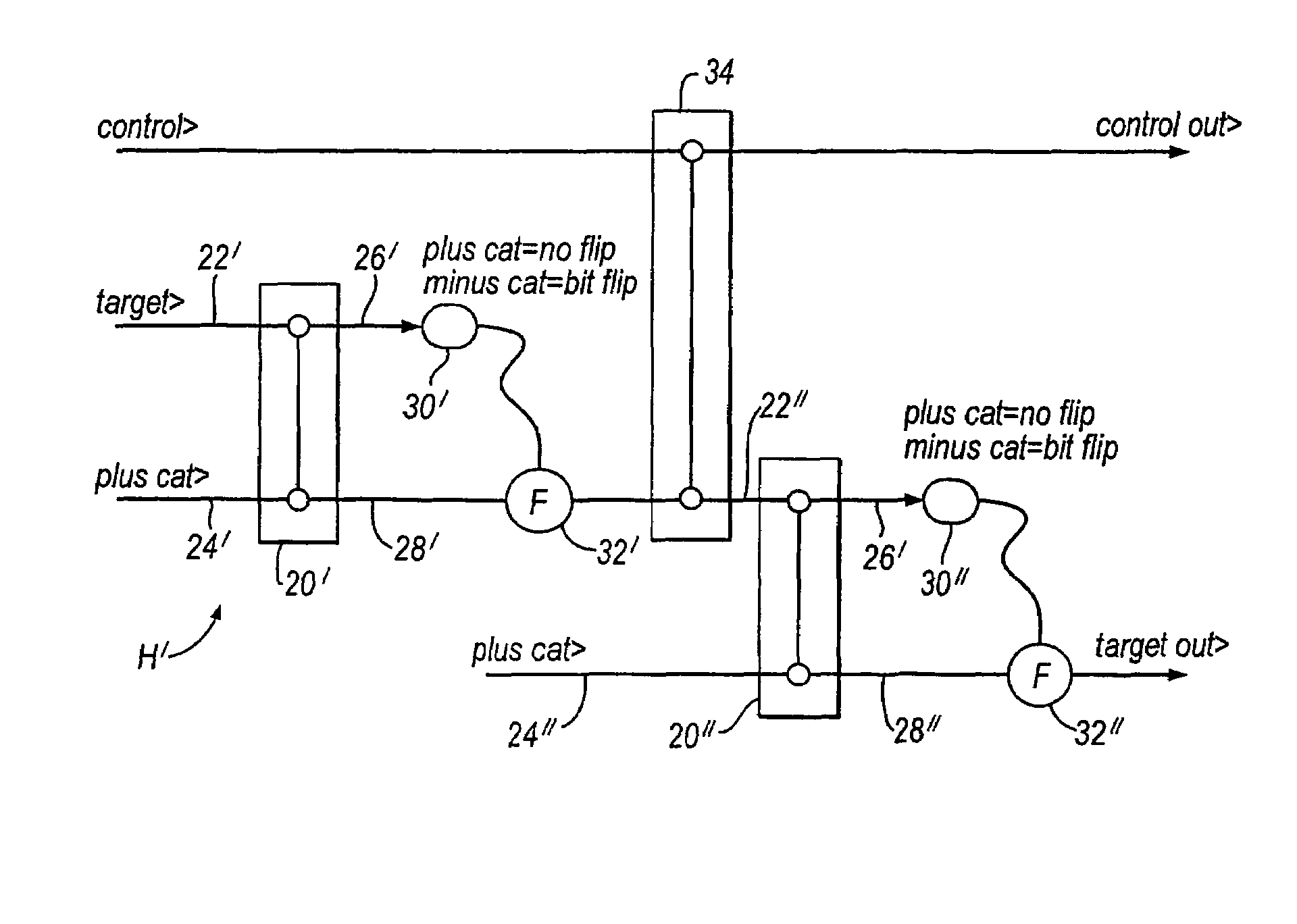
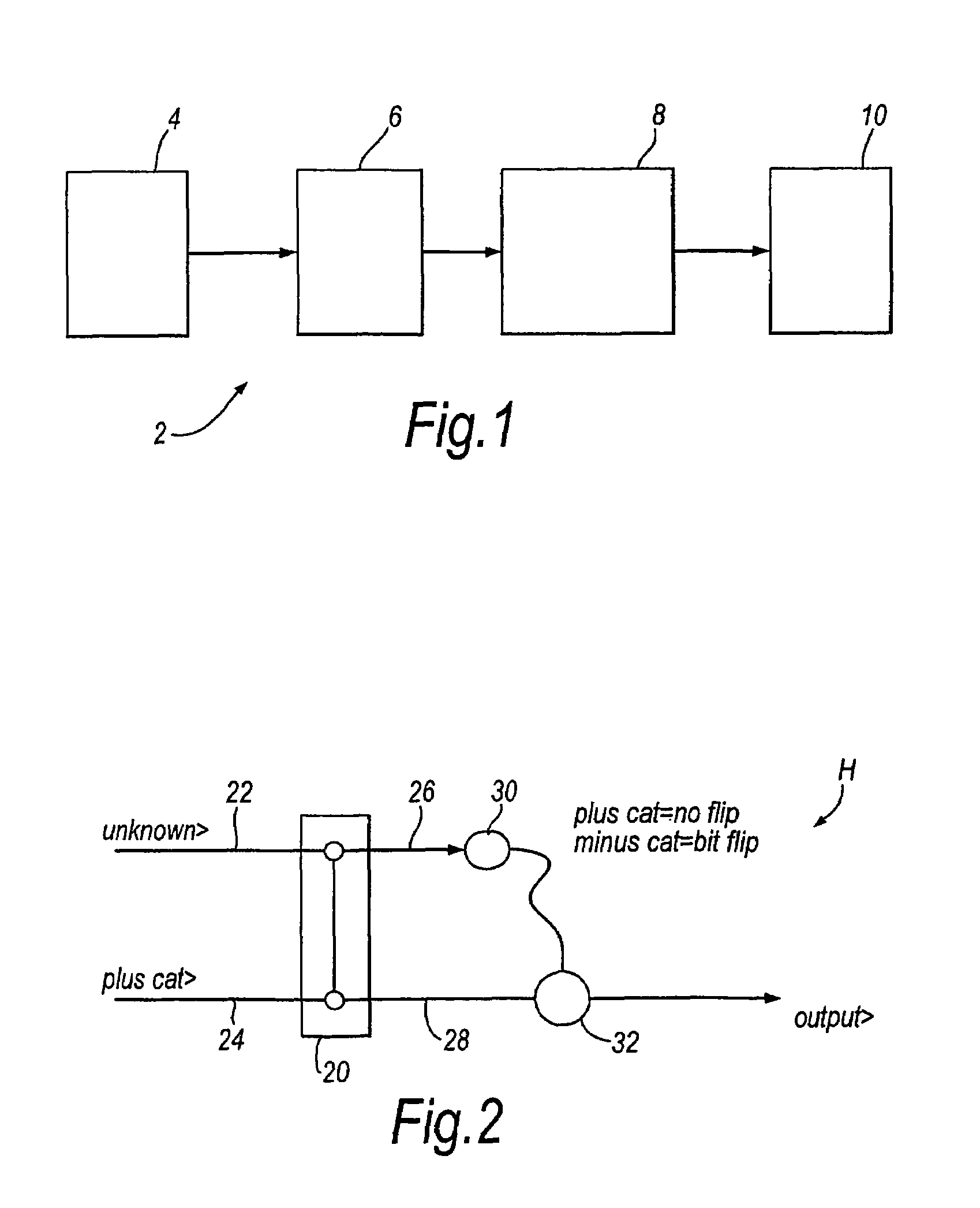
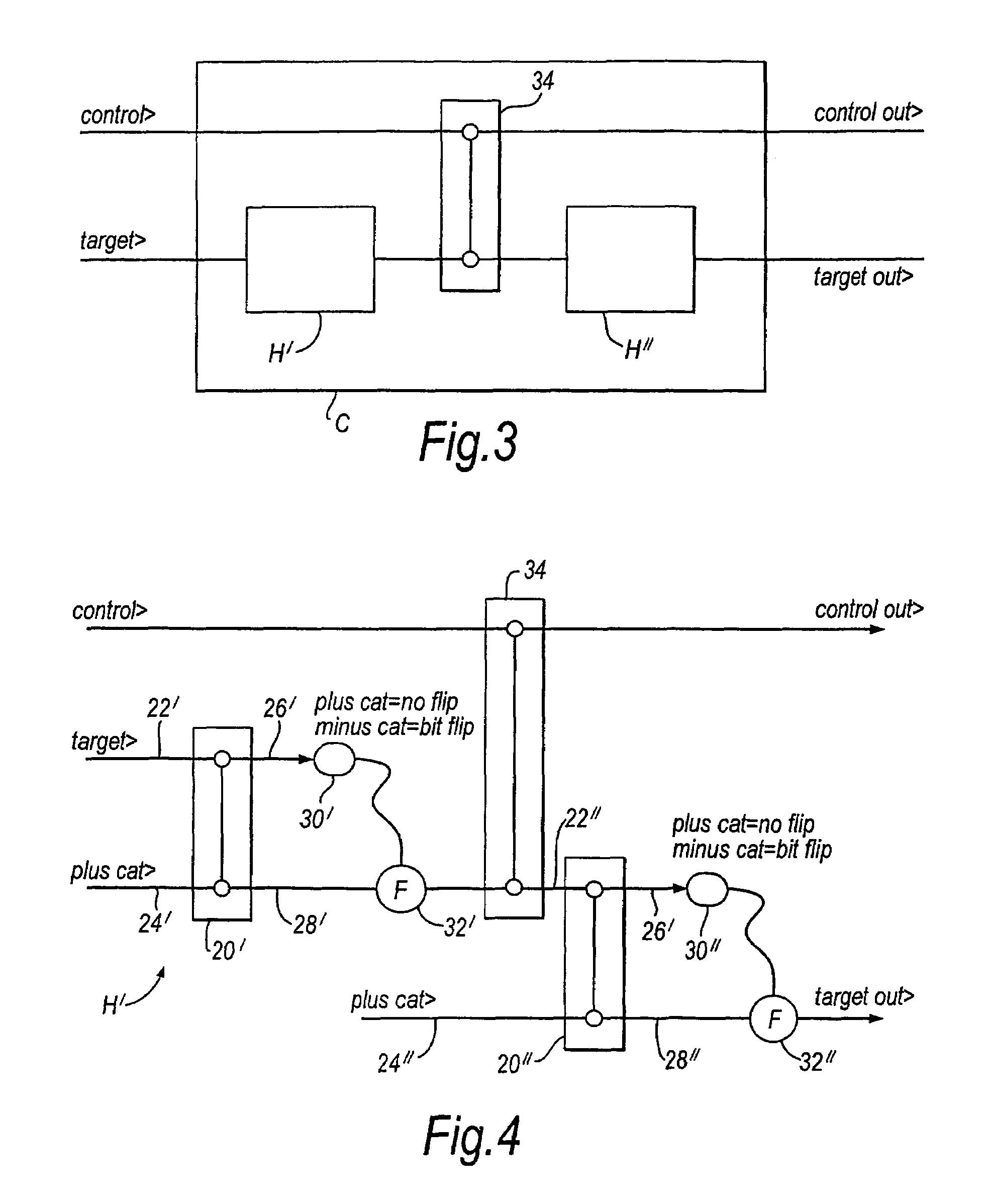
Patents
Literature
121 results about "Quantum information processing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Quantum information processing
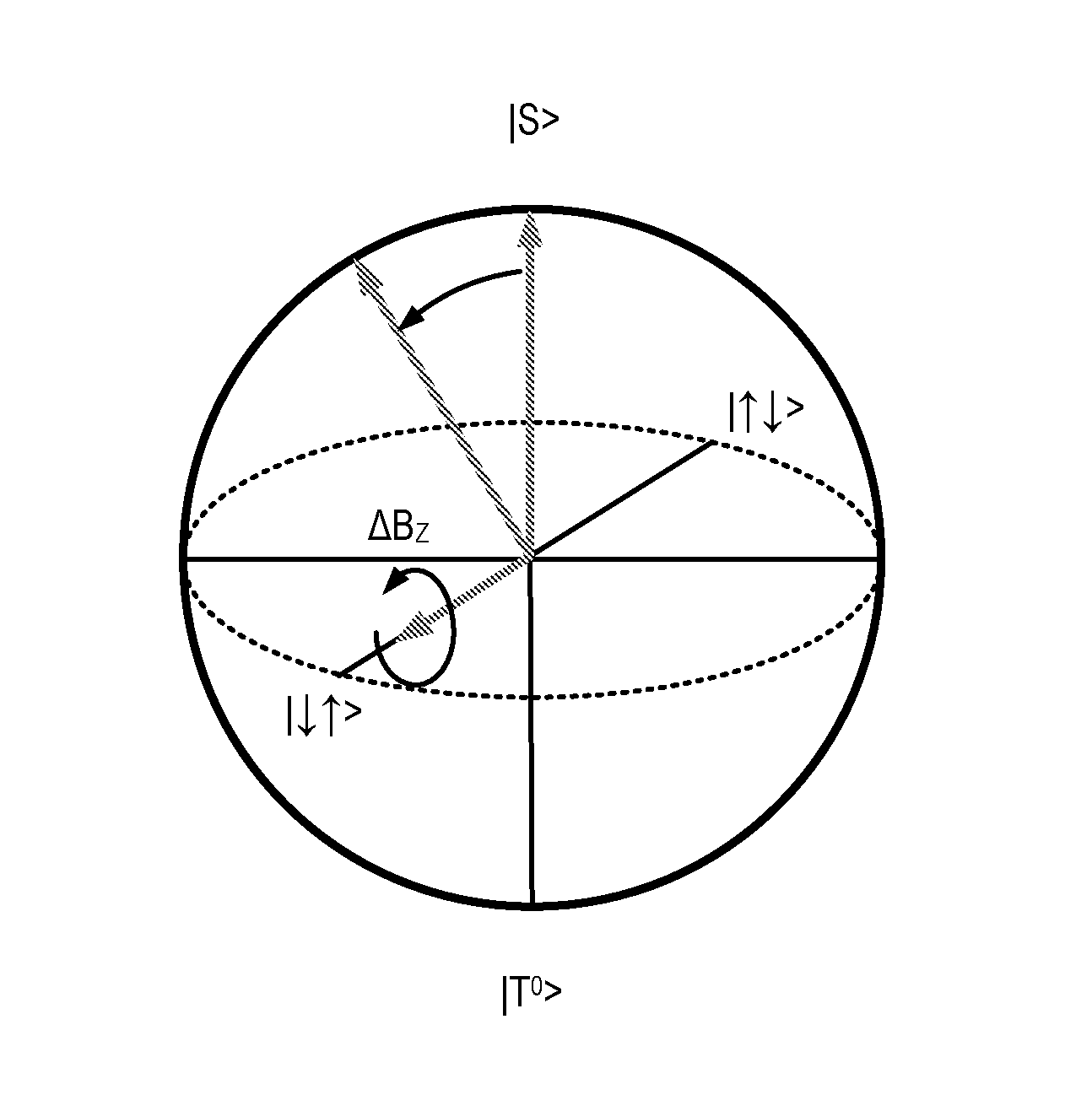
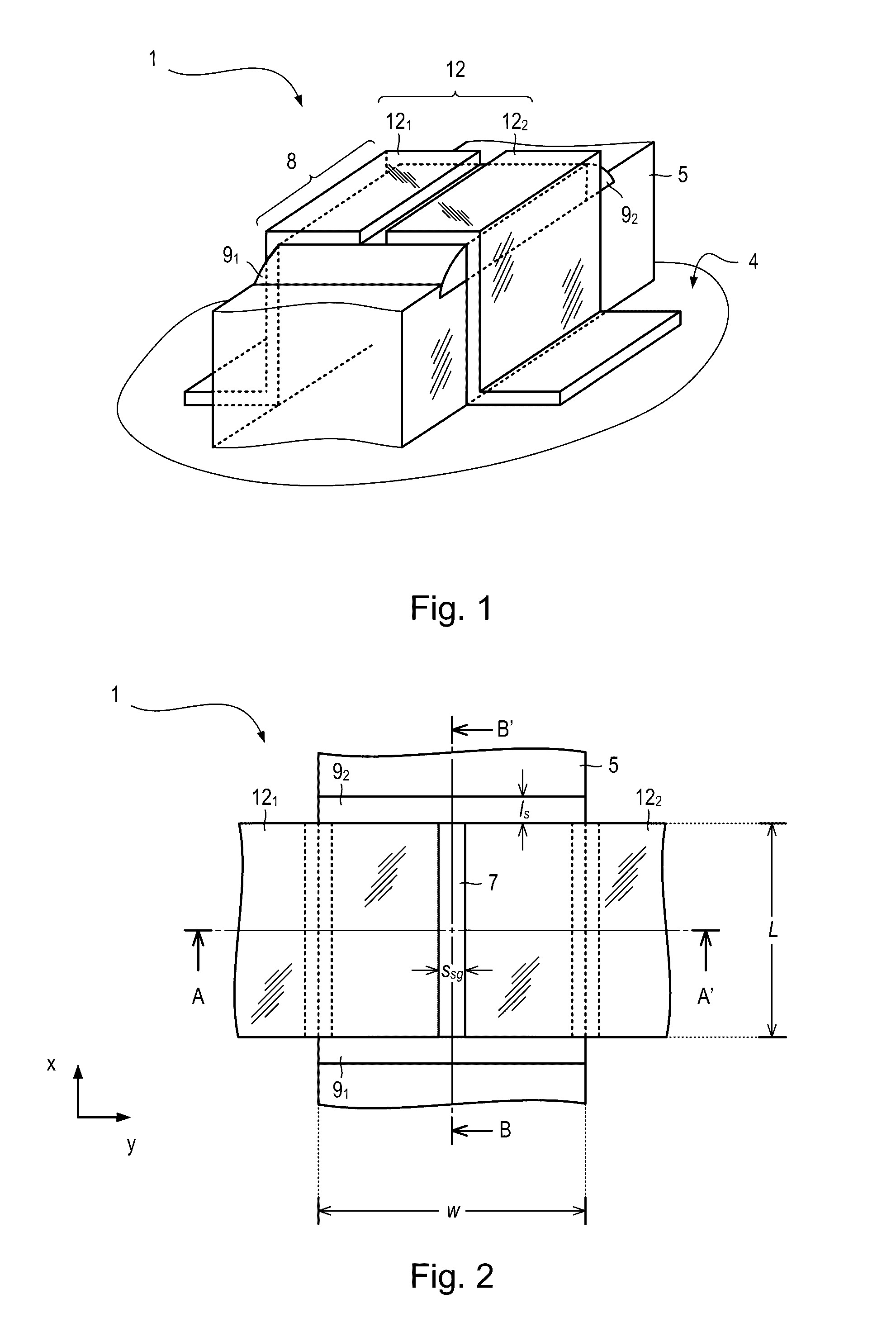
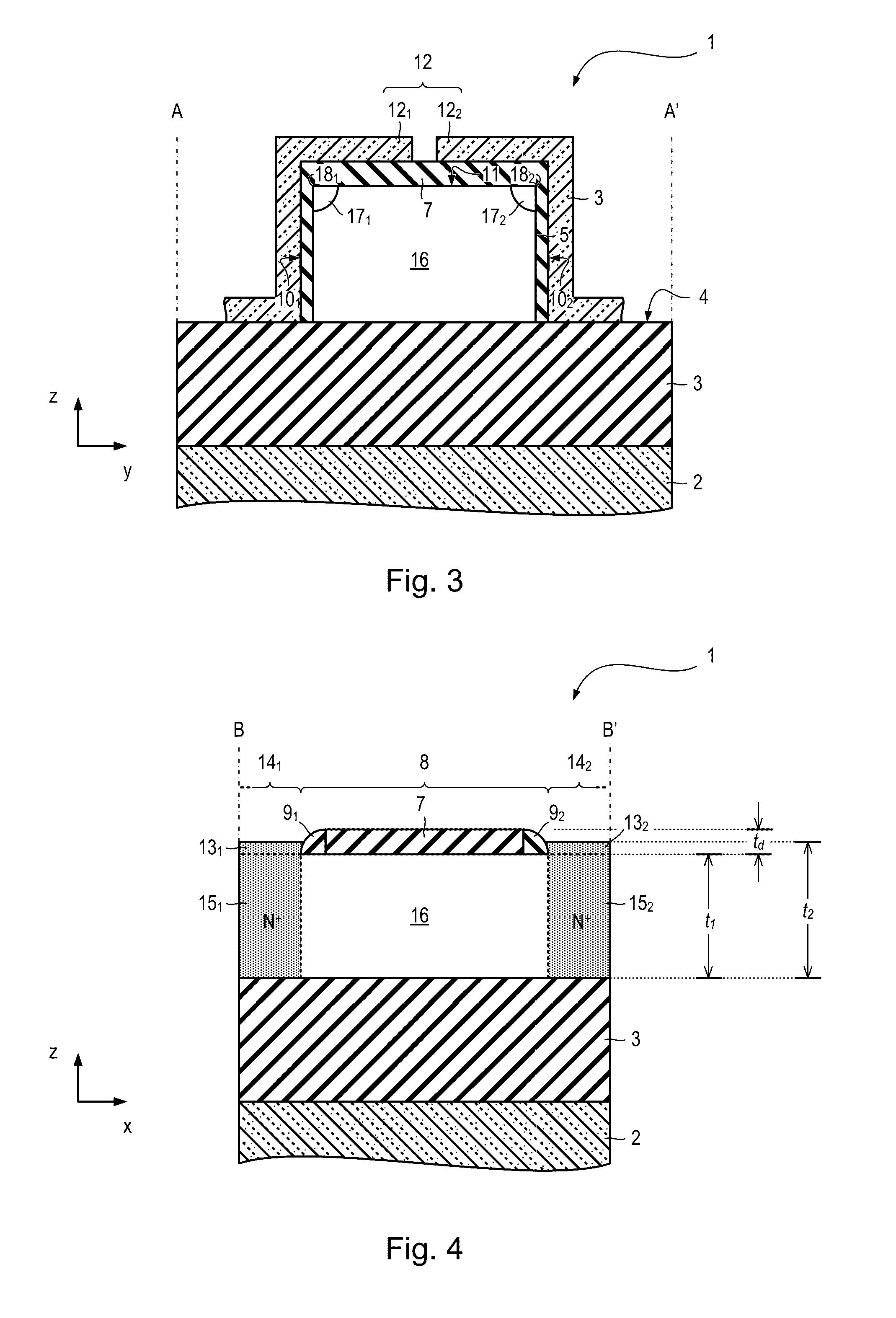
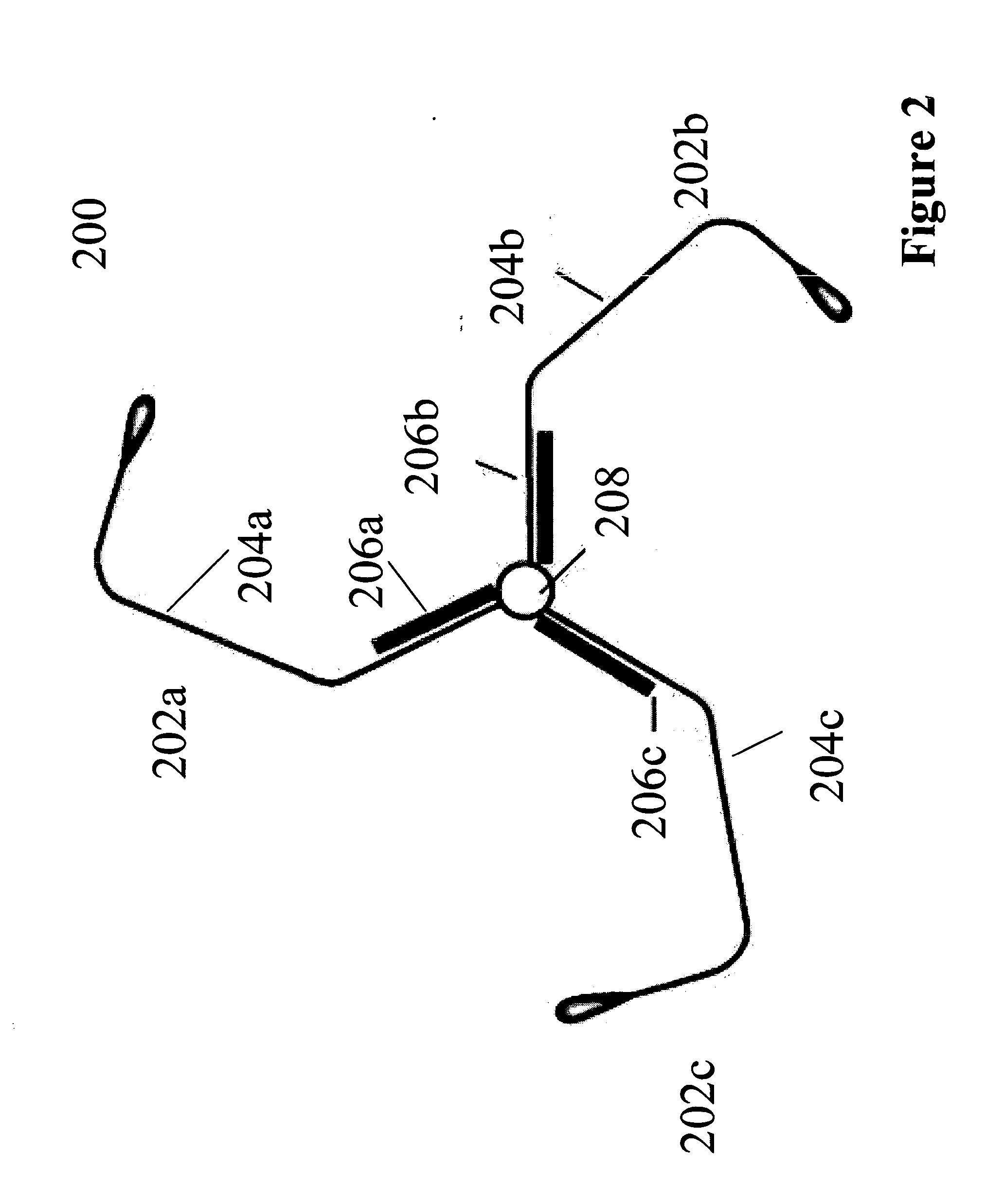
Quantum information processing apparatus and methods are described. The apparatus comprises a device for defining a qubit and a reflectometry circuit for reading out a state of the qubit. The device comprises a semiconductor nanowire extending along a first direction having first and second obtuse or acute edges running along the first direction, gate dielectric overlying the first and second edges of the nanowire and a split gate running across a section of the nanowire in a second, transverse direction, the split gate comprising first and second gates overlying the first and second edges respectively. The reflectometry circuit comprises a resonator coupled to the first or second gate.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Method and apparatus for single-photon source and quantum memory
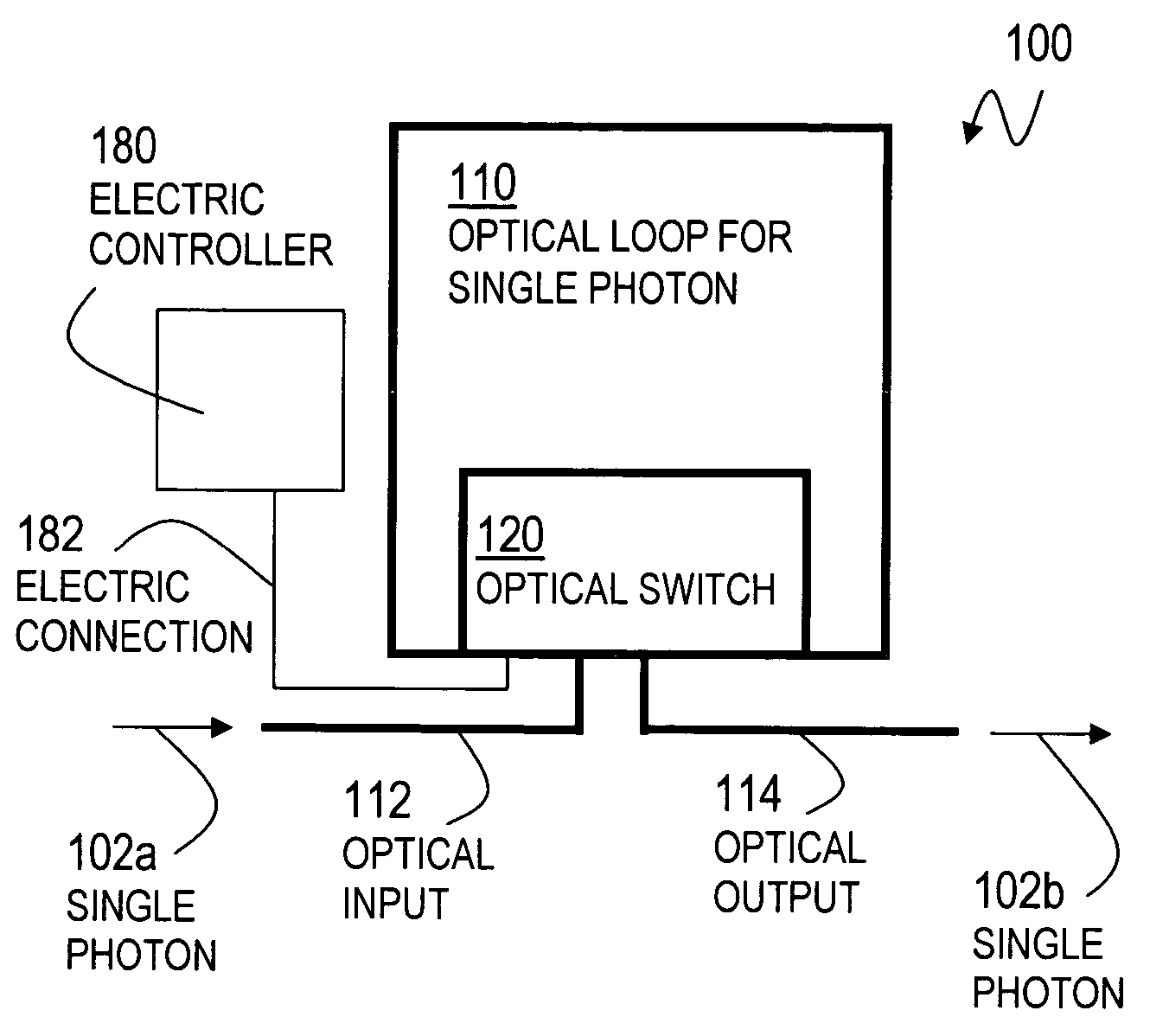
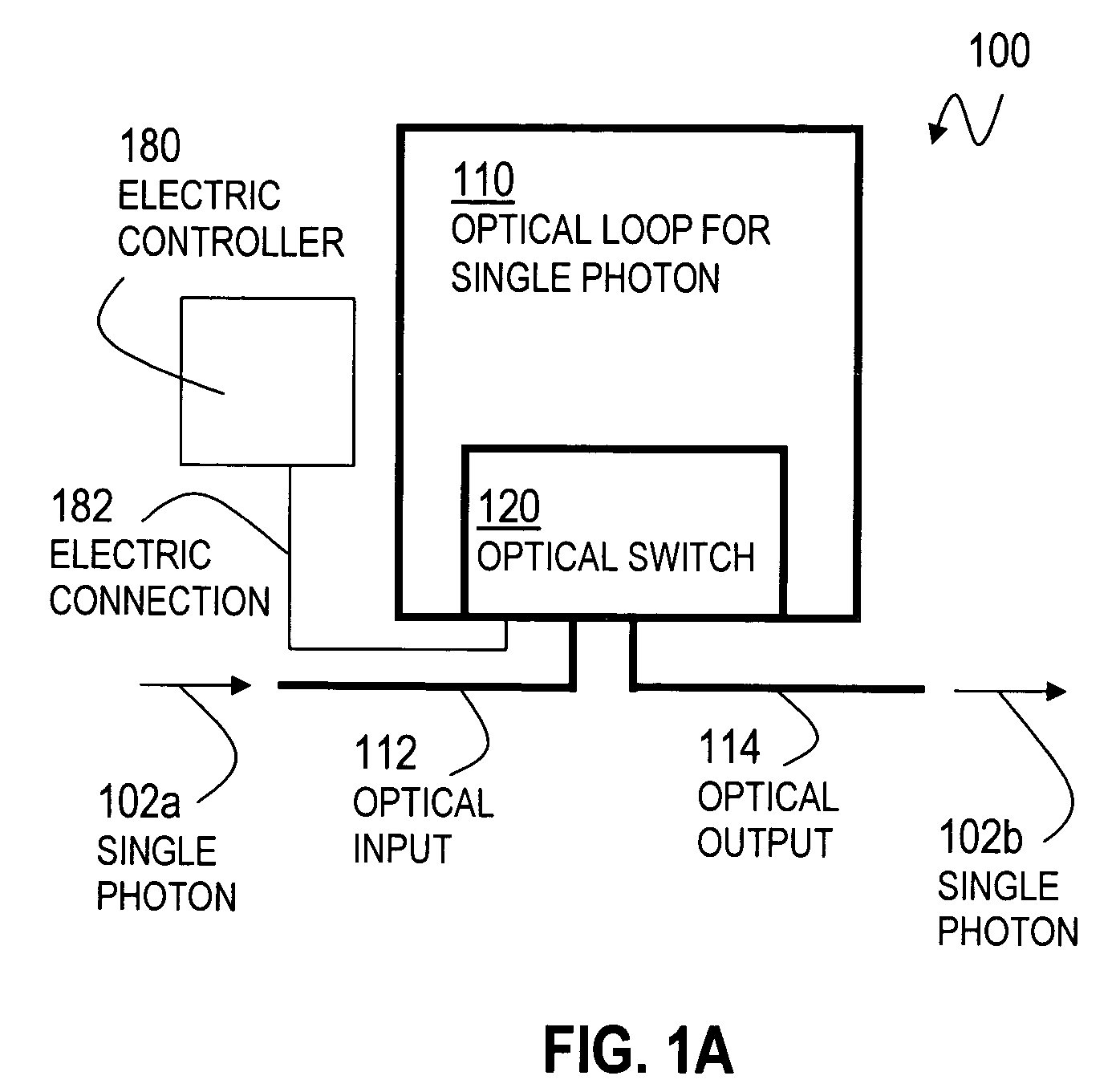
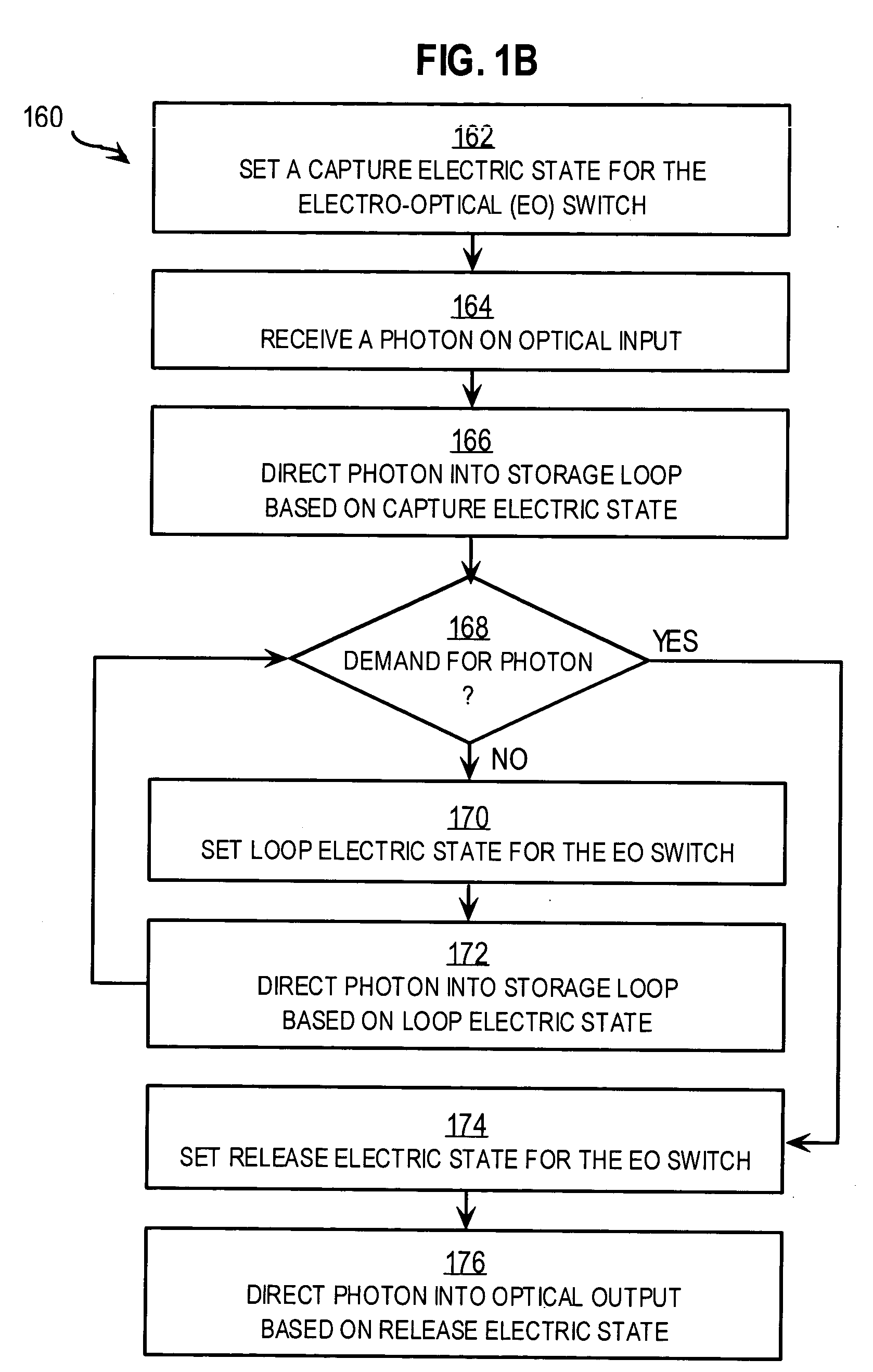
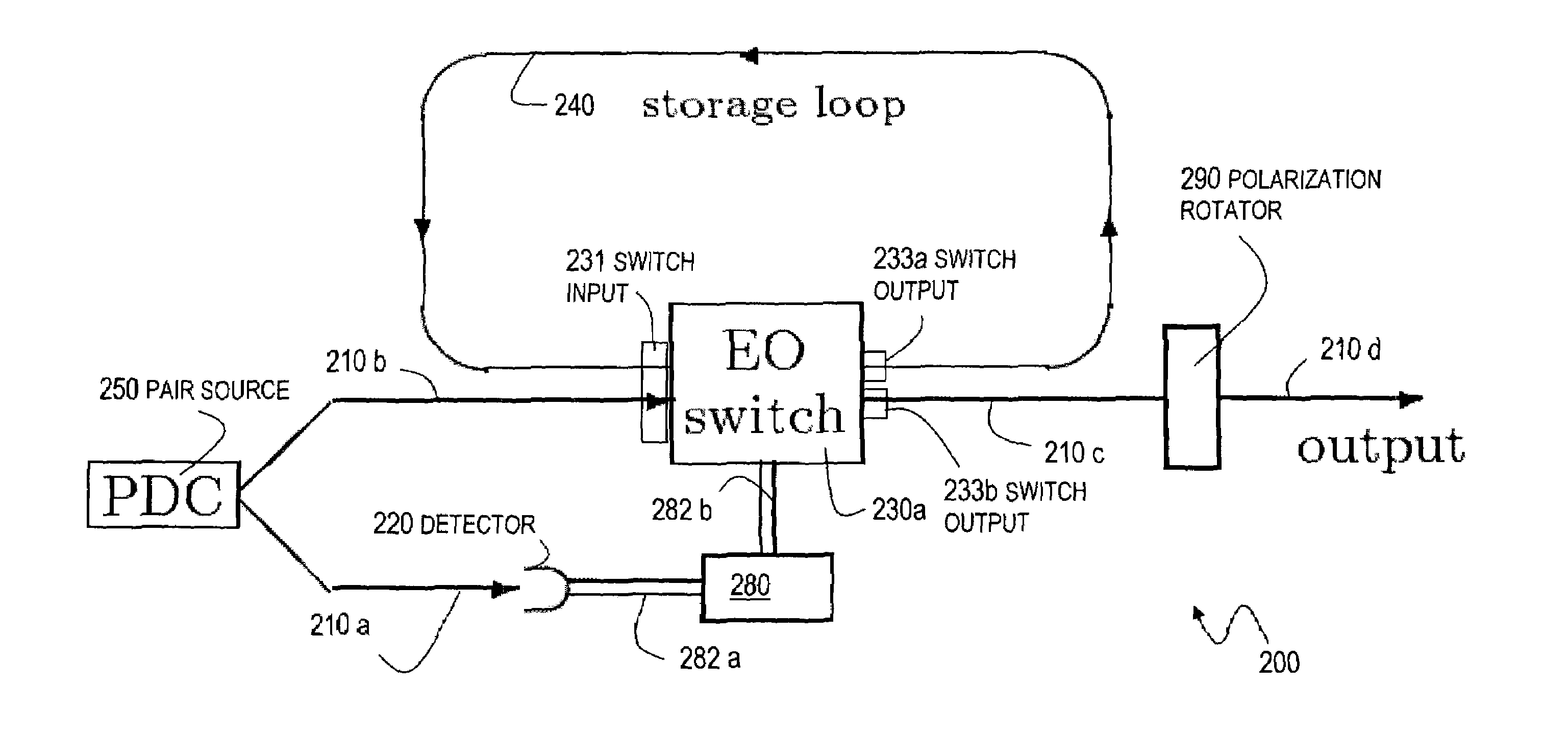
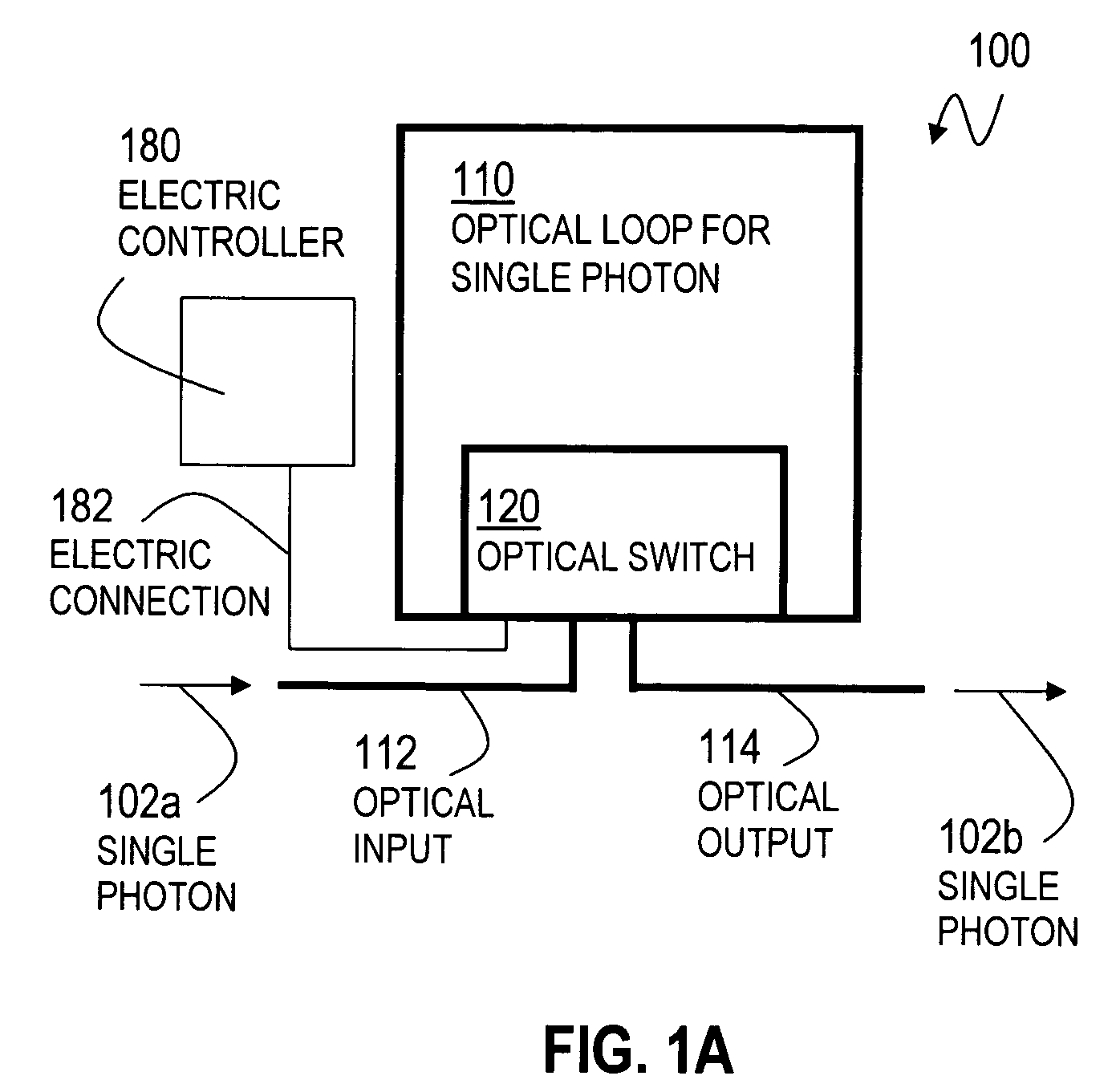
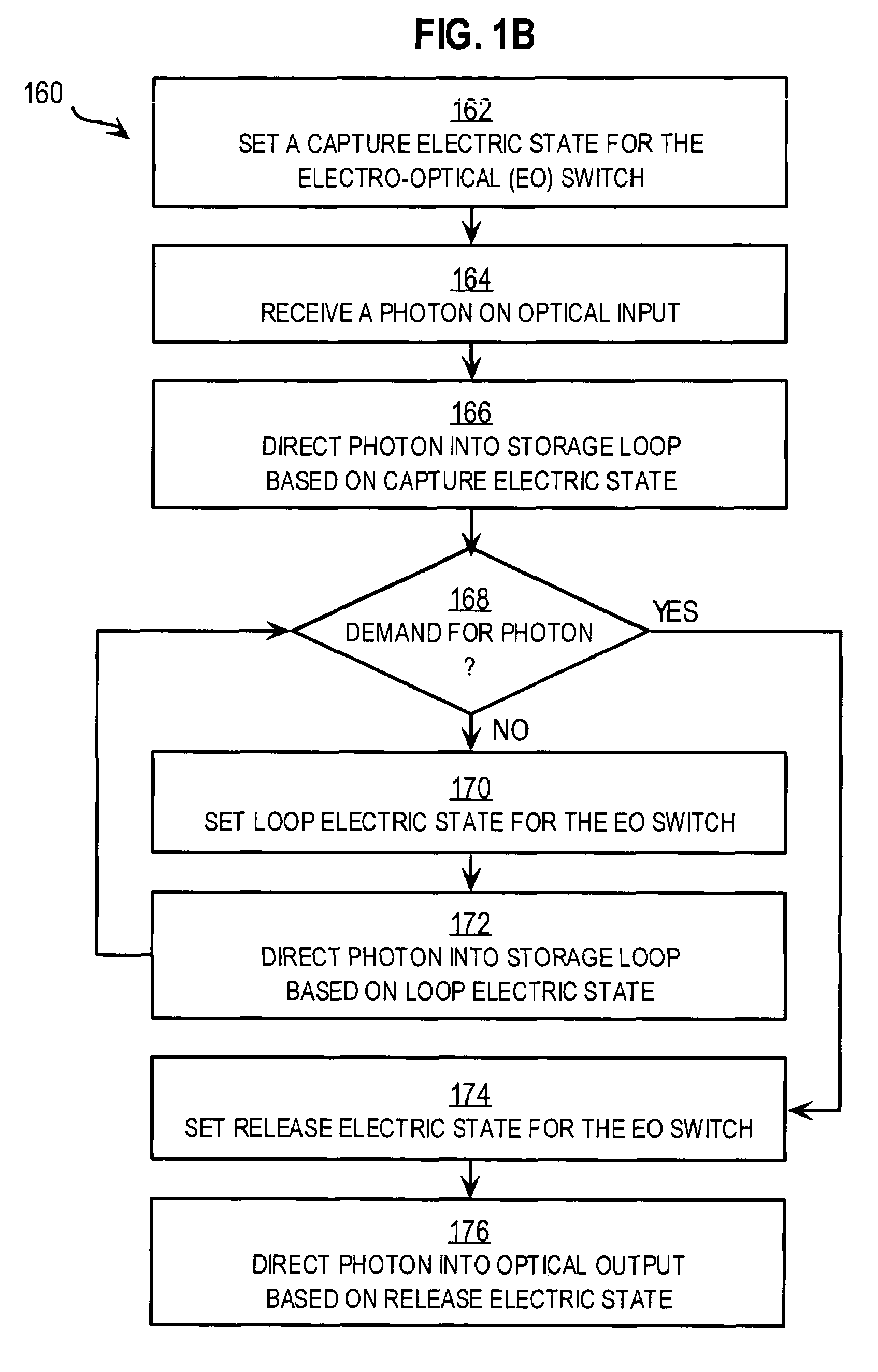
An optical switch and optical storage loop are used as the basis of a single-photon source and a quantum memory for photonic qubits. To operate as a single-photon source, the techniques include a source of a pair of photons, such as a parametric down-conversion crystal, which is known to emit photons in pairs. The detection of one member of the pair activates the switch, which re-routes the other member into the storage loop. The stored photon is then known to be circulating in the loop, and can be switched out of the