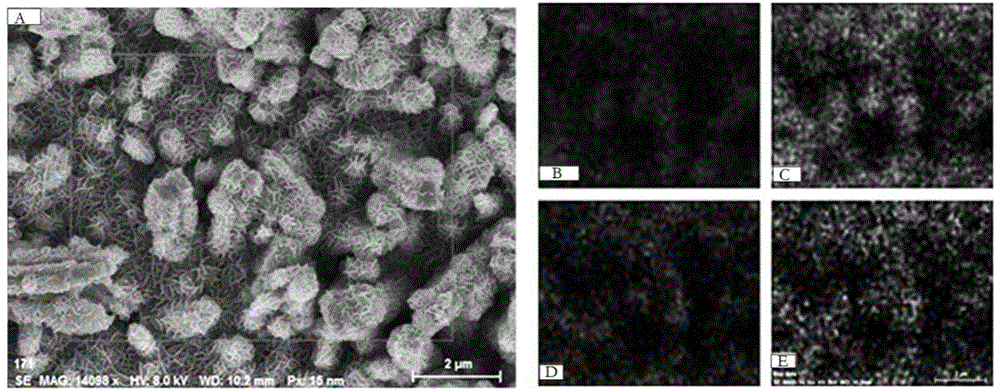
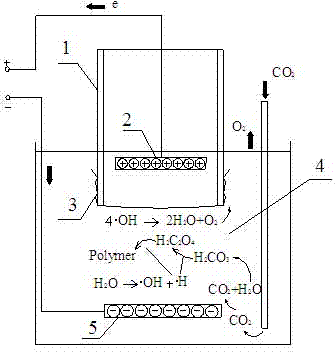
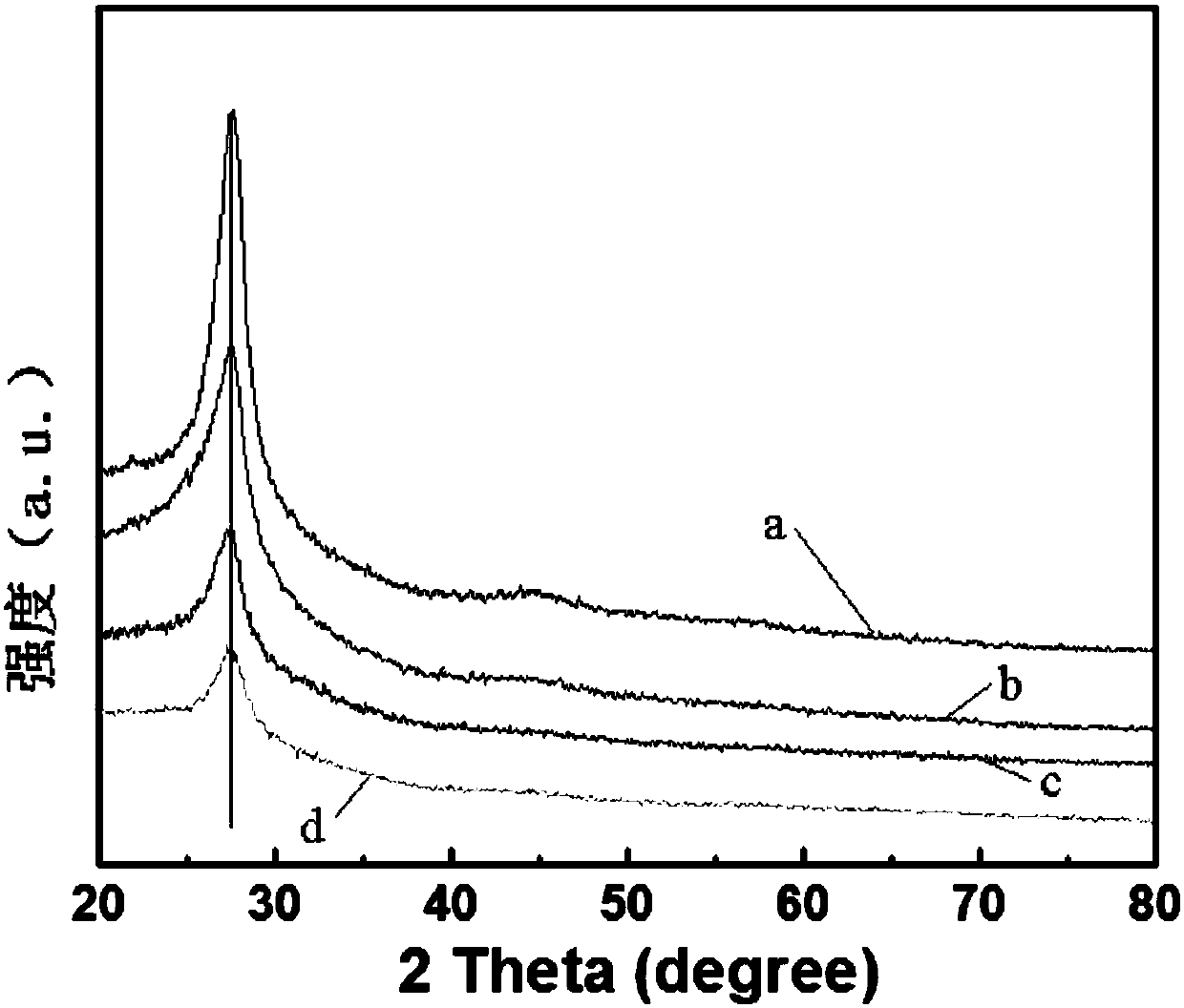
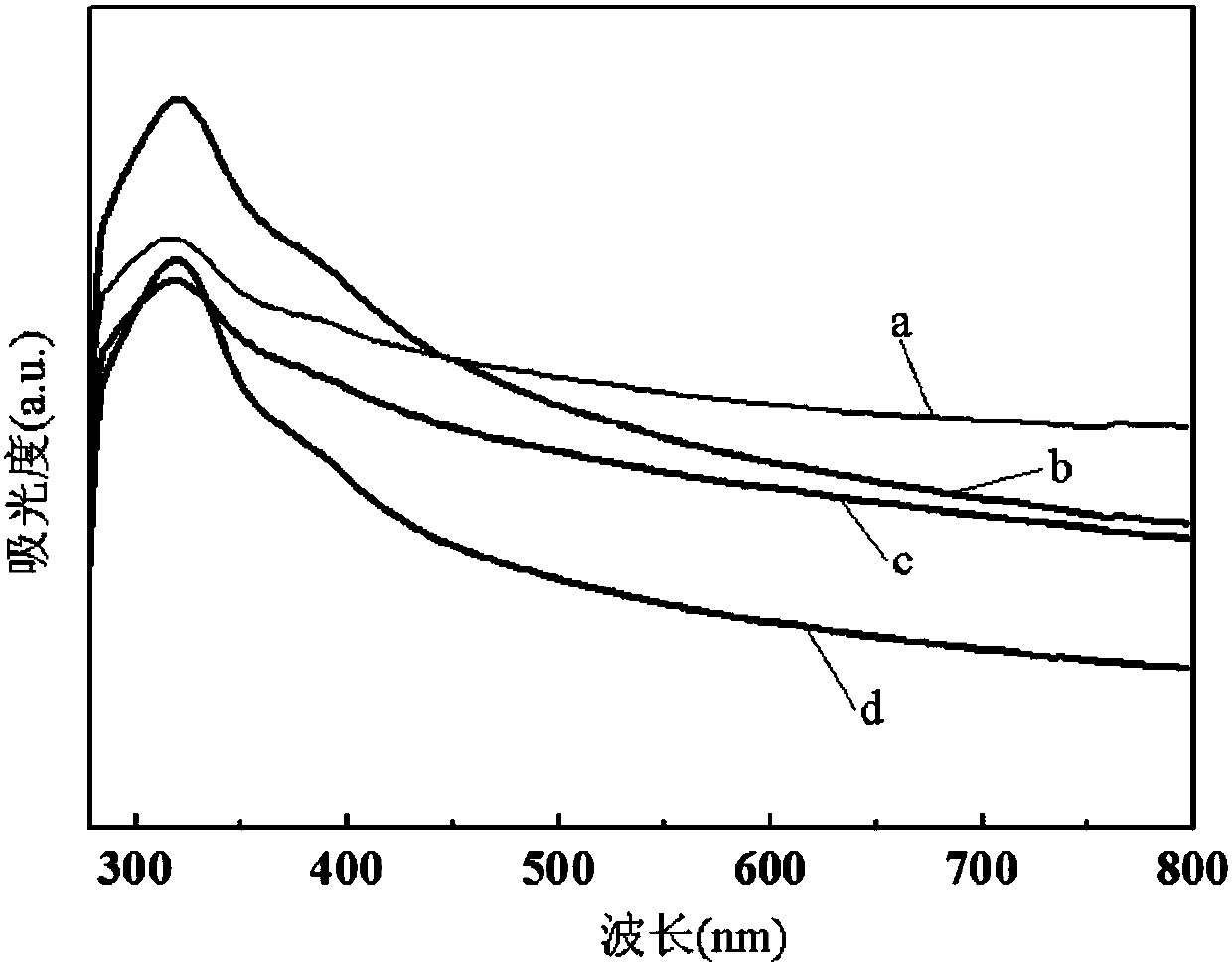
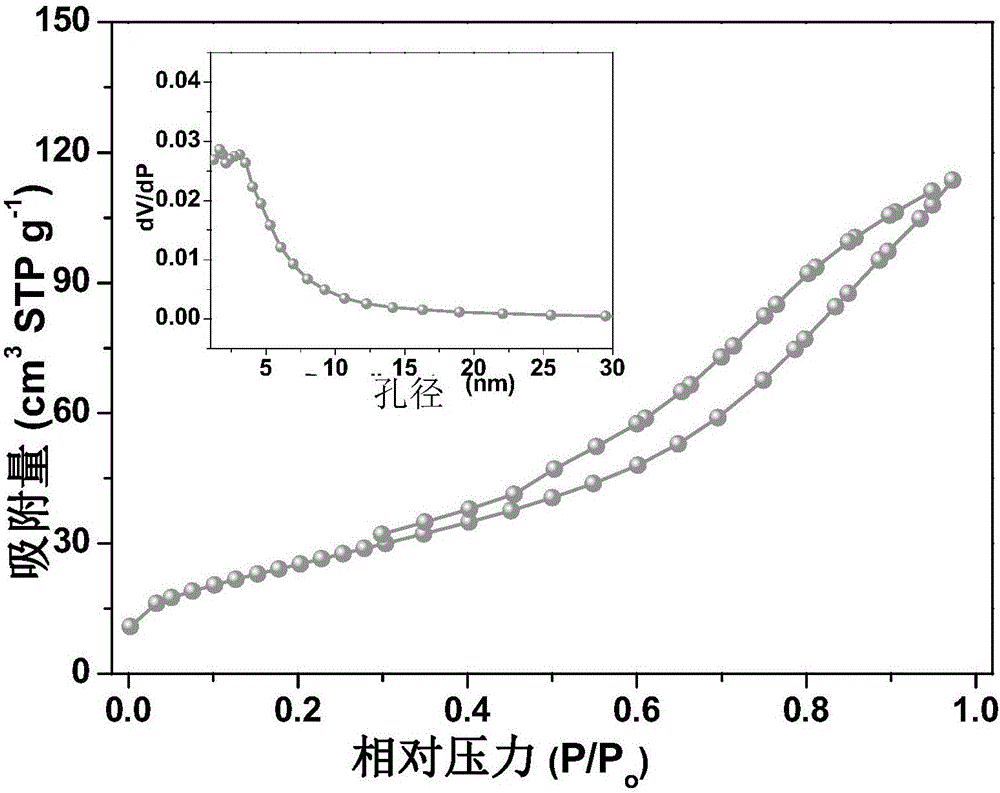
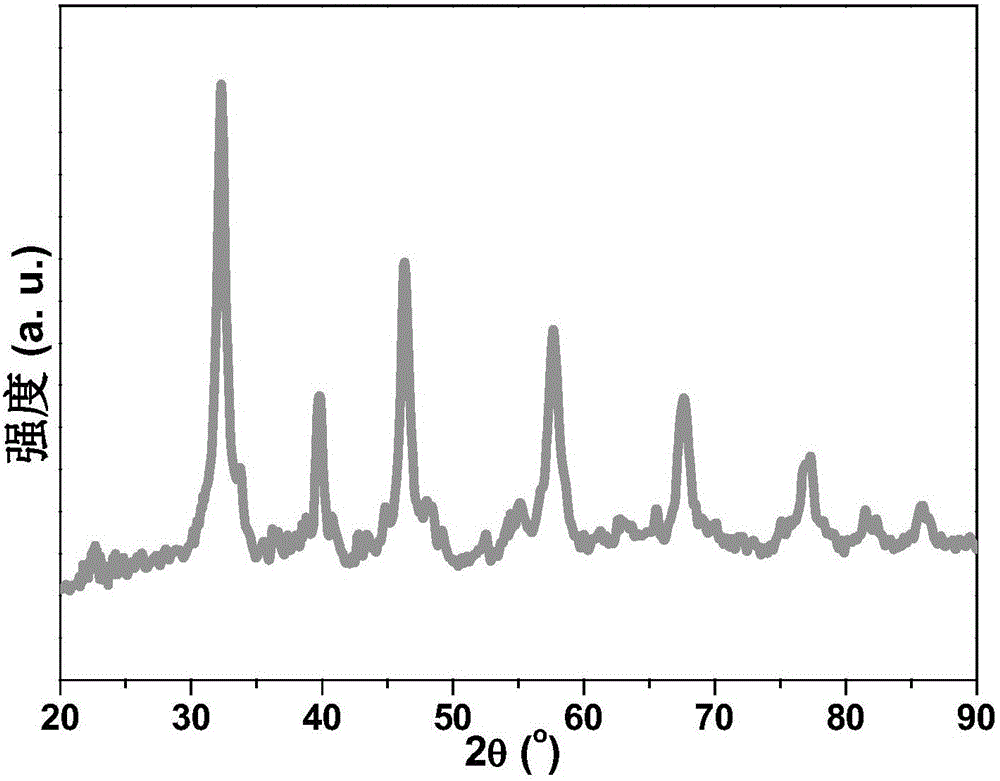
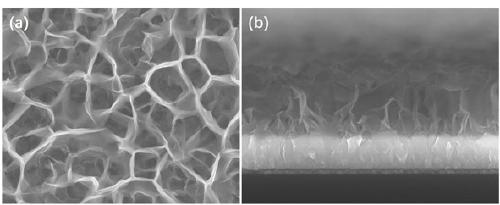
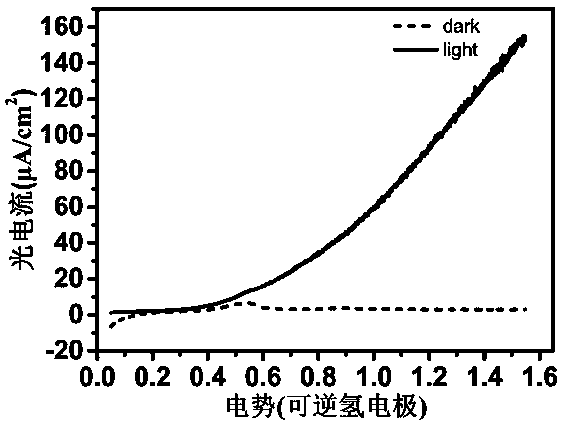
Patents
Literature
75 results about "Artificial photosynthesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Artificial photosynthesis is a chemical process that biomimics the natural process of photosynthesis to convert sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide into carbohydrates and oxygen. The term artificial photosynthesis is commonly used to refer to any scheme for capturing and storing the energy from sunlight in the chemical bonds of a fuel (a solar fuel). Photocatalytic water splitting converts water into hydrogen and oxygen and is a major research topic of artificial photosynthesis. Light-driven carbon dioxide reduction is another process studied that replicates natural carbon fixation.
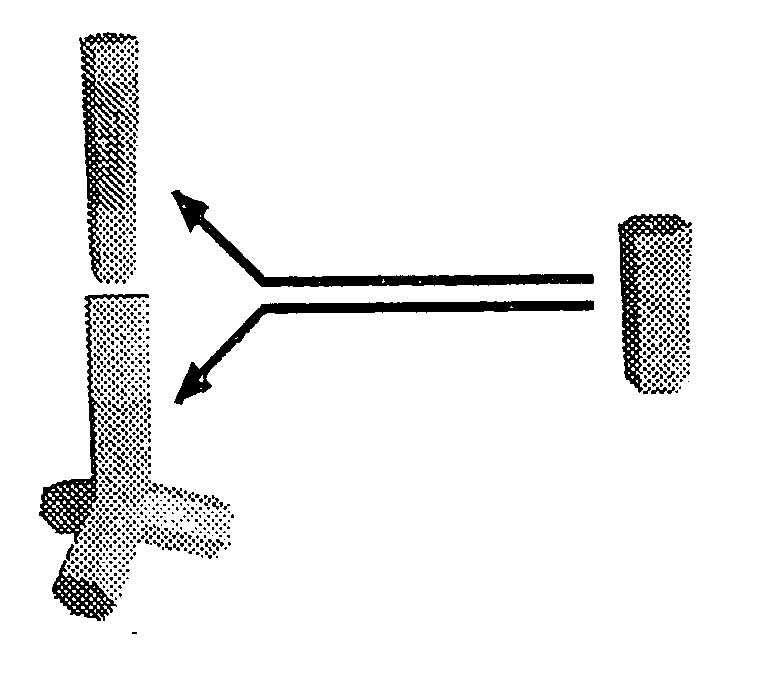
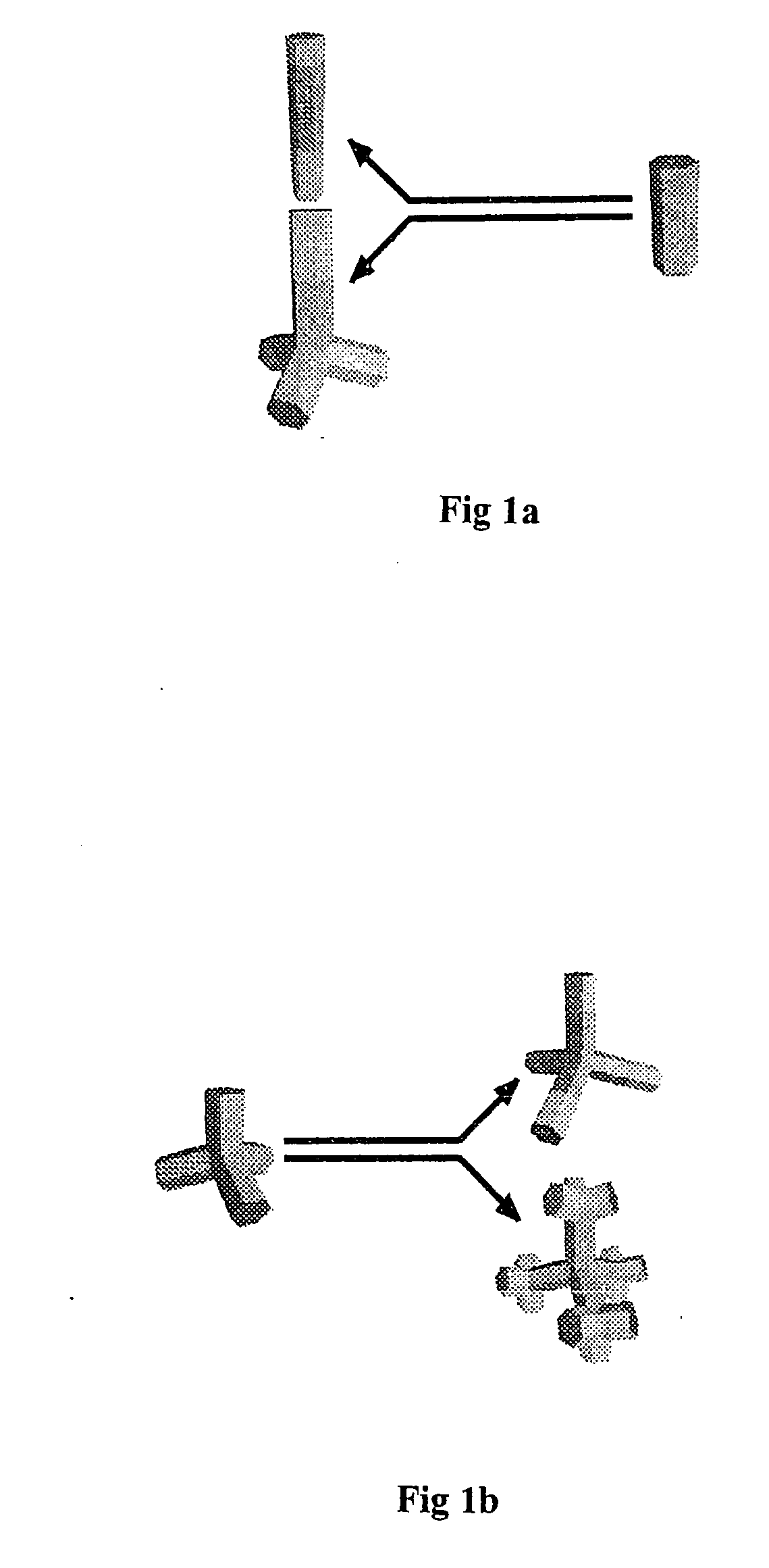
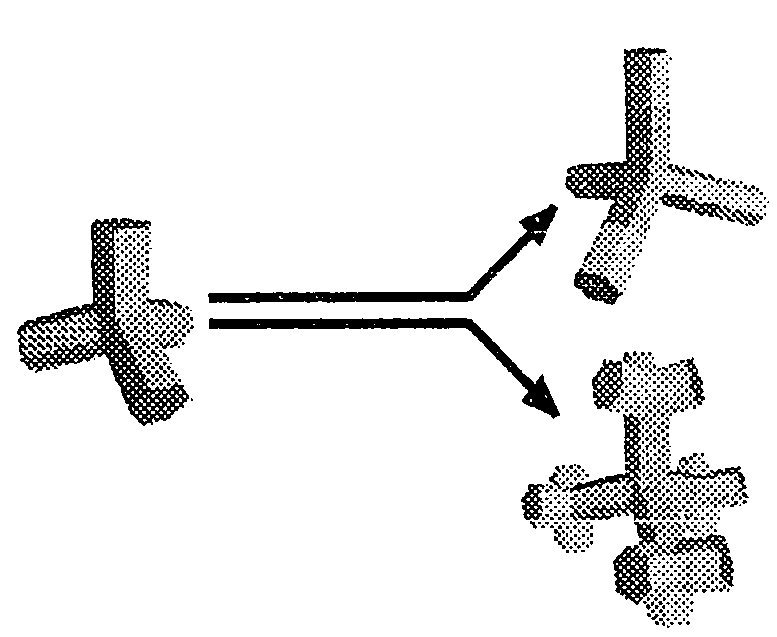
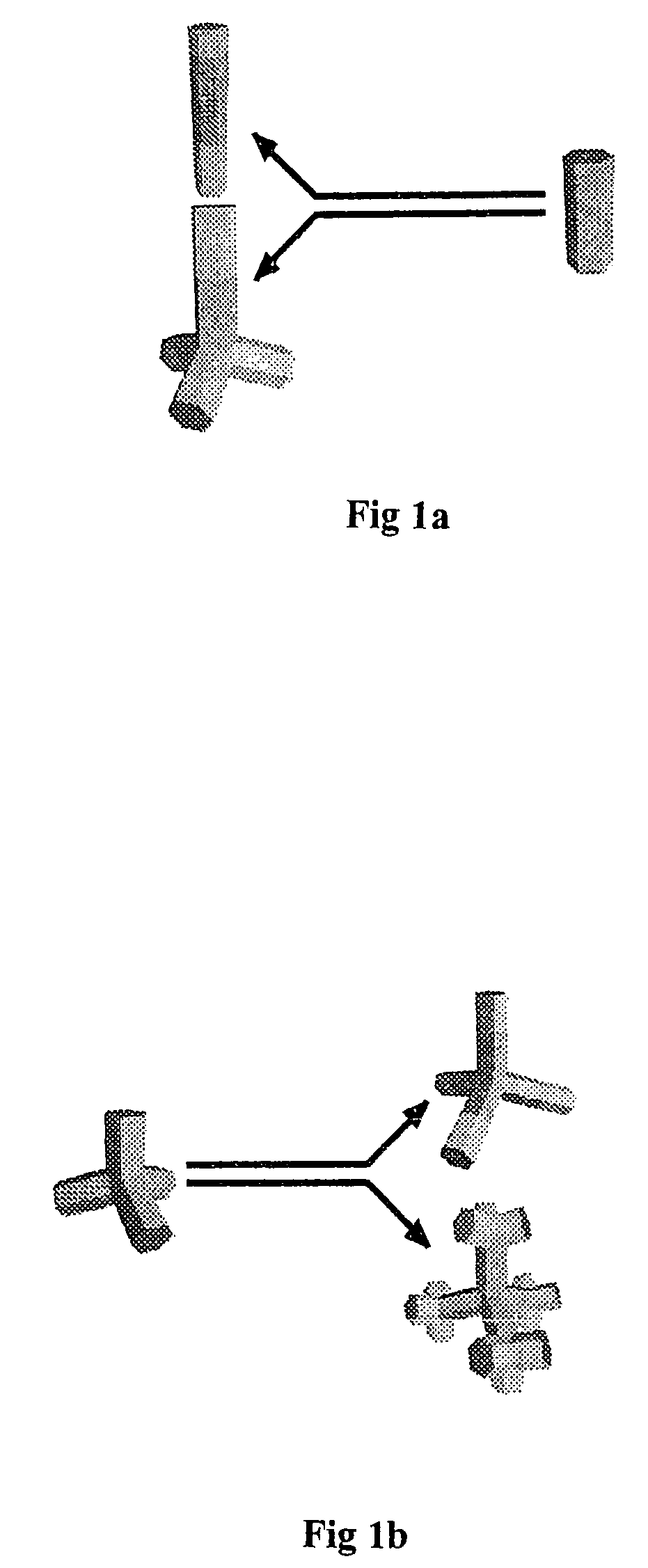
Nanocrystals with linear and branched topology
InactiveUS20050211154A1Quantum computersPolycrystalline material growthInformation processingThree-dimensional space
Disclosed herein are nanostructures comprising distinct dots and rods coupled through potential barriers of tuneable height and width, and arranged in three dimensional space at well defined angles and distances. Such control allows investigation of potential applications ranging from quantum information processing to artificial photosynthesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Nanocrystals with linear and branched topology
InactiveUS7303628B2Quantum computersPolycrystalline material growthThree-dimensional spaceNanocrystal
Disclosed herein are nanostructures comprising distinct dots and rods coupled through potential barriers of tuneable height and width, and arranged in three dimensional space at well defined angles and distances. Such control allows investigation of potential applications ranging from quantum information processing to artificial photosynthesis.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
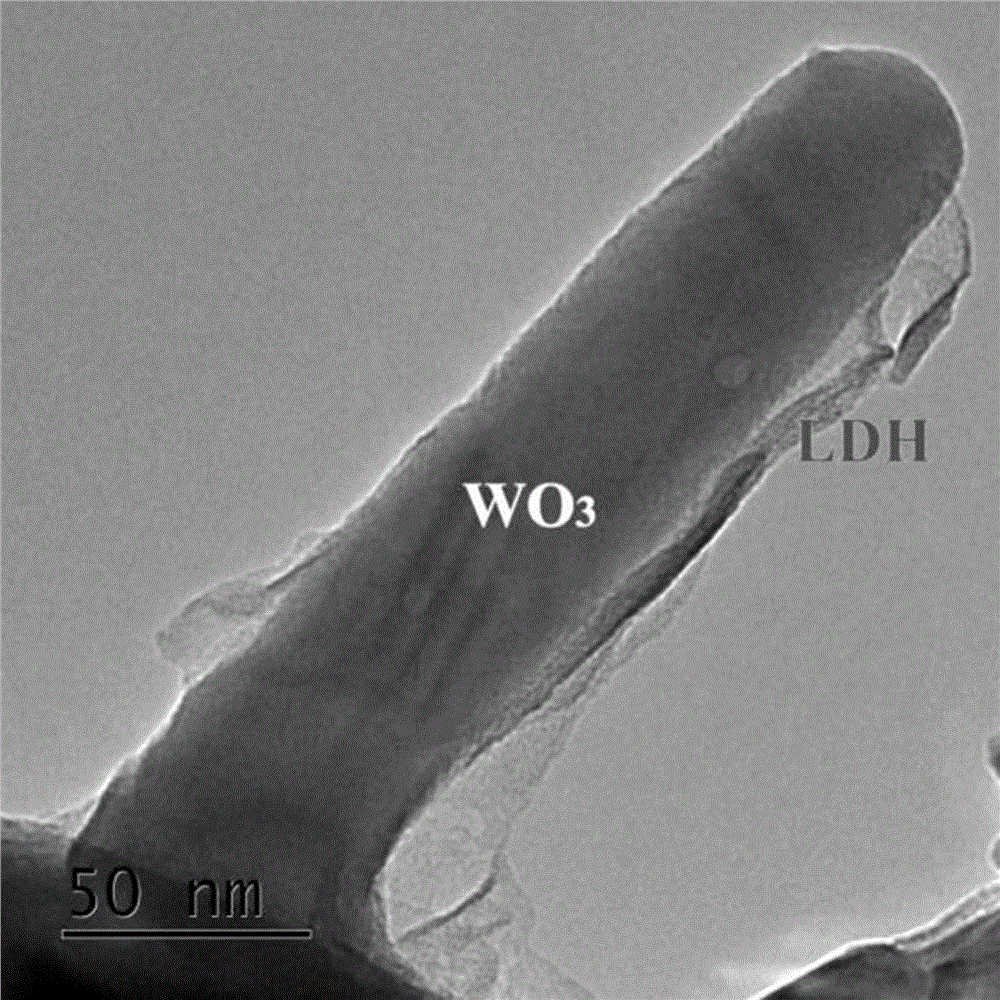
Preparation method for WO3-LDH composite film for photoelectrocatalytic water decomposition
ActiveCN106222685APhotooxidative water splitting current density is highImprove separation efficiencyCellsAir atmosphereComposite film
The invention relates to a preparation method for a WO3-LDH (Layered double hydroxide) composite film for photoelectrocatalytic water decomposition. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving ammonium tungstate and concentrated hydrochloric acid into water to obtain a solution, stirring the solution and transferring the solution into a lining of a high-pressure reaction kettle, and inserting pre-treated conductive glass FTO; then, carrying out solvothermal reaction, naturally cooling the room temperature, washing and drying the conductive glass, and carrying out thermal treatment for at least one hour at a temperature being 450-500 DEG C under air atmosphere, thereby obtaining a WO3 film; and the WO3 film as a working electrode, taking an aqueous solution of nickel nitrate and iron nitrate as electrolyte, depositing NiFe-LDH on the surface of the WO3 film under constant current, finally obtaining the WO3-LDH composite film. The product prepared by the preparation method has high photoelectric conversion efficient, low photooxidation water take-off potential, and has a wide application prospect in the fields such as photocatalytic degradation, photoelectrocatalytic water decomposition, artificial photosynthesis and photo-assisted energy storage batteries.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Method for electric field-induced conversion of water and CO2 to organic polymer
ActiveCN104213148AReduce consumptionIncreased efficiency of artificial photosynthesisElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionOxygenArtificial photosynthesis
