Patents
Literature
427 results about "Grid network" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
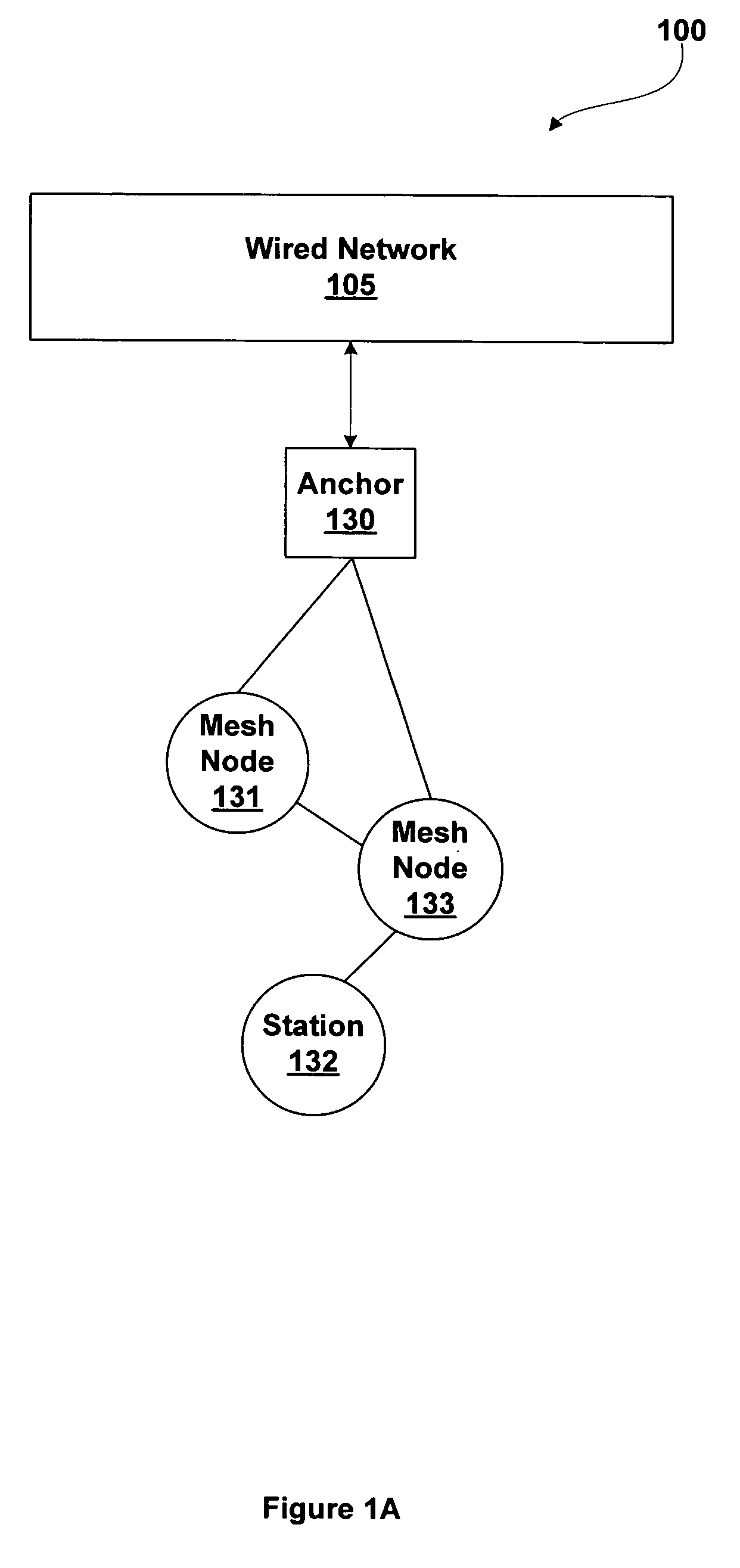
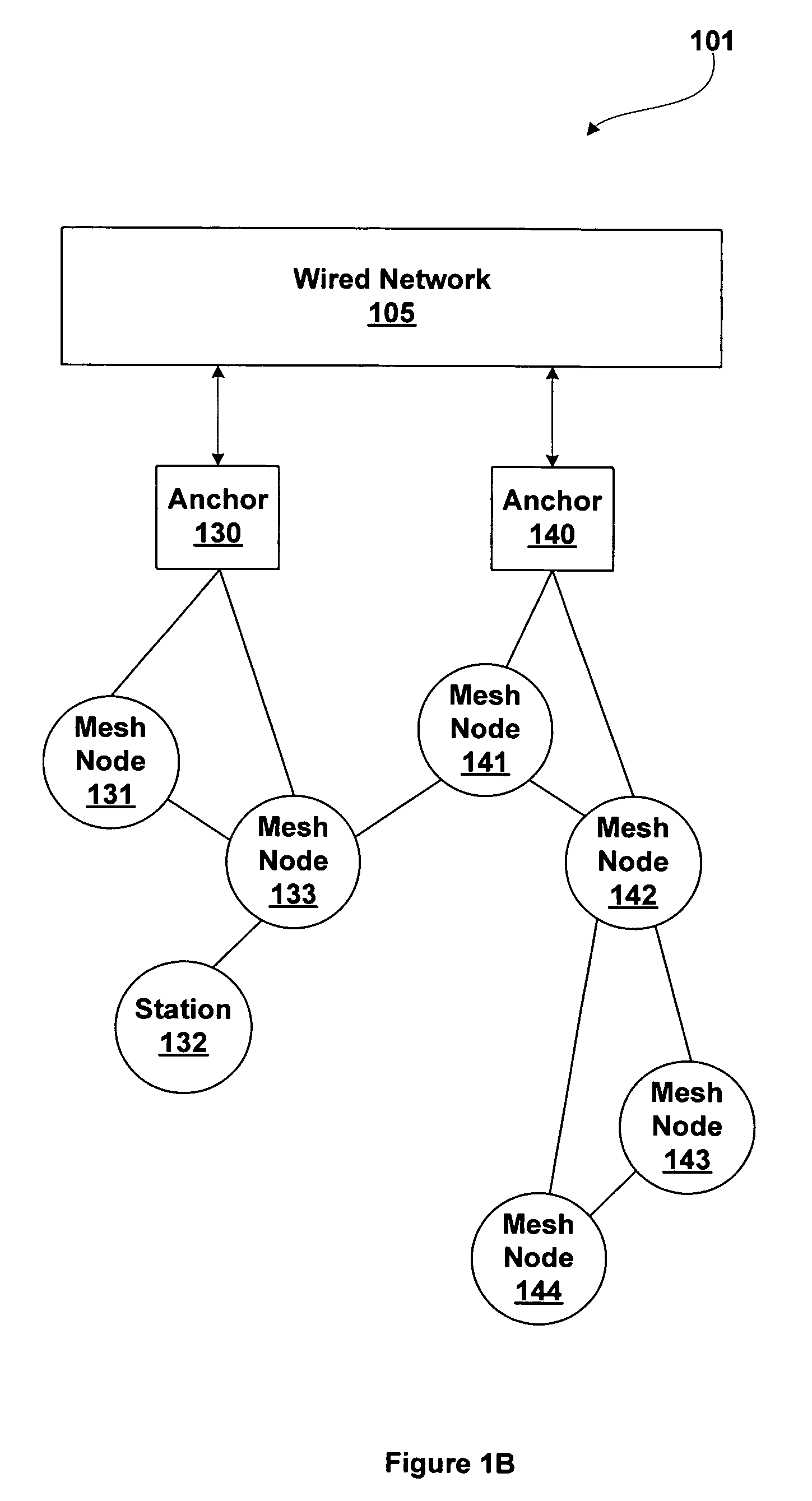
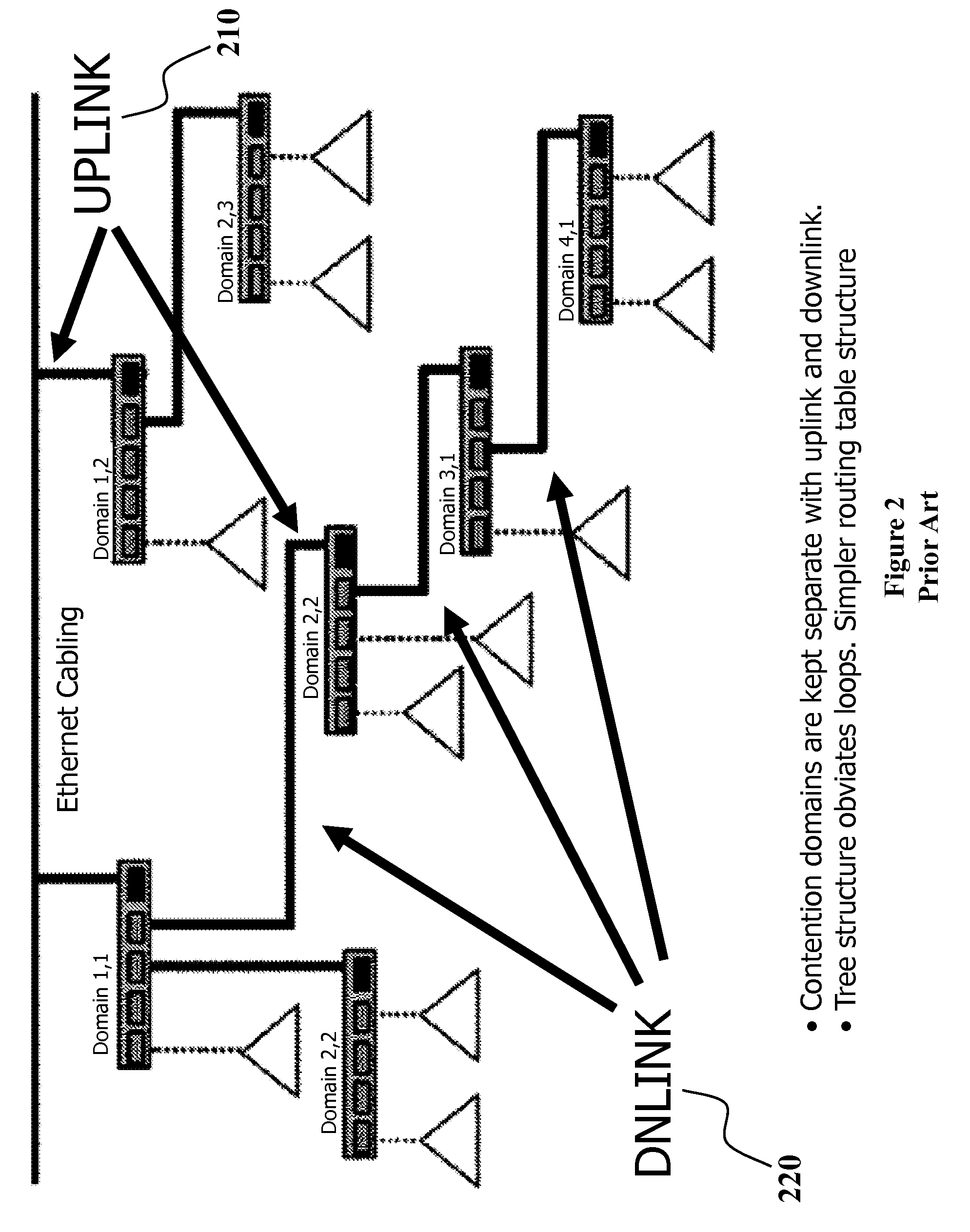
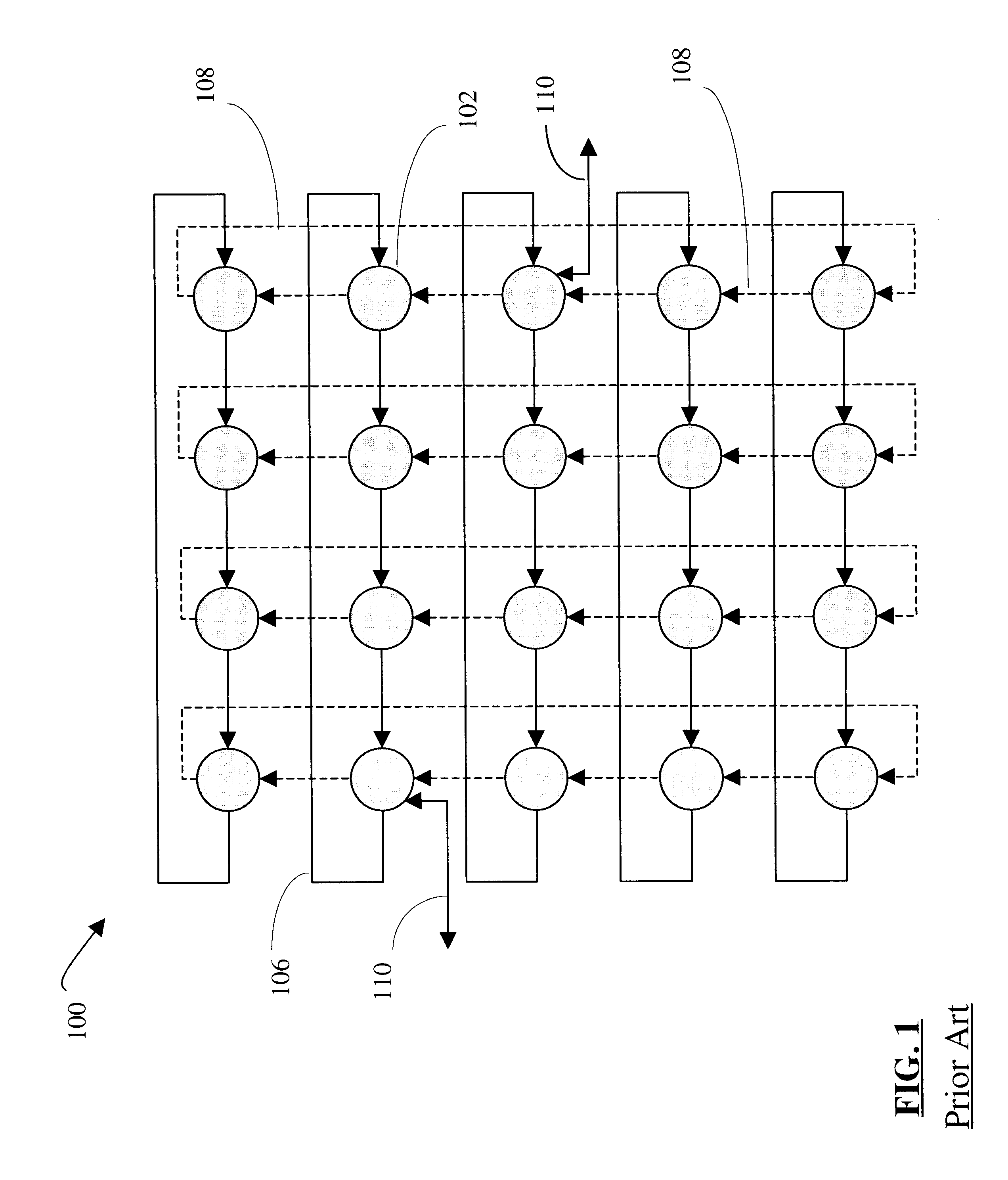
A grid network is a computer network consisting of a number of (computer) systems connected in a grid topology. In a regular grid topology, each node in the network is connected with two neighbors along one or more dimensions. If the network is one-dimensional, and the chain of nodes is connected to form a circular loop, the resulting topology is known as a ring. Network systems such as FDDI use two counter-rotating token-passing rings to achieve high reliability and performance. In general, when an n-dimensional grid network is connected circularly in more than one dimension, the resulting network topology is a torus, and the network is called "toroidal". When the number of nodes along each dimension of a toroidal network is 2, the resulting network is called a hypercube.
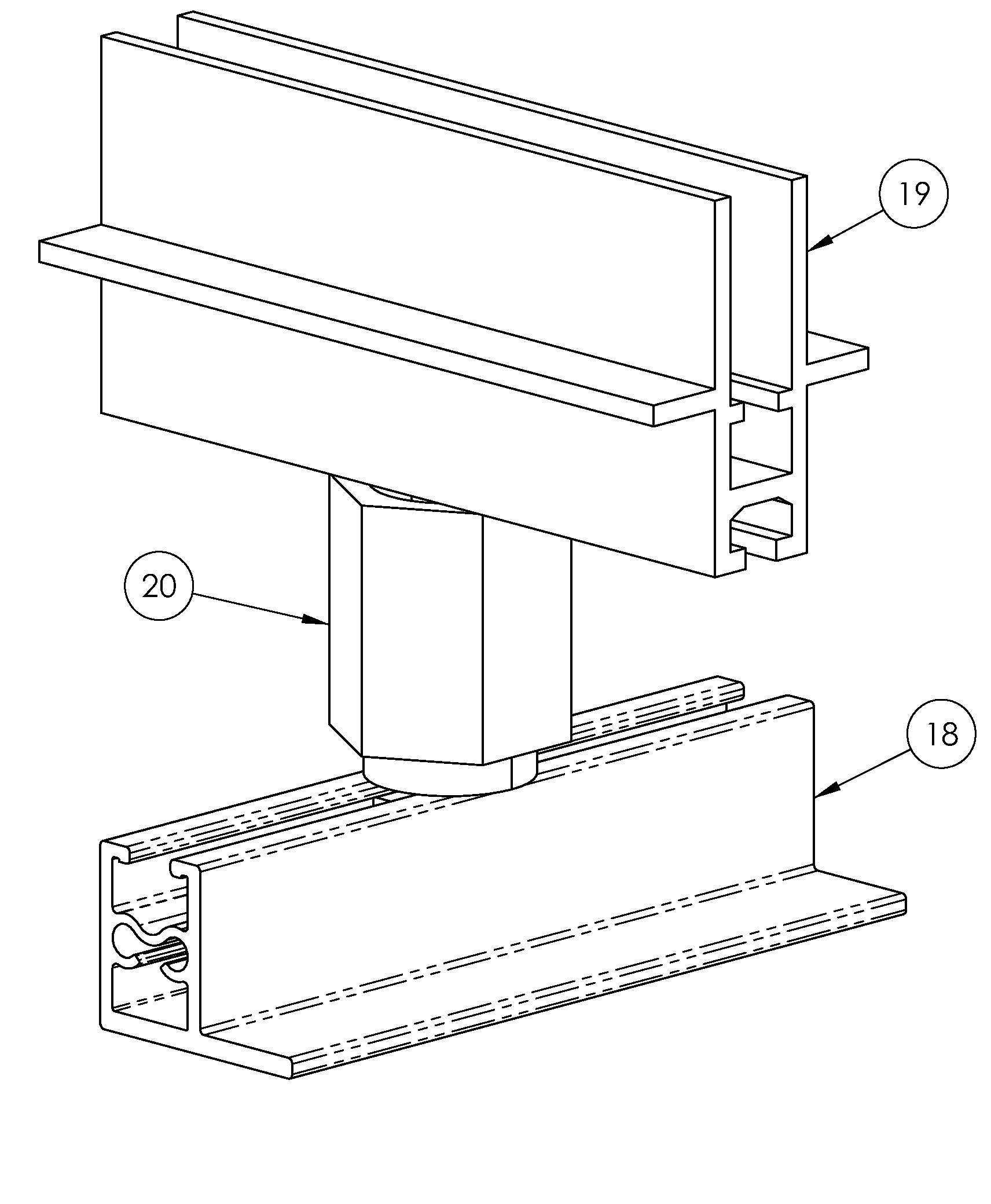
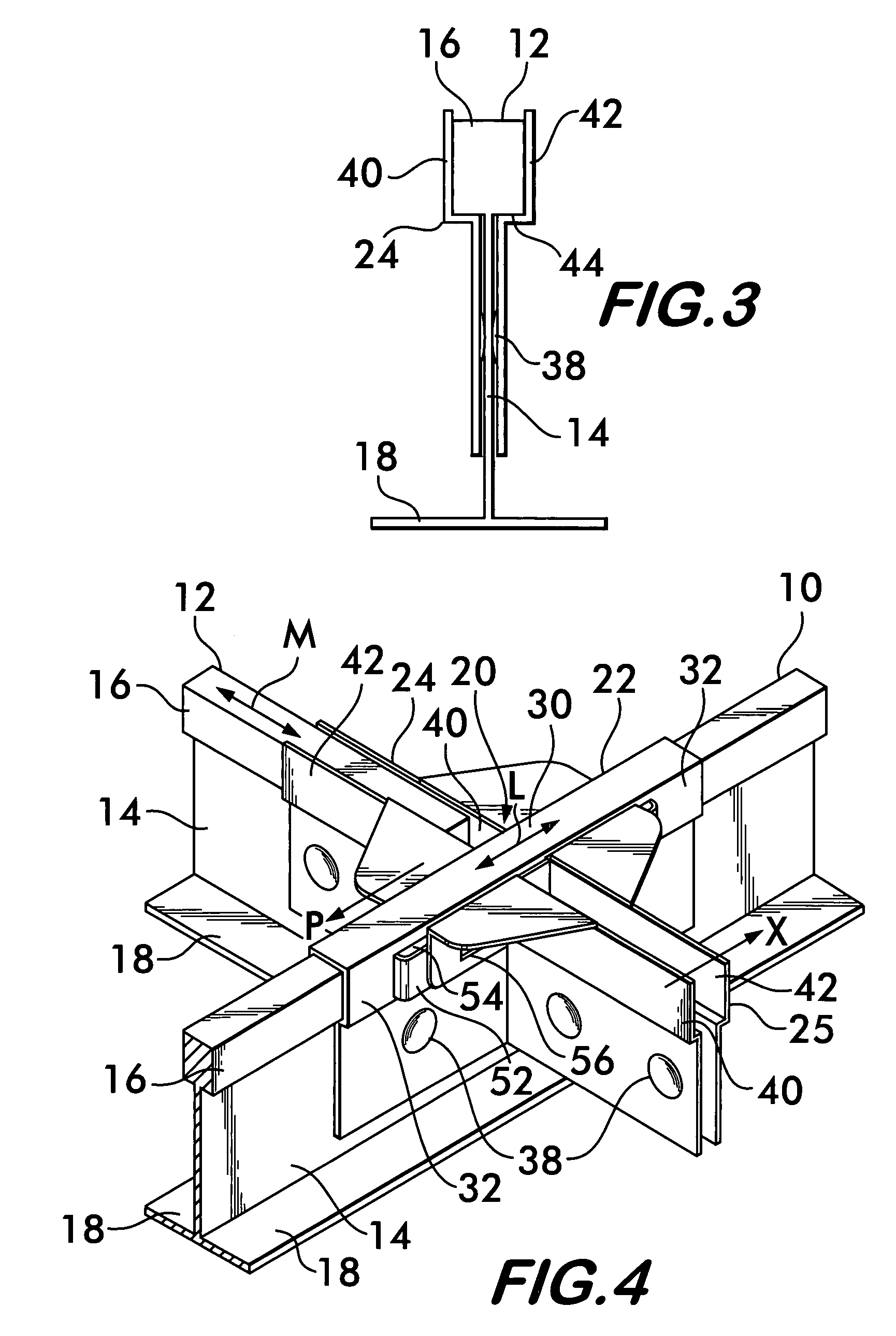
Photovoltaic mounting system with locking connectors, adjustable rail height and hinge lock
InactiveUS20090282755A1Cost-effectiveTurn easilyPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityPhotovoltaic mounting system
A cam-actuated connection device joins rail mounting members of a photovoltaic panel array. The connection device slides within channels of mounting members until the members are in a properly positioned grid. When in position, the connection device is rotated to lock the mounting members in a rigid grid network. The connecting device can be subsequently loosened, repositioned and locked into position. The rail-mounting members create a grid for installation of multiple PV panels. The mounting rail allows the unit to remain relatively compact in nature but still covers a wide range of PV panel thicknesses. The rail system has a hinged connection with the mounting rail that allows an installer to assemble the module in a near perpendicular fashion to the mounting rail, make the required electrical connections and then lower the PV module into its working position. The unit is then locked into its working position.
