Patents
Literature
357 results about "Acoustic lens" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultrasound pulmonary vein isolation
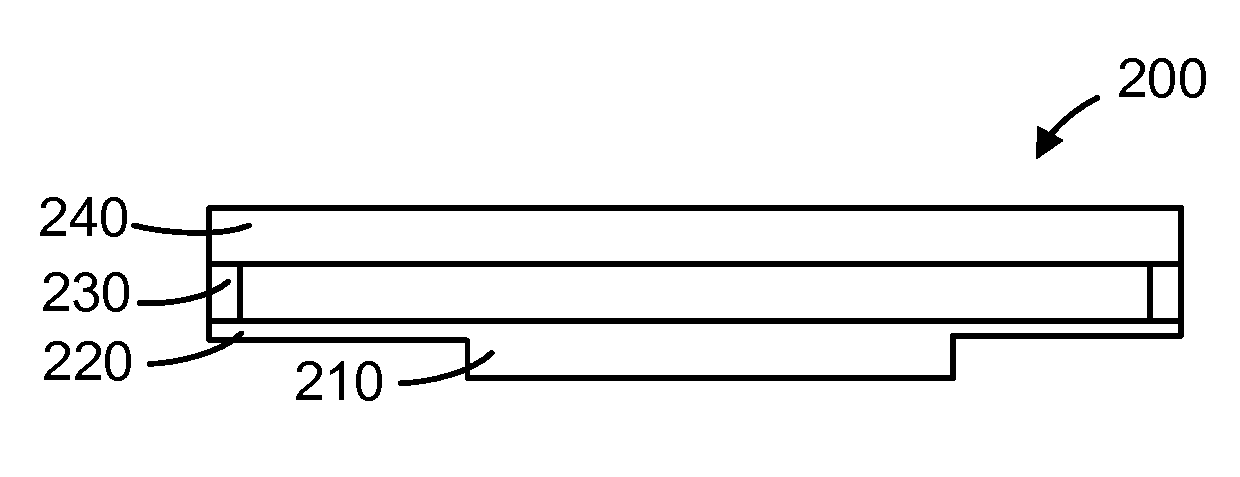
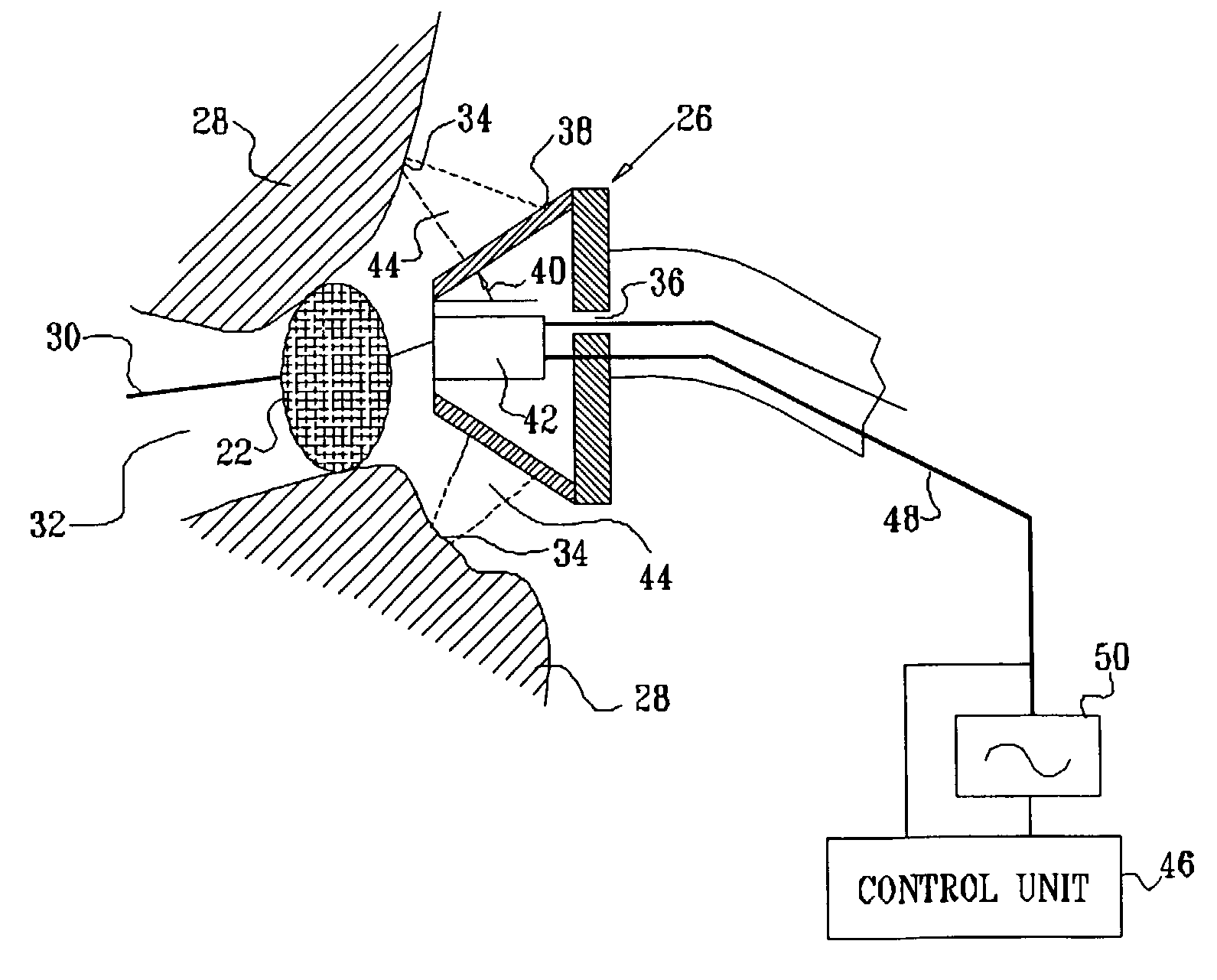
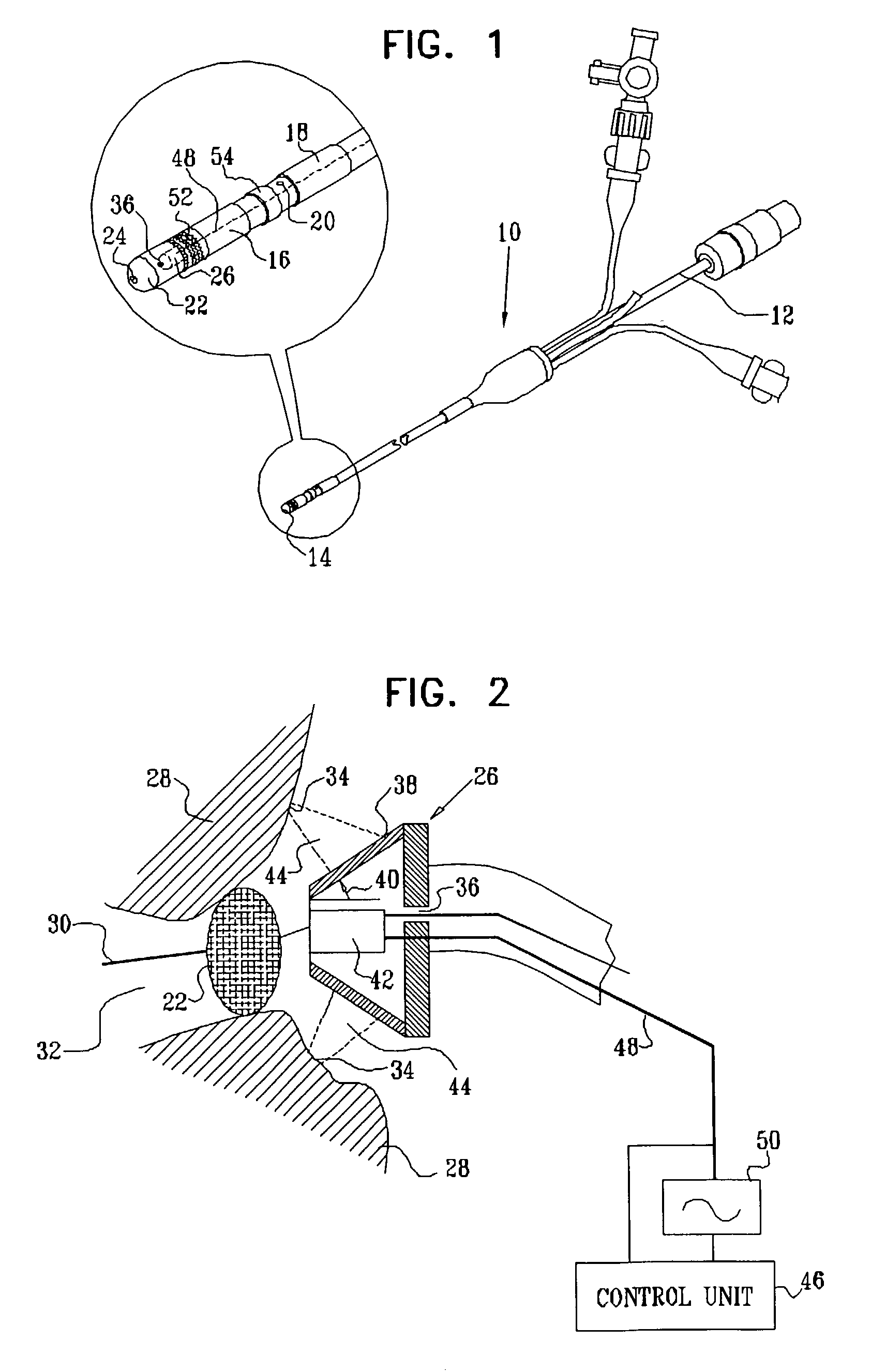
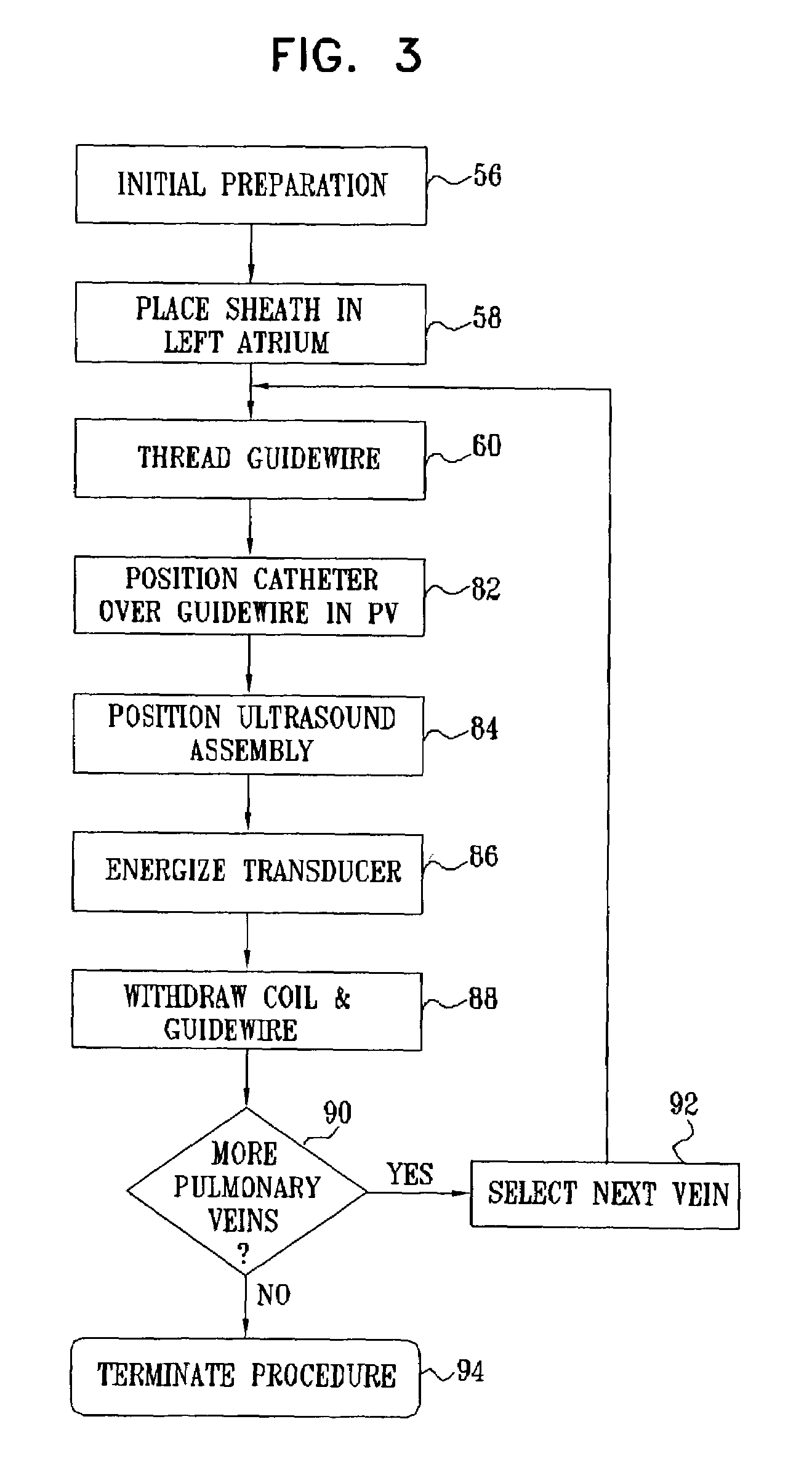
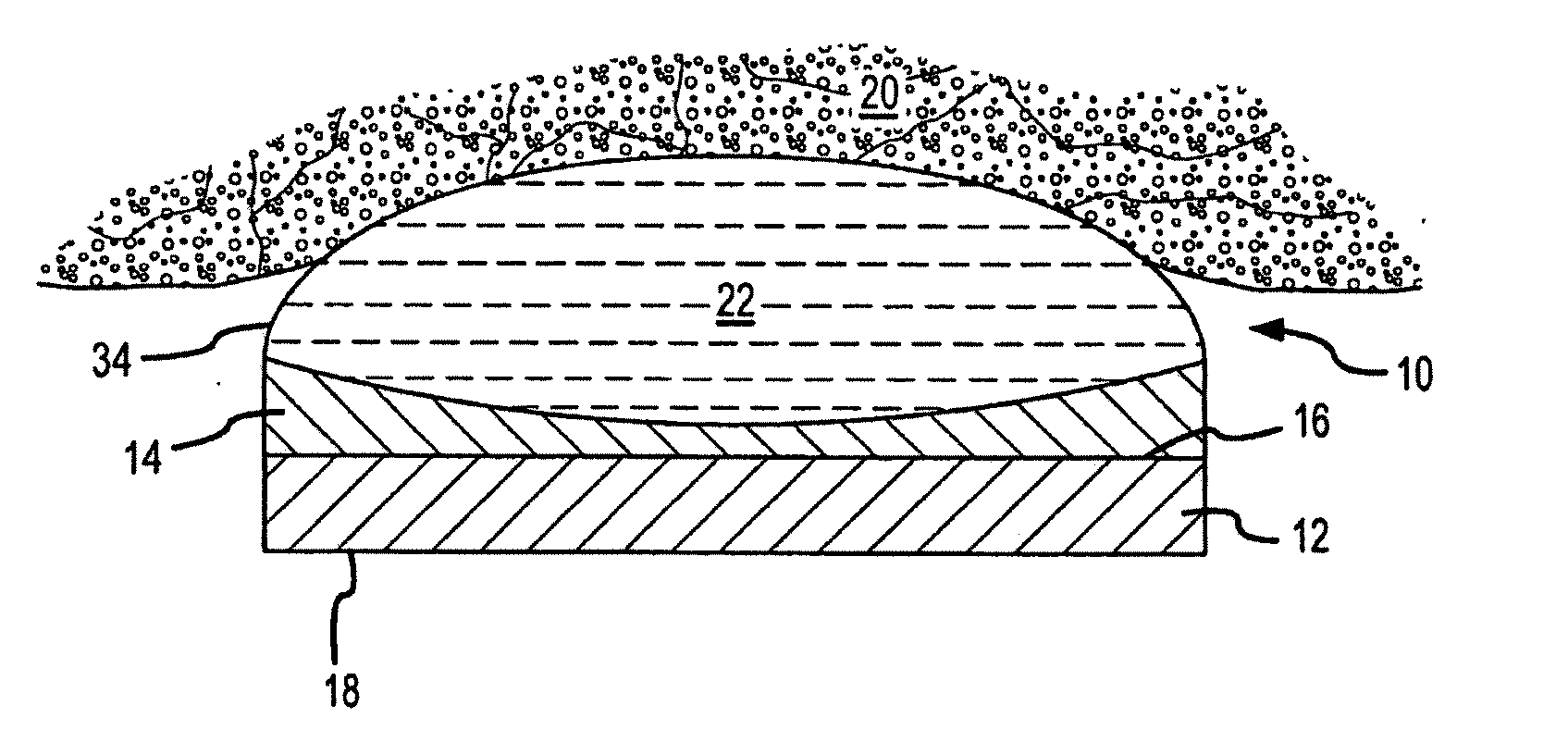
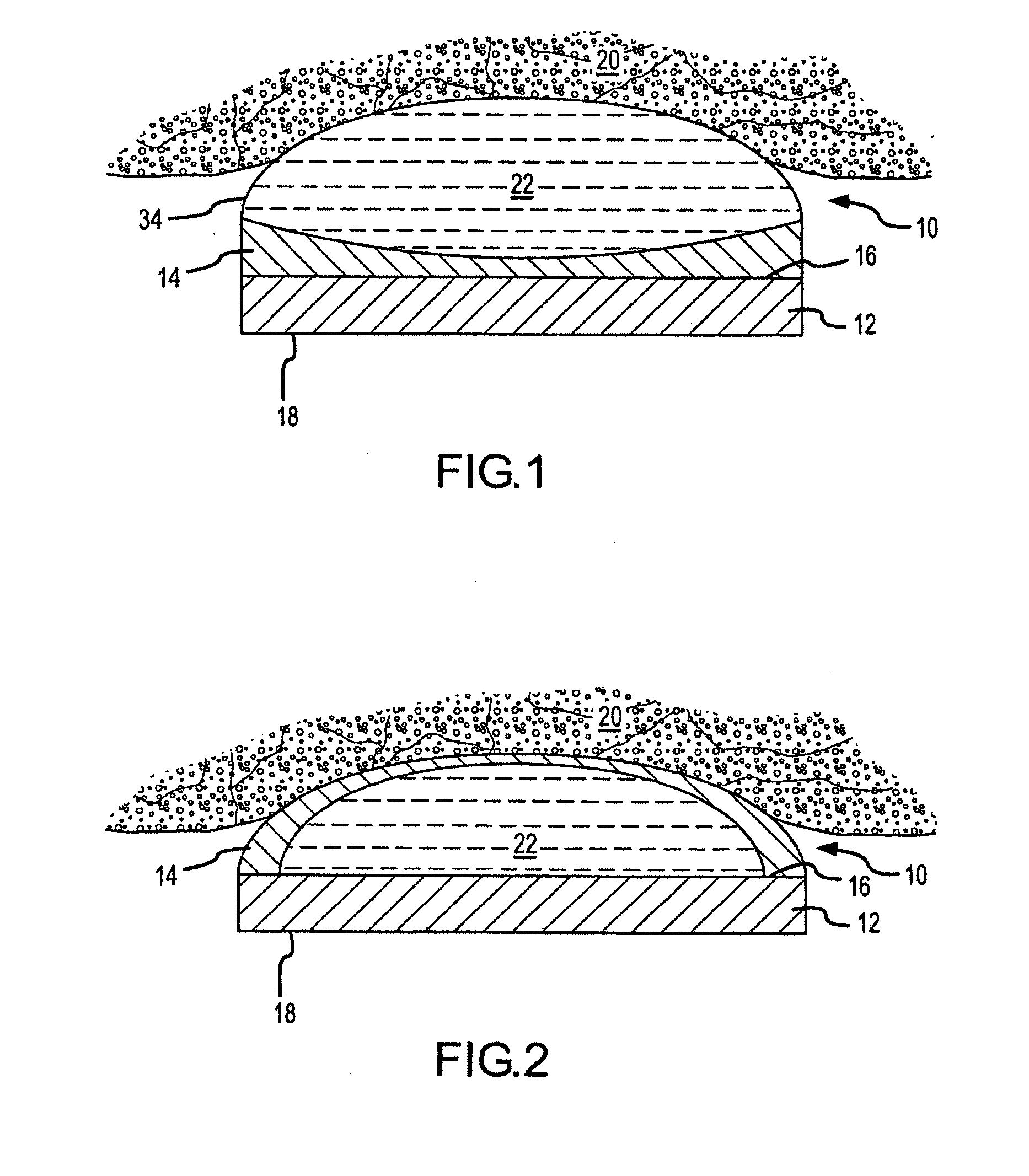
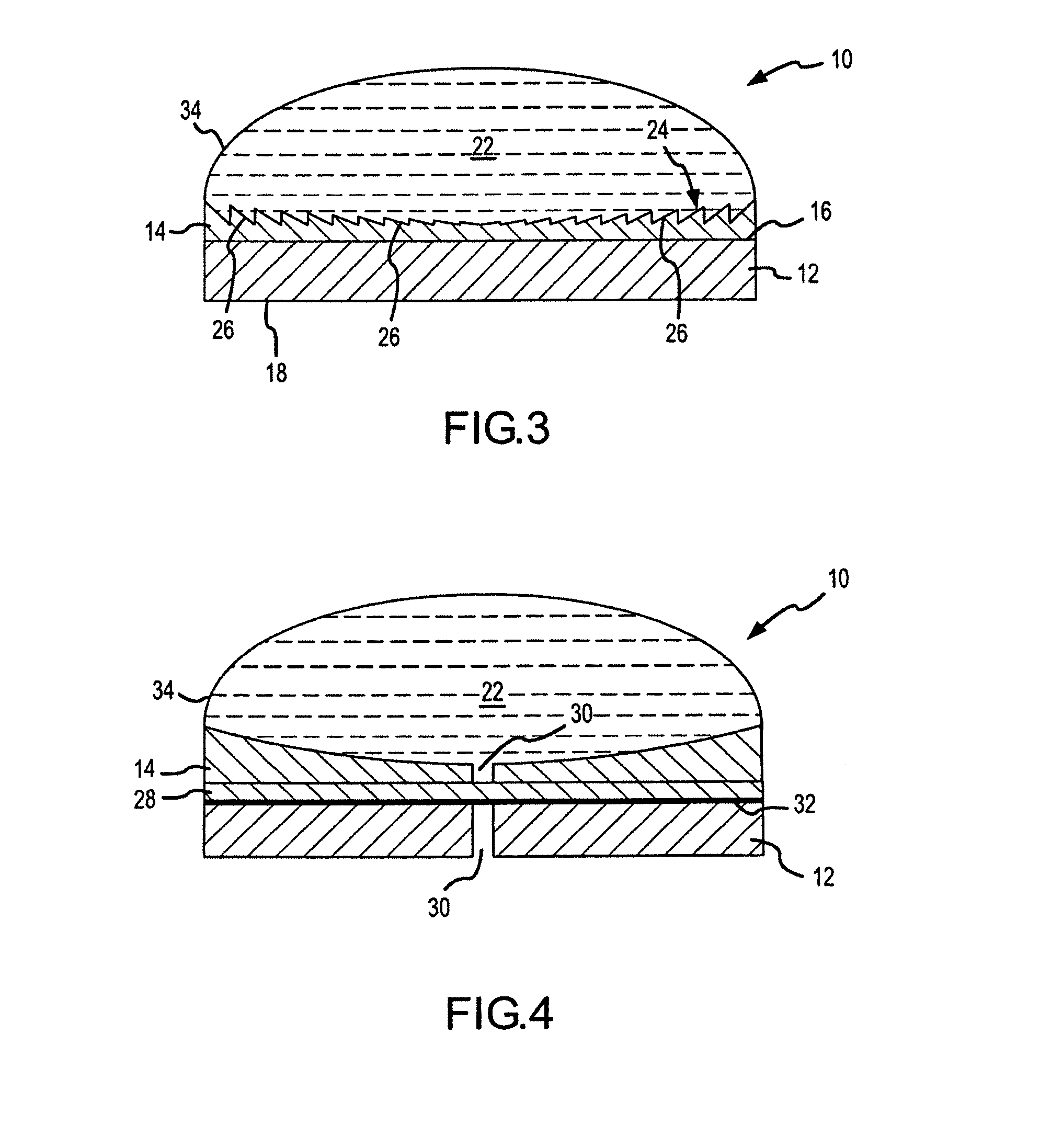
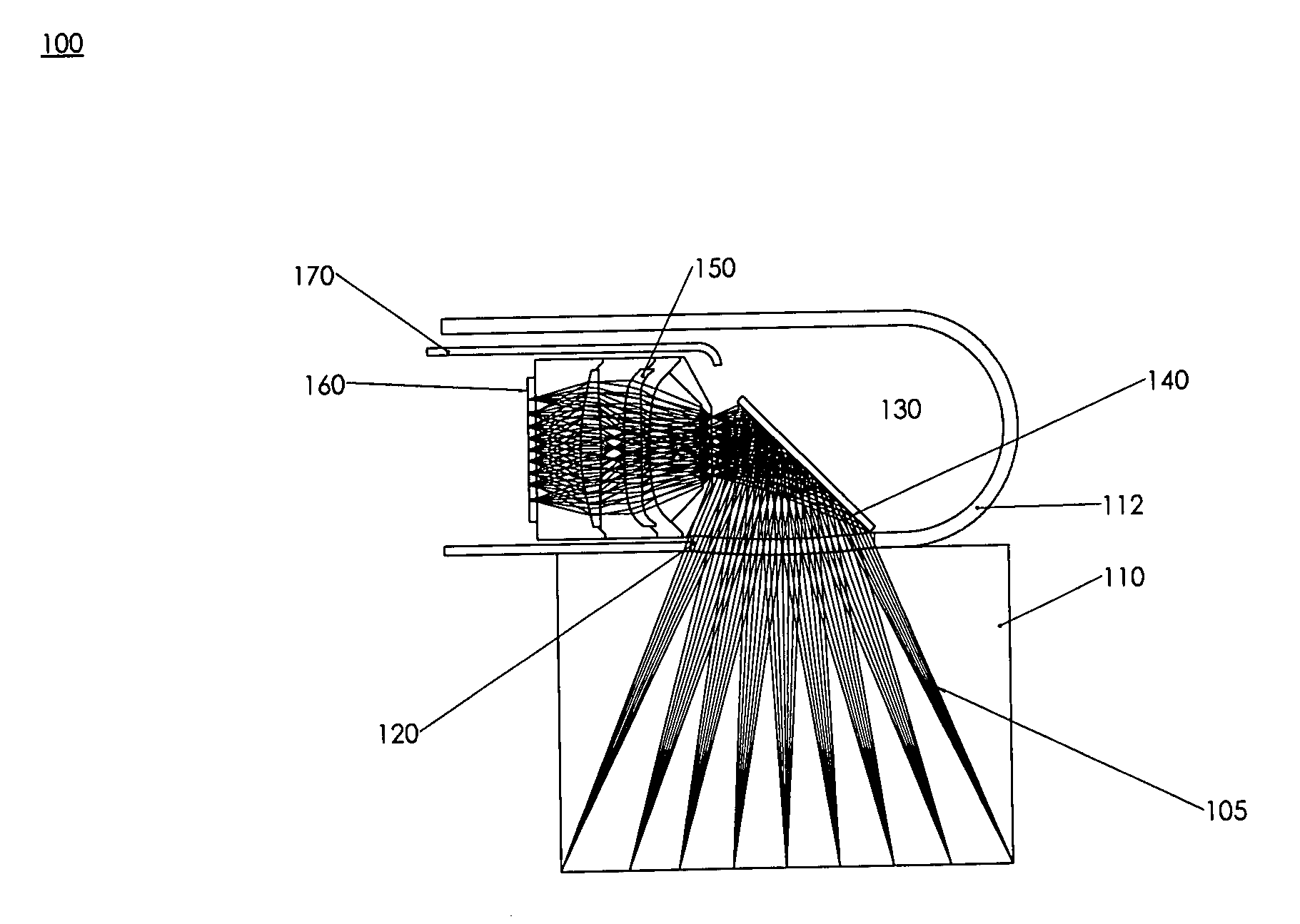
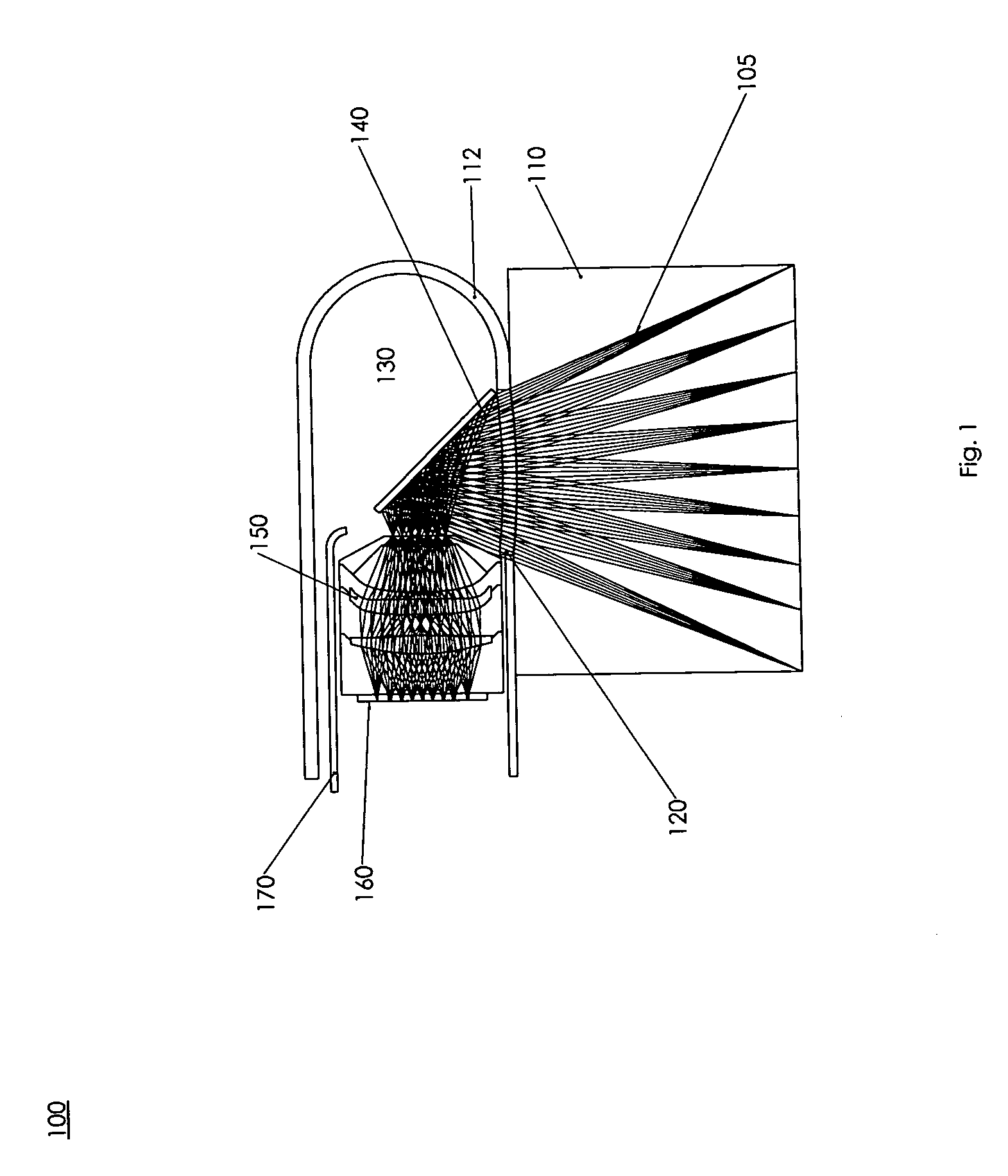
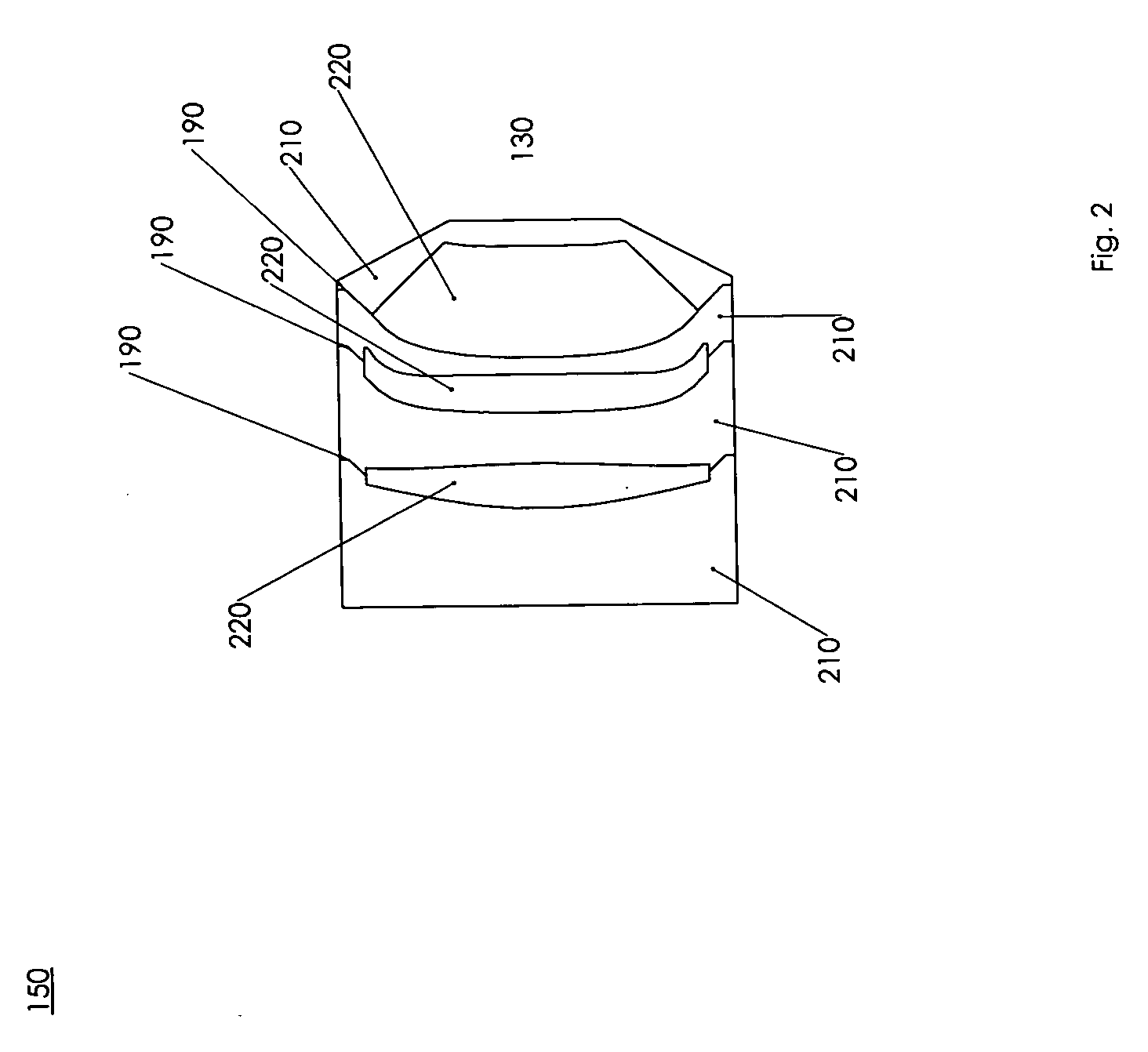
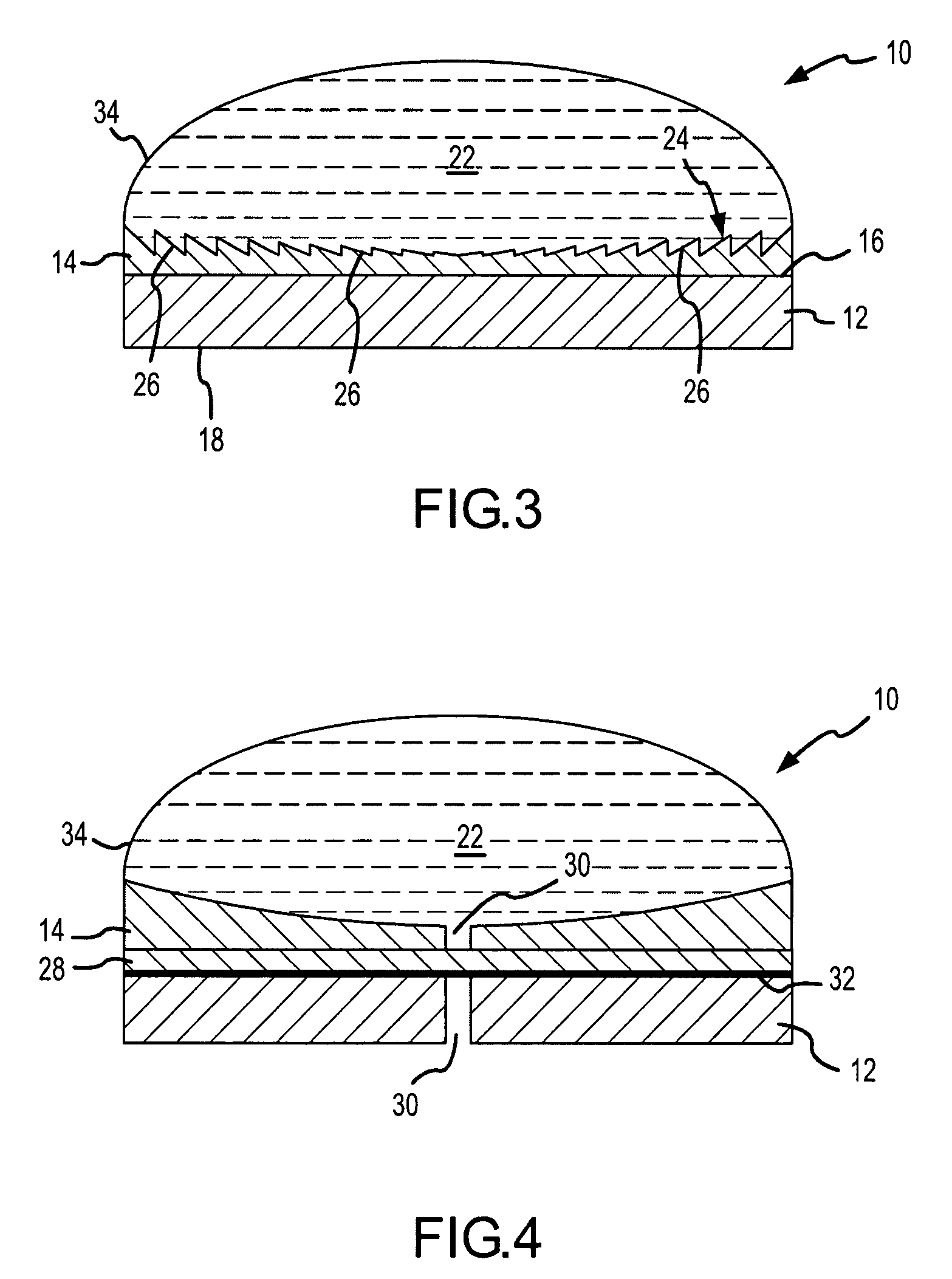
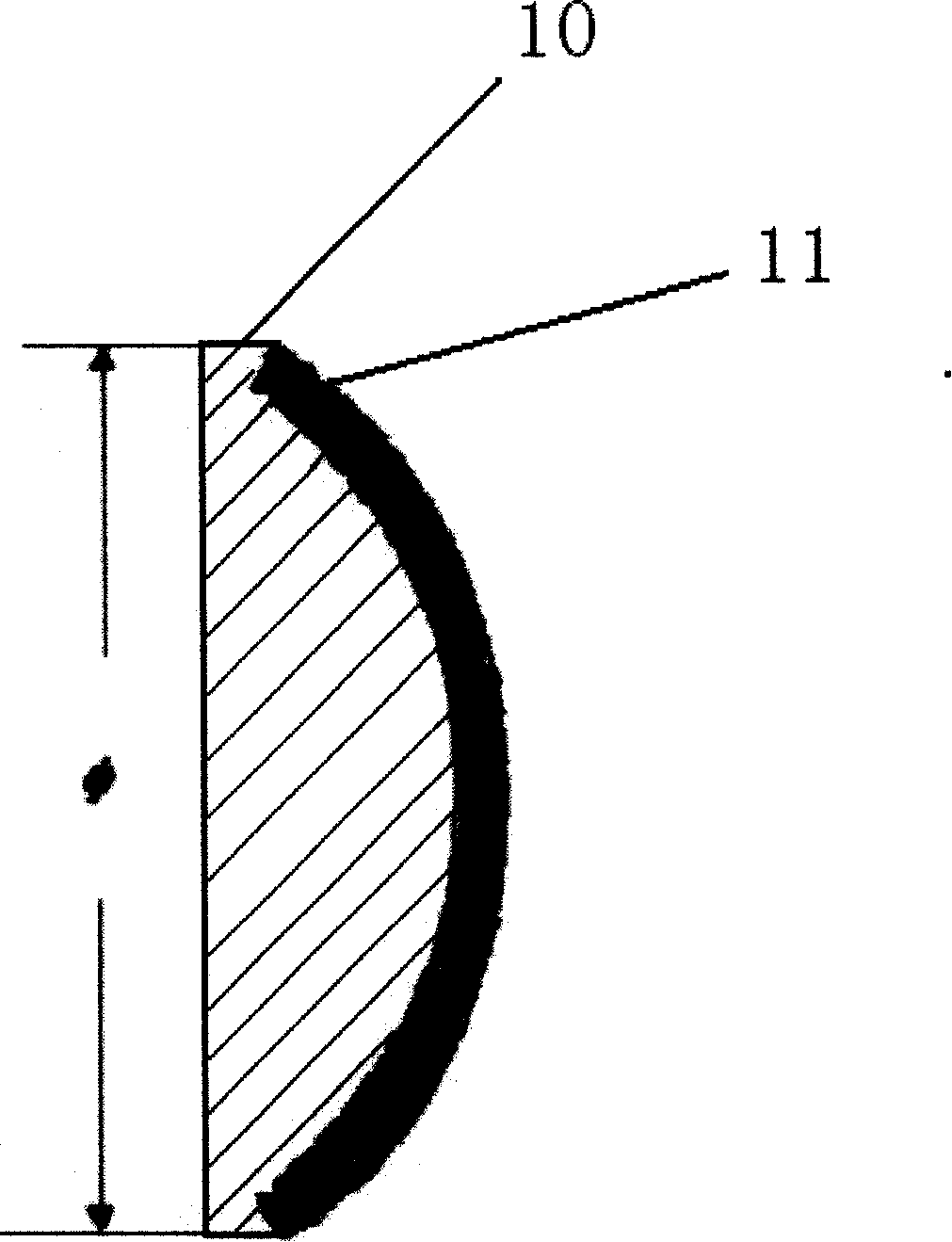
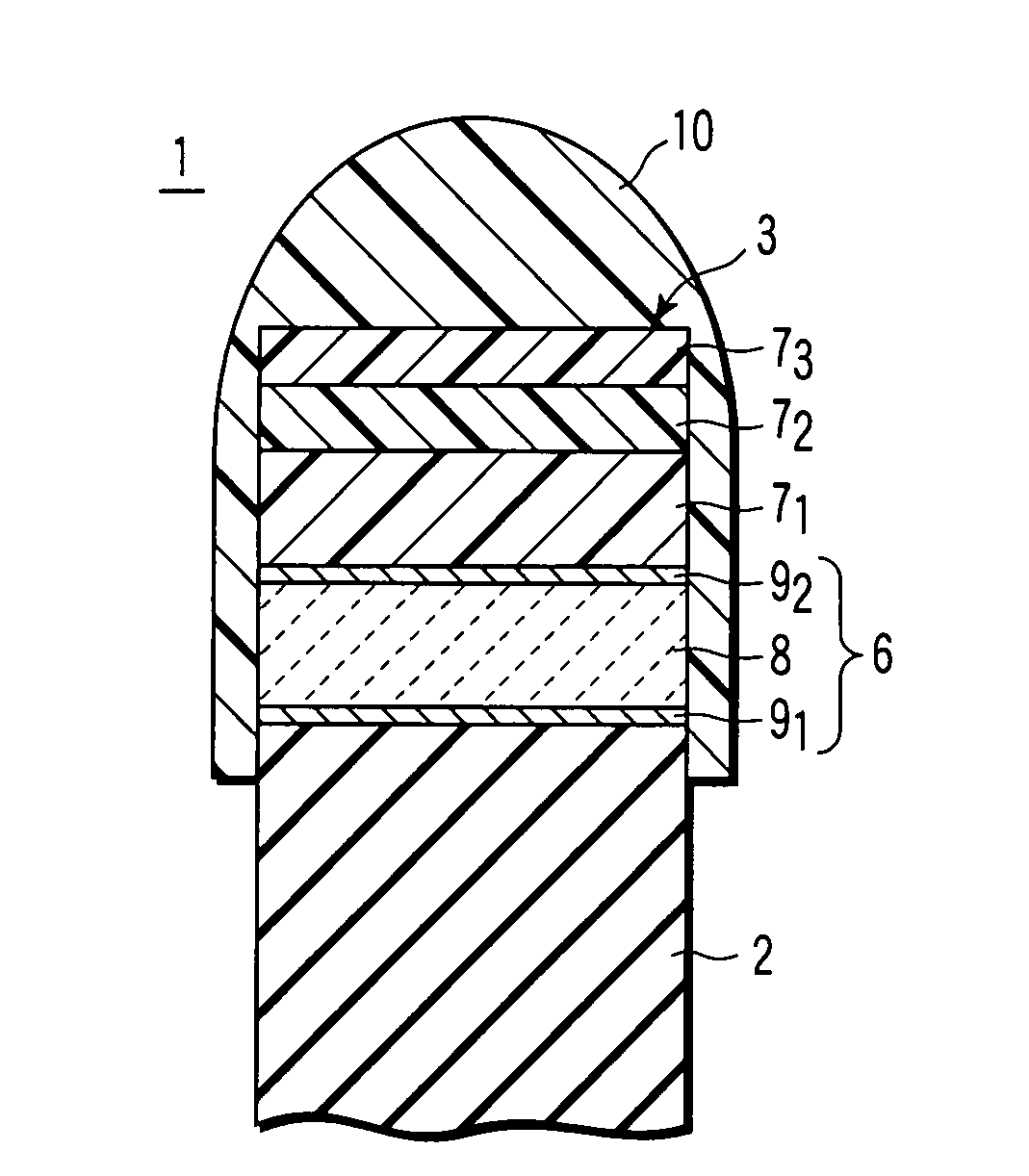
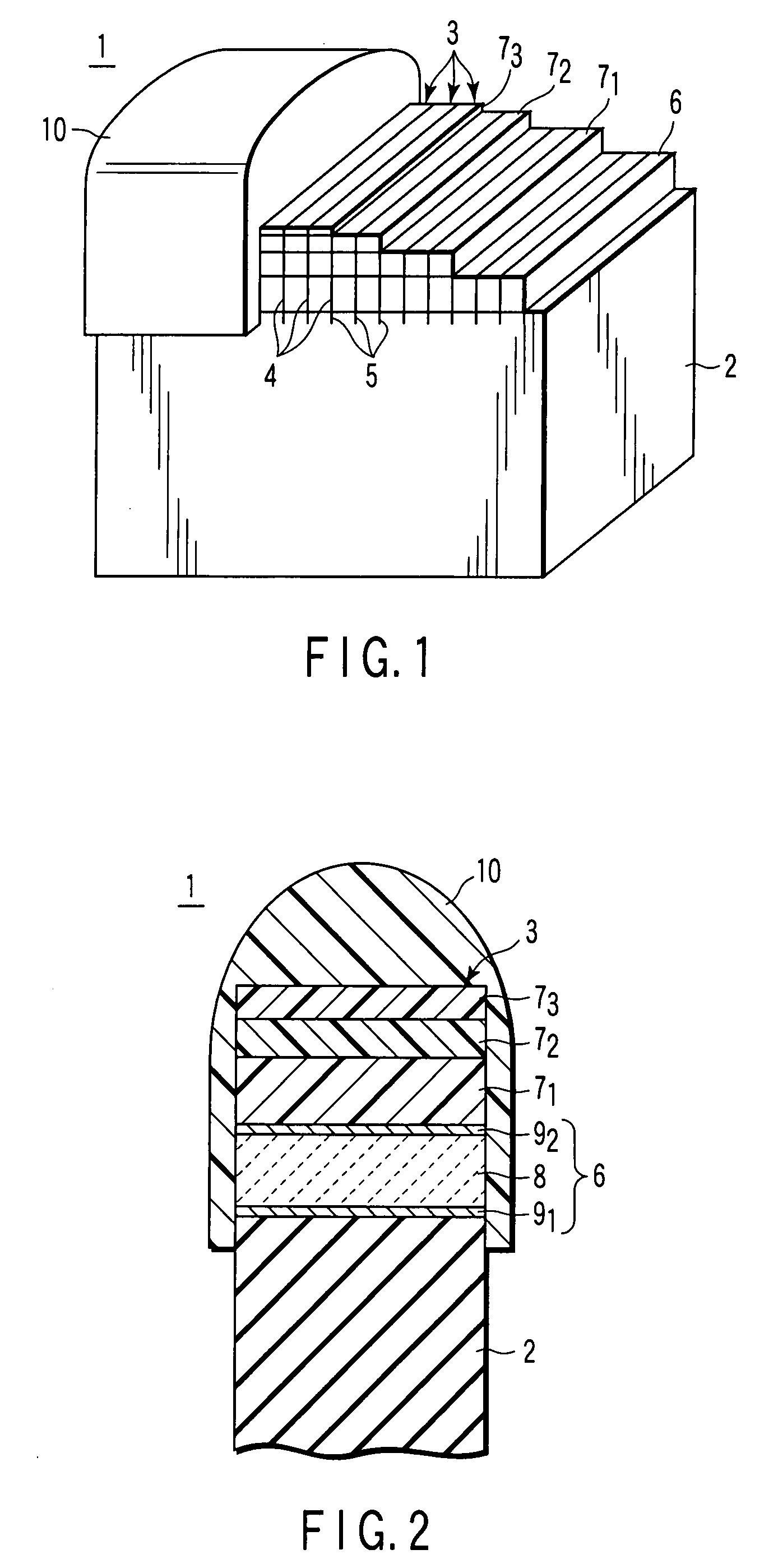
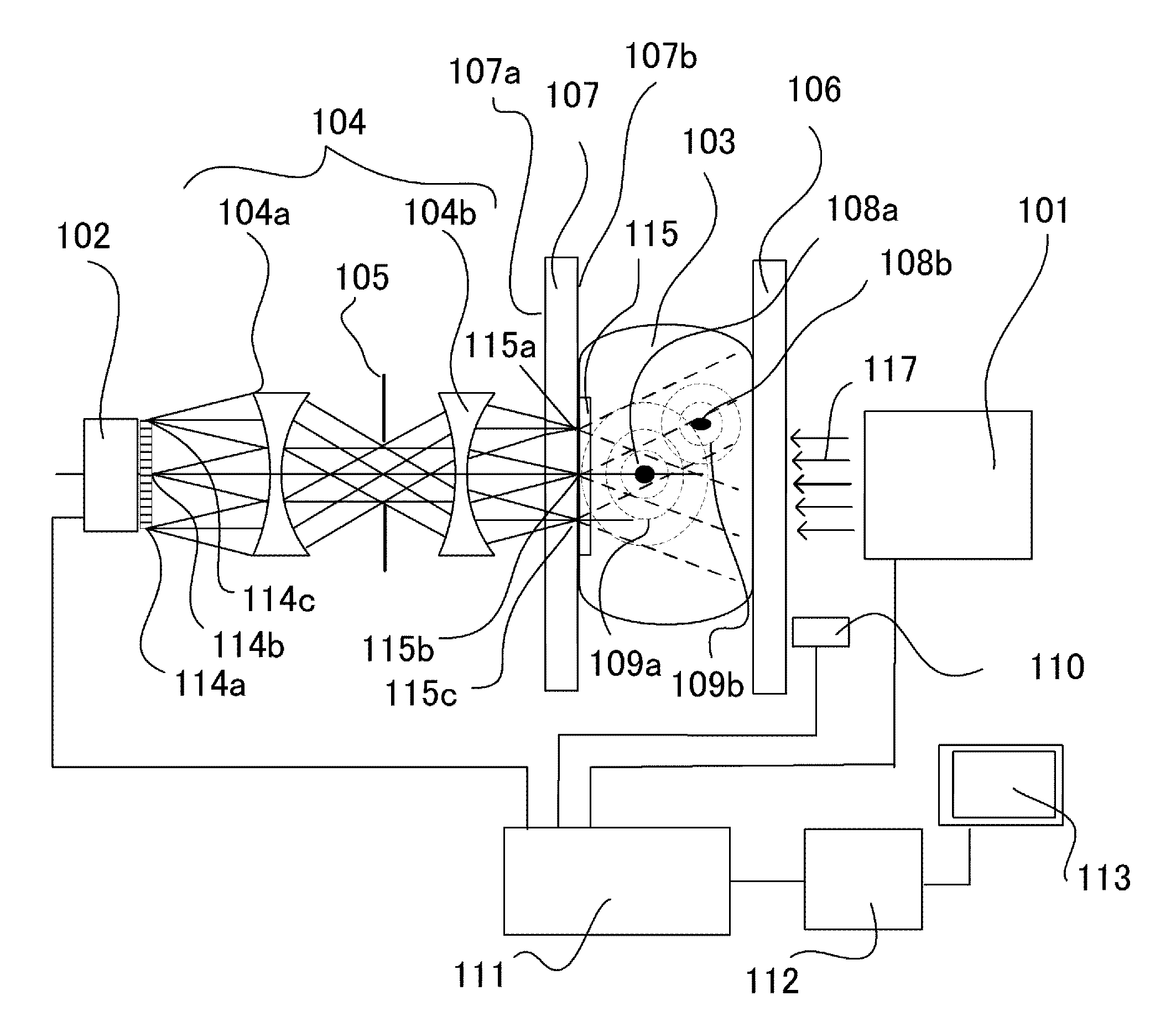
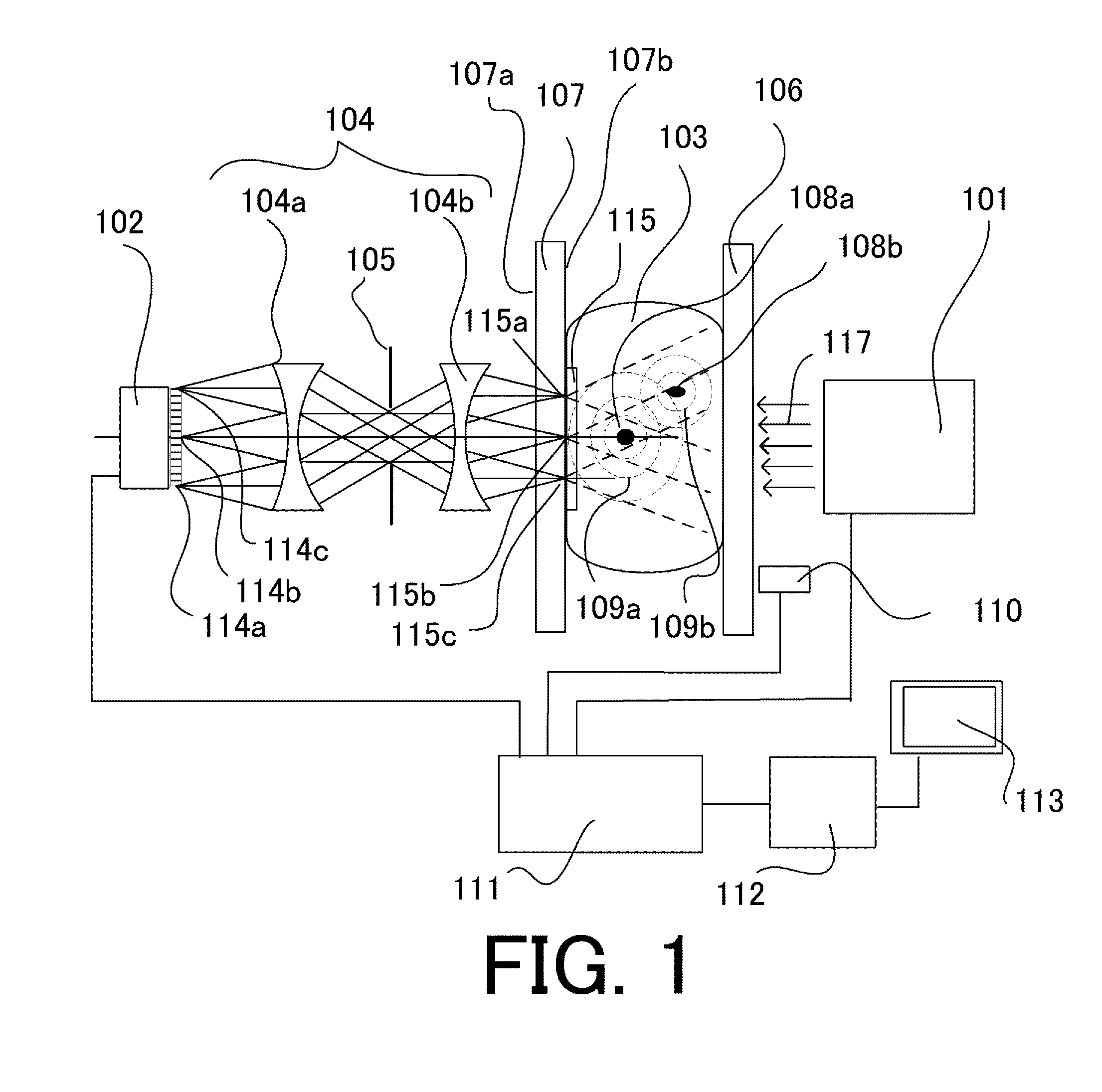
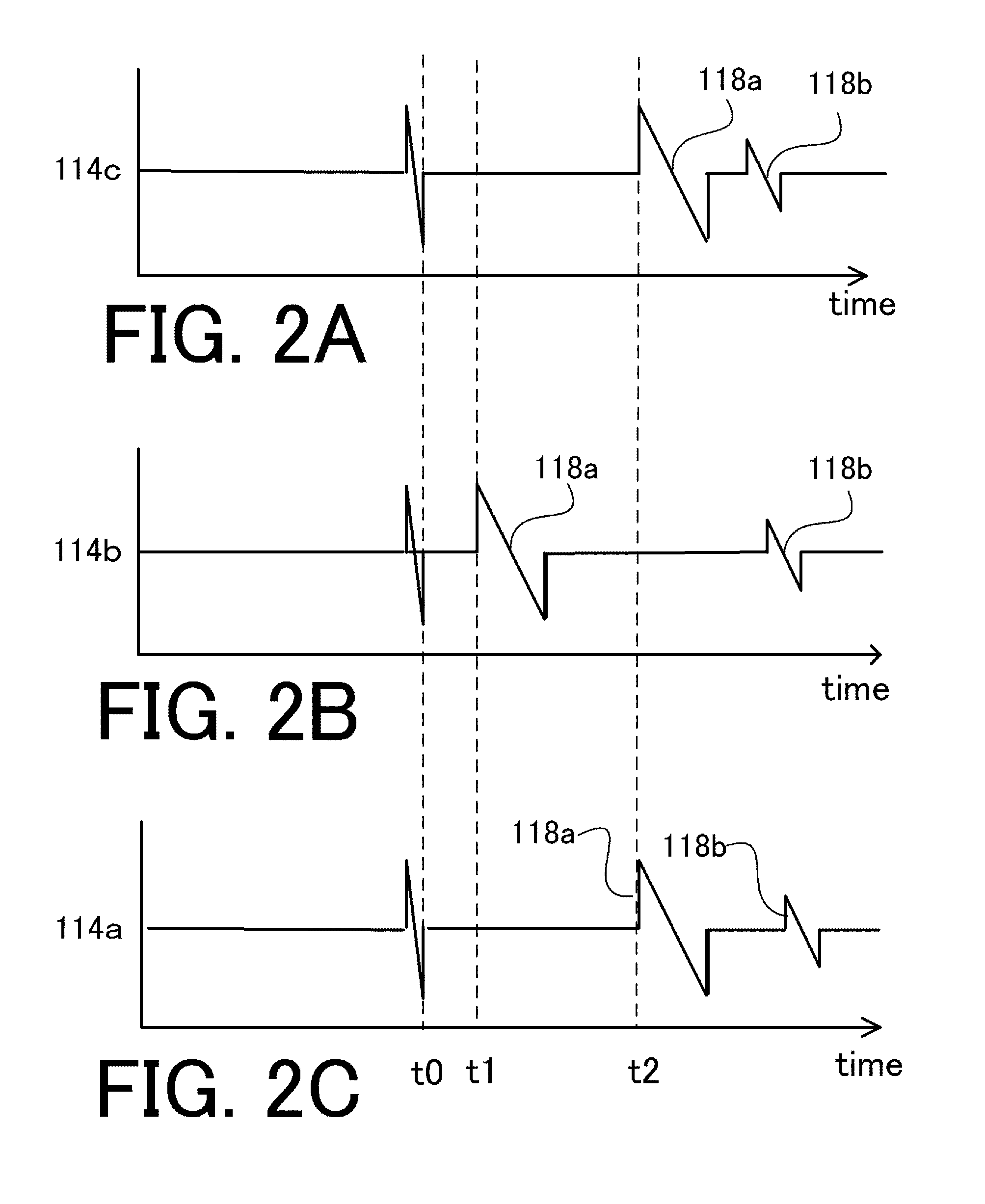
A catheter introduction apparatus provides an ultrasound assembly for emission of ultrasound energy. In one application the catheter and the ultrasound assembly are introduced percutaneously, and transseptally advanced to the ostium of a pulmonary vein. An anchoring balloon is expanded to center an acoustic lens in the lumen of the pulmonary vein, such that energy is converged circumferentially onto the wall of the pulmonary vein when a transducer is energized. A circumferential ablation lesion is produced in the myocardial sleeve of the pulmonary vein, which effectively blocks electrical propagation between the pulmonary vein and the left atrium.
Owner:BIOSENSE
Ultrasound apparatus with treatment lens
An ultrasound apparatus comprising an ultrasound transducer having a geometric focus; an acoustic lens assembly acoustically coupled to the ultrasound transducer; wherein the acoustic lens assembly includes a focal layer that serves to increase relative acoustic pressure in a treatment region proximal to the transducer's geometric focus.
Owner:ULTHERA INC
Ultrasound imaging with acquisition of imaging data in perpendicular scan planes
InactiveUS6537220B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrotherapyUltrasound imagingSonification
