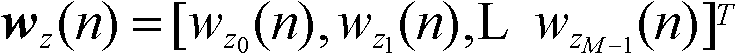Patents
Literature
154 results about "Cross correlation matrix" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
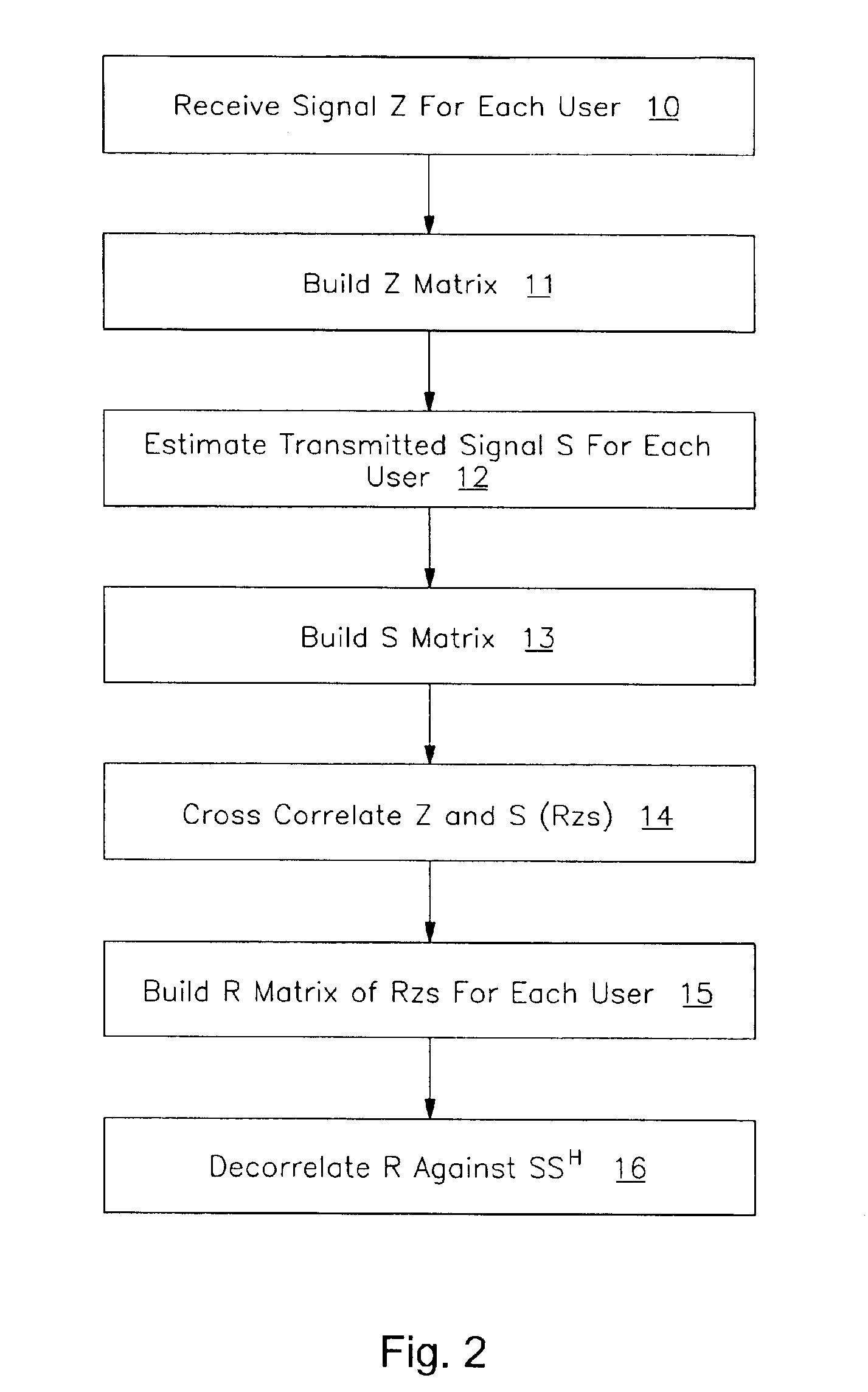
Method for determining similarities between data sequences using cross-correlation matrices and deformation functions
InactiveUS20050102107A1Character and pattern recognitionBiological testingCross correlation matrixMinimum cost path
A method compares a first data sequence with a second data sequence. A cross-correlation matrix of distances between all possible pairs of values of the first and second data sequences is constructed. A minimum cost path between diagonally opposing corners of the cross-correlation matrix is determined. The minimum cost path is projected onto a transfer function that maps between the first data sequence and the second data sequence. Then, the minimum cost path is projected onto a deformation function that corresponds to a similarity between the first data sequence and the second data sequence.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Method for self-correction of array error of multi-input multi-output radar system
ActiveCN101251597AHigh Target Angle Estimation AccuracyEffective correctionRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMulti inputRadar systems
The invention discloses a self-correction method of a multi-input multi-output radar system array error, relating to the radar technical field. The method aims to carry out self correction of the reliant amplitude and phase error of a receiving array azimuth on the premise that the transmitting array of a multi-input multi-output radar system. The implementation process of the method is as follows: firstly, by means of the two corrected transmitting array elements of the multi-input multi-output radar system, orthogonal signals are transmitted; then, the echo signals of the transmitting array elements are separated by means of the orthogonality of transmitting signal through adopting a matched filtering method; an auto correlation matrix and a cross correlation matrix are established by means of the echo signals; a real guide vector and a target angle of an array are estimated by means of a rotary invariant subspace method; finally, by means of the real guide vector and the target angle of the array obtained through estimation, the array azimuth reliant amplitude and phase error can be corrected. The self-correction method can be used in the array error correction field of a multichannel radar system.
Owner:XIAN CETC XIDIAN UNIV RADAR TECH COLLABORATIVE INNOVATION INST CO LTD
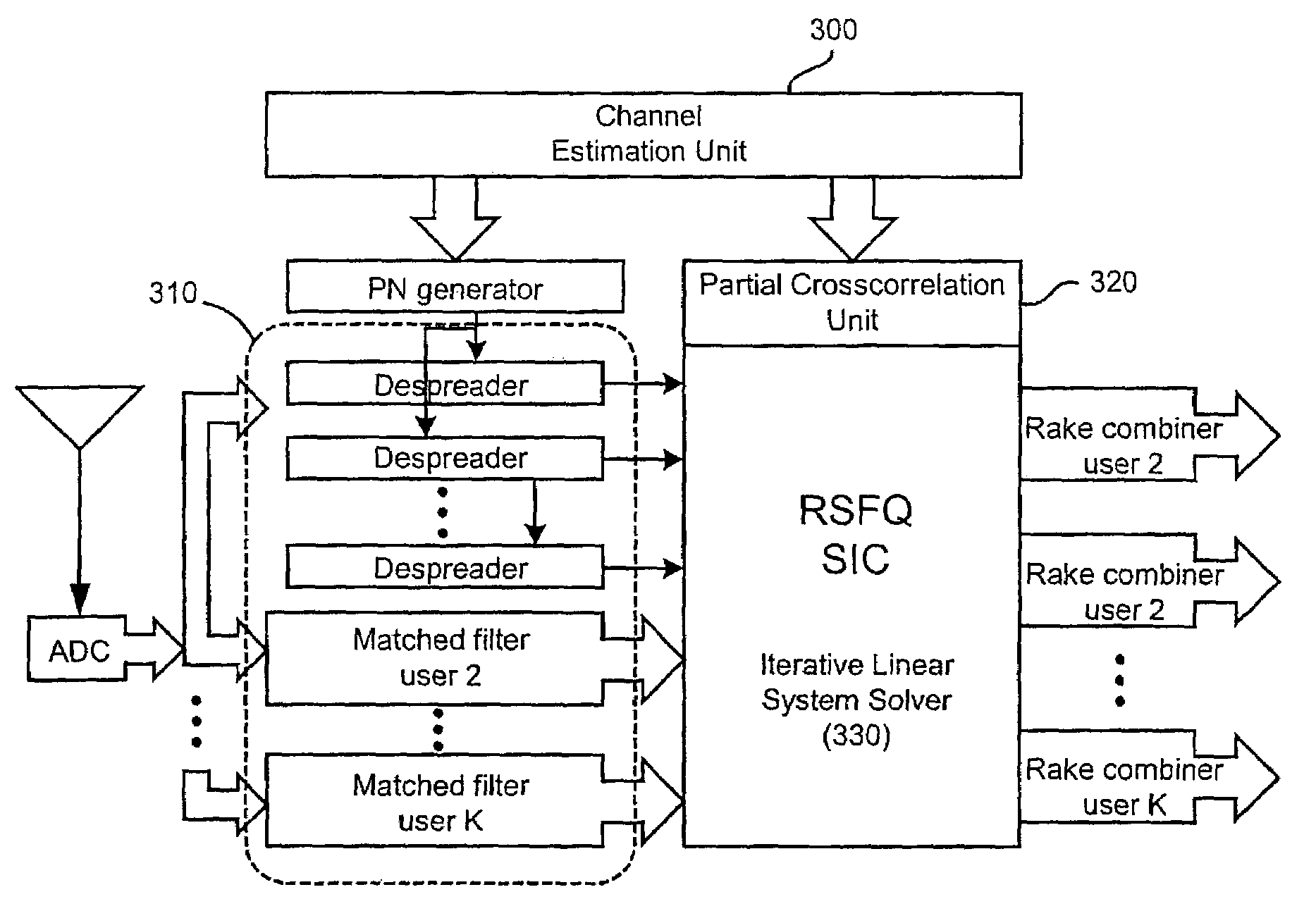
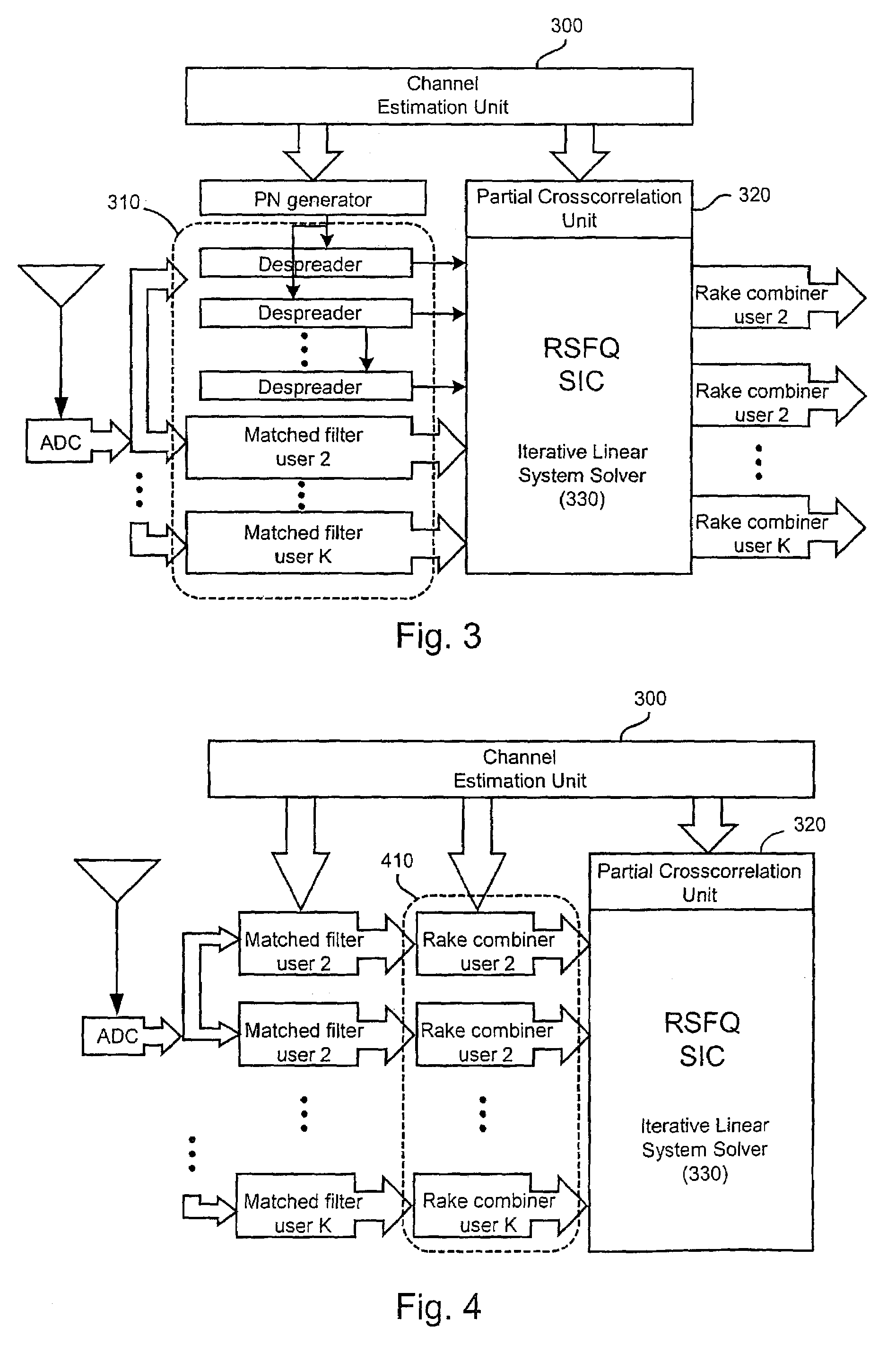
Method and apparatus for multi-user detection using RSFQ successive interference cancellation in CDMA wireless systems
InactiveUS7440490B2Reduce distractionsIncrease uplink capacityRadio transmissionInterference cancellerSystem capacity
A method and apparatus for using a multi-user detector for reducing multiple access interference (MAI) in a direct sequence CDMA wireless system such as W-CDMA. A superconducting rapid single flux quantum (RSFQ) RF digital receiver operating in combination with an RSFQ successive interference canceller (SIC) is located in the base stations of the wireless system. In the present invention, the RSFQ SIC is a vector machine capable of processing the cross-correlation matrices using an iterative method to decorrelate the user binary code sequences from the input signal in which the interference components are removed. According, the reduction in interference results in a significant increase in system capacity while improving cellular coverage area.
Owner:KIDIYAROVA SHEVCHENKO ANNA +2
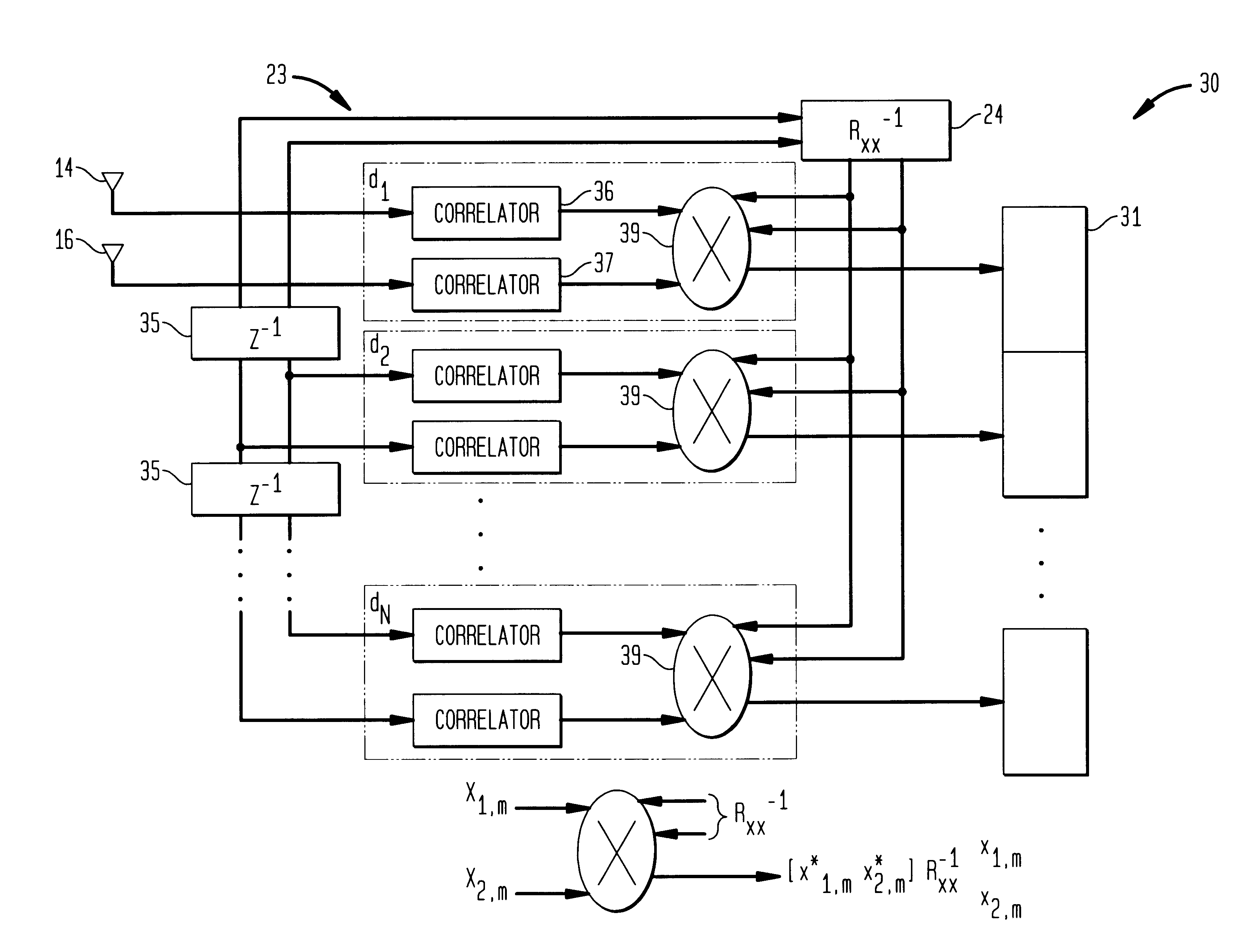
Code division multiple access system and method of operation with improved signal acquisition and processing
InactiveUS6549565B1Computational complexity is reducedGood synchronizationSpatial transmit diversityCode division multiplexSignal qualitySignal processing circuits
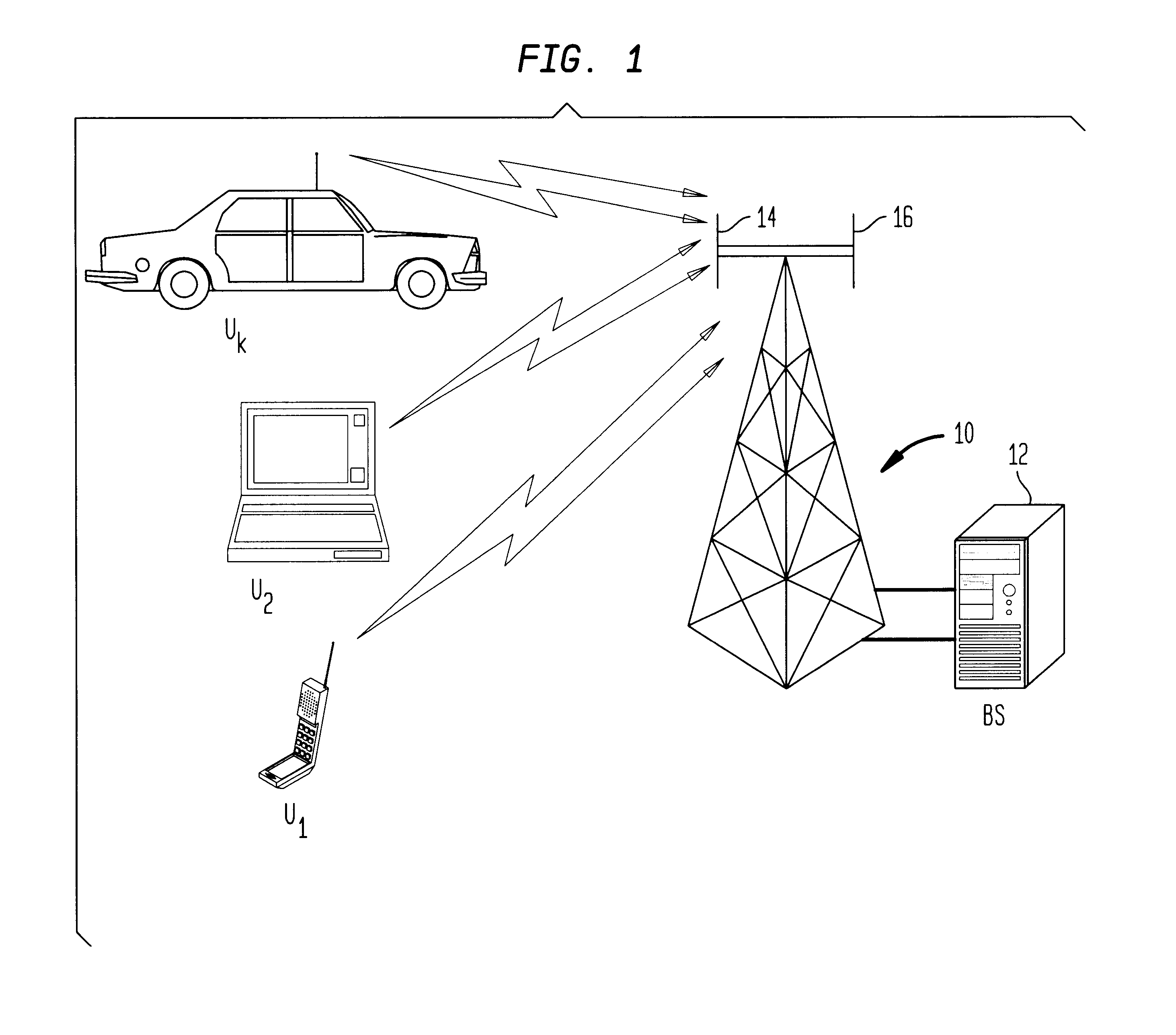
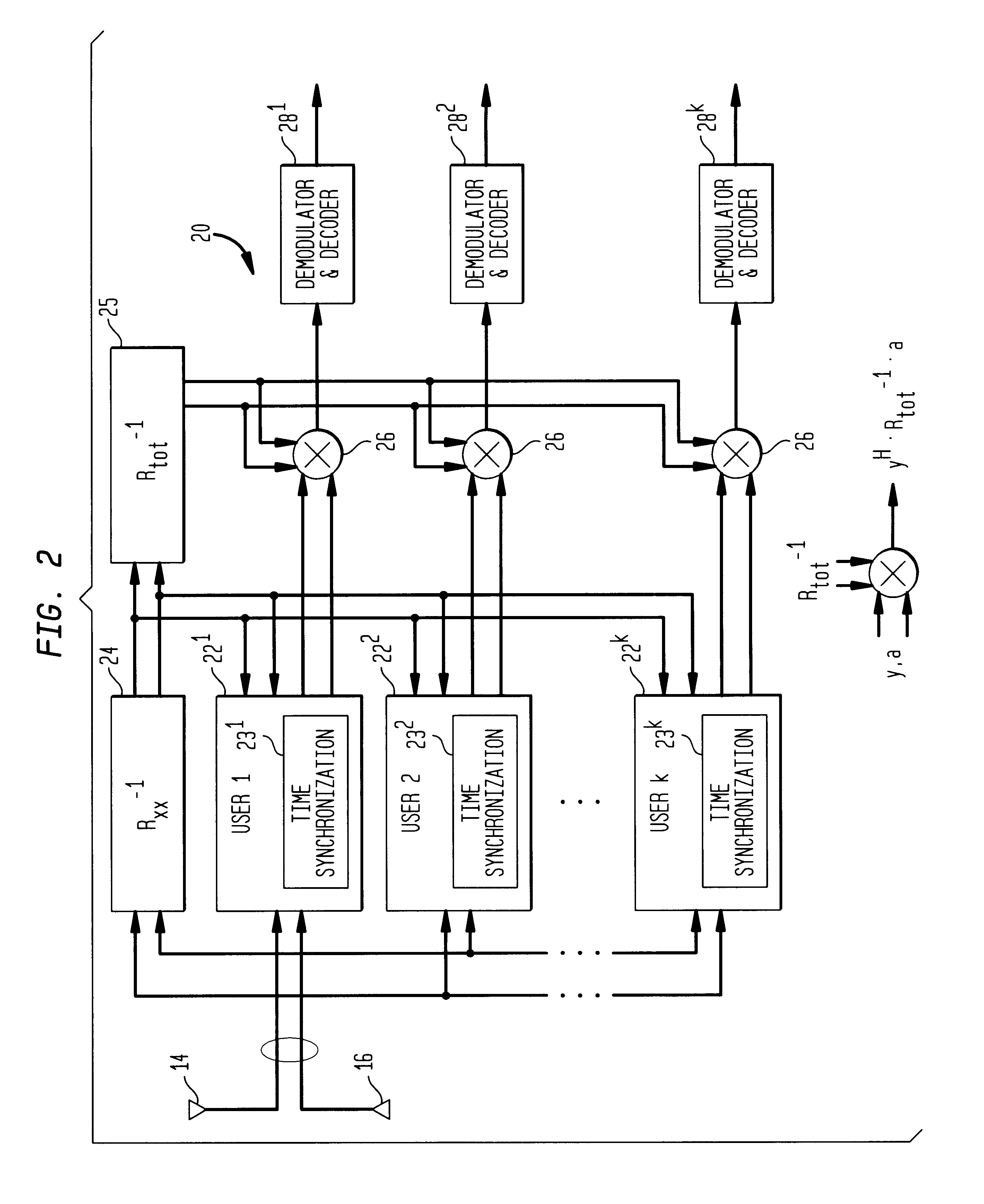