loop at a later time chosen by the user, providing a single photon for potential use in a variety of quantum information processing applications. To operate as a quantum memory for photonic qubits, a single-photon in an arbitrary initial polarization state is coherently stored in the loop, and coherently switched out of the loop when needed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
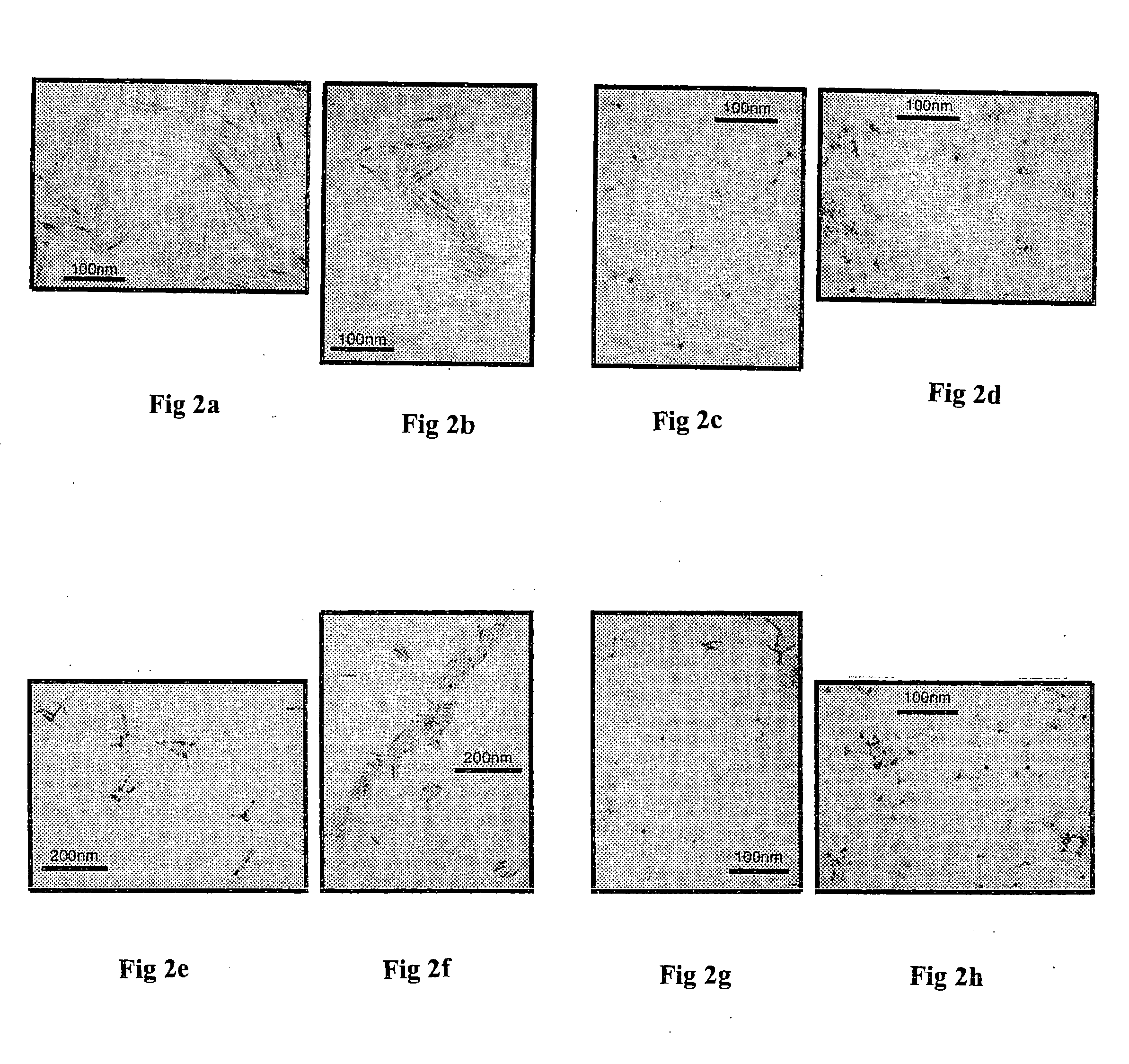
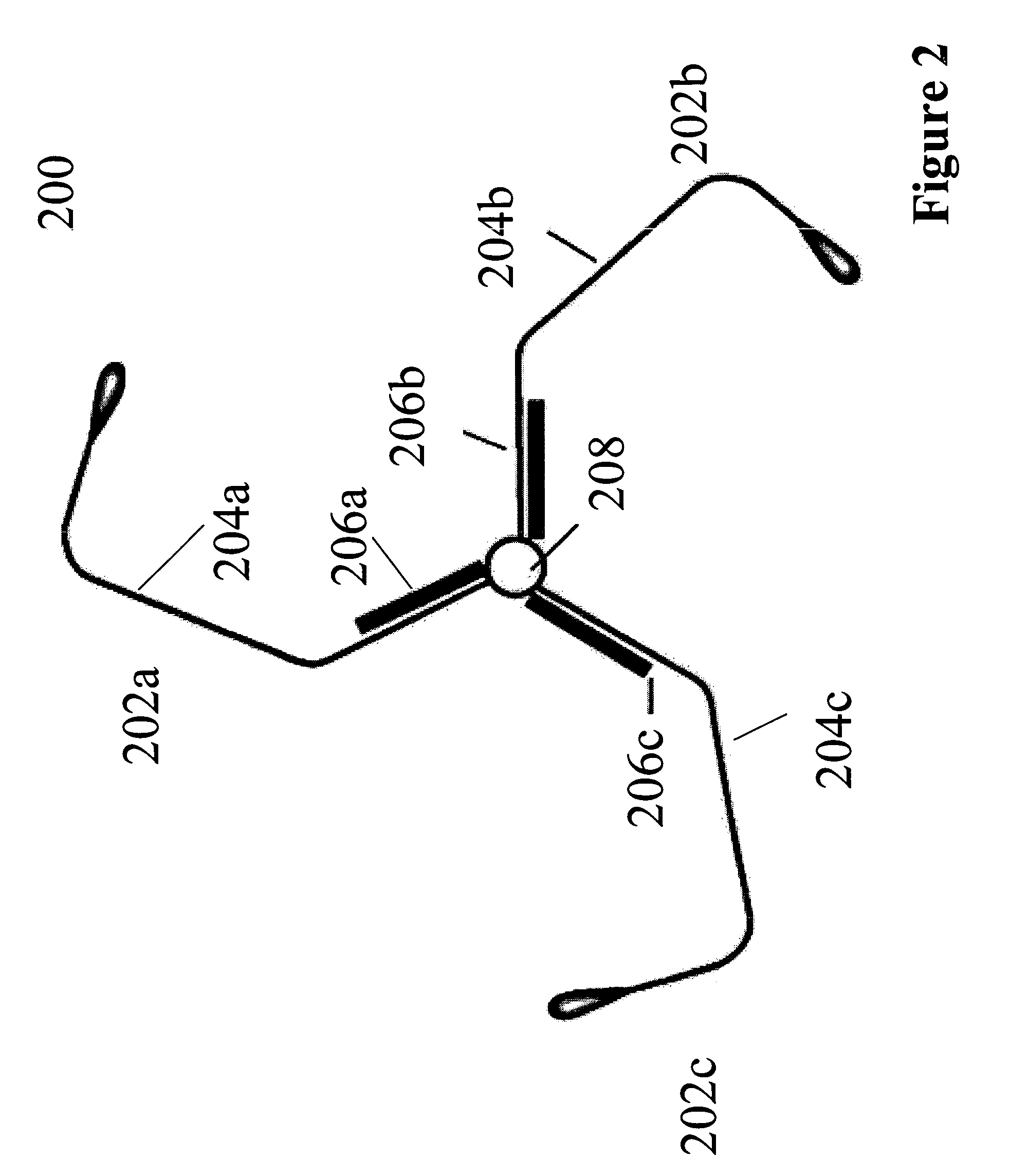
Nanocrystals with linear and branched topology
InactiveUS20050211154A1Quantum computersPolycrystalline material growthInformation processingThree-dimensional space
Disclosed herein are nanostructures comprising distinct dots and rods coupled through potential barriers of tuneable height and width, and arranged in three dimensional space at well defined angles and distances. Such control allows investigation of potential applications ranging from quantum information processing to artificial photosynthesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
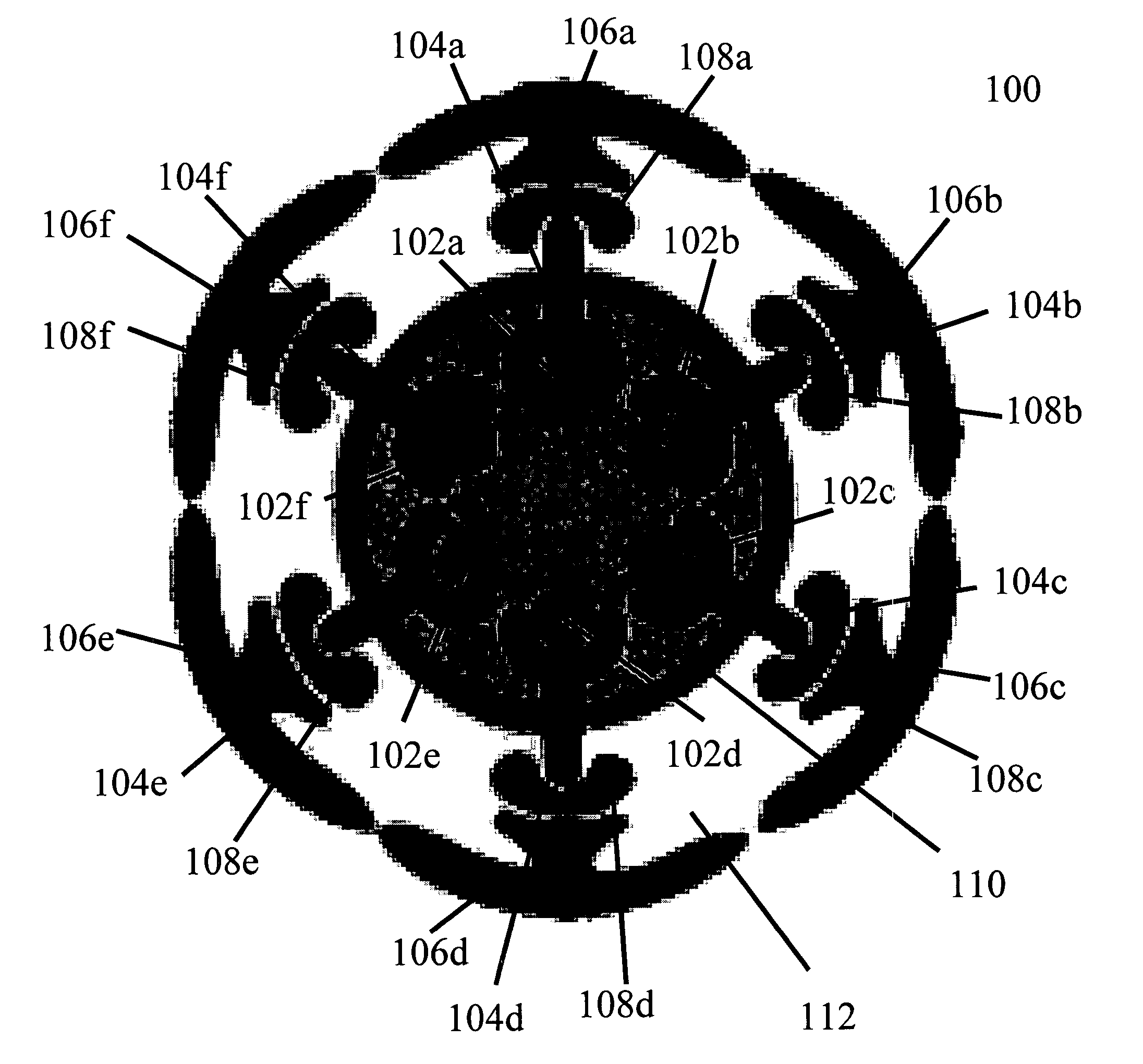
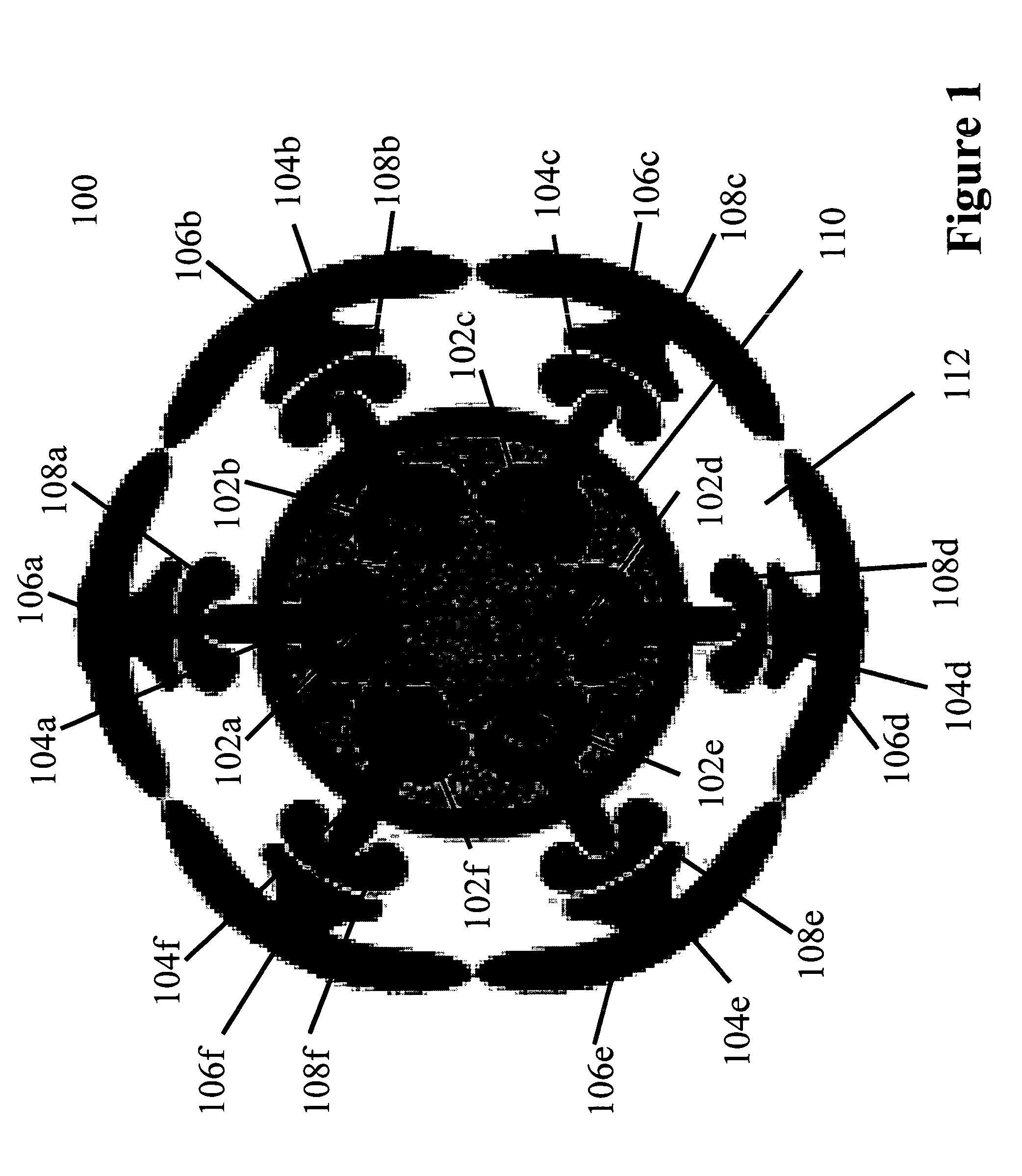
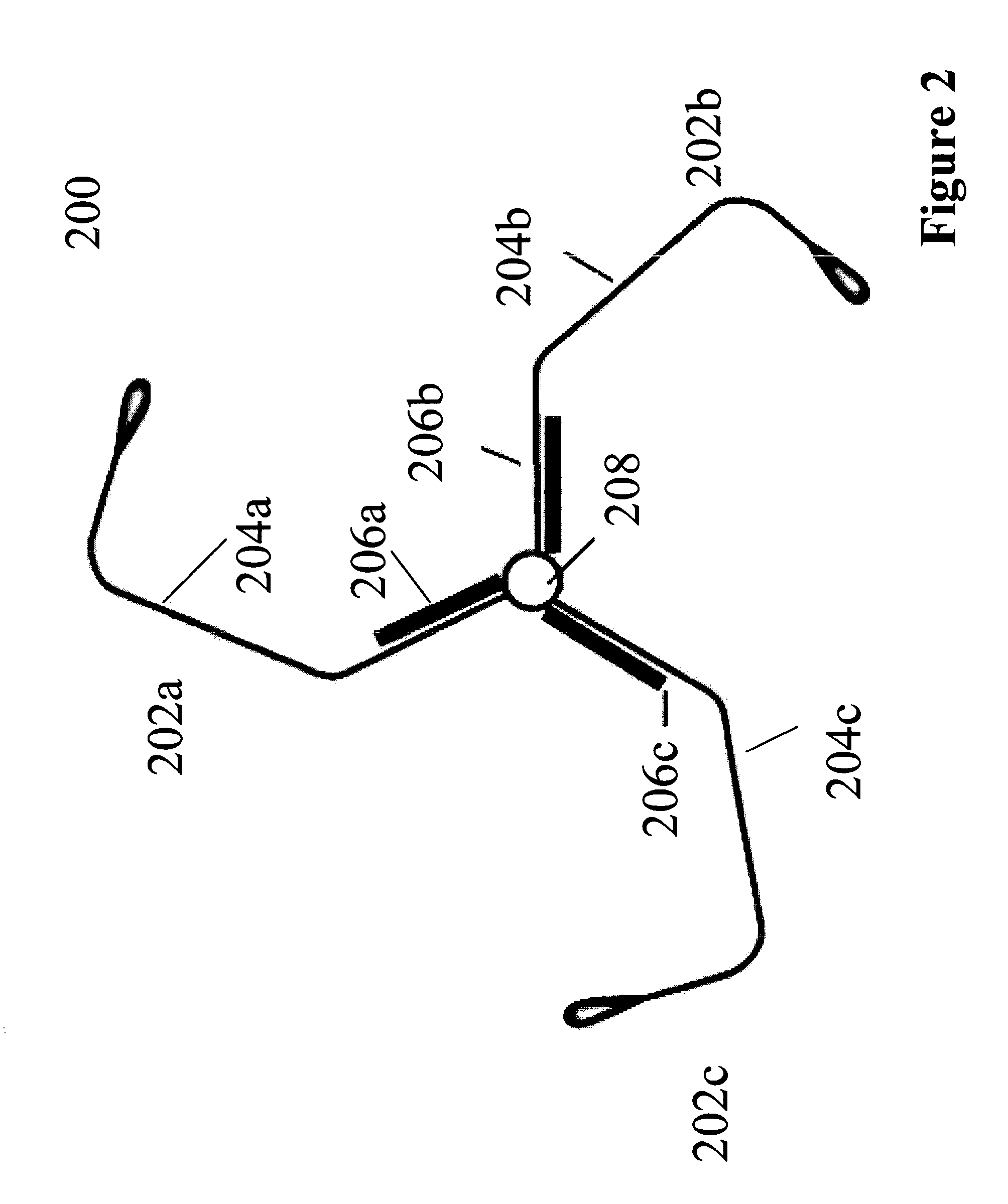
Quantum information processing elements and quantum information processing platforms using such elements
ActiveUS7219018B2Inhibition of charge transferReduce restrictionsQuantum computersMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein moleculesSelf assembled
Owner:METAQOR
Nanocrystals with linear and branched topology
InactiveUS7303628B2Quantum computersPolycrystalline material growthThree-dimensional spaceNanocrystal
Disclosed herein are nanostructures comprising distinct dots and rods coupled through potential barriers of tuneable height and width, and arranged in three dimensional space at well defined angles and distances. Such control allows investigation of potential applications ranging from quantum information processing to artificial photosynthesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
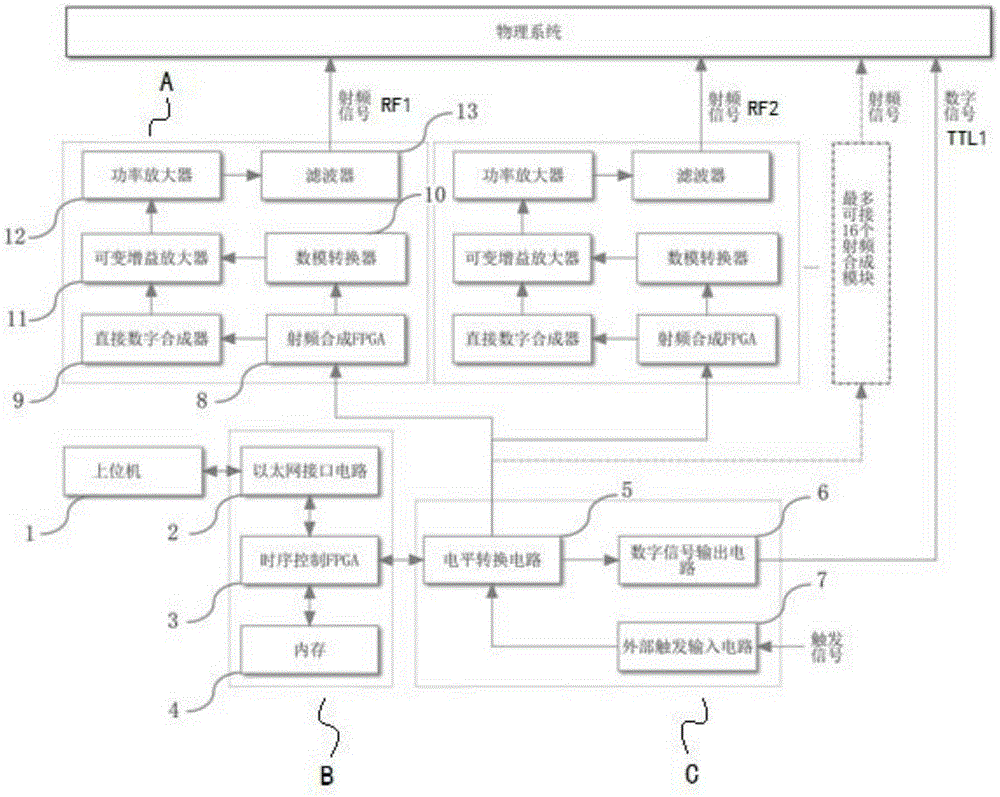
