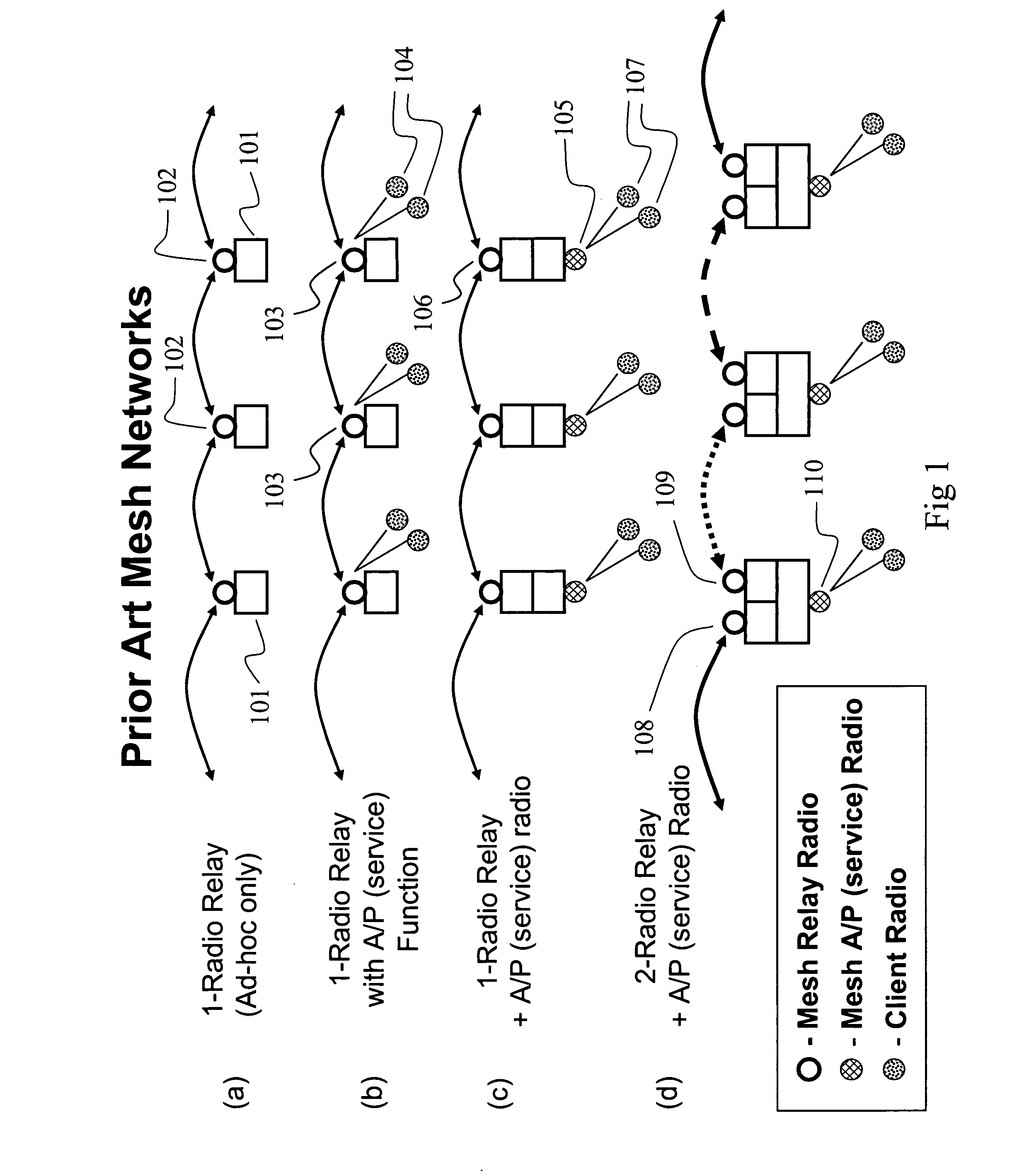
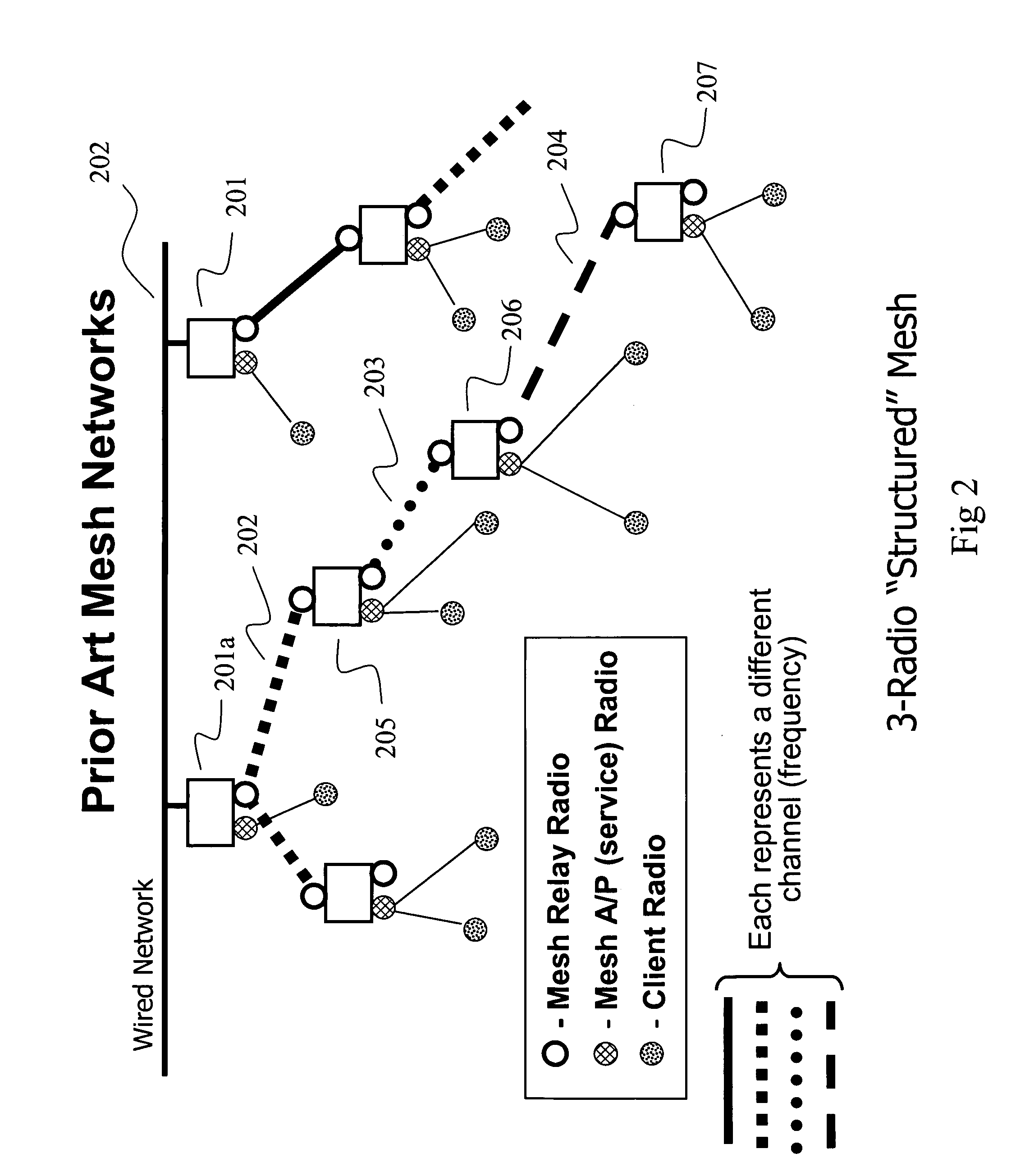
Patents
Literature
553 results about "Mesh node" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
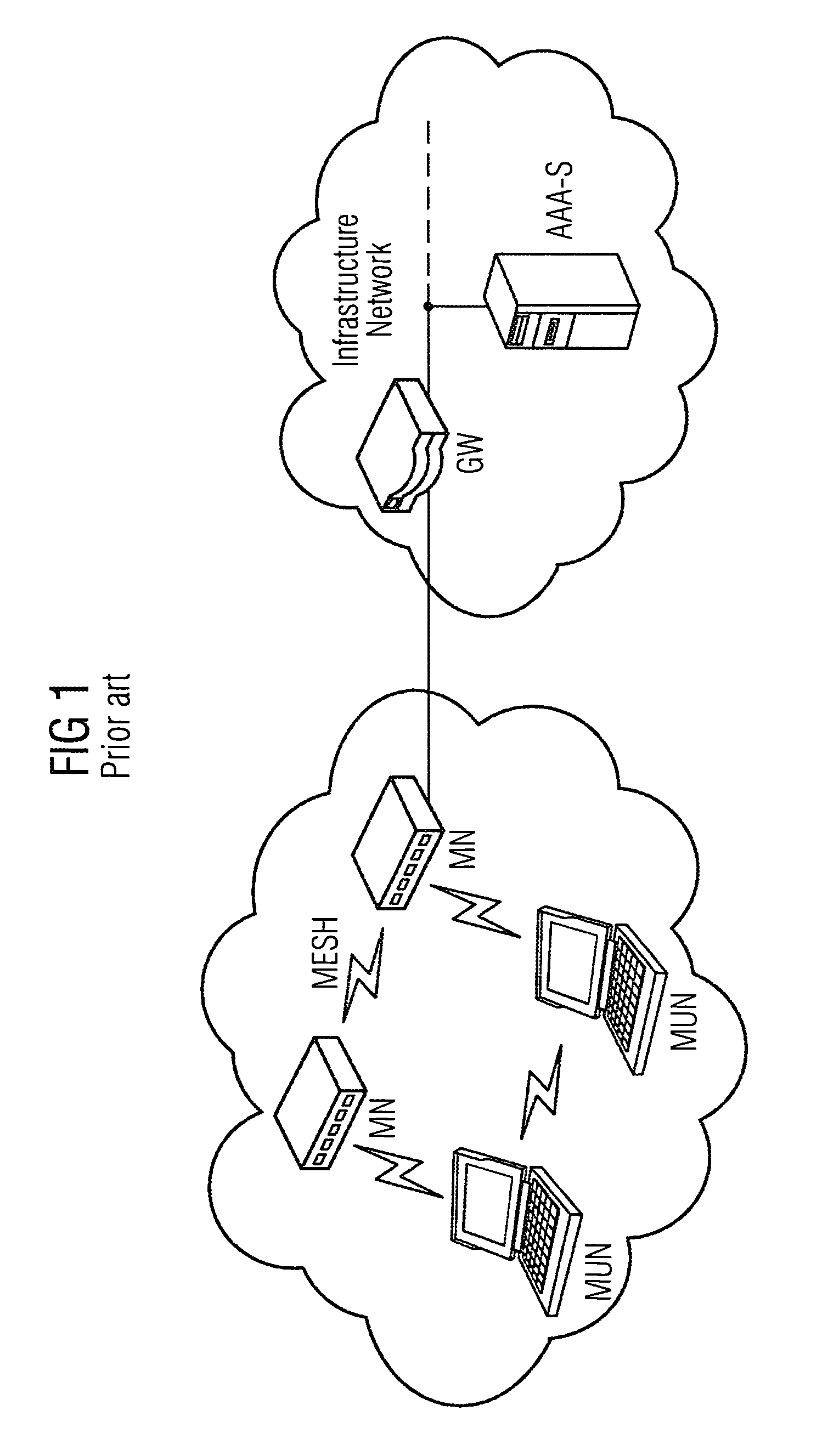
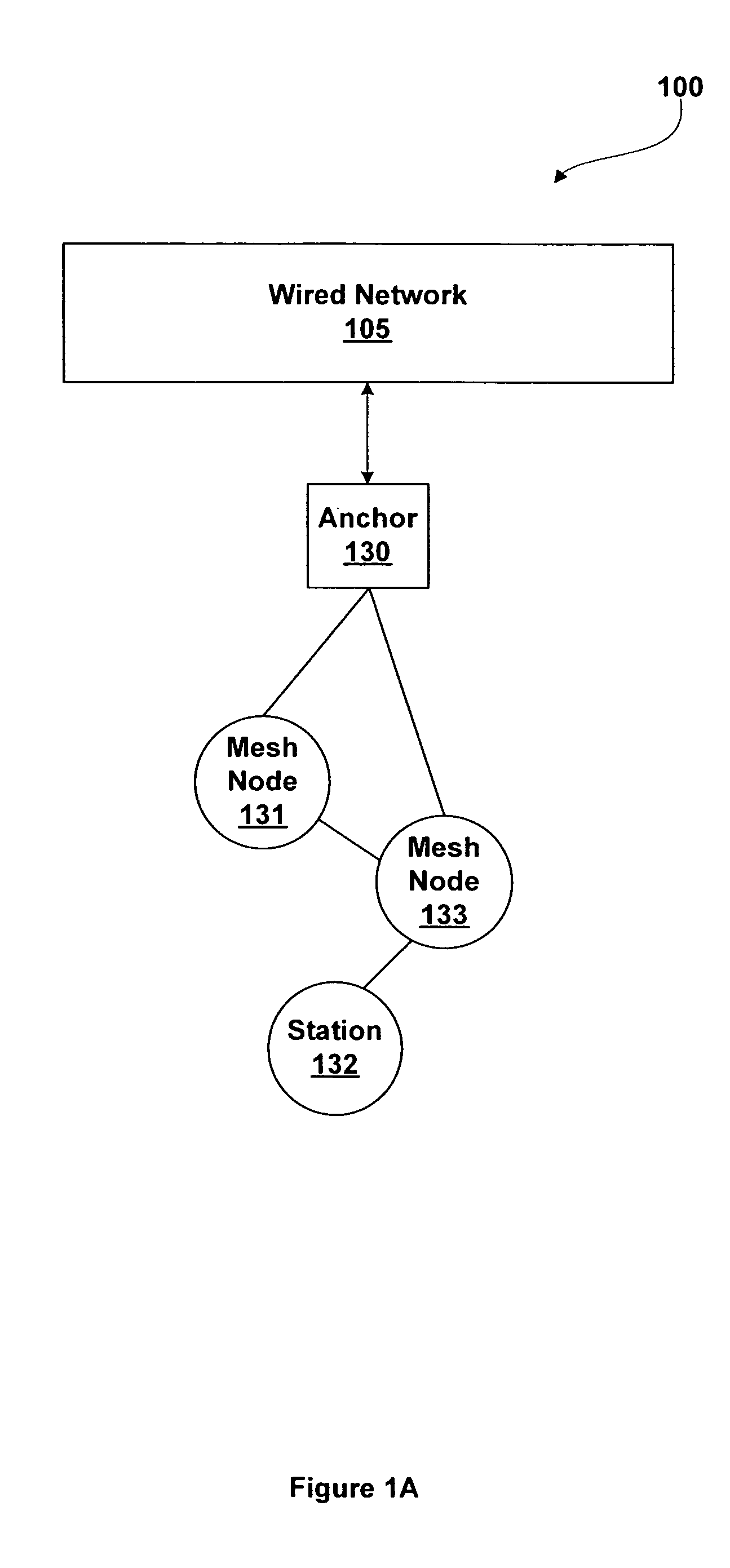
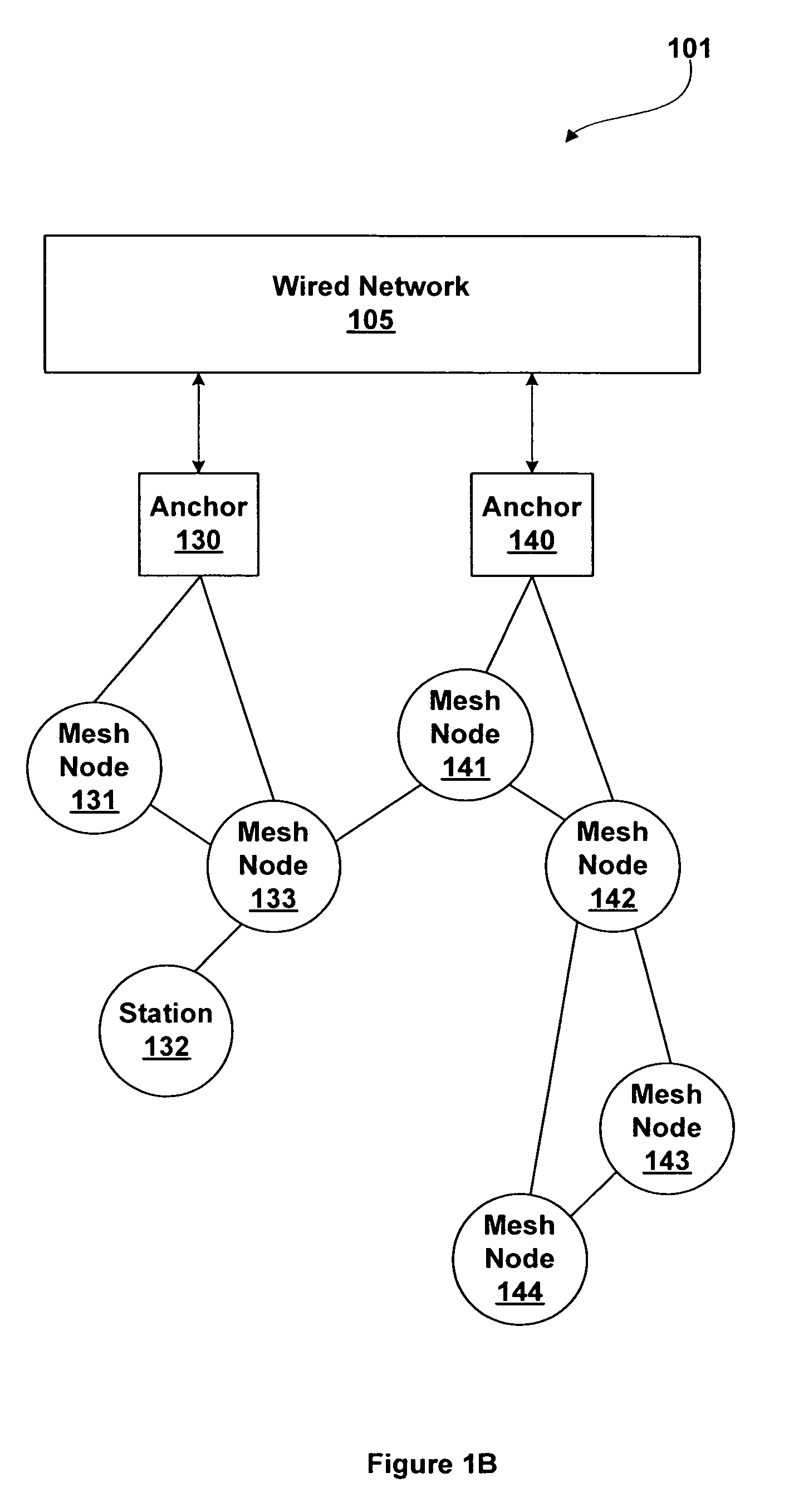
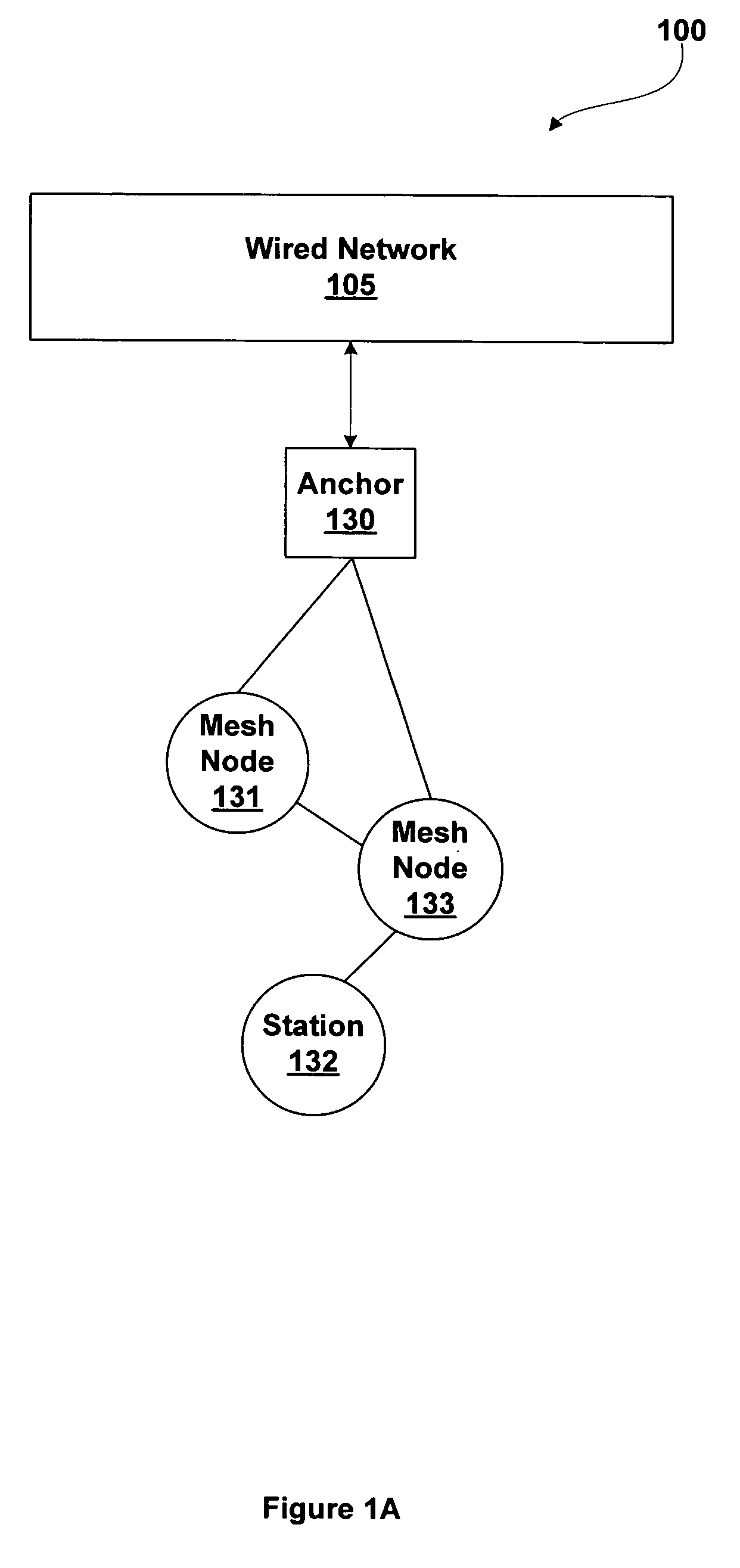
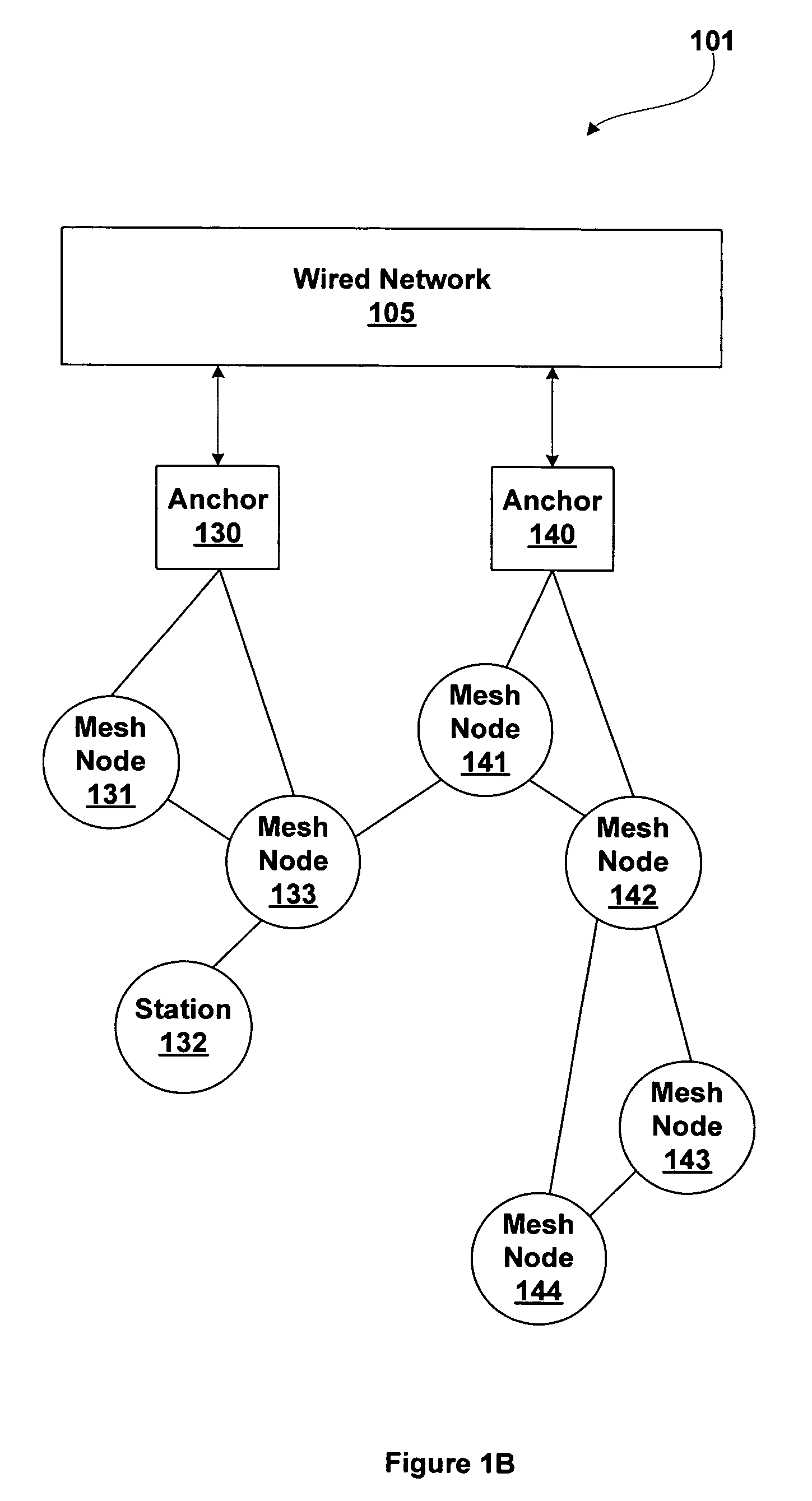
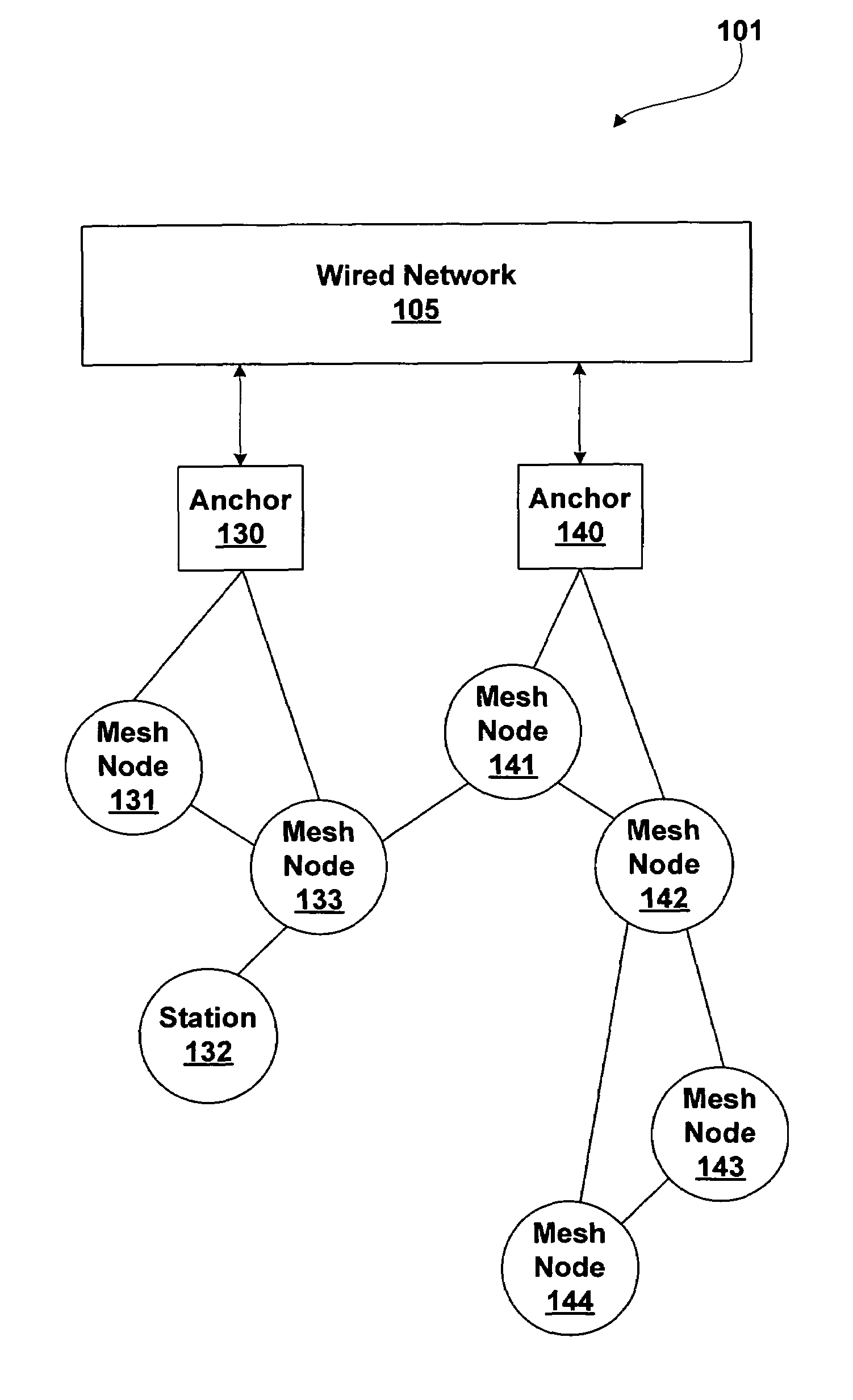
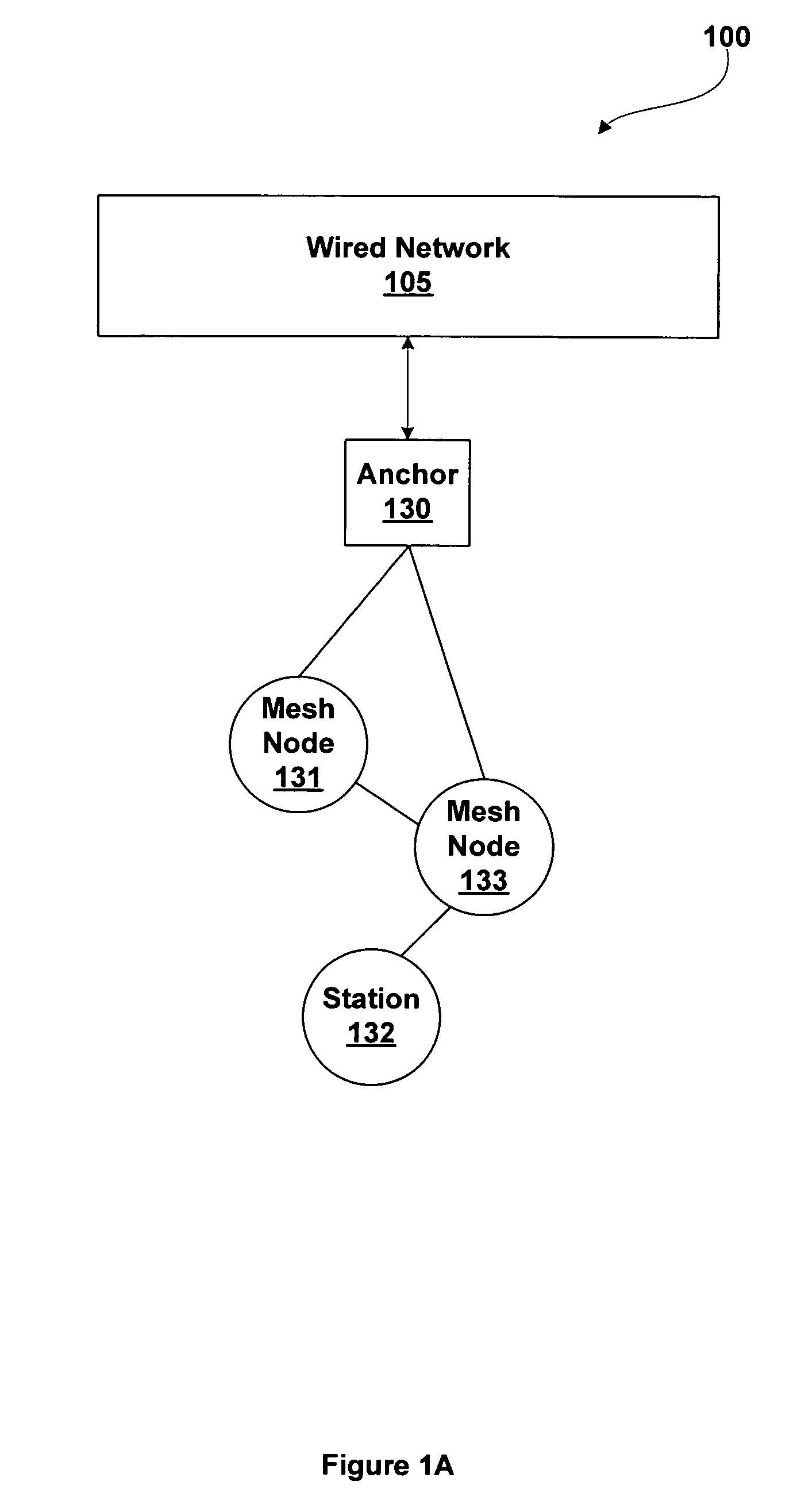
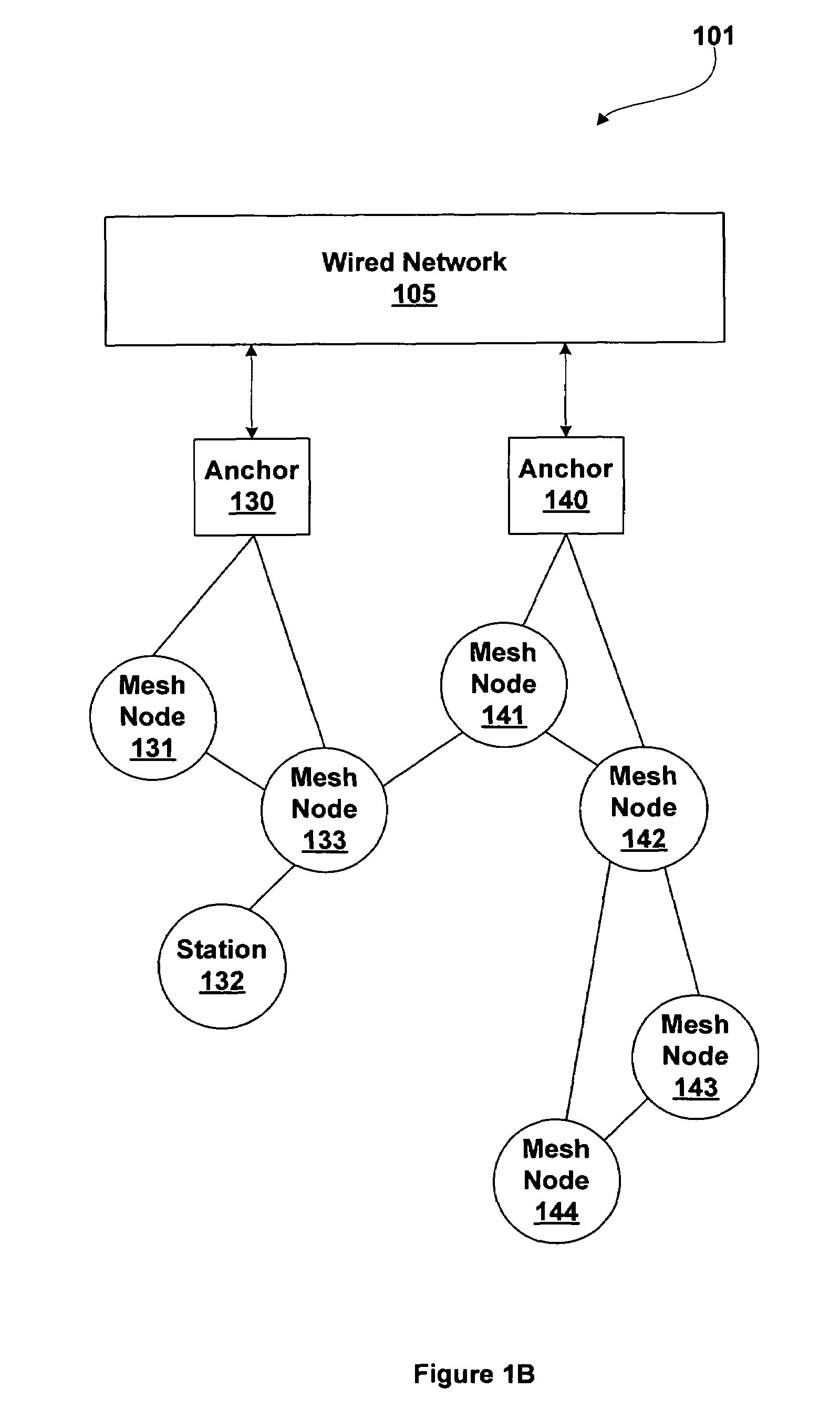
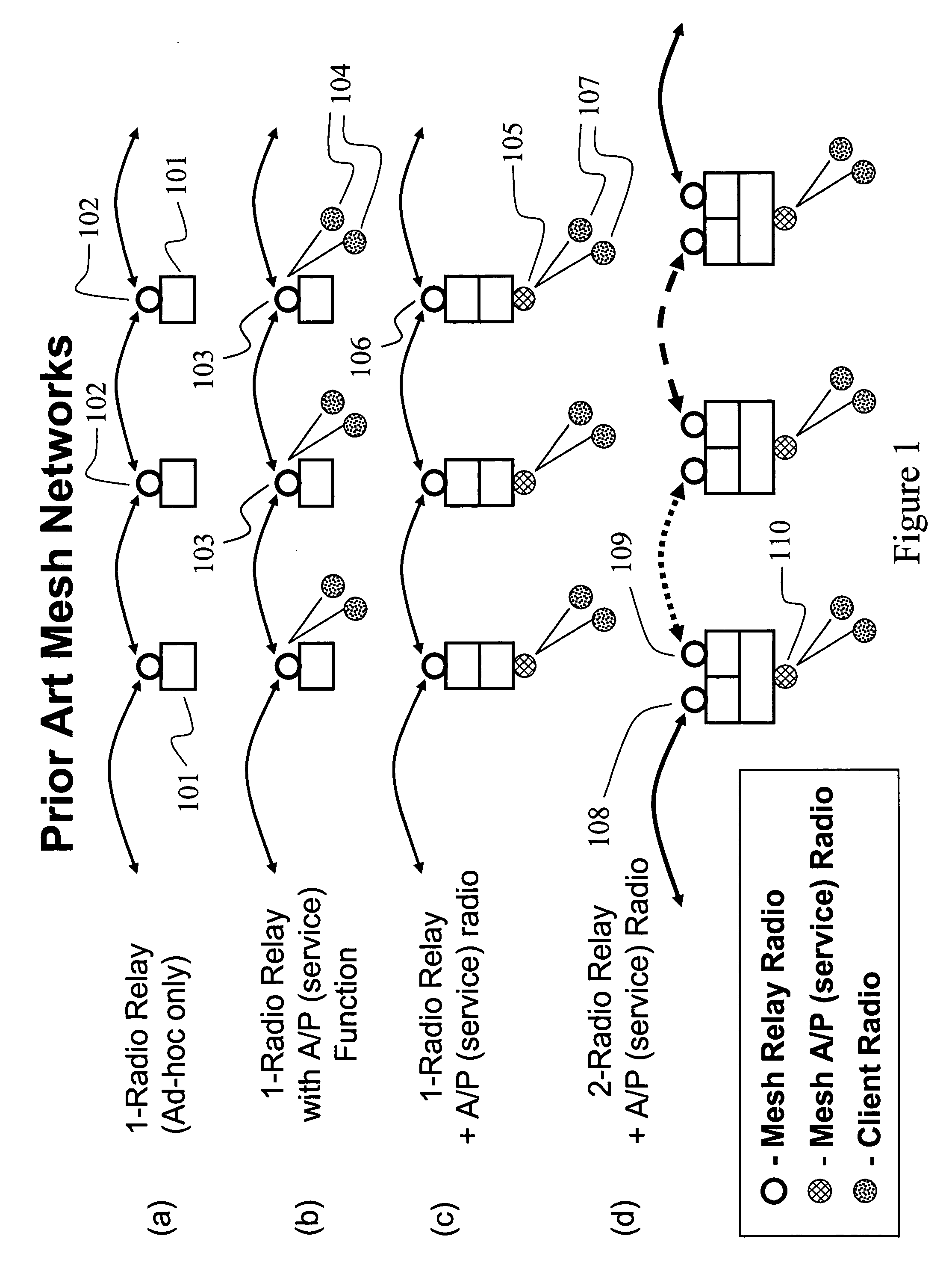
