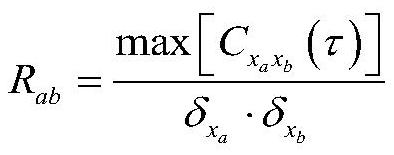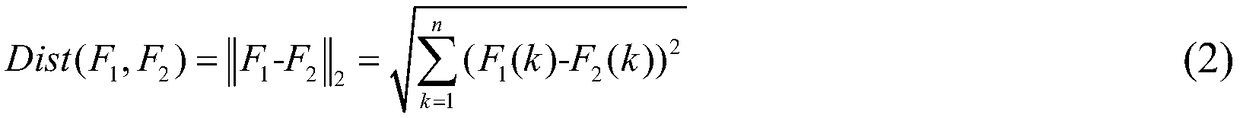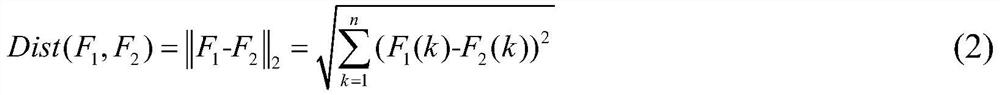Patents
Literature
32 results about "Spectral distance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The log-spectral distance (LSD), also referred to as log-spectral distortion, is a distance measure (expressed in dB) between two spectra. The log-spectral distance between spectra () and ^ is defined as: = ∫ − [ ^ ()], where () and ^ are power spectra. Unlike the Itakura–Saito distance, the log-spectral distance is symmetric.. In speech coding log spectral distortion for a given ...
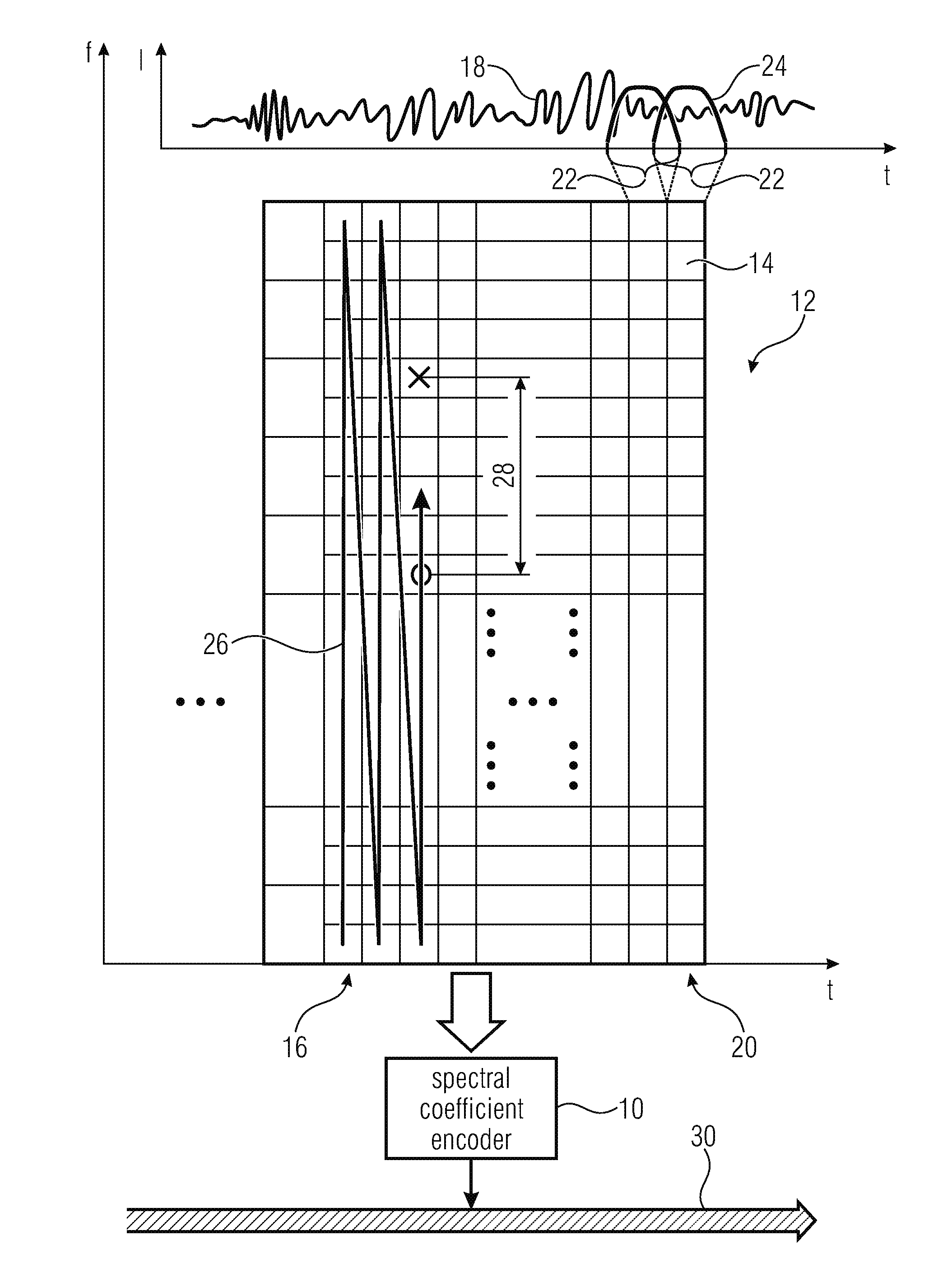
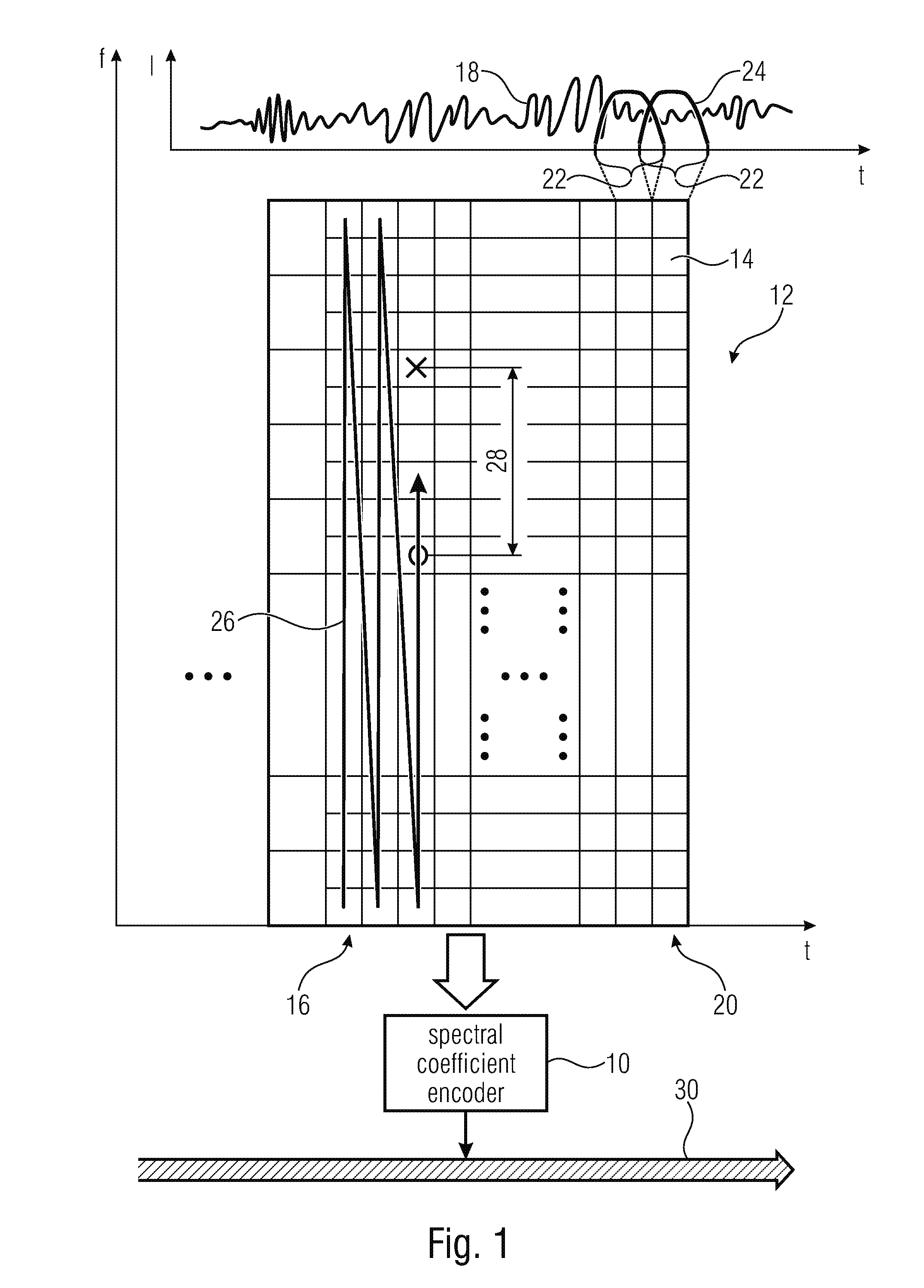
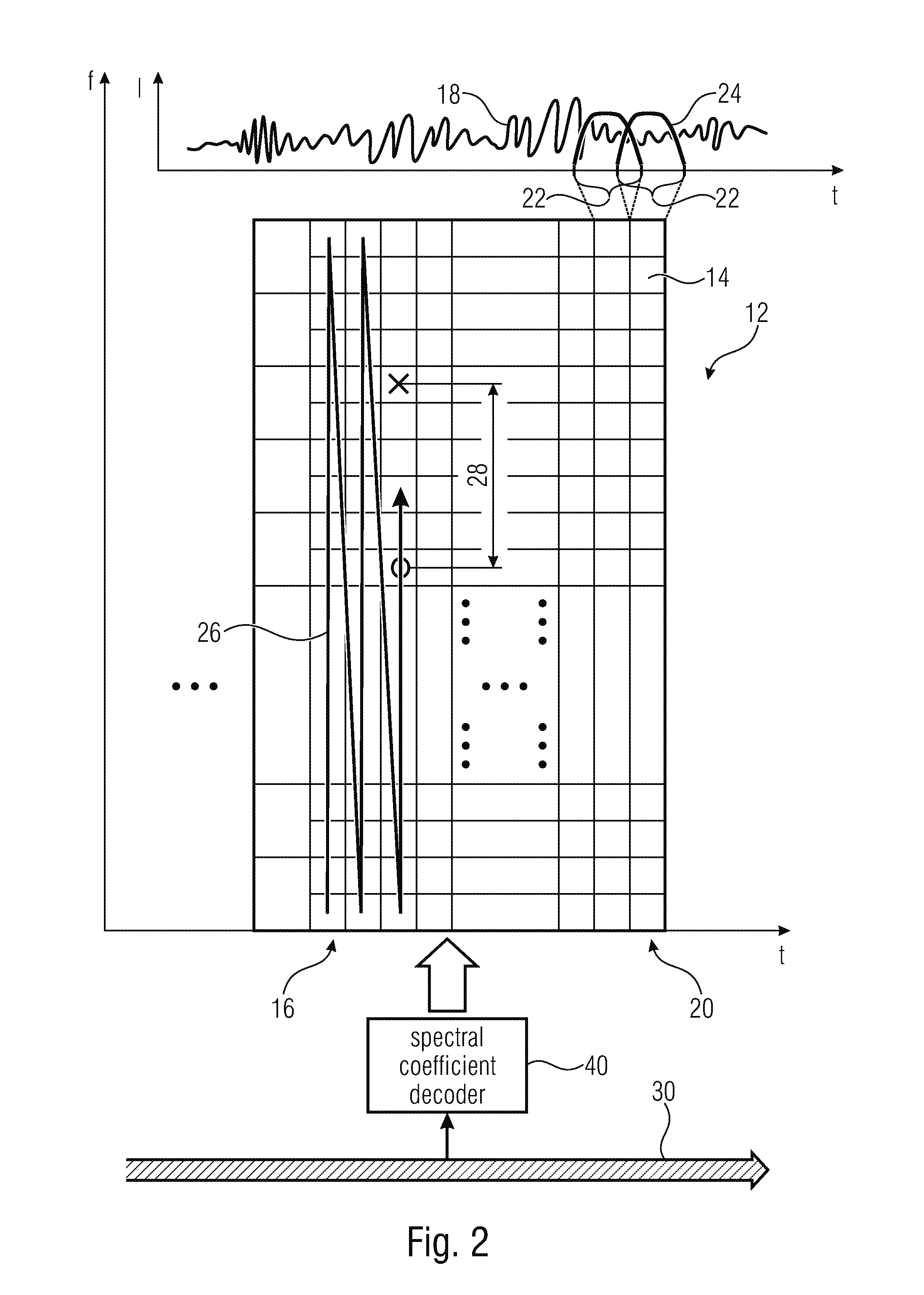
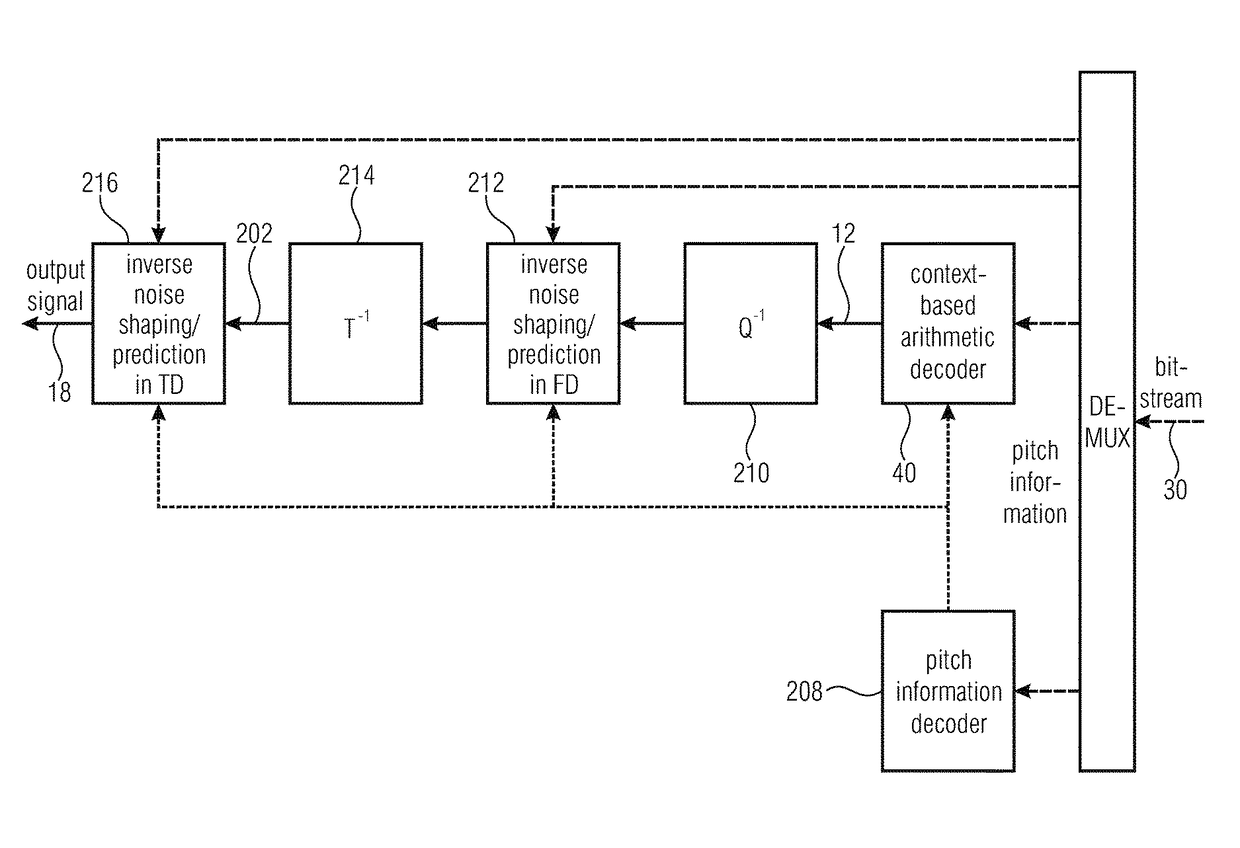
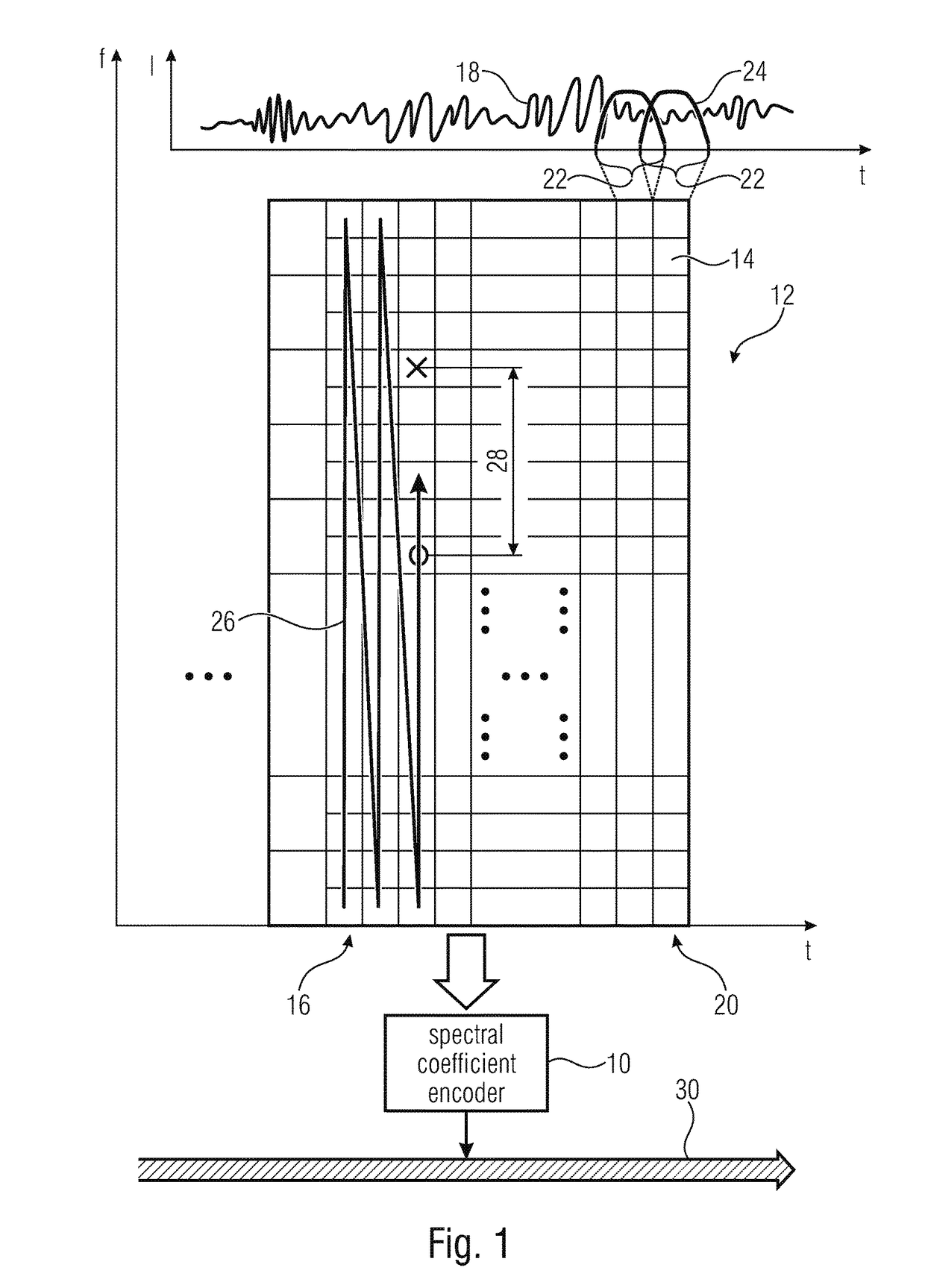
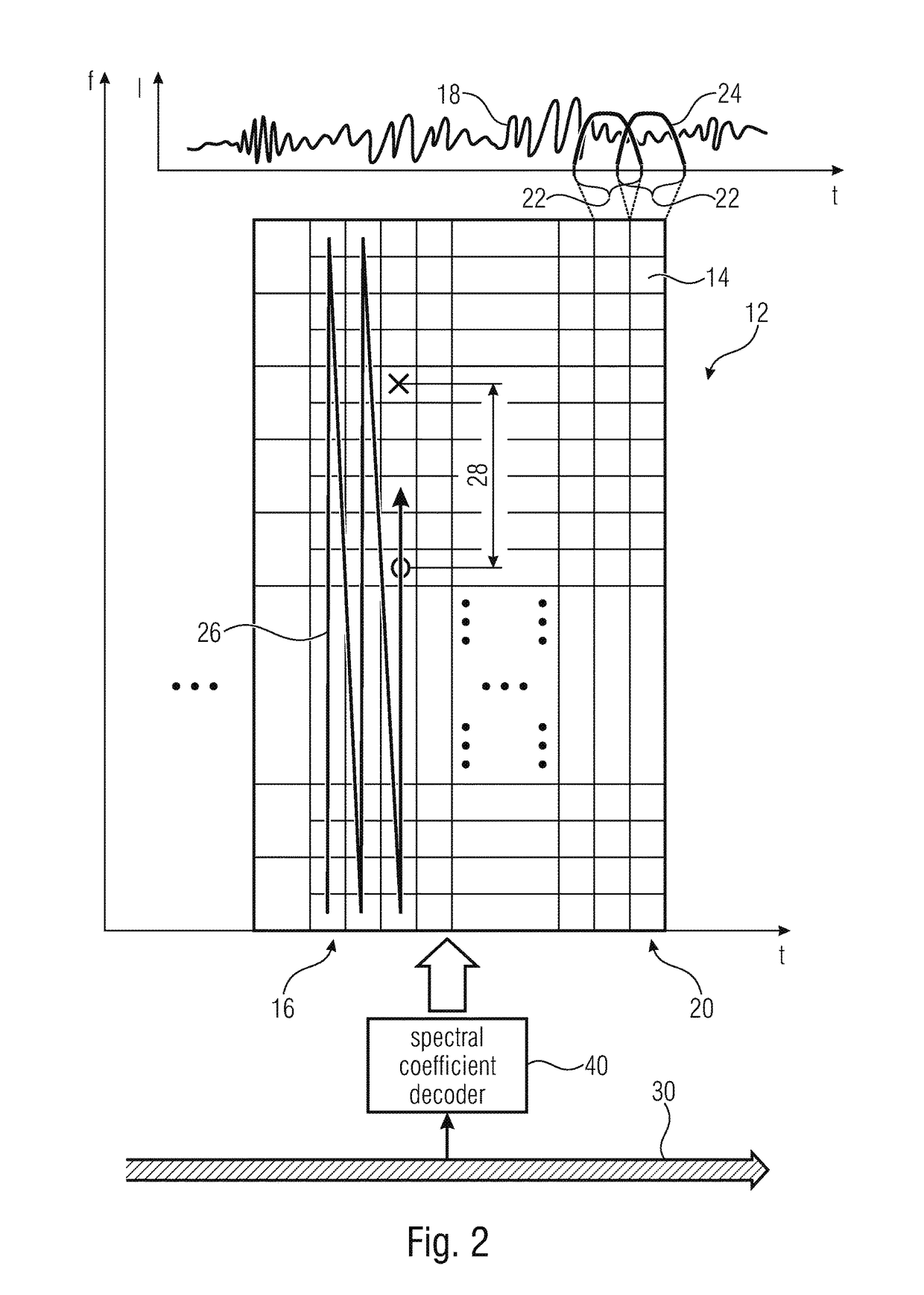
Coding of spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal
ActiveUS20160307576A1Enhancing entropy coding efficiencyImprove coding efficiencySpeech analysisCode conversionFrequency spectrumHarmonic
A coding efficiency of coding spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal is increased by en / decoding a currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficient by entropy en / decoding and, in doing so, performing the entropy en / decoding depending, in a context-adaptive manner, on a previously en / decoded spectral coefficient, while adjusting a relative spectral distance between the previously en / decoded spectral coefficient and the currently en / decoded spectral coefficient depending on an information concerning a shape of the spectrum. The information concerning the shape of the spectrum may have a measure of a pitch or periodicity of the audio signal, a measure of an inter-harmonic distance of the audio signal's spectrum and / or relative locations of formants and / or valleys of a spectral envelope of the spectrum, and on the basis of this knowledge, the spectral neighborhood which is exploited in order to form the context of the currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficients may be adapted to the thus determined shape of the spectrum, thereby enhancing the entropy coding efficiency.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
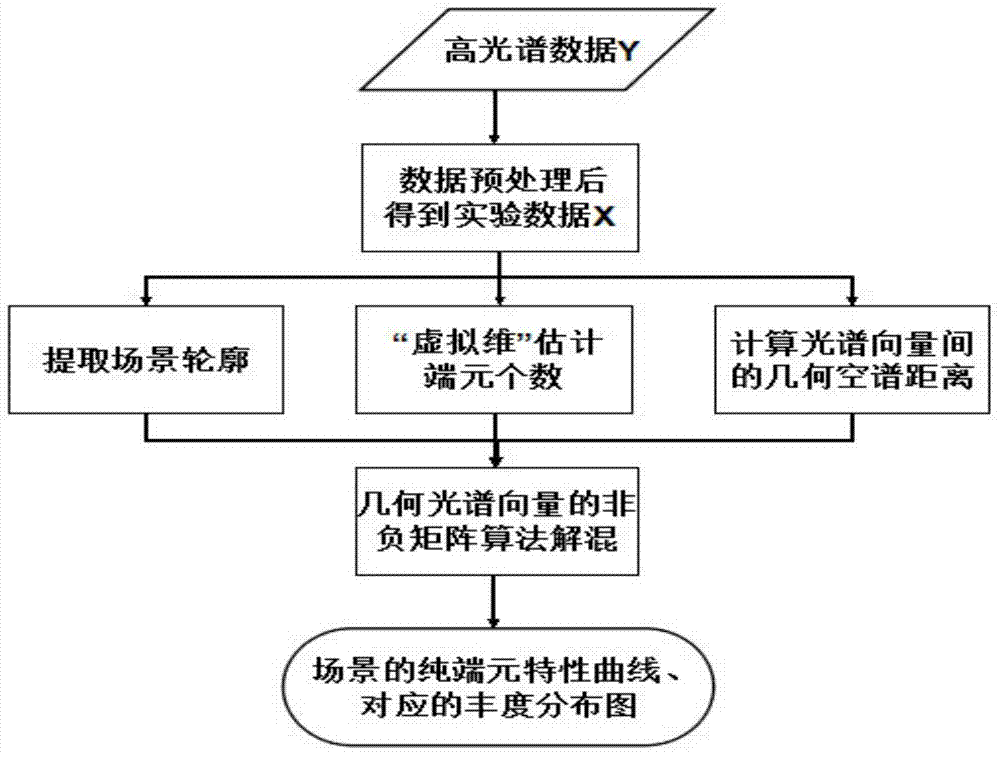
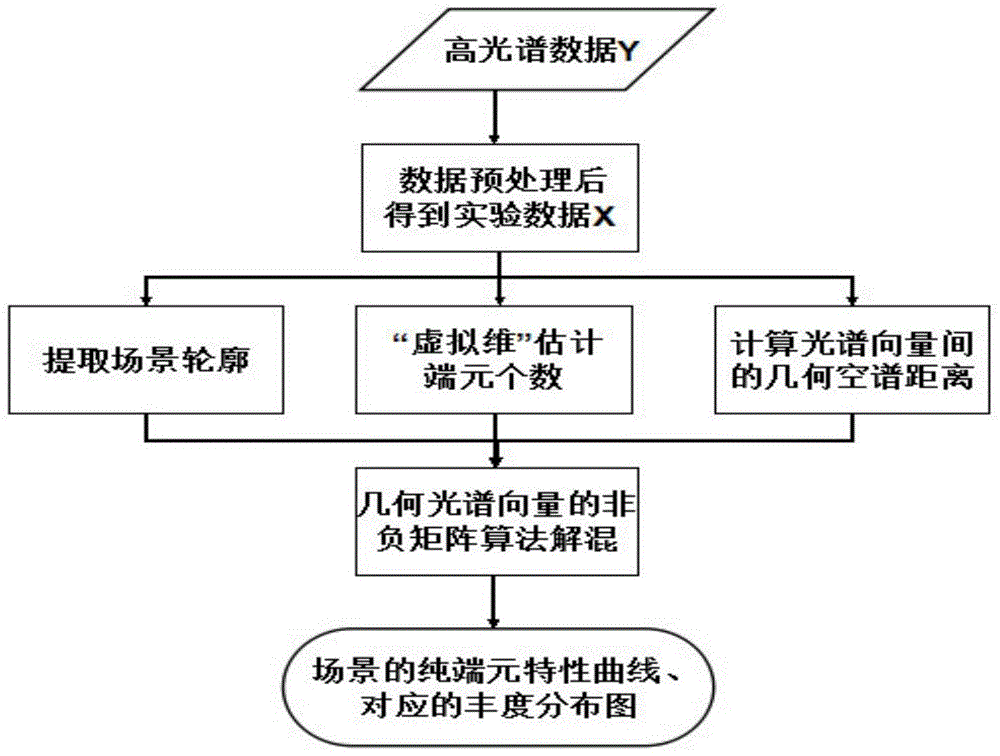
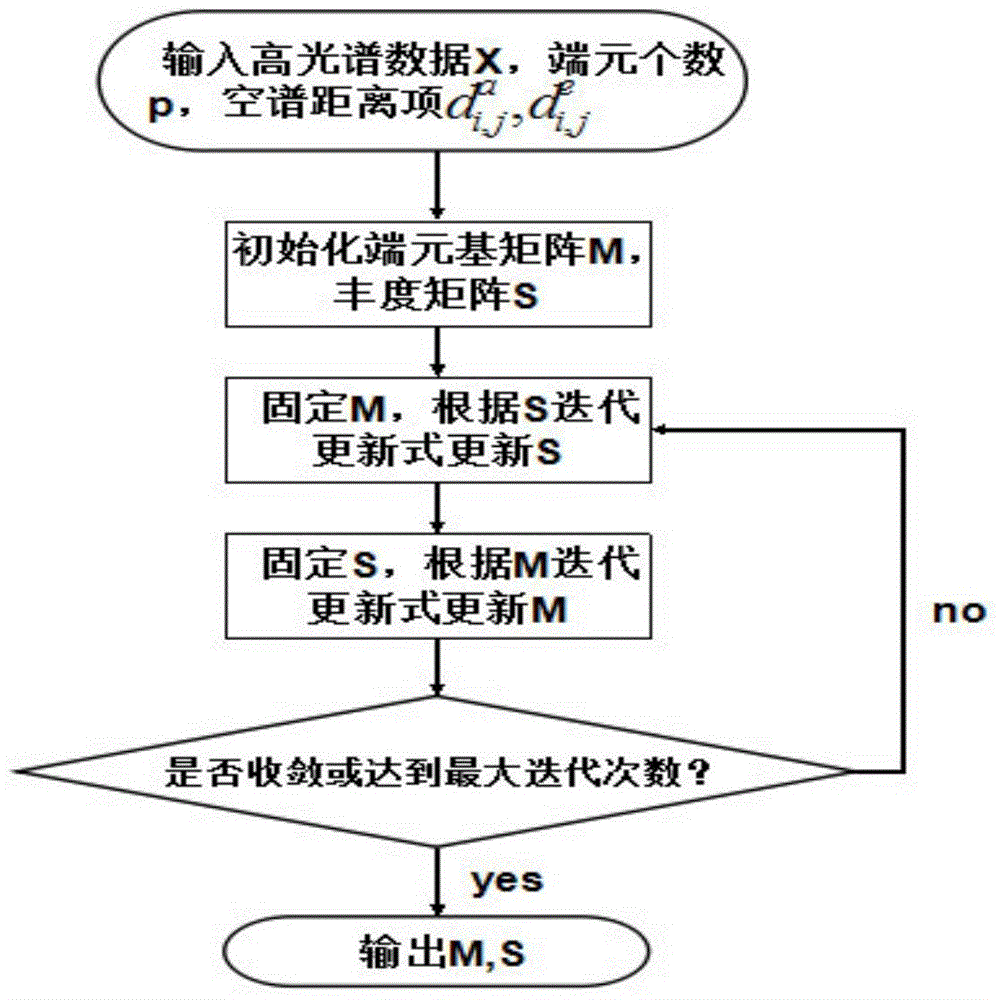
Hyper-spectral mixed pixel decomposition method based on geometric spatial spectral structure information
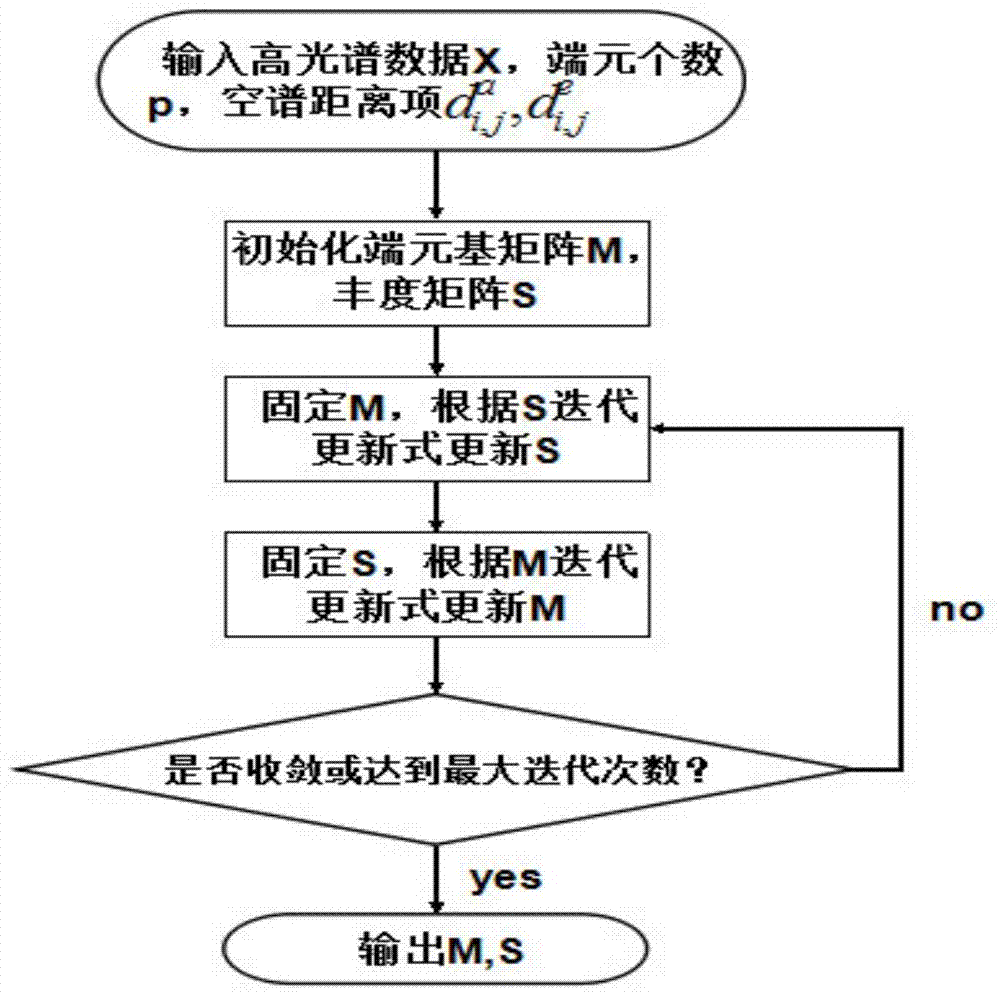
