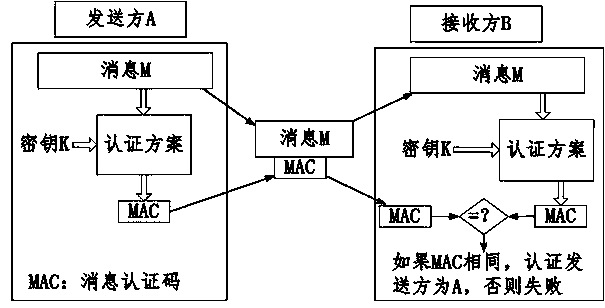
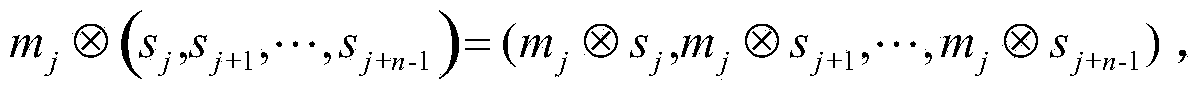Patents
Literature
213 results about "Quantum cryptography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
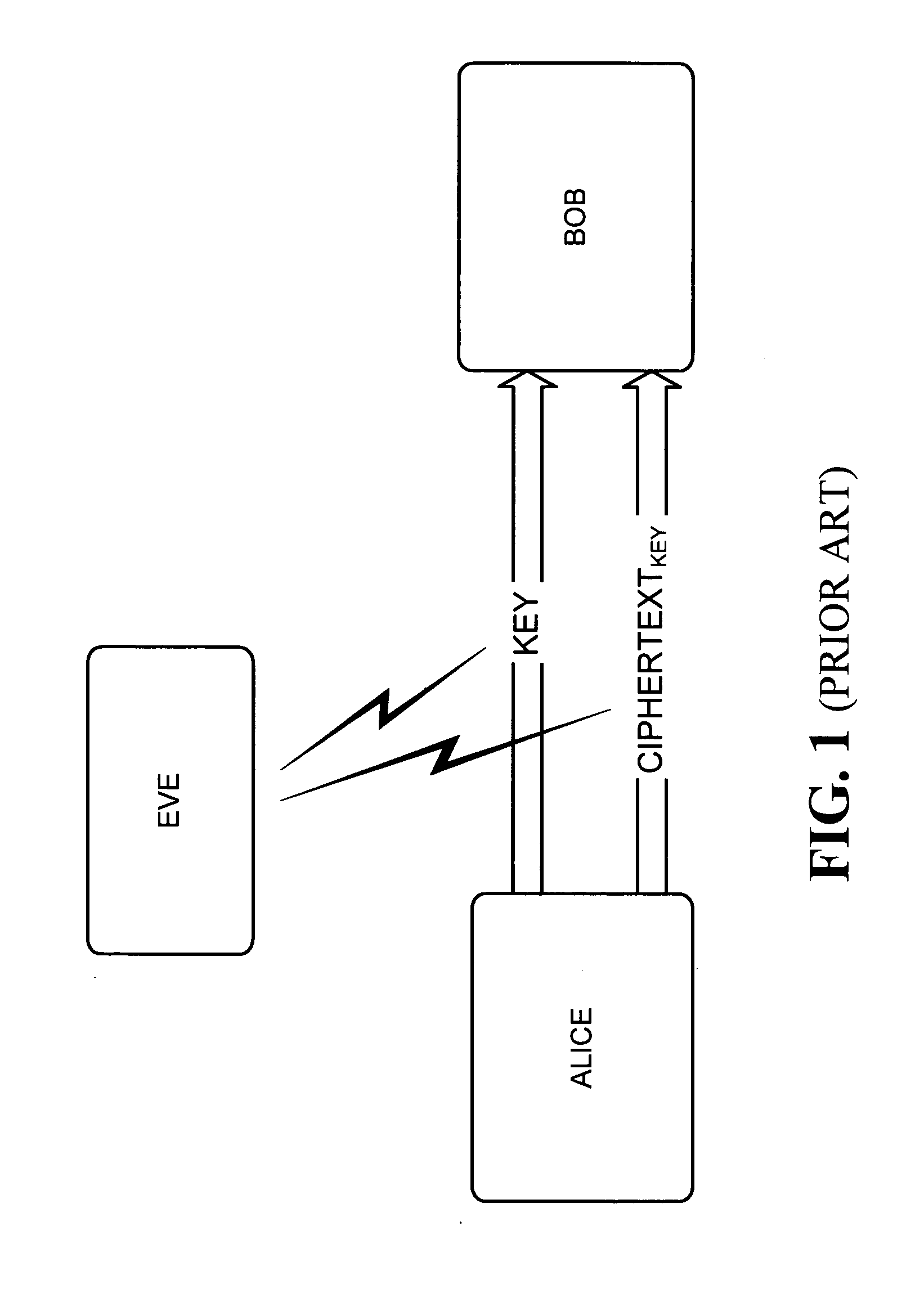
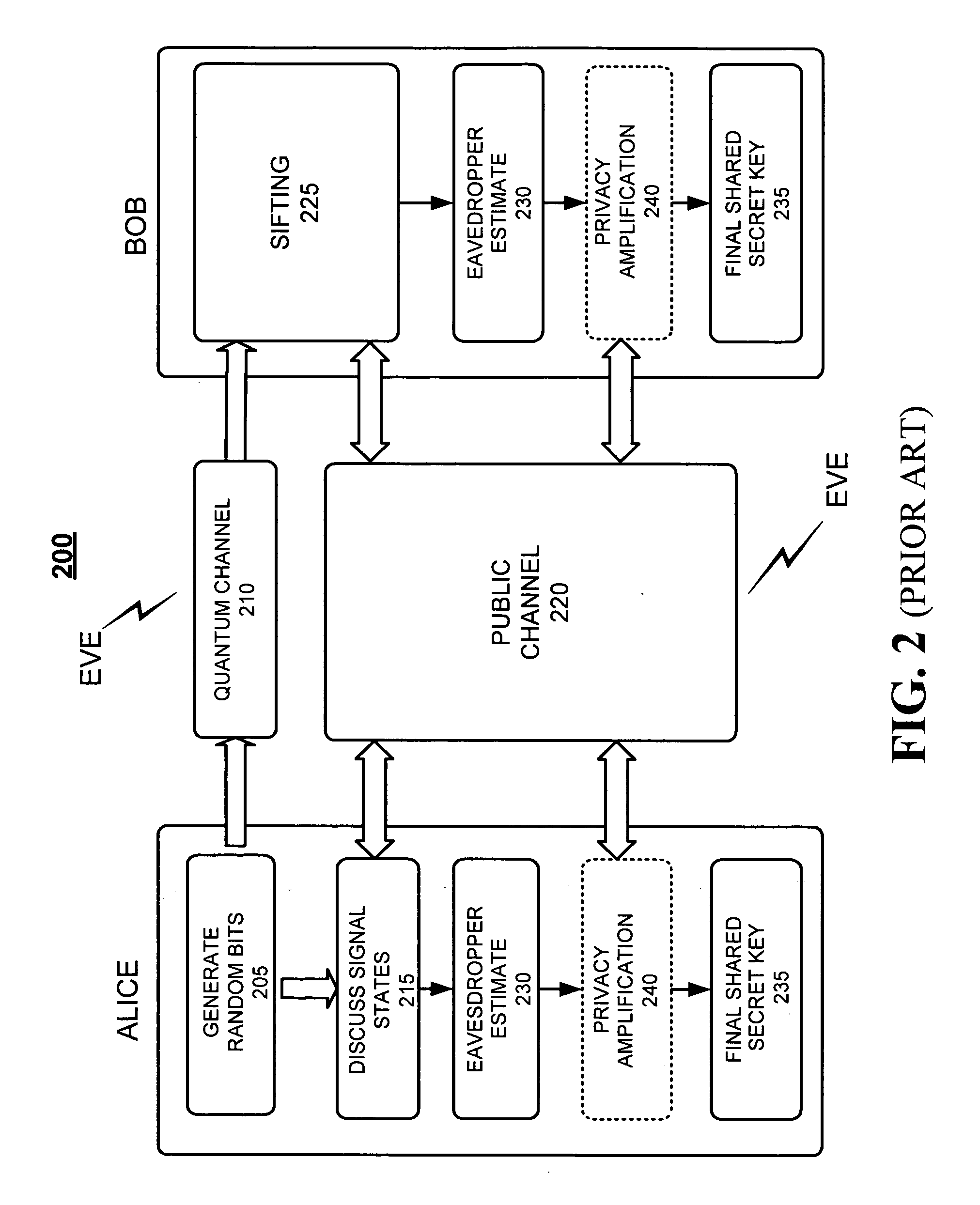
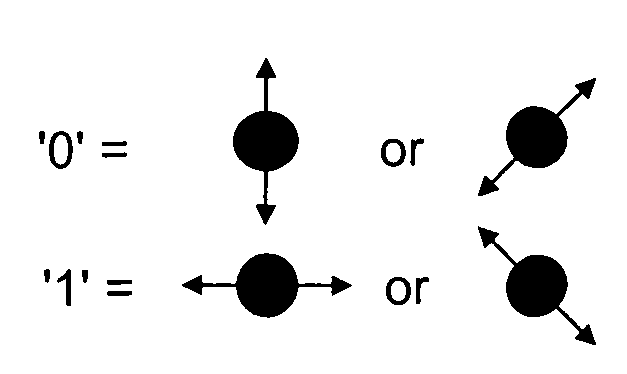
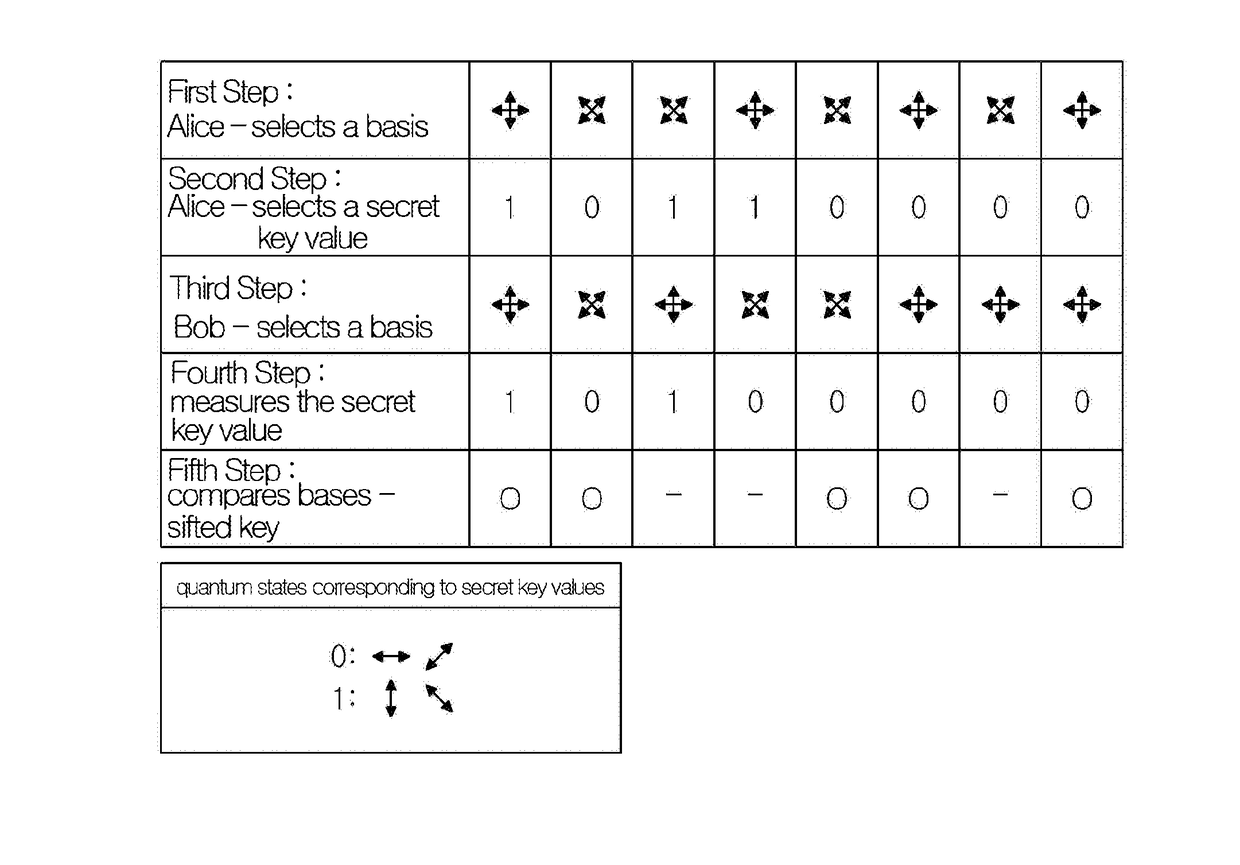
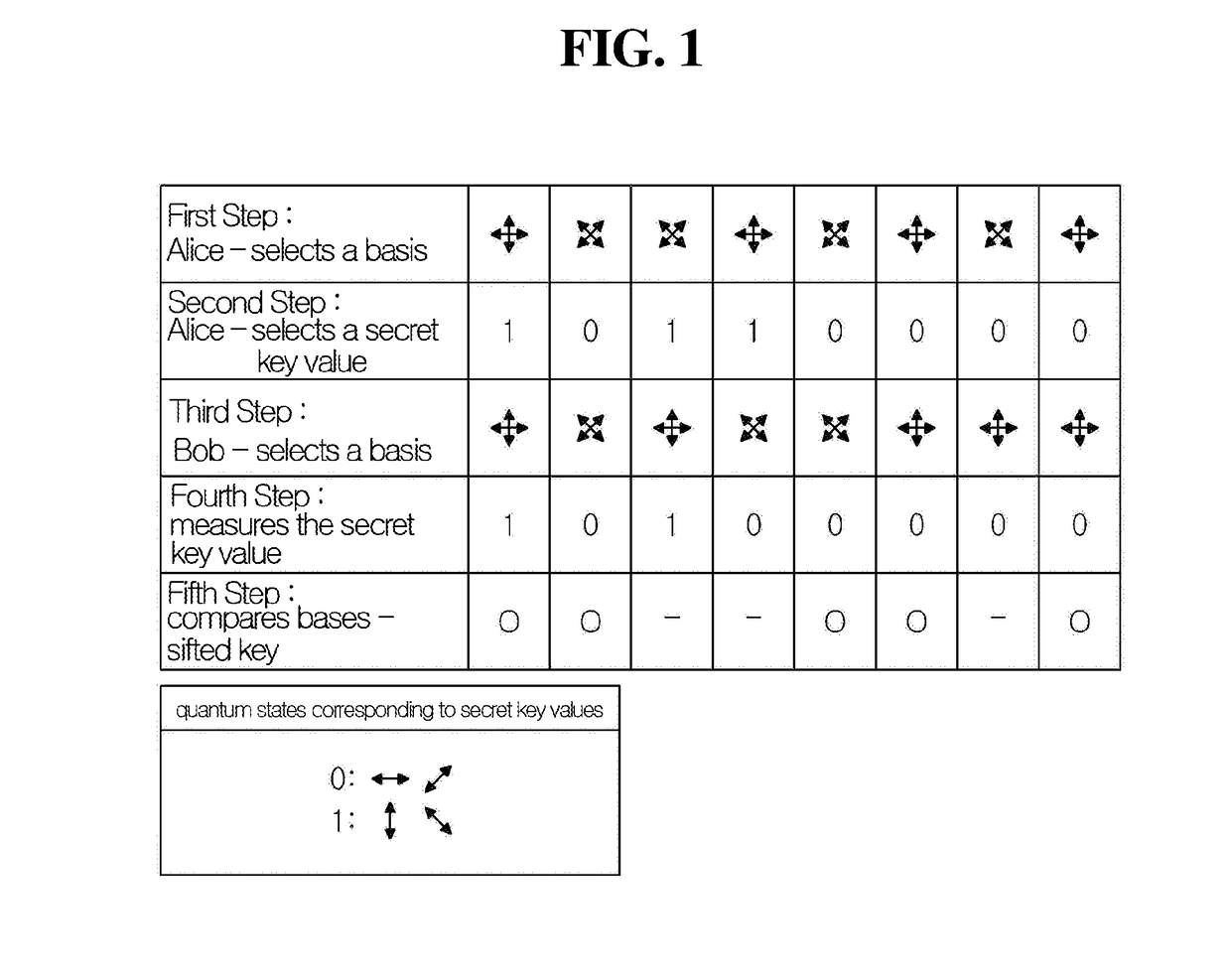
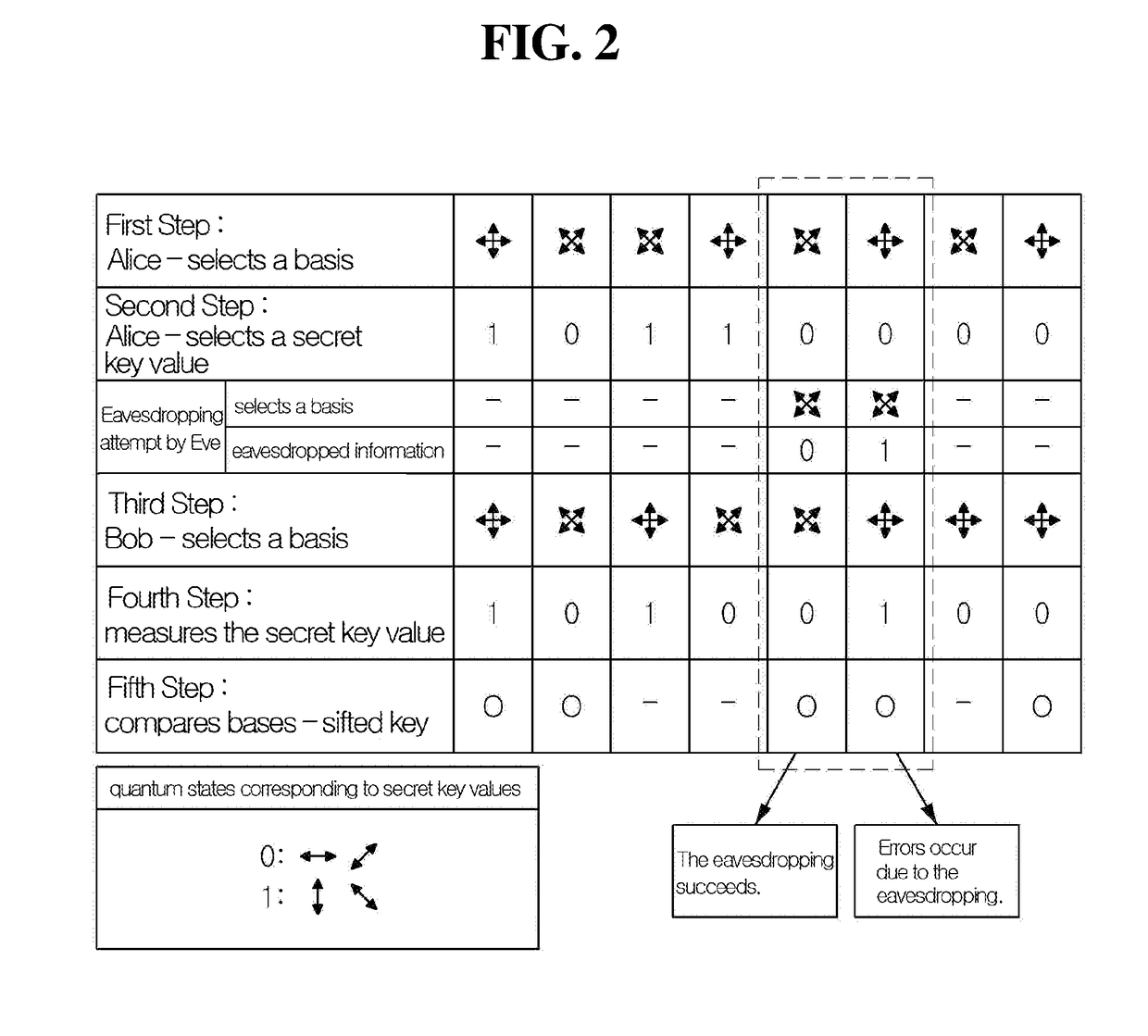
Quantum cryptography is the science of exploiting quantum mechanical properties to perform cryptographic tasks. The best known example of quantum cryptography is quantum key distribution which offers an information-theoretically secure solution to the key exchange problem. The advantage of quantum cryptography lies in the fact that it allows the completion of various cryptographic tasks that are proven or conjectured to be impossible using only classical (i.e. non-quantum) communication. For example, it is impossible to copy data encoded in a quantum state. If one attempts to read the encoded data, the quantum state will be changed (no-cloning theorem). This could be used to detect eavesdropping in quantum key distribution.
