Multiparty quantum privacy comparison method based on d-level cat state and d-level Bell state entanglement swapping
An entanglement exchange, quantum technology, applied in the field of quantum cryptography, which can solve the problem that semi-loyal TP cannot obtain secrets
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0167] 1. Application example of MQPC method
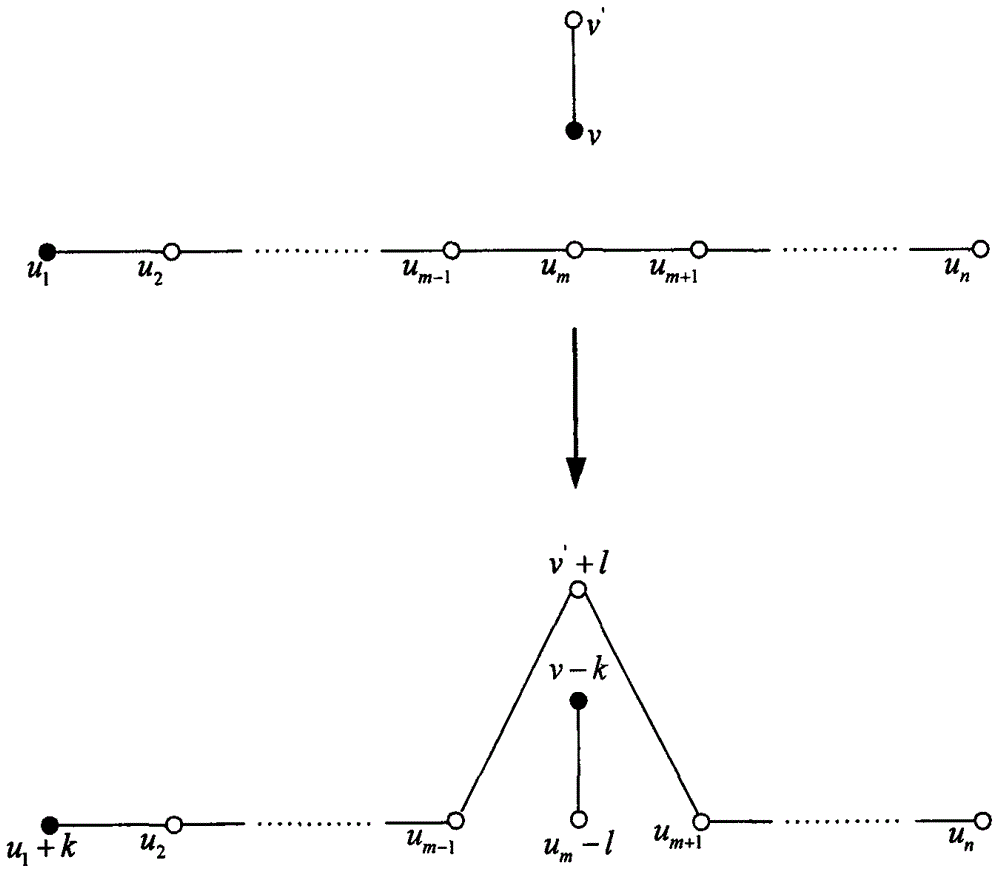
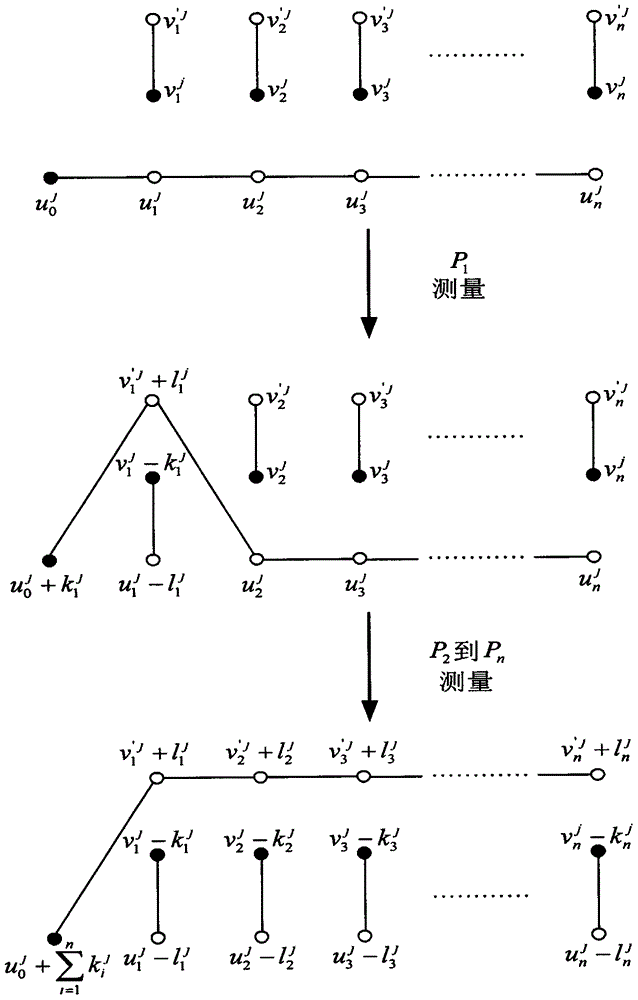
[0168] here with x i The first bit of (ie ) as an example to illustrate the method of the present invention. P i By applying to |Ψ(0,0)> produce to encode (which is ). Then, P i The label in the cat state is The particle and her Bell state are labeled as The particle imposes a d-level Bell state measurement. In this way, the label in the cat state is The particle and her Bell state are labeled as The particles exchange entanglement. at P 1 , P 2 ,...,P n After completing the measurement of the d-level Bell state, the first cat state sent back to the TP has a label TP calculation and from Subtract from to get that is if So if So These two situations mean modn=0. otherwise, mod n ≠ 0. In this way, it is completed from P 1 , P 2 ,...,P n The equality comparison of the 1st bit of the secret.
[0169] 2. Discussion
[0170] Since the wiretapping detection process can be considered...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com