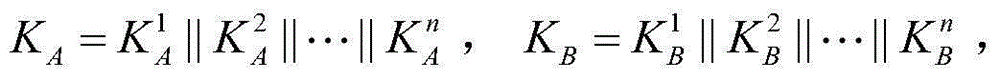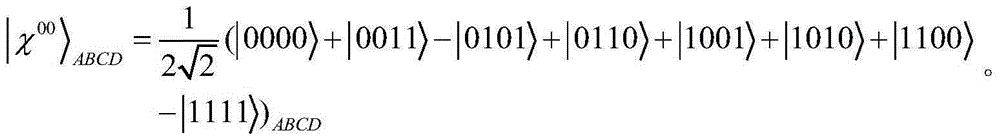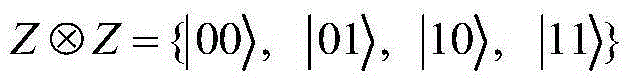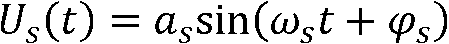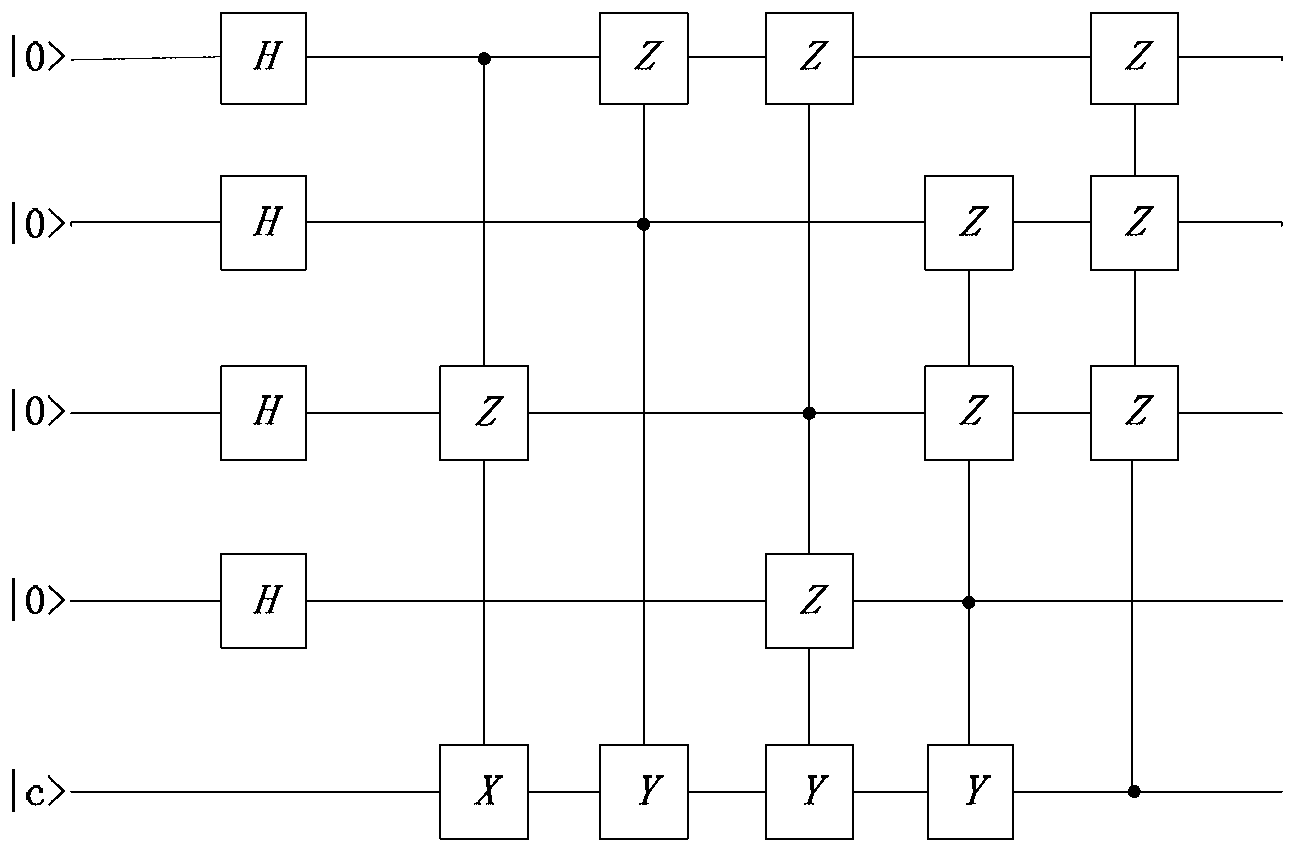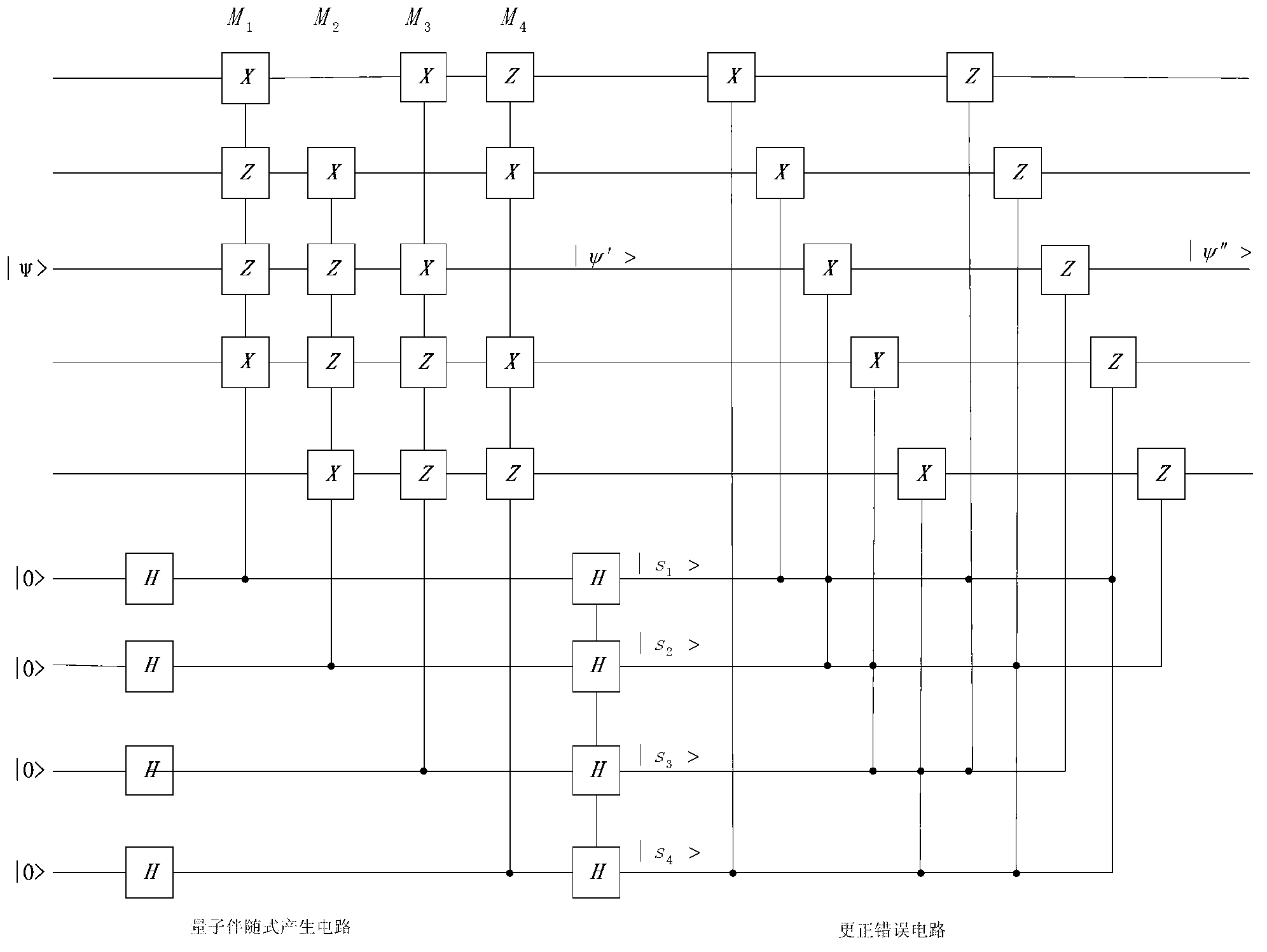Patents
Literature
89 results about "Quantum noise" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, quantum noise refers to the uncertainty of a physical quantity that is due to its quantum origin. In certain situations, quantum noise appears as shot noise; for example, most optical communications use amplitude modulation, and thus, the quantum noise appears as shot noise only. For the case of uncertainty in the electric field in some lasers, the quantum noise is not just shot noise; uncertainties of both amplitude and phase contribute to the quantum noise. This issue becomes important in the case of noise of a quantum amplifier, which preserves the phase. The phase noise becomes important when the energy of the frequency modulation or phase modulation of waves is comparable to the energy of the signal (which is believed to be more robust with respect to additive noise than an amplitude modulation).
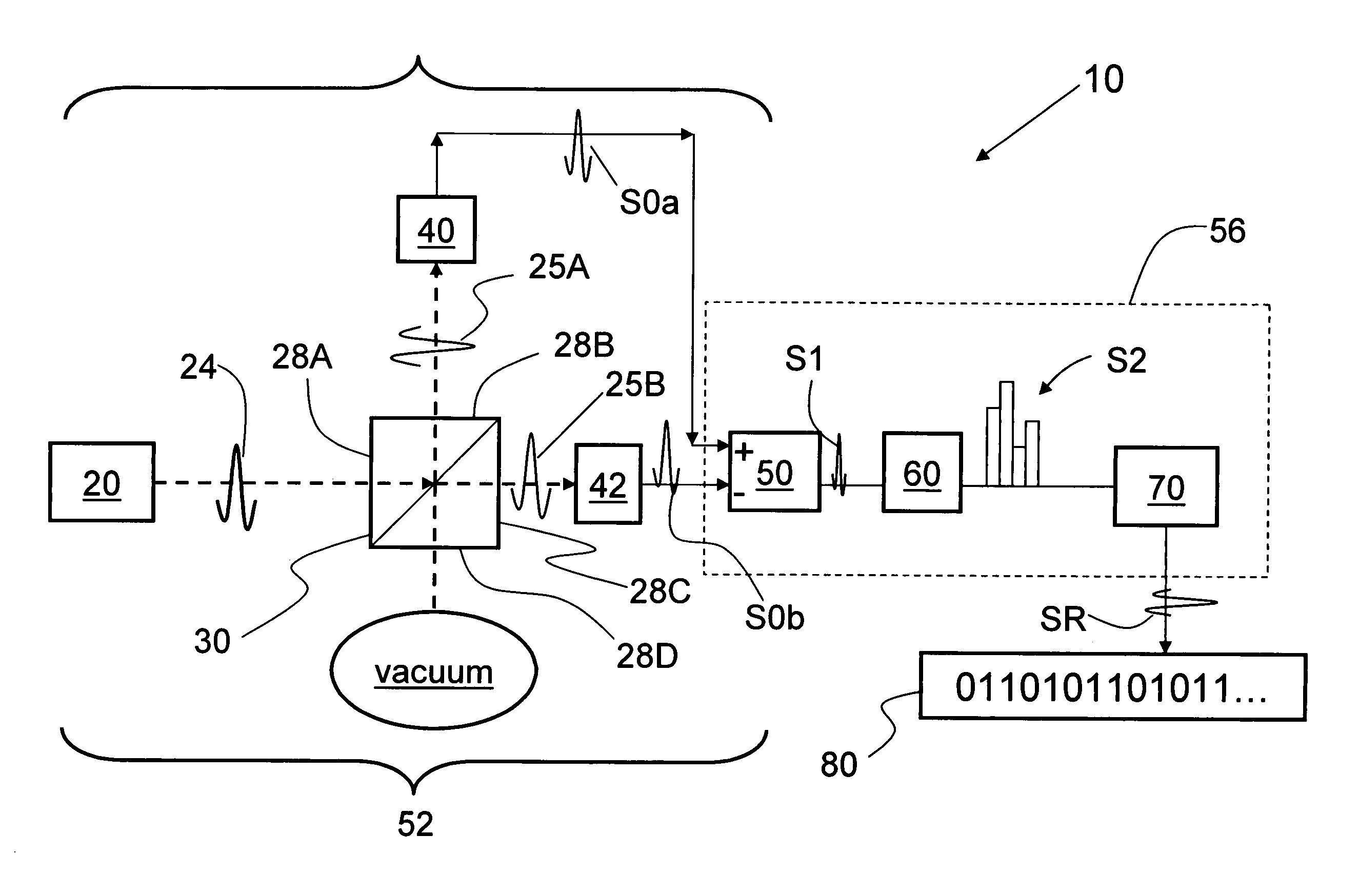
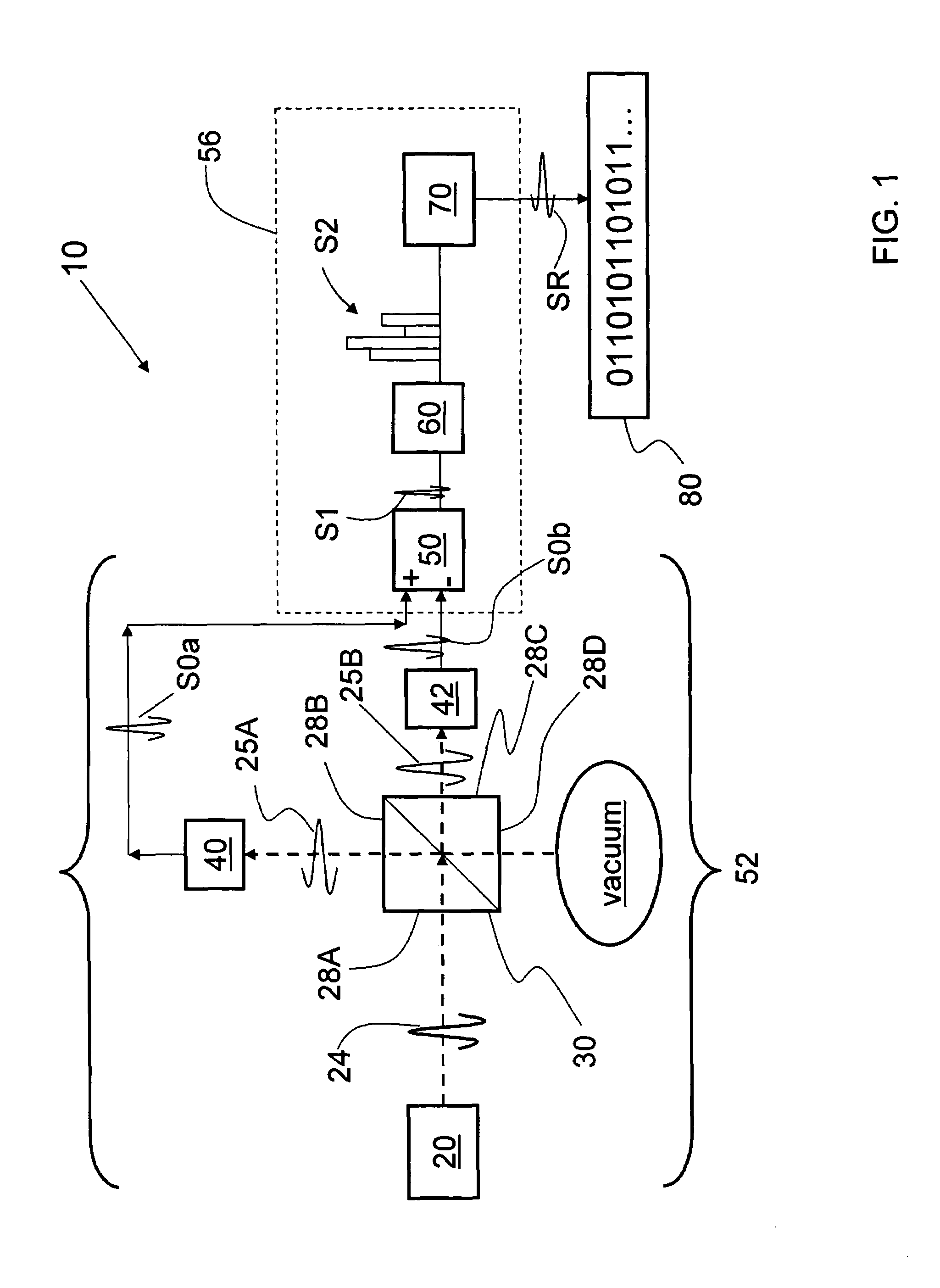
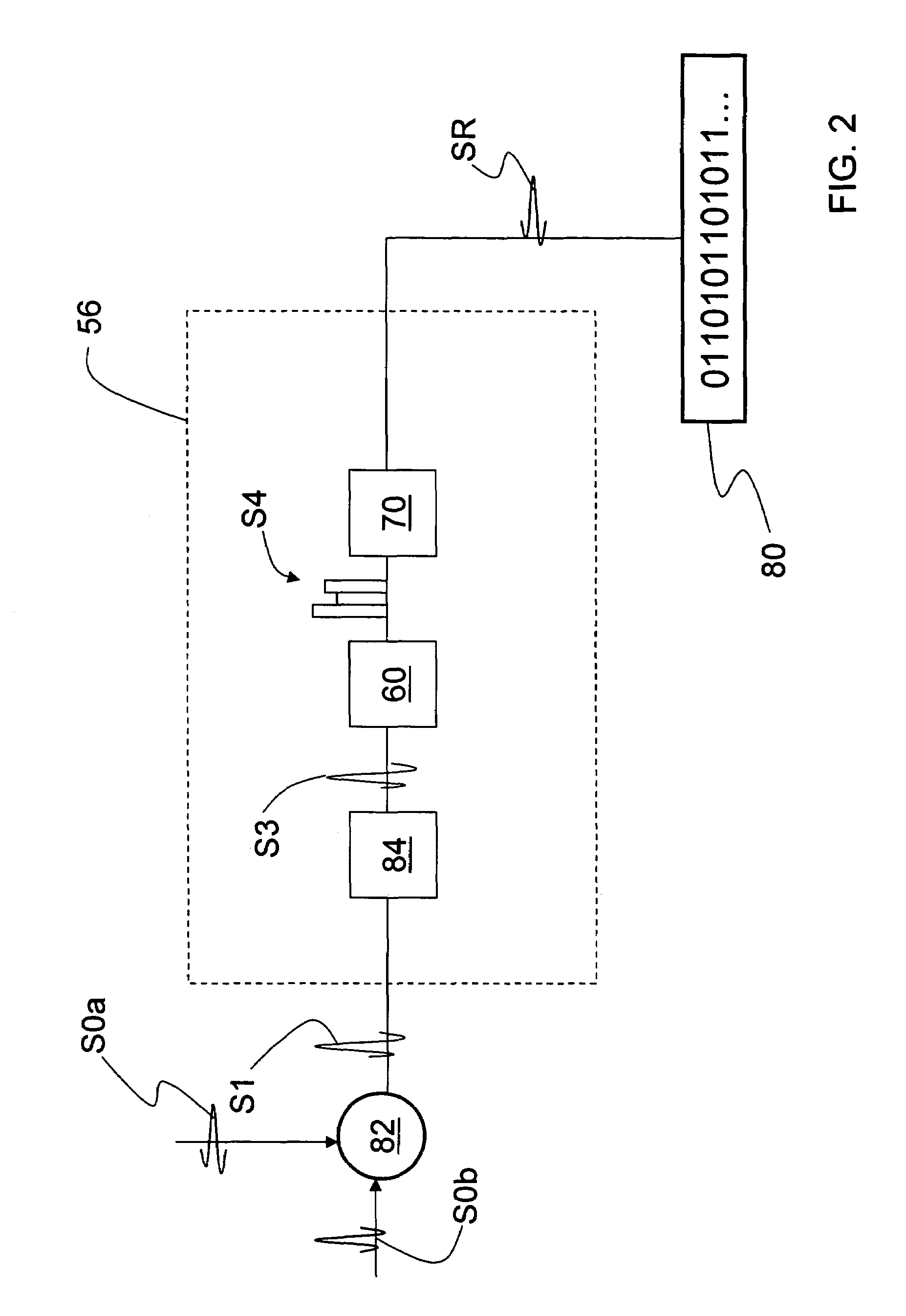
Quantum noise random number generator
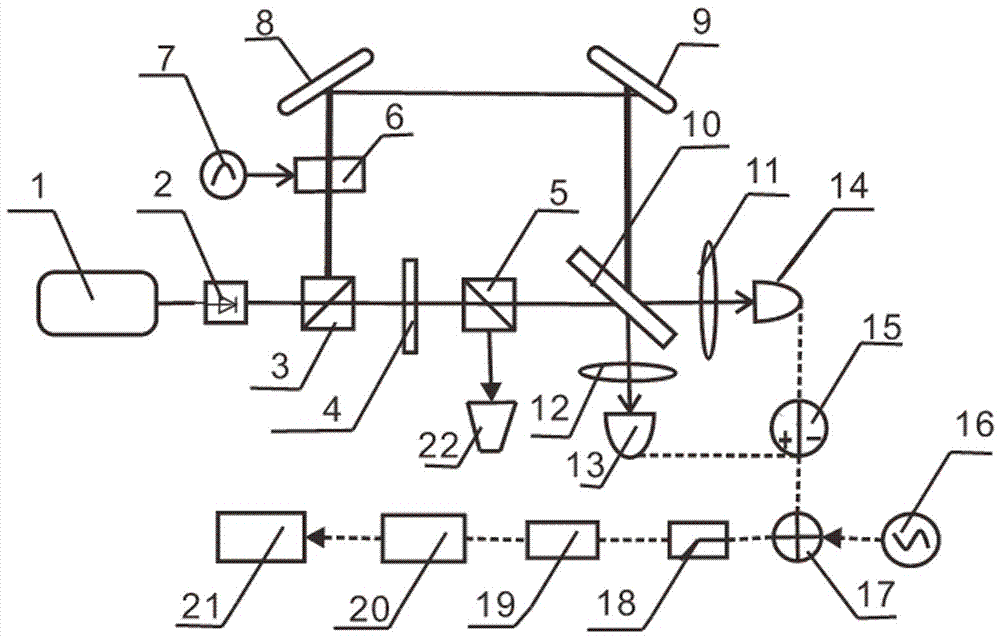
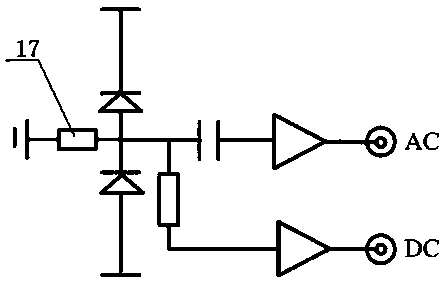
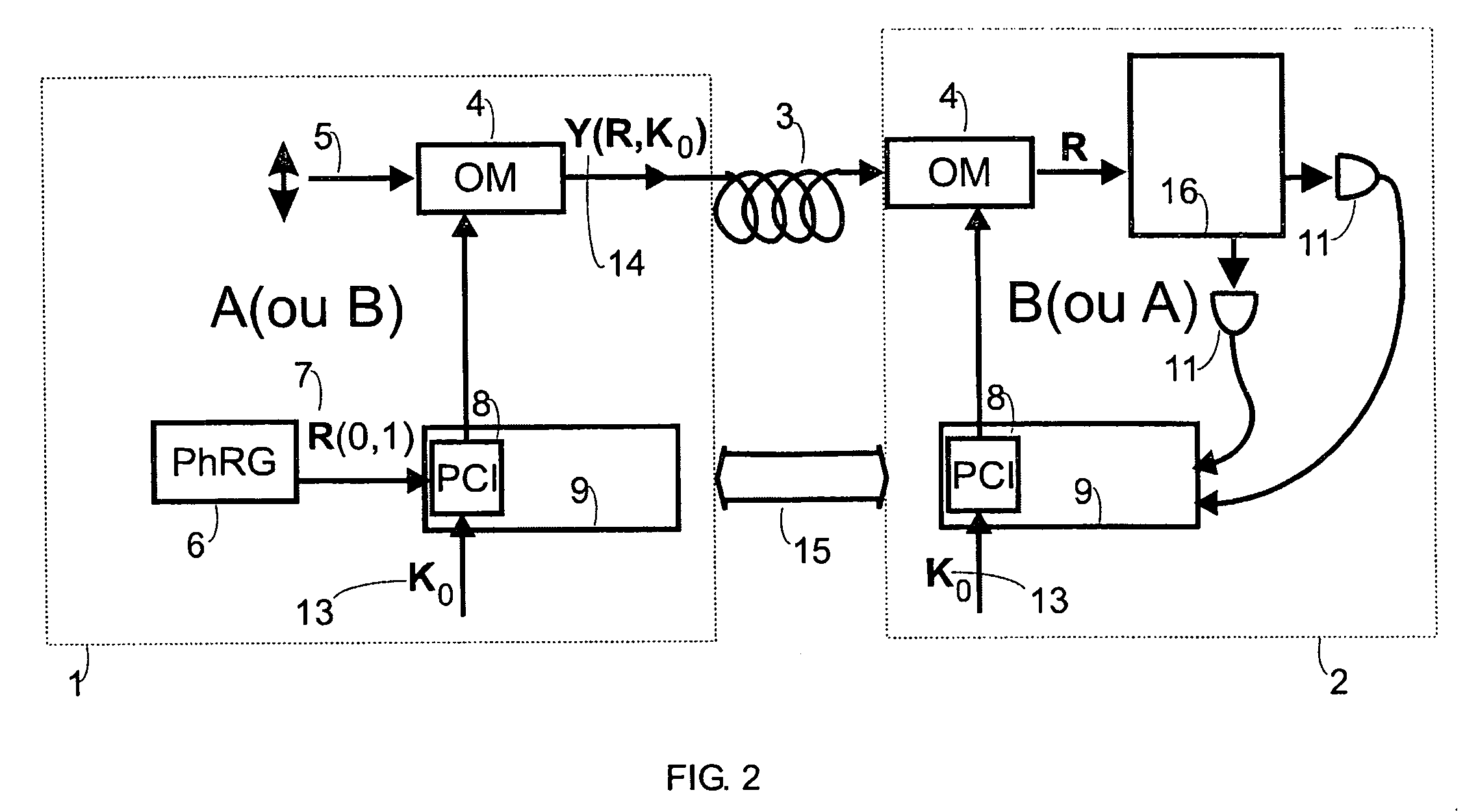
A quantum noise random number generator system that employs quantum noise from an optical homodyne detection apparatus is disclosed. The system utilizes the quantum noise generated by splitting a laser light signal using a beamsplitter having four ports, one of which receives one of which is receives the laser light signal, one of which is connected to vacuum, and two of which are optically coupled to photodetectors. Processing electronics process the difference signal derived from subtracting the two photodetector signals to create a random number sequence. Because the difference signal associated with the two photodetectors is truly random, the system is a true random number generator.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
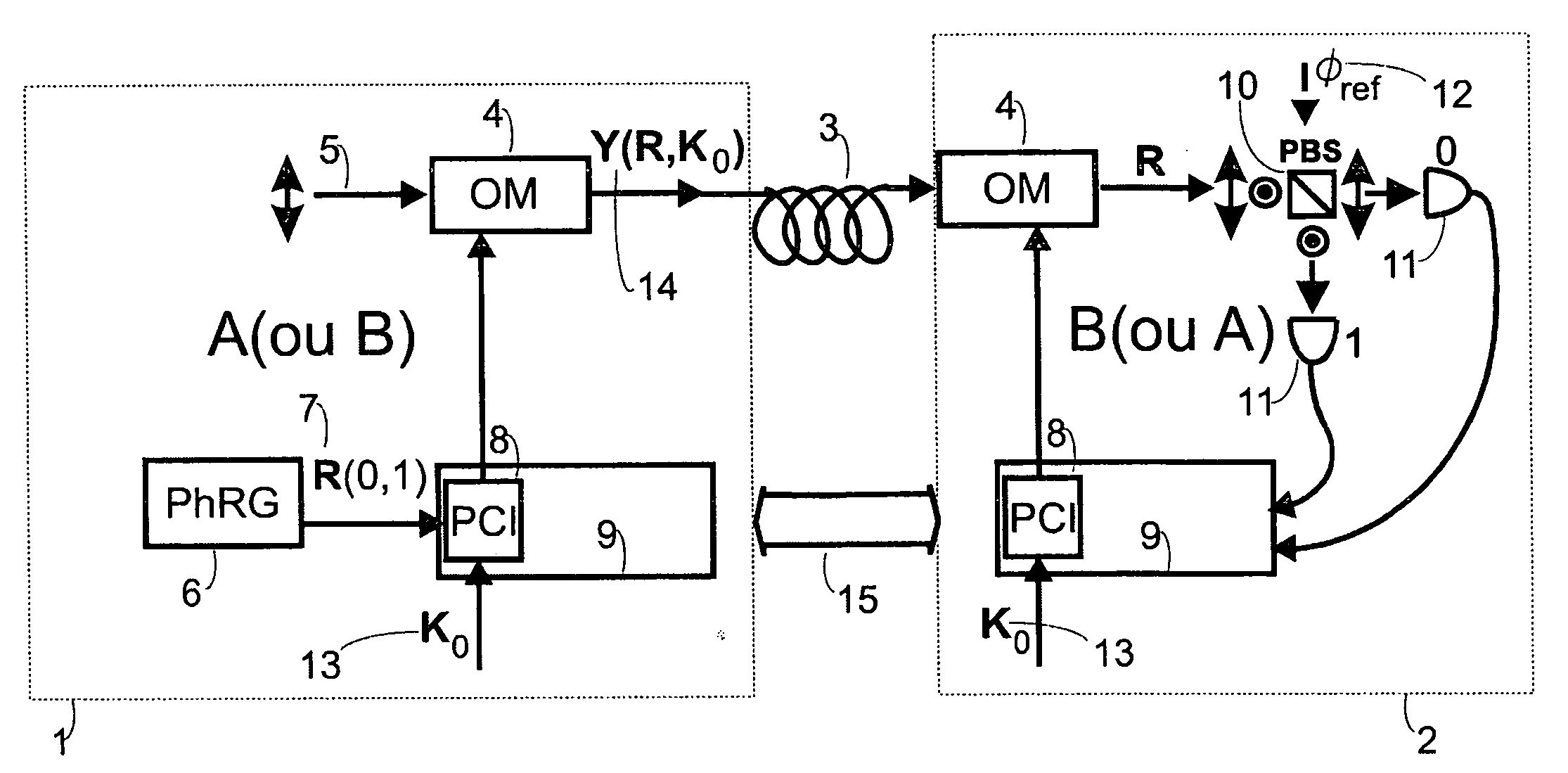
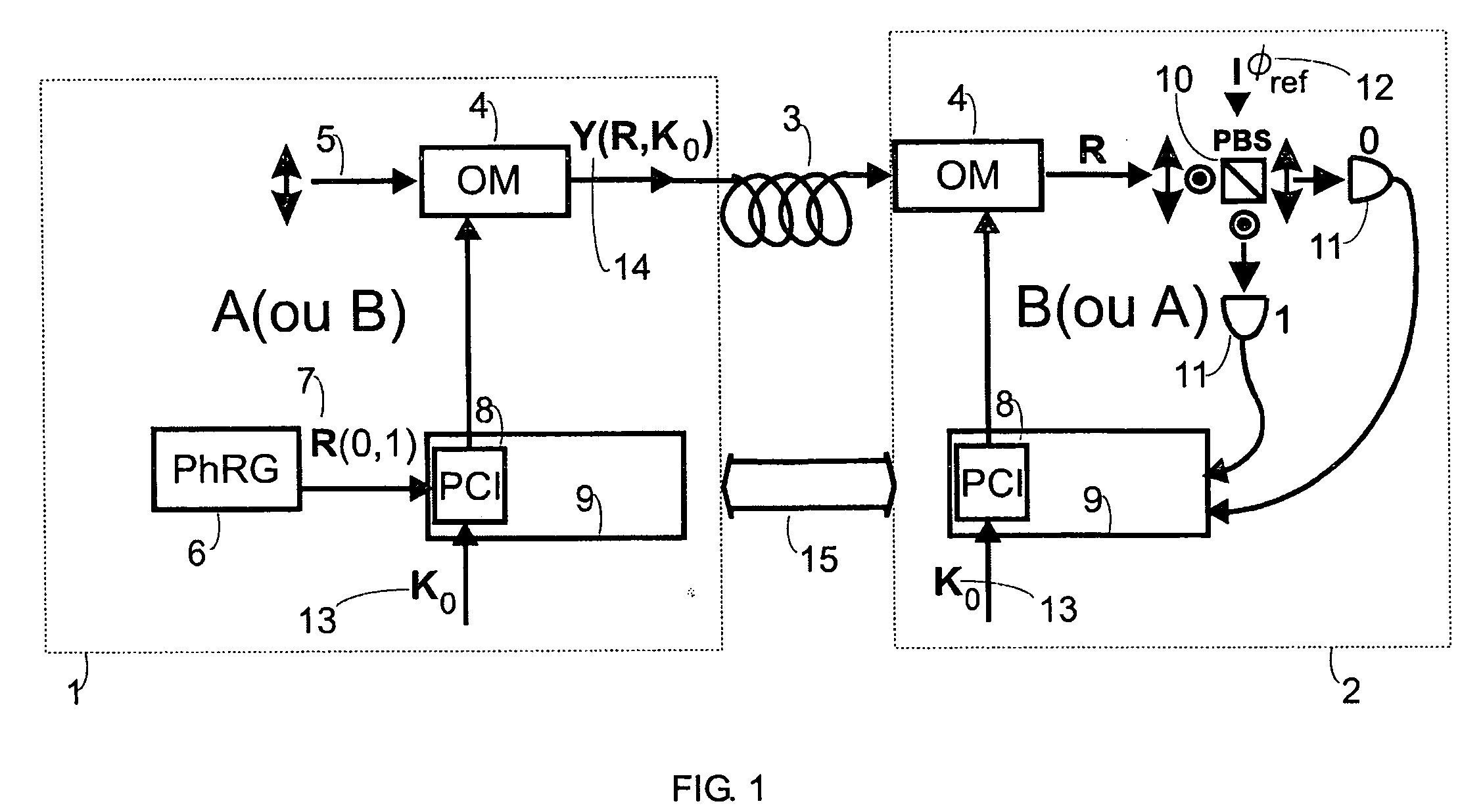
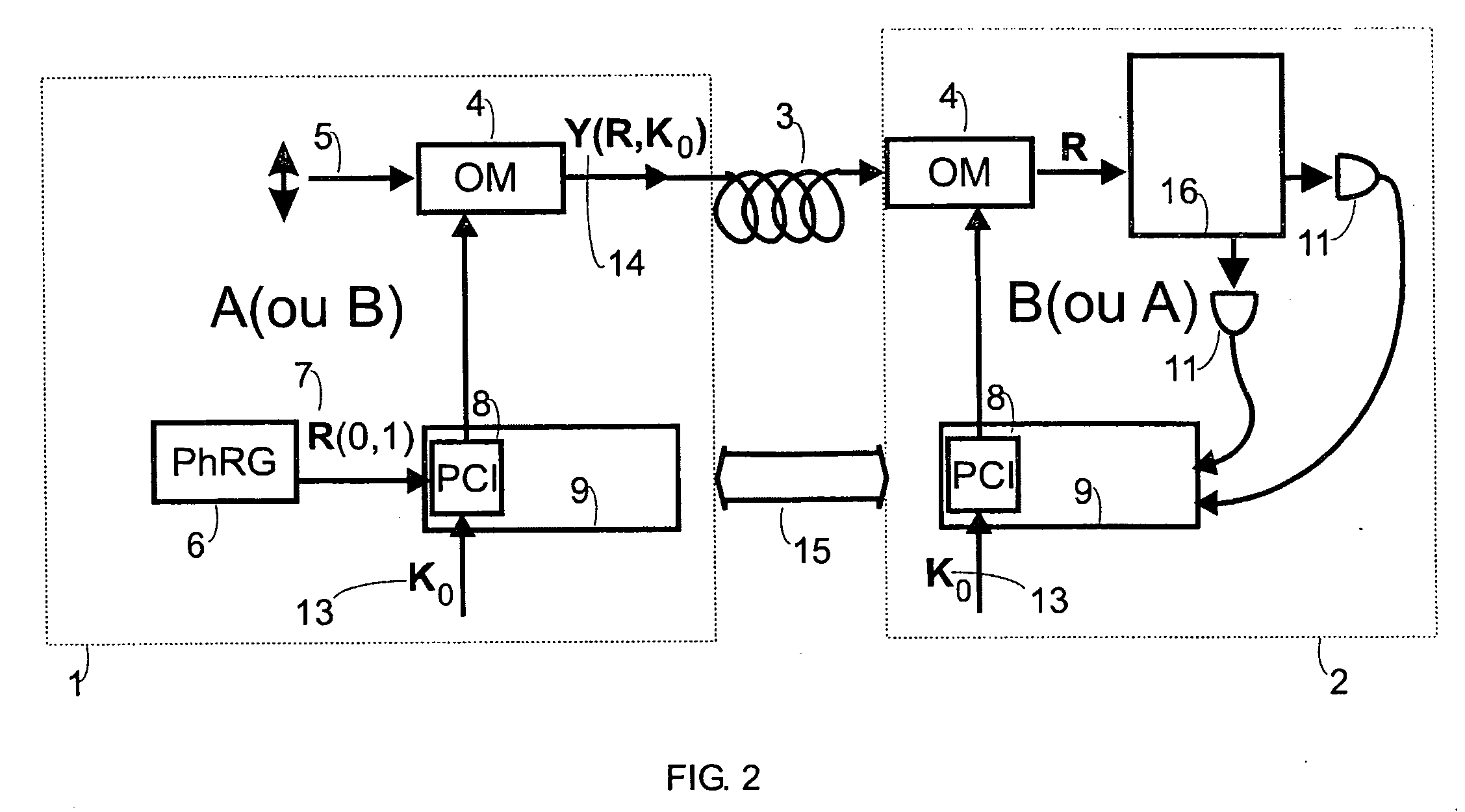
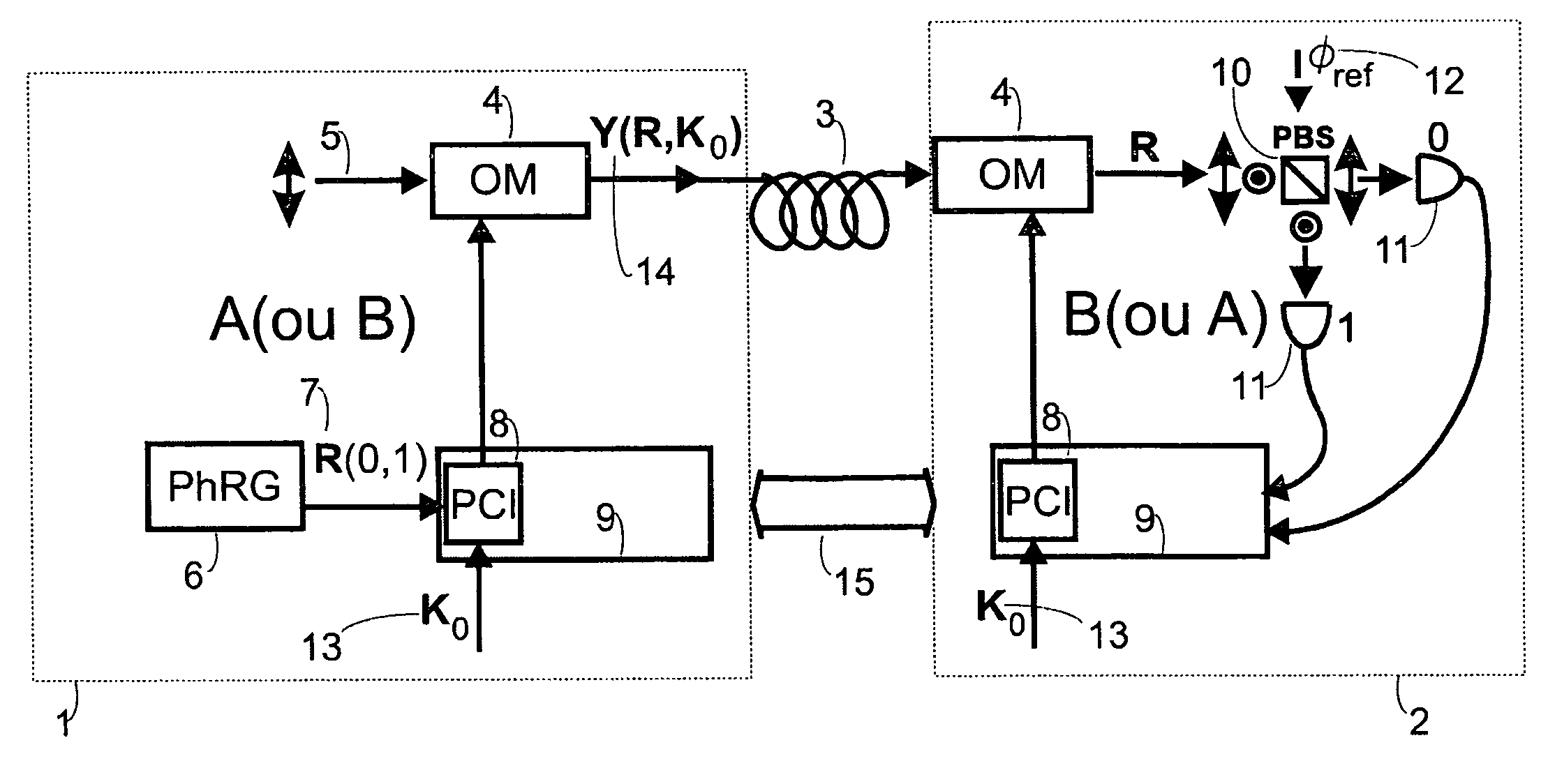
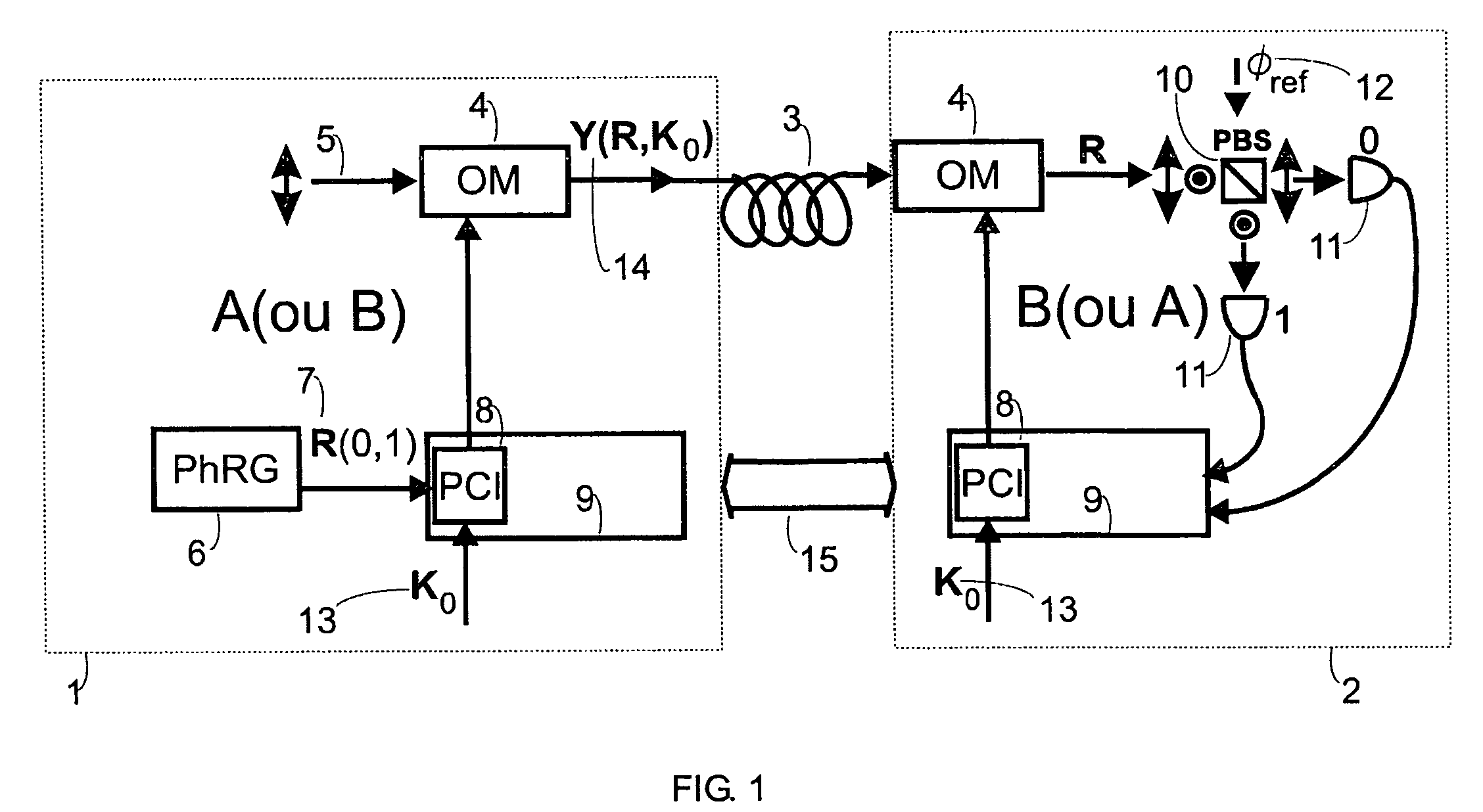
Fast multi-photon key distribution scheme secured by quantum noise
ActiveUS20050152540A1Fast and secure key distributionRaise the ratioKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareQuantum noise