A Code Division Multiple Access system and method of operation provides reduced interference for received signals and improved signal acquisition and processing with reduced computational complexity. The system includes a base station coupled to an antenna array of at least two or more antennas and serving a plurality of users. A receiver in the base station includes a universal inverse cross-correlation matrix coupled to the antenna array, a signal acquisition and a signal processing circuit serving each user. Each signal acquisition circuit comprises a series of delay stages in which the incoming antenna signals in each stage are correlated with a spreading code and combined in a multiplier coupled to the universal inverse cross-correlation matrix which facilitates improved time delay estimation for signal acquisition. Each multiplier combines the correlated signals of the stage with the output of the universal inverse cross-correlation matrix to provide a signal amplitude representative of the signal energy in an antenna path for a given time period, with individual delays separated by a half of chip period. The amplitudes for each of the delay stages are captured in buffers which contain threshold information for selection of the strongest received signal. The signal processing circuit combines the strongest received signal with a channel estimate and the universal inverse matrix output in a multiplier to provide an output signal for demodulation and decoding with improved signal quality due to (a) reduced interference, (b) improved synchronization for signal acquisition and processing, and (c) the universal inverse cross-correlation matrix reducing computational complexity in signal acquisition and signal processing.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
3D MIMO (Three-dimensional Multiple Input Multiple Output) statistical channel modeling method based on actual measurement
ActiveCN107425895ASolve non-positive definite problemsHigh precisionSpatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringCross correlation matrixStatistical analysis
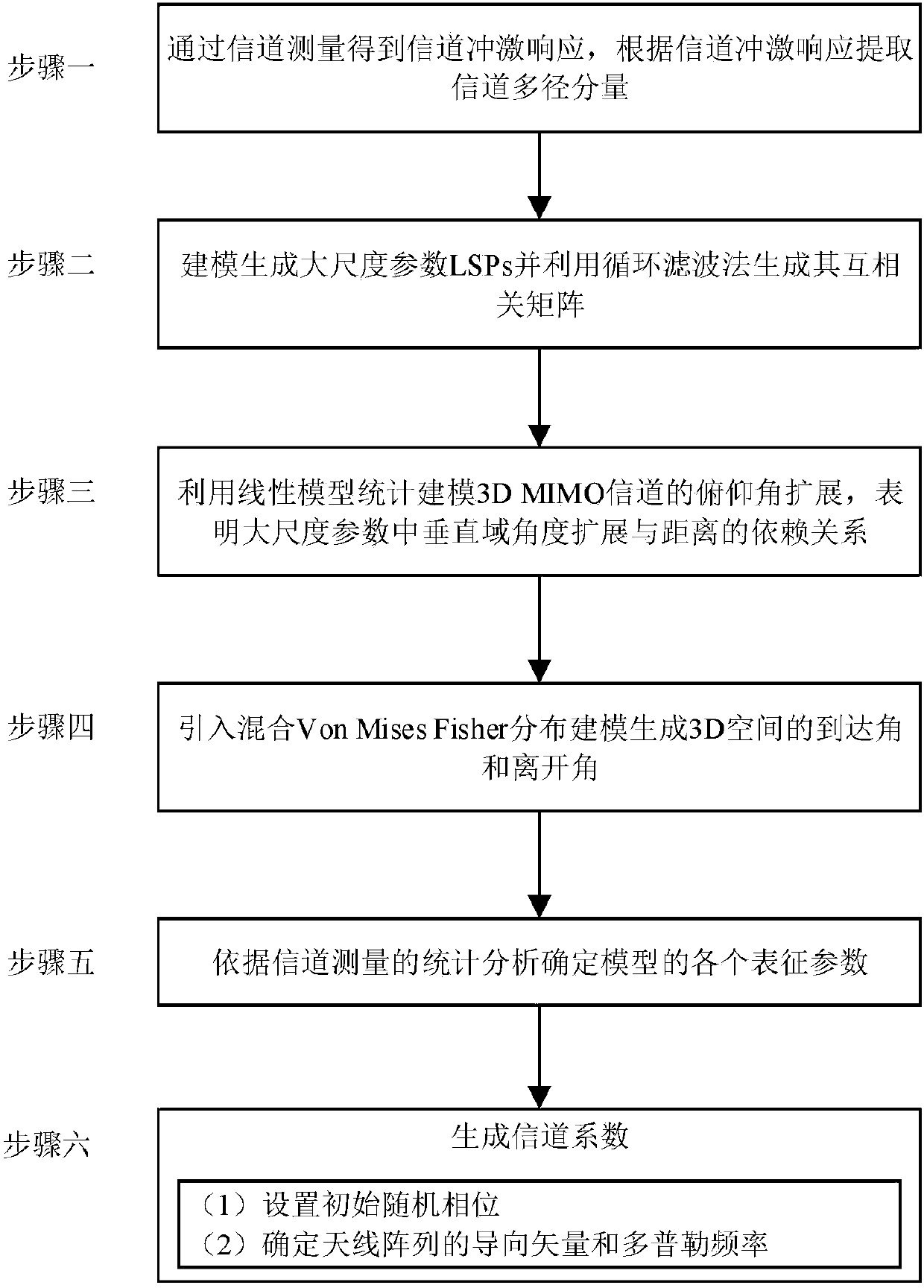
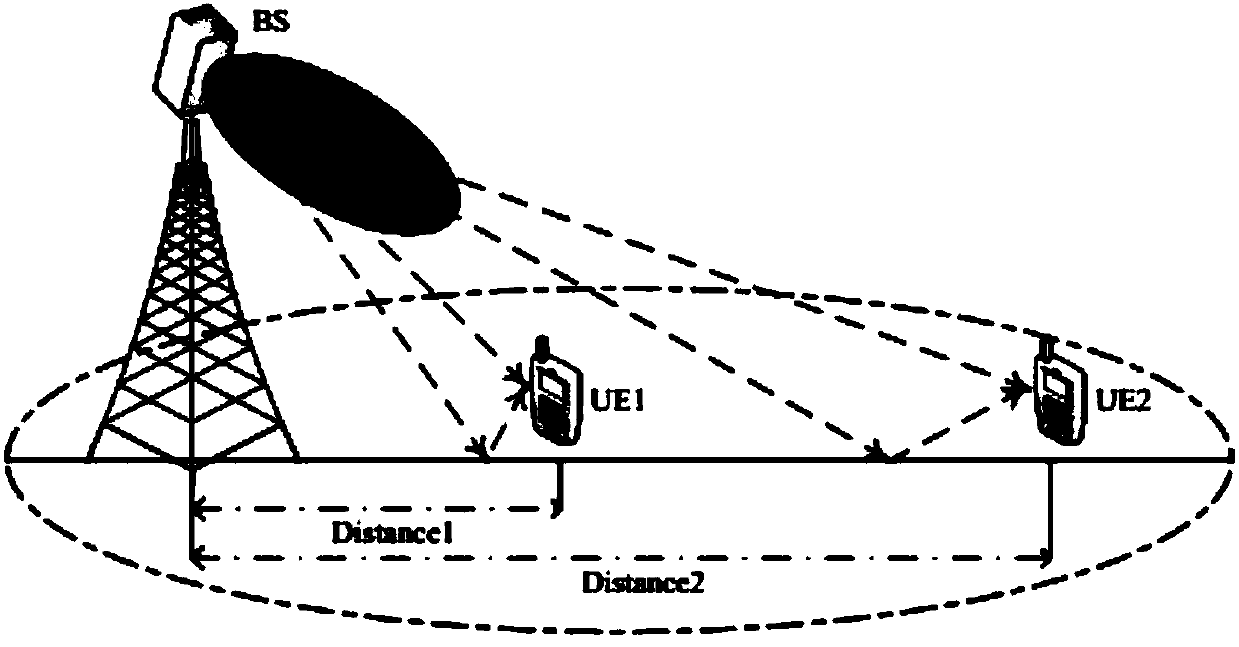
The invention belongs to the technical field of wireless communications, and discloses a 3D MIMO (Three-dimensional Multiple Input Multiple Output) statistical channel modeling method based on actual measurement, which effectively and accurately reflects the real three-dimensional channel environment and improves the accuracy of a channel model. Statistical characteristics of large scale parameters are extracted through external field measurement, and a cross correlation matrix of large scale parameters is generated to solve the non-positive problem of the matrix in the existing model; a linear model is used to make a statistics of elevation spread of the modeled 3D MIMO channel, which increases the dependence of vertical domain angle spread and distance; a sub-diameter azimuth and a sub-diameter elevation dependent on each other are randomly generated through the mixed Von Mises Fisher distribution; and according to the statistical analysis of the external field measurement, each characterization parameter of the channel model is determined, and a 3D MIMO channel coefficient is generated. The 3D MIMO statistical channel modeling method based on the actual measurement provided by the invention expands the application of the 3D MIMO channel model, and provides a powerful tool for accurately and efficiently evaluating a related algorithm of a 3D MIMO system.
Owner:广州市埃特斯通讯设备有限公司
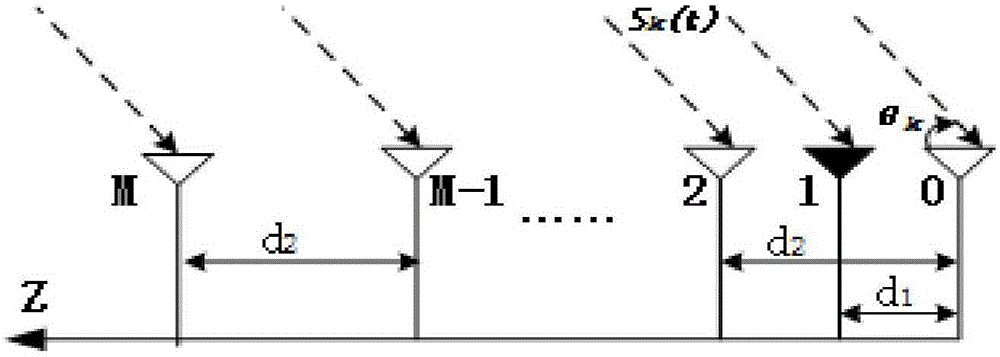
Sparse L-shaped array and two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof
InactiveCN106054123ASmall amount of calculationThe parameters are accurateRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDirection/deviation determining electromagnetic systemsCross correlation matrixDecomposition
The invention discloses a sparse L-shaped array and a two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of wireless mobile communication. The sparse L-shaped array comprises a first subarray formed by a sparse uniform linear array, the array element space of which is equal to the wavelength, and an auxiliary array element, and a second subarray formed by an arbitrary sparse linear array, the minimum array element space of which is smaller than or equal to a half wavelength. The shared array element of the two linear arrays is a reference array element, and the distance between the auxiliary array element and the reference array element is the half wavelength. The two-dimensional DOA estimation method is characterized by, to begin with, calculating an autocorrelation matrix according to received data of the second subarray, carrying out characteristic decomposition on the autocorrelation matrix and then, estimating a corresponding second angle, and carrying out calculation to obtain an information source autocorrelation matrix based on the second angle; and obtaining an array manifold matrix of the first subarray according to a cross-correlation matrix of the received data of the two subarrays and the information source autocorrelation matrix, thereby finishing estimation of a first angle corresponding to the first subarray, and obtaining the two-dimensional DOA. Complexity is low, and DOA estimation precision is high.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
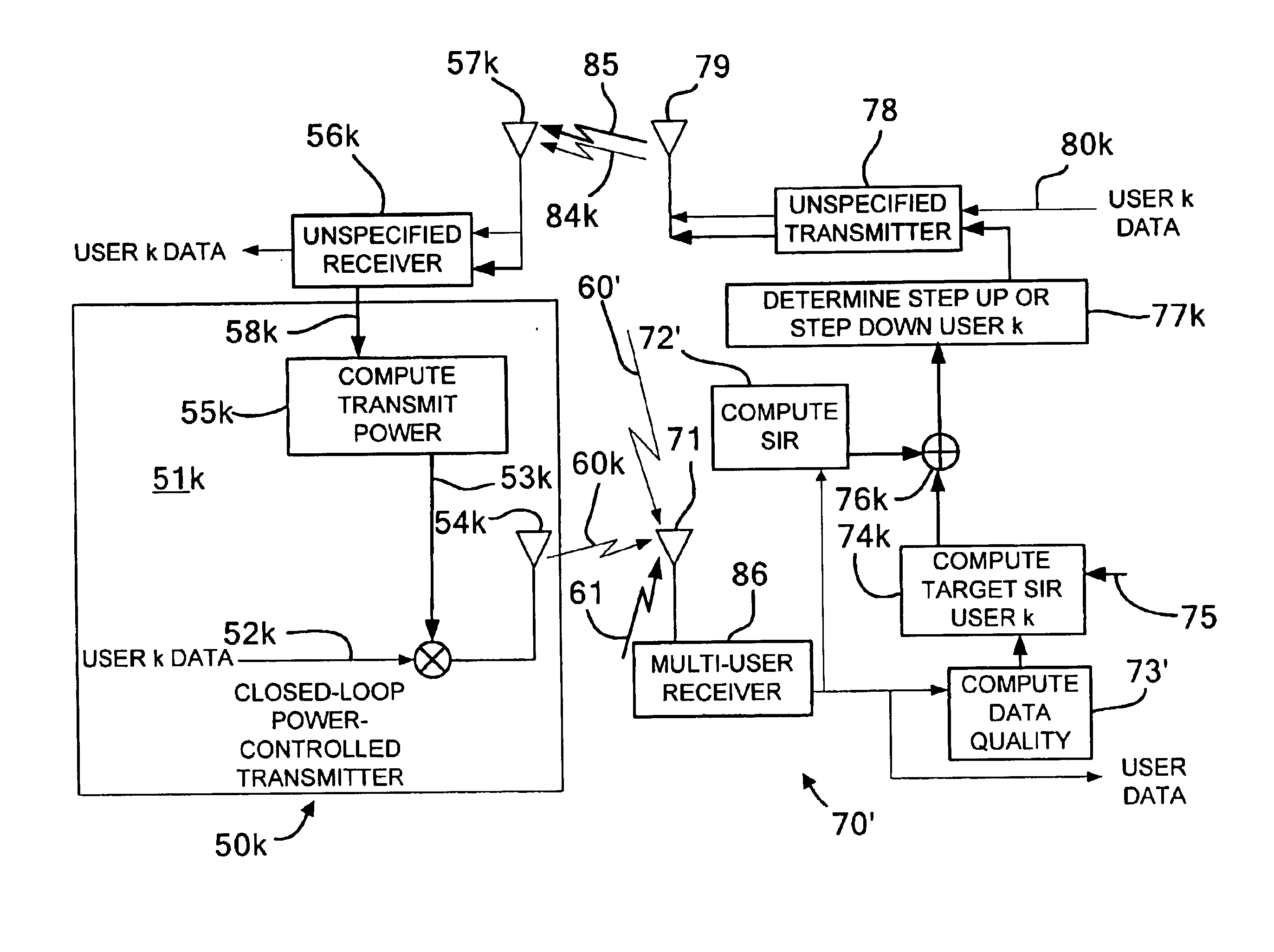
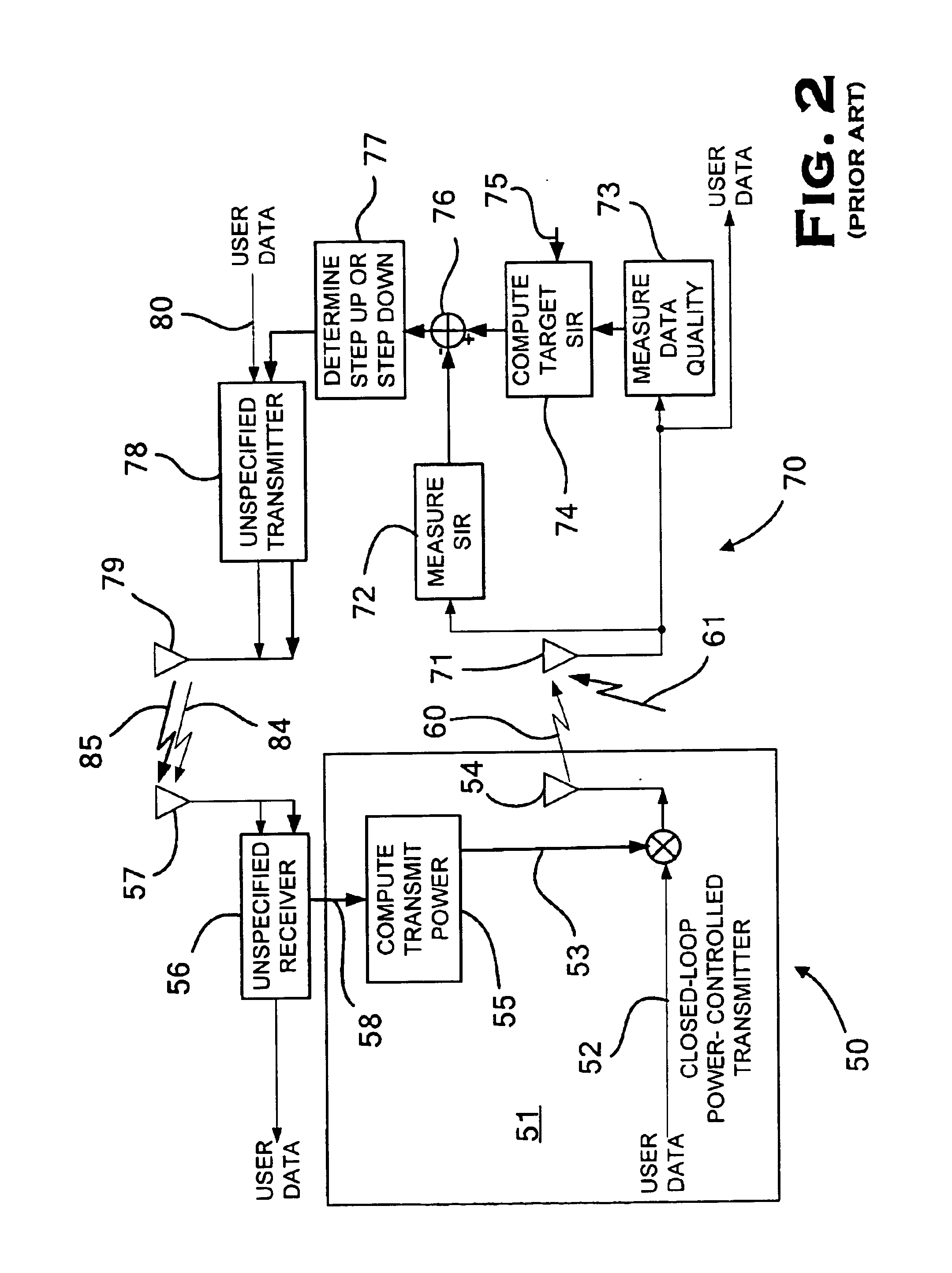
