Patents
Literature
547results about "Tungsten/molybdenum carbide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Proppants With Carbide and/or Nitride Phases
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Method of using carbide and/or oxycarbide containing compositions
InactiveUS20020121460A1Facilitated DiffusionHigh porosityMaterial nanotechnologyHydrocarbon by isomerisationFluid phaseChemical reaction
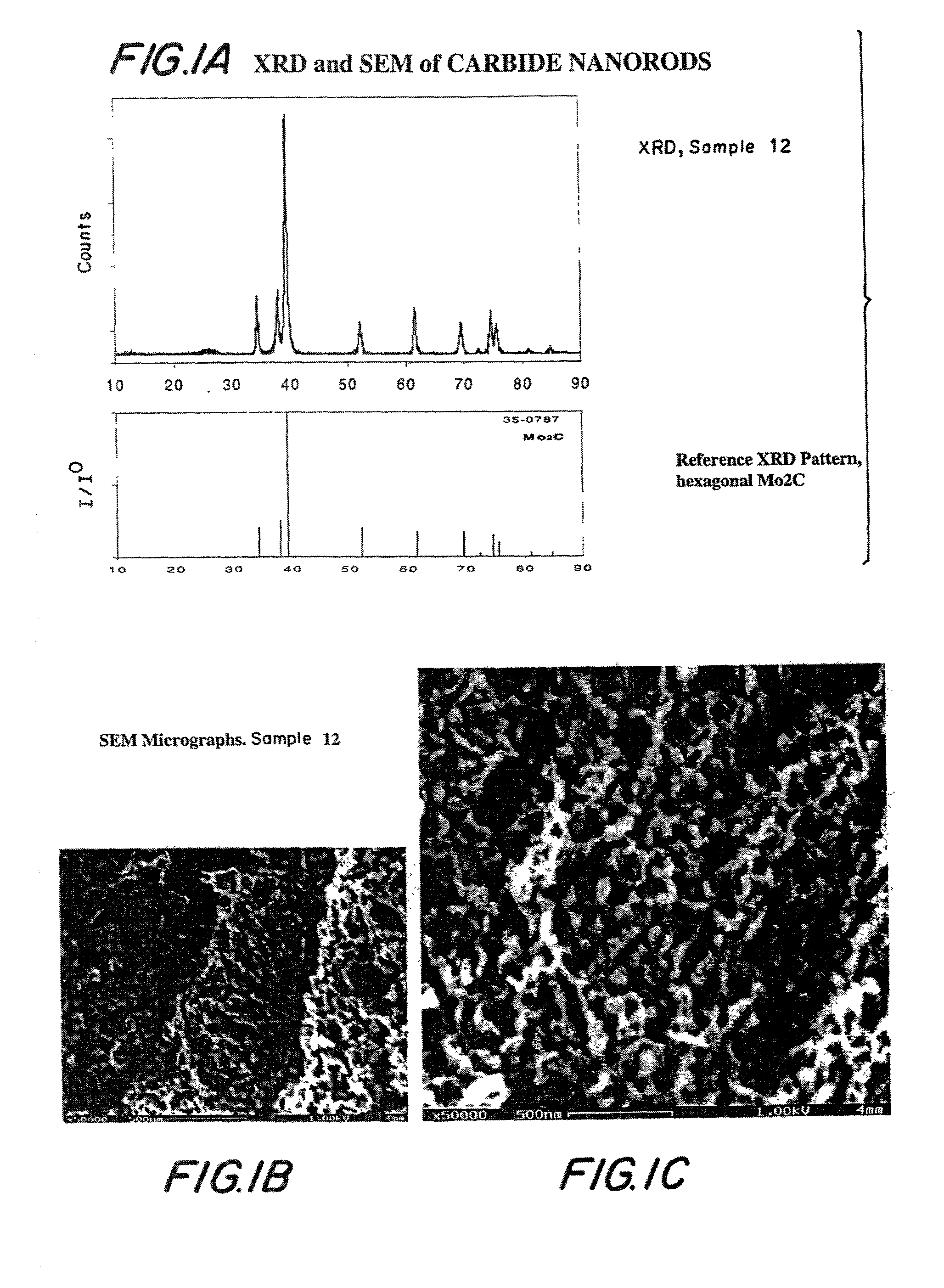
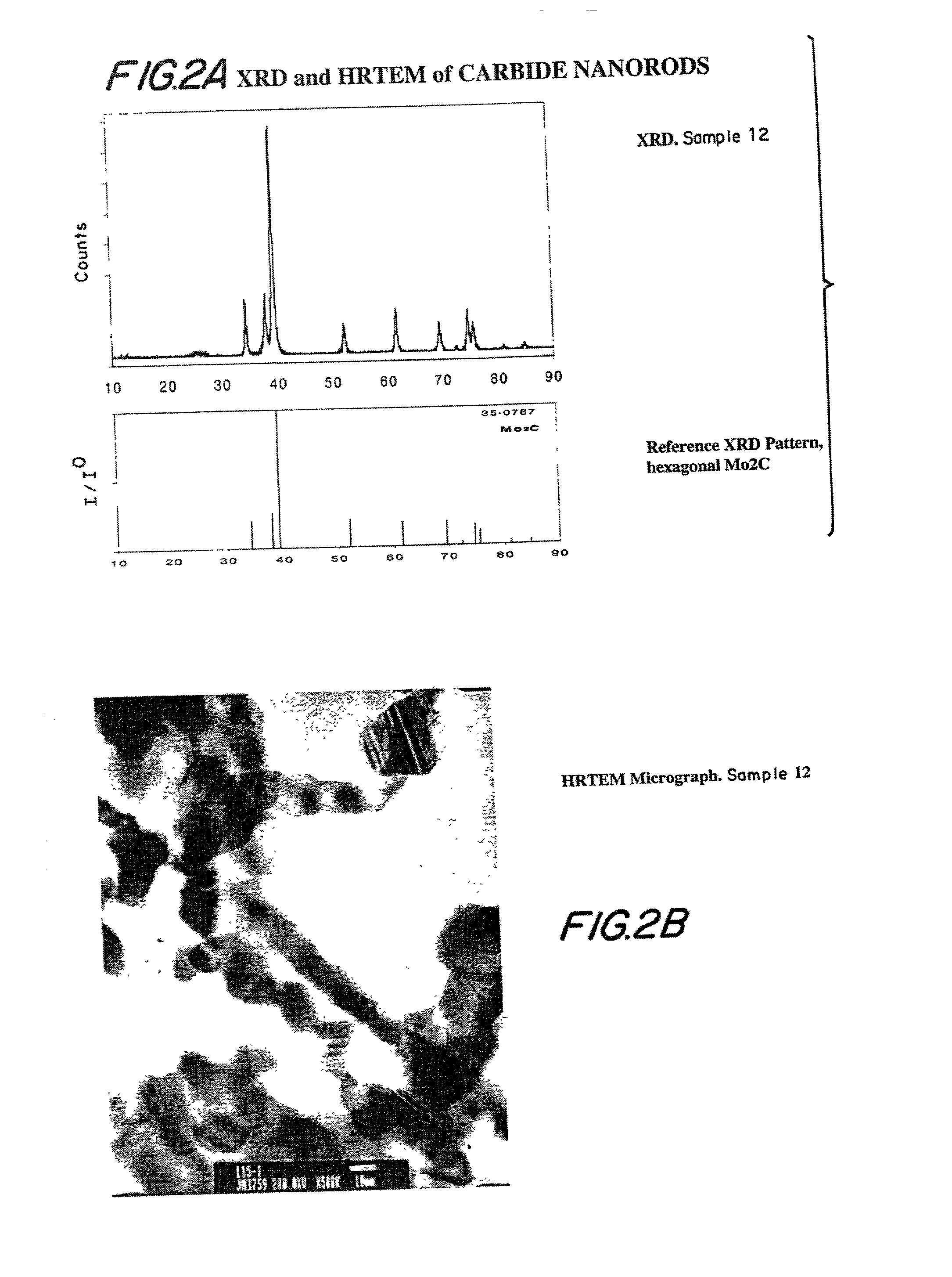
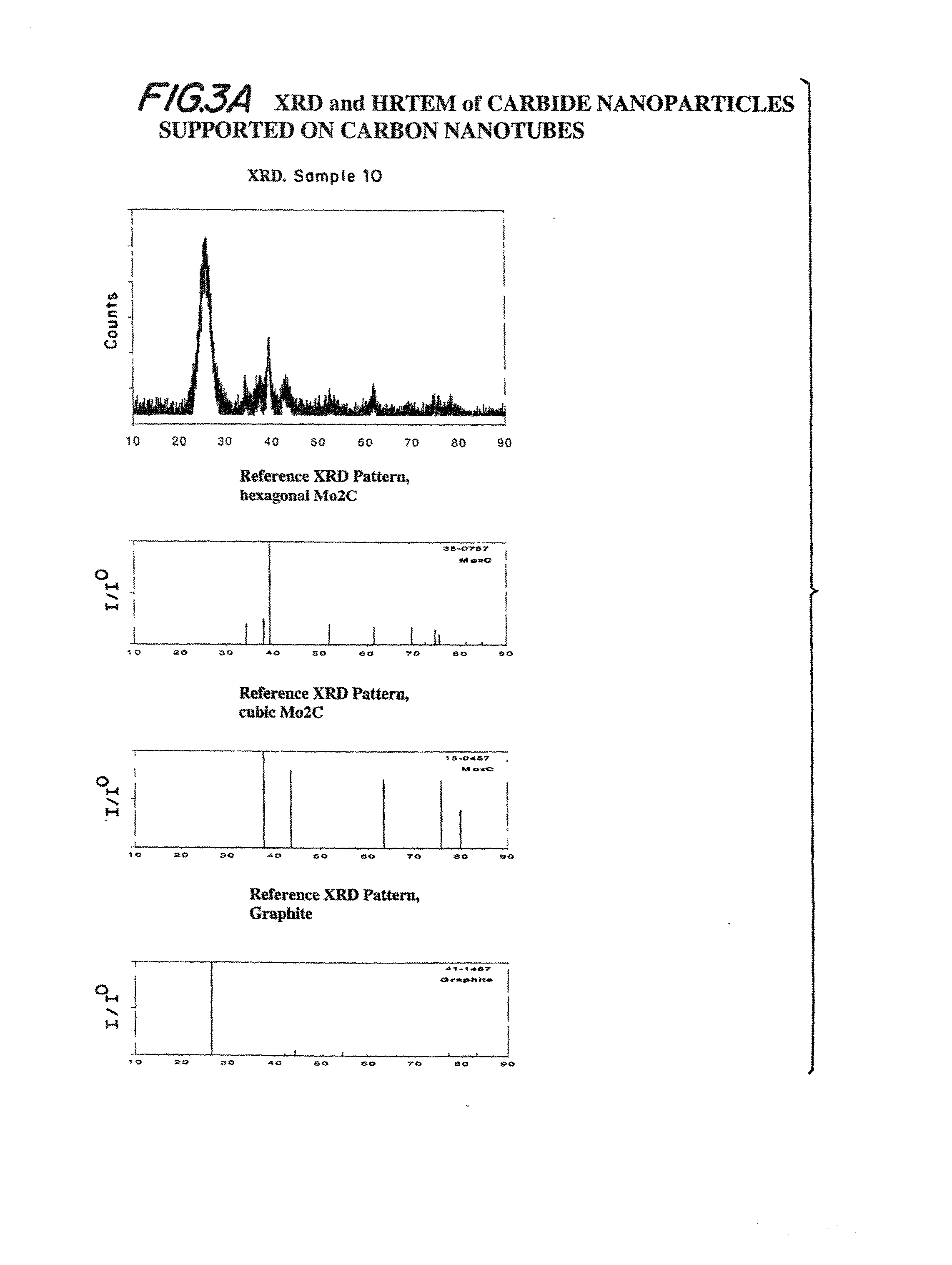
Compositions including carbide-containing nanorods and / or oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing carbides and oxycarbides and methods of making the same are provided. Rigid porous structures including oxycarbide-containing nanorods and / or carbide containing nanorods and / or carbon nanotubes bearing carbides and oxycarbides and methods of making the same are also provided. The compositions and rigid porous structures of the invention can be used either as catalyst and / or catalyst supports in fluid phase catalytic chemical reactions. Processes for making supported catalyst for selected fluid phase catalytic reactions are also provided.
Owner:HYPERION CATALYSIS INT
Process for the preparation of metal carbides having a large specific surface from activated carbon foams
InactiveUS6217841B1Easy accessPhysical/chemical process catalystsTransuranic element compoundsActivated carbonCarbide
The invention relates to a silicon carbide or metal carbide foam to be used as a catalyst or catalyst support for the chemical or petrochemical industry or for silencers, as well as the process for producing the same.The foam is in the form of a three-dimensional network of interconnected cages, whose edge length is between 50 and 500 micrometres, whose density is between 0.03 and 0.1 g / cm3 and whose BET surface is between 20 and 100 m2 / g. The carbide foam contains no more than 0.1% by weight residual metal and the size of the carbide crystallites is between 40 and 400 Angstroms.The production process consists of starting with a carbon foam, increasing its specific surface by an activation treatment using carbon dioxide and then contacting the thus activated foam with a volatile compound of the metal, whose carbide it is wished to obtain.
