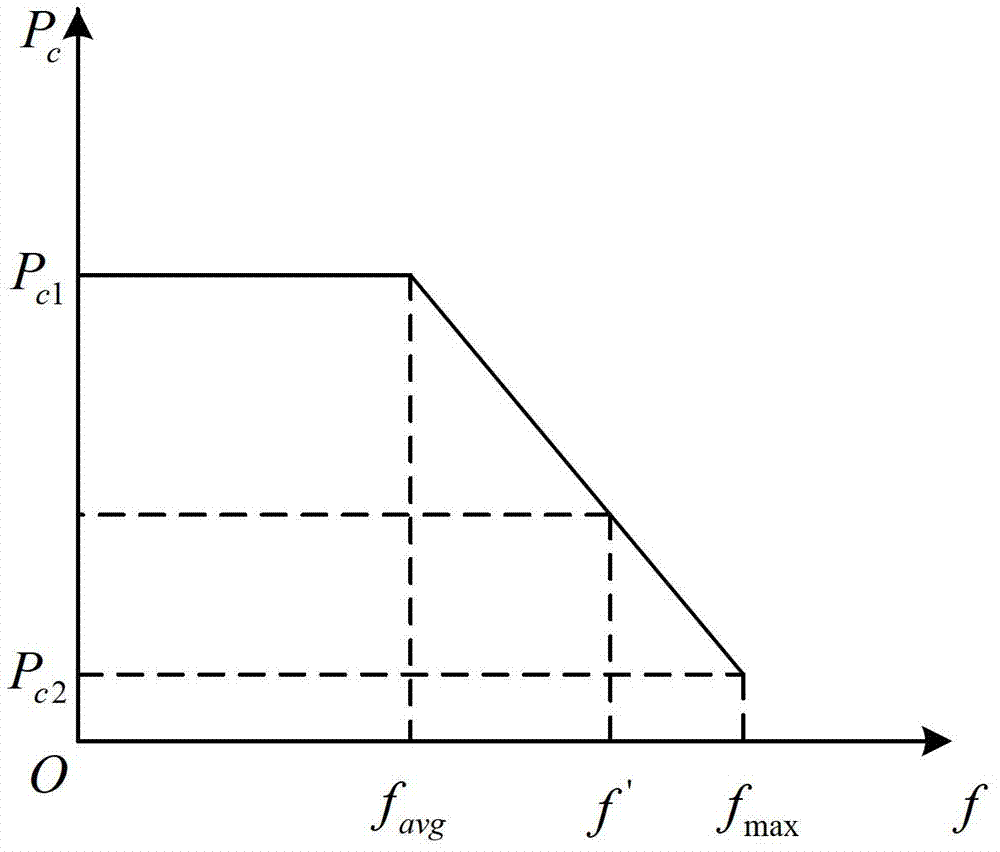
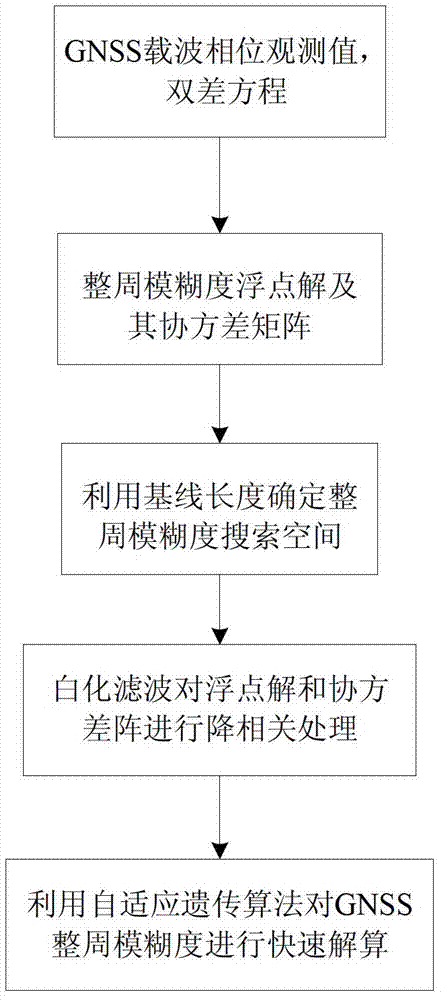
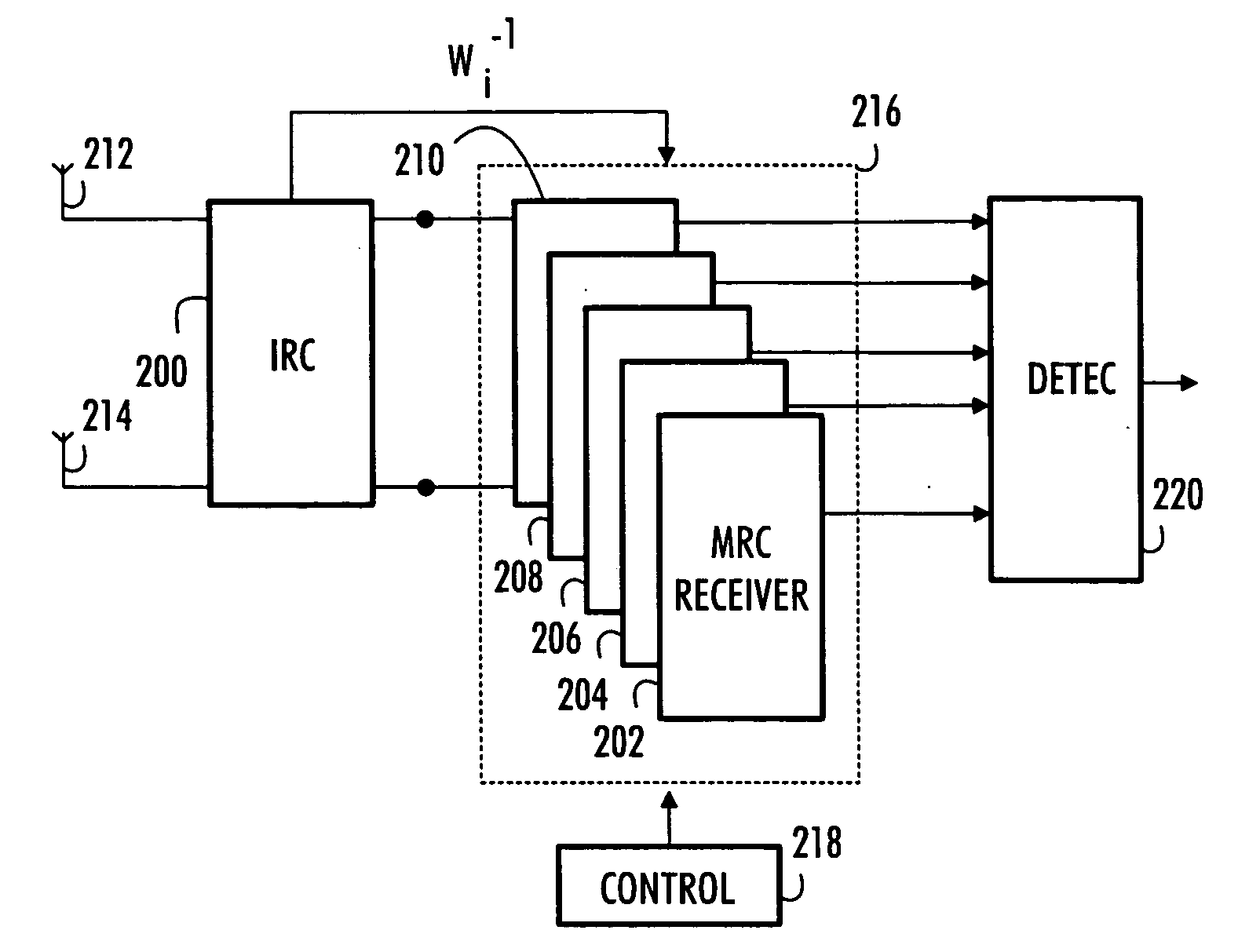
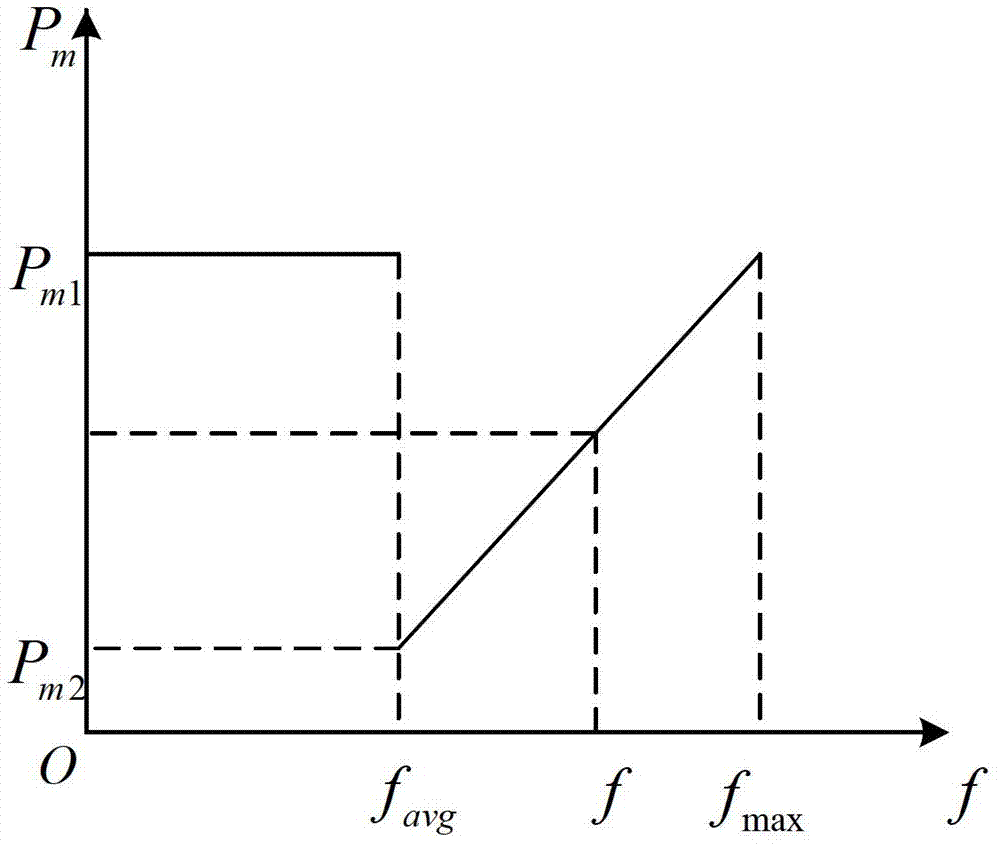Patents
Literature
108 results about "Whitening filter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
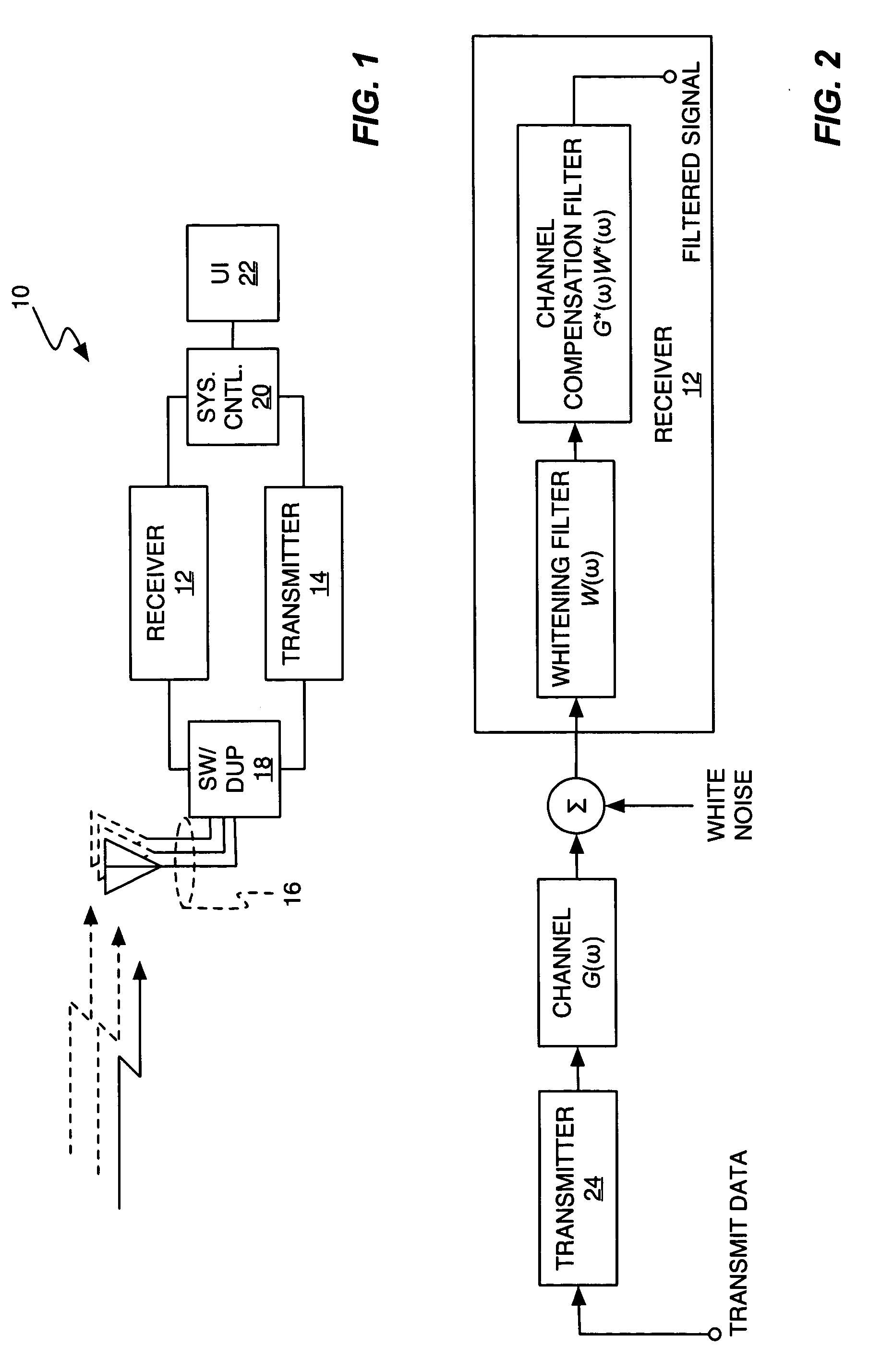
Whitening matched filter for use in a communications receiver
InactiveUS6862326B1Improve performanceMultiple-port networksDigital technique networkIir filteringChannel impulse response
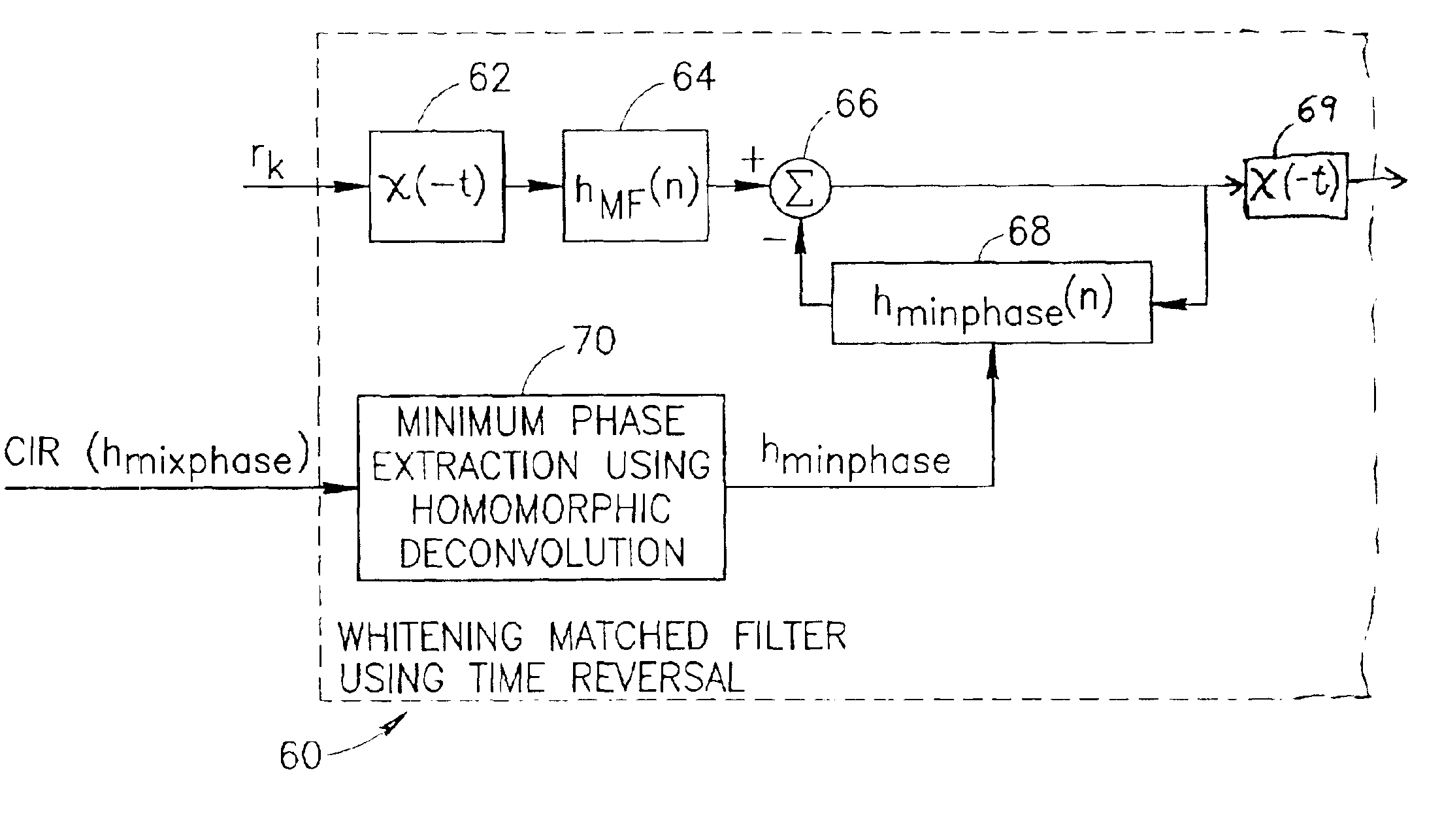
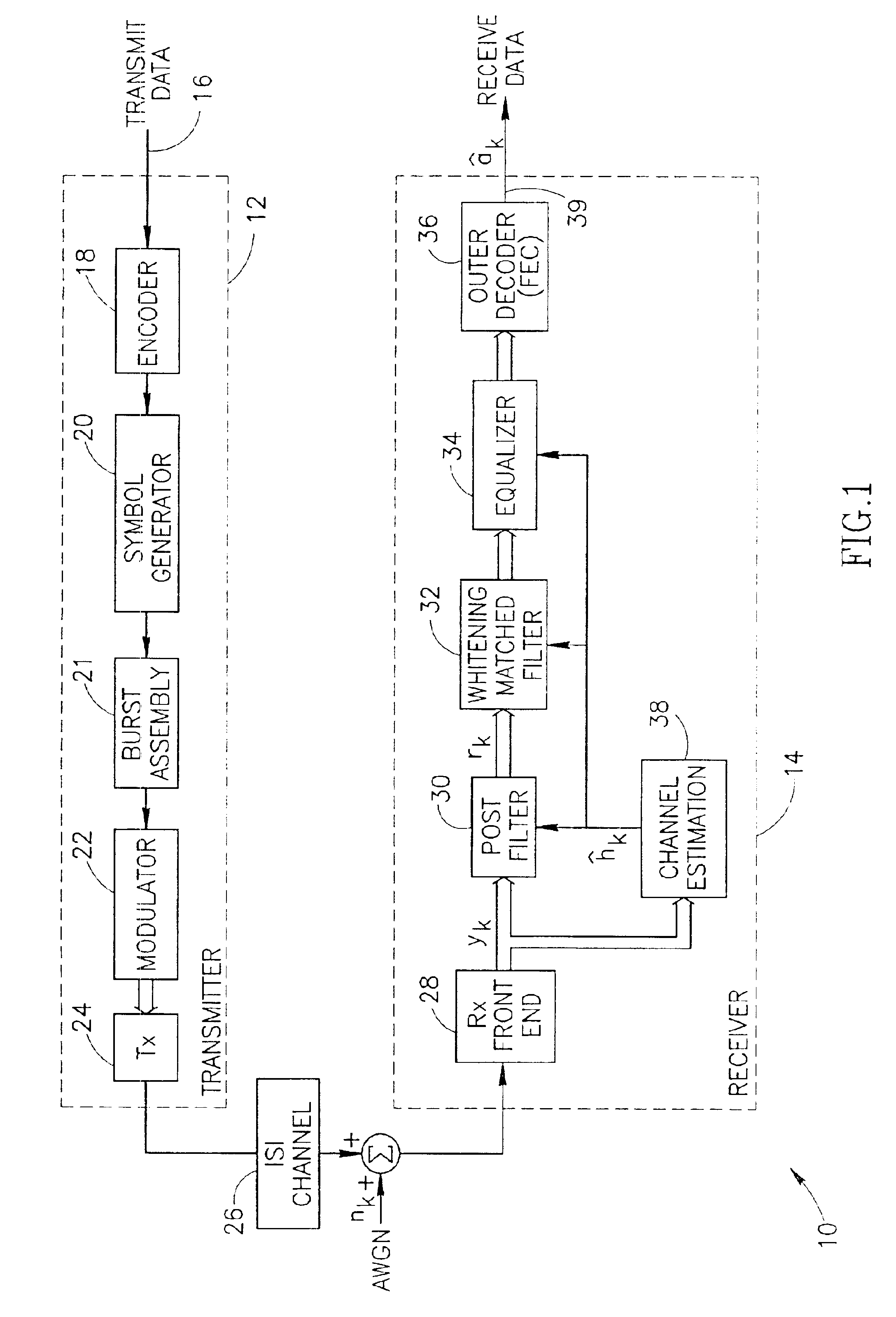
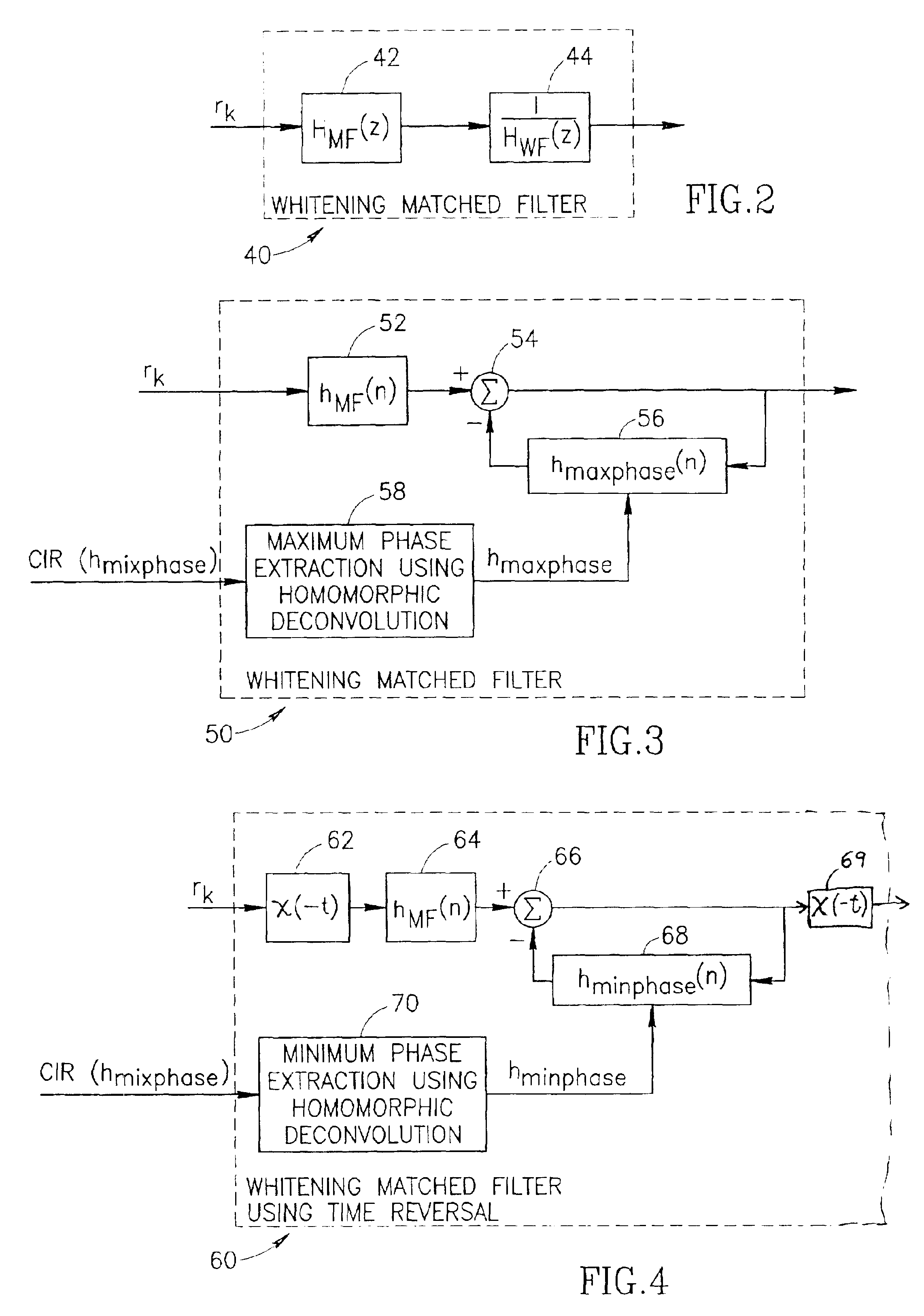
A novel and useful whitening matched filter (WMF) for use in a communications receiver. The WMF is constructed by cascading a matched filter and a noise-whitening filter. The response of the matched filter is derived from the time reversed complex conjugate of the channel impulse response. The whitening filter is derived by extracting the minimum phase portion of the mixed phase channel impulse response using homomorphic deconvolution. The whitening filter is implemented using either an FIR or IIR filter adapted to process the data received before and after the training sequence using a minimum phase system in a direction in time opposite to that of the direction of corresponding data sample processing performed by the equalizer.