Owner:POWERMOUNT SYST +1
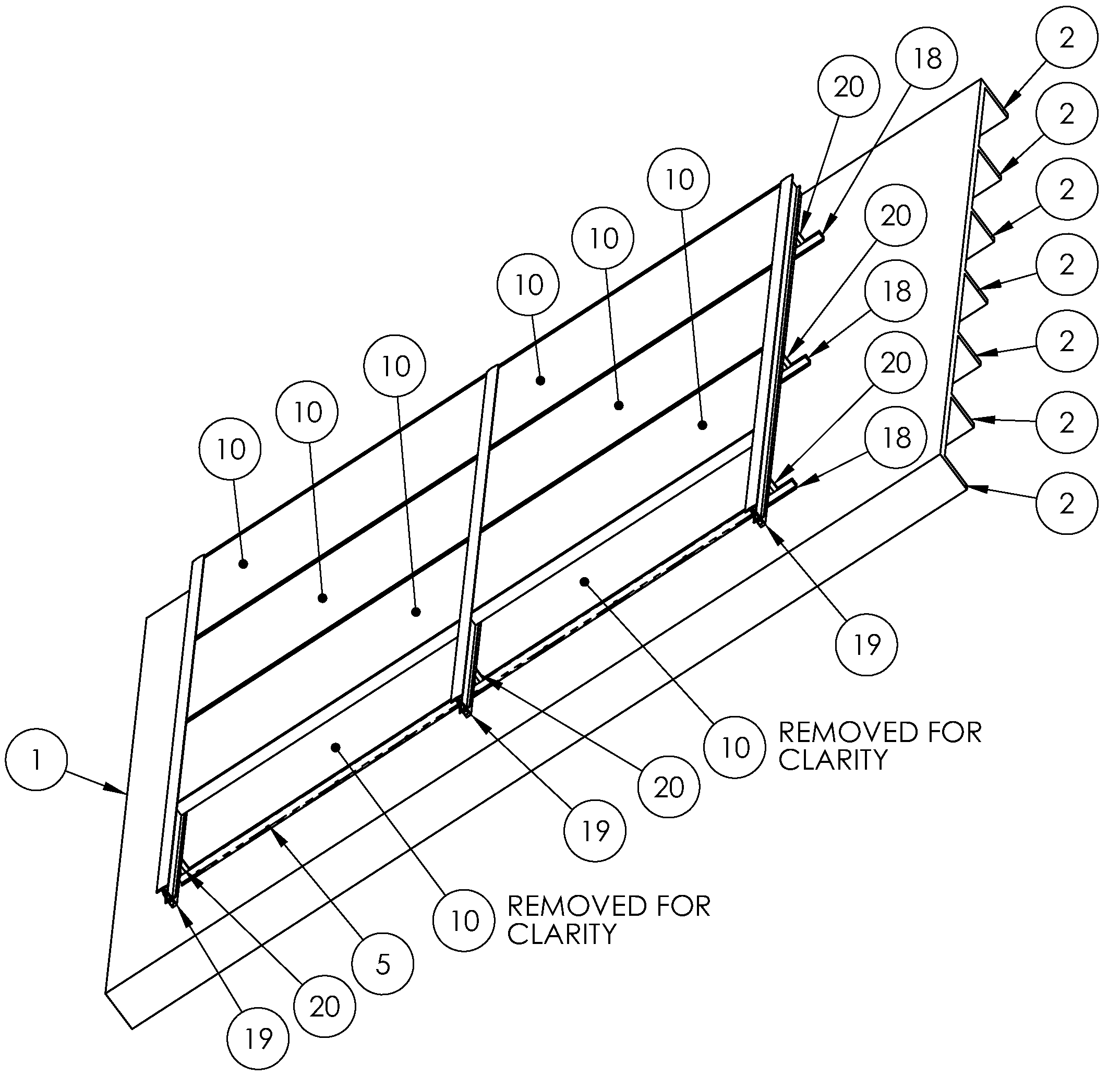
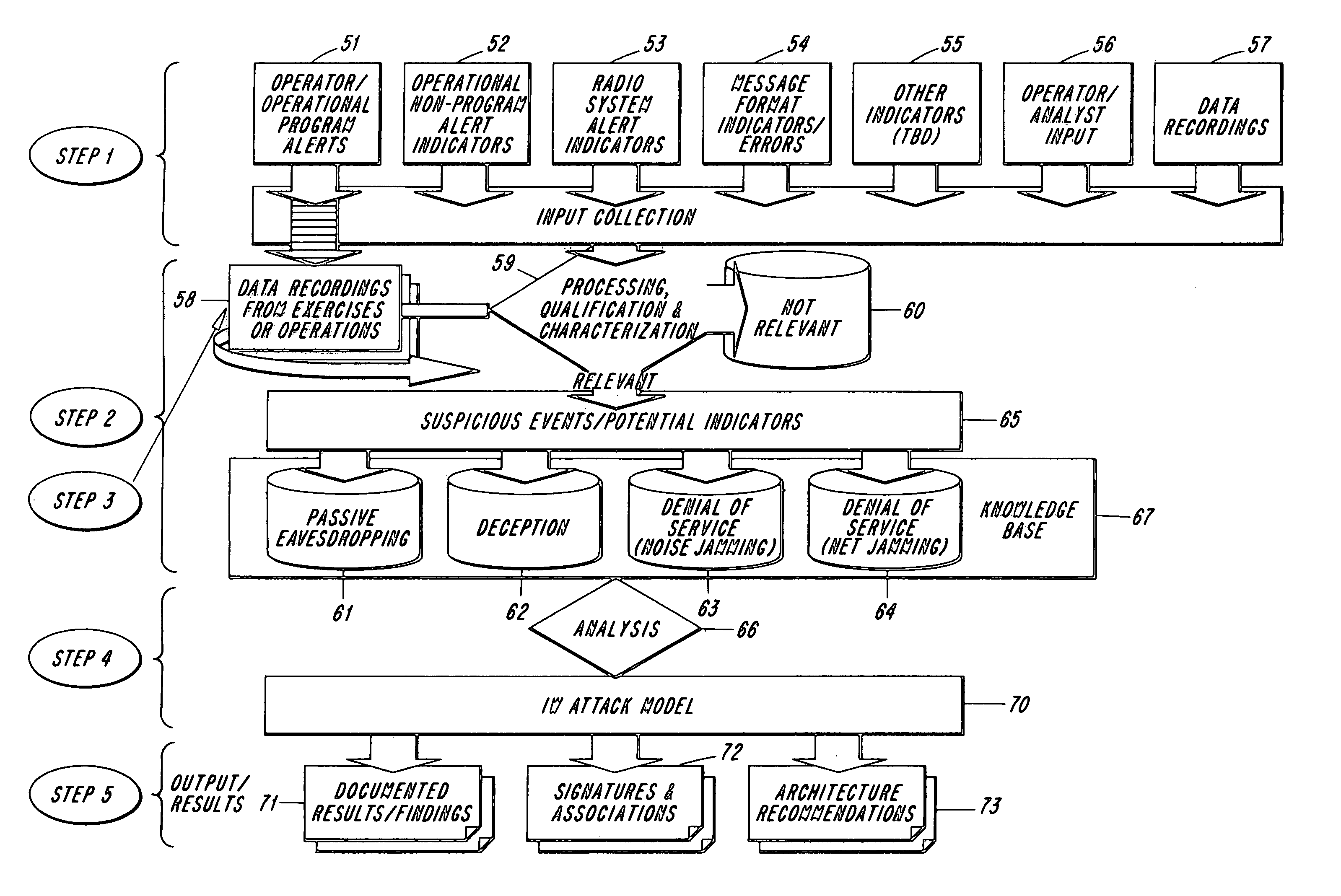
Methodology for the detection of intrusion into radio frequency (RF) based networks including tactical data links and the tactical internet
InactiveUS7068998B2Solid comprehensionEnhance information resiliencyUnauthorised/fraudulent call preventionMemory loss protectionInformation analysisAttack model
The present invention provides strategies for detecting intrusions in wireless environments, and the strategies are based on innovative applications of information analysis as well as other information correlating techniques. The key to detecting intrusions in a RF based environment is to understand the normal spectrum of behavior so that deviations can be detected and analyzed. For a wireless communications grid, this process requires empirical knowledge about how the radios work together as components of the information grid, and how this grid network is managed. Once normal behavior has been characterized, anomalous behavior can be identified. Potential intrusions into the wireless network can be analyzed and an attack model can be created. The attack model can be utilized as the basis for initiating appropriate adaptive responses.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
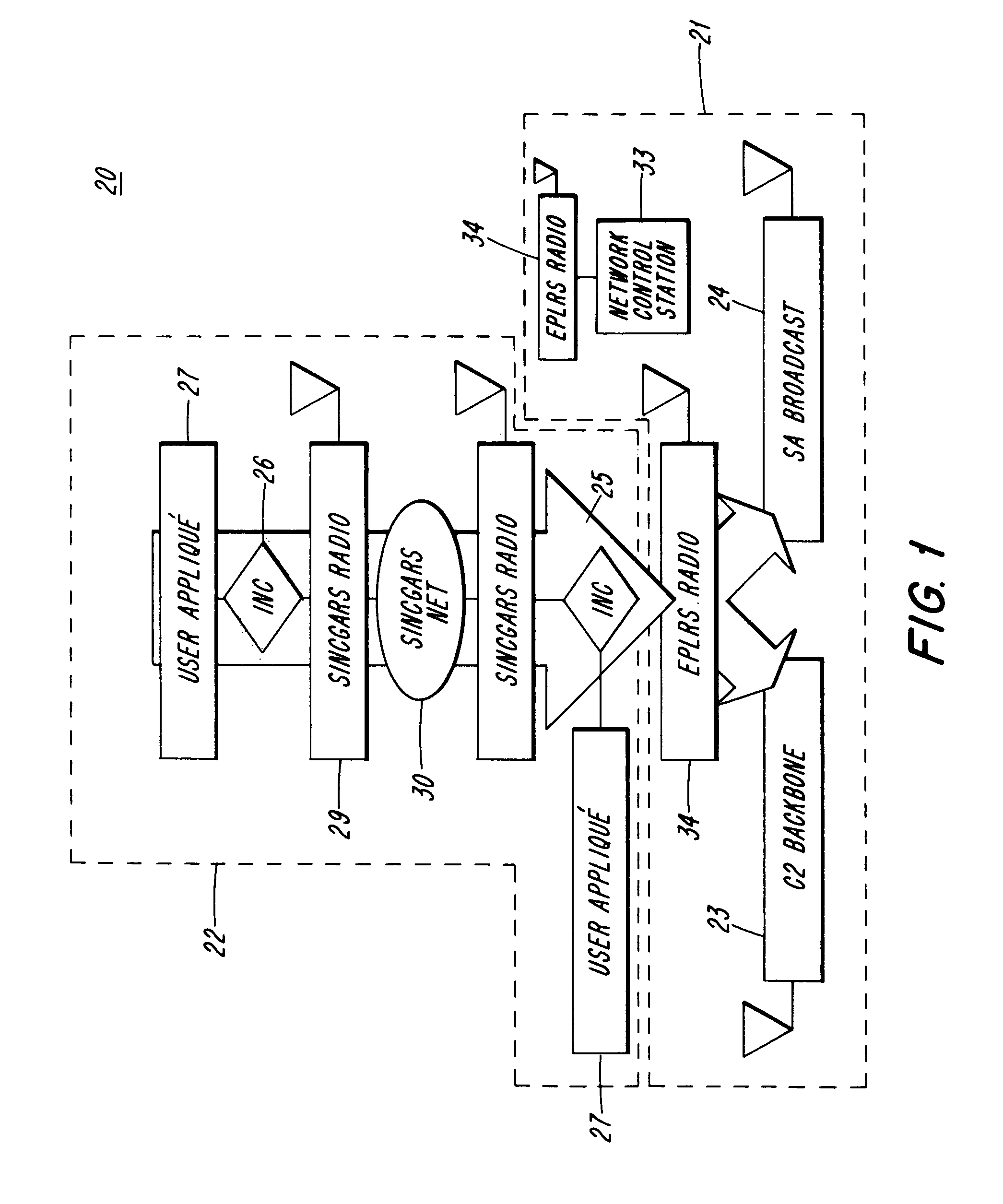
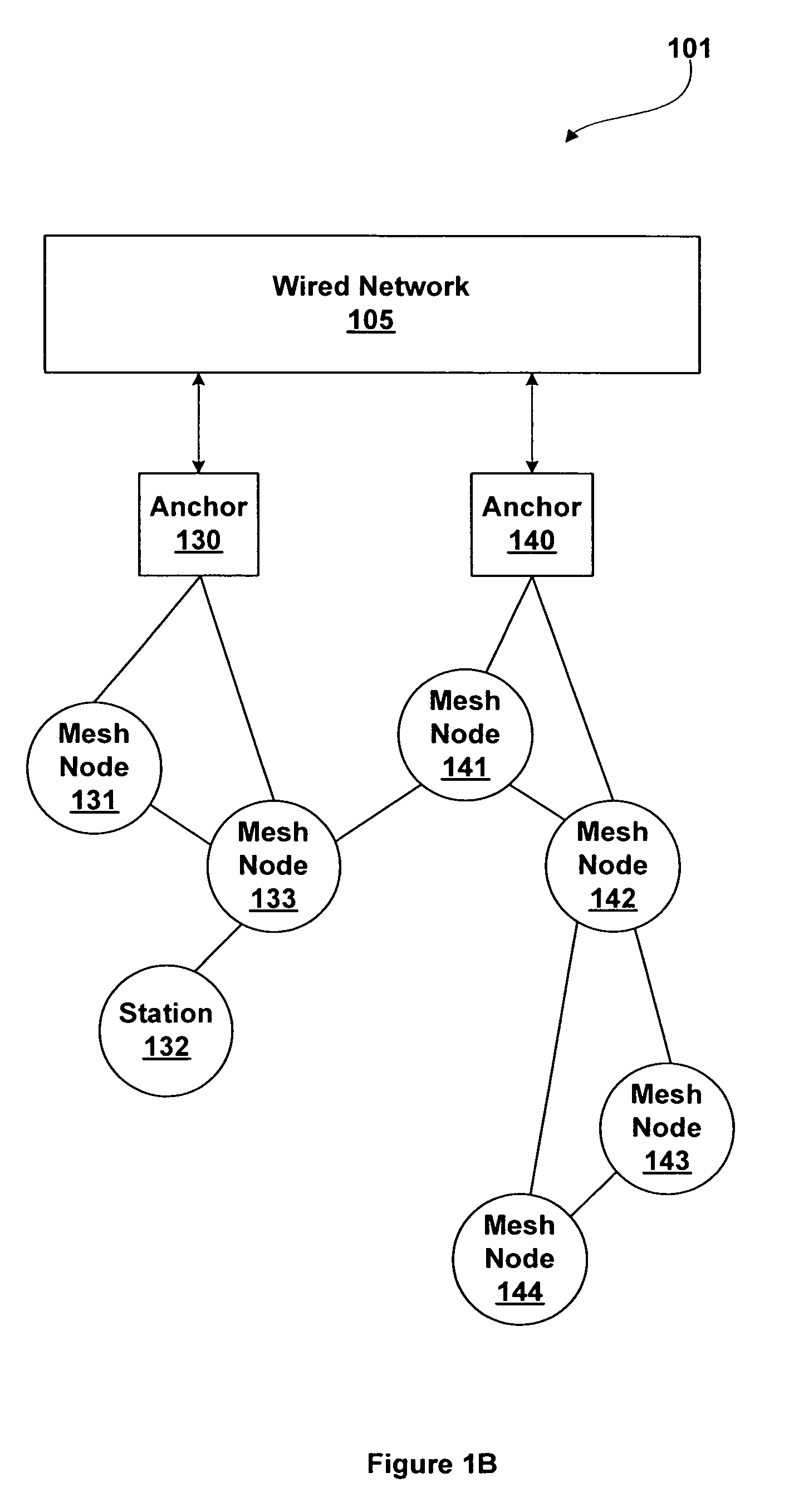
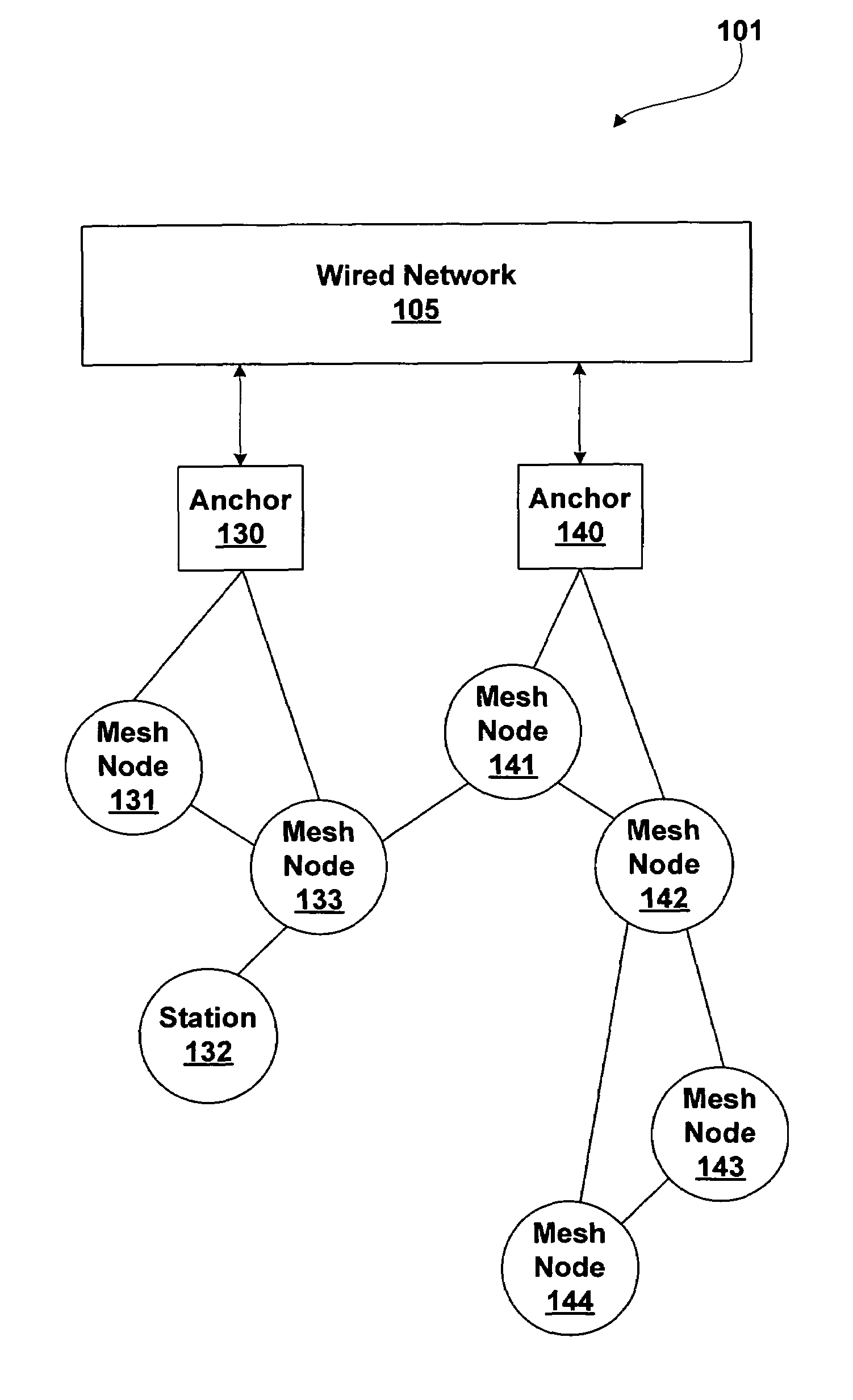
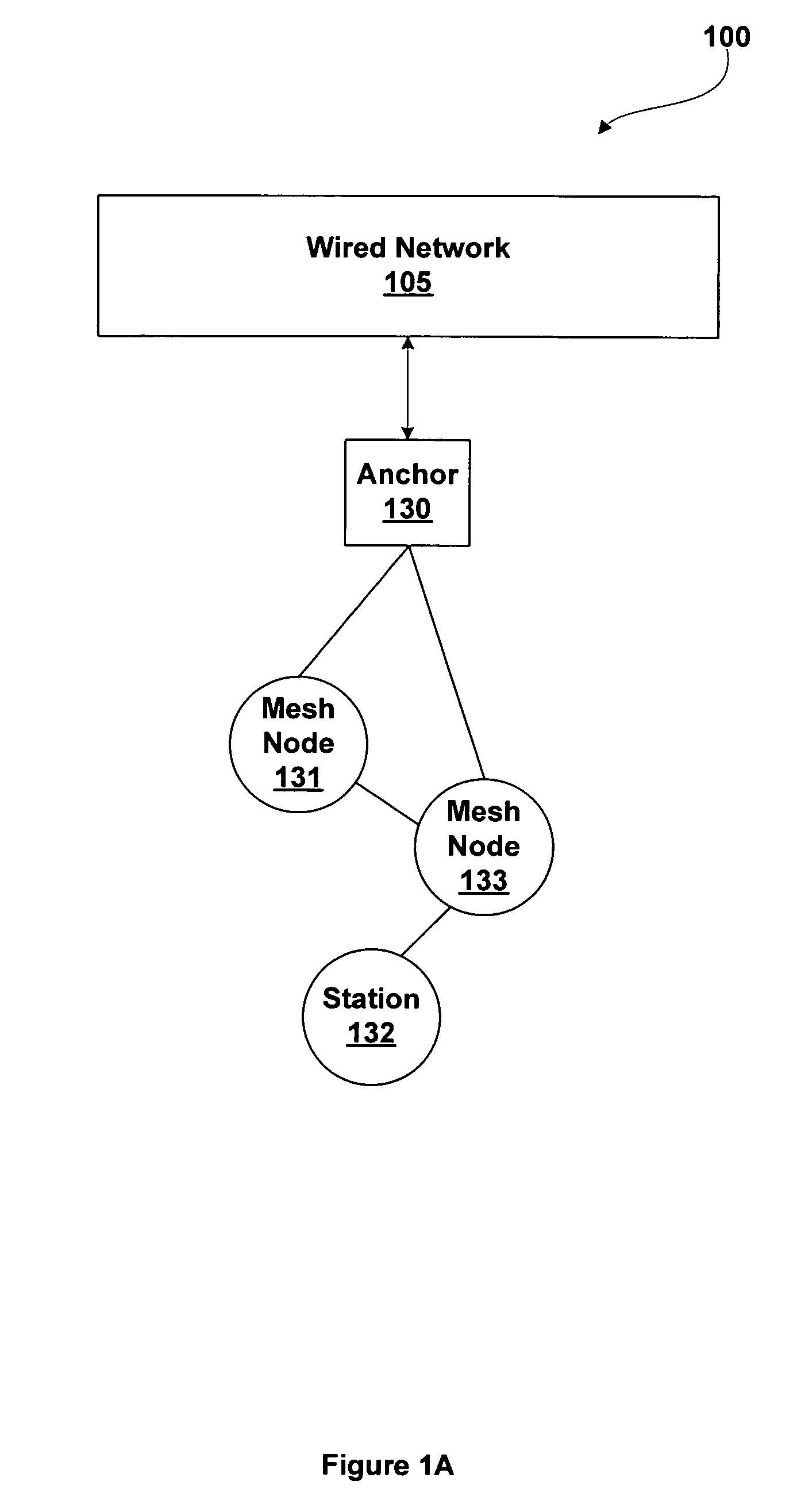
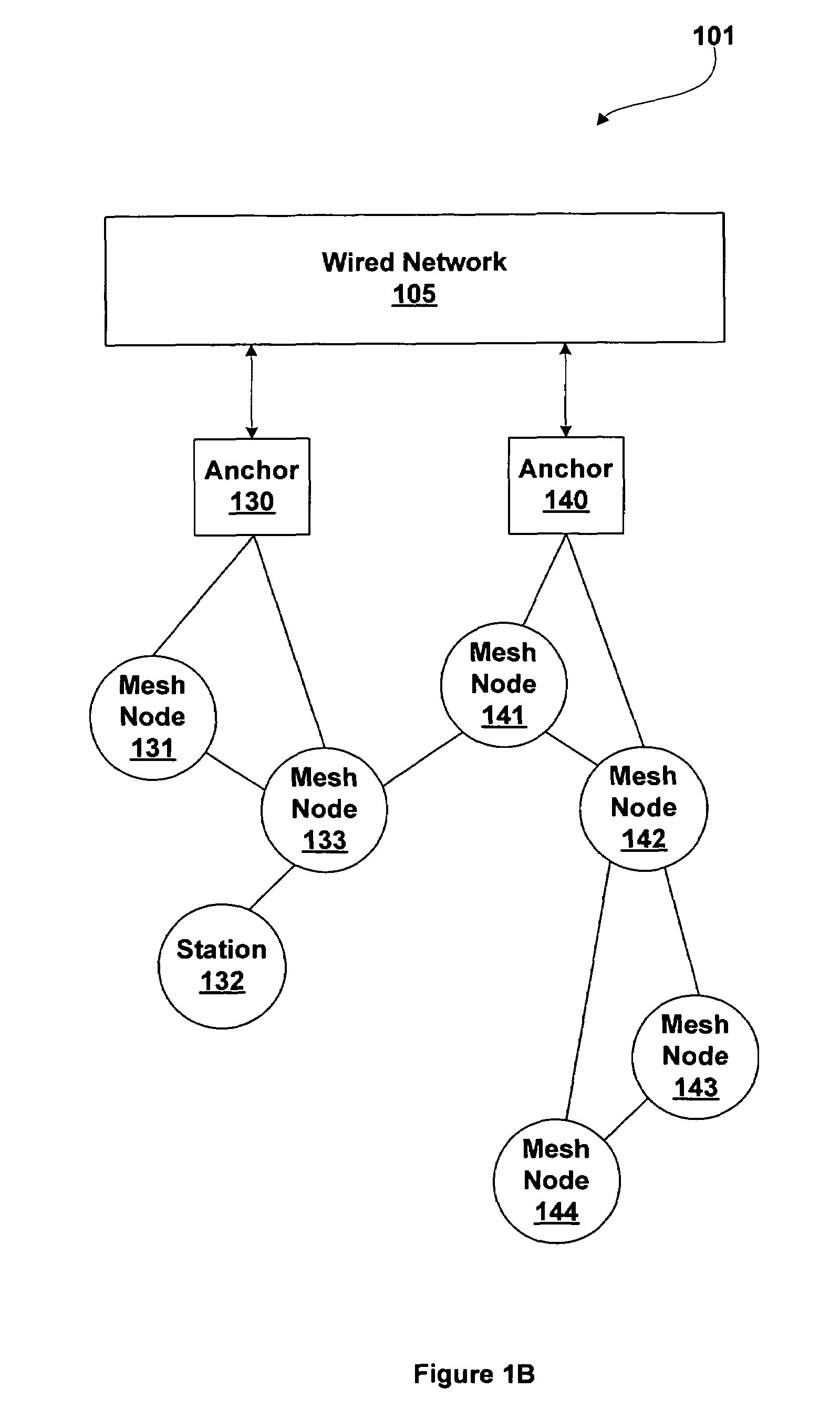
Extended service set mesh topology discovery
ActiveUS7522540B1Network topologiesData switching by path configurationGrid networkWireless computing
A system and methods for wireless computing devices to become mesh member nodes within a self-configuring mesh network includes mechanisms for neighbor discovery and sharing of a common topology database including mesh topology and mesh network information. Each mesh node may use the topology database to determine optimized routing paths within the mesh network. Mesh member nodes are configured to detect and communicate topology changes and measured mesh network attributes to other members of the self-configuring wireless network.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
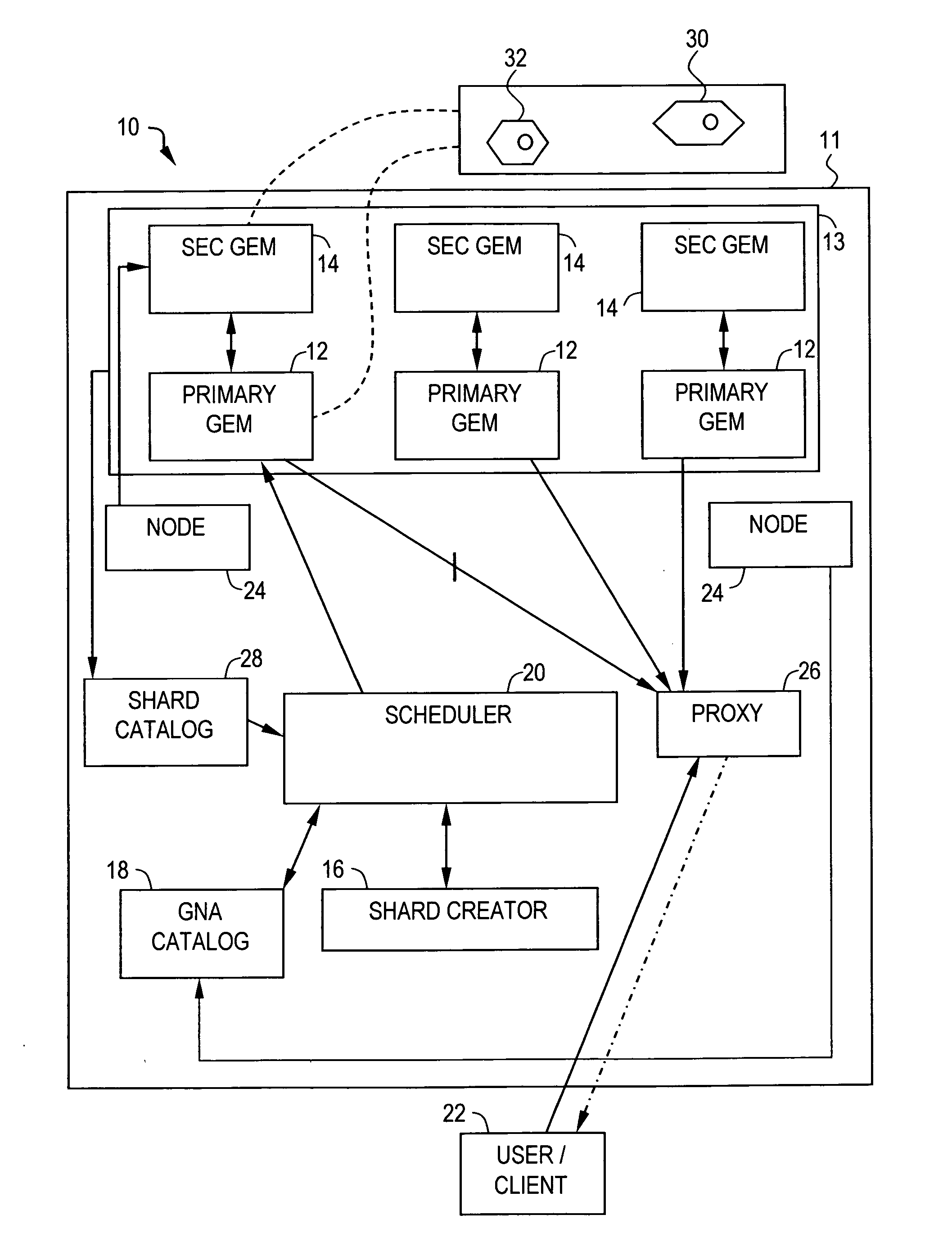
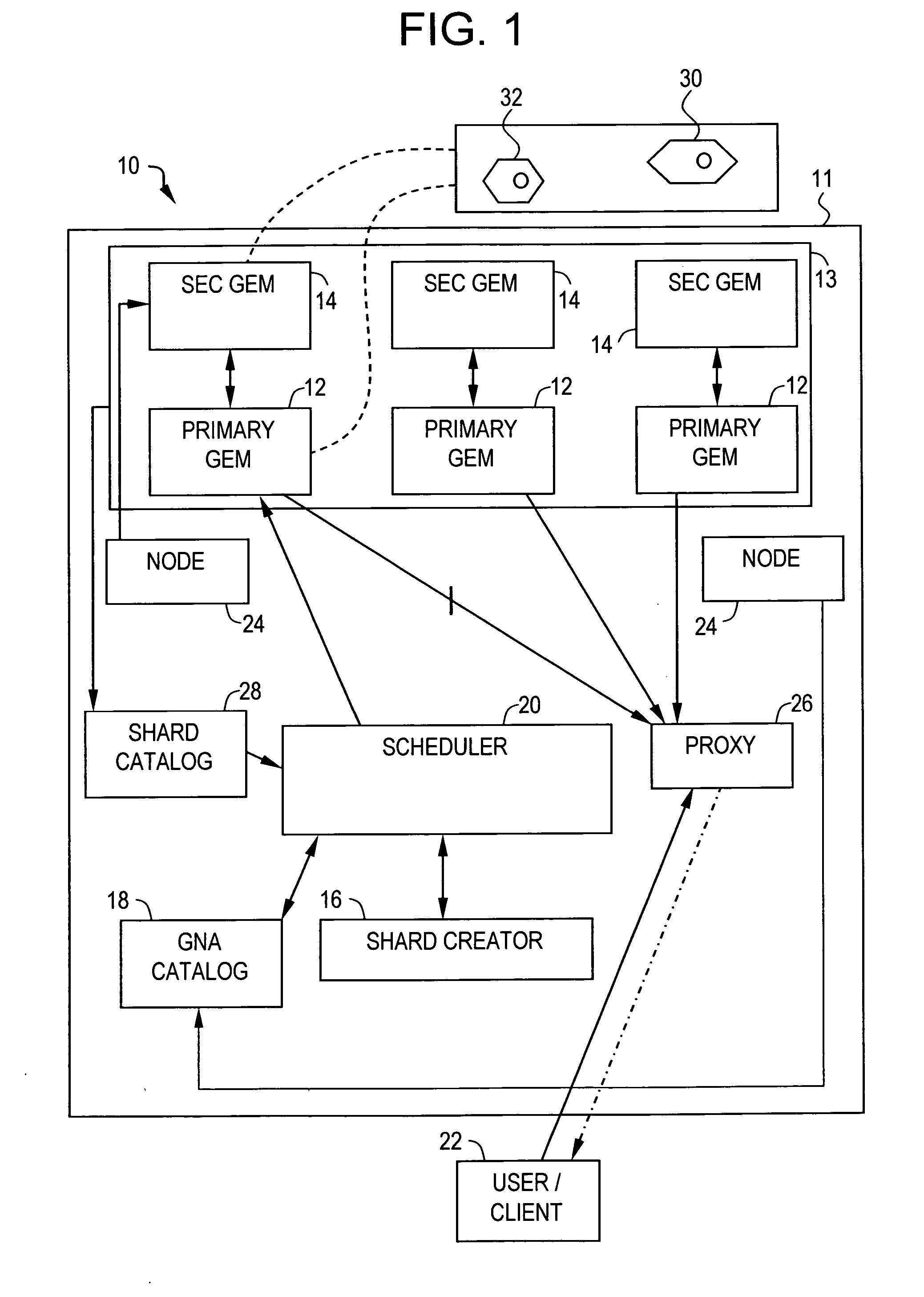
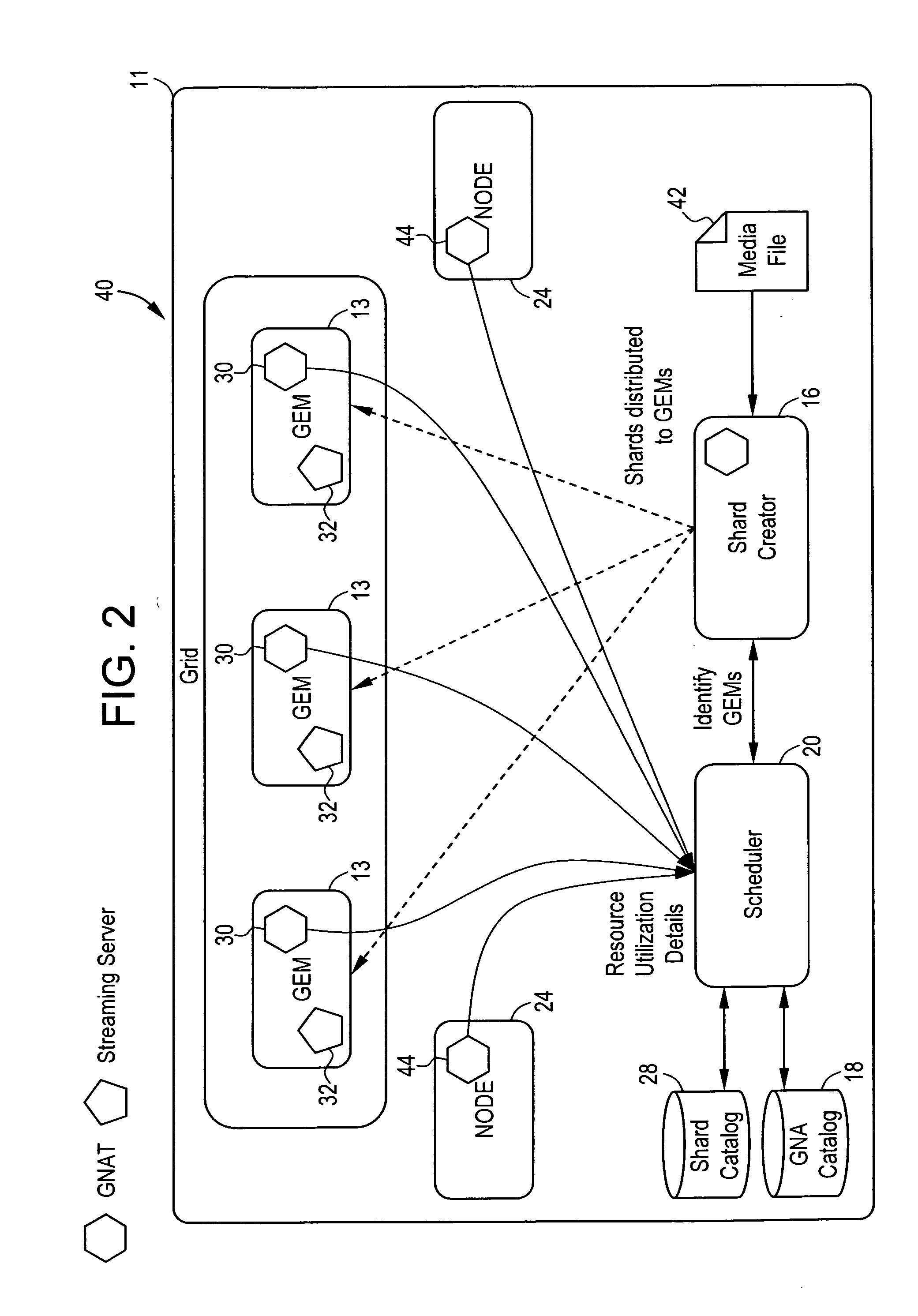
Video on demand system and methods thereof
ActiveUS20070083617A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsMultiple digital computer combinationsPower gridGrid network
A method for transmitting a video data over a grid infrastructure network is disclosed. The method includes receiving a request from at least one user for viewing the video data and identifying a plurality of attributes from a plurality primary grid enabled mini servers (GEMS), wherein the plurality of primary GEMS together form the grid network. The method further includes partitioning video data into a plurality of discrete fragments using a shard creator indicative of the plurality of attributes in each of the plurality of primary GEMS and allocating the plurality of discrete fragments among the plurality of primary GEMS based on the plurality of attributes of each of the plurality of primary GEMS. The method also includes decoding the plurality of discrete fragments of the video data using a streaming server for transmitting the video data to the at least one user.
