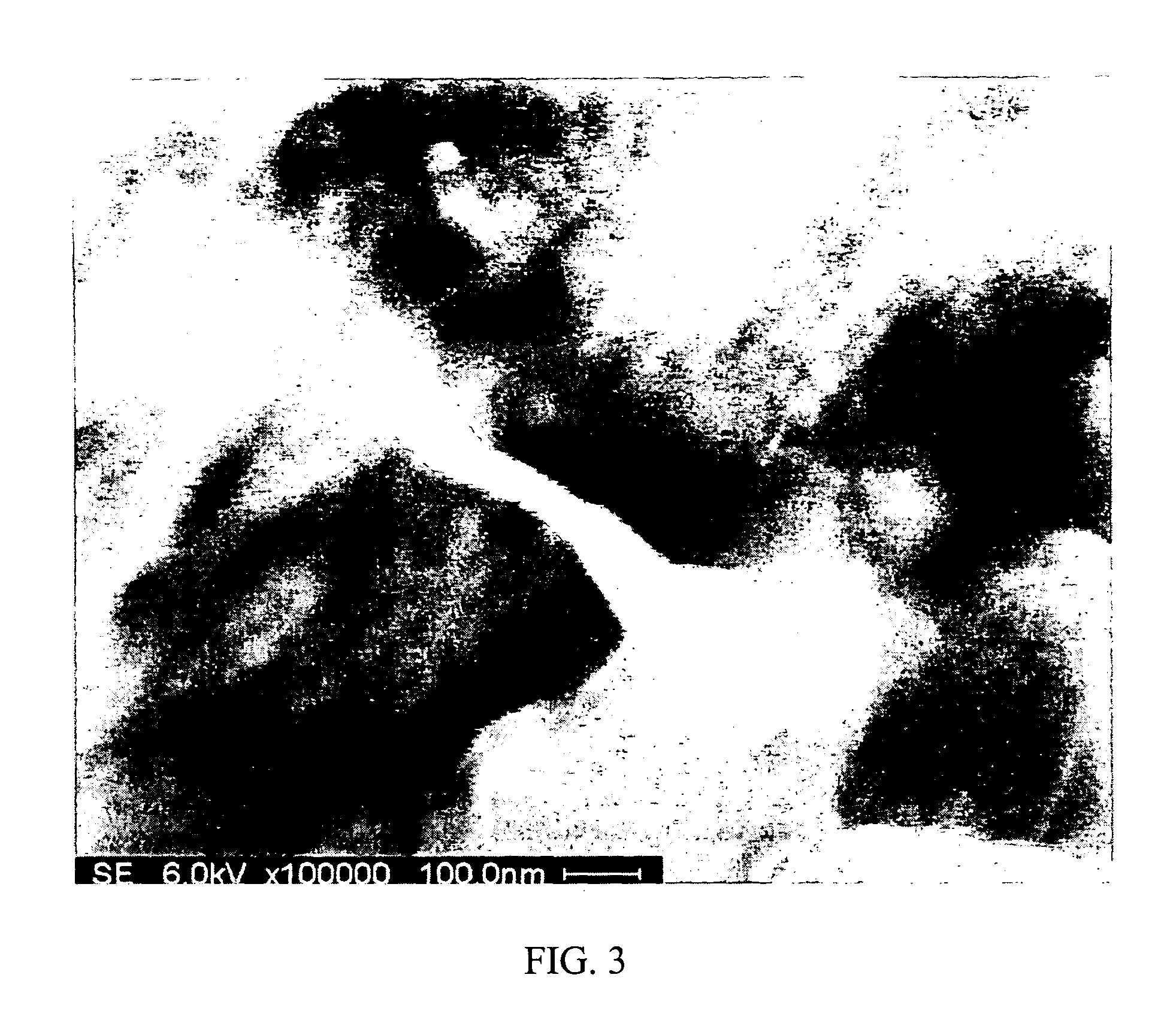Patents
Literature
102 results about "Polymethylpentene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymethylpentene (PMP), also known as poly(4-methyl-1-pentene), is a thermoplastic polymer of 4-methyl-1-pentene. It is used for gas permeable packaging, autoclavable medical and laboratory equipment, microwave components, and cookware. It is commonly called TPX, which is a trademark of Mitsui Chemicals.
Multi-layer plastic articles and methods of making the same
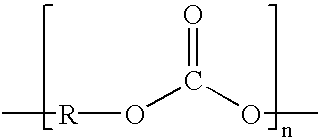
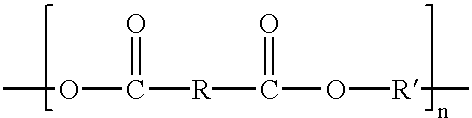
A three-dimensional, multi-layer plastic product that is resistant to damage caused by environmental factors such as heat, chemicals, desiccants, oxygen, and / or weather is disclosed. The multi-layer product includes an engineering resin layer affixed to a commodity resin layer. The engineering resin layer of the multi-layer film may be directly fused to the commodity resin or post-consumer regrind layer. Alternatively, the engineering resin layer may be tied to the commodity resin or post-consumer regrind layer through the use of one or more adhesive and / or tie layers. The commodity resin layer may be manufactured from an economical polymer material such as a polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene or post-consumer regrind. Suitable engineering resins may be any of a variety of suitable materials such as a polysulphone, polymethylpentene, polyester, polycarbonate, polyetherimide, nylon, polyarylate, polyphenylenesulphide, polyphenylene oxide, polyethersulphone, aromatic polyketone, liquid crystal polymer, and mixtures thereof, for example, a method for manufacturing a three-dimensional multi-layer plastic product is also disclosed which includes the steps of providing an extruded or laminated sheet comprising an engineering resin layer, thermoforming a three-dimensional shell from the sheet, and injection molding a commodity resin layer onto the thermoformed shell.
