Patents
Literature
612 results about "Authentication scheme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
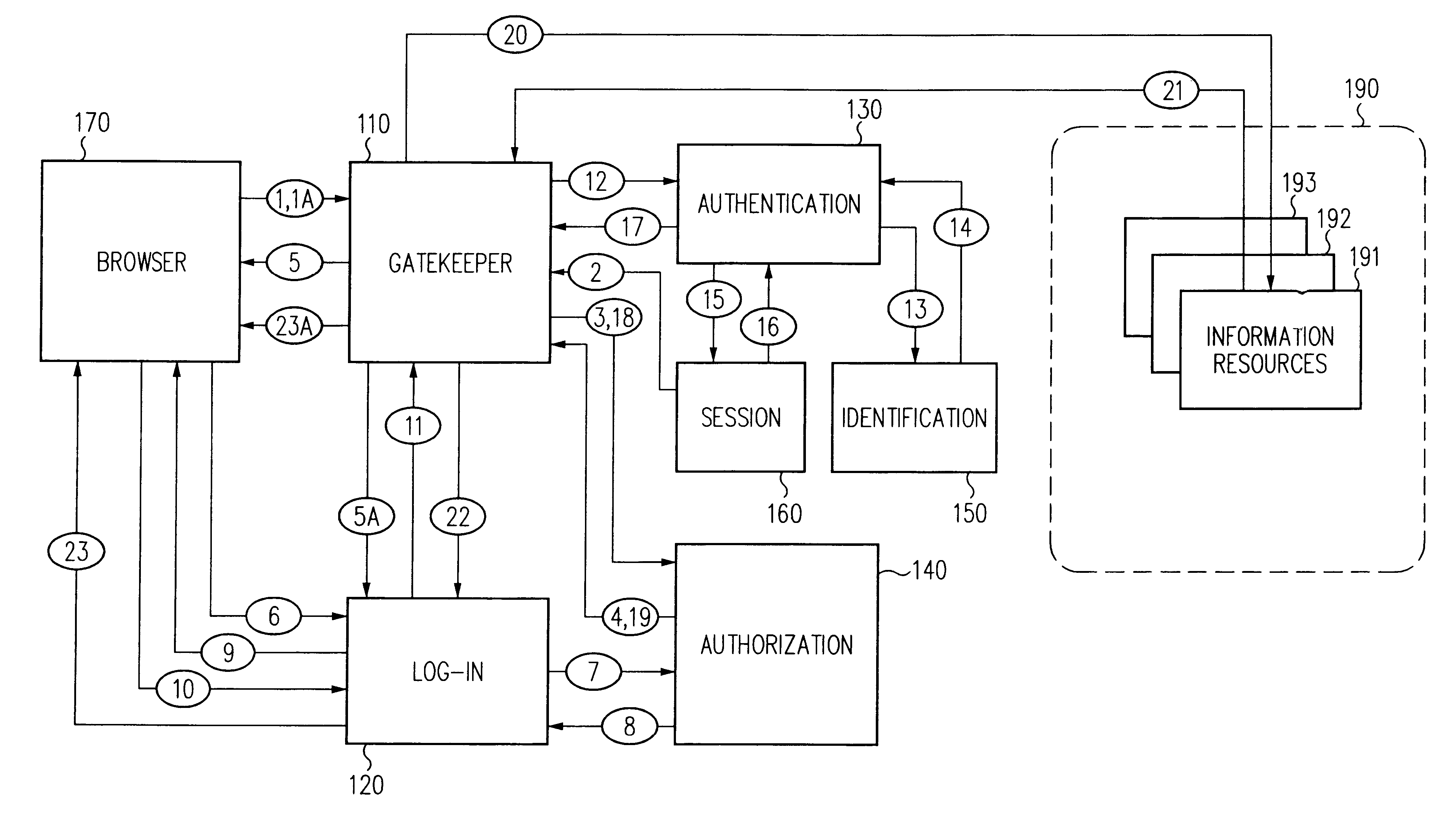
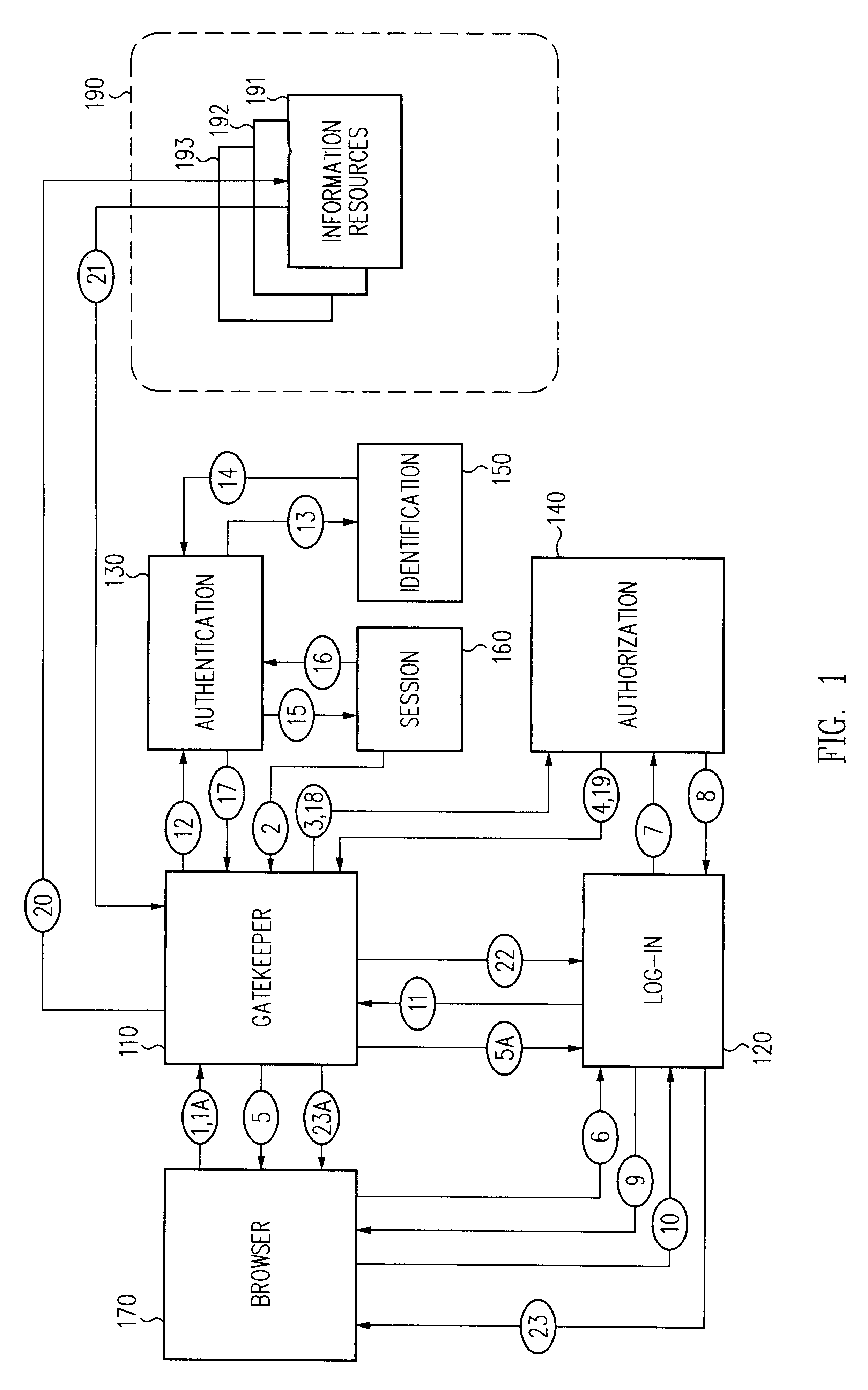
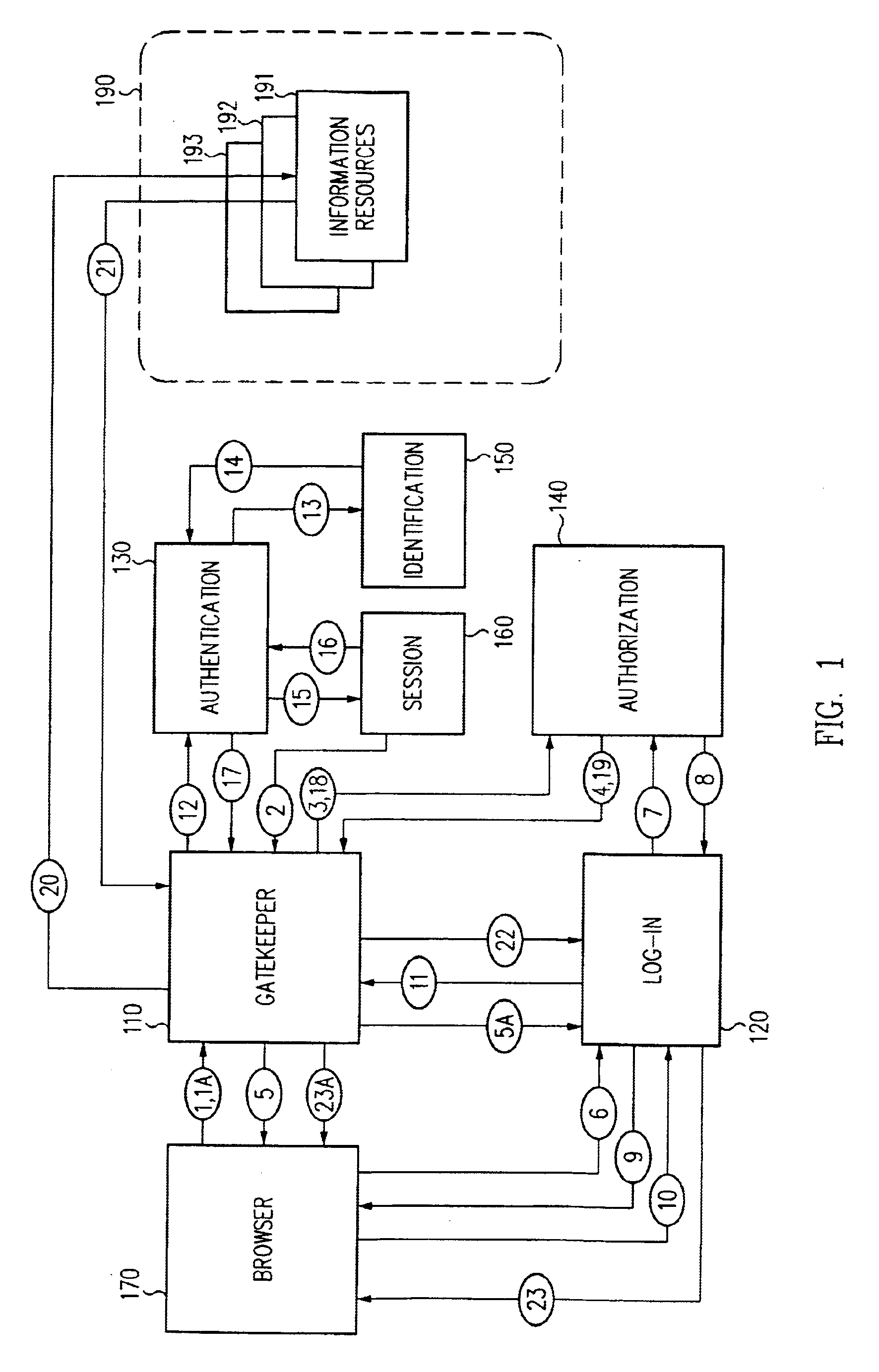
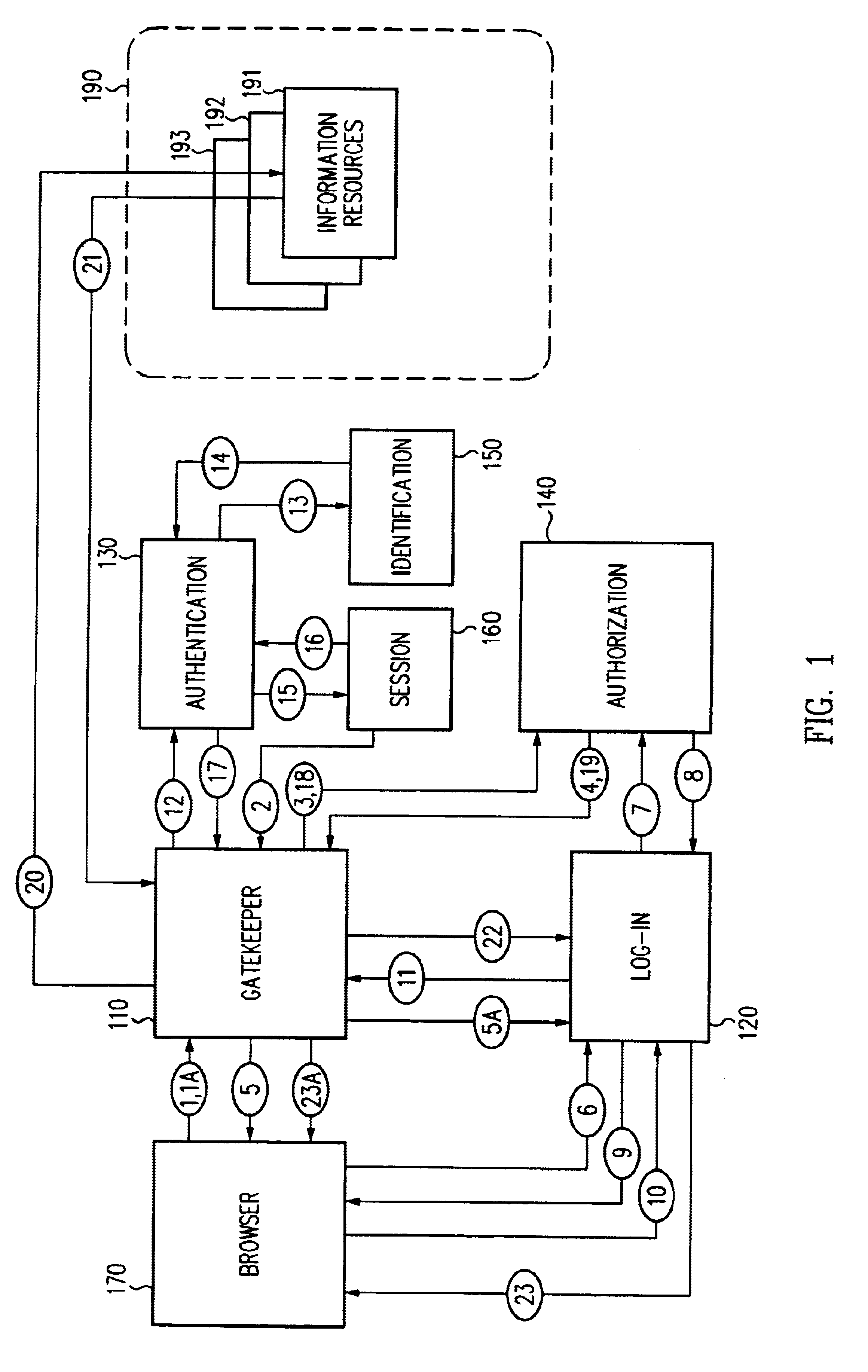
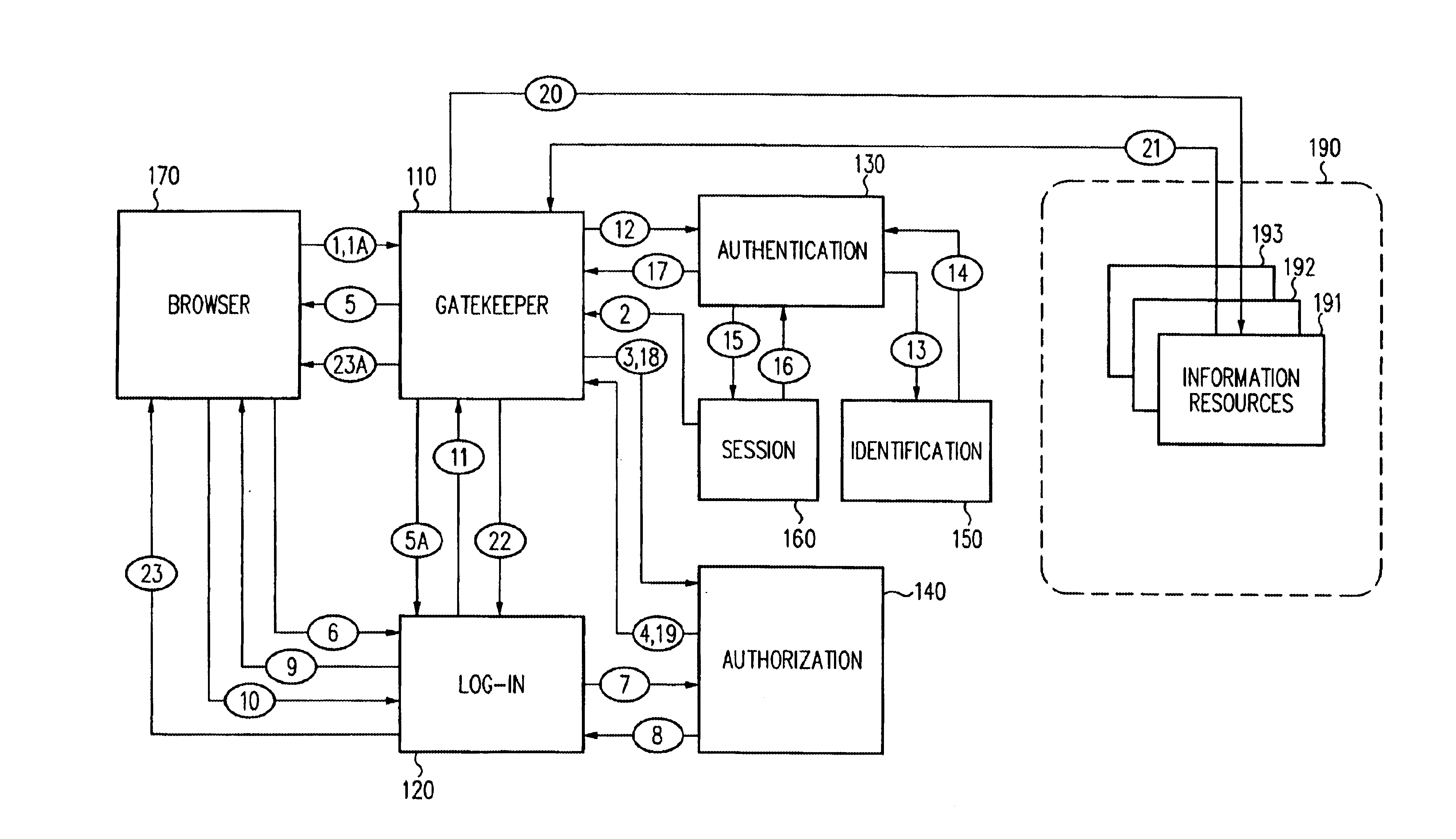
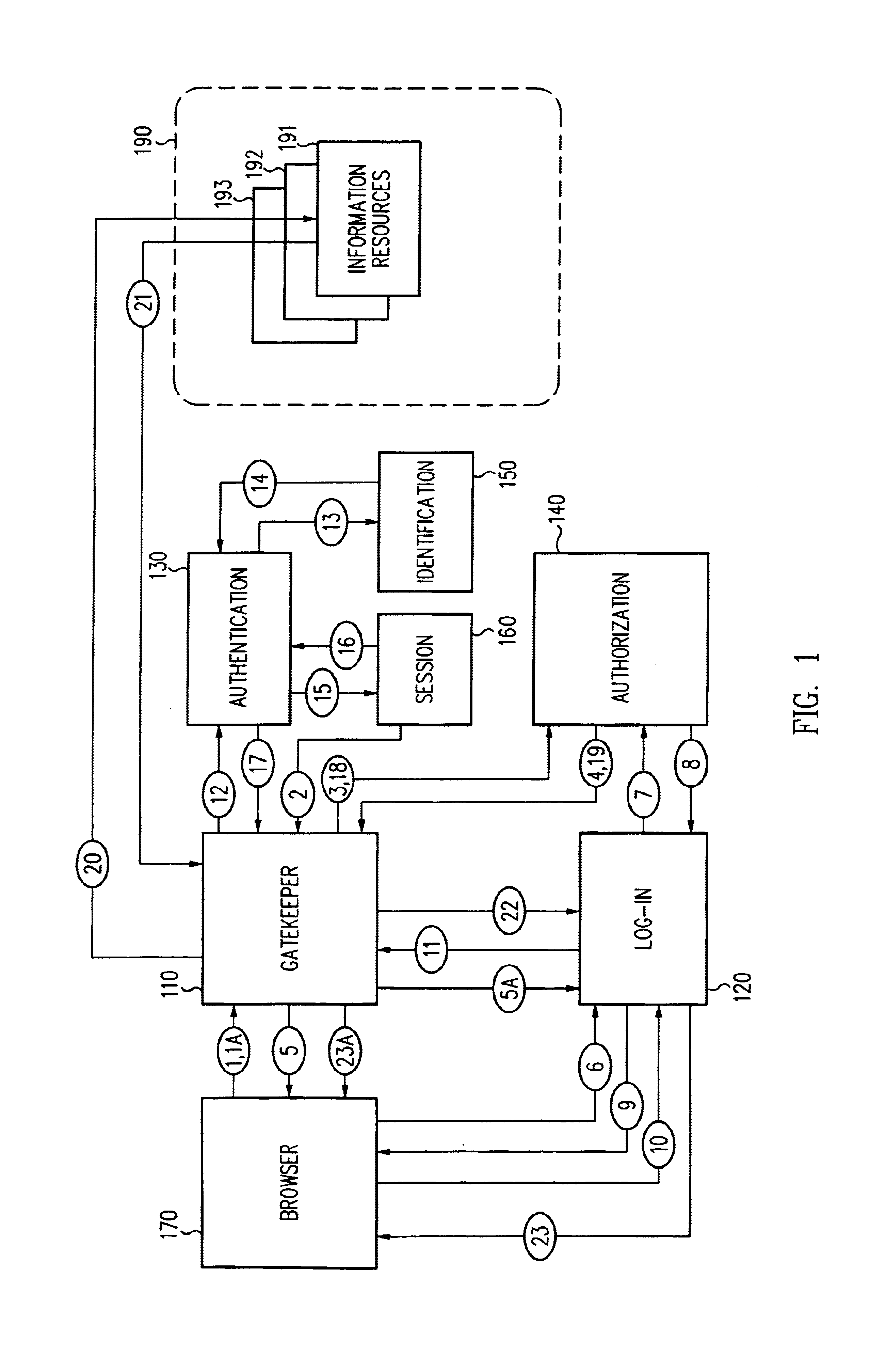
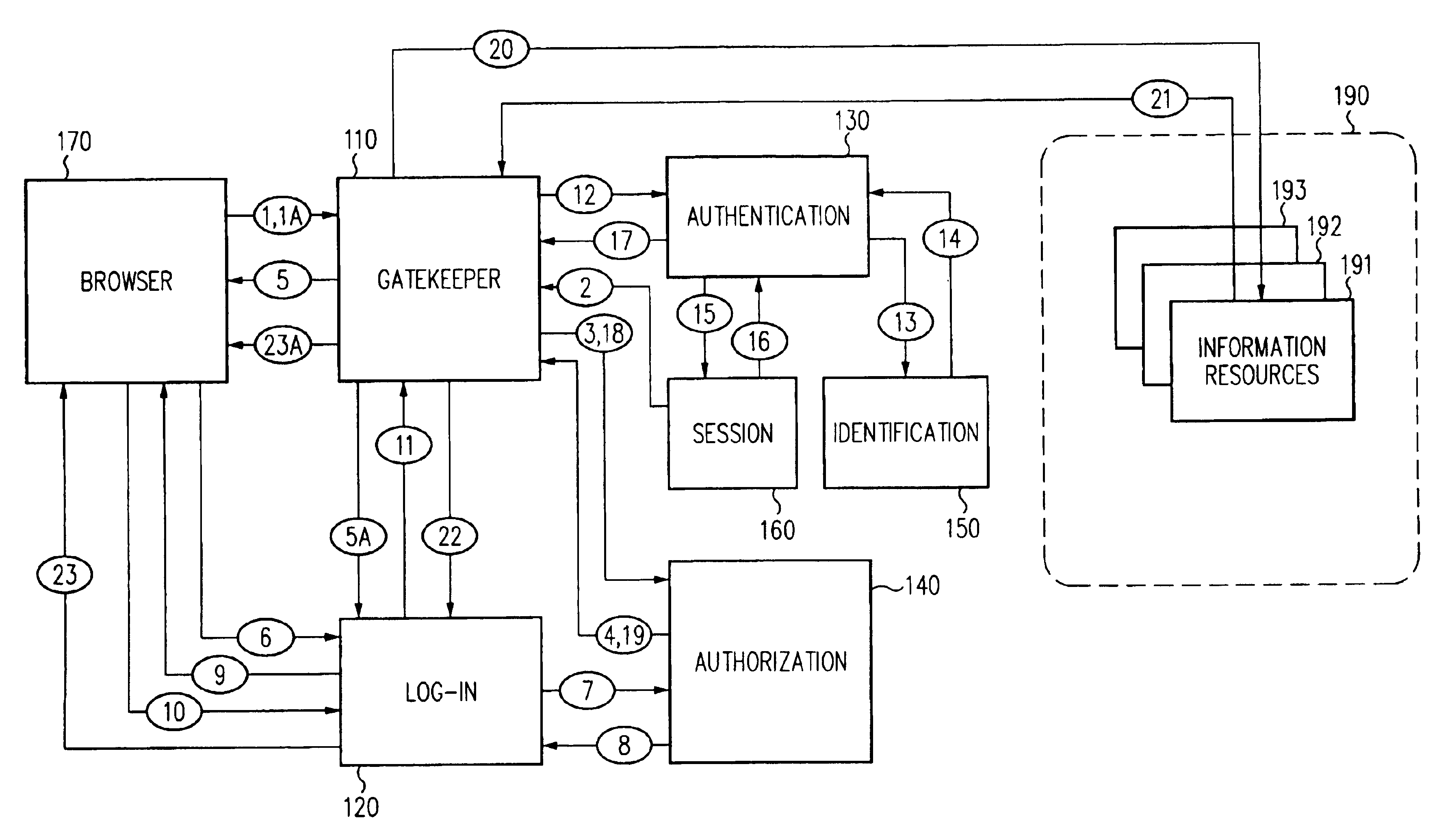
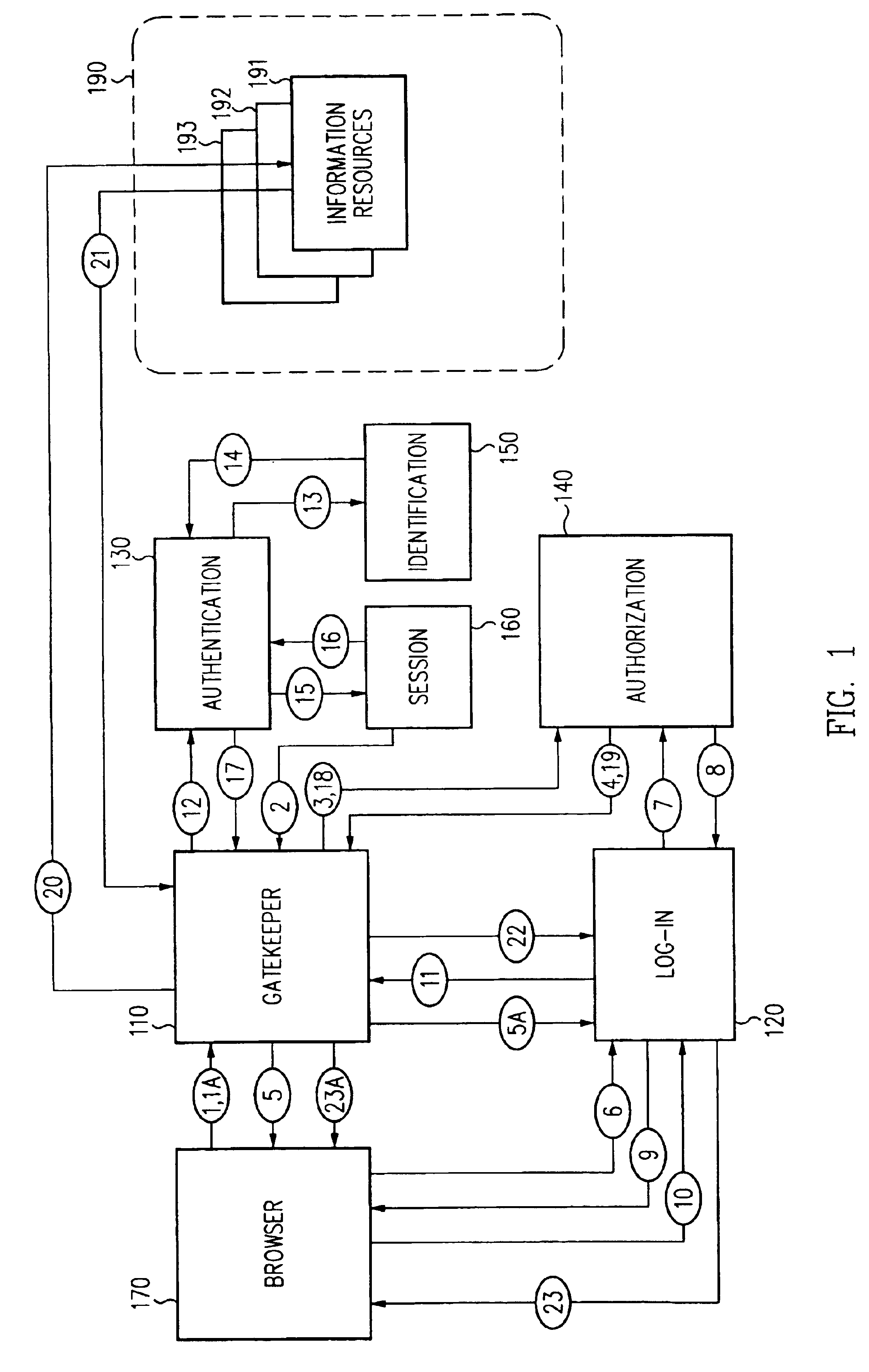
Authentication Schemes. Authentication schemes provide a way to collect credentials and determine the identity of a user. During authentication, Web Agents communicate with the Policy Server to determine the proper credentials that must be retrieved from a user who is requesting resources.