A key distribution scheme comprising a generation and reception system and a specific operation protocol is described. This system allows fast and secure key distribution in optical channels by two stations A and B. One or two true-random physical sources are used to generate random bits and a random sequence received provides the cipher to the following one to be sent. A starting shared secret key is used and the method can be described as a one-time-pad unlimited extender. The minimum probability of error in signal determination by an eavesdropper can be set arbitrarily close to the pure guessing level of one-half and the security of the method comes from the quantum noise of light as well as from the starting secret key. This system allows for optical amplification without security degradation within its operational boundaries.
Owner:SMARTPLUG
Optical phase conjugation laser diode
A phase-conjugating resonator that includes a semiconductor laser diode apparatus that comprises a phase-conjugating array of retro-reflecting hexagon apertured hexahedral shaped corner-cube prisms, an electrically and / or optically pumped gain-region, a distributed bragg reflecting mirror-stack, a gaussian mode providing hemispherical shaped laser-emission-output metalized mirror. Wherein, optical phase conjugation is used to neutralize the phase perturbating contribution of spontaneous-emission, acoustic phonons, quantum-noise, gain-saturation, diffraction, and other intracavity aberrations and distortions that typically destabilize any stimulated-emission made to undergo amplifying oscillation within the inventions phase-conjugating resonator. Resulting in stablized high-power laser-emission-output into a single low-order fundamental transverse cavity mode and reversal of intra-cavity chirp that provides for high-speed internal modulation capable of transmitting data at around 20-Gigabits / ps.
Owner:HENRICHS JOSEPH REID
Bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for X-ray image
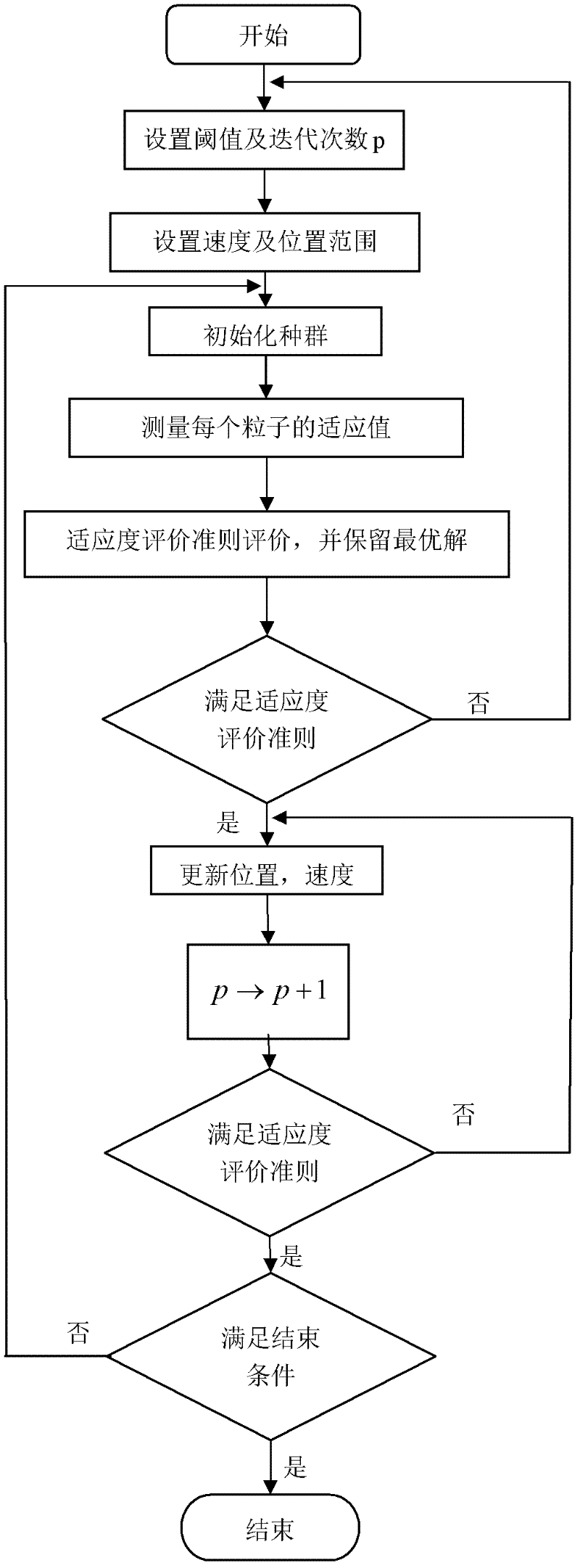
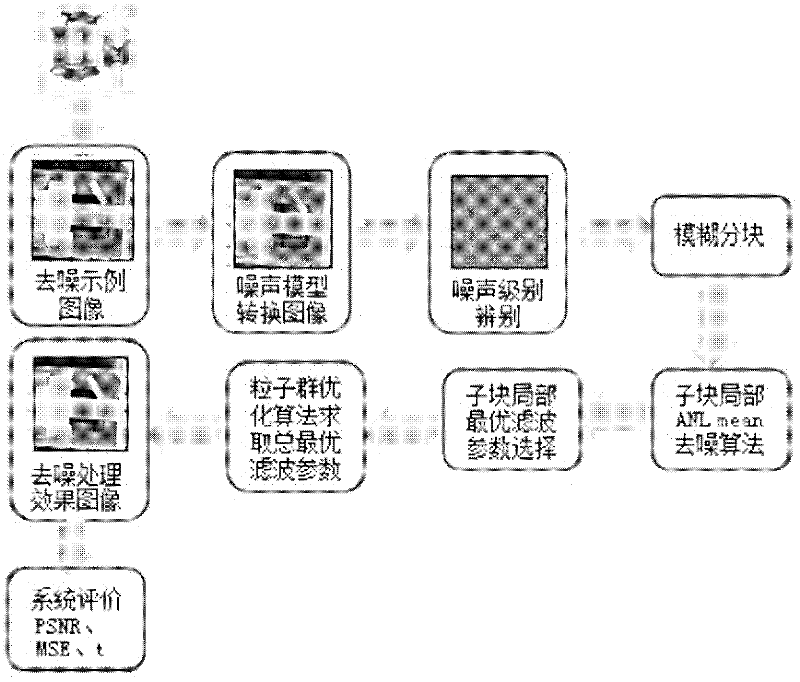
The invention provides a bivariate nonlocal average filtering de-noising method for an X-ray image. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) a selecting method of a fuzzy de-noising window; and 2) a bivariate fuzzy adaptive nonlocal average filtering algorithm. The method has the beneficial effects that in order to preferably remove the influence caused by the unknown quantum noise existing in an industrial X-ray scan image, the invention provides the bivariate nonlocal fuzzy adaptive non-linear average filtering de-noising method for the X-ray image, in the method, a quantum noise model which is hard to process is converted into a common white gaussian noise model, the size of a window of a filter is selected by virtue of fuzzy computation, and a relevant weight matrix enabling an error function to be minimum is searched. A particle swarm optimization filtering parameter is introduced in the method, so that the weight matrix can be locally rebuilt, the influence of the local relevancy on the sample data can be reduced, the algorithm convergence rate can be improved, and the de-noising speed and precision for the industrial X-ray scan image can be improved, so that the method is suitable for processing the X-ray scan image with an uncertain noise model.