Link-quality estimation method and components for multi-user wireless communication systems
InactiveUS6879813B2Power managementTransmission control/equalisingCross correlation matrixResponse characteristics
Received signal characteristics of multiple concurrently received channels are determined using an analytical approach for computation in lieu of the measurement based approach of the prior art. A receiving wireless transmit receive unit (WTRU) and method are provided for processing concurrent communication signals from a plurality of transmitting WTRUs that concurrently transmit successive data blocks in a plurality of K forward channels. The receiving WTRU preferably has a receiver configured to receive successive data blocks of K concurrent transmissions transmitted from the transmitting WTRUs on the respective K forward channels. A processor is configured to compute individual channel characteristics for each forward channel k based on the characteristics of data signals received on all K forward channel. The processor is preferably configured to successively compute instantaneous Signal to Interference Ratio values for each forward channel j (iSIRj), for integers j=1 to K, based on a cross correlation matrix of channel response characteristics of K concurrently received data blocks and to selectively compute an average value that is used for the computing the individual channel characteristics for the forward channel k. The individual channel characteristics are advantageously used for power control or for the processing of the data blocks received on the respective forward channels.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
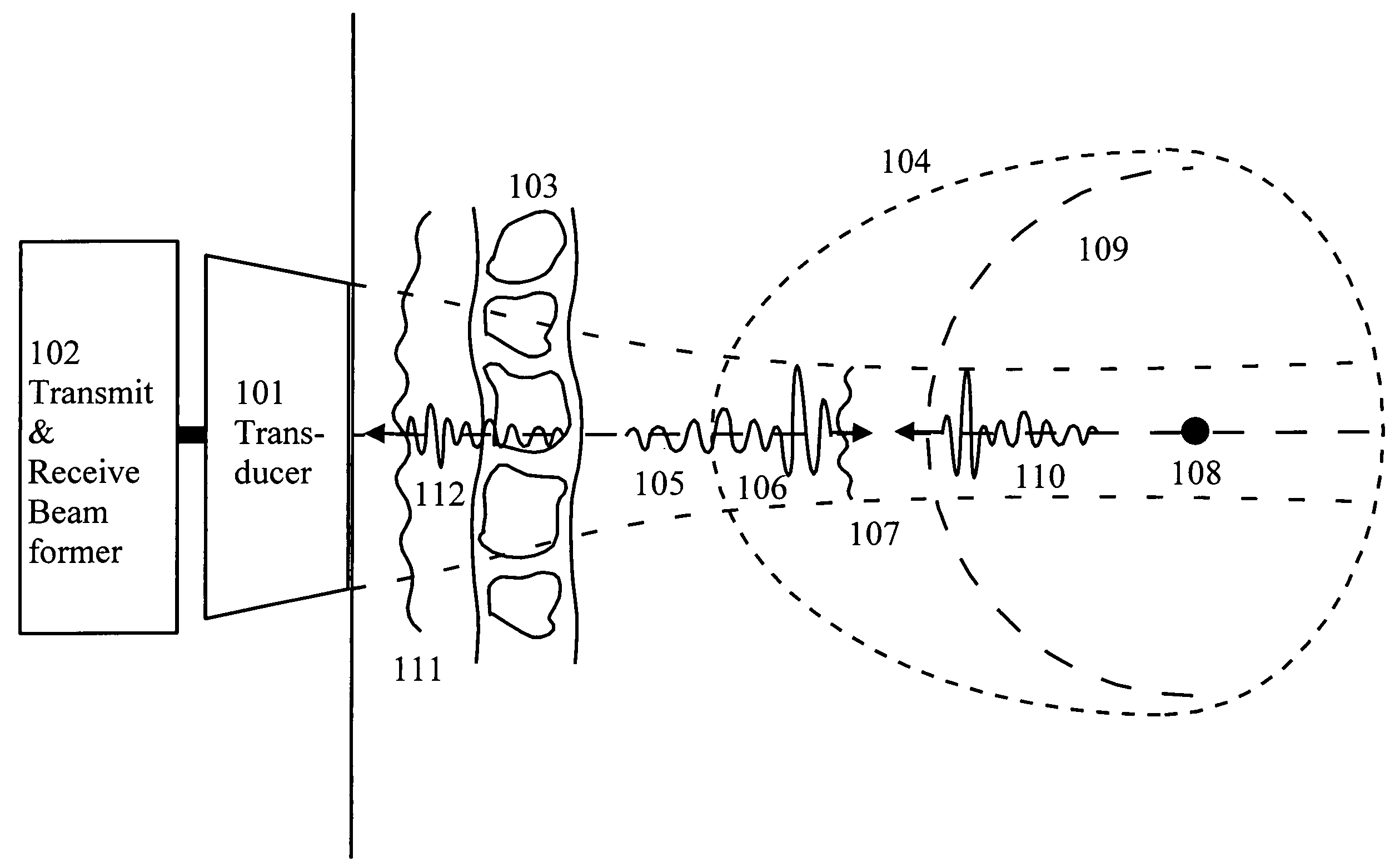
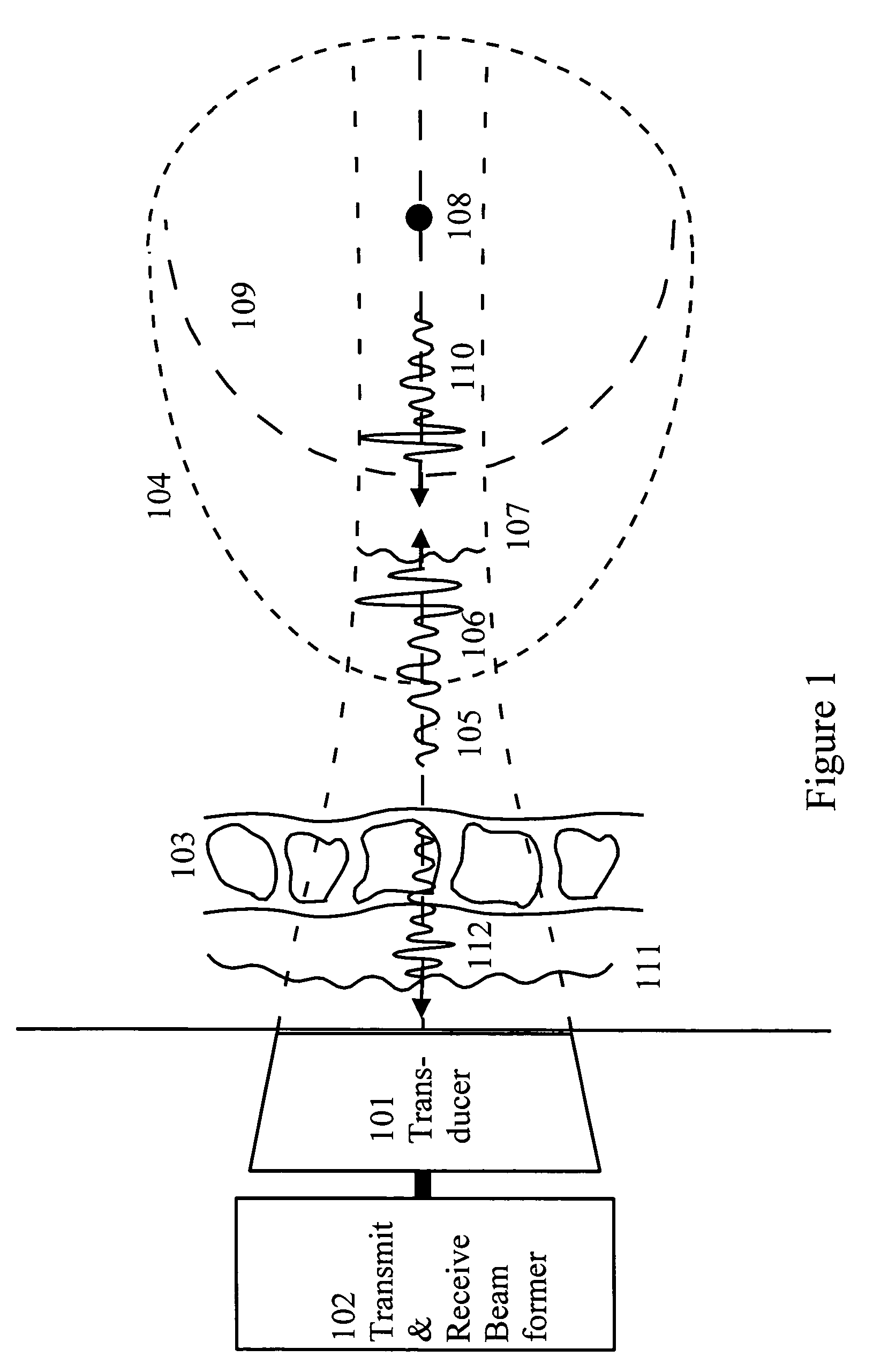
Corrections for wavefront aberrations in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS7273455B2Power maximizationComputationally efficientUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsFeature vectorUltrasound imaging
An estimation method for correction filters for wavefront aberration correction in ultrasound imaging is given. The aberration is introduced due to spatial variations of the ultrasound propagation velocity in heterogeneous tissue. The correction filters are found as eigenvectors of the cross-correlation matrix of the element signals. In particular, the eigenvectors with a small spatial linear / plane phase component is sought. Detailed methods for calculating the eigenvectors are given.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +2
Single user detection user equipment
InactiveUS20020126646A1Network traffic/resource managementRadio transmissionFrequency spectrumCross correlation matrix
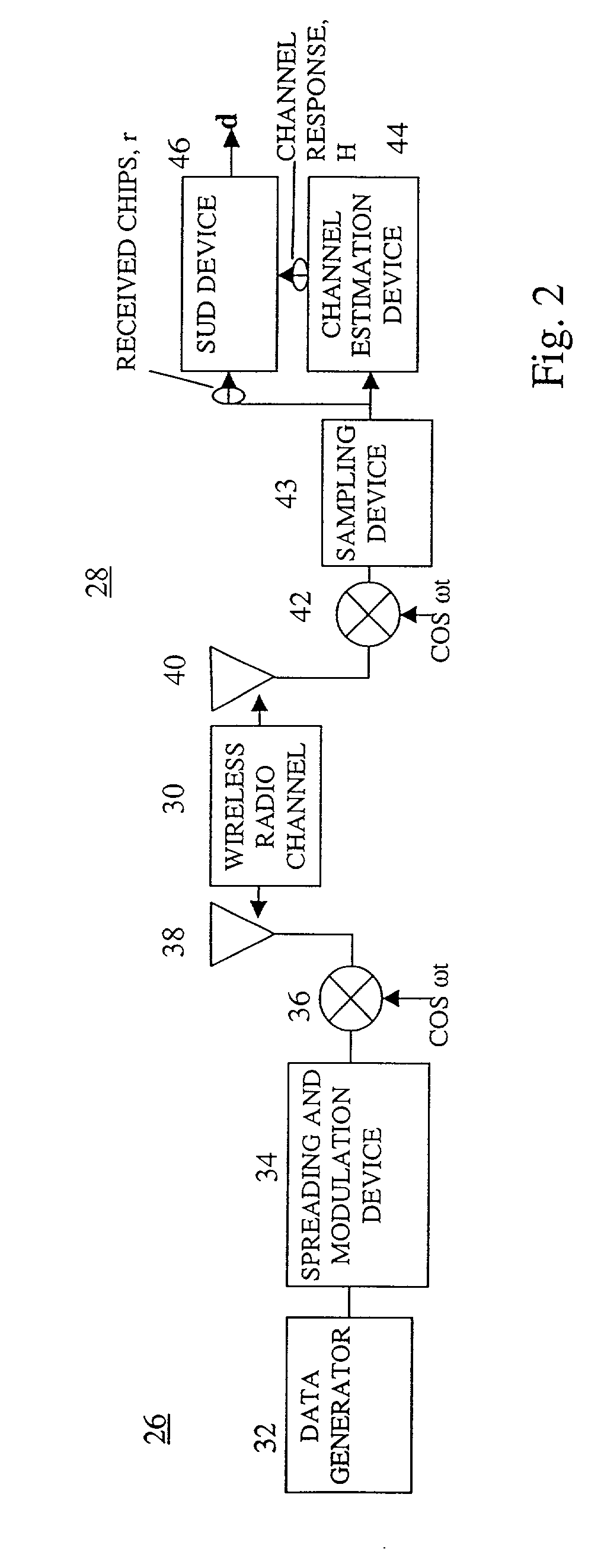
A code division multiple access user equipment is used in receiving a plurality of data signals over a shared spectrum. Each received data signal experiences a similar channel response. A combined signal of the received data signals is received over the shared spectrum. The combined signal is sampled at a multiple of the chip rate. A channel response is estimated. A cross correlation matrix is determined using the estimated channel response. A subblock of the cross correlation matrix is selected. A Cholesky factor for the subblock is determined. The Cholesky factor is extended. The spread data vector is determined using the extended Cholesky factor, a version of the channel response and the samples. Data of the data signals is estimated using the spread data vector.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL TECH CORP
Massive MIMO array emulation
ActiveUS20170019154A1Spatial transmit diversityTransmission monitoringCross correlation matrixEngineering
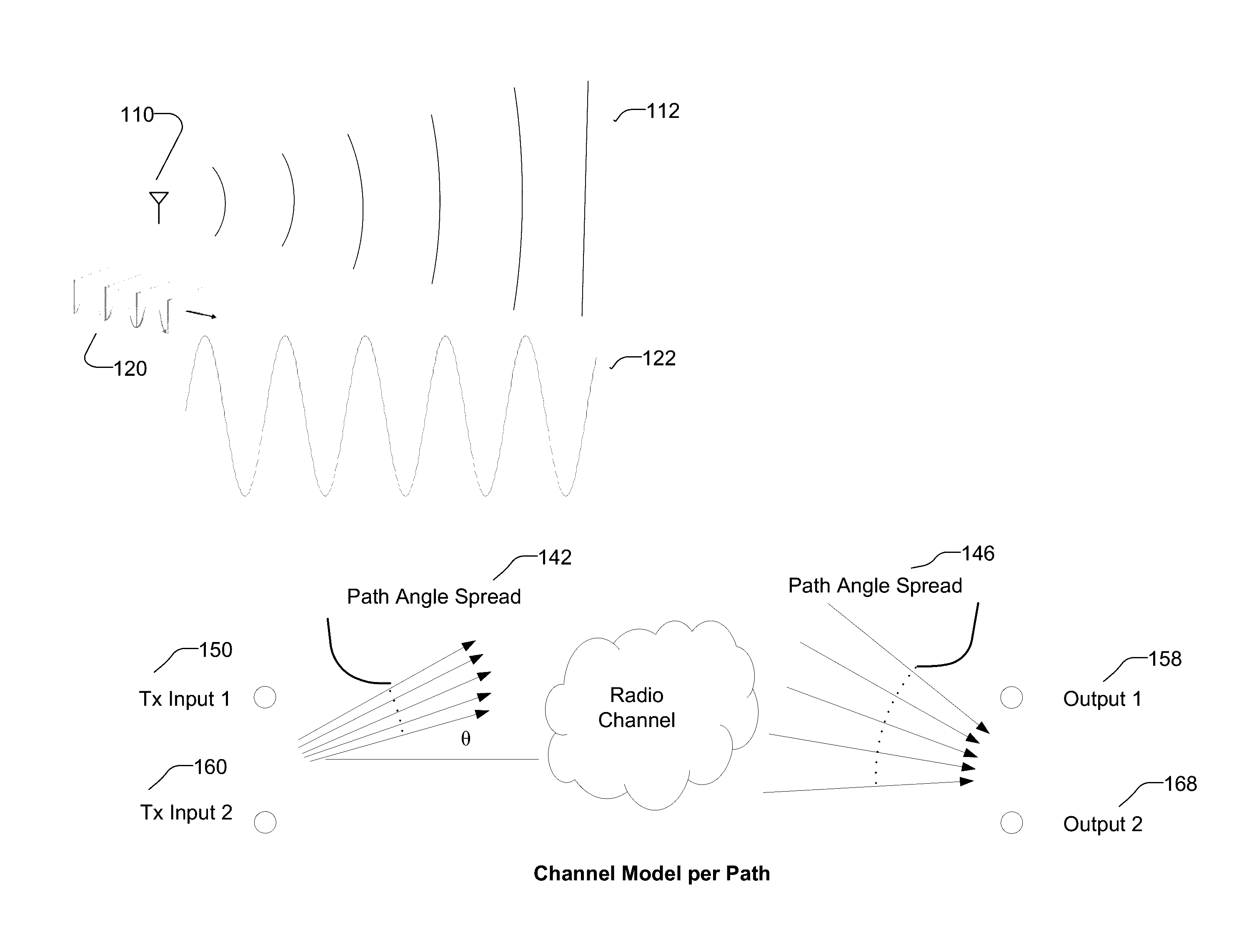
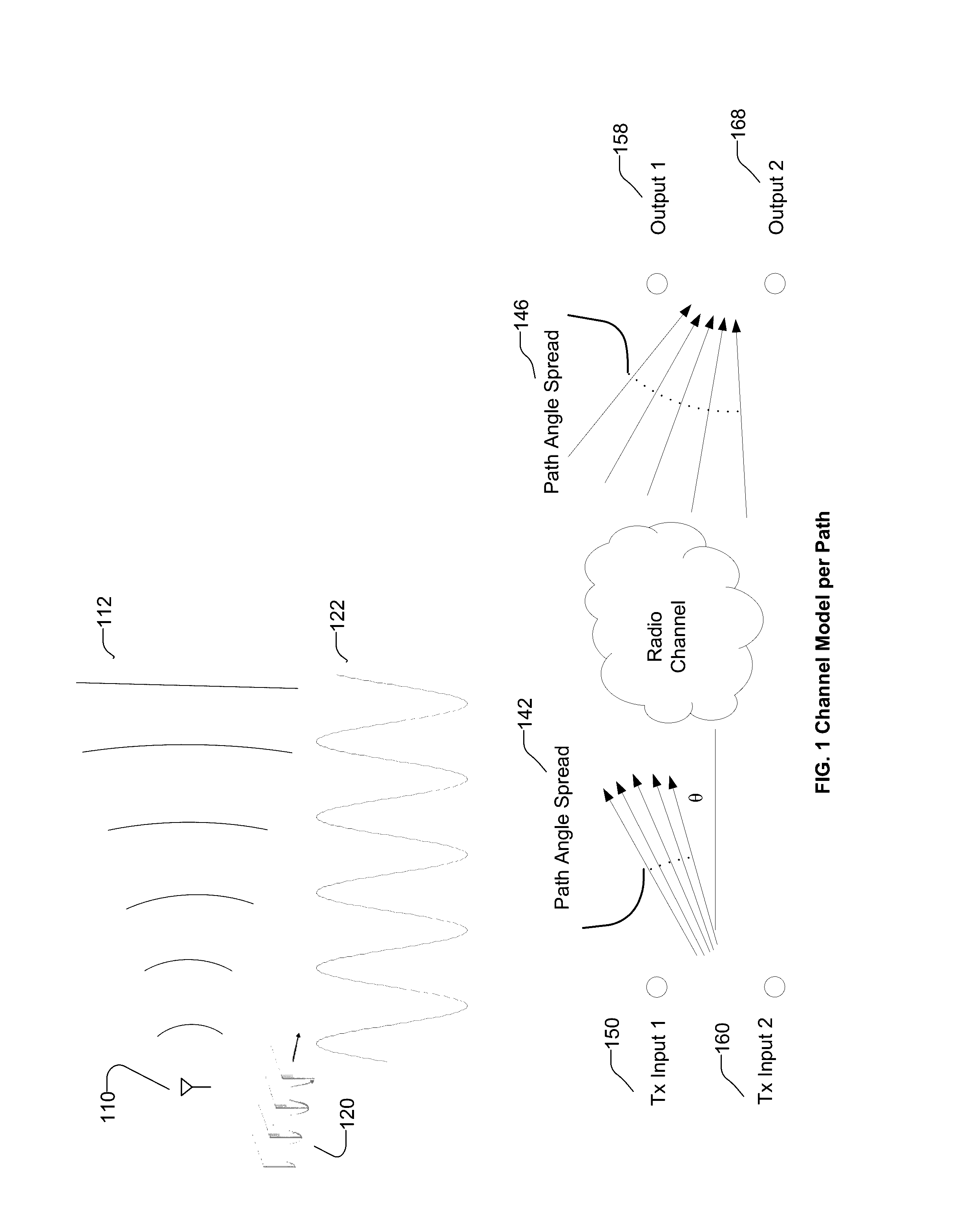
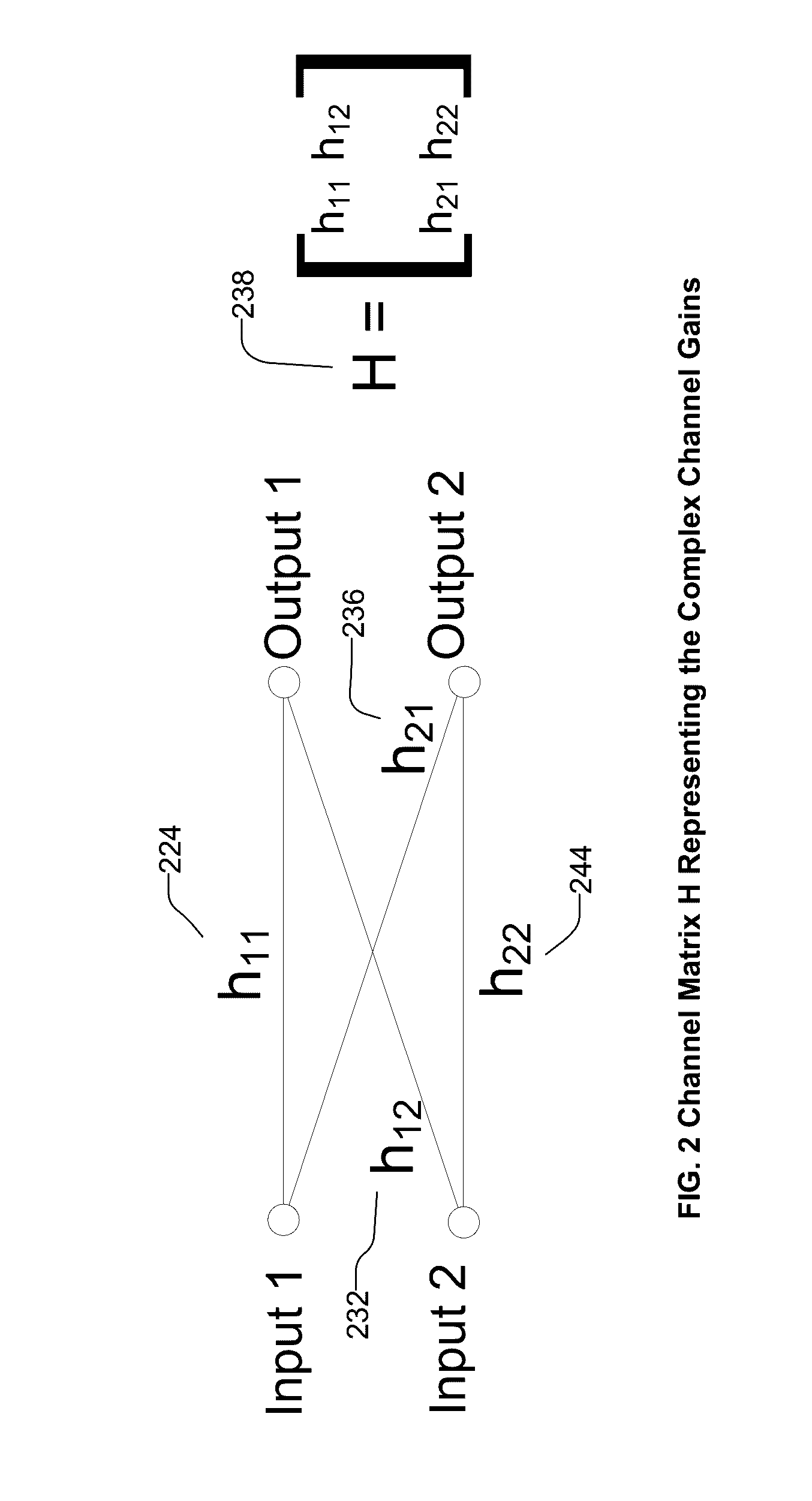
The disclosed technology relates to systems and methods for emulating a massive MIMO beamforming antenna array of arbitrary size—a channel model between a transmitter and a receiver, with one or more signal paths having respective amplitudes, angles of arrival, angle spreads, and delays. The disclosed technology includes defining a complete channel model H, calculating the correlation matrix for the channel, grouping the base antenna elements of the antenna array by combinations of signal and polarization, and calculating observed beamforming power of each group of the base elements, by applying a cross-correlation matrix to determine observed power signals and delay of each signal at each remote antenna element of the user equipment. Emulation includes supplying cross-correlated signals to remote antenna elements of user equipment during a RF test of the user equipment. Disclosed technology includes a channel emulator that generates output streams for testing user equipment for multiple users.