Owner:CENT NAT DE LA RECHERCHE SCI
Uniform macromeritic tungsten powder and method for preparing tungsten carbide powder
The invention discloses a uniform macromeritic tungsten powder and a method for preparing macromeritic tungsten carbide powder. During reduction, water vapor and hydrogen or a mixture thereof is sentinto a reducing furnace, and tungsten oxide powder materials or mixture materials of tungsten oxide powder and tungsten powder, which are pushed into the reducing furnace, are reduced to metallic tungsten powder by controlling the partial pressure ratio (PH2O / PH2) of the water vapor and the hydrogen sent into the reducing furnace and the temperature of the furnace. By the adjustment of technological parameters, macromeritic tungsten powder of multiple grades in the range of 10-100 micrometers can be prepared. The prepared macromeritic tungsten powder has the advantages of comparatively uniformgranularity, integrated crystallization, attractive appearance and high purity. After the carbonization of the macromeritic tungsten powder, uniform macromeritic tungsten carbide powder of 12-115 micrometers can be prepared. The invention can be used for producing macromeritic and super macromeritic hard alloy products of more than 4 micrometers and can be also used for the surface spray coating,the spray welding and the like of hard-surface materials.
Owner:ZHUZHOU HARD ALLOY GRP CO LTD
Proppants with carbide and/or nitride phases
Owner:HALLIBURTON ENERGY SERVICES INC
Molybdenum and tungsten nanostructures and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS20130281285A1Reduce overpotentialReduce productionMaterial nanotechnologyNitrogen compoundsHydrogenNanoparticle
The present invention provides molybdenum and tungsten nanostructures, for example, nanosheets and nanoparticles, and methods of making and using same, including using such nanostructures as catlysts for hydrogen evolution reactions.
Owner:BROOKHAVEN SCI ASSOCS
Physical forms of MXene materials exhibiting novel electrical and optical characteristics
ActiveCN107001051ANitrogen-metal/silicon/boron binary compoundsTitanium carbideElectrical conductorOptical property
Owner:DREXEL UNIV
Synthesis method of nano-molybdenum carbide
InactiveCN103936008ALarge specific surface areaSmall particle sizeTungsten/molybdenum carbideSynthesis methodsFiltration