Owner:INFOSYS TECH LTD (IN)
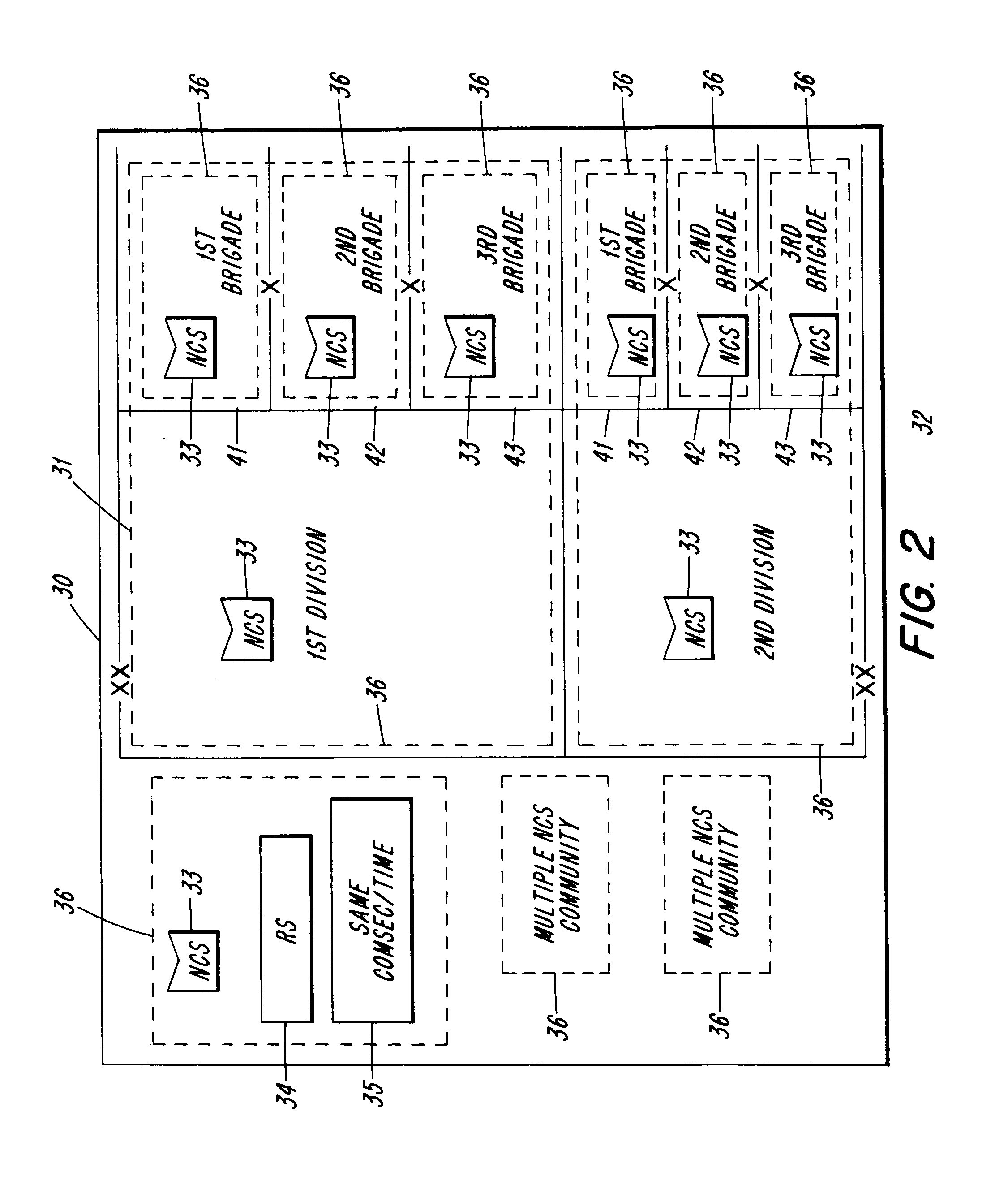
Grouping mesh clusters
InactiveUS7321316B2High bandwidthReduce in quantityElectric signal transmission systemsLevel controlSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Cluster systems
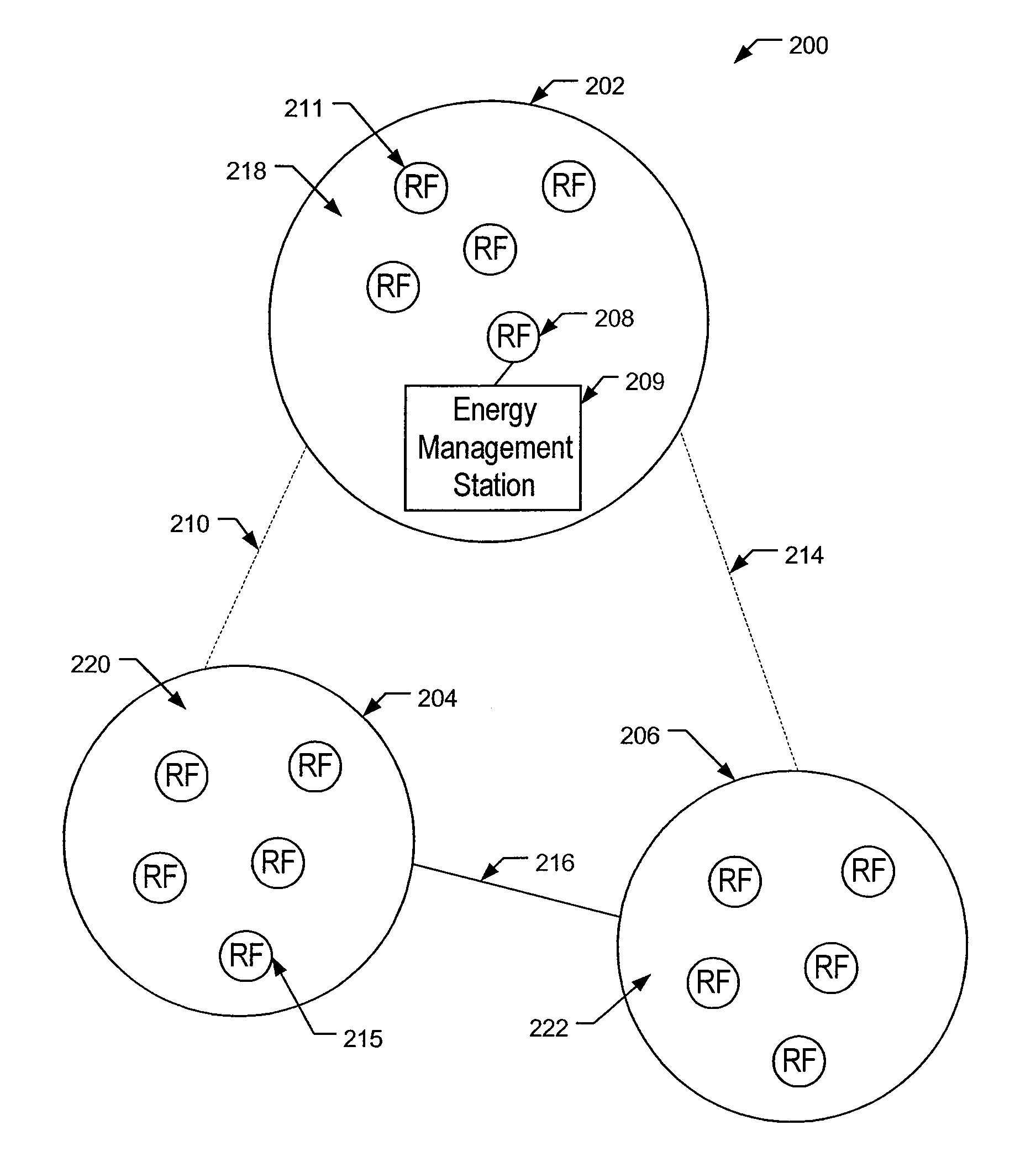
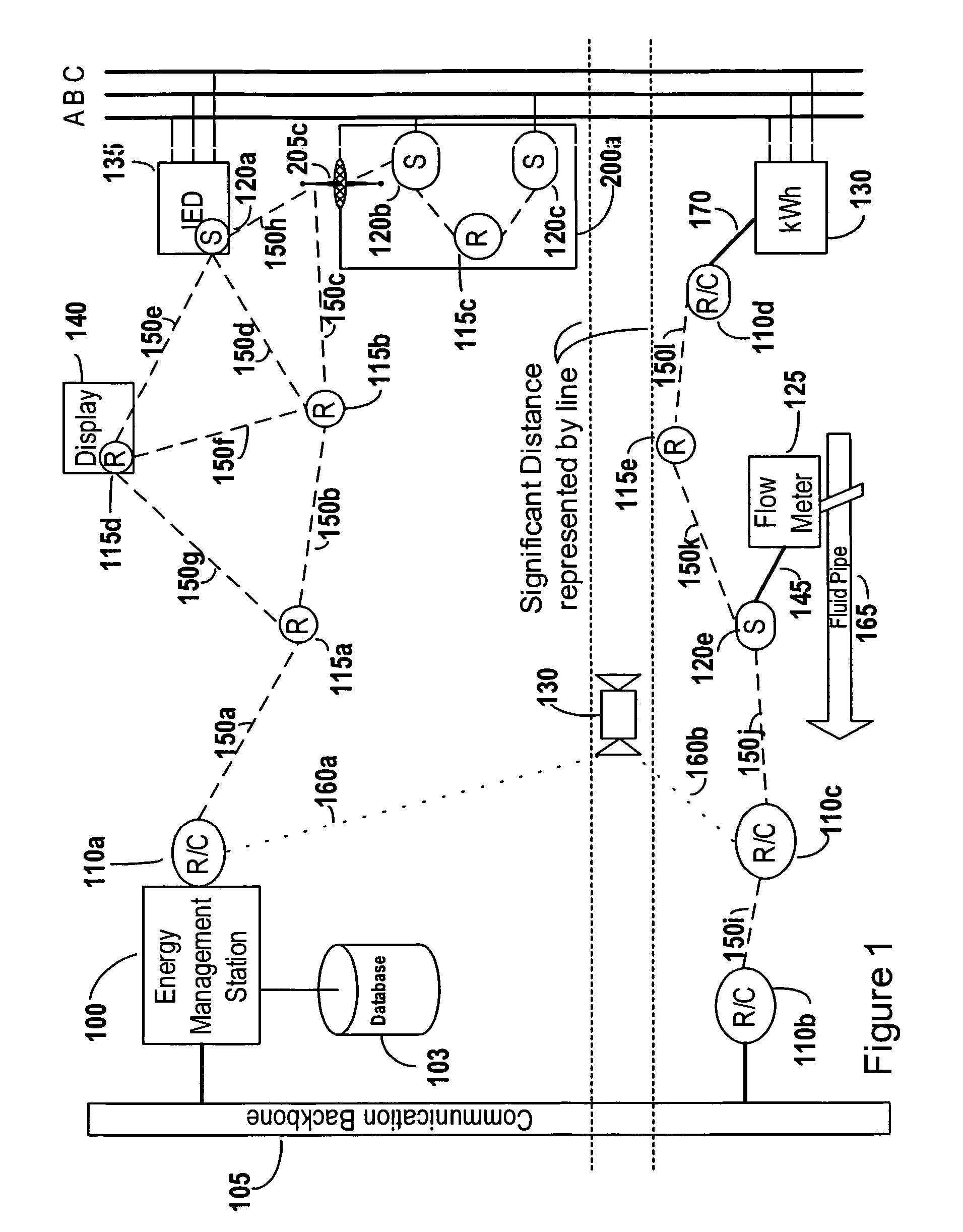
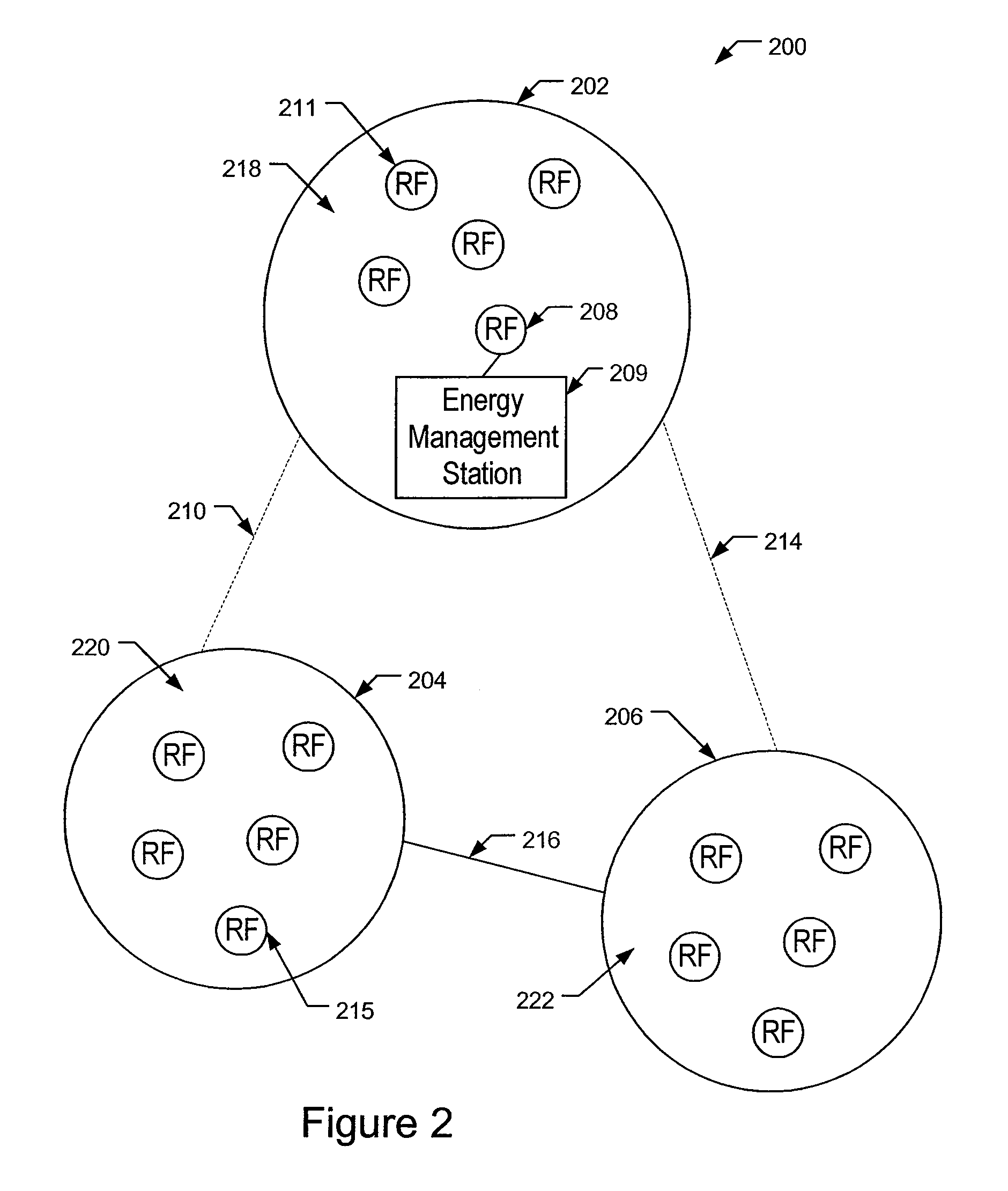
Systems and methods for grouping mesh networks. Mesh networks enable energy data to be transferred from an energy sensing device to a destination device using various networks and reduces the need to install metering stations. Embodiments of the invention join or group mesh networks that otherwise are not able to communicate. The connections between the grouped mesh networks can be passive using directional antennas or passive antennas or active using higher power RF devices, solar repeaters, mobile mesh devices, etc. The energy data is routed in a smart manner, by performing load balancing at gateways, by monitoring the signal to noise ratio of available communication paths, etc. Mesh clusters can also be created to define low power clusters, address blocking clusters, and frequency based clusters. Grouping clusters facilitates the efficient transfer of energy data from an energy sensing device to a energy management station.
Owner:POWER MEASUREMENT LTD
Extended service set mesh path selection
ActiveUS7606175B1Frequency-division multiplex detailsNetwork topologiesGrid networkWireless computing
A system and methods for wireless computing devices to become mesh member nodes within a self-configuring mesh network includes mechanisms for neighbor discovery and sharing of a common topology database including mesh topology and mesh network information. Each mesh node may use the topology database to determine optimized routing paths within the mesh network. Mesh member nodes are configured to detect and communicate topology changes and measured mesh network attributes to other members of the self-configuring wireless network.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
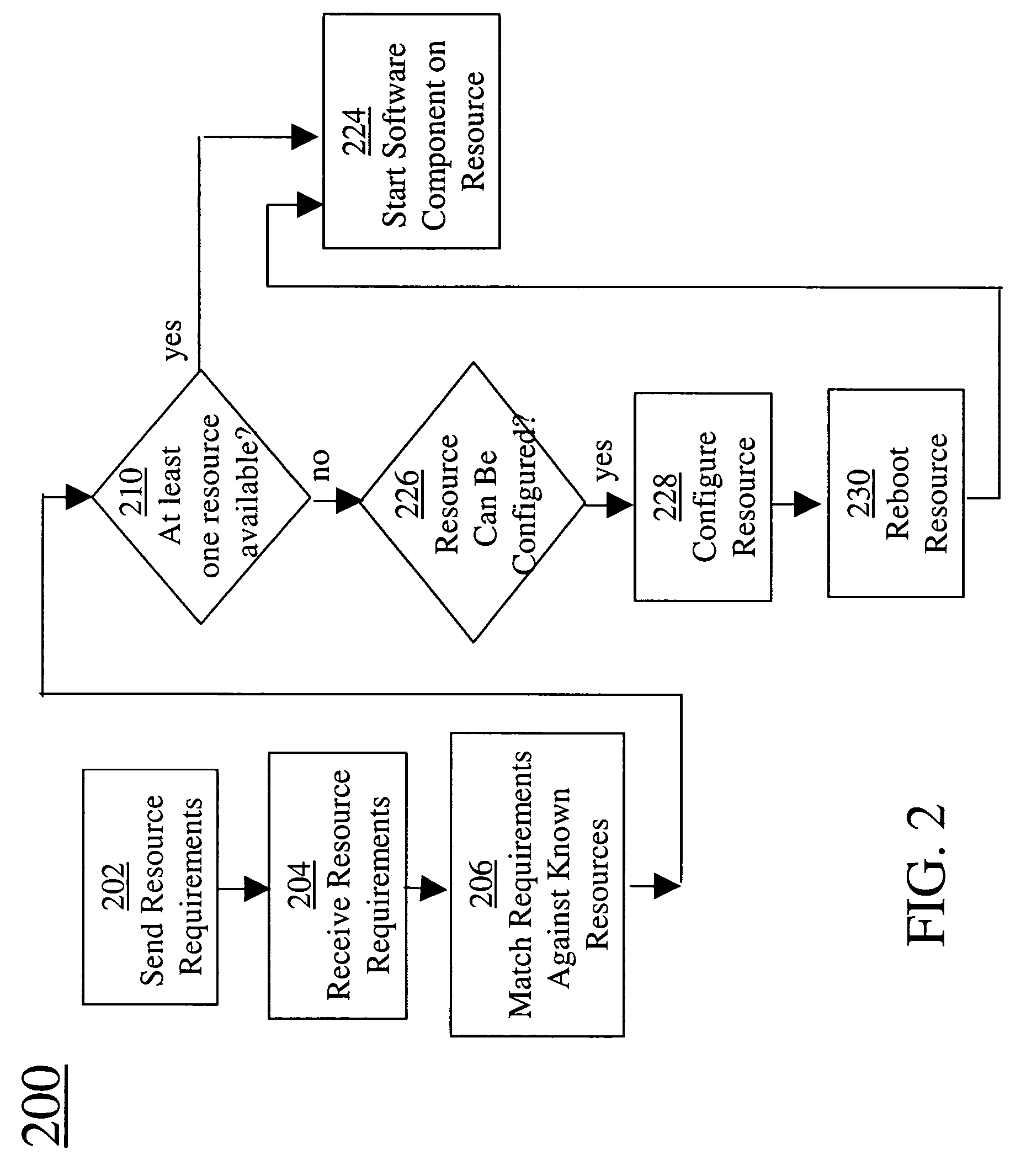
Grid compute node software application deployment
ActiveUS7810090B2Fulfil requirementsMultiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsOperational systemGrid network
A method including, in a grid network, determining available compute devices for installation and execution of an application, the application requiring a specific operating system. The method also includes, in response to determining that there are no available compute devices having the specific operating system, sending a request to install the specific operating system and a grid manager through a link to a management system. The method also includes installing the specific operating system on one of a plurality of compute devices controlled by the management system and linking the one of a plurality of compute devices controlled by the management system to the grid network. Lastly, the method includes installing the application on the one of a plurality of compute devices controlled by the management system.