Owner:RUBBERMAID
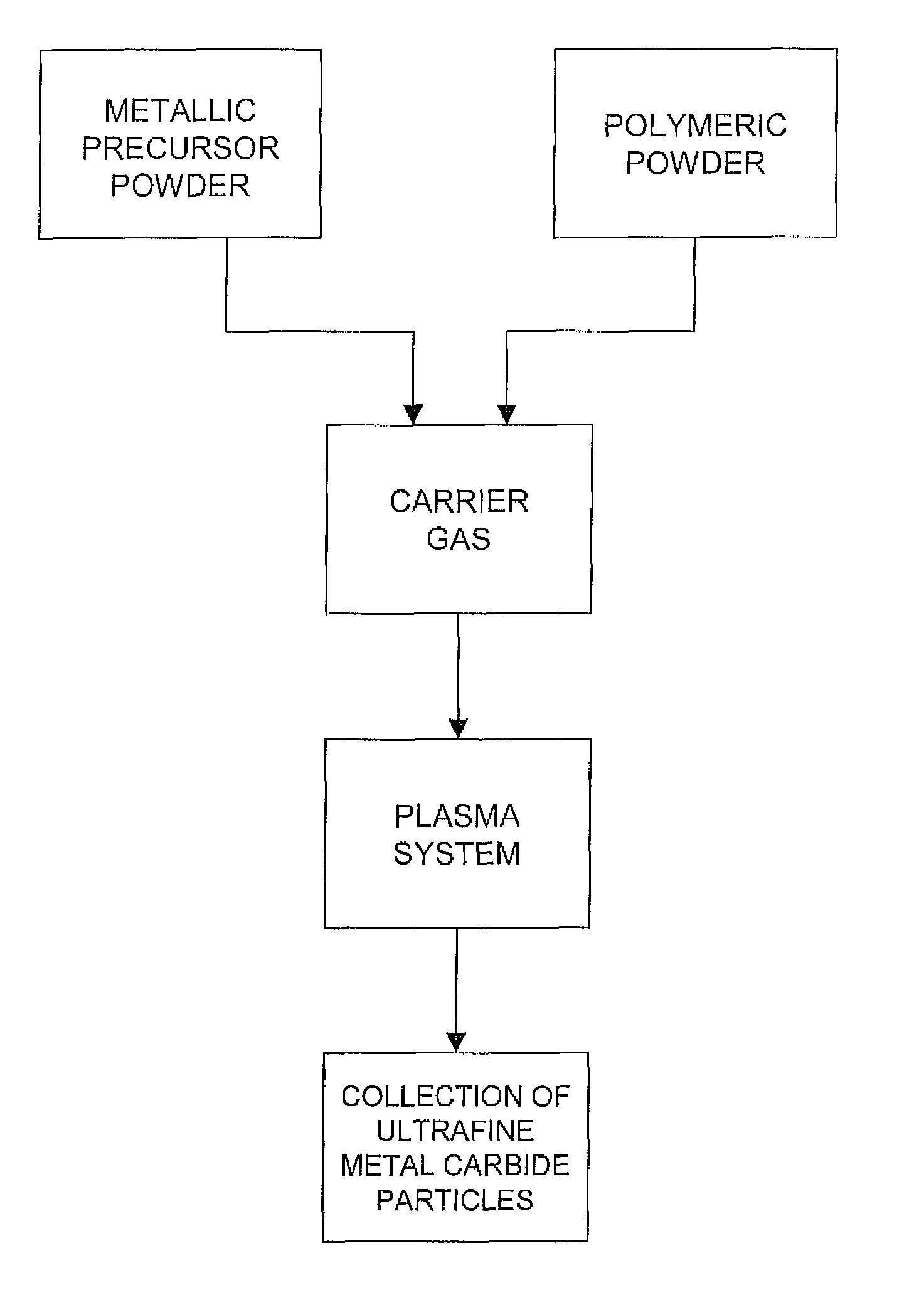
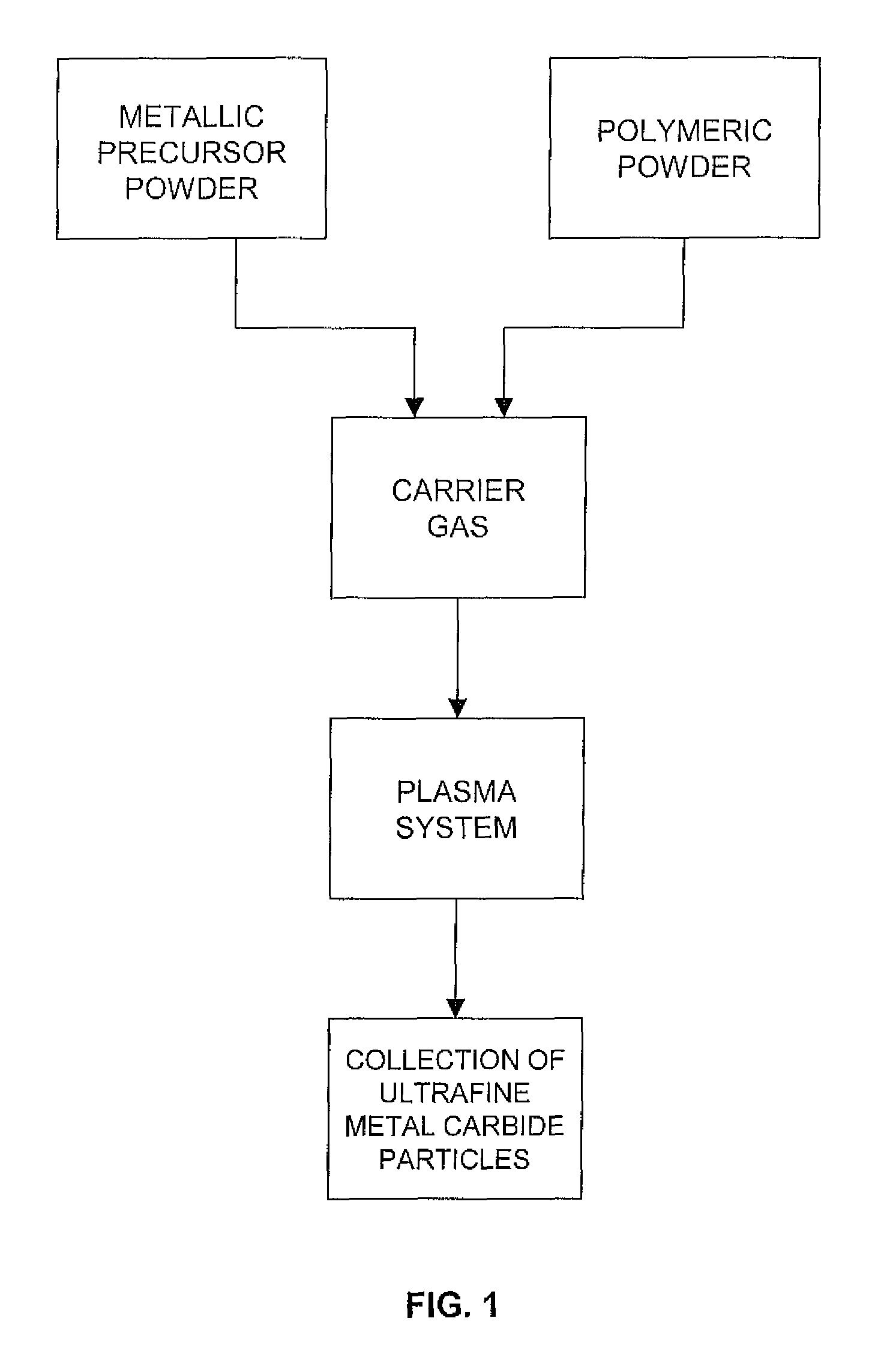
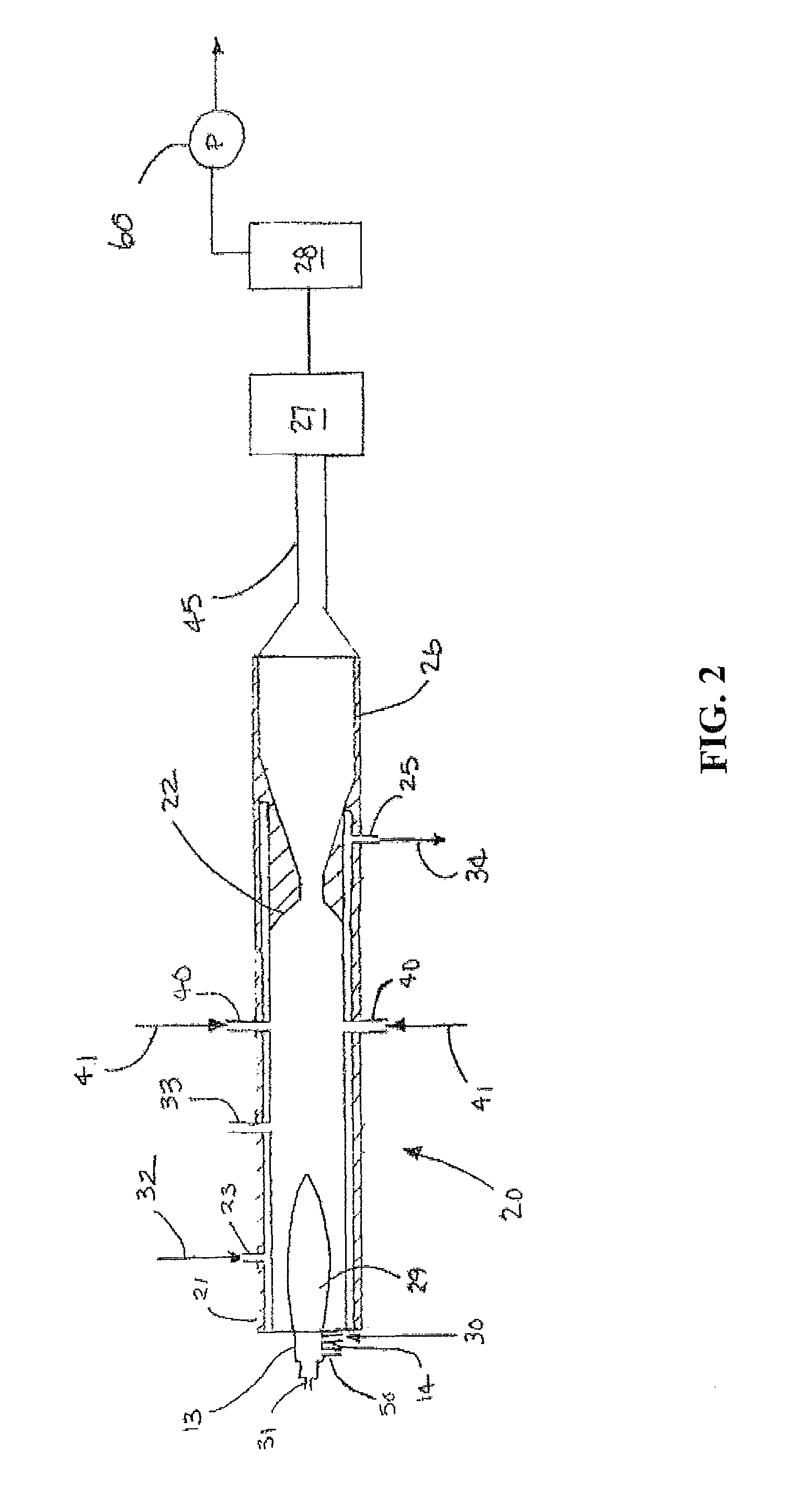
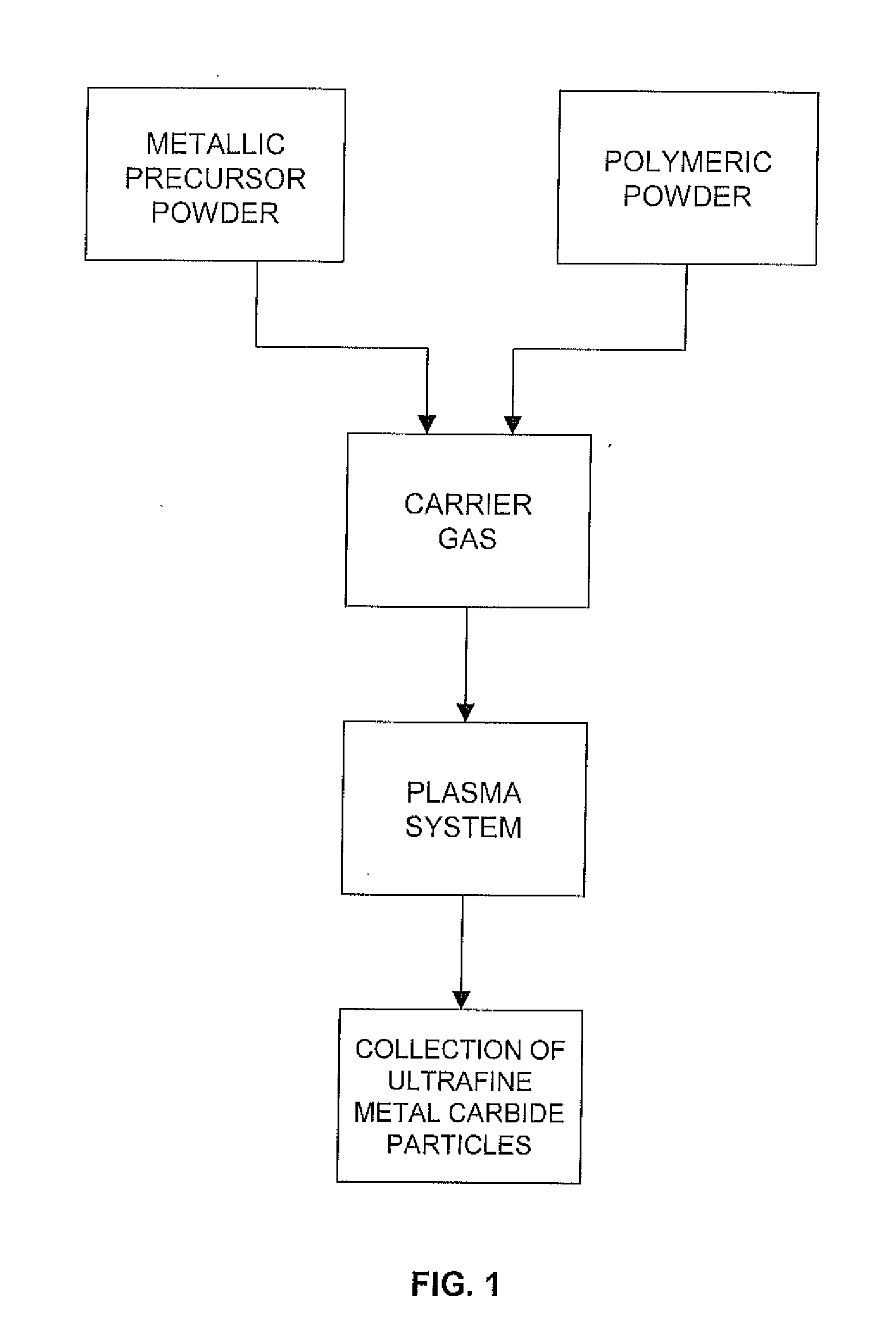
Production of ultrafine metal carbide particles utilizing polymeric feed materials
The production of ultrafine metal carbide powders from polymeric powder and metallic precursor powder starting materials is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the polymeric powder may comprise polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyester, polybutylene, nylon, polymethylpentene and the like. The metal precursor powder may comprise pure metals, metal alloys, intermetallics and / or metal-containing compounds such as metal oxides and nitrides. In one embodiment, the metal precursor powder comprises a silicon-containing material, and the ultrafine powders comprise SiC. The polymeric and metal precursor powders are fed together or separately to a plasma system where the feed materials react to form metal carbides in the form of ultrafine particles.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
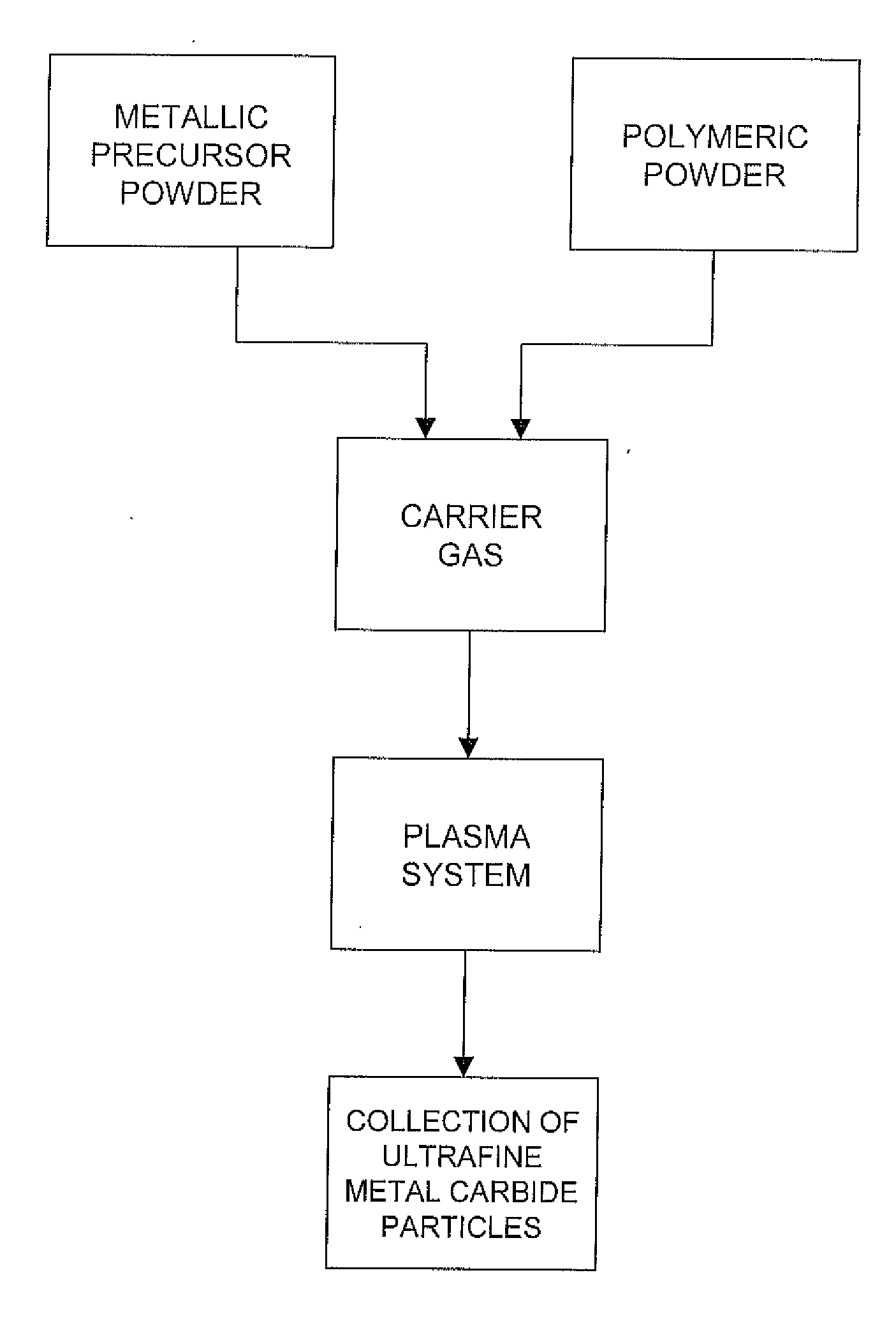
Production of ultrafine metal carbide particles utilizing polymeric feed materials
The production of ultrafine metal carbide powders from polymeric powder and metallic precursor powder starting materials is disclosed. In certain embodiments, the polymeric powder may comprise polypropylene, polyethylene, polystyrene, polyester, polybutylene, nylon, polymethylpentene and the like. The metal precursor powder may comprise pure metals, metal alloys, intermetallics and / or metal-containing compounds such