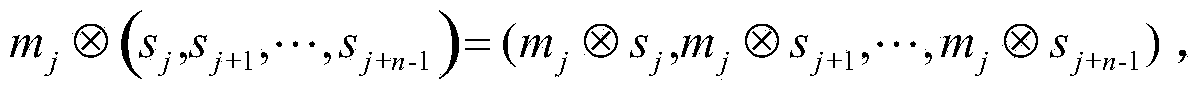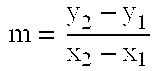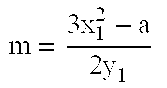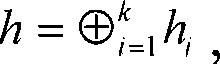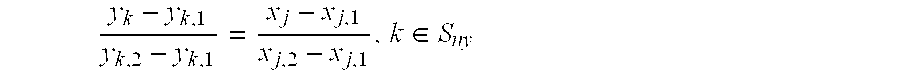Patents
Literature
114 results about "Hash-based message authentication code" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
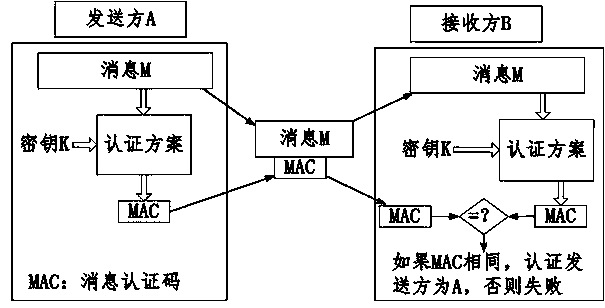
In cryptography, an HMAC (sometimes expanded as either keyed-hash message authentication code or hash-based message authentication code) is a specific type of message authentication code (MAC) involving a cryptographic hash function and a secret cryptographic key. It may be used to simultaneously verify both the data integrity and the authenticity of a message, as with any MAC. Any cryptographic hash function, such as SHA-256 or SHA-3, may be used in the calculation of an HMAC; the resulting MAC algorithm is termed HMAC-X, where X is the hash function used (e.g. HMAC-SHA256 or HMAC-SHA3). The cryptographic strength of the HMAC depends upon the cryptographic strength of the underlying hash function, the size of its hash output, and the size and quality of the key.
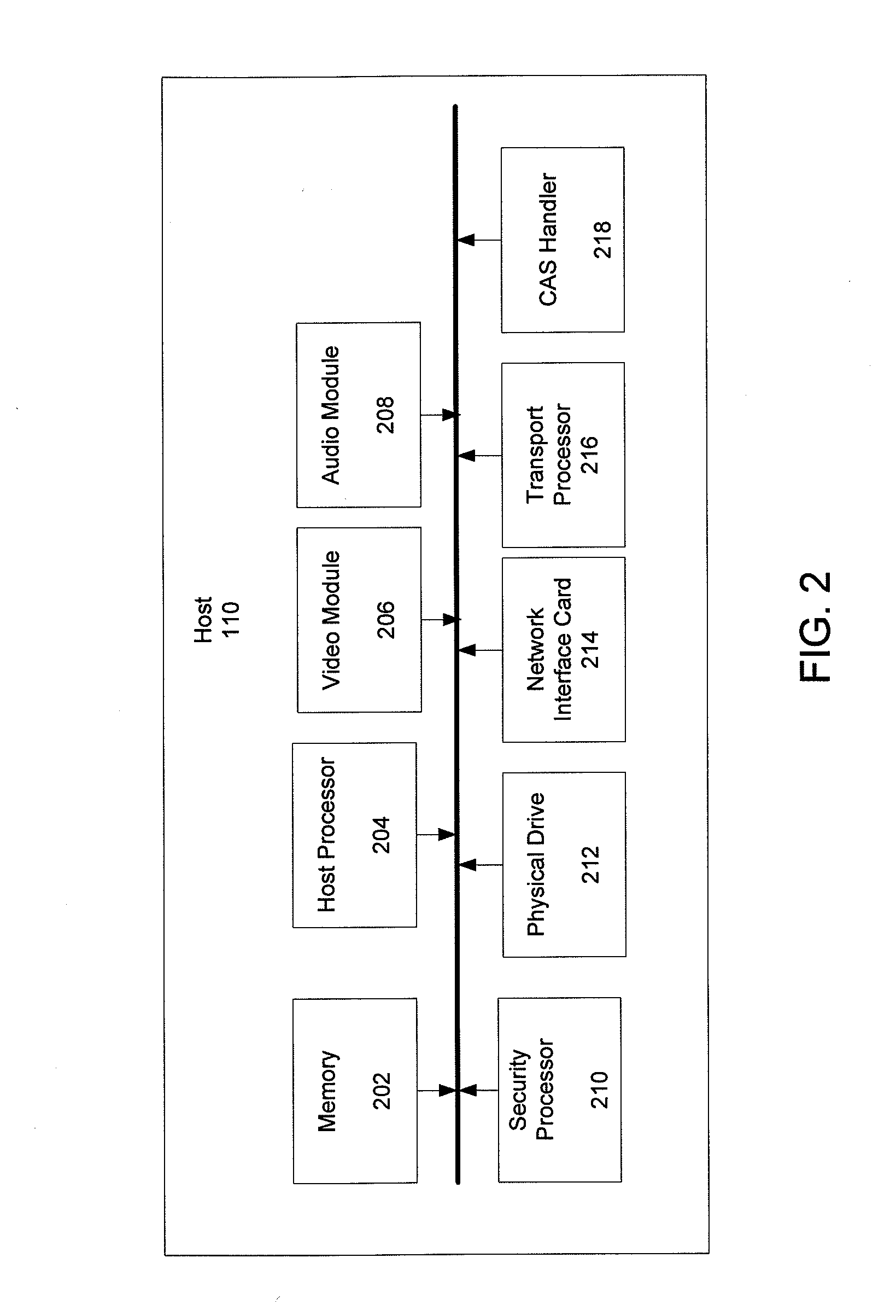
Method for securing a computing device with a trusted platform module-tpm
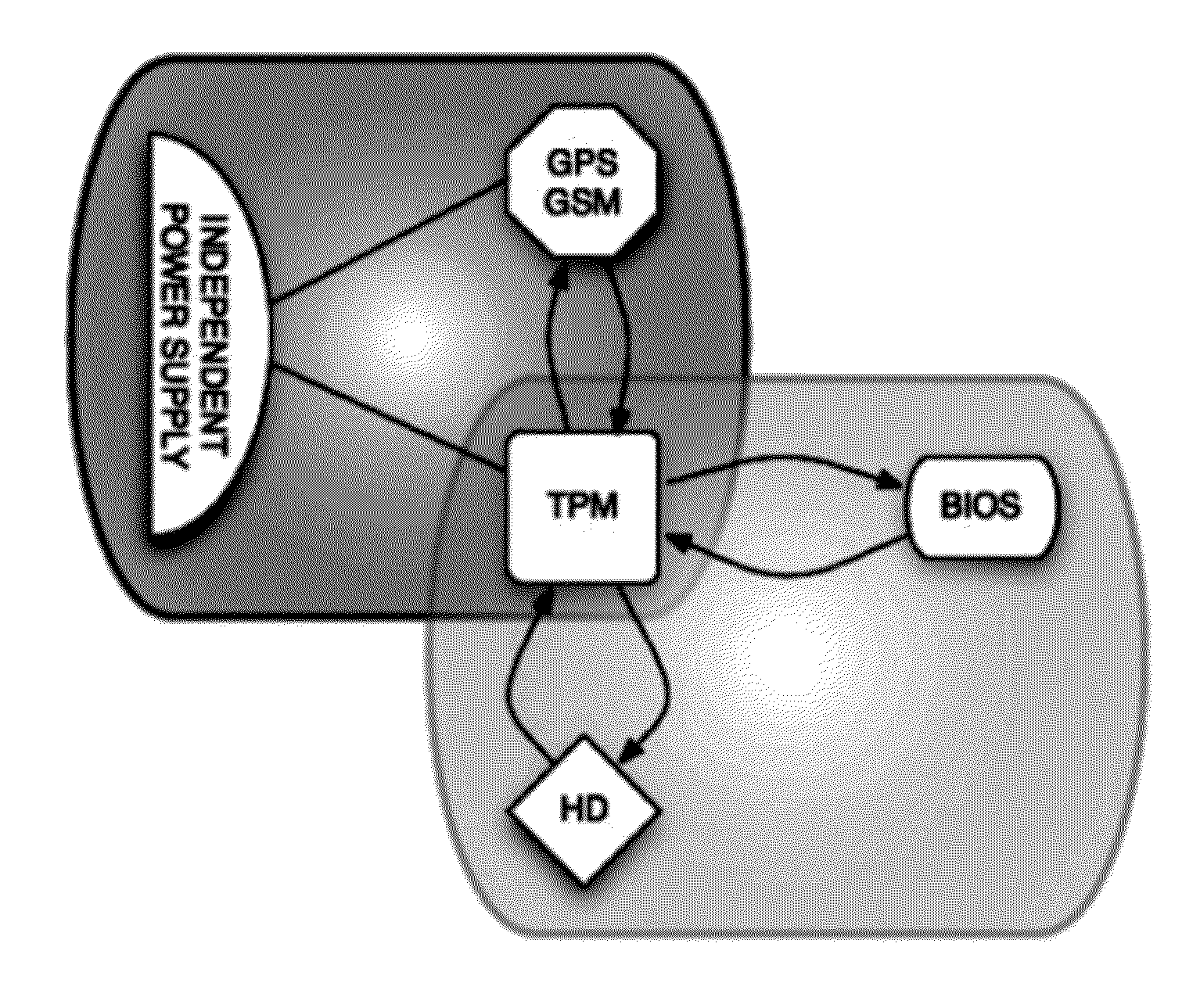
InactiveUS20120151223A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringExternal storageHash-based message authentication code
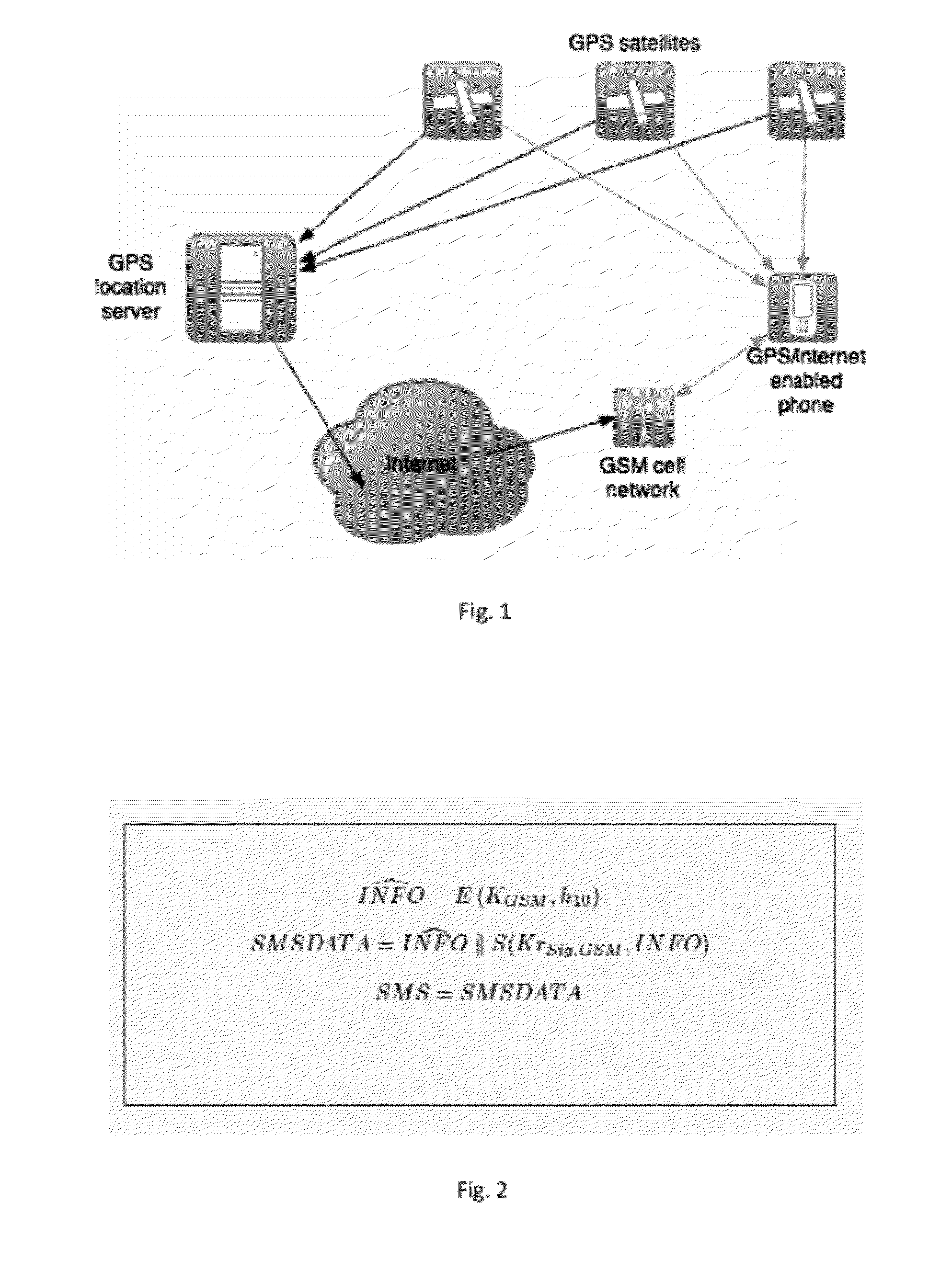
Methods, systems and computer program products for securing a computing device with data storage, power-on firmware—BIOS, geolocation and mobile data module—GPS / GSM, and a Trusted Platform Module—TPM, including establishing a shared-secret between the BIOS and the TPM, requesting the TPM to generate suitable encryption keys, namely for encrypting the data storage, supplying the user of the computing device suitable keys for external storage, calculating a hash-based message authentication codes over the BIOS, MBR, unique ID of the TPM, unique ID of the GPS / GSM module and unique ID of the BIOS; using user provided password and / or token device; using mobile data messages to secure the device if misplaced.
Owner:UNIV DE LISBOA
Authenticated Communication Between Security Devices
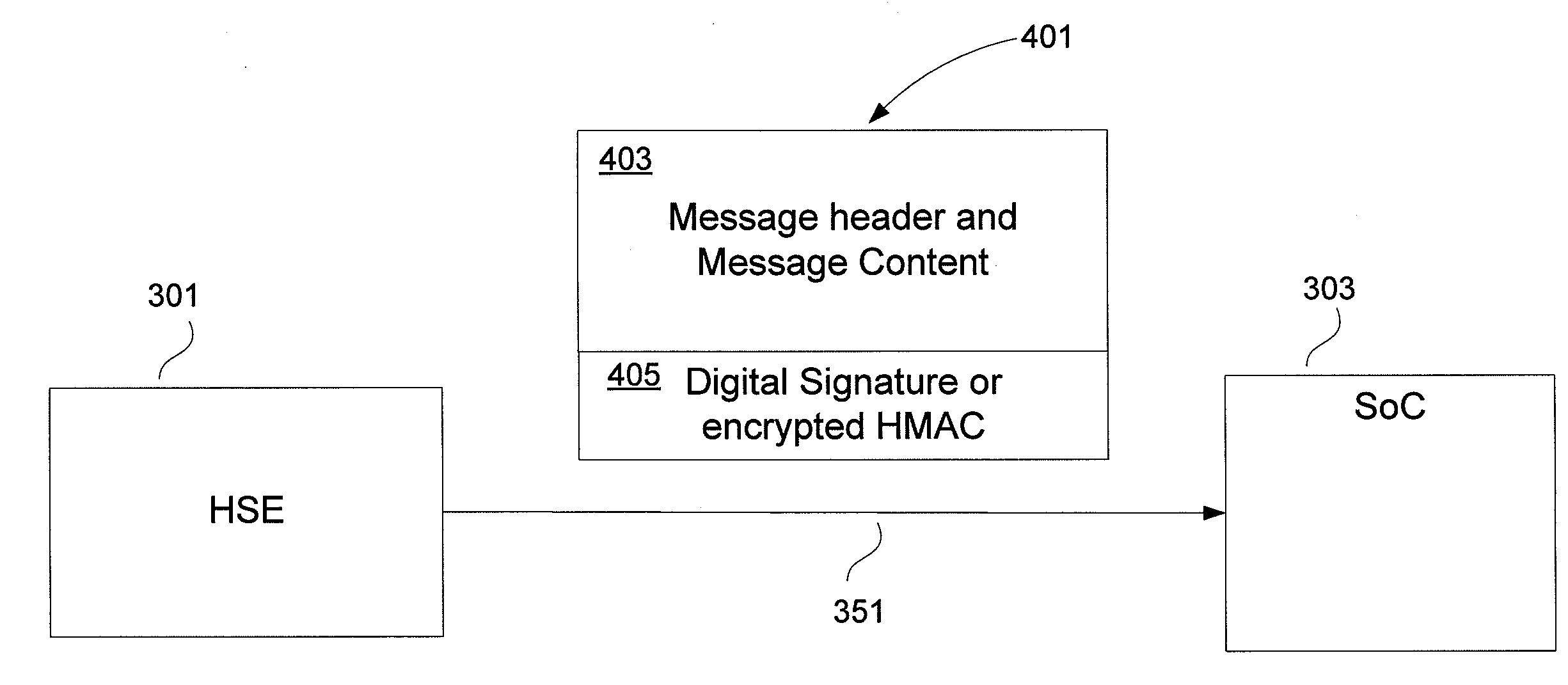
ActiveUS20100217985A1User identity/authority verificationTelevision systemsConditional access systemsDigital signature
Apparatuses, computer readable media, and methods establishing and maintaining trust between security devices for distributing media content are provided. Two security devices bind to establish an initial trust so that security information can be exchanged. Subsequently, trust is refreshed to verify the source of a message is valid. In an embodiment, the security devices may comprise a security processor and a system on a chip (SoC) in a downloadable conditional access system. Trust may be refreshed by a security device inserting authentication information in a message to another security device, where authentication information may assume different forms, including a digital signature (asymmetric key) or a hash message authentication code (HMAC). Trust may also be refreshed by extracting header information from the message, determining state information from at least one parameter contained in the header information, and acting on message content only when the state information is valid.
Owner:COMCAST CABLE COMM LLC
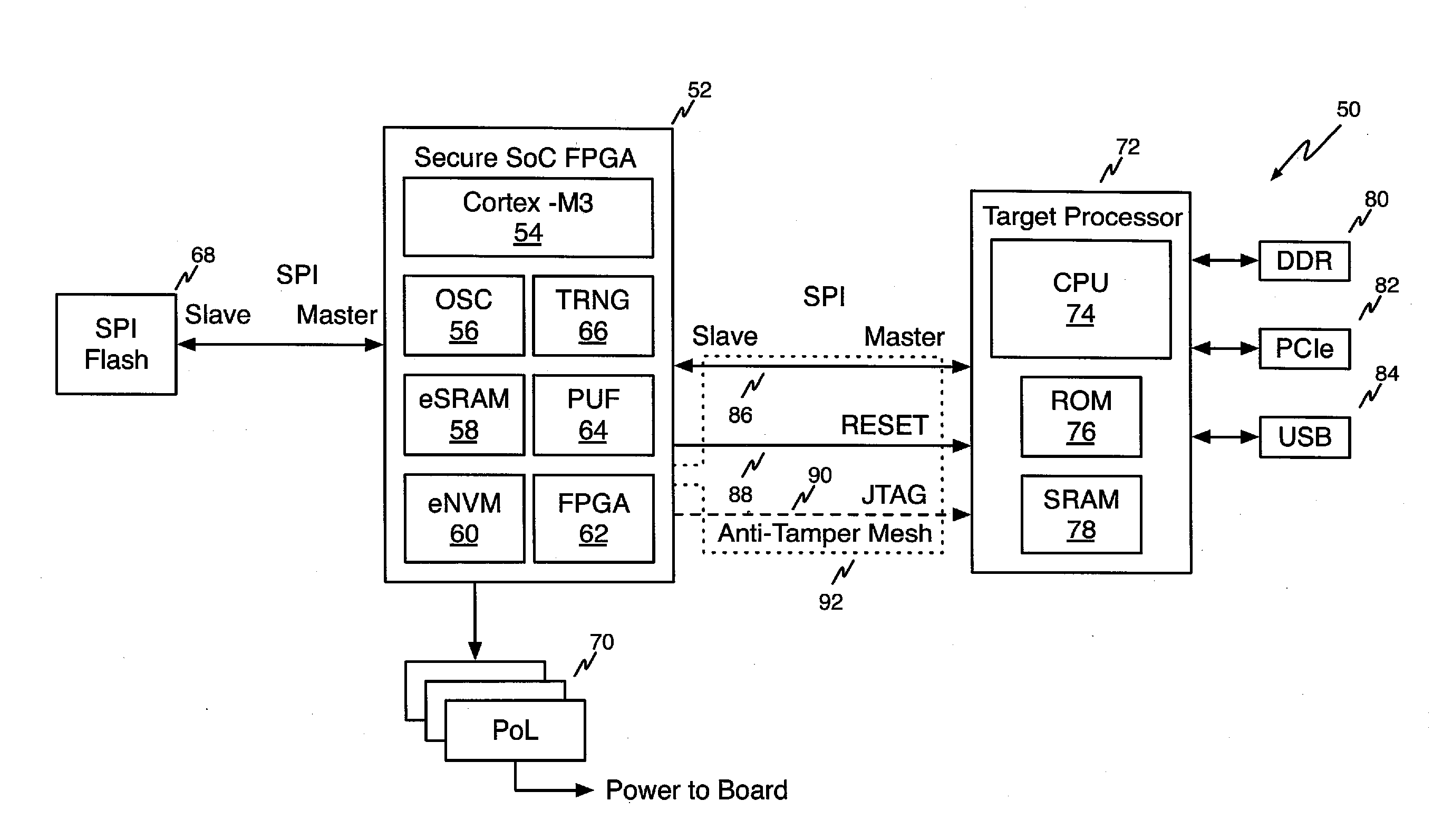
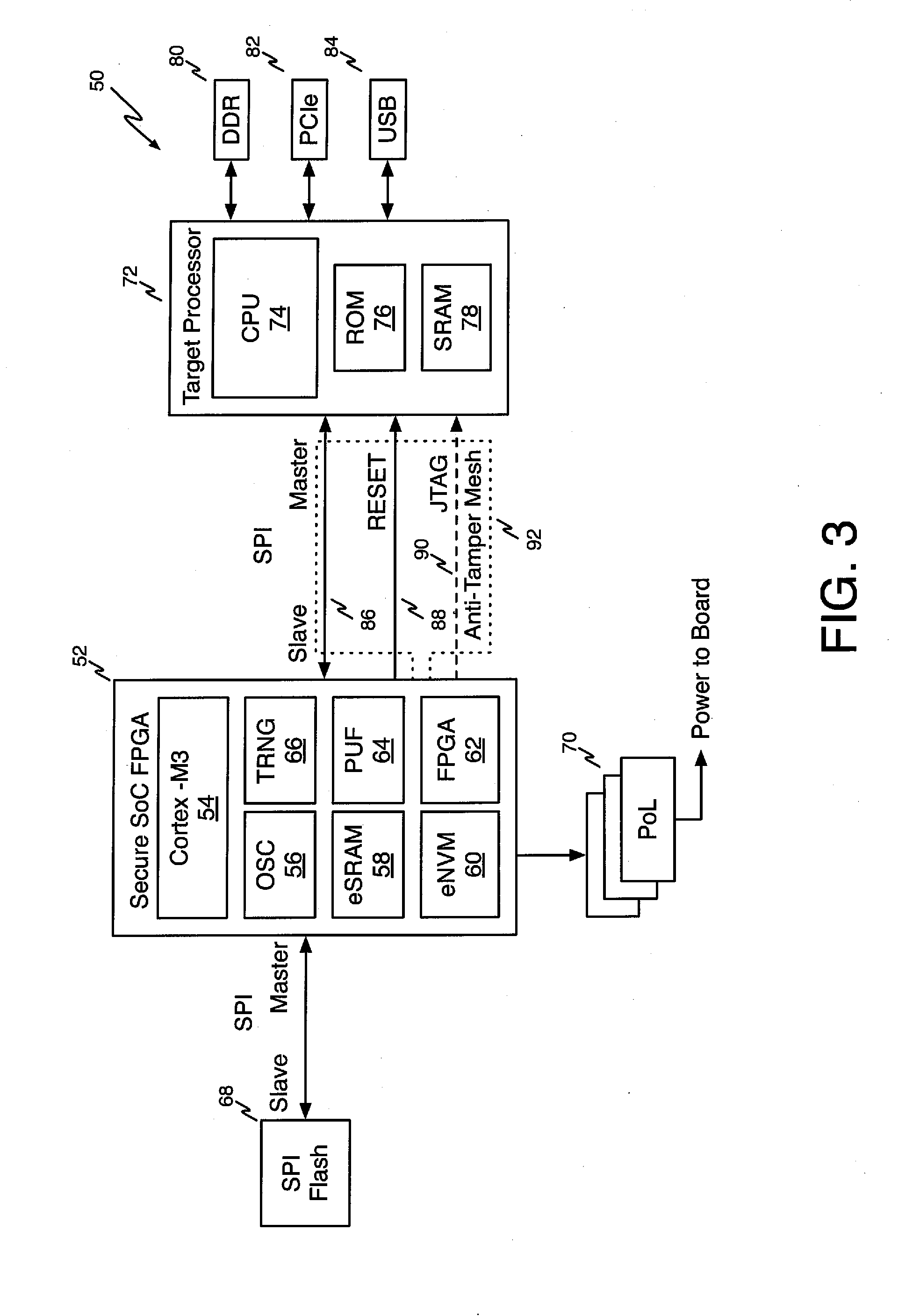
Secure Boot for Unsecure Processors
ActiveUS20150012737A1Improve securityDifficult to overwriteDigital computer detailsDigital data authenticationComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
A method for securely booting a target processor in a target system from a secure root of trust includes computing a message authentication code from boot code to be provided to the target processor, including an obfuscated algorithm for recreating the message authentication code in the target processor, serving the boot code to the target processor, executing the boot code to recreate the message authentication code in the target processor, serving the message authentication code back to the root of trust, comparing the returned message authentication code with the message authentication code generated in the root of trust, continuing execution of the boot code data if the returned message authentication code matches the message authentication code, and applying at least one penalty to the target system if the returned message authentication code does not match the message authentication code generated in the root of trust.