Owner:SAP AG
Photovoltaic mounting system with locking connectors, adjustable rail height and hinge lock
InactiveUS8176693B2Turn easilyQuick and securePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityPhotovoltaic mounting system
Owner:POWERMOUNT SYST +1
Mesh networking using point coordination function
ActiveUS7502354B1Raise the possibilityTime-division multiplexData switching by path configurationGrid networkWireless computing
A system and methods for wireless computing devices to become mesh member nodes within a self-configuring mesh network includes mechanisms for neighbor discovery and sharing of a common topology database including mesh topology and mesh network information. Each mesh node may use the topology database to determine optimized routing paths within the mesh network. Mesh member nodes are configured to detect and communicate topology changes and measured mesh network attributes to other members of the self-configuring wireless network.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
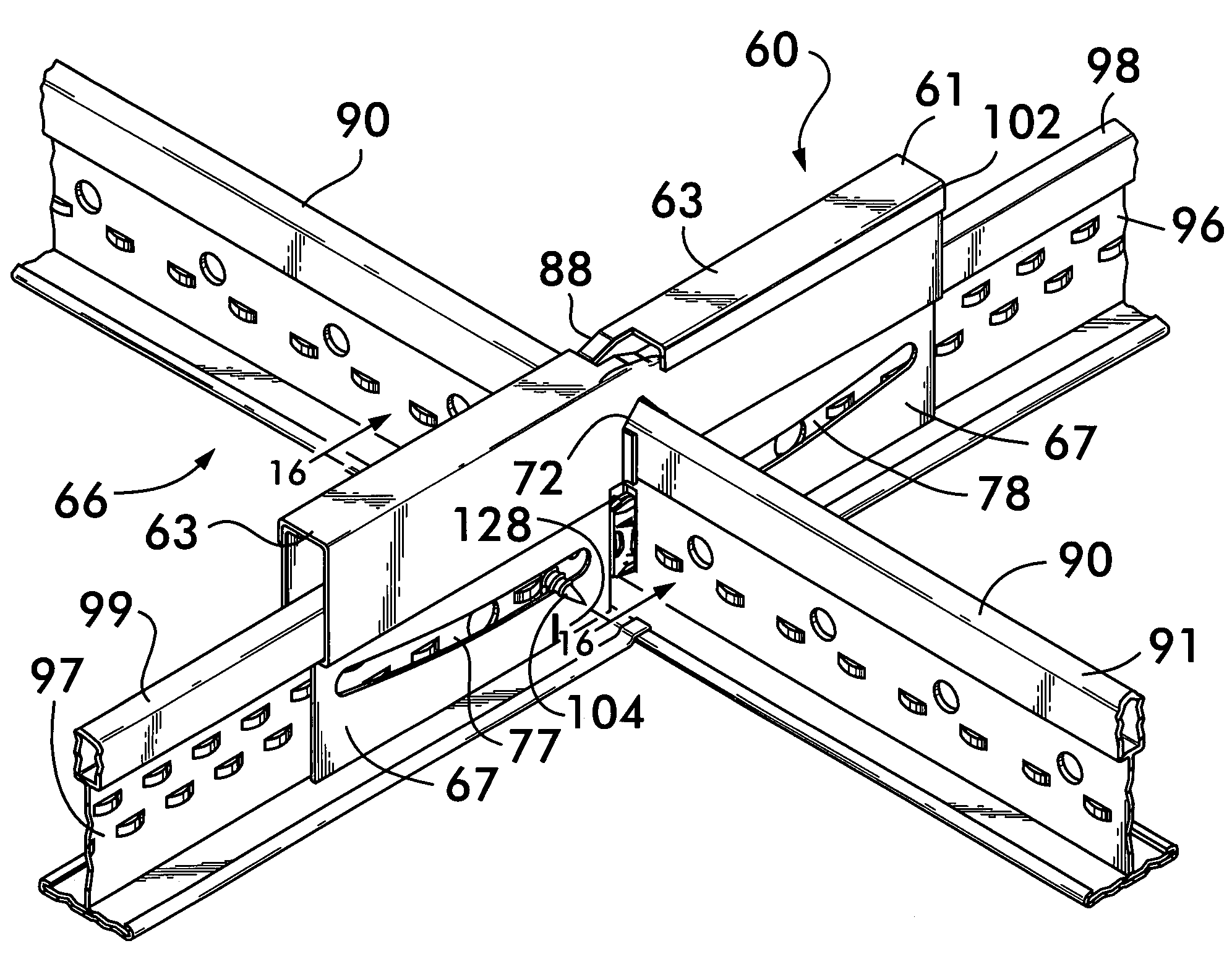
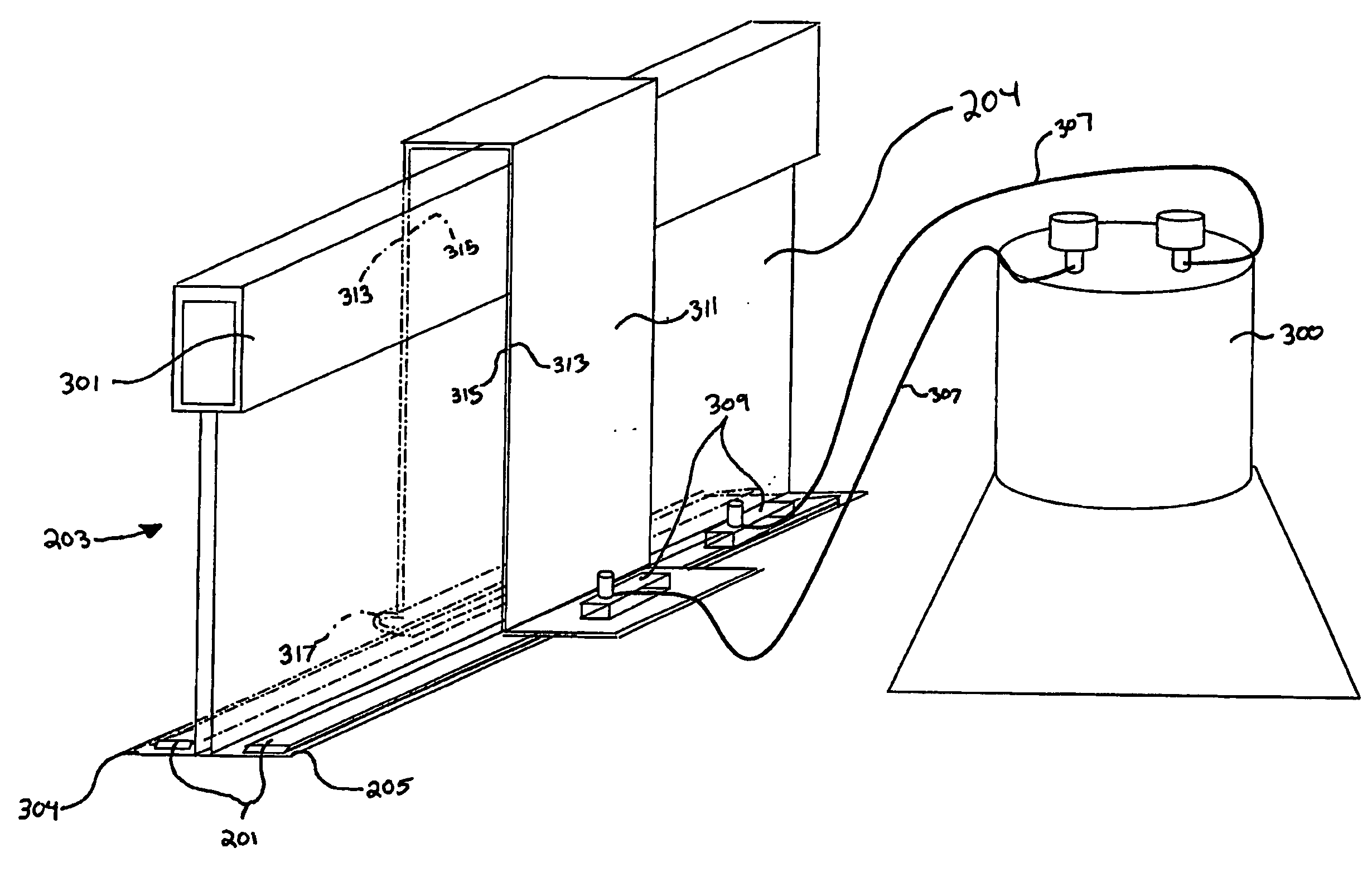
Suspended ceiling grid network utilizing seismic separation joint clips
ActiveUS20080060306A1Preserving aesthetic appealImprove structural strengthCeilingsWallsGrid networkEngineering
Joint clips of the invention are used in grids for suspended ceilings, at selected intersections, to create separate areas of ceiling that move independently of one another during an earthquake, to prevent a buildup of momentum in the entire ceiling. In one embodiment disclosed herein, the clips extend laterally of a selected main beam, and are formed of a pair of loosely connected identical segments that are slidably secured to a selected main beam by a cut-out in the segments. The clip extends laterally across a selected main beam and slidably receives the end of a cross beam in a pocket of the clip that extends laterally on each side of the selected main beam.
Owner:WORTHINGTON ARMSTRONG VENTURE
Systems and methods for advanced energy settlements, network-based messaging, and applications supporting the same on a blockchain platform
Owner:CAUSAM ENERGY INC
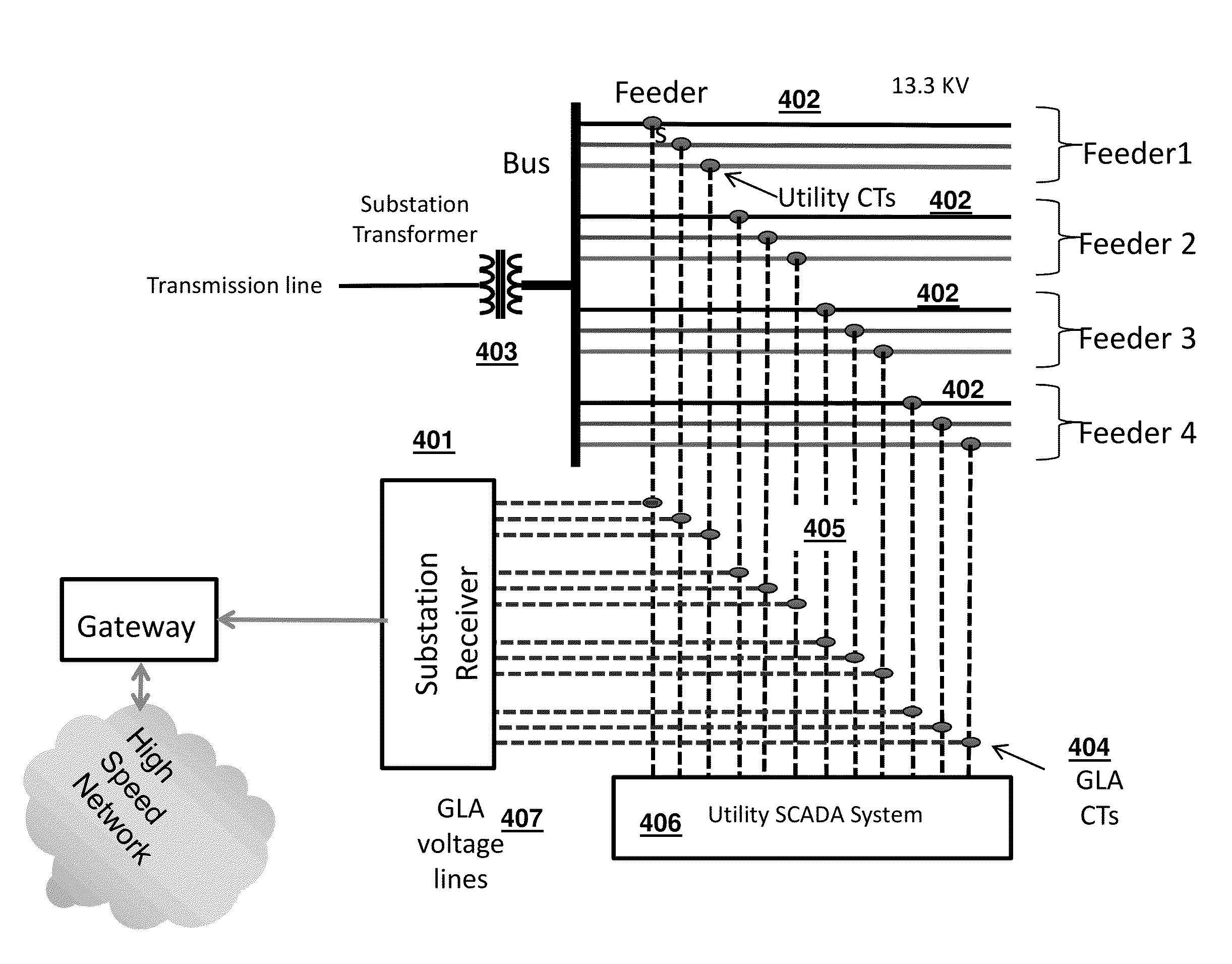
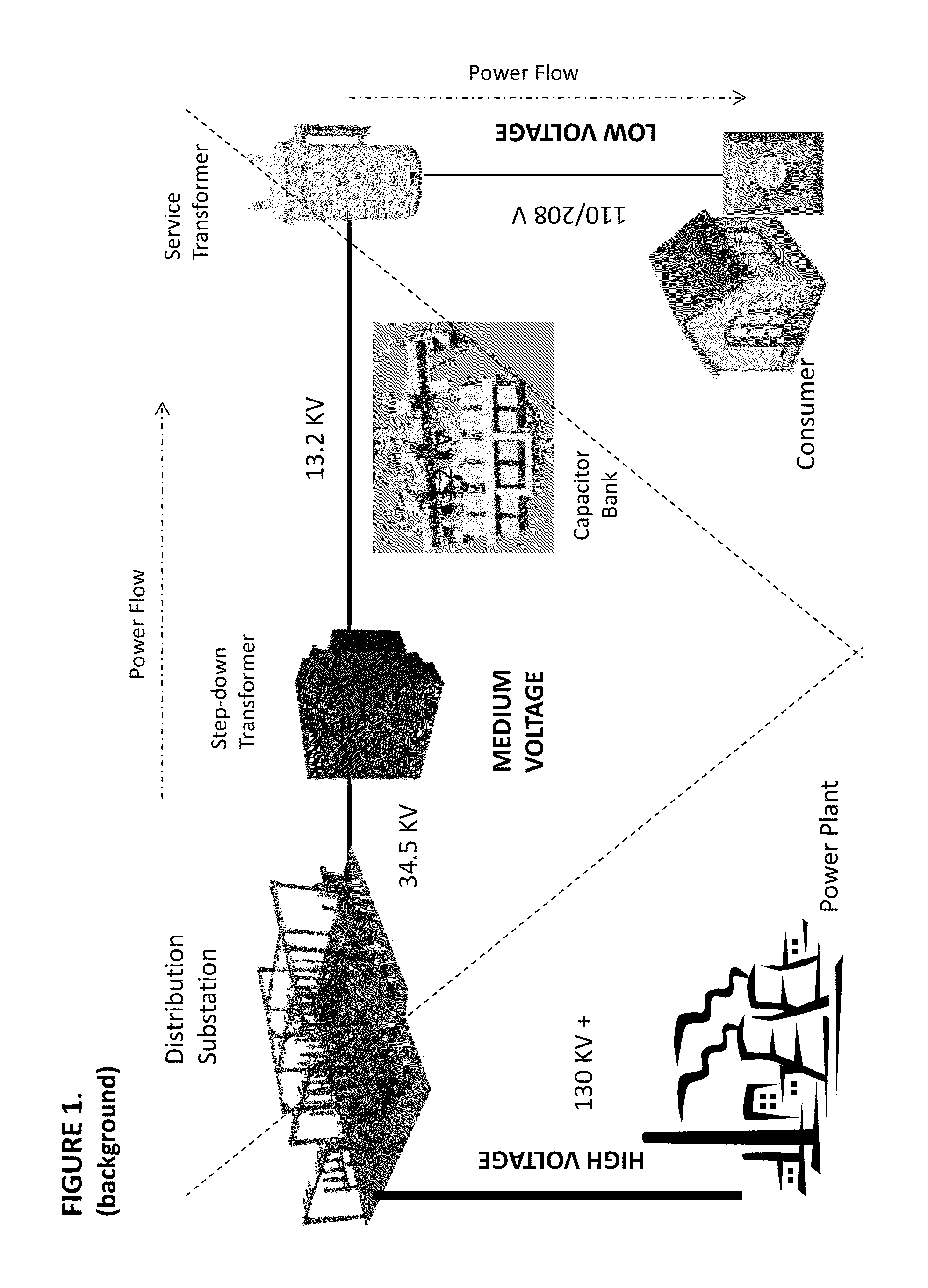
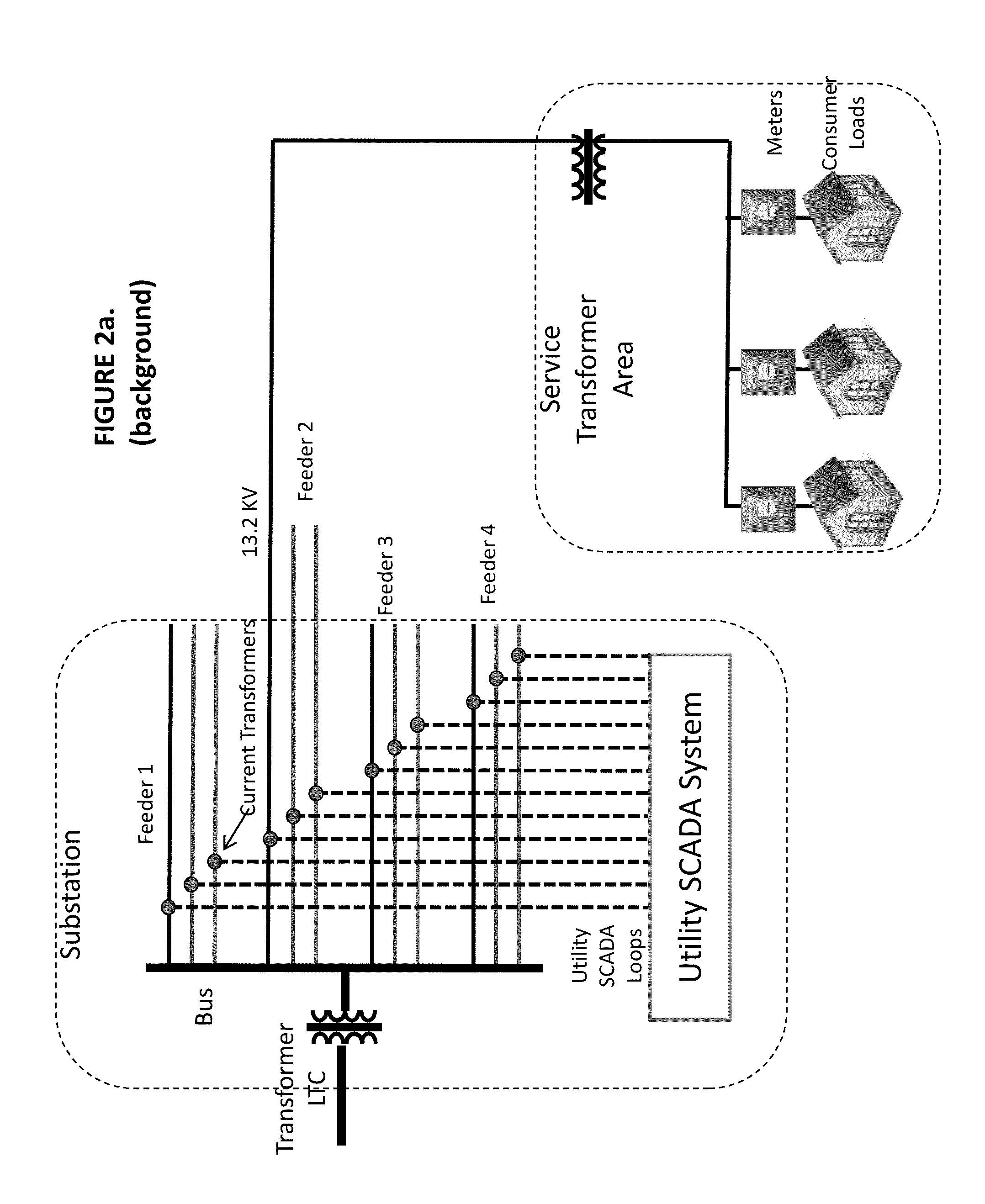
A system and method for inferring schematic and topological properties of an electrical distribution grid
InactiveUS20140233662A1Reduce bitrateLimited amountData processing applicationsCircuit arrangementsTopological orderGrid network
A system and method for inferring schematic and topological properties of an electrical distribution grid is provided. The system may include Remote Hubs, Subordinate Remotes, a Substation Receiver, and an associated Computing Platform and Concentrator. At least one intelligent edge transmitter, called a Remote Hub Edge Transmitter, may transmit messages on the electrical distribution grid by injecting a modulated current into a power main that supplies an electric meter. The Subordinate Remotes, Remote Hubs, the Substation Receiver, and the associated Computing Platform and Concentrator may contain processing units which execute stored instructions allowing each node in the network to implement methods for organizing the on-grid network and transmitting and receiving messages on the network. The Substation Receiver, Computing Platform and Concentrator may detect and infer schematic grid location attributes of the network and publish the detected and inferred attributes to other application systems including geospatial information systems maintaining the logical and physical network model.
Owner:TRC +1
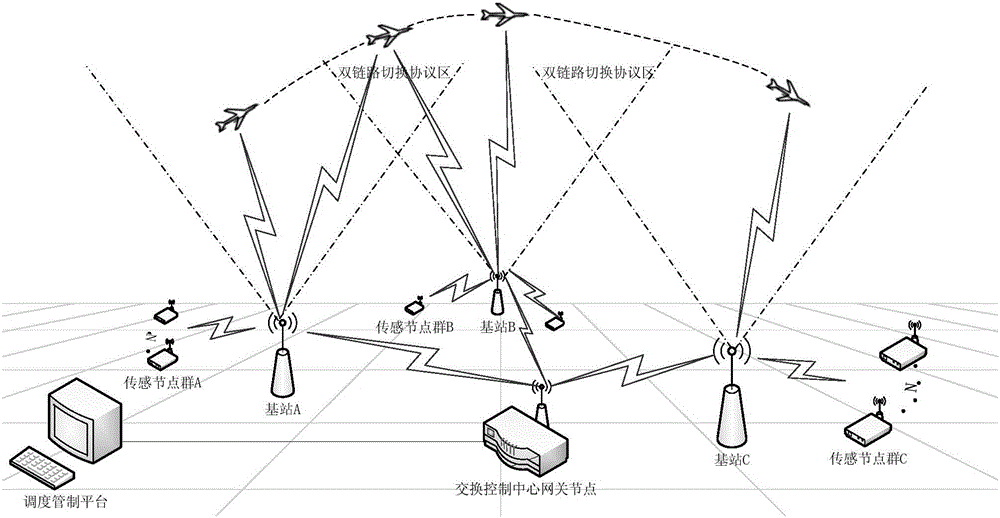
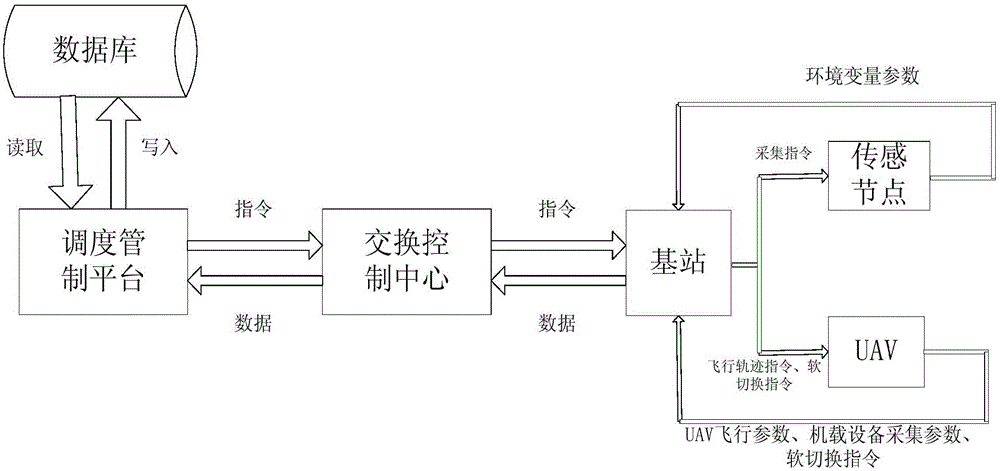
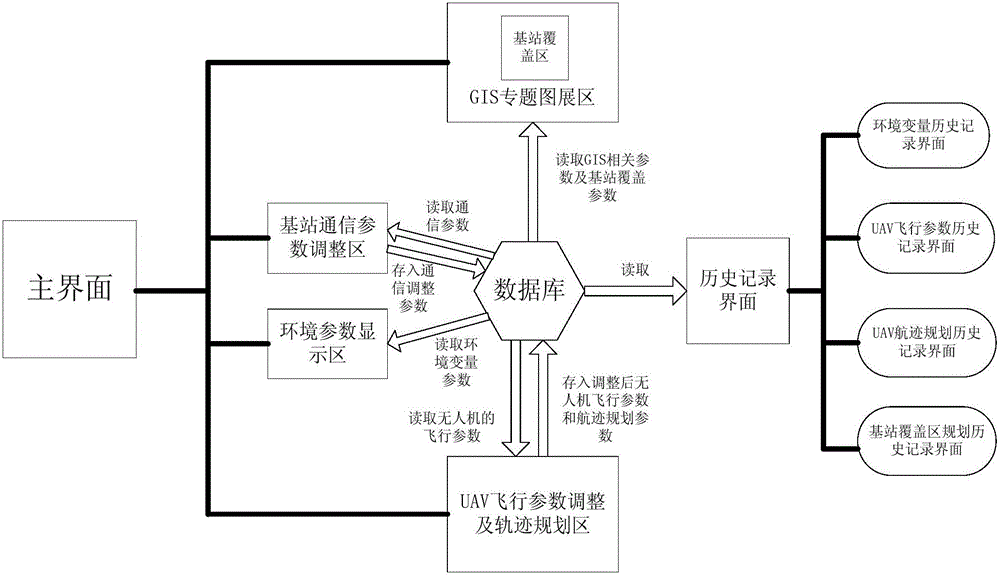
Ground-air wireless sensor network communication device and method compatible with UAV
ActiveCN105828345AExpandable and flexibleEliminate signal blind spotsNetwork topologiesTransmissionGrid networkNetwork communication
The invention discloses a ground-air wireless sensor network communication device compatible with a UAV. The device comprises a sensing monitoring system, a mobile platform system, an integrated Wi-Fi network communication system and a dispatching control platform. The sensing monitoring system indicates that in a sensor network, sensor nodes randomly scattered in a monitored region monitor specific variable objects in a target region in real time. The mobile platform system comprises UAVs for mounting Wi-Fi network communication modules, wherein the controllability of the flying speeds and the paths of the UAVs is realized by using rotor vertical lifting platforms. The integrated Wi-Fi network communication system indicates a structure which takes a Wi-Fi communication mode as the main and refers to a cellular mobile communication network. The dispatching control platform is a set of software platform which is used for controlling flying paths of the unmanned aerial vehicles and collecting wireless network topology control information and environment variable information. According to the device, grid network development demands can be satisfied; and through establishment of the UAV communication network taking the network as the center, sufficient stability and reliability and high interconnection and interoperability can be realized.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Suspended ceiling grid network utilizing seismic separation joint clips
ActiveUS7614195B2Preserving aesthetic appealImprove structural strengthCeilingsWallsGrid networkEngineering
Joint clips of the invention are used in grids for suspended ceilings, at selected intersections, to create separate areas of ceiling that move independently of one another during an earthquake, to prevent a buildup of momentum in the entire ceiling. In one embodiment disclosed herein, the clips extend laterally of a selected main beam, and are formed of a pair of loosely connected identical segments that are slidably secured to a selected main beam by a cut-out in the segments. The clip extends laterally across a selected main beam and slidably receives the end of a cross beam in a pocket of the clip that extends laterally on each side of the selected main beam.