The invention belongs to the technical field of remote sensing data processing, and particularly discloses a mixed pixel decomposition method based on geometric spatial spectral structure information, so as to solve the problems that classifications of hyper-spectral image mixed pixel point surface features are not distinct and distribution is not accurate. The method comprises steps: 1) hyper-spectral data are inputted, and the data are arranged in a matrix after pretreatment; 2) a VD method is used for estimating the number of pure end members; 3) an edge contour of the image is extracted; 4) a formula for computing a spatial distance is brought forward according to the edge and the position; 5) a formula for computing a spectral distance is brought forward according to spectral statistic information; 6) a geometric spatial spectral binding term is built according to the spatial distance and the spectral distance, and the binding term is added to an NMF model; and 7) an output end member matrix and an abundance matrix are unmixed in new NMF algorithm, and the scene surface feature classifications and the distribution ratio are judged. The method is well applicable to different hyper-spectral data, and compared with the prior method, the precision of mixed pixel decomposition is improved, and great value is provided for target detection and recognition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Detection method of gasoline properties based on weighted absorbance and similar samples
ActiveCN104990894AHigh precisionAvoid inaccurate classificationMolecular entity identificationMaterial analysis by optical meansModel sampleSpectral database
The invention provides a detection method of gasoline properties based on weighted absorbance and similar samples, the detection method comprises the steps of calculating the correlation coefficient R between a sample to be detected and a known sample on basis of the gasoline properties and the absorbance of the known sample after the near infrared spectroscopy of the sample to be detected and the known sample is conventionally pretreated; taking the correlation coefficient R as a weight, the weighted sample absorbance is obtained and the weighted absorbance matrix is established; calculating the score matrix of the weighted absorbance matrix by adopting a principal component analytical method; selecting the first principal component and the second principal component in the score matrix to obtain a new score matrix; calculating the mahalanobis distance according the new score matrix, selecting the similar samples which are nearest to the mahalanobis distance of the sample to be detected in the known spectral database as modeling samples, and performing prediction on the sample to be detected. According to the detection method provided by the invention, the effect of gasoline properties on the spectral distance is fully considered, the phenomenon that the classification is not accurate can be effectively avoided, so that the prediction accuracy of a model is finally improved. An important guarantee can be provided for accurately measuring the gasoline properties and timely adjusting the operating parameters.