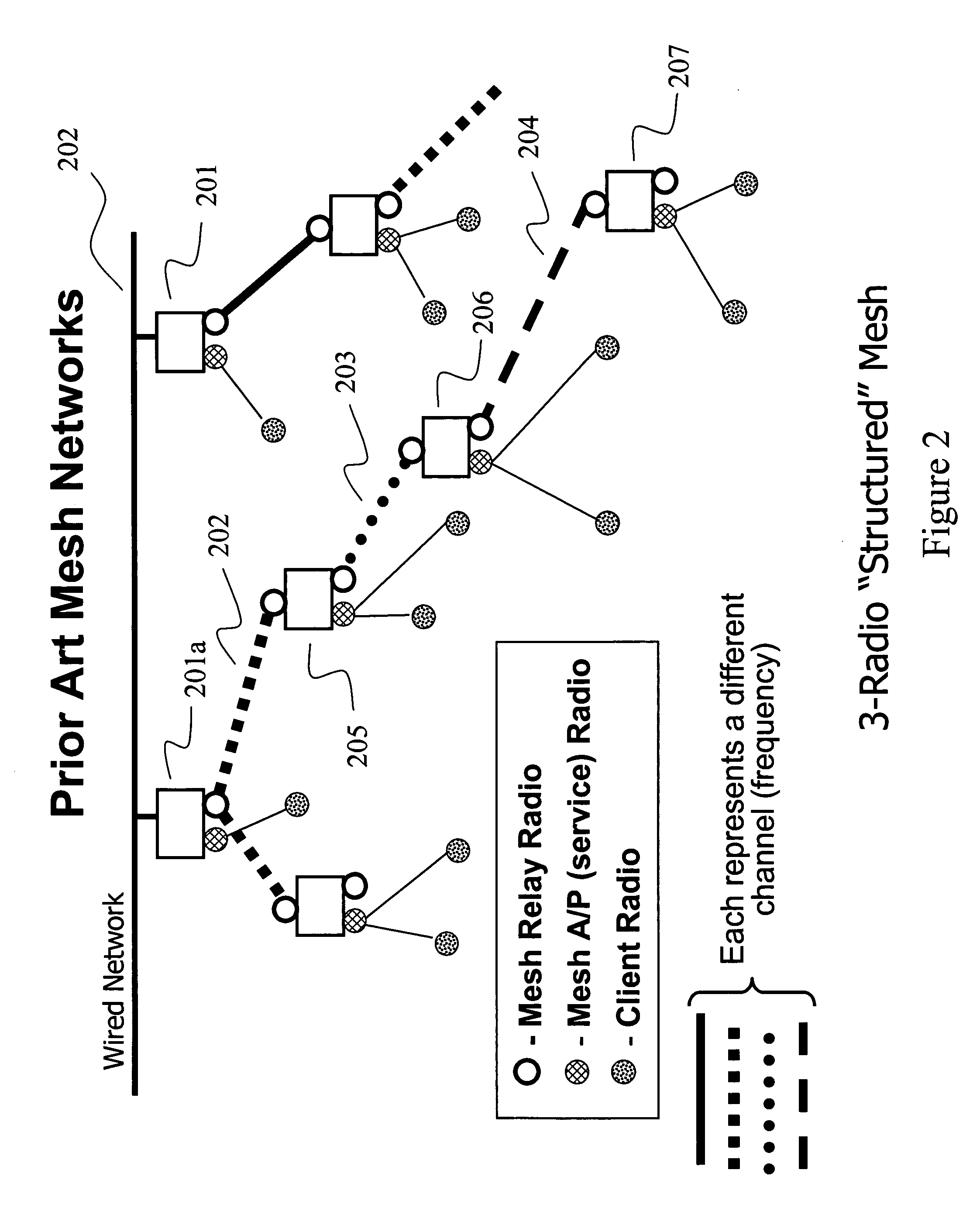
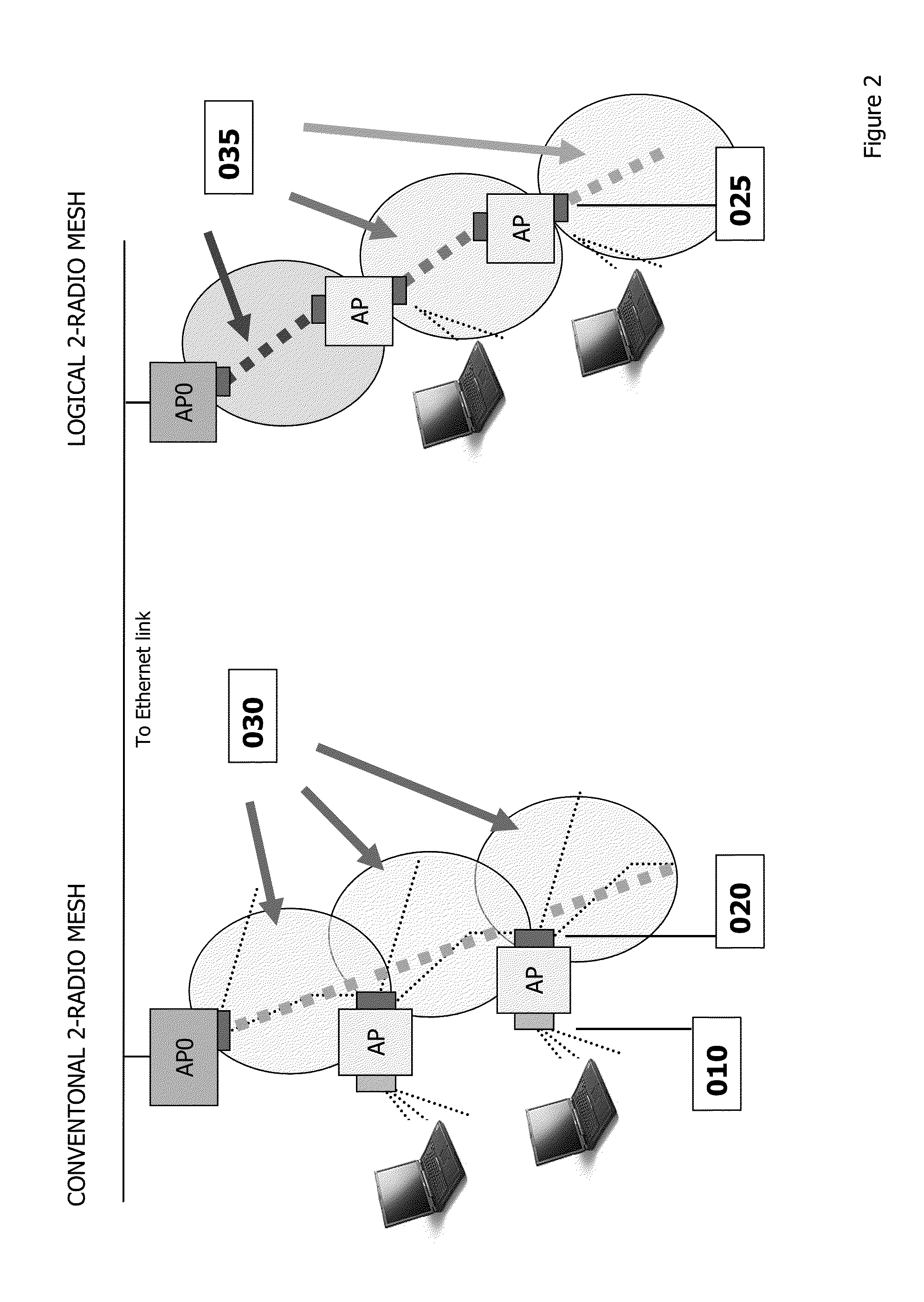
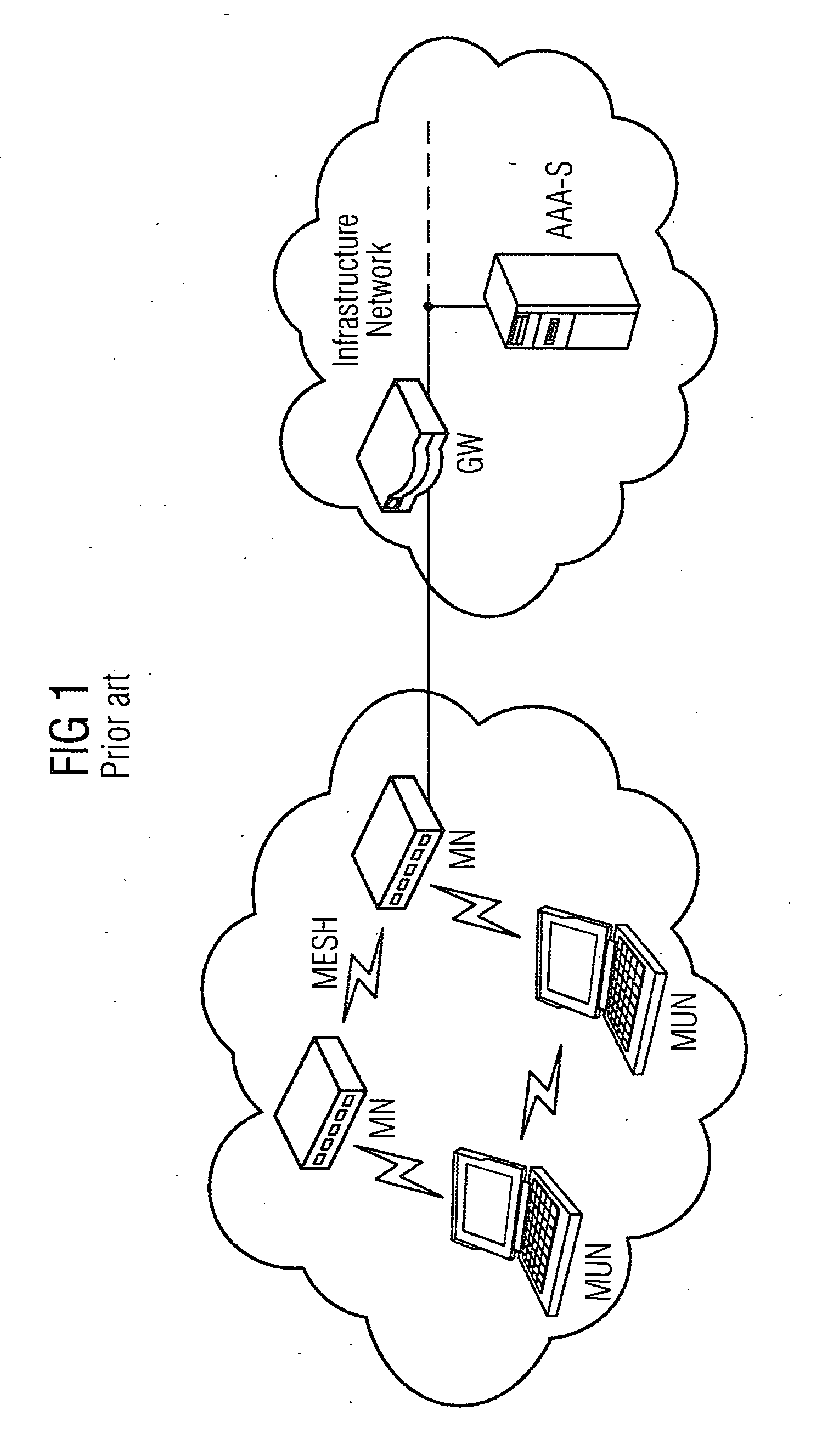
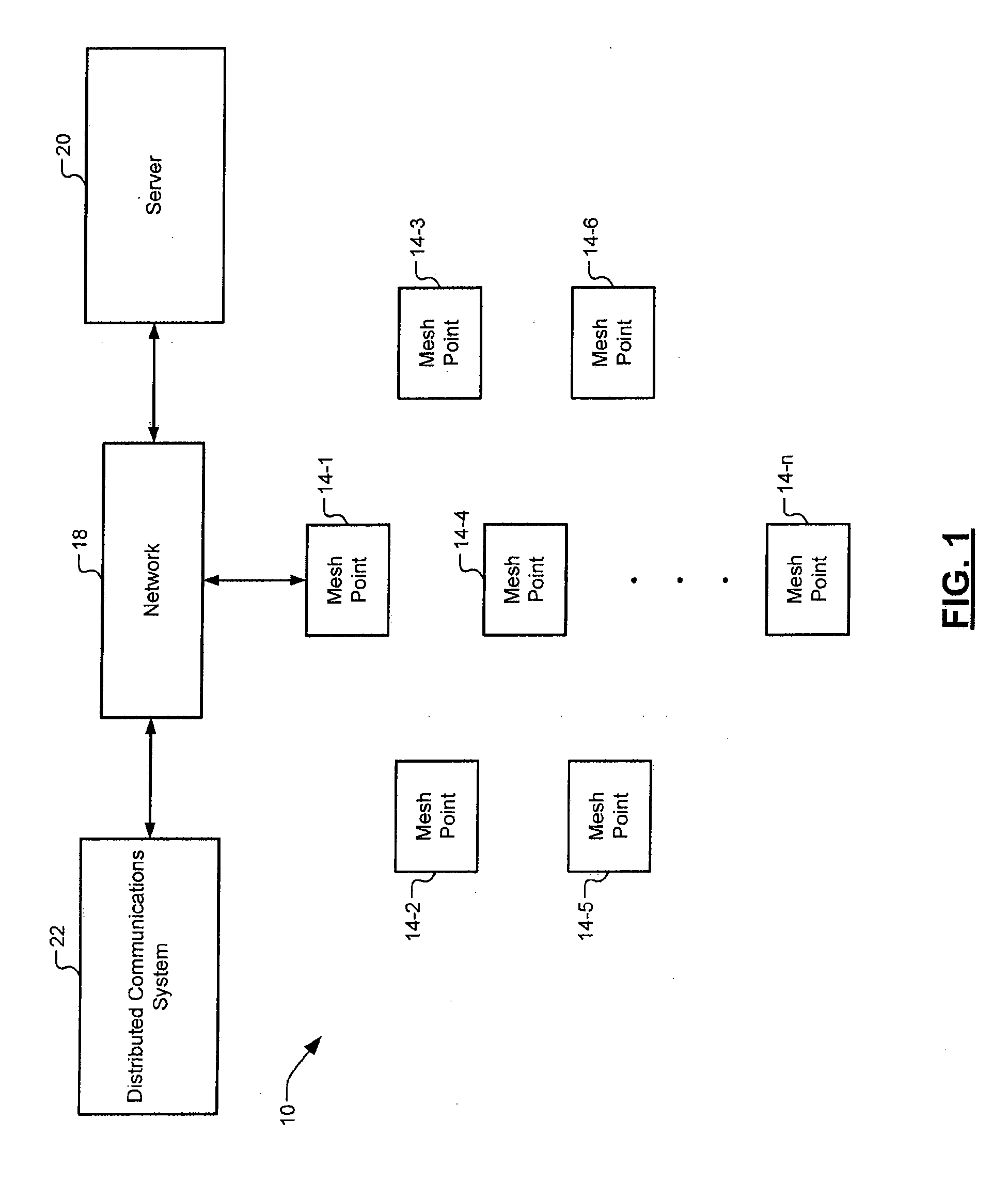
A mesh node is a node on a mesh network. This node can be anything with a network transceiver. Mesh nodes communicate with each other and use some sort of ad hoc networking protocol to route messages amongst themselves without the need for a traditional, hierarchical routing model. This also allows for nodes to join, move among, and drop out of the network without having to make administrative changes.