Owner:MICROSEMI SOC
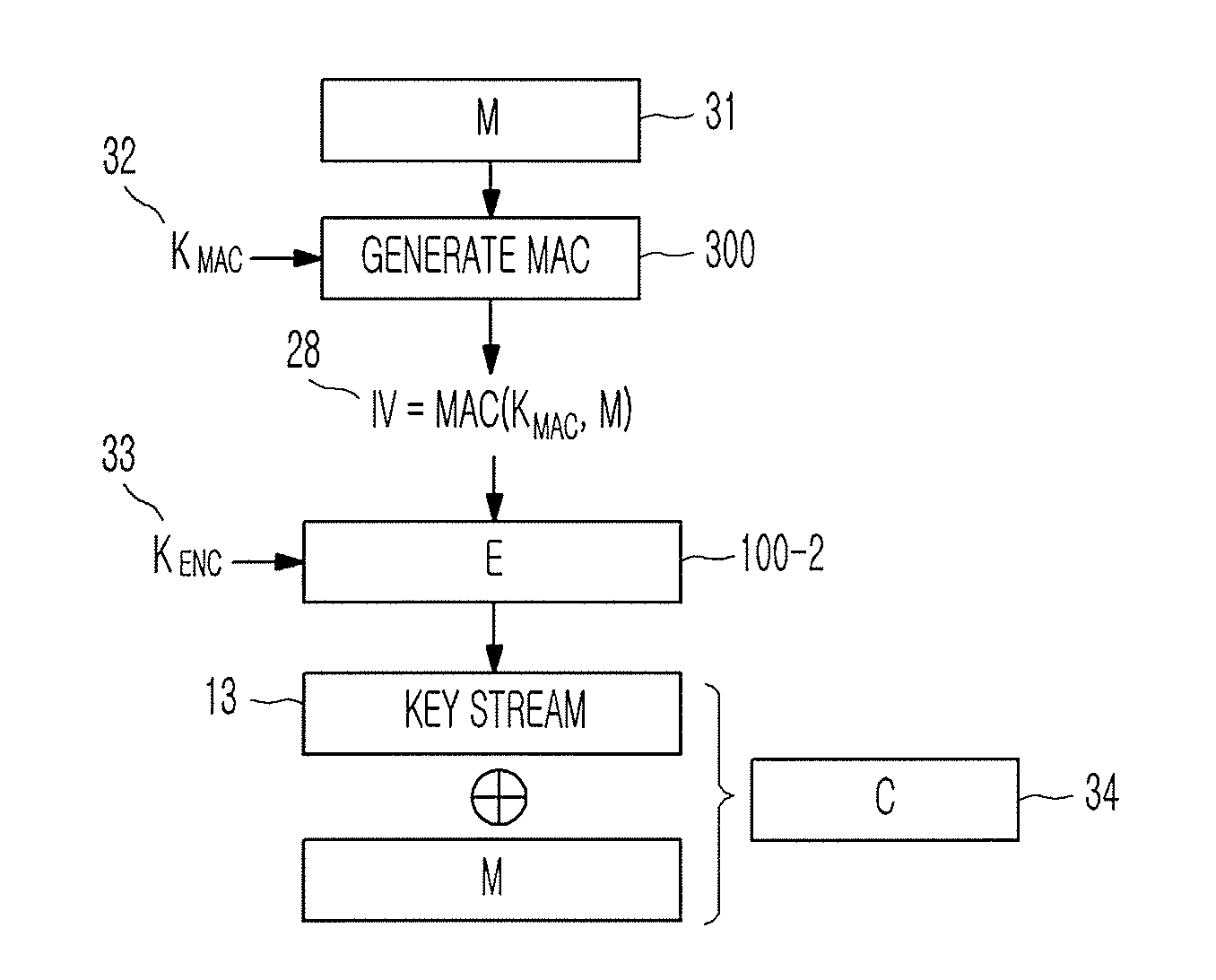
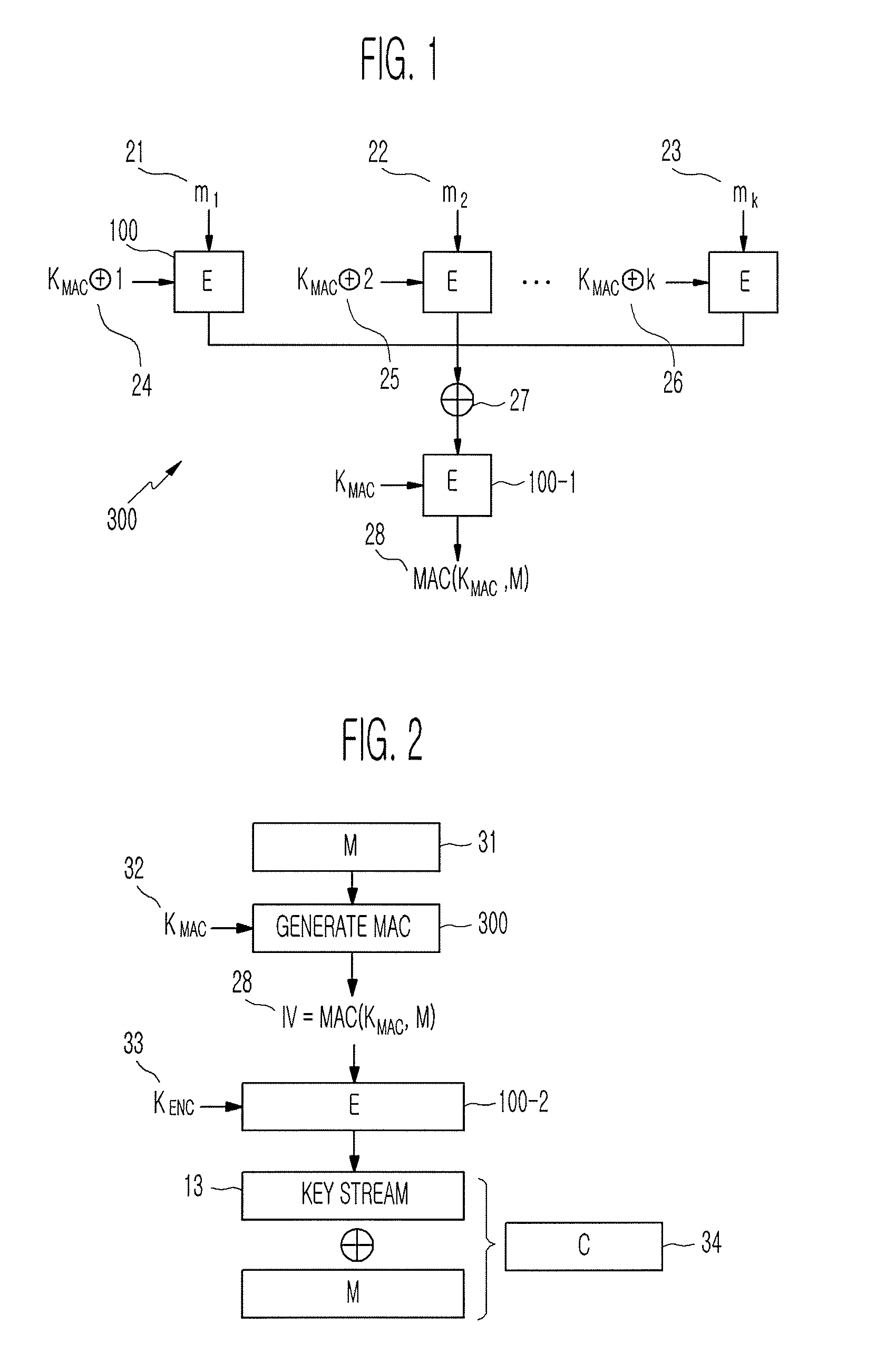
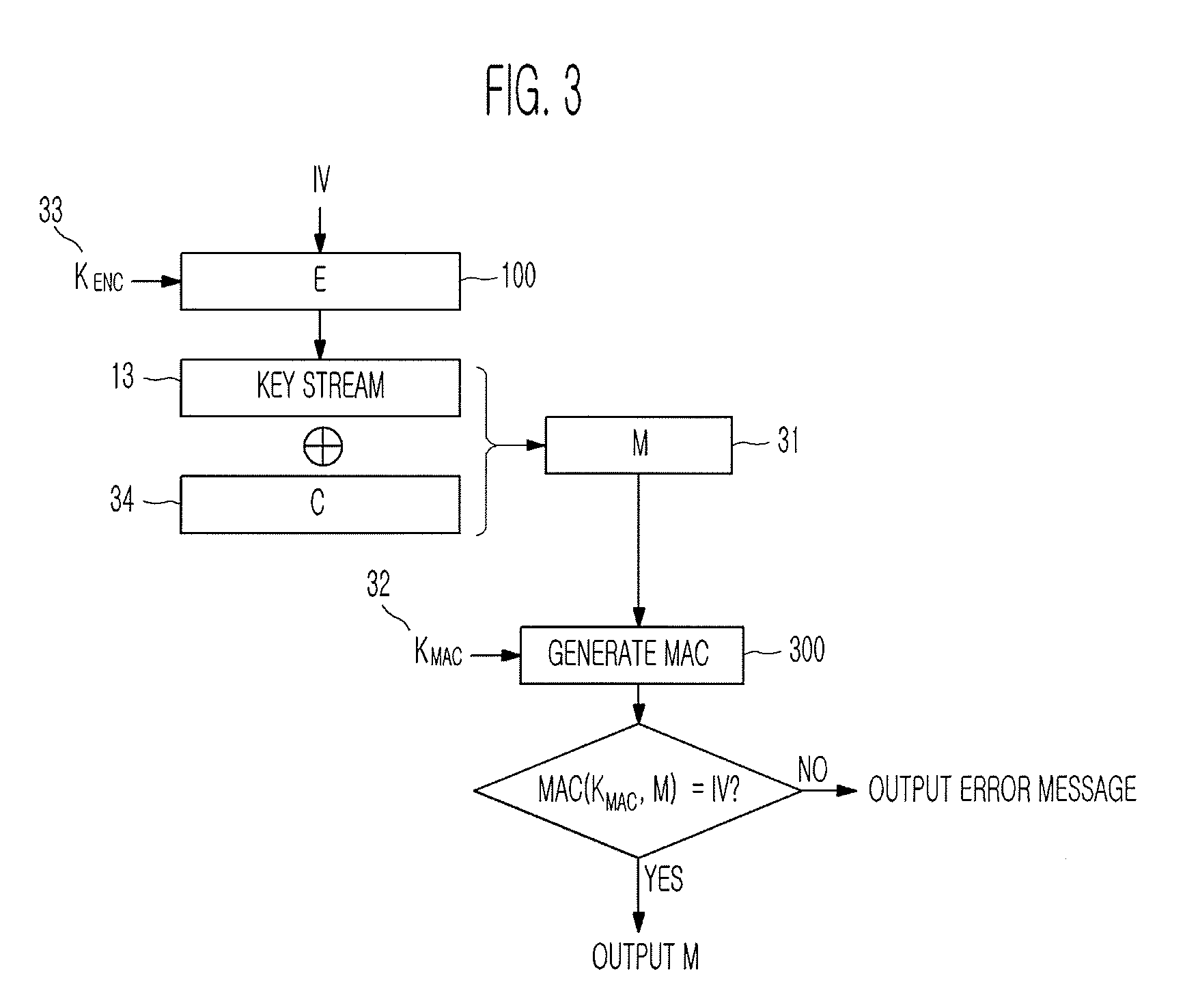
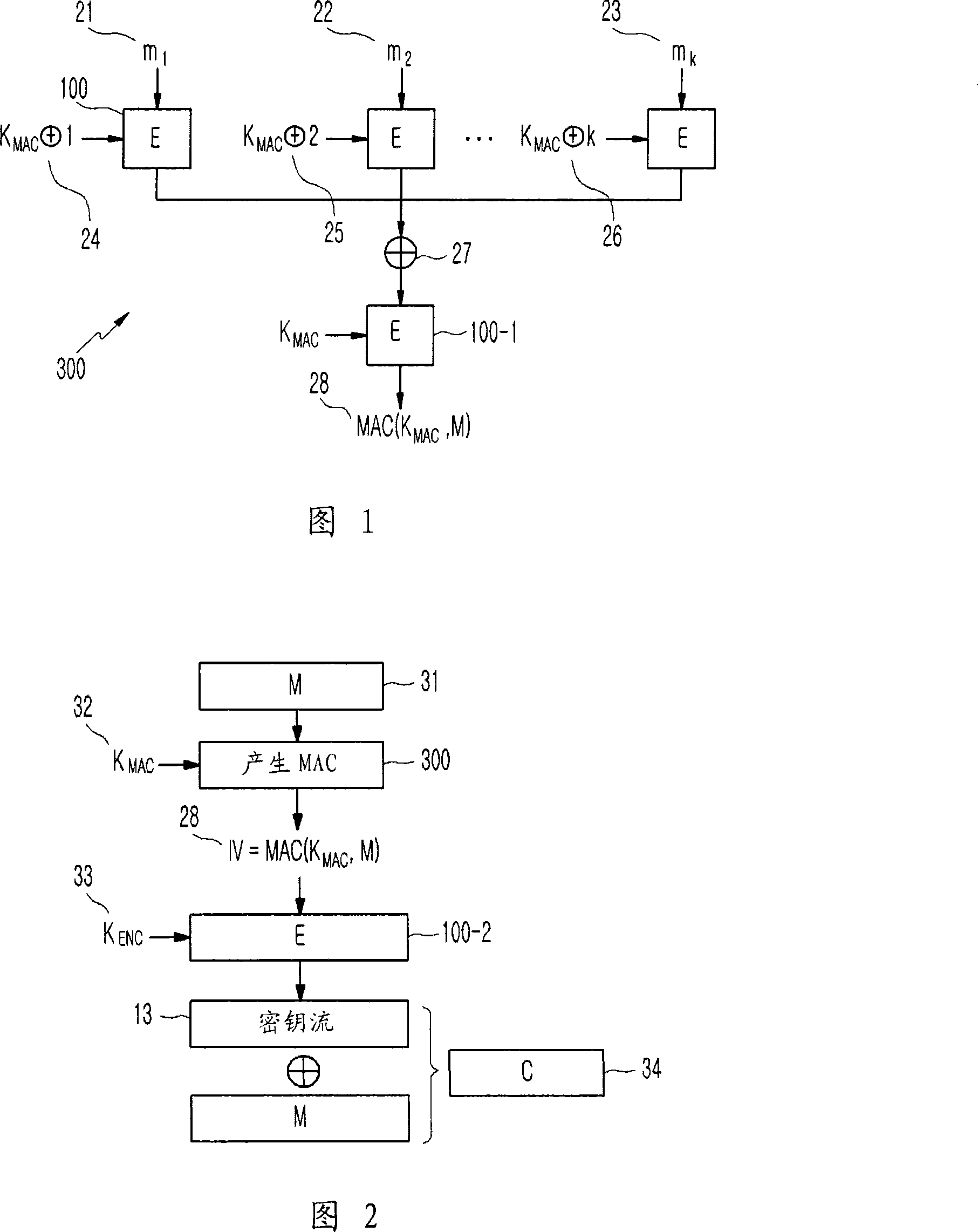
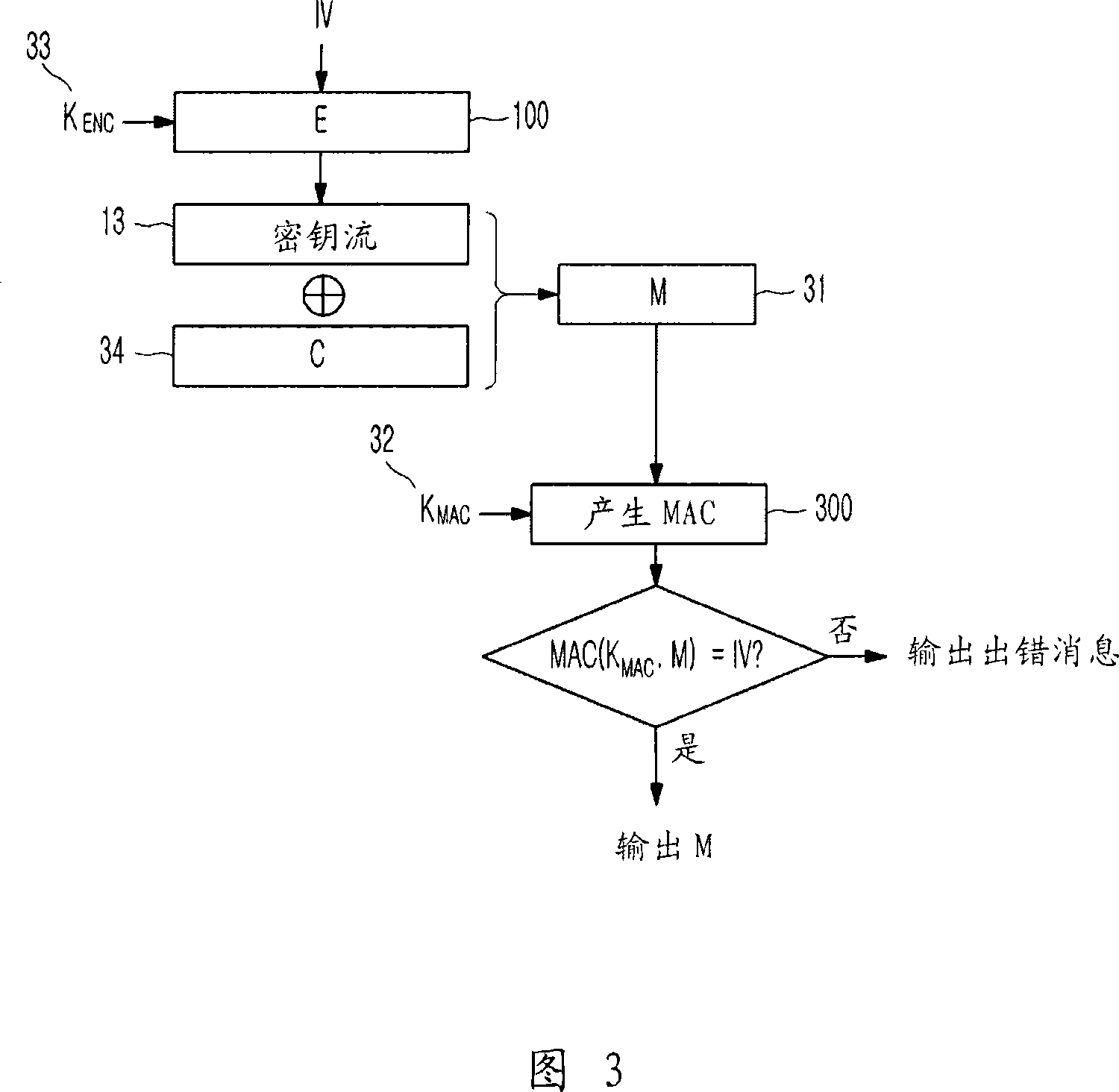
Method of generating message authentication code using stream cipher and authentication/encryption and authentication/decryption methods using stream cipher
InactiveUS20080112561A1Secret communicationSecuring communicationComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
Provided are a method of generating a Message Authentication Code (MAC) using a stream cipher, and authentication / encryption and authentication / decryption methods using a stream cipher.According to the methods, authentication / encryption is performed using a MAC generated using a stream cipher as an initialization vector of the stream cipher. Therefore, it is unnecessary to use a random number generation algorithm to generate the initialization vector, and thus implementation efficiency can be improved.In addition, upon generation of a MAC, a plurality of key stream generators perform computation for a plurality of message blocks, respectively. Therefore, the message blocks are computed in parallel at a time, and thus computation efficiency is excellent.