The invention relates to a synthesis method of nano-molybdenum carbide. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: dissolving a molybdenum precursor in hydrogen peroxide, dissolving carbohydrates in water, mixing the molybdenum precursor with the carbohydrates, stirring, loading a mixed solution into a hydrothermal kettle, and performing hydrothermal treatment to obtain a black product; cooling the black product, then washing and performing suction filtration on the product, drying, baking in a passivation gas atmosphere, replacing with passivation gas when the temperature is reduced to room temperature, and performing passivation treatment to obtain the nano-molybdenum carbide. The synthesis method provided by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, easiness in control, economical efficiency, reasonableness and large specific surface area with mesoporous structure.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
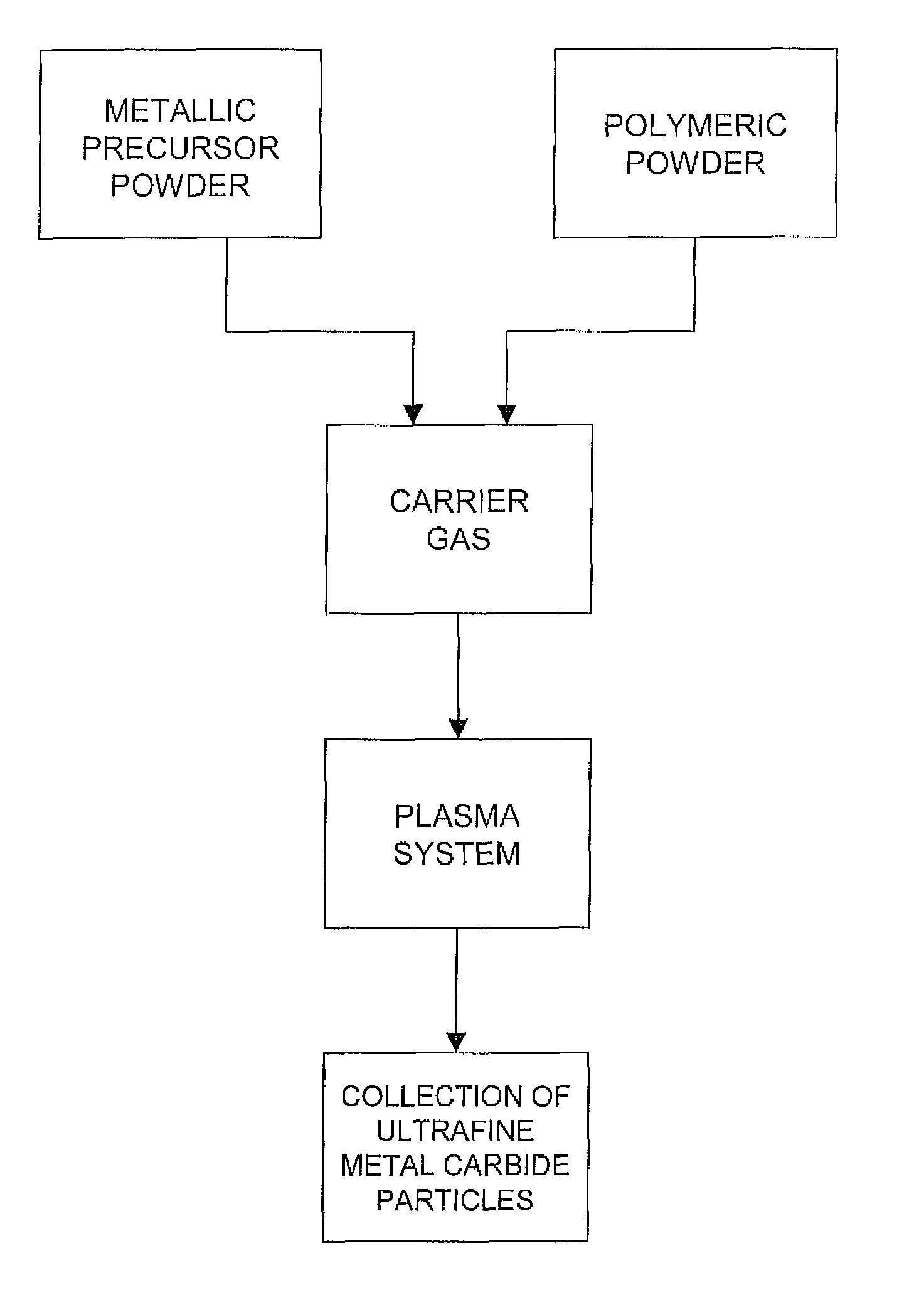
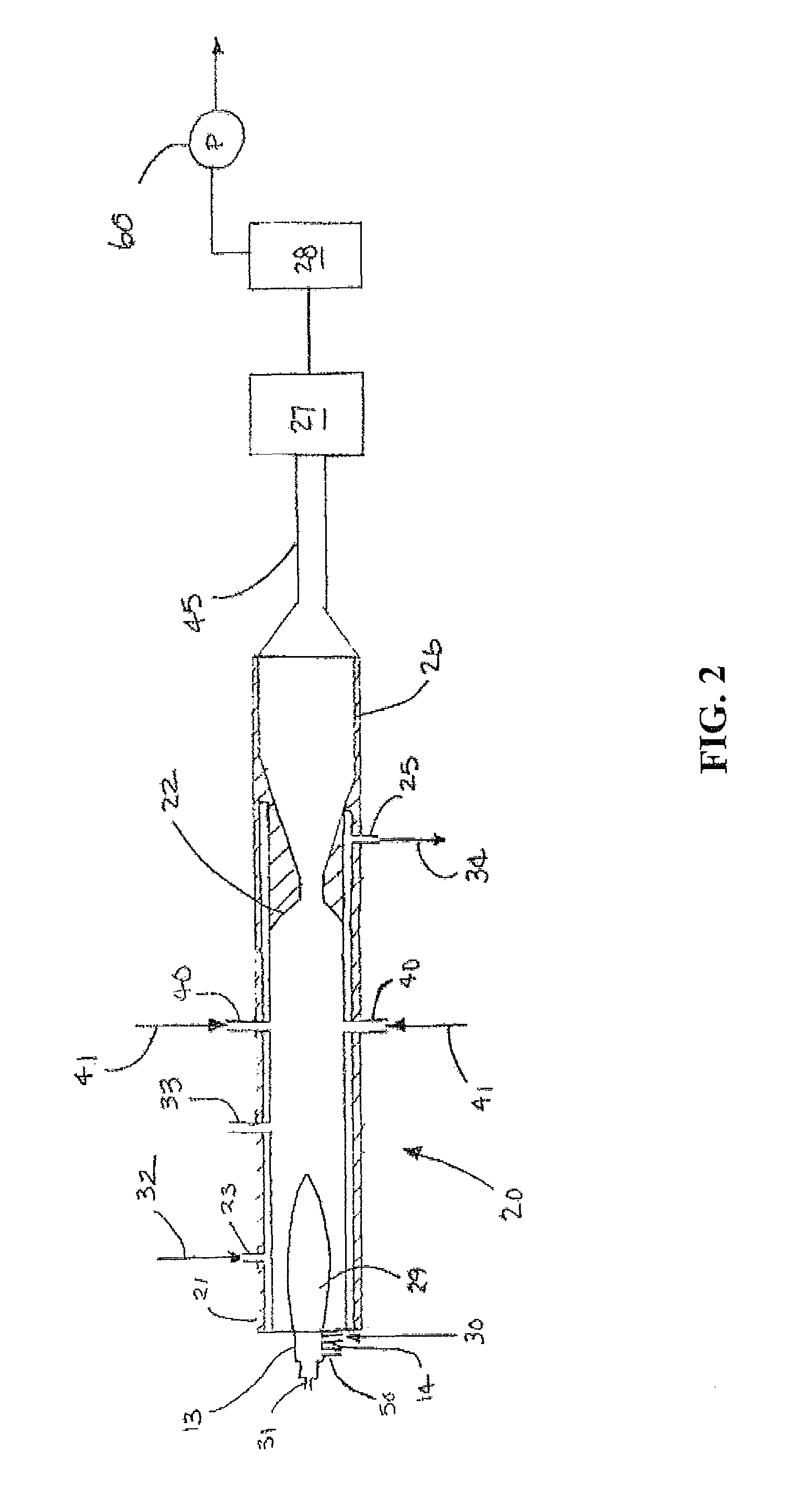
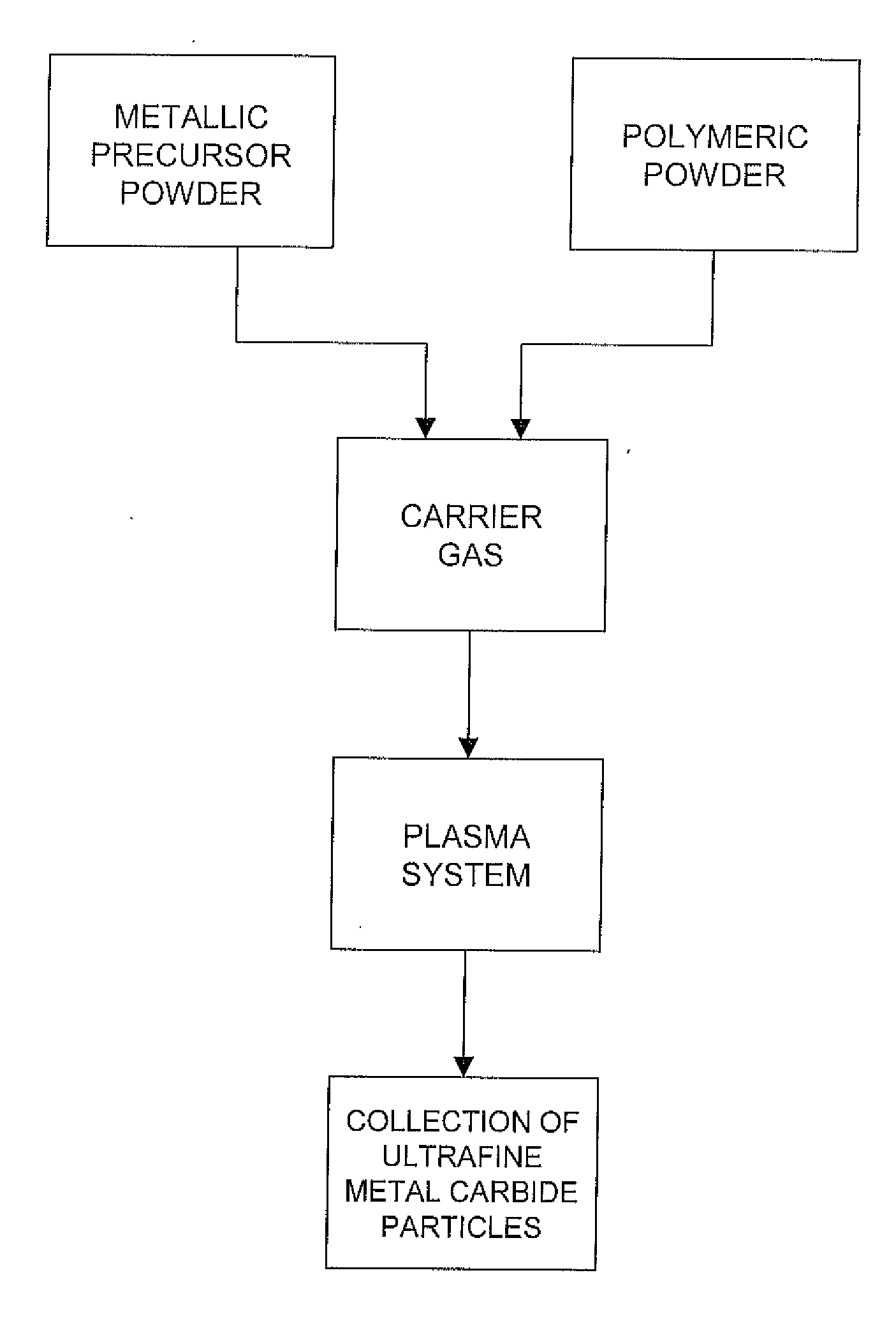
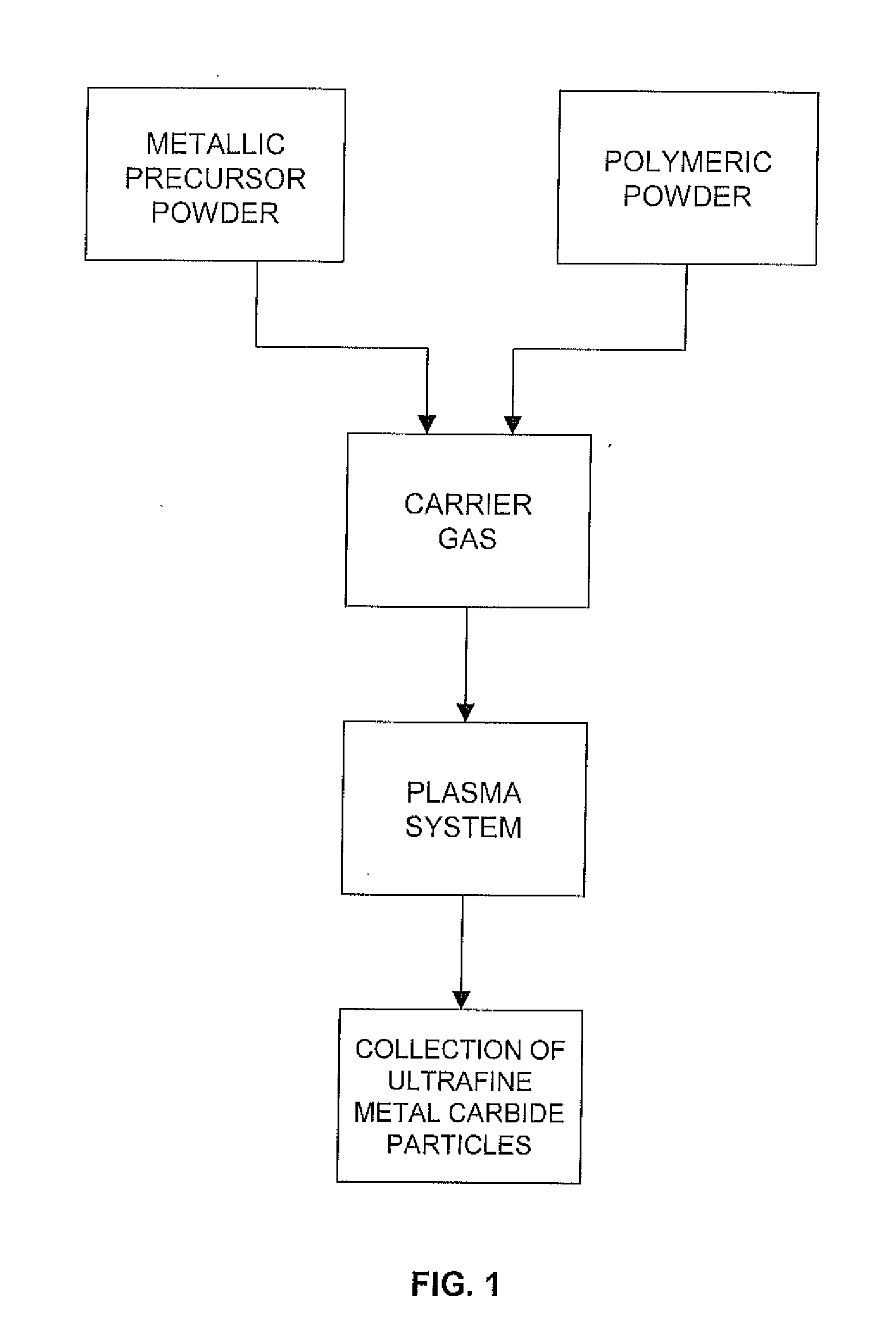
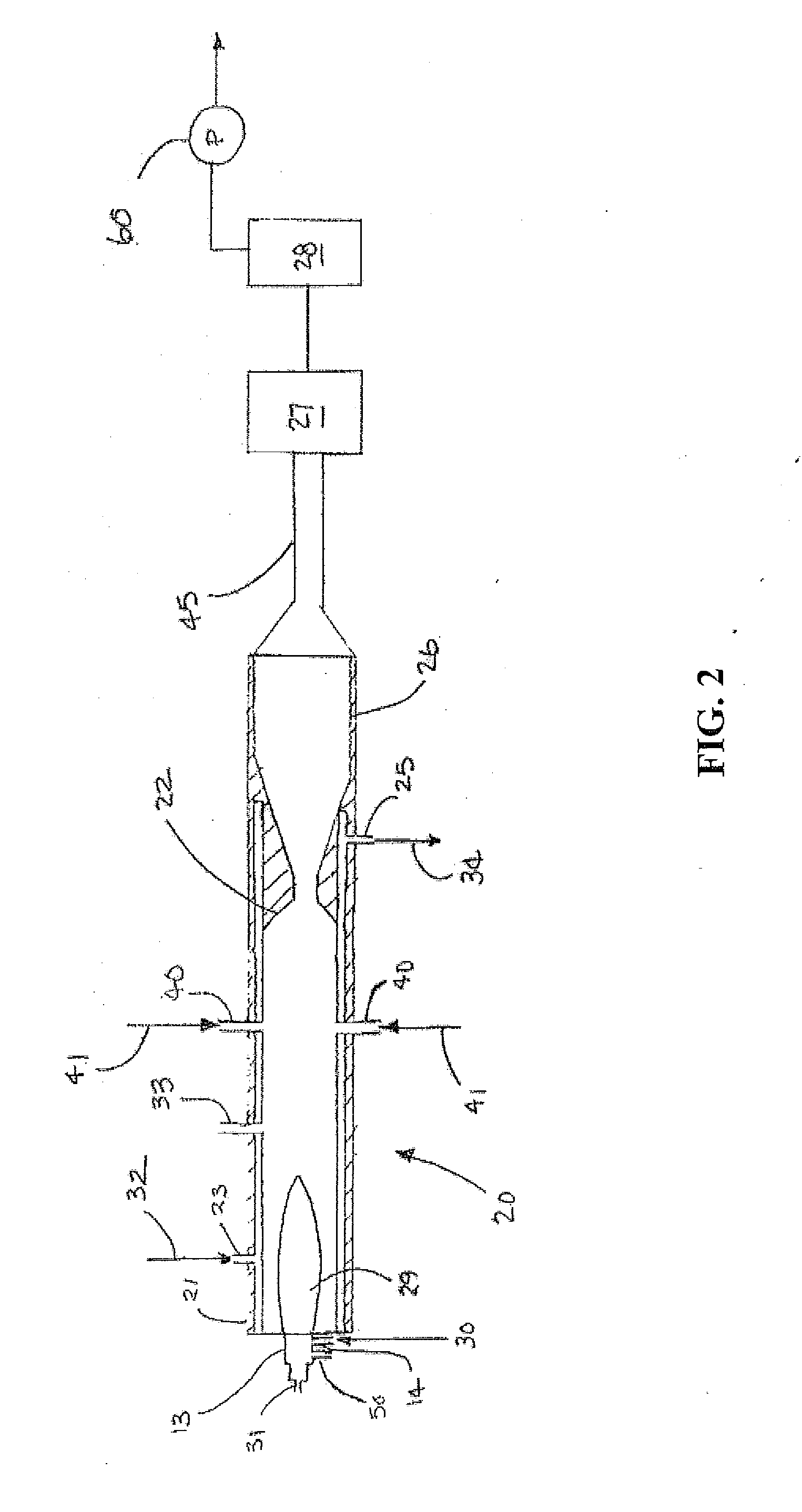
Production of ultrafine metal carbide particles utilizing polymeric feed materials
The production of ultrafine metal carbide powders from polymeric powder and metallic precursor powder starting materials is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the polymeric powder may comprise polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyester, polybutylene, nylon, polymethylpentene and the like. The metal precursor powder may comprise pure metals, metal alloys, intermetallics and / or metal-containing compounds such as metal oxides and nitrides. In one embodiment, the metal precursor powder comprises a silicon-containing material, and the ultrafine powders comprise SiC. The polymeric and metal precursor powders are fed together or separately to a plasma system where the feed materials react to form metal carbides in the form of ultrafine particles.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
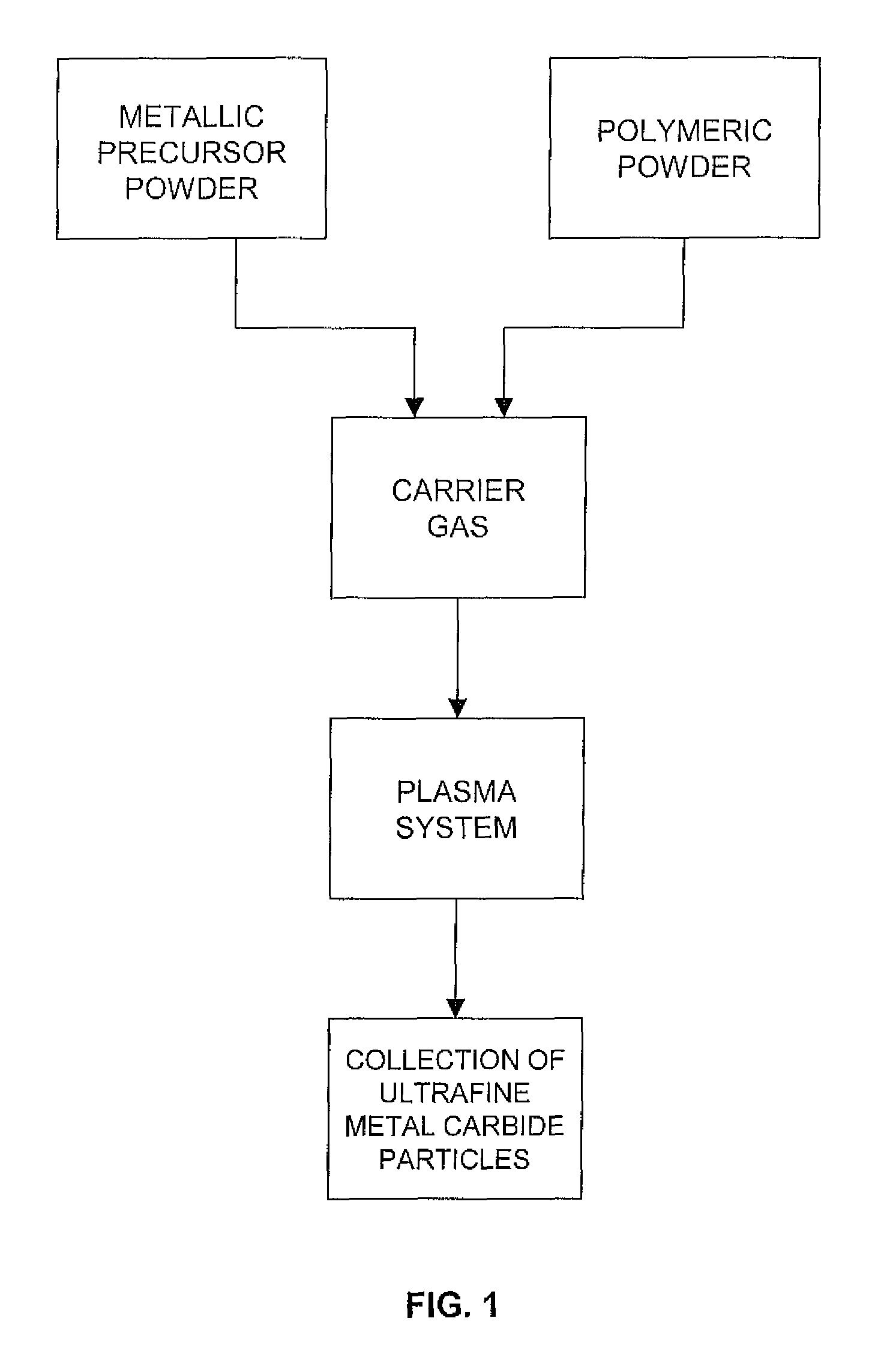
Production of ultrafine metal carbide particles utilizing polymeric feed materials
The production of ultrafine metal carbide powders from polymeric powder and metallic precursor powder starting materials is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the polymeric powder may comprise polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyester, polybutylene, nylon, polymethylpentene and the like. The metal precursor powder may comprise pure metals, metal alloys, intermetallics and / or metal-containing compounds such as metal oxides and nitrides. In one embodiment, the metal precursor powder comprises a silicon-containing material, and the ultrafine powders comprise SiC. The polymeric and metal precursor powders are fed together or separately to a plasma system where the feed materials react to form metal carbides in the form of ultrafine particles.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