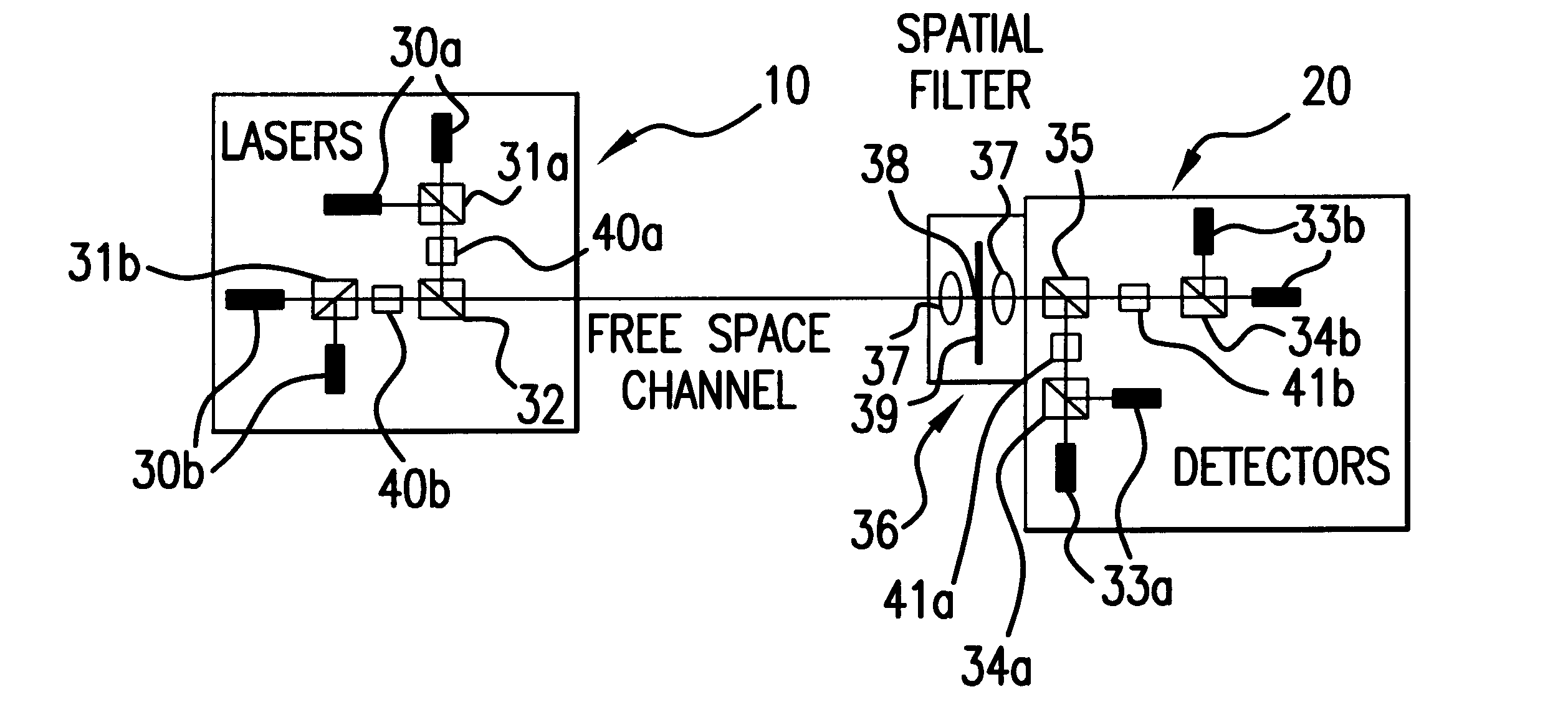
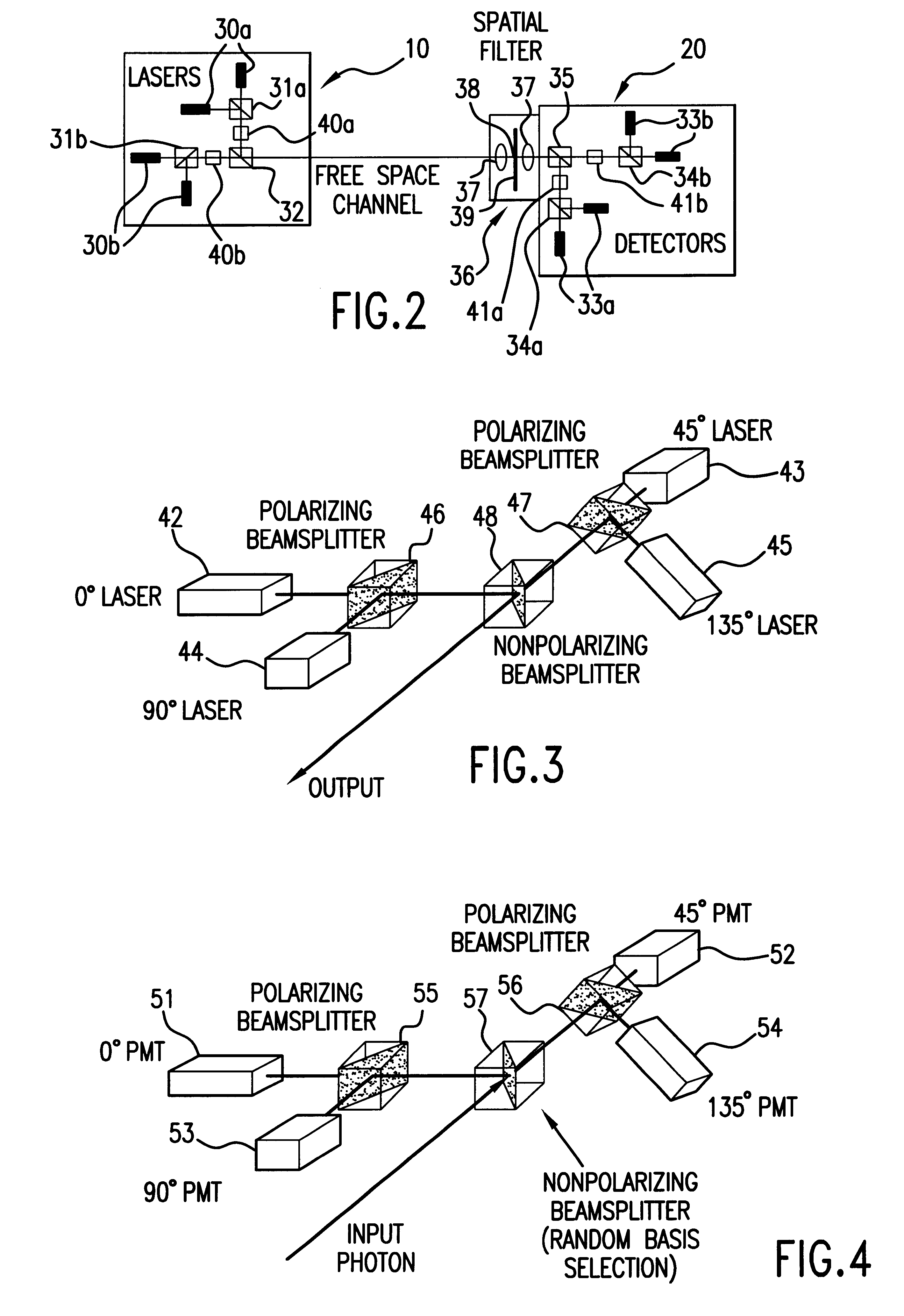
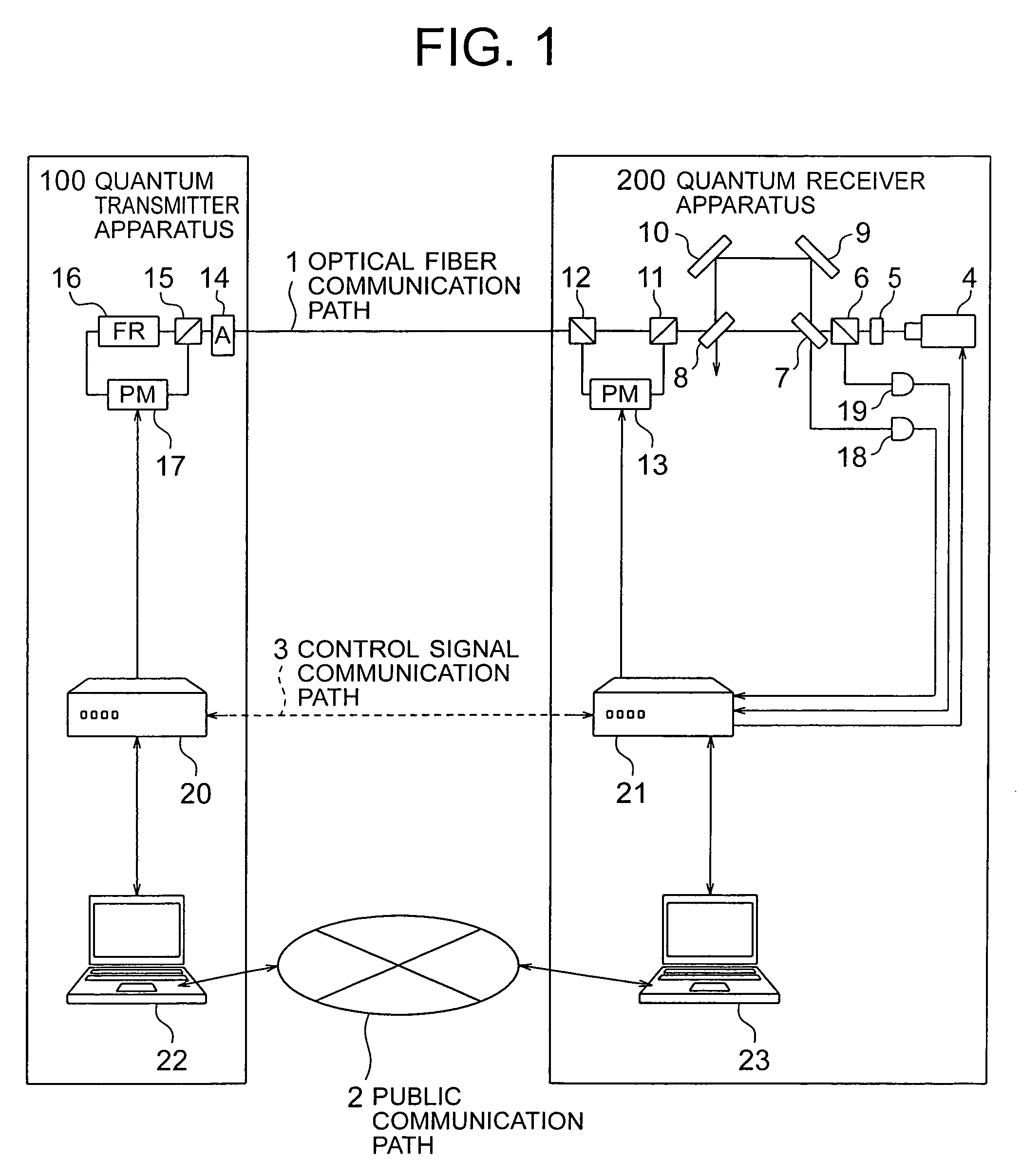
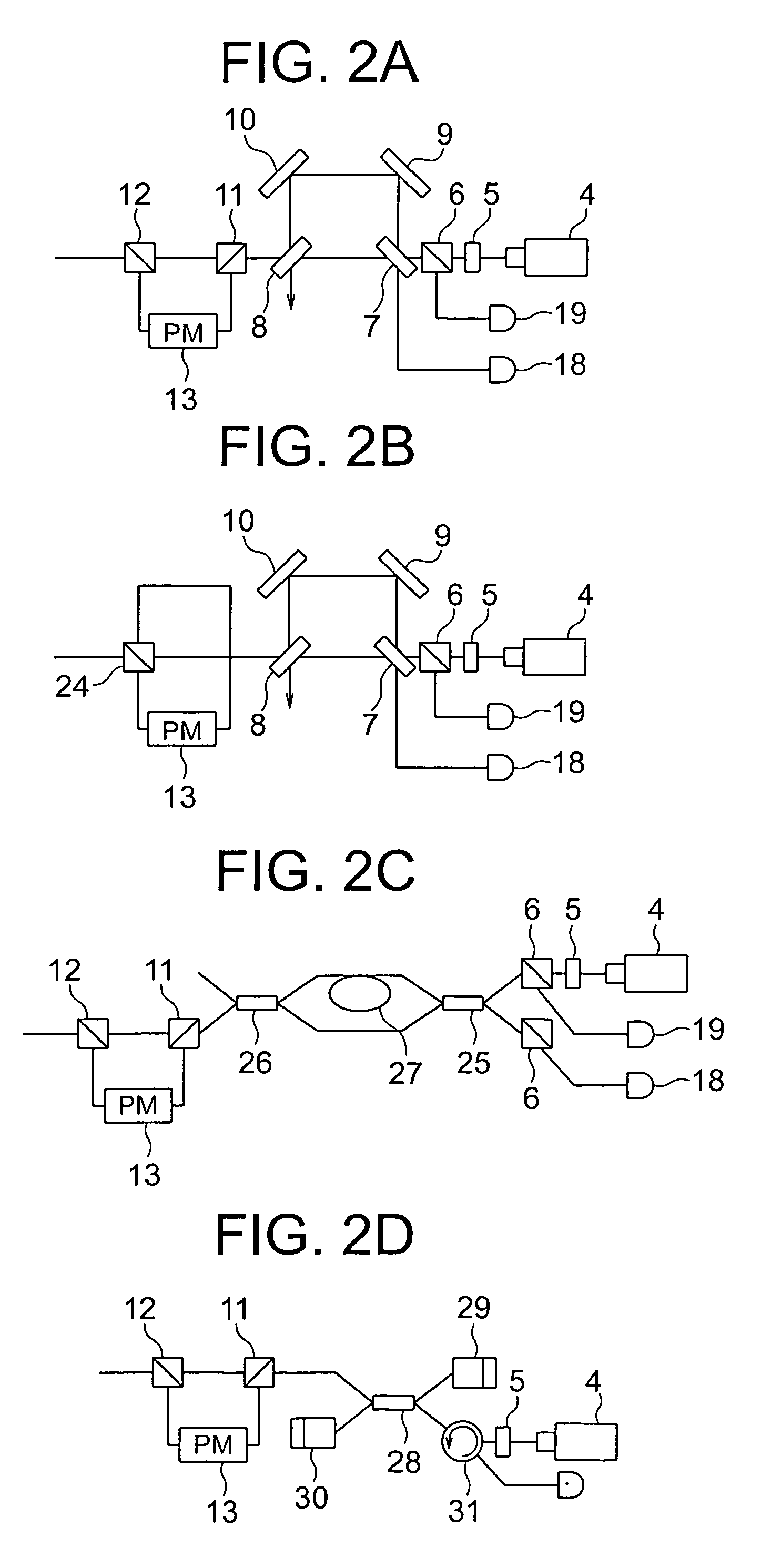
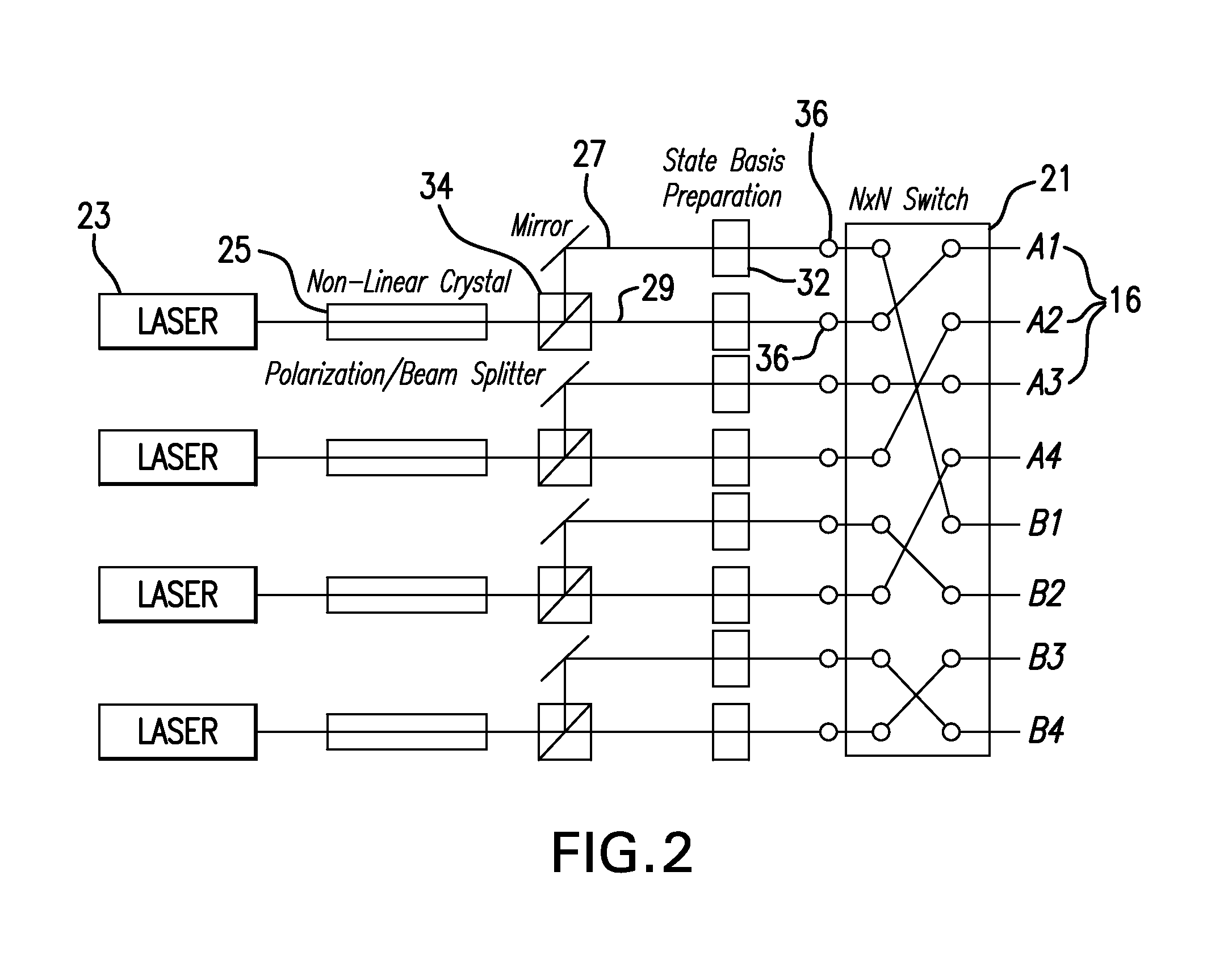
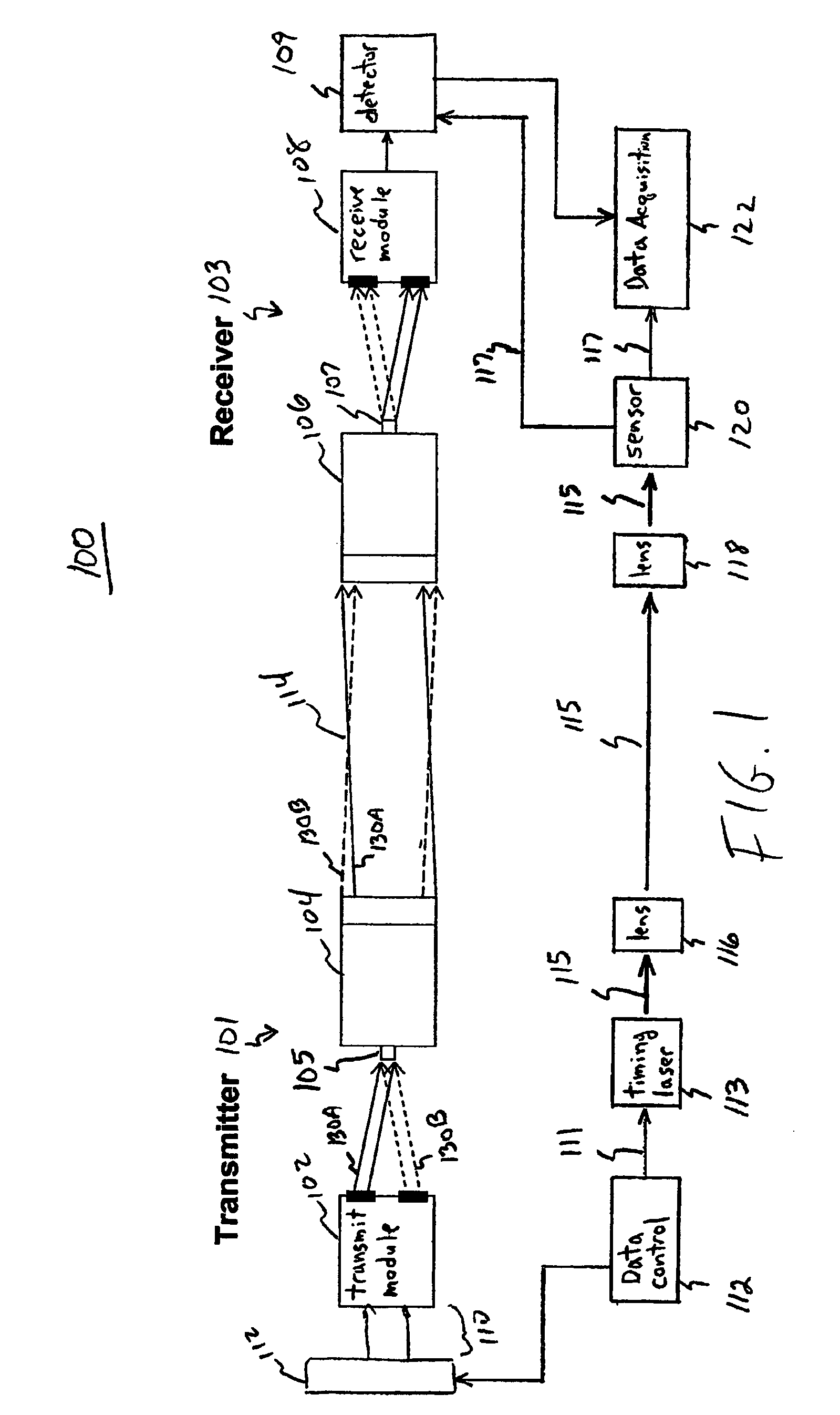
Free-space quantum cryptography system
InactiveUS6289104B1Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationOptoelectronicsPolarization beam splitter
A system and method for quantum key delivery in a single-photon, free-space cryptography scheme including a transmitter and a receiver. The transmitter includes two pairs of photon sources, each of which represents a specific photon polarization direction. The first pair of photon sources represents a first polarization basis while the remaining pair of photon sources represents a second polarization basis. The first and second polarization basis are rotated with respect to each other so as to produce non-orthogonal polarization eigenstates. A transmitter polarizing beamsplitter corresponding to each of the pairs of the photon sources is provided whereby the polarizations of each of the photon sources of each pair of photon sources are recombined. A transmitter non-polarizing beamsplitter is provided whereby the recombined polarizations are combined for output to the receiver. The receiver includes a set of optics inversely disposed with respect to the optics of the transmitter and two pairs of photon detectors.
Owner:ILLINOIS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20050036624A1Reduce bitrateIncrease bitrateKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelHilbert space
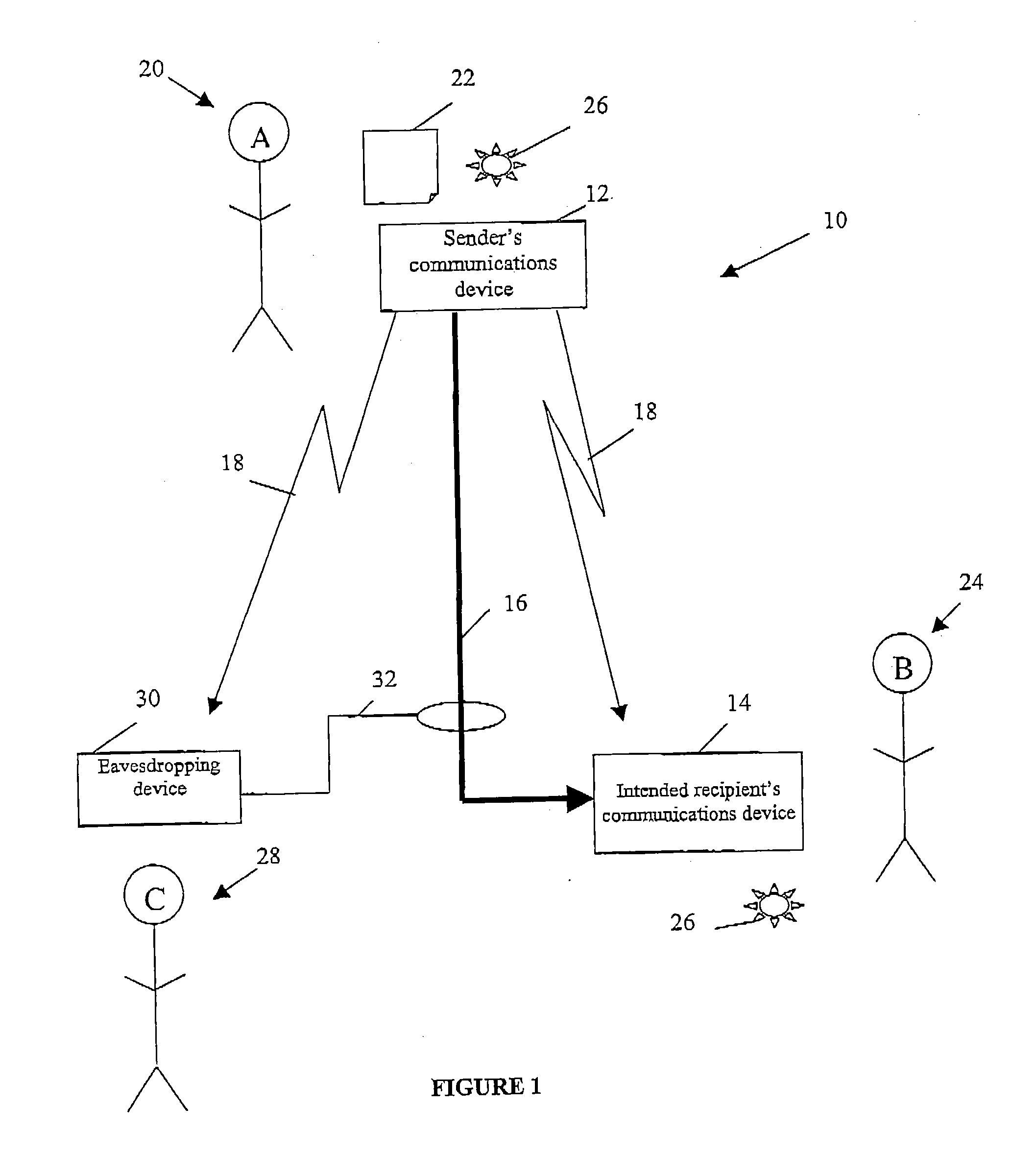
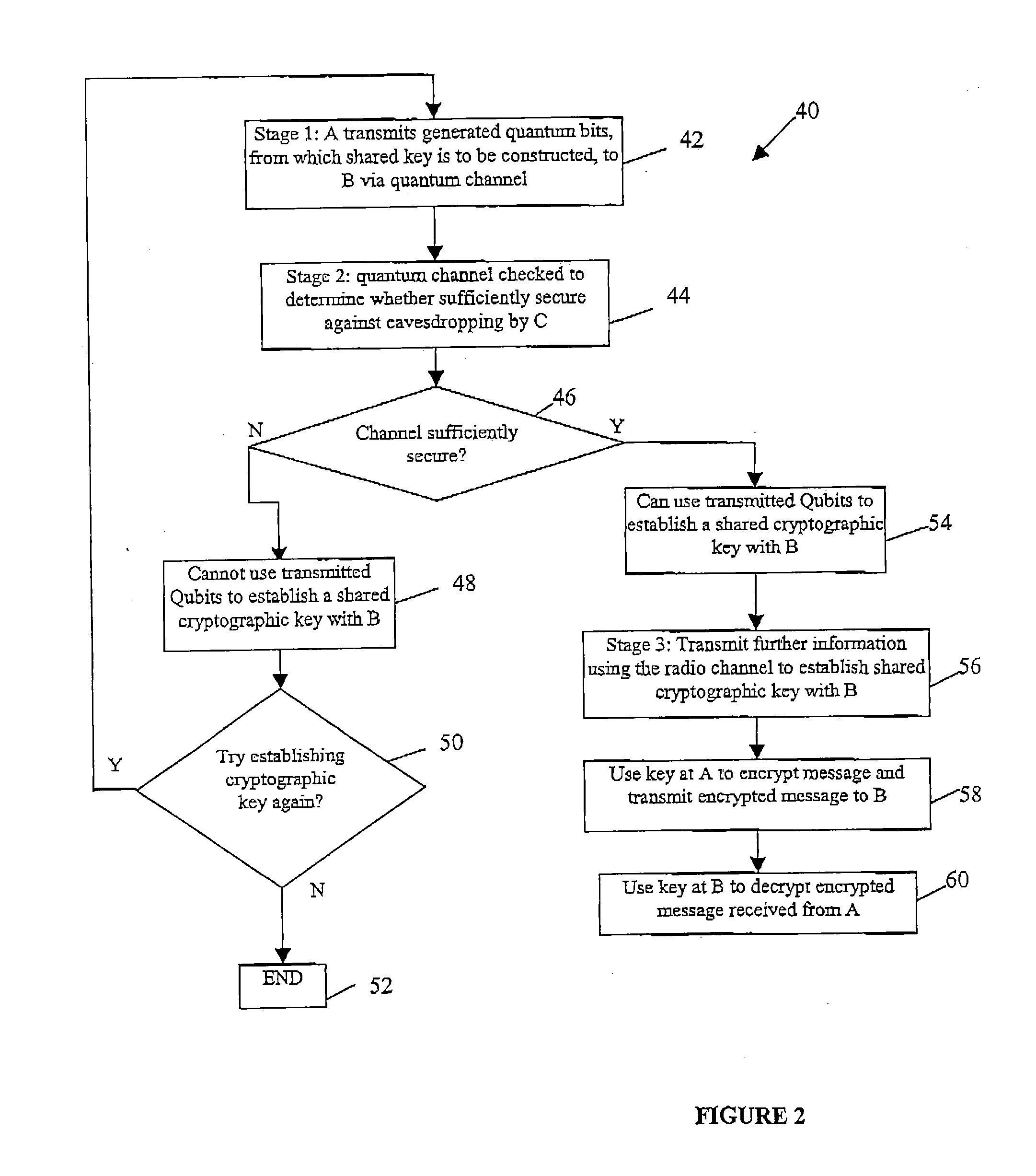
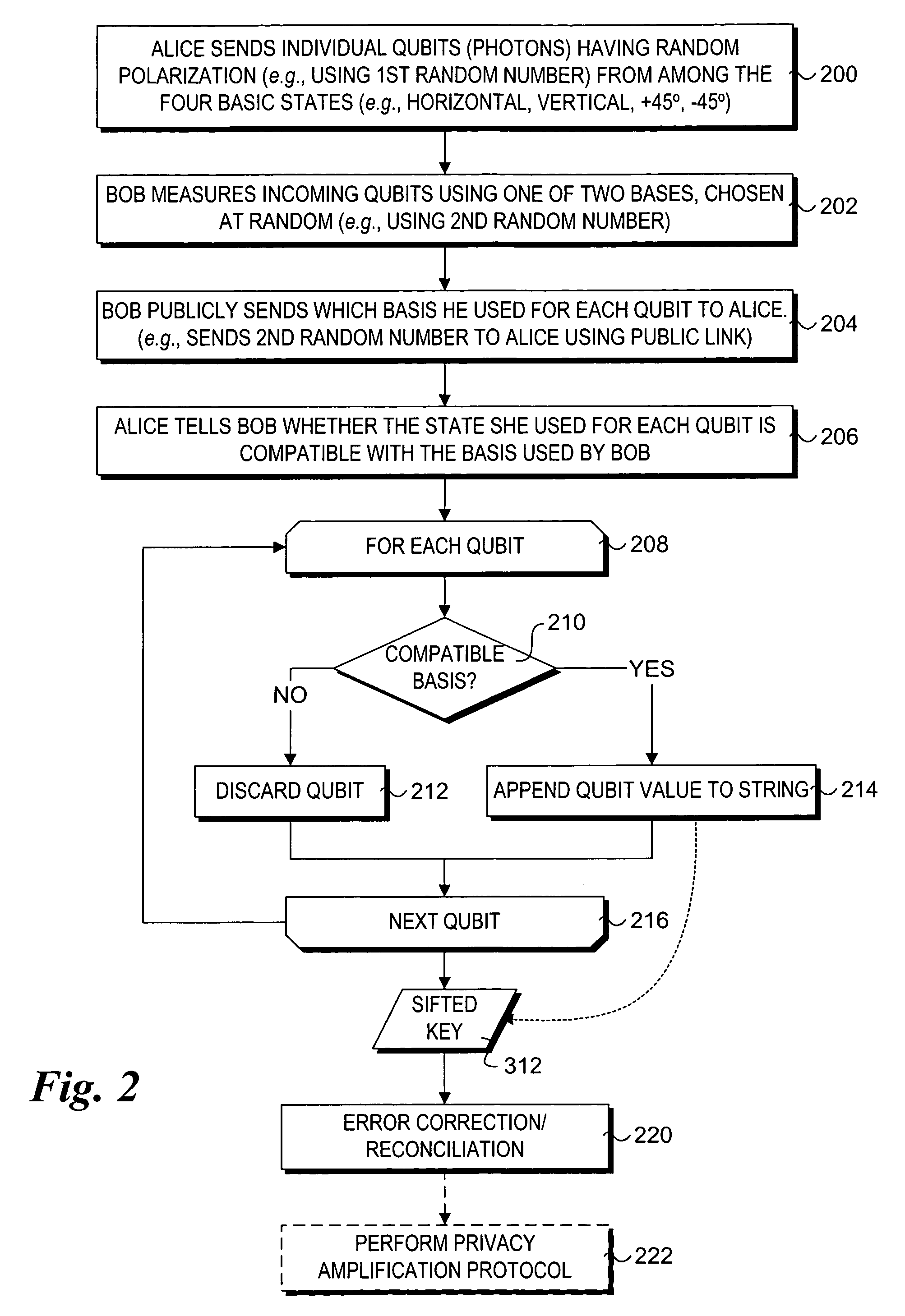
A method of establishing a shared secret random cryptographic key between a sender and a recipient using a quantum communications channel is described. The method comprises: generating a plurality of random quantum states of a quantum entity, each random state being defined by a randomly selected one of a first plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting the plurality of random quantum states of the quantum entity via the quantum channel to a recipient, measuring the quantum state of each of the received quantum states of the quantum entity with respect to a randomly selected one of a second plurality of bases in Hilbert space, transmitting to the recipient composition information describing a subset of the plurality of random quantum states, analysing the received composition information and the measured quantum states corresponding to the subset to derive a first statistical distribution describing the subset of transmitted quantum states and a second statistical distribution describing the corresponding measured quantum states, establishing the level of confidence in the validity of the plurality of transmitted random quantum states by verifying that the first and second statistical distributions are sufficiently similar, deriving a first binary sting and a second binary string, correlated to the first binary string, respectively from the transmitted and received plurality of quantum states not in the subset, and carrying out a reconciliation of the second binary string to the first binary string by using error correction techniques to establish the shared secret random cryptographic key from the first and second binary strings.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP +1
Method and apparatus for polarization-insensitive quantum cryptography
InactiveUS6529601B1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesCommunications systemSingle polarization
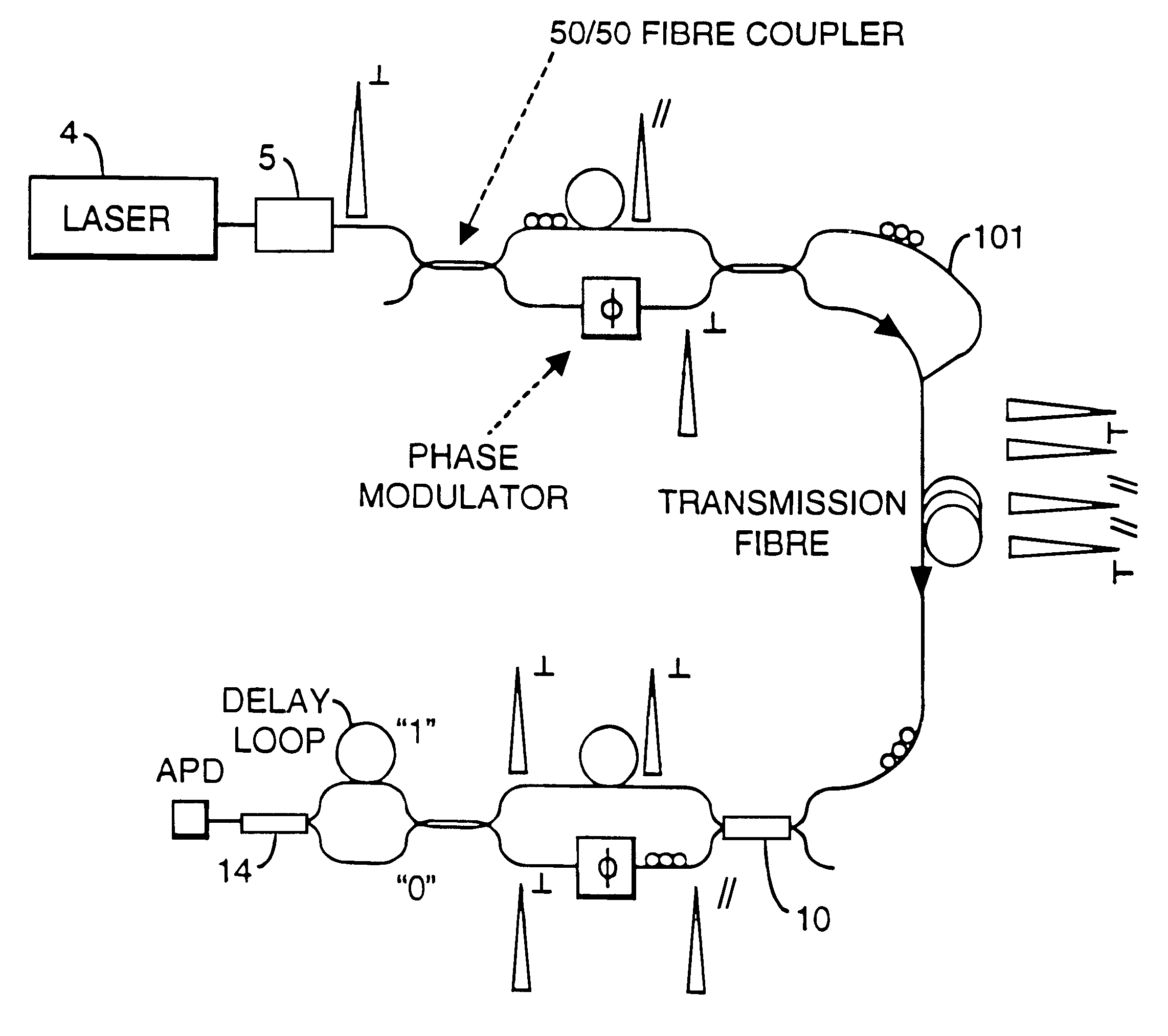
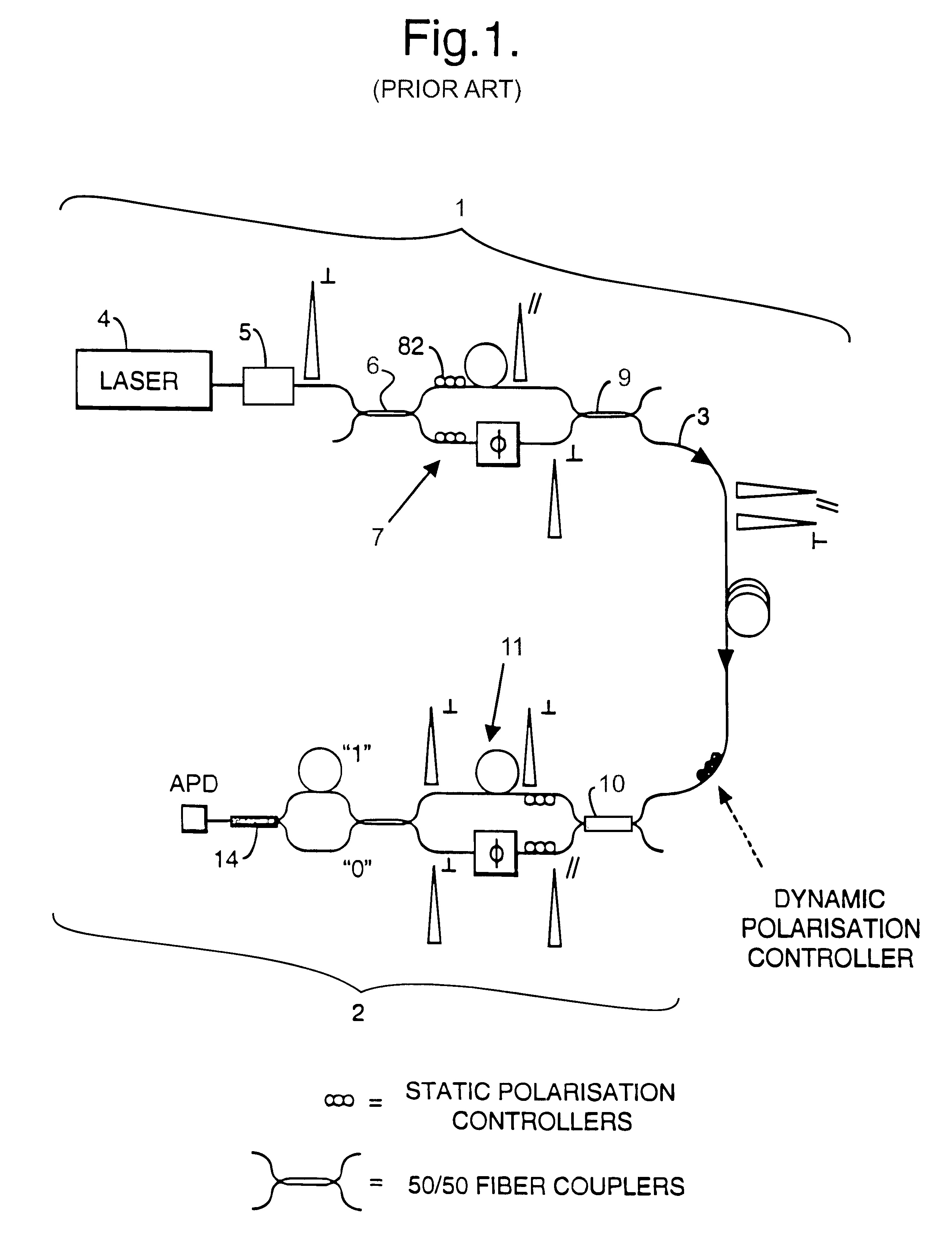