Owner:SPIRENT COMM
Double-base MIMO radar angle estimating method based on cross-correlation matrixes
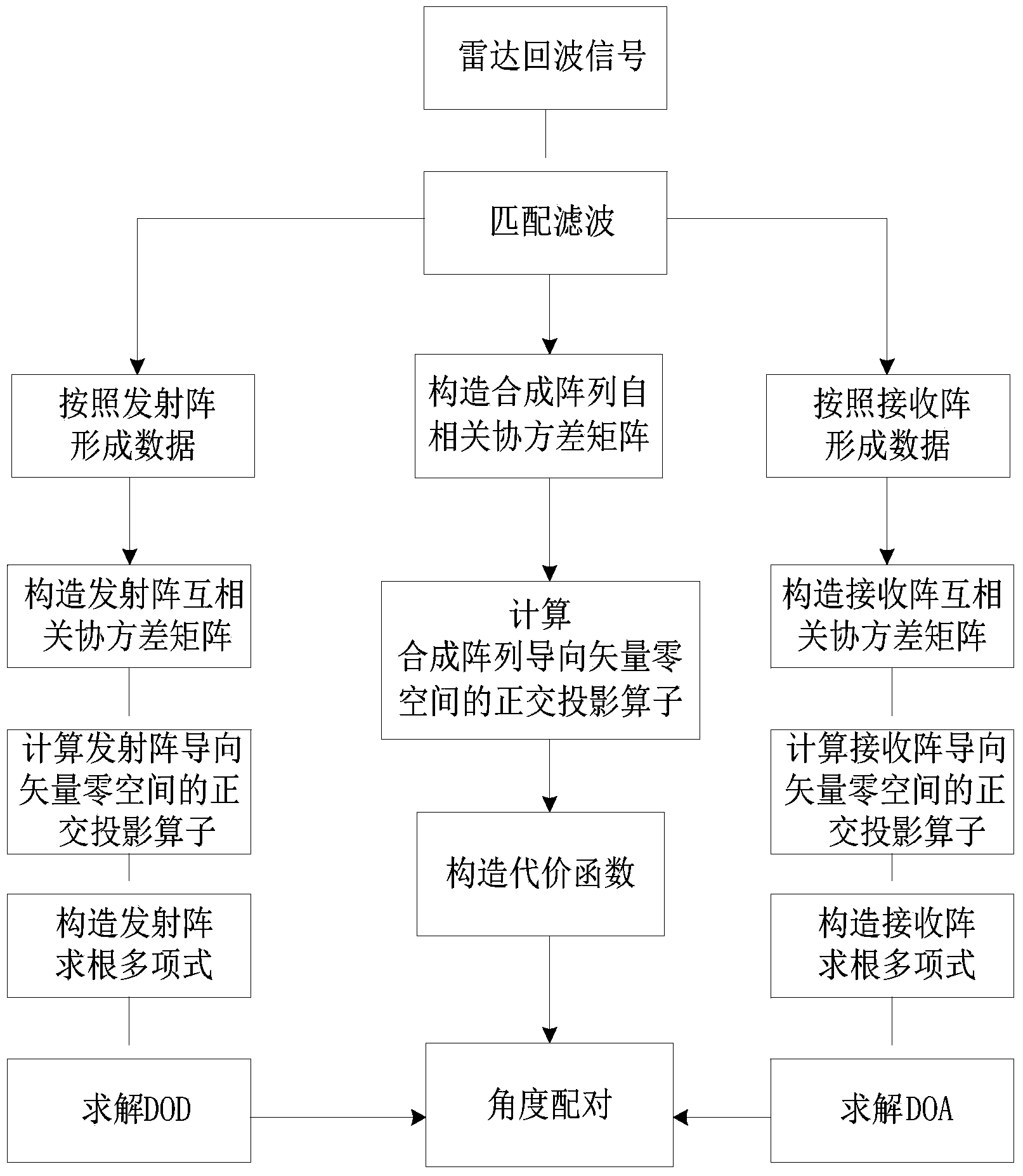
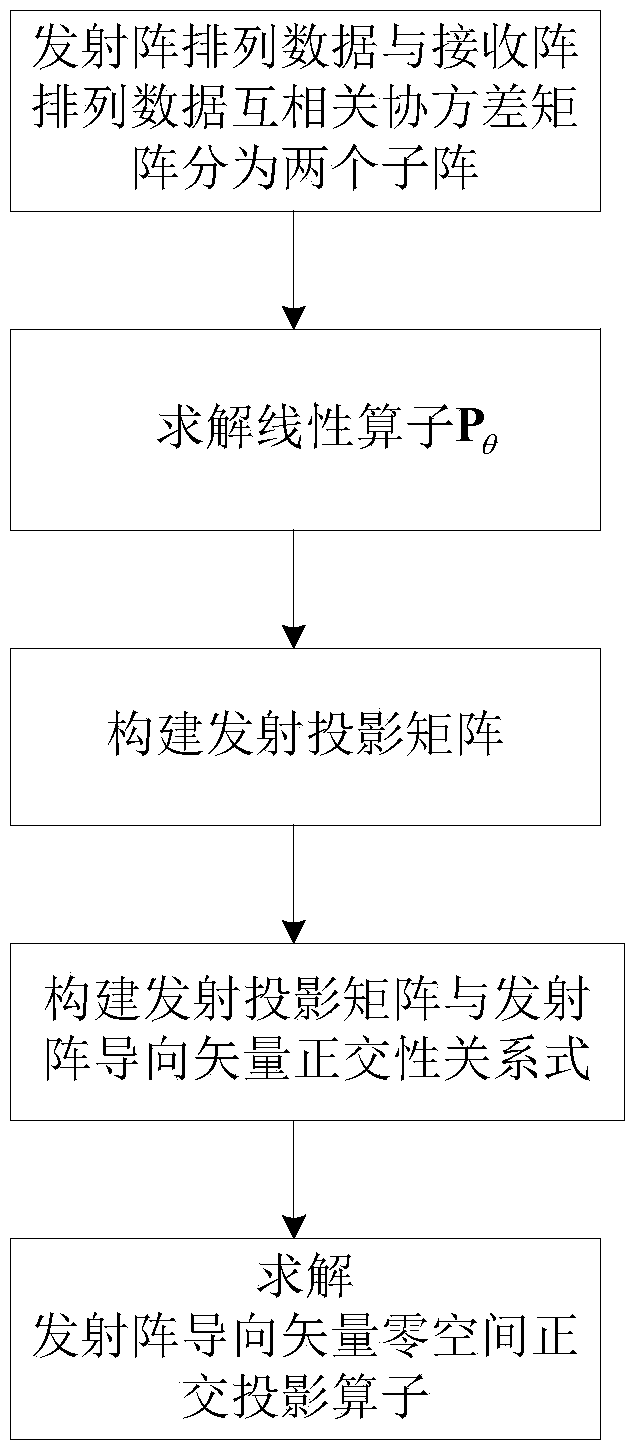
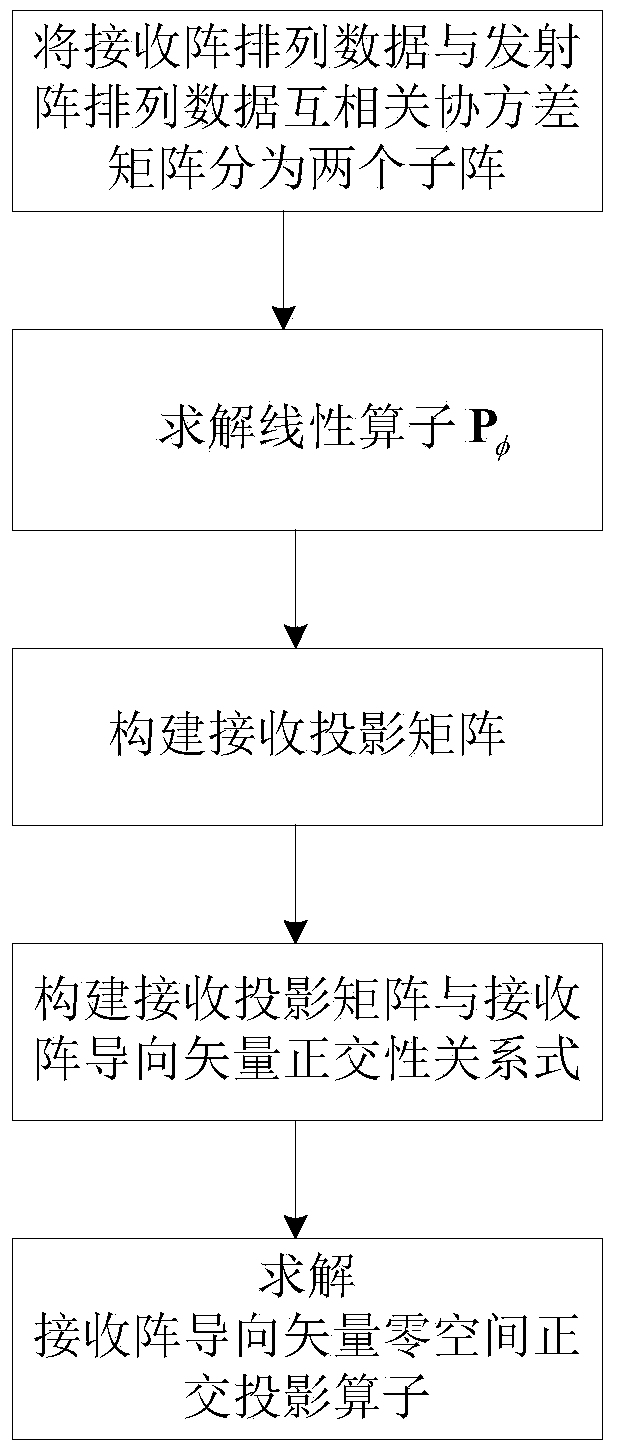
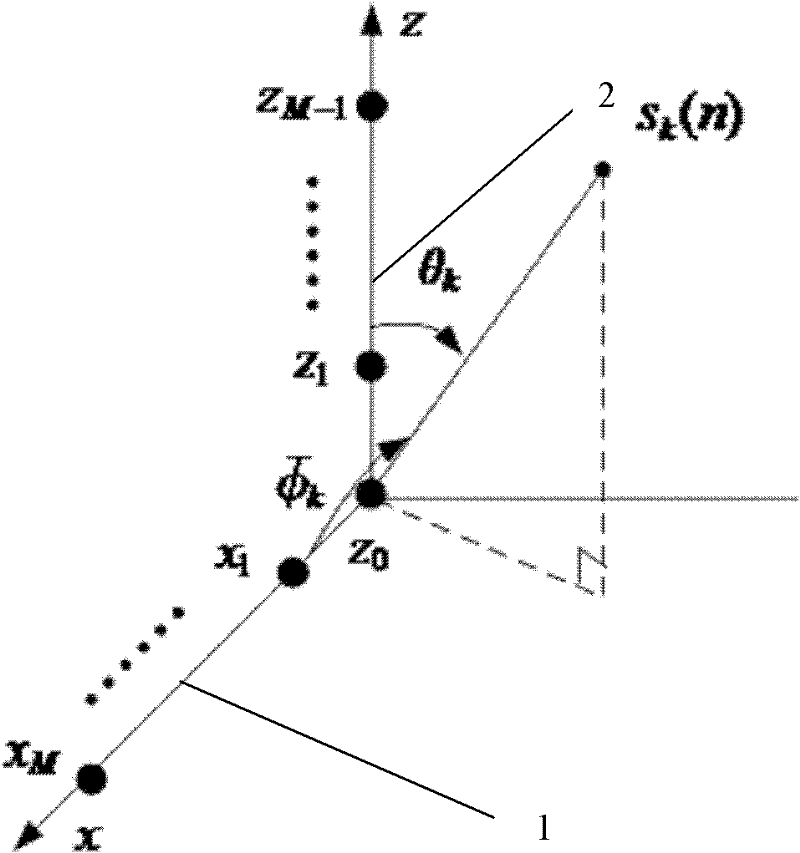
InactiveCN103760547AReduce the influence of angle estimationImprove estimation accuracyDirection findersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionCross correlation matrixFiltration
The invention discloses a double-base MIMO radar angle estimating method based on cross-correlation matrixes. The method mainly solves that problem that a double-base MIMO radar angle is large in calculation and complex in computation. The achieving steps are as follows: (1) conducting matching and filtering on a radar echo signal, and forming data according to an emission array and a receiving array; (2) respectively constructing cross covariance matrixes by utilizing the formed data; (3) respectively obtaining rectangular projection operators in guide vector null space of the emission array and the receiving array through linear independence of a covariance matrix row vector; (4) obtaining the position of a target relative to the emission array and the receiving array; (5) respectively obtaining rectangular projection operators in guide vector null space of a synchronized array through linear independence of an autocorrelation covariance matrix row vector of the data after matching and filtration, and constructing a cost function for matching angles. The double-base MIMO radar angle estimating method based on cross-correlation matrixes achieves high-precision MIMO radar target angle estimation with small calculation and can be used for locating a target in a radar and communication.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
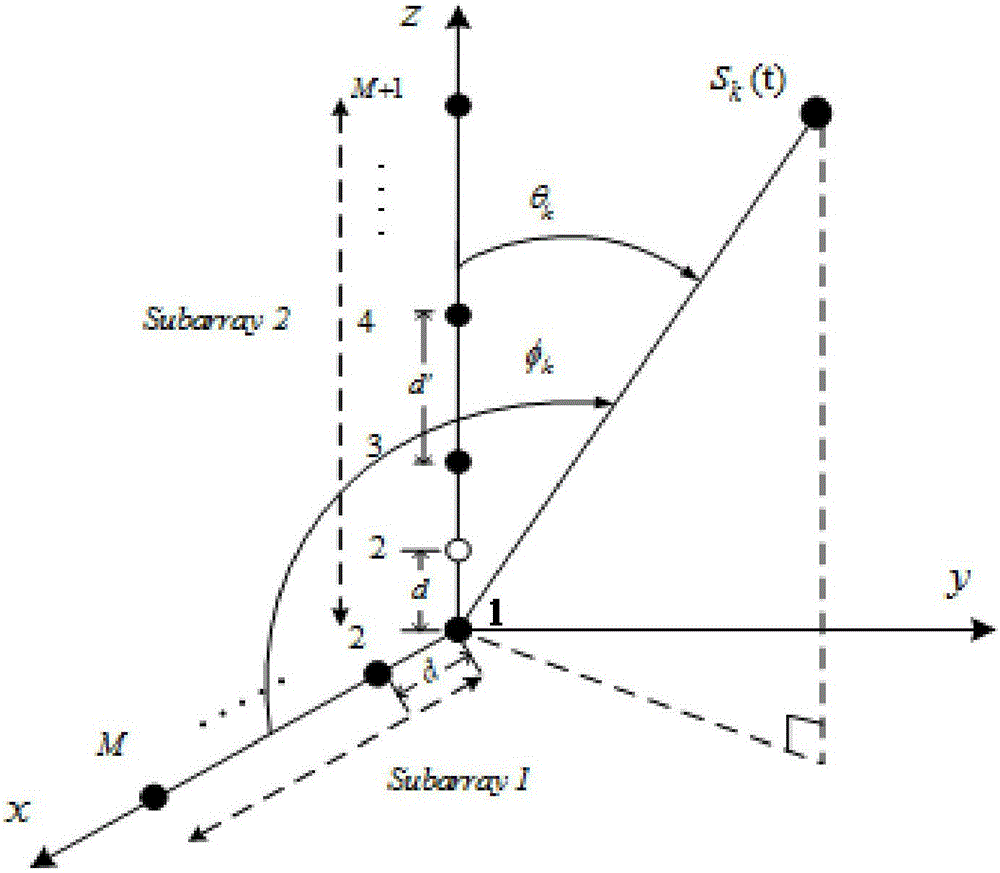
Device for estimating two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of coherent signals based on L array and method thereof
InactiveCN102253363ARadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsCross correlation matrixDecomposition
The invention provides a device for estimating two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of coherent signals based on an L array and a method thereof. The method is characterized by carrying out communication connection on a longitudinal x-direction equidistant linear subarray antenna, a vertical z-direction equidistant linear subarray antenna, an instantaneous correlation computation device, an instantaneous correlation matrix computation device, a linear operation sub-estimation device, a DOA estimation device and a DOA angle pairing device, utilizing a subarray averaging technology to carry out decorrelation on the incident signals, simultaneously implementing linear operation on cross-correlation matrices of L array received data to obtain null space, firstly estimating an angle of pitch and an azimuth angle respectively, then paring the angle of pitch and the azimuth angle and finally obtaining the azimuth angle according to the geometrical relationship, and the method dispenses with eigen-decomposition and has high computation efficiency.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Beam forming method adapted to wide band CDMA system
InactiveCN1549473AEasy to implementSimple compositionSpatial transmit diversityAntenna arraysTime domainCode division multiple access
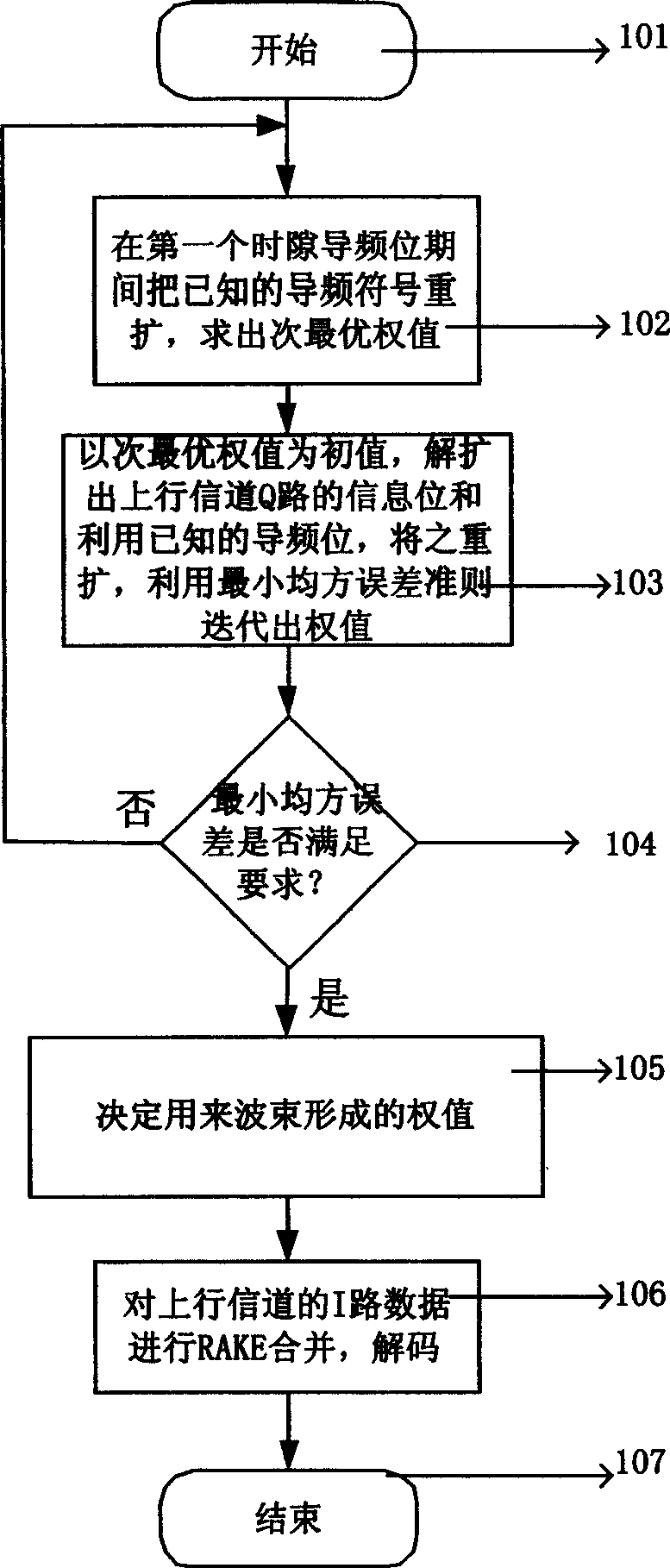
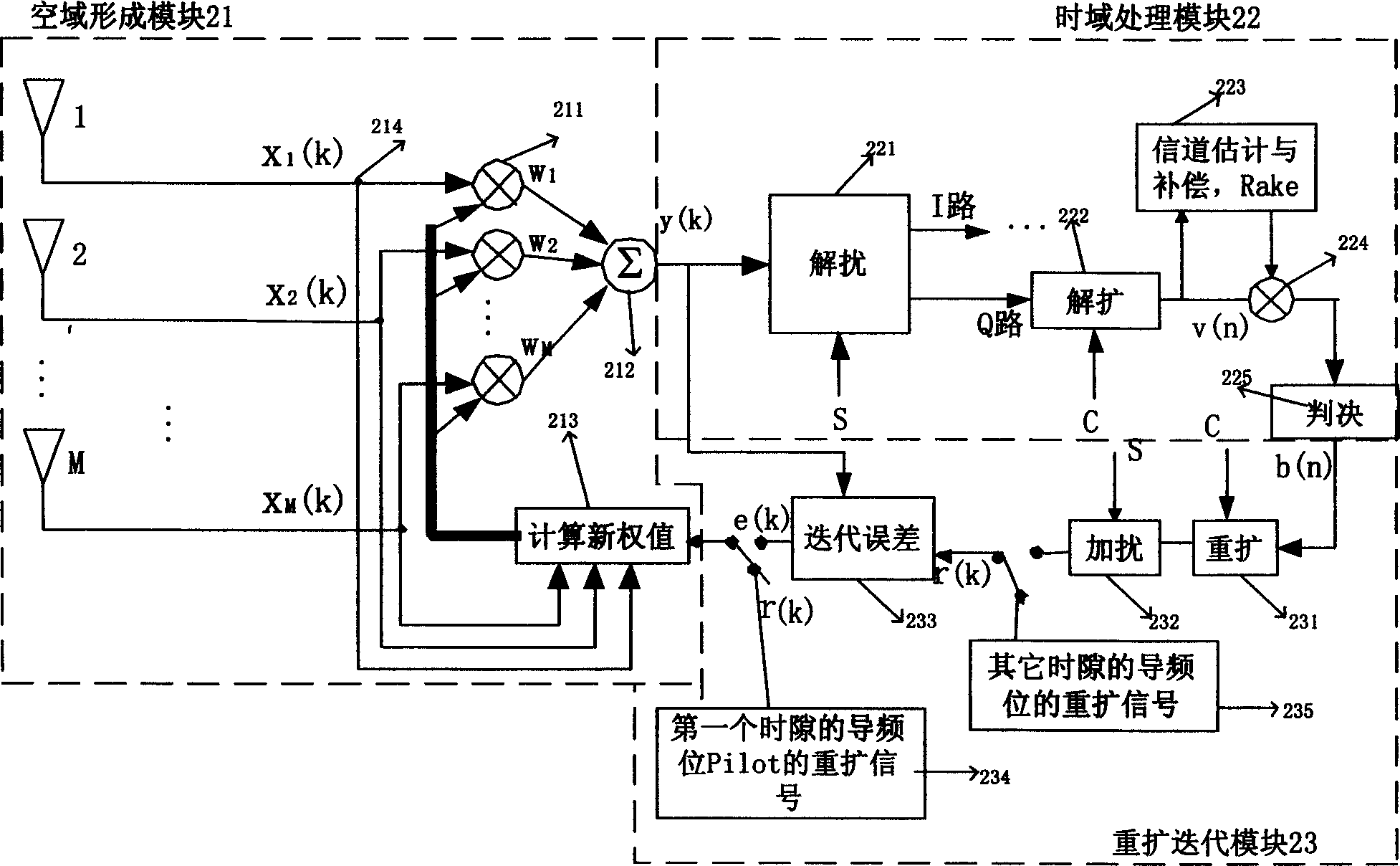
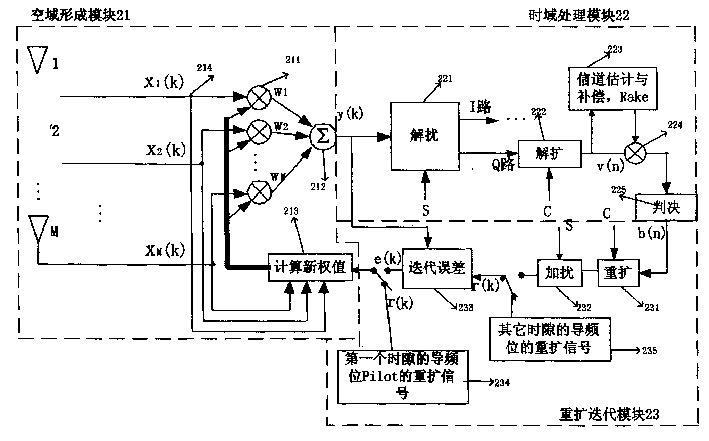
The present invention relates to a beam forming method applicable in wide-band code-division multiple access system, which comprises the steps of carrying out the spatial processing on array signals, wherein the array signals are baseband signals X aligned in time delay; during the pilot bit period of a first time slot, performing the cross-correlation operation on a symbol obtained through respreading and scrambling a known pilot symbol in an uplink channel for each frame as a reference signal and the baseband signals X, so as to obtain a cross-correlation matrix r*r=E[Xr*]; calculating a suboptimum weighted value till all pilot bits in the first time slot are over; during the periods of information symbol bits and other time slots, performing the iteration operation on the suboptimum weighted value as an initial value, the respread and scrambled signals of despread and descrambled information symbol bits and the respread and scrambled signals of known pilot bits as reference signals respectively, based on the principle of the minimum mean square error, so as to figure out a self-adaptive suboptimal weighted value W=r*r; and forming beams by means of the suboptimal weighted value W to obtain Y=W*X. The beam forming method simplifies the structure of the system and also greatly reduces the technical difficulty and the amount of calculation.