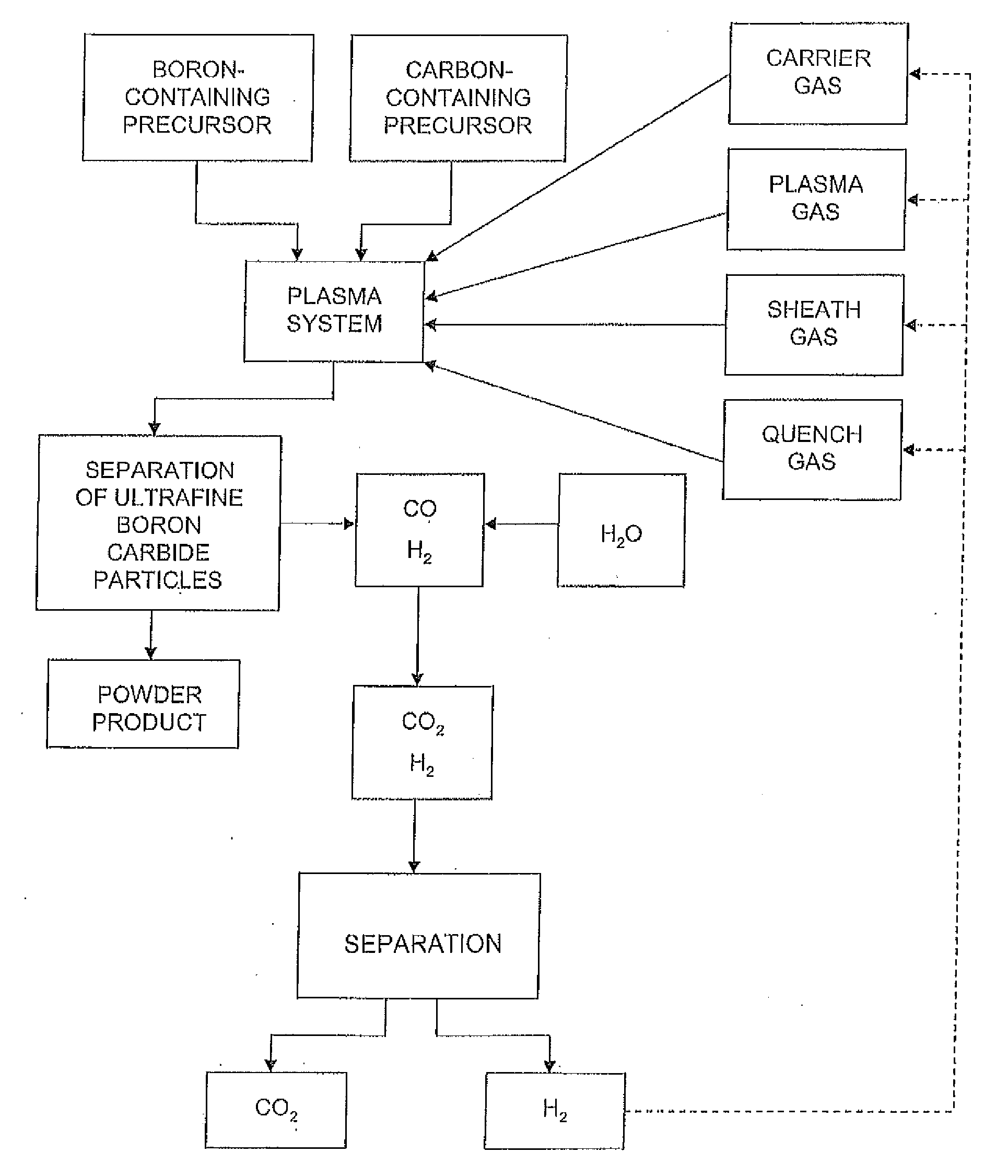
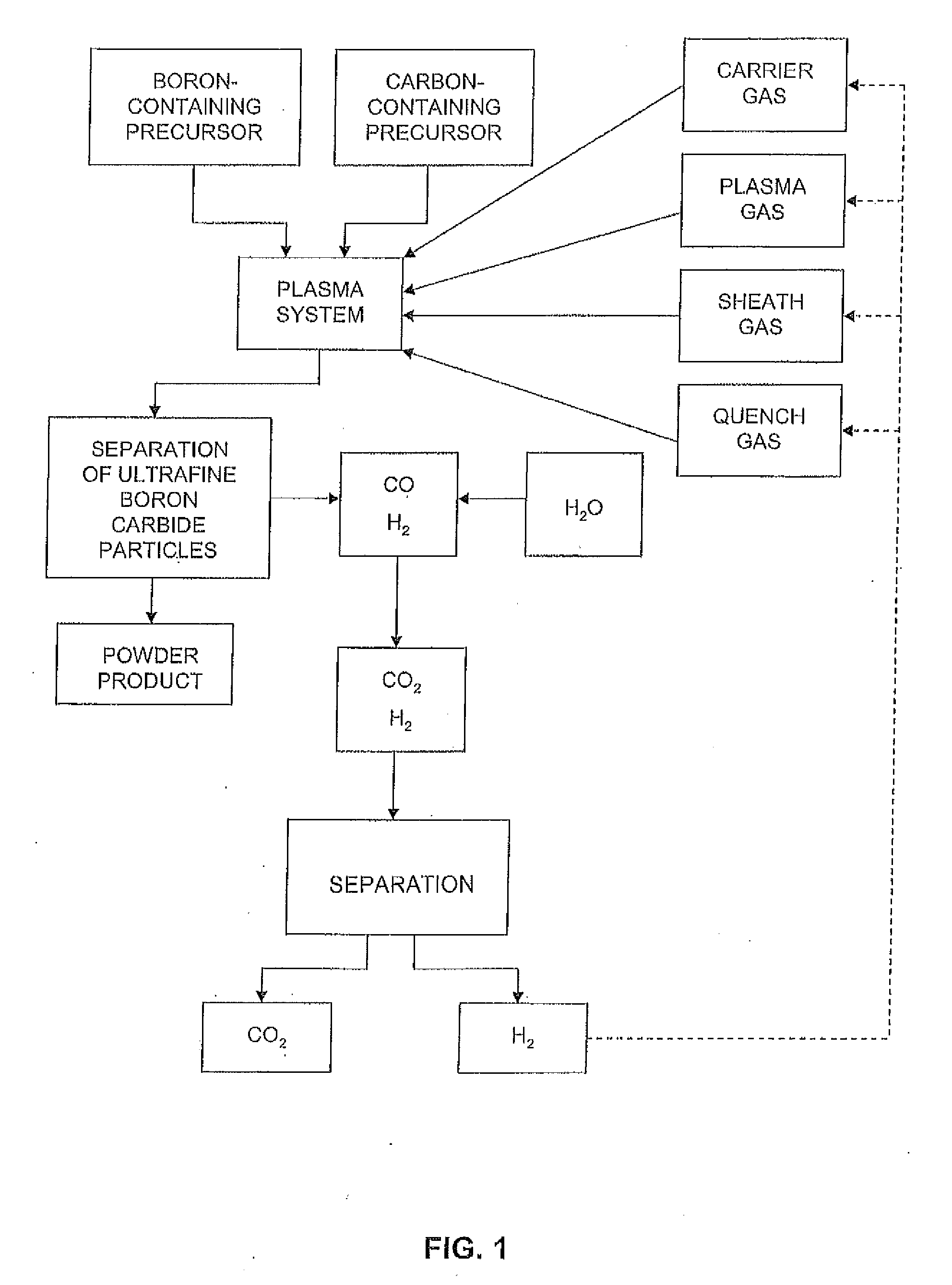
Methods for the production of ultrafine metal carbide particles and hydrogen
A method for producing ultrafine metal carbide particles and hydrogen is disclosed. The method includes introducing a metal-containing precursor and a carbon-containing precursor into a thermal reaction chamber, heating the precursors in the thermal reaction chamber to form the ultrafine metal carbide particles from the precursors and to form carbon monoxide and hydrogen, collecting the ultrafine doped metal carbide particles, converting at least a portion of the carbon monoxide to carbon dioxide and generating additional hydrogen, and recovering at least a portion of the hydrogen.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
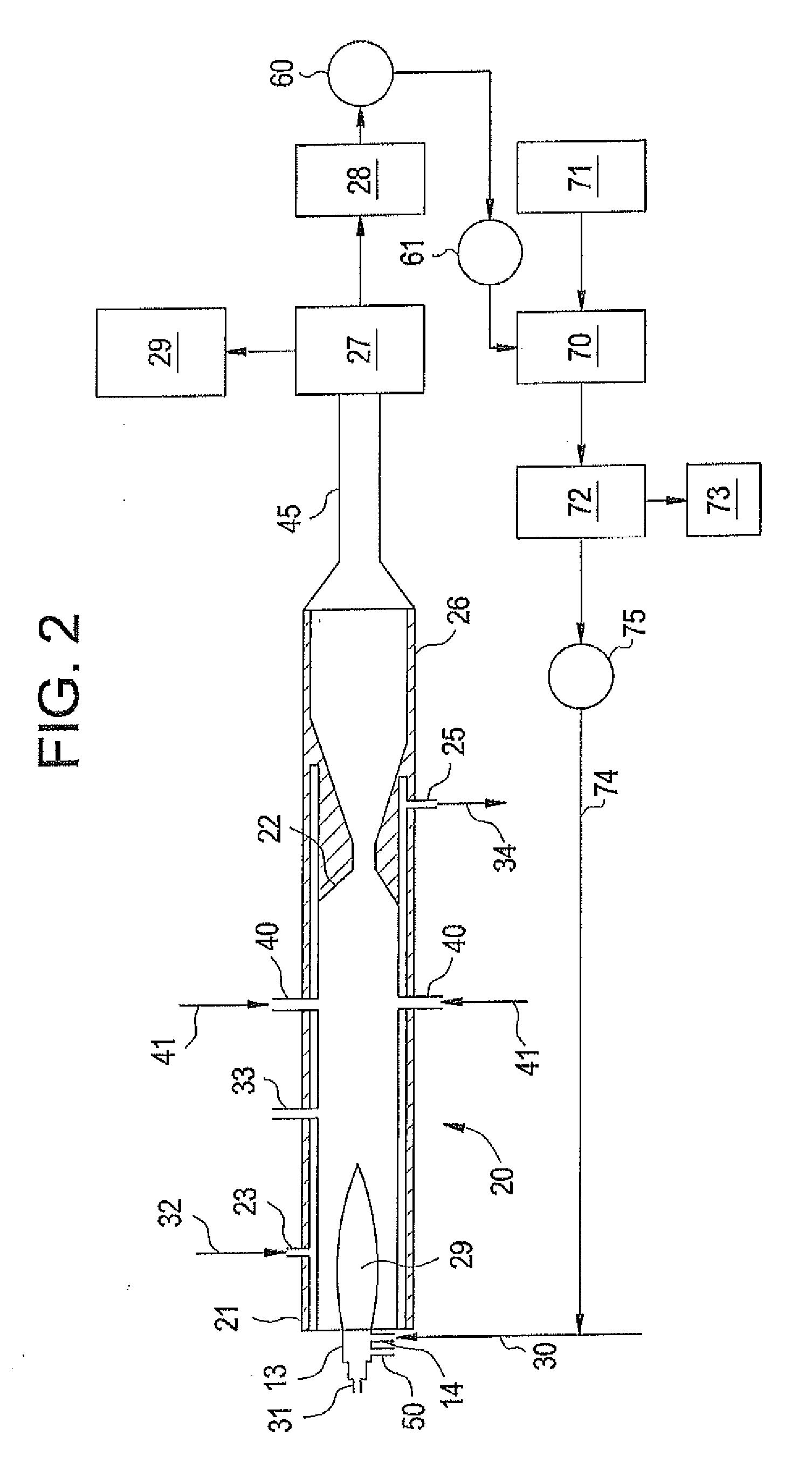
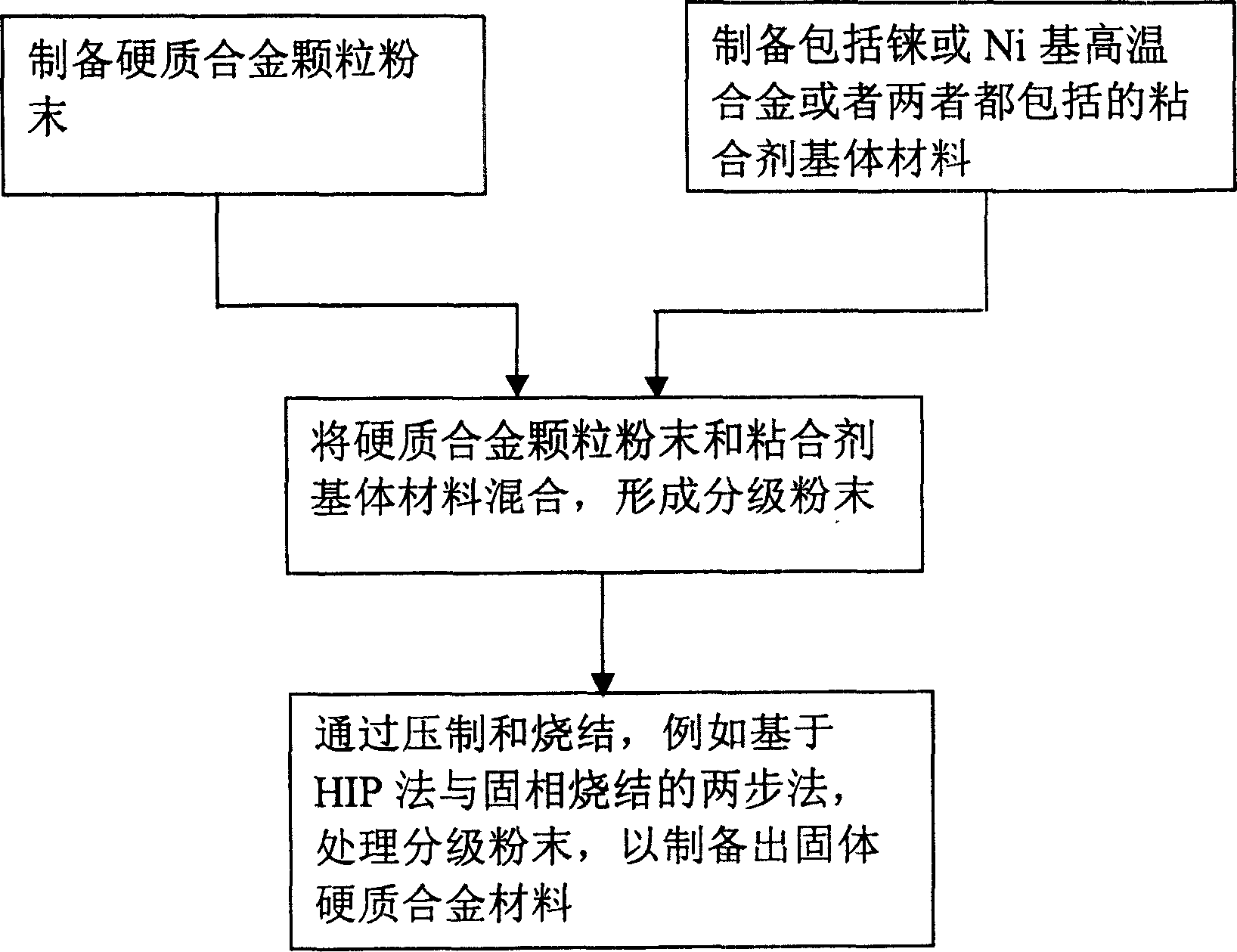
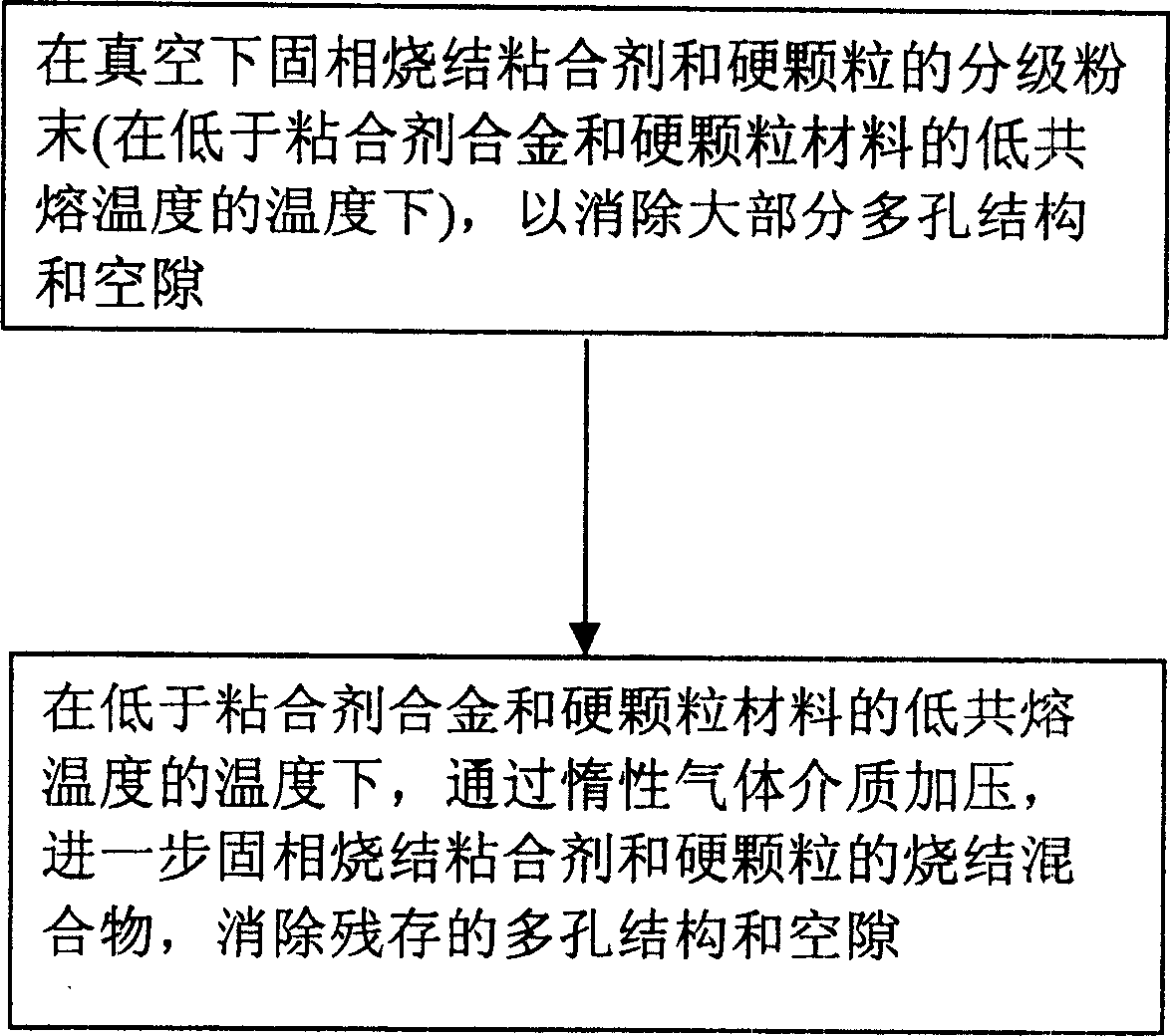
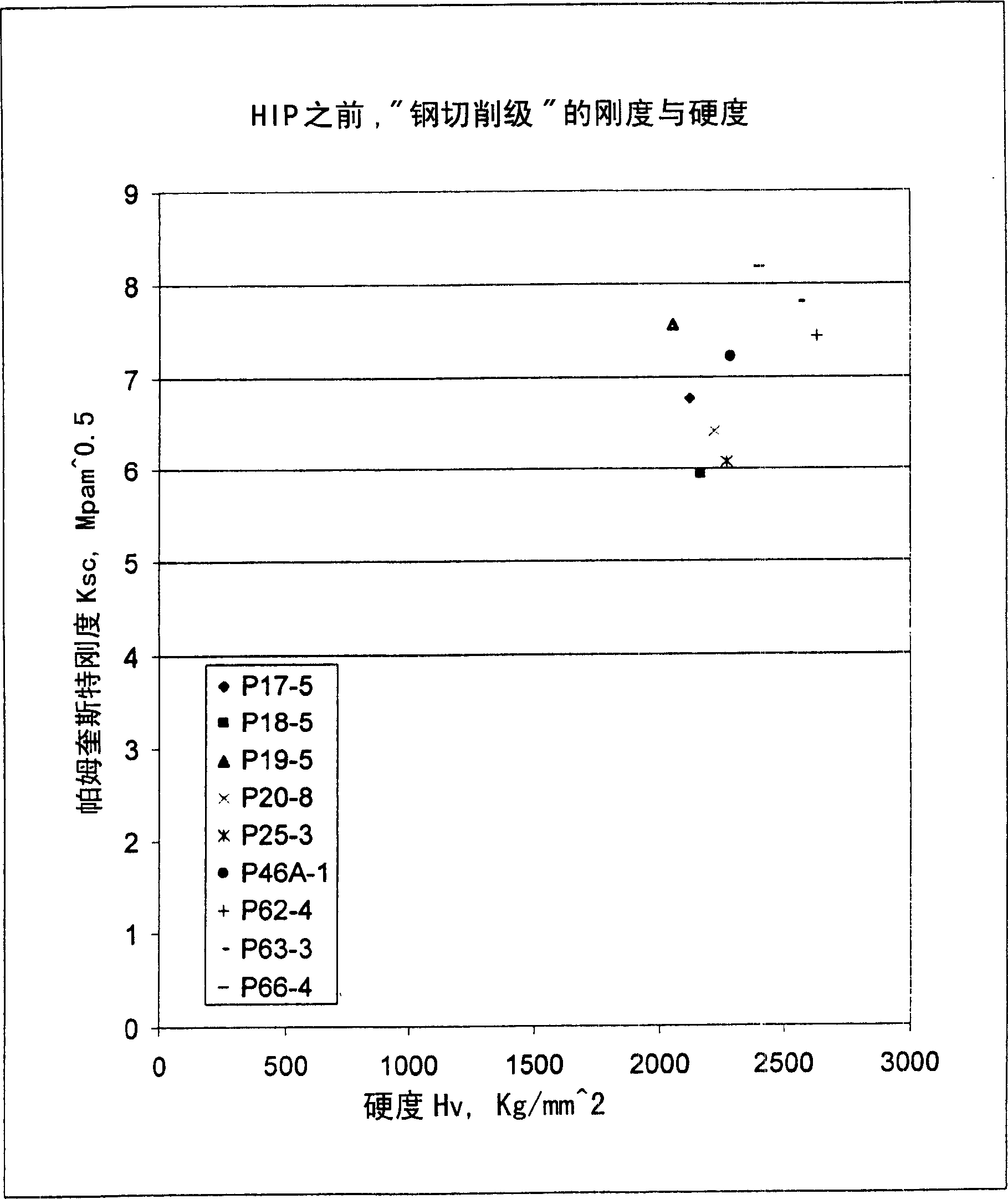
Compositions and fabrication methods for hardmetals
InactiveCN1592795AHigh hardnessAccelerated corrosionTungsten/molybdenum carbideRheniumCemented carbide
Hardmetal compositions each including hard particles having a first material and a binder matrix having a second, different material comprising rhenium or a Ni-based superalloy. A two-step sintering process may be used to fabricate such hardmetals at relatively low sintering temperatures in the solid-state phase to produce substantially fully-densified hardmetals.
Owner:竹箐工程有限公司
Method for producing fluids having suspended ultrasmall particles using multi-carbide grinding media
InactiveUS20050159494A1Increase mass densityExtreme hardnessPigmenting treatmentOther chemical processesCarbideHardness
Grinding media, including shaped media such as spheres or rods ranging in size from about 0.5 micron to 100 mm in diameter, are formed from a multi-carbide material consisting essentially of two or more carbide-forming elements and carbon, with or without carbide-forming elements in their free elemental state. The media have extremely high mass density, extreme hardness, and extreme mechanical toughness.
Owner:PRIMET PRECISION MATERIALS
Sintering process of superfine pure WC without adhering phase
The present invention is sintering process of superfine pure WC without adhering phase, and belongs to the field of powder metallurgy and hard material application. Superfine WC powder maintained in vacuum or inert gas atmosphere as material is densified in high strength graphite mold, set together with the mold between the upper and lower electrodes inside plasma sintering apparatus, which is then vacuumized to 5Pa, and electrically heated in the sintering temperature and pressed for sintering. The