A communication system uses quantum cryptography for the secure distribution of a key. A single-photon signal is phase-modulated and transmitted over a pair of time-multiplexed transmission paths. With each original single-photon signal in a given one of the transmission paths, a duplicate signal is transmitted. The duplicate is identically modulated and orthogonally polarized. At the receiver, the outputs of the two paths are combined interferometrically. A single polarization-insensitive measurement is derived from the combined contributions of the orthogonally polarized signals.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
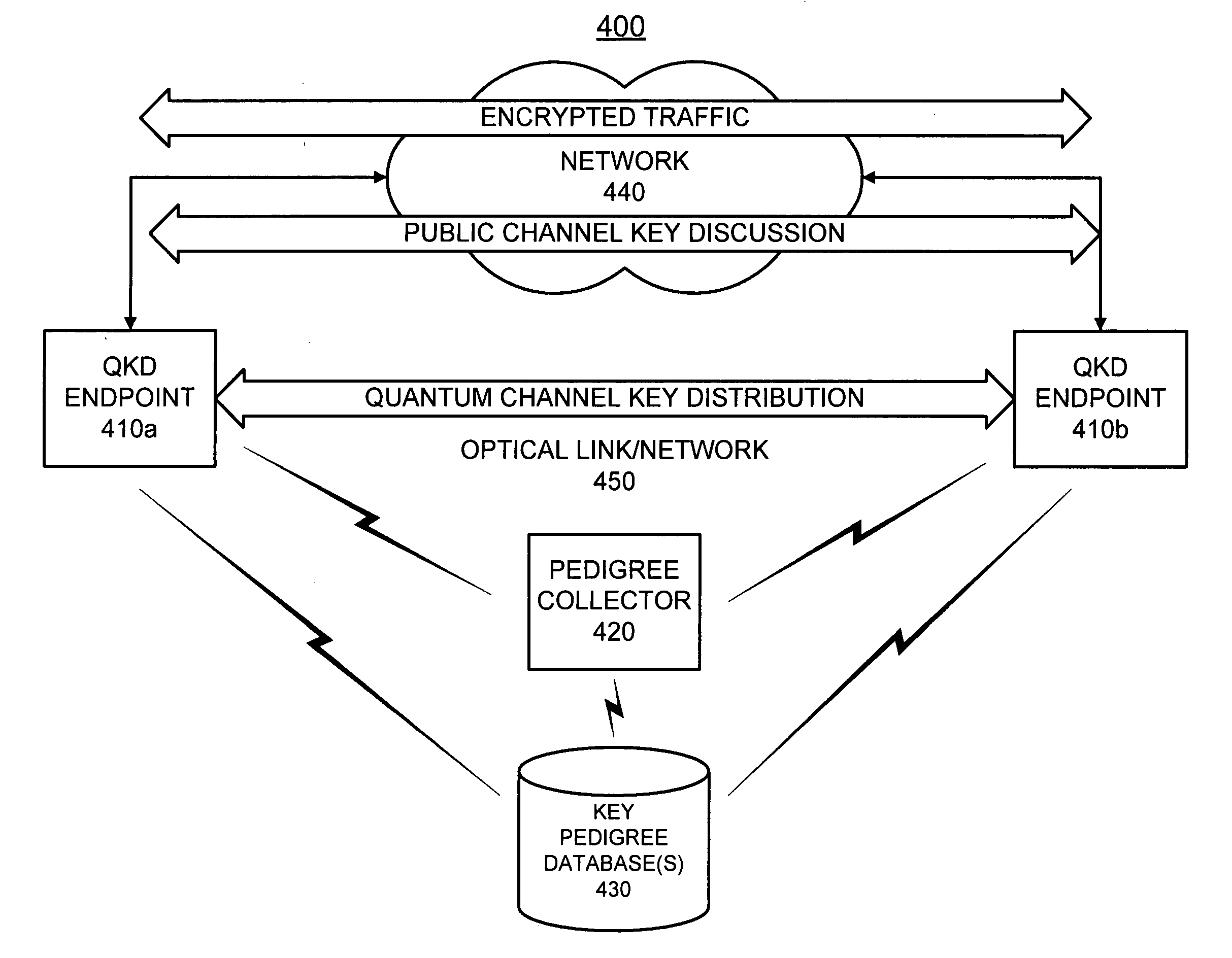
Pedigrees for quantum cryptography
ActiveUS20070192598A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationQuantumInformation system
A system stores pedigrees that include details of how and when each of multiple blocks of encryption key material were distributed between two endpoints using quantum cryptographic techniques. The system receives an indication of a possible quantum cryptographic security violation and accesses the stored pedigrees to identify one or more of the multiple blocks of encryption key material that may have been compromised.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Systems and methods for path set-up in a quantum key distribution network
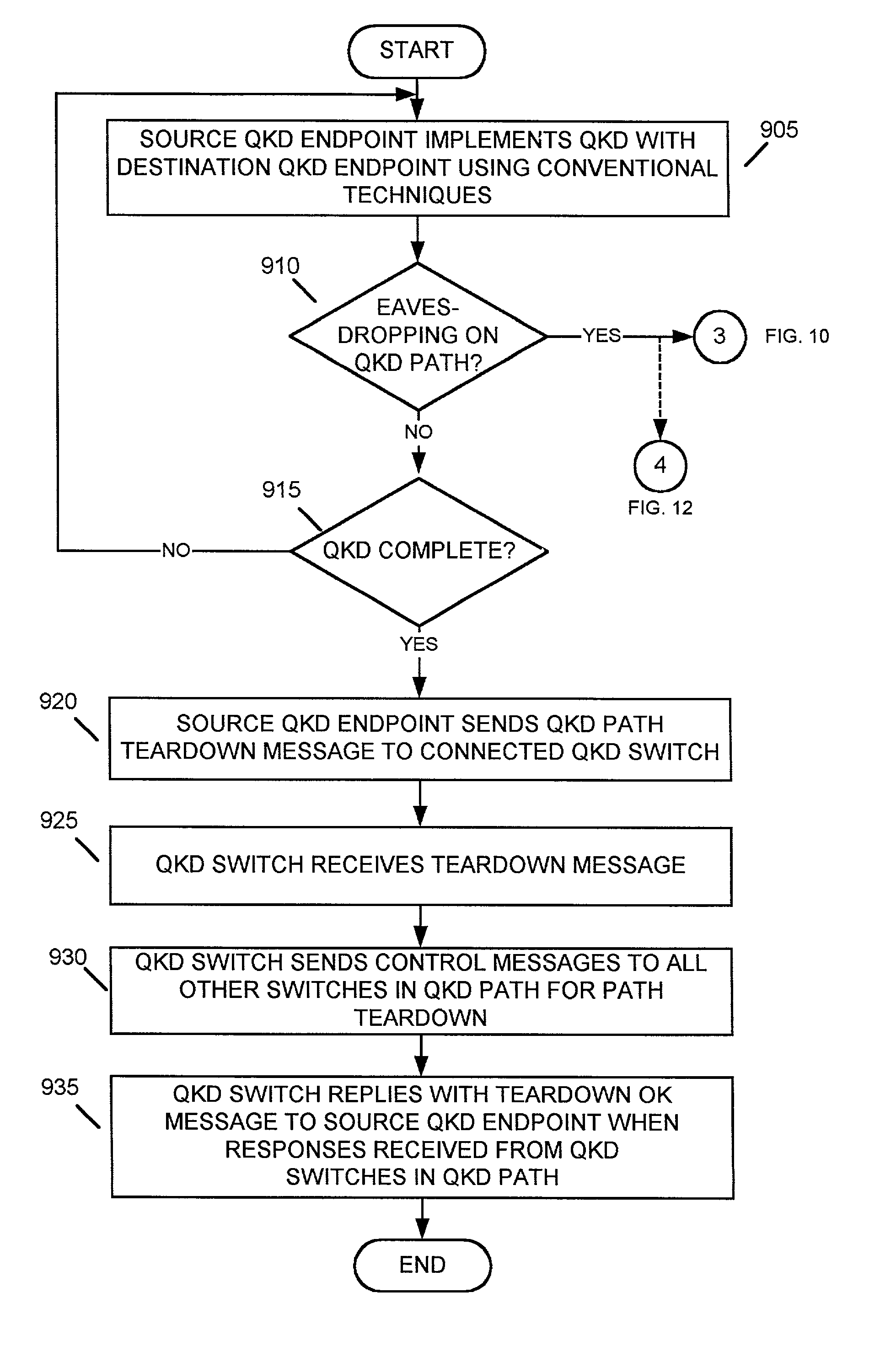
InactiveUS7068790B1Low costReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsKey distributionEavesdropping
A system establishes a path for distributing data through an optical network (115). The system includes an optical switch (205a) and a data distribution endpoint (105a). The optical switch (205a) establishes a first encryption key distribution path through the optical network (115), the first encryption key distribution path including multiple optical switches and optical links. The data distribution endpoint (105a) determines whether eavesdropping has occurred on the first encryption key distribution path using quantum cryptography. The optical switch (205a) further establishes a second data distribution path through the optical network (115) responsive to the eavesdropping determination. The second encryption key distribution path includes multiple optical switches and optical links.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Method to support secure network booting using quantum cryptography and quantum key distribution
A method and system to support secure booting and configuration. The mechanism employs an optical link comprising a quantum channel that is used to send data encoded as quantum bits (qubits) via respective photons. Qubits encoded using a first random basis at the client and are sent to the boot server, which processes the qubits using a second random basis to extract the encoded data. A public channel is used to send data indicative of the second random basis to the client. A symmetric quantum key is then derived a both the client and the boot server using a comparison of the random basis' and the original and extracted data. The scheme enables the presence of an eavesdropper to be detected on the quantum channel. A DHCP message exchange is employed to obtain a network address, and, optionally, be provided with a network address for one or more boot servers. A boot image request is made to the boot server by the client, and a subsequent boot image is downloaded via a secure channel facilitated by the symmetric quantum key.
Owner:INTEL CORP
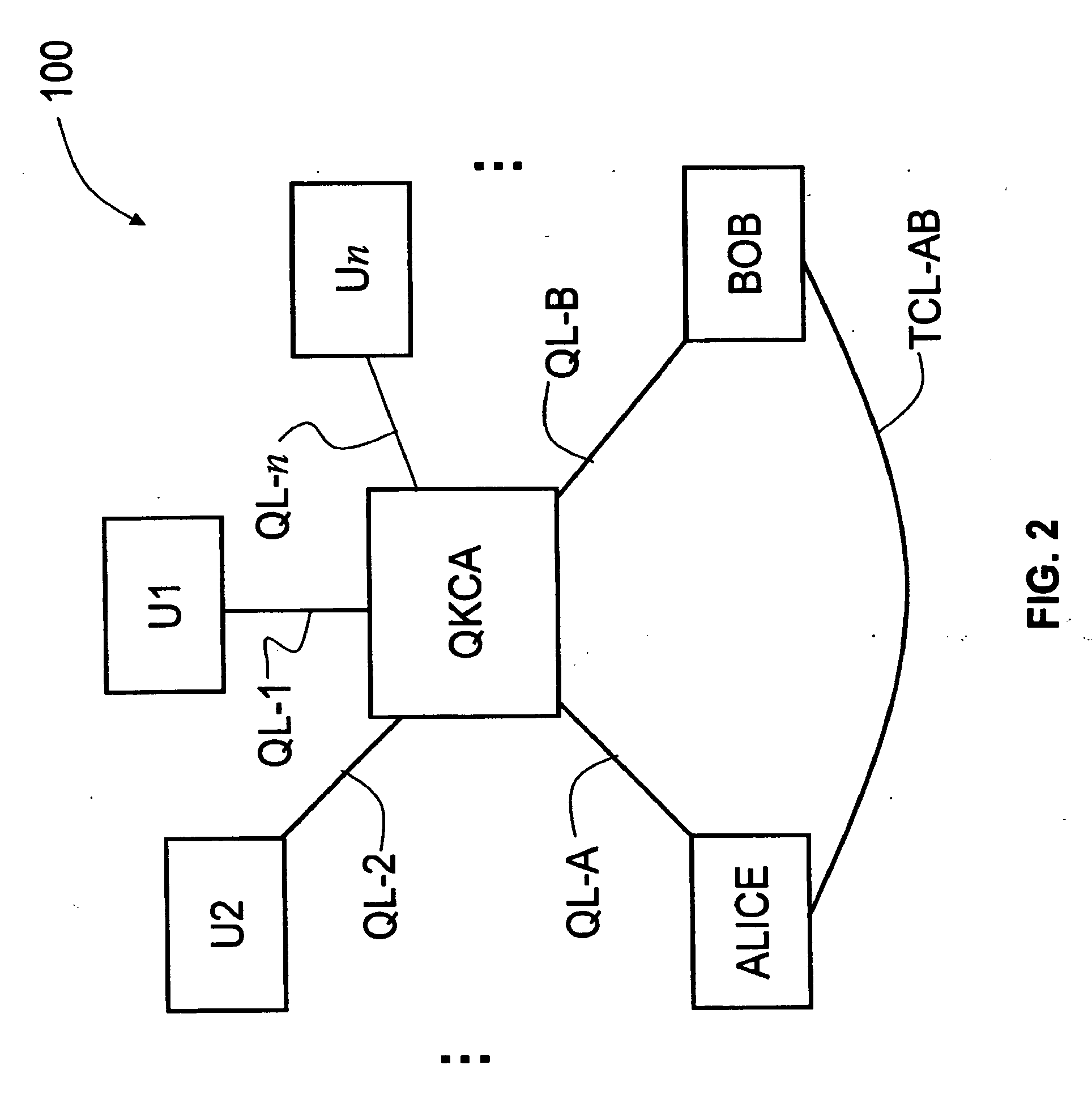
Key Management and User Authentication for Quantum Cryptography Networks
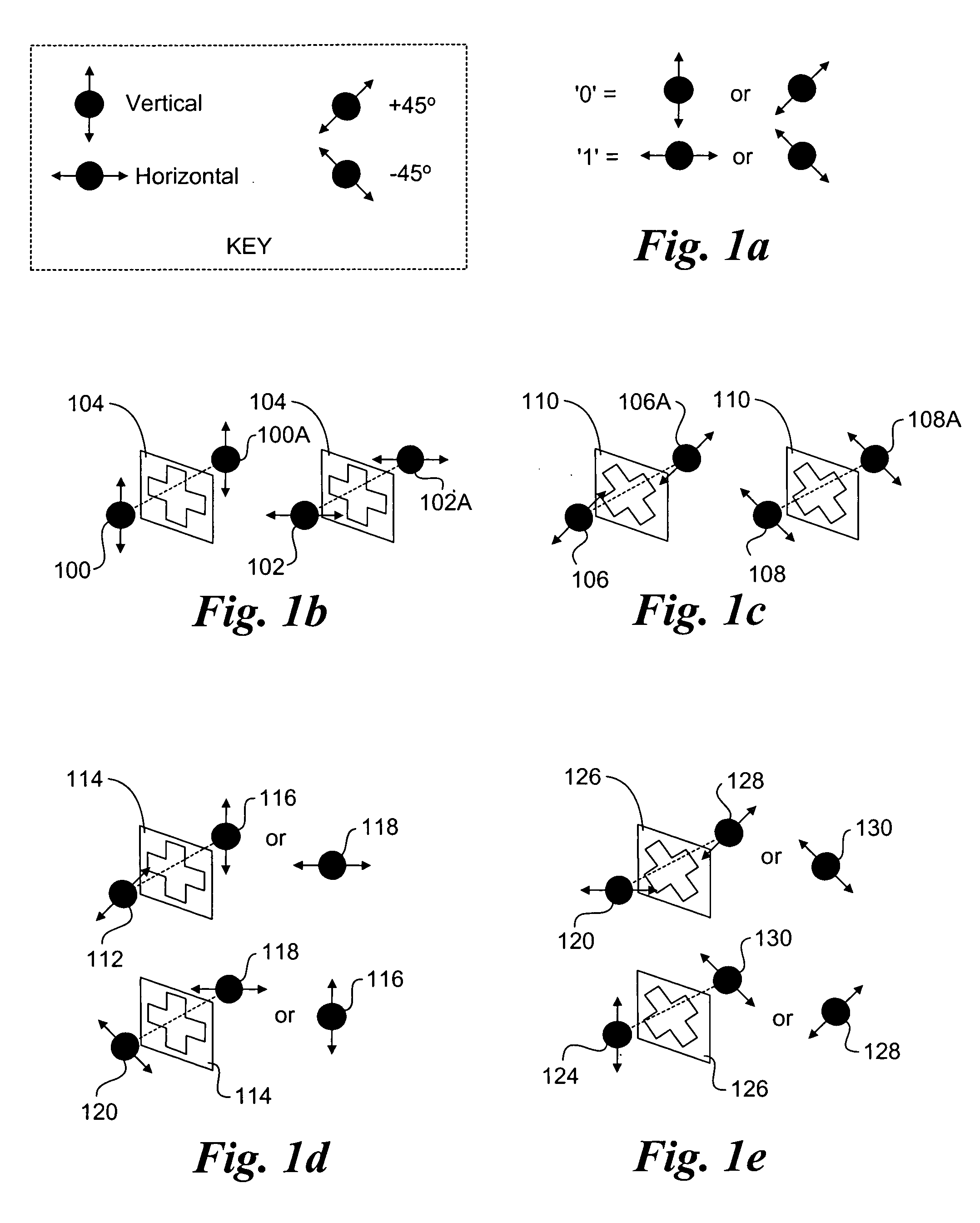
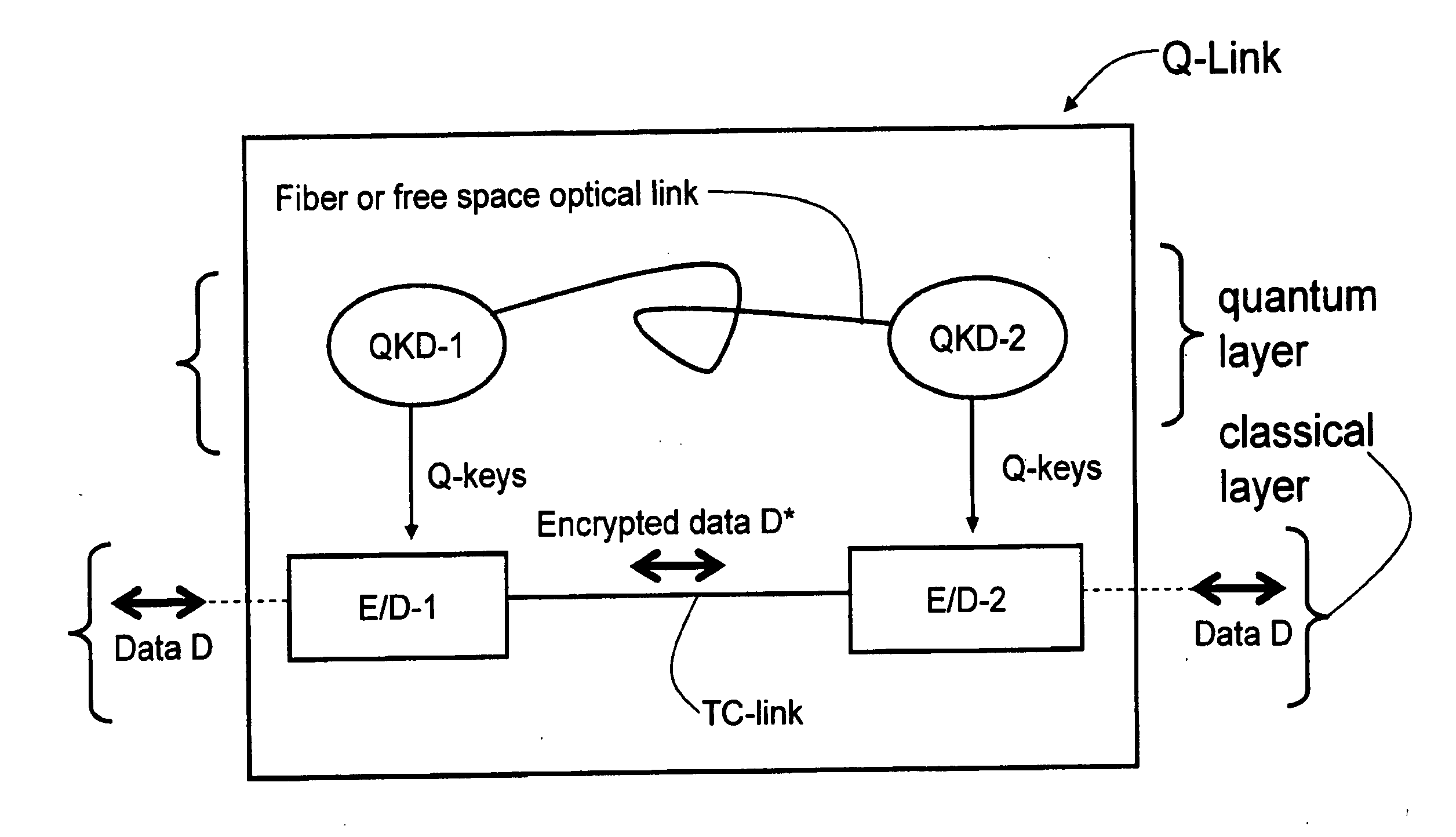
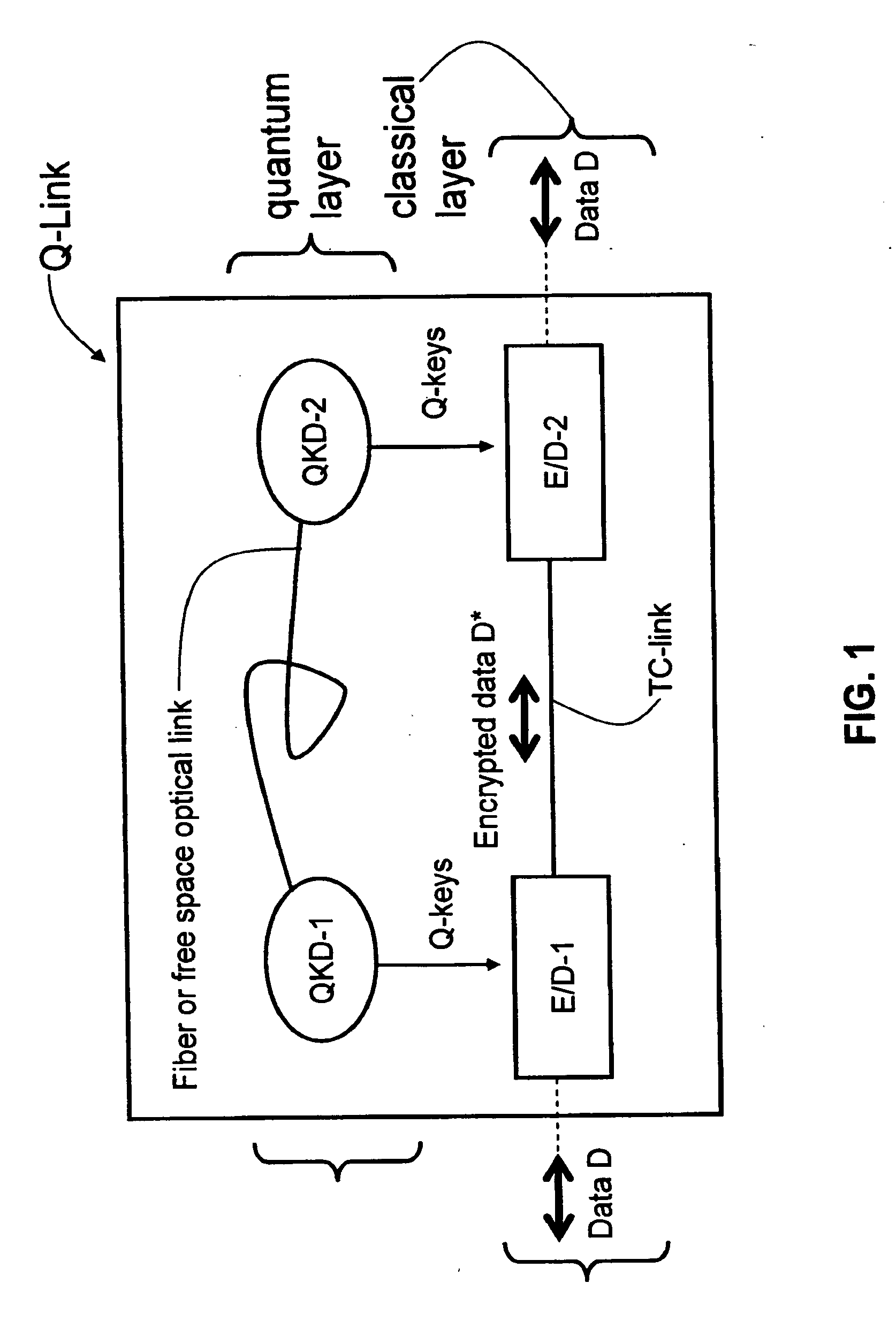
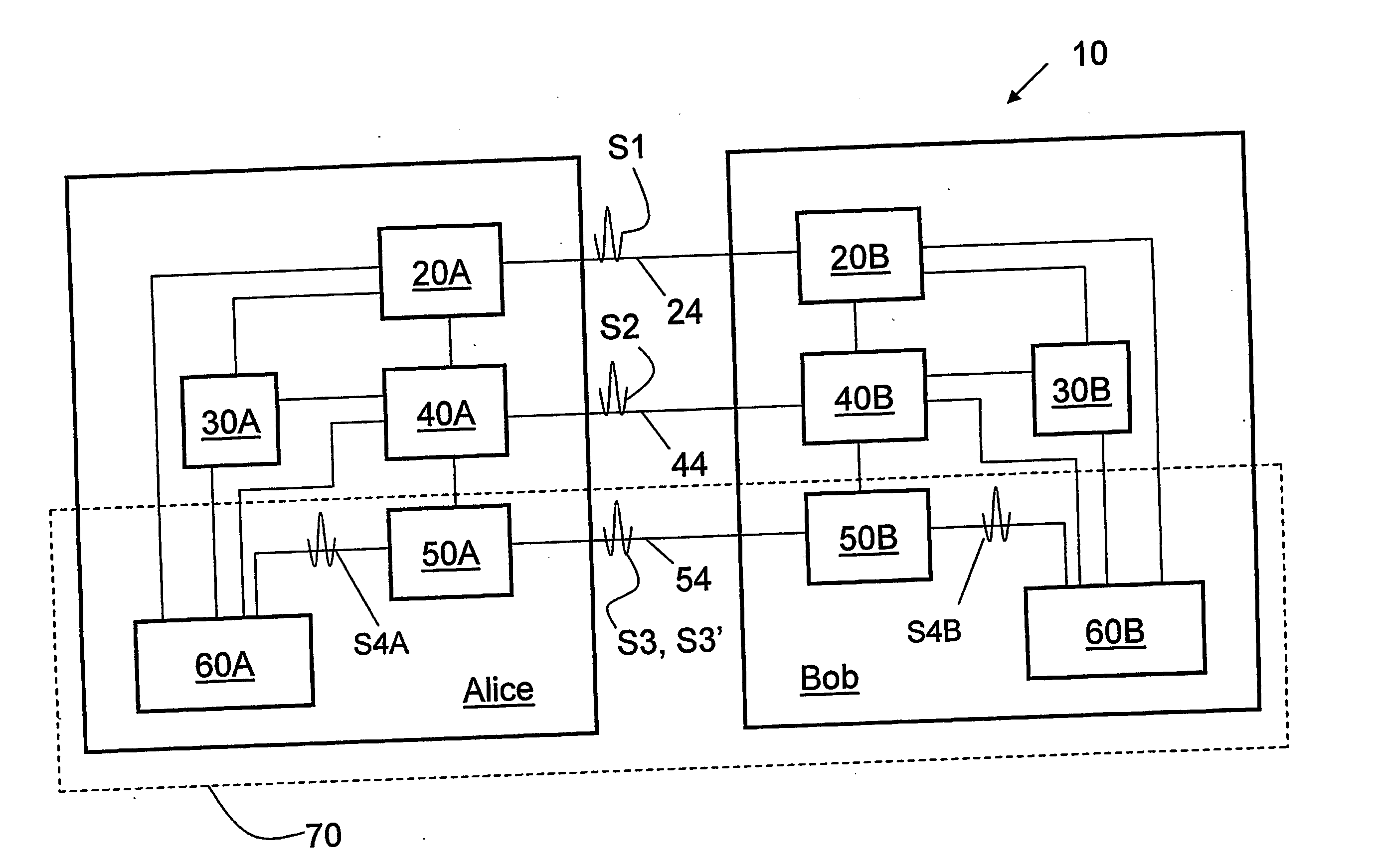
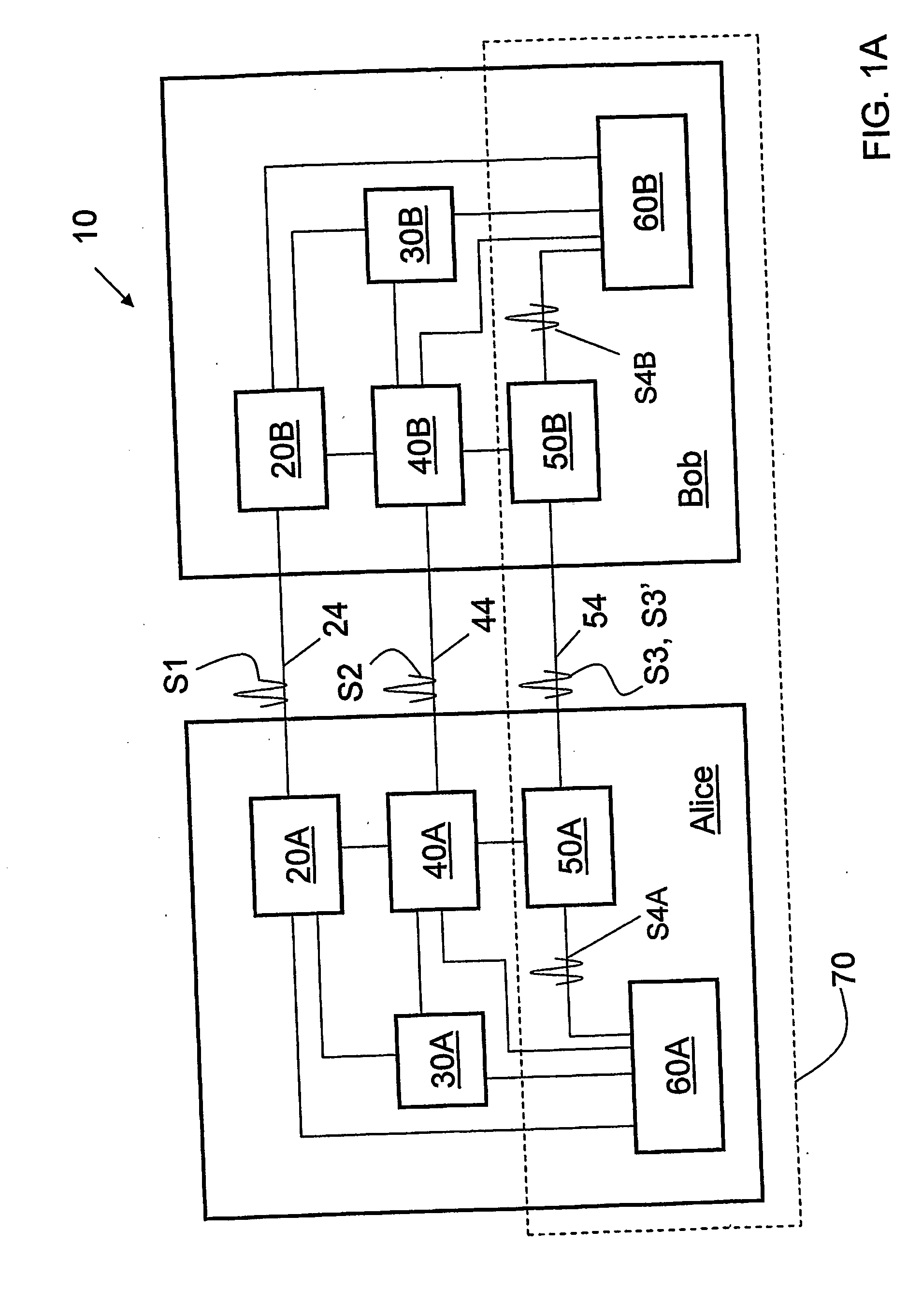
ActiveUS20090175452A1Key distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesAlice and BobTelecommunications link