Owner:COMSYS COMM & SIGNAL PROC
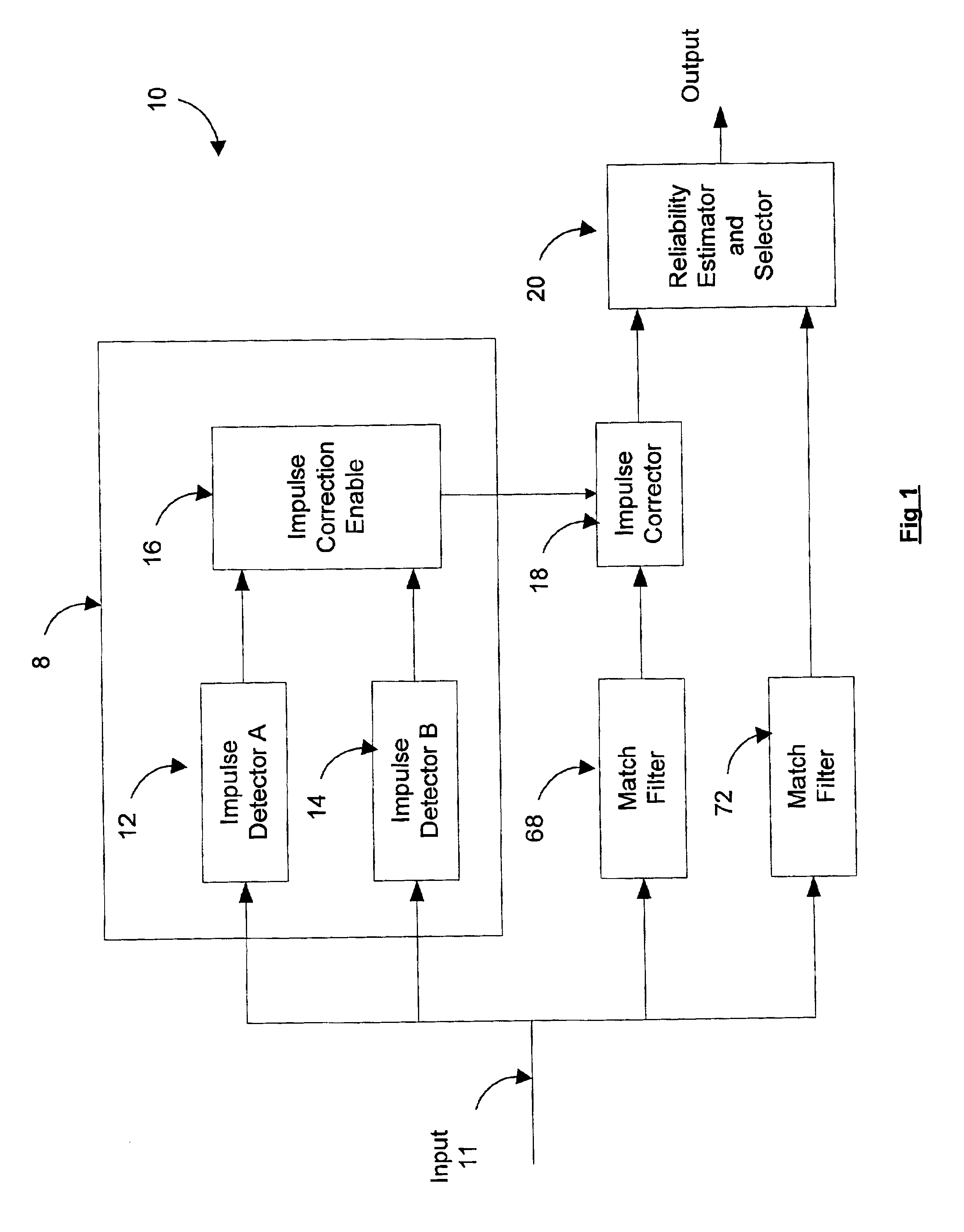
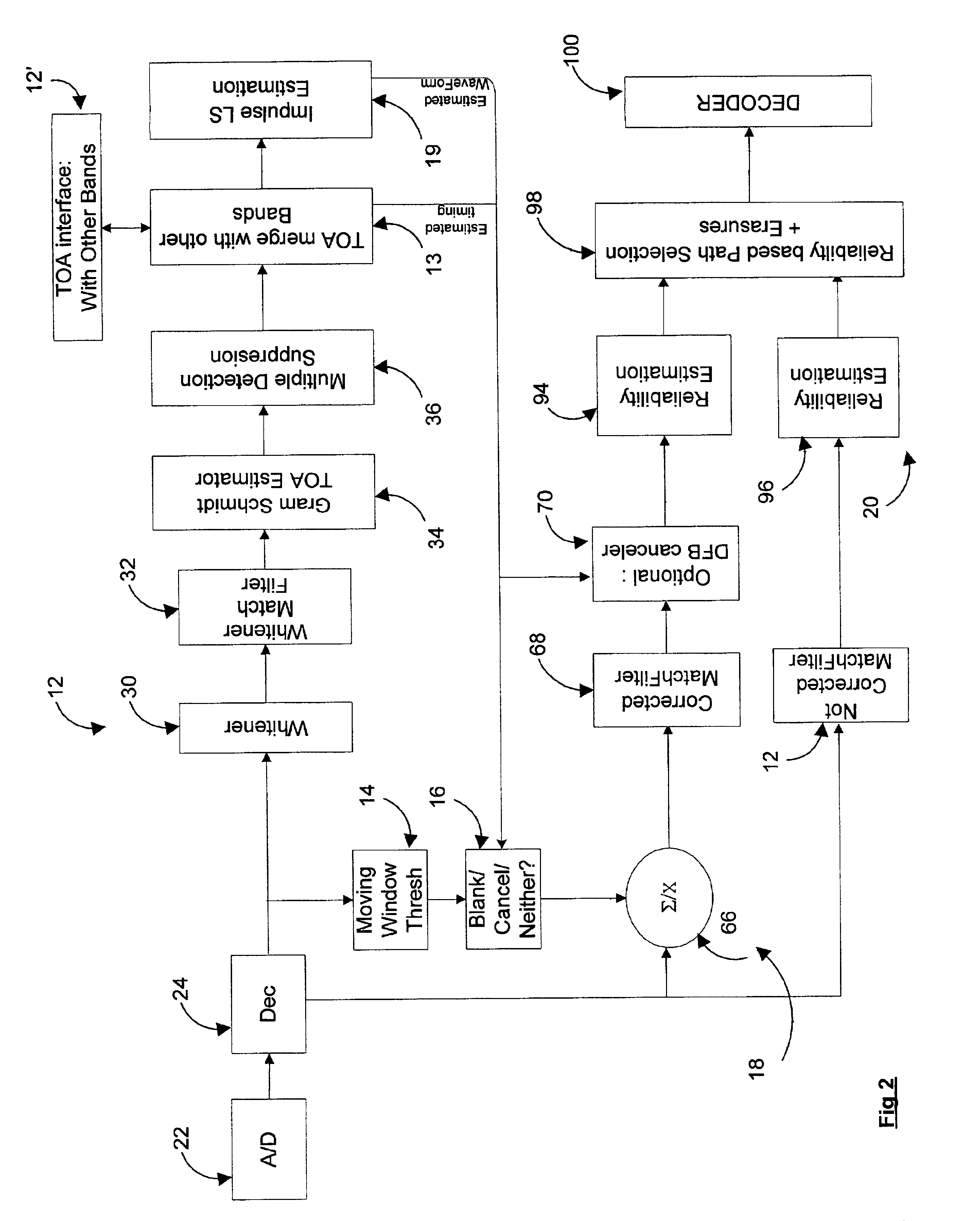
Method and system for detecting, timing, and correcting impulse noise
InactiveUS6920194B2Solve their vulnerability to impulse noiseLess complexDc level restoring means or bias distort correctionMulti-frequency code systemsData signalGram schmidt
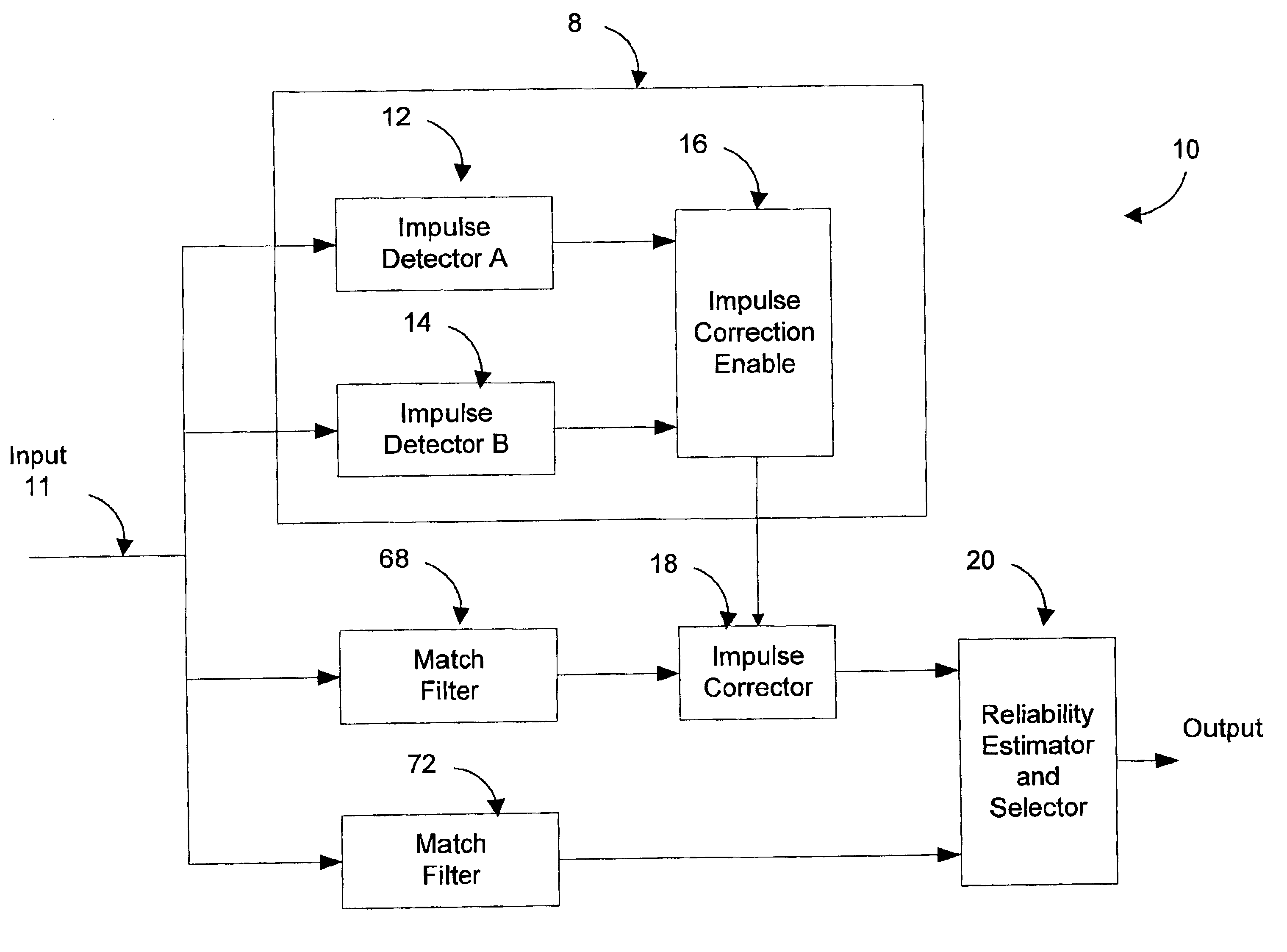
A system for detecting and correcting impulse noise present on an input data signal includes an impulse detector module receiving an input data signal and producing as output an correction enable signal indicating when an impulse correction is required. An impulse corrector module receives the input data signal and a correction enable signal and produces a corrected data signal, e.g., having the impulse canceled or blanked, as output. A reliability estimator and selector module receives the corrected data signal and the input data signal and selects as output the input signal which is more reliable. In one embodiment, the impulse detector includes first and second complementary impulse detectors, the outputs of which are analyzed by an enable and correction module to produce an impulse detection signal with improved accuracy. Preferably, the enable and correction module also indicates the most appropriate type of impulse correction in accordance with the detection signals from the complementary detectors. A novel system and method of detecting impulses based on Gram Schmidt techniques is also presented. In this method, one or more channels of a multi-channel data signal are kept free of data. When a whitening filter is applied, impulses on these quiet channels are emphasized. The Gram Schmidt technique exploits this fact to provide for improved impulse detection. The system can be modified to detect other types of low dimensionality noise.
Owner:RPX CORP
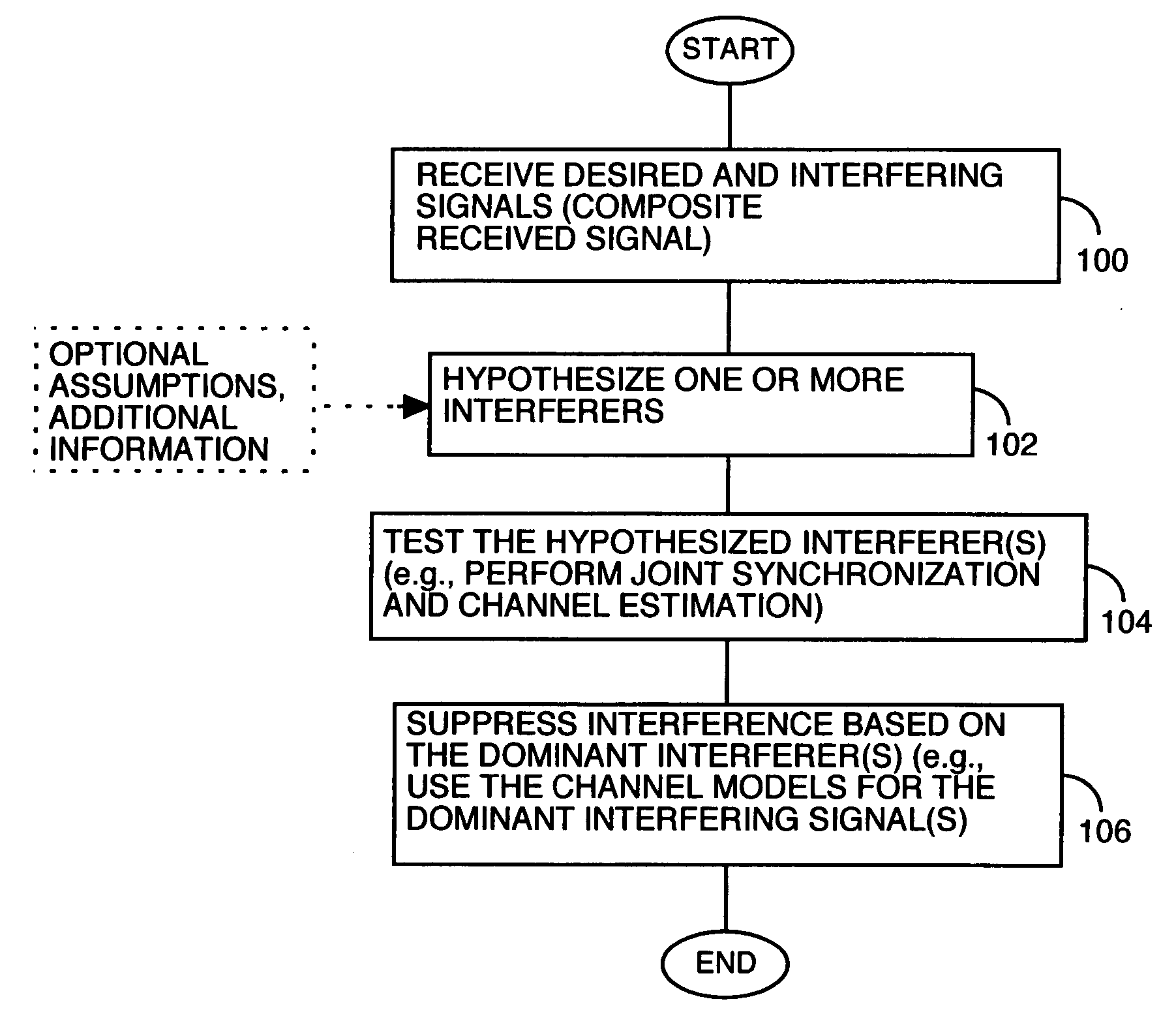
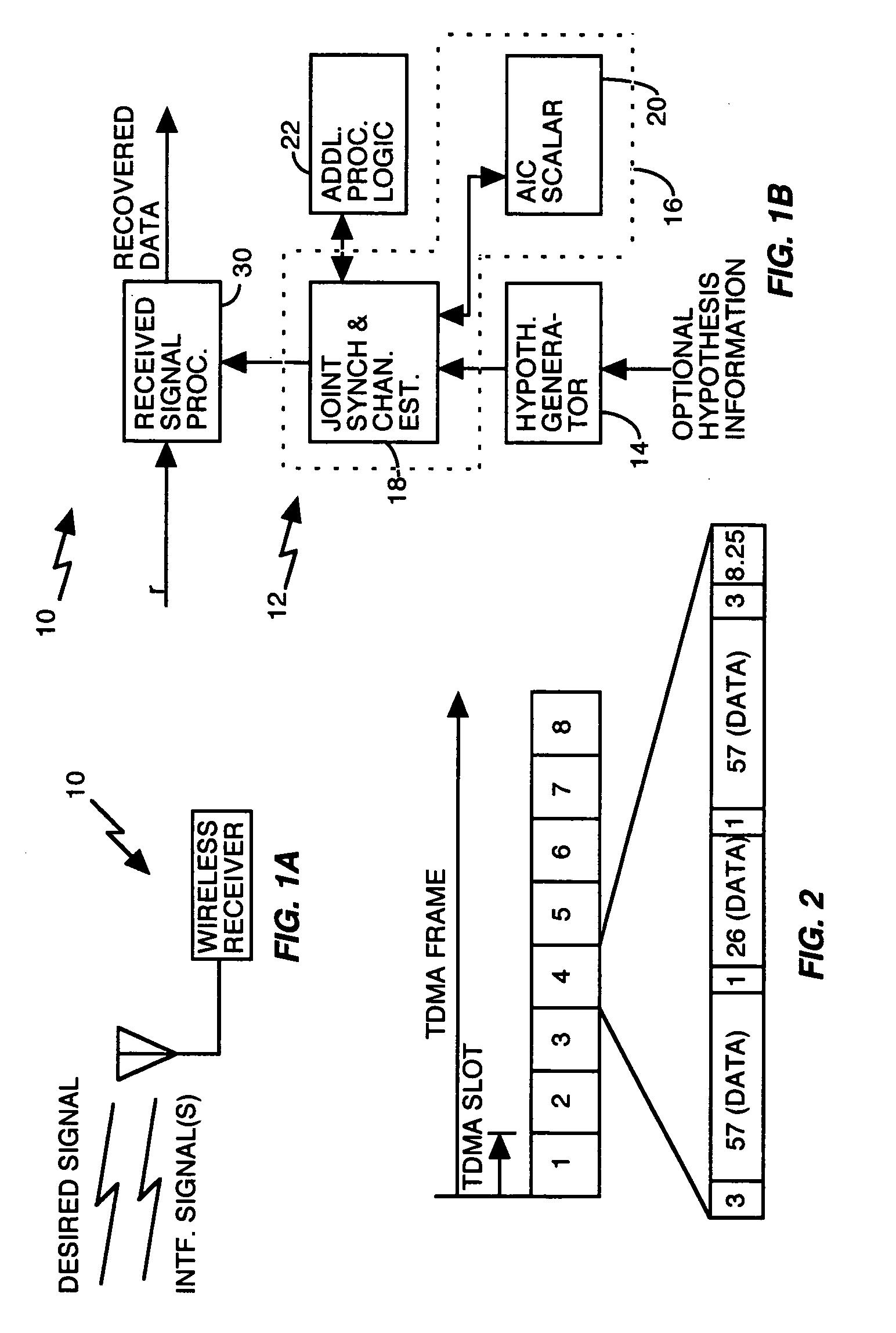
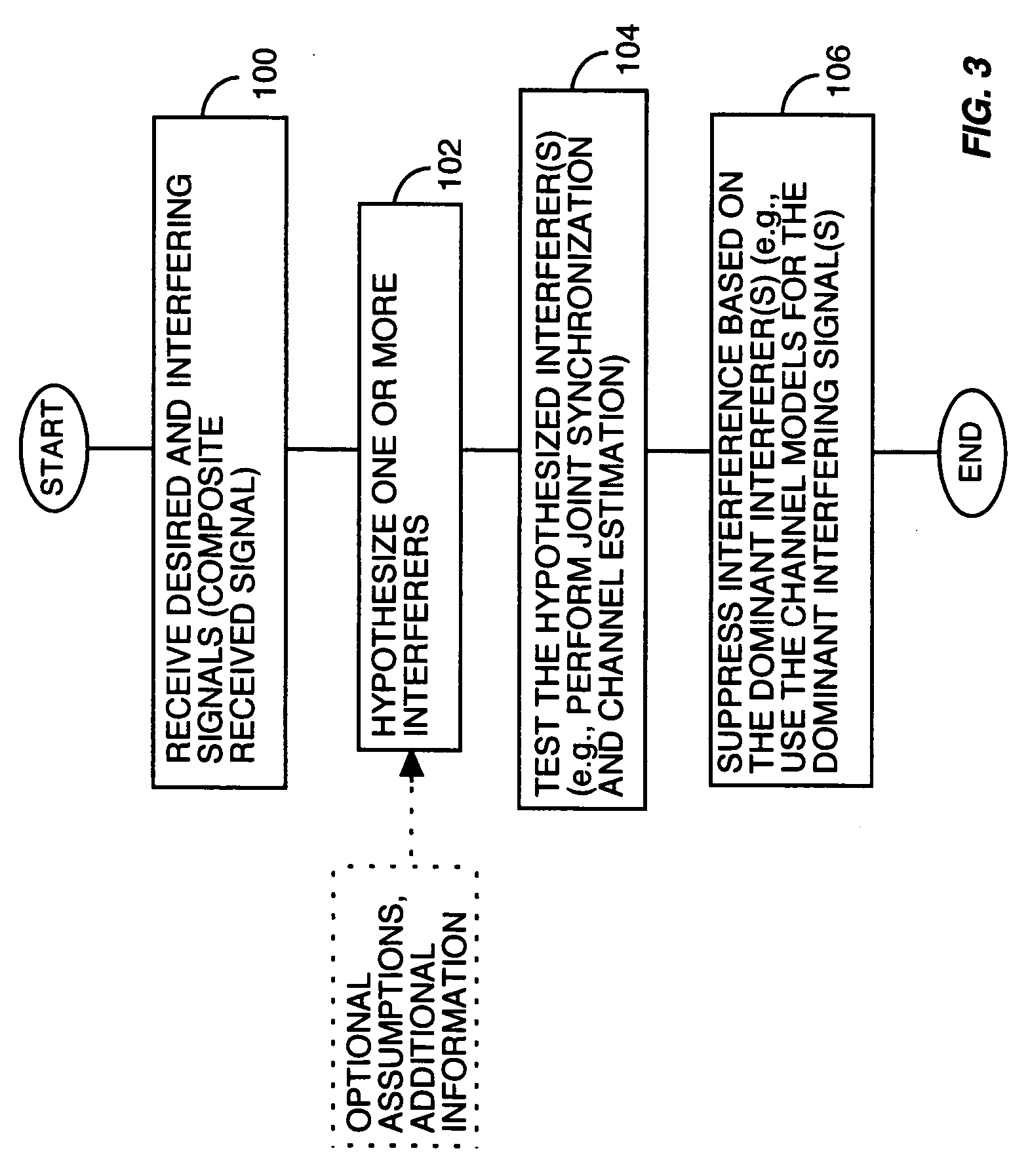
Method and apparatus for multi-user interference determination an rejection
InactiveUS20050095985A1Synchronisation signal speed/phase controlTransmission monitoringMulti user interferenceChannel models
A receiver circuit identifies one or more interfering signals received with a desired signal by generating and evaluating one or more hypothesized interferers. By testing these hypotheses, such as through joint synchronization and channel estimation for the desired signal and the one or more hypothesized interferers, the circuit identifies which hypothesized interferer(s) best correspond to the dominant interfering signal(s) actually received. Channel models thus obtained for the dominant interferer(s) may be used in, for example, generating a whitening filter used in interference suppression, or jointly demodulating the desired and interfering signal(s).
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
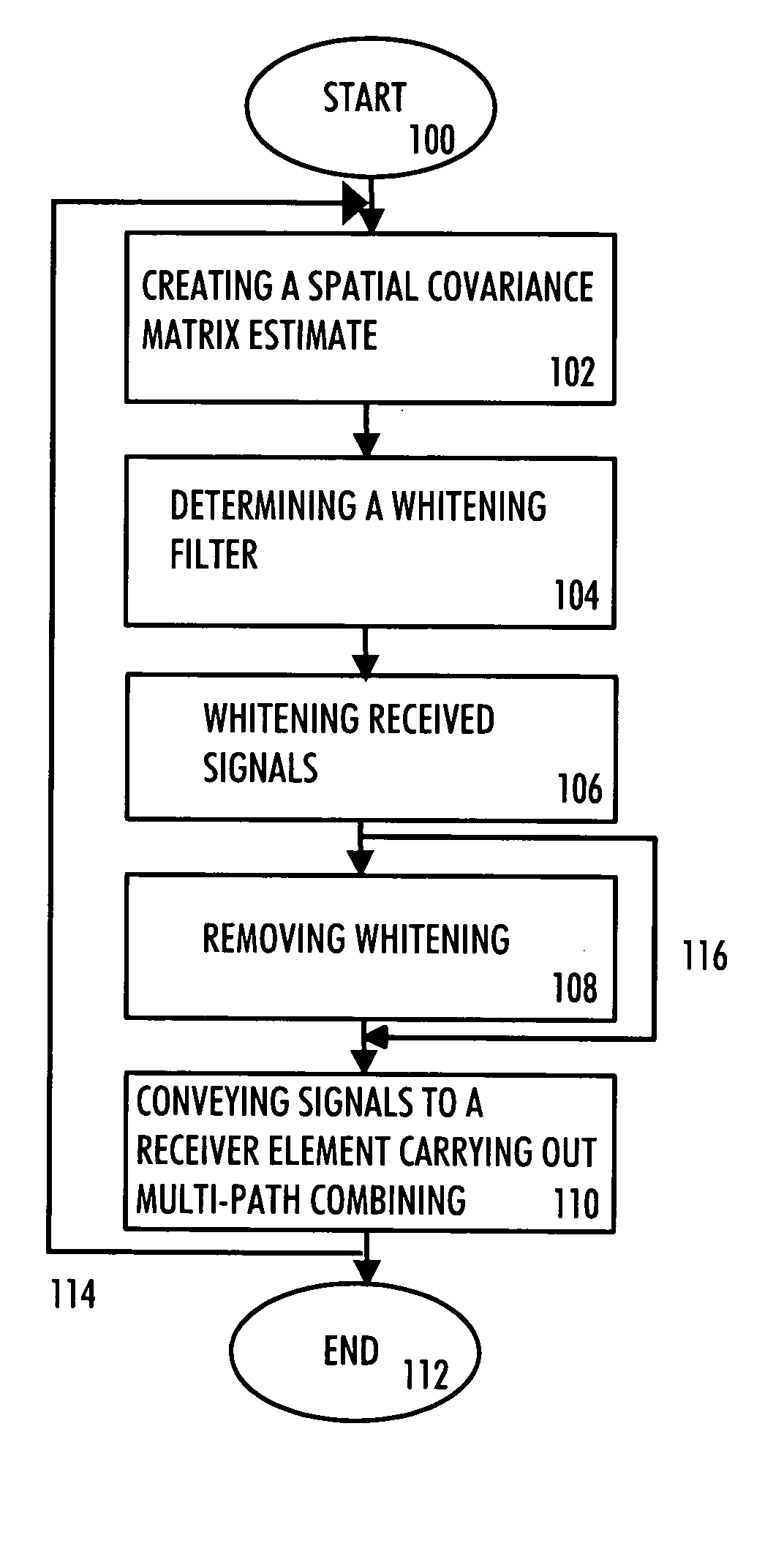
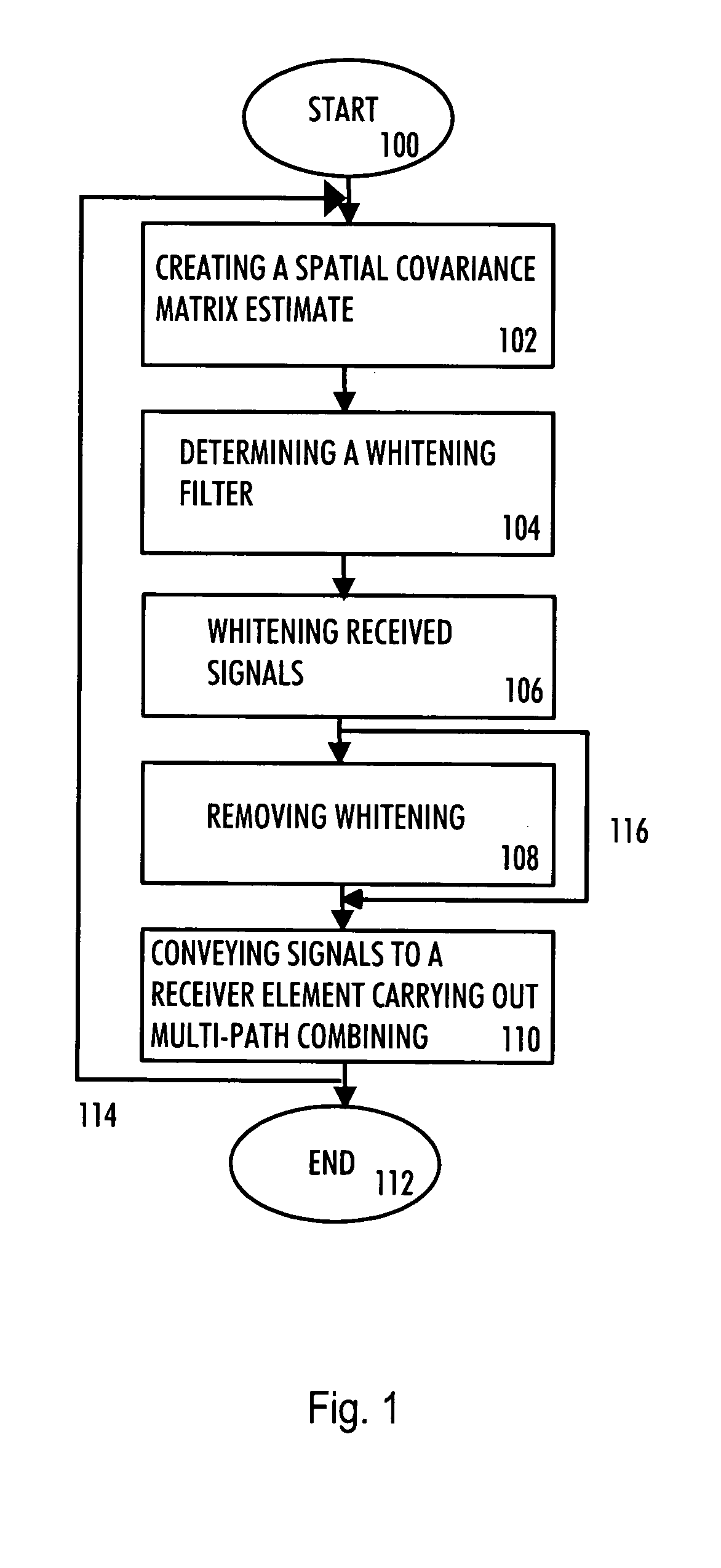
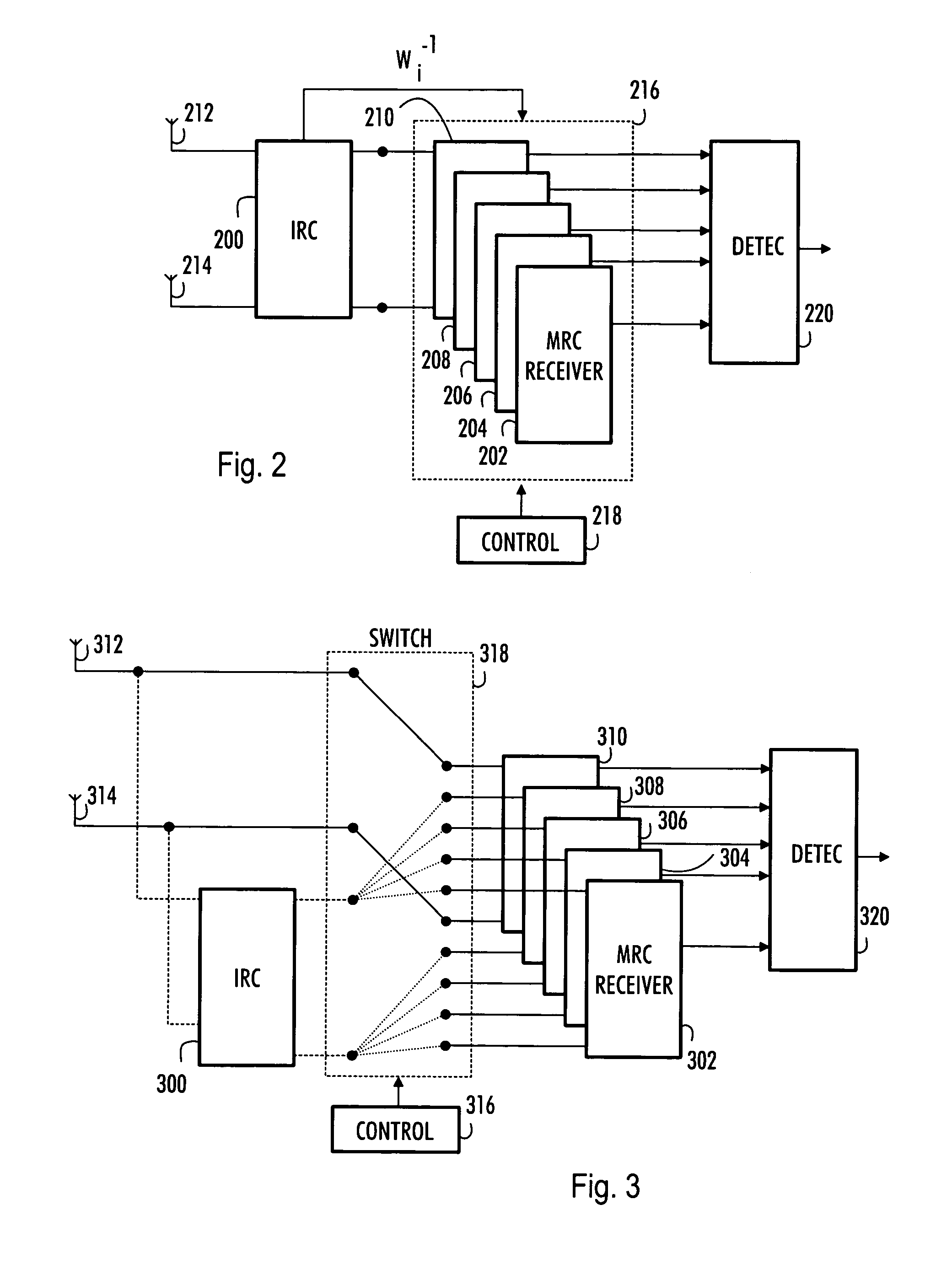
Communication method, receiver and base station
InactiveUS20050101253A1Reduce the impact of interferenceReduce impactSpatial transmit diversityPolarisation/directional diversityConjugate transposeEngineering
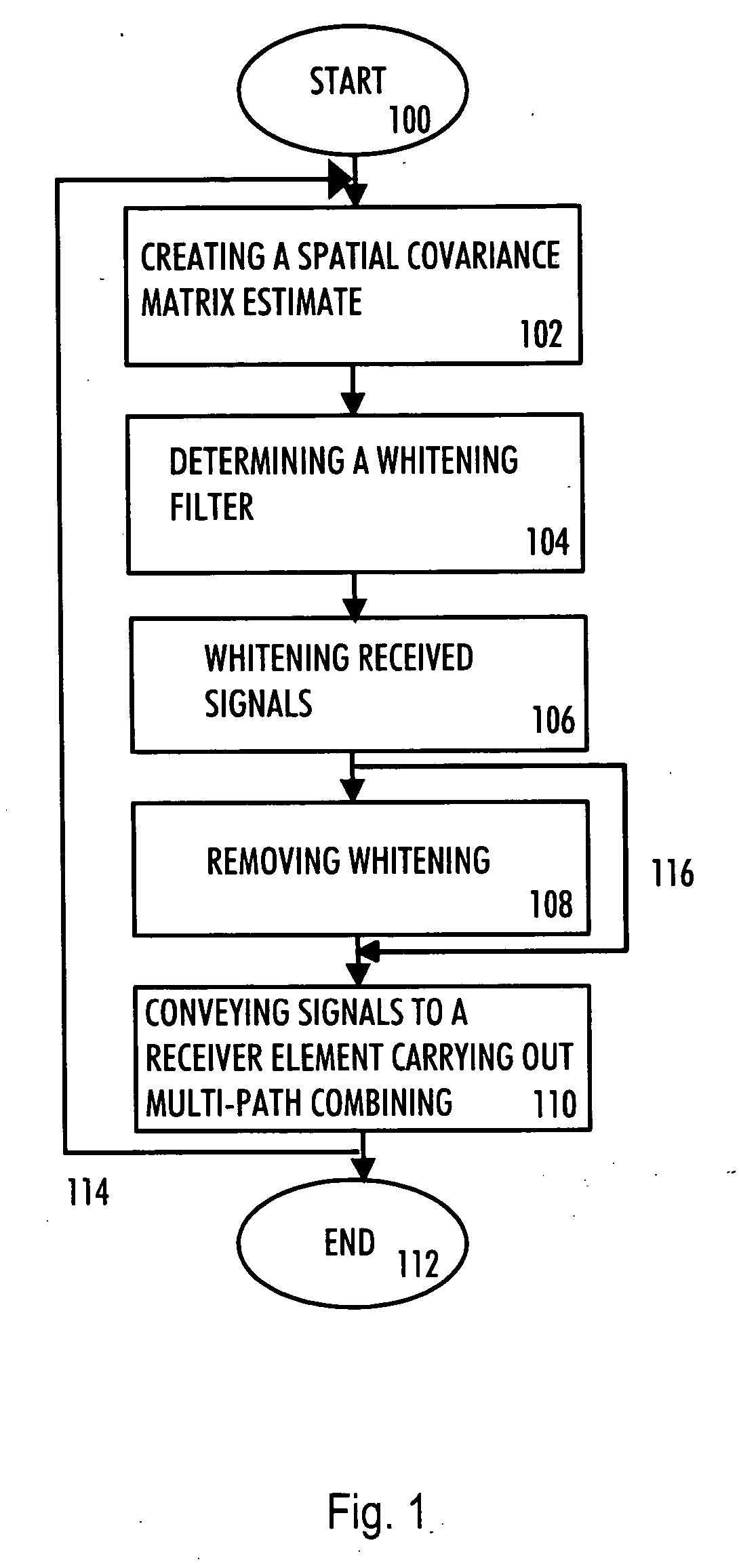
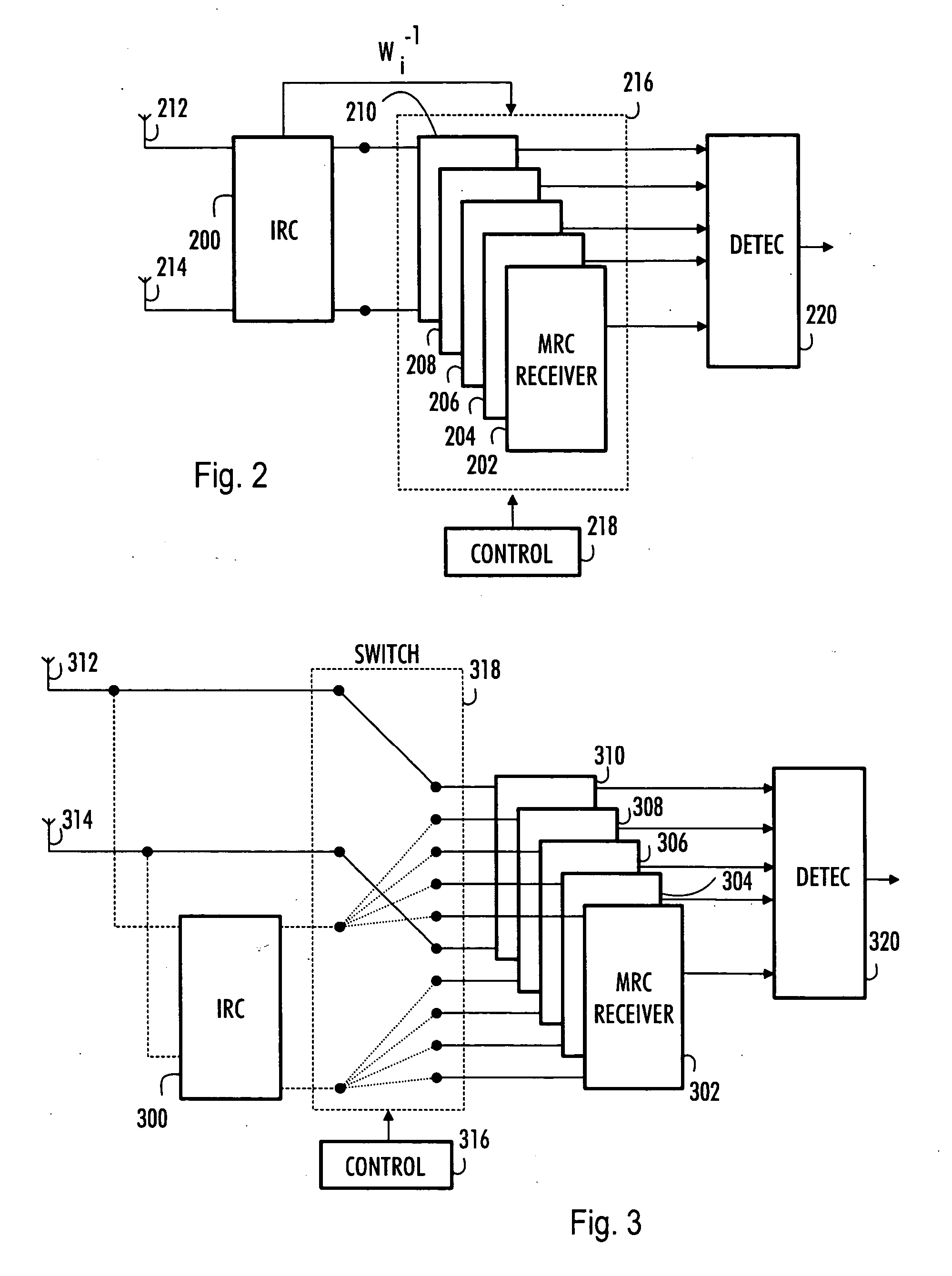
A multi-user receiver which uses at least two antenna elements and in which the influence of interference is reduced, the receiver comprises: means (200) for pre-filtering a wideband antenna signal, the pre-filtering means being determined on the basis of a spatial covariance matrix estimate, which spatial covariance matrix estimate is obtained from wideband antenna signals by sampling, arranging sampled values into a signal vector and by multiplying the signal vector by its conjugate transpose vector, means (210, 218) for removing the whitening from signals of predetermined users by using an inverse matrix of the matrix used in the whitening filter, means (202, 204, 206, 208, 210) for performing multi-path combining and multi-antenna combining.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
Systems and methods for interference cancellation in a radio receiver system
ActiveUS20090154620A1Error preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionRound complexityInterference cancelation
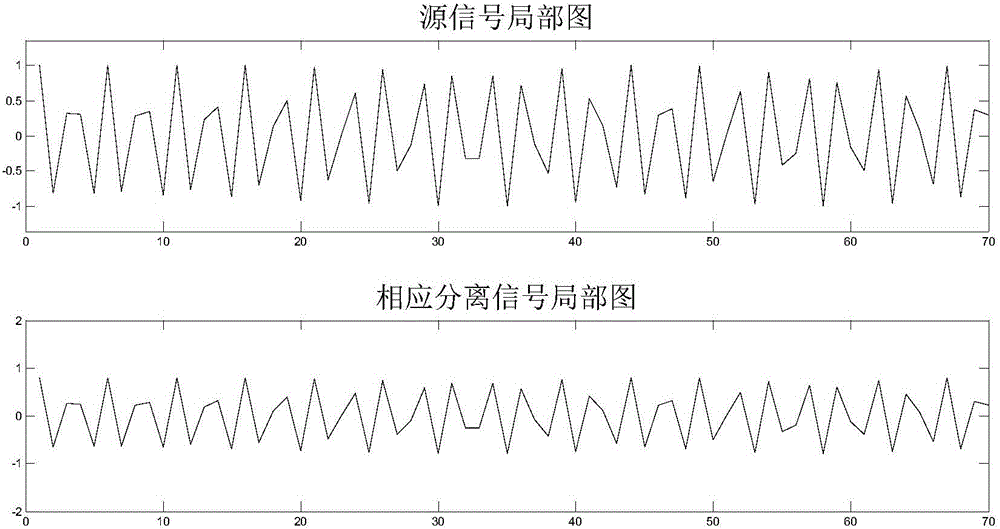
