Patents
Literature
389 results about "Trust level" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
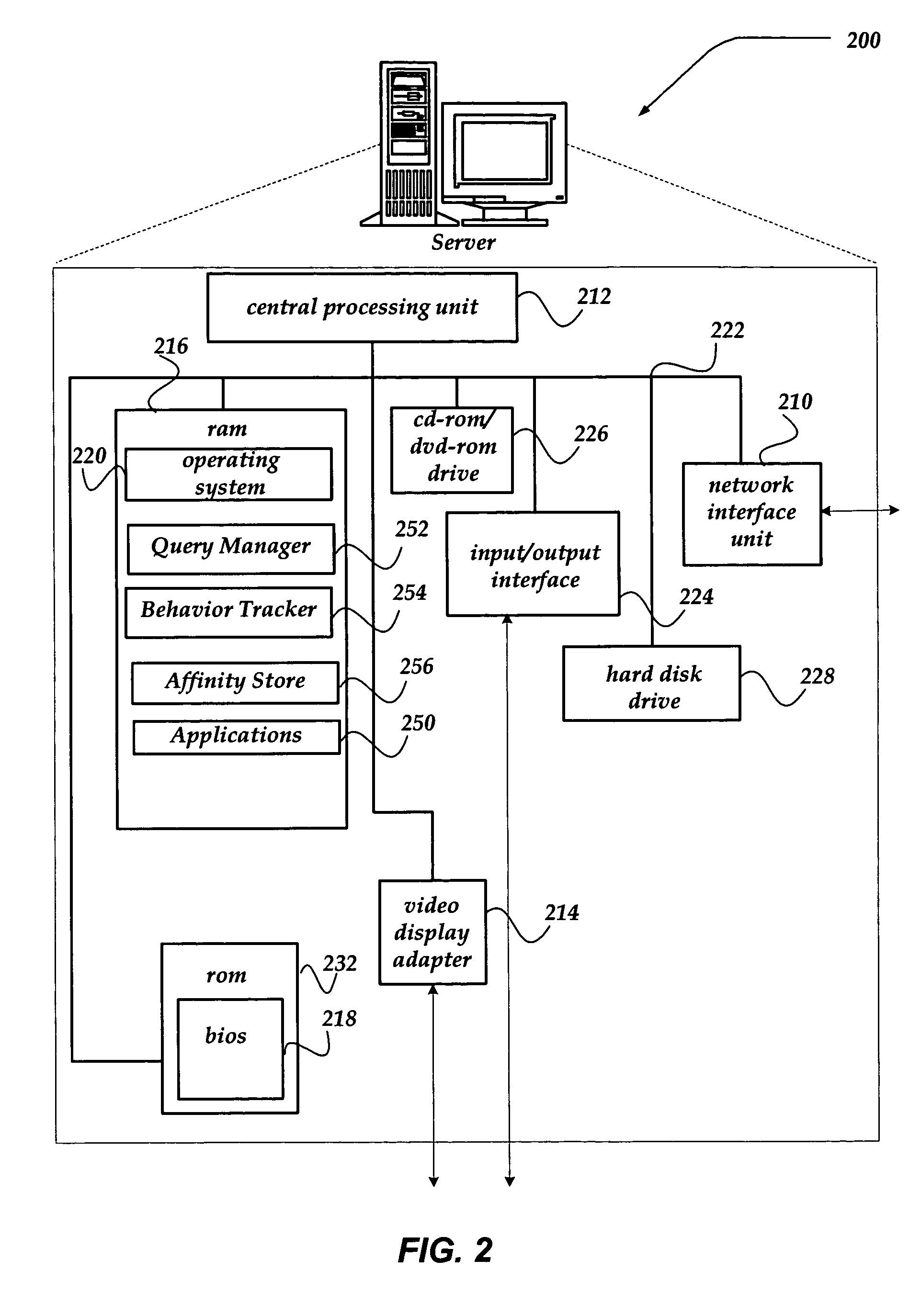
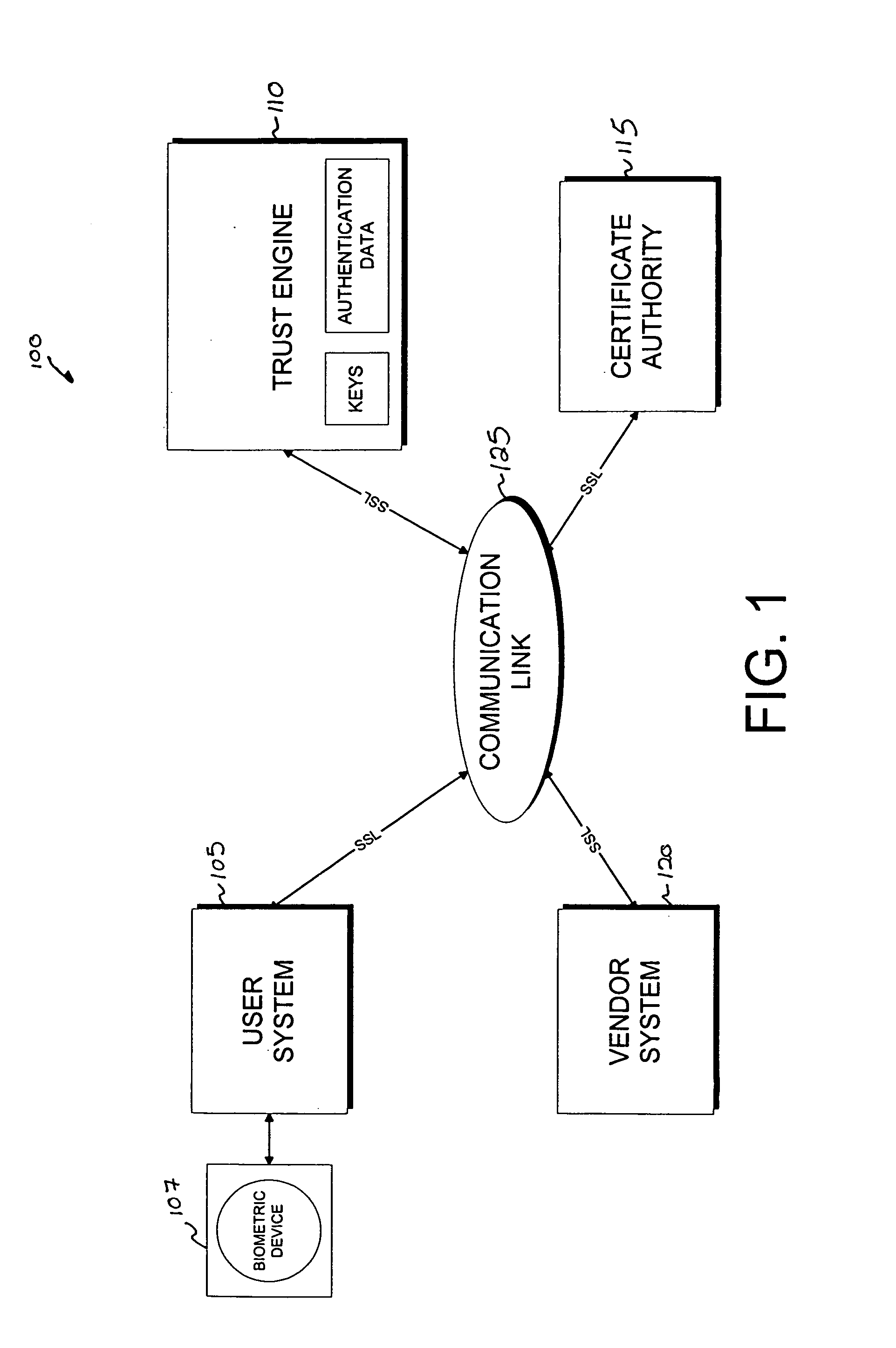
Trust Level. The Trust Level determines the actions that a program is allowed to perform. The Trust Levels are Super, Trusted, Restricted, Ask, Kill, and No Enforcement. A program’s Trust Level setting is determined by its policy. ZoneAlarm security software assigns policies to known programs automatically.
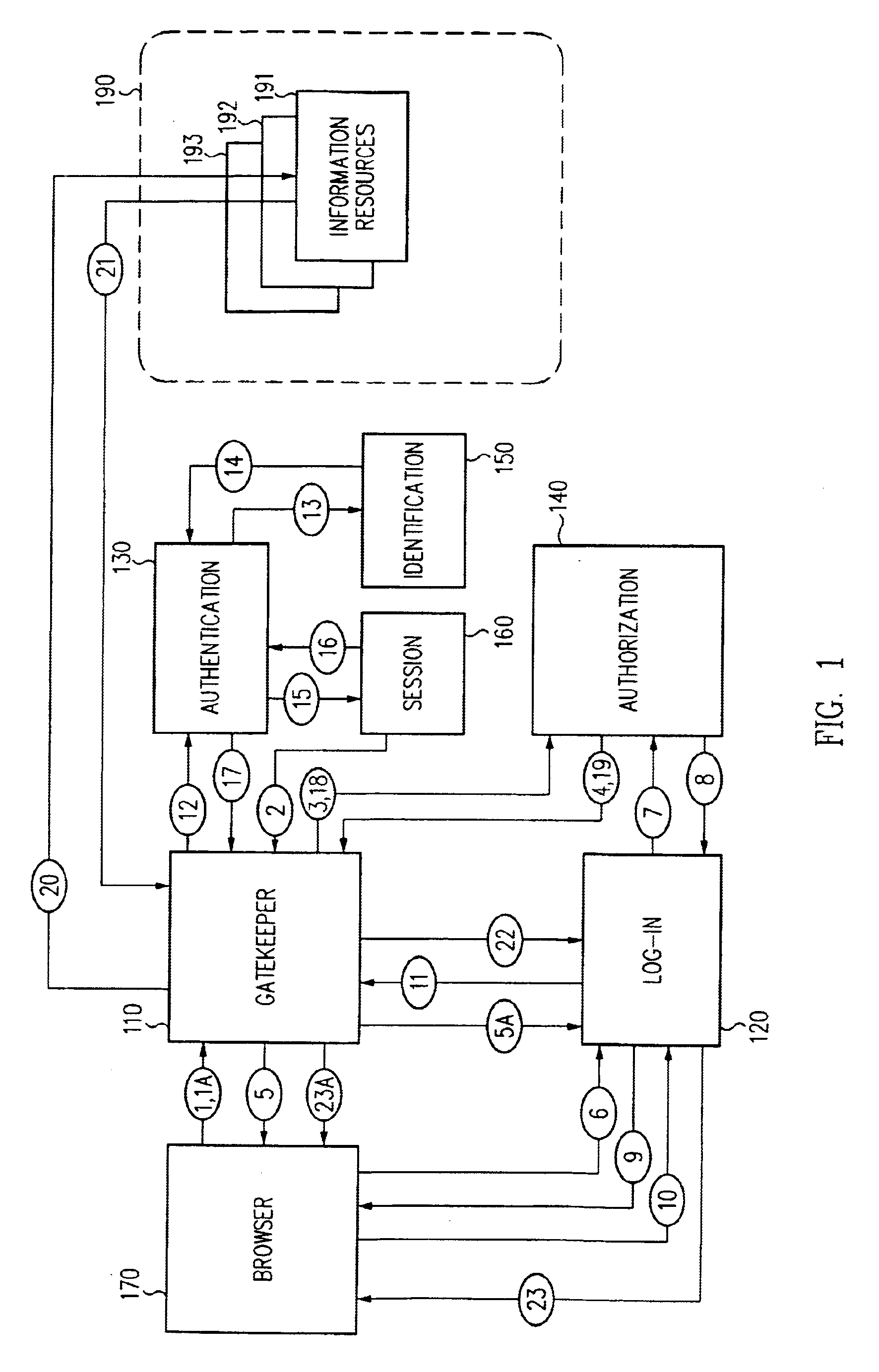
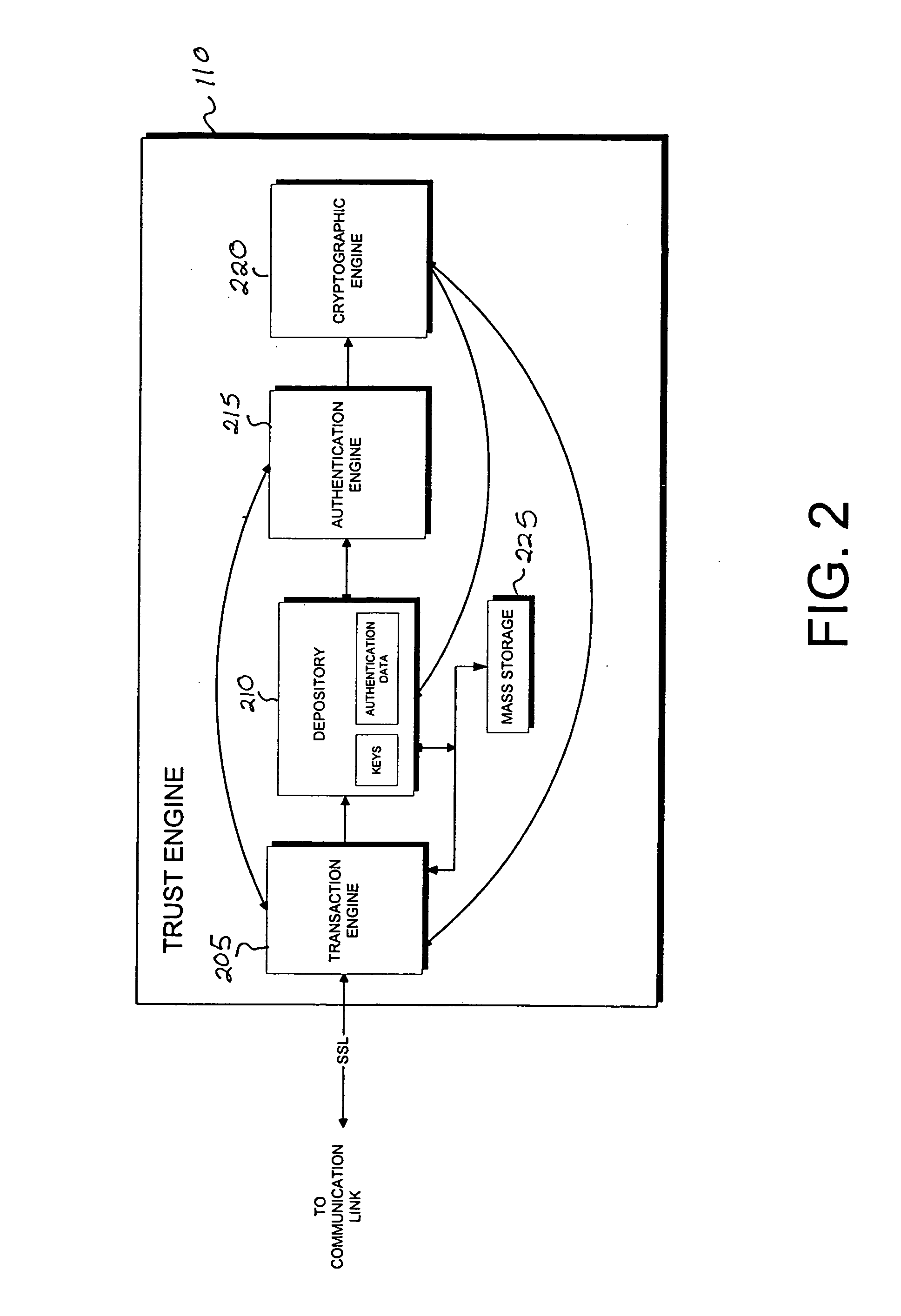
Distributed administration of access to information
InactiveUS6408336B1Digital data processing detailsMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkInformation resource
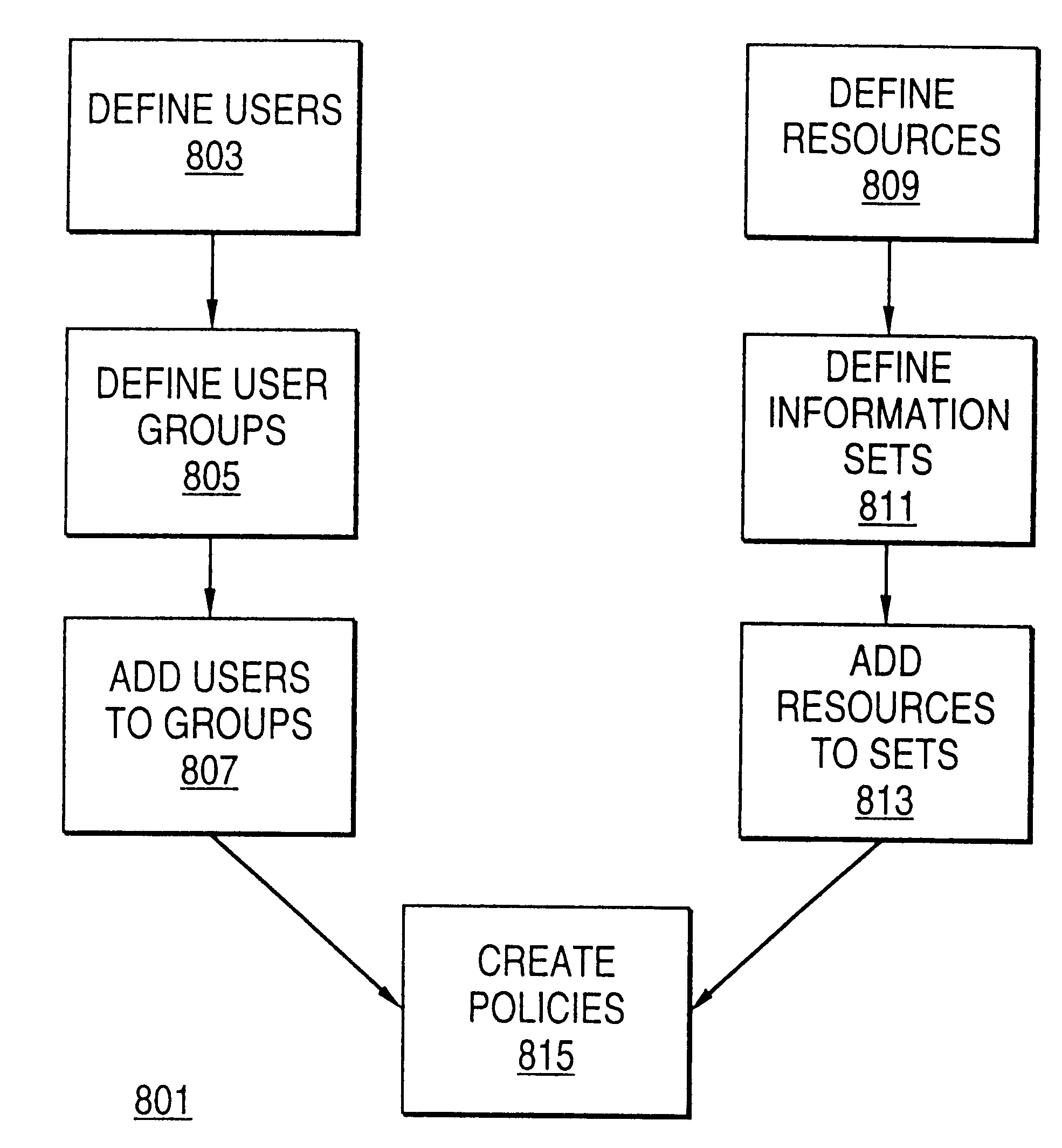
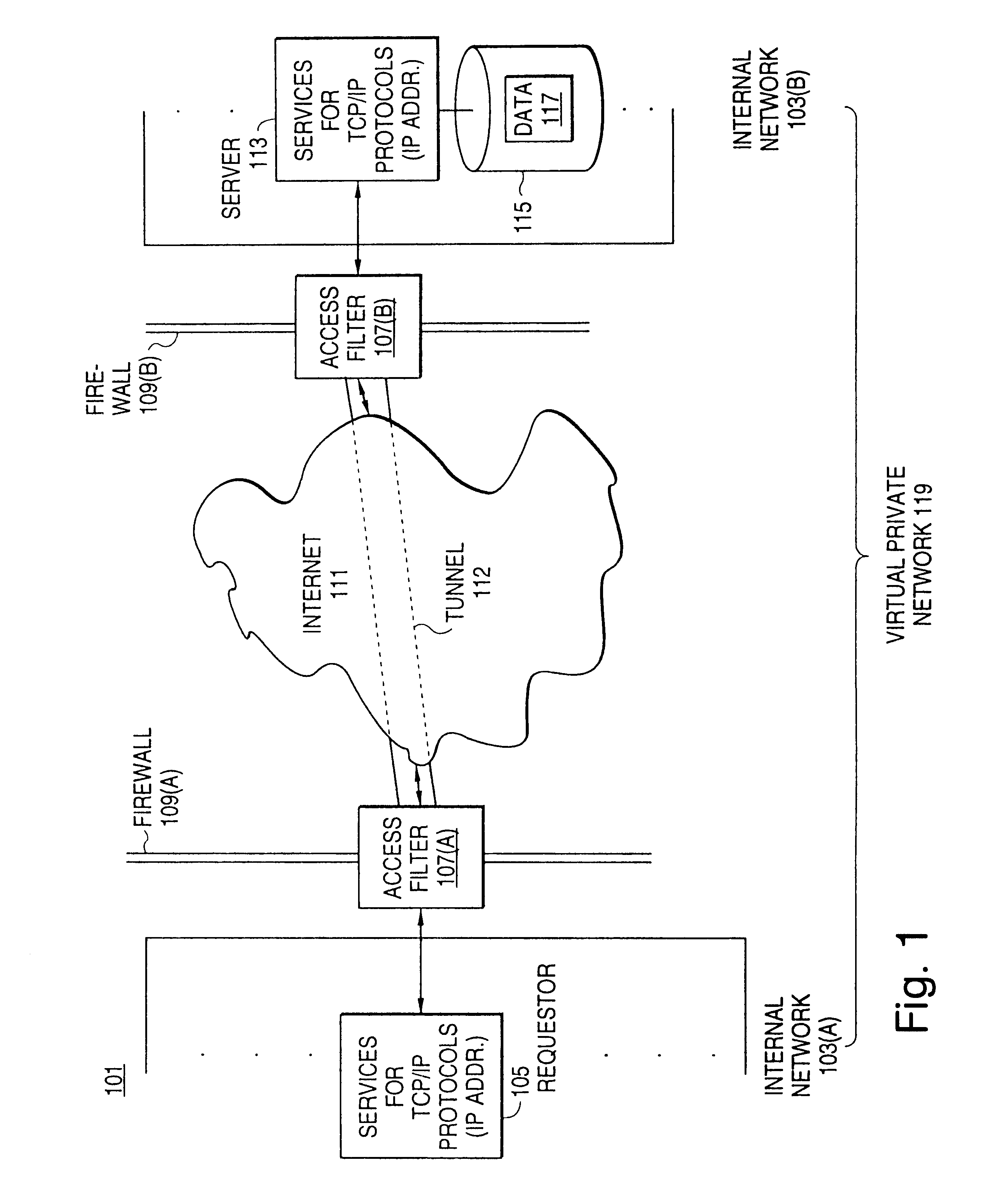
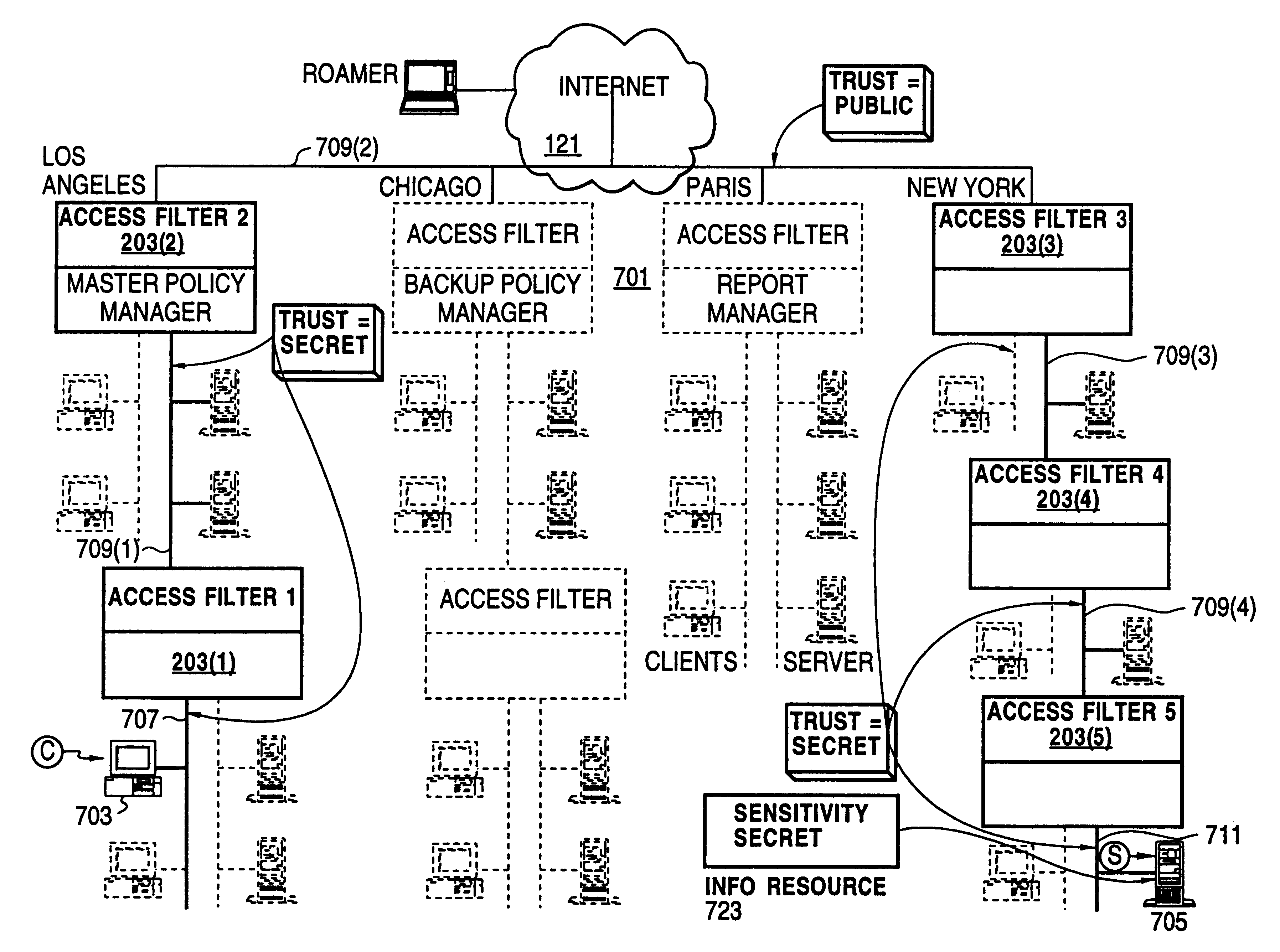
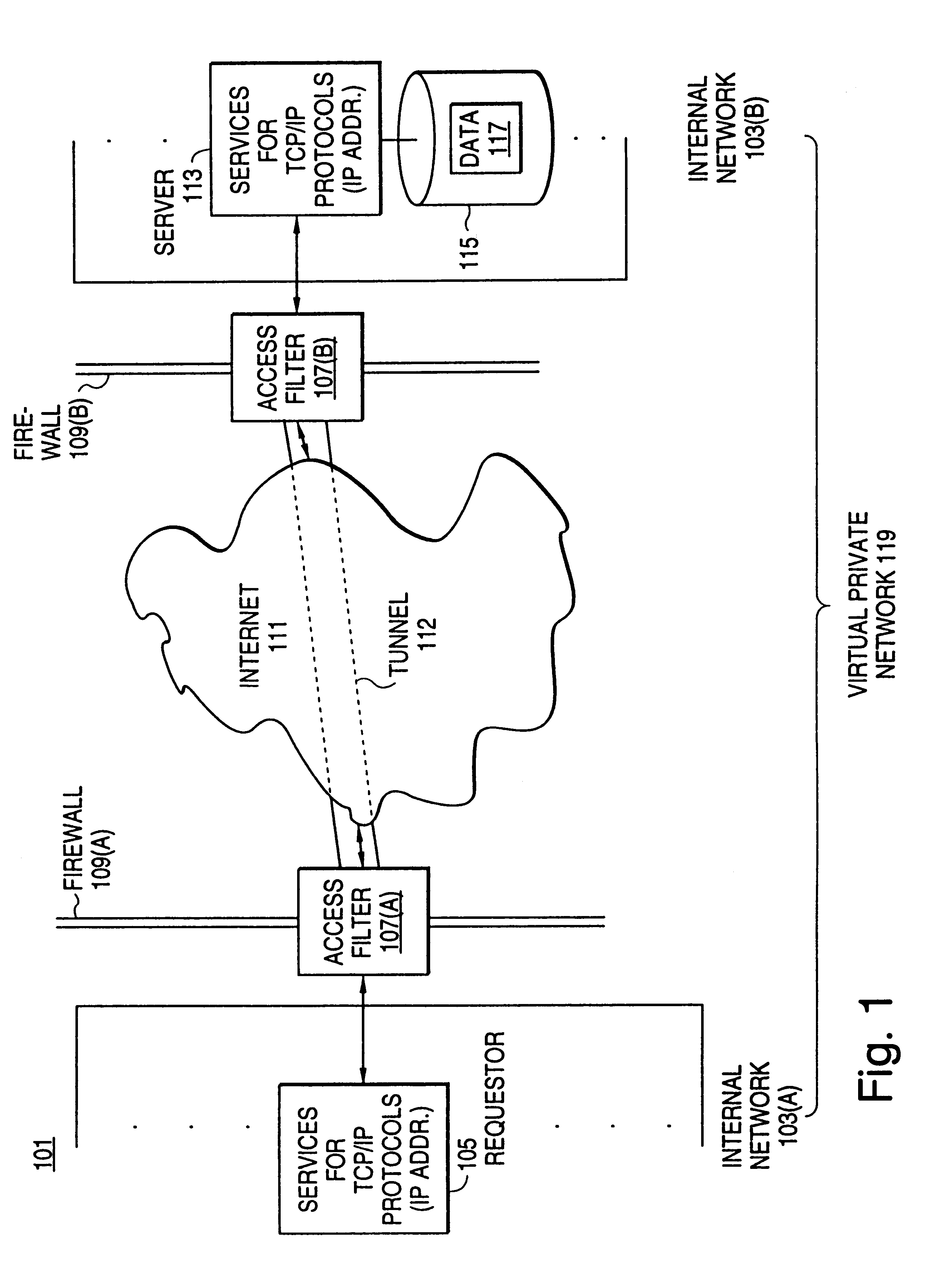
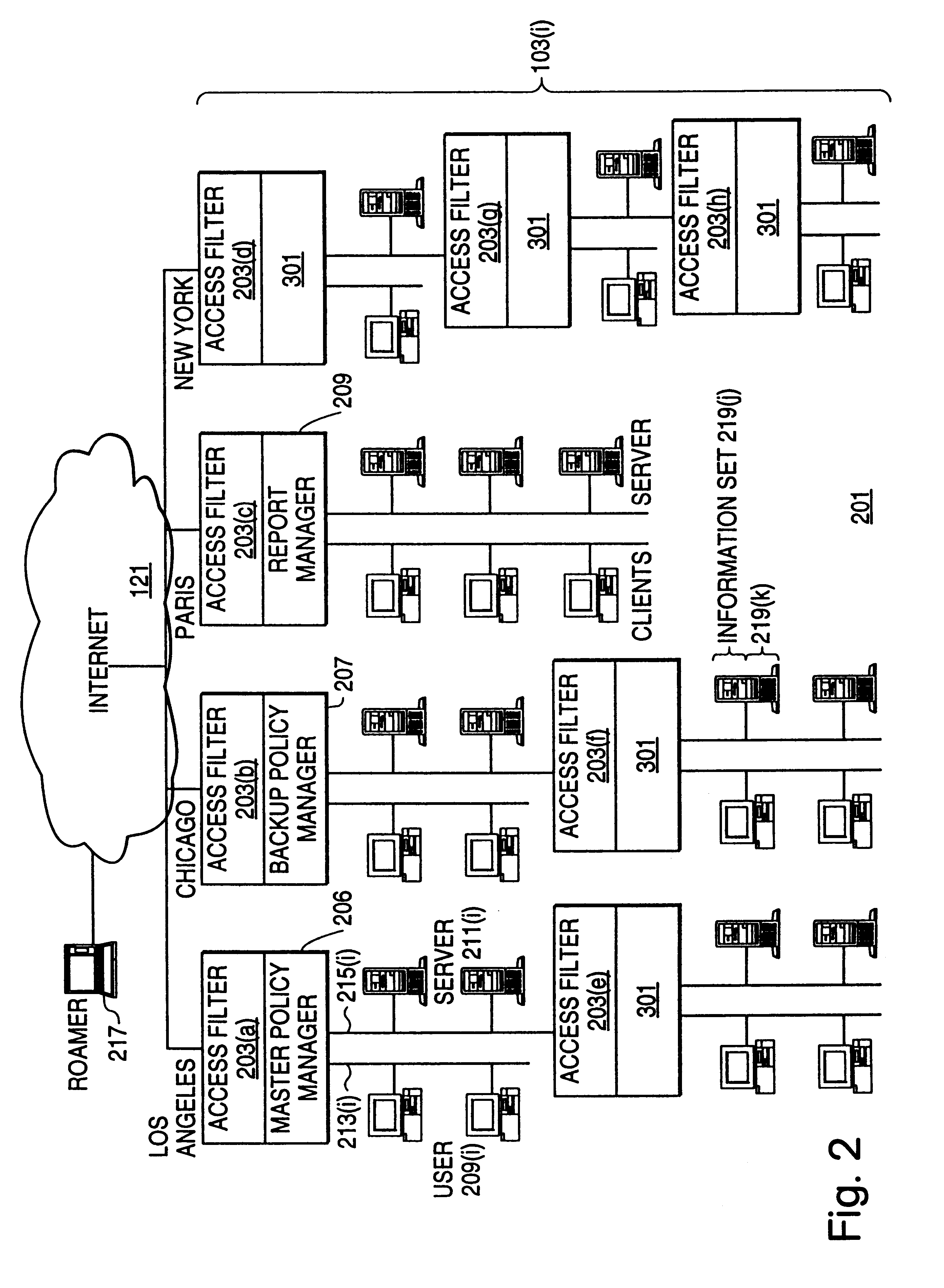
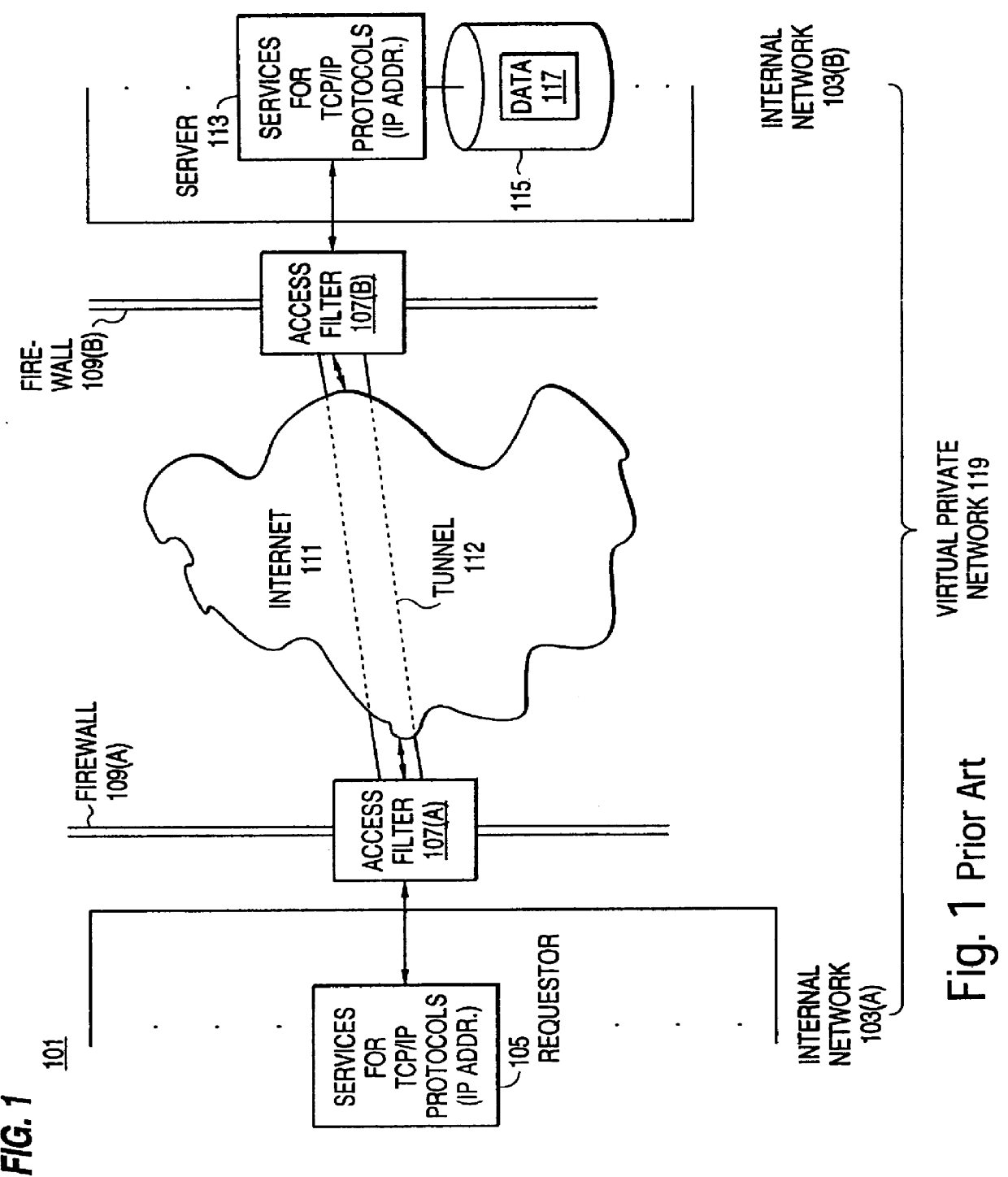
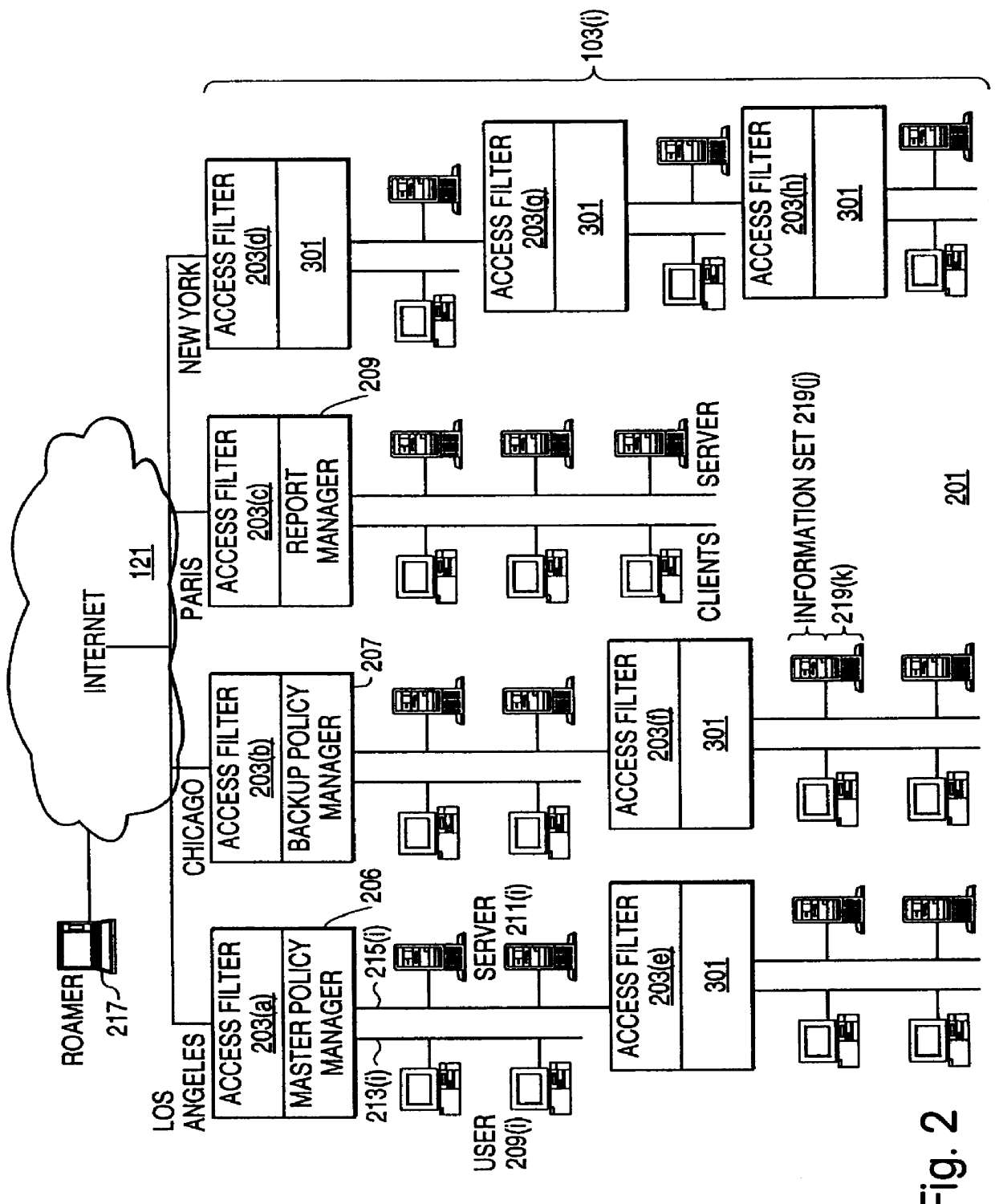
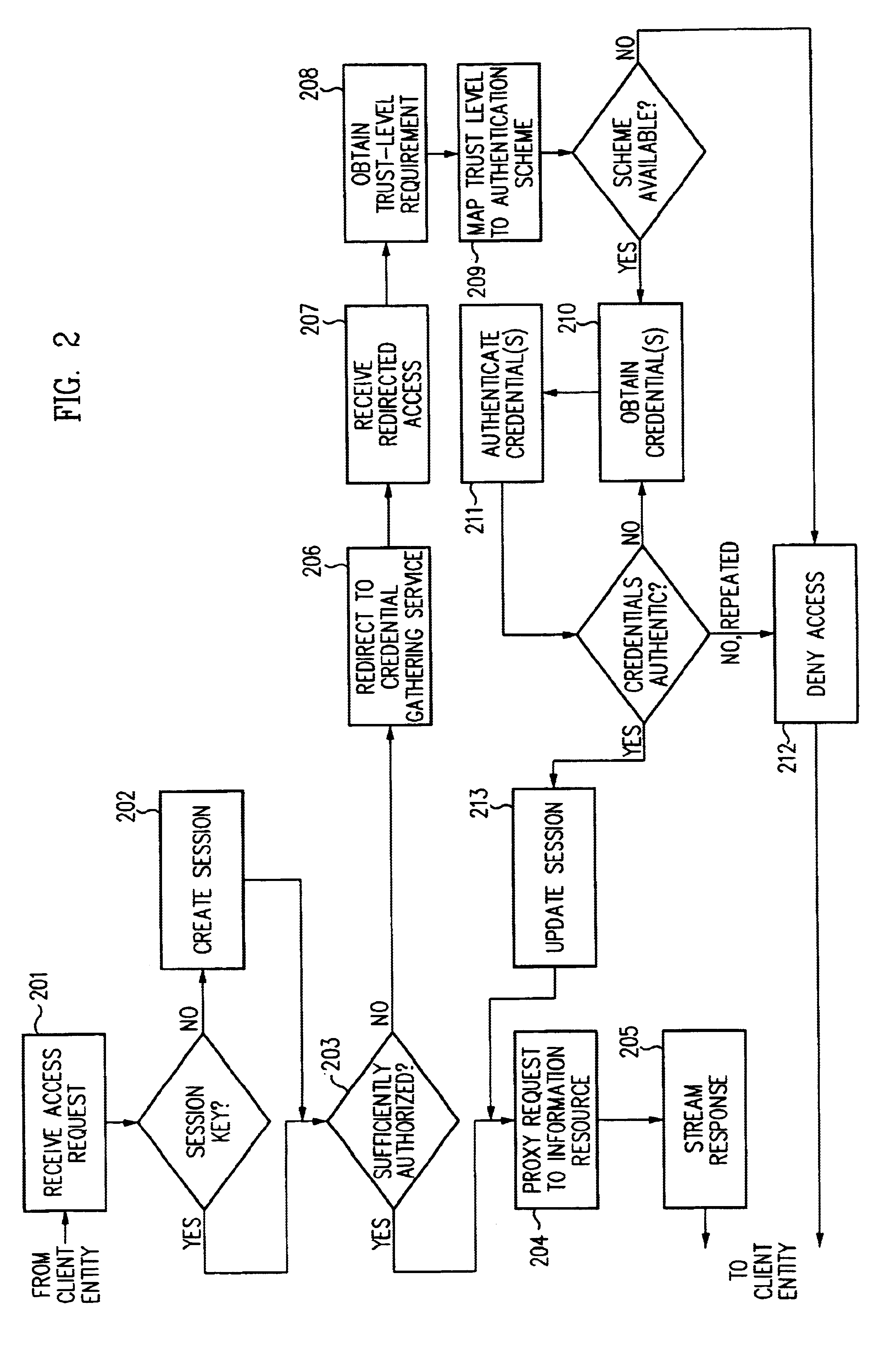
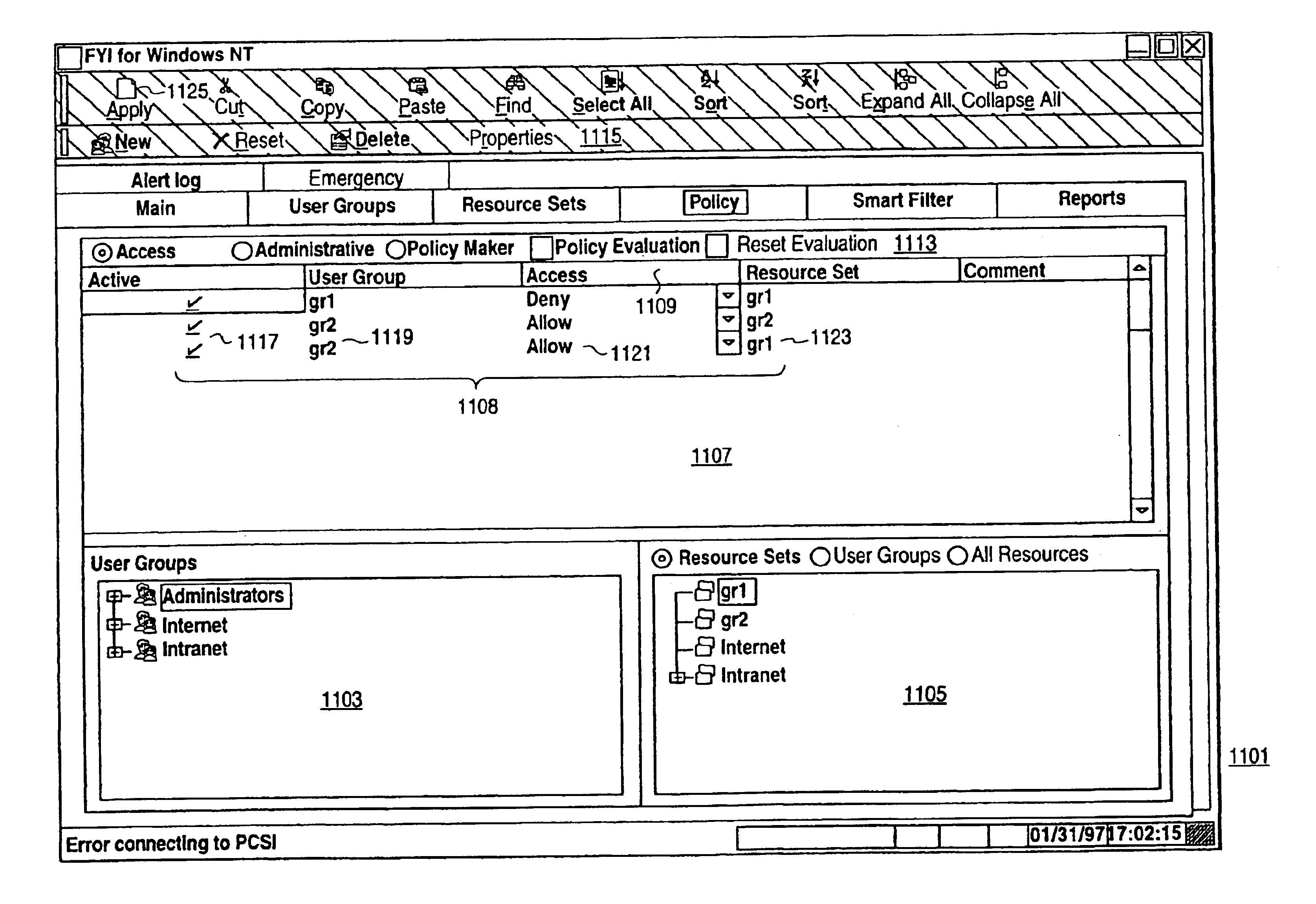
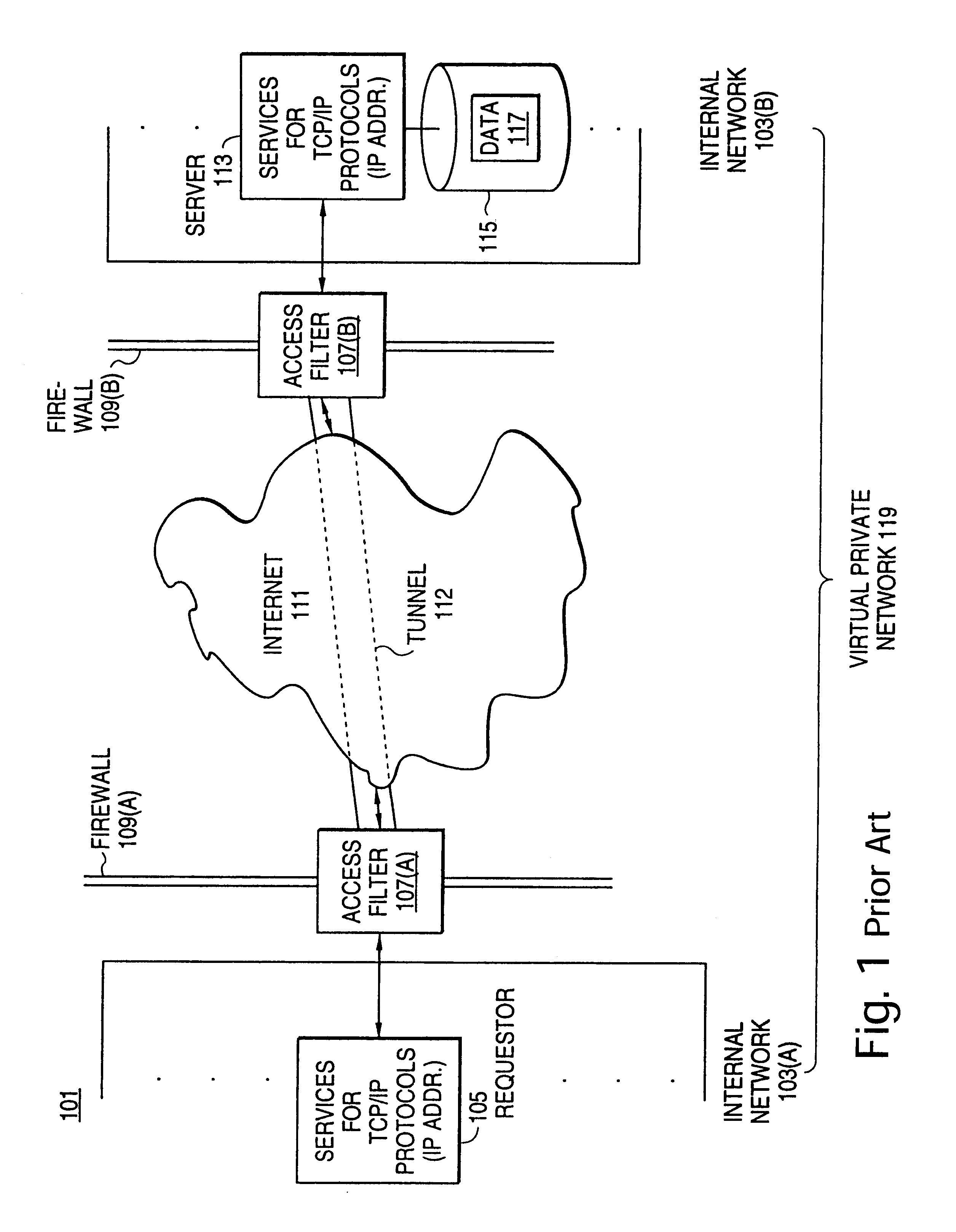
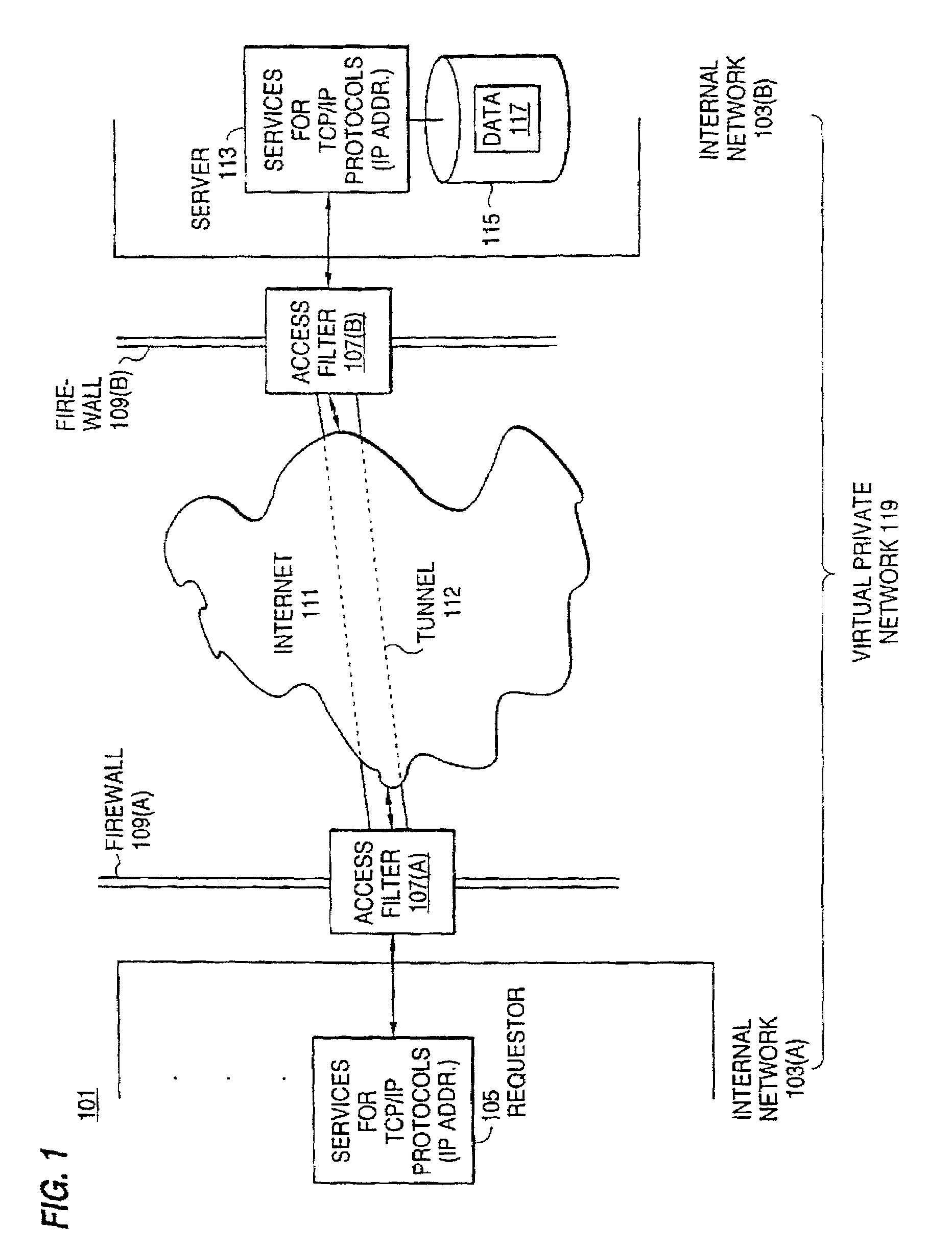
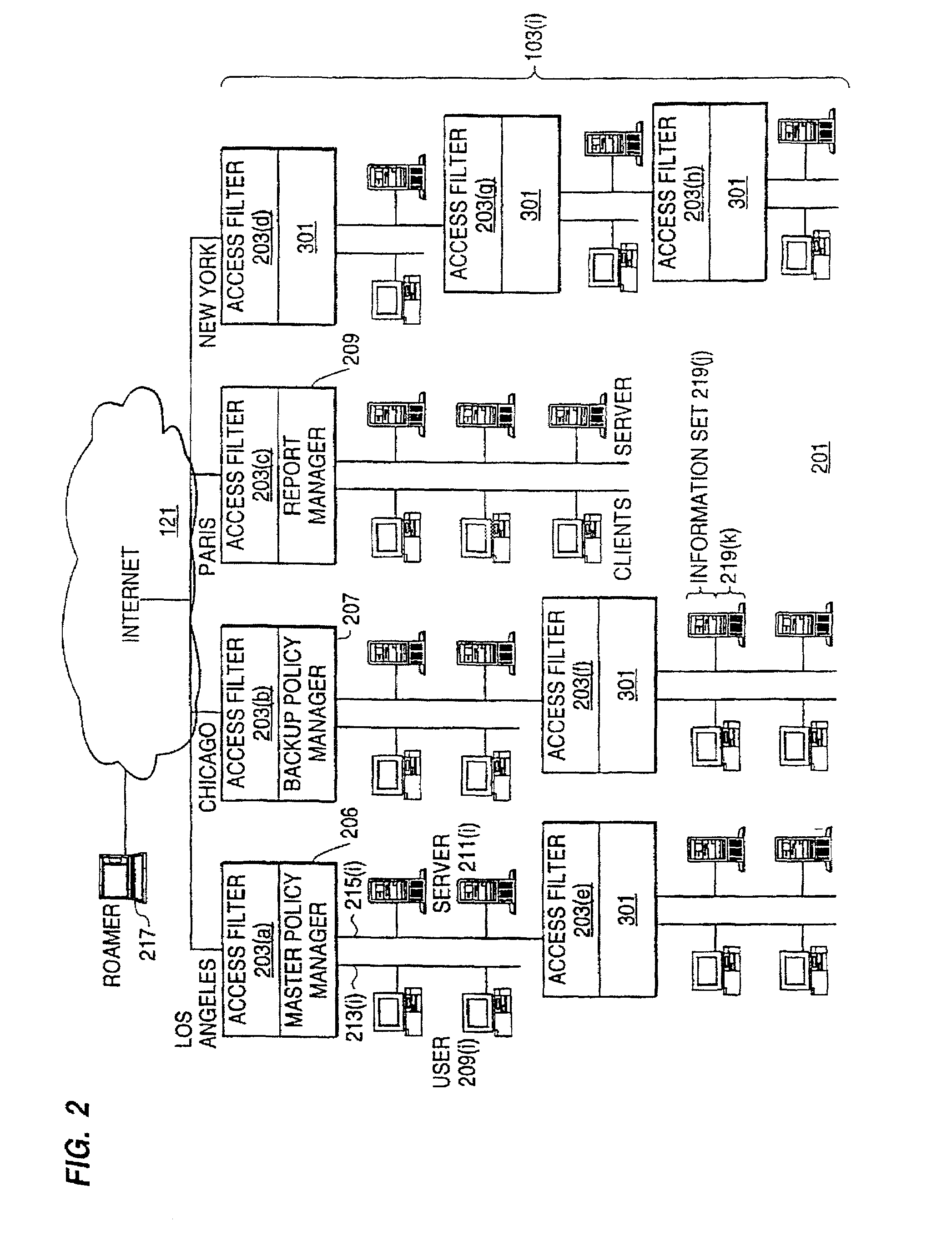
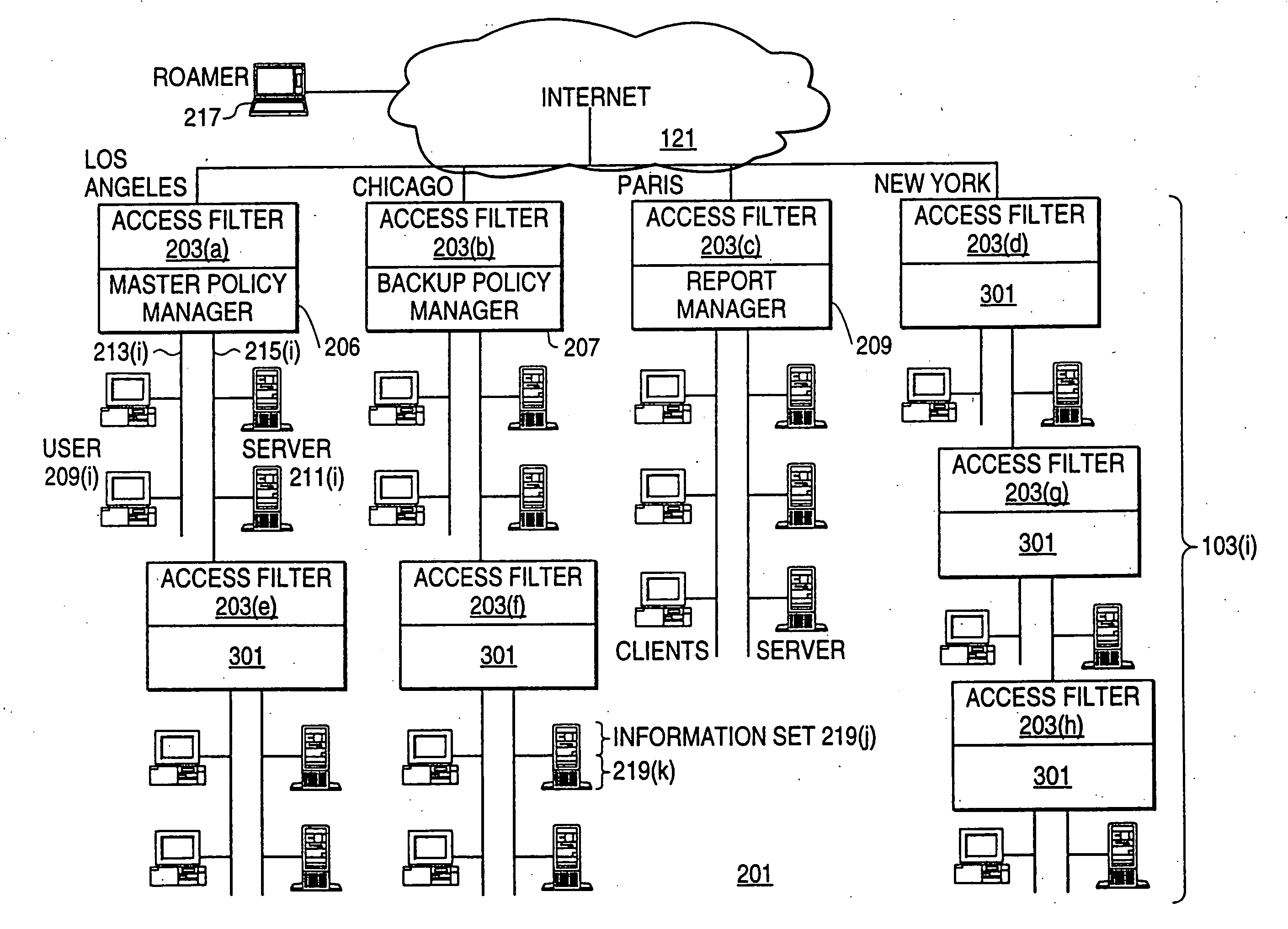
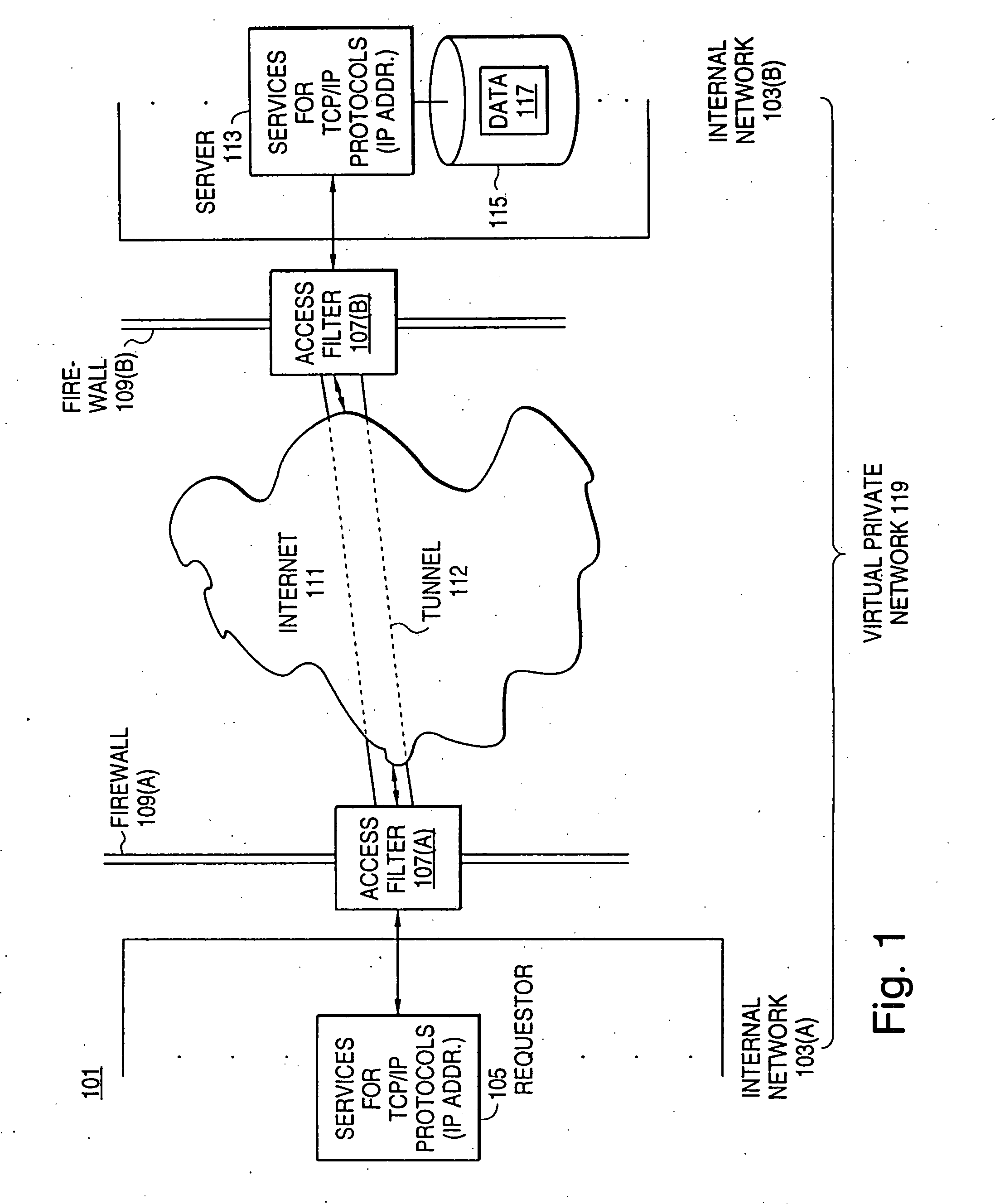