Key management and user authentication systems and methods for quantum cryptography networks that allow for users securely communicate over a traditional communication link (TC-link). The method includes securely linking a centralized quantum key certificate authority (QKCA) to each network user via respective secure quantum links or “Q-links” that encrypt and decrypt data based on quantum keys (“Q-keys”). When two users (Alice and Bob) wish to communicate, the QKCA sends a set of true random bits (R) to each user over the respective Q-links. They then use R as a key to encode and decode data they send to each other over the TC-link.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
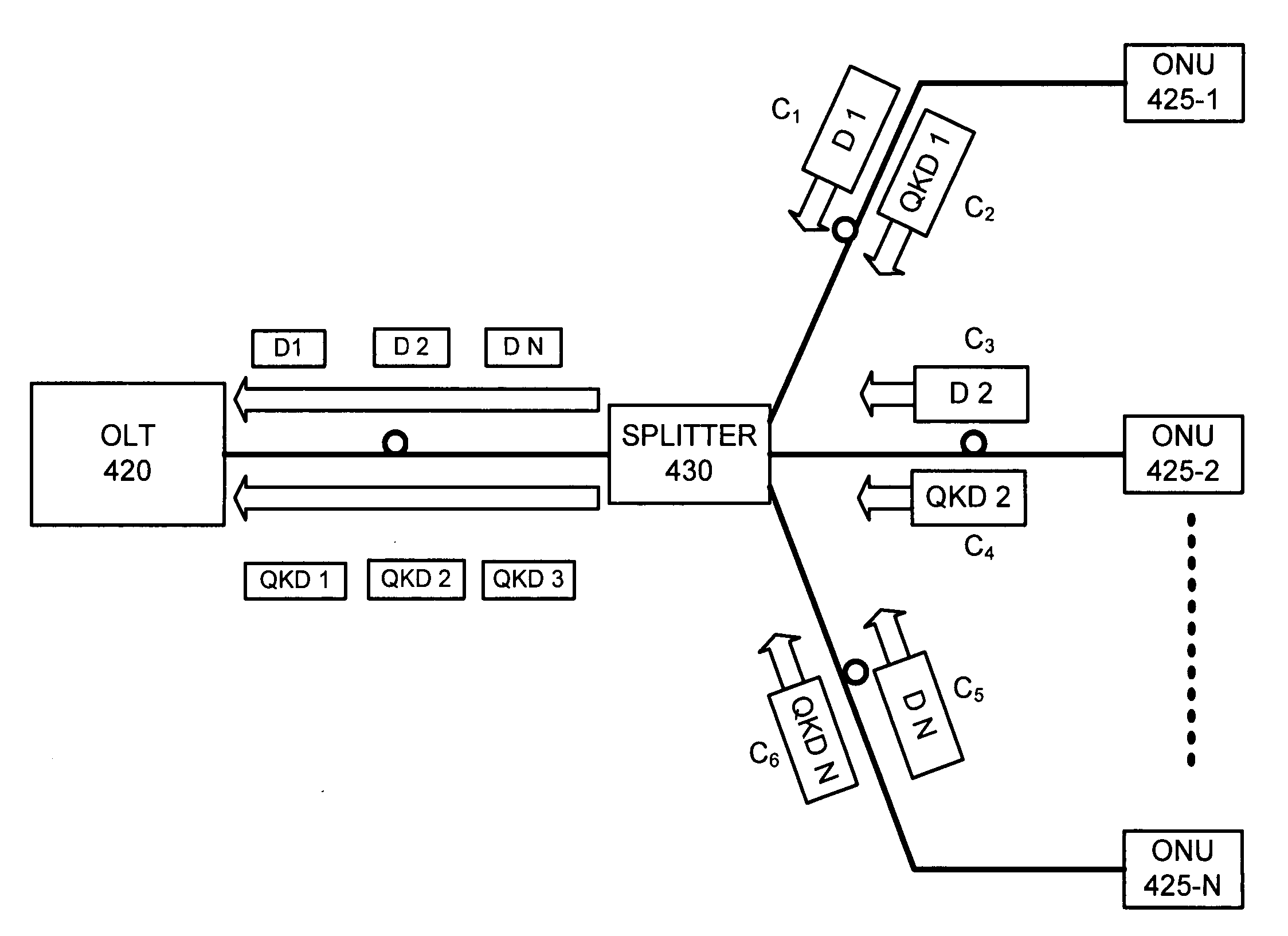
Quantum cryptography on a multi-drop optical network
InactiveUS20070133798A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsSecret communicationOptical network unitQuantum
A system includes an optical network unit and a head-end or central office connected to a multi-drop optical network. The optical network unit transmits dim optical pulses via the multi-drop optical network using quantum cryptographic mechanisms to distribute encryption key symbols, where the dim optical pulses include one of single-photon optical pulses or weak attenuated optical pulses. The head-end or central office detects the dim optical pulses from the optical network unit, derives the encryption key symbols from the detected dim optical pulses, and encrypts data transmitted to the optical network unit using the encryption key symbols.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
Quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method
ActiveCN103001875AConvenient for dynamic expansionFast convergenceKey distribution for secure communicationData switching networksRefresh cycleRoute server
The invention discloses a quantum cryptography network dynamic routing method. According to the method, dynamic routing selection of encryption communication is performed by utilizing quantum cryptography according to changes of the quantum key quantity between relay nodes of a quantum cryptography network. According to the method, a route server is arranged for the relay nodes of the whole quantum cryptography network, and topology refresh cycles of the quantum cryptography network are set; in each topology refresh cycle, each relay node collects and processes state information of the relay node and reports results to the route server. After the route server collects the topology state information of each relay node, quantum cryptography network topology state information of a next topology refresh cycle is generated and sent to all the relay nodes of the quantum cryptography network. According to the quantum cryptography network topology state information obtained from the route server, a target relay node is calculated and determined to be a next skip route of communication data of a random other relay node according to a shortest path law through each relay node.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF QUANTUM SCI & TECH +2
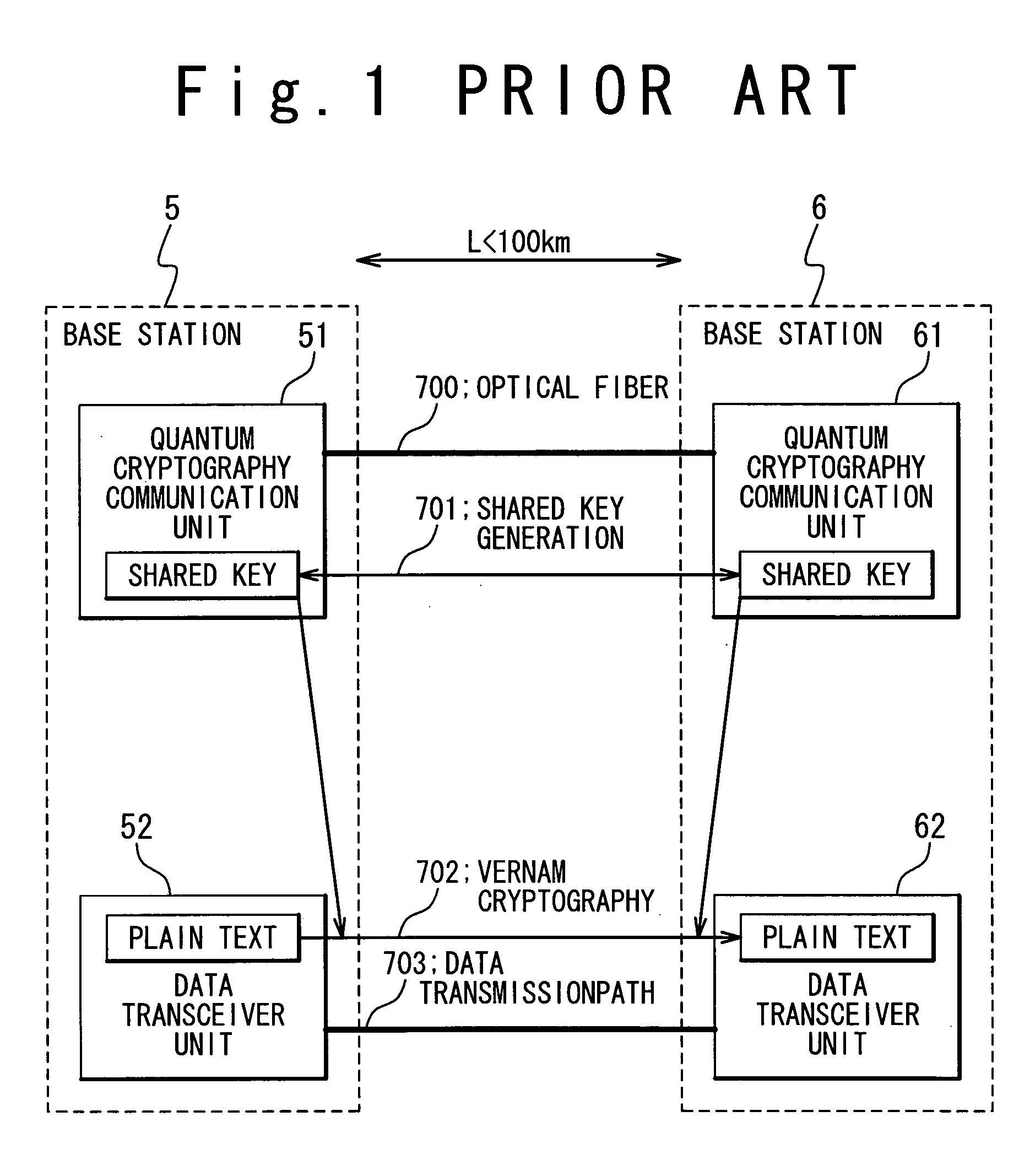
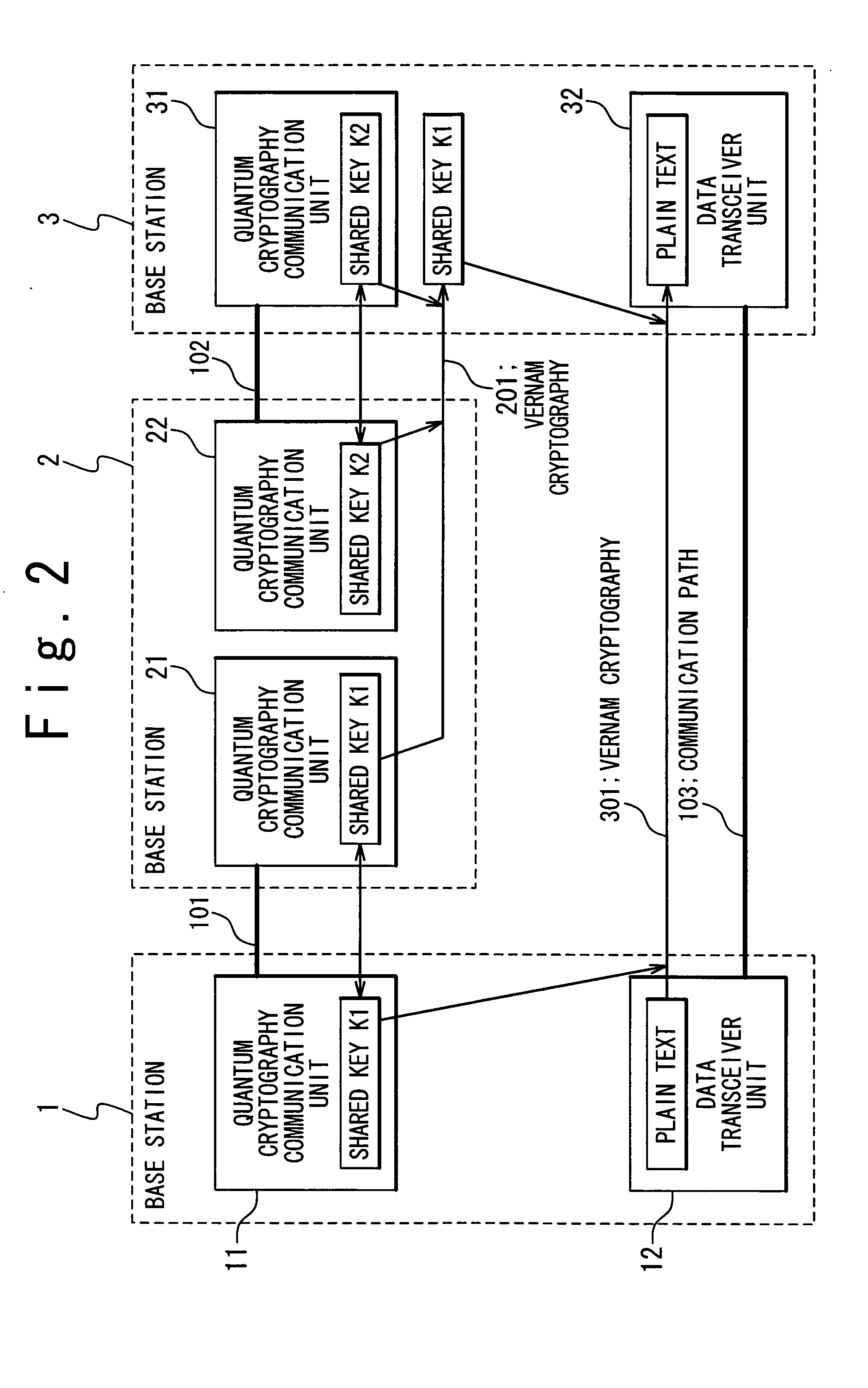
Quantum cryptography communication system and quantum cryptography key distributing method used in the same
ActiveUS20050078826A1Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesCommunications systemCommunication unit
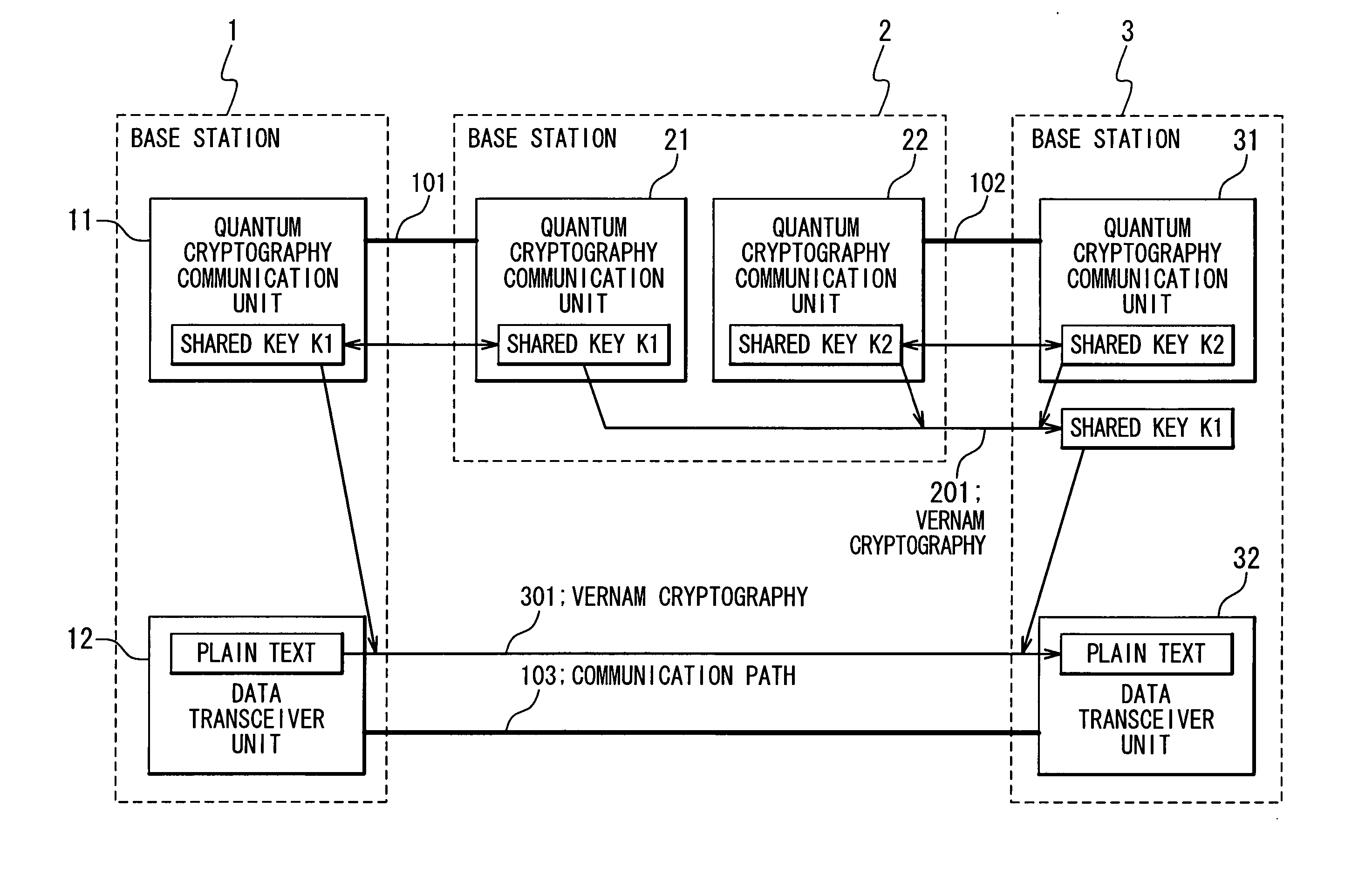
A quantum cryptography communication system includes a first data communication unit; a second data communication unit connected with the first data communication unit by a first optical fiber; and a third data communication unit connected with the second data communication unit by a second optical fiber. A first shared key is generated in the first data communication unit and the second data communication unit, and a second shared key is generated in the second data communication unit and the third data communication unit. The second data communication unit encrypts the first shared key by using the second shared key and then transmits the encrypted first shared key to the third data communication unit on the second optical fiber, and the third data communication unit decrypts the encrypted first shared key by using the second shared key to reproduce the first shared key.