A system and method for interference cancellation is provided to cancel / greatly reduce the interference of a wireless network. The interferers are separated from a desired signal using independent component analysis by hypothesizing the transmitting sequence. An optional whitening filter is used after the signal separation to improve the signal conditioning. The separated signal is processes by a second pass channel estimation to improve the signal channel estimation and is fed to MLSE algorithm, such as a Viterbi algorithm, for signal detection. The system and method provides significant gain over all previous methods with no limitation to the frequency type or specific interference profile such as the ratio of the dominant interferer to the other interferers. It is possible to separate the interferers without prior knowledge of the specific parameters of the interferers and with much less complexity than conventional joint demodulation detection methods. The algorithm employed is considered a blind estimation approach which makes it attractive for wireless devices that have limited power resources.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Method and apparatus for suppressing communication signal interference
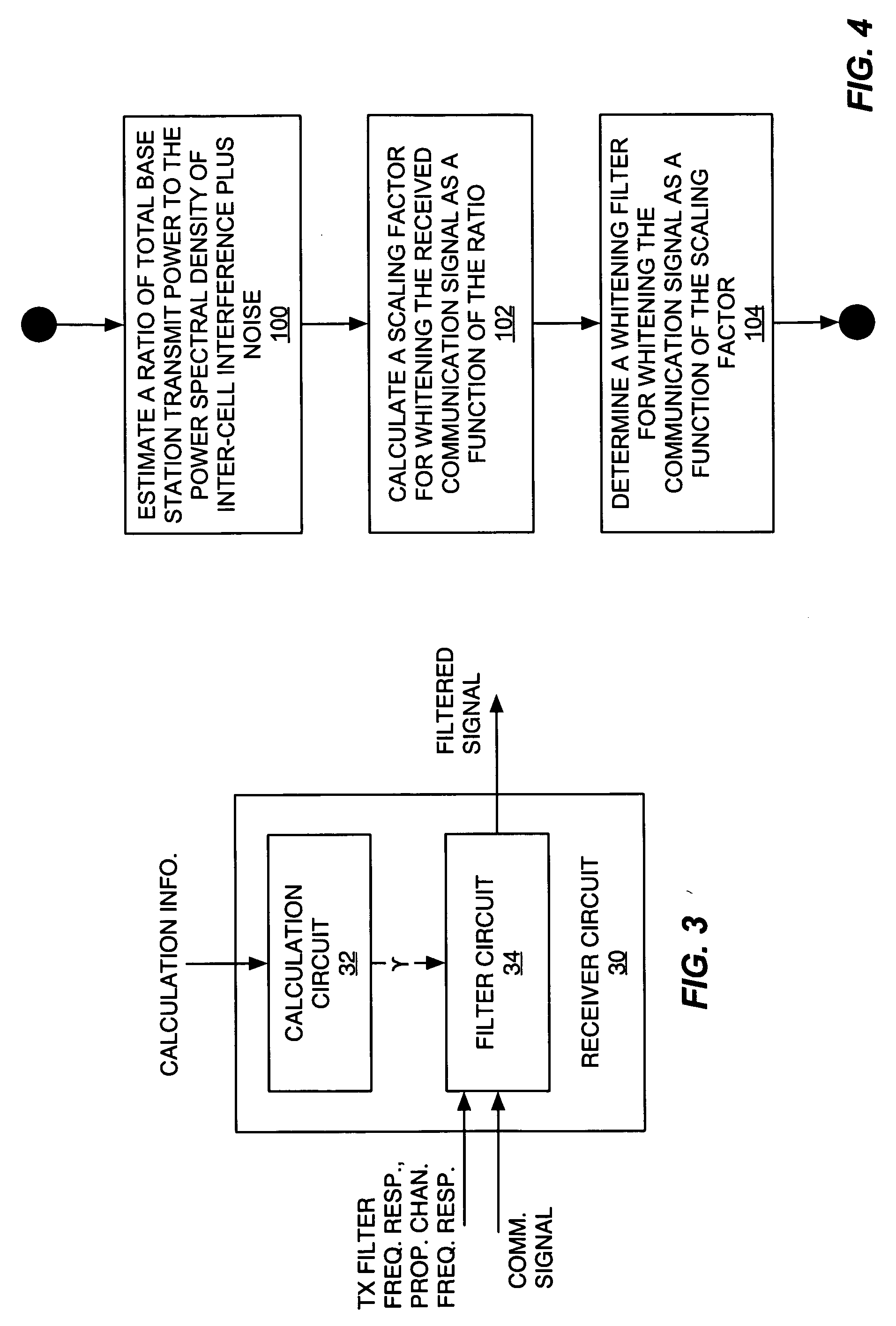
InactiveUS20060072485A1Reduce computational complexityEasy constructionError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionTransmitted powerEngineering
A frequency domain representation of a whitening filter is made to depend on essentially one unknown, namely, a scaling factor that is based on an estimated ratio of total base station power to the power spectral density (PSD) of inter-cell interference plus noise. In turn, that scaling factor can be computed based on the modeling terms used in a parametric model of the impairment correlations for a received communication signal. Preferably, the model comprises an interference impairment term scaled by a first model fitting parameter, and a noise impairment term scaled by a second model fitting parameter. Further, the scaling factor can be computed by directly estimating total base station transmit power and the PSD of inter-cell interference plus noise. In any case, the whitening filter can be used in whitening a received communication signal in conjunction with channel equalization processing or RAKE receiver processing, for example.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
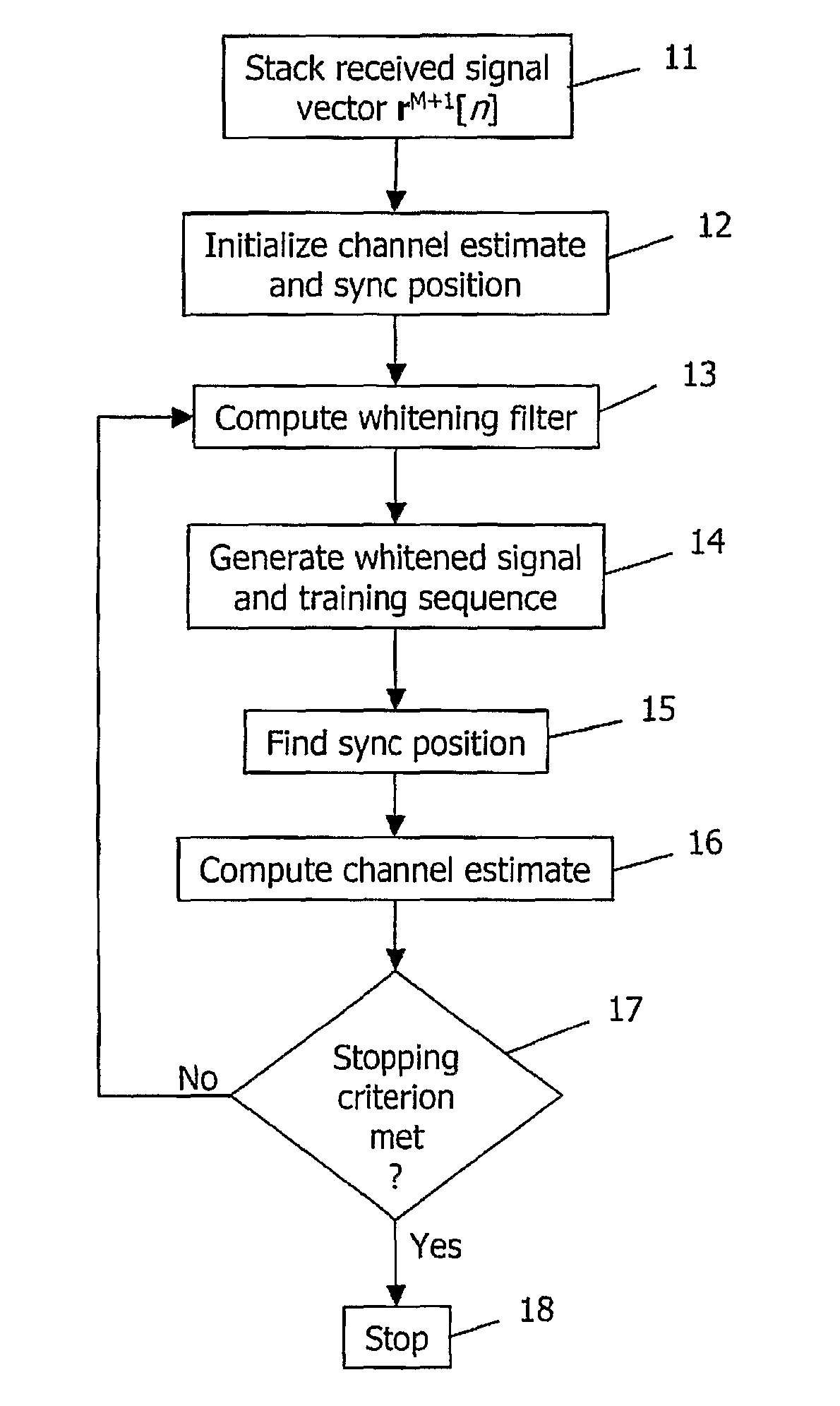
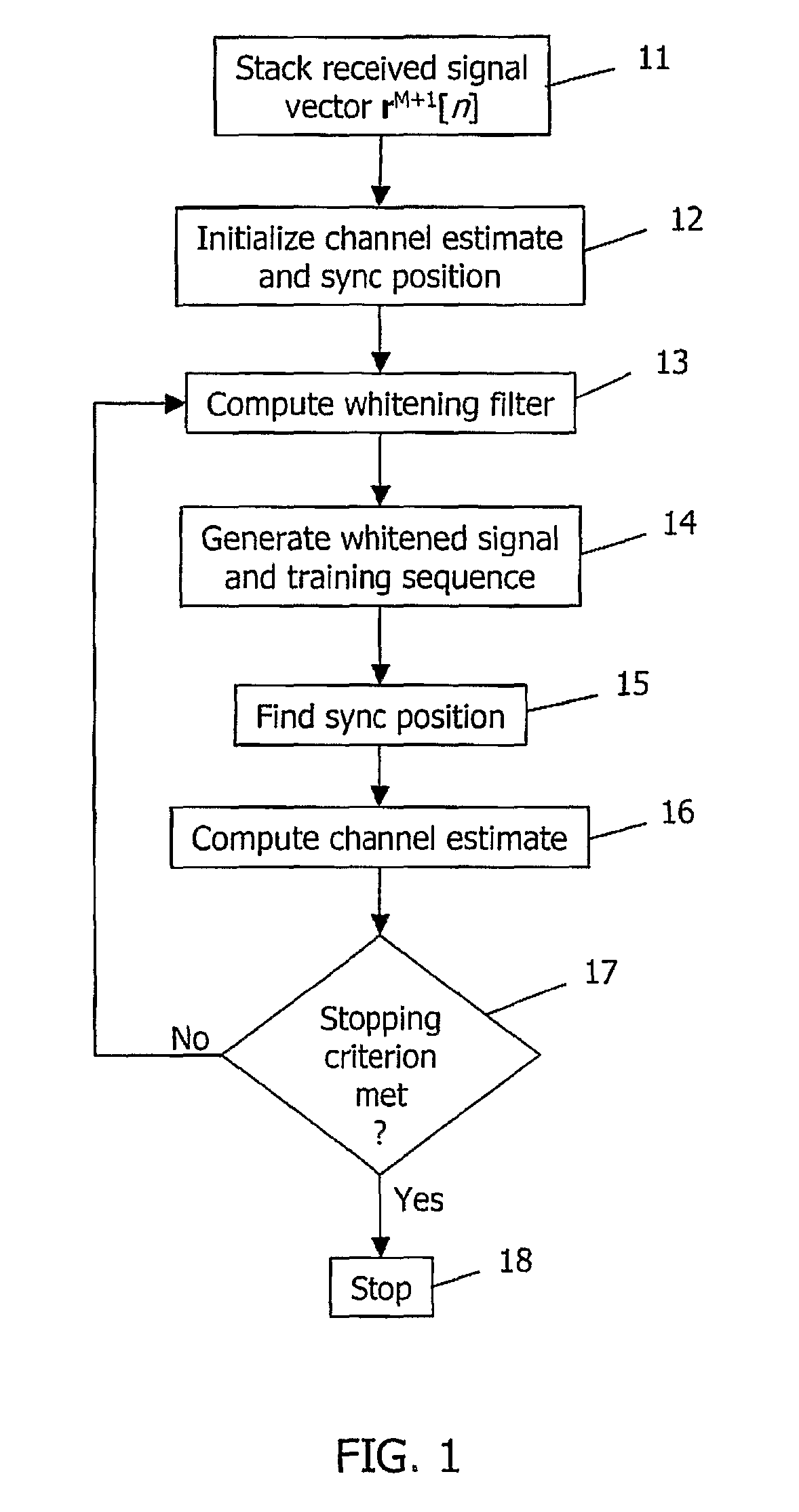
Method and device for synchronization and channel estimation in a radio receiver
ActiveUS20100248666A1Amplitude-modulated carrier systemsTransmission monitoringRadio receiverComputer science
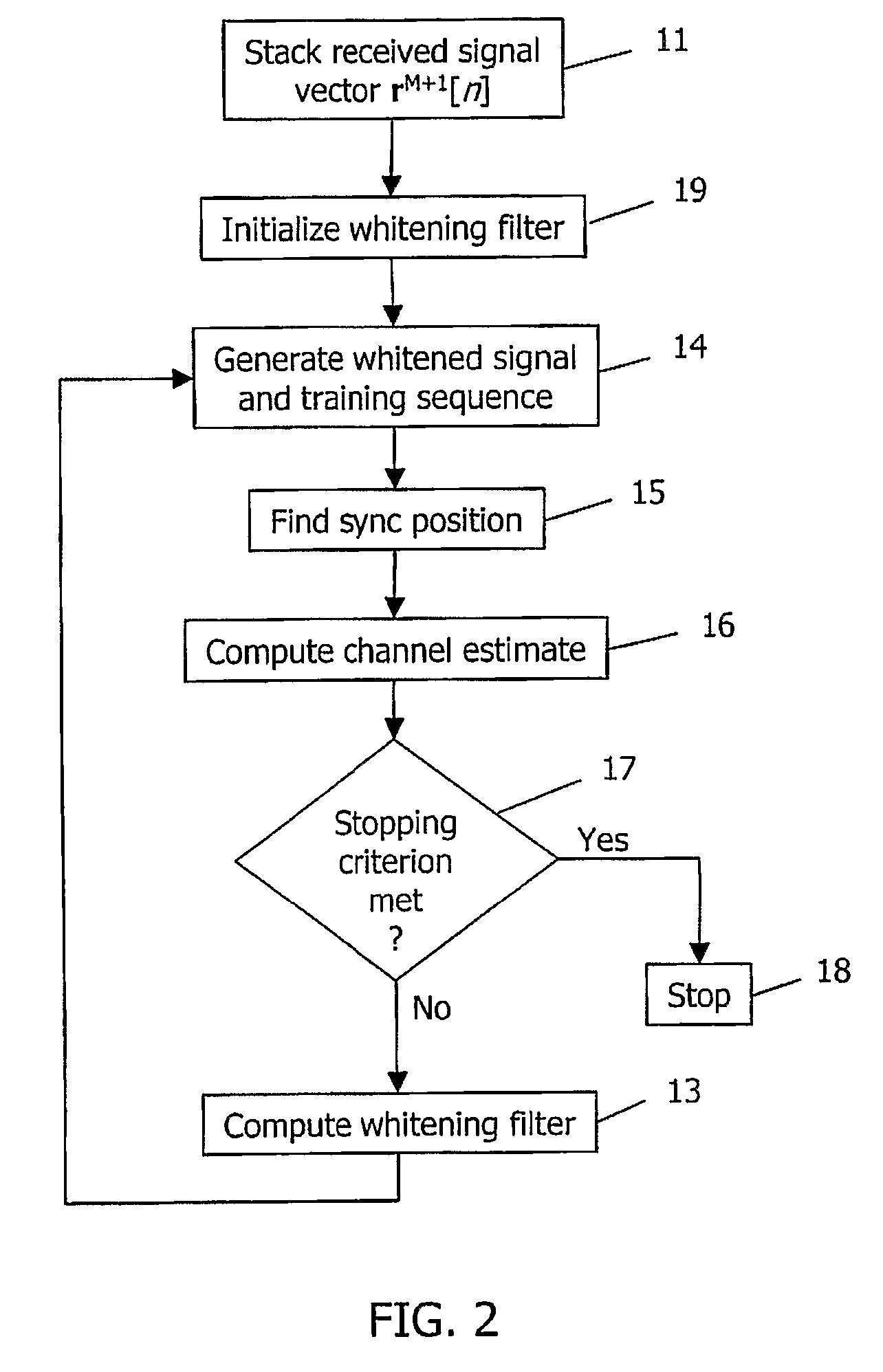
A device and method in a radio receiver for generating synchronization and channel estimation information based on three parameters consisting of a synchronization position, at least one whitening filter parameter, and a channel estimate. A spatially and temporally stacked signal model is generated by stacking successive samples of temporally adjacent received signal vectors and corresponding training vectors. Initial estimates of a first one or two of the three parameters are then generated based on the spatially and temporally stacked signal model. The rest of the three parameters are then computed based on the initial estimates of the first one or two parameters. If a stopping criterion is met, the method ends and the parameters are used to process the signal. If the stopping criterion is not met, additional iterations are performed to improve the synchronization and estimation information.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Systems and methods for interference cancellation in a multiple antenna radio receiver system
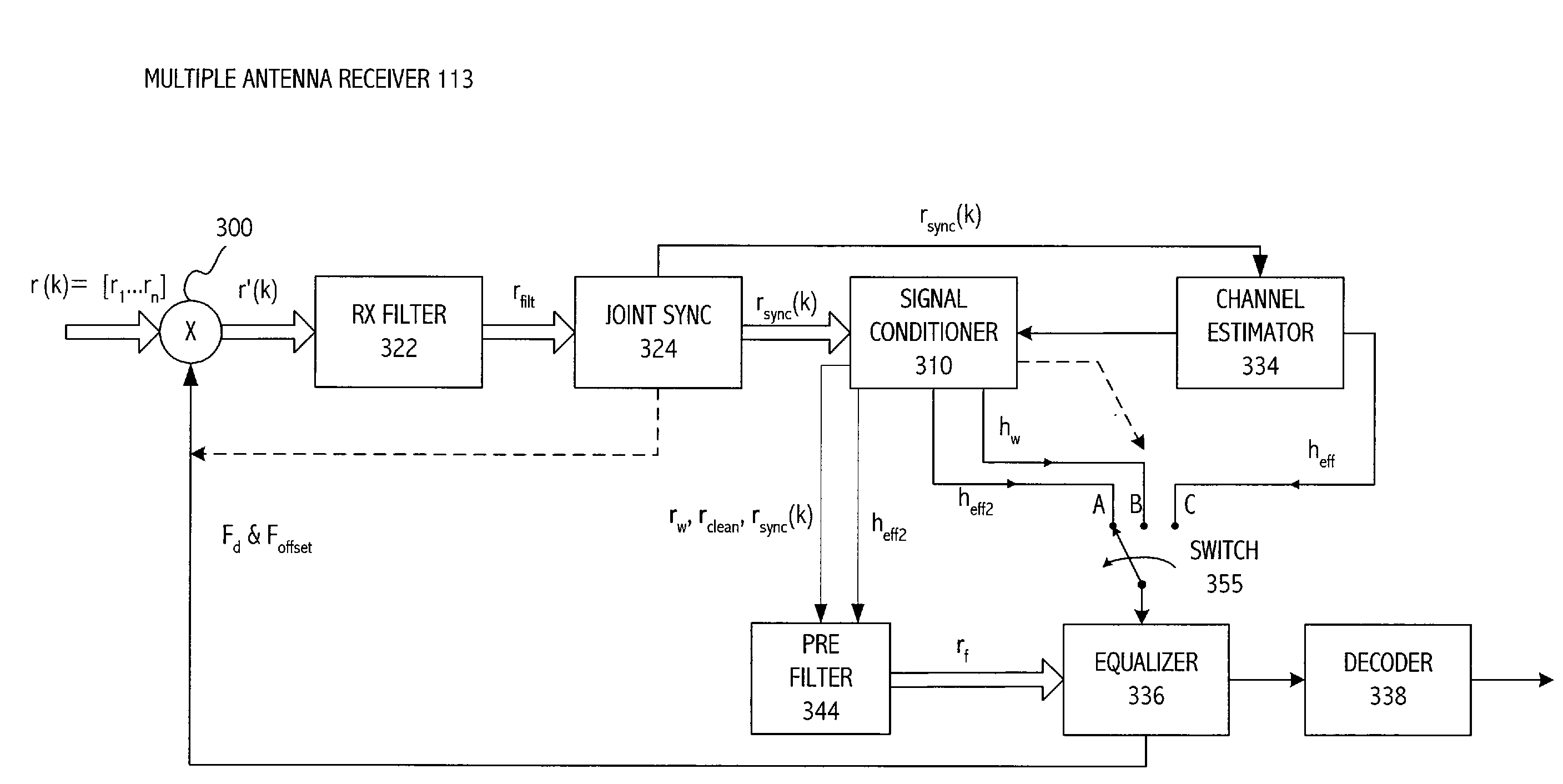
ActiveUS20070263744A1Quality improvementLarge capacityPolarisation/directional diversityError prevention/detection by diversity receptionRadio receiverEngineering
Interference cancellation is implemented for a multiple antenna system. The multiple antenna receiver is provided that includes a whitening filter coupled to receive processed signals corresponding to signals received at respective antennas, and to generate whitened signals corresponding to each of the received signals, having a colored noise component whitened. The whitening filter coupled to determine the whitened signals, at least in part, utilizes symbols corresponding to the signals received by the plurality of antennas. A signal separator is coupled to supply the whitening filter with processed received signals having interference components reduced as compared to received signals.
