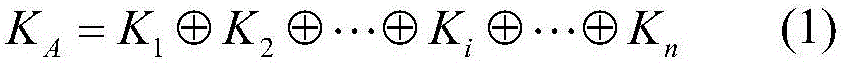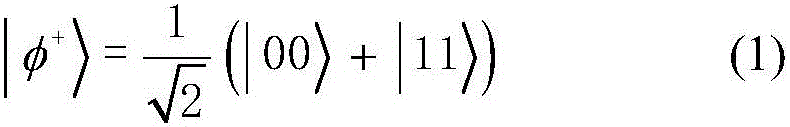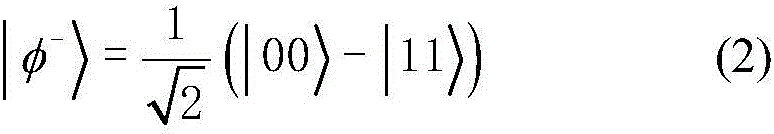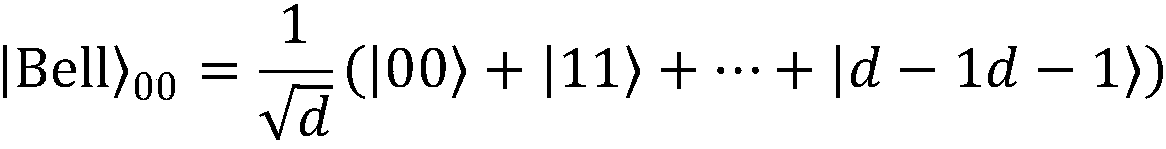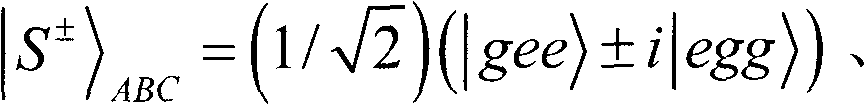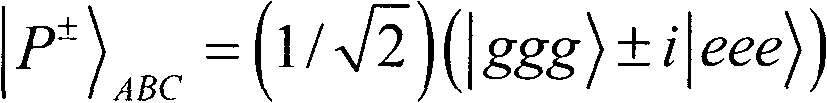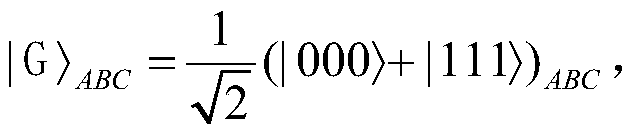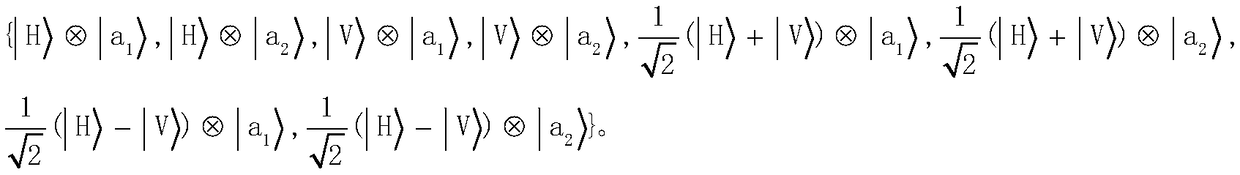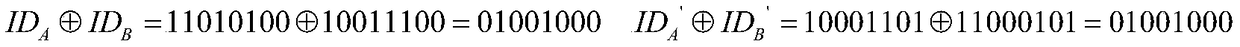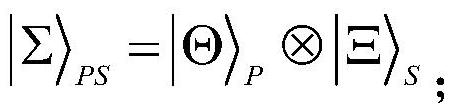Patents
Literature
152 results about "Bell state" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
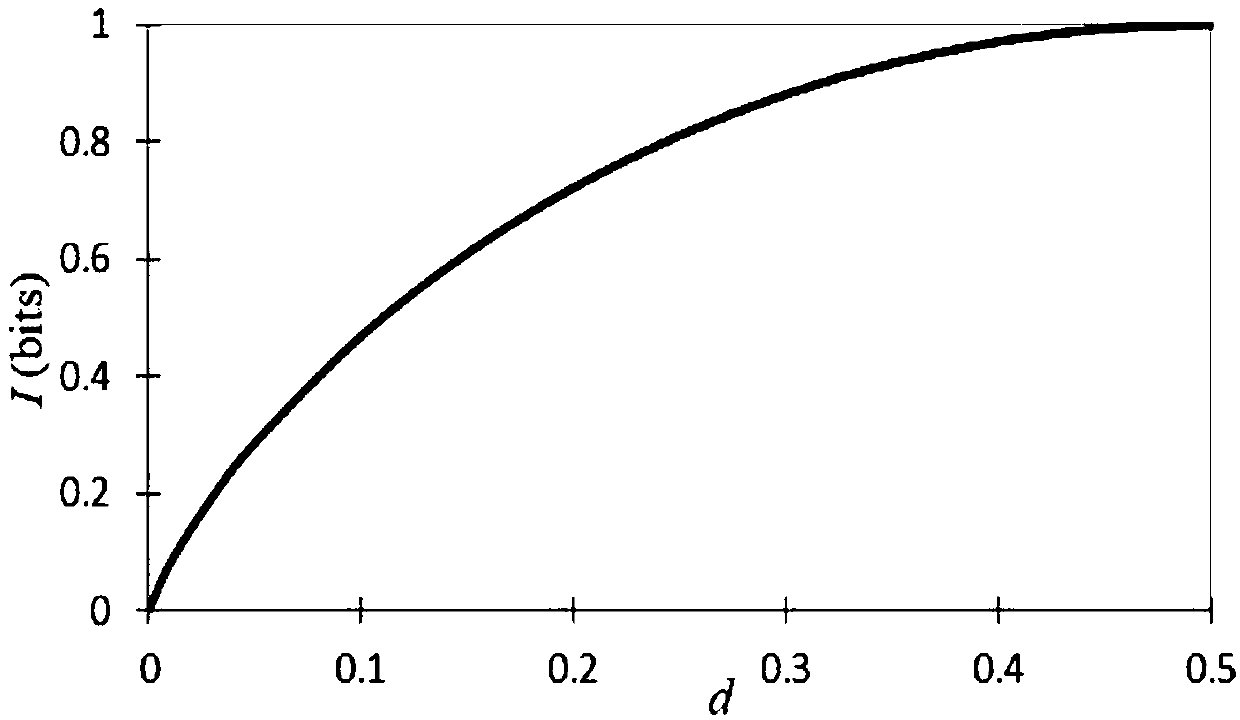
The Bell states, a concept in quantum information science, are specific quantum states of two qubits that represent the simplest (and maximal) examples of quantum entanglement. The Bell states are a form of entangled and normalized basis vectors. This normalization implies that the overall probability of the particle being in one of the mentioned states is 1: 〈Φ|Φ〉=1. Entanglement is a basis-independent result of superposition.
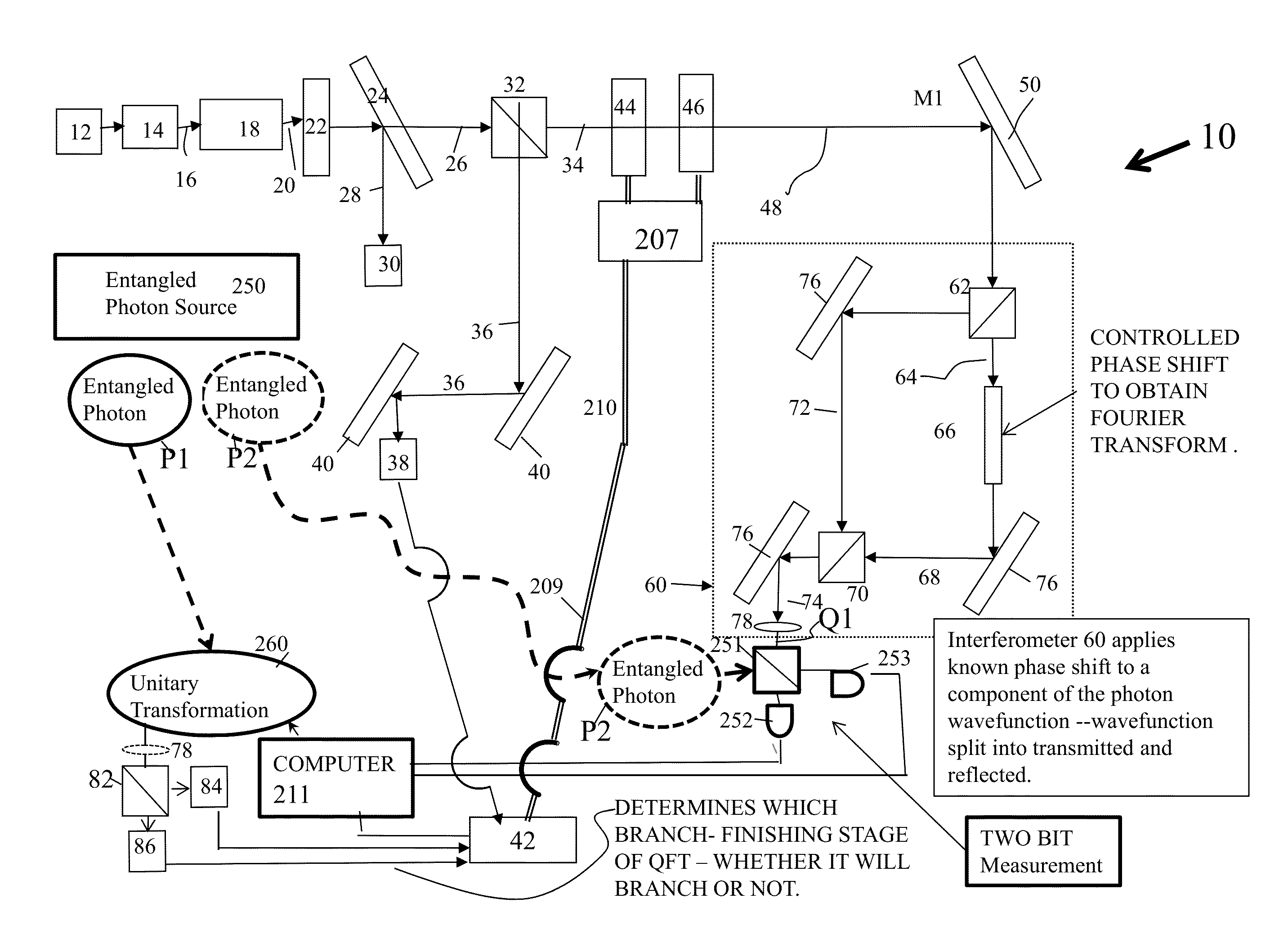
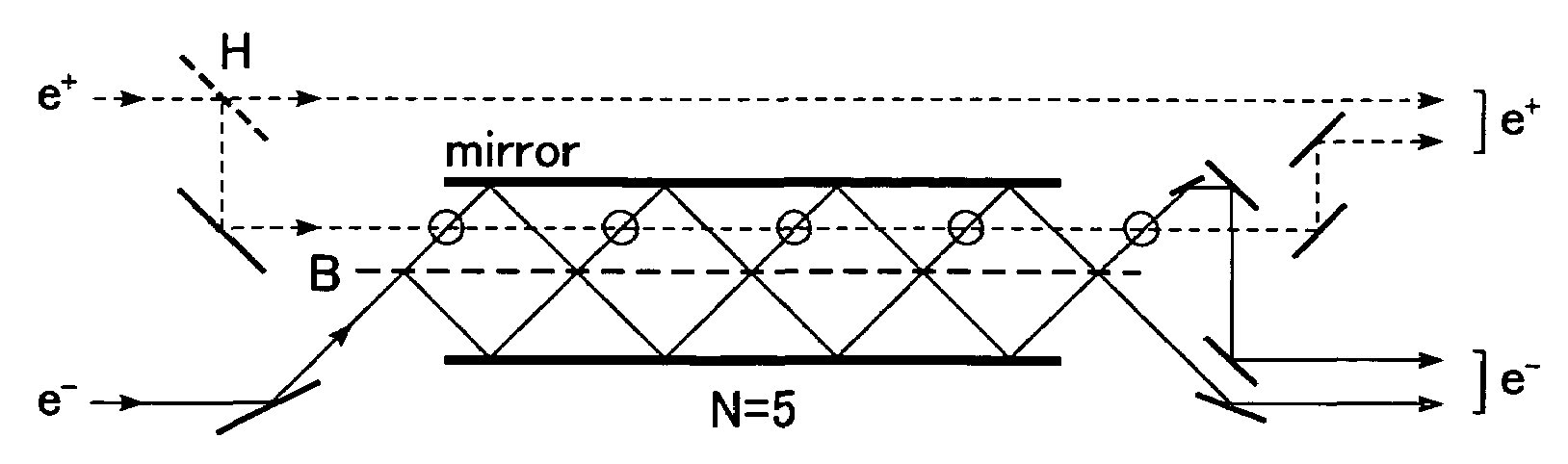
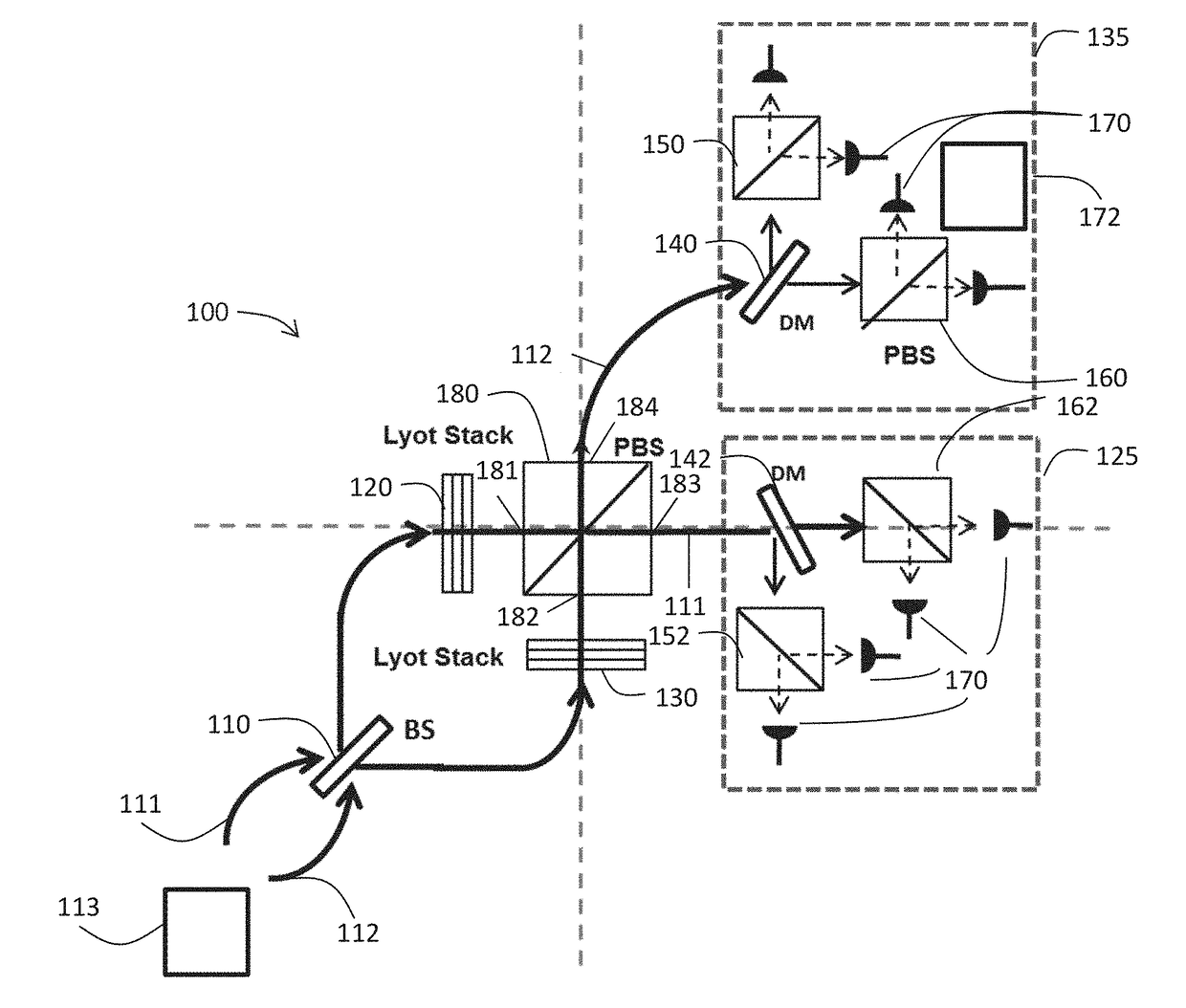
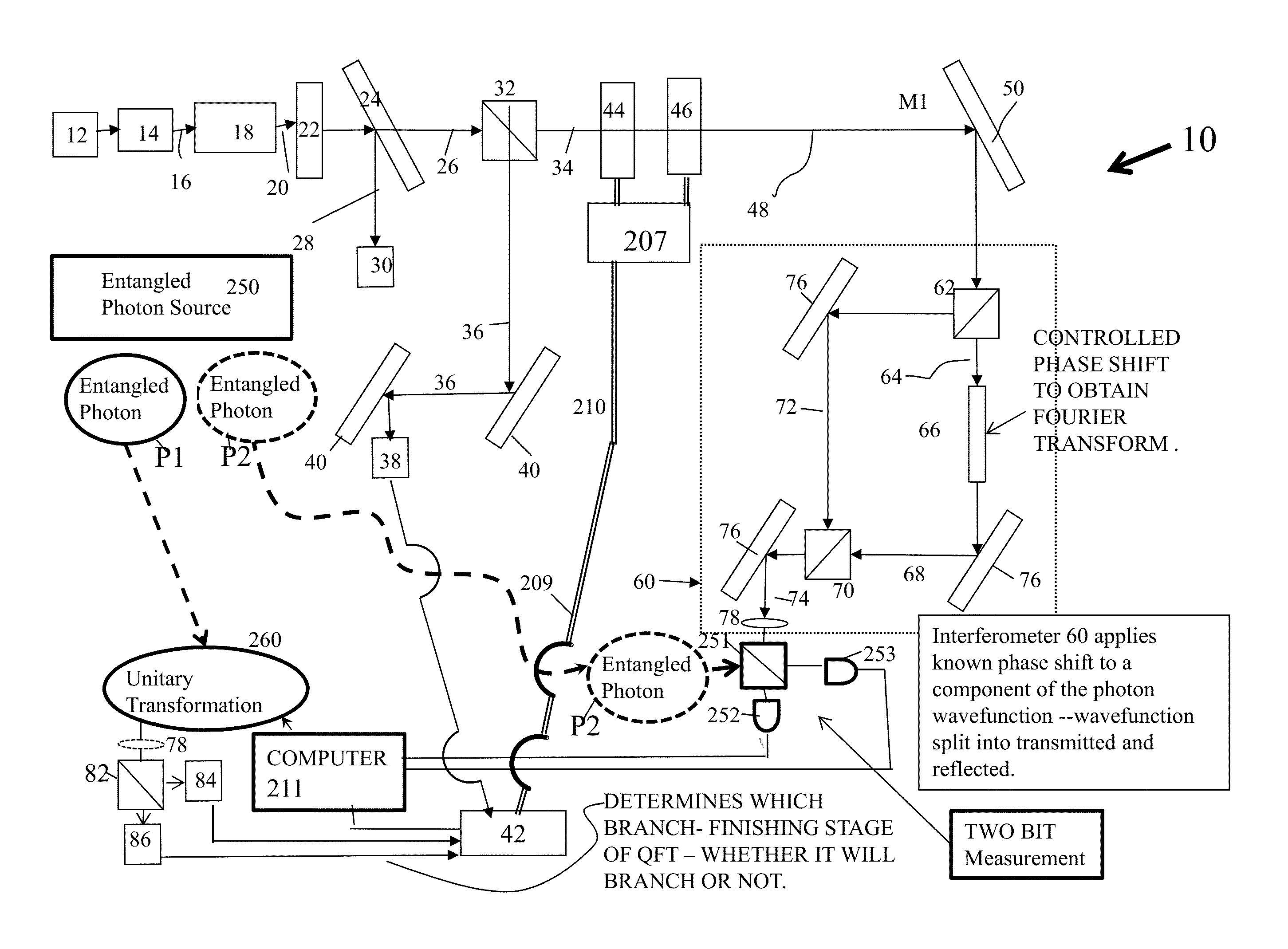
System and method for quantum based information transfer
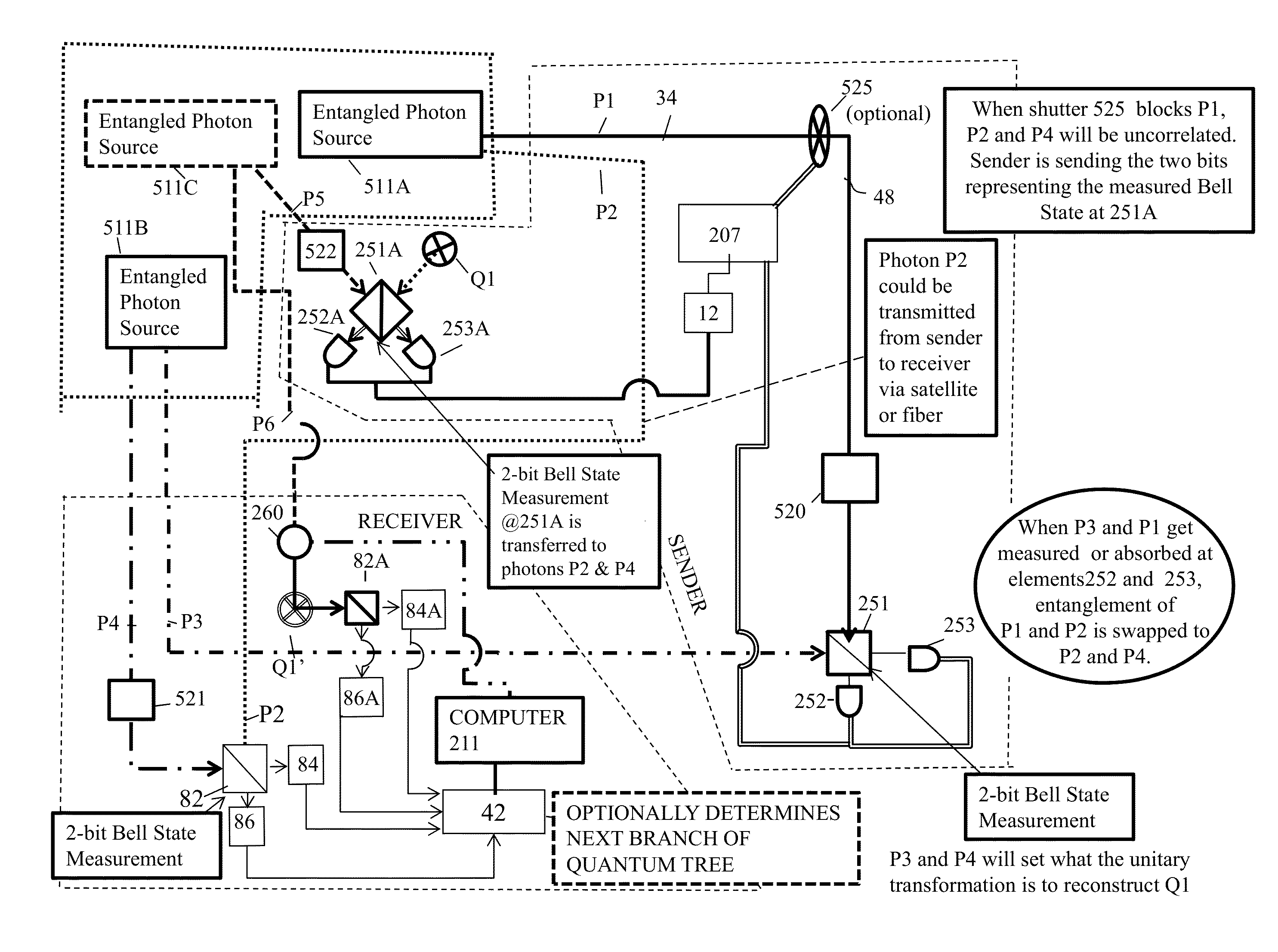
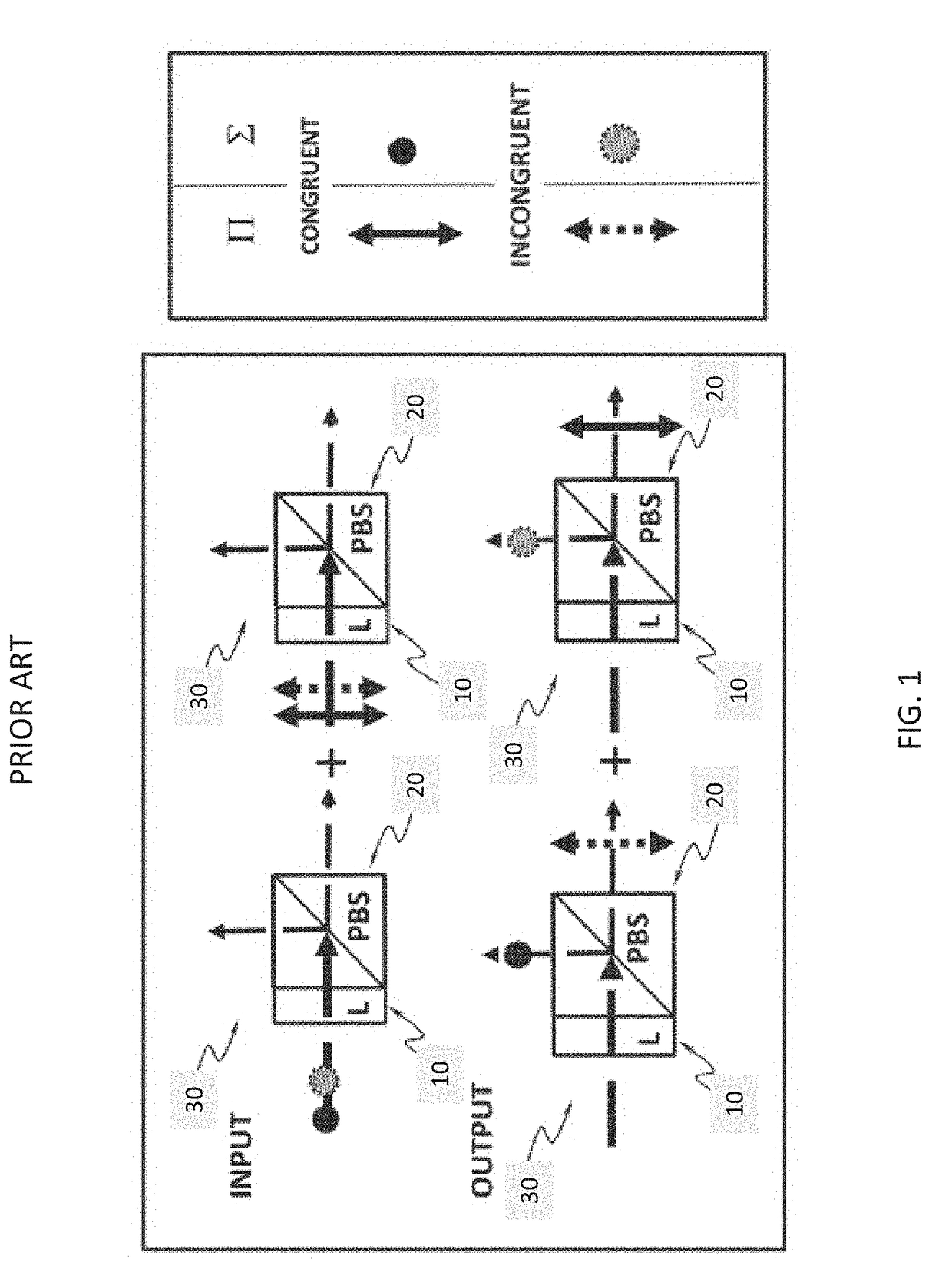