Owner:NEC CORP
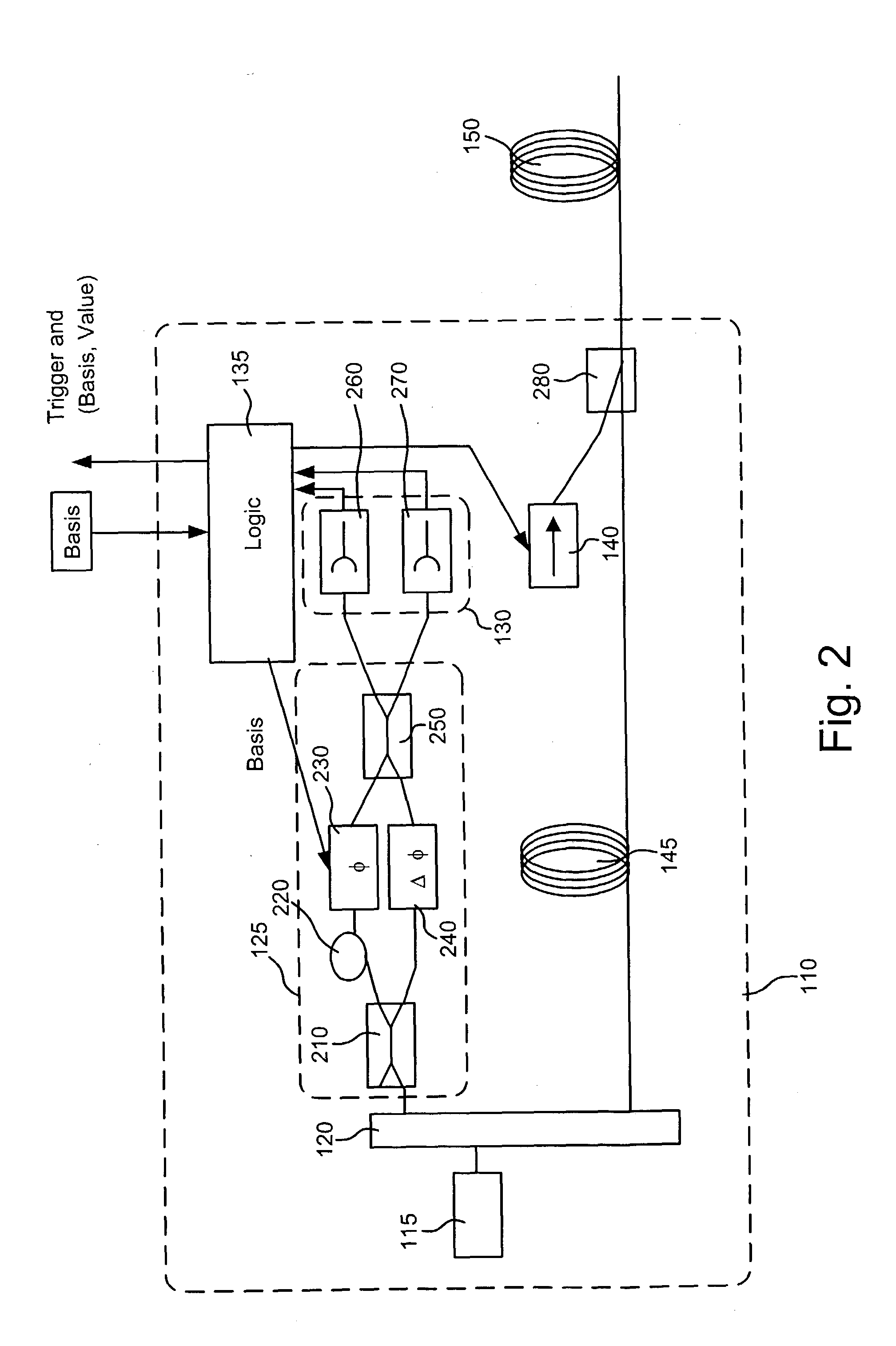
Kd systems with robust timing
QKD systems having timing systems and timing method that allow for QKD to be performed in actual field conditions associated with practical commercial applications of quantum cryptography. The QKD system includes optical modems in each QKD station. Each modem has a circulator with an optical receiver and an optical transmitter coupled to it. One of the optical modems includes two phase lock loops and the other optical modem includes a phase lock loop and a transmit clock. Synchronization pulses are exchanged between the optical modems over a timing channel to synchronize the operation of the QKD system. The phase lock loops serve to lock a receive timing domain to a transmit time domain to ensure proper encoding and detection of weak quantum signals exchanged between the QKD stations.
Owner:MAGIQ TECH INC
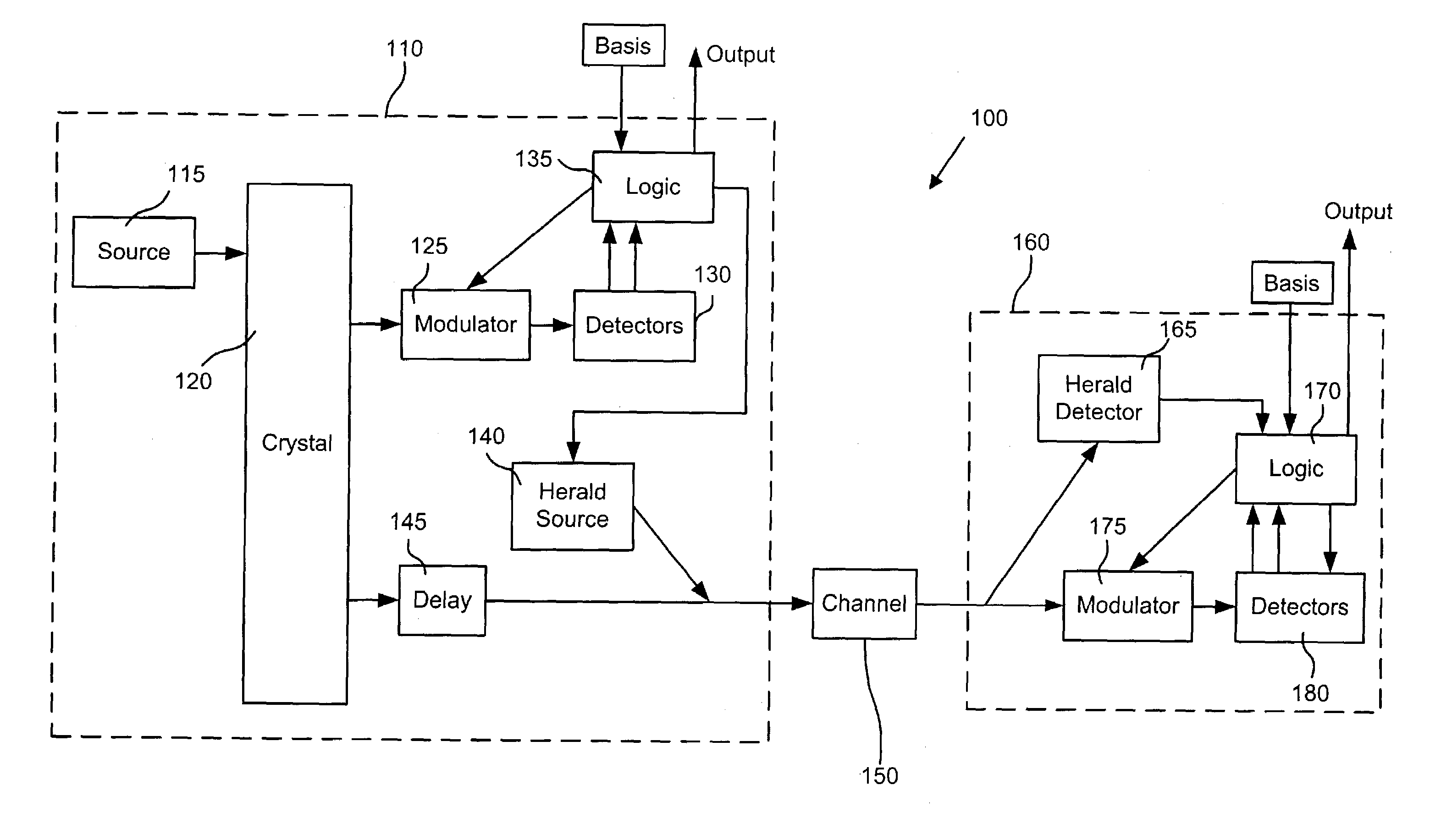
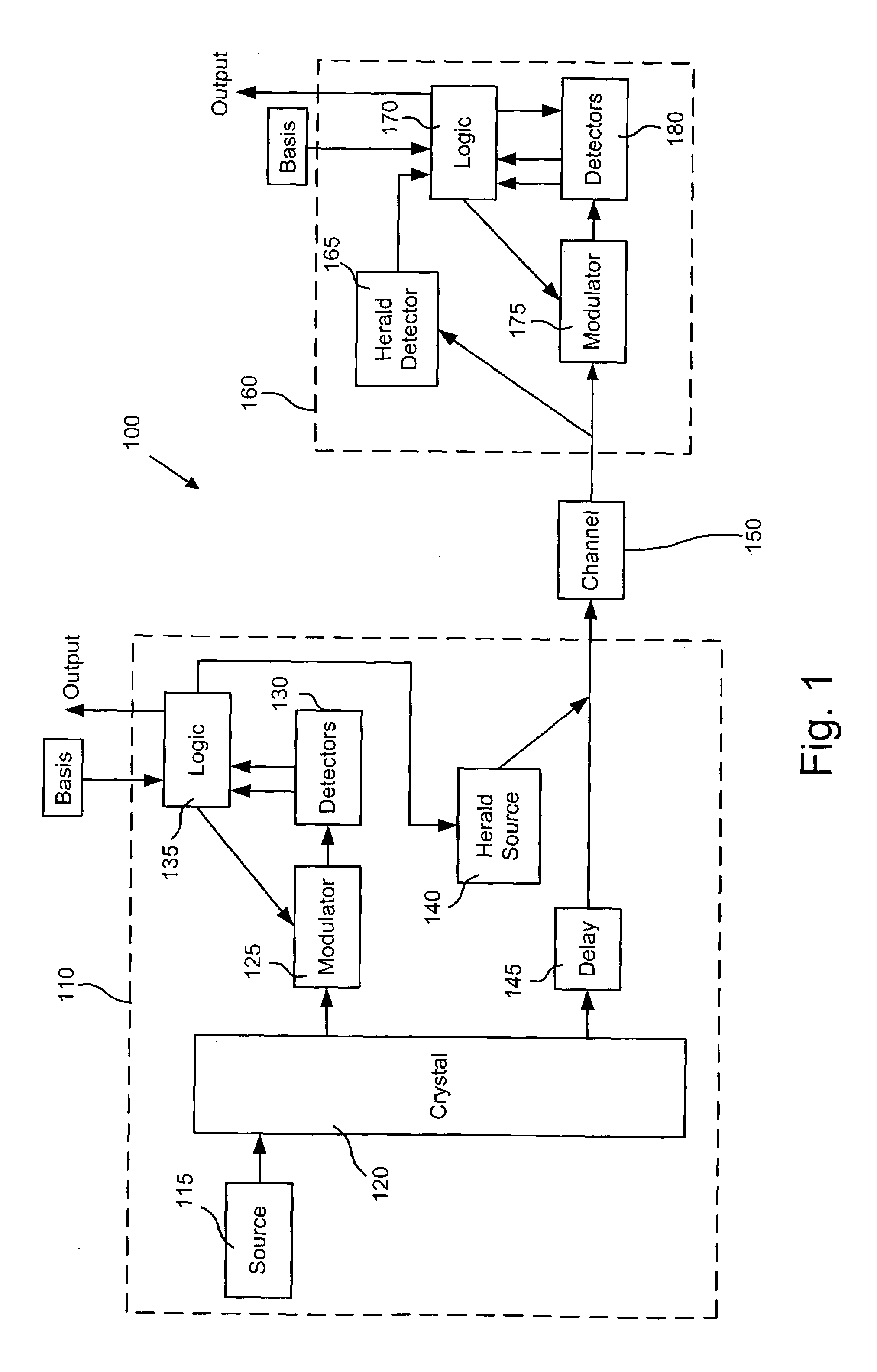
Chip-scale transmitter for quantum cryptography
A quantum cryptographic key distribution (QKD) transmitter includes an integrated photonic circuit configured to distribute encryption key material using quantum cryptographic mechanisms. The integrated photonic circuit further includes a first photon source, an interferometer coupled to the first photon source and a phase modulator coupled to the interferometer and configured to modulate a phase of photons emitted by the first photon source.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
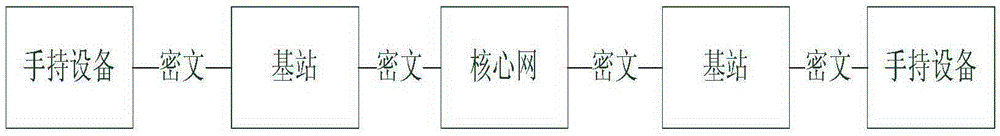
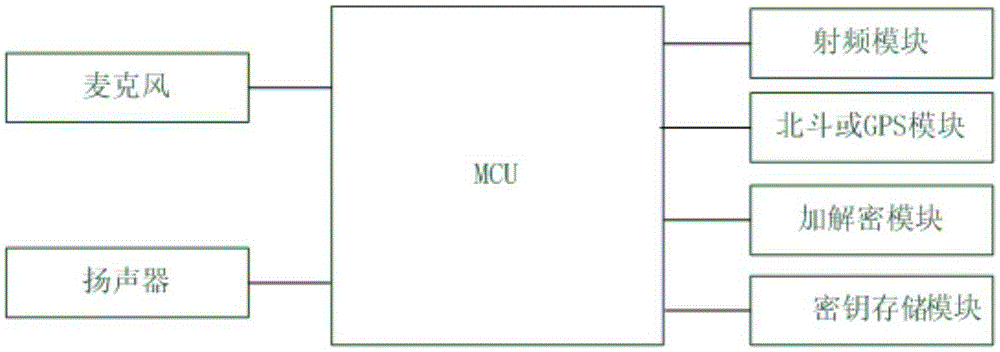
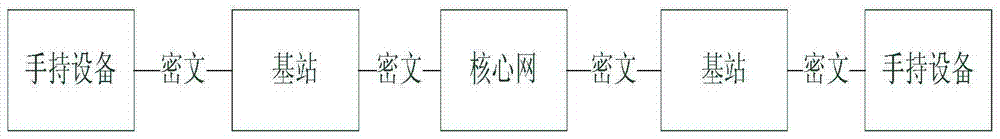
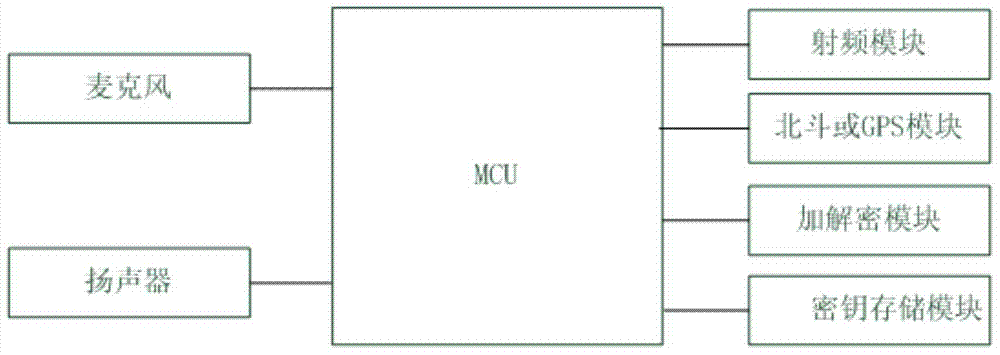
End-to-end hand-held device encryption method based on quantum cryptography and system
InactiveCN105337726AImprove securityIncrease independenceKey distribution for secure communicationHand heldHand held devices
The invention discloses an end-to-end hand-held device encryption method based on quantum cryptography and a system. The encryption method comprises following steps of storing quantum keys; initiating a call; synchronizing the quantum keys; performing synchronous confirmation; answering the call; and performing encryption communication. In the encryption communication, an MCU of a main calling end injects quantum communication keys Ksa into an encryption and decryption model; an MCU of a called end injects the quantum communication keys Ksa into the encryption and decryption model; the MCU of the called end using the quantum communication keys to encrypt the data; the encrypted data is sent out via a radio frequency module of the called end; a radio frequency module of the main calling end injects the received encrypted data into the encryption and decryption model for decryption; and after being decrypted, the data is played by a loudspeaker of the main calling end or displayed via a touch type display. The invention also discloses an end-to-end hand-held device encryption system based on quantum cryptography. The encryption method and system are highly safe, independent and easy, quick and simple to deploy.
Owner:ANHUI QASKY QUANTUM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Quantum cryptographic communication apparatus
InactiveUS7894604B2Key distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesOptoelectronicsQuantum emitter
Provided is a quantum cryptography communication apparatus capable of preventing a go photon pulse from being phase modulated and also capable of freely selecting any repetitive frequency of a light source. In the quantum cryptography communication apparatus, a quantum receiver apparatus includes: a light source; an optical path loop having a multiplexing / interfering means for generating time difference twin photon pulses from the photon pulses of the light source and for multiplexing and causing interference between a signal optical pulse corresponding to a retrograde quantum and a reference optical pulse; a bypass optical path having a phase modulator for phase modulating only the received reference optical pulse; and a photon detector for observing the interfered light passed through the optical path loop, and a quantum transmitter apparatus includes: a polarized wave rotating means for rotating polarization planes of the twin photon pulses at a right angle in a non-reciprocal manner; a phase modulator for phase modulating and returning the signal optical pulse passed through the polarized wave rotating means, to the quantum receiver apparatus; and a beam attenuating means.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
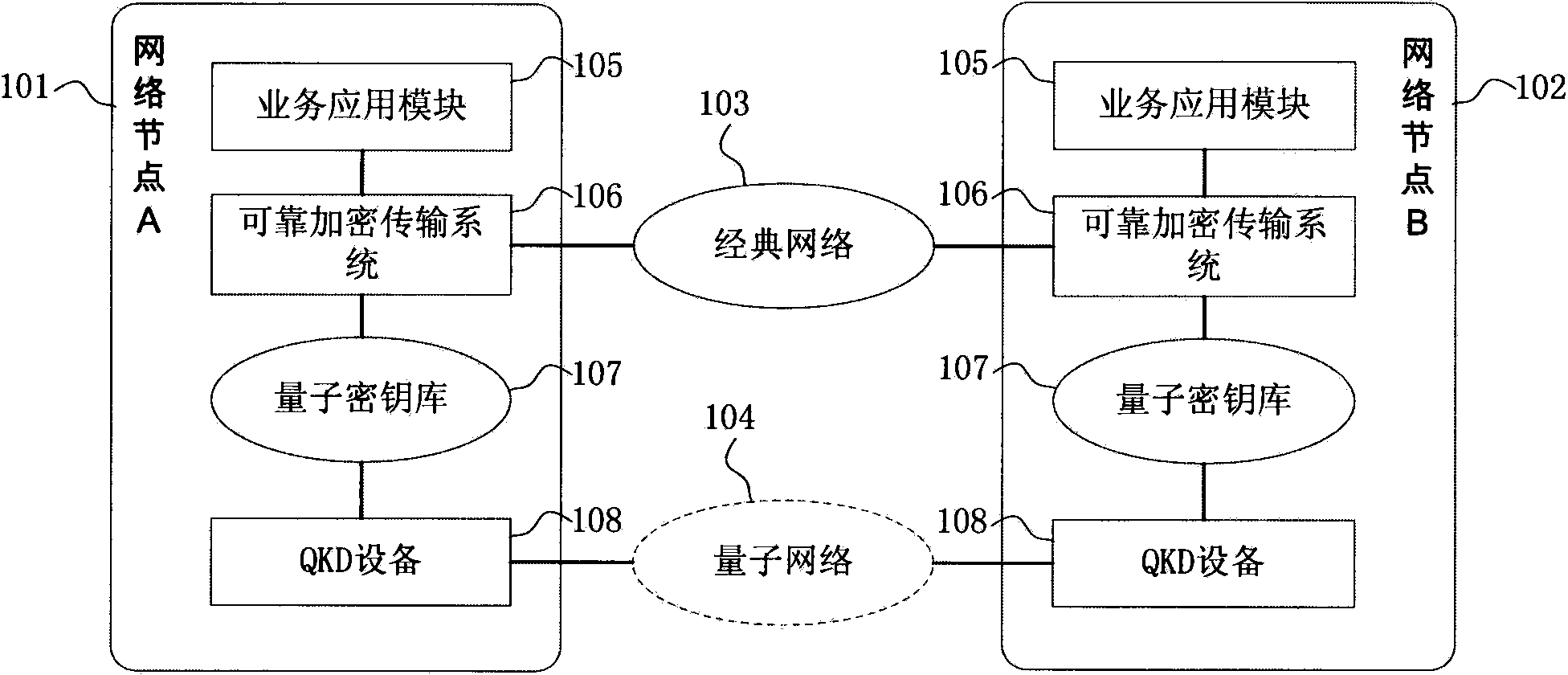
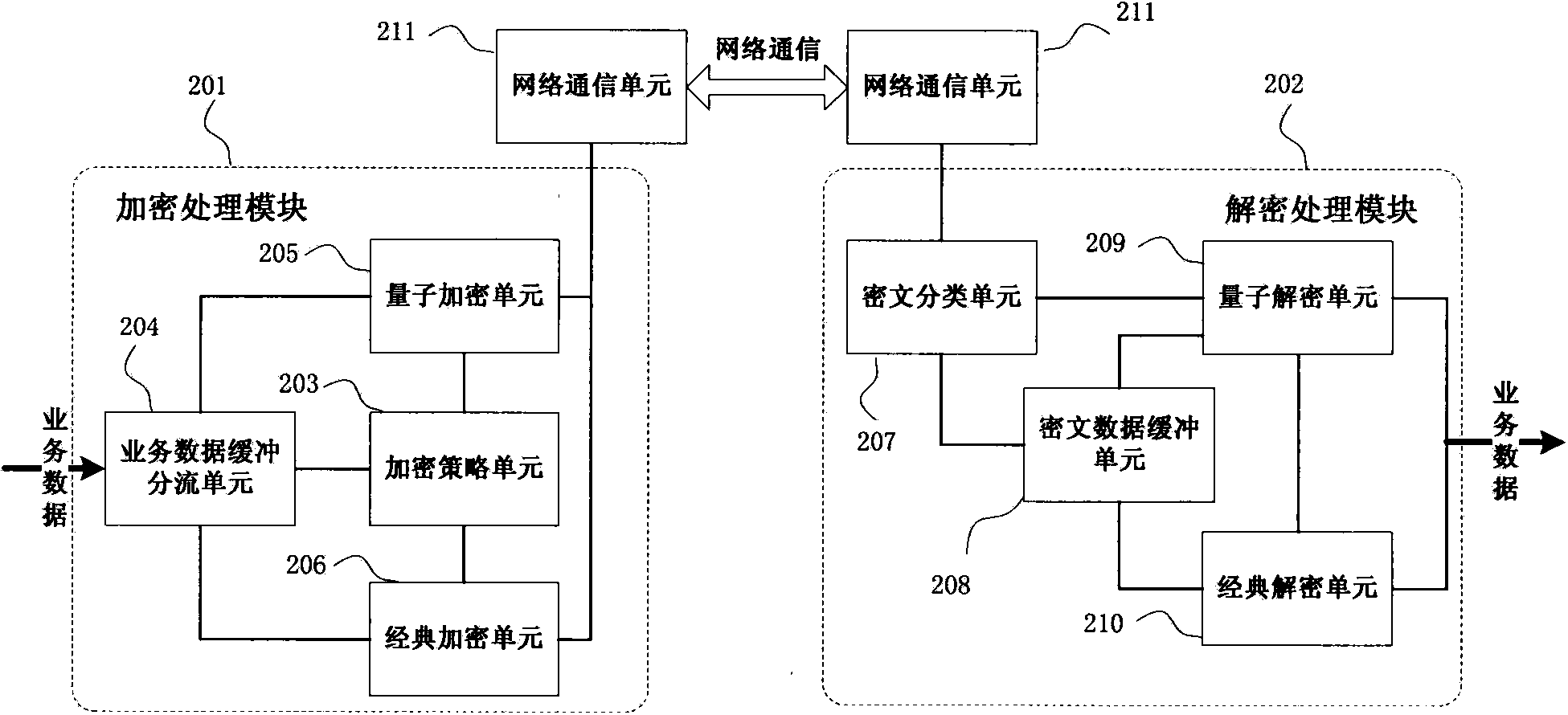
Reliable encryption transmission system and method of quantum cryptography network
ActiveCN103840936AImprove continuityImprove reliabilityKey distribution for secure communicationSynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesCiphertextDependability
The invention provides a reliable encryption transmission system of a quantum cryptography network. The reliable encryption transmission system comprises an encryption processing module and a decryption processing module, the encryption processing module is composed of an encryption strategy unit, a service data buffering shunt unit, a classic encryption unit and a quantum encryption unit, and the decryption processing module is composed of a cryptograph classification unit, a cryptograph data buffering unit, a classic decryption unit and a quantum decryption unit. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a reliable encryption transmission method of the quantum cryptography network. The classic encryption mode and the quantum one-time pad encryption mode are adopted for transmitting service data in a shunt mode, the shunt proportion of the service data can be timely and correspondingly changed according to changes of the quantum secret key supply-demand relationship, on the basis that the safety is guaranteed, the continuity of service data encryption transmission is improved, and the reliability of service data encryption transmission is improved. Meanwhile, the consumption of quantum secret key data is reduced, quantum secret key generation loads of the quantum cryptography network are reduced, and the cost of service data encryption transmission of the quantum cryptography network is reduced.