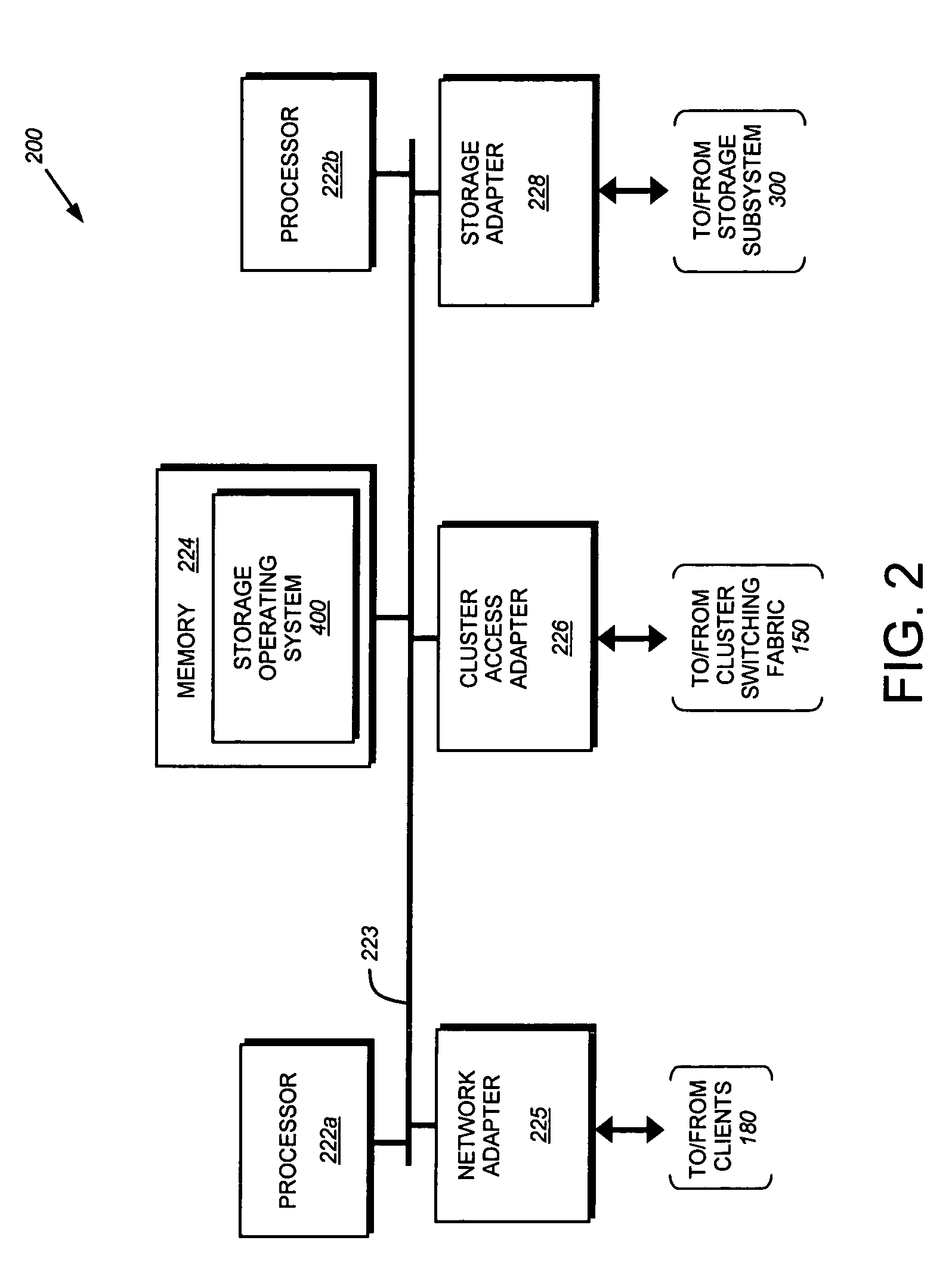
Log-on service providing credential level change without loss of session continuity
InactiveUS6609198B1Volume/mass flow measurementMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation resourceTrust level
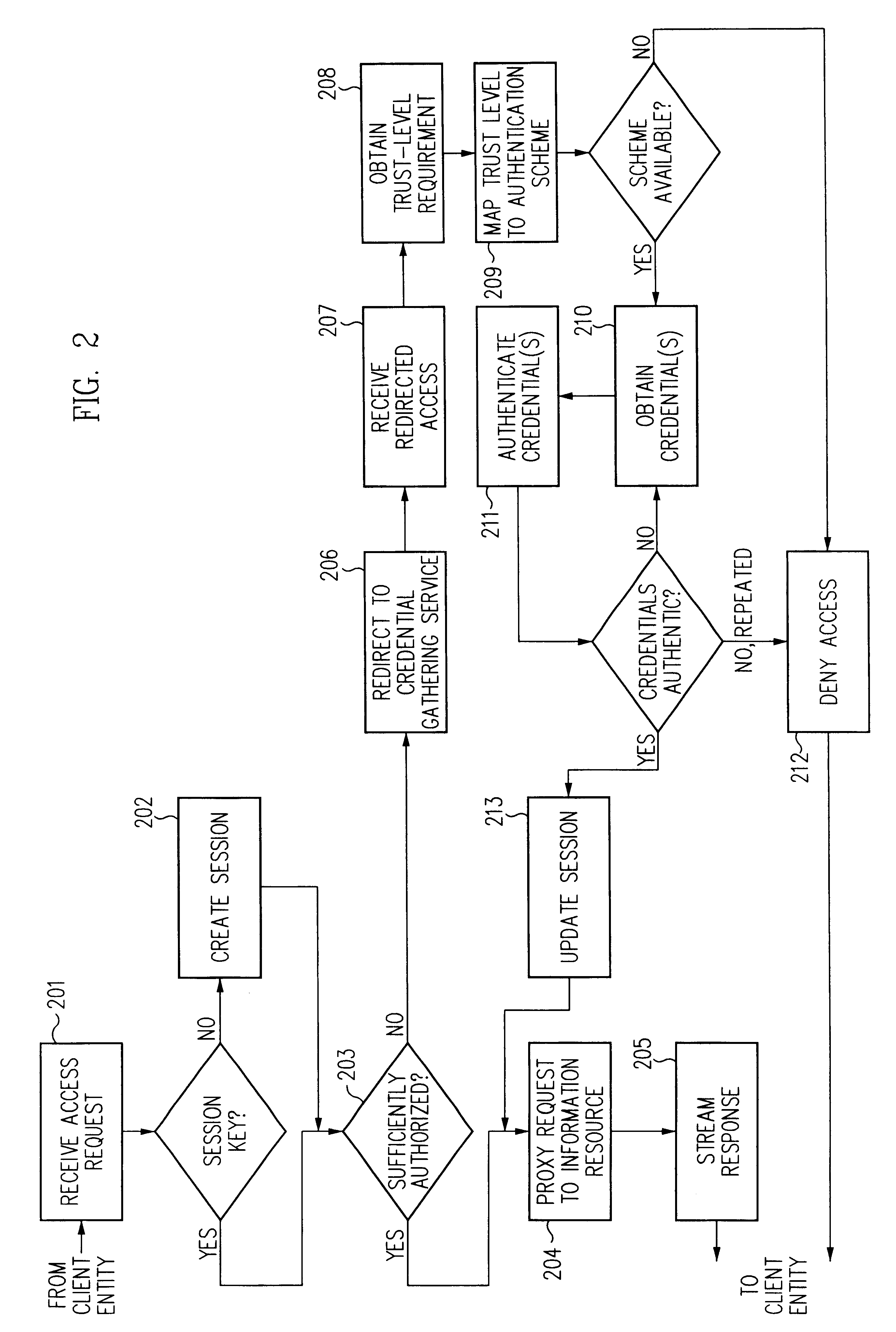
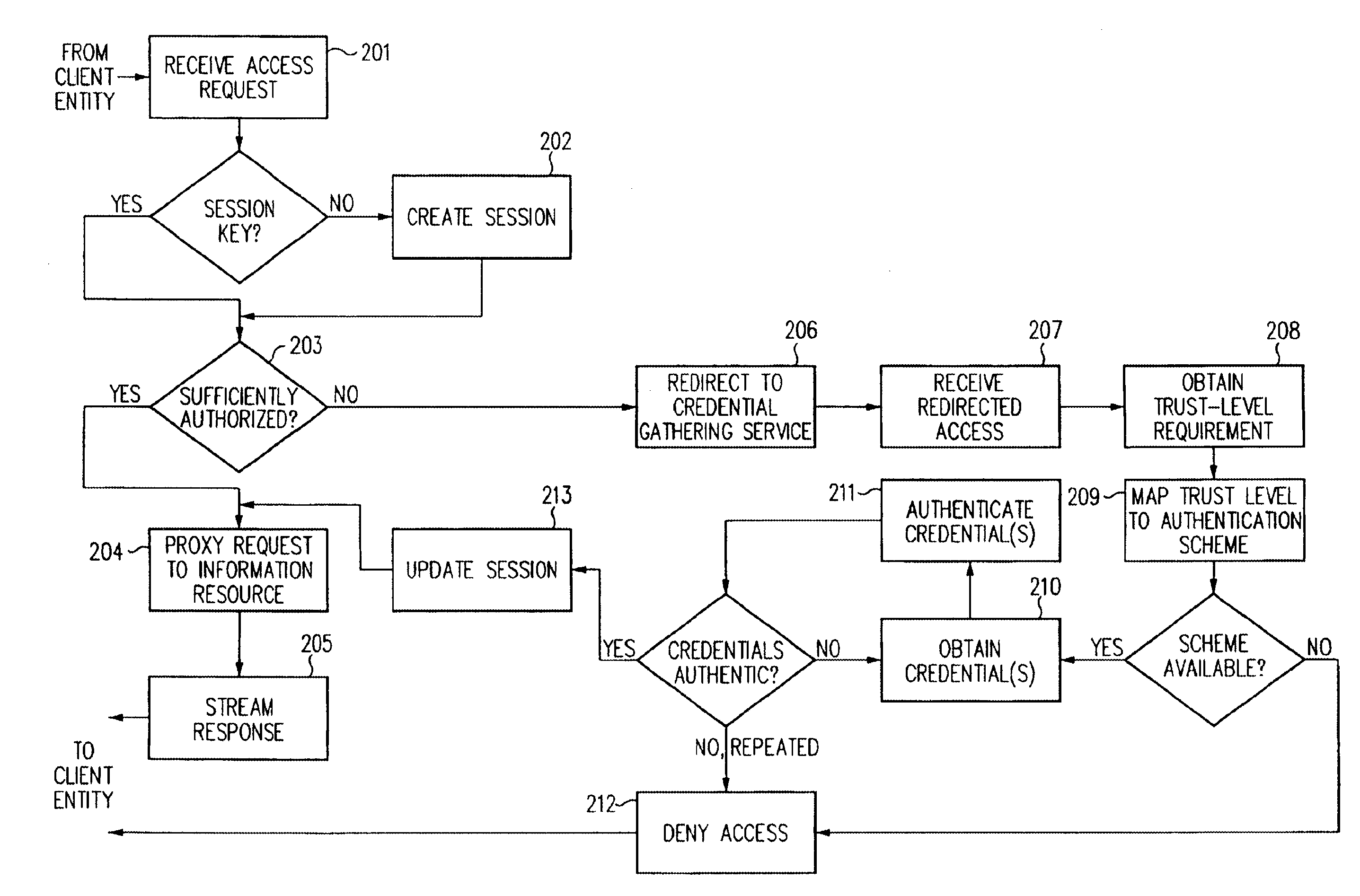
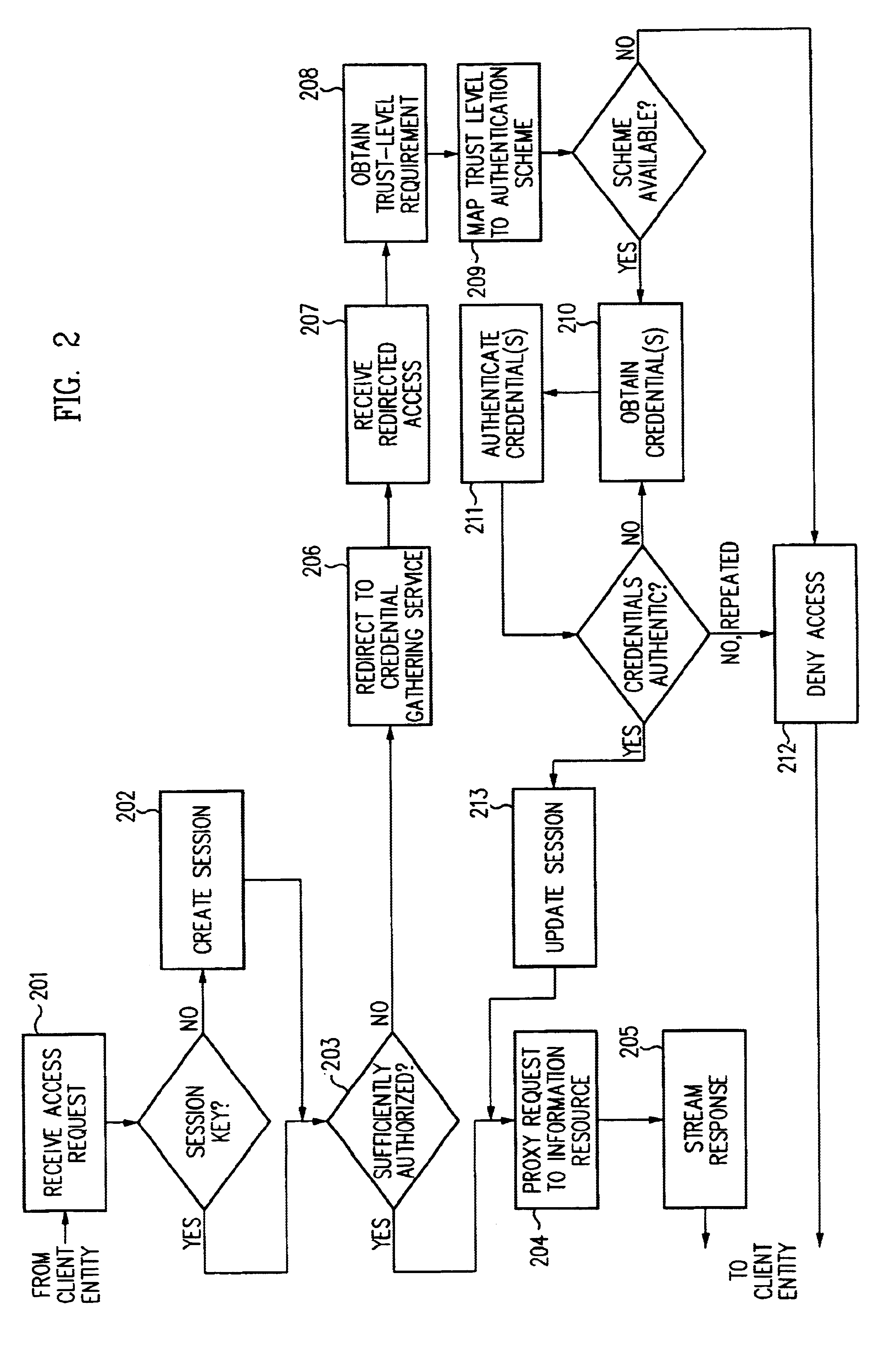
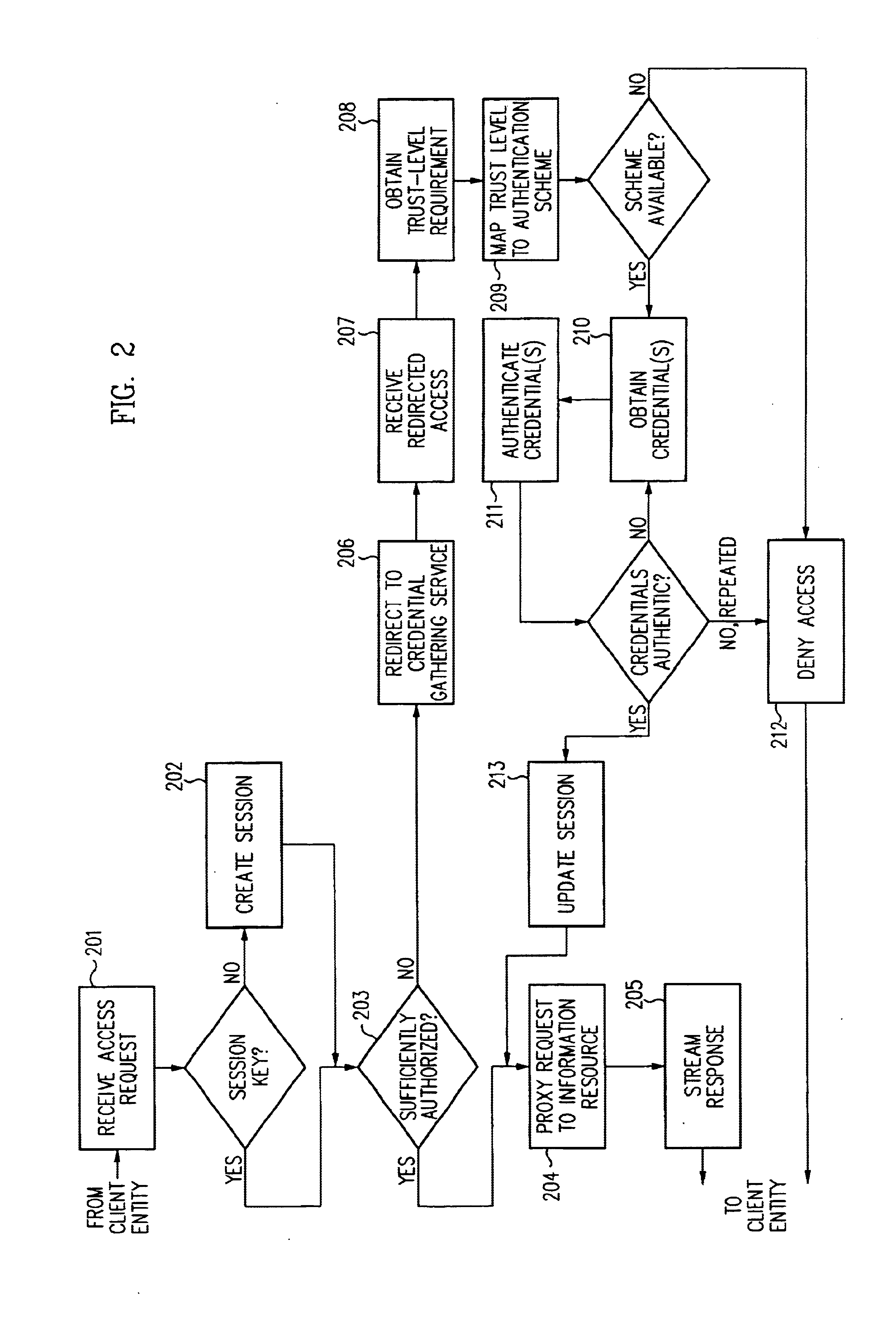
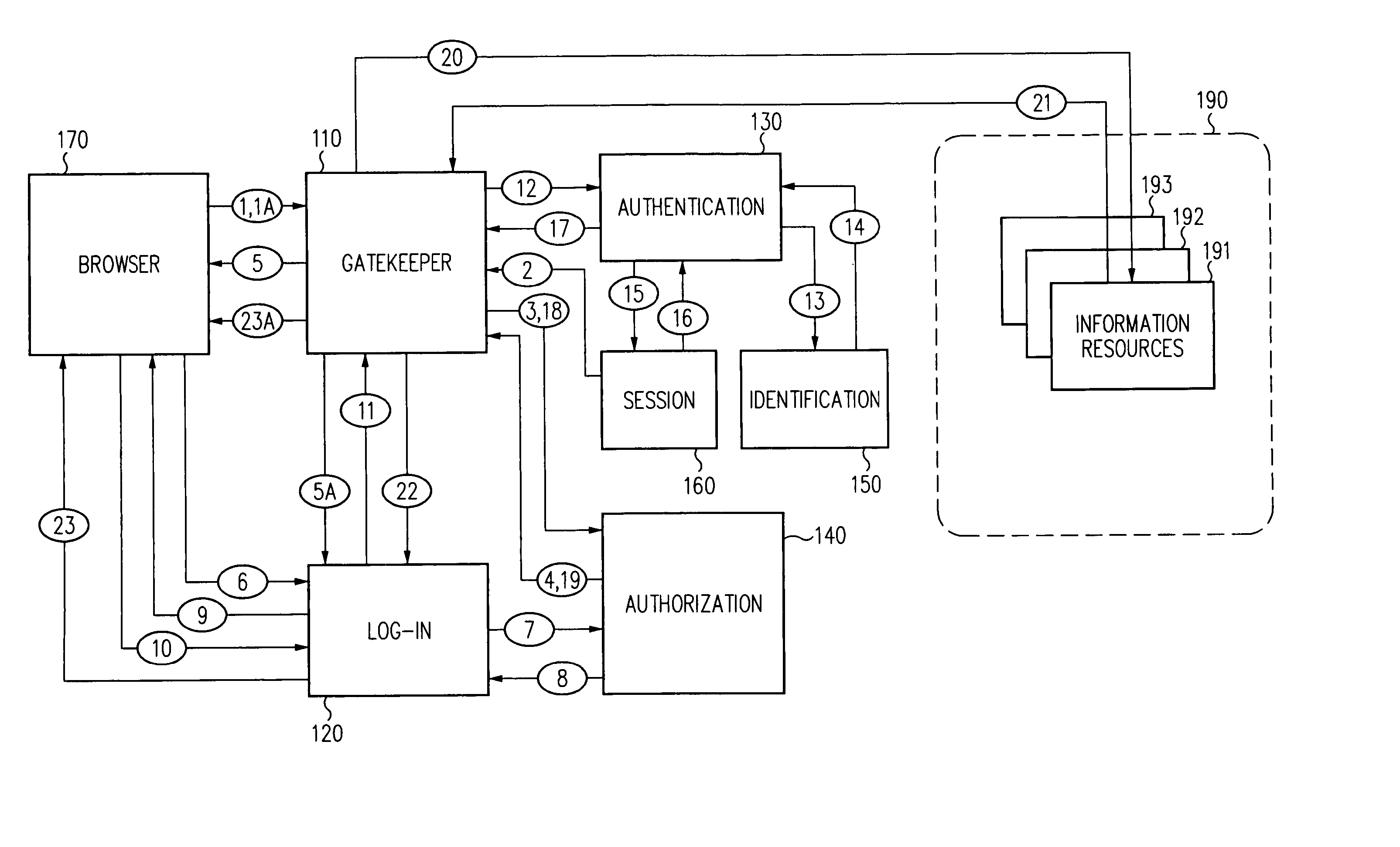
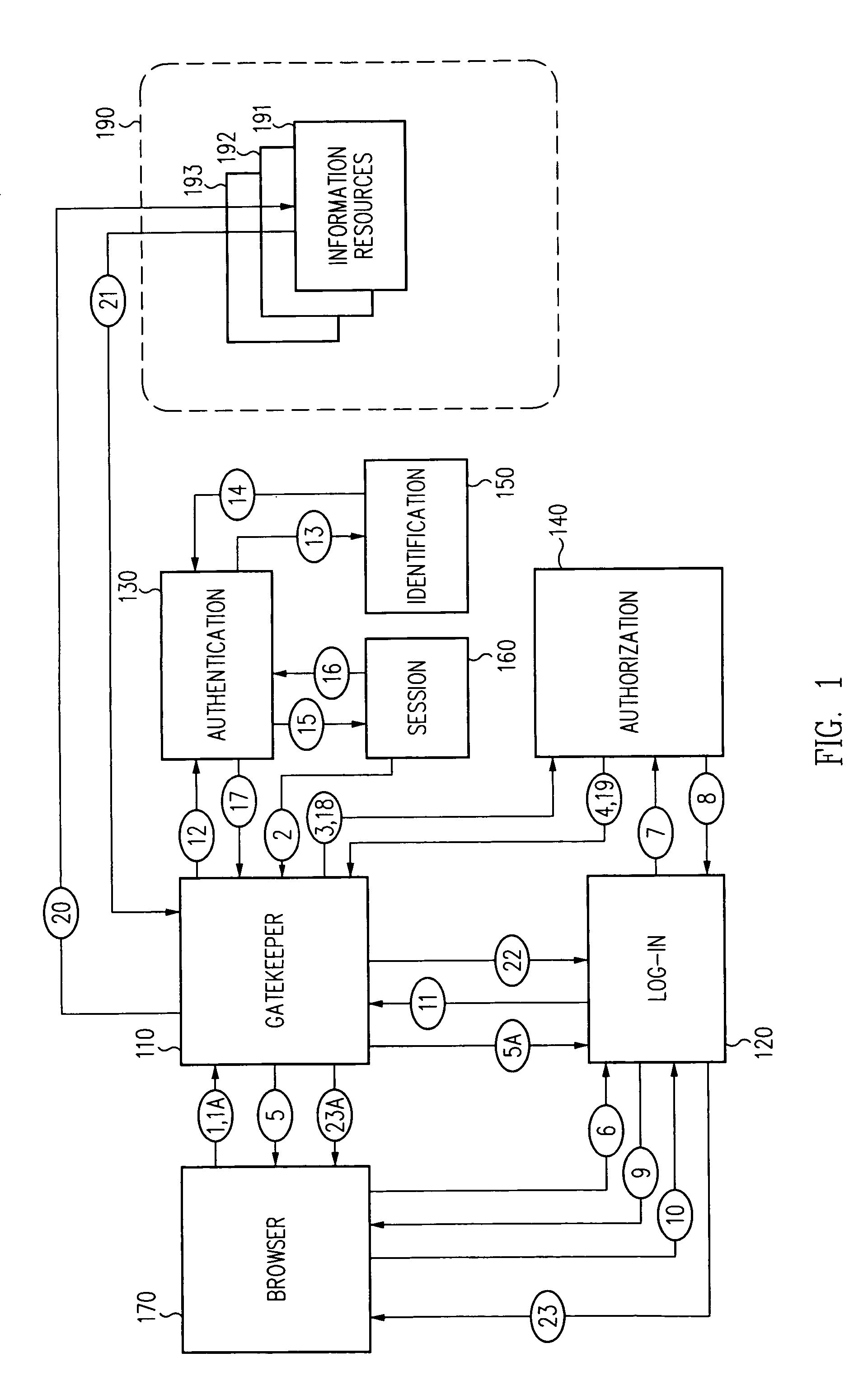
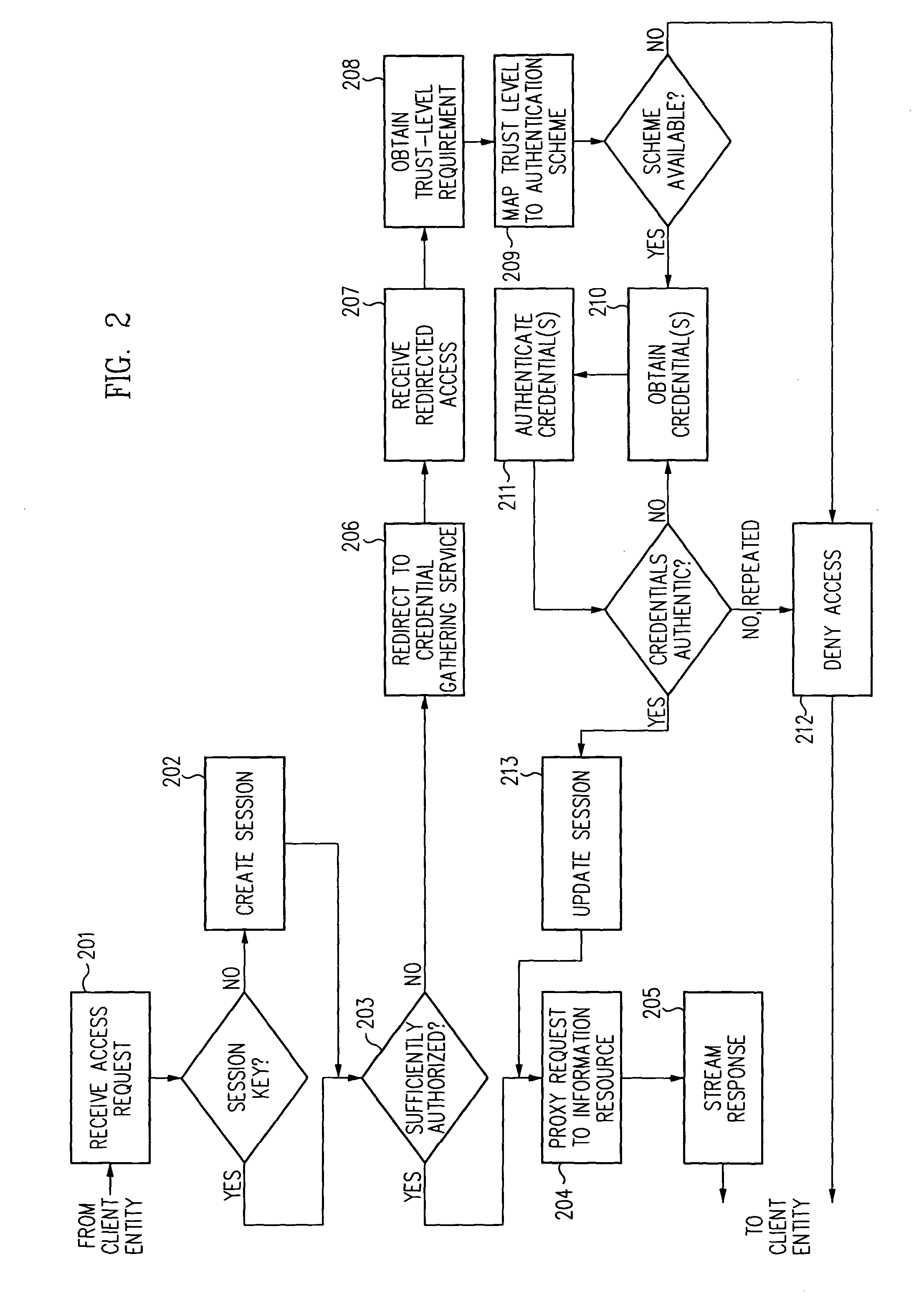
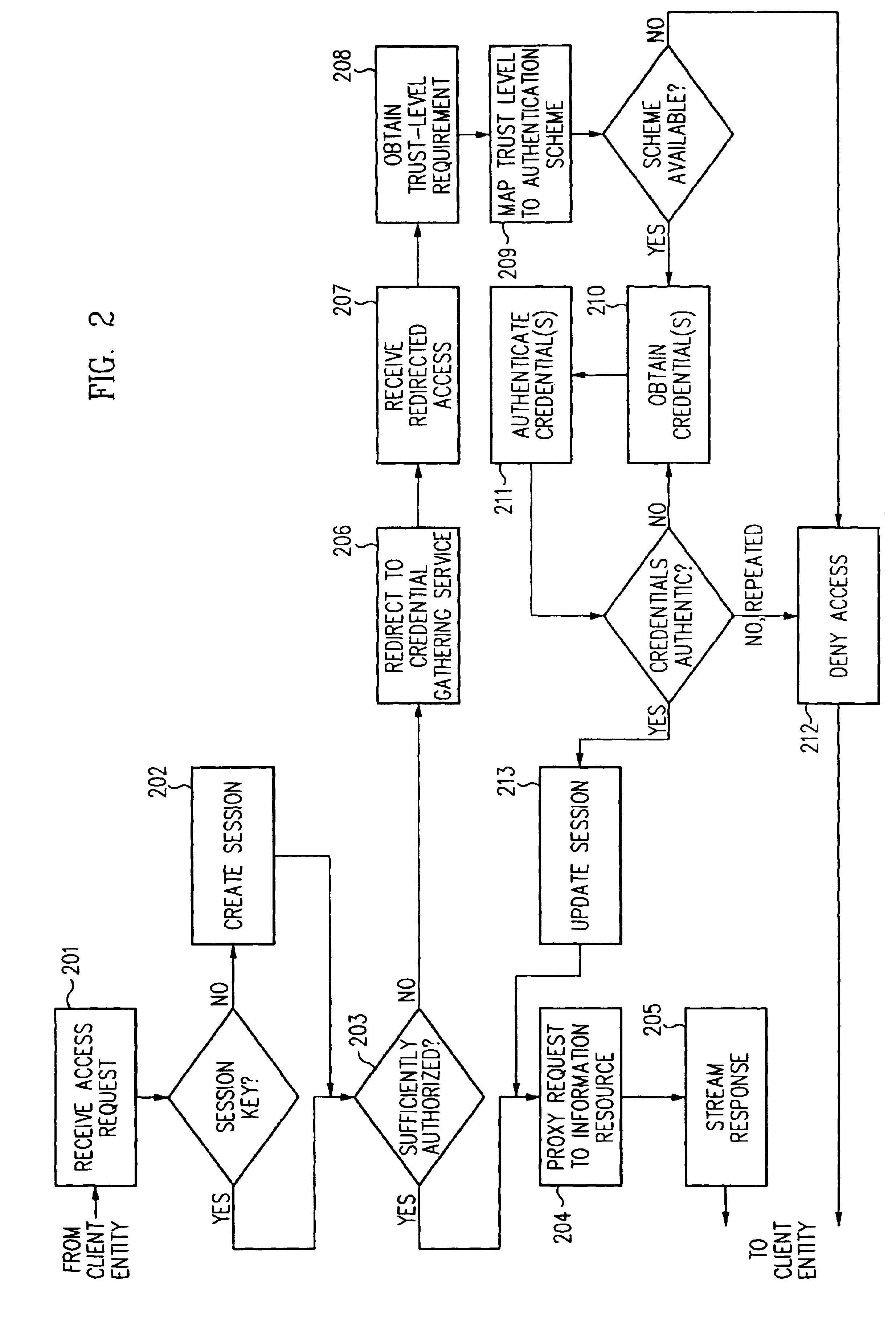
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided for multiple information resources. Rather than specifying a single authentication scheme for all information resources, the security architecture associates trust-level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are employed depending on the trust-level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed. Once credentials have been obtained for an entity and the entity has been authenticated to a given trust level, access is granted, without the need for further credentials and authentication, to information resources for which the authenticated trust level is sufficient. The security architecture allows upgrade of credentials for a given session. This capability is particularly advantageous in the context of a single, enterprise-wide log-on. An entity (e.g., a user or an application) may initially log-on with a credential suitable for one or more resources in an initial resource set, but then require access to resource requiring authentication at higher trust level. In such case, the log-on service allows additional credentials to be provided to authenticate at the higher trust level. The log-on service allows upgrading and / or downgrading without loss of session continuity (i.e., without loss of identity mappings, authorizations, permissions, and environmental variables, etc.).