Owner:ZTE CORP
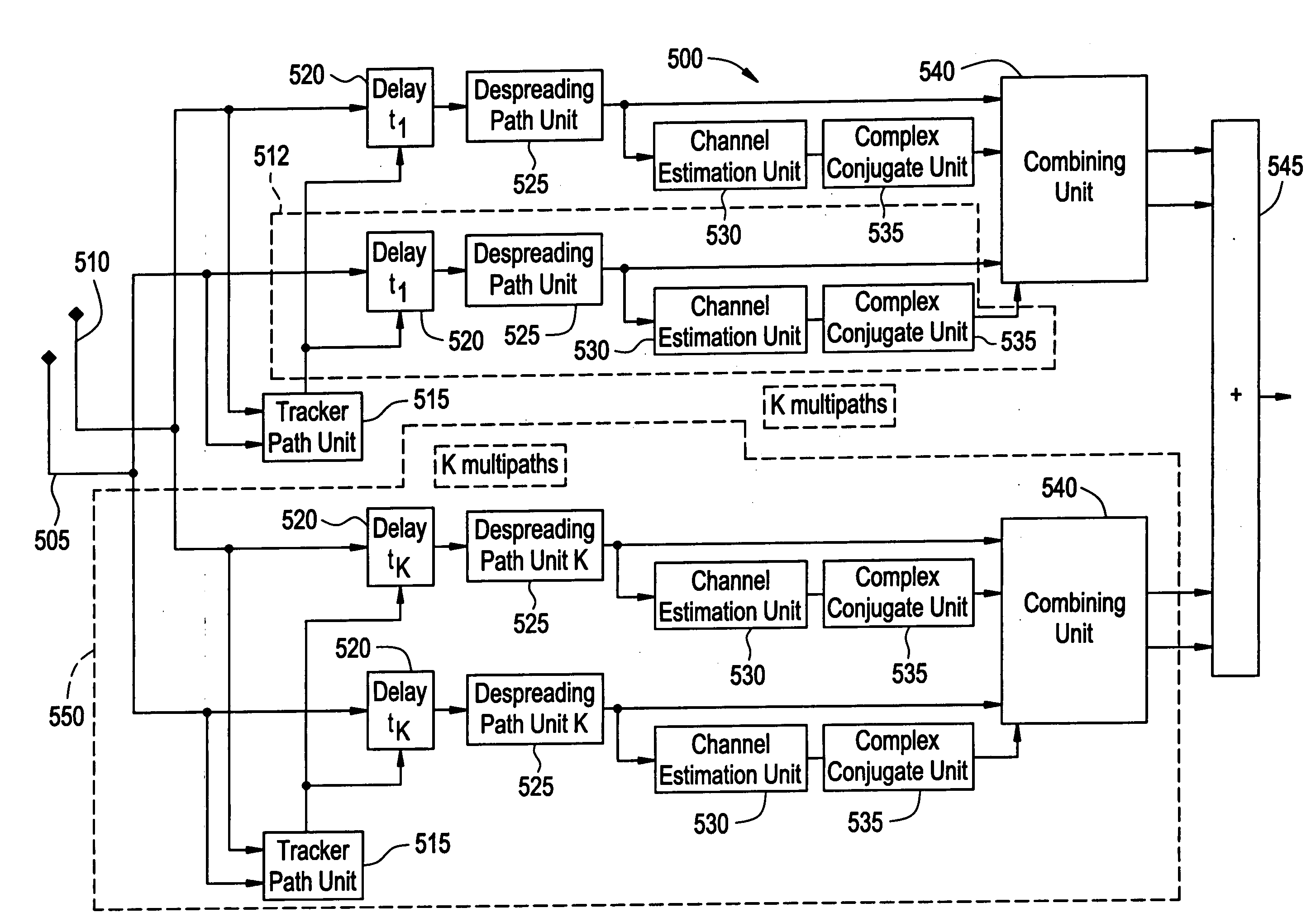
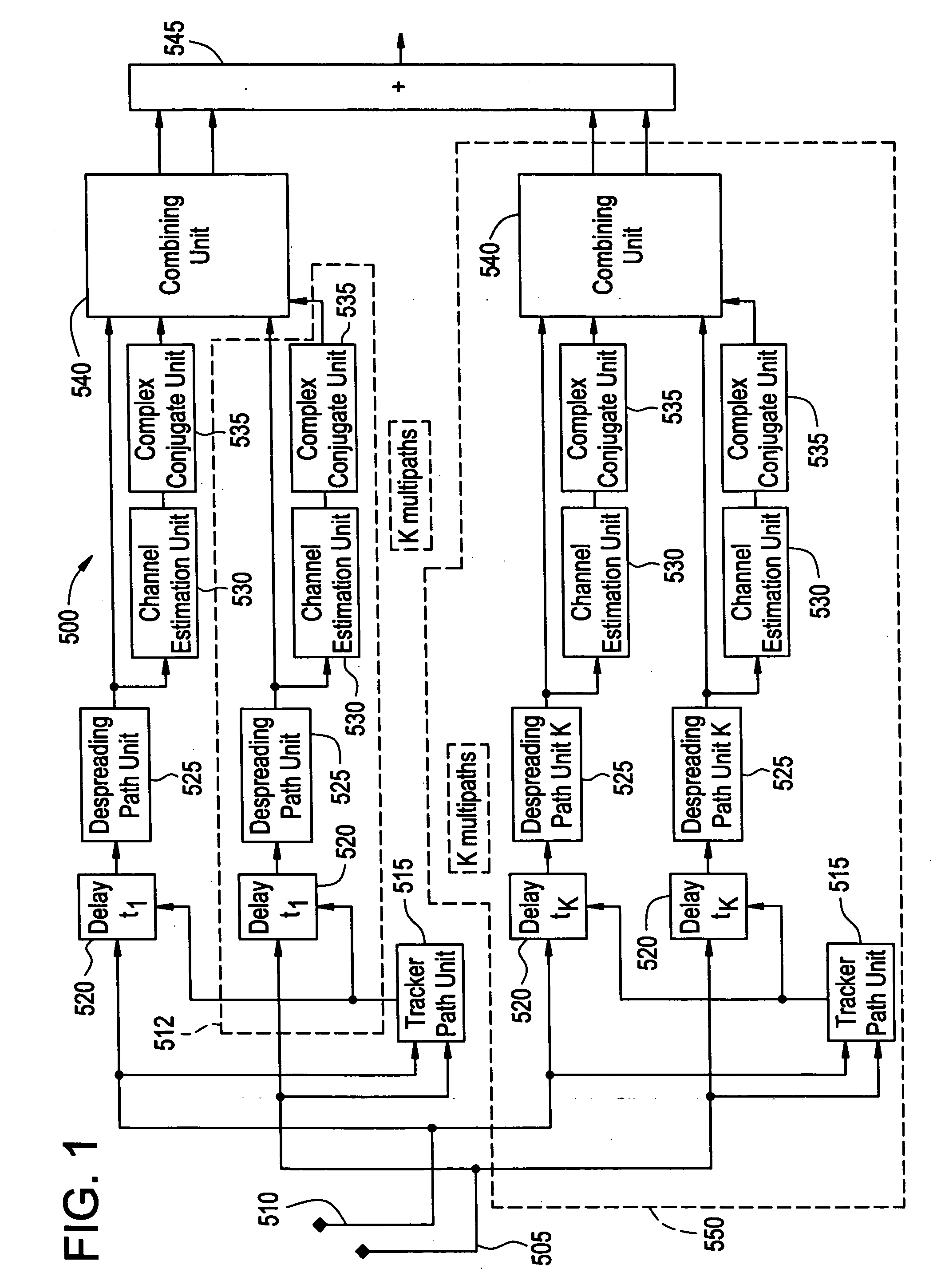
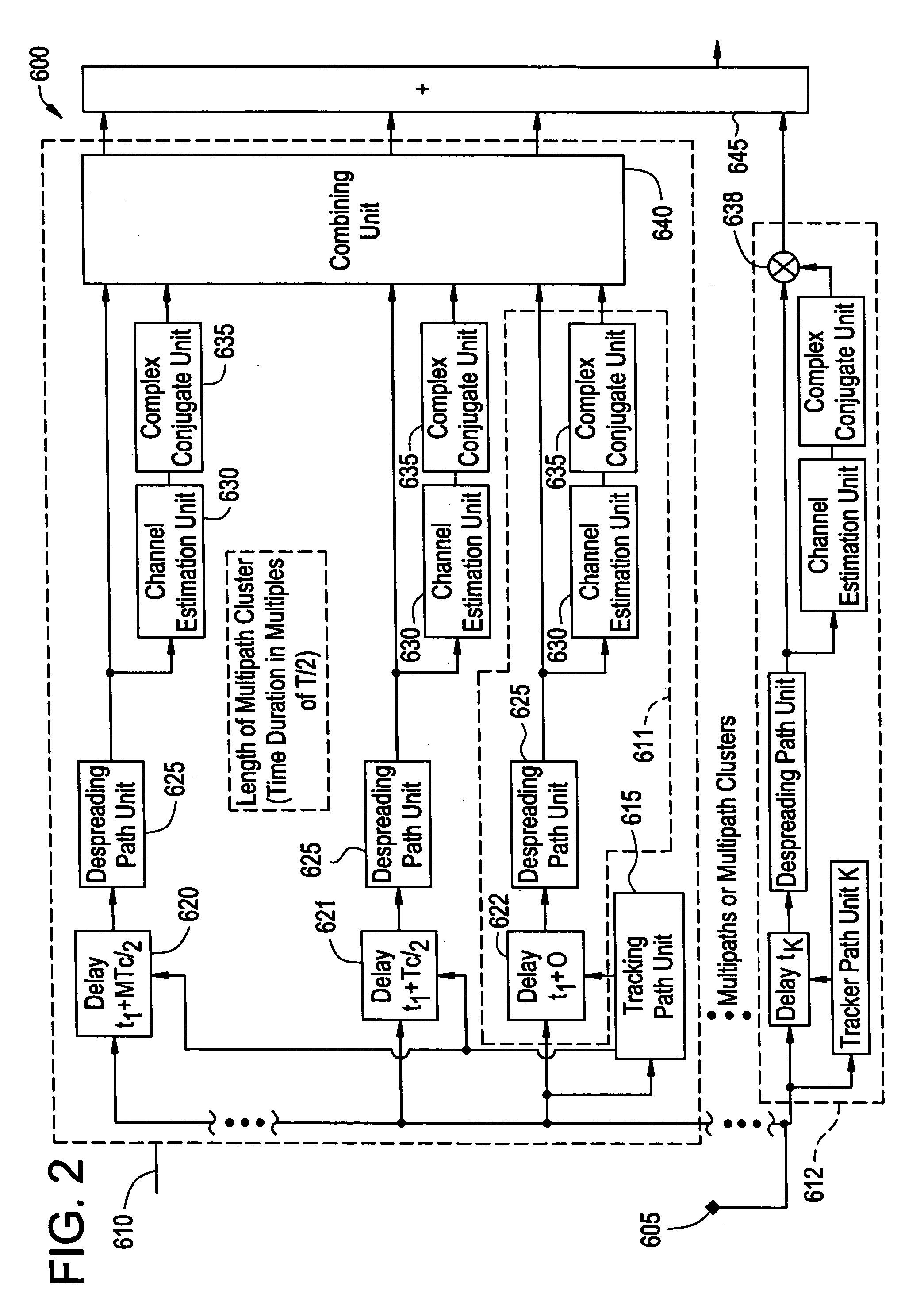
Method of processing multi-path signals
InactiveUS20060126705A1Time-division multiplexAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsCross correlation matrixEngineering
In the method of processing signals, multi-path signals are received, channel estimates for the received multi-path signals are determined, and a combining operation is applied to the multi-path signals, the combining operation being a function of a correlation matrix of the received multi-path signals, a correlation matrix of estimates for channels of the received multi-path signals, a cross-correlation matrix of the channels and channel estimates for the received multi-path signals, and the channel estimates.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
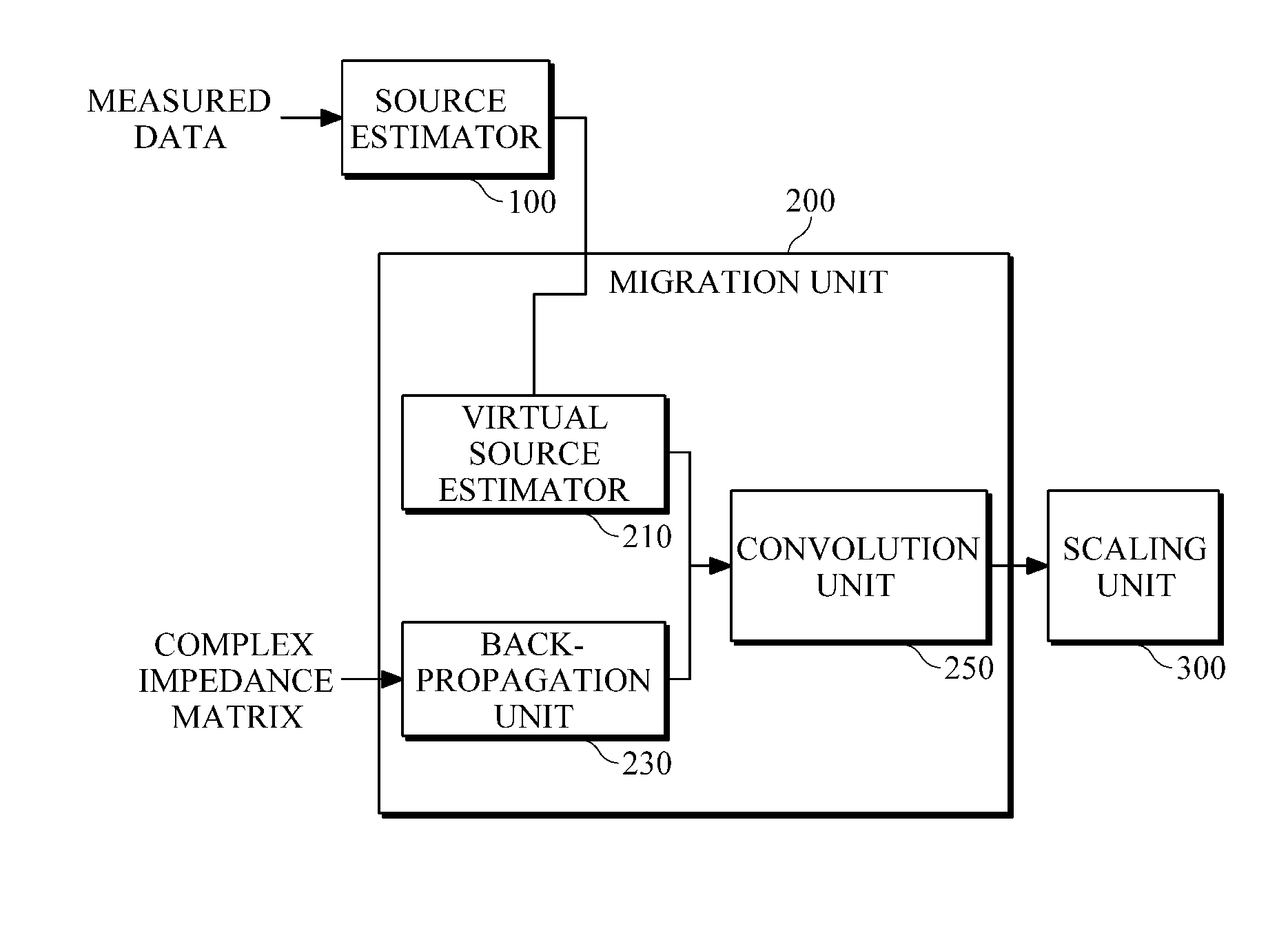
Method and apparatus for time-domain reverse-time migration with source estimation
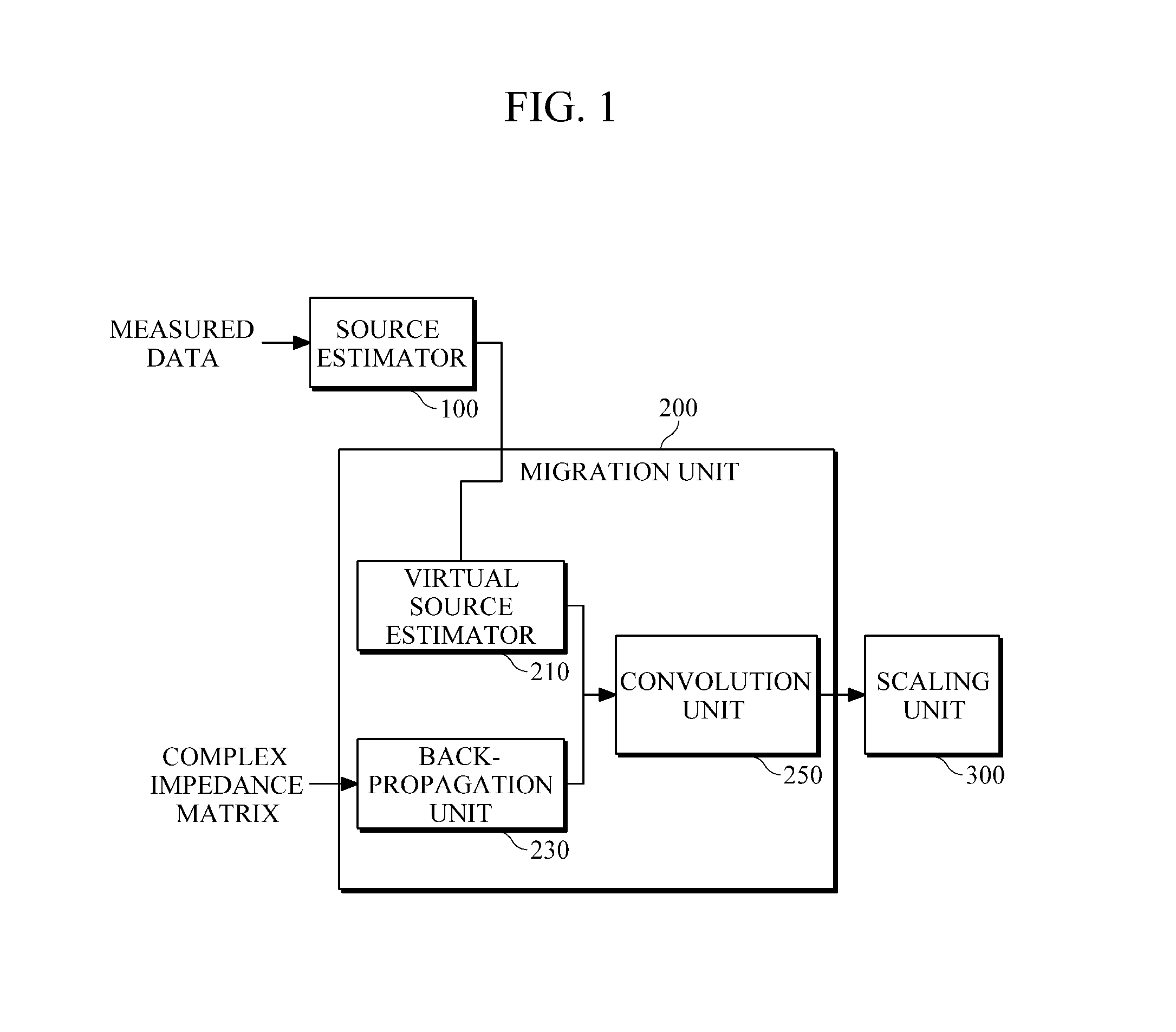
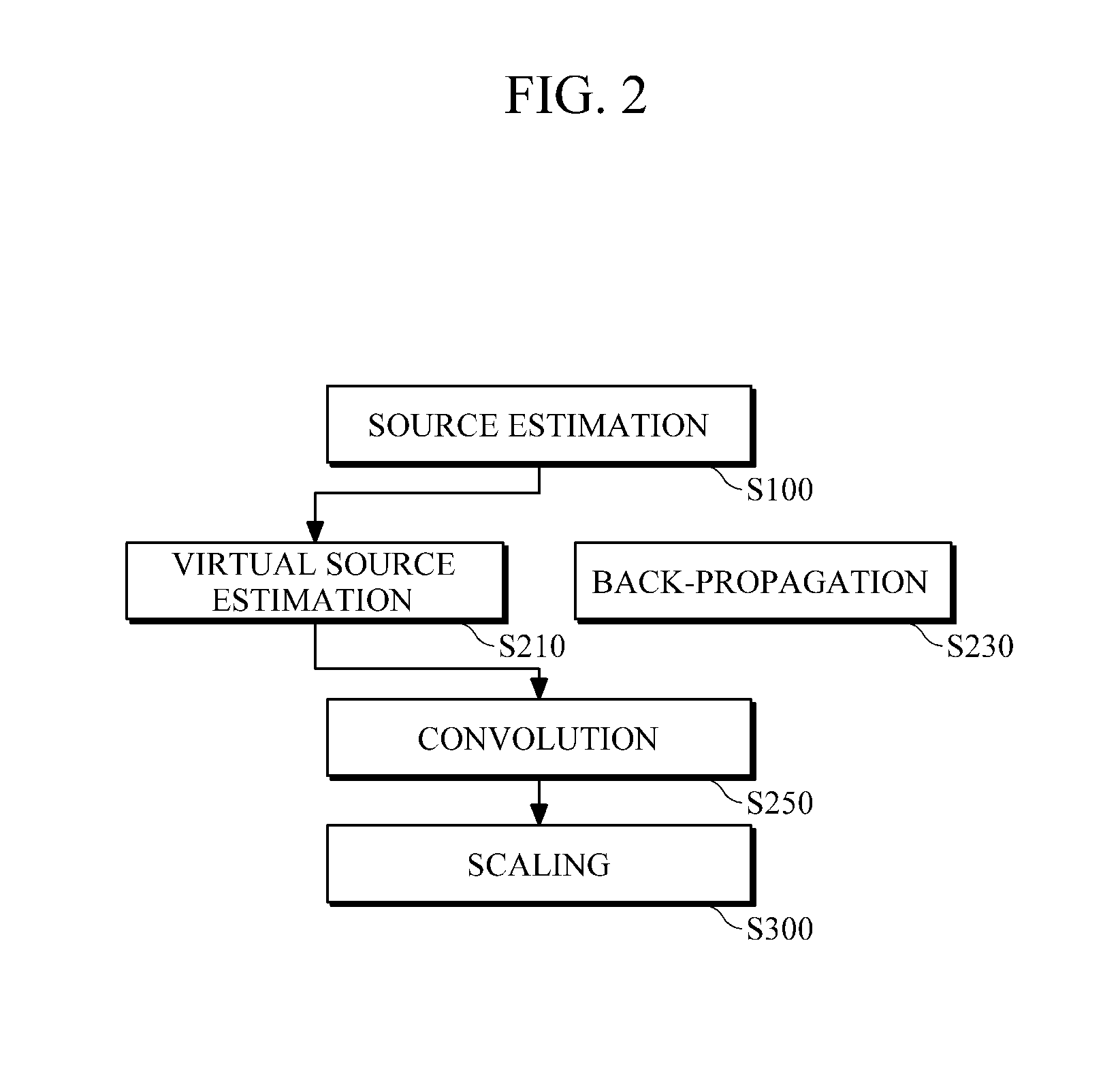
Provided is seismic imaging, particularly, a time-domain reverse-time migration technique for generating a real subsurface image from modeling parameters calculated through waveform inversion, etc. A reverse-time migration apparatus according to an example includes a source estimator configured to estimate sources by obtaining transmission waveforms from data measured by a plurality of receivers, through waveform inversion, and a migration unit configured to receive information about the estimated sources, and to perform reverse-time migration in the time domain. The source estimator estimates sources, by solving first-order matrix equation including a Toeplitz matrix composed of autocorrelation values of the Green's function, and a cross-correlation matrix of measured data and the Green's function, through Levinson Recursion. In more detail, the migration unit includes a back-propagation unit configured to back-propagate the measured data; a virtual source estimator configured to estimate virtual sources from the sources estimated by the source estimator; and a convolution unit that configured to convolve the back-propagated data with the virtual sources and output the results of the convolution.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Soft decision-based decorrelator for estimating spatial signatures in a wireless communications system
InactiveUS6931262B2Spatial transmit diversitySubstation equipmentCommunications systemCross correlation matrix
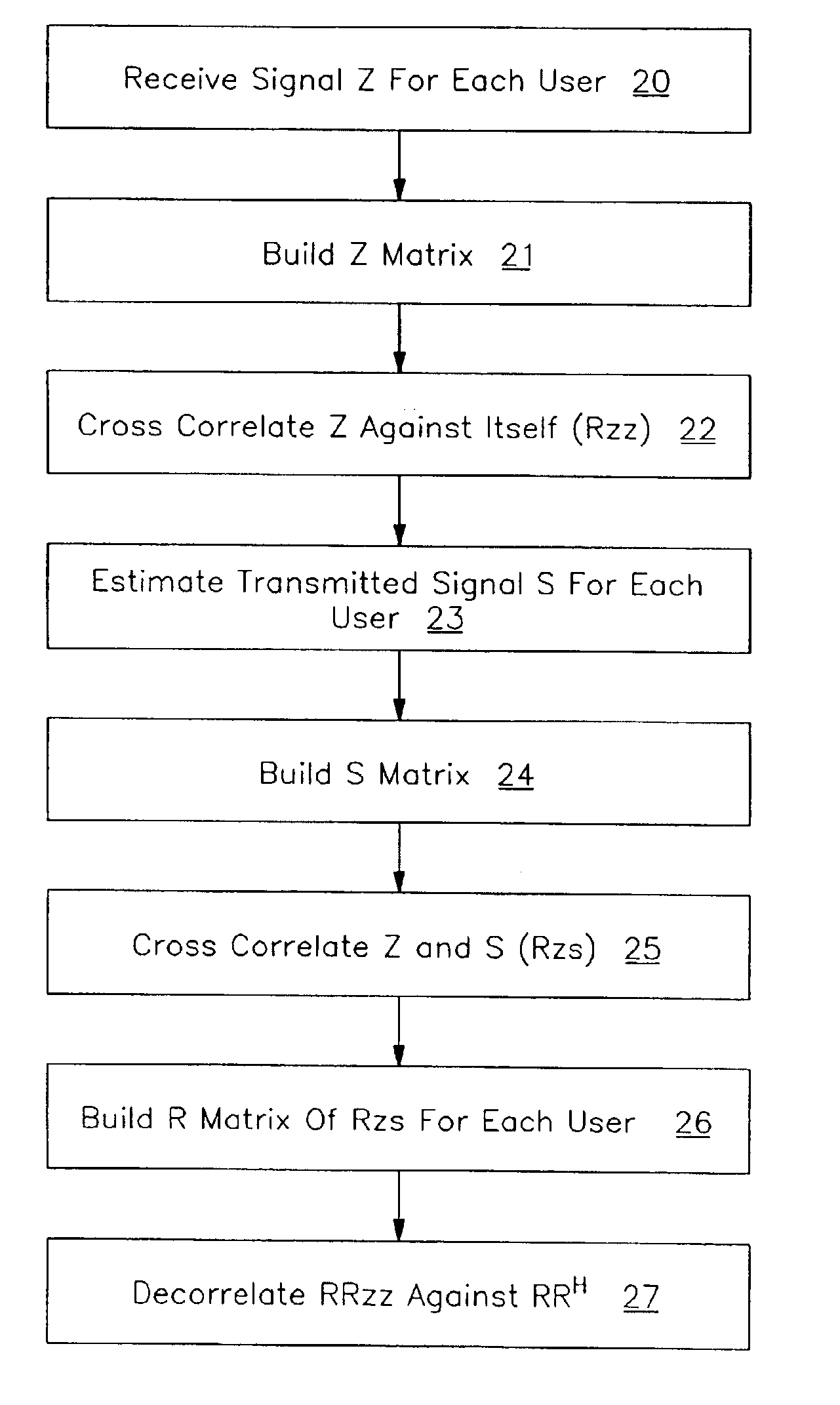
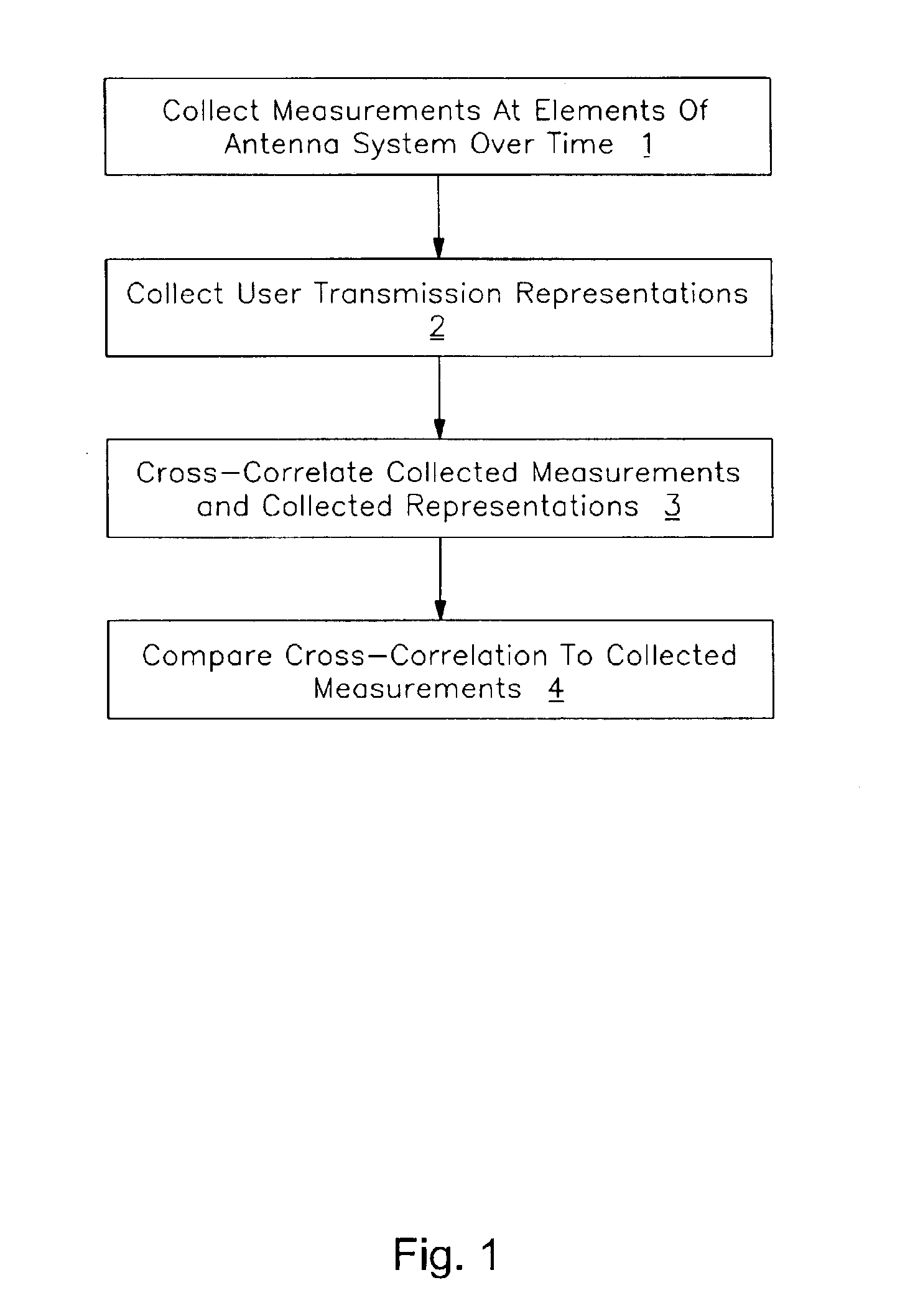
Spatial and temporal characteristics of received radio signals in a multiple user radio system can be estimated based on signals received from the users. In one embodiment, the invention includes measuring radio frequency signals received at different elements of an antenna system over time, the received signals corresponding at least in part to transmissions received from a system user, accumulating the signal measurements into a first matrix, and generating a second matrix representing the transmissions of the system user. The invention further includes cross-correlating the first and second matrices to form a first cross-correlation matrix, cross-correlating the first matrix with itself to form a second cross-correlation matrix, and multiplying the second cross-correlation matrix with a product of the first cross-correlation matrix to form a fifth matrix in which the elements of the fifth matrix characterize the radio channel traversed by transmissions of the system user.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Partial sparse L array and two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof
InactiveCN106019213AImprove direction finding accuracyLow costRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsDecompositionCross correlation matrix
