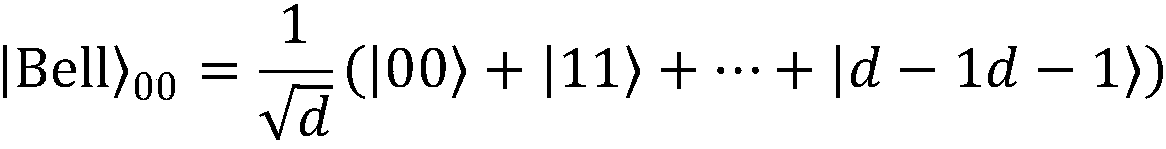Disordered high capacity multiparty quantum key agreement method based on high energy level bell state
A multi-party quantum and key agreement technology, applied in the field of disordered high-capacity multi-party quantum key agreement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
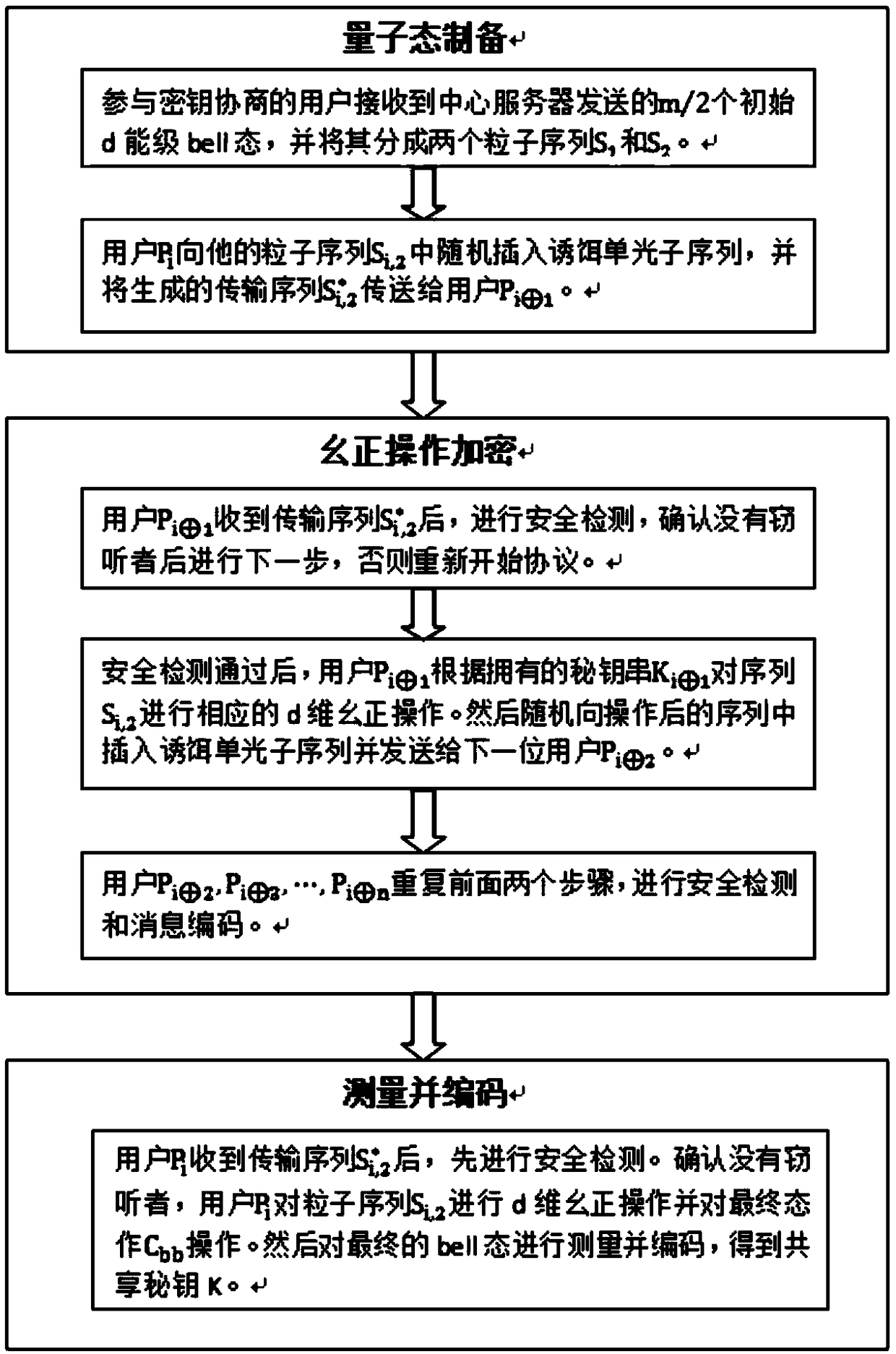
[0058] Such as figure 1 As shown, this embodiment is based on a disordered high-capacity multi-party quantum key agreement method based on a high-energy-level bell state. All users perform corresponding d-dimensional unitary operations on the transmission sequence, and finally the initial sender determines the system by quantum measurement. The final state, so as to encode the negotiated secret key K, the specific steps are as follows:
[0059] Suppose there are n users P i (i=1, 2...n) participate in the quantum key agreement, and they have all passed the identity authentication of the network center server in advance. Each user has a set of d-ary key sequence K with length m (m is a positive integer divisible by 2) i :
[0060] K 1 =(K 1,1 , K 1,2 …K 1,m )
[0061] K 2 =(K 2,1 , K 2,2 …K 2,m )
[0062] ...