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Single sign-on framework with trust-level mapping to authentication requirements
InactiveUS6892307B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordInformation resource
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided for multiple information resources. Rather than specifying a single authentication scheme for all information resources, the security architecture associates trust-level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are associated with trust levels and a log-on service obtains credentials for an entity commensurate with the trust-level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed. Once credentials have been obtained for an entity and the entity has been authenticated to a given trust level, access is granted, without the need for further credentials and authentication, to information resources for which the authenticated trust level is sufficient.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Access management system and method employing secure credentials
InactiveUS6668322B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInformation resourceTrust level
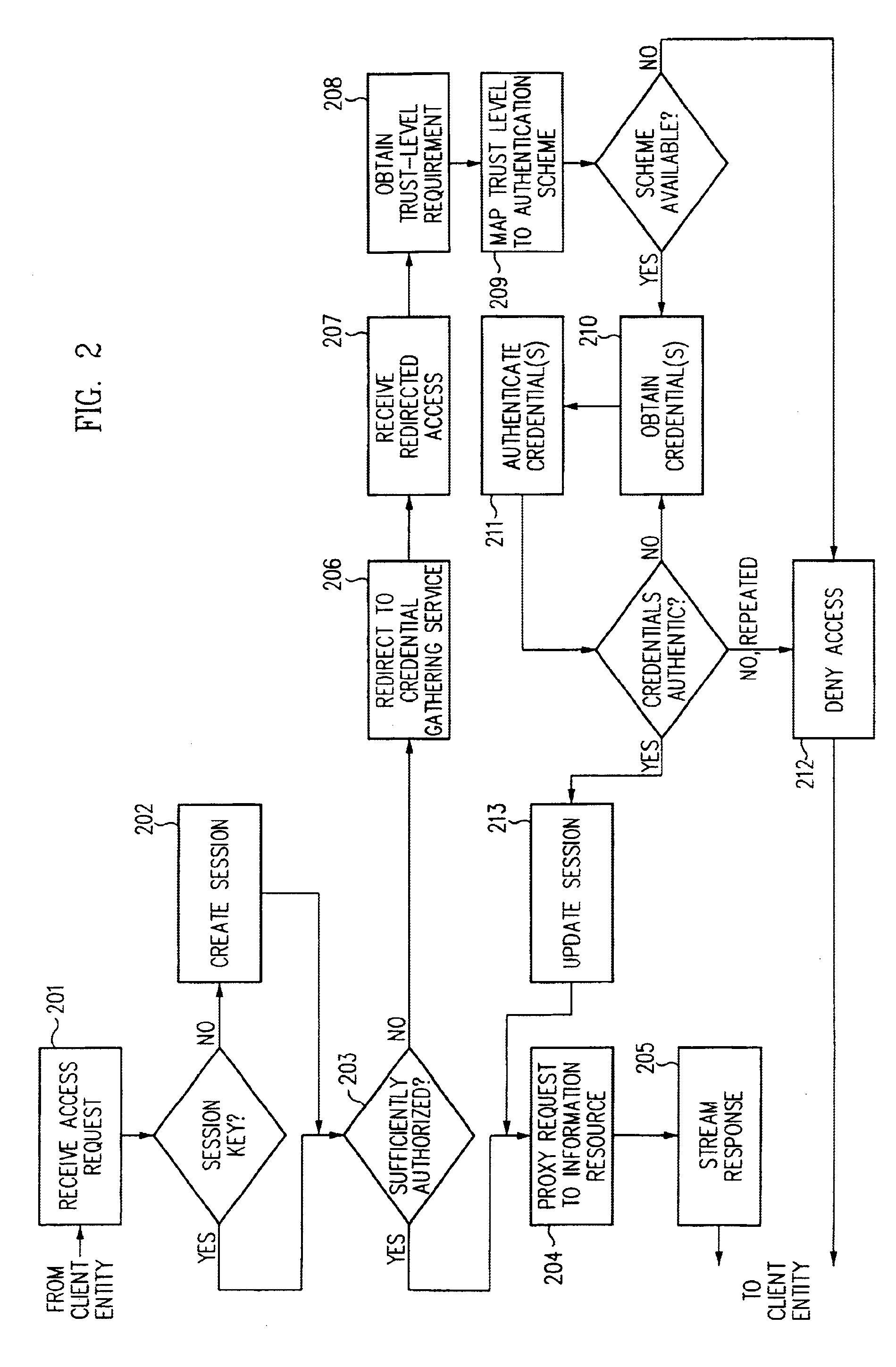
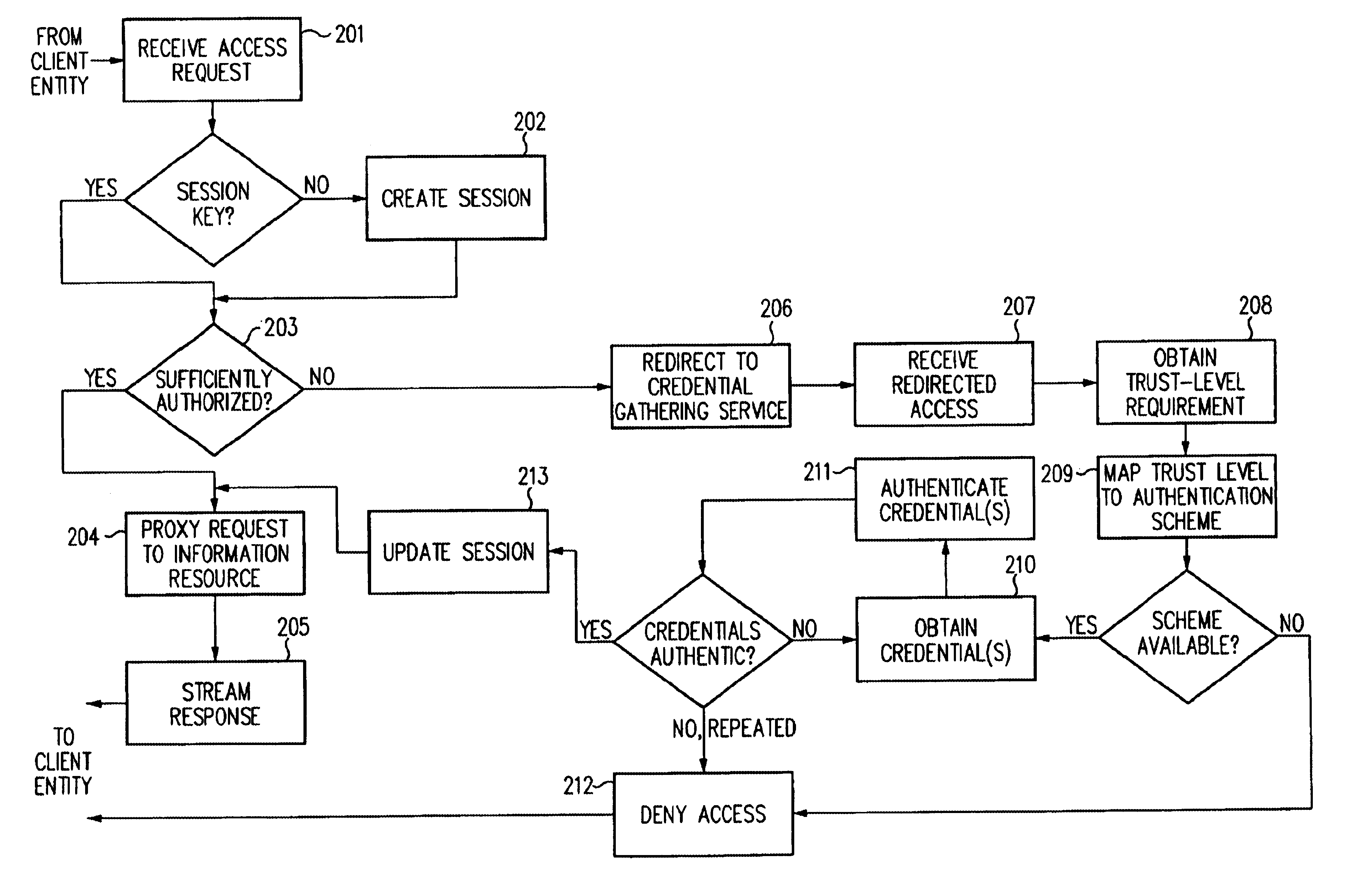
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided. Session credentials are used to maintain continuity of a persistent session across multiple accesses to one or more information resources, and in some embodiments, across credential level changes. Session credentials are secured, e.g., as a cryptographically secured session token, such that they may be inspected by a wide variety of entities or applications to verify an authenticated trust level, yet may not be prepared or altered except by a trusted authentication service. Some embodiments of the present invention associate trust level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are associated with trust levels, and in some embodiments, with environmental parameters. For example, in one configuration, a login service obtains login credentials for an entity commensurate with the trust level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed and with environment parameters that affect the sufficiency of a given credential type. Once login credentials have been obtained for an entity and have been authenticated to a given trust level, session credentials are issued and access is granted to information resources for which the trust level is sufficient. Advantageously, by using the session credentials access is granted without the need for further login credentials and authentication. In some configurations, session credentials evidencing an insufficient trust level may be remedied by a session continuity preserving upgrade of login credential.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Security architecture with environment sensitive credential sufficiency evaluation
InactiveUS6691232B1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation resourceTrust level
By including environment information in a security policy, a security architecture advantageously allows temporal, locational, connection type and / or client capabilities-related information to affect the sufficiency of a given credential type (and associated authentication scheme) for access to a particular information resource. In some configurations, time of access, originating location (physical or network) and / or connection type form a risk profile that can be factored into credential type sufficiency. In some configurations, changing environmental parameters may cause a previously sufficient credential to become insufficient. Alternatively, an authenticated credential previously insufficient for access at a given trust level may be sufficient based on a changed or more fully parameterized session environment. In some configurations, the use of session tracking facilites (e.g., the information content of session tokens) can be tailored to environmental parameters (e.g., connection type or location). Similarly, capabilities of a particular client entity (e.g., browser support for 128-bit cipher or availablity of a fingerprint scanner or card reader) may affect the availability or sufficiency of particular authentication schemes to achieve a desired trust level.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
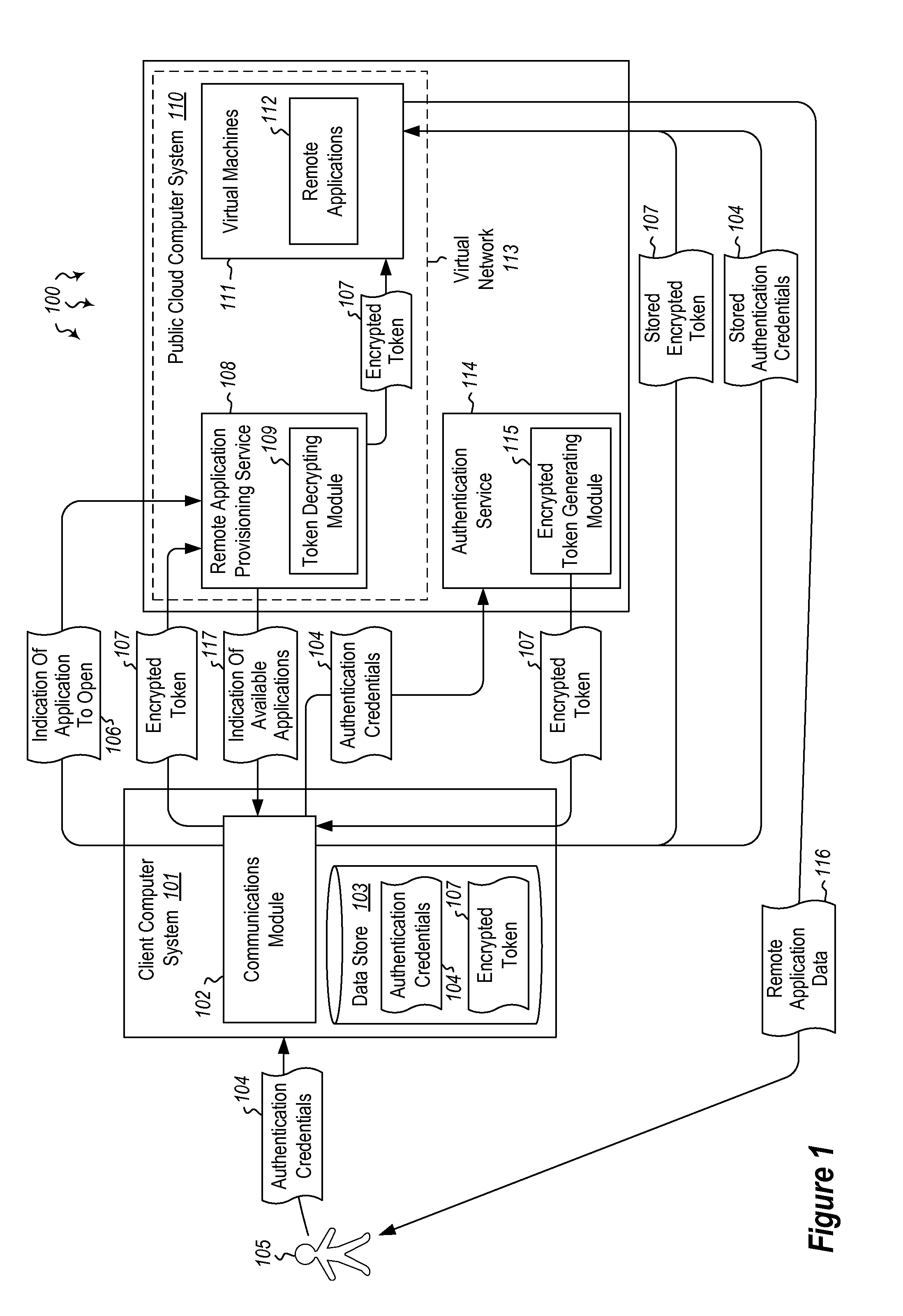
User authentication in a cloud environment
ActiveUS20140373126A1Well formedDigital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsInternet Authentication ServiceData memory
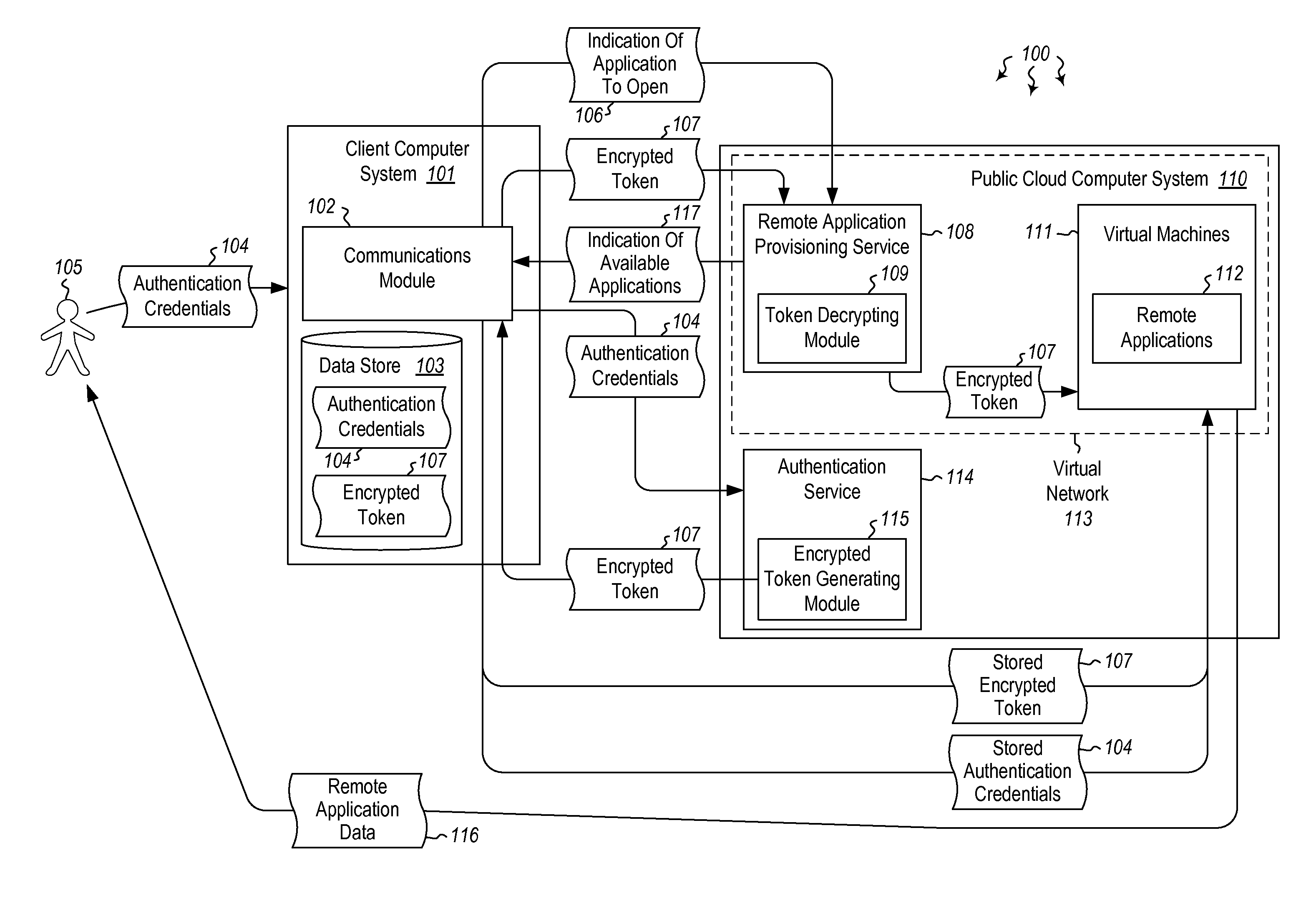
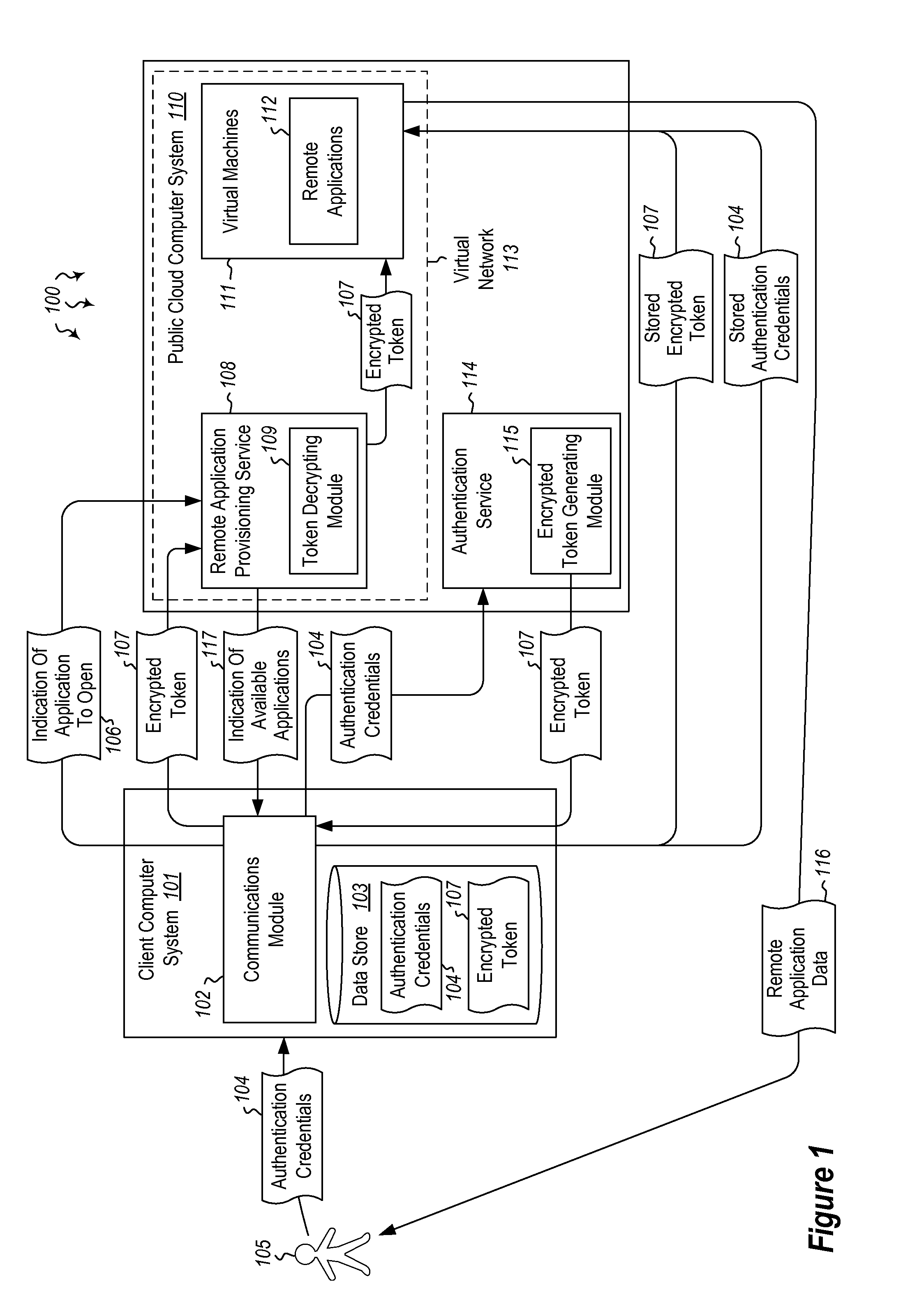
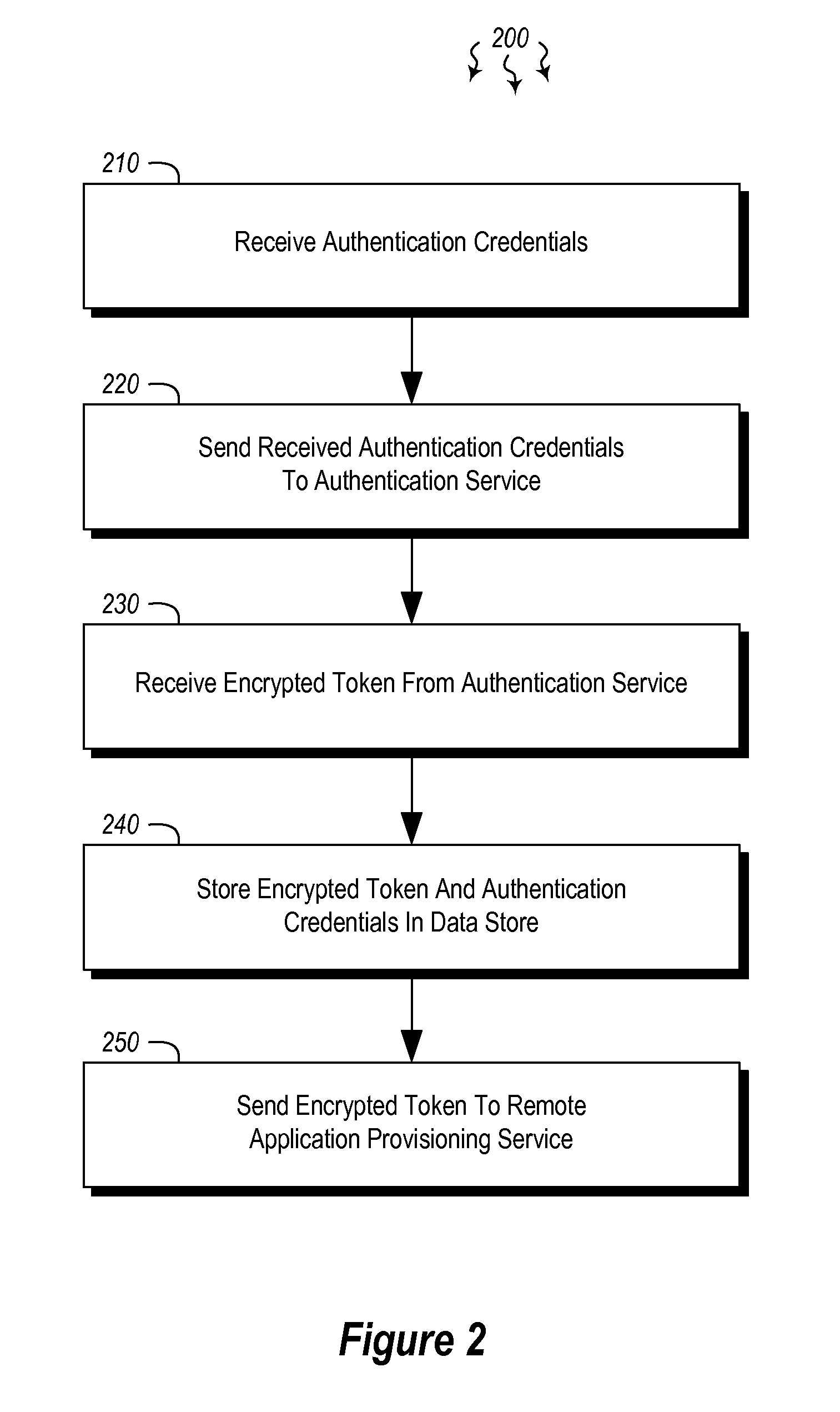
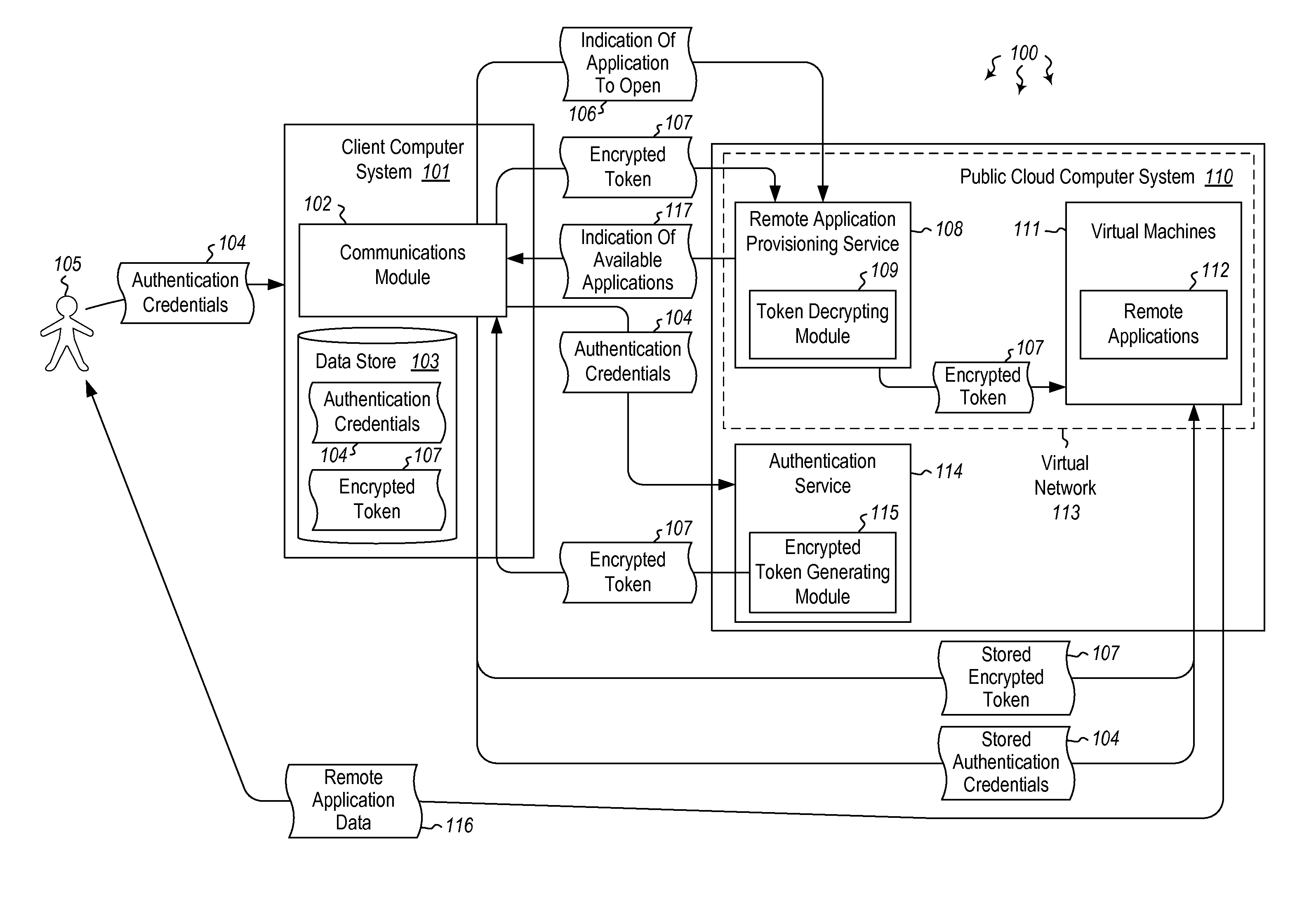
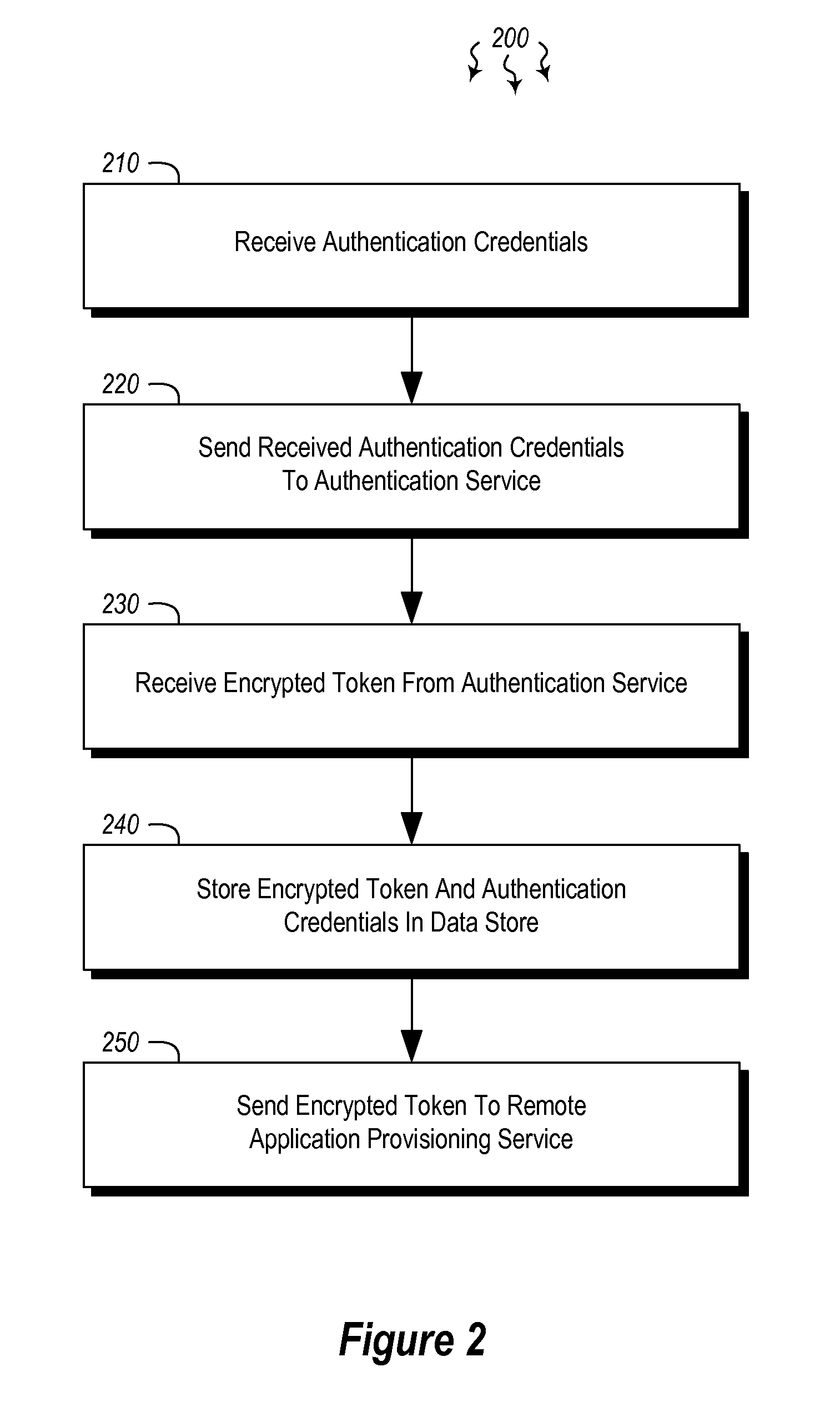
Embodiments are directed to authenticating a user to a remote application provisioning service. In one scenario, a client computer system receives authentication credentials from a user at to authenticate the user to a remote application provisioning service that provides virtual machine-hosted remote applications. The client computer system sends the received authentication credentials to an authentication service, which is configured to generate an encrypted token based on the received authentication credentials. The client computer system then receives the generated encrypted token from the authentication service, stores the received encrypted token and the received authentication credentials in a data store, and sends the encrypted token to the remote application provisioning service. The encrypted token indicates to the remote application provisioning service that the user is a valid user.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
User authentication in a cloud environment
ActiveUS9124569B2Digital data processing detailsDigital data authenticationInternet Authentication ServiceData memory
Embodiments are directed to authenticating a user to a remote application provisioning service. In one scenario, a client computer system receives authentication credentials from a user at to authenticate the user to a remote application provisioning service that provides virtual machine-hosted remote applications. The client computer system sends the received authentication credentials to an authentication service, which is configured to generate an encrypted token based on the received authentication credentials. The client computer system then receives the generated encrypted token from the authentication service, stores the received encrypted token and the received authentication credentials in a data store, and sends the encrypted token to the remote application provisioning service. The encrypted token indicates to the remote application provisioning service that the user is a valid user.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