Owner:NAINFOX CO LTD
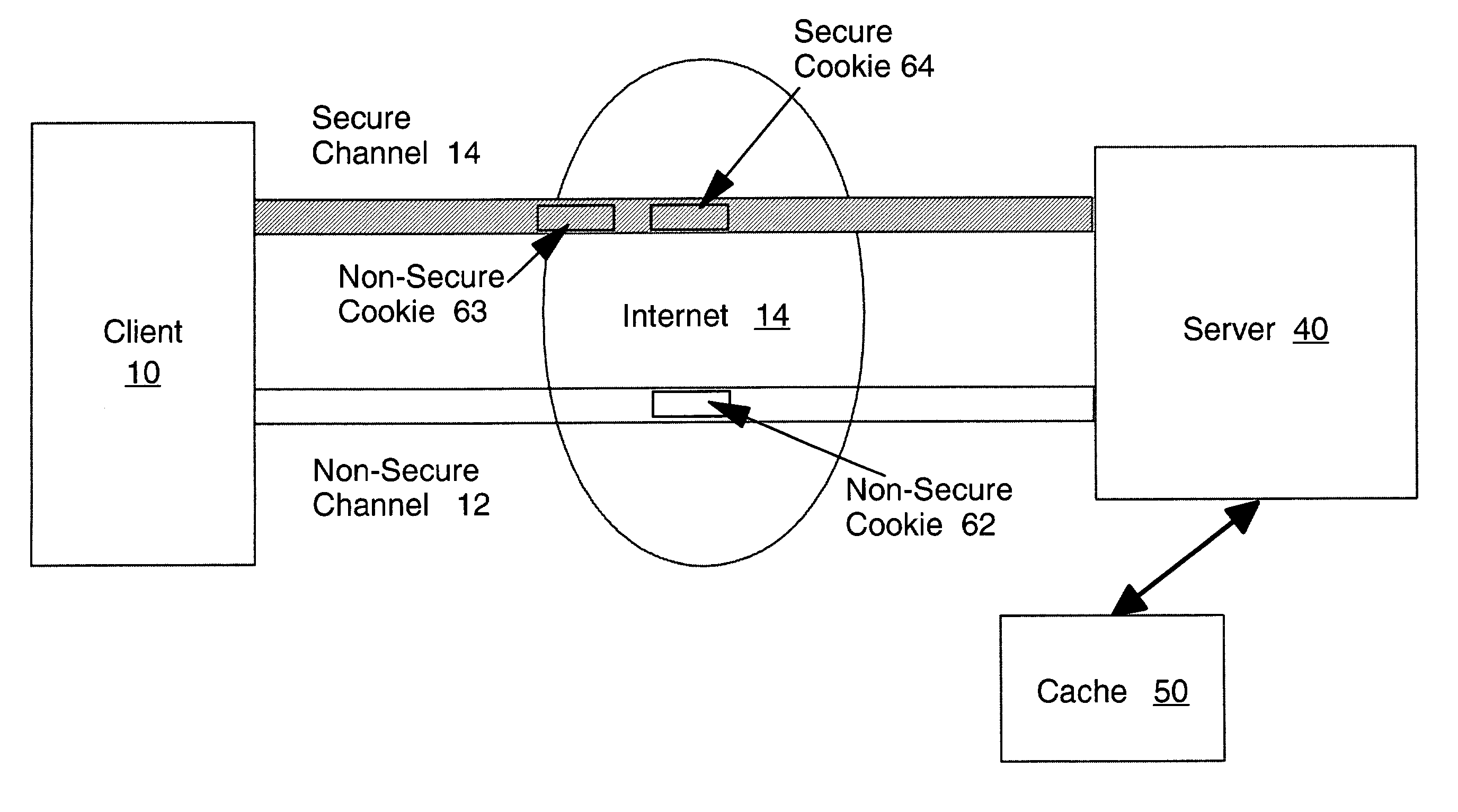
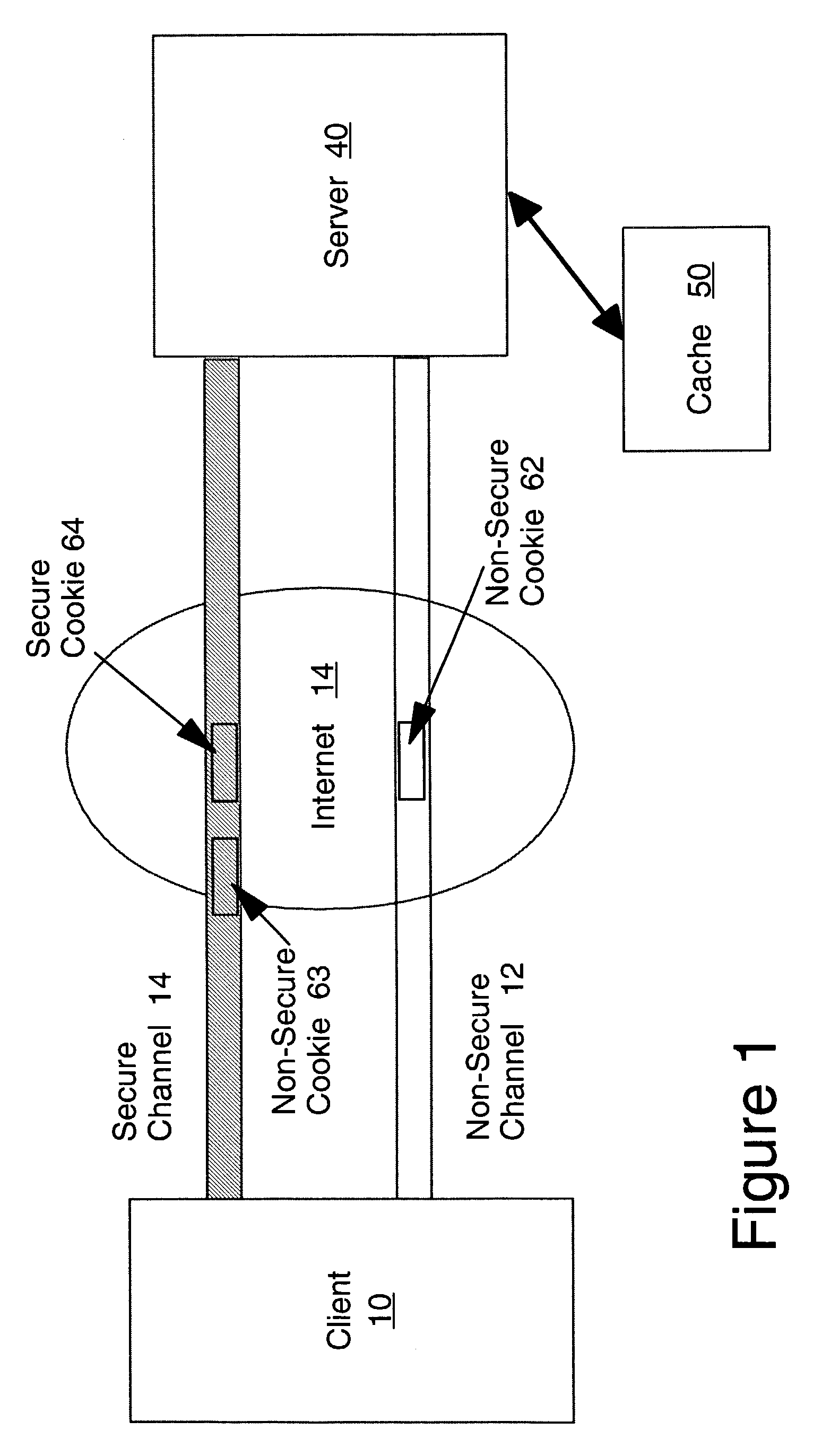
Secure cache of web session information using web browser cookies
InactiveUS7197568B2Not be easily alteredDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsWeb browserHash-based message authentication code
A secure method and system for accessing a cache for web session is provided using web browser cookies. The cache for the web session data uses an encoded identifier, determined using for example the Keyed-Hash Message Authentication Code, based on information identifying a client. The client communication is accompanied by a cookie (persistent state object) that also includes the identifier encoded in the same manner. This encoded identifier in the received cookie is used for accessing the cached data. Where a secure communication channel is available, such as a secure socket layer (SSL connection), a second cookie which is only transmitted over SSL is used as a signature for the first cookie.
Owner:IBM CORP
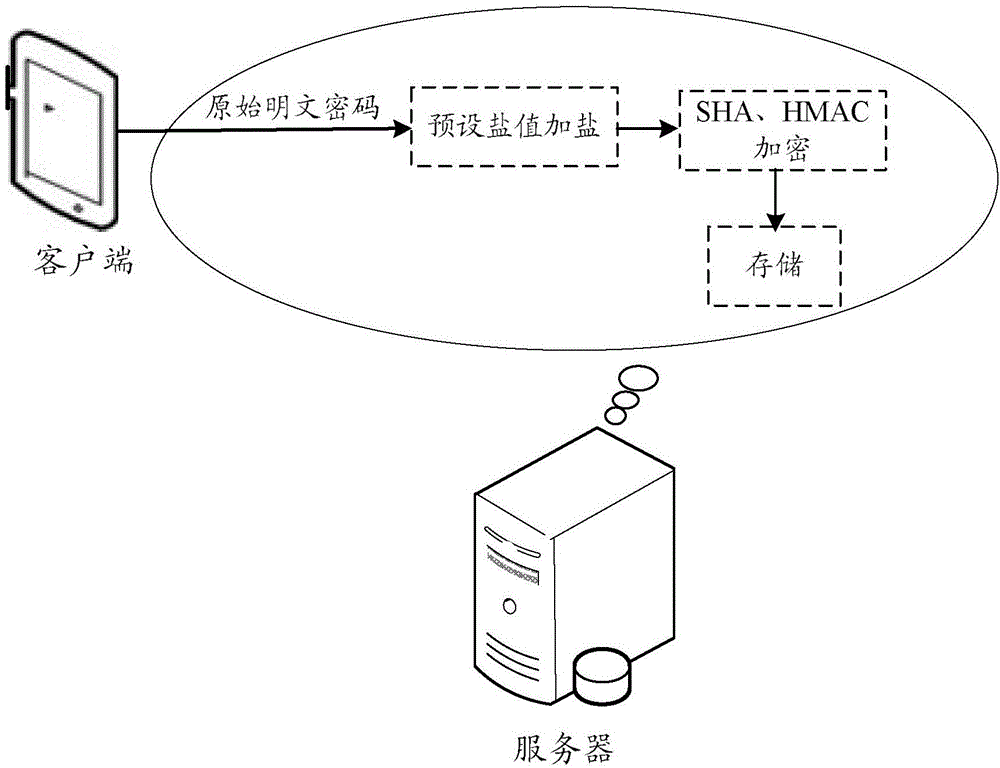
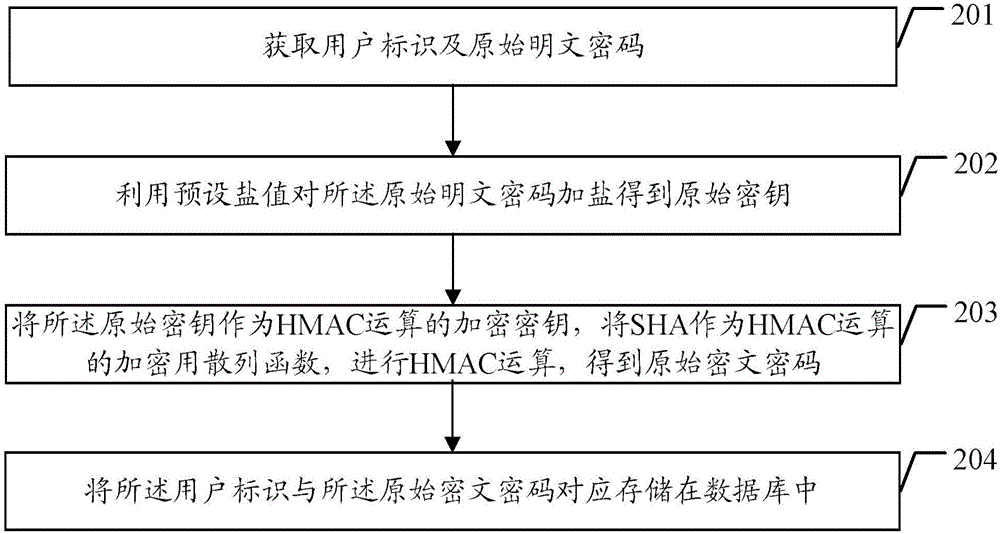
Password protecting method and device
ActiveCN106656476AEnsure safetyReduce the risk of being leakedKey distribution for secure communicationEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHash functionPassword
The embodiment of the present invention discloses a password protecting method and device, wherein, the password protecting method comprises: obtaining user identification and an original clear text password; adding salts to the original clear text password with a preset salt value to obtain an original key; using the original key as an encryption key of Hash-based message authentication code HMAC operation; using a secure Hash algorithm SHA as an encryption hash function of the HMAC operation to carry out the HMAC operation to obtain an original cryptograph password; and storing the user identification and the original cryptograph password correspondingly in a database. The embodiment of the present invention is able to assure the password security, and reduce the risk of password disclosing.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
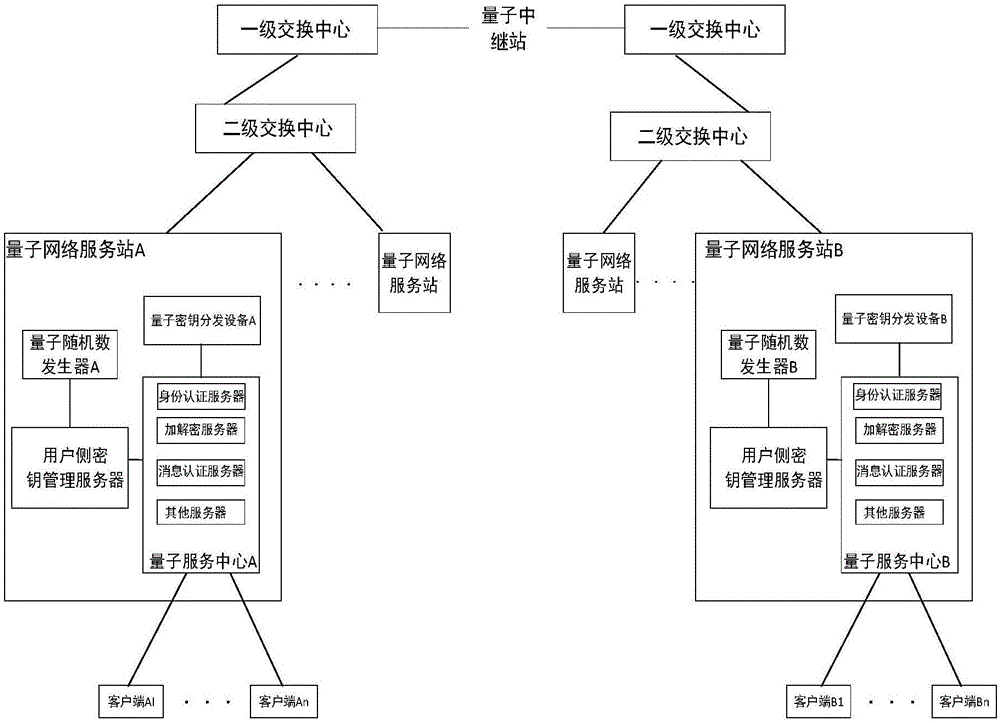
Message authentication method and system
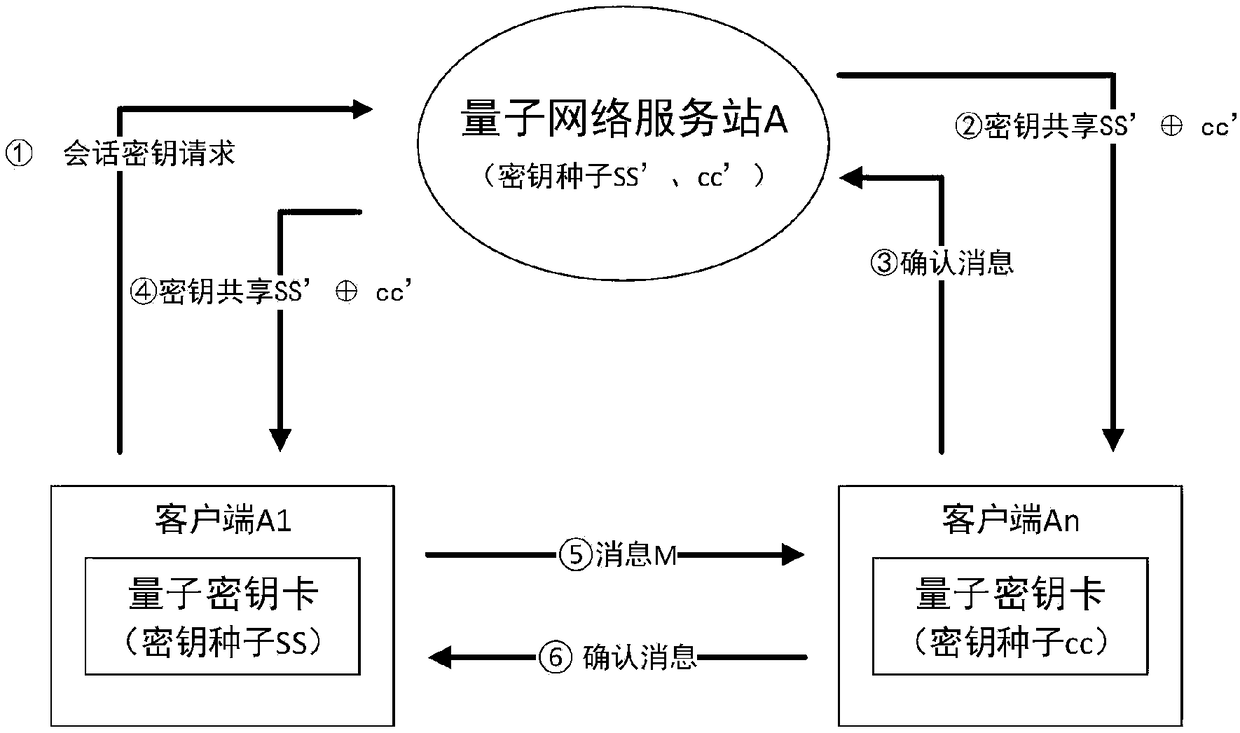
ActiveCN106411525AEnsure safetyGuaranteed correctnessKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHash-based message authentication codeQuantum network
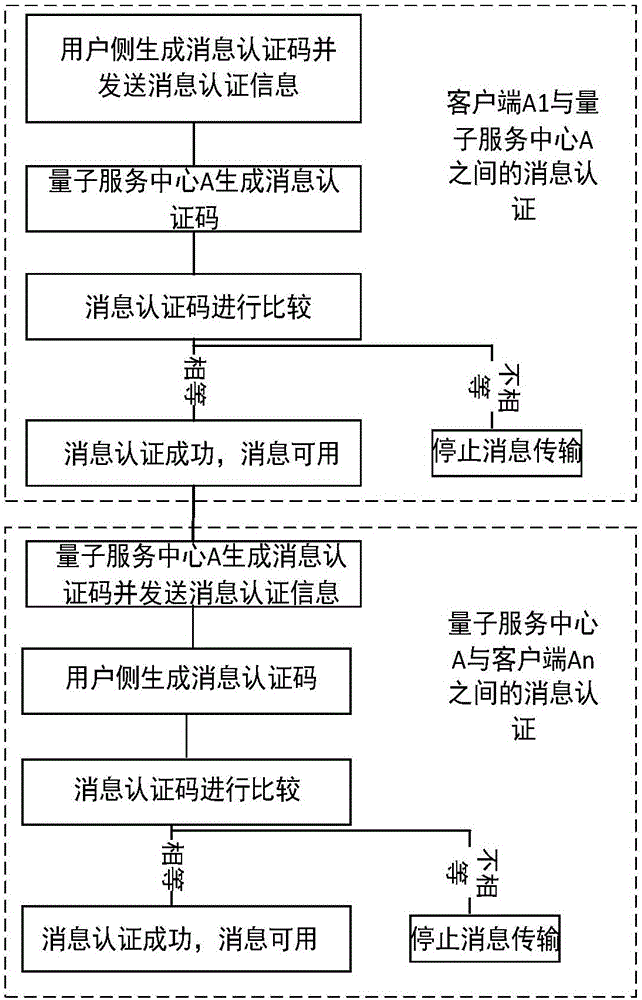
The invention discloses a message authentication method and a message authentication system, wherein the message authentication system comprises a quantum network service station and a client side; the quantum network service station is configured at a network side; the client side is configured at a user side; Interaction of message authentication information carrying message authentication codes is carried out between the client side and the network side; comparative authentication is carried out by comparison of the respectively generated message authentication codes; a quantum key card is also arranged; the network side generates true random numbers to respectively store in the quantum key card and the network side, so that corresponding user side keys are formed; and the user side keys of the quantum key card and the network side are respectively used for generating the message authentication codes to perform comparative authentication. According to the message authentication method and system disclosed by the invention, advantages of the existing classical communication network are utilized; in combination with keys generated by a true random number generator and quantum key distribution, information data can be transmitted to a receiver only after stage-by-stage mutual message authentication is carried out; therefore, the correctness of the information data is ensured better; and furthermore, the security also cannot be reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SHENZHOU QUANTUM NETWORK TECH CO LTD
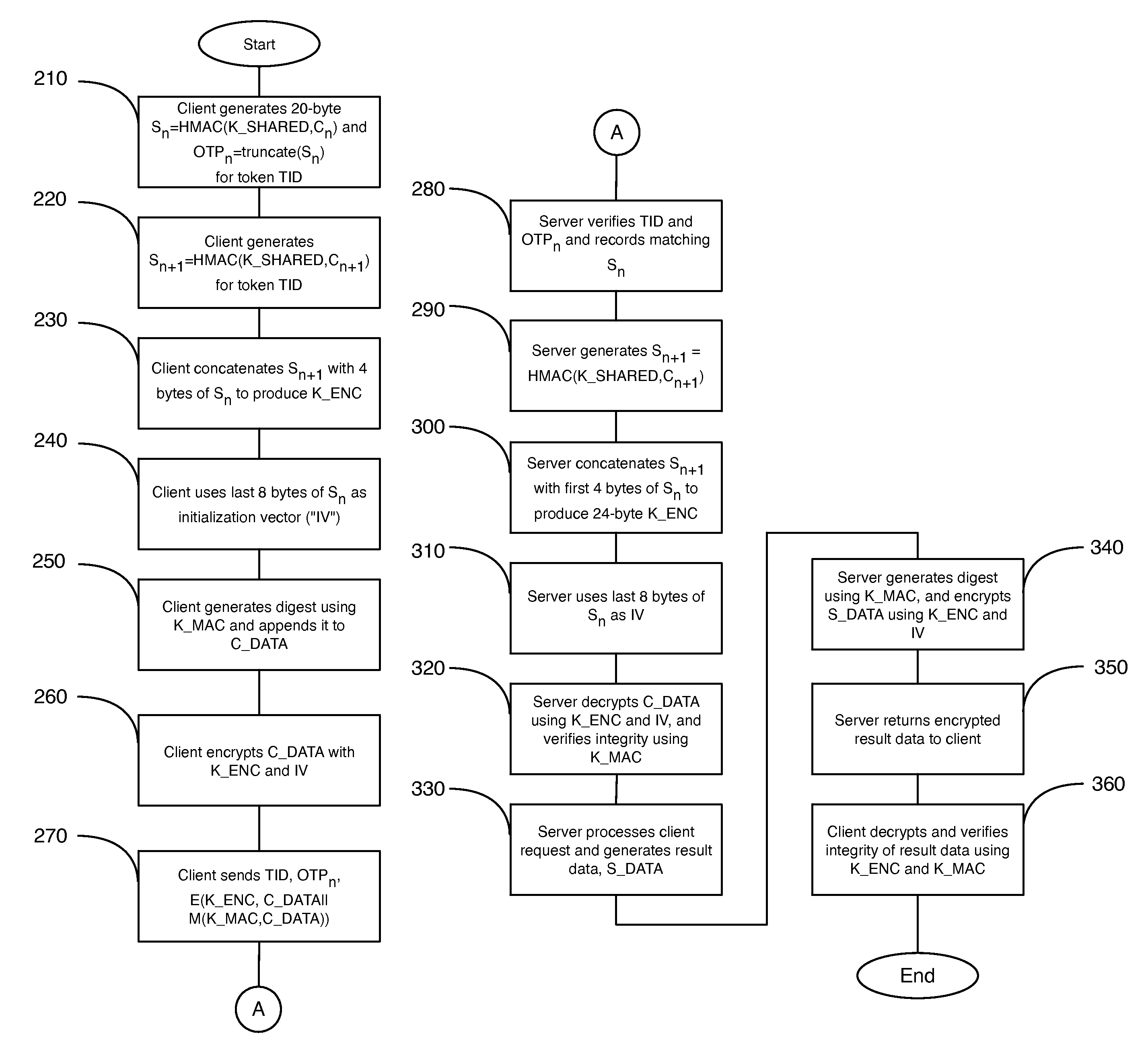
Method and system for secure communication using hash-based message authentication codes
ActiveUS20110238989A1User identity/authority verificationPayment architectureSecure communicationHash-based message authentication code
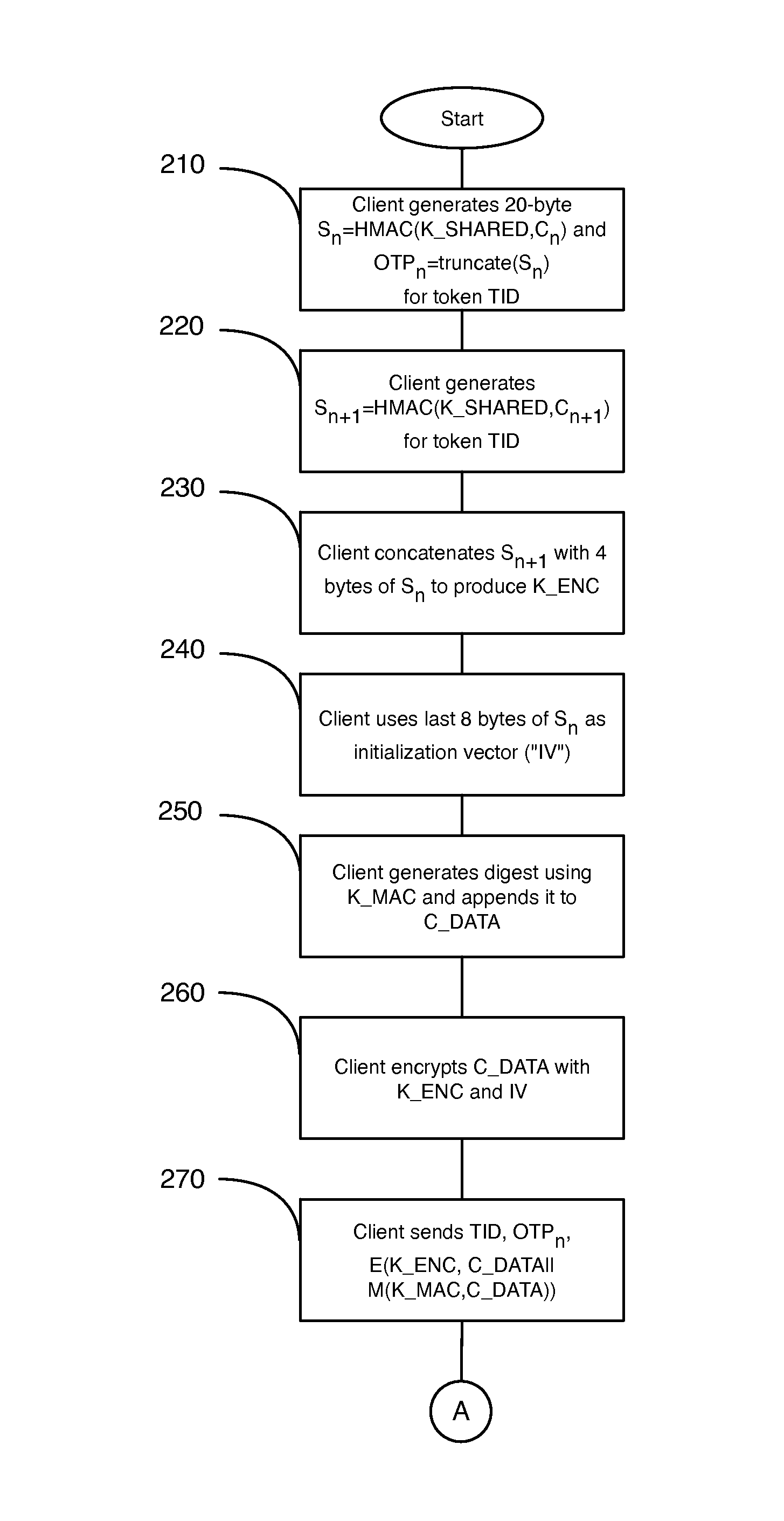
A system and method for secure communication is provided. A first hash-based message authentication code is generated from a shared secret and a first counter value stored in storage of a computing device. A second hash-based message authentication code is generated from such shared secret and a second counter value. An encryption key is derived from a function of the first hash-based message authentication code and the second hash-based message authentication code. A message is encrypted using the encryption key, and communicated via a network interface of the computing device.