Owner:南京富岛信息工程有限公司
Method of Processing Spectrometric Data
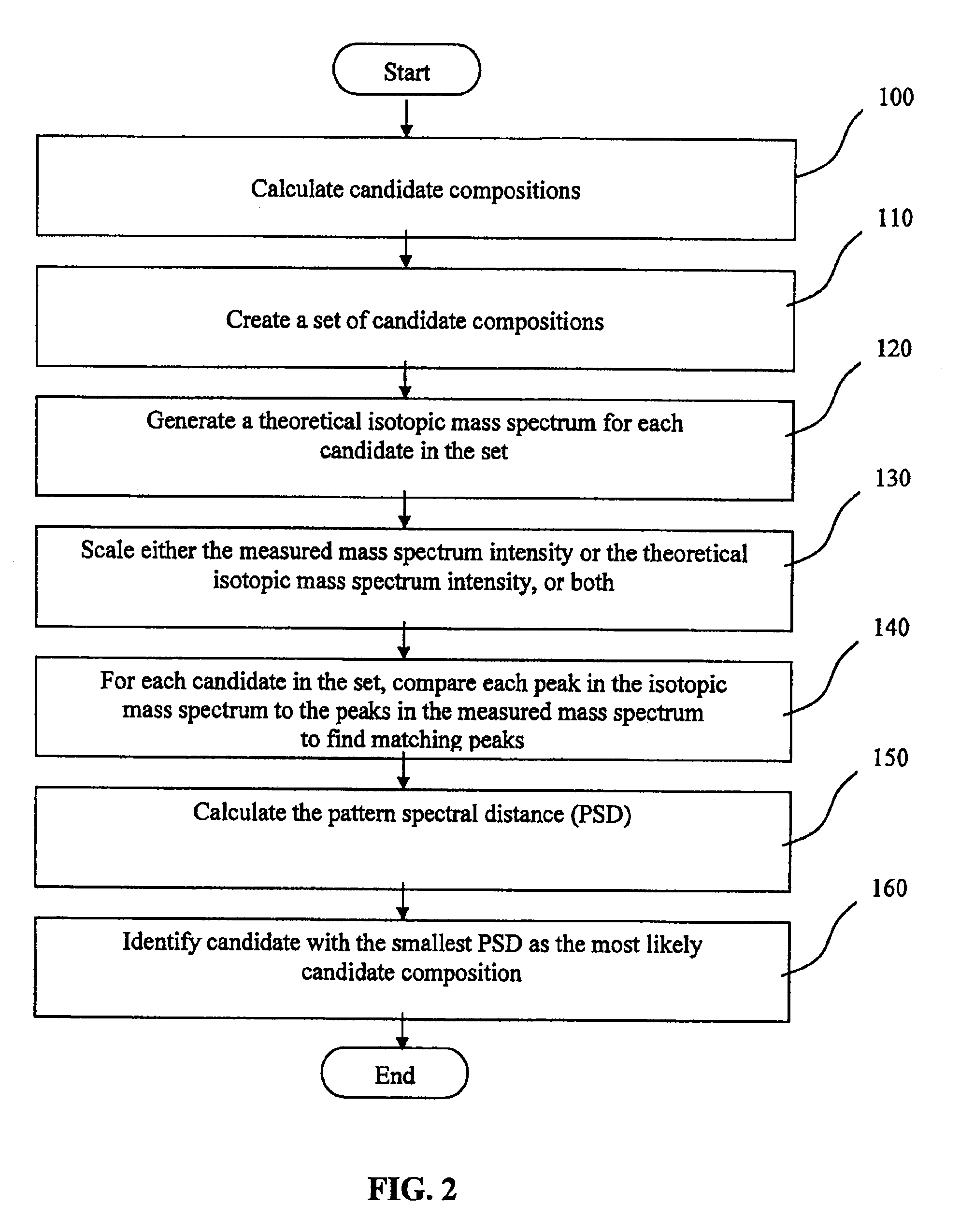
ActiveUS20090299653A1Increase valueReduce the differenceMolecular entity identificationIsotope separationPhysical chemistryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
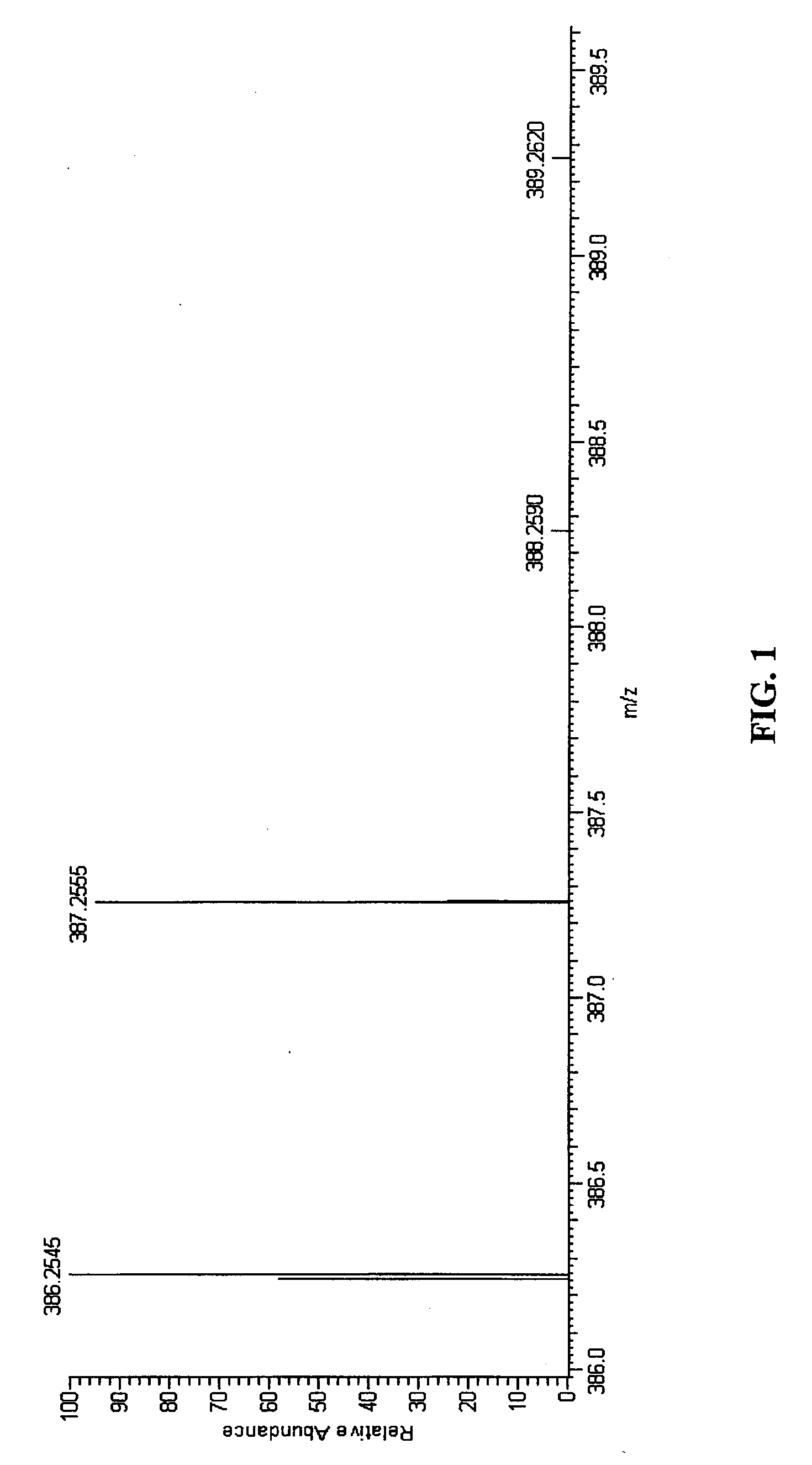
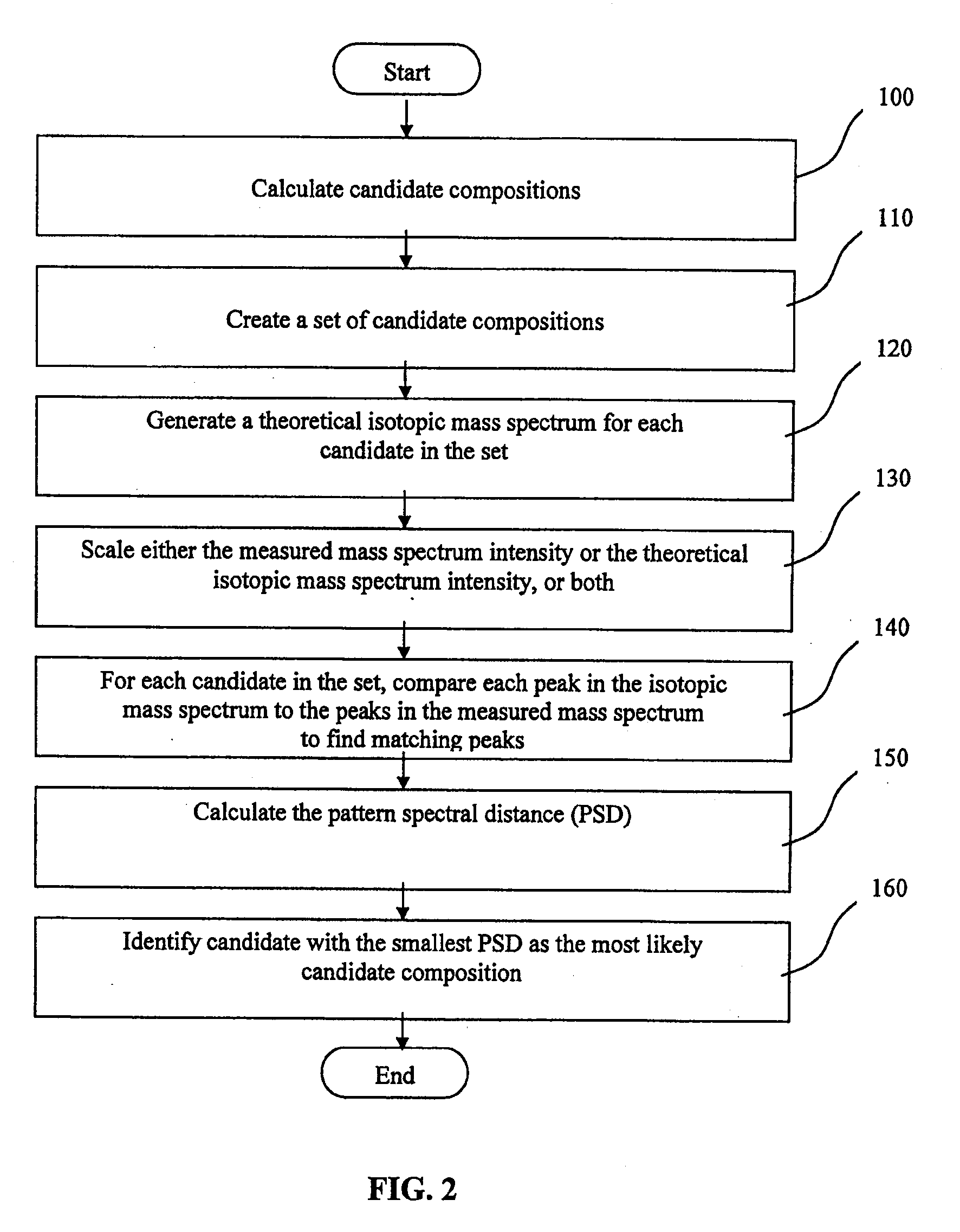
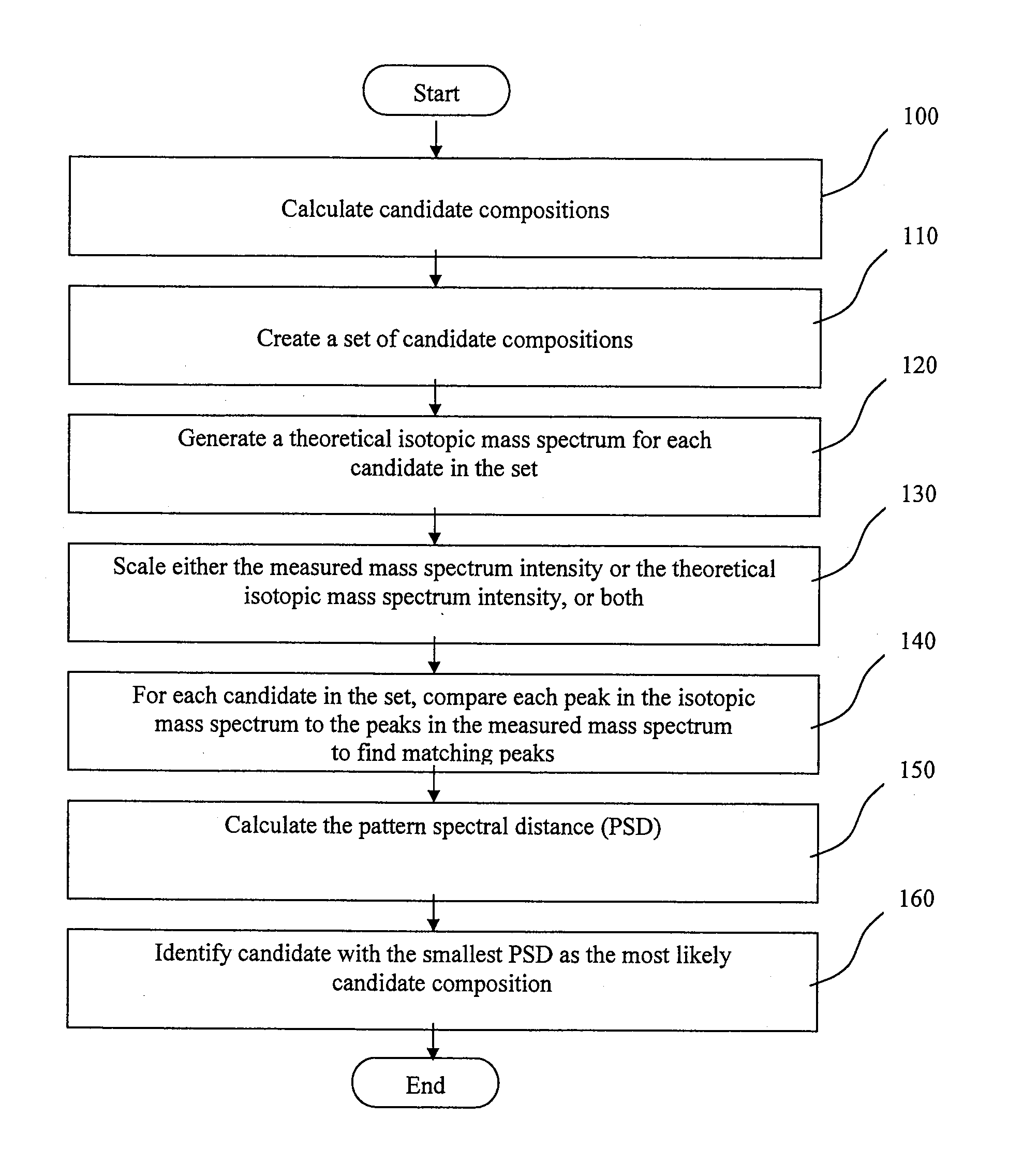
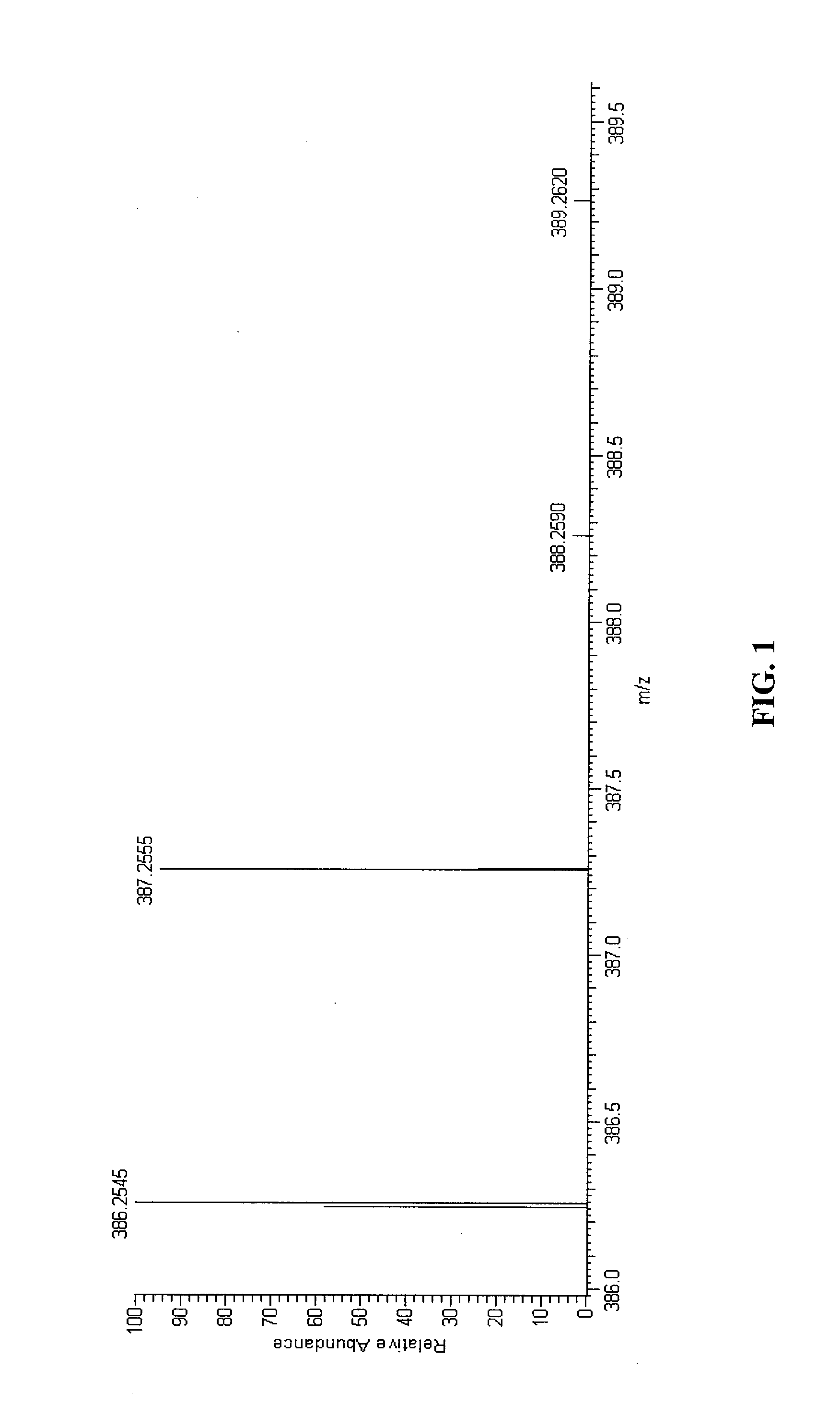
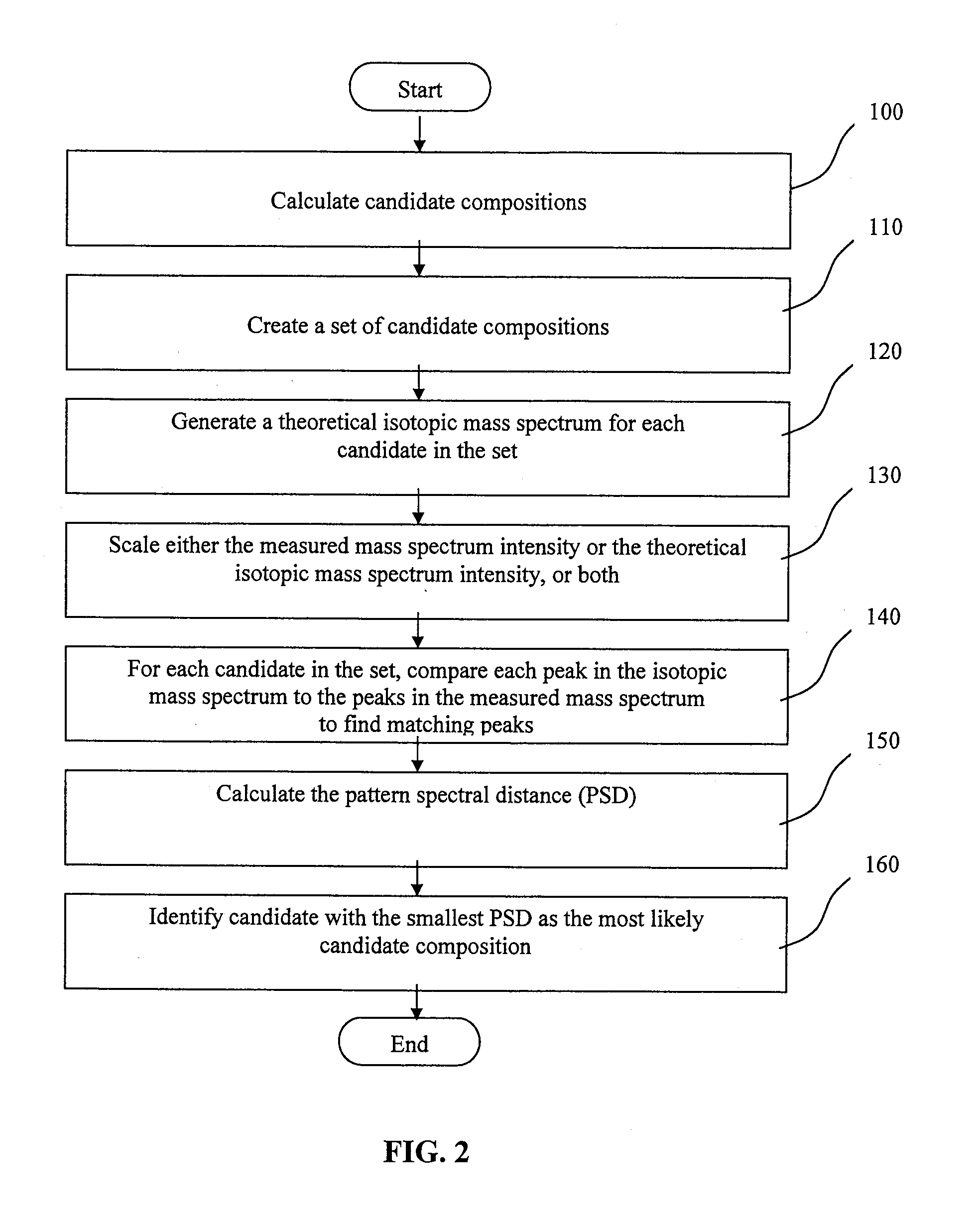
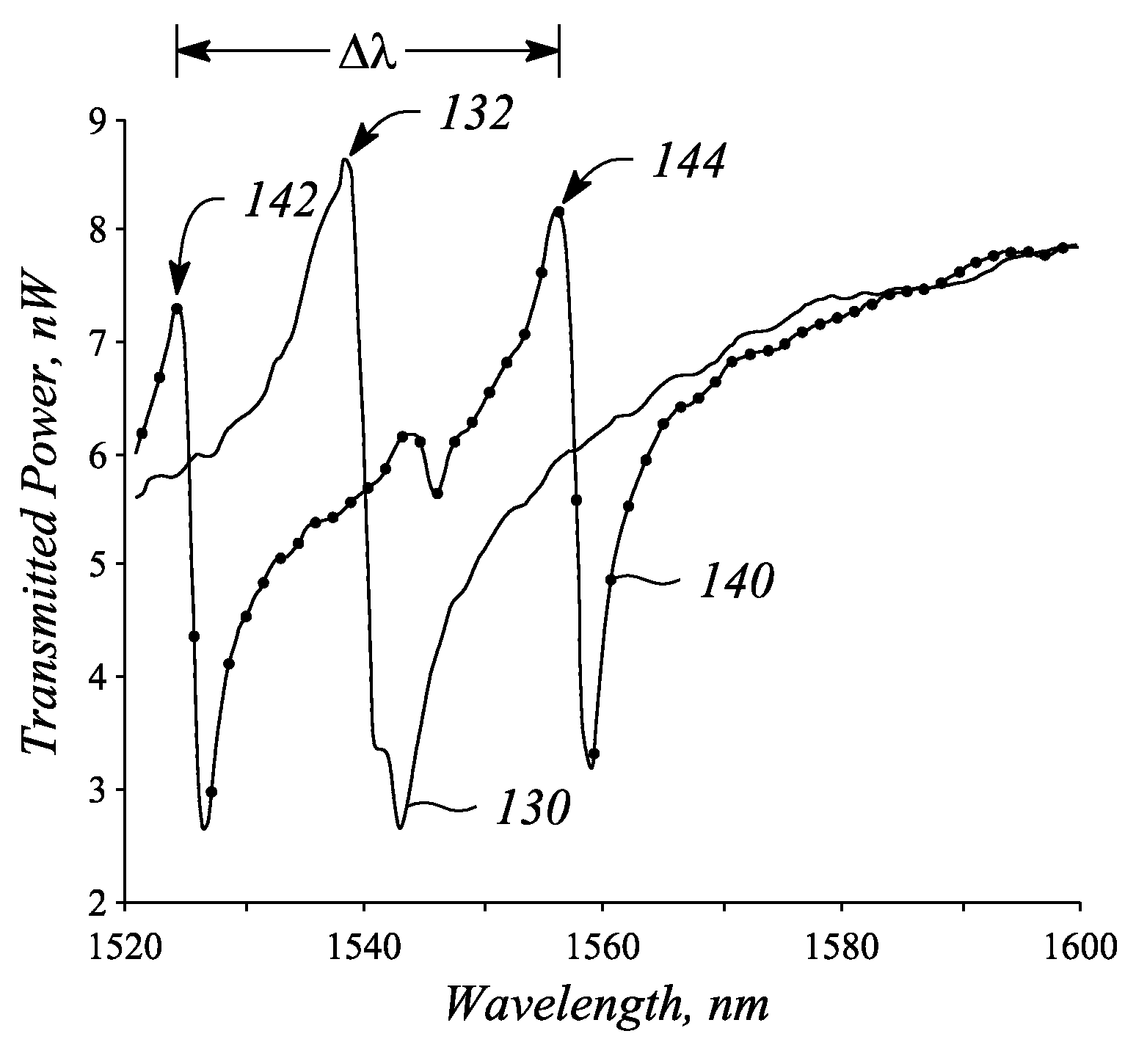
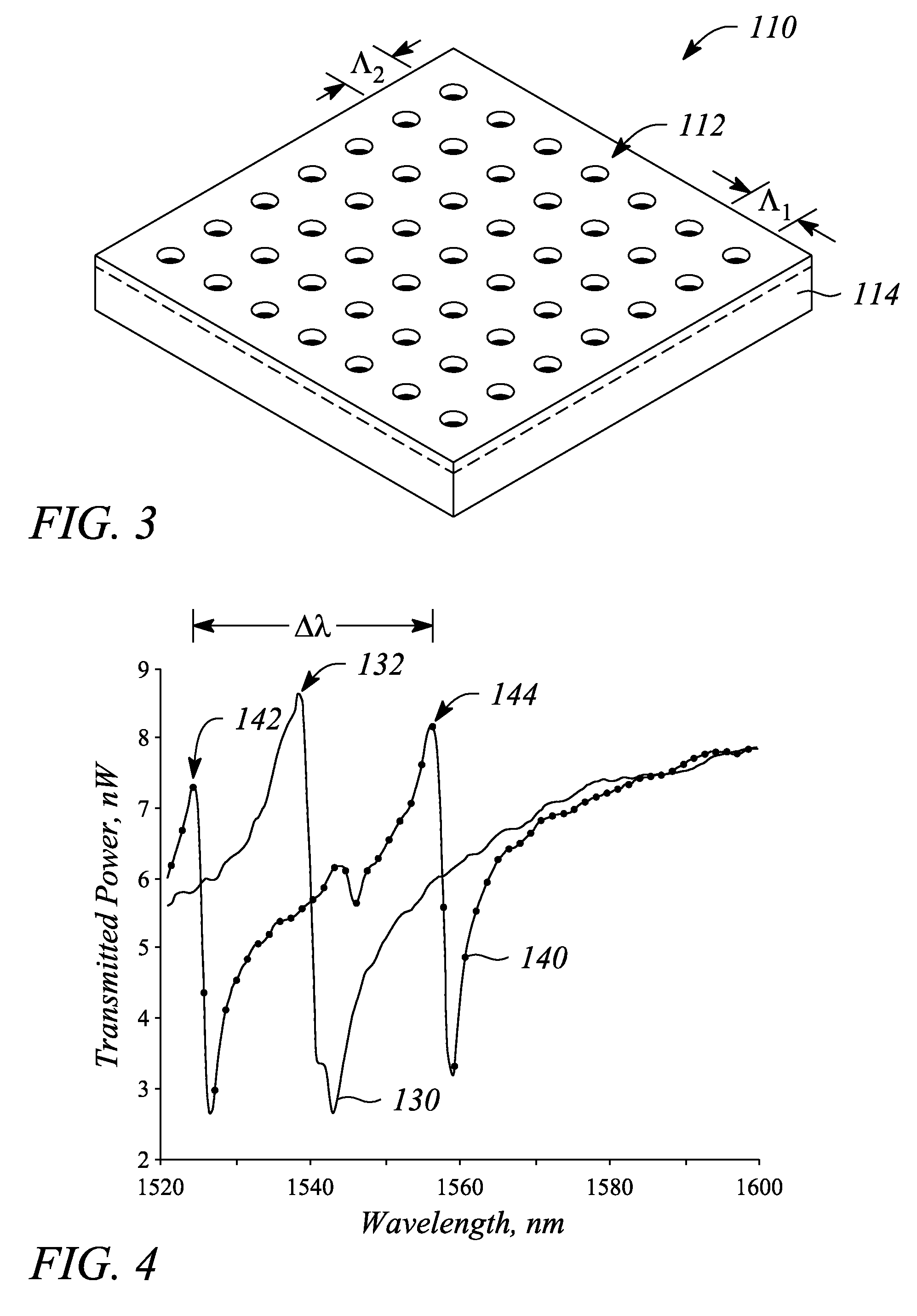
A method of characterising a sample from spectrometric data using calculation of spectral distance values is disclosed, for use in the field of mass spectrometry. Molecular formula assignment of peaks in mass spectral data is difficult and time-consuming, and the invention provides a computer implemented method of finding a most likely elemental composition of a measured spectral peak of interest. The method analyses isotopic peaks in a portion of the spectrum, using both their mass positions and intensities, to determine a spectral distance between those peaks and isotopic peaks of a candidate composition, finding peaks that match (140). A pattern spectral distance is determined (150) to provide a measure of the correspondence between a set of those peaks in the measured spectrum and peaks of each of a number of candidate compositions. The spectral fit is used to determine a most likely candidate composition.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
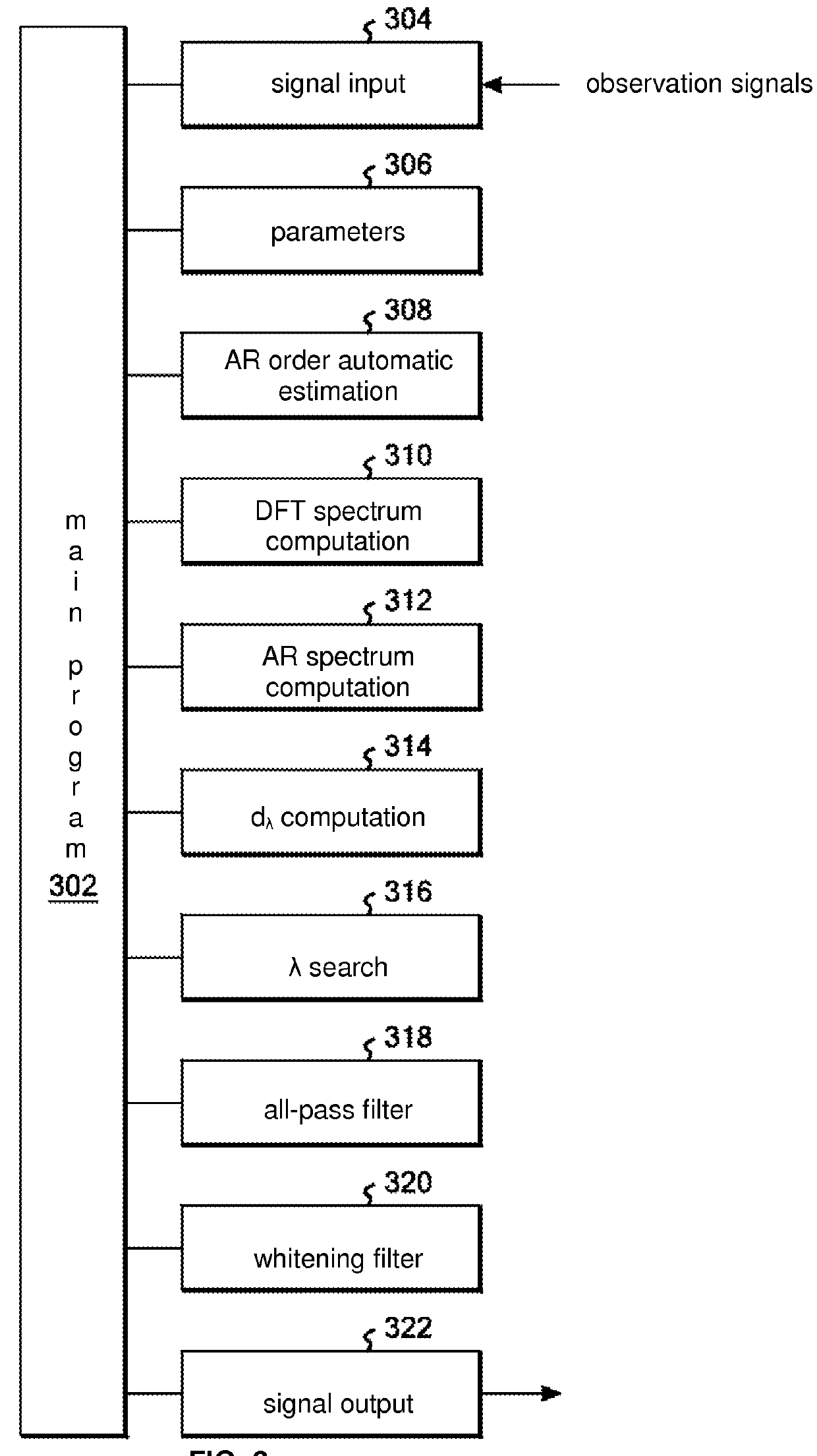
Whitening filter configuration method, program, and system
InactiveUS20140040340A1Relatively small errorLower ratioDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringDiscrete Fourier transform
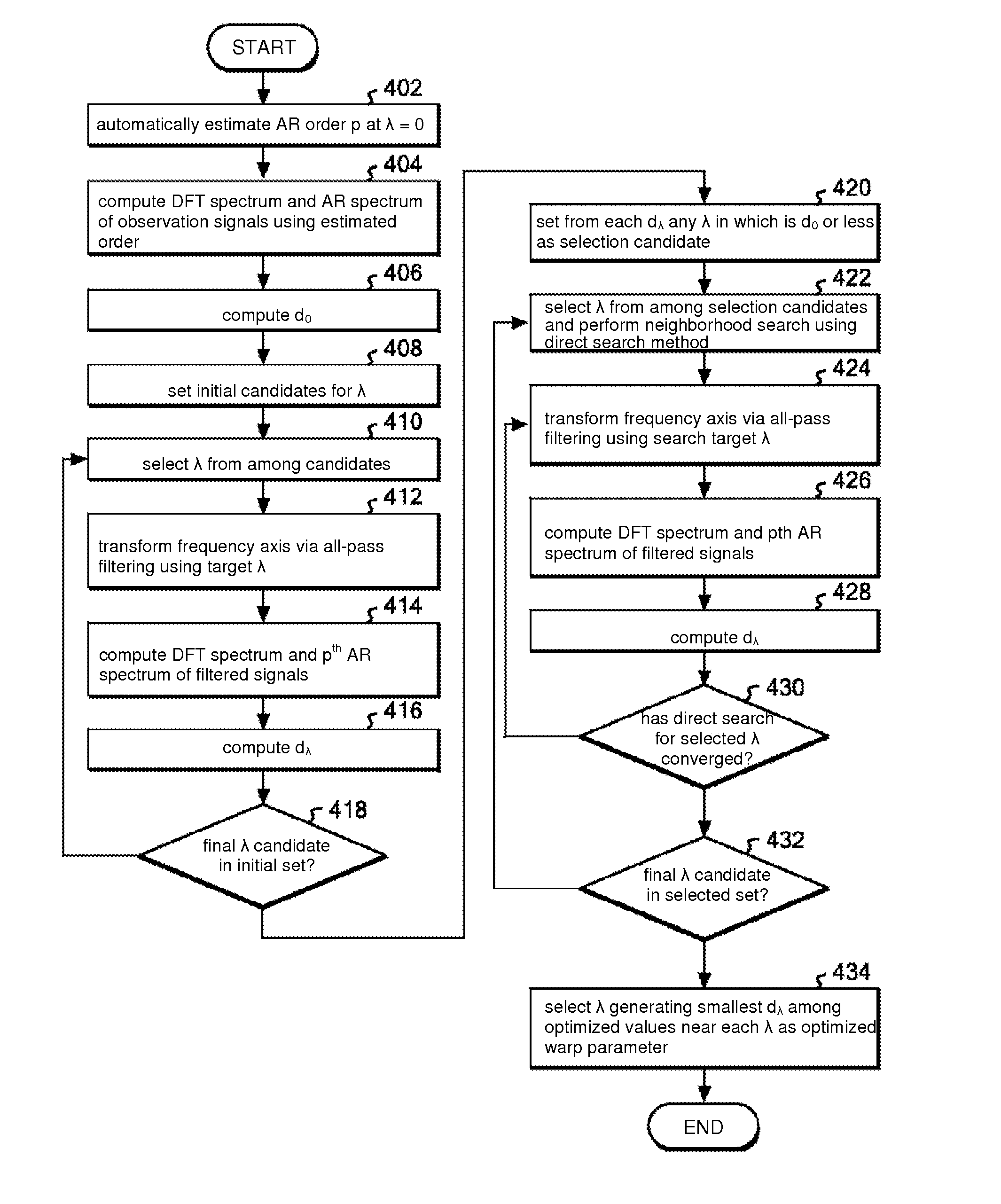
A system is configured so that signals passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ are whitening-filtered, and so that the frequency axis is restored by an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ. This optimizes the whitening filter by determining the optimum λ. First, the AR order p is automatically estimated using λ=0. A spectral distance dλ is computed using a discrete Fourier transform spectrum value passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ and a discrete AR spectrum value passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ. The λ which minimizes the spectral distance dλ is set as the warp parameter, and a whitening filter is configured in which the warp parameter has been optimized.