Owner:SHANDONG INST OF QUANTUM SCI & TECH
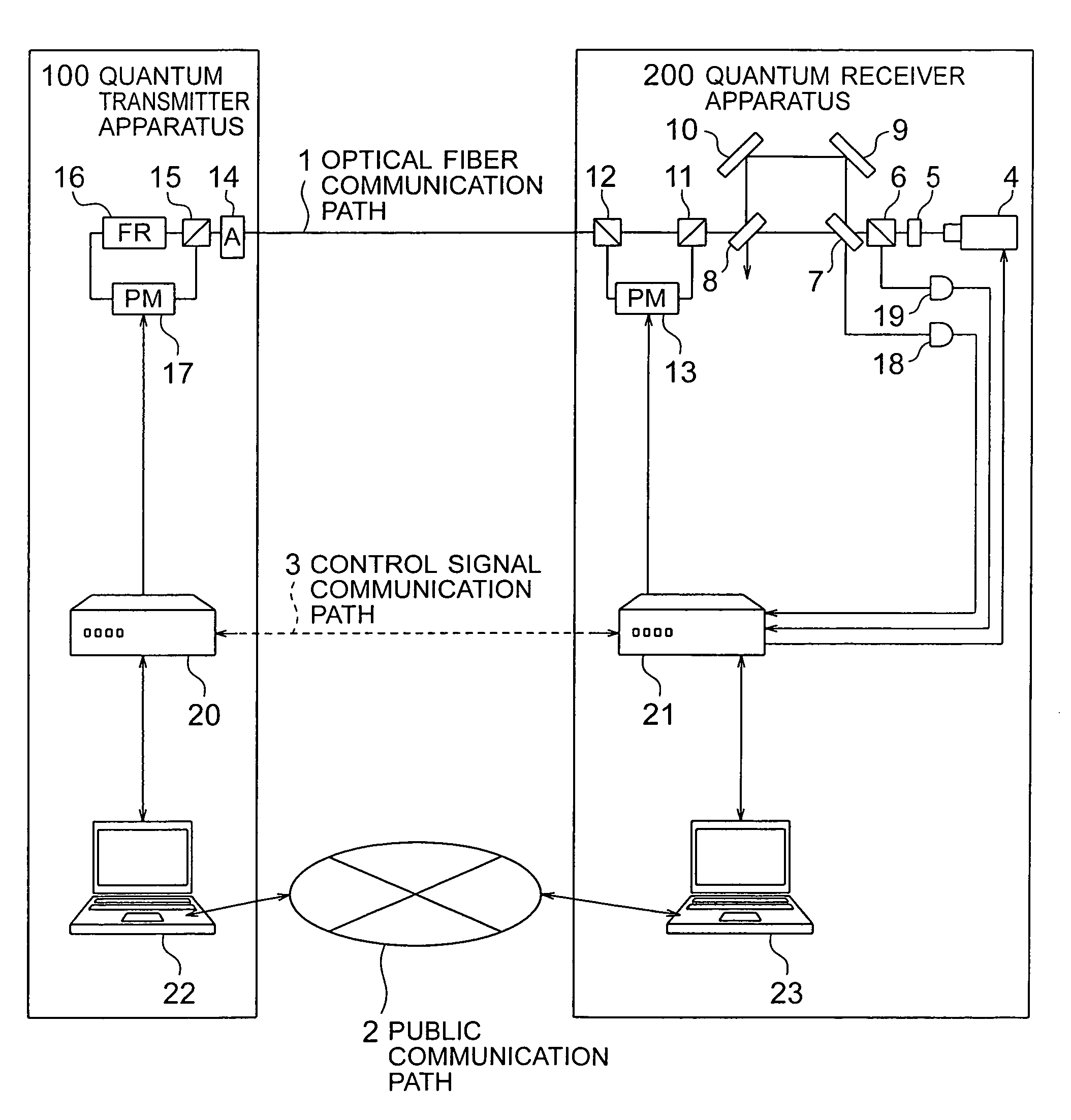
High-speed autocompensation scheme of quantum key distribution
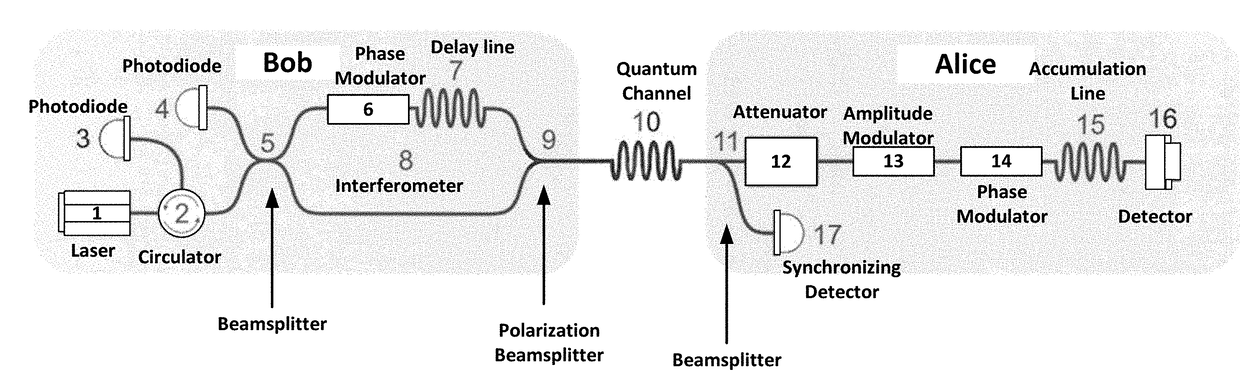
ActiveUS20180191496A1Key distribution for secure communicationPhotonic quantum communicationBeam splitterQuantum channel
The invention relates to quantum cryptography, and includes a communication system for transmitting a cryptographic key between the ends of a channel, including a transmitting node (Alice) comprising a beam splitter, an electro-optical attenuator, an amplitude modulator, a phase modulator, a storage line, a Faraday mirror, a synchronization detector; a receiving node (Bob) that includes avalanche photodiodes, a beam splitter, a circulator, a delay line, a phase modulator, a polarizing beam splitter, a Mach-Zehnder interferometer, and also a quantum channel for connecting these nodes. In this case, for the storage line is placed between the electro-optical phase modulator of the sender and the Faraday mirror. The limiting frequency of the laser pulse repetition at a fixed value of their width is increased, which makes it possible to use an autocompensation circuit at a frequency corresponding to the width of the laser pulse, which is the maximum possible result.
Owner:QRATE LLC
Quantum cryptography service network implementation structure
ActiveUS20110317836A1Eliminate needExtend the reach of the quantum keySynchronising transmission/receiving encryption devicesSecret communicationTelecommunications networkTerminal equipment
In order to overcome the limitation of the prior art quantum key terminal equipment not being able to operate across different segments, the present invention discloses a quantum cryptography service network implementation technique to let a point-to-point quantum key equipment in one segment be redesigned to cooperate with other quantum key equipment in other segments to form a quantum key service network. As opposed to the prior art technique of having each segment generates its own quantum key, the present invention can map one pair of quantum key equipment with another pair of quantum key equipment, or map multiple pairs of quantum key equipment connected in series to have quantum keys entirely or partly shared by the quantum key equipment. Therefore, the generated quantum keys can be used across different segments. Each node in the quantum key service network can provide the quantum key to nearby telecommunication equipment in the telecommunication network of the same premises.
Owner:CHUNGHWA TELECOM CO LTD
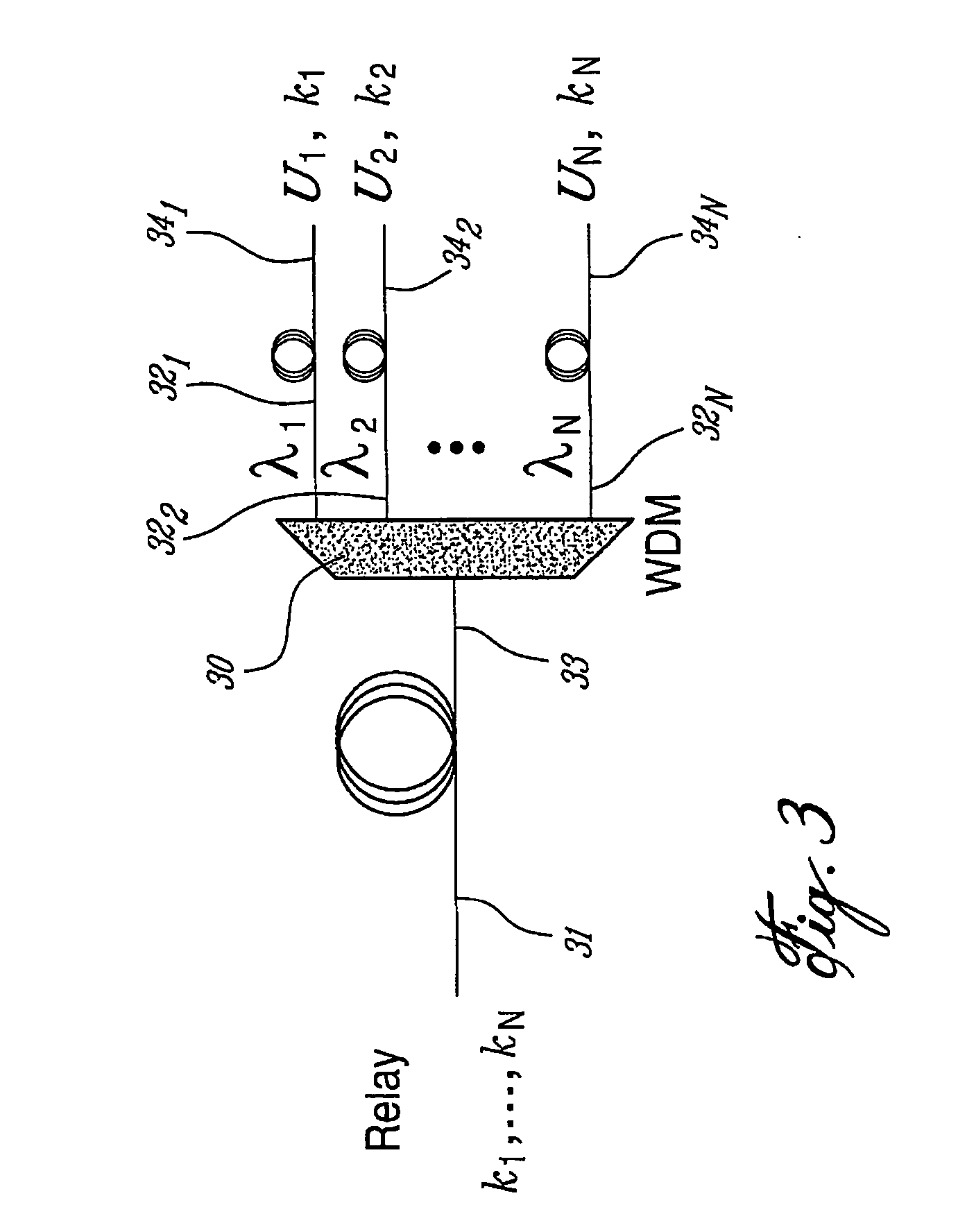
Multi-user quantum cryptography method and system using wavelength division multiplexing
InactiveUS20060002563A1Key distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationMultiplexerLength wave
A multi-user quantum cryptography system and method are described herein. The system comprises a relay including a quantum information server so configured as to generate quantum information communications having different wavelengths and a multiplexer so configured as to separate the different quantum information communications generated by the quantum information server by their wavelength and to supply each communication to a respective user.
Owner:BUSSIERES FELIX +2
Handheld device encryption method and system based on quantum cryptography
InactiveCN104780040AKey distribution for secure communicationSecurity arrangementComputer hardwareHand held devices
The invention discloses a handheld device encryption method based on the quantum cryptography. The method comprises steps as follows: quantum key storage, call making by a calling terminal, key synchronization at a called terminal, synchronization determination at the called terminal, call answering at the calling terminal, key synchronization at the calling terminal, synchronization determination at the calling terminal, cryptographic communication and key updating, wherein communication session keys Ksa used by the calling terminal and the called terminal have life cycles; after the communication session keys Ksa of the calling terminal and the called terminal reach the set states respectively in a communication process, the communication session keys Ksa are replaced with new the communication session keys Ksb, the communication session keys Ksb are injected into encryption and decryption modules of the calling terminal and the called terminal after replacement is succeeded, and the calling terminal and the called terminal adopt the communication session keys Ksb for cryptographic communication. The invention further discloses a handheld device encryption system based on the quantum cryptography. The method and the system have high safety, high independence, convenience in deployment, rapidness and simplicity.
Owner:ANHUI QASKY QUANTUM SCI & TECH CO LTD
System and method for quantum cryptography
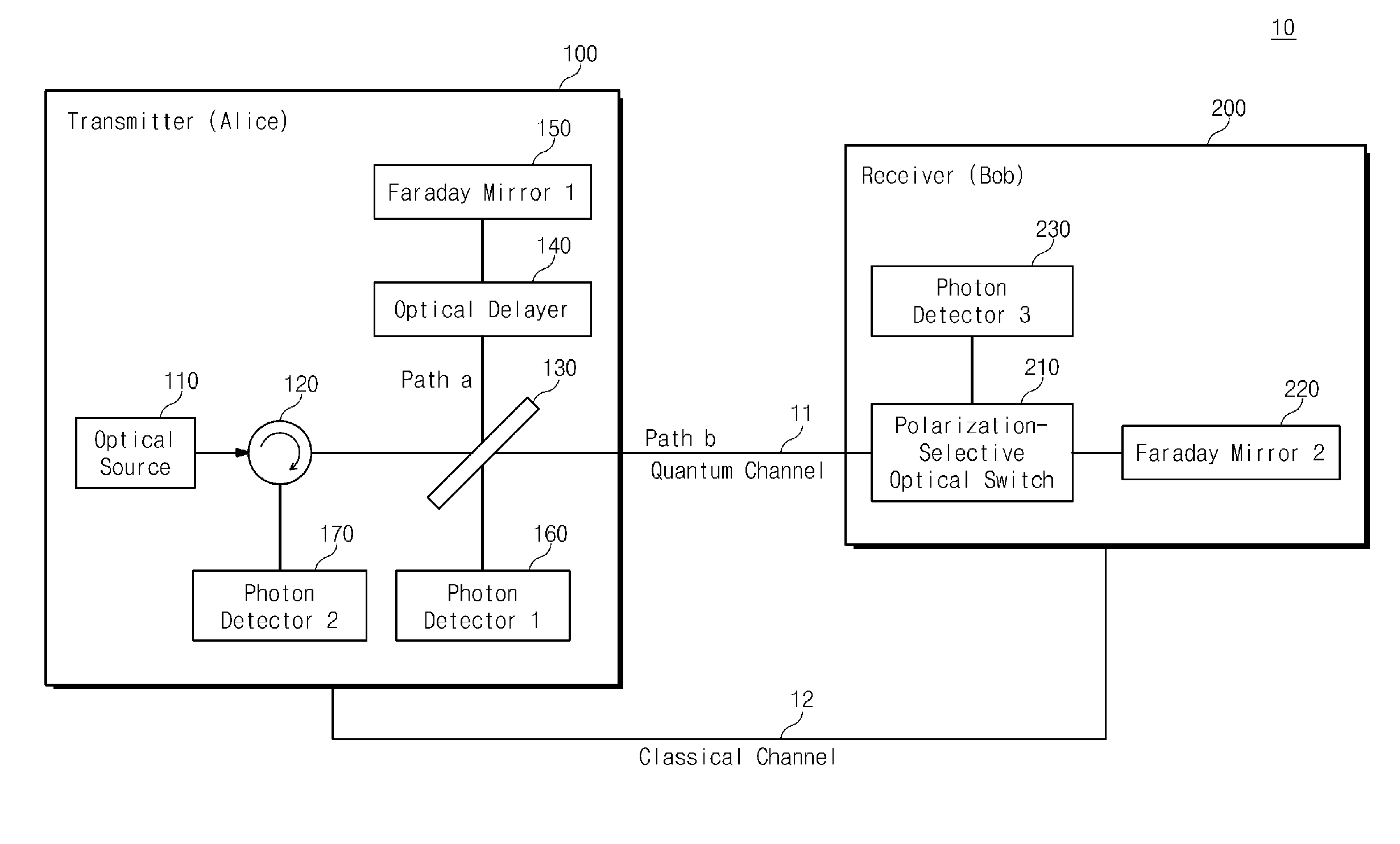
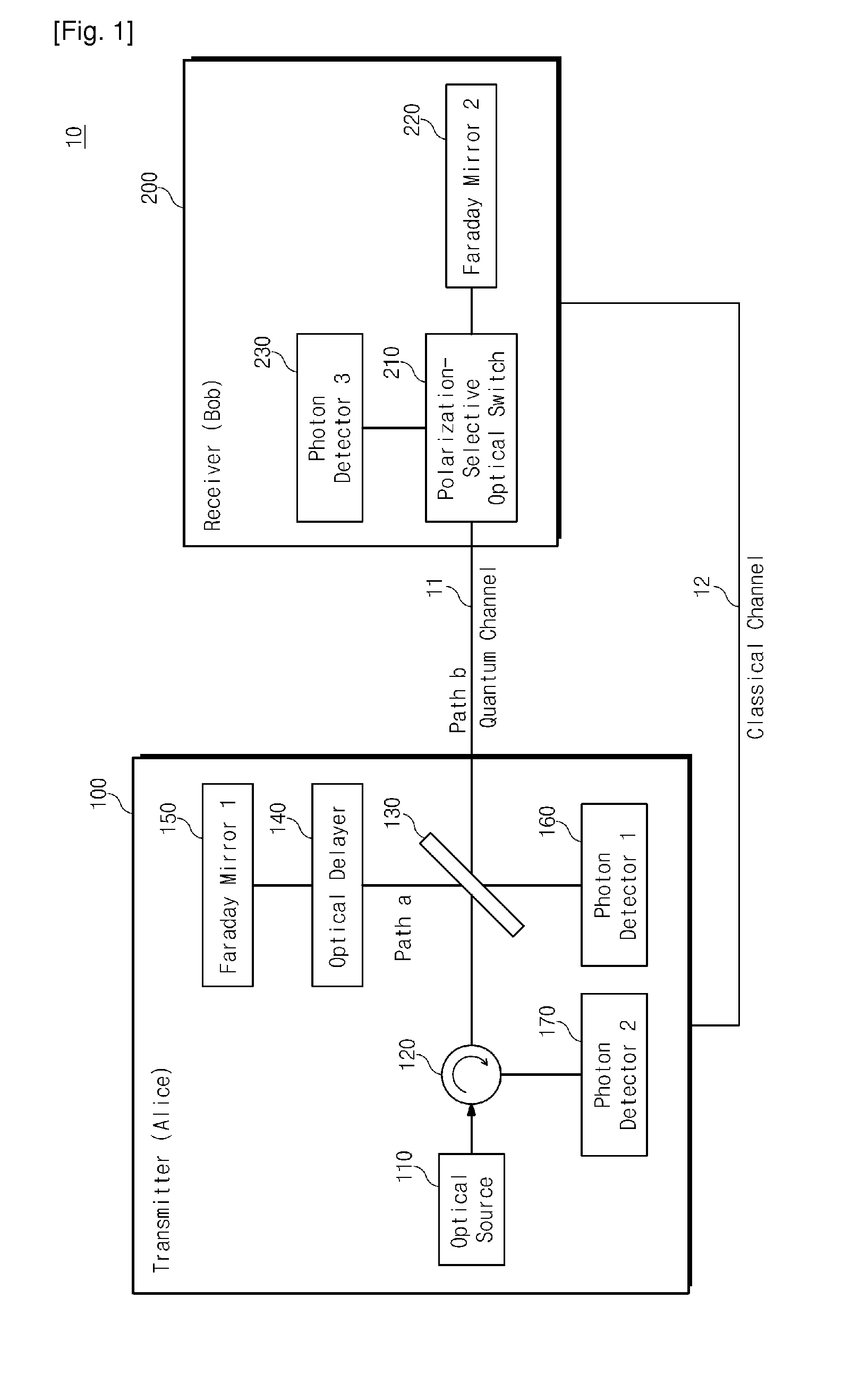
InactiveUS20110075839A1Guaranteed safe generationEfficient detectionKey distribution for secure communicationQuantum channelQuantum system
Provided are a system and a method for quantum cryptography. The method includes generating the same quantum cryptography key in a transmitter and a receiver by measuring a composite-quantum-system made of a plurality of sub-quantum-systems in each of the transmitter and the receiver connected to each other through a quantum channel, wherein a part of the sub-quantum-systems is confined within the transmitter in order not to expose the entire composite-quantum-system to an outside of the transmitter and the composite-quantum-system cannot be determined without disturbing the composite-quantum-system at the outside of the transmitter.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
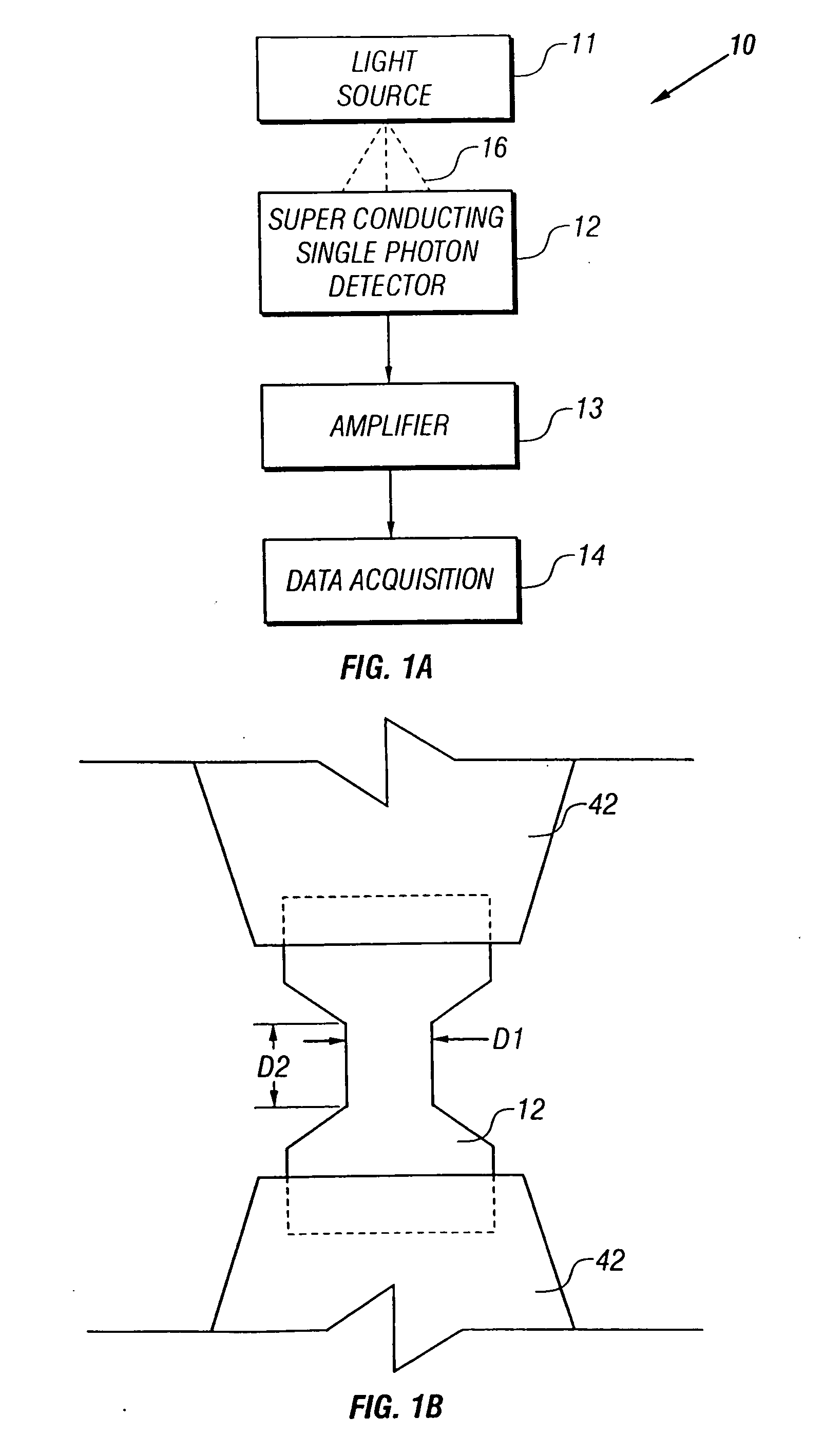
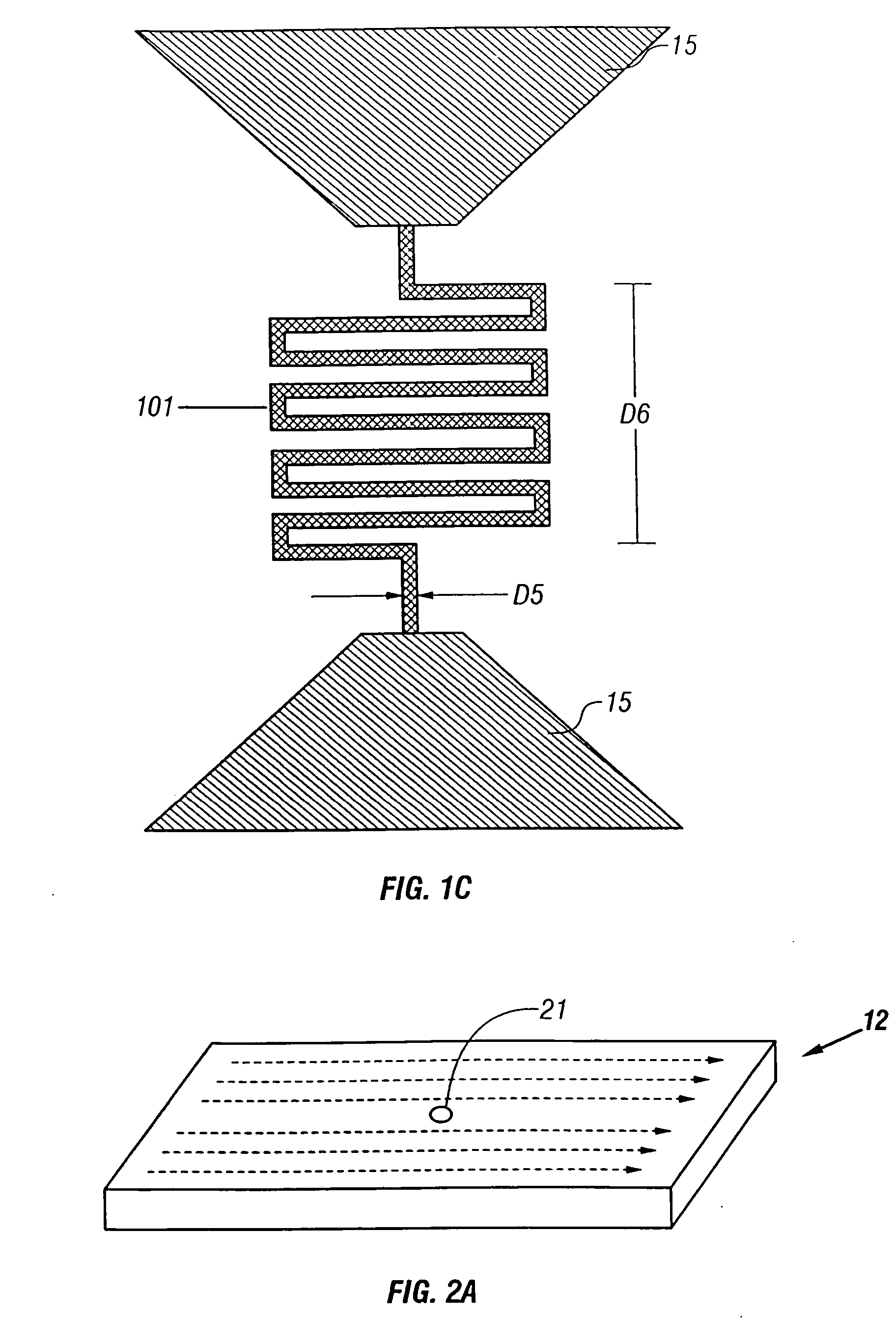
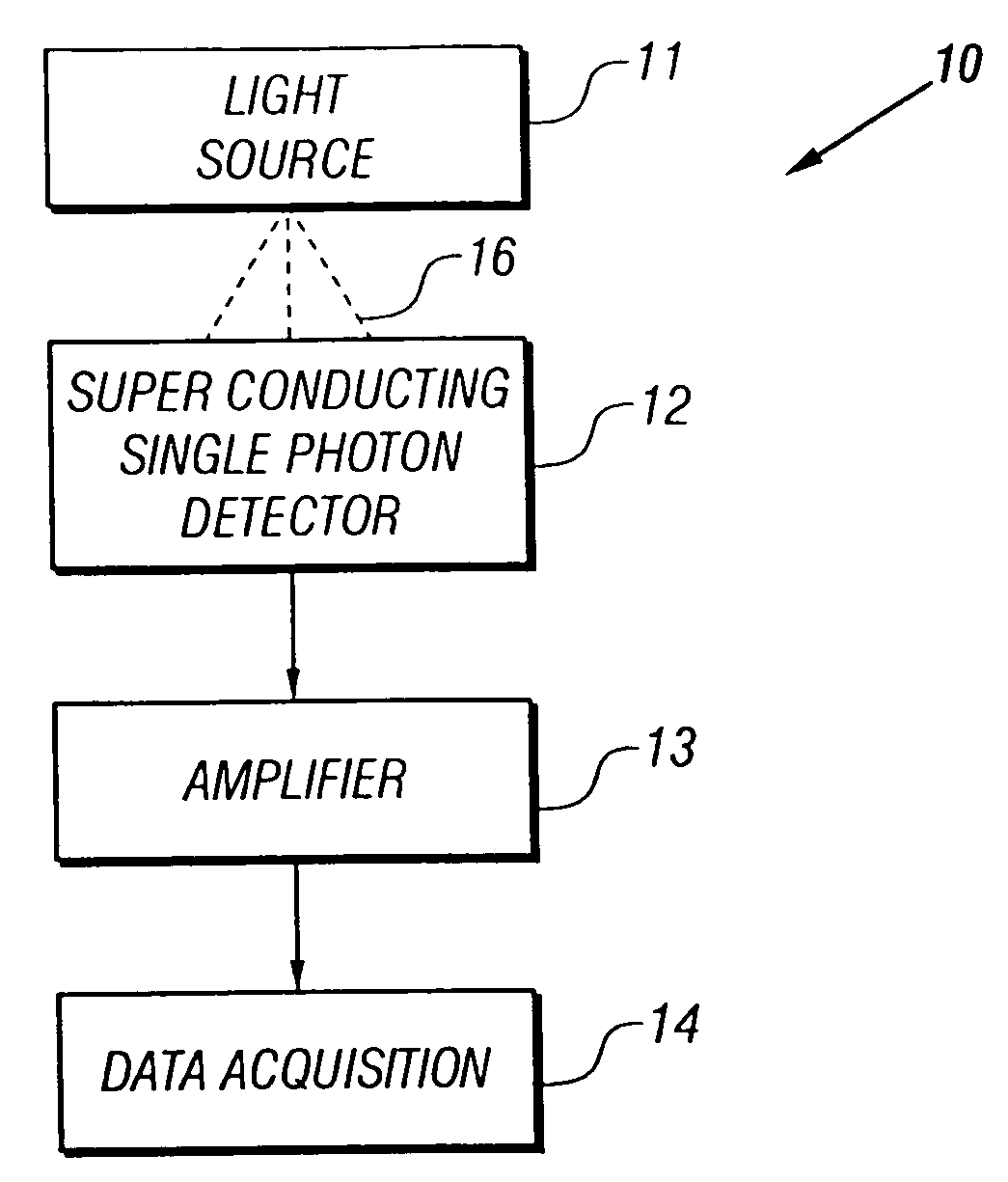
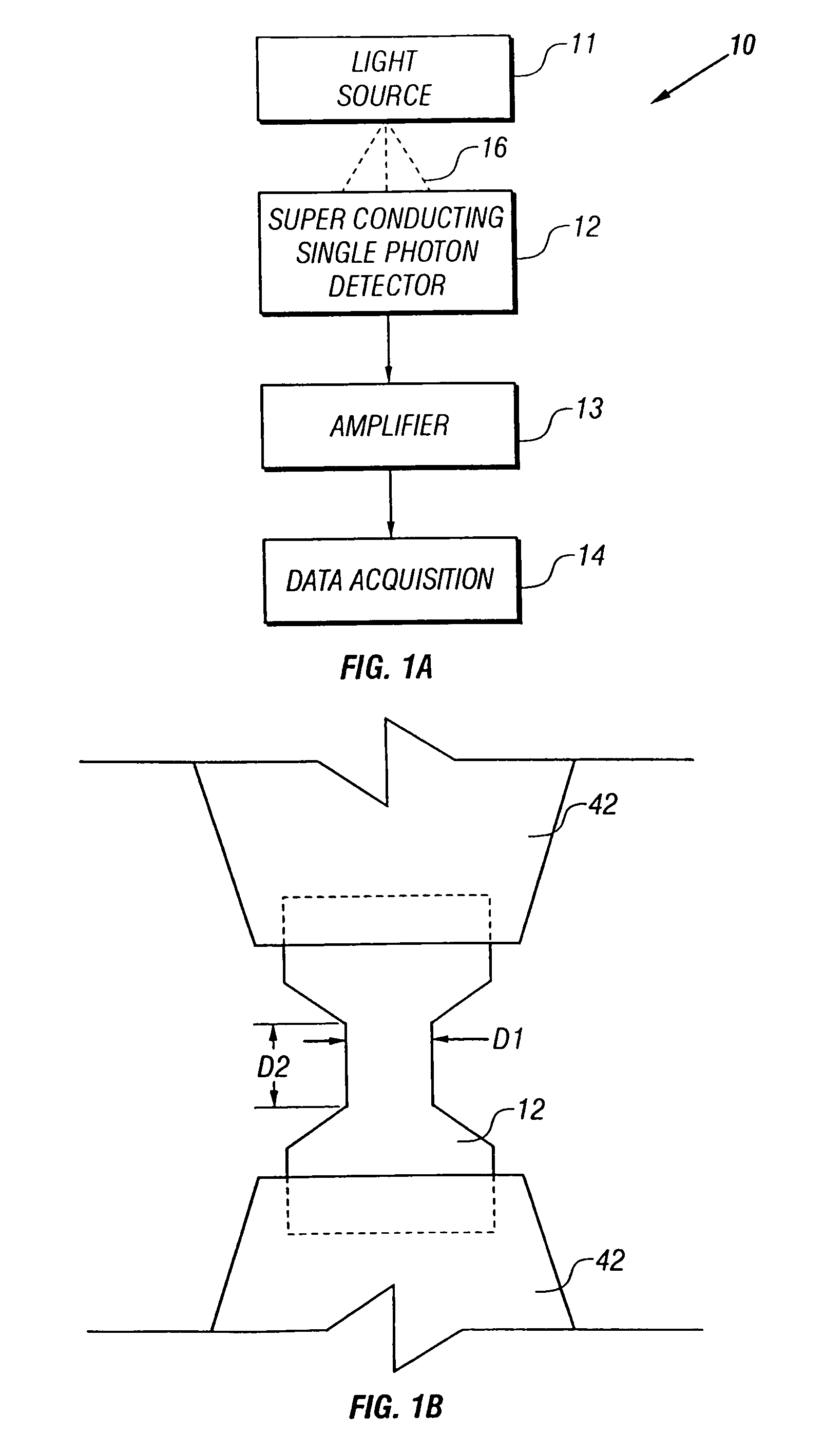
Superconducting single photon detector
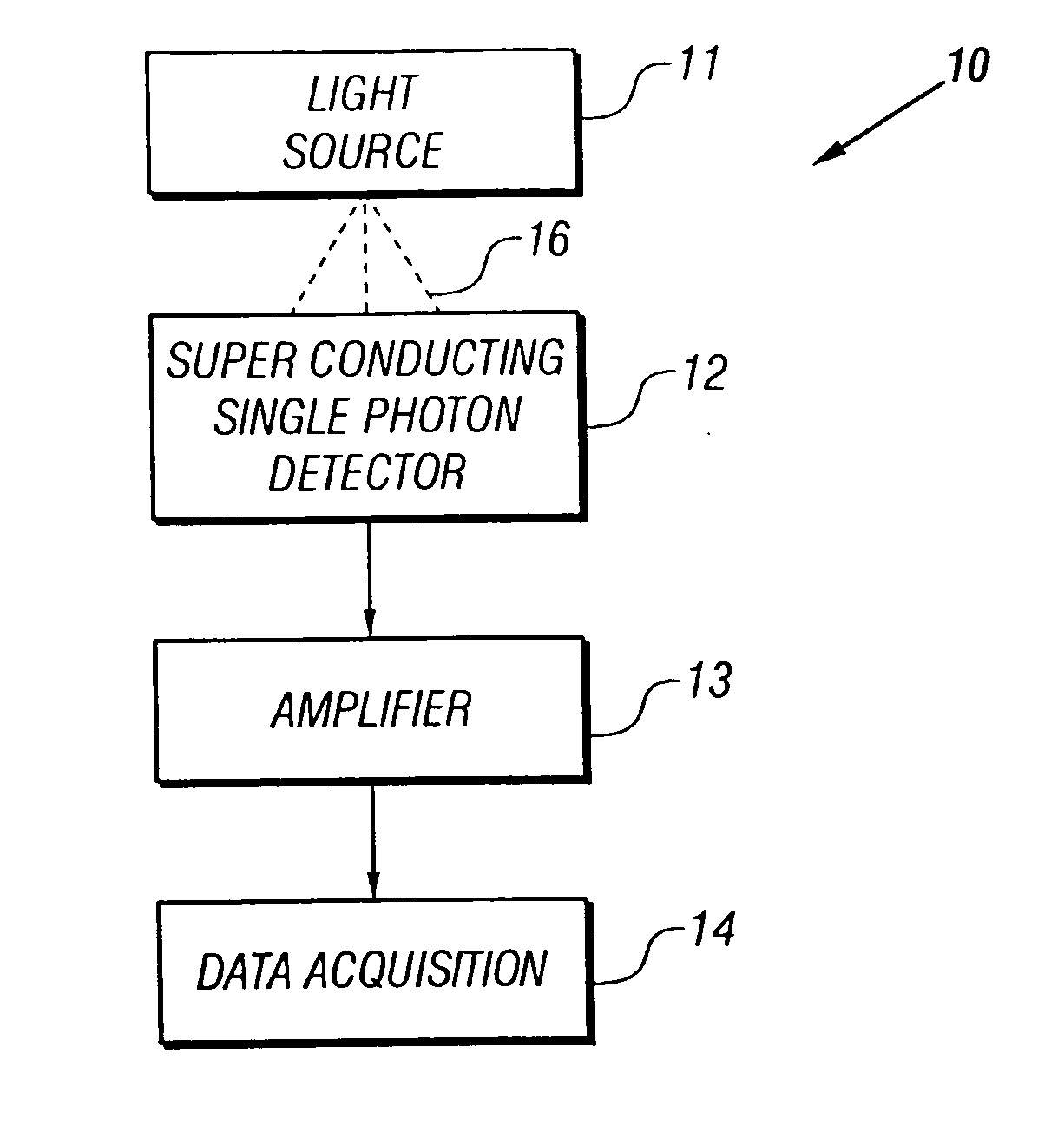
InactiveUS20050051726A1Improve quantum efficiencyIncrease surface areaSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDevice materialSuperconductor classification
