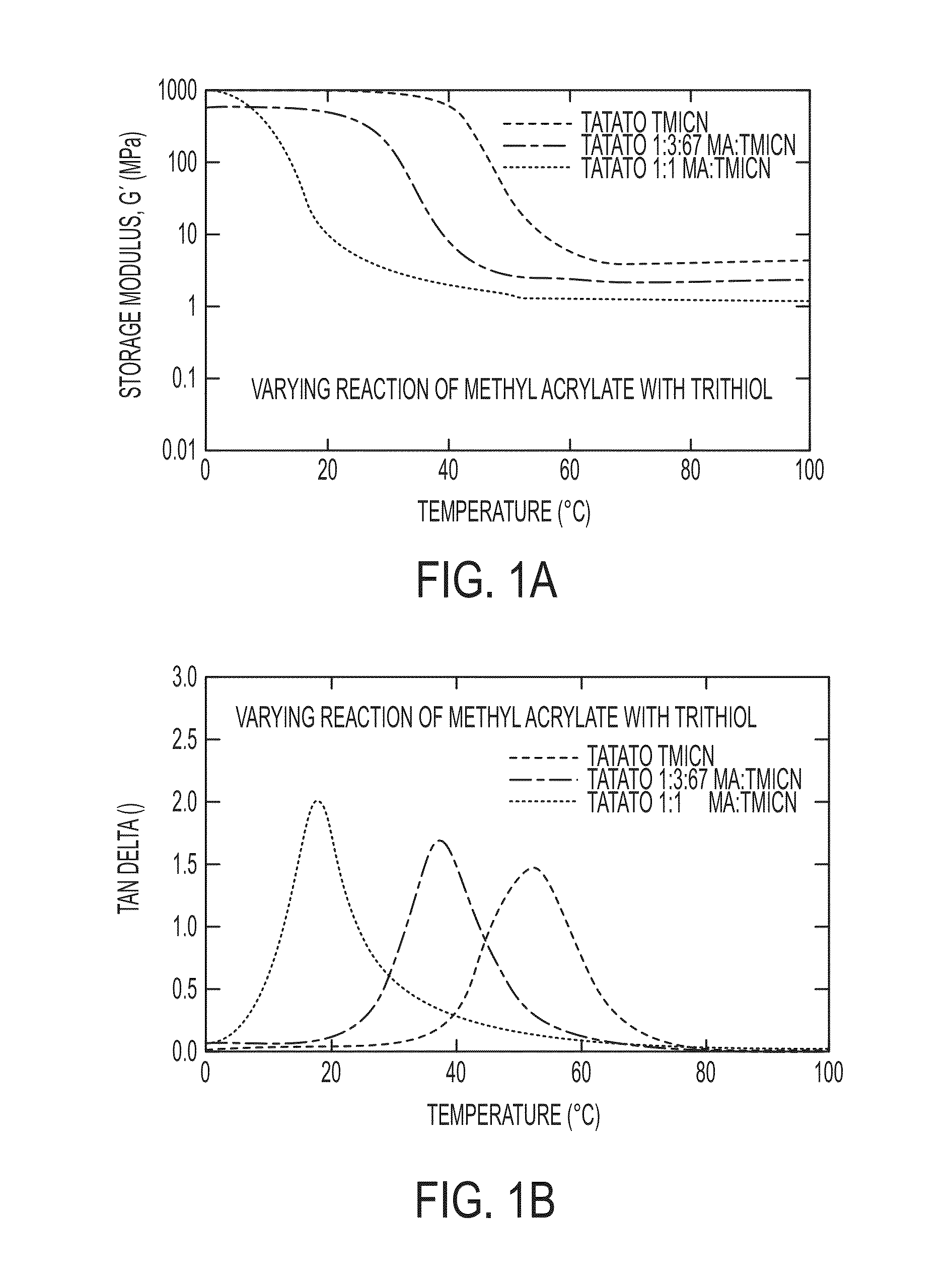
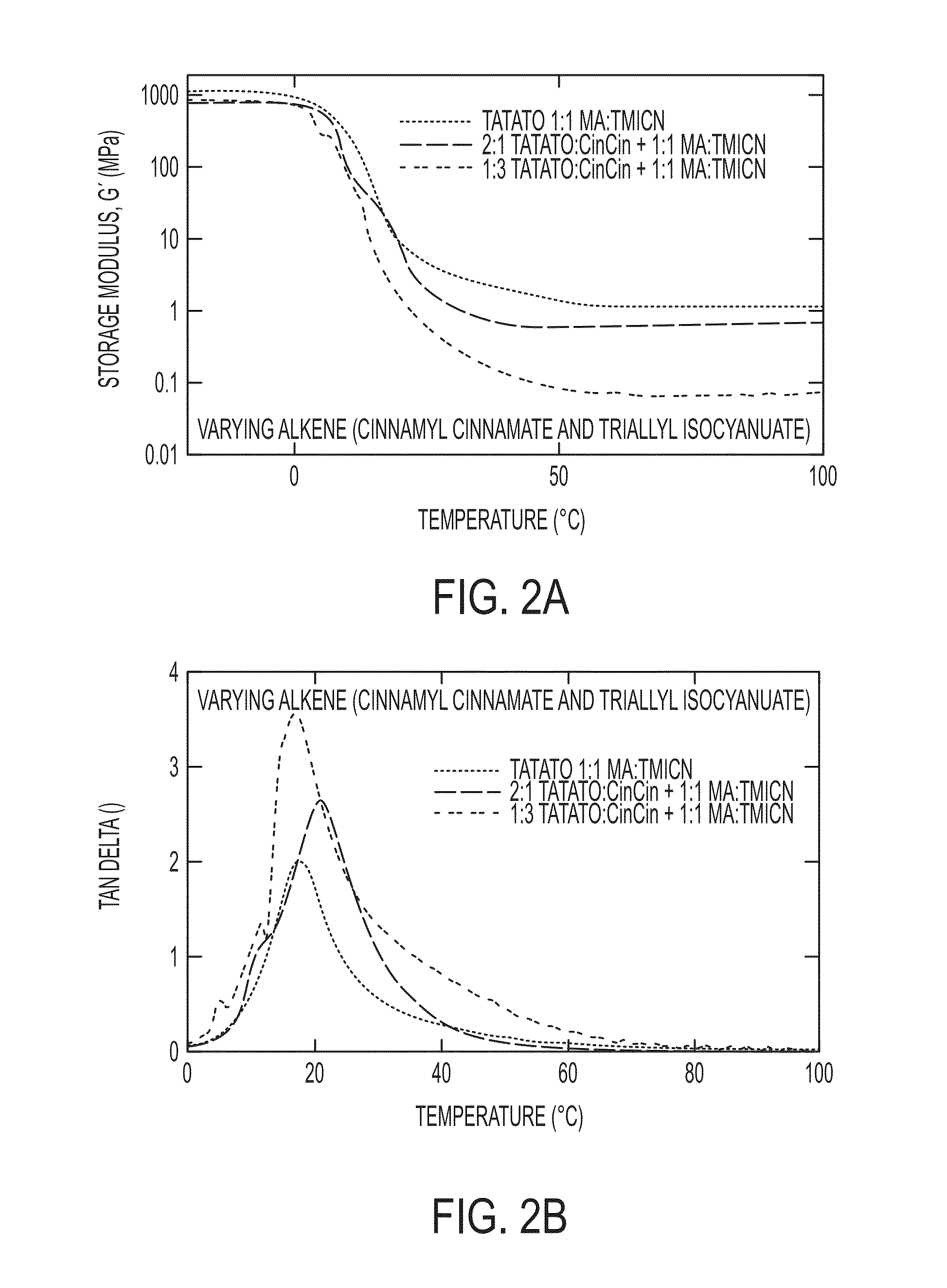
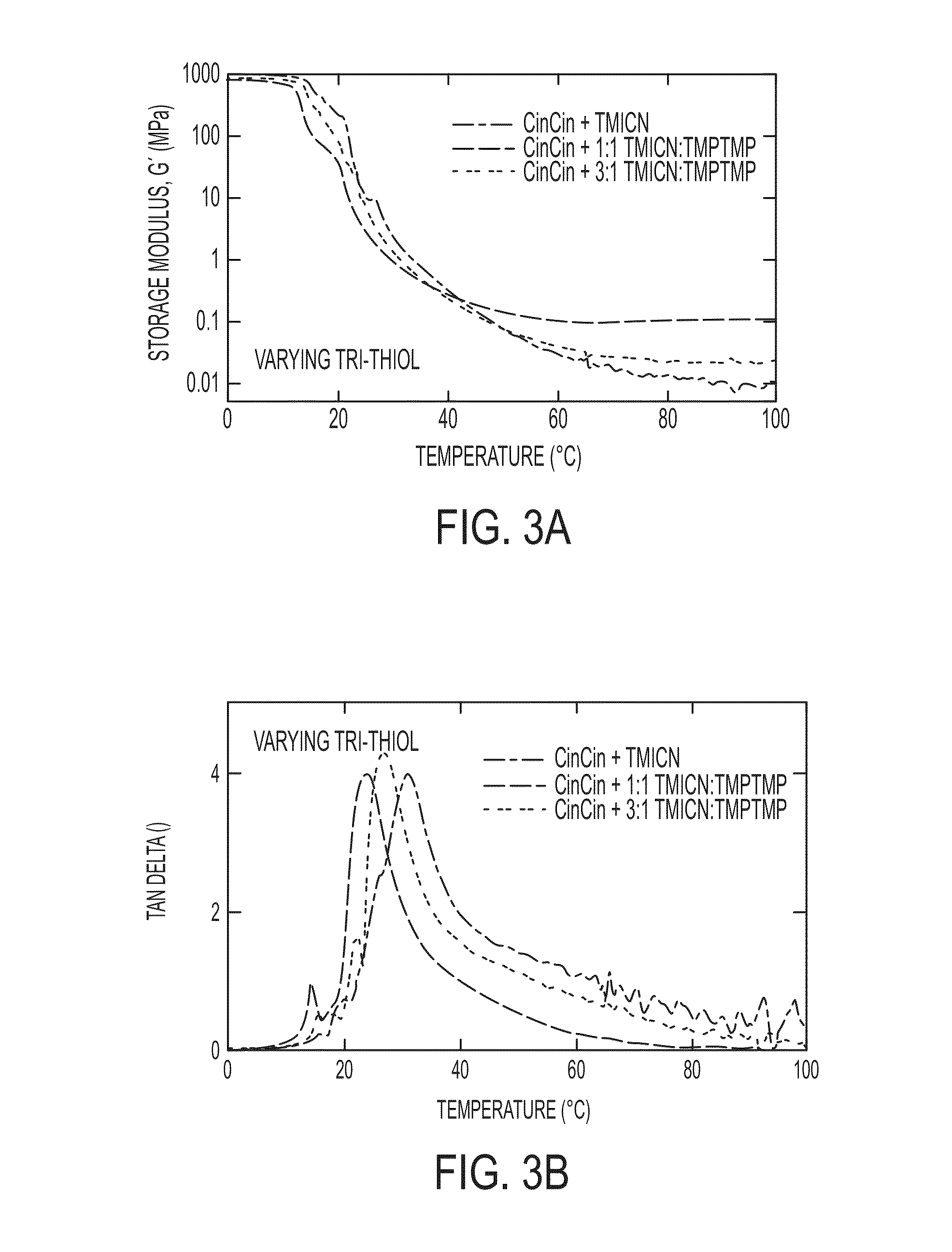
Softening materials based on thiol-ene copolymers
Embodiments of the invention are directed to softening amorphous polymeric materials based on a combination of thiol, acrylate, ene and epoxy monomers. These materials can soften to the modulus of tissue, have a sharp transition and are highly tunable. The materials have a glassy modulus of 1-7 GPa and exhibit a rubbery plateau in modulus that can range from 100 MPa down to as low as 0.03 MPa, which is at or below the modulus of tissue. They have potential uses as materials for near net shape processing such as casting, stereolithography, reaction injection molding, fused deposition molding and various other forms of 3D printing.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Method of manufacturing a component and thermal management process