A system for communicating data comprising sender and receiver subsystems; at least one data input; at least one entangled photon source; first photons of the pairs of entangled photons outputted by the at least one photon source being processed by one of the sender or receiver subsystem; second photons of the pairs of entangled photons being processed by the other of the sender or receiver subsystem; a photonic element configured to receive the first photons of the pairs of entangled photons and enable interference therebetween; at least one absorber configured to absorb the first photons after passage through the beam splitter, the absorbance of the first photons operating to transfer the properties of the entanglement to the second photons of the pairs of entangled photons; and a Bell state measurement element operatively associated with the receiver subsystem configured to measure the second photons of the pairs of entangled photons.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
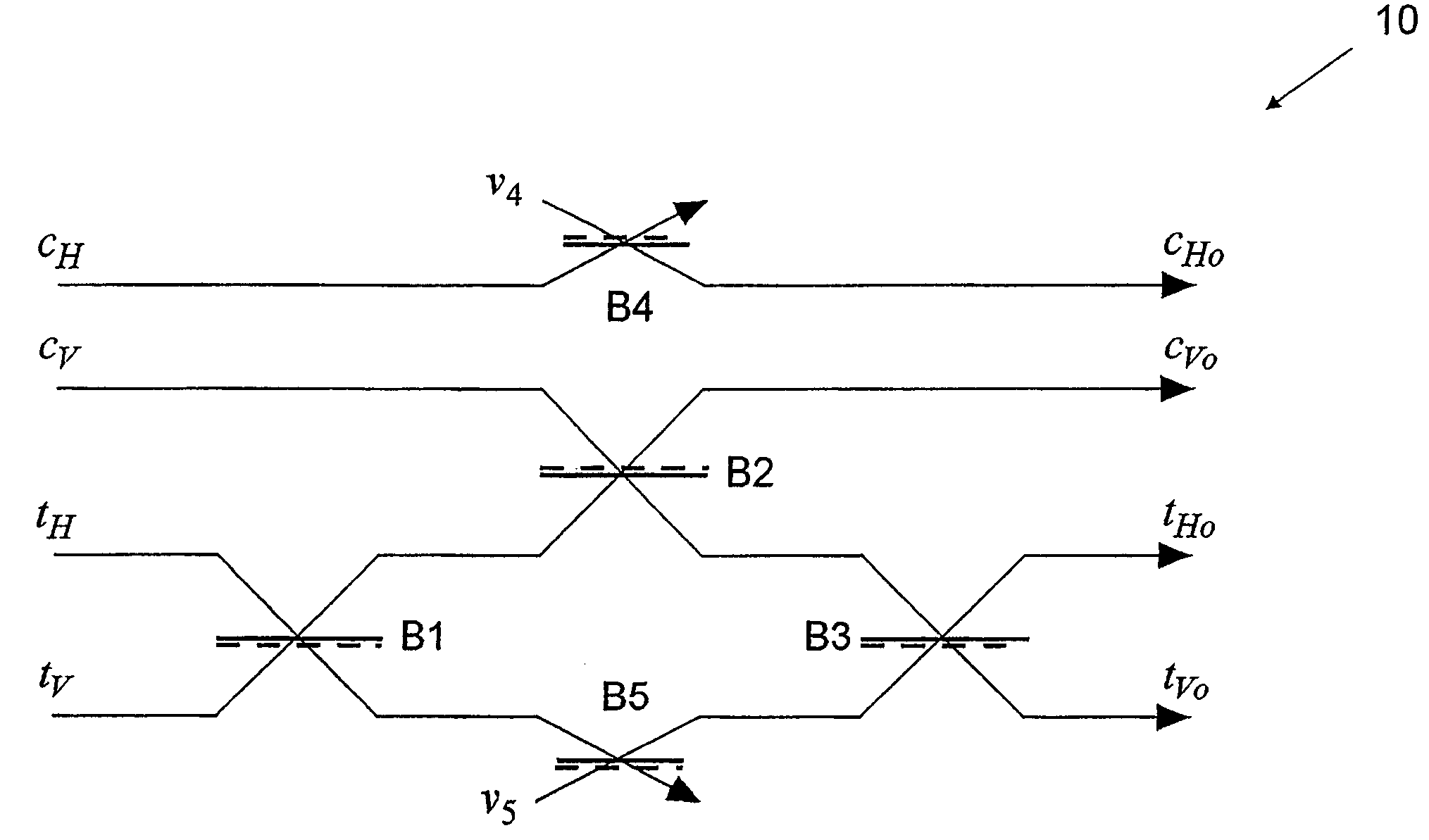
Quantum optical CNOT gate
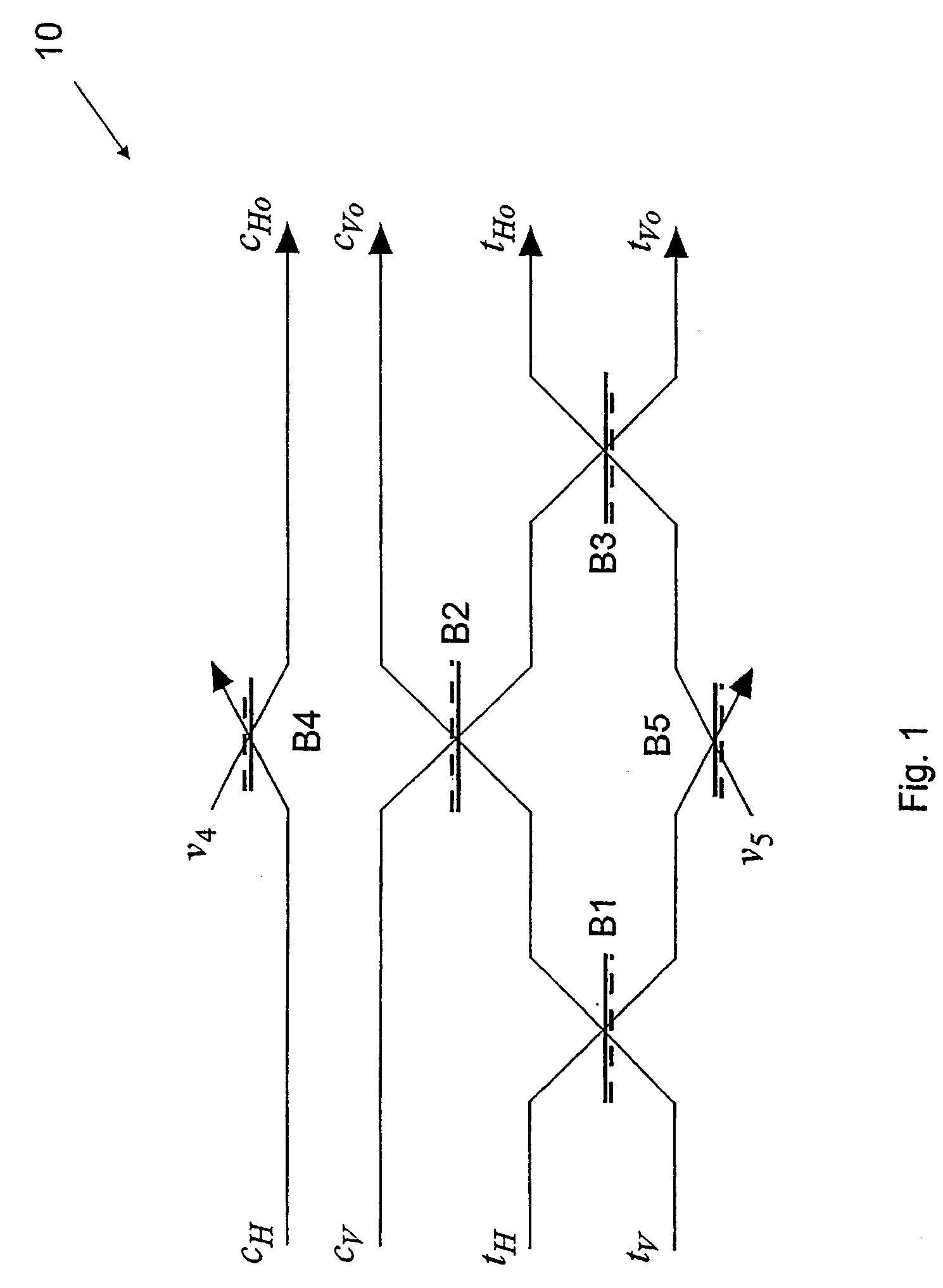
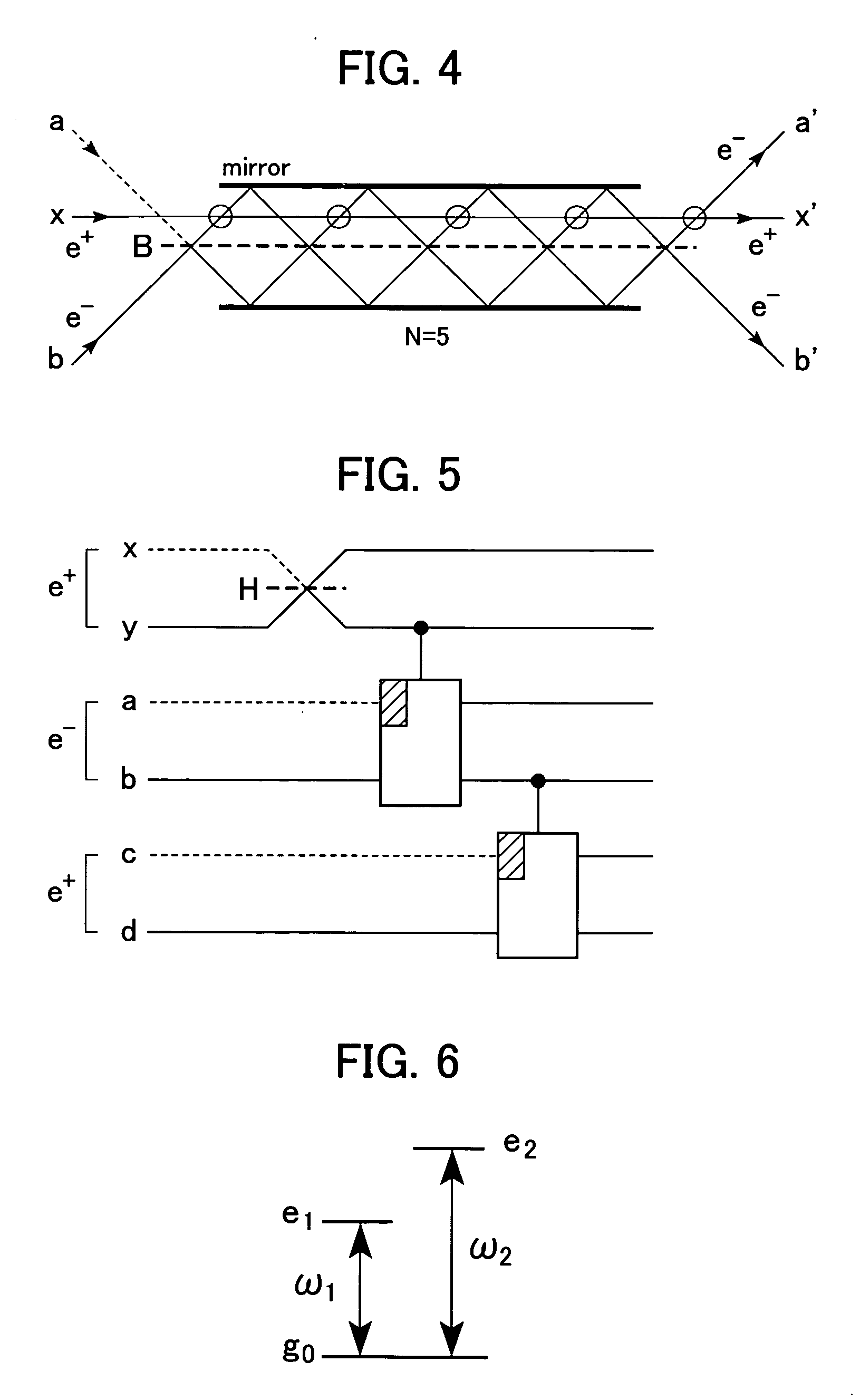
A nondeterministic quantum CNOT gate (10) for photon qubits, with success probability 1 / 9, uses beamsplitters (B1–B5) with selected reflectivities to mix control and target input modes. It may be combined with an atomic quantum memory to construct a deterministic CNOT gate, with applications in quantum computing and as a Bell-state analyser.