Owner:AT&T MOBILITY II LLC
Adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS (Global Navigation Satellite System) integer ambiguity acquisition method
InactiveCN102736094AReduce correlationAvoid complex calculationsSatellite radio beaconingDouble differenceInteger ambiguity
The invention discloses an adaptive genetic algorithm-based single-frequency GNSS integer ambiguity acquisition method. The method includes the following steps: step 1: acquiring the observed data of a GNSS carrier phase, and establishing a double-difference observation equation for the GNSS carrier phase; step 2: according to the double-difference observation equation obtained in step 1, utilizing the least square method to acquire the float solution and corresponding covariance matrix of GNSS integer ambiguity; step 3: utilizing known base length as a constraint condition to determine the search space of integer ambiguity; step 4: utilizing the whitening filter method to decorrelate the float solution and covariance matrix of integer ambiguity obtained in step 2; step 5: according to anobjective function, determining a fitness function, determining each operating parameter in the adaptive genetic algorithm, finally, introducing the adaptive genetic algorithm into fast solution on integer ambiguity, and searching the optimal solution of integer ambiguity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Communication method, receiver and base station
InactiveUS20070072551A1Reduce the impact of interferenceReduce impactSpatial transmit diversityTransmission noise suppressionConjugate transposeEngineering
A multi-user receiver which uses at least two antenna elements and in which the influence of interference is reduced, the receiver comprises: means (200) for pre-filtering a wideband antenna signal, the pre-filtering means being determined on the basis of a spatial covariance matrix estimate, which spatial covariance matrix estimate is obtained from wideband antenna signals by sampling, arranging sampled values into a signal vector and by multiplying the signal vector by its conjugate transpose vector, means (210, 218) for removing the whitening from signals of predetermined users by using an inverse matrix of the matrix used in the whitening filter, means (202, 204, 206, 208, 210) for performing multi-path combining and multi-antenna combining.
Owner:NOKIA SOLUTIONS & NETWORKS OY
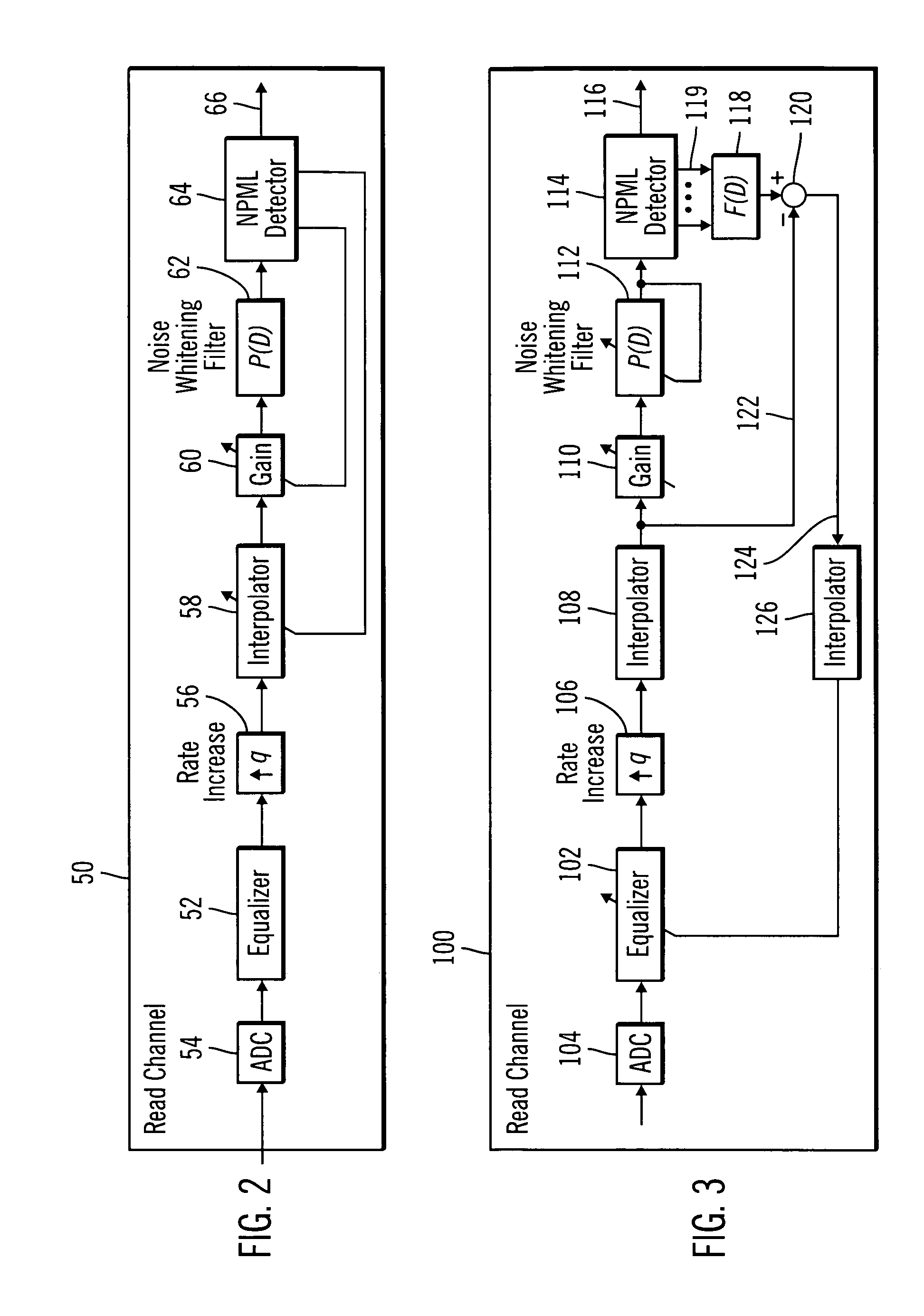
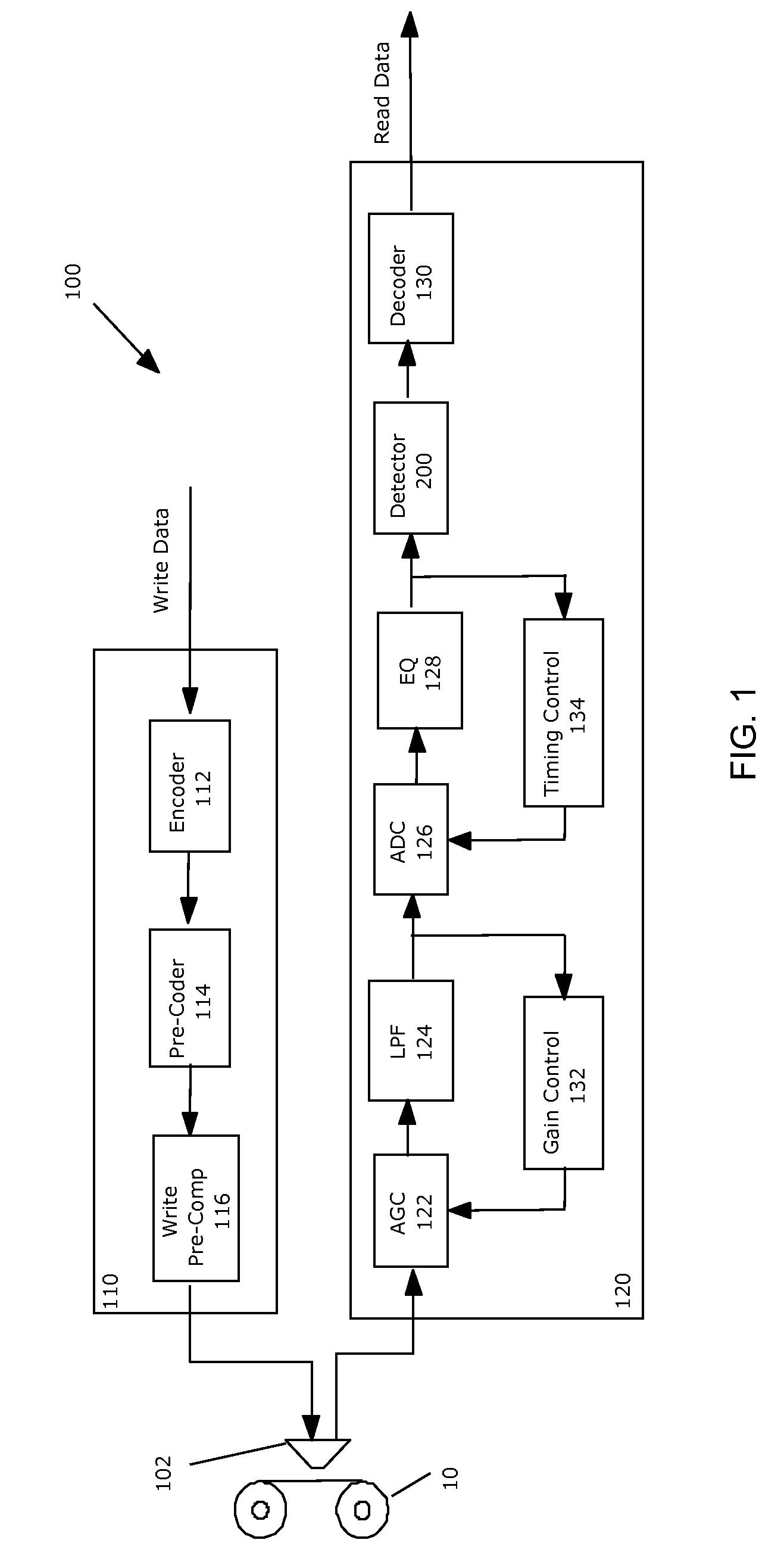
Asynchronous read channel shaped toward generalized partial response characteristics
InactiveUS7522367B2Modification of read/write signalsRecord information storageTime domainComputer science
Provided is an asynchronous read channel shaped toward generalized partial response characteristics. The read channel is incorporated in a storage device to process signals read from a storage medium. An equalizer receives asynchronous input read signals and shapes the input read signals toward a desired fixed characteristic in an asynchronous time domain. An interpolator transforms the read signal from the equalizer in the asynchronous time domain to a synchronous time domain. A noise whitening filter processes the read signal shaped toward the desired fixed characteristic to produce an output read signal shaped towards a generalized partial response polynomial. A detector receives the read signal shaped towards the generalized partial response polynomial in the synchronous time domain to determine an output value comprising data represented by the input read signals.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Adaptive differential pulse code modulation system and method utilizing whitening filter for updating of predictor coefficients
An improved technique for processing digital audio signals is provided wherein adaptation of predictor coefficients in an ADPCM environment is caused to converge in a rapid and computationally efficient manner. The technique employs a whitening filter to generate a filtered reconstructed signal which is utilized to update, or adapt, the prediction coefficients of a pole-based predictor.
Owner:POLYCOM INC
Whitening filter configuration method, program, and system
InactiveUS20140040340A1Relatively small errorLower ratioDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringDiscrete Fourier transform
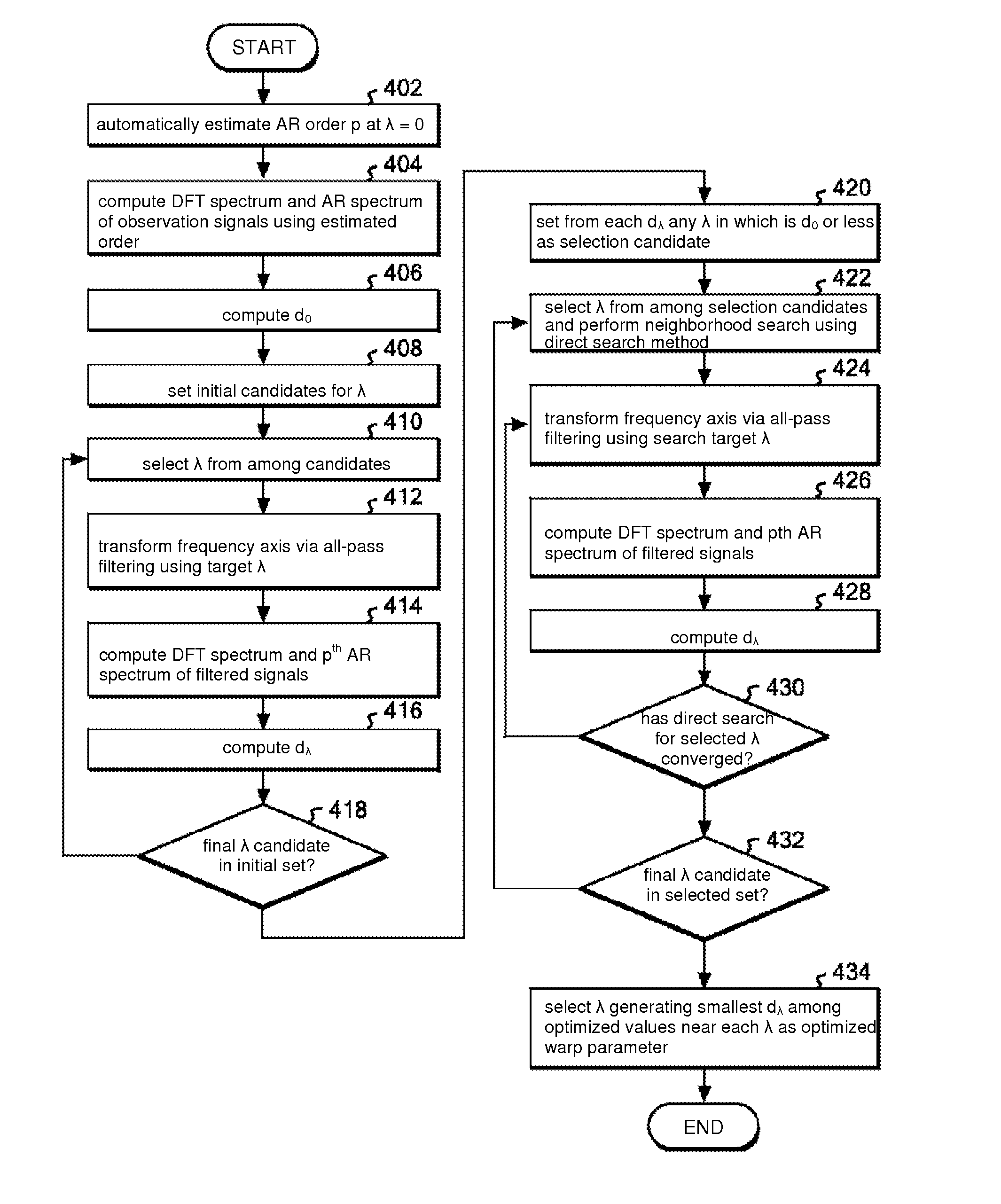
A system is configured so that signals passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ are whitening-filtered, and so that the frequency axis is restored by an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ. This optimizes the whitening filter by determining the optimum λ. First, the AR order p is automatically estimated using λ=0. A spectral distance dλ is computed using a discrete Fourier transform spectrum value passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ and a discrete AR spectrum value passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ. The λ which minimizes the spectral distance dλ is set as the warp parameter, and a whitening filter is configured in which the warp parameter has been optimized.
Owner:IBM CORP
Method of designing watermark in consideration of wiener attack and whitening filtered detection
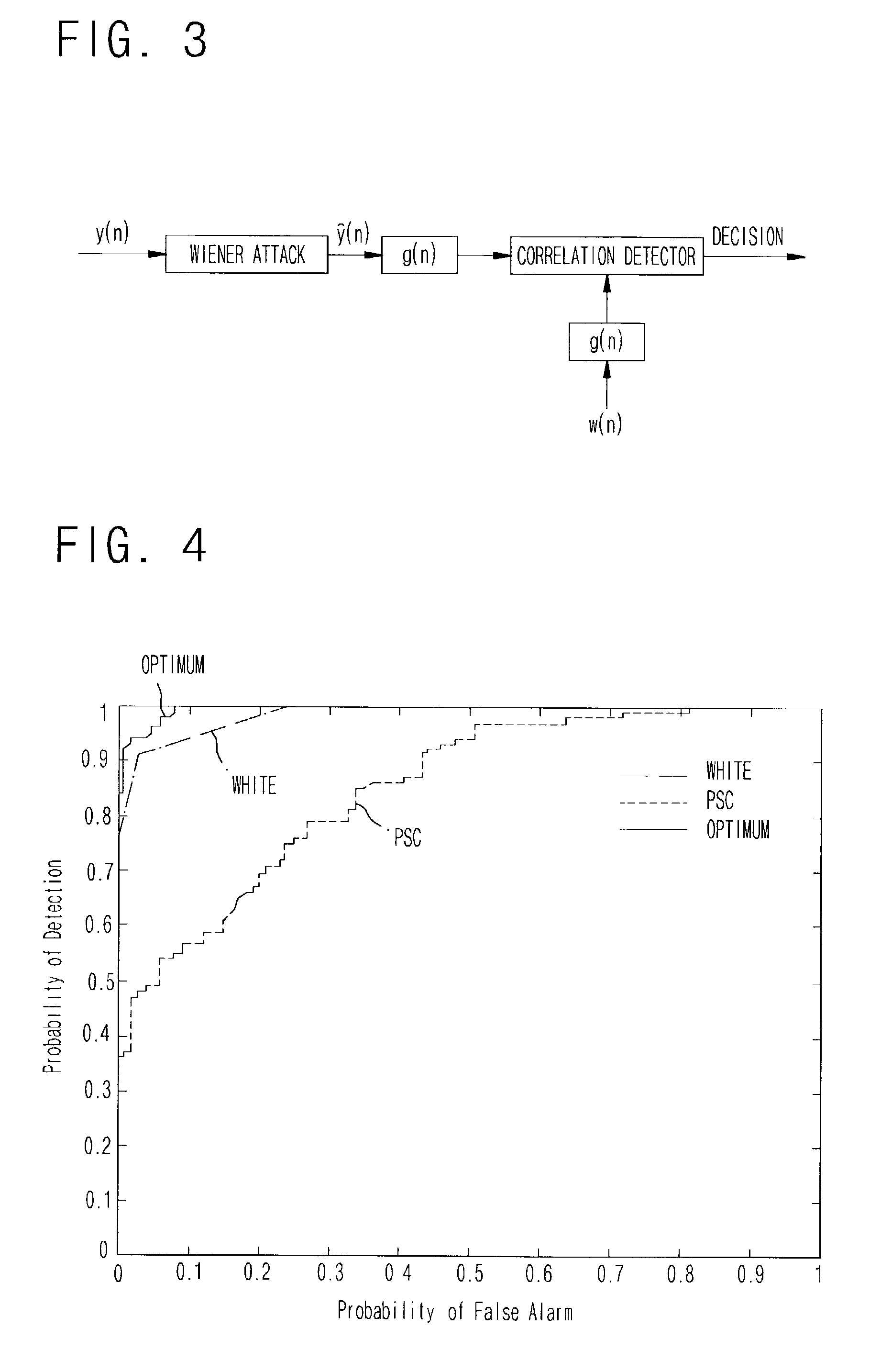
InactiveUS7076081B2Easy to detectEliminate the problemUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionHypothesisEngineering
Disclosed a method of designing a watermark having the power spectral density optimized so that the detection performance can be improved by employing the whitening filtered detection after the Wiener attack. The power spectral density of the watermark is designed using an optimization method that can improve the entire detection performance by reflecting the gain of the whitening filter after the Wiener attack. A higher detection gain is obtained using the whitening filter after the Wiener attack, and the expected value of the difference between test statistics of the two hypotheses that the watermark exists and the watermark does not exist, respectively, is maximized to optimize the detection performance. Regarding the expected value of the difference between the test statistics as an objective function, the power spectral density of the watermark, which corresponds to a maximum differentiated value of the power spectral density of the watermark using the Lagrange multiplier method, is obtained.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
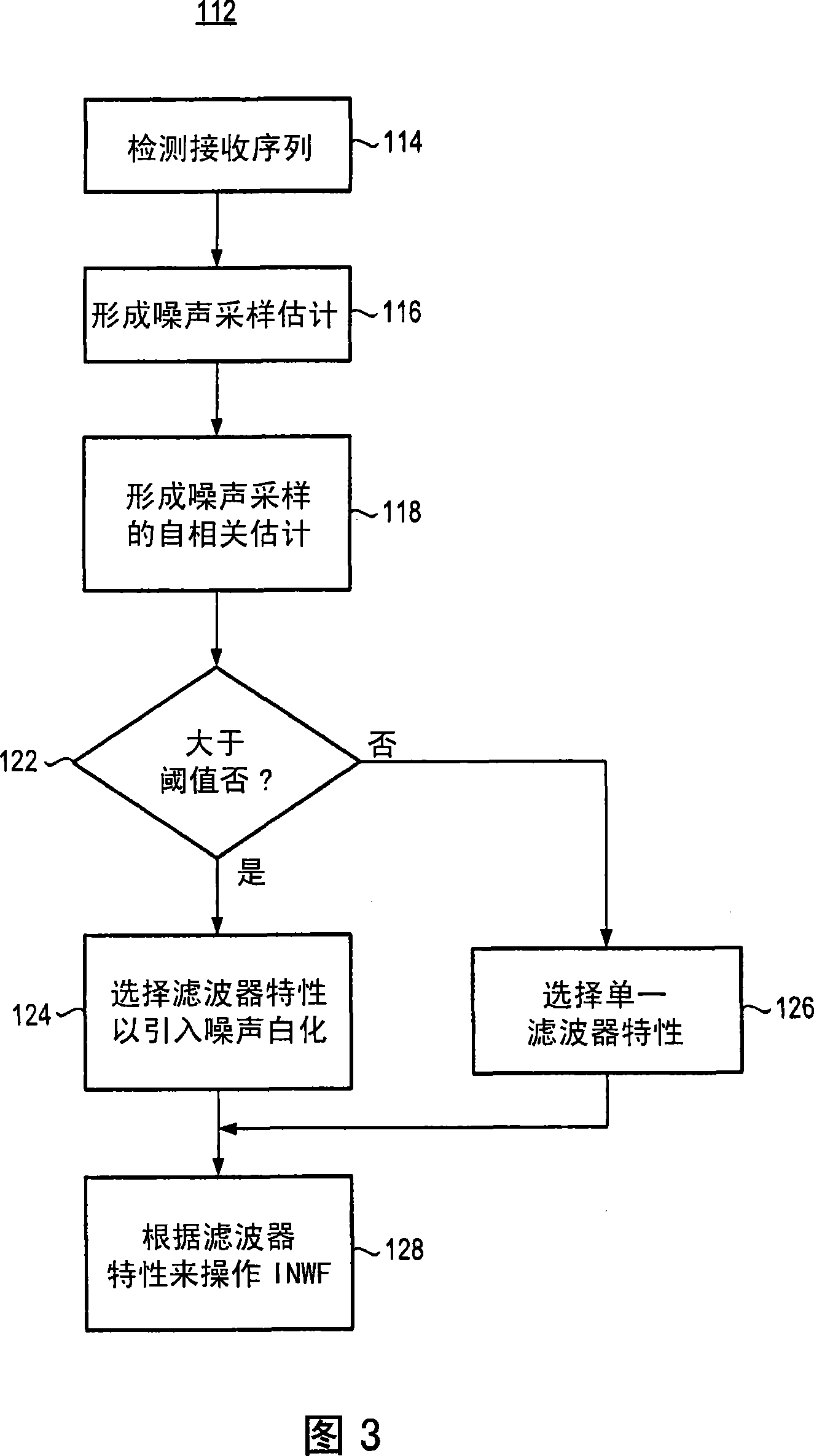
Apparatus and method for filtering a receive signal
InactiveCN101242626ARadio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmission for post communicationTransceiverCellular communication systems
Apparatus, and an associated method, for the receive part of a receiving station, such as a mobile station or other transceiver of a cellular communication system. Selection is made of filter characteristics to be exhibited by an adaptive, input noise whitening filter. A noise estimator estimates a noise component of a noise sequence. An autocorrelation estimator estimates the noise-component autocorrelation. A determination is made as to whether the autocorrelation exceeds a threshold. If so, filter characteristics are selected to cause the input noise whitening filter to operate to inject whitening noise into the received sequence.