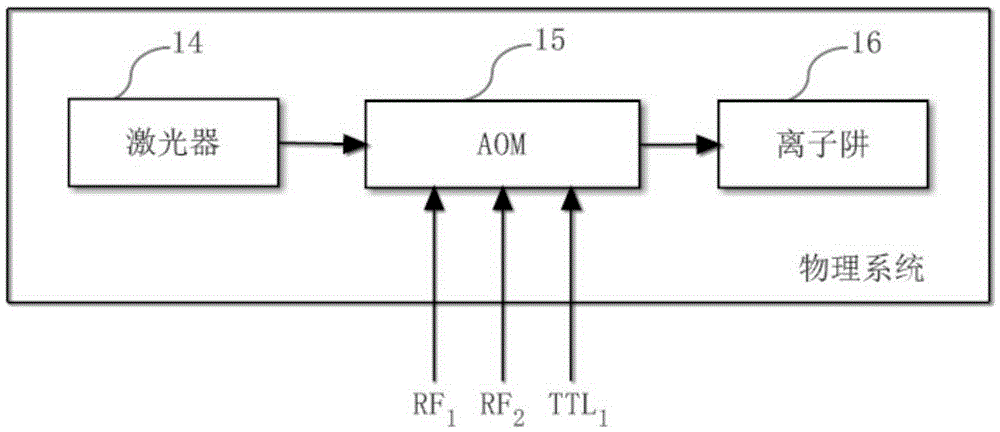
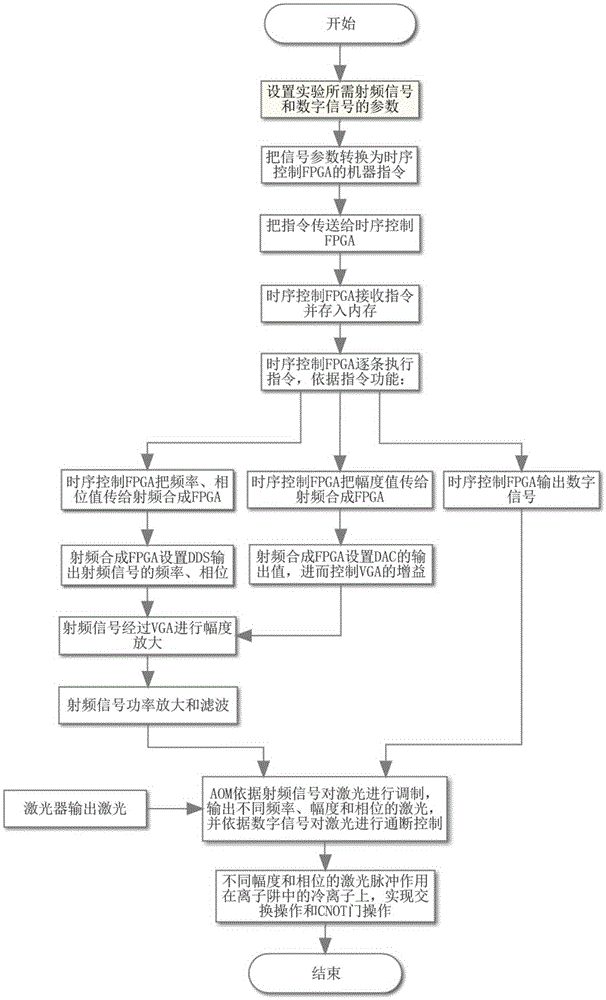
Sequential control signal generation method and device of cold ion quantum information processor
ActiveCN105281886ARealize intuitive descriptionAvoid duplication of workSynchronising arrangementControl signalRadio frequency signal
The invention provides a sequential control signal generation method of a cold ion quantum information processor. Radio frequency signal and digital signal parameters are set through a principal computer command on a principal computer; the principal computer command is converted into a machine command which is transmitted to a sequential control FPGA; the sequential control FPGA executes the machine command and digital signals and radio frequency signals are output through a conversion module and a radio frequency synthesis module. The invention also provides a sequential control signal generation device of a cold ion quantum information processor. The device comprises a principal computer, a sequential control module, a radio frequency synthesis module and a conversion module. According to the invention, sequential control signals for experiments are described intuitively; programmed principal computer commands can be used repeatedly, so that repeated work is prevented and improvement can be made according to experiment results conveniently; the parameters such as the frequency, the phase and the amplitude of radio frequency signals can be changed conveniently; multiple paths of control signals can be controlled accurately to work cooperatively; the extendibility is great.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF PHYSICS & MATHEMATICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
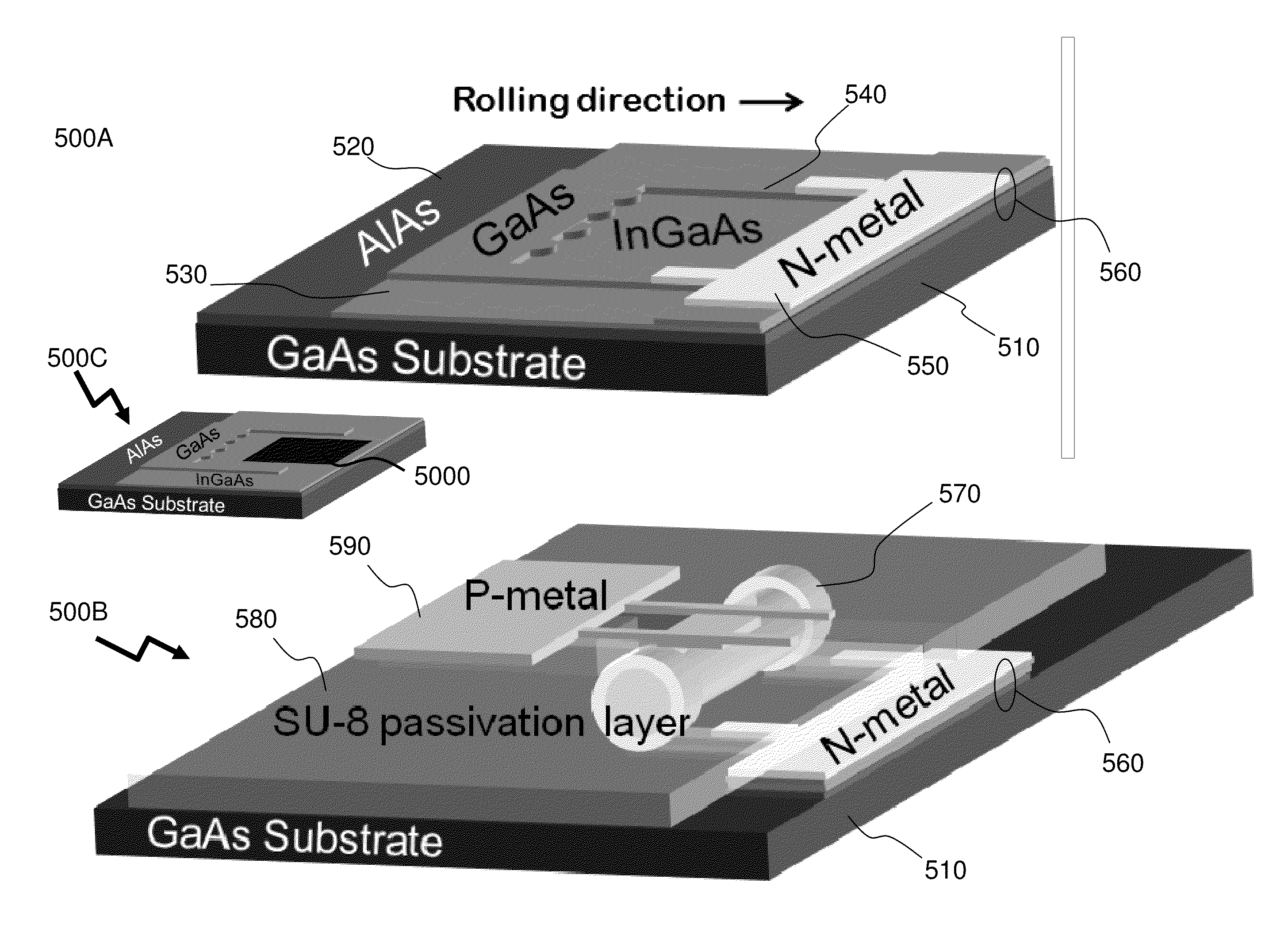
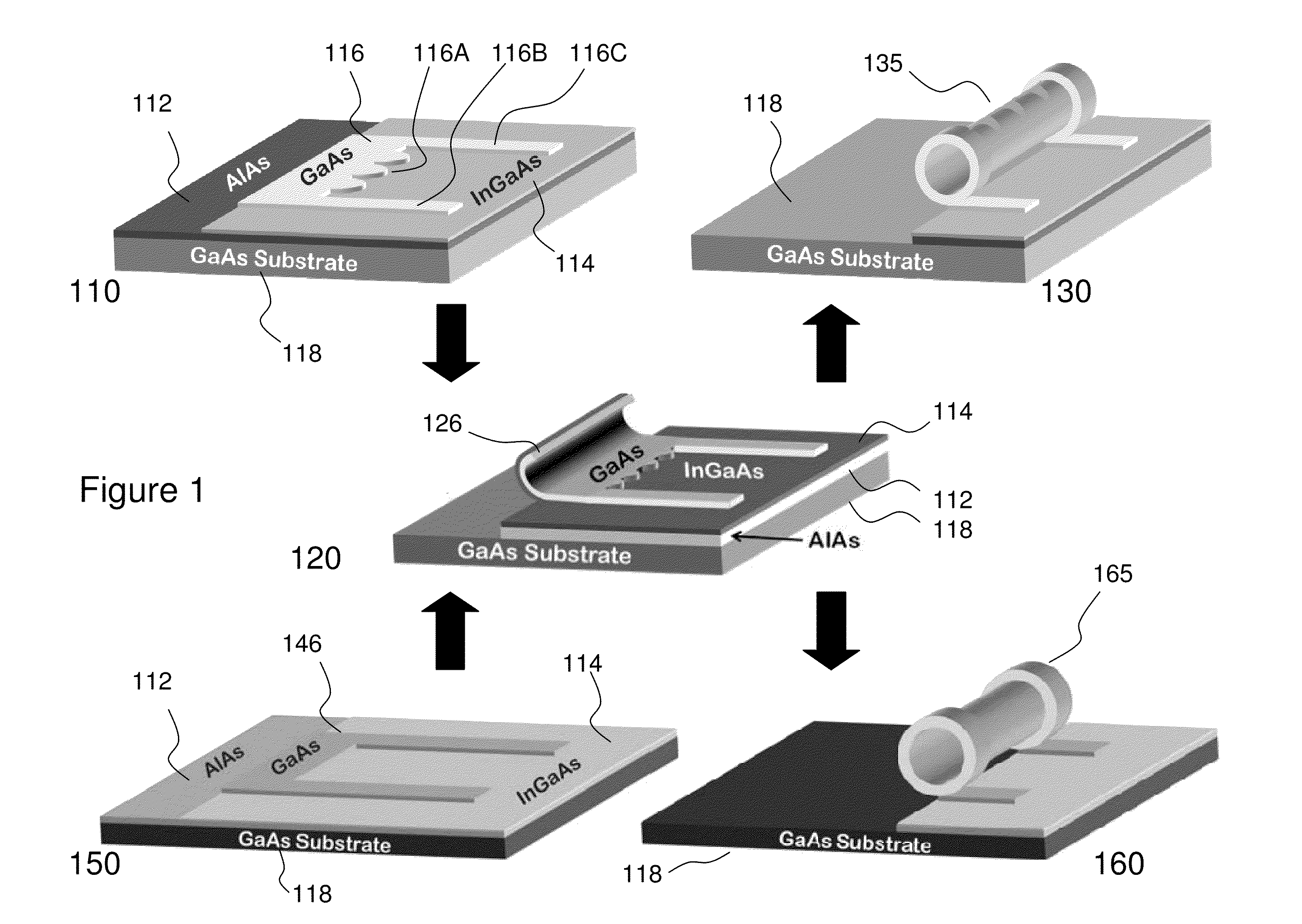
Method for Fabricating Optical Semiconductor Tubes and Devices Thereof
ActiveUS20110163421A1NanoinformaticsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingManufacturing technologyHigh density