Owner:WORTHINGTON ARMSTRONG VENTURE
Electrified ceiling framework
InactiveUS20080087464A1Safely and conveniently to and unconnectedConveniently routedCoupling device connectionsFlat/ribbon cablesElectricityLow voltage
An electrified ceiling framework system having a plurality of grid elements forming a grid network arranged in a substantially planar arrangement. A conductive material is disposed on a surface of at least one of the plurality of grid elements. The conductive material is electrically connected to a low voltage power source and has a contact surface connectable to a low voltage device.
Owner:WORTHINGTON ARMSTRONG VENTURE
Method for making battery plates
InactiveUS20050150092A1Improve adhesionExtend battery lifePrimary cellsElectrode carriers/collectorsElectrical batteryGrid network
A method of making a plurality of battery plates includes forming a strip including a plurality of battery grids. Each battery grid includes a grid network bordered by a frame element and includes a plurality of spaced apart grid wire elements. Each grid wire element has opposed ends joined to one of a plurality of nodes to define a plurality of open spaces in the grid network. The method also includes deforming at least a portion of a plurality of the grid wire elements such that the deformed grid wire elements have a first transverse cross-section at a point intermediate their opposed ends that differs from a second transverse cross-section taken at at least one of their opposed ends. The method also includes applying a lead alloy coating to the strip, applying battery paste to the strip, and cutting the strip to form a plurality of battery plates.
Owner:CPS TECH HLDG LLC
Electrified ceiling framework
InactiveUS7762821B2Safely and conveniently connected to and unconnectedConveniently routedCoupling device connectionsFixed installationElectricityLow voltage
An electrified ceiling framework system having a plurality of grid elements forming a grid network arranged in a substantially planar arrangement. A conductive material is disposed on a surface of at least one of the plurality of grid elements. The conductive material is electrically connected to a low voltage power source and has a contact surface connectable to a low voltage device.
Owner:WORTHINGTON ARMSTRONG VENTURE
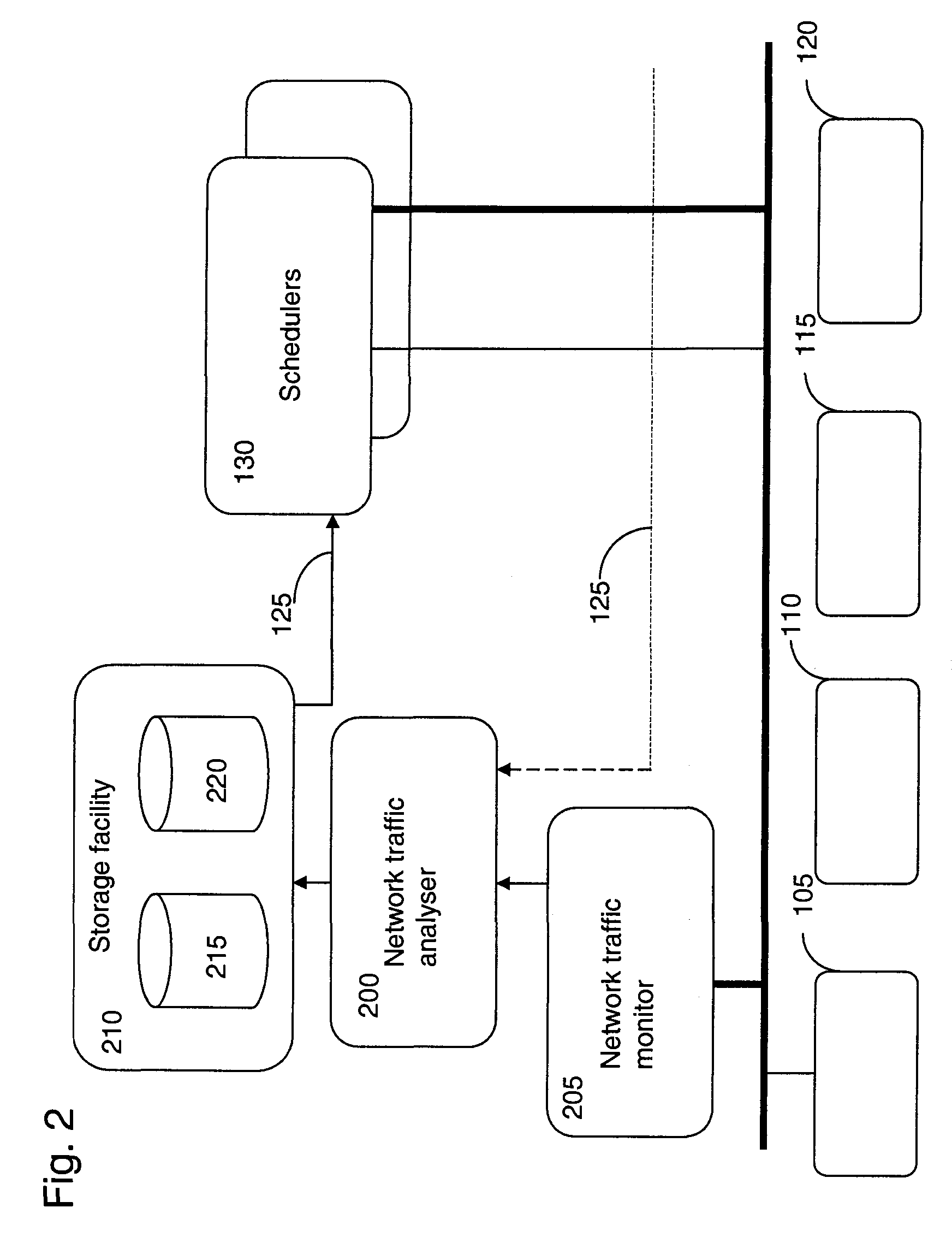
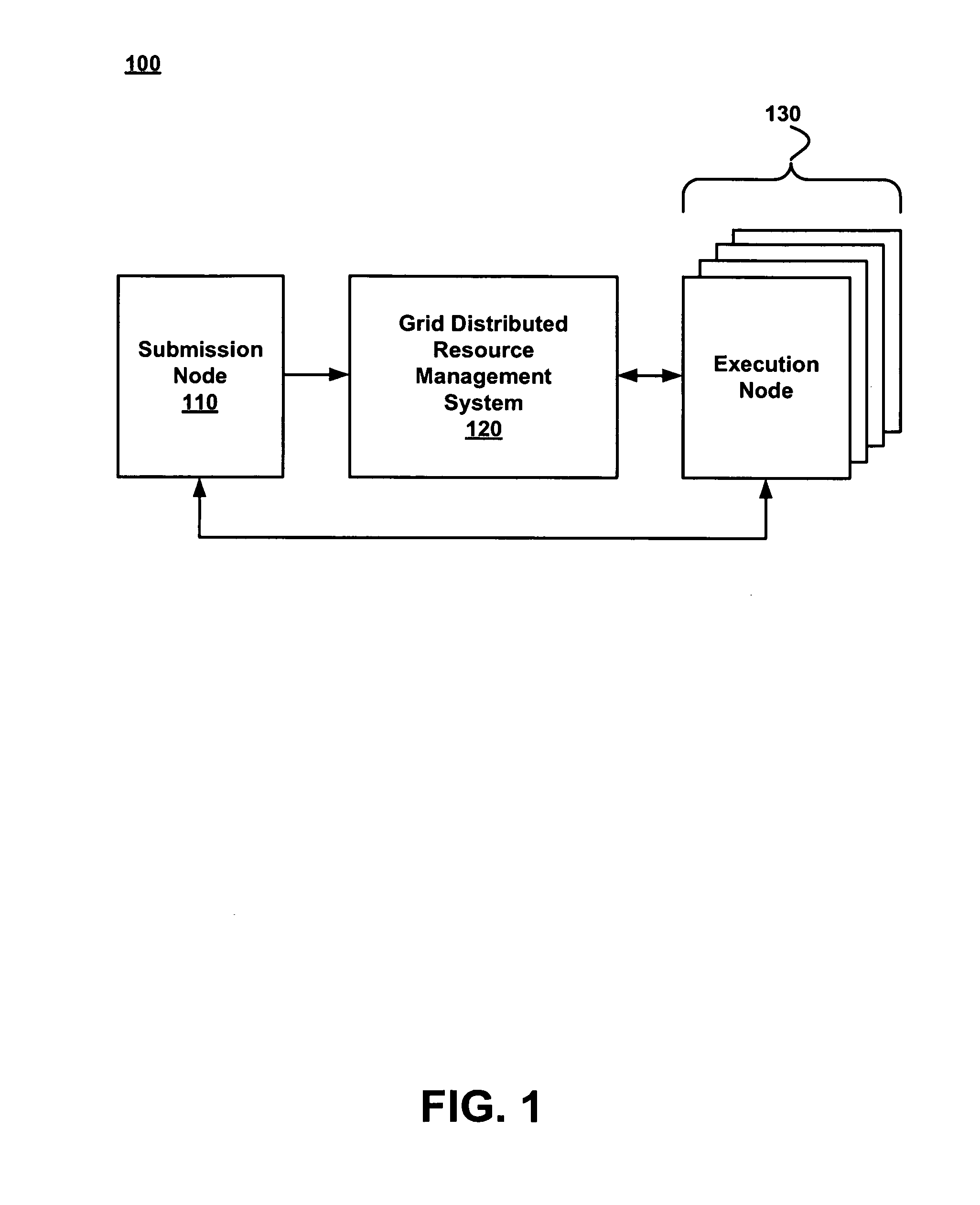
Method and system for determining a plurality of scheduling endpoints in a grid network
InactiveUS20070016590A1Reduce network trafficInformed decisionDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsData setTime segment
A method for determining a plurality of scheduling endpoints in a grid network, each scheduling endpoint comprising a device for processing job requests communicated across the network, the method comprising the steps of: examining a communication across the network in order to determine a current activity status of a requesting device; identifying an activity history for the requesting device; comparing the current activity status with the activity history to derive a statistical data set; and analysing the statistical data set to derive a time period in which the requesting device is available for processing job requests.
Owner:LINKEDIN
Power distribution method and network topology method for smart grid management, and apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20110054709A1Good extensibilityIncrease flexibilityMechanical power/torque controlLevel controlElectric power transmissionDistribution method
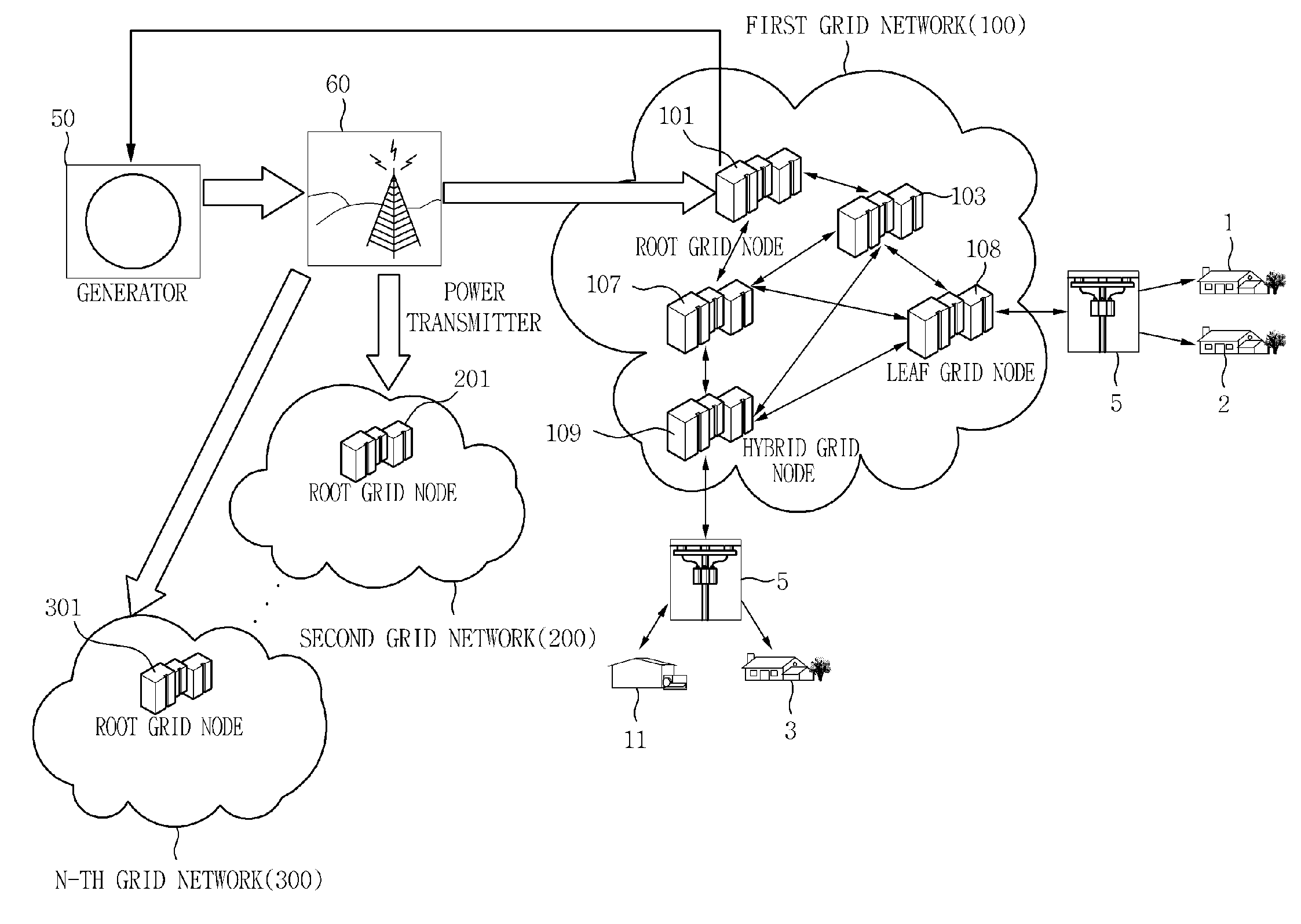
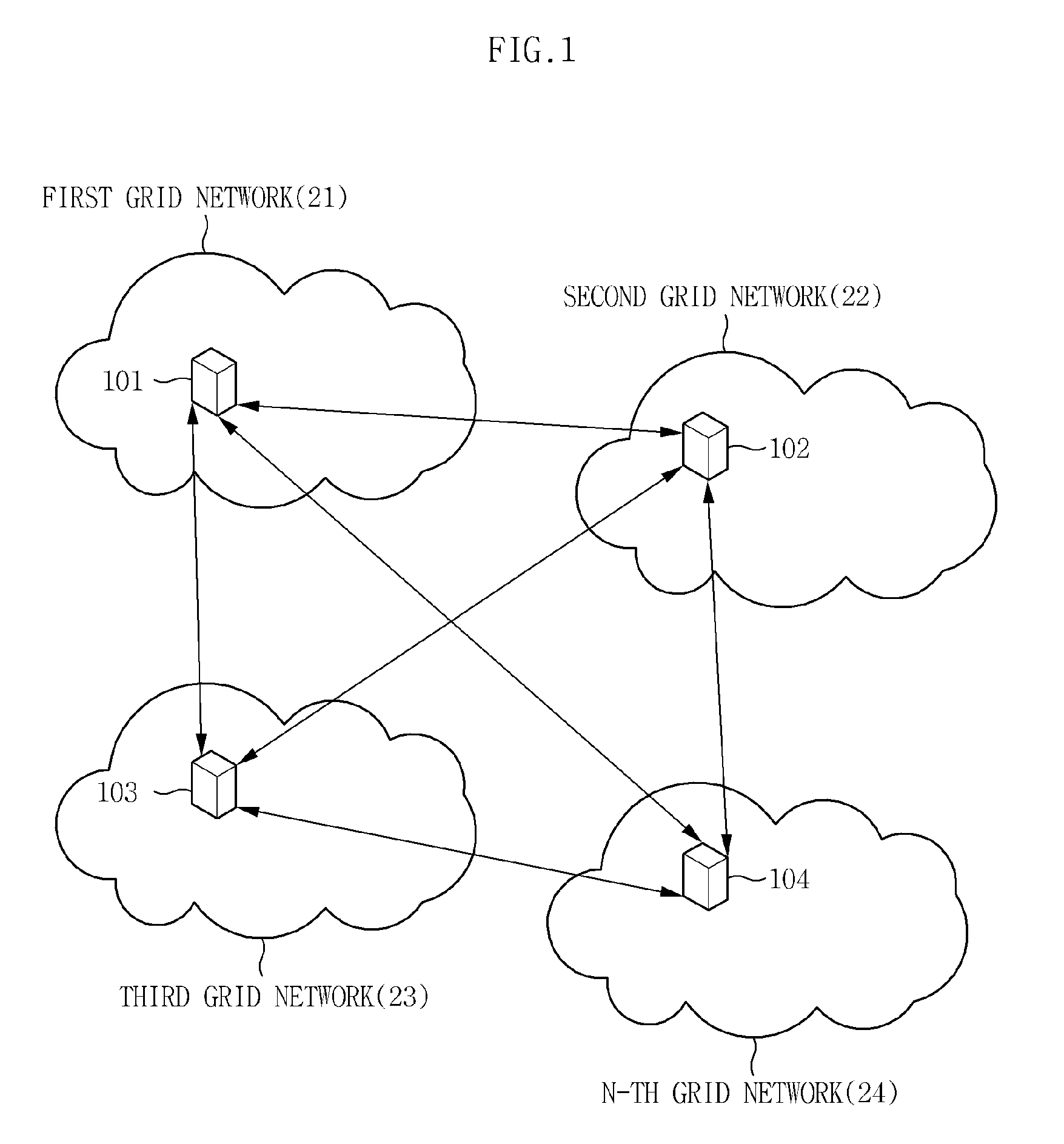
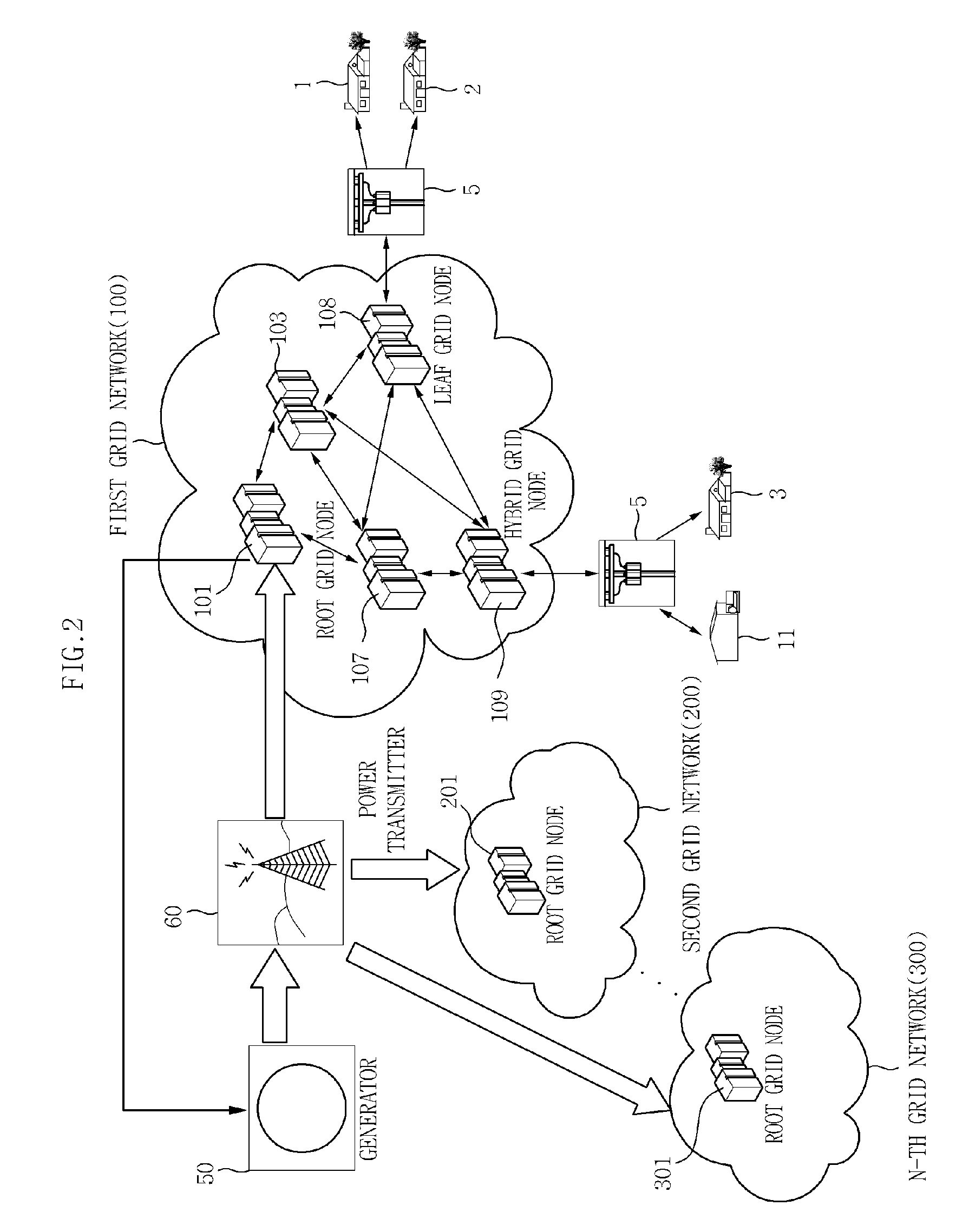
Provided is a power distribution apparatus that includes: a neighboring node information collection unit collecting power distribution amount information and physical distance information between grid nodes from neighboring grid nodes belonging to the same grid network; and a power transmission target node selecting unit allocating priorities to the neighboring grid nodes by using the power distribution amount information and the distance information and selecting a neighboring grid node having the highest priority as a neighboring power transmission grid node by comparing the priorities allocated to the neighboring grid nodes.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
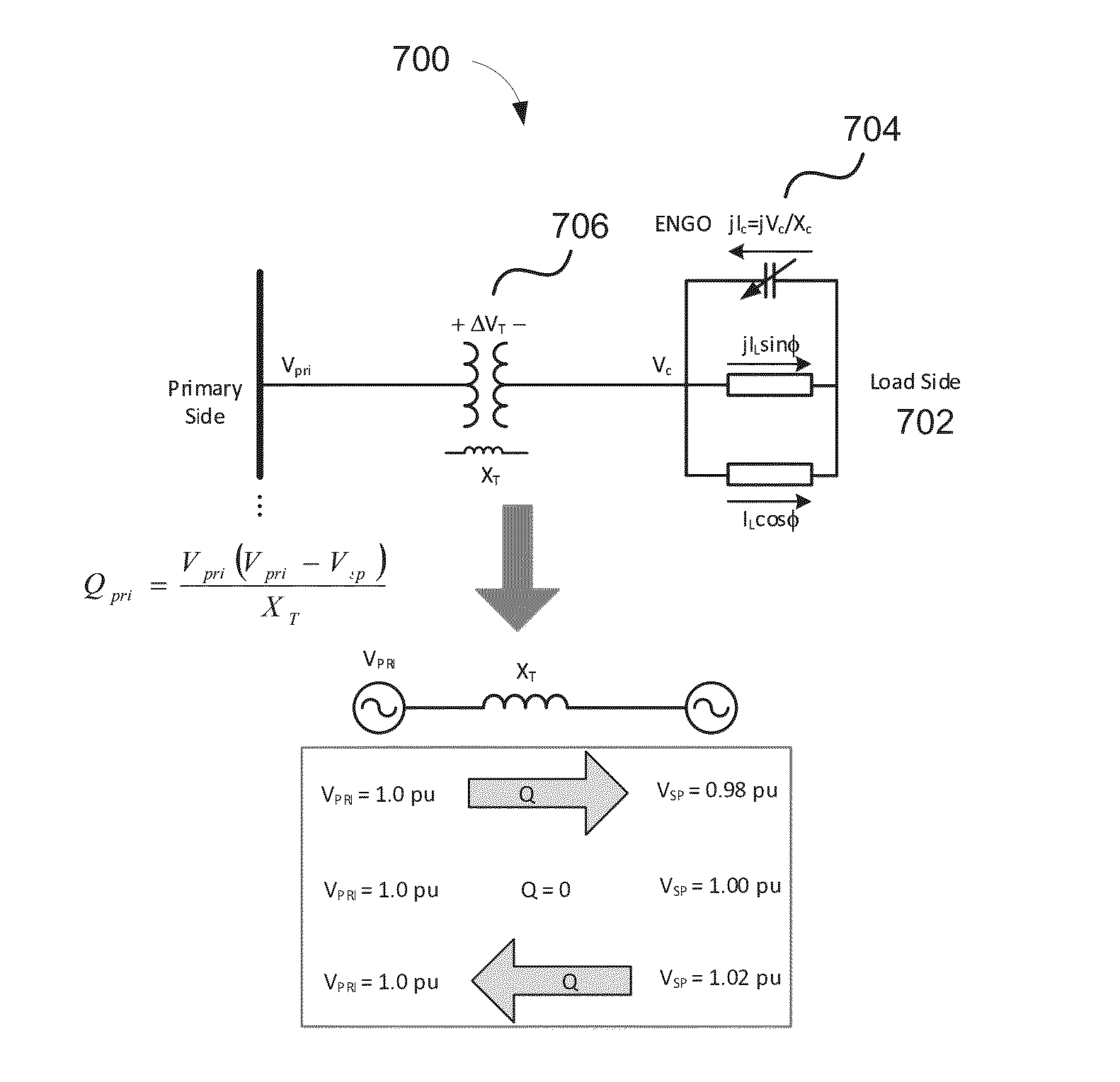
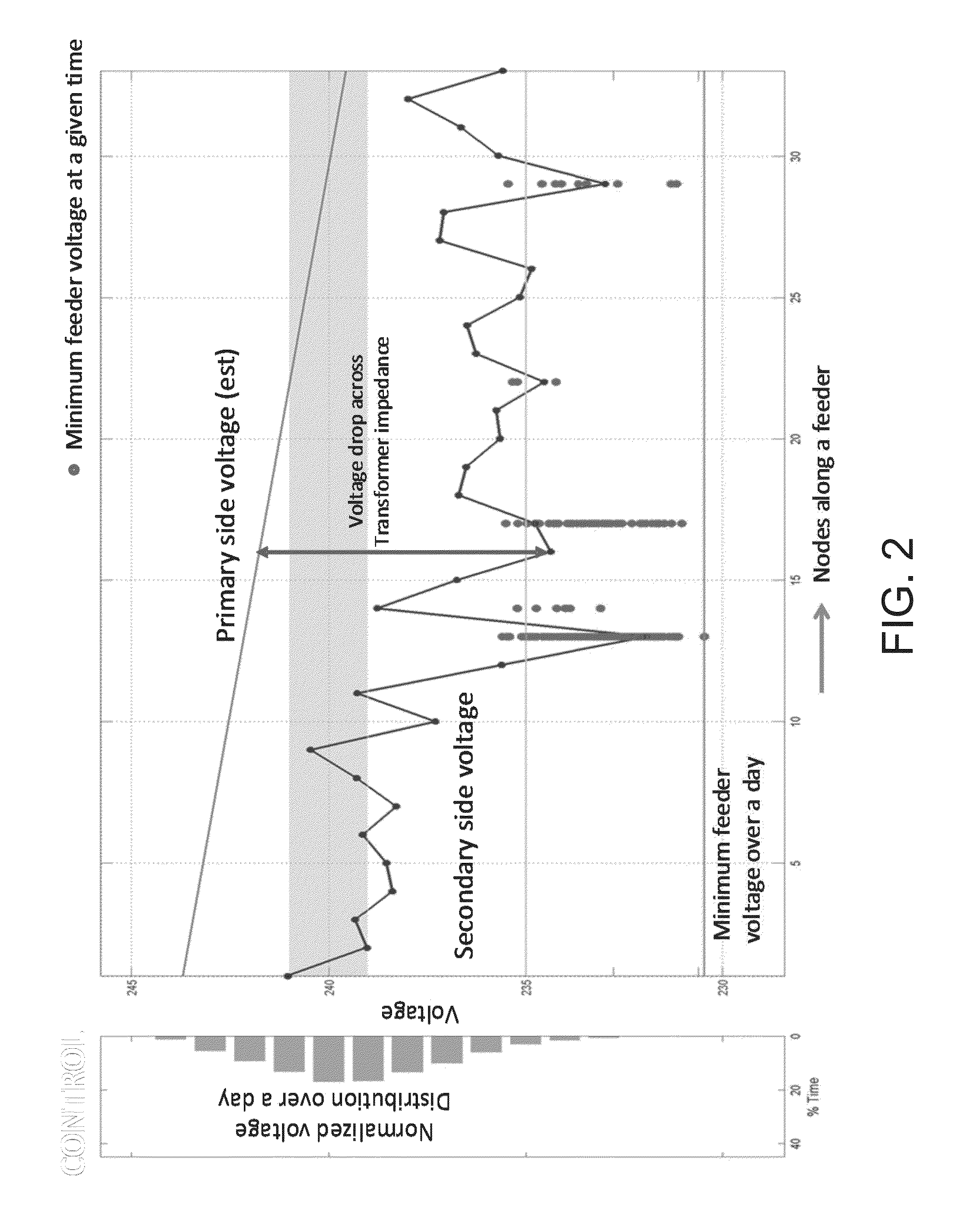
Optimizing voltage and var on the electric grid using distributed var sources
ActiveUS20150311718A1Reactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationPower factorElectric power system
A plurality of edge of network grid volt ampere reactive (VAR) sources are provided in a power system in order to effectuate control at a customer level, which in turn effectuates control at a feeder level, which in turn effectuates control of an entire power system or wide area electric grid network. By optimally selecting voltage setpoints and applying such voltage setpoints to the plurality of edge of network grid VAR sources, the power system can be configured to self-balance, power factor compensation can be determined without the need for measuring load power factor. Moreover, traditionally volatile voltages at the feeder can be flattened, and VAR control can be realized.