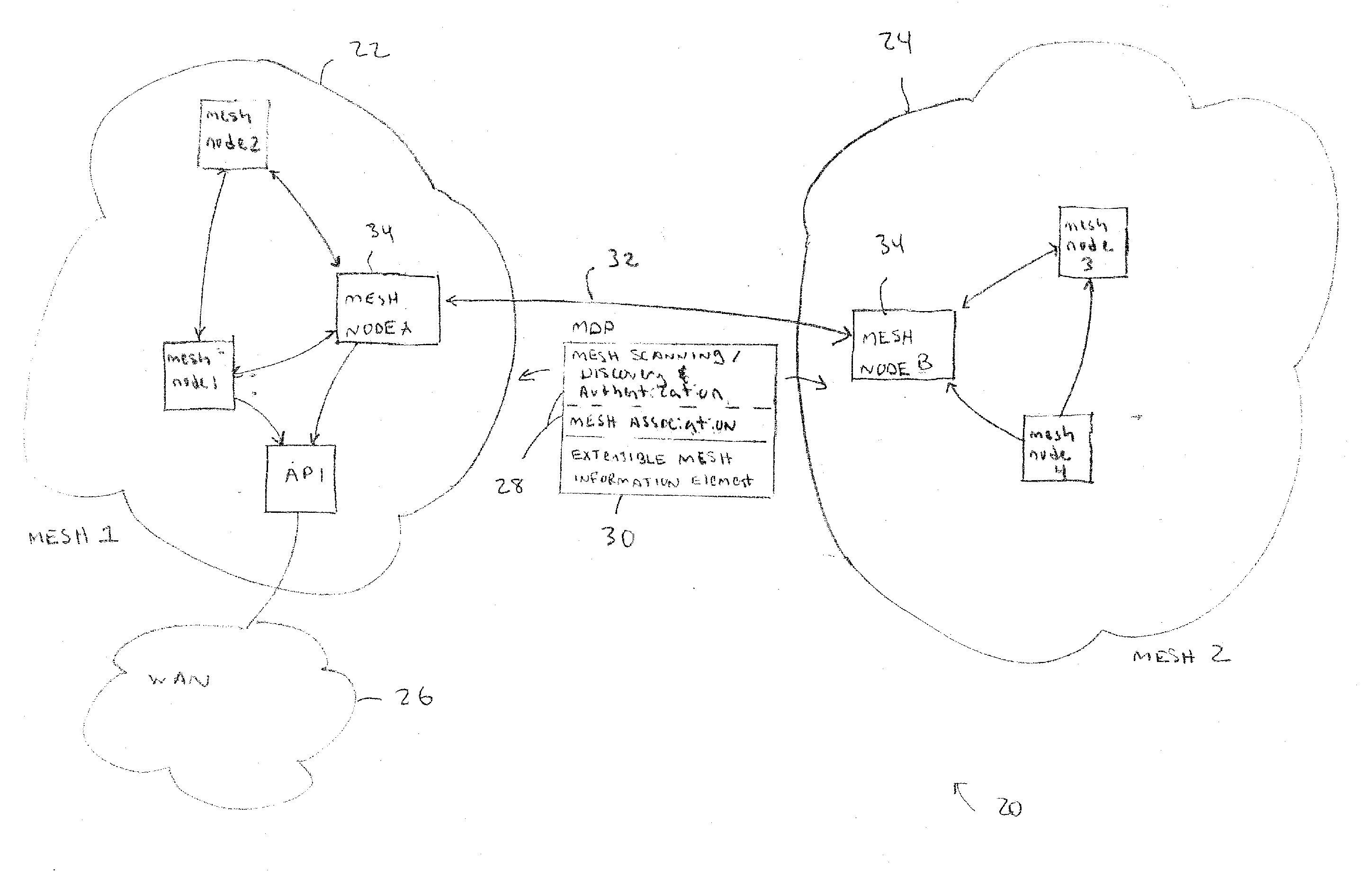
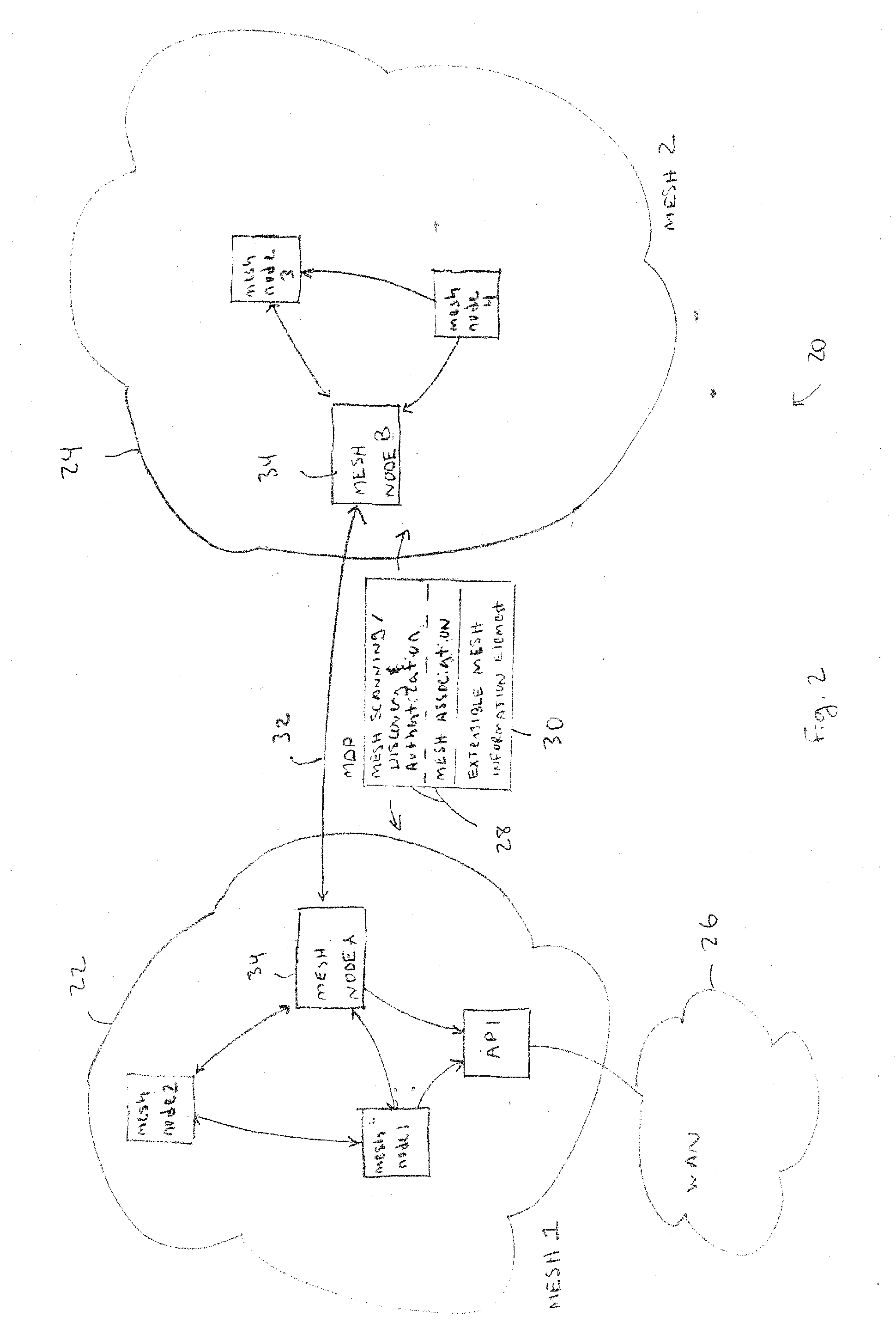
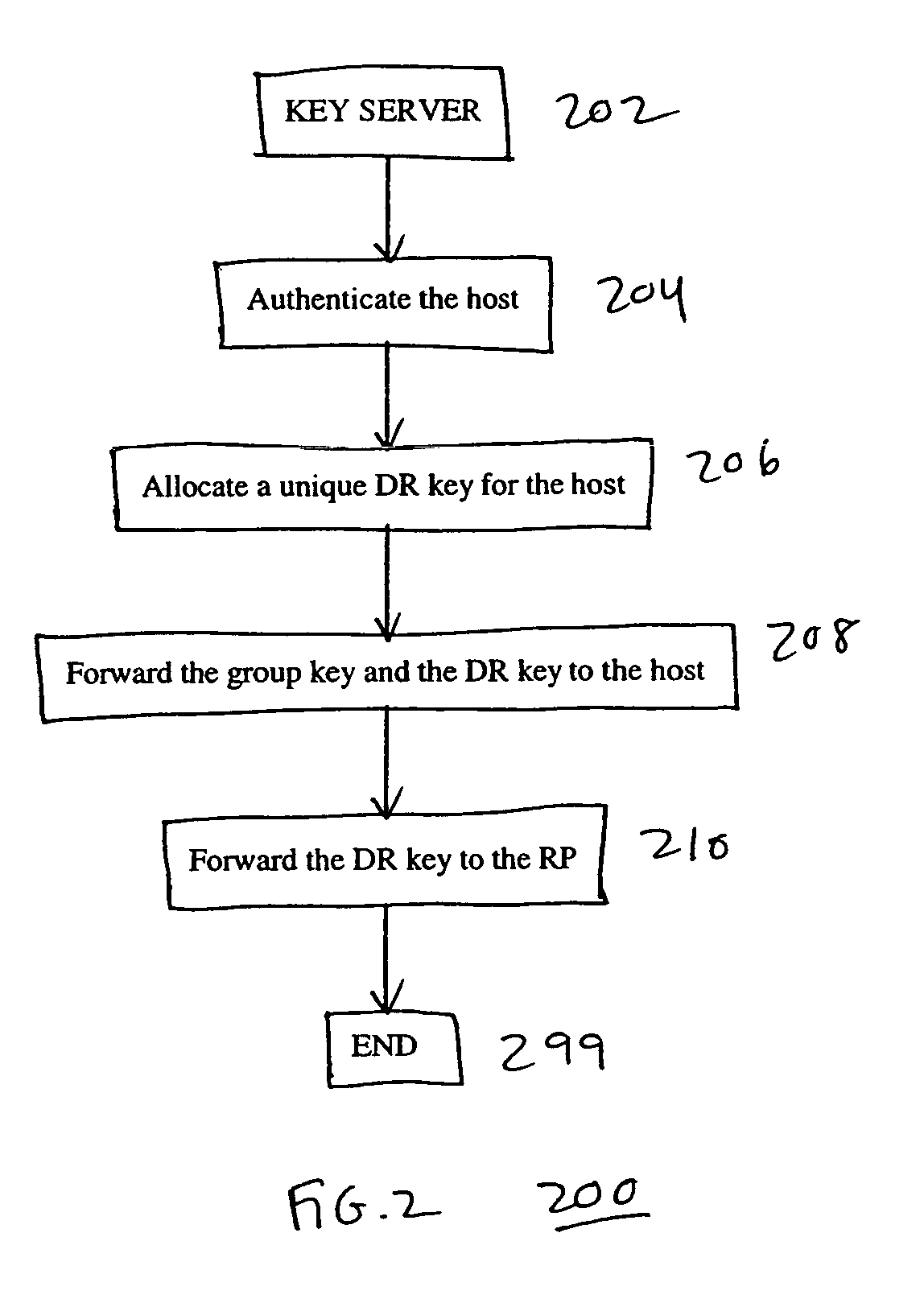
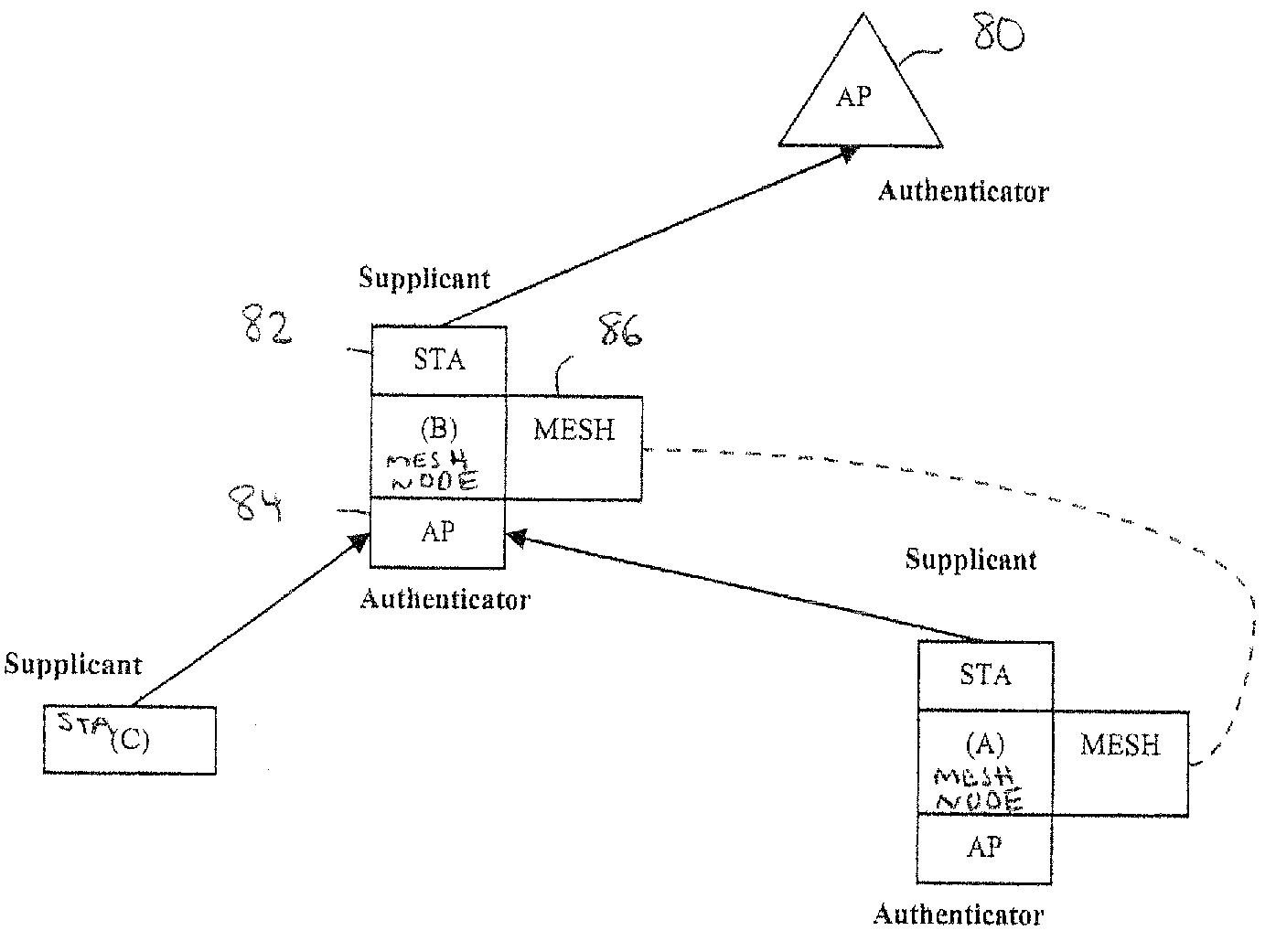
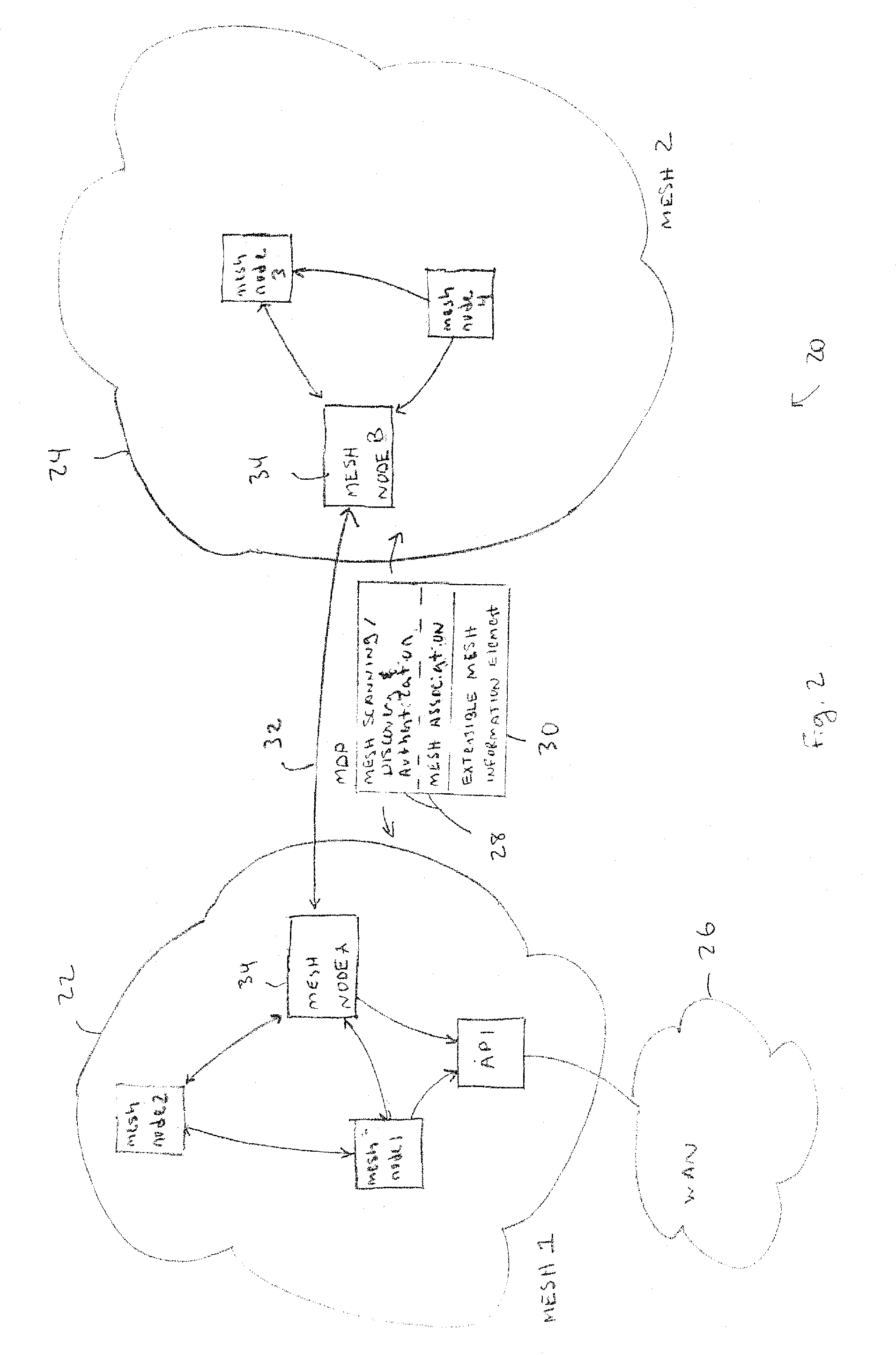
Discovery and authentication scheme for wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS20070189249A1Readily apparentError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsOpen Systems InterconnectionMesh node
Wireless network devices discover individual mesh nodes and networks of mesh nodes. An association is formed on the basis of peer-to-peer interactions at layer-1, layer-2 and / or higher layers of the Open System Interconnect (OSI) model. In particular, the system uses Beacon, Probe Request, Probe Response, Association Request, Association Response, and Disassociation frames and introduces a new Extensible Mesh Information Element (EMIE) used by mesh nodes to discover, authenticate, and associate with other peer nodes.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Secure wireless local area network
InactiveUS7174564B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordNetwork addressing
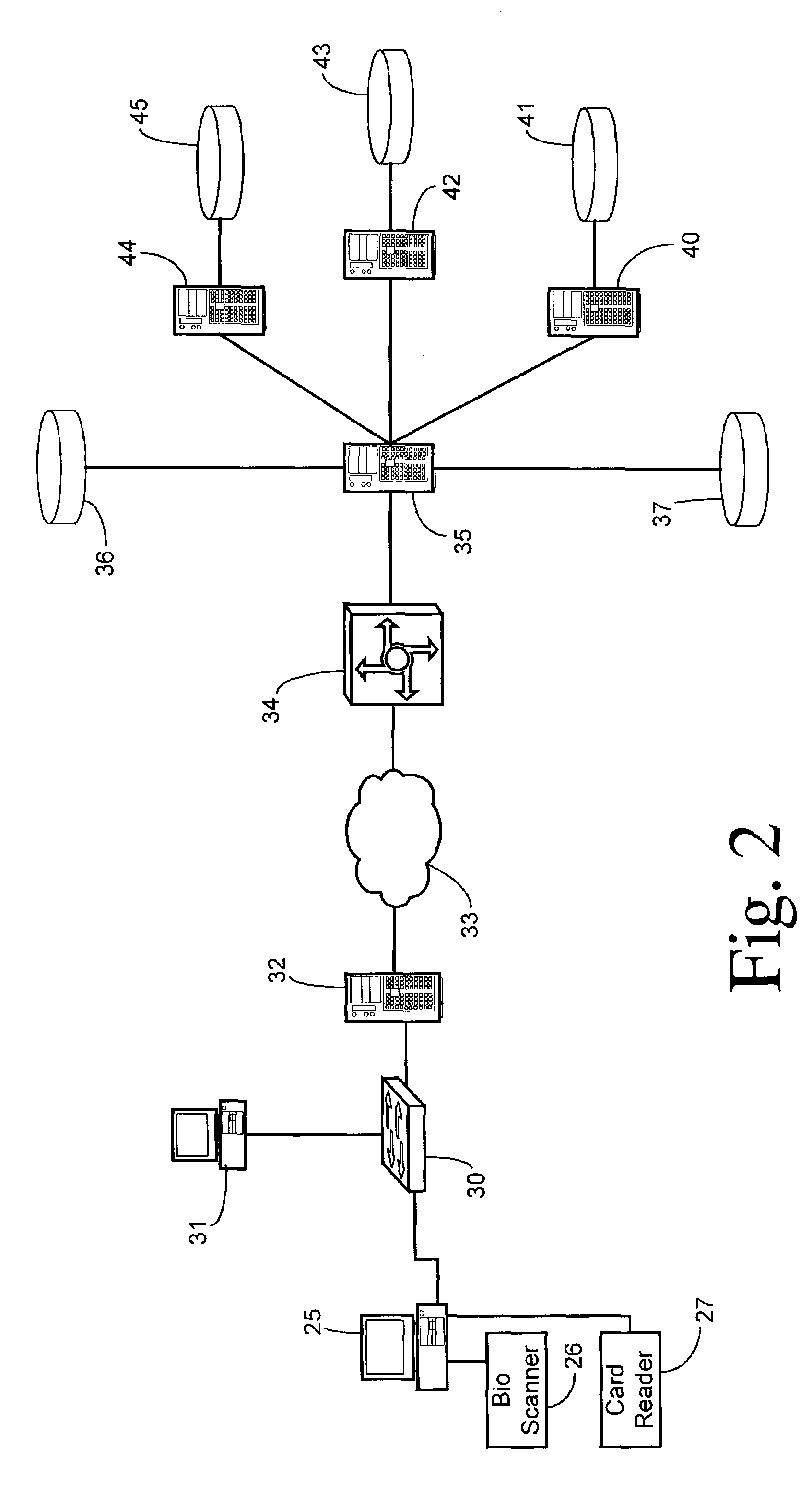
The secure wireless local area network of the present invention includes a single wired network that supports both wired and wireless devices. The network addresses security concerns by including an authentication server that services a plurality of access points. Each access point includes a first authentication device that generates and transmits a first authentication message to the corresponding wireless device over an air channel. The first authentication message includes encrypted validating information about the access point including an access point key that uniquely identifies the access point. Each wireless device includes a second authentication device. The wireless device receives the first authentication message and determines whether the access point is authorized to connect to the wired network. If the access point is valid, the second authentication device responds to the first authentication message by generating and transmitting a second authentication message to the access point. The second authentication message includes encrypted validating information about the wireless device and operator, e.g., a device key and the operator's logon name and password. The access point determines the authenticity of the wireless device by decrypting the portion of the second authentication message that includes the device key. If the wireless device is valid, the AP opens a control channel with the authentication server. The AP transmits the first and second authentication messages to the authentication server. If the authentication server validates the access point and the operator's logon name and password, it will authorize access to the wired network.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Log-on service providing credential level change without loss of session continuity
InactiveUS20040210771A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInformation resourcePassword
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided for multiple information resources. Rather than specifying a single authentication scheme for all information resources, the security architecture associates trust-level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are employed depending on the trust-level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed. Once credentials have been obtained for an entity and the entity has been authenticated to a given trust level, access is granted, without the need for further credentials and authentication, to information resources for which the authenticated trust level is sufficient.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
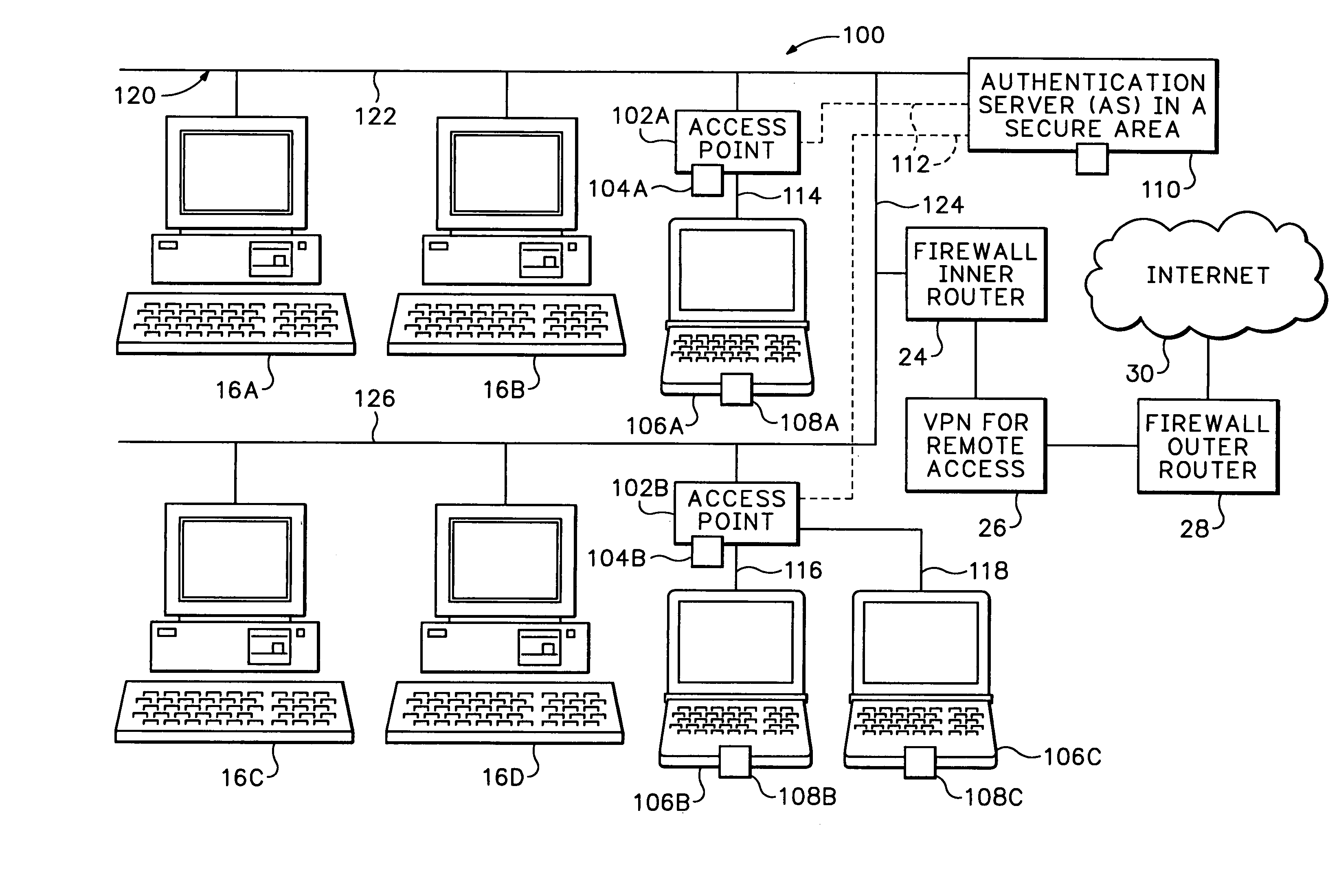
Biometric authentication of a client network connection
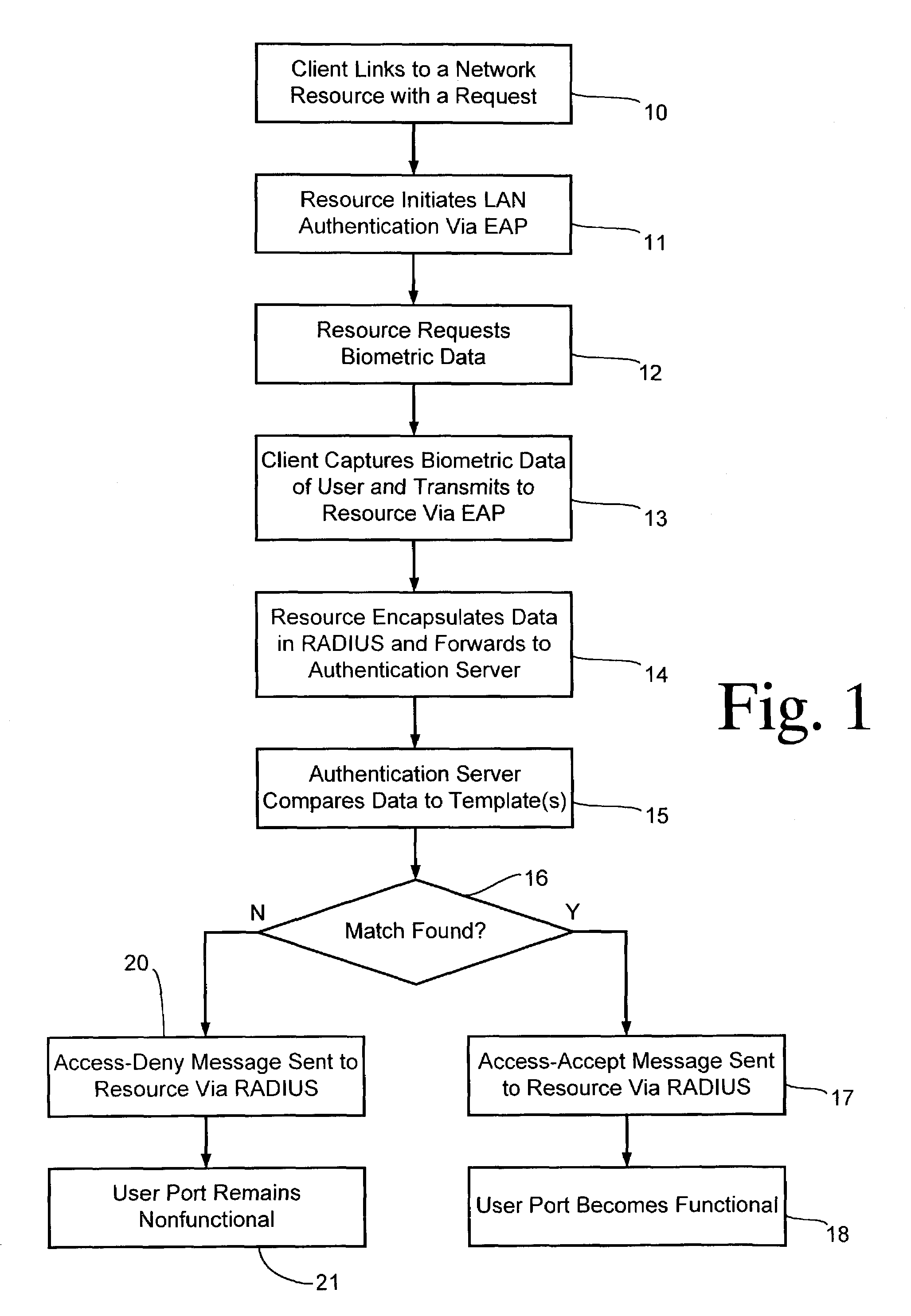
InactiveUS7249177B1Low costDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionBiometric dataNetwork connection
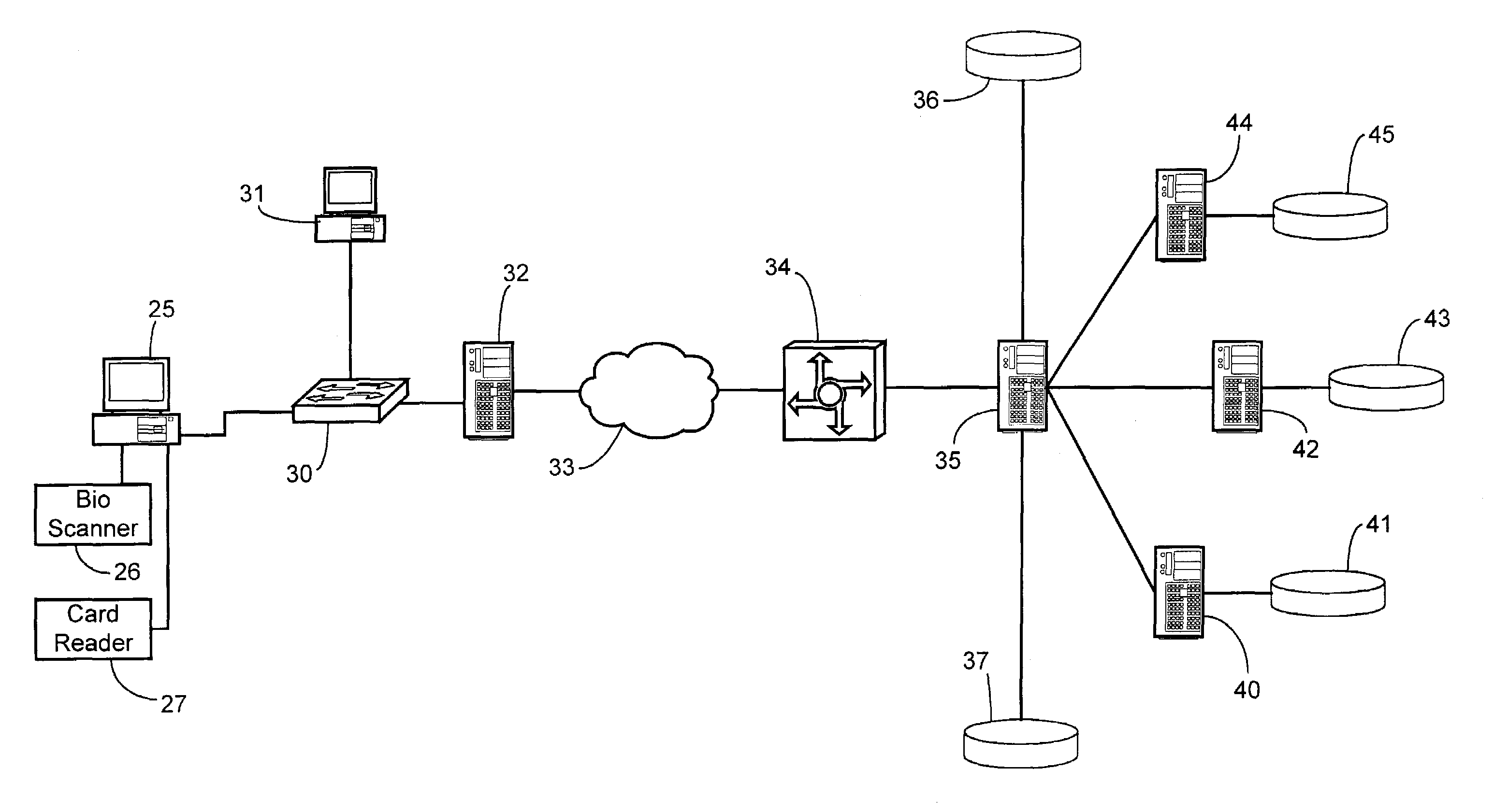
A client is authenticated to a network resource wherein the client is coupled to a biometric sensor. The client signals a request to the network resource (e.g., by connecting to an access point). The network resource initiates a point-to-point LAN authentication protocol between the network resource and the client. The network resource requests biometric data from the client via the LAN authentication protocol (optionally either before or after authenticating with other credentials). The client captures biometric data of an attendant user of the client. The client transmits the captured biometric data to the network resource via the LAN authentication protocol. The network resource encapsulates the biometric data in the LAN authentication protocol into an authentication server protocol and forwards the encapsulated biometric data to an authentication server. The authentication server compares the biometric data to a biometric template stored in conjunction with the authentication server for making a determination whether the attendant user should be granted access to the network resource. The authentication server sends either an access-accept message or an access-deny message in the authentication server protocol to the network resource in response to the determination. The network resource grants access to the client only after receiving an access-accept message.
Owner:SPRINT CORPORATION
Web site authentication
ActiveUS20080109657A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationWeb siteInternet Authentication Service
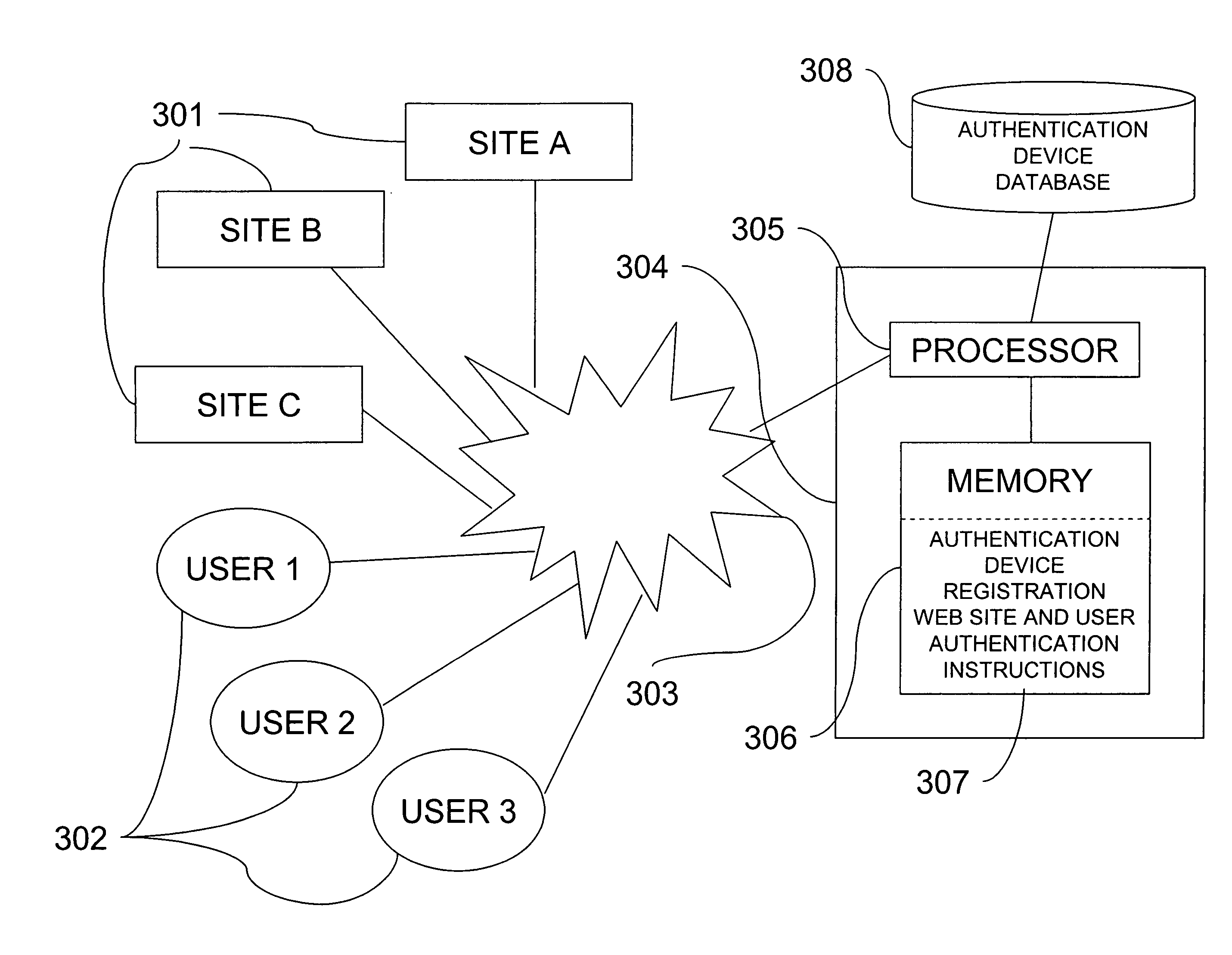
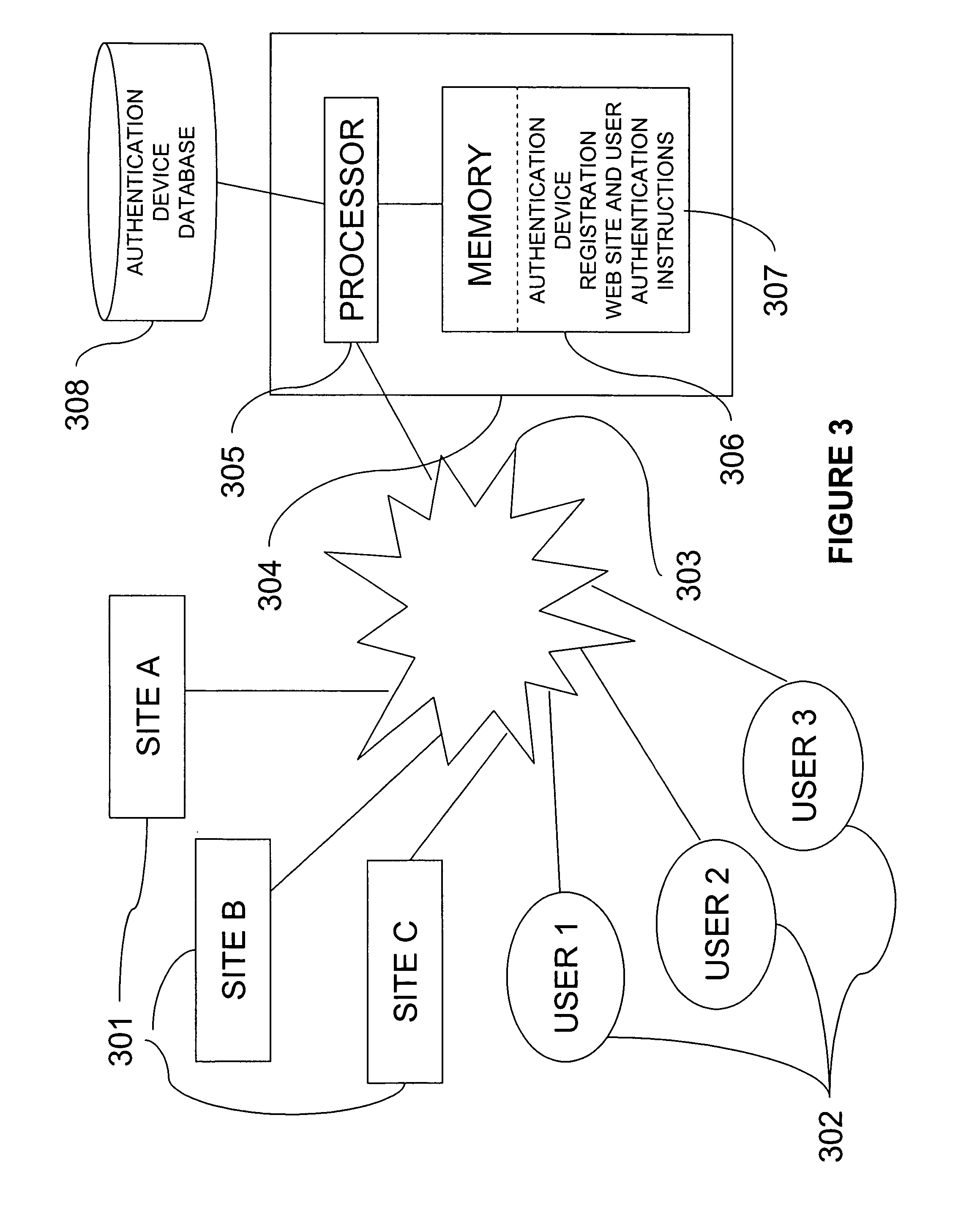
A web site can be authenticated by a third party authentication service. A user designates an authentication device that is a shared secret between the user and the authentication service. A web site page includes a URL that points to the authentication service. The URL includes a digital signature by the web site. When the user receives the page, the user's browser issues a request to the authentication service, which attempts to authenticate the digital signature. If the authentication is successful, it sends the authentication device to the user computer.