The invention discloses a method or electric field-induced conversion of water and CO2 to an organic polymer. The method is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps: dissociating water by using the induction effect of an electric field with water and CO2 as base raw materials and an electric field induced reactor as a reaction device to generate hydrogen free radicals and hydroxy free radicals; converting the hydroxy free radicals with transition metal ions as a catalyst to form water and oxygen; and reacting water with CO2 in an aqueous solution system to generate carbonic acid, reacting carbonic acid with the hydrogen free radicals to generate oxalic acid, and continuously reacting oxalic acid and its derivative with the hydrogen free radical reaction to generate the organic polymer. The method can substantially improve the production efficiency and rate of the hydrogen free radicals, generates a large quantity of the hydrogen free radicals, greatly improves the artificial photosynthesis efficiency, and promotes the synthesis of carbohydrate and the organic polymer with complex structure.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Preparation method and application of crumpled graphite phase carbon nitride
InactiveCN107311126AImprove photocatalytic performanceImprove surface electronic structureCatalyst carriersNitrogen and non-metal compoundsArtificial photosynthesisRaw material
Relating to a preparation method of graphite phase carbon nitride and application thereof, the invention provides a preparation method of crumpled graphite phase carbon nitride and application thereof. The invention aims to solve the technical problem of low activity of graphite phase carbon nitride used as a carrier for photocatalysis of formic acid to produce hydrogen at present. The preparation method includes: 1. mixing of melamine with glyoxal, and condensation reflux; 2. sintering; and 3. pickling, condensation reflux and centrifugation. The crumpled graphite phase carbon nitride prepared by the method provided by the invention can be used as a catalyst carrier. The invention employs a simple thermal decomposition method to synthesize the crumpled graphite phase carbon nitride catalyst carrier, the crumpled graphite phase carbon nitride not only maintains the photocatalytic performance of the graphite phase carbon nitride material itself, and also can be used as the catalyst carrier to improve the photocatalytic performance of the catalyst. The method has the characteristics of simple preparation and low raw material cost, and is easy for industrial production. The obtained crumpled graphite phase carbon nitride has potential application value in the fields of photolysis of water, artificial photosynthesis, organic pollutant degradation, carbon dioxide reduction, catalyst carriers and the like.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
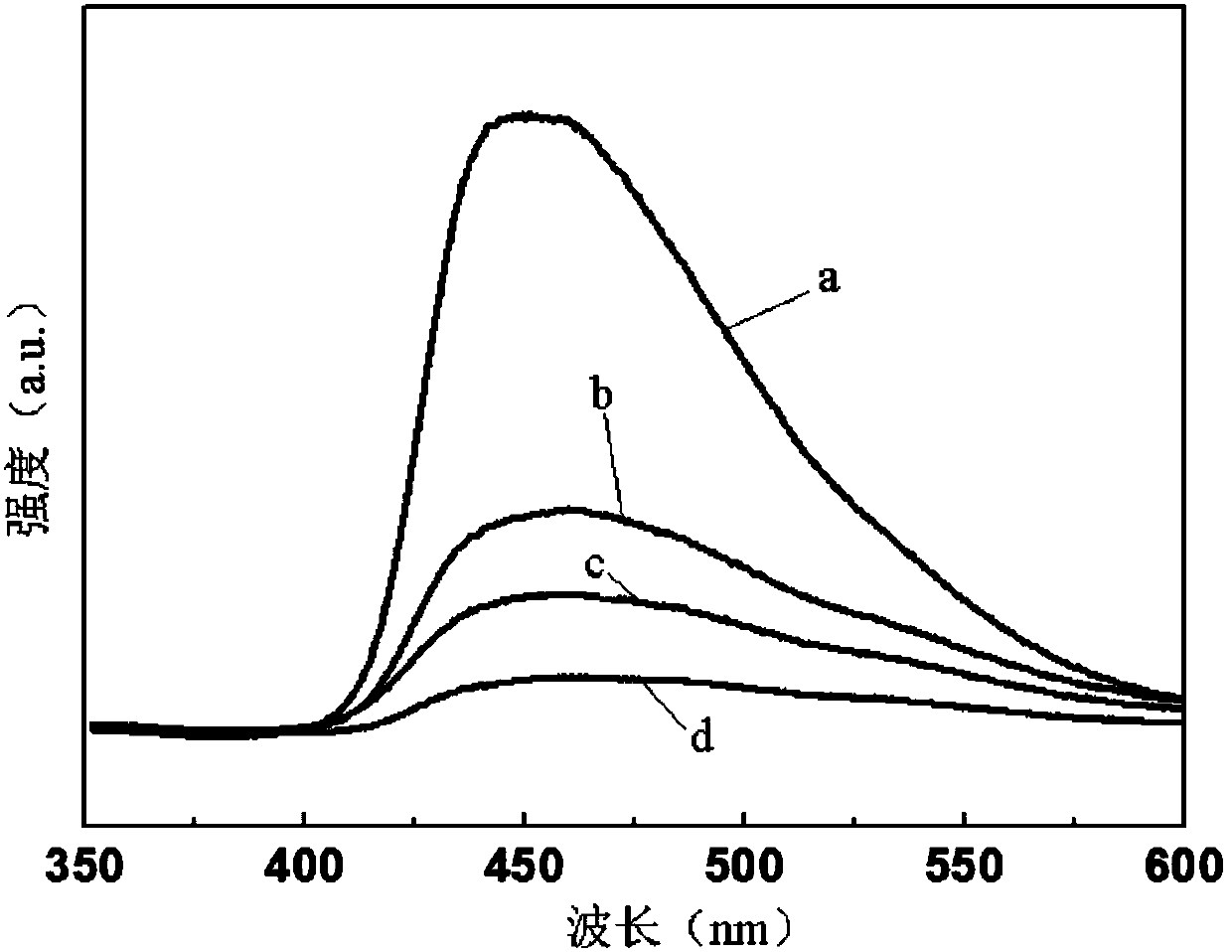
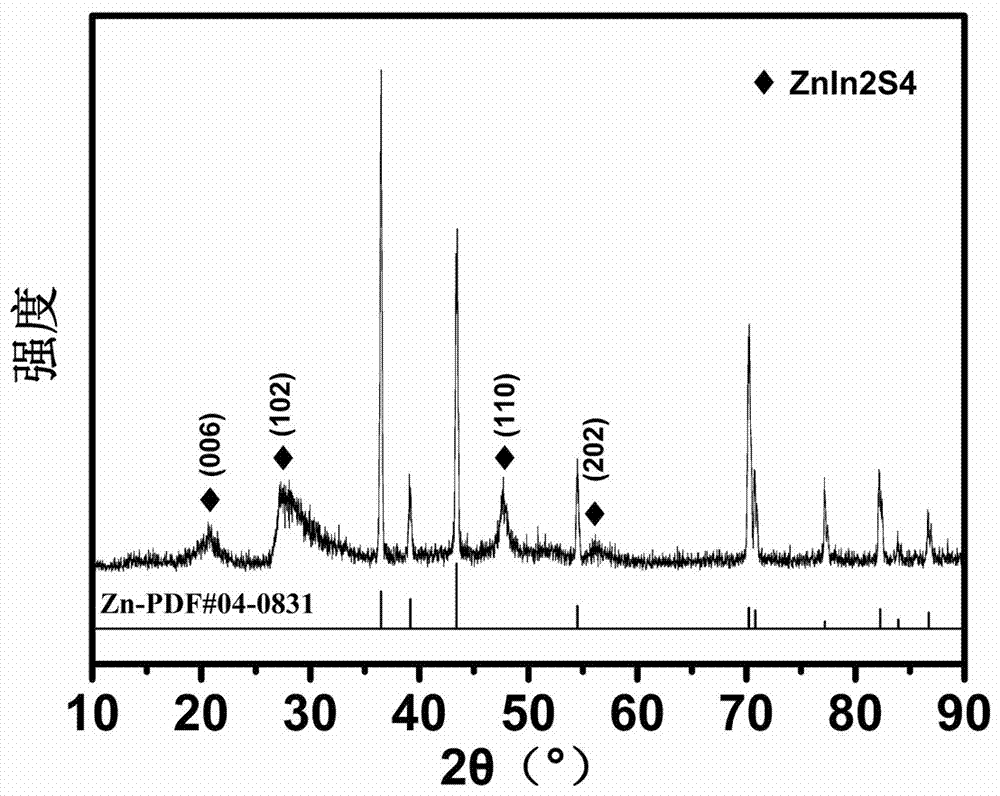
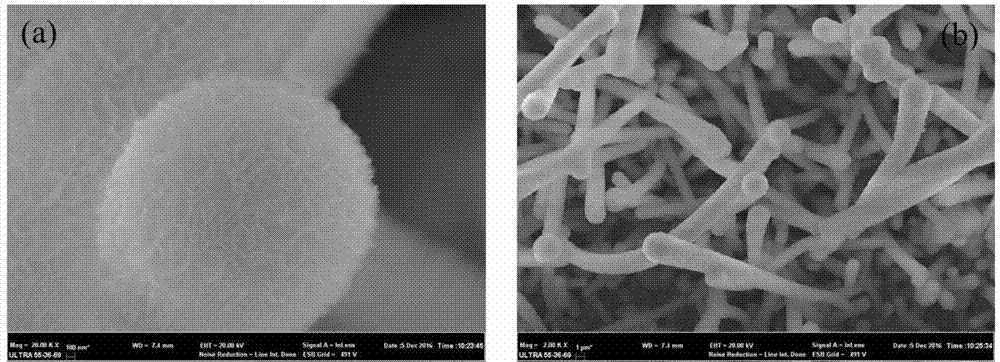
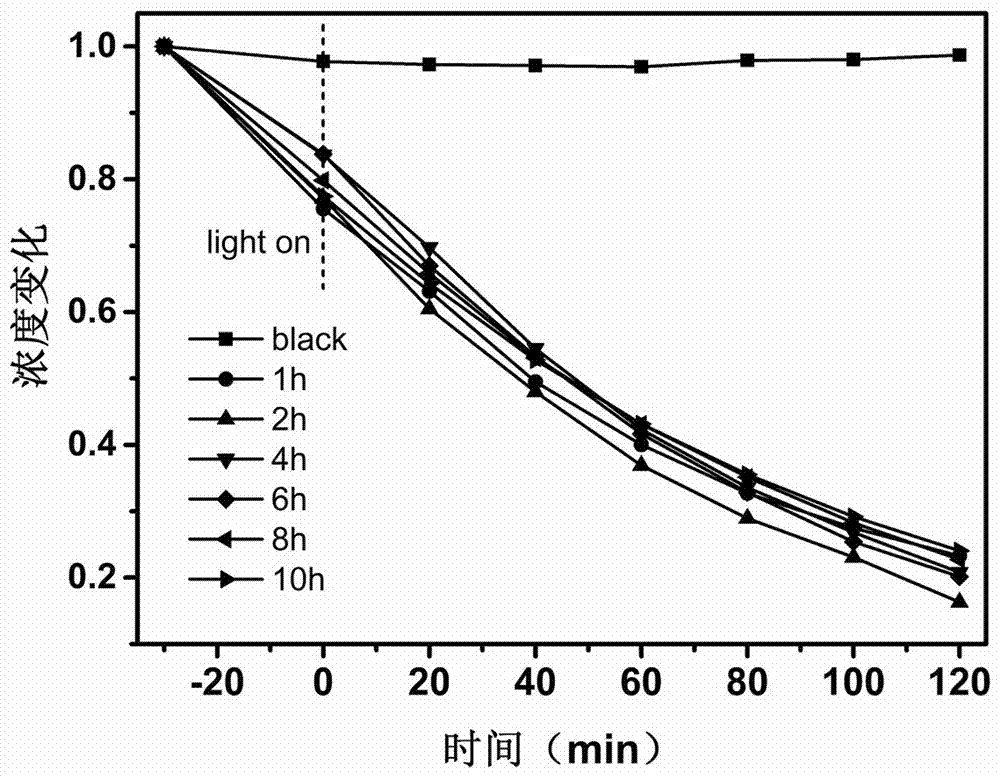
Three-dimensional flower-sheet-shaped sulfur-indium-zinc micro-nanowire array as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107282070ARaw material acquisitionEasy to getMaterial nanotechnologyPhysical/chemical process catalystsIndiumTrapping
The invention discloses a three-dimensional flower-sheet-shaped sulfur-indium-zinc micro-nanowire array as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. According to the preparation method, a pretreated zinc sheet is taken as a substrate, an indium source and a sulfur source are taken as precursors, the temperature and time of solvothermal reaction are controlled, and therefore, the ZnIn2S4 micro-nanowire array is prepared. The three-dimensional flower-sheet-shaped sulfur-indium-zinc micro-nanowire array prepared by virtue of the preparation method is initiated from a solid substrate and has the excellent characteristics of high specific surface area, low reflectivity, good light trapping property, relatively few defects, capability in repeated use and the like; and the preparation method is simple, low in cost and non-toxic and environment-friendly and has huge application prospects in the fields of photocatalytic hydrogen generation, photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants, artificial photosynthesis, photocatalytic sterilization, solar cells and the like, and the process is easily controlled.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