sintered sample is then taken out. The process has temperature raising speed of 180 deg.c / min, sintering temperature of 1400-1600 deg.c, and temperature maintaining period of 0-8 min. The no-adhesive phase super-pure WC material is sintered in the SPS technology process, the process is simple, low in cost and short in production period, and the obtained hard material has superior performance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method of micro-nano molybdenum carbide powder
InactiveCN107352543AGuaranteed to dissolveAvoid contactTungsten/molybdenum carbideMicro nanoMolybdate
The invention discloses a preparation method of micro-nano molybdenum carbide powder. The preparation method comprises the specific steps that an organic precursor serves as a carbon source, molybdate serves as a molybdenum source, fused salt serves as a reaction medium, high-temperature processing, washing and drying are conducted in sequence in an air environment, and the micro-nano molybdenum carbide powder is prepared. The preparation method is quick in reaction speed, and the reaction time is effectively shortened. Besides, the fused salt exists between the generated solid-phase molybdenum carbide particles in the reaction process, so that the mutual bonding between the particles can be stopped, and the agglomeration phenomenon can be reduced. In the method, no special atmospheric conditions are needed, the micro-nano molybdenum carbide material can be prepared at a relatively low temperature; the process is simple, the preparation conditions are mild, and a large scale of production is easy to achieve.
Owner:DONGGUAN UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of transition metal carbide material
InactiveCN1751990ASynthesis temperature is lowImprove conversion rateTungsten/molybdenum carbideFiberCrucible
A process for preparing the carbide of transition metal includes such steps as putting carbon in crucible, covering it by assistant and transition metal, heating to 600-1300 deg.C at 0.1-30 deg.C / min under protection of Ar gas or in vacuum, holding the temp for 0.1-200 hr, cooling, boiling the crucible in water, taking the carbide, water washing and drying.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of making multi-carbide spherical grinding media
Grinding media, including shaped media such as spheres or rods ranging in size from about 0.5 micron to 100 mm in diameter, are formed from a multi-carbide material consisting essentially of two or more carbide-forming elements and carbon, with or without carbide-forming elements in their free elemental state. The media have extremely high mass density, extreme hardness, and extreme mechanical toughness.