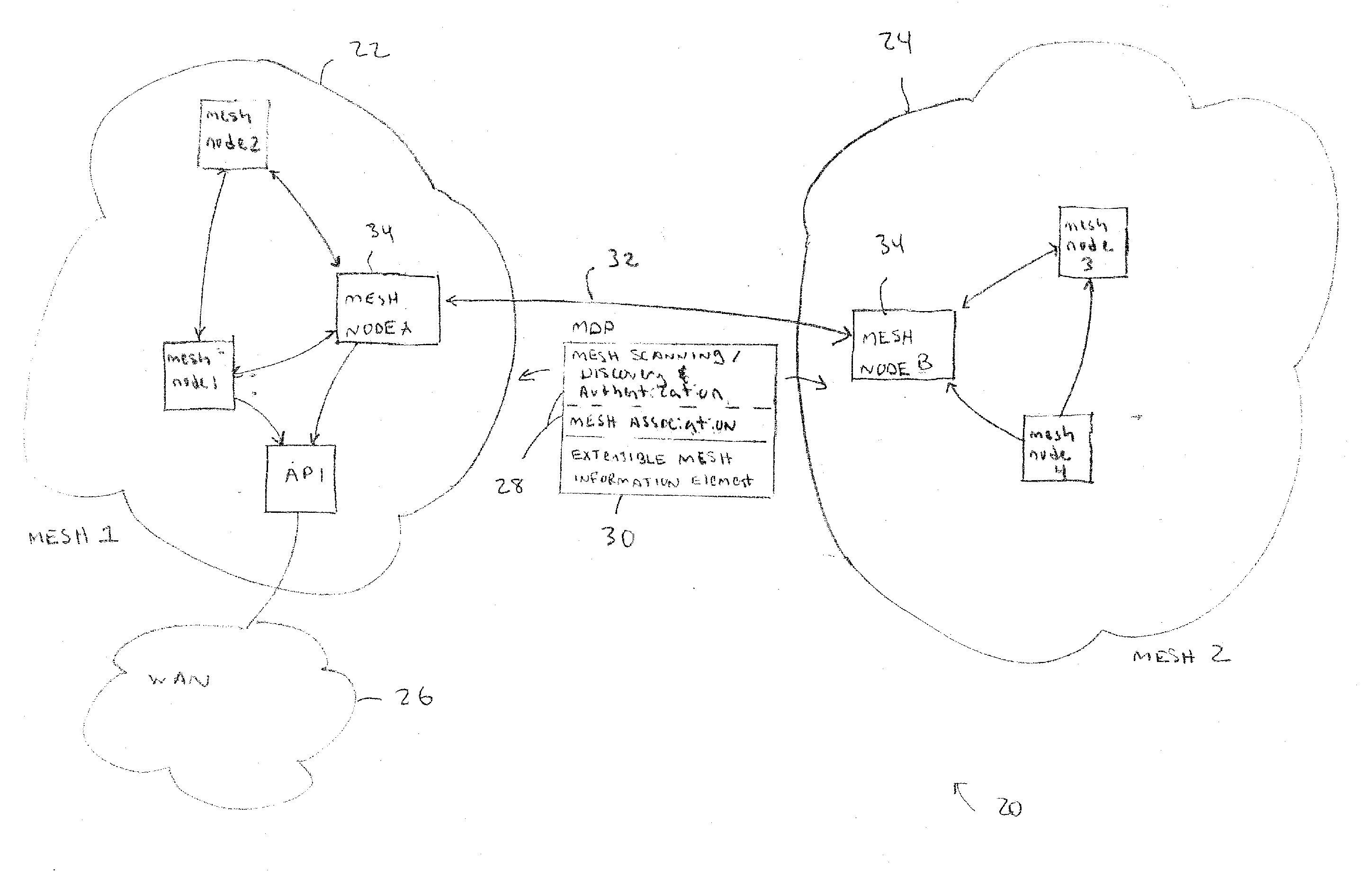
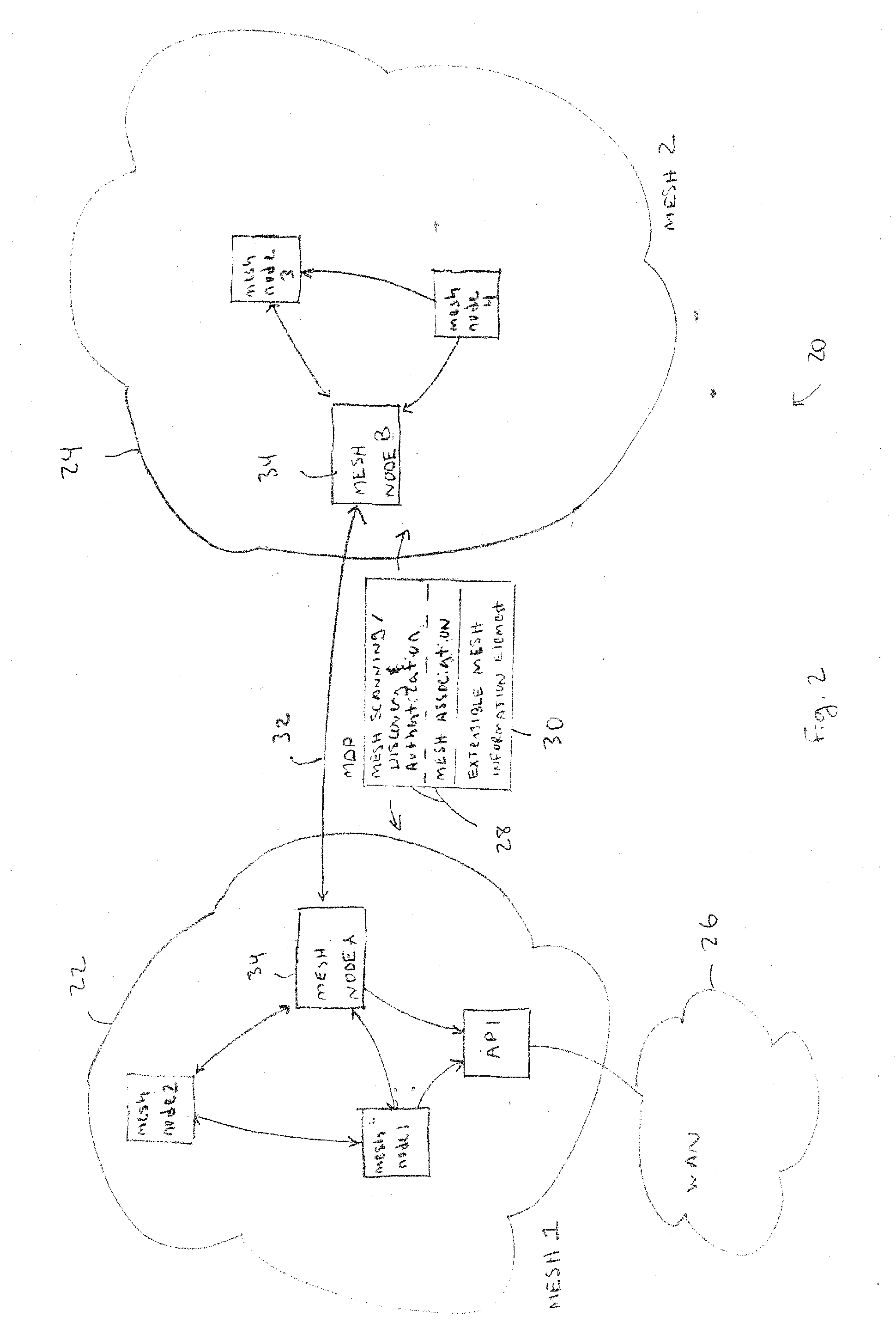
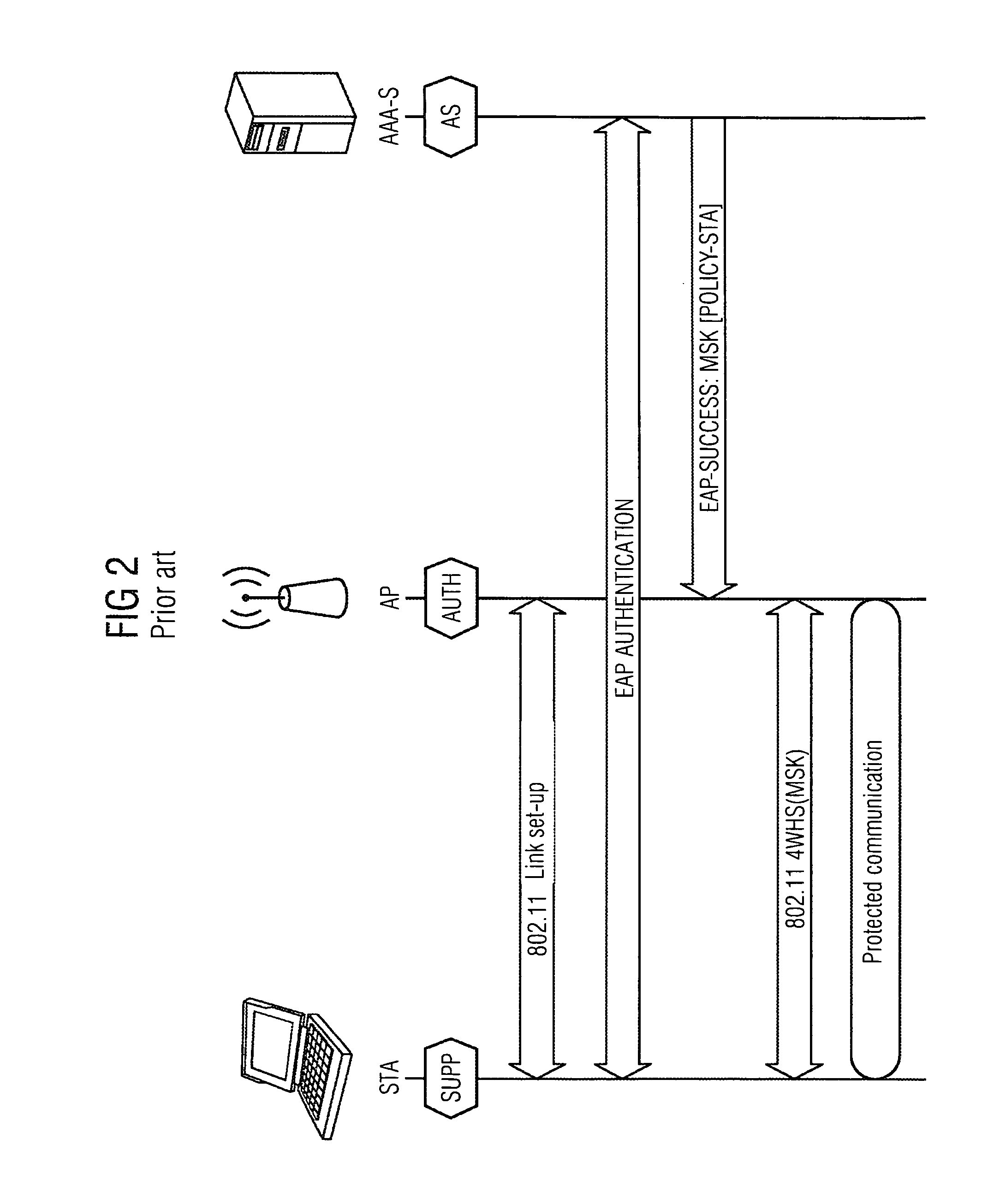
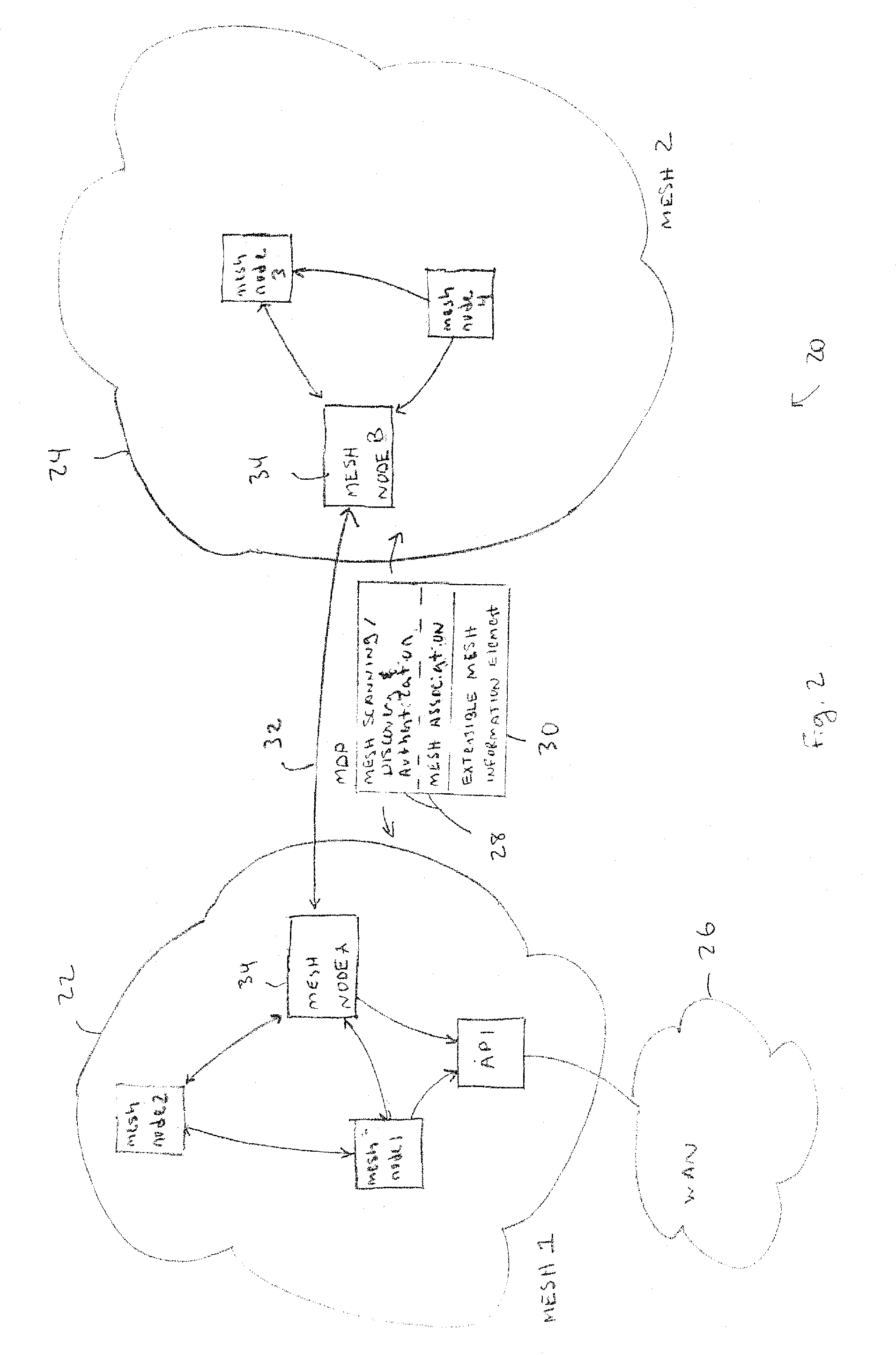
Discovery and authentication scheme for wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS20070189249A1Readily apparentError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsOpen Systems InterconnectionMesh node
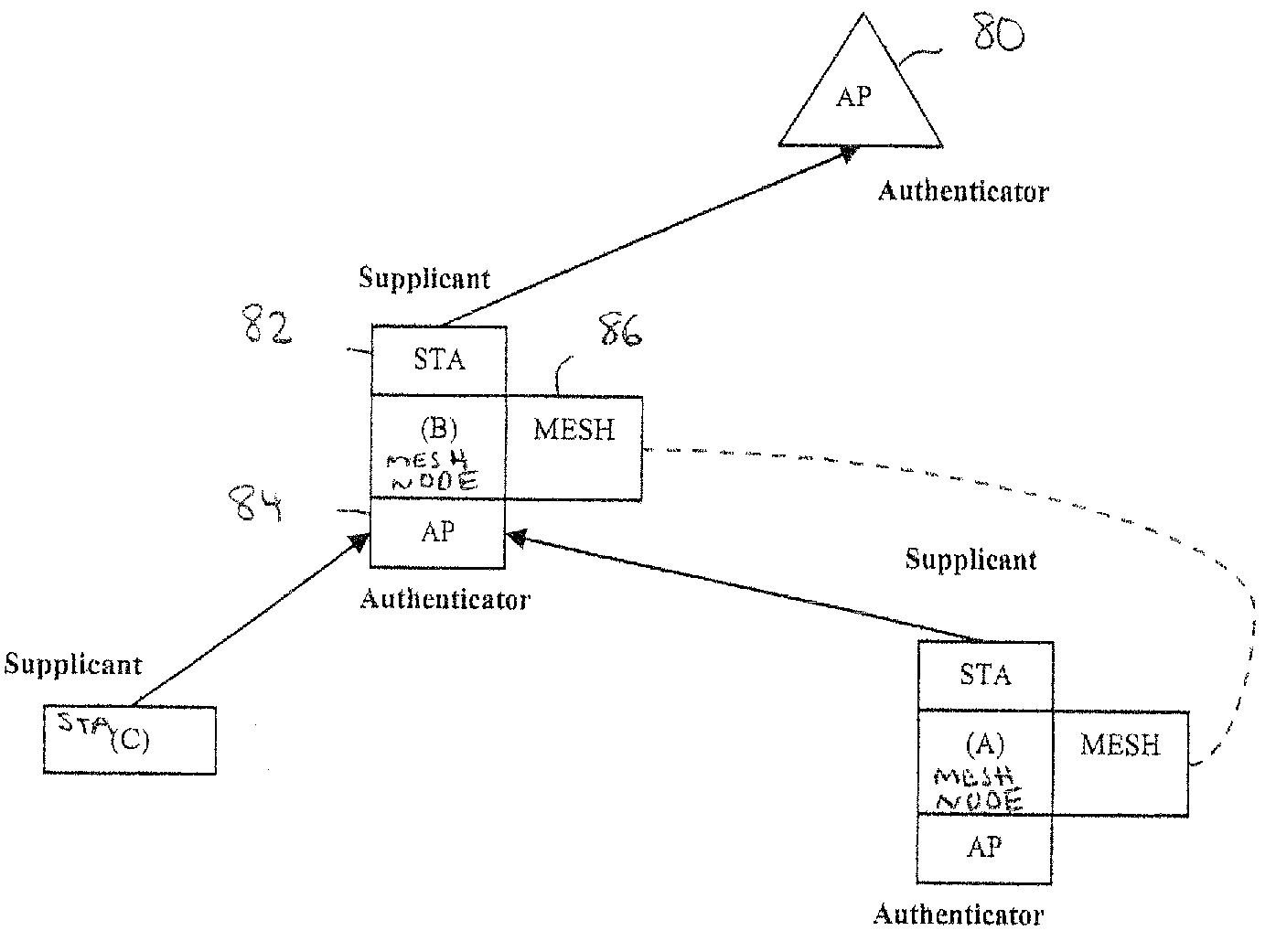
Wireless network devices discover individual mesh nodes and networks of mesh nodes. An association is formed on the basis of peer-to-peer interactions at layer-1, layer-2 and / or higher layers of the Open System Interconnect (OSI) model. In particular, the system uses Beacon, Probe Request, Probe Response, Association Request, Association Response, and Disassociation frames and introduces a new Extensible Mesh Information Element (EMIE) used by mesh nodes to discover, authenticate, and associate with other peer nodes.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Method and arrangement for providing a wireless mesh network
ActiveUS8122249B2Small loadReduce signaling overheadUser identity/authority verificationNetwork topologiesProxy serverMesh node
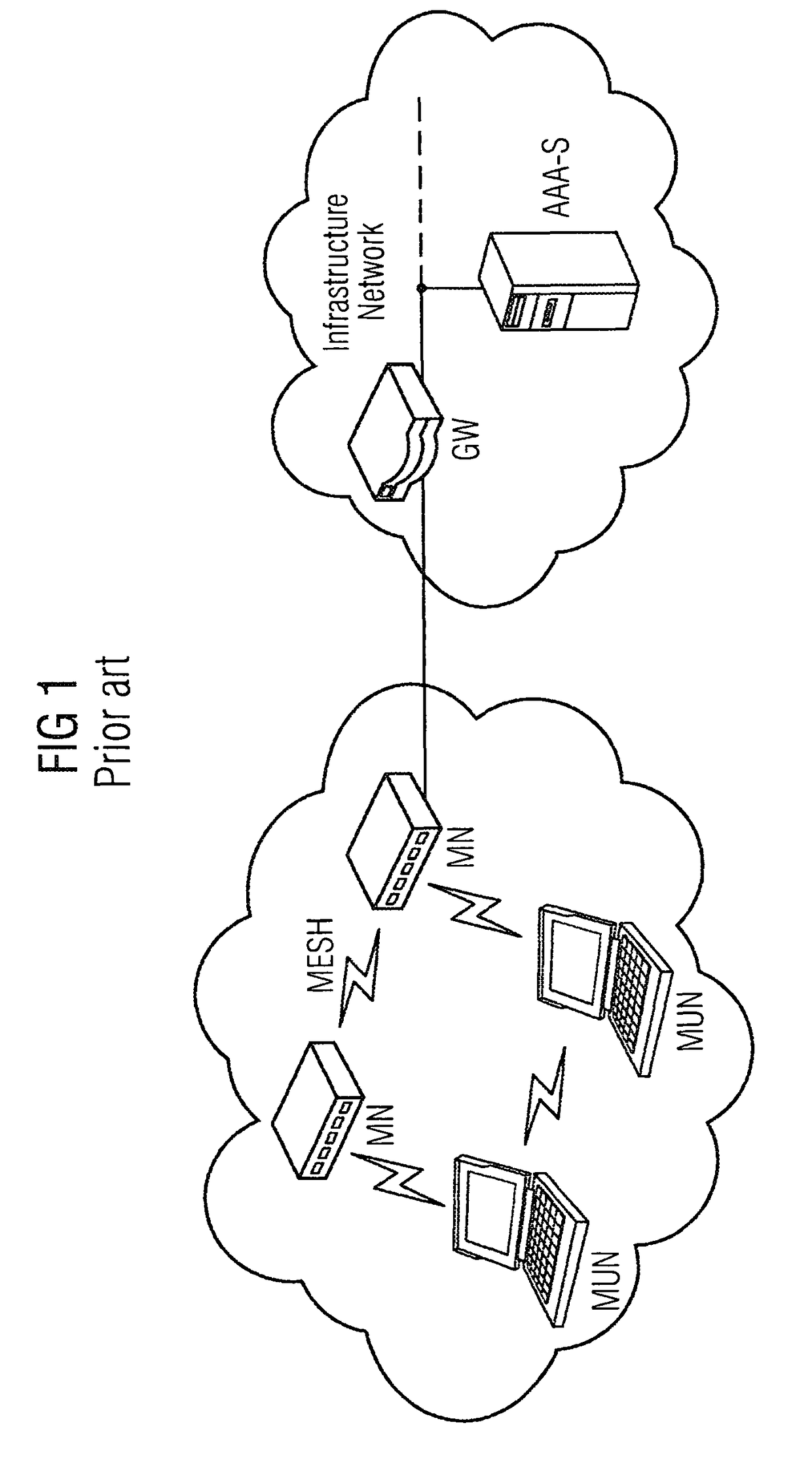
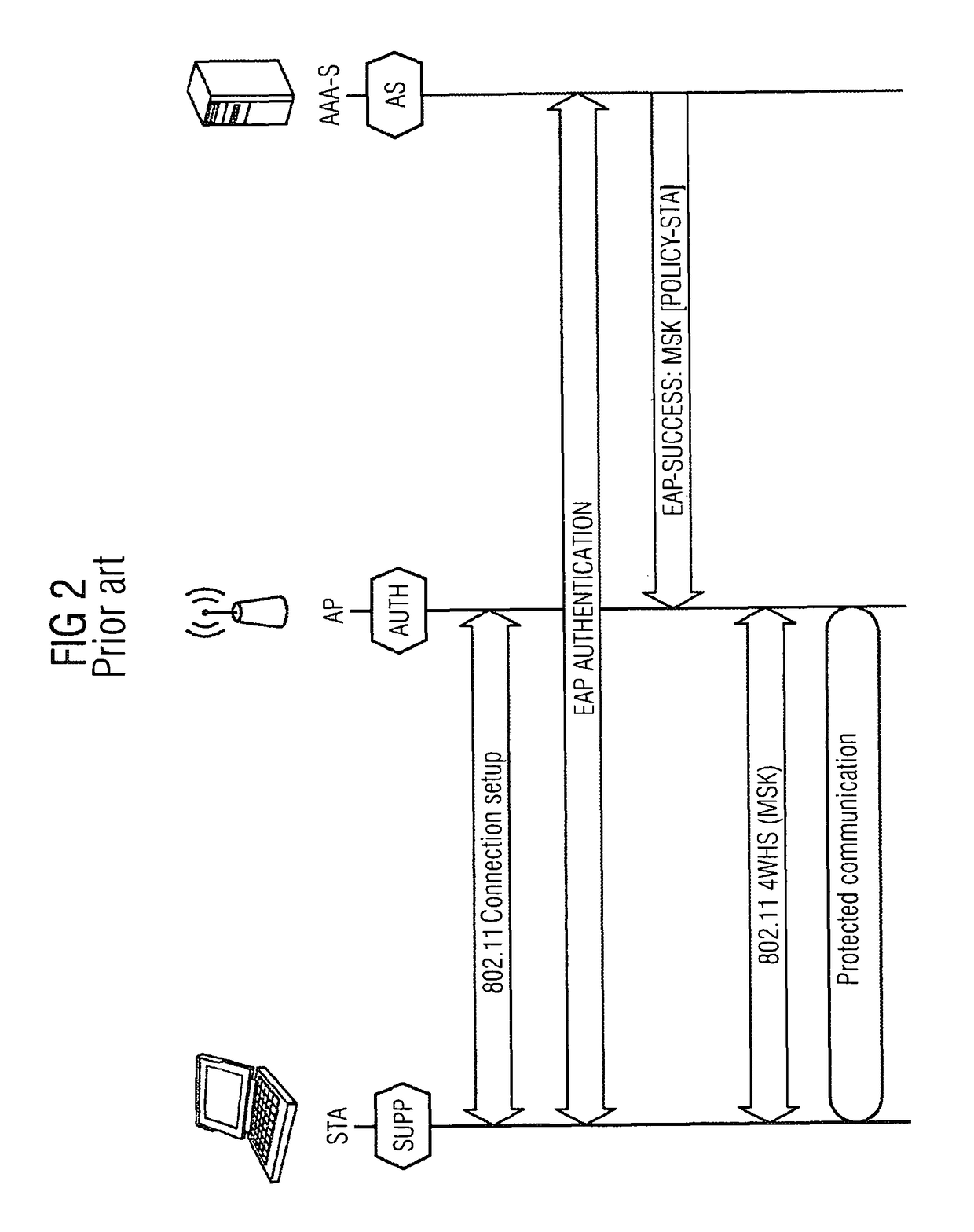
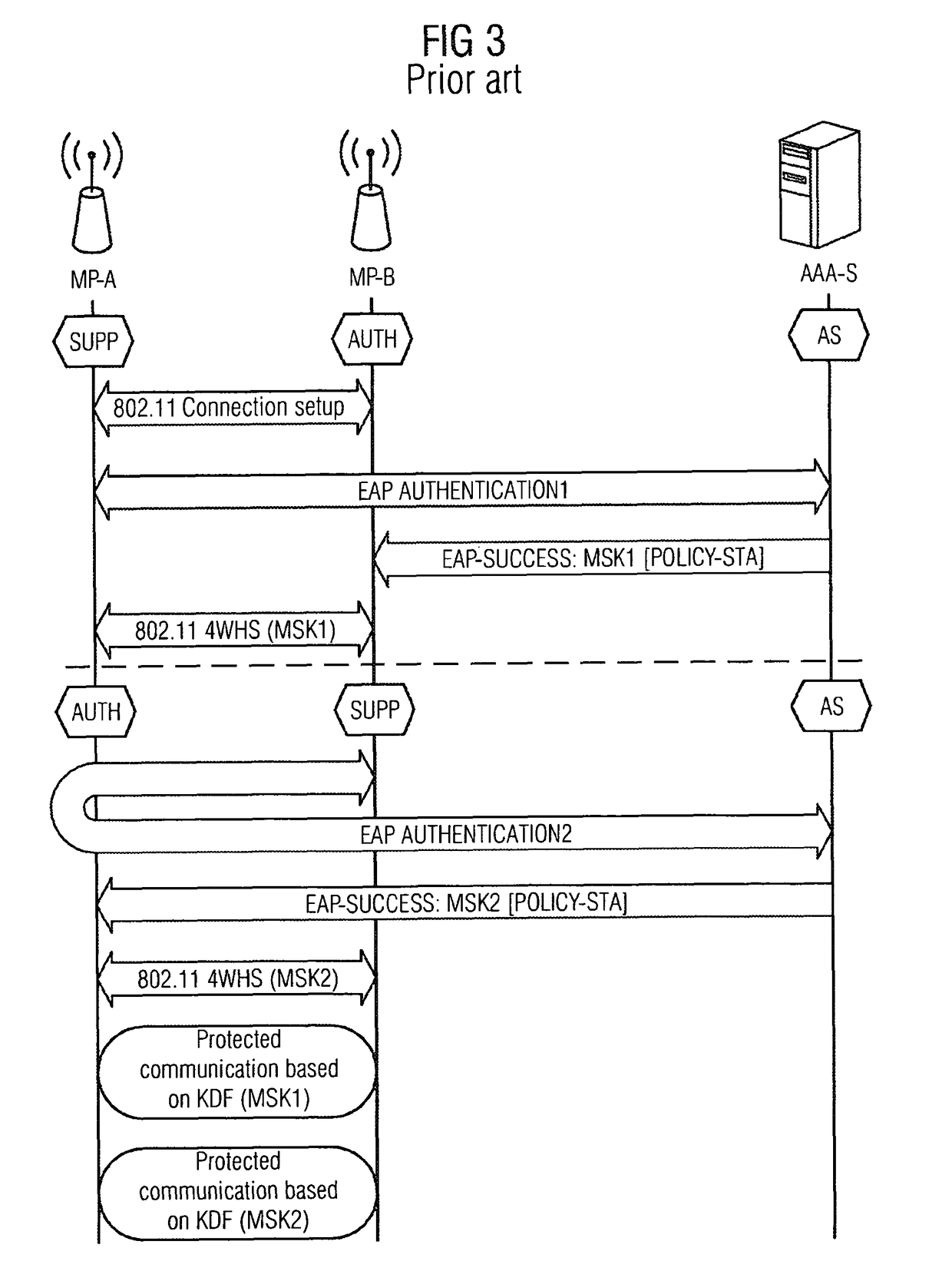
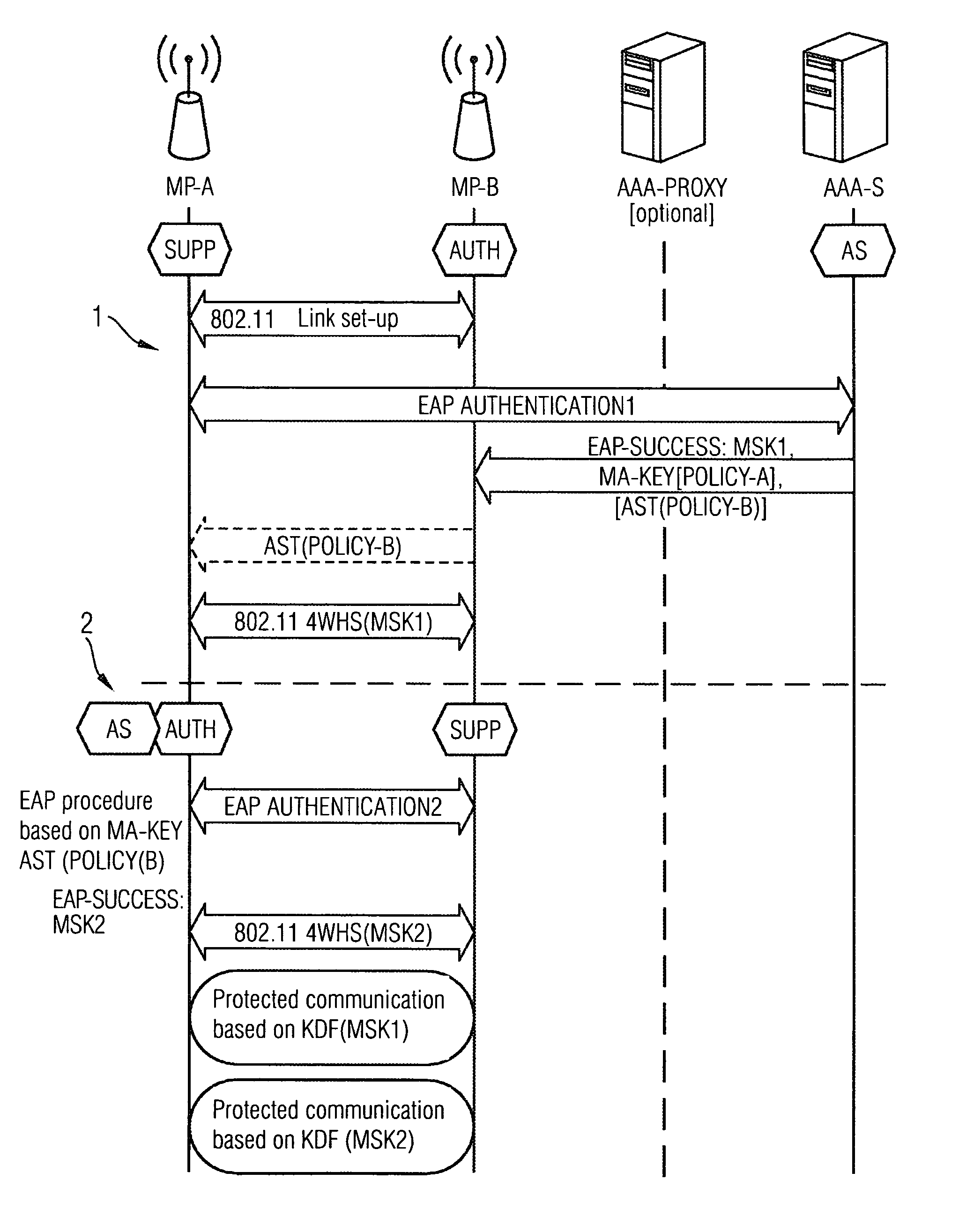
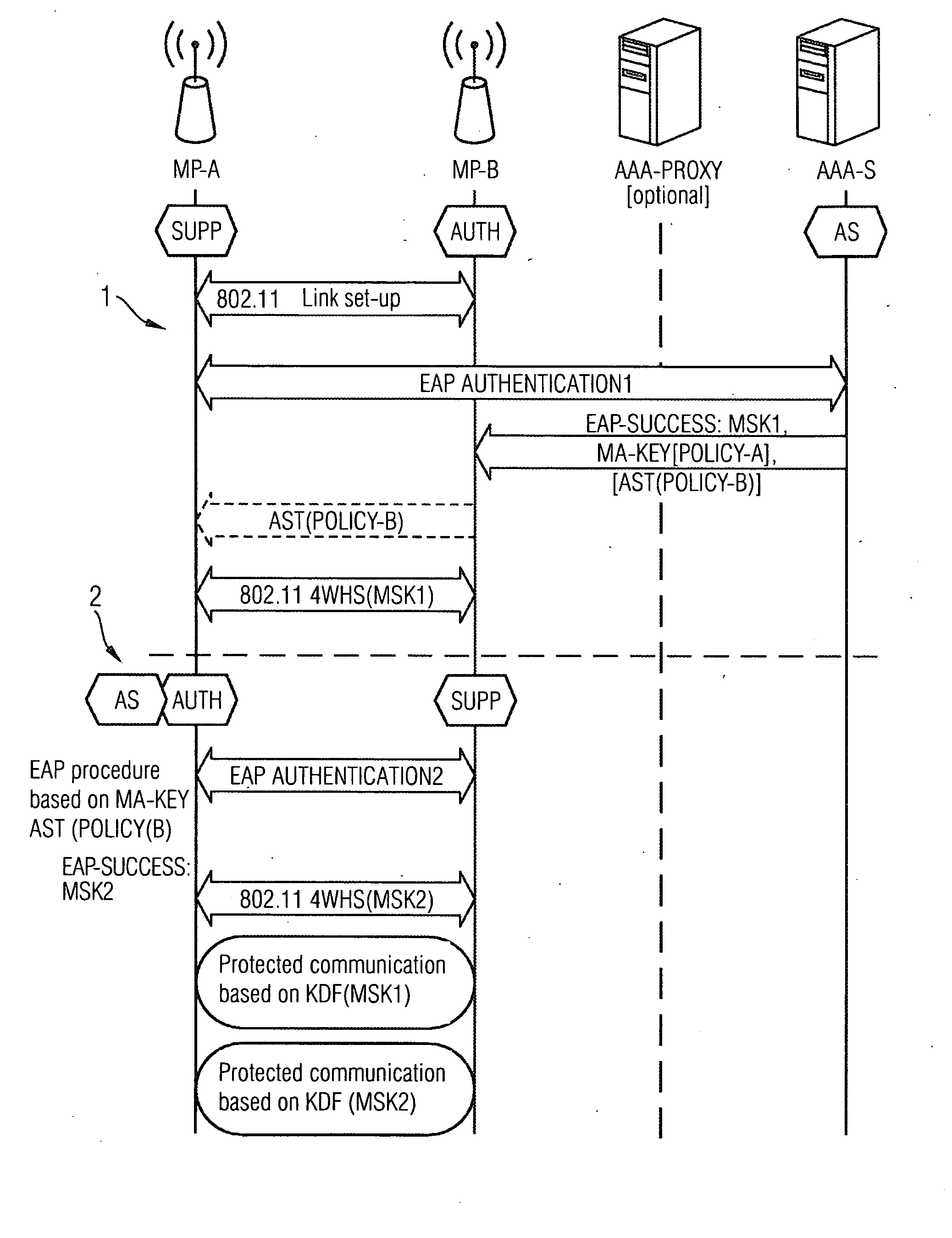
Provided are a method and an arrangement for creating a wireless mesh network in which a new node is provided that is connected between mesh nodes and an AAA server located in an infrastructure network. Based on basic encoding data that is available to the new node following successful initial authentication of a first mesh node, the new node performs the authentication similar to a proxy server instead of an AAA server, particularly for a limited time, during subsequent authentication attempts.