Complementary conjugated polyelectrolyte complexes as electronic energy relays
ActiveUS20190006545A1Light-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureArtificial photosynthesisElectronic energy transfer
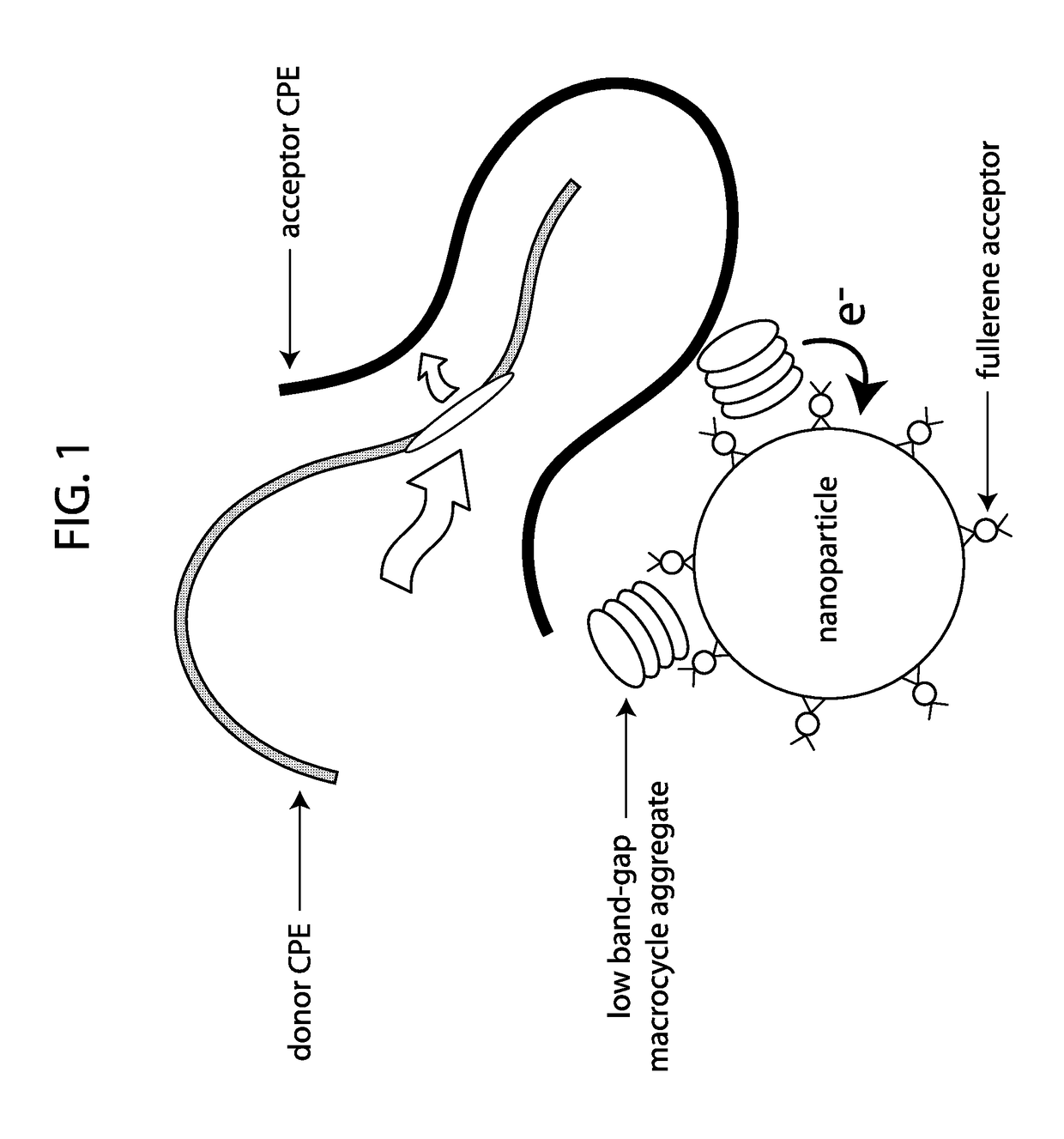
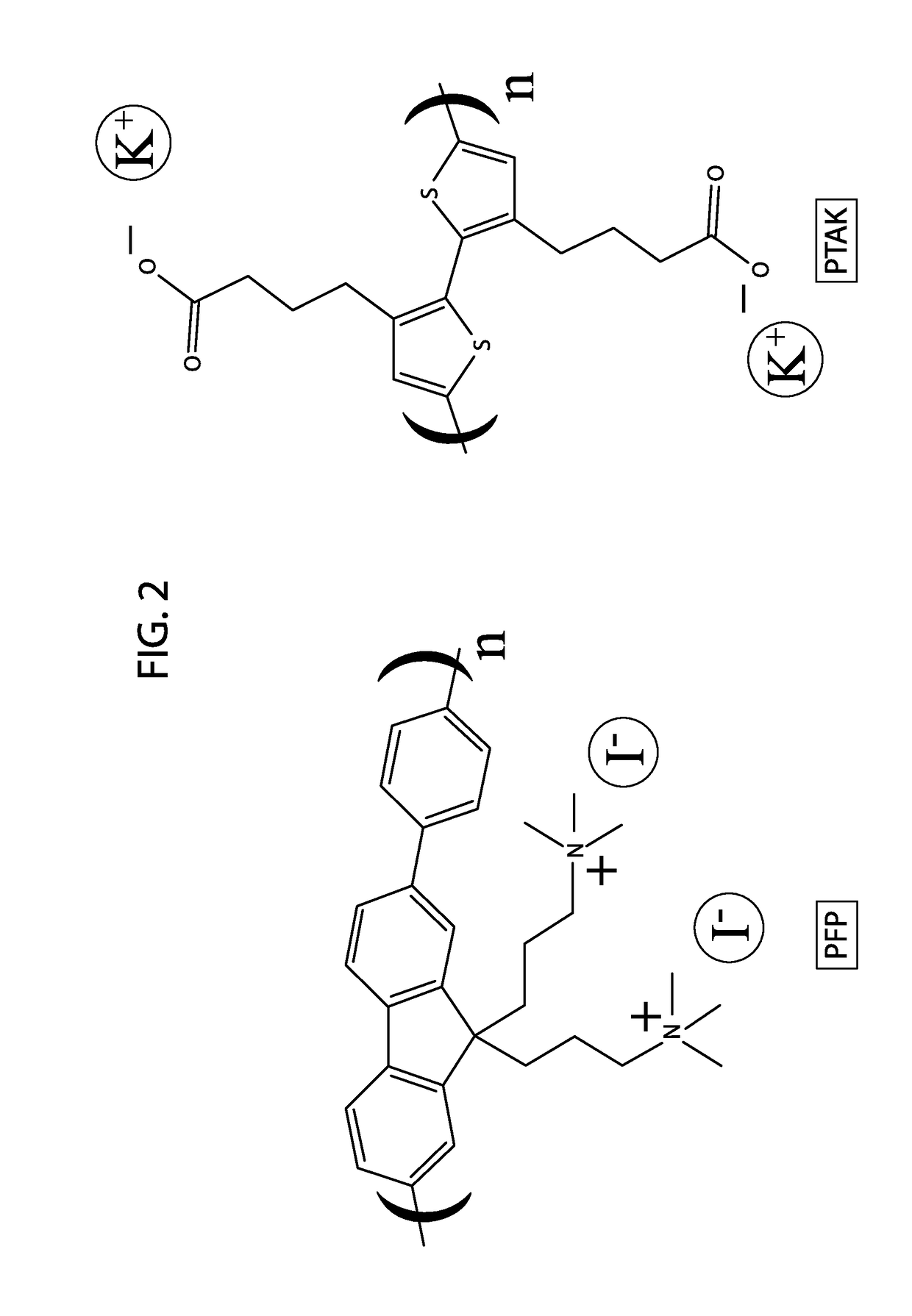
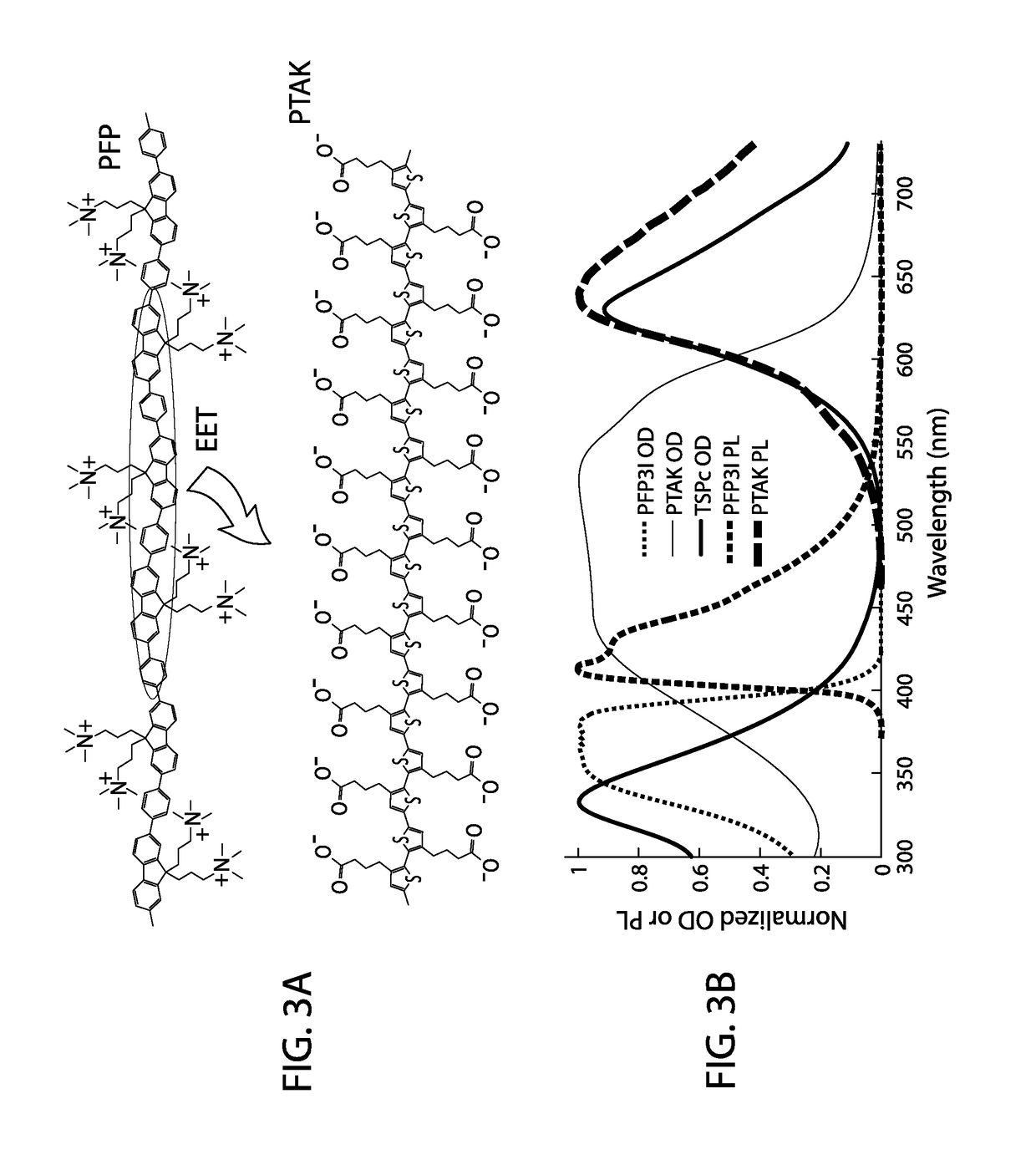
The present invention generally relates to artificial photosystems and methods of their use, for example in artificial photosynthesis, wherein the artificial photosystems comprise one or more light-harvesting antenna (LHA) comprising a conjugated polyelectrolyte (CPE) complex (CPEC) comprising a donor CPE and an acceptor CPE, wherein the donor CPE and acceptor CPE are an electronic energy transfer (EET) donor / acceptor pair.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
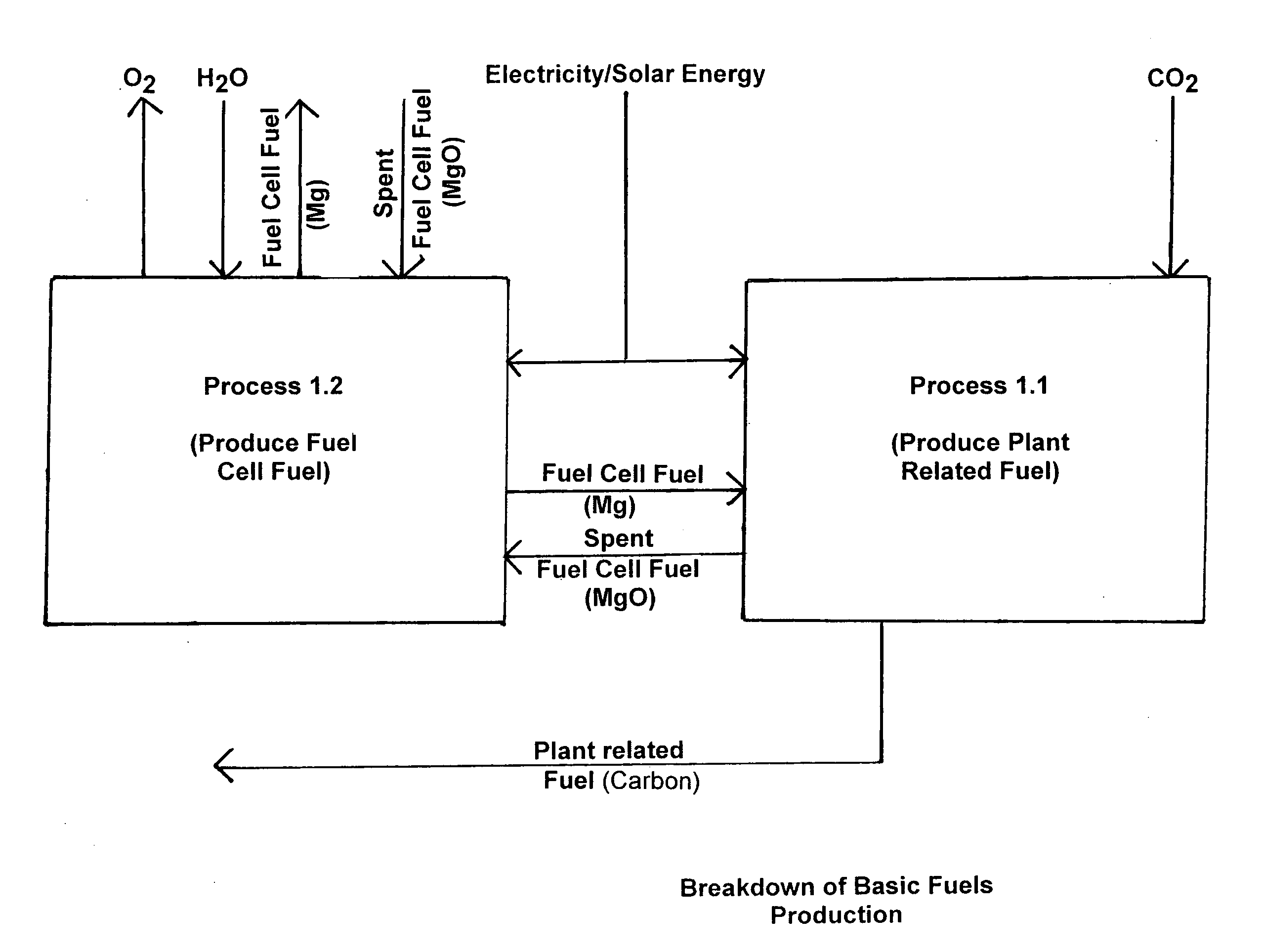
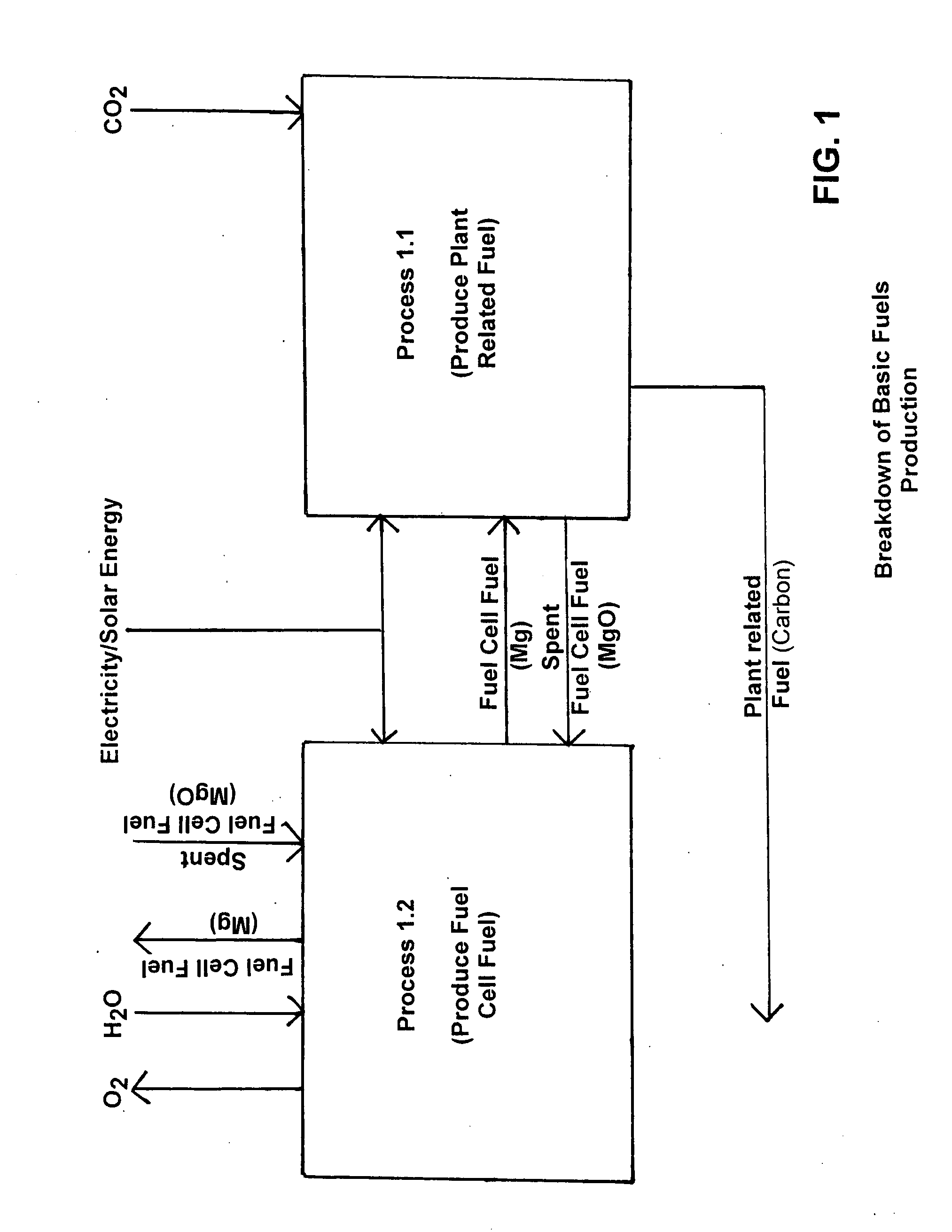
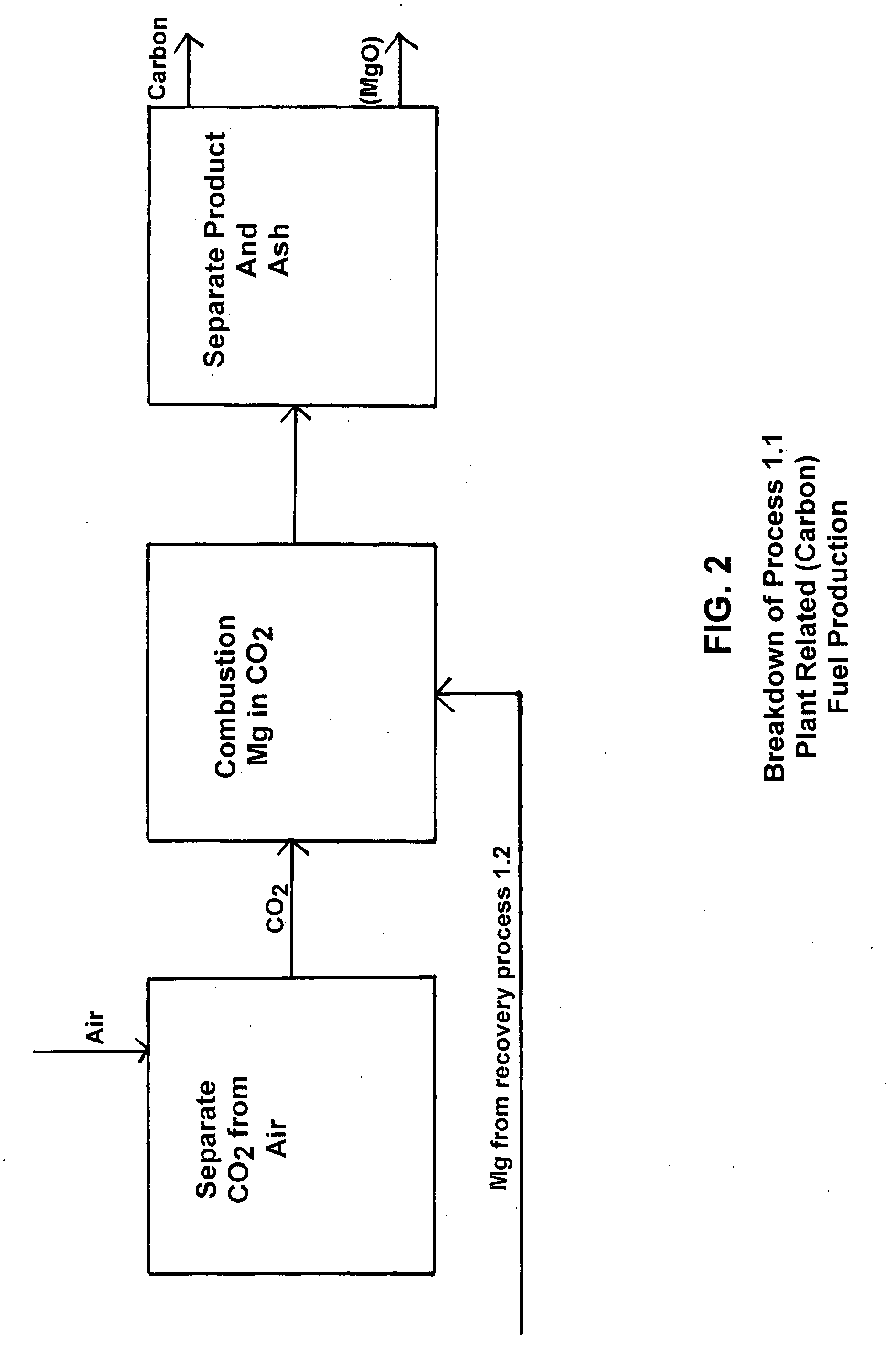
Fuel production from atmospheric CO2 and H20 by artificial photosynthesis and method of operation thereof
The present invention relates generally to reduction of atmospheric carbon dioxide and to fuel production, and more specifically, to carbonaceous fuel production by means of utilization of atmospheric carbon dioxide and water by “artificial photosynthesis”, as defined herein and methods of operation thereof.
Owner:YOUNG EDGAR D
Electrochemical preparation method of BiOBr/Bi12SiO20 composite film photocatalyst and application of BiOBr/Bi12SiO20 composite film photocatalyst
ActiveCN110624575AEasy to useOvercoming the insufficiency of not being easy to separateCatalyst activation/preparationCarbon monoxideComposite filmSynthesis methods
The invention discloses an electrochemical preparation method of a BiOBr / Bi12SiO20 composite film photocatalyst and application of the BiOBr / Bi12SiO20 composite film photocatalyst, belonging to the fields of in-situ preparation of Bi-based composite materials, solar photocatalyst immobilization technology and artificial photosynthesis. The problems that existing synthesis methods are high in energy consumption and have difficulty in separation of powder catalysts from reaction systems can be solved. According to the invention, a BiOBr / Bi12SiO20 immobilized composite film is through one-step electrochemical synthesis at room temperature with a Bi plate, NaBr and Na2SiO3.9H2O as raw materials, water / EG as a solvent, nitric acid or a sodium hydroxide solution as an agent for adjusting a pH value and a Ti plate as a negative pole. The preparation method has the advantages of usage of cheap and easily available raw materials, no need for high temperature and high pressure, mild and controllable reaction conditions, easy operation, environment-friendly process, and no generation of harmful byproducts.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
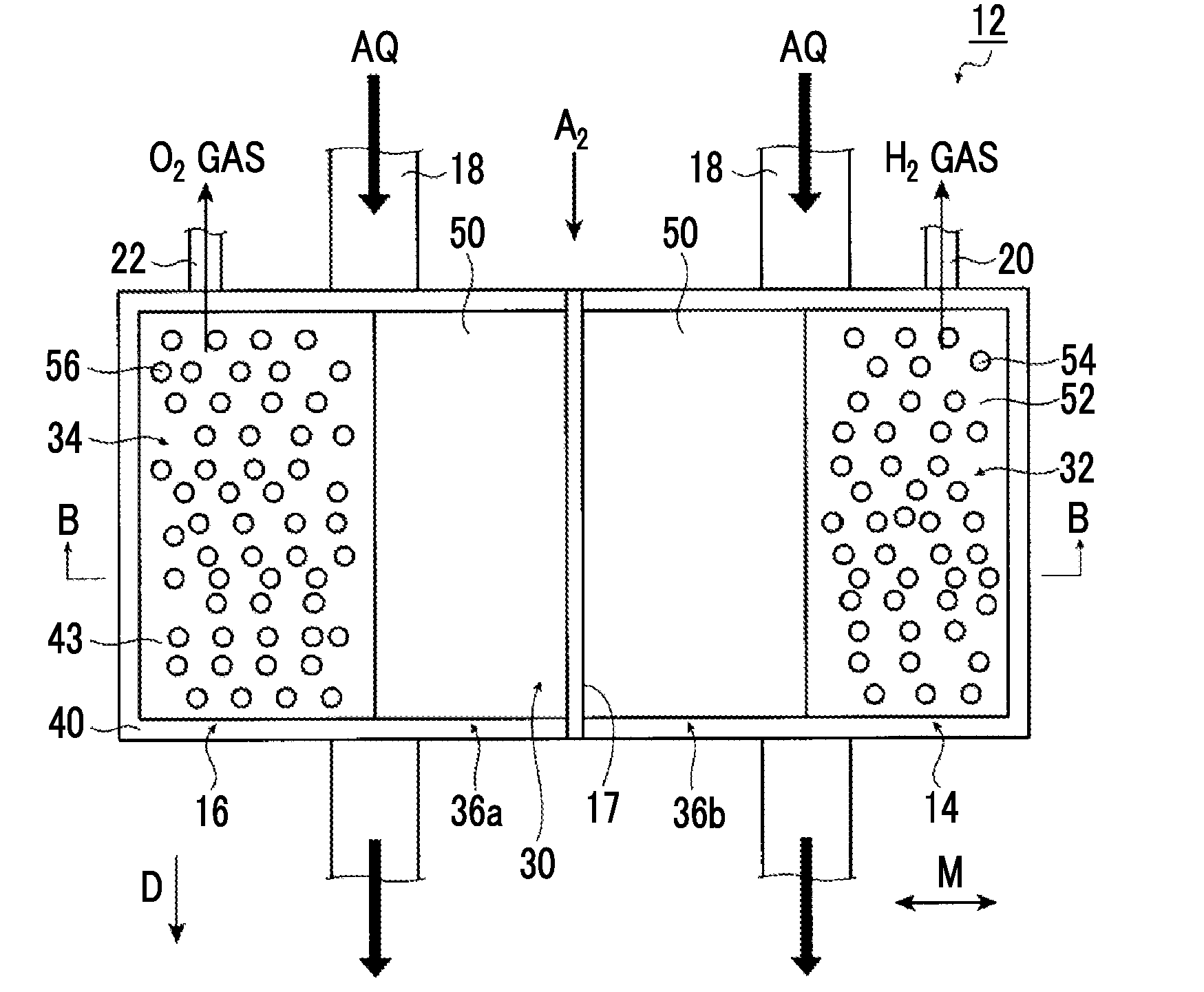
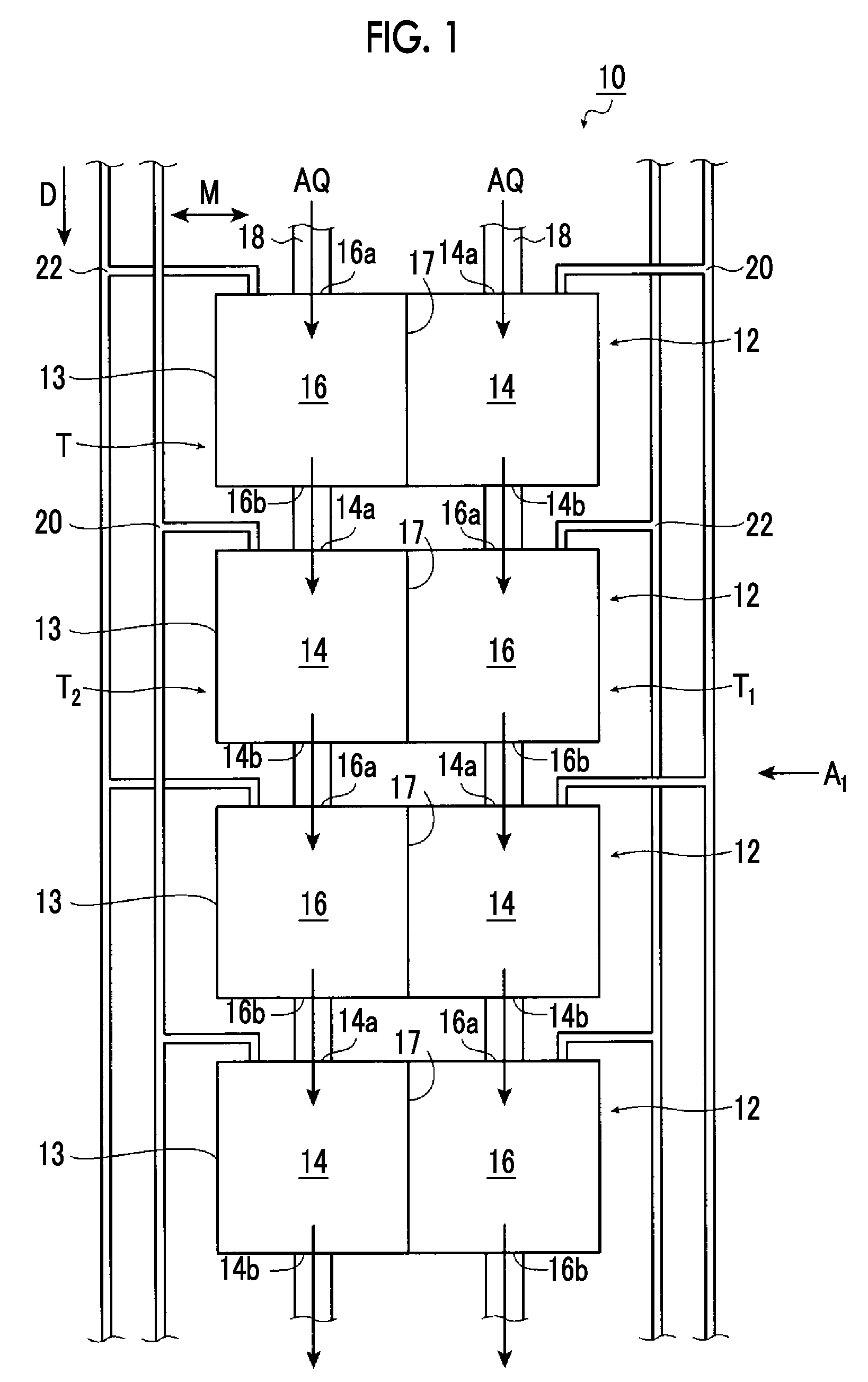
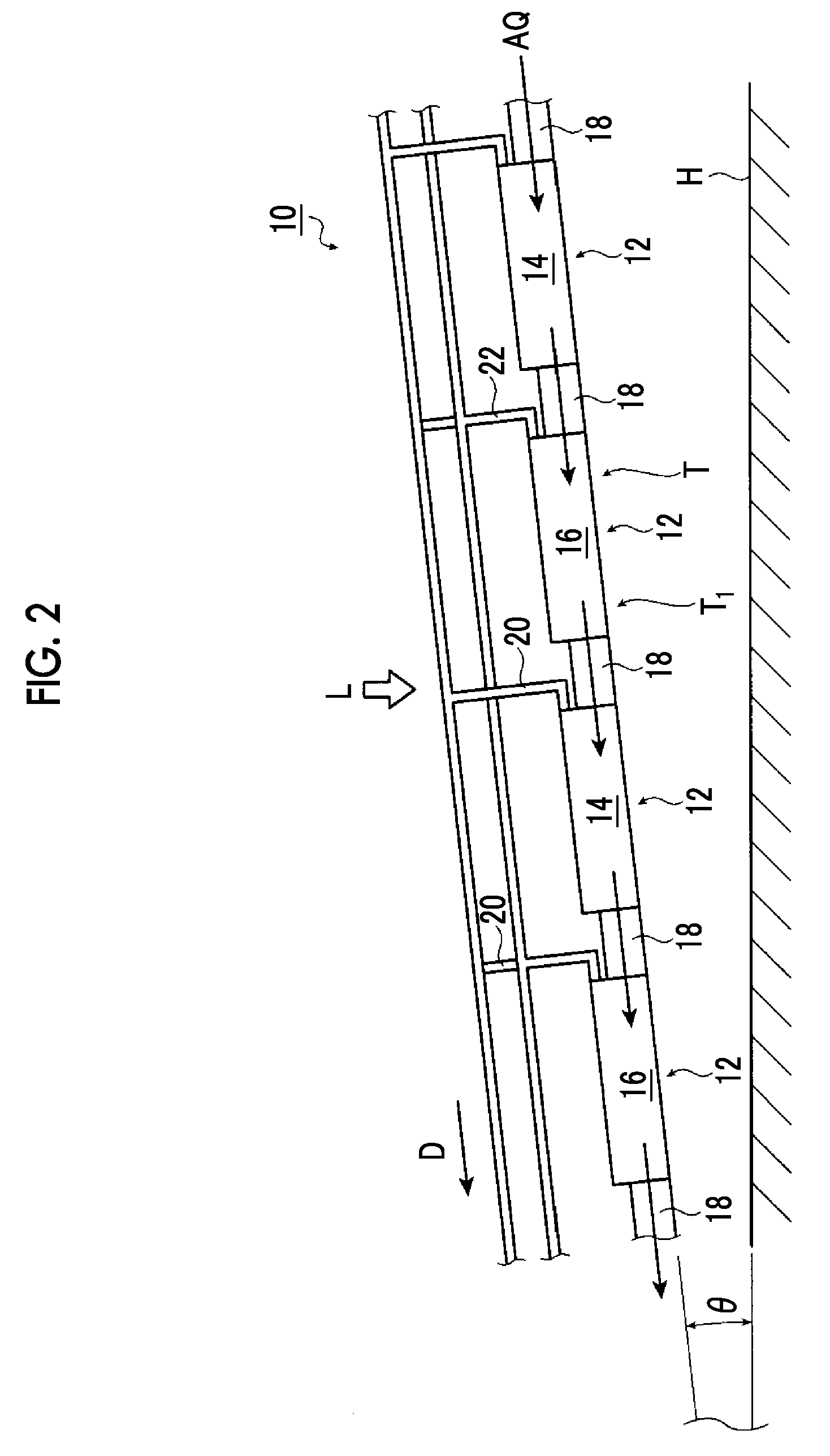
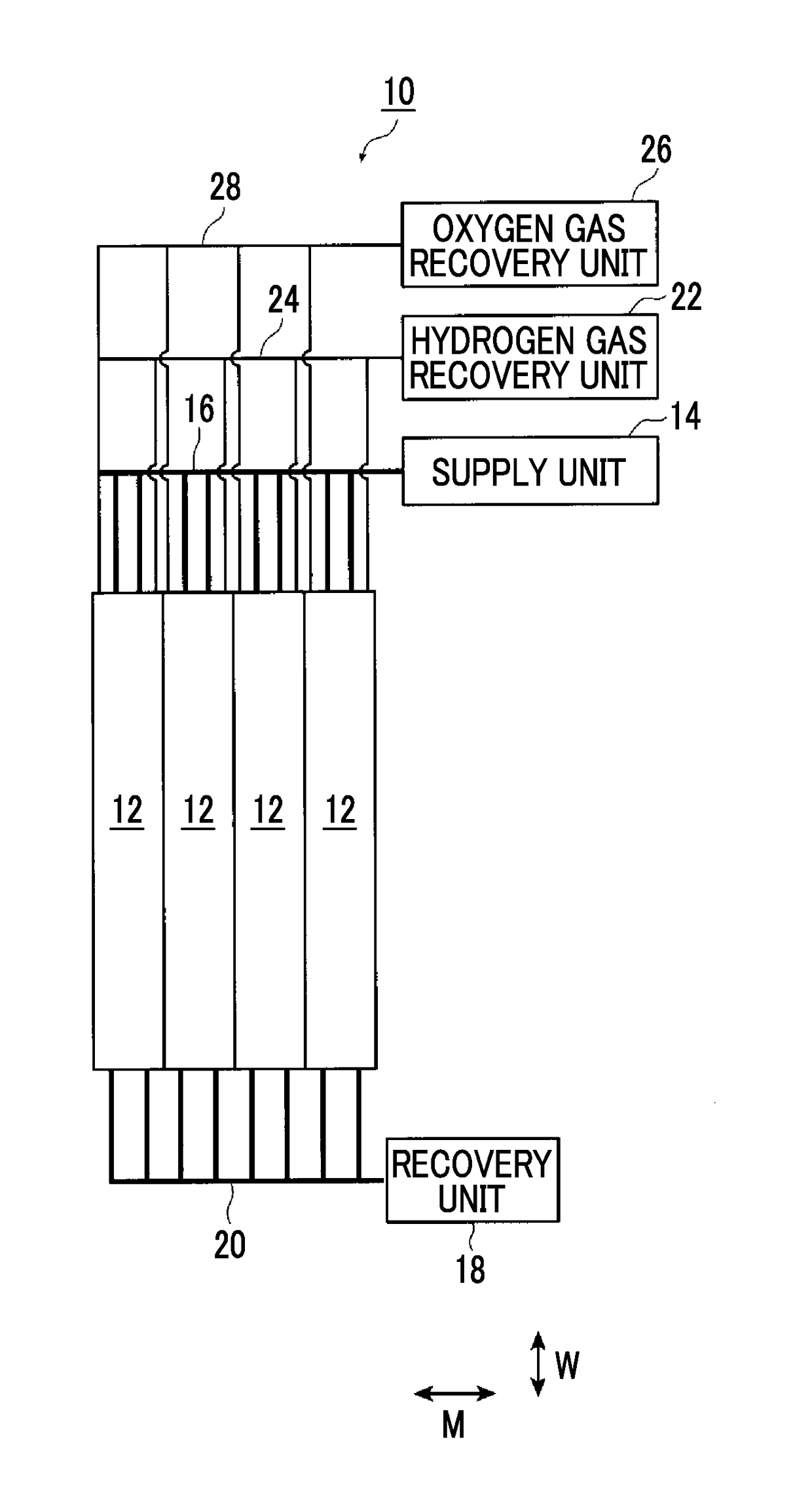
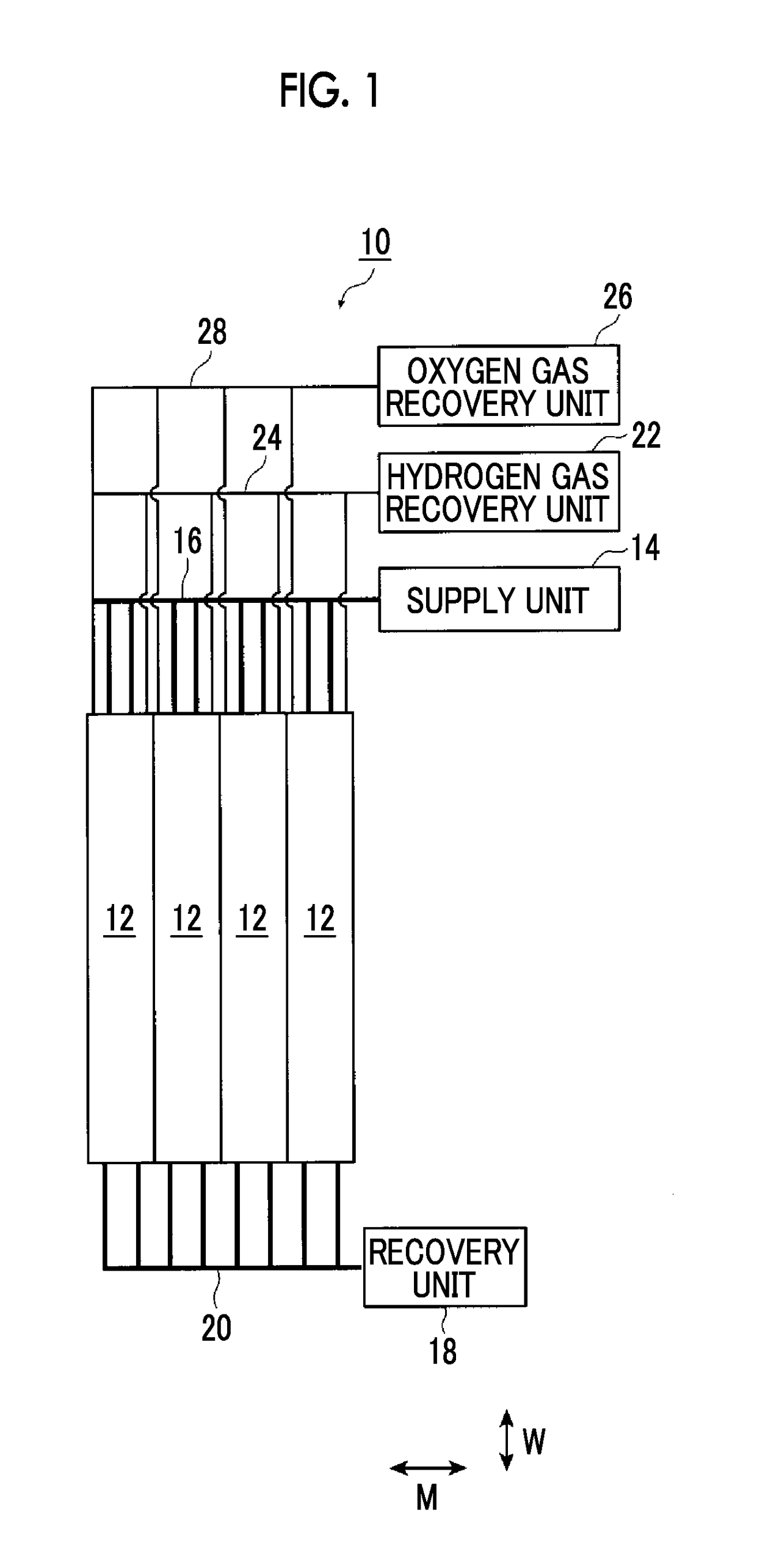
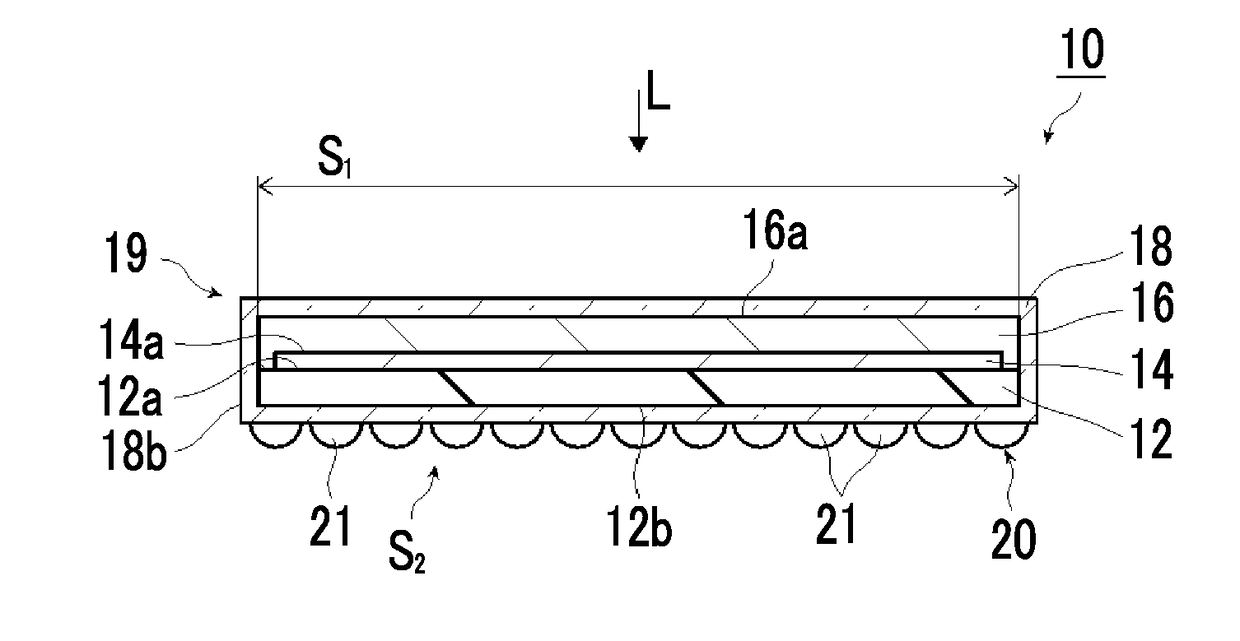
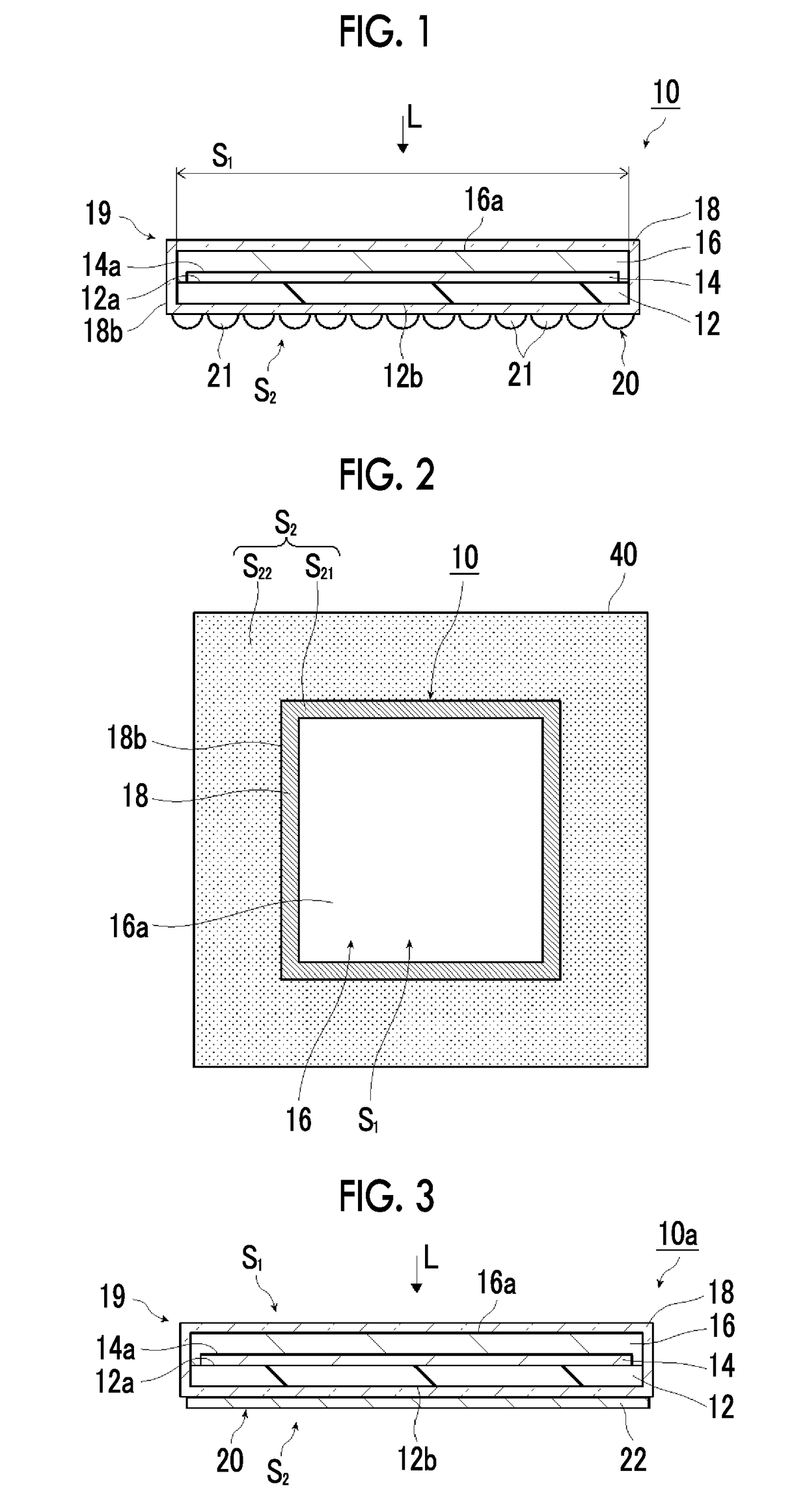
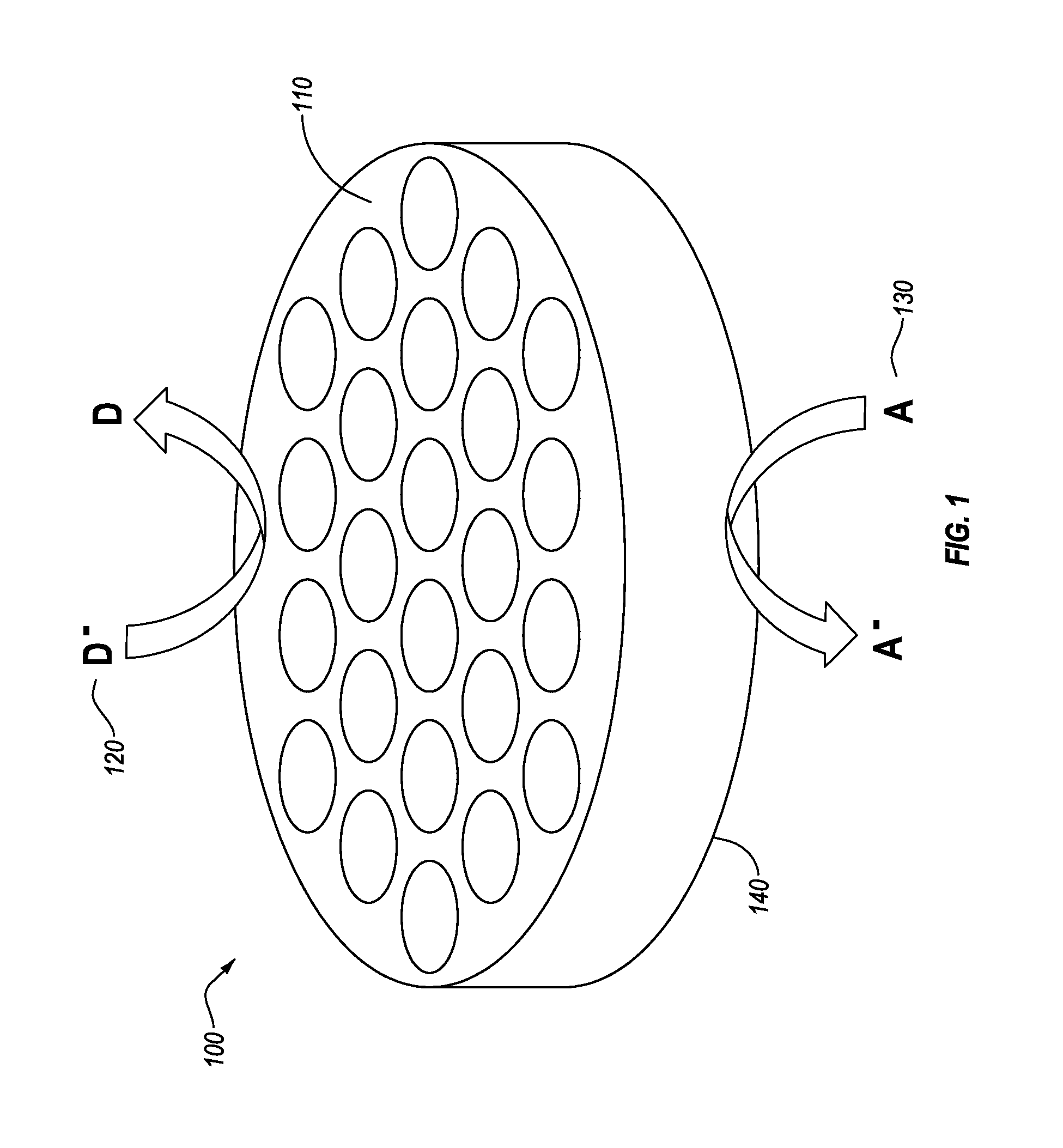
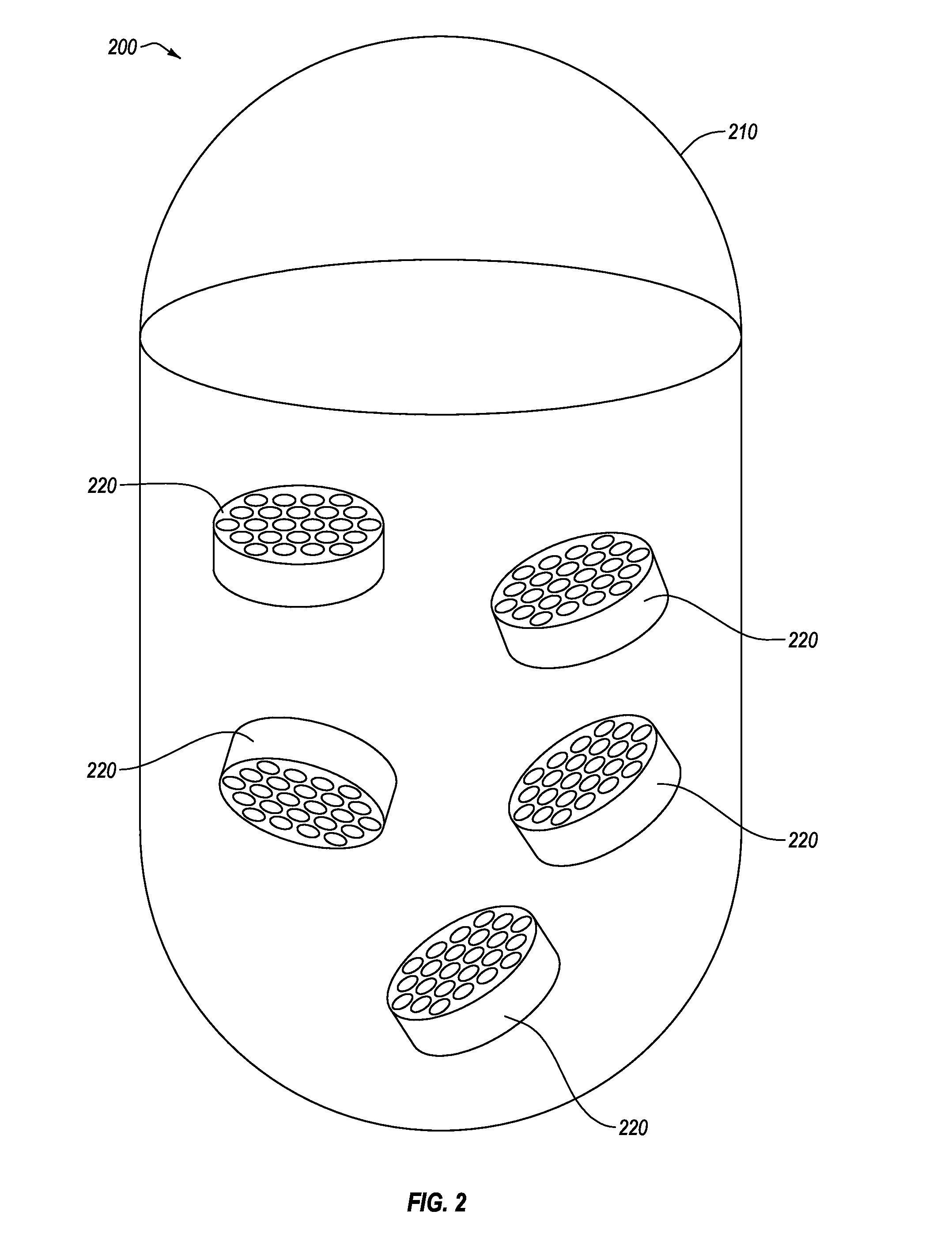
Artificial-photosynthesis array
InactiveUS20160281244A1Reduce mixKeep concentrationCellsFinal product manufactureHydrogenPhysical chemistry
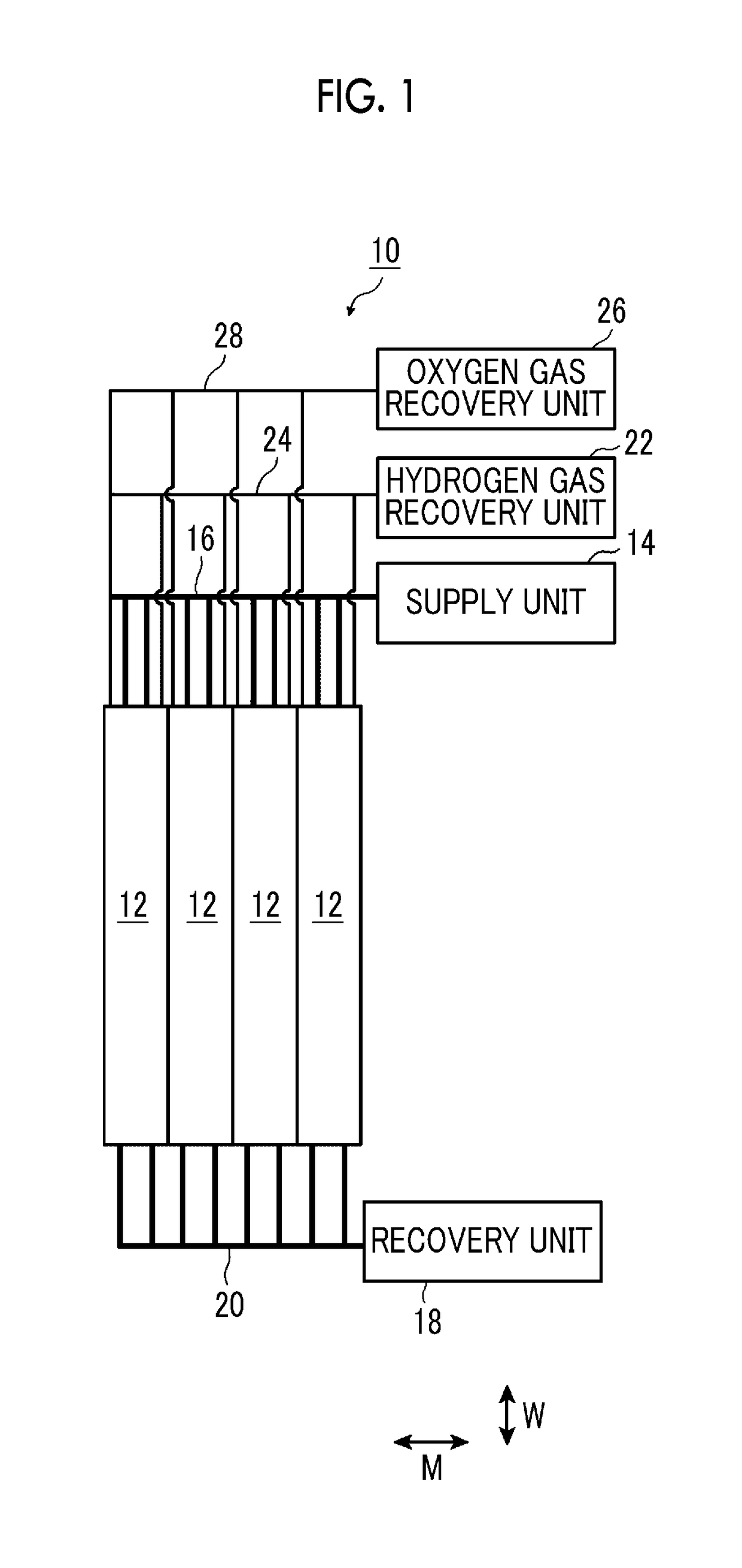
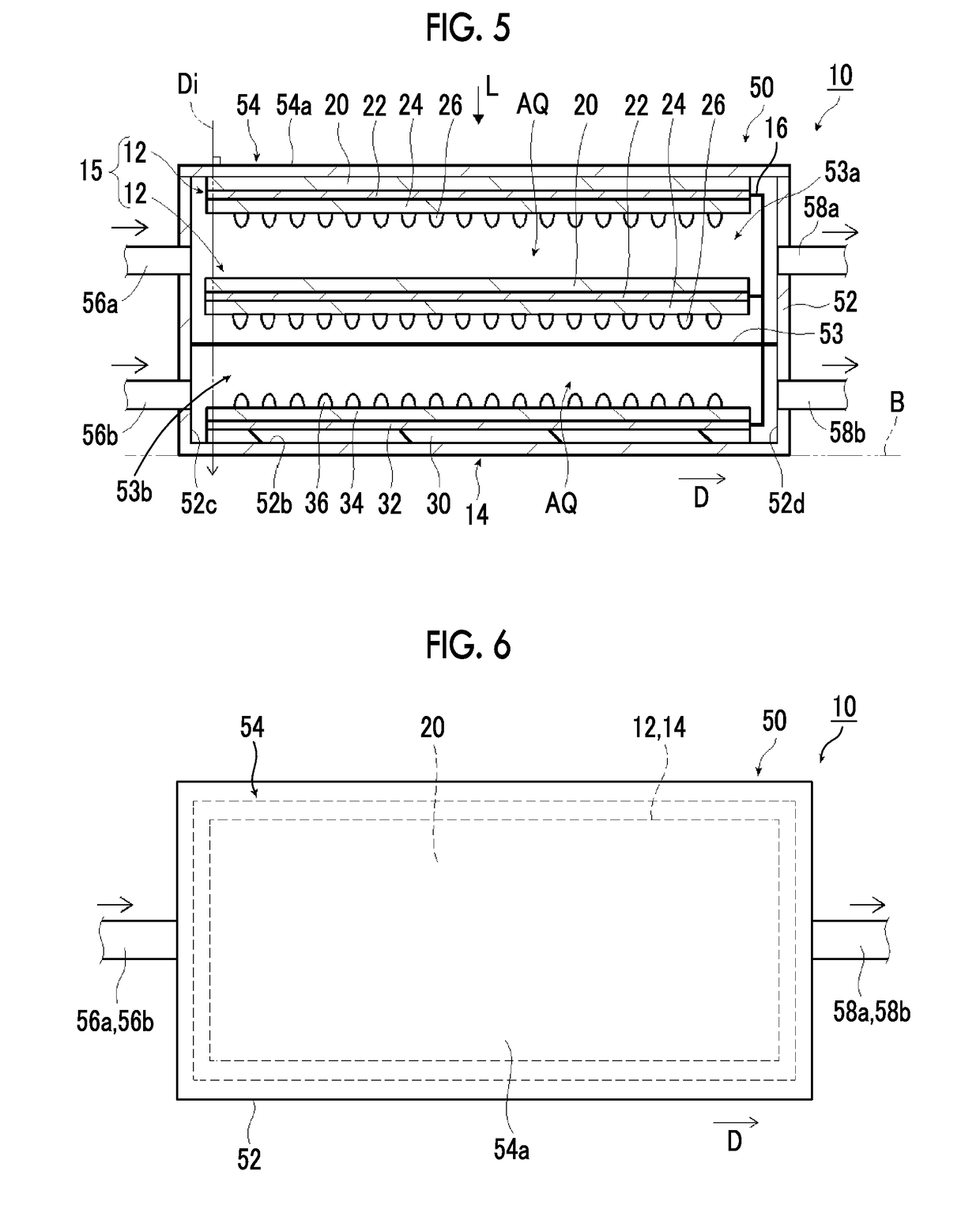
Provided is an artificial-photosynthesis array configured of artificial-photosynthesis modules which have been arranged in one or more rows and which receive light and decompose a supplied aqueous electrolyte solution to thereby obtain hydrogen gas and oxygen gas. The artificial-photosynthesis modules each includes an electrolytic chamber for hydrogen where hydrogen gas is generated and an electrolytic chamber for oxygen where oxygen gas is generated, the chambers being isolated from each other. The electrolytic chambers for hydrogen and electrolytic chambers for oxygen of the artificial-photosynthesis modules are alternately connected so that the electrolytic chamber for hydrogen of each artificial-photosynthesis module is connected to the electrolytic chamber for oxygen of another module and the electrolytic chamber for oxygen of each artificial-photosynthesis module is connected to the electrolytic chamber for hydrogen of another module.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +2