A single-photon detector includes a superconductor strip biased near its critical current. The superconductor strip provides a discernible output signal upon absorption of a single incident photon. In one example, the superconductor is a strip of NbN (niobium nitride). In another example, the superconductor strip meanders to increase its probability of receiving a photon from a light source. The single-photon detector is suitable for a variety of applications including free-space and satellite communications, quantum communications, quantum cryptography, weak luminescence, and semiconductor device testing.
Owner:DCG SYST +1
Superconducting single photon detector
InactiveUS7049593B2Improve quantum efficiencyIncrease surface areaRadiation pyrometrySolid-state devicesSuperconductor classificationLuminescence
A single-photon detector includes a superconductor strip biased near its critical current. The superconductor strip provides a discernible output signal upon absorption of a single incident photon. In one example, the superconductor is a strip of NbN (niobium nitride). In another example, the superconductor strip meanders to increase its probability of receiving a photon from a light source. The single-photon detector is suitable for a variety of applications including free-space and satellite communications, quantum communications, quantum cryptography, weak luminescence, and semiconductor device testing.
Owner:DCG SYST +1
Mobile device having quantum cryptographic security function for mobile commerce, and authentication method
ActiveUS20170324552A1Improve securityLow costKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageQuantum gateCommunication device
Disclosed herein are technologies regarding a communication device and server which are capable of cryptographic communication based on quantum cryptography. The communication device includes: a quantum signal generation unit configured to generate a series of first quantum signals by using a first quantum filter; an optical transmission unit configured to send the series of first quantum signals to a server; and a processor configured to select the first quantum filter based on a series of randomly generated first quantum states, and to control the quantum signal generation unit to generate the series of first quantum signals by using the first quantum filter.
Owner:FIRST QUANTUM INC
Method and system for using quantum cryptography in safe IP communication
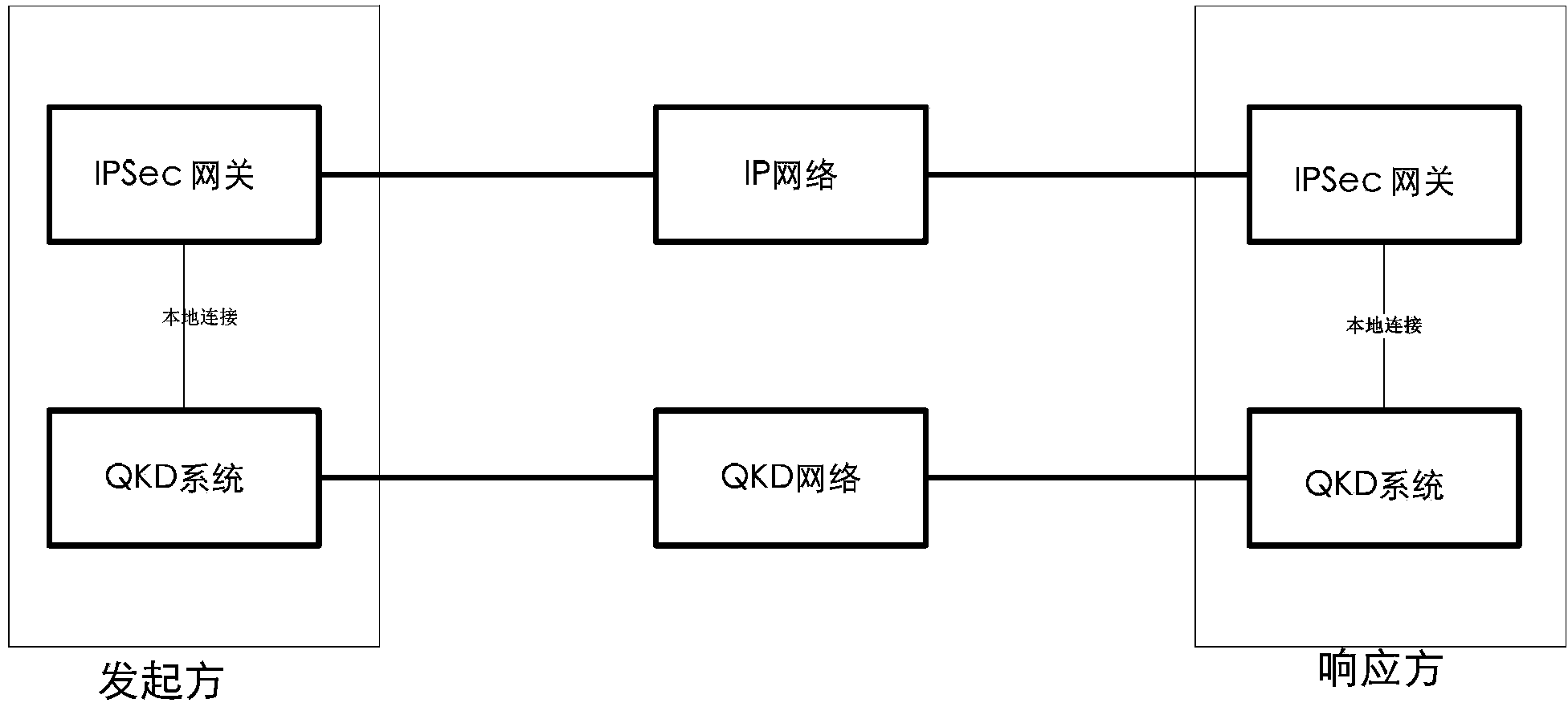
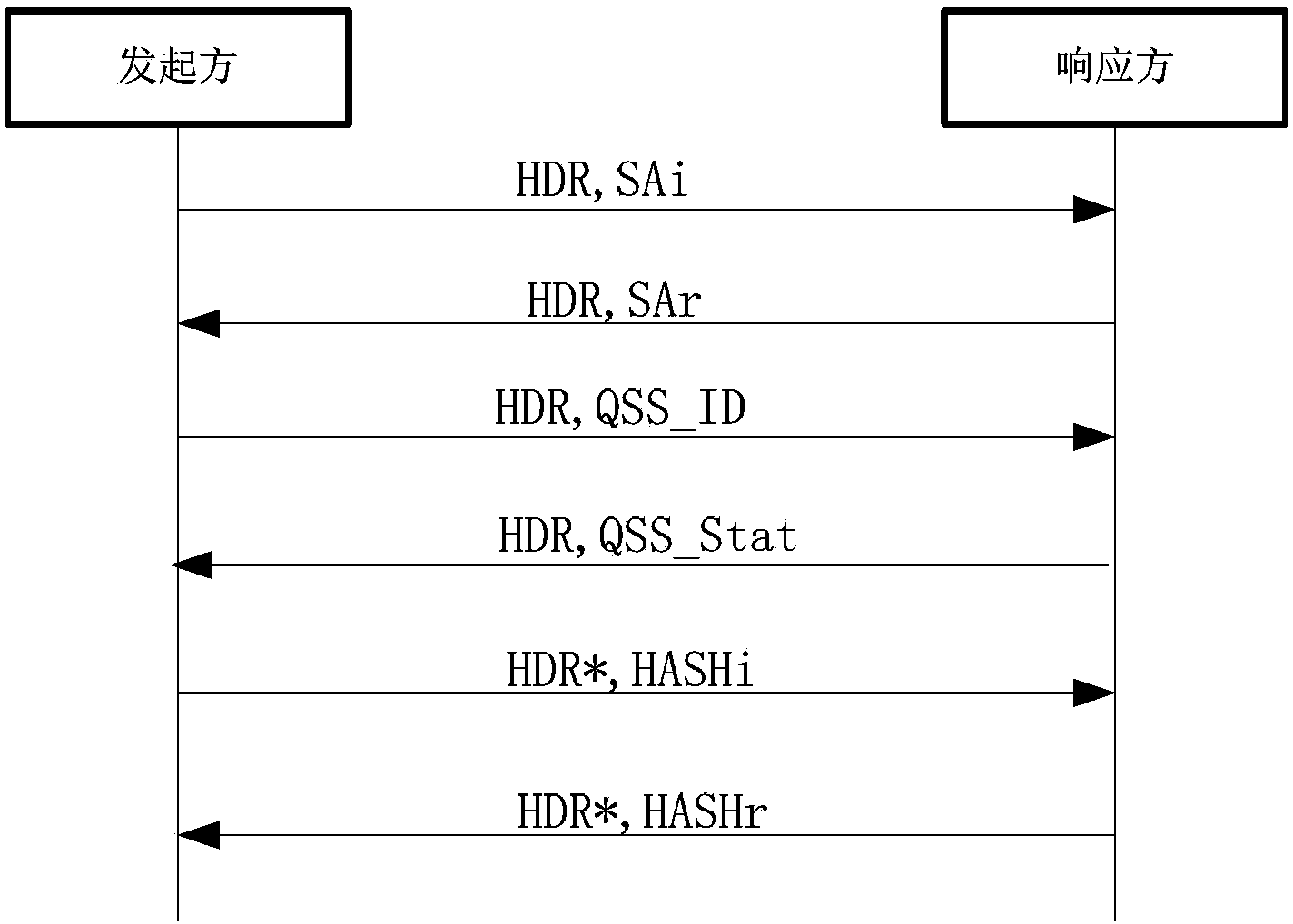
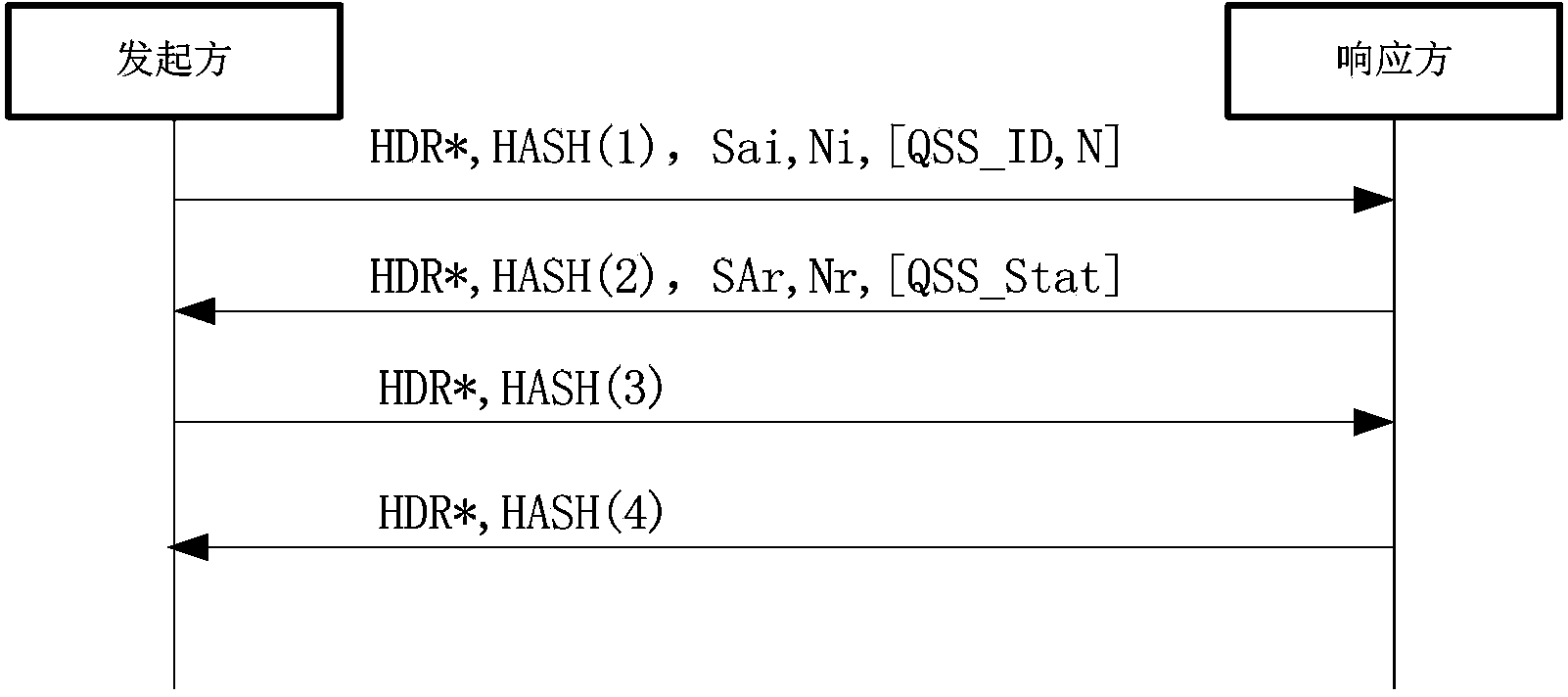
ActiveCN103441839AImprove securityFix compatibility issuesKey distribution for secure communicationKey exchangeIPsec
The invention provides a method and system for using the quantum cryptography in safe IP communication. The method is on the basis of a framework defined by an ISAKMP and comprises the following steps that quantum keys are distributed and a shared secret is established; IQKE SA negotiation is conducted; IPSec SA negotiation is conducted; session keys are generated. According to an IQKE protocol defined by the method and system, the framework defined by the ISAKMP is adopted and is independent of a standard IKE protocol, the problem existing in the compatibility of the standard IKE protocol and a QKD system can be avoided so that the safety of the quantum keys generated by the IPSec through the QKD system can be enhanced; in addition, according to the IQKE protocol, the quantum keys generated by the QKD system are adopted and serve as pre-shared keys, so that the adoption of the typical key exchange algorithm is not needed and the complexity of key negotiation is reduced. QIKE and QKD can be conducted in parallel; according to the QKD system with the low speed, the key storage technology is adopted; according to the QKD system with the high speed, OTP encryption can be achieved, so that the unconditional safety is achieved. The method and system are significant for improvement of the safety of IP communication.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Quantum key distribution system and method based on continuous variable measurement equipment independence
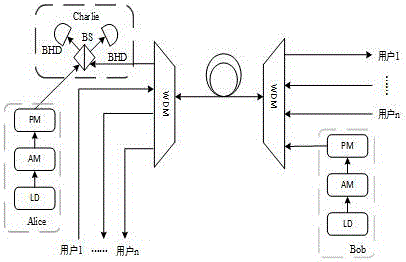
InactiveCN106685658AObvious advantage of metropolitan area networkKey distribution for secure communicationAlice and BobKey generation
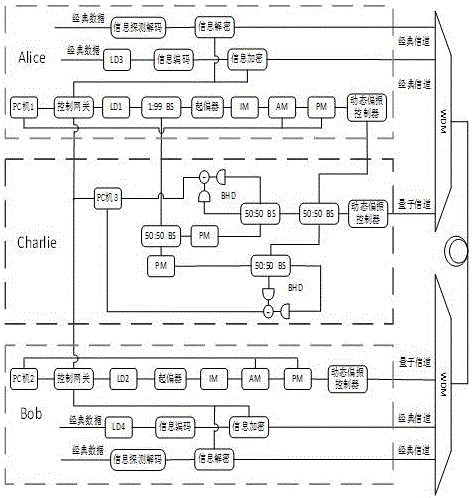
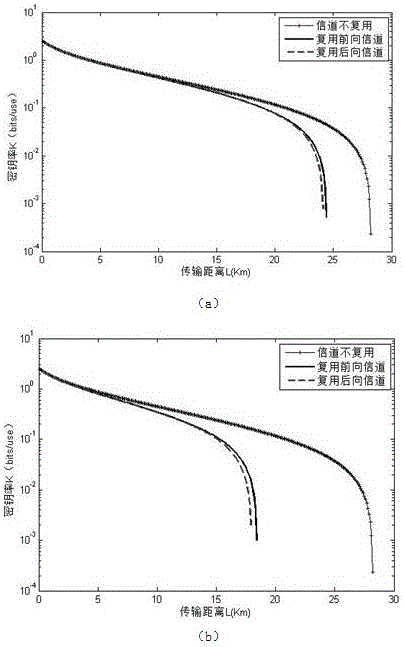
The invention provides a quantum key distribution system and method based on continuous variable measurement equipment independence. The quantum key distribution system comprises a sender Alice and a receiver Bob, and is characterized in that the receiver Bob is connected with a balance homodyne detector BHD through a wavelength division multiplexer WDM; the sender Alice is connected with the balance homodyne detector BHD at Alice and Bob ends; after a continuous wave laser device (LD) passes through an intensity modulator (IM), light pulse is formed by attenuation; Gaussian-modulation encoding of a coherent state is finished after the light pulse is processed by an amplitude modulator (AM) and a phase modulator (PM) under the control of a random number generated by a PC (Personal Computer) machine; then a result is sent to a third party Charlie; generated noises have relatively small influences on the system; influences on a safety key generation speed of the system, caused by forward transmission and backward transmission of a channel can be ignored; and advantages of a metropolitan area network based on a CV-MDIQKD quantum cryptography communication system are very obvious, and a foundation can be laid for commercialized and networked application in the future.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Incorruptible public key using quantum cryptography for secure wired and wireless communications
ActiveUS20160112192A1Communication securitySecure transmissionKey distribution for secure communicationElectric digital data processingFuture proofQuantum
A hardware system and encryption method that generates encryption keys based on quantum mechanical phenomena that can be delivered directly, over public wired and wireless channels, to communicating devices. The encryption strength is derived from physical phenomena and not mathematical complexity and, therefore, is “future proof” against advances in computational power. The present invention allows pre-existing networked devices to communicate securely within a geographically defined “protection zone.”