Owner:SYMANTEC CORP
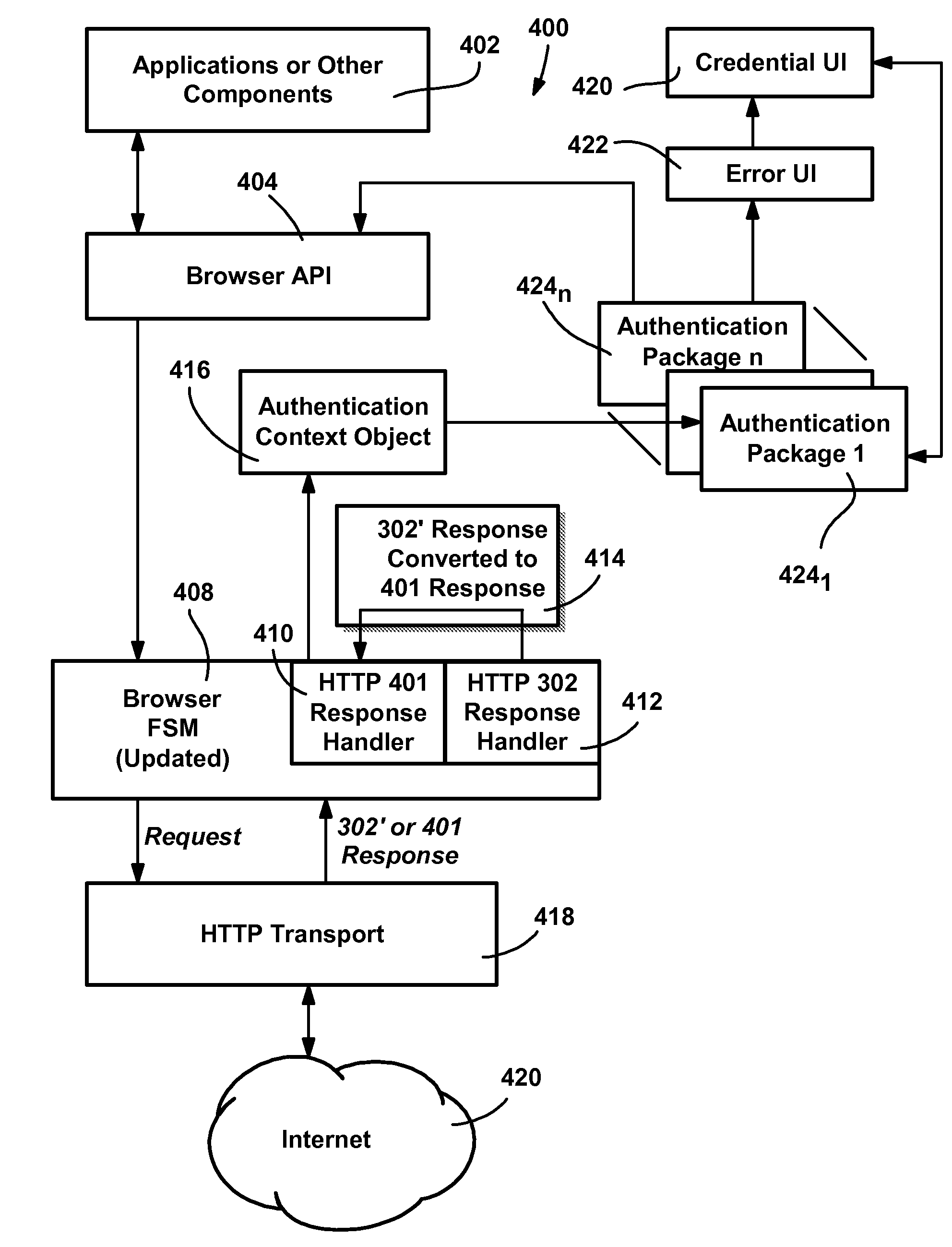
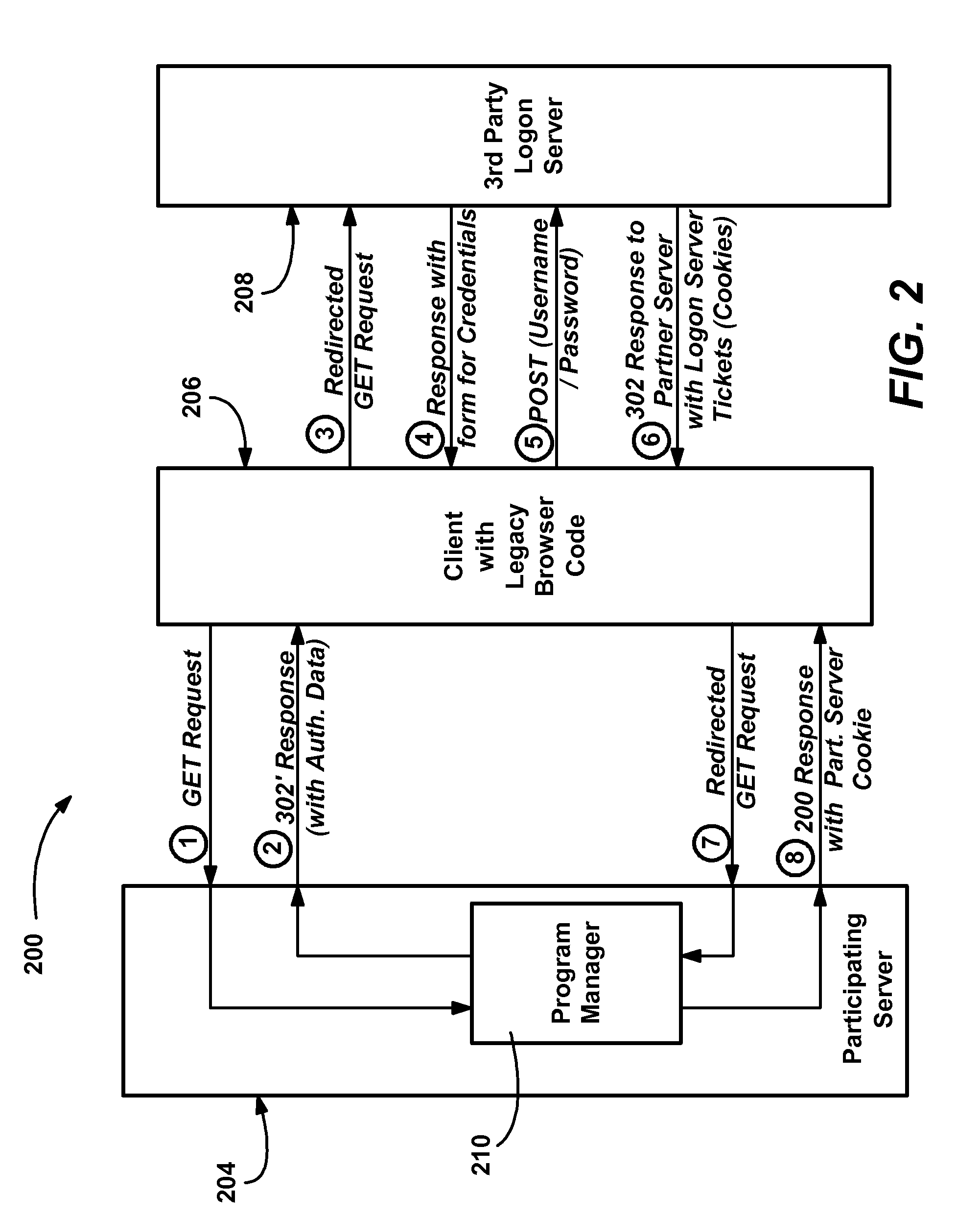
Method and system of integrating third party authentication into internet browser code
InactiveUS7191467B1Random number generatorsUser identity/authority verificationThird partyThe Internet
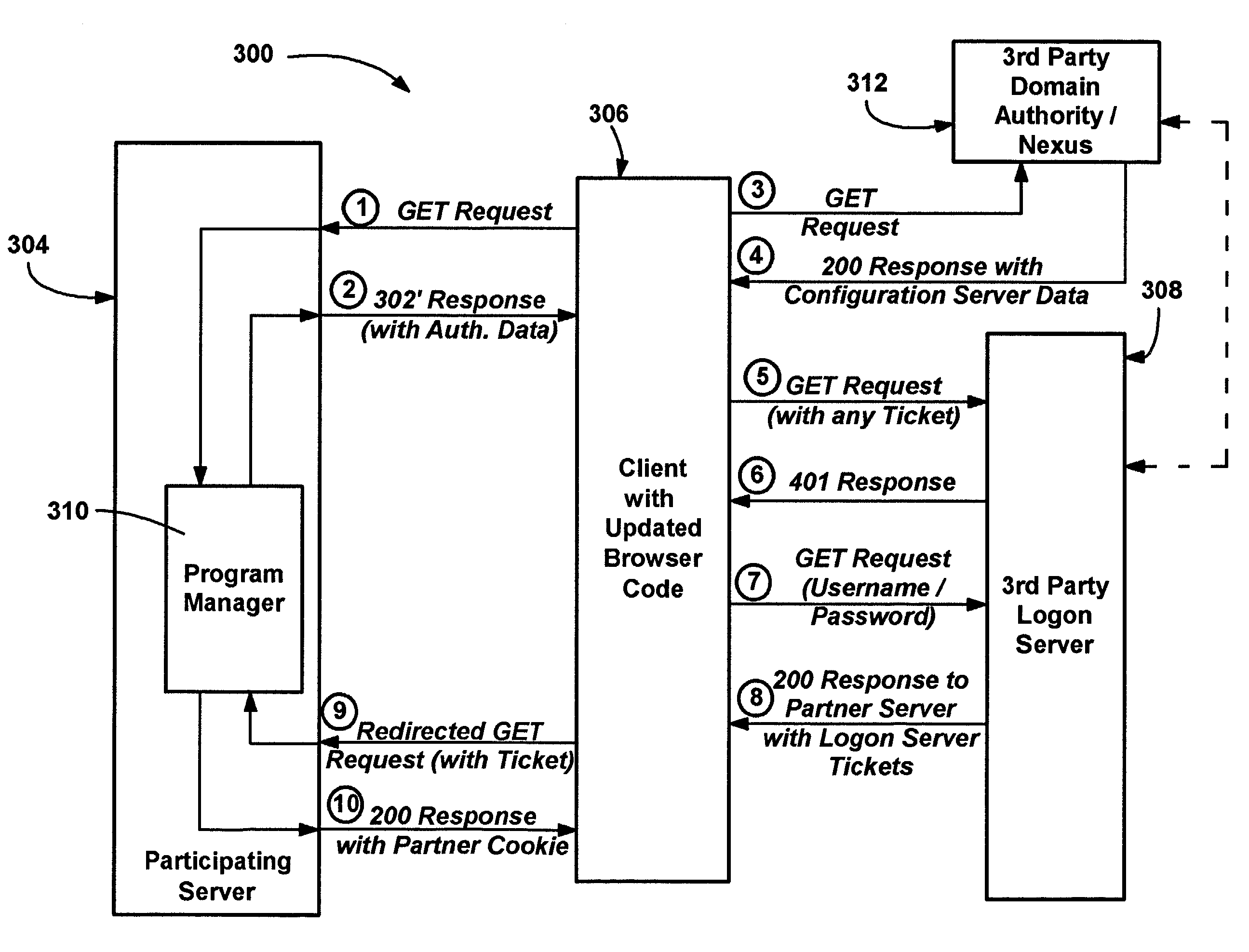
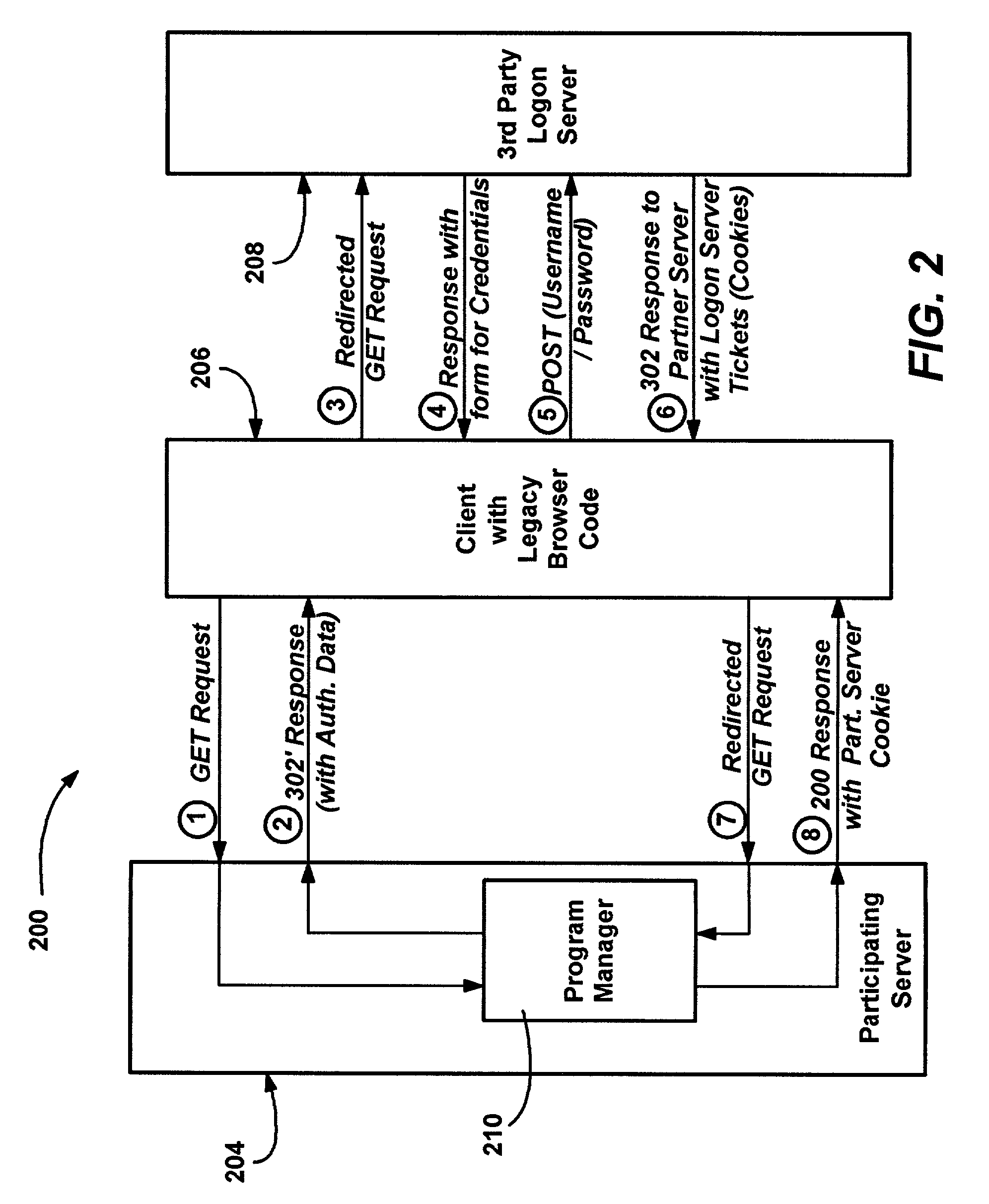
A method and system for using an Internet client's local authentication mechanism in systems having updated browser code, so as to enable third party authentication according to an authentication scheme specified by a participating server on clients with updated browser code, while not breaking clients with legacy browser code. A redirect response from a server has authentication data added thereto such that updated browser code can detect the data's presence and enable the use of local security mechanisms for authentication purposes with the server-specified authentication scheme, including local credential entry for verification at a third party login server. At the same time, if such a redirect response is received by prior browser code, the added data is ignored while conventional redirection occurs, such that third party authentication may be performed via redirection to a third party's Internet page that provides a form for credential entry.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system of integrating third party authentication into internet browser code
InactiveUS20060185021A1Improve responseKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsThird partyThe Internet
A method and system for using an Internet client's local authentication mechanism in systems having updated browser code, so as to enable third party authentication according to an authentication scheme specified by a participating server on clients with updated browser code, while not breaking clients with legacy browser code. A redirect response from a server has authentication data added thereto such that updated browser code can detect the data's presence and enable the use of local security mechanisms for authentication purposes with the server-specified authentication scheme, including local credential entry for verification at a third party login server. At the same time, if such a redirect response is received by prior browser code, the added data is ignored while conventional redirection occurs, such that third party authentication may be performed via redirection to a third party's Internet page that provides a form for credential entry.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
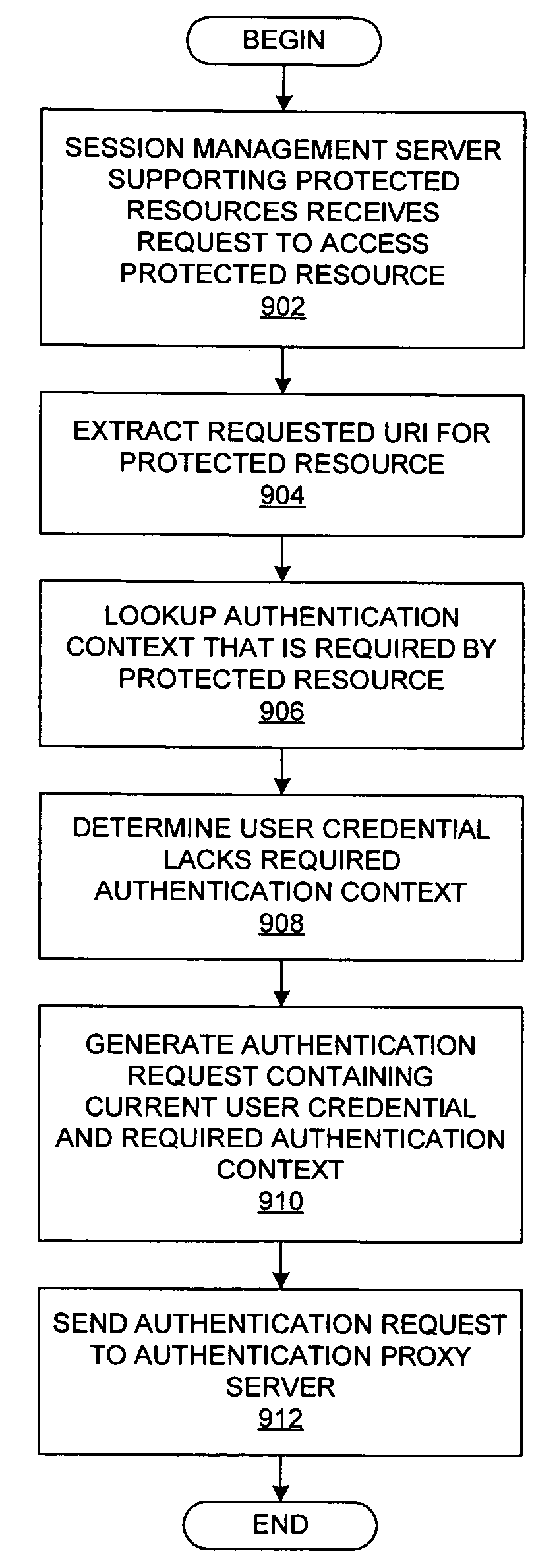
Method and system for extending authentication methods
ActiveUS20080134305A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationSession managementA domain
A method is presented for managing authentication credentials for a user. A session management server performs session management with respect to the user for a domain that includes a protected resource. The session management server receives a request to access the protected resource, which requires authentication credentials that have been generated for a first type of authentication context. In response to determining that authentication credentials for the user have been generated for a second type of authentication context, the session management server sends to an authentication proxy server a first message that contains the authentication credentials for the user and an indicator for the first type of authentication context. The session management server subsequently receives a second message that contains updated authentication credentials for the user that indicate that the updated authentication credentials have been generated for the first type of authentication context.
Owner:FINJAN BLUE INC
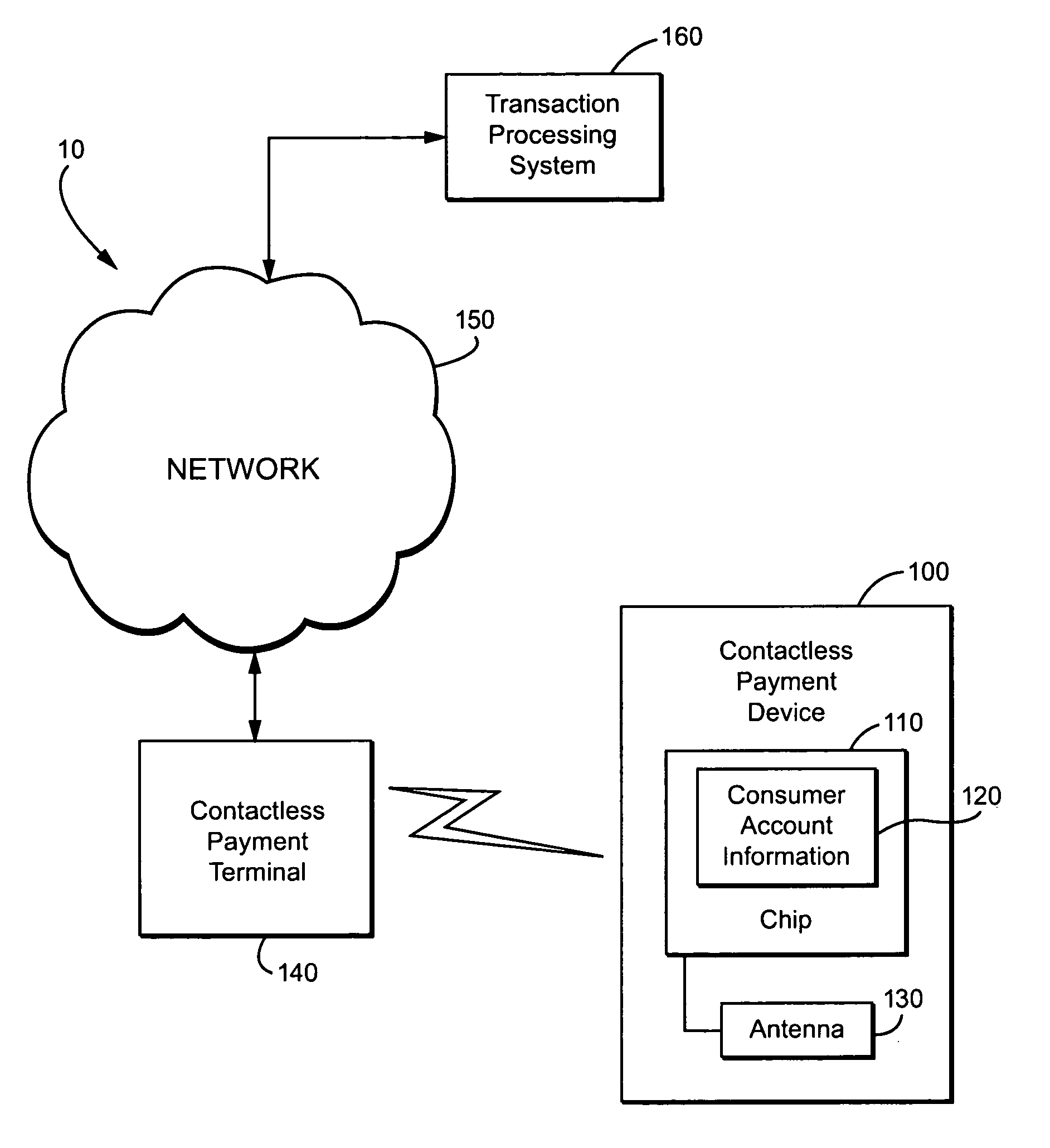
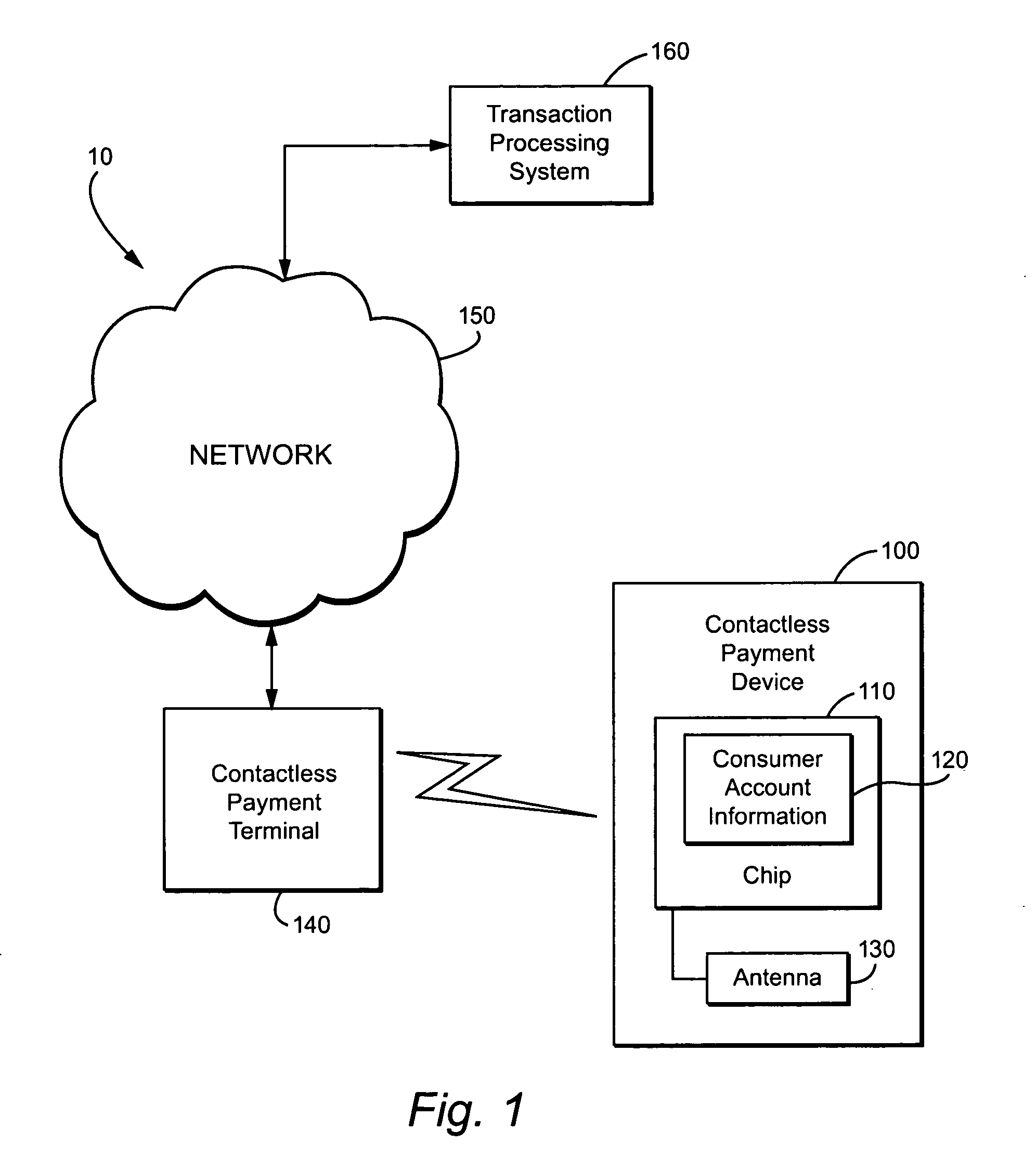
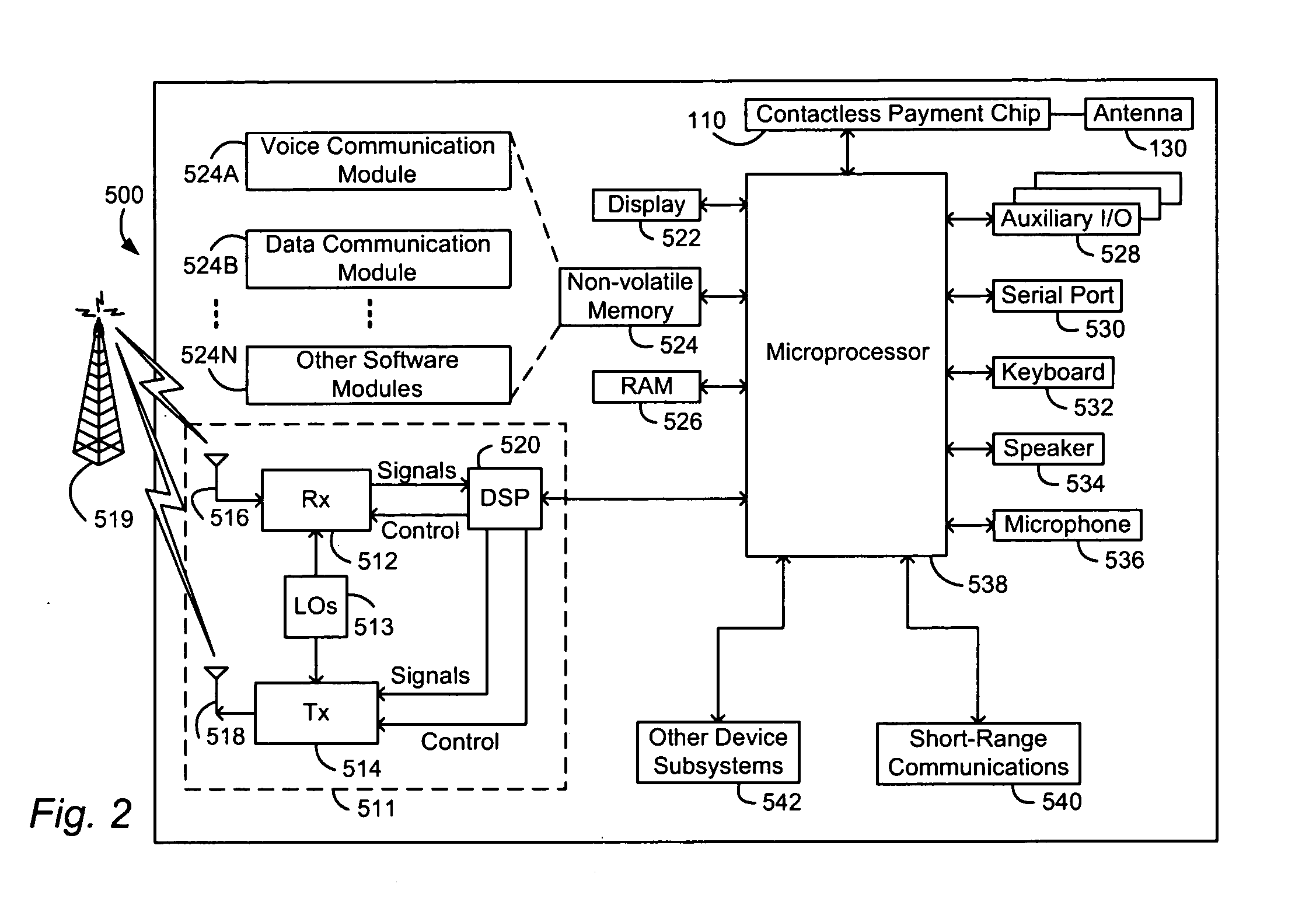
Method and apparatus for contactless payment authentication
ActiveUS20070152035A1Efficient and accurate and easy to implementMaintain conveniencePayment architectureSensing record carriersPaymentPassword protection
The present disclosure relates generally to the authentication of contactless payments attempted by a device having embedded contactless payment functionality. In particular, the disclosure is directed to systems and methods that utilize authentication schemes that already exist on a device in which the contactless payment functionality is embedded. One example of such authentication schemes is the use of password protection to lock or unlock the device in which the contactless payment functionality is embedded. Using the password protection functionality may provide varying levels of authentication protection based on the desires of the user. A number of exemplary uses of such a method and apparatus are disclosed herein.
Owner:MALIKIE INNOVATIONS LTD
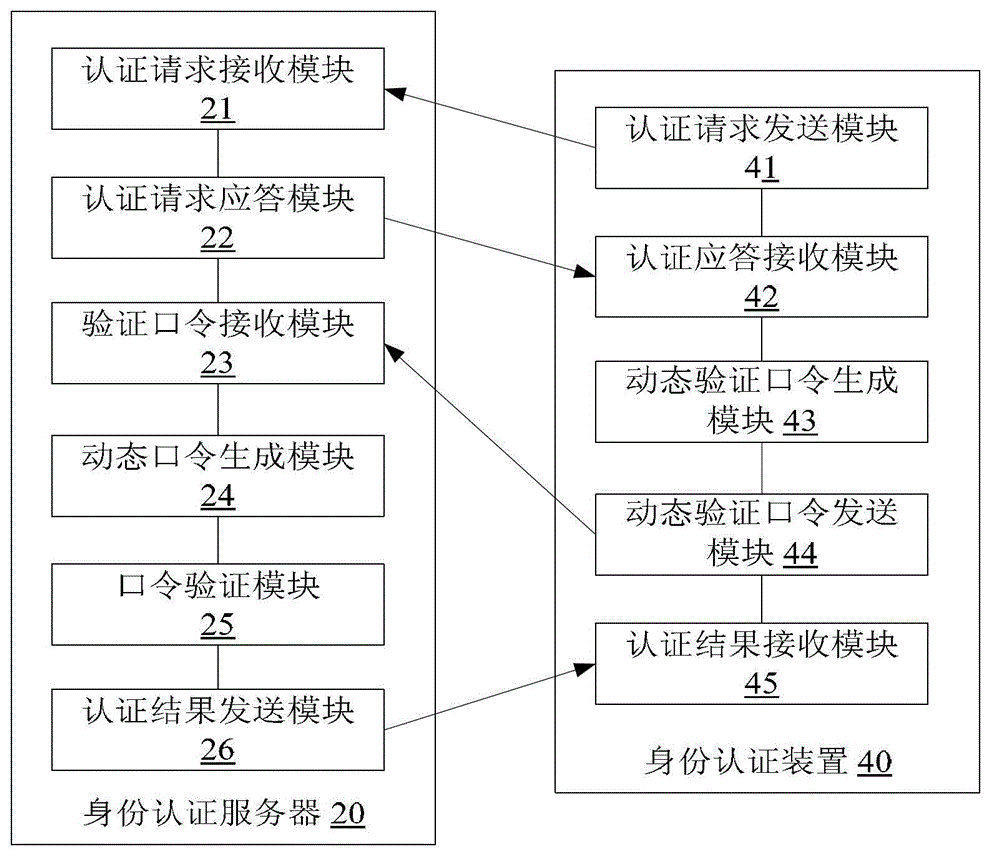
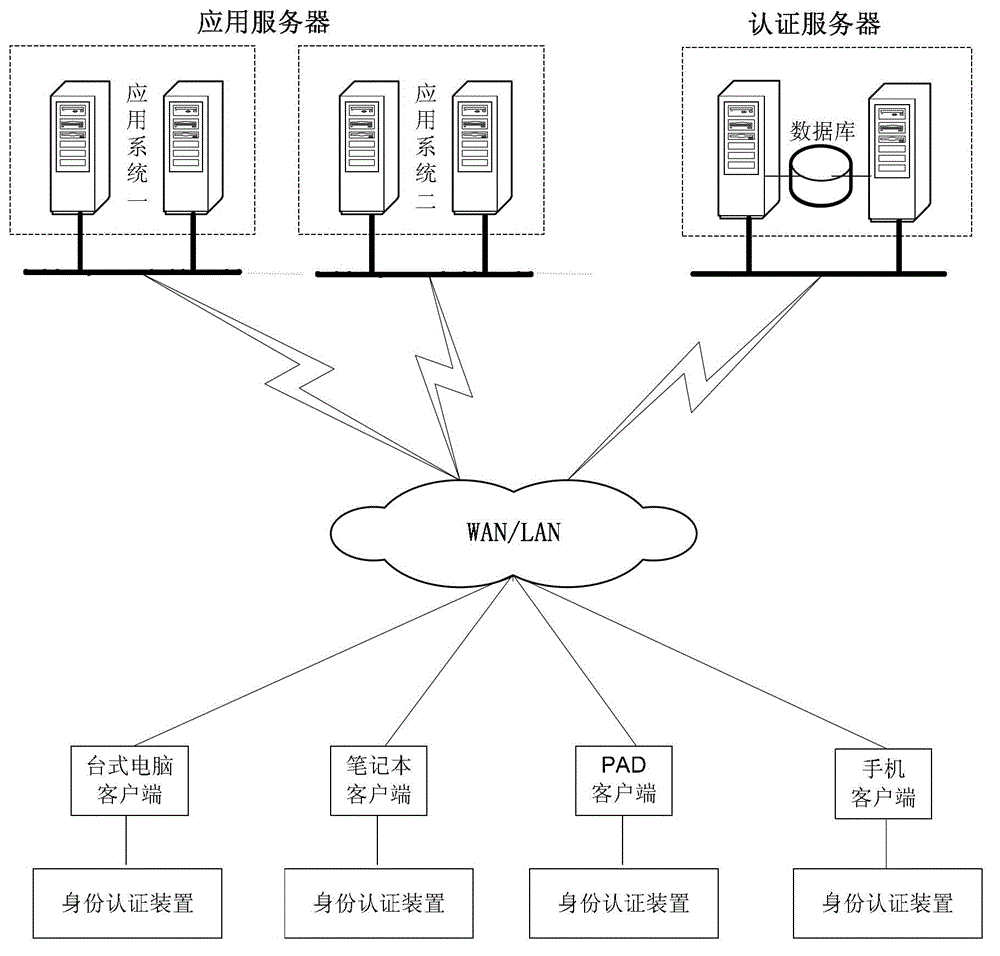
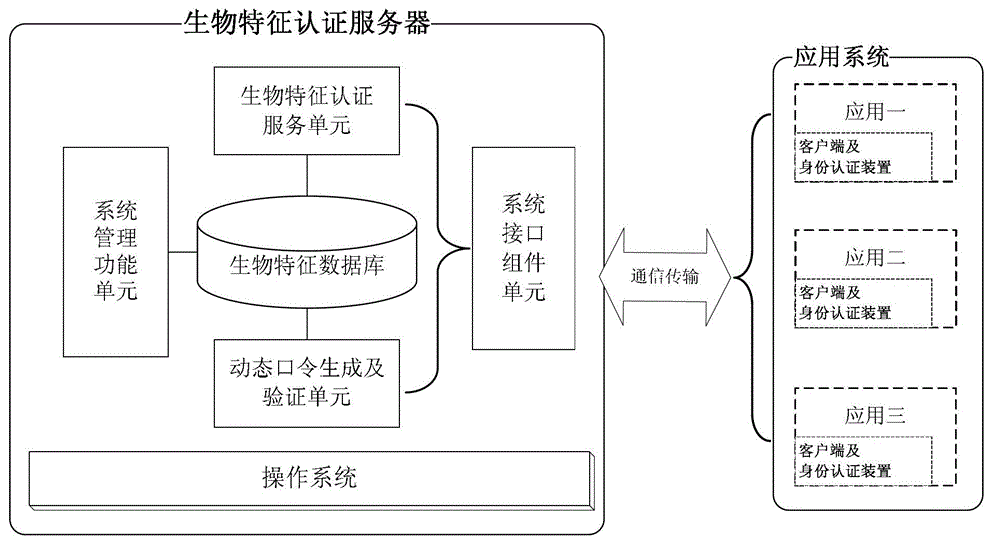
Identity authentication method, identity authentication server and identity authentication device
ActiveCN102916968AImprove securityEnsure safetyKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationPasswordAuthentication server
The invention discloses an identity authentication method, an identity authentication server and an identity authentication device. The method comprises the steps that the authentication server receives a biological characteristic authentication request sent by a client, returns challenges generated randomly to the client and receives a dynamic verification password sent by the client, wherein the dynamic verification password is generated by the client time when the challenges are received, the challenges, a biological characteristic of a user and a first seed key prestored in the client; the authentication server generates a dynamic password according to the time of the authentication server when the dynamic verification password is received, the challenges, the biological characteristic of the user and a second seed key; and the authentication server verifies whether the dynamic password is consistent with the dynamic verification password and returns an identity authentication result to the client according to a verification result. With the adoption of the identity authentication method, the identity authentication server and the identity authentication device, the safety of the dynamic password is ensured through the biological characteristic, and the authenticity and reliability of the identity authentication of the user are guaranteed.