Owner:THE UNIV OF QUEENSLAND
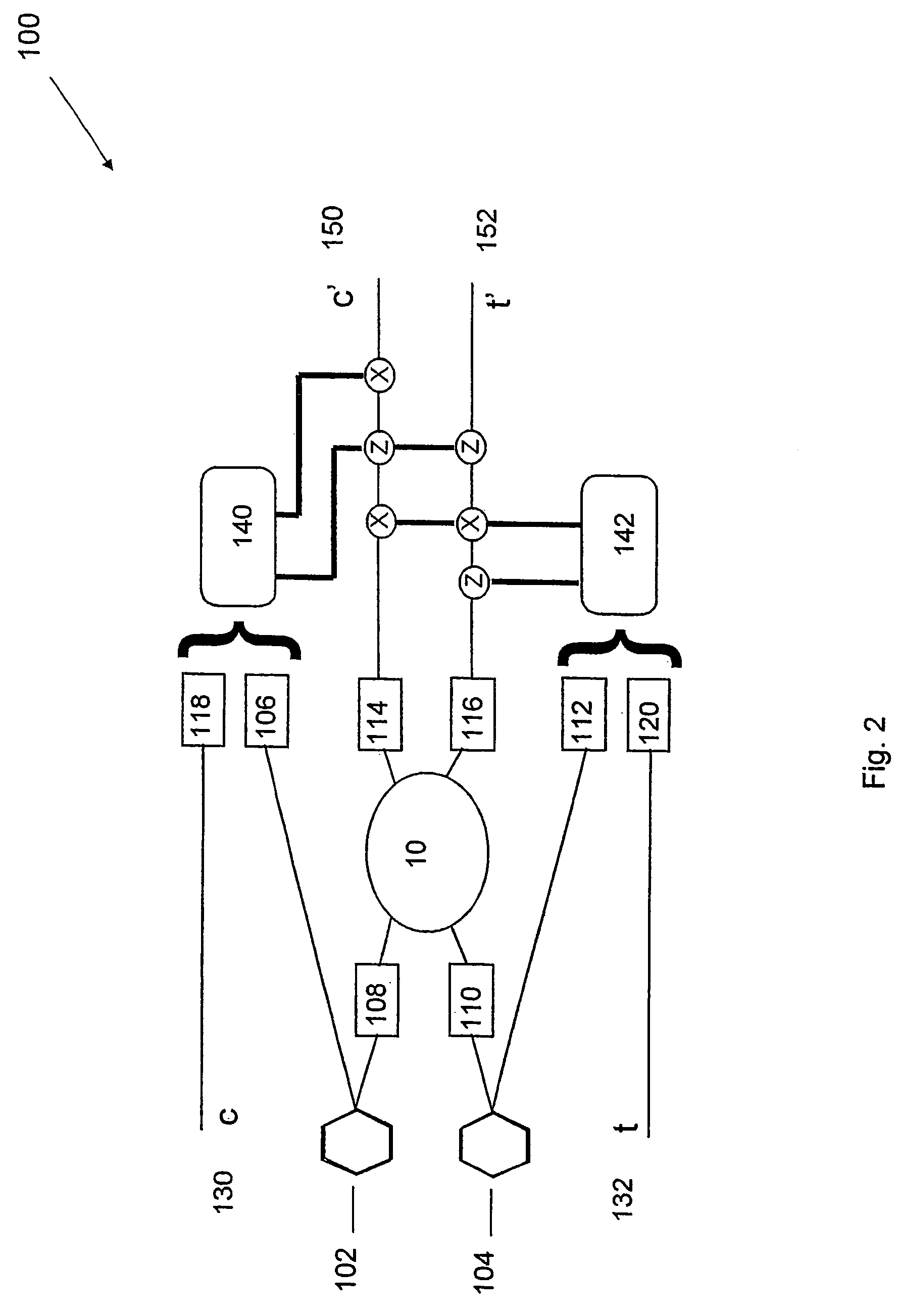
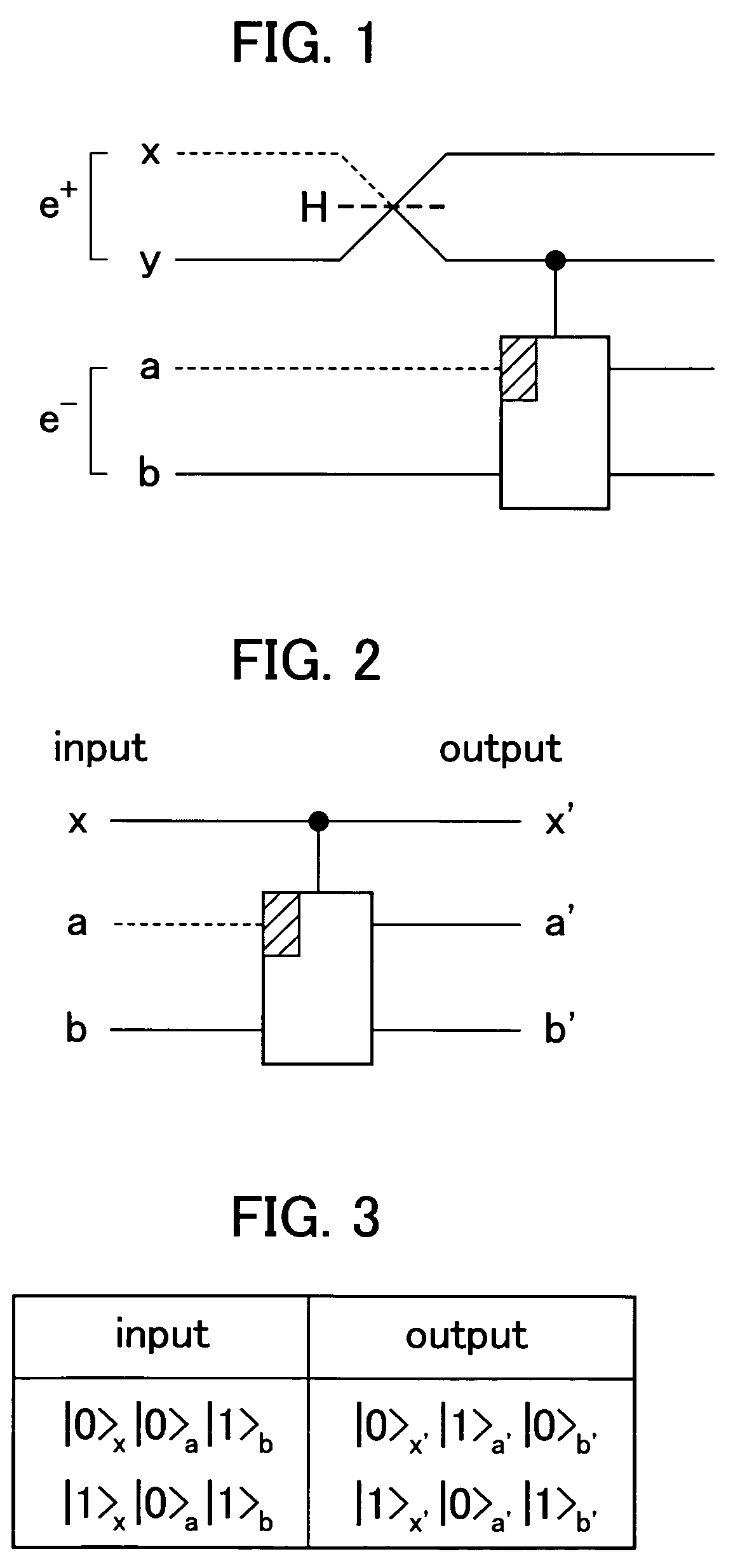
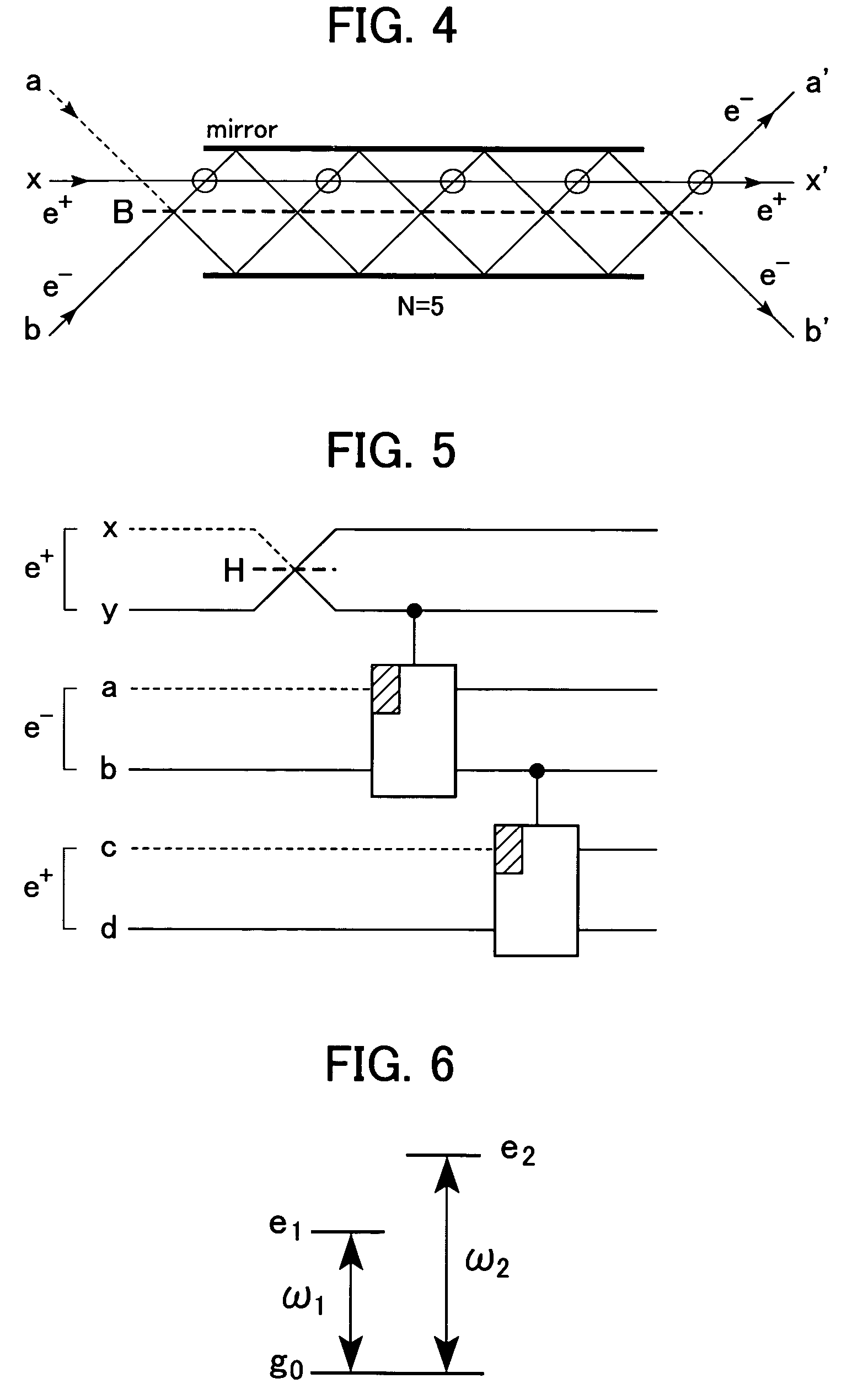
Quantum-state-generating apparatus, Bell measurement apparatus, quantum gate apparatus, and method for evaluating fidelity of quantum gate
InactiveUS20050133780A1Promote generationQuantum computersComputing operations for integration/differentiationBell stateBeam splitter
An apparatus for generating a quantum state of a two-qubit system including two qubits, each qubit being represented by a particle which invariably travels through one of two paths, includes a quantum gate composed of an interferometer for implementing an-interaction-free measurement. The apparatus receives two particles having no correlation and generates a Bell state with asymptotic probability 1. A Bell measurement of a state of a two-qubit system is performed by observing a quantum gate composed of the interferometer after the quantum gate has processed the state and selecting the state from the Bell bases. An approximate fidelity of a quantum gate composed of the interferometer is calculated, if an absorption probability with which a first particle absorbs a second particle in the interferometer is less than 1, under the condition that the number of times the second particle hits beam splitters in the interferometer is sufficiently large.
Owner:CANON KK
Controlled bi-directional quantum secure direct communication protocol free of information leakage
Bi-directional quantum secure direct communication aims at enabling two legal communication parties to exchange secret information of each other simultaneously. The invention provides a controlled bi-directional quantum secure direct communication protocol free of information leakage. In the protocol, two legal communication parties Alice and Bob are controlled by a controller Charlie to achieve exchange of the secret information of each other without information leakage. The protocol utilizes measuring relevancy after entanglement swapping of 3 Bell states to solve an information leakage problem. In addition, the protocol only uses the Bell states as quantum resources, only Bell measuring is required to be conducted, and the controlled bi-directional quantum secure direct communication protocol is convenient to achieve.