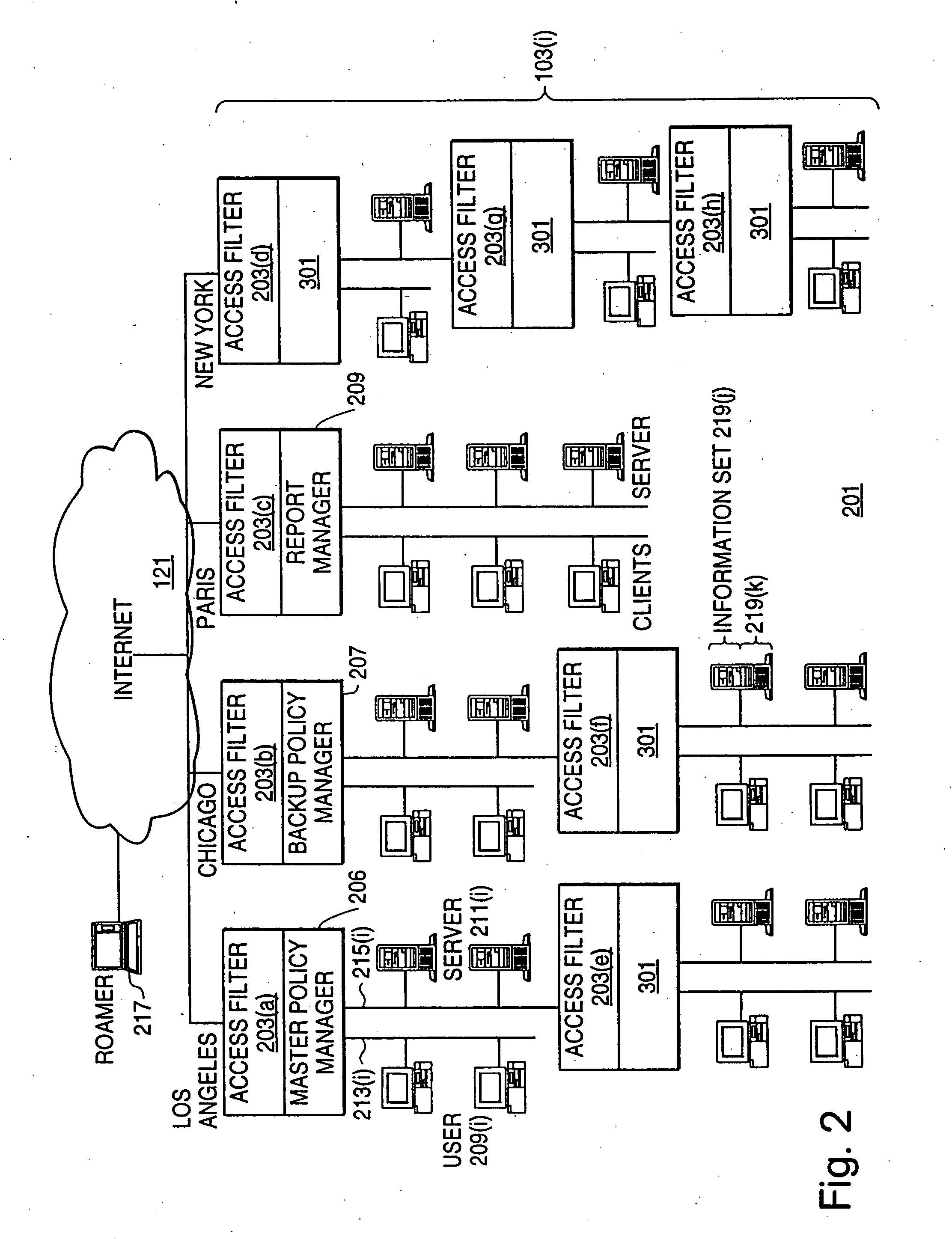
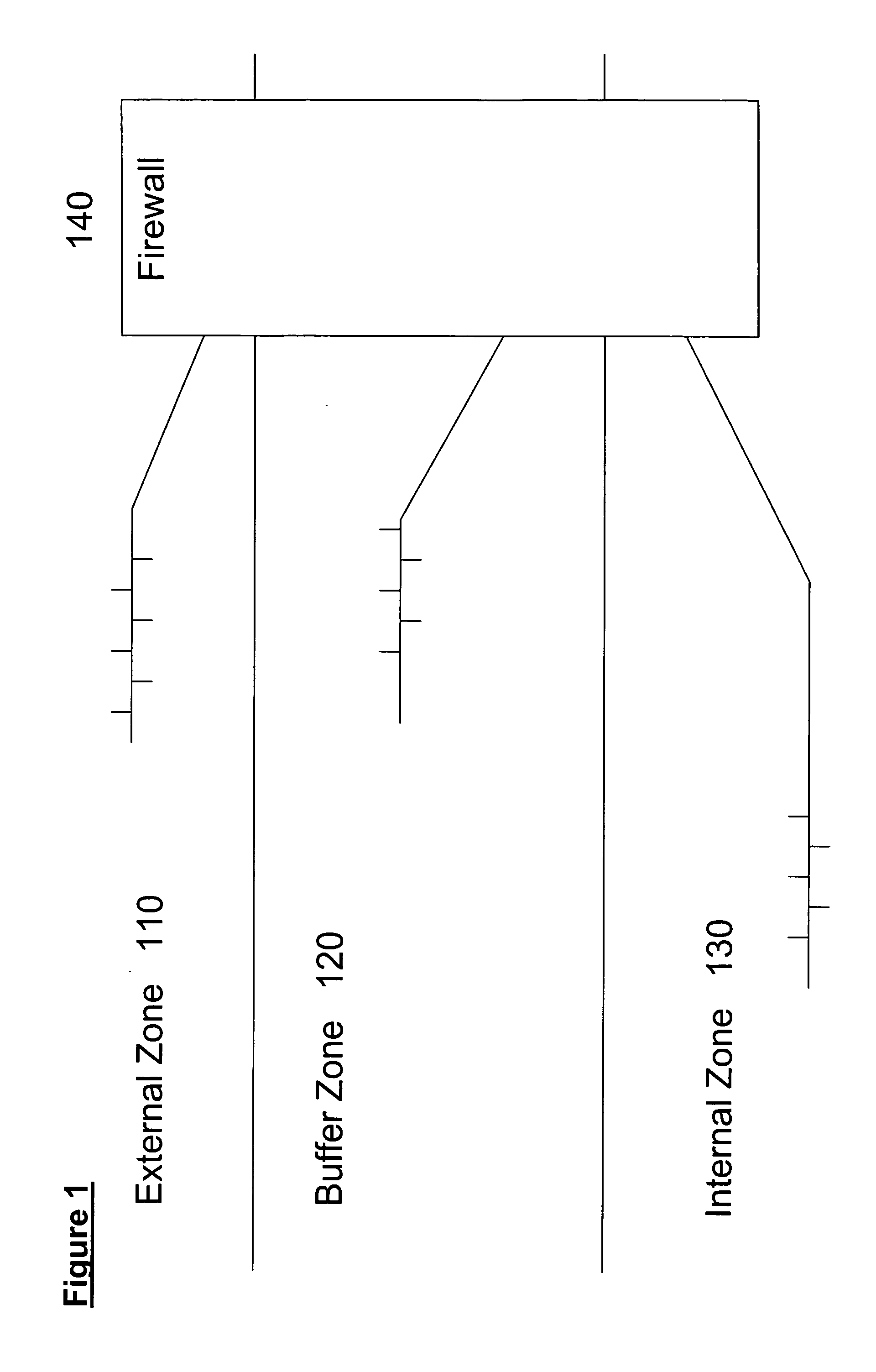
A scalable access filter that is used together with others like it in a virtual private network to control access by users at clients in the network to information resources provided by servers in the network. Each access filter use a local copy of an access control data base to determine whether an access request made by a user. Changes made by administrators in the local copies are propagated to all of the other local copies. Each user belongs to one or more user groups and each information resource belongs to one or more information sets. Access is permitted or denied according to of access policies which define access in terms of the user groups and information sets. The rights of administrators are similarly determined by administrative policies. Access is further permitted only if the trust levels of a mode of identification of the user and of the path in the network by which the access is made are sufficient for the sensitivity level of the information resource. If necessary, the access filter automatically encrypts the request with an encryption method whose trust level is sufficient. The first access filter in the path performs the access check and encrypts and authenticates the request; the other access filters in the path do not repeat the access check.