Owner:IQVIA INC
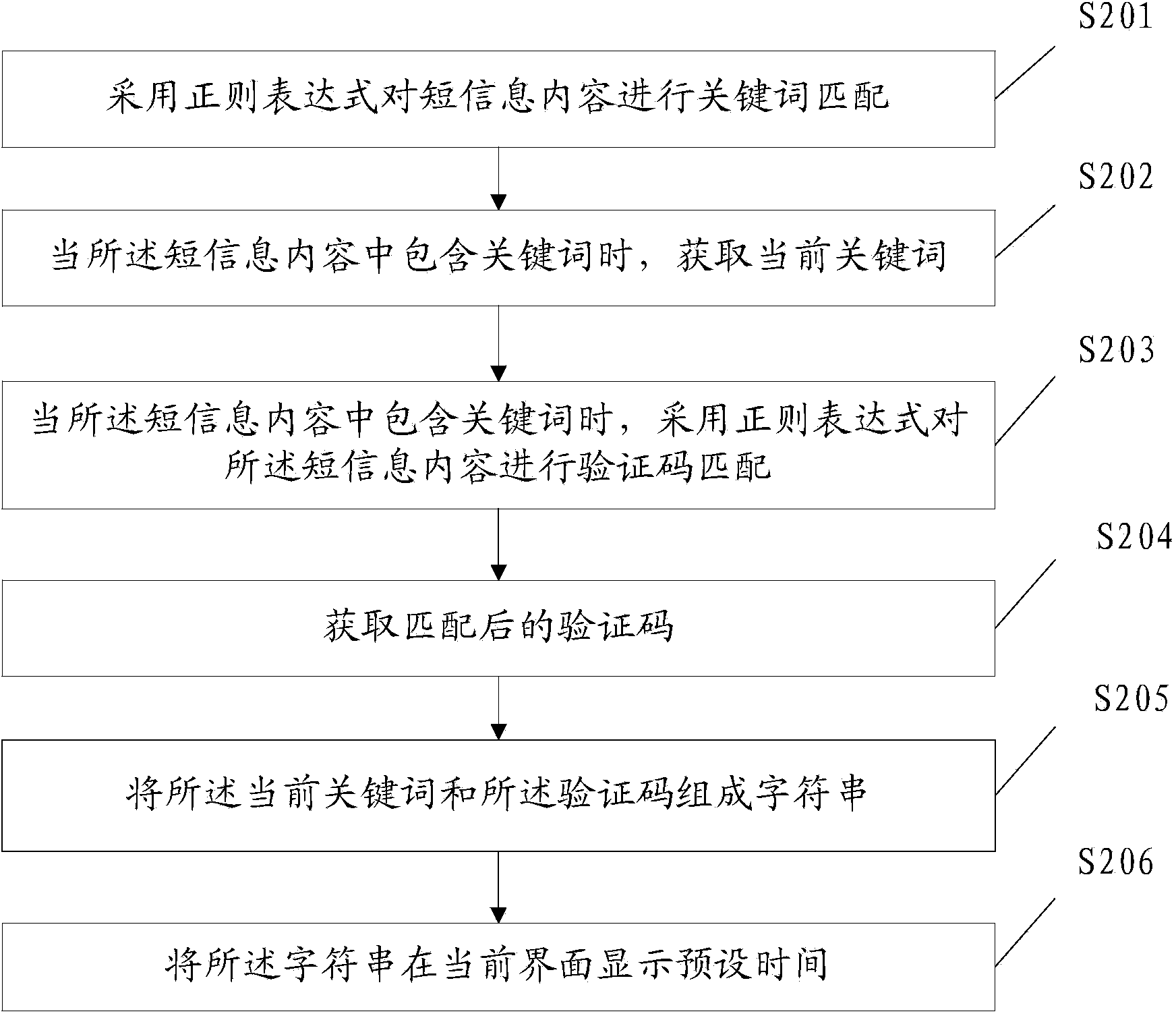
Short message authentication code residing method and device
ActiveCN103902740AImprove experienceEasy to fillUnstructured textual data retrievalDigital data authenticationUser needsHash-based message authentication code
The invention provides a short message authentication code residing method and device. The method includes the steps that a regular expression is adopted to conduct keyword matching to the short message content; when the short message content contains the keyword, the regular expression is adopted to conduct authentication code matching to the short message content so as to obtain the post-matching authentication code; the preset time of the authentication code is displayed at the present interface. The method is capable of automatically extracting the authentication code in the short message and displaying the preset time at the present interface, the user can fill in the authentication code according to the displayed authentication code on the authentication code interface within the preset time, the user needs not to remember the authentication code, and the user needs not to frequently switch from the short message application and the present application. According to the short message authentication code residing method and device, the authentication code is directly displayed on the present interface of the authentication code, the filling in of the authentication code needs only one step, that is, filling in the authentication code by manual inputting, so that the process of filling in the authentication code of the user is greatly facilitated and user experience is improved.
Owner:BEIJING BYTEDANCE NETWORK TECH CO LTD
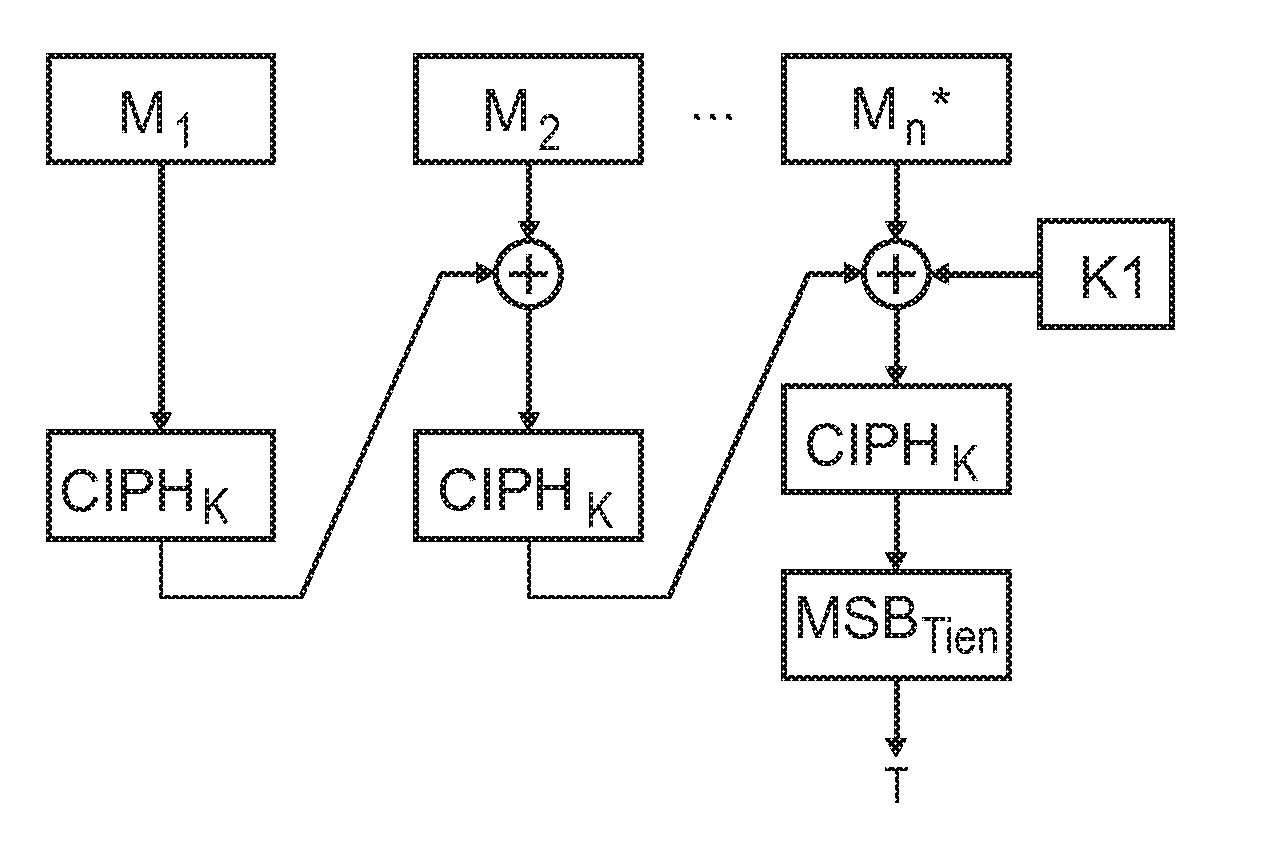
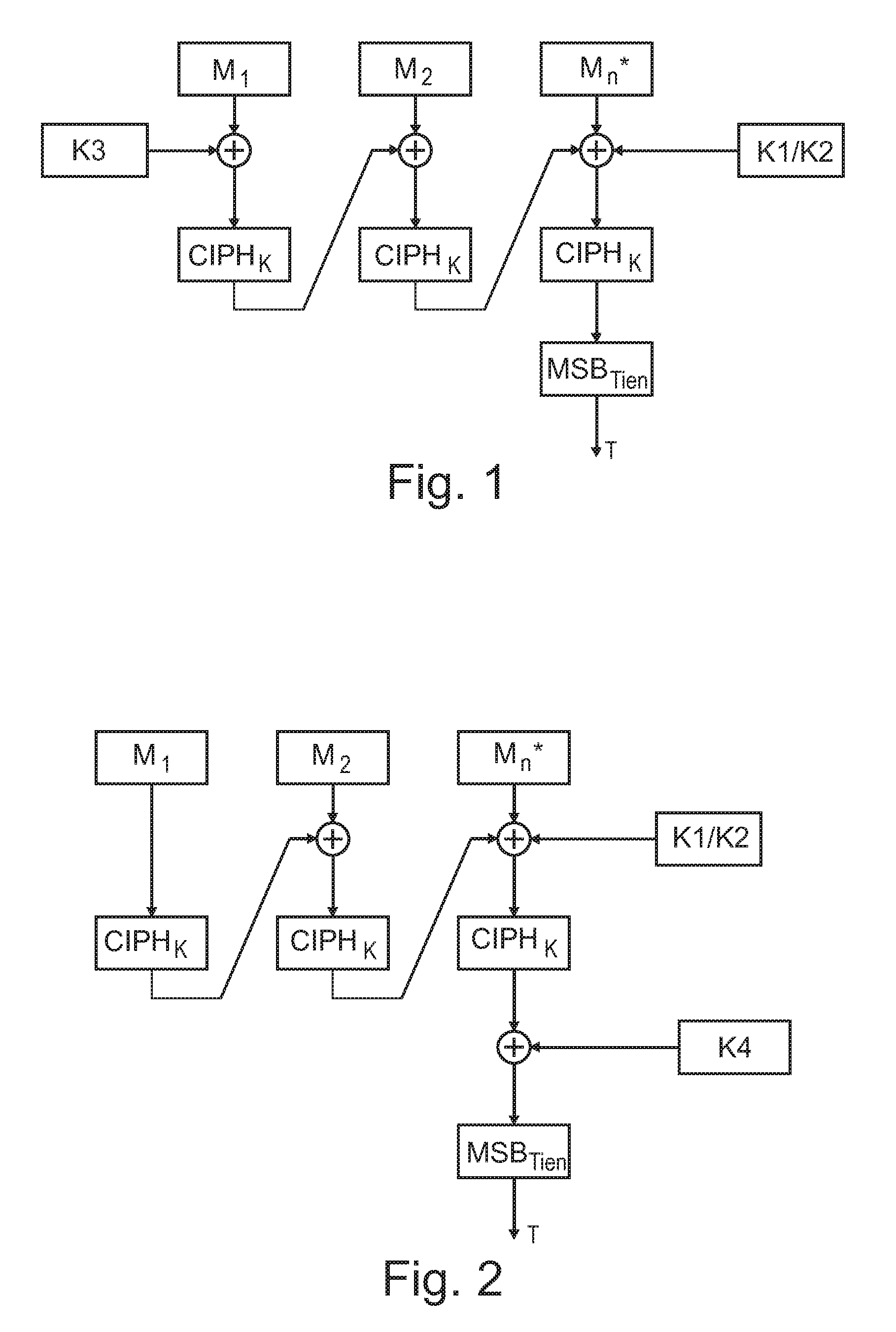
Device for generating a message authentication code for authenticating a message
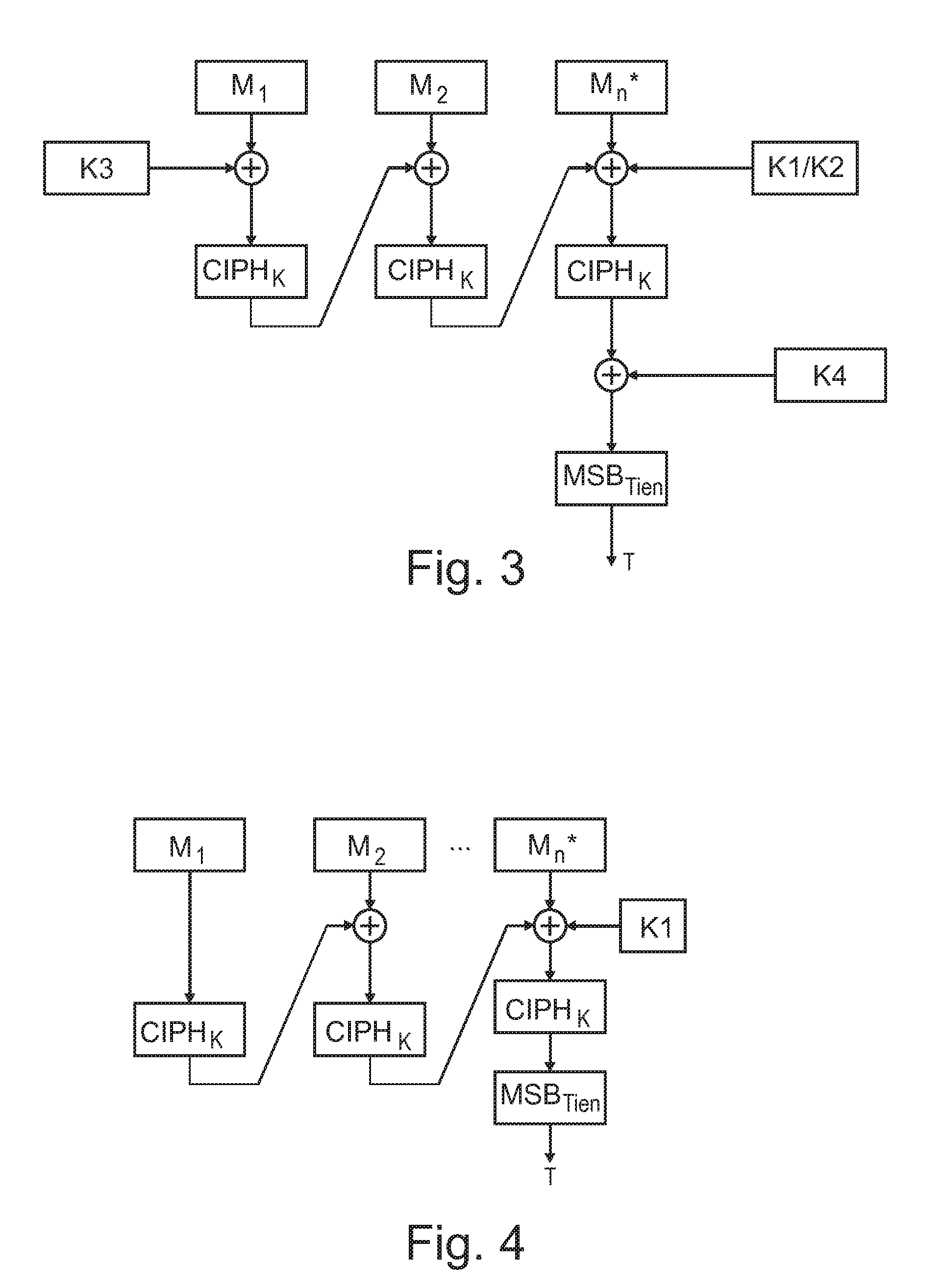
ActiveUS20110051927A1Increase authenticityImprove integritySecret communicationCryptographic attack countermeasuresComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
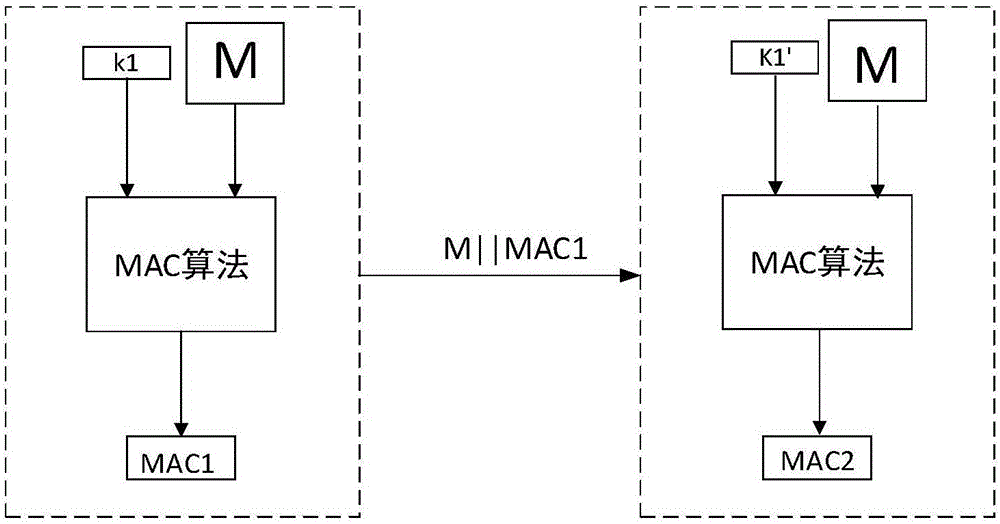
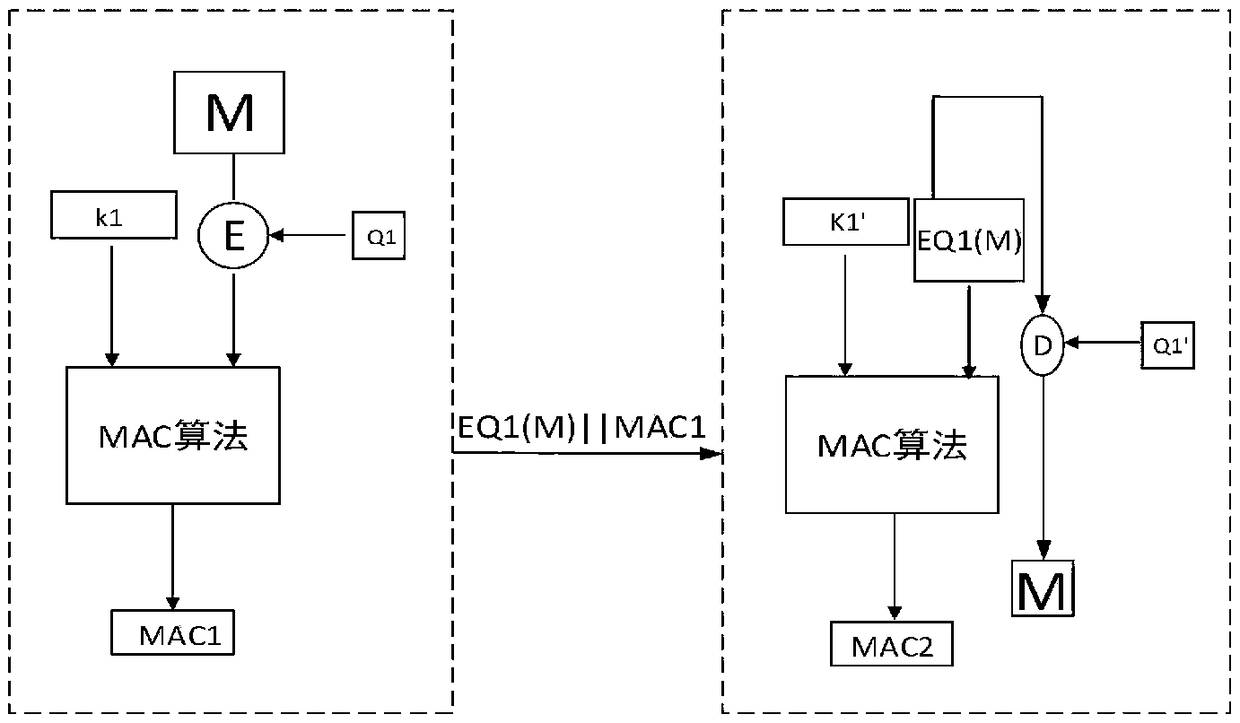
Device for generating a message authentication code for authenticating a message, wherein the message is divided in blocks (M) with a specified block length, the device comprising a generating unit for generating the message authentication code based on a message by using a block cipher algorithm, and an encrypting unit for performing an exclusive disjunction on the last block with a first key (K1, K2) and for performing an exclusive disjunction on the first and / or the last block additionally with a second key (K3, K4) for generating the message authentication code.