Owner:SENTIENT ENERGY TECH LLC
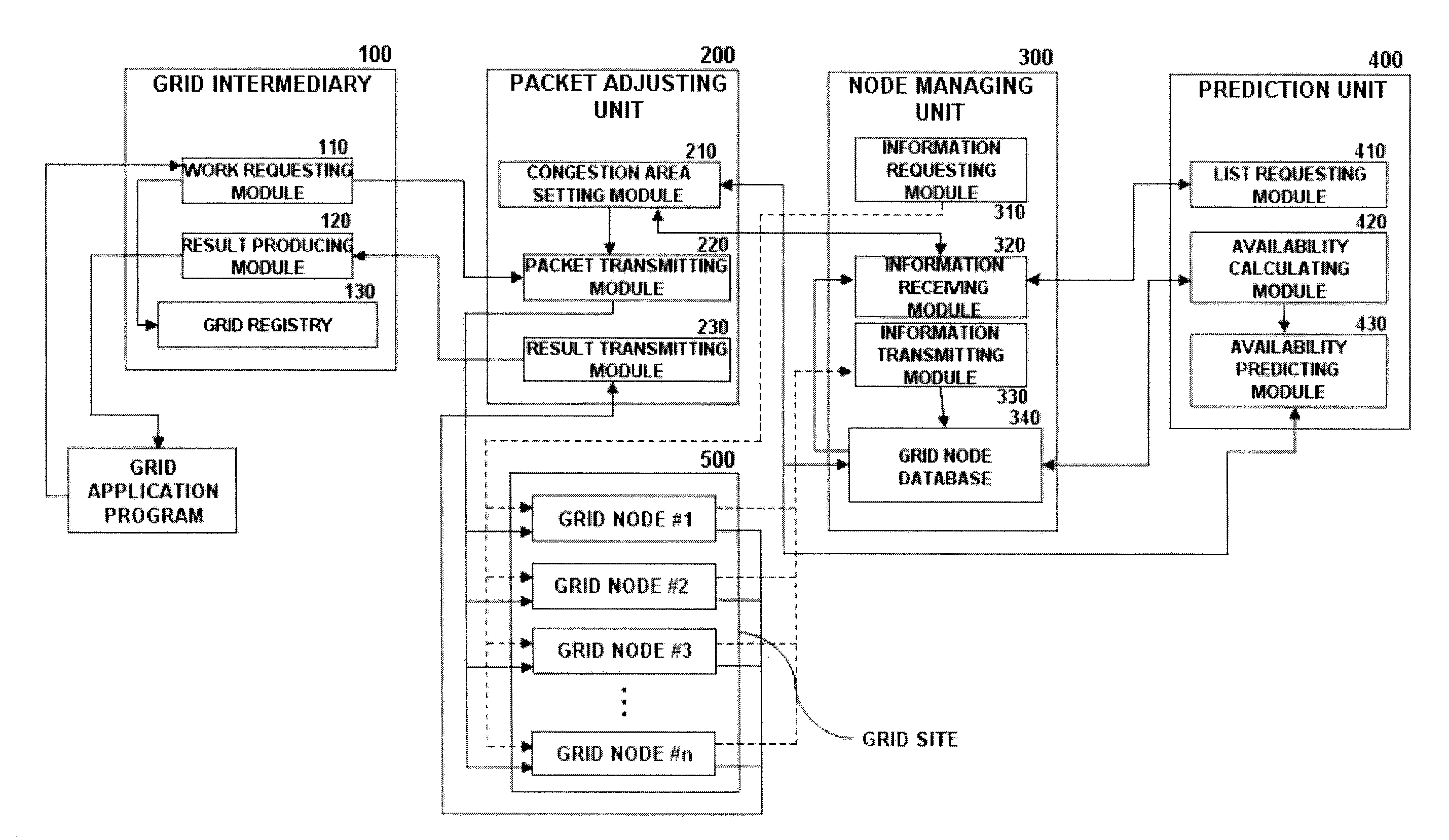
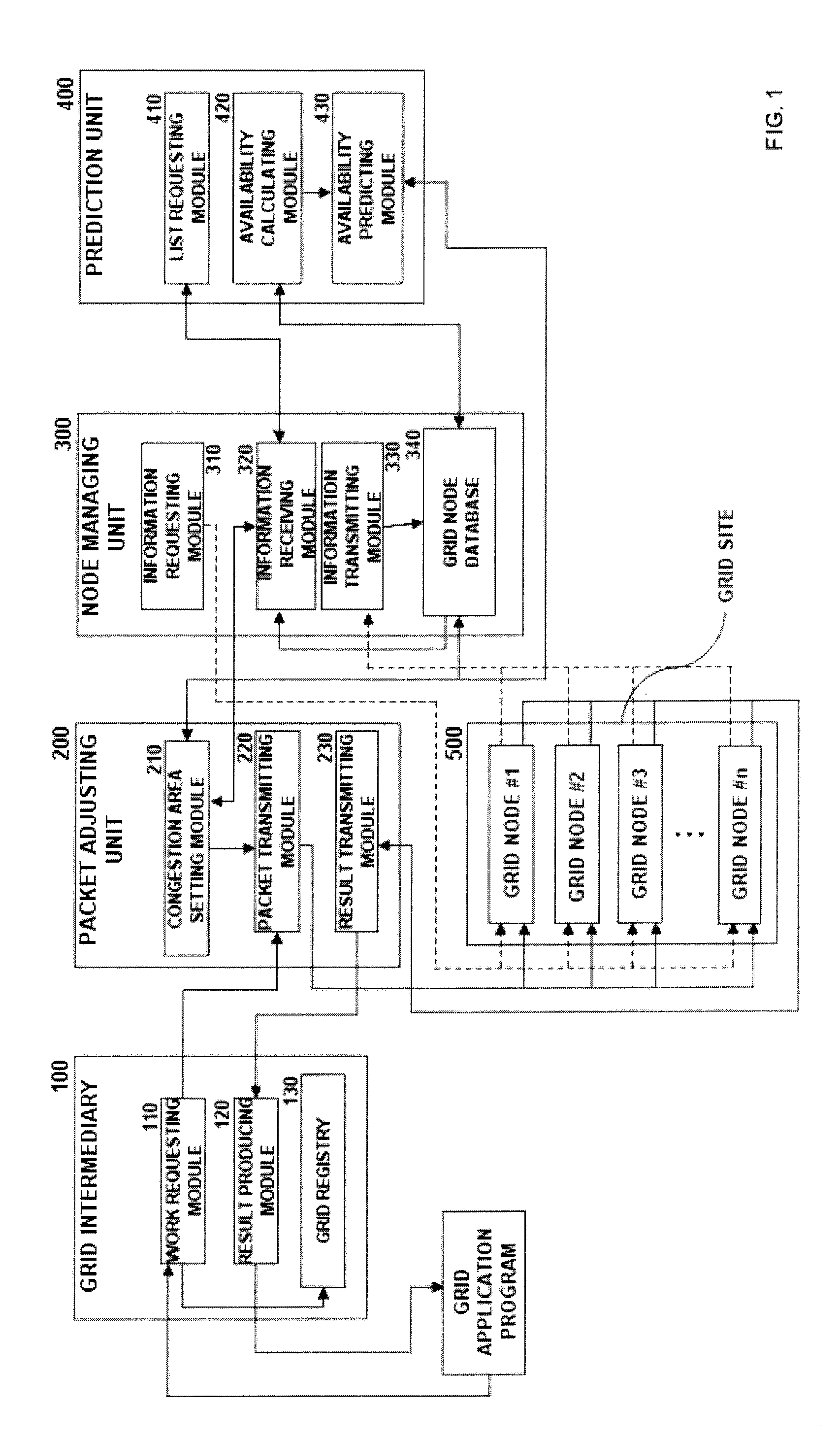
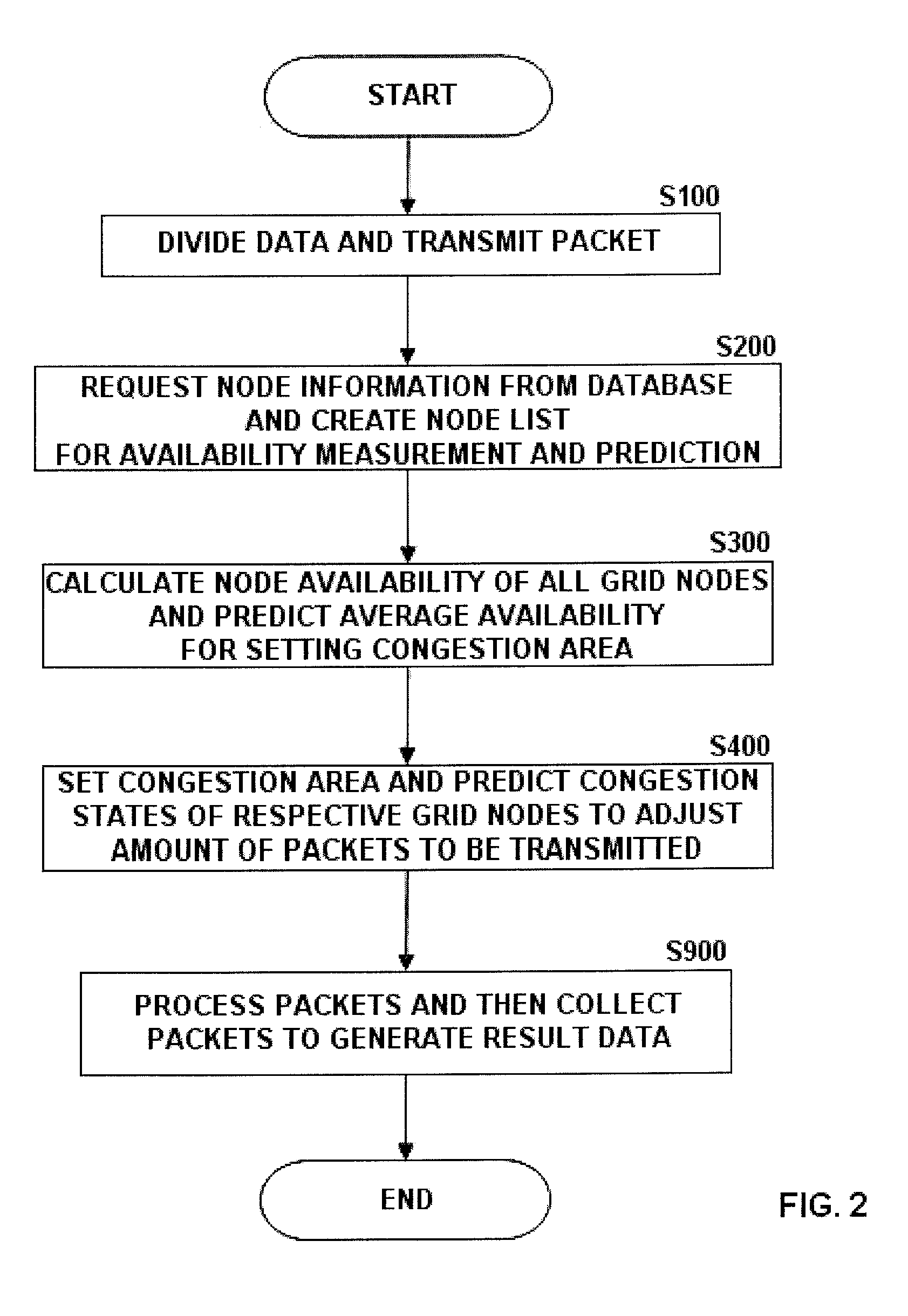
Node availability prediction-based grid network congestion control device and method therefor
InactiveUS20080298240A1High bandwidthHigh network delayError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of servicePacket loss
A system and method are disclosed, which controls congestion to efficiently transmit data through a network of grid node network in a grid computing environment where a large amount of data is processed. The system and method are performed in such a way that, according to a grid application program's request for distributed processing a large amount of data, the data is divided into packets, the node availability of respective nodes distributed in the grid network is measured with consideration to the bandwidth and the queue size of available grid nodes to avoid and control network congestion that may occur when the packets are processed by distributed processing using the respective nodes, the average node availability of all nodes is predicted using a statistical method, a threshold is calculated based on the predicted average node availability to set a dynamic congestion area representing the congestion level of the respective nodes, and the amount of packet transmission is controlled based on the congestion area. As the grid nodes are managed by controlling congestion, packet loss and packet delay are reduced and the rate of packet processing and the rate of node use are increased. Therefore, data can be stably transmitted to the grid user through the network with an improvement in the Quality of Service (QoS).
Owner:IND COLLABORATION FOUND OF INHA UNIV
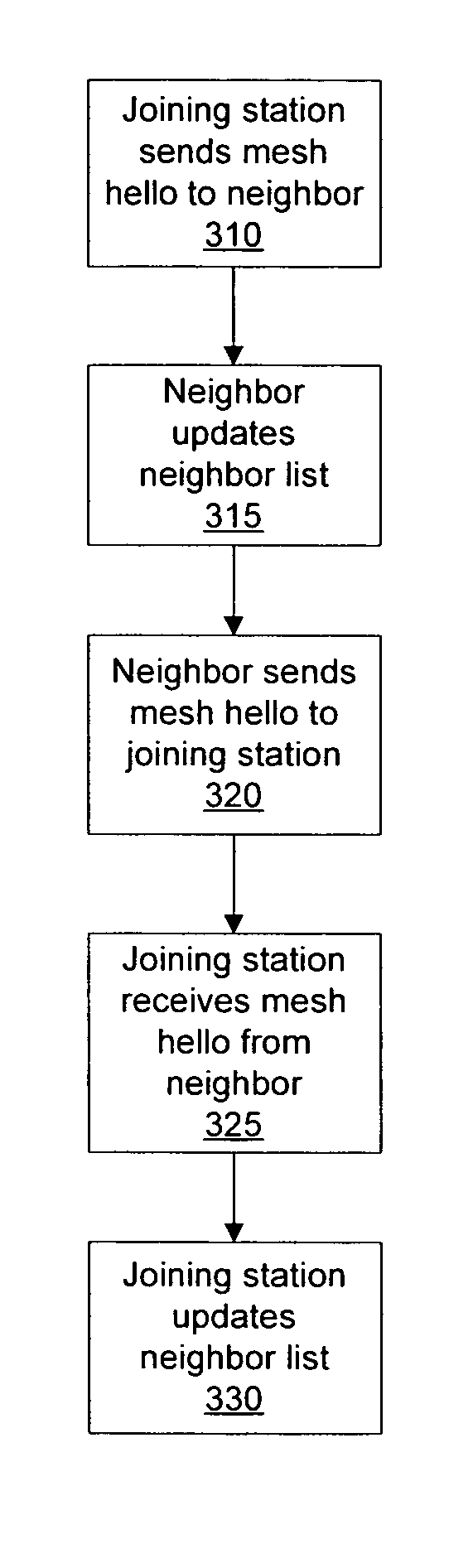
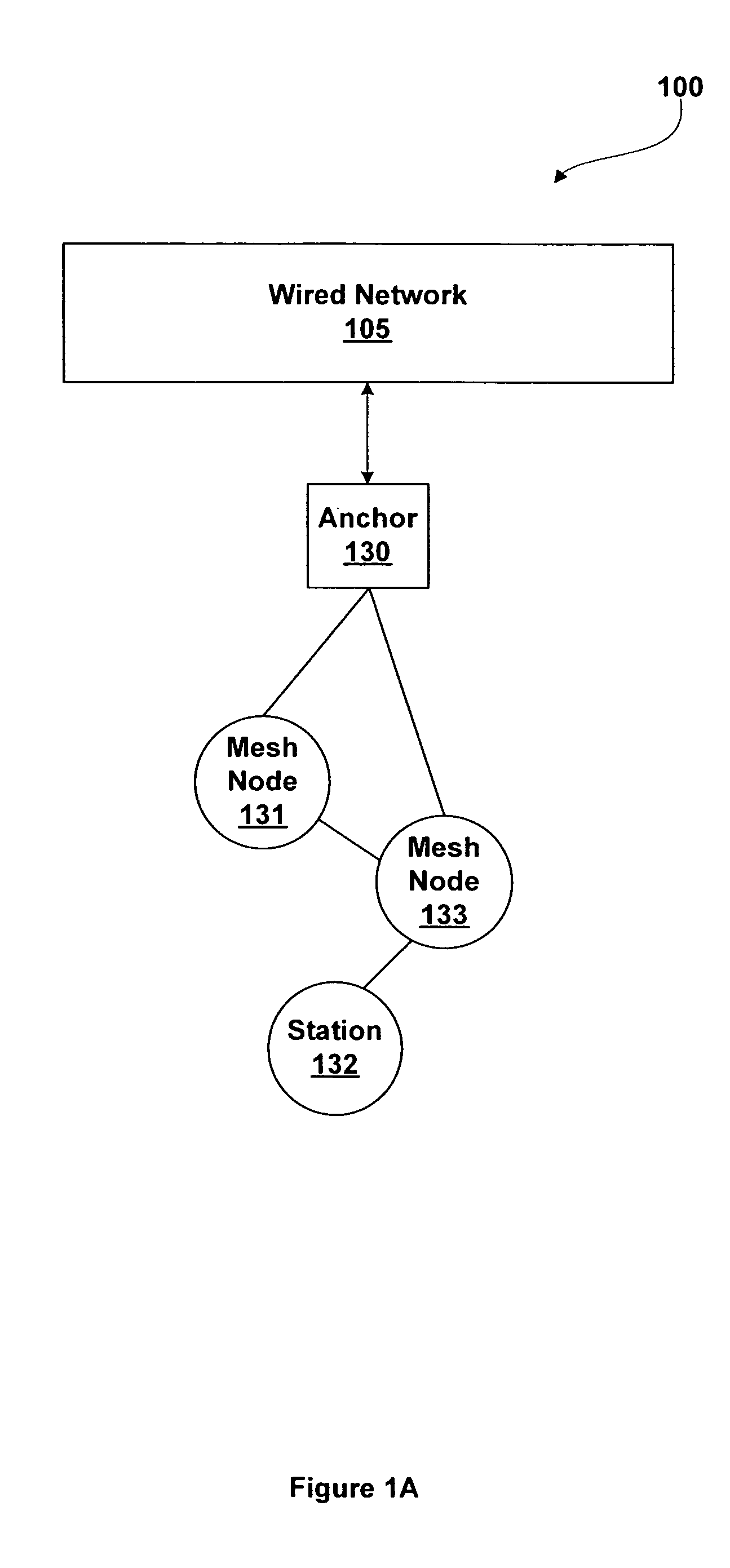
Persistent Mesh for Isolated Mobile and Temporal Networking
ActiveUS20100177703A1Maintain structureStay connectedNetwork topologiesWireless commuication servicesWireless mesh networkIp address
A structured wireless mesh network is disclosed where a tree-like connection topology is formed. In one embodiment, each node has separate uplink and downlink radios operating on different channels. When a cluster of such nodes becomes isolated as in the case of a mobile mesh application, a node in the cluster according to this invention acts as a root node thus enabling the tree structure to persist, even in isolation. Example methods of joining sub networks are disclosed that guide the joining of mesh networks and channel management. Nodes that may operate in isolation also support a distributed DHCP capability such that IP addresses are assigned to clients even when a connection to a central DHCP server is unavailable.
Owner:DYNAMIC MESH NETWORKS
Method for designing ultralow-power wireless data transmission network
ActiveCN105792305AReduce power consumptionImprove work efficiencyPower managementTransmission systemsGrid networkWireless data transmission
The invention discloses a method for designing an ultralow-power wireless data transmission network. The method comprises the following steps of designing the data transmission network; establishing low-power communication; designing route communication; carrying out node registration; and automatically maintaining a network fault. The designed grid network has self-adaptive and automatic intelligent negotiation networking capability of each node, the network can compute an optimal route automatically and bypass the fault nodes of the individual nodes automatically. In the whole system, all nodes can work in a low-power mode of intermittent power supply, and a centralizer can be in a low-power mode or a normal power mode. The whole network supports bidirectional communication between the centralizer and the nodes, the nodes can transmit the meter reading data to the centralizer, and the centralizer can issue the control information to the appointed nodes, so that the working efficiency is higher.