Owner:DROPBOX
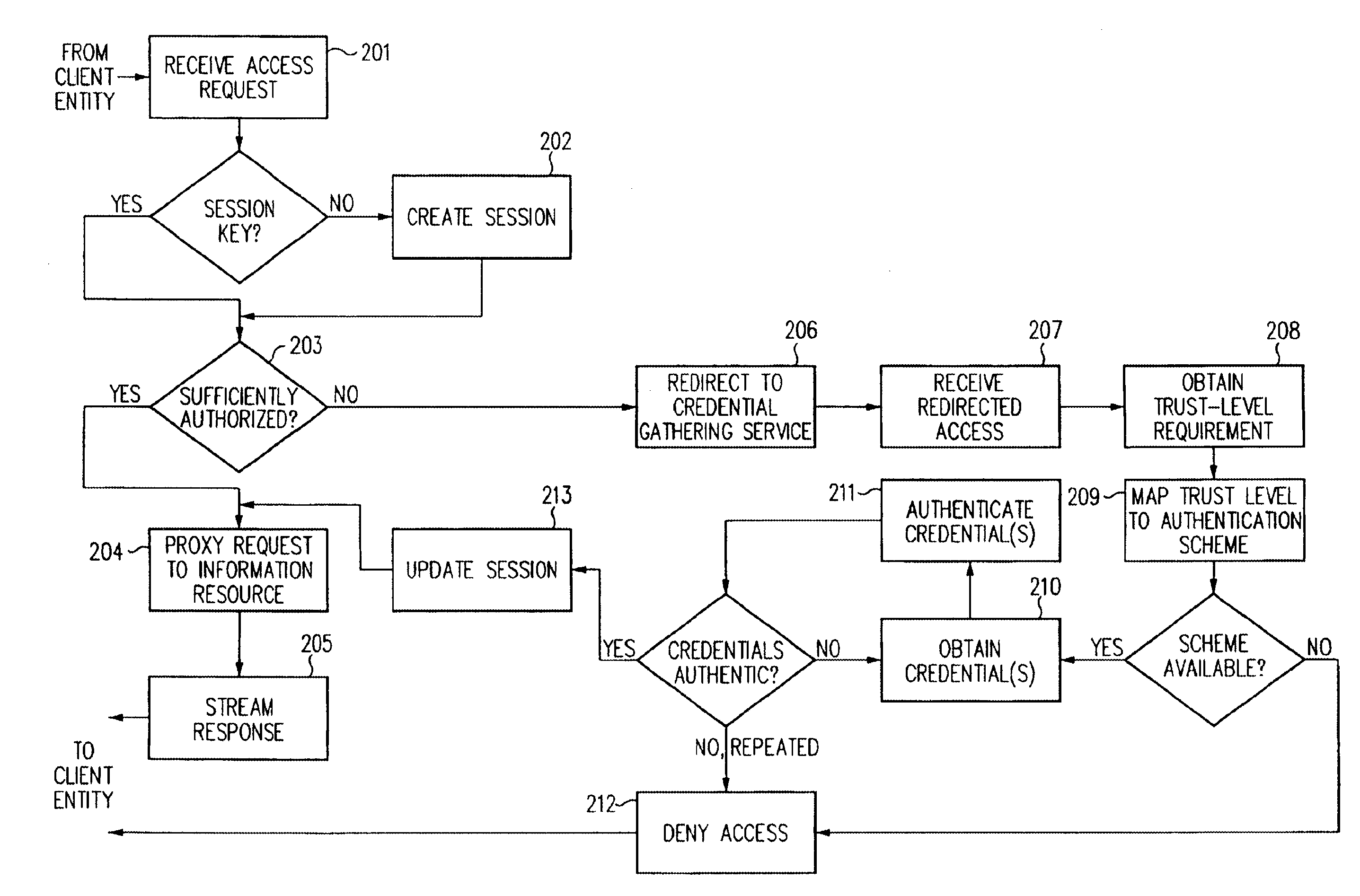
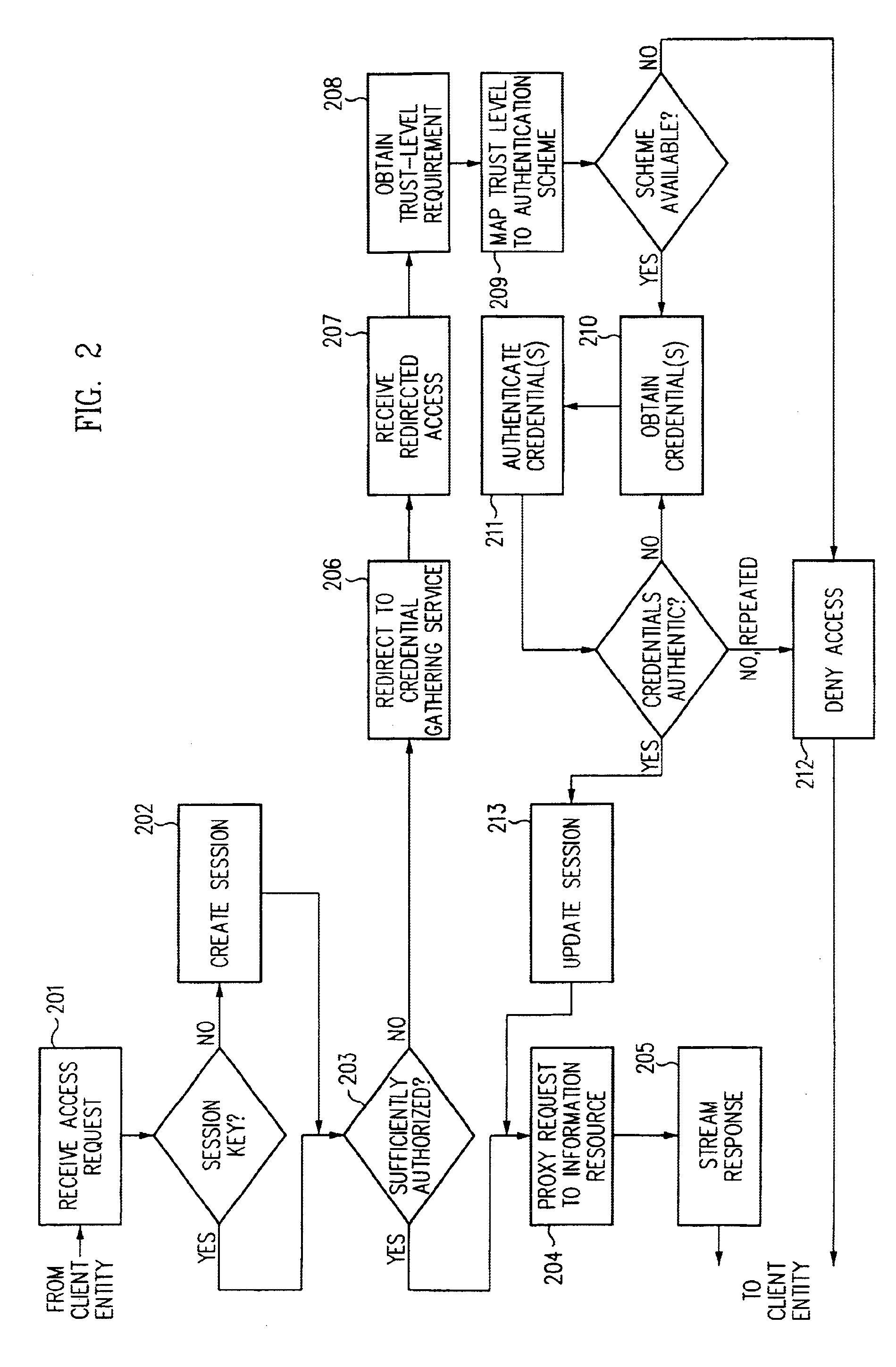
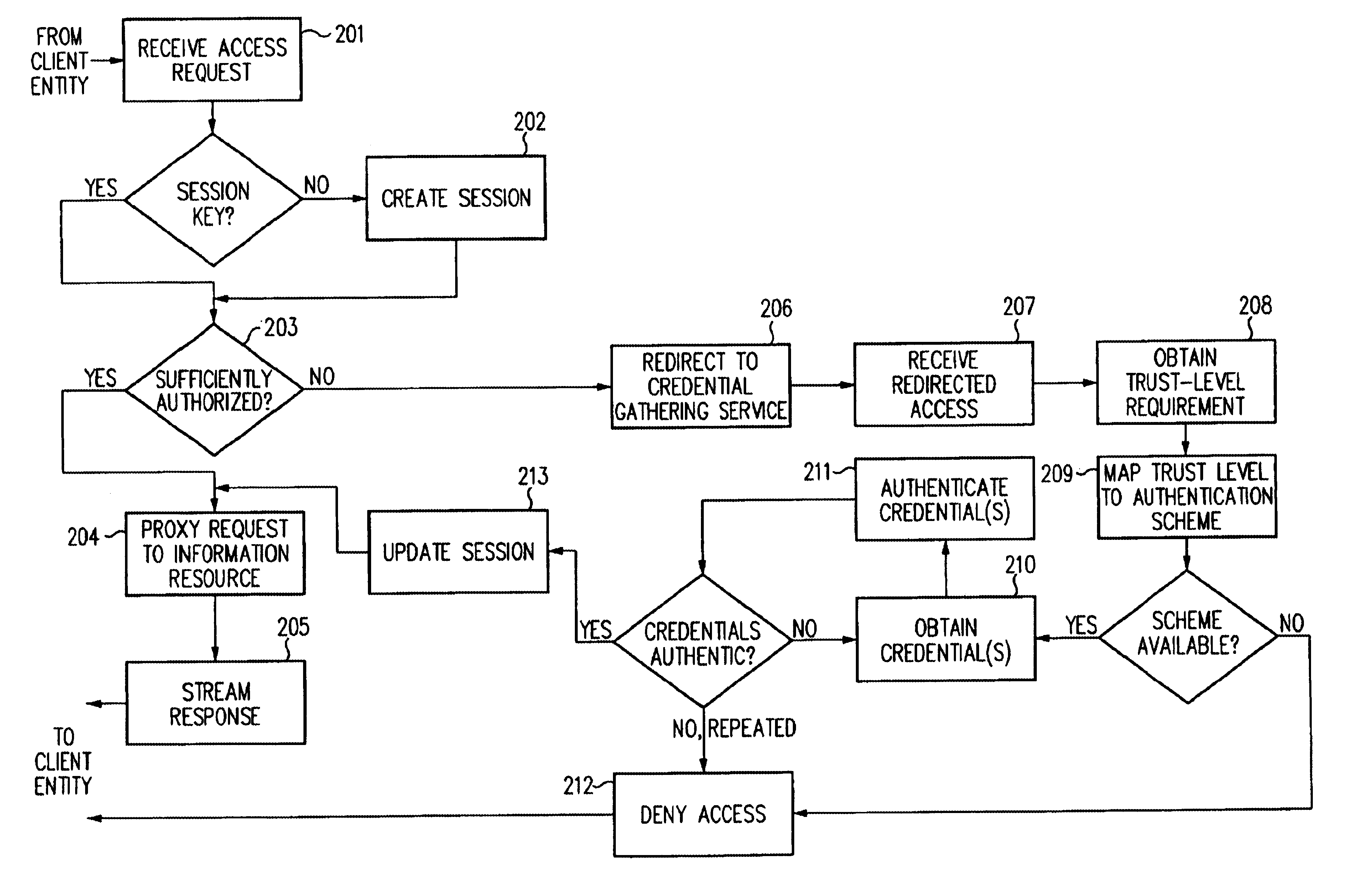
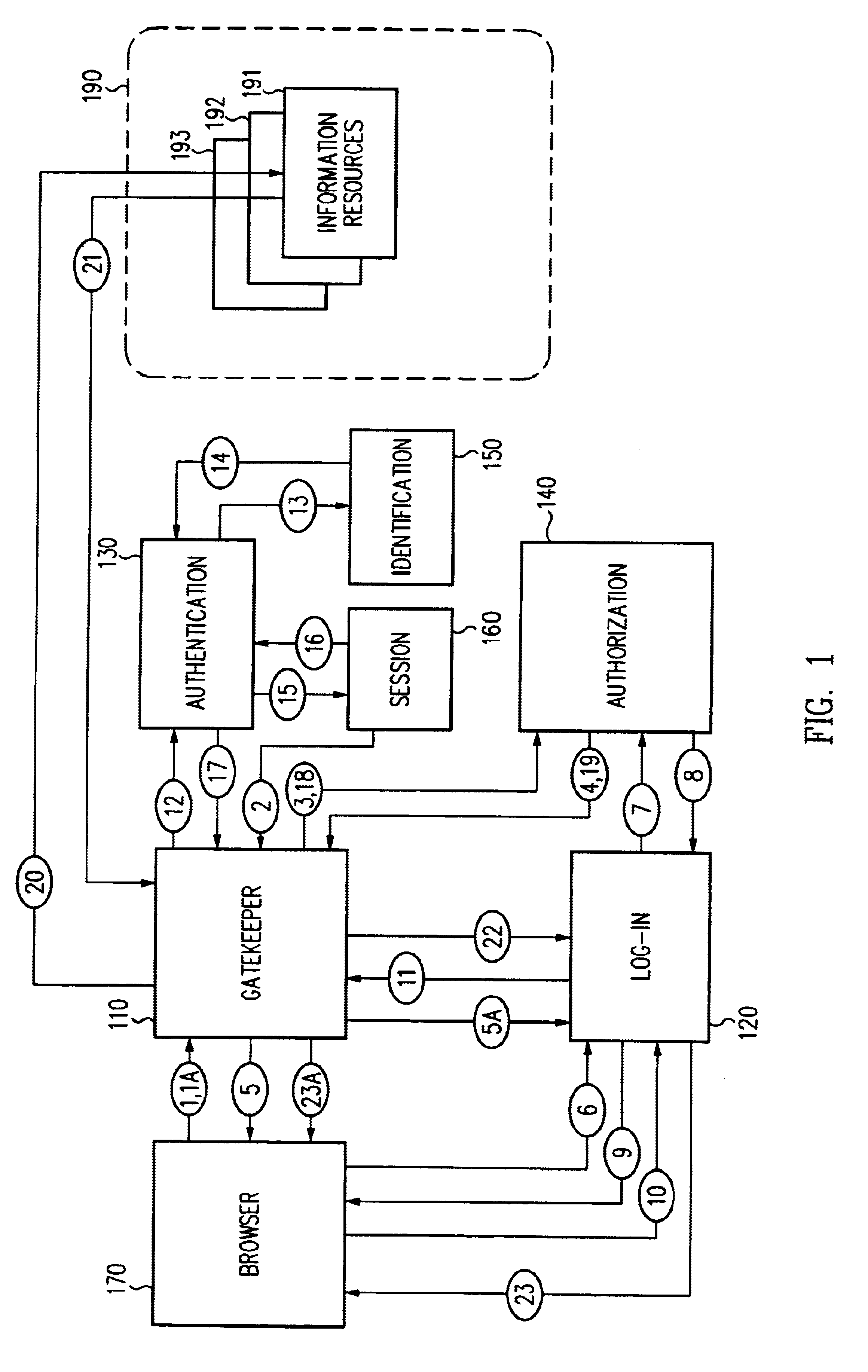
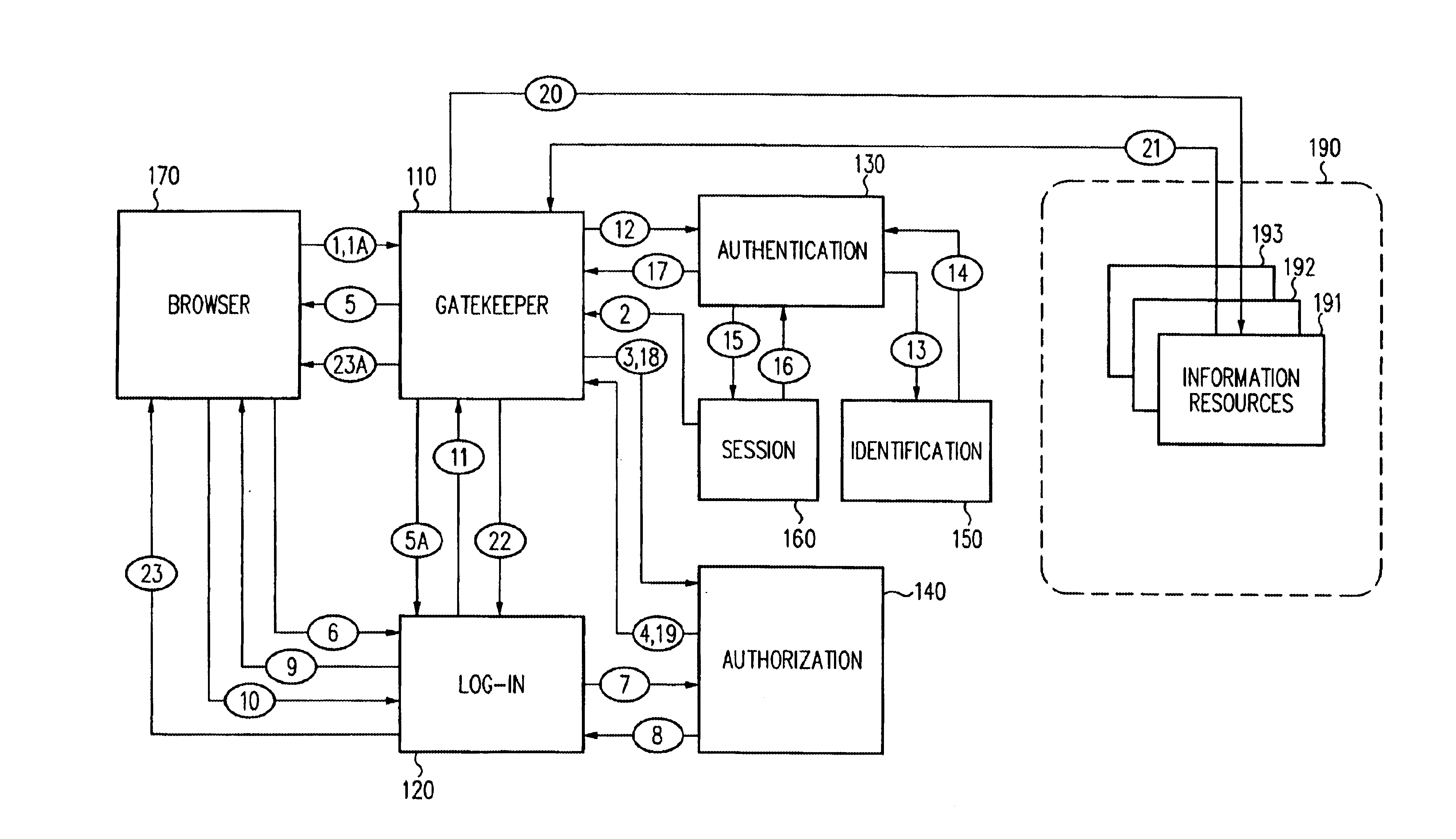
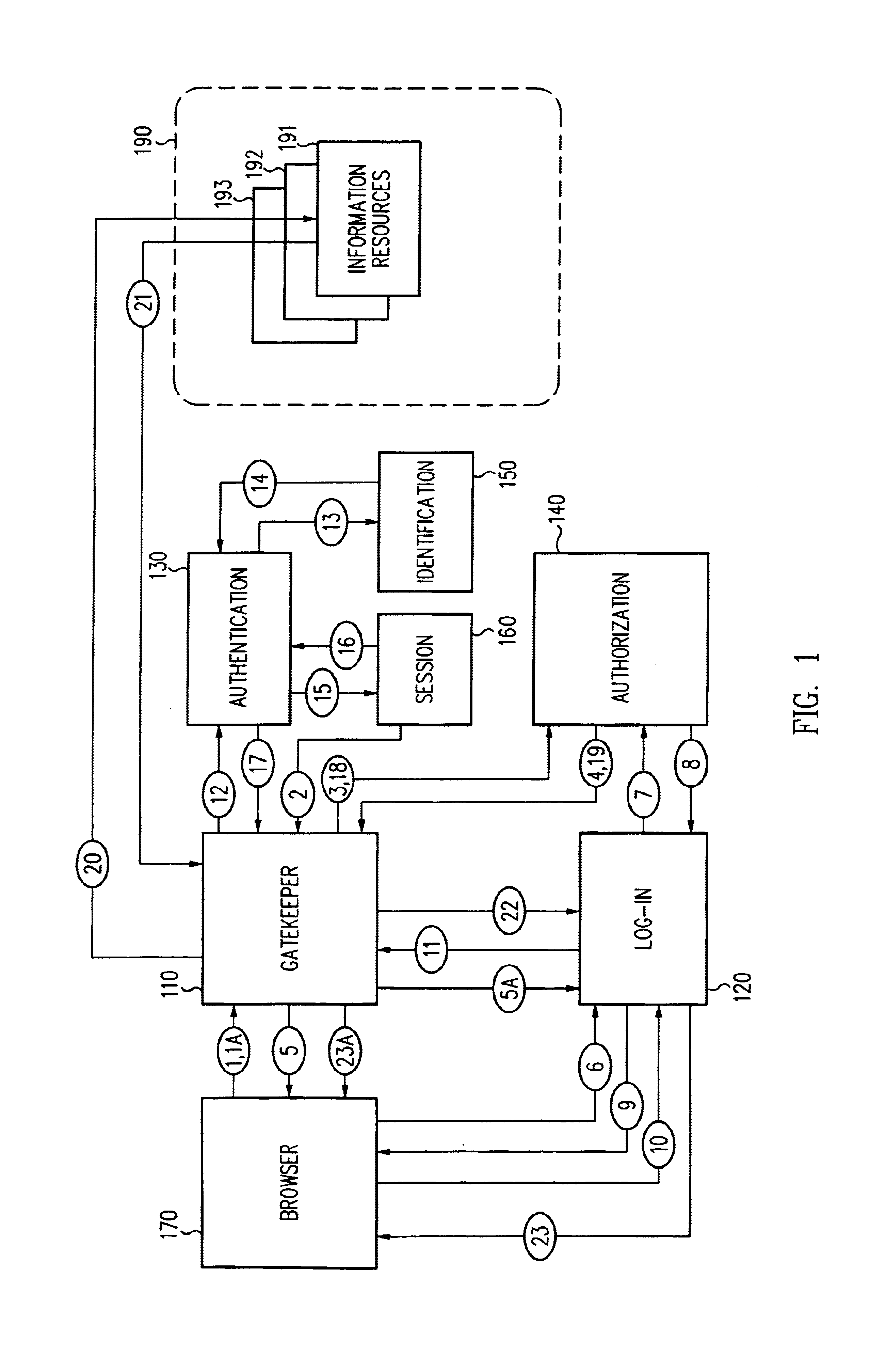
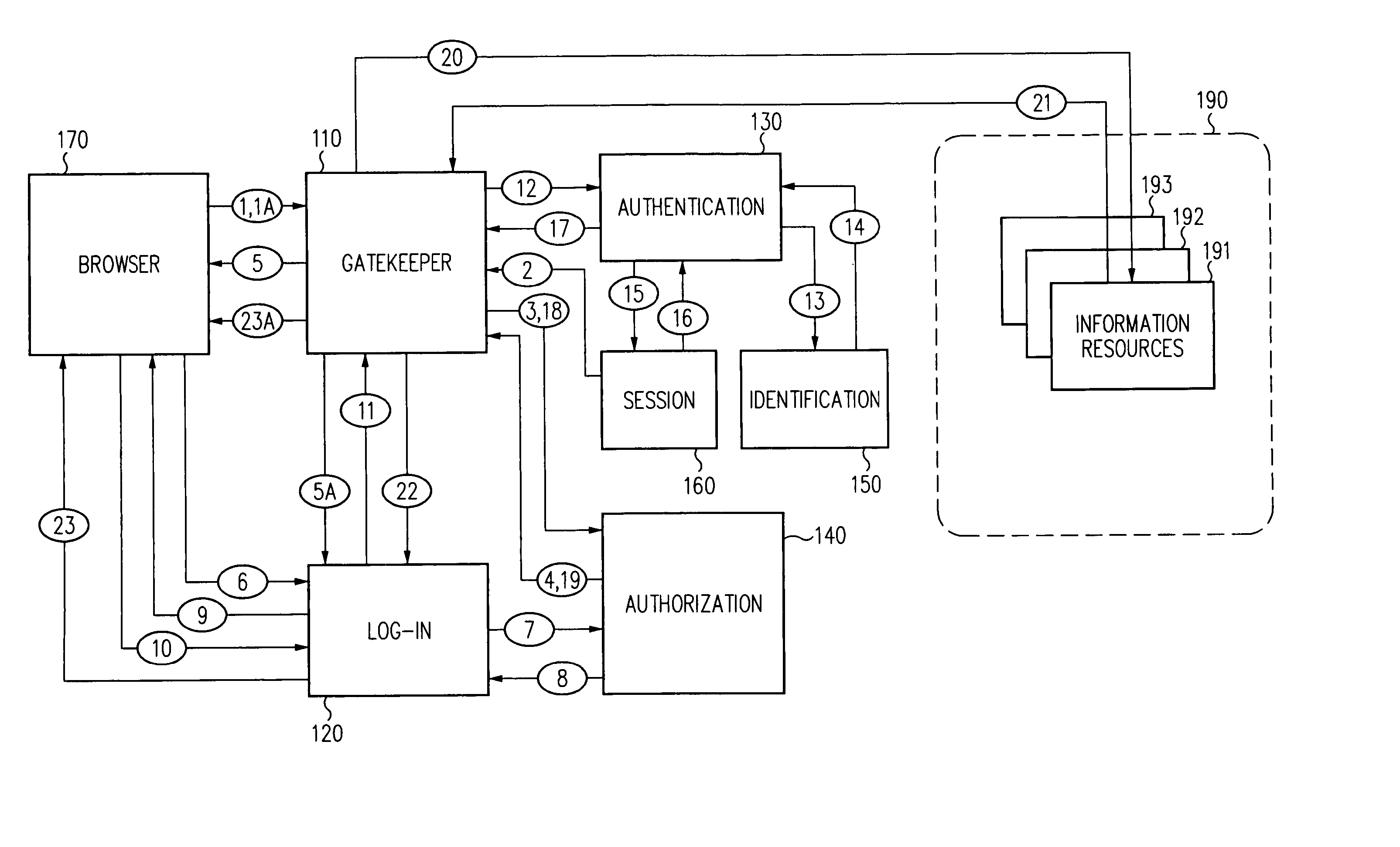
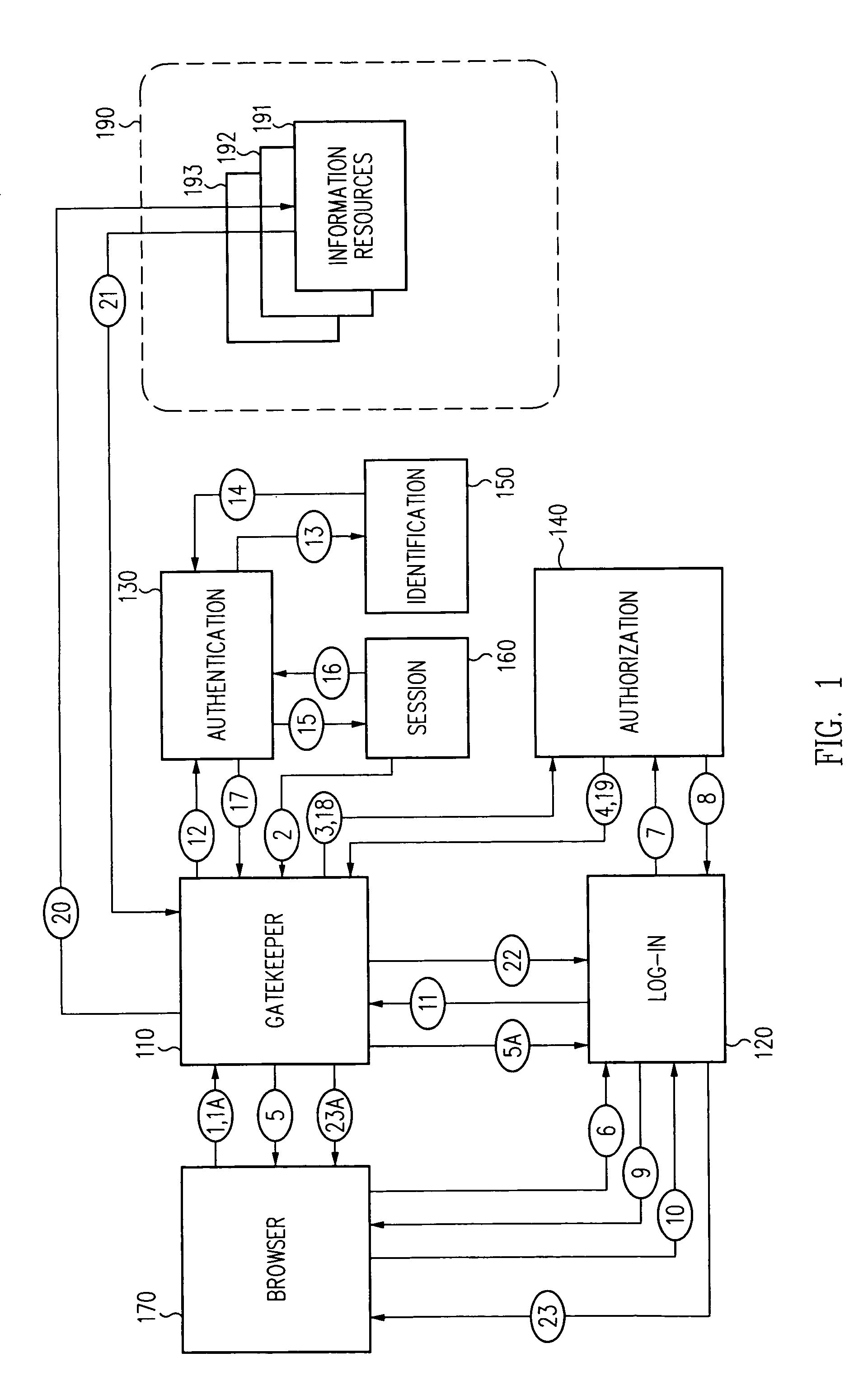
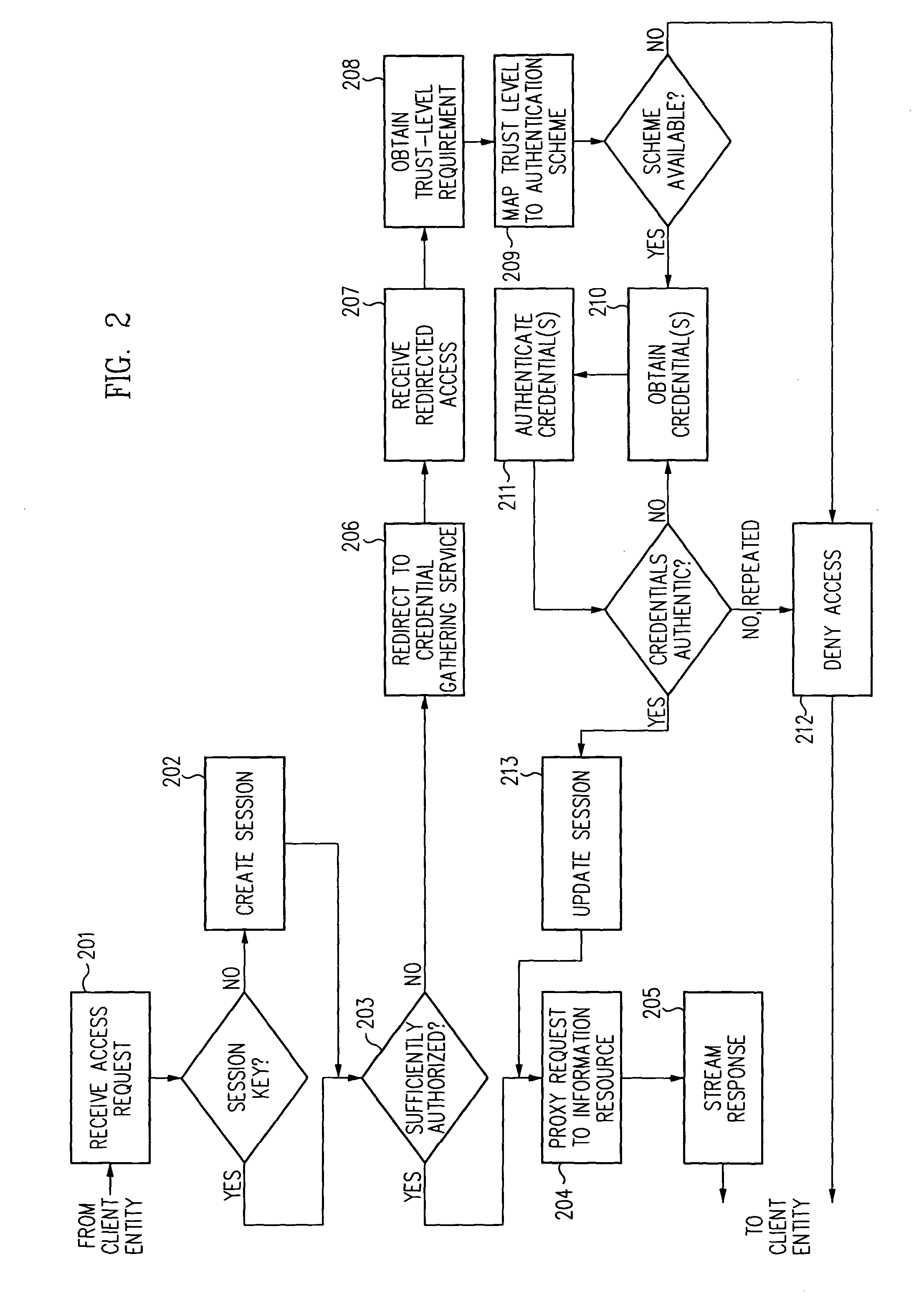
Log-on service providing credential level change without loss of session continuity
InactiveUS6609198B1Volume/mass flow measurementMultiple digital computer combinationsInformation resourceTrust level
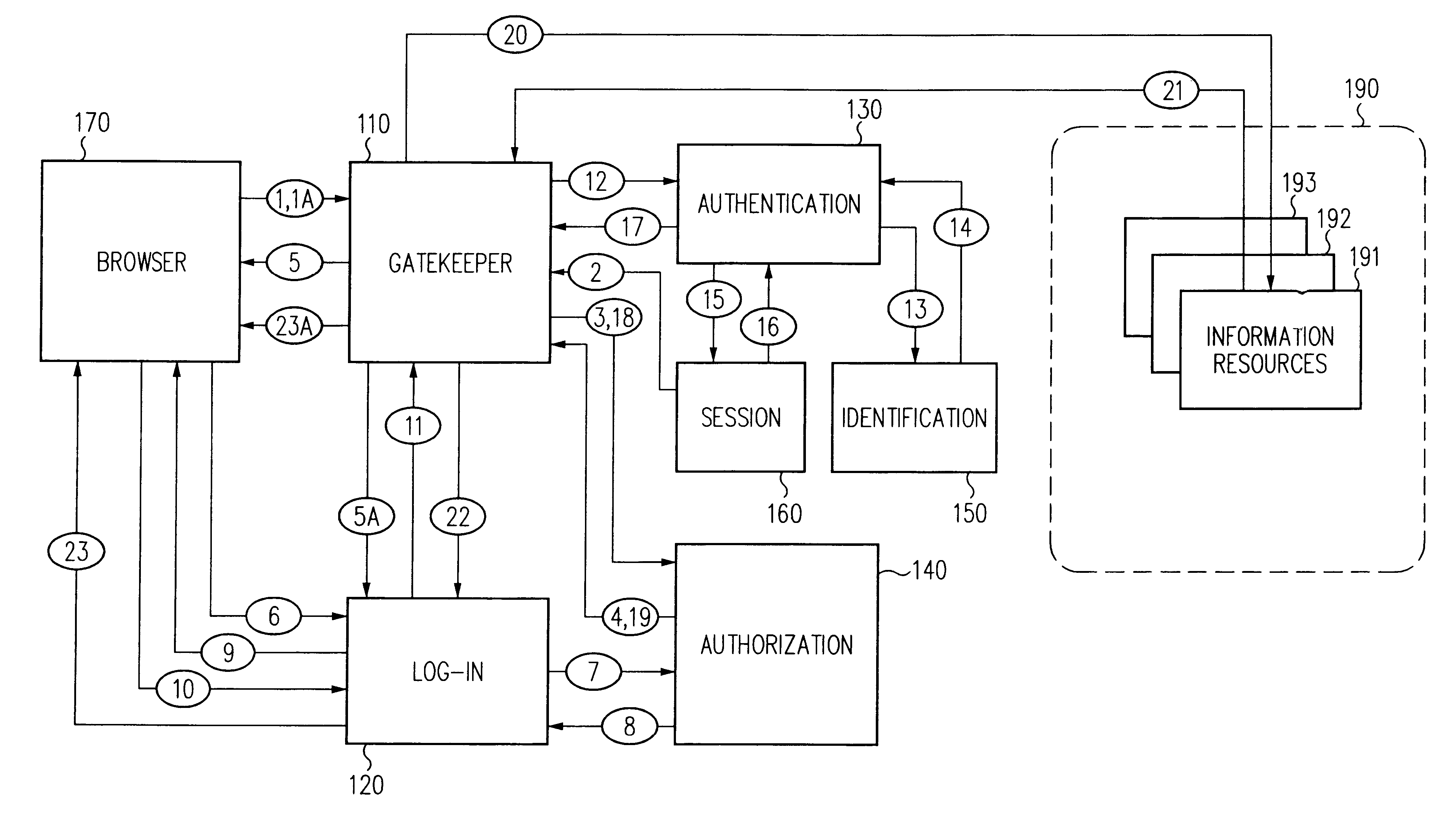
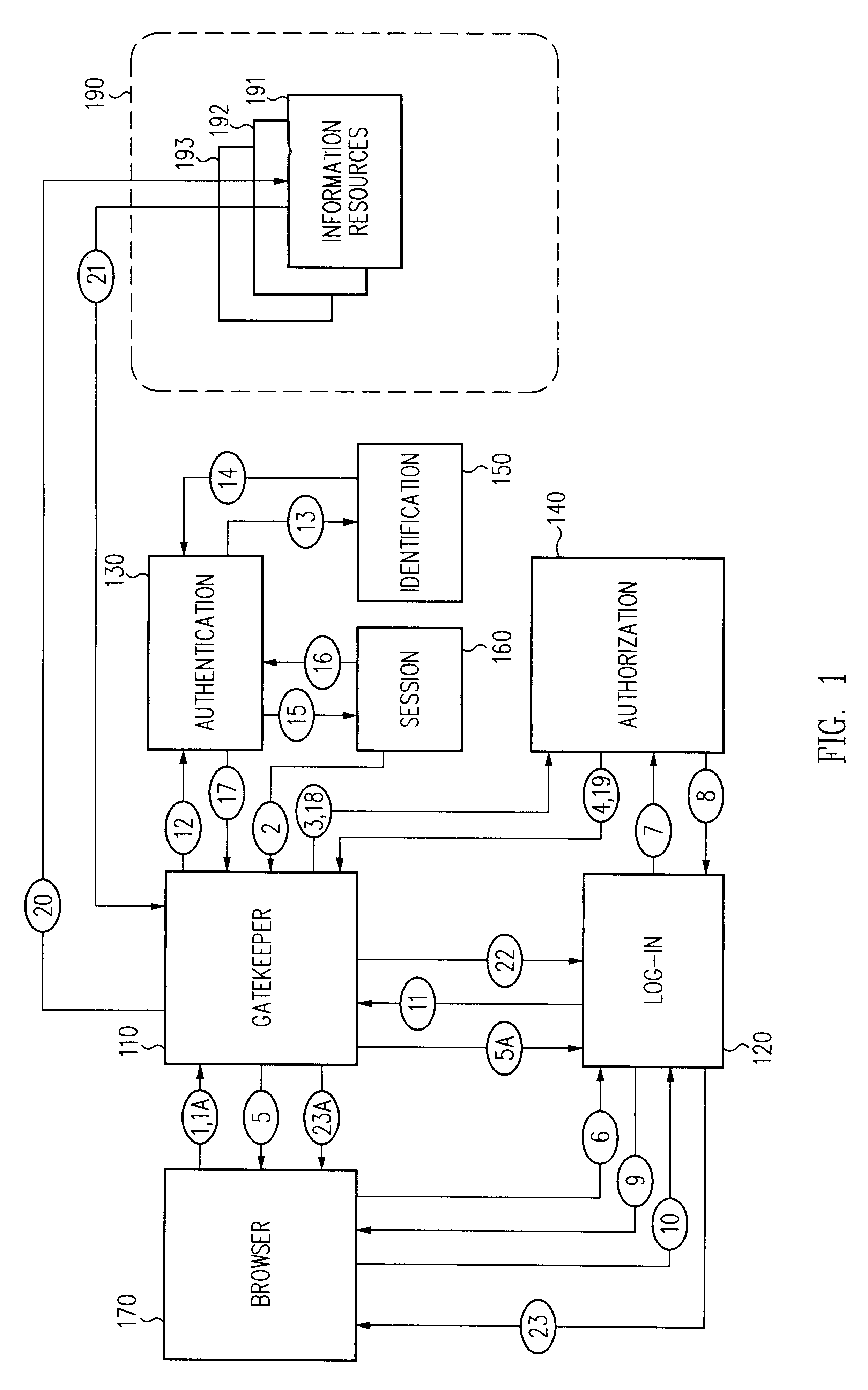
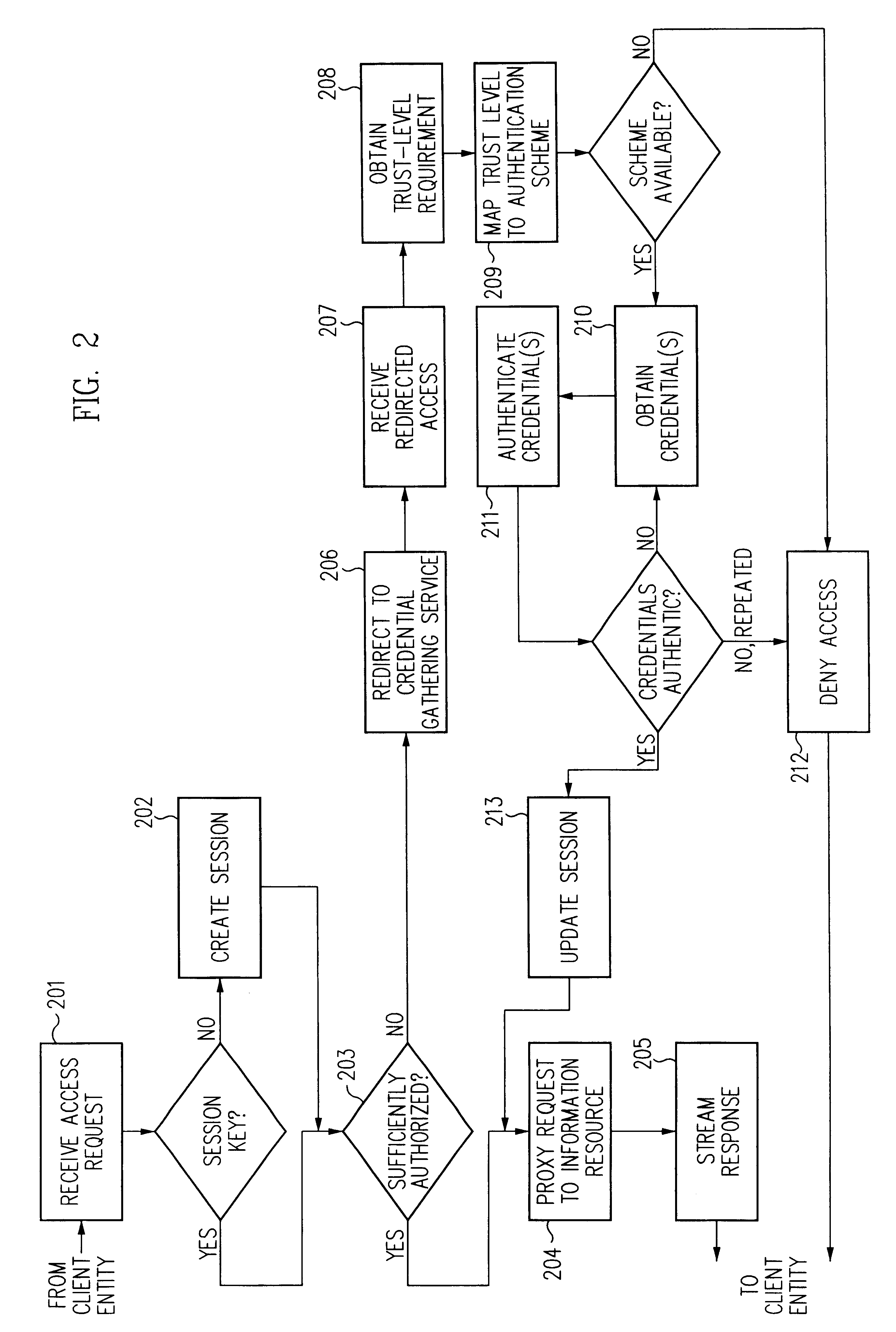
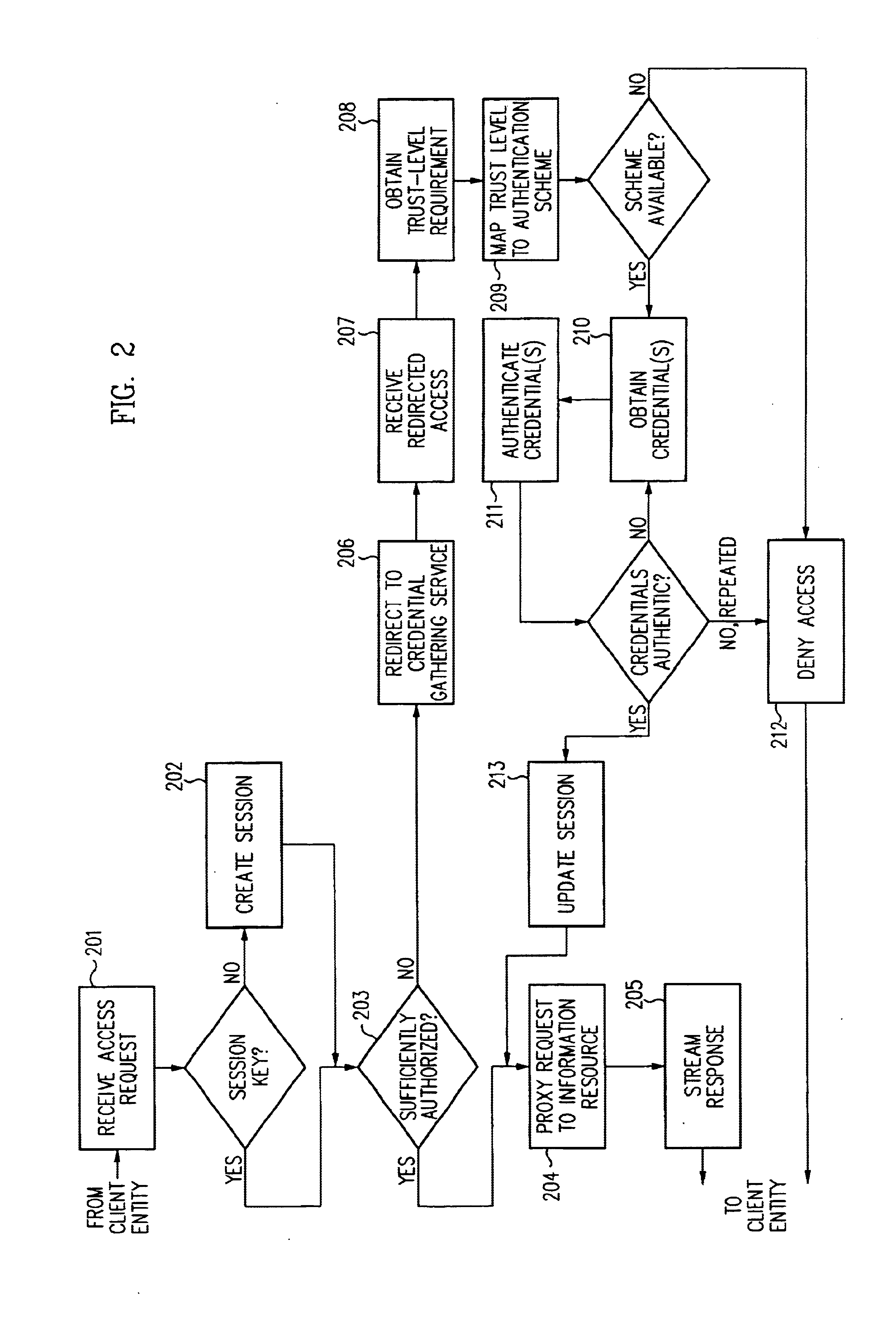
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided for multiple information resources. Rather than specifying a single authentication scheme for all information resources, the security architecture associates trust-level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are employed depending on the trust-level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed. Once credentials have been obtained for an entity and the entity has been authenticated to a given trust level, access is granted, without the need for further credentials and authentication, to information resources for which the authenticated trust level is sufficient. The security architecture allows upgrade of credentials for a given session. This capability is particularly advantageous in the context of a single, enterprise-wide log-on. An entity (e.g., a user or an application) may initially log-on with a credential suitable for one or more resources in an initial resource set, but then require access to resource requiring authentication at higher trust level. In such case, the log-on service allows additional credentials to be provided to authenticate at the higher trust level. The log-on service allows upgrading and / or downgrading without loss of session continuity (i.e., without loss of identity mappings, authorizations, permissions, and environmental variables, etc.).
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Secure delivery of information in a network
InactiveUS6178505B1User identity/authority verificationData switching networksPrivate networkInformation resource
A scalable access filter that is used together with others like it in a virtual private network to control access by users at clients in the network to information resources provided by servers in the network. Each access filter use a local copy of an access control data base to determine whether an access request made by a user. Changes made by administrators in the local copies are propagated to all of the other local copies. Each user belongs to one or more user groups and each information resource belongs to one or more information sets. Access is permitted or denied according to of access policies which define access in terms of the user groups and information sets. The rights of administrators are similarly determined by administrative policies. Access is further permitted only if the trust levels of a mode of identification of the user and of the path in the network by which the access is made are sufficient for the sensitivity level of the information resource. If necessary, the access filter automatically encrypts the request with an encryption method whose trust level is sufficient. The first access filter in the path performs the access check and encrypts and authenticates the request; the other access filters in the path do not repeat the access check.
Owner:DROPBOX
Techniques for eliminating redundant access checking by access filters
InactiveUS6105027AData processing applicationsMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkInformation resource
A scalable access filter that is used together with others like it in a virtual private network to control access by users at clients in the network to information resources provided by servers in the network. Each access filter uses a local copy of an access control data base to determine whether an access request is made by a user. Changes made by administrators in the local copies are propagated to all of the other local copies. Each user belongs to one or more user groups and each information resource belongs to one or more information sets. Access is permitted or denied according to of access policies which define access in terms of the user groups and information sets. The rights of administrators are similarly determined by administrative policies. Access is further permitted only if the trust levels of a mode of identification of the user and of the path in the network by which the access is made are sufficient for the sensitivity level of the information resource. If necessary, the access filter automatically encrypts the request with an encryption method whose trust level is sufficient. The first access filter in the path performs the access check and encrypts and authenticates the request; the other access filters in the path do not repeat the access check.
Owner:DROPBOX
Single sign-on framework with trust-level mapping to authentication requirements
InactiveUS6892307B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPasswordInformation resource
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided for multiple information resources. Rather than specifying a single authentication scheme for all information resources, the security architecture associates trust-level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are associated with trust levels and a log-on service obtains credentials for an entity commensurate with the trust-level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed. Once credentials have been obtained for an entity and the entity has been authenticated to a given trust level, access is granted, without the need for further credentials and authentication, to information resources for which the authenticated trust level is sufficient.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Access management system and method employing secure credentials
InactiveUS6668322B1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInformation resourceTrust level