Semiconductor micro- and nanotubes allow the incorporation of ordered structures such as quantum wells and quantum dots into them providing the potential for ultralow threshold micro- and nanoscale lasers for use in applications such as future ultrahigh-speed photonic systems as well as quantum information processing. According to the invention a means of manufacturing these with high reproducibility, low processing complexity, and at high densities is provided. Also provided is a means of releasing these micro- and nanotubes with low stress and a method of “pick-and-place” allowing micro- and nanotubes to be exploited in devices integrated on substrates that are either incompatible with the manufacturing technique or where the area of substrate required to manufacture them is detrimental to the cost or performance of the circuit.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Modular array of fixed-coupling quantum systems for quantum information processing
A quantum information processing system includes a first composite quantum system, a second composite quantum system, a plurality of electromagnetic field sources coupled to the system and an adjustable electromagnetic coupling between the first composite quantum system and the second composite quantum system.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
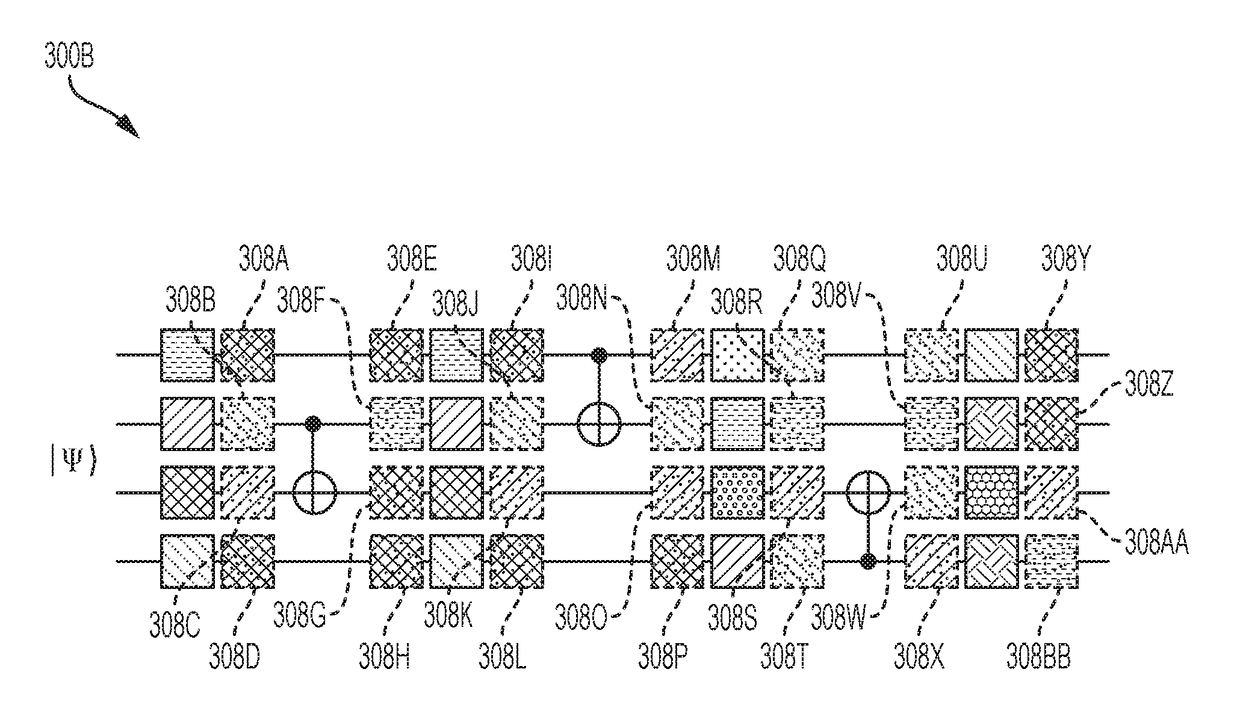
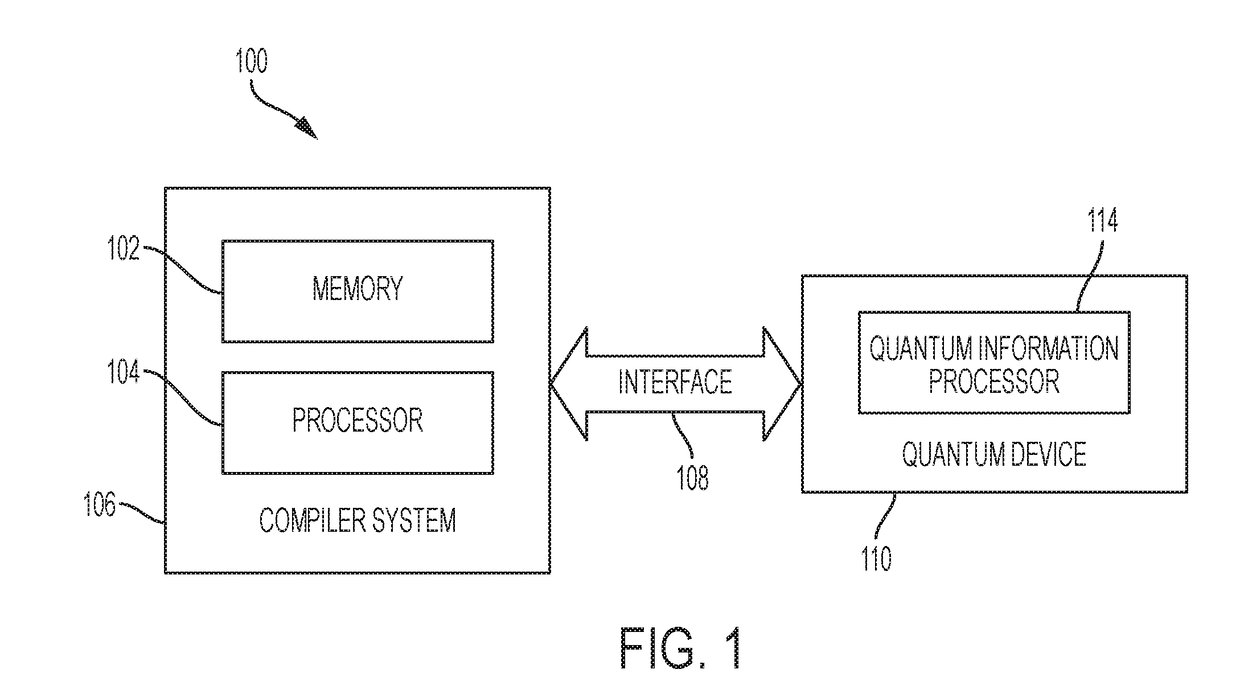
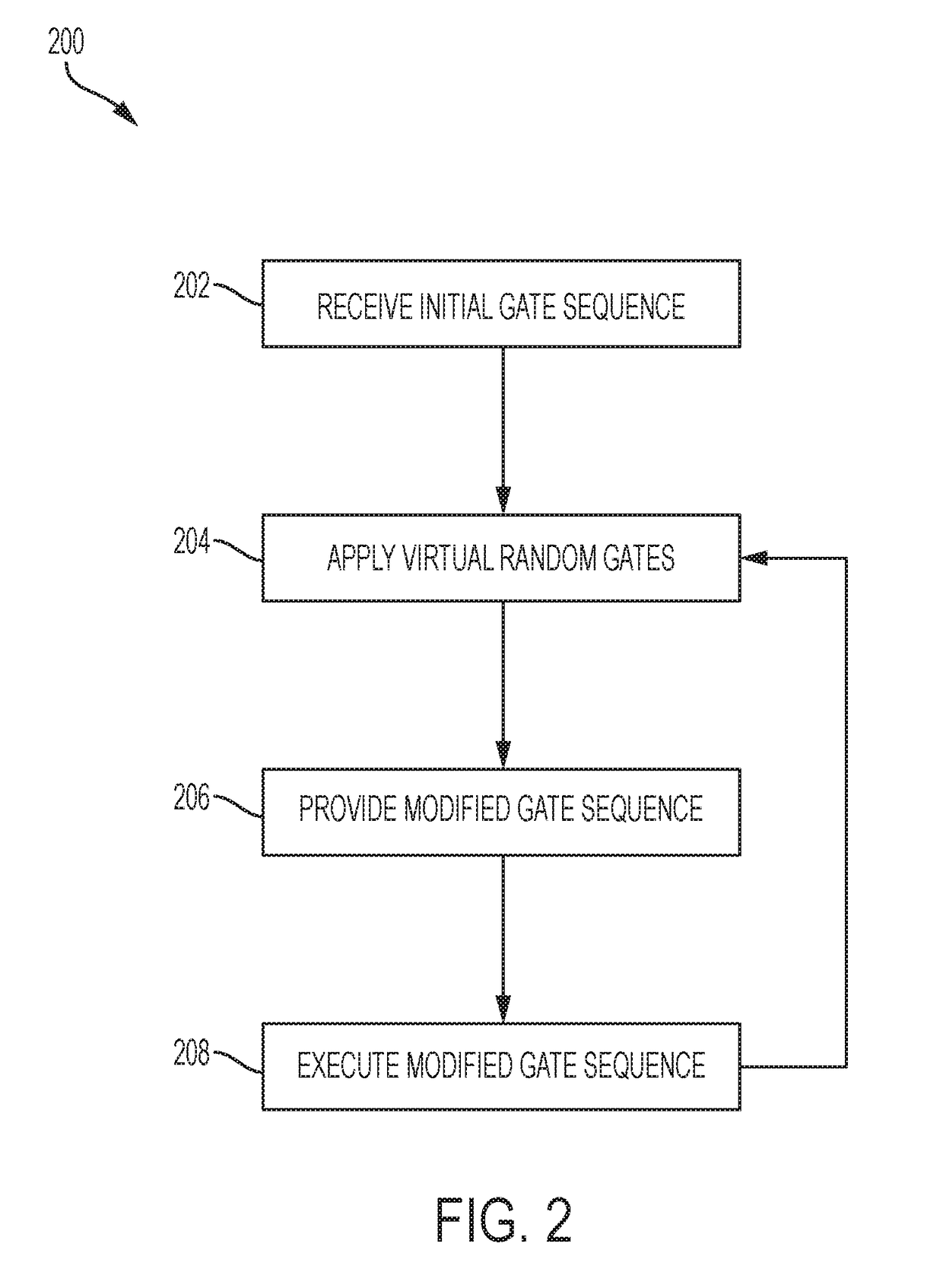
Randomized Compiling for Quantum Computation
In a general aspect, randomized compiling techniques for quantum computing are described. In some aspects, an initial quantum-logic gate sequence is received. A modified quantum-logic gate sequence is generated by applying virtual random gates to the initial quantum-logic gate sequence, such that the initial quantum-logic gate sequence is logically equivalent to the modified quantum-logic gate sequence. The modified quantum-logic gate sequence can be provided to a quantum information processor for execution.