Owner:NXP BV
Method and device for generating approximate message authentication codes
InactiveUS6851052B1Other decoding techniquesUser identity/authority verificationHash-based message authentication codeChecksum
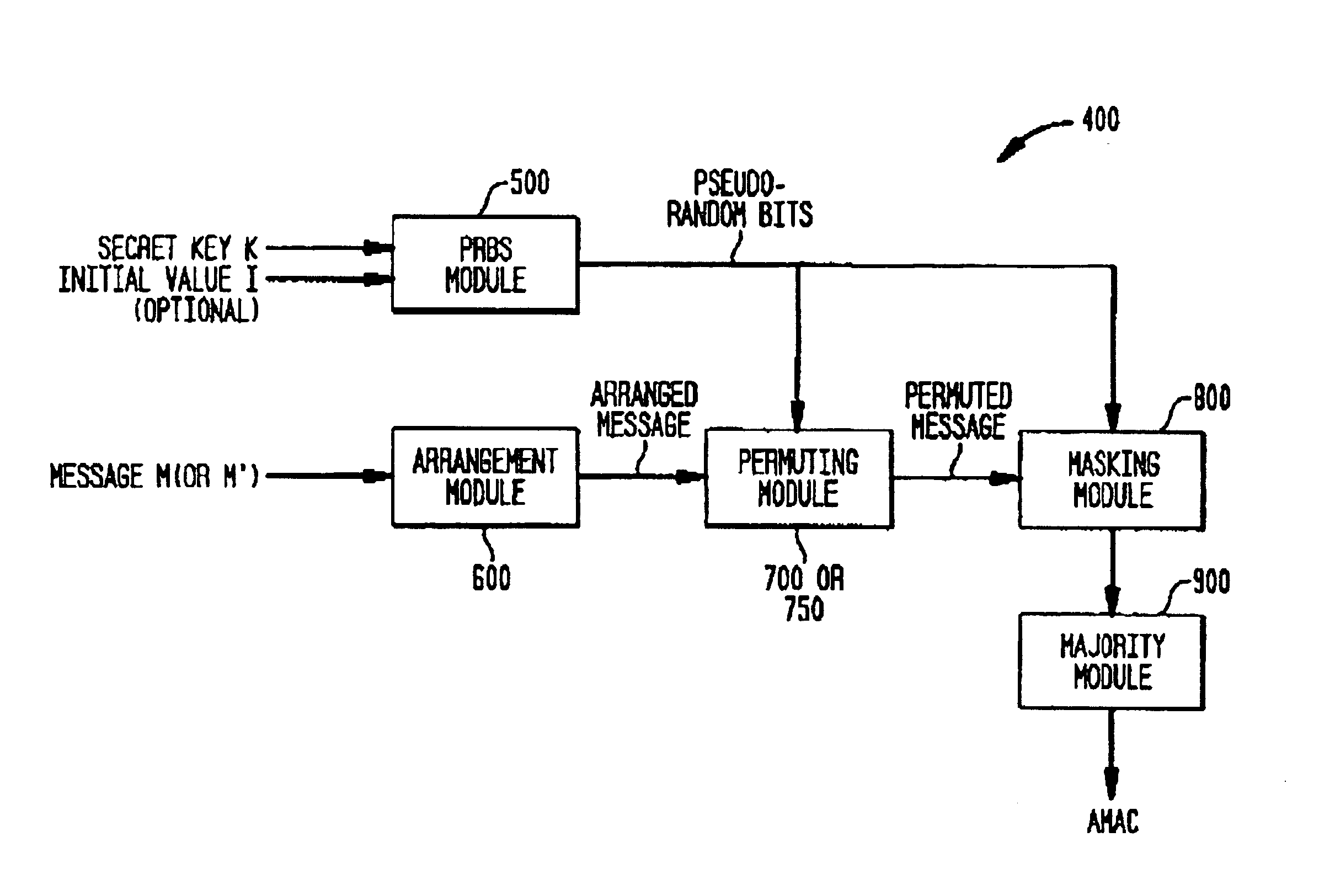
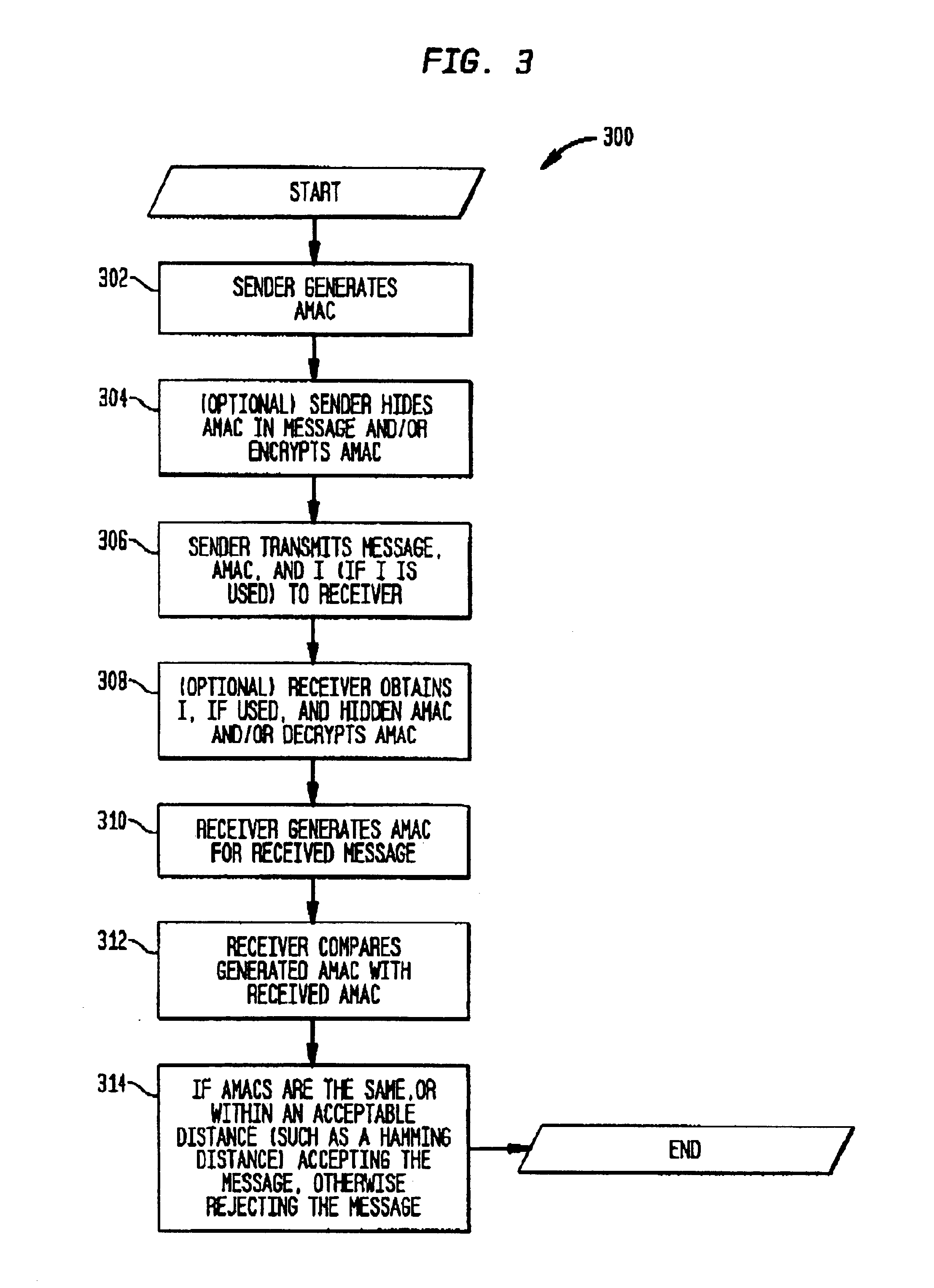
An approximate message authentication code (AMAC) which, like conventional message authentication codes, provides absolute authentication of the origin of the message, yet provides an approximate integrity check for the content of the message. The approximate integrity check will be computed probabilistically and will likely be the same for messages having only a small percentage of different bits. A distance measure on the AMACs, such as a Hamming distance measure, may be used to determine whether the number of bit differences between the messages is likely to be within an acceptable amount. The AMAC is a probabilistic checksum based on a shared key. The AMAC uses the message and a shared key as inputs. Optionally, an initial value may also be used as an input. In one version of the invention, the data in the message M are permuted and arranged (physically or logically) into a table having |A| bits in each column and T2 rows, where T is may be an odd integer. The permuted data are masked, for example, to generate an unbiased, independent, identically distributed set of bits (1 s and 0 s). Taking T rows at a time, the majority bit value for each column is determined and that majority value is used to generate a new row. This procedure is repeated on the T new rows of majority bits. The resulting |A| bits is the AMAC.
Owner:NYTELL SOFTWARE LLC
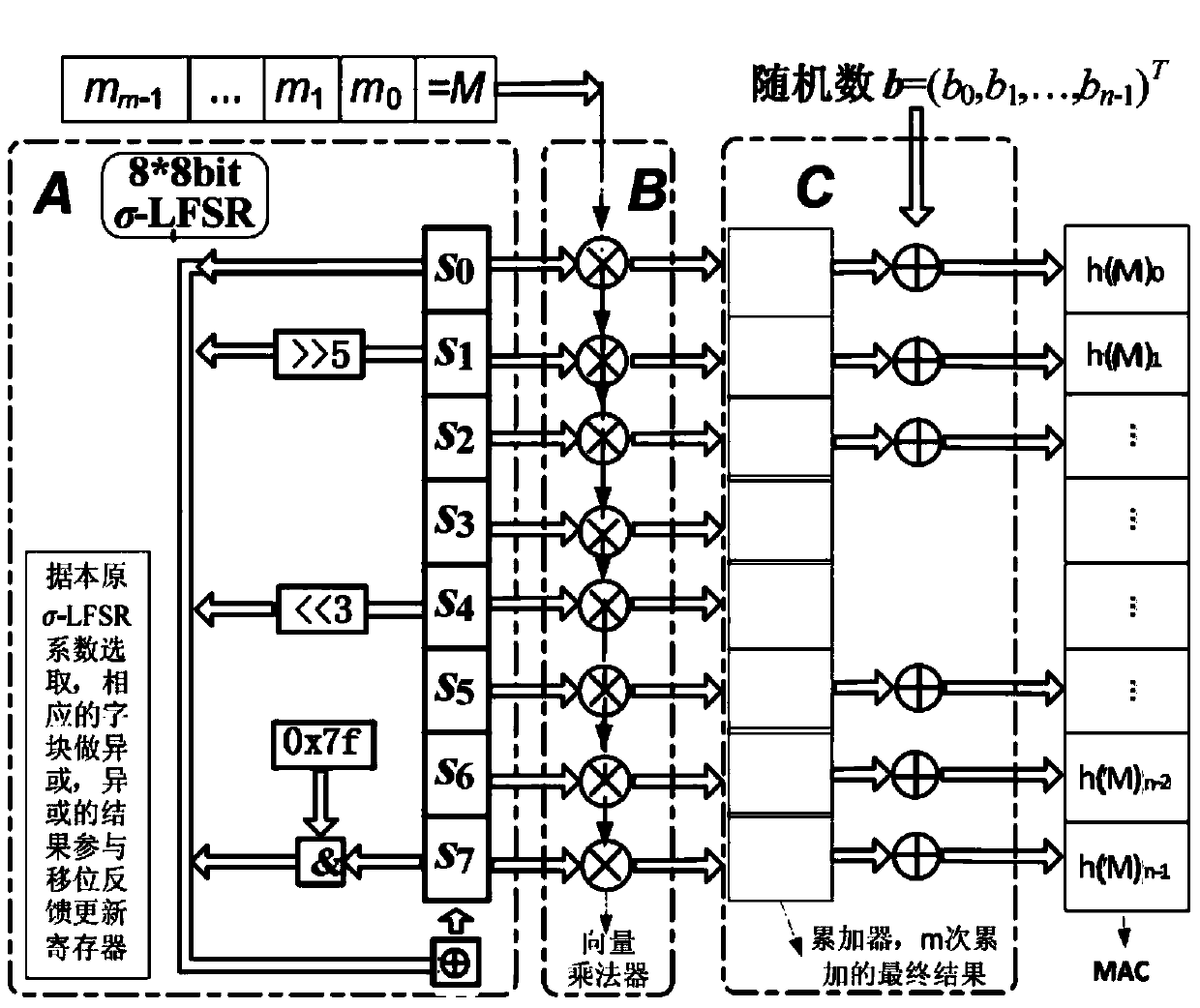
Efficient generic Hash function authentication scheme suitable for quantum cryptography system
ActiveCN104270247AEnsure safetyReduce complexityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHash functionHash-based message authentication code
The invention discloses an efficient generic Hash function authentication scheme suitable for a quantum cryptography system. In the scheme, a word-based design way is adopted. The scheme comprises the following steps: initializing a shared key of both parties and a word linear feedback shift register; performing vector multiplication on an authentication message and a register state in sequence by using an iteration and vector multiplier of the word linear feedback shift register; performing accumulation through an accumulator; performing exclusive or processing on a random number to obtain a message authentication code; and transmitting an authentication message and the message authentication code to the other party to realize an identity authentication function. The authentication scheme disclosed by the invention is clear in design principle, a design way is open, and any manual security defect does not exist; through the authentication scheme, an ideal safety security attribute can be achieved, and an efficient identity authentication function can be provided for the quantum cryptography system; and the authentication scheme has the characteristics of low occupation of resources, high portability and high platform adaptability.
Owner:THE PLA INFORMATION ENG UNIV
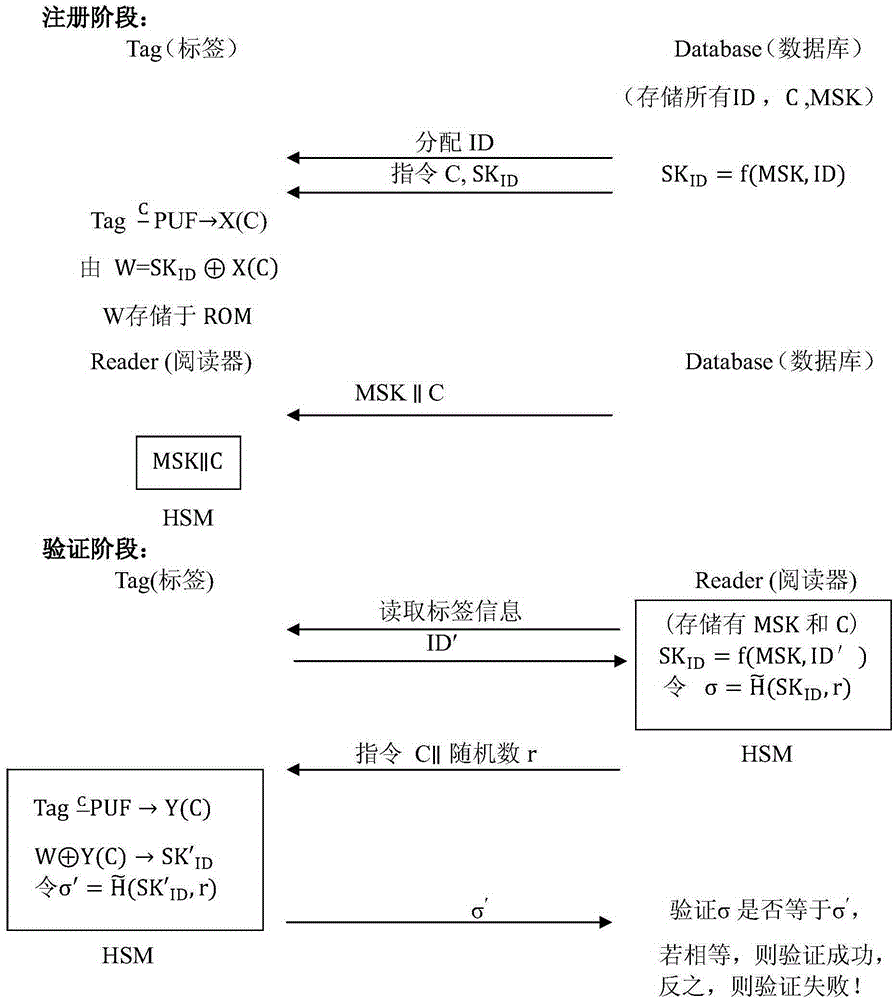
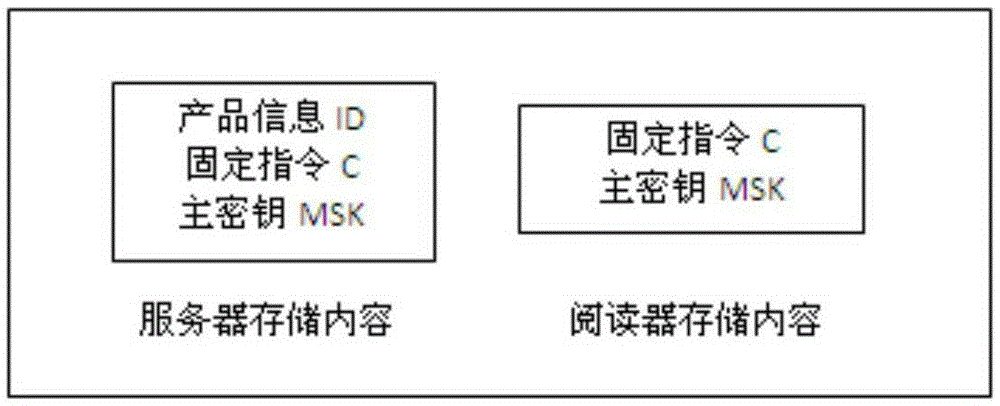
Effective novel anti-counterfeiting method based on physical unclonable function
InactiveCN105354604ALow priceEnsure safetyCo-operative working arrangementsCommerceComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
The present invention relates to an effective novel anti-counterfeiting method based on a physical unclonable function. The method comprises: storing a master key MSK, ID and an instruction C sent to an RFID tag in a server-side database; and storing critical auxiliary data W in ROM of the RFID tag, storing the master key MSK and instruction C by a hardware security module in a reader so as to implement off-line authentication and the security of information protection. By determining a response Y (C) generated by stimulating PUF by virtue of the instruction C and a private-key SKID calculated by the auxiliary data W, then by virtue of a message authentication code generated by hashing, the message authentication code is compared with the message authentication code corresponding to the private-key SKID obtained by hashing in a registration phase to verify whether the two are equal or not so as to implement product authentication. The method has the characteristics of being relatively low in storage complexity, relatively high in query efficiency, simple and convenient in authentication process, small in calculation cost, hard to be maliciously cloned and difficult to be stolen in critical information and the like.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Data transmission ciphering and integrity checking method
ActiveCN101478548ACheck integrityAddress tamperingTransmissionSecurity arrangementHash-based message authentication codeData node
The invention relates to an encryption and integrality check method of a data-transmission belonging to the electric communication technique field. In the invention, an originating node and a destination node share a root key not known by attackers, the root key and message authentication codes of all the prior transferred data generate an encryption key for encrypting the prior transferred data; at the present an encrypted data and a message authentication code corresponding the data node are transferred from the originating node to the destination node. The invention can encrypt and check the data transferred between the nodes and have advantages of safety and high performance.
