M-Algorithm multiuser detector with correlation based pruning
a detector and correlation-based technology, applied in the direction of amplitude demodulation, line-fault/interference reduction, baseband system details, etc., can solve the problems of multiple-access interference, inability to realize real-time operation, and inability to achieve real-time operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
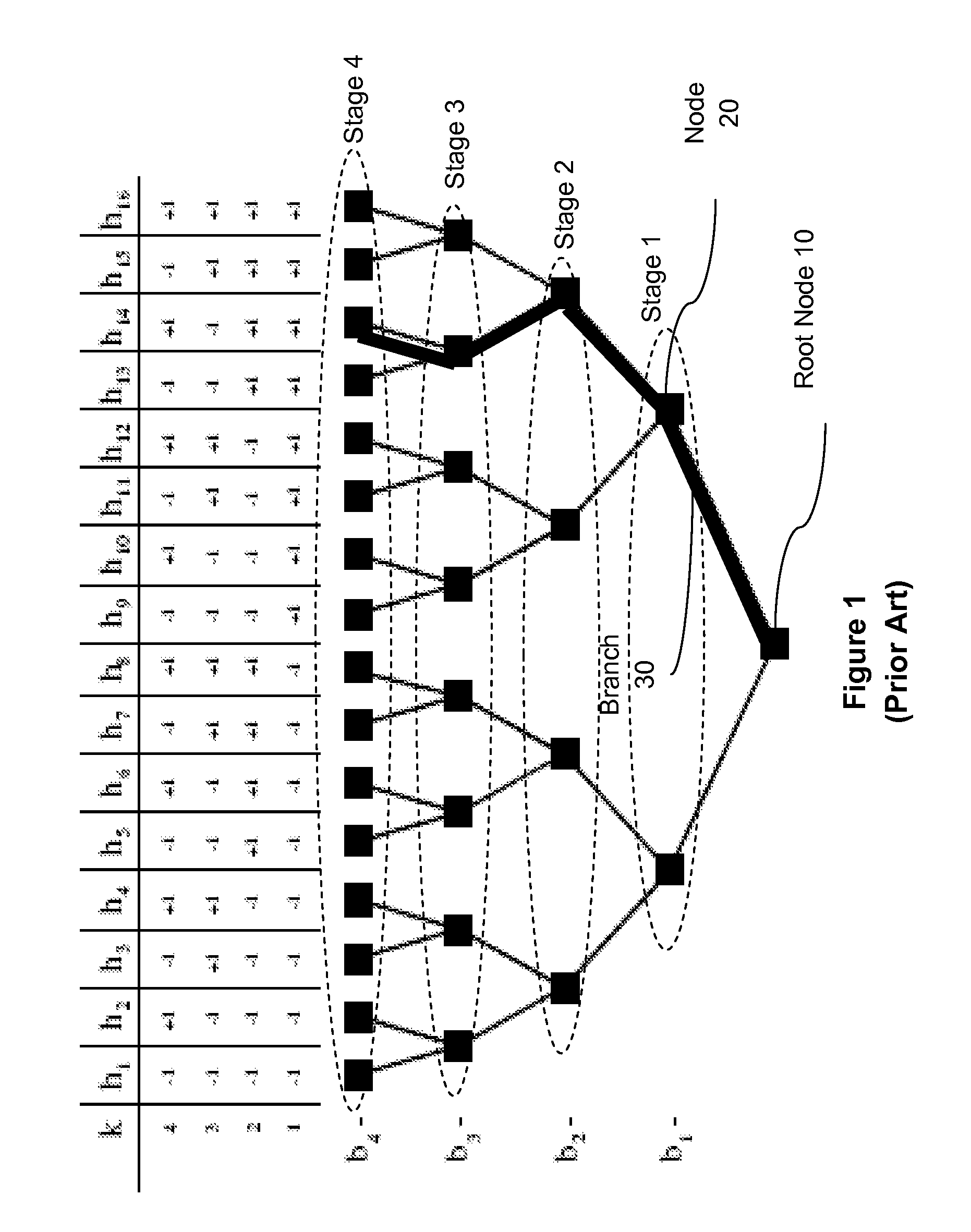
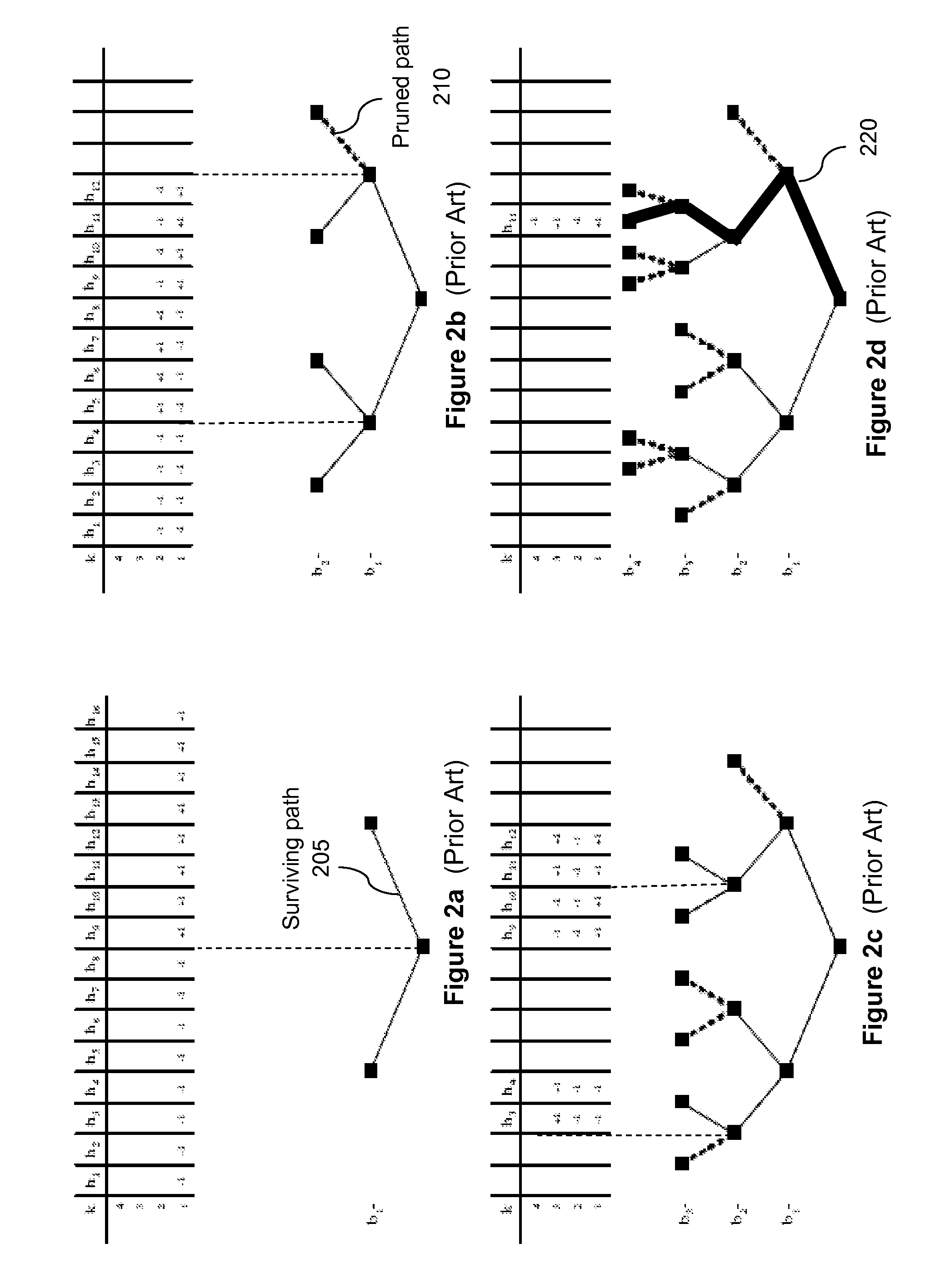
[0042]In a general embodiment, the present invention describes a method for decreasing complexity in multiuser detector receivers by discarding some hypotheses based on the amount of correlation between paths in incremental decisions. The computational savings is realized by pruning a tree search algorithm at intermediate steps of the decision process. Metrics are proposed for determining if and when a branch should be pruned. In addition, a method for ordering users when solving the tree search is also described.
[0043]The term “signature waveform” as used herein denotes the impulse response of the channel through which the signal passes. The term “channel” as used herein includes not only the propagation channel and antenna effects, but also any filtering used in the transmitters and receiver. In addition, in a direct sequence spread spectrum system, it would also include the spreading code.
[0044]A MUD receiver jointly demodulates co-channel interfering digital signals. Multiuser d...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com