Hydrogen generation electrode and artificial photosynthesis module
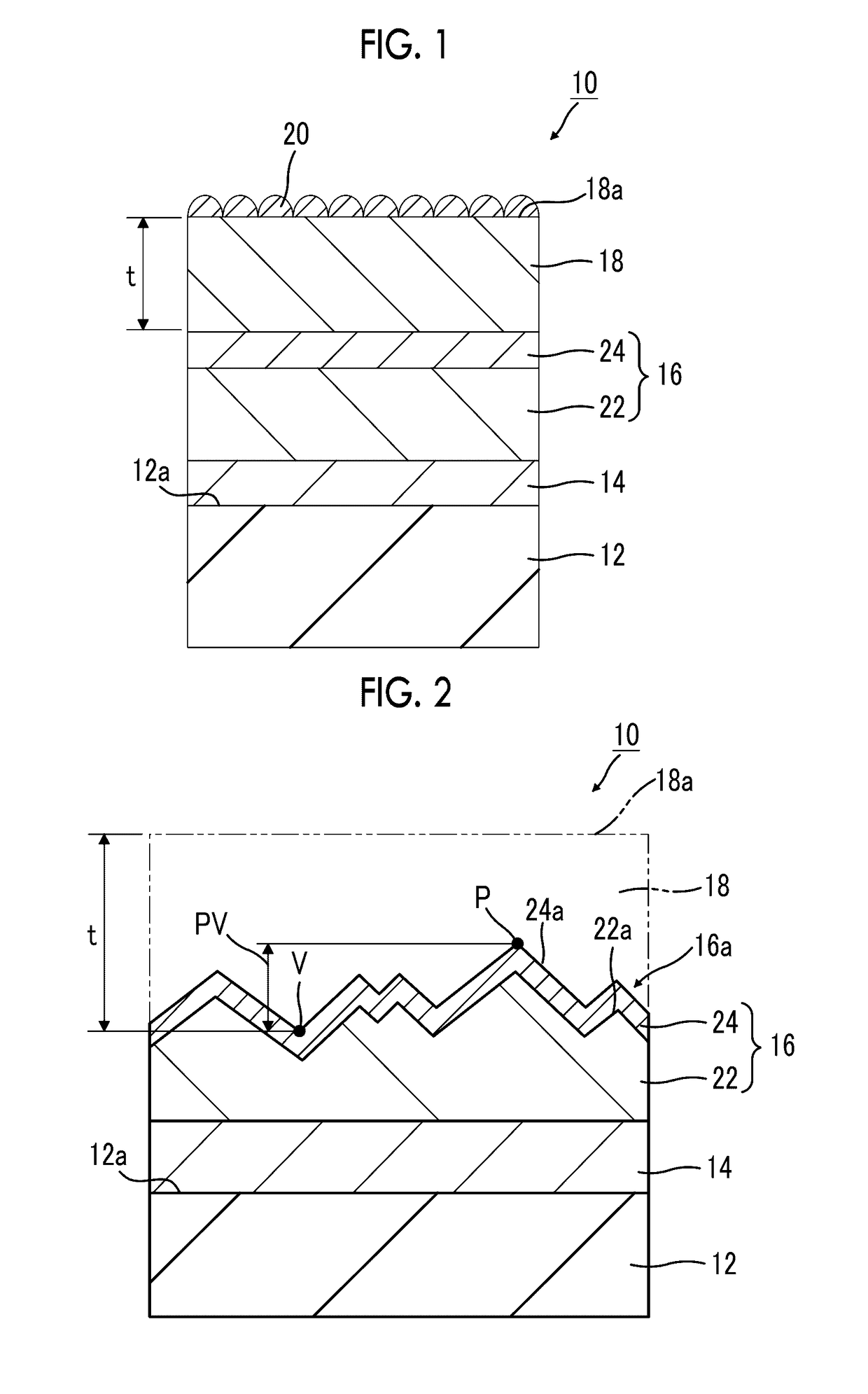
A hydrogen generation electrode is used for an artificial photosynthesis module that decomposes an electrolytic aqueous solution into hydrogen and oxygen with light. The hydrogen generation electrode has a conductive layer, an inorganic semiconductor layer that is provided on the conductive layer and has a pn junction, and a functional layer that covers an inorganic semiconductor layer. The steam permeability of the functional layer is 5 g / (m2·day) or less.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +2
Preparation method of Bi/Cu catalyst for artificial photosynthesis
ActiveCN112342568AHigh reduction selectivityElectrolytic organic productionElectrodesPtru catalystReactive deposition
The invention relates to a preparation method of a Bi / Cu catalyst for artificial photosynthesis, which comprises the following steps of preparing an electrodeposition solution: adding bismuth chlorideBiCl3 and sodium citrate C6H9Na3O9 into a hydrochloric acid solution with the concentration of 1 mol / L or above, and sufficiently stirring the solution until the BiCl3 is completely dissolved and thesolution is transparent, thereby obtaining the electrodeposition solution, and electro-deposition reaction: forming a pair of electrodes by taking foamy copper as a cathode and a carbon rod as an anode, then immersing the electrodes into the prepared electrodeposition solution, carrying out constant-potential deposition reaction, and depositing 3-6 C charge quantity to obtain the Bi / Cu catalyst.Due to the fact that replacement reaction occurs under the acidic condition, Cu on the surface of the copper substrate is replaced into a solution and then deposited on the substrate again, and the coralline Bi / Cu catalyst with copper as a framework is formed. The Bi / Cu catalyst prepared through artificial photosynthesis has very high CO2 reduction selectivity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV +1
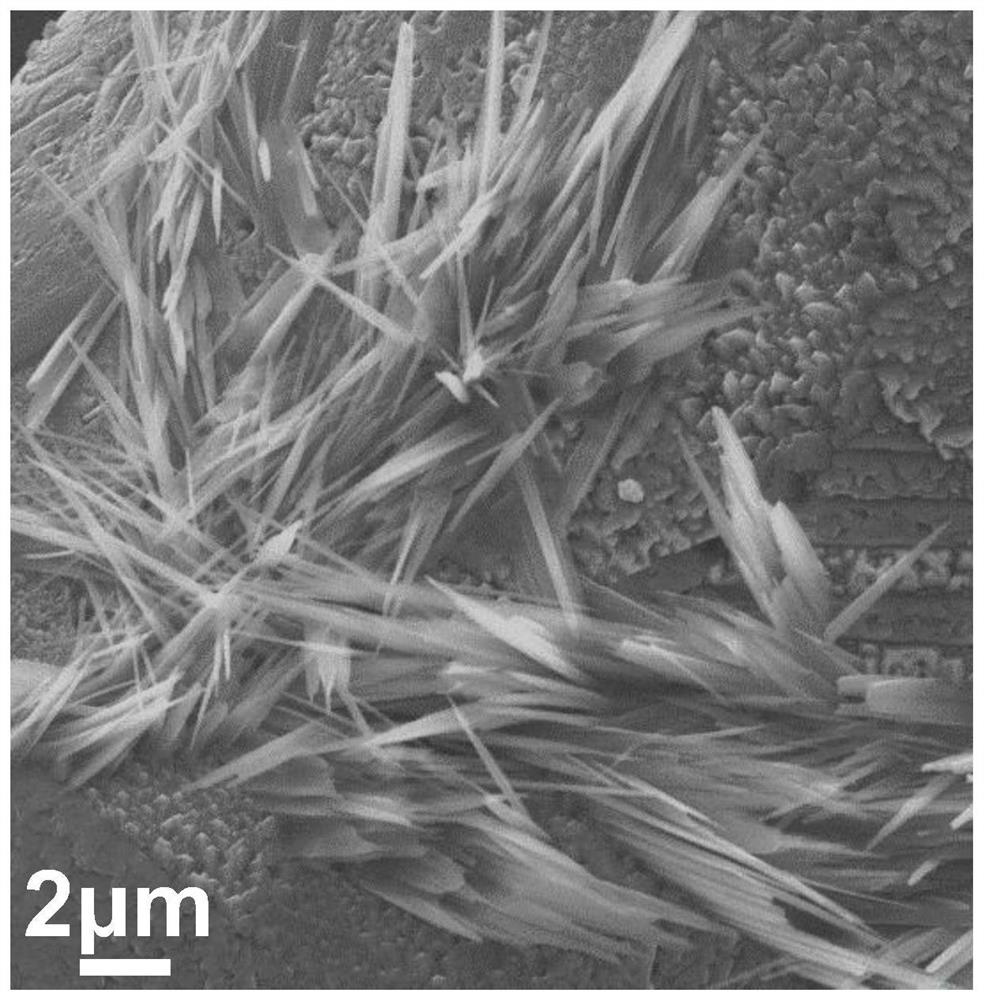
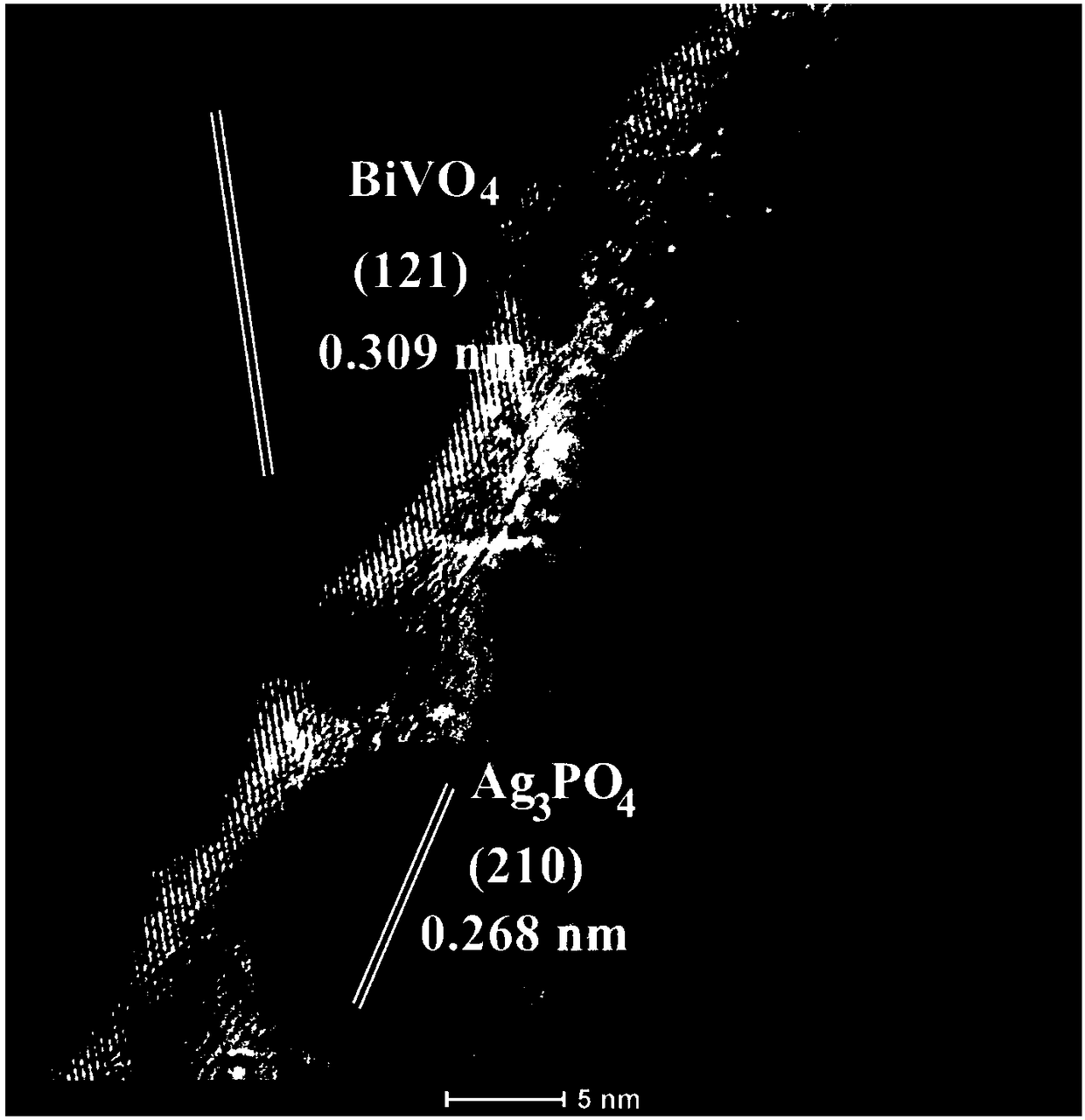
Production method of BiVO4/Ag3PO4 film for photoelectrocatalytic water decomposition
ActiveCN108355688AEasy to separateLow onset potentialPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesDecompositionBismuth vanadate
The invention discloses a production method of a BiVO4 / Ag3PO4 film for photoelectrocatalytic water decomposition, and belongs to the field of inorganic nonmetal materials. The method comprises the following steps: Step 1, preparing a bismuth vanadate seed layer precursor solution; Step 2, producing a bismuth vanadate seed layer; Step 3, producing a bismuth vanadate film; and Step 4, depositing Ag3PO4 by a three-electrode system. The BiVO4 / Ag3PO4 film produced by the method has the advantages of high photoelectric conversion efficiency, low initial potential of water photooxidation, and broad application prospects in the fields of photocatalytic degradation, photoelectrocatalytic water decomposition, artificial photosynthesis, light-assisted energy storage batteries and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
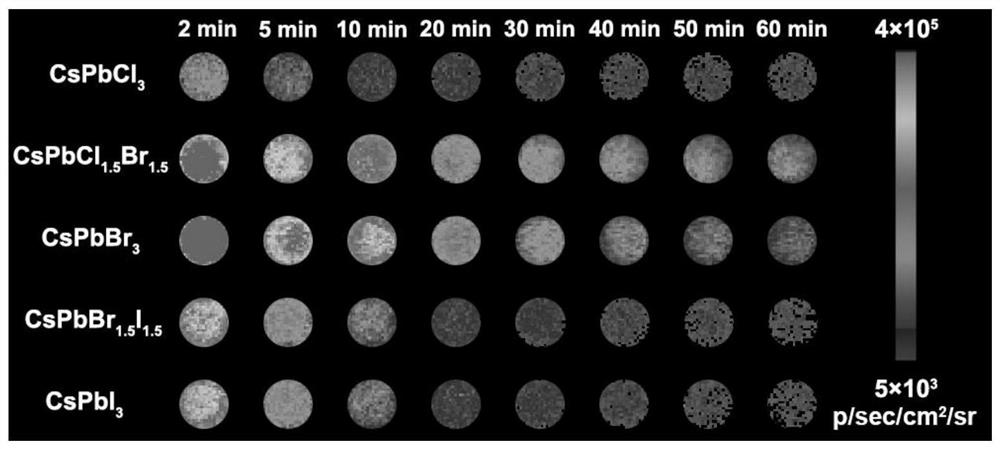
Application of metal halide perovskite CsPbX3 in photocatalytic bionic biosynthesis
ActiveCN112569971AIncrease productionEmbodies long afterglow luminous propertiesPhysical/chemical process catalystsFermentationQuantum yieldArtificial photosynthesis
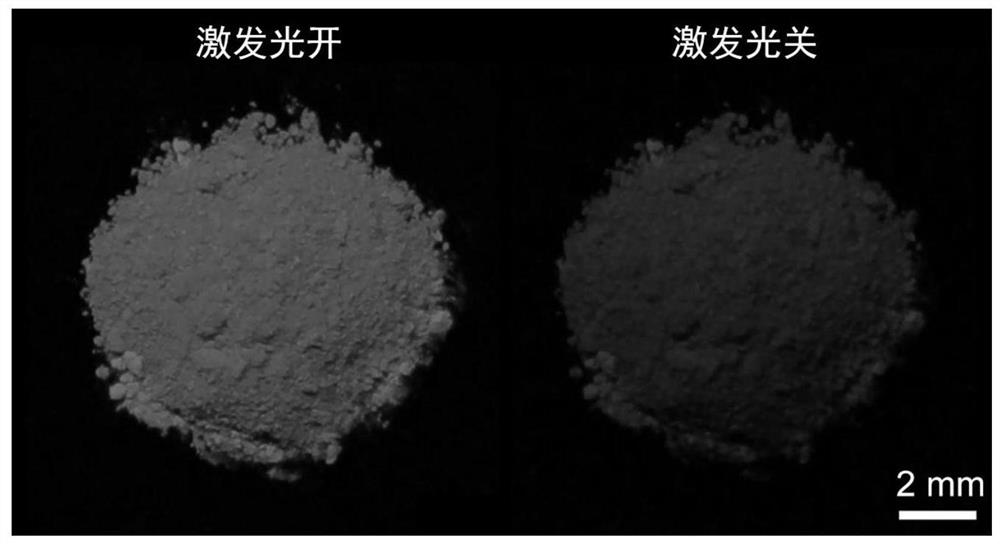