The invention discloses a partial sparse L array and a two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof. Two subarrays for the L array, the array element interval of the first subarray is half of a wavelength, and the array element interval of the second subarray is n times of the wavelength; and an auxiliary array element distanced half of the wavelength away from a reference array element is arranged on the second subarray. During DOA estimation processing, the subarrays are respectively placed on an x axis and a z axis, and by use of a feature that a cross-correlation matrix is not affected by noise, cross correlation of receiving data is solved, and a signal subspace is extracted; by use of translation invariability of a ULA and the signal subspace, a rotation matrix of a z-axis array flow type matrix is solved, possible pitch angle estimation values are obtained by performing feature value decomposition on the rotation matrix, and then defuzzificaiton processing is performed on estimation results based on the auxiliary array element; and then based on this, a source waveform and an x-axis array flow type matrix are estimated, and corresponding azimuths are solved. The partial sparse L array and the two-dimensional DOA estimation method thereof are applied to radar, sonar and the like, and have the advantages of low realization cost, low computation quantity and high direction finding precision.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
SAR calculation for multichannel mr transmission systems
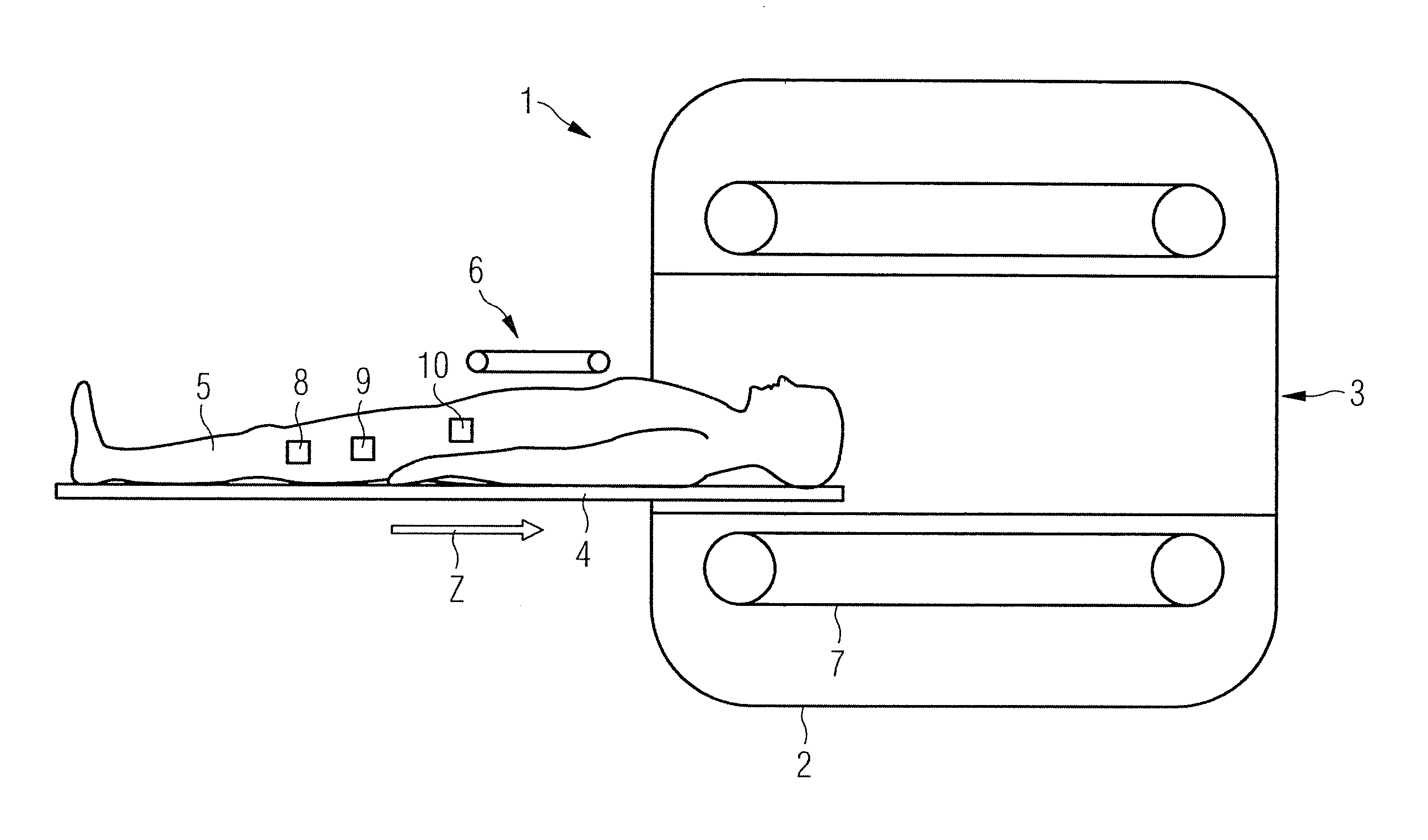
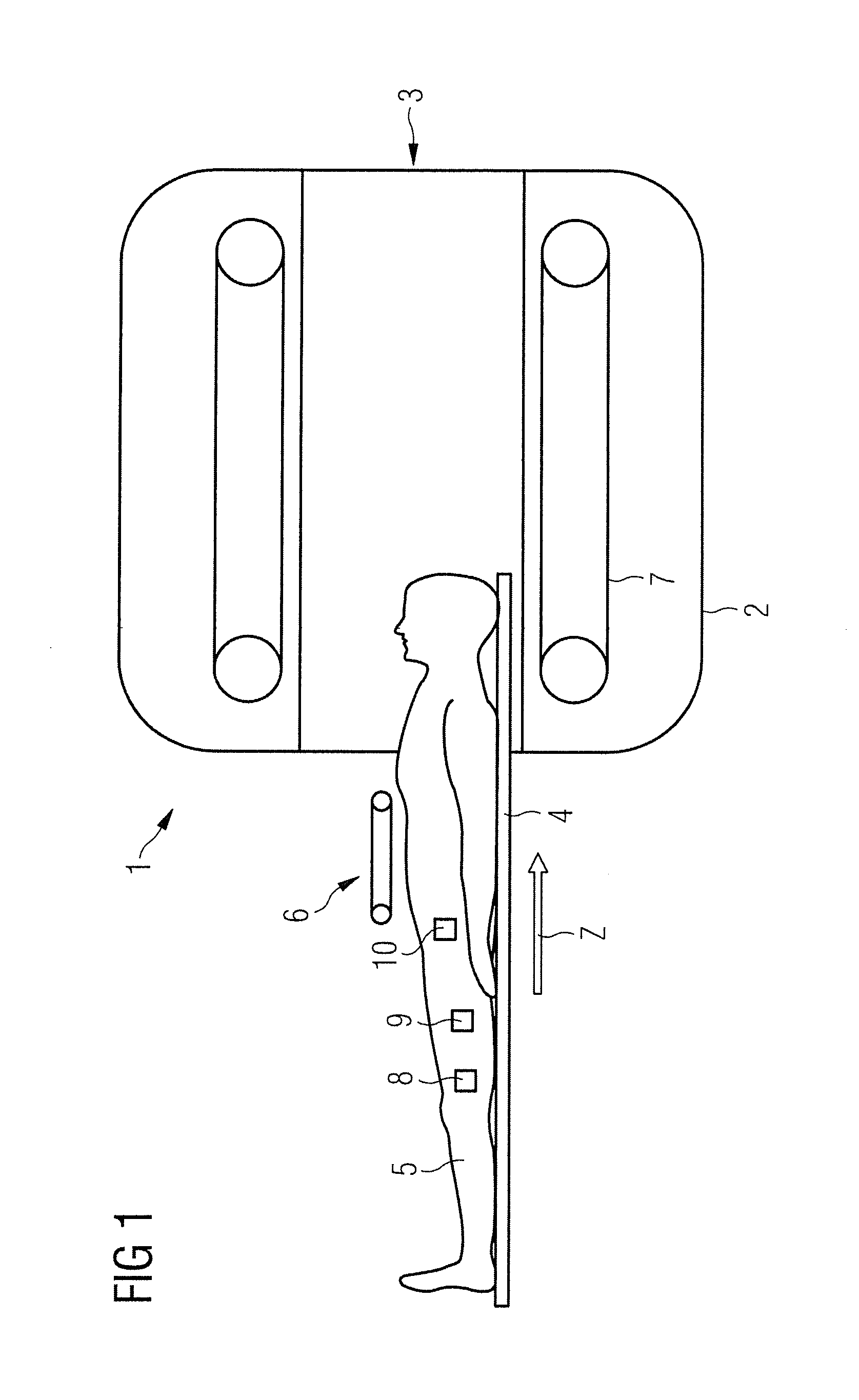
ActiveUS20100327868A1Efficient and accelerated calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCross correlation matrixResonance
In a device and a method to determine SAR for a magnetic resonance tomography transmission system with multiple antenna elements, a single-column cross-correlation matrix of an antenna element matrix of antenna element values of multiple antenna elements of the magnetic resonance tomography transmission system is determined for each of multiple points in time or time periods. These single-column cross-correlation matrices are added into a sum cross-correlation matrix over a summation time period and the sum cross-correlation matrix is multiplied with a hotspot sensitivity matrix. The hotspot sensitivity matrix represents the sensitivities in at least one direction at a number of hotspot points in a subject located in the magnetic resonance tomography transmission system. The product of the sum cross-correlation matrix and the hotspot sensitivity matrix is multiplied with a value representing the dielectricity at least one hotspot point in order to determine a respective SAR value for hotspot points. If at least one SAR value exceeds a predetermined upper limit, the voltage applied to at least one antenna element or the current flowing in at least one antenna element is reduced or deactivated.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
M-Algorithm multiuser detector with correlation based pruning
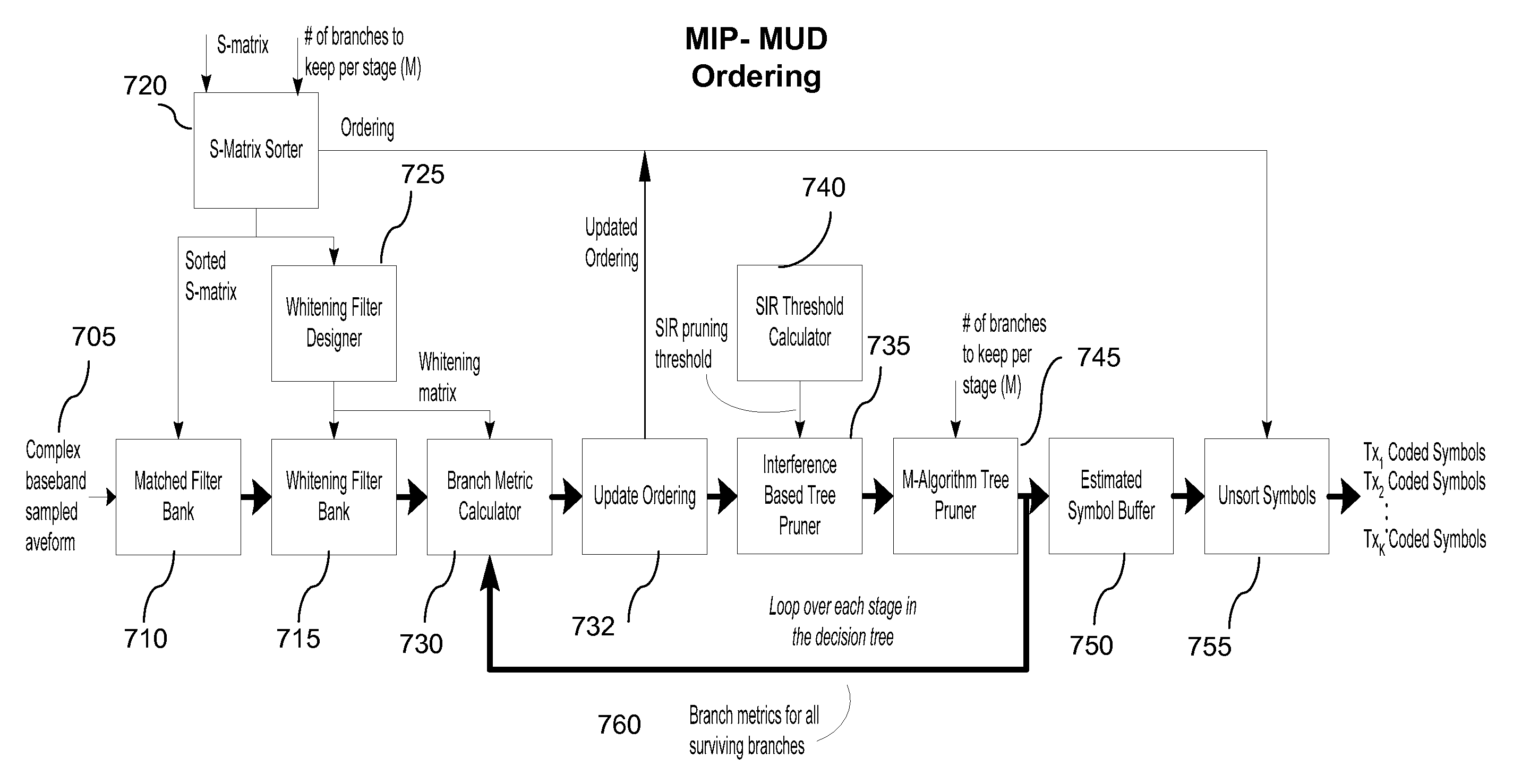
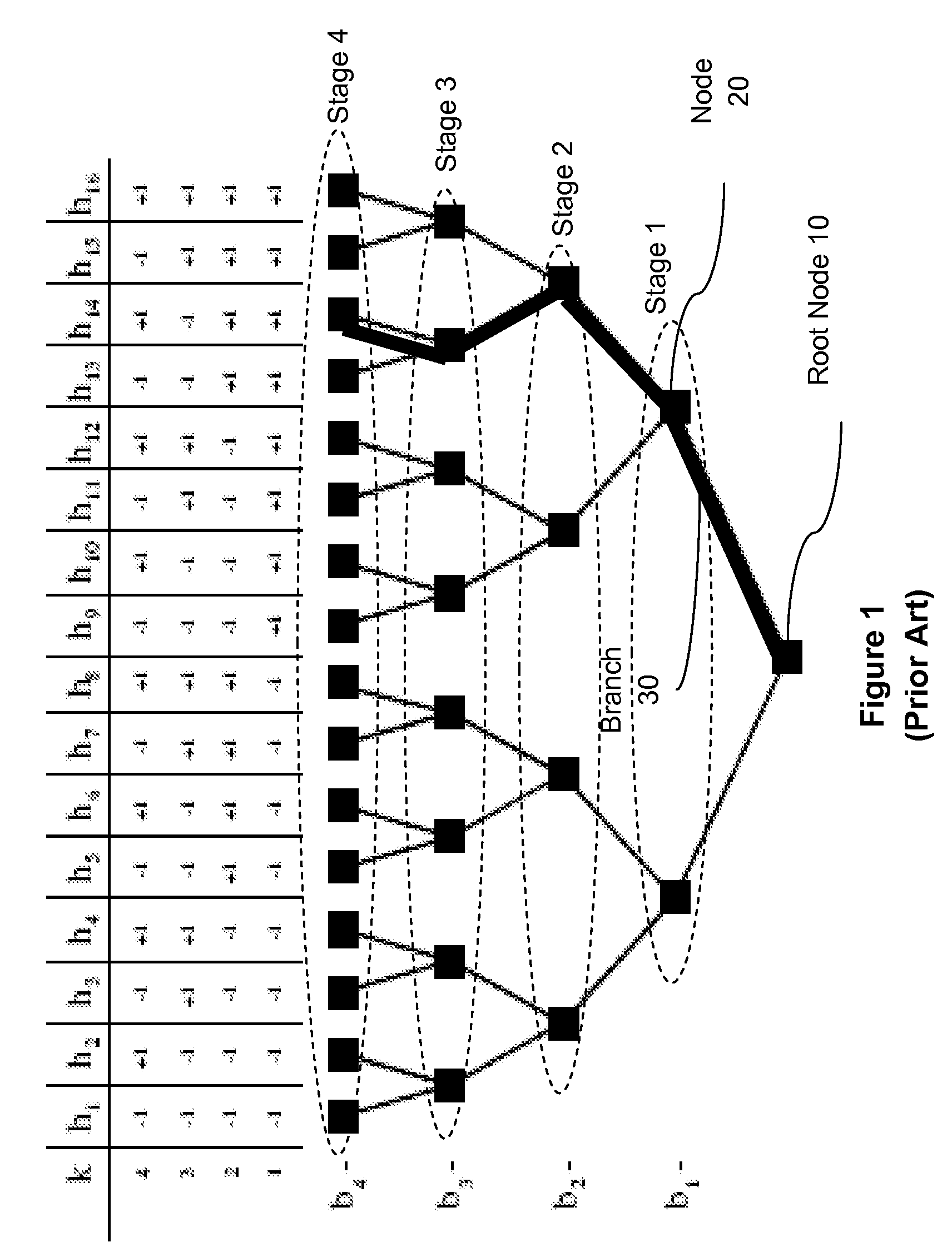
ActiveUS7613228B2Line-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsHypothesisRound complexity
A multiuser detector system with correlation based pruning including a parameter estimation module adapted to receive complex signals, and to produce estimated signature waveforms for each of K co-channel interfering signals. Pre-processing the estimated signature waveforms using an S-matrix module and producing a more valid set of hypotheses, wherein the S-matrix module uses apriori knowledge of an unnormalized cross correlation matrix, and processing the more valid set of hypotheses for pruning with an M-algorithm in a multiuser detector module. An improvement to the M-algorithm in which the interference structure based on the signal correlation matrix used during the optimization process aids in selecting a better subset of hypotheses to test. This approach has the benefit of reducing computational complexity and improving performance over the existing M-algorithm.