as metal oxides and nitrides. In one embodiment, the metal precursor powder comprises a silicon-containing material, and the ultrafine powders comprise SiC. The polymeric and metal precursor powders are fed together or separately to a plasma system where the feed materials react to form metal carbides in the form of ultrafine particles.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
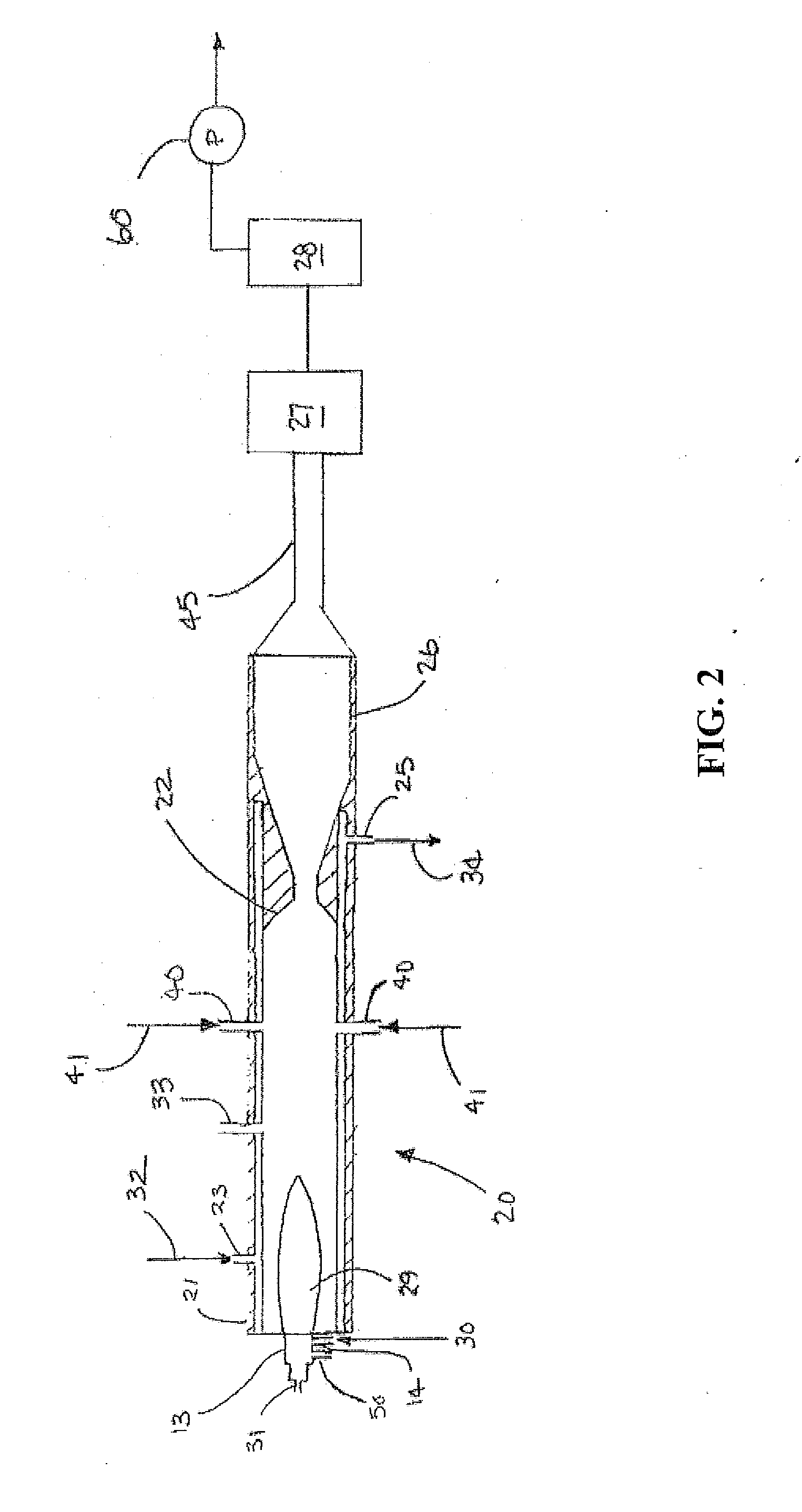
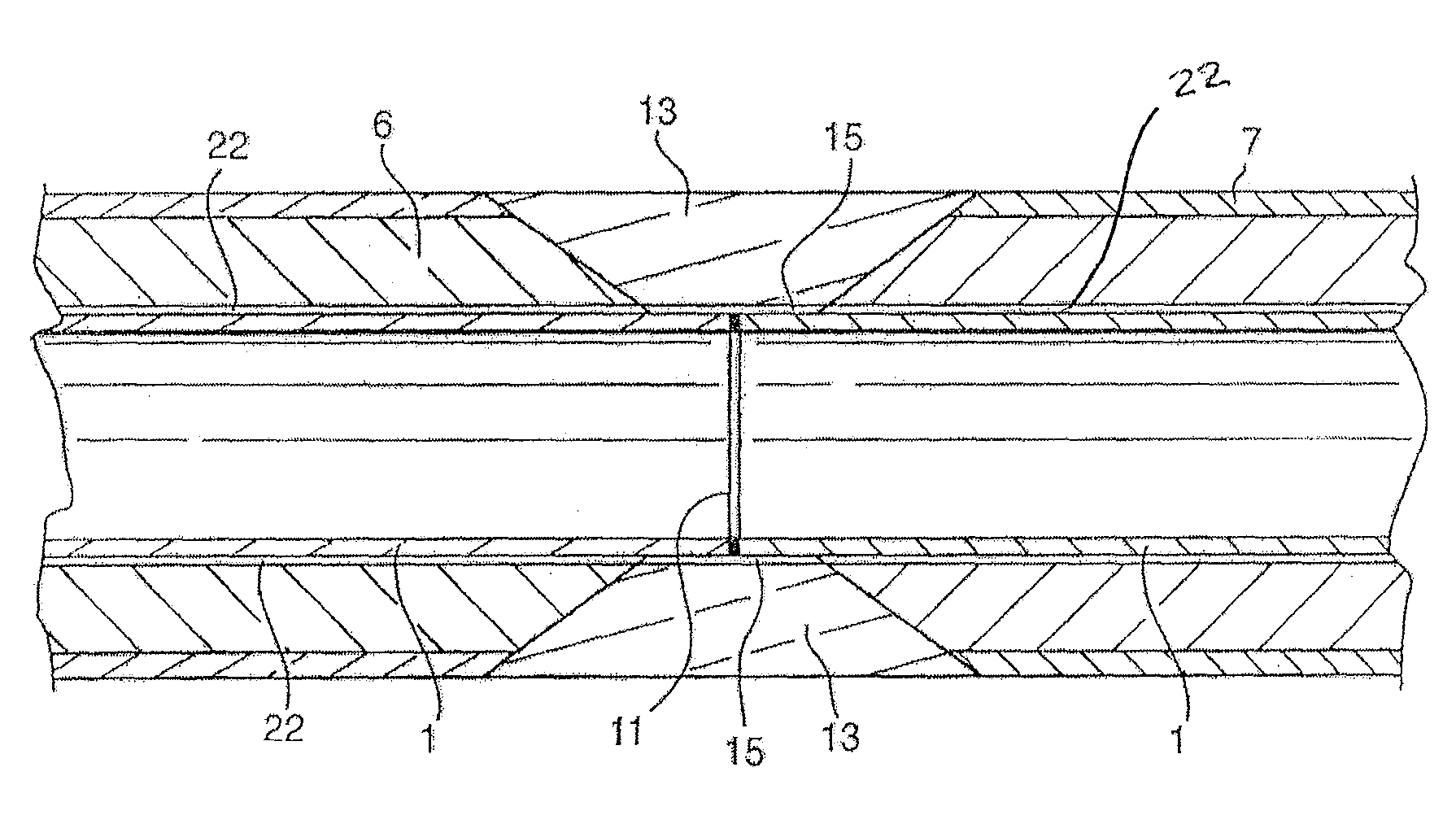
High temperature resistant insulation for pipe
ActiveUS8397765B2Low thermal conductivityImprove thermal stabilityThermal insulationSynthetic resin layered productsElastomerPolyetherimide
A polymeric composition for insulating fluid and / or gas transport conduits, such as off-shore oil and gas pipelines operating at temperatures of 130° C. or higher in water depths above 1,000 meters. The outer surface of the conduit is provided with at least one layer of solid or foam insulation comprising a high temperature resistant thermoplastic having low thermal conductivity, high thermal softening point, high compressive strength and high compressive creep resistance. The high temperature resistant thermoplastic is selected from one or more members of the group comprising: polycarbonate; polyphenylene oxide; polyphenylene oxide blended with polypropylene, polystyrene or polyamide; polycarbonate blended with polybutylene terephthalate, polyethylene terephthalate, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, acrylonitrile styrene acrylate, or polyetherimide; polyamides, including polyamide 12 and 612 and elastomers thereof; polymethylpentene and blends thereof; cyclic olefin copolymers and blends thereof; and, partially crosslinked thermoplastic elastomers, also known as thermoplastic vulcanizates or dynamically vulcanized elastomers.