The invention relates to the technical field of luminescent materials, in particular to application of metal halide perovskite CsPbX3 in photocatalytic biomimetic synthesis, and the long afterglow luminescent property of the metal halide perovskite CsPbX3 is applied to photocatalytic biosynthesis. According to the invention, the long afterglow luminescence time of the metal halide perovskite CsPbX3 is as long as 1 h or more. The long-afterglow luminescence of the metal halide perovskite CsPbX3 is applied to photocatalytic biosynthesis, and the yield of photocatalytic biosynthesis can be increased by long-life photo-induced electrons of the perovskite. The application of the perovskite material in the aspect of energy can be expanded, and new inspiration is brought to the development of artificial photosynthesis. According to the photocatalytic biosynthesis system constructed in the invention, the light quantum yield is as high as 3.24%, and the important value of the long afterglow luminescence property of perovskite to the photocatalytic activity is embodied.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
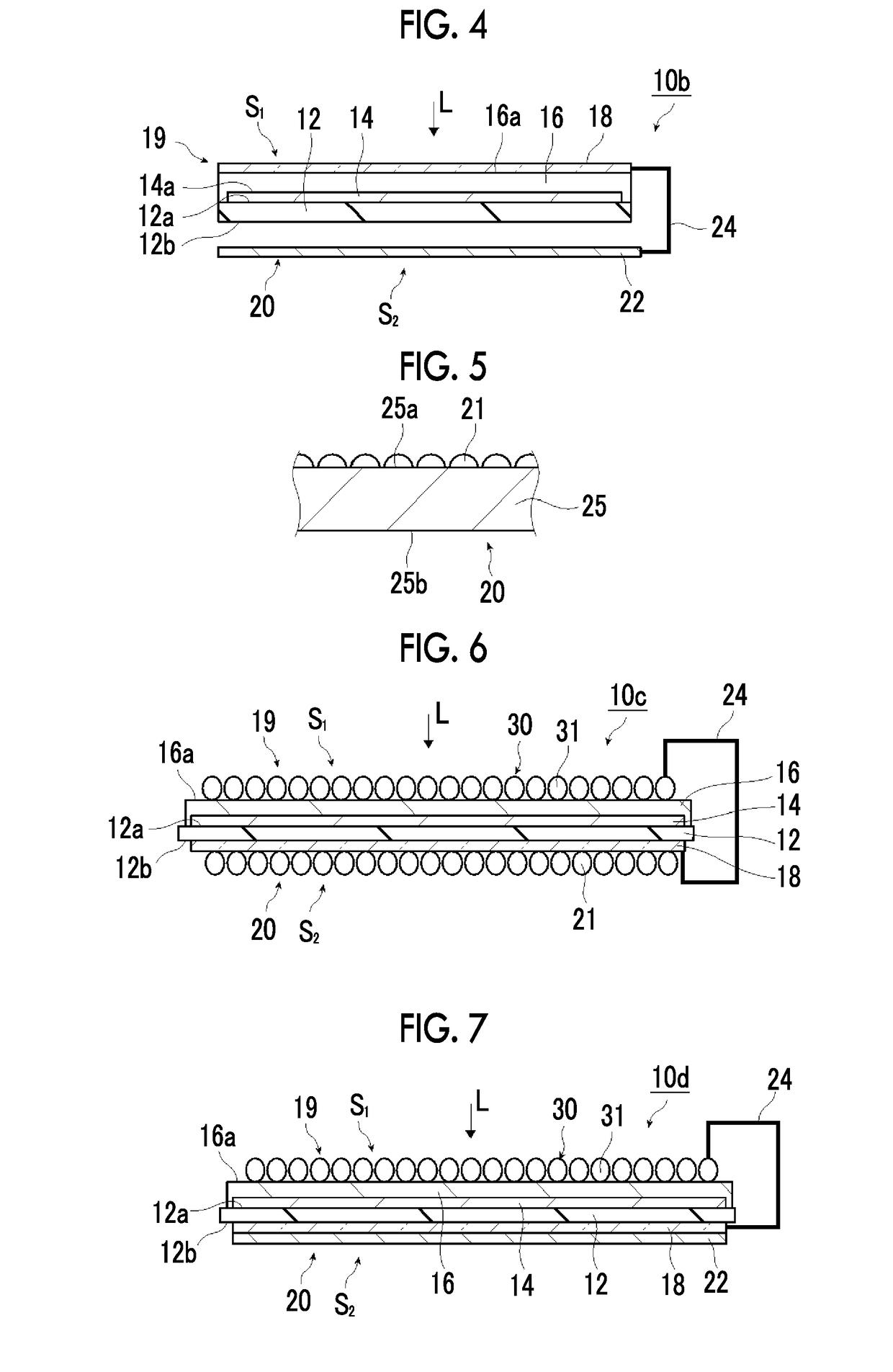
Photocatalyst electrode, artificial photosynthesis module, and artificial photosynthesis device
ActiveUS20190112721A1Improve creation efficiencyLittle resistanceCellsMultiple component coatingsHydrogenElectrical conductor
Provided are a photocatalyst electrode, an artificial photosynthesis module, and an artificial photosynthesis device that have low electrical resistance, even in a case where the area is increased, in a case where a transparent conductive layer is used. The photocatalyst electrode is a photocatalyst electrode that has a substrate, a transparent conductive layer, a photocatalyst layer, and a linear metal electrical conductor, and splits water with light to produce a gas. The substrate, the transparent conductive layer, and the photocatalyst layer are laminated in this order, and the linear metal electrical conductor is in contact with the transparent conductive layer. The artificial photosynthesis module has the oxygen evolution electrode that splits the water with the light to produce oxygen, and a hydrogen evolution electrode that splits the water with the light to produce hydrogen. The oxygen evolution electrode and the hydrogen evolution electrode are disposed in series in a traveling direction of the light. At least one of the oxygen evolution electrode or the hydrogen evolution electrode has the configuration of the above-described photocatalyst electrode. The artificial photosynthesis device has the artificial photosynthesis module, and circulates and utilizes water.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
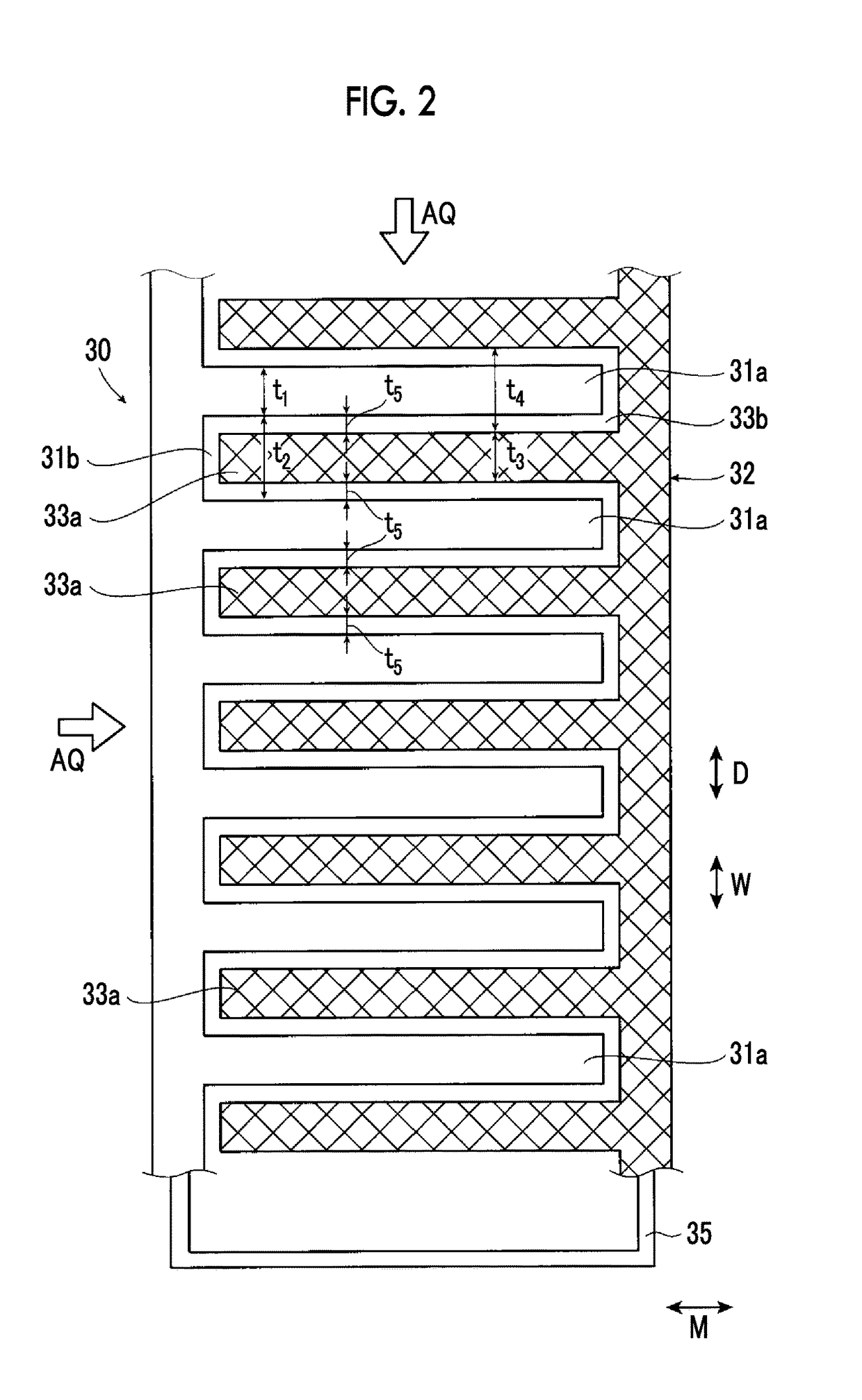
Artificial photosynthesis module
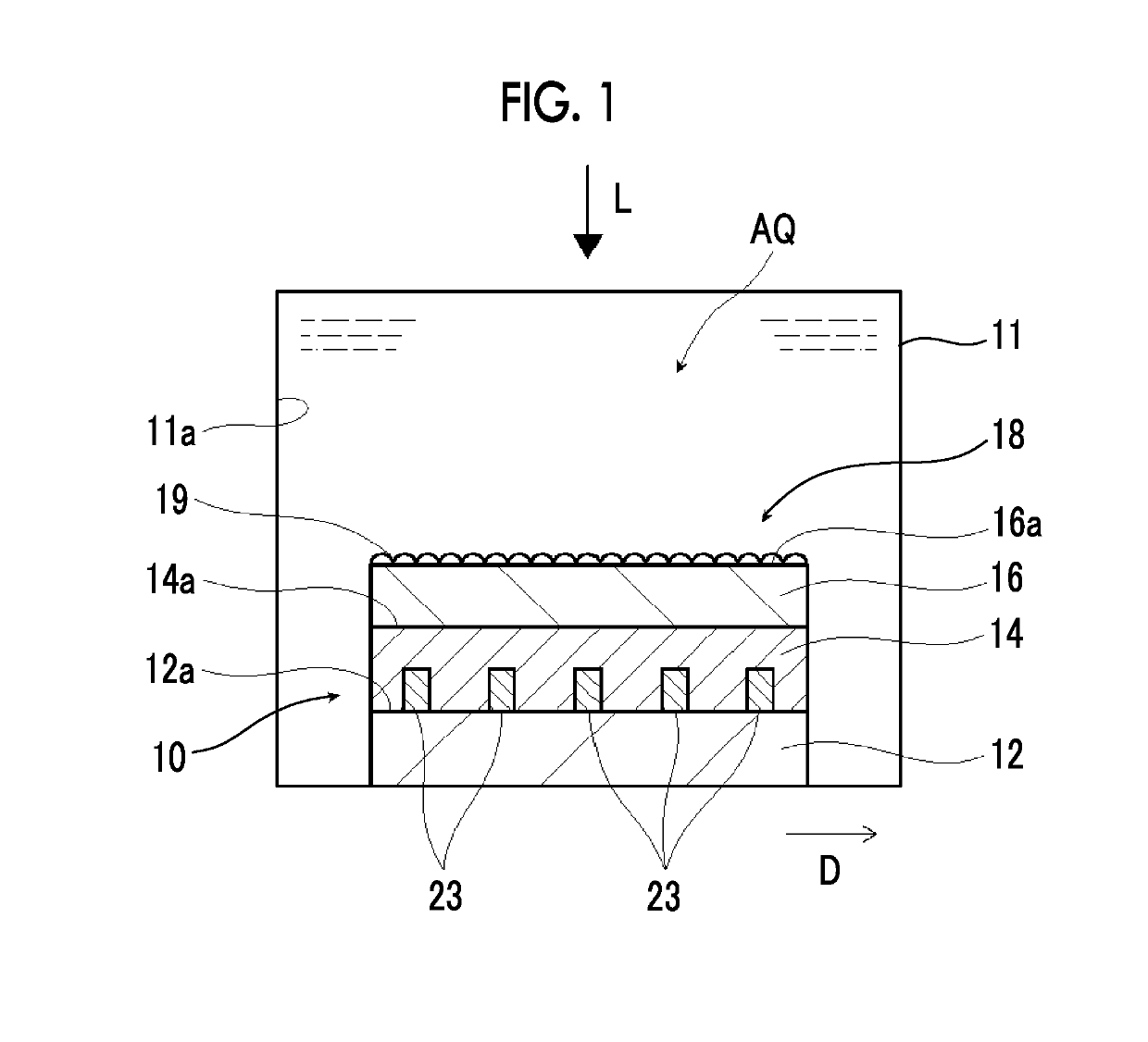
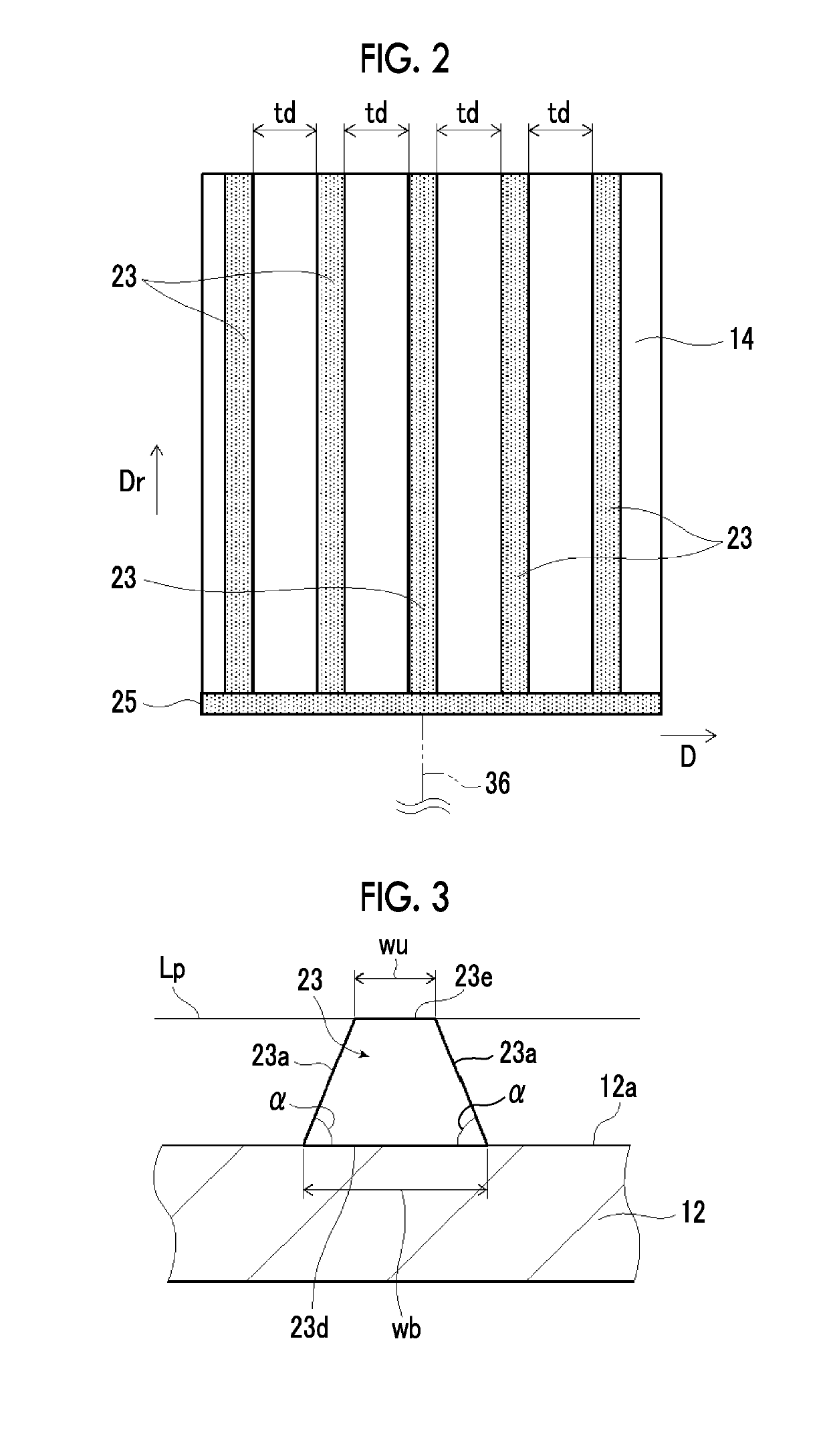
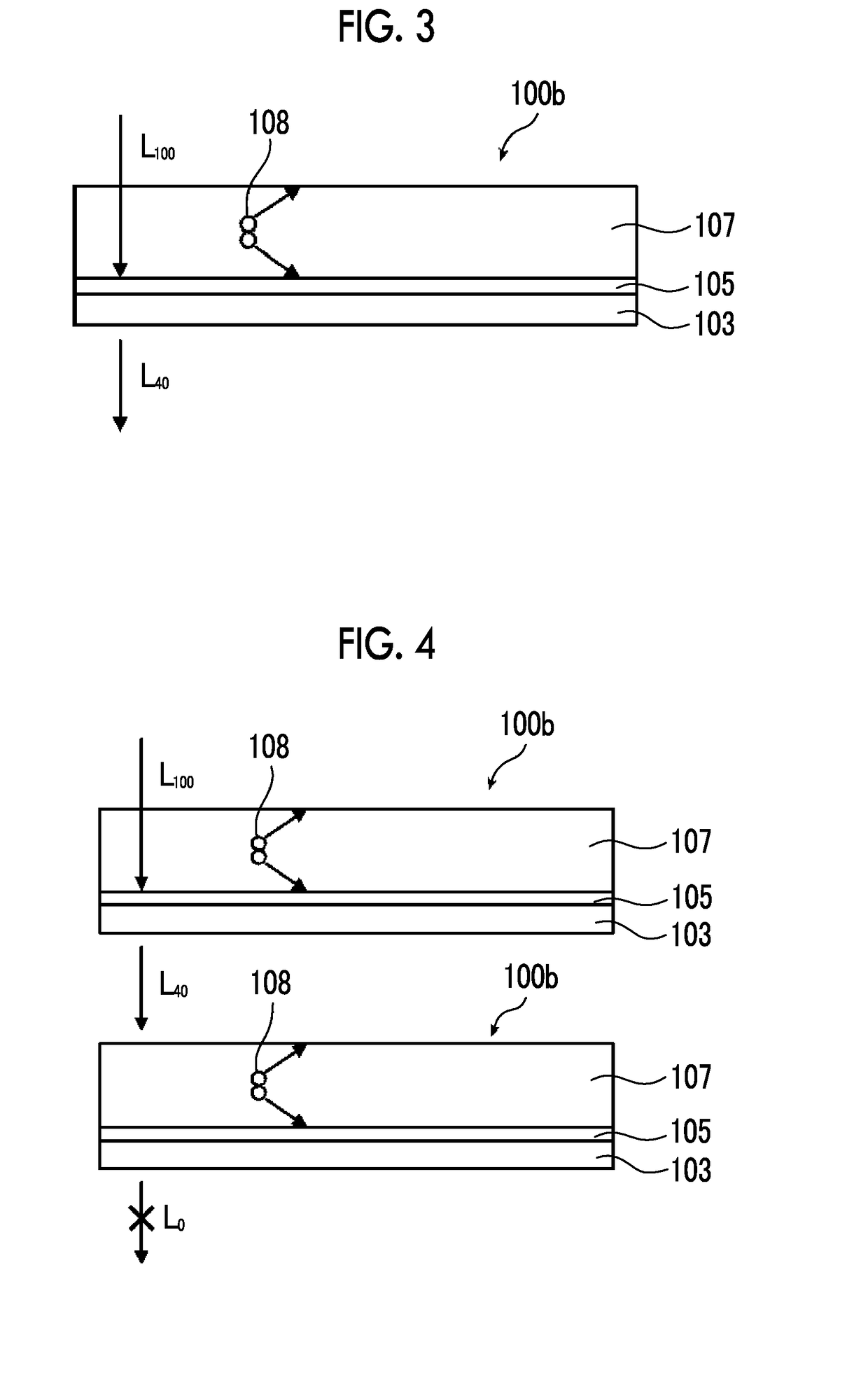
InactiveUS20170191172A1Improve electrolysis efficiencyImprove efficiencyCellsLight-sensitive devicesHydrogenDecomposition
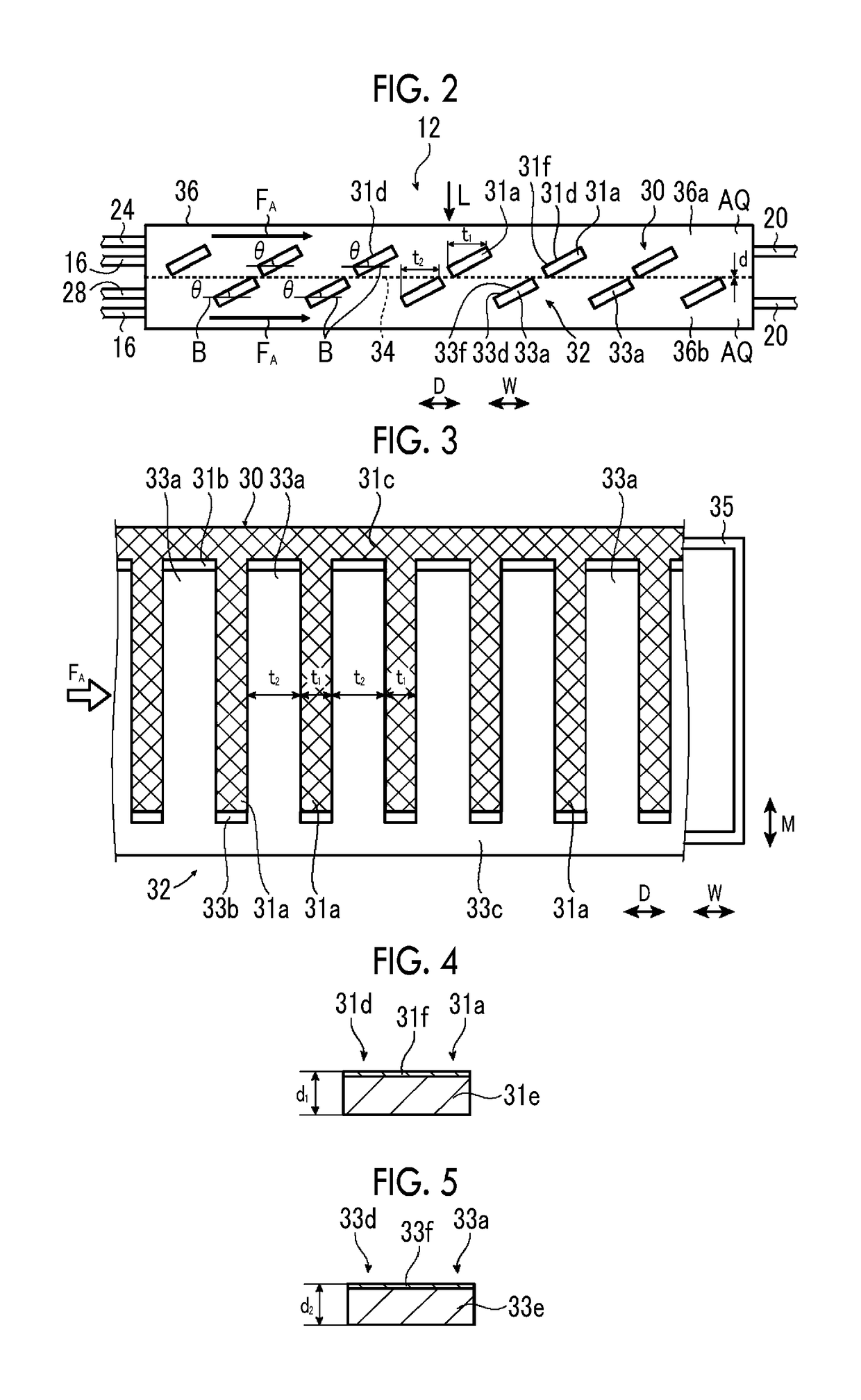
An artificial photosynthesis module is used for decomposition of an electrolytic aqueous solution into hydrogen and oxygen by light. The artificial photosynthesis module has an oxygen generation electrode having a first protrusion and a first recess alternately arranged thereon, and a hydrogen generation electrode having a second protrusion and a second recess alternately arranged thereon. The hydrogen generation electrode and the oxygen generation electrode are in contact with the electrolytic aqueous solution, and at least one electrode of the hydrogen generation electrode or the oxygen generation electrode includes a conductive layer and a photocatalyst layer provided on the conductive layer. The hydrogen generation electrode and the oxygen generation electrode are arranged side by side, the second protrusion of the oxygen generation electrode faces the first recess of the hydrogen generation electrode in an arrangement direction, and the first protrusion faces the second recess in the arrangement direction.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
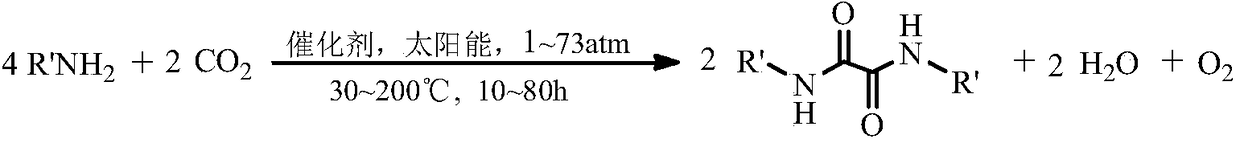
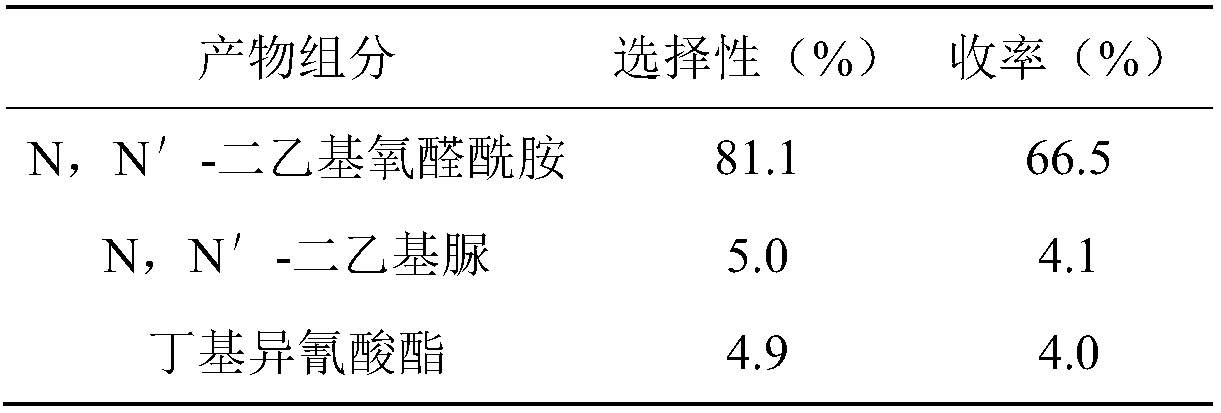
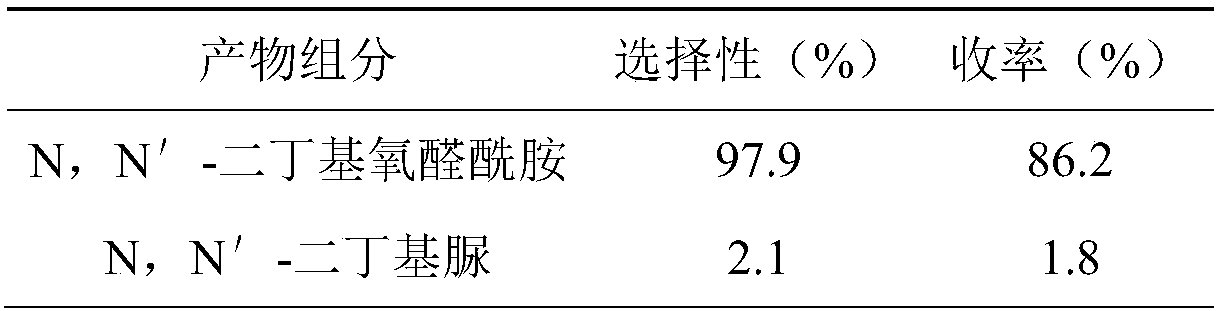
Method for synthesizing N,N'-dialkyl oxalamide by using artificial photosynthesis effect, and derivative thereof