[0063] K n =(K n,1 , K n,2 …K n,m )
[0064] Step 1: Every legitimate user participating in the key negotiation receives m / 2 initial d-level bell stat...
Embodiment 2
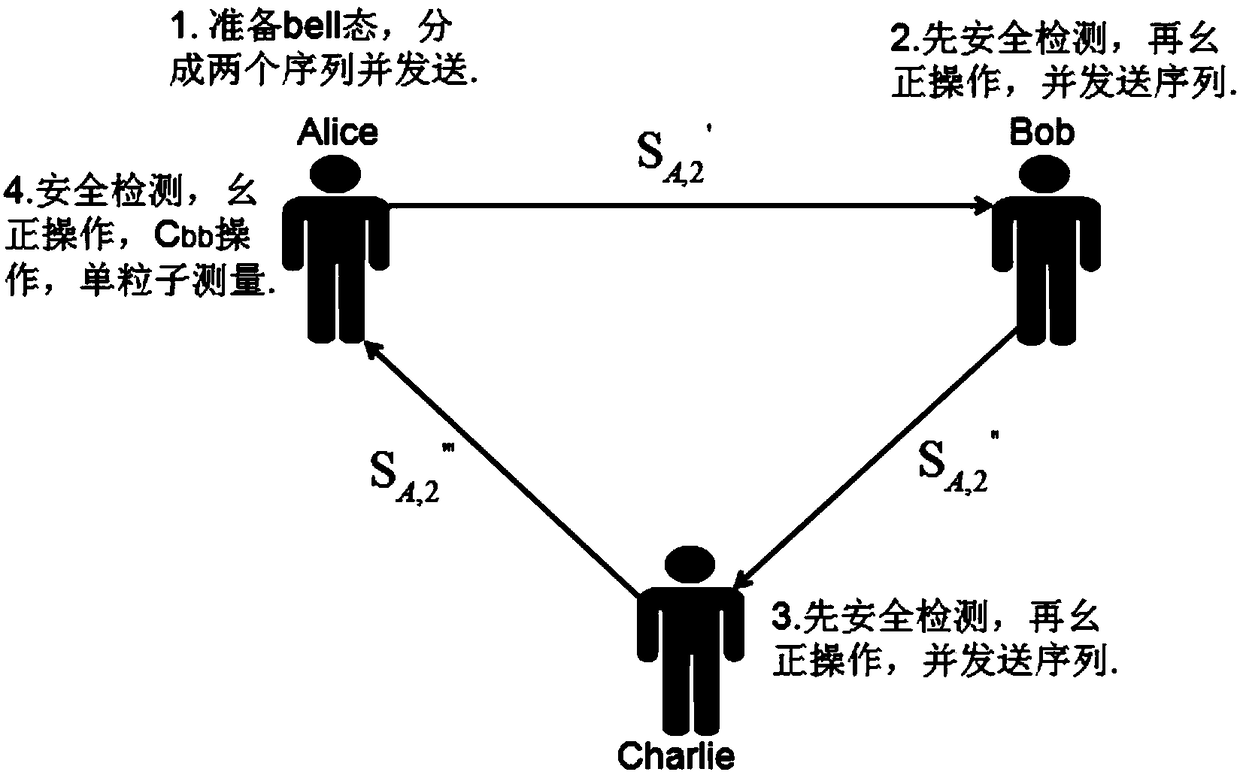
[0103] Such as figure 2 As shown, this embodiment is based on a disordered high-capacity multi-party quantum key agreement method based on a high-energy-level bell state. Taking a three-party particle key agreement method based on a three-energy-level bell state as an example, it includes:
[0104] Step 1: Assume that there are three users Alice, Bob and Charlie participating in the key negotiation. They have all passed the identity authentication of the network center server in advance, and each user has a set of 9-ary key sequences with a length of 2: K A =(12), K B =(69),K C =(23). In order to be consistent with the dimension of the bell state, the user needs to preprocess the key sequence first, according to the formula:
[0105]
[0106] The user can convert the key sequence into a 3-ary key sequence of 4: K A =(0102),K B =(2120),K C =(0212). After the preprocessing, Alice, Bob, and Charlie all received the two initial 3-level bell states sent by the network ce...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com