Owner:浙江海宁经编产业园区开发有限公司
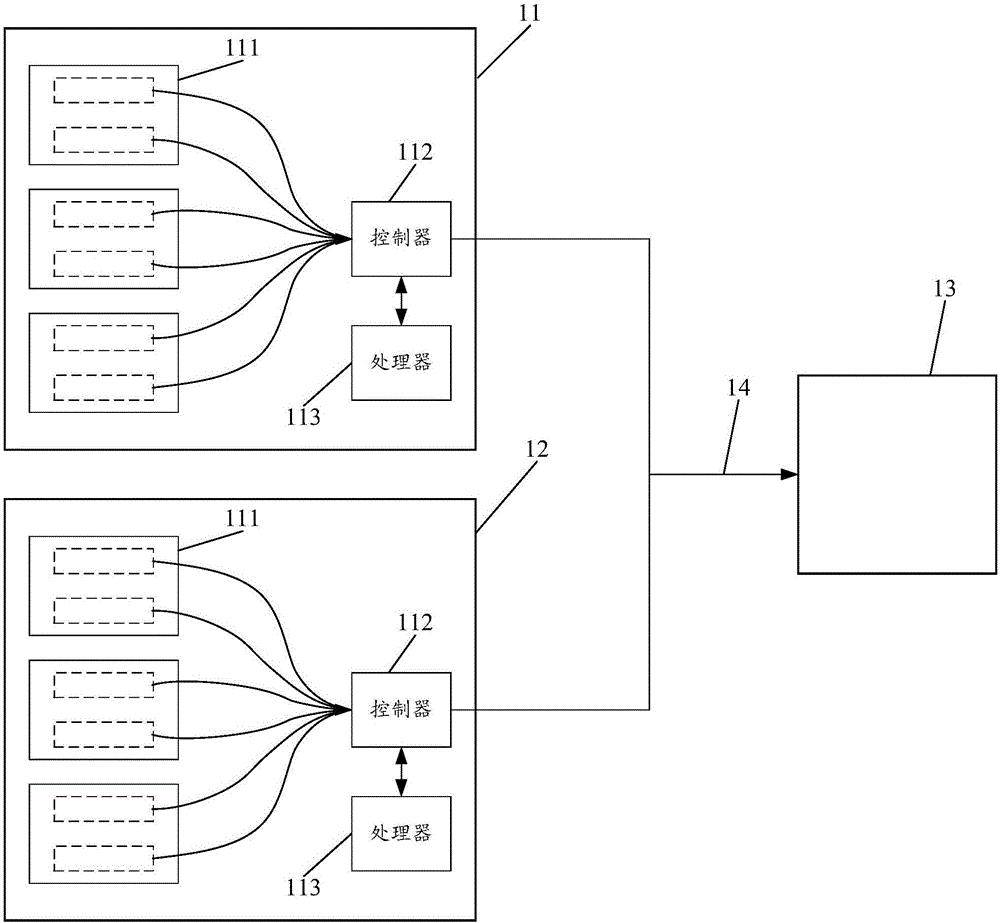
System and method for measuring device-independent quantum key distribution (QKD)
ActiveCN106712940AEnable secure distributionReduce the numberKey distribution for secure communicationBell stateThird party
The invention provides a system and method for measuring device-independent quantum key distribution (QKD). The system comprises a first-party device, a second-party device and a third-party device which are connected through a transmission channel, wherein both the first-party device and the second-party device comprise a controller, a processor and multiple lasers; the multiple lasers are used for respectively preparing the signal states and decoy states corresponding to two eigenstates of the signal measurement base and decoying the two decoy states of the measurement base; the controller selects one of the two groups of measurement bases, selects the signal states or the decoy states prepared by the corresponding lasers according to the selected measurement bases, and sends the signal states or the decoy states to the third-party device; the processor implements key post-processing on the received measurement results to obtain a secure key; and the third-party device implements Bell-state measurement on the received quantum state and releases the measurement results. By adopting the system and method provided by the invention, the number of the adopted lasers can be reduced without decreasing the performance of a QKD system, and thus the cost of the device can be lowered, the complexity of the device can be reduced, and more space of the client device can be saved.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Quantum secret sharing method based on Bell state
InactiveCN106712945ARealize secret sharingReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationBell stateQuantum efficiency
The invention discloses a quantum secret sharing method based on a Bell state. The quantum secret sharing method is characterized by comprising a secret distributor and n participants, the secret distributor distributes a random secret to the n participants, wherein each participant obtains a sub-secret, when the n participants accumulate all sub-secrets, the originally shared secret can be restored, and any information of the shared secret cannot be obtained less than n participants. By adoption of the quantum secret sharing method disclosed by the invention, the problems of participant fraud, low security, complexity and efficiency of channels in the existing quantum secret sharing process are solved, the quantum and classical resources can be saved, the operation complexity is reduced, and higher quantum efficiency is ensured.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Measurement device independent quantum key distribution system and method
ActiveCN107332627AIncreased complexityReduce transmission efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBell stateMeasurement device
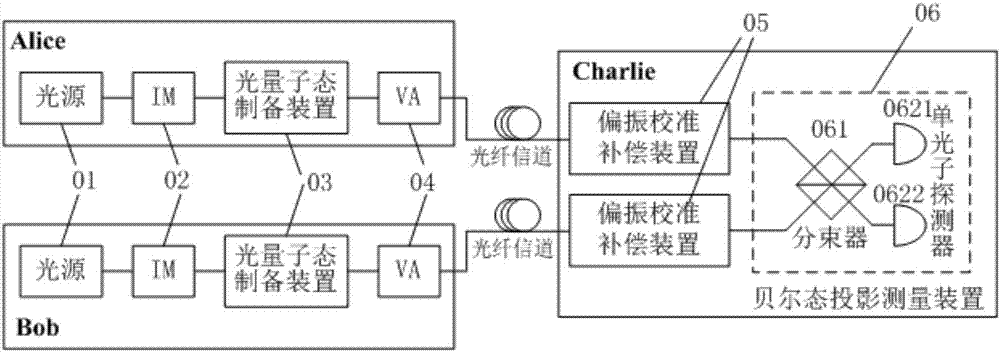
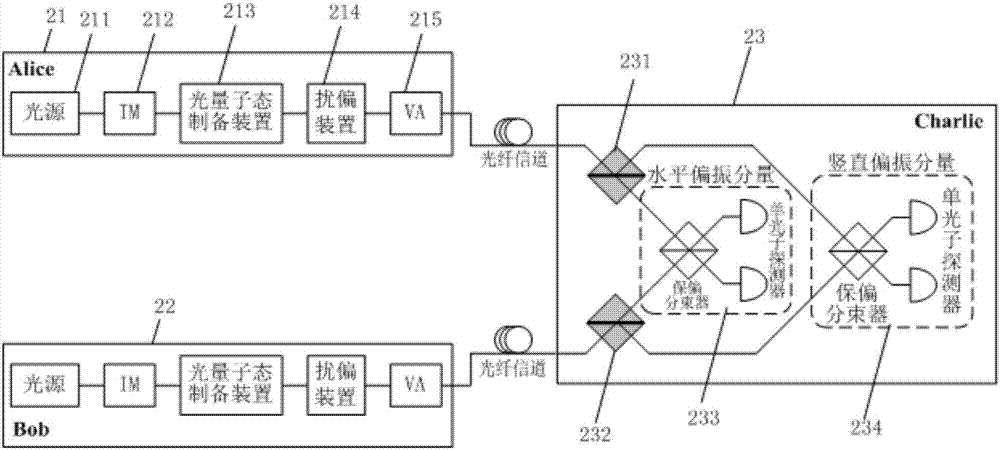
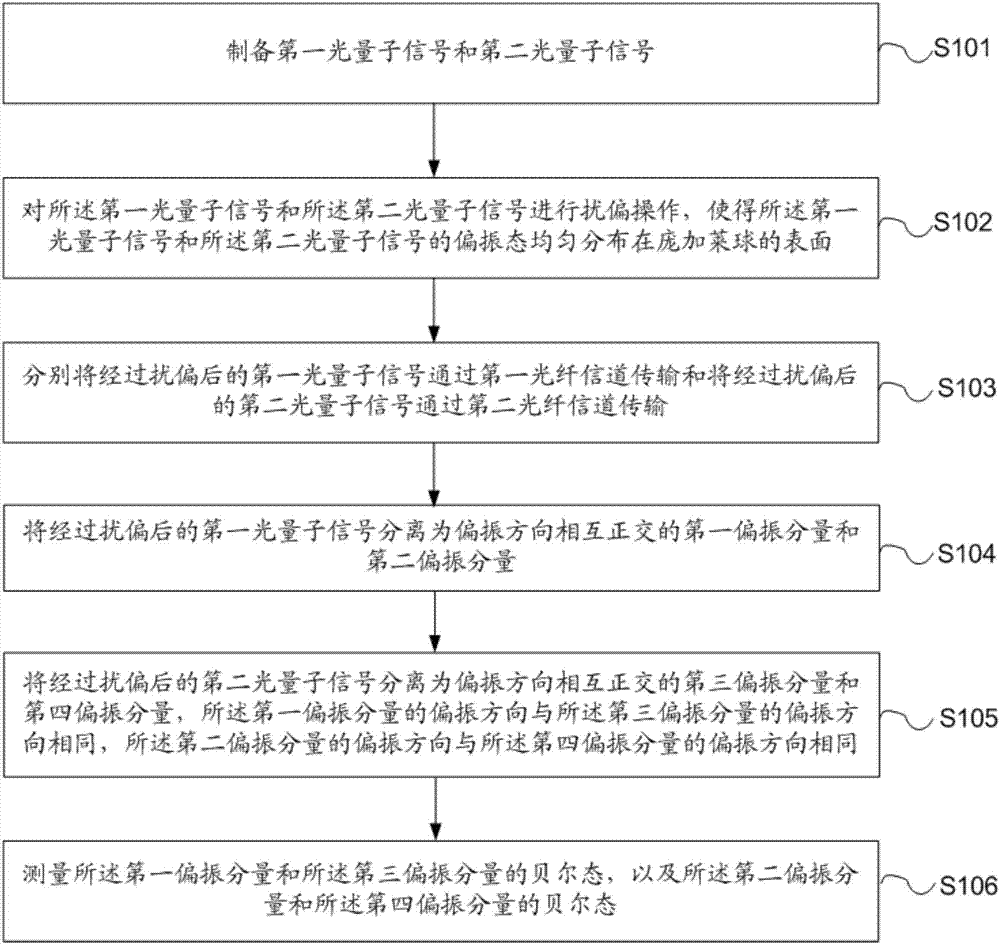
The invention provides a measurement device independent quantum key distribution system and method. Polarization scrambling is carried out on polarization states of light pulse signals or light quantum signals at quantum state preparation sending ends, so the polarization states of the light pulse signals or the light quantum signals are uniformly distributed on the surface of a Poincare sphere, and the two ways of polarization scrambled light pulse signals or light quantum signals are transmitted to a measuring end for Bell state projection measurement through independent optical channels. At the measuring end, each way of light quantum signal is separated into two orthogonal polarization components, the polarization directions of the two ways of orthogonal polarization components are the same, and the Bell state projection measurement is carried out on the polarization components with the same polarization direction.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
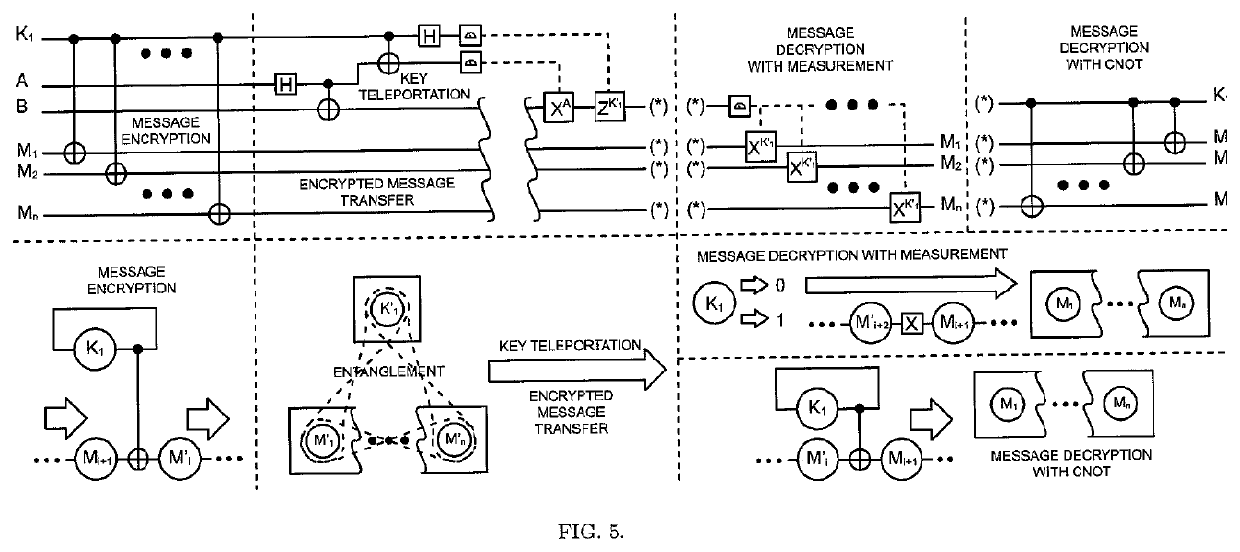
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) for entanglement encryption of quantum information
InactiveUS20210058244A1Quantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationInformation processingQuantum teleportation
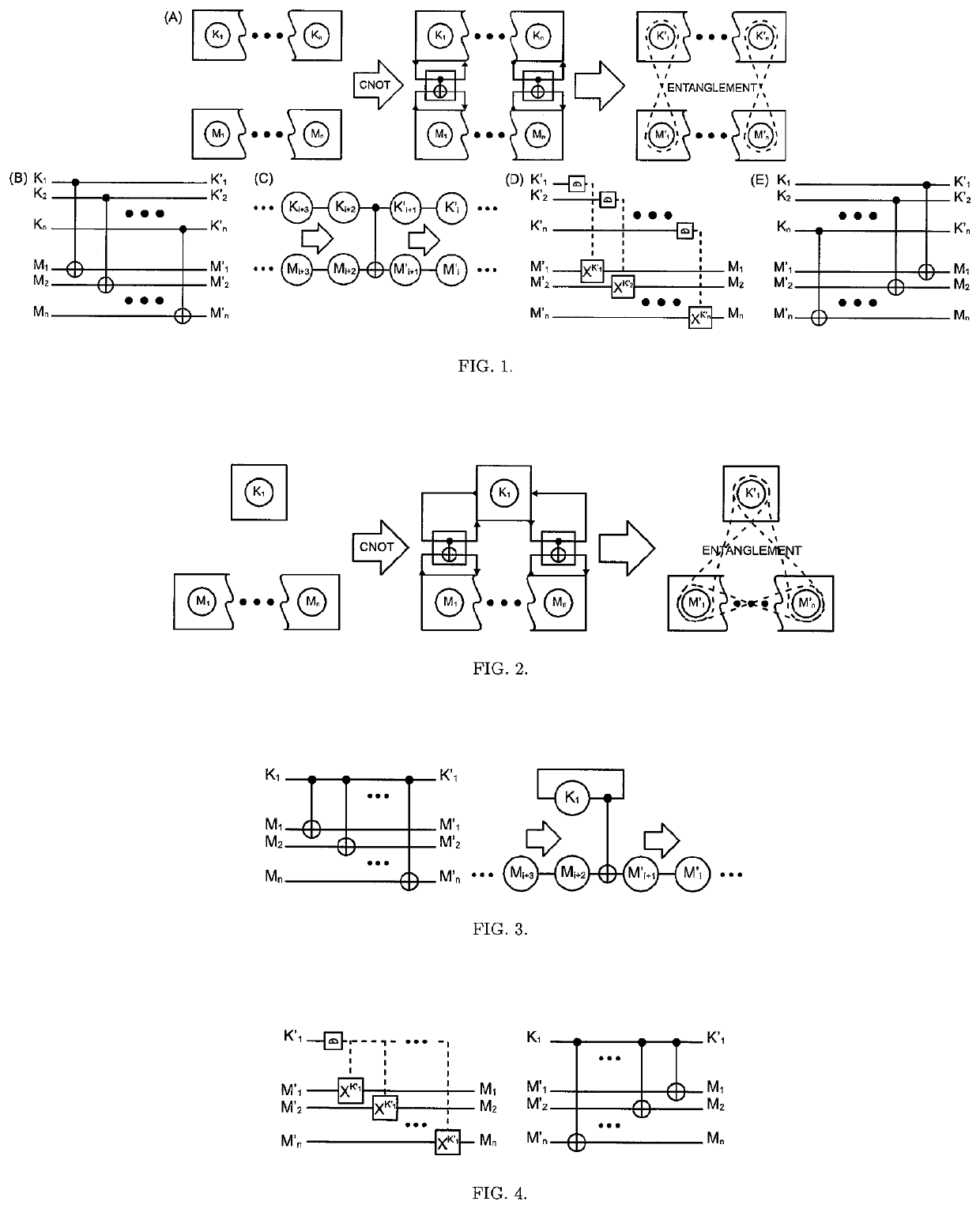
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) protocol and its generic implementing device constitute a novel, maximally efficient scheme for encryption of quantum information with a quantum key of just a single qubit in an arbitrary unknown quantum state. The OQP enables encryption of the quantum information of n qubits register with a single qubit key upon provision of a multi-qubit entanglement between the single qubit key and the n qubits of the quantum message by the iterative application of the CNOT gate on the same key qubit (control input) and subsequent qubits of the message (target input). This results in an entanglement of all n+1 qubits, which locks original quantum information qubits and the single qubit of the key in a jointly entangled state that cannot be disentangled without the single qubit key. In order to decrypt the quantum message (by its disentanglement) one needs to have the qubit key and either reverse the protocol (applying CNOT operations in the reversed order) or simply measure the entangled key qubit and then depending on the outcome either straightforwardly obtain the decrypted quantum message or its quantum negation (dealt with by again applying quantum negation on all of the message qubits thus restoring their original states). The OQP protocol and its implementing device is proposed one hundred years after the classical One-Time Pad (Vernam cipher) was invented in 1917. The main differences between two schemes show how much quantum and clasical information differ. It is of course impossible to unconditionally securely encrypt classical sequence of n bits with just 1 bit of a key or guarantee that the random key that can be used for this purpose of n bits length (same as of the message) could not be copied. In contrast both these features are possible for the quantum information as described upon the proposed invention. The main characteristic of the OQP protocol to use only a single qubit as the key to enable information-theoretic security of n qubits quantum information encryption follows from the introduction in the invention of the multi-qubit entanglement, which is a non-local, topological and non-classical phenomenon giving quantum information significant edge over its classical counterpart. The main application of the OQP protocol and its implementing generic device is to lock quantum information with the single key qubit in order to prevent any unauthorized access to it (not only a classical access upon a measurement, but more importantly a quantum access by a quantum information processing device). This application can be also extended to communication scenario jointly with the Quantum Teleportation, which without OQP requires pre-sharing of n pairs of Bell states between Alice and Bob to securely communicate n qubits long quantum message, whereas in contrast with the OQP protocol just one pair of Bell state is required to securely teleport only the single qubit key for the OQP encrypted quantum message sent through an insecure quantum channel and still be access-protected from Eve (an adversary).