ActiveCN108084046ARealize direct resource utilizationOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid amides preparationArtificial photosynthesisPhotochemistry
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing N,N'-dialkyl oxalamide by using an artificial photosynthesis effect, and a derivative thereof. Under a condition of existence of a catalyst, organic amine and CO2 are synthesized to obtain the N,N'-dialkyl oxalamide and the derivative thereof. The method aims to provide the method for preparing the N,N'-dialkyl oxalamide by direct recycling utilization of flue gas carbon dioxide from a coal-fired power plant.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
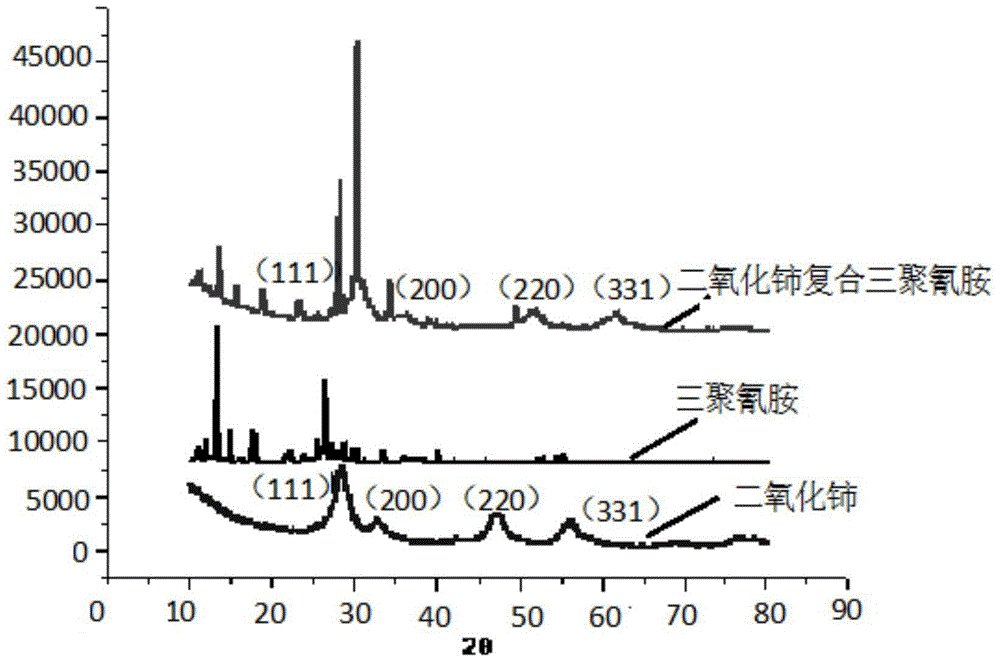
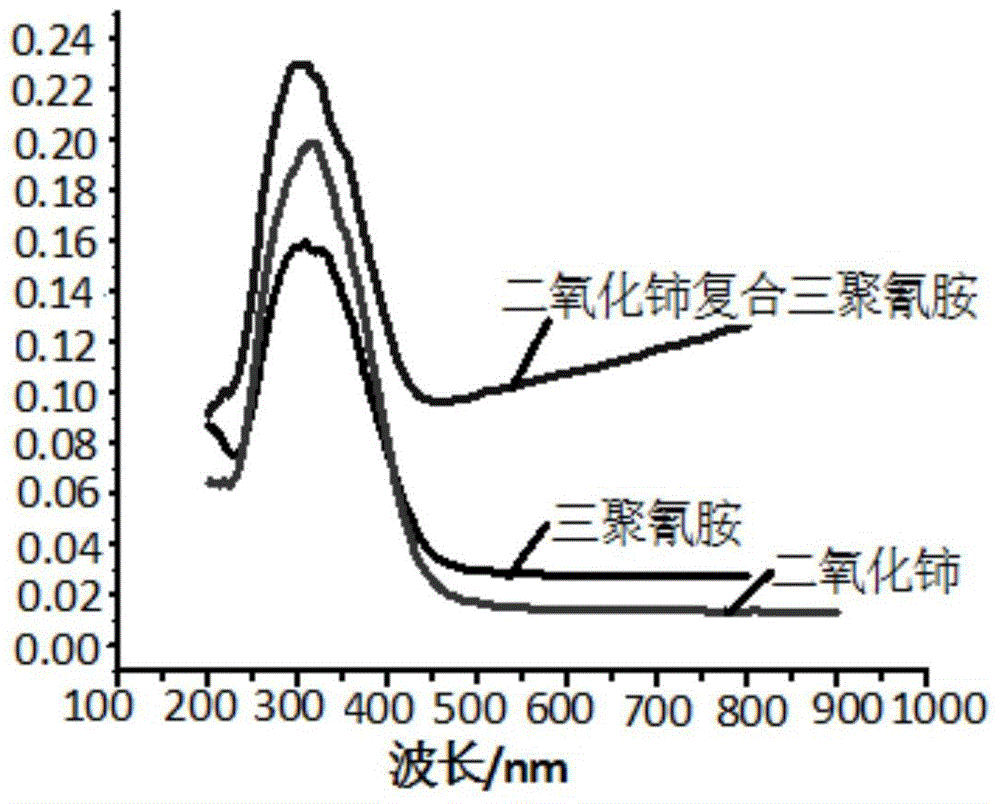
Synthetic method of biological structural carbon/cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material
InactiveCN106563436AEnhance the effect of photolysis of water to produce hydrogenReduce typesCatalyst carriersHydrogen productionAir atmosphereCerium
The invention provides a synthetic method of a biological structural carbon / cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material. The synthetic method comprises the following steps: leaf pretreatment is carried out, plant leaves are soaked in mixed liquor of dilute hydrochloric acid, absolute ethyl alcohol and distilled water, then is taken out, is cleaned with the distilled water, and is soaked in the mixed liquor of dilute hydrochloric acid, absolute ethyl alcohol and the distilled water; a cerium solution is prepared, a pretreated leaf template is soaked in the cerium solution, is taken out, is washed with the distilled water, and is dried; the treated leaf template is calcined under nitrogen atmosphere protection, then is calcined in an air atmosphere, and is subjected to natural cooling, and the biological structural carbon / cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material is obtained. The synthetic method of the biological structural carbon / cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material adopts a relatively simple chemical technology, the reaction requires no complicated equipment, the varieties of required chemical raw materials are few, the cost is low, the experiment repeatability is good, the biological structural carbon / cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material has very high photocatalysis value, a utilization ratio of visible light by the biological structural carbon / cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material can be raised substantially, the effect of photocatalytically splitting of water into hydrogen of the biological structural carbon / cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material under sunlight can be improved, and the biological structural carbon / cerium oxide artificial photosynthesis material has wide potential application value.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Gallium-nitride-based device for artificial photosynthesis and preparation method thereof
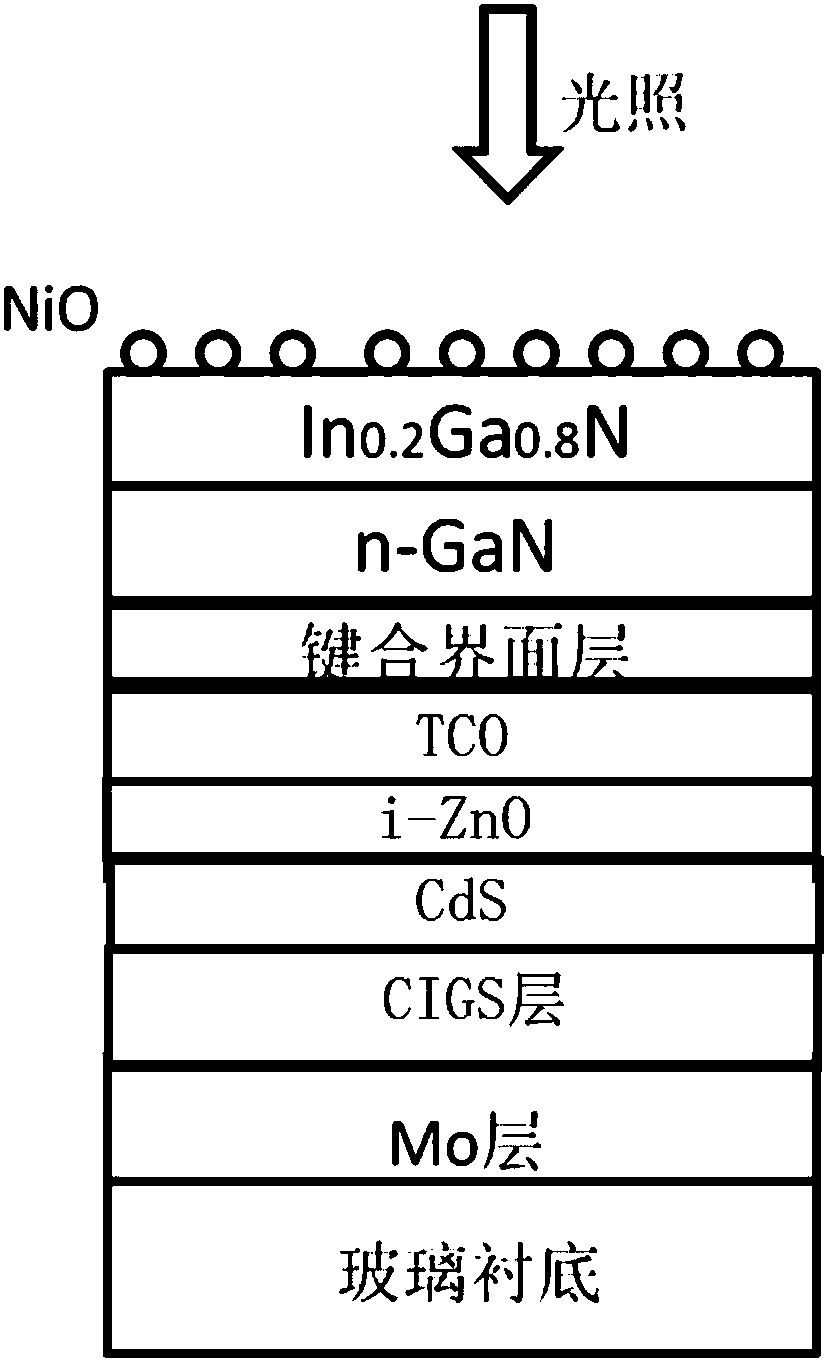
ActiveCN107845848AHigh absorption coefficientImprove stabilityMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationBond interfaceNew energy
The invention discloses a gallium-nitride-based device for artificial photosynthesis. The gallium-nitride-based device comprises a glass substrate, a molybdenum layer, a CIGS (Copper-Indium-Gallium-Selenide) layer, a CdS layer, an intrinsic ZnO layer, a TCO layer, a bonding interface layer, a GaN layer, an InGaN layer and an NiO nanoparticle layer from bottom to top. The gallium-nitride-based device is prepared by the following steps: depositing the molybdenum layer on the glass substrate, performing coevaporation to grow the CIGS layer on the molybdenum layer, then depositing the CdS layer, the ZnO layer and the TCO layer in sequence; growing the InGaN layer on the GaN substrate; bonding the GaN substrate on the TCO layer by a bonding technology, then growing the NiO nanoparticle layer onthe surface of the InGaN layer and obtaining the gallium-nitride-based device for the artificial photosynthesis. The gallium-nitride-based device disclosed by the invention has the advantages of highabsorption coefficient, easy current regulation and high stability, can be used in the artificial photosynthesis as a photoanode material and plays a very important role in reducing carbon-dioxide emission and developing and utilizing new energy.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Artificial photosynthesis system and application thereof