Owner:KEYSIGHT TECH CANADA INC
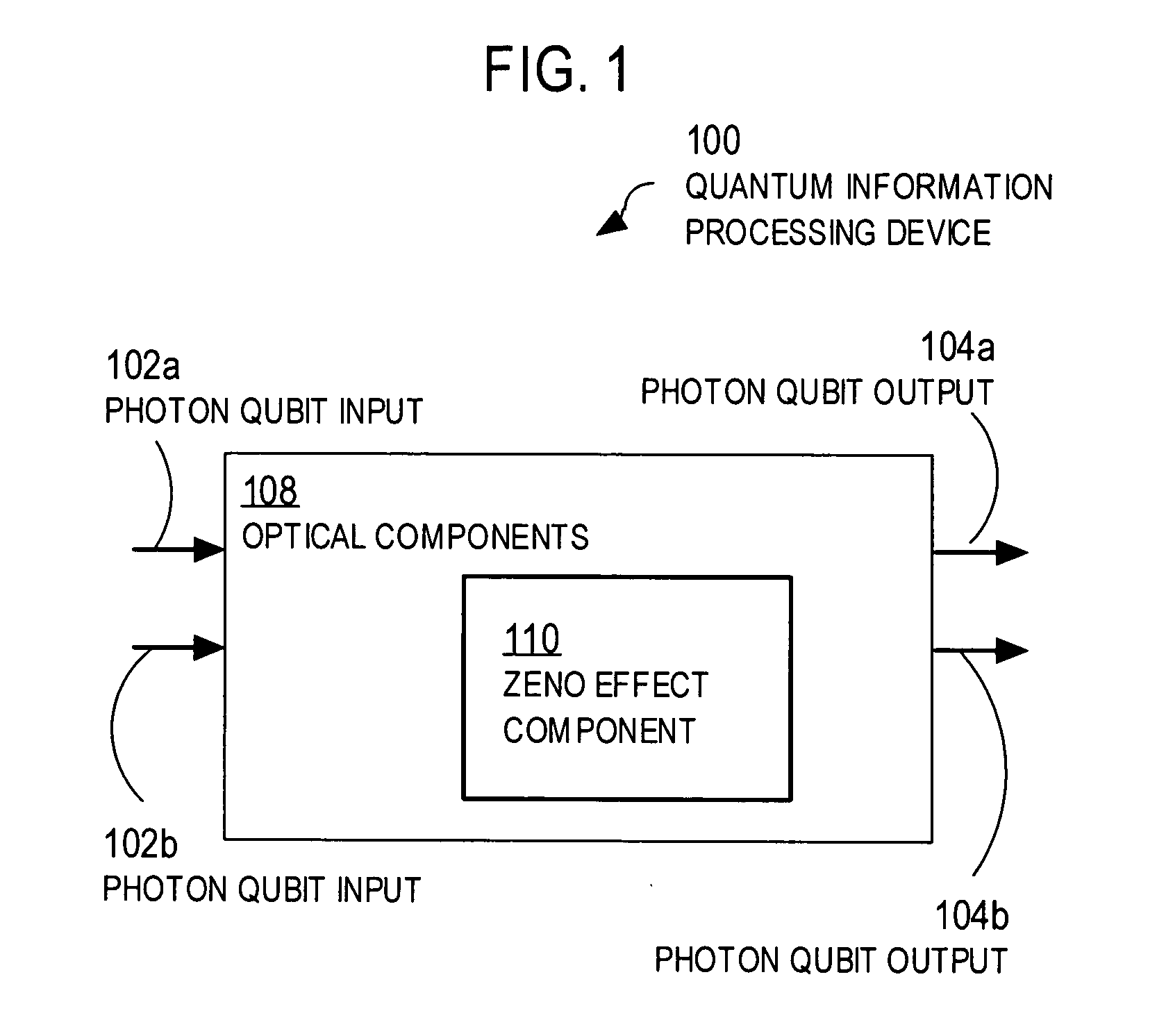
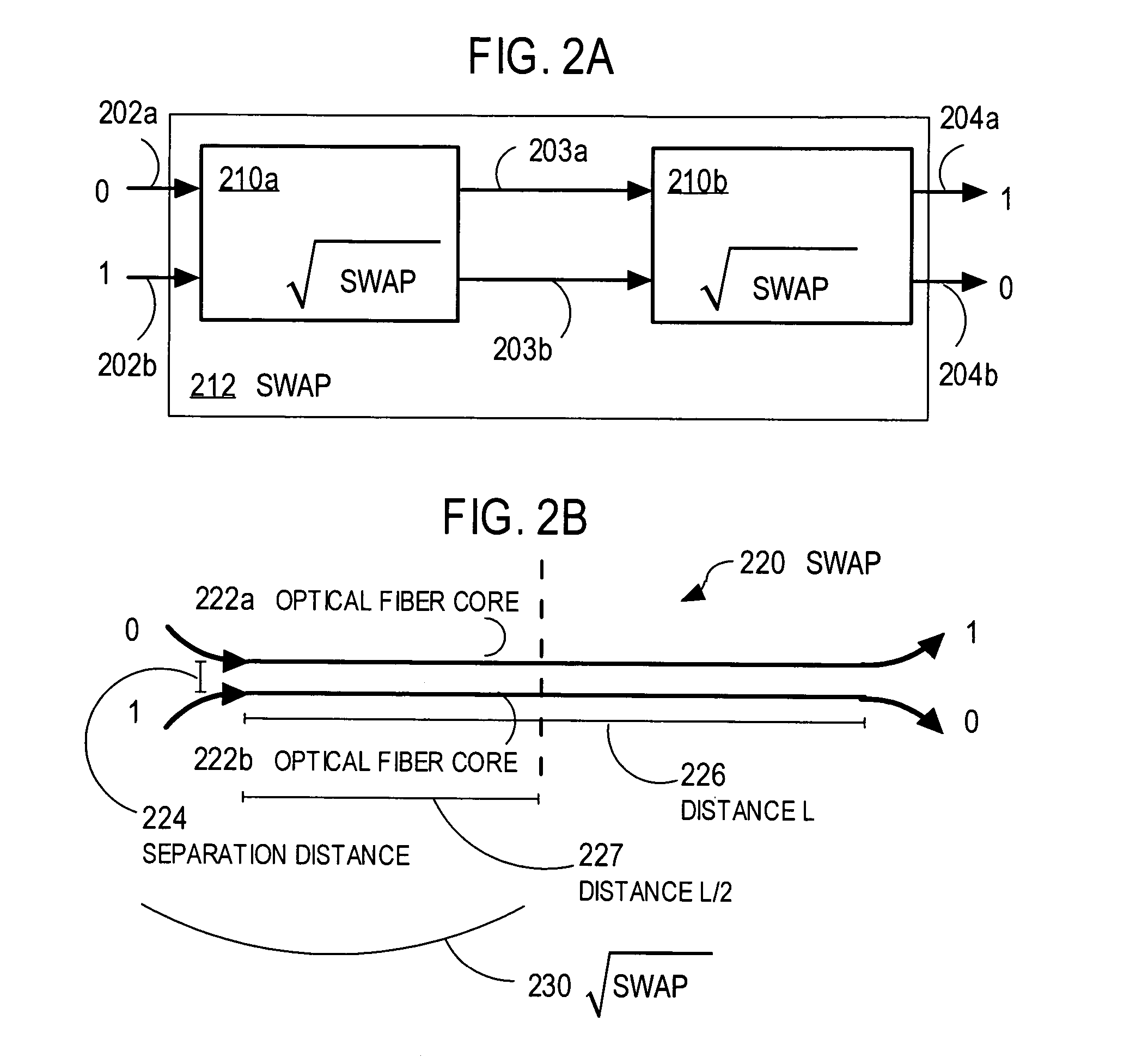
Techniques for quantum processing with photons and the Zeno effect
ActiveUS20050117836A1Small spacingReduce error rateQuantum computersComputing operations for integration/differentiationInformation processingQuantum Zeno effect
Techniques are provided that use the quantum Zeno effect to implement practical devices that use single photons as the qubits for quantum information processing. In the quantum Zeno effect, a randomly-occurring event is suppressed by frequent measurements to determine whether the event has occurred. The same results can be obtained by using atoms or molecules or ions to react to the occurrence of the event. Techniques include directing one or more input qubits onto a device and applying a quantum Zeno effect in the device. The quantum Zeno effect is applied by consuming one or more photons in the device under conditions in which photons, that would otherwise be output by the device, do not represent a result of a particular quantum information processing operation. Devices implemented using the quantum Zeno effect can operate with low error rates without the need for high efficiency detectors and large number of ancilla.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
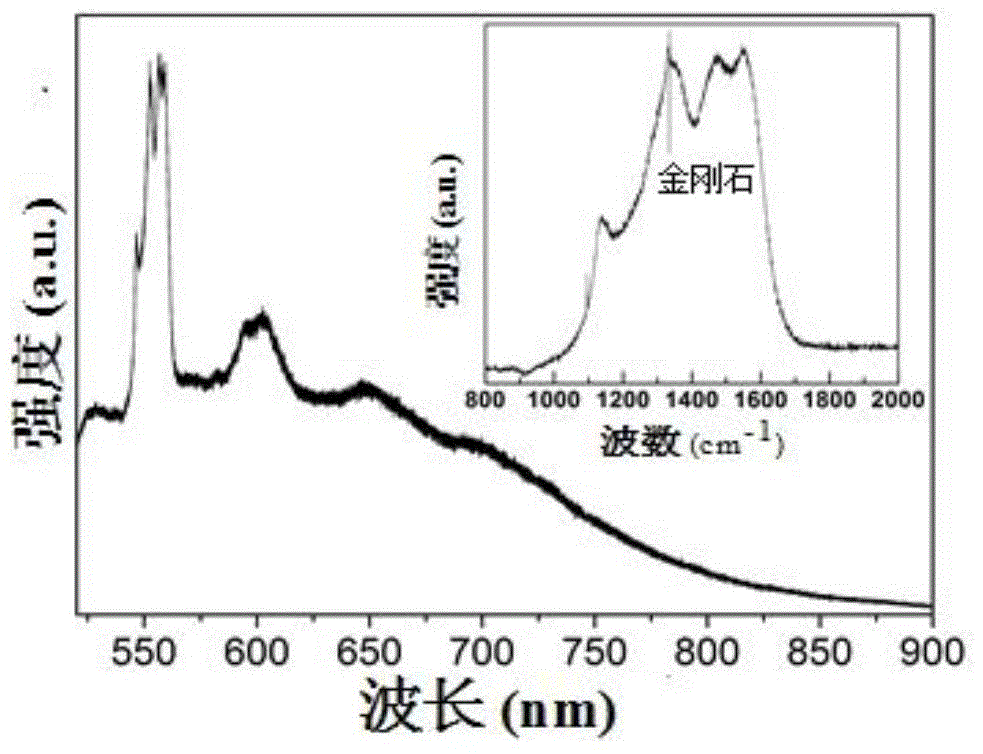
Nano-diamond film with Si-V luminescence and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104060237AWith Si-V light emitting performanceSi-V has strong luminous performanceMaterial nanotechnologyChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseDisplay device
The invention provides a nano-diamond film with Si-V luminescence and a preparation method thereof. The nano-diamond film is prepared on a single crystal silicon substrate by use of a hot filament chemical vapor deposition method; heat preservation is performed on the film for 5-150 minutes in air at a temperature ranging from 500 to 700 DEG C, and then the nano-diamond film with Si-V luminescence is obtained. The nano-diamond film prepared has relatively high Si-V luminescence intensity which has very important scientific significance and engineering value for the application of the nano-diamond film in the fields such as single photon sources, quantum information processing, photoelectric devices, biomarkers, semiconductor devices and field emission displays.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Quantum computational systems
ActiveUS20060045269A1Public key for secure communicationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsQuantum electrodynamicsUniversal quantum simulator
Apparatus and methods for performing quantum computations are disclosed. Such quantum computational systems may include quantum computers, quantum cryptography systems, quantum information processing systems, quantum storage media, and special purpose quantum simulators.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
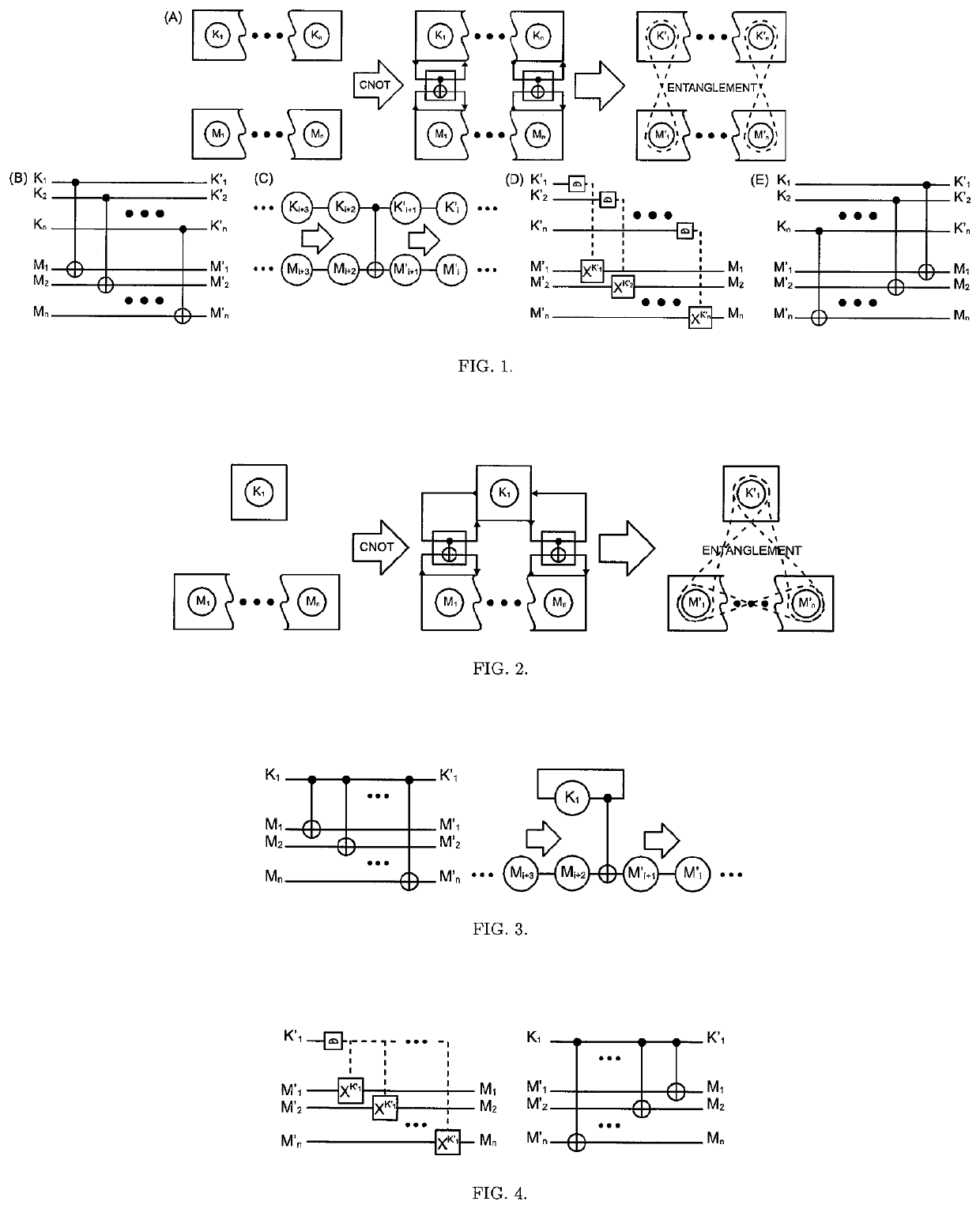
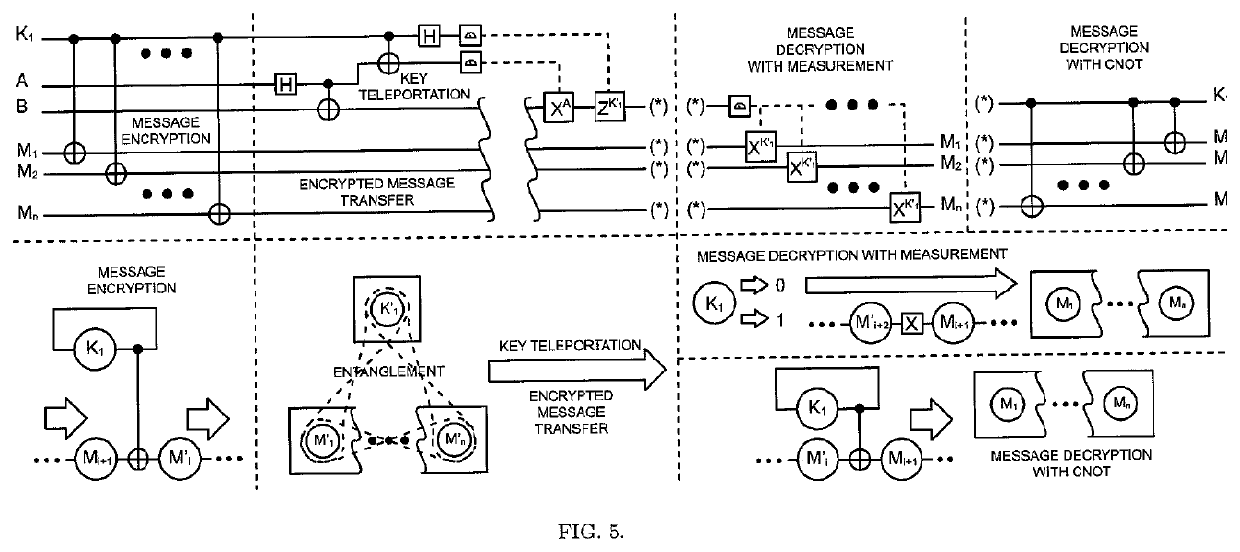
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) for entanglement encryption of quantum information
InactiveUS20210058244A1Quantum computersKey distribution for secure communicationInformation processingQuantum teleportation
The One-Qubit Pad (OQP) protocol and its generic implementing device constitute a novel, maximally efficient scheme for encryption of quantum information with a quantum key of just a single qubit in an arbitrary unknown quantum state. The OQP enables encryption of the quantum information of n qubits register with a single qubit key upon provision of a multi-qubit entanglement between the single qubit key and the n qubits of the quantum message by the iterative application of the CNOT gate on the same key qubit (control input) and subsequent qubits of the message (target input). This results in an entanglement of all n+1 qubits, which locks original quantum information qubits and the single qubit of the key in a jointly entangled state that cannot be disentangled without the single qubit key. In order to decrypt the quantum message (by its disentanglement) one needs to have the qubit key and either reverse the protocol (applying CNOT operations in the reversed order) or simply measure the entangled key qubit and then depending on the outcome either straightforwardly obtain the decrypted quantum message or its quantum negation (dealt with by again applying quantum negation on all of the message qubits thus restoring their original states). The OQP protocol and its implementing device is proposed one hundred years after the classical One-Time Pad (Vernam cipher) was invented in 1917. The main differences between two schemes show how much quantum and clasical information differ. It is of course impossible to unconditionally securely encrypt classical sequence of n bits with just 1 bit of a key or guarantee that the random key that can be used for this purpose of n bits length (same as of the message) could not be copied. In contrast both these features are possible for the quantum information as described upon the proposed invention. The main characteristic of the OQP protocol to use only a single qubit as the key to enable information-theoretic security of n qubits quantum information encryption follows from the introduction in the invention of the multi-qubit entanglement, which is a non-local, topological and non-classical phenomenon giving quantum information significant edge over its classical counterpart. The main application of the OQP protocol and its implementing generic device is to lock quantum information with the single key qubit in order to prevent any unauthorized access to it (not only a classical access upon a measurement, but more importantly a quantum access by a quantum information processing device). This application can be also extended to communication scenario jointly with the Quantum Teleportation, which without OQP requires pre-sharing of n pairs of Bell states between Alice and Bob to securely communicate n qubits long quantum message, whereas in contrast with the OQP protocol just one pair of Bell state is required to securely teleport only the single qubit key for the OQP encrypted quantum message sent through an insecure quantum channel and still be access-protected from Eve (an adversary).
Owner:COMPSECUR SP ZOO
Quantum information processing elements and quantum information processing platforms using such elements
ActiveUS7216038B2Inhibition of charge transferReduce restrictionsQuantum computersMicrobiological testing/measurementProtein moleculesSelf assembled
The invention in various embodiments is directed to quantum information processing elements and quantum information processing platforms employing such elements. In one aspect, the quantum information processing elements are formed with self-assembling protein molecules.
Owner:METAQOR
Method and apparatus for single-photon source and quantum memory
An optical switch and optical storage loop are used as the basis of a single-photon source and a quantum memory for photonic qubits. To operate as a single-photon source, the techniques include a source of a pair of photons, such as a parametric down-conversion crystal, which is known to emit photons in pairs. The detection of one member of the pair activates the switch, which re-routes the other member into the storage loop. The stored photon is then known to be circulating in the loop, and can be switched out of the loop at a later time chosen by the user, providing a single photon for potential use in a variety of quantum information processing applications. To operate as a quantum memory for photonic qubits, a single-photon in an arbitrary initial polarization state is coherently stored in the loop, and coherently switched out of the loop when needed.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Quantum information processing elements and quantum information processing platforms using such elements
ActiveUS7219017B2Inhibition of charge transferReduce restrictionsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsLaser detailsProtein moleculesInformation handling
The invention in various embodiments is directed to quantum information processing elements and quantum information processing platforms employing such elements. In one aspect, the quantum information processing elements are formed with self-assembling protein molecules.
Owner:METAQOR
Systems, devices, and methods to interact with quantum information stored in spins
A quantum information processing device including a semiconductor substrate. An optical resonator is coupled to the substrate. The optical resonator supports a first photonic mode with a first resonator frequency. The quantum information processing device includes a non-gaseous chalcogen donor atom disposed within the semiconductor substrate and optically coupled to the optical resonator. The donor atom has a transition frequency in resonance with the resonator frequency. Also disclosed herein are systems, devices, articles and methods with practical application in quantum information processing including or associated with one or more deep impurities in a silicon substrate optically coupled to an optical structure.