Owner:PRIMET PRECISION MATERIALS
Metal carbides and process for producing same
InactiveUS20060051281A1Minimize stress concentrationIncreased tortuosityMaterial nanotechnologyInorganic material artificial filamentsQuantum wellCarbide
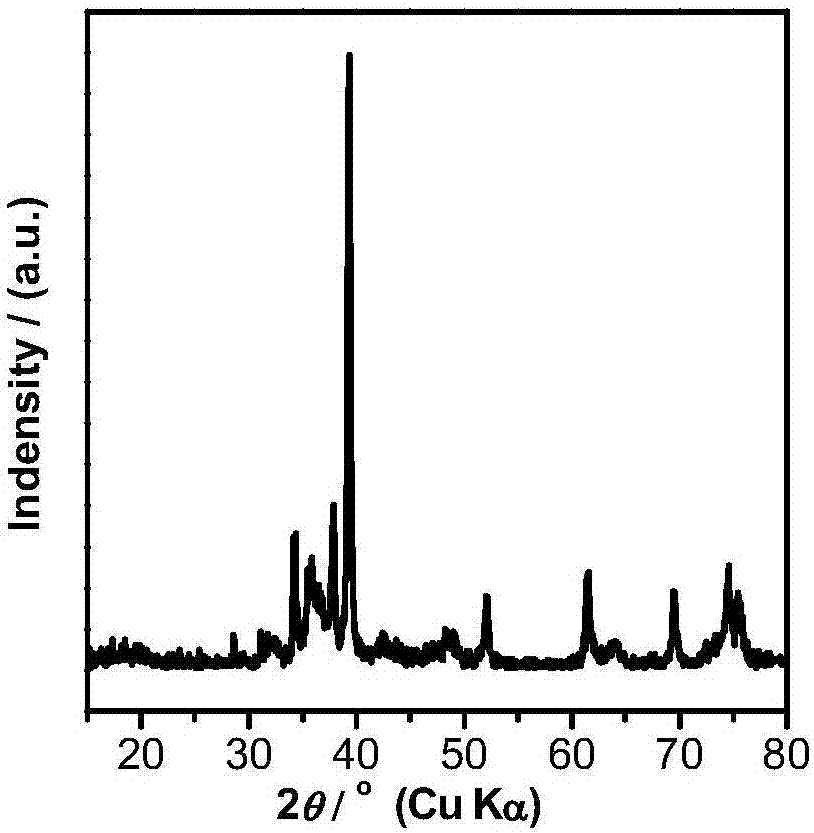
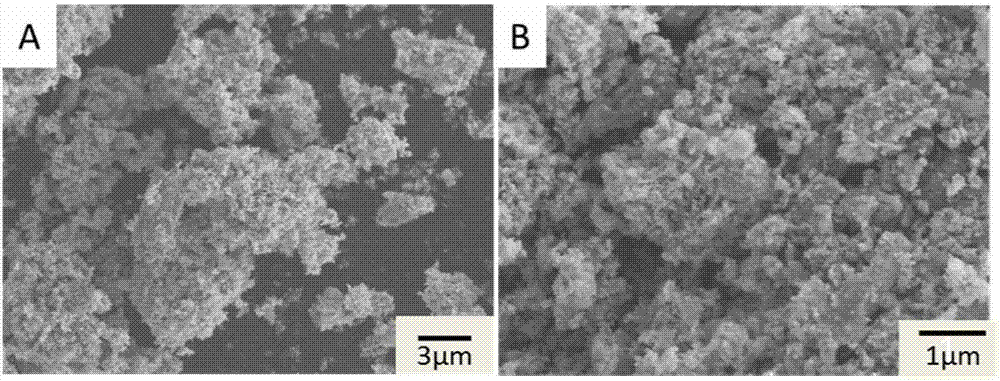
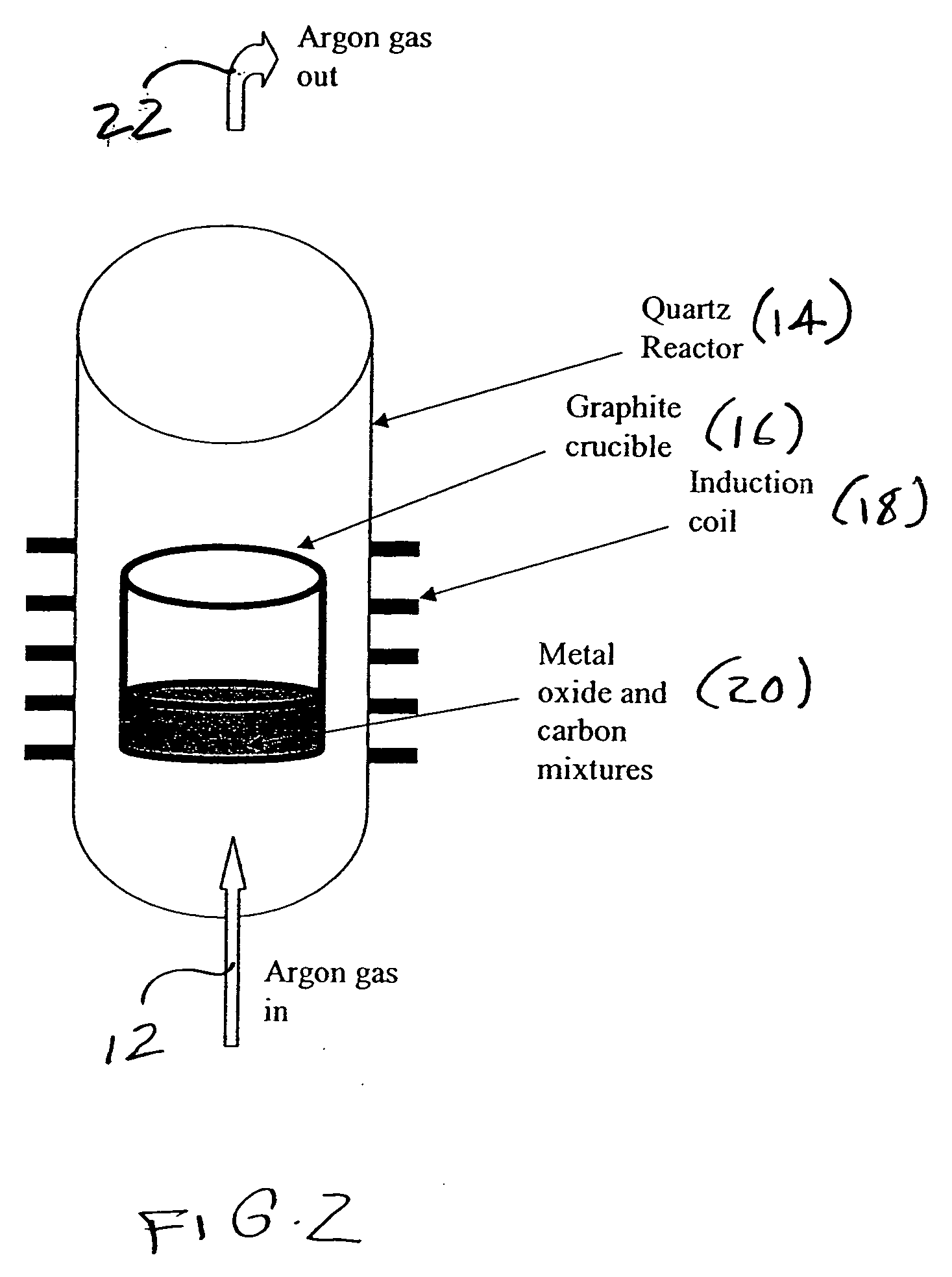
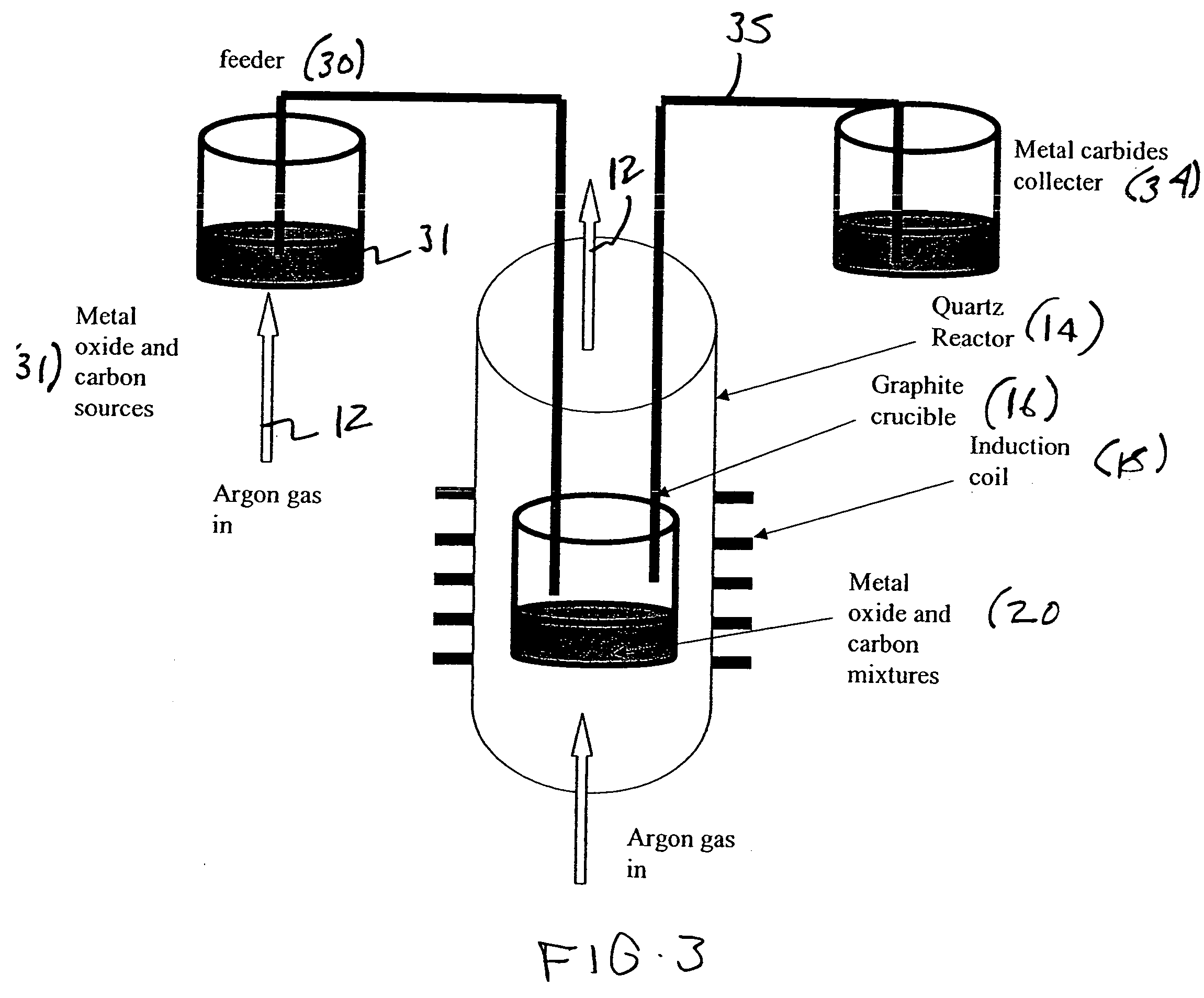
A metal carbide composition and a process for synthesizing metal carbides, through a single step process, wherein oxides of different metals, including, but not limited to Si, Ti, W, Hf, Zr, V, Cr, Ta, B, Nb, Al, Mn, Ni, Fe, Co, and Mo were physically mixed with spherical or filamentateous nano structured carbon, and inductively heated to a certain temperature range (900-1900° C.) where the metal oxide reacts with carbon to form different metal carbides. The process retains the original morphology of the starting carbon precursor in the resultant metal carbides. This method also produces highly crystalline metal nano-carbides. The metal carbide products would have applications in high temperature thermoelectric devices, quantum wells, optoelectronic devices, semi-conductors, body armour, vehicle armour, catalysts, and as discontinuous reinforced agents in metal such as aluminum and other alloys.
Owner:COLUMBIAN CHEM CO
Carburized monotungsten and ditungsten carbide eutectic particles, materials and earth-boring tools including such particles, and methods of forming such particles, materials, and tools
Earth-boring tools for drilling subterranean formations include a particle-matrix composite material comprising a plurality of at least partially carburized monotungsten carbide and ditungsten carbide eutectic particles dispersed throughout a matrix material. In some embodiments, the particles are at least substantially fully carburized monotungsten carbide and ditungsten carbide eutectic particles. In further embodiments, the particles are generally spherical or at least substantially spherical. Methods of forming such particles include exposing a plurality of monotungsten carbide and ditungsten carbide eutectic particles to a gas containing carbon. Methods of manufacturing such tools include providing a plurality of at least partially carburized monotungsten carbide and ditungsten carbide eutectic particles or at least substantially completely carburized monotungsten carbide and ditungsten carbide eutectic particles within a matrix material.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Method for producing an ultrasmall device using multi-carbide grinding media
Grinding media, including shaped media such as spheres or rods ranging in size from about 0.5 micron to 100 mm in diameter, are formed from a multi-carbide material consisting essentially of two or more carbide-forming elements and carbon, with or without carbide-forming elements in their free elemental state. The media have extremely high mass density, extreme hardness, and extreme mechanical toughness.