A method of manufacturing a component and a method of thermal management are provided. The methods include forming at least one portion of the component, printing a cooling member of the component and attaching the at least one portion to the cooling member of the component. The cooling member includes at least one cooling feature. The at least one cooling feature includes at least one cooling channel adjacent to a surface of the component, wherein printing allows for near-net shape geometry of the cooling member with the at least one cooling channel being located within a range of about 127 (0.005 inches) to about 762 micrometers (0.030 inches) from the surface of the component. The method of thermal management also includes transporting a fluid through at least one fluid pathway defined by the at least one cooling channel within the component to cool the component.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Process for producing a shaped foam article
InactiveUS20110091688A1Reduce warpageReduce crackingLayered productsThin material handlingPolymer scienceCold formed
The invention relates to an improved method of cold forming a shaped foam article wherein the improvement is using a near net-shaped foam blank cut from a foam plank having a vertical compressive balance equal to or greater than 0.4 to produce the shaped foam article.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
High throughput preparation and analysis of materials
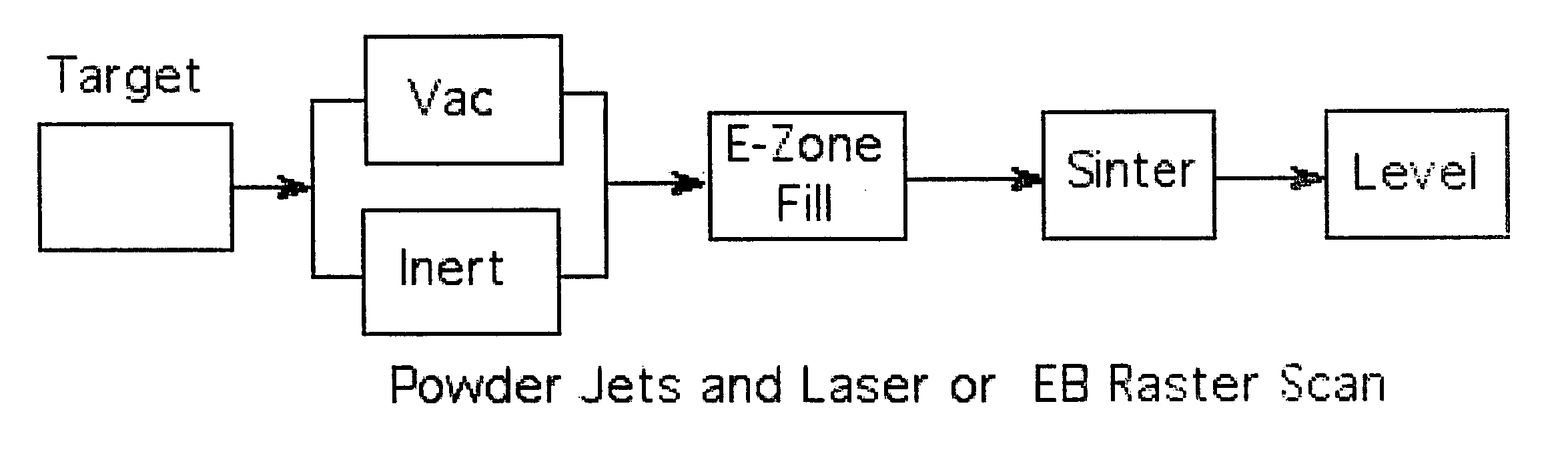
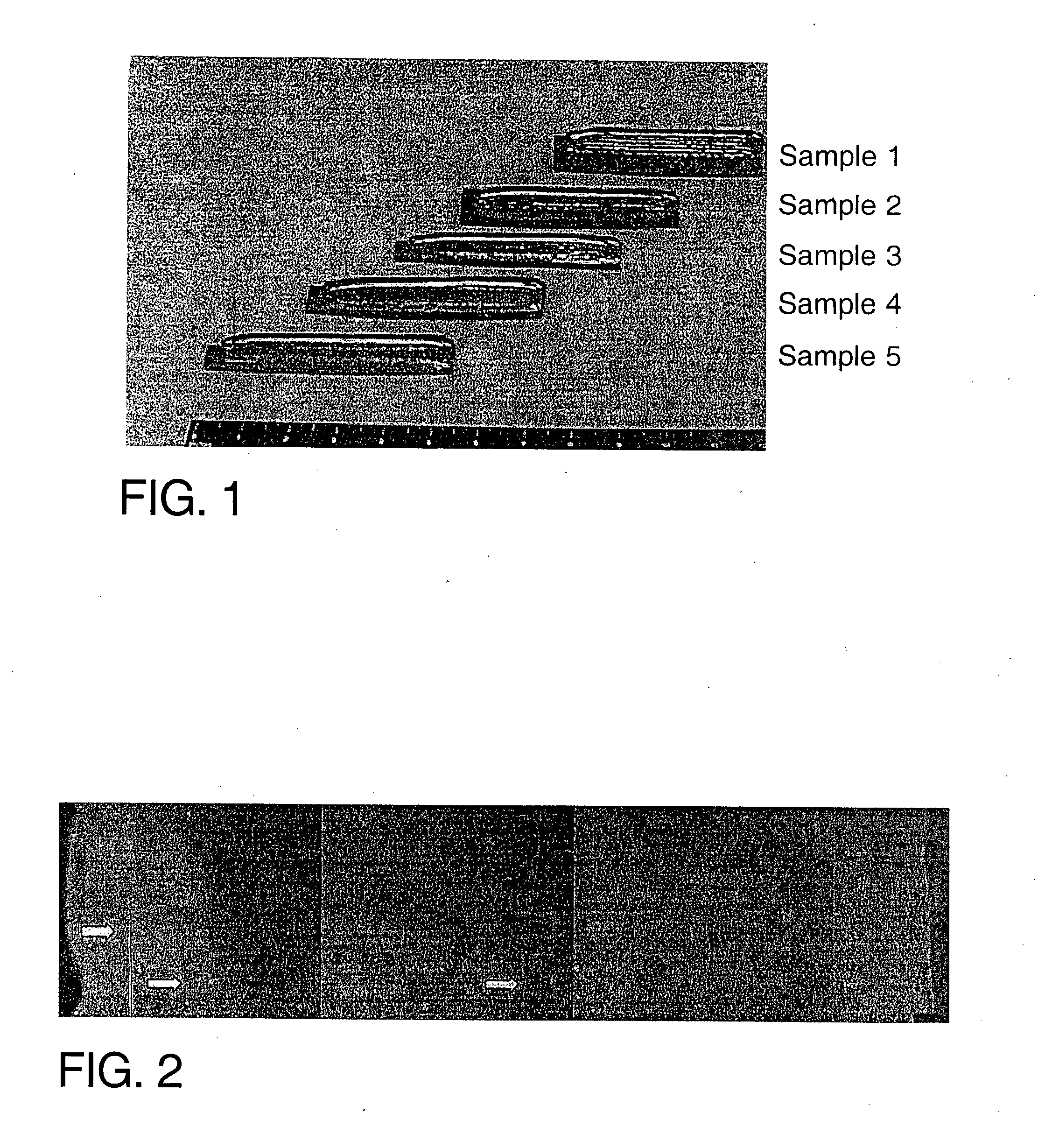
A rapid throughput method for the preparation, analysis or both of libraries of material samples is provided. According to the method, a plurality of samples is provided. Providing the plurality of samples can include a variety of sample formation techniques including, but not limited to, extruding, milling, compression preparation, rotary mixing, microcentrifugation, molding and casting. Preferably, the samples are solidified into a near net shape configuration appropriate for testing of properties or characteristics of the samples.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Fully-dense discontinuously-reinforced titanium matrix composites and method for manufacturing the same