Owner:COMPSECUR SP ZOO
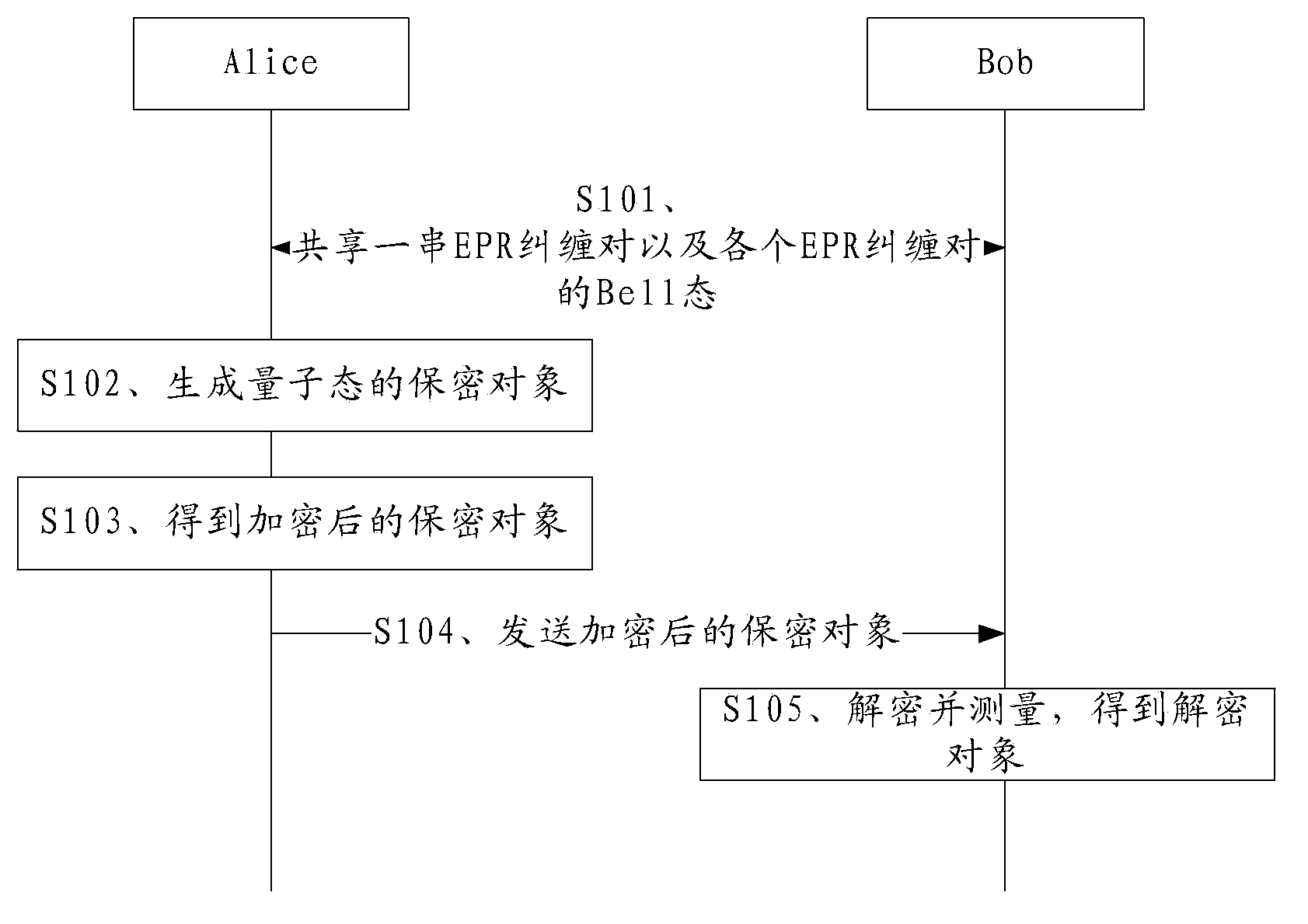
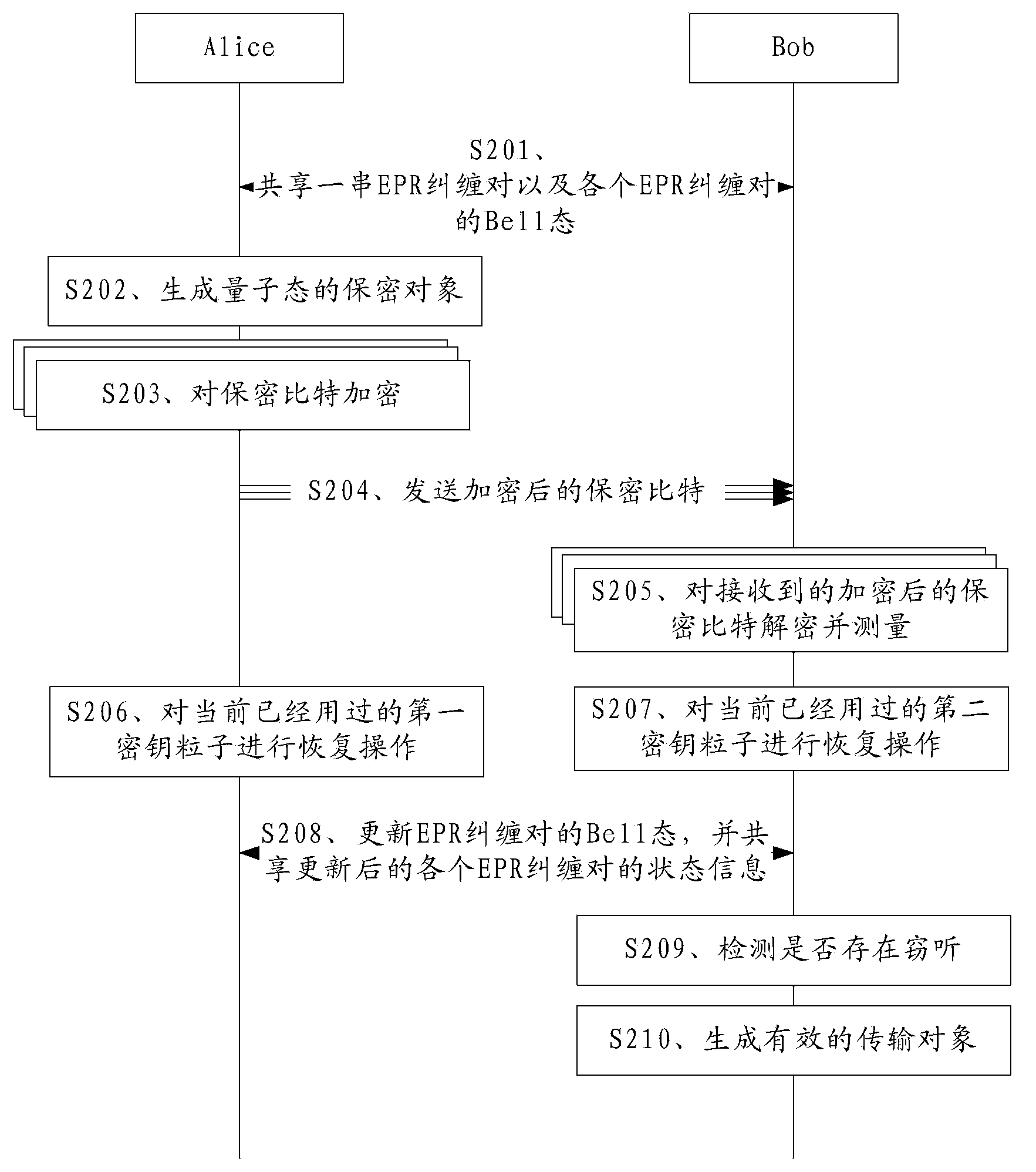
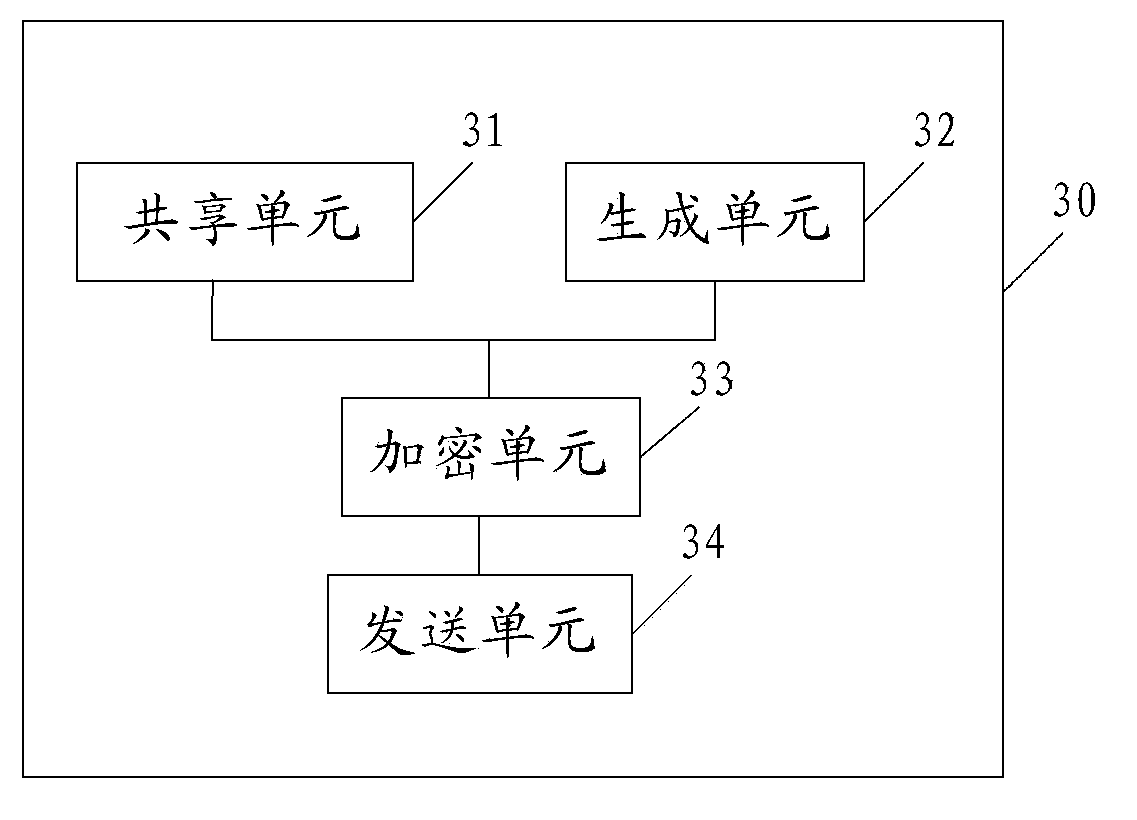
Quantum secrecy transmission method and device
ActiveCN104104500AReduce the probability of effective decipheringImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareBell state
The embodiment of the invention discloses a quantum secrecy transmission method and device, relates to the technical field of security, and is used for reducing effective decoding probability of interception information intercepted by eavesdroppers in the process of quantum secrecy transmission. The method comprises the steps that a sender and a receiver share a string of EPR entanglement pairs and state information of each EPR entanglement pair; each EPR entanglement pair is randomly in any one of two different types of Bell states or any one of at least three types of Bell states; a quantum state secrecy object is generated; the quantum state secrecy object comprises multiple secrecy bits; the secrecy bits are encrypted by utilizing first secret key particles so that the secrecy object after encryption is obtained; the secrecy object after encryption is sent to the receiver so that the secrecy object after encryption is decrypted and measured by the receiver by utilizing second secret key particles according to the Bell state of the EPR entanglement pairs so that a classic state decryption object is obtained; and the classic state decryption object comprises multiple decryption bits.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
Continuous variable quantum entanglement source generating device
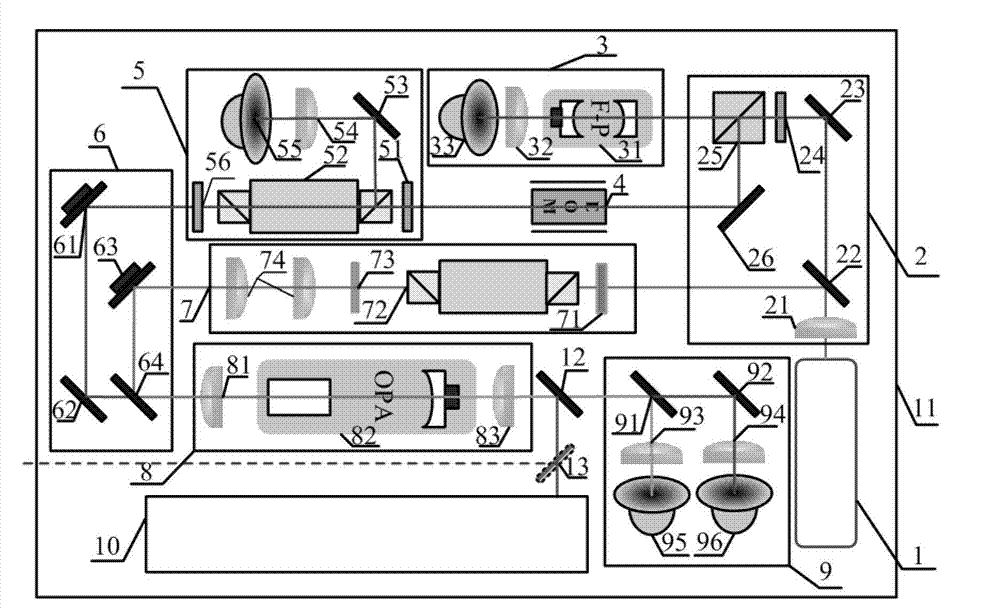
ActiveCN103176329ASolve temperature problemsSolve the influence of dust, etc.Non-linear opticsBell stateOptical parametric amplifier
The invention provides a continuous variable quantum entanglement source generating device. The device comprises a laser module, a beam split coupling module, a laser reference cavity module, a phase modulator, an optical parametric amplifier locking module, an anti-phase regulating and locking module, an isolator and beam shaping module, an optical parametric amplifier module, a detection system module and a Bell state direct detection system module, wherein the modules are all fixed on each base plate, and after being subjected to sealing treatment, the modules are sequentially fixed at corresponding positions of an entanglement source total base plate, and a polysulfone cover covers nonlinear crystals in the optical parametric amplifier module for heat preservation. The entanglement source generating device is beneficial to improvement of stability, reliability, operability and exchangeability and is easy for productization, mass production, and the like.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
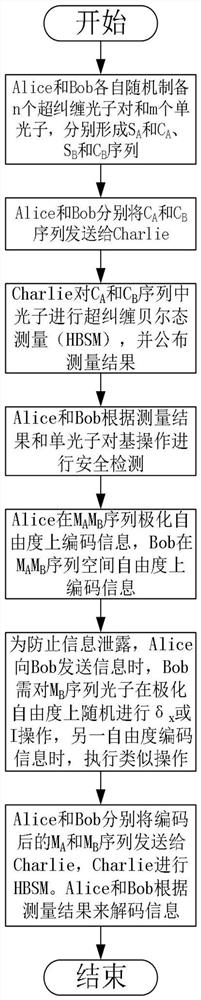
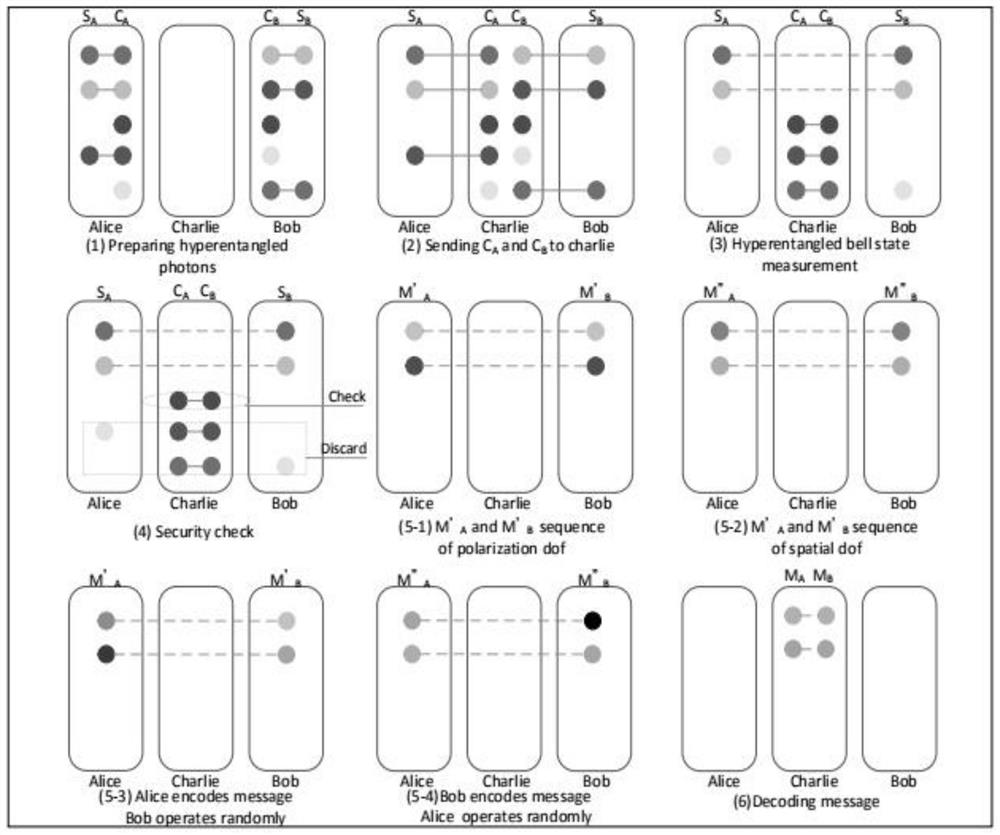
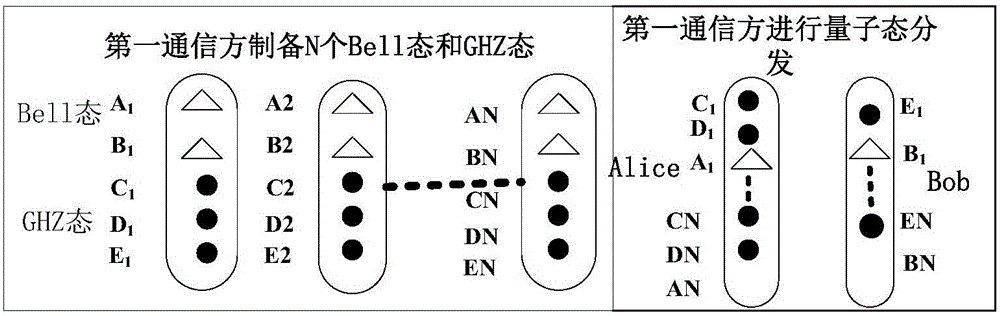
Three-party quantum secure direct communication method based on hyper-entangled Bell state
ActiveCN107786280AReduce loss rateImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBell stateQuantum secure direct communication
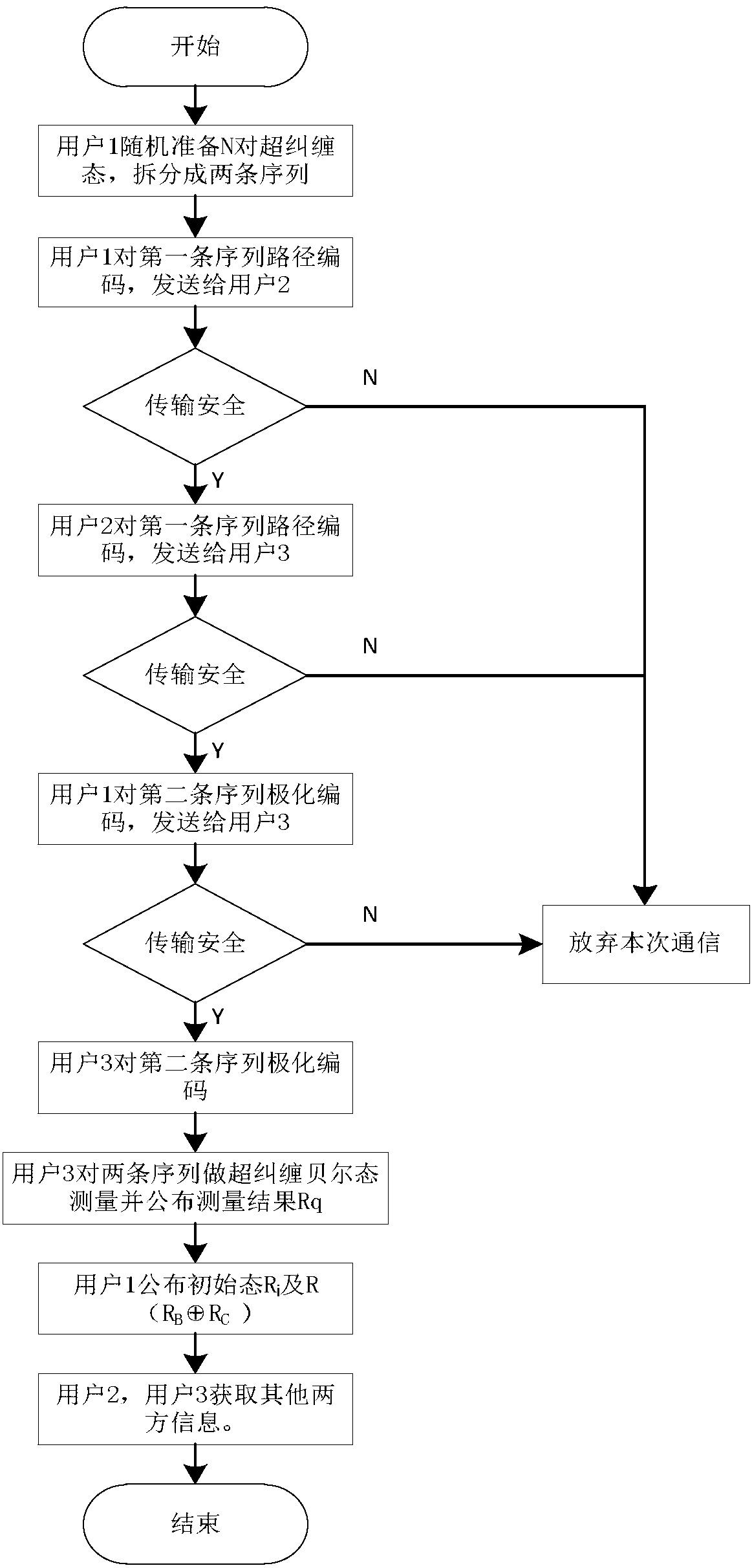
The invention discloses a three-party quantum secure direct communication method based on a hyper-entangled Bell state, including the following steps: a user 1 randomly prepares N hyper-entangled Bellstates and splits the Bell states into two sequences; the user 1 encodes a first sequence path and sends the path to a user 2; the user 2 encodes the path after confirming that no eavesdropping exists and sends the path to a user 3; the user 3 notifies the user 1 to send a second sequence after confirming that no eavesdropping exists; the user 1 performs polarization encoding on the second sequence and sends the second sequence to the user 3; the user 3 performs polarization encoding on the second sequence, performs joint hyper-entangled Bell state measurement on the two sequences, and publishes measurement results; the user 1 acquires encoding information of the user 2 and the user 3 respectively; the user 1 announces an initial state Ri and the encoding information R of the user 3 on XOR of the user 2; and the users 2 and 3 acquire the encoding information of the other two parties. According to the scheme of the invention, the transmission is only performed for three times, the probability of photon loss caused by channel loss can be greatly reduced, the security detection can be provided, and the security of transmission can be fully improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Quantum secret key distribution method with function of bidirectional identity authentication
ActiveCN106685654AImprove efficiencyImprove communication efficiencyKey distribution for secure communicationComputer hardwareBell state
The invention discloses a quantum secret key distribution method with a function of bidirectional identity authentication, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the interception detection, identity authentication and secret key distribution based on Bell state entangle properties, and then completing the identity authentication and secret key distribution through primary quantum sequence transmission; firstly detecting the channel safety, secondly carrying out the identity authentication, and finally carrying out the secret key distribution. According to the invention, the method carries out the interception detection, identity authentication and secret key distribution based on Bell state entangle properties, and then completes the identity authentication and secret key distribution through primary quantum sequence transmission, thereby improving the utilization efficiency of particles and communication efficiency, and enabling a protocol to be more concise. The protocol has the characteristic of zero knowledgeability during identity authentication. Even if a user is simulated, a simulator still cannot obtain any valuable information in the communication, thereby further guaranteeing the information safety of the user. When two sides need to carry out the secret key distribution, the protocol firstly detects the channel safety, secondly carries out the identity authentication, and finally carries out the secret key distribution.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Semi-quantum secure direct communication protocol based on Bell state
ActiveCN108881215AHigh efficiency of quantum communicationGuaranteed execution securityKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBell stateInformation transmission
The invention belongs to the field of quantum security communication, and discloses a semi-quantum secure direct communication method and system based on a Bell state. Two users participate in the execution of a present protocol, the first participating user has advanced quantum functions, can prepare the Bell state, and can use a Bell base to measure a quantum state and has a quantum storage function; the second participating user only has basic quantum functions, specifically: measurement: using a classical base {|0), |1)} to measure quanta, generating a quantum |1) (|0)) in an opposite state according to a measurement result |0) (|1) ), and sending the quantum; reflection: after receiving the quantum, directly sending the quantum to a sender without any modification; and disorder: disturbing the sending sequence of the quantum sequence by using the delay technology. The protocol proposed by the invention is a semi-quantum secure direct communication protocol, which improves the communication efficiency of the protocol while ensuring the absolute security of secret information transmission.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
System and method for quantum based information transfer
A system for communicating data comprising sender and receiver subsystems; at least one data input; at least one entangled photon source; first photons of the pairs of entangled photons outputted by the at least one photon source being processed by one of the sender or receiver subsystem; second photons of the pairs of entangled photons being processed by the other of the sender or receiver subsystem; a photonic element configured to receive the first photons of the pairs of entangled photons and enable interference therebetween; at least one absorber configured to absorb the first photons after passage through the beam splitter, the absorbance of the first photons operating to transfer the properties of the entanglement to the second photons of the pairs of entangled photons; and a Bell state measurement element operatively associated with the receiver subsystem configured to measure the second photons of the pairs of entangled photons.