Owner:UNIFY PATENTE GMBH & CO KG
Method and arrangement for providing a wireless mesh network
ActiveUS8495360B2Communication securitySimple and appropriateDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationComputer scienceMesh node
A method and an arrangement are provided wherein a newly added mesh node does not require a link to the AAA server for the purpose of authentication. Authentication is carried out using a node which is already present in the mesh network and which has a link to the AAA server.
Owner:UNIFY PATENTE GMBH & CO KG
Communication protocol for a wireless mesh architecture
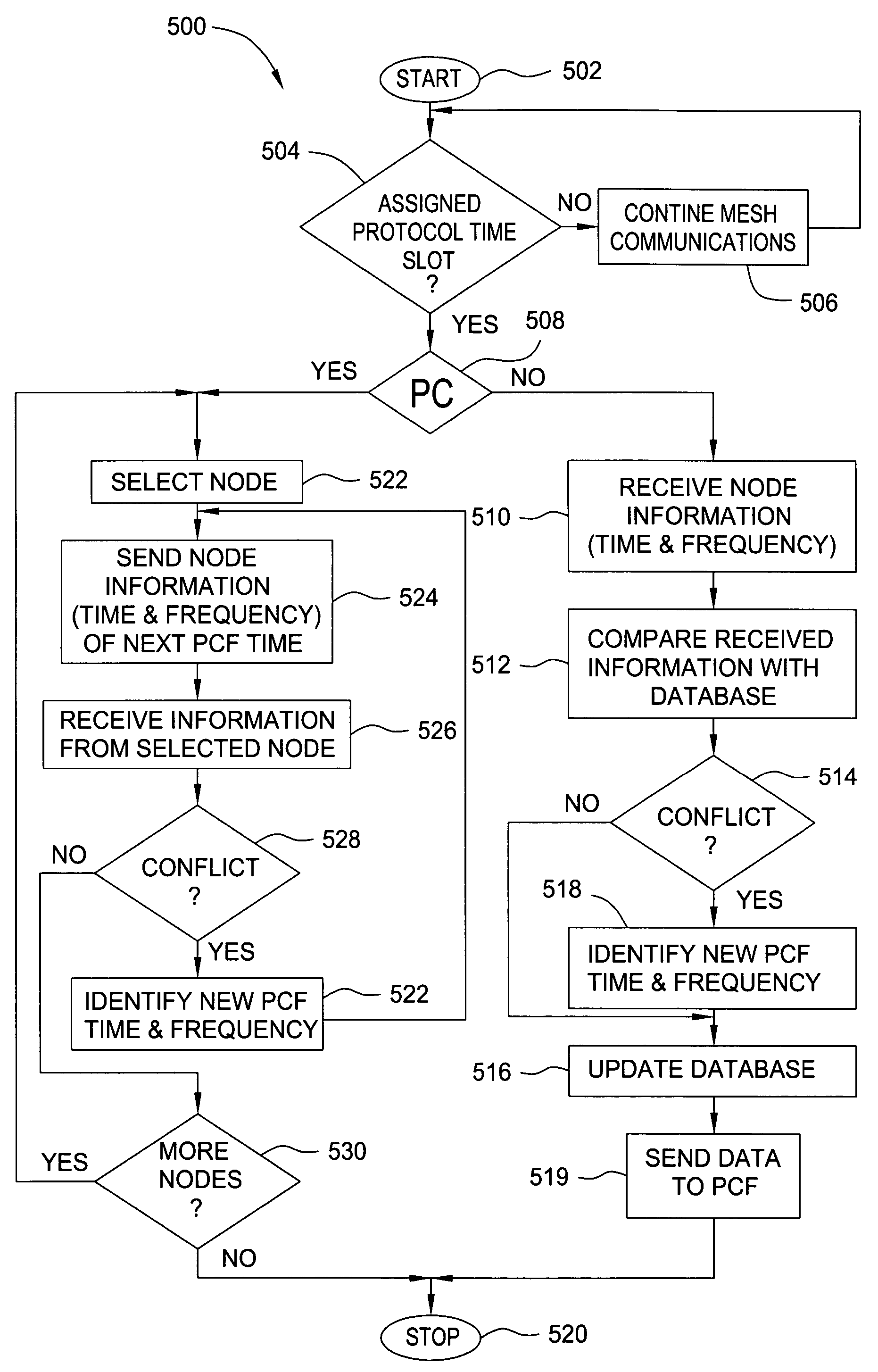
A wireless mesh communication protocol that dynamically assigns communication time-slots and frequencies to mesh nodes. A first node is established as a PC that sequentially polls other nodes. A second node responds at a predetermined time with information that includes database records, and then a third node responds similarly. The second node is then established as the PC and the first node is polled during dynamically allocated time-slots and on a frequency that depend on the second node's database records. The third node is then established as a PC and acts similarly. In both cases the first node responds by sending information and data records. The first node is then re-established as the PC. The first node then polls the second and third nodes at times and frequencies that depend on the first node's database records.
Owner:TRILLIANT NETWORKS
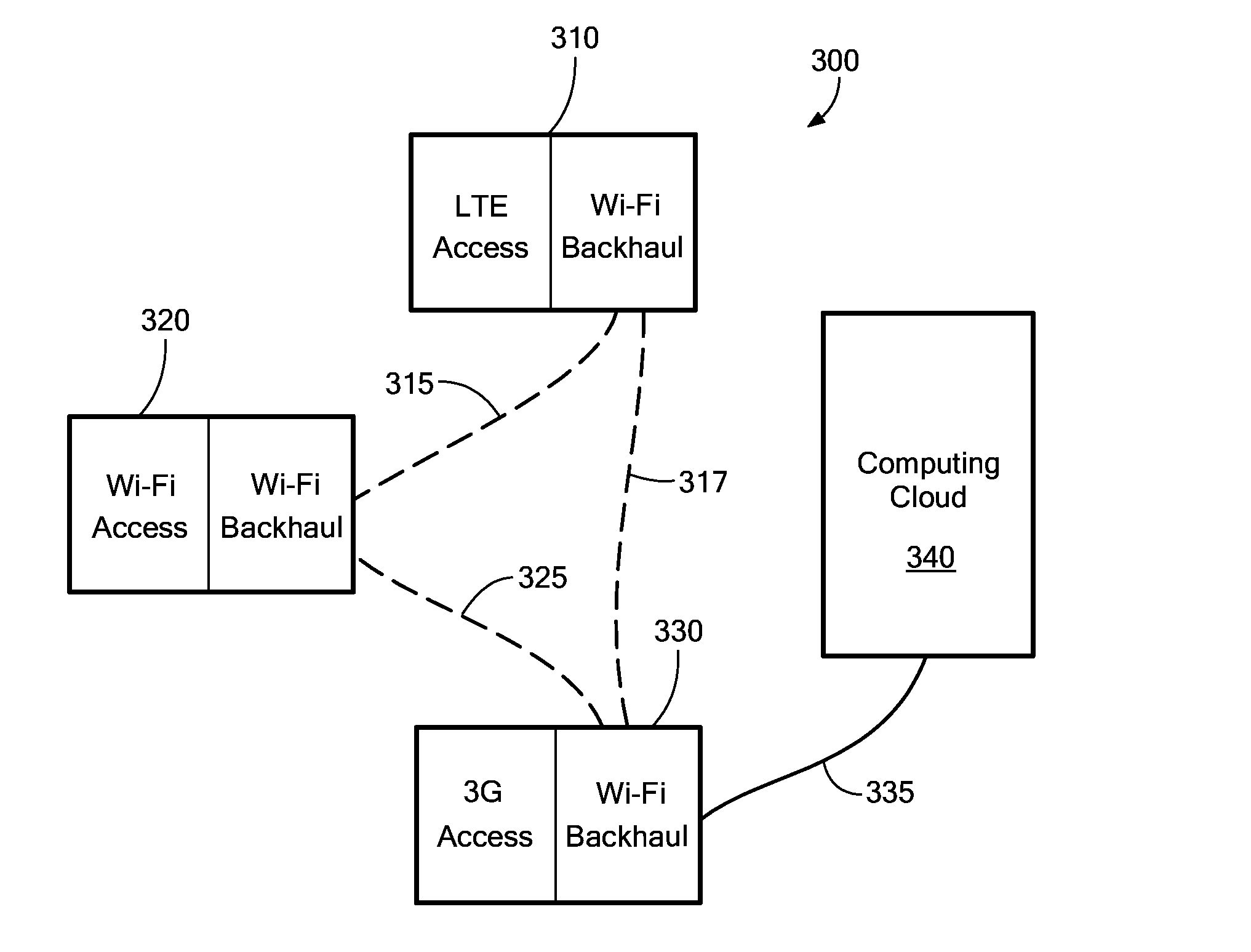
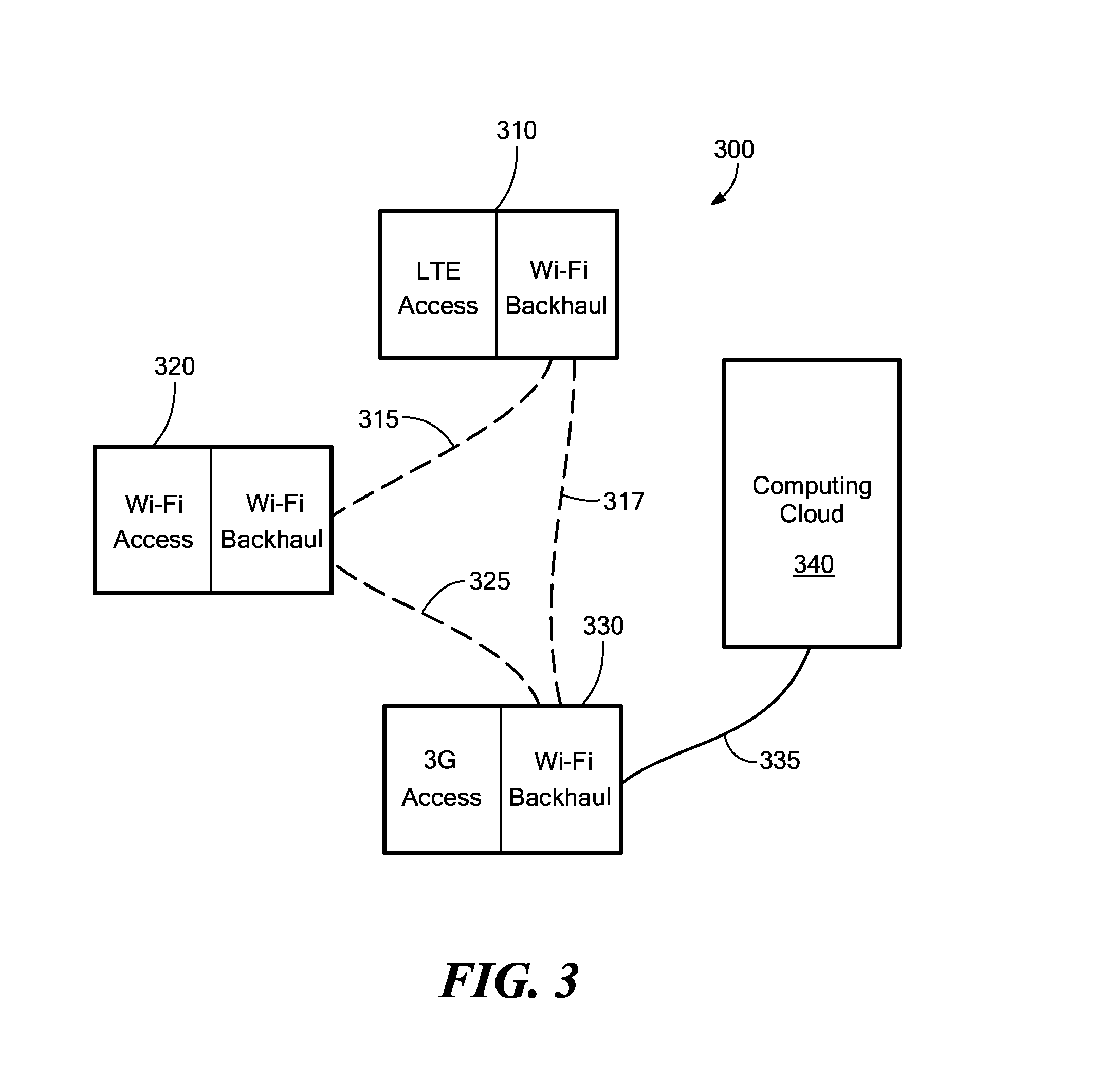
Dynamic Multi-Access Wireless Network Virtualization
ActiveUS20140133456A1Network topologiesWireless commuication servicesWireless network virtualizationMulti access
We disclose systems and methods of dynamically virtualizing a wireless communication network. The communication network is comprised of heterogeneous multi-RAT mesh nodes coupled to a computing cloud component. The computing cloud component virtualizes the true extent of the resources it manages and presents an interface to the core network that appears to be a single base station.
Owner:PARALLEL WIRELESS
Extended service set mesh topology discovery
ActiveUS7522540B1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationGrid networkWireless computing
A system and methods for wireless computing devices to become mesh member nodes within a self-configuring mesh network includes mechanisms for neighbor discovery and sharing of a common topology database including mesh topology and mesh network information. Each mesh node may use the topology database to determine optimized routing paths within the mesh network. Mesh member nodes are configured to detect and communicate topology changes and measured mesh network attributes to other members of the self-configuring wireless network.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Discovery and authentication scheme for wireless mesh networks
InactiveUS7814322B2Error preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsOpen Systems InterconnectionMesh node
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
System and method for spanning tree cross routes
InactiveUS20070110024A1Easy to routeData switching by path configurationWireless communicationRouting tableNetwork packet
A spanning tree cross-route protocol for establishing mesh-like cross routes in an underlying wireless spanning tree topology. A cross route spans branches of the tree topology to provide a more optimal route between any two nodes in the wireless network. The cross route can span multiple spanning trees. Each mesh node maintains a cross route table. When a packet is received, the node determines whether there is an entry for the destination node in the cross route table. If there is an entry for the destination node in the cross route table, the packet is forwarded via the cross route; otherwise, the packet is forwarded via the spanning tree.
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Chirp networks
ActiveUS20150304879A1Low costEfficient transportError preventionTransmission systemsPacket lossRouting table
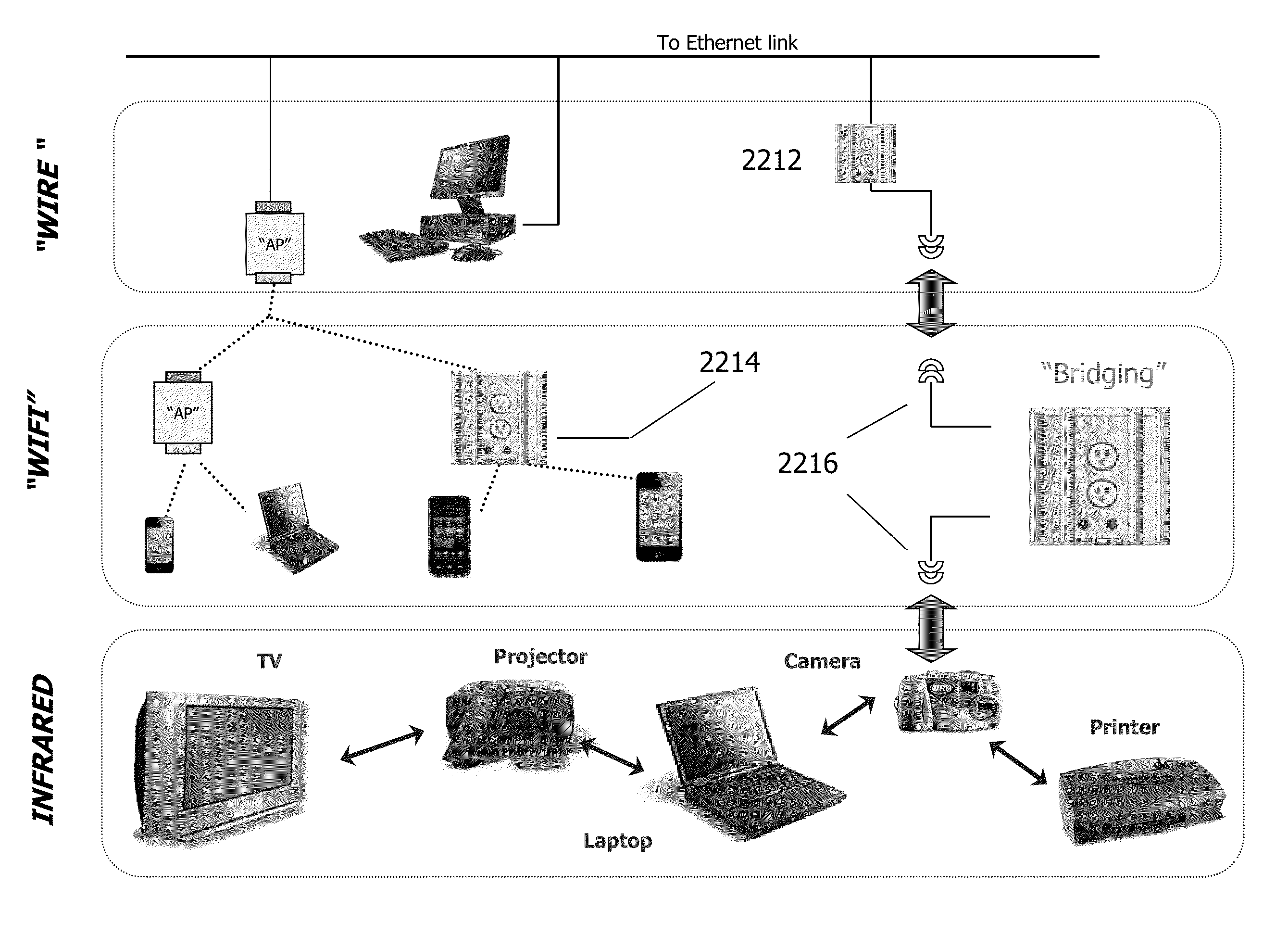
A network combining wireless and wired elements is described, using a multi-slot modular mesh node to house diverse transceiver elements (e.g. IR, Wi-Fi, Powerline). A radio agnostic tree based mesh network is formed, based on what type of wireless links are formed on the uplink and downlink of the backhaul and what type of radios are used for the Access Points AP. In addition to servicing IP based clients (e.g. Wi-Fi, WiMax, Bluetooth), the modular mesh nodes APs may also serve as receivers / collectors for low cost chirp devices. The method of transport is standard IP based packets yet security is inherent in this chirp-based implementation: only mesh nodes are privy to the routing tables that indicate that packet addresses are not IP. Multiple methods to obfuscate packet flow are presented. An organic approach to providing category / class based form of data type identification is proposed, to support a (dynamic) M2M Social Network Applications in-device discovery, registration and control are presented.
Owner:MESHDYNAMICS
Extended service set mesh path selection
ActiveUS7606175B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesGrid networkWireless computing
A system and methods for wireless computing devices to become mesh member nodes within a self-configuring mesh network includes mechanisms for neighbor discovery and sharing of a common topology database including mesh topology and mesh network information. Each mesh node may use the topology database to determine optimized routing paths within the mesh network. Mesh member nodes are configured to detect and communicate topology changes and measured mesh network attributes to other members of the self-configuring wireless network.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
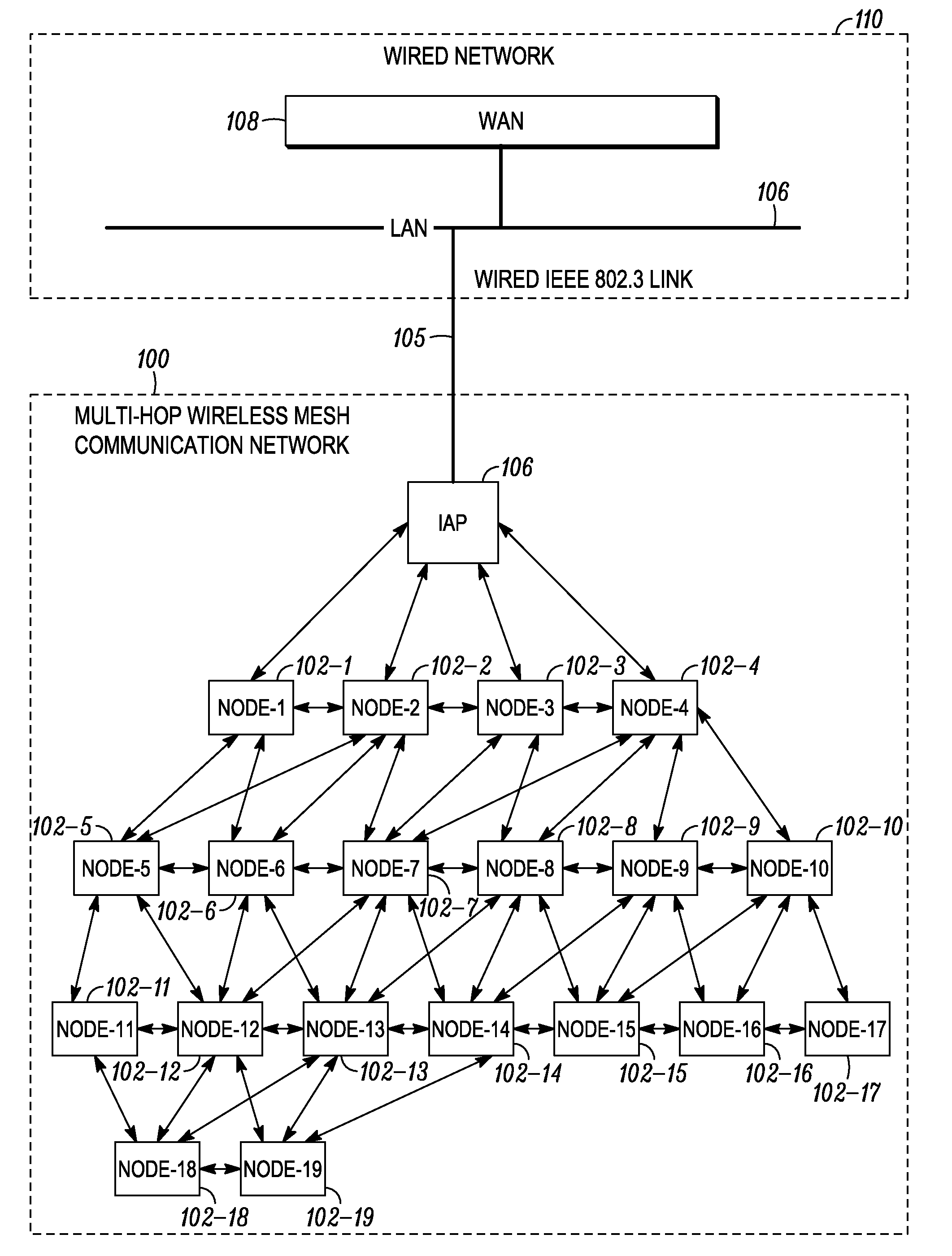
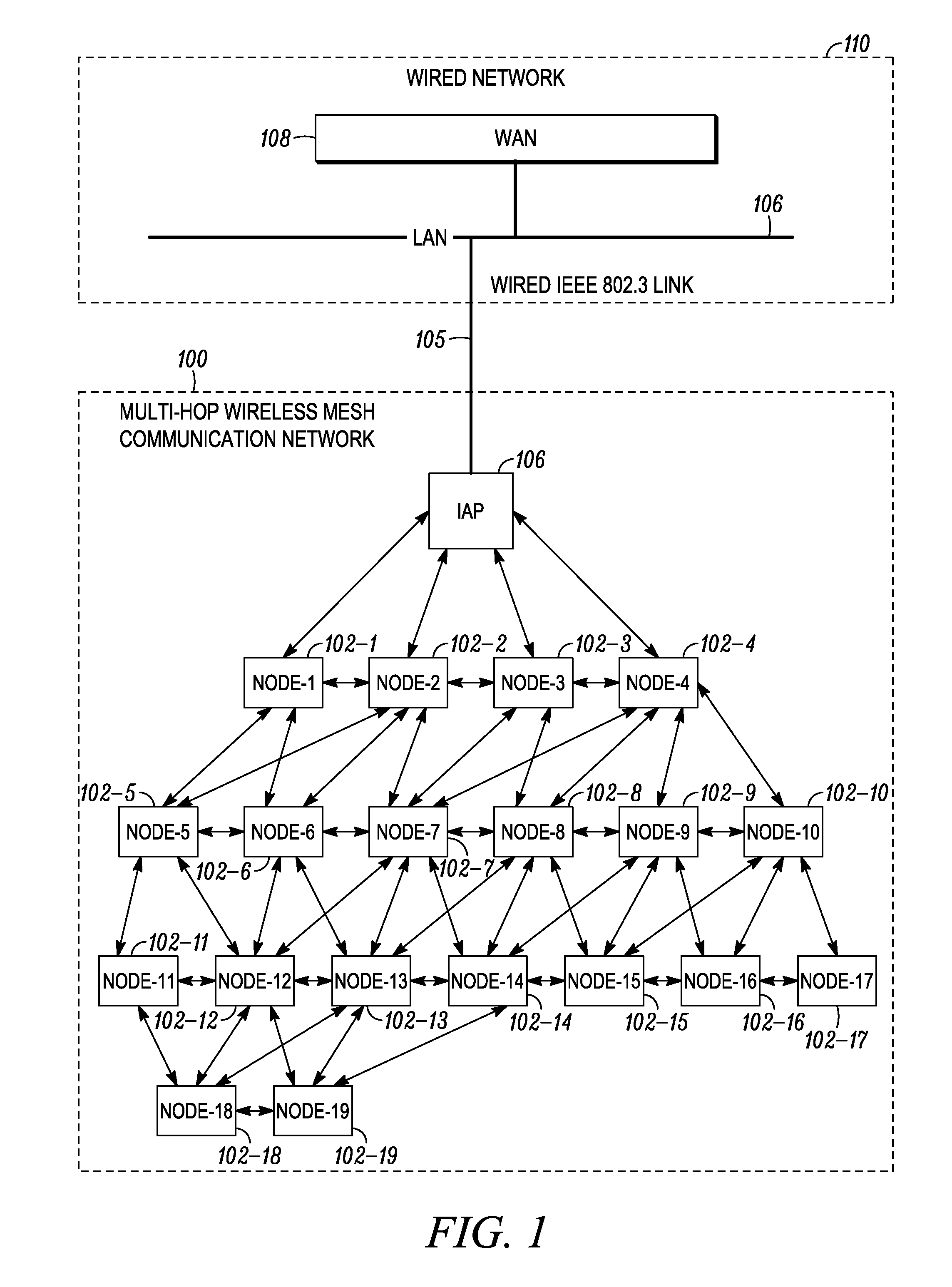
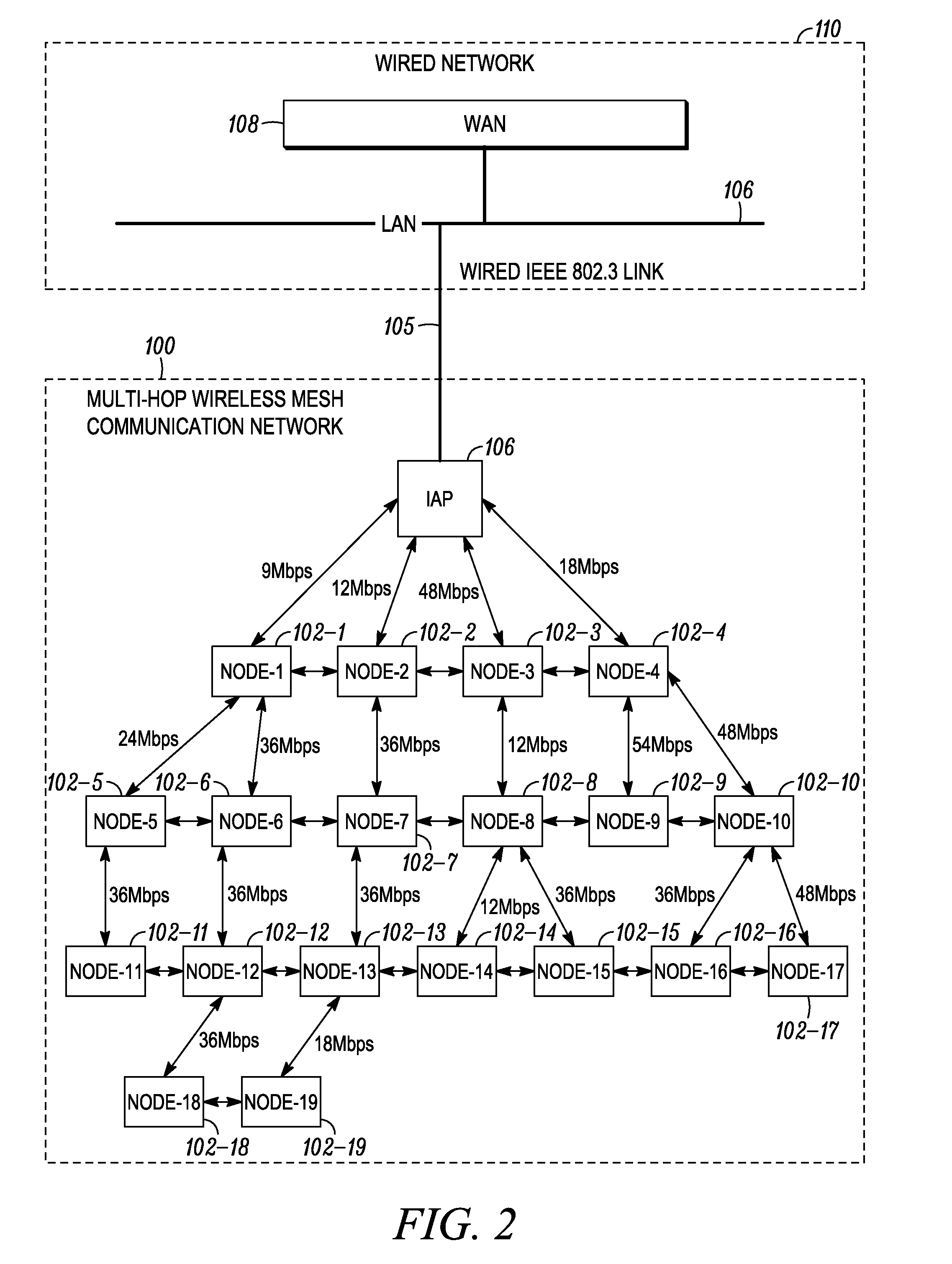
System and method for improving efficiency and reliability of broadcast communications in a multi-hop wireless mesh network
InactiveUS20100157888A1Wireless commuication servicesData switching networksBroadcast packetTelecommunications
Systems and methods are provided for improving efficiency and reliability of broadcast transmission in a multi-hop wireless mesh communication network. In some implementations, systems and methods are provided for a leaf mesh node to acknowledge reception of a broadcast packet broadcast by an Intelligent Access Point (IAP), and for allowing the IAP to determine whether to re-communicate the broadcast packet that it had previously re-transmitted when no acknowledgment is received from a leaf mesh node.