Owner:SHAWCOR LTD
Fibrous structures derived from renewable resources
Disclosed herein are co-formed fibrous structures that are composed of (a) a plurality of filaments that have a biobased content of at least about 25% and selected from the group consisting of polypropylene, polyethylene, polymethylpentene, polybutylene-1, polyisobutylene, ethylene propylene copolymer, ethylene propylene diene monomer copolymer or rubber, and mixtures thereof; and, (b) a solid additive including a cellulosic fiber. The solid additive is present in an amount of at least about 30 wt. %, based on the total weight of the fibrous structure. The co-formed fibrous structures of the invention can themselves be articles, such as, paper, fabrics, and absorbent pads.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
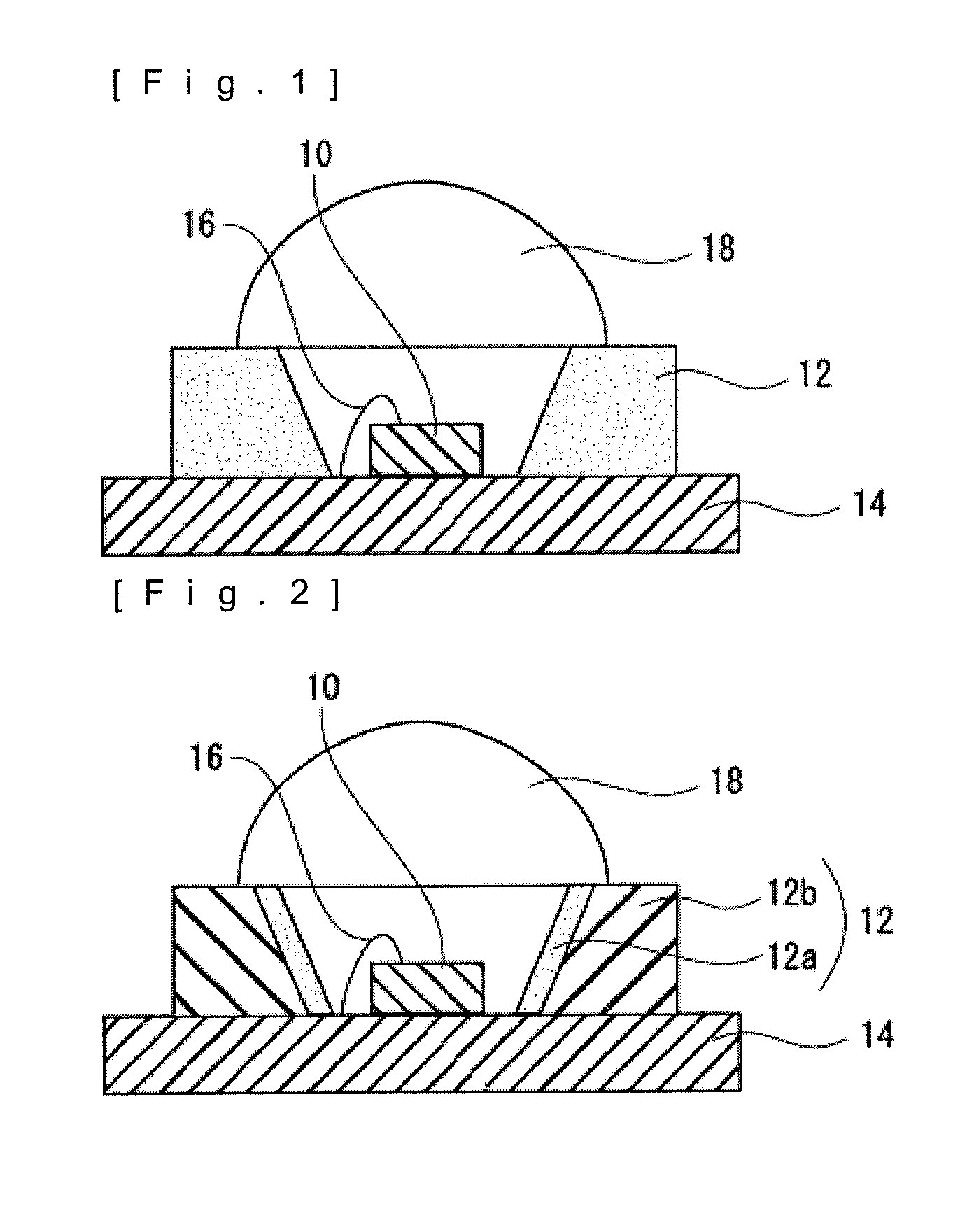
Electron beam curable resin composition, resin frame for reflectors, reflector, semiconductor light emitting device, and method for producing molded body
InactiveUS20150041839A1Improve heat resistanceLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsPolymer scienceCross linker
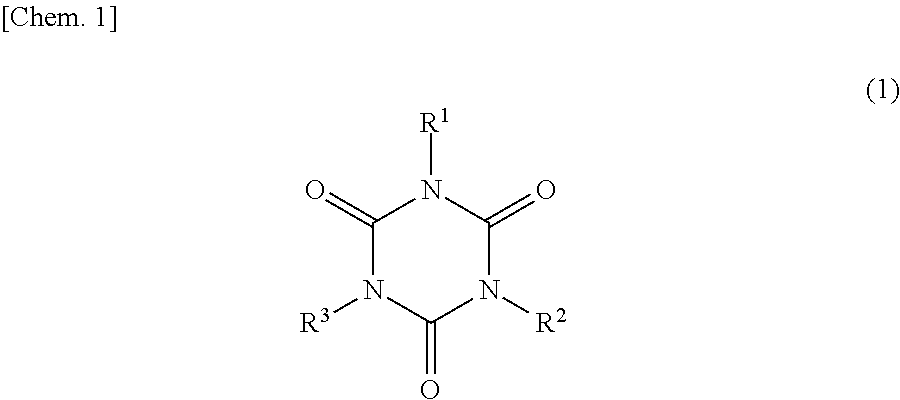
Provided are an electron beam curable resin composition including polymethylpentene, and a crosslinking agent, in which the crosslinking agent has a saturated or unsaturated ring structure, at least one atom among atoms forming at least one ring is bonded to any allylic substituent of an allyl group, a methallyl group, an allyl group through a linking group, and a methallyl group through a linking group, and a molecular weight is 1,000 or less, a resin frame for reflectors using the resin composition, a reflector, and a molding method using the resin composition.
Owner:DAI NIPPON PRINTING CO LTD
Release liner/layer, system and method of using the same with additive manufacturing
InactiveUS20160176112A1Easy to removeEasy to replaceManufacturing platforms/substratesLayered productsPolyolefinThermoforming
Release liner forming structures and methods of making and using the same. The methods of making the release liner include thermoforming and sheet bending. The flexible release liner may be used in conjunction with a rigid, transparent supporting surface. The release liner may be developed from a flexible sheet formed into a deformable resin fluid vat. A release layer, and additional structure if desired, can be formed of or include plastic, such as polyolefin or fluoropolymer. In some instances, the polyolefin is, or includes, polymethylpentene or a fluropolymer is fluorinated ethylene propylene. The optical and other properties of the release layer can be altered with treatments and other materials to, for example, reduce over-penetration of a light beam or deform a release layer.
Owner:FULL SPECTRUM LASER
Polyester articles having simulated metallic or pearlescent appearance
ActiveUS20120165422A1Less expensiveAntifouling/underwater paintsPaints with biocidesPolyesterPolymer science
A polyester article is made to appear lustrously metallic or pearlescent by the addition of polymethylpente and non-metallic, non-pearlescent colorant; and optionally other functional additives. The colorant can be one or more pigments, one or more dyes, or combination thereof. A stretch blow molded plastic article, such as a bottle, using the polymethylpentene in the polyester can simulate the appearance of a metallic surface or a pearlescent luster even though non-metallic and non-pearlescent colorants are used.
Owner:AVIENT CORP
Non-crosslinked flame-retardant resin compsition, and an insulated wire and a wire harness using the same
InactiveUS20070048524A1Sufficient flame retardancySolve the lack of flexibilityPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSpecial tyresAdditive ingredientPliability
To provide a non-crosslinked flame-retardant resin composition possessing sufficient flame retardancy, mechanical properties, flexibility and workability, and also delivering excellent heat resistance over a long period of time as it is hard to be molten when used under high temperature environment and its material is not deteriorated even if used in contact with a vinyl chloride resin material and the like, and an insulated wire and a wiring harness using the same. The composition includes (A) a non-crosslinked base resin which contains a propylene resin containing 50 wt % or more of propylene monomer and a thermoplastic resin of which a melting point is 180° C. or more, (B) a metallic hydrate, (C) a hindered phenolic antioxidant, (D) a sulfurous antioxidant, and (E) a metallic oxide. Polymethylpentene, an imidazole compound and an oxide of zinc are preferably utilized as the thermoplastic resin, the ingredients (D) and (E), respectively. The composition is used as an insulated covering material for a non-halogenous insulated wire, which is used in a wire bundle of the wiring harness.
Owner:AUTONETWORKS TECH LTD +2
Low surface energy blends useful in the manufacture of ovenable containers
InactiveUS20050100695A1Facilitated releaseHigh level of starchSynthetic resin layered productsCellulosic plastic layered productsPolyesterLow-density polyethylene
A laminate useful in the manufacture of ovenable grease resistant food containers, which have the added advantage of good release from the food products, particularly those containing high levels of starch and sugar. The laminate of the present invention includes a substrate, preferably of a paperboard, a layer of grease resistant material, such as polyamide, polyester, polyvinyl chloride, polytetrafluoroethylene, or polyvinyl alcohol, etc., or nylon, a tie layer of low density polyethylene or linear low density polyethylene modified with maleic anhydride, and a food contact release layer comprising a blend of polypropylene and polymethylpentene. In the preferred embodiment, the grease resistant layer, the tie layer and the food contact release layer are coextruded onto a paperboard substrate.
Owner:INT PAPER CO
Battery separator with antistatic properties
A battery separator comprising: a microporous polyolefin film having from 0.1% to 50% by weight of a block copolymer including a polyetheresteramide monomer. In this battery separator the polyolefin is selected from the group consisting of: polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutylene, polymethylpentene, mixtures thereof, and copolymers thereof. Preferably the polyolefin is polyethylene, mixtures of polyethylene and copolymers of polyethylene, or polypropylene, mixtures of polypropylene and copolymers of polypropylene and has less than or equal to 5% by weight of the block copolymer. In the battery separator of the invention, the microporous film generally has a thickness of no greater than 200 microns, a porosity in the range of 10 to 90%, and a pore size in the range of 0.005 micron to 1.5 micron.