Owner:IBM CORP
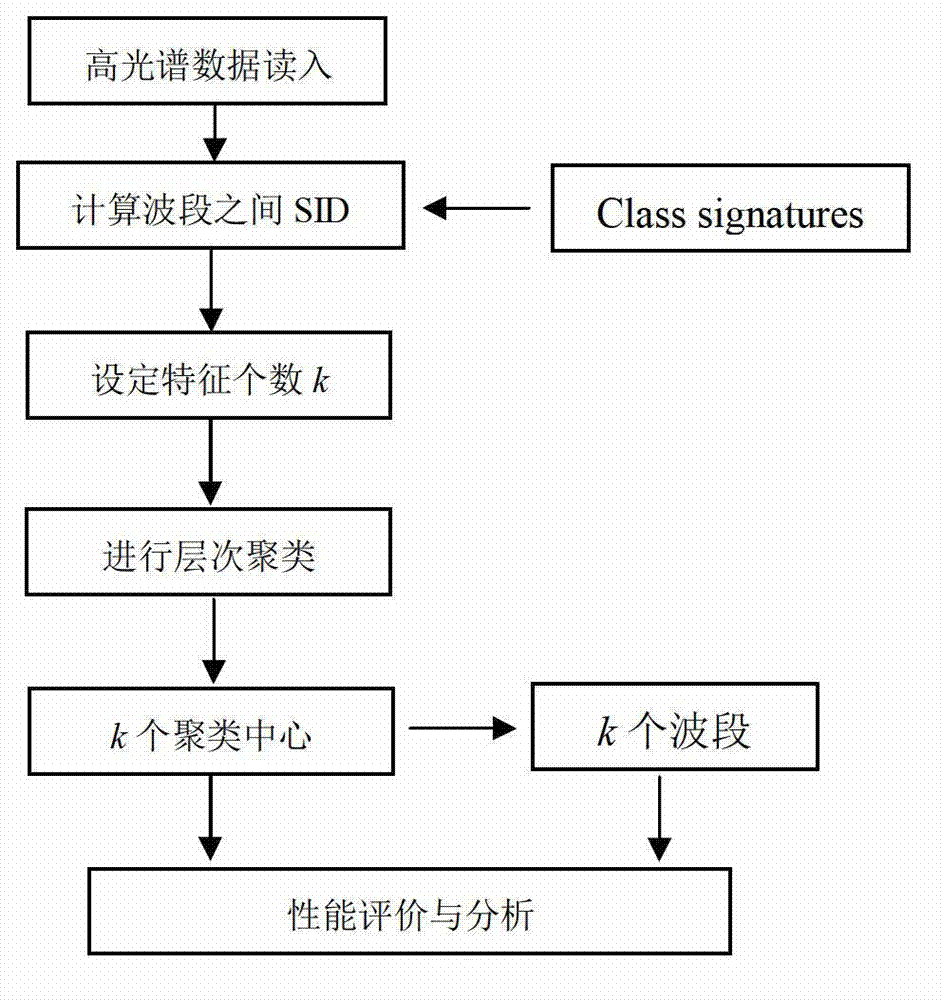
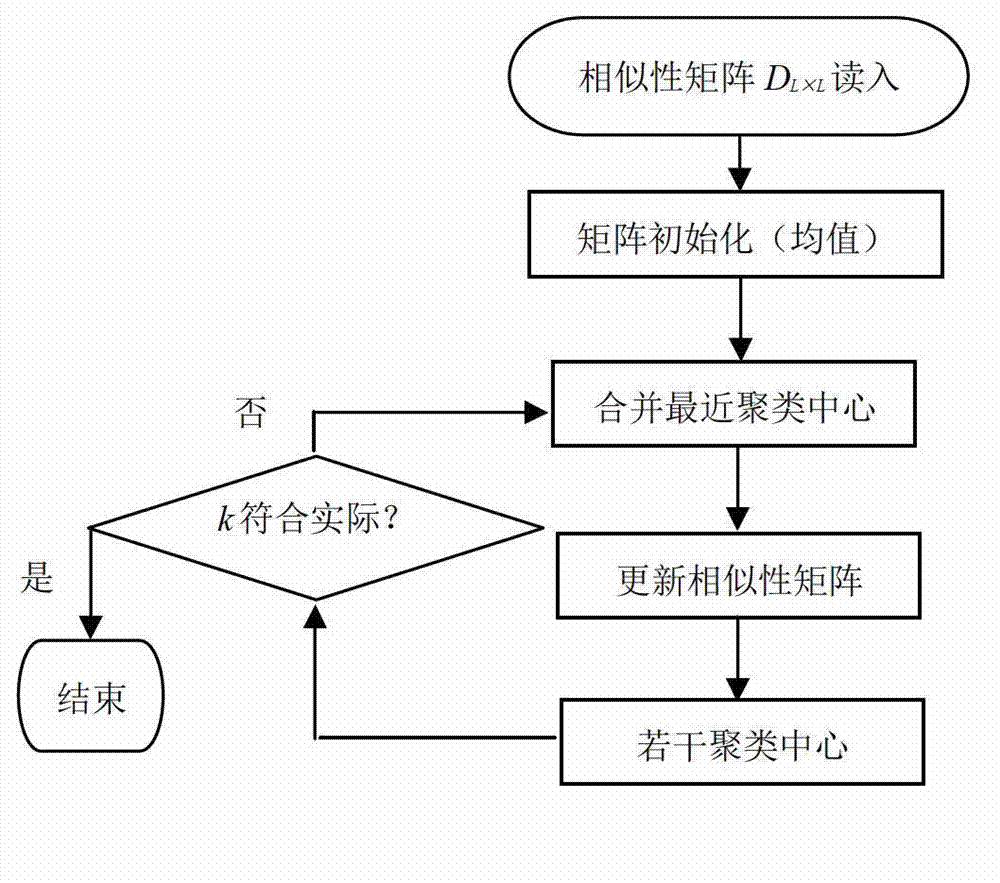
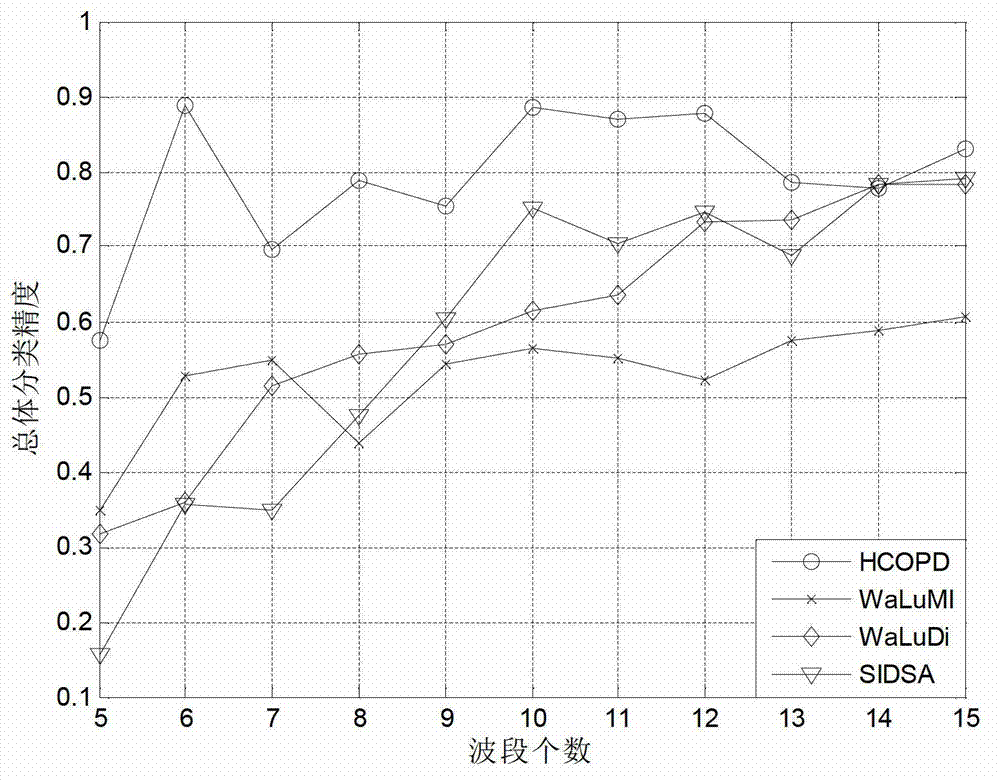
Hyperspectral remotely-sensed data dimensionality reduction method based on improved hierarchical clustering
InactiveCN102903114AImprove classification accuracySmall amount of calculationImage analysisFeature extractionData information
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remotely-sensed data dimensionality reduction method based on improved hierarchical clustering. The hyperspectral remotely-sensed data dimensionality reduction method comprises the following steps of: selecting hyperspectral remotely-sensed image data to be analyzed, wherein the hyperspectral remotely-sensed image data comprise L wave bands; calculating a spectral distance between every two wave bands by a security identification (SID) algorithm to acquire a clustering center extracted for setting a spectral distance matrix and a number k of wave bands to be selected; performing clustering analysis on the image data by a hierarchical clustering method based on a similarity distance matrix; acquiring k clustering center data to finish a feature extraction process; and selecting the most representative wave band from each clustering center to acquire k wave bands to finish a feature selection process. By the method, the dimensionality reduction efficiency can be improved; and the data information loss caused by the conventional hyperspectral remotely-sensed data dimensionality reduction method is reduced.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Method of Processing Spectrometric Data
InactiveUS20140379279A1Reduce the differenceImprove correct assignmentMolecular entity identificationParticle separator tube detailsElemental compositionMass spectrometry
A method of characterising a sample from spectrometric data using calculation of spectral distance values is disclosed, for use in the field of mass spectrometry. Molecular formula assignment of peaks in mass spectral data is difficult and time-consuming, and the invention provides a computer implemented method of finding a most likely elemental composition of a measured spectral peak of interest. The method analyses isotopic peaks in a portion of the spectrum, using both their mass positions and intensities, to determine a spectral distance between those peaks and isotopic peaks of a candidate composition, finding peaks that match (140). A pattern spectral distance is determined (150) to provide a measure of the correspondence between a set of those peaks in the measured spectrum and peaks of each of a number of candidate compositions. The spectral fit is used to determine a most likely candidate composition.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
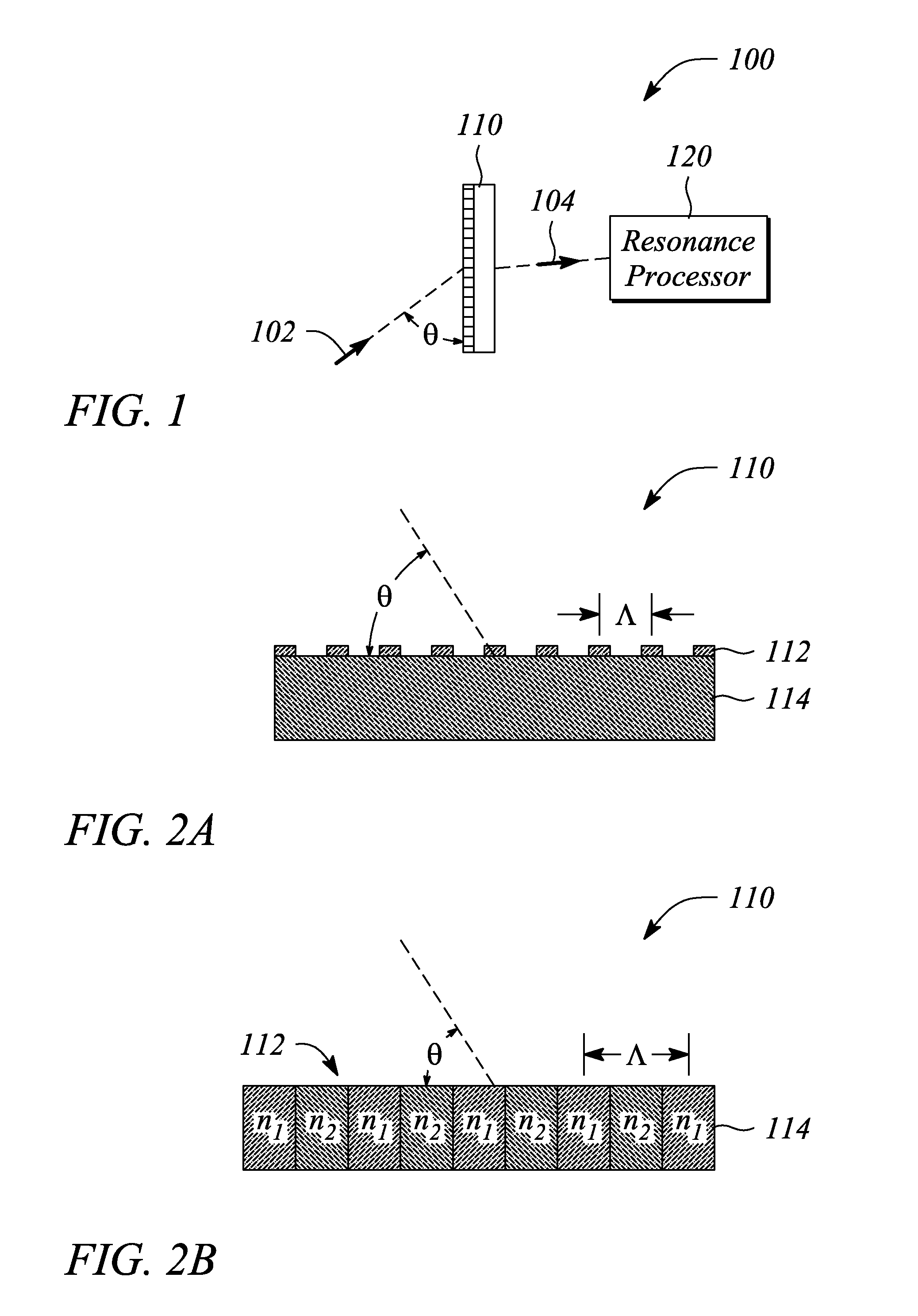
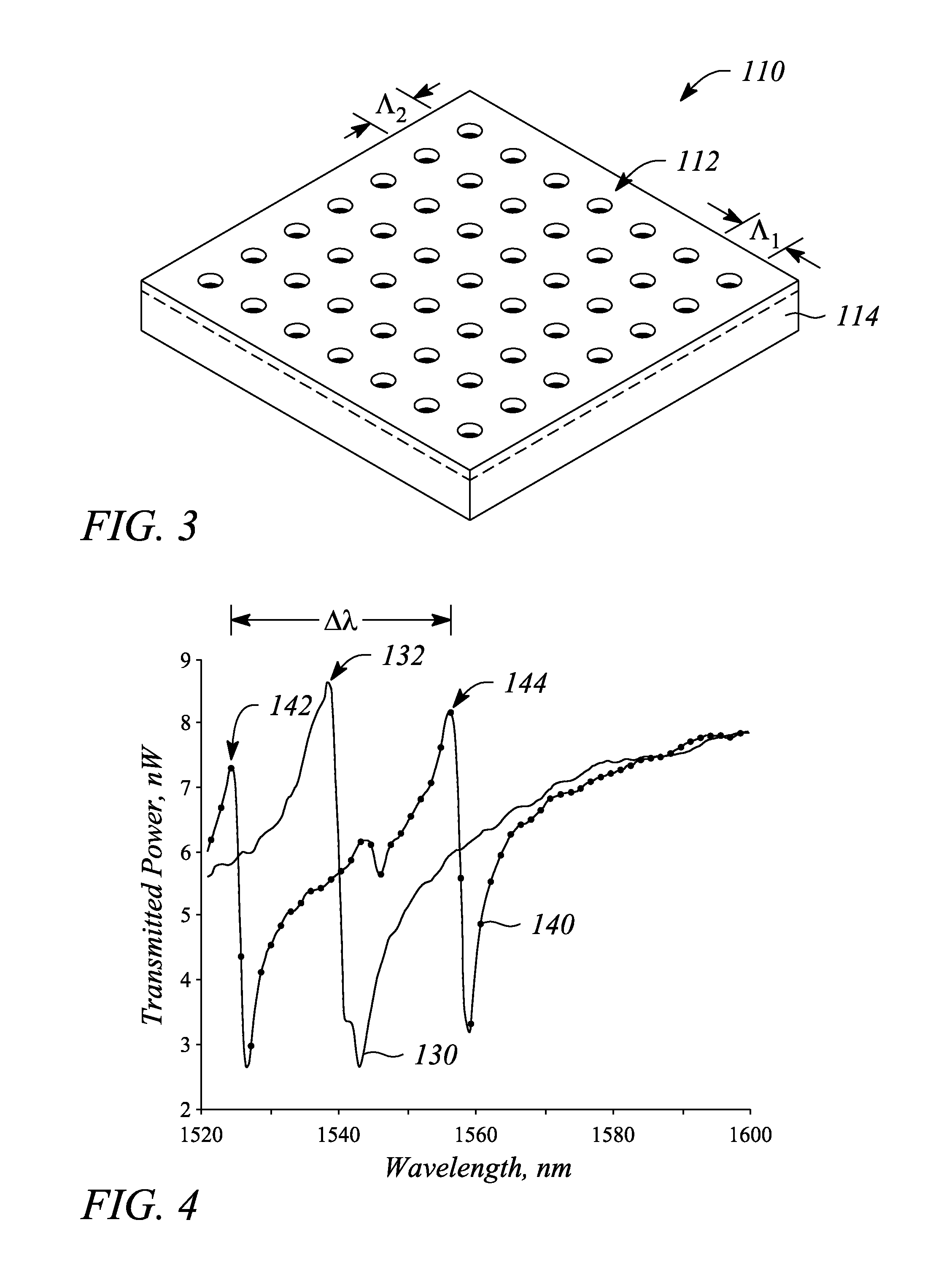
Angle sensor, system and method employing guided-mode resonance
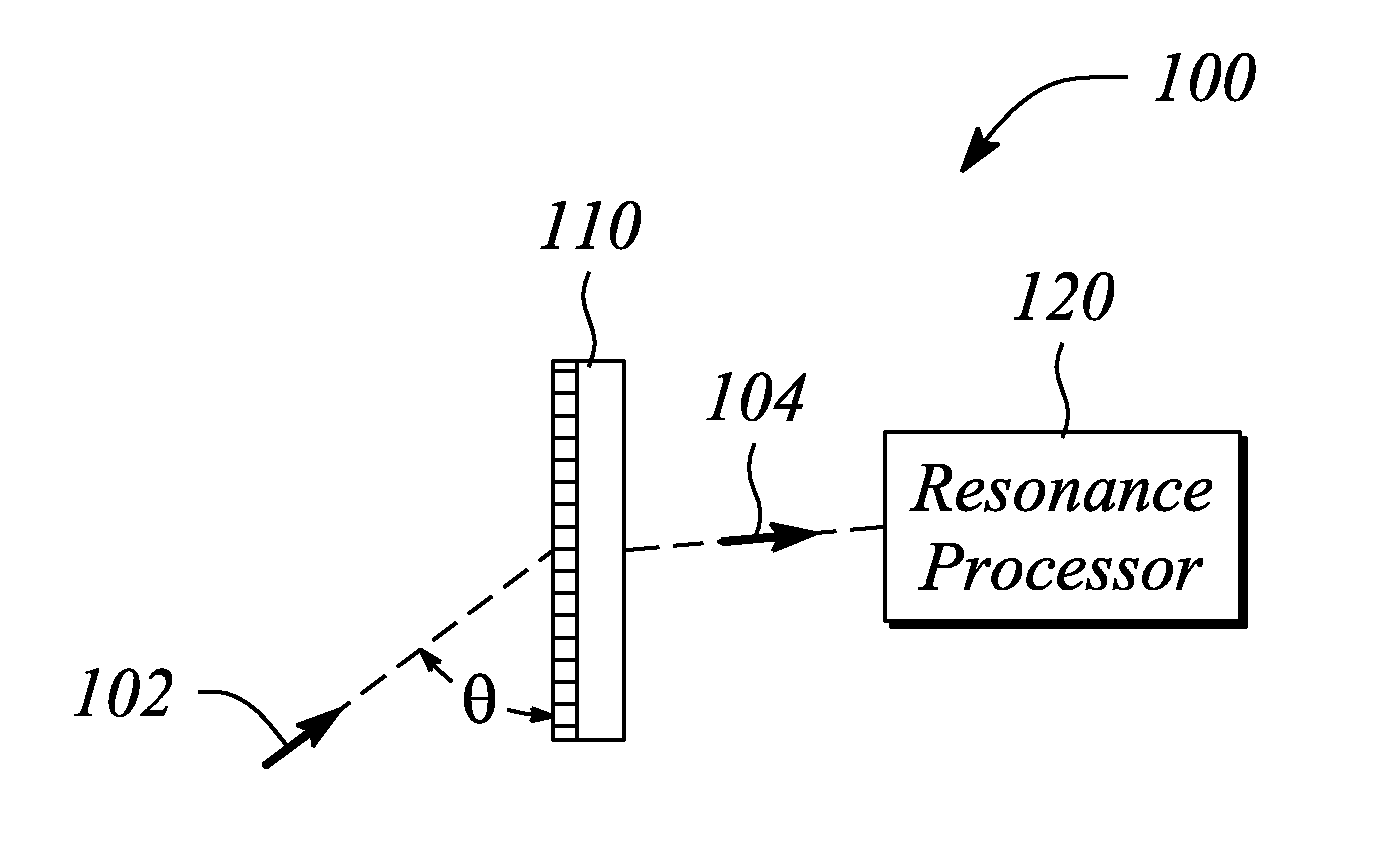
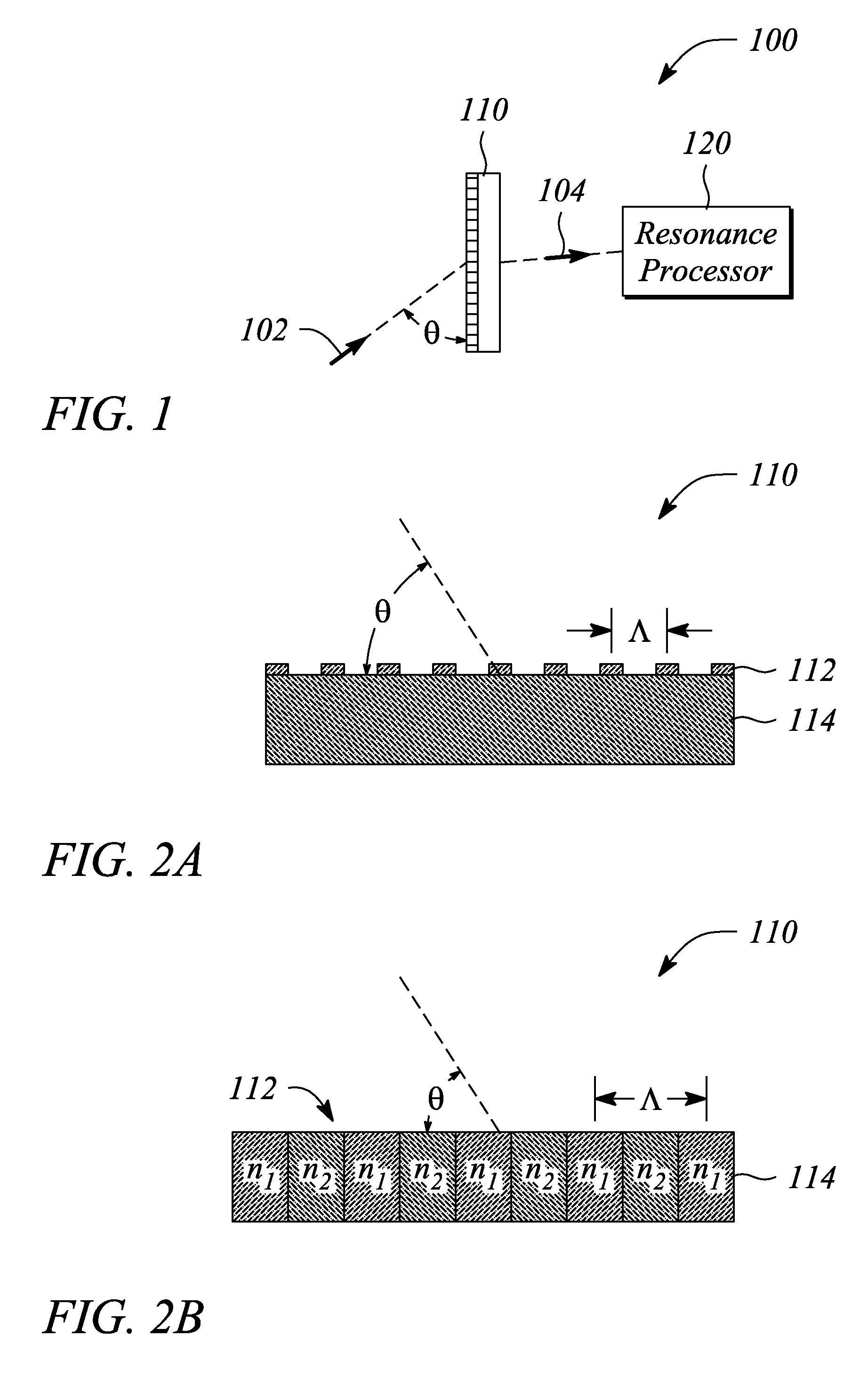
An angle sensor, system and method employ a guided-mode resonance. The angle sensor includes a guided-mode resonance (GMR) grating and a resonance processor. The resonance processor determines an angle of incidence of a signal incident on the GMR grating. The resonance processor uses a guided-mode resonance response of the GMR grating to the signal to determine the angle of incidence. The angle sensing system includes the GMR grating, the resonance processor and further includes an optical source that produces the signal. The method includes providing a GMR grating, detecting a guided-mode resonance produced in the GMR grating when subjected to an incident signal, and determining an angle of incidence of the incident signal from one or both of a number of and a spectral distance between guided-mode resonances present in a response of the GMR grating to the incident signal.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