Owner:MOTOROLA SOLUTIONS INC
Multi-channel mesh nodes employing stacked responses
ActiveUS20100061350A1Error prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementTransceiverNetwork packet
Rather than using a large number of transceivers (transmitter / receiver pairs) operating in parallel, Access Points with multiple channels are used to aggregate, or stack, transmitted response communications, e.g., transmitting multiple acknowledgements (ACKs) in a single packet to one or more sources of received packets. The method includes sending on a plurality of channels, by each of a plurality of respective first nodes, a communication to a second node, receiving on the plurality of channels, by the second node, the communication from each of the plurality of first nodes and sending, by the second node, a transmission that contains a response to each communication that was successfully received from each of the plurality of first nodes. The response to each of the plurality of first nodes is part of a single message sent by the second node.
Owner:ITRON NETWORKED SOLUTIONS INC
Communication protocol for a wireless mesh architecture
A wireless mesh communication protocol that dynamically assigns communication time-slots and frequencies to mesh nodes. A first node is established as a PC that sequentially polls other nodes. A second node responds at a predetermined time with information that includes database records, and then a third node responds similarly. The second node is then established as the PC and the first node is polled during dynamically allocated time-slots and on a frequency that depend on the second node's database records. The third node is then established as a PC and acts similarly. In both cases the first node responds by sending information and data records. The first node is then re-established as the PC. The first node then polls the second and third nodes at times and frequencies that depend on the first node's database records.
Owner:TRILLIANT NETWORKS
Mesh networking using point coordination function
ActiveUS7502354B1Raise the possibilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationGrid networkWireless computing
A system and methods for wireless computing devices to become mesh member nodes within a self-configuring mesh network includes mechanisms for neighbor discovery and sharing of a common topology database including mesh topology and mesh network information. Each mesh node may use the topology database to determine optimized routing paths within the mesh network. Mesh member nodes are configured to detect and communicate topology changes and measured mesh network attributes to other members of the self-configuring wireless network.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Combined directional and mobile interleaved wireless mesh network
InactiveUS20070183439A1Improve acceleration performanceImprove performanceNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationOmnidirectional antennaDirectional antenna
A combined fixed directional and mobile omnidirectional interleaved wireless mesh network is described where the fixed mesh nodes have directional antennas facing in horizontally orthogonal directions. The antennas can be focused to have a horizontal beam width of less than ninety degrees in order to achieve greater strength of signal and radiation. Each directional node can have multiple radios that communicate on separate channels, such that packets propagated through the mesh network can utilize any channel to enter or leave a particular node. The combined network also includes mobile nodes that utilize multiple radios, each connected to an omnidirectional antenna and operating on a different channel. The mobile nodes can maintain constant communication with the directional nodes as they move between various quadrants covered by the directional nodes. The mobile nodes can also maintain connections to each other even during the loss of communication with the fixed directional nodes.
Owner:SECOND SIGHT MEDICAL PRODS +1
Chirp networks
A wire-less / Wired mesh network is described, using a multi-slot modular mesh node to house diverse transceiver elements (e.g. IR, Wi-Fi, Powerline). A radio agnostic tree based mesh network is formed, based on what type of wire-less links are formed on the uplink and downlink of the backhaul and what type of radios etc are used for the Access Points AP, see FIG. 17,23.In addition to servicing IP based clients (e.g. Wi-Fi, WiMax, Bluetooth), the modular mesh nodes APs may also serve as receivers / collectors for low cost chirp devices. These devices are not “agile” and therefore contentious. APs, servicing these devices, alleviate potential contention by multiple means including: sending out a “incoming” CTS, efficient delivery through container based schedulable bus deliveries, and its reverse (moving chirp transmission times to be sequential).Multiple approaches for “pollen” to reach the intended “flower” in a timely manner are described. The method of transport is standard IP based packets yet security is inherent in this pollen-flower based system: only mesh nodes are privy to the routing tables that indicate that packet addresses are not IP. Multiple options to further obfuscate packet flow are presented.A multi-agent based approach driving business process flow is described. Such agents can also provide specialized mesh network routing e.g. navigation agents for chirp devices.Tree based routing and logical radio abstractions are revisited.An organic approach to providing category / class based form of data type identification is proposed, to efficiently match publishers and subscribers, based on the type of data being sought. A private, secure and natively Publish / Subscribe M2M community is engendered at the edge. It has loosely, dynamic and ad hoc couplings to big data servers, also operating on their own private exchange / market place, using a real time publish / subscribe infrastructure with content categories used as part of pollen identification.
Owner:DYNAMIC MESH NETWORKS
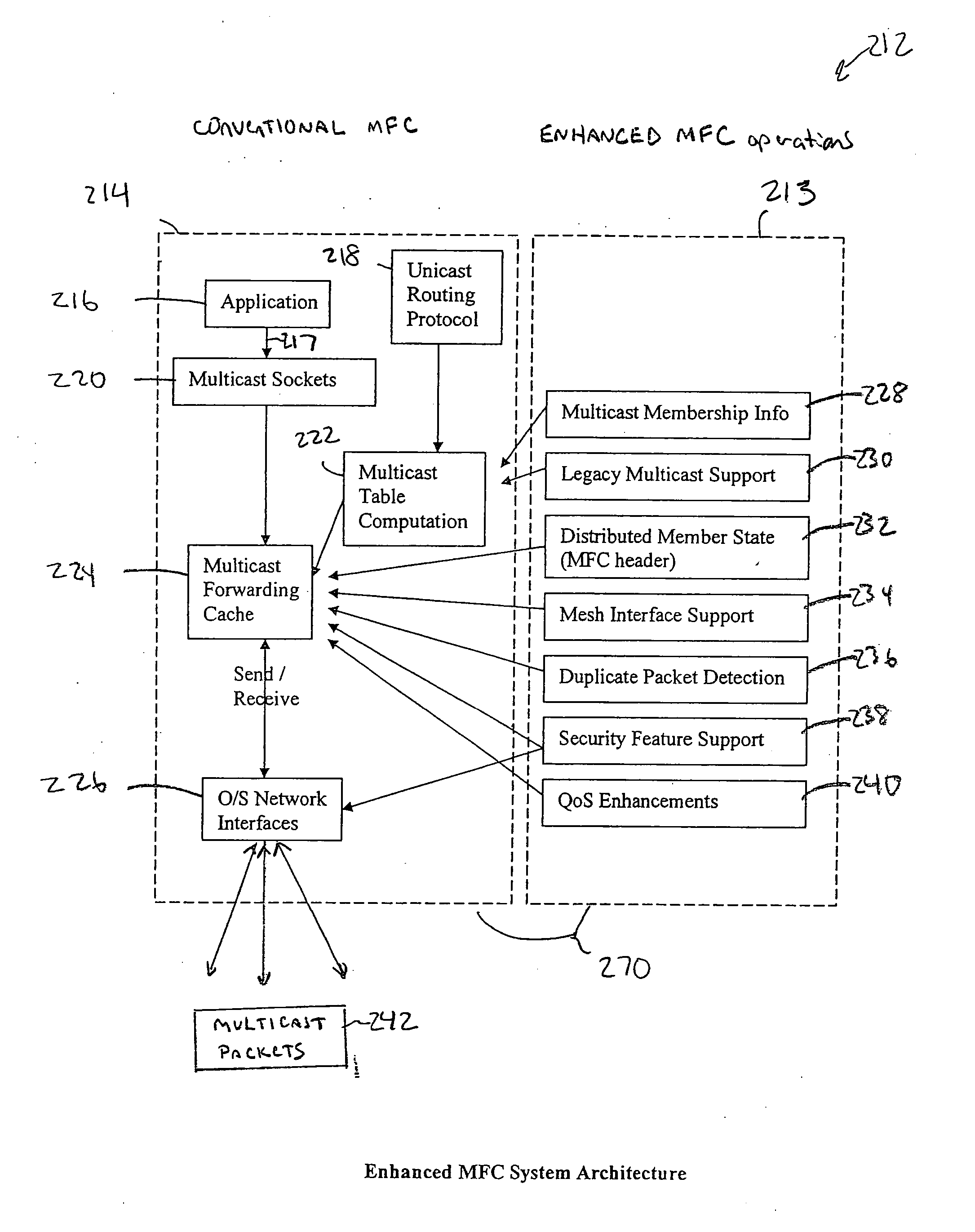
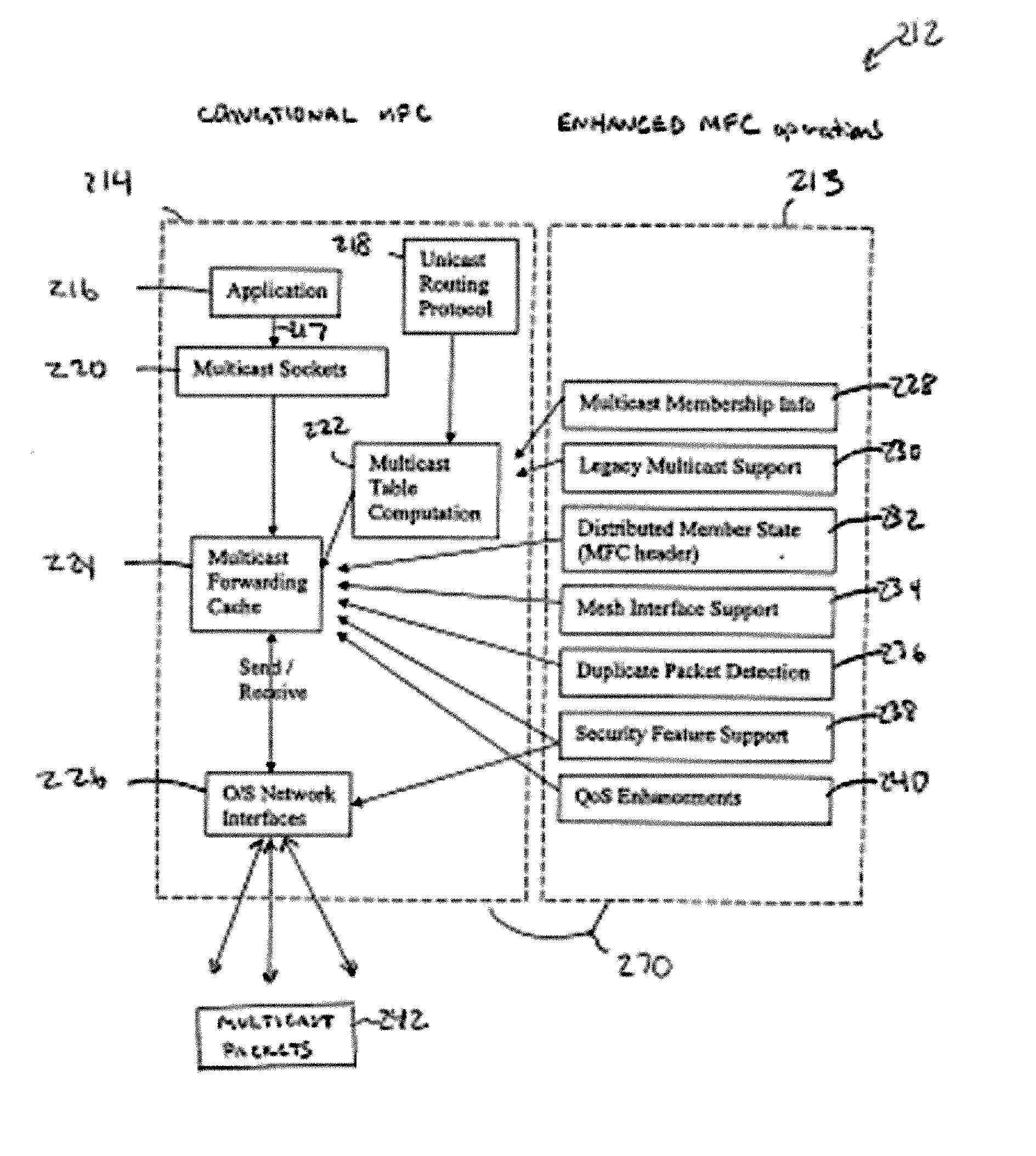
Enhanced multicast forwarding cache (eMFC)
InactiveUS20050175009A1Maintaining backwards compatibilityMaintain securityTime-division multiplexWide area networksQuality of serviceDistributed services
An Enhanced Multicast Forwarding Cache (eMFC) supports multicast transmissions in mobile mesh networks. The enhanced MFC is designed to support mesh node mobility, quality of service, and security requirements that are particular to mesh networks. To achieve these goals, the enhanced MFC draws from a global state maintained by a unicast routing protocol, multicast aware applications, and distributed services. The eMFC distributes this derived global state through the use of an eMFC-specific multicast packet header. Information contained within the eMFC header is also used to collect and derive multicast traffic statistics at each mesh node. To maintain backwards compatibility, multicast traffic without the eMFC-specific header is also honored by the MFC. Mobile mesh network specific interfaces, such as radio interfaces, as well as conventional interface types are supported. Security is maintained through the use of authentication and encryption techniques.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Grid proxy architecture for network resources
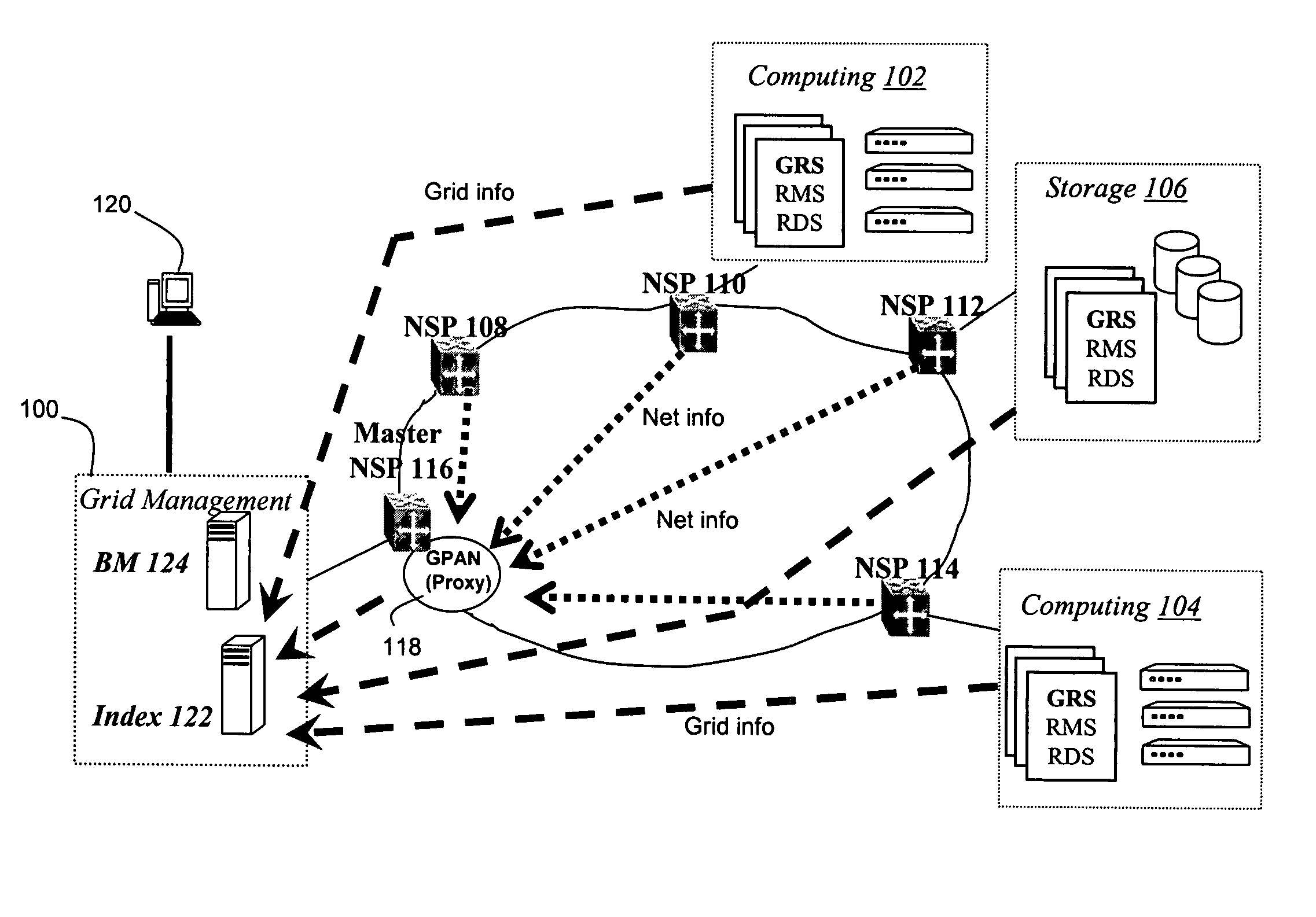
ActiveUS8078708B1Facilitate reservationFacilitate resourceMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram controlGrid resourcesResource based
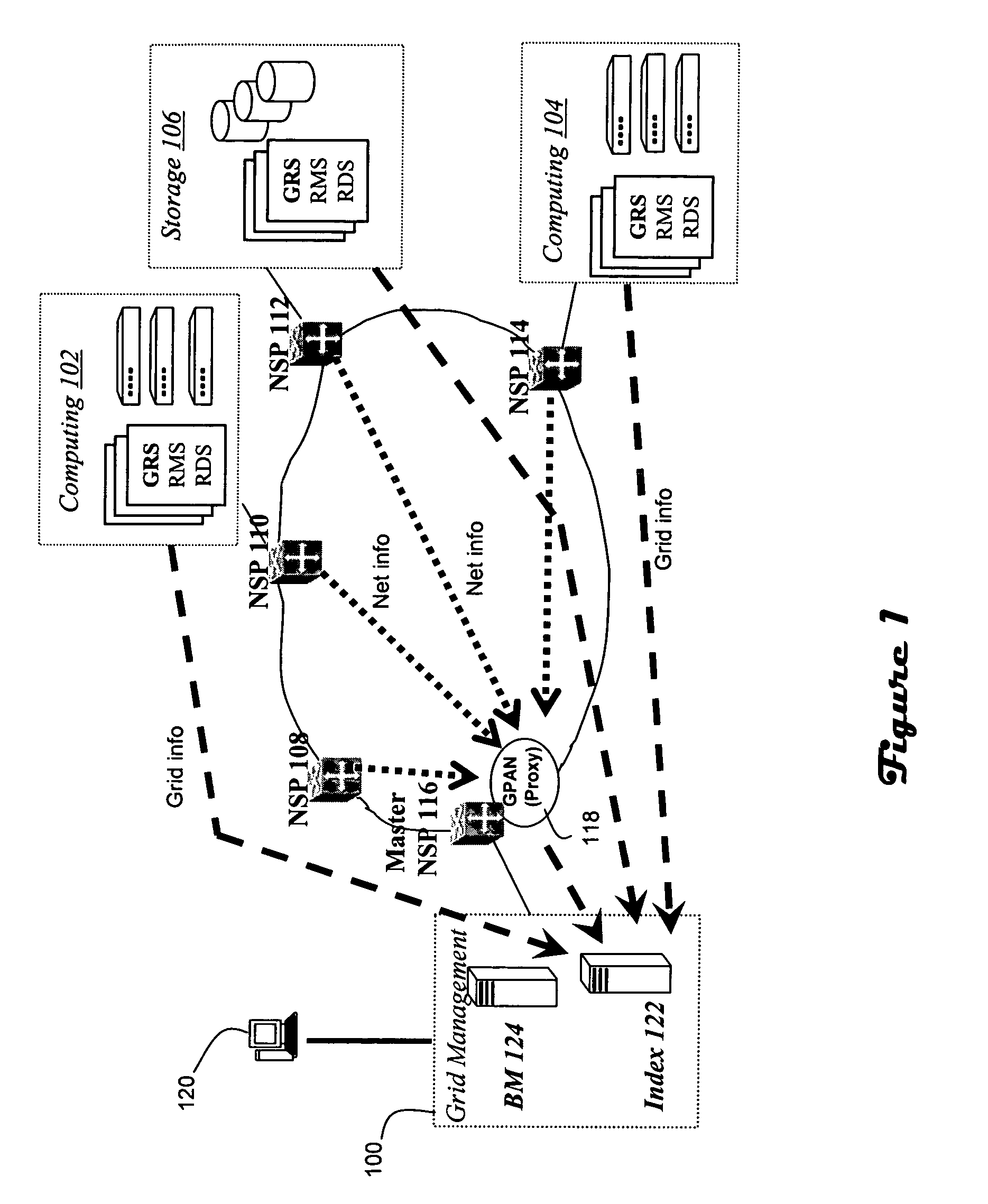
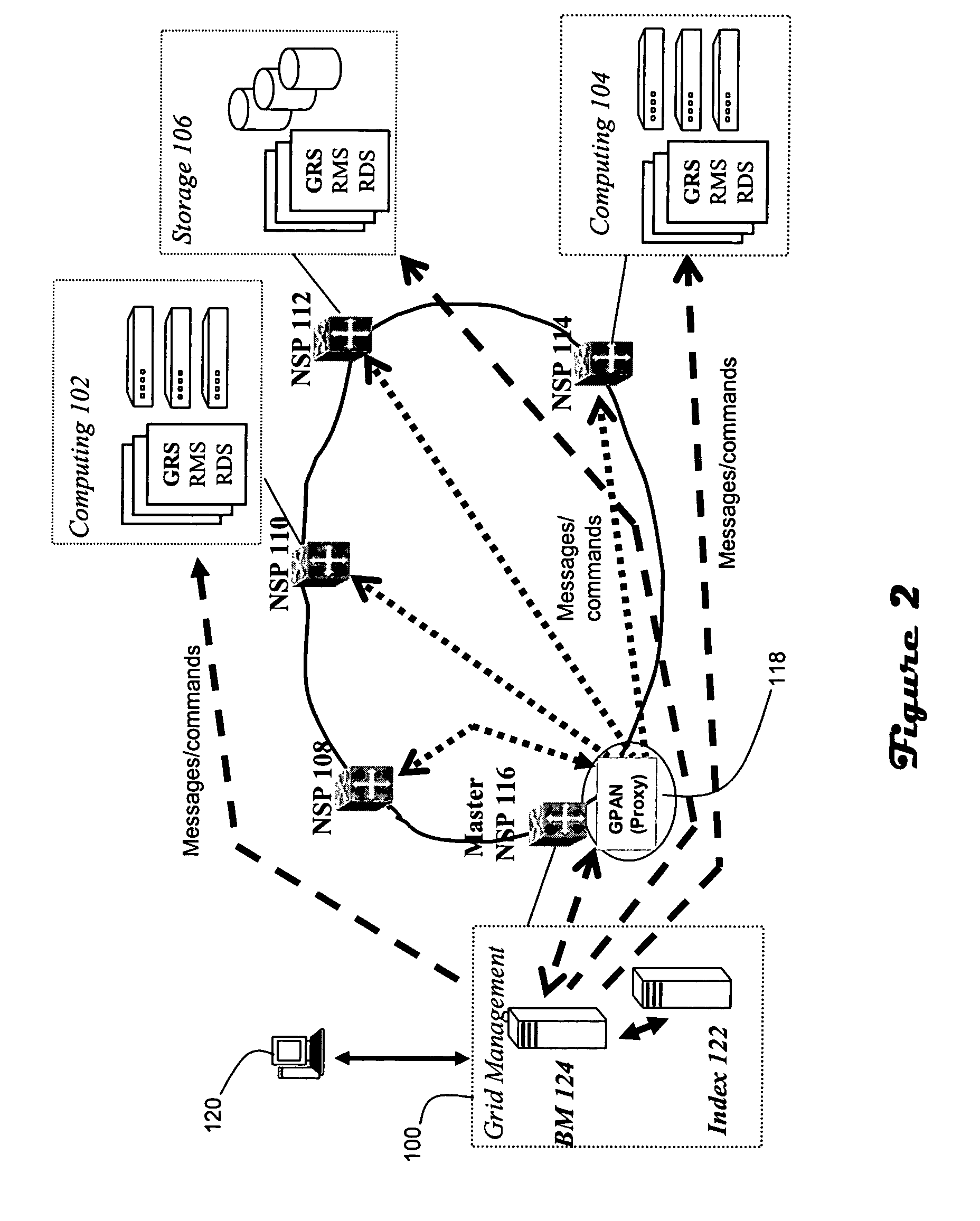
A Grid Proxy Architecture for Network Resources (GPAN) is proposed to allow Grid applications to access resources shared in communication network domains. GPAN bridges Grid services serving user applications and network services controlling network devices through its proxy functions such as resource data and management proxies. Working with Grid resource index and broker services, GPAN employs distributed network service peers (NSP) in network domains to discover, negotiate and allocate network resources such as bandwidth for Grid applications. An elected master NSP is the unique Grid node that runs GPAN and represents the whole network to share network resources to Grids without Grid involvement of network devices. GPAN provides the Grid Proxy service (GPS) to interface with Grid services and applications, and the Grid Delegation service (GDS) to interface with network services to utilize network resources. Resource-based XML messaging is employed for the GPAN proxy communication.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and Arrangement for Providing a Wireless Mesh Network
ActiveUS20100228980A1Simple and appropriate implementationReduce loadKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsMesh nodeAuthentication
A method and an arrangement are provided wherein a newly added mesh node does not require a link to the AAA server for the purpose of authentication. Authentication is carried out using a node which is already present in the mesh network and which has a link to the AAA server
Owner:UNIFY GMBH & CO KG
ENHANCED MULTICASE FORWARDING CACHE (eMFC)
InactiveUS20060029074A2Time-division multiplexWide area networksQuality of serviceDistributed services
Abstract of the DisclosureAn Enhanced Multicast Forwarding Cache (eMFC) supports multicast transmissions in mobile mesh networks. The enhanced MFC is designed to support mesh node mobility, quality of service, and security requirements that are particular to mesh networks. To achieve these goals, the enhanced MFC draws from a global state maintained by a unicast routing protocol, multicast aware applications, and distributed services. The eMFC distributes this derived global state through the use of an eMFC-specific multicast packet header. Information contained within the eMFC header is also used to collect and derive multicast traffic statistics at each mesh node. To maintain backwards compatibility, multicast traffic without the eMFC-specific header is also honored by the MFC. Mobile mesh network specific interfaces, such as radio interfaces, as well as conventional interface types are supported. Security is maintained through the use of authentication and encryption techniques.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
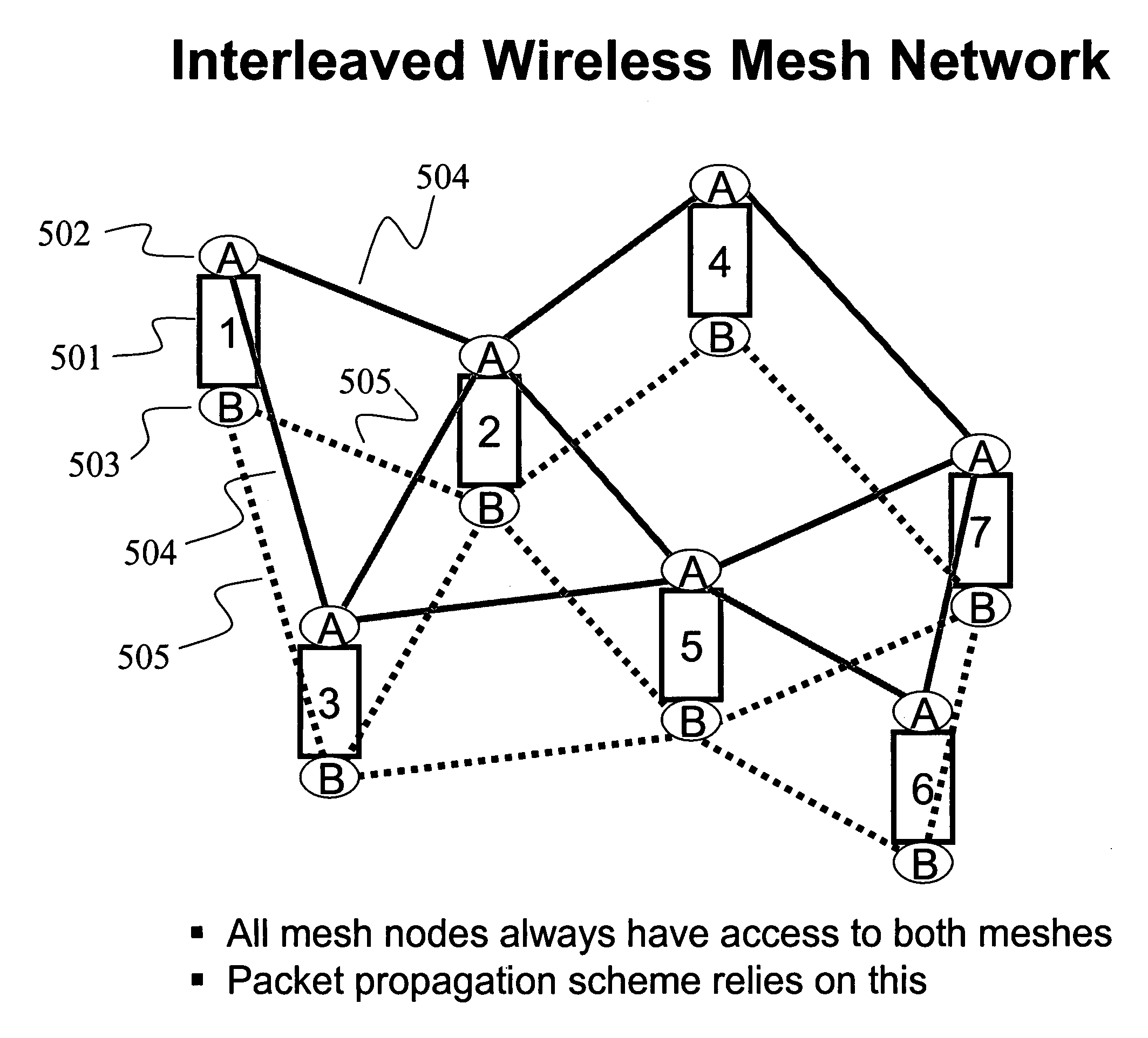
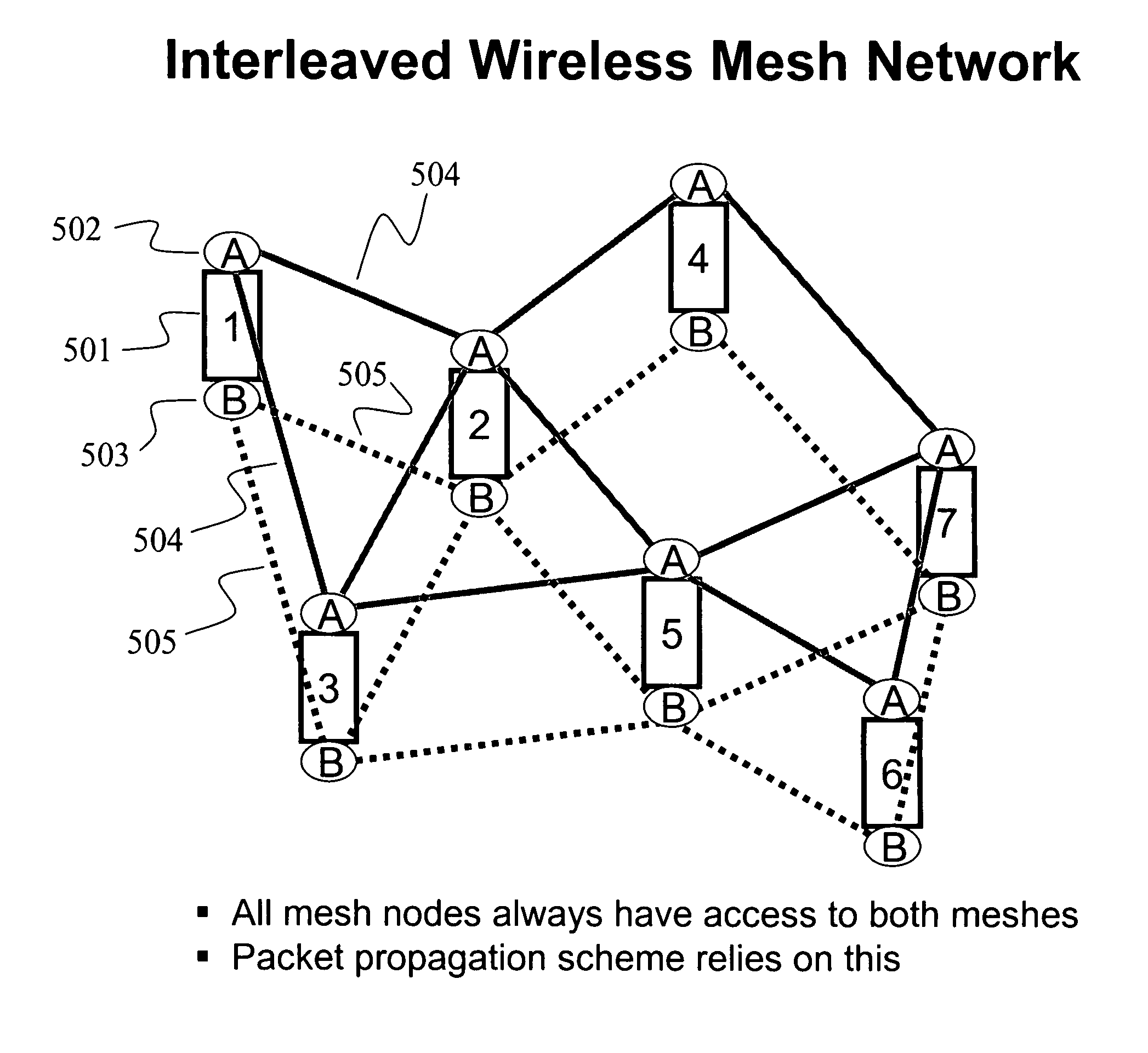
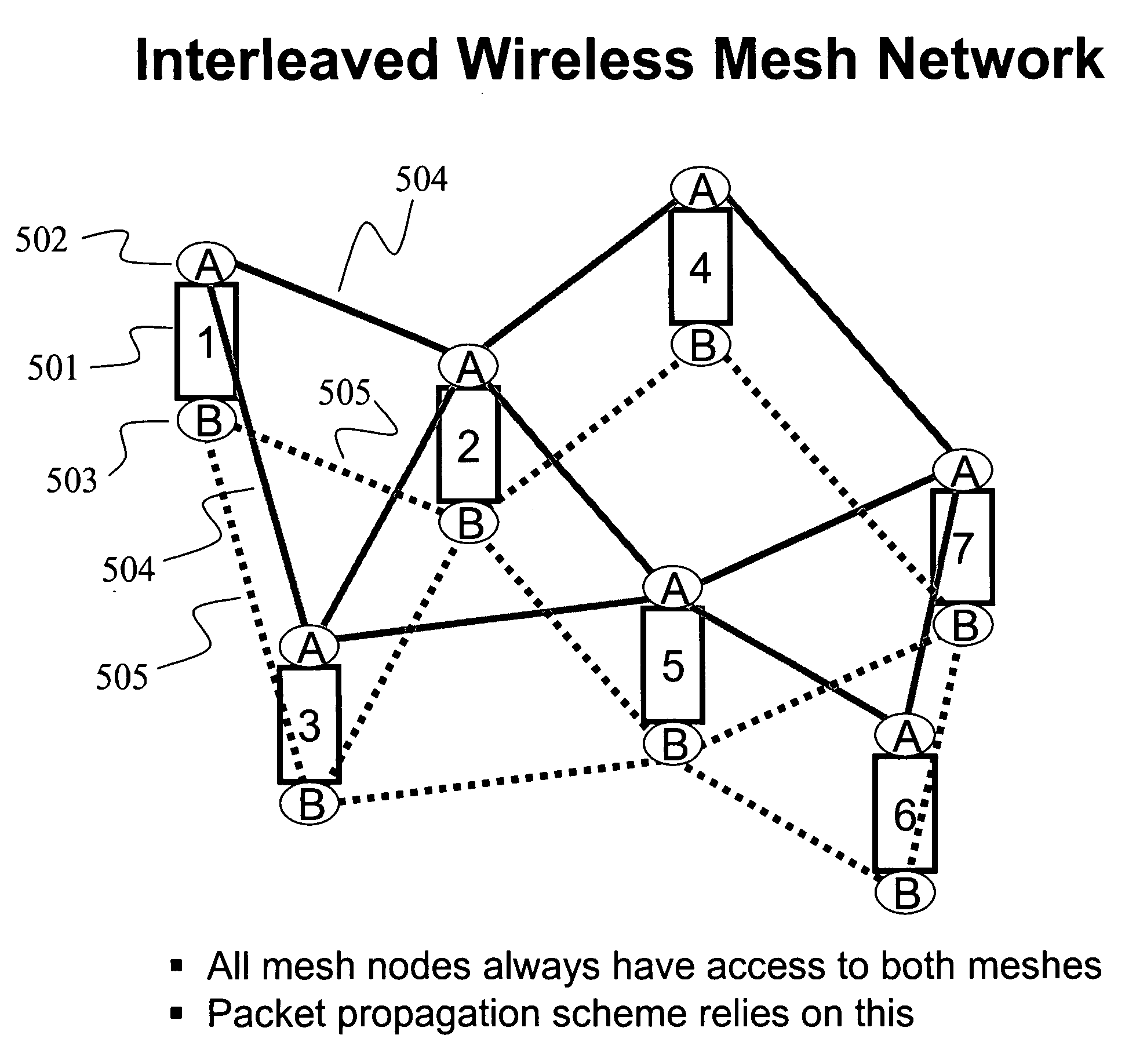
Interleaved wireless mesh network
InactiveUS20070160020A1Improve acceleration performanceImprove performanceNetwork traffic/resource managementNetwork topologiesParallel computingAlternative methods
An interleaved wireless mesh network is described where each mesh node always has at least two radios that have access to at least two parallel meshes, and where a packet stream may utilize either or both of these parallel meshes for any given hop, using the parallel (physical) meshes as a single (logical) mesh. Here, two sequentially adjacent packets in a particular packet stream may travel on the same mesh or on different meshes for any given hop, thereby enabling the performance of a specific sequential packet stream to be doubled. Dynamic frequency selection (DFS) operations can be performed by the parallel meshes upon sensing radar interference on a channel used by either mesh. While one mesh is performing the DFS, packets may continue to be propagated on the alternative mesh, thereby enabling continuous and uninterrupted data flow throughout the network.