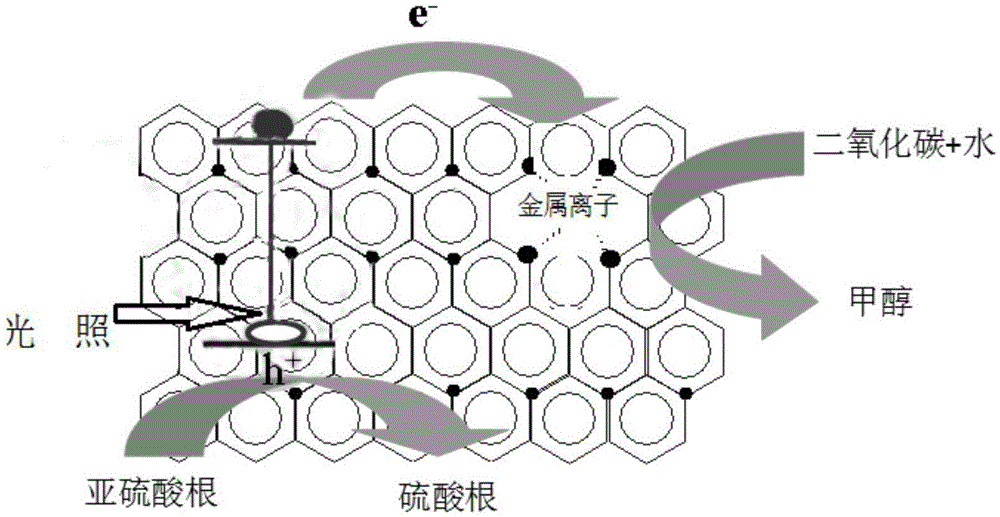
InactiveCN105728048AImprove accessibilityHigh selectivityOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsSemiconductor materialsArtificial enzyme
The invention discloses an artificial photosynthesis system and an application thereof. The artificial photosynthesis system comprises an artificial enzyme carrier, a light capture agent and an artificial enzyme, wherein the artificial enzyme comprises a coordination compound formed by metal ions and more than two nitrogen-atoms in melamine molecule in the artificial enzyme carrier. The artificial photosynthesis system contains 0.5-6wt% of melamine. The artificial photosynthesis system provided by the invention takes the melamine as the photosensitizer and the artificial enzyme carrier and the coordination compound formed between metal ions and nitrogen-atoms as the artificial enzyme, so that the selectivity of the photocatalytic reduction products to methyl alcohol is increased. The artificial photosynthesis system provided by the invention puts forward taking the semiconductor material ceric oxide coupling metal complex as the artificial enzyme for constructing a theoretical model for the artificial photosynthesis system, so that the applications of the semiconductor material CeO2 and melamine in the photocatalysis field are widened, the photocatalyst preparation process according to the invention is simple and the raw materials are low-cost and easily acquired.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Photocatalyst electrode and artificial photosynthesis module
InactiveUS20180290129A1Improve reaction efficiencyImprove efficiencyCellsCatalyst activation/preparationOptoelectronicsArtificial photosynthesis
A photocatalyst electrode decomposes water with light to generate gas. The photocatalyst electrode has a laminate including a substrate, a conductive layer provided on a surface of the substrate, and a photocatalyst layer provided on a surface of the conductive layer, and a first co-catalyst electrically connected to the photocatalyst layer. The light is incident from the surface side of the photocatalyst layer of the laminate, and in a case where a region where the light is incident on the surface of the photocatalyst layer and above the surface is defined as a first region and the region other than the first region is defined as a second region, the first co-catalyst is provided at least in the second region. The first co-catalyst and the photocatalyst layer are electrically connected to each other by at least one of a transparent conductive layer provided on the surface of the photocatalyst layer or a wiring line.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
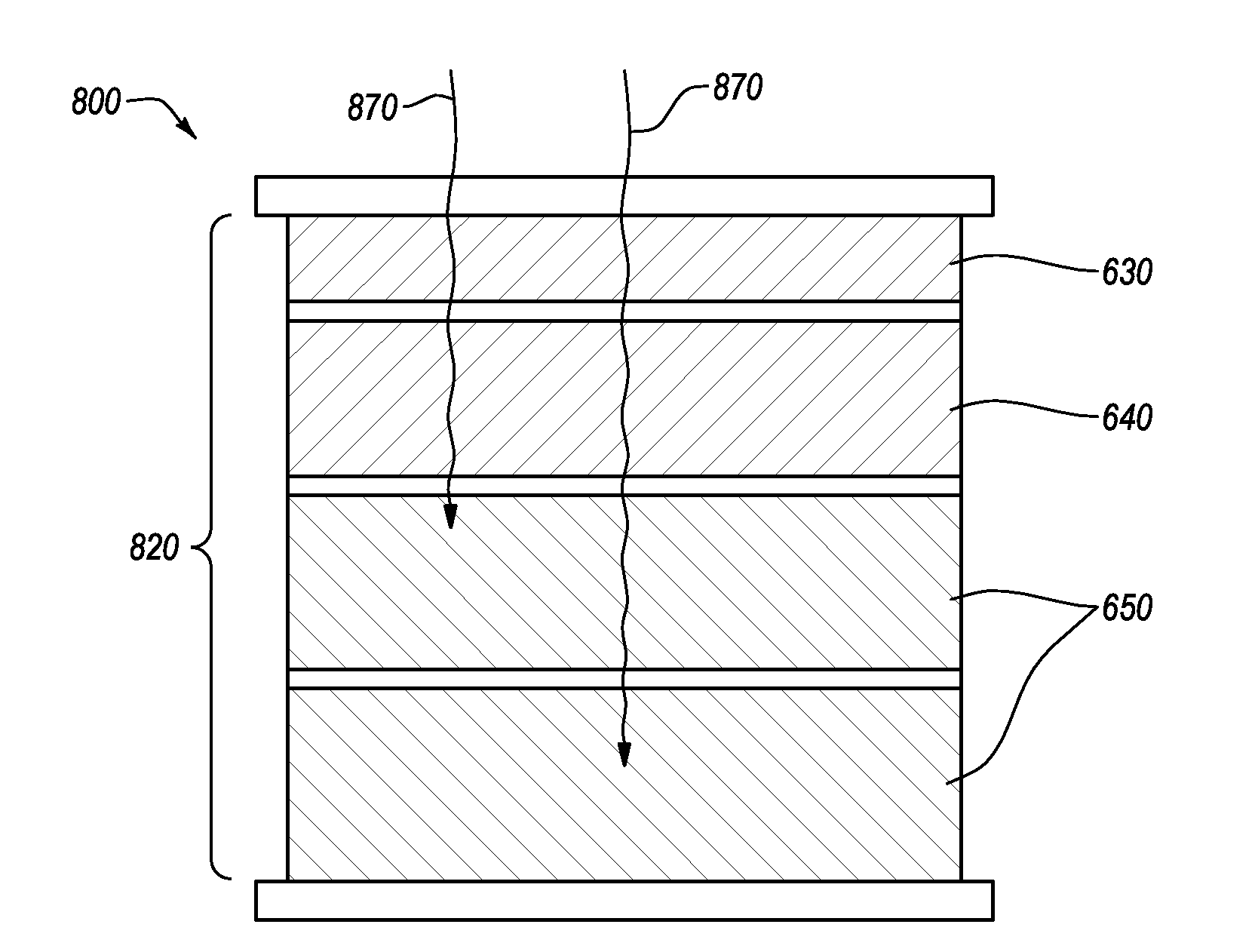
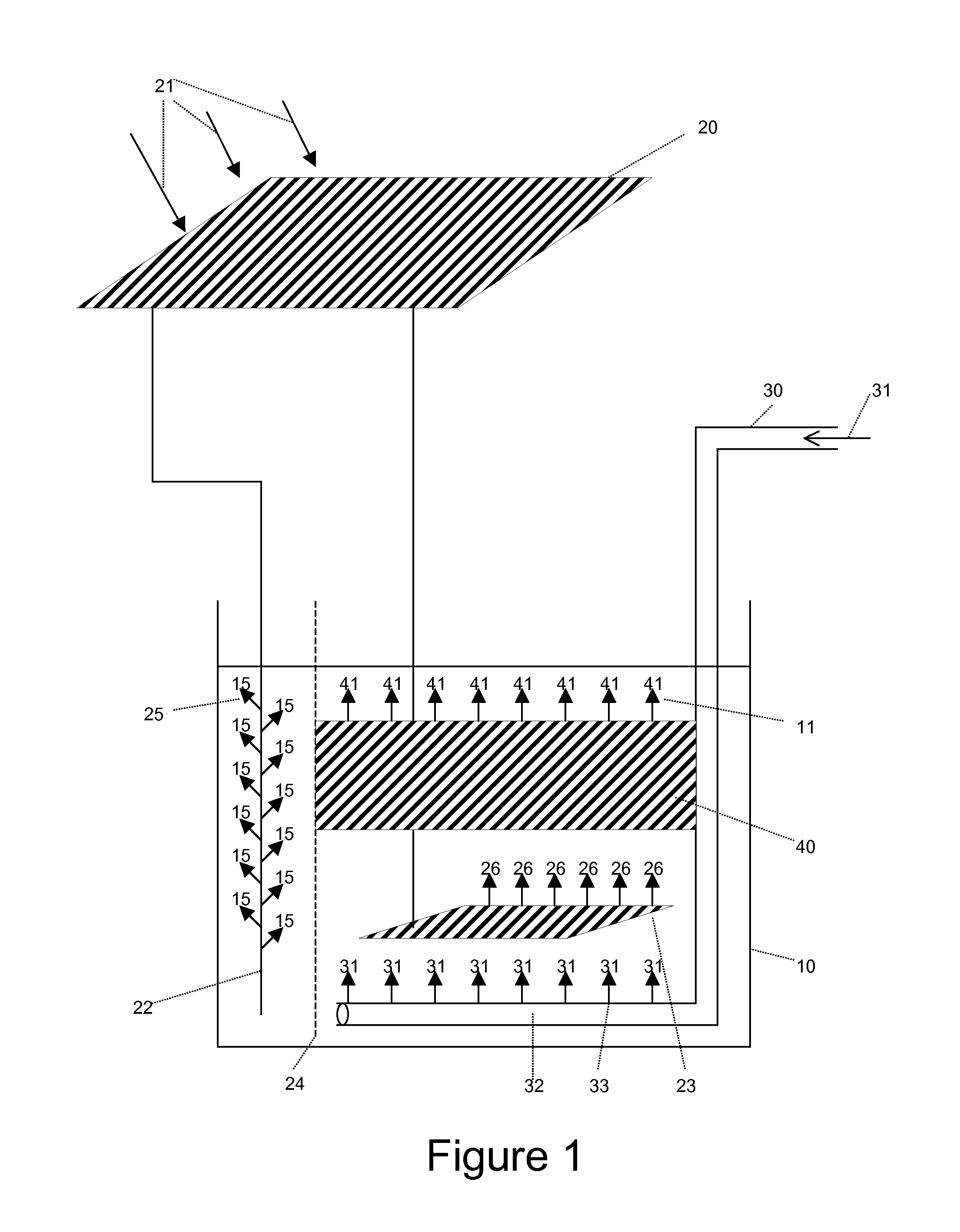
Multi-junction artificial photosynthetic cell with enhanced photovoltages
ActiveUS20160076154A1Sufficient energyEfficient and stable mannerCellsLight-sensitive devicesSchottky barrierRedox
A multi-junction artificial photosynthetic unit includes an active element with a plurality of semiconducting layers, with metal layers deposited between the semiconductor layers appropriately forming Schottky barrier junctions or ohmic junctions with a surface of an adjacent semiconductor layer. The active element is formed within a protective structure formed of porous aluminum oxide. Successive layers of the active element can be formed within the protective structure, and additional layers and junctions can be added until desired photovoltages are achieved. A photoreactor for the production of fuels and chemicals driven by solar-powered redox reactions includes a bag reactor filled with a feedstock solution. A plurality of multi-junction photosynthetic units are placed in the feedstock solution to drive the redox reactions and produce the desired fuels and chemicals.