Owner:COLLISION COMM INC
Method for determining similarities between data sequences using cross-correlation matrices and deformation functions
InactiveUS7328111B2Analogue computers for chemical processesCharacter and pattern recognitionCross correlation matrixCorrelation ratio
A method compares a first data sequence with a second data sequence. A cross-correlation matrix of distances between all possible pairs of values of the first and second data sequences is constructed. A minimum cost path between diagonally opposing corners of the cross-correlation matrix is determined. The minimum cost path is projected onto a transfer function that maps between the first data sequence and the second data sequence. Then, the minimum cost path is projected onto a deformation function that corresponds to a similarity between the first data sequence and the second data sequence.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC RES LAB INC
Estimation algorithm for two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of L-shaped array by adopting time-frequency analysis
InactiveCN106772224AEliminate the effects ofImprove robustnessRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsFrequency spectrumCross correlation matrix
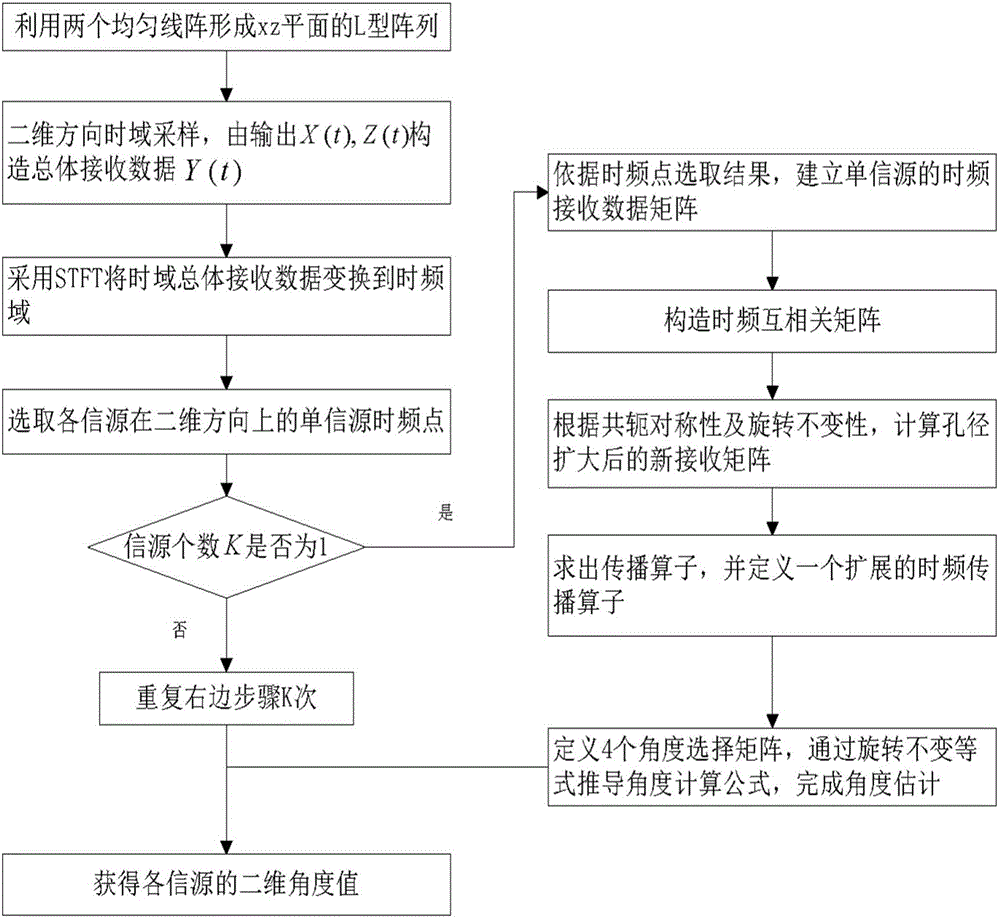
The invention discloses an estimation algorithm for two-dimensional direction of arrival (DOA) of an L-shaped array by adopting time-frequency analysis. The estimation algorithm disclosed by the invention mainly aims at solving the problem of two-dimensional DOA estimation of time-frequency spectrum aliasing and spatial neighborhood information sources and is suitable for low signal to noise ratio and underdetermined conditions. The estimation algorithm is realized by the following steps: firstly, forming the L-shaped array on an xz plane by using two uniform linear arrays to construct total receiving data; secondly, transforming the total receiving data into a time-frequency domain by adopting STFT (Short Time Fourier Transform); thirdly, selecting single information source time-frequency points of all the information sources in a two-dimensional direction, and establishing a time-frequency receiving data matrix of single information sources; fourthly, constructing a time-frequency cross correlation matrix; fifthly, calculating a novel receiving matrix subjected to aperture expansion; sixthly, based on a propagation operator principle, defining a propagation operator subjected to the aperture expansion; seventhly, constructing an angle selection matrix, and calculating the two-dimensional DOA according to rotational invariance among sub-matrixes. According to the estimation algorithm disclosed by the invention, estimation precision of the time-frequency spectrum aliasing and spatial neighborhood information sources and the success rate are improved, high robustness of noises is realized, and required number of array elements can be reduced.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Image-segmentation-based registration method of polarized InSAR image in repeated passing
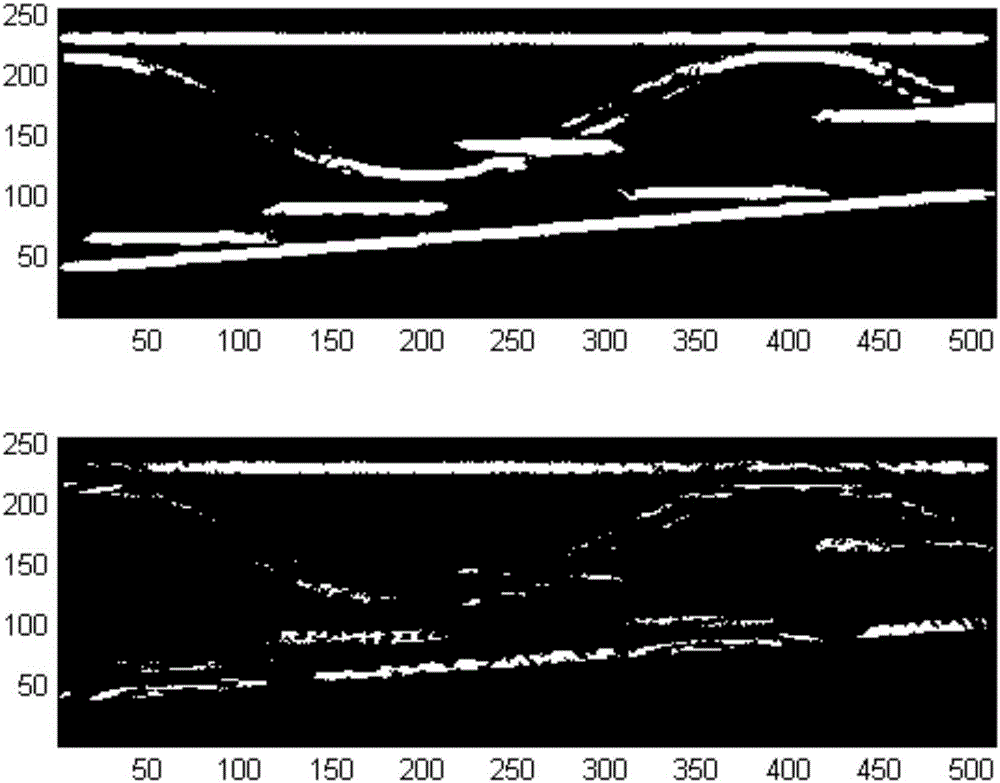
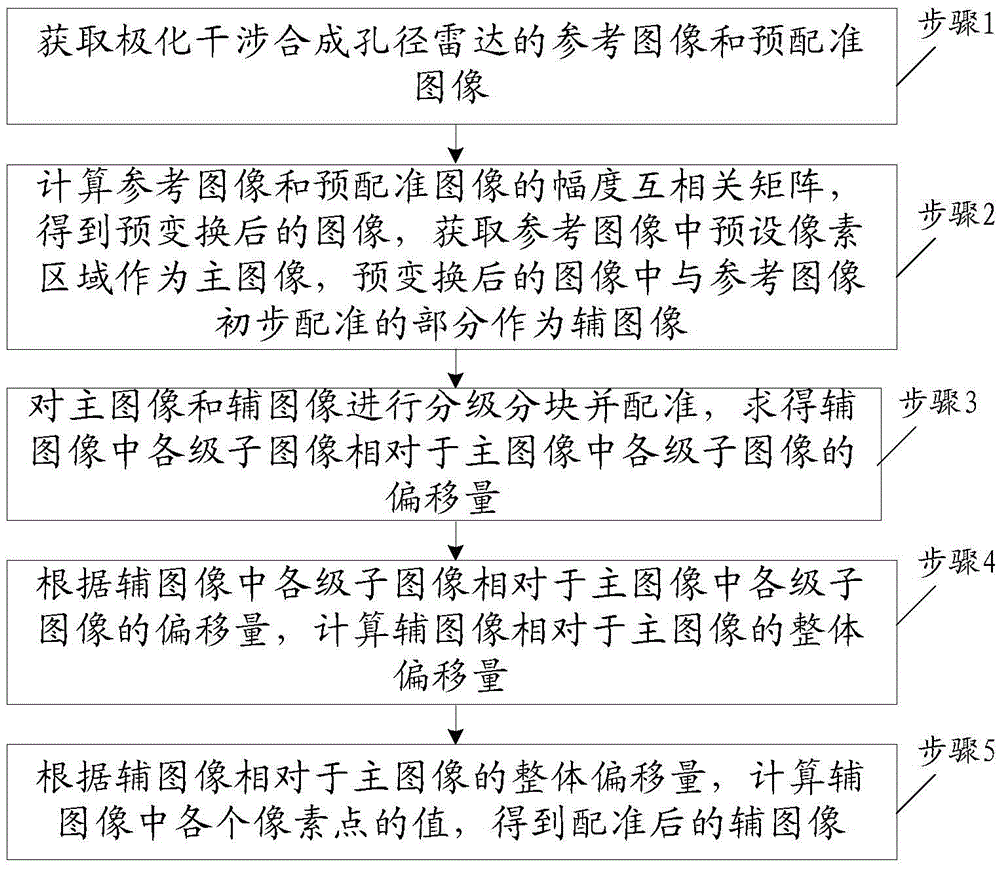
ActiveCN105425216AOffset is accurateExact searchRadio wave reradiation/reflectionInterferometric synthetic aperture radarCross correlation matrix
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of polarized interferometric synthetic aperture radar detection, discloses an image-segmentation-based registration method of a polarized InSAR image in repeated passing. The method comprises: a reference image and a pre-registered image of a polarized interferometric synthetic aperture radar are obtained; an amplitude cross-correlation matrix of the reference image and the a pre-registered image is calculated and common position parts of the reference image and a pre-converted image are obtained and then are used as a main image and an auxiliary image respectively; graded registration is carried out on the main image and the auxiliary image, thereby obtaining offsets of sub images at all levels in the auxiliary image relative to sub images at all levels in the main image; according to the offsets of sub images at all levels in the auxiliary image relative to sub images at all levels in the main image, an overall offset of the auxiliary image relative to the main image is calculated; and on the basis of the overall offset of the auxiliary image relative to the main image, values of all pixel points in the auxiliary image are calculated and then an auxiliary image after registration is obtained.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
A device and method for two-dimensional direction of arrival estimation based on L-shaped array
InactiveCN102279381AReduce mistakesAvoid the eigenvalue decomposition processRadio wave finder detailsRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsElevation angleCross correlation matrix
The invention relates to an L-shaped array-based two-dimensional wave arrival direction estimating device and a method thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring cross correlation matrixes by using a right angle folding ruler L-shaped array antenna which is formed by vertically connecting one end of an equal-distance linear sub-array antenna in a longitudinal direction x withone end of an equal-distance linear sub-array antenna in a vertical direction z, and according to observation data which is acquired from the equal-distance linear sub-array antenna in the longitudinal direction x and the equal-distance linear sub-array antenna in the vertical direction z; independently acquiring an azimuth angle estimation value and an elevation angle estimation value through linear operation; and automatically accomplishing the process of matching an azimuth angle with an elevation angle by minimizing an azimuth angle and elevation angle cost function. Thus, the characteristic value decomposition process is avoided, complexity is reduced, a few estimation errors are generated, and precision is high.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Automatically-registered two-dimensional direction-of-arrival estimation device and method thereof
InactiveCN102142879AAvoid Angle Matching ProblemsSpatial transmit diversityCross correlation matrixDecomposition
The invention discloses an automatically-registered two-dimensional direction-of-arrival estimation device and a method thereof. In the method, the pitch angle in an arrival direction is estimated first and then the azimuth angle in the arrival direction is estimated according to the pitch angle by connecting longitudinal x-directional equidistant linear sub-array antennae, vertical z-directional equidistant linear sub-array antennae, a correlation matrix calculation device, a subspace estimation device and an arrival direction estimation device in a communication way, decorrelating an incident signal by utilizing a sub-array averaging technology, and simultaneously obtaining zero space by implementing a linear operation on a cross-correlation matrix of L-array received data. In the method, eigenvalue decomposition does not need to be performed, and the problem of angle matching is avoided.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
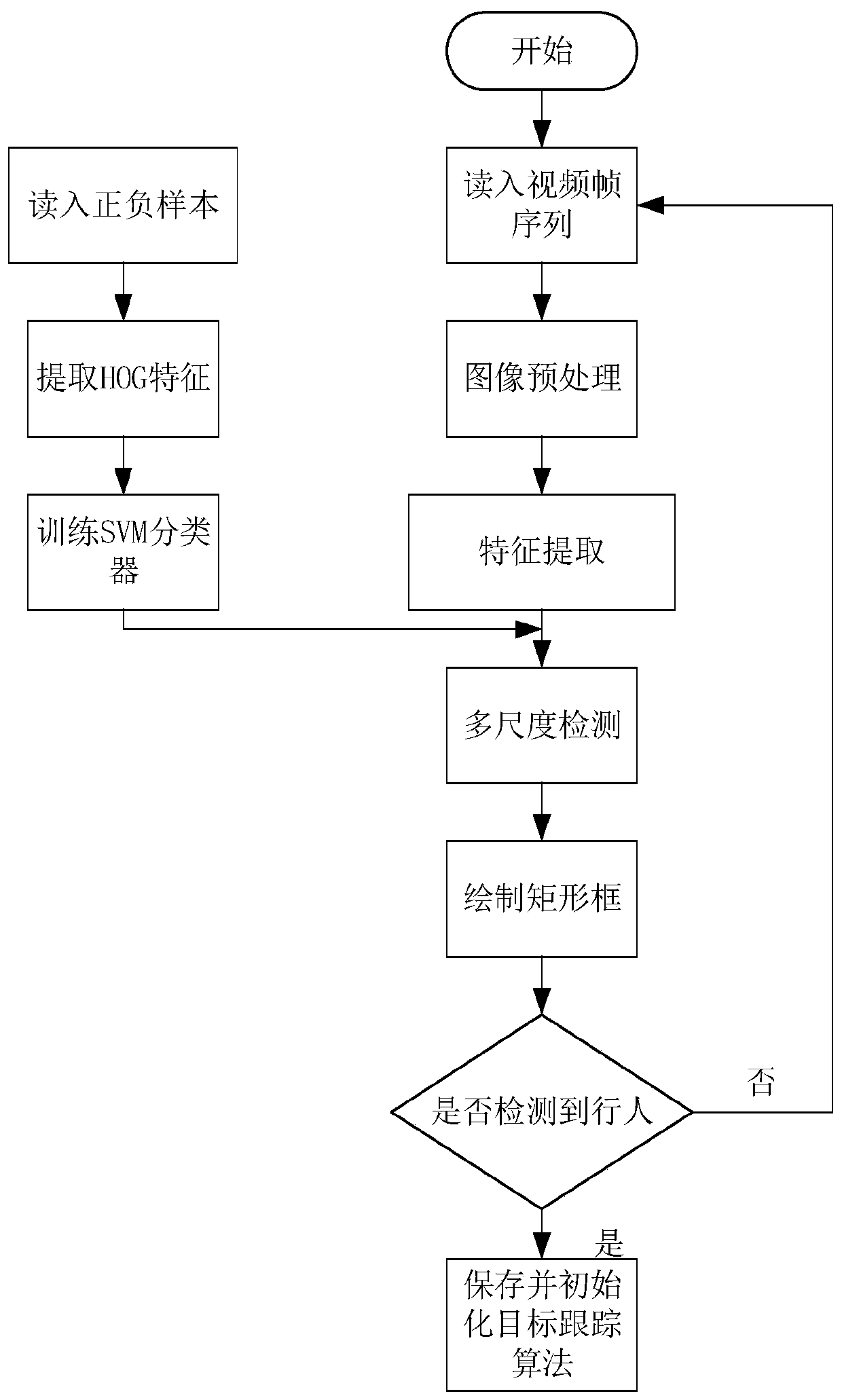
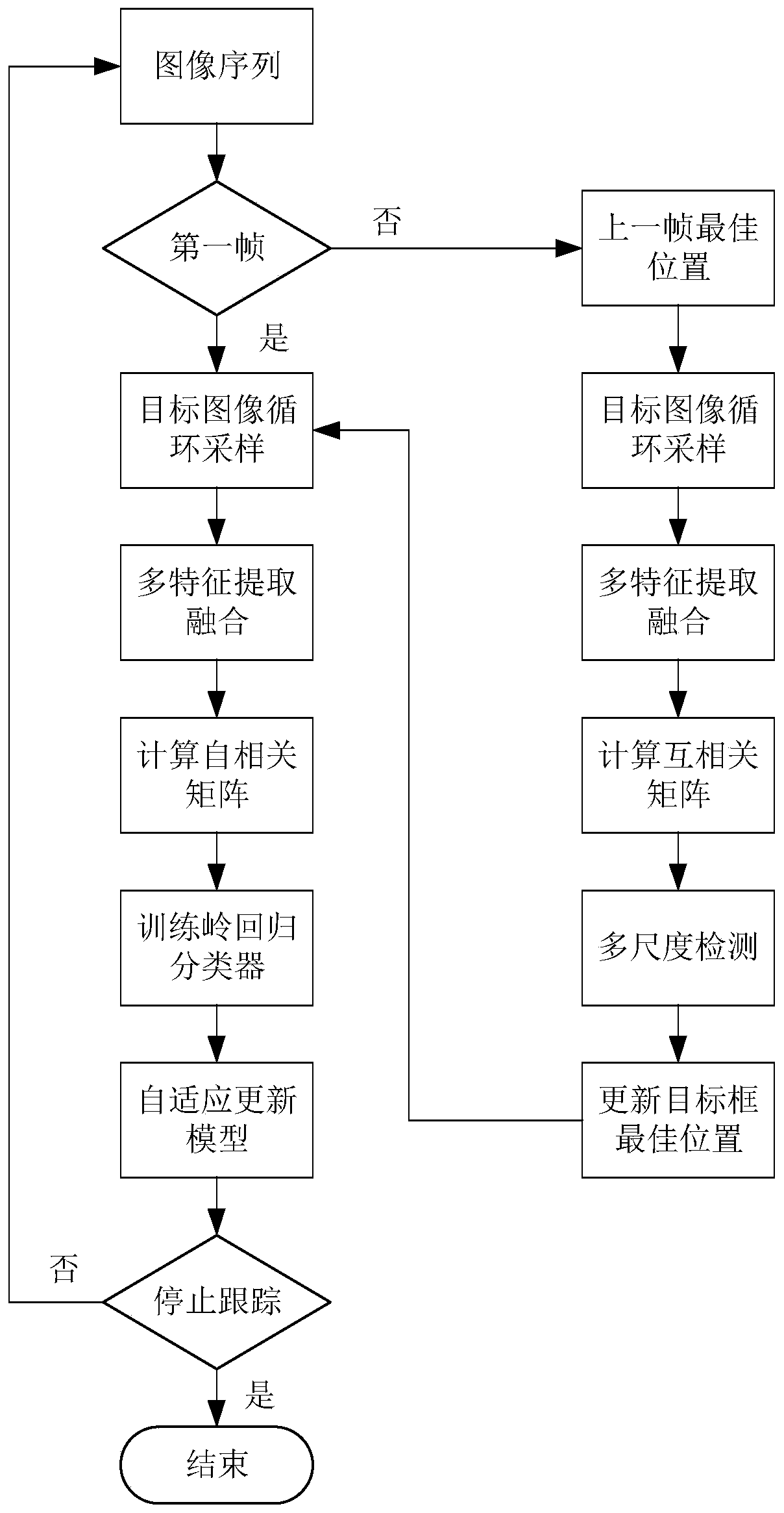
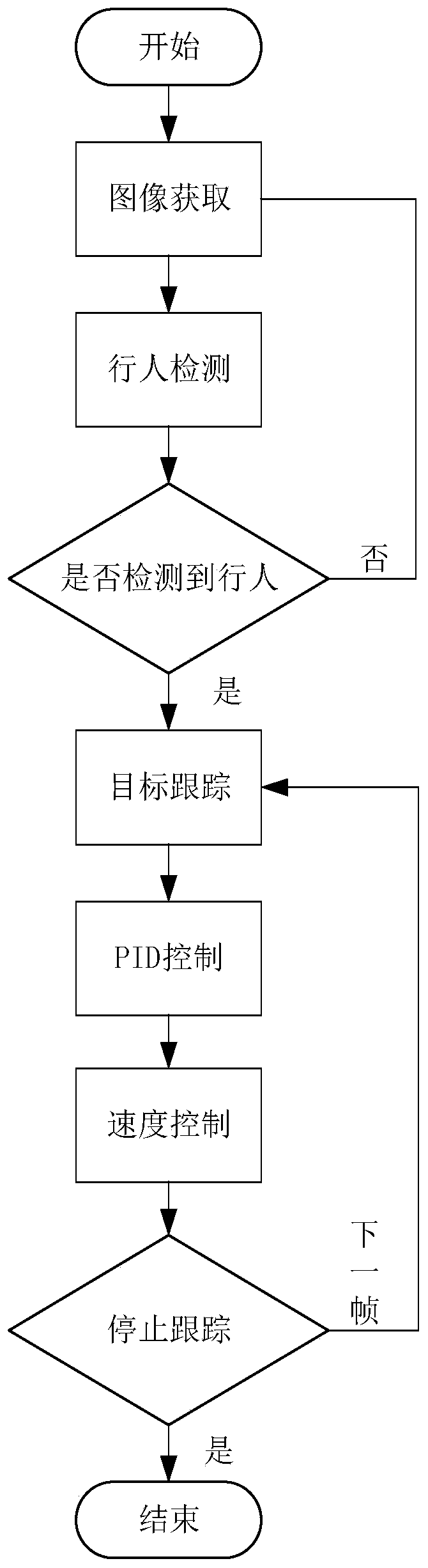
Kernel correlation filtering target tracking method suitable for pedestrian following of mobile robot