Method of processing spectrometric data
ActiveUS8831888B2Reduce the differenceImprove correct assignmentMolecular entity identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionPhysical chemistryMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A method of characterizing a sample from spectrometric data using calculation of spectral distance values is disclosed, for use in the field of mass spectrometry. Molecular formula assignment of peaks in mass spectral data is difficult and time-consuming, and the invention provides a computer implemented method of finding a most likely elemental composition of a measured spectral peak of interest. The method analyzes isotopic peaks in a portion of the spectrum, using both their mass positions and intensities, to determine a spectral distance between those peaks and isotopic peaks of a candidate composition, finding peaks that match (140). A pattern spectral distance is determined (150) to provide a measure of the correspondence between a set of those peaks in the measured spectrum and peaks of each of a number of candidate compositions. The spectral fit is used to determine a most likely candidate composition.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCI BREMEN
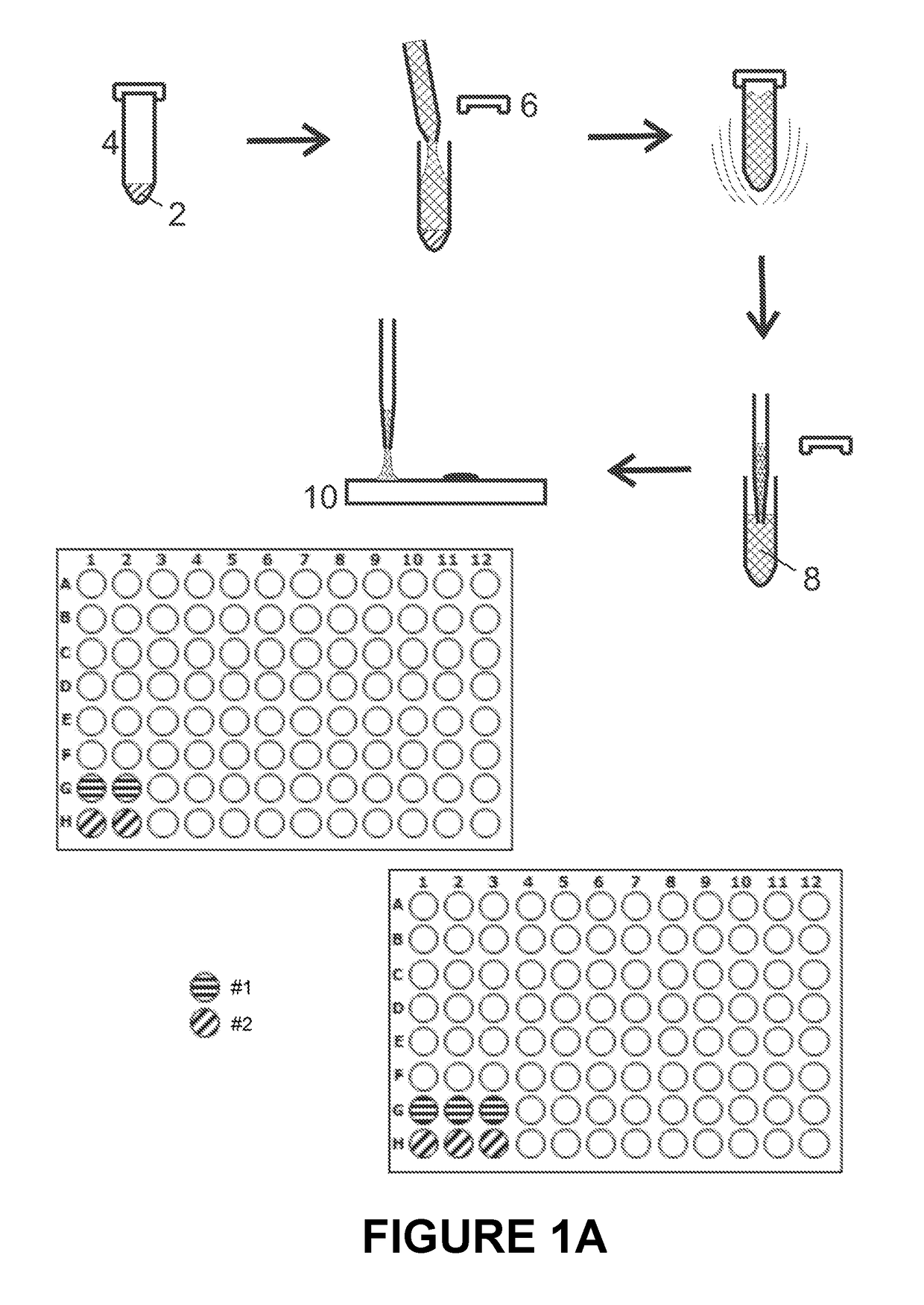
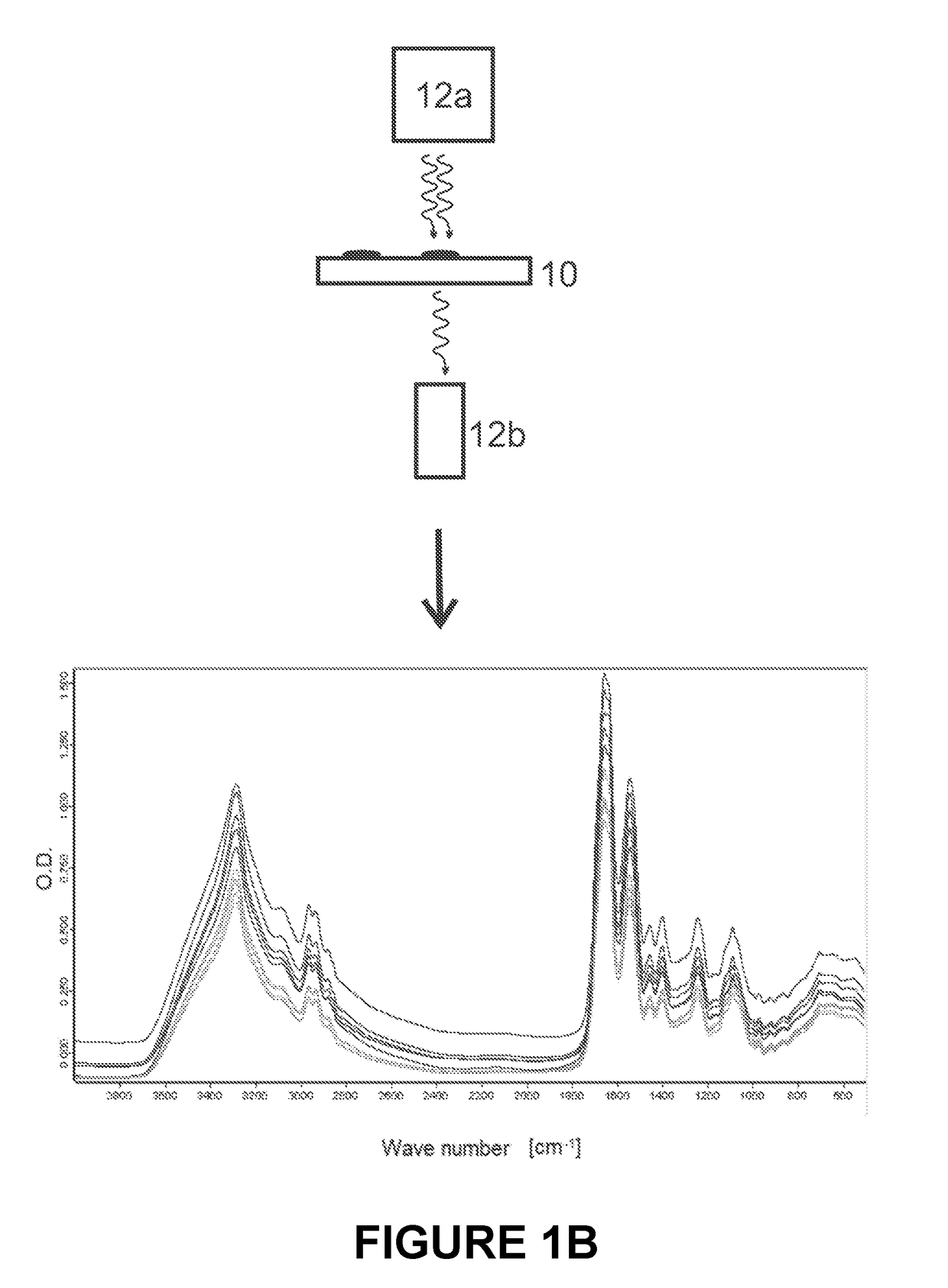
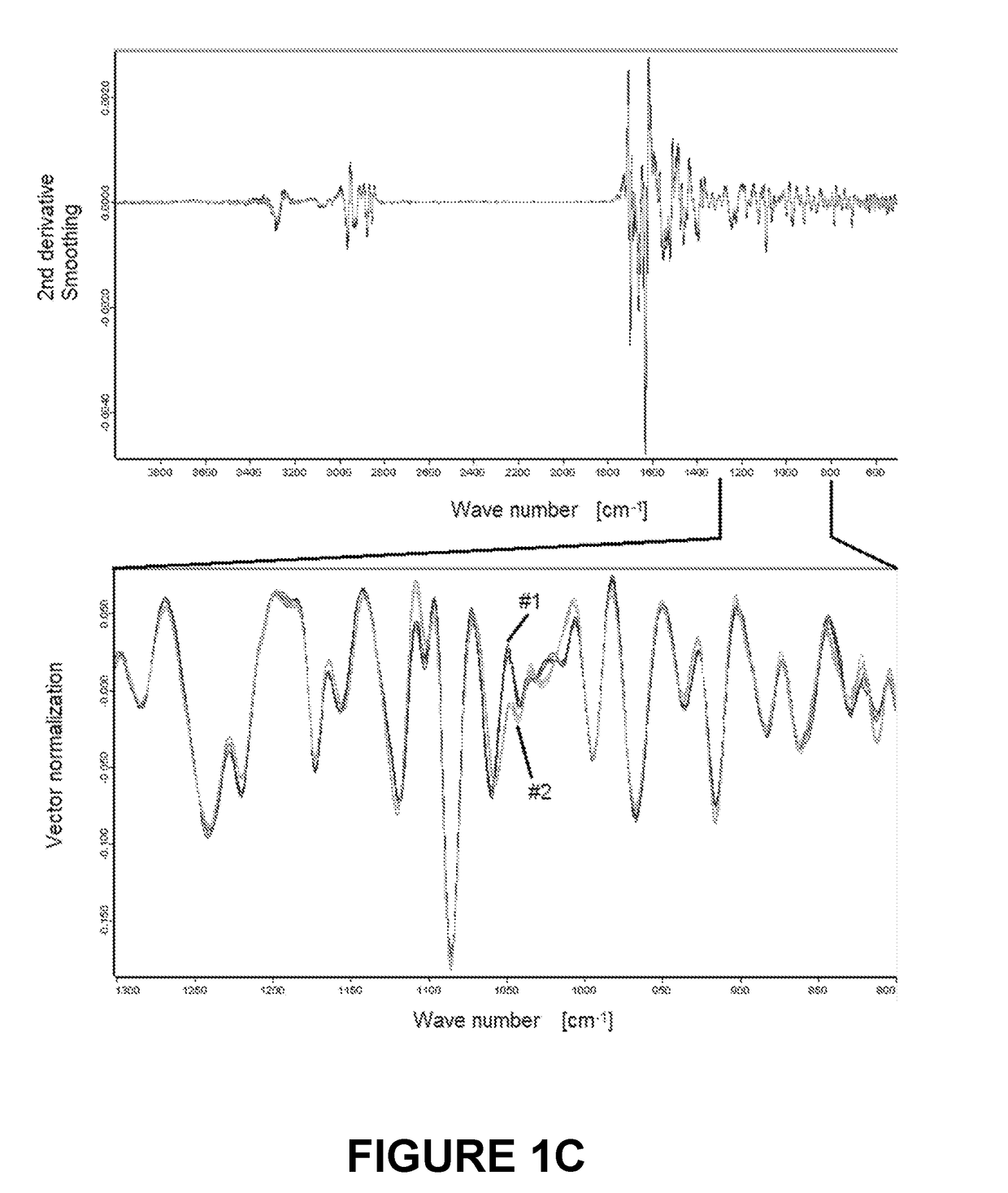
Microbial test standard for use in infrared spectrometry
ActiveUS20180306711A1Suitable for storageExtended shelf lifeMicrobiological testing/measurementPreparing sample for investigationMicrobiologySpectral distance
The invention relates to a microbial test standard for use in infrared spectrometry which has at least two resealable vessels which are liquid-tight when closed, each of which contains a predefined amount of dried biomass of a microorganism. The microorganisms in the different vessels differ in at least one characteristic, which is selected in particular from the group comprising species, subspecies, strain, serovar, pathovar, toxivar and variety, and the difference manifests itself in a predefined intermicrobial spectral distance. The disclosure furthermore comprises a method of using the microbial test standard.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
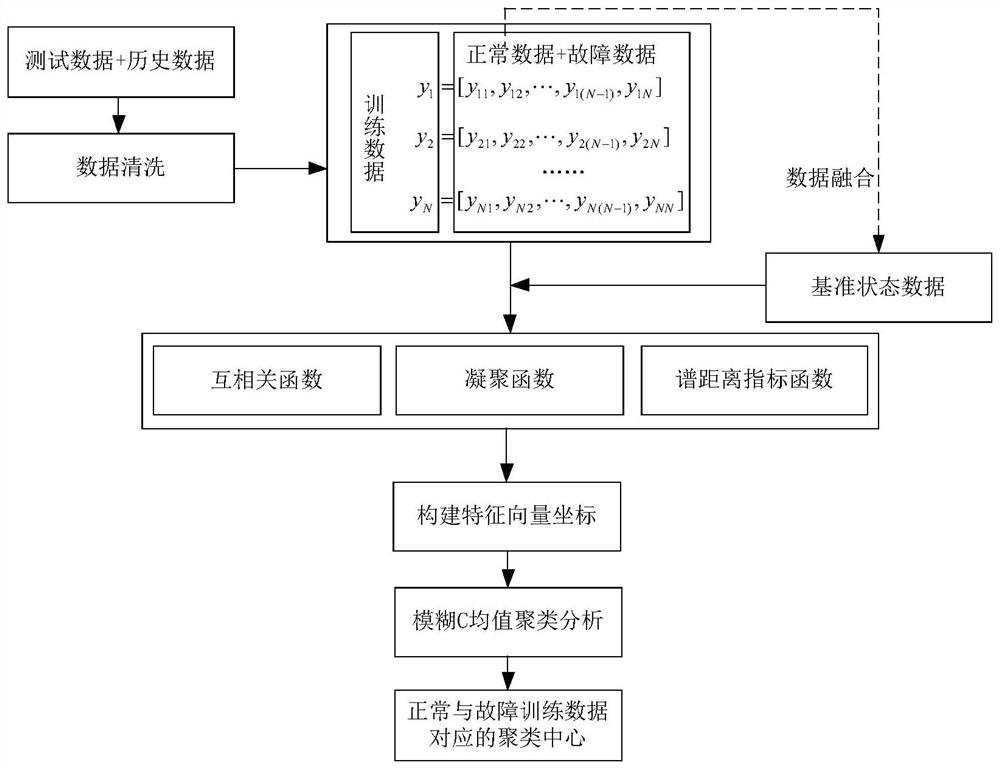
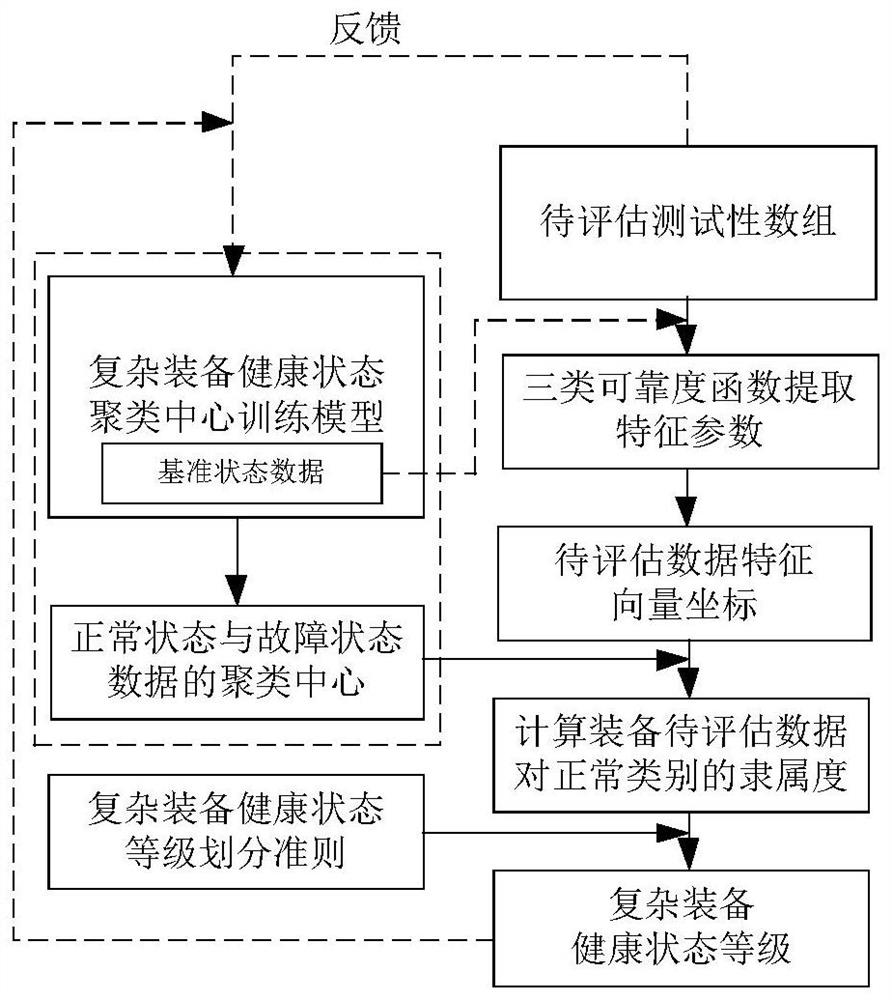
Complex equipment health state assessment method
PendingCN114266289AImprove accuracyReduce chanceCharacter and pattern recognitionEngineeringFeature parameter
The invention discloses a complex equipment health state assessment method, which assesses to-be-assessed data by establishing a complex equipment health state clustering center training model to judge the health level of complex equipment, and fuses normal state data of the complex equipment into a group of reference normal state data. And further calculating characteristic parameters, namely a cross correlation coefficient, a condensation coefficient and a spectral distance index, as three-dimensional characteristic vector coordinates of each group of training data. Performing clustering analysis on the feature vector array to obtain a clustering center training model, calculating a membership degree and an assessment health level of the to-be-assessed data to the clustering center in a normal state according to an Euclidean distance from the to-be-assessed data to the clustering center, then performing sampling mechanism analysis on the to-be-assessed data, judging the accuracy of an assessment result, and obtaining the assessment result of the to-be-assessed data. And meanwhile, the extracted to-be-evaluated data which is evaluated completely and accurately is added into the training data of the complex equipment, so that the accuracy and the stability of subsequent evaluation work are improved.