Owner:RES IN MOTION LTD
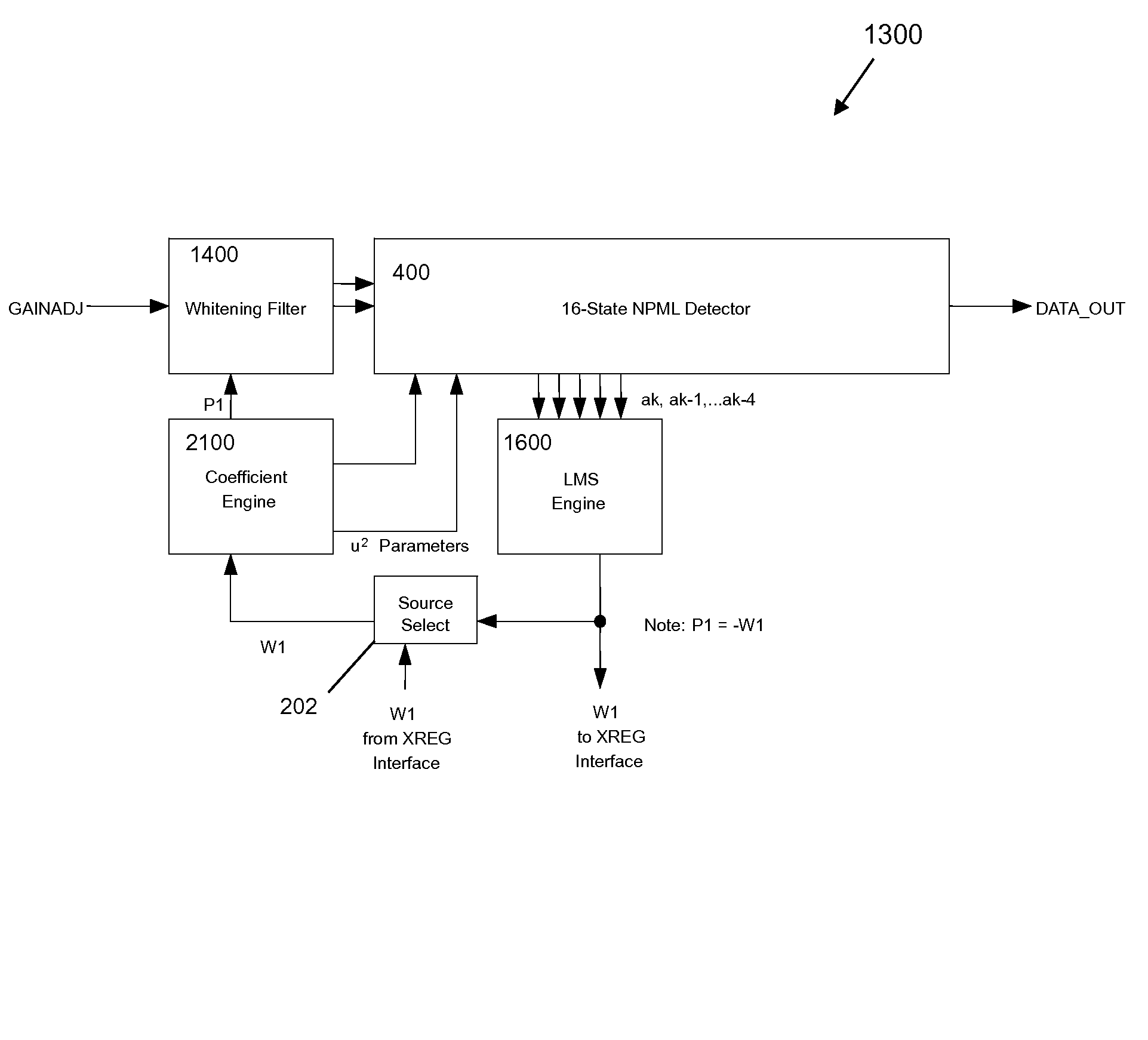
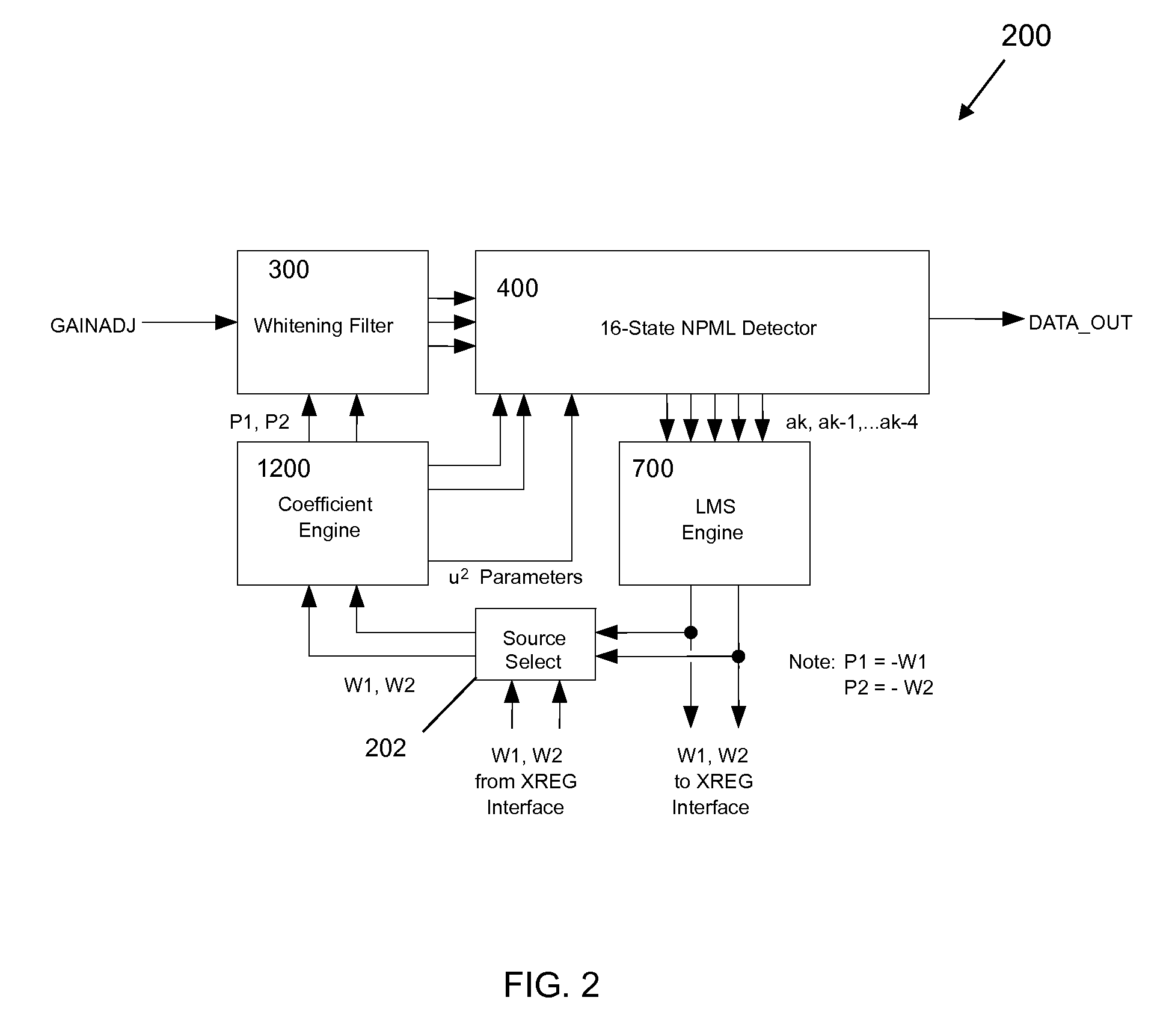
16-state adaptive noise predictive maximum-likelihood detection system
InactiveUS8077764B2Reduce in quantityAvoid disadvantagesMultiple-port networksDelay line applicationsMaximum likelihood detectionEngineering
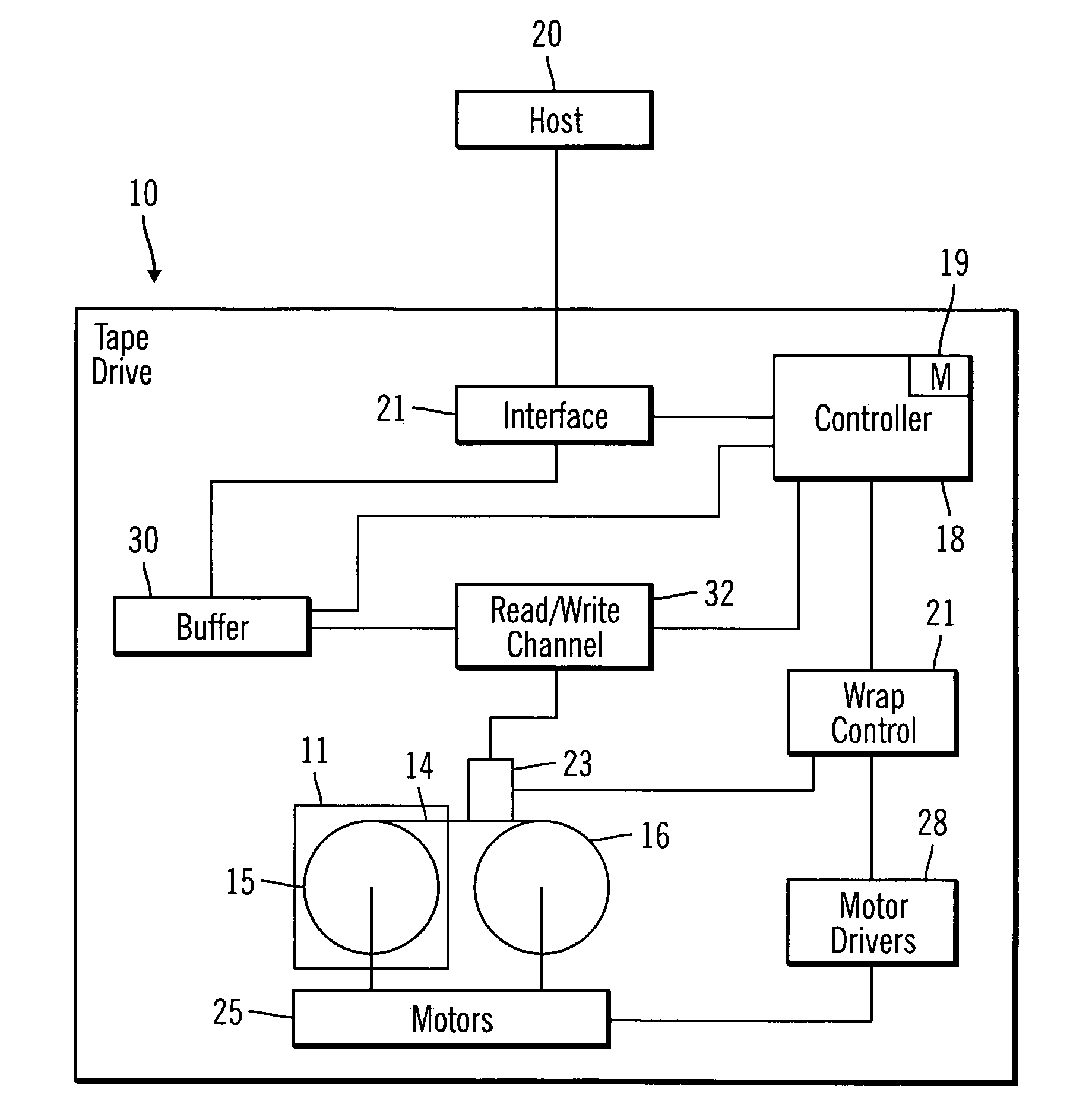
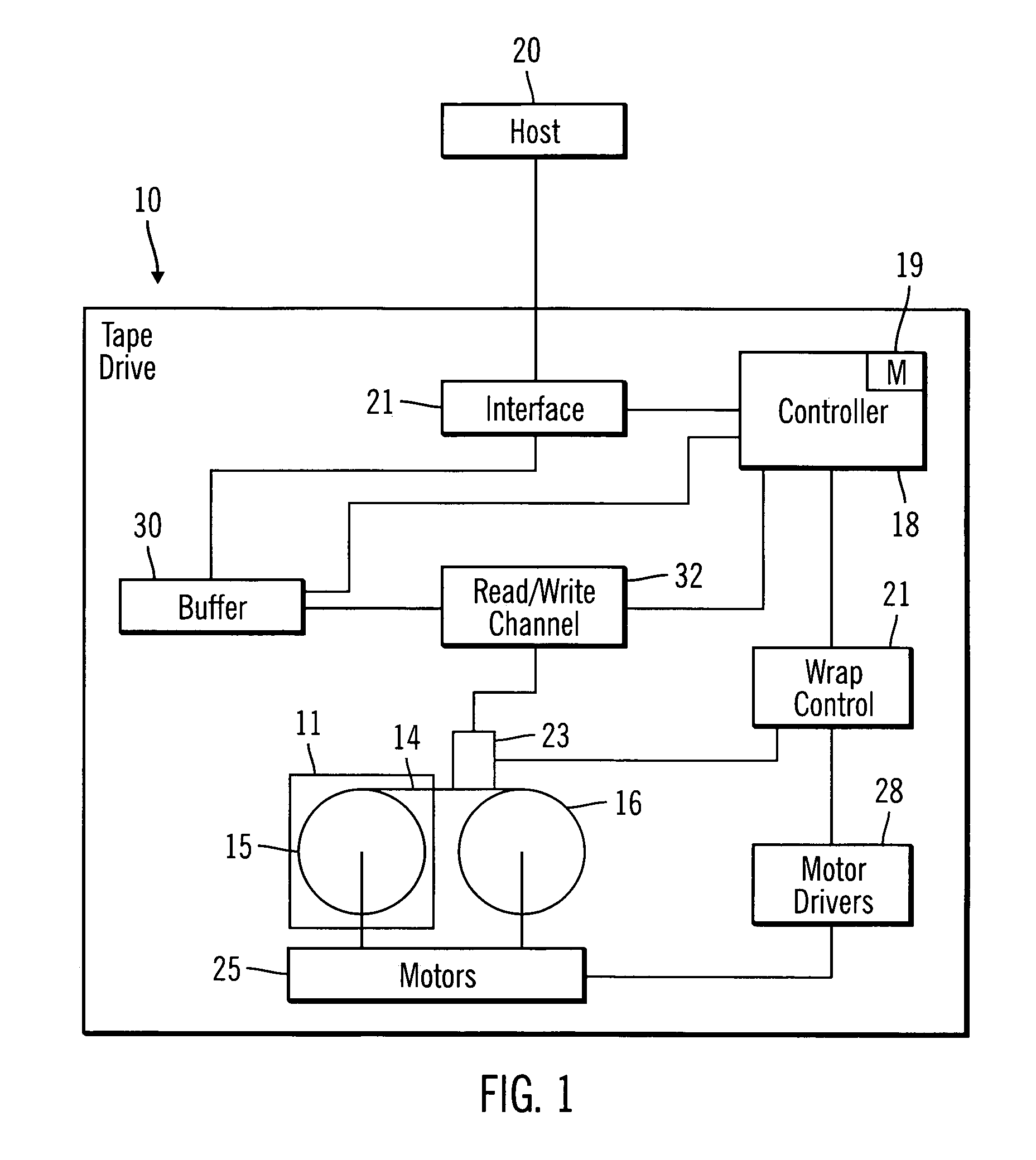
A 16-State adaptive NPML detector is provided for a tape drive which addresses weaknesses of a conventional fixed, 8-state EPR4 detector. Rather than having a fixed target channel, the detector is programmable to allow a range of target channels and can support “classical” partial response channels such as PR4 or EPR4 by programming predictor or whitening filter coefficients. In one embodiment, two filter coefficients may be set via XREG inputs or dynamically determined through the use of an LMS algorithm allowing the detector to adapt the predictor coefficients as data is being read. Another embodiment provides a detector for an EPR4 target in which the whitening filter has one coefficient. Components of the detection system include the detector itself, an LMS engine, a coefficient engine and a noise predictive or whitening filter. Coefficients from the LMS engine may be loaded or stored dynamically based upon conditions in the tape drive.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image target detection method based on quotient space granular computing
InactiveCN102053248ARadio wave reradiation/reflectionPolarimetric synthetic aperture radarDomain of discourse
A polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image target detection method based on quotient space granular computing relates to the field of remote sensing, and solves the problem that the traditional detection method is inflexible and cannot acquire comprehensive detection results. The method comprises the following steps: a full polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image is pretreated; a multicomponent dispersion model, a polarimetric similarity parameter and a polarimetric whitening filter are respectively adopted to treat the polarimetric synthetic aperture radar image, and the target detection is carried out to obtain three coarsness spaces; the quotient space theory is utilized for synthesis of the three coarsness spaces, including the synthesis of domains of discourse and the synthesis of attributes; and the attributes of synthetic domains of discourse are utilized to re-determine and re-divide undetermined elements, and an acquired result is combined with the synthetic domains ofdiscourse so as to obtain the fine grit space of the detection result, that is, the comprehensive and optimized detection result. The method solves the problem that the traditional polarimetric characteristics and polarimetric detection arithmetic are inflexible and limited in the target detection of a building with complicated dispersion characteristics.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Colored interference indentification
InactiveUS20050227663A1Improve communication performanceError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorTransmission monitoringHueWhitening filter
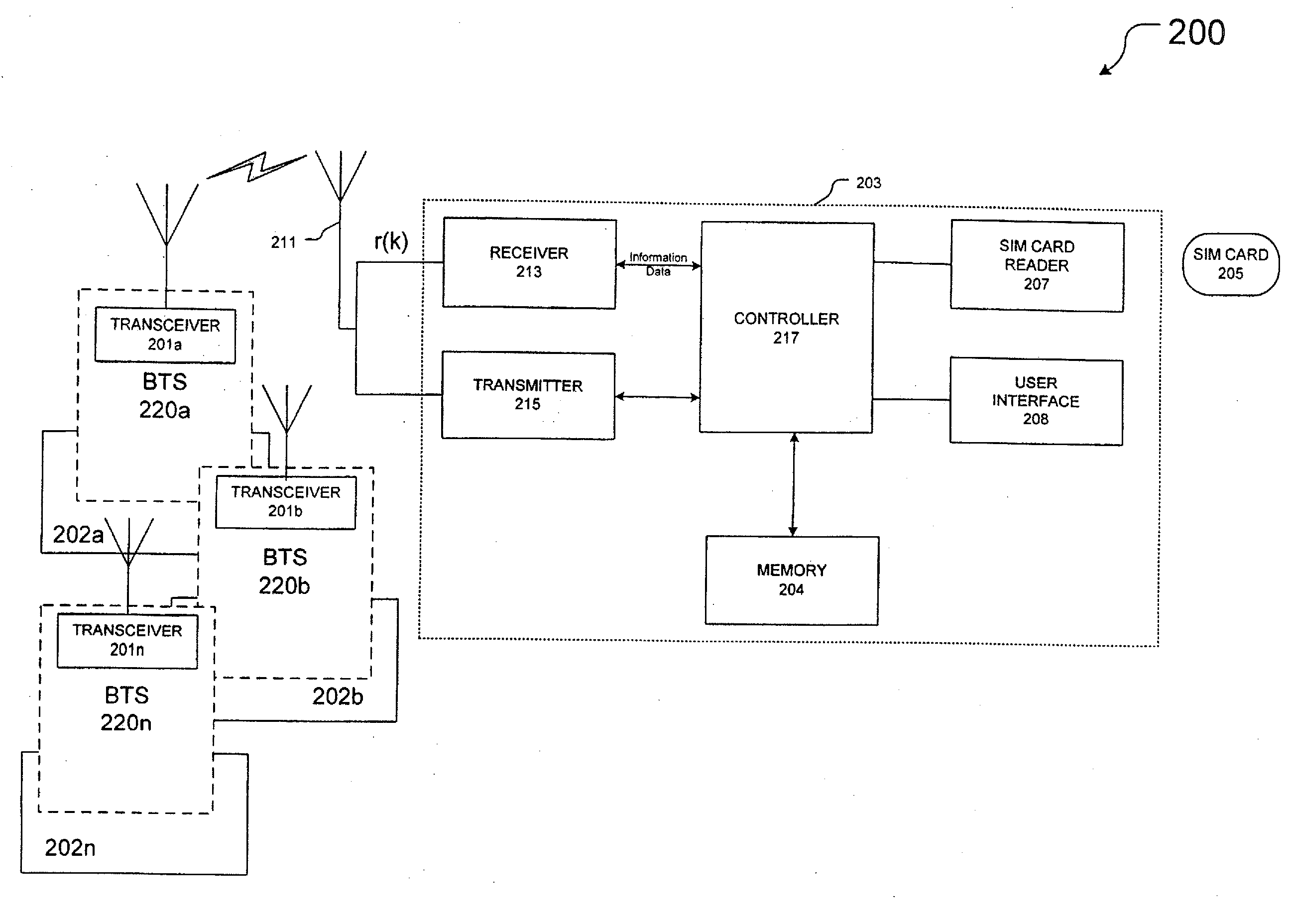
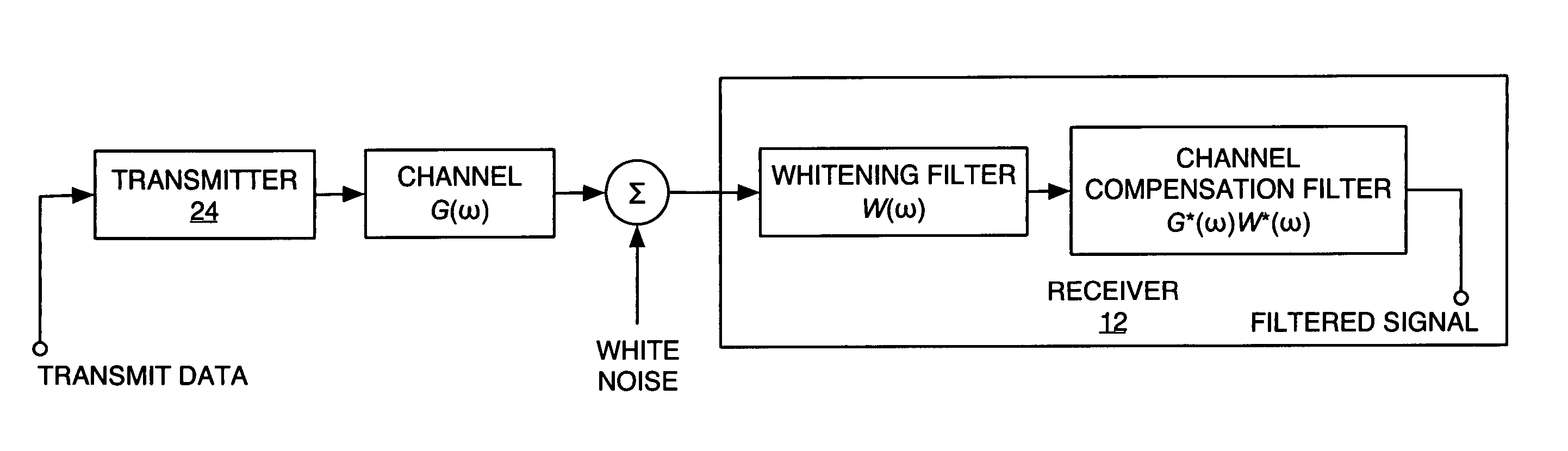
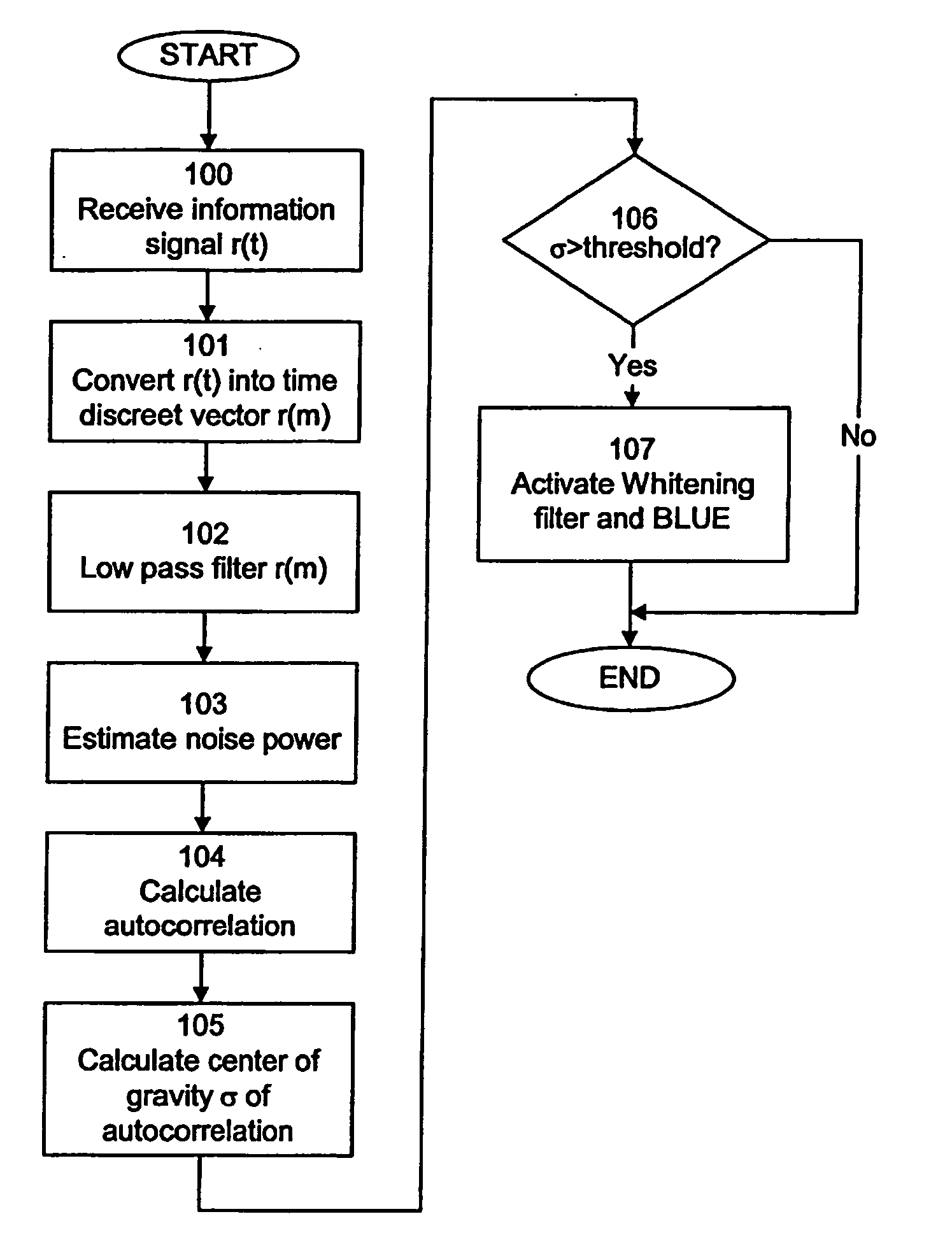
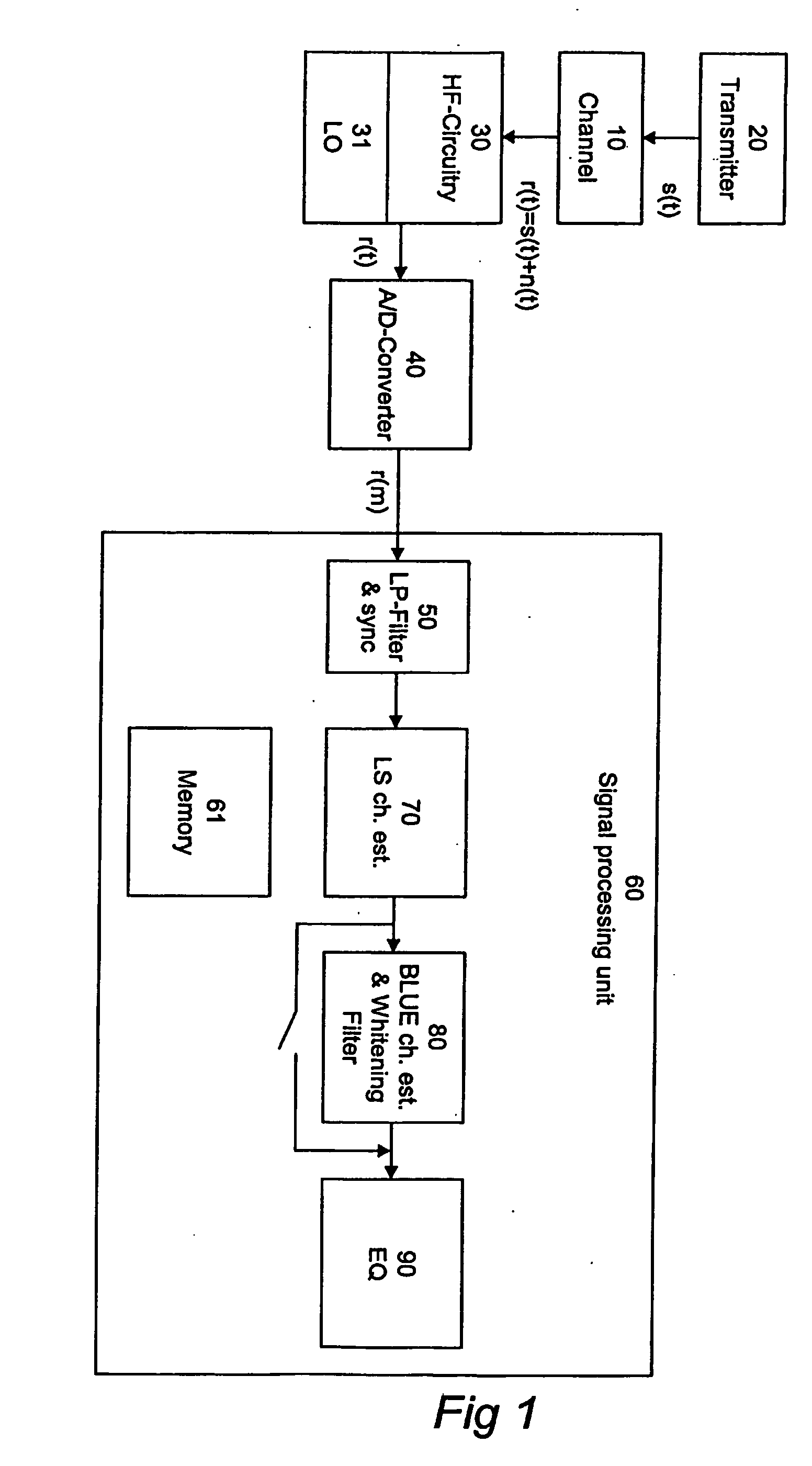
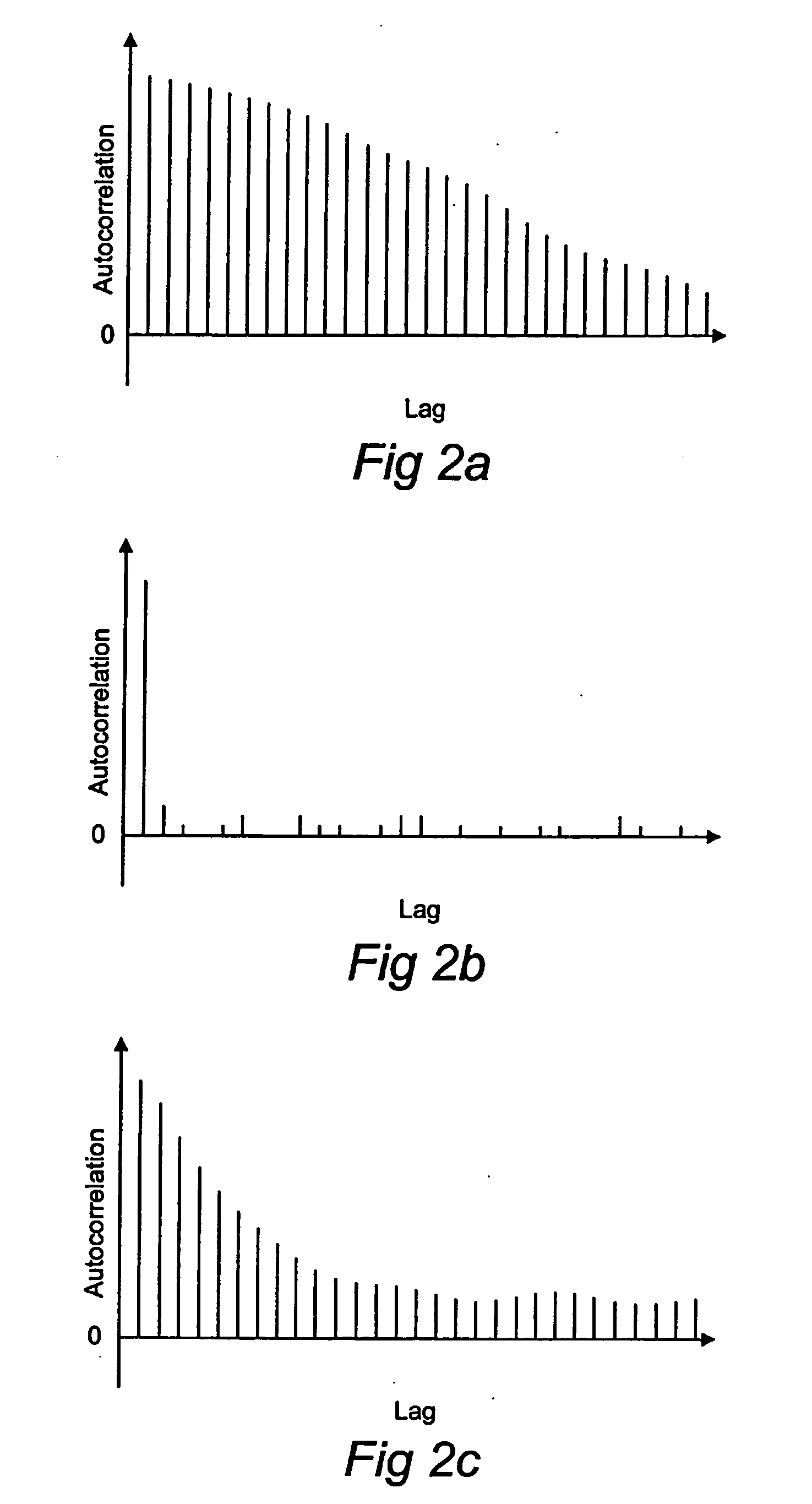
A method and apparatus for receiving a communication signal r(t) subject to noise n(t) over a communication channel (10) is disclosed. The method comprises the steps of: receiving (100) the communication signal r(t) comprising the noise n(t), estimating (103) the amount of noise n(t) in the communication signal r(t), and determining (105) the hue of the estimated amount noise n(t), wherein the received communication signal r(t) is passed through a whitening filter if the hue of the noise n(t) is greater than a predetermined threshold level.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Multispectral imaging system and methods of use
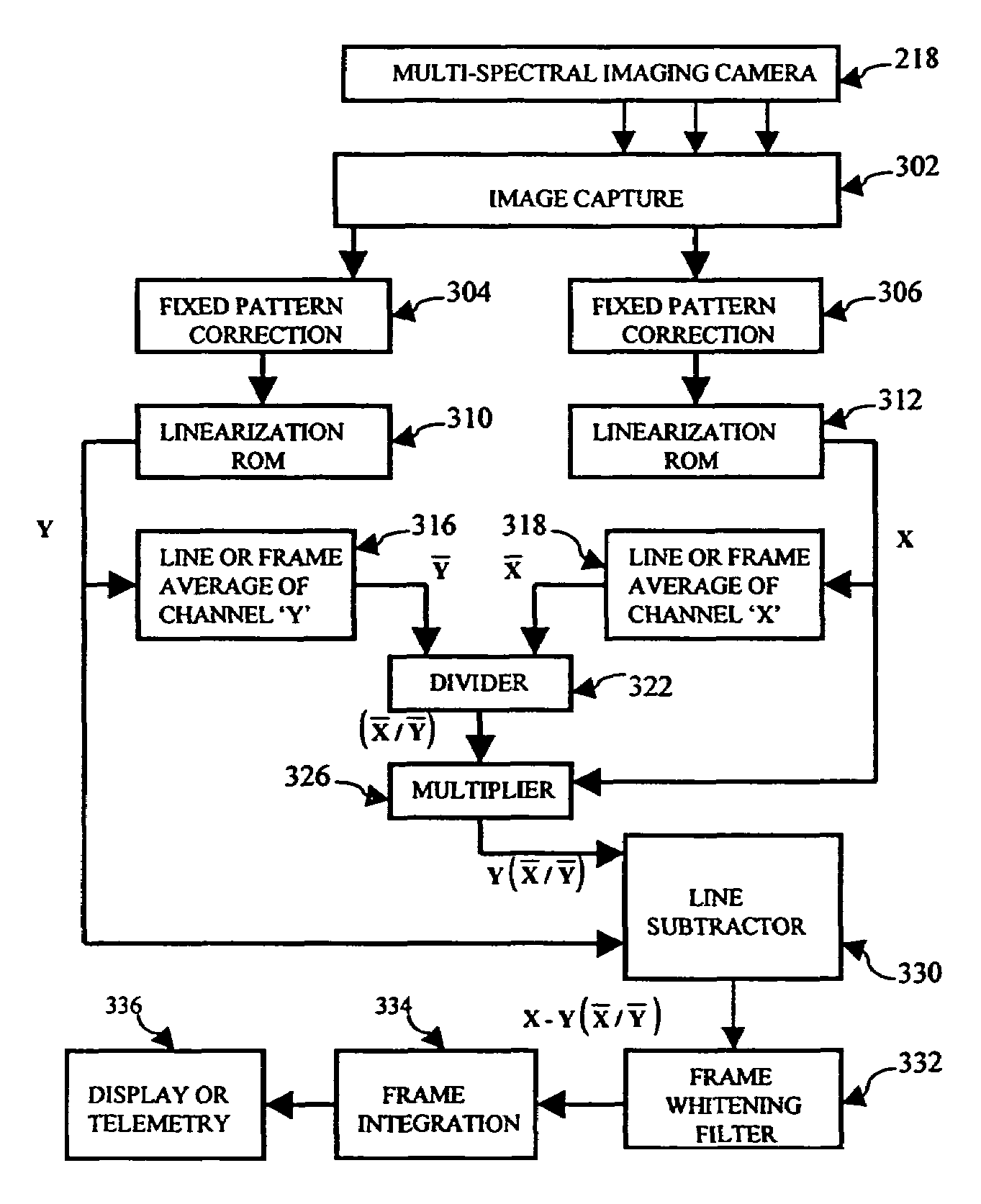
The multispectral imaging system provides detection of low contrast objects on or below the surface of a body of water through the elimination of most of the surface reflected light clutter components from multispectral images. The images are processed by taking the weighted difference of two or more spectral components and applying a demeaning or whitening filter to the result. The images can then be frame averaged where the appropriate corrections for motion, magnification, rotation, and translation have been applied. The resultant imagery can then be displayed to an operator or transmitted to a remote location.