Owner:US SEC THE ARMY THE
Multiparty quantum privacy comparison method based on d-level cat state and d-level Bell state entanglement swapping
The invention provides a multiparty quantum privacy comparison method based on d-level cat state and d-level Bell state entanglement swapping. A half-loyal third party is allowed to do on own will but cannot conspire with any party; in the invention, n parties encode their own secrets by use of a unitary operation, and the equality of the secrets of the n parties can be compared by only executing once. The external attack and the participant attack are resisted in the premise of not adopting a quantum key to produce a key to guarantee the security. One party cannot obtain the secrets of other parties except the circumstance that their secrets are completely same. The half-loyal third party cannot obtain any information about the secret of these parties except the comparison result.
Owner:嘉兴市顺凯鹿科技有限公司
Disordered high capacity multiparty quantum key agreement method based on high energy level bell state
ActiveCN108809644AReduce the difficulty of measurementLow equipment requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationBell stateHigh energy
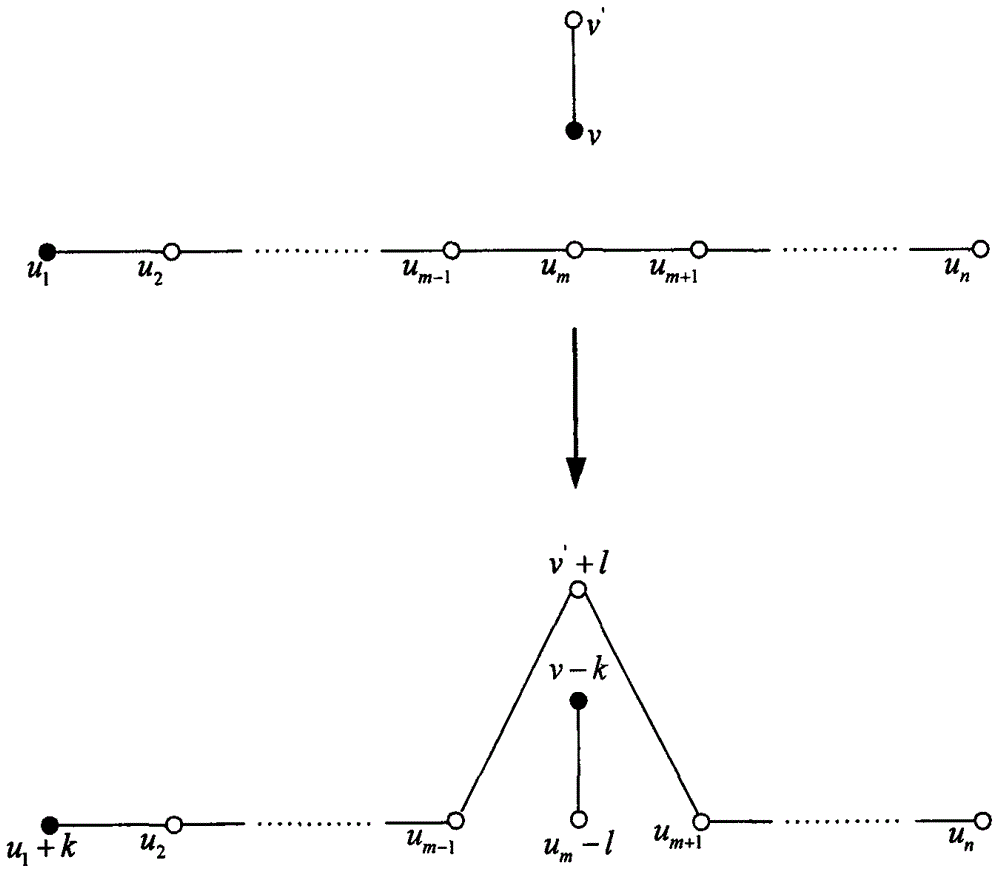
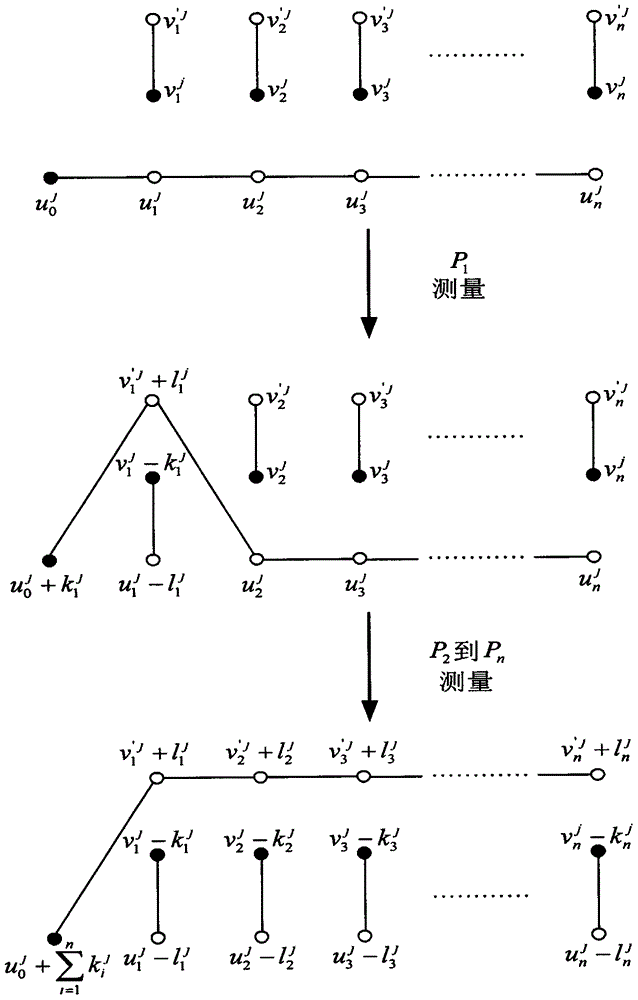
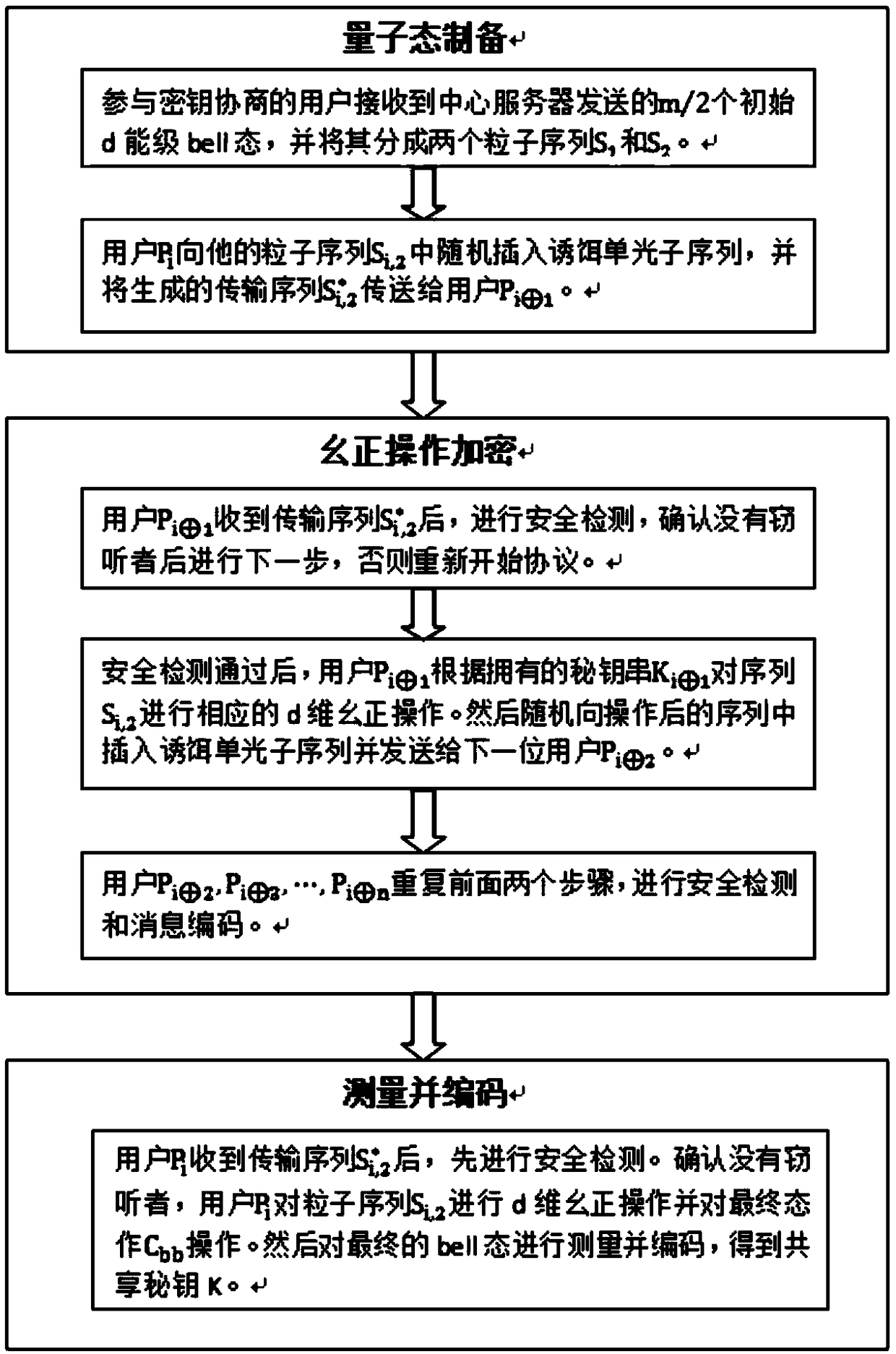
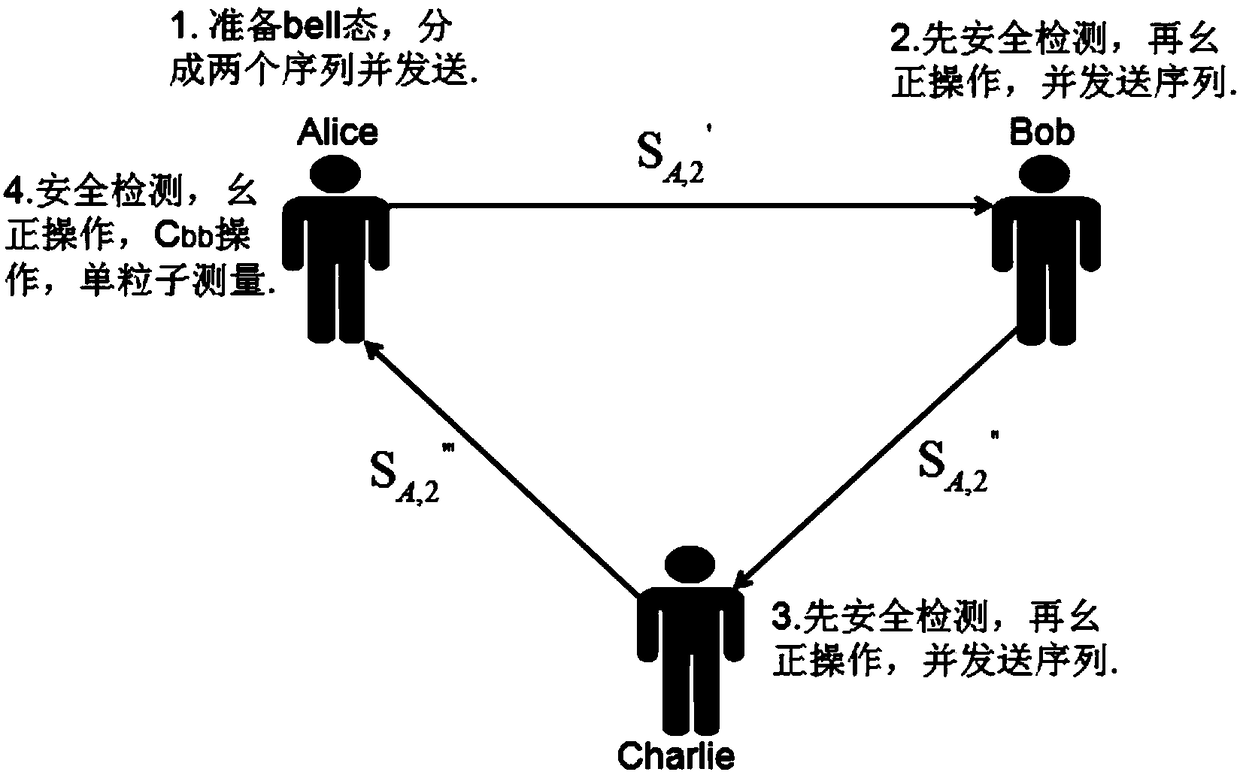
The invention relates to a disordered high capacity multiparty quantum key agreement method based on a high energy level bell state, which is designed for providing a more flexible and efficient quantum key sharing mode. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: dividing an initial bell state into two particle sequences Si, 1 and Si, 2, inserting a bait single photon sequence into the particle sequence Si, 2, forming a transmission sequence (represented as a formula in specification) and then sending the transmission sequence to the next user (represented as a formulain specification) to confirm security, and then performing d-dimension unitary operation for the particle sequence according to content of owned key sequence (represented as a formula in specification), inserting the bait single photon sequence in an operation result, sending the result to the next user (represented as a formula in specification), and repeating the steps above to perform security detection and message coding by the users (represented as a formula in specification). When the user Pi receives the particle sequence S1, 2 sent out by itself, after confirming security, the user Pi performs the d-dimension unitary operation for the particle sequence. The user Pi performs two qudit unitary operations for the finally recycled d-energy level bell state, and respectively performssingle particle measurement based on a base H and a base Z for a first particle and a second particle of the bell state.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Quantum voting system and method based on quantum teleportation
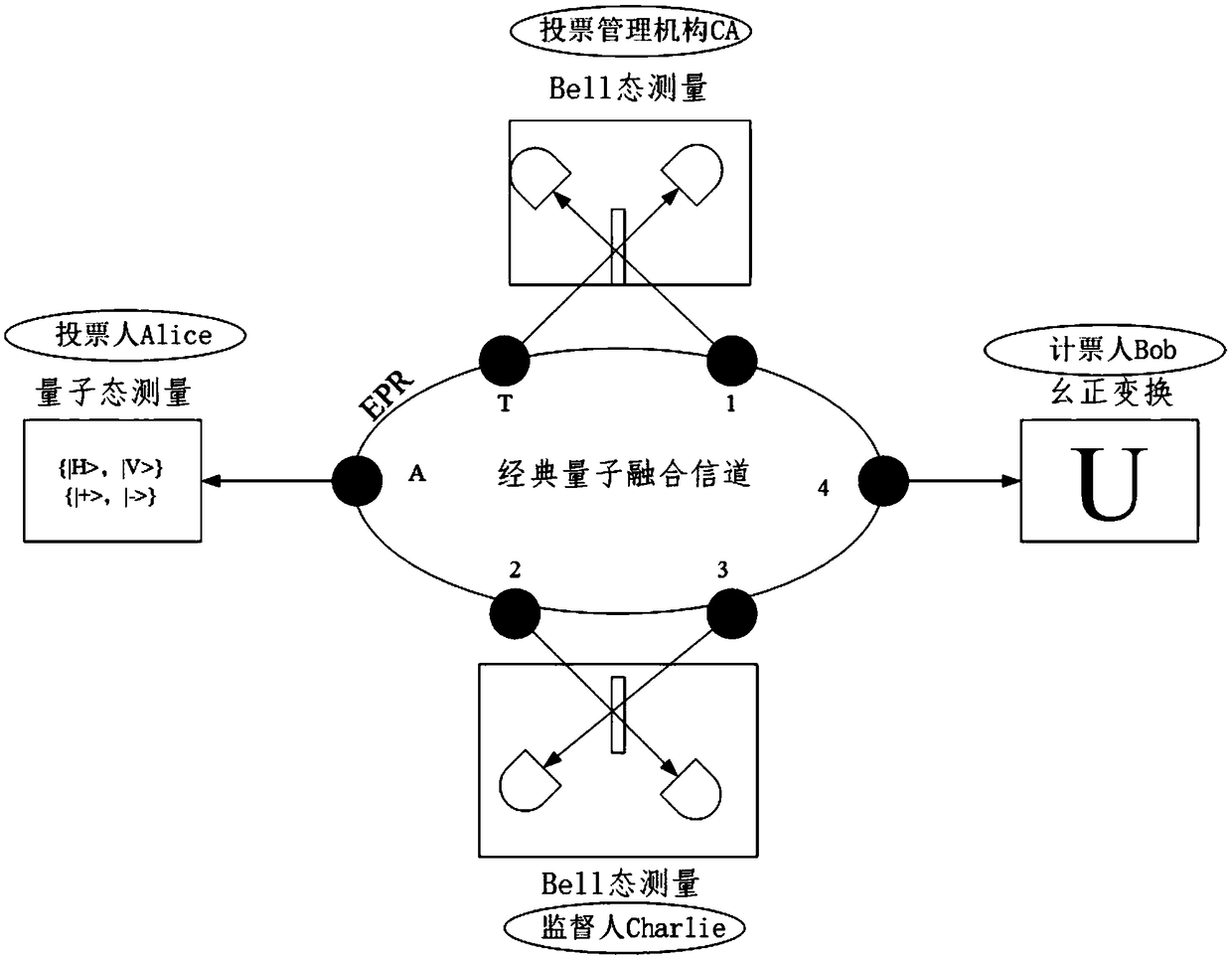
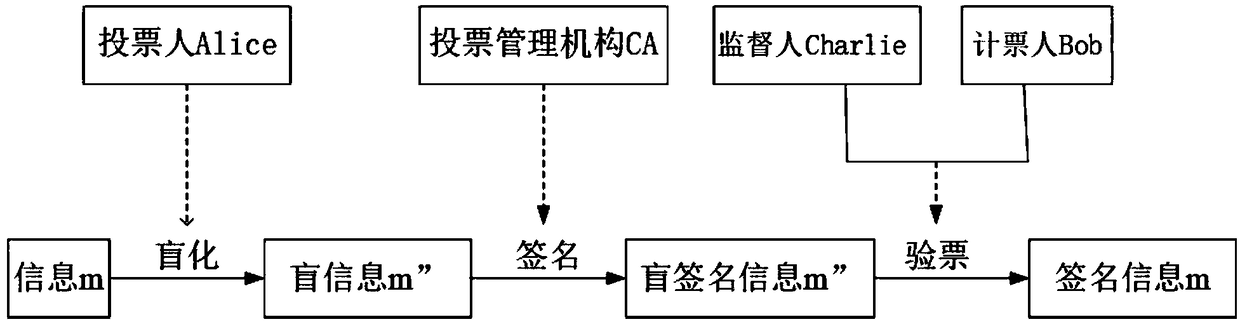
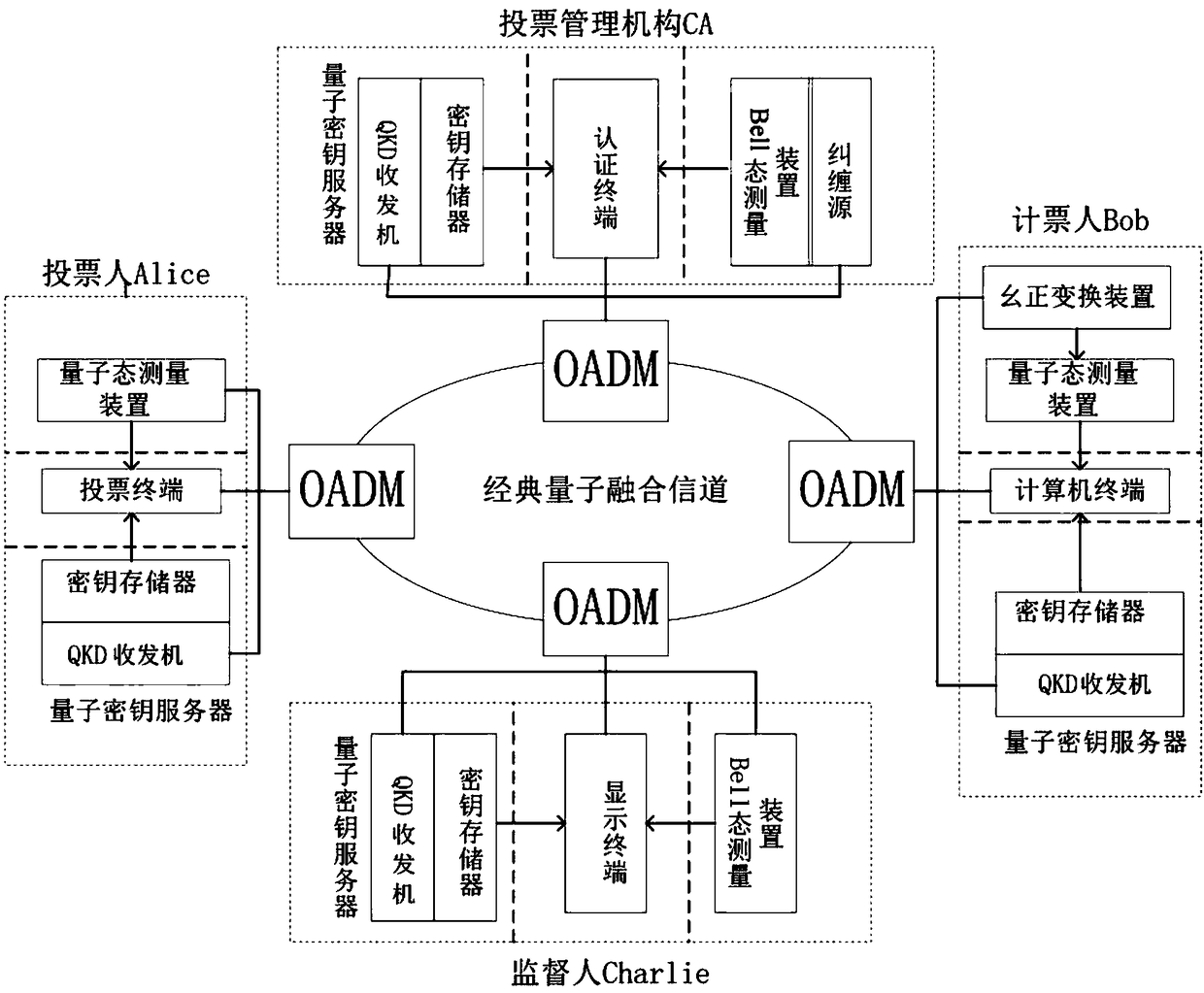
PendingCN108880790AGuaranteed legalityEnsure safetyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationBell stateMeasurement device
The invention discloses a quantum voting system and method based on quantum teleportation. The quantum voting system comprises a voter Alice, a voting management organization CA, a supervisor Charlie,a teller Bob and four OADMs, wherein the voter Alice comprises a first a quantum key server, a voting terminal and a first quantum state measurement device; the voting management organization CA comprises a second quantum key server, an authentication terminal, an entanglement source and a first Bell state measurement device; the supervisor Charlie comprises a third quantum key server, a displayterminal and a second Bell state measurement device; and the teller Bob comprises a fourth quantum key server, a computer terminal, a unitary transformation device and a second quantum state measurement device. The quantum voting system disclosed by the invention ensures the security of the whole voting process by the coherence of entangled particles, a QKD protocol, a one-time-one-encryption encryption algorithm and quantum channel eavesdropping detection. In addition, the quantum voting system disclosed by the invention transmits the classical and quantum information through different wavelengths in the same optical fiber, so that the cost of an application can be greatly reduced, and the practicability is improved
Owner:GUANGDONG INCUBATOR TECH DEV CO LTD
Quantum-state-generating apparatus, Bell measurement apparatus, quantum gate apparatus, and method for evaluating fidelity of quantum gate
InactiveUS7180645B2Promote generationQuantum computersComputing operations for integration/differentiationBell stateMeasurement device