Owner:BEIJING EYECOOL TECH CO LTD +1
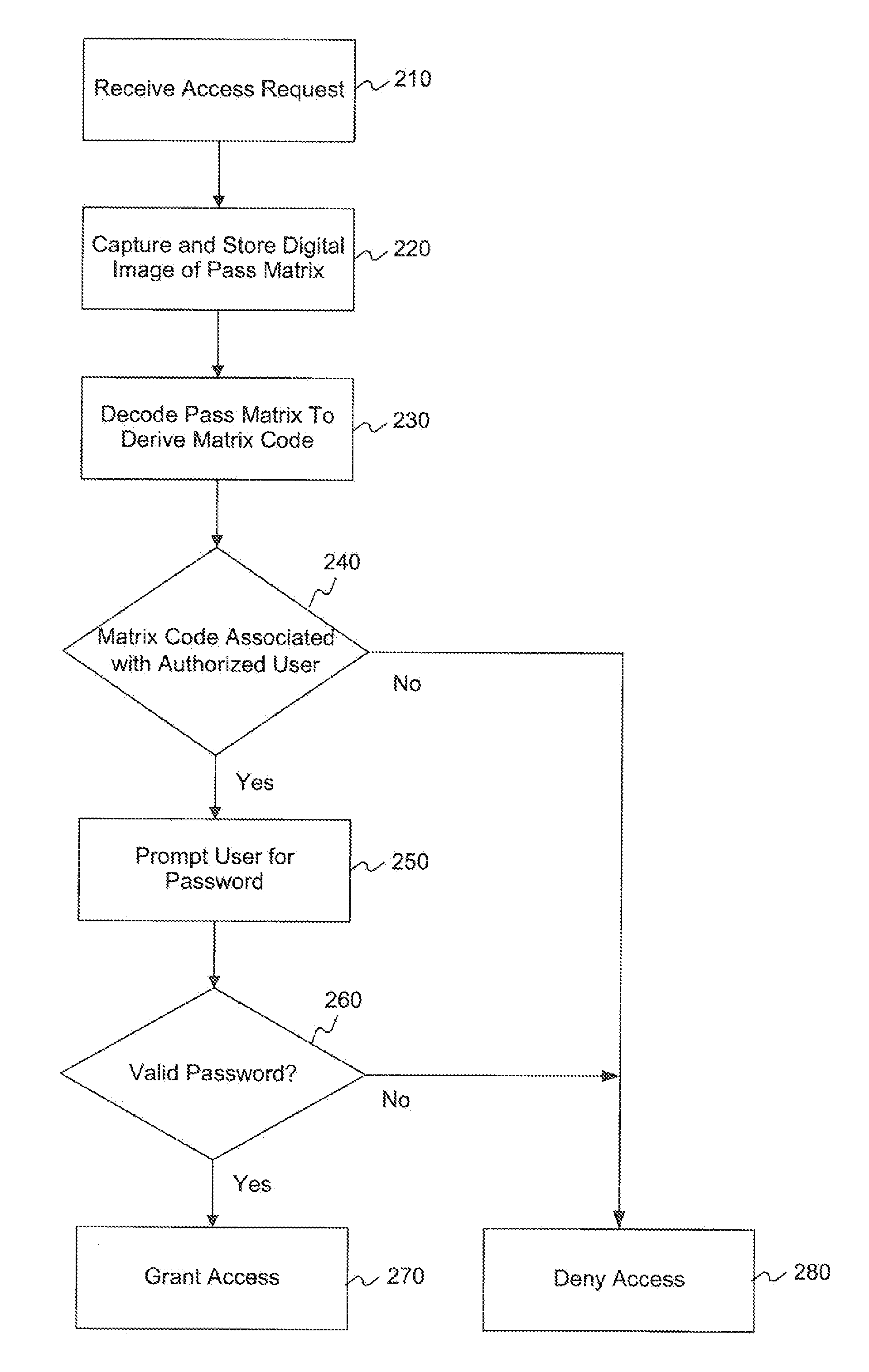
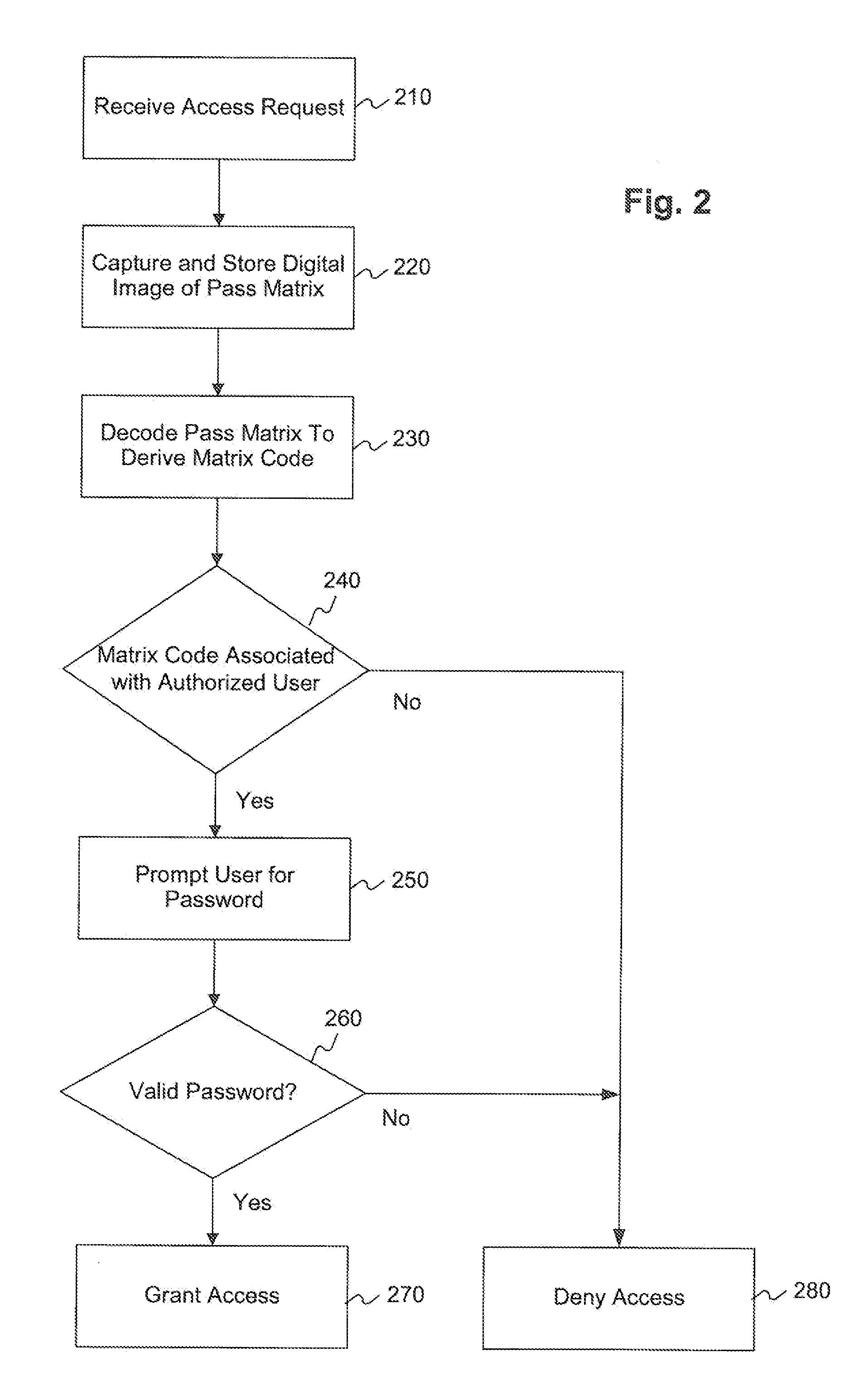
Multi-factor authentication using digital images of barcodes
ActiveUS20130031623A1Easy to operateReduce memory loadDigital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer graphics (images)Password
Methods, systems, and computer-readable media for implementing a multi-factor authentication scheme utilizing barcode images in computing devices, such as standard mobile devices and smartphones having no native hardware support for reading barcodes other than standard digital camera componentry for capturing digital images of real-world phenomena. A mobile device may be configured by software to require a user, as a first authentication factor, to present a barcode, such as a Quick Response (QR) Code for image scanning using digital camera componentry built into the mobile device. The device analyzes the digital image of the barcode to decode the barcode into its encoded character data. If the device recognizes the character data as valid, then, as a second authentication factor, the device prompts the user to enter a valid password associated with the barcode. If the user-entered barcode is also valid, then the device may grant the user access.
Owner:XEROX CORP
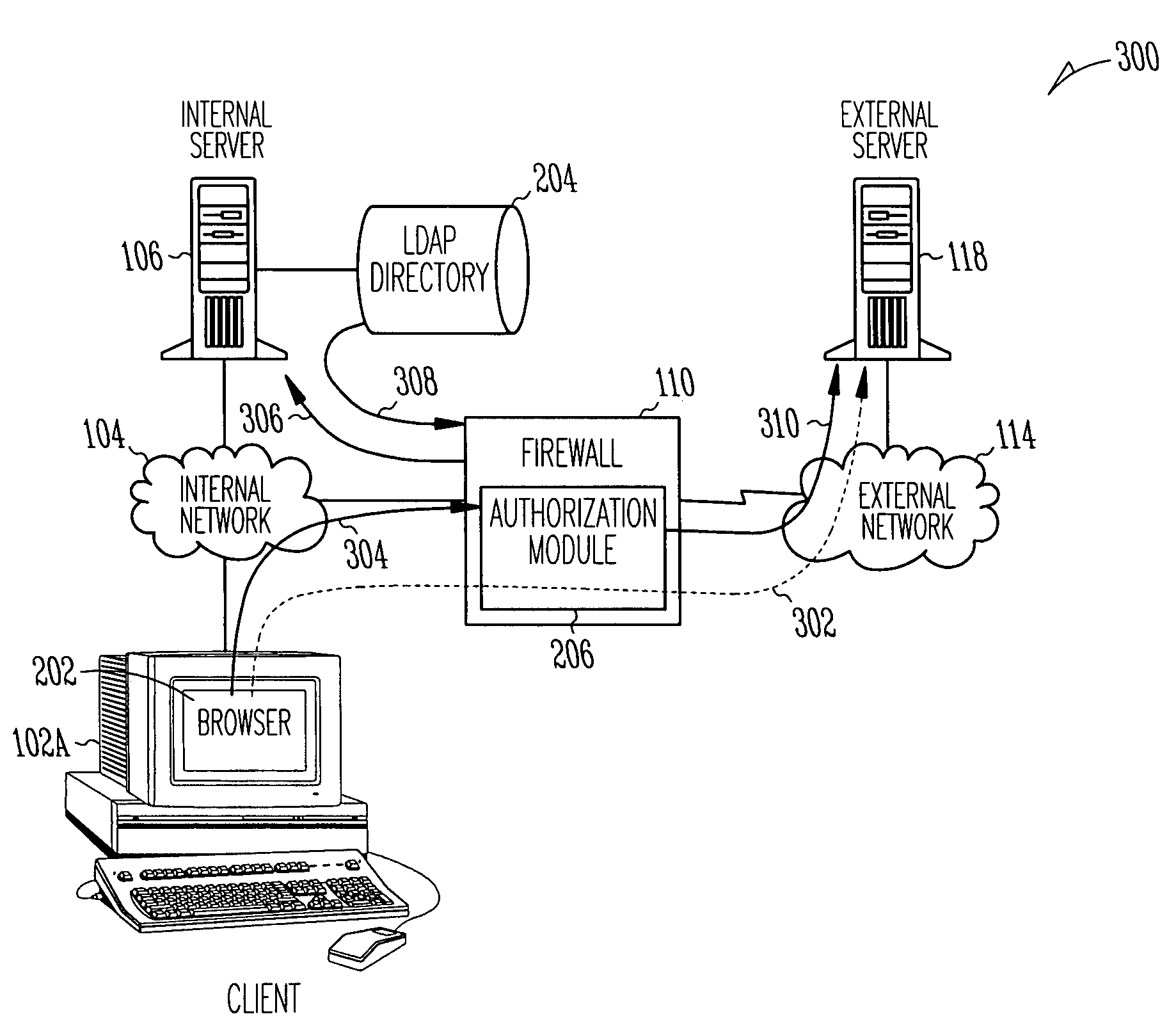
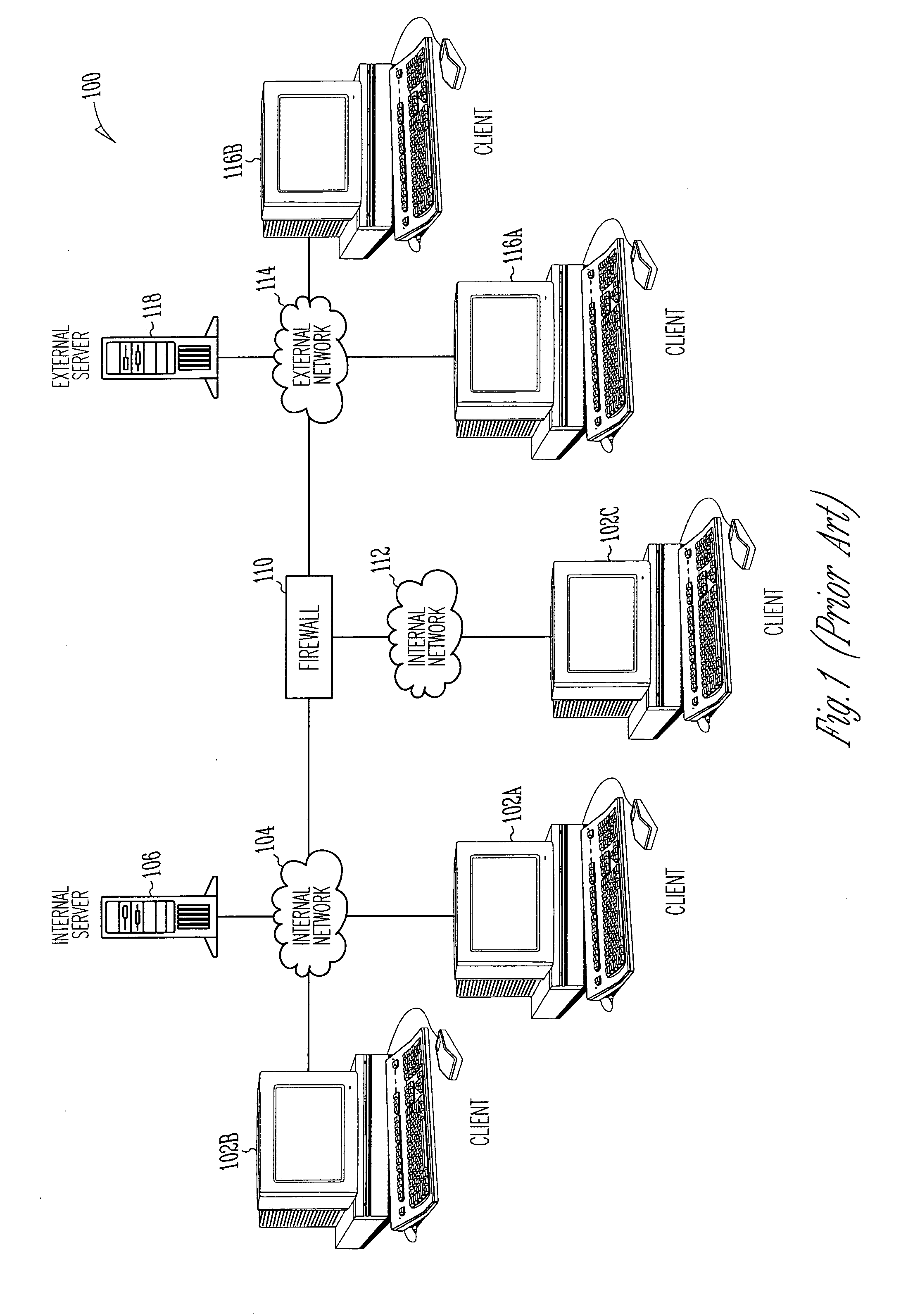
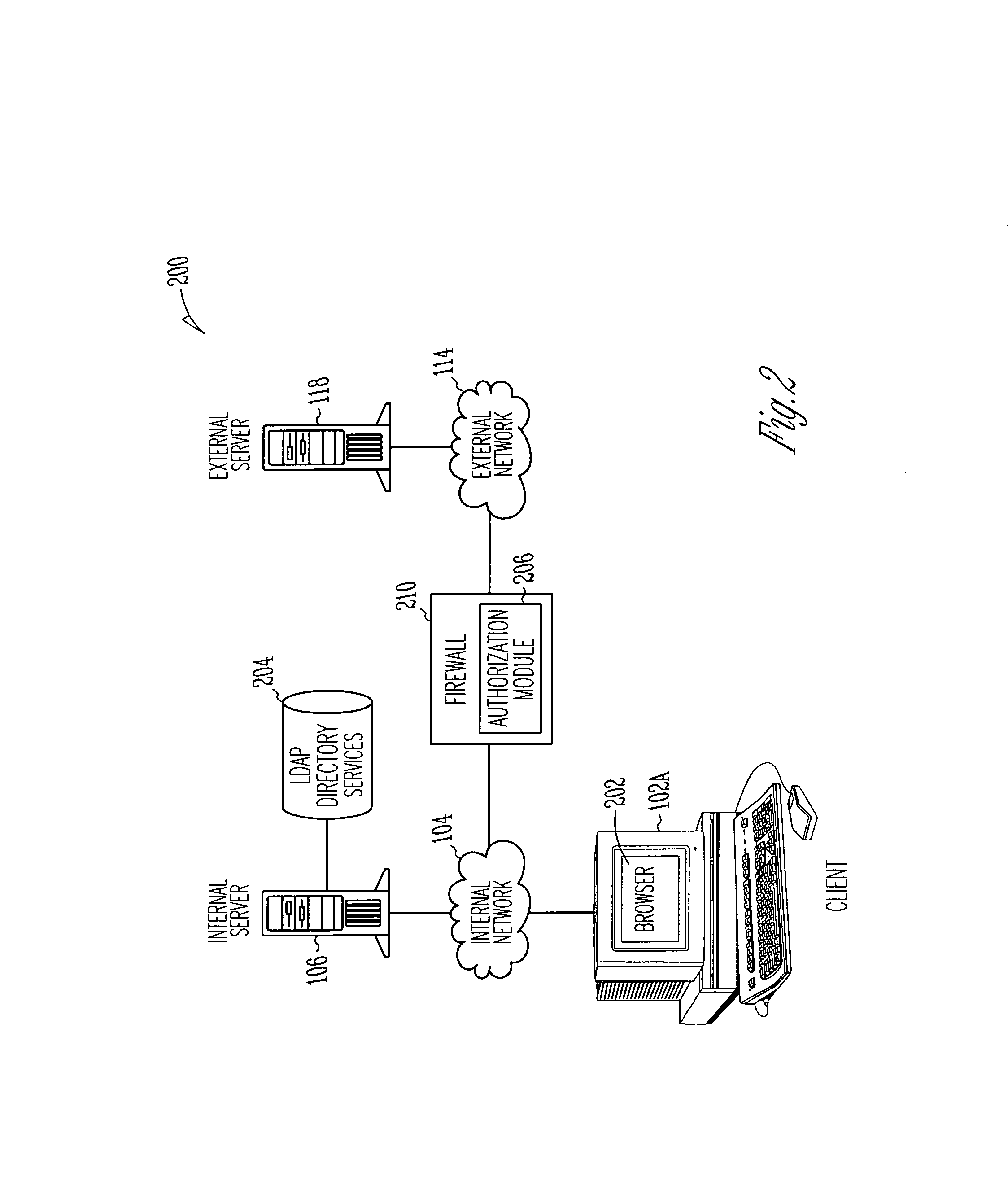
System, method and computer program product for authenticating users using a lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) directory server
InactiveUS7185361B1Great degreeFlexible specificationsData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsGraphical user interface
A system, method and computer program product for providing authentication to a firewall using a lightweight directory access protocol (LDAP) directory server is disclosed. The firewall can be configured through a graphical user interface to implement an authentication scheme. The authentication scheme is based upon a determination of whether at least part of one or more LDAP entries satisfy an authorization filter.
Owner:MCAFEE LLC
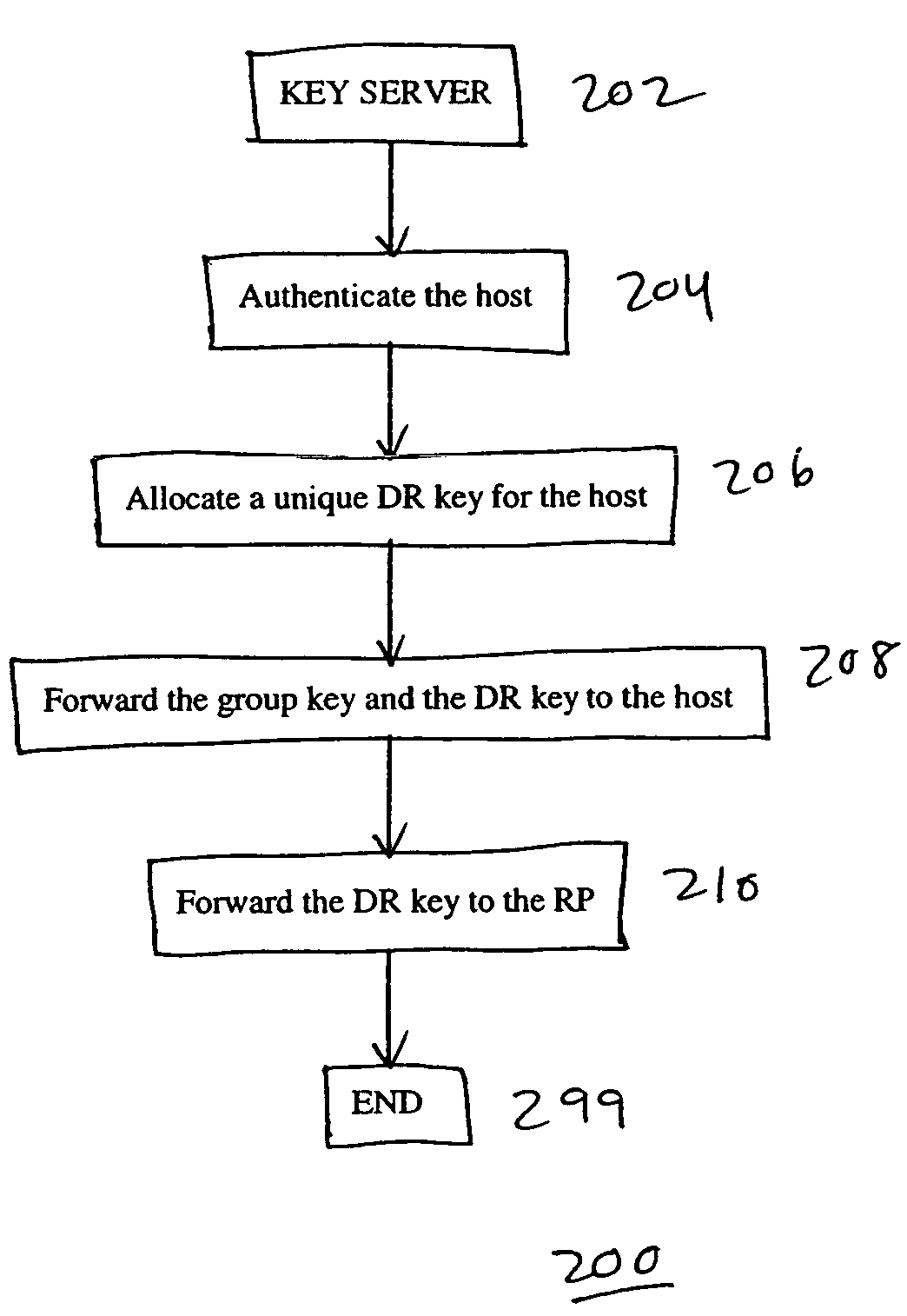
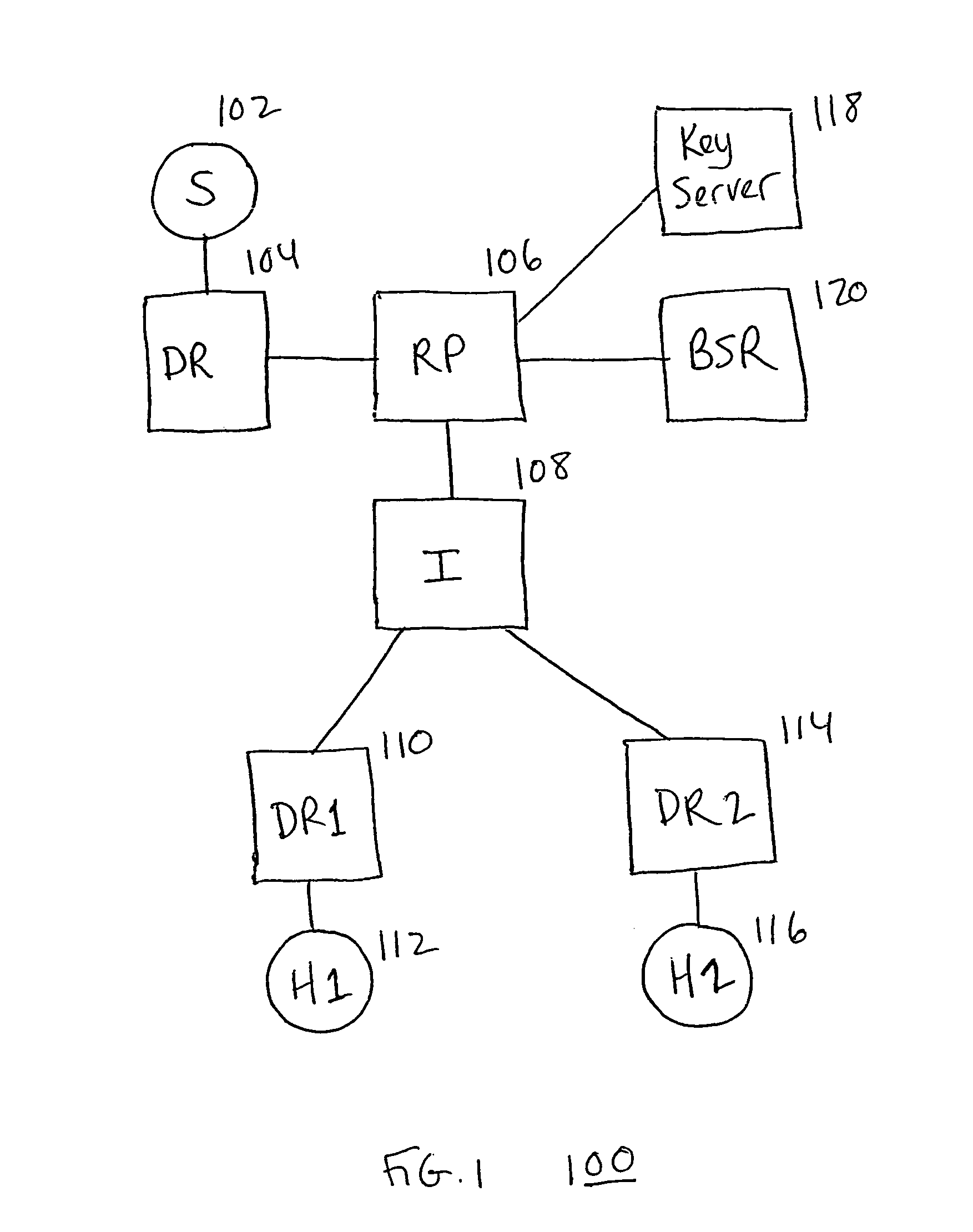
System, device, and method for controlling access in a multicast communication network
InactiveUS7360084B1User identity/authority verificationDigital computer detailsDistribution treeNetwork packet
A system, device, and method for controlling access in a multicast communication network uses a centralized host authentication scheme to prevent unauthorized hosts from joining a shared multicast distribution tree. Each authorized host is allocated a unique authentication key, which is used by the designated router to encode the PIM join message and by the rendezvous point router to authenticate the PIM join message. If the PIM join message is authentic, then each PIM router from the rendezvous point router to the designated router establishes appropriate multicast routes to route multicast packets to the host. If the PIM join message is not authentic, then multicast packets are prevented from reaching the host.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Discovery and authentication scheme for wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS7814322B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsOpen Systems InterconnectionMesh node
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
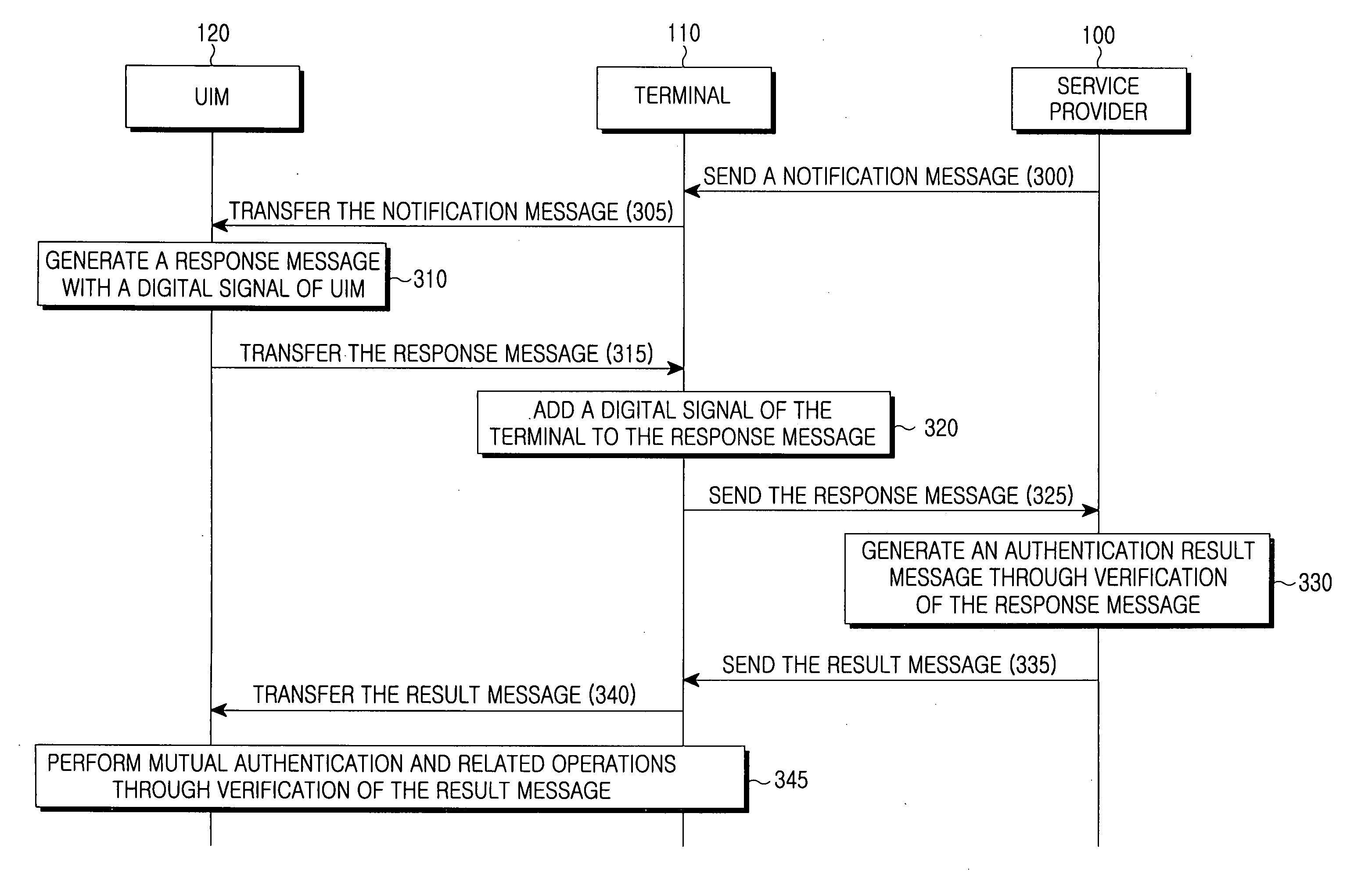
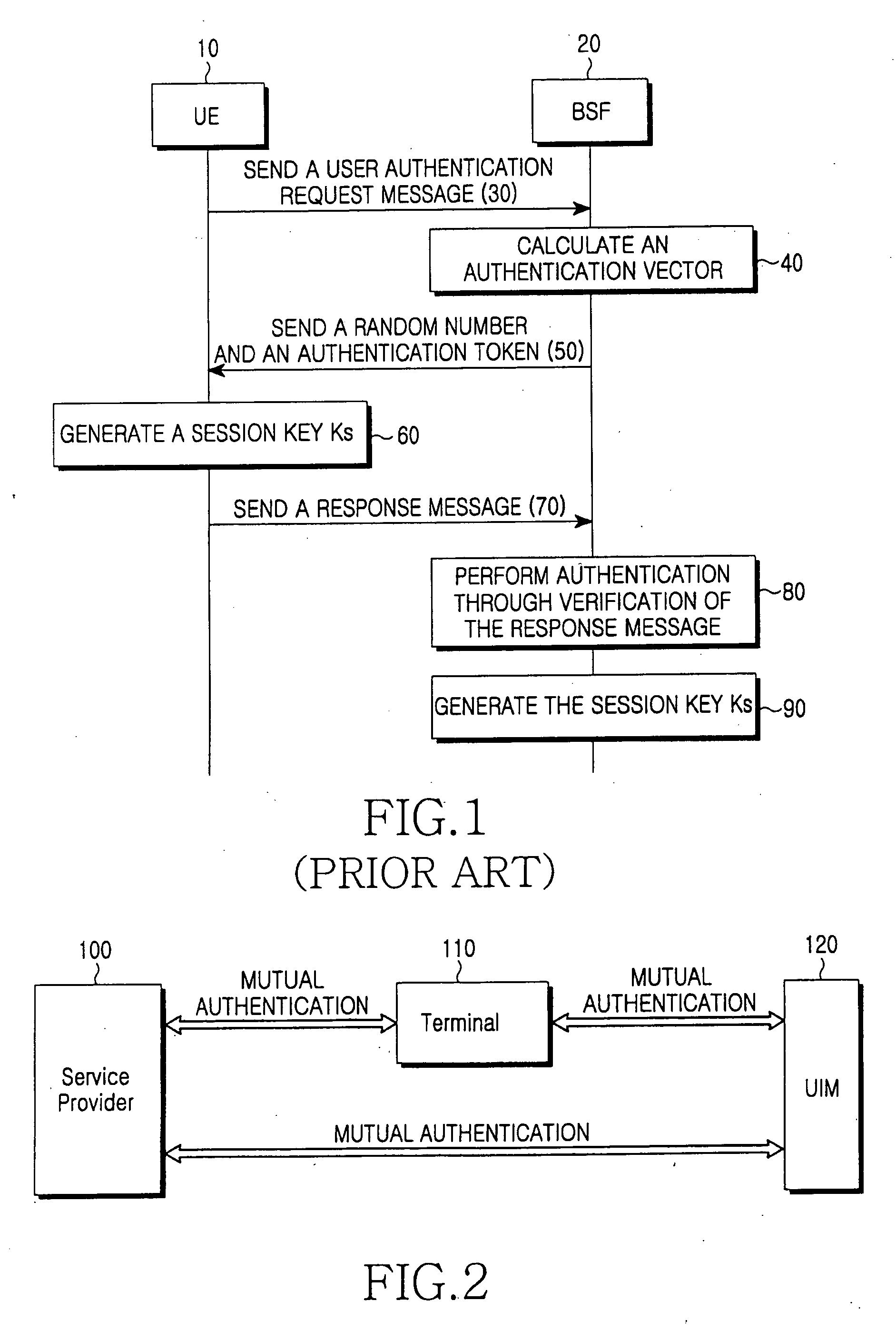
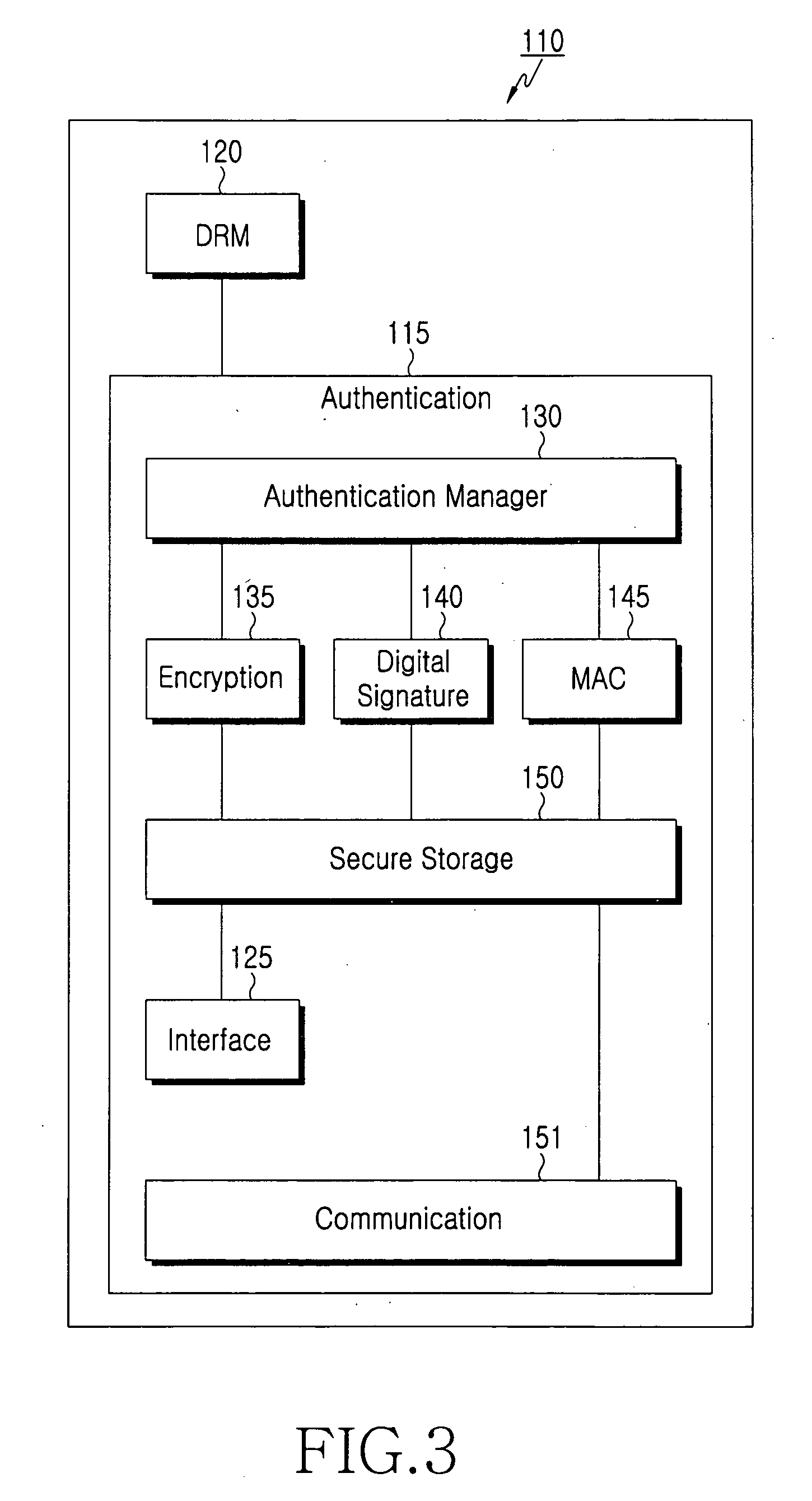