An ultrasonic imaging array has two independent, interleaved linear subarrays occupying a common array face. The subarrays are independently steerable and focusable in different imaging planes. The subelements making up the elements in of the subarrays is preferably quadrilateral. Adjacent subelements in each element are electrically connected via an interconnect portion such that the interconnect portion connecting each pair of adjacent subelements in each element is substantially linear and is aligned with the diagonals of the adjacent subelements. A preferred acoustic lens is curved in both azimuth and elevation directions, whereby the subarrays are independently focusable. By transmitting in one plane and simultaneously receiving in a different, orthogonal plane, a system including the array can image a 3-D region of interest (ROI). In a volumetric embodiment of the invention two orthogonal B-mode images of a structure within the ROI are displayed simultaneously. The user may then trace the outlines of the images and the system therefrom calculates the volume of the structure.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
High intensity focused ultrasound transducer with acoustic lens
ActiveUS20080194967A1Low costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound attenuationSonification
A high intensity focused ultrasound transducer includes an ultrasonic emitter having a surface that emits ultrasonic energy along a beam path, at least one low attenuation polymeric ultrasonic lens acoustically coupled to the surface in the beam path of the ultrasonic energy, such that the lens can direct the ultrasonic energy in at least one direction, and at least one stress mitigation feature, such as a kerf, a heat sink, or an acoustic matching layer, to mitigate thermal expansion mismatch stresses within the transducer. For manufacturing simplicity, the first surface is typically either flat or monotonically curvilinear. The lens may take a variety of shapes, including Fresnel features, and may focus, collimate, or defocus the ultrasonic energy. Any orientation and positioning of the at least one ultrasonic lens relative to the first ultrasonic emitter is contemplated. Manufacture is further simplified by molding, casting, or thermoforming the lens.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