Owner:CELGARD LLC
Containers and peelable seal containers of new non-PVC material
The present invention provides a flowable materials container. The container has a first sidewall and a second sidewall sealed together along a peripheral seam to define a fluid chamber. At least one sidewall is a film having at least one layer of blend of a first component selected from the group of: (1) ethylene and α-olefin copolymers having a density of less than about 0.915 g / cc, (2) ethylene copolymerized with lower alkyl acrylates, (3) ethylene copolymerized with lower alkyl substituted alkyl acrylates and (4) ionomers, the first component being present in an amount from about 99% to about 55% by weight of the blend, a second component in an amount by weight of the blend from about 45% to about 1% and consists of one or more polymers of the group: (1) propylene containing polymers, (2) polybutene polymers, (3) polymethylpentene polymers, (4) cyclic olefin containing polymers and (5) bridged polycyclic hydrocarbon containing polymers; and the film has a modulus of elasticity when measured in accordance with ASTM D882 of less than about 60,000 psi, an internal haze when measured in accordance with ASTM D1003 of less than about 25%, an internal adhesion ranking of greater than about 2, a sample creep at 120° C. under 27 psi loading of less than or equal to 150% for a film having a thickness of from about 5 mils to about 15 mils, and the film can be heat sealed into a container having seals wherein the seals remain intact when the container is autoclaved at 121° C. for one hour.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC
Microporous membrane, method for producing same, and battery separator using same
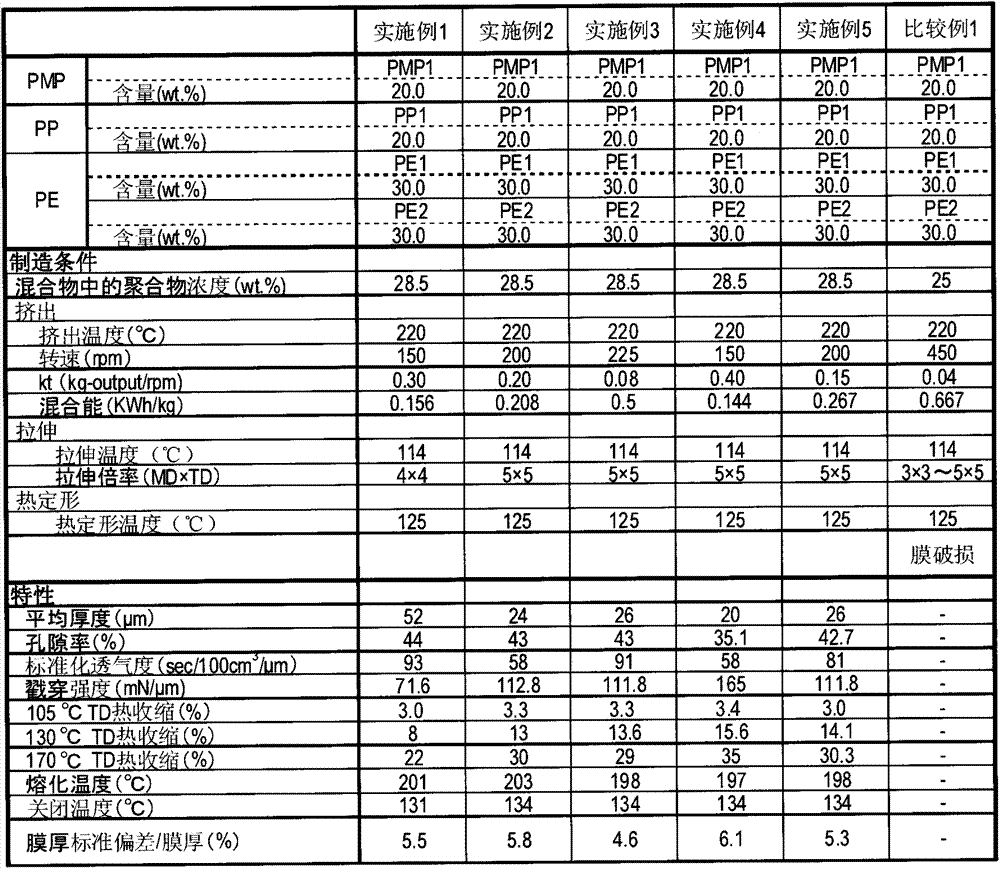
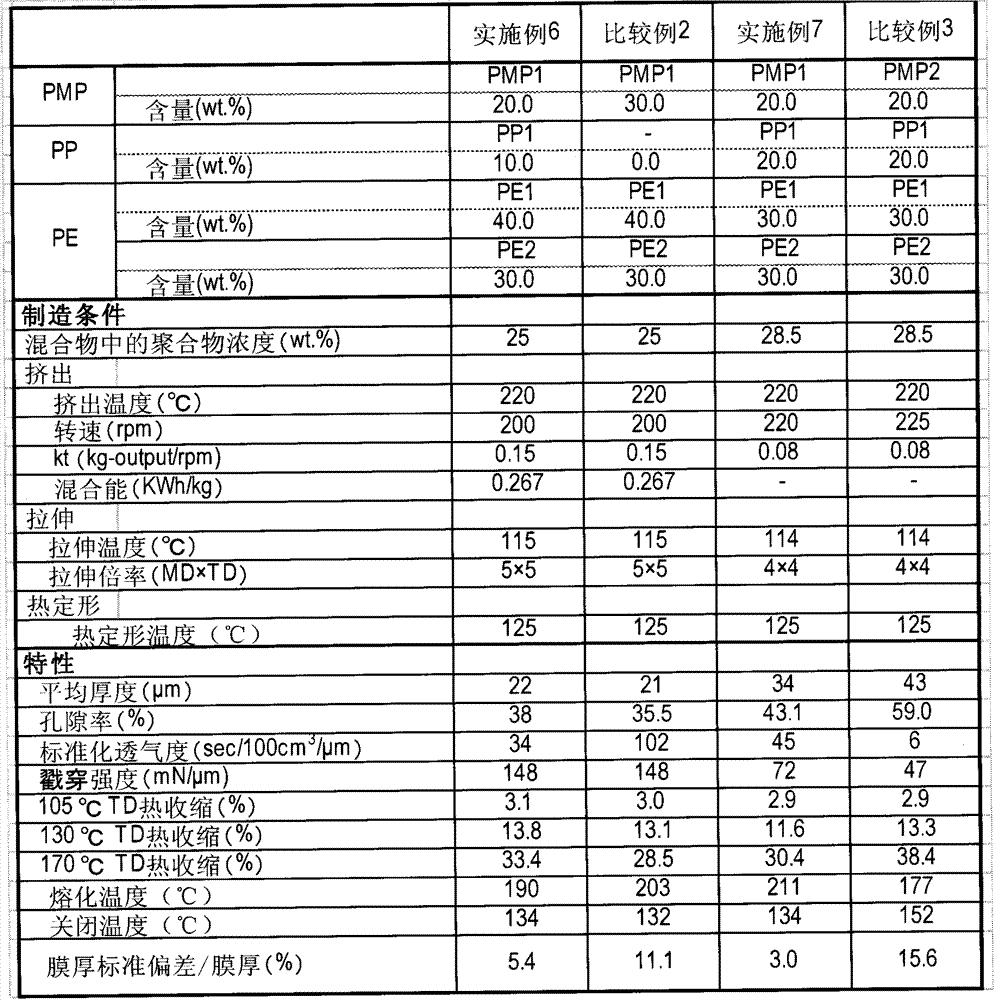
InactiveUS20130302696A1High meltdown temperatureLow shutdown temperatureCell component detailsMotive system fuel cellsPhysical chemistryPolymethylpentene
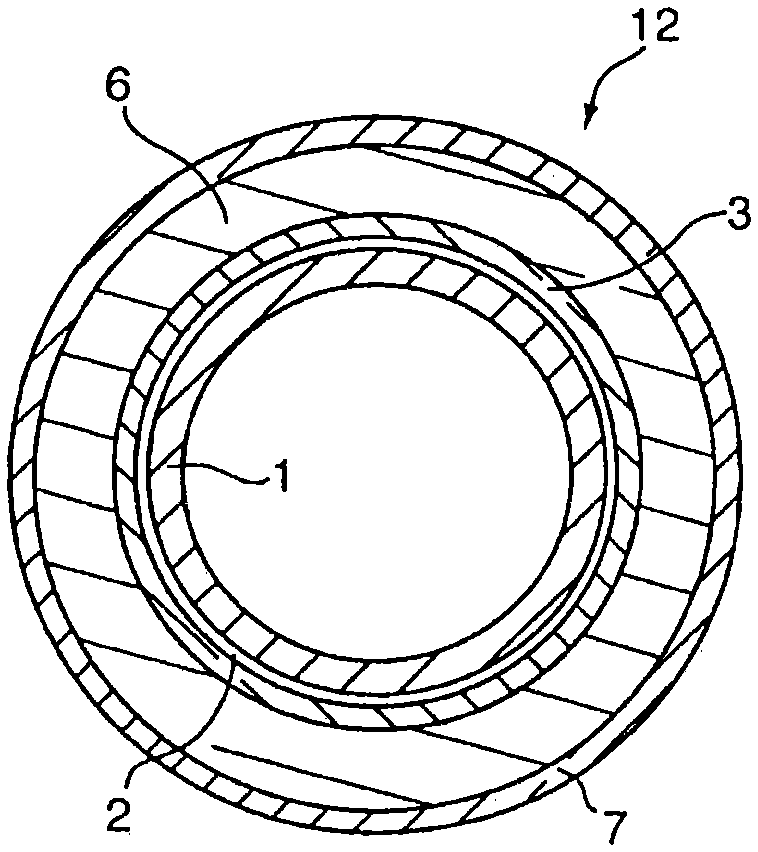
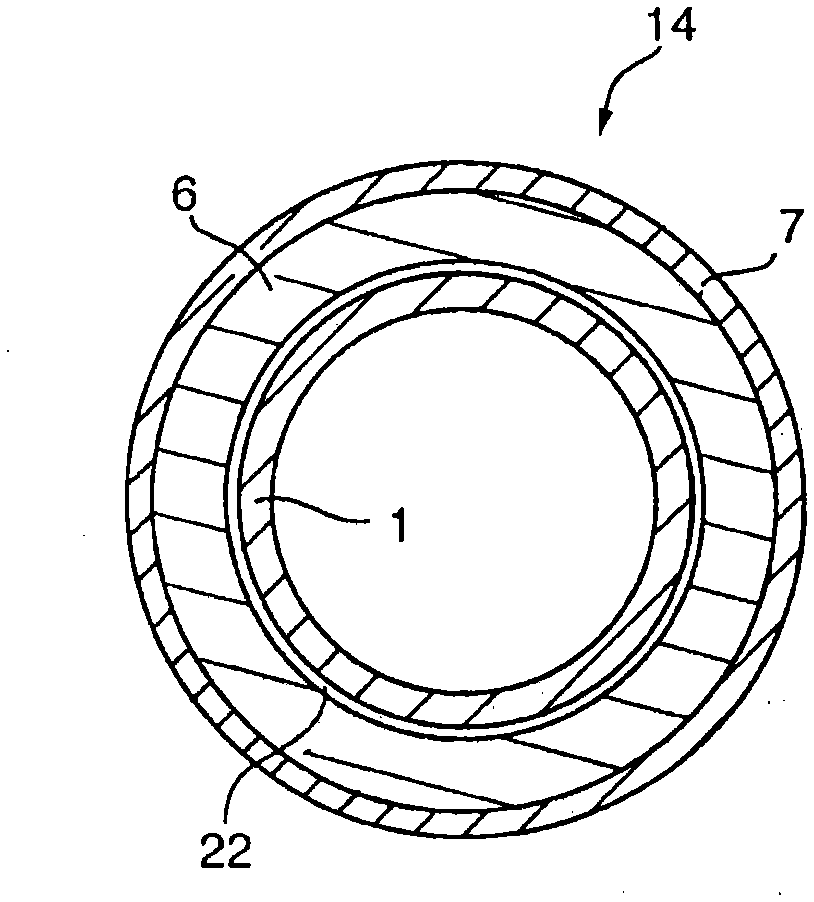
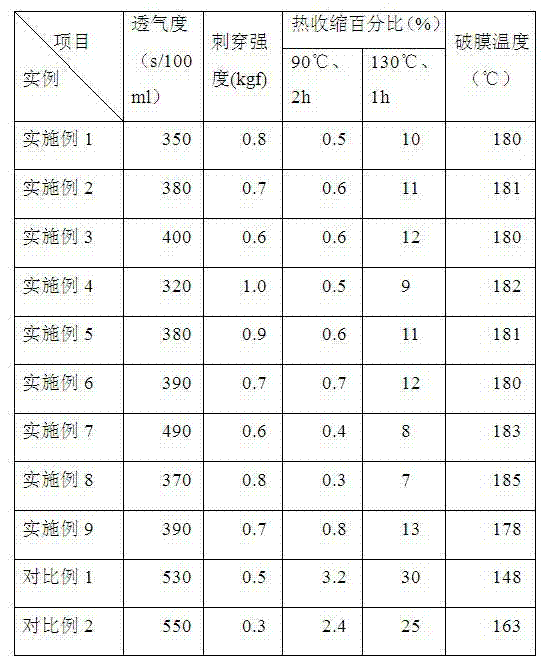
The present invention is a microporous membrane comprising polymethylpentene (a), polyethylene (b), and polypropylene (c), the microporous membrane having a meltdown temperature of 180° C. or higher, a TD heat shrinkage at 170° C. of 35% or less, and a thickness change ratio per thickness of 10% or less.An object of the present invention is to provide a microporous membrane having a high meltdown temperature, a low shutdown temperature, and resistance to heat shrinkage at high temperatures, which cannot be obtained by the prior art.
Owner:TORAY BATTERY SEPARATOR FILM
Composite film for film bioreactor and method for preparing same
ActiveCN101444703AImprove support strengthImprove mechanical stabilitySemi-permeable membranesTreatment using aerobic processesOrganic filmPolyester
The invention provides a composite film for film bioreactor, mainly comprising a porous material supporting layer and an organic film layer which is attached to the surface of the supporting layer; wherein, the porous material supporting layer is formed by sintering one or more than two polymer materials as follows: polytetrafluor ethylene, polyethylene, polypropylene, polymethylpentenes and polystyrene; the film material of the organic film layer consists of one or more than two polymers as follows: polyether sulfone, polysulphones, polyacrylic acid ester, polybutene, polyamides, PEEK, polycellulose ester, polyacrylonitrile, polyvinyl alcohol, polystyrene, polyphenylene oxide, polyester carbonates, polyurethanes, polyacrylate, polyoxyethylene, and polysiloxanes. The composite film has high supporting strength, good mechanical stability, stable structural shape, convenient cleaning and replacement, and can be applicable to various high-pressure environments, with the surface film not easy to be fallen and damaged.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Polyester articles having simulated metallic or pearlescent appearance
A polyester article is made to appear lustrously metallic or pearlescent by the addition of polymethylpentene and non-metallic, non-pearlescent colorant; and optionally other functional additives. The colorant can be one or more pigments, one or more dyes, or combination thereof. A stretch blow molded plastic article, such as a bottle, using the polymethylpentene in the polyester can simulate the appearance of a metallic surface or a pearlescent luster even though non-metallic and non-pearlescent colorants are used.