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided. Session credentials are used to maintain continuity of a persistent session across multiple accesses to one or more information resources, and in some embodiments, across credential level changes. Session credentials are secured, e.g., as a cryptographically secured session token, such that they may be inspected by a wide variety of entities or applications to verify an authenticated trust level, yet may not be prepared or altered except by a trusted authentication service. Some embodiments of the present invention associate trust level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are associated with trust levels, and in some embodiments, with environmental parameters. For example, in one configuration, a login service obtains login credentials for an entity commensurate with the trust level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed and with environment parameters that affect the sufficiency of a given credential type. Once login credentials have been obtained for an entity and have been authenticated to a given trust level, session credentials are issued and access is granted to information resources for which the trust level is sufficient. Advantageously, by using the session credentials access is granted without the need for further login credentials and authentication. In some configurations, session credentials evidencing an insufficient trust level may be remedied by a session continuity preserving upgrade of login credential.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Security architecture with environment sensitive credential sufficiency evaluation
InactiveUS6691232B1Digital data processing detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionInformation resourceTrust level
By including environment information in a security policy, a security architecture advantageously allows temporal, locational, connection type and / or client capabilities-related information to affect the sufficiency of a given credential type (and associated authentication scheme) for access to a particular information resource. In some configurations, time of access, originating location (physical or network) and / or connection type form a risk profile that can be factored into credential type sufficiency. In some configurations, changing environmental parameters may cause a previously sufficient credential to become insufficient. Alternatively, an authenticated credential previously insufficient for access at a given trust level may be sufficient based on a changed or more fully parameterized session environment. In some configurations, the use of session tracking facilites (e.g., the information content of session tokens) can be tailored to environmental parameters (e.g., connection type or location). Similarly, capabilities of a particular client entity (e.g., browser support for 128-bit cipher or availablity of a fingerprint scanner or card reader) may affect the availability or sufficiency of particular authentication schemes to achieve a desired trust level.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Push-Pull Based Content Delivery System
InactiveUS20080059631A1Maximize QoSImprove scalabilityDigital computer detailsTelevision systemsClosed loop feedbackPush pull
QoS is built into a peer network within existing Internet infrastructure itself lacking QoS, by enabling a network peer to continuously discern the network's ability to deliver to that peer a particular Content Object (distributed in groups of component Packages among neighboring VOD peers) within predetermined times. Content Objects are divided into groups of component Packages and distributed to Clusters of neighboring network peers, enhancing QoS upon subsequent retrieval. Tracking Files (lists of network peers storing Package groups) and Tracking Indexes (lists of network peers storing Tracking Files) are generated to facilitate “on demand” Content Objects retrieval. Dynamically monitoring network traffic (including VOD functionality, bandwidth and reliability) creates “distributed closed-loop feedback,” and in response, attributes of individual network peers (e.g., Trust Level and membership within a particular Cluster) are modified, and “content balancing” functions performed (e.g., redistribution of Package groups among network peers) enables maintaining high QoS.
Owner:VODDLER GRP
Distributed administration of access to information
InactiveUS6785728B1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsMultiple digital computer combinationsPrivate networkInformation resource
A scalable access filter that is used together with others like it in a virtual private network to control access by users at clients in the network to information resources provided by servers in the network. Each access filter use a local copy of an access control data base to determine whether an access request made by a user. Changes made by administrators in the local copies are propagated to all of the other local copies. Each user belongs to one or more user groups and each information resource belongs to one or more information sets. Access is permitted or denied according to of access policies which define access in terms of the user groups and information sets. The rights of administrators are similarly determined by administrative policies. Access is further permitted only if the trust levels of a mode of identification of the user and of the path in the network by which the access is made are sufficient for the sensitivity level of the information resource. If necessary, the access filter automatically encrypts the request with an encryption method whose trust level is sufficient. The first access filter in the path performs the access check and encrypts and authenticates the request; the other access filters in the path do not repeat the access check.
Owner:DROPBOX
Generalized policy server
InactiveUS7272625B1Easy to handleMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionPolicy decisionTrust level
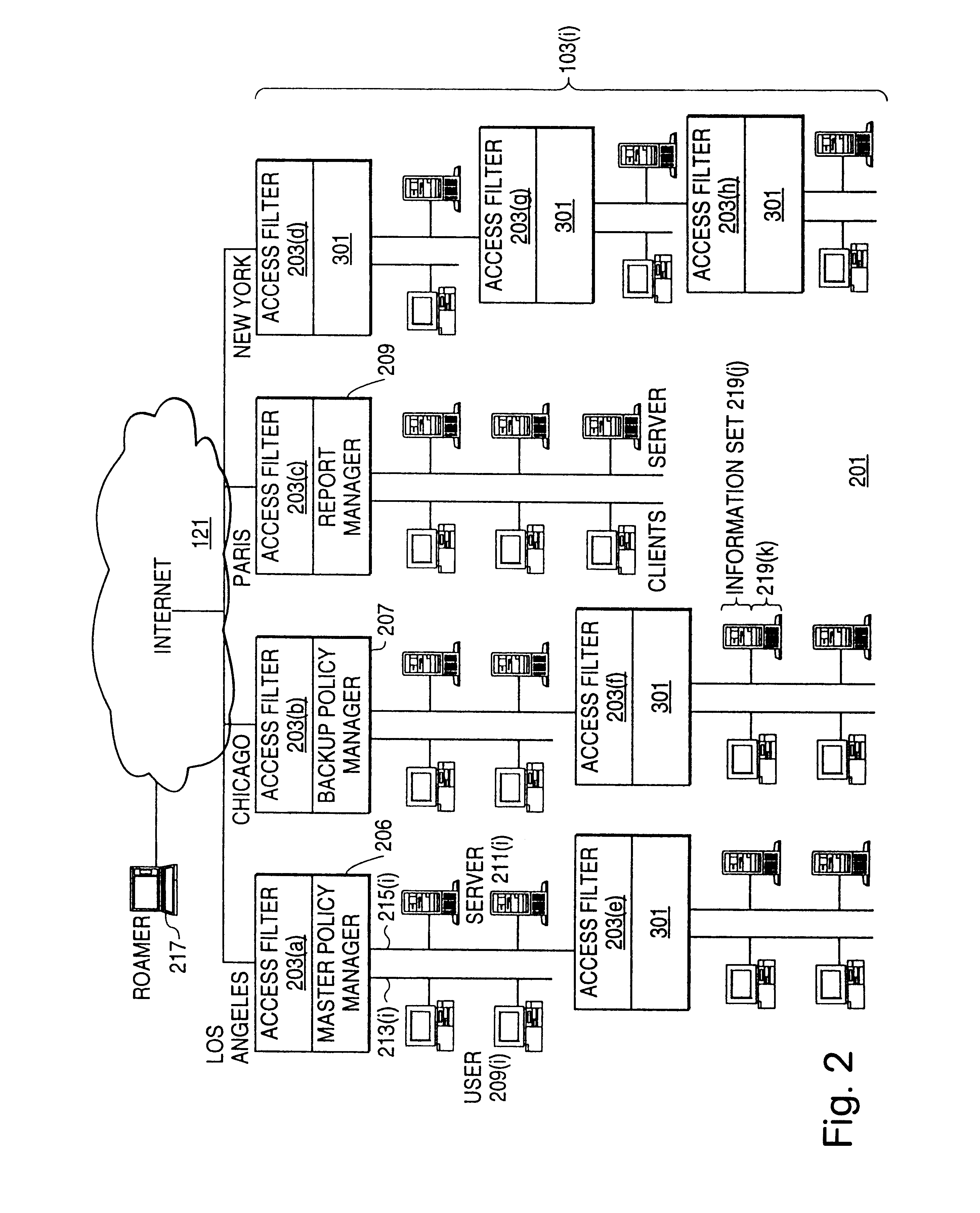
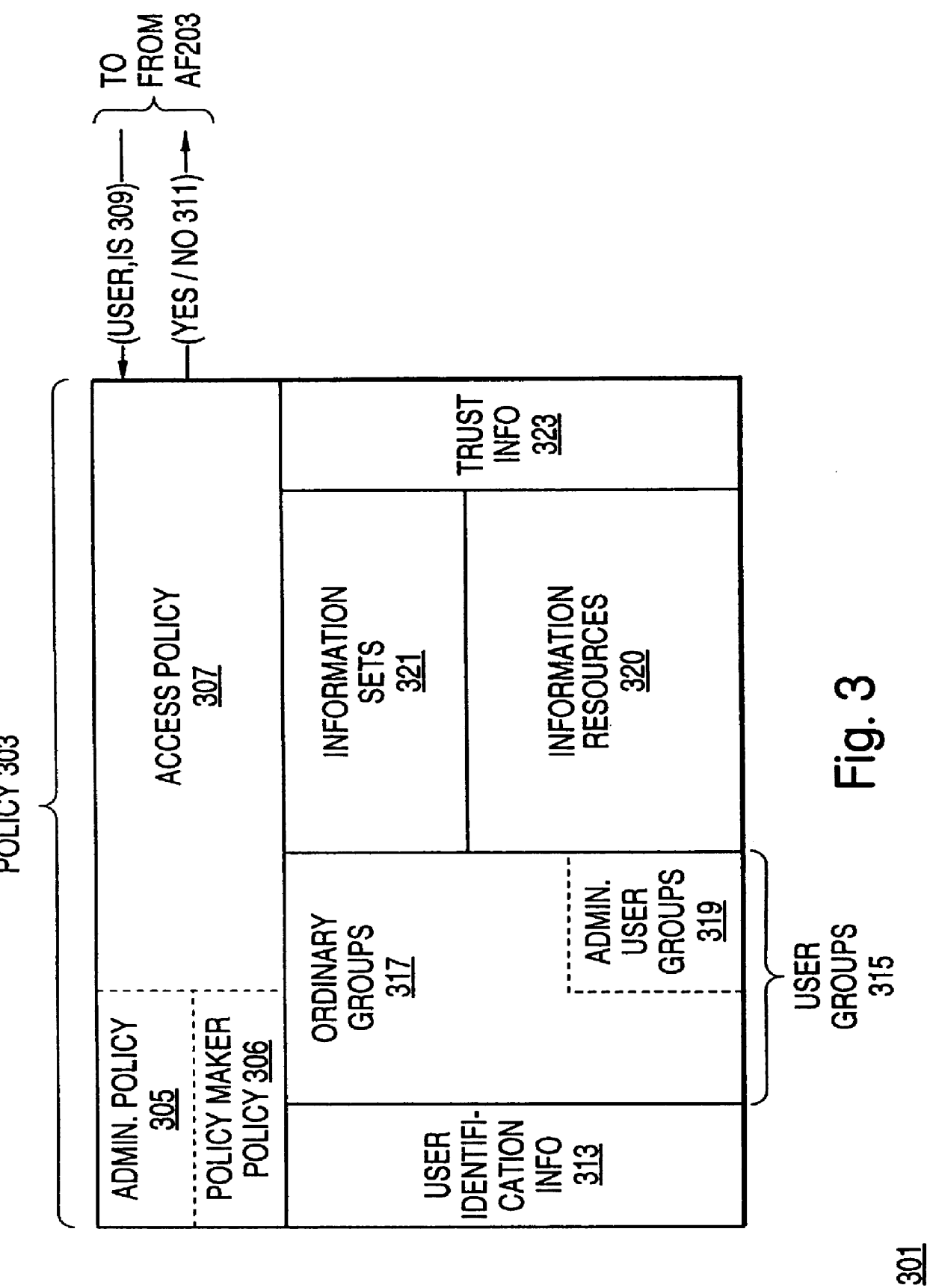
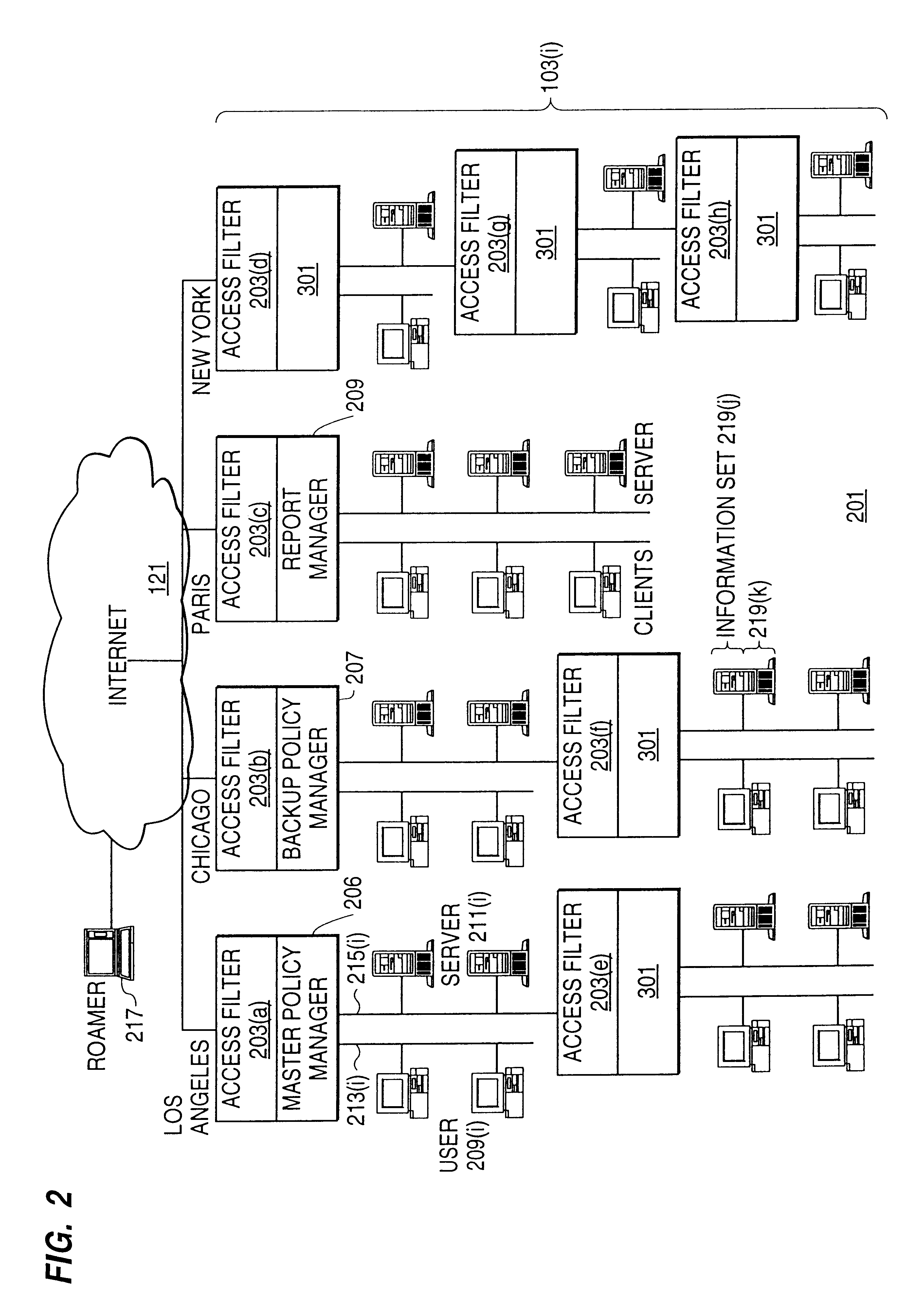
A policy system includes the policy server (2617); a policy database (2619) which located at policy decision point (2723); the access / response entity (2603); resource server (2711); policy message (2725) and policy enforcement point (2721). System connected through public network (2702) or internal network (103). The access filter (107, 203, 403) control access by use a local copy of an access control data base to determine whether an access request made by a user. Changes made by administrators in the local copies are propagated to all of the other local copies. Access is permitted or denied according to of access policies (307) which define access in terms of the user groups (FIGS. 9-12) and information sets (FIGS. 13A-18). The rights of administrators are similarly determined by administrative policies (FIGS. 23A-C). Access is further permitted only if the trust levels of the network by which is made by the sufficient access (FIGS. 25-29). A policy server component of the access filter has been separated from the access filter and the policies have been generalized to permit administrators of the policy server to define new types of actions and new types of entities. Policies may now further have specifications for time intervals during which the policies are in force and the entities may be associated with attributes that specify how the entity is to be used when the policy applies.