High intensity focused ultrasound transducer with acoustic lens
A focused ultrasound transducer includes a first ultrasonic emitter and at least one metallic ultrasonic lens acoustically coupled thereto. The emitter generates ultrasonic energy that propagates along a beam path projecting therefrom. The at least one metallic ultrasonic lens is positioned at least partially in the beam path so that it can direct (e.g., focus, defocus, and / or collimate) in at least one direction (or along at least one plane) at least some of the ultrasonic energy propagating from the emitter. The metallic lens may be formed by extrusion, by molding (e.g., diecast molding or thermoforming), or by sintering (e.g., powder metallurgy). The metallic lens also advantageously functions as a heat sink, improving thermal performance of the ultrasound transducer.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Teleoperation unmanned submersible for detecting and disposing submarine target
The invention discloses a teleoperation unmanned submersible for detecting and disposing a submarine target, and is applied to the field of detecting and disposing technologies for submarine targets in the limpidity water area and the muddy water area. A power propulsion device of the teleoperation unmanned submersible comprises four screw propellers installed on a submersible body frame, wherein a cable interface and a signal interface are combined so as to form a photoelectric composite cable interface; underwater detection equipment comprises submersible front detection equipment and submersible lower detection equipment; a forward follow-up bright light searching lamp, a follow-up glimmer camera and an acoustic lens of a detection sonar are fixedly installed on a pitching rotation cradle head; the pitching rotation cradle head generates pitching rotation relative to the submersible body frame so as to adjust detection and viewing angles of the submersible front detection equipment fixed on the pitching rotation cradle head; and submersible position and attitude sensor group realize exact locating on positions and attitudes of an ROV (remotely-operated vehicle), thereby improving the service property of the unmanned submersible, and expanding the application area of the unmanned submersible.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Ultrasonic probe and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus using the same