Owner:YUN NAN ELECTRIC TEST & RES INST GRP CO LTD ELECTRIC INST +1
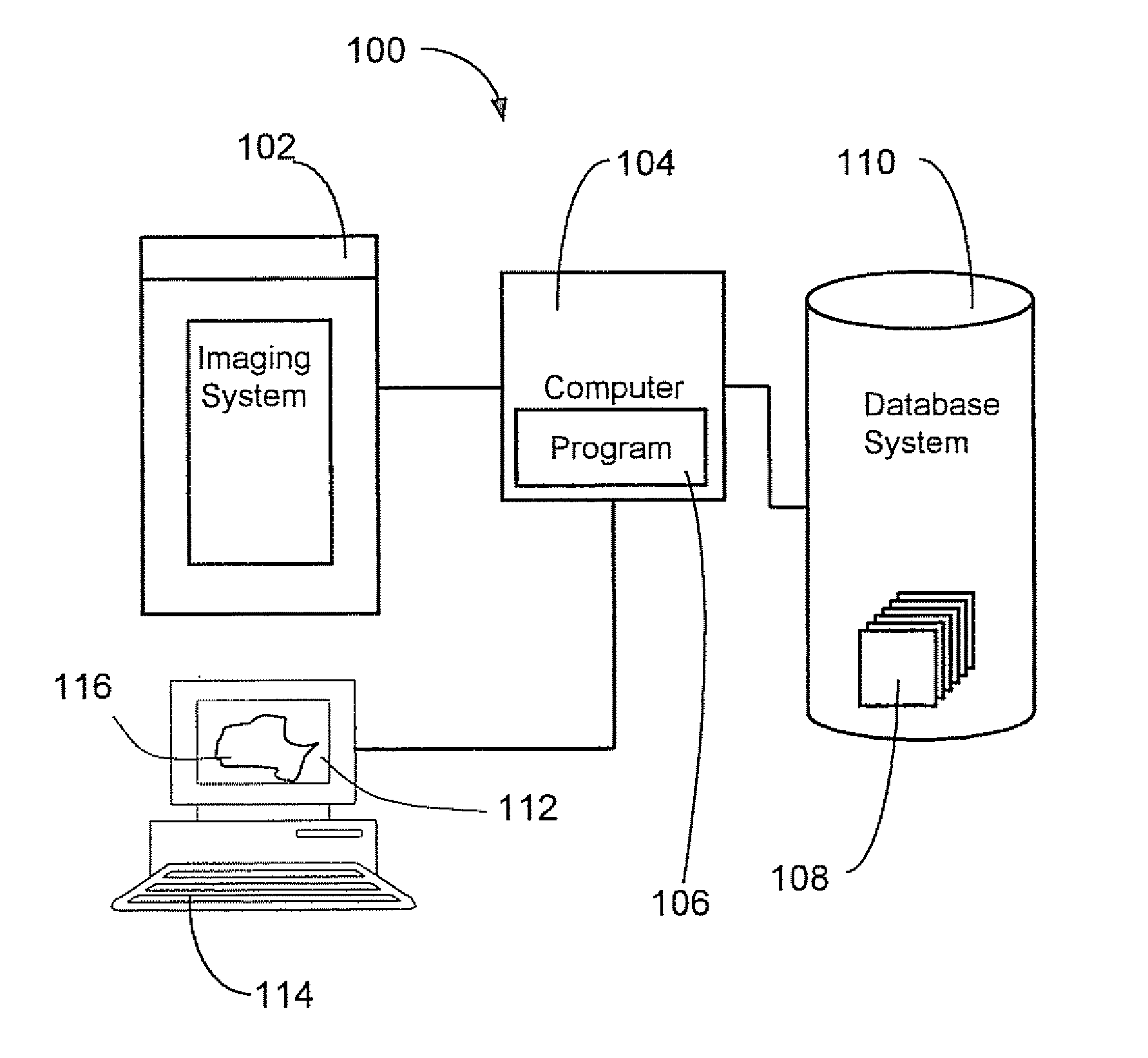
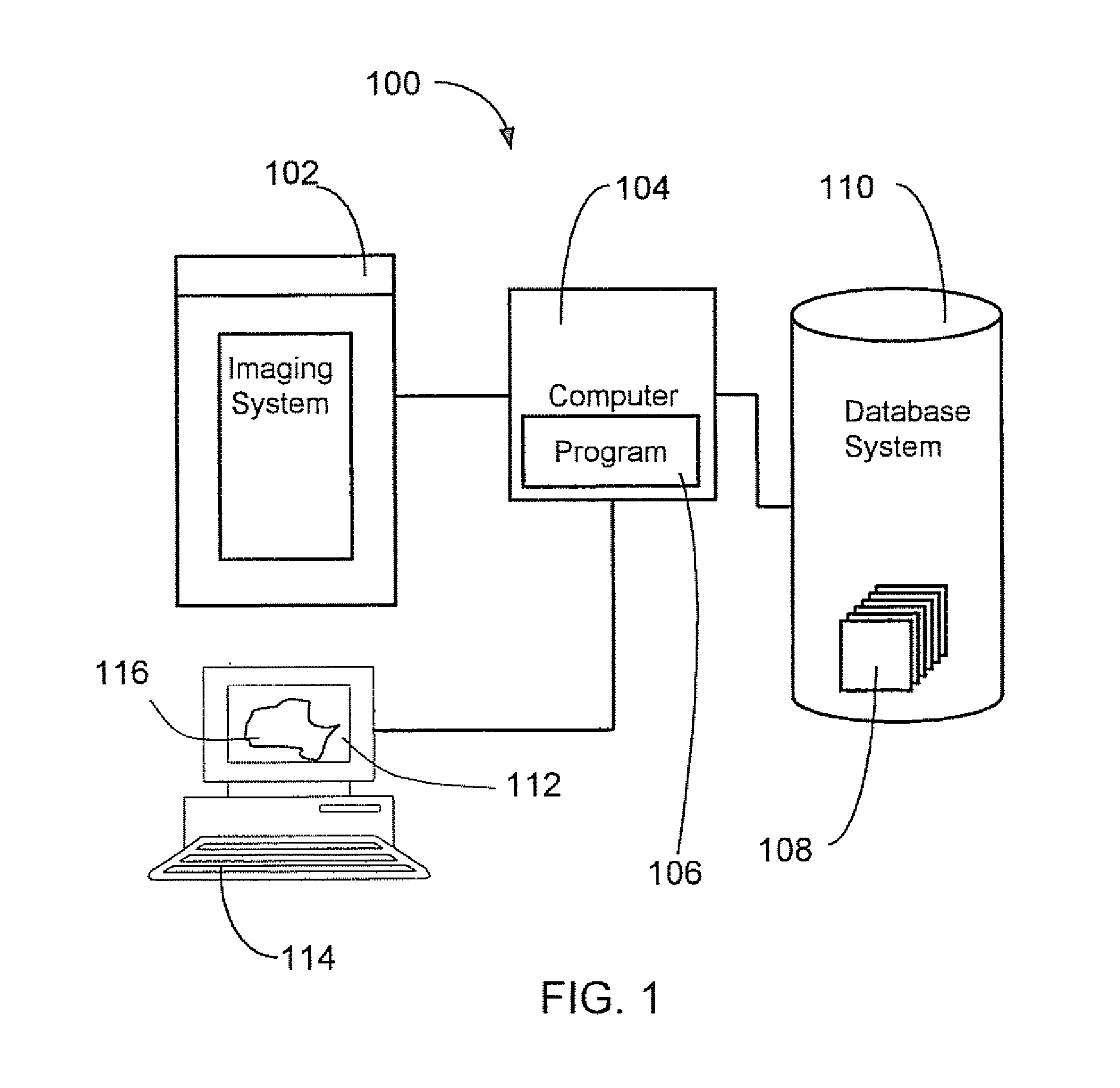
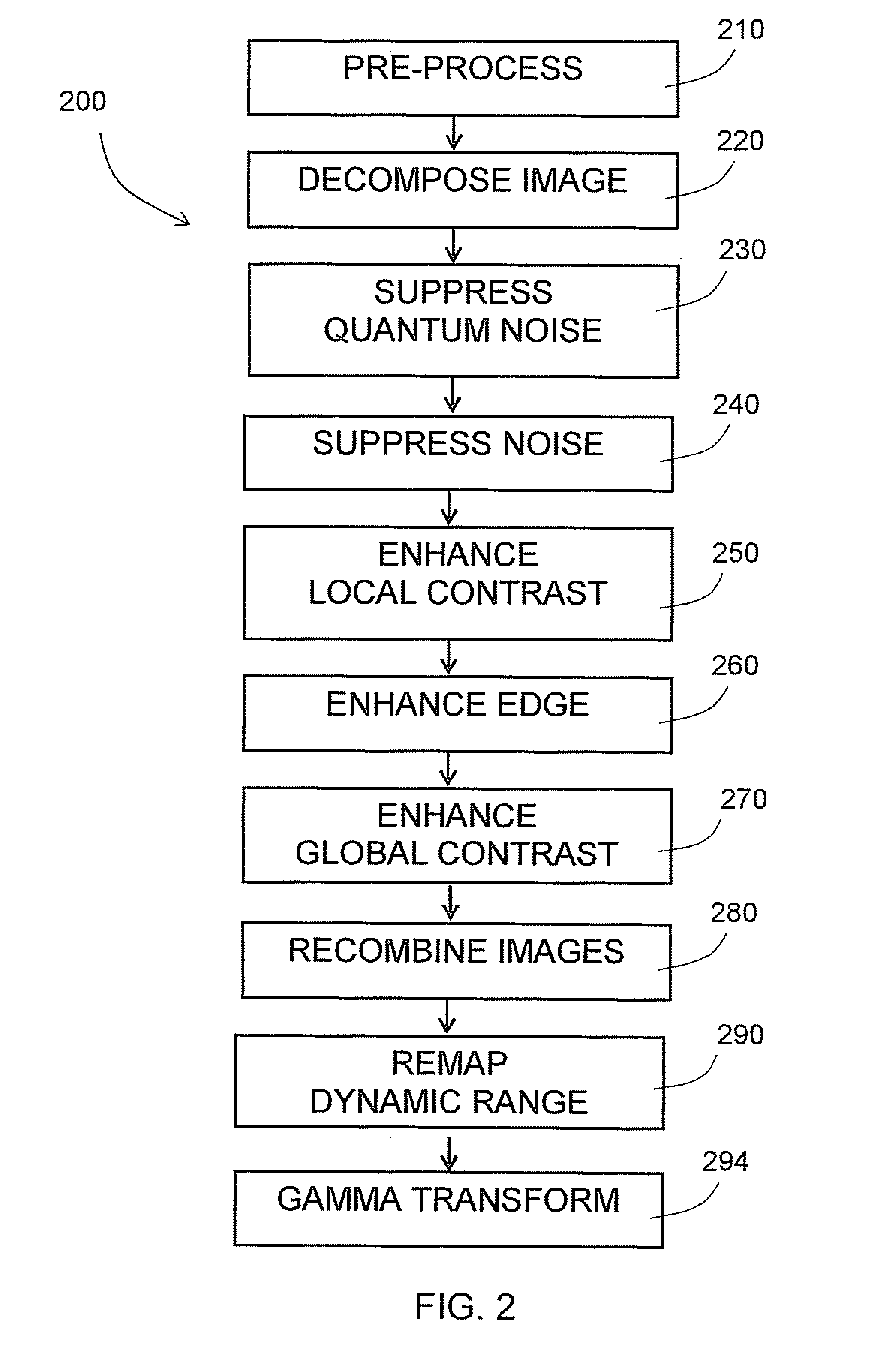
Method and system for enhancing digital images
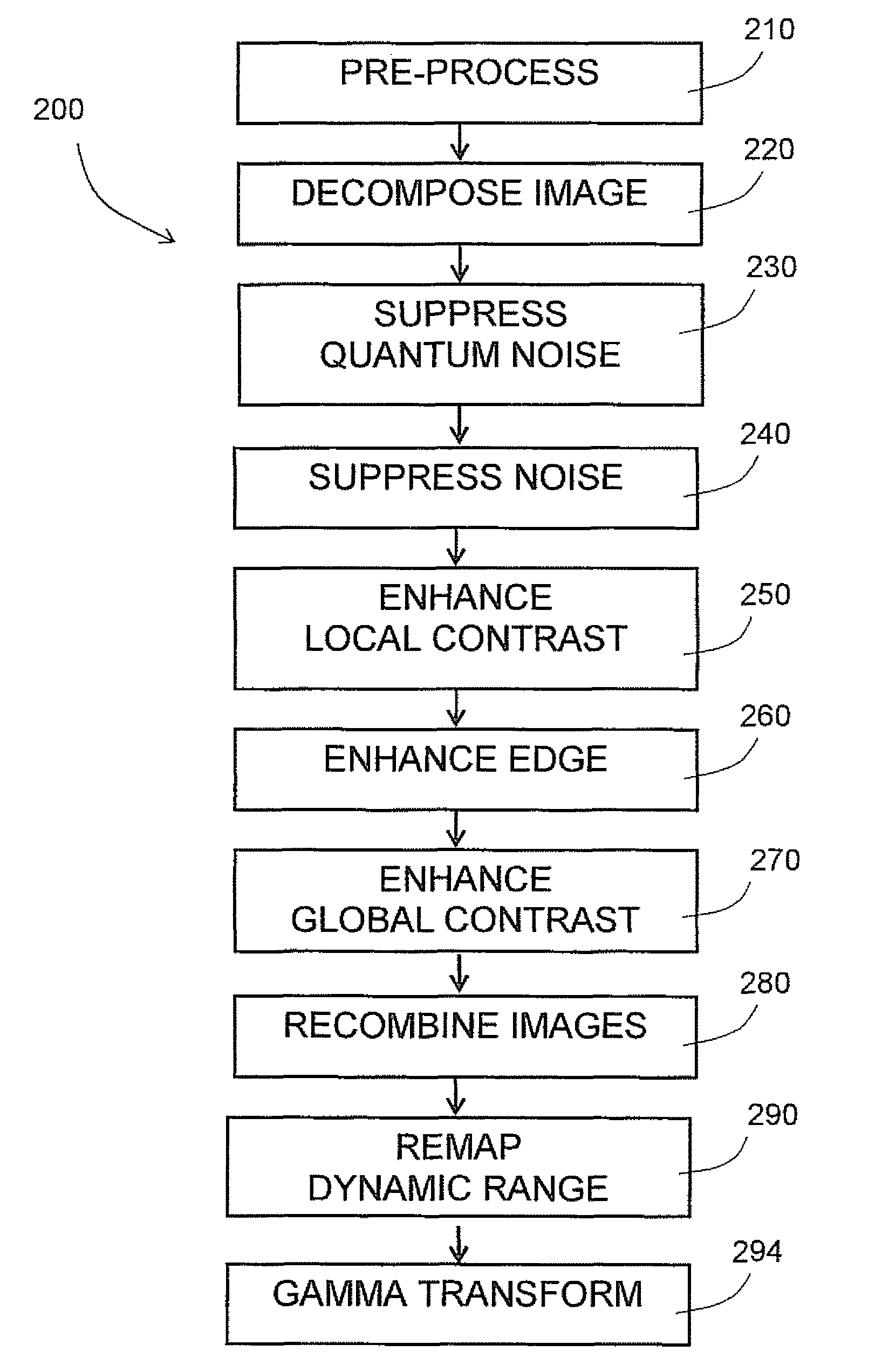
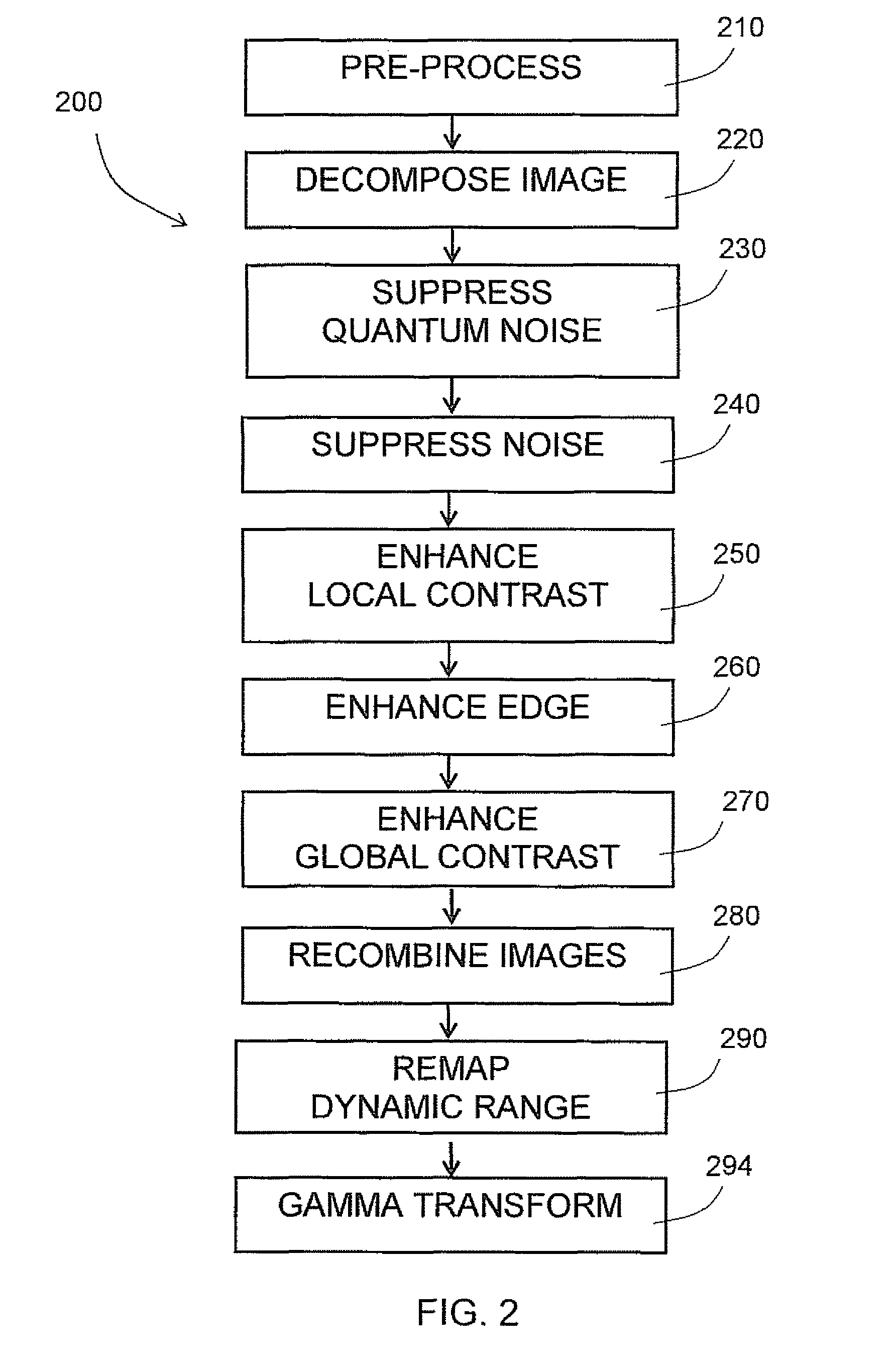
A system and method for enhancing digital images is described. A digital image is transformed into a series of decomposed images in frequency bands, or different resolution grids. A decomposed image is noise suppressed and contrast enhanced. Representative value of signal at each pixel is computed based on contributions to signals from pixels in a neighborhood of the pixel. Lookup tables are applied to pixel values to selectively enhance signal in a predetermined range of signal strength. Another set of lookup tables are applied to pixel values to suppress noise components contained therein. Optionally, operations are applied to decomposed images to suppress quantum noise, enhance object edges or enhance global contrast, among others. These decomposed images, after signal enhancement and noise suppression, are then recombined to result in an enhanced image.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
Quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state
ActiveCN105227301AHigh qubit efficiencyResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobComputer hardware
The invention discloses a quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state, comprising the following steps that: step 1, Alice and Bob randomly generate respective classical keys; step 2, Alice prepares the GHZ state and divides all particles into sequences, inserts decoy photons into one of the sequences and then transmits the sequence to Bob; step 3, Bob measures the decoy photons, Alice calculates an error rate, if the error rate is low, a step 4 is executed, otherwise, the step 2 is executed again; step 4, Alice and Bob respectively perform measurement and obtain the measurement result of each other; step 5, Alice executes unitary transformation and obtains a new sequence, and Alice transits the sequence with the inserted decoy photons to Bob; step 6, Bob measures the decoy photons, and Alice calculates the error rate, if the error rate is low, a step 7 is executed, and otherwise, the step 2 is executed again; step 7, Alice calculates a shared key of both sides; step 8, Bob generates the shared key. The quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state can resist participant attack, outside attack and Trojan horse attack. The quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state is safe in both a noiseless quantum channel and a quantum noisy channel. Moreover, quantum bit efficiency of the quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state is higher than the existing protocols.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Chaotic signal production method and device based on uncertainty quantum noise
ActiveCN108712212AHigh bandwidthSolve problems with deterministic delay characteristicsLaser output parameters controlPhotonic quantum communicationSpectrum analyzerLow-pass filter
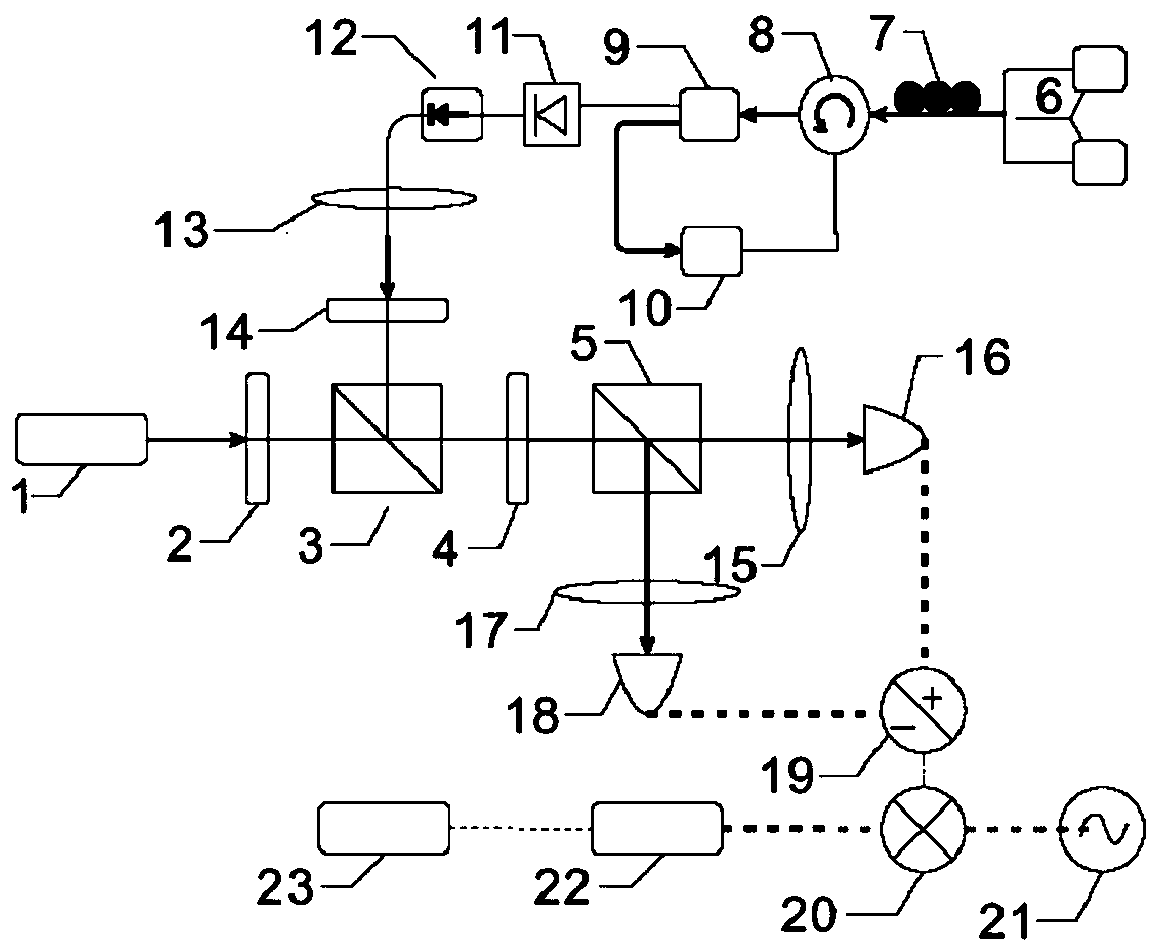
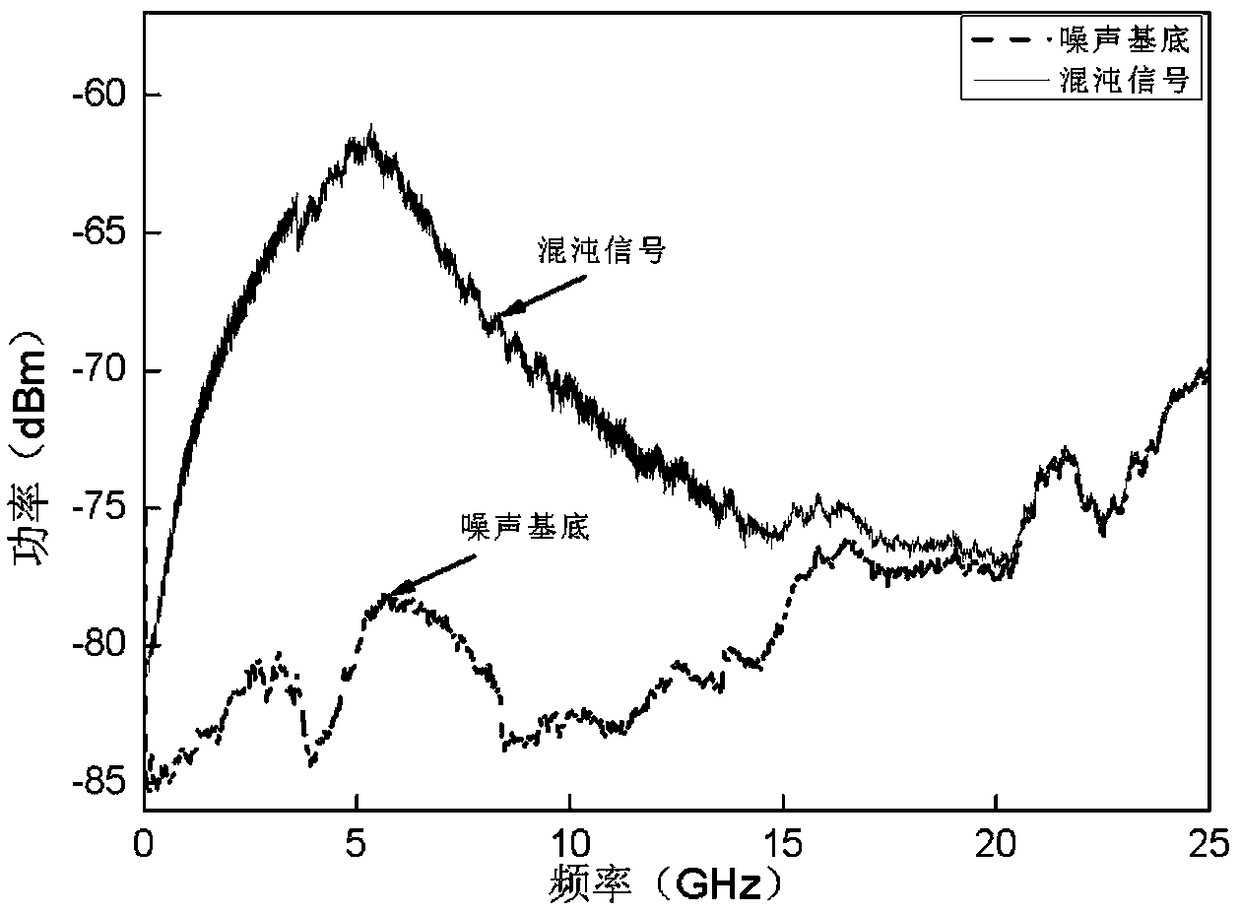
The invention belongs to the field of the secret communication, and provides the chaotic signal production method and device based on the uncertainty quantum noise. The method comprises the followingsteps: S1, preparing a chaotic light source, a slave laser and a signal laser; S2, injecting the chaotic light field into the slave laser, observing an output light field of the slave laser through aspectrum analyzer, and regulating the intensity and the polarization state of the chaotic light field injected into the slave laser until the output light field of the slave laser is the chaotic lightfield; S3, enabling the light emitted from the signal laser to be incident to a balance homodyne detection system to produce the quantum noise signal, performing frequency mixing on the signal and the radio frequency signal, injecting into a modulation port of the slave laser after passing through the low-pass filter, modulating the slave laser, thereby enabling the output light field of the slave laser to be the chaotic signal with the uncertainty. The delay feature of the chaotic signal can be inhibited, and the method can be extensively applied to the chaotic signal production field.