Owner:MARSHMAN RES +1
Log-on service providing credential level change without loss of session continuity
InactiveUS20040210771A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationInformation resourcePassword
A security architecture has been developed in which a single sign-on is provided for multiple information resources. Rather than specifying a single authentication scheme for all information resources, the security architecture associates trust-level requirements with information resources. Authentication schemes (e.g., those based on passwords, certificates, biometric techniques, smart cards, etc.) are employed depending on the trust-level requirement(s) of an information resource (or information resources) to be accessed. Once credentials have been obtained for an entity and the entity has been authenticated to a given trust level, access is granted, without the need for further credentials and authentication, to information resources for which the authenticated trust level is sufficient.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Variable trust levels for authentication
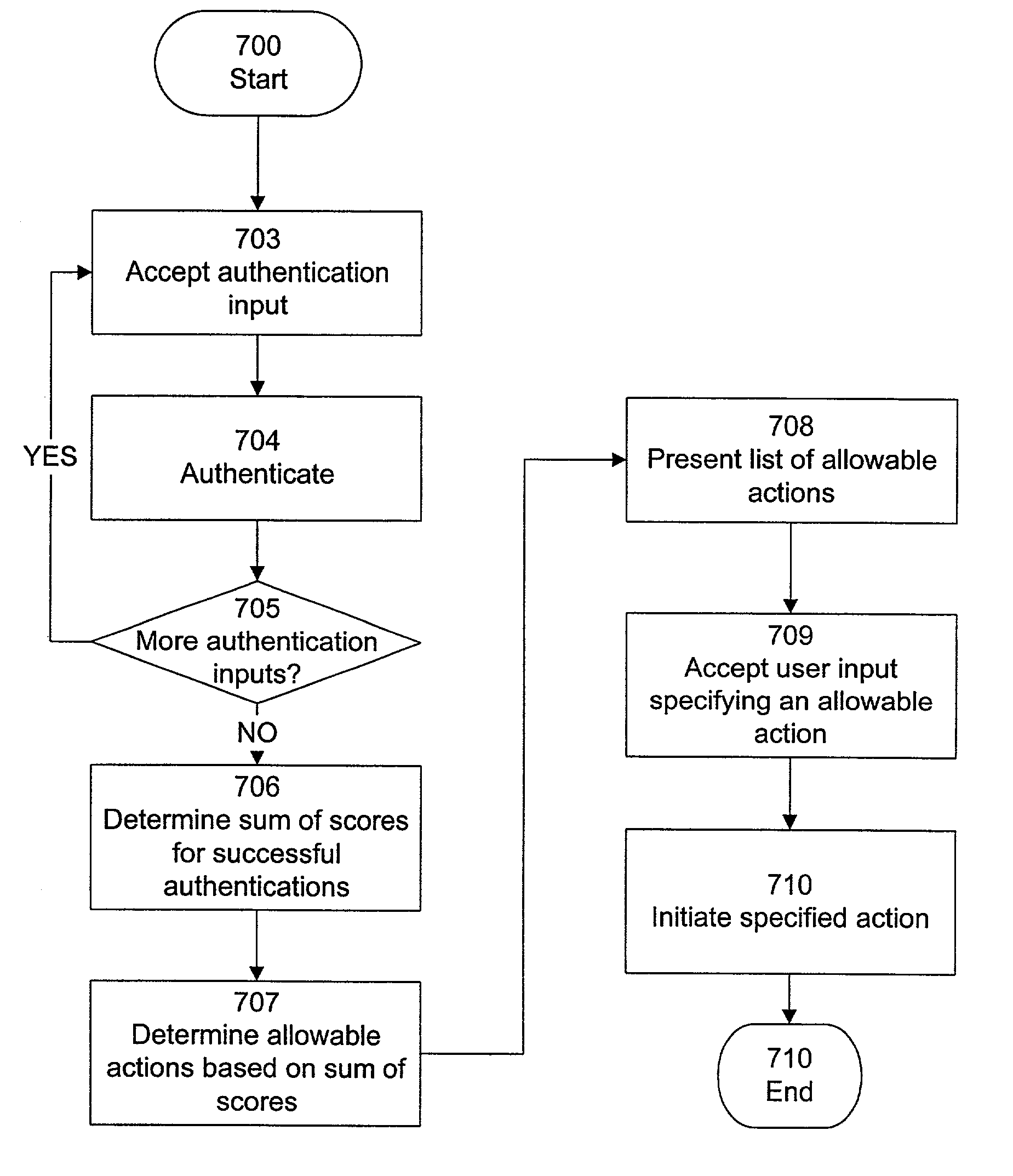
InactiveUS7086085B1Good flexibilityHigh scoreDigital data processing detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsInternet privacyTrust level
A level of trust is determined based on a combination of scores for one or more successful authentications. Scores indicate relative degrees of reliability for authentications, so that differing authentication methods may correspond to different scores. The determined level of trust can then be used to allow or deny access to a resource, and can be used to specify the type of access that is allowed, if applicable.
Owner:ILUMIN CORP
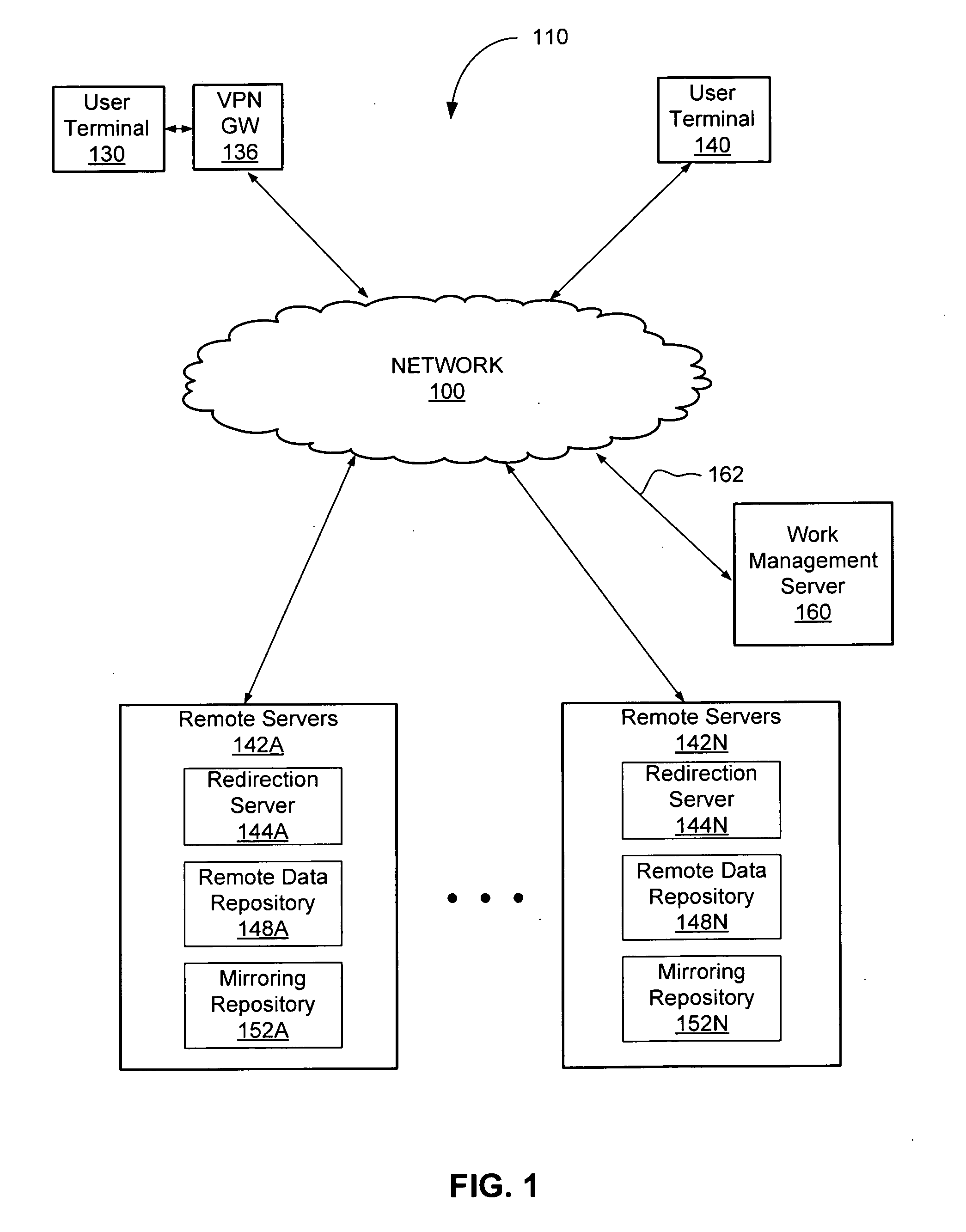
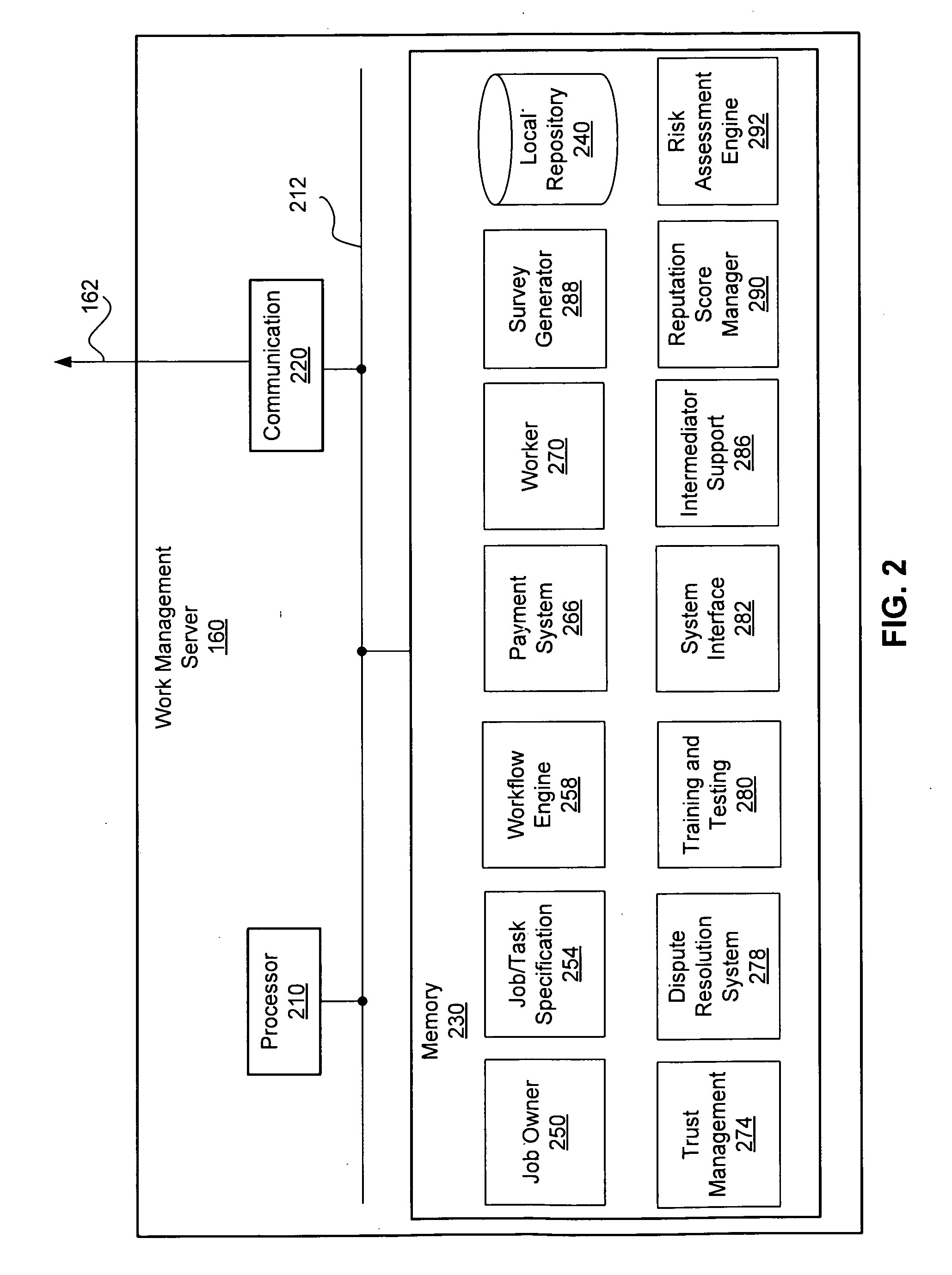
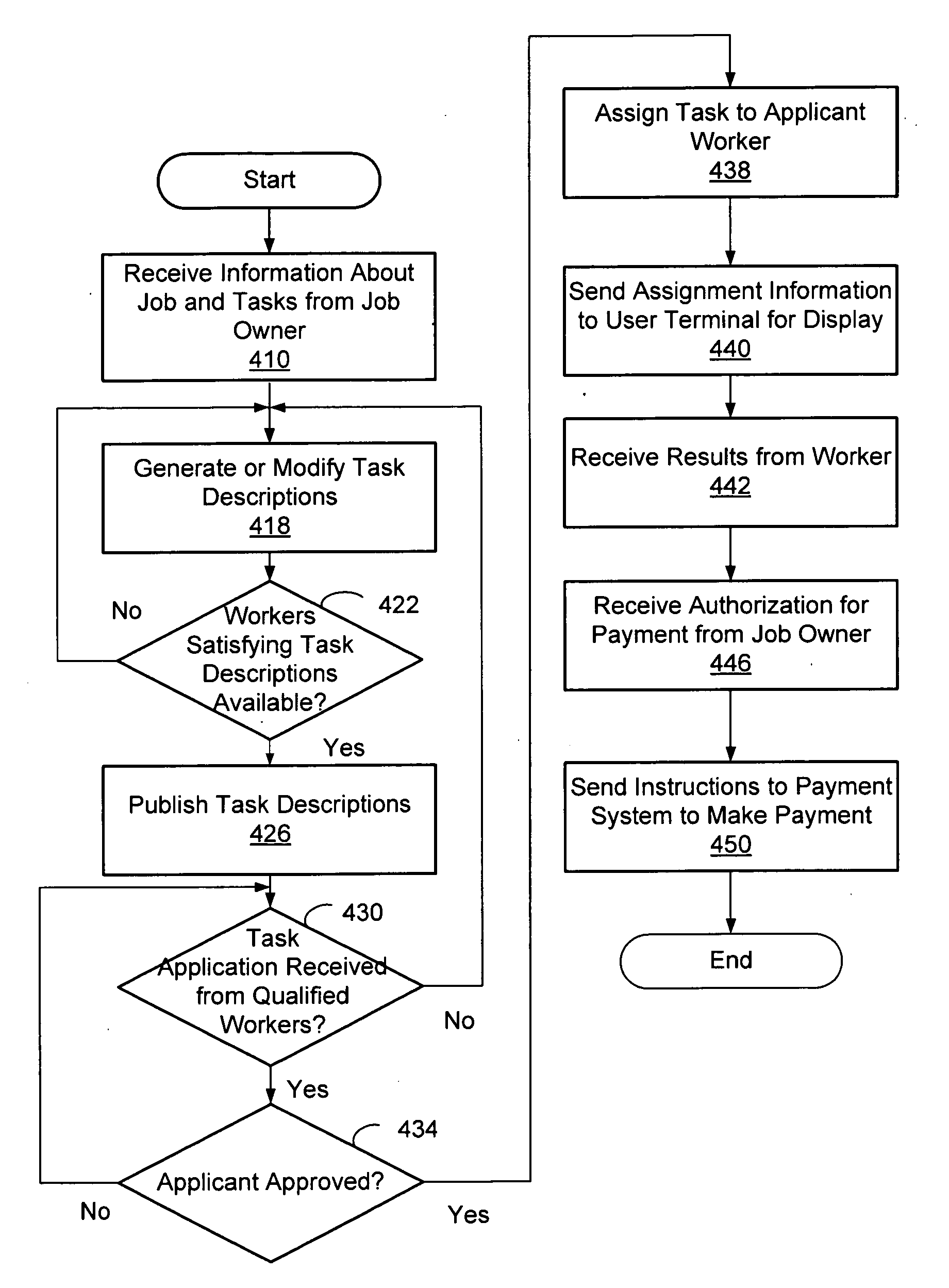
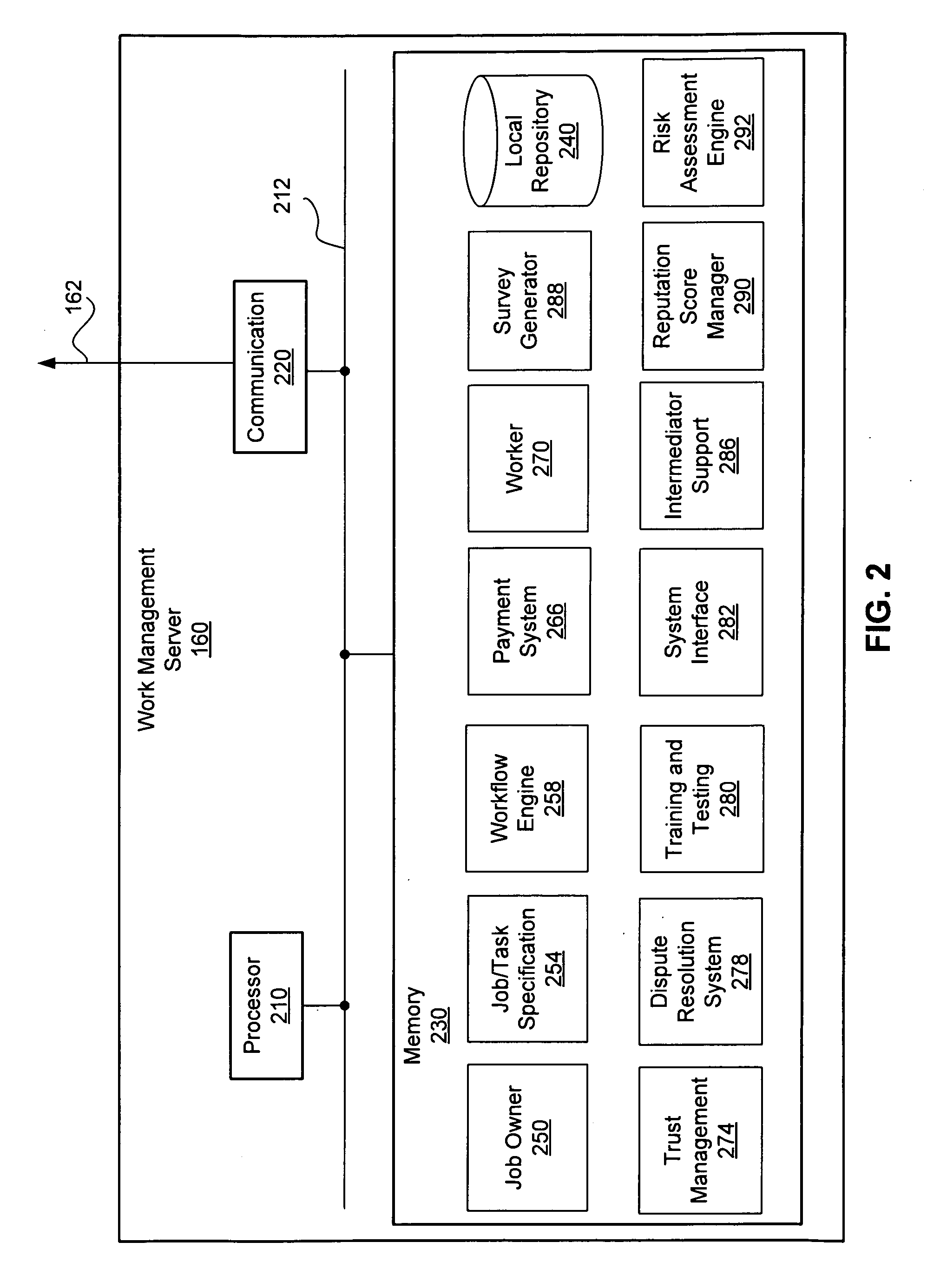
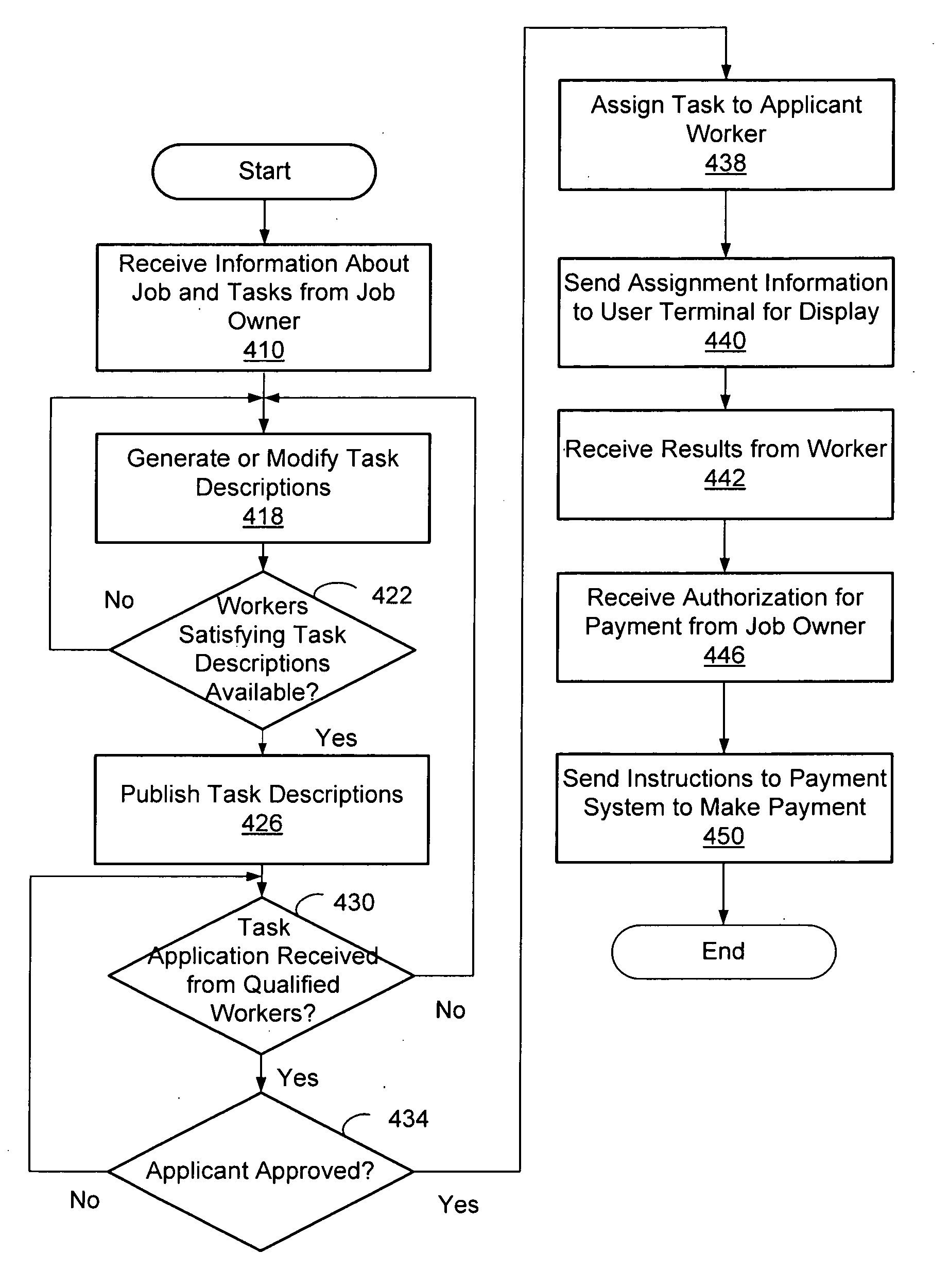
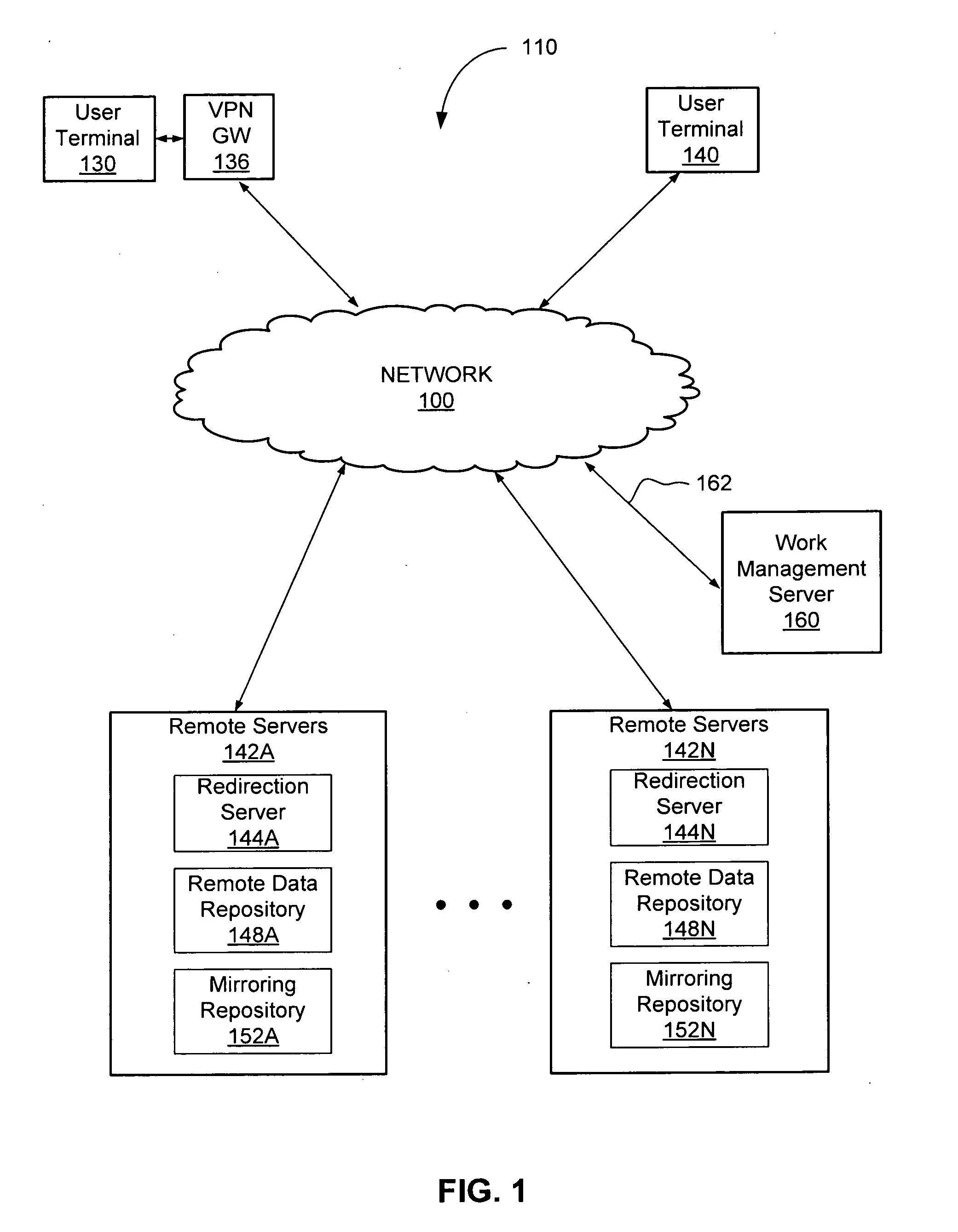
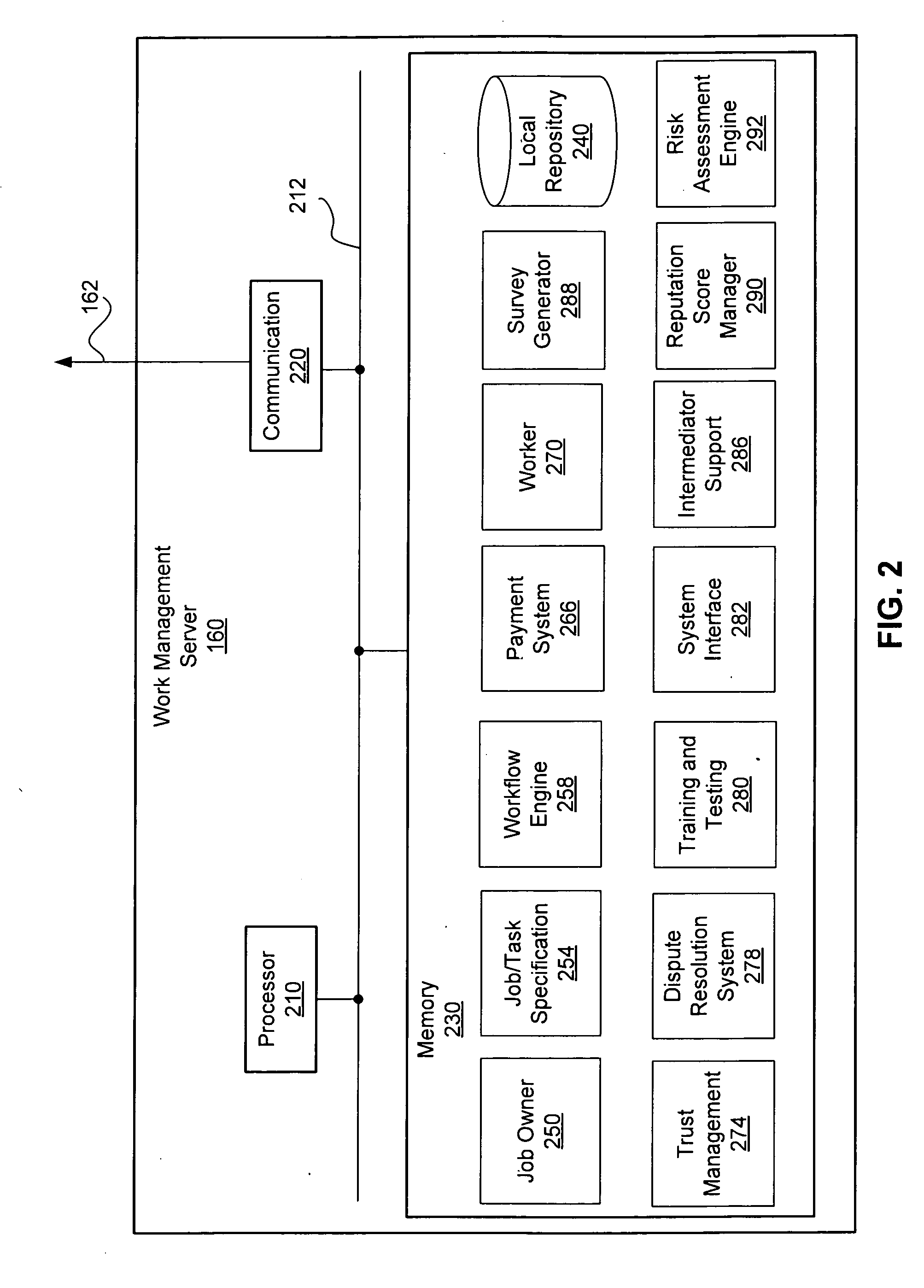
Trust Level Based Task Assignment in an Online Work Management System
ActiveUS20090204471A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPaymentJob description
An online work management system provides a marketplace for multiple job owner and workers. The job owners provide a job description that defines task. The job description may be processed to generate task descriptions that may be published for workers' application. The task descriptions specify the qualification or restrictions for workers to have the task assigned. The online work management system also provides various functions supporting coordination and management of task assignment such as determining the trust level of the user's identity, search the tasks or workers, monitoring the progress of job, managing payment to workers, training and testing the workers, evaluating the review by the job owners, and generation of surveys.