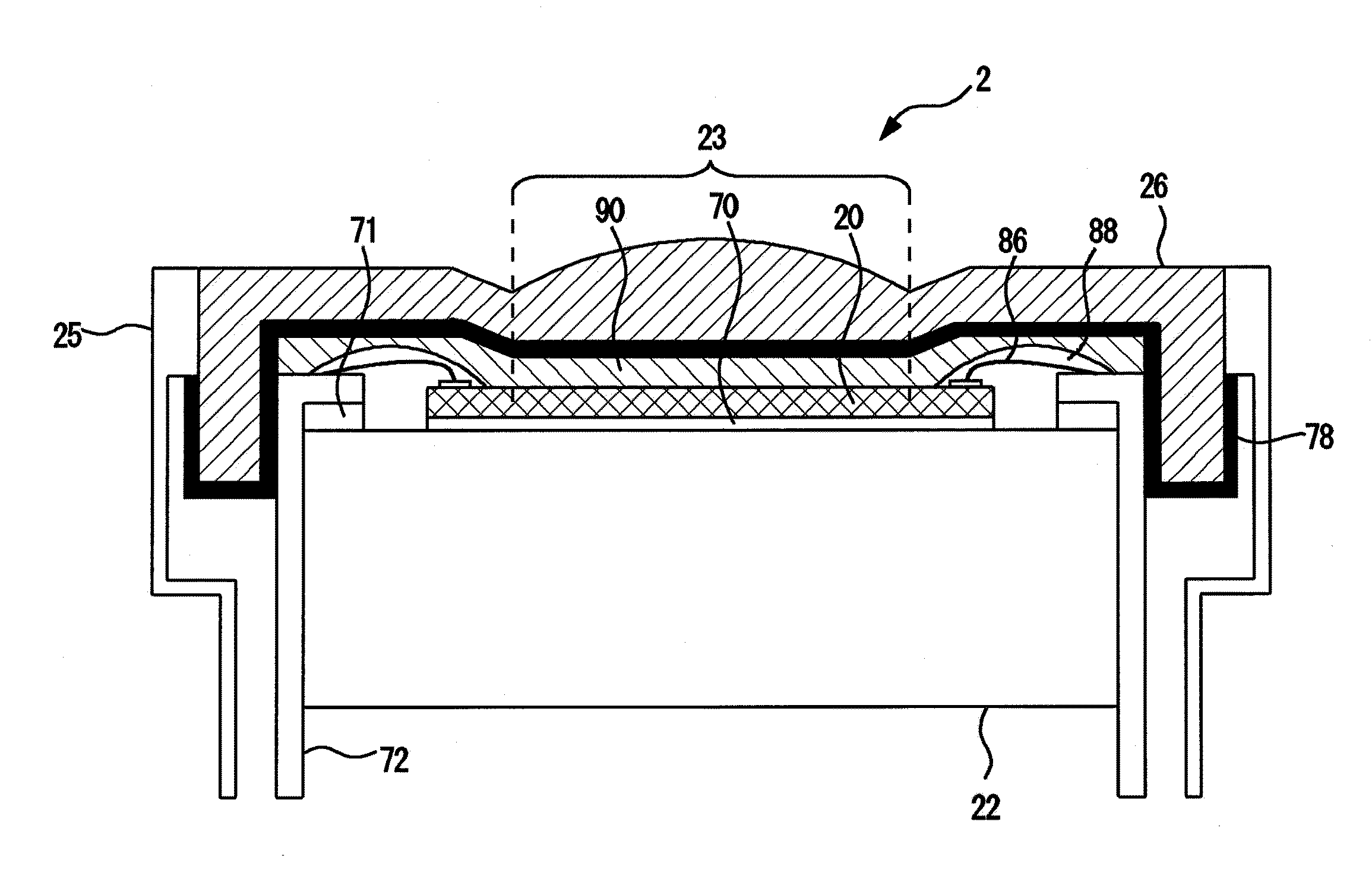
ActiveUS8758253B2Prevent leakageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectromechanical coupling coefficientAcoustic lens
An ultrasonic probe is disclosed which includes a cMUT chip having a plurality of vibration elements whose electromechanical coupling coefficient or sensitivity is changed according to a bias voltage and transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves, an acoustic lens arranged above the cMUT chip, and a backing layer arranged below the cMUT chip. An electric leakage preventing unit is provided at the ultrasonic wave transmission / reception surface side of the acoustic lens or between the acoustic lens and the cMUT chip. The electric leakage preventing unit can be, for example, an insulating layer such as a ground layer. Such a structure makes it is possible to provide an ultrasonic probe capable of preventing electric leakage from the ultrasonic probe to an object to be examined so as to improve the electric safety and an ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus using the probe.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
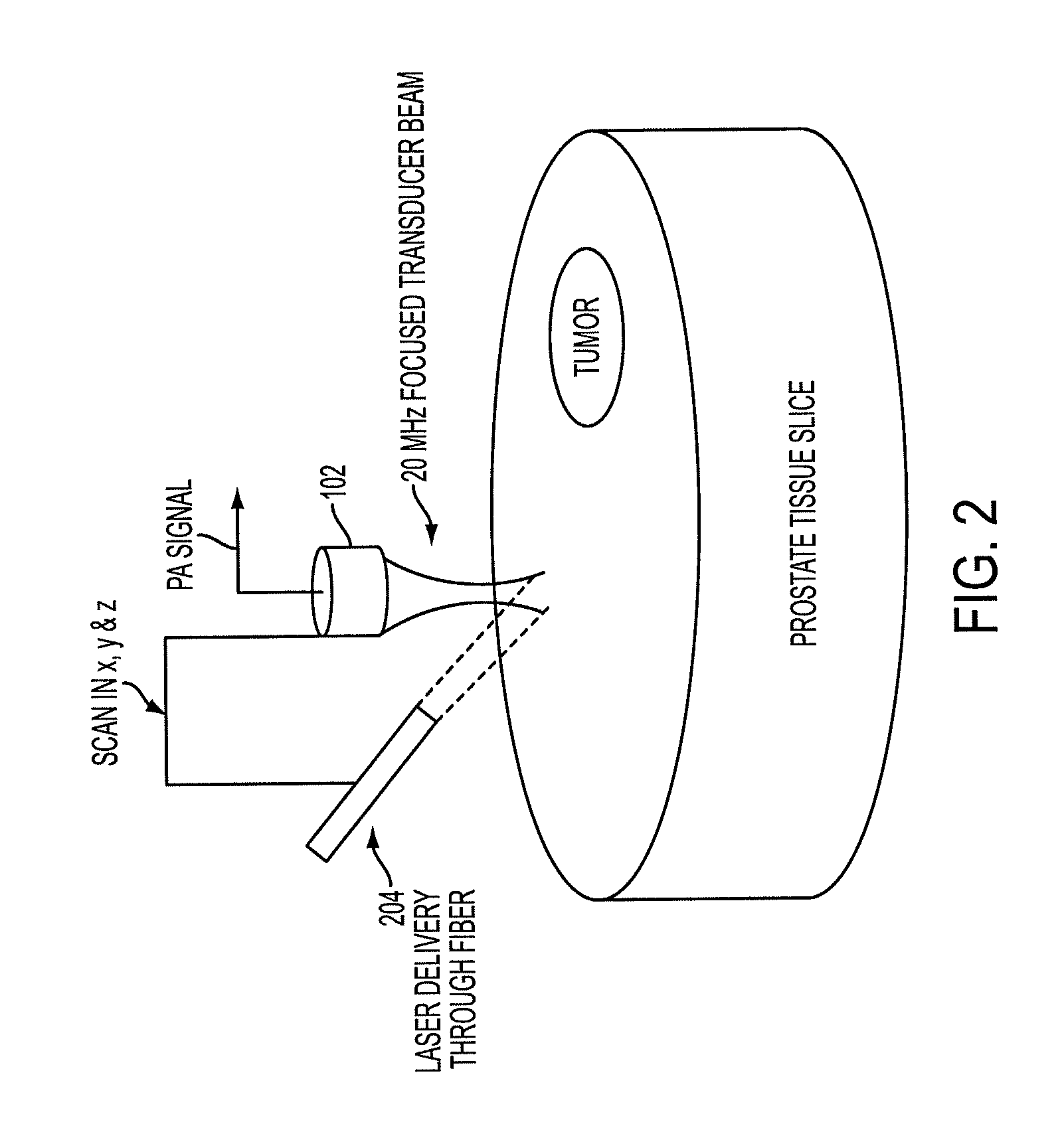
Low-cost device for c-scan photoacoustic imaging
ActiveUS20100016717A1Small sizeLow costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsSensor arraySonification
The prostate gland or other region of interest is stimulated with laser light, resulting in ultrasound waves (photoacoustic effect) which are focused by an acoustic lens and captured by a specific 1- or 2D sensor array and subsequently displayed as a C-scan on a computer screen. The amplitude of the ultrasound waves generated by laser stimulation is proportional to the optical absorption of the tissue element at that spatial location. Variability in tissue absorption results in C-scan image contrast. The photoacoustic imaging is combined with an ultrasound C-scan image produced with a plane ultrasound wave applied to the region of interest.