Owner:CHINA AEROSPACE STANDARDIZATION INST
Method for judging maintenance and update of octane number model
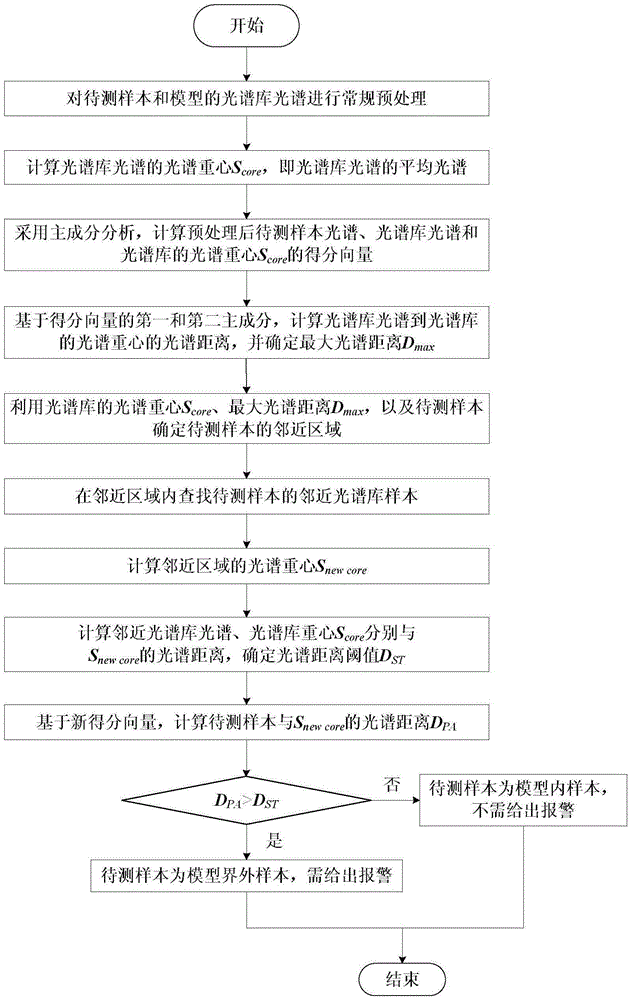
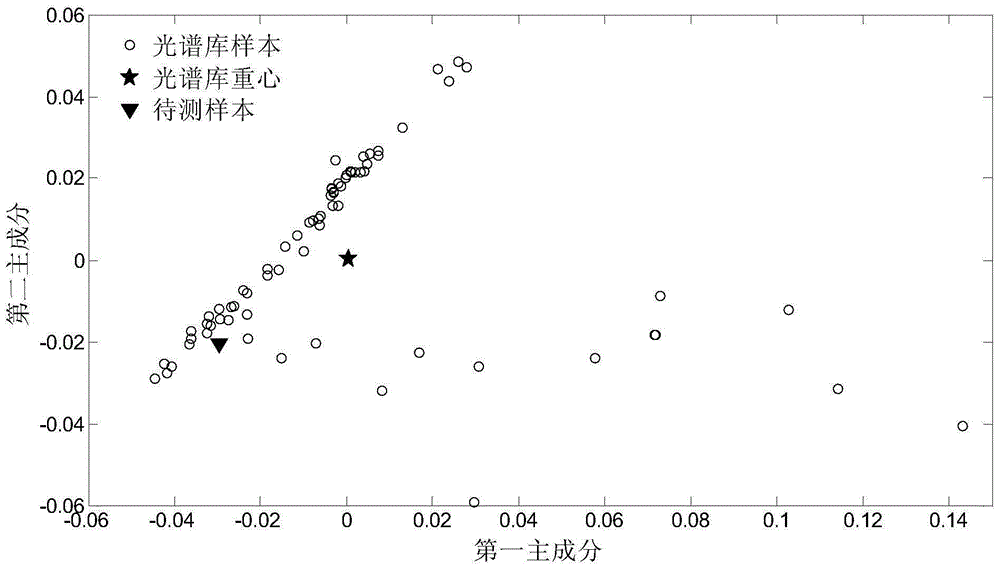
ActiveCN105184004AImprove forecast accuracyGuaranteed prediction accuracyProgram loading/initiatingSpecial data processing applicationsDemarcation pointComputer science
The invention disclose a method for judging maintenance and update of an octane number model. The method is characterized by adopting a spectral distance threshold to serve as a demarcation point to judge whether a sample to be tested is a model out-of-bound sample or not, and if yes, alarming is conducted to remind staff to conduct maintenance and update on an existing model. After an alarming signal is received, the staff conduct a standard test on current components to be tested and added to the model to improve the prediction accuracy of the model. Compared with a traditional method for maintaining and updating in a specified time, by means of the method for maintaining and updating according to needs, on the premise that the prediction accuracy of the model is guaranteed, time and manpower resources are greatly saved.
Owner:南京富岛信息工程有限公司
Angle sensor, system and method employing guided-mode resonance
An angle sensor, system and method employ a guided-mode resonance. The angle sensor includes a guided-mode resonance (GMR) grating and a resonance processor. The resonance processor determines an angle of incidence of a signal incident on the GMR grating. The resonance processor uses a guided-mode resonance response of the GMR grating to the signal to determine the angle of incidence. The angle sensing system includes the GMR grating, the resonance processor and further includes an optical source that produces the signal. The method includes providing a GMR grating, detecting a guided-mode resonance produced in the GMR grating when subjected to an incident signal, and determining an angle of incidence of the incident signal from one or both of a number of and a spectral distance between guided-mode resonances present in a response of the GMR grating to the incident signal.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
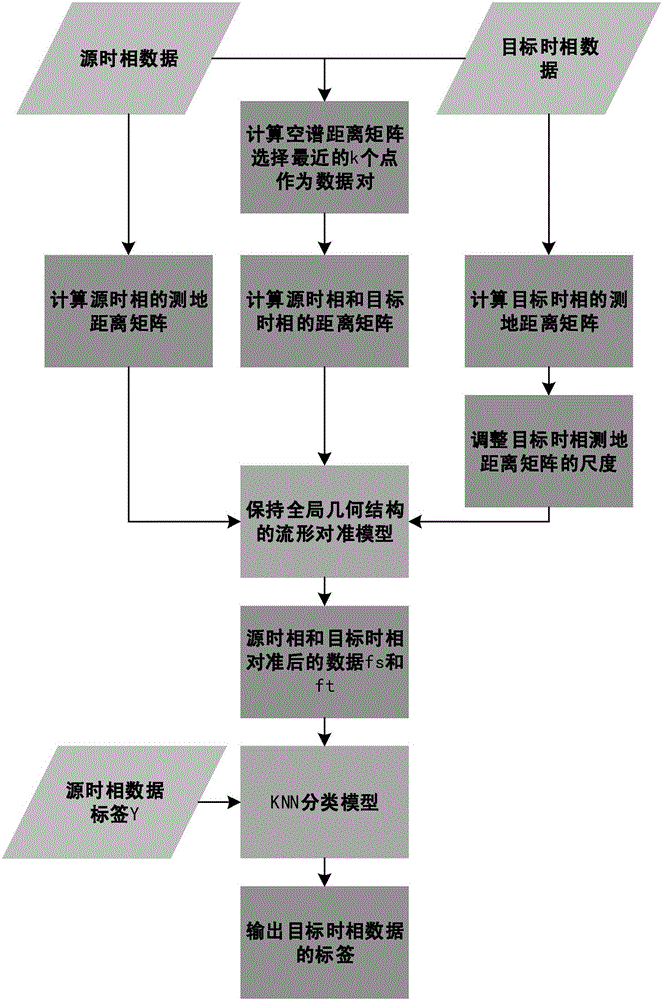
Multi-temporal hyper-spectral image classification method based on spatial-spectral feature preserving global geometric structure
ActiveCN106503754AImplement classificationEasy accessCharacter and pattern recognitionHyperspectral data classificationDistance matrix
Disclosed is a multi-temporal hyper-spectral image classification method based on a spatial-spectral feature preserving global geometric structure. The invention relates to a multi-temporal hyper-spectral remote sensing image classification method. The invention aims to solve the problem that a hyper-spectral multi-temporal data tag is hard to acquire, and classification of data of a target time phase by direct use of hyper-spectral data of a source time phase is unreliable under the condition of obvious spectral drift of an image. The method specifically comprises the following steps: (1) inputting X<s> and X<t> and the spatial coordinates Z1, Z2 thereof, and a tag vector Y of corresponding category in each line of X<s>; (2) calculating the spatial-spectral distance of X<s> and X<t>, and selecting nearest points as a data pair needing matching; (3) calculating D<s, s>, D<t, t>, and D<s, t>, adjusting the scale of the data set, and building a distance matrix D; (4) getting the mapping matrixes alpha and beta of X<s> and X-wavy line<t> in an alignment space, and getting projections f<s> and f<t>; and (5) performing classification using a KNN classification model according to f<s> and f<t> as well as a tag Y corresponding to f<s> to get a classification tag of the target time phase. The method is used in the field of image classification.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Coding of spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal
A coding efficiency of coding spectral coefficients of a spectrum of an audio signal is increased by en / decoding a currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficient by entropy en / decoding and, in doing so, performing the entropy en / decoding depending, in a context-adaptive manner, on a previously en / decoded spectral coefficient, while adjusting a relative spectral distance between the previously en / decoded spectral coefficient and the currently en / decoded spectral coefficient depending on an information concerning a shape of the spectrum. The information concerning the shape of the spectrum may have a measure of a pitch or periodicity of the audio signal, a measure of an inter-harmonic distance of the audio signal's spectrum and / or relative locations of formants and / or valleys of a spectral envelope of the spectrum, and on the basis of this knowledge, the spectral neighborhood which is exploited in order to form the context of the currently to be en / decoded spectral coefficients may be adapted to the thus determined shape of the spectrum, thereby enhancing the entropy coding efficiency.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
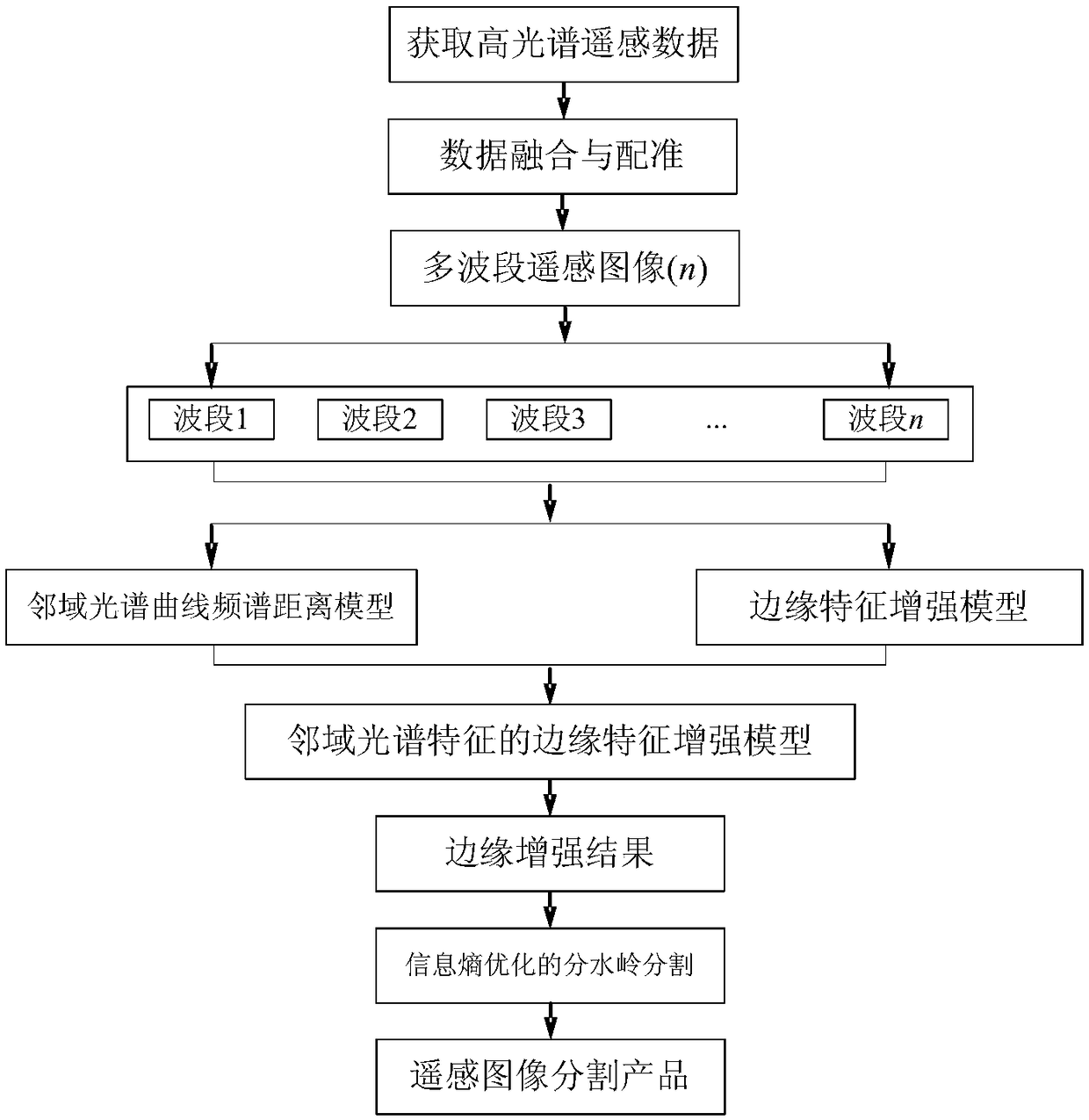
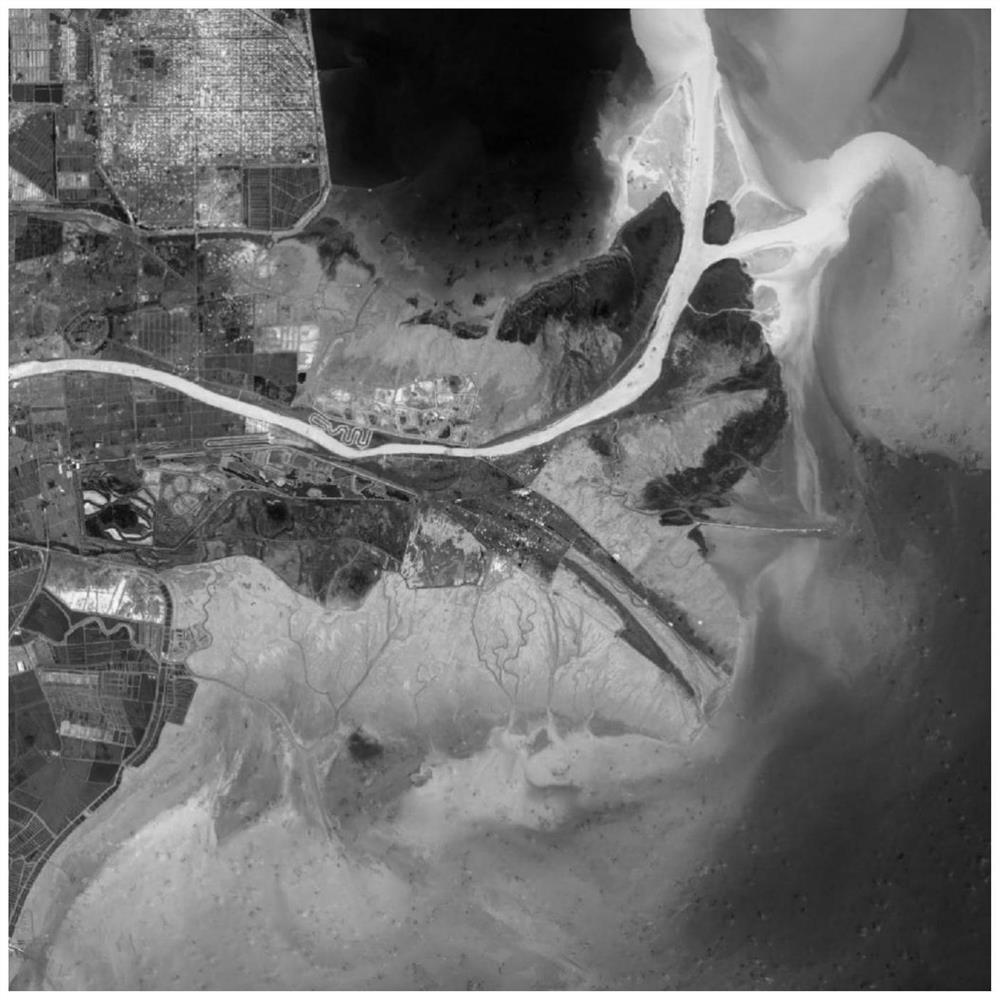
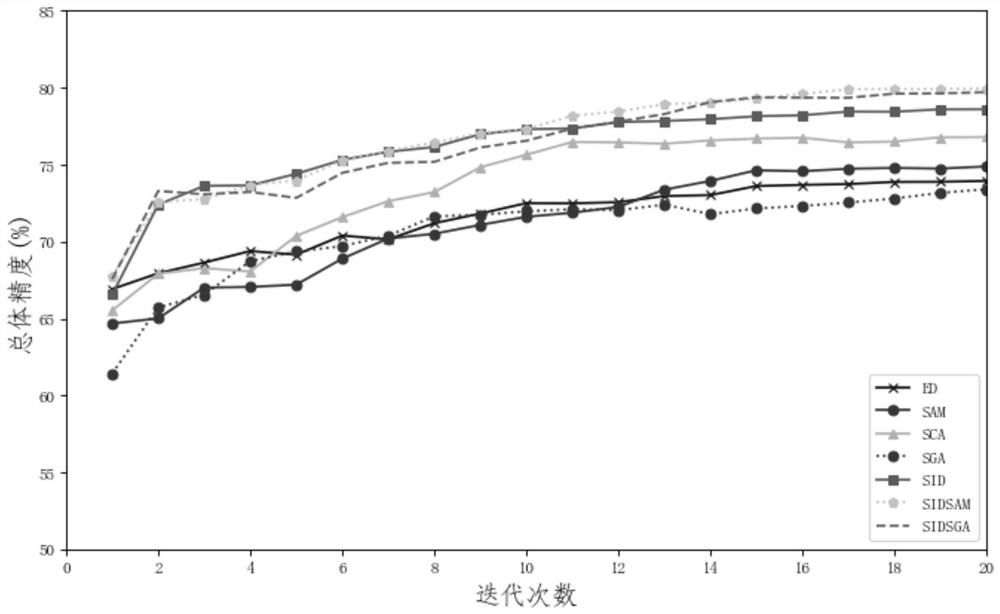
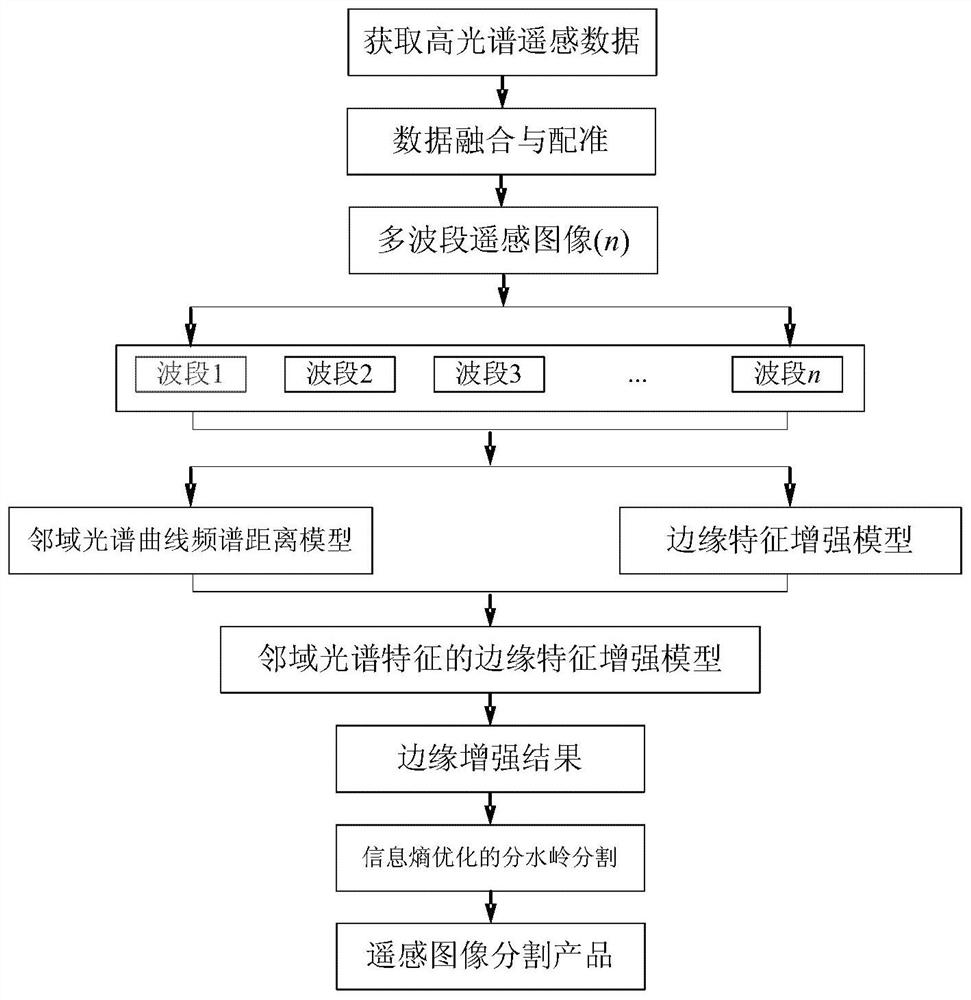
A hyperspectral remote sensing image segmentation method based on spectral distance of spectral curve
ActiveCN109377507ASuppress oversegmentationResolve weak edgesImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral curveFrequency spectrum
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image segmentation method based on a spectral curve spectral distance. Firstly, a neighborhood spectral curve spectral distance model of a targetpixel is constructed. The Hilbert transform is used to obtain the odd-even filtering results by convolution operation, and the square root of the sum of squares of the odd-even filtering results is used as the local energy to construct the edge feature enhancement model. The edge feature enhancement model based on neighborhood spectral features is obtained by combining the two methods, which is used to obtain the edge feature enhancement results. The result of edge feature enhancement is input into watershed segmentation algorithm as gradient data, And the watershed segmentation algorithm isoptimized to achieve high-precision segmentation of remote sensing images, which can effectively suppress the over-segmentation phenomenon of hyperspectral remote sensing images, and solve the technical problems that weak edges and pseudo-edges in hyperspectral remote sensing images affect the segmentation results of remote sensing images.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
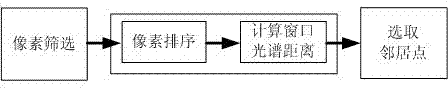
Neighbor point searching method and system for spectral image dimensionality reduction
ActiveCN104268558AAvoid the effects of searchImprove accuracyGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionImage geometrySpectral distance