Owner:山西墨丘利科技有限公司
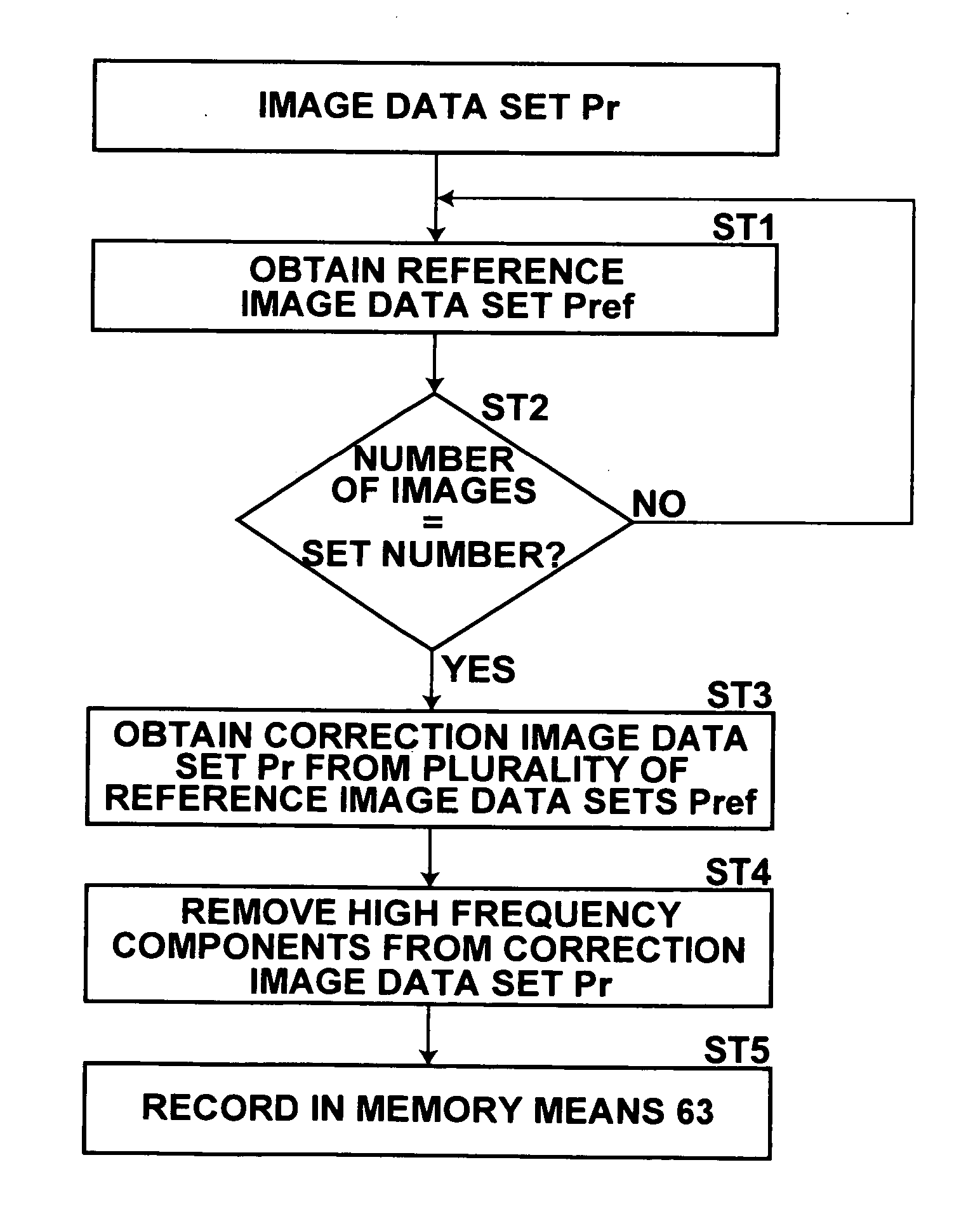
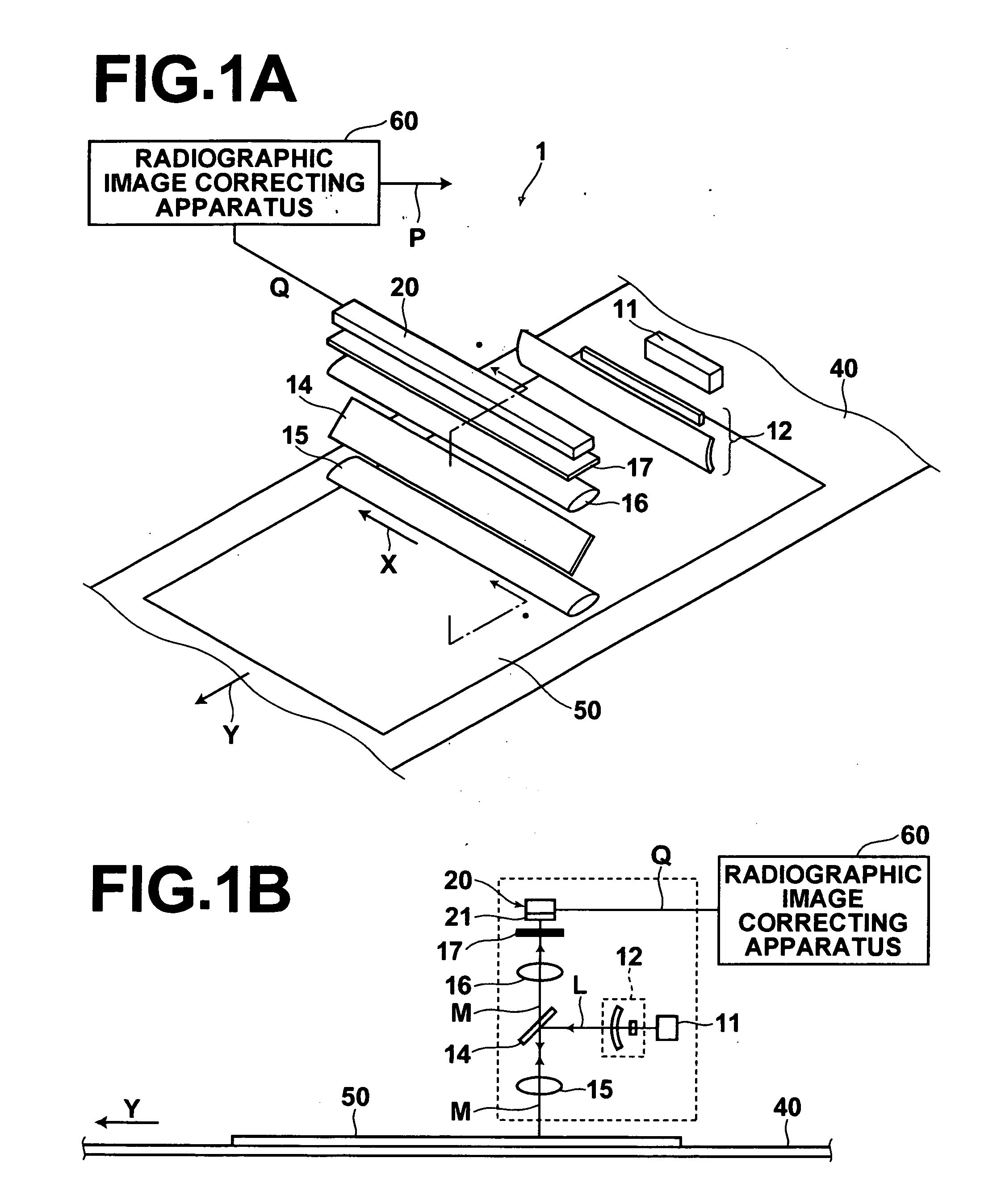
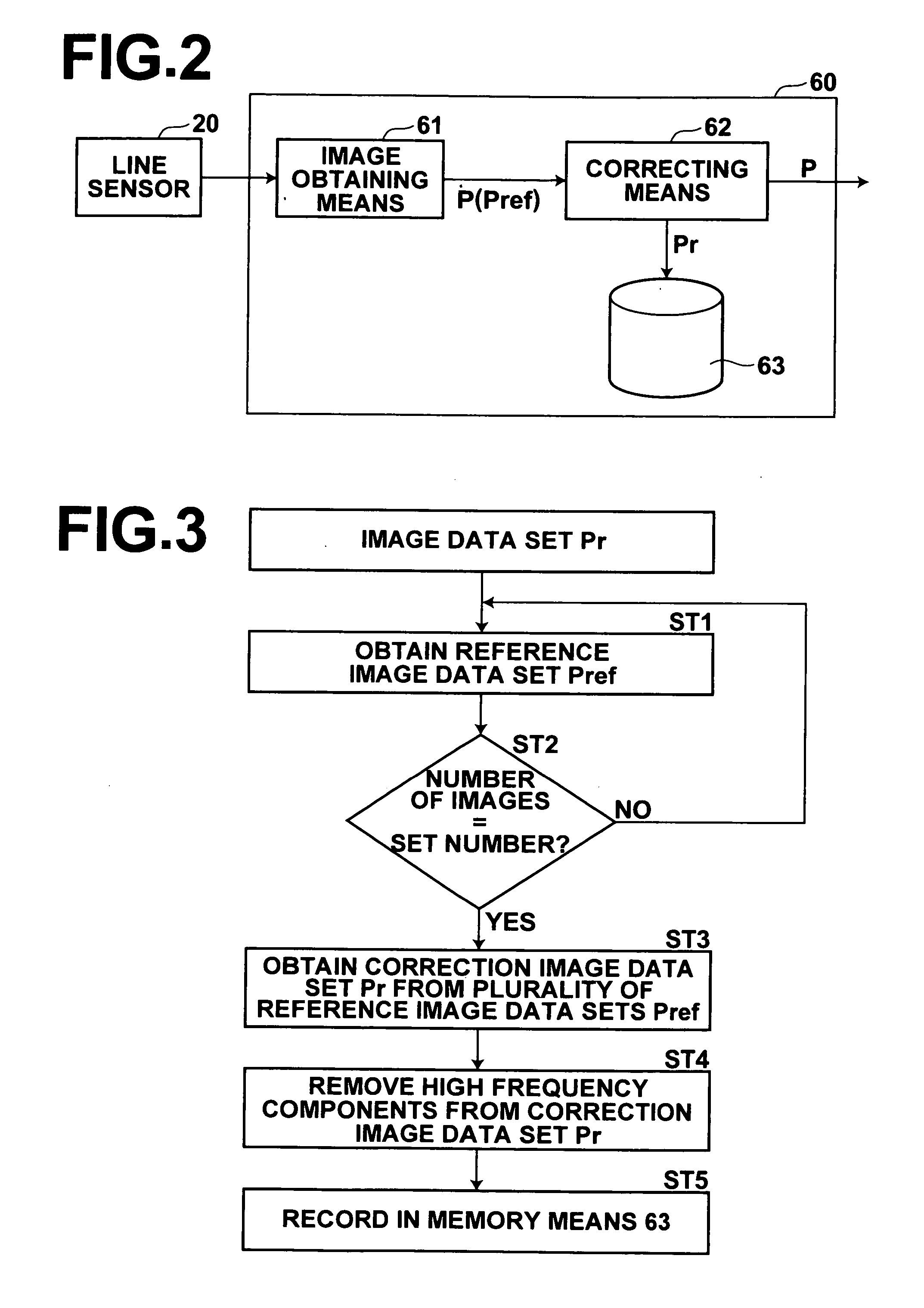
Method and apparatus for correcting radiographic images
InactiveUS20060210135A1Structural noise can be correctedAvoid positioningImage enhancementImage analysisData setReference image
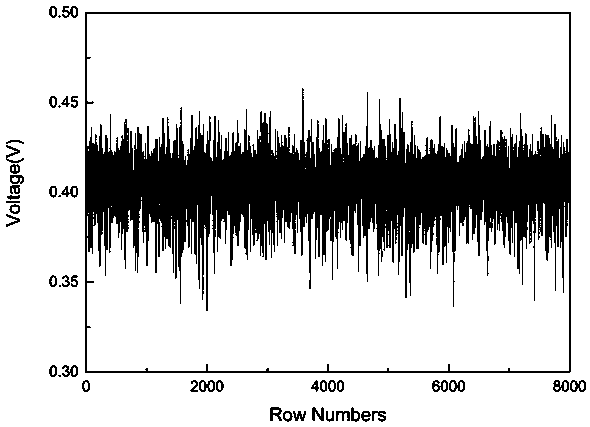
Structural noise is accurately removed by a radiographic image correcting apparatus. A correction image data set, generated from a reference image data set obtained from a stimulable phosphor sheet onto which radiation has been uniformly irradiated, that includes at least four times the amount of structural noise compared to quantum noise, is recorded in a memory means. A correcting means corrects a radiographic image data set, employing the correction image data set recorded in the memory means.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Method for producing random quantum number at high speed based on vacuum state quantum fluctuation
ActiveCN107220026AIncrease spawn rateIncreased entropy contentRandom number generatorsGeneration ratePhase space
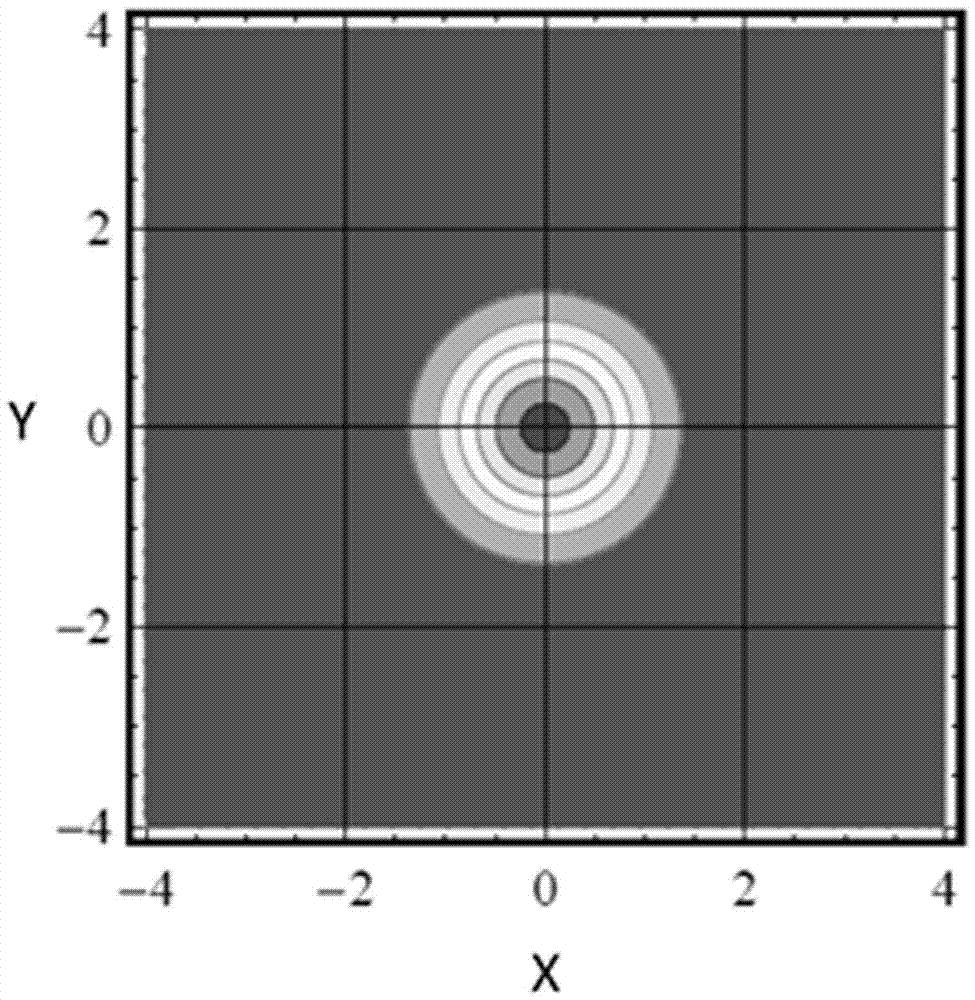
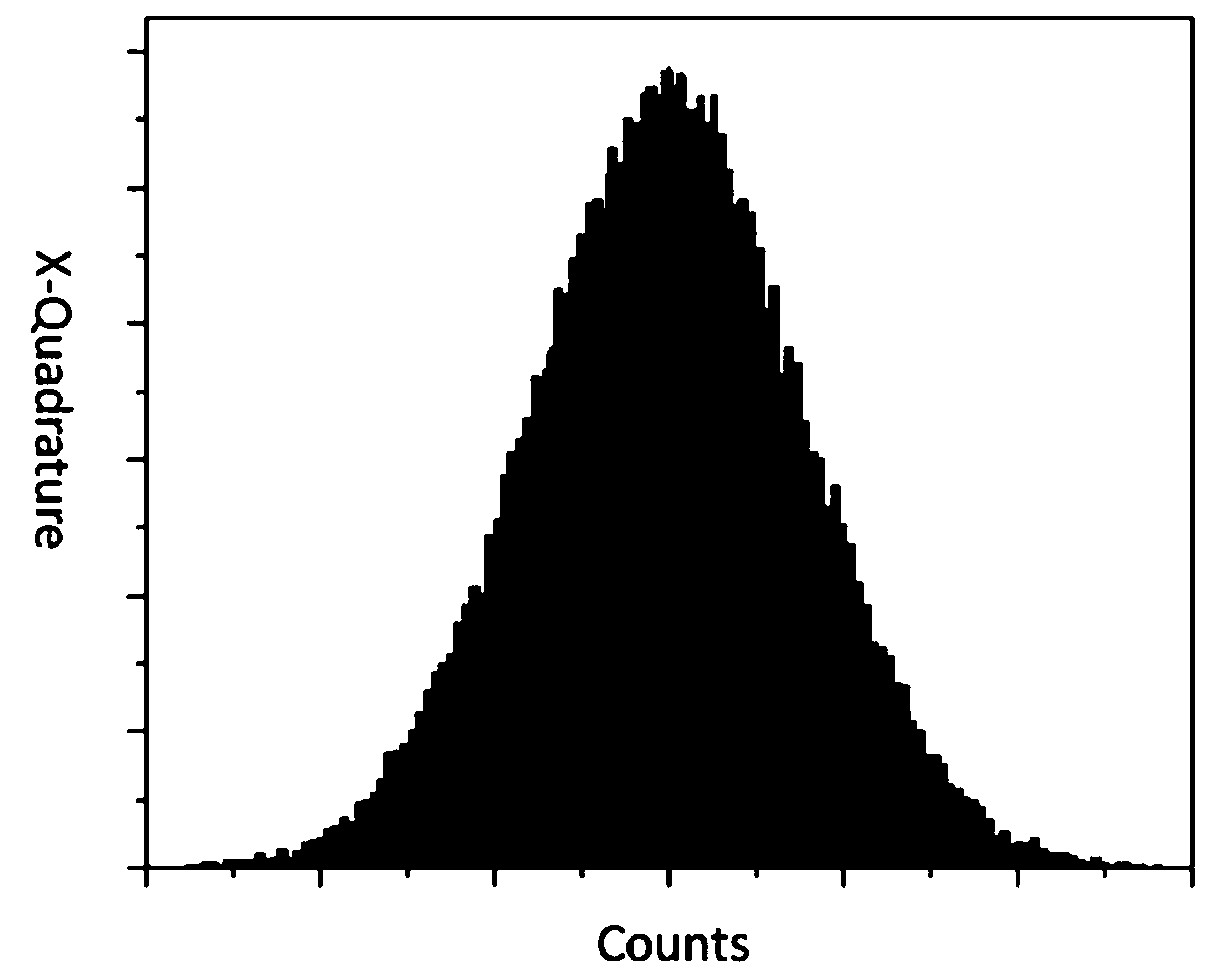
The invention relates to a high-speed true random quantum number generating method, in particular to a method for producing random quantum number at high speed based on vacuum state quantum fluctuation. The problem that the production speed of an existing vacuum random quantum number generator is lower is solved. According to the specific scheme, the high-speed true random quantum number generating method mainly comprises the following steps that the translation effect of Gaussian distribution is firstly exerted to a vacuum state in a phase space, amplification of vacuum-state orthogonal amplitude component noise in the phase space is achieved, and the entropy content introduced by quantum noise in a system is increased; the true random bits which can be extracted in data postprocessing are increased; the background light of a homodyne detection system is strengthened, the sensitivity of the detection system to vacuum noise is improved, and a vacuum noise measurement value is amplified, so that the framing amount of vacuum noise statistics, namely sampling quantization bits are remarkably increased. By adopting the method, the vacuum random quantum number generating rate is effectively improved, and a new means is provided for manufacturing of high-speed random quantum number generators.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Four-particle x state-based two-party quantum key agreement protocol
ActiveCN105245332AHigh qubit efficiencySecure and confidential communicationKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum noiseConvolution
The invention discloses a four-particle x state-based two-party quantum key agreement protocol. The protocol includes following steps that: step 1, Alice and Bob negotiate on quantum-state codes; step 2, Alice prepares n x-state|x<00>>ABCD, and divides all the particles into four ordered sequences, and selects out 2m decoy photons and inserts the decoy photons into the sequences and transmits the sequences to Bob; step 3, Bob measures corresponding decoy photons with a correct measurement base, and informs Alice of measurement results; Alice compares the measurement results and the initial states of the decoy photons, and calculates an error rate, and executes step 4 if the error rate is low, otherwise, executes step 2; and step 4, Alice performs Bell measurement on the particles, Bob executes Z convolution Z-base measurement on the sequences, and Alice and Bob both obtain a shared key. The protocol of the invention can resist existing participant attacks, external attacks and Troy Trojan horse attacks; and the protocol is safe in a noise-free quantum channel and a quantum noise channel. The quantum bit efficiency of the protocol of the invention is higher than that of an existing secure multi-particle entangled state-based quantum key agreement protocol.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Passive mode-locked fiber laser device
InactiveCN103944042AClock jitter is smallShorten the lengthActive medium shape and constructionMode locked fiber laserBandpass filtering
The invention relates to a passive mode-locked fiber laser device which includes a laser pumping source and a unidirectional annular resonant cavity. The unidirectional annular resonant cavity includes a wavelength division multiplexer, an Er doped fiber, a first optical-fiber collimator, a second optical-fiber collimator, a first 1 / 4 glass slide, a second 1 / 4 glass slide, a photoisolator, a bandpass filter, a polarization beam splitter and a 1 / 2 glass slide. The passive mode-locked fiber laser adopts nonlinear polarization rotation mode locking and utilizes the highly doped optical fiber as a gain medium so that the length of a laser cavity is reduced and the repeating frequency of the laser device is increased. Through introduction of the bandpass filter into the laser cavity, stray components and noises in the cavity are filtered so that clock jitter resulted from quantum noises is reduced. Through management of chromatic dispersion of the laser cavity, narrower pulses can be generated and wider frequency spectrum can also be obtained and intensity noises of the laser device are also reduced so that the passive mode-locked laser device is widely applicable to the field of optical-analog-digital system (OAD).