Owner:MICRO BIZ VENTURES
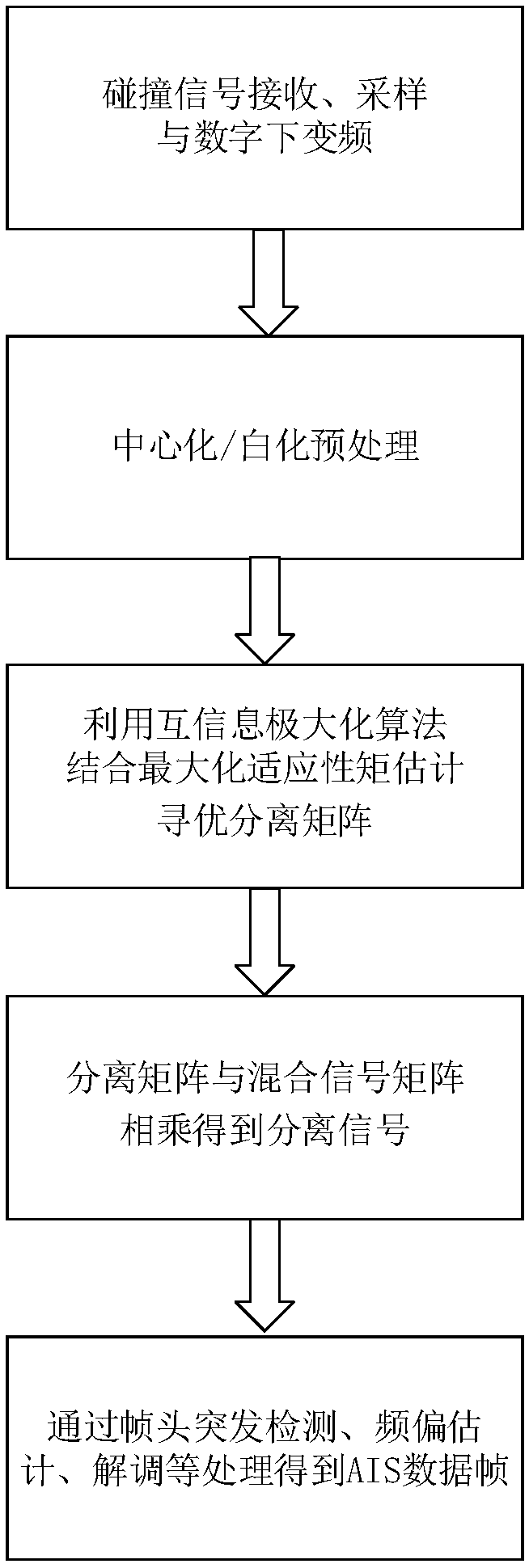
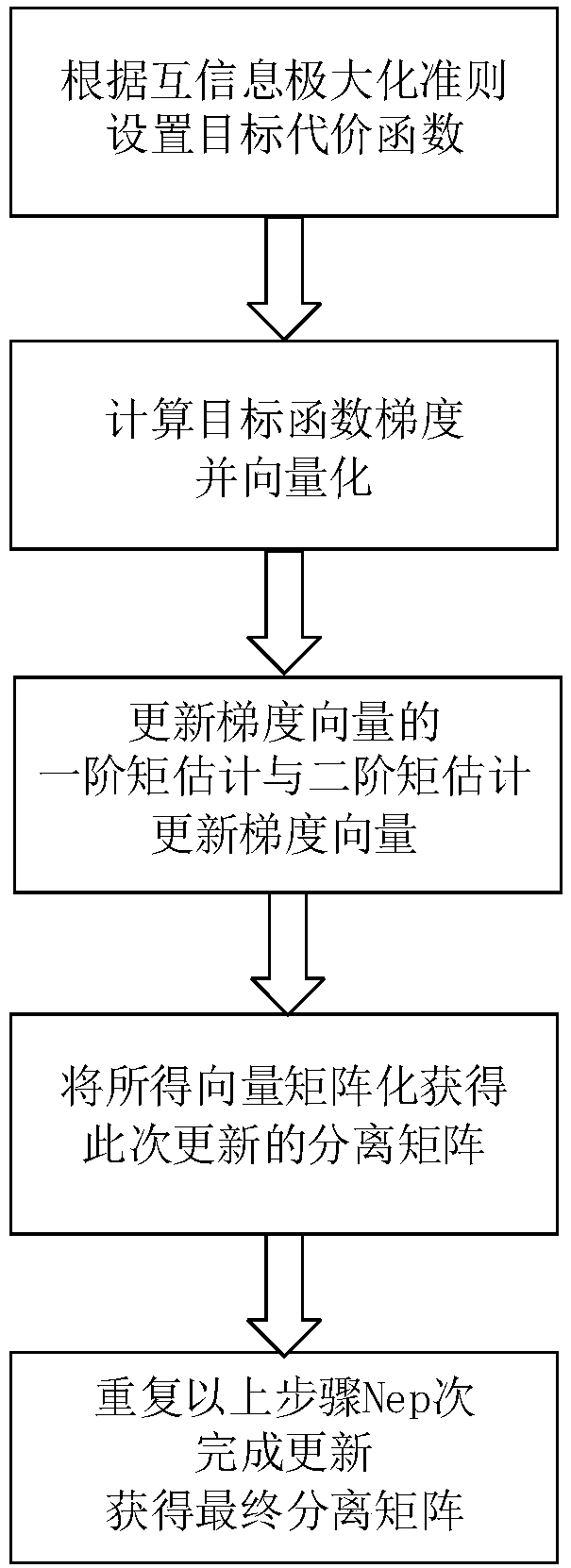
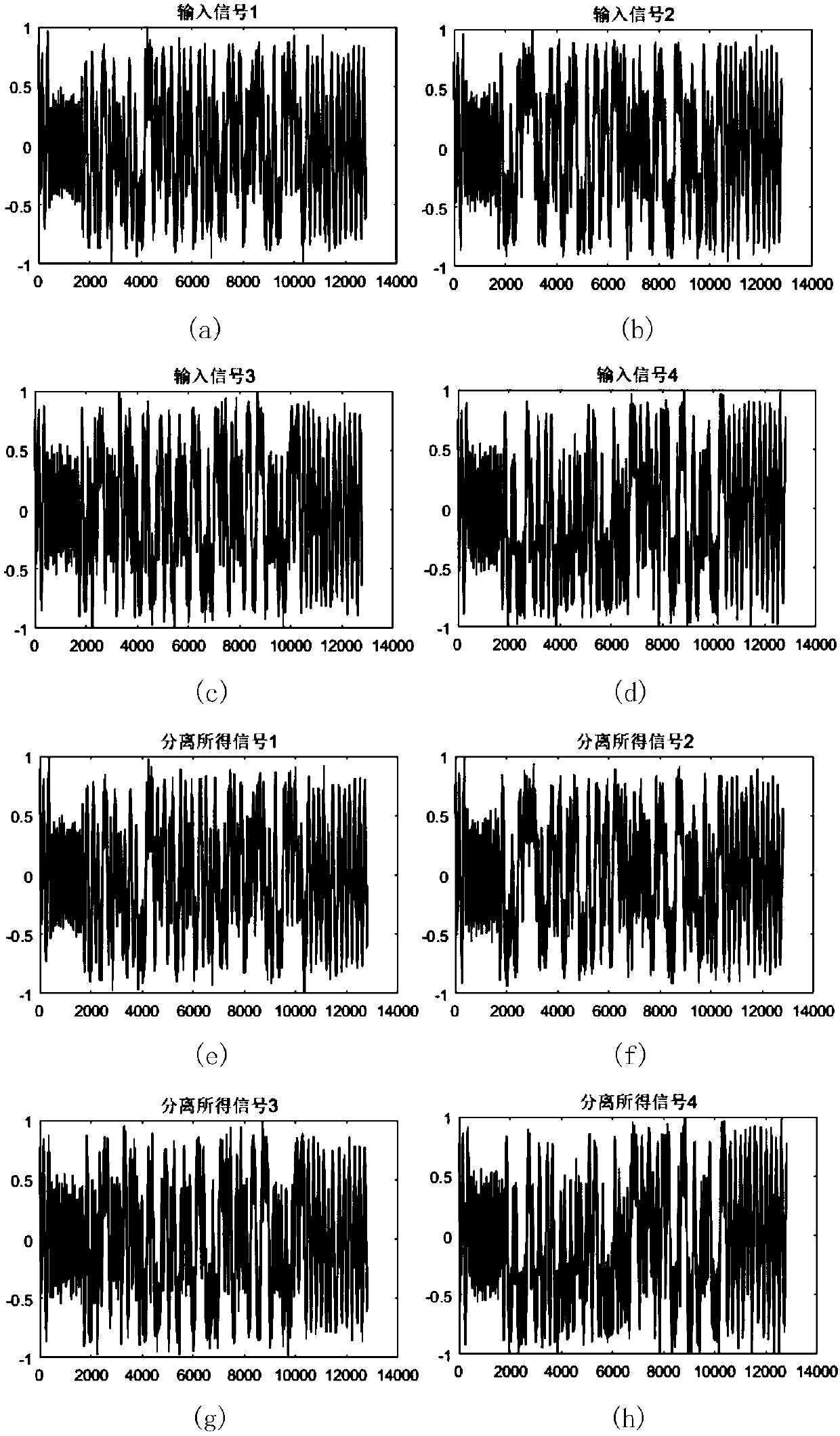
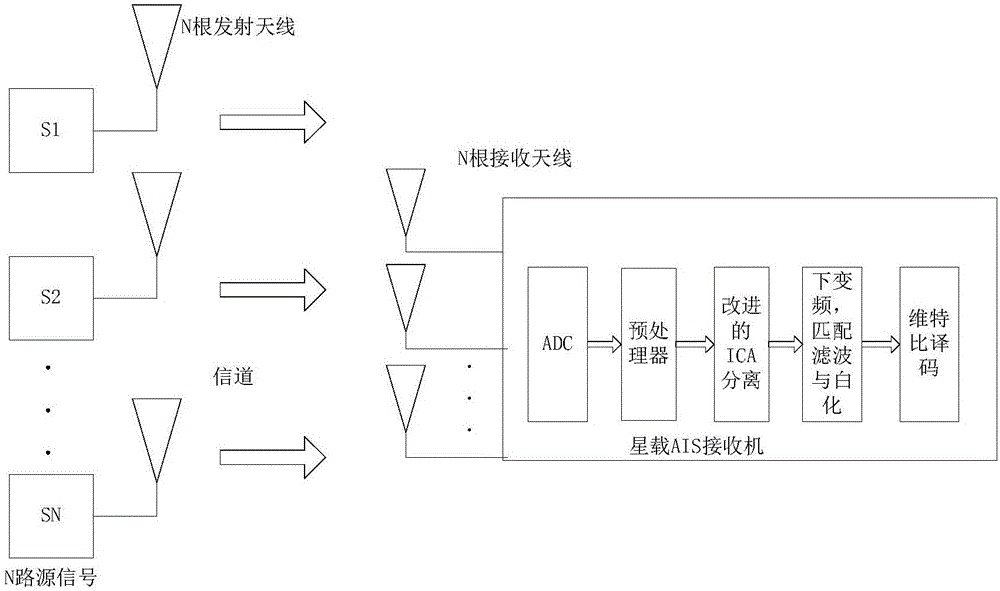
Satellite-borne AIS collision signal separation method based on adaptive moment estimation
ActiveCN108574525AAchieve adaptiveImprove estimation accuracyRadio transmissionTransmitter/receiver shaping networksDigital down conversionMatrix optimization
The invention discloses a satellite-borne AIS collision signal separation method based on adaptive moment estimation. The method specifically comprises the steps of sampling received AIS collision signals to obtain N ways of receiving signals, and carrying out digital down conversion processing to obtain an observation signal matrix; preprocessing the observation signal matrix, and carrying out collision removal processing through combination of mutual information maximization and maximum adaptive moment estimation and a signal separation algorithm, thereby obtaining N ways of separated signals; carrying out frame header burst detection, frequency offset estimation, symbol timing synchronization and whitening filtering processing on the N ways of separated signals; and carrying out decoding processing through utilization of a Viterbi algorithm, thereby obtaining valid data frames. According to the method, the maximum adaptive moment estimation is introduced into the mutual informationmaximization algorithm, the estimation precision of a separation matrix is improved, moreover, the time required for matrix optimization and collision removal is reduced, the timeliness is relativelyhigh, and the method is relatively applicable to a satellite-borne AIS receiving system.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
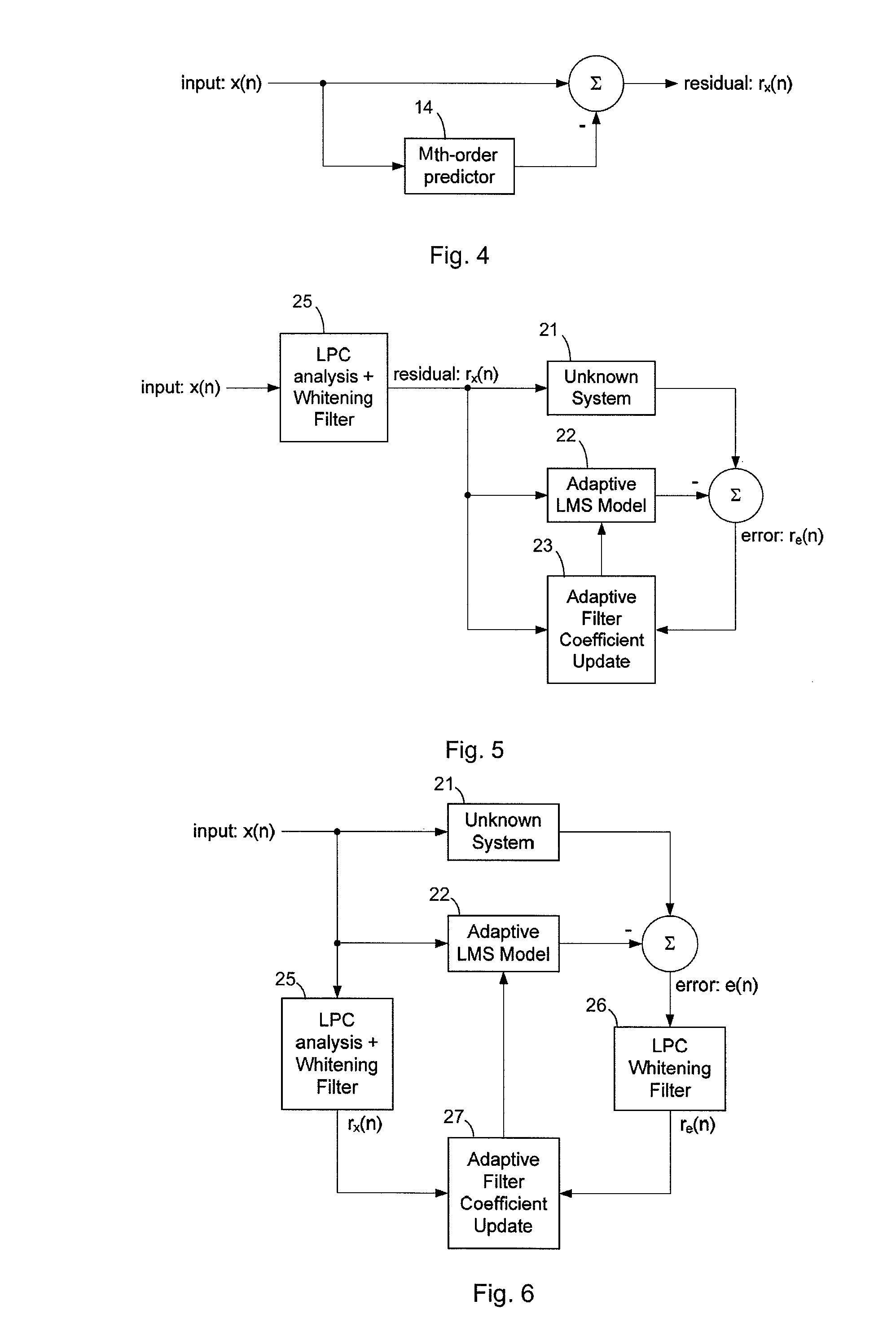
Method for Determining Updated Filter Coefficients of an Adaptive Filter Adapted by an LMS Algorithm with Pre-Whitening
ActiveUS20110158363A1Improve approximation accuracyErrorMultiple-port networksAdaptive networkAdaptive filterPre whitening
The application relates to a method for determining at least one updated filter coefficient of an adaptive filter (22) adapted by an LMS algorithm. According to the method, filter coefficients of a first whitening filter (25′) are determined, in particular filter coefficients of an LPC whitening filter. The first whitening filter (25′) generates a filtered signal. A normalization value is determined based on one or more computed values obtained in the course of determining the filter coefficients of the first whitening filter (25′). The normalization value is associated with the energy of the filtered signal. At least one updated filter coefficient of the adaptive filter (22) is determined in dependency on the filtered signal and the normalization value. Preferably, updated filter coefficients for all filter coefficients of the adaptive filter (22) are determined.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
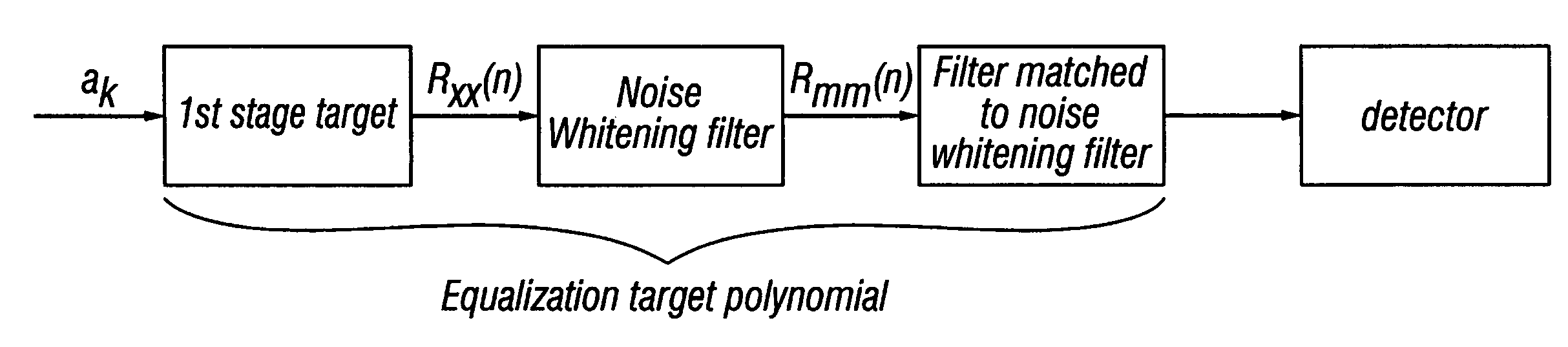
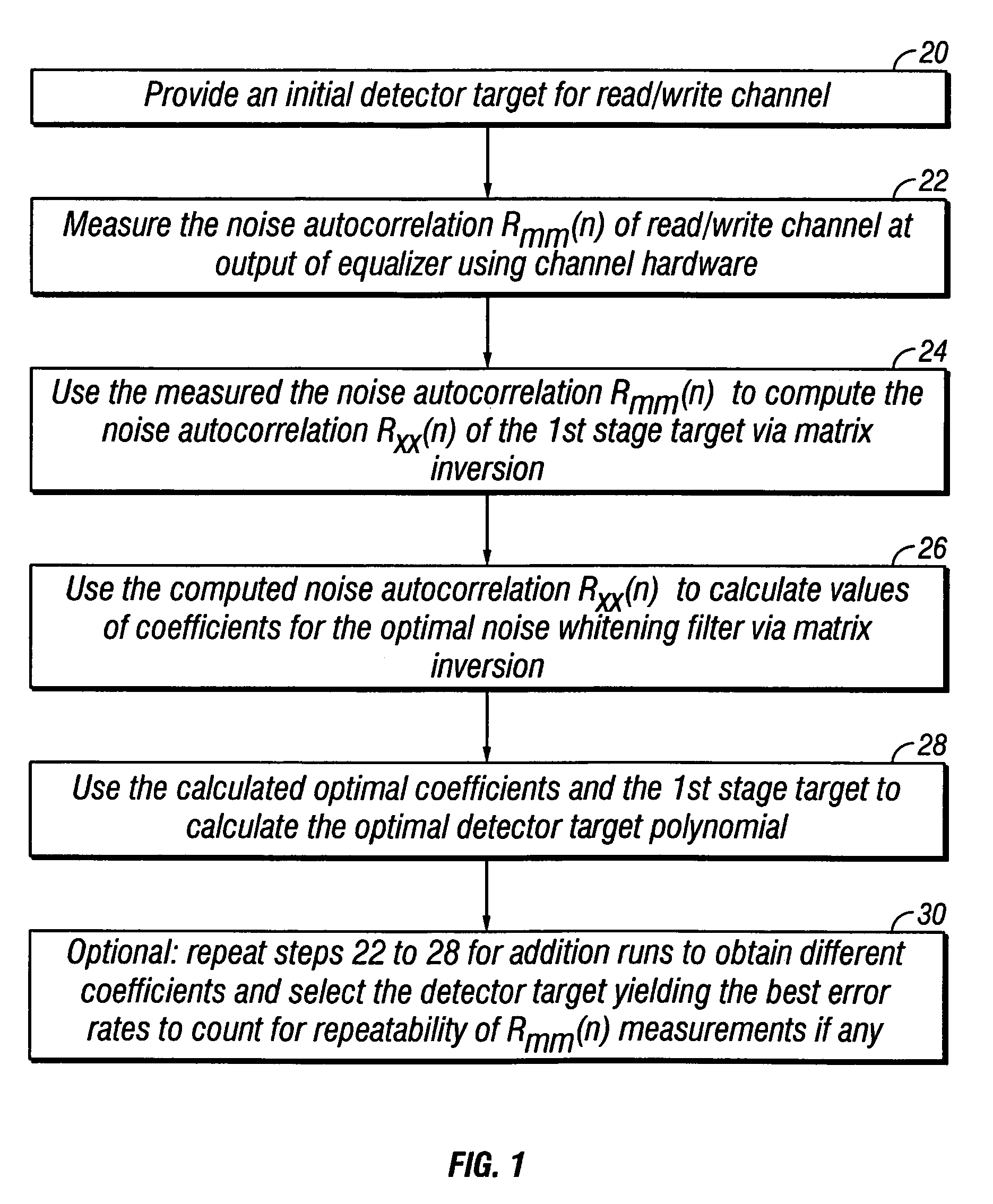
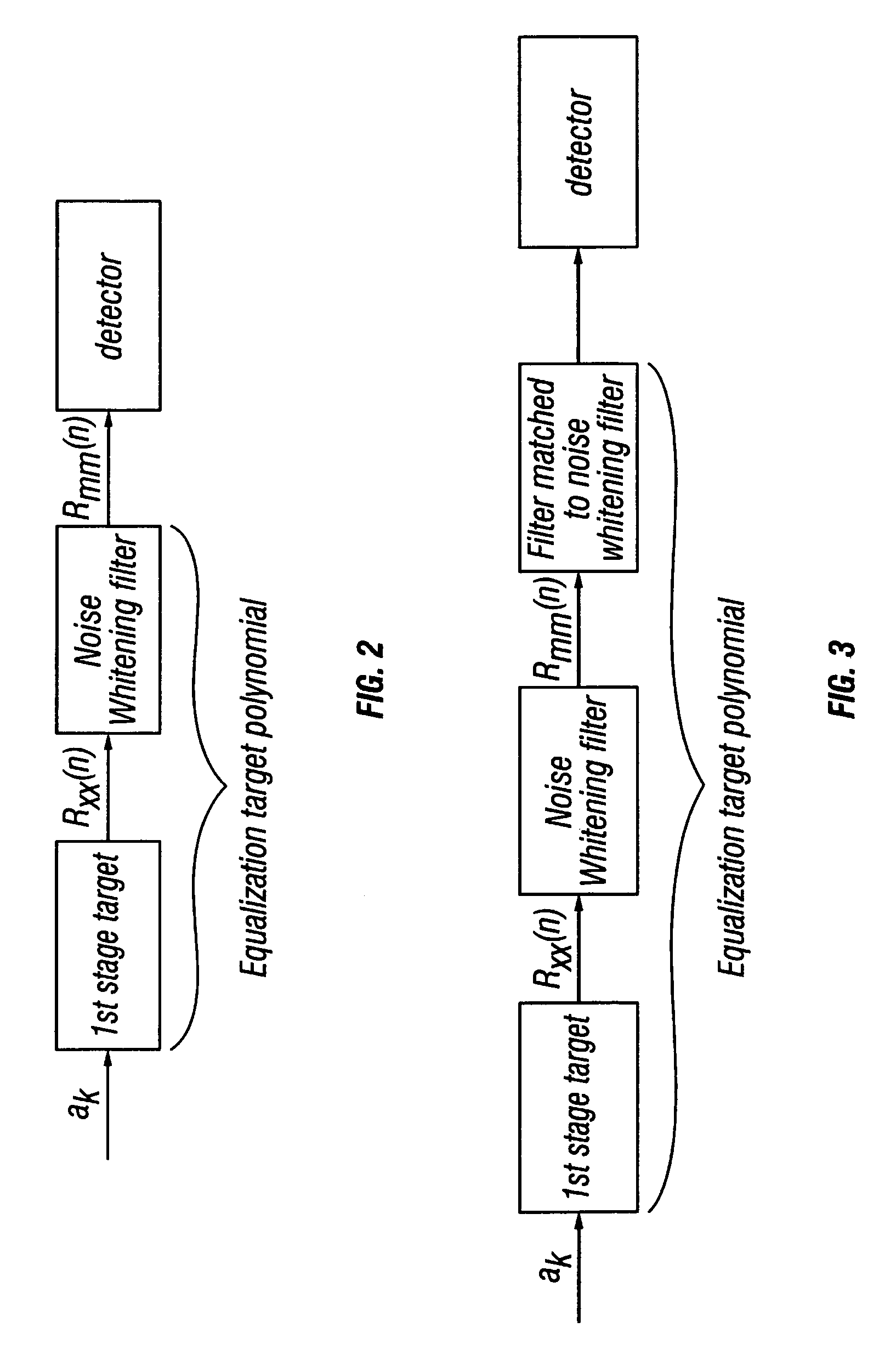
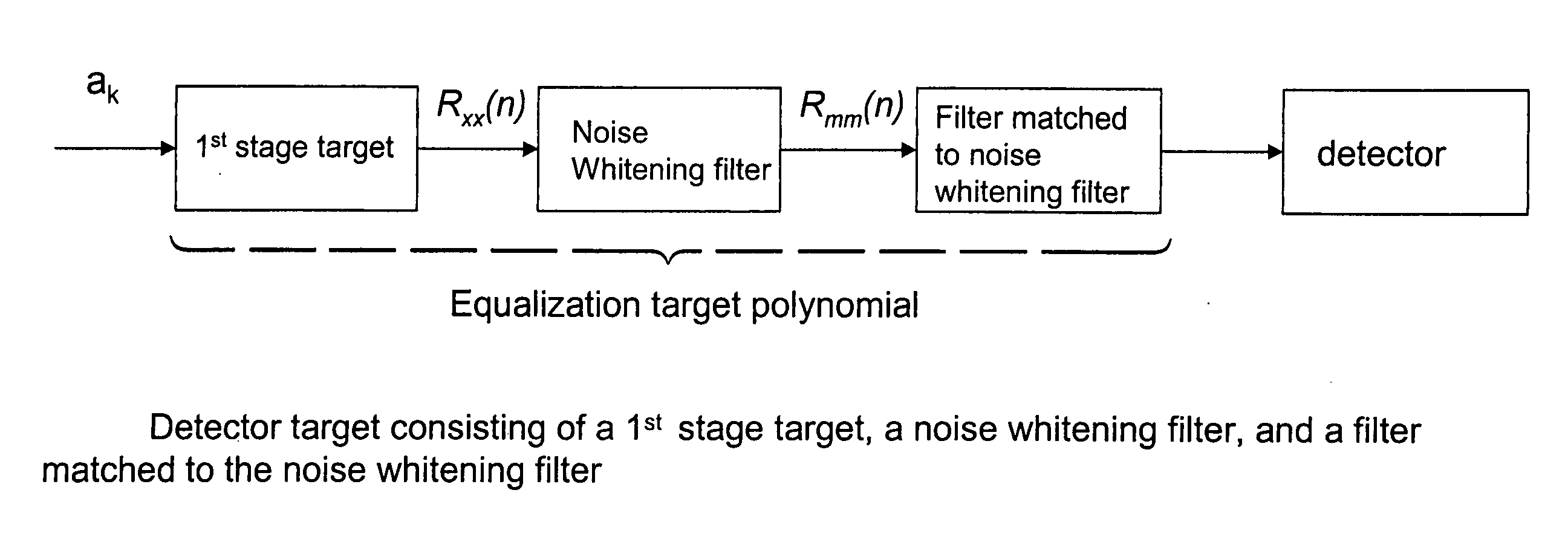
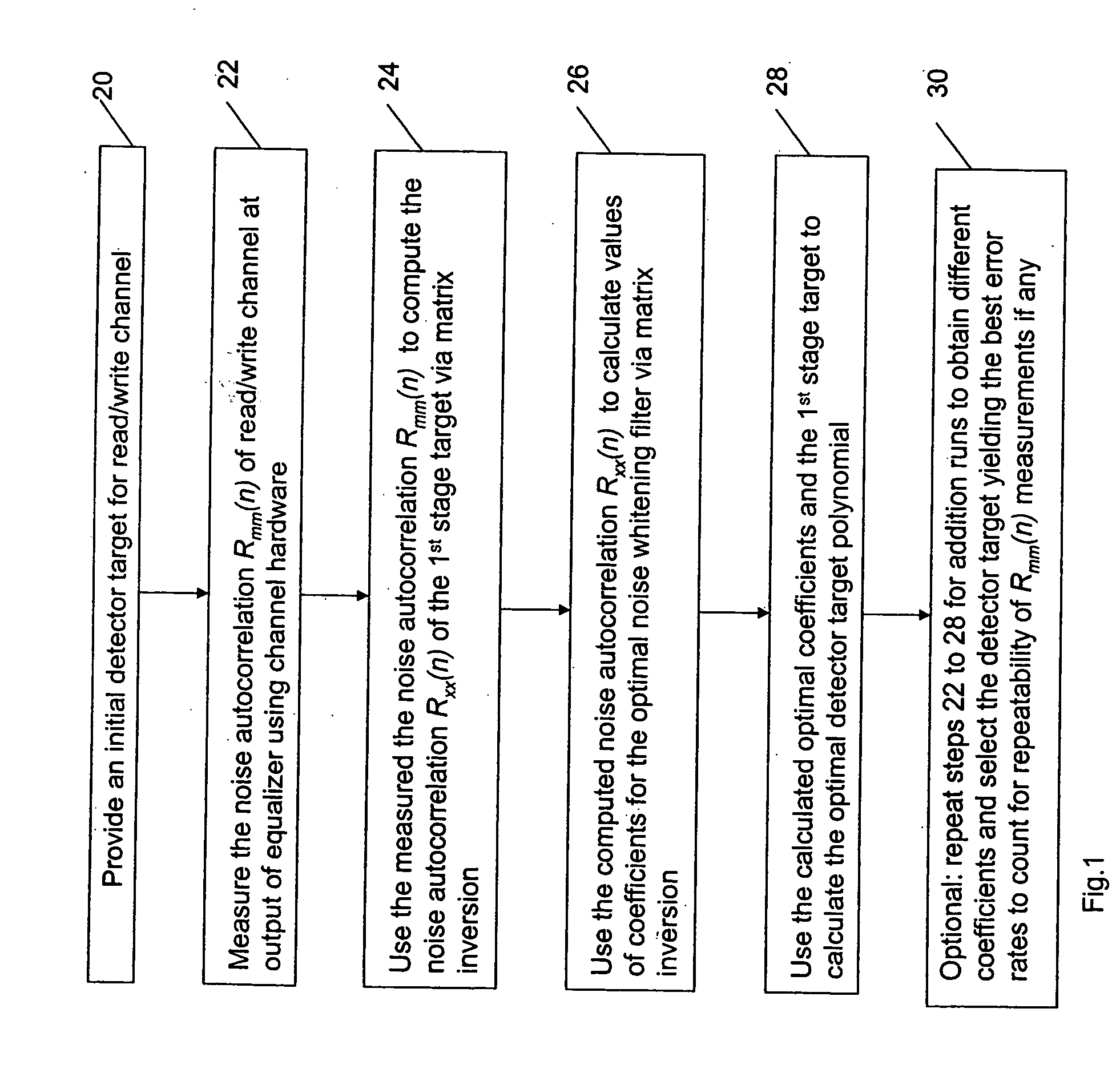
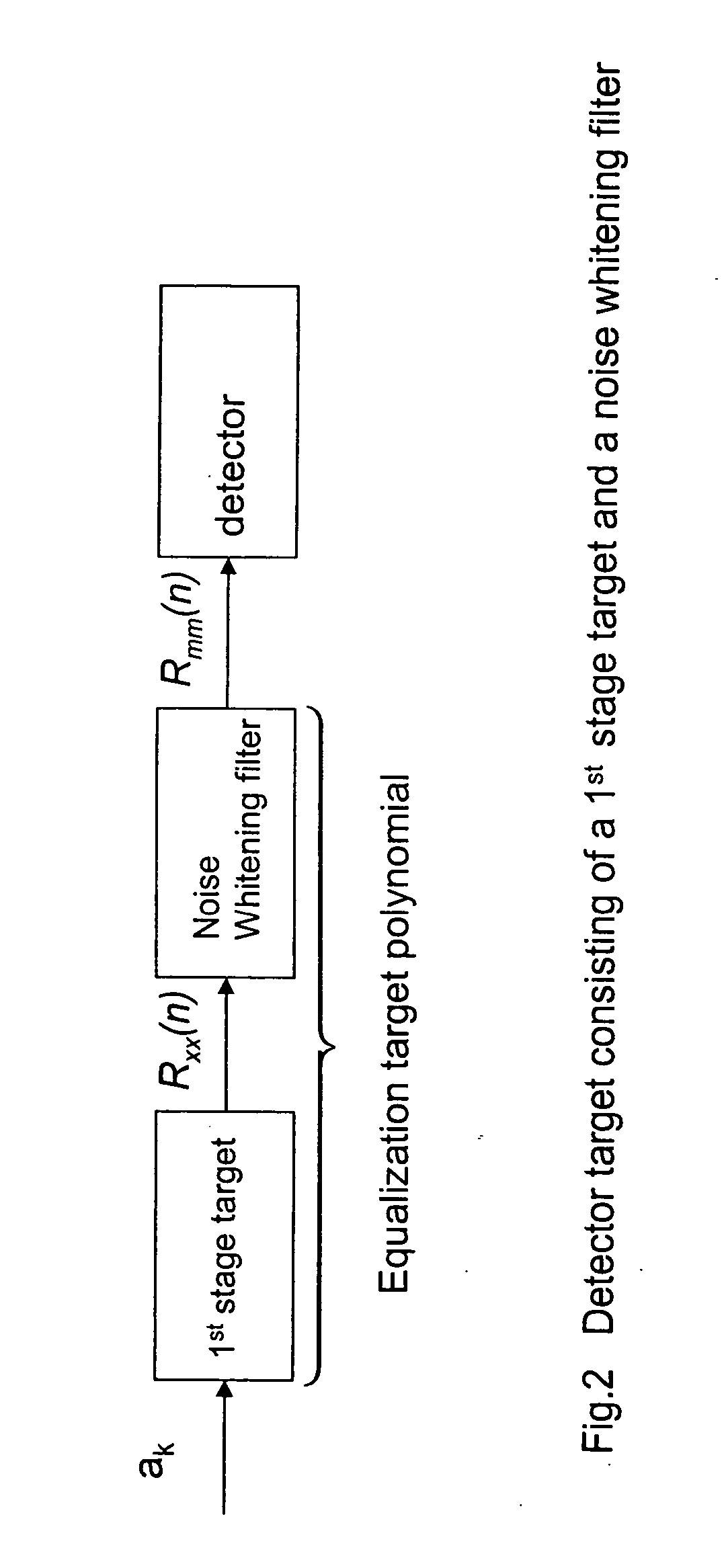
Optimizing detector target polynomials in read/write channels to achieve best error rate performance in disk drives
InactiveUS7424074B2Improve performanceModification of read/write signalsSignal processing for reducing noiseComputer scienceWhitening filter
Embodiments of the invention provide techniques for optimizing the detector target polynomials in read / write channels to achieve the best error rate performance in recording devices. In one embodiment, a method of obtaining a detector target polynomial of a read / write channel to achieve best error rate performance in a recording device comprises: providing an initial detector target for the read / write channel; measuring a noise autocorrelation of the read / write channel at the output of equalizer using channel hardware; computing a noise autocorrelation at the output of the 1st stage target based on the measured noise autocorrelation of the read / write channel at the output of equalizer; calculating optimal coefficients for the noise whitening filter; and obtaining the optimal detector target polynomial of the read / write channel using the calculated coefficients for noise whitening filter.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
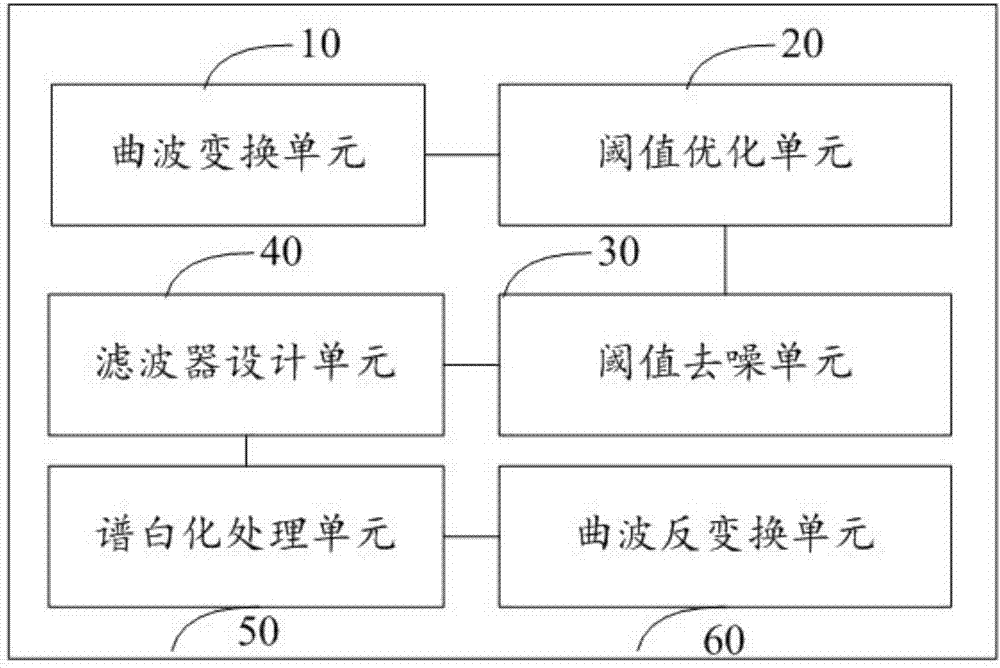
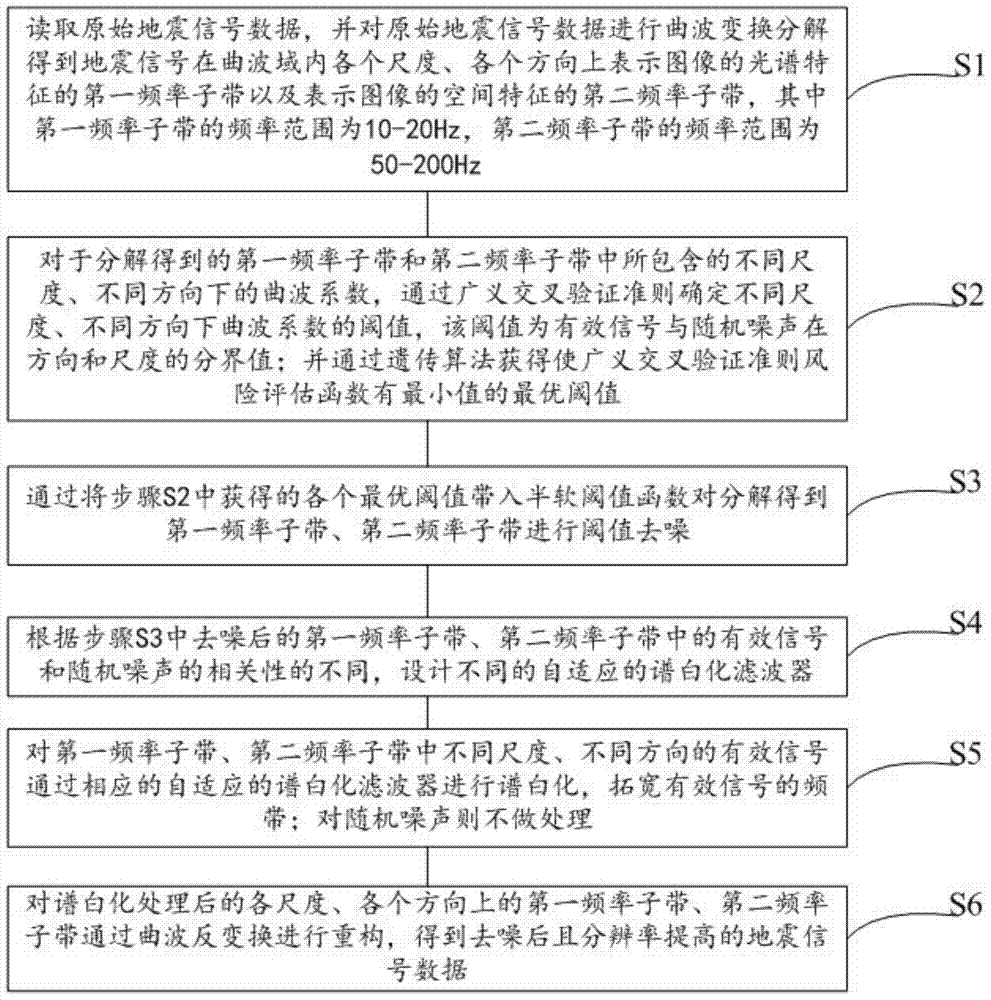
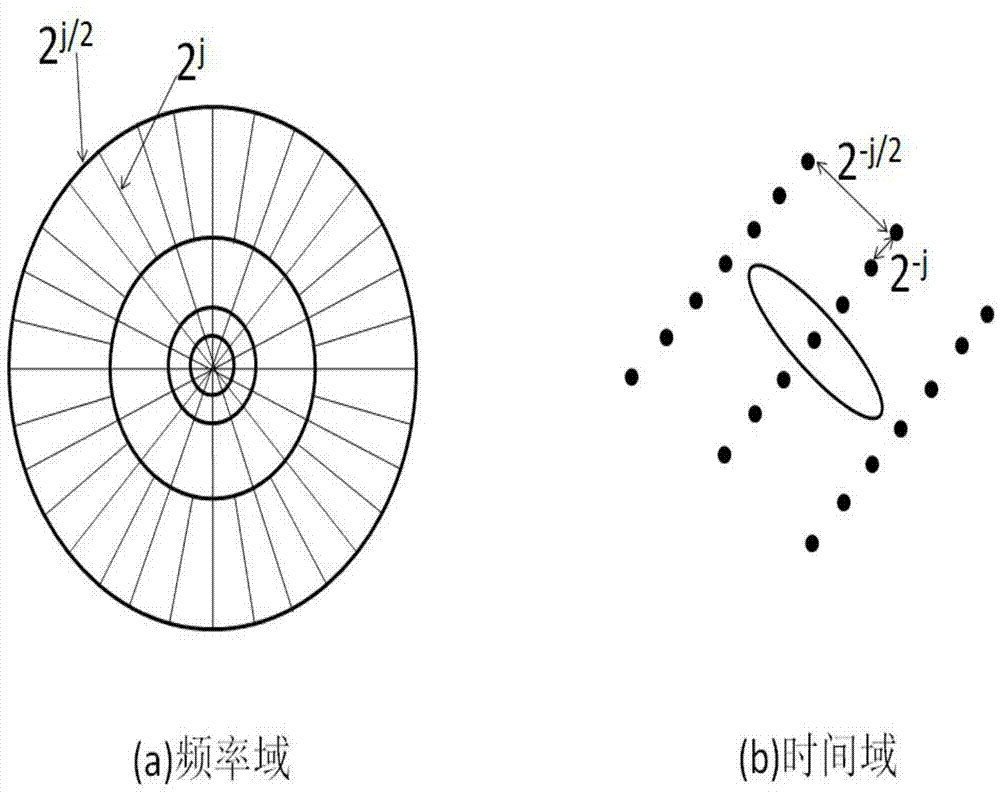
System and method for eliminating random noise in seismic signals
InactiveCN104849757AHigh-resolutionFilter out noise interferenceSeismic signal processingRandom noiseTransformation unit