Owner:FOLUSHA FORTE
Interleaved and directional wireless mesh network
ActiveUS20070153817A1Improve acceleration performanceImprove performanceNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationComputer networkDirectional antenna
A directional and interleaved wireless mesh network is described where mesh nodes have directional antennas facing in horizontally orthogonal directions. The antennas can be focused to have a beam width of less than ninety degrees in order to achieve greater strength of signal and radiation. Each mesh node can have two radios that communicate on separate channels, such that packets propagated through the mesh network can utilize either channel in order to hop from one node to the next. Each radio can be connected to four orthogonally directed antennas in order to enable communication with adjacent nodes. Alternatively, a separate independent radio can be connected to each antenna in order to achieve greater simultaneity of transmission and reception to the node. For example, two such radio-antenna combinations can be facing in each of the four orthogonal directions, each of the two combinations operating on a different RF channel.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
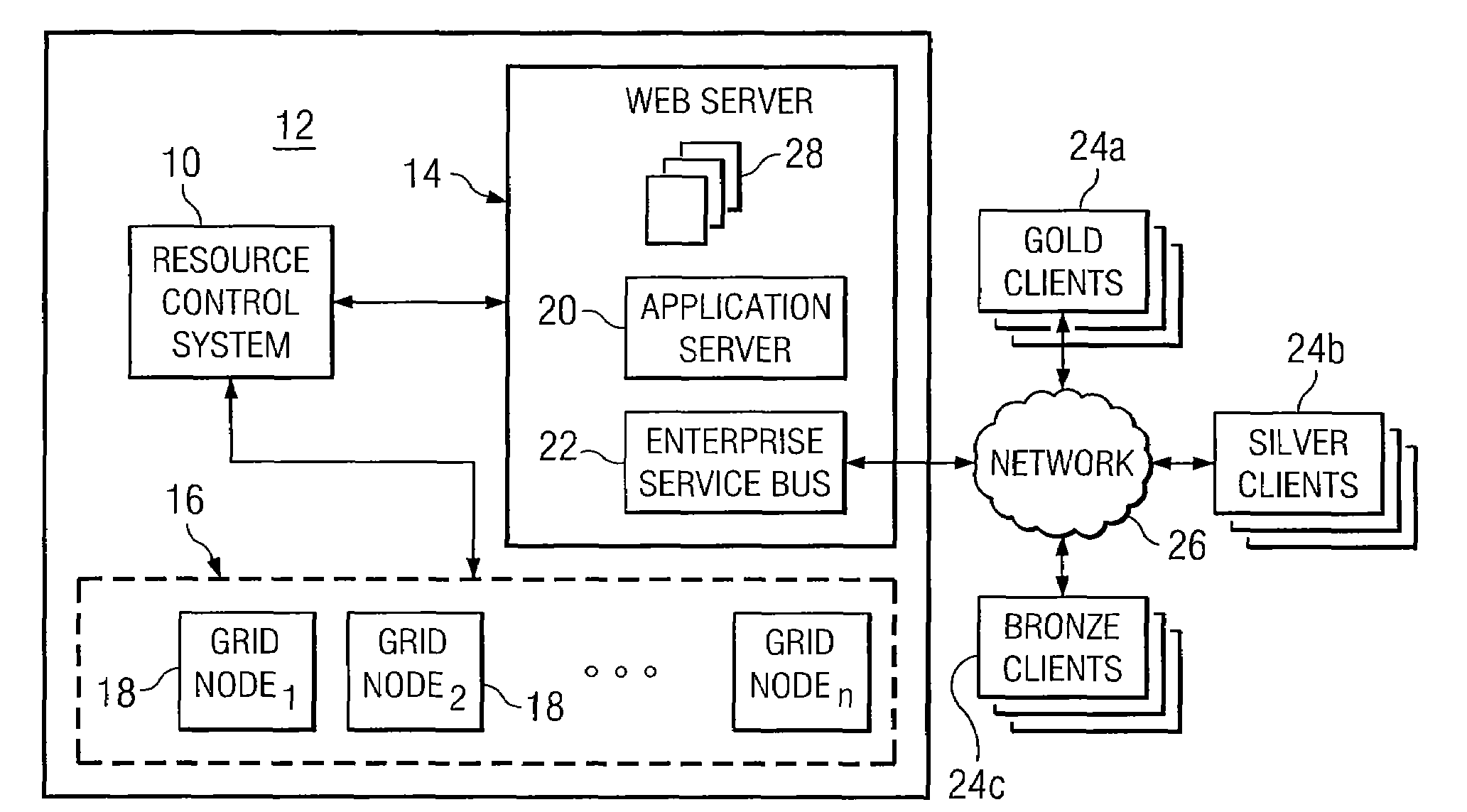
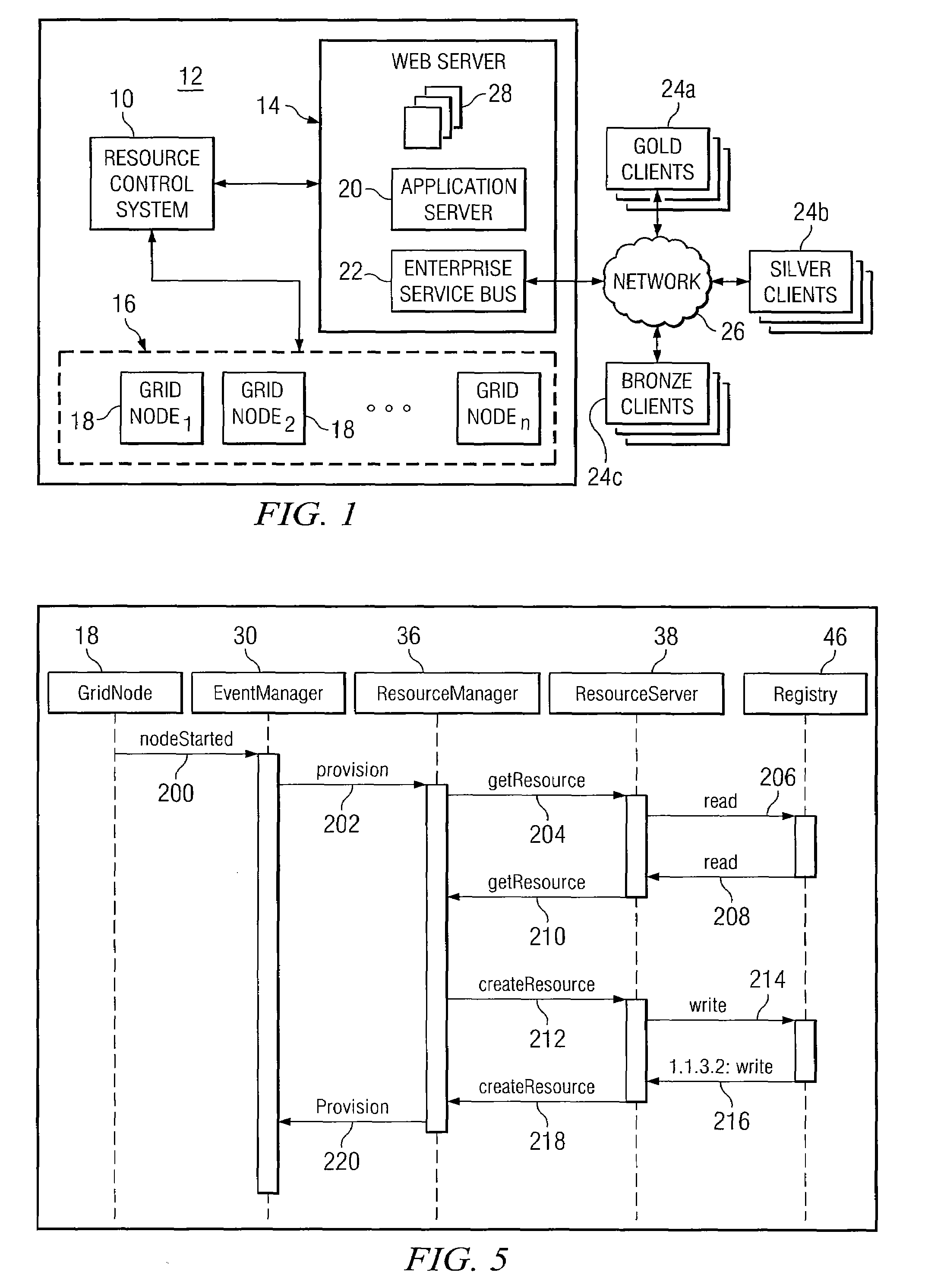
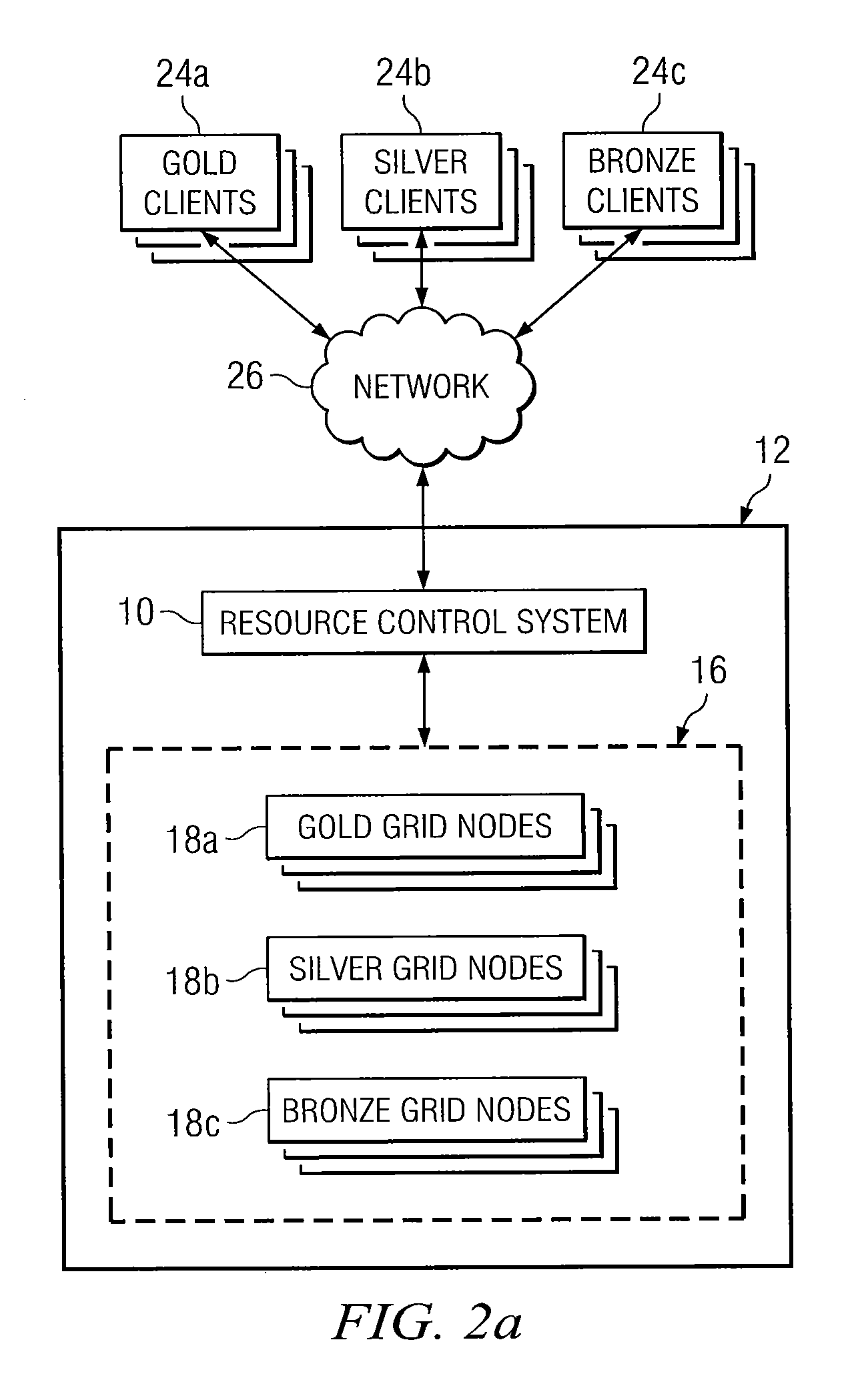
System and Method for Allocating Resources in a Distributed Computing System
ActiveUS20100262695A1Reduce idle timeReduce computing power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTError detection/correctionQuality of serviceMaximum level
According to a particular embodiment of the present invention, a system and method for allocating resources in a distributed computing system are provided. In one embodiment, a distributed computing system includes a computing grid including a plurality of grid nodes, a web server configured in a service-oriented architecture and operable to provide one or more business applications to a plurality of clients by executing one or more services on the plurality of grid nodes, and a resource control system communicatively coupled to the web server. The resource control system is operable to receive one or more performance parameters of the business applications executed on the plurality of grid nodes, provision one or more of the grid nodes in response to the performance parameters falling below a predetermined minimum level, and un-provision one or more of the grid nodes in response to the performance parameters exceeding a predetermined maximum level. The plurality of clients comprises a plurality of client subsets, each client subset requiring a respective quality of service, and each of the grid nodes in the computing grid is assigned a particular client subset for which to execute services.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