The invention is suitable for the manufacture of flat or shaped titanium matrix composite articles having improved mechanical properties such as lightweight plates and sheets for aircraft and automotive applications, heat-sinking lightweight electronic substrates, bulletproof structures for vests, partition walls and doors, as well as for sporting goods such as helmets, golf clubs, sole plates, crown plates, etc. A fully-dense discontinuously-reinforced titanium matrix composite (TMMC) material comprises (a) a matrix of titanium or titanium alloy as a major component, (b) ceramic and / or intermetallic hard particles dispersed in the matrix in the amount of ≦50 vol. %, and (c) complex carbide- and / or silicide particles at least partially soluble in the matrix at the sintering or forging temperatures such as Ti4Cr3C6, Ti3SiC2, Cr3C2, Ti3AlC2, Ti2AlC, Al4C3, Al4SiC4, Al4Si2C5, Al8SiC7, V2C, (Ti,V)C, VCr2C2, and V2Cr4C3 dispersed in the matrix in the amount of ≦20 vol. %. The method for manufacturing TMCC is comprised of the following steps: (a) preparing a basic powdered blend containing matrix alloy or titanium powders, dispersing ceramic and / or intermetallic powders, and powders of said complex carbide- and / or silicide particles, (b) preparing the Al—V master alloy containing ≦5 wt. % of iron, (c) preparing the Al—V—Fe master alloy fine powder having a particle size of ≦20 μm, (d) mixing the basic powdered blend with the master alloy powder to obtain a chemical composition of TMCC, (e) compacting the powder mixture at room temperature, (f) sintering at the temperature which provides at least partial dissolution of dispersed powders, (g) forging at 1500-2300° F., and (h) cooling. The resulting TMCC has density over 98% and closed discontinuous porosity after sintering that allows making hot deformation in air without encapsulating. The invention can be used to produce near-full density near-net shape parts from titanium matrix composite materials with acceptable mechanical properties without a hot deformation.