The present invention provides a system and a method for eliminating the random noise in seismic signals, which comprises a curvelet transformation unit, a threshold optimization unit, a threshold de-noising unit, a filter design unit, a spectral whitening processing unit, and a curvelet inverse-transformation unit. The curvelet transformation unit is used for reading original seismic signal data, and obtaining first frequency sub-bands and second frequency sub-bands in various scales and all directions within a curvelet domain through decomposing the data based on the wavelet transformation process. The threshold optimization unit is used for determining the threshold values of curvelet coefficients in various scales and all directions, and obtaining an optimized threshold based on the genetic algorithm, wherein the optimized threshold is set in such a manner that the risk assessment function of the generalized cross validation criteria has a minimum value. The threshold de-noising unit is used for conducting the threshold de-noising treatment on the first and second frequency sub-bands obtained through the decomposing process. The filter design unit is used for designing different self-adaptive spectral whitening filters. The spectral whitening processing unit is used for conducting the spectral whitening treatment on effective signals of the first frequency sub-bands and the second frequency sub-bands in various scales and all directions. The curvelet inverse-transformation unit is used for reconstructing the signals through the curvelet inverse-transformation process to obtain de-noised seismic signal data of higher resolution.
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
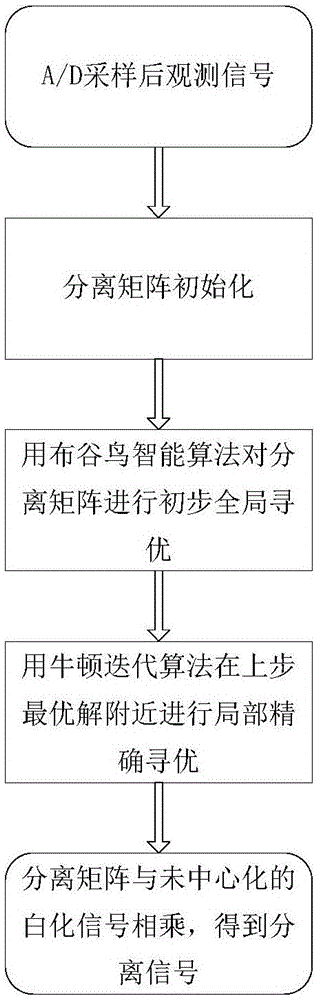
Satellite-borne AIS conflicting signal separation method based on improved independent component analysis
ActiveCN106506060AEasy to separateSimple structureRadio transmissionChannel estimationAnalog-to-digital converterVIT signals
The invention discloses a satellite-borne AIS conflicting signal separation method based on improved independent component analysis. The method comprises the following steps: sampling by an analog-to-digital converter to form N channel receiving data; performing centralization processing and whitening processing on N paths of received observation signals; obtaining N paths of separation signals from the matrix preprocessed by the observation signals by using an improved ICA method based on the cuckoo algorithm and the Newton iterative algorithm; performing digital down-conversion, matched filtering and whitening filtering on the obtained N paths of separation signals; and decoding the N paths of separation signals after the whitening filtering by using the viterbi algorithm to obtain N AIS data frames. According to the satellite-borne AIS conflicting signal separation method disclosed by the invention, no frequency deviation, phase shift or amplitude estimation is required, a satellite-borne AIS receiver structure is simplified, and the satellite-borne load is relieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method of and apparatus for noise whitening filtering
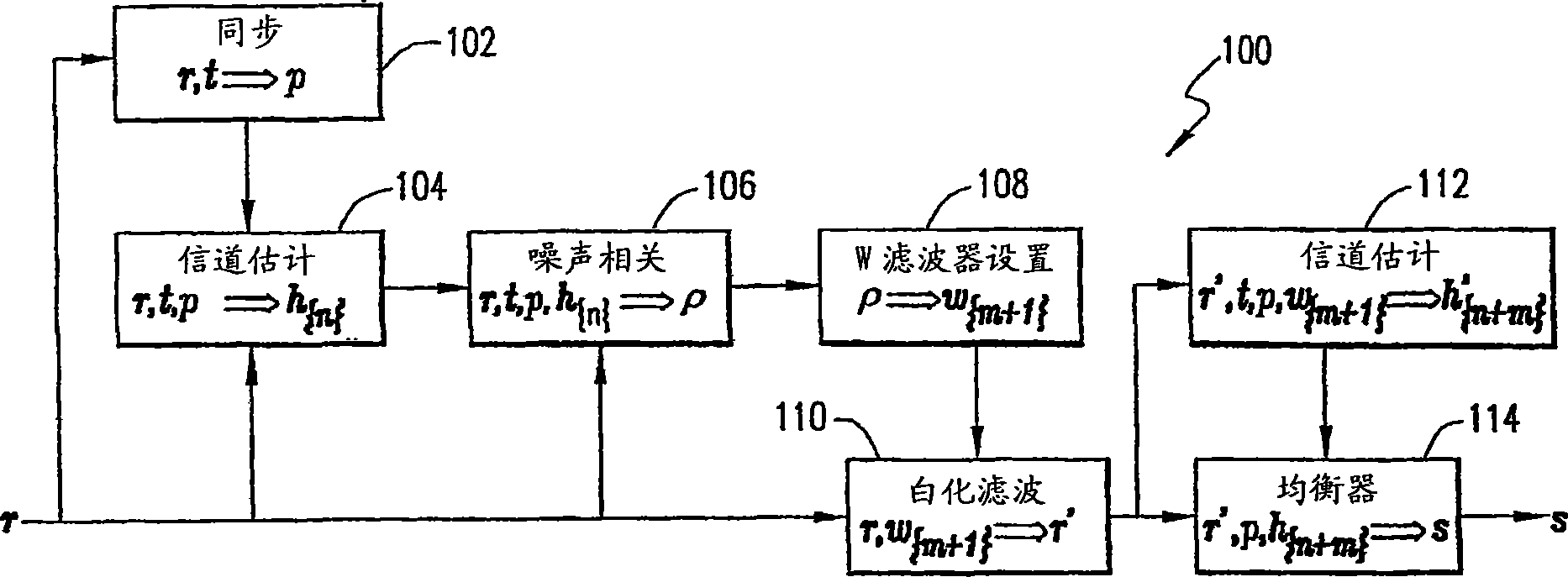
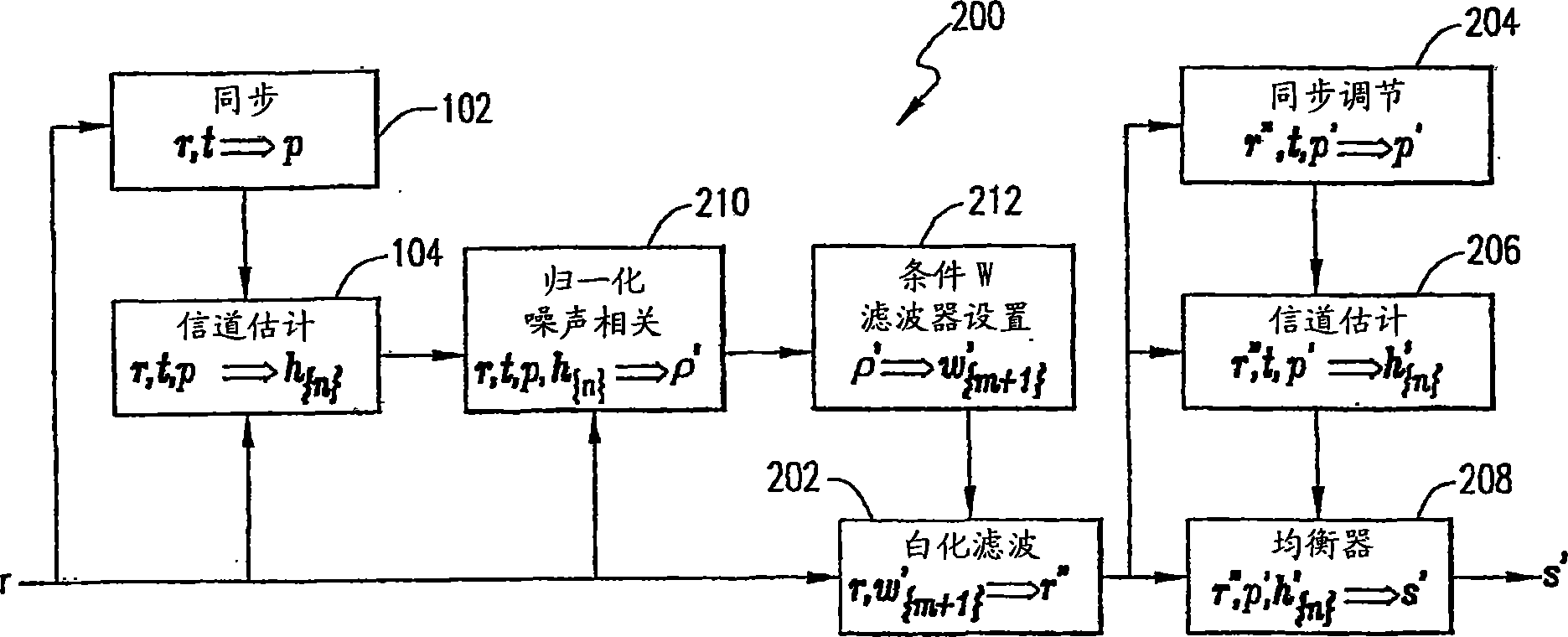
A method of and apparatus for reducing interference in a received signal. A normalized noise correlate is determined (210) using the received signal and a first channel estimate (104) of the received signal. Conditional whitening-filter settings are determined (212) using the normalized noise correlate (210). A whitening filter (202) is applied to the received signal in accordance with the conditional whitening-filter settings (212). A synchronization adjustment of an updated received signal is performed (204). A second channel estimate, which is of the same span as the first channel estimate, is determined (206) using an updated synchronization position and the updated received signal.
Owner:OPTIS WIRELESS TECH LLC
Method for processing a digital input signal of a channel equalizer
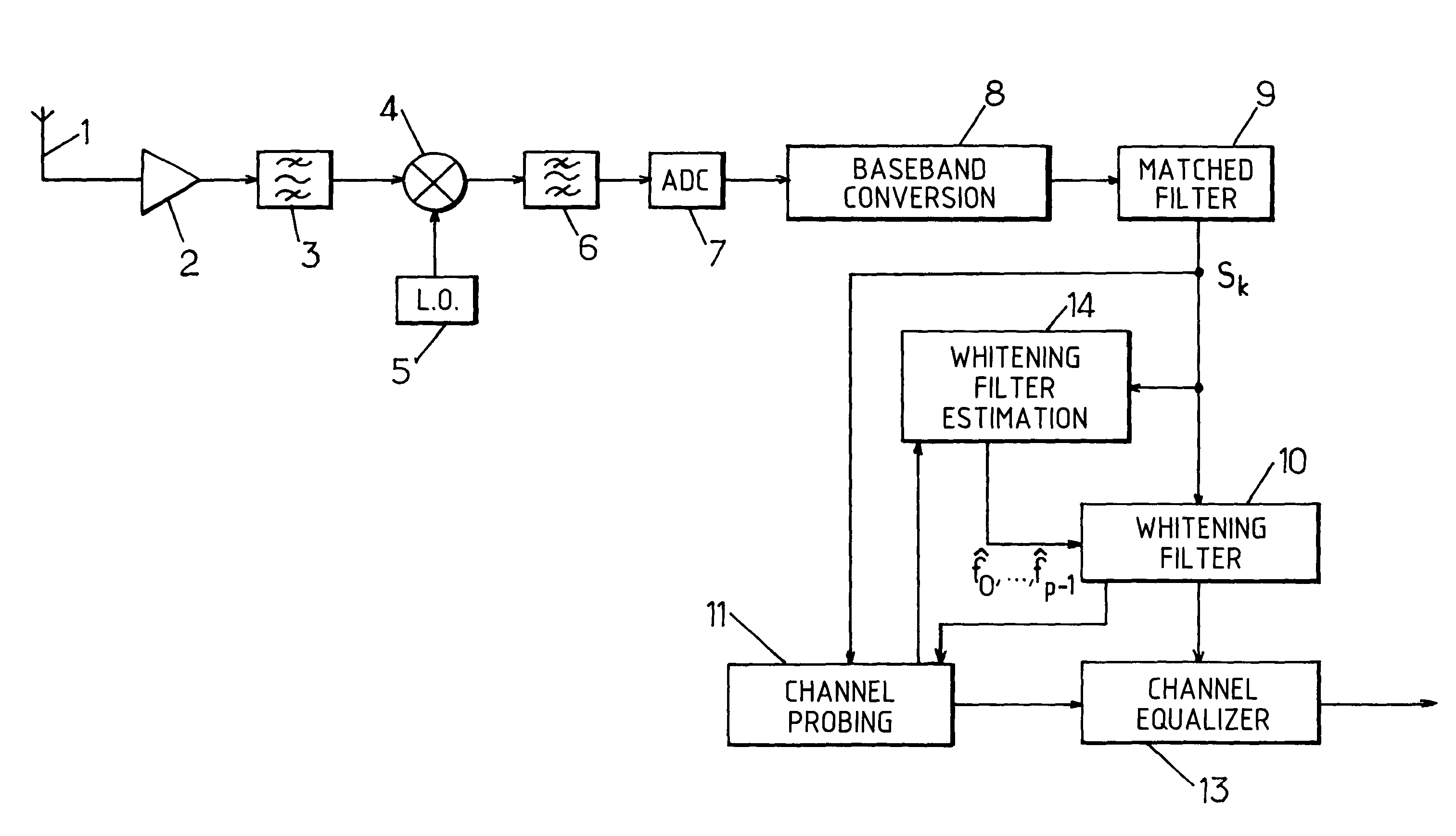
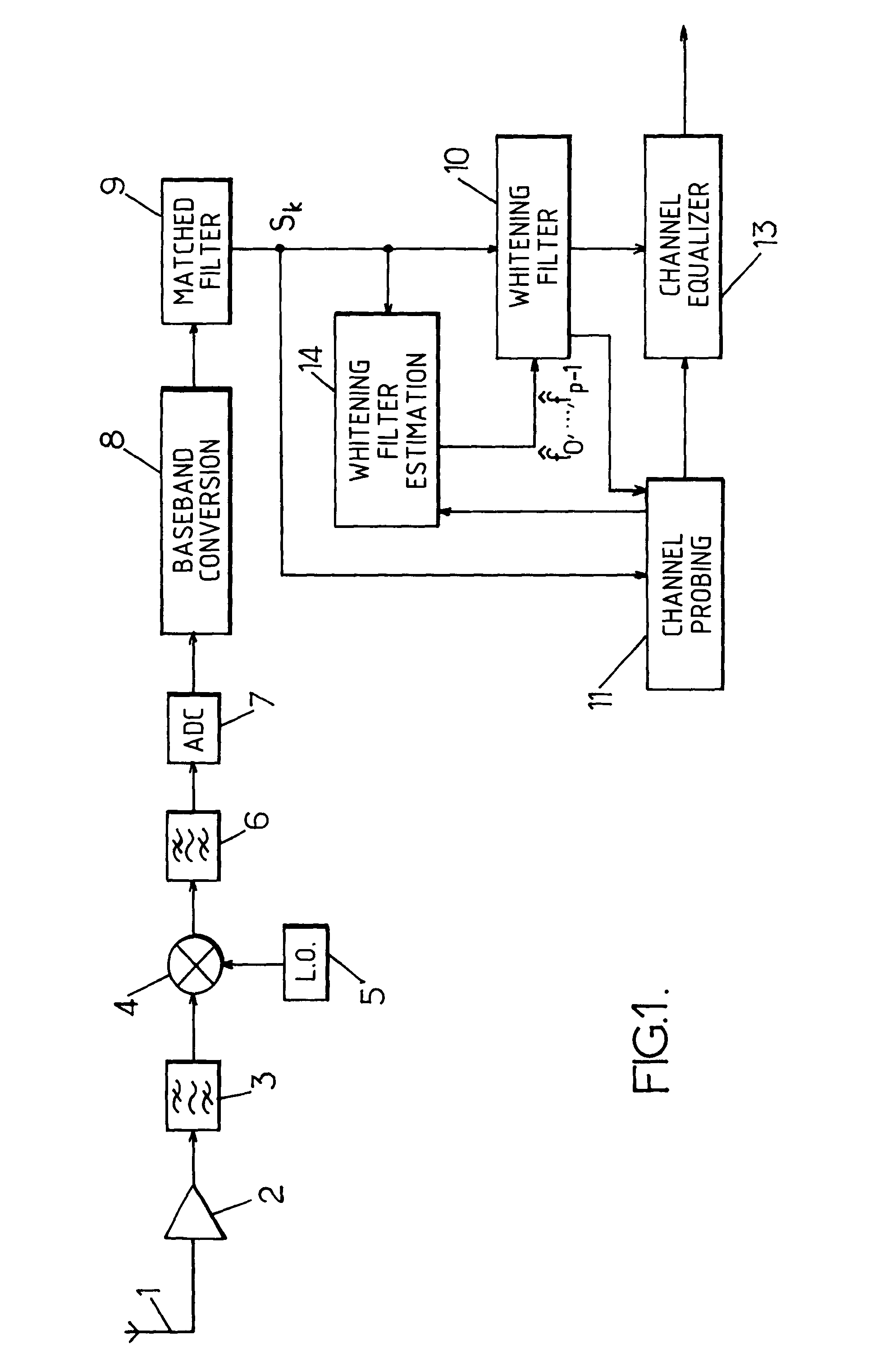
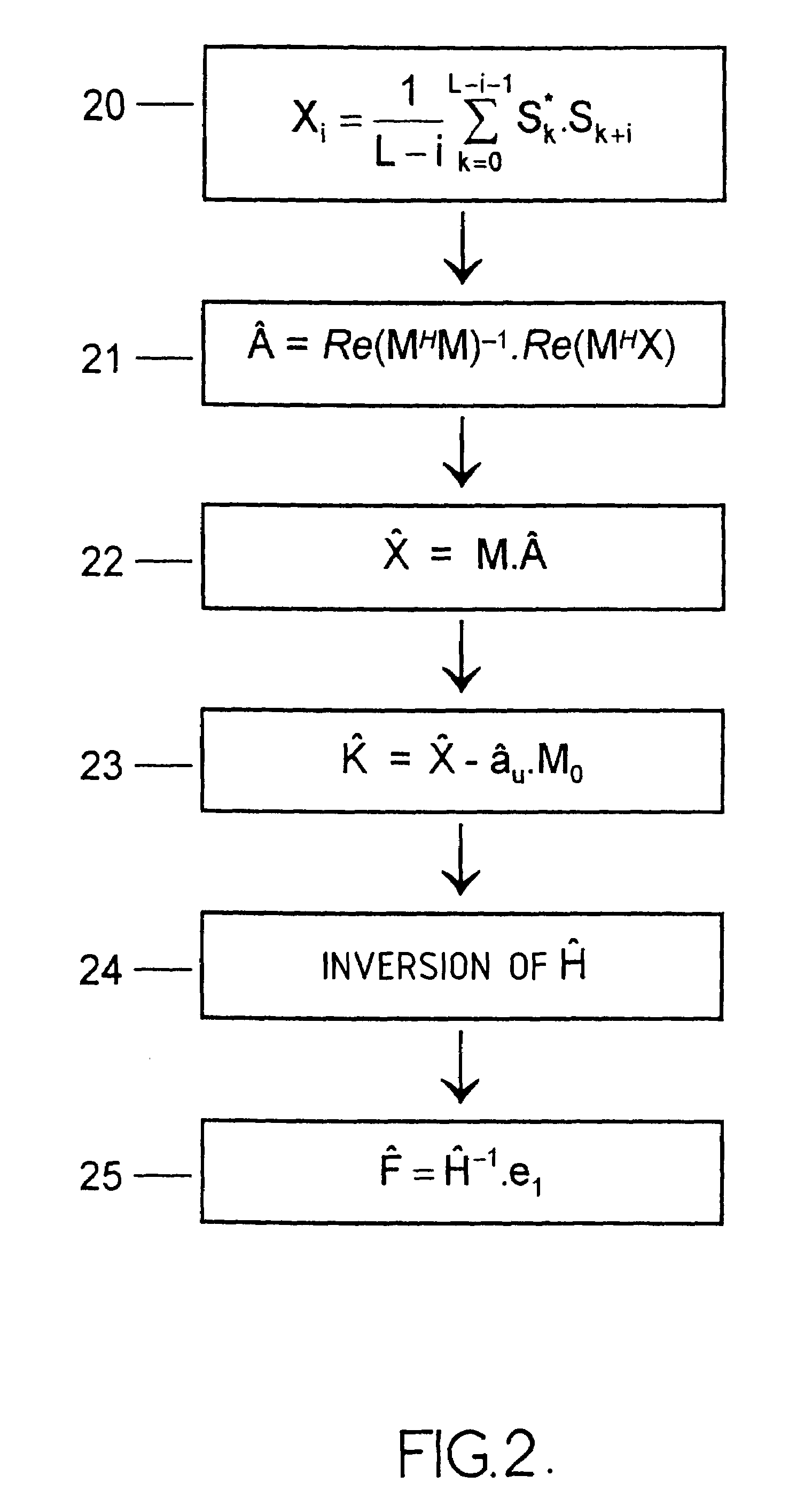
InactiveUS7257174B2Reliable estimateError preventionLine-faulsts/interference reductionMatched filterChannel equalizer
A baseband digital signal block is processed at an output of a matched filter and at an input of a channel equalizer. This signal is fed to a whitening filter estimated for the block by taking into account interfering signals in the frequency band of the useful signal and in one or more adjacent bands. To this end, an autocorrelation vector, calculated form the block of received signal is projected onto different directions corresponding to predetermined correlation vectors relating to the useful signal, to signals which may be present in the adjacent bands and to the thermal noise. The coefficients of the whitening filter are then derived from the sum of the projected vectors, by taking into account the energy of the useful signal if the latter has not been cancelled prior to the computation of the autocorrelations.