Owner:PHOTONIC INC
Single particle layer nano-diamond film and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104762607AEasy to operateChemical vapor deposition coatingDisplay deviceElectrochemical electrode
The invention provides a single particle layer nano-diamond film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: polishing a monocrystalline silicon piece by using a diamond, and then cleaning and drying to obtain a monocrystalline silicon substrate; putting the monocrystalline silicon substrate in hot filament chemical vapor deposition equipment; by taking acetone as a carbon source, bringing acetone to a reaction chamber in a hydrogen bubbling manner, wherein the flow rate of hydrogen to acetone is 200: 90, the distance from a hot filament to the monocrystalline silicon substrate is 7mm, the reaction power is 1600-2300W, and the working air pressure is 1.63Kpa, no bias voltage is applied in the reaction process, the film growing time is 10-50 minutes; and after growth, dropping the temperature and cooling under a condition of not introducing hydrogen, thus obtaining the single particle layer nano-diamond film which is 300-700nm thick. The film is relatively strong in Si-V light-emitting property and has a broad application prospect in the field of single-photon sources, quantum information processing, optoelectronic devices, electrochemical electrodes, biomarkers, semiconductor apparatuses, field emission displays and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Quantum information processing device and method
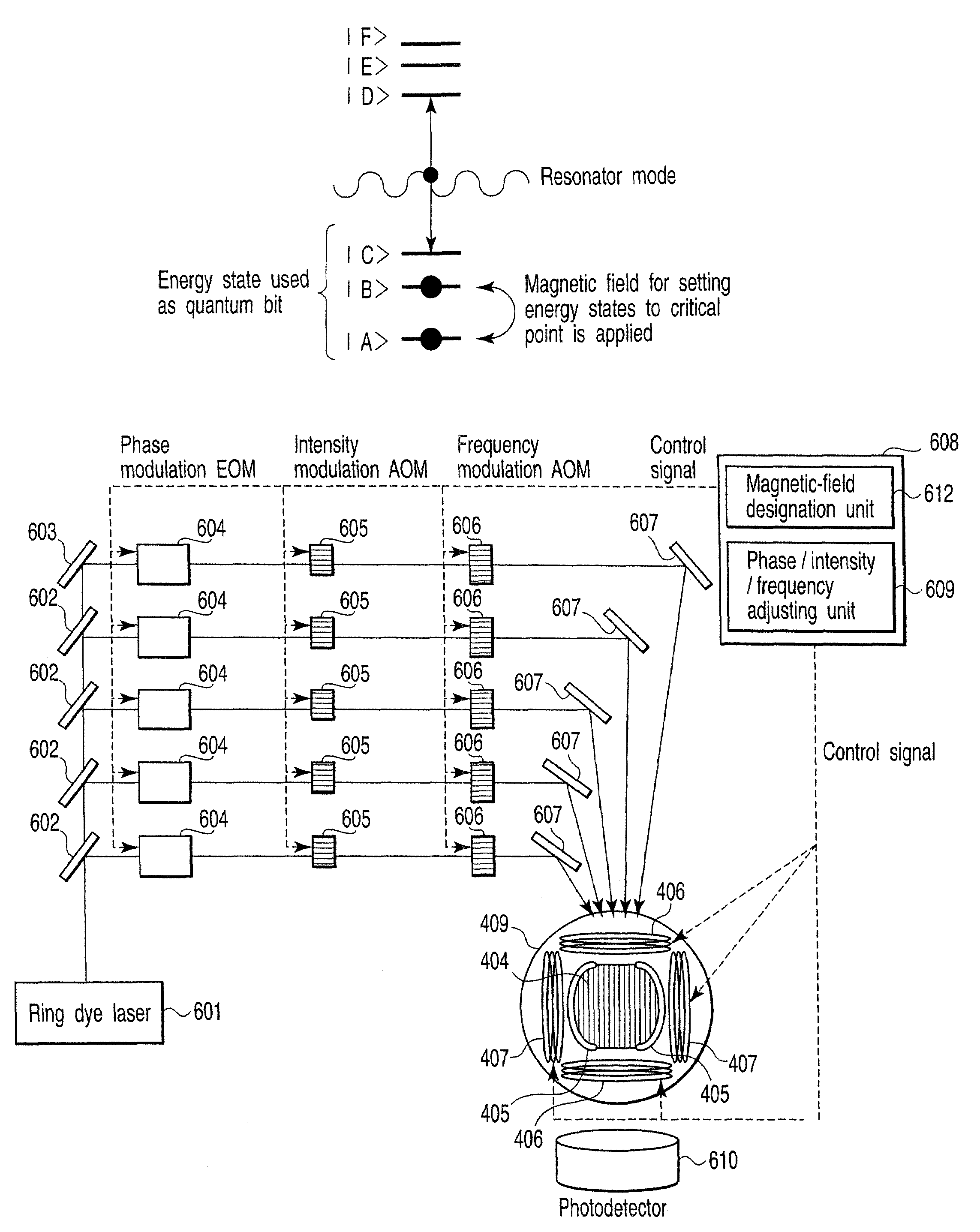
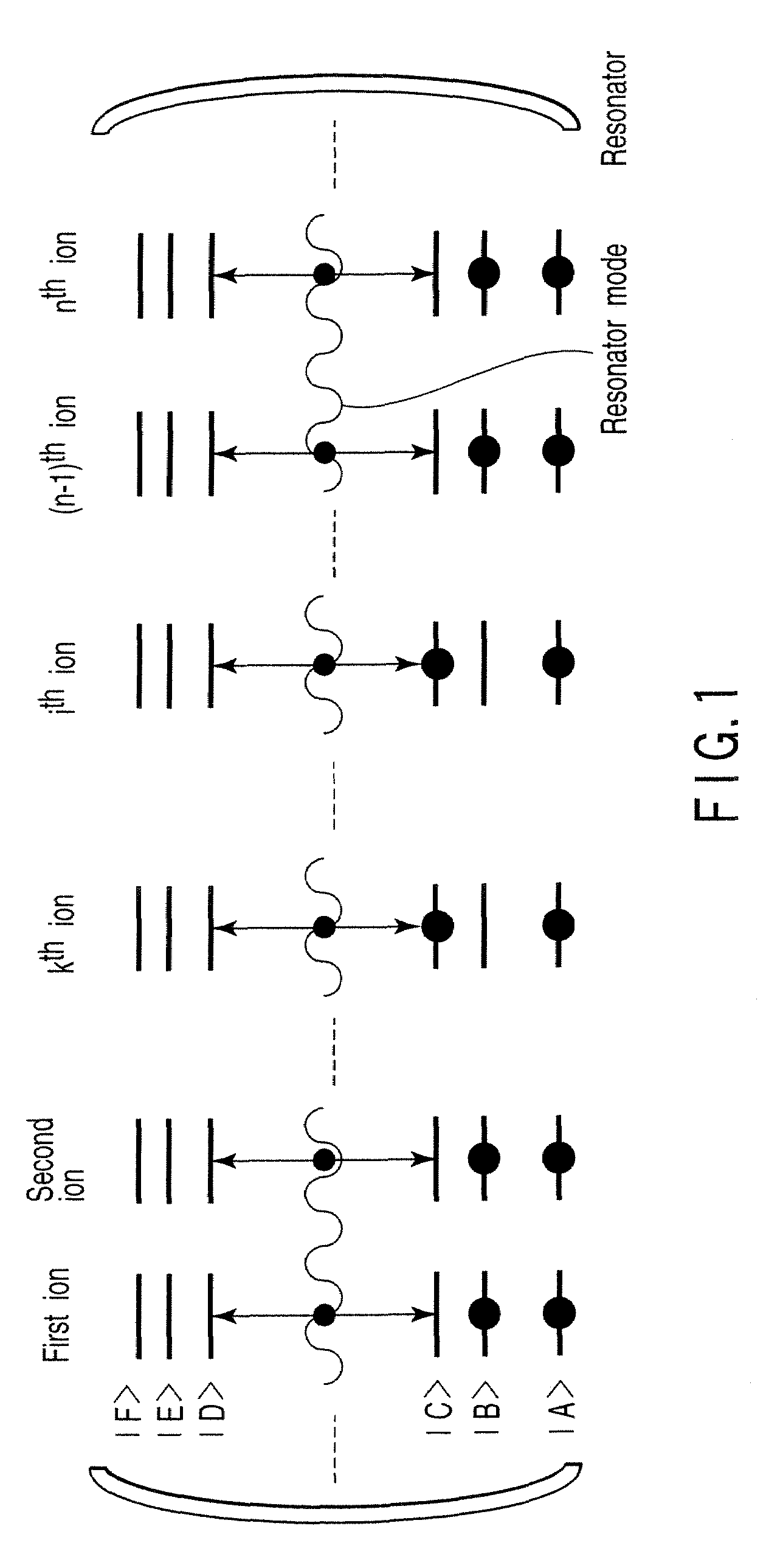
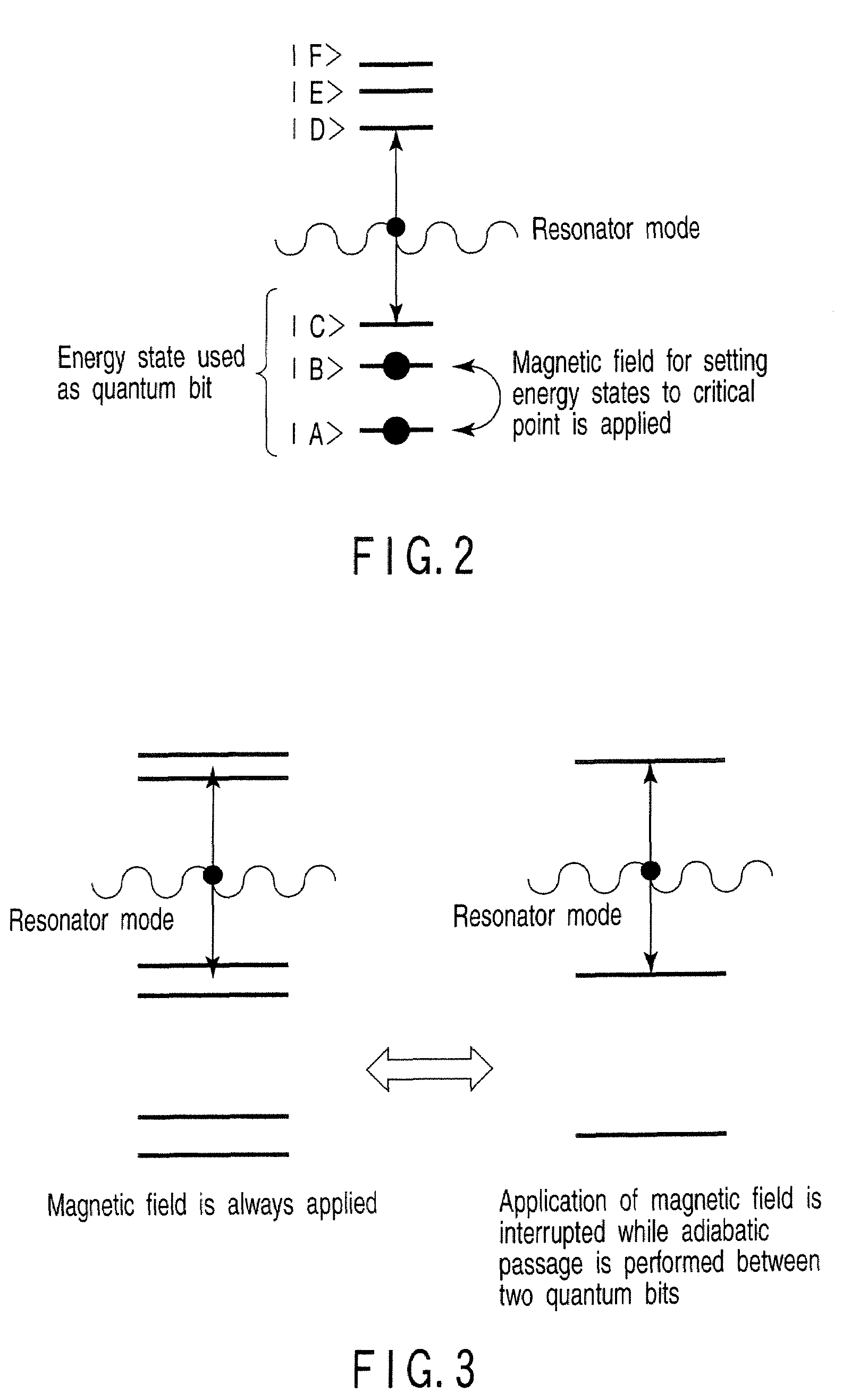
Quantum information processing device includes resonator incorporating material containing physical systems, each of physical systems having at least four energy states, transition between two energy states of at least four energy states, and transition energy between at least two energy states of at least four energy states, at least four energy states being non-degenerate when magnetic field fails to be applied to physical systems, transition resonating in resonator mode that is in common between physical systems, each of at least four energy states representing a quantum bit, transition energy being shifted when magnetic field is applied to physical systems, and magnetic-field application unit configured to apply magnetic field having direction and intensity to material, to eliminate linear transition energy shift between two energy states included in physical systems, each of two energy states included in physical systems being with excluding two energy states resonating in resonator mode.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
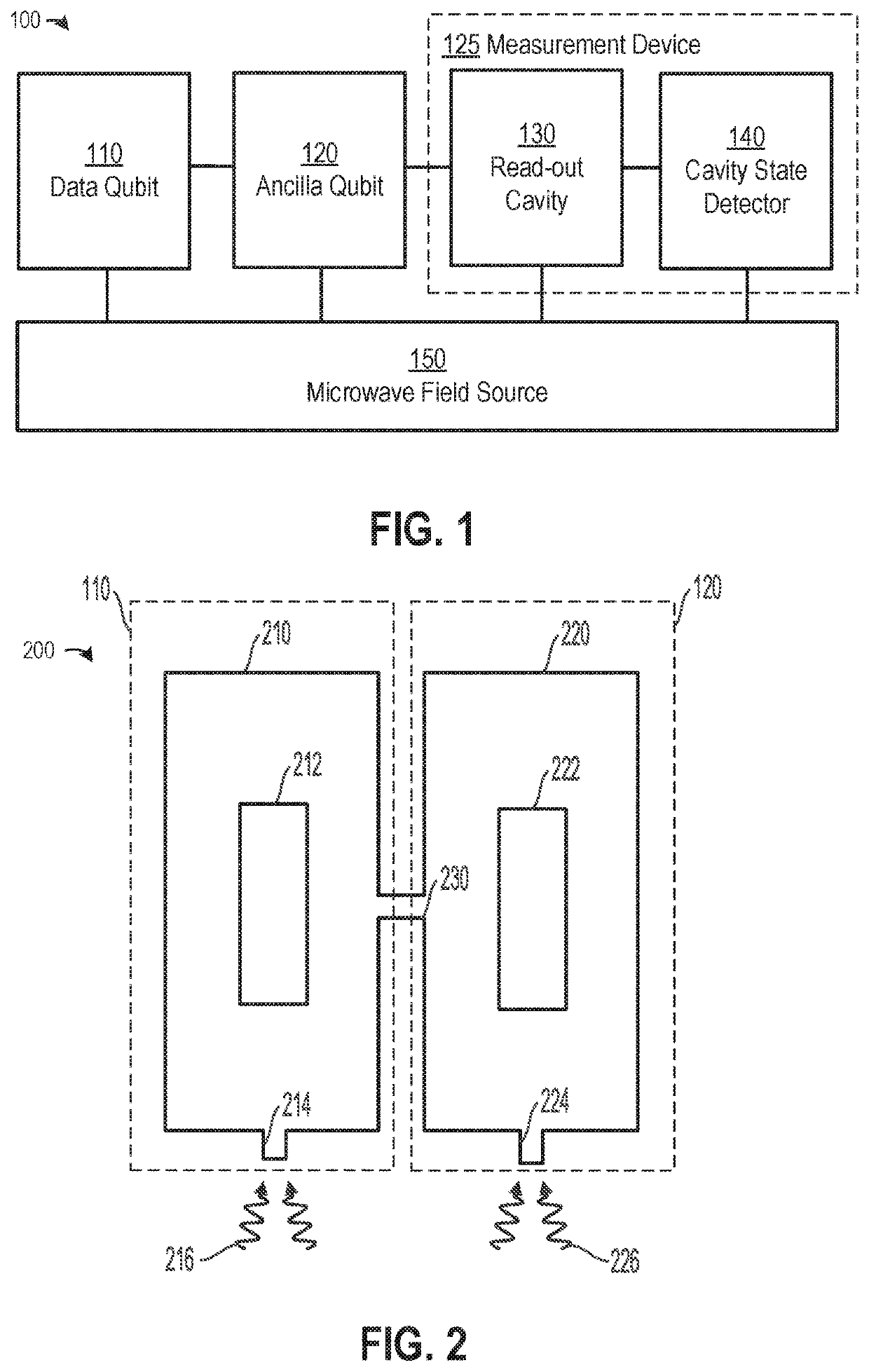
Quantum information processing with an asymmetric error channel
Techniques for performing quantum information processing using an asymmetric error channel are provided. According to some aspects, a quantum information processing includes a data qubit and an ancilla qubit, the ancilla qubit having an asymmetric error channel. The data qubit is coupled to the ancilla qubit. The ancilla qubit may be driven with a stabilizing microwave field to create the asymmetric error channel.
Owner:YALE UNIV
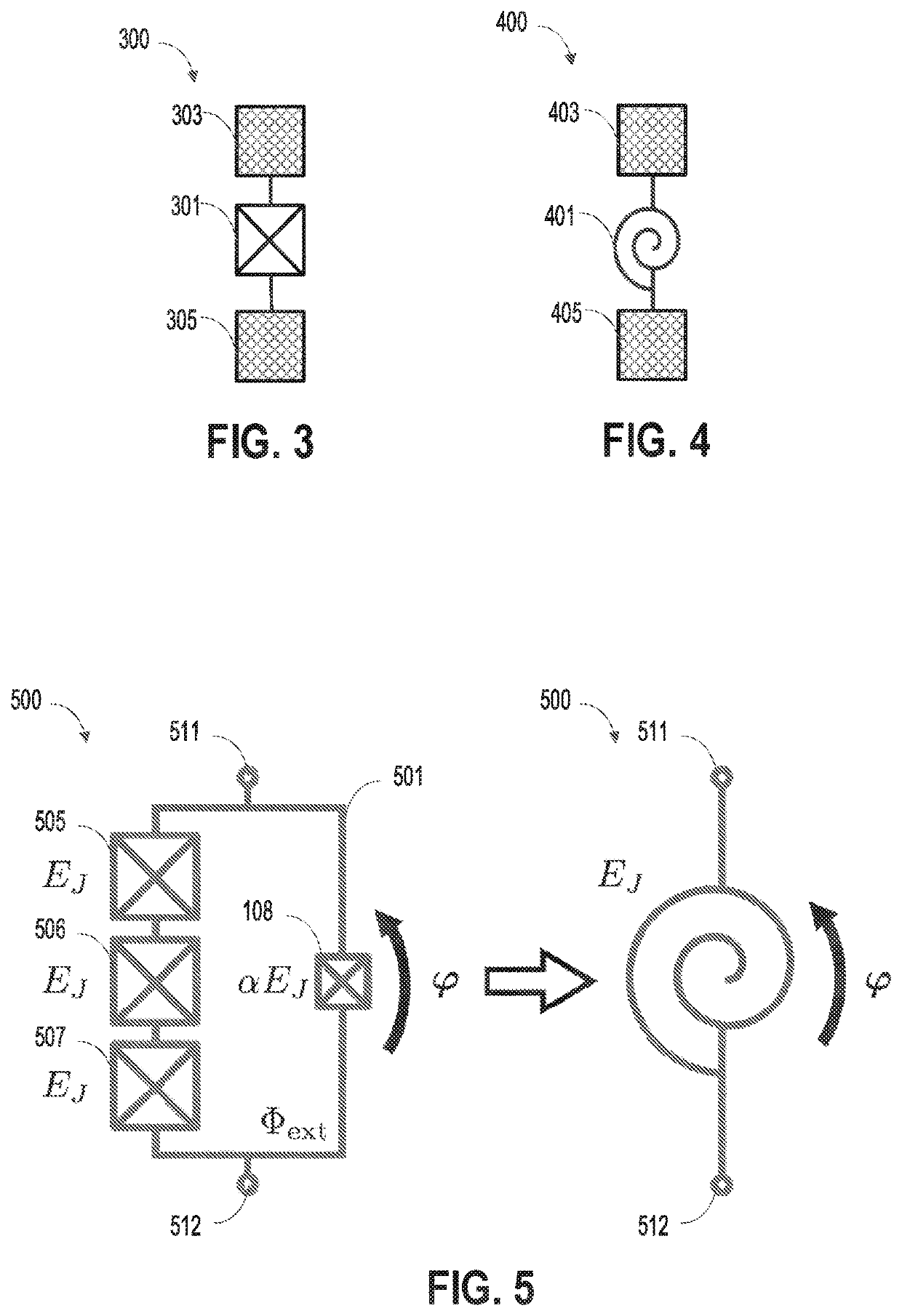
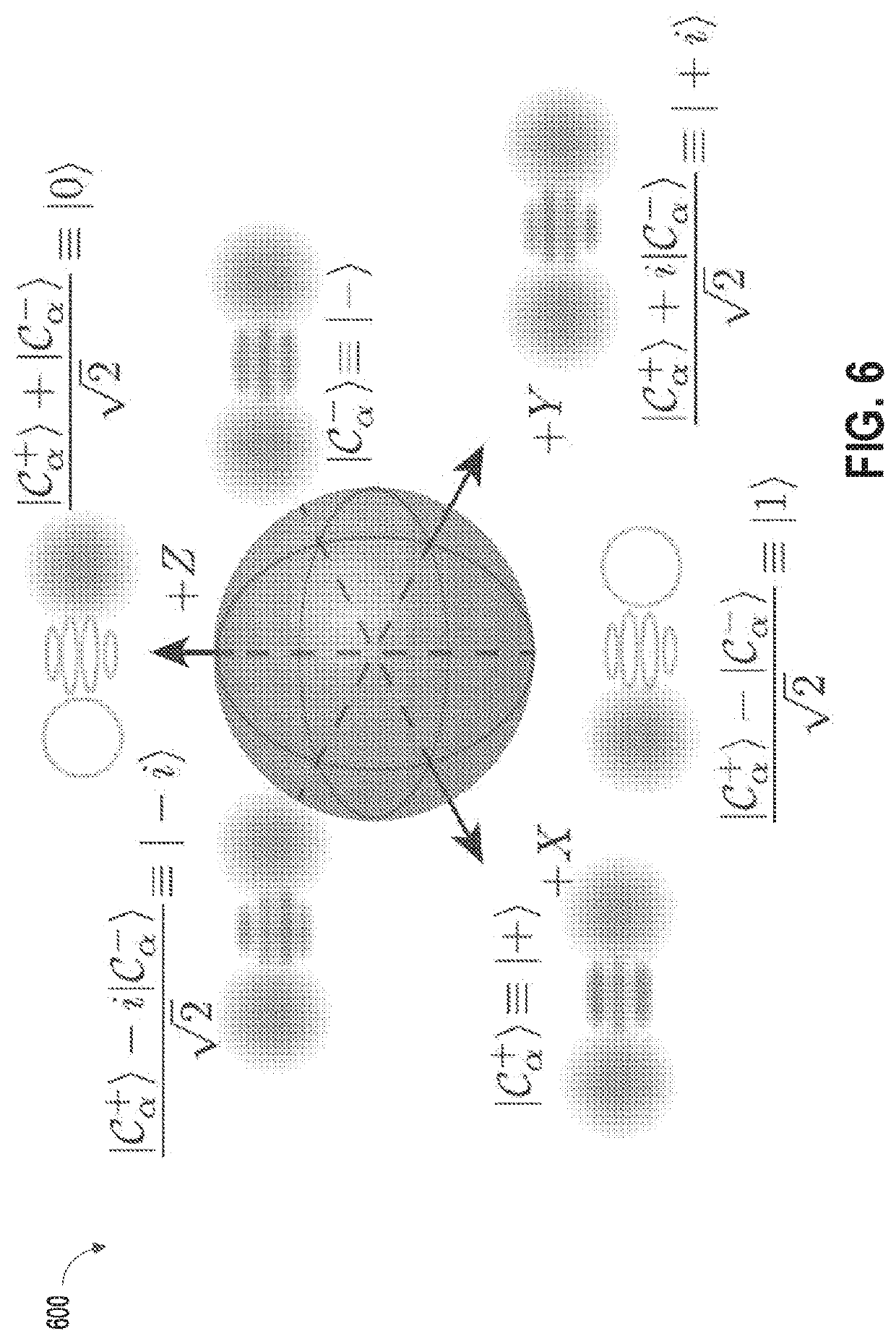
Quantum coherent systems and operations
Nonlinear elements (200) can efficiently implement quantum information processing systems such as controlled phase shifters (400), non-absorbing detectors including parity detectors (1290), quantum subspace projections (600), non-absorbing Bell state analyzers (800), non-absorbing encoders / entanglers (1200), and fundamental quantum gates such as CNOT gates (1300). The non-absorbing detectors (1640, 1650) permit improvements in the efficiency of a probabilistic quantum gate (1720) by permitting reuse of the same photonic resources during multiple passes through the probabilistic gate (1720).