PendingCN109858415AAchieve goal trackingHigh precisionCharacter and pattern recognitionScale modelFeature vector
The invention discloses a kernel correlation filtering target tracking method suitable for pedestrian following of a mobile robot. The kernel correlation filtering target tracking method comprises thesteps of utilizing SVM pedestrian classifier based on OpenCV to detect and initialize target position and target area; constructing a training sample according to the target area of the current frame, and performing multi-feature extraction and weighted fusion to obtain a feature vector; constructing a ridge regression model classifier for target tracking by taking a kernel autocorrelation cyclicmatrix in a Fourier space as input and taking a regression value as output, and calculating to obtain a learning weight coefficient; reading in the next frame, constructing a detection sample according to the target position of the previous frame, and forming a cross-correlation matrix with the training sample; establishing a scale pyramid and combining bilinear interpolation to obtain target detection areas of different scale models, calculating to obtain the maximum response and updating the target position; and training and updating the target tracking ridge regression model classifier again. According to the method, the target can be effectively captured, multi-level scale adaptive transformation is achieved, and good robustness and real-time performance are achieved.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
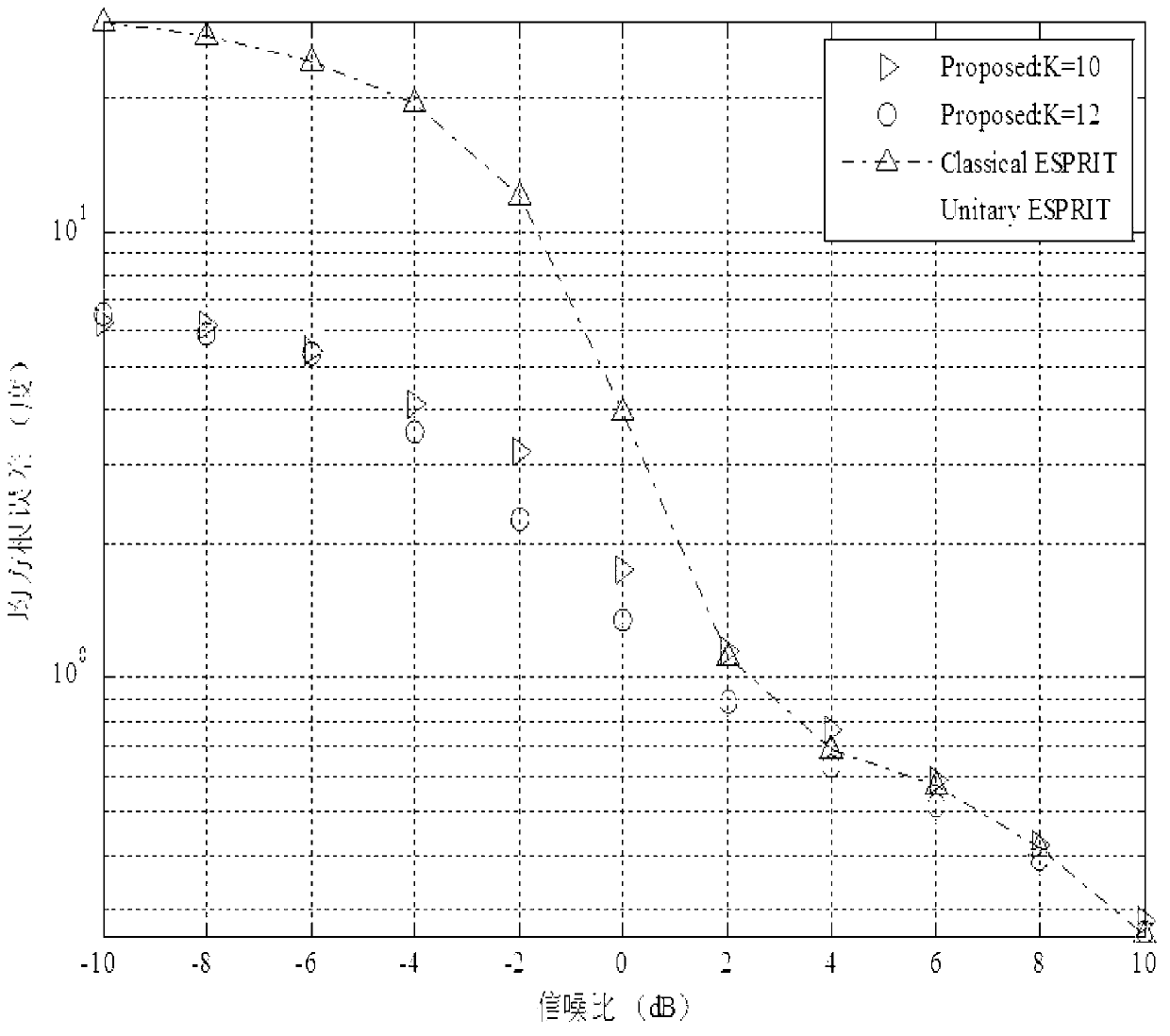
Low-complexity DOA estimation method and system
ActiveCN103344940AAvoid decompositionReduce complexityMulti-channel direction-finding systems using radio wavesCross correlation matrixEstimation methods
The invention provides a low-complexity DOA estimation method and system. According to the low-complexity DOA estimation method, unitary transformation is carried out on sample data, data obtained after transformation are divided into two parts, an autocorrelation matrix of and a cross-correlation matrix of and are calculated, and the real part of the autocorrelation matrix and the real part of the cross-correlation matrix are extracted. The low-complexity DOA estimation method and system has the advantages that only a subsample covariance matrix of two real number fields needs to be calculated, a signal subspace is constructed through the method, construction of the covariance matrix of the whole sample and eigenvalue decomposition are avoided, and complexity is further lowered.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
M-algorithm multiuser detector with correlation based pruning
ActiveUS20070036250A1Line-faulsts/interference reductionAmplitude-modulated carrier systemsRound complexityHypothesis
A multiuser detector system with correlation based pruning including a parameter estimation module adapted to receive complex signals, and to produce estimated signature waveforms for each of K co-channel interfering signals. Pre-processing the estimated signature waveforms using an S-matrix module and producing a more valid set of hypotheses, wherein the S-matrix module uses apriori knowledge of an unnormalized cross correlation matrix, and processing the more valid set of hypotheses for pruning with an M-algorithm a multiuser detector module. An improvement to the M-algorithm in which the interference structure based on the signal correlation matrix used during the optimization process aids in selecting a better subset of hypotheses to test. This approach has the benefit of reducing computational complexity and improving performance over the existing M-algorithm
Owner:COLLISION COMM
Method and system for detection of broadband energy
InactiveUS7009912B1Direction finders using ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wavesRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLine sensorFrequency spectrum
A system and related method for the detection of low power broadband signal sources in a high noise environment. The system uses multiple collinear arrays of sensors to receive data signals. The sensor-to-sensor spacing within the arrays is greater than one-half the wavelength of the center frequency associated with the broadband spectrum of interest. The signals are processed using nonlinear spectral estimation to remove periodic signals from the data signals to obtain broadband data. A cross correlation matrix is formed from the broadband data. Nonlinear spectral estimation is applied to the cross correlation matrix to determine the angular direction of the low power broadband signal sources with respect to the arrays.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Method for estimation of probe shape in charged particle beam instruments
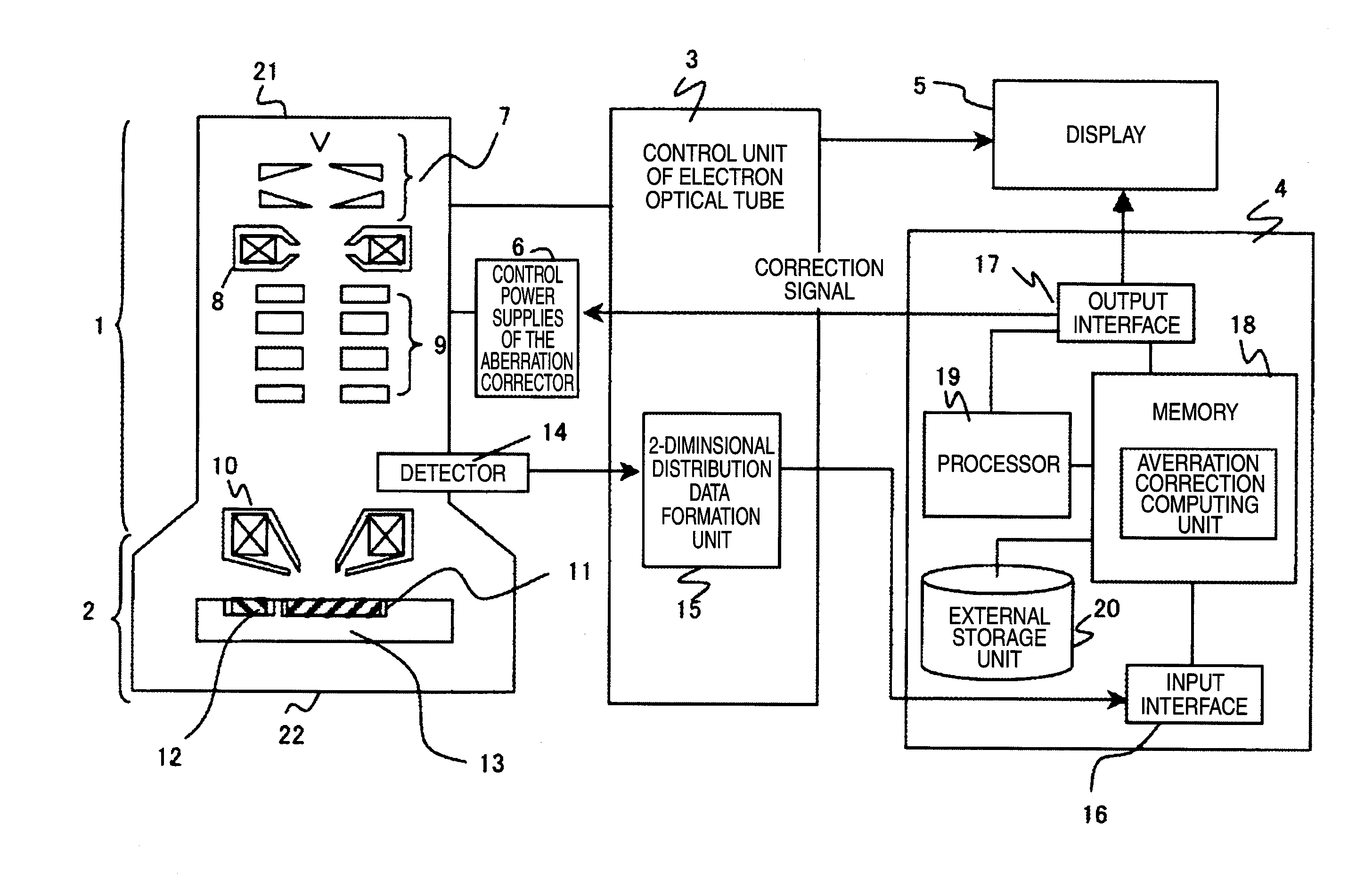
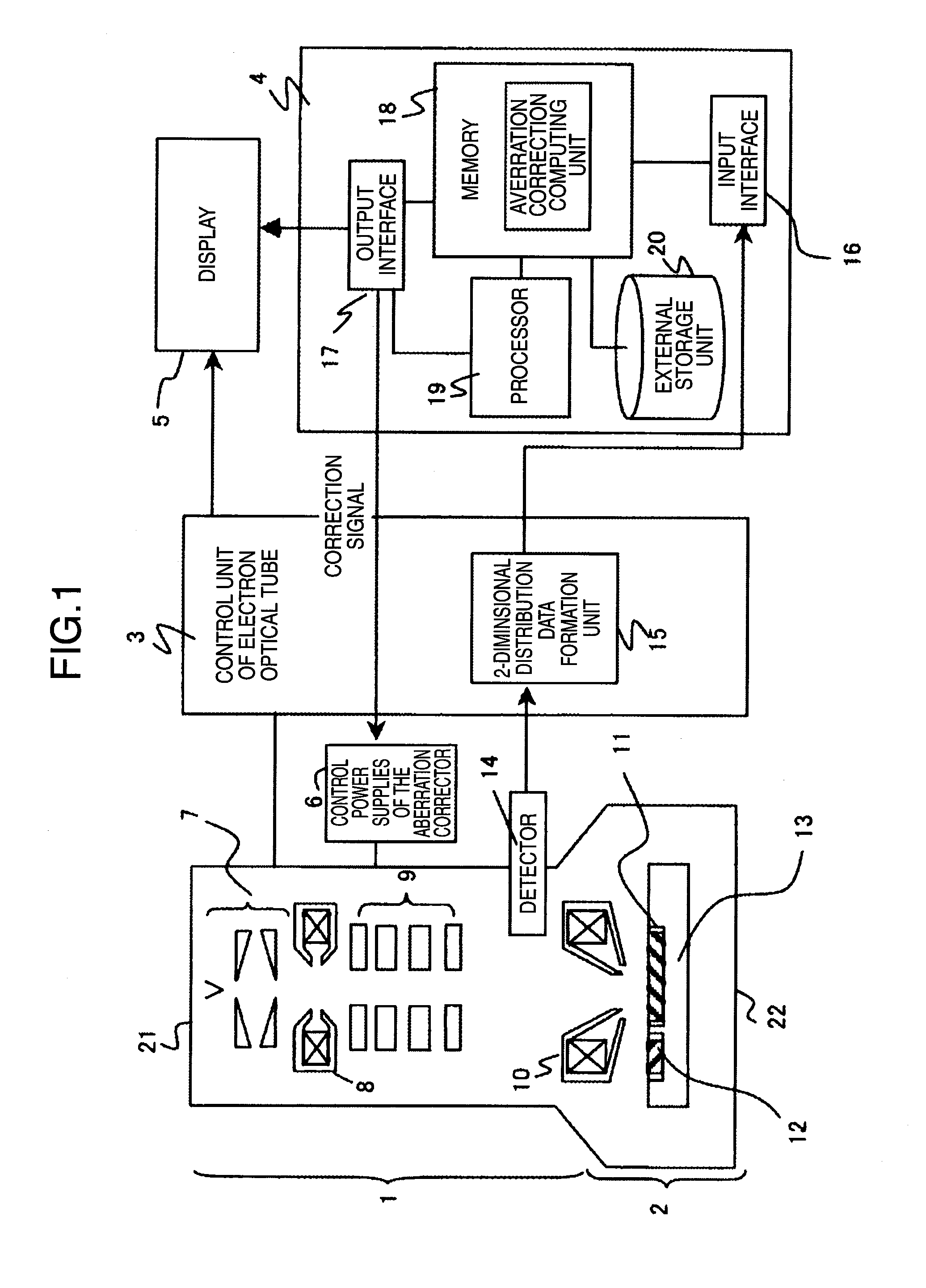
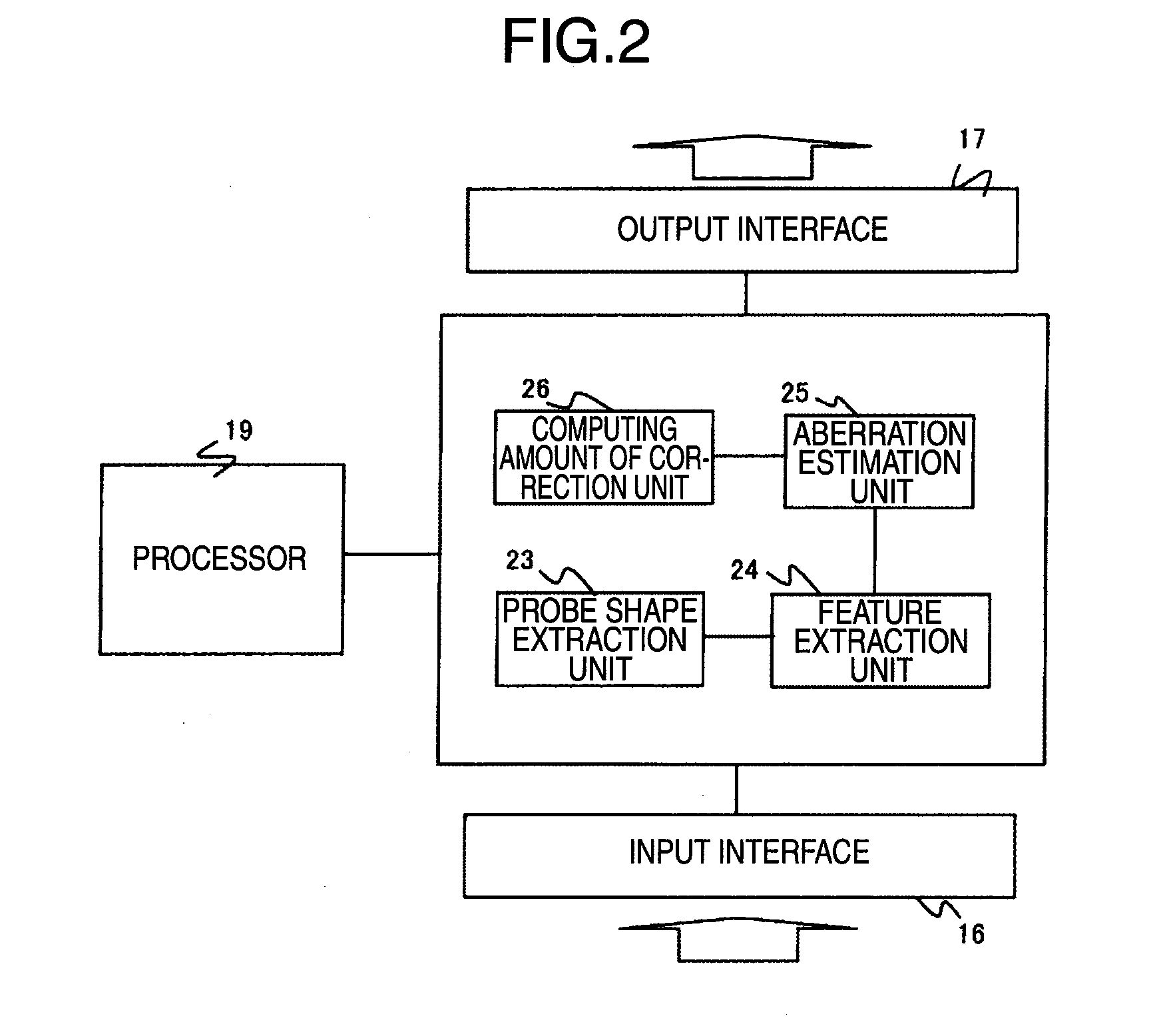
InactiveUS20100264309A1Improve accuracySuitable for automationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesCross correlation matrixScanning electron microscope
A method for estimation of a probe shape, in a scanning electron microscope provided with an aberration corrector, and the method is designed so as to obtain a probe image, by inputting to a computer an image taken in a just-focused state and an image taken in a de-focused state, as an image data; preparing a correlation window by automatically determining a size of a correlation window image, based on an input data size and an output data size; executing cross-correlation calculation between the correlation window and a reference area; and repeating this calculation while shifting the reference area, so as to obtain a cross-correlation matrix, in order to stably obtain the probe image, without receiving effects of use conditions or noises.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Multi-channel speech enhancement method
ActiveCN102969000AAccurate estimateOvercoming Noise Energy FluctuationsSpeech analysisTime domainGeneralized eigenvalue decomposition
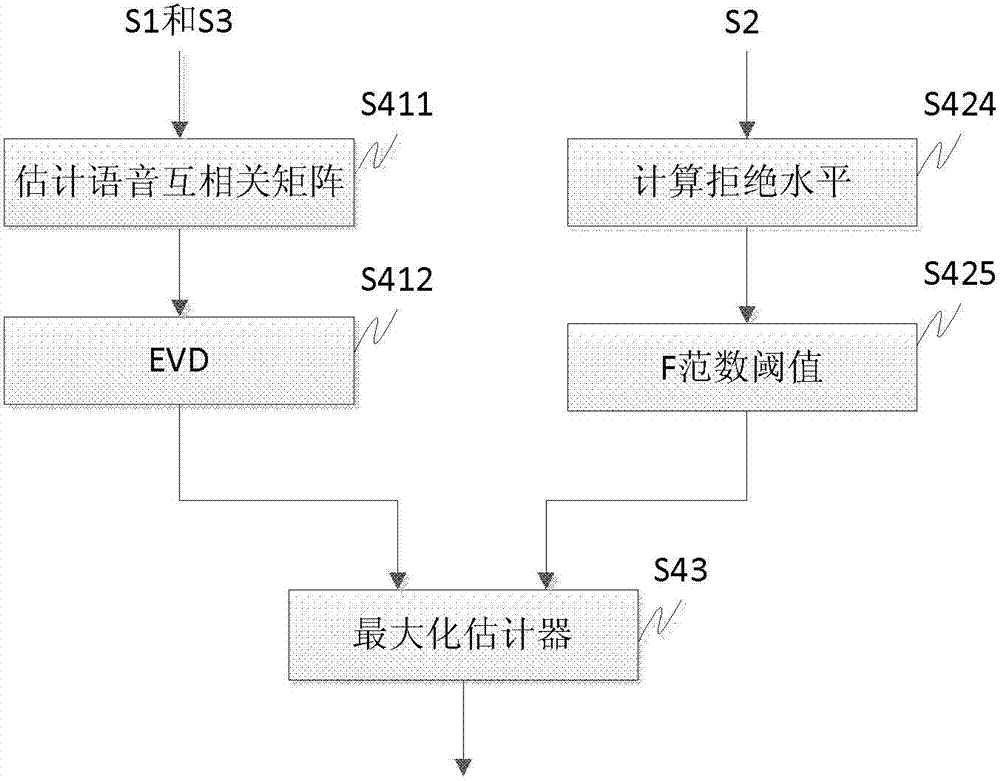
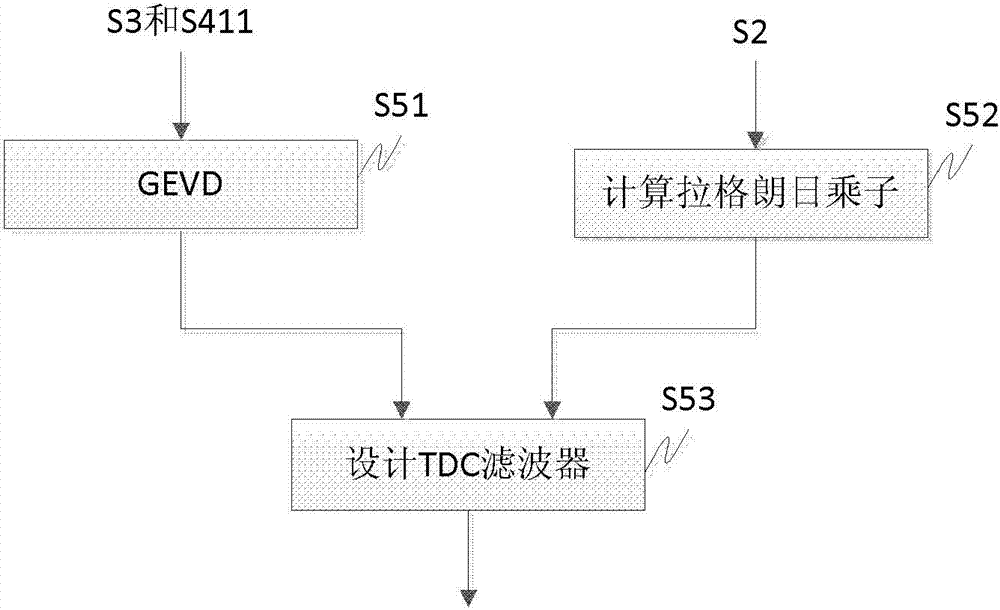
The invention discloses a multi-channel speech enhancement method in which a norm F is used for presenting the dimension of a signal subspace. The method comprises the following steps of: step 1, acquiring a multi-channel speech signal y(t) with a noise via a microphone array which is composed of N microphones, and calculating the noisy speech cross-correlation matrix Ryy of the multi-channel speech signal y(t), wherein t represents a discrete time point; step 2, estimating an additive noise cross-correlation matrix by virtue of a noise estimation algorithm; step 3, estimating a pure speech cross-correlation matrix by virtue of the noisy speech cross-correlation matrix Ryy and the additive noise cross-correlation matrix; step 4, estimating the dimension of the signal subspace by virtue of the pure speech cross-correlation matrix; step 5, performing generalized eigenvalue decomposition, and obtaining a time-domain constraint linear signal estimator by combining the dimension of the signal subspace and a Lagrangian multiplier mu; and step 6, filtering the multi-channel speech signal y(t) by virtue of the time-domain constraint linear signal estimator to obtain the enhanced speech.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com