The invention provides a neighbor point searching method and system for spectral image dimensionality reduction. The method includes the steps of screening pixels of a window where current pixels are located and eliminating the pixels greatly interfered by noise and other factors; sequencing the current pixels and pixels in a window where pixels to be compared are located, and calculating the spectral distance between the current pixels and the window where the pixels to be compared are located; selecting multiple pixels with the highest similarity as neighbor points of the current pixels. According to the method, spatial information is fully used, a searching process is not influenced by changes of geometrical morphology of images through sequencing, spatial robustness is achieved, some noise pollution points are well prevented, the found neighbor points are more accurate, and data dimensionality reduction performance of hyperspectral images is improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Whitening filter configuration method, program, and system
InactiveUS9252745B2Improve the level ofReduce impactDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsEngineeringDiscrete Fourier transform
A system is configured so that signals passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ are whitening-filtered, and so that the frequency axis is restored by an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ. This optimizes the whitening filter by determining the optimum λ. First, the AR order p is automatically estimated using λ=0. A spectral distance dλ is computed using a discrete Fourier transform spectrum value passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ and a discrete AR spectrum value passed through an all-pass filter using warp parameter λ. The λ which minimizes the spectral distance dλ is set as the warp parameter, and a whitening filter is configured in which the warp parameter has been optimized.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
A near-infrared anomaly spectral identification method based on knn
ActiveCN109459409BIdentify and removeImprove forecast accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansNear infrared spectraHyperparameter
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Method for detecting contents of glucose in cell culture mediums by utilizing Raman spectroscopy
The invention provides a method for detecting contents of glucose in cell culture mediums by utilizing Raman spectroscopy. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) preparing a series of standard glucose solution with a concentration from 0.1 g / L to 350 g / L by using glucose, placing the standard glucose solution in a cuvette of a Raman spectrometer, setting a laser projection distance as 1-2mm and acquiring spectral signals by utilizing the Raman spectrometer; and 2) establishing a standard model according to characteristic peaks and concentrations of Raman spectrums of the standard glucose solution with different concentrations. The method for detecting contents of glucose in cell culture mediums by utilizing Raman spectroscopy is applied to the field of veterinary cell culture medium detection, and does not have hemoglobin interference factors; and at the same time, the interference factors are eliminated through adjusting Raman spectral distances and wavelength time. Comparedwith the existing glucose solution detection technology in the field of veterinary biological products, the method has the characteristics of being fast, simple, accurate and sensitive.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HUSBANDRY IND
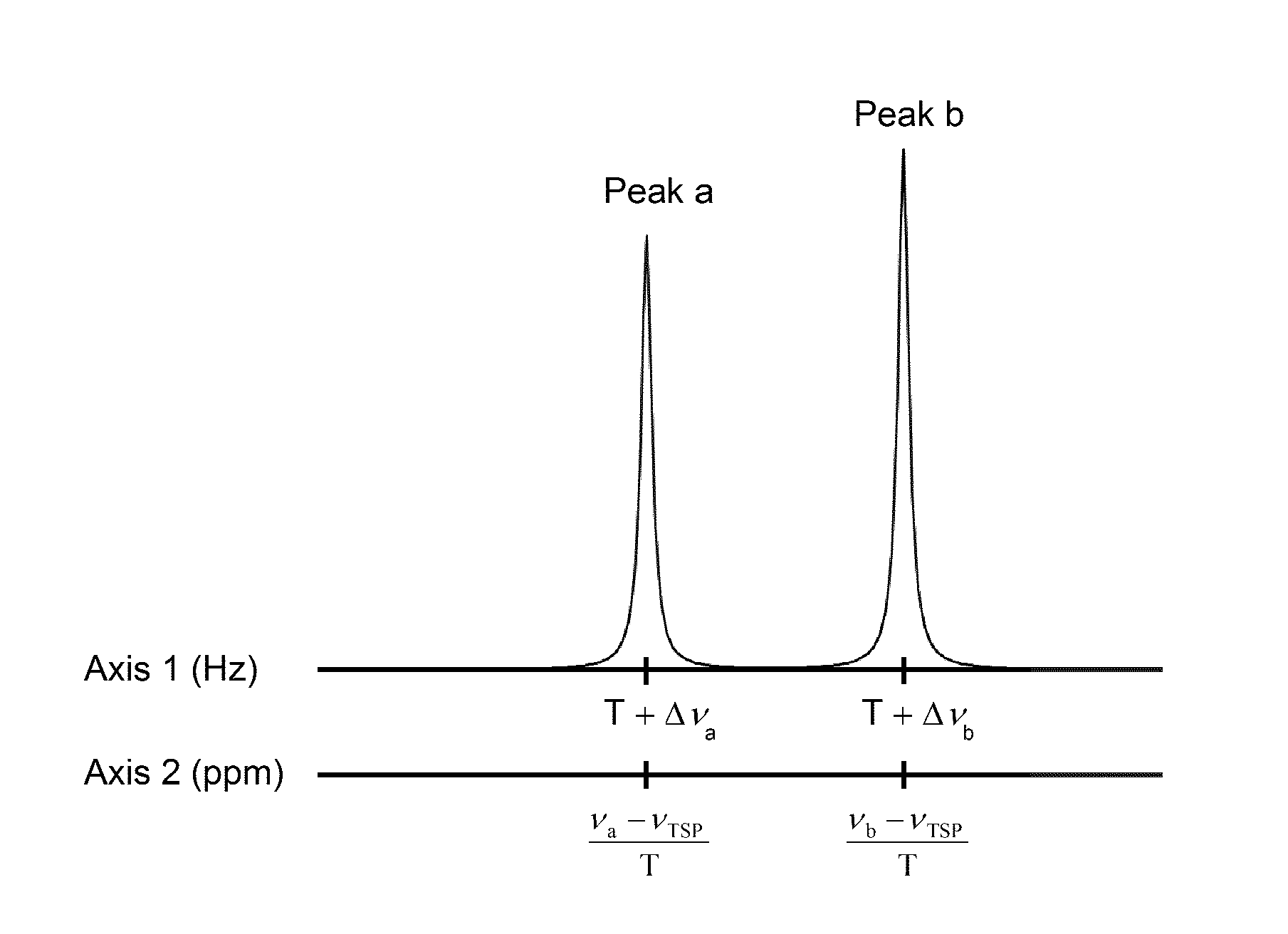
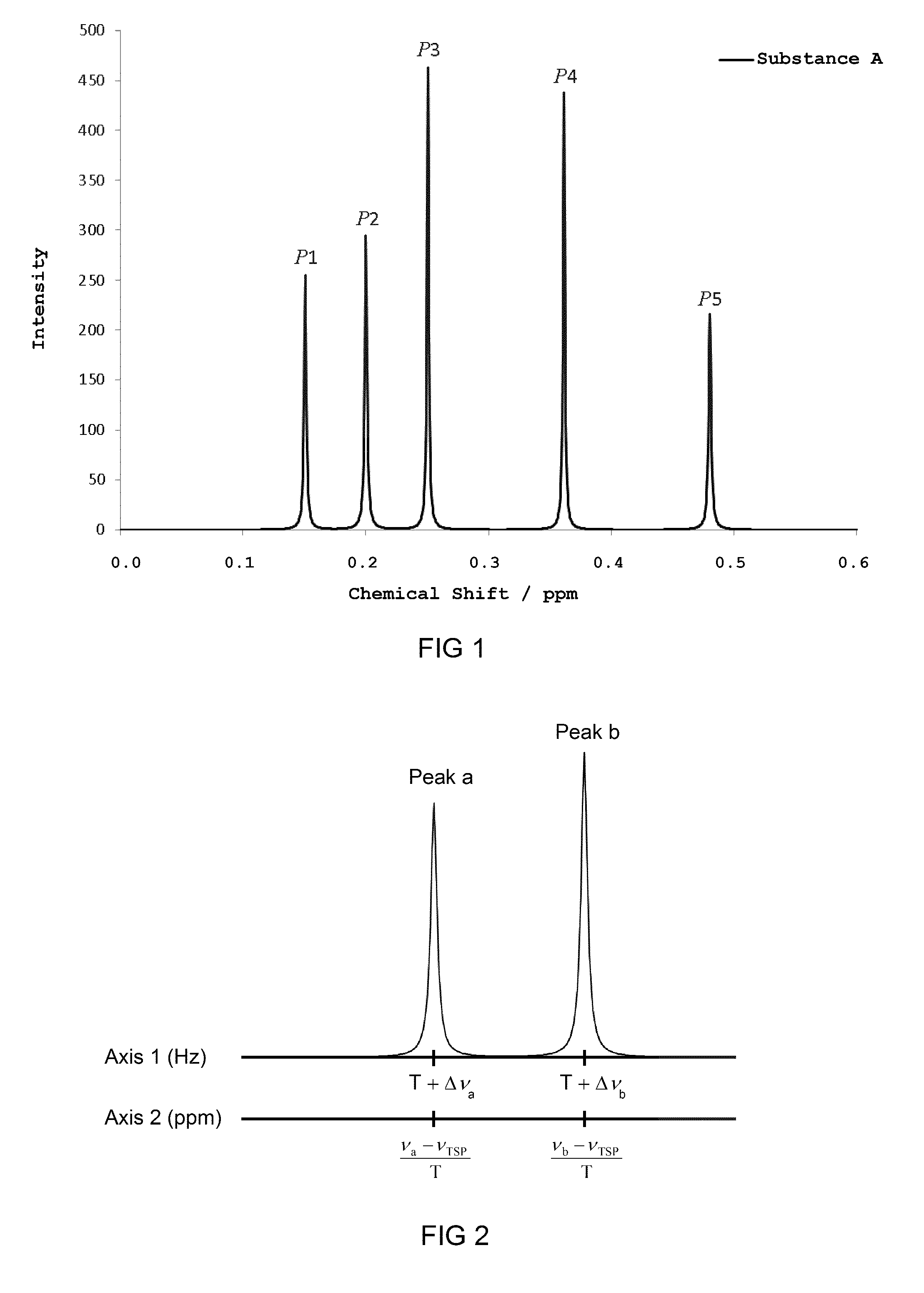
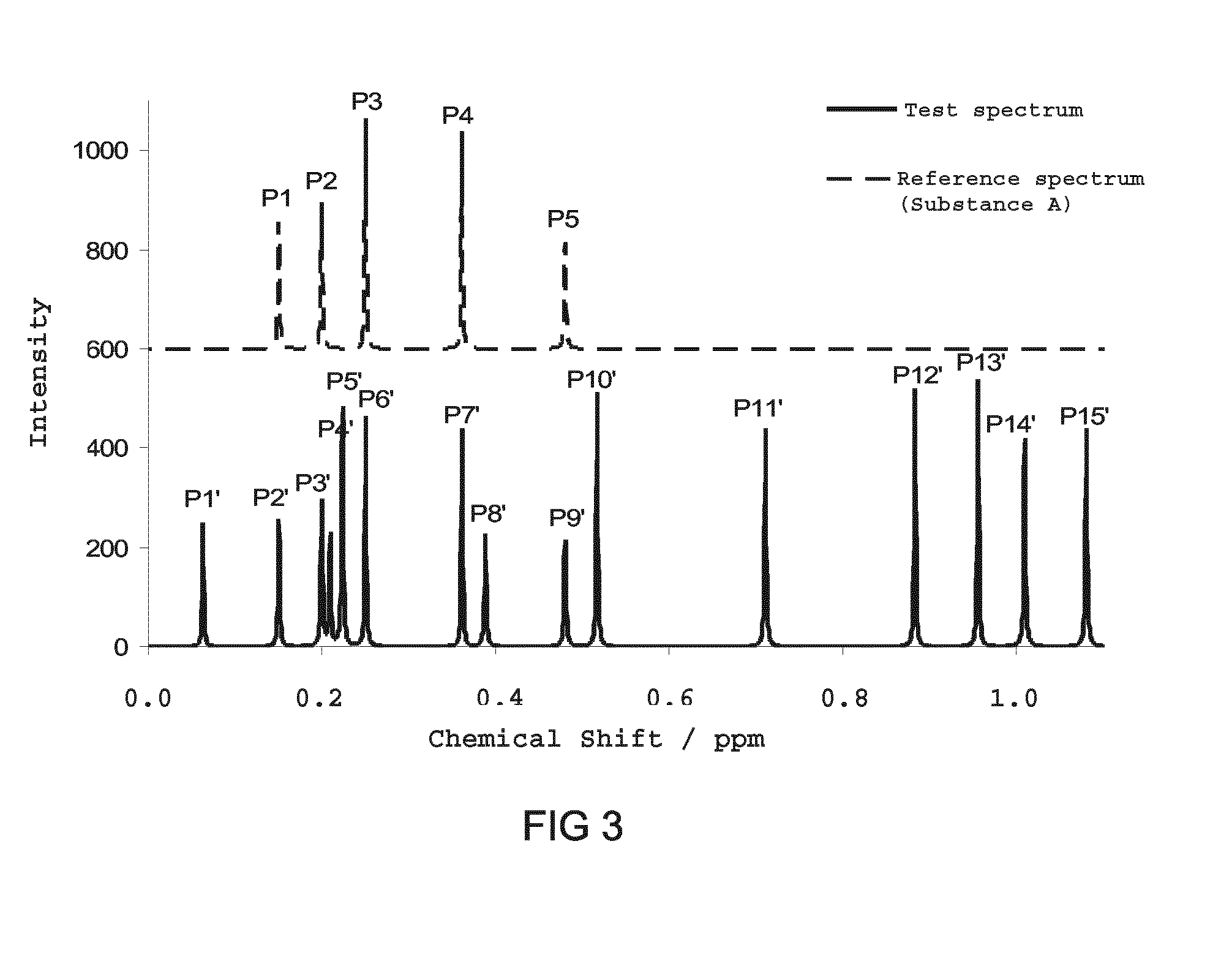
Method for substance identification from NMR spectrum
ActiveUS9285444B2Reduce effortSave resourcesMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceSpectral distanceRatio value
The present invention relates to a method which allows for an automatic substance identification on the basis of an NMR spectrum. In the scope of the method, determining a multitude of integral ratio values, in each case from at least two integral values of the NMR spectrum, takes place, wherein each integral ratio value specifies the ratio of the height and / or area of the underlying spectral values, and determining a multitude of distance values, in each case from at least two position values of the NMR spectrum, takes place, wherein each distance value specifies the spectral distance between the underlying spectral values. The integral ratio values and the distance values are then used for substance identification.
Owner:NUMARES
Image category recognition method and device and electronic equipment
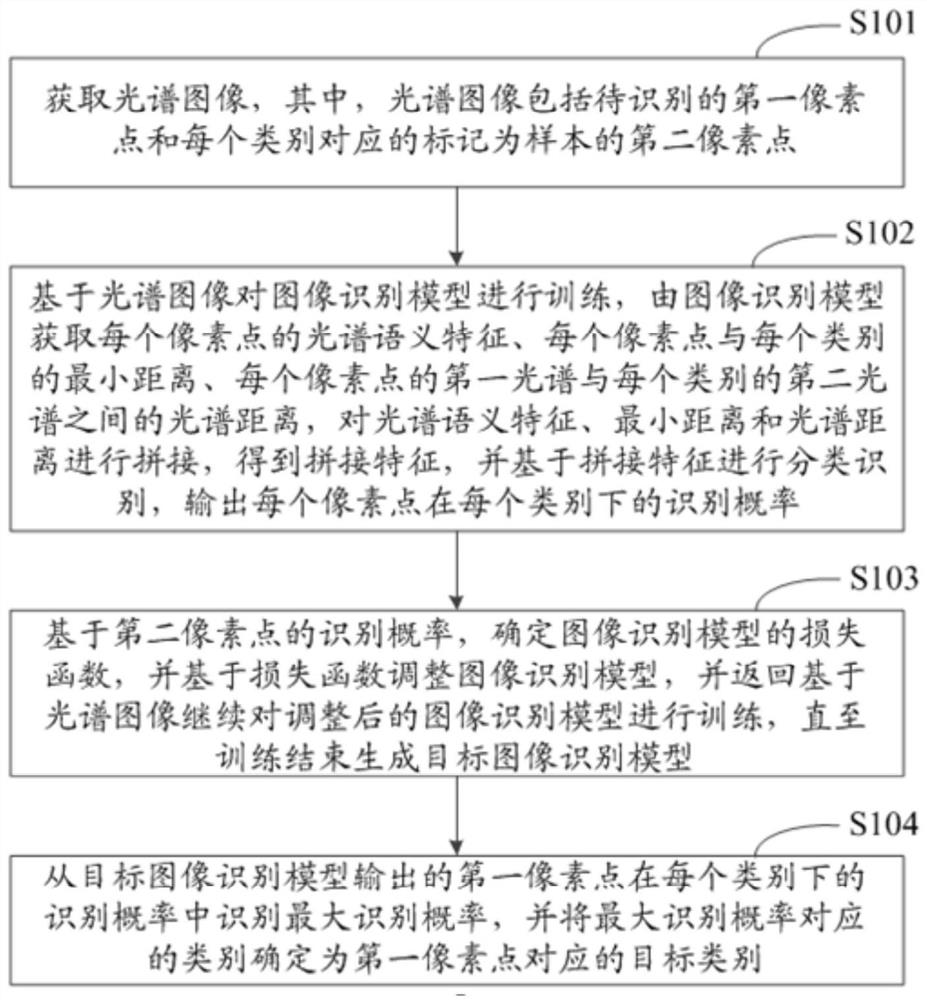
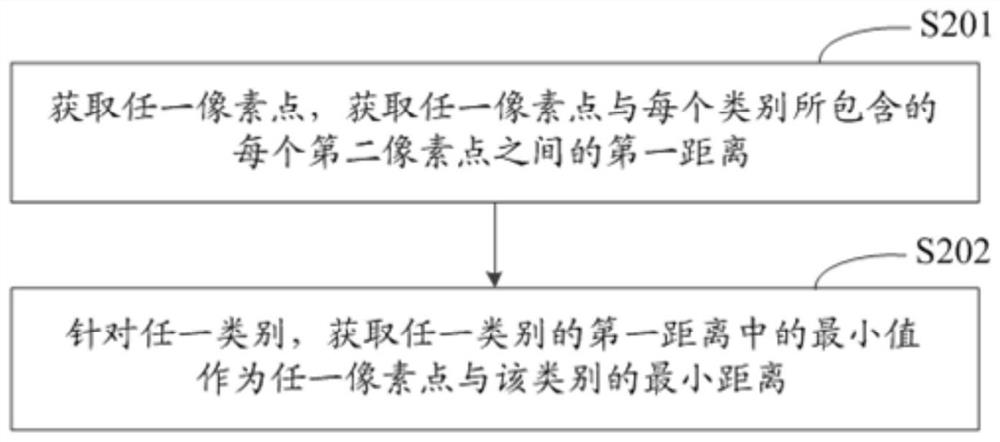
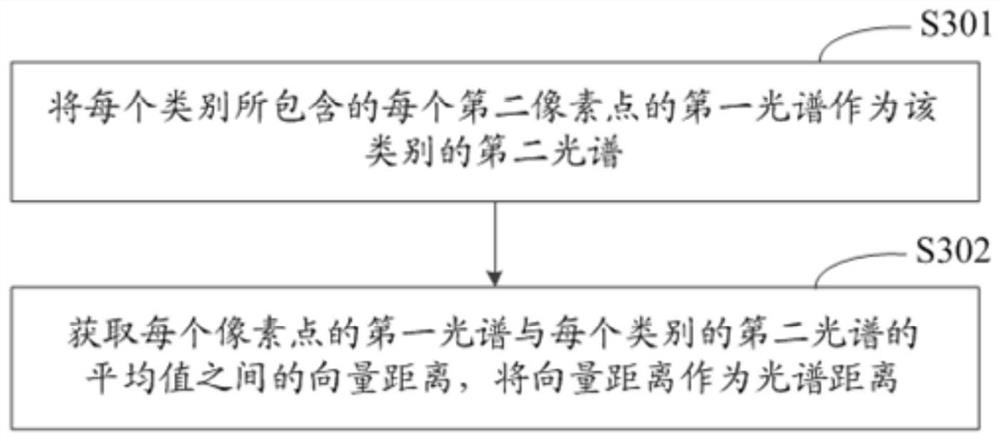
ActiveCN113191261AEasy to understandScene recognitionNeural architecturesCategory recognitionVisual perception
The invention discloses an image category recognition method and device and electronic equipment, and relates to the technical field of artificial intelligence, in particular to the technical field of computer vision and deep learning. The specific implementation scheme is as follows: acquiring a spectral image; and training an image recognition model based on the spectral image, obtaining the spectral semantic feature of each pixel point, the minimum distance between each pixel point and each category, and the spectral distance between the first spectrum of each pixel point and the second spectrum of each category by the image recognition model, and performing classification recognition based on the splicing features. Outputting the recognition probability of each pixel point; based on the recognition probability of the second pixel point, determining and adjusting an image recognition model based on a loss function; the maximum recognition probability is recognized from the recognition probabilities of the first pixel points output by the target image recognition model under each category, the category corresponding to the maximum recognition probability is determined as the target category corresponding to the first pixel points, the number of needed samples is small, and the labeling cost is low.
Owner:BEIJING BAIDU NETCOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Multi-temporal Hyperspectral Image Classification Method Preserving Global Geometry Structure Based on Spatial Spectral Features
ActiveCN106503754BImplement classificationEasy accessCharacter and pattern recognitionData setHyperspectral data classification
The invention relates to a multi-temporal hyperspectral image classification method for maintaining global geometric structure based on spatial spectral features, and the invention relates to a multi-temporal hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method. The purpose of the present invention is to solve the problem that it is difficult to obtain hyperspectral multi-temporal data tags and the image has obvious spectral drift, and the problem of unreliable classification of target time-phase data by directly using the hyperspectral data of the source time-phase. The specific process is: 1. Input X s with X t and their spatial coordinates Z 1 ,Z 2 , and X s The corresponding category label vector Y for each row; 2. Calculate X s ,X t The space spectrum distance selects the nearest point as the data pair that needs to be matched; 3. Calculate D s,s ,D t,t and D s,t , adjust the scale of the data set, and construct the distance matrix D; 4. Obtain X s , of the mapping matrices α and β in the alignment space, so that the projection f s and f t ; Five, use f s and f t and f s The corresponding label Y is classified by the KNN classification model to obtain the classification label of the target phase. The invention is used in the field of image classification.