Owner:长春思拓电子科技有限责任公司 +1
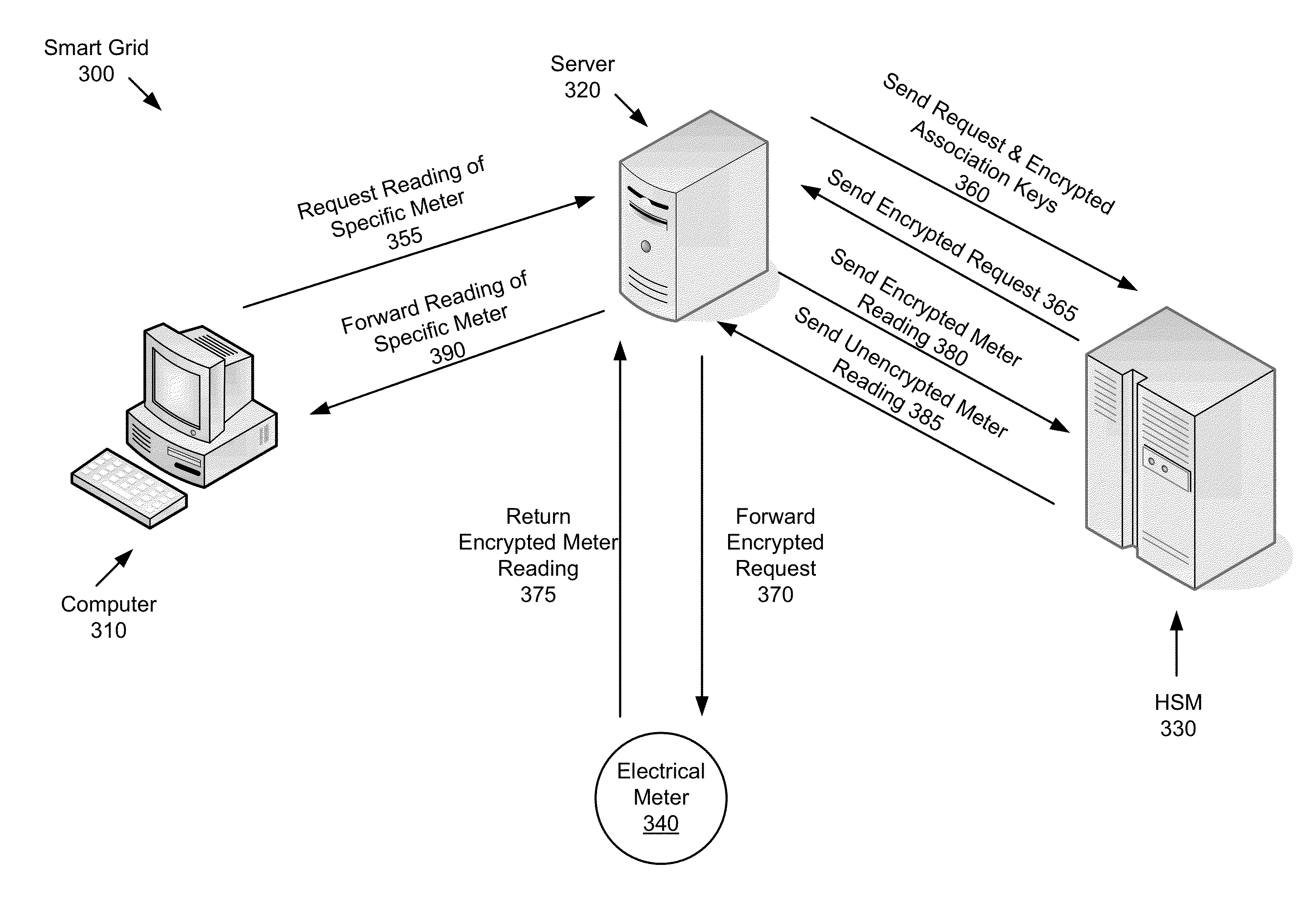
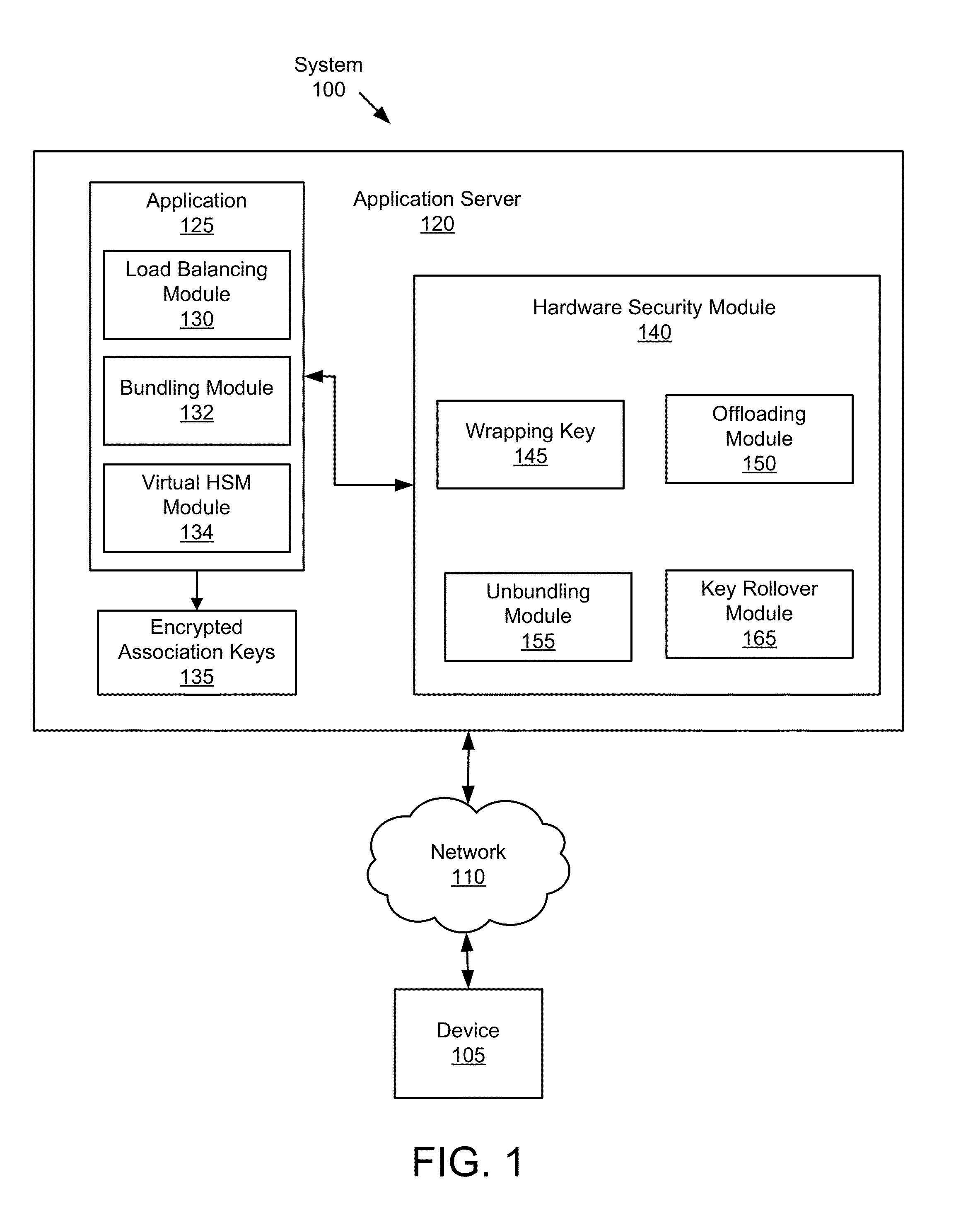
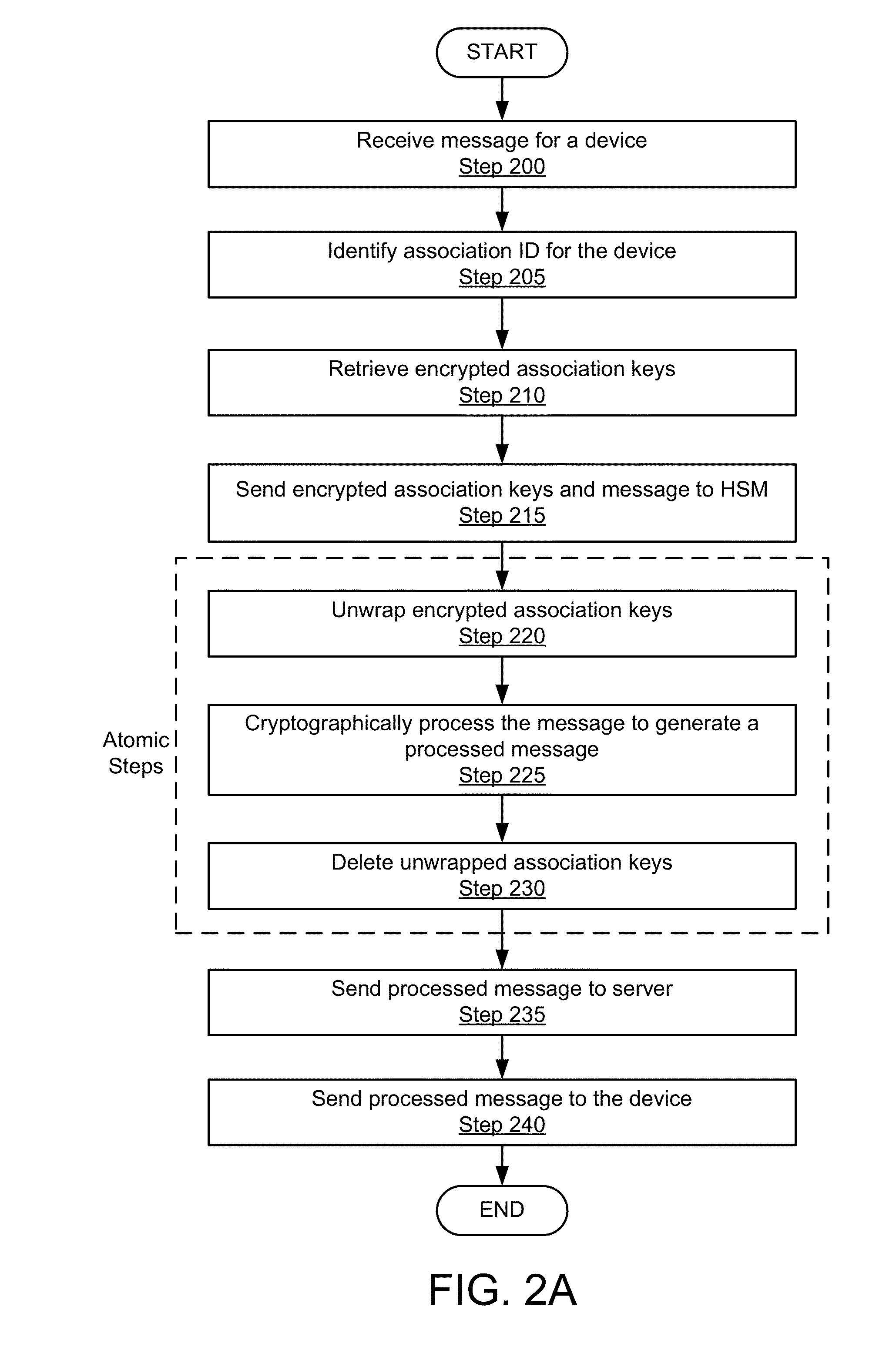
System and method for enabling a scalable public-key infrastructure on a smart grid network
ActiveUS20140281483A1Remote meteringInformation technology support systemComputer hardwareHardware security module
A method for enabling a scalable public-key infrastructure (PKI) comprises invoking a process of receiving a message for a device, identifying an association ID for the device, retrieving encrypted association keys stored on the server for communicating with the device, the encrypted association keys encrypted using a wrapping key stored on a Hardware Security Module (HSM). The method further comprises sending the message and the encrypted association keys to the HSM, unwrapping, by the HSM, the encrypted association keys to create unwrapped association keys, cryptographically processing the message to generate a processed message, deleting the unwrapped association keys, sending the processed message to the device, and invoking, concurrently and by a second application, the process.
Owner:SILVER SPRING NETWORKS
Multi-dimensional lattice network
InactiveUS6853635B1Increase the number ofImprove transmission performanceData switching by path configurationMultiple digital computer combinationsRouting tableGrid network
Owner:ROCKSTAR CONSORTIUM INC
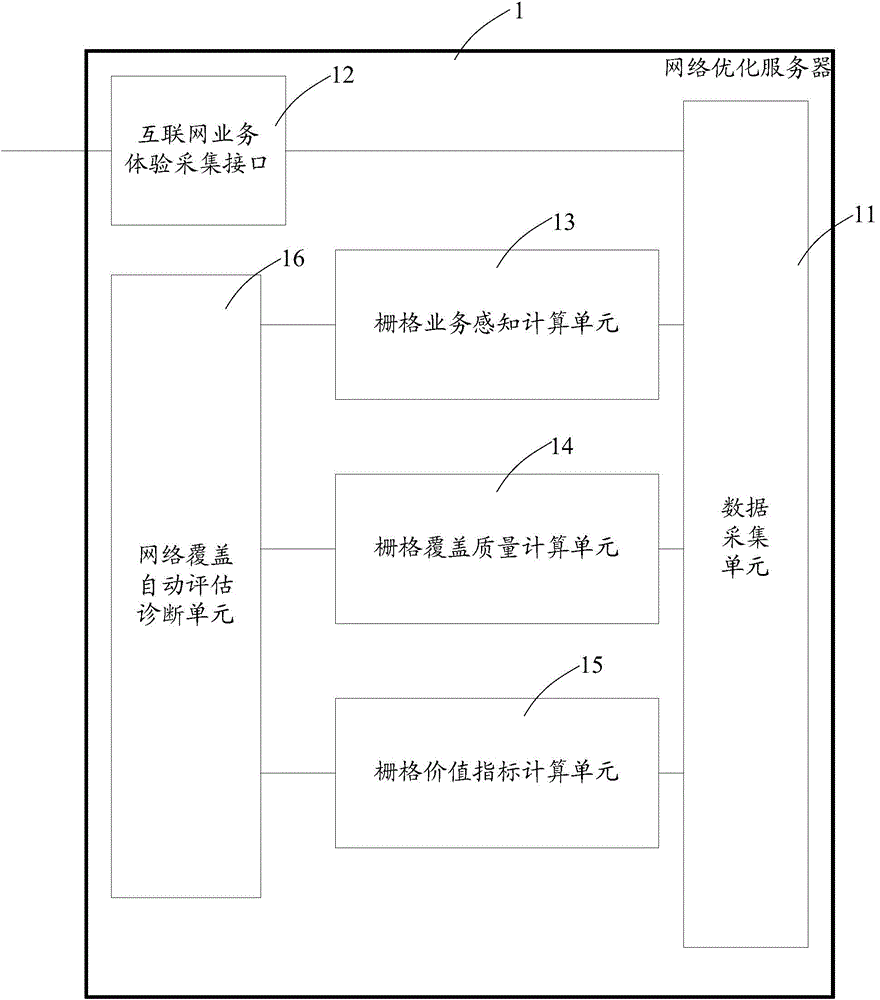
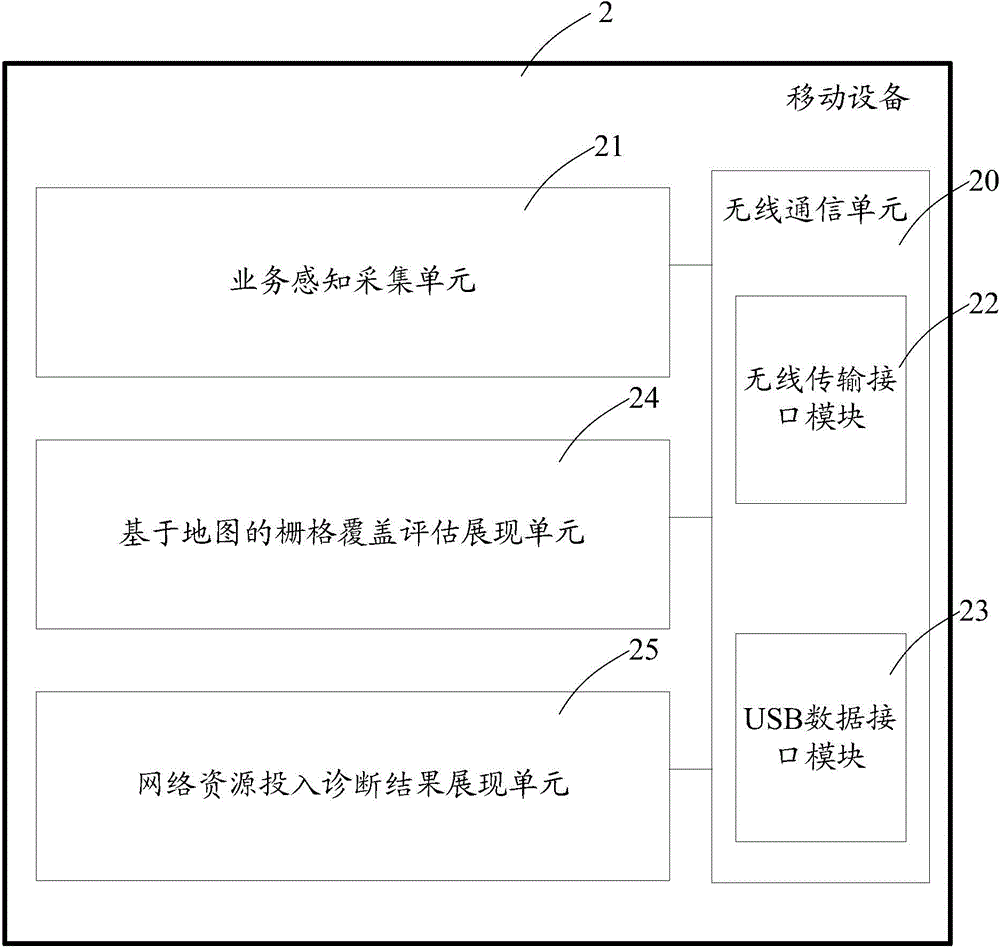
Network optimization server, mobile device of realizing network optimization and system of realizing network optimization
The embodiment of the present invention provides a network optimization server, a mobile device of realizing network optimization and a system of realizing network optimization. The network optimization server comprises a data acquisition unit used for obtaining and storing the business perception data, the network performance data and the business usage data; a grid business perception calculating unit for calculating the comprehensive business perception scores of the different grids based on the business perception data and according to a corresponding relation of a base station and the grids; a grid coverage quality calculating unit for calculating the comprehensive quality index scores of the different grids according to the corresponding relation of the base station and the grids; a grid value index calculating unit for calculating the comprehensive value indexes of the different grids according to the corresponding relation of the base station and the grids; a network coverage automatic assessment and diagnosis unit for determining a network resource investment comprehensive evaluation score of the grid network coverage optimization by the comprehensive business perception scores, the comprehensive quality index scores and the comprehensive value indexes of the grids, and by utilizing an expert system rule engine, and matching a corresponding optimization diagnosis suggestion. According to the present invention, the optimization diagnosis suggestion is formed automatically.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP ZHEJIANG
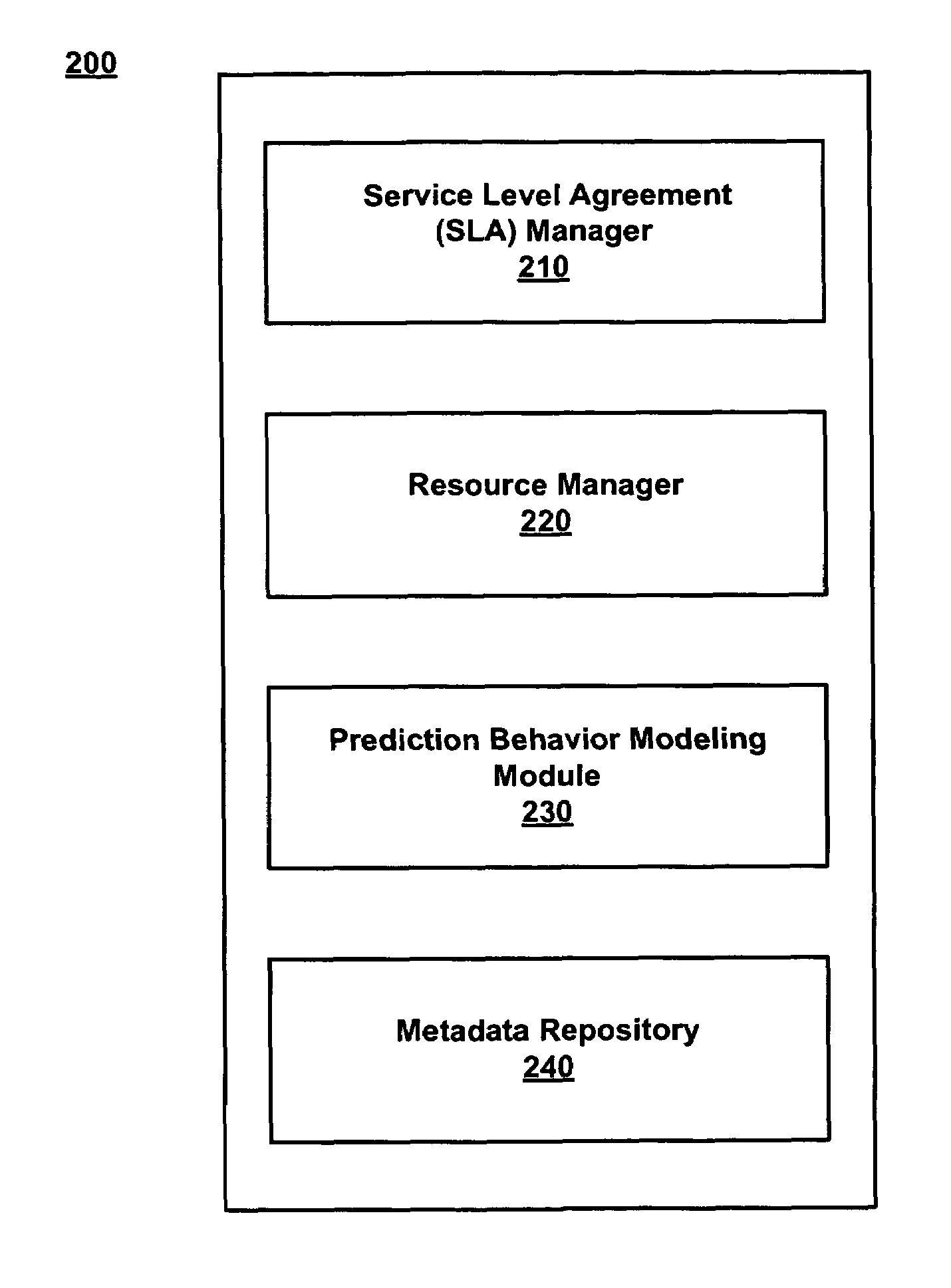
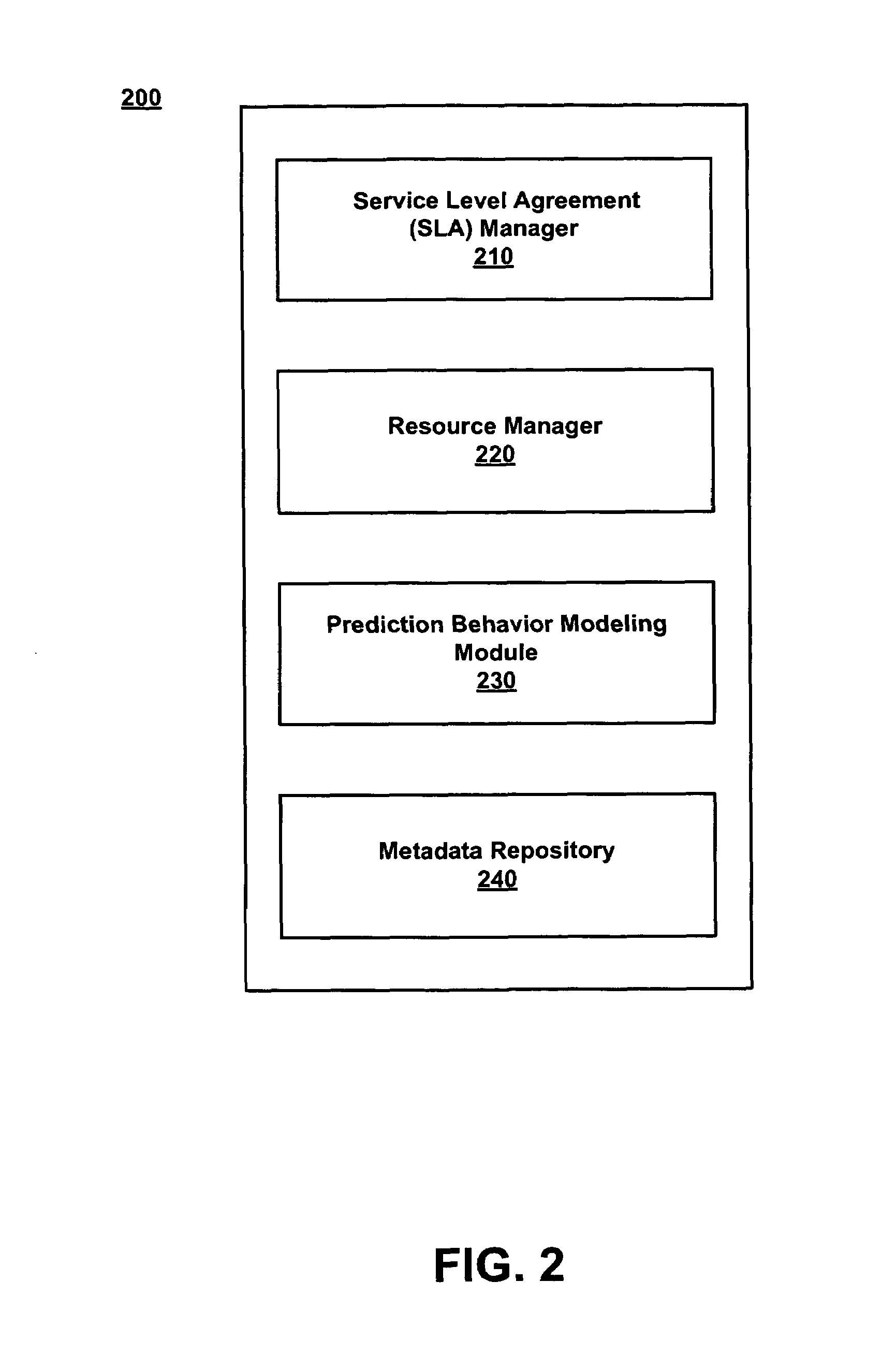
Grid network management via automatic trend analysis of a service level agreement
ActiveUS7672923B1Digital computer detailsKnowledge representationService-level agreementService level requirement
A method for managing a GRID network. The method includes performing trend analysis of a job type repeatedly processed by the GRID network to anticipate a future load on the GRID network associated with the job type. The job type is associated with a service level agreement (SLA). At least one internal performance metric of the GRID network is measured to monitor current GRID network status. The future load that is anticipated is compared with the at least one performance metric to predict future satisfaction of the SLA.