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Method and apparatus for quantum information processing using entangled neutral-atom qubits
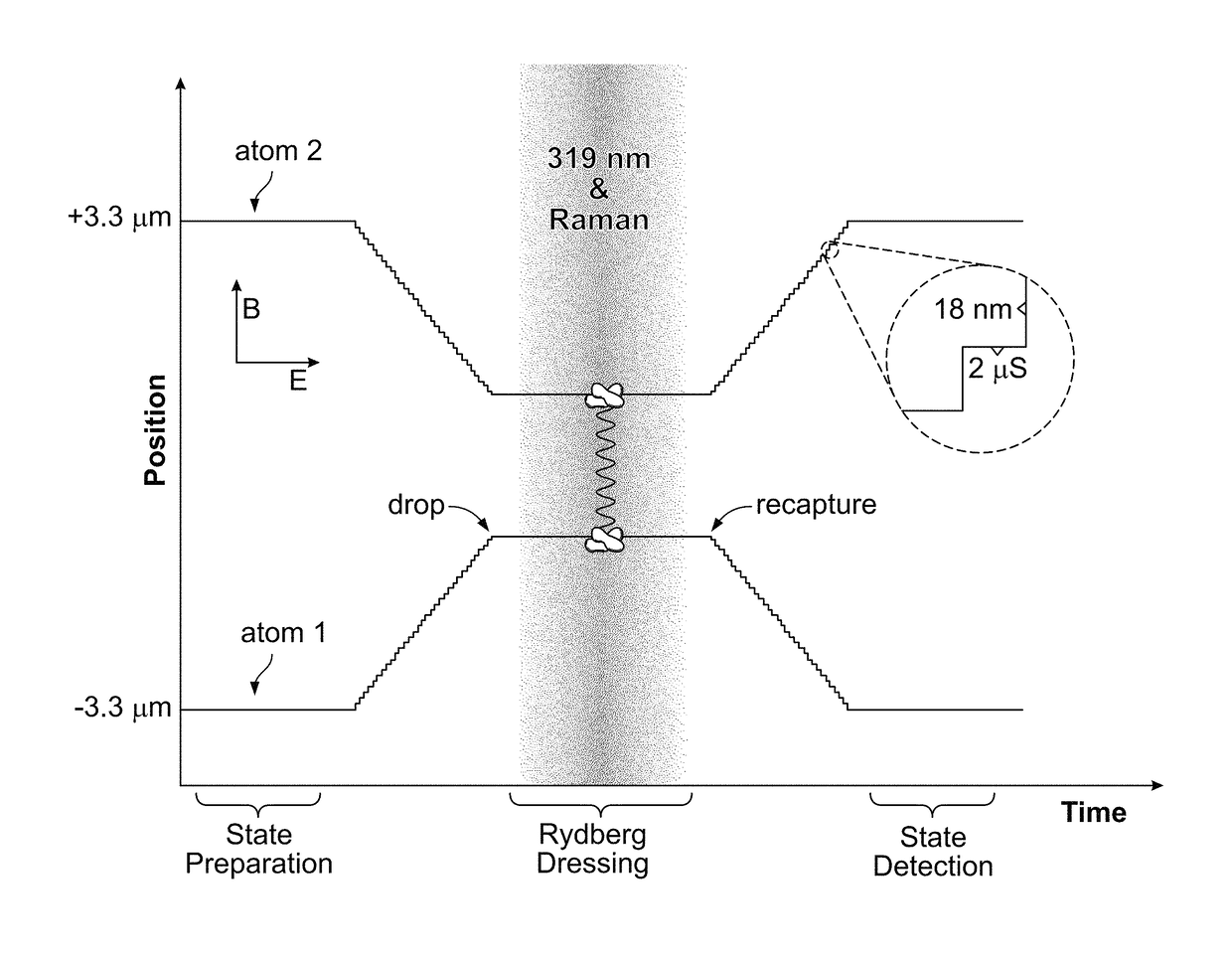
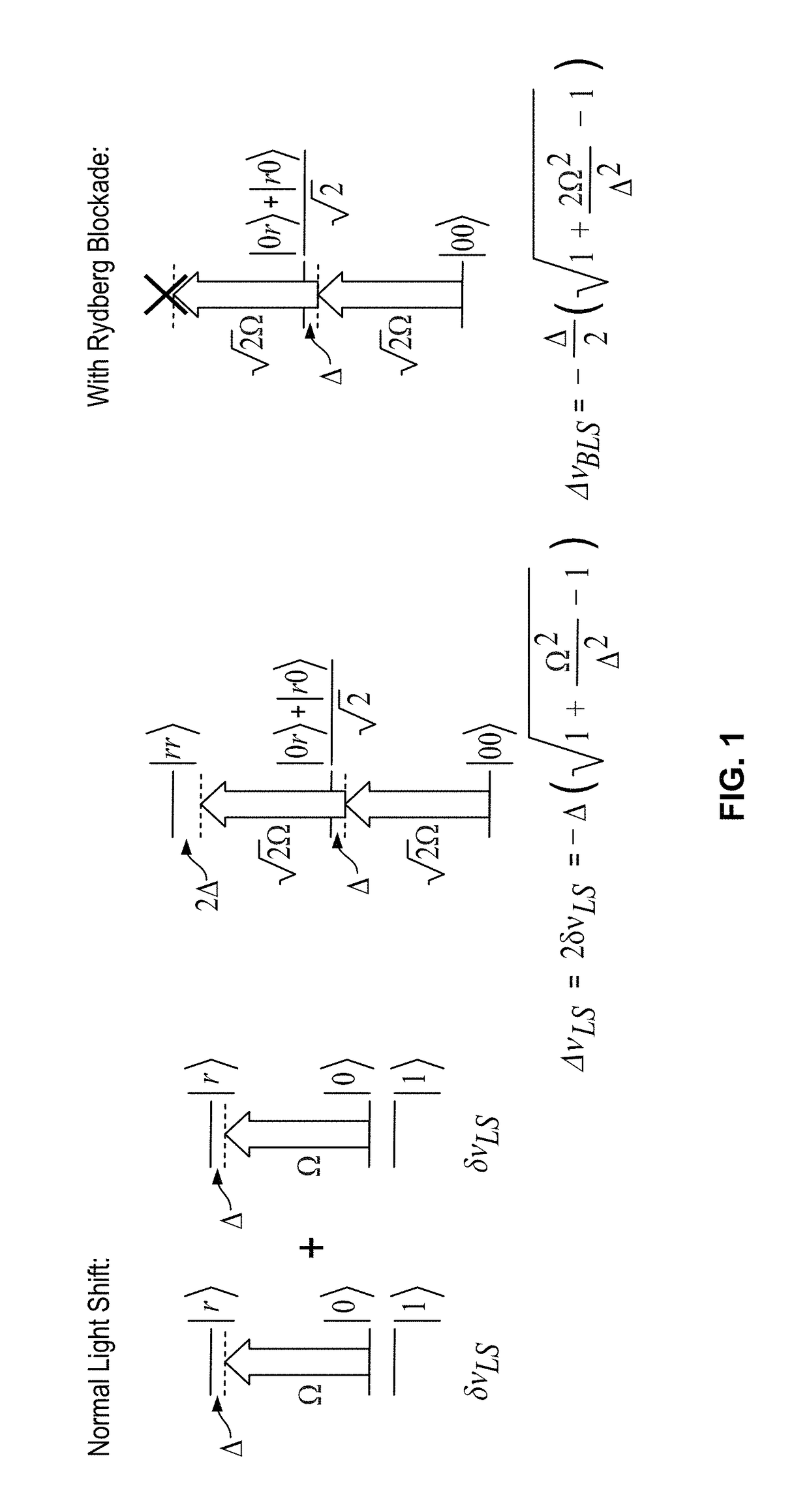
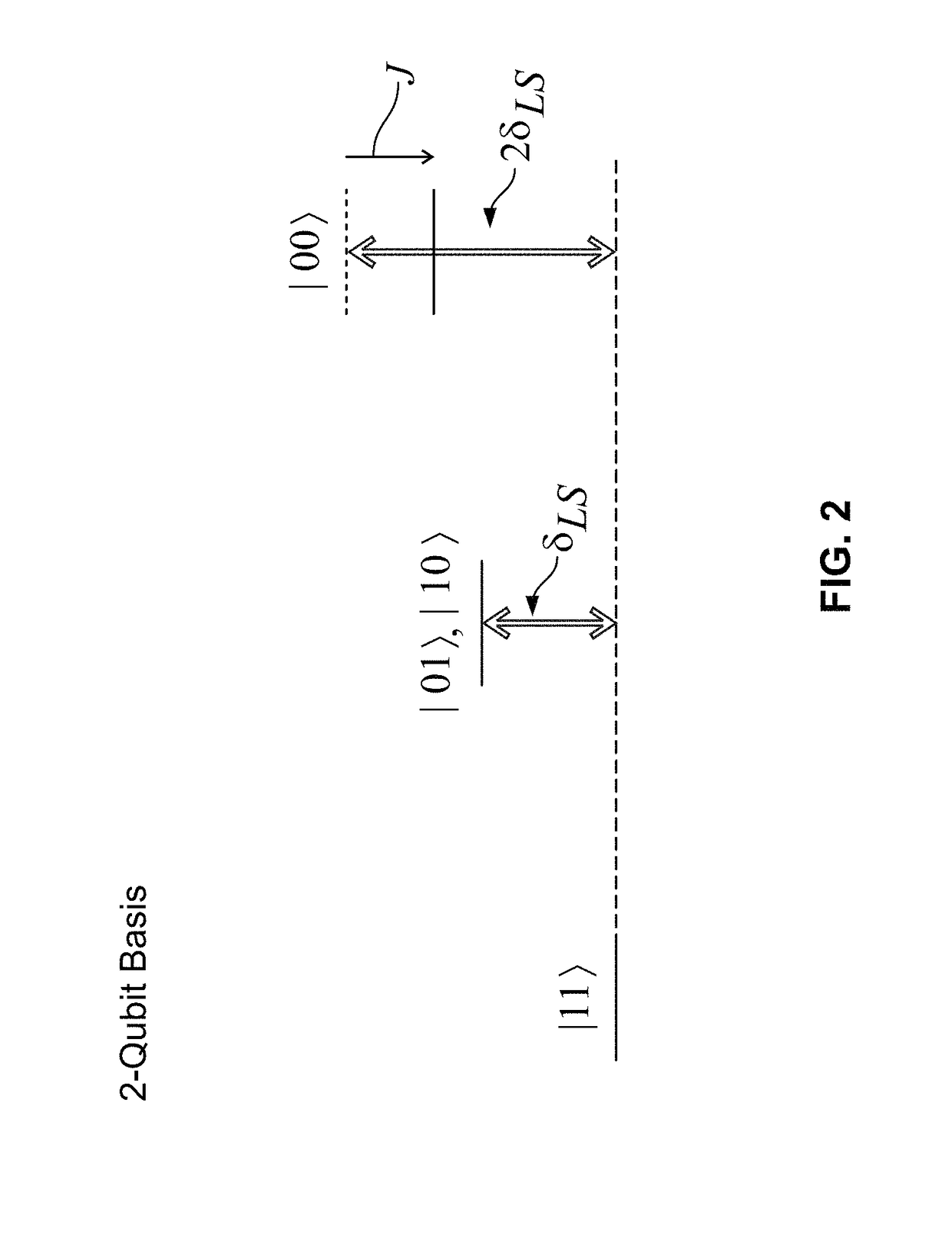
A method for preparing an entangled quantum state of an atomic ensemble is provided. The method includes loading each atom of the atomic ensemble into a respective optical trap; placing each atom of the atomic ensemble into a same first atomic quantum state by impingement of pump radiation; approaching the atoms of the atomic ensemble to within a dipole-dipole interaction length of each other; Rydberg-dressing the atomic ensemble; during the Rydberg-dressing operation, exciting the atomic ensemble with a Raman pulse tuned to stimulate a ground-state hyperfine transition from the first atomic quantum state to a second atomic quantum state; and separating the atoms of the atomic ensemble by more than a dipole-dipole interaction length.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Quantum information processing method and apparatus
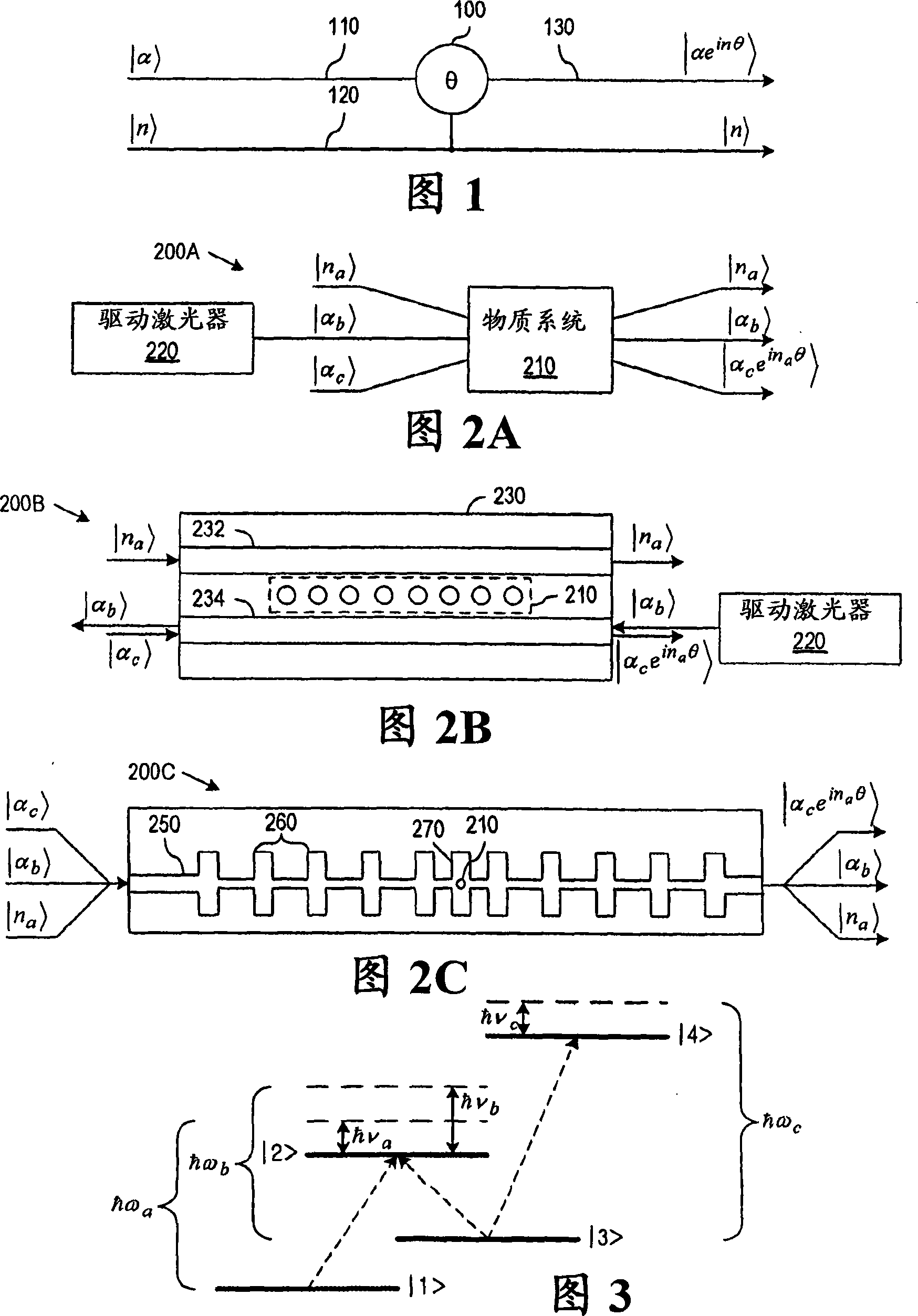
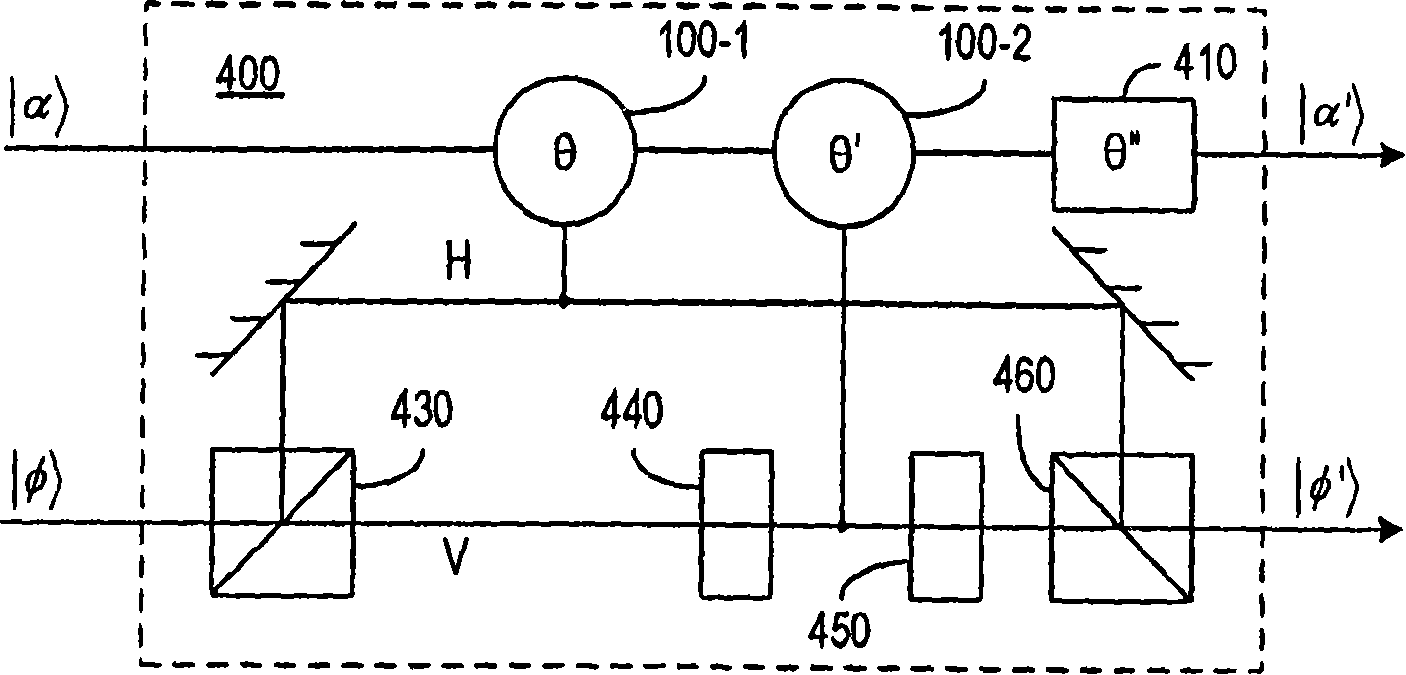
InactiveUS7346246B2Improve efficiencyQuantum computersNanoinformaticsInformation processingCoherent states
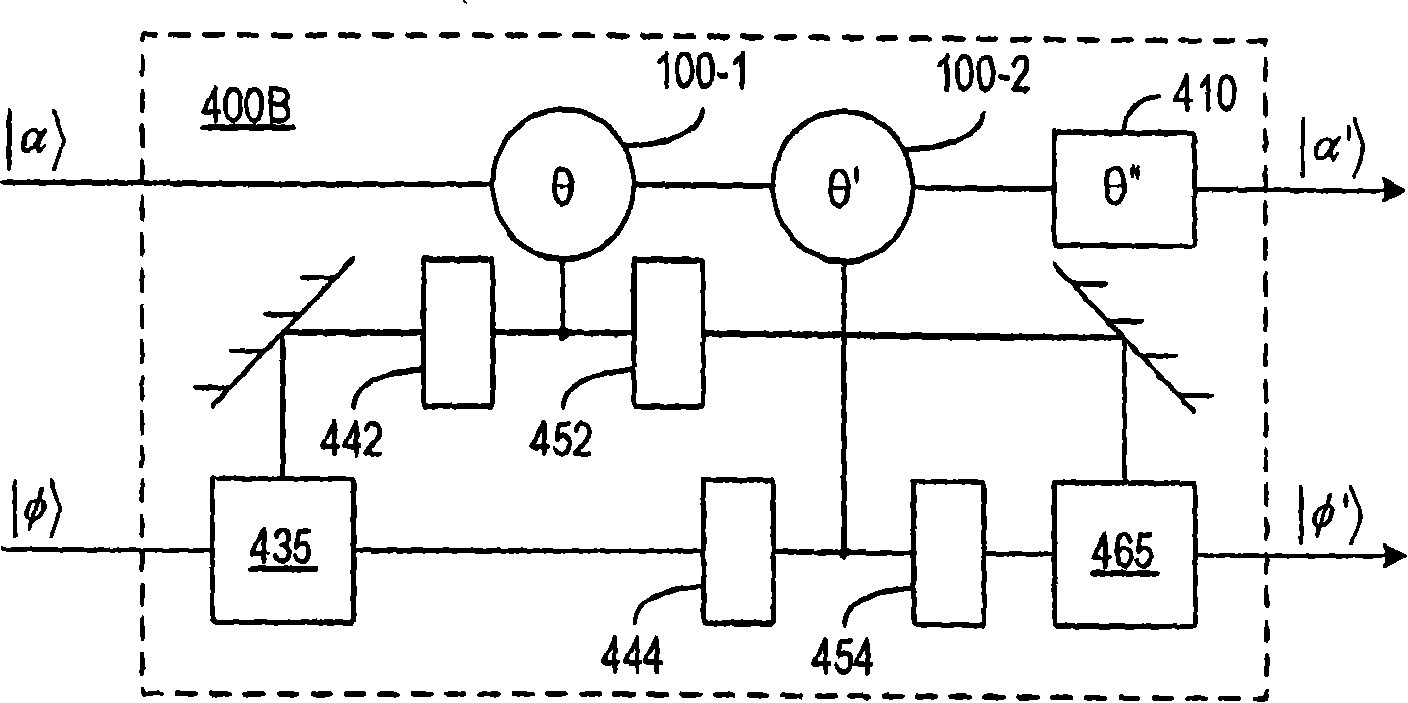
A method and apparatus for quantum information processing is disclosed in which logical qubits |0>L and |1>L are respectively encoded by different near orthogonal coherent states |β> and |α>, where <α|β>=0, |α> and |β> being the computational basis states for the qubits, for example, in which logical qubits |0>L and |1>L are respectively encoded by different ones of the vacuum state |0> and a multi-photon optical coherent state |α> which states are the computational basis states for the qubits. This provide an efficient scheme for linear optics quantum processing which is deterministic and for which qubit readout can use homodyne detection which is highly efficient. The invention finds application in quantum computation and quantum communication.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Single granule layer nanometer diamond film with strong Si-V luminescence, and production method thereof
ActiveCN104831253ASi-V luminous intensity enhancementIncreased Si-V luminous intensityMaterial nanotechnologyChemical vapor deposition coatingGas phaseDisplay device
The invention provides a single granule layer nanometer diamond film with strong Si-V luminescence, and a production method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: producing a single granule layer nanometer diamond film with the thickness of 500-700nm on a monocrystalline silicon substrate by adopting a hot filament chemical vapor deposition technology; and carrying out heat insulation on the film in 600DEG C air for 10-50min to produce the single granule layer nanometer diamond film with strong Si-V luminescence. The nanometer diamond film obtained in the invention has single granule layer characteristics and has a thickness of 500-700nm, the speak shape of the Si-V luminescence peak of the film is sharp, the Si-V luminescence intensity is greatly improved, and the preparation is of great scientific and engineering significance to realize application of the film in fields of single photon sources, quantum information processing, photoelectron devices, biological markers, semiconductor devices and field emission displays.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Unentangled quantum blind signature method and system based on quantum walking
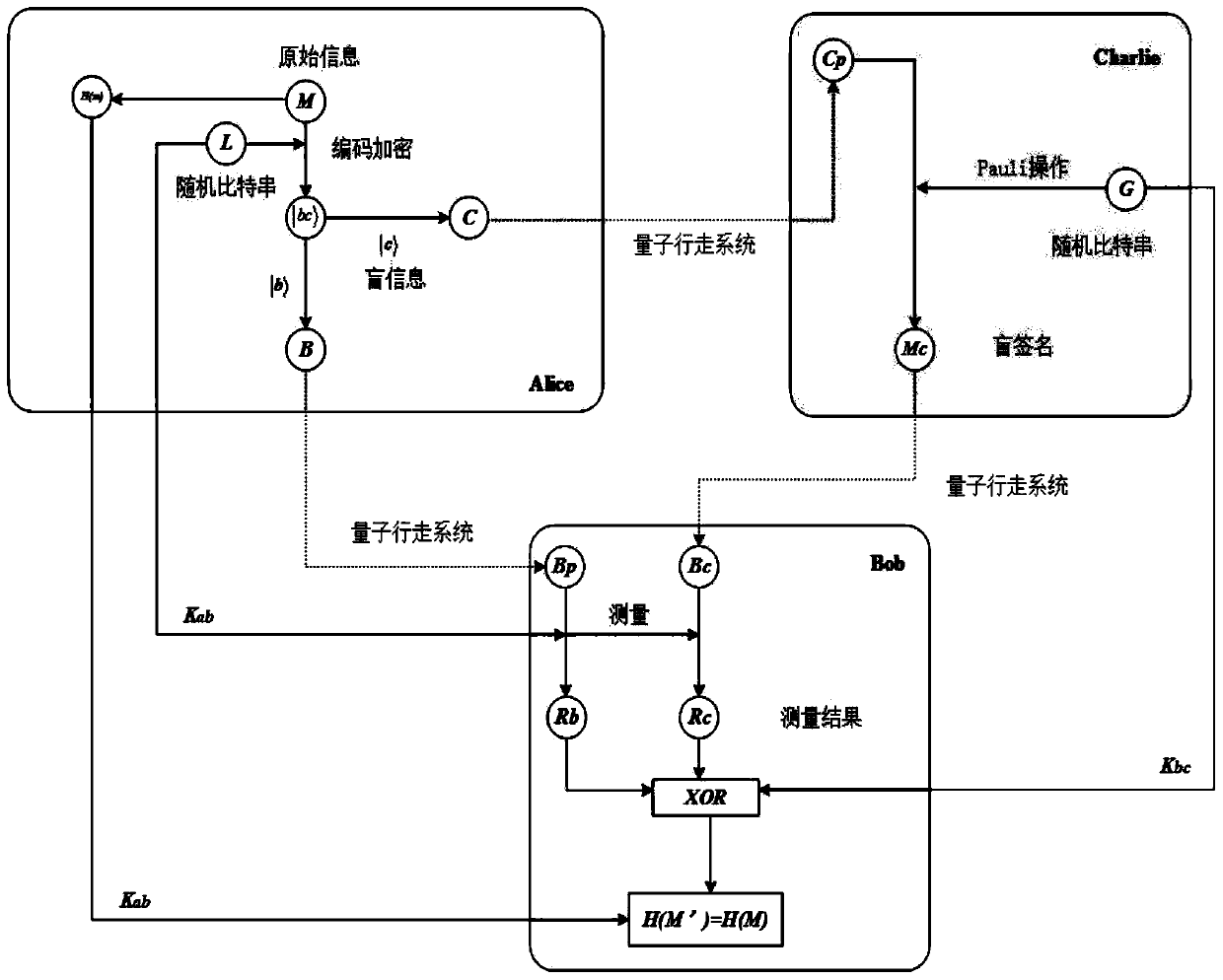
ActiveCN110213060AProven robustnessAchieve the effect of one-time pad (OTP)Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationE-commerceBlind signature
The invention belongs to the technical field of quantum information processing, and discloses an unentangled quantum blind signature method and system based on quantum walking, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out the coding and blind information through employing four single event states in combination with a blind coding rule of a message in the coding stage of the message; in the invisible transmission process of the coded particles, using quantum walking to achieve invisible transmission of the coded particles, wherein entanglement is spontaneously generated on the invisible transmission seed particles, which is used for resisting negative attacks of signers and denial attacks of verifiers and further used for preventing attackers from forgery signatures. The method comprises secret key updating, the effect of one-time encryption (OTP) is achieved, and therefore a next execution scheme does not need secret key redistribution any more; security analysis shows that the scheme of the invention satisfies the characteristics of unforgeability, undeniable property and blindness, can also resist entanglement attack, and is very suitable for use in electronic commerce or electronic payment systems.