Owner:PRIMET PRECISION MATERIALS
Matrix powder for matrix body fixed cutter bits
A matrix powder for forming a matrix bit body, the matrix powder essentially consisting of a plurality of carbide particles having a particle size distribution of ±20% of a median particle size; and a plurality of metal binder particles is disclosed.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Method for synthesizing carbide nano powder by solid-phase reaction
InactiveCN101891192AControl morphologyRaw materials are easy to getTungsten/molybdenum carbideReaction temperatureMixed materials
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing carbide nano powder by a solid-phase reaction, which comprises the following steps of: mixing a silicon source or a metal source, a carbon source, magnesium powder and elementary iodine according to a mol ratio of 1: (0.05-2): (1-25): (1.25-12), sealing the mixed material in an autoclave, and placing the autoclave in a drying box to perform a reaction for 6 to 48 hours at the temperature of between 100 and 500 DEG C; and washing, separating and drying the product to obtain the carbide nano powder. In the invention, glucose or maltose which universally exists in the natural world is used as the carbon source to avoid using a chlorine-containing carbon source such as carbon tetrachloride and tetrachloroethylene which have bad influences on an operation environment, and the reaction temperature and the reaction pressure are relatively mild, so that the method for synthesizing carbide nano powder by the solid-phase reaction has a potential for mass production.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Methods for producing titanium metal using multi-carbide grinding media
InactiveUS20050155455A1Increase mass densityExtreme hardnessOther chemical processesDiamondTitanium metalCarbide
Grinding media, including shaped media such as spheres or rods ranging in size from about 0.5 micron to 100 mm in diameter, are formed from a multi-carbide material consisting essentially of two or more carbide-forming elements and carbon, with or without carbide-forming elements in their free elemental state. The media have extremely high mass density, extreme hardness, and extreme mechanical toughness.
Owner:PRIMET PRECISION MATERIALS
Method for preparing nano-stage tungsten carbide powder
ActiveCN101264888AImprove performanceShort processNanostructure manufactureTungsten/molybdenum carbideNano carbonNanometre
The invention discloses a nano-tungsten carbide powder (particle size is less than or equal to 0.2Mum, carbon compound Cc is more than or equal to 6.10%) preparation method. The preparation takes nano-tungsten (particle size is less than or equal to 0.2Mum) powder and nano-carbon black as materials and comprises a plurality of steps: put the nano-tungsten powder and nano-carbon black into a container; pass the inert gas in the container and mix and stir nano-tungsten powder and nano-carbon black in a state of inert gas the protection; in mixing, add 0.5-3% organic and active materials; after the mixed powder is uniformly mixed, press the mixed powder into pieces under the pressure of 500kg / cm2 -- 1500kg / cm 2 and calcine the pressed pieces (W+C) to make the nano-tungsten powder and tungsten carbide nano-carbon black form tungsten carbide(WC); after the formation of tungsten carbide(WC), adopt the method of airflow grinding to grind and break up the tungsten carbide into nano-tungsten carbide powder. The method has advantages of short technological process, small investment, high yield and great improvement for production quality and stability and is an environment-friendly preparation method.
Owner:XIAMEN GOLDEN EGRET SPECIAL ALLOY +1
Matrix powder for matrix body fixed cutter bits
A matrix powder for forming a matrix bit body, the matrix powder essentially consisting of a plurality of carbide particles having a particle size distribution of ±20% of a median particle size; and a plurality of metal binder particles is disclosed.
Owner:SMITH INT INC
Preparation method of tungsten carbide nanopowder
InactiveCN102190299AHigh purityReduce the introductionNanostructure manufactureTungsten/molybdenum carbideOrganic acidResidual carbon
The invention provides a preparation method of tungsten carbide nanopowder. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a tungsten-carbon precursor by using soluble tungsten salt and organic acid as raw materials through a sol-gel method, and then carrying out heat treatment on the tungsten-carbon precursor to obtain the tungsten carbide nanopowder. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple and practical, avoids the multistep control mode of the traditional preparation methods, saves energy, and is suitable for industrial production; and the tungsten carbide nanopowder prepared by the invention has the advantages of uniform and small particle size (smaller than 50 nm), low aggregation degree, low impurity content and low residual carbon content (lower than 0.5wt%).
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
In-situ synchronous synthesizing method of tungsten carbide/graphitic carbon nano complexes
ActiveCN101456552AEvenly distributedWidely distributed and cheapTungsten/molybdenum carbideState of artCarbonization
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing a tungsten carbide / graphite carbon nano composition through in-situ synchronization, which relates to a method for preparing the tungsten carbide / graphite carbon nano composite. The method solves the problem of nonuniform tungsten carbide distribution in the prior art for preparing the tungsten carbide / graphite carbon nano composite. The method comprises: firstly, pretreatment of carbon sources; secondly, dissolution of a graphitized catalyst and tungsten sources into a solvent, addition of the pretreated carbon sources, and dispersion; thirdly, pre-carbonization; fourthly, heat treatment; fifthly, acid treatment; and sixthly, physical activation or chemical activation. The method has the advantages of simple technology, uniform tungsten carbide distribution, small environmental pollution, low cost and simple required equipment, and is easy to realize commercialization.
Owner:佛山市菲玛斯新材料科技有限公司
Synthesis of stephanoporate molybdenum carbide nano-wire
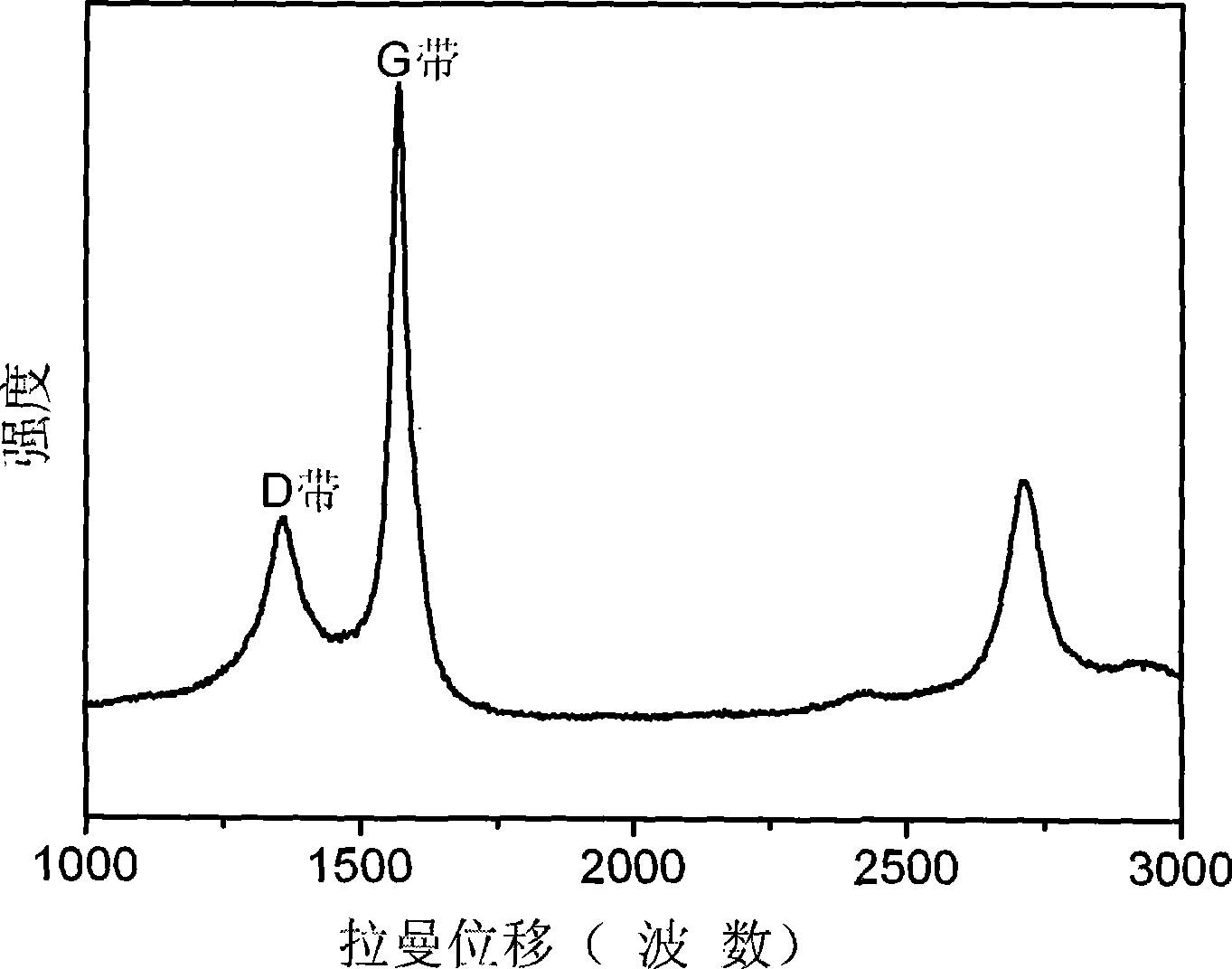
InactiveCN101367521AHigh surface areaSmall surface areaTungsten/molybdenum carbideMolybdateGranularity
The invention relates to the technical field of the nanometer material, and relates to a method for synthesizing the porous molybdenum carbide nanometer wire, and adopts the following steps: molybdate is dissolved in the water, and the mol concentration of the molybdenum atom is 0.02 to 1.5 mol / L; organic amine is filled in, and the mol ratio between the organic amine and the molybdenum atom is 20.0 to 1.0: 1; inorganic acid is dropped into the solution, and the pH value is adjusted to be 3 to 6 until the white precipitate appears; the reaction solution is moved into an oil bath with the temperature of 30 to 60 DEG C to be reacted for 6 to 24 hours; (5) the product is washed, pumped, filtered and dried; the product is baked in the inert gases atmosphere at the temperature of 675 to 750 DEG C for 4 to 10 hours. The invention has the advantages that abundant nanometer hole structure is arranged between the nanometer particles, the granularity of the molybdenum carbide is small, the molybdenum carbide has rich porous structure and large specific surface area, the carbon on the surface is small, thereby favoring the secondary assembling of the catalyst and having wide application fields; the productivity can reach 95 percent or more; the conditions are simple and easy to be controlled; the preparation efficiency is high; the invention has favorable application and industrialization prospect.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Submicron narrow particle size distribution type tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder and preparation method thereof
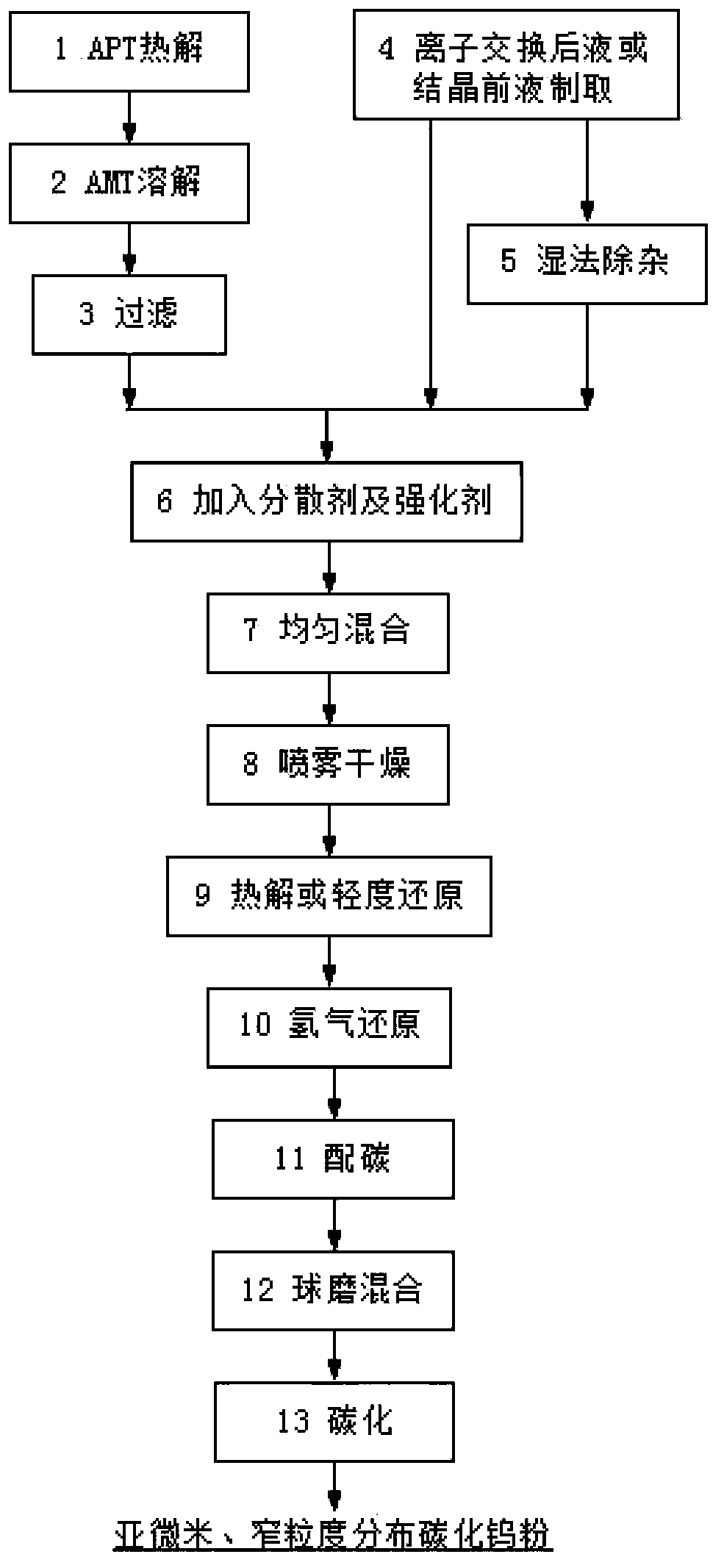
ActiveCN103570020AControllable wall thicknessPurity does not affectTungsten/molybdenum carbideTungstateKetone
The invention relates to submicron narrow particle size distribution type tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the field of metallurgic powder preparation of refractory metal powder. The submicron narrow particle size distribution type tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder are characterized in that the average particle size is 0.1 to 1.0 micron, and the maximum particle size is not greater than twice of the average particle size. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking an ammonium tungstate solution as a raw material and a high molecular surfactant as a dispersing agent; reinforcing the dispersion effect through alcohol or ketone; quickly crystallizing and drying by spray drying to obtain fine particle hollow thin-walled spherical ammonium tungstate crystals; and performing pyrolysis, hydrogen gas reduction and carbonizing; and then generating submicron narrow particle size distribution type tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder in situ. According to the preparation method, the submicron narrow particle size distribution type tungsten powder and tungsten carbide powder can be prepared in situ; and the technology is reformed and upgraded on the basis of the existing production condition of the enterprise, so that the scale production is easily realized, the production efficiency is high, and the effect is great.