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Low-frequency balanced zero beat photodetector
ActiveCN105157829AReduce the impactImprove signal-to-noise ratioPhotometry electrical circuitsCapacitanceLow noise
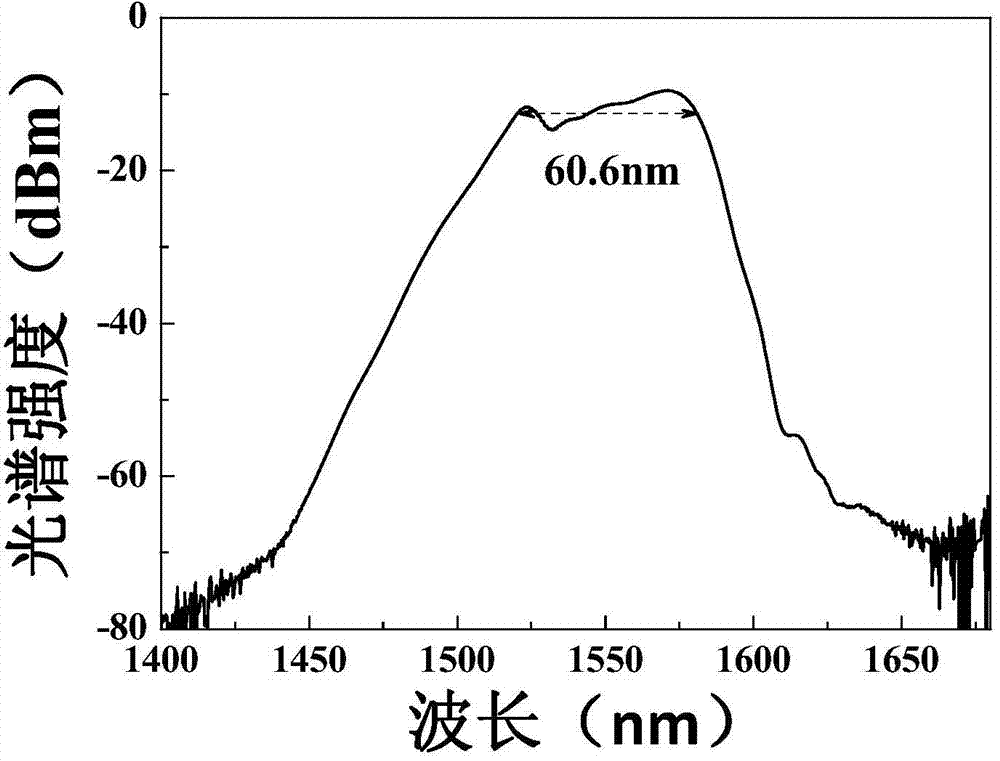
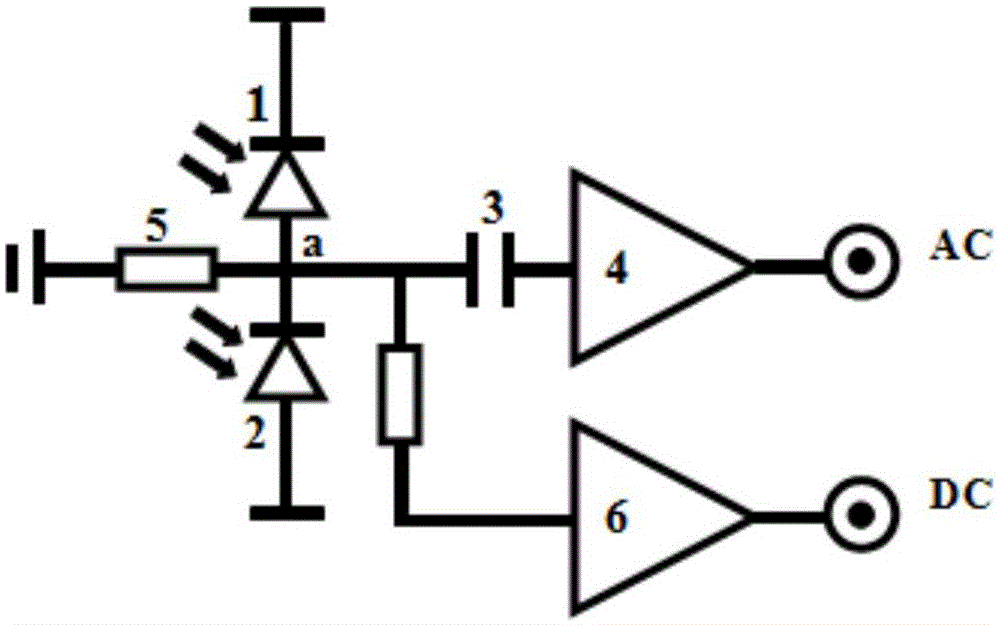
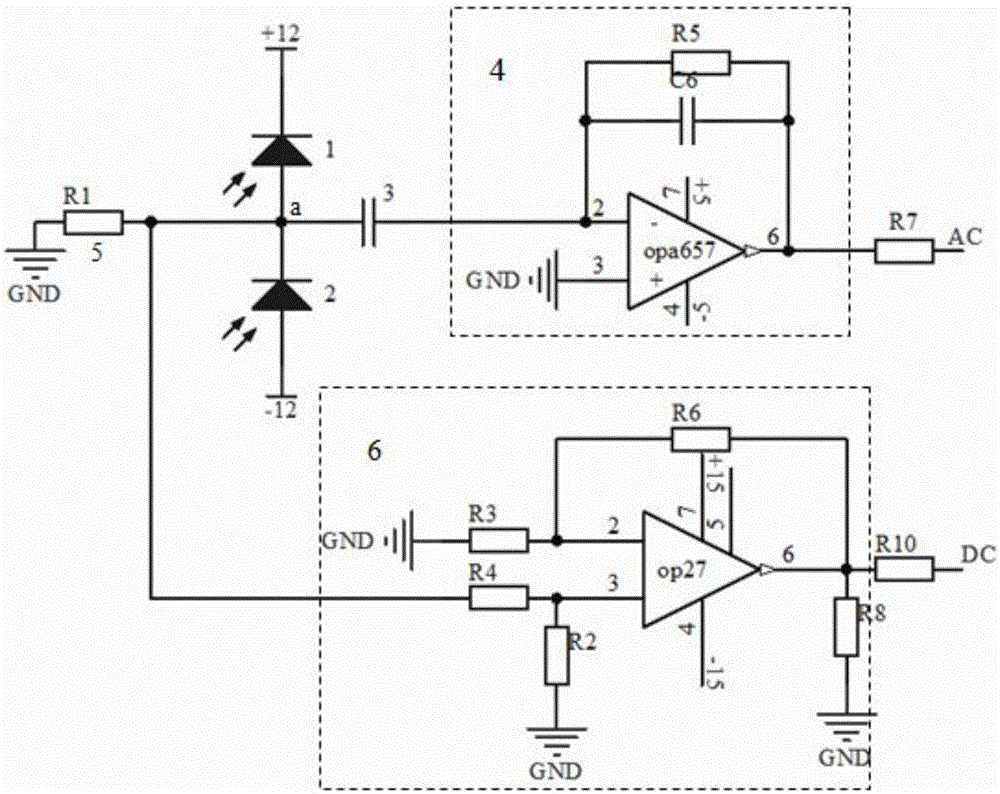
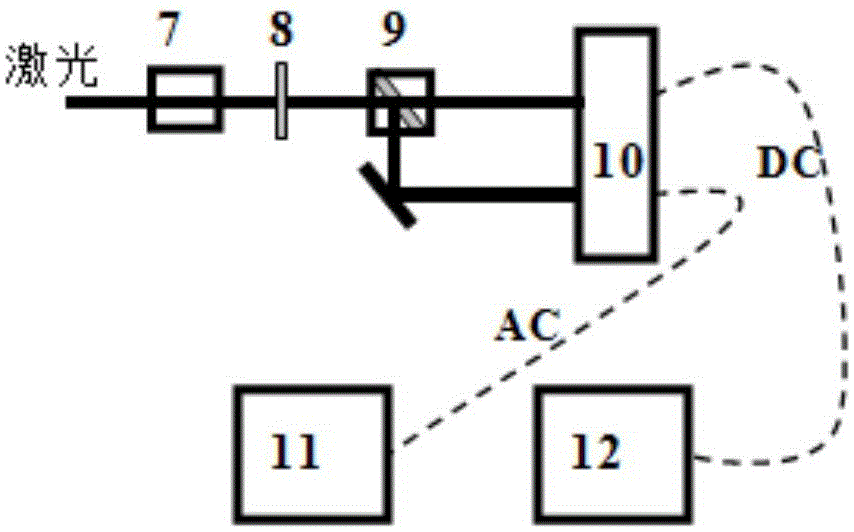
The invention provides a low-frequency balanced zero beat photodetector, which can be used for detecting quantum noises of a laser at the frequency of 50Hz-200kHz and measuring the compression noise spectrum of a non-classical light field in this band. The photodetector comprises a first PIN photodiode (1) and a second PIN photodiode (2) which are of high quantum efficiency, an AC coupling capacitor (3), a low-frequency transimpedance amplifying circuit (4), a DC sampling resistor (5) and a DC same direction proportion amplifying circuit (6). The AC output of the photodetector has the advantages of high gain, low noise, high common mode rejection ratio and so forth, and the photodetector also has a DC output and can monitor the change in the light intensity.
Owner:华科微磁(北京)光电技术有限公司
A random number generation method based on chaotic amplified quantum noise
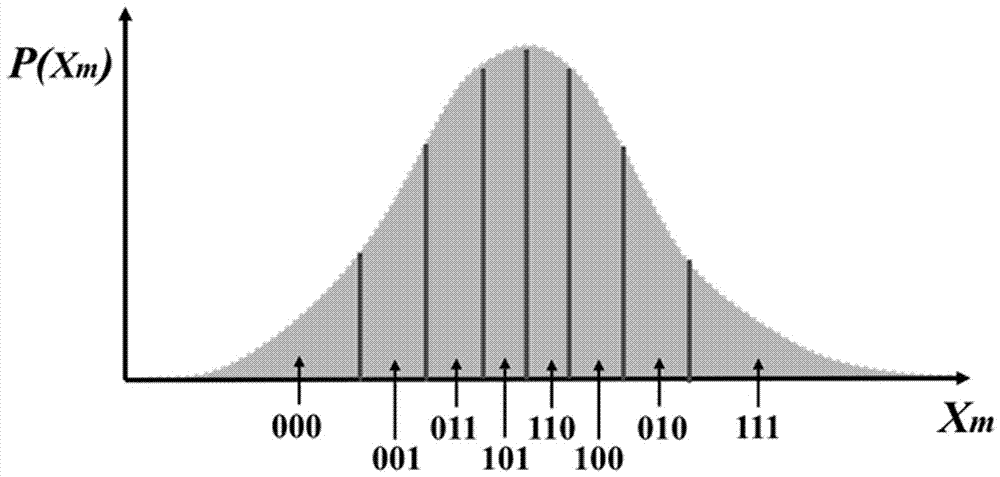
The invention relates to a true random number generator, in particular to a random number generation method based on chaotic amplification quantum noise. The scheme mainly includes the following steps: Firstly, the proportion of electronic noise and quantum spontaneous emission noise in the initial steady state of chaotic laser without feedback is measured and analyzed, and the proportion of quantum noise entropy content is determined; The natural invariant probability distribution of the chaotic system is determined. Based on the distribution, the frame threshold is set to ensure that the distribution probability in each threshold interval is equally divided, the random bits are generated by binary conversion, and the true random sequences are extracted by the generalized hash function. The method of the invention realizes the effective improvement of the generation rate of the vacuum quantum random number, and provides a new method for preparing a high-entropy and high-reliability true random number generator.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Laser Doppler velocity-measuring system with all-optical fiber light-frequency modulation
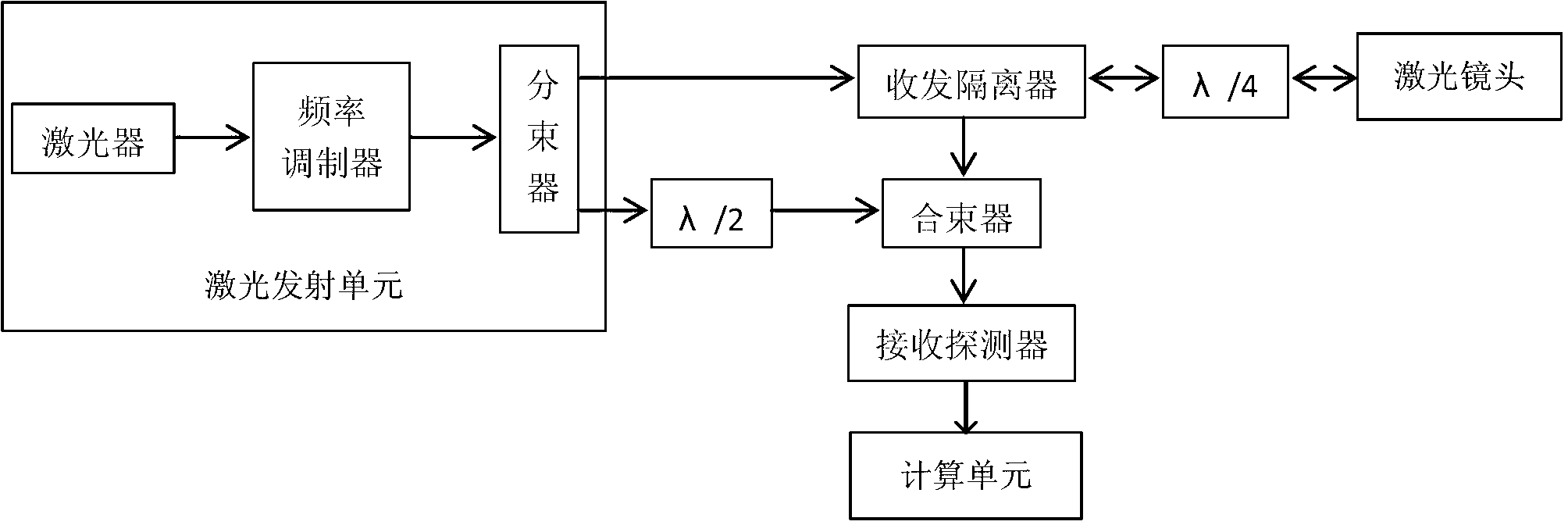
InactiveCN102854511AReduce power consumptionReduce volumeFluid speed measurementElectromagnetic wave reradiationFiberDoppler velocity
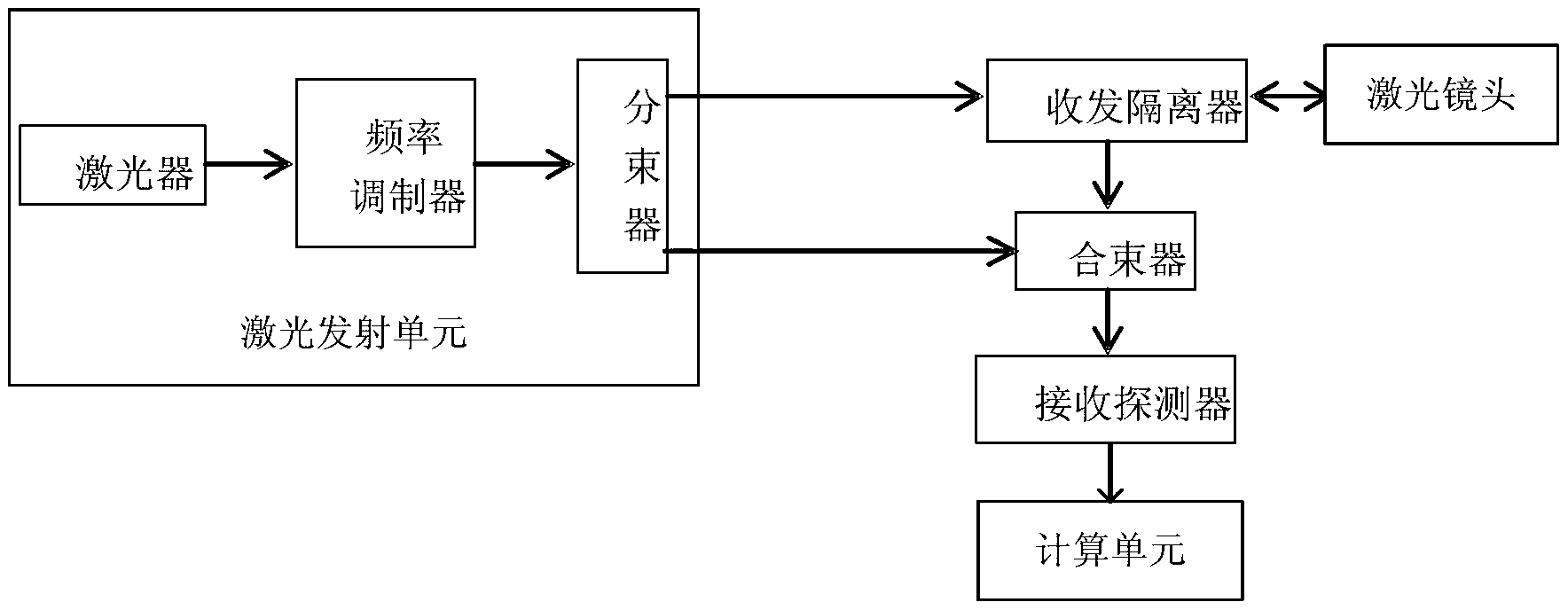
The invention discloses a laser Doppler velocity-measuring system with all-optical fiber light-frequency modulation. The system comprises a laser emission unit, a transceiving isolator, a laser lens, a beam combiner, a receiving detector and a computation unit, and the all optical functional units or devices are connected mutually by optical fibers. By using the system, the detection sensitivity of a laser Doppler velocity-measuring technology reaches quantum noise theory limit, and an optical system of the laser Doppler velocity-measuring technology is upgraded completely. A laser Doppler velocity-measuring meter using a new technology has the advantages that the power consumption is lower, the volume is smaller, the weight is lighter, the structure layout is more reasonable, the construction is more convenient, a transmitting lens and a receiving lens become one, no sensitiveness to impact vibration and high-low temperature changes exists, and requirement for cleanness degree of environment is low.
Owner:11TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GROUP CORP
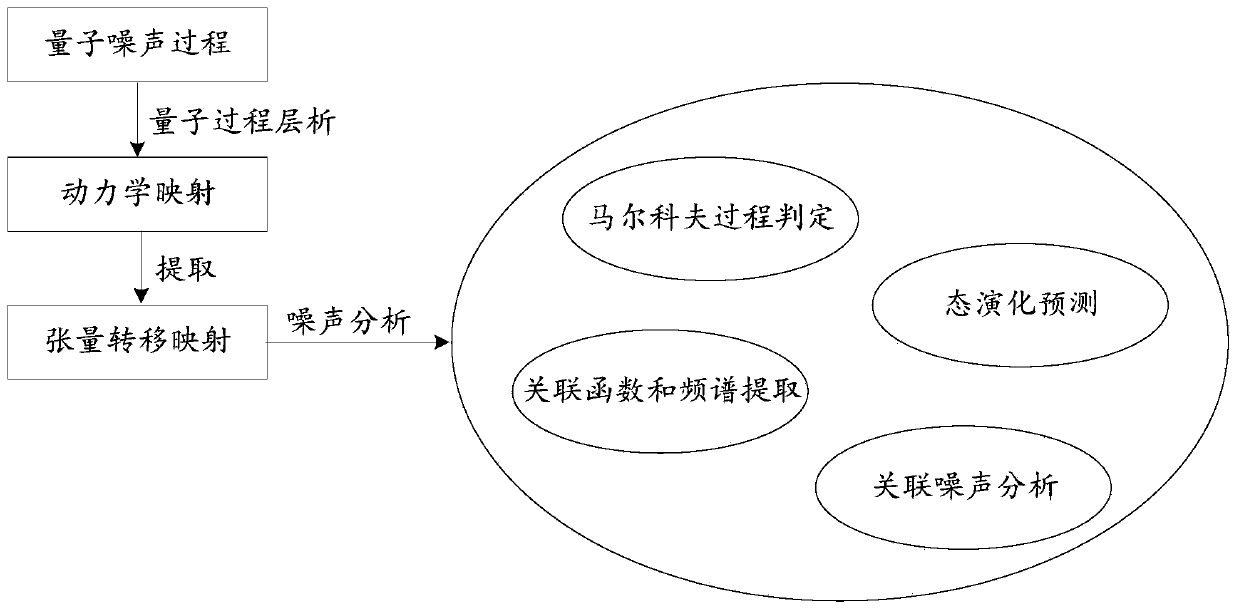
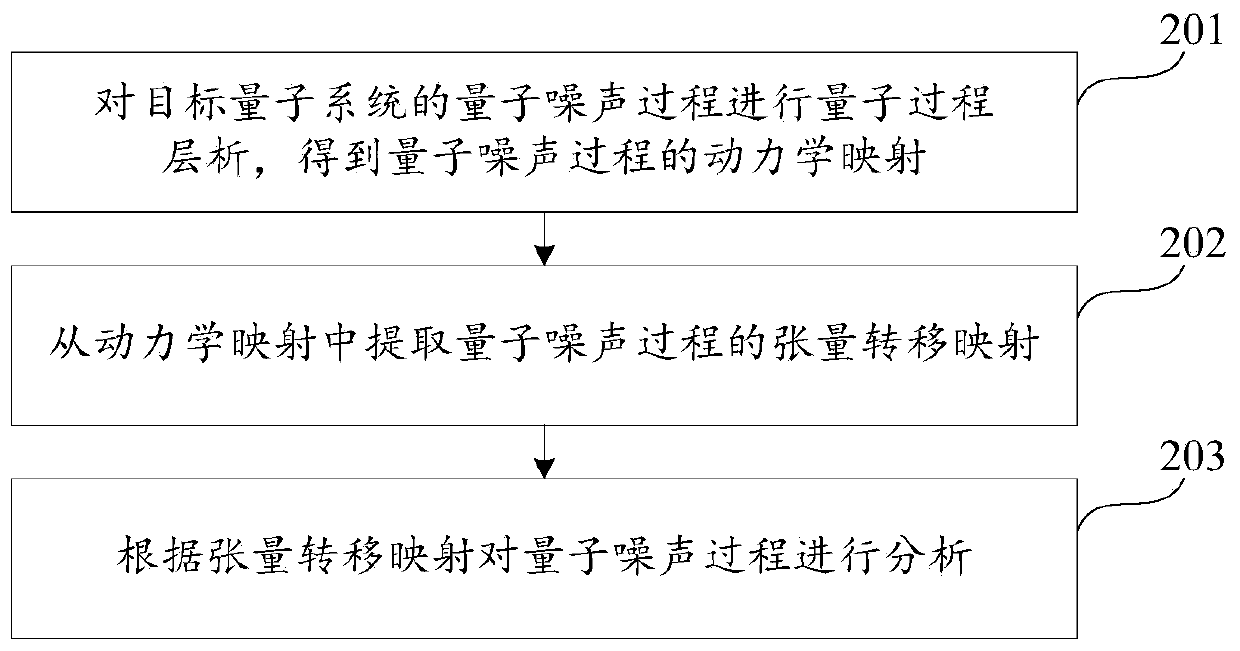
Quantum noise process analysis method and device, equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN110210073AEasy to analyzeAccurate analysisQuantum computersMathematical modelsQuantum technologyQuantum noise
The invention discloses a quantum noise process analysis method and device, equipment and a storage medium, and belongs to the technical field of quantum. The quantum noise process analysis method comprises the following steps: carrying out quantum process chromatography on a quantum noise process of a target quantum system to obtain dynamic mapping of the quantum noise process; extracting tensortransfer mapping of the quantum noise process from the dynamic mapping; and analyzing the quantum noise process according to the tensor transfer mapping, wherein the tensor transfer mapping is used for representing the dynamic evolution of the quantum noise process, namely, the evolution law of the dynamic mapping of the quantum noise process along with time is embodied. Therefore, the quantum noise process is analyzed based on tensor transfer mapping of the quantum noise process, and compared with pure quantum process chromatography, richer and more comprehensive information about the quantumnoise process can be obtained, so that the quantum noise process is analyzed more accurately and comprehensively.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Two-party quantum key negotiation protocol based on three-particle GHZ state