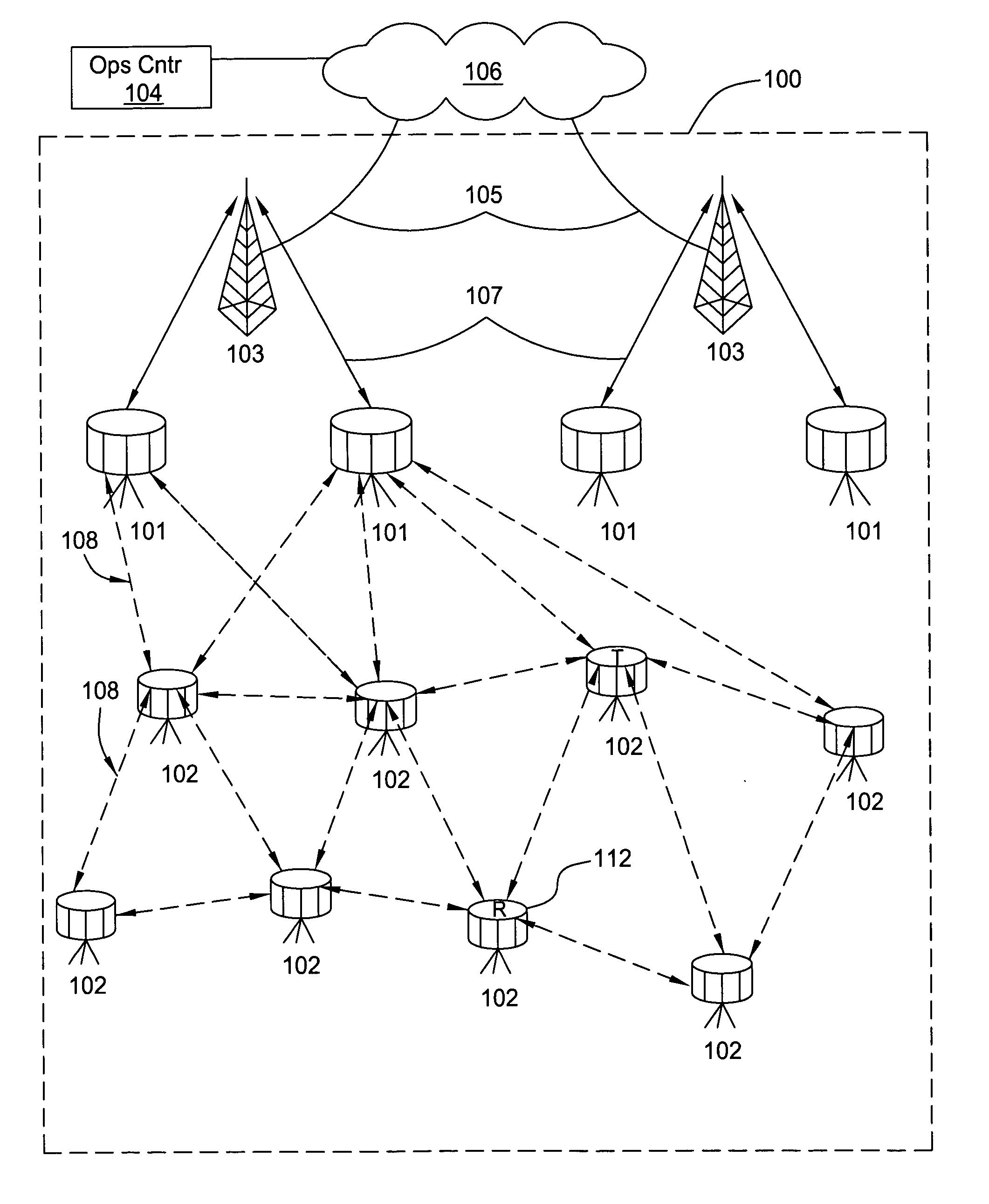
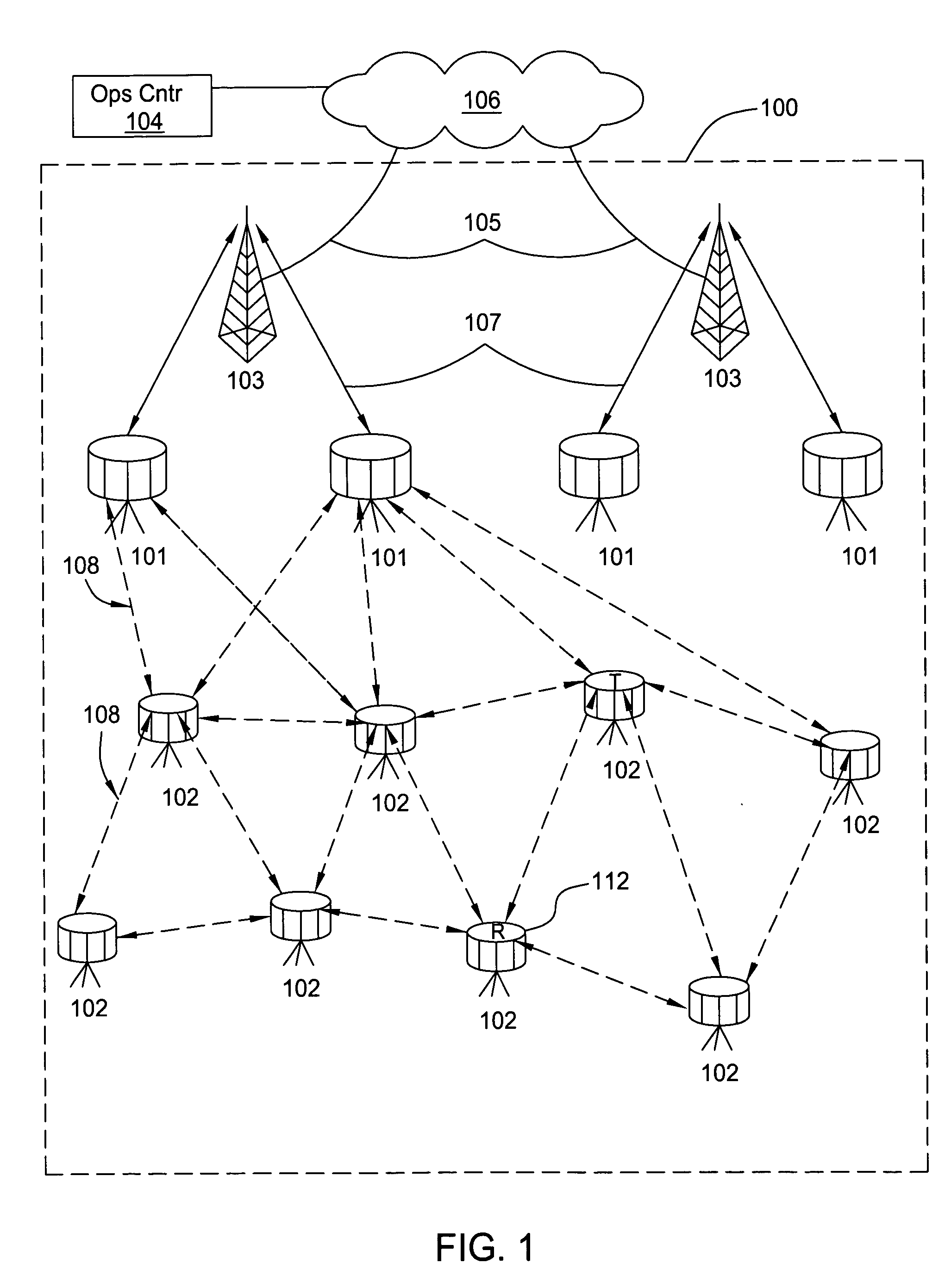
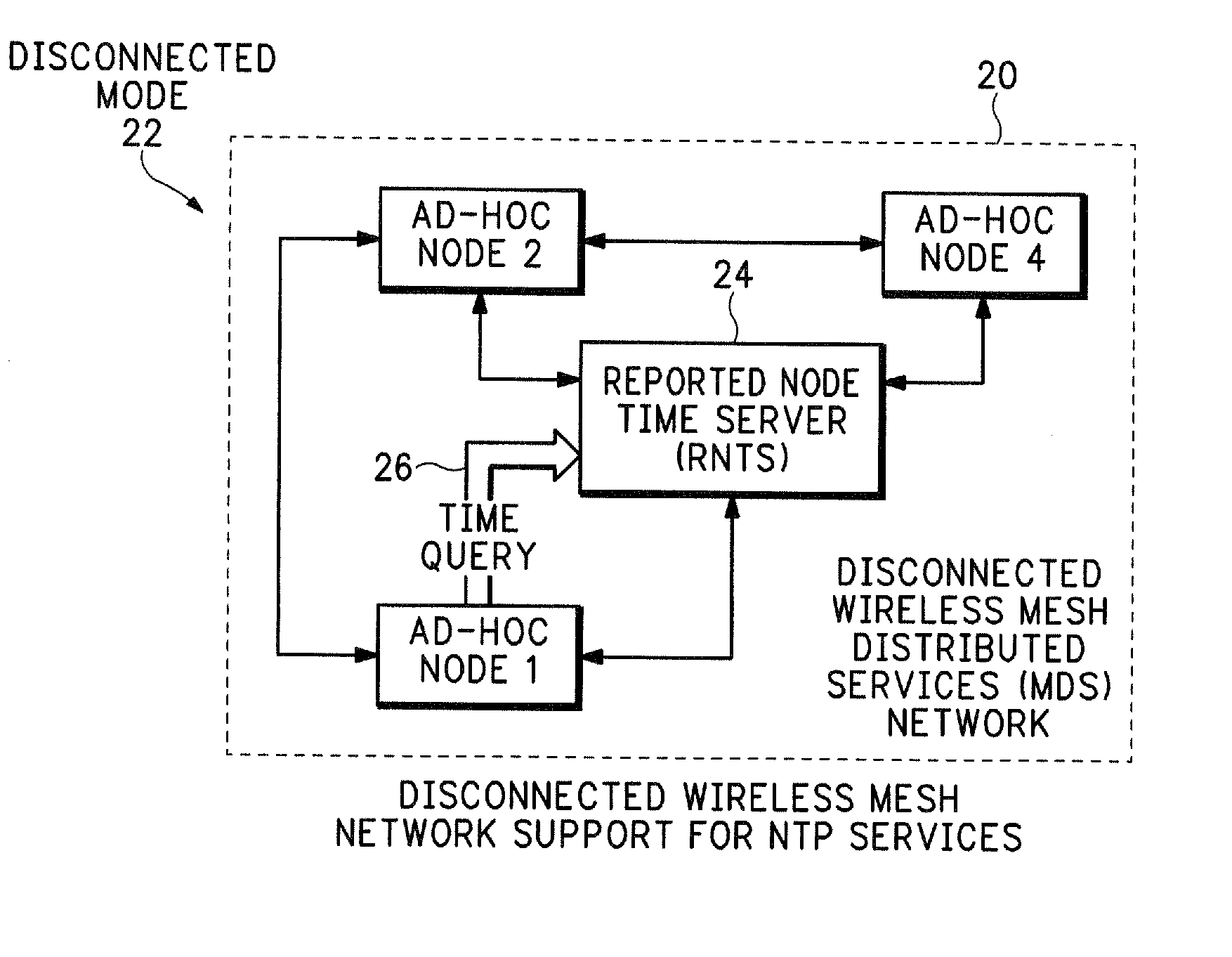
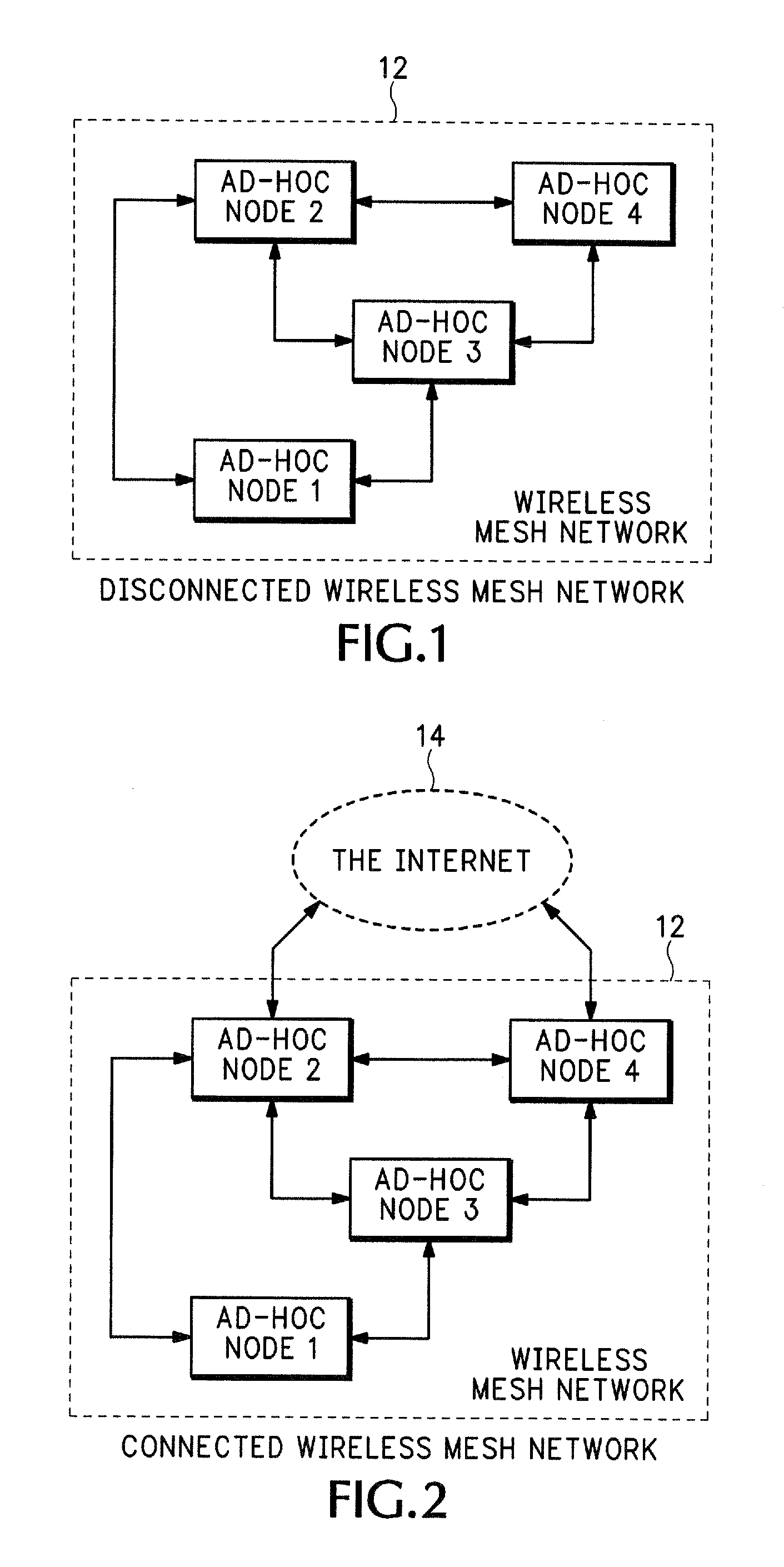
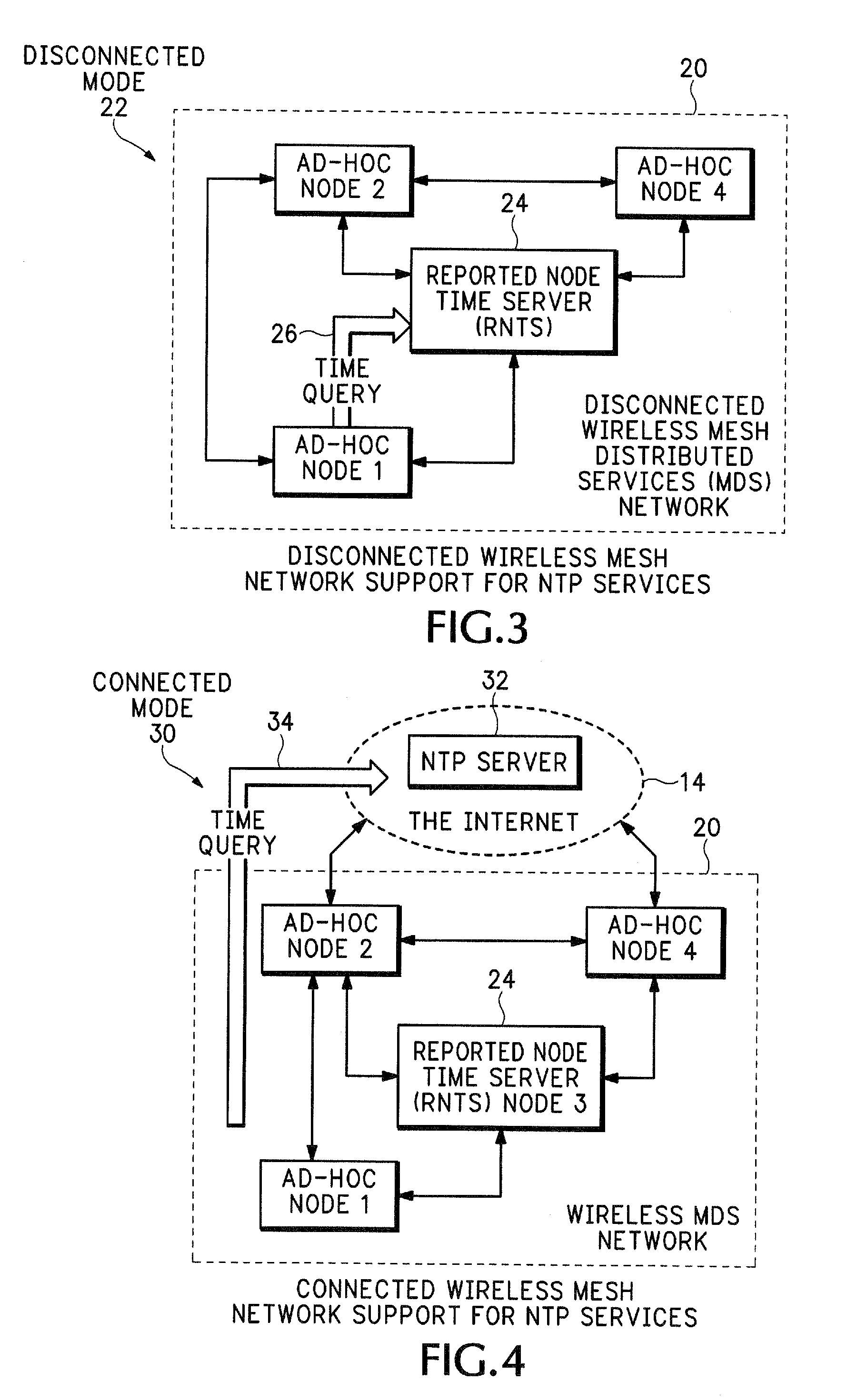
Distributed services for mesh networks
InactiveUS20070140239A1Readily apparentNetwork topologiesData switching by path configurationClient-sideDistributed services
Nodes in a mesh network are configured to access centralized Internet Protocol (IP) services whenever the Internet infrastructure is accessible and then dynamically switch to providing the IP services locally in the mesh network when the Internet infrastructure is not accessible and operate through collaborative cooperation. In one embodiment, a Reported Node Time Server (RNTS) is elected when the mesh network is disconnected. In another embodiment, a Mesh Network Name Cache (MNNC) protocol pre-provisions each mesh node with the names and addresses of all other mesh nodes. In another embodiment, a Mesh Address Allocation Protocol (MAAP) provides DHCP services for DHCP clients in the mesh network.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
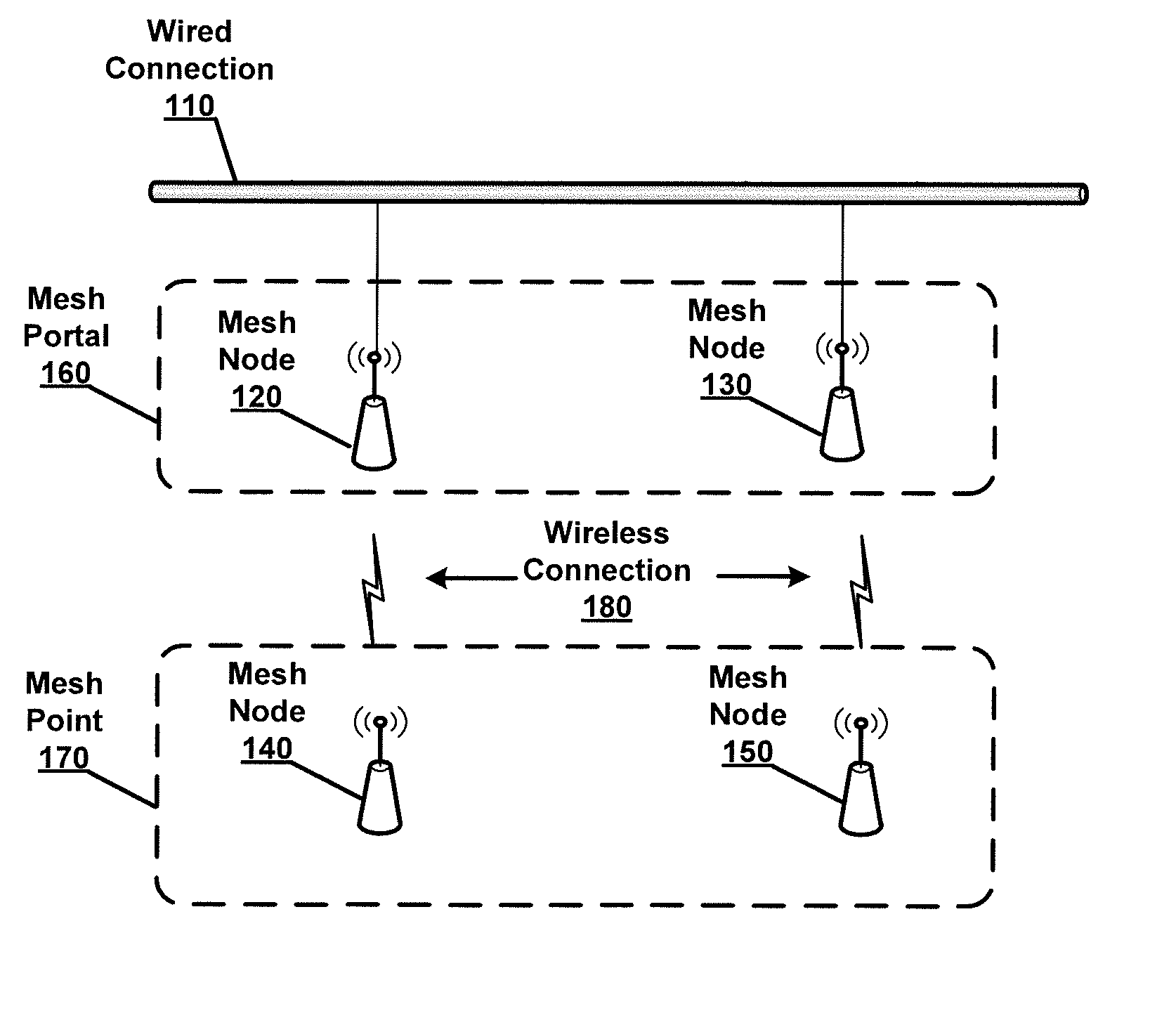
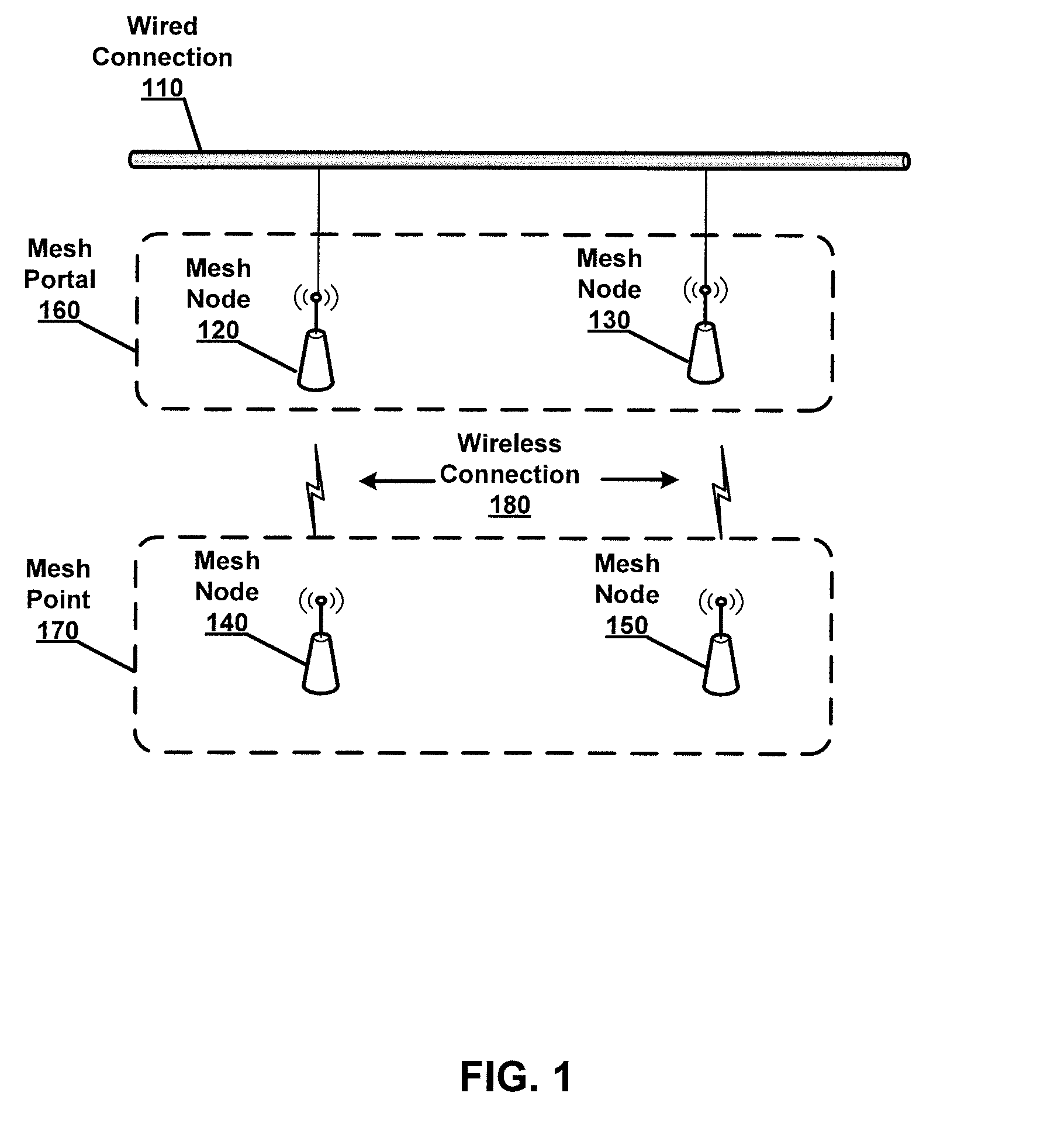
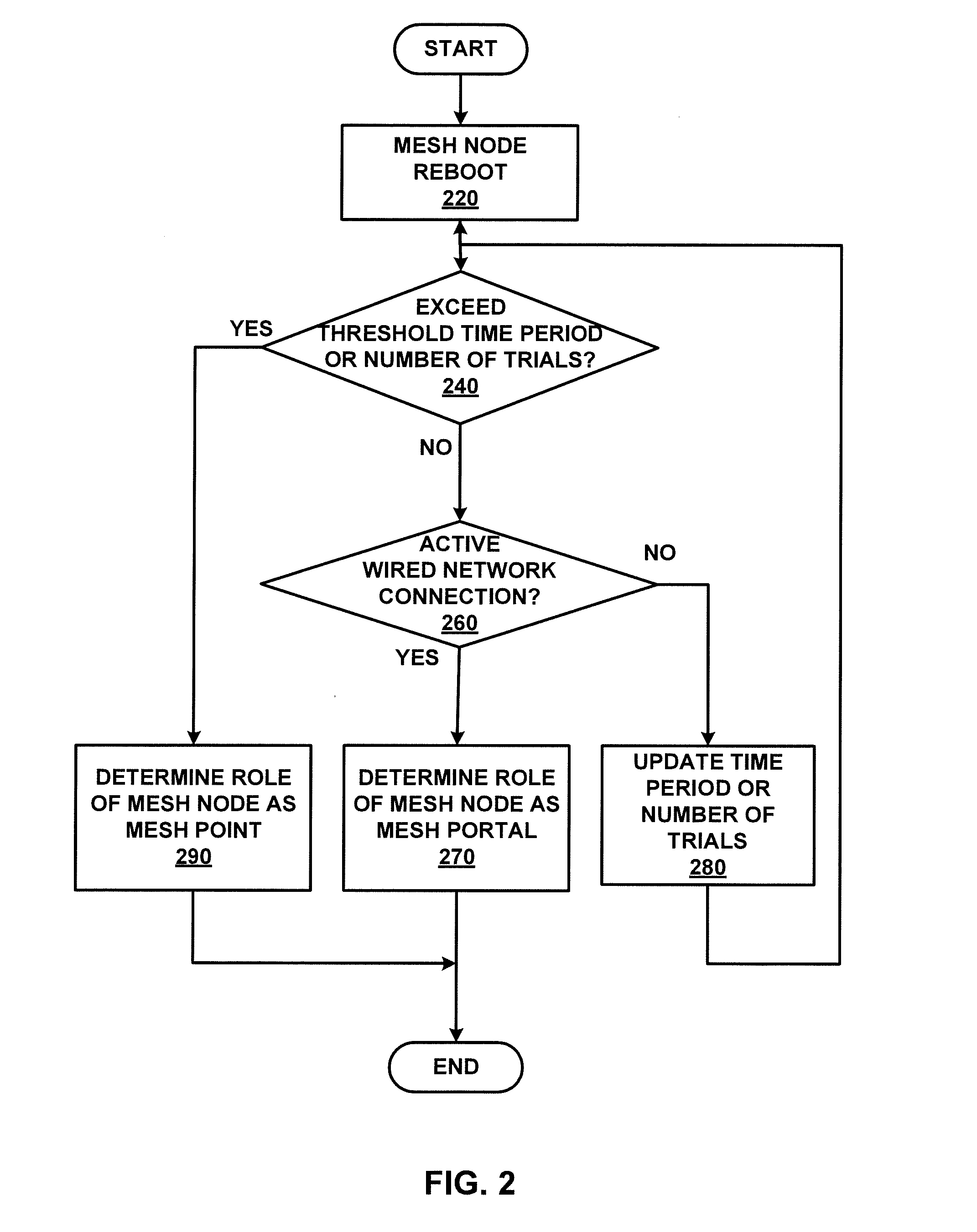
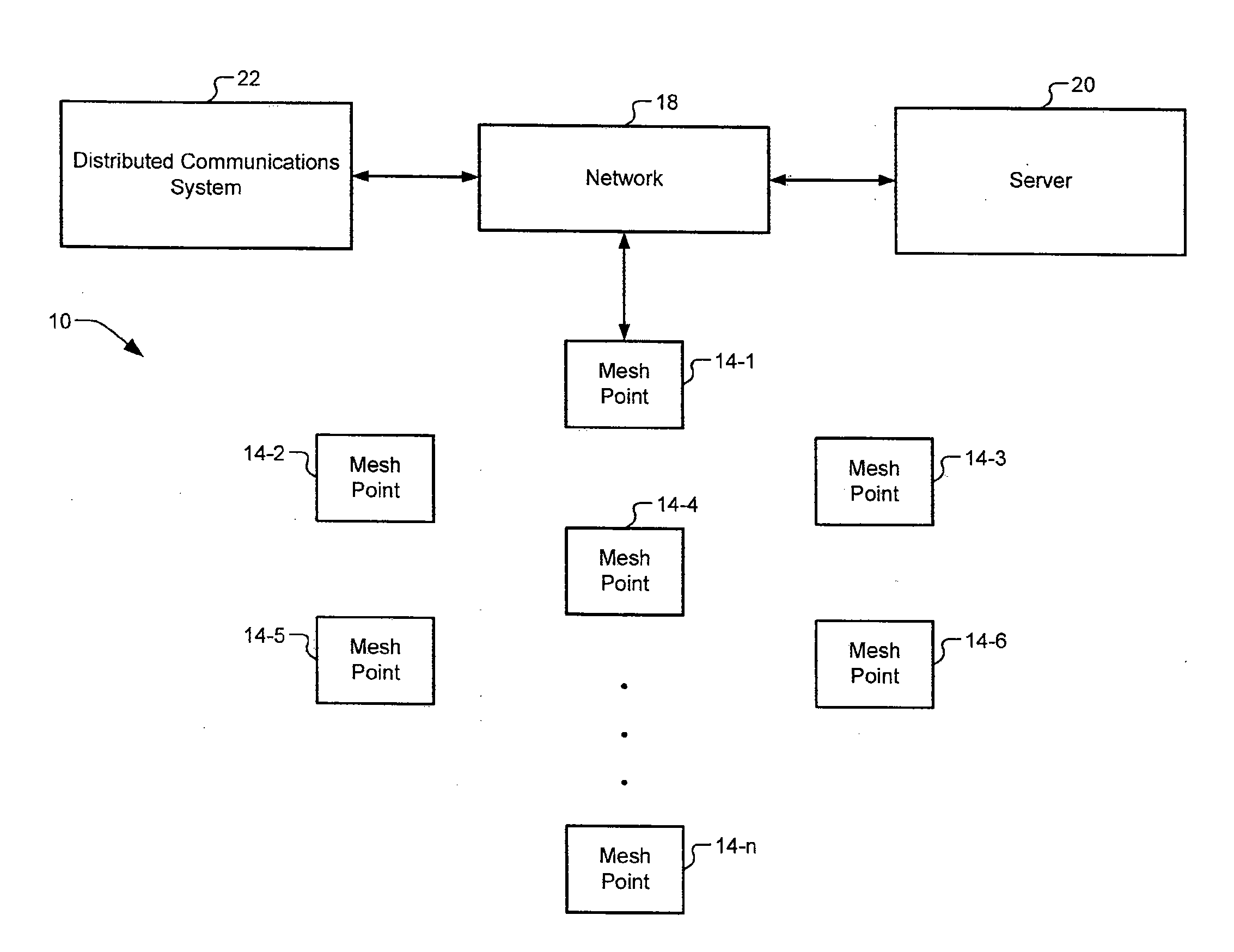
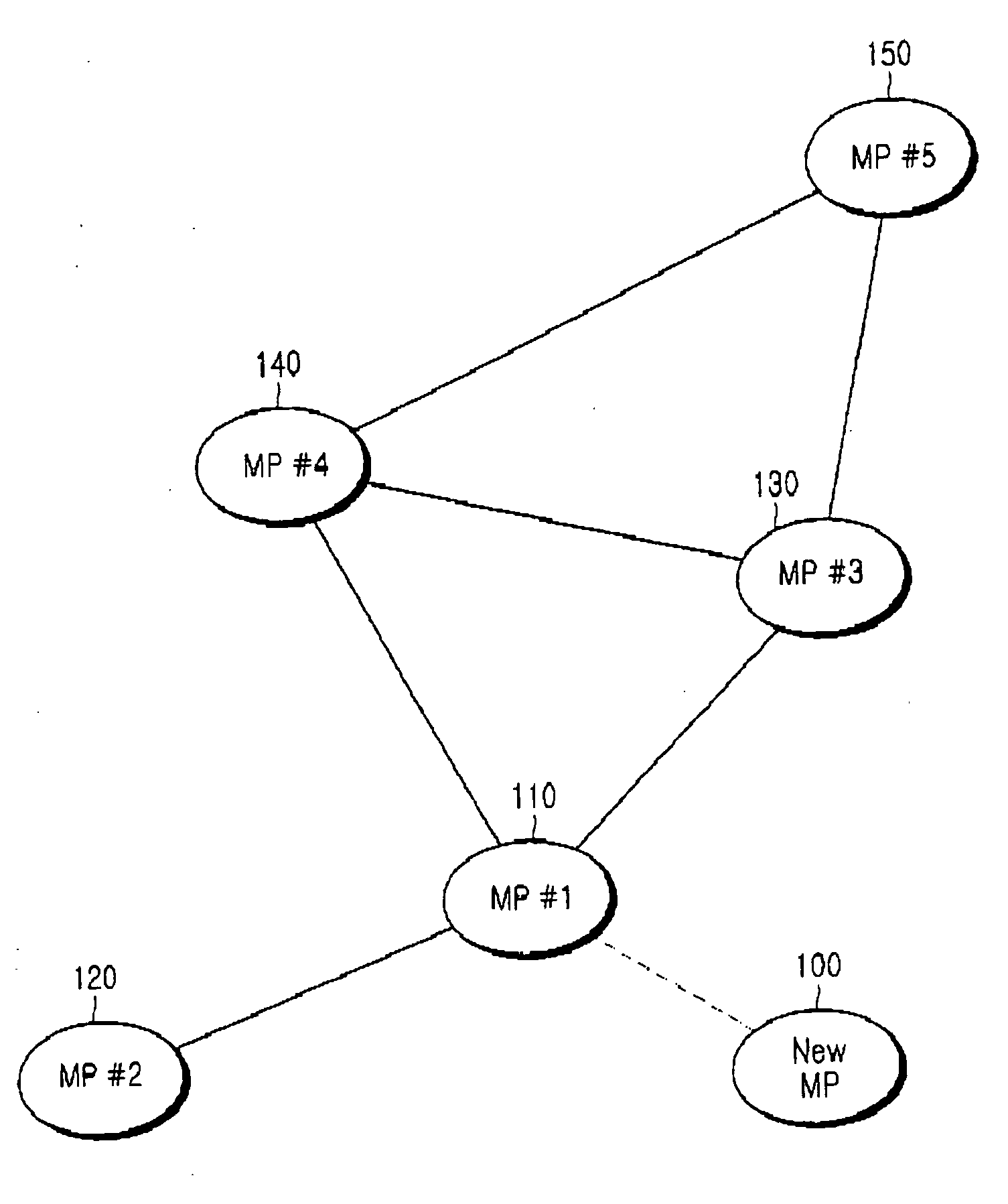
Mesh Node Role Discovery and Automatic Recovery
Embodiments of the present disclosure provide for configuring and managing mesh nodes during occasional failure of mesh nodes or addition of new mesh nodes. The disclosed system first determines whether a mesh node is a mesh portal or a mesh point. If it is a mesh portal, the mesh node will advertise its capacity as a mesh portal to other mesh nodes in the network. If it is a mesh point, the mesh node attempts to automatically recover connection to the wireless mesh network if it identifies a unique wireless network based on its associated network identifier. If more than one network identifiers are discovered, the mesh node delays establishing connection to the wireless mesh network until a selection is received.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Dense mesh network communications
ActiveUS20090310516A1Network traffic/resource managementBroadcast transmission systemsTransceiverNetwork communication
A frame groupcast system for a mesh node in a mesh network having a plurality of mesh nodes includes a transceiver that receives a groupcast frame and a groupcast determination module that determines whether to forward the received groupcast frame based on at least one measurement.