Owner:VALTRUS INNOVATIONS LTD +1
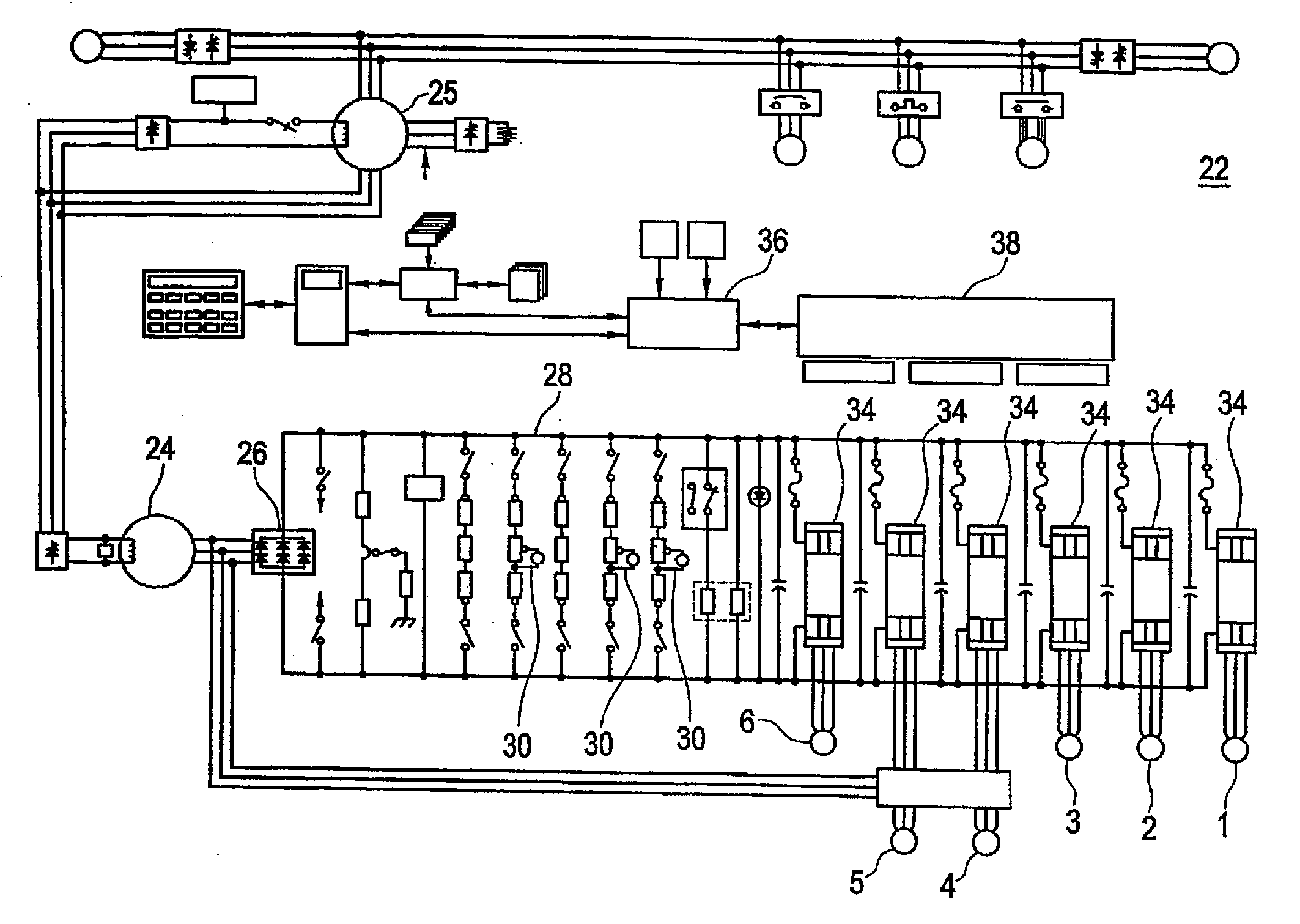
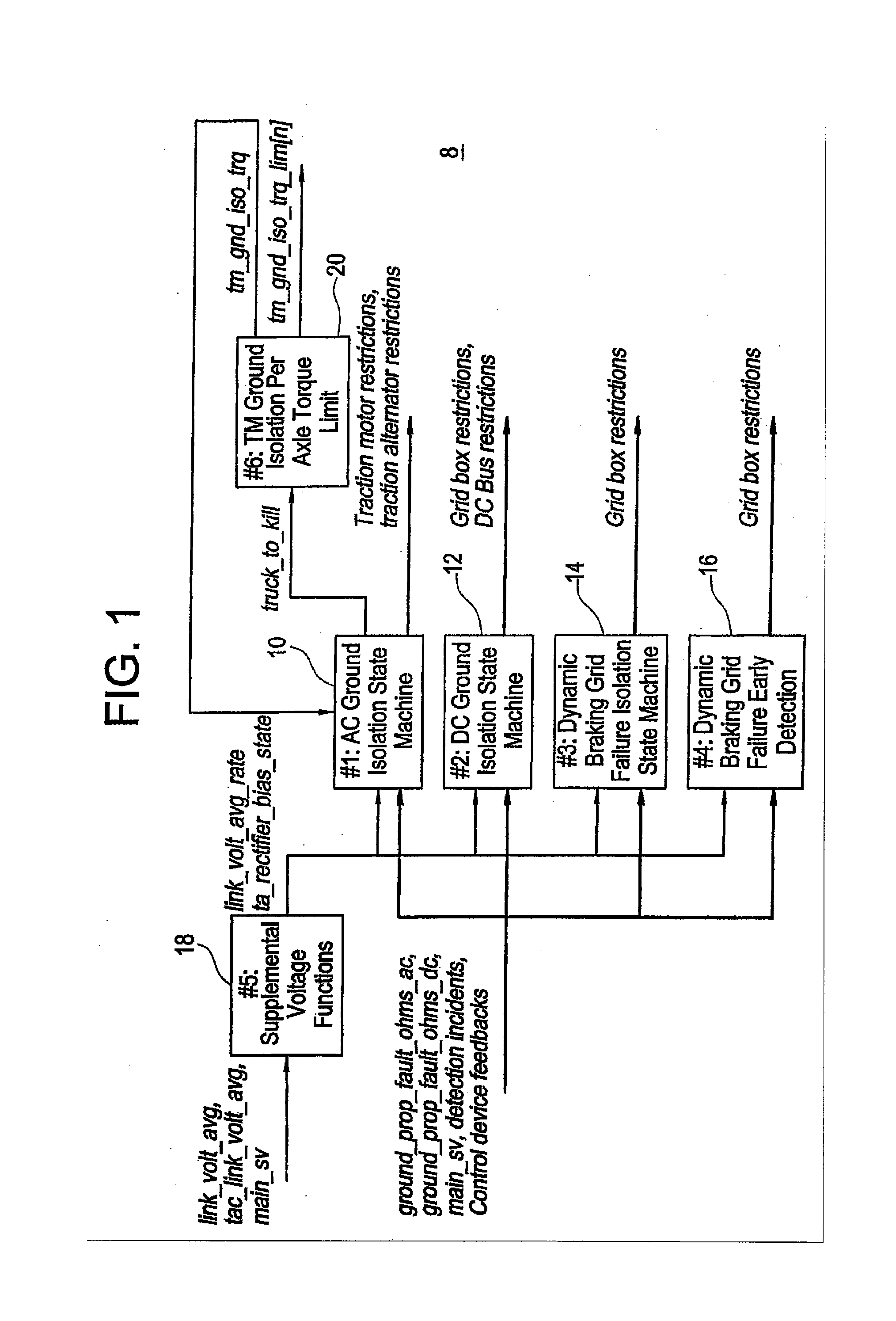
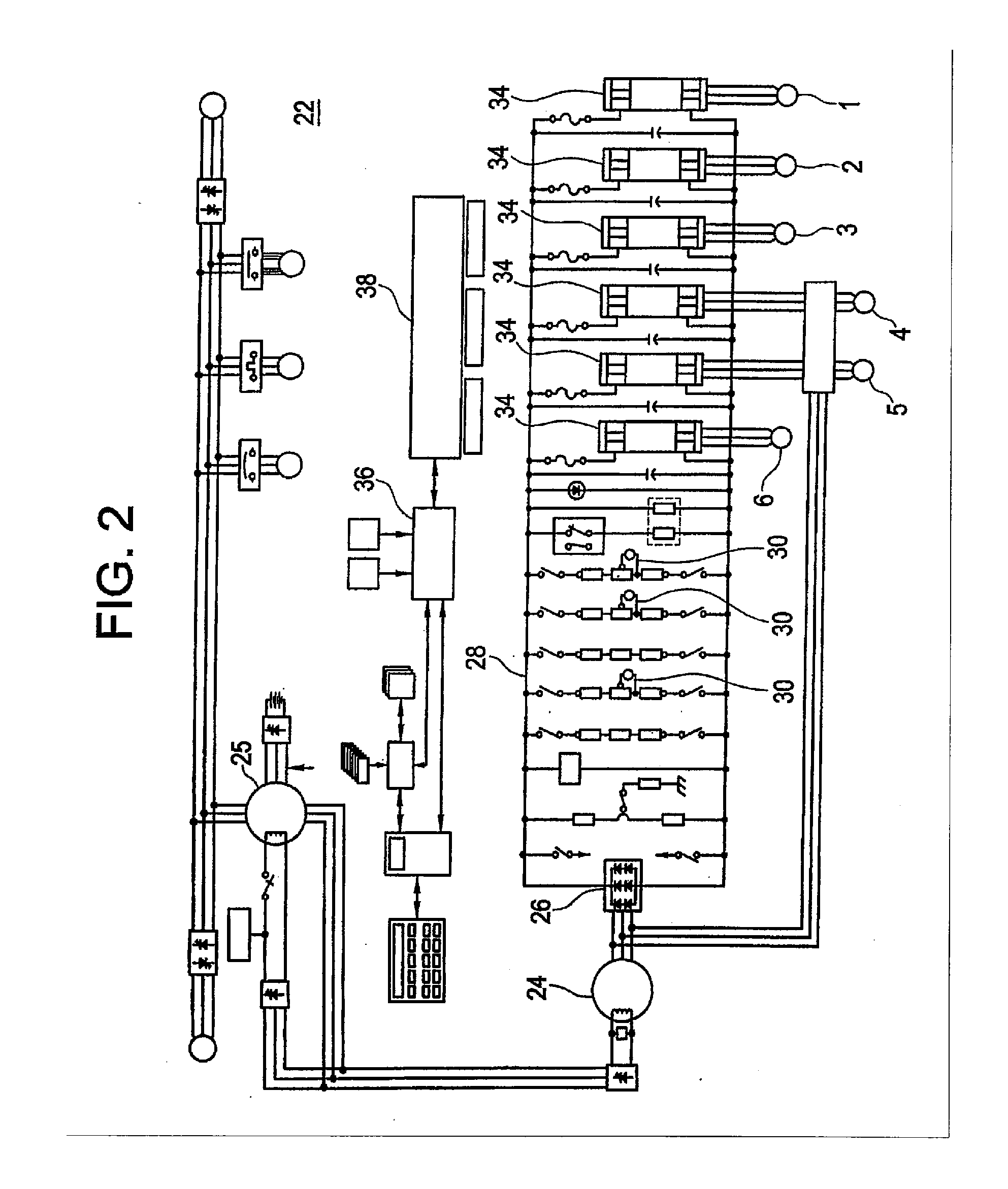
Method, System, and Computer Software Code for Detection and Isolation of Electrical Ground Failure and Secondary Failure
In an off-road vehicle having a resistor grid network and a blower system as part of a braking system operable to determine at least one of a resistor failure and a blower failure, the system including a first series of resistors connected in series, a second series of resistors connected in series, a blower cross to at least one of the first series of resistors and the second series of resistors, a sensor proximate at least one of the first series of resistors, the second series of resistors, and the blower, wherein each individual resistor in the first series connected in parallel to an individual resistor in the second series, and wherein when at least one of a current value, blower speed, and voltage value changes, the grid network is disconnected.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
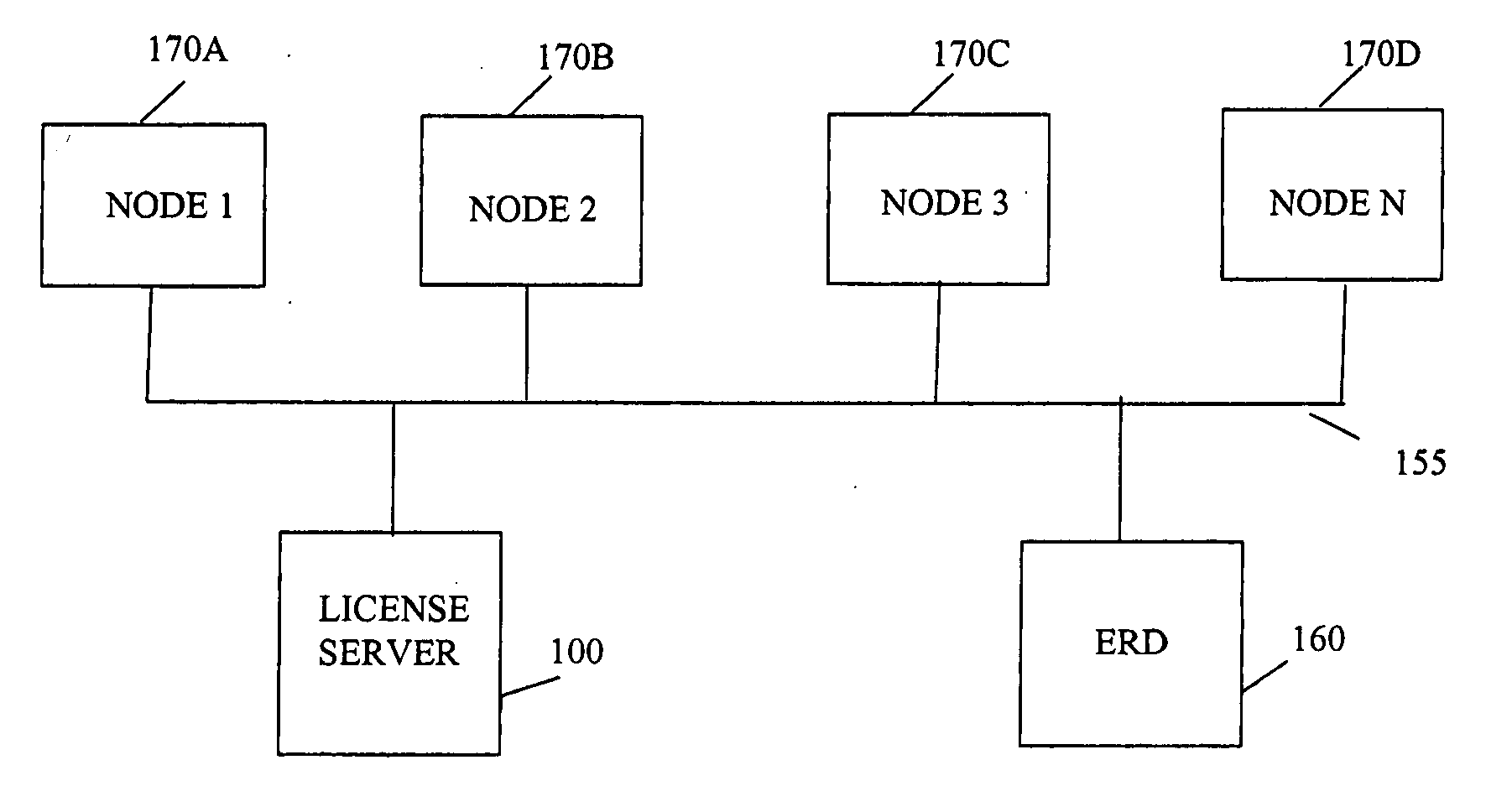
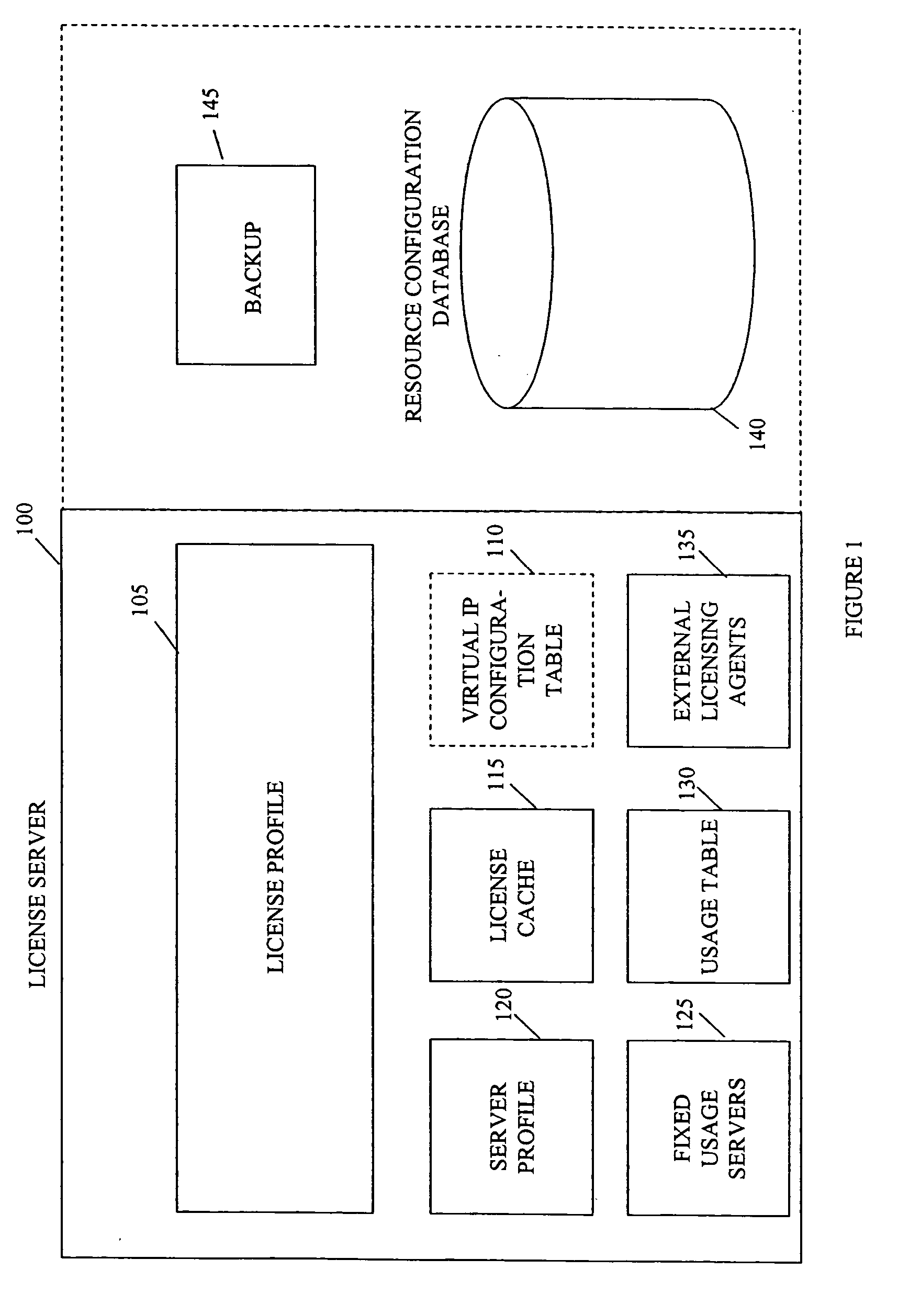
Grid licensing server and fault tolerant grid system and method of use
ActiveUS20060282519A1Short response timeResource allocationDigital computer detailsCapacity provisioningGrid network
A system and method for managing licensed and non-licensed resources in a grid network is provided. A license server receives and processes requests for a license and determines whether a license is available and, if necessary, causes a new configuration to be created on a server for satisfying the request. A new grid node may also be created and configured to be added to the grid for creating additional capacity for grid processing. The configuration may be performed at a time prior to an actual need by the grid, perhaps due to a faulted node, and quickly brought on-line with a simple configuration update. The new grid node may also have a virtual IP address reassigned to quickly redirect processing from the faulted node to the newly configured node. Also, an external resource dispatcher may add new resources such as storage or processing capacity to the grid and may coordinate the new resources with the license server.
Owner:KYNDRYL INC
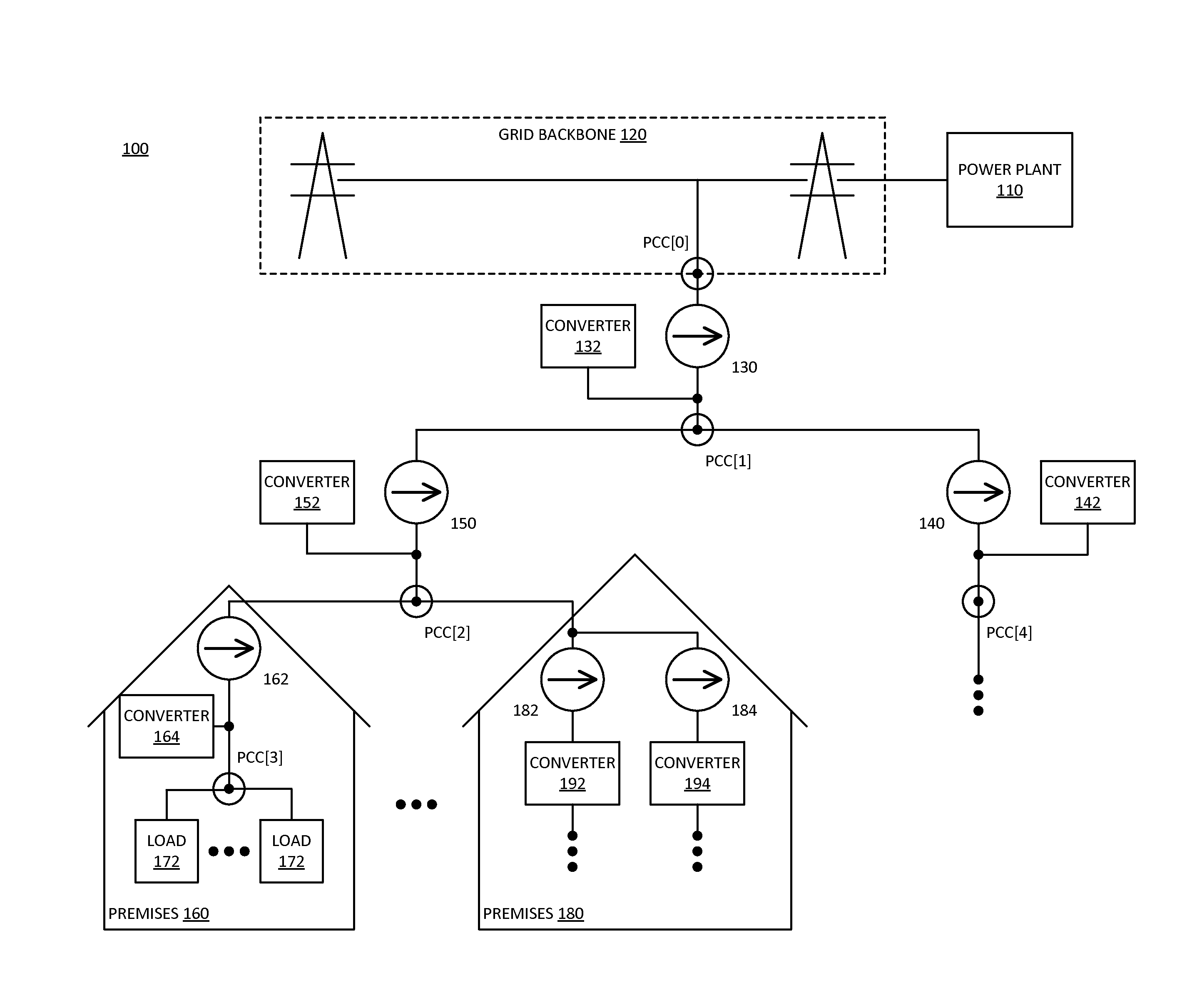
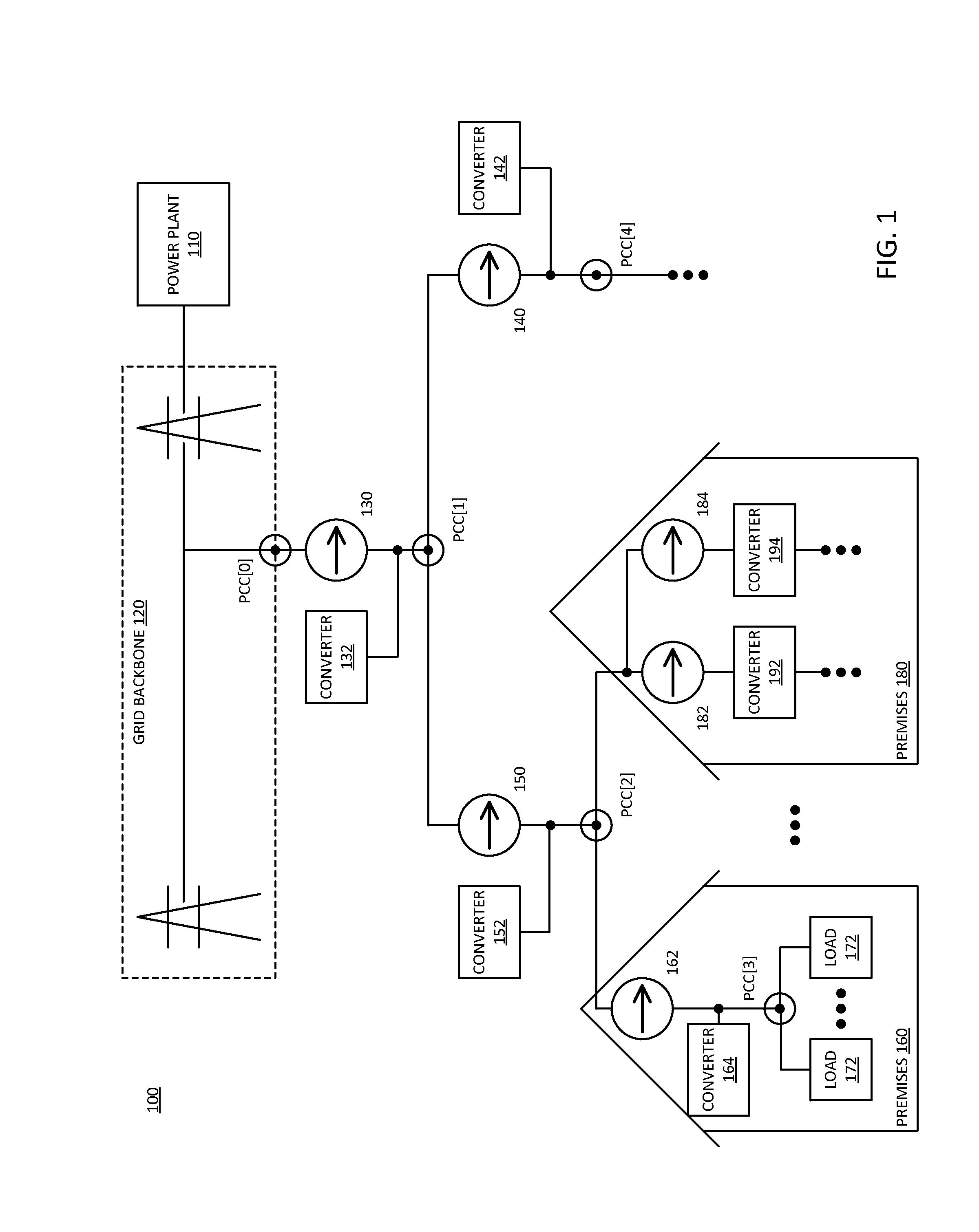
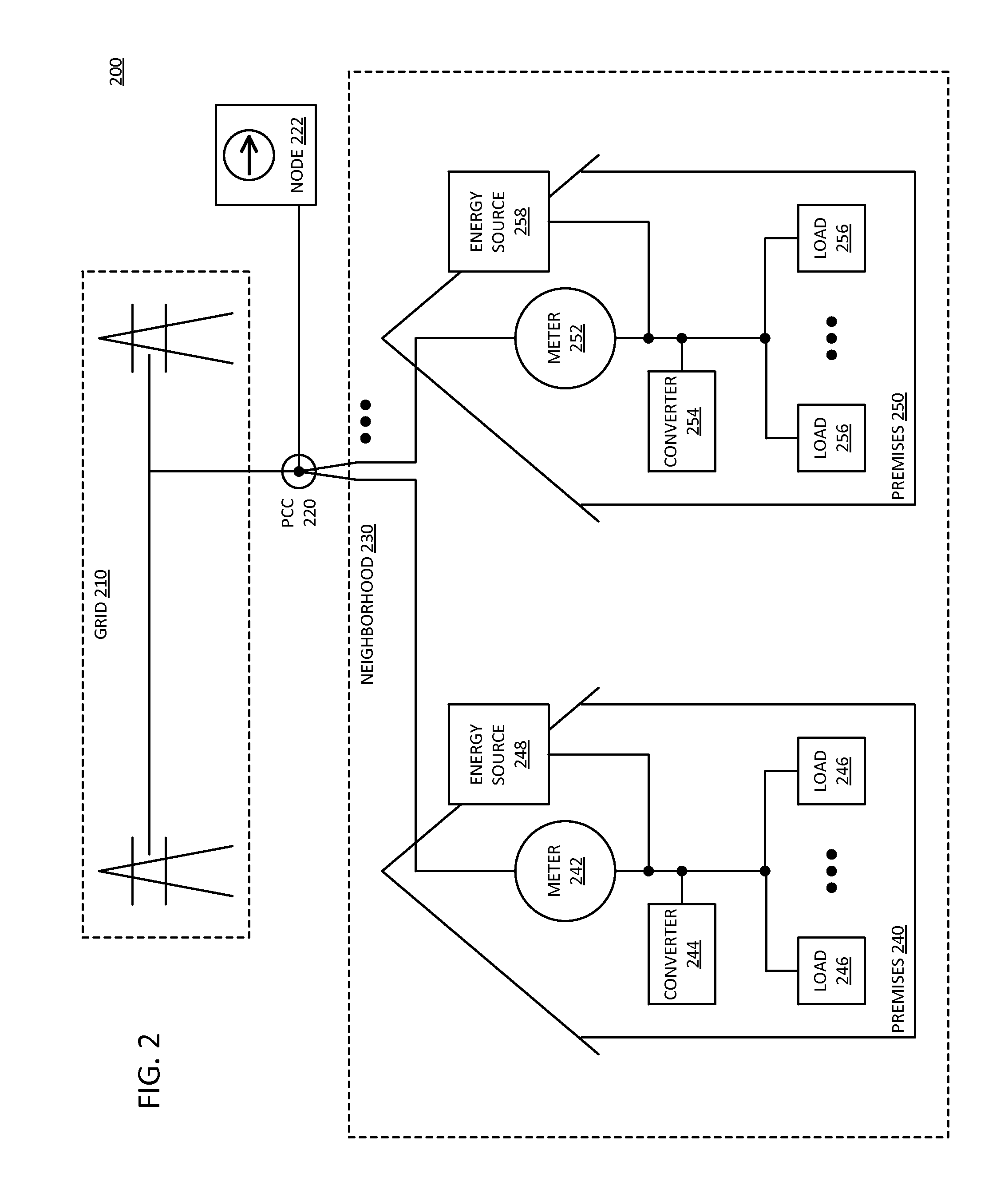
Local metering response to data aggregation in distributed grid node
Data aggregation enables a local control response at a consumer node of a distributed grid network. A consumer node includes a local energy meter. The meter receives multiple inputs indicating an electrical condition of the grid network and local operating conditions. The meter can aggregate the grid network and local operation conditions inputs with power demand for a local load coupled to the consumer side of the point of common coupling monitored by the energy meter. The energy meter calculates a mix of real and reactive power to output from a local energy source, based on the aggregated data. A local power converter outputs the calculated power from the local energy source.
Owner:XSLENT ENERGY TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com