An apparatus for generating a quantum state of a two-qubit system including two qubits, each qubit being represented by a particle which invariably travels through one of two paths, includes a quantum gate composed of an interferometer for implementing an-interaction-free measurement. The apparatus receives two particles having no correlation and generates a Bell state with asymptotic probability 1. A Bell measurement of a state of a two-qubit system is performed by observing a quantum gate composed of the interferometer after the quantum gate has processed the state and selecting the state from the Bell bases. An approximate fidelity of a quantum gate composed of the interferometer is calculated, if an absorption probability with which a first particle absorbs a second particle in the interferometer is less than 1, under the condition that the number of times the second particle hits beam splitters in the interferometer is sufficiently large.
Owner:CANON KK
Quantum steganography protocol based on quantum electrodynamics (QED)
The quantum steganography aims to realize covert communication of classified information through a quantum hidden channel. The quantum steganography has important applications in multiple aspects, such as covert communication and quantum identity authentication. The invention provides a quantum steganography protocol based on quantum electrodynamics (QED). The quantum steganography protocol is not influenced by cavity leakage and thermal cavity field. The classified information is secretly transmitted through the entanglement exchange between a GHZ state and a Bell state and Hadamard operation in the cavity QED. When the quantum steganography decodes the 2-bit classified information, only local independent measurement is required to be performed; and moreover, the capacity of the hidden channel can be improved to 4 bits.
Owner:唐山安生纸制品制造有限公司
Quantum coherent systems and operations
Nonlinear elements (200) can efficiently implement quantum information processing systems such as controlled phase shifters (400), non-absorbing detectors including parity detectors (1290), quantum subspace projections (600), non-absorbing Bell state analyzers (800), non-absorbing encoders / entanglers (1200), and fundamental quantum gates such as CNOT gates (1300). The non-absorbing detectors (1640, 1650) permit improvements in the efficiency of a probabilistic quantum gate (1720) by permitting reuse of the same photonic resources during multiple passes through the probabilistic gate (1720).
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Remote quantum state preparation method based on quantum remote control
InactiveCN109257172AImprove efficiencyEase of physical implementationKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBell stateQuantum nonlocality
The invention provides a method for simultaneously realizing remote state preparation and quantum remote control. The remote quantum state preparation method based on quantum remote control utilizes the quantum nonlocality of a three-particle GHZ state to simultaneously perform the remote preparation of an arbitrary single-particle state and realize the remote rotation on the particle state. The invention has the advantages that: the invention is based on sharing a three-particle GHZ state to complete the scheme of preparing arbitrary single-particle quantum state and loading rotation control;compared with the intuitive solution, the protocol of the invention has higher efficiency; only Pauli operator, controlled NOT gate, Bell state measurement, single particle measurement, EPR state, GHZ state and the like are use in the scheme of the invention, which is easy to be physically realized.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
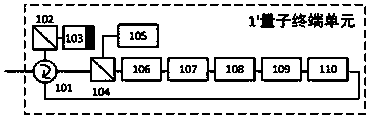
Plug-and-play measuring device independent quantum key distribution network system and method
ActiveCN109450628AEnsure consistencyReduce consumptionKey distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBell stateQuantum channel
The invention discloses a plug-and-play measuring device independent quantum key distribution network system and a method. The method includes steps: a quantum relay unit emits two channels of pulses,the pulses are respectively transmitted to two designated quantum terminal units through a quantum channel, the quantum terminal units encode the input light pulses and transmit the pulses back to the quantum relay unit through the quantum channel, and the quantum relay unit conducts a Bell-state analysis on the pulses modulated through the quantum terminal units, obtains a result and publishes the result through a classic channel; and the quantum terminal units compare the above result and local encoding information, obtains a screening node and selects a part for error code rate detection,if the result is safe, the communication is successful, and if the result is not safe, the communication is given up and restarted. The problems of the influence of the environment on photon polarization in practical application and key distribution multi-user application in the network are solved.