Owner:KAPSCH CARRIERCOM FRANCE
Apparatus and methods for suppression of interference among disparately-modulated signals
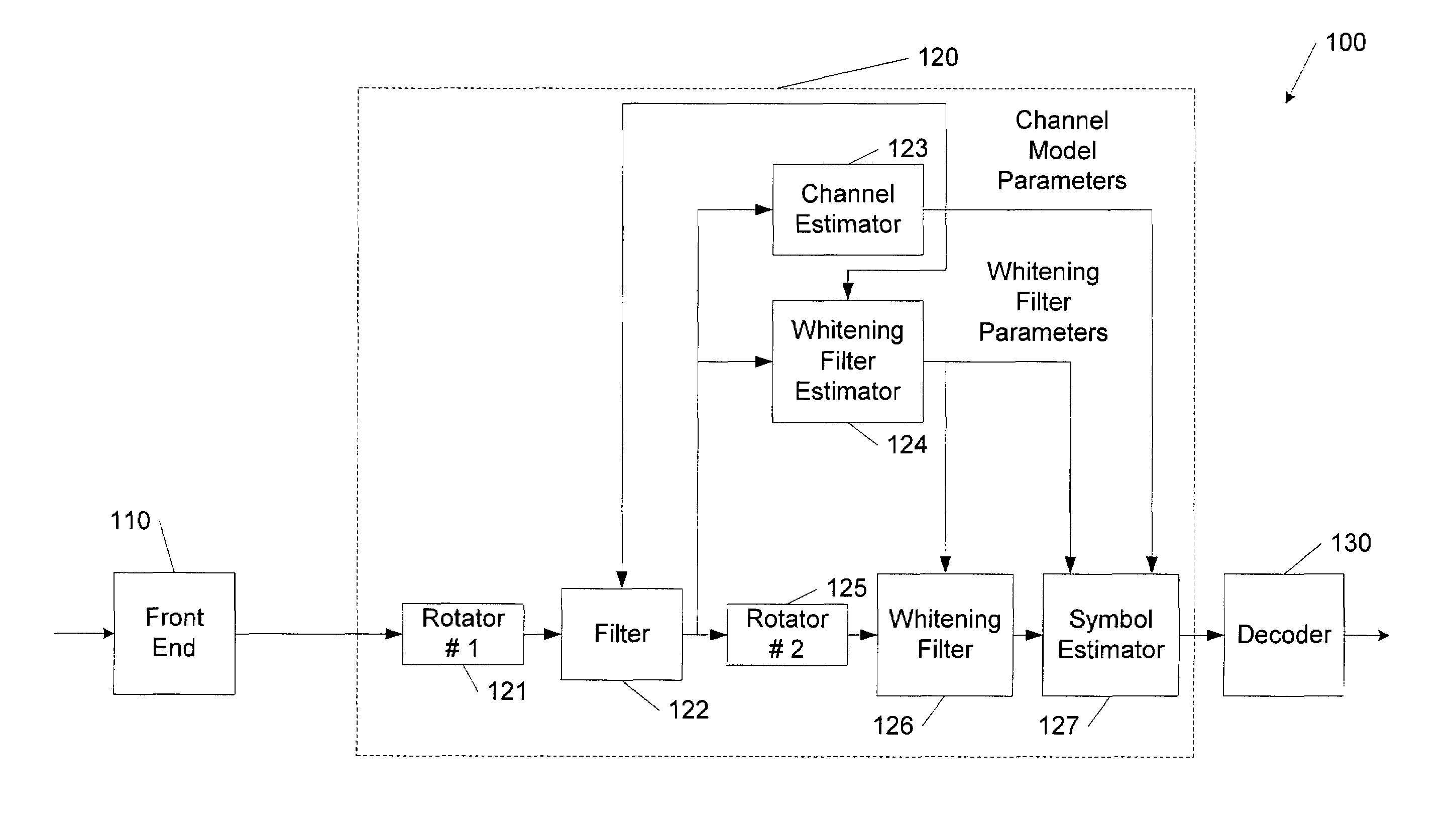
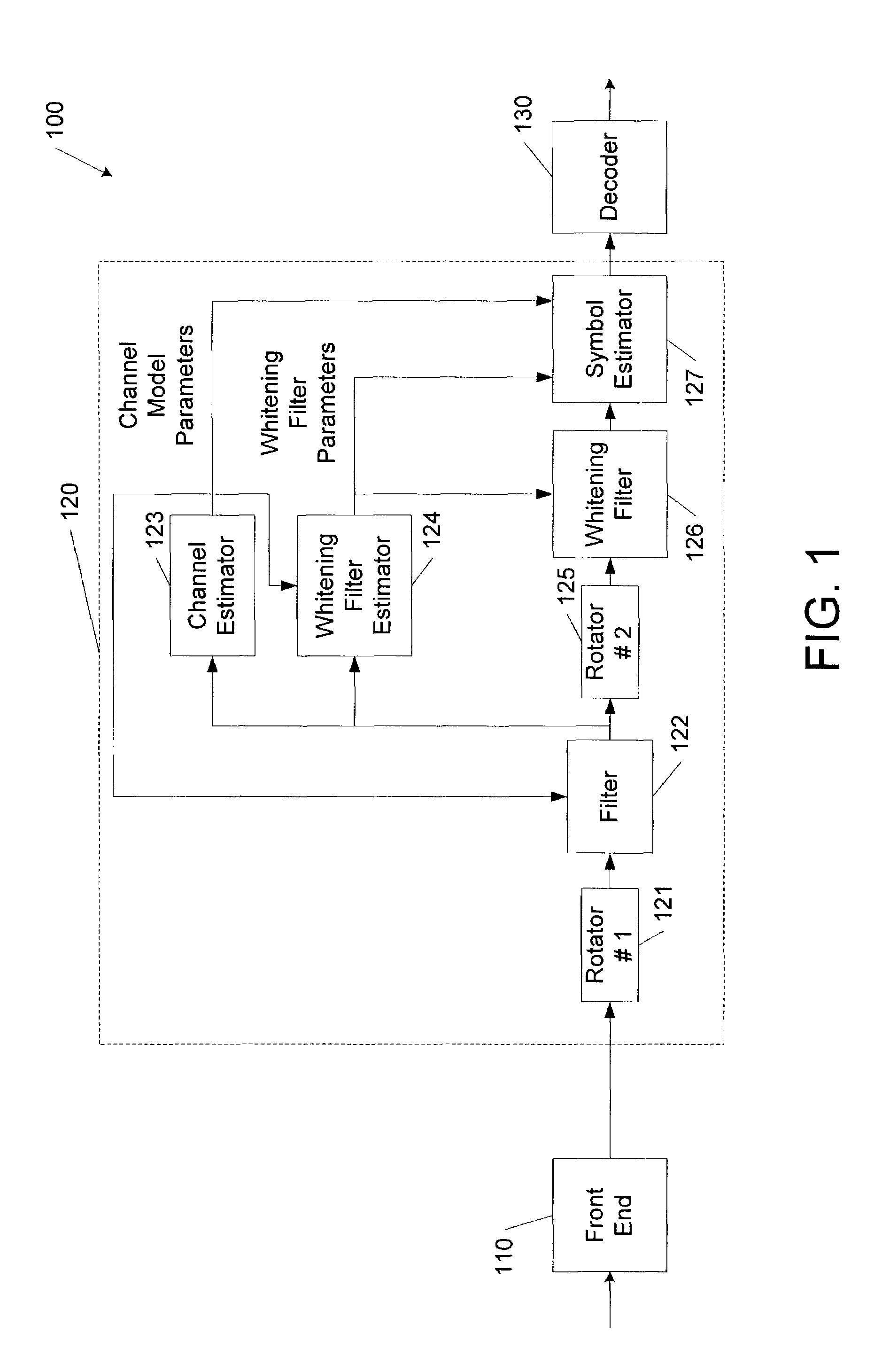
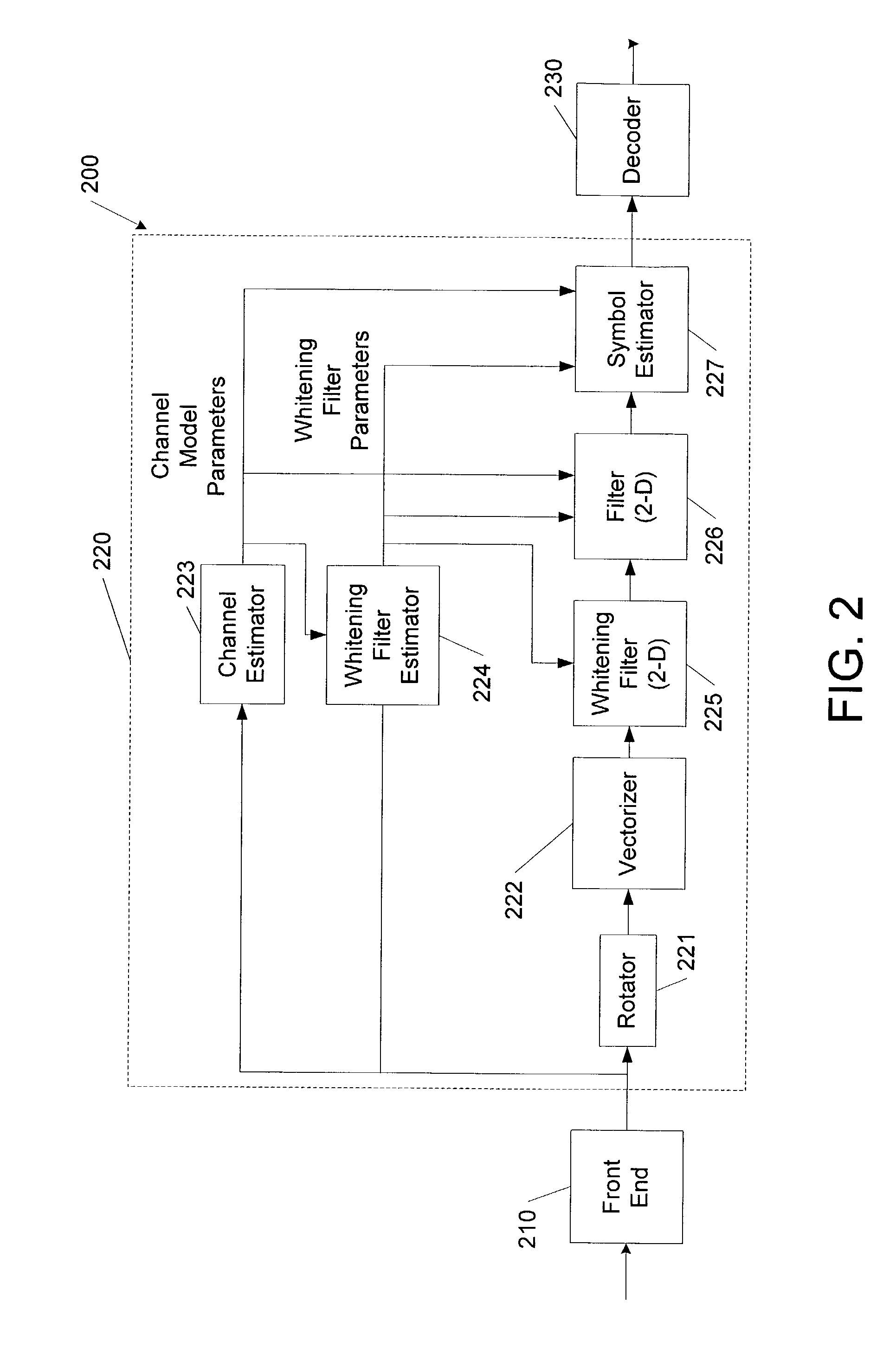
Information is recovered from a composite signal including first and second component signals modulated according to respective first and second modulations, for example, 8-PSK and GMSK. The composite signal is processed based on predetermined characteristics of the first and second modulations, for example, signal rotations, to generate a channel model for the first component signal and a whitening filter for the second component signal. The composite signal is filtered according to the whitening filter to generate a filtered signal. A symbol hypothesis for a symbol of the first component signal is evaluated using a metric with respect to the filtered signal that is a function of the whitening filter and the channel model, for example, in a multidimensional Viterbi symbol estimation algorithm. The invention may be embodied as methods, apparatus and computer program products.
Owner:ERICSSON INC
Ground clutter suppression method based on whitening filter
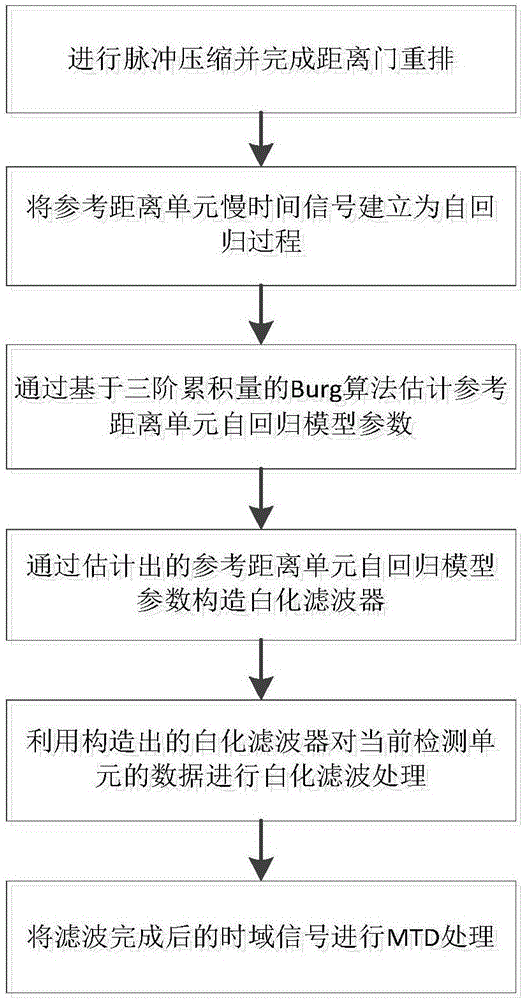
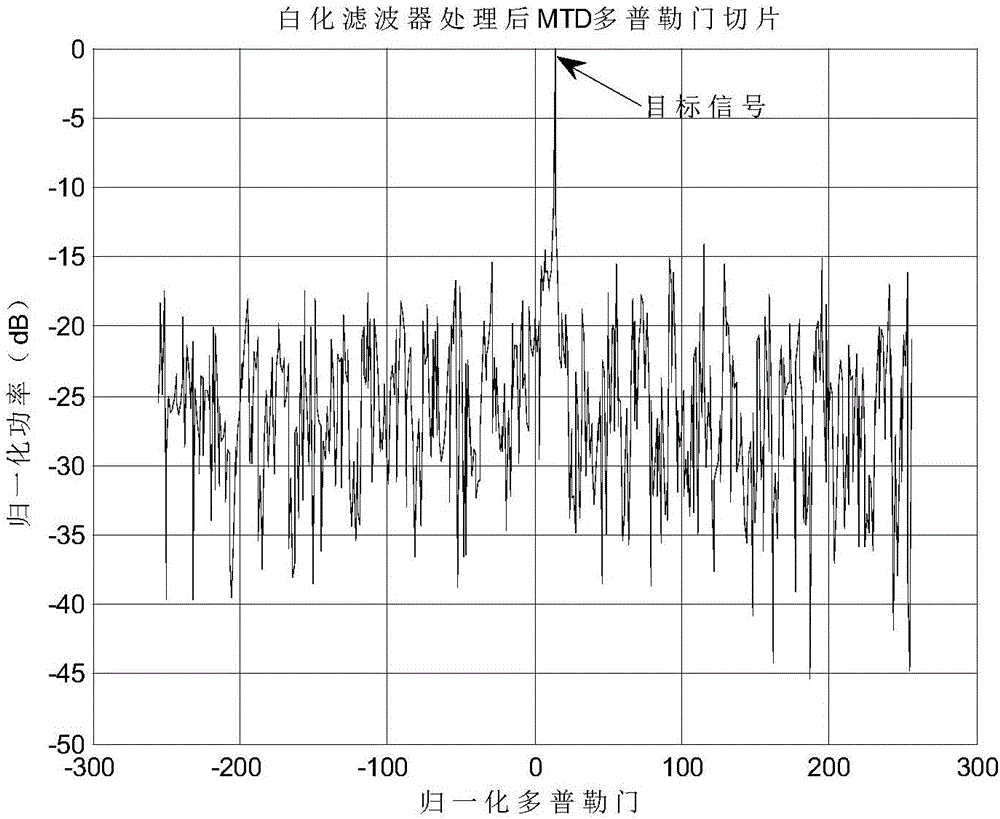
InactiveCN106199539AReduce the impactSuppress clutterWave based measurement systemsTime domainModel parameters
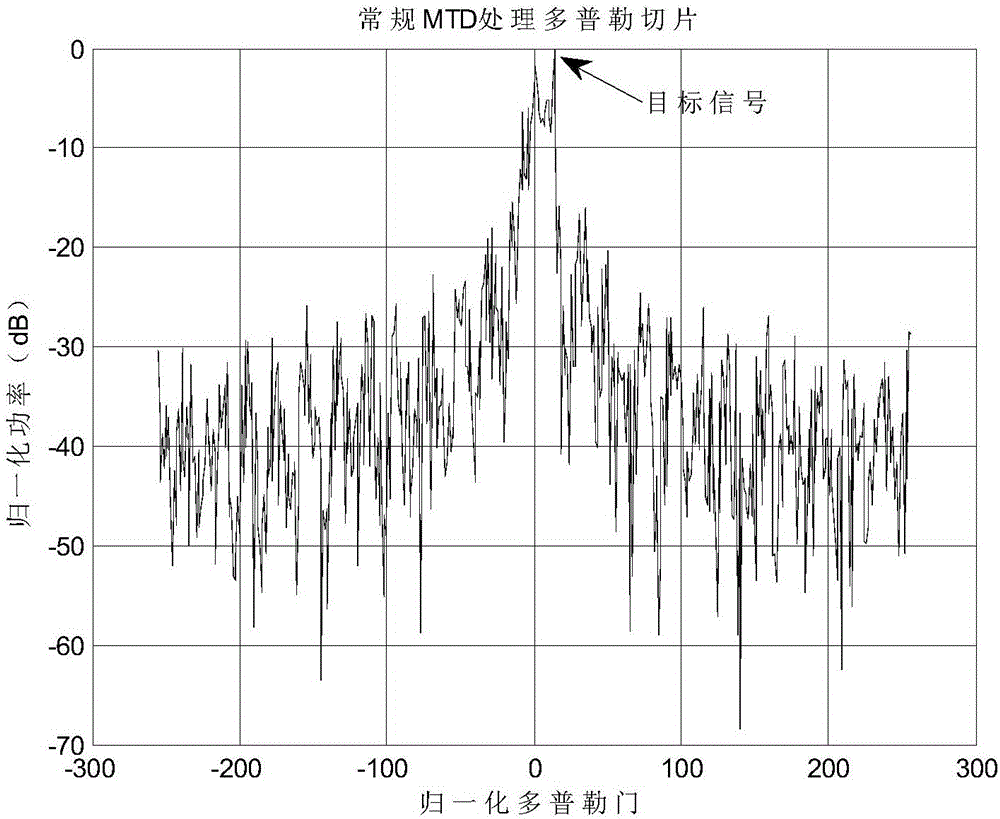
The invention discloses a ground clutter suppression method based on a whitening filter. The method comprises the steps of subjecting radar echo data containing clutters and noises to the pulse compression treatment, rearranging data according to range gates, setting the K-th range gate after the pulse compression treatment as a reference unit, establishing a self-regression process based on the radar echo data in the slow-time dimension, estimating the self-regression model parameters of the reference unit according to the Burg algorithm based on three-order cumulants, constructing a whitening filter based on the self-regression model parameters of the reference unit, subjecting the data of a current detection unit to the whitening and filtering treatment by using the constructed whitening filter, and subjecting filtered time domain signals to the moving target detection treatment. According to the technical scheme of the invention, clutters for a moving target with a low velocity can be effectively inhibited, and clutters originally aggregated in the vicinity of the zero frequency can also be effectively inhibited. The power is dispersed, so that clutters appear in the form of approximate white noises in the frequency domain. After the power dispersing process, the influence of clutters on the detection of the moving target with the low velocity is obviously reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Receiving method of ship automatic identification system, receiver and communication satellite
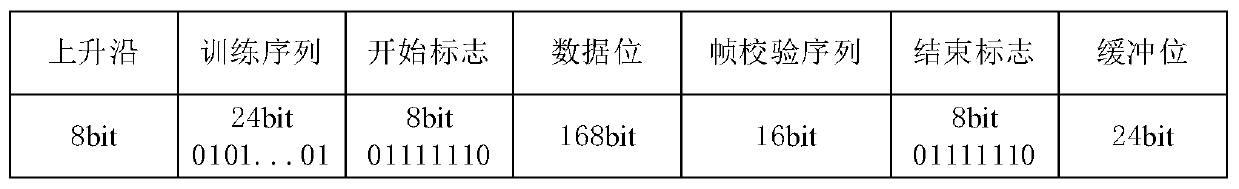
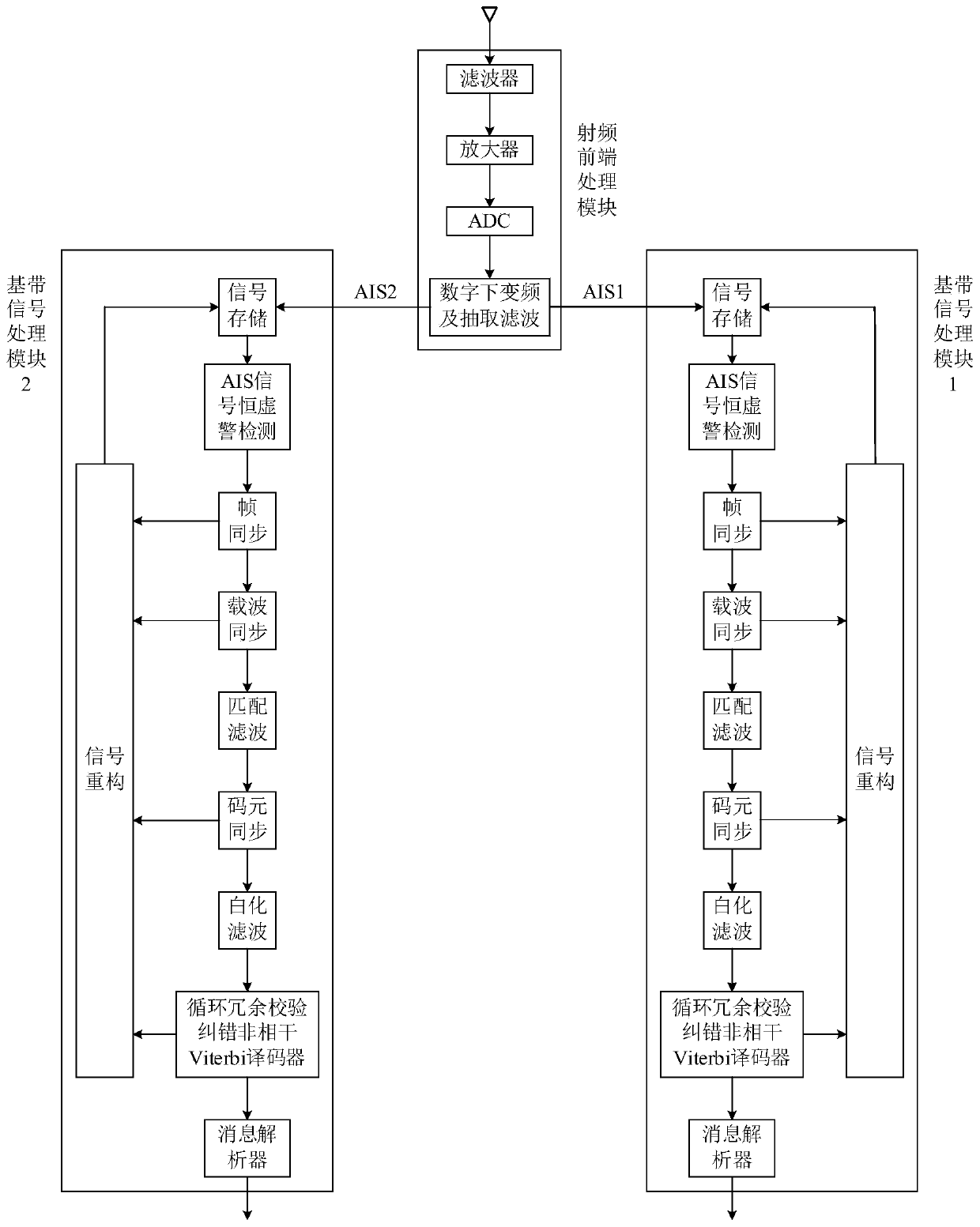
ActiveCN110011724ATroubleshoot technical issues with poor demodulation performanceReduce frame error rateCarrier regulationRadio transmissionIntermediate frequencyResource saving
The invention discloses a receiving method of a ship automatic identification system, a receiver and a communication satellite. The receiving method comprises the following steps: receiving an AIS radio frequency signal, filtering and amplifying, carrying out analog-to-digital conversion, carrying out multi-stage orthogonal down-conversion and decimation filtering, storing, carrying out constant false alarm rate inspection, carrying out carrier synchronization, carrying out matched filtering, carrying out code element synchronization, carrying out whitening filtering, and carrying out demodulation decoding. The receiver comprises a radio frequency front-end processing module and a baseband signal processing module. wherein the radio frequency front-end processing module is used for performing intermediate frequency filtering and power amplification, radio frequency sampling, orthogonal down-conversion and decimation filtering processing on a received radio frequency signal to obtain abaseband signal, and the baseband signal processing module is used for performing detection, synchronization and demodulation decoding on an AIS message in the AIS baseband signal. The method has thetechnical characteristics of excellent demodulation performance, resource saving and collision signal processing.
Owner:SHANGHAI SPACEFLIGHT INST OF TT&C & TELECOMM
Optimizing detector target polynomials in read/write channels to achieve best error rate performance in disk drives
InactiveUS20060235919A1Good error rate performanceImprove performanceModification of read/write signalsSignal processing for reducing noiseComputer scienceChannel use
Embodiments of the invention provide techniques for optimizing the detector target polynomials in read / write channels to achieve the best error rate performance in recording devices. In one embodiment, a method of obtaining a detector target polynomial of a read / write channel to achieve best error rate performance in a recording device comprises: providing an initial detector target for the read / write channel; measuring a noise autocorrelation of the read / write channel at the output of equalizer using channel hardware; computing a noise autocorrelation at the output of the 1st stage target based on the measured noise autocorrelation of the read / write channel at the output of equalizer; calculating optimal coefficients for the noise whitening filter; and obtaining the optimal detector target polynomial of the read / write channel using the calculated coefficients for noise whitening filter.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com