Owner:HYPERSOLAR +1
Artificial photosynthesis
Disclosed is a process for storing solar energy in organic compounds. The process comprises providing a water source and a carbon source. Water present in the water source is activated using solar energy. Activated water is reacted with the carbon source to form an organic compound comprising hydrogen and carbon. The organic compound has higher energy content than the carbon source.In a specific embodiment the organic compound is used as a fuel in an electricity-generating device, such as a fuel cell. In this embodiment the preferred organic compound is methanol.
Owner:CLIMEWORKS
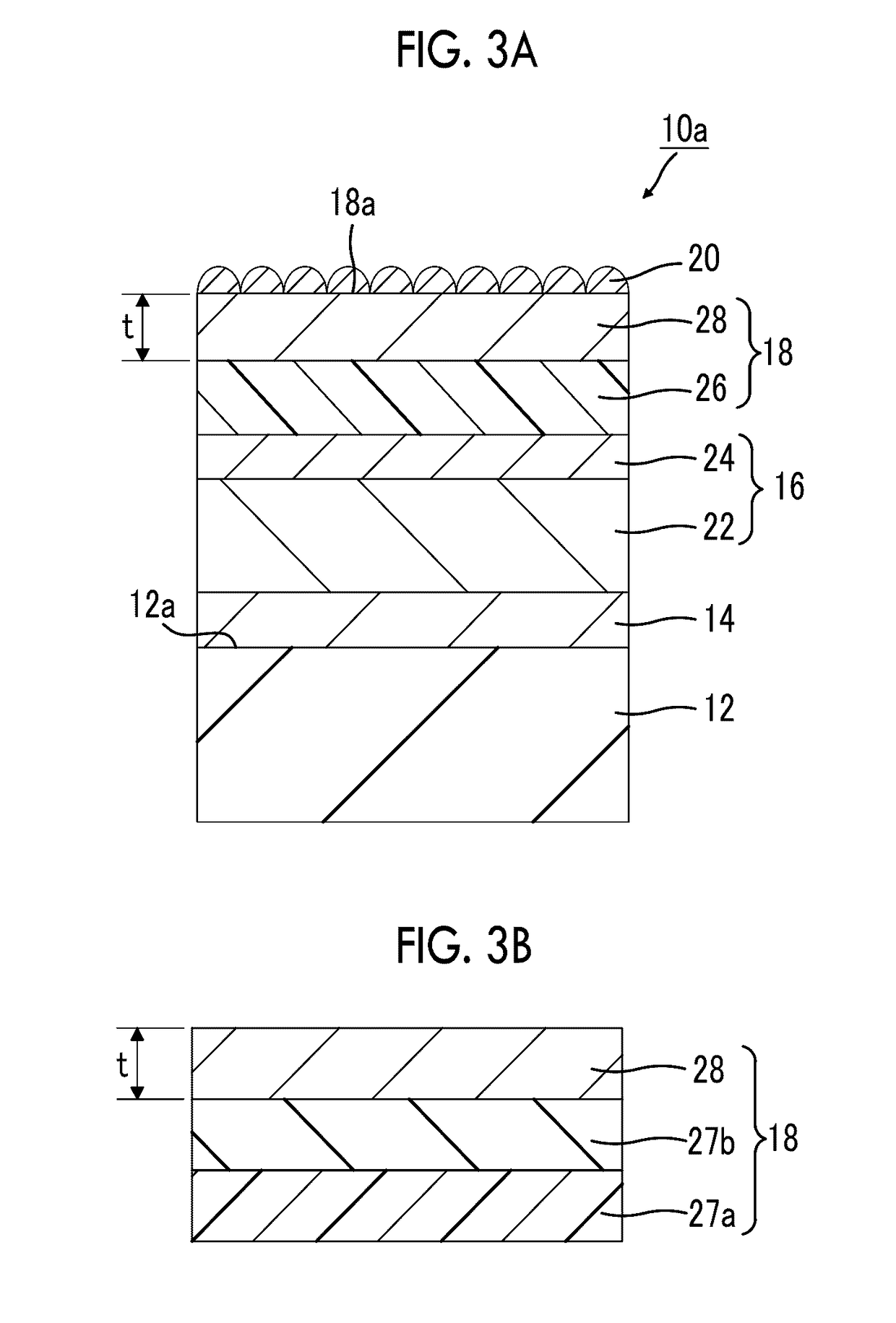
Artificial photosynthesis module
InactiveUS20180258542A1Improve energy conversion efficiencyExcellent onset potentialCellsElectrode with substrate and coatingHydrogenEngineering
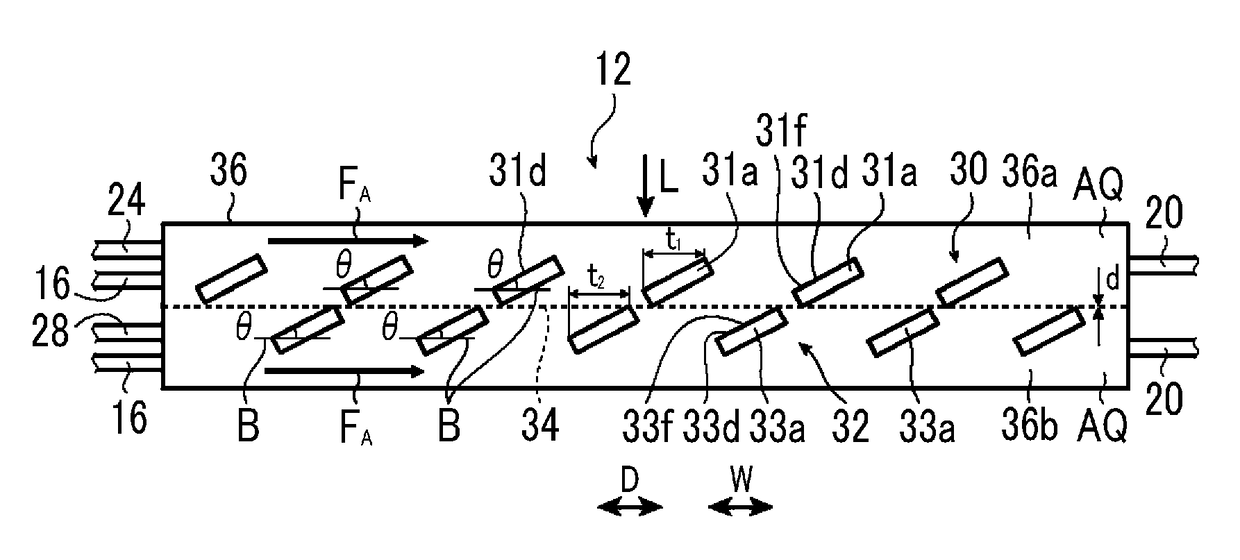
In an artificial photosynthesis module, a plurality of first electrode portions of a hydrogen generation electrode are disposed side by side with a gap, and each of a plurality of second electrode portions of an oxygen generation electrode is disposed at a gap between the first electrode portions of the hydrogen generation electrode as seen from the hydrogen generation electrode side with respect to the diaphragm. A first photocatalyst layer of at least one first electrode portion of the hydrogen generation electrode or a second photocatalyst layer of at least one of the second electrode portions of the oxygen generation electrode is tilted with respect to a flow direction of an electrolytic aqueous solution, or a projecting part is provided on a surface of the first photocatalyst layer of at least one first electrode portion of the hydrogen generation electrode or a surface of the second photocatalyst layer of at least one second electrode portion of the oxygen generation electrode.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Artificial photosynthesis module
ActiveUS20180361363A1Improve reaction efficiencyImprove efficiencyCellsOxygen/ozone/oxide/hydroxideHydrogenOptoelectronics
An artificial photosynthesis module includes an oxygen generation electrode having a first photocatalyst layer that decomposes water with light to generate oxygen, and has a first substrate, a first conductive layer, a first photocatalyst layer, and a first co-catalyst, and a hydrogen generation electrode that decomposes water with light to generate hydrogen and has a second substrate, a second conductive layer, a second photocatalyst layer, and a second co-catalyst. This provides an artificial photosynthesis module with high reaction efficiency.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
Carbon nitride composite material and preparation method and application thereof in artificial photosynthesis
PendingCN113663723AEasy to prepareRaw materials are easy to getOrganic compound preparationOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCarbon compositesCharge carrier mobility
The invention relates to a carbon nitride composite material and a preparation method and application thereof in photosynthesis, and belongs to the technical field of environment and new energy materials. calcining a carbon-nitrogen compound twice to generate a graphite-phase carbon nitride nanosheet; and fully grinding the graphite-phase carbon nitride nanosheet and diimine pyromellitic acid, and calcining in inert gas to generate the diimine pyromellitic acid / graphite-phase carbon nitride composite material. The diimine phthalate / graphite-phase carbon nitride composite material disclosed by the invention is combined with the biological enzyme, and due to excellent visible light responsiveness, high carrier mobility, relatively high visible light utilization efficiency and specificity of the biological enzyme, the efficiency of catalytic production of formic acid is high, the product selectivity is good, and the material has a wide application prospect in the aspect of producing clean energy in artificial photosynthesis.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for preparing ordered mesoporous strontium titanate
The invention discloses a method for preparing ordered mesoporous strontium titanate. The method comprises the following steps: dissolving a nonionic surfactant, phenol-formaldehyde resin, tetrabutyl titanate, strontium acetate and concentrated hydrochloric acid in ethanol, carrying out stirring so as to obtain an orange solution, then, transferring the orange solution into a flat-bottomed vessel, carrying out solvent-induced self-assembly for at least 24 hours, and then, carrying out thermal polymerization for at least 12 hours at the temperature of 80 DEG C to 100 DEG C so as to form an orange film; and then, carrying out high-temperature heat treatment sequentially in an inert atmosphere and an air atmosphere, thereby obtaining a white ordered mesoporous strontium titanate film. The product prepared by the method is large in specific surface area, uniform in pore passage and high in orderliness and has a broad application prospect in the fields of photocatalytic degradation, photoelectrocatalytic water decomposition, artificial photosynthesis, photo-assisted energy storage batteries and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Preparation method of zinc indium sulfide nanosheet array film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a ZnIn2S4 nanosheet array film. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, depositing a layer of In2S3 nano film on FTO conductive glass by utilizing a chemical method; then sputtering a layer of zinc on the surface; finally, taking an indium source and a sulfide source as precursors, and controlling the heat reaction temperature and time ofa solvent to obtain a ZnIn2S4 nanosheet array. The prepared ZnIn2S4 nanosheet is of an ultrathin structure and is 5-6nm in thickness; the ZnIn2S4 nanosheet has high crystallizing performance, high trapping performance, recyclable performance and other outstanding properties; in addition, the method is simple in preparation; the process is easily controlled; the cost is low; the method is nontoxicand environmentally friendly and has huge application prospects in the fields such as the fields of photocatalytic hydrogen generation, organic pollutant photocatalytic degradation and artificial photosynthesis.
Owner:SHANGHAI NAT ENG RES CENT FORNANOTECH
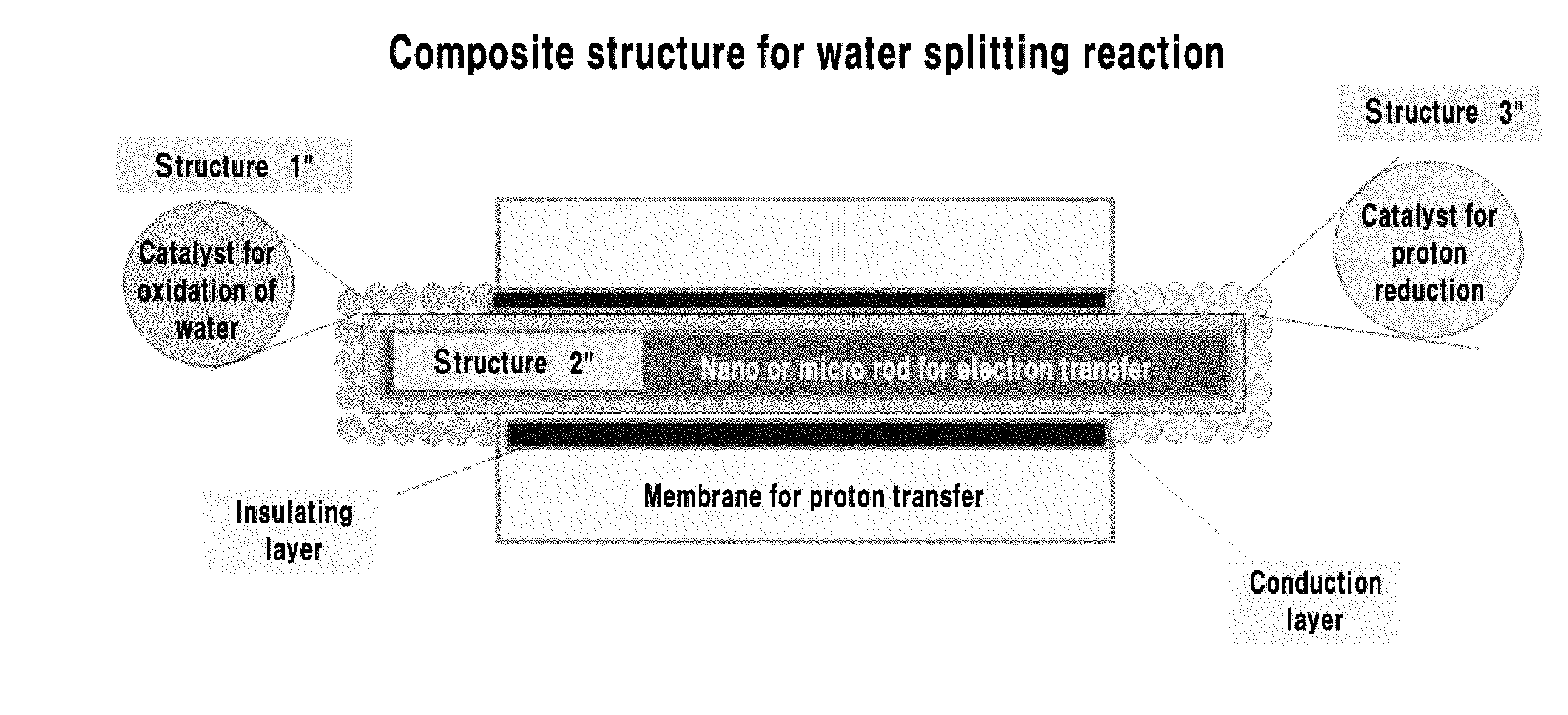
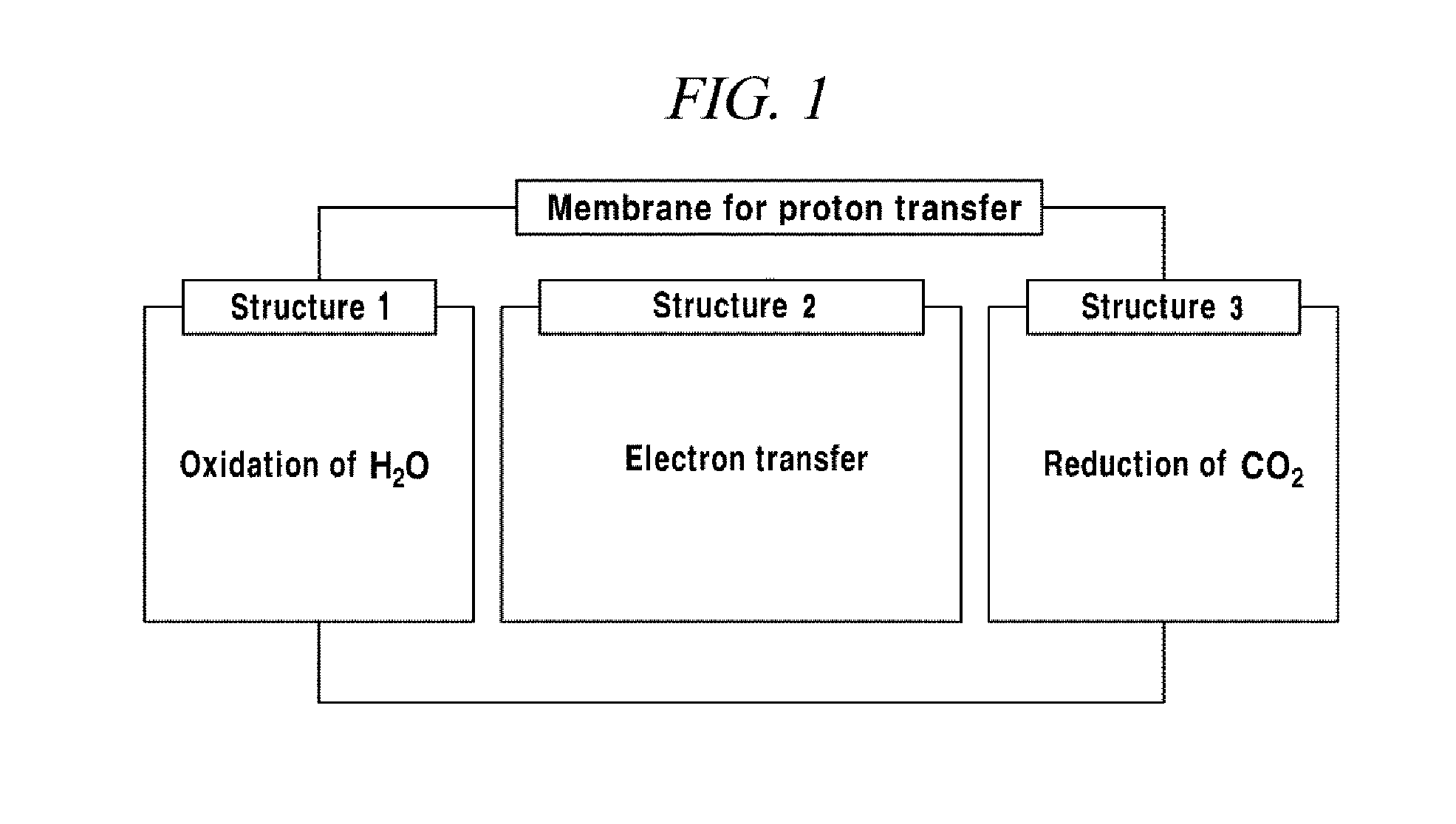
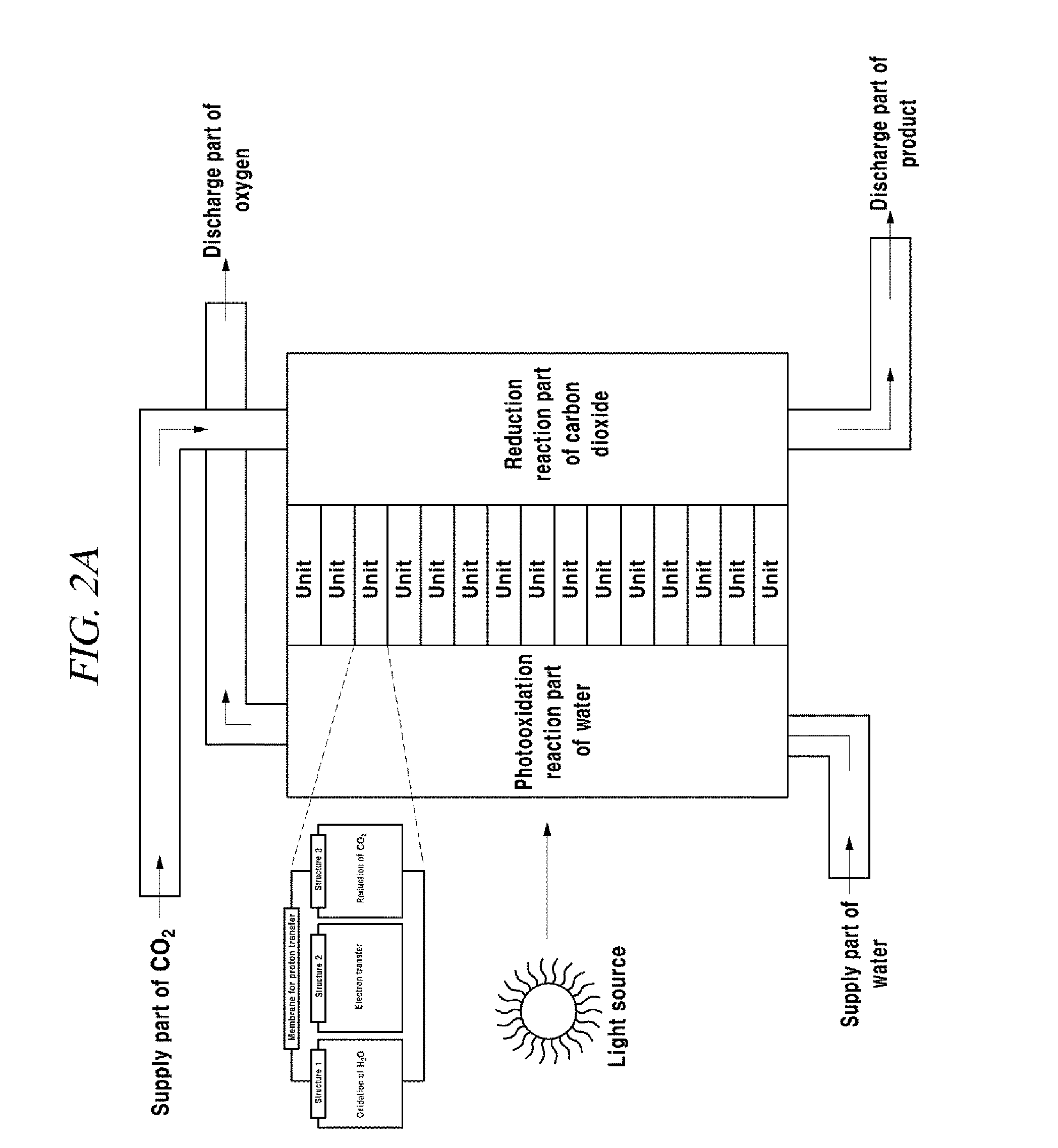
Composite structure for an artificial photosynthesis reaction and integrated reaction device for artificial photosynthesis including same, and composite structure for a water splitting reaction and integrated reaction device for water splitting including same
ActiveUS20140120000A1Improve energy efficiencyProductsHydrocarbon from carbon oxidesArtificial photosynthesisChemistry
The present disclosure relates to a novel composite structure for artificial photosynthesis reaction and an integrated reaction device for artificial photosynthesis including the same, and a novel composite structure for water splitting reaction and an integrated reaction device for water splitting including the same.
Owner:SOGANG UNIV RES FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com