Owner:AVIENT CORP
155 DEG C high-strength, oil-resistant and flame-retardant polyolefin high-speed extruded thin-wall material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a 155 DEG C high-strength, oil-resistant, halogen-free and flame-retardant polyolefin high-speed extruded thin-wall material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: preparing main base material particles, namely adding ethylene propylene diene monomer (EPDM) rubber, copolymer of poly(4-methyl amylene), an ethylene-octene copolymer polyolefin elastomer (POE), a compound antioxidant, polyethylene wax serving as a lubricating agent, methyl phenyl silicone oil and a rheological agent into a high-speed mixer for mixing, performing melt extrusion, pelletizing on the underwater die surface, dehydrating the particles, and drying to prepare the main base material particles; preparing auxiliary base material particles, namely adding silicone rubber, nitrile silicone rubber, EPDM rubber, an antioxidant RD, a high-efficiency expanded halogen-free flame retardant and talcpowder into an internal mixer for internal mixing, and performing extrusion granulation; adding the prepared main base material particles and auxiliary base material particles into the high-speed mixer for mixing, performing melt extrusion, pelletizing on the underwater die surface, dehydrating the particles, and drying to prepare a finished product. The high-strength, oil-resistant, halogen-free and flame-retardant polyolefin high-speed extruded thin-wall material has oil resistance, flame retardance, high-temperature resistance, wear resistance and high strength.
Owner:中广核拓普(湖北)新材料有限公司
High teMPERATURE resistant insulating for pipe
The invention provides a polymeric composition for insulating fluid and / or gas transport conduits, such as off-shore oil and gas pipelines operating at temperatures of 130 DEG C or higher in water depths above 1,000 metres. The outer surface of the conduit is provided with at least one layer of solid or foam insulation comprising a high temperature resistant thermoplastic having low thermal conductivity, high thermal softening point, high compressive strength and high compressive creep resistance. The high temperature resistant thermoplastic is selected from one or more members of the group comprising: polycarbonate; polyphenylene oxide; polyphenylene oxide blended with polypropylene, polystyrene or polyamide; polycarbonate blended with polybutylene terephthalate, polyethylene terephthalate, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene, acrylonitrile styrene acrylate, or polyetherimide; polyamides, including polyamide 12 and 612 and elastomers thereof; polymethylpentene and blends thereof; cyclic olefin copolymers and blends thereof; and, partially crosslinked thermoplastic elastomers, also known as thermoplastic vulcanizates or dynamically vulcanized elastomers.
Owner:SHAWCOR LTD
Non-crosslinked flame-retardant resin composition, and an insulated wire and a wire harness using the same
InactiveUS7713620B2Solve the lack of flexibilitySufficient propertyPlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSpecial tyresPliabilityPolymethylpentene
To provide a non-crosslinked flame-retardant resin composition possessing sufficient flame retardancy, mechanical properties, flexibility and workability, and also delivering excellent heat resistance over a long period of time as it is hard to be molten when used under high temperature environment and its material is not deteriorated even if used in contact with a vinyl chloride resin material and the like, and an insulated wire and a wiring harness using the same. The composition includes (A) a non-crosslinked base resin which contains a propylene resin containing 50 wt % or more of propylene monomer and a thermoplastic resin of which a melting point is 180° C. or more, (B) a metallic hydrate, (C) a hindered phenolic antioxidant, (D) a sulfurous antioxidant, and (E) a metallic oxide. Polymethylpentene, an imidazole compound and an oxide of zinc are preferably utilized as the thermoplastic resin, the ingredients (D) and (E), respectively. The composition is used as an insulated covering material for a non-halogenous insulated wire, which is used in a wire bundle of the wiring harness.
Owner:AUTONETWORKS TECH LTD +2
Battery separator film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102956858AImprove breathabilityHigh strengthCell component detailsLow-density polyethylenePower battery
The invention provides a battery separator film, wherein film materials comprise a polyethylene mixture and polymethylpentene. The polyethylene mixture comprises ultrahigh-molecular-weight polyethylene and high-density polyethylene. The invention also provides a preparation method of the battery separator film. According to the invention, air permeability of the separator film provided by the invention is substantially improved, pore-closing temperature is substantially reduced, piercing strength is substantially increased, and film rupture temperature is substantially increased. Therefore, a safer protection performance is provided for batteries. The film and the method are more suitable to be applied in power batteries.