Owner:观源(上海)科技有限公司
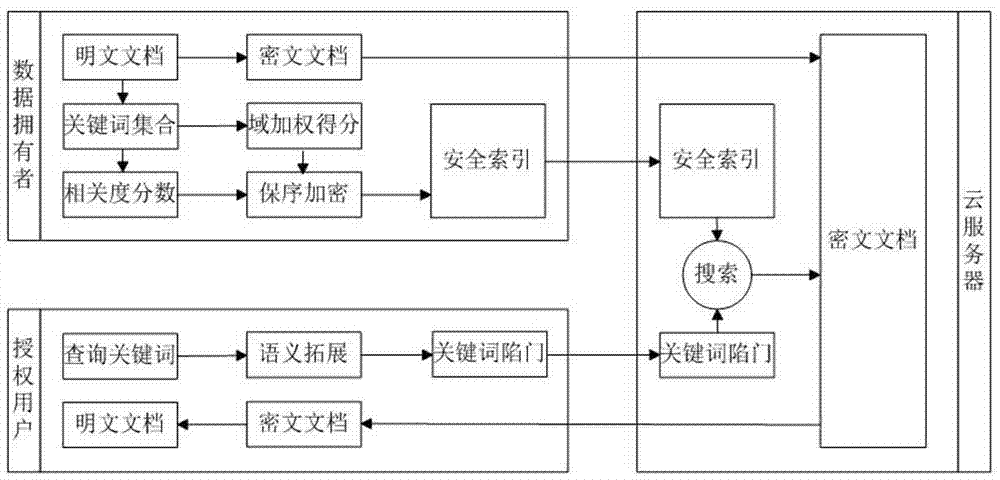
Semantic fuzziness searchable encryption method capable of realizing sorting verifiability
ActiveCN106997384ASemantic Fuzzy Search ImplementationAccurate sortingEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesDigital data protectionSorting algorithmCiphertext
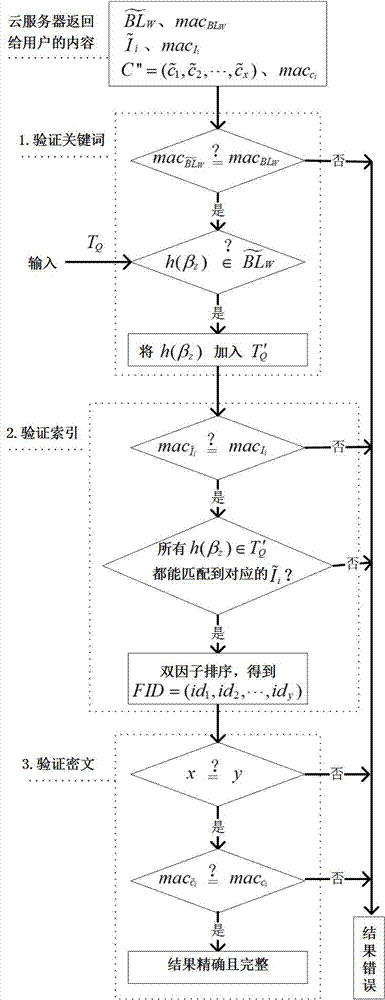
The invention relates to a semantic fuzziness searchable encryption method capable of realizing sorting verifiability. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, importing a relevancy score and a domain weighting score to obtain a more accurate index structure; then, on the basis of a WordNet dictionary set, carrying out semantic extension on query keywords, integrating semantic similarity with an encryption score to design a dual-factor sorting algorithm, and carrying out accurate sorting on a search result; and finally, applying a Bloom filter and a message authentication code to carry out comprehensive and effective verification on keywords, indexes and ciphertexts. By use of the method, semantic fuzziness search can be realized, search results can be sorted, and a sorting verifiability function is supplemented on the basis of the accuracy and the integrity of a verification result of an existing verifiable scheme.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
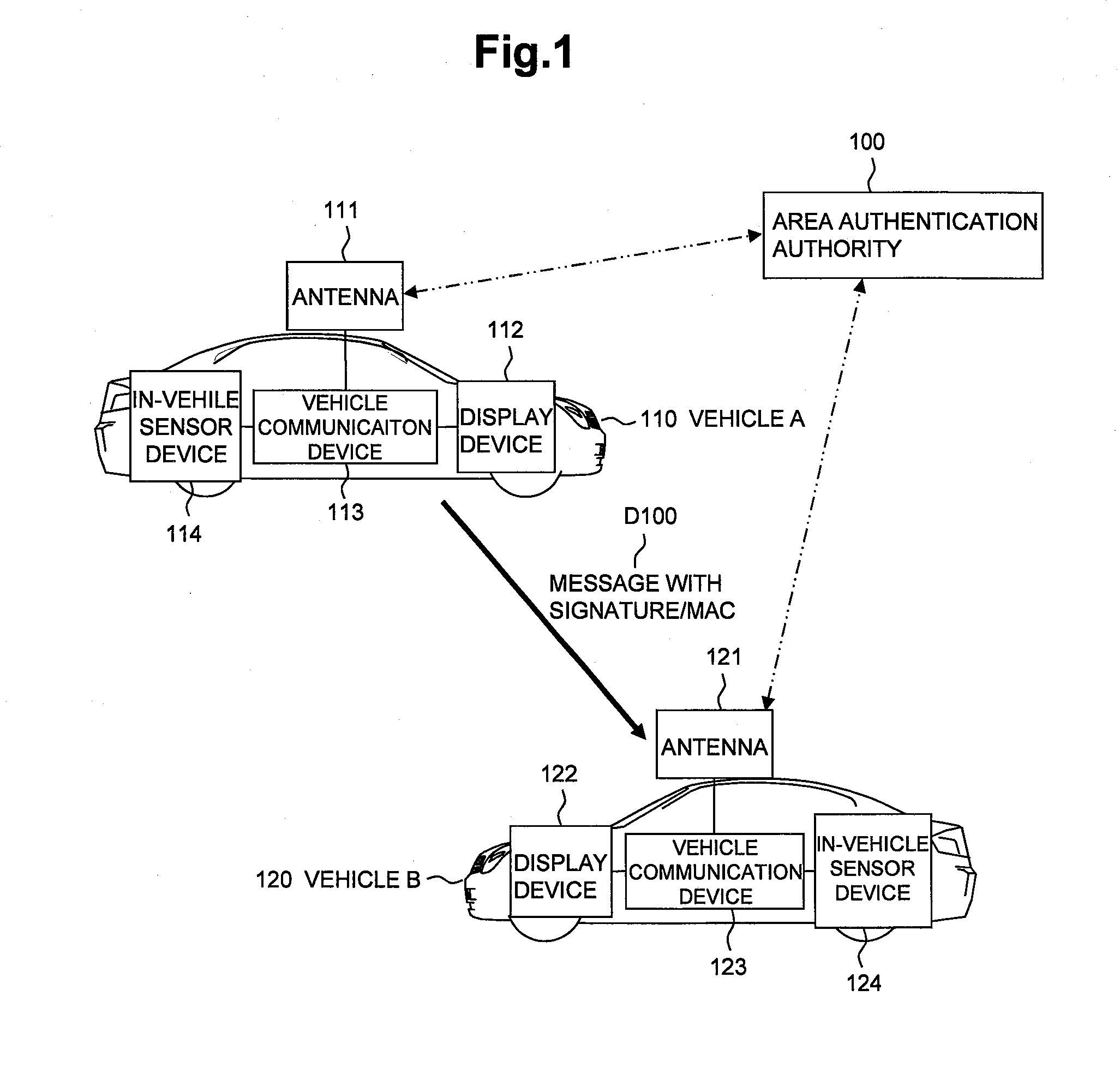
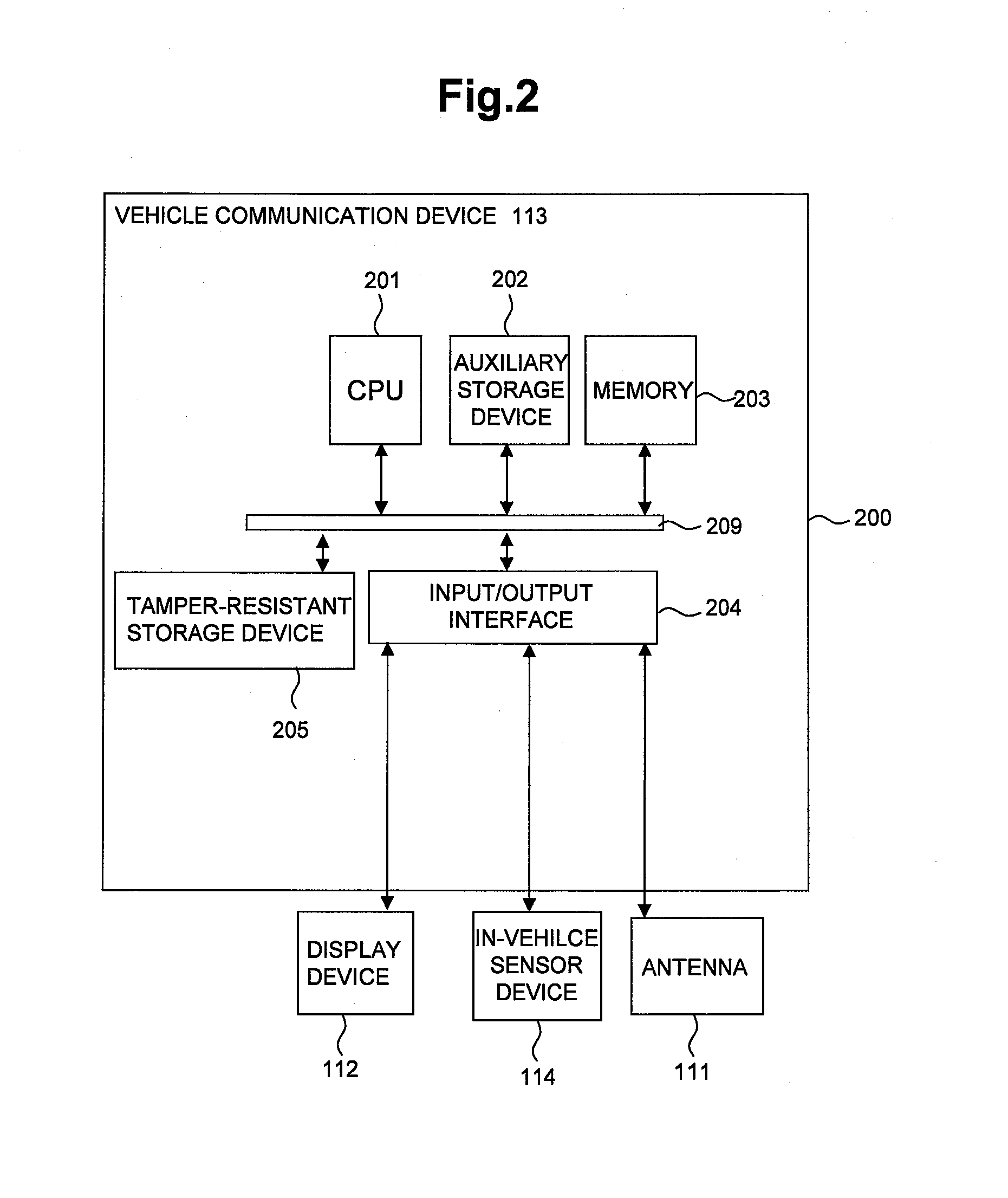
An inter-vehicle message anonymous authentication method and system in an Internet of Vehicles environment
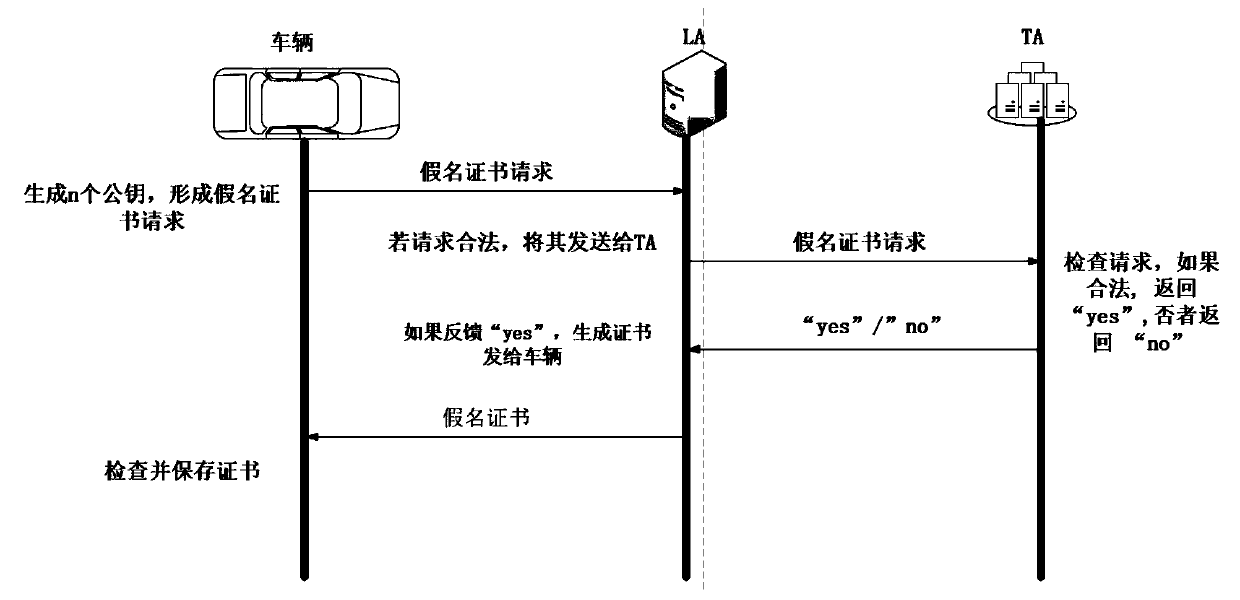
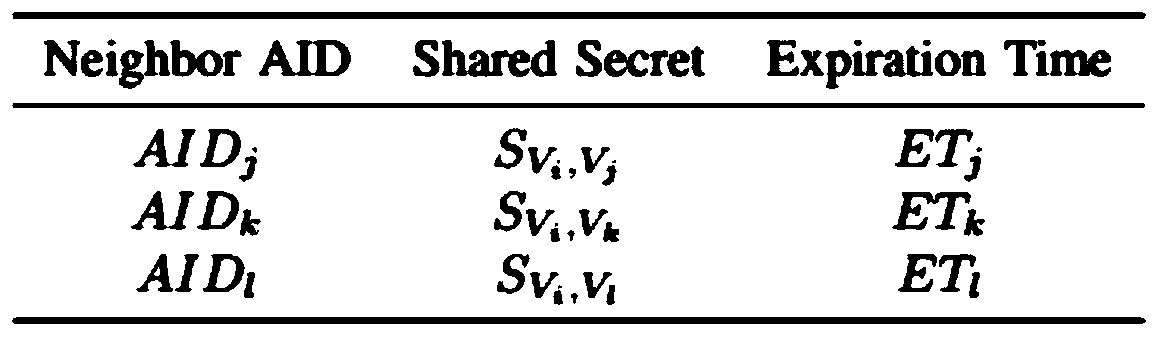
ActiveCN109788482AShort timeMeet privacy requirementsKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationHash-based message authentication codeThe Internet
The invention relates to an inter-vehicle message anonymous authentication method and system in an Internet of Vehicles environment, in the method, each vehicle has a unique identity, and in communication, a short-term pseudonymous certificate needs to be obtained through TA authentication in advance and is used for proving the legal identity of the vehicle. The vehicle negotiates with each neighbor vehicle a communication authentication secret key through the pseudonym certificate, and then based on the communication secret key, signature and signature verification can be realized through simple and rapid HMAC. Compared with a previous message authentication mode, the method has the advantages that the time required for message authentication each time is shortened on the whole, and the environment of vehicle information communication is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Wireless communications device and authentication processing method
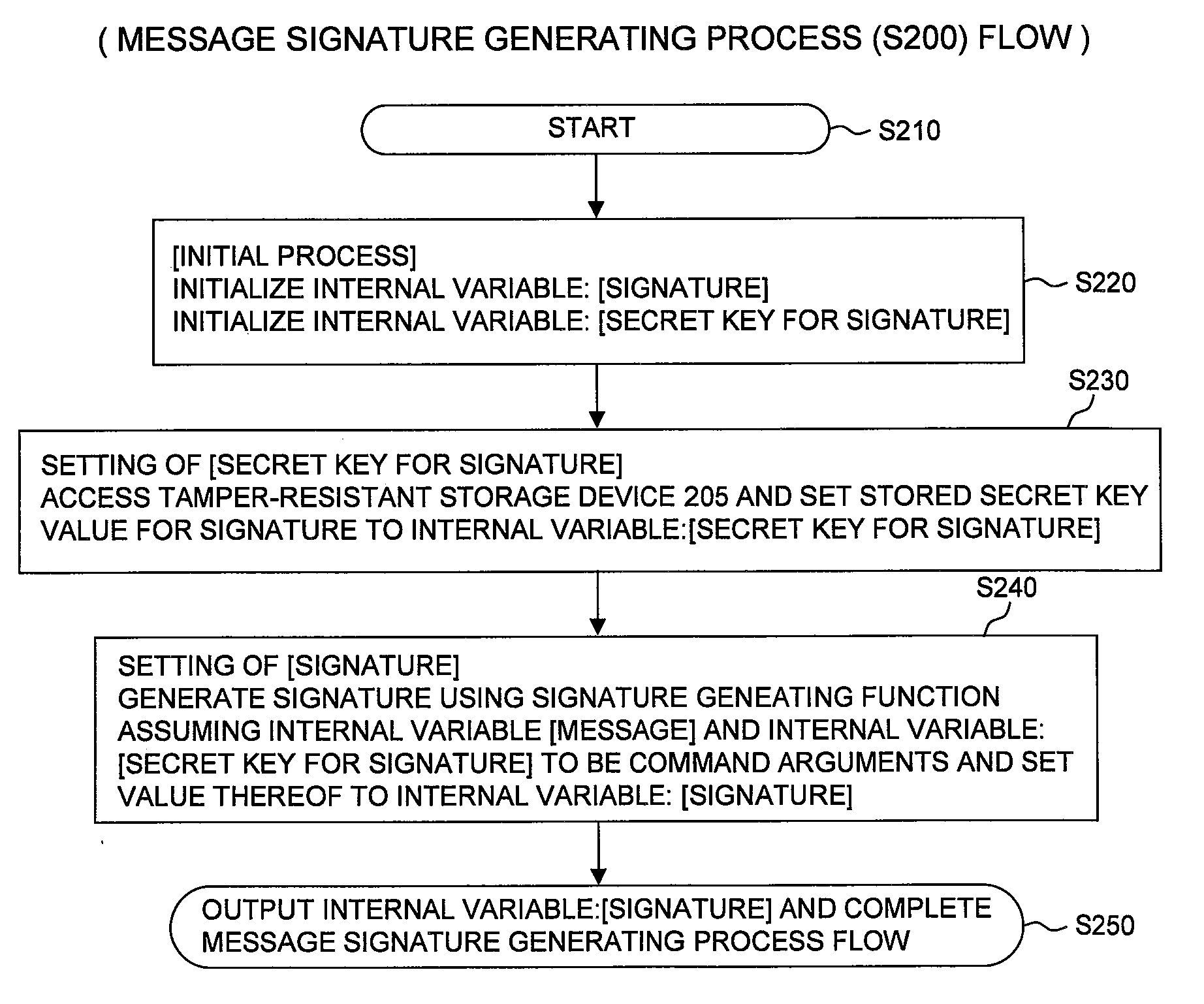
ActiveUS20120311340A1Multiple keys/algorithms usageUser identity/authority verificationHash-based message authentication codeDigital signature
An authentication method is provided which is capable of performing message authentication within an allowable time regardless of the magnitude of the number of messages and performing message authentication high in accuracy within a range for which the allowable time allows. Upon transmission by wireless communications with another mobile or a fixed station, a message authentication code of communication data and a digital signature are generated (S200 and S300). The generated message authentication cod and digital signature are transmitted with being added to the communication data. Upon reception, whether authentication should be done using either one of the message authentication code and the digital signature included in received information is determined according to its own state for the authentication (S400 and S500). This state includes, for example, a load state of a central processing unit or the like that performs an authentication process.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Method and system for secure communication using hash-based message authentication codes
ActiveUS8560849B2User identity/authority verificationPayment architectureSecure communicationHash-based message authentication code
A system and method for secure communication is provided. A first hash-based message authentication code is generated from a shared secret and a first counter value stored in storage of a computing device. A second hash-based message authentication code is generated from such shared secret and a second counter value. An encryption key is derived from a function of the first hash-based message authentication code and the second hash-based message authentication code. A message is encrypted using the encryption key, and communicated via a network interface of the computing device.
Owner:IQVIA INC
Message authentication method and system based on quantum key card
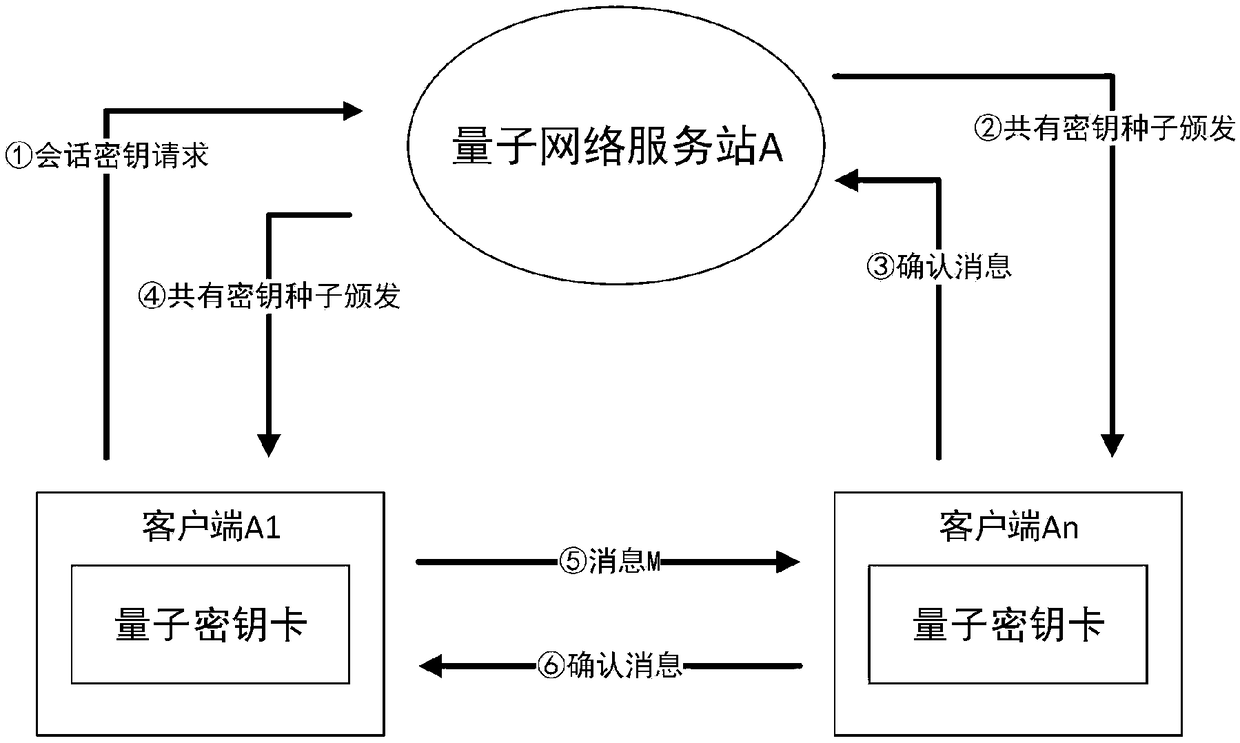
ActiveCN108173649AEnsure safetyReduce consumptionKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
The invention discloses a message authentication method based on a quantum key card, and a message authentication method. The message authentication system comprises a quantum network service stationconfigured at a network side and two clients configured at a user side to participate the message authentication, each client is configured with a quantum key card, two clients directly or indirectlyacquire a common key seed through the quantum network service station at the network side when performing the message authentication; two clients respectively generate message authentication codes byusing the owned common key seed in the corresponding quantum key card, and correspondingly implements message authentication at the user side. When two clients perform the message authentication, thecommon key seed is acquired through the quantum network service station at the network side, the generation and the comparison authentication of the message authentication code are performed at the user side, the security of the data transmission is guaranteed, and the consumption on the data processing resource at the network side is lowered.
Owner:RUBAN QUANTUM TECH CO LTD
Secure wireless communication
ActiveUS20090103728A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesHash-based message authentication codeCryptographic protocol
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Handshake method and system based on datagram secure transmission protocol
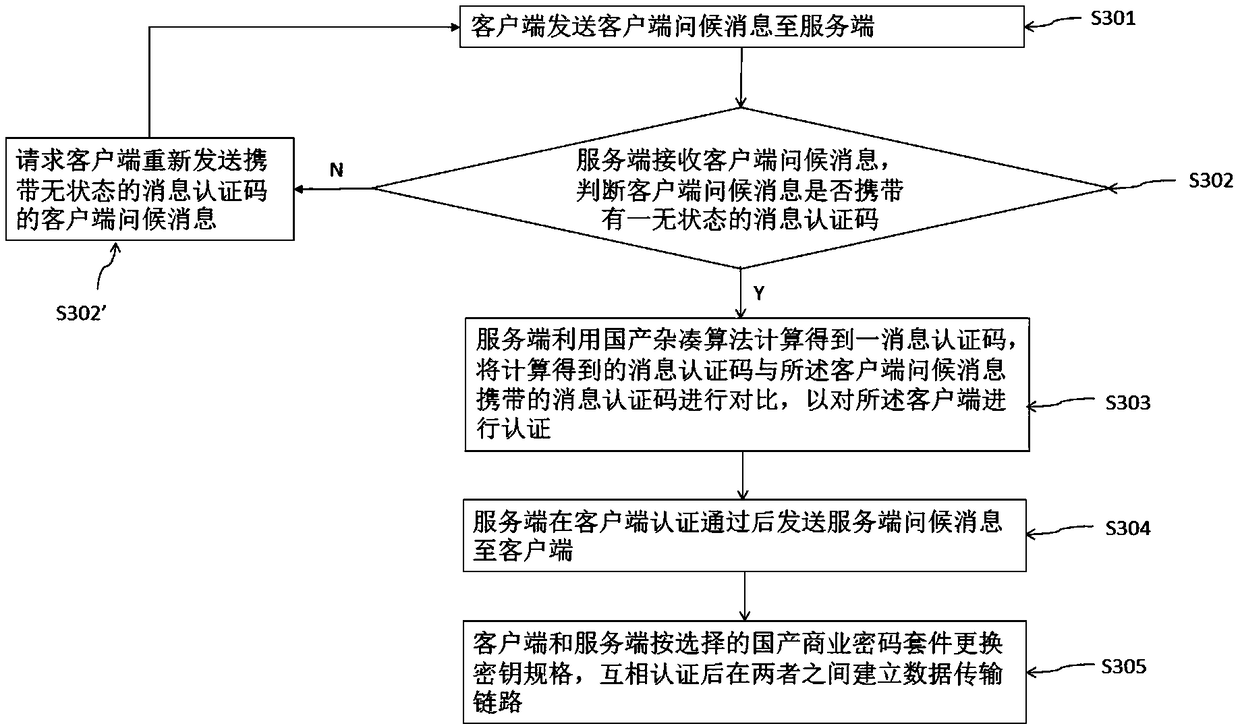
ActiveCN108650227ASatisfy the needs of safety, autonomy and controllabilityTake advantage ofKey distribution for secure communicationTransmission protocolComputer hardware
The invention refers to a handshake method and a handshake system based on a datagram secure transmission protocol. The handshake method comprises: sending a client greeting message to the server by the client, wherein the client greeting message contains a list of all domestic commercial cipher suites supported by the client; receiving and determining whether the client greeting message carries astateless message authentication code by the server: if so, calculating to obtain a message authentication code by using a domestic hash algorithm, and comparing with the message authentication codecarried by the client greeting message to authenticate the client; sending a server greeting message to the client after the authentication, and informing the client of the domestic commercial ciphersuite selected by the client; and replacing the key specification according to the selected domestic commercial cipher suite by the client and the server, thereby establishing a data transmission link. The invention is capable of meeting the requirement of self-controllable information security in China and fully utilizing the unique advantages of the domestic encryption algorithm, and is compatible with the original DTLS protocol, and convenient for horizontal expansion.