Owner:ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
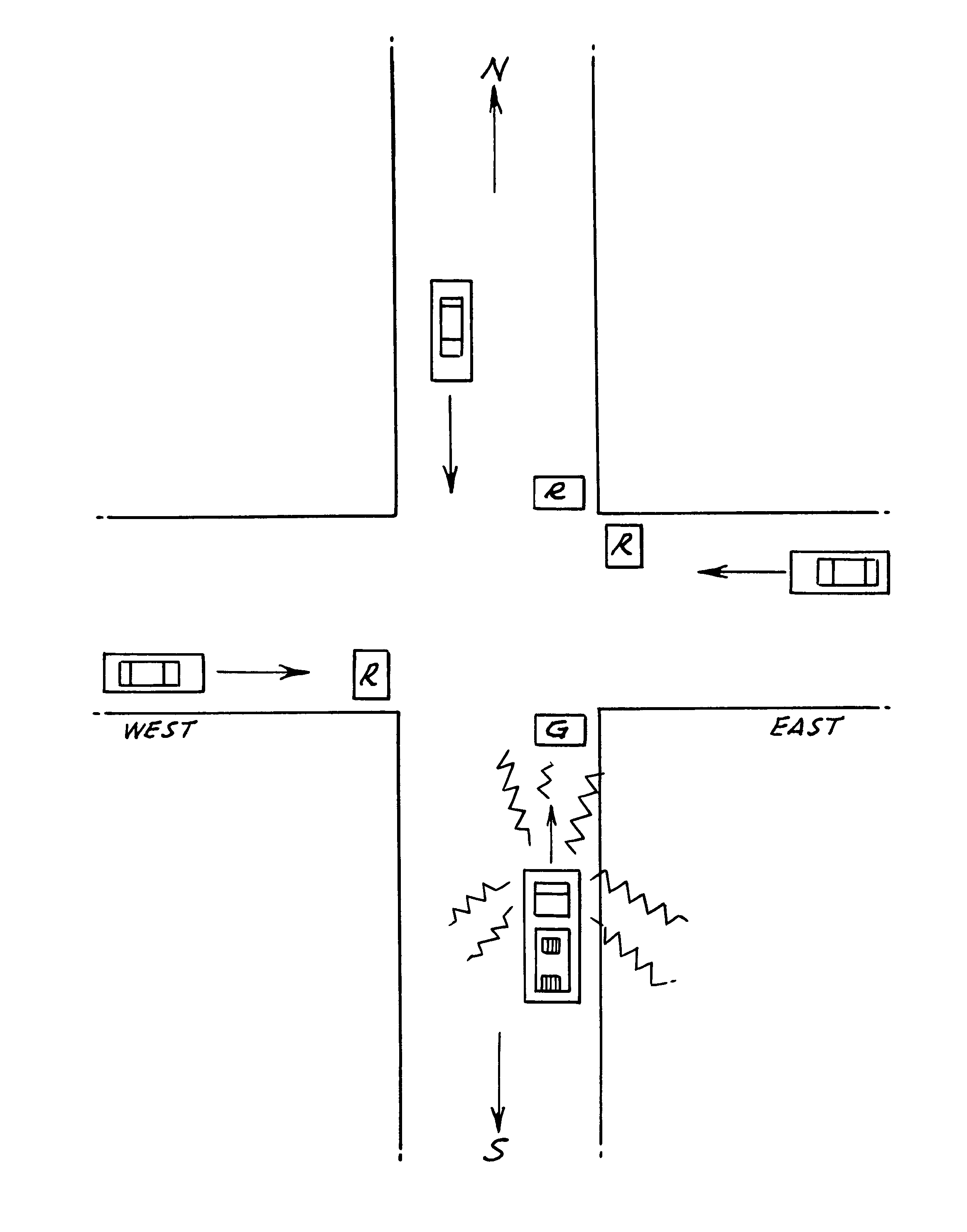
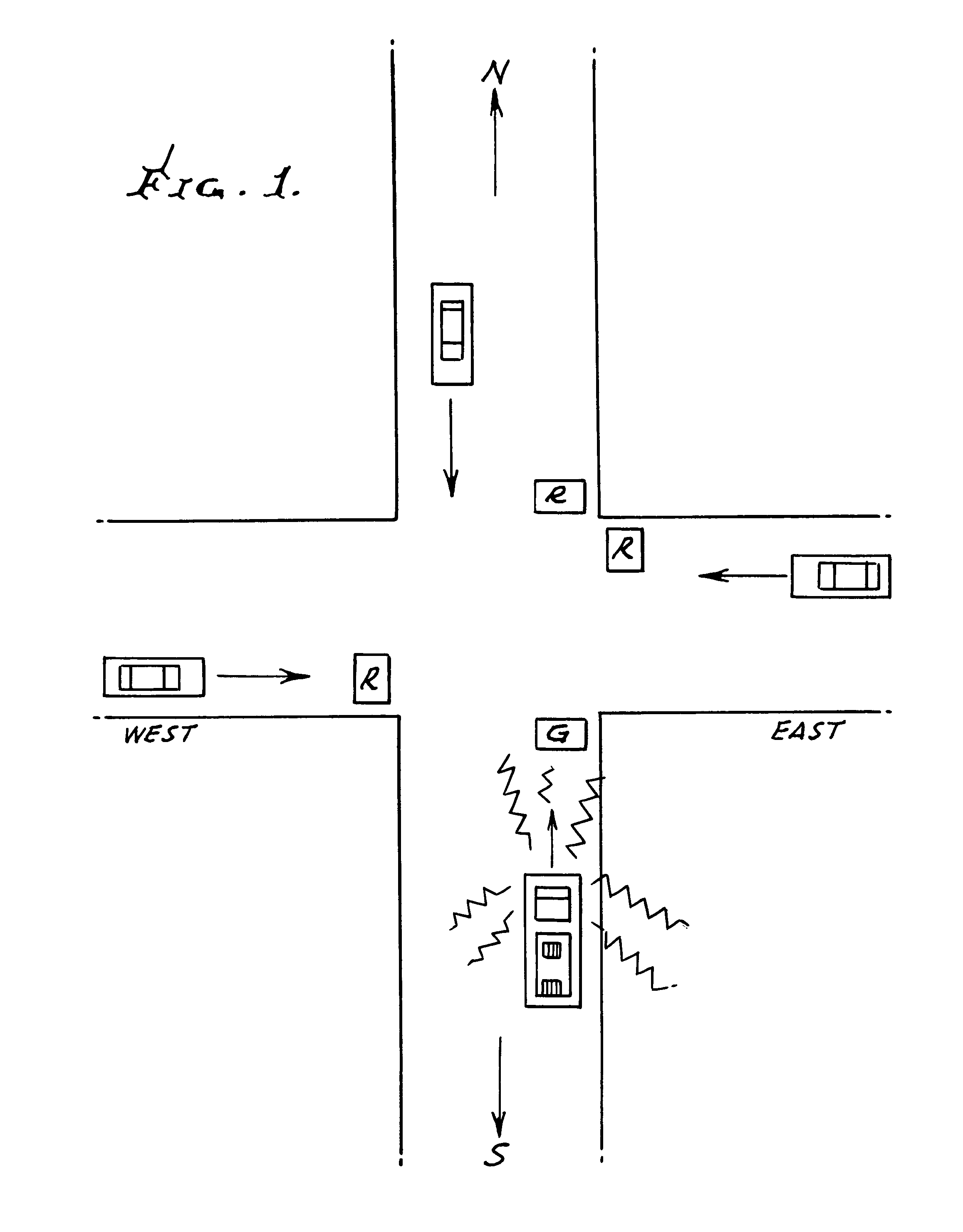
Methods and apparatus for electronically detecting siren sounds for controlling traffic control lights for signalling the right of way to emergency vehicles at intersections or to warn motor vehicle operators of an approaching emergency vehicle
InactiveUS8094040B1Improve discriminationEliminating extraneous soundControlling traffic signalsSequence controlDriver/operator
A siren sensor for detecting siren sounds emitted from emergency vehicles and electronic processing circuits for detecting and identifying the siren sounds electronically to control the traffic signal lights at an intersection to permit only the emergency vehicle to travel through an intersection with the right of way. The method and apparatus utilizes an acoustic horn in combination with a microphone for receiving the siren sounds and converting them to corresponding electrical signals. A conventional horn is modified to function as an acoustic lens to filter and amplify the siren sounds applied to the microphone. The modified acoustic horn and microphone combination comprise a tuned and directional audio sensor sensitive in the frequency range of an emergency vehicle siren. The electronic signal processing circuitry amplifies the resulting microphone signals to obtain the maximum sensitivity to the frequency spectrum of siren sounds. Detectors tuned to a harmonic of the siren signals is utilized for eliminating extraneous sounds along with unique filtering to band pass only sounds in siren frequency spectrum to a phase locked loop detector. The validity of the detected signal is verified by tracking a portion of the siren signal in pre-selected increment under time constraints to lock up and unlock the detector to verify a valid siren sound signal has been detected and provides a valid output signal for use in controlling a conventional traffic light sequencing control or to warn a motorist of an approaching emergency vehicle.