Owner:BYD CO LTD
Highly-transparent optical polyester film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104943305AEasy to processOvercome foggingSynthetic resin layered productsElectrical equipmentPolyesterSandwich like
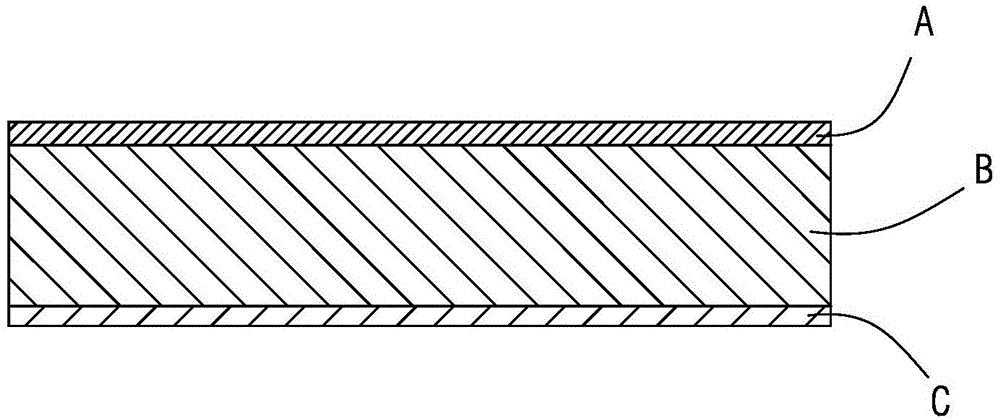
The invention provides a highly-transparent optical polyester film and a preparation method thereof. The highly-transparent optical polyester film comprises a layer A, a layer B and a layer C which are integrally formed into a three-layer stratified structure, wherein the layer A is a surface layer; the layer B is a sandwich layer; the layer C is a bottom layer; the layer A comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 85-95% of modified polyester for films, and 5-15% of nanometer polymethylpentene particles or nanometer styrene butadiene resin particles; the layer B comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 95-99% of super bright polyester for films and 1-5% of a heat stabilizer; the layer C comprises the following raw materials in percentage by weight: 85-95% of modified polyester for films, and 5-15% of the nanometer polymethylpentene particles or the nanometer styrene butadiene resin particles. Non-transparent anti-bonding particles (an anti-bonding agent) which are commonly used in the prior art need not to be added into the raw materials of the high-transparent optical polyester film, so that the processability of the high-transparent optical polyester film is improved; meanwhile, fogging is avoided, and the light transmittance and the glossiness of the high-transparent optical polyester film are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU SHUANGXING COLOR PLASTIC NEW MATERIALS
Polymer/carbon nanotube composites, methods of use and methods of synthesis thereof
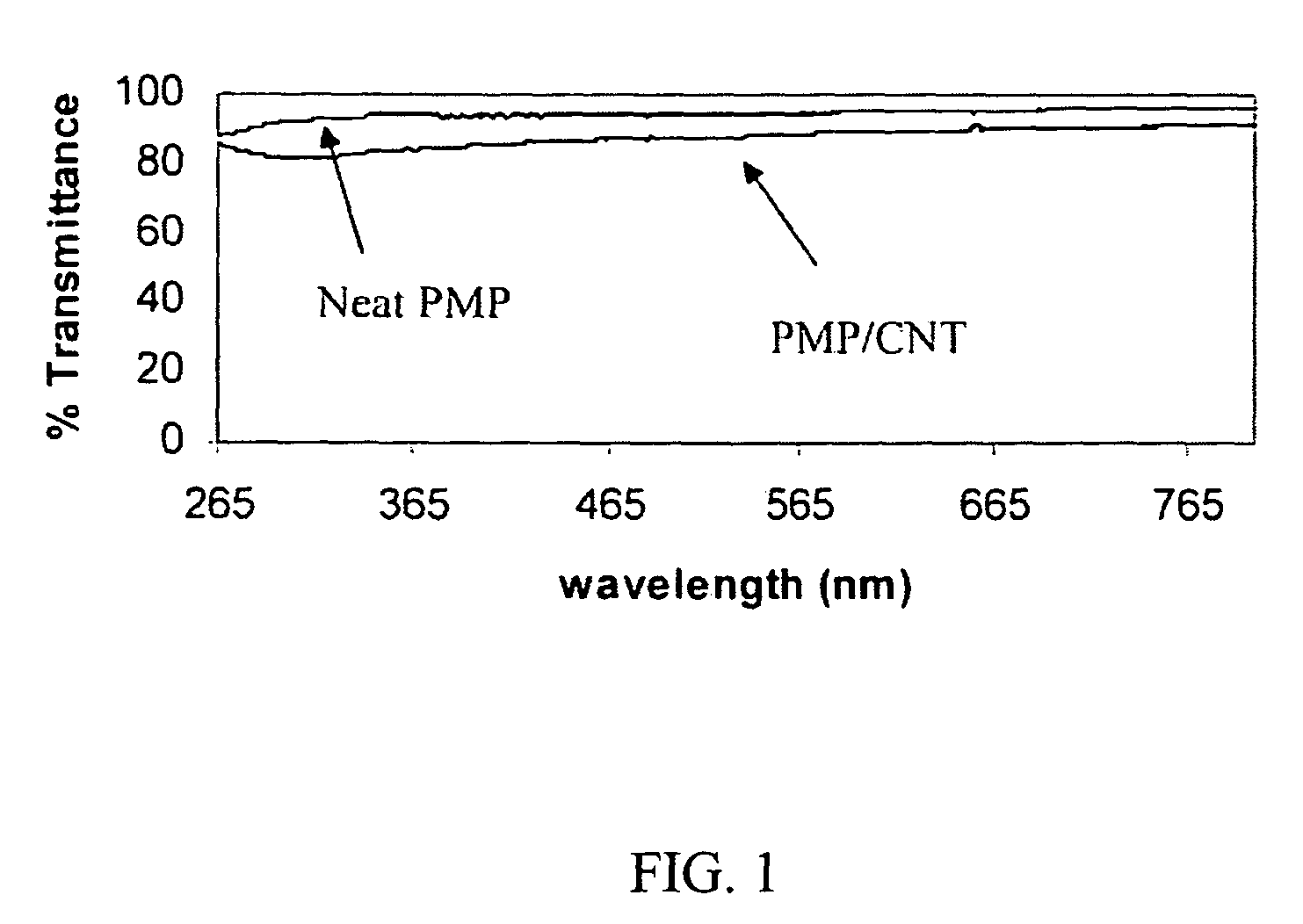
Polymer / carbon nanotube composites including single-wall or multi-wall carbon nanotubes incorporated into the matrix of a polymer are provided. These composites can be used in environments exposed to galactic cosmic radiation. Accordingly, the composites are useful in deep space applications like space vehicles, space stations, personal equipment as well as applications in the biomedical arts and atom splitting research. The composites can be modified with organic dyes containing at least one phenyl ring and the resulting doped composite is useful as a radiation detector. The preferred polymer is poly(4-methyl-1-pentene). At low nanotube concentrations (i.e., about 0.5 wt % or less), the composites exhibit transparent optical qualities. At higher nanotube concentrations (i.e., about 0.6 wt % or more), the composites are non-transparent.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
Polymethylpentene conjugate fiber or porous polymethylpentene fiber and fiber structure comprising same
ActiveUS20150051308A1Highly uniform in pore sizeColor depthOther chemical processesFoundry mouldsYarnOptoelectronics
Provided are a polymethylpentene conjugate fiber, which is capable of imparting to a lightweight polymethylpentene fiber an ability to develop a vivid and deep color, and a porous polymethylpentene fiber, which has a lightweight, a high pore diameter uniformity and a high porosity retention ratio against an external force, said polymethylpentene conjugate fiber and said porous polymethylpentene fiber being appropriately usable as a fiber structure for woven knitted goods, non-woven fabrics, yarns, cotton waddings, etc. The polymethylpentene conjugate fiber is characterized by having an island-in-sea structure wherein the sea component comprises a polymethylpentene-based resin and the island component comprises a thermoplastic resin. The porous polymethylpentene fiber, which comprises a polymethylpentene-based resin, is characterized in that the coefficient of variation (CV) of pore diameter at the fiber cross section is 1-50%.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Poly (4-methylpentene) and SiO2 microsphere composite film and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a poly (4-methylpentene) and SiO2 microsphere composite film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) heating and stirring poly (4-methylpentene) (TPX) and a solvent for dissolution at the temperature of 0-90 DEG C to obtain a poly (4-methylpentene) solution; (2) adding SiO2 microspheres into the obtained poly (4-methylpentene) solution to obtain a TPX-SiO2 microsphere composite solution; and (3) dripping the obtained TPX-SiO2 microsphere composite solution on a substrate, then putting the substrate into a sealed container, and after the solvent is evaporated, obtaining the poly (4-methylpentene) and SiO2 microsphere composite film.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Battery separator with antistatic properties