Owner:芽米科技(广州)有限公司
Simple and reliable method for preparing any Werner state
ActiveCN107608158AEasy to adjustHighly integratedNon-linear opticsOptical elementsMixed statesSpontaneous parametric down-conversion
The invention discloses a simple and reliable method for preparing any Werner state, comprising a step of preparing an entanglement light source, in which photon pairs are entangled by using laser topump nonlinear crystals to generate a spontaneous parametric down conversion process, and a step of constructing a controllable depolarized channel, in which a completely mixed state is introduced byacting the controllable depolarized channel on one photon. Sandwich-shaped crystals are adopted for the nonlinear crystals and comprise two BBO crystals and a real zero-order half-wave plate disposedbetween the two BBO crystals. The controllable depolarized channel is composed of a Sagnac ring, a complete destructive phase channel and a state superposition portion, the Sagnac ring is of a rectangular structure, and a half-wave plate is disposed between two reflectors thereof; the complete destructive phase channel is composed of two destructive phase crystals and a half-wave plate therebetween; and the state superposition portion comprises a BS. The simple and reliable method is convenient to adjust and high in feasibility, and can be applied to the fields of quantum information processing and quantum communication.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Device and system for measuring orbital angular momentum spectrum of light beam
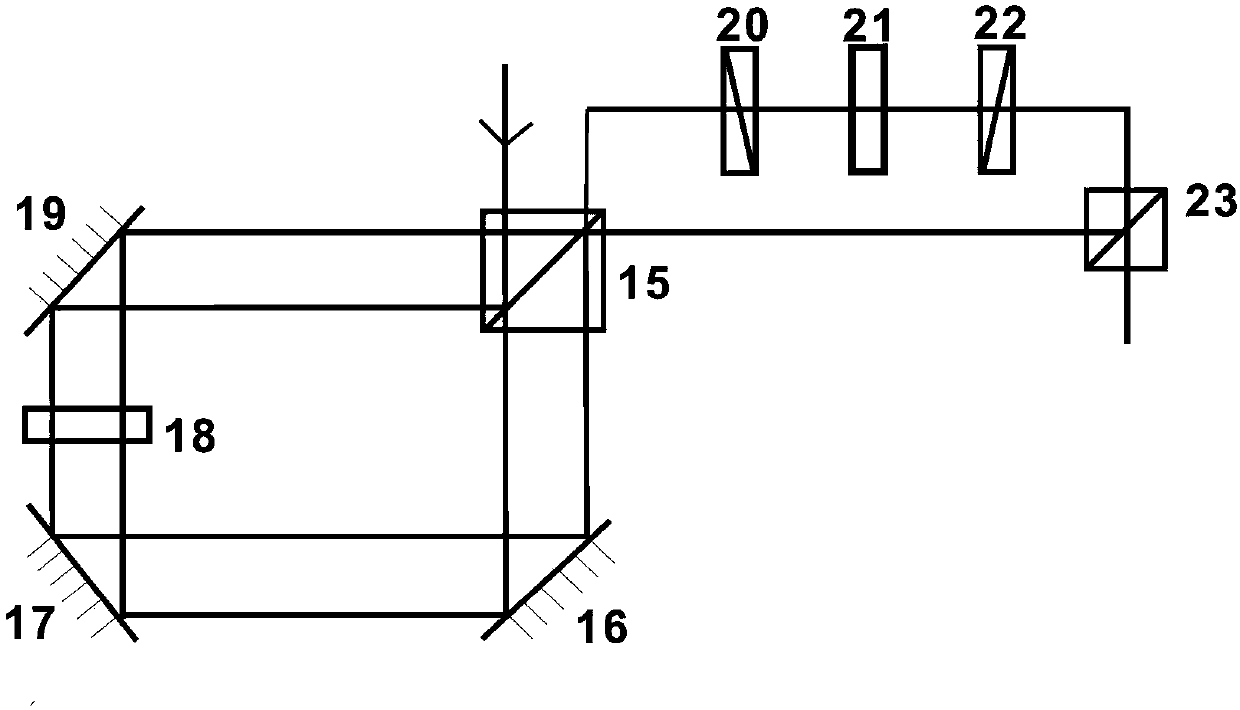
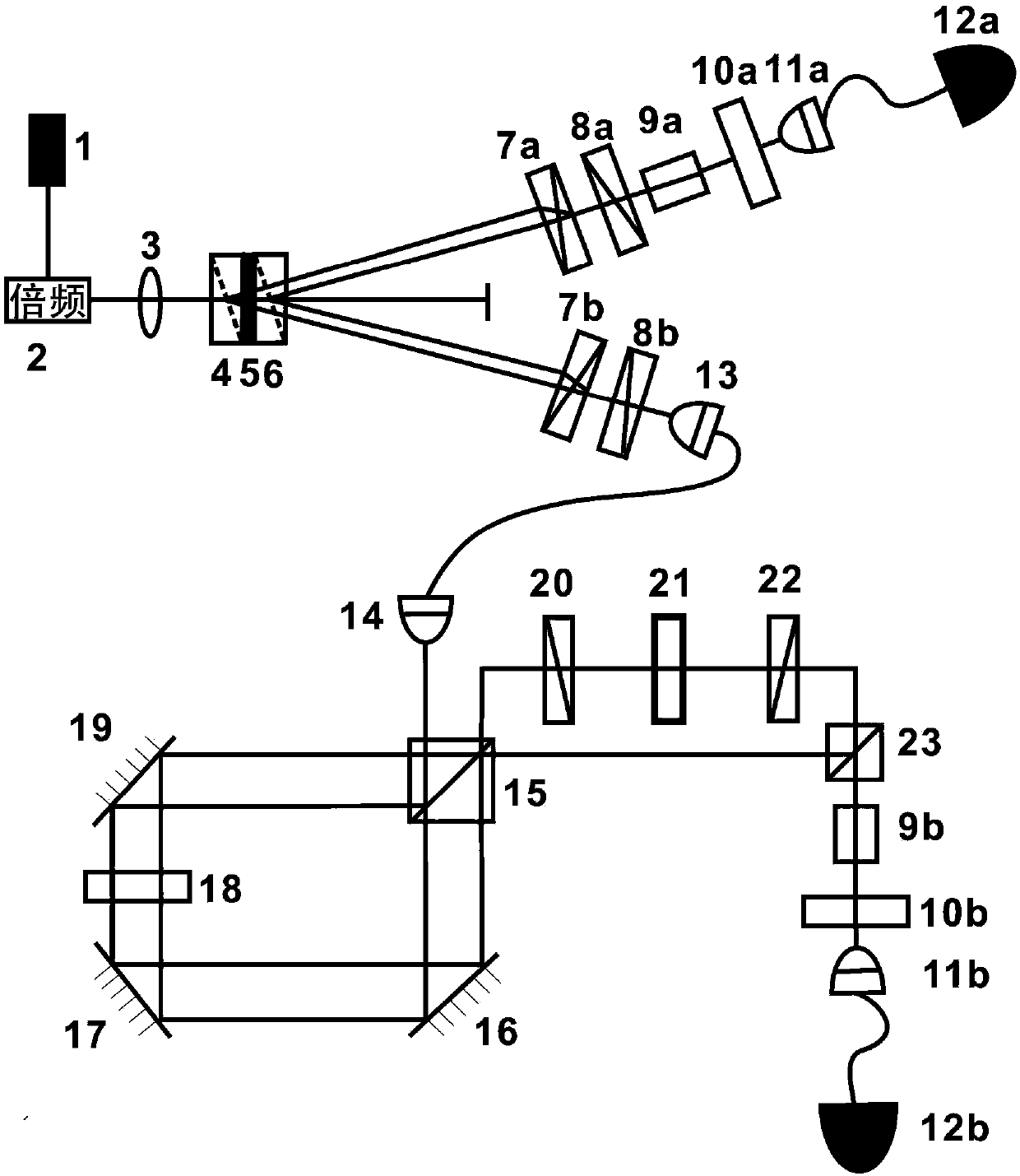
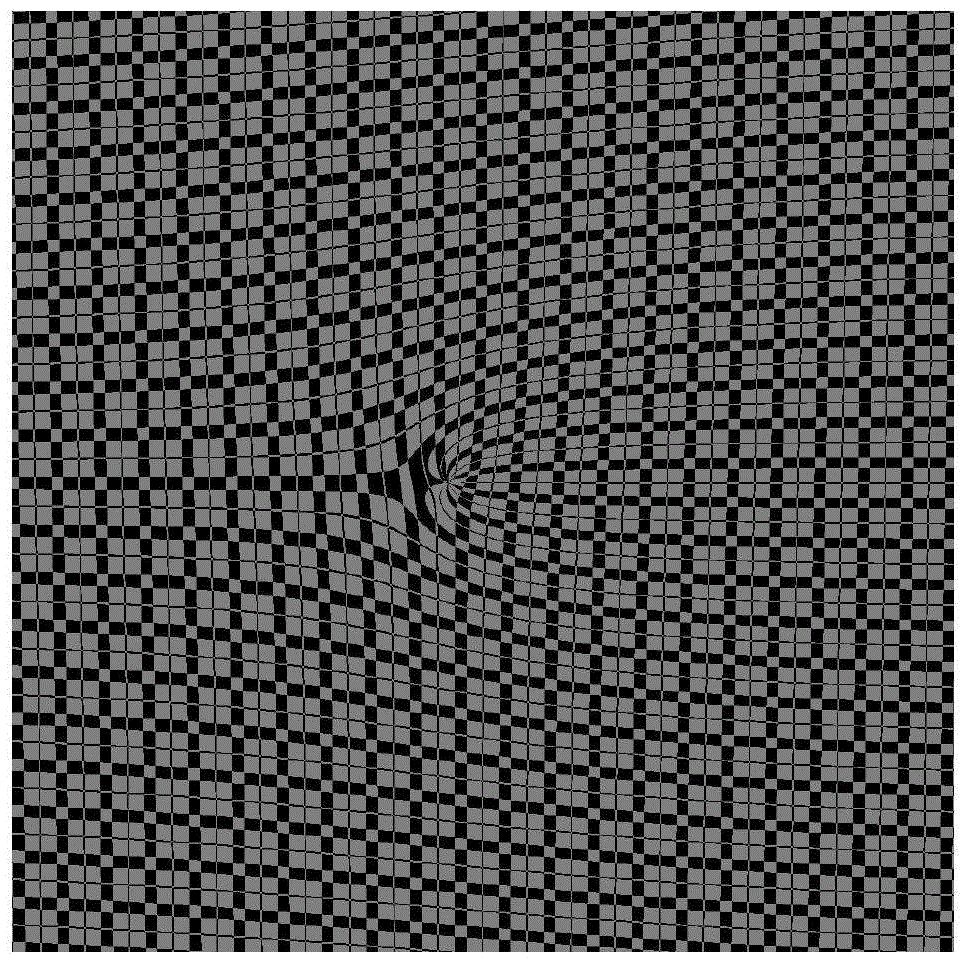
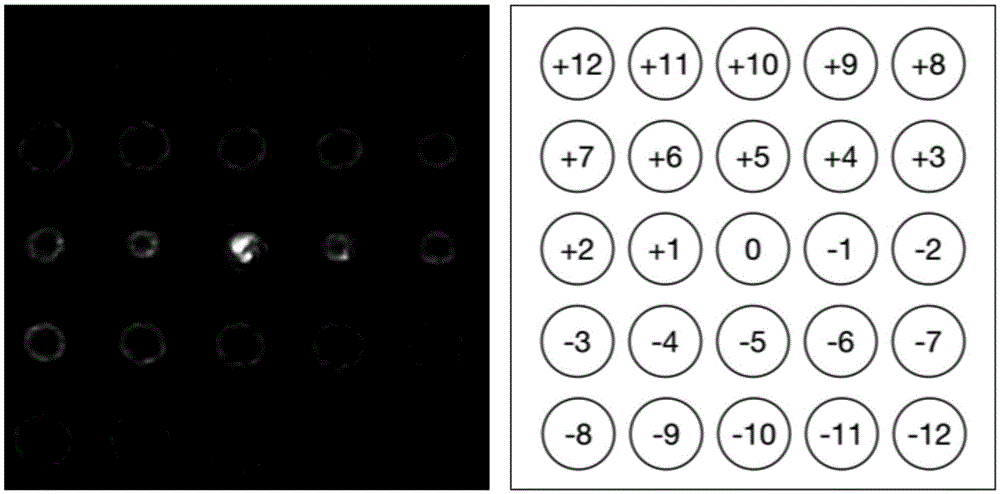
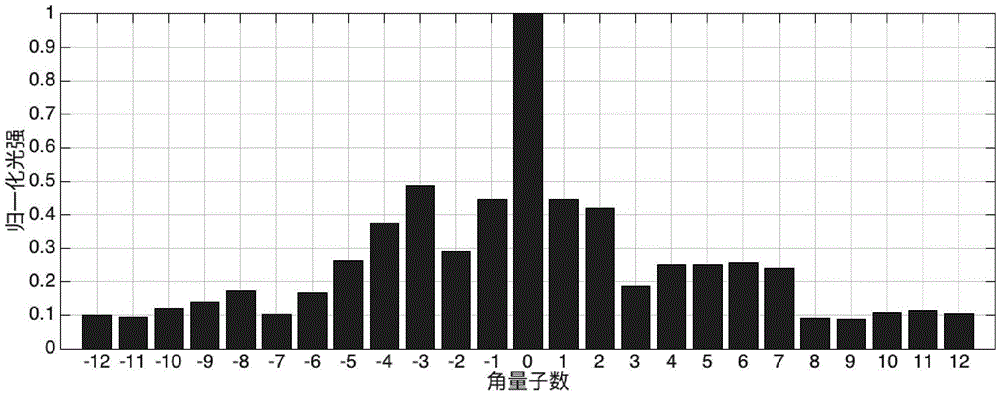
The invention discloses a device and system for measuring the orbital angular momentum spectrum of a light beam. The device just needs to enable a to-be-measured light beam to be transmitted in an optical axis direction of a system, and obtains a far-field diffraction spot gray scale pattern at a receiving end. The orbital angular momentum spectrum of the incident light beam can be obtained through a calculation system provided by the invention. The device is very simple, and the optical path is easy to adjust. The device is higher in operability, and just needs to obtain the far-field diffraction spot gray scale pattern, wherein other operations are automatically completed by a host. Compared with the conventional technology of orbital angular momentum spectrum measurement, the device and system are improved greatly. The device and system can be used for the technology of light communication, the field of quantum information processing and the technology of optical tweezers.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for realizing quantum circuit design through quantum Haar wavelet transformation
The invention provides a method for realizing quantum circuit design through quantum Haar wavelet transformation, and belongs to the field of quantum information processing. According to the method, the existing quantum Fourier transform implementing technology is perfected and improved, and implementing circuits of two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet transformation and two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet inverse transformation are established separately by using extended tensor product and basic quantum bit gate (comprising quantum bit controlled door and single quantum bit gate). Based on analysis of the complex rates of the implementing circuits of the quantum Haar wavelet transformation and the quantum Haar wavelet inverse transformation, the complex rates of the implementing circuits of the two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet transformation and the two pieces of multi-layer quantum Haar wavelet inverse transformation are Theta(n2) for one data set with 2n elements, and other typical and rapid Haar wavelet transformation cannot achieve the aim. The method is suitable for the fields of algorithms such as compression, denoising, encryption and decryption of images of actual information processing application, and has important significance in popularization of perfection and application of a quantum computing theory.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method and system for quantum information processing and computation
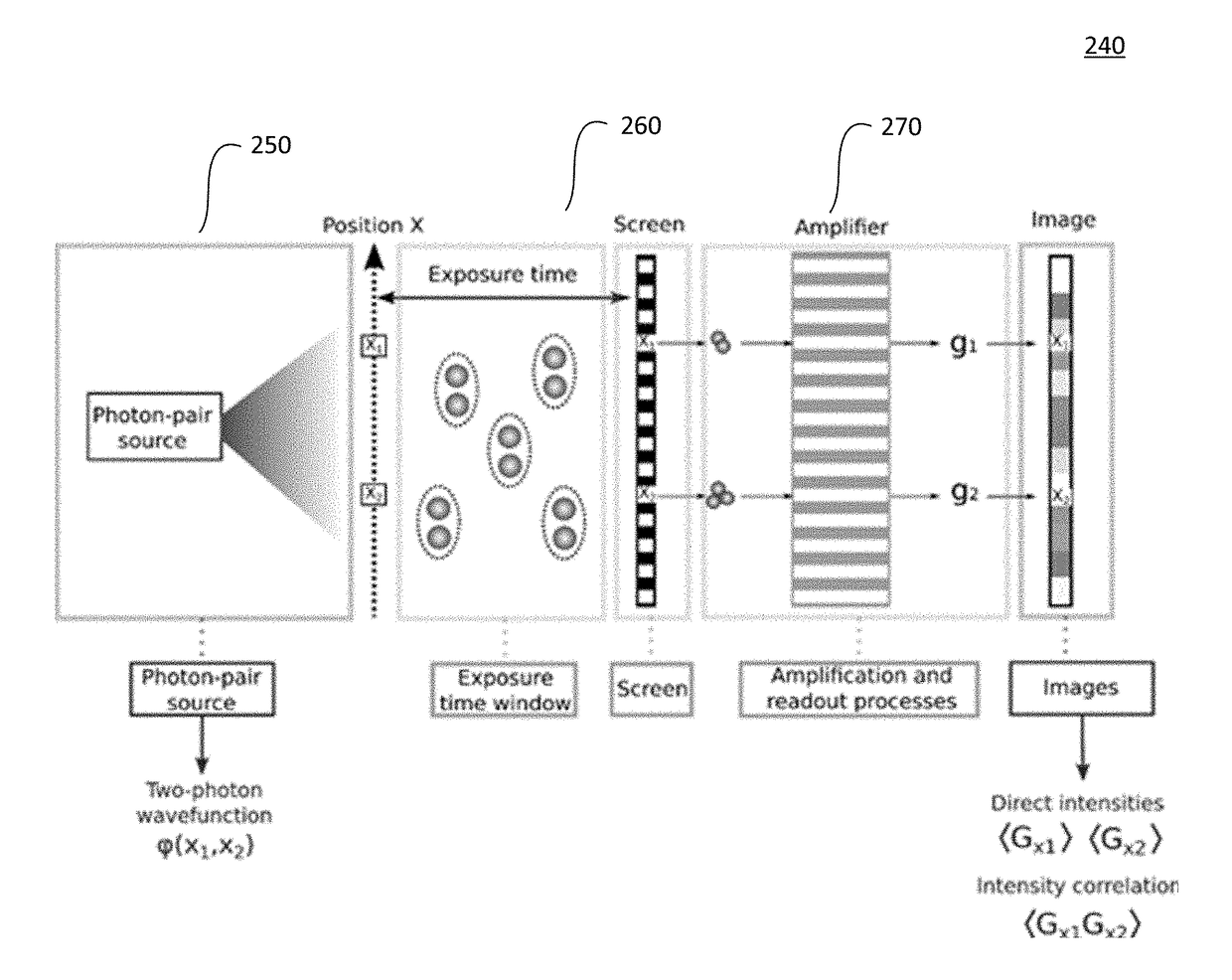
PendingUS20180032896A1Well formedQuantum computersImage enhancementInformation processingSpatial light modulator
A quantum information processing system comprises a light source, a detector, at least one spatial light modulator and at least one optical lens. The light source is configured to provide a beam of entangled photons. The at least one optical lens is configured to project the resultant beam onto the spatial light modulator, either by direct imaging or by performing a full or partial optical Fourier transform. Said spatial light modulator includes a plurality of discrete pixels and is configured to select one or more of the plurality of discrete pixels to generate a resultant beam from said beam of entangled photons. The resultant beam from said spatial light modulator is projected onto the detector. For optical computation, such as search algorithms, the configuration and projections are repeated to find the optimal solution.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
Quantum information processing elements and quantum information processing platforms using such elements
ActiveUS20050059020A1Inhibition of charge transferReduce restrictionsQuantum computersMicrobiological testing/measurementInformation processingProtein molecules
The invention in various embodiments is directed to quantum information processing elements and quantum information processing platforms employing such elements. In one aspect, the quantum information processing elements are formed with self-assembling protein molecules.
Owner:METAQOR
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com