Owner:QUBITEKK
Quantum cryptography based on phase entangled photons
A quantum cryptography system [100] may include a transmitter [110] configured to generate entangled first and second photons, modulate and detect the first photon, and transmit detection information and the second photon. The system [100] may also include a receiver [160] configured to modulate the second photon. The receiver [160] may also be configured to detect the second photon based on the detection information.
Owner:RAYTHEON BBN TECH CORP
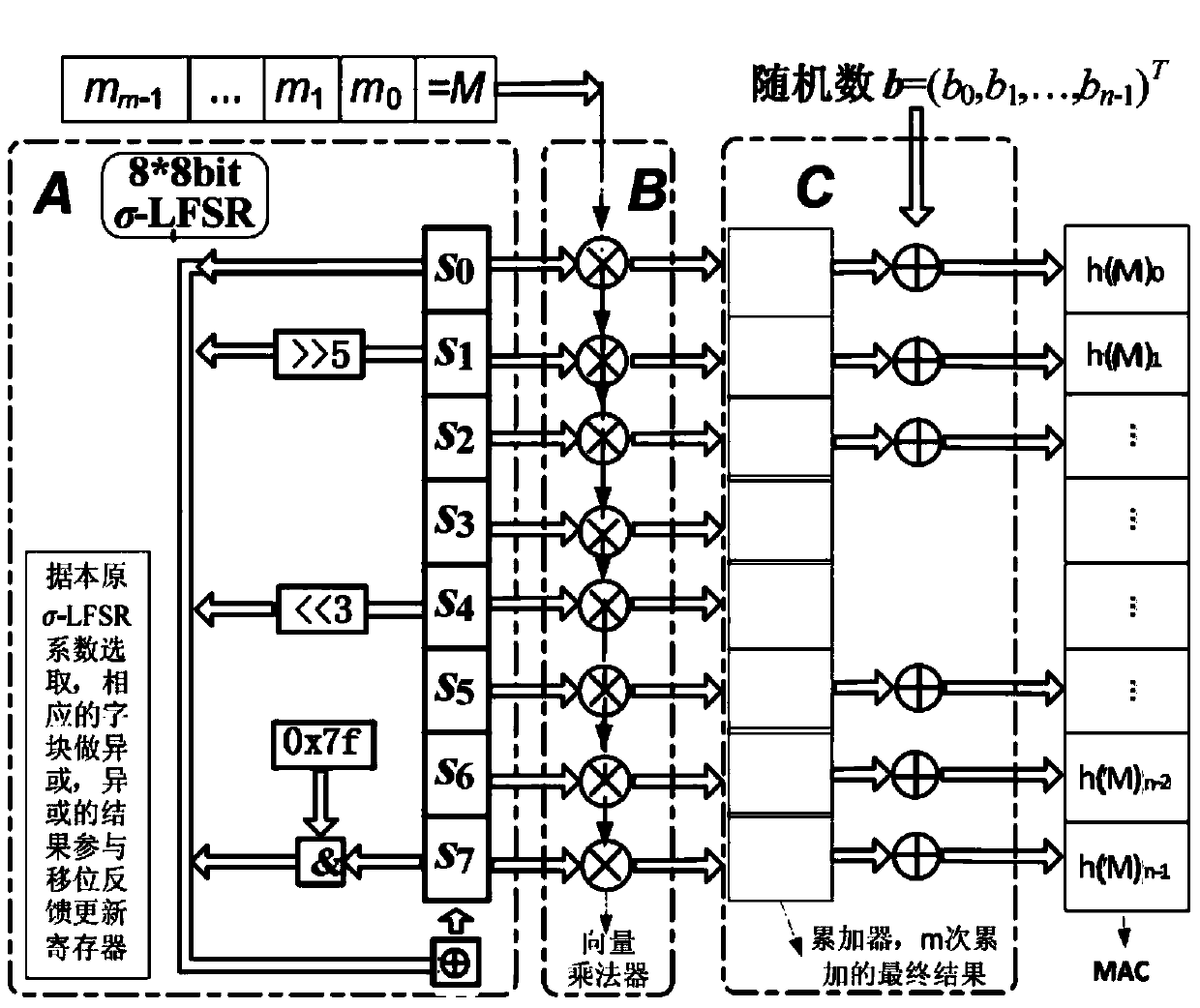
Efficient generic Hash function authentication scheme suitable for quantum cryptography system
ActiveCN104270247AEnsure safetyReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHash functionHash-based message authentication code
The invention discloses an efficient generic Hash function authentication scheme suitable for a quantum cryptography system. In the scheme, a word-based design way is adopted. The scheme comprises the following steps: initializing a shared key of both parties and a word linear feedback shift register; performing vector multiplication on an authentication message and a register state in sequence by using an iteration and vector multiplier of the word linear feedback shift register; performing accumulation through an accumulator; performing exclusive or processing on a random number to obtain a message authentication code; and transmitting an authentication message and the message authentication code to the other party to realize an identity authentication function. The authentication scheme disclosed by the invention is clear in design principle, a design way is open, and any manual security defect does not exist; through the authentication scheme, an ideal safety security attribute can be achieved, and an efficient identity authentication function can be provided for the quantum cryptography system; and the authentication scheme has the characteristics of low occupation of resources, high portability and high platform adaptability.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
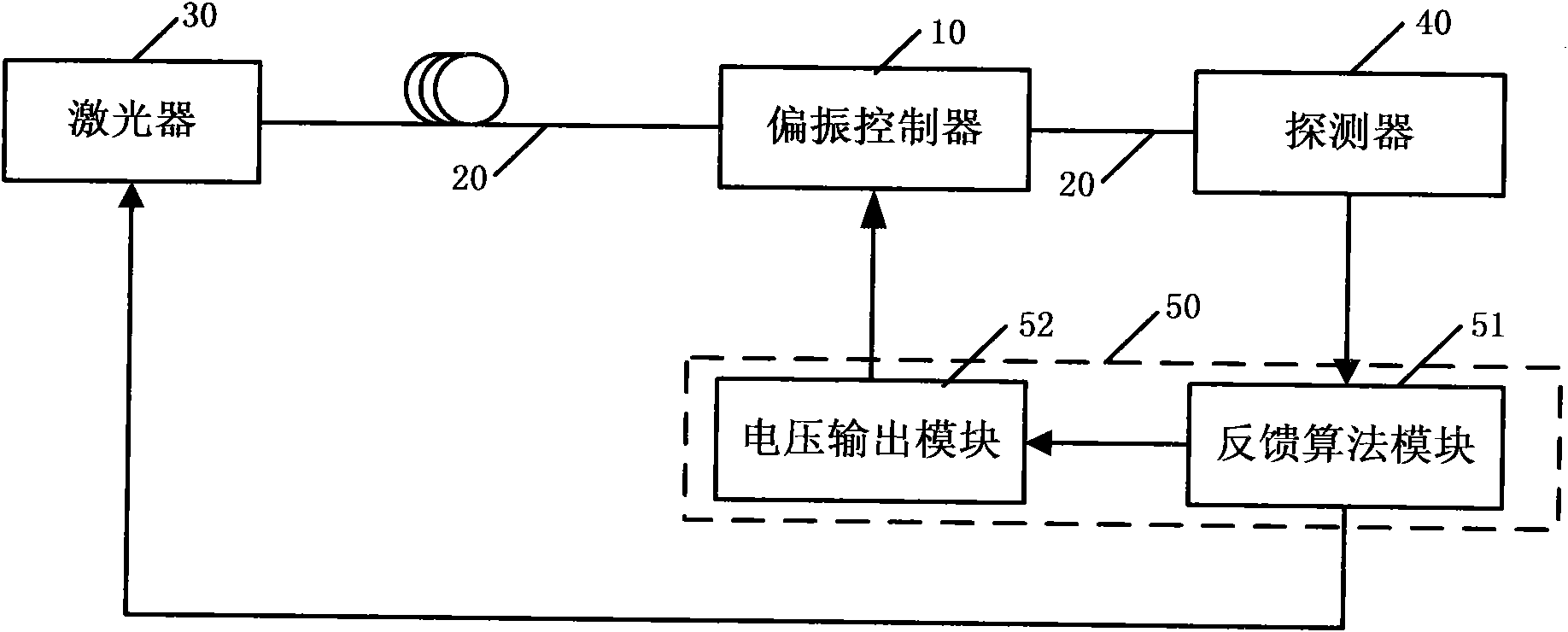
Quantum cryptography distributing polarization feedback system and implementation method thereof
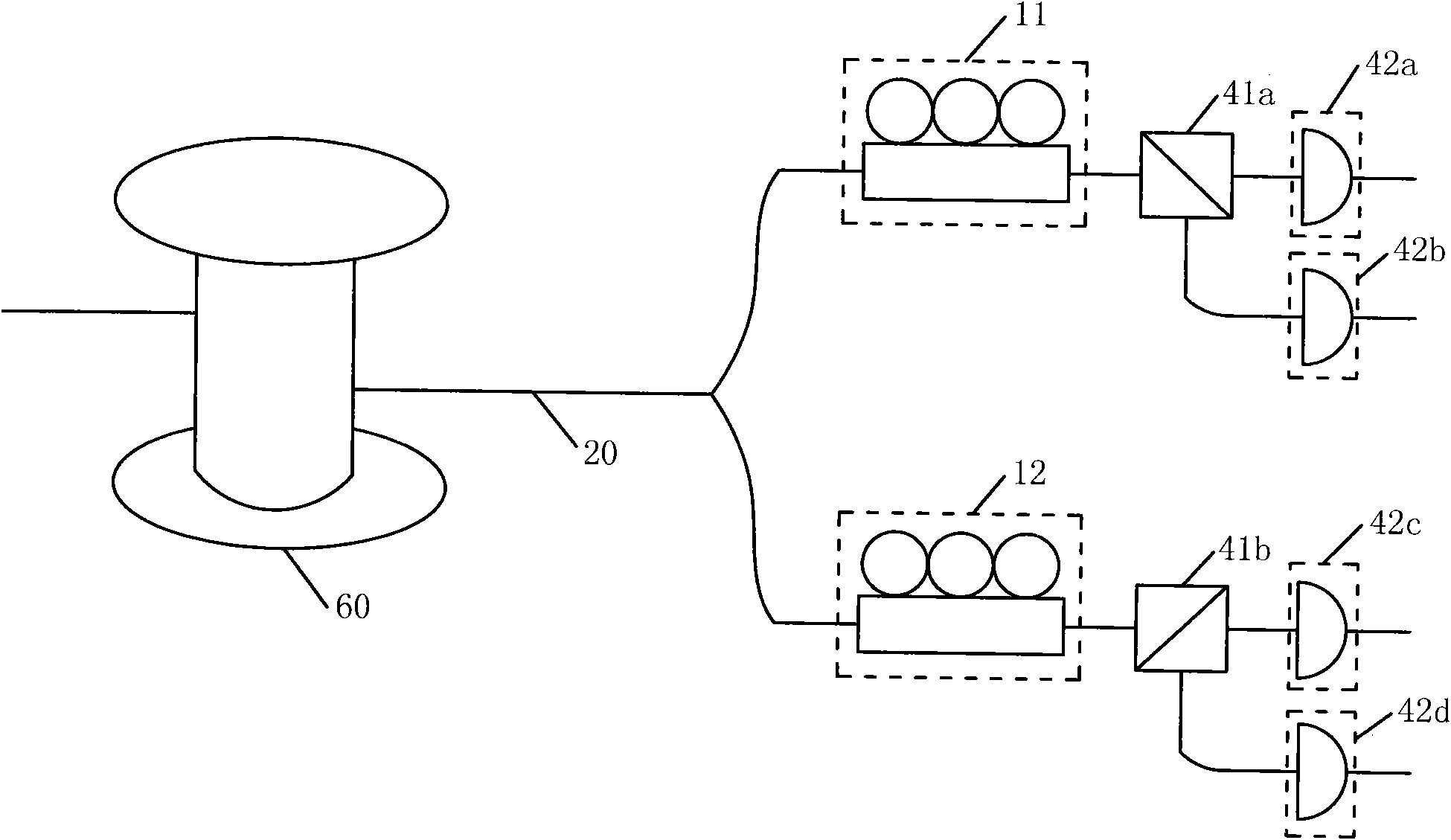
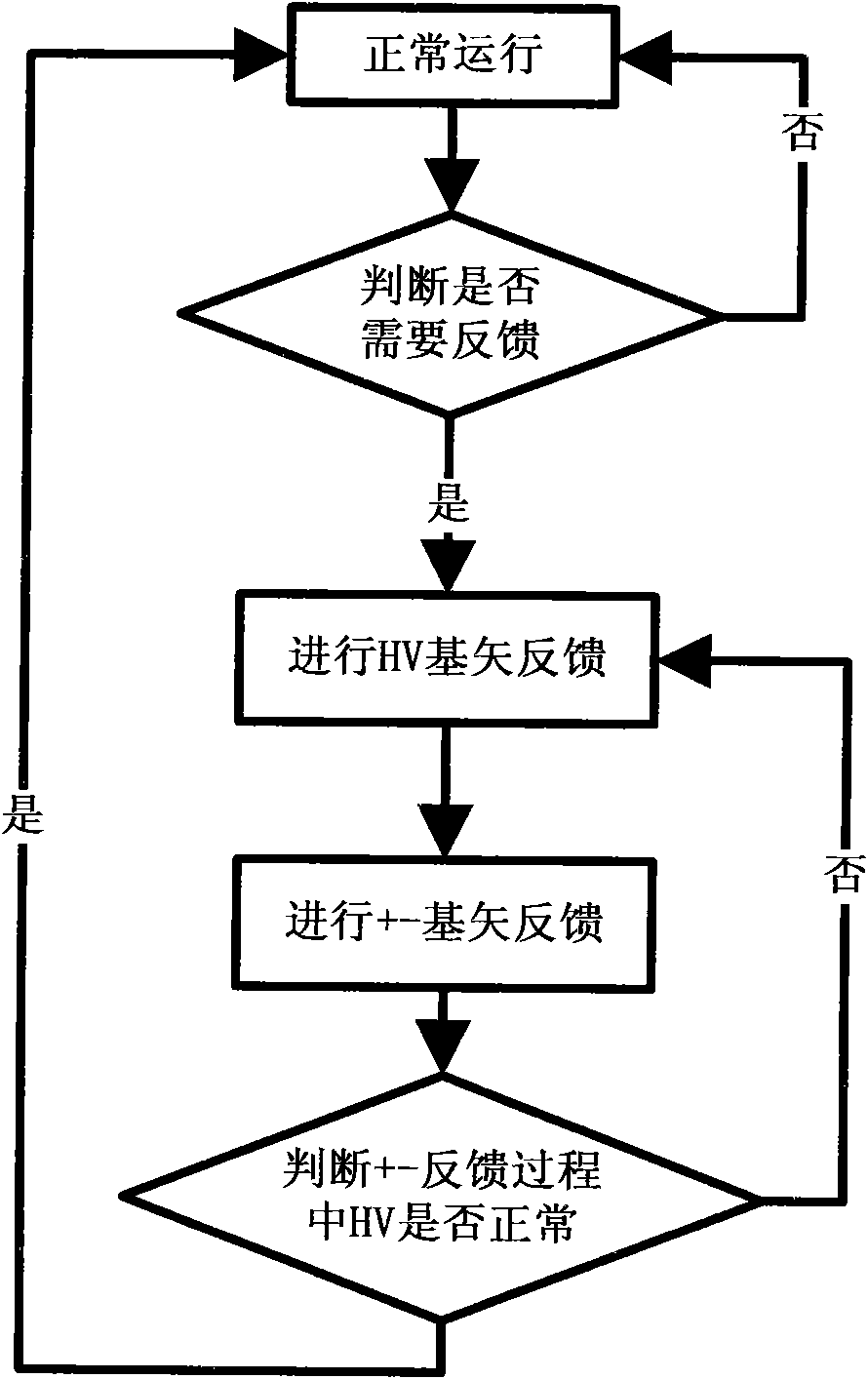
The invention relates to an implementation method of a quantum cryptography distributing polarization feedback system comprising the steps of: a signal generated by a laser entering a polarization controller and a detector through a channel optical fiber in order, when the signal enters the detector, the detector beginning to count; when a system error rate is bigger than a pre-setting value, a polarization feedback module working; the laser sending out special polarized light, the polarization feedback module sending out a polarization feedback signal to the polarization controller, and the polarization controller adjusting the output signal according to the voltage variation. The implementation method also comprises the following steps of: initiating a polarization feedback by a receiver, transmitting orders through reliable connection of a sender and the receiver, controlling the sender to send polarized lights, and adjusting the polarization to the required state by the receiver through controlling the polarization controller of a corresponding HV / +- basis vector. The polarization feedback module controls the laser of the sender to emit light in different polarization directions according to needs, feeds the light back at the receiver and compensates the influences brought by the disturbance of the channel optical fiber.
Owner:QUANTUMCTEK
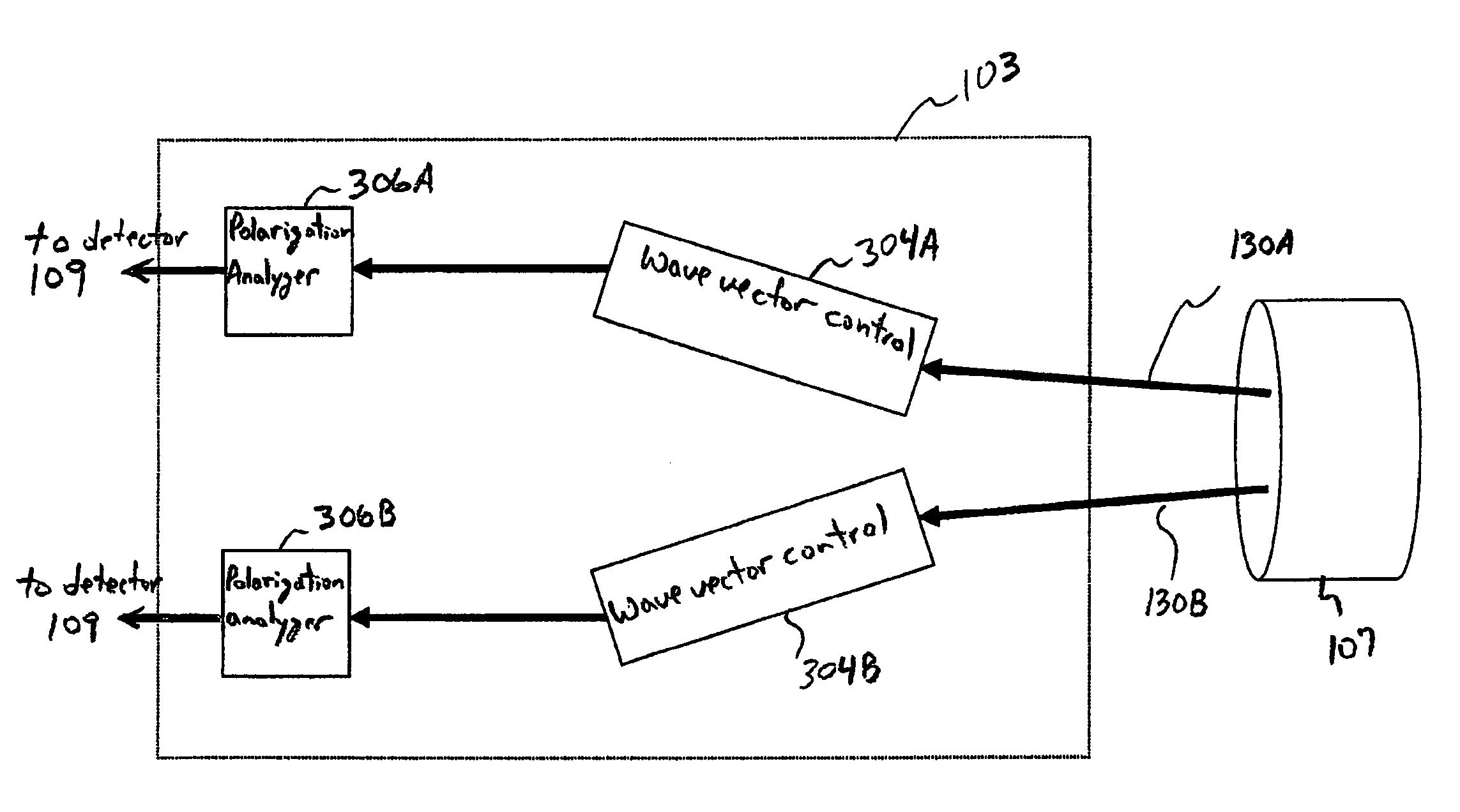
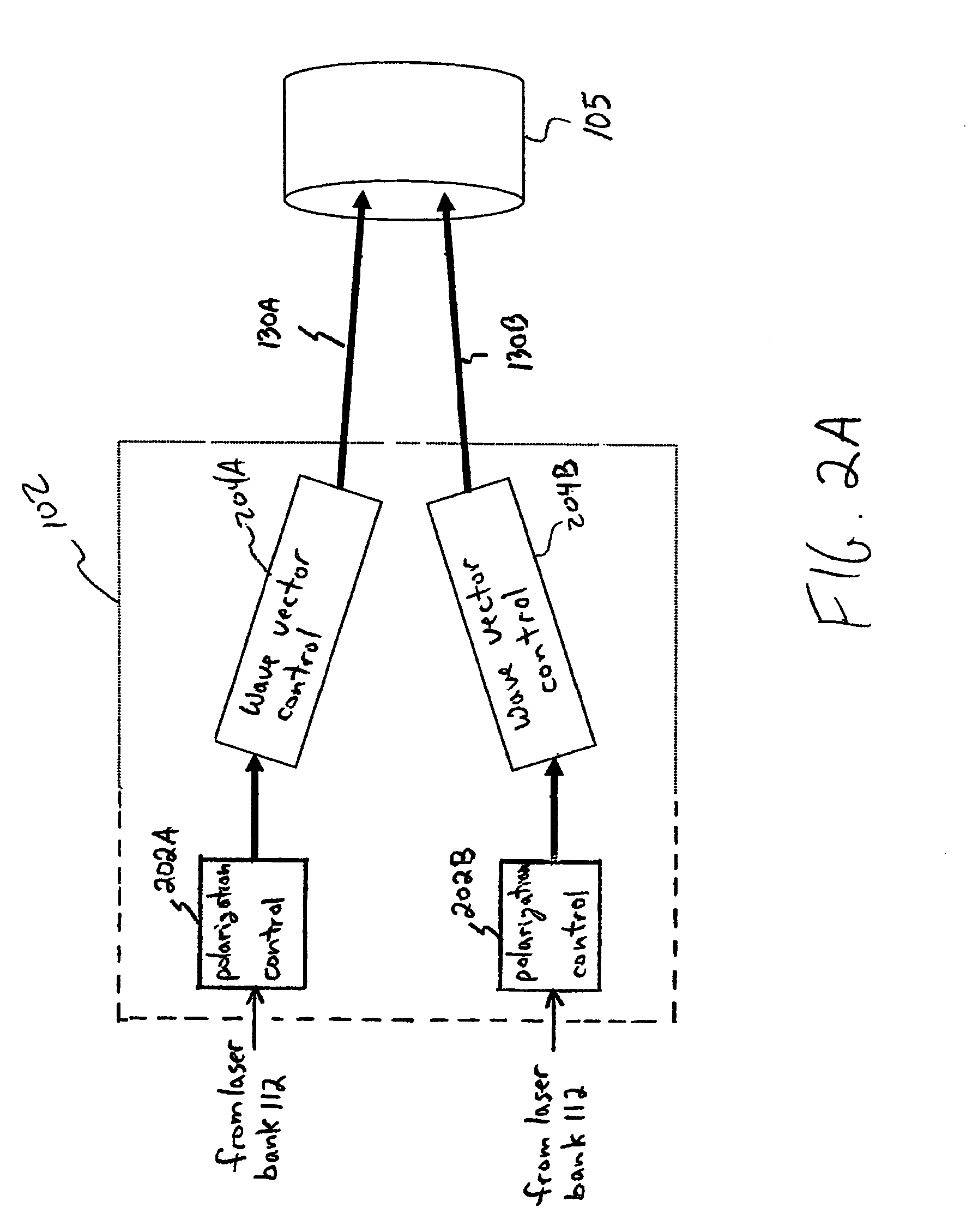
System and method for wave vector multiplexed laser communication
ActiveUS7639948B2Key distribution for secure communicationWavelength-division multiplex systemsMultiplexingLight beam
Wave vector division multiplexing (“WVDM”) is a method of free-space multiplexing for optical communications. In WVDM, wave vectors of individual laser beams are manipulated so that each individual laser beam has a unique wave vector. These individual laser beams are multiplexed into an aggregate beam, which is transmitted to a receiver. The receiver separates the individual laser beams on the basis of their unique wave vectors. One area where WVDM is useful is in quantum cryptography. WVDM can also be combined with traditional wavelength division multiplexing (“WDM”) to increase throughput even further.
Owner:MITRE SPORTS INT LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com