Owner:CELGARD LLC
Preparation method for material with high density fixed biologically functional molecule
InactiveCN101810888AKeep aliveEasily control physical propertiesPreparing sample for investigationSurgerySide chainPolyethylene glycol
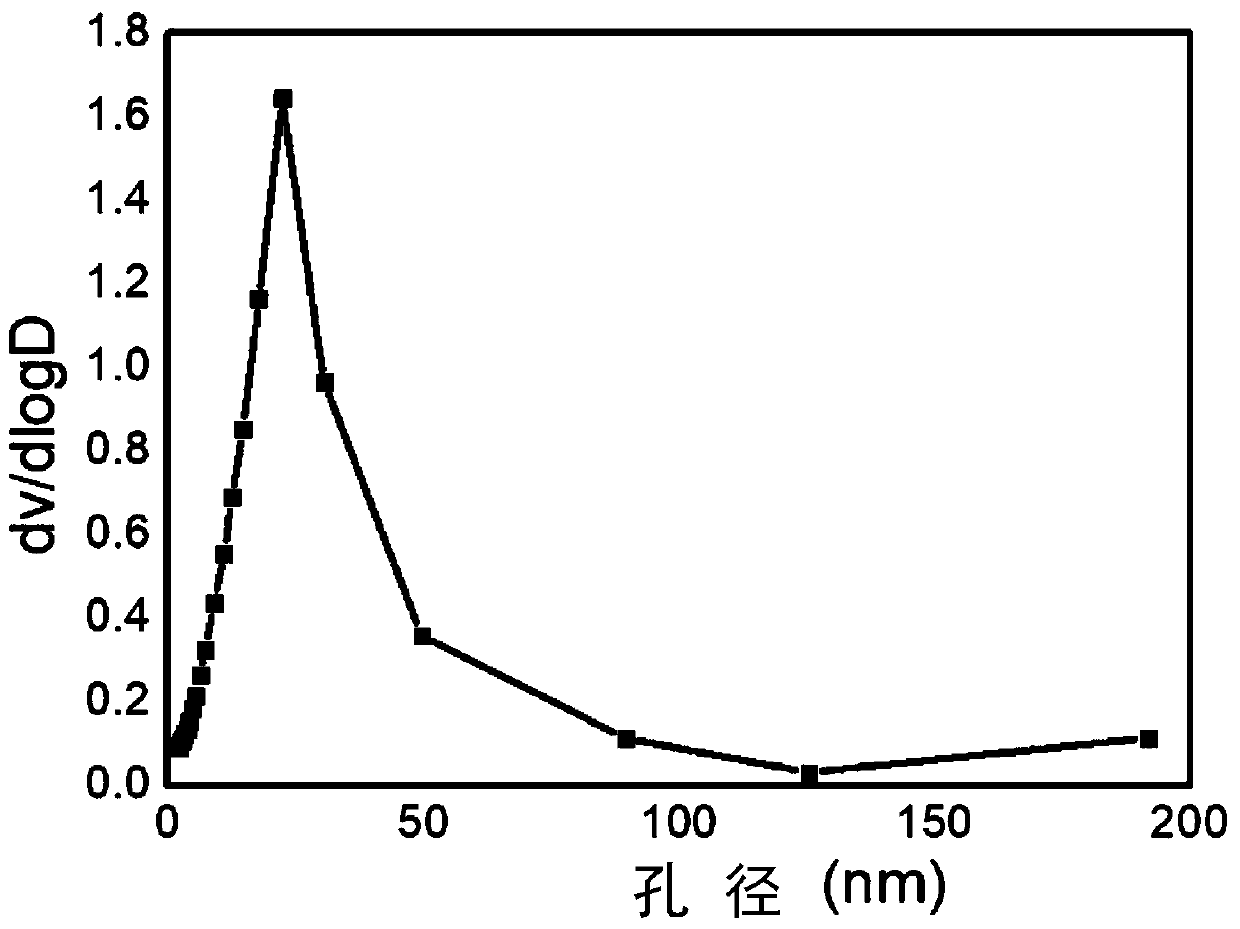
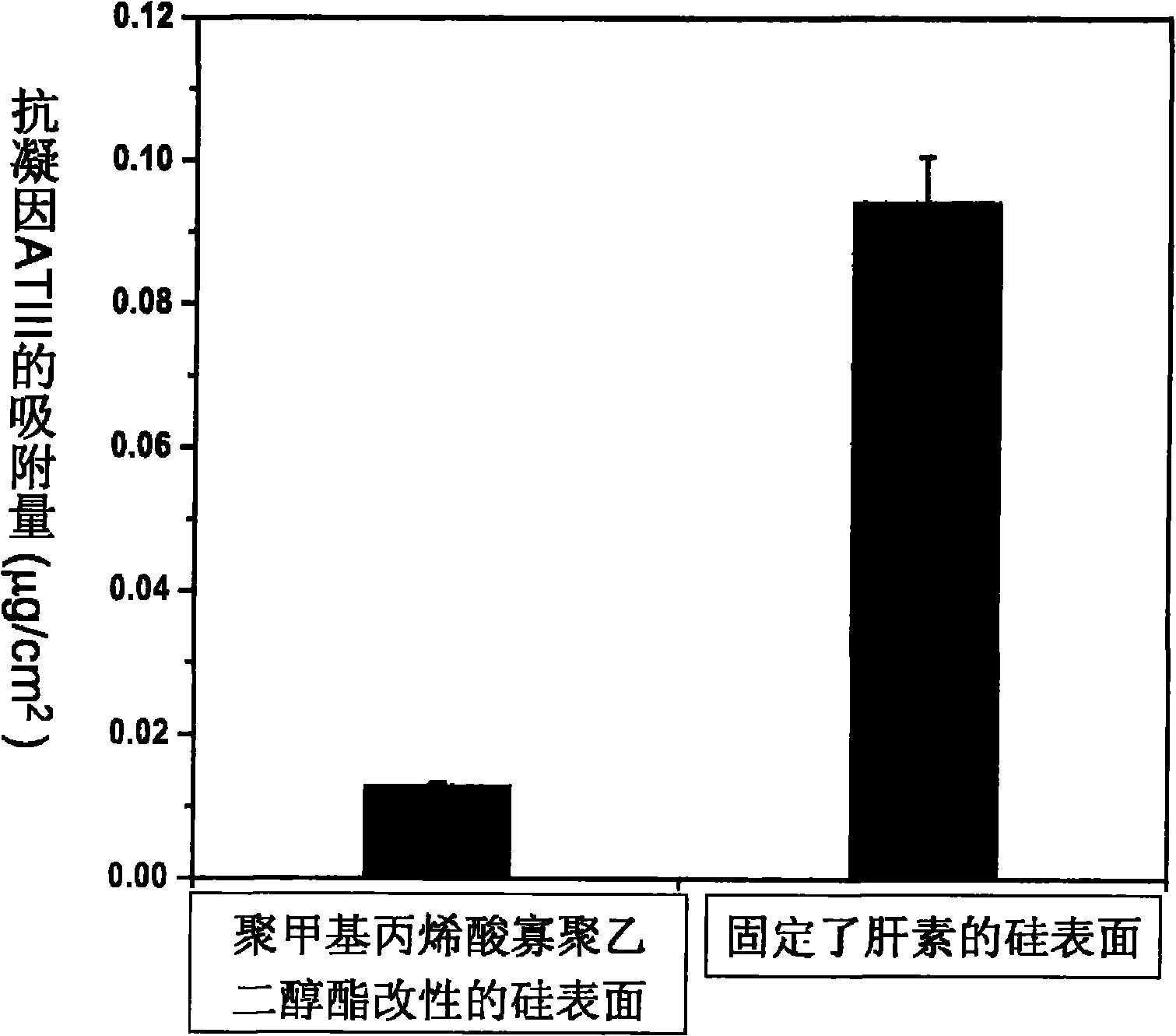
The invention relates to a preparation method for material with bioactivity functional surface, which comprises the steps of: grafting polymethylacrylic acid oligomerization gylcol ester (POEGMA) with excellent rejecting non-specific protein adsorption capacity on the surface of the material by an atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) technique; then grafting polymethylpentene acryloyl oxylsuccinimide at the tail end of the POEGMA by using a secondary initiation of ATRP; and fixing biological molecules containing amino in a high-density way by using a larger number of active ester group contained in the side chain of PNHSMA. The bioactivity functional surface provided by the method can obviously increase the grafting density of the surfaces of the biological molecules, simultaneously reduces the undesirable influence caused by non-specific protein adsorption, effectively keeps the activity of the fixed biological molecules and can fix various biological molecules and is suitable for more extensive biomedical fields.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Microporous film, process for production of the film, and use of the film
ActiveUS20130164598A1Improve balanceHigh meltdown temperatureSynthetic resin layered productsSecondary cellsPolymethylpenteneChemistry
The invention relates to microporous polymeric membranes suitable for use as battery separator film. The membrane comprises polyethylene, polypropylene, and polymethylpentene. The invention also relates to a method for producing such a membrane, batteries containing such membranes as battery separators, methods for making such batteries, and methods for using such batteries.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
High-cross section difference resistant high-temperature release liner and preparation process
PendingCN107234764AImprove performanceSimple structureSynthetic resin layered productsFlat articlesPolyolefinEngineering
Owner:昆山致信天城电子材料有限公司
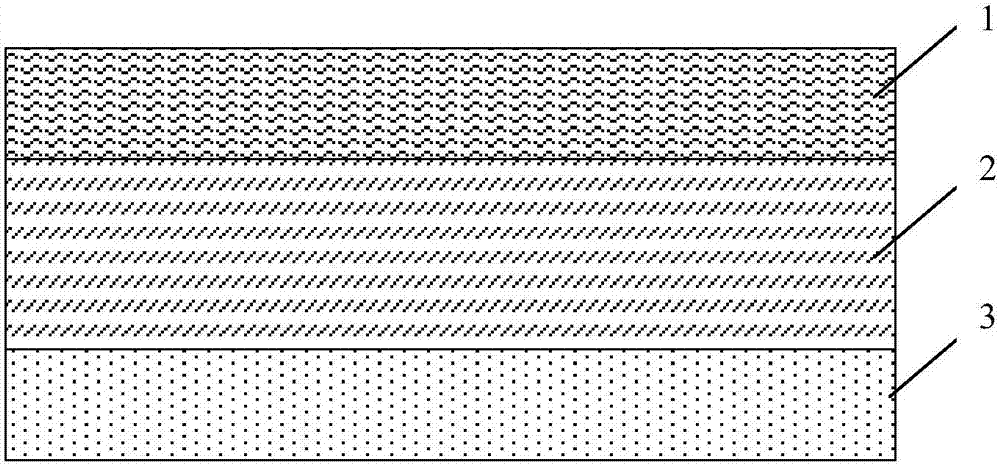
Multi-layer microporous film
ActiveUS20120077073A1Semi-permeable membranesCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersPolymer sciencePolymethylpentene
The invention relates to microporous membranes having at least two layers, a first layer comprising polymethylpentene and a second layer which comprises a polymer and has a composition that is not substantially the same as that of the first layer. The invention also relates to methods for making such membranes and the use of such membranes as battery separator film in, e.g., lithium ion batteries.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Microporous membrane, method for producing same, and battery separator using same
ActiveCN103328552AHigh melting temperatureLow shutdown temperatureHybrid capacitor separatorsCell component detailsMembrane thicknessPolymethylpentene
The present invention is a microporous membrane which contains (a) a polymethyl pentene, (b) a polyethylene and (c) a polypropylene and which has a meltdown temperature of 180 DEG C or more, a TD thermal shrinkage at 170 DEG C of 35% or less, and a thickness variation rate per membrane thickness of 10% or less. The purpose of the present invention is to provide a microporous membrane that has high meltdown temperature, low shutdown temperature and resistance to thermal shrinkage at high temperatures, which have not been achieved by conventional technology.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
An acoustic lens for an ultrasound array
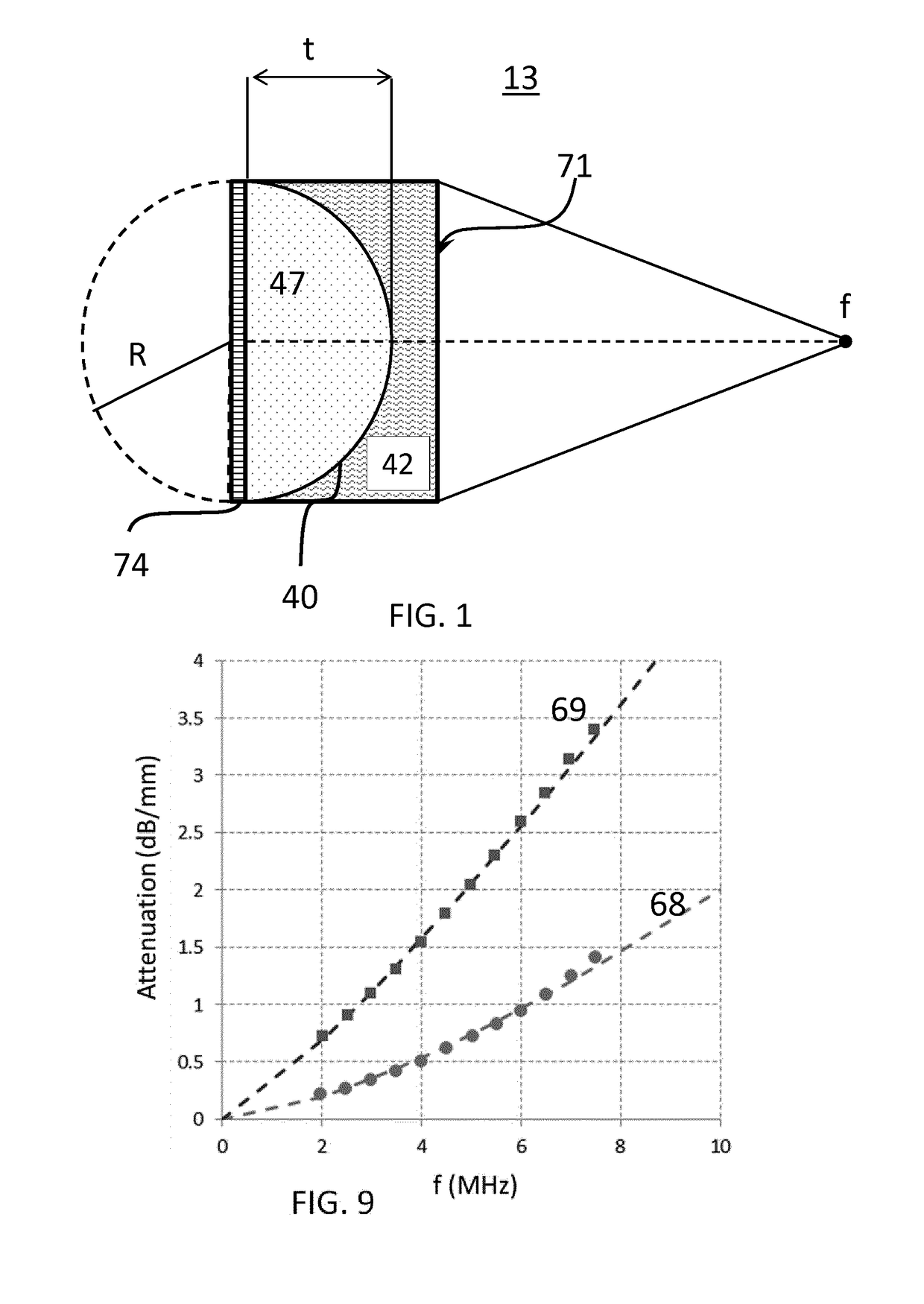
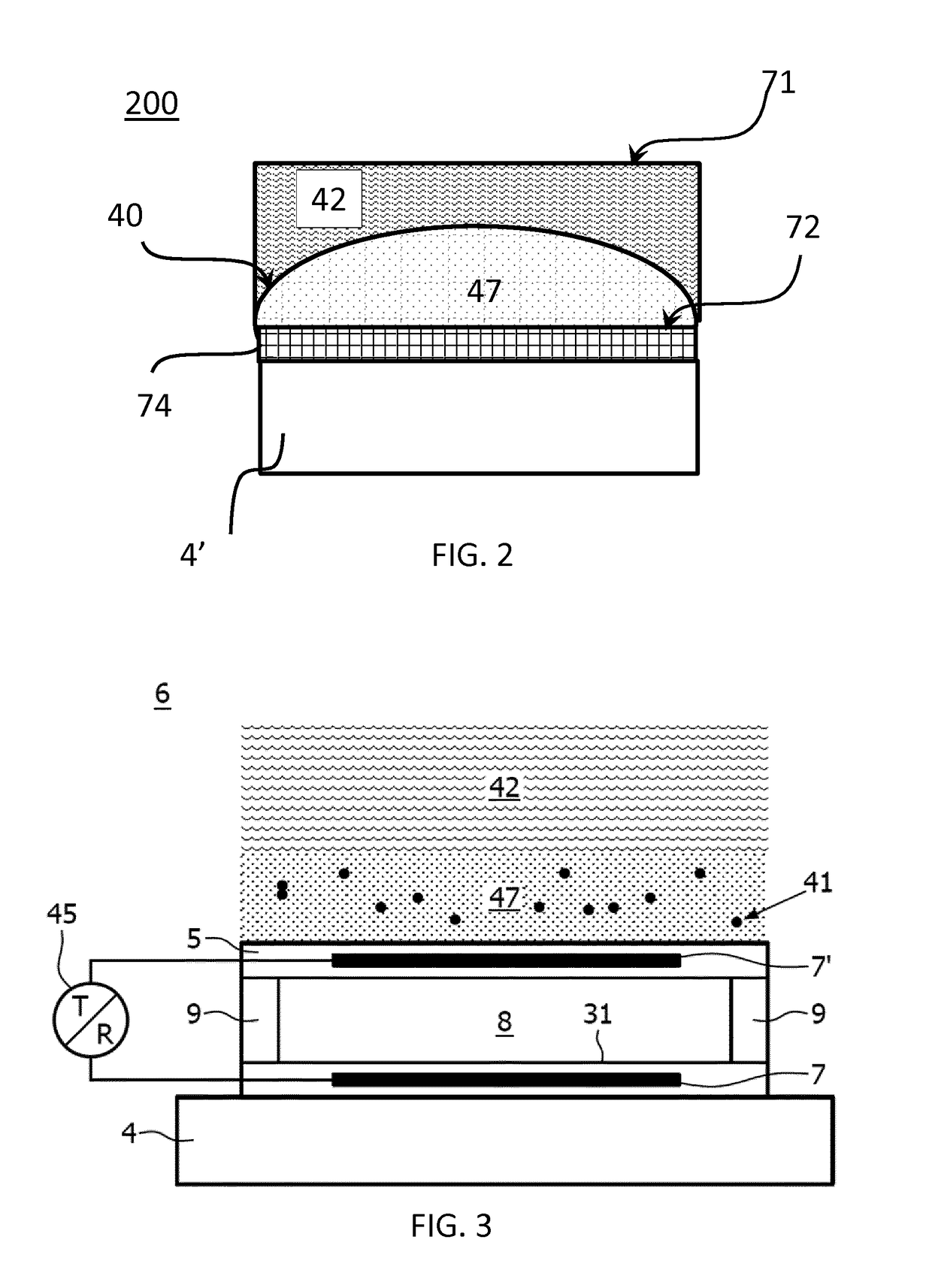
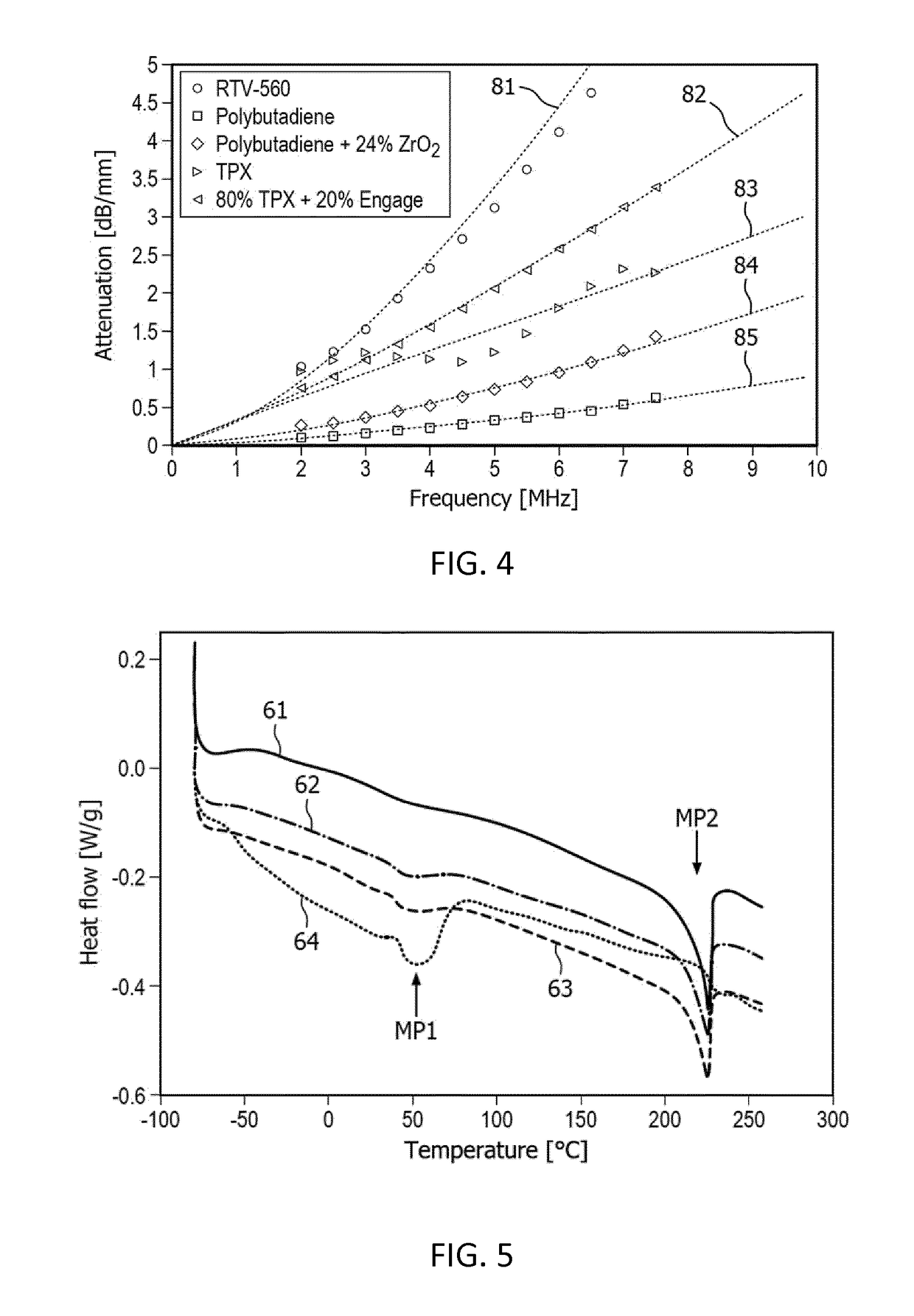
ActiveUS20180374471A1Improved acoustic wave propagationImproved wave propagationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElastomerPolyolefin
An acoustic lens suitable for a CMUT array (74) is provided. The acoustic lens comprising: a first layer (47) comprising a thermoset elastomer having a polymeric material selected from hydrocarbons, wherein the first layer has an inner surface (72) arranged to face the array and an outer convex shaped surface (40) arranged to oppose the inner surface; and a second layer (42) coupled to the outer surface of the first layer and comprising thermoplastic polymer polymethylpentene and an elastomer selected from the polyolefin family (POE) blended therein, wherein the outer layer located at the outer surface of the acoustic window layer, wherein the first layer has a first acoustic wave velocity (v1) and the second layer has a second acoustic wave velocity (v2), said second velocity is larger than the first acoustic wave velocity.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com