Owner:CLEARSHIFT CORP
System and method of information filtering using measures of affinity of a relationship
A system, apparatus, and method are directed towards enabling information filtering using measures of an affinity of a relationship between subscribers of an online portal system. The affinity of a relationship may be determined based, in part, on the tracking of various online behaviors of and between subscribers of the portal system. Any of a variety of behaviors may be tracked, including message communications between subscribers, participation in instant messaging groups, purchases, activities, categories, and so forth. Such behaviors may be employed to determine a level of trust (or affinity) between subscribers of the portal system. This affinity measurement may be used to filter various information, including, but not limited to, product recommendations, ratings, polling queries, advertising, social network communications, personal ads, search results, and the like. Moreover, this affinity measurement may also be employed to perform message spam detection.
Owner:SLACK TECH LLC
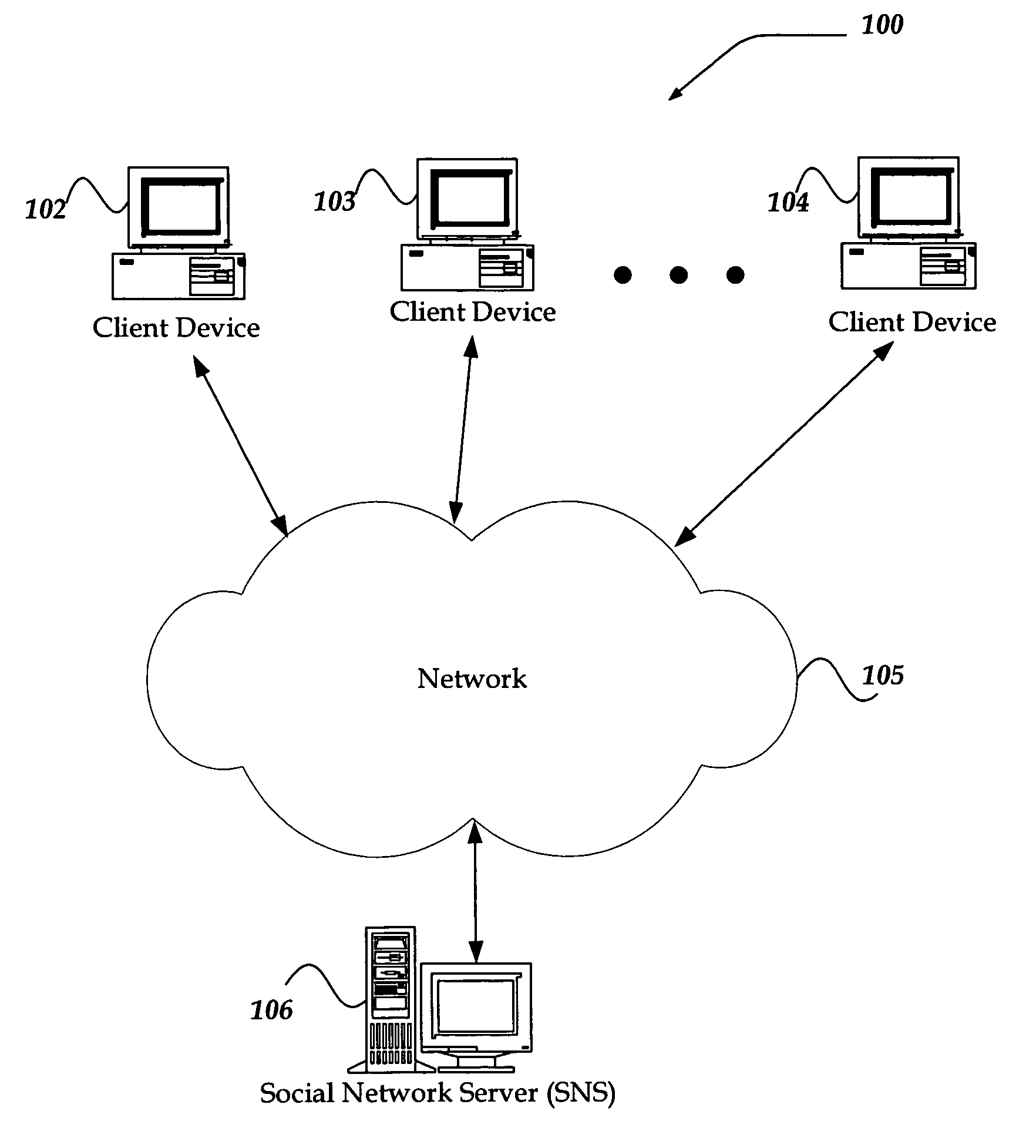
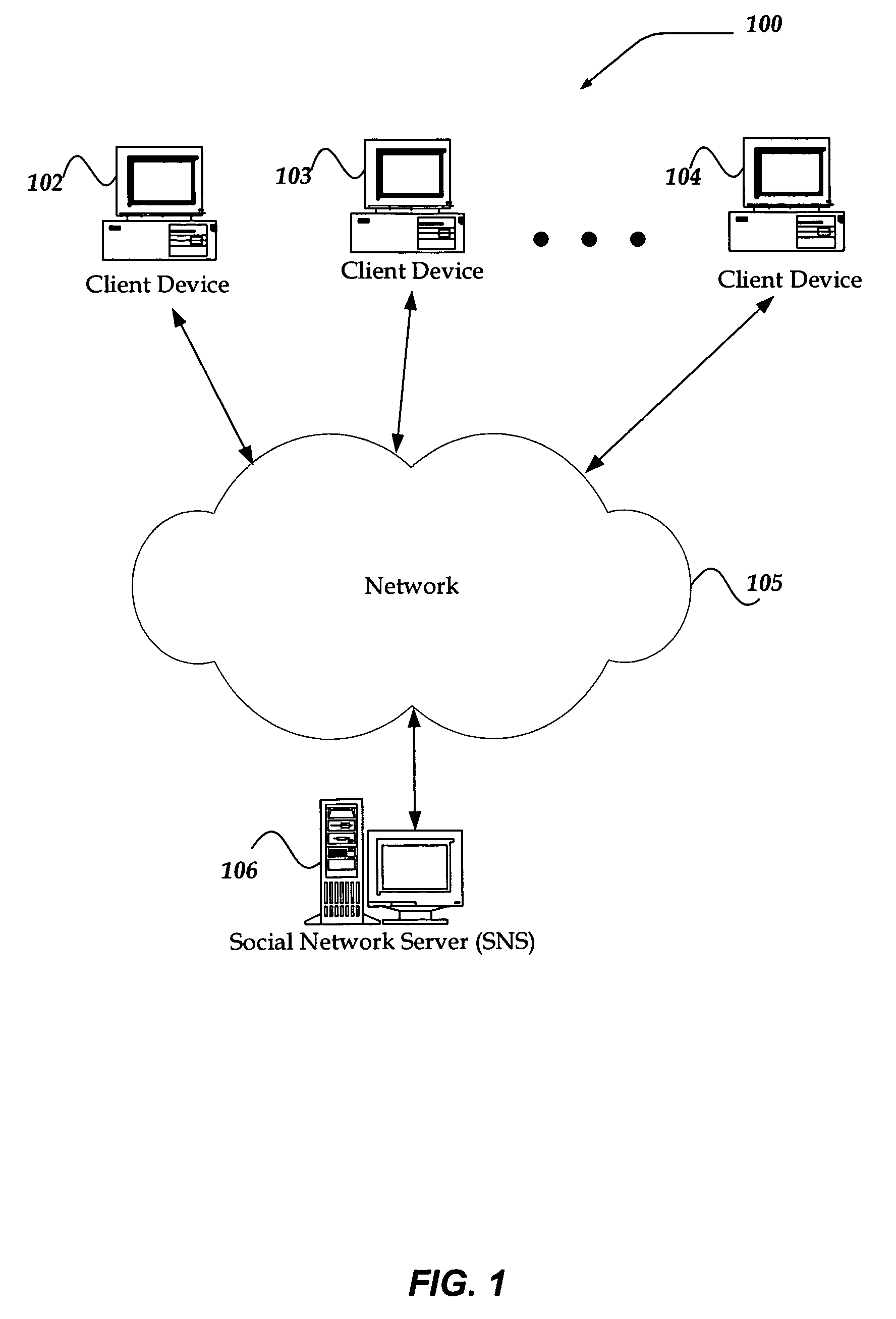
System and method for determining a trust level in a social network environment
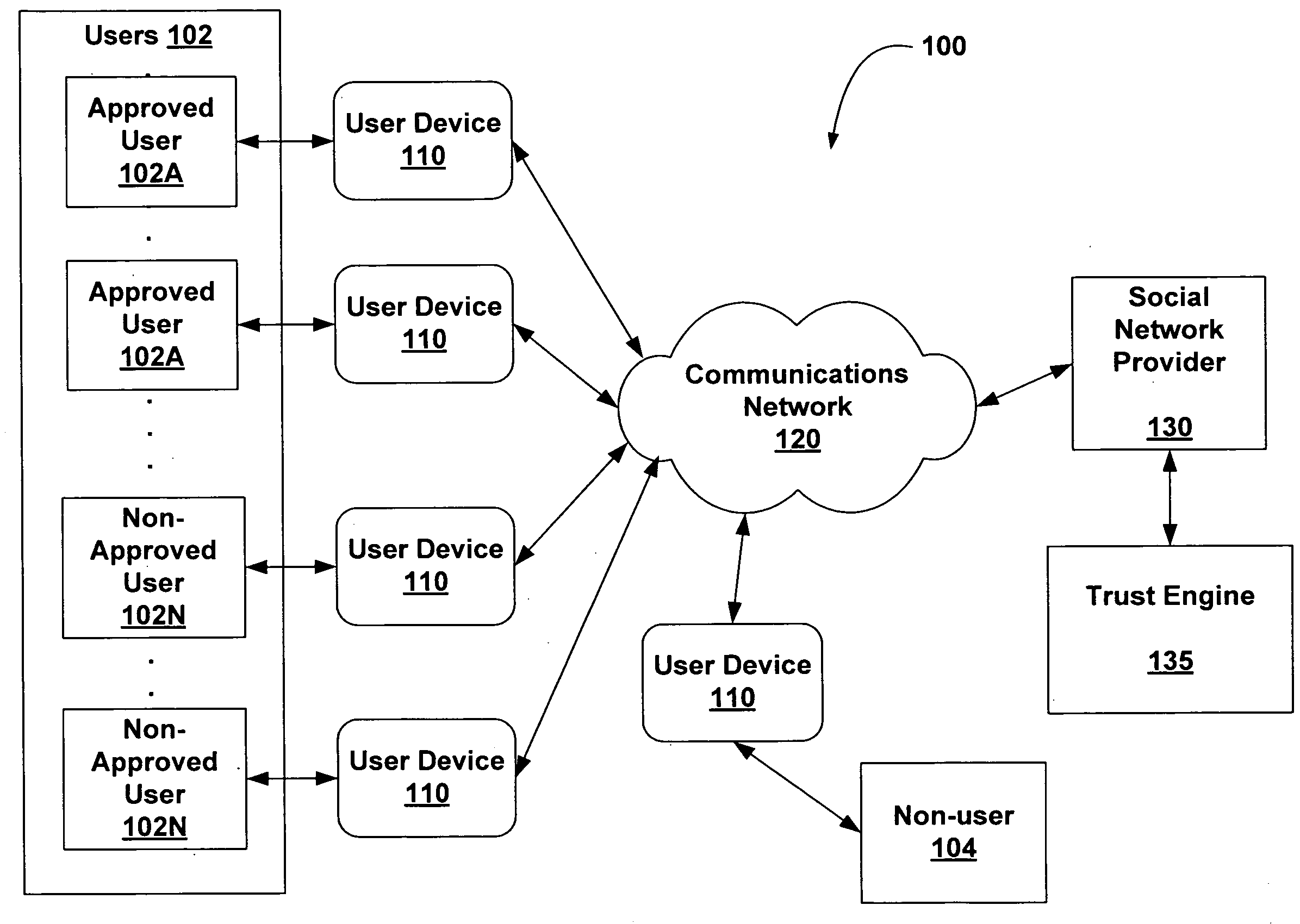
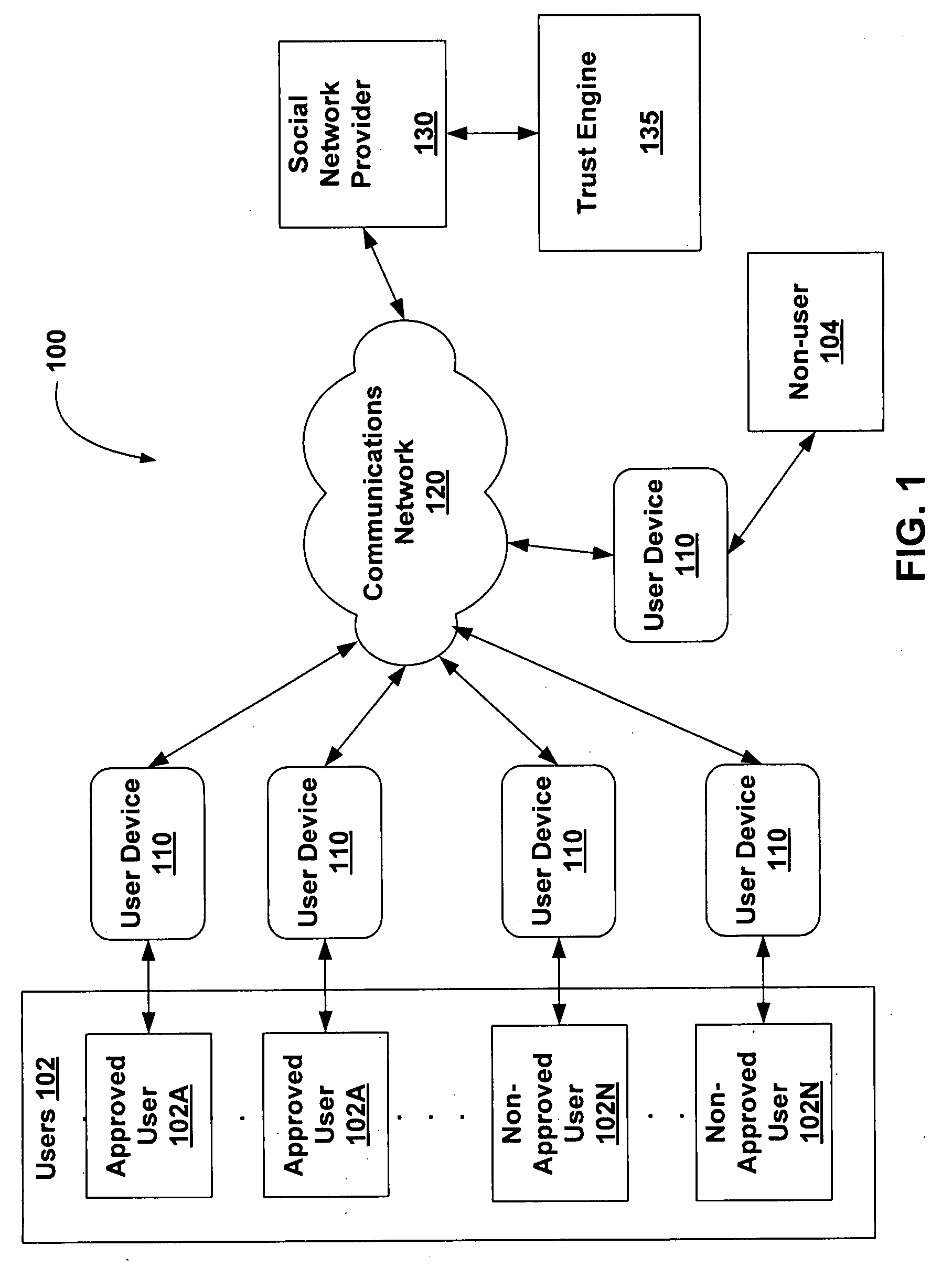
ActiveUS20080189768A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsInternet privacyTrust level
A system and method for determining a trust level for a non-approved user in a social network is described. The method includes monitoring requests for social network interactions between an approved user and the non-approved user and determining if each interaction requested is of a first type or a second type. The method further includes increasing a first trust value when the interaction requested is of the first type and increasing a second trust value when the interaction requested is of the second type. The method further includes determining the trust level based on the first trust value and the second trust value. The method further includes changing the status of the non-approved user to an approved user based on the trust level, the first trust value and / or the second trust value.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
Policy driven, credential delegation for single sign on and secure access to network resources
ActiveUS20070277231A1Wide rangeMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionNetwork conditionsTrust level
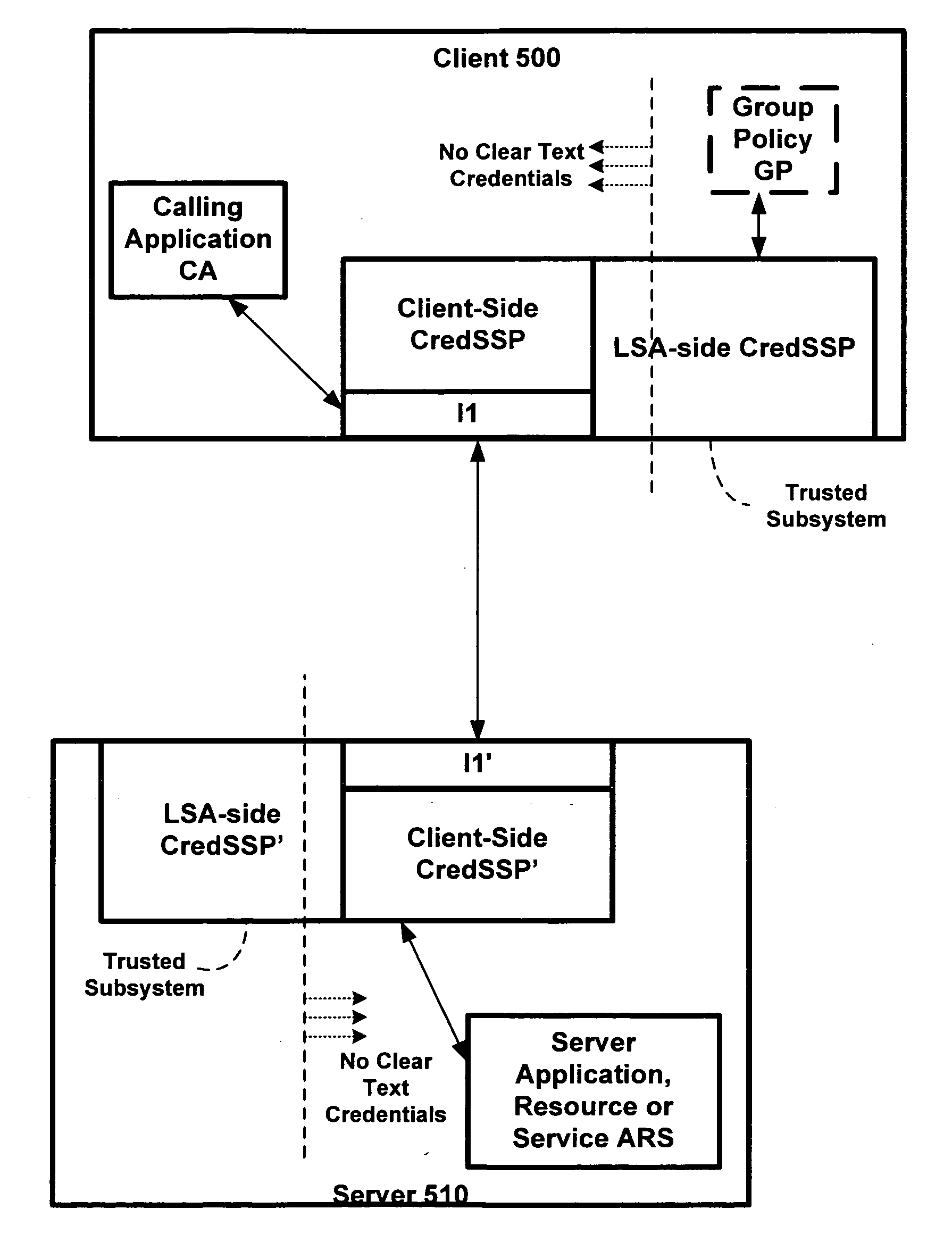
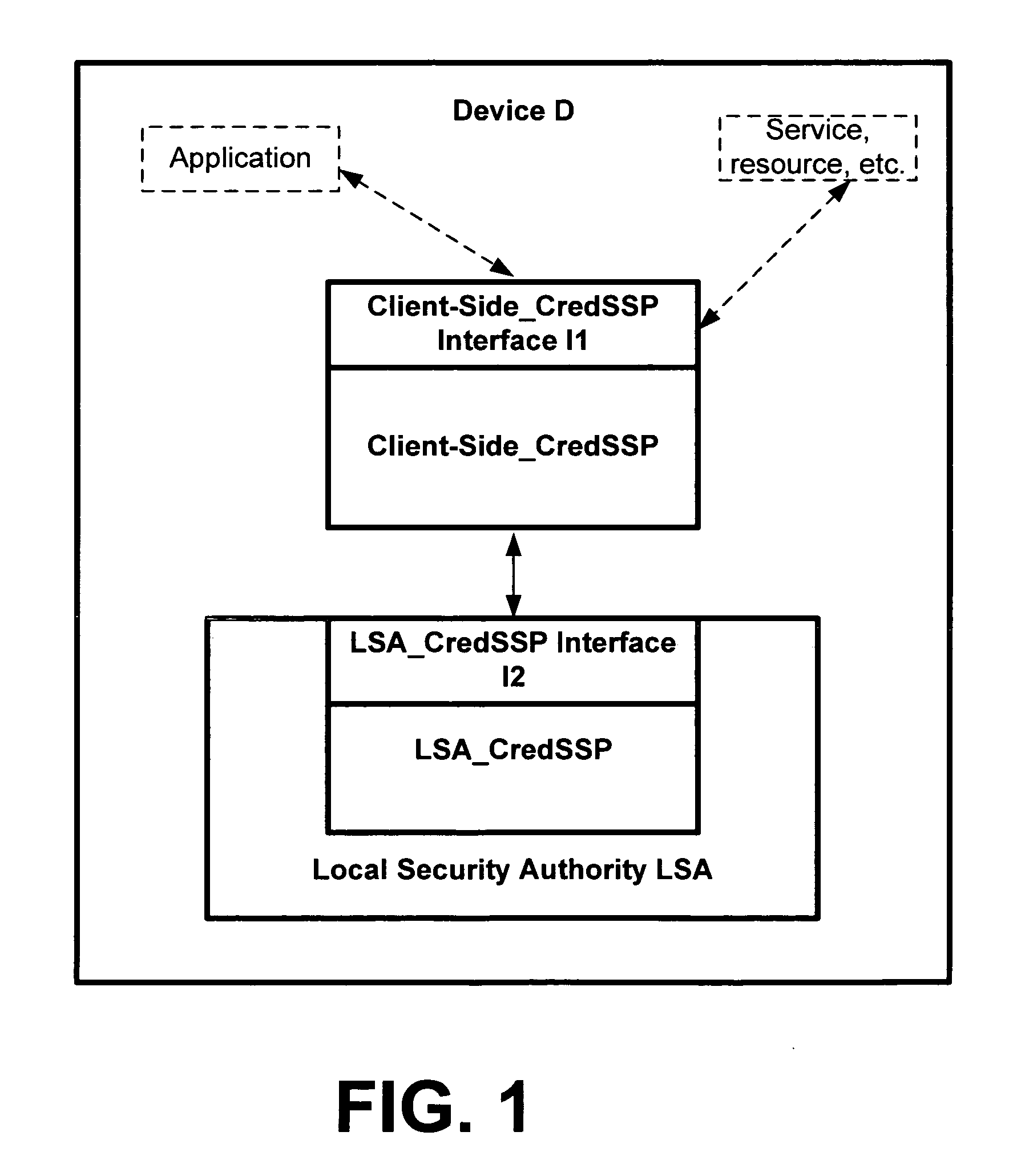
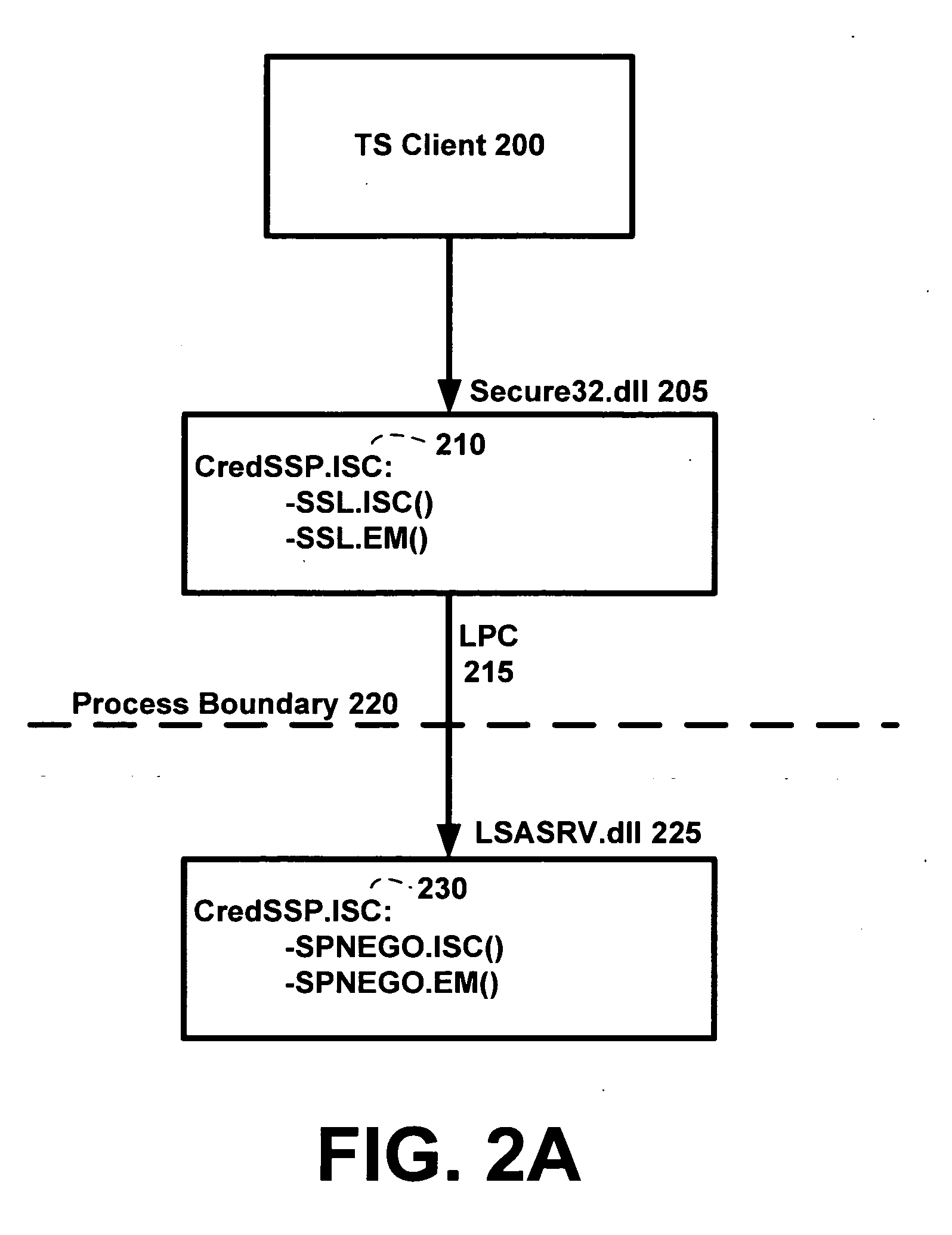
A credential security support provider (Cred SSP) is provided that enables any application to securely delegate a user's credentials from the client, via client side Security Support Provider (SSP) software, to a target server, via server side SSP software in a networked computing environment. The Cred SSP of the invention provides a secure solution that is based in part upon a set of policies, including a default policy that is secure against a broad range of attacks, which are used to control and restrict the delegation of user credentials from a client to a server. The policies can be for any type of user credentials and the different policies are designed to mitigate a broad range of attacks so that appropriate delegation can occur for given delegation circumstances, network conditions, trust levels, etc. Additionally, only a trusted subsystem, e.g., a trusted subsystem of the Local Security Authority (LSA), has access to the clear text credentials such that neither the calling application of the Cred SSP APIs on the server side nor the calling application of the Cred SSP APIs on the client side have access to clear text credentials.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Context sensitive dynamic authentication in a cryptographic system
InactiveUS7260724B1Minimal compute resourceAvoid the needUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsInternet privacyTrust level
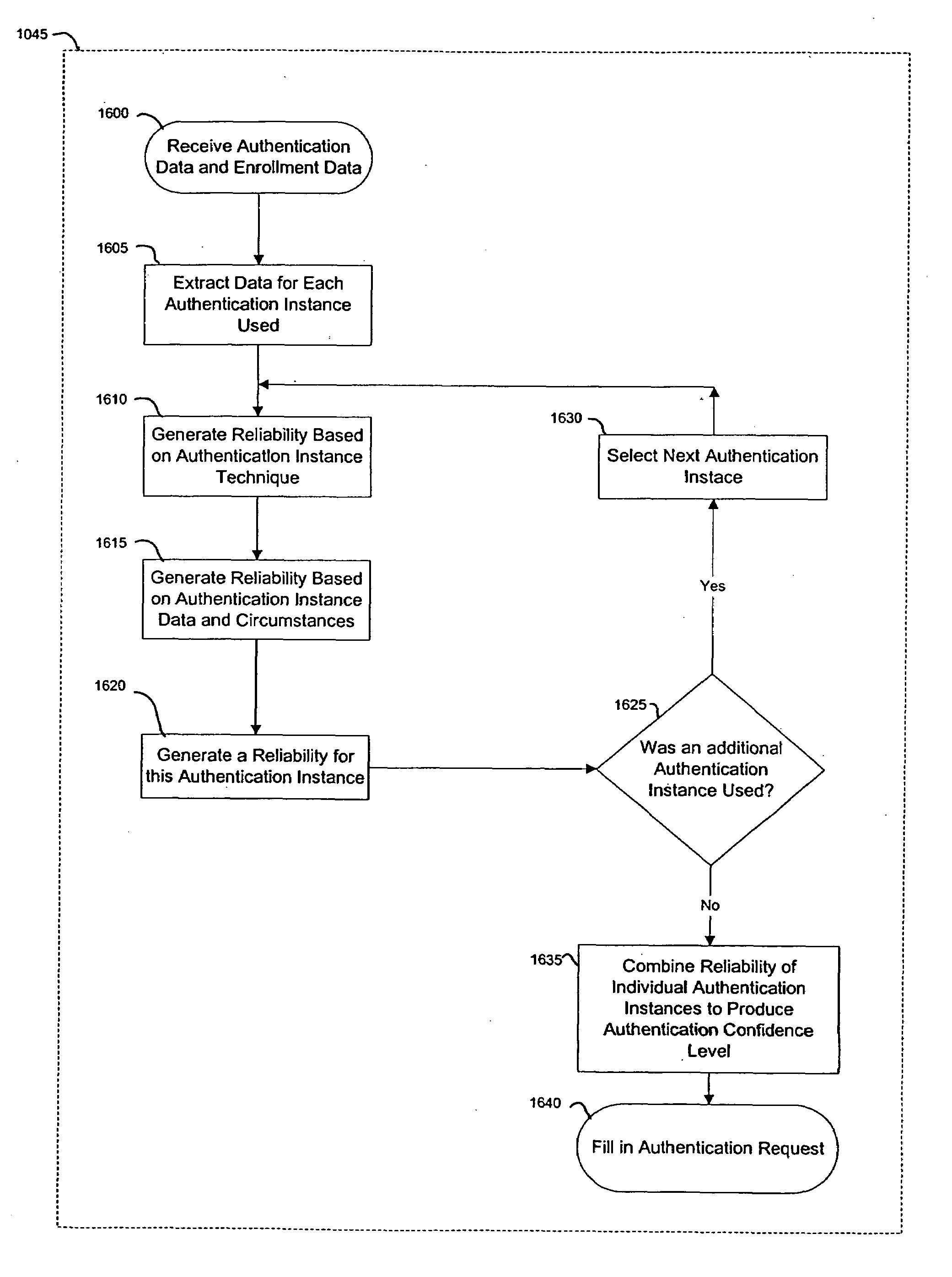
A system for performing authentication of a first user to a second user includes the ability for the first user to submit multiple instances of authentication data which are evaluated and then used to generate an overall level of confidence in the claimed identity of the first user. The individual authentication instances are evaluated based upon: the degree of match between the user provided by the first user during the authentication and the data provided by the first user during his enrollment; the inherent reliability of the authentication technique being used; the circumstances surrounding the generation of the authentication data by the first user; and the circumstances surrounding the generation of the enrollment data by the first user. This confidence level is compared with a required trust level which is based at least in part upon the requirements of the second user, and the authentication result is based upon this comparison.
Owner:SECURITY FIRST INNOVATIONS LLC
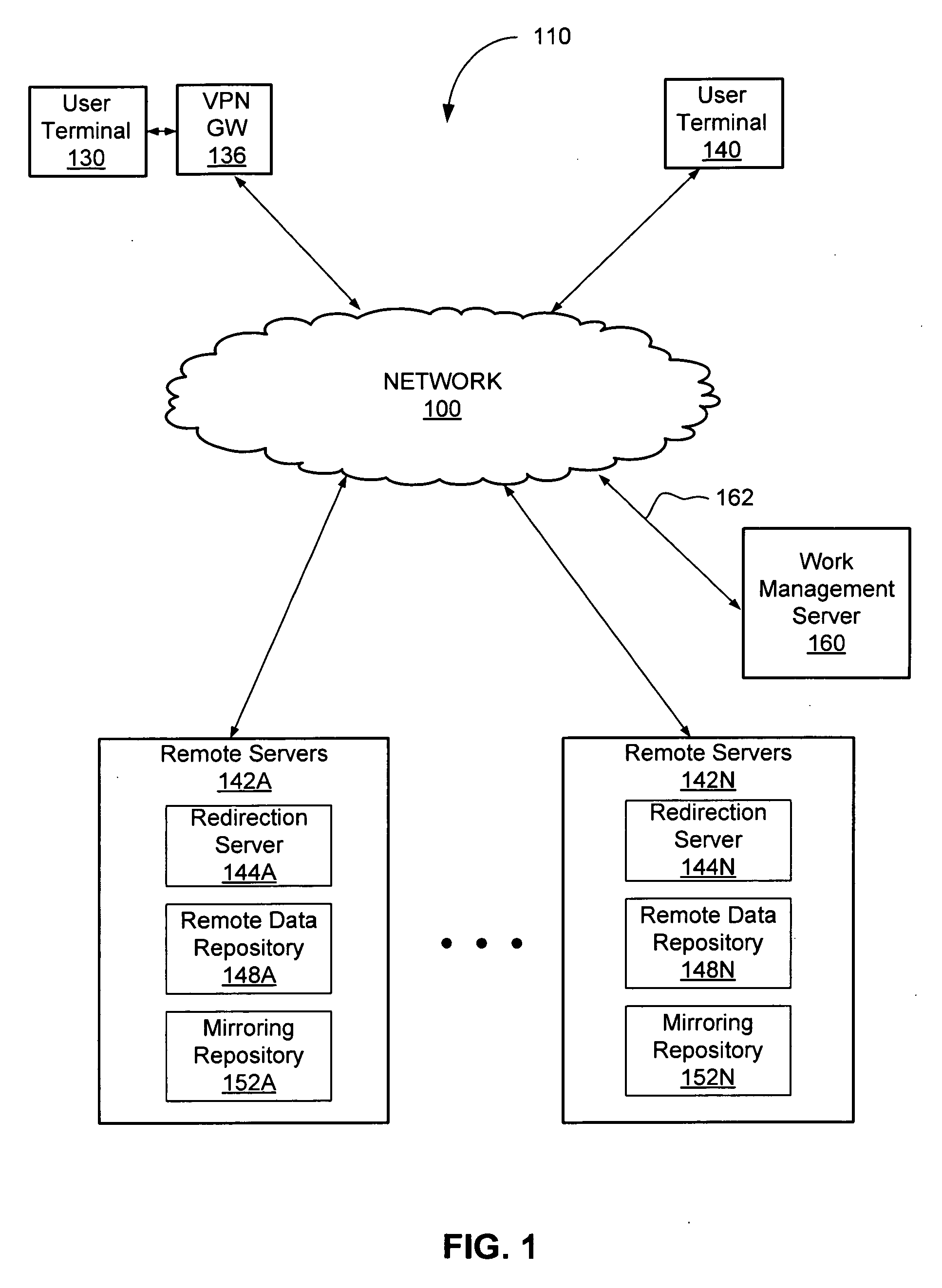
Online Work Management System with Job Division Support
Owner:CLEARSHIFT CORP
Multilevel Assignment of Jobs and Tasks in Online Work Management System
An online work management system provides a marketplace for multiple job owner and workers. The job owners provide a job description that defines task. The job description may be processed to generate task descriptions that may be published for workers' application. The task descriptions specify the qualification or restrictions for workers to have the task assigned. The online work management system also provides various functions supporting coordination and management of task assignment such as determining the trust level of the user's identity, search the tasks or workers, monitoring the progress of job, managing payment to workers, training and testing the workers, evaluating the review by the job owners, and generation of surveys.