Owner:SUZHOU KEDA TECH
Elliptic curve-based message authentication code
InactiveUS20100169658A1Finite divisionUser identity/authority verificationElliptic curve discrete logarithm problemComputer hardware
The elliptic curve-based message authentication code is a computational method for improving the security of existing message authentication code (MAC) generating methods through the use of elliptic curve cryptography. Particularly, the message authentication codes and elliptic curve cryptography are based on an elliptic curve discrete logarithm problem, which is well known in mathematics to be a computationally hard problem.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
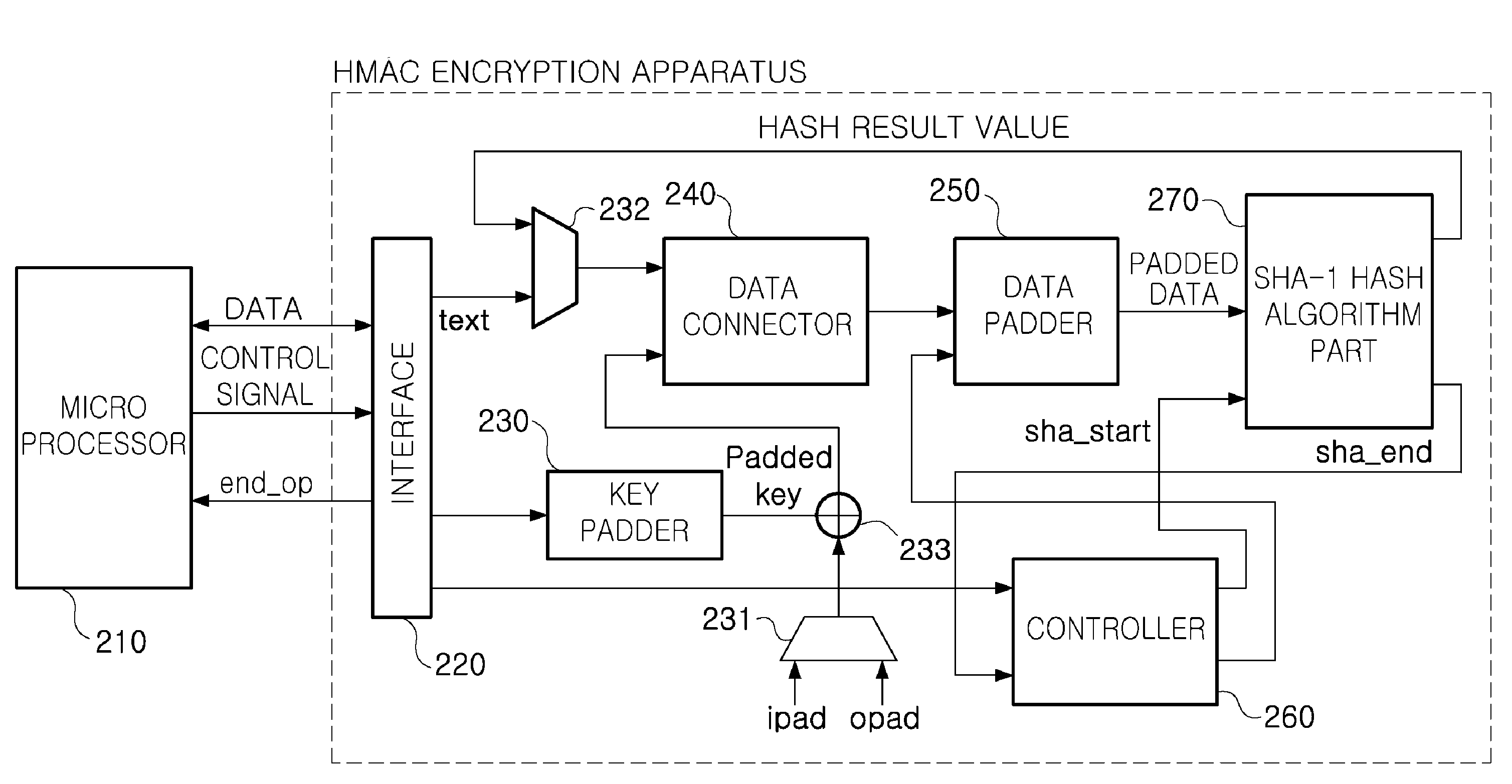
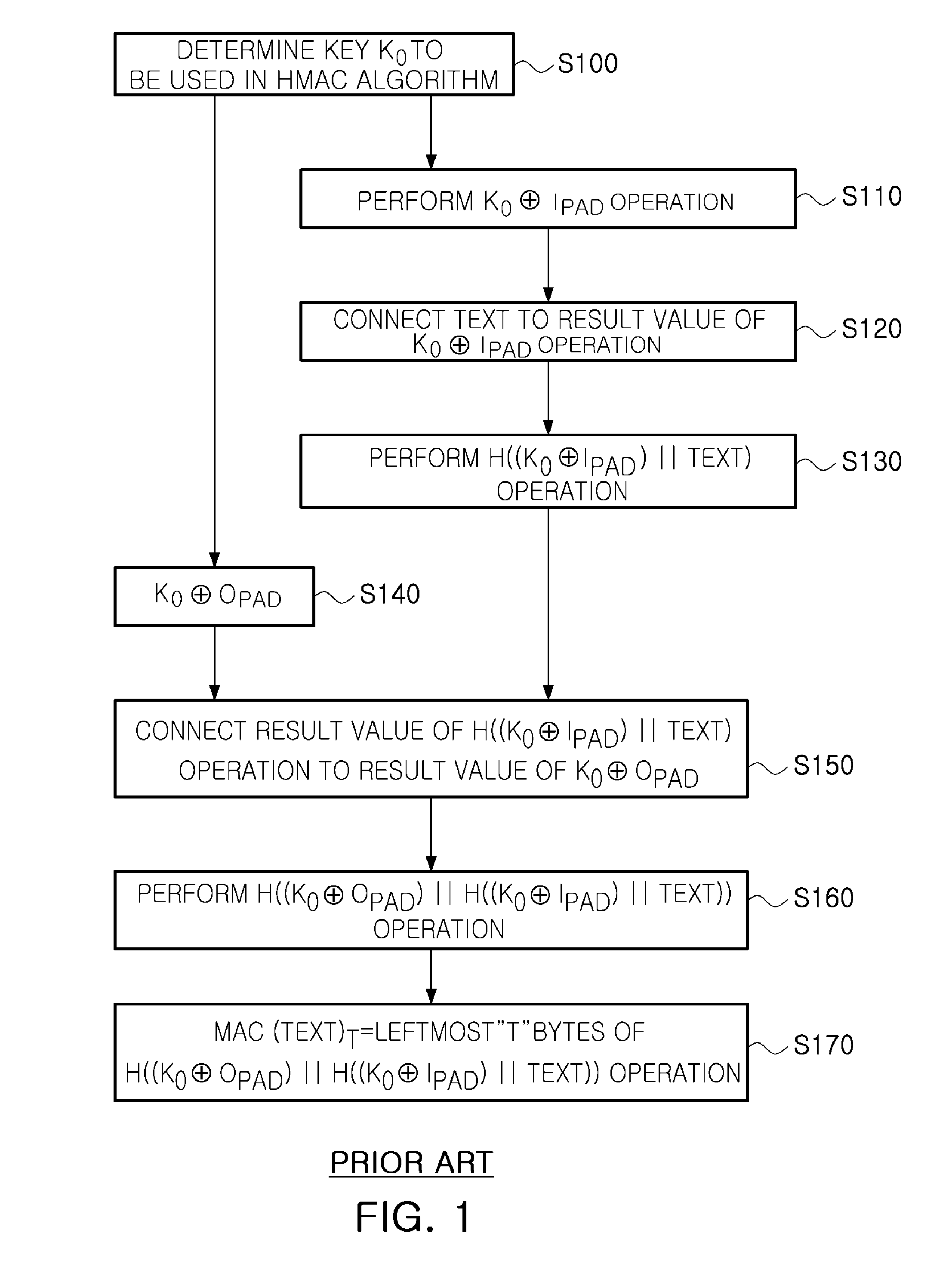
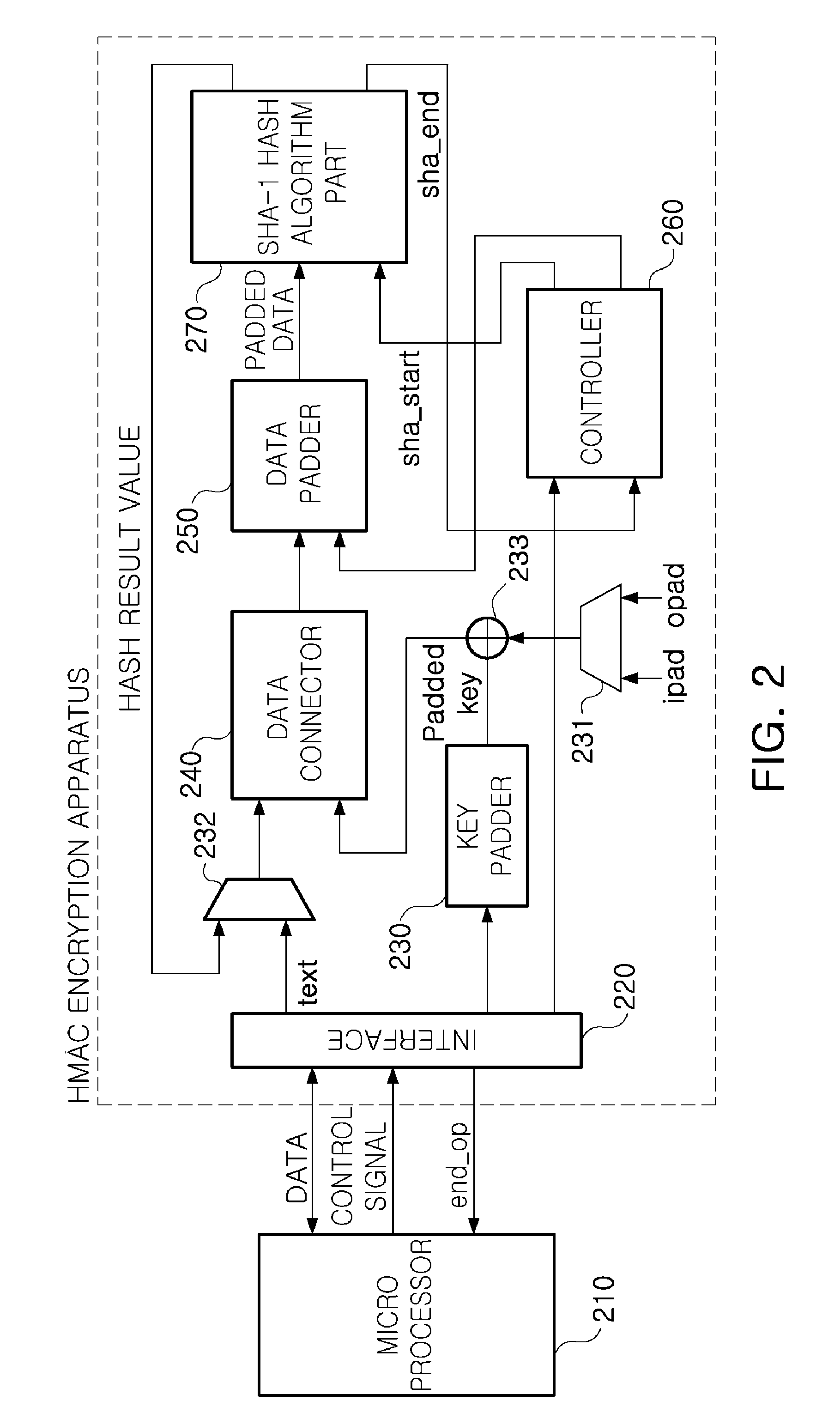
Low power hmac encryption apparatus
InactiveUS20100031052A1Privacy protectionReduce power consumptionDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationData connectionHash-based message authentication code
There are provided a low power SHA-1 hash algorithm apparatus having a low power structure and optimized to a trusted platform module (TPM) applied to a mobile trusted computing environment and a low power keyed-hash message authentication code (HMAC) encryption apparatus using the low power SHA-1 hash algorithm apparatus, the HMAC encryption apparatus including: a key padder padding key data for HMAC algorithm; an XOR operator XOR operating the padded key data and a padding constant; a data connector connecting a text to be encrypted, to data obtained by the XOR operating; a data padder padding the connected data; an SHA-1 hash algorithm part performing an SHA-1 hash algorithm on the padded data; a data selector selecting and applying one of a result of the SHA-1 hash algorithm and the text to be encrypted, to the data connector; and a controller controlling operations of the key padder, data connector, and data padder, a sequence of performing a hash algorithm of the SHA-1 hash algorithm part, and storing an operation result to read data required for performing an encryption operation and store data with memory.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
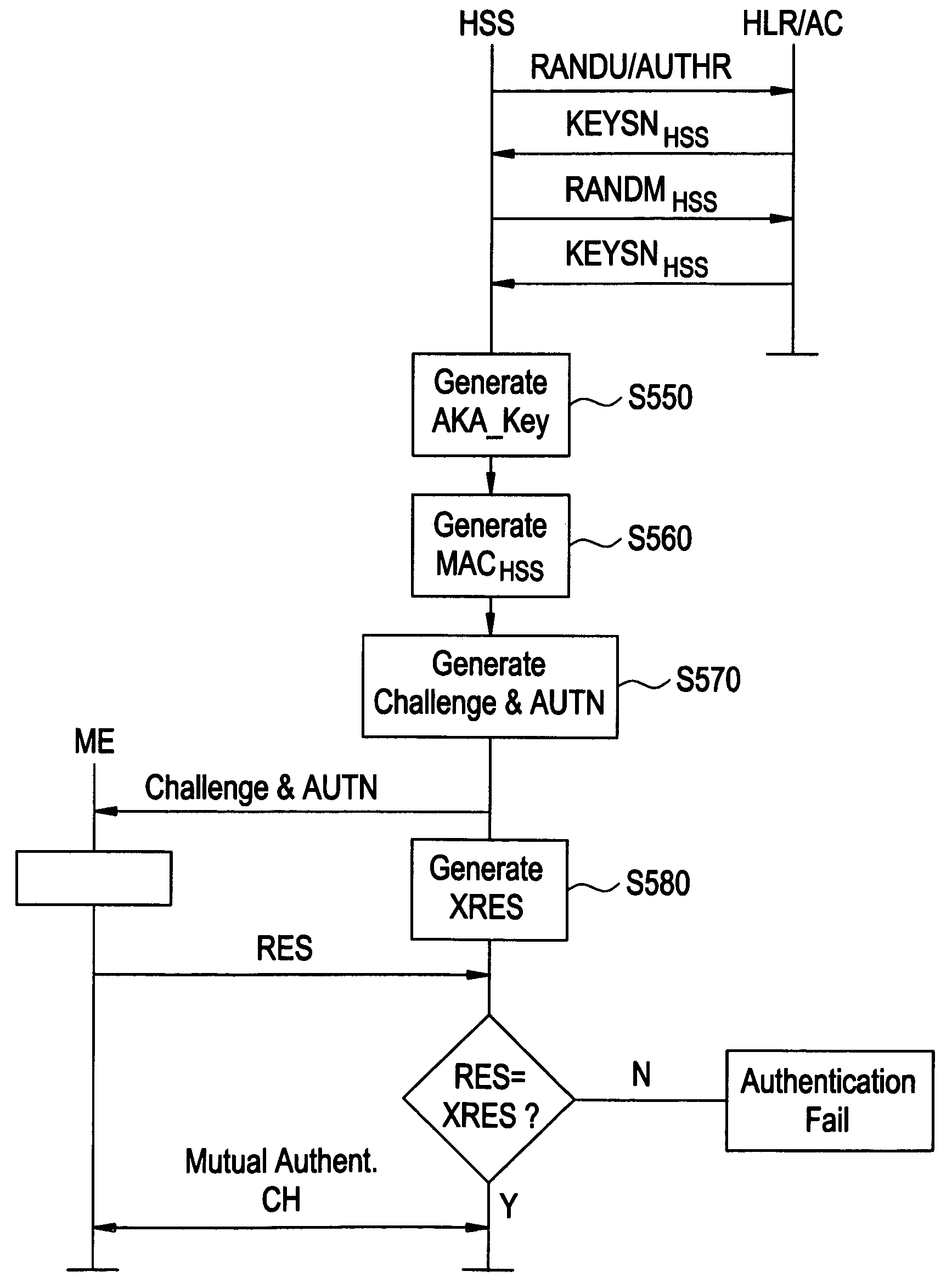
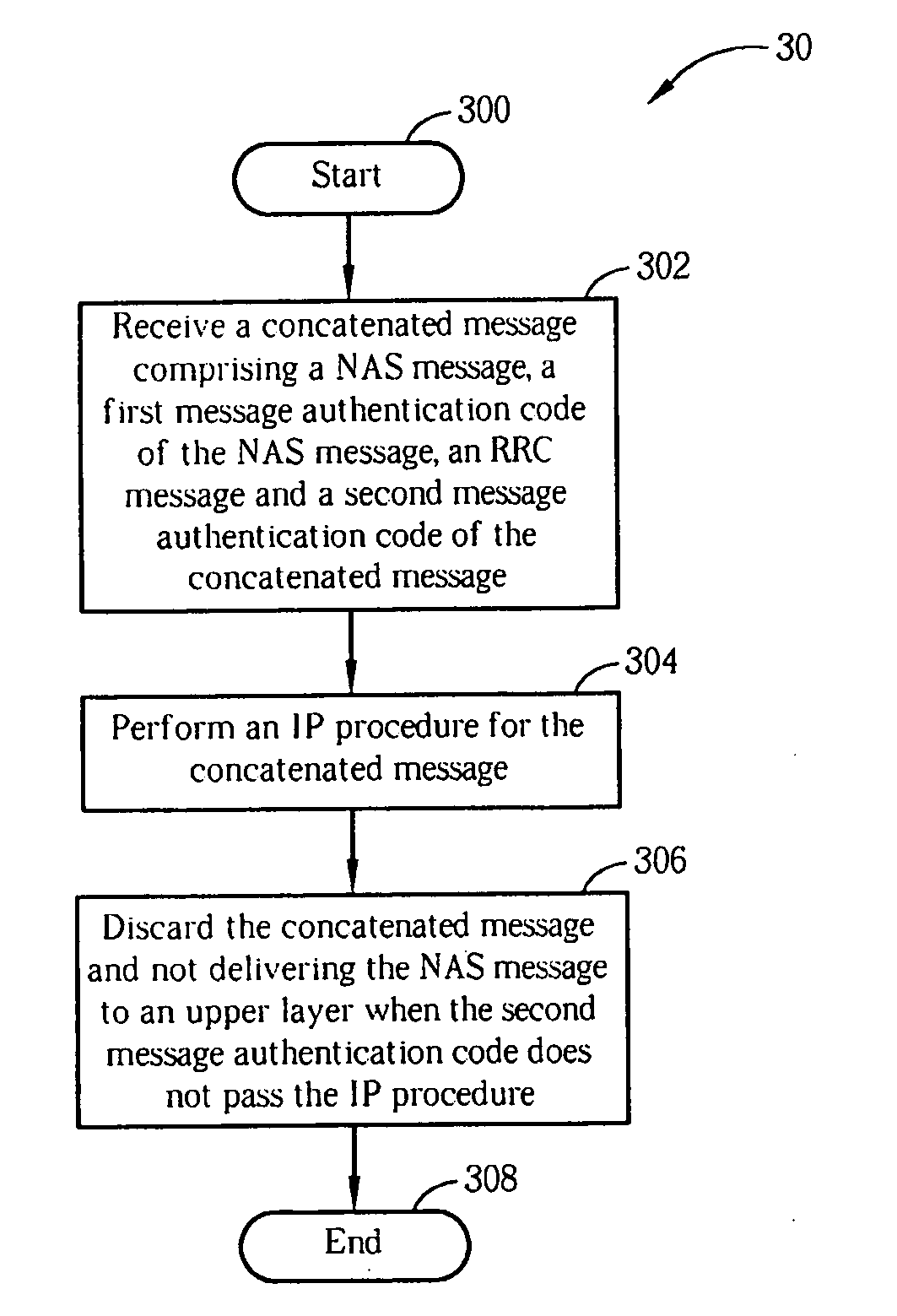
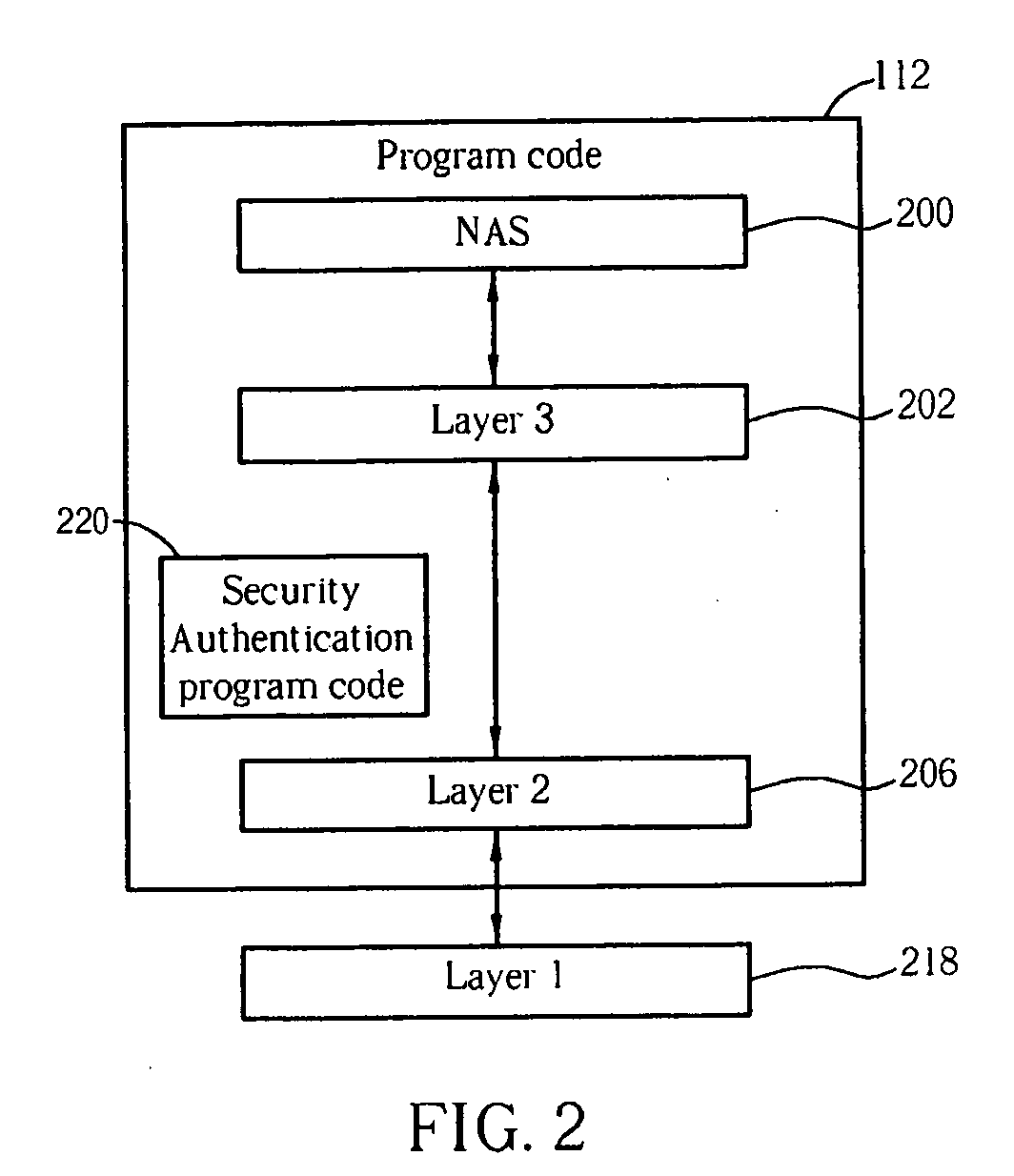
Method and apparatus for performing integrity protection in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS20080120728A1Ensure correct executionDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsHash-based message authentication codeWireless communication systems
A method for performing integrity protection in a receiver of a wireless communications system includes receiving a concatenated message including a Non-Access Stratum message, a first message authentication code of the Non-Access Stratum message, a Radio Resource Control message and a second message authentication code of the concatenated message, performing an integrity protection procedure for the concatenated message, and discarding the concatenated message and not delivering the Non-Access Stratum message to an upper layer when the second message authentication code does not pass the integrity protection procedure.
