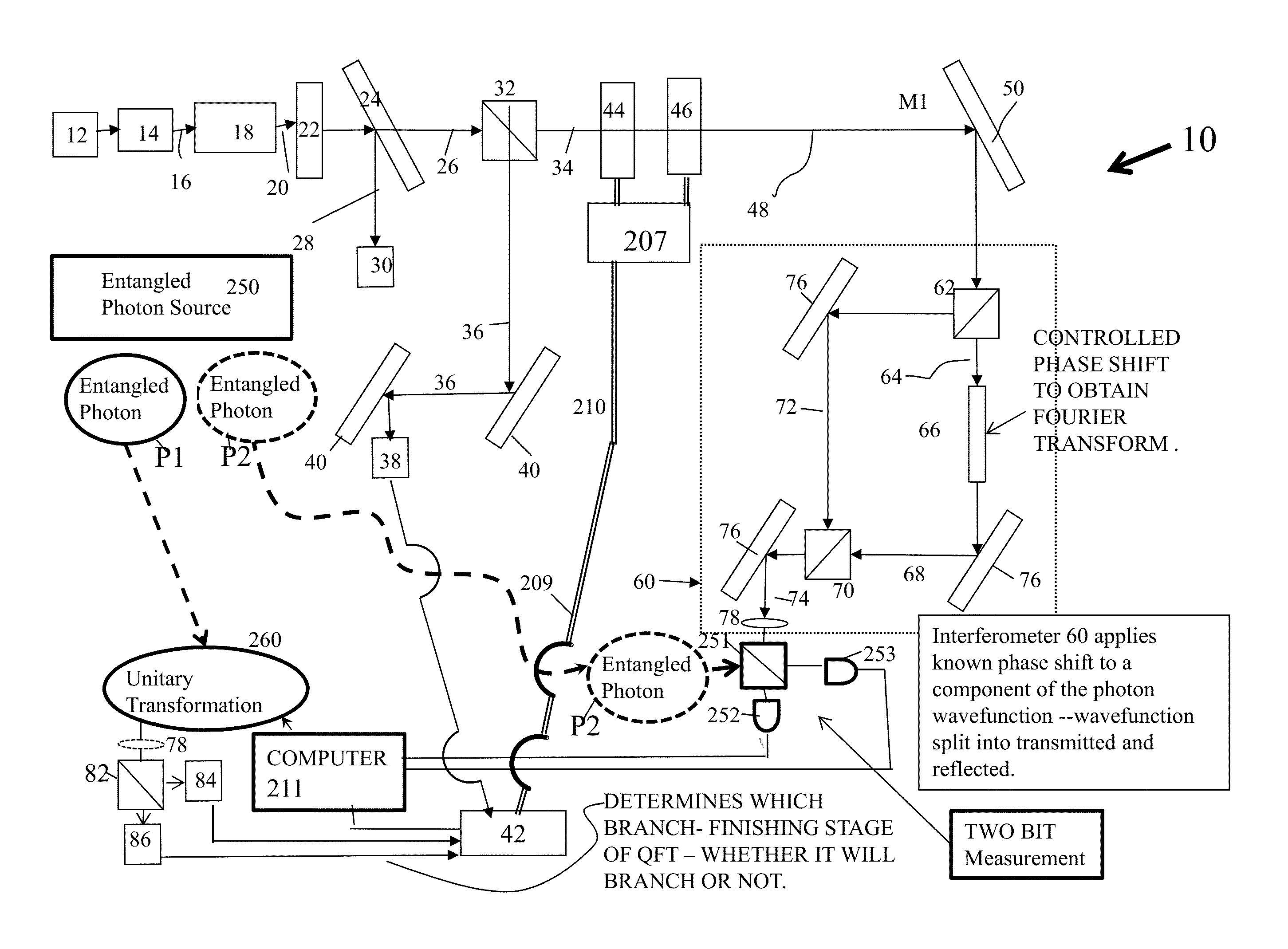
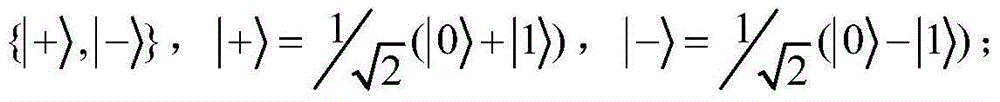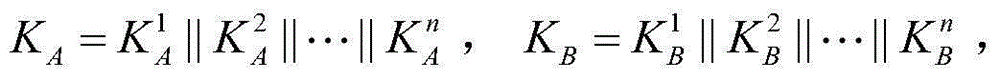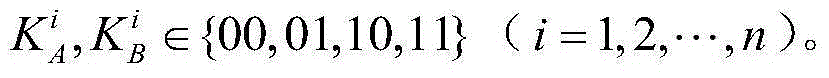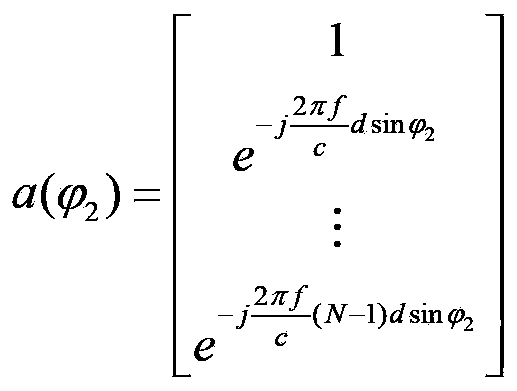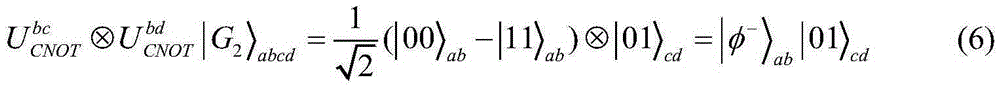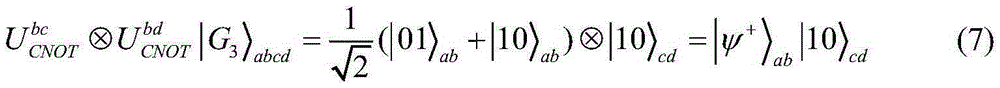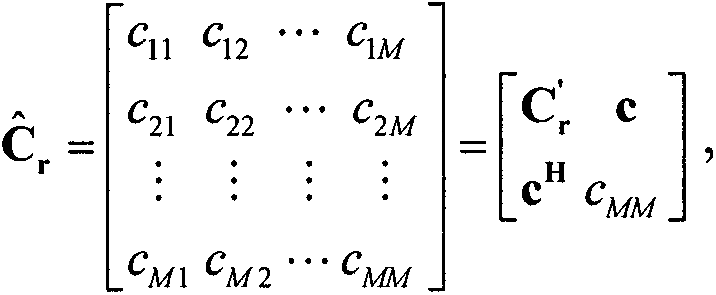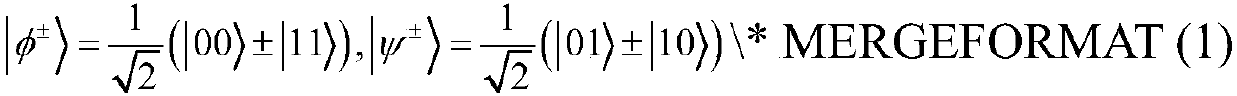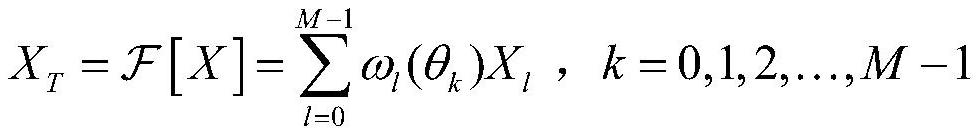Patents
Literature
132 results about "Unitary transformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
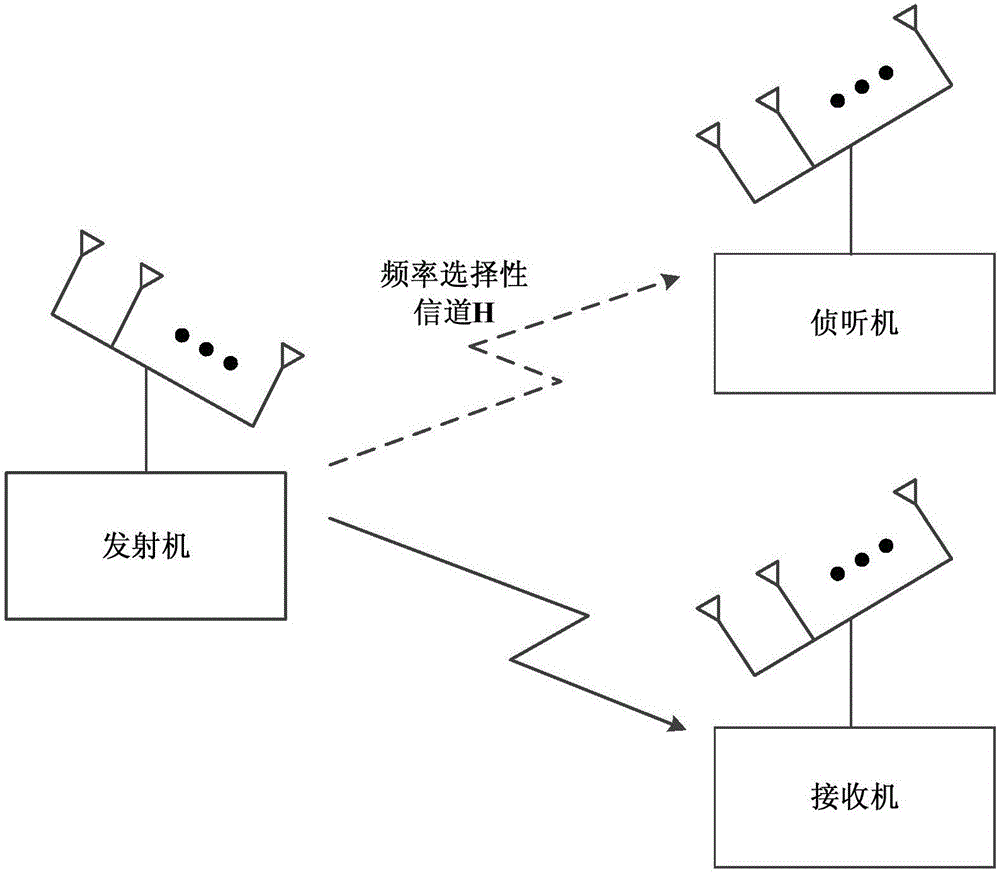
In mathematics, a unitary transformation is a transformation that preserves the inner product: the inner product of two vectors before the transformation is equal to their inner product after the transformation.
Quantum computing method and quantum computer
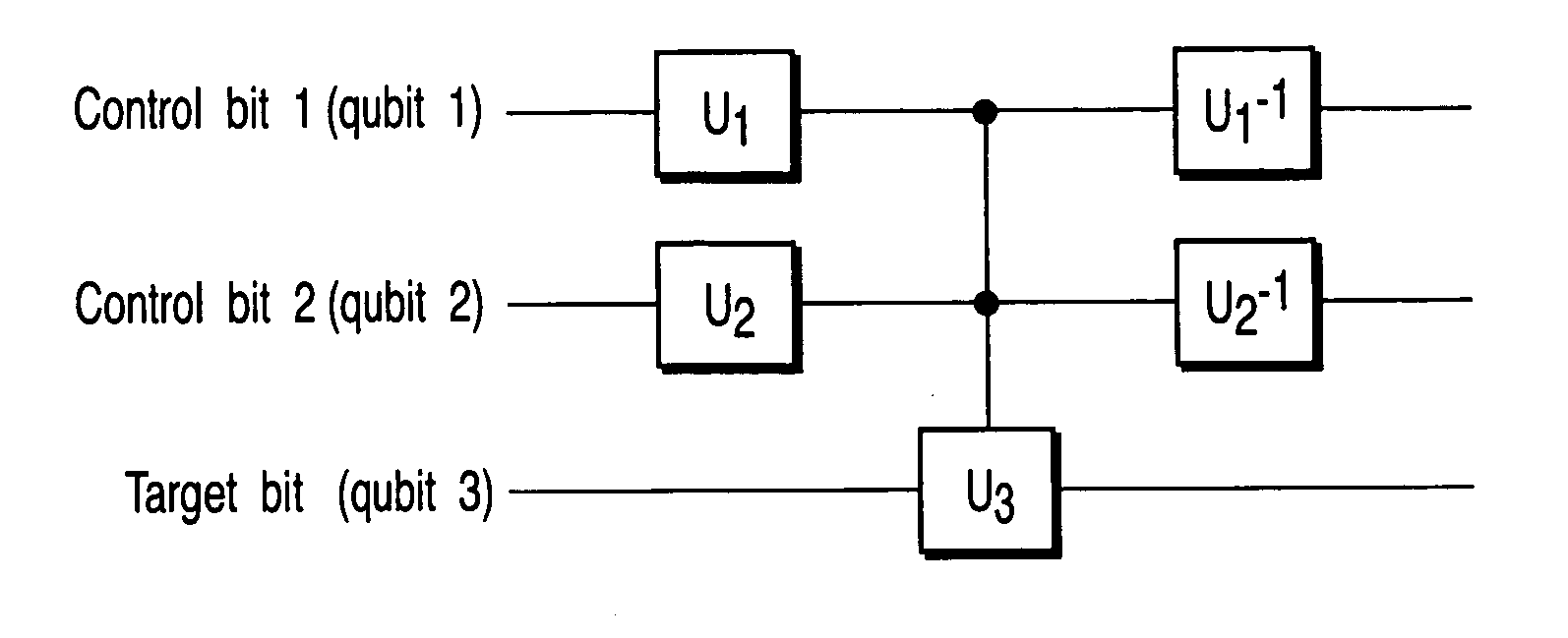
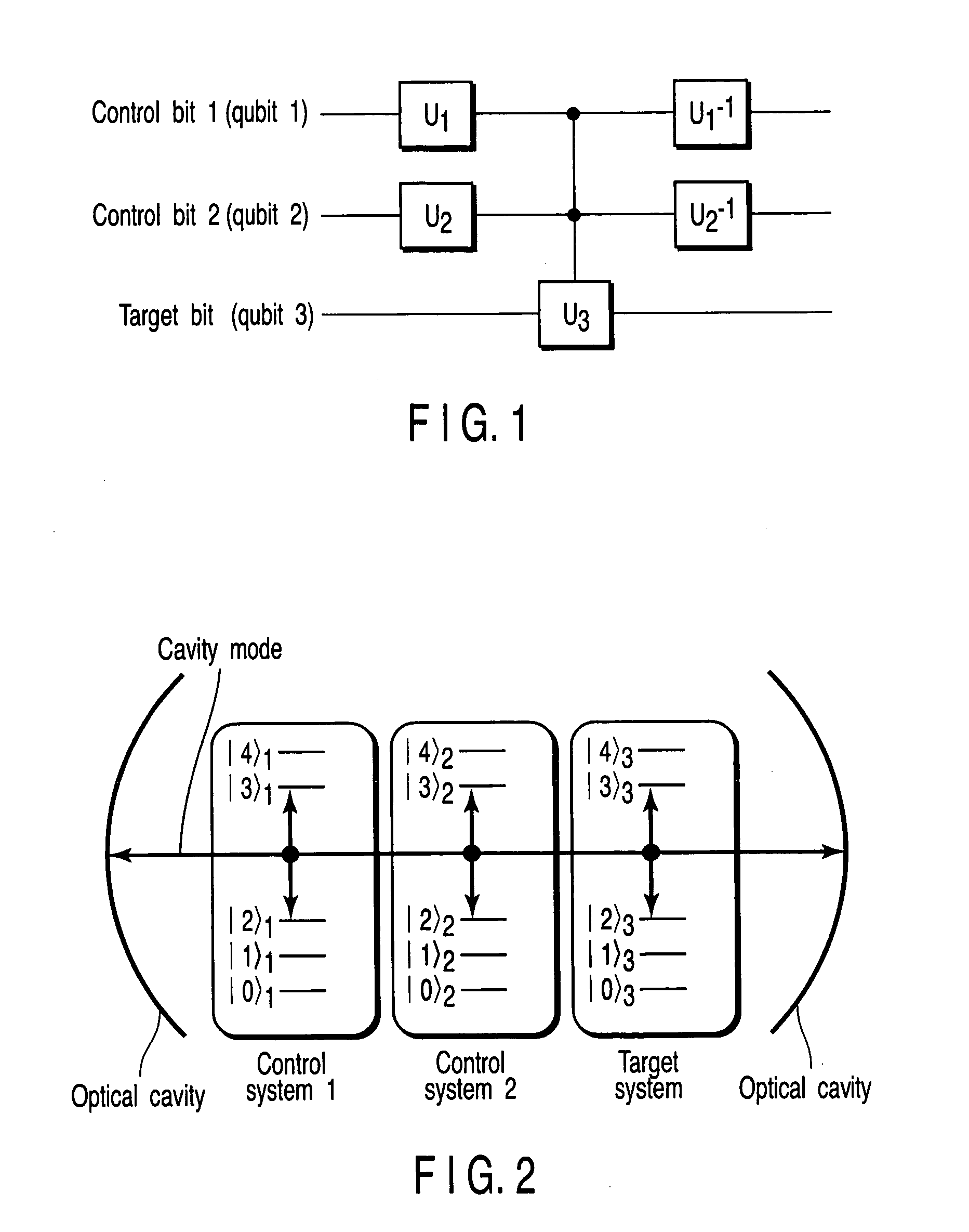
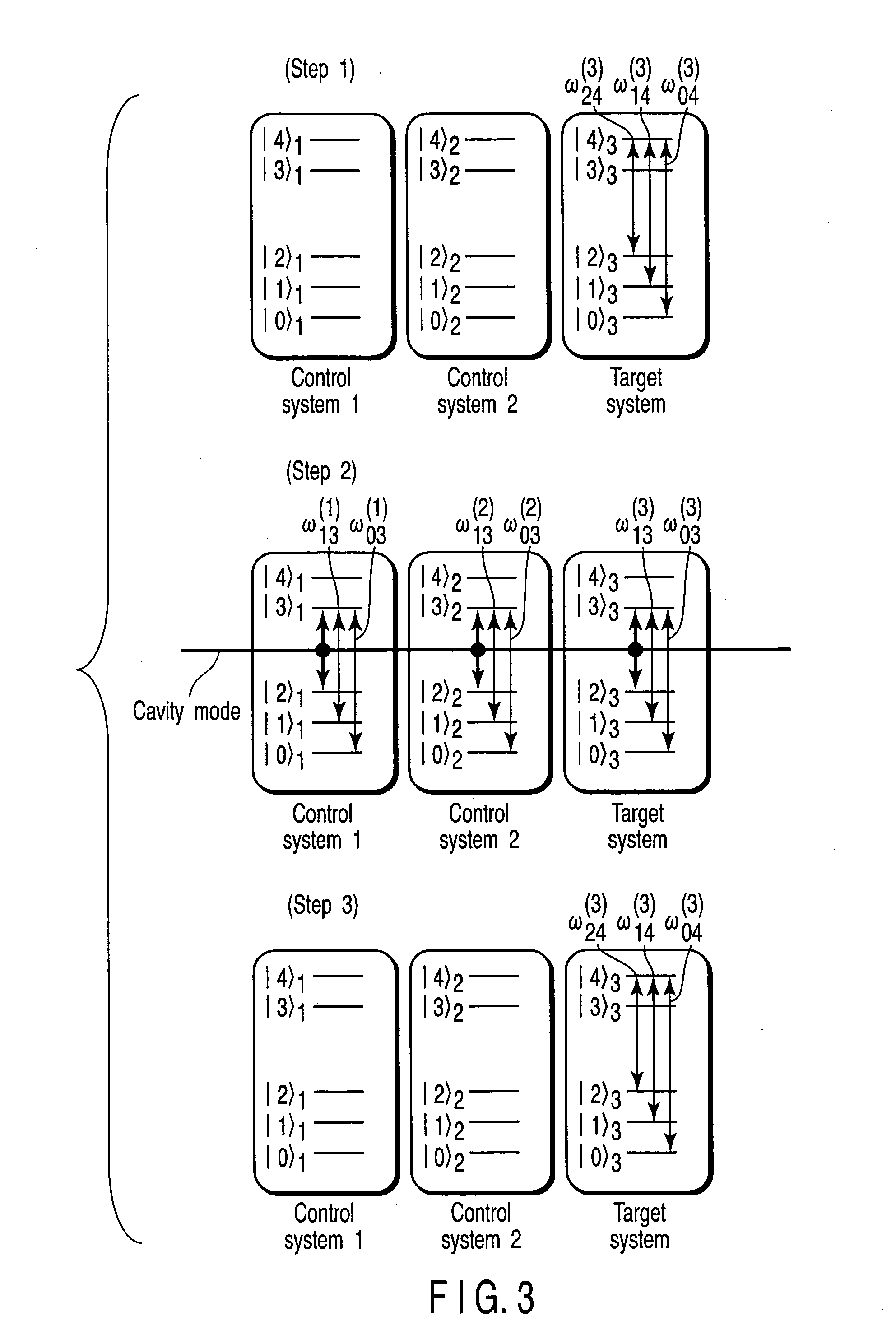
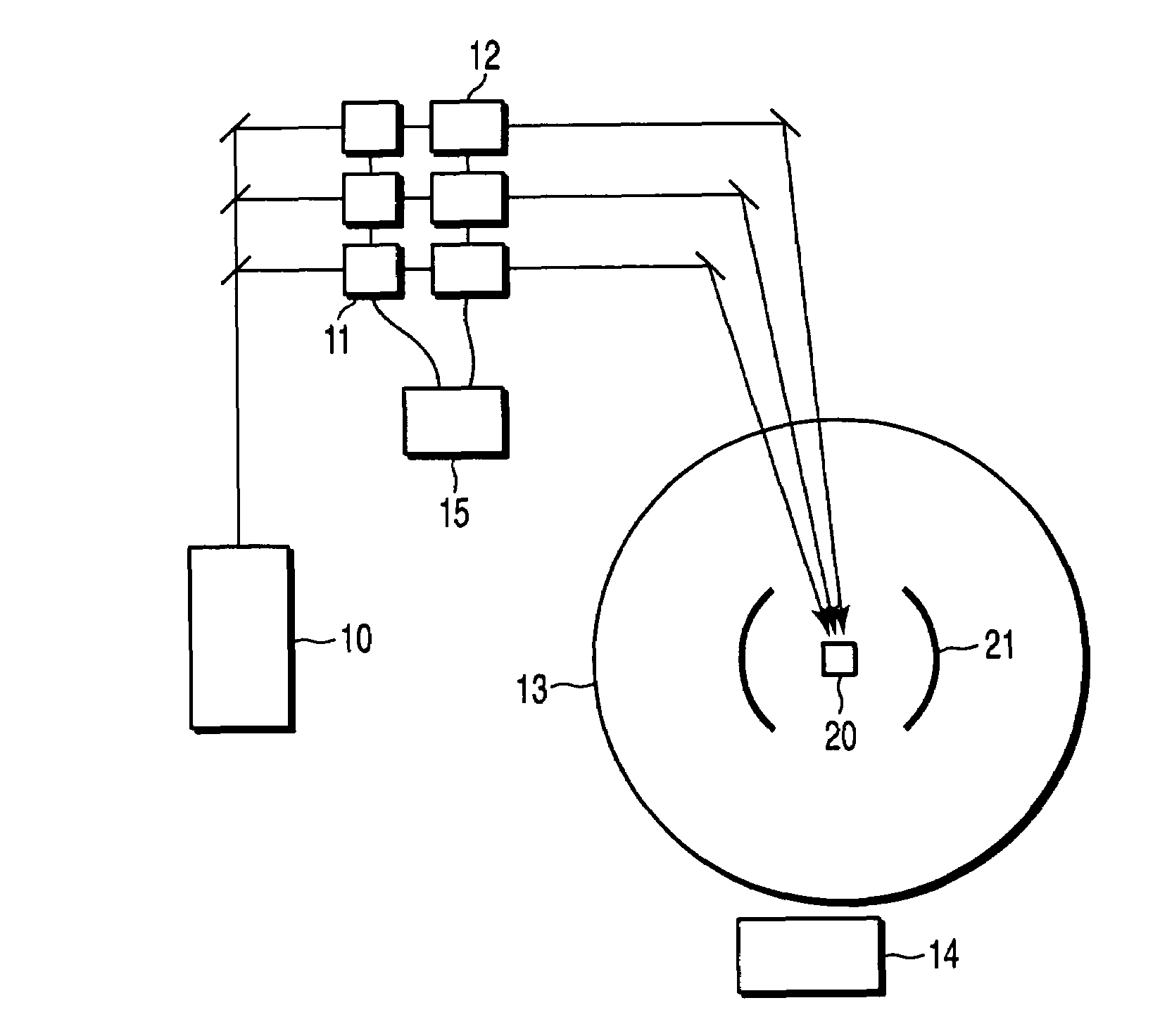
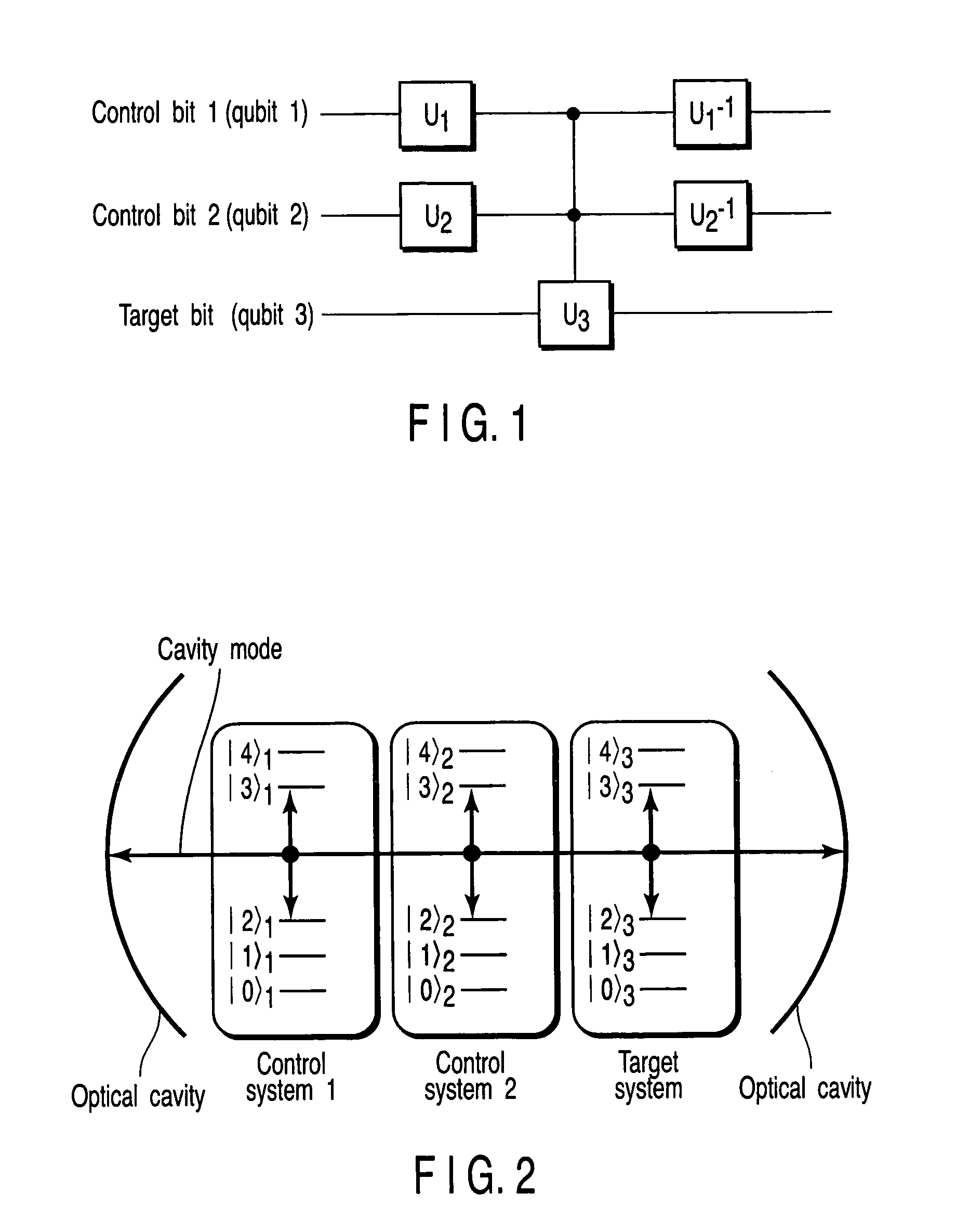
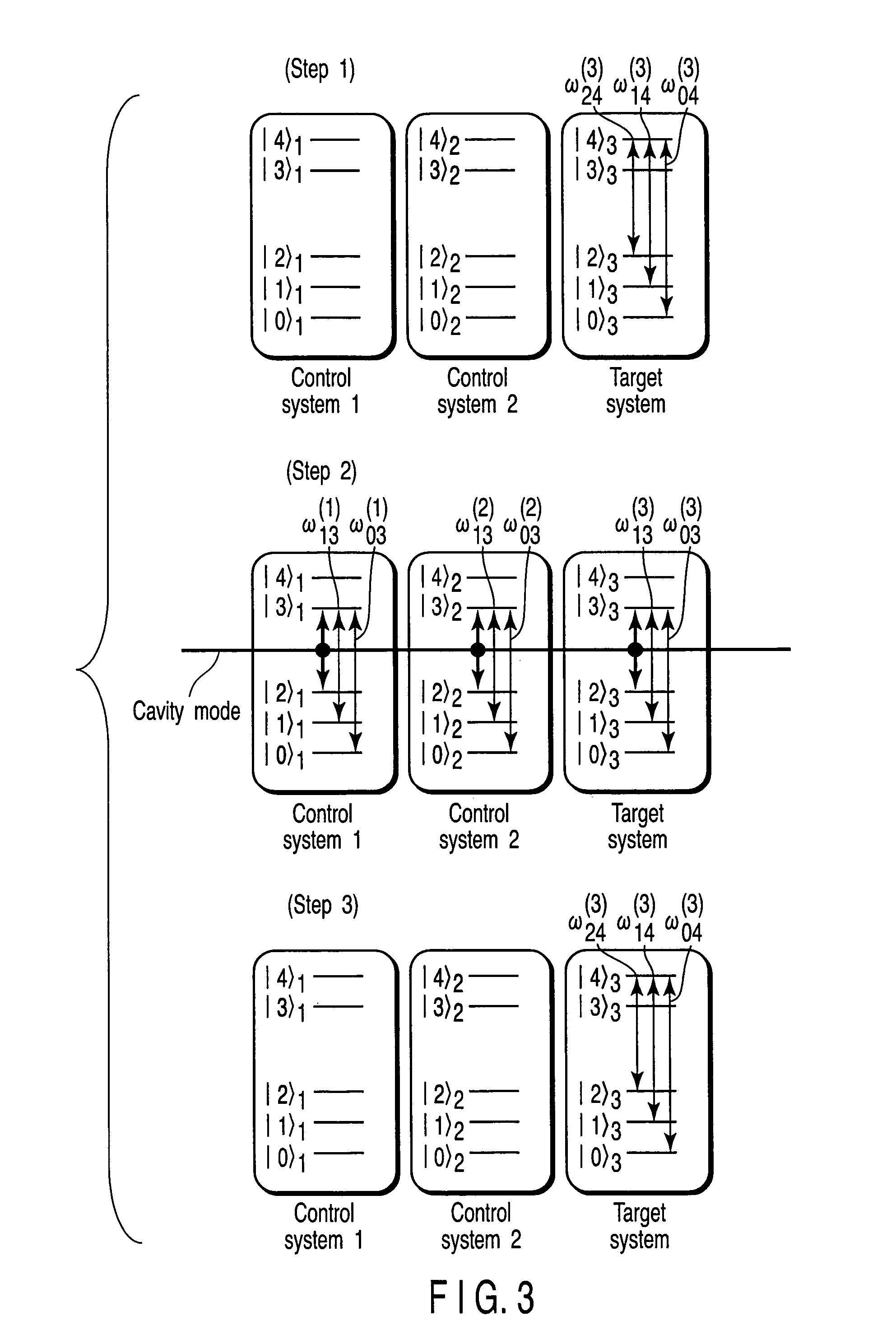
An (N+1) number of physical systems each having five energy levels |0>, |1>, |2>, |3>, and |4>, a qubit being expressed by |0> and |1>, are provided in an optical cavity having a cavity mode resonant with |2>-|3>, such that an N number of control systems and a target system are prepared. The target system is irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|4>, |1>-|4>, and |2>-|4> to change a superposed state |c> to |2>. All of the physical systems are irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|3> and |1>-|3>, and a phase of the light pulse resonant with the target system is shifted by a specific value dependent on a unitary transformation U. The target system is irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|4>, |1>-|4>, and |2>-|4>, with a phase difference between them being set to a specific value dependent on the unitary transformation U, to return |2> to |c>.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
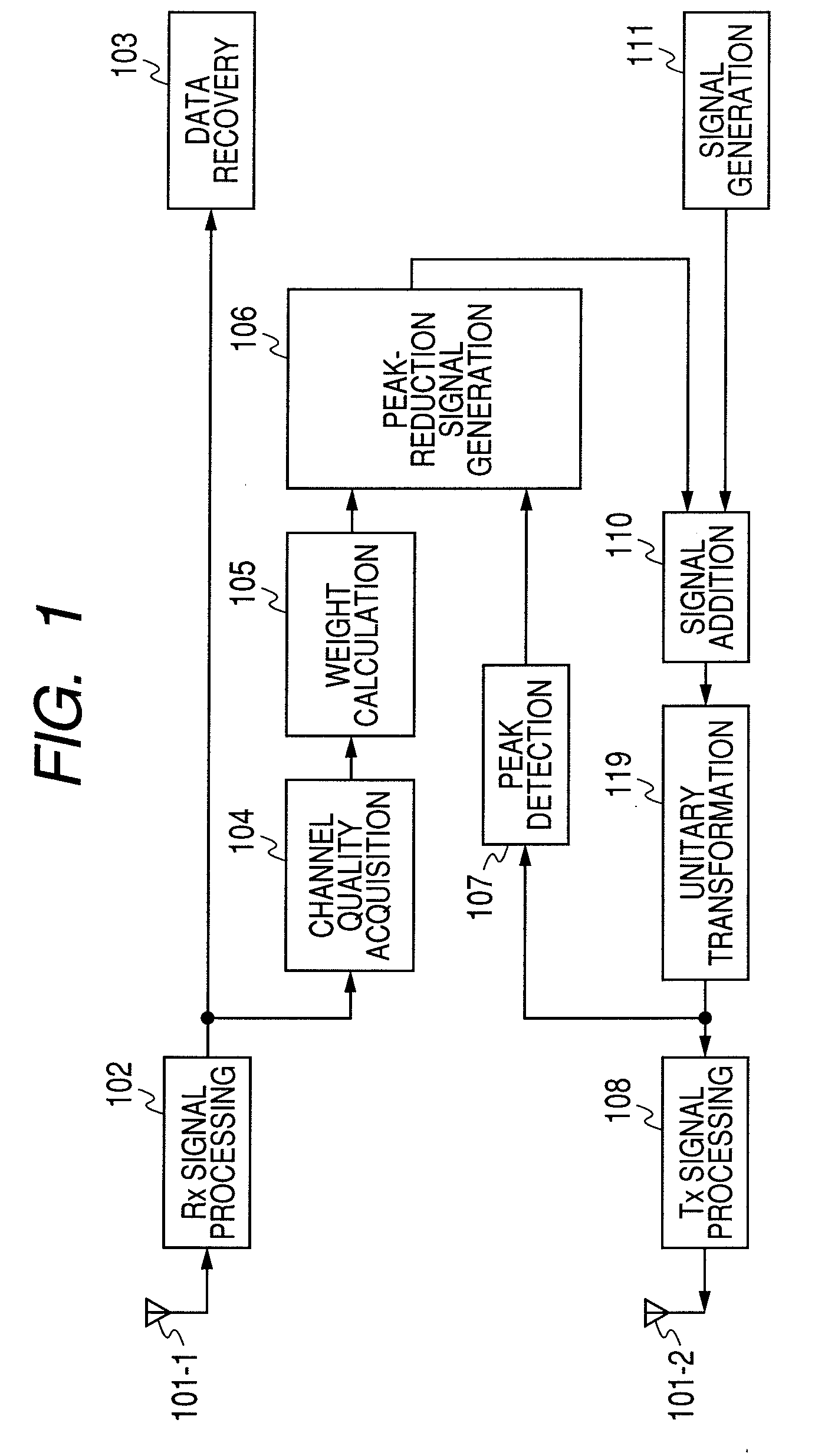
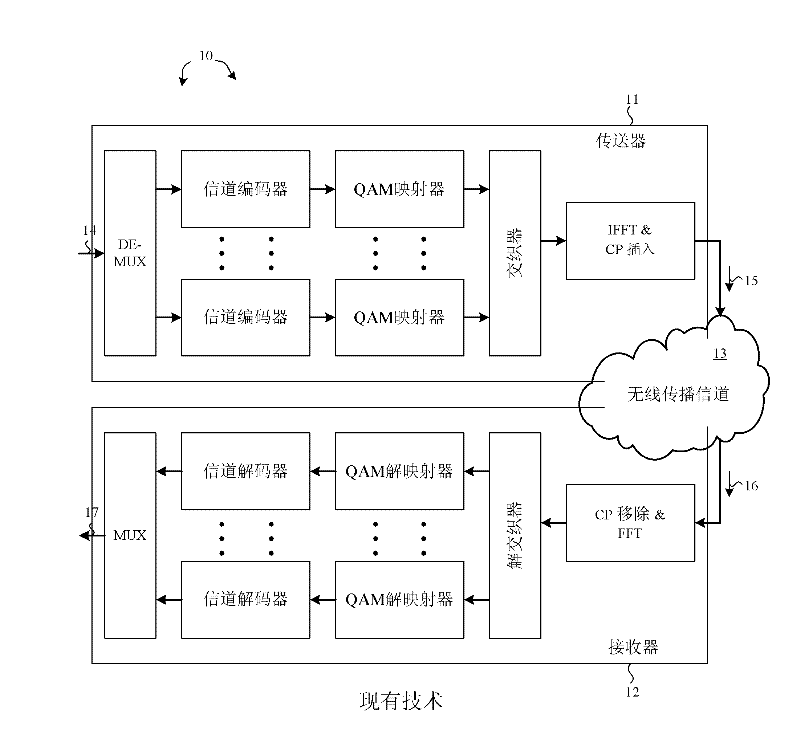
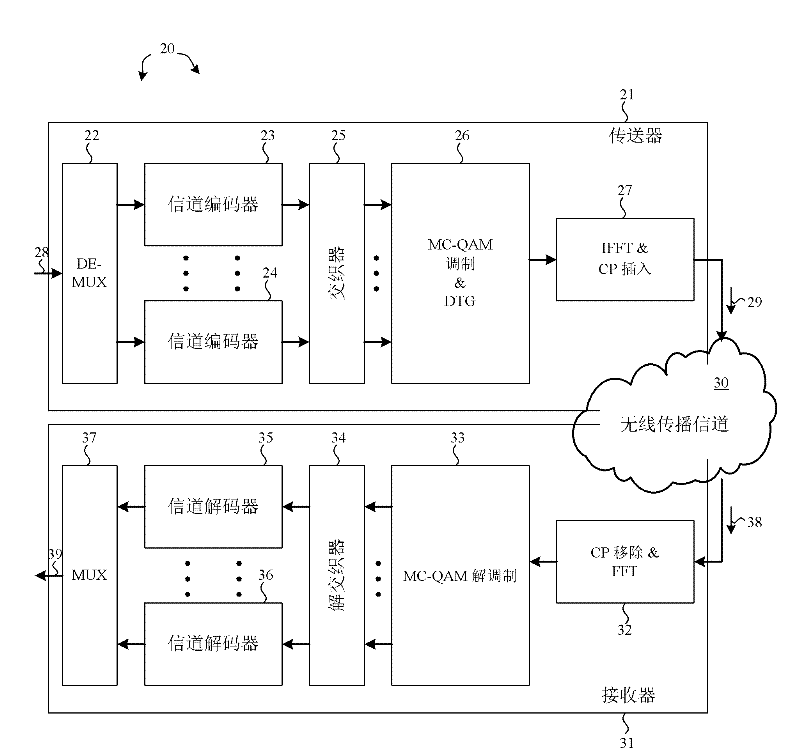
Apparatus and Method for Peak Suppression in Wireless Communication Systems
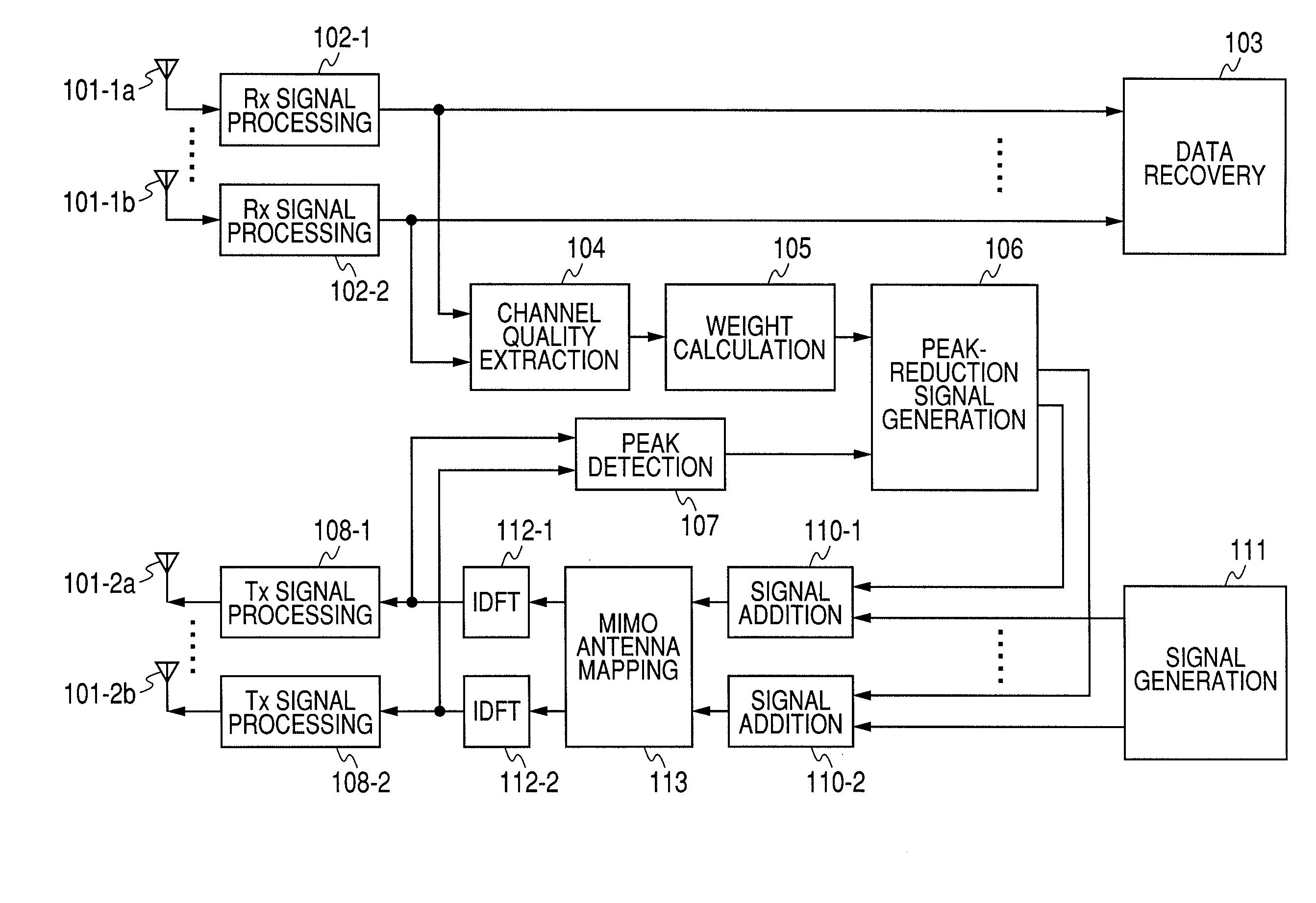
InactiveUS20090060070A1Suppressing peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR)Prevent degradationCriteria allocationSecret communicationCommunications systemPeak value
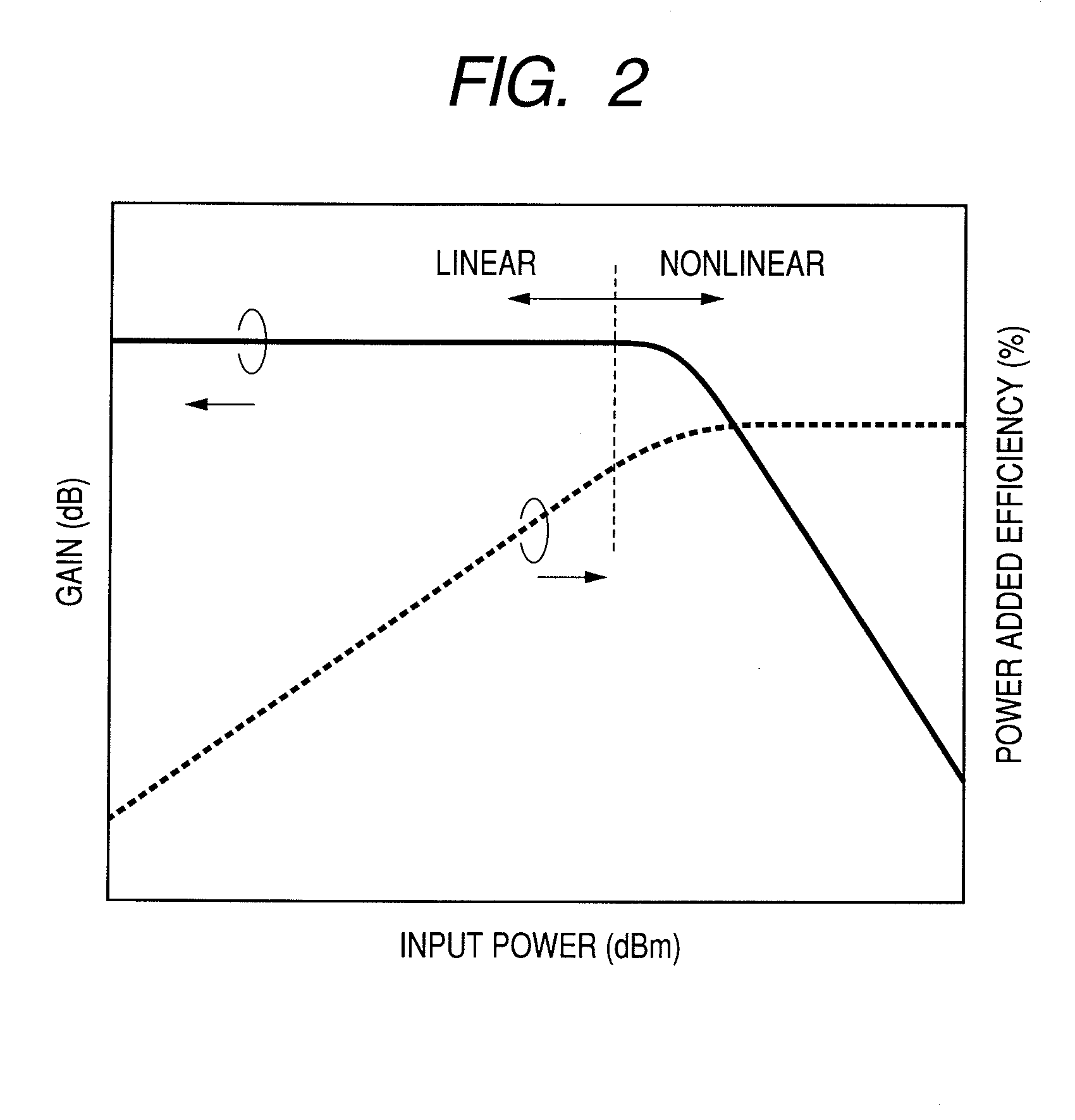
A method for suppressing the peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) while limiting deterioration in signal characteristics in wireless communication devices utilizing wireless communication methods (OFDM method, MIMO method) for multiplexing and sending multiple signals. A weight calculator unit sets a large weight for transmit signals whose channel quality is poor, relative to the weight of each base component based on the acquired channel quality. A peak detector unit detects the peak from the signal string after unitary conversion, and extracts a distortion component to apply for suppressing the peak. A peak suppression signal generation unit calculates the peak signal from the distortion component and weight of each base component, to add to each base component, and adds the peak suppression signal to each base component prior to unitary transformation.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
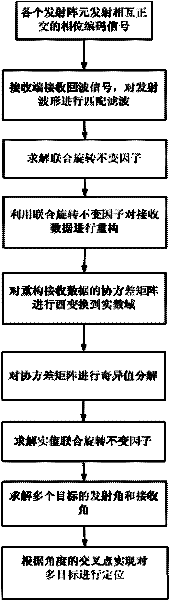
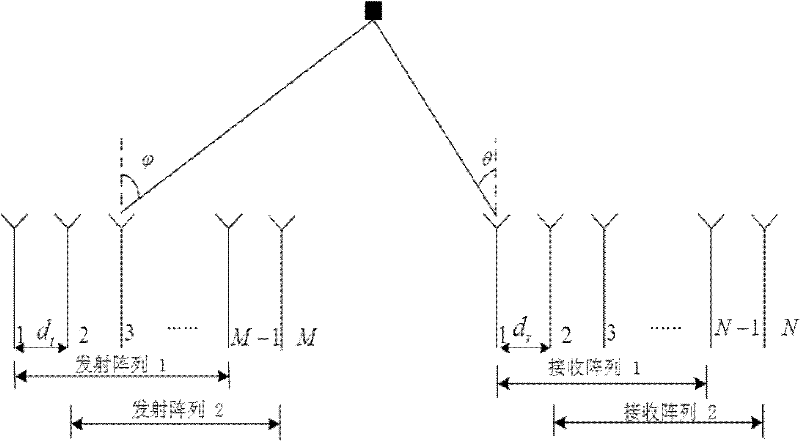
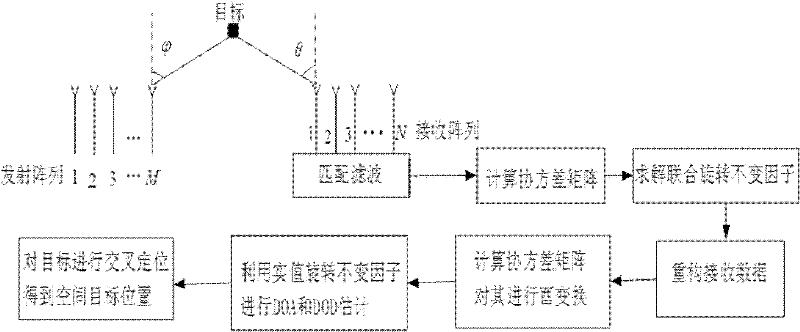
Multi-target location method of bistatic common-address multi-input-multi-output radar
InactiveCN102213761AHigh precisionAvoid simultaneous application to the transmitterRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSingular value decompositionDomain name
The invention provides a multi-target location method of a bistatic common-address multi-input-multi-output radar. The method comprises the following steps of: transmitting mutual orthogonal phase coded signals by M transmitting array elements; receiving the phase coded signals by N receiving array elements; performing matching filtering on the received phase coded signals by a matching filter ofeach receiver which is used for receiving the array elements; reconfiguring covariance matrix of signal data subjected to matching filtering; performing unitary transformation on the reconfigured covariance matrix to obtain the covariance matrix of a real number field; performing singular value decomposition on the covariance matrix of the real number field; estimating emission angles and acceptance angles of a plurality of objects by utilizing actual value combination spinning invariant factor; and realizing multi-target location according to a cross point of the two angles to obtain the position of a space object. According to the method, the combination spinning invariant factor is adopted to reconfigure the receiving data so as to improve the estimation performance of an object; and the covariance matrix of the real number field is obtained through unitary transformation, and characteristic decomposition is performed on the covariance matrix of the real number field so as to be favorable for real-time processing and realization on hardware.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
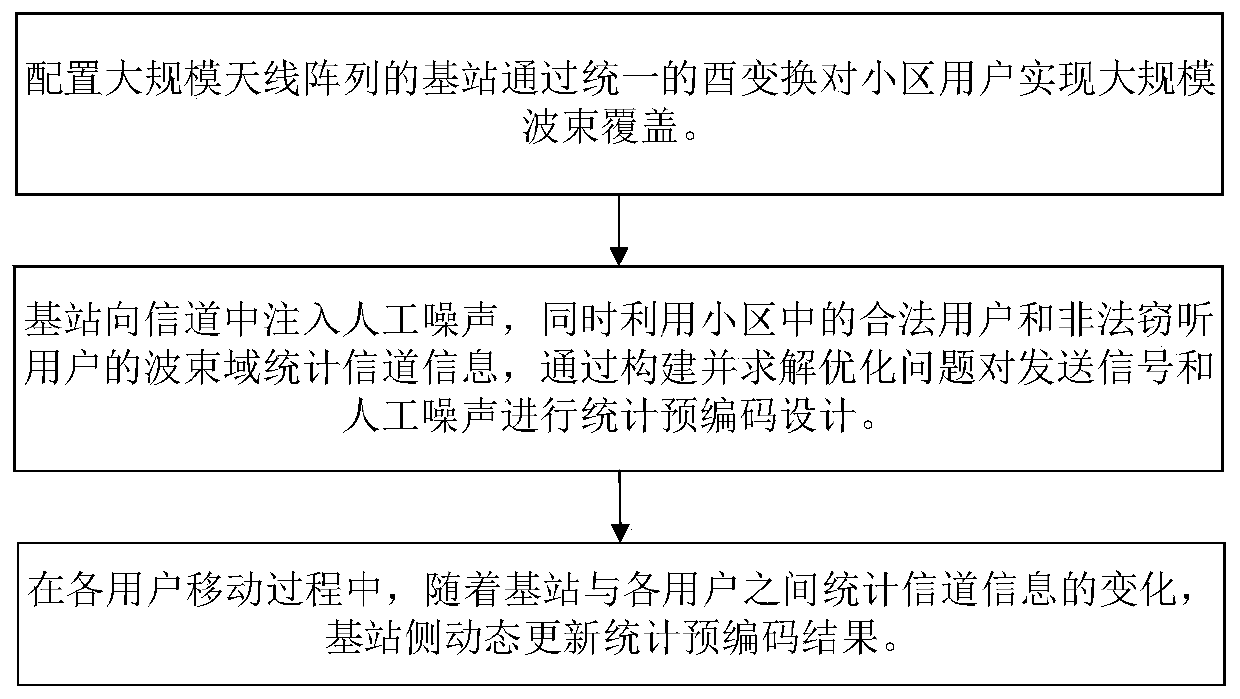
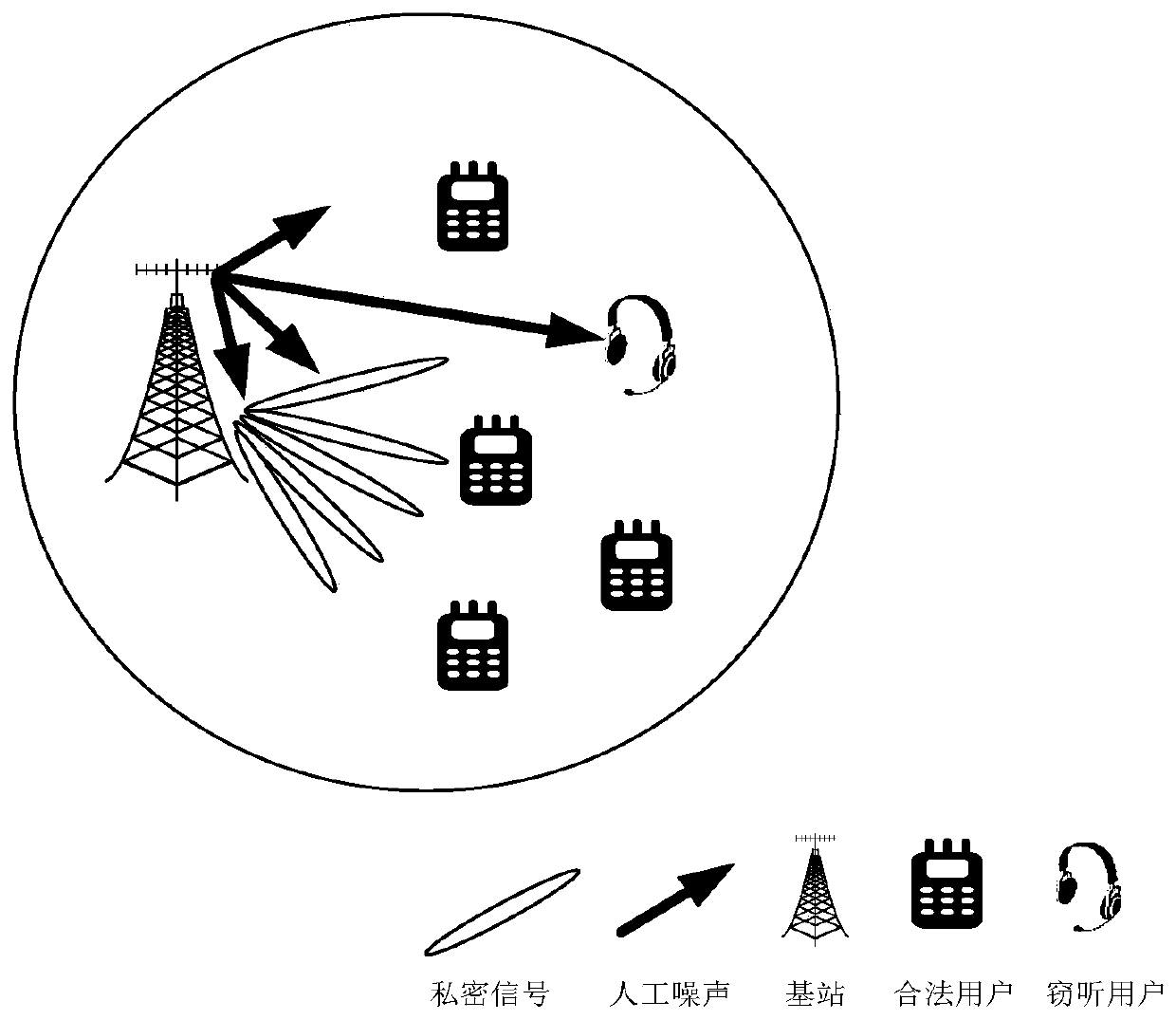
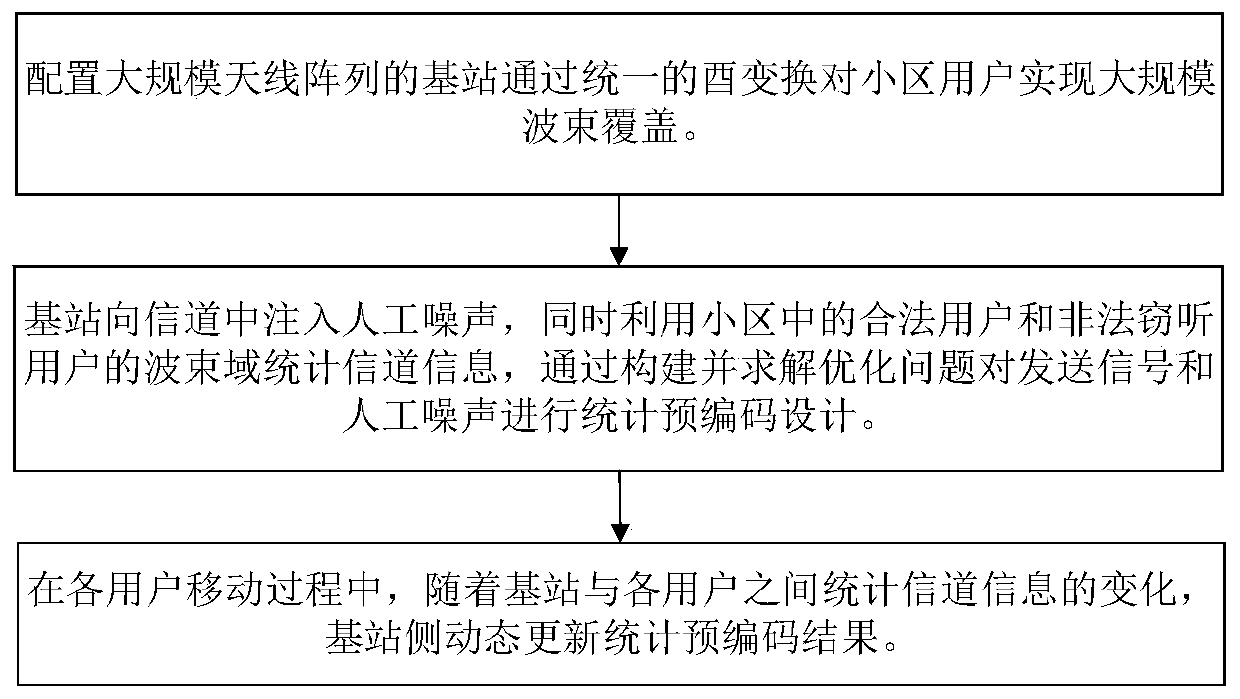
Artificial noise assisted large-scale MIMO security statistical precoding method
ActiveCN109981153AImprove efficiencyImprove spectral efficiencyRadio transmissionSecure transmissionEngineering