Owner:CORNETT ROBERTT H +1
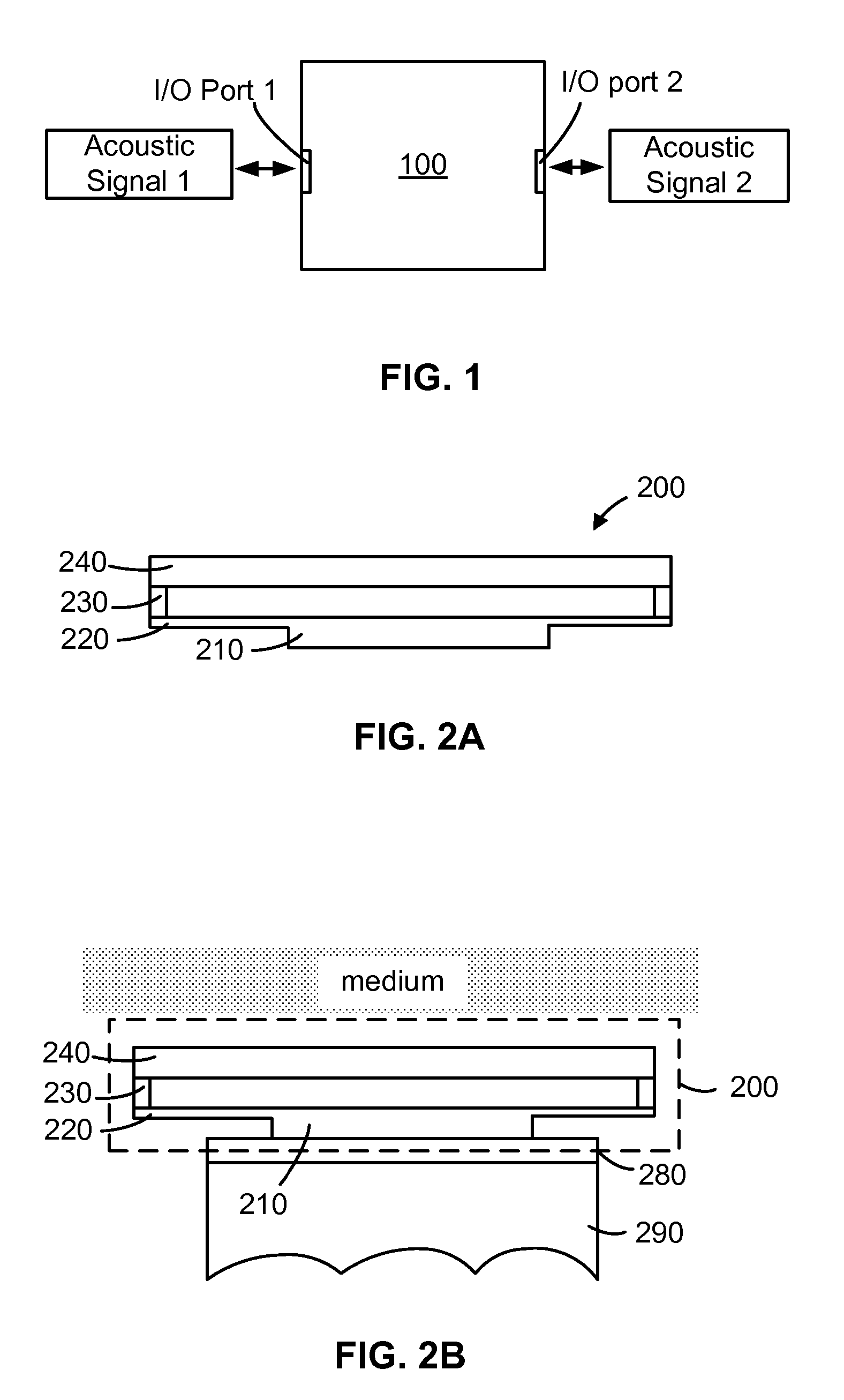
MEMS acoustic filter and fabrication of the same
ActiveUS20070046396A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesImpedence networksAcoustic lensAcoustic filters
A MEMS acoustic filter has a MEMS resonator and at least two acoustic I / O ports to alter an input acoustic signal to an output acoustic signal. The first I / O port is adapted for interfacing with a medium, and the second I / O port for passing an acoustic signal to an acoustic transducer. Multiple MEMS resonators may be stacked to form a high order acoustic filter. An array of MEMS acoustic filters may be designed to function as an acoustic lens. The MEMS acoustic filter is particularly useful with an ultrasonic transducer, such as PZT and MUT. Fabrication methods to make the same are also disclosed.
Owner:KOLO MEDICAL (SUZHOU) CO LTD
Phase plug and acoustic lens for direct radiating loudspeaker
ActiveUS20110168480A1Minimize distortionMinimize insertion lossLoudspeaker screensCabinetsEngineeringAcoustic lens
A phase plugs or acoustic lens improves the directional audio performance of a loudspeaker. Application of the improved directional audio performance to a sound system in a listening area may improve the performance of the audio system. Configuration of the acoustic lens or phase plug may include both symmetrical and asymmetrical features to provide an improved frequency response and directivity. The improved loudspeaker may provide improved an improved listing location, for example, in a vehicle.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Acoustic imaging probe incorporating photoacoustic excitation
Various embodiments of the present invention provide for a photoacoustic imaging probe for use in a photoacoustic imaging system, whereby the probe is comprised of a cohesive composite, acoustic lens incorporating aspheric geometry and exhibiting low or practically no measurable dispersion of acoustic waves constructed of at least one material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively low acoustic velocity and at least one other material with a low acoustic impedance and attenuation and a relatively high acoustic velocity. The probe is housed in a conduit filled with a low acoustic velocity and low acoustic impedance fluid such as water or mineral oil. The lens may be designed as a telecentric lens, an acoustic zoom lens, a catadioptric lens, or a reflective lens. The lens focuses acoustic waves on an acoustic imager which detects the image. The acoustic imager may be designed as a 2 dimensional array of transducers. Research to date indicates that within the range of acoustic frequencies of interest, 1 MHz-50 MHz and preferable 2 MHz-10 MHz, there exists little velocity variation within the materials of interest, and the lens design approach may currently be considered to be essentially monochromatic. The acoustic waves can be generated when an emitting light source illuminates a test subject comprising materials that generate acoustic waves at differing intensities and / or frequencies when illuminated with light, for example tissue containing blood vessels, wherein the blood vessels excite and generate an acoustic pulse. The probe has an acoustic window made of a material with low acoustic impedance which allows the acoustic pulse to enter the probe without distortion and then may be reflected by a mirror onto the acoustic lens. The probe may include the emitting light source and an optical window to allow light emitting from said light source to illuminate the test subject.
Owner:ARNOLD STEPHEN C
Ultrasonic device, ultrasonic probe, electronic equipment, and ultrasonic imaging apparatus
ActiveUS20140208853A1Improve reliabilityAvoid damageAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesUltrasonic imagingAcoustic lens
Provided is an ultrasonic device including: an ultrasonic element array substrate having a plurality of ultrasonic elements that each include a piezoelectric body; an acoustic lens secured via an acoustic matching layer to a surface, formed with the ultrasonic elements, of the ultrasonic element array substrate; and a support member secured to a surface, opposite to the surface formed with the ultrasonic elements, of the ultrasonic element array substrate, wherein the support member is formed to have a larger area, in plan view in the thickness direction of the ultrasonic element array substrate, and a higher bending stiffness than the ultrasonic element array substrate, and the acoustic lens is formed to have a lower bending stiffness than the ultrasonic element array substrate. The above-described ultrasonic device further includes an acoustic matching layer filled between the ultrasonic element array substrate and the acoustic lens.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Device and method for high intensity focused ultrasound ablation with acoustic lens