Method for inclusive authentication and management of service provider, terminal and user identity module, and system and terminal device using the method
ActiveUS20060281442A1Unauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsPublic key authenticationNetworked system
Disclosed are a method and a system for mutual inclusive authentication between a service provider, a terminal and a user identity module. The authentication system is configured in a structure that can interact with a public key infrastructure of the current network security environment and can be independently used in a specific network system. The inclusive authentication method is divided into public key authentication and symmetric key authentication. Mutual authentication can be made between a service provider, a terminal and a user identity module using any of the two authentication schemes. Then a user can access content on any terminal device using the content license based on the user's identity.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
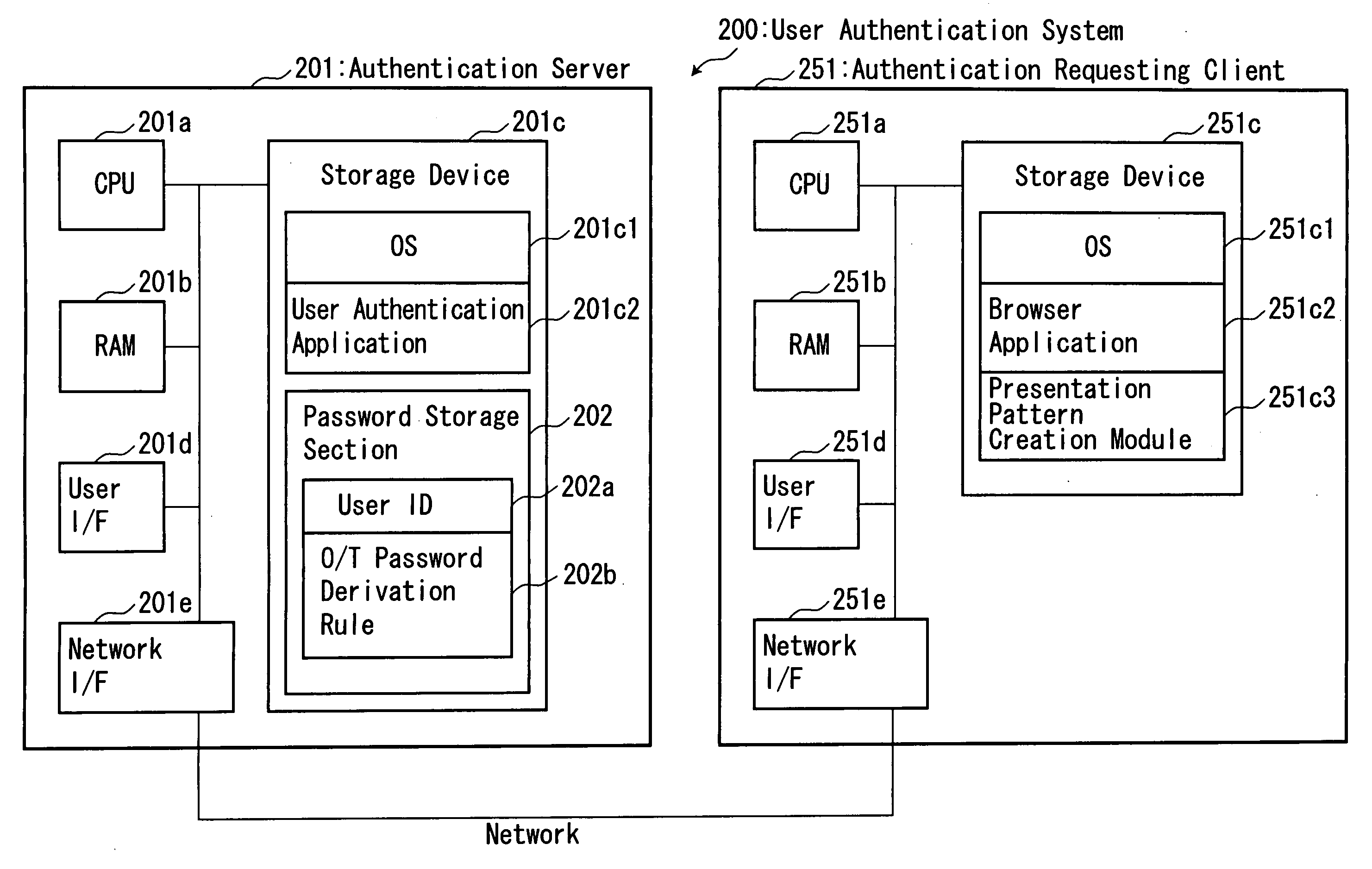
System and method for user authentication
ActiveUS20070226784A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser authenticationAuthentication server
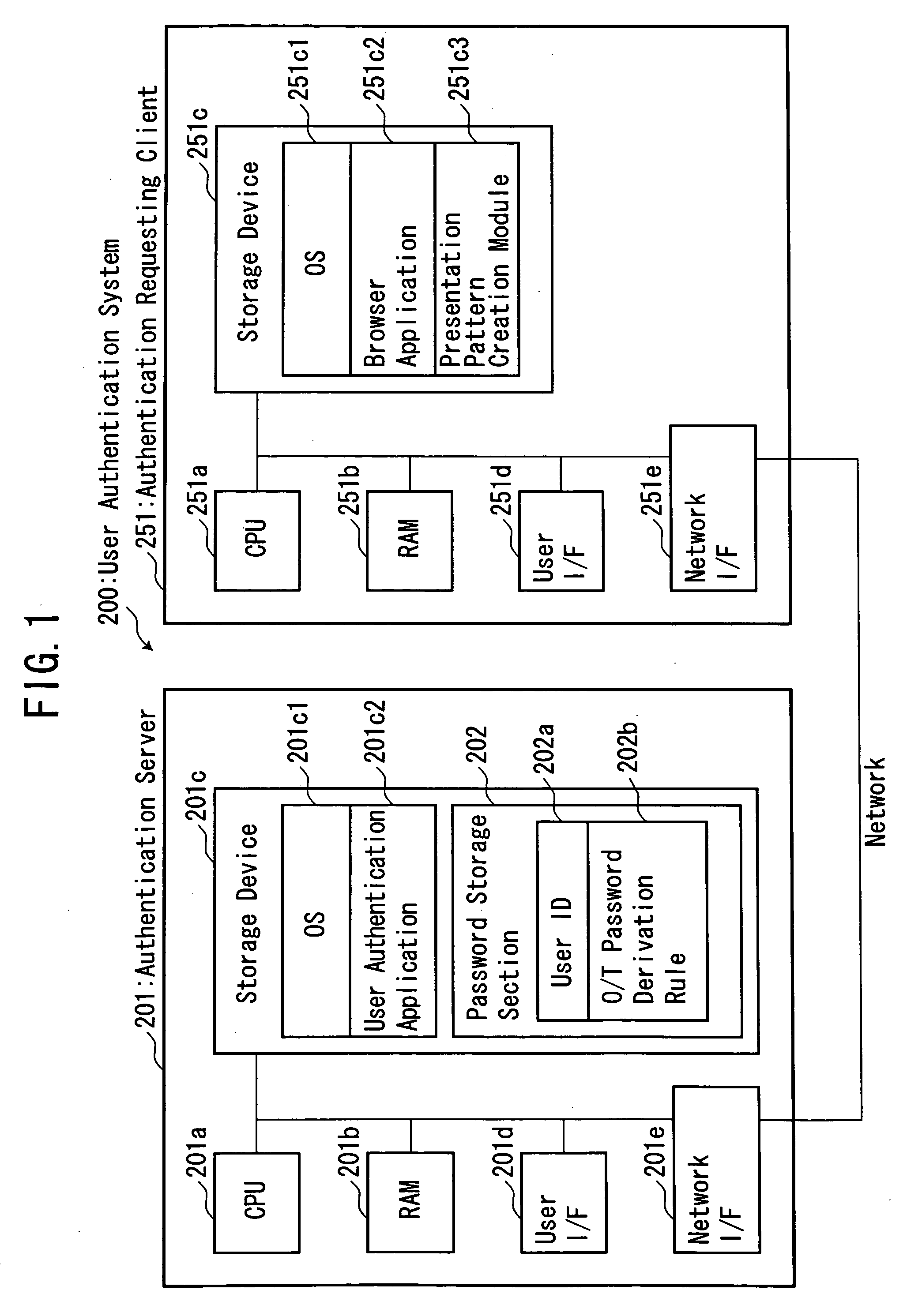
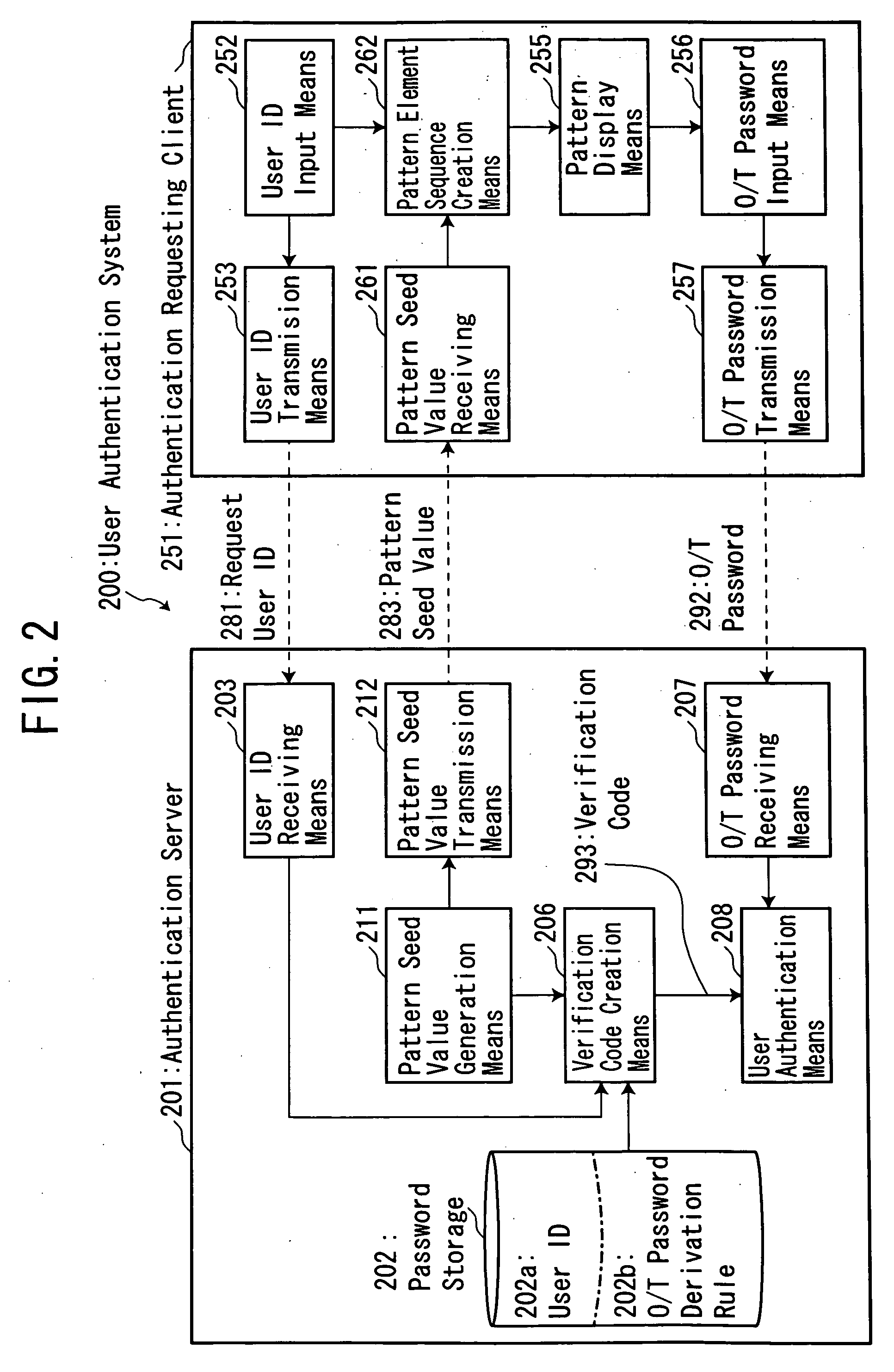
Disclosed is a user authentication system, which is designed to present a presentation pattern to a user subject to authentication, and apply a one-time-password derivation rule serving as a password of the user to certain pattern elements included in the presentation pattern at specific positions so as to create a one-time password. An authentication server is operable to generate a pattern seed value adapted to be combined with a user ID so as to allow a presentation pattern to be uniquely determined, and transmit the generated pattern seed value to an authentication-requesting client. The authentication-requesting client is operable to display a presentation pattern created based on an entered user ID and the received pattern seed value and in accordance with a given pattern-element-sequence creation rule, so as to allow the user to enter therein a one-time password, and transmit the entered one-time password to the authentication server. The authentication server is operable to duplicate the presentation pattern so as to create a verification code, and compare between the received one-time password and the created verification code, so as to carry out user authentication. The present invention provides a matrix authentication scheme capable of reducing the risk of password leakage.
Owner:CSE CO LTD
Identification and authentication management
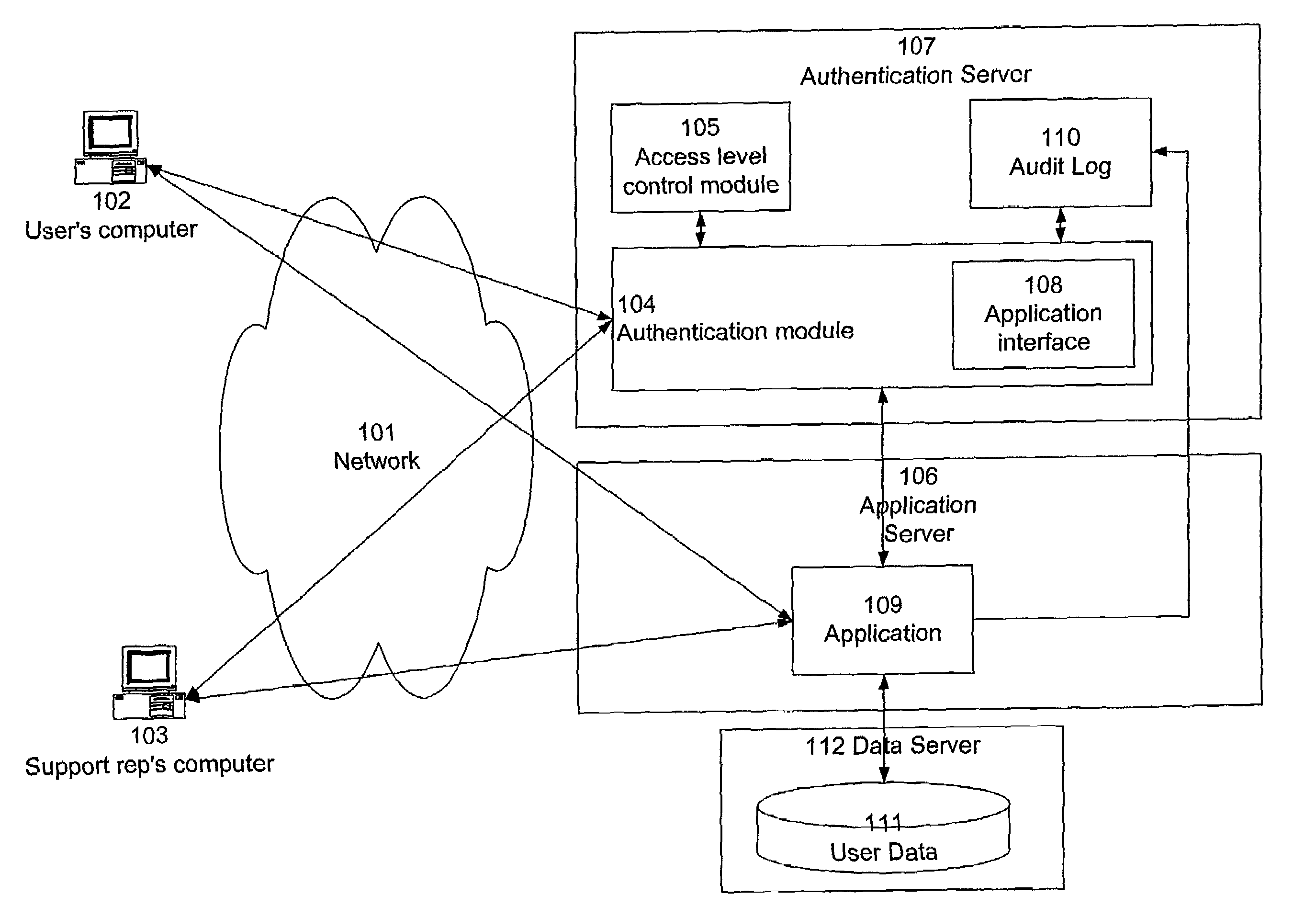
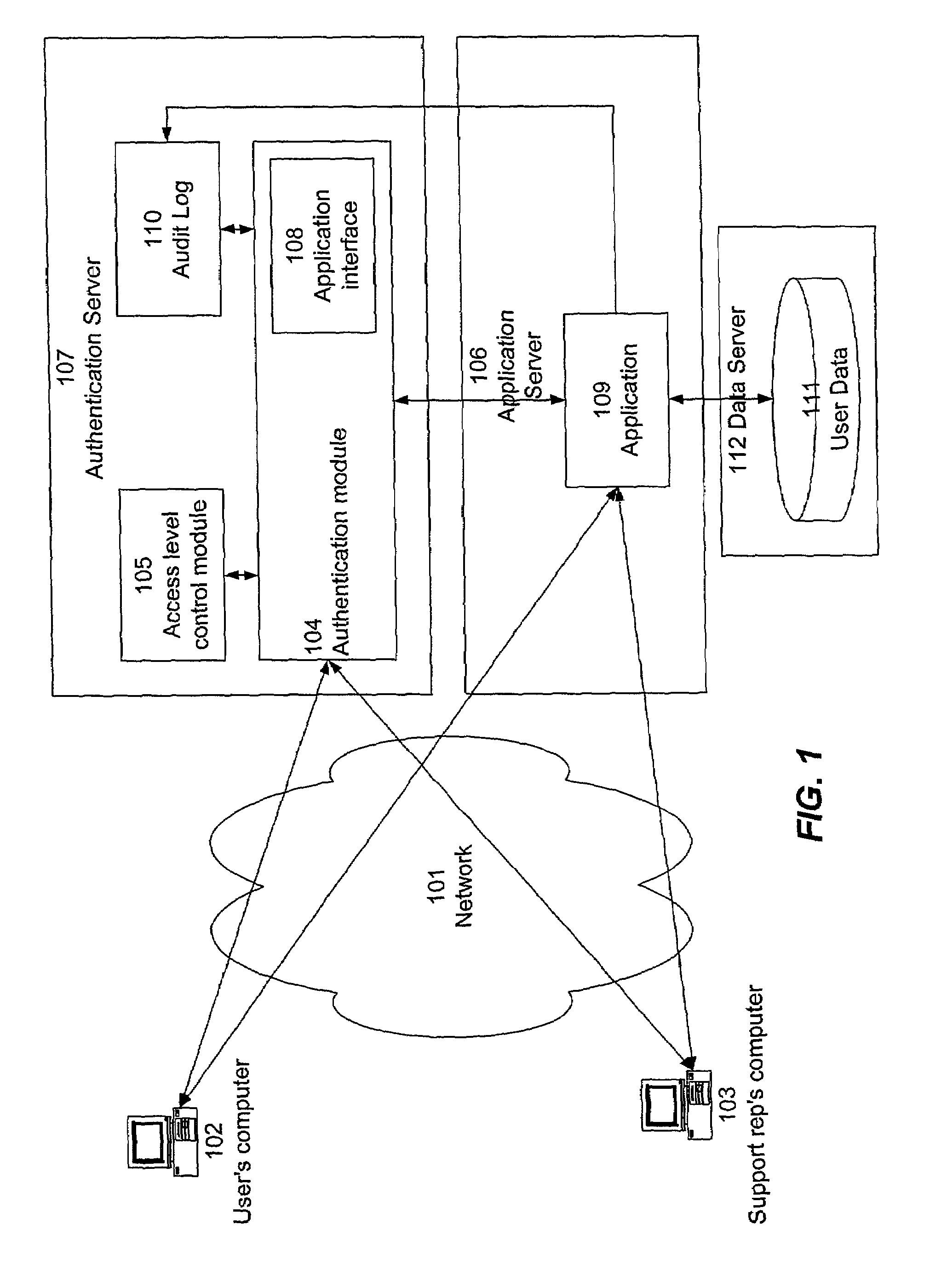
ActiveUS7117529B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationUser inputPassword
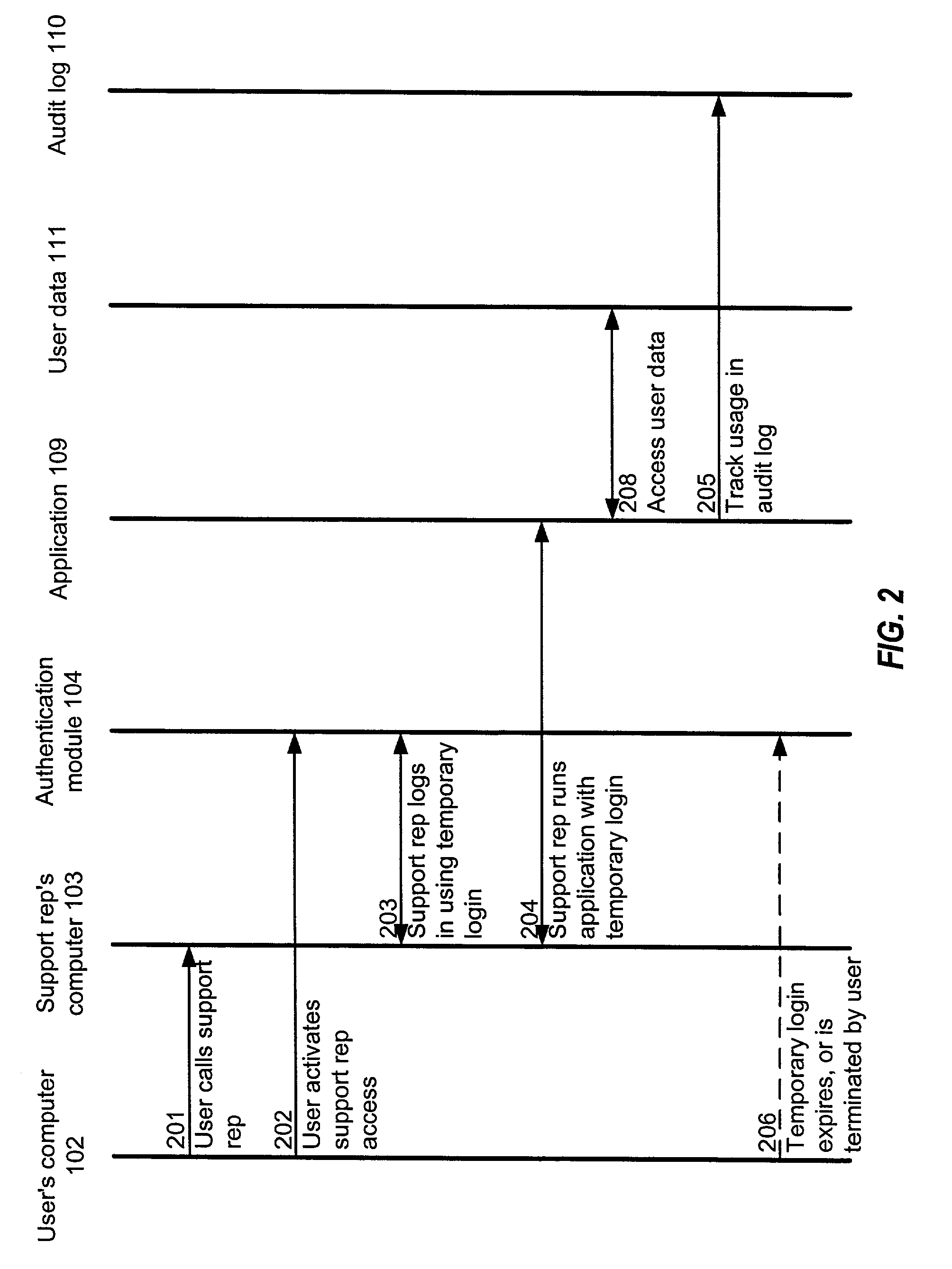
An identification and authentication scheme maintains control relationships among identities in order to allow a user to dynamically grant or deny permission for a technical support representative to access the user's data, while allowing the user to retain ultimate control over access to the data. Interactions entered by the representative can be distinguished from those entered by the user, while execution paths for representative-entered interactions are configured so that, to an application, the representative-entered transactions appear substantially identical to user-entered transactions. Technical support representatives are thereby able to duplicate users' problems to enable diagnosis and resolution of problems without requiring users to reveal their passwords or login credentials.