Owner:NXP USA INC
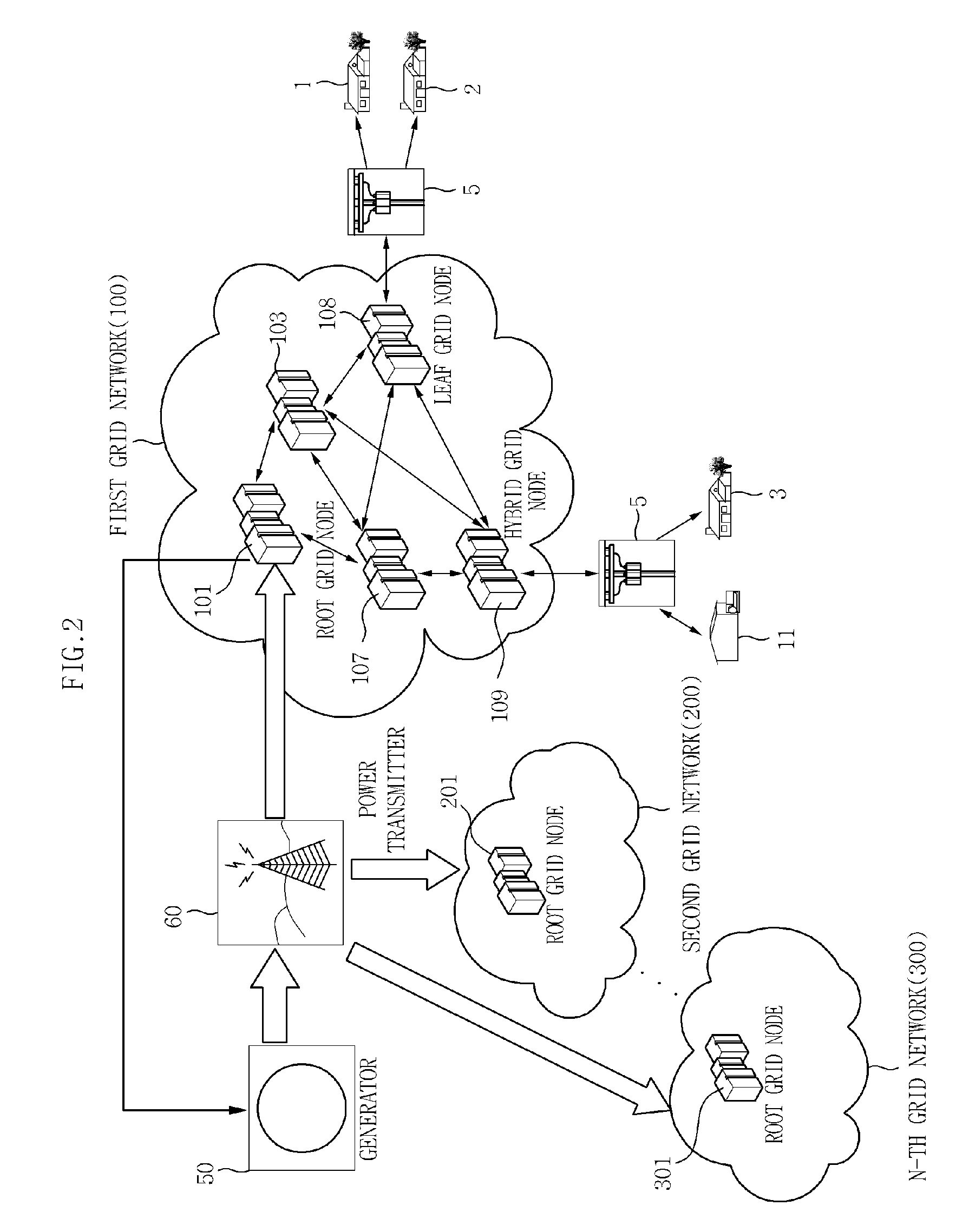
Power distribution method and network topology method for smart grid management, and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20110054709A1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilityMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectric power transmissionDistribution method
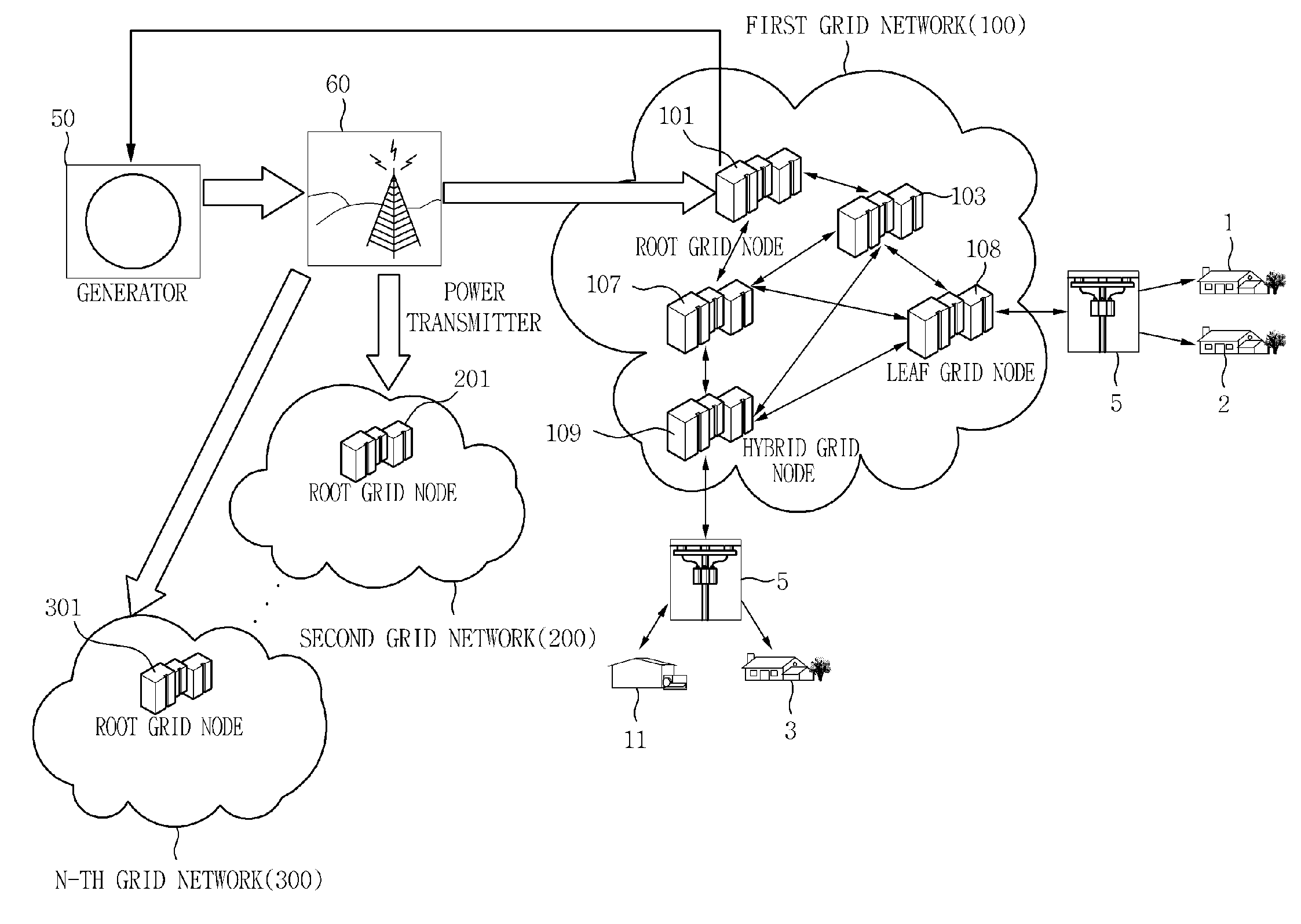
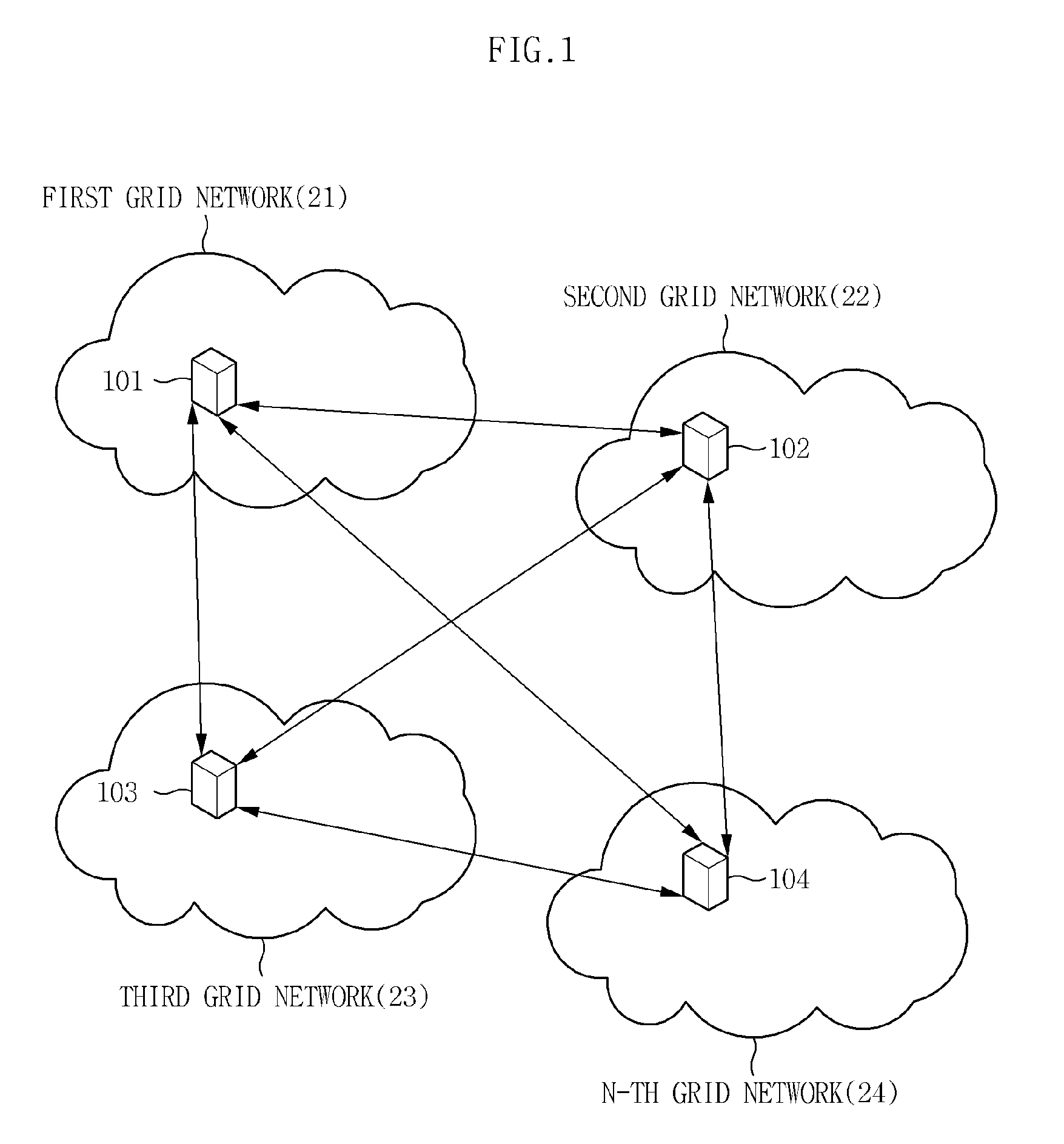
Provided is a power distribution apparatus that includes: a neighboring node information collection unit collecting power distribution amount information and physical distance information between grid nodes from neighboring grid nodes belonging to the same grid network; and a power transmission target node selecting unit allocating priorities to the neighboring grid nodes by using the power distribution amount information and the distance information and selecting a neighboring grid node having the highest priority as a neighboring power transmission grid node by comparing the priorities allocated to the neighboring grid nodes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
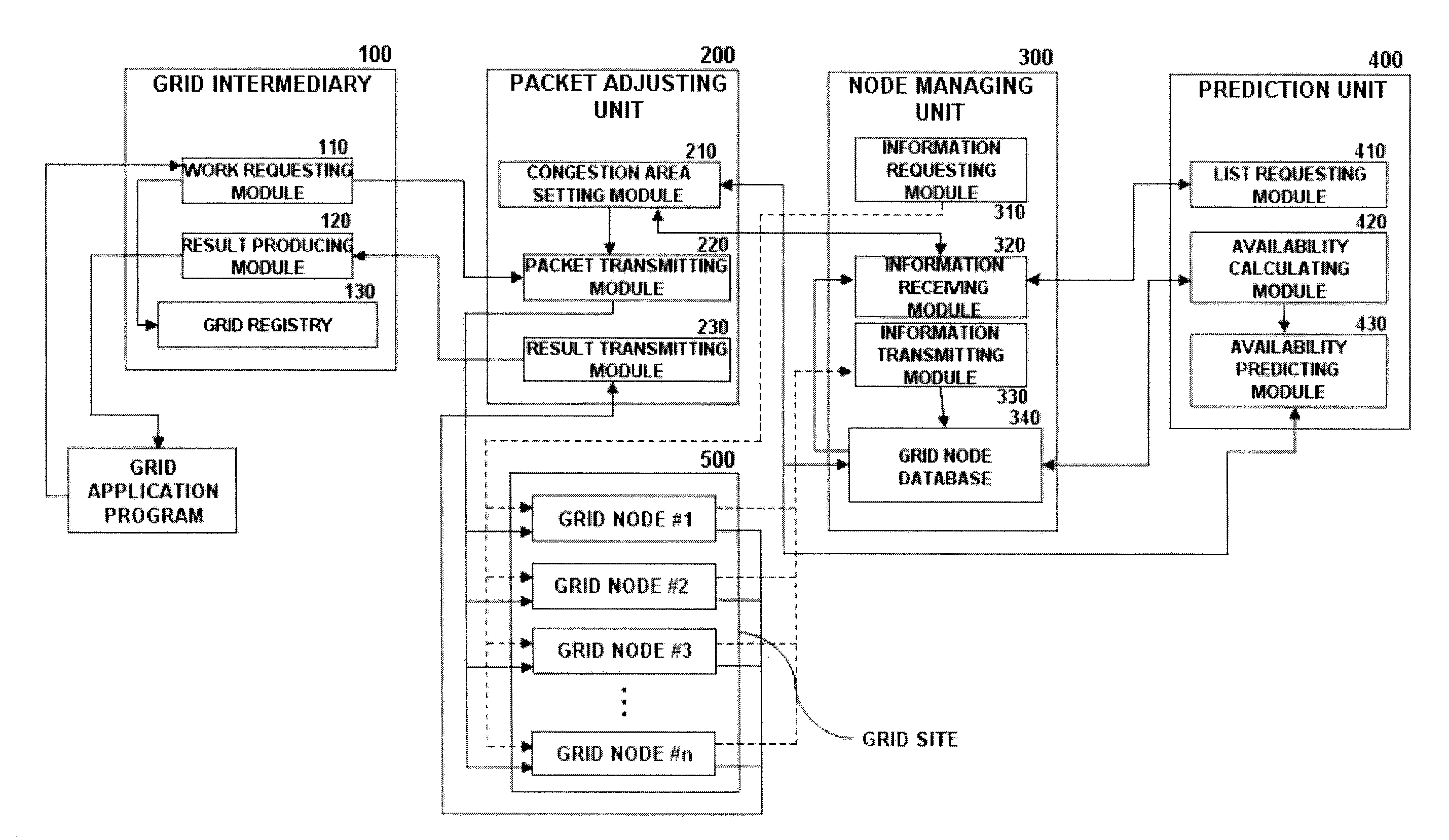
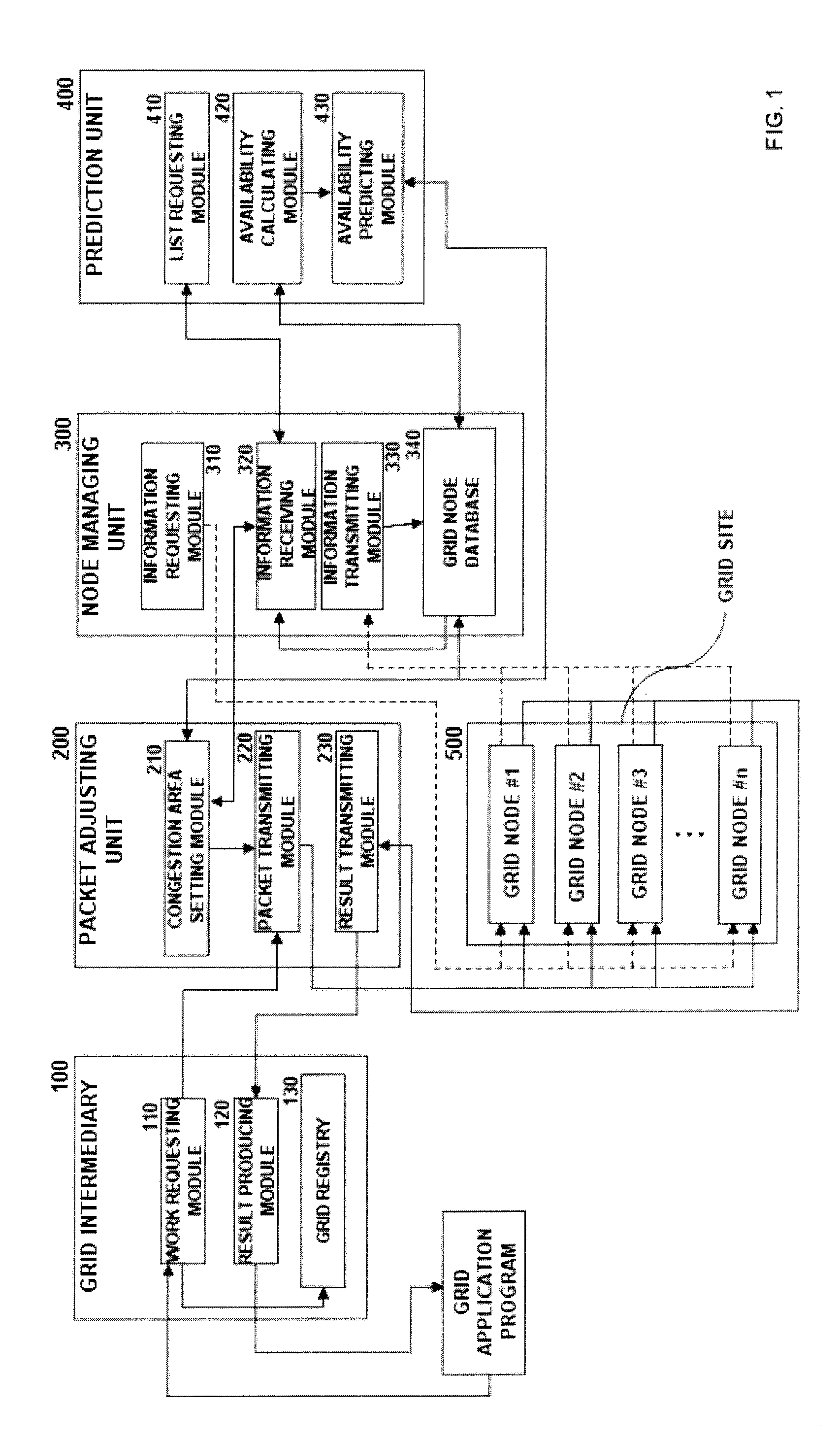
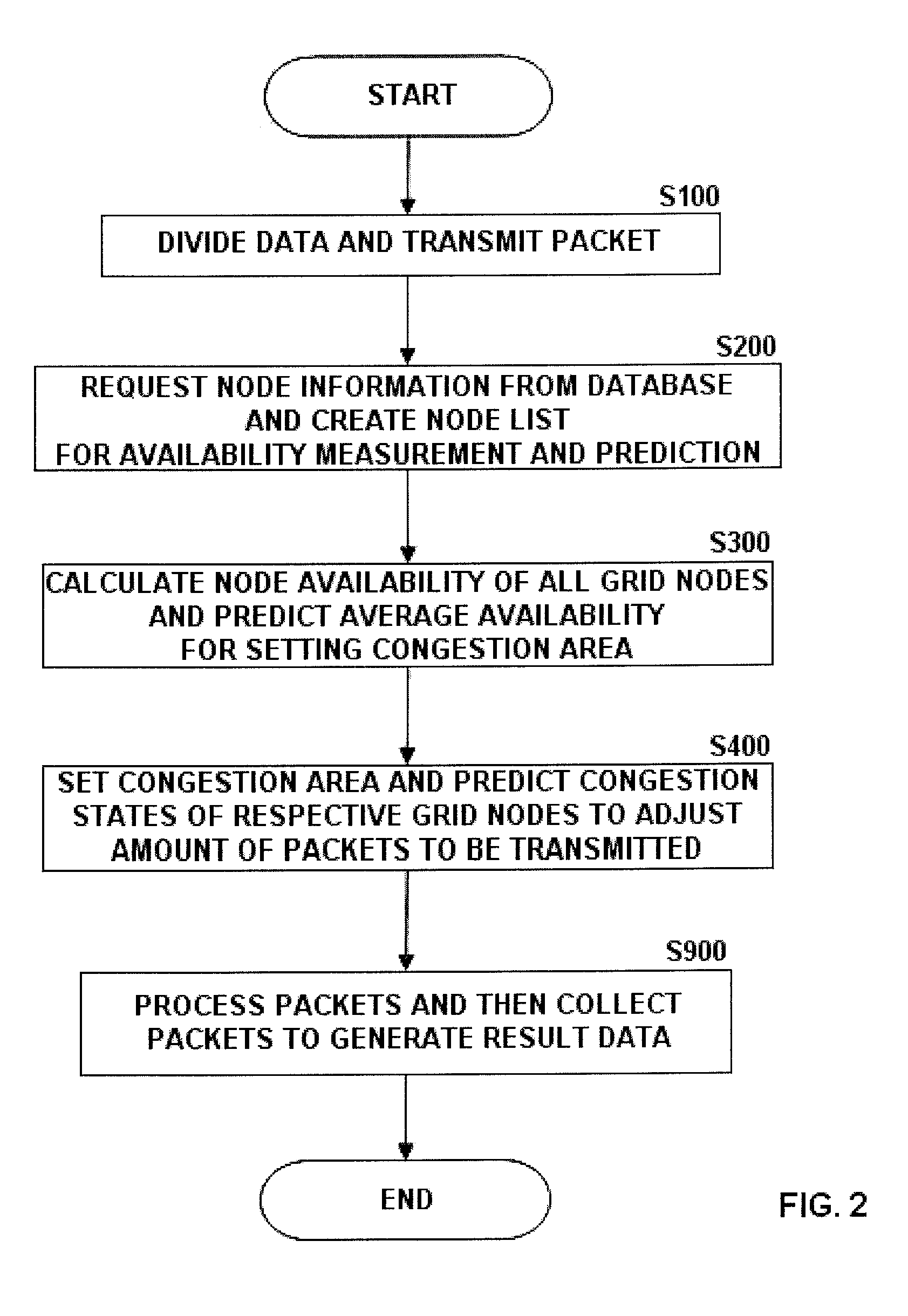
Node availability prediction-based grid network congestion control device and method therefor
InactiveUS20080298240A1High bandwidthHigh network delayError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
A system and method are disclosed, which controls congestion to efficiently transmit data through a network of grid node network in a grid computing environment where a large amount of data is processed. The system and method are performed in such a way that, according to a grid application program's request for distributed processing a large amount of data, the data is divided into packets, the node availability of respective nodes distributed in the grid network is measured with consideration to the bandwidth and the queue size of available grid nodes to avoid and control network congestion that may occur when the packets are processed by distributed processing using the respective nodes, the average node availability of all nodes is predicted using a statistical method, a threshold is calculated based on the predicted average node availability to set a dynamic congestion area representing the congestion level of the respective nodes, and the amount of packet transmission is controlled based on the congestion area. As the grid nodes are managed by controlling congestion, packet loss and packet delay are reduced and the rate of packet processing and the rate of node use are increased. Therefore, data can be stably transmitted to the grid user through the network with an improvement in the Quality of Service (QoS).
Owner:IND COLLABORATION FOUND OF INHA UNIV
Multicast traffic management within a wireless mesh network
ActiveUS20140269487A1Network topologiesBroadcast transmission systemsComputer networkAir traffic management
The present disclosure relates to a management of multicast traffic within a wireless mesh network. In some embodiments, a wireless mesh network includes a plurality of mesh nodes and a central server in communication with at least one of the mesh nodes of the plurality of mesh nodes. In some embodiments, the central server is configured to generate one or more rules for at least one of the mesh nodes to enable a change in a pre-routing parameter in a packet header. In some embodiments, the central server includes a rules-based engine configured to generate and convey one or more traffic shaping rules in response to sensing traffic conditions.
Owner:VIVINT INC
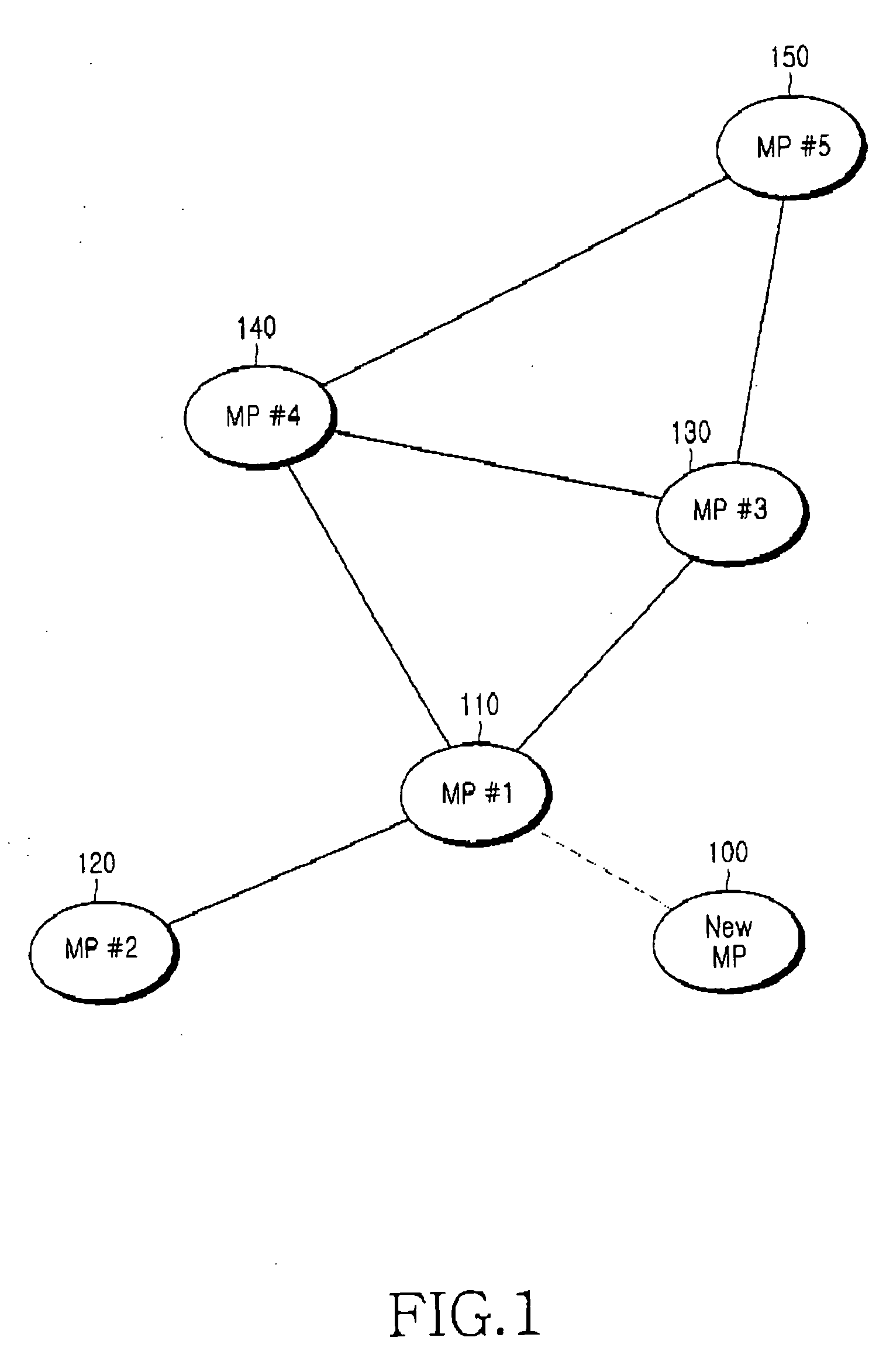
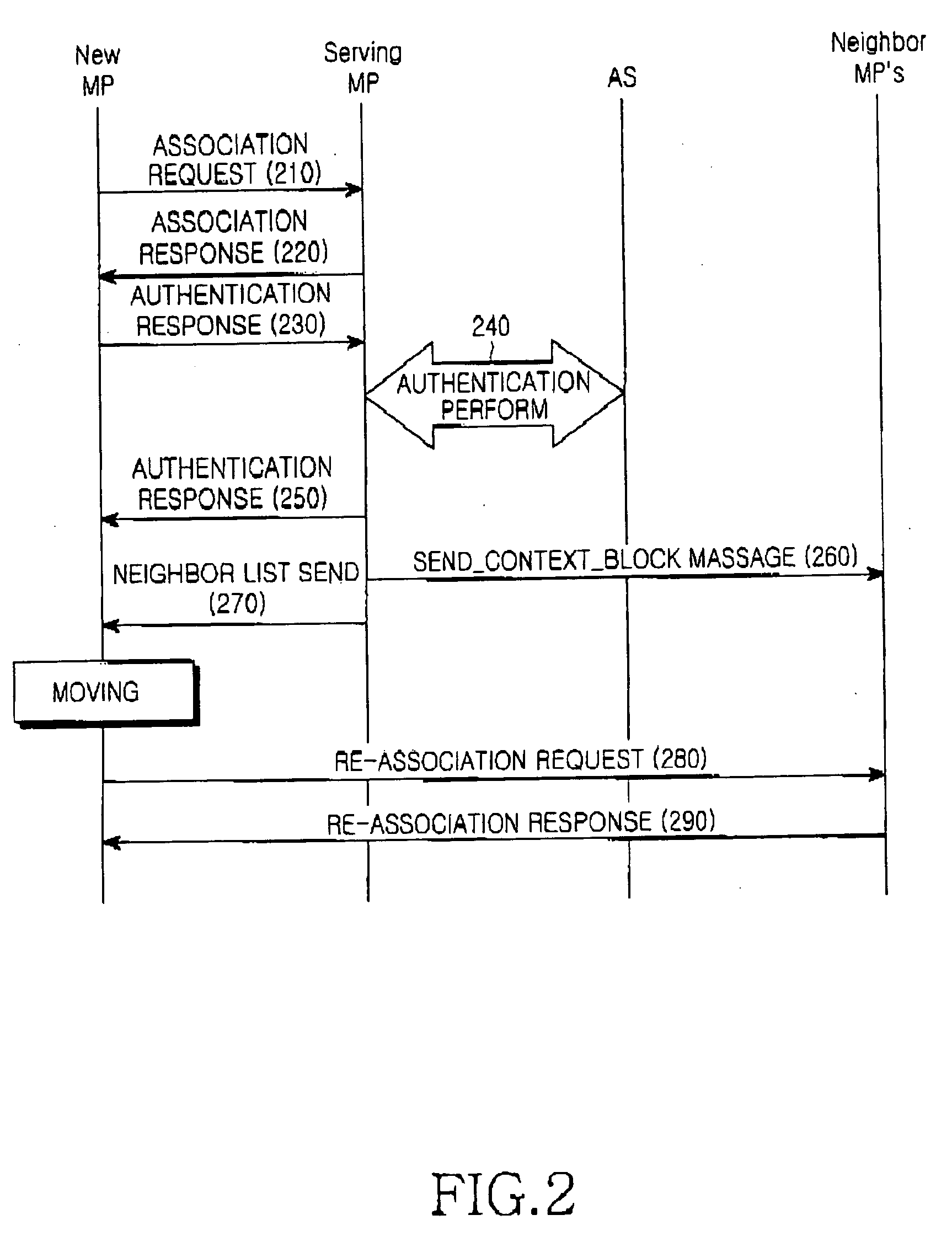
Mesh node association method in a mesh network, and mesh network supporting the same
InactiveUS20070011435A1Minimize timeUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionEavesdropping prevention circuitsComputer networkComputer science
A mesh network has a plurality of mesh nodes, including a moving mesh node. A serving mesh node initially associates with the moving mesh node at the request of the moving mesh node, transmits context information due to the initial association to at least one neighbor mesh node, and transmits information on the at least one neighbor mesh node to the moving mesh node. The at least one neighbor mesh node stores the context information received from the serving mesh node, and re-associates with the moving mesh node using the context information at the request of the moving mesh node.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com