ActiveCN105490804AFair establishmentSecure and confidential communicationKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareAlice and Bob
The present invention discloses a two-party quantum key negotiation protocol based on a three-particle GHZ state, comprising the following steps: step 1: Alice and Bob negotiate codes of quantum states; step 2: Alice prepares n+q GHZ states and divides all the particles into sequences; Alice sends a sequence SC to Bob; step 3: Bob selects and measures q sample particle(s); Alice selects measurement bases to measure corresponding particles; Bob calculates an error rate; and if the error rate is low, step 4 is performed, otherwise step 2 is performed; step 4: Alice performs a Bell measurement on two particles with the same sequence number in the sequences; Bob performs X-base measurement on the particles in the sequences; and Alice and Bob respectively obtain the same shared key according to measurement results and the codes of the quantum states. According to the present invention, the two-party quantum key negotiation protocol can resist existing participant attacks and external attacks as well as Trojan horse attacks, is safe in noiseless quantum channels and quantum noise channels, and can achieve a relatively high quantum bit efficiency.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
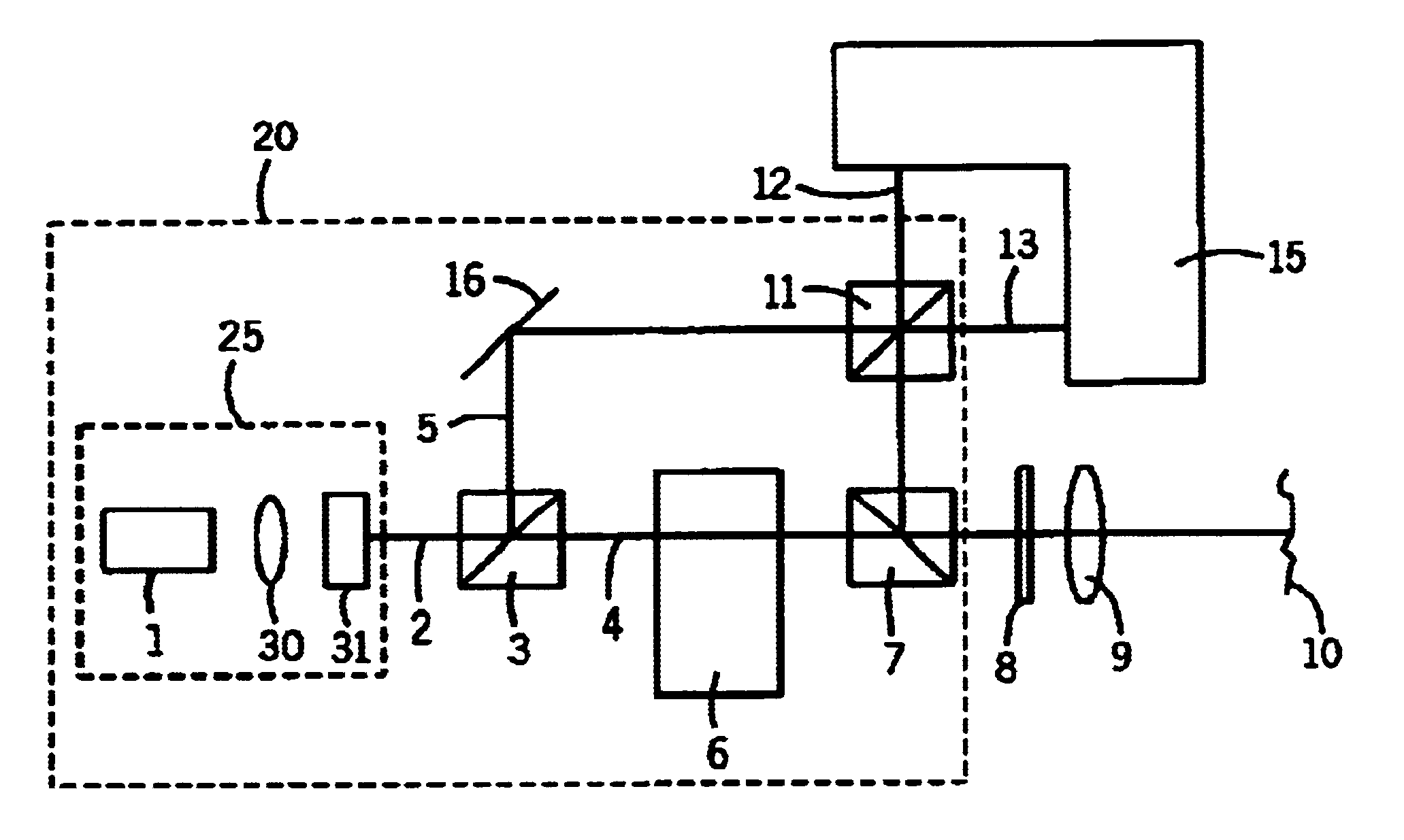
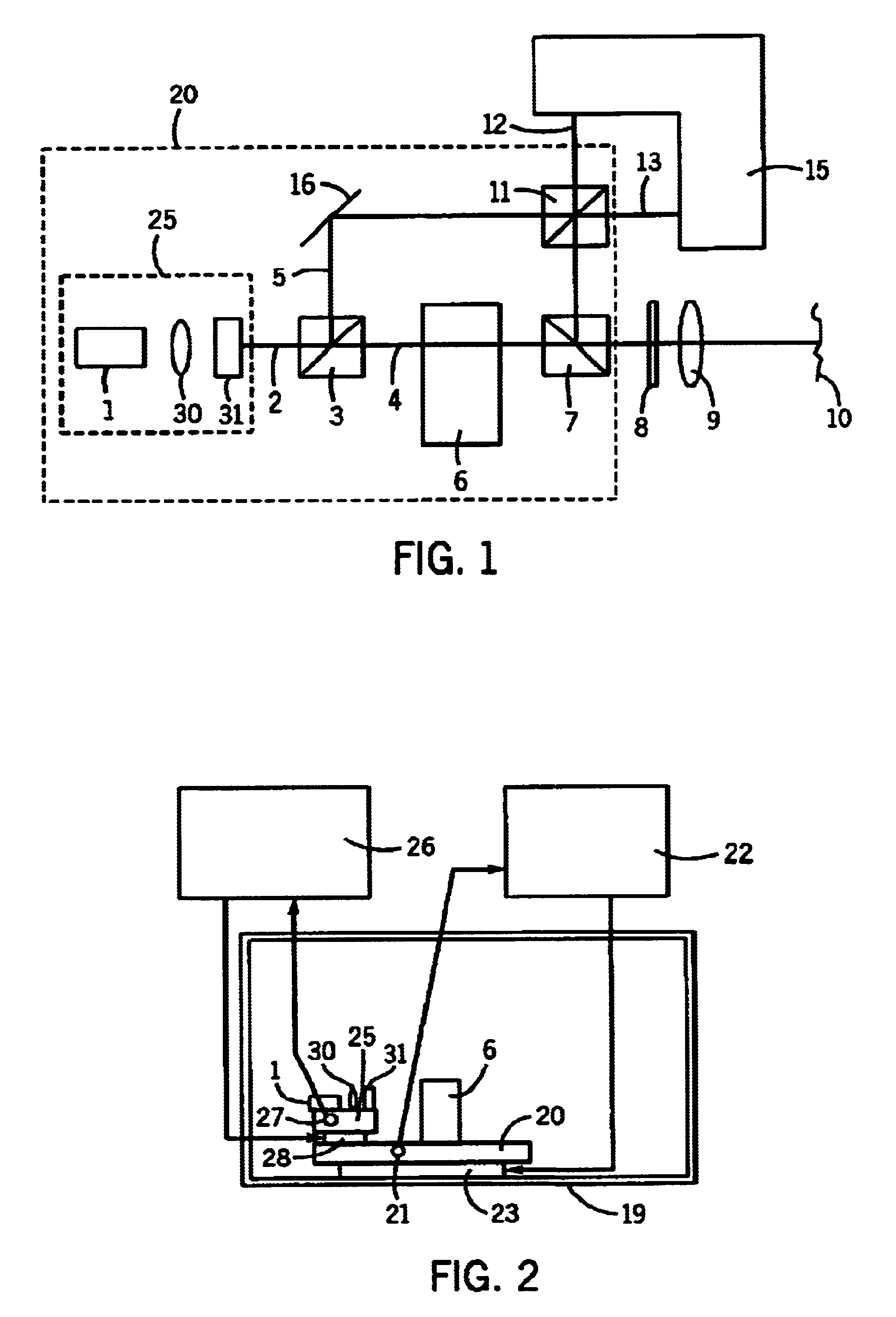
Device for the non-contacting measurement of an object to be measured, particularly for distance and/or vibration measurement
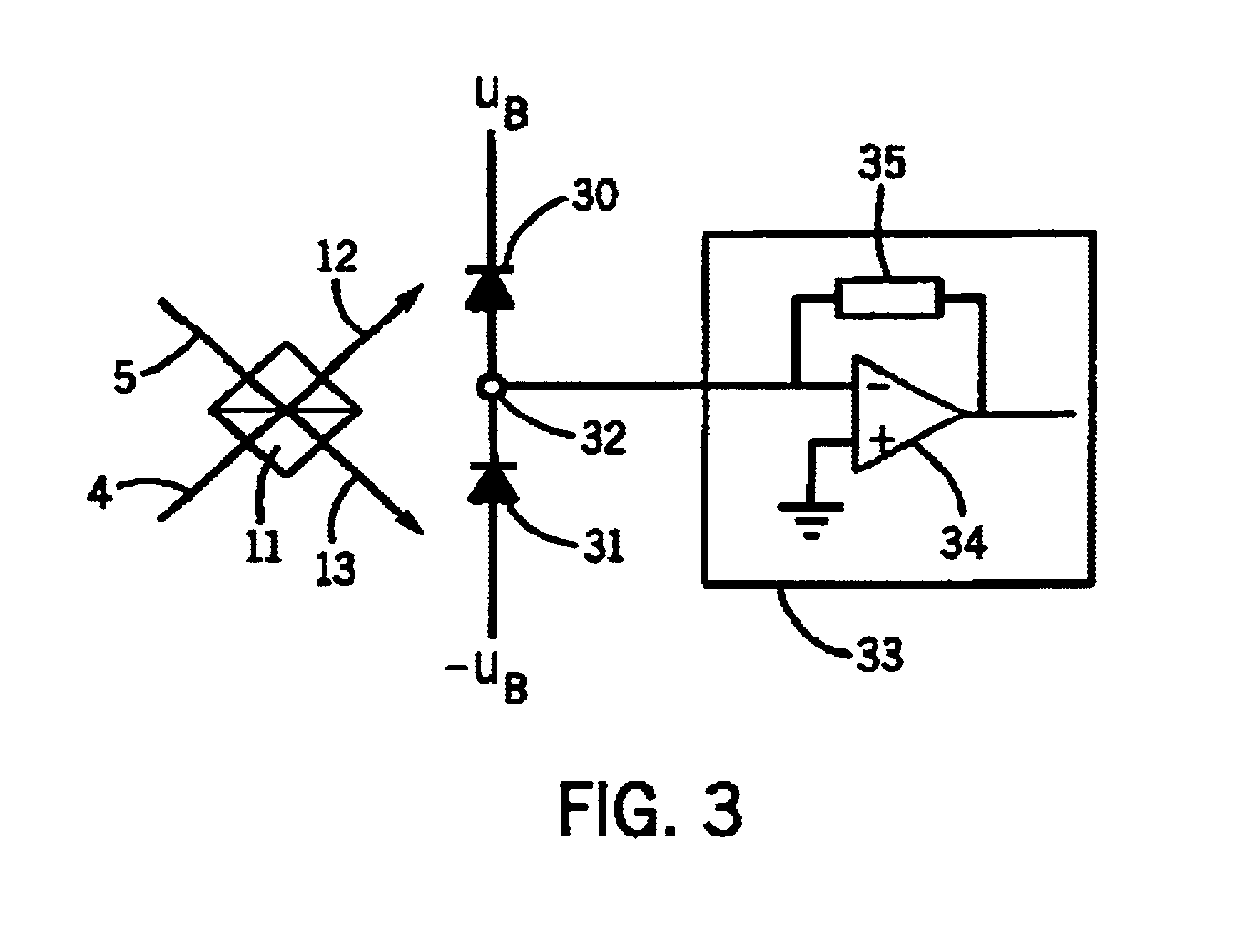
InactiveUS6844936B2High measurement accuracyStructural economyInterferometersUsing optical meansVibration measurementAudio power amplifier
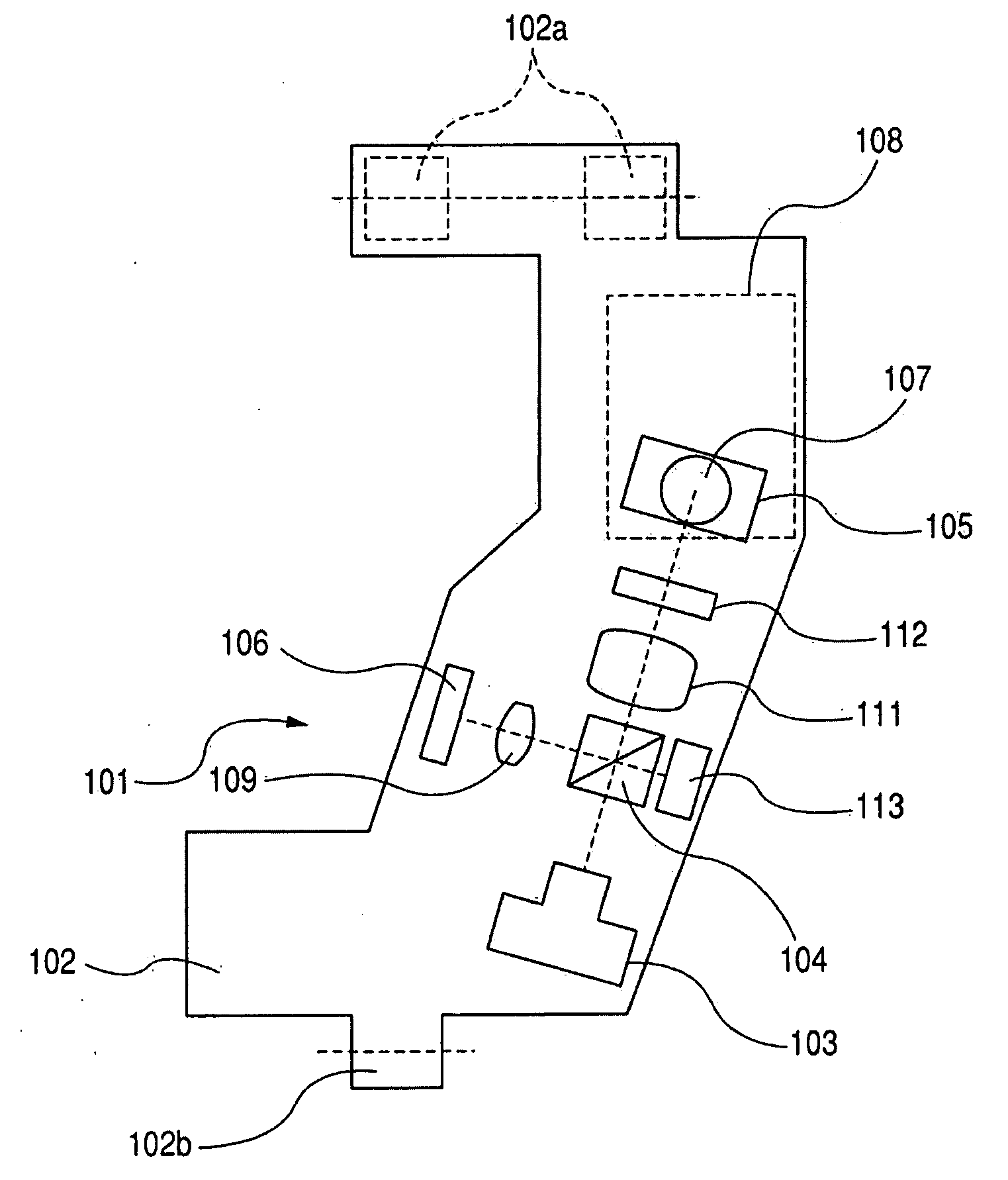
A device for the non-contacting measurement of an object to be measured, particularly for distance and / or vibration measurement, has at least one laser light source, optical devices for splitting the light into object light (4) and reference light (5) for interacting with the object to be measured and for superimposing object light and reference light following the interaction of the object light with the object to be measured, preferably a frequency shift device in the form of a Bragg cell for producing a frequency shift between the object light and the reference light and a detecting device (15) for converting reference light and object light into electrical signals suitable for further processing. The detecting device has at least two series-connected optoelectronic transducers in the form of photodiodes (30, 31). Between the transducers is located a tap (32) for tapping a difference signal which, for further processing, is supplied to a transimpedance circuit (33) associated with one of the transducers. Thus, there is a subtraction of photodiode currents prior to processing in an amplifier circuit in a balanced detection arrangement. This inexpensively permits measurements at high reference light power with resolutions in the quantum noise limit range.
Owner:ZENNER HANS PETER
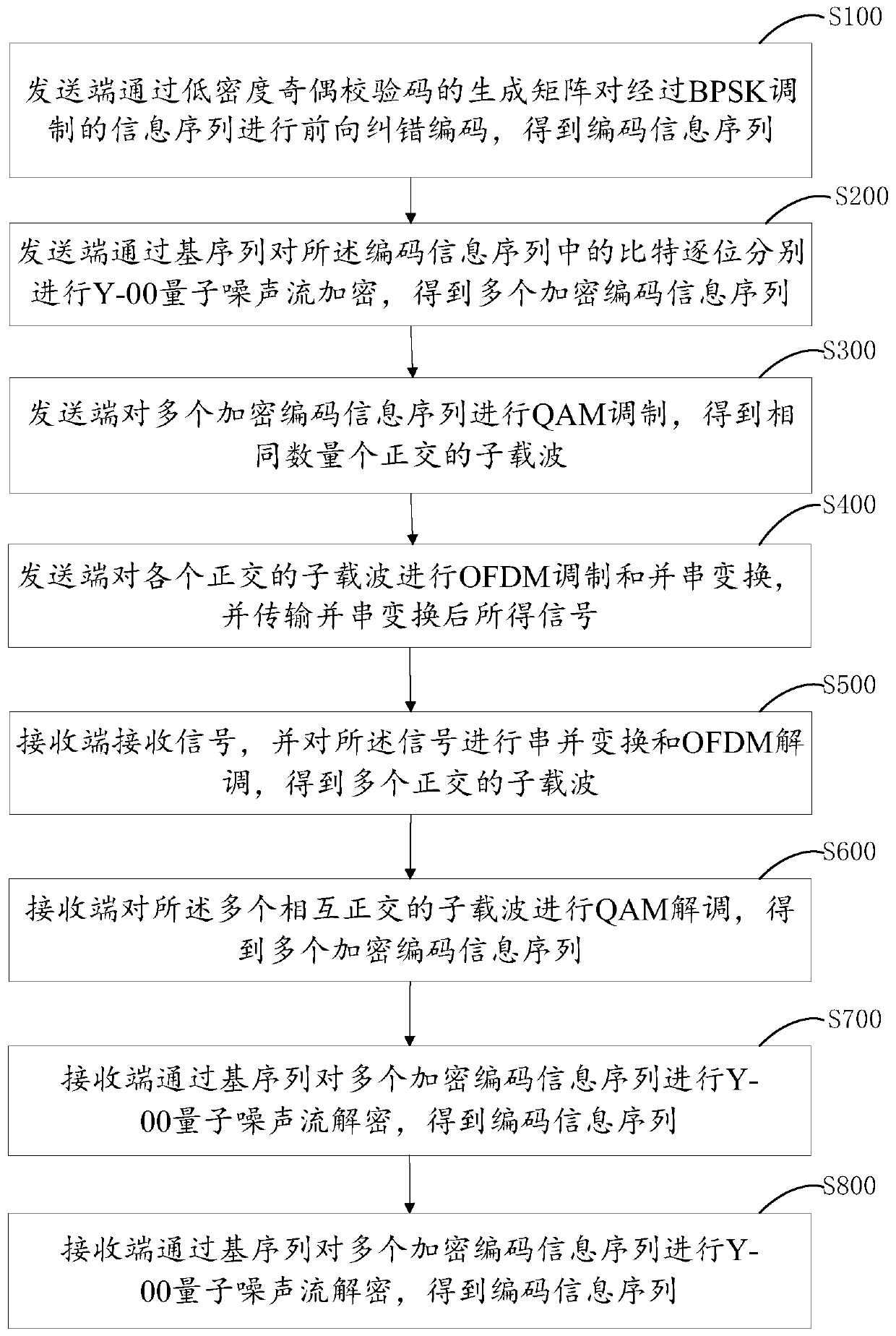
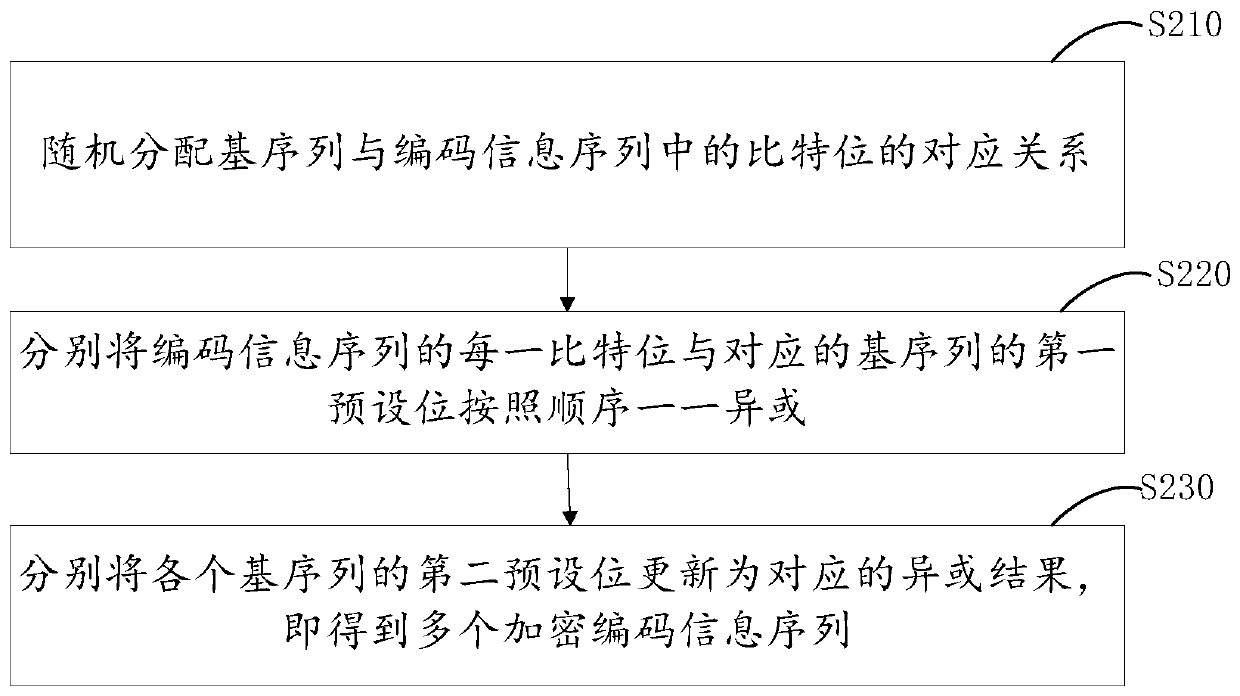
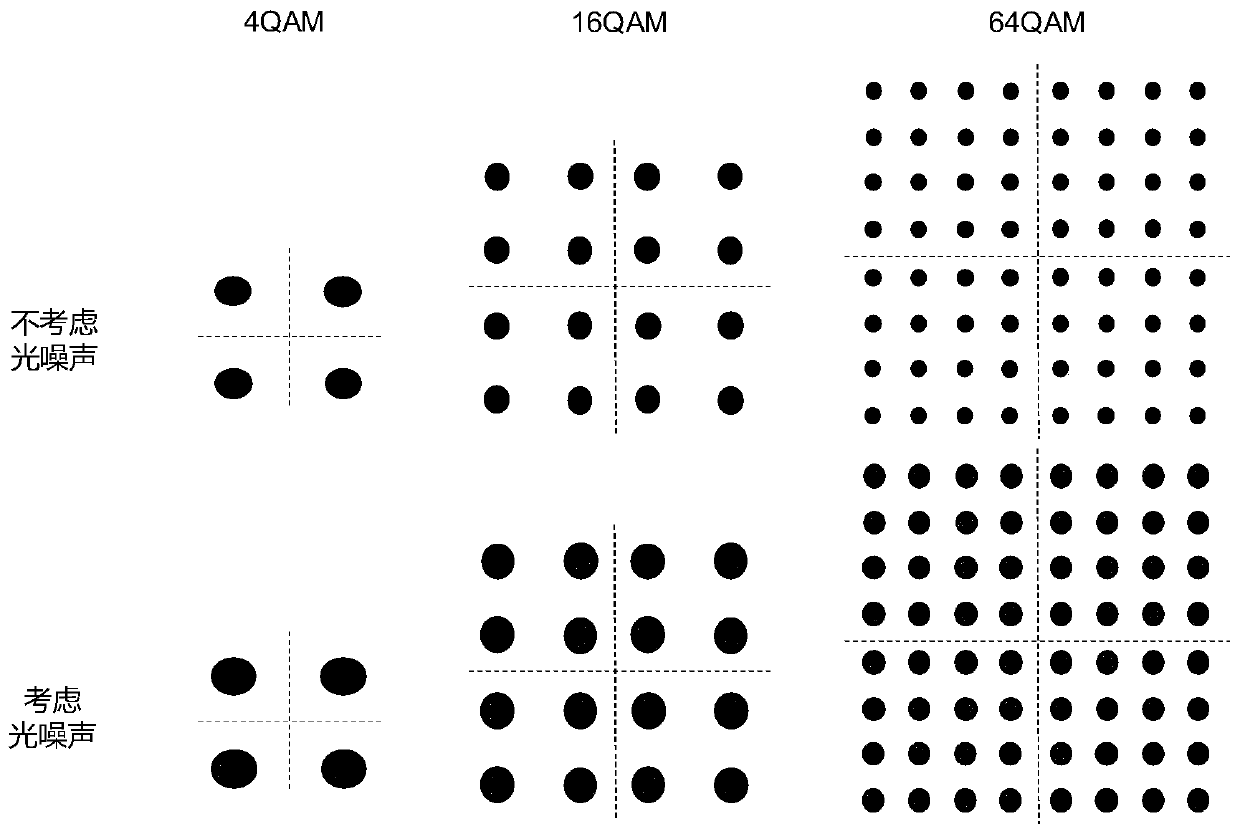
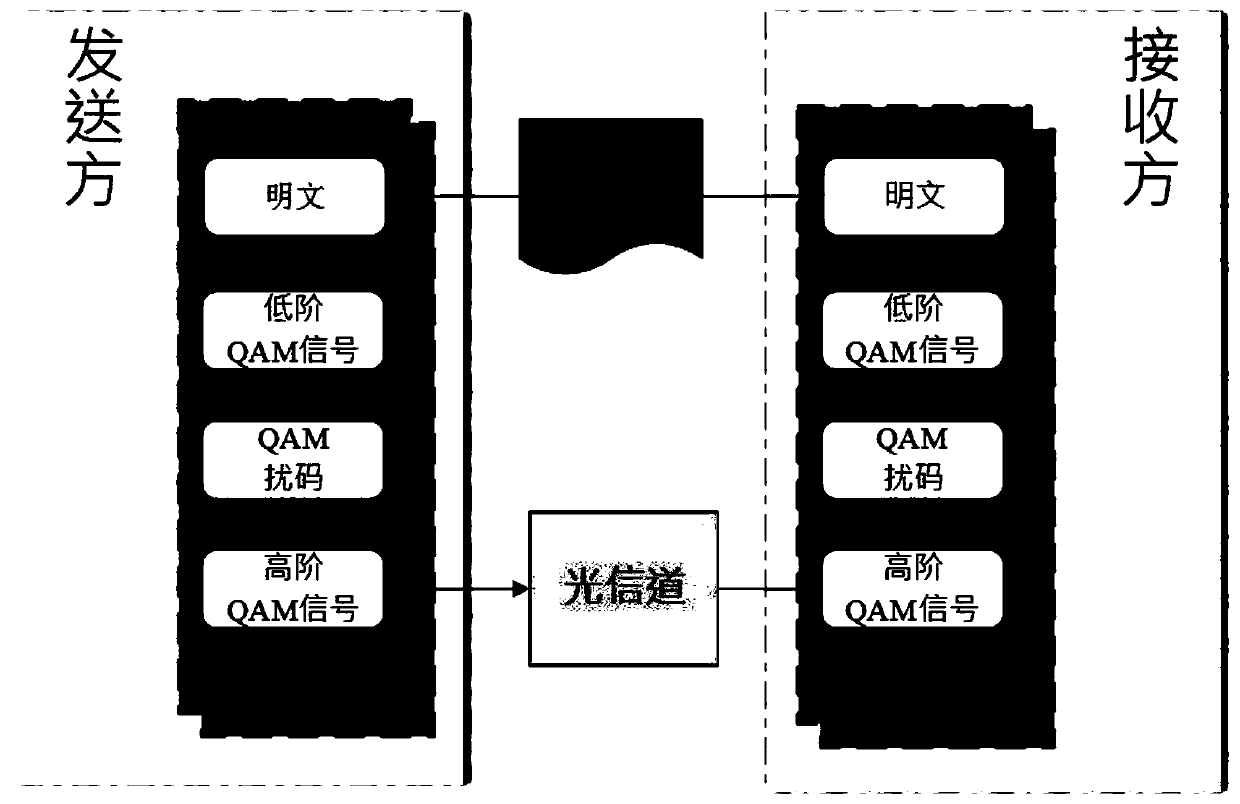
Y-00 quantum noise stream encryption transmission method with low bit error rate
ActiveCN111342958AReduce energy consumptionReduce bit error rateKey distribution for secure communicationError preventionQam modulationCarrier signal
The invention provides a Y-00 quantum noise stream encryption transmission method with a low bit error rate. The method comprises the steps that a transmitting end carries out the forward error correction coding of an information sequence modulated by BPSK through a generation matrix of a low-density parity check code, and obtains a coded information sequence; the sending end performs Y-00 encryption on bits in the coded information sequence bit by bit through the base sequence to obtain a plurality of encrypted coded information sequences; the sending end performs QAM modulation on the plurality of encrypted coded information sequences; the sending end performs OFDM modulation and parallel-serial conversion on each orthogonal subcarrier and transmits the orthogonal subcarriers; a receiving end receives the signals, and performs serial-parallel conversion and OFDM demodulation; the receiving end demodulates the plurality of orthogonal subcarriers QAM to obtain a plurality of encryptedcoded information sequences; the receiving end performs Y-00 decryption on the plurality of encrypted coded information sequences through the base sequence to obtain an information sequence subjectedto BPSK modulation; and the receiving end performs iterative computation through an LDPC FEC decoder to obtain an information sequence to be transmitted.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
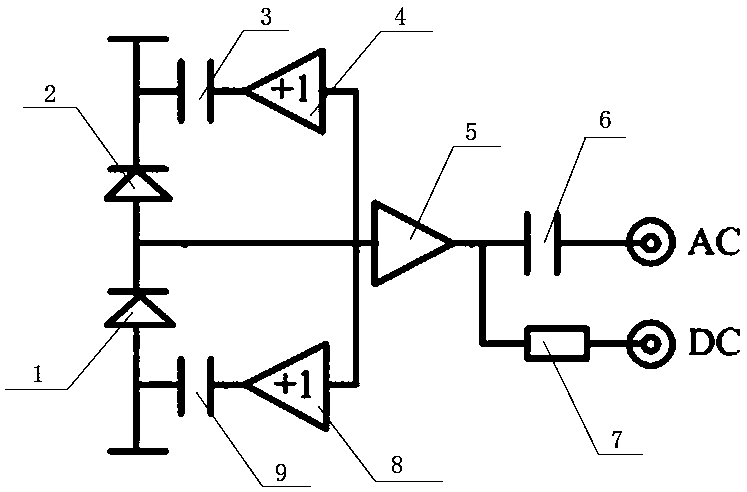
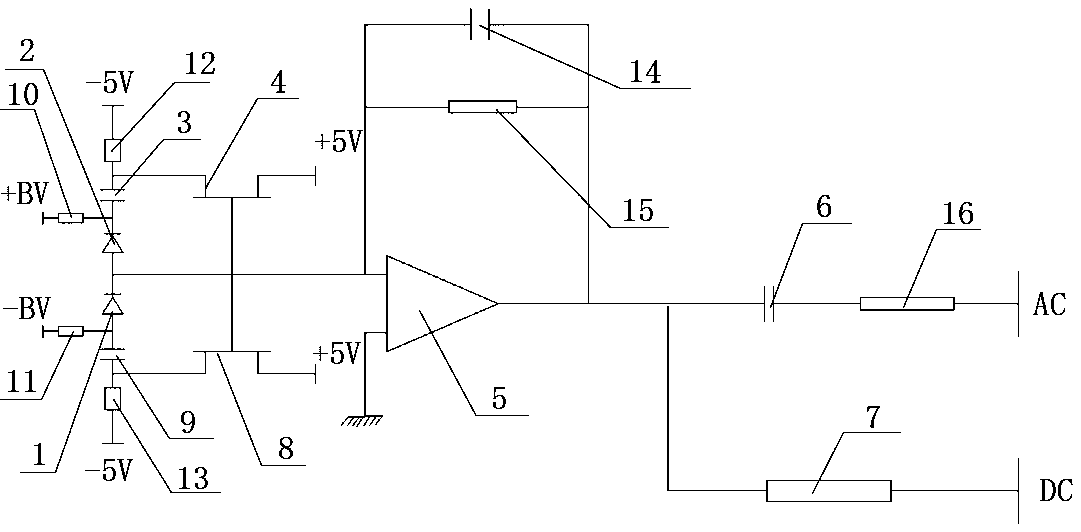
Low-frequency low-noise balanced homodyne detector