Owner:INTUIT INC
Encrypted communication method and system
InactiveUS20050273843A1Maintain confidentialityMaintain integrityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsCommunications systemPassword
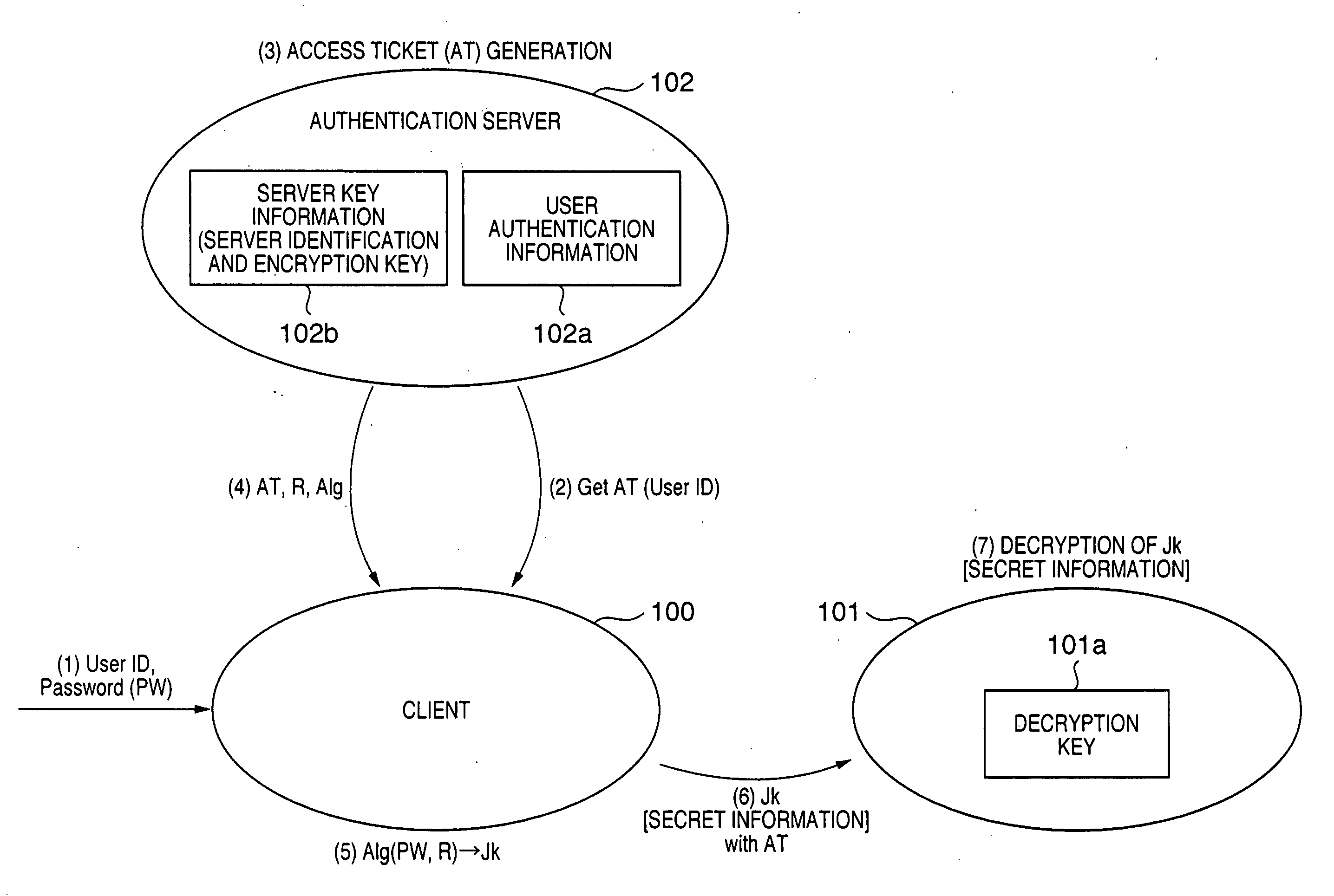
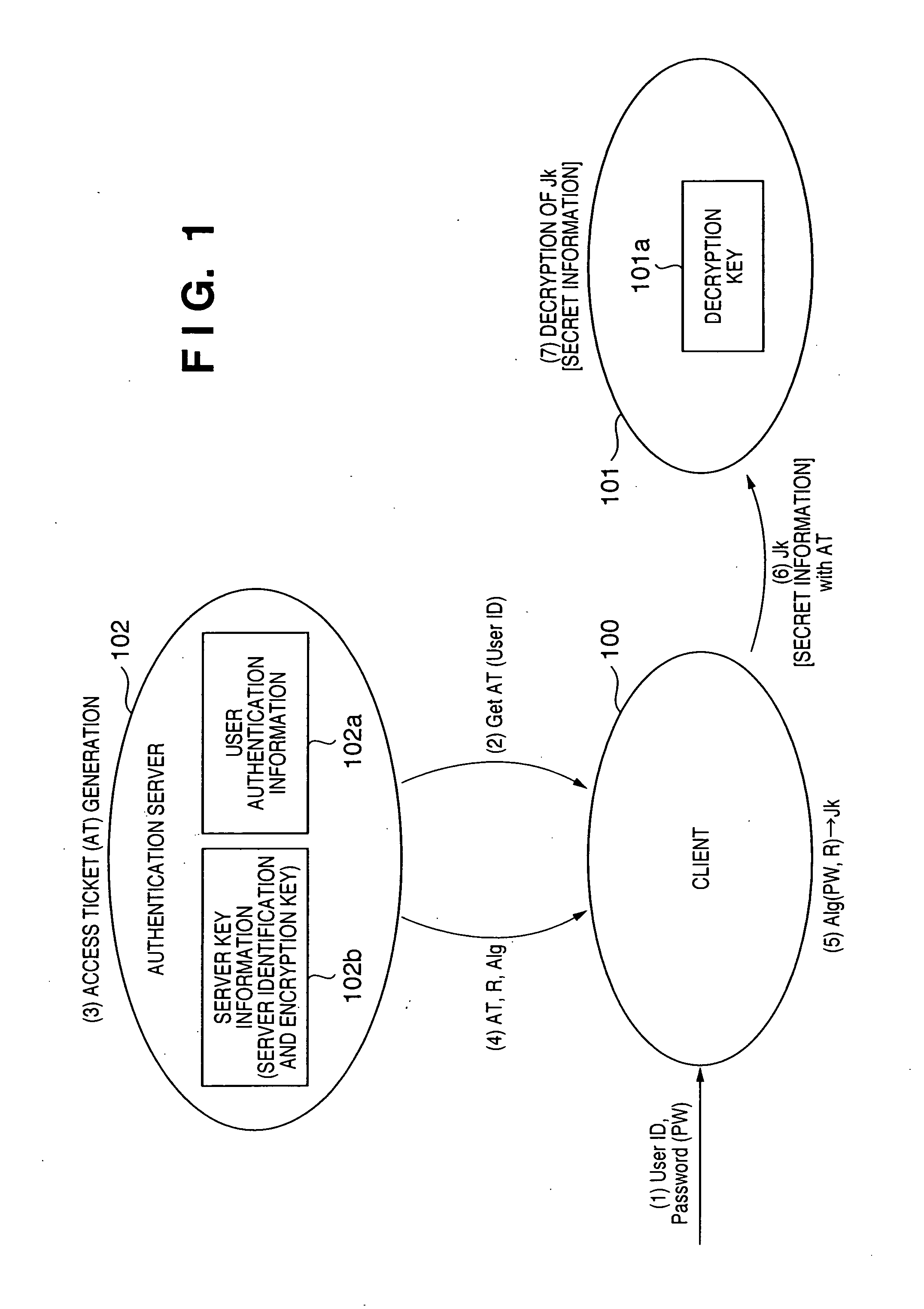
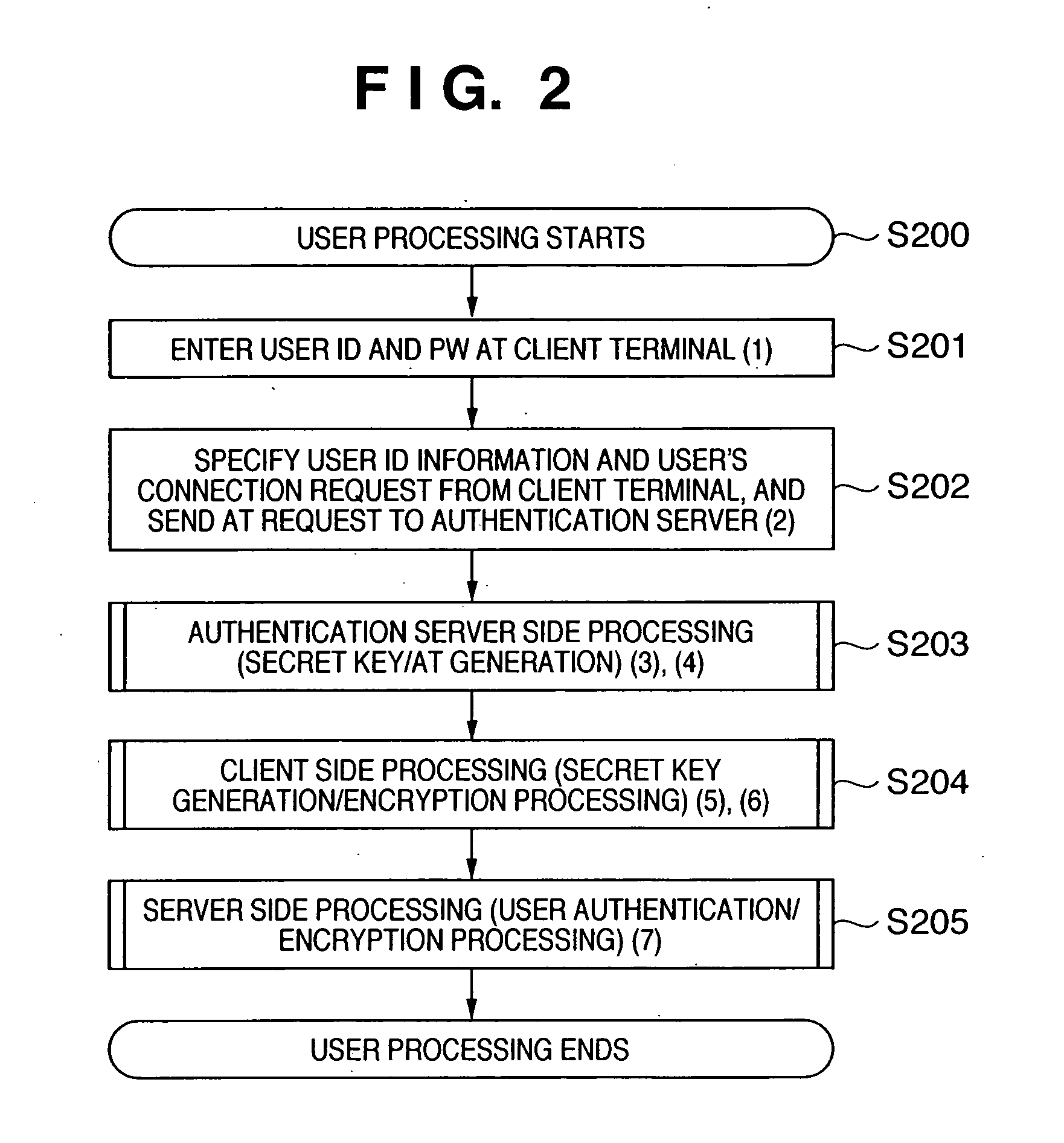
An encrypted communication system according to the present invention comprises an authentication server in which a user password and an encryption key of a server were registered, a client involved in utilization by a user, and a server providing a service. According to the encrypted communication system, shared credentials for the client and the server to conduct encrypted communication are generated separately by the authentication server and the client based on mutually shared information, a ticket is generated in which the credentials that were generated by the authentication server are encrypted with the encryption key by the authentication server, and the client encrypts information to be sent using the credentials generated by the client and attaches the ticket that was acquired from the authentication server to the encrypted information to send the encrypted information and the ticket to the server.
Owner:CANON KK
Methods, apparatuses and systems for transparently intermediating network traffic over connection-based authentication protocols
ActiveUS7343398B1Easy to deployTransparently fits into existing NTLM environmentMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionTraffic capacityComputer network
Methods, apparatuses and systems allowing for the transparent intermediation of network traffic over connection-based authentication protocols. In one embodiment, the present invention allows a proxy to be placed into an NTLM or HTLMv2 environment and have it transparently ensure that NTLM transactions are handled appropriately, such that the proxy can interact (optimize / accelerate) with the authenticated content without breaking the authentication scheme. Embodiments of the present invention provide a proxy solution that is easily deployed and transparently fits into an existing NTLM environment.
Owner:CA TECH INC
System and method for ensuring security with multiple authentication schemes
InactiveUS7308580B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsThird partyInternet privacy
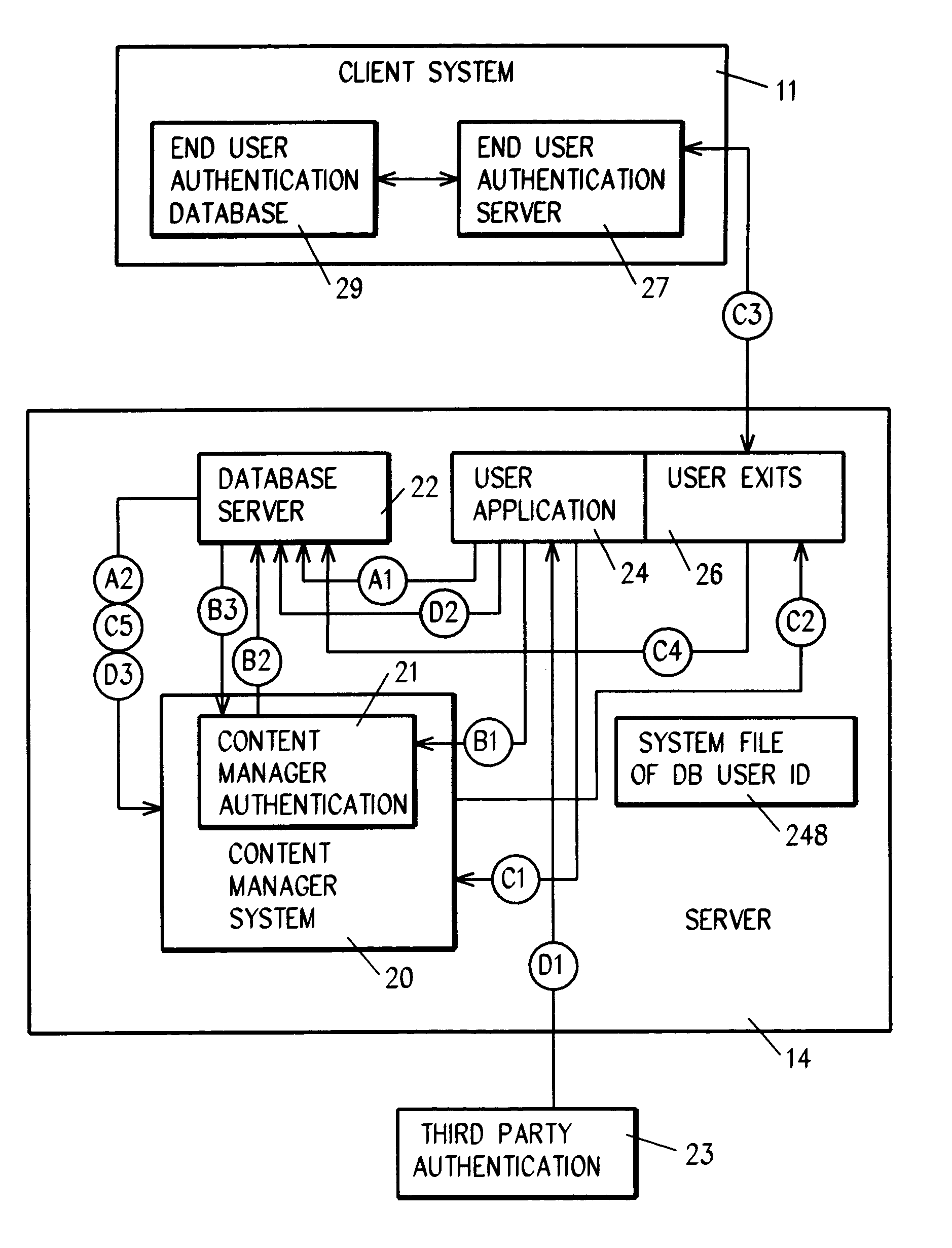
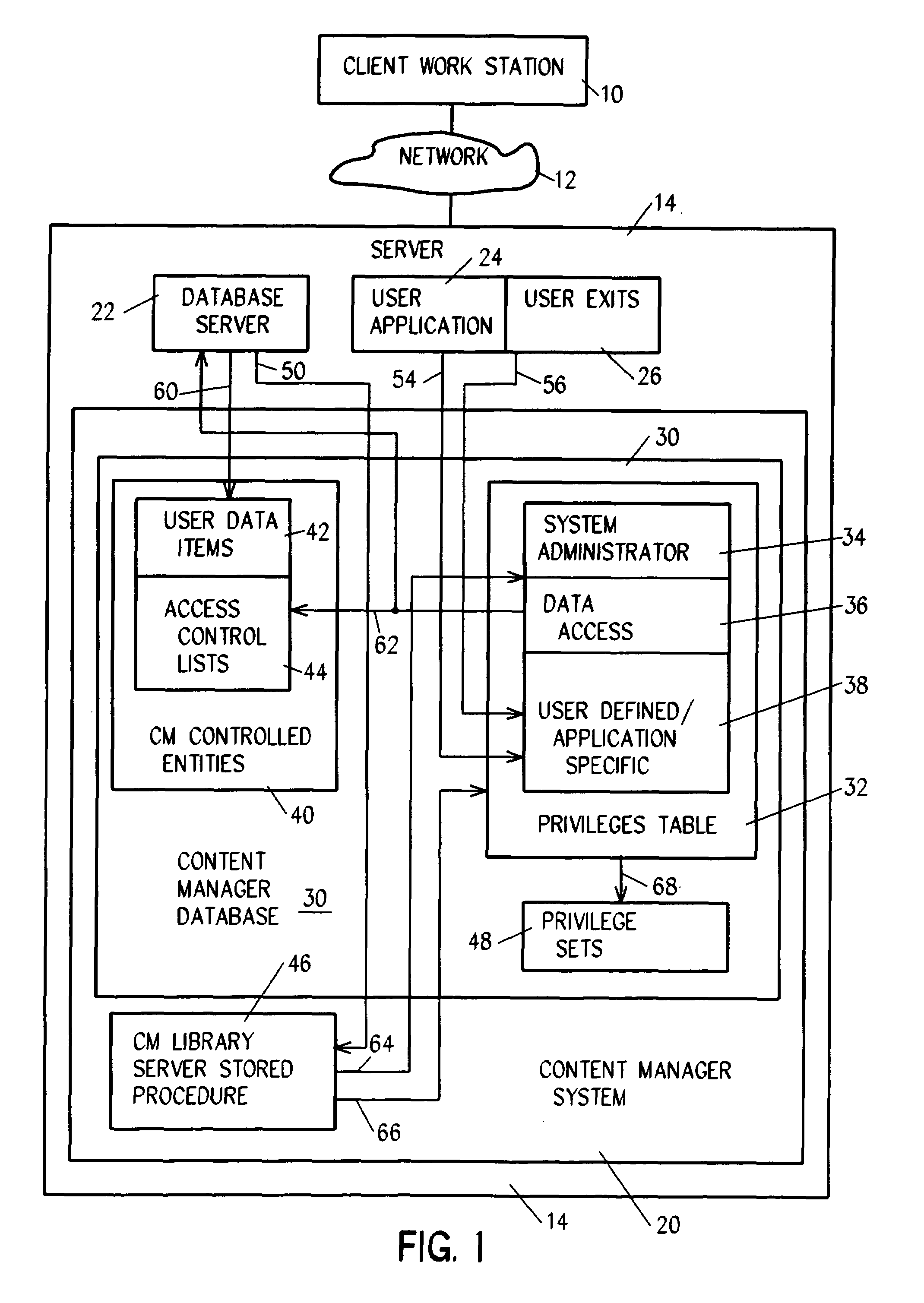
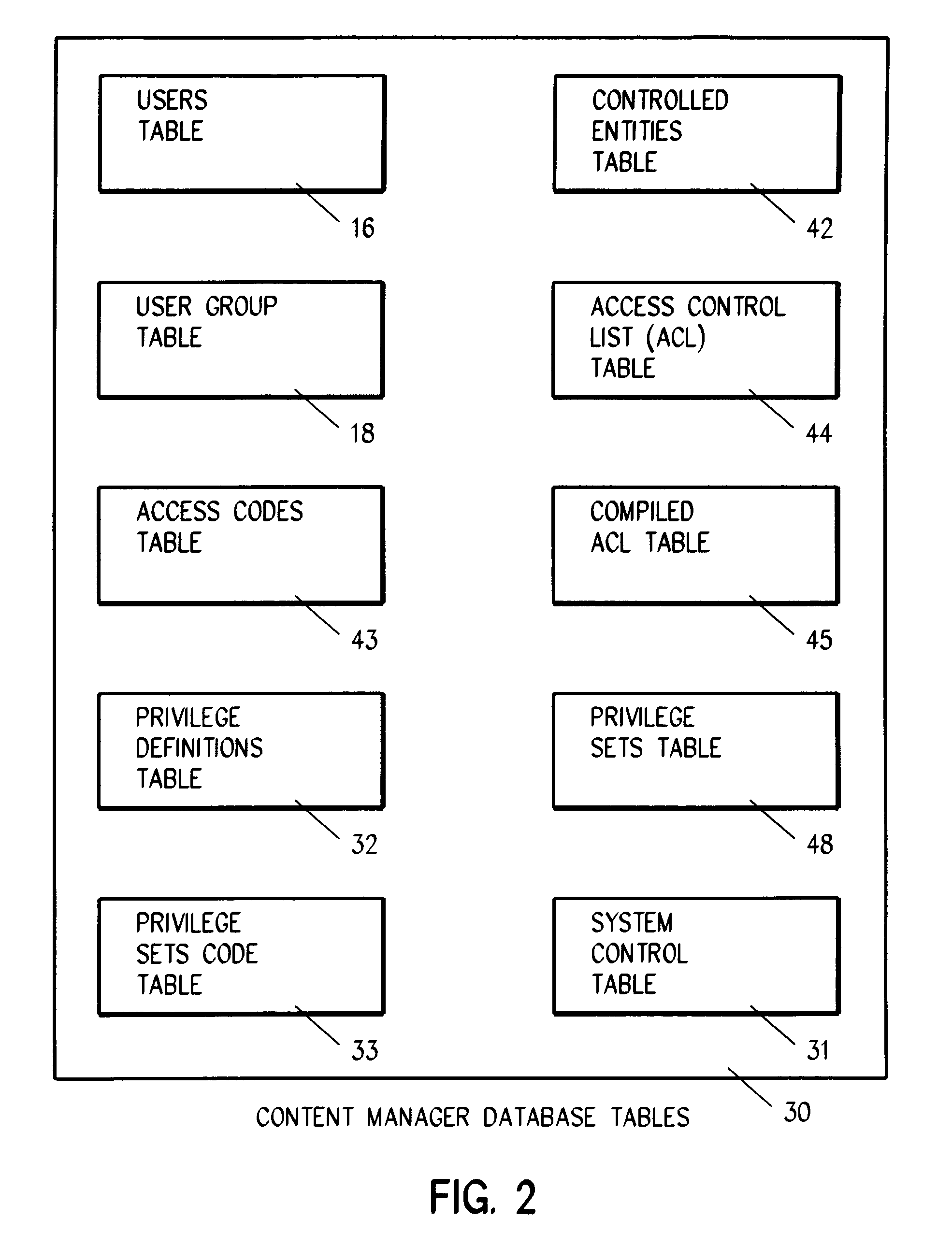
System for authenticating a user for logon to a content manager running on top of a database manager. A connect procedure connects the user to a database manager; and then a logon procedure logs on the user to the content manager selectively responsive to the user connecting to the database manager; the user being authenticated by a third party by way of a user exit or a trusted logon environment and privilege; or the user being authenticated by the content manager.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for a sidecar authentication mechanism
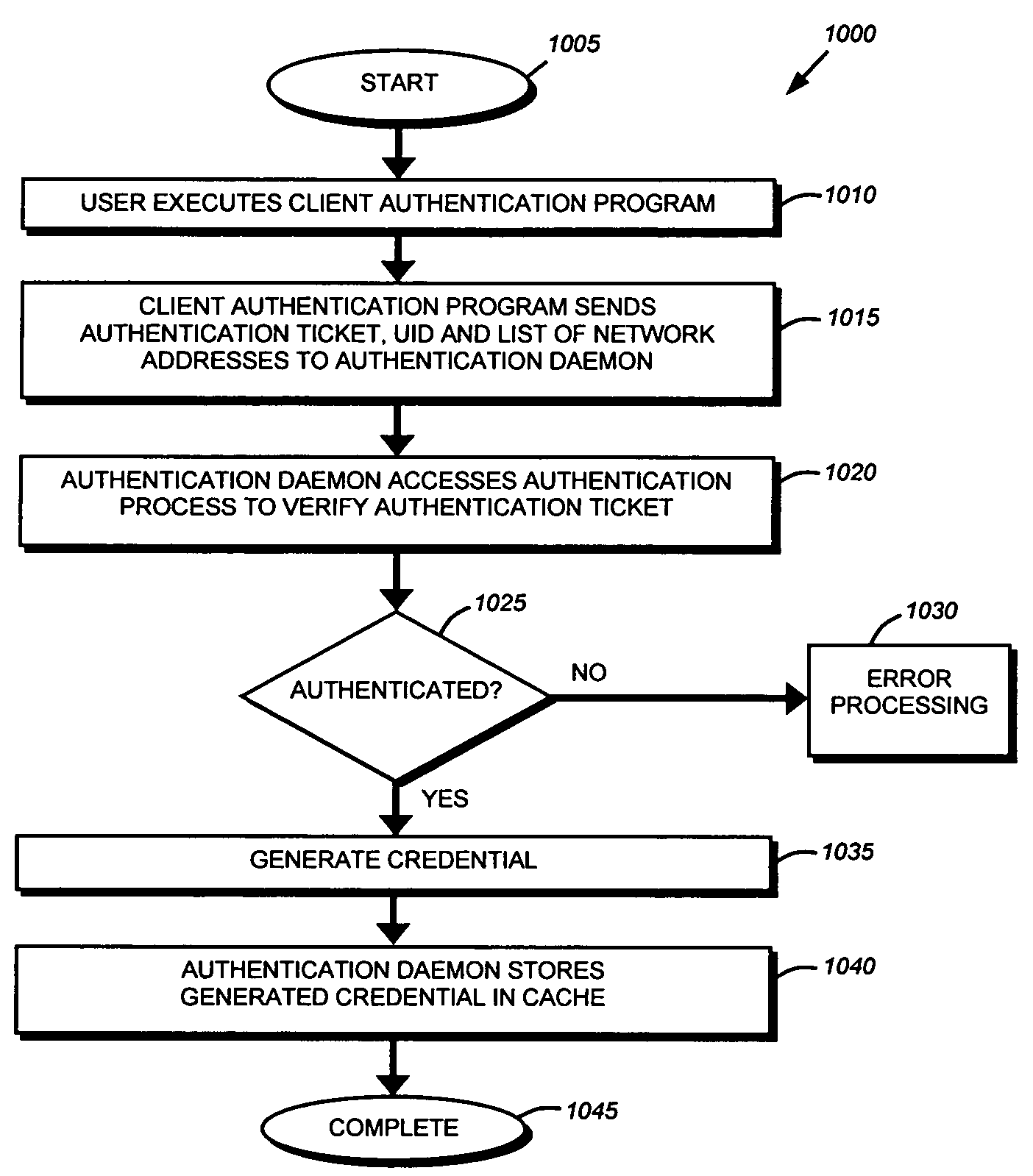
ActiveUS7519813B1Improve securityExpand accessDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationProgram validationFile system
A system and method for authenticating an unauthenticated file level protocol using a sidecar authentication mechanism. A client transmits an authentication ticket, UID and list of network addresses to an authentication daemon of a storage system. The authentication daemon verifies the user identity and generates a file system credential that is stored in a cache indexed by an authentication tuple. Received data access operations from a client are compared to authentication tuples by UID and network address and the file system utilizes the stored credential for processing the data access operation.
Owner:NETWORK APPLIANCE INC
Log-on service providing credential level change without loss of session continuity
InactiveUS6944761B2Improve abilitiesDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordInformation resource
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided for multiple information resources. Rather than specifying a single authentication scheme for all information resources, the security architecture associates trust-level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are employed depending on the trust-level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed. Once credentials have been obtained for an entity and the entity has been authenticated to a given trust level, access is granted, without the need for further credentials and authentication, to information resources for which the authenticated trust level is sufficient.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Scored Factor-Based Authentication
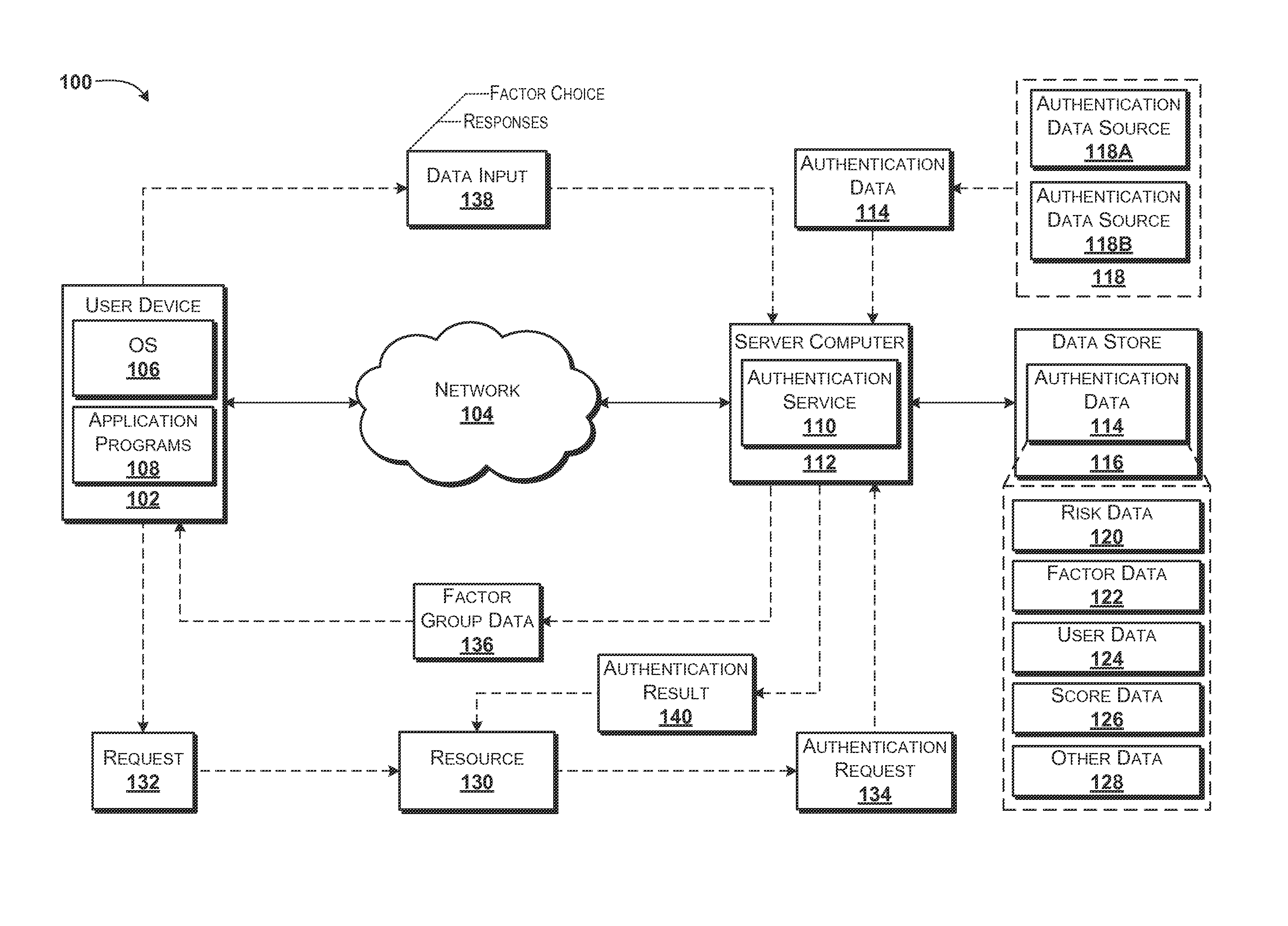
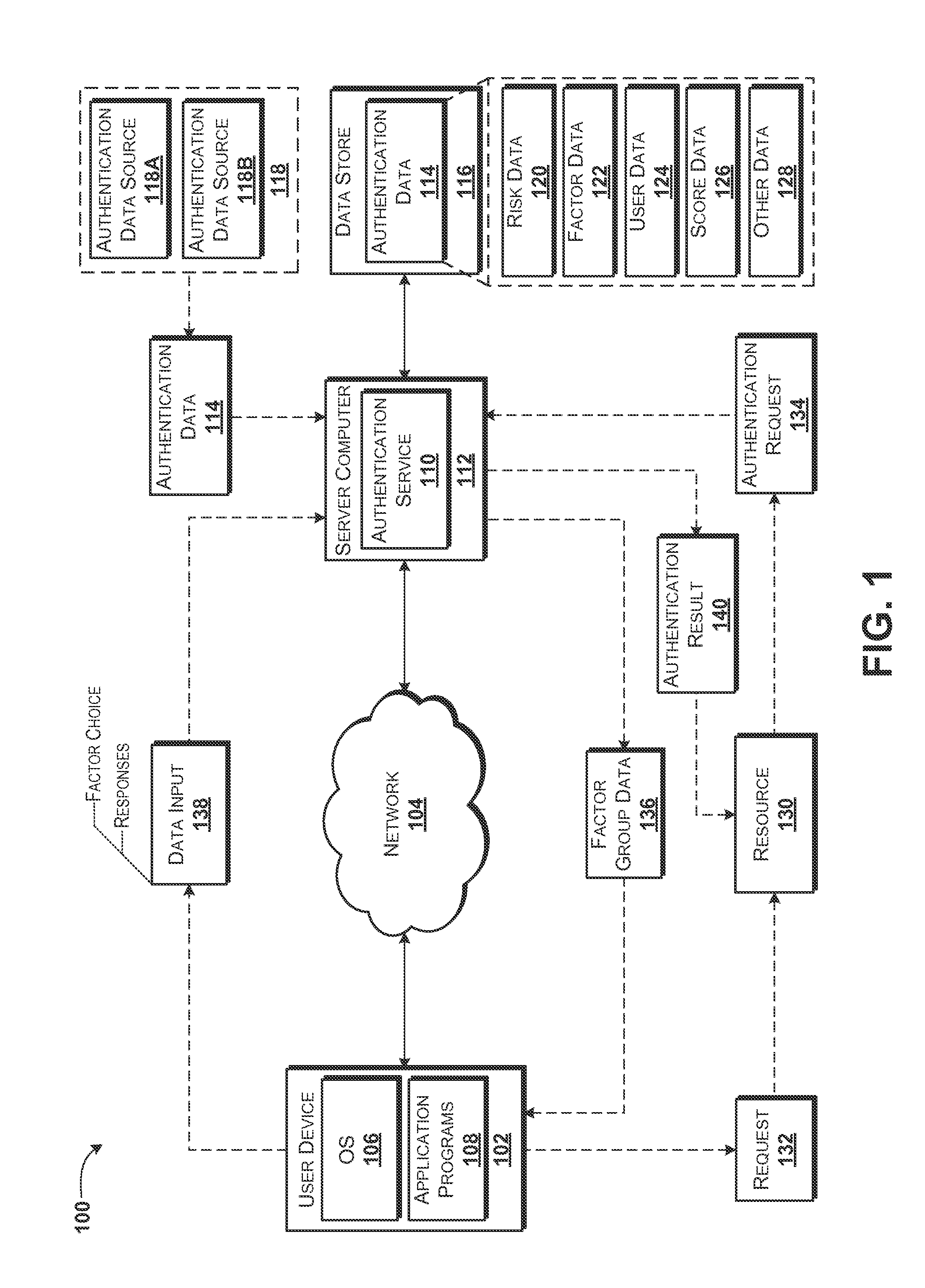
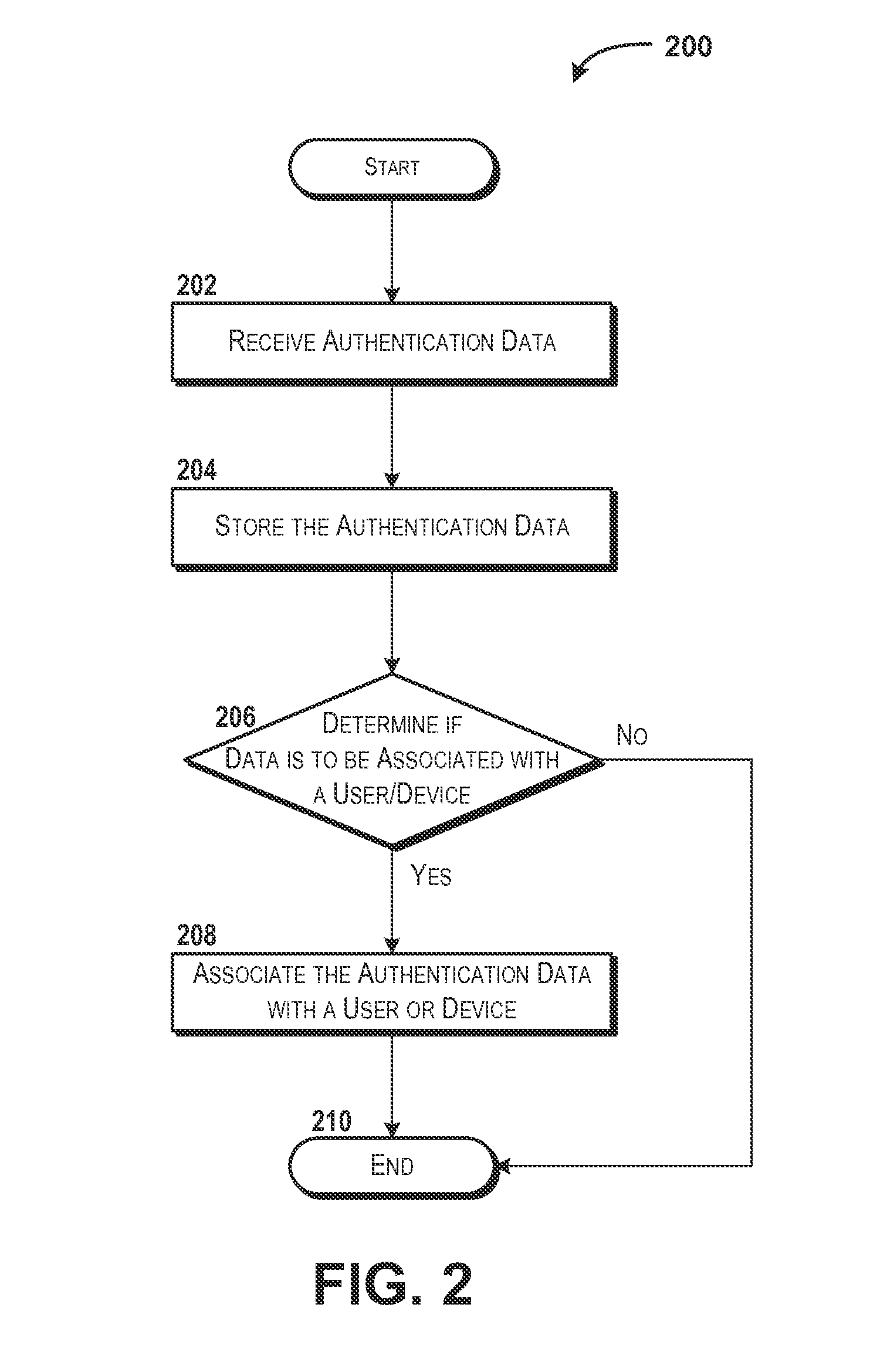
ActiveUS20150089585A1Improve security levelDigital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsFactor baseAuthentication server
Concepts and technologies are disclosed herein for scored factor-based authentication. A verification service can receive an authentication request from a requestor, wherein the authentication request identifies a transaction. The verification service can determine a risk associated with the transaction, an authentication score based upon the risk, a plurality of groups of authentication factors, each of which the authentication score. The verification service can provide factor group data identifying the plurality of groups of authentication factors to the requestor.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Fast byzantine paxos
ActiveUS7620680B1Accurate authenticationProvide securityMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDigital signatureClient-side
A distributed computing system can operate in the face of malicious failures on the part of some of its constituent devices, and provide a minimum of message delays between receiving a client request and providing a response, when each device within the system verifies the sender of any message it receives, and the propriety of the message. The sender can be verified through message authentication schemes or digital signature schemes. The propriety of a message can be verified by receiving a sufficiently large number of equivalent, properly authenticated messages. If the number of malicious devices is represented by the variable “M”, a sufficient number of equivalent, properly authenticated messages to verify that the message is true can be any number of messages greater than M. Furthermore, to verify that a leader device is not maliciously submitting different proposals to different devices using the same proposal number, a quorum of devices can be required to select a proposal, where a quorum is a sufficiently large number of devices such that any other quorum has, as a majority of its devices, non-malicious devices from the first quorum. Therefore, the distributed computing system can operate properly with M number of malicious failures and F number of total failures, and with a minimum of message delays, if the number of constituent devices in the distributed computing system is greater than 3F+2M. Additionally, if the distributed computing system can revert to a more traditional algorithm if too many devices fail or become malicious, it can use a message-delay-reducing algorithm while having as few as 2Q+F+2M+1 constituent devices, where Q is the number of devices that can fail and still allow the system to use a message-delay-reducing algorithm.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com