The invention provides an artificial noise assisted large-scale MIMO security statistical precoding method. In the method, a cell base station is configured with a large-scale antenna array, and large-scale beam coverage is realized on the whole cell by utilizing a unified unitary transformation matrix. The base station uses beam domains of legal users and eavesdropping users in a cell to count channel information and injects artificial noise into the channel to reduce the decoding capability of the eavesdropping users, and performs statistical precoding design on the signals sent to each legal user and the artificial noise sent to the eavesdropping users according to the criterion of maximizing the system reachable traversal security and rate lower bound. In the moving process of each legal user and each eavesdropping user, the base station intermittently acquires statistical channel information and dynamically updates a statistical precoding result. According to the invention, the problem that the base station side only knows the design of the beam domain secure transmission signal of the statistical channel information is solved, the realization complexity is reduced, and meanwhile, the introduction of artificial noise improves the security of system transmission.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state
ActiveCN105227301AHigh qubit efficiencyResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobComputer hardware
The invention discloses a quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state, comprising the following steps that: step 1, Alice and Bob randomly generate respective classical keys; step 2, Alice prepares the GHZ state and divides all particles into sequences, inserts decoy photons into one of the sequences and then transmits the sequence to Bob; step 3, Bob measures the decoy photons, Alice calculates an error rate, if the error rate is low, a step 4 is executed, otherwise, the step 2 is executed again; step 4, Alice and Bob respectively perform measurement and obtain the measurement result of each other; step 5, Alice executes unitary transformation and obtains a new sequence, and Alice transits the sequence with the inserted decoy photons to Bob; step 6, Bob measures the decoy photons, and Alice calculates the error rate, if the error rate is low, a step 7 is executed, and otherwise, the step 2 is executed again; step 7, Alice calculates a shared key of both sides; step 8, Bob generates the shared key. The quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state can resist participant attack, outside attack and Trojan horse attack. The quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state is safe in both a noiseless quantum channel and a quantum noisy channel. Moreover, quantum bit efficiency of the quantum key agreement protocol based on GHZ state is higher than the existing protocols.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Controlled quantum security direct communication method based on four particle cluster states
ActiveCN107222307AMaintain entanglementLong cycleKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationAlice and BobQuantum secure direct communication
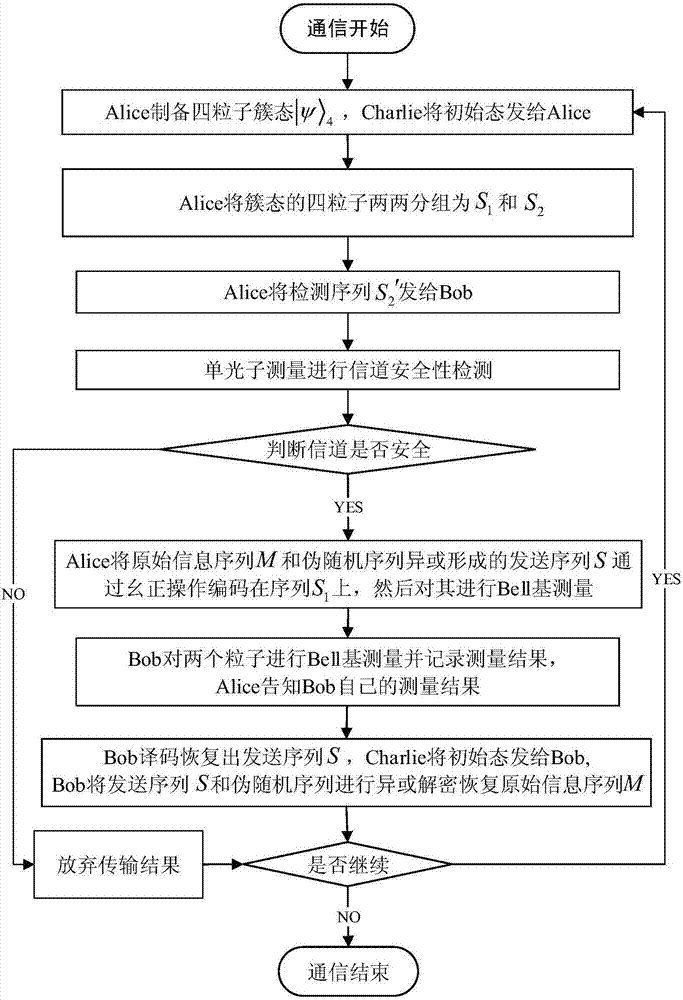
The invention discloses a controlled quantum security direct communication method based on four particle cluster states. Alice and Bob respectively serve as a legal information sender and a legal information receiver during a quantum communication process, and Charlie serves as a credible scheme control party; information security is achieved by randomly inserting a single photon to perform measurement-based comparison detection, and communication starts after security detection; Alice uniformly divides the prepared four particle cluster states into two groups, after being subjected to an XOR operation with a pseudorandom sequence, the sent information is encoded on the two particles reserved by Alice via unitary transformation. Alice performs Bell-based measurement on reserved particles, and sends measurement information to Bob, and Bob recovers the original sequence via an initial state sent by Charlie after the measurement information is compared. The four particle cluster states used by the method has good entanglement, connectivity and damage resistance, only the receiver Bob in the method gets the permission of the controller Charlie, Bob can recover the original information, so that the information can be effectively prevented from being attacked during a transmission process, and an implementation process is simple.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Target low elevation estimation method based on real number field generalized multiple-signal sorting algorithm
InactiveCN103364772AReduce operational complexityHeavy computationWave based measurement systemsHat matrixSorting algorithm
The invention discloses a target low elevation estimation method based on a real number field generalized multiple-signal sorting algorithm. The target low elevation estimation method includes the implementation steps of (1) sampling radar received back waves, (2) using sample data to calculate a sampling covariance matrix, (3) carrying out spatial smoothing and unitary transformation on the sampling covariance matrix to obtain a real number field covariance matrix (4) carrying out eigenvalue decomposition on the real number field covariance matrix to obtain a noise projection matrix, (5) constructing a real number field guiding vector manifold, (6) using the noise projection matrix and the real number field guiding vector manifold to constructing a spatial spectrum, conducting two-dimensional angle searching on the spatial spectrum and obtaining an initial angle estimated value, (7) using the initial angle estimated value to estimate a multi-path attenuation coefficient, constructing a secondary spatial spectrum and obtaining an angle estimated value through the two-dimensional angle searching, and (8) comparing the two angles in the estimated values, and considering the maximum angle as the target elevation value. According to the target low elevation estimation method, the algorithm complexity is reduced, and the angle estimation performance of a radar under the low signal-to-noise ratio is improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Mutual coupling condition-oriented bistatic MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) radar angle estimation method