ActiveUS20080194965A1Low costUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyUltrasound attenuationLight beam
A high intensity focused ultrasound transducer includes an ultrasonic emitter having a surface that emits ultrasonic energy along a beam path, at least one low attenuation polymeric ultrasonic lens acoustically coupled to the surface in the beam path of the ultrasonic energy, such that the lens can direct the ultrasonic energy in at least one direction, and at least one stress mitigation feature, such as a kerf, a heat sink, or an acoustic matching layer, to mitigate thermal expansion mismatch stresses within the transducer. For manufacturing simplicity, the first surface is typically either flat or monotonically curvilinear. The lens may take a variety of shapes, including Fresnel features, and may focus, collimate, or defocus the ultrasonic energy. Any orientation and positioning of the at least one ultrasonic lens relative to the first ultrasonic emitter is contemplated. Manufacture is further simplified by molding, casting, or thermoforming the lens.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Ultrasonic probe and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20080098816A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMultiple-port networksResin-Based CompositeZinc
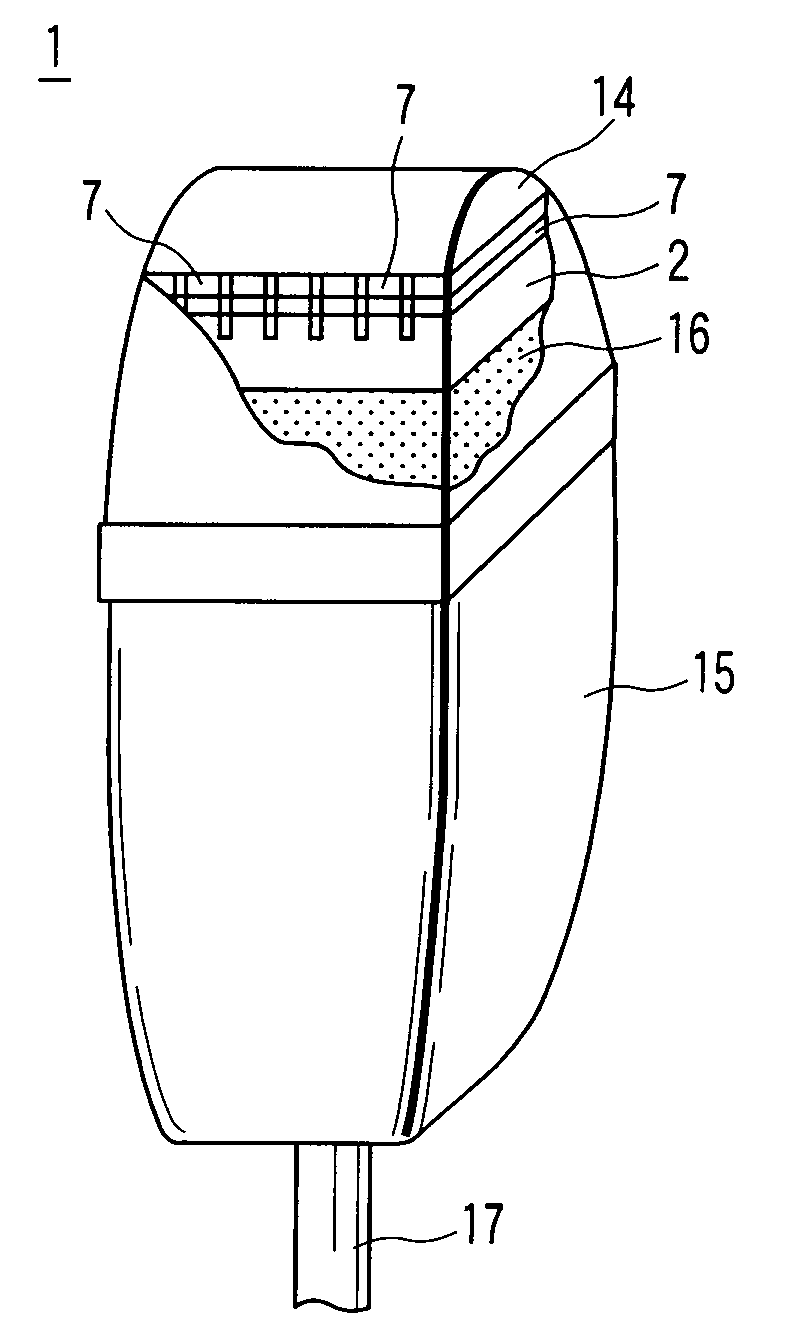
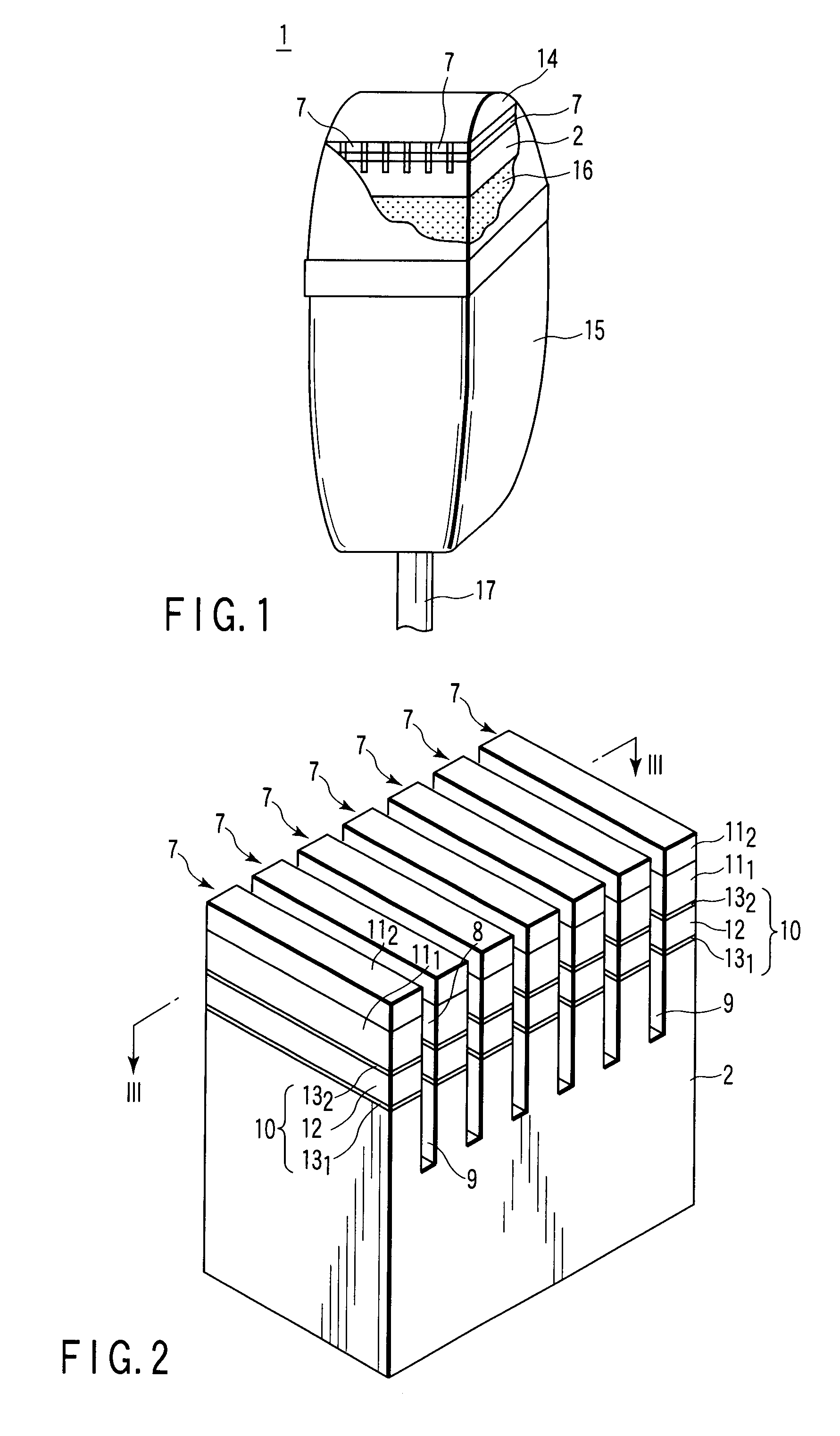
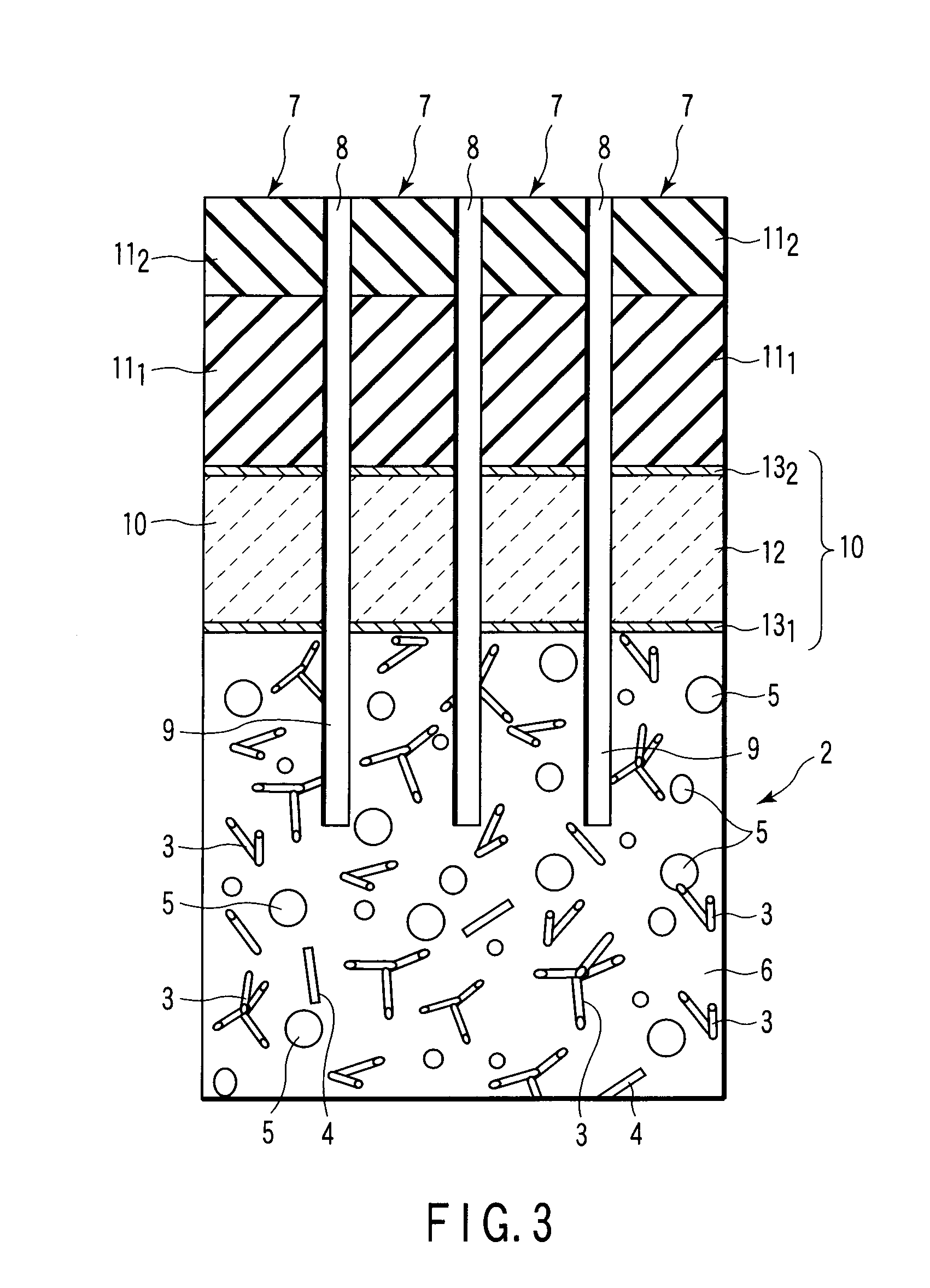
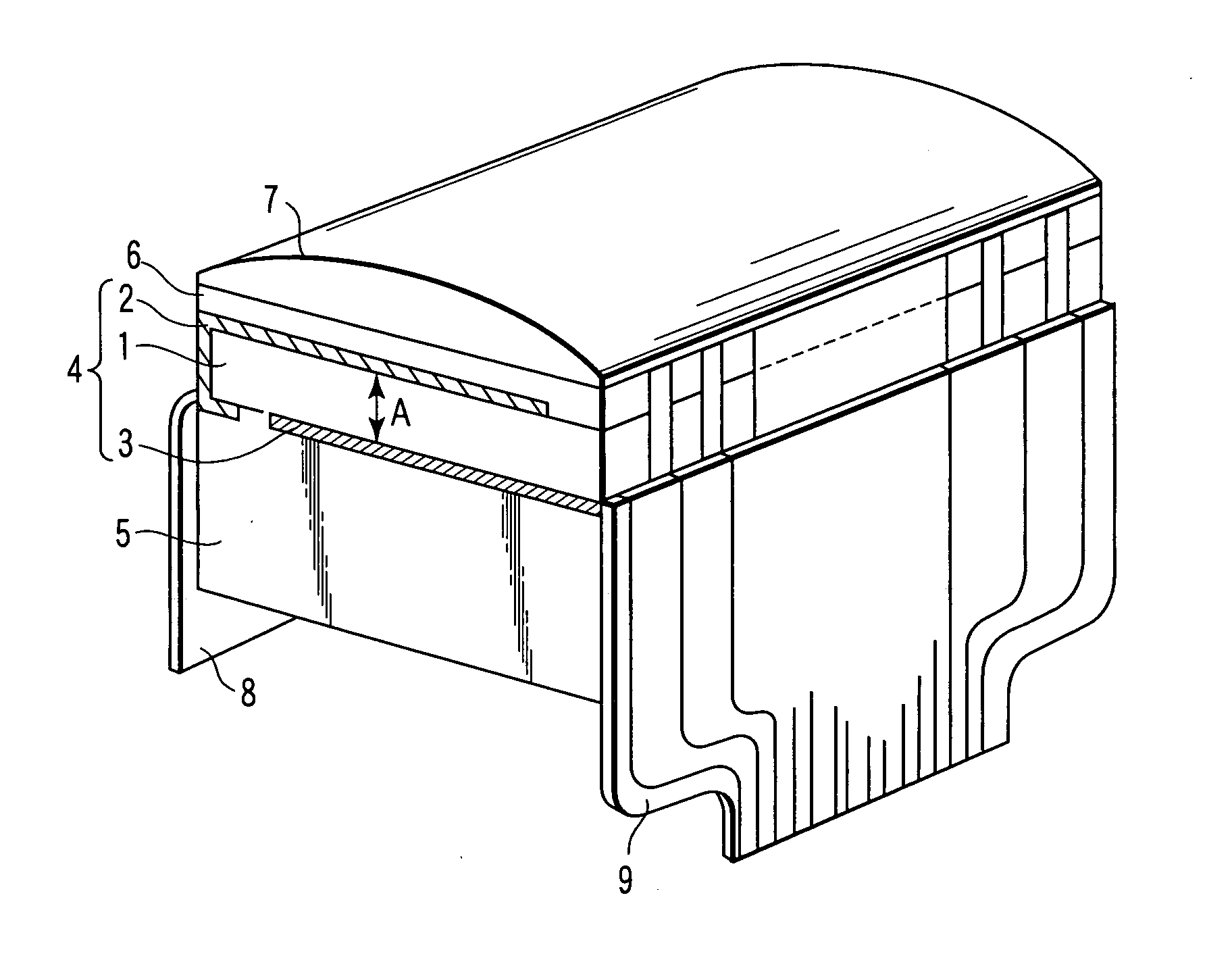
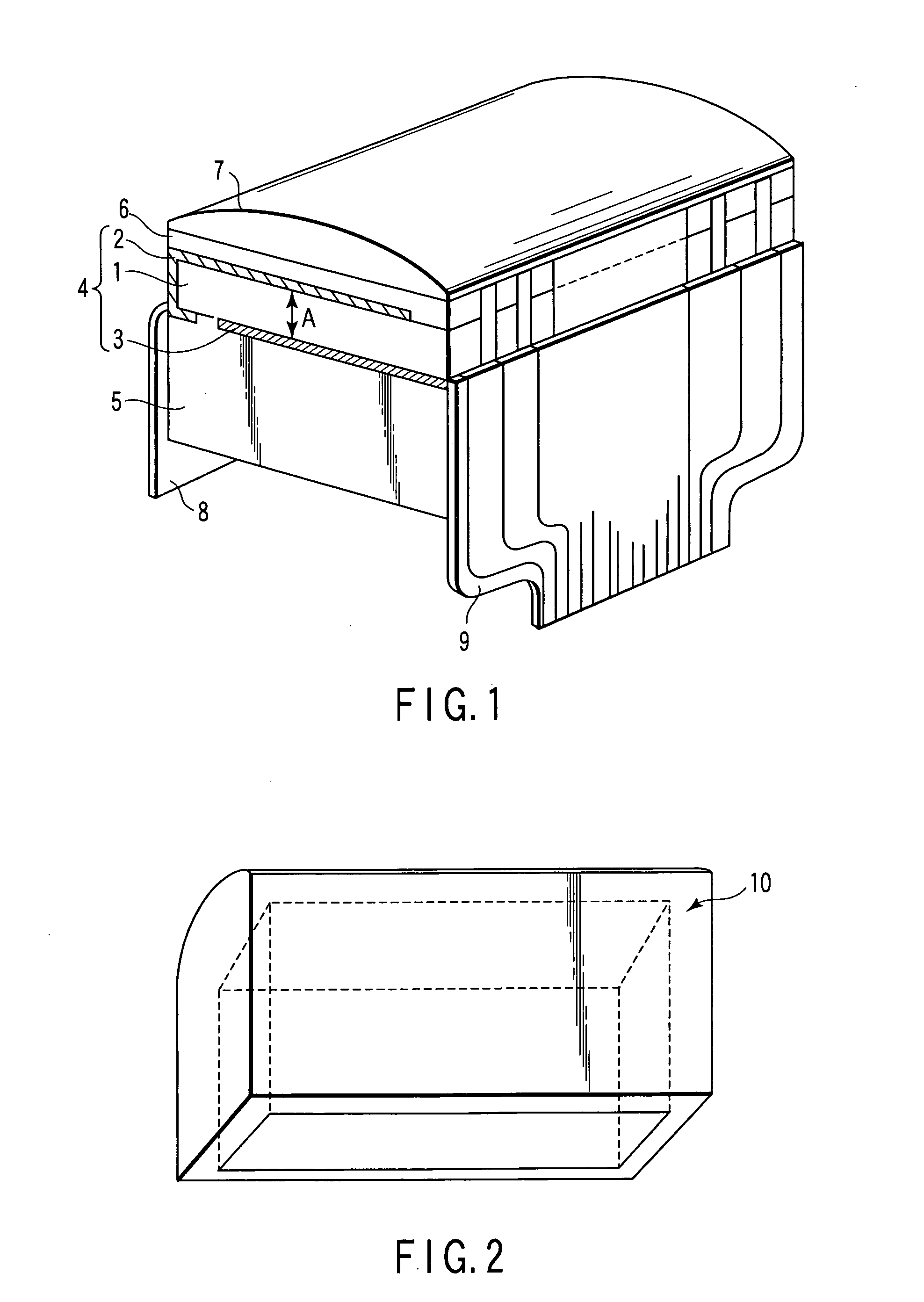
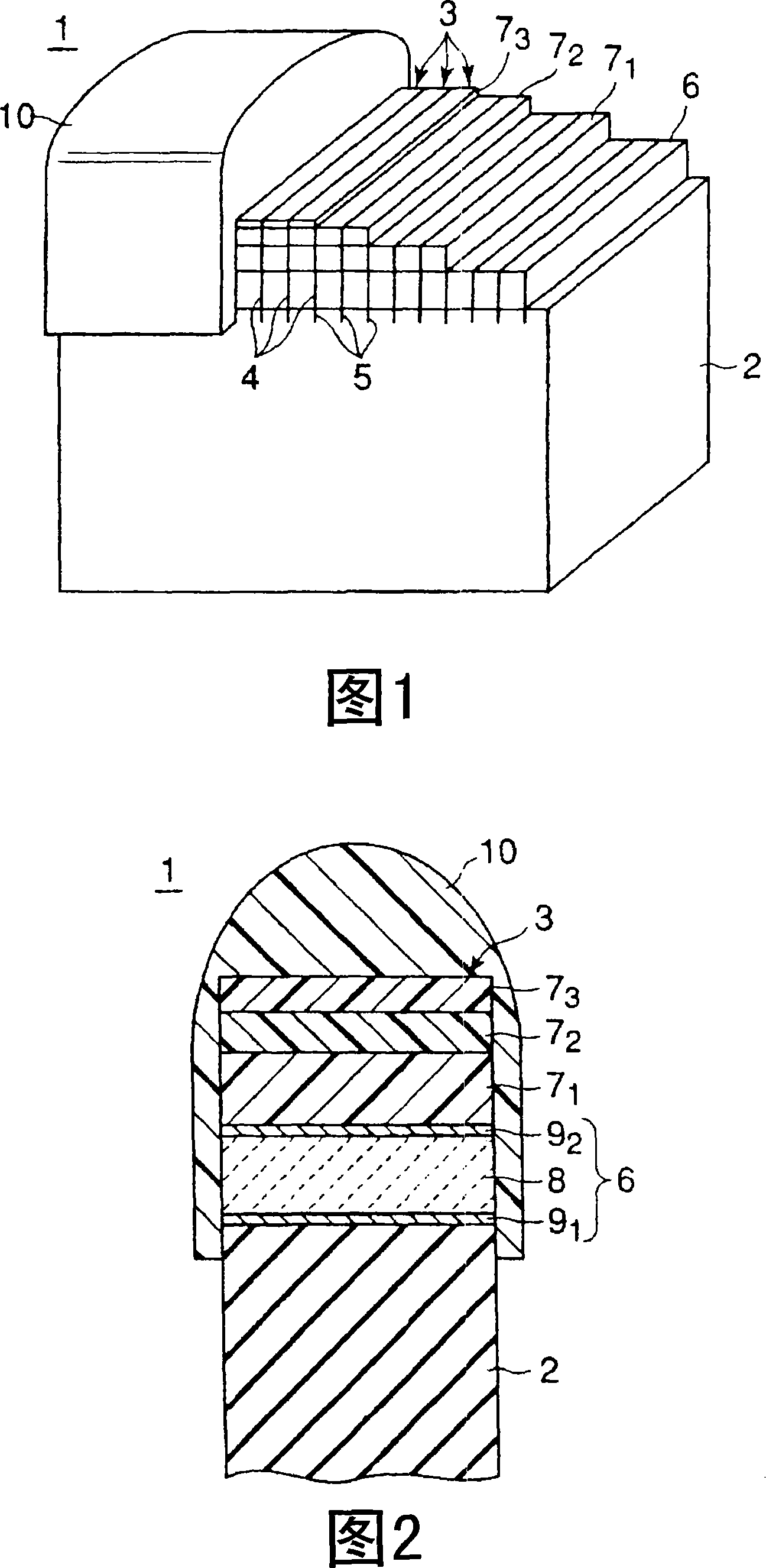
An ultrasonic probe comprises an acoustic backing layer made of a composite resin material including a resin and a plurality of bonded fibers contained the resin, each of the bonded fibers being formed of a plurality of zinc oxide fibers bonded to each other at one edge portions and extending in different directions in the other edge portions, the composite resin material exhibiting an acoustic impedance of 1.3 to 6 MRayls at 25° C., a plurality of channels arranged on the acoustic backing layer with space, each channel having a piezoelectric element and an acoustic matching layer formed on the piezoelectric element, and an acoustic lens formed to cover at least the surface of the acoustic matching layer of each channel.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
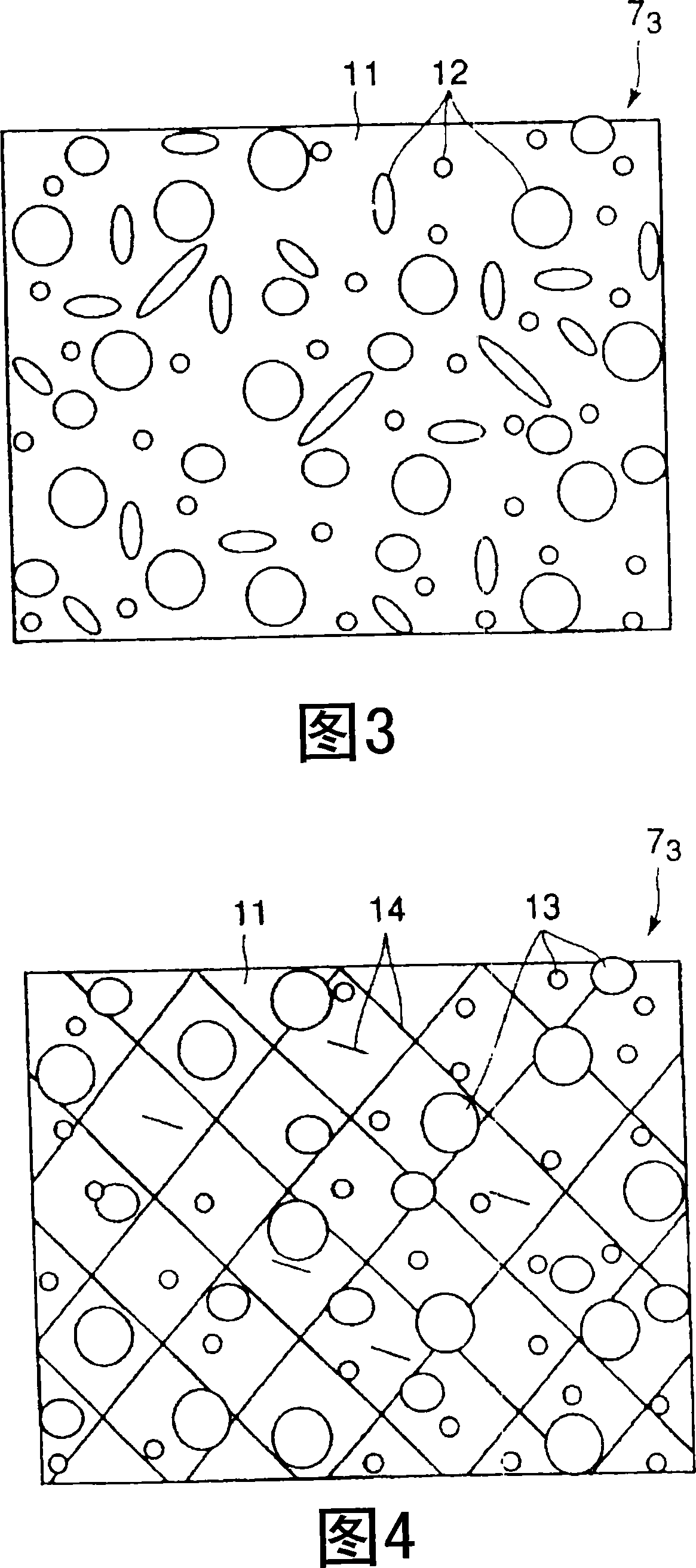
Acoustic lens composition, ultrasonic probe, and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20050070801A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesUltrasonic attenuationAcoustic lens
Provided is an acoustic lens composition which comprises 40 wt % or more of silicone rubber and 15 to 60 wt % of a zinc oxide powder, suppresses ultrasonic attenuation, and has superior molding properties.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Ultrasonic probe, method for manufacturing the same and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20110071396A1Avoid dysfunctionMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesElectrical transducersElectromechanical coupling coefficientAdhesive
An ultrasonic probe is provided with a CMUT chip having a plurality of transducer elements that change electromechanical coupling coefficients or sensitivities in accordance with a bias voltage to transmit and receive ultrasonic waves, an electric conducting layer formed on the ultrasonic irradiation side of the CMUT chip, an acoustic lens arranged on the ultrasonic irradiation side of the CMUT chip, an insulating layer formed in the direction opposite to the ultrasonic irradiation side of the acoustic lens, a housing unit that stores the CMUT chip in which the electric conducting layer and the insulating layer are fixed with an adhesive and the acoustic lens, wherein the insulating layer is formed by the material that includes at least either silicon oxide or paraxylene to prevent a solvent of the adhesive from soaking into the adhered portion.