Owner:ADVANCE MATERIAL PRODS ADMA PRODS
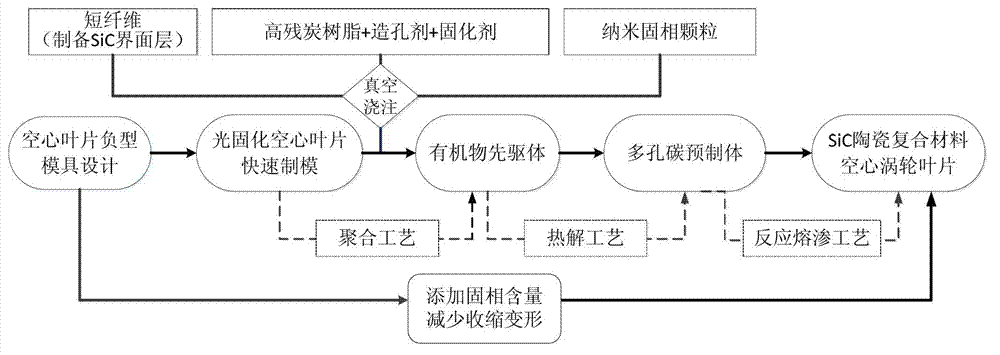
Preparation method of fiber-toughened SiC ceramic-based composite material three-dimensional member
The invention discloses a preparation method of a fiber-toughened SiC ceramic-based composite material three-dimensional member. The method comprises the following steps: adding fiber to liquid-state high char yield resin, pouring to a photo-curing mold, performing polymerization and curing on the resin, then manufacturing a controllable porous carbon preform through a thermolysis method, then performing high-temperature siliconizing, and preparing a SiC ceramic matrix by in-situ reaction of silicon on a carbon support to realize the manufacturing of the SiC ceramic-based composite material three-dimensional member. The method has the characteristics of near net shape formed variable cross-section complex structure, no crack defects, short production period, low cost and the like, and can be applied to development and manufacturing of blades of engines and other aerospace high-temperature-resistant complex structure parts.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