Owner:CLEARSHIFT CORP
Methods and apparatus for enabling a dynamic network of interactors according to personal trust levels between interactors
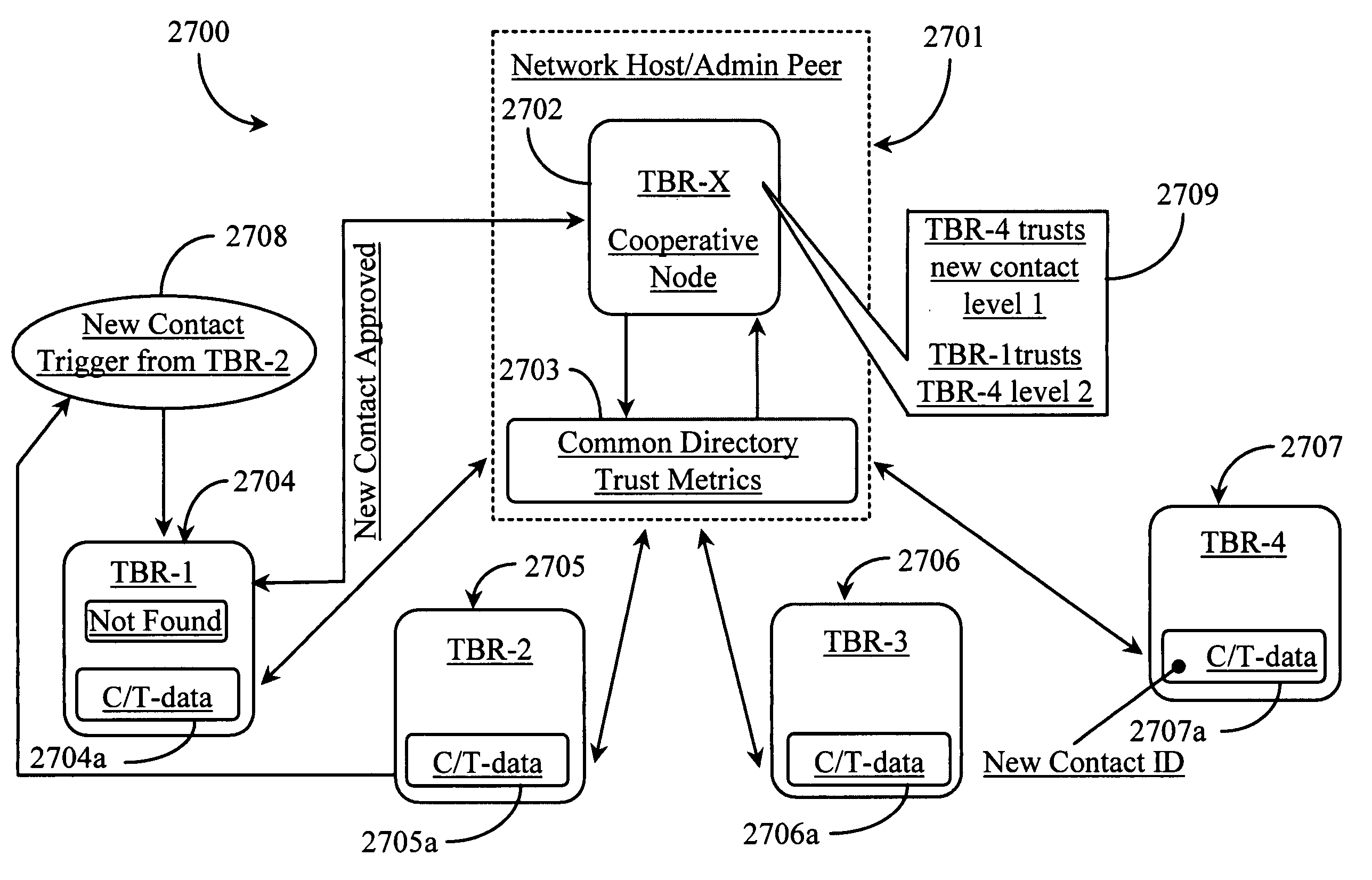
A system for causing routing of a communication event includes a sending platform for initiating and sending the communication event, a communications network for carrying the communication event, a receiving platform for receiving the communication event for final routing, and a router resident at least in the receiving platform for preparing and executing or forwarding for execution a routing instruction for handling the incoming communication event or notification thereof, the routing instruction thus executed, overriding a default routing instruction, the overriding routing instruction initiated upon discovery by the router of some level of trust metric between the sender and intended recipient of the event.
Owner:FORTE INTERNET SOFTWARE
Method and apparatus for sharing content among multiple users
InactiveUS20090216859A1Digital data processing detailsComputer security arrangementsInternet privacyTrust level
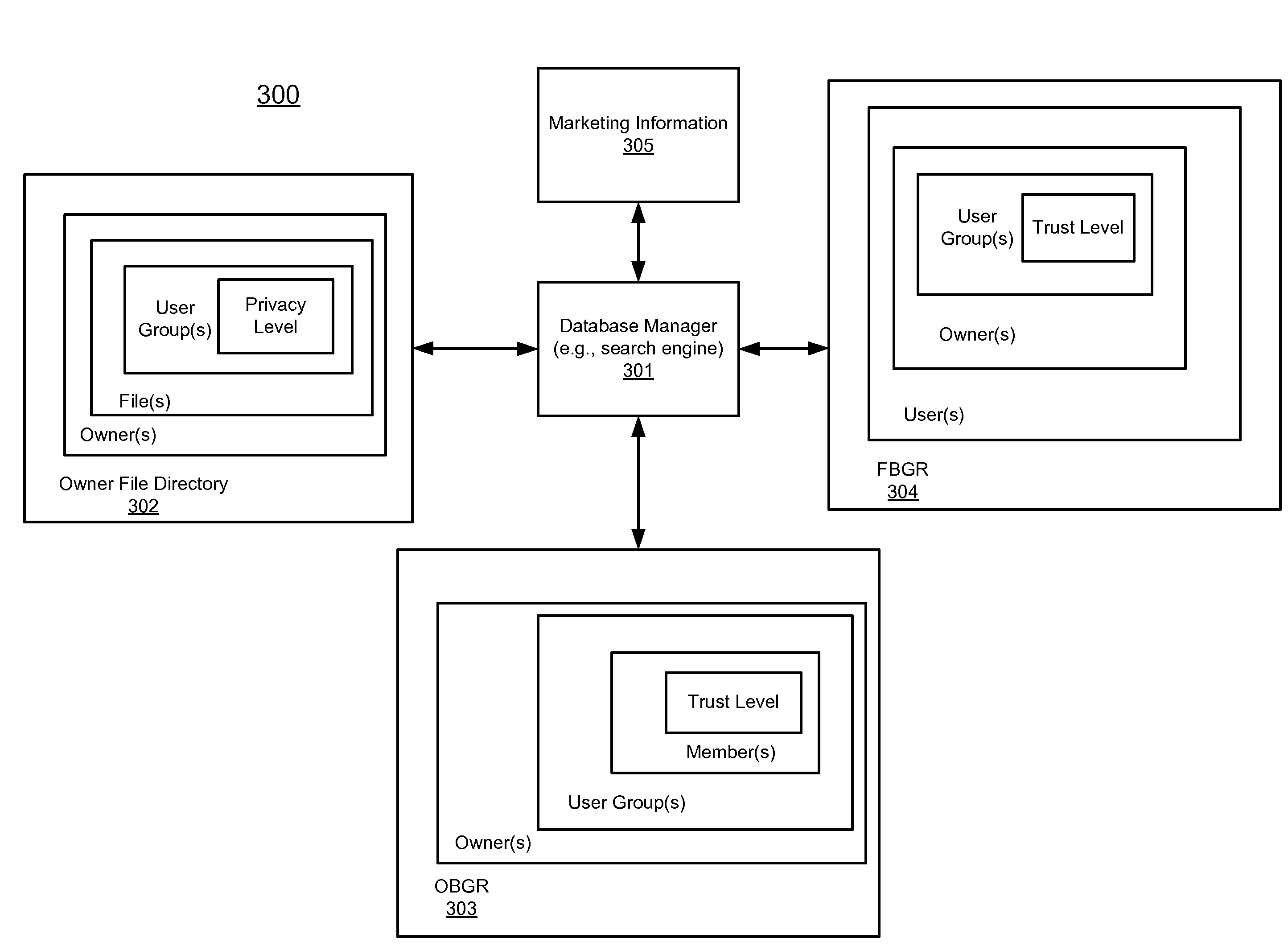
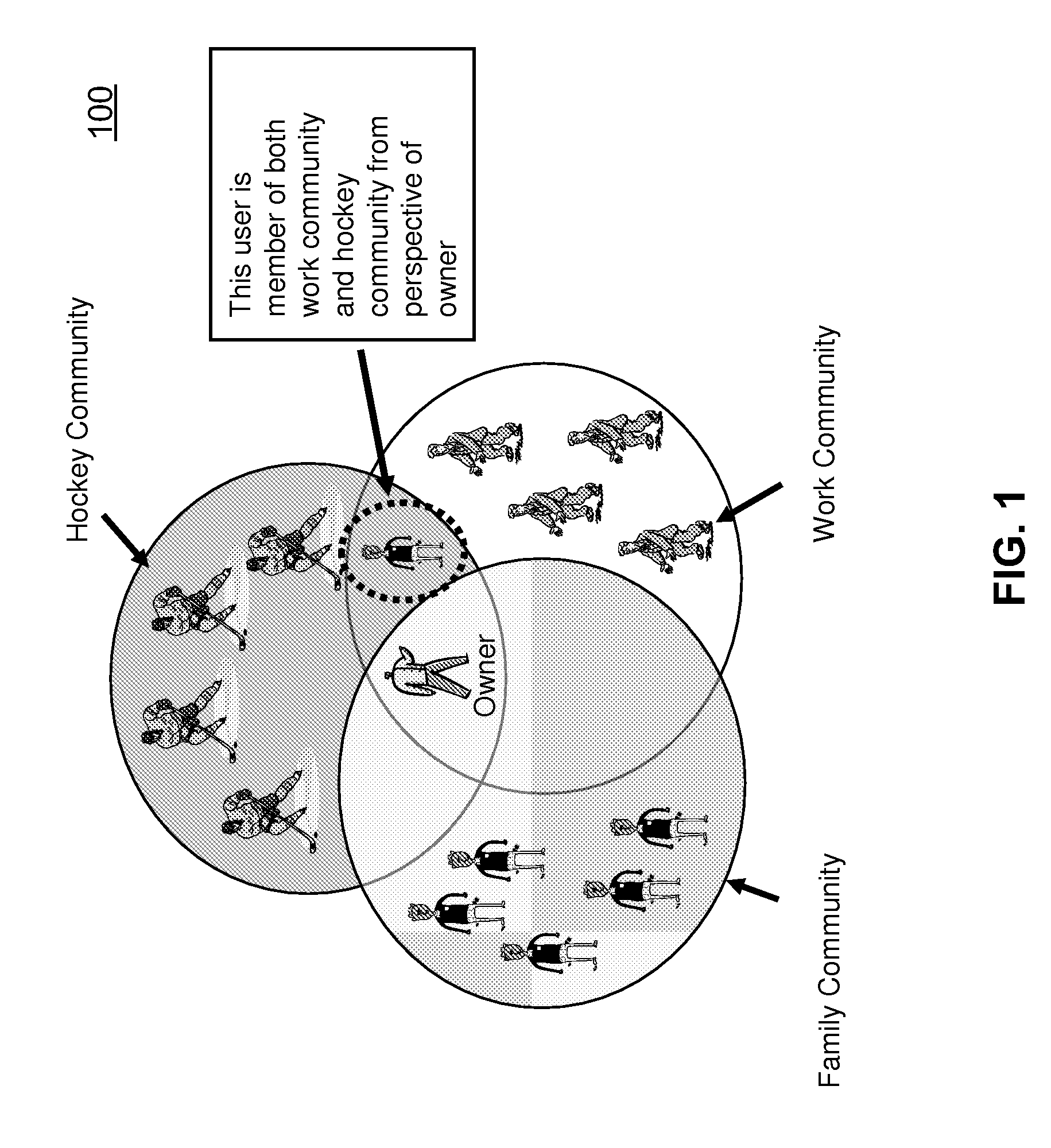
Techniques for sharing content among multiple users are described herein. According to one embodiment, content is received from an owner to be shared among multiple members of one or more communities, where the owner defines the one or more communities. In response to the received content, a privacy level associated with the content to be shared is determined, where the privacy level is assigned by the owner. A trust level associated with each member of the one or more communities is determined, where each member is associated with a trust level assigned by the owner previously to represent a relationship between each member and the owner. The content is shared among selected members of the one or more communities if trust levels of the selected members and the privacy level associated with the content satisfy a predetermined relationship. Other methods and apparatuses are also described.
Owner:WILLIAMS SUSAN BARNHARDT
Trusted virtual machine as a client
InactiveUS20090172781A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrust levelClient-side
The embodiments provide generating a dedicated virtual machine image (DVMI) including functionality for a target service provider and launching the DVMI in the host device as a dedicated virtual machine (DVM). A measurement of the DVMI and / or the launched DVM, as a Trusted Dedicated Virtual Machine (TDVM), is transmitted to the target service provider server. The target service provider determines a trust level for the TDVM, based upon the measurement and provides a level of service by the target service provider server to the TDVM, according to the trust level of the TDVM.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Methods and Apparatus for Delegated Authentication
ActiveUS20080313719A1Easy maintenanceOvercome problemsDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationTrust levelAuthentication server
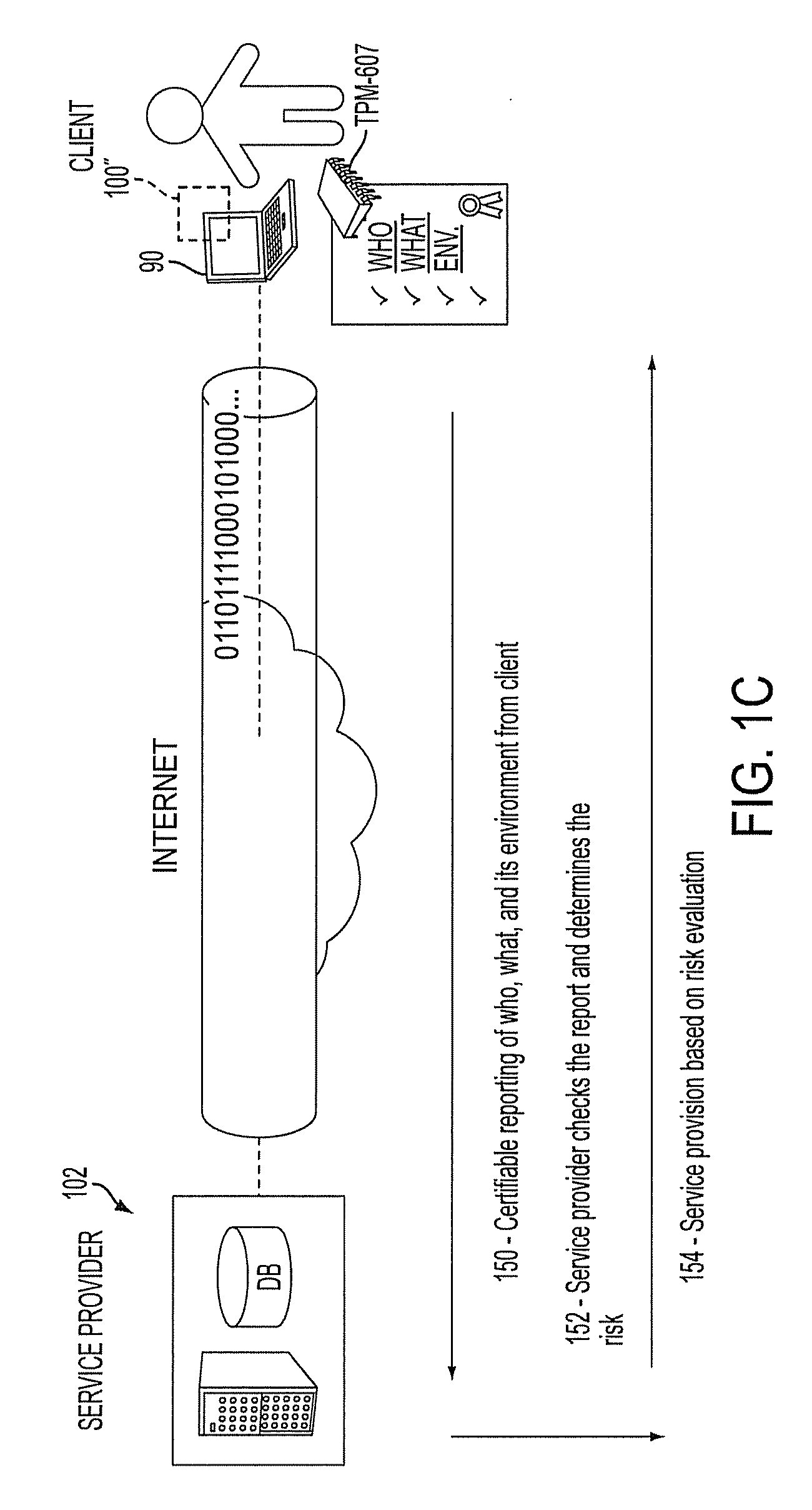
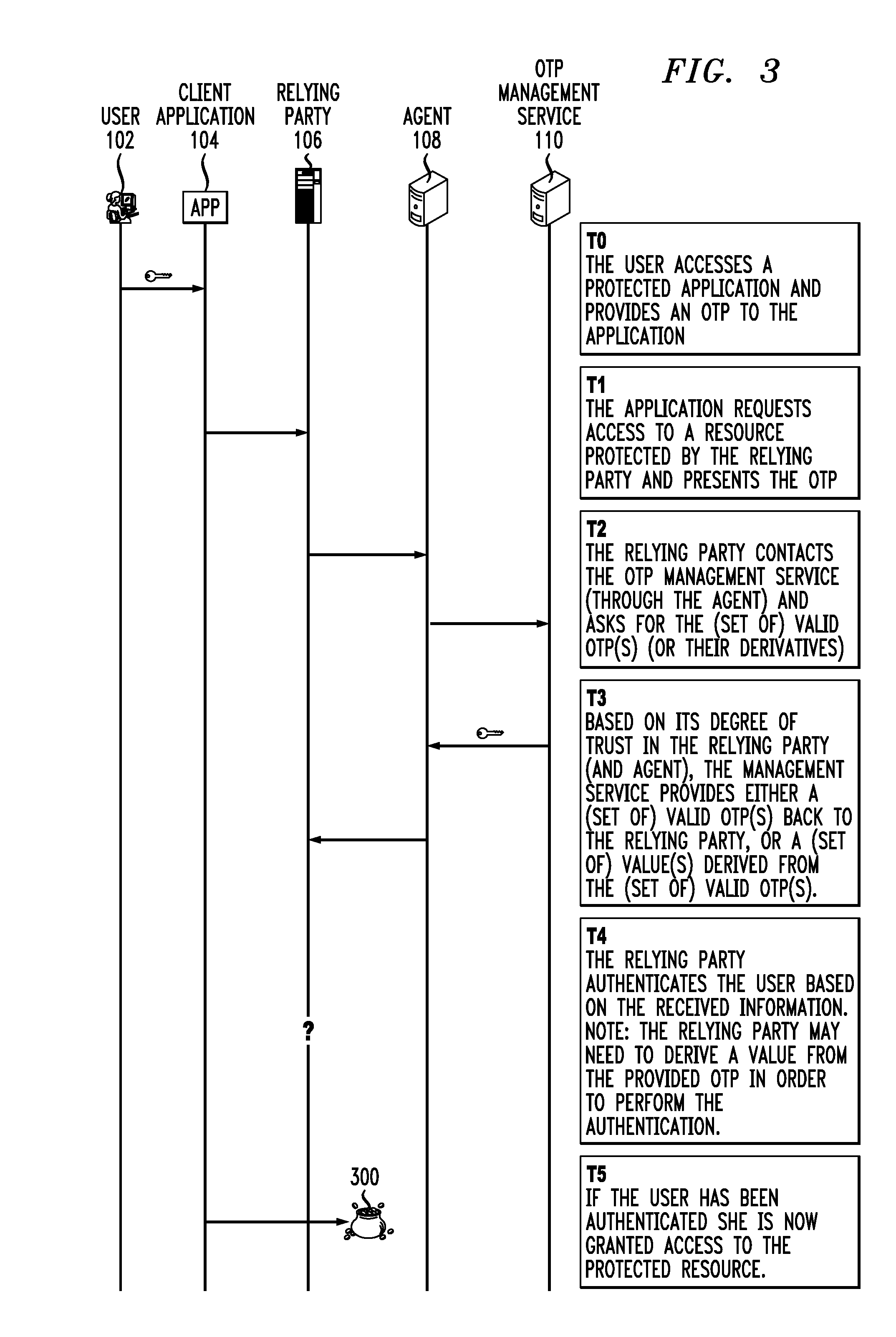
An authentication-delegating service implemented in an authentication server or other processing device is configured to receive a request from a relying party for delegated authentication information associated with a particular user, to determine a level of trust associated with the relying party, and to provide the delegated authentication information to the relying party if the relying party has a sufficient level of trust, so as to permit the relying party to authenticate the user based on the delegated authentication information. The delegated authentication information has the property that the user can be presently authenticated based on such information. The delegated authentication information may comprise, for example, at least one value derived from a one-time password or other authentication credential of the particular user. The authentication-delegating service may be graded to provide different types of delegated authentication information based on respective levels of trust that may be associated with relying parties.
Owner:RSA
Generalized policy server
InactiveUS20080028436A1Easy to handleError preventionTransmission systemsPathPingInformation resource
A scalable access filter that is used together with others like it in a virtual private network to control access by users at clients in the network to information resources provided by servers in the network. Each access filter use a local copy of an access control database to determine whether an access request made by a user. Changes made by administrators in the local copies are propagated to all of the other local copies. Each user belongs to one or more user groups and each information resource belongs to one or more information sets. Access is permitted or denied according to of access policies which define access in terms of the user groups and information sets. The rights of administrators are similarly determined by administrative policies. Access is further permitted only if the trust levels of a mode of identification of the user and of the path in the network by which the access is made are sufficient for the sensitivity level of the information resource. If necessary, the access filter automatically encrypts the request with an encryption method whose trust level is sufficient. The first access filter in the path performs the access check and encrypts and authenticates the request; the other access filters in the path do not repeat the access check. A policy server component of the access filter has been separated from the access filter and the policies have been generalized to permit administrators of the policy server to define new types of actions and new types of entities for which policies can be made. Policies may now further have specifications for time intervals during which the policies are in force and the entities may be associated with attributes that specify how the entity is to be used when the policy applies.
Owner:QUEST SOFTWARE INC +1
Method of providing secure access to computer resources
InactiveUS20070101400A1Easy accessLow level of trustDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer resourcesTrusted authority
A method of providing varying levels of secure access to computer resources. A certificate is used to identify a particular data requester and the certificate is authenticated using asymmetrical encryption techniques, such as public-private key pairs. One or more trust authorities may be consulted to ascribe a trust level to the certificate, which is an indication of the veracity of the identity of the data requester. Individual system users may set differing levels of access to a number of shared system resources for a particular data requester. The authenticated and verified data requester is then provided with the pre-set level of access to the desired shared resource. The level of access to a particular shared system resource therefore depends upon the user the data is being accessed through, the authenticated identity of the data requester, and their ascribed trust level. The shared resource may comprise data and / or an application module that is accessed or executed through a secure symmetric encryption tunnel.
Owner:OVERCOW CORP
Systems and methods for determining trust levels for computing components using blockchain
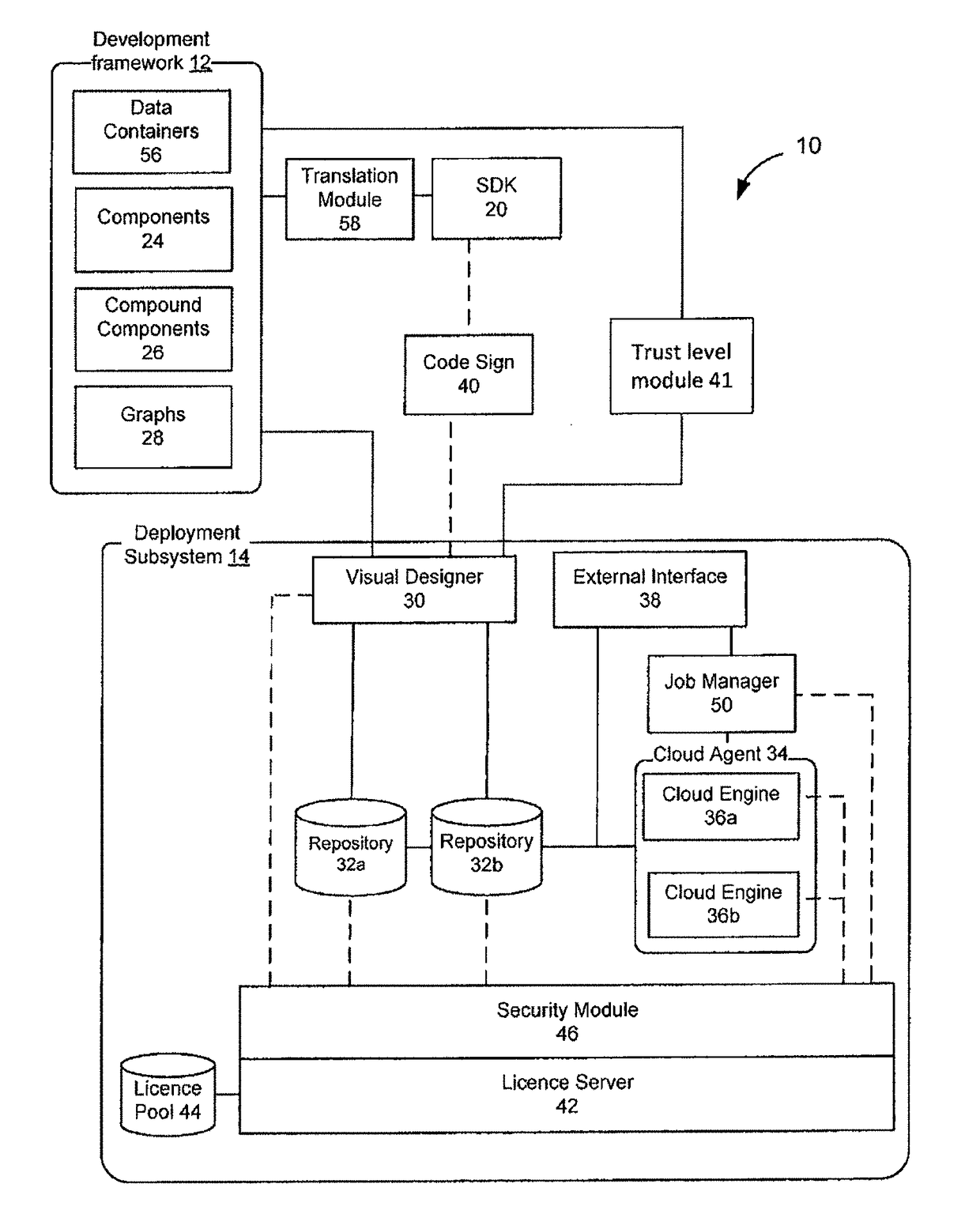
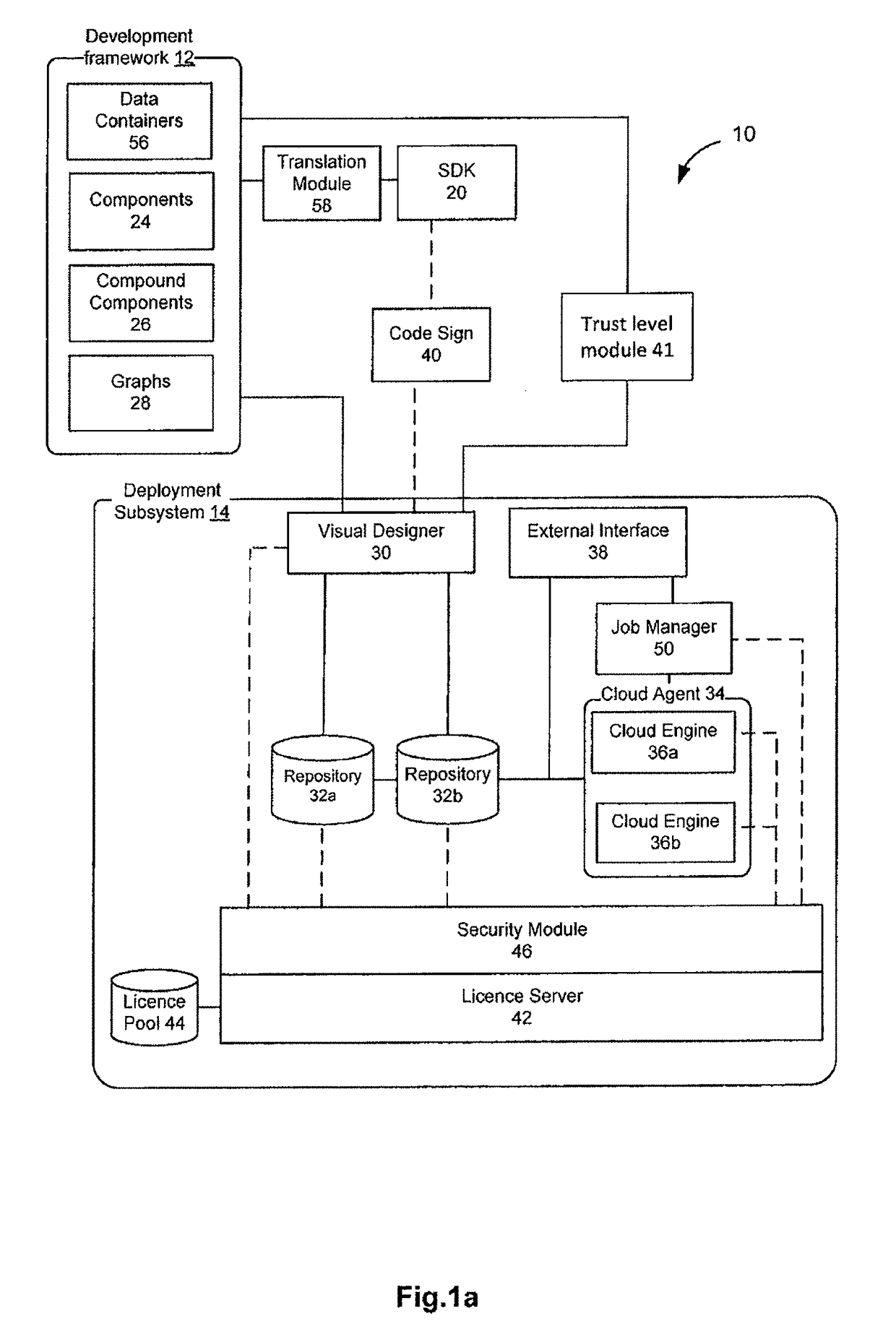
ActiveUS20180157825A1Acceptable performanceCryptography processingDigital data protectionGraphicsInternet privacy
Systems and methods for determining trust levels for components of a computing application using a blockchain. The system may include a development framework, a trust matrix, a trust level calculation module, a visual design subsystem, and a deployment subsystem, where trust levels are associated with components, combinations of components, graphs, and blueprints, where trust levels relate to categories of use.