Owner:HITACHI MEDICAL CORP
Ultrasonic probe for intra-cavity diagnosis and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20060184035A1Less heat energySuppress feverUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationFlexible circuits
A diagnostic ultrasonic probe for use in body cavities has at its tip an ultrasonic transducer array, which has a layered structure wherein a flexible circuit board, an electric circuit, a backing material, a piezoelectric element array, an acoustic impedance matching layer and an acoustic lens are formed atop another on a supporting member. The electric circuit includes at least one of amplifiers for amplifying echo signals from ultrasonic transducers, switches for switching over between sending the echo signals from the ultrasonic transducers and receiving drive signals for exciting the ultrasonic transducers, a multiplexer for selective-switching between the echo signals as well as between the drive signals, an A / D converter for converting the echo signals from an analog form to a digital form, and a D / A converter for converting the drive signals from a digital form to an analog form.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +2
Ultrasonic transducer system
ActiveUS20080156577A1Improve featuresEfficient productionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesApodizationAcoustic lens
An improved acoustic lens and an improved ultrasonic transducer system comprising an improved acoustic lens and related methods are provided. The improved acoustic lens may have a uniform loss along an elevation axis or may have a loss along the elevation axis that provides for an apodization of an acoustic signal. The improved acoustic lens may be a multi-component lens. In a two-component lens embodiment, the inner lens component, for interfacing with a transducer, may have a concave outer surface and the outer lens component may have a flat or convex outer surface. In a three-component lens embodiment, the inner lens component, for interfacing with a transducer, may have a concave outer surface, the middle lens component may have a concave outer surface and the outer lens component may have a flat or convex outer surface.
Owner:SOUND TECH
Magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method and imaging system
ActiveCN102788836AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringSource imagingAcoustic lens
The invention discloses a magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging method, comprising the steps of applying pulse excitation on a conductive target imaging body in a static magnetic field, generating an inductive vortex in the conductive target imaging body, and generating a Lorentz force by the interaction of the inductive vortex and the static magnetic field so as to cause the vibration of mass points in the imaging body to generate ultrasonic signals; receiving image signals of the ultrasonic signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body by using an array ultrasonic probe on a focal plane of an acoustic lens, imaging the received image signals of each mass point in the conductive target imaging body, so that each mass point image signal is proportional to the Lorentz force divergence of a corresponding point in the conductive target imaging body, and a Lorentz force divergence image of the conductive target imaging body or a reconstructed image according to current density rotation can be obtained according to the image signals of the ultrasonic signals detected by the array ultrasonic probe. A magneto-acoustic microscopic imaging system using the imaging method disclosed by the invention comprises a synchronous trigger and control module (1), an excitation source, an imaging system and a week signal detecting system.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Continuous-focus ultrasound lens
InactiveUS20070197917A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsFocus ultrasoundUltrasound imaging
The depth of focus in the elevation plane of an acoustic ultrasound transducer is extended. The ultrasound transducer comprises an acoustic element, said element having a substantially uniform frequency amplitude characteristic across its spatial extent and transmitting an ultrasound beam when excited, an acoustic lens positioned in front of said element, said lens having a cross sectional profile comprising (1) a curved portion with a curved front surface and a back surface facing said transducer element, said curved lens portion providing a focal point at a first focal range, and (2) a pair of linear portions with linear front surfaces and back surfaces facing said transducer element, said linear portions positioned on either side of said curved portion, and said linear portions providing continuous focusing at imaging ranges after said first focal depth of said curved portion. The broadband frequency characteristic of said element means that all frequencies are focused at all focal points, which makes the invention particularly useful for harmonic ultrasound imaging.
Owner:B K MEDICAL
High intensity focused ultrasound transducer with accoustic lens
InactiveUS20080189932A1Low costLine/current collector detailsElectrical transducersLight beamHigh intensity
A focused ultrasound transducer includes a first ultrasonic emitter and at least one metallic ultrasonic lens acoustically coupled thereto. The emitter generates ultrasonic energy that propagates along a beam path projecting therefrom. The at least one metallic ultrasonic lens is positioned at least partially in the beam path so that it can direct (e.g., focus, defocus, and / or collimate) in at least one direction (or along at least one plane) at least some of the ultrasonic energy propagating from the emitter. The metallic lens may be formed by extrusion, by molding (e.g., diecast molding or thermoforming), or by sintering (e.g., powder metallurgy). The metallic lens also advantageously functions as a heat sink, improving thermal performance of the ultrasound transducer.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Photoacoustic apparatus
InactiveUS20100058870A1Information obtainMultiple-port networksMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesAcoustic waveAcoustic lens
A photoacoustic apparatus includes an acoustic lens configured to collect a acoustic wave, an acoustic detector configured to detect the acoustic wave collected by the acoustic lens, a driver configured to move at least one of the acoustic detector and the acoustic lens so as to measure the acoustic wave generated from an object to be measured due to a photoacoustic effect, and a controller configured to output a first measurement signal resulting from the acoustic wave that is generated from a first position in the object, and to eliminate a second measurement signal resulting from the acoustic wave that is generated from a second position different from the first position in the object.
Owner:CANON KK
Phase control focusing ultrasound wave source device
InactiveCN101190436AFocusAvoid damageUltrasound therapyMechanical vibrations separationFocus ultrasoundTreatment effect
The invention discloses a phase-control focusing ultrasonic source device, comprising a plurality of transducer array elements used for emitting ultrasonic and a bearing part used for bearing the transducer array elements. The transducer array elements are in cylinder shape; a piezoelectricity wafer on the top of the array element can be in round convex shape or round concave shape, or the top of the cylindrical array element is provided with a round piezoelectricity flat piece as well as an acoustic lens; the bottom of the array element is provided with a base which is bonded into a whole with the piezoelectricity wafer; the bearing part is a sphere concave surface; all the transducer array elements are born to the bearing part to lead all the piezoelectricity wafers to be arranged in sphere concave surfaces; the plurality of transducer array elements are connected with a phase control device which adjusts the phases of all array element emitting signals by using electronic technology, thus adjusting focus position and focusing direction. The invention has the advantages of reinforcing the focusing performance of the sphere phase-control arrays, being used for high-strength focusing ultrasonic therapy equipment, only destroying tumor tissue without damaging normal tissue, thus improving therapeutic effect.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Array-type ultrasonic probe and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveCN101081169ALow decay rateLow machinabilityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesHeat resistanceHardness
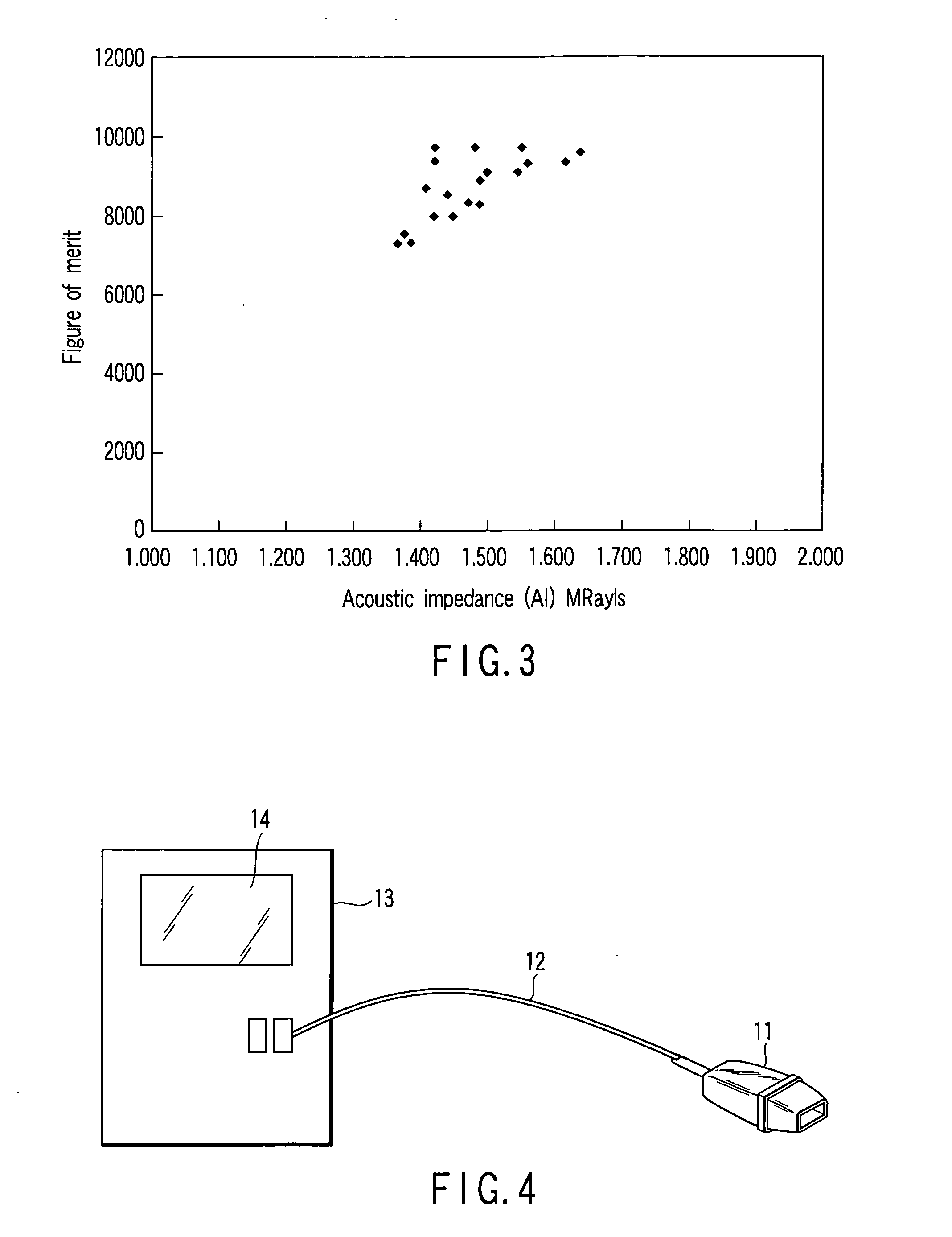
Disclosed is an array ultrasonic probe, including a plurality of channels arranged with spaces, each channel having a piezoelectric element and a laminated acoustic matching layer structure formed of at least three layers and arranged on the piezoelectric element, a backing on which the piezoelectric element of each channel is mounted and having trenches in which are formed at places corresponding to the spaces, and an acoustic lens formed to cover at least the surface of the uppermost acoustic matching layer of each channel, wherein the uppermost acoustic matching layer comprises a silicone resin-containing mixture having a Shore hardness D not lower than 40 at 25 DEG C., and exhibits an acoustic impedance of 1.8 to 2.5 MRayls at 25 DEG C.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Array-type ultrasonic probe and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus
InactiveUS20070282204A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsHardnessAcoustic lens
Disclosed is an array ultrasonic probe, including a plurality of channels arranged with spaces, each channel having a piezoelectric element and a laminated acoustic matching layer structure formed of at least three layers and arranged on the piezoelectric element, a backing on which the piezoelectric element of each channel is mounted and having trenches in which are formed at places corresponding to the spaces, and an acoustic lens formed to cover at least the surface of the uppermost acoustic matching layer of each channel, wherein the uppermost acoustic matching layer comprises a silicone resin-containing mixture having a Shore hardness D not lower than 40 at 25° C., and exhibits an acoustic impedance of 1.8 to 2.5 MRayls at 25° C.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Phase plug and acoustic lens for direct radiating loudspeaker
ActiveUS8181736B2Reduce distortionReduce insertionLoudspeaker screensCabinetsEngineeringAcoustic lens
A phase plugs or acoustic lens improves the directional audio performance of a loudspeaker. Application of the improved directional audio performance to a sound system in a listening area may improve the performance of the audio system. Configuration of the acoustic lens or phase plug may include both symmetrical and asymmetrical features to provide an improved frequency response and directivity. The improved loudspeaker may provide improved an improved listing location, for example, in a vehicle.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Acoustic lens system
ActiveUS7316290B2Reduced dimensionWiden high-frequency coveragePiezoelectric/electrostrictive microphonesMicrophonesAcoustic lensLoudspeaker
A loudspeaker includes a frame, a magnet coupled to the frame and a diaphragm secured to the frame. An acoustic lens may be positioned in front of the diaphragm. An aperture extends through the acoustic lens. The acoustical directivity pattern of the loudspeaker may be modified by the acoustic lens to improve the uniformity of the off axis vs. on axis sound pressure level.
Owner:HARMAN INT IND INC
Ultrasonic probe and ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus using the same
ActiveUS20100036257A1Prevent leakageImprove securityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSemiconductor electrostatic transducersElectromechanical coupling coefficientAcoustic lens
Provided is an ultrasonic probe including: a cMUT chip having a plurality of vibration elements whose electromechanical coupling coefficient or sensitivity is changed according to a bias voltage and transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves; an acoustic lens arranged above the cMUT chip: and a backing layer arranged below the cMUT chip.Electric leakage preventing means is provided at the ultrasonic wave transmission / reception surface side of the acoustic lens or between the acoustic lens and the cMUT chip.The electric leakage preventing means is, for example, an insulating layer such as a ground layer.By using such a structure, it is possible to provide an ultrasonic probe capable of preventing electric leakage from the ultrasonic probe to an object to be examined so as to improve the electric safety and an ultrasonic diagnostic apparatus using the probe.
Owner:FUJIFILM HEALTHCARE CORP
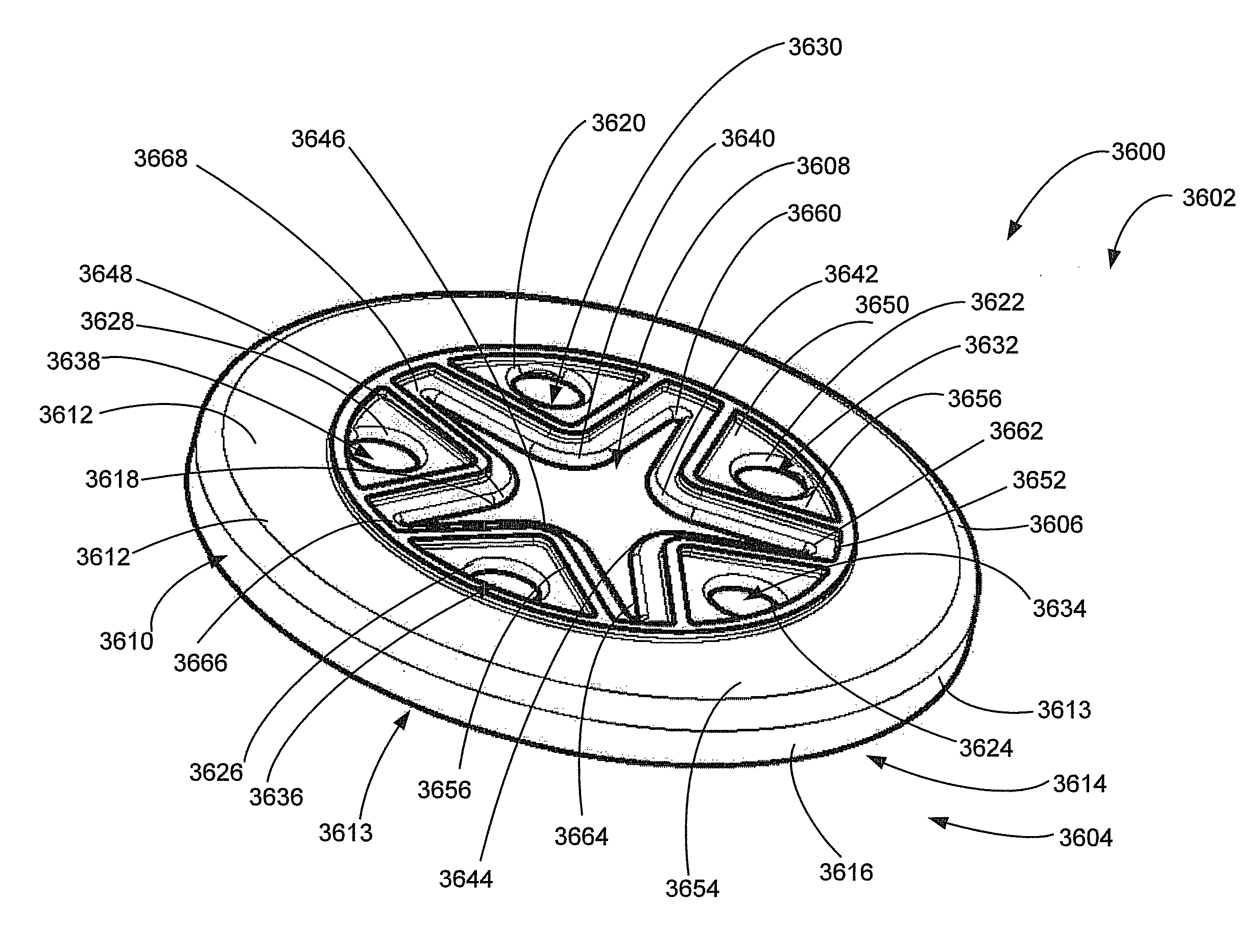
Measuring apparatus
InactiveUS20120130222A1Less degradation of resolutionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMeasurement deviceMeasuring instrument
A measuring apparatus is used, the apparatus including a probe having an element detecting an acoustic wave that has propagated through an object, an acoustic lens disposed between the probe and the object, and a signal processor obtaining object information from an electrical signal based on the acoustic wave detected by the element of the probe. The probe is disposed at a position where the element of the probe is made acoustically conjugate to a surface on a probe side of the object by the acoustic lens.
Owner:CANON KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com