ActiveCN107290730ARespond effectivelyReduce mutual coupling effectsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsComplex mathematical operationsComputation complexityArray element
The present invention discloses a mutual coupling condition-oriented bistatic MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) radar angle estimation method. According to the method, radar data which have been subjected to matched filtering are expressed as a third-order tensor model by means of the multi-dimensional structure of array signals; since a uniform linear array mutual coupling matrix has a strip-shaped Toeplitz feature, the common scale conversion feature of a part of an array element directional matrix is utilized to eliminate the influence of mutual coupling; on the basis of a forward-backward smoothing technique and a unitary transformation technique, the augmented output trilinear model of decoupling-post data is constructed; and joint DOD (direction-of-departure) and DOA (direction-of-arrival) estimation is related with the trilinear model; and a target DOD and DOA are estimated through the least squares method. Compared with a traditional algorithm, the bistatic MIMO (multiple-input multiple-output) radar angle estimation method under the mutual coupling condition can effectively deal with situations where mutual coupling exists between a transmitting array and a receiving array, can automatically match the estimated DOD and DOA, and can reduce computational complexity by using a feature that trilinear decomposition only involves real number operation.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Method and system for performing quantum bit commitment protocol
InactiveUS20100150349A1Secret communicationSecuring communicationComputer hardwareUnitary transformation
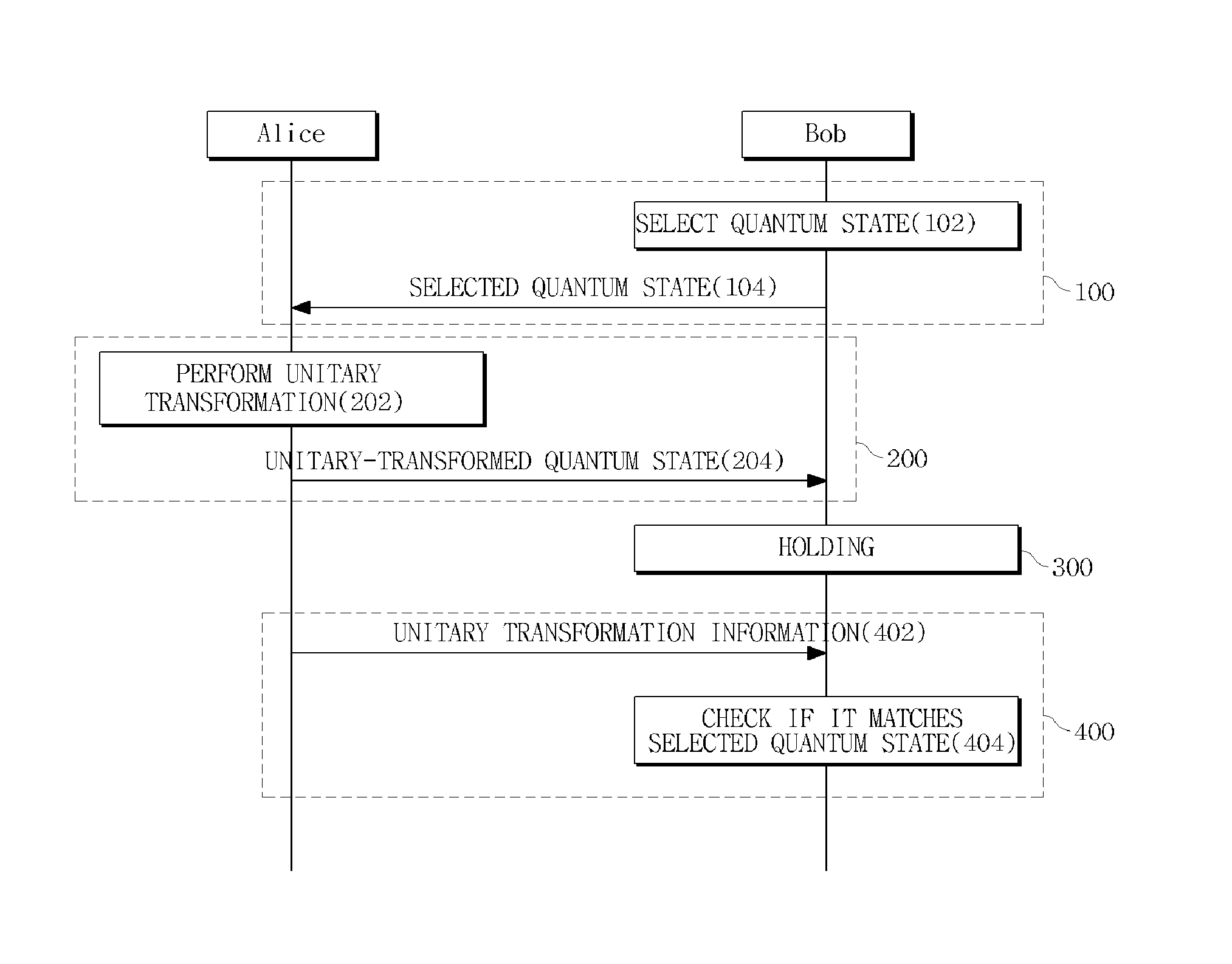
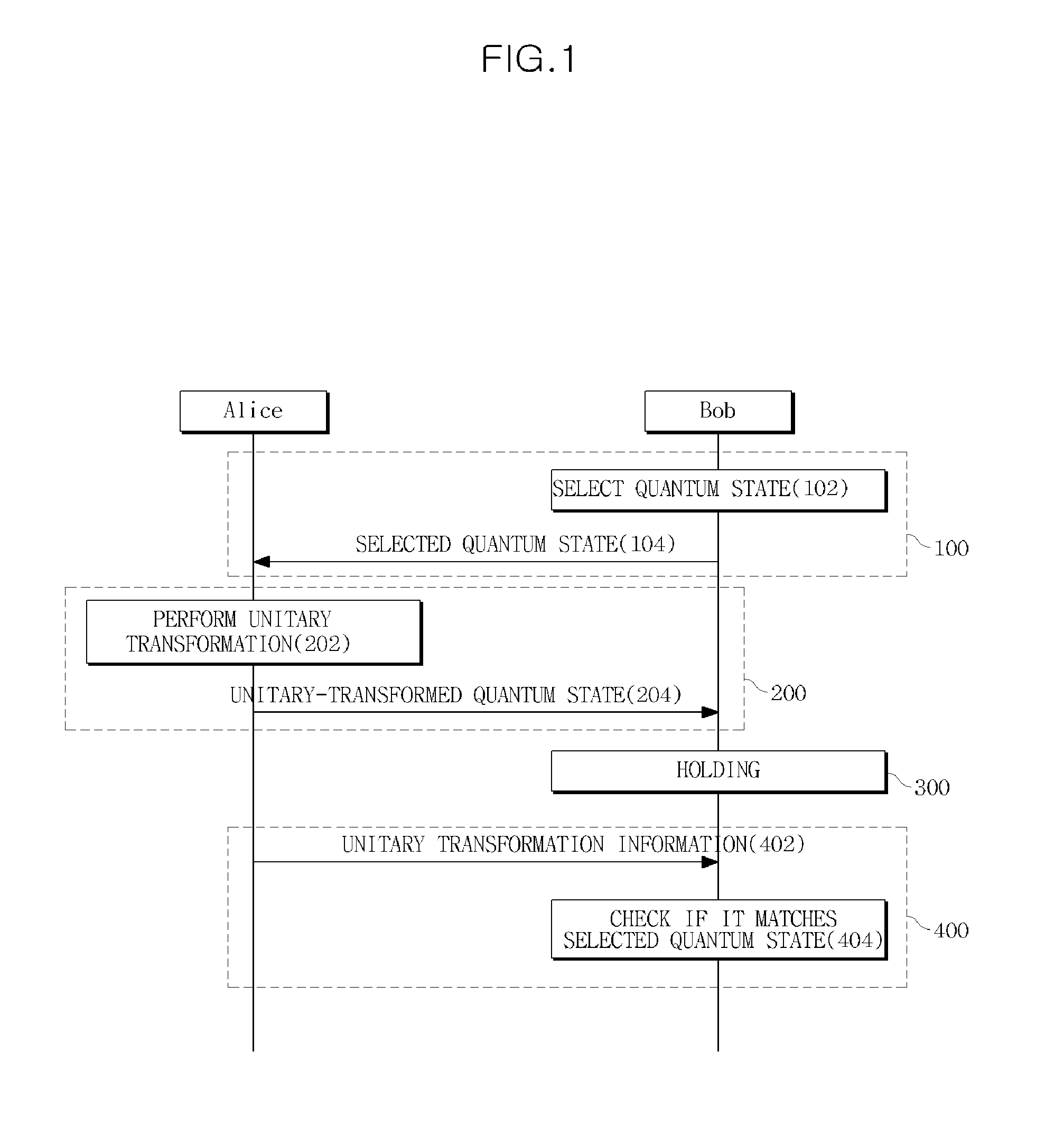
A method and system for performing a quantum bit commitment protocol is provided. The method of performing a quantum bit commitment protocol to send bit information from a first party to a second party includes a pre-commit phase to randomly select and send, by the second party, a quantum state to the first party; a commit phase to perform, by the first party, a unitary transformation on the quantum state to combine the bit information with the quantum state and send the unitary-transformed quantum state to the second party; a hold phase to hold the unitary-transformed quantum state for a predetermined time period; and a reveal phase to provide, by the first party, information about the unitary transformation to the second party to open the bit information to the second party. The reveal phase may include a verification process to check if the opened bit information matches the bit information committed in the commit phase. For example, the verification process may be performed by checking if a quantum state obtained by performing an inverse unitary transformation of the unitary-transformed quantum state matches the quantum state selected in the pre-commit phase.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Differential non-Gauss operation radioactivity continuous variable quantum key distribution method
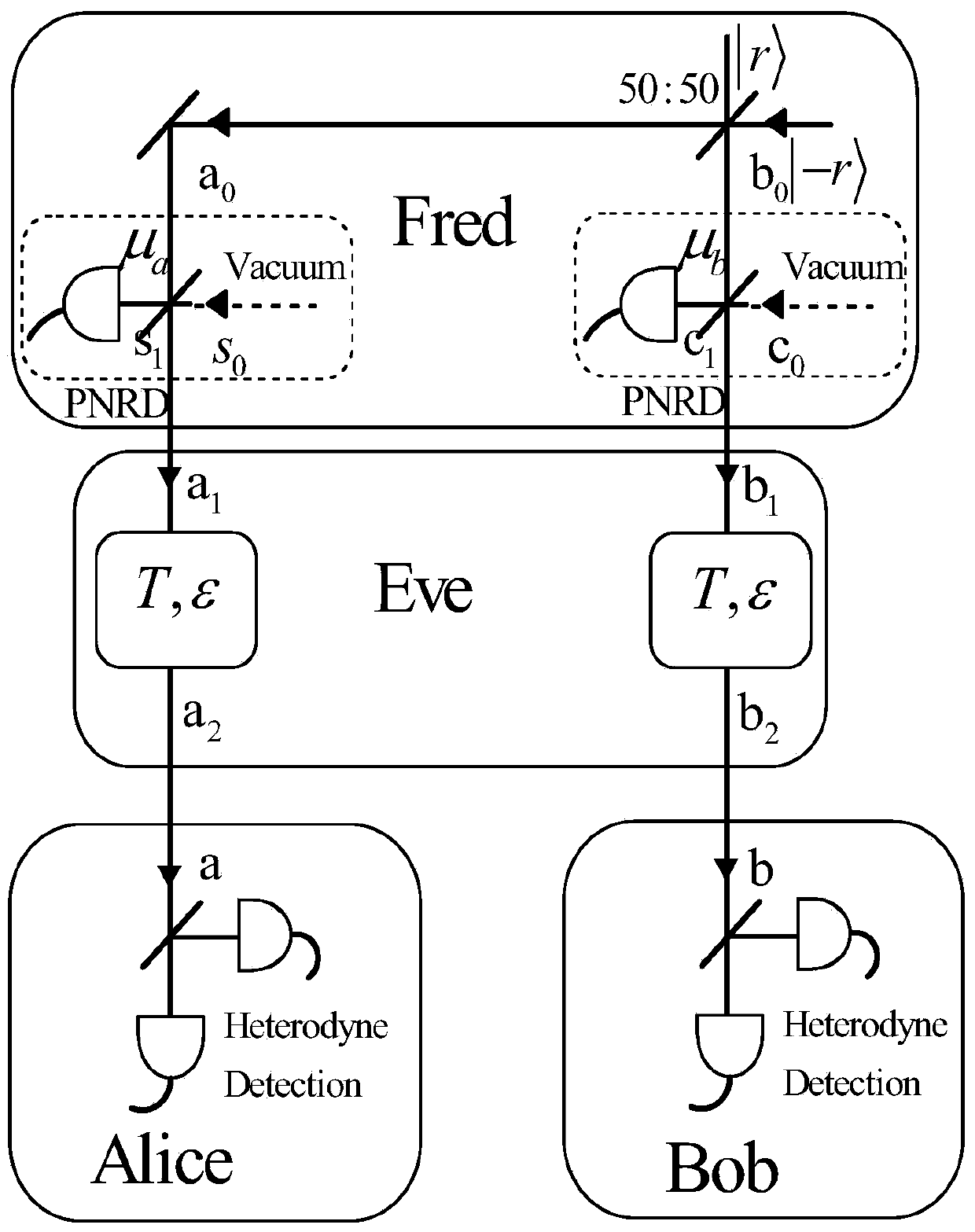
InactiveCN103746799AImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobCommunications system
The invention discloses a differential non-Gauss operation radioactivity continuous variable quantum key distribution method. A trusted third party Fred prepares a dual-mode vacuum compression state which is marked as rho[ab] by use of a laser generator, a photon undergoes beam dividing of the dual-mode vacuum compression state rho[ab] and then undergoes double-mode unitary transformation Uab<^> to commonly generate a double-mode vacuum compression state phi>a0b0, at the moment, the output modes of the photon are respectively marked as a0 and b0, photon subtraction operation is used to realize non-Gauss operation to respectively obtain a mode a1 and a mode b1, when Alice and Bob receive photon output modes a2 and b2 transmitted by a noise channel, a heterodyne detector is utilized to perform detection for secret negotiation and error correction, and finally, a secret key is extracted and obtained for data encryption. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: non-Gauss modulation is realized at a source by use of a photon number distinguishing detector, and the security of secret key transmission in a quantum communication system is improved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Low-complexity DOA estimation method and system
ActiveCN103344940AAvoid decompositionReduce complexityMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesCross correlation matrixEstimation methods