Owner:黑龙江省工研院资产经营管理有限公司
Hyperspectral Mixed Pixel Decomposition Method Based on Geometric Spatial Spectral Structure Information
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
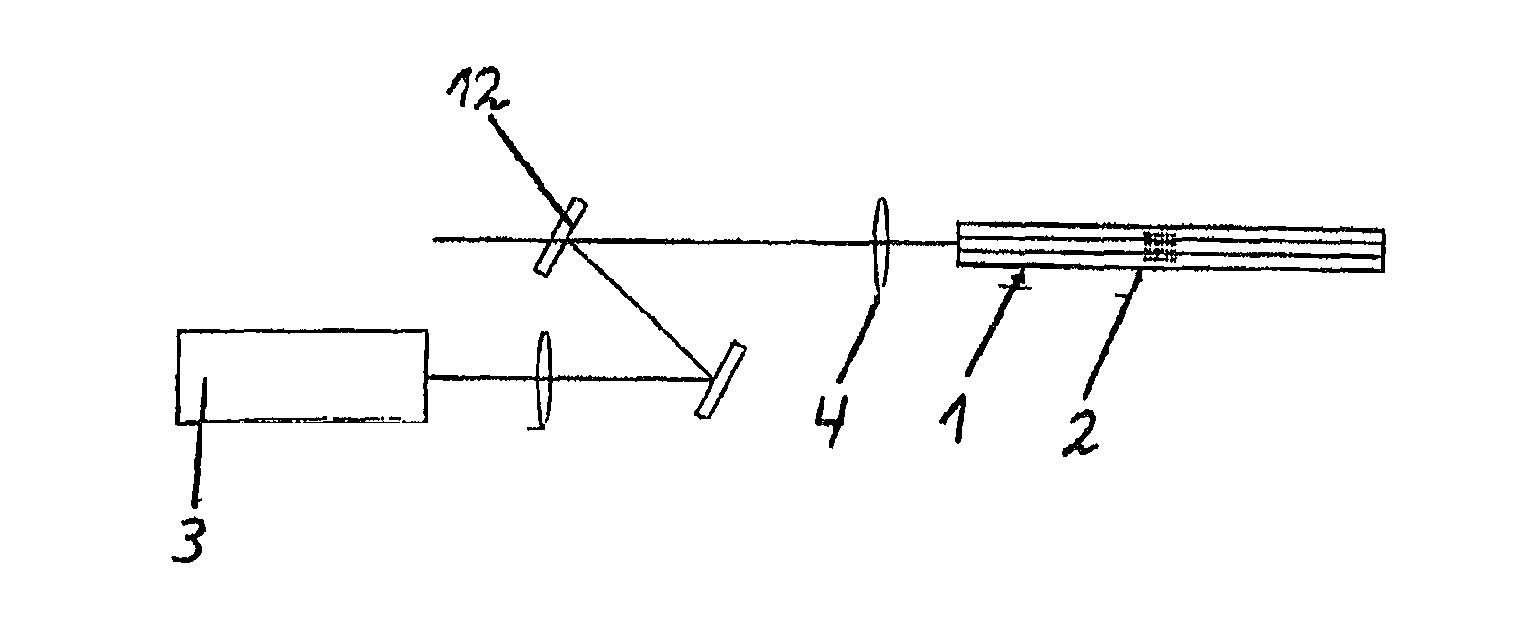
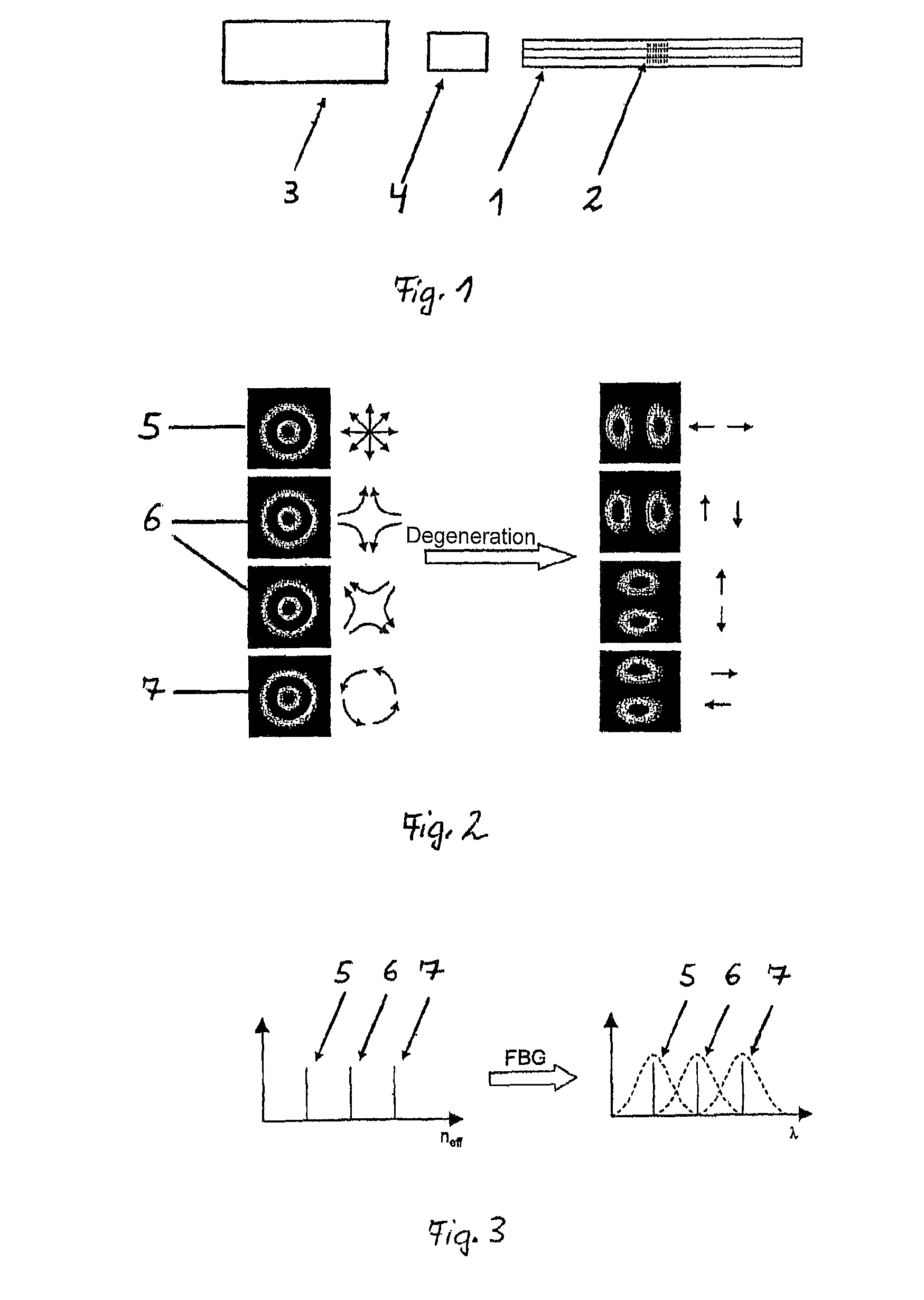
Generation of azimuthally or radially polarized radiation in optical waveguides
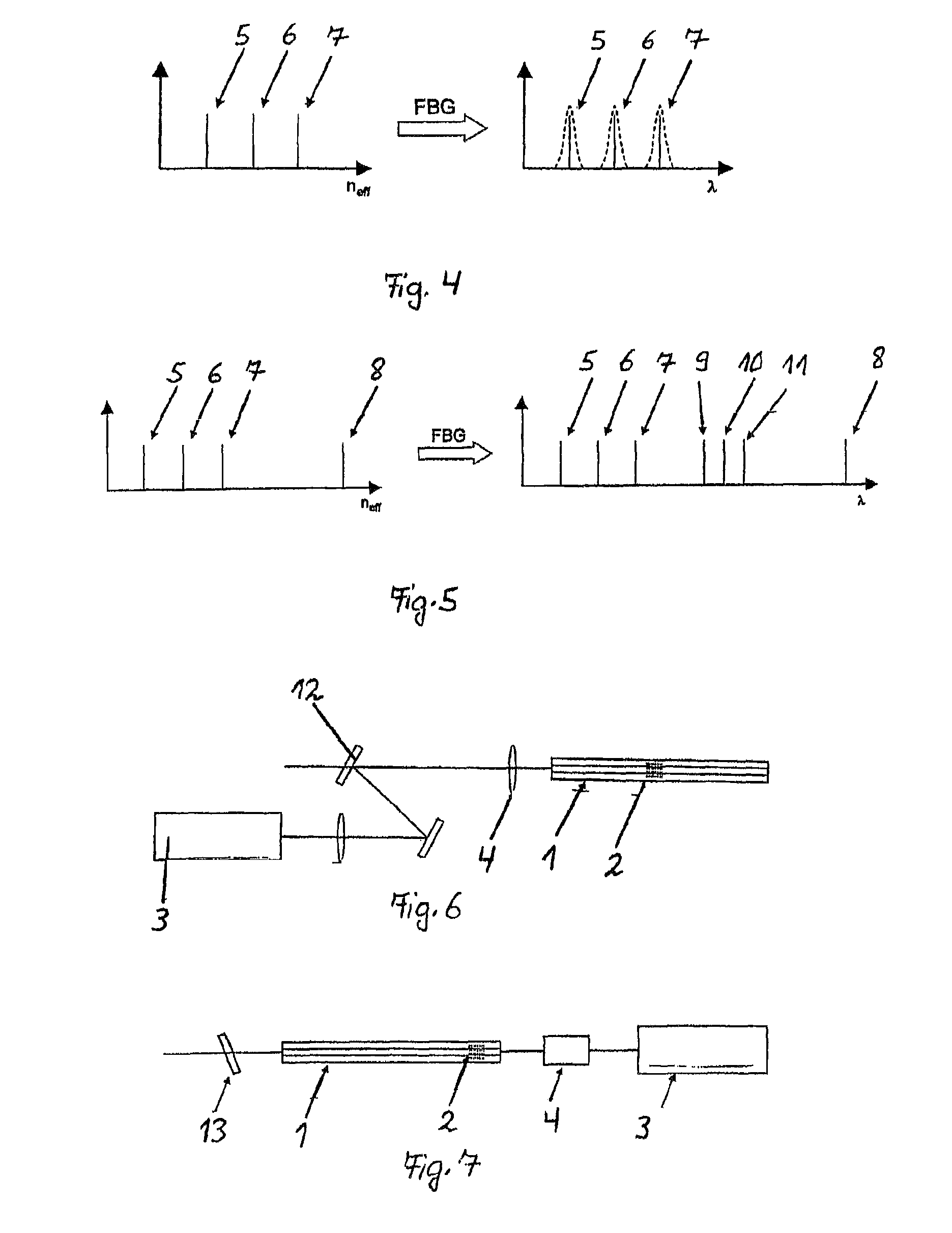
InactiveUS9459403B2Simple and stable and cost-effectiveOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium shape and constructionGratingFiber Bragg grating
The invention relates to an apparatus for generating azimuthally or radially polarized radiation by means of an optical waveguide (1), wherein the optical waveguide (1) has a structure which is suitable for conducting azimuthally or radially polarized modes (5, 7). The invention proposes that the azimuthally or radially polarized modes (5, 7) in the optical waveguide (1) have different effective refractive indices and, within the optical waveguide (1), a narrow-band grating (2) is arranged, in particular a fiber Bragg grating (2) which is designed such that the spectral distance between two azimuthally or radially polarized resonant modes (5, 7) is equal to or greater than the associated spectral bandwidth.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV +1
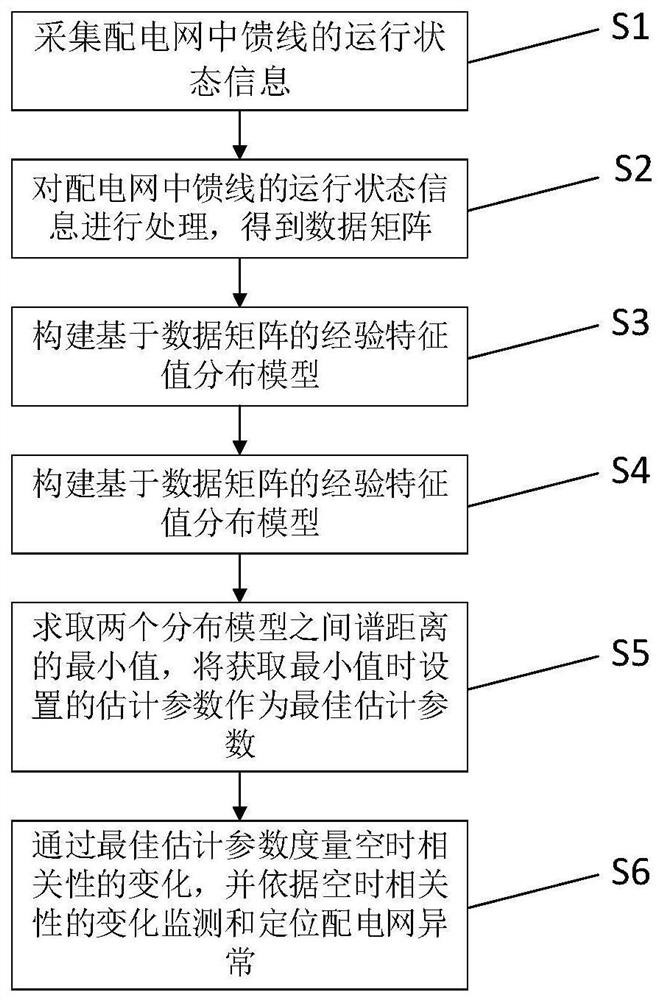
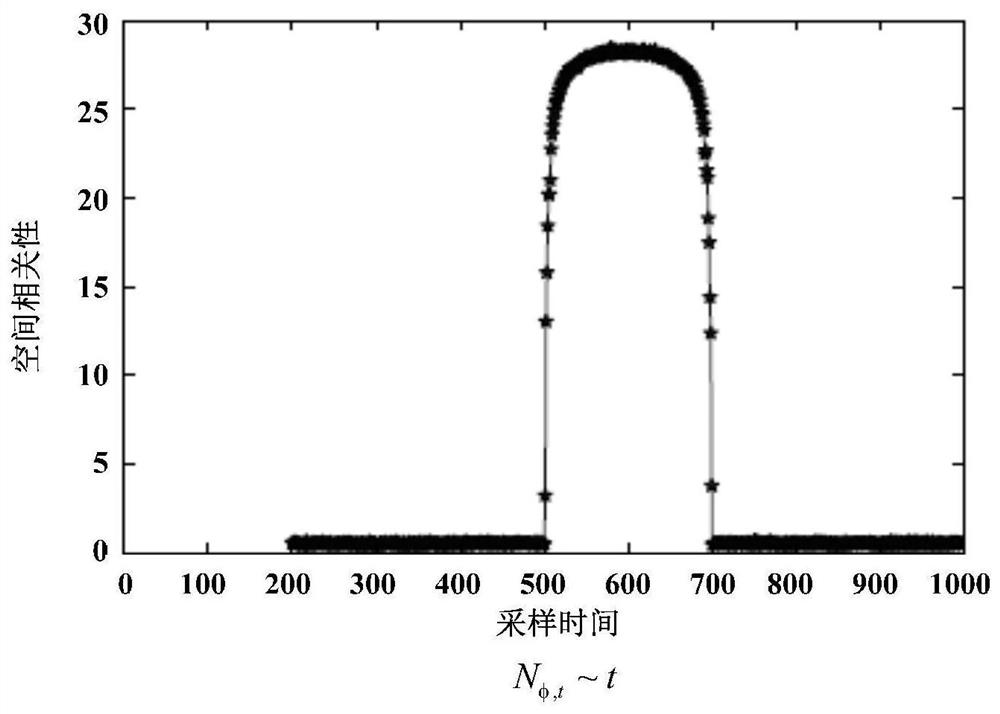
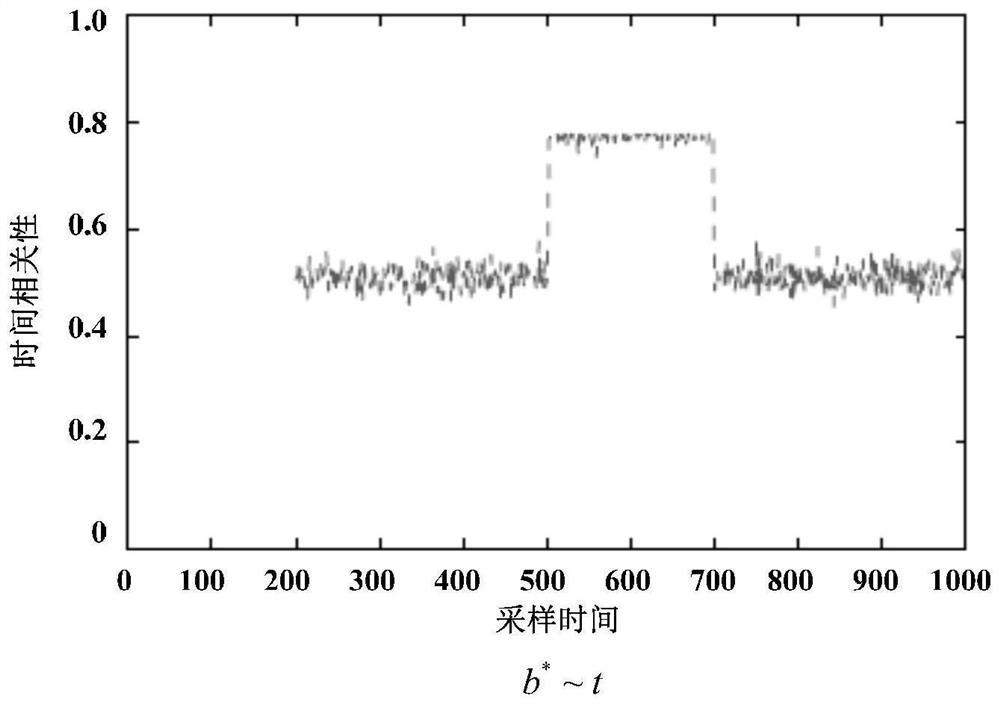
Power distribution network abnormity monitoring and positioning method based on monitoring data space-time correlation
The invention discloses a power distribution network abnormity monitoring and positioning method based on monitoring data space-time correlation. The method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting operation state information of a feeder line in a power distribution network; s2, processing the operation state information of the feeder line in the power distribution network to obtain a data matrix; s3, constructing an empirical characteristic value distribution model based on the data matrix; s4, constructing an empirical characteristic value distribution model based on a residual matrix space-time correlation structure; s5, solving the minimum value of the spectral distance between the two empirical feature value distribution models, and taking an estimation parameter set when the minimum value is obtained as an optimal estimation parameter; and S6, measuring the change of the space-time correlation through the optimal estimation parameter, and monitoring and positioning the abnormity of the power distribution network according to the change of the space-time correlation. According to the method, priori knowledge about the complex topology of the power distribution network does not need to be foreseen, and the method has very high robustness for tiny random fluctuation and measurement errors in the network and is beneficial to reducing the false alarm rate.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Multi-manifold-based multi-temporal hyperspectral image classification method
ActiveCN106778490BImplement classificationEasy accessScene recognitionComputer visionHyperspectral image classification
A multi-manifold-based multi-temporal hyperspectral image classification method, the invention relates to a multi-temporal hyperspectral remote sensing image classification method. The purpose of the present invention is to solve the problem of how to use complementary information of multiple time phases to solve the difficulty in obtaining multi-time phase hyperspectral data tags and the obvious spectral drift between time phase maps. The specific process is: 1. Input X s1 ,X s2 ,X t and their spatial coordinates L 1 , L 2 , L 3 , and Y 1 , Y 2 ; Two, calculate d 13 , d 23 , d 12 , each type of sample in the source image selects k samples with the smallest spatial spectral distance in the target image, and obtains three sets of data pairs that need to be matched; 3. Calculate D s1,s1 、D s2,s2 、D t,t , and D s1,s2 、D s1,t 、D s2,t ; 4. Adjust X s2 ,X t The data scale of the multi-manifold distance matrix D is constructed; 5. Get the projection f s1 , f s2 , f t 6. Obtain the classification label of the target phase. The invention is used in the field of image classification.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
A method for removing thick clouds from optical remote sensing images based on constructing virtual images
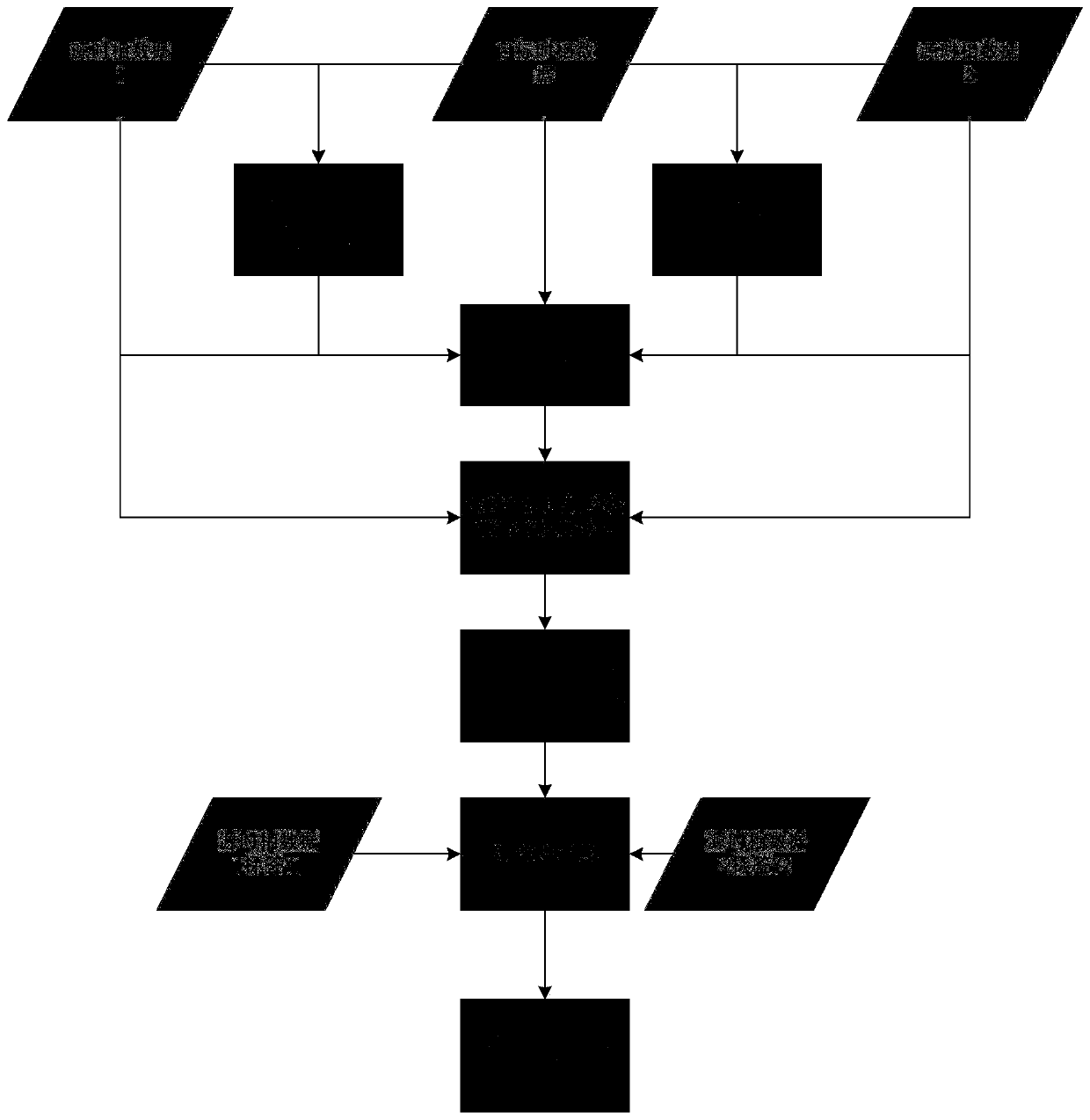