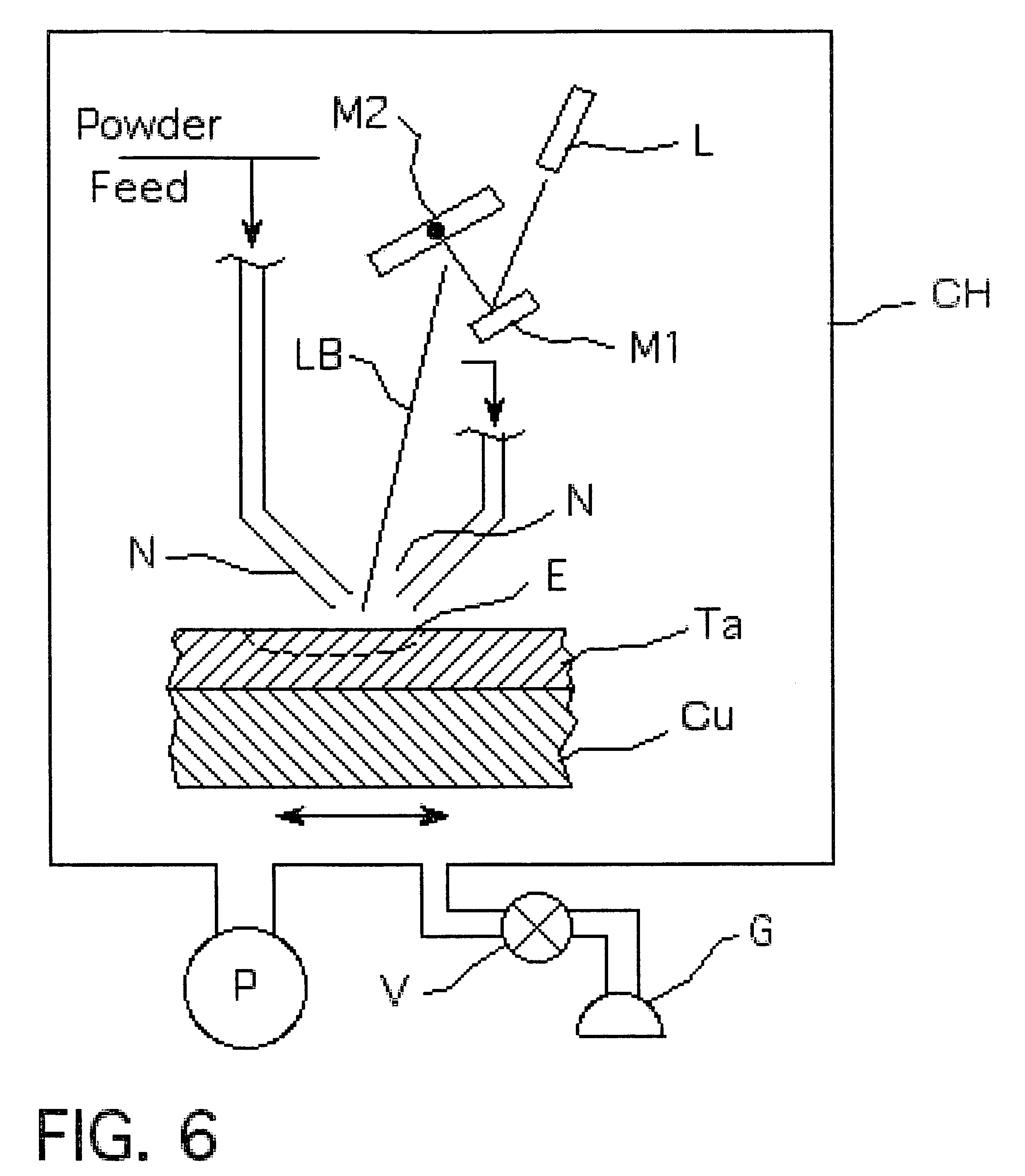
Refractory metal and alloy refining by laser forming and melting
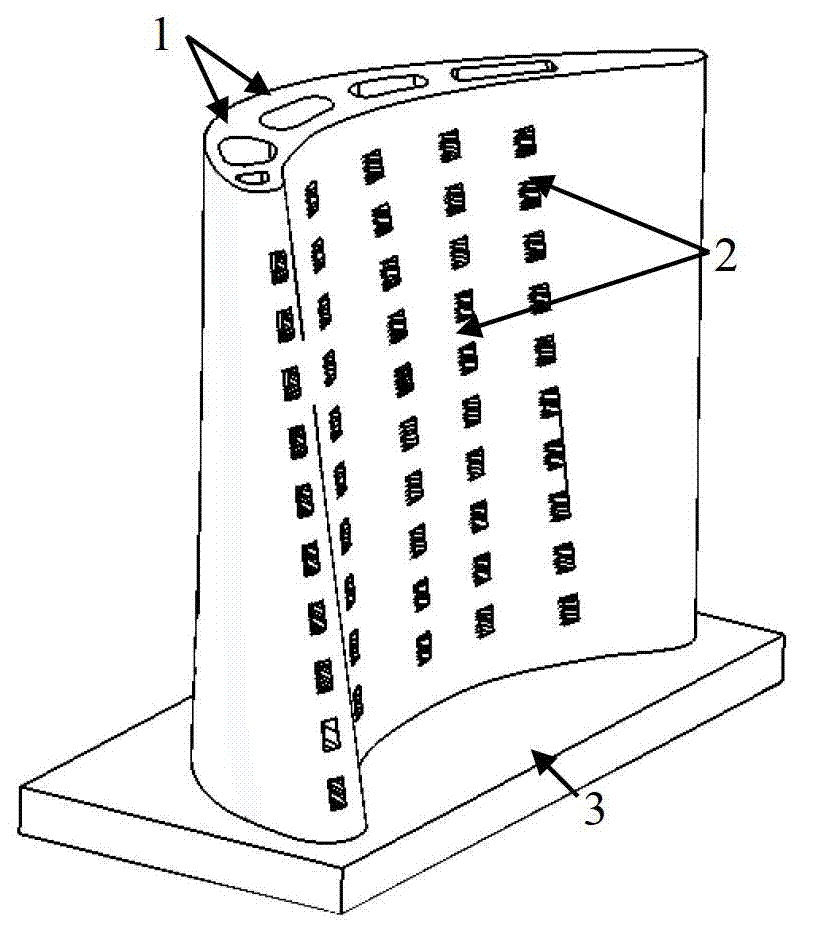
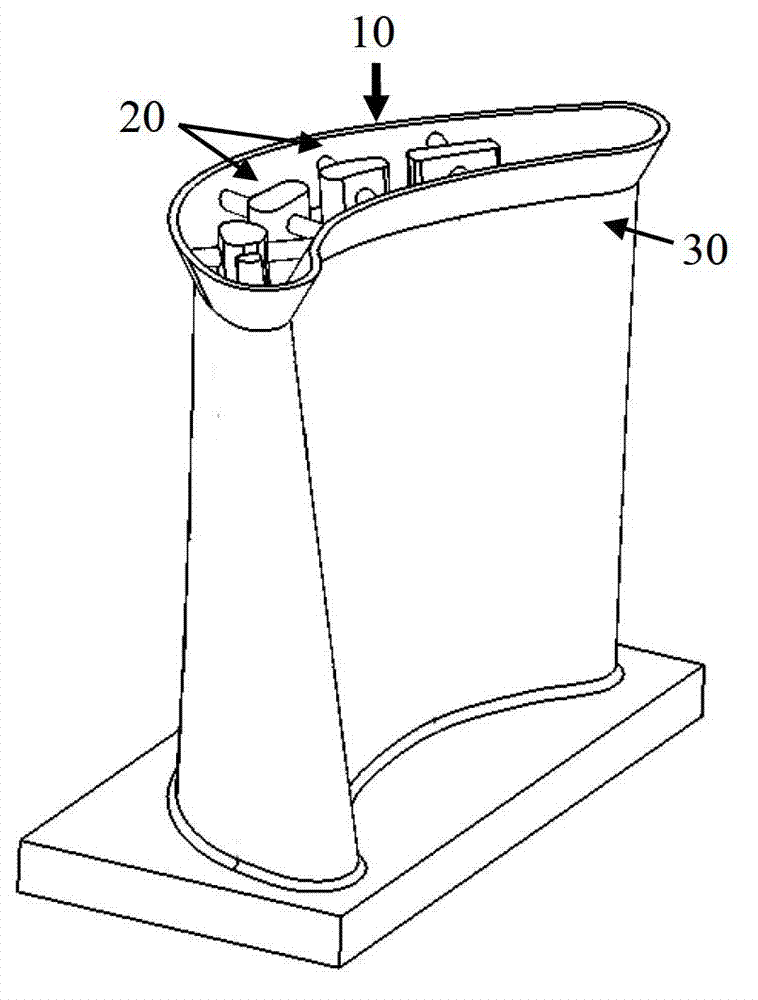
ActiveUS7651658B2Improve throughputMore consistencyRadiation applicationsVacuum evaporation coatingNiobiumNear net shape
A process to chemically refine and consolidate tantalum, niobium and their alloys to a fabricated product of net shape or near-net shape with higher throughput, more consistency, and lower manufacturing costs compared to prior art routes or rejuvenate damaged and deteriorated refractory metal parts. Powder metal is loaded into hoppers to be fed into laser forming / melting equipment. A suitable substrate is loaded into a laser forming / melting chamber onto which the powder will be deposited and consolidated in a point-scan process. As the powder is fed onto successive points of the surface of the substrate in linear traces, the laser is used to heat and partially melt the substrate and completely melt the powder. A combined deposition and melt beam traces the substrate surface repeatedly over a selected area to build up a dense coating of controlled microstructure in multiple layers. A fully dense deposit is built up that becomes the desired shape.
Owner:MATERION NEWTON INC
Method for producing rapidly renewable chitinous material using fungal fruiting bodies and product made thereby
The method of growing a fungal fruiting body requires exposing a mycelium of a desired organism type to environmental conditions sufficient to induce fruiting of fungal primordium in the organism type followed by enclosing the fungal primordium within a mold of a designated shape representing a near net shape volume of a desired final product. The fungal primordium is allowed to grow and fill the mold to form a mass of fungal tissue equivalent in shape to the designated shape of the mold after which the mass of fungal tissue is removed from the mold and dried.
Owner:ECOVATIVE DESIGN LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com