Owner:INNOVATIVE SONIC
Method of generating message authentication code using stream cipher and authentication/encryption and authentication/decryption methods using stream cipher
InactiveCN101202623AError preventionData stream serial/continuous modificationComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
Provided are a method of generating a Message Authentication Code (MAC) using a stream cipher, and authentication / encryption and authentication / decryption methods using a stream cipher. According to the methods, authentication / encryption is performed using a MAC generated using a stream cipher as an initialization vector of the stream cipher. Therefore, it is unnecessary to use a random number generation algorithm to generate the initialization vector, and thus implementation efficiency can be improved. In addition, upon generation of a MAC, a plurality of key stream generators perform computation for a plurality of message blocks, respectively. Therefore, the message blocks are computed in parallel at a time, and thus computation efficiency is excellent.
Owner:奈福克斯有限公司
Light-overhead and flexible wireless sensor message authentication method
The present invention relates to a wireless sensor message authentication method, which is characterized by an authentication scheme of any message authentication code applied to any secure message authentication code (MAC); an authentication scheme using the concept of error correcting code (ECC) and applied to any binary ECC to provide different feature; flexible technique tuning required throughput and faulty data detection capability by adjusting the ECC in use; end-to-end authentication; and XOR operation conducted to original MAC to secure light overhead.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
Method to authenticate packet payloads
ActiveUS8245032B2Improve the immunityEffective blockingError prevention/detection by using return channelUser identity/authority verificationHash-based message authentication codeTransport agent
An architecture for authenticating packets is provided that includes: an input 322 operable to receive a packet, the packet comprising at least one of a transport, session and presentation header portion and a transport agent 312 operable to compute a first message authentication code based on at least some of the contents of the packet and compare the first message authentication code with a second message authentication code in the at least one of a transport, session, and presentation header portion to authenticate the packet.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Elliptical polynomial-based message authentication code
InactiveUS20100166176A1Readily apparentEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesUser identity/authority verificationComputer hardwareHash-based message authentication code
The elliptic-polynomial based Message Authentication Code (MAC) provides MAC generation methods based on the elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem. It is well known that an elliptic polynomial discrete logarithm problem is a computationally “difficult” or “hard” problem. The methods use both an elliptic polynomial polynomial and its twist, even if the polynomial and its twist are not isomorphic. Since both the polynomial and its twist are used, multiple x- and y-coordinates can be used to embed bit strings into a point that satisfies the elliptic polynomial, and the embedding process is non-iterative, so that the time required to embed the bit string is independent of the bit string content.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Securing computer log files
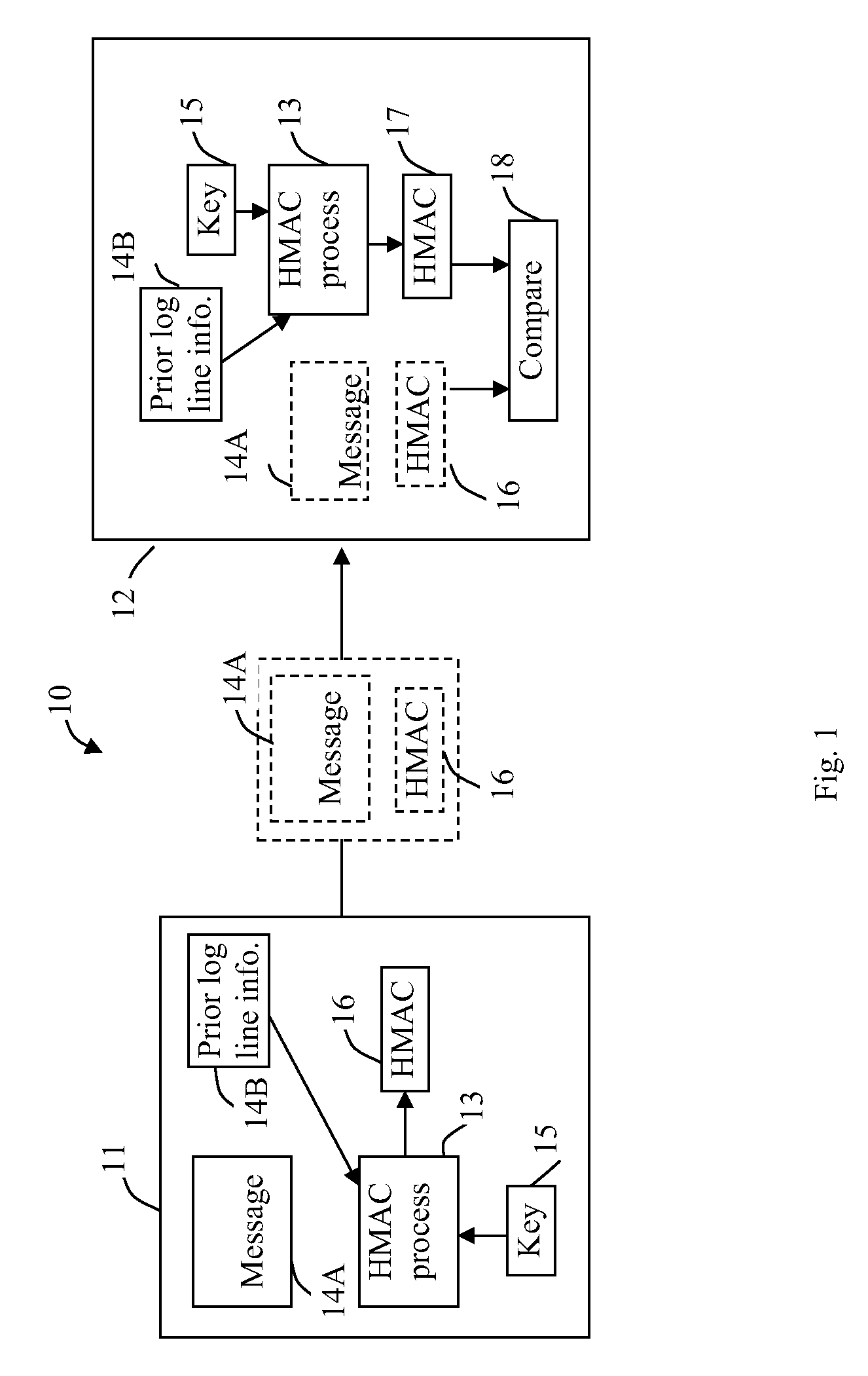
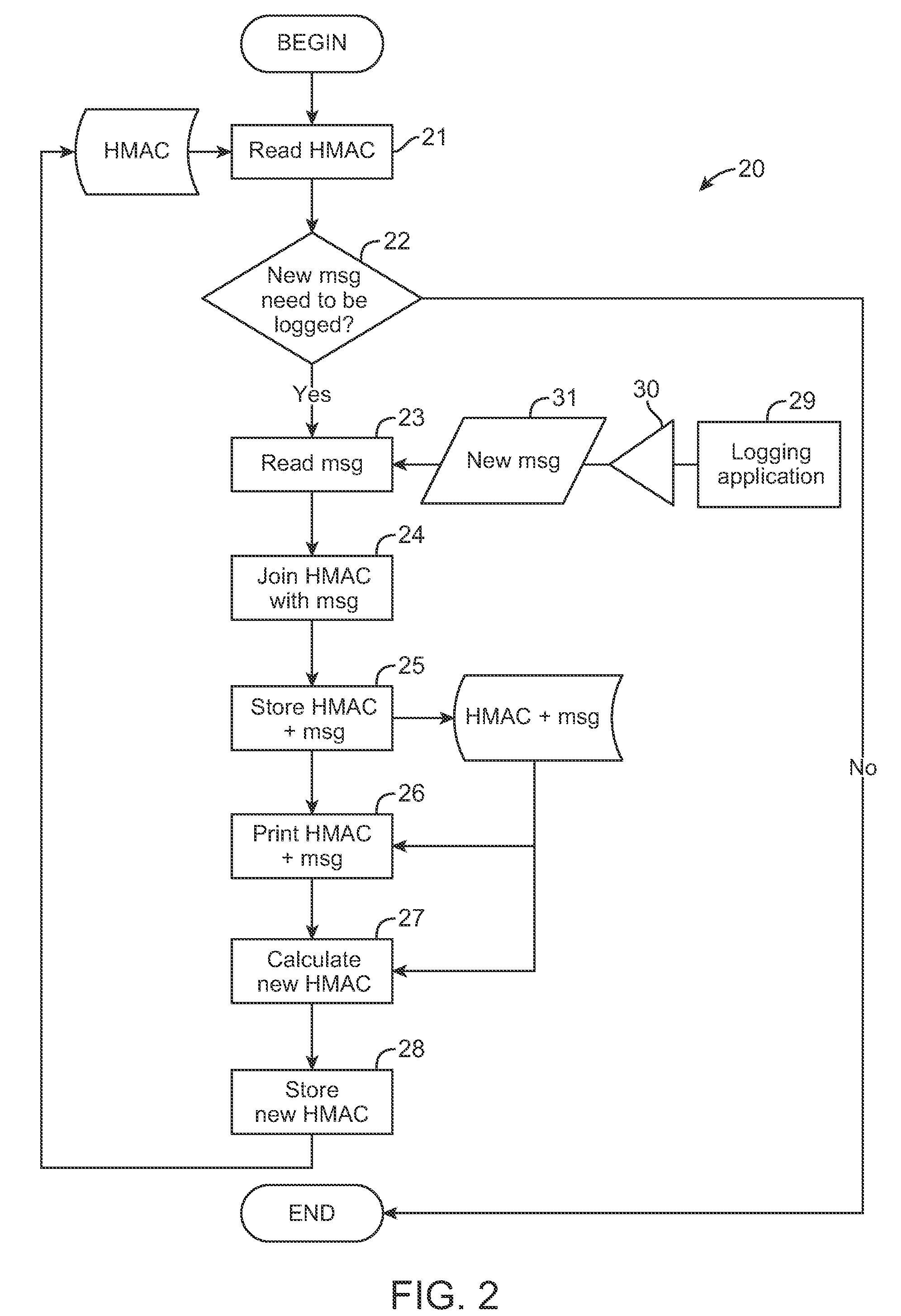
InactiveUS20100218002A1Unauthorized memory use protectionHardware monitoringLogbookHash-based message authentication code
A log file is secured. One implementation involves maintaining a log file including one or more log entries in a storage device connected to a computer, and entering a new log entry by generating a new message authentication code based on a preceding log entry including a preceding message authentication code, and applying the message authentication code to the new log entry.
Owner:IBM CORP
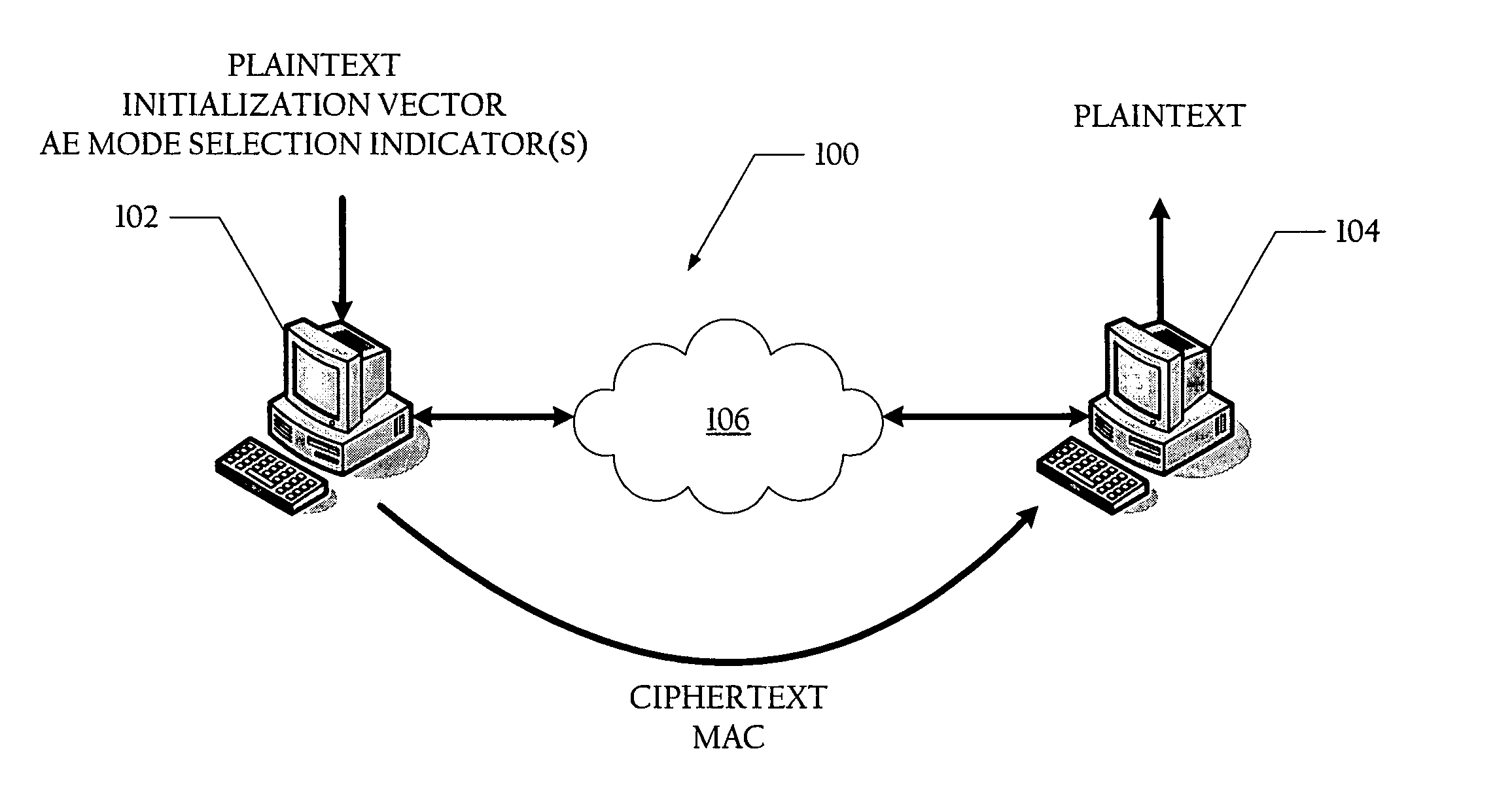
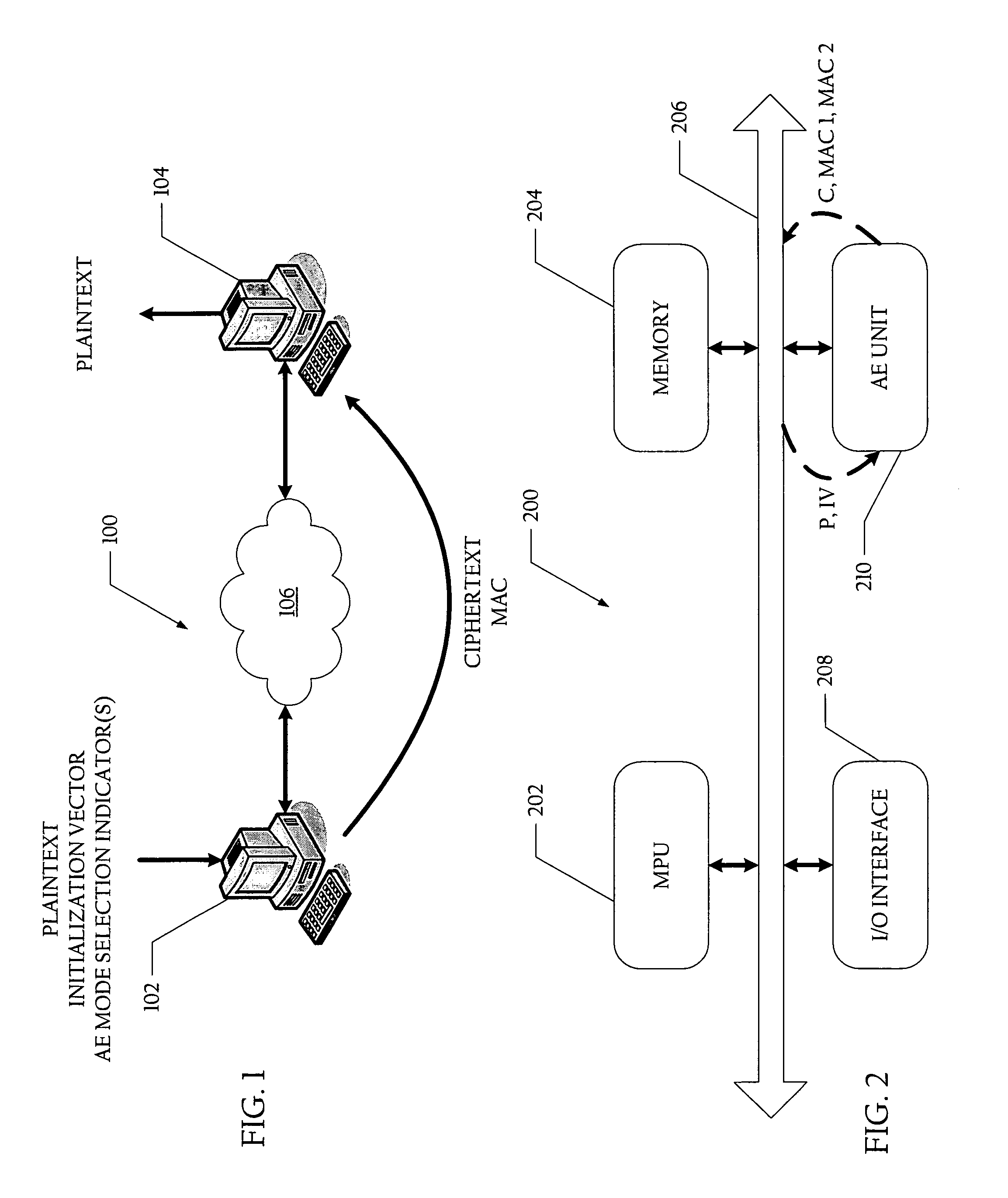
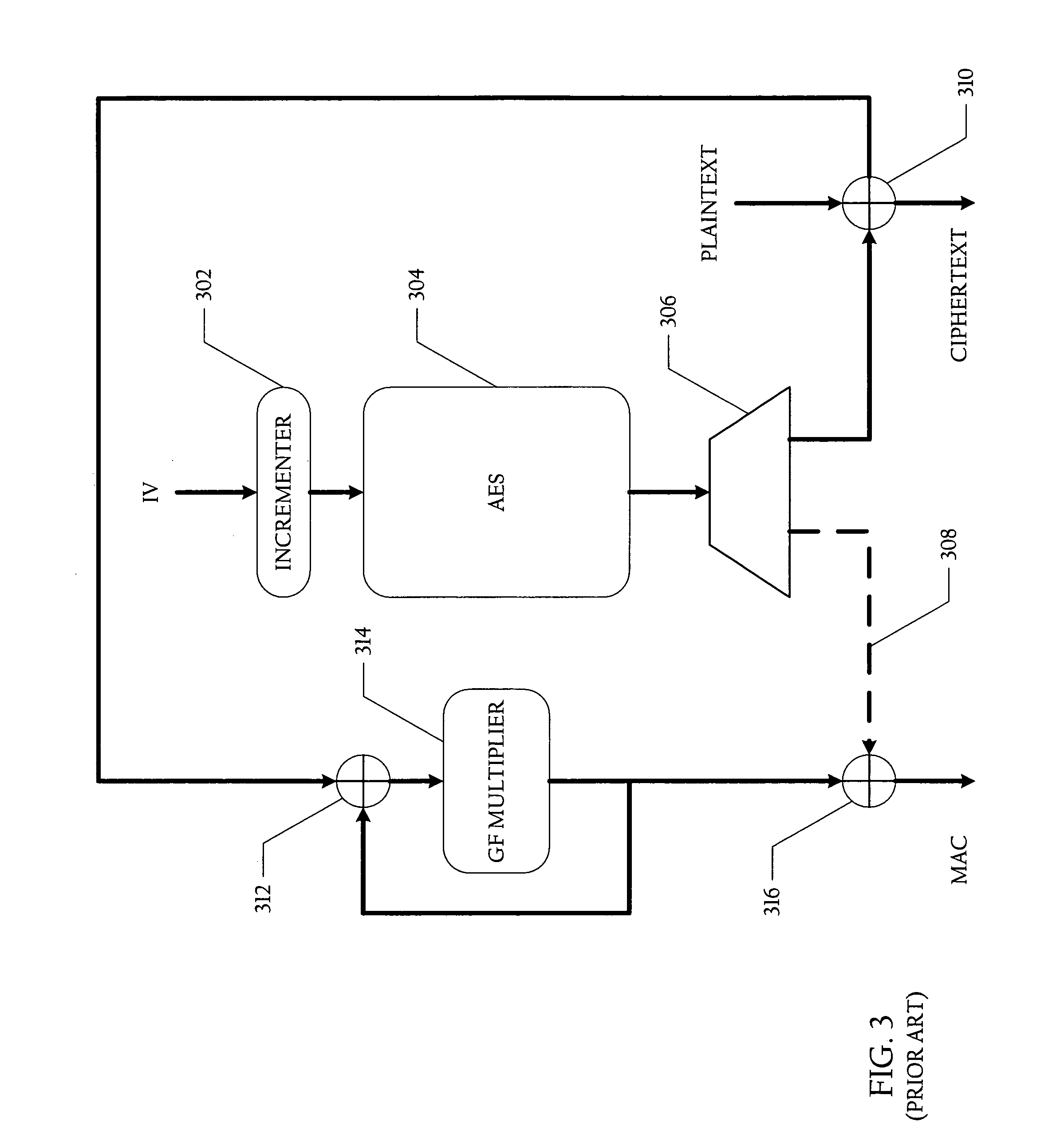
Method and system for generating ciphertext and message authentication codes utilizing shared hardware
A method and system for generating ciphertext and message authentication codes utilizing shared hardware are disclosed. According to one embodiment, a method is provided of generating ciphertext message data and message authentication codes utilizing shared authenticated encryption unit hardware. In the described embodiment, plaintext message data is received at an authenticated encryption unit which comprises first and second authenticated encryption hardware modules. Thereafter, a first message authentication code (MAC) associated with a first authenticated encryption mode and a second MAC associated with a second authenticated encryption mode are generated. More specifically, the first MAC is generated utilizing the plaintext message data and first authenticated encryption hardware module and ciphertext message data and the second MAC are generated utilizing the plaintext message data and second authenticated encryption hardware module.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com