Owner:GRIMAT ENG INST CO LTD
Method for manufacturing nanophase TiC-based composite powders by metallothermic reduction
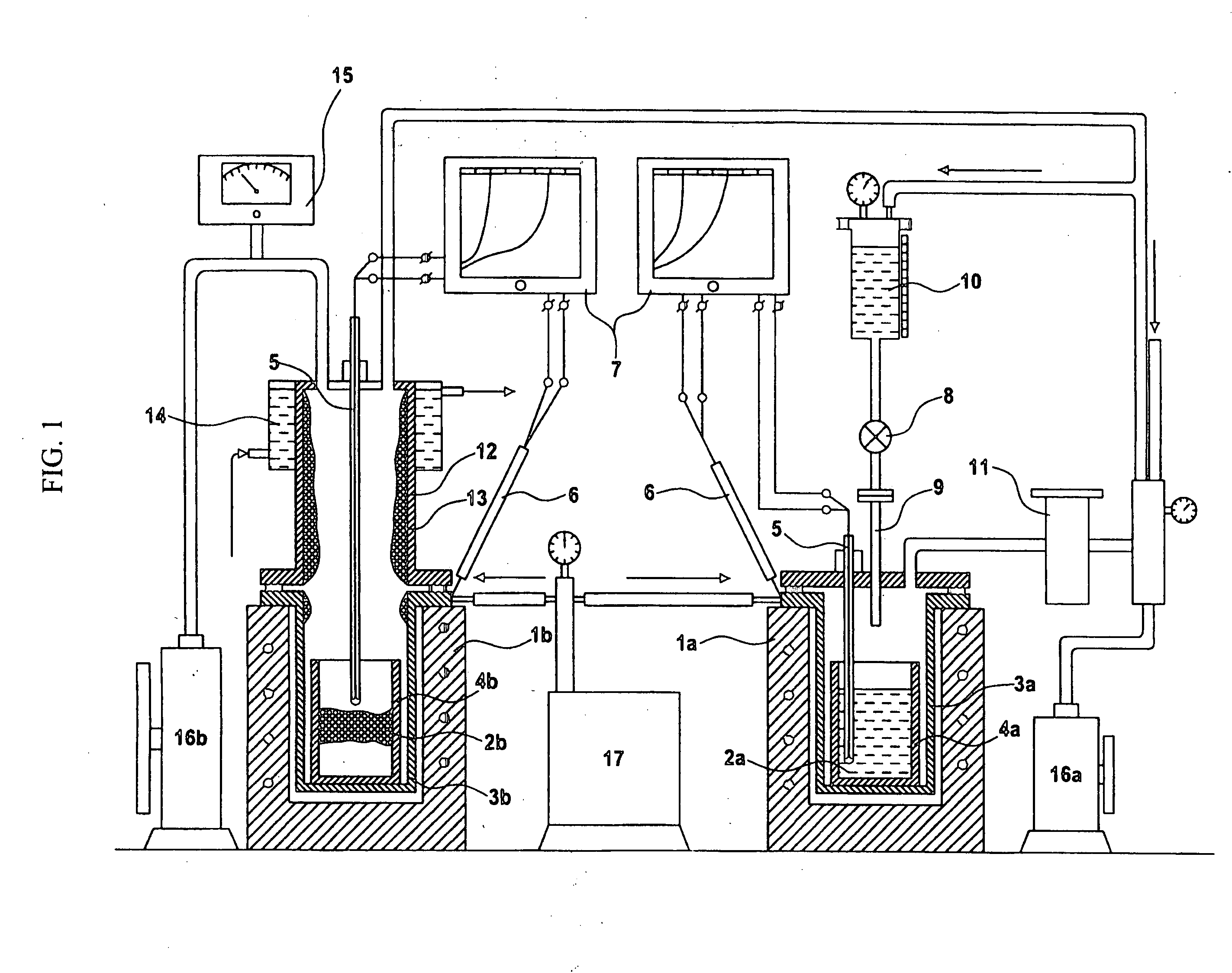
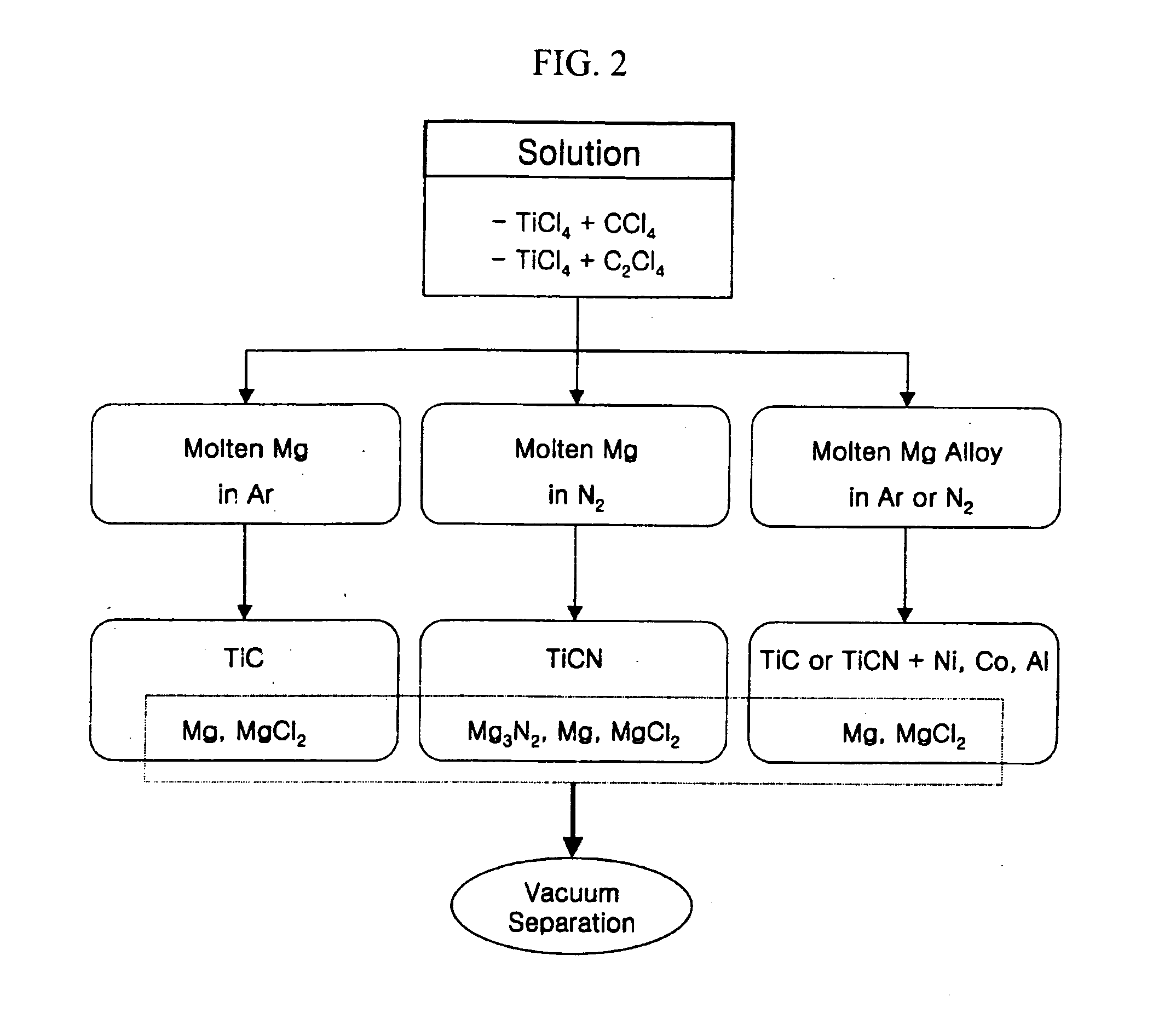
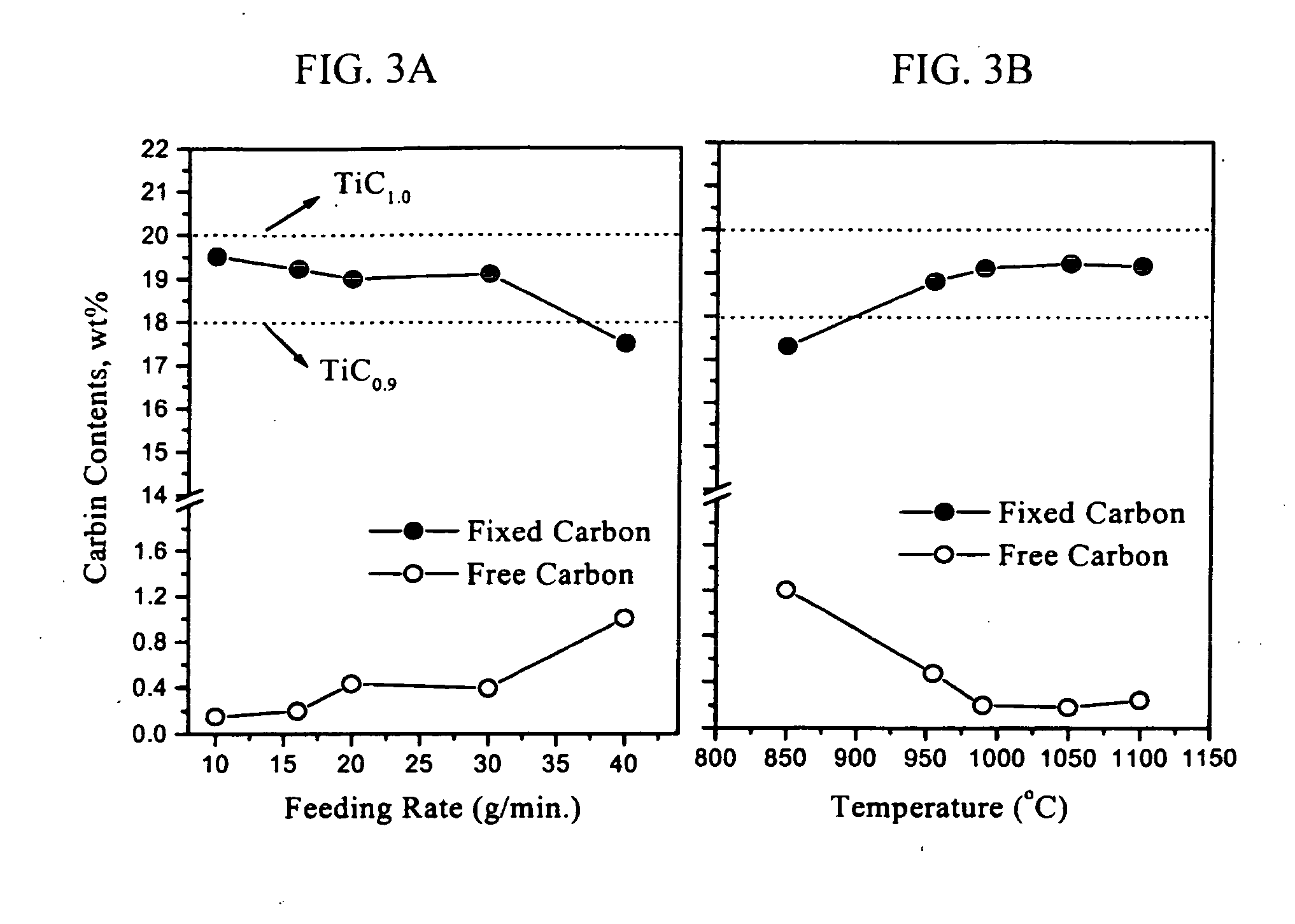
Disclosed herein is a method for economically manufacturing high quality TiC powder, TiCN powder or ultrafine nanophase TiC+Ni (Co, Al) and TiCN+Ni (Co, Al) composite powders by means of metallothermic reduction. The method comprises the steps of preparing a starting solution of titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4) in a carbon chloride, feeding the starting solution into a closed container containing molten magnesium (Mg) under inert atmosphere, vacuum-separating unreacted liquid-phase Mg and magnesium chloride (MgCl2) remaining after reduction of magnesium from the closed container, and collecting a TiC compound from the closed container. TiC powder, TiCN powder or ultrafine nanophase TiC+Ni (Co, Al) and TiCN+Ni (Co, Al) composite powders having a particle size of a few tens nm can be manufactured in a simpler manner using economically advantageous starting materials such as titanium tetrachloride and carbon chlorides.
Owner:KOREA INST OF MASCH & MATERIALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com