Owner:IMAGINE COMM
System for executing program using virtual machine monitor and method of controlling the system
InactiveUS20090165133A1Improve system stabilityImprove stabilityMemory loss protectionUnauthorized memory use protectionOperational systemControl system
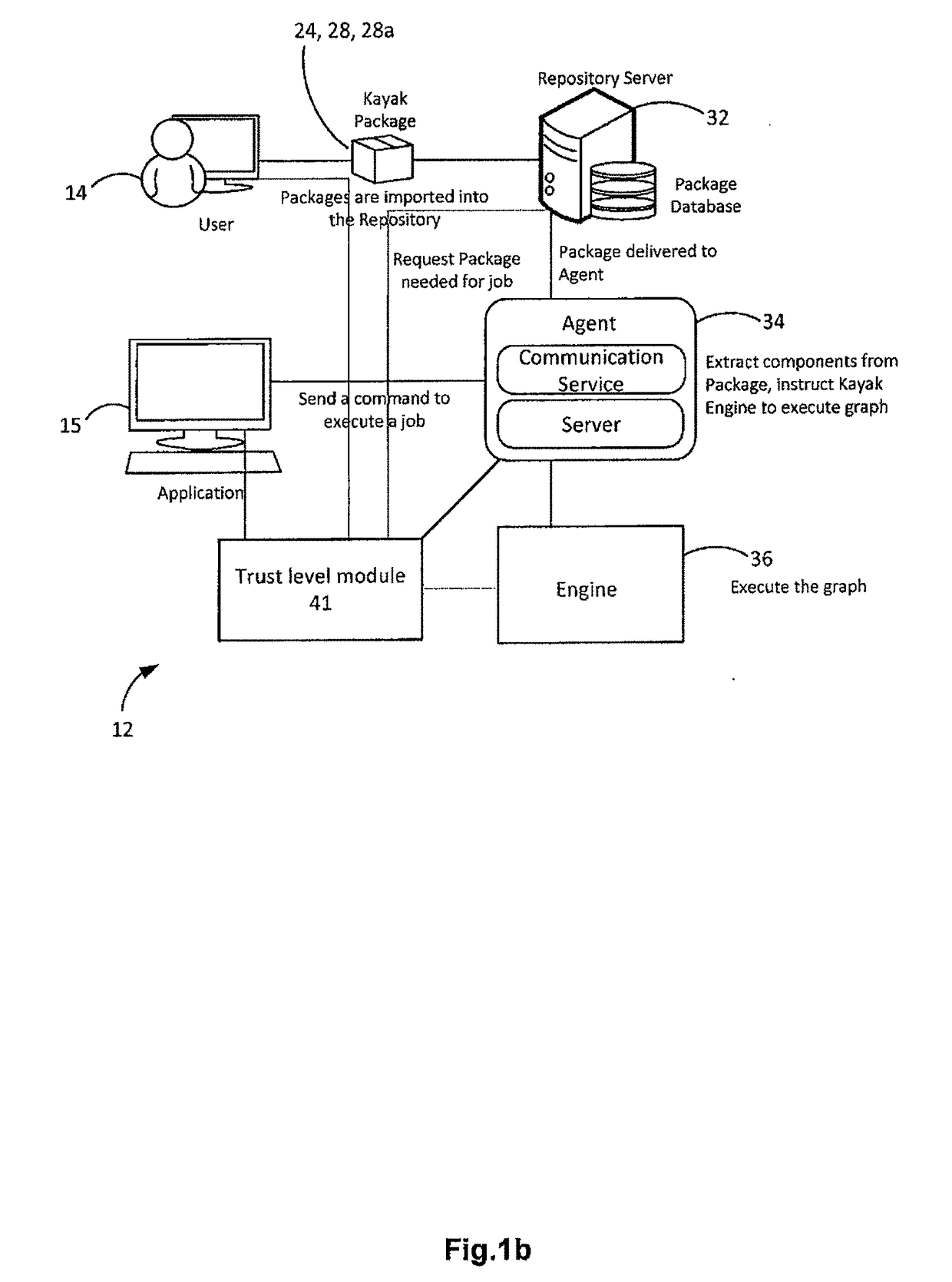
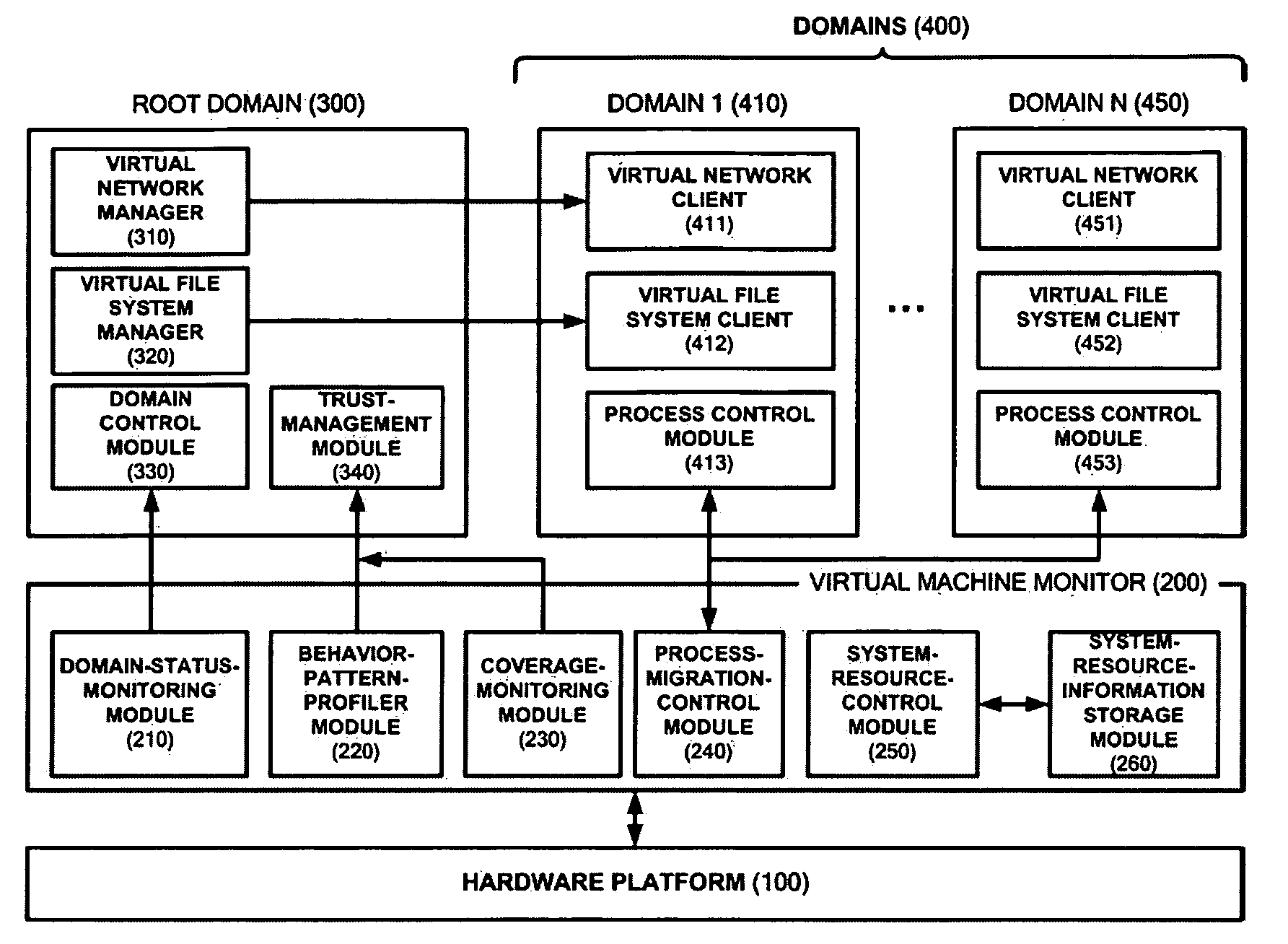
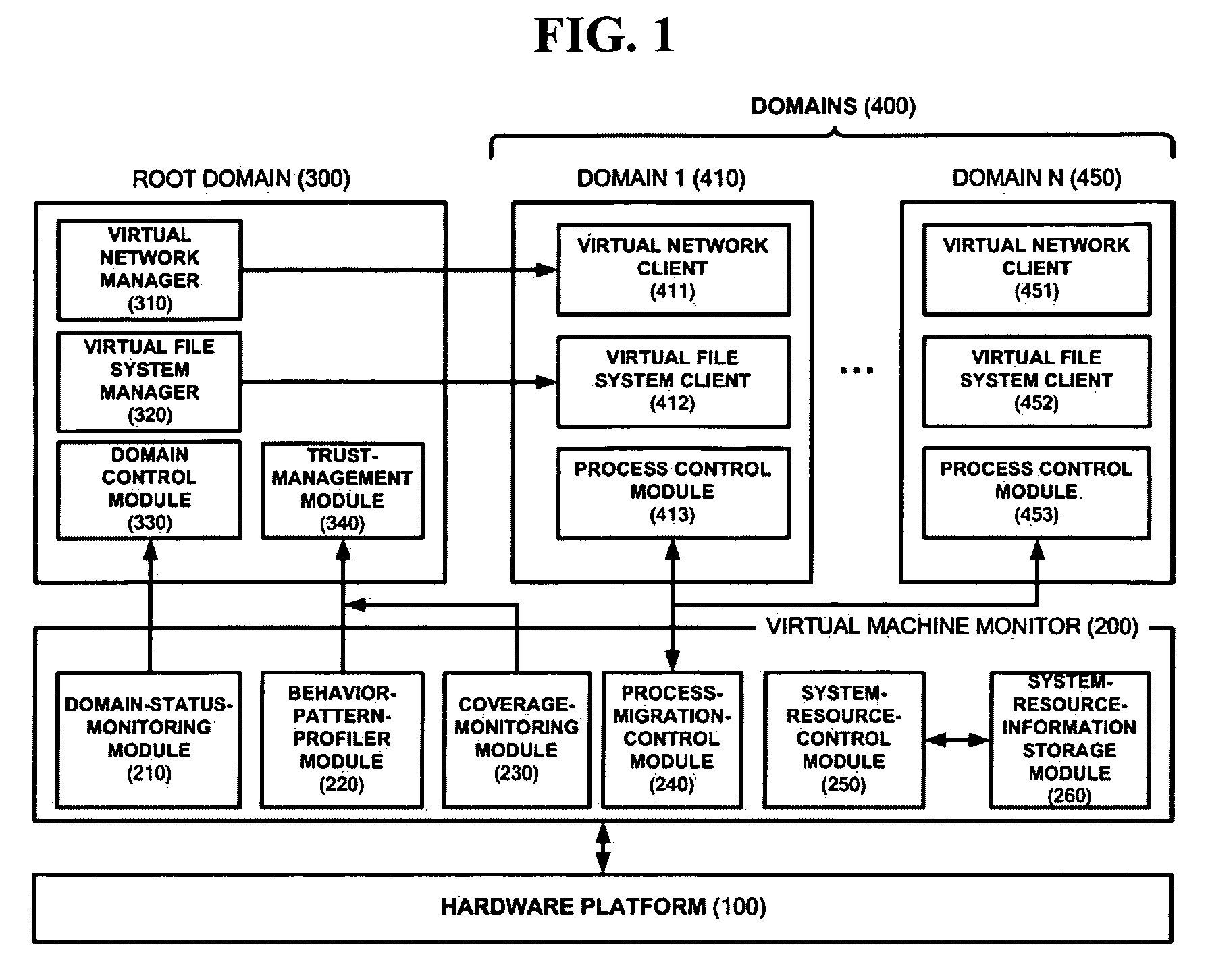
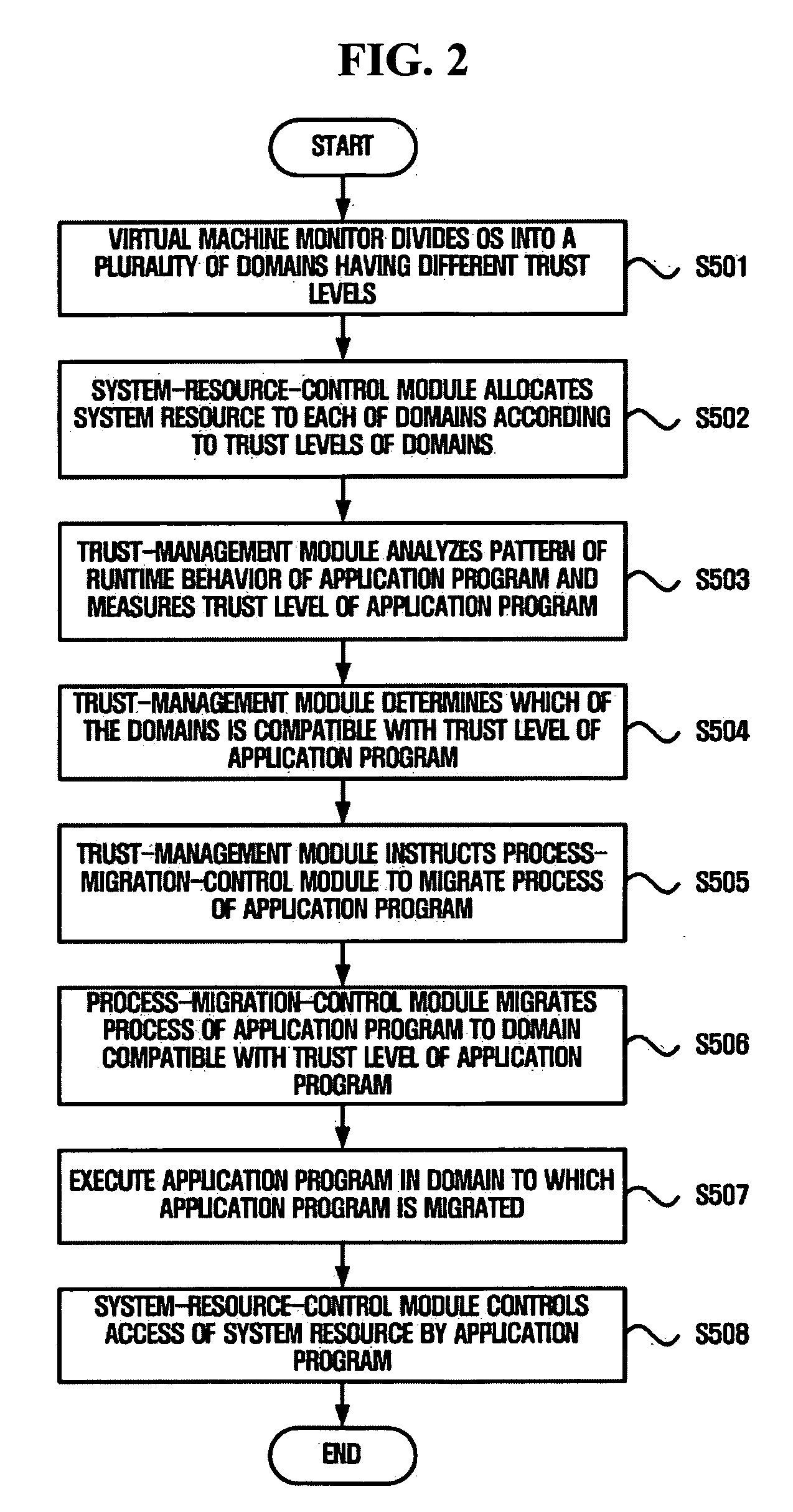
A system for executing a program using a virtual machine monitor and a method of controlling the system are provided. The system includes a virtual machine monitor which divides an operating system (OS) into at least one root domain and a plurality of domains having different trust levels, and a trust-management module which is included in the root domain and periodically measures the trust level of an application program currently being executed in the OS. The virtual machine monitor executes the application program in one of the domains in consideration of the trust level of the application program. The method includes dividing an OS into at least a root domain and a plurality of domains having different trust levels by using a virtual machine monitor, enabling the root domain to periodically measure the trust level of an application program currently being executed in the OS, and executing the application program in one of the domains according to the trust level of the application program.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multiple Means of Trusted Translation
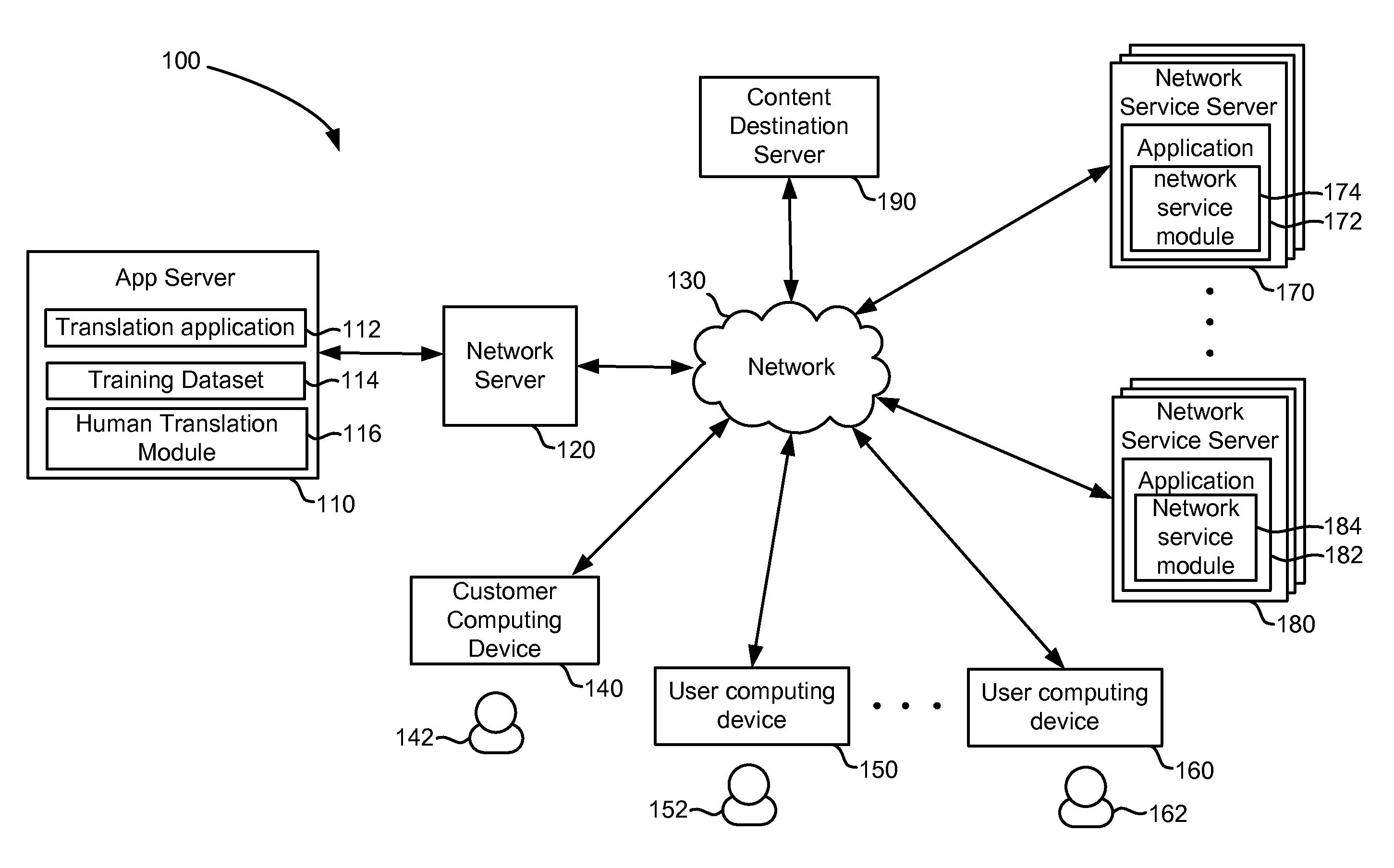
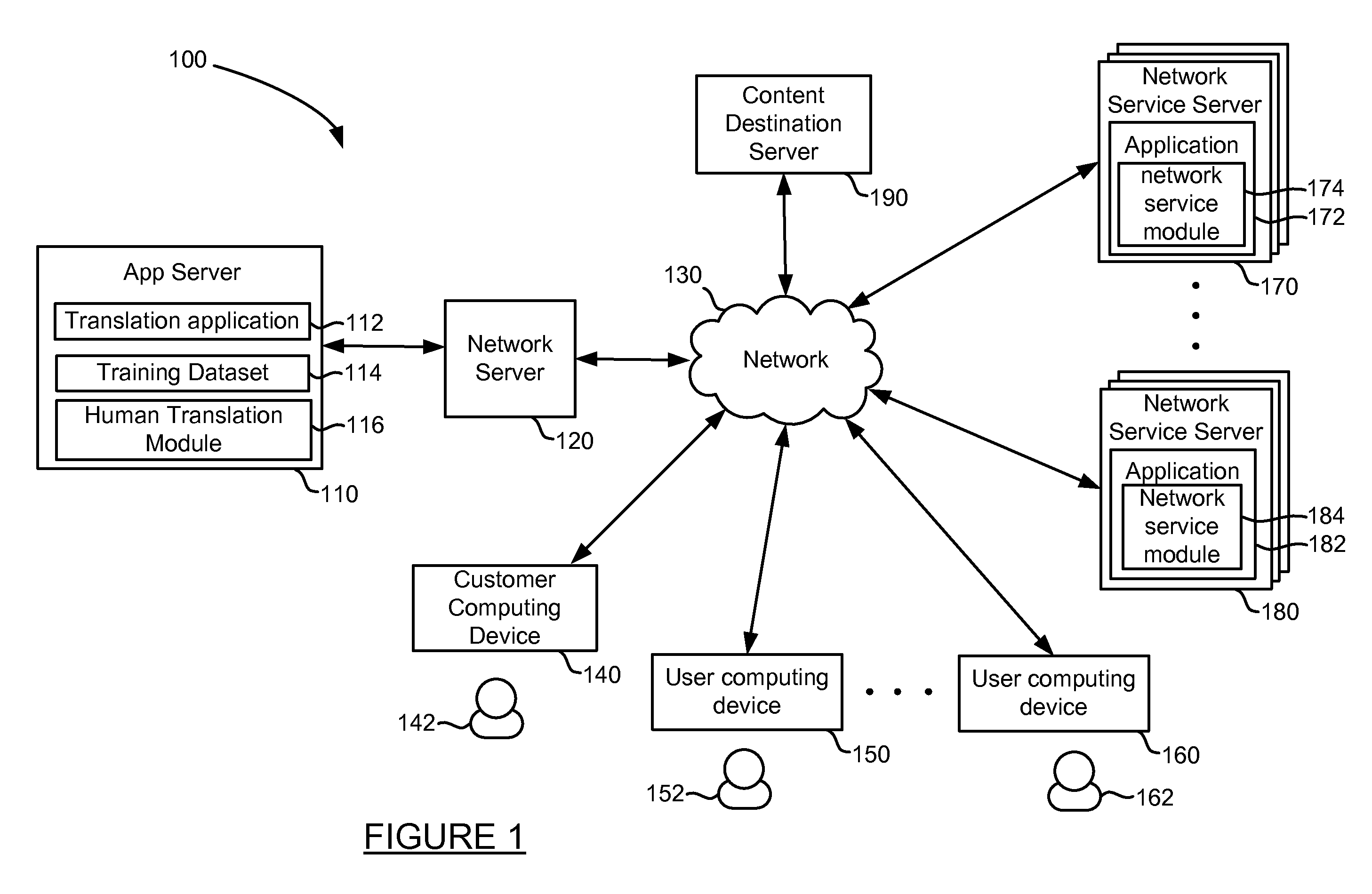
ActiveUS20110082684A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsTrust levelApplication software
Customers having a translation project to select a translation method from a variety of options, ranging from a completely human translation to a completely automated translation. For human translations, translation job information may be communicated through one or more network service modules which execute within a network service application, such as a web-based networking application. A network service module may register a user having an account with the network service application as a translator and communicate translation jobs to the user. One or more users who express interest in performing the translation are selected to perform a translation job, each job comprising at least a portion of the translation project. After a user provides a translation for the translation job, the translation is analyzed to generate a trust level prediction for the translation. A user translation profile may be updated after each translation to reflect the user's performance.
Owner:SDL INK
Data transfer security
ActiveUS20060190606A1Memory loss protectionDigital data processing detailsInternet privacyTrust level
An apparatus for protecting against computer malware, comprising: a data inputter for intercepting data units flow, a trust level assigner, associated with the data inputter, for assigning to each of the data units a respective trust level, an isolated-processing environment, operable to process the data units in an isolated manner and configured to send copies of the processed data units out of the isolated-processing environment, and a processing environment selector, associated with the trust level assigner and the isolated-processing environment, operable to determine if a data unit is to be executed on the isolated-processing environment, in accordance with the respective trust level.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Providing Machine-Generated Translations and Corresponding Trust Levels
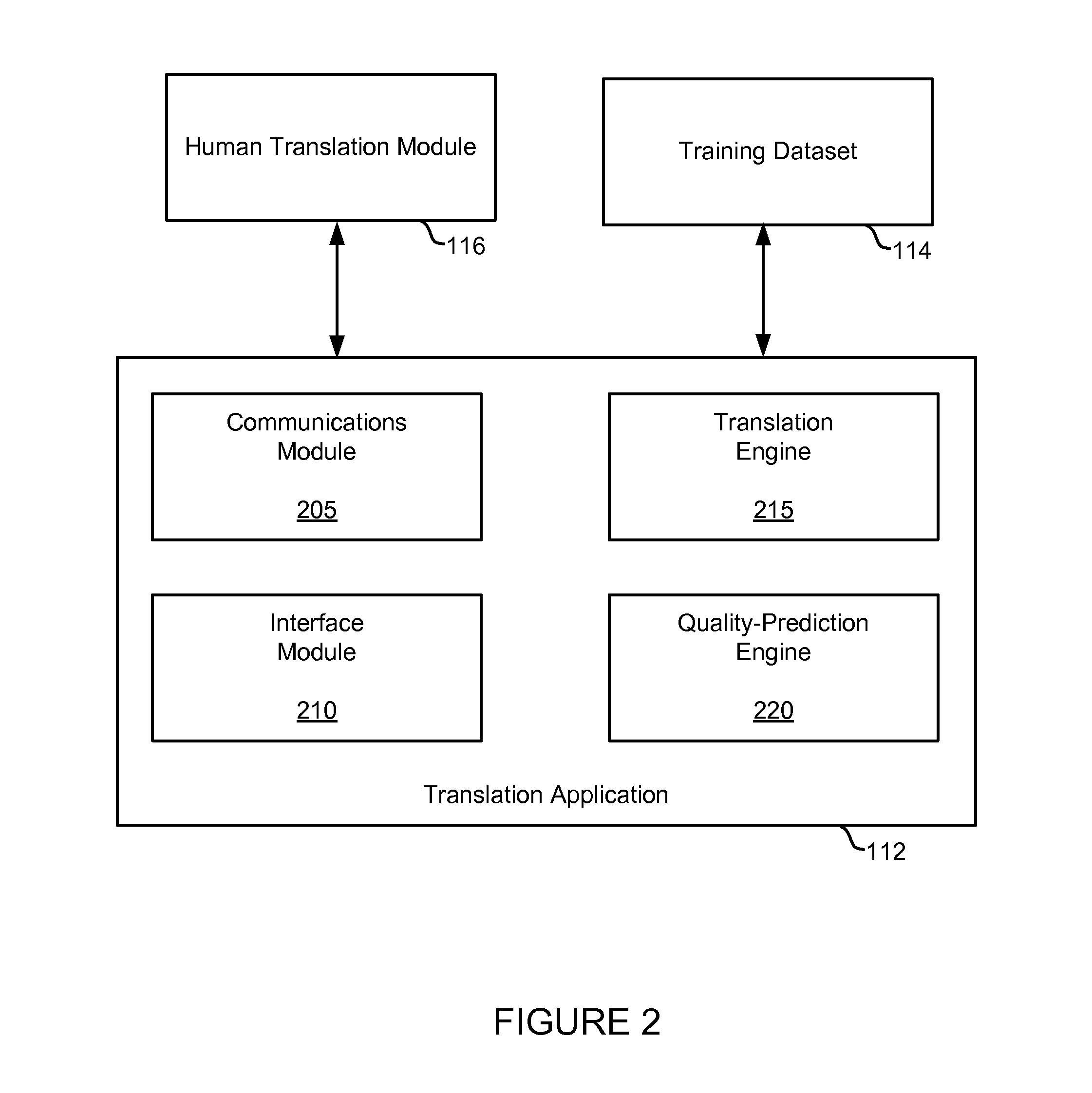
ActiveUS20110082683A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsTrust levelMachine translation
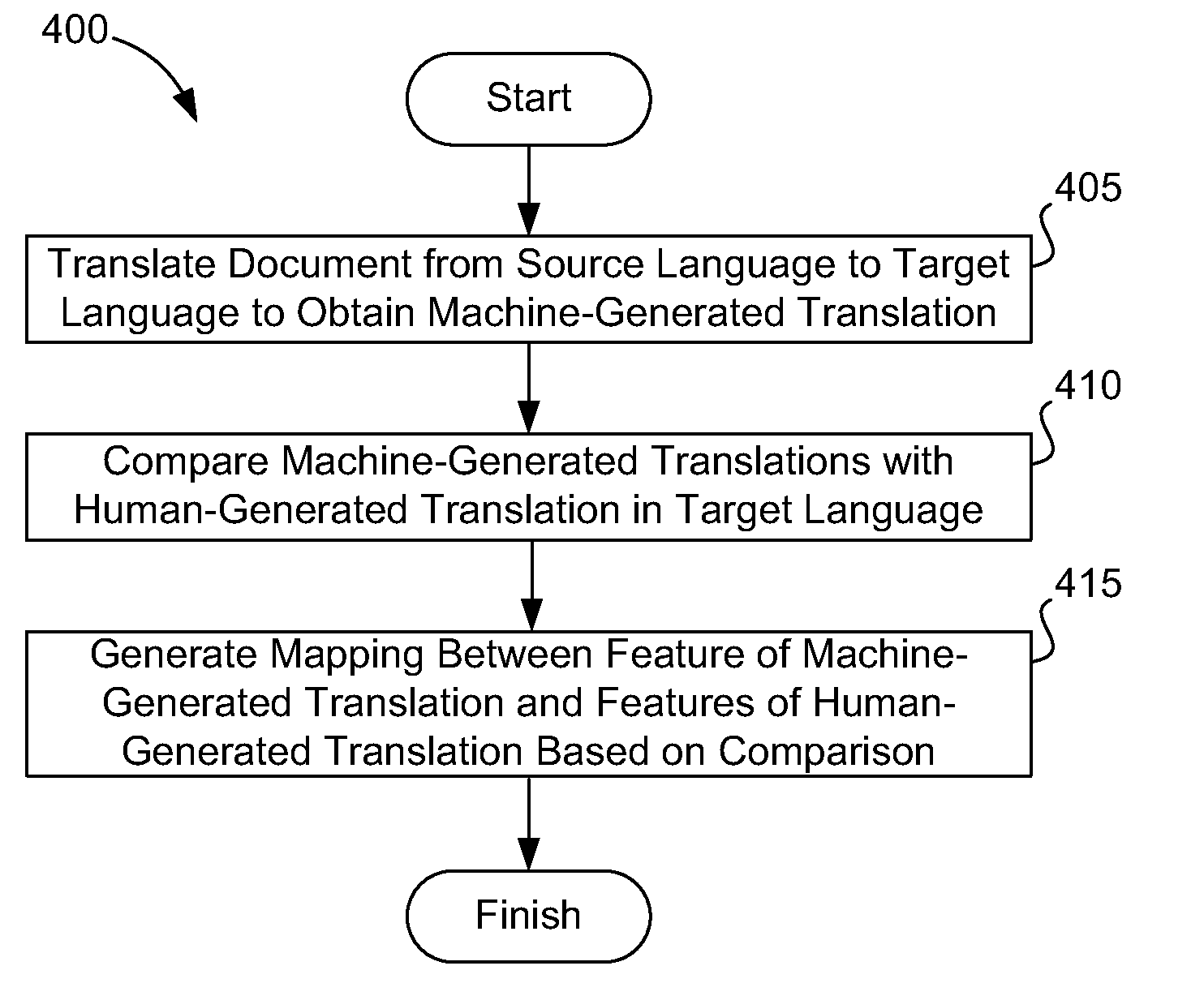
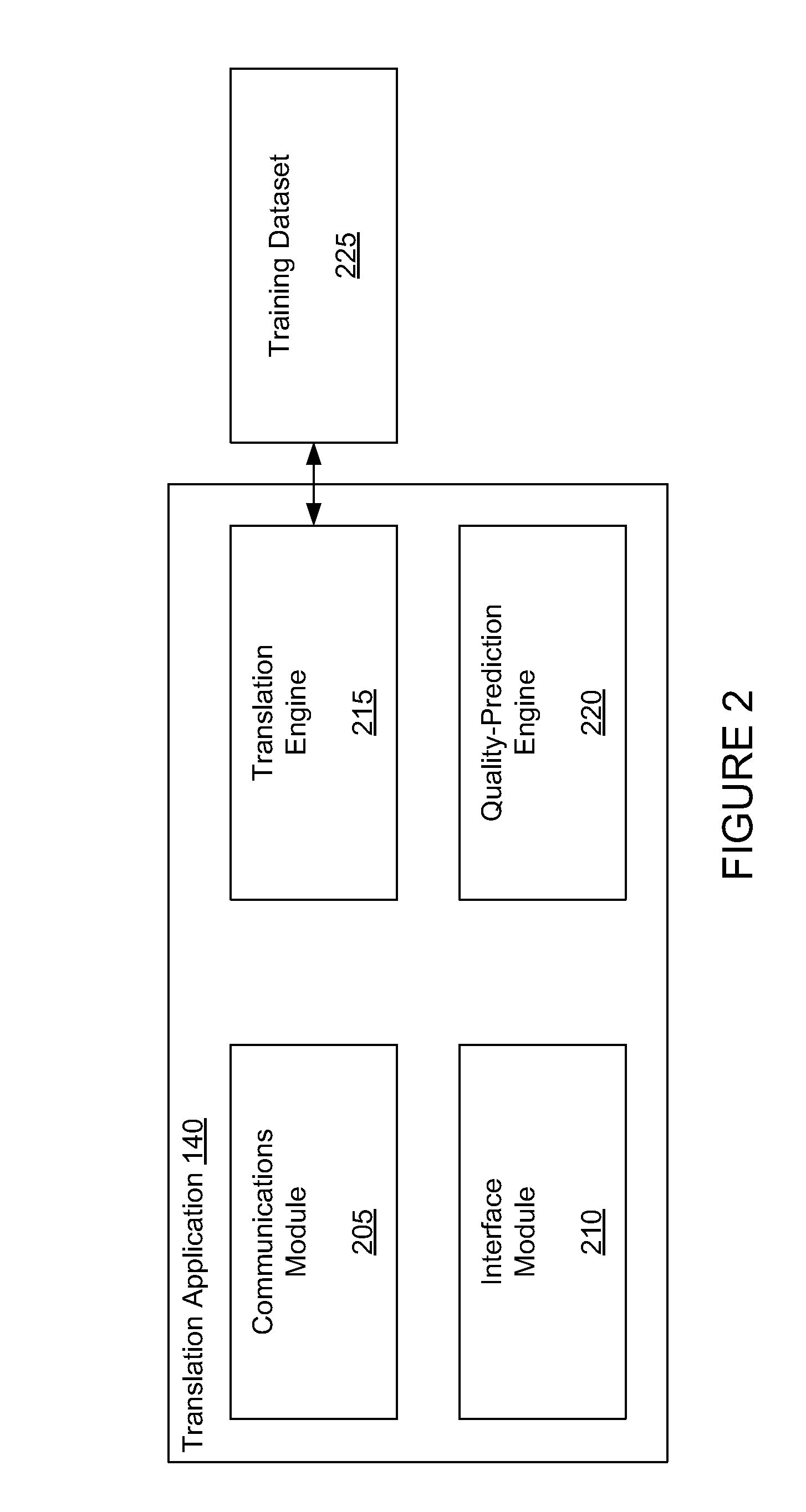
A quality-prediction engine predicts a trust level associated with translational accuracy of a machine-generated translation. Training a quality-prediction may include translating a document in a source language to a target language by executing a machine-translation engine stored in memory to obtain a machine-generated translation. The training may further include comparing the machine-generated translation with a human-generated translation of the document. The human-generated translation is in the target language. Additionally, the training may include generating a mapping between features of the machine-generated translation and features of the human-generated translation based on the comparison. The mapping may allow determination of trust levels associated with translational accuracy of future machine-generated translations that lack corresponding human-generated translations. Machine-generated translations may then be credibly provided by translating a document from a source language to a target language by executing a machine-translation engine stored in memory to obtain a machine-generated translation, predicting a trust level of the machine-generated translation by executing a quality-prediction engine stored in memory, and outputting the machine-generated translation and the trust level.
Owner:SDL INK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com