Owner:GUANGDONG INCUBATOR TECH DEV CO LTD
Quantum key distribution method based on single photon multi-degree of freedom irrelevant to measurement device
ActiveCN109194479AIncrease profitImprove bit rateKey distribution for secure communicationMeasurement deviceDecoy state
The present invention provides a quantum key distribution method based on a single photon multi-degree of freedom irrelevant to a measurement device. The method employs spaces and polarization singlephotons to perform coding on a polarization freedom and a space path freedom and sends the spaces and polarization single photons after coding to a third-party measurement device. The third-party measurement device is employed to perform hyper-entangled Bell state analysis to achieve complete distinguishing of 16 Bell states. Compared to a quantum key distribution protocol scheme irrelevant to anoriginal measurement device, the information is encoded on two degrees of freedom, and a non-linear optical condition is employed to perform complete distinguishing of the 16 Bell states so as to effectively utilize the safe keys and improve the channel capacity. Besides, in order to respond to the safety hole of photon number separation attack, a decoy state technology is used. The quantum key distribution method based on a single photon multi-degree of freedom irrelevant to a measurement device can greatly improve the utilization of the code forming rate and the safe keys and can ensure thereliability and the safety of the transmission process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
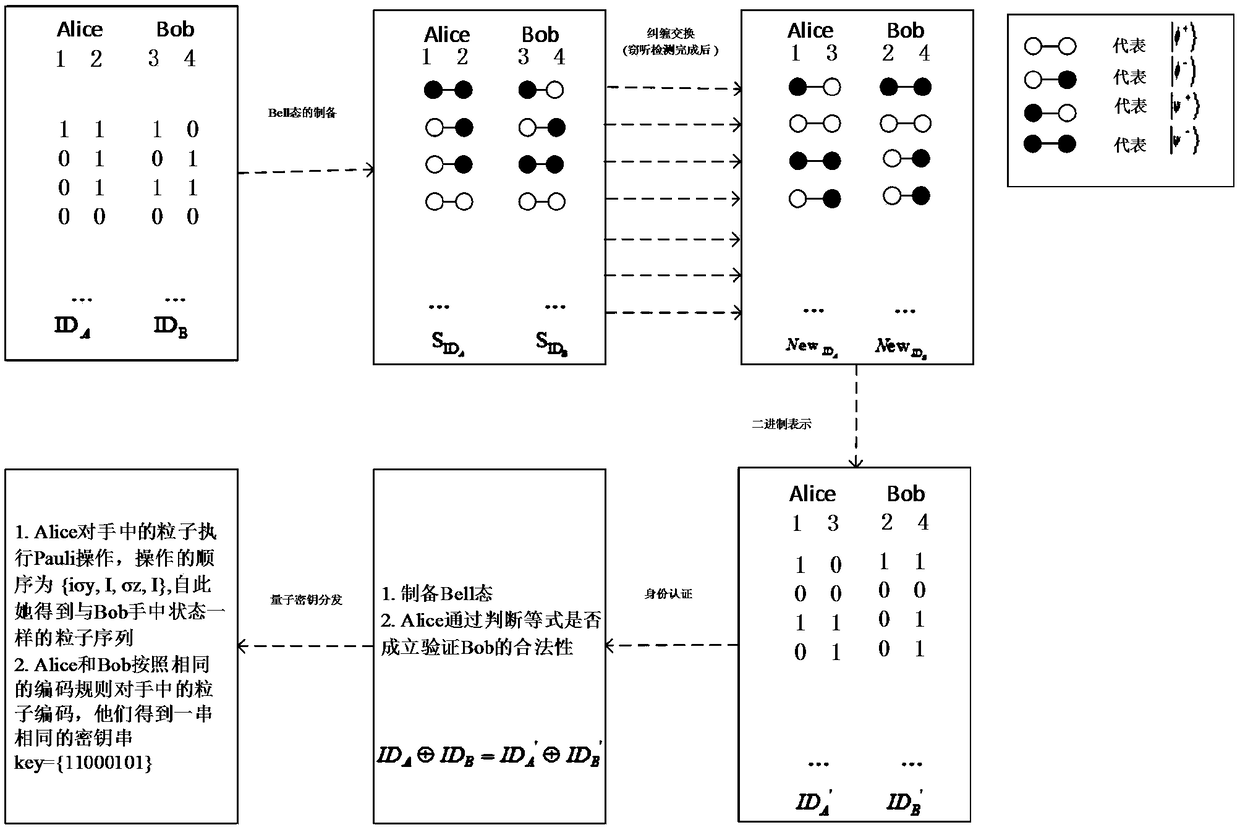
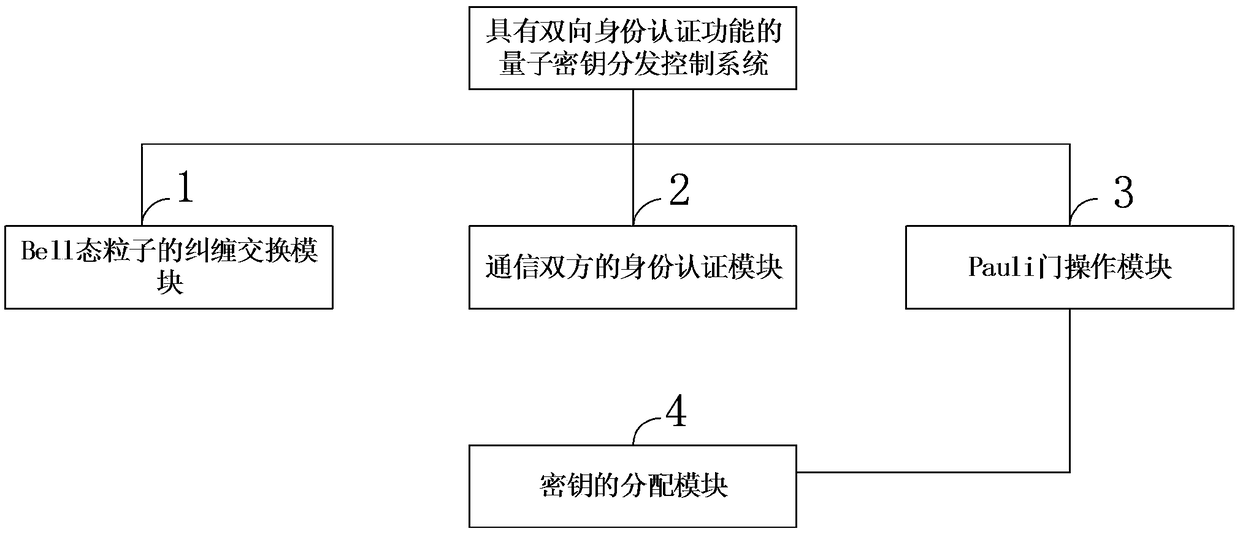
Quantum key distribution method and system with bidirectional identity authentication function
ActiveCN109327308AThe certification process is simple and practicalIncrease profitKey distribution for secure communicationBell stateQuantum gate
The invention belongs to the technical field of network information and discloses a quantum key distribution method and system with a bidirectional identity authentication function. A communication participant uses a binary character string representing the user identity to carry out preparation of a Bell state; encoding and particle exchange are carried out according to a same convention; Bell-based measurement is finished so as to achieve entanglement exchange of the Bell-state particles; after a bitwise XOR operation is carried out, a Pauli gate operation is carried out on any side of bothsides of communication so that the particles in the hand are converted into the Bell-state particles the same as the particles on the opposite side; and both the sides of communication can obtain a same binary character string so as to finish the distribution of secret keys. The quantum key distribution method and system with a bidirectional identity authentication function in the invention improve the use ratio of resources produced during authentication of both the sides of communication; according to the agreement announced by both the sides of communication can identity authentication andkey distribution be realized without the intervention of a third side; the required quantum state is the Bell state of two particles; and the preparation is relatively easy.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV OF INFORMATION TECH
Fermionic bell-state analyzer and quantum computer using same
ActiveUS20080142787A1Easy to implementEliminate needQuantum computersNanoinformaticsBell stateDevice material
The Bell-state analyzer includes a semiconductor device having quantum dots formed therein and adapted to support Fermions in a spin-up and / or spin-down states. Different Zeeman splittings in one or more of the quantum dots allows resonant quantum tunneling only for antiparallel spin states. This converts spin parity into charge information via a projective measurement. The measurement of spin parity allows for the determination of part of the states of the Fermions, which provides the states of the qubits, while keeping the undetermined part of the state coherent. The ability to know the parity of qubit states allows for logic operations to be performed on the qubits, i.e., allows for the formation of (two-qubit) quantum gates, which like classical logic gates, are the building blocks of a quantum computer. Quantum computers that perform a parity gate and a CNOT gate using the Bell-state analyzer of the invention are disclosed.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
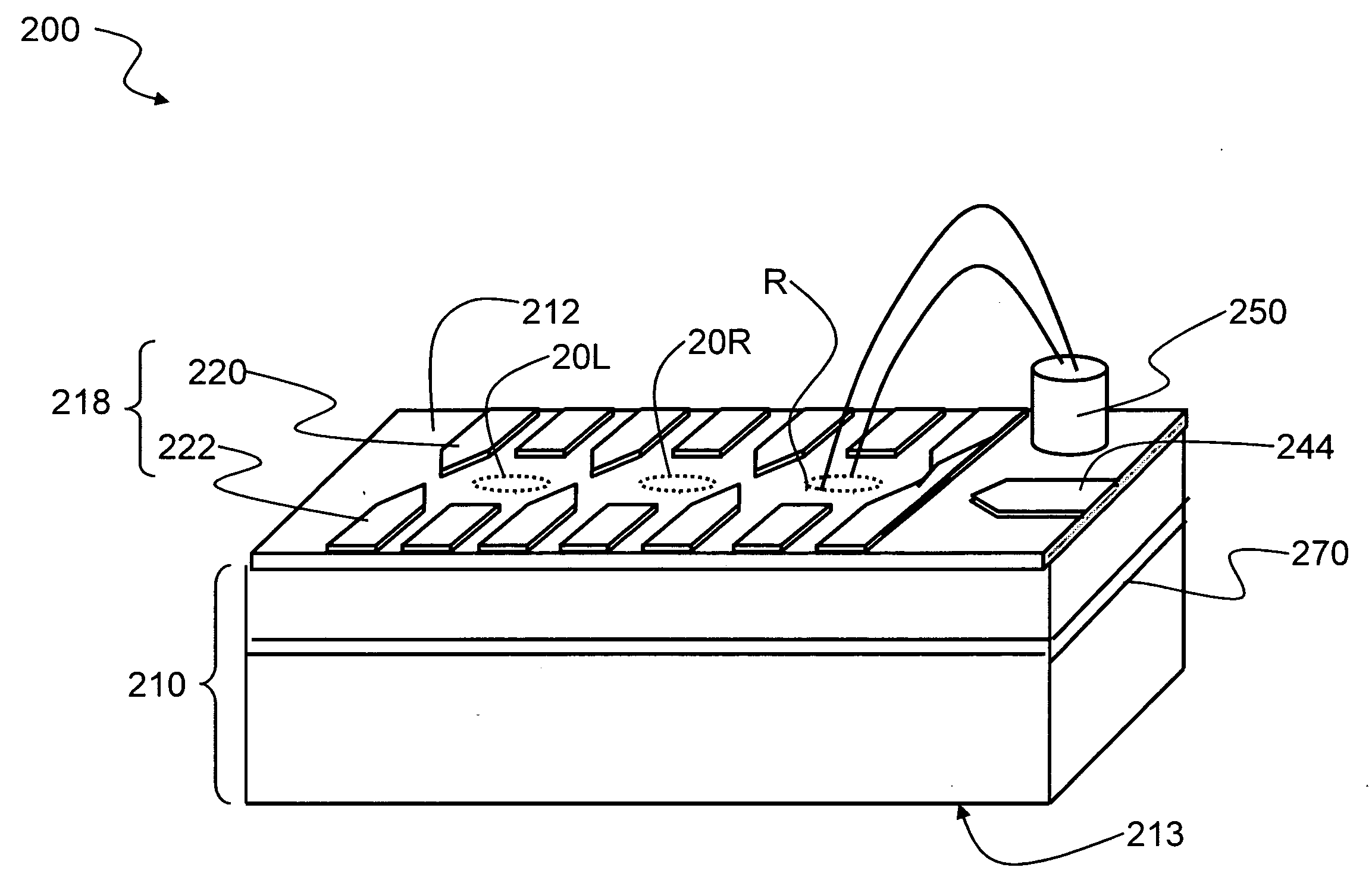
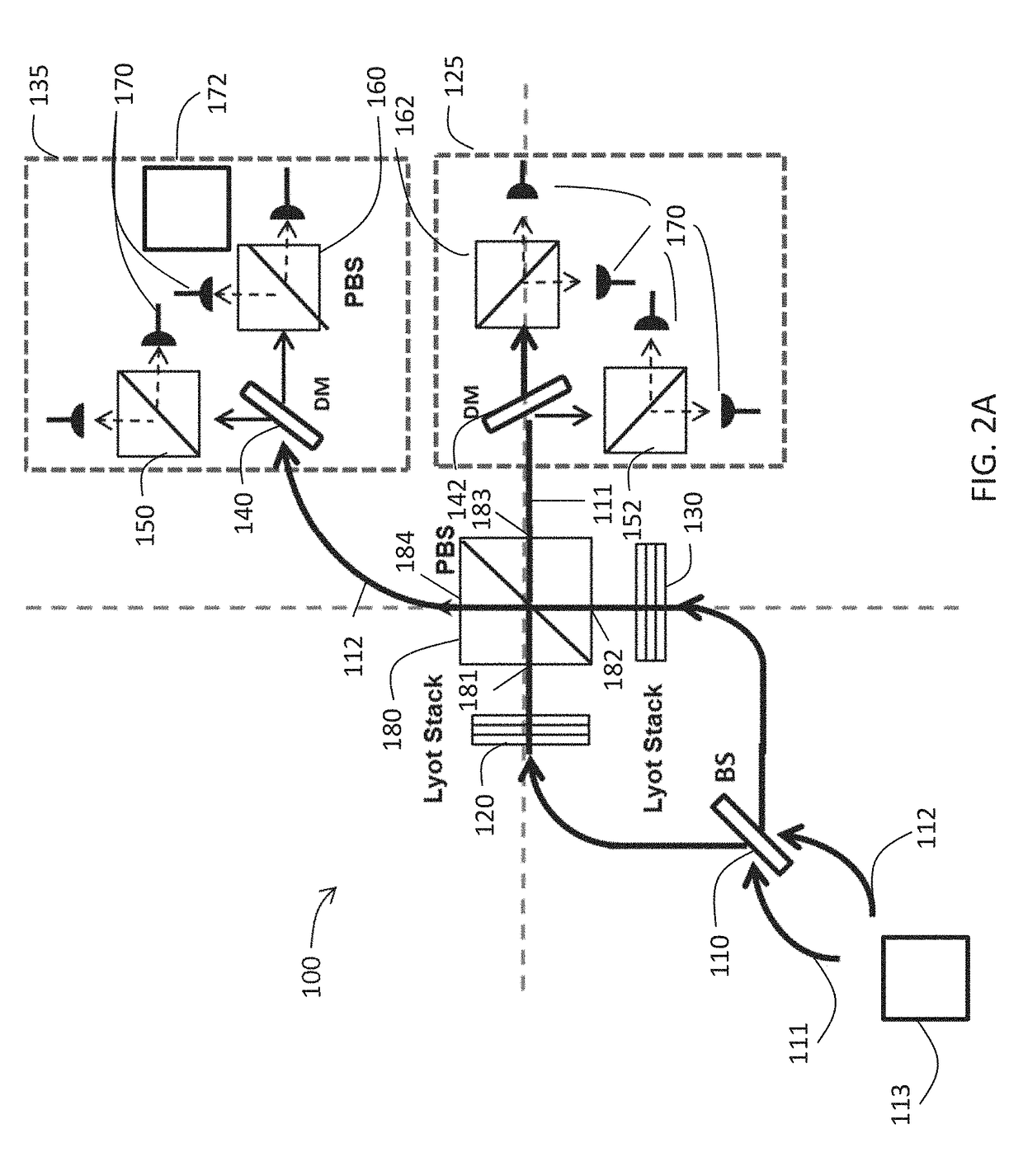
Hyper-Entangled Photon Server System and Associated Methods
ActiveUS20180241480A1Quantum computersEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesBell stateBeam splitter
A hyper-entanglement photon server (i.e., hub) employs non-degenerate frequencies input as entangled photon pairs into a beam splitter. The beam splitter splits probability amplitudes into two sets of bunched superposition states plus two sets of anti-bunched superposition states. The amplitudes pass through identical Lyot filters and then either enter a polarization beam splitter, where the bunched and anti-bunched states switch identities, or merely advance unchanged to awaiting users at two distinct and spatially-displaced positions (i.e., spokes). The Lyot filters change the output amplitudes from rotationally invariant superpositions of generalized Bell States to rotationally non-invariant superpositions of generalized Bell states. All hubs and spokes pre-share operating key material (a security method called KCQ) that may be continually updated by shared stream ciphers seeded by fresh key material engendered by hub-to-spoke quantum communication.
Owner:GOVERNMENT OF THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE AIR FORCE
Quantum dialogue method irrelevant to measurement equipment based on hyper-entanglement
ActiveCN112272062AIncrease channel capacityImprove communication efficiencyPhotonic quantum communicationElectromagnetic transmission optical aspectsBell stateQuantum secure direct communication
The invention discloses a quantum dialogue method irrelevant to measuring equipment based on super-entanglement. The method comprises the following steps that two communication parties randomly prepare a super-entanglement state and a single photon respectively to form corresponding photon sequences; the third detection party performs hyper-entangled Bell state measurement on the photon sequence sent by the communication party and publishes a measurement result, and the communication party performs security detection according to the measurement result; two communication parties simultaneouslyencode information at different degrees of freedom and randomly perform security detection encoding, and the process is similar to quantum secure direct communication at different degrees of freedom;and the two communication parties send the coded photon sequence to the detection party, the detection party performs hyper-entangled Bell state measurement again and publishes a result, and the communication party decodes information according to the result to complete dialogue. According to the method, bidirectional quantum secure direct communication can be realized, communication efficiency is effectively improved, meanwhile, security holes related to measurement equipment and information leakage can be eliminated, and the method has relatively high flexibility, i.e., information codes ondifferent degrees of freedom do not influence each other.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Broadcasting communication technique of quantum network
InactiveCN101944994APrevent cheatingAvoid mistakesKey distribution for secure communicationBroadcast systems controlBell stateQuantum network
The invention provides a novel quantum broadcasting communication scheme. Only one difference from the transmitting party in the traditional quantum broadcasting protocol is as follows: the scheme realizes that two transmitting parties simultaneously transmit the united confidential information of the two parties to multiple legal receiving parties. In the scheme, the transmitting parties respectively share the multiparticle GHZ state with all the receiving parties, and then the transmitting parties carry out the single particle measurement and publish the check bit; after carrying out inaccurate Bell measurement, each receiving party simultaneously acquires the united confidential information of the transmitting parties according to the result and the check bit; the quantum characteristic ensures the unconditional safety of the protocol; and the application of the induced quantum photon leads the protocol to have detectability on bugging. The communication model can be applied to the fields of the safe democratic decision in a quantum network, the united signal control and the like. In the implementing process of the scheme, the transmitting party only needs to carry out single particle measurement, the receiving party carries out Bell measurement, but only partial Bell state measuring result needs to be distinguished, all the measuring results needs to be inaccurately distinguished, thus the scheme is easy to implement in the quantum network.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
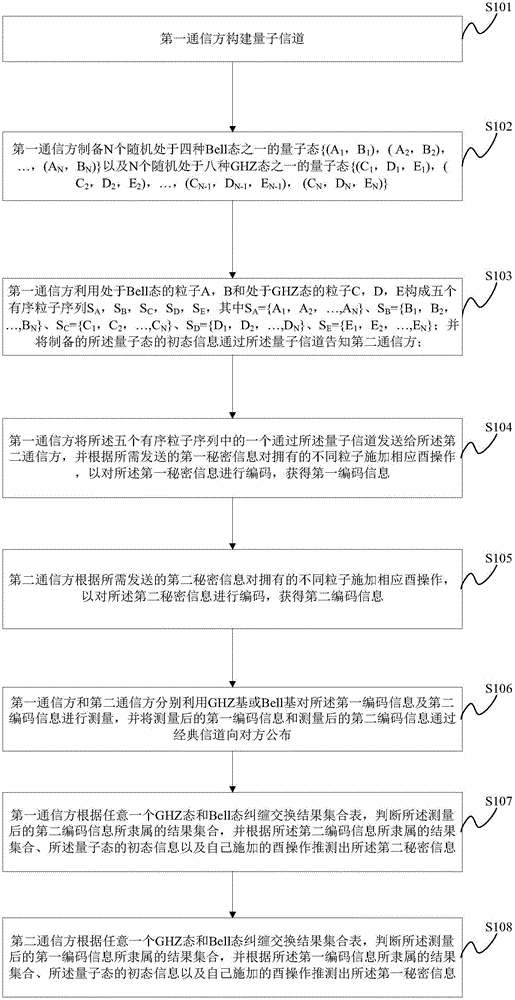
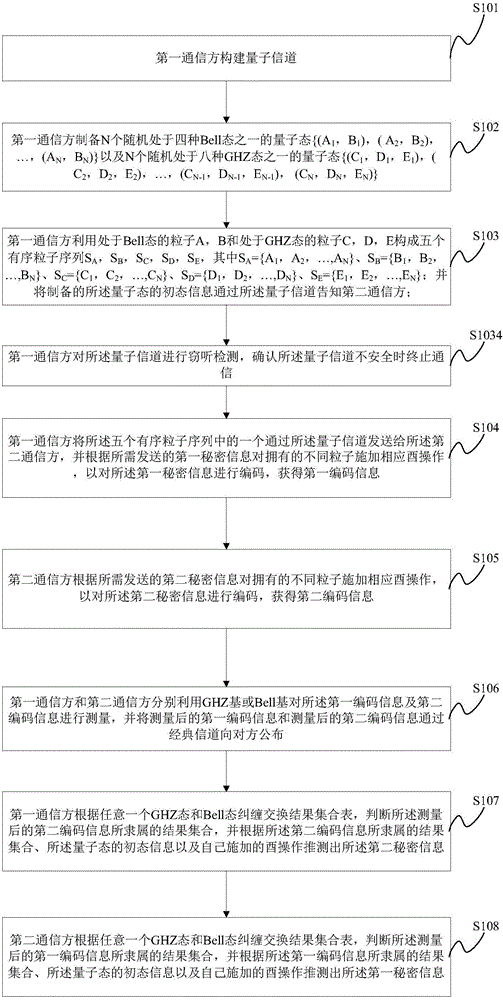
Quantum dialogue method for asymmetric capacity based on GHZ state and Bell state
ActiveCN105933114AReduce leakageImprove confidentialityKey distribution for secure communicationBell stateConfidentiality
The invention discloses a quantum dialogue method for an asymmetric capacity based on a GHZ state and a Bell state. The quantum dialogue method for the asymmetric capacity based on the GHZ state and the Bell state uses the Bell state and the GHZ state to perform quantum communication simultaneously, so that a quantum communication process with the asymmetric capacity with three-bit secrete information in one party and two-bit secrete information in the other party in a round of quantum communication process can be realized. Besides, in a whole communication process, only first measured encoding information and second measured encoding information need to be published once through a classical channel, so that the possibility of information leakage in the communication process is reduced. Further, a first communication party and a second communication party in the communication process do not need to truly transfer first secrete information and second secrete information to the other party through quantum information, so that the confidentiality of the quantum dialogue method for the asymmetric capacity based on the GHZ state and the Bell state can be greatly improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Quantum based information transfer system and method
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA THE AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE ARMY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com