The invention provides a low-complexity DOA estimation method and system. According to the low-complexity DOA estimation method, unitary transformation is carried out on sample data, data obtained after transformation are divided into two parts, an autocorrelation matrix of and a cross-correlation matrix of and are calculated, and the real part of the autocorrelation matrix and the real part of the cross-correlation matrix are extracted. The low-complexity DOA estimation method and system has the advantages that only a subsample covariance matrix of two real number fields needs to be calculated, a signal subspace is constructed through the method, construction of the covariance matrix of the whole sample and eigenvalue decomposition are avoided, and complexity is further lowered.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Quantum voting system and method based on quantum teleportation
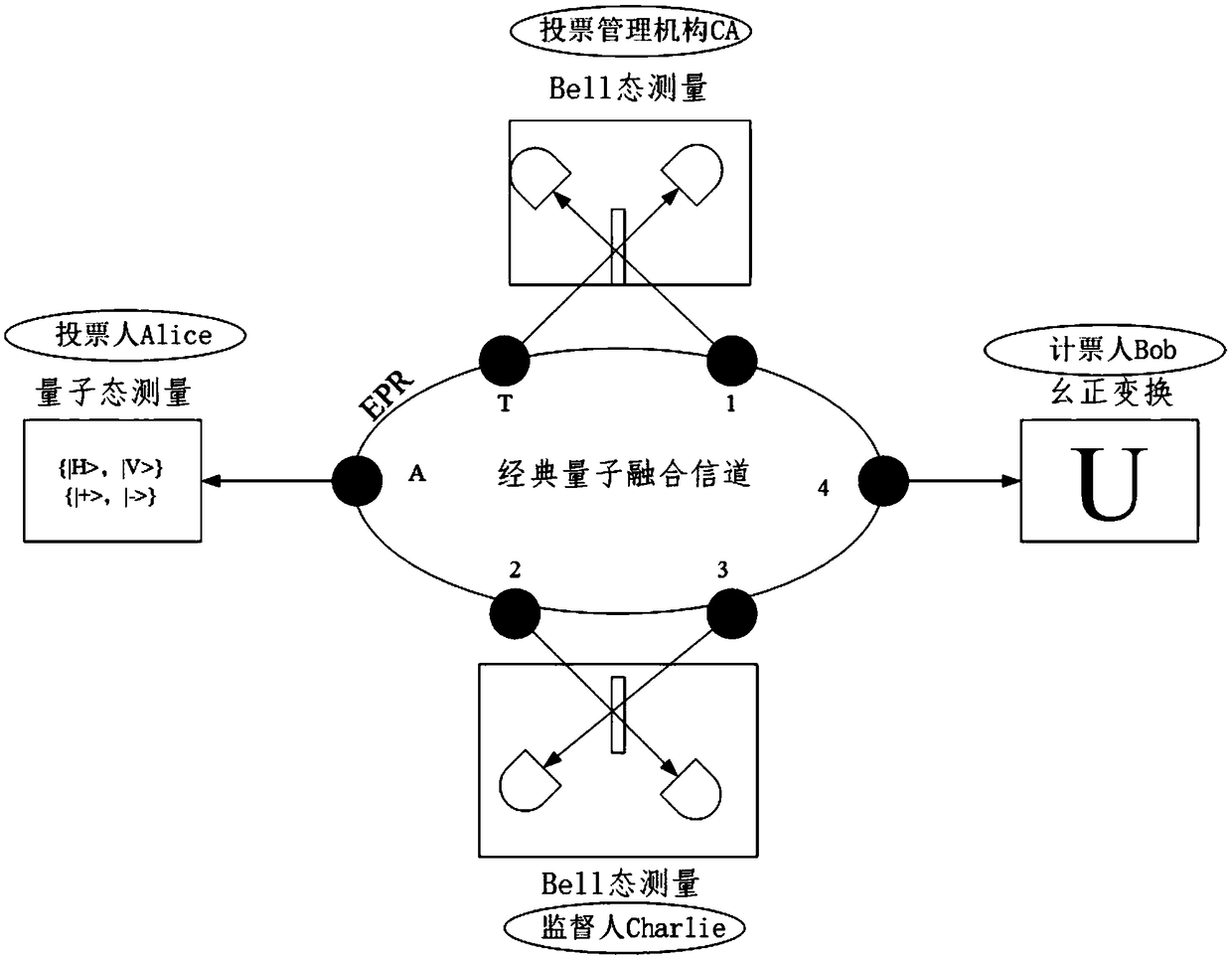
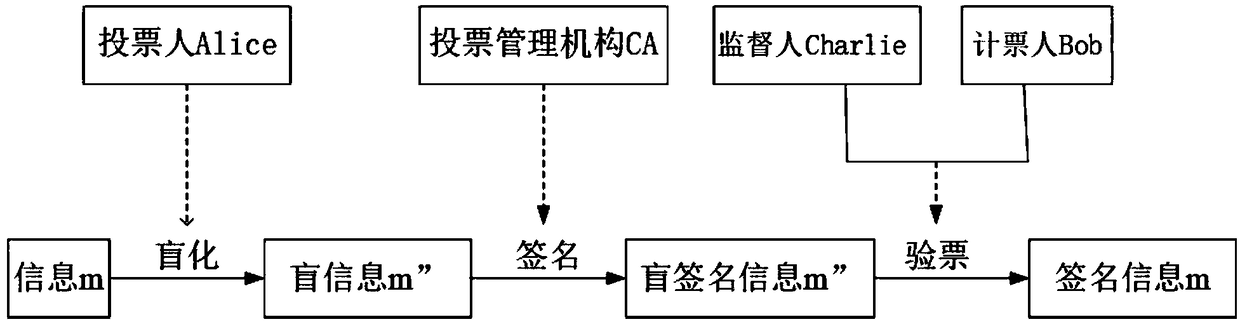
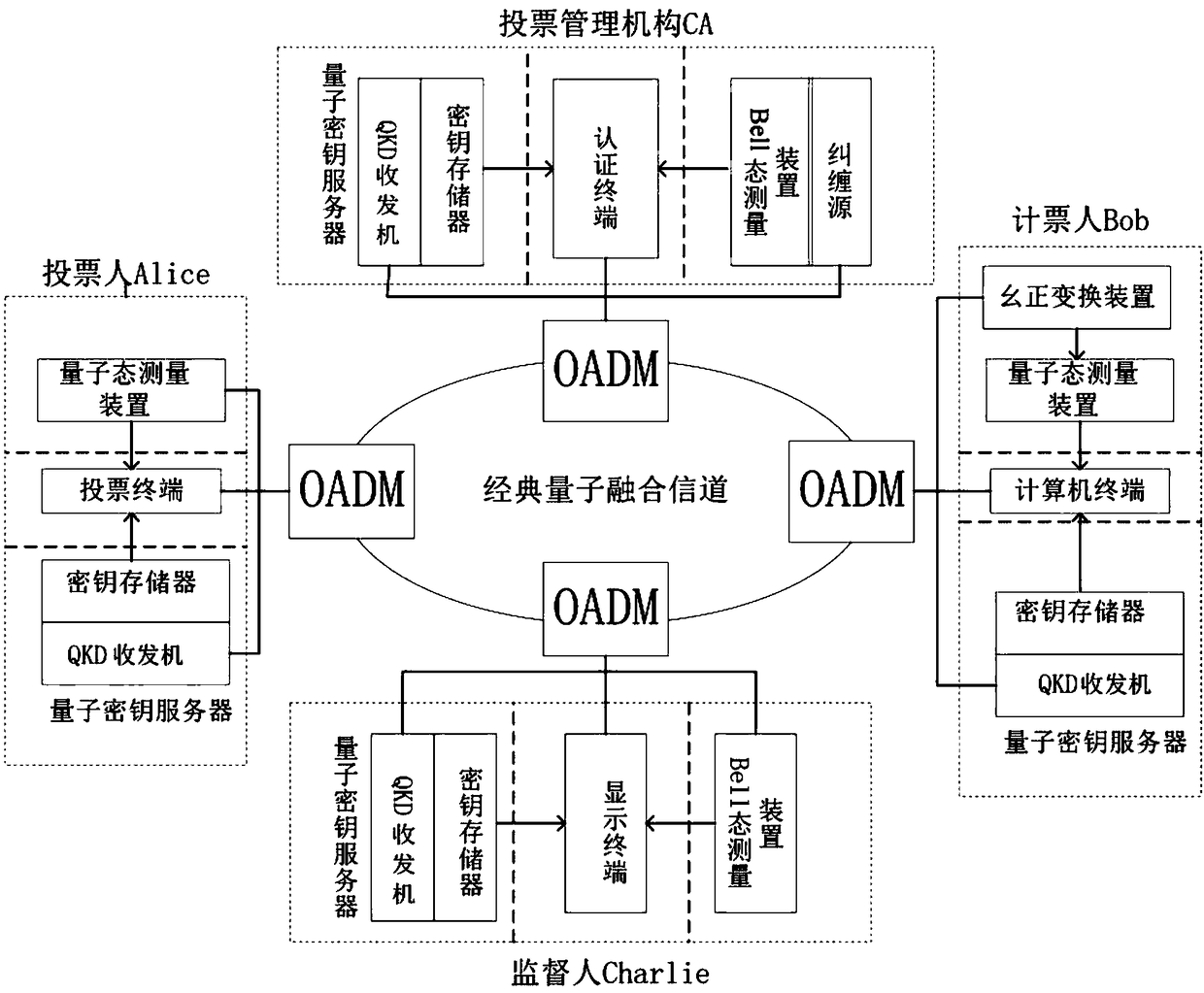
PendingCN108880790AGuaranteed legalityEnsure safetyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationBell stateMeasurement device
The invention discloses a quantum voting system and method based on quantum teleportation. The quantum voting system comprises a voter Alice, a voting management organization CA, a supervisor Charlie,a teller Bob and four OADMs, wherein the voter Alice comprises a first a quantum key server, a voting terminal and a first quantum state measurement device; the voting management organization CA comprises a second quantum key server, an authentication terminal, an entanglement source and a first Bell state measurement device; the supervisor Charlie comprises a third quantum key server, a displayterminal and a second Bell state measurement device; and the teller Bob comprises a fourth quantum key server, a computer terminal, a unitary transformation device and a second quantum state measurement device. The quantum voting system disclosed by the invention ensures the security of the whole voting process by the coherence of entangled particles, a QKD protocol, a one-time-one-encryption encryption algorithm and quantum channel eavesdropping detection. In addition, the quantum voting system disclosed by the invention transmits the classical and quantum information through different wavelengths in the same optical fiber, so that the cost of an application can be greatly reduced, and the practicability is improved
Owner:GUANGDONG INCUBATOR TECH DEV CO LTD
Methods and apparatus for power allocation and/or rate selection for ul mimo/simo operations with par considerations
A method for a wireless communication includes receiving or storing a peak to average (PAR) back off value; and applying the PAR back off value to determine the transmission power and rate for SIMO and MIMO transmissions. In one aspect, the PAR back off value is at least partially based on modulation type. In another aspect, the PAR back off value is more for higher order QAM than for QPSK. The power allocation algorithm for different UL MIMO schemes is described as follows. For MIMO without antenna permutation (e.g. per antenna rate control), different PAR back off values are considered for different data streams. For MIMO with antenna permutation or other unitary transformation such as virtual antenna mapping or precoding, the PAR back off are determined based on combined channel. The transmission data rate depends on power and also the receiver algorithms such as a MMSE receiver or MMSE-SIC receiver.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Four-particle GHZ state-based two-party quantum key agreement protocol
ActiveCN105245331AHigh qubit efficiencyResist attackKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobSerial code
The invention discloses a four-particle GHZ state-based two-party quantum key agreement protocol. The protocol includes the following steps that: step 1, Alice and Bob randomly generate respective classic keys and negotiate on functions; step 2, Alice selects n four-particle GHZ combination and separation sequences, and randomly inserts decoy photons into three sequences and transmits the new sequences to Bob; step 3, Bob measures the decoy photons, and Alice calculates an error rate; step 4, Alice executes CNOT operation on every three corresponding particles with the same serial numbers in the sequences by twice; step 5, Alice executes unitary transformation so as to obtain new sequences, and selects out the decoy photons and inserts the decoy photons into the sequences and transmits the sequences to Bob; step 6, Bob measures the decoy photons; Alice compares measurement results and calculates an error rate, and step 7 is executed if the error rate is low, otherwise, the method returns to step 2; step 7, Alice generates a shared key; and step 8, Bob generates a shared key. With the four-particle GHZ state two-party quantum key agreement protocol of the invention adopted, existing participant attacks and the external attacks can be resisted. The quantum bit efficiency of the protocol is much higher than that of an existing protocol.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Quantum computing method and quantum computer
An (N+1) number of physical systems each having five energy levels |0>, |1>, |2>, |3>, and |4>, a qubit being expressed by |0> and |1>, are provided in an optical cavity having a cavity mode resonant with |2>-|3>, such that an N number of control systems and a target system are prepared. The target system is irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|4>, |1>-|4>, and |2>-|4> to change a superposed state |c> to |2>. All of the physical systems are irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|3> and |1>-|3>, and a phase of the light pulse resonant with the target system is shifted by a specific value dependent on a unitary transformation U. The target system is irradiated with light pulses resonant with |0>-|4>, |1>-|4>, and |2>-|4>, with a phase difference between them being set to a specific value dependent on the unitary transformation U, to return |2> to |c>.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Multi-antenna spectrum sensing method and device suitable for broadband system
InactiveCN103118394AShorten the perception timeImprove spectrum utilizationSpatial transmit diversityWireless communicationFrequency spectrumSignal subspace
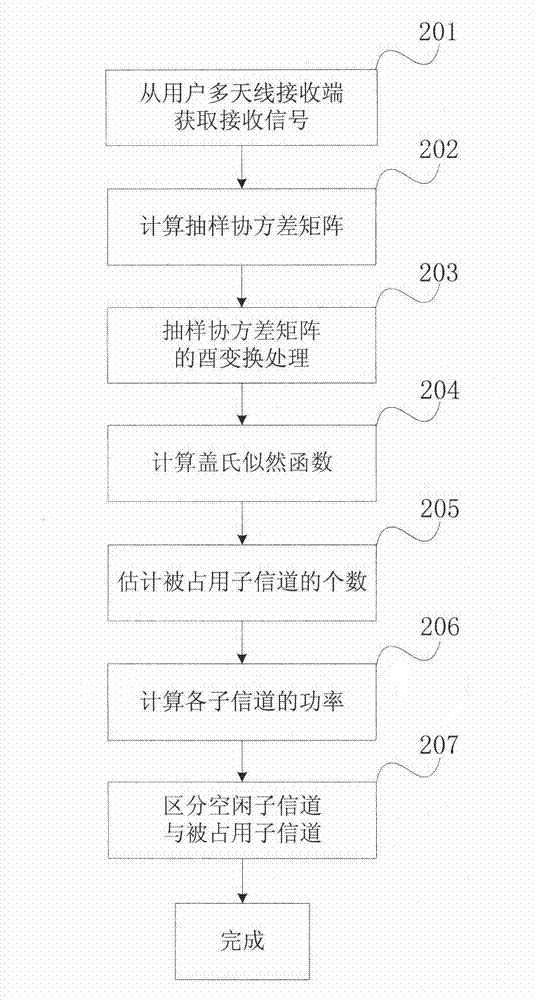
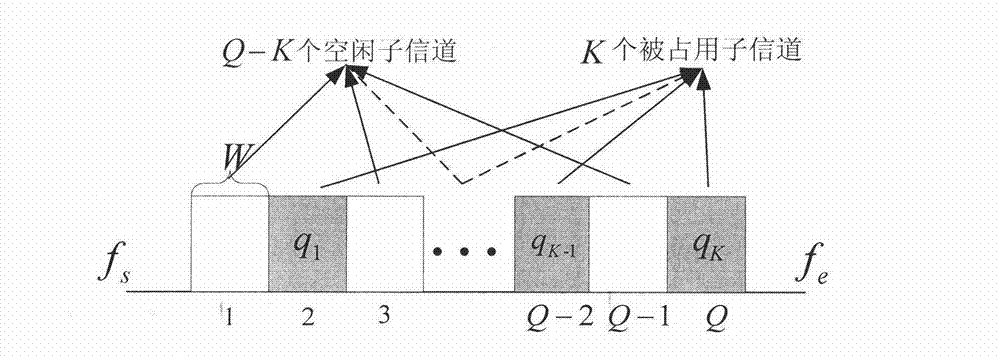
The invention discloses a multi-antenna spectrum sensing method and a device suitable for a broadband system. All component channels of the broadband system are detected simultaneously. First, unitary transformation treatment is conducted to the sampling covariance matrix of receiving signals, based on the galeazzi likelihood function and the Gerschgorin radii of noise, the number of occupied component channels is estimated, and then according the size of power of the component channels, the positions of the occupied component channels are judged, and free component channels and the occupied component channels are determined. Compared with a traditional broadband spectrum sensing method, the multi-antenna spectrum sensing method suitable for the broadband system is characterized in that a traditional subjective judgment threshold does not rely on, however, the orthogonality of channel subspace and noise subspace is used to judge; apriori information of noise power is of no need, and robustness is achieved to the uncertainty of the noise. By means of the multi-antenna spectrum sensing method suitable for the broadband system, the influence of the uncertainty of the noise on system performance can be effectively restrained, sensing time is shortened, and spectrum efficiency is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
In-solid nuclear spin quantum calculation device
InactiveUS20050021927A1Reduce in quantityAdjustable frequencyQuantum computersMagnetic measurementsCoplanar waveguideElectron
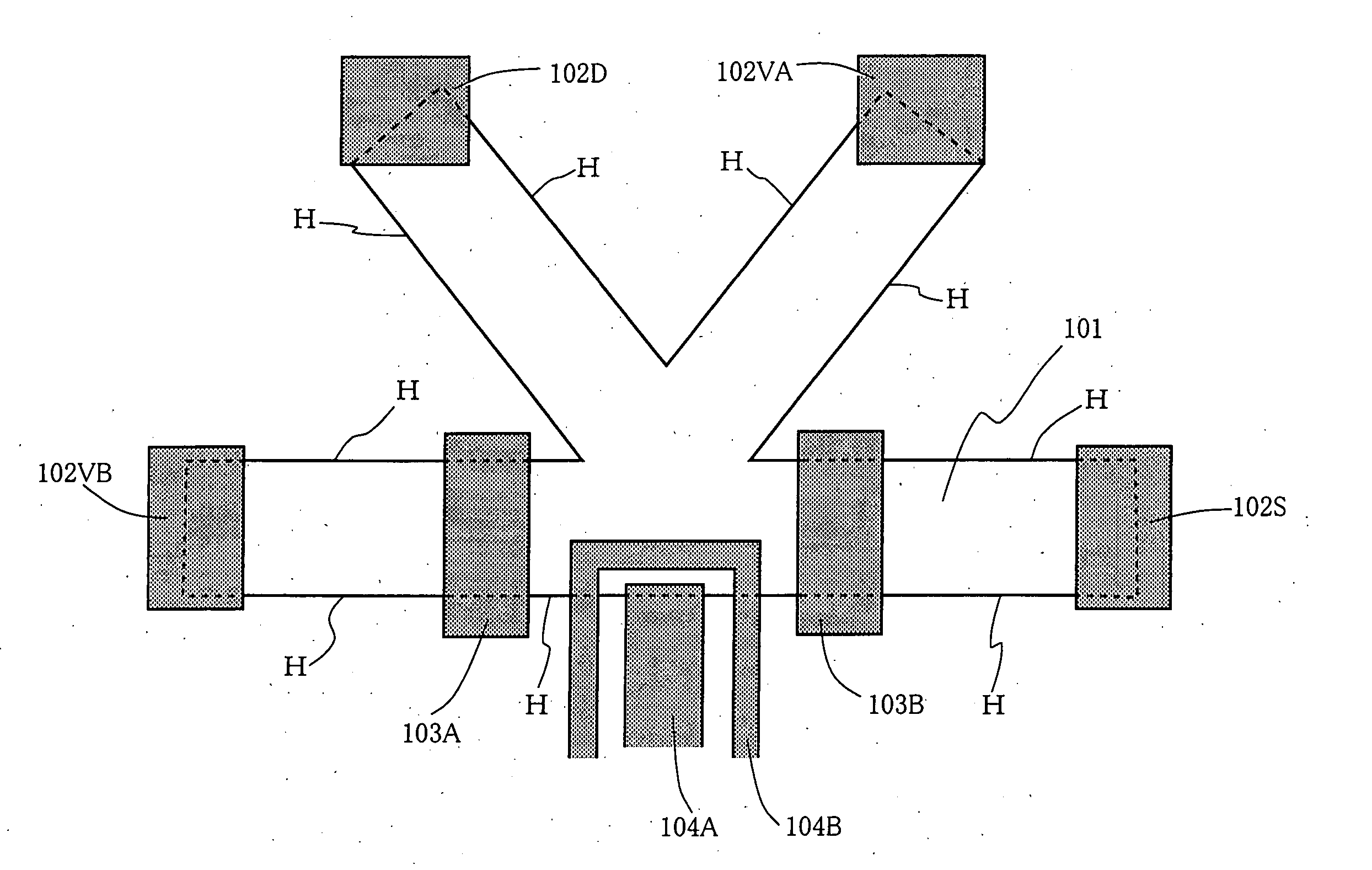
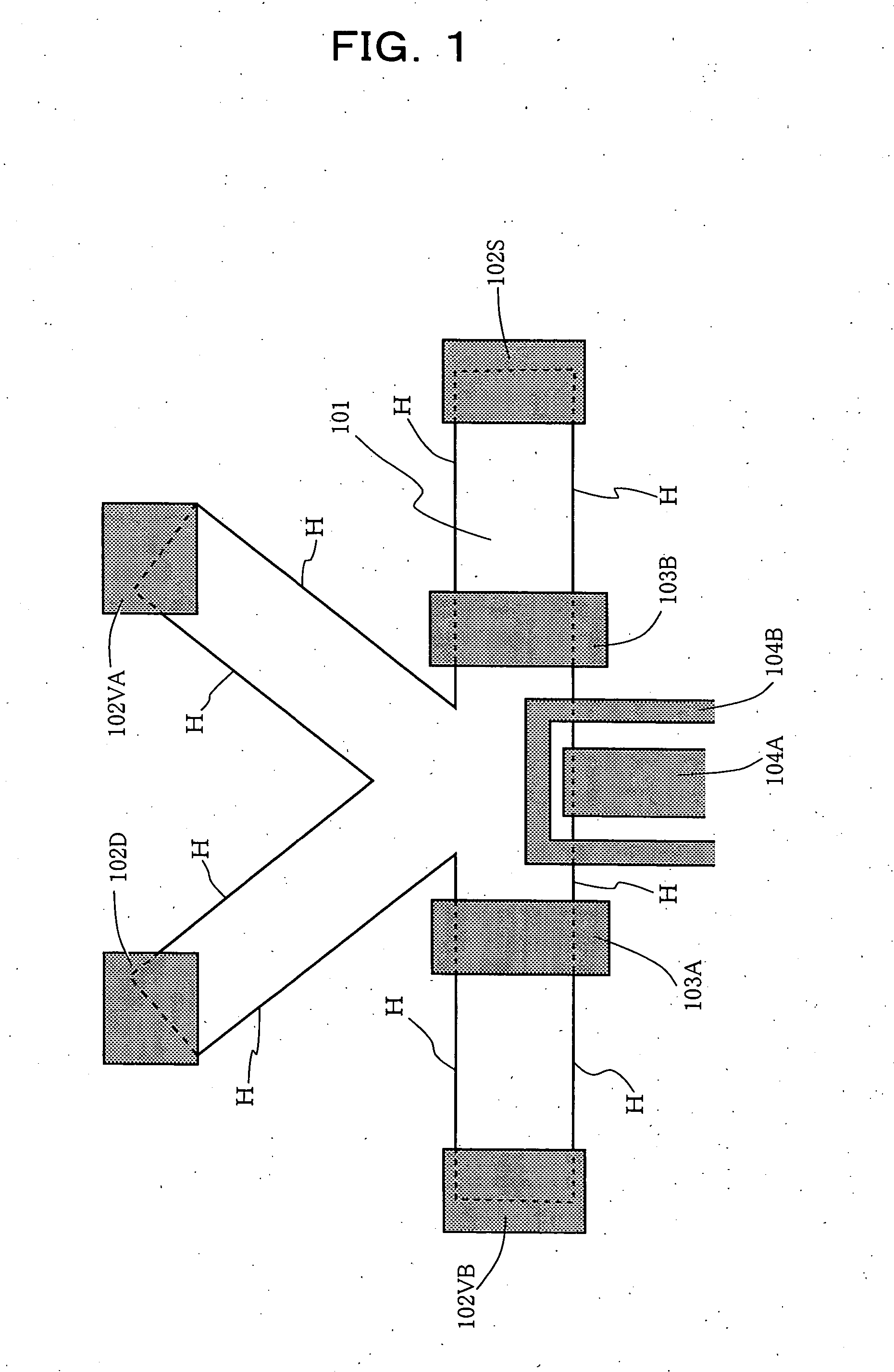
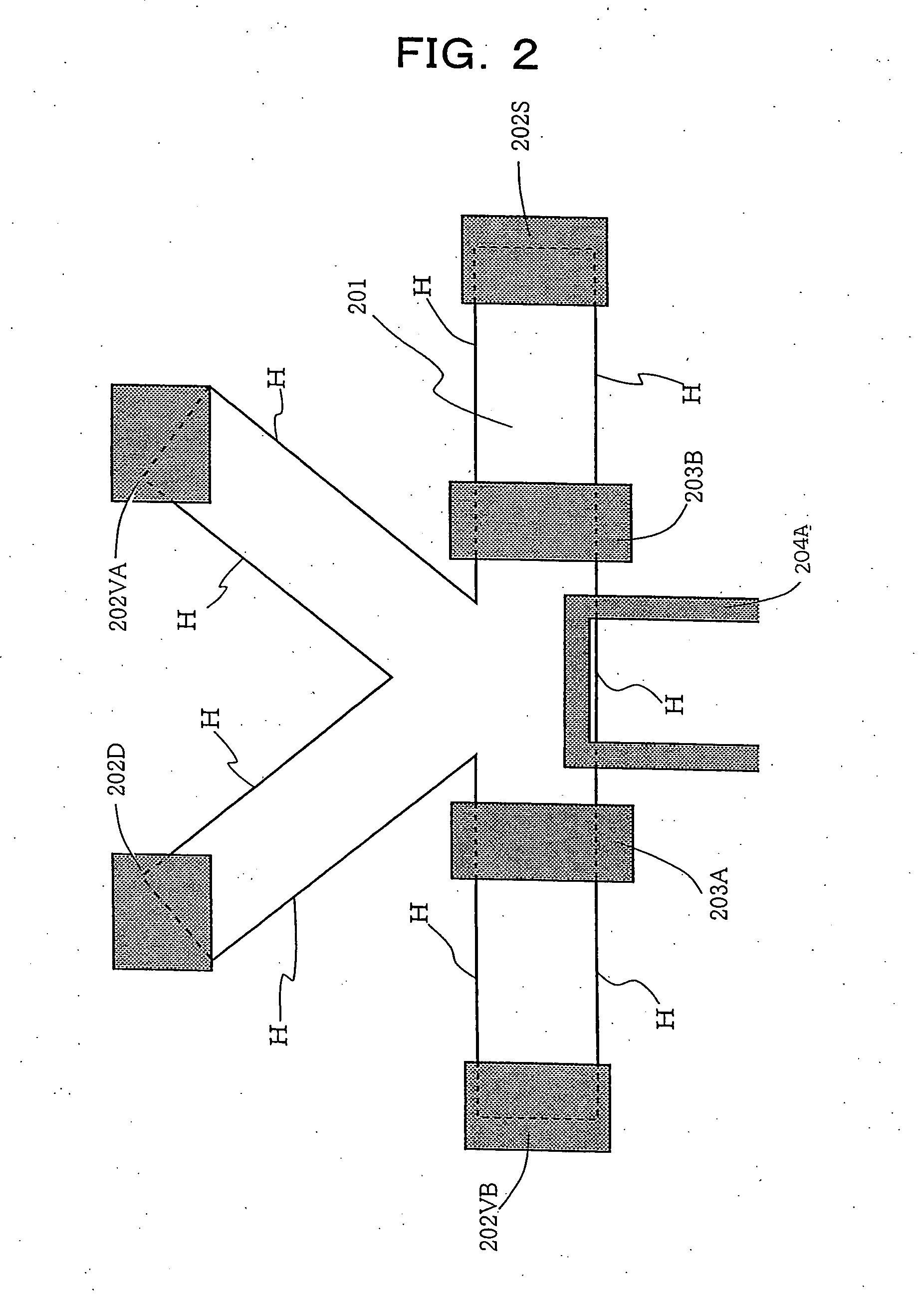
A voltage is applied across gate electrodes (103A) and (103B) in a two-dimensional electronic system (101) placed under a magnetic field, and the polarity of an electric current passed between ohmic electrodes (102D) and (102S) is selected to bring about inversion of electron spins based on a non-equilibrium distribution of electrons in a quantum Hall edge state and to initialize the polarization of nuclear spins. An oscillatory electric field of a nuclear magnetic resonance frequency is applied to coplanar waveguides (104A) and (104B) to control the nuclear spin polarization. The controlled spin polarization is read out by measuring the Hall resistance from ohmic electrodes (102VA) and (102VB). An in-solid nuclear spin quantum processor device can be manufactured by attaching a microfine metal gate structure to a quantized Hall effect element that is realized in a semiconductor two-dimensional system, and allows a limited number of nuclear spins to be controlled, initialized, subjected to a unitary transformation, and read out.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) detection method for multiple input multiple output-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM)
ActiveCN102111354AReduce processing timeBaseband system detailsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionNoise levelAlgorithm
The invention discloses a linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) detection method for multiple input multiple output-orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (MIMO-OFDM). The method comprises the following steps of: presetting a detection systolic array by adopting an estimated noise level value obtained from a channel estimation module, performing Givens rotation on a multi-antenna channel matrix, simultaneously performing unitary transformation on data received by a plurality of antenna, and finally solving linear equations by using a back substitution method to obtain an estimated value of a space division multiplexing signal. The processing method is implemented according to a sub-carrier sequence. Compared with the conventional methods, the LMMSE detection method for the MIMO-OFDM has the advantages that: a calculated amount is far less than that of the conventional systolic array Givens rotation-based quick response (QR) decomposition performed on the multi-antenna channel augmented matrix, and the processing time is relatively shorter.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Quantum based information transfer system and method
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
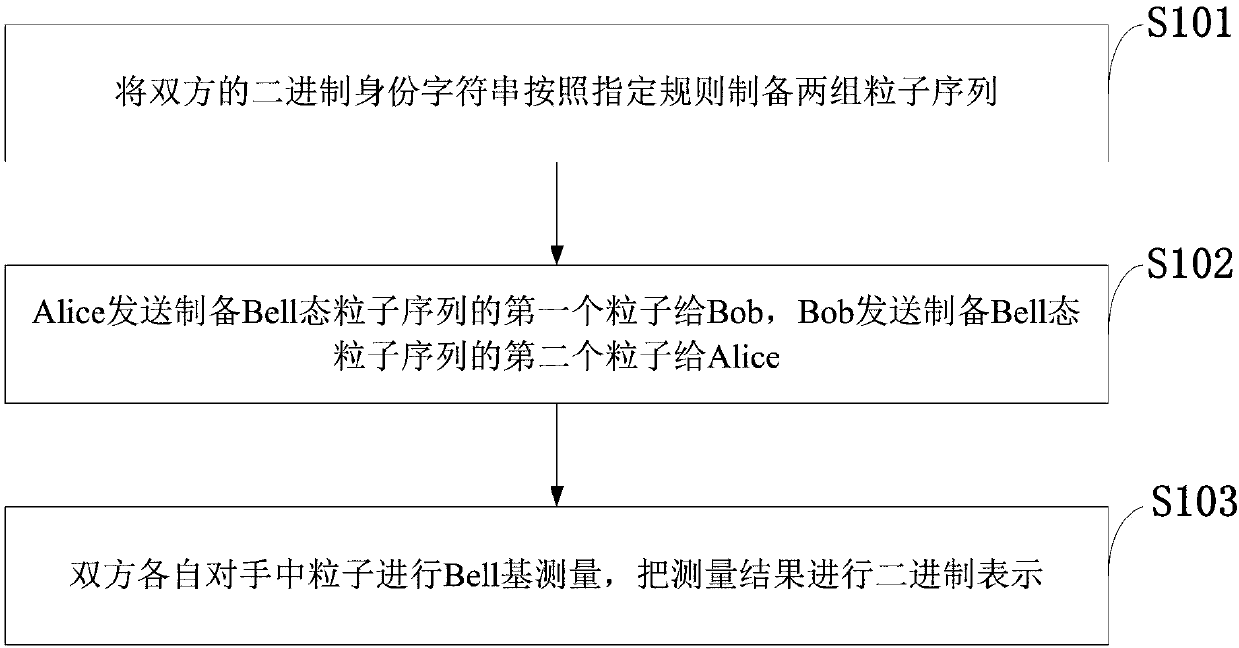
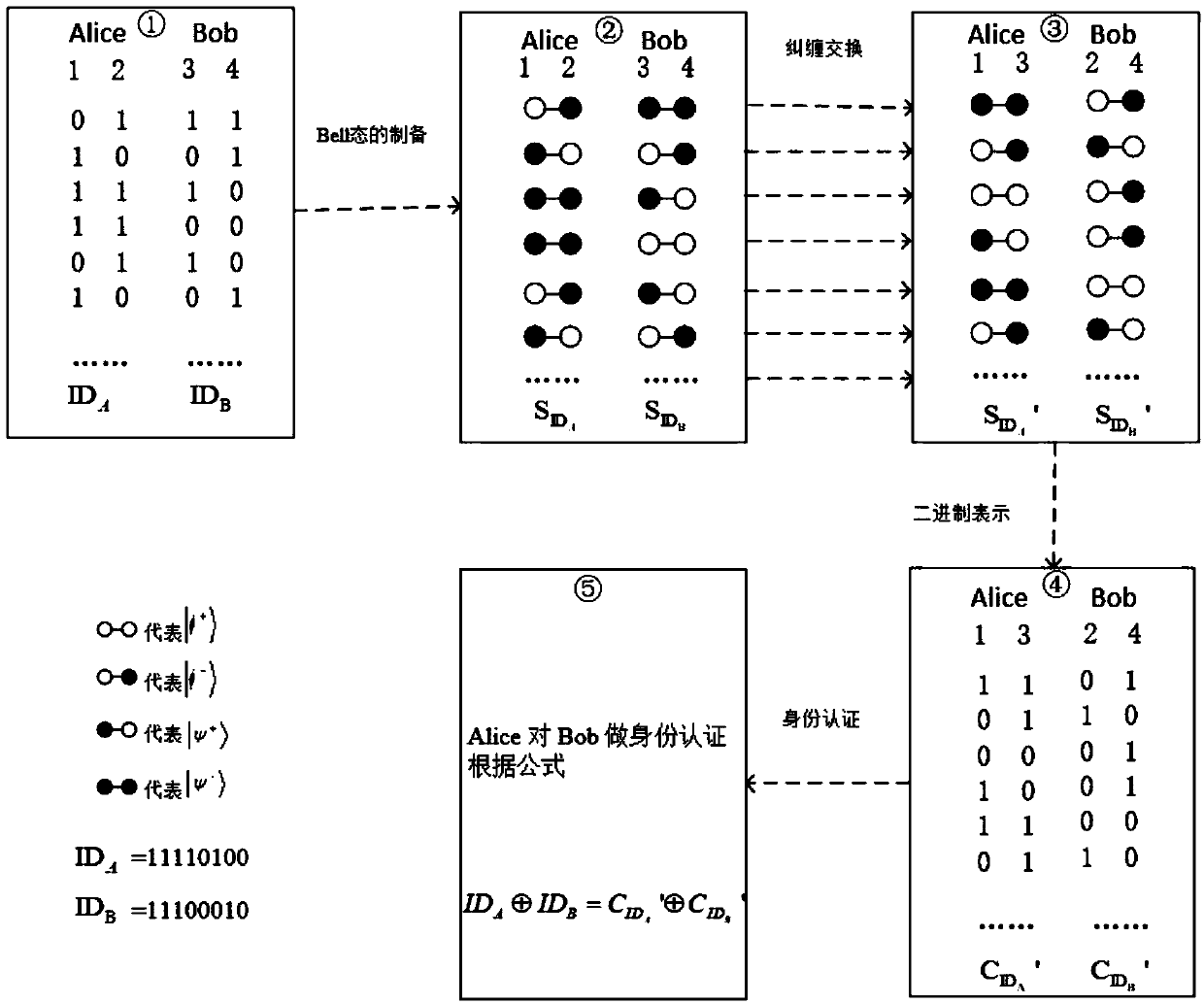
Quantum identity authentication method, computer, computer program and readable storage medium
InactiveCN108092770AResist attackWon't leakKey distribution for secure communicationBell stateComputer hardware
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum communications, and discloses a quantum identity authentication method, a computer, a computer program and a readable storage medium. The methodcomprises the steps that binary identity strings of both sides are used for preparing two groups of particle sequences according to specified rules; Alice sends a first particle used for preparing aBell-state particle sequence to Bob, and Bob sends a second particle used for preparing the Bell-state particle sequence to Alice; Bell-based measurement is conducted on particles in the two sides, and the measurement results are subjected to binary representation. In the identity authentication process, no unitary transformation is needed in the Bell-state transmission process, and information transmission can be achieved simply by executing Bell-state measurement and a bitwise exclusive OR operation. In practical application, achievement of the protocol is achieved by only depending on Bell-state accurate preparation and Bell-state reliable measurement, and the protocol can resist impersonation attack.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
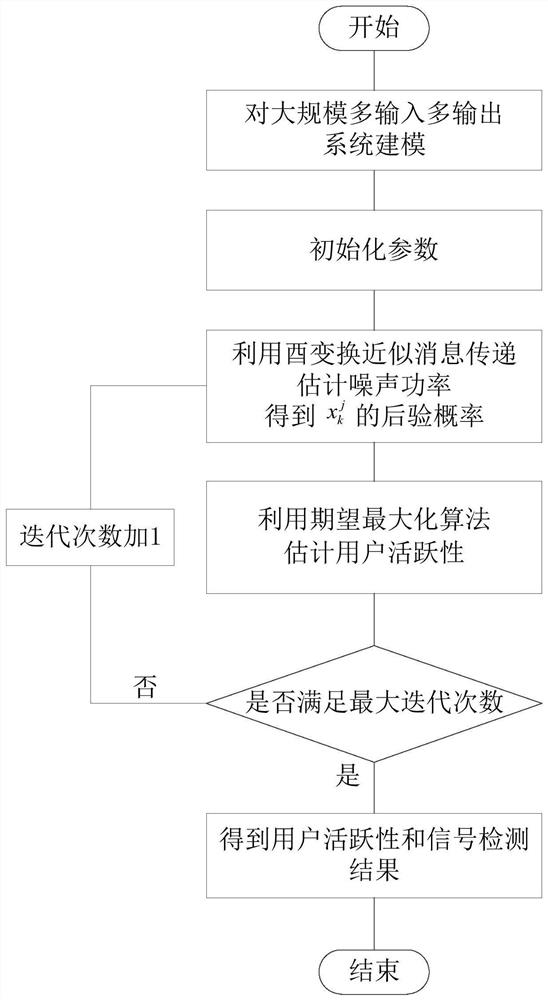
User activity and signal joint detection method for large-scale MIMO system
ActiveCN112242861AAchieve estimatesIt is estimated that the effect is goodError preventionRadio transmissionExpectation–maximization algorithmMessage delivery
The invention discloses a user activity and signal joint detection method for a large-scale MIMO system. The method comprises the steps: enabling the number of IoT equipment to be greater than the number of antennas configured at a base station side, transmitting an M-ary quadrature amplitude modulation symbol at each time slot at each active IoT equipment of an uplink, and enabling the transmitting symbol of inactive IoT equipment to be 0 at each time slot, wherein each antenna on the base station side receives signals in each time slot; considering the condition that the noise power is unknown, estimating the noise power by utilizing unitary transformation approximate message passing, obtaining a posterior probability of transmitting symbols, and performing user activity detection according to the posterior probability and an expectation maximization algorithm, thereby finally obtaining a signal detection result, namely, estimating a matrix formed by symbols transmitted by all IoT equipment in all time slots. The method has the advantages that the noise power does not need to be known, the method better conforms to the actual situation, and the method can still have good detection performance under the condition that the number of active IoT devices is close to the number of base station side antennas.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Knowledge assisted space-time adaptive processing method integrating generalized symmetrical structure information
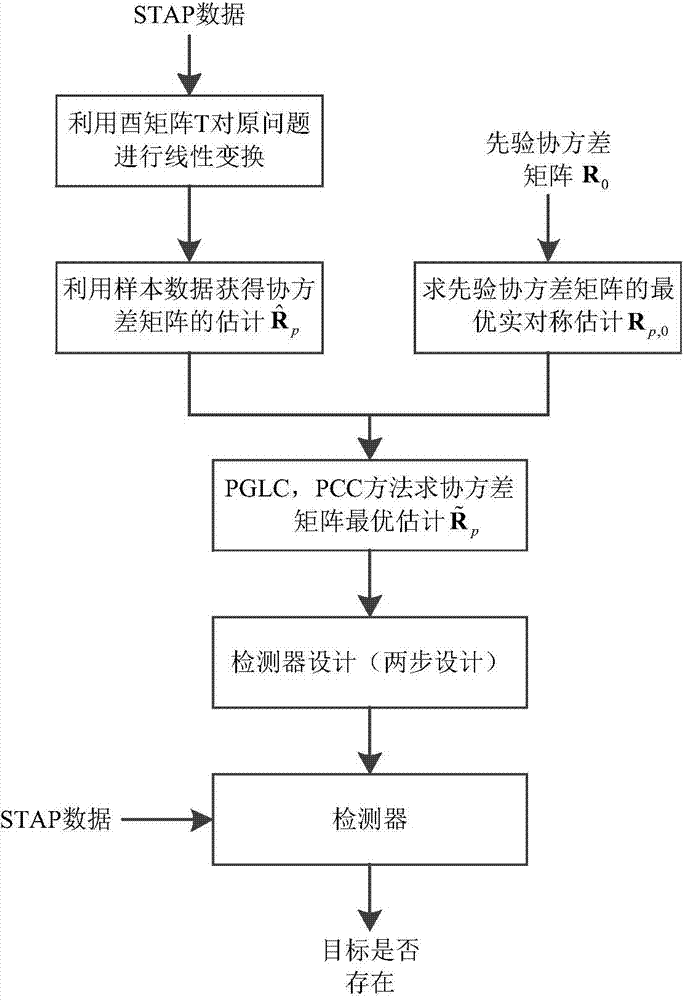
InactiveCN104215939AReduce demandEasy to detectWave based measurement systemsAlgorithmSpace-time adaptive processing
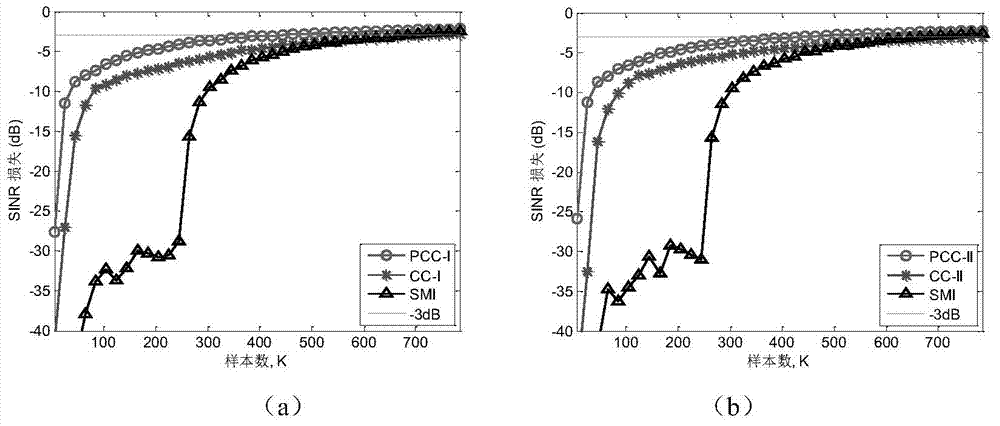
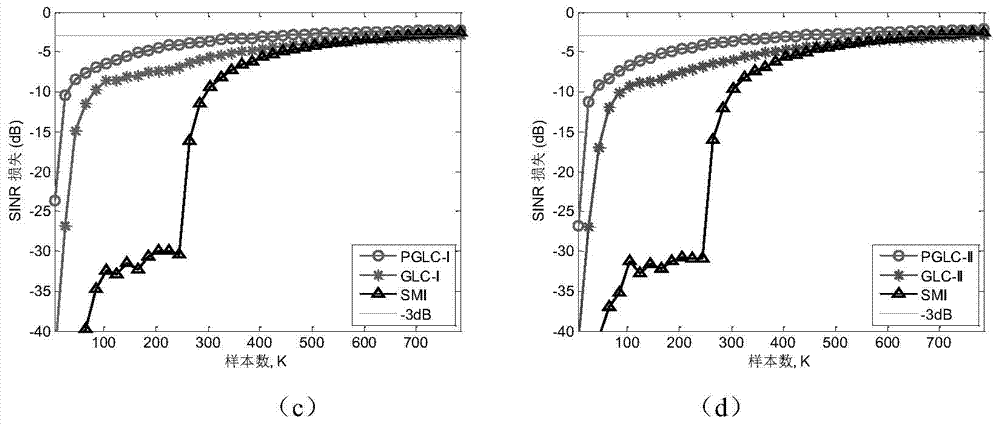
The invention provides a knowledge assisted space-time adaptive processing method integrating generalized symmetrical structure information. The knowledge assisted space-time adaptive processing method integrating the generalized symmetrical structure information comprises steps of (1) performing linear transformation through an unitary transformation matrix and transforming an original space-time adaptive processing problem to be in a form which is equivalent to the original space-time adaptive processing problem to enable a covariance matrix of the original space-time adaptive processing problem to be transferred into a real symmetric matrix in the same dimension from a generalized symmetric matrix; (2) obtaining an estimation of the transformed covariance matrix according to sample data; (3) solving an optimal real symmetric estimation of a prior covariance matrix under the minimum Euclidean distance; (4) solving a minimum mean square error estimation through a generalized linear combination and convex combination method in combination with training samples and the prior covariance matrix; (5) obtaining detector forms under part of uniform model and random non-uniform model assumption according to a two-step design and achieving target detection. The knowledge assisted space-time adaptive processing method integrating the generalized symmetrical structure information has the advantages of effectively reducing demanded quantity of the training samples during covariance matrix estimation in the space-time adaptive processing, remarkably improving the detector performances and being simple in achievement.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
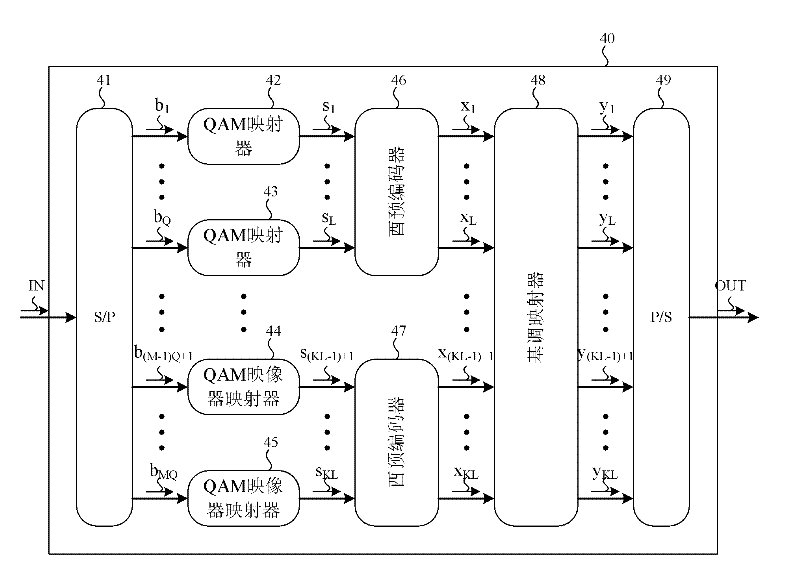
Dynamic tone grouping and encoding for multi-carrier quadrature amplitude modulation in ofdm
ActiveCN102224761AError preventionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsChannel state informationSubcarrier pairing
The invention provides a transmitter, a method for the transmitter and a subcarrier pairing method. The method for the transmitter firstly includes that a sequence of coded and interleaved bits is de-multiplexed into a number of bit-streams. Each bit-stream is mapped into a sequence of Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) symbols, which are grouped into non-overlapping sets of QAM symbols. Unitary transformation is then applied on the QAM symbols to produce groups of complex signals. Finally, the complex signals are dynamically mapped to subcarrier groups based on tone mapping information to improve link performance. The tone mapping information is derived from information associated with each OFDM subcarrier, such as Channel State Information (CSI). The OFDM subcarriers are grouped into subcarrier groups according to the tone mapping information such that the channel quality of each subcarrier group is balanced. The inventive transmitter, the method for the transmitter and the subcarrier pairing method can improve the whole efficiency of the channel link.
Owner:MEDIATEK SINGAPORE PTE LTD SINGAPORE
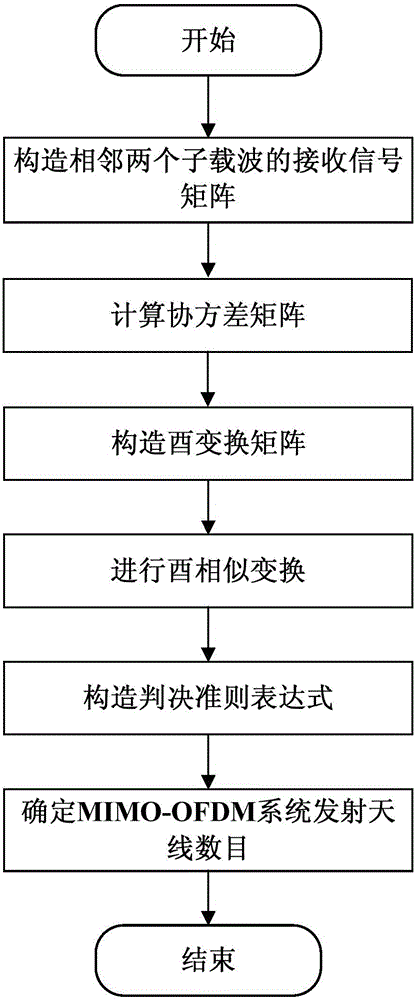
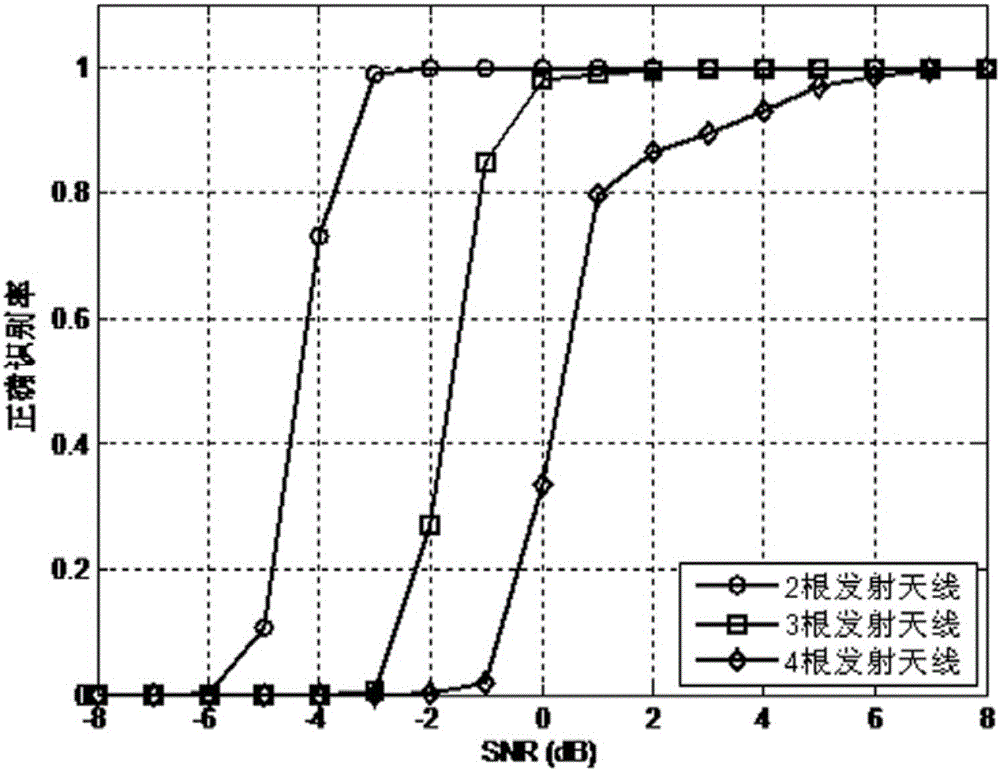
Matrix Gerschgorin circle based transmitting antenna number blind estimation method
ActiveCN106059639AImprove reliabilityImprove robustnessSpatial transmit diversityBaseband system detailsCarrier signalEngineering
The invention invention discloses a matrix Gerschgorin circle based transmitting antenna number blind estimation method. Efficient estimation of the number of transmitting antennas of an MIMO-OFDM system is realized without utilizing prior information such as a pilot frequency in the conditions of a frequency selective fading channel and residential frequency deviation. The matrix Gerschgorin circle based transmitting antenna number blind estimation method mainly comprises the steps of (1) constructing a received signal matrix of two adjacent sub-carriers; (2) calculating a covariance matrix; (3) constructing a unitary transformation matrix; (4) performing unitary similarity transformation; (5) constructing a judgment criterion expression; and (6) determining the number of the transmitting antennas. The matrix Gerschgorin circle based transmitting antenna number blind estimation method solves the problems of blind identification of the number of the transmitting antenna in the malicious conditions of the frequency selective fading channel, a low signal to noise ratio and residential frequency deviation.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
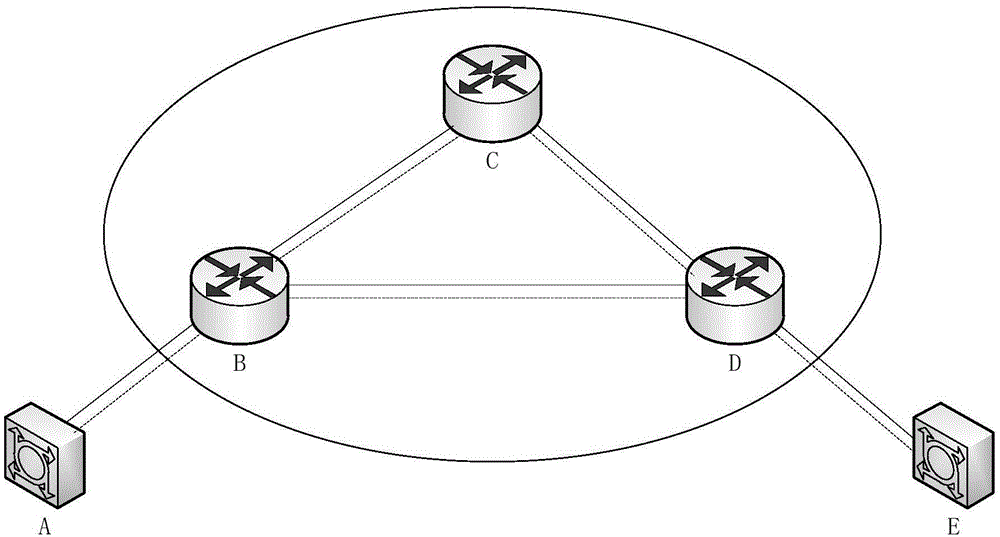
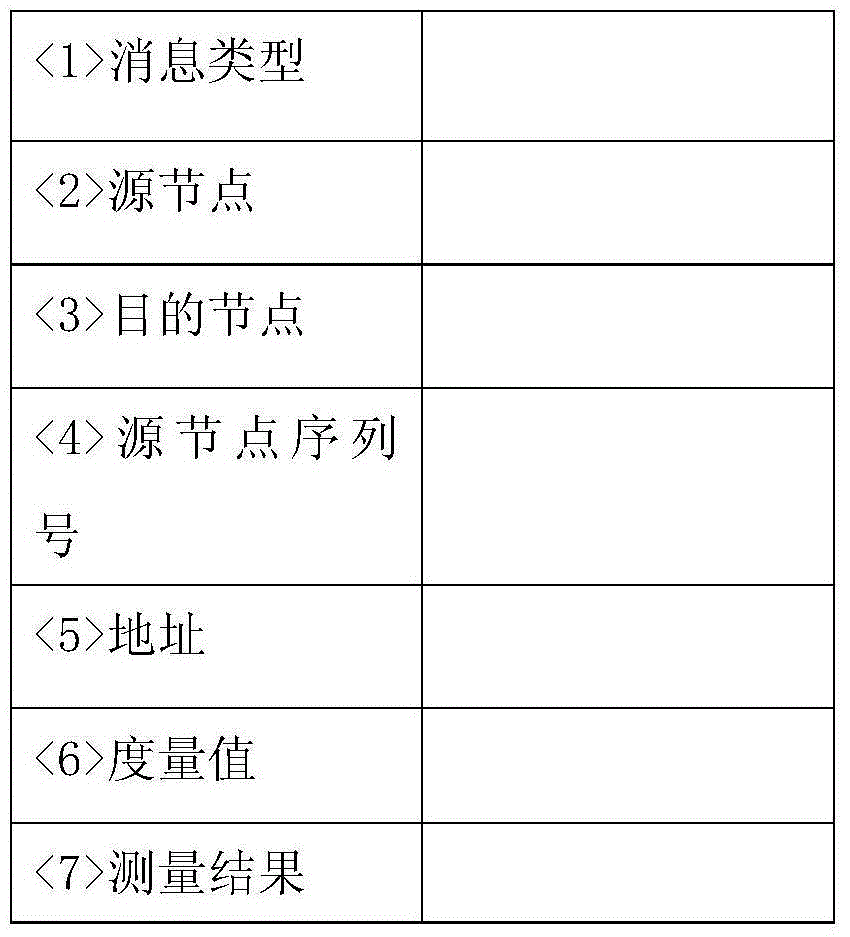
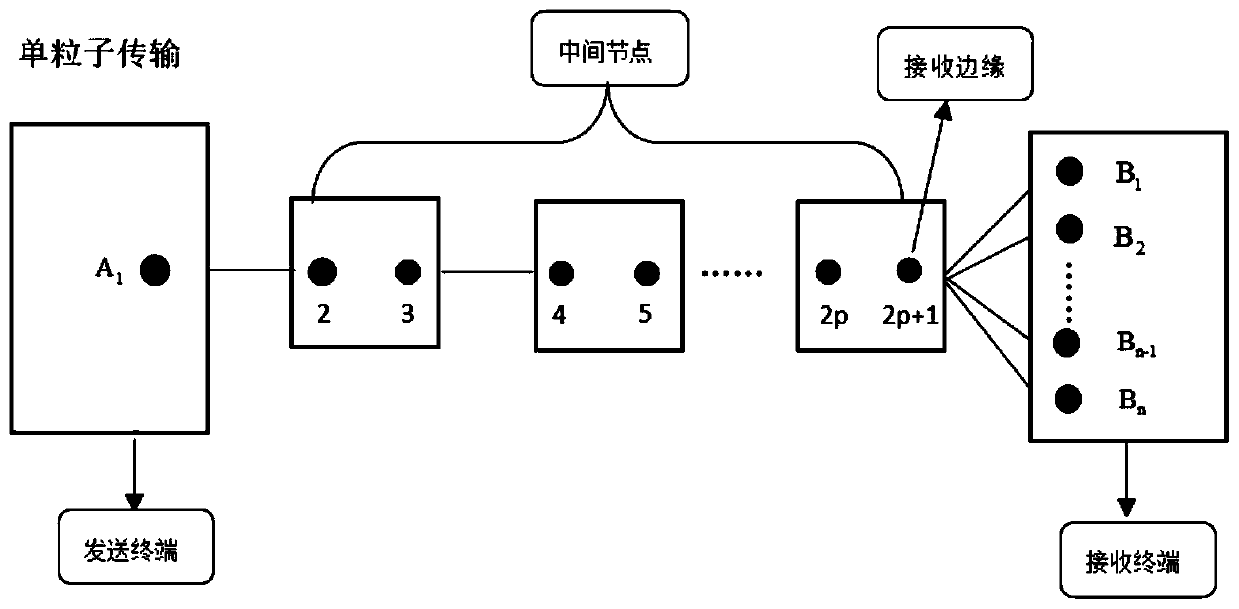
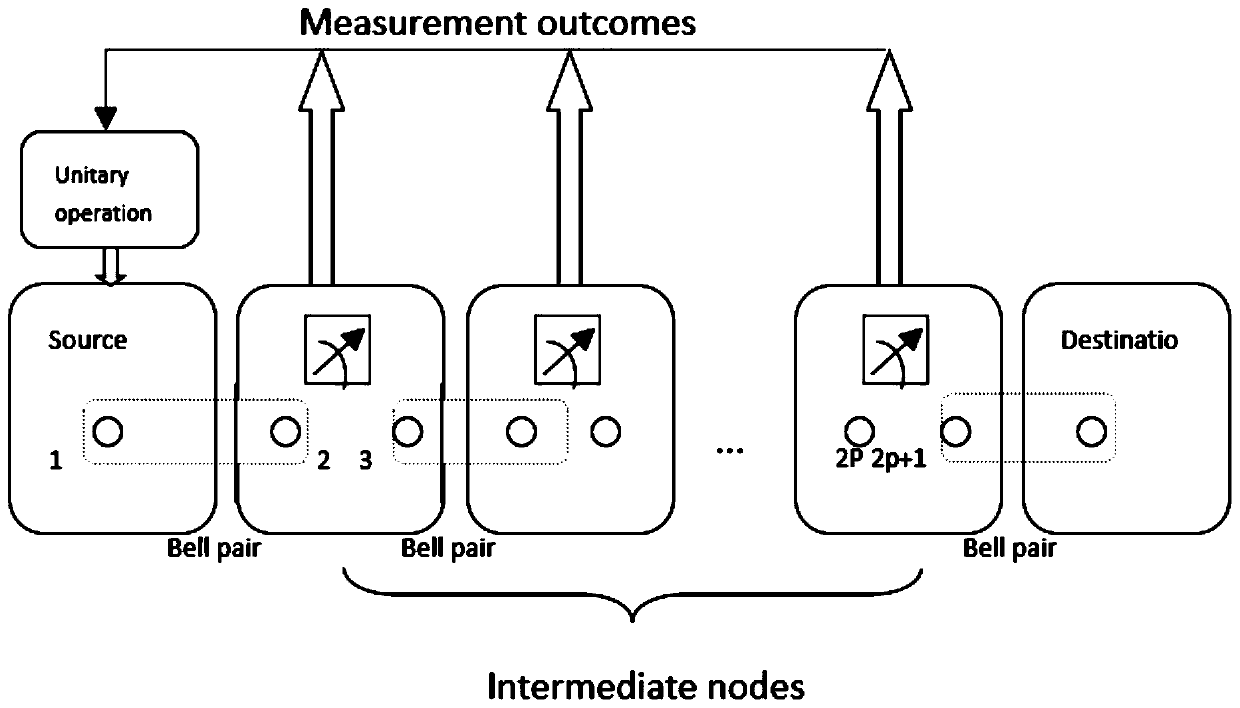
Routing method for quantum Mesh network
ActiveCN105099902ASafe deliveryReliable deliveryKey distribution for secure communicationData switching networksUnitary transformationInformation transfer
The invention discloses a routing method for a quantum Mesh network. A source node originates a route request to a backbone network edge node connected with the source node and the backbone network edge node sends the route request to a backbone network; a backbone network edge node connected with a destination node performs routing and makes a route reply; each node receiving a reply message on the route performs Bell state measurement and transmits a route reply message carrying a measurement result to the source node; after the source node performs the Bell state measurement, all the measurement results are transmitted to the backbone network edge node connected with the destination node along the selected route; the edge node sends all the measurement results to the destination node; and the destination node processes all the measurement results and obtains a quantum state carrying information by virtue of unitary transformation. The routing method for the quantum Mesh network is capable of providing safer and more reliable quantum information transfer; in addition, the Bell state measurement is performed in the process of establishing a route, so that the time delay of information transmission can be reduced and the transmission efficiency can be improved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Anti-detection transmission method based on extended weighted fractional Fourier transform
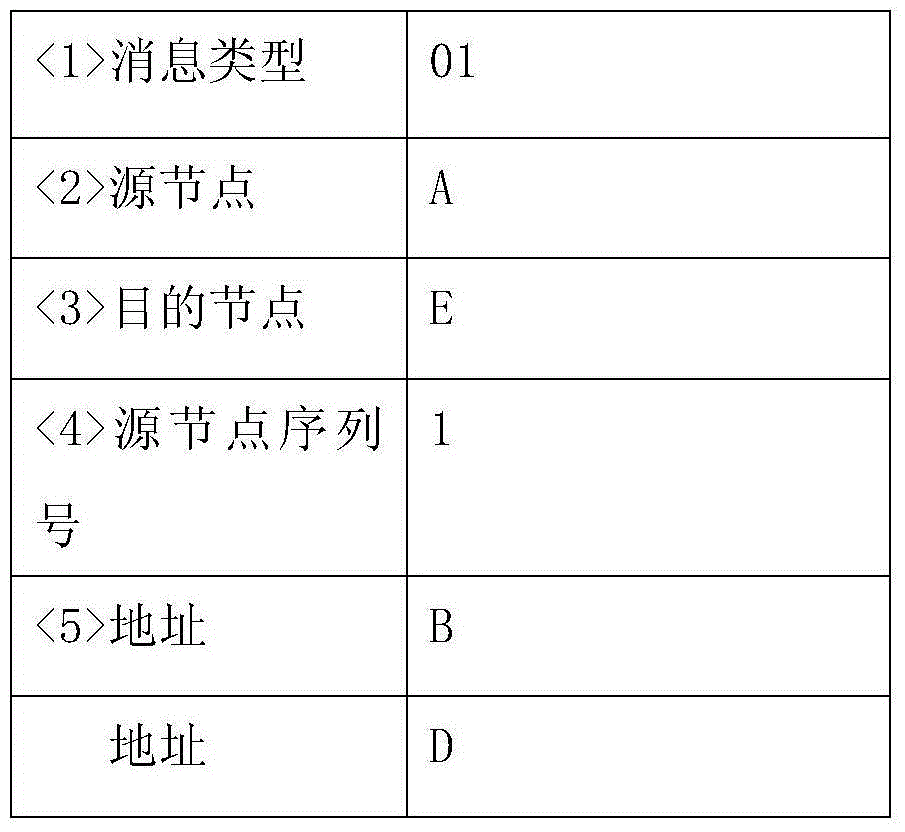
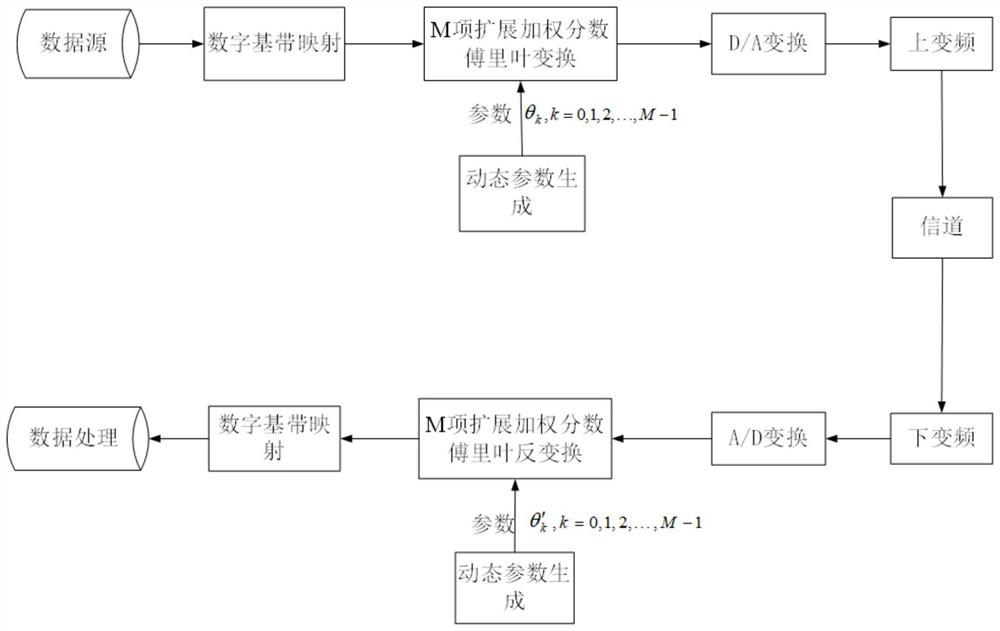
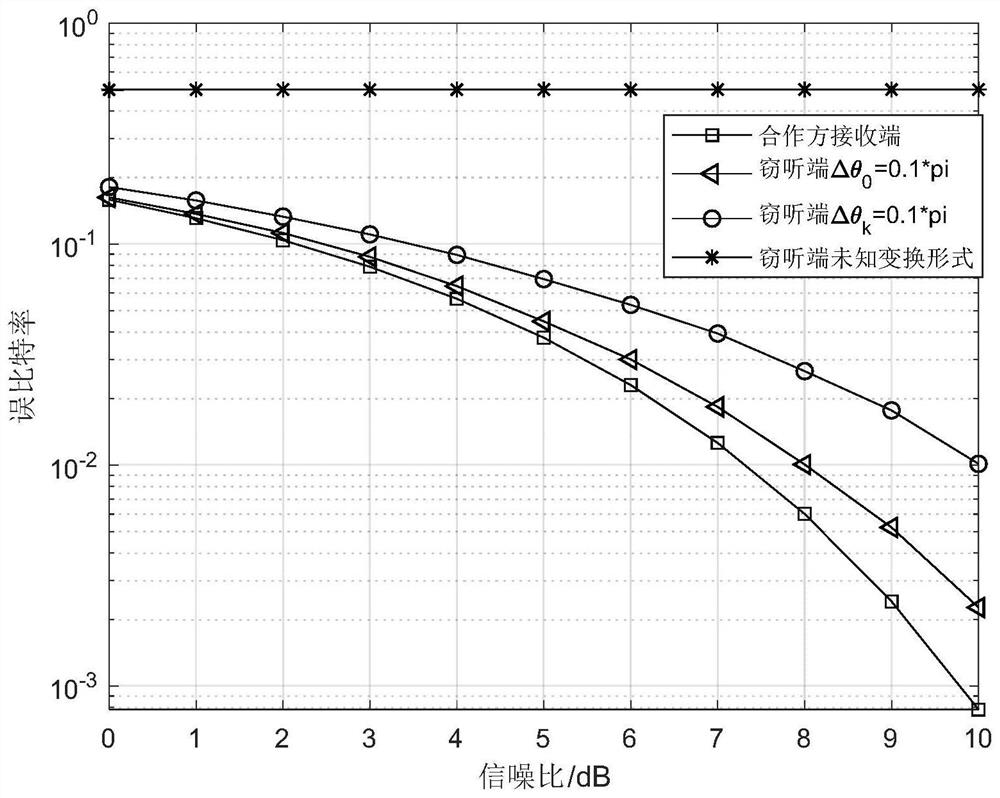
ActiveCN111614590AParameter sensitivity is goodImproved anti-scan capabilityPhase-modulated carrier systemsSecurity arrangementCommunications systemComputation complexity
The invention discloses an anti-detection transmission method based on extended weighted fractional Fourier transform, and belongs to the technical field of communication. According to the invention,the problem of poor anti-eavesdropping end interception performance of the existing communication method is solved. According to the invention, M extended weighted fractional Fourier transforms are introduced into the signal processing process to realize the enhancement of the anti-interception performance of the signal transform domain. For a partner, due to unitary transformation, sending data can be recovered by correct inverse transformation according to a parameter key shared with a sending end; for an eavesdropping end, because the extended weighted transformation has a plurality of transformation parameters and the transformation parameters are mutually independent, the calculation complexity of decoding all the transformation parameters is greatly improved. Therefore, the anti-interception performance of the system is effectively improved, the possibility that the communication information is cracked illegally and violently is reduced, and the physical layer safety performanceof the communication system is improved. The method is suitable for the technical field of secret communication.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Complete polarization synthetic aperture radar target decomposition method for adaptive selection unitary transformation
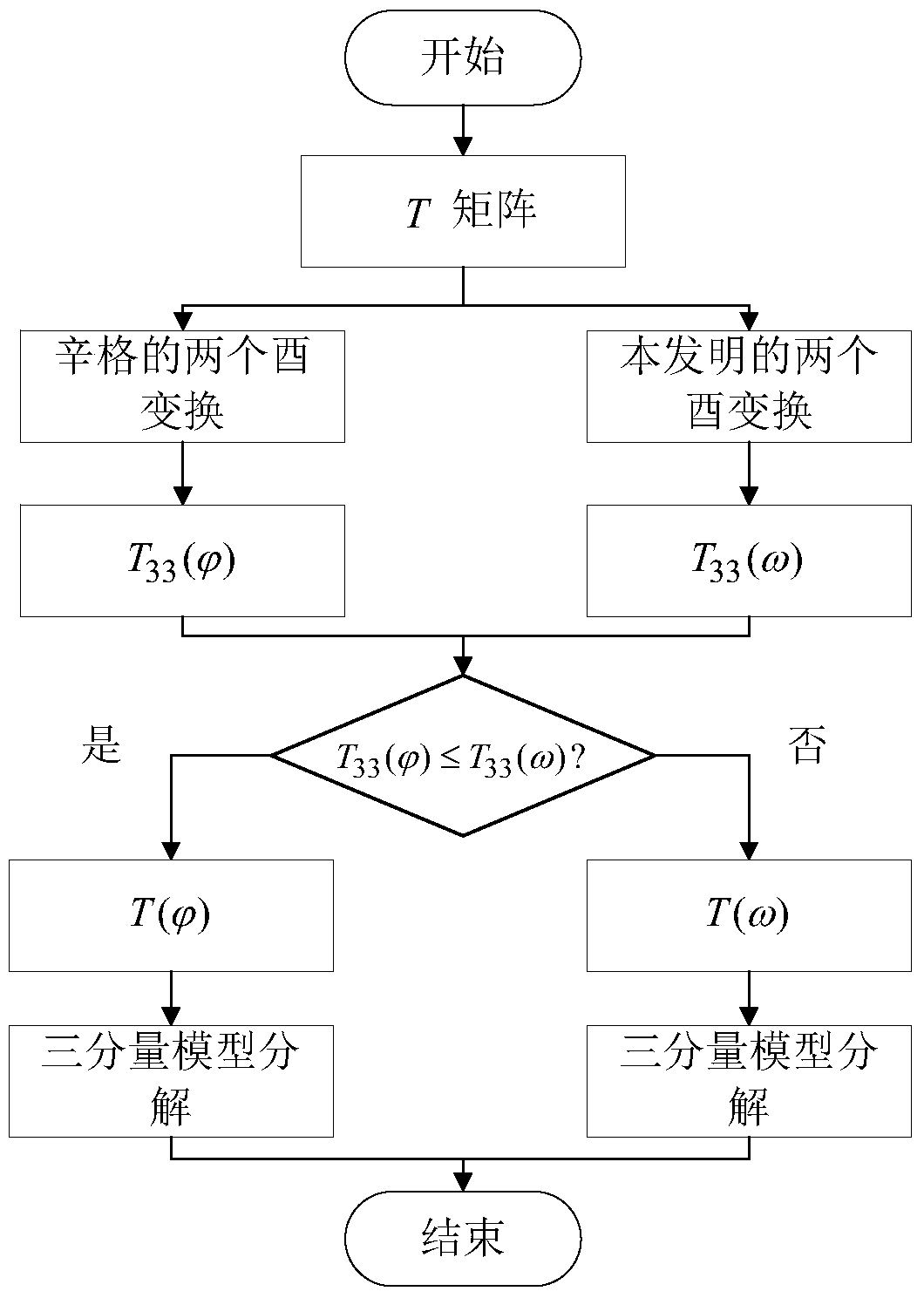
InactiveCN104698447ASuppressing Scatter Overestimation ProblemsLess freedomRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarOmega
The invention provides a complete polarization synthetic aperture radar target decomposition method for adaptive selection unitary transformation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) performing two unitary transformations for singh for data coherence T matrix of the complete polarization synthetic aperture radar to obtain the matrix, (the formula is as shown in specification); (2) performing other two unitary transformations for the coherence T matrix to obtain the matrix T(omega), wherein the first unitary transformation is used for performing the spiral angle compensation and restraining the volume scattering excessive estimation of model decomposition, the second unitary transformation is used for further restraining the volume scattering excessive estimation and reducing one degree of freedom of the coherence T matrix; (3) comparing with element (the formula is as shown in specification) of the matrix (the formula is as shown in specification) with the element T33(omega) of the matrix T(omega); if (the formula is as shown in specification), and (the formula is as shown in specification), otherwise, T is equal to T(omega); (4) performing three-component model decomposition on coherence T matrix. The two unitary transformations for singh in the step (1) or the two unitary transformations in the step (2) can be selected for the coherence T matrix in a self-adaption mode by the method according to the real situation of the object, and the volume scattering excessive estimation problem of the model decomposition can be effectively restrained.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
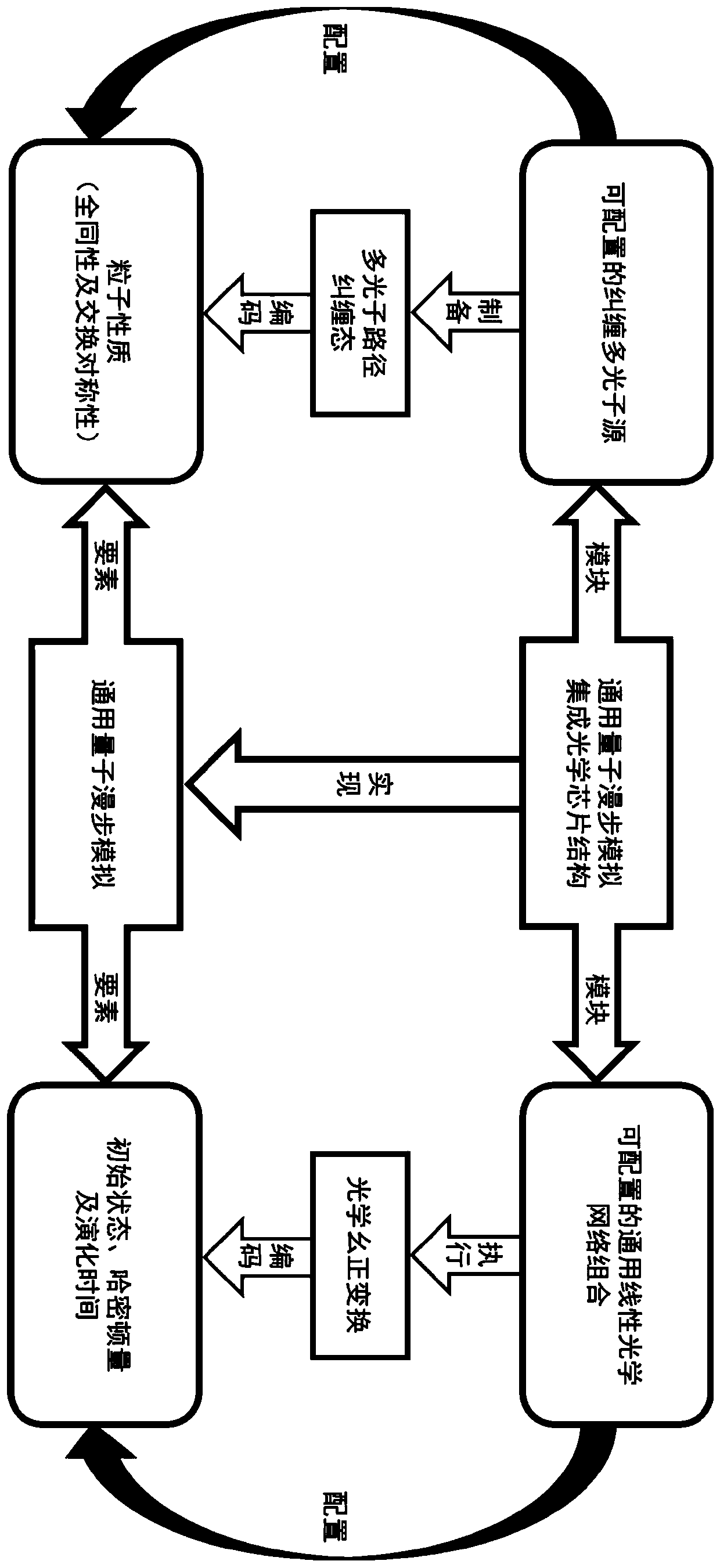
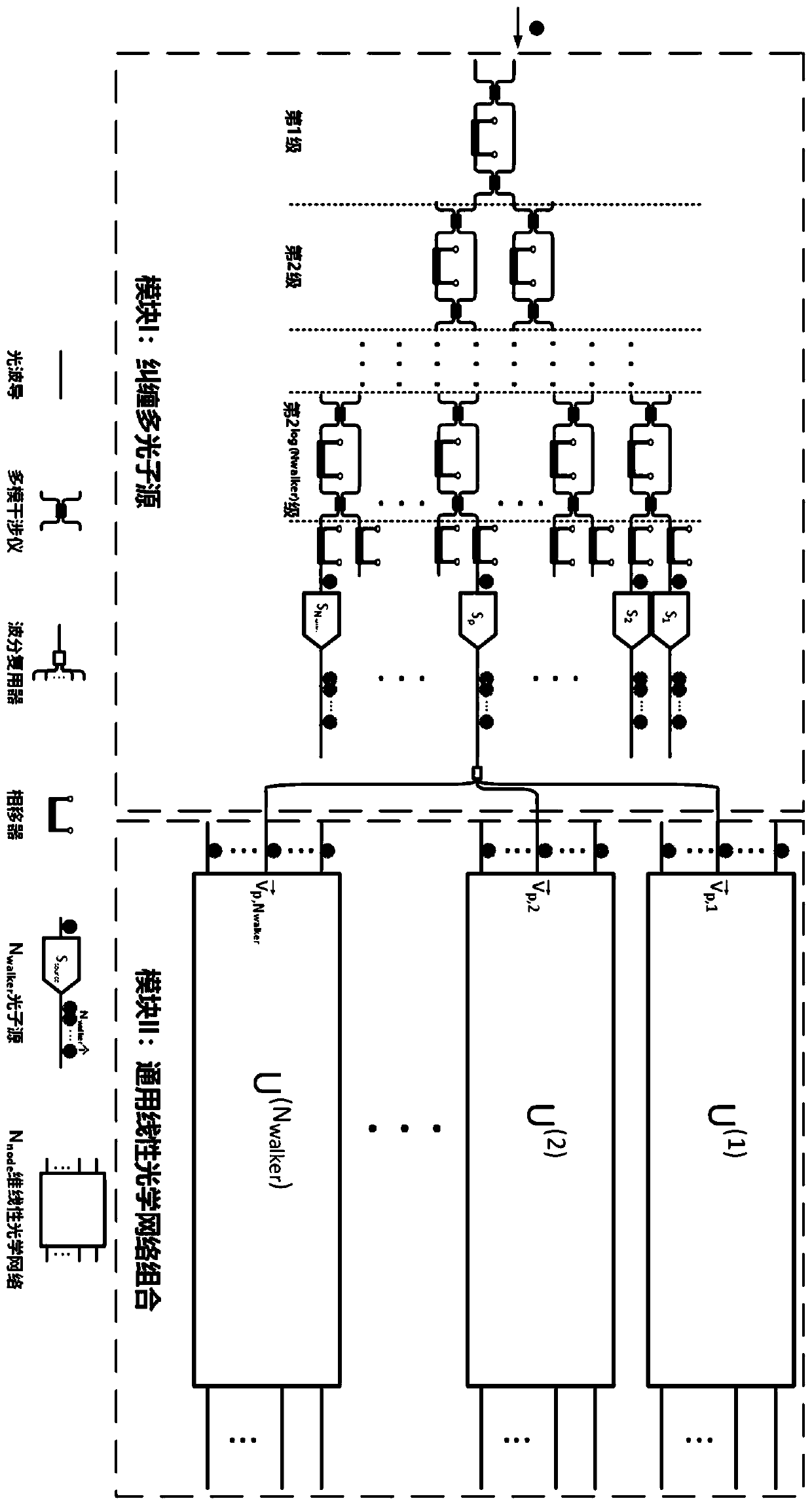
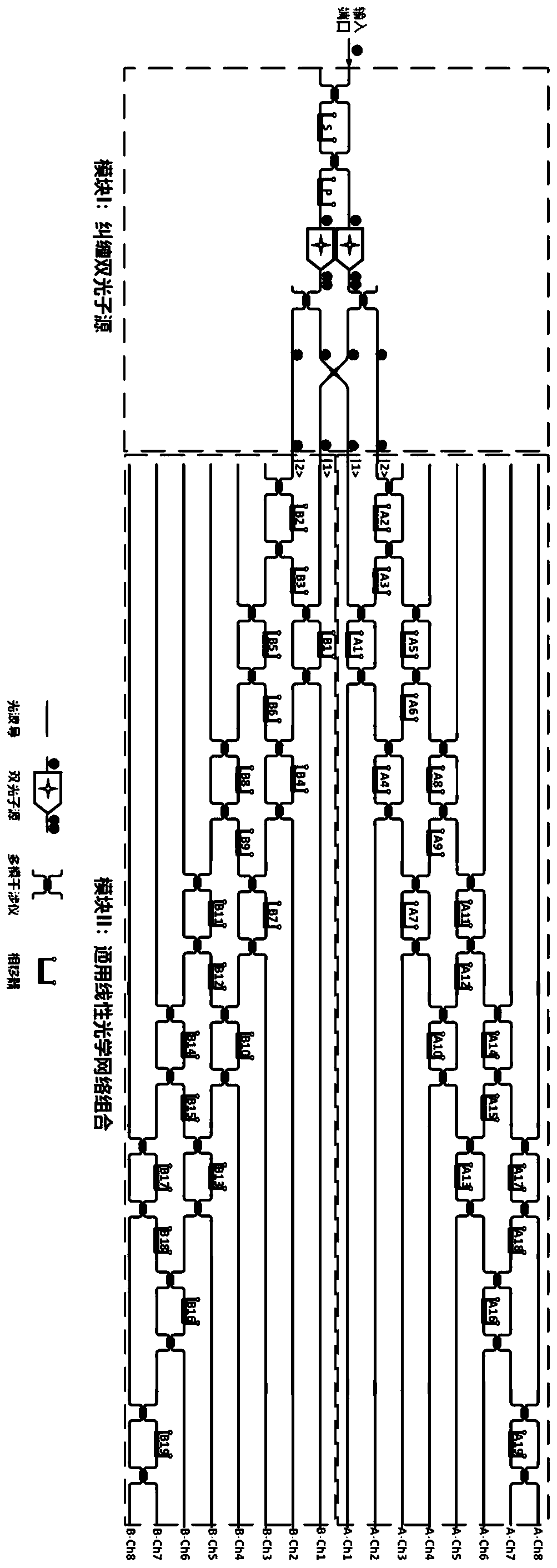
Universal quantum walk analog chip structure based on integrated optics
ActiveCN111478735AQuantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationParticle physicsAnalog chip
The invention discloses a universal quantum walk analog chip structure based on integrated optics. A multi-photon source capable of preparing a multi-photon path entangled state and a linear optical network capable of achieving unitary transformation are organically combined and used in cooperation, and the corresponding relation among the on-chip multi-photon path entangled state, the unitary transformation, the quantum walking state of multi-particle quantum walking and the walking process is established. Optical unitary transformation is realized by regulating and controlling a multi-photonpath entangled state prepared by a multi-photon source and a universal linear optical network; the chip structure can carry out general quantum walk simulation with configurable elements such as evolution Hamiltonian quantity, evolution time, initial evolution state, particle properties (such as particle isotropy and particle exchange symmetry) and the like of multi-particle quantum walk.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
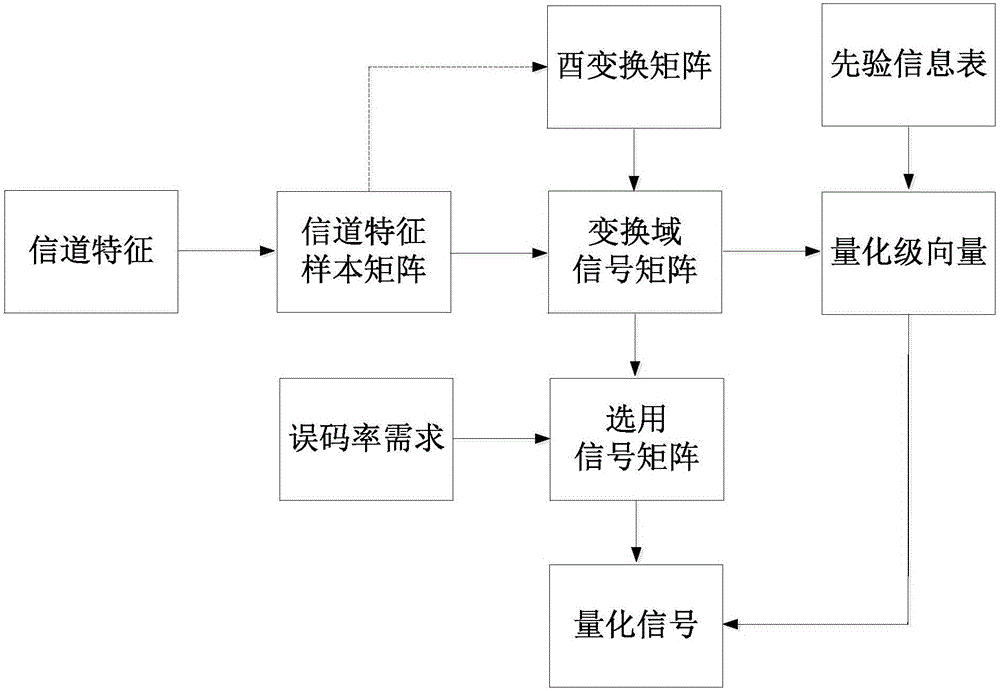
Wireless channel characteristic stepwise quantification method based on unitary transformation preprocessing
ActiveCN106027242AGood preprocessingImprove consistencyKey distribution for secure communicationPropogation channels monitoringSecure communicationHigh rate
The invention discloses a wireless channel characteristic stepwise quantification method based on unitary transformation preprocessing. The method comprises the following steps: making a party A and a party B in wireless communication perform unitary-transformation-based preprocessing on channel detection results; quantifying preprocessed signal vectors with different signal-to-noise ratios with different quantification levels; and finally, using generated quantification bit streams as inputs of subsequent wireless channel key generation steps such as an information reconciliation step. Through adoption of the method, the consistency of the channel detection results of the party A and the party B in the wireless communication can be improved effectively; the auto-correlation of the channel detection results is lowered; and the two parties of the communication can generate quantification bit streams with high rate, high consistency and low redundancy. The method is applied to the field of wireless channel key generation, can be specifically applied to the fields of secure communications, military communications and the like, and can be extended to a multi-node communication scene. Through adoption of the method, the security of a wireless communication system is enhanced.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
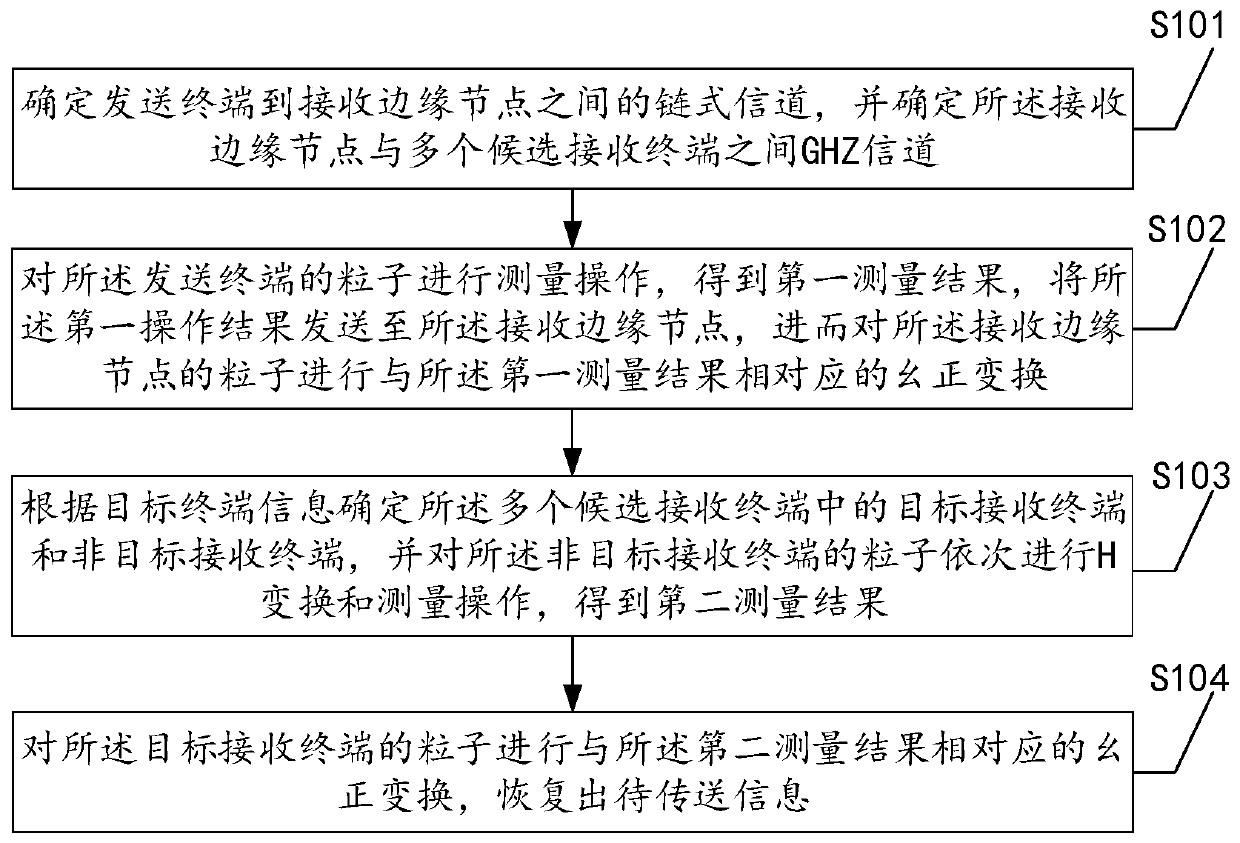
Quantum communication method and system for terminal delay selection
ActiveCN110212978AImprove transmission efficiencyReduce latencyPhotonic quantum communicationInformation transmissionTime delays
The invention discloses a quantum communication method and system for terminal delay selection, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the measurement operation of particles of a sending terminal, and obtaining a first measurement result; performing unitary transformation corresponding to the first measurement result on the particles of the receiving edge node; sequentially performing Htransformation and measurement operation on the particles of the non-target receiving terminal to obtain a second measurement result; and carrying out unitary transformation corresponding to the second measurement result on the particles of the target receiving terminal, and recovering the to-be-transmitted information. Visibly, according to the scheme, under the condition that the receiving terminal is not completely determined, the particle state can start the transmission behavior, the receiving edge node can select the receiving terminal while the particle state is in channel transmission,and after the final receiving terminal is determined, the particles have transmitted most paths, so that the time delay is effectively reduced, and finally information receiving is completed. The quantum communication process of selecting the terminal is delayed under the condition that the terminal is uncertain, and the information transmission efficiency is improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com