ActiveCN108362377AElectronic Noise ReductionLow Common Mode Rejection RatioPhotometry electrical circuitsLow noiseLow frequency band
The invention relates to the field of squeezed state optical field quantum noise measurement. A low-frequency low-noise balanced homodyne detector includes a differential circuit composed of two photodiodes, a bootstrapping current-voltage conversion circuit composed of two bumpers and a trans-impedance operation amplifier (5), and an AC and a DC output circuit composed of a first capacitor (6) and a first resistor (7) separately. According to the invention, through quantitative analysis of input current total noise of the low-frequency low-noise balanced homodyne detector in a low frequency band and since a sampling resistor in a traditional detector is removed and the bootstrapping current-voltage converter is adopted, the electronic noise of the low-frequency low-noise balanced homodynedetector within a frequency of 20 Hz to 200kHz is reduced substantially and requirements for high gain, high common-mode rejection ratio, simple structure and low cost are met.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Quantum encryption method based on chaotic sequence
InactiveCN109889338AImprove securityImprove decoding performanceKey distribution for secure communicationTransceiverSecure transmission
The invention discloses a quantum encryption method based on a chaotic sequence. The invention discloses a quantum encryption method based on a chaotic sequence. The method comprises the following steps of: performing quantitative judgment on a chaotic sequence in a chaotic state to generate a binary sequence with enough length; the method is used as key information of a quantum noise encryption system, quantitative decision function is as follows; using the chaotic sequence to generate a chaotic signal, and the chaotic signal is used to generate a chaotic signal. The chaotic signal is used togenerate a chaotic signal; and the sender and the receiver only need to share three key parameters, namely iteration times, a logistic map coefficient and a chaotic sequence length, so that a matchedpassword sequence can be automatically generated. The beneficial effects of the method are as follows: compared with a traditional quantum encryption system, the quantum encryption system has the advantages that the cracked risk and the safe transmission difficulty of the long password sequence are considered, the long chaotic sequence generated by the chaotic function is used as the password sequence of the quantum encryption system, and therefore safe decoding of information can be achieved only by sharing key parameters of the chaotic function between legal transceivers.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
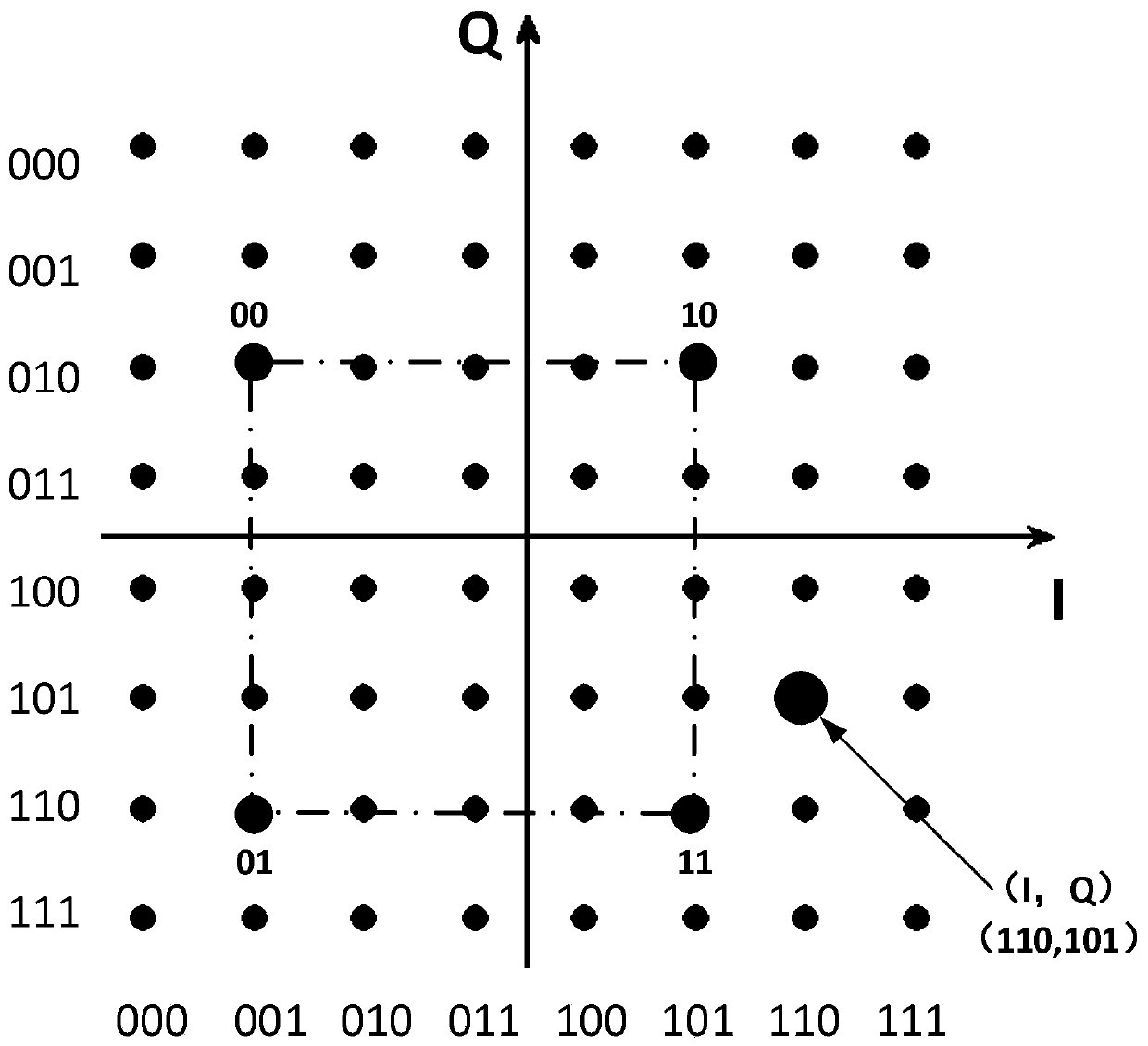
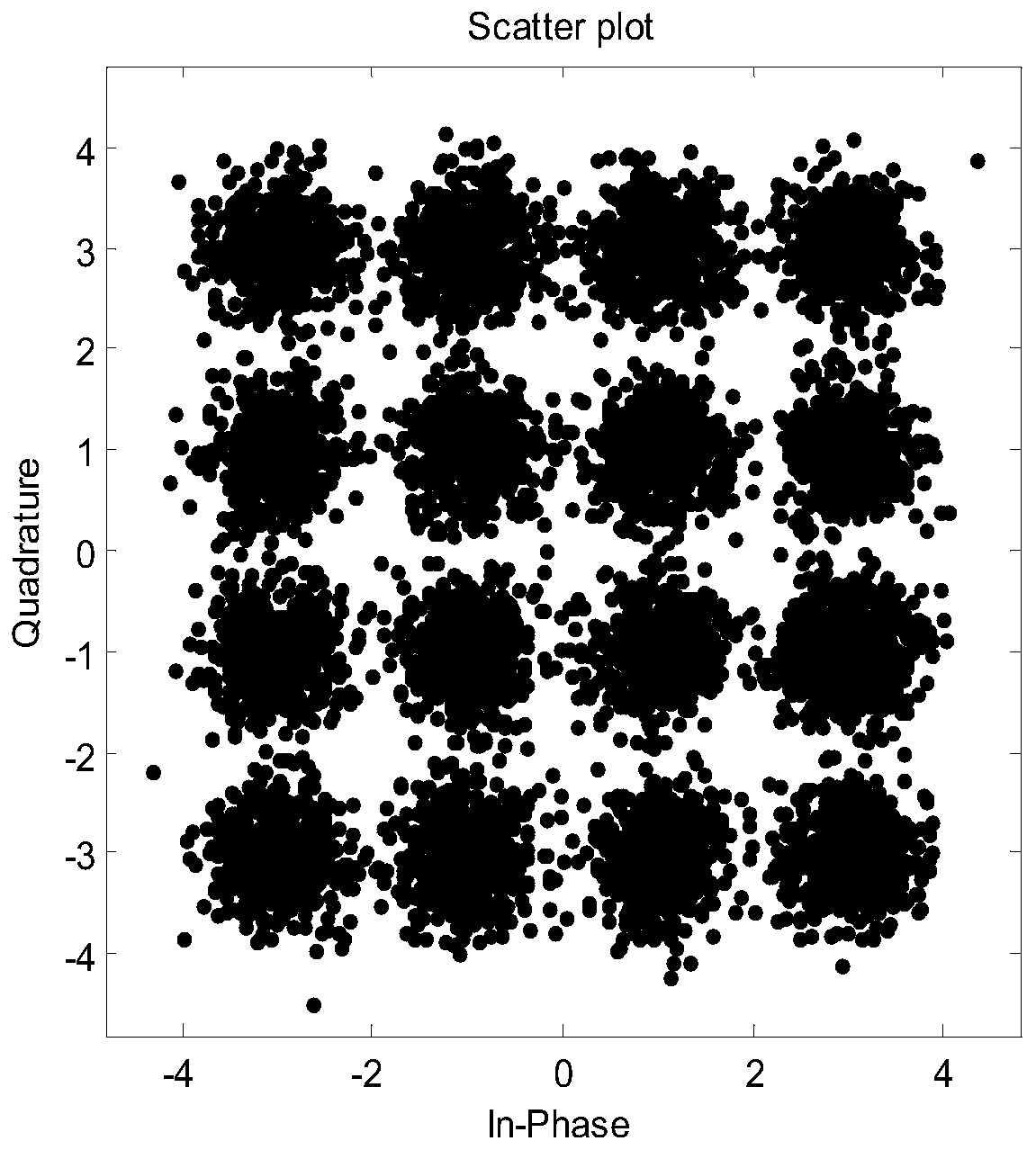
Quantum noise stream encryption system and encoding and decoding method based on one-dimensional chaotic sequence
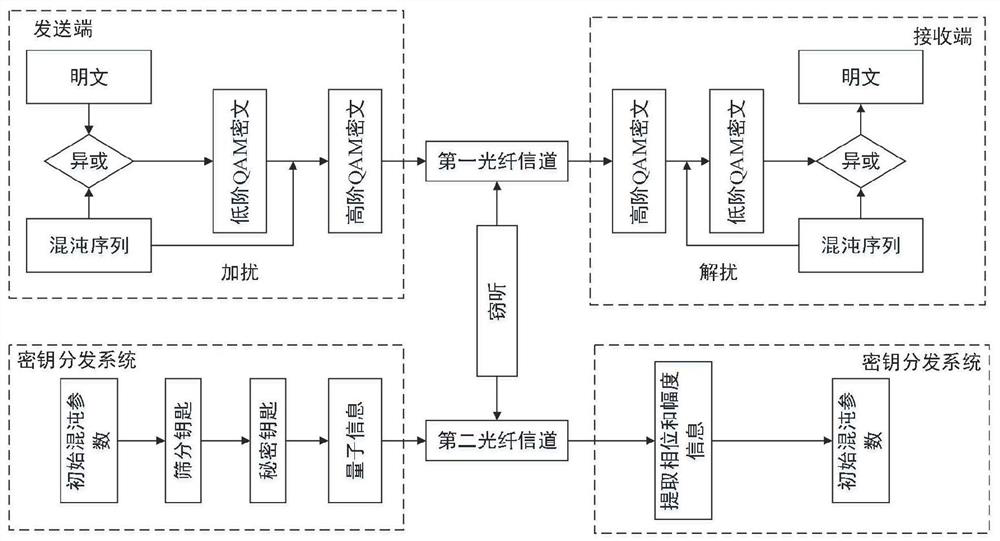
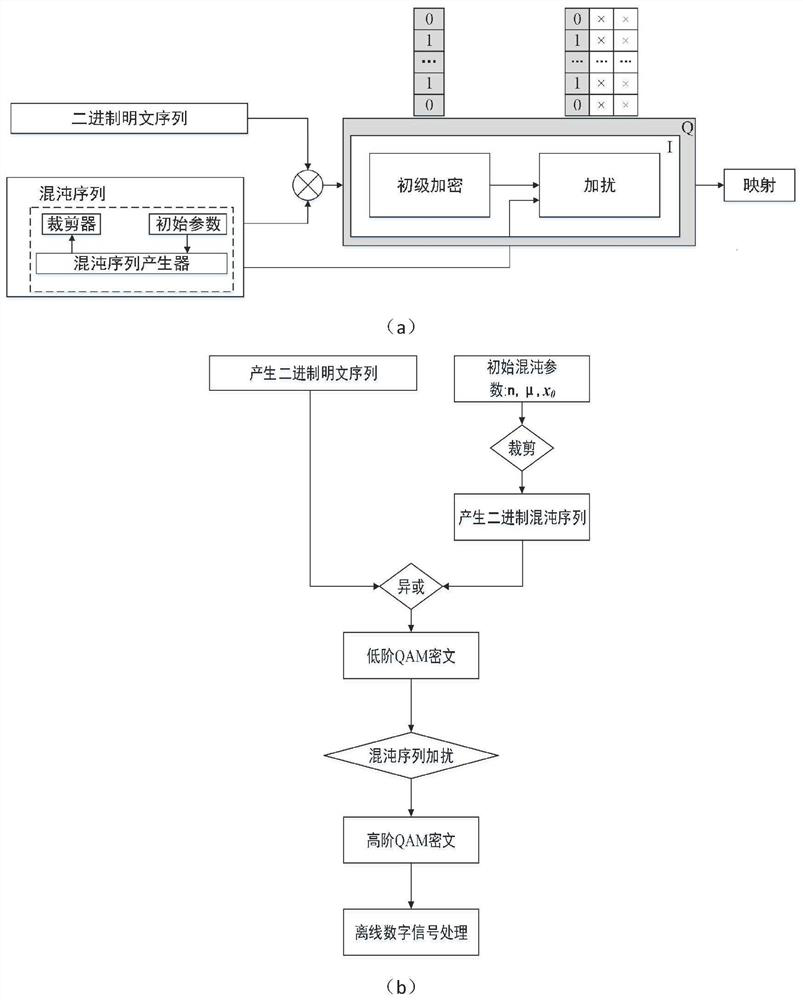
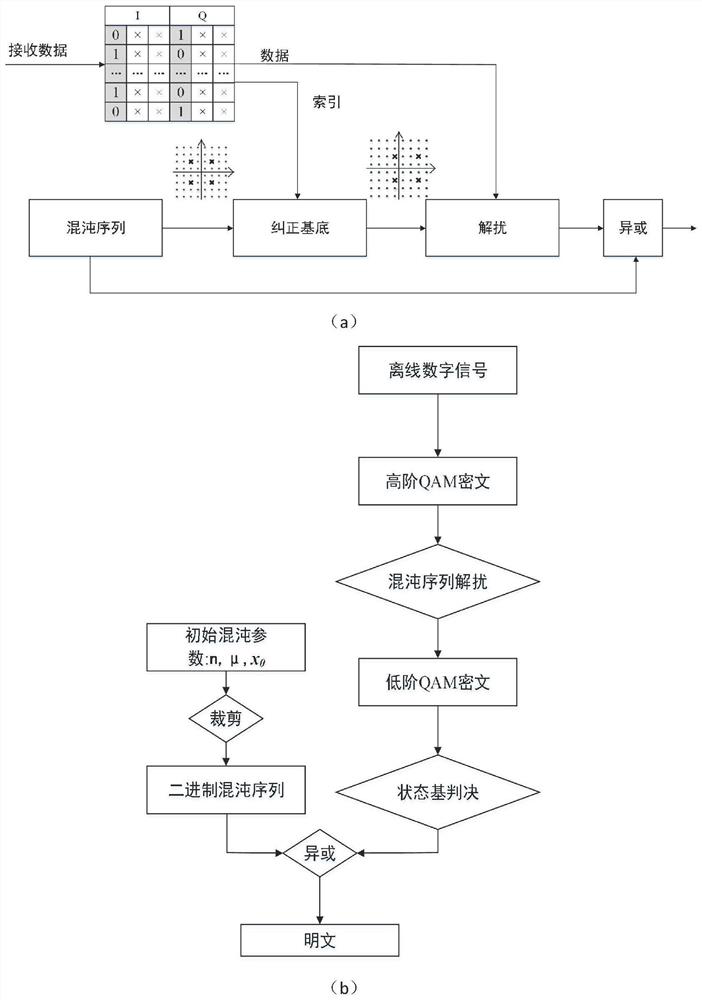
PendingCN113225174AGood effectReduce bit error rateSecuring communication by chaotic signalsDigital signal processingDecoding methods
The invention relates to a quantum noise stream encryption system based on a one-dimensional chaotic sequence and a coding and decoding method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining a binary chaotic sequence; respectively carrying out one-by-one exclusive-or operation on the binary chaotic sequence and the I / Q component of the binary plaintext information, and mapping to obtain a low-order QAM ciphertext; increasing the digits of the low-order QAM ciphertext by using a QNSC technology, and mapping to obtain a high-order QAM ciphertext; performing offline digital signal processing on the high-order QAM ciphertext, and transmitting the high-order QAM ciphertext to a receiving end through a first optical fiber channel. The coding and decoding method is improved, the effect of a state base during decoding is expanded, the bit error rate is reduced, and the safety is high.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
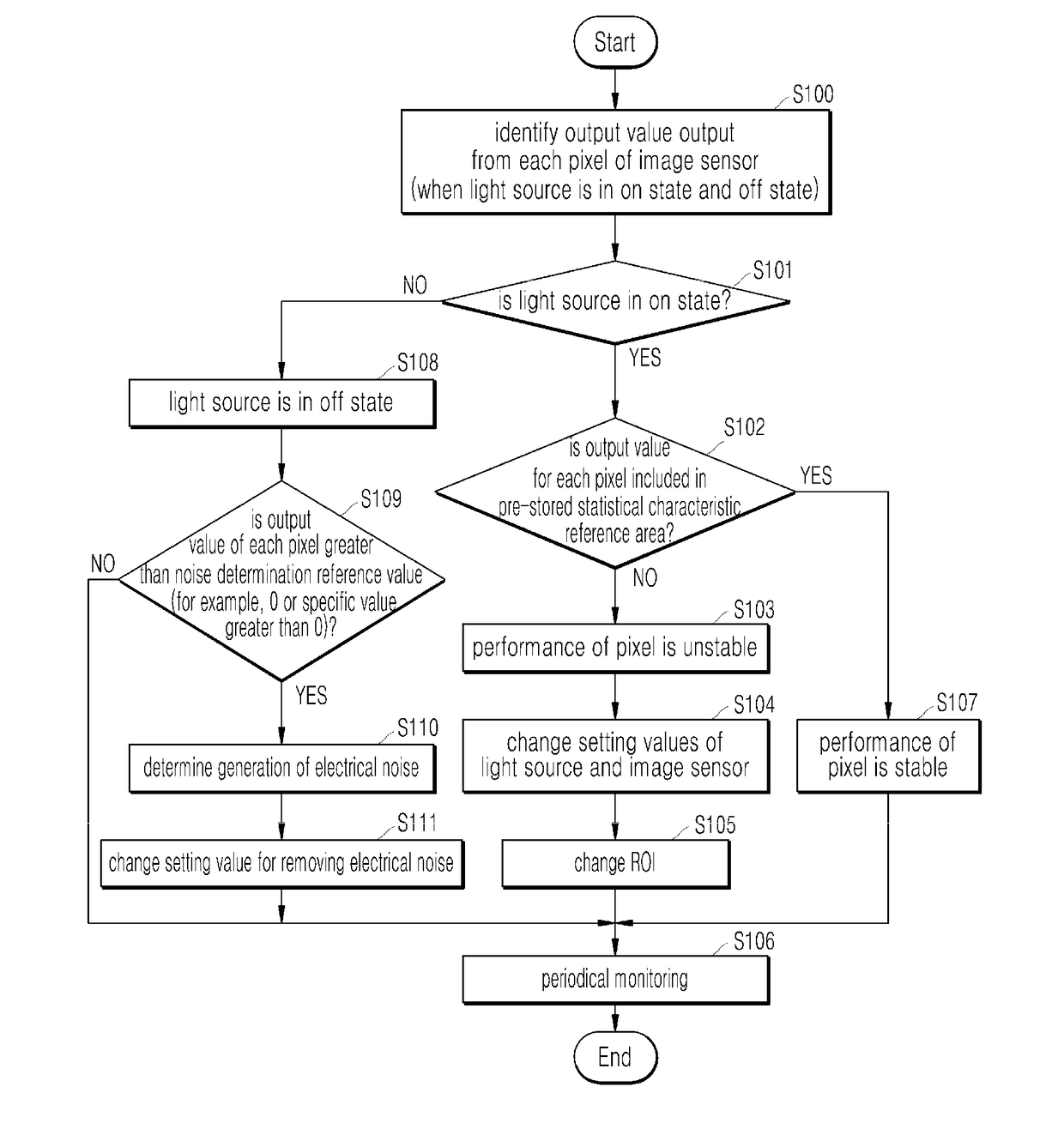
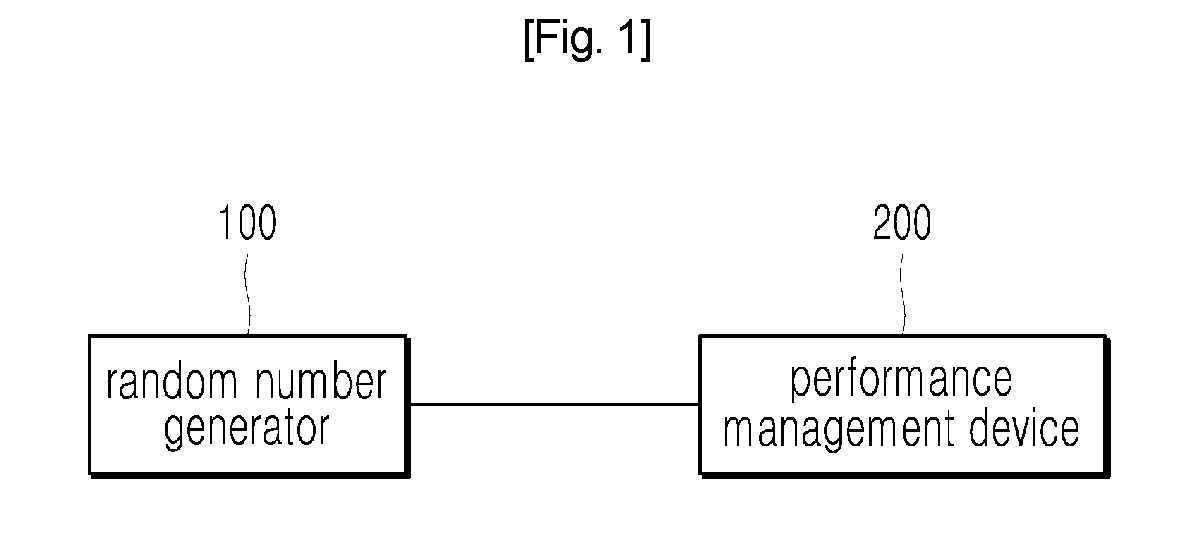
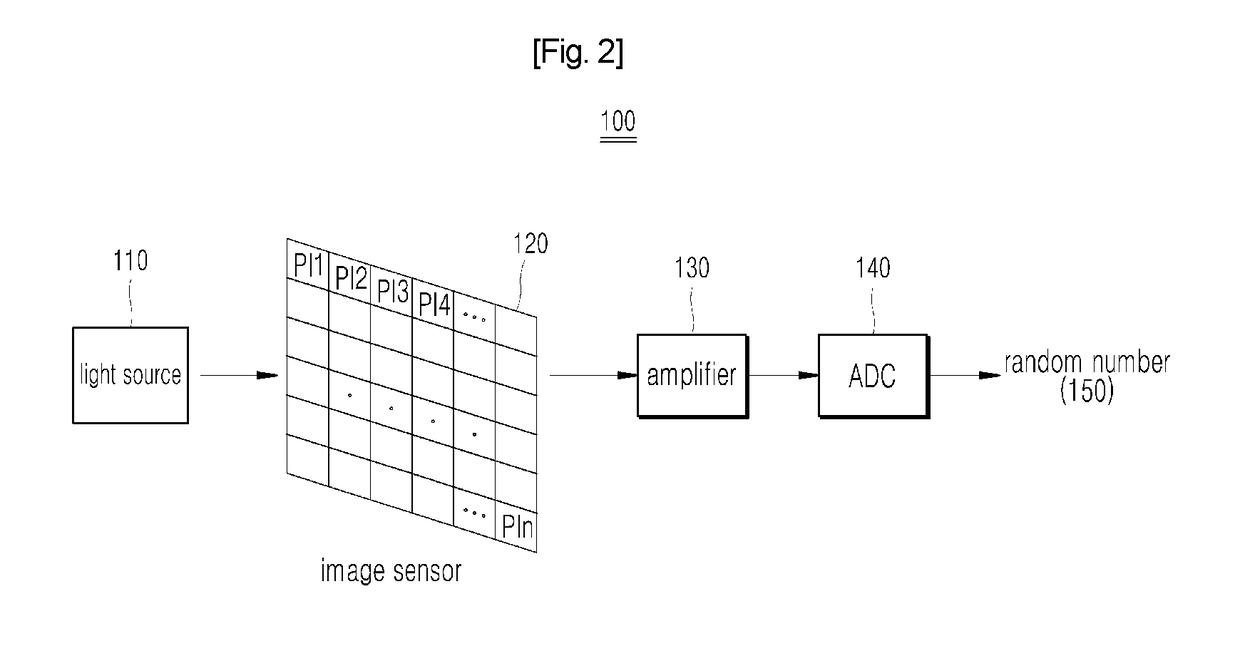
Device and method for managing performance of quantum noise-based random number generator
ActiveUS20180260192A1Sufficient randomnessMinimize biasKey distribution for secure communicationPhotometry using reference valueQuantum noiseNumber generator
The present invention presents a device and method for managing the performance of a quantum noise-based random number generator, the device ensuring the performance stability of a random number generator on the basis of an output value for each pixel, which is outputted in correspondence to an optical strength value of an optical signal emitted from a light source and inputted into each pixel, so as to be capable of outputting, within a certain range regardless of devices, a value of an entropic signal outputted from an image sensor, thereby enabling sufficient randomness to be continuously maintained while minimizing deviation between pixels.
Owner:ID QUANTIQUE SA
Fast multi-photon key distribution scheme secured by quantum noise
ActiveUS7831050B2Fast and secure key distributionRaise the ratioKey distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareQuantum noise
A key distribution scheme comprising a generation and reception system and a specific operation protocol is described. This system allows fast and secure key distribution in optical channels by two stations A and B. One or two true-random physical sources are used to generate random bits and a random sequence received provides the cipher to the following one to be sent. A starting shared secret key is used and the method can be described as a one-time-pad unlimited extender. The minimum probability of error in signal determination by an eavesdropper can be set arbitrarily close to the pure guessing level of one-half and the security of the method comes from the quantum noise of light as well as from the starting secret key. This system allows for optical amplification without security degradation within its operational boundaries.
Owner:SMARTPLUG
An X-ray photon counting detector consistency calibration method based on deep learning
ActiveCN109697476AEasy CalibrationAccurately determineMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionCluster algorithmProjection image
The invention discloses an X-ray photon counting detector consistency calibration method based on deep learning. The method comprises the following steps: 1, bad pixel positioning: analyzing a projection image by using a clustering algorithm to obtain bad pixel coordinates; and 2, classifying and compensating the bad pixels: classifying the bad pixels by using correlation analysis to obtain the positions of the bad pixels of the detector, and calibrating the positions. And 3, noise elimination of the projection image: using the label data to train the convolutional neural network to eliminatenoise in the projection image, and completing consistency calibration of the X-ray photon counting detector. According to the method, the coordinates of the defective pixels of the detector are obtained by analyzing the rear-end projection image and are calibrated, so that the positions of the defective pixels of the detector can be more accurately determined, the quantum noise in the projection image is completely eliminated, and the method is more convenient and quicker than the existing front-end calibration.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and device for suppressing chaotic delay by using broadband spontaneous emission quantum noise
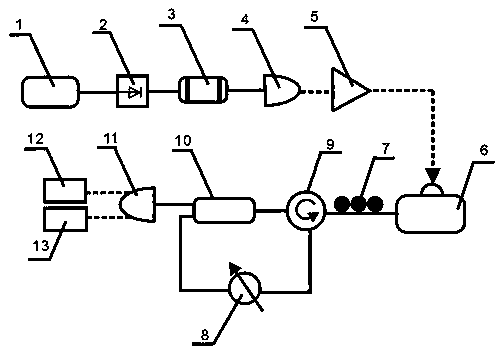
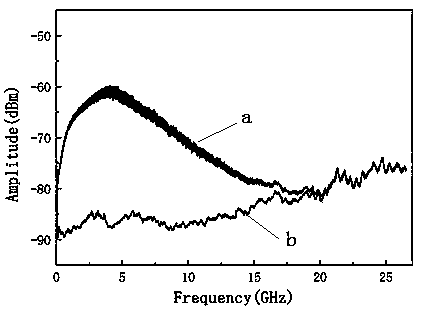
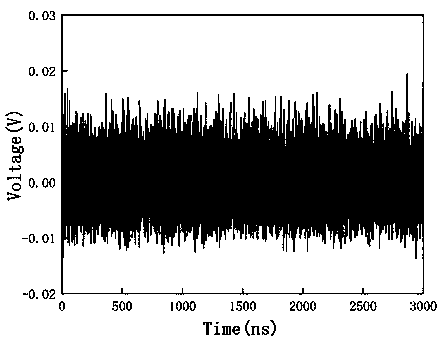
ActiveCN110571641AControllable frequency bandwidthMeet application needsLaser detailsLaser output parameters controlSecure communicationQuantum noise
The invention relates to chaotic laser, in particular to a method and a device for suppressing chaotic delay by using broadband spontaneous emission quantum noise, which solves the problem that the existing chaotic signal generation system has delay characteristics. The device for suppressing chaotic delay by using broadband spontaneous emission quantum noise comprises a broadband spontaneous emission quantum noise system and a continuous chaotic laser signal generation system to construct a broadband spontaneous emission quantum noise preparation system. Chaos is modulated by generating continuous chaotic laser signals and broadband spontaneous emission quantum noise. The broadband spontaneous emission quantum noise adopted by the invention can provide uncertain initial values for chaoticsignals, so that the final chaotic signals cannot be predicted and become chaotic signals with uncertainty, chaotic laser delay characteristics can thus be effectively suppressed, and the method andthe device can be used in the field of secure communication.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
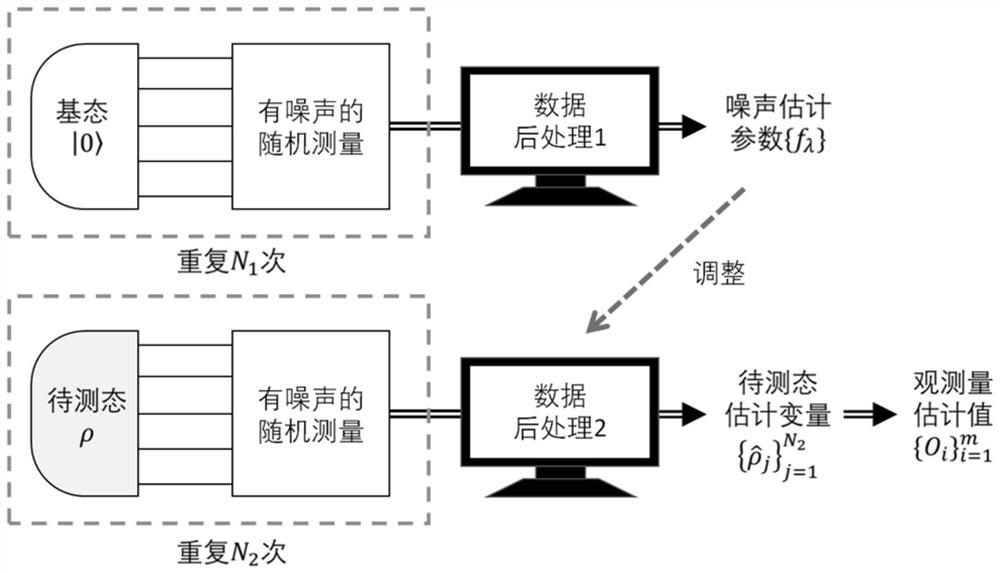
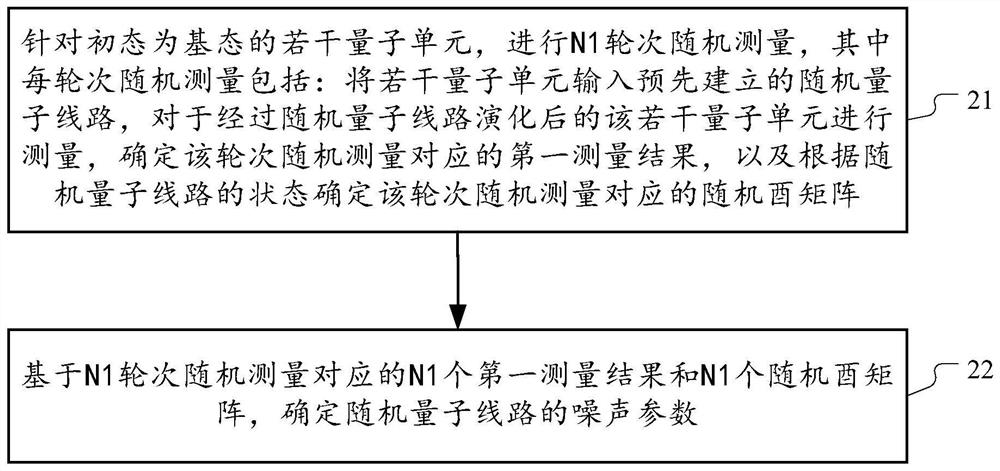
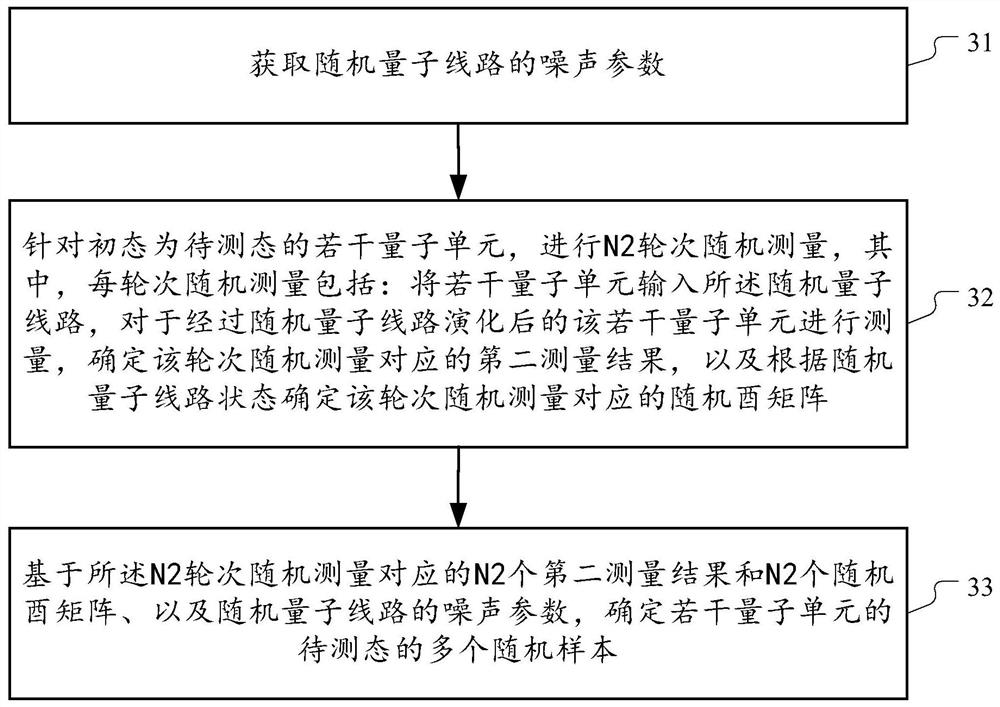
Quantum noise determination method and quantum state estimation method
The embodiment of the invention provides a method for determining quantum circuit noise and a quantum state estimation method, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out N1 rounds of random measurement for a plurality of quantum units whose initial states are ground states, wherein each round of random measurement comprises the steps: inputting the plurality of quantum units into a pre-established random quantum circuit, measuring the plurality of quantum units evolved by the random quantum circuit, determining a first measurement result corresponding to the round of random measurement, and determining a random unitary matrix corresponding to the round of random measurement according to the state of the random quantum circuit; and determining noise parameters of the random quantum circuit based on N1 first measurement results corresponding to N1 rounds of random measurement and N1 random unitary matrixes. And determining a plurality of random samples of the to-be-measured state of the plurality of quantum units based on the noise parameter and N2 second measurement results and N2 random unitary matrixes obtained by random measurement of N2 rounds on the plurality of quantum units of the to-be-measured state.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor based on quantum enhancement
PendingCN110260800AAchieve ultra-high sensitivity measurementAvoid stressUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyGratingSpectrum analyzer
The invention discloses a micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor based on quantum enhancement. The micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor comprises a laser, a 2*1 coupler, a filter, an erbium-doped fiber amplifier, a filter, a fiber polarization controller, a fiber polarization beam splitter, a dispersion displacement fiber, a coarse wavelength division multiplexer, a fiber isolator, a fiber Bragg grating, a micro-cantilever beam, a balance detector and a spectrum analyzer. According to the invention, quantum entangled double light beams generated after four-wave frequency mixing are used, the quantum entangled double light beams have high quantum correlation, the intensity difference quantum noise of each mode is reduced, the detection light and the reference light quantum correlation noise are subtracted to generate a noise substrate lower than the shot noise limit, so that signals annihilated under the quantum noise can be detected, and thus, ultra-high sensitivity measurement of micro-displacement breaking through the quantum noise limit is achieved. The micro-cantilever beam fiber grating micro-displacement sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, safety, reliability and the high practical value.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
Method and system for enhancing digital images
A system and method for enhancing digital images is described. A digital image is transformed into a series of decomposed images in frequency bands, or different resolution grids. A decomposed image is noise suppressed and contrast enhanced. Representative value of signal at each pixel is computed based on contributions to signals from pixels in a neighborhood of the pixel. Lookup tables are applied to pixel values to selectively enhance signal in a predetermined range of signal strength. Another set of lookup tables are applied to pixel values to suppress noise components contained therein. Optionally, operations are applied to decomposed images to suppress quantum noise, enhance object edges or enhance global contrast, among others. These decomposed images, after signal enhancement and noise suppression, are then recombined to result in an enhanced image.
Owner:MERATIVE US LP
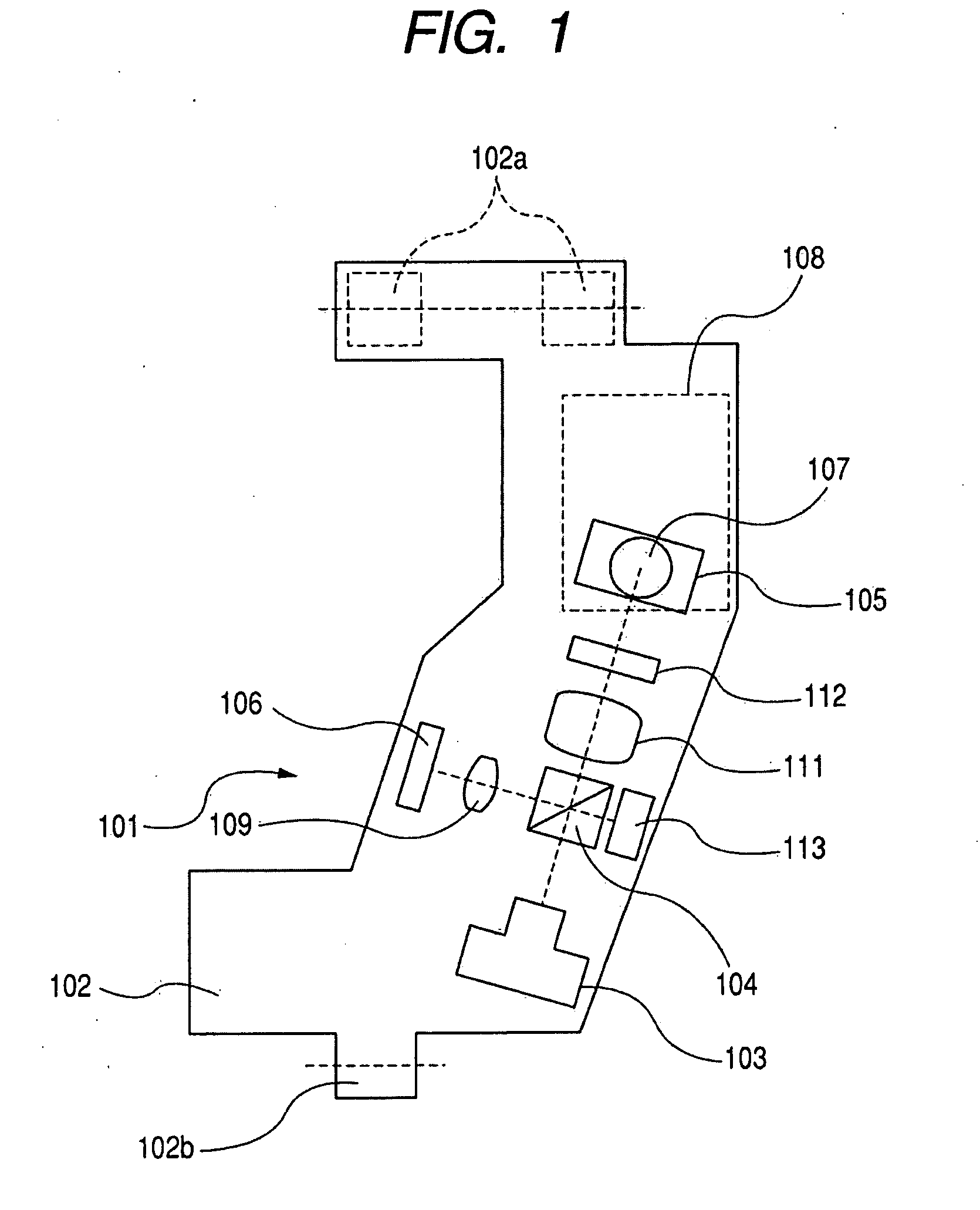
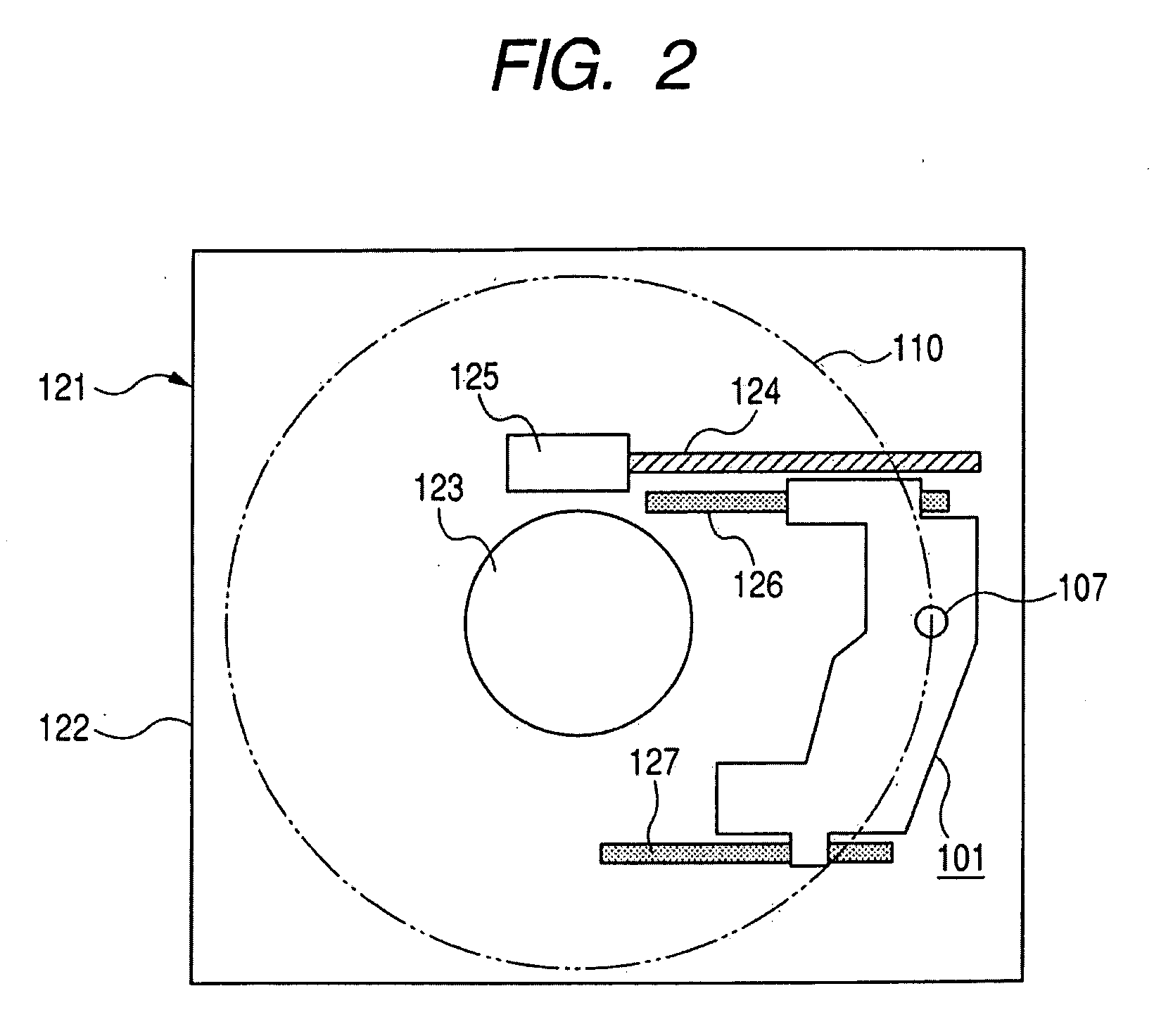
Optical disk apparatus and optical pickup
InactiveUS20090175152A1Improve cooling effectIncreasing size and thicknessOptical beam sourcesRecord information storageOptical pickupSignal quality
Provided is an optical disk apparatus that suppresses shortening of the life time of a light source, degradation of the signal quality involved in an increase in quantum noise, and lowering of the slope efficiency, which are caused by a temperature increase of the light source by a lowering in the heat radiation performance of the light source due to size reduction or thickness reduction of the apparatus. As a specific structure, the optical disk apparatus includes an optical pickup including: a light source; a light source drive circuit; an optical base housing an optical system for guiding light emitted from the light source to a disk-shaped recording medium; a first heat radiation member connected to the light source; and a second heat radiation member connected to the light source drive circuit.
Owner:CANON KK
Quantum error correction coding method applicable to high-voltage overhead power lines
ActiveCN103067093AReduce complexityEase difficultyError preventionPower distribution line transmissionElectric power systemQuantum noise
The invention discloses a quantum error correction coding method applicable to high-voltage overhead power lines. Quantum equipment is respectively arranged in converting stations at two ends of an electric power overhead line, one end of the electric power overhead line is a sending end, the other end of the electric power overhead line is a receiving end, and the sending end and the receiving end adopt a [5, 1] stable disc quantum error correction coding technology. The quantum error correction coding method applicable to the high-voltage overhead power lines carries out system analysis in an electric system for the first time, chooses the quantum error correction of coding technology which is applicable to the environment of electric power aerial optical cables, solves the problems of signal error detecting and recovery in quantum noise caused by an electric power hyperbaric environment, and explores a scheme applicable to long-distance quantum signal encoding and decoding among the converting stations. The quantum error correction of coding method applicable to the high-voltage overhead power lines has the advantages of providing convenience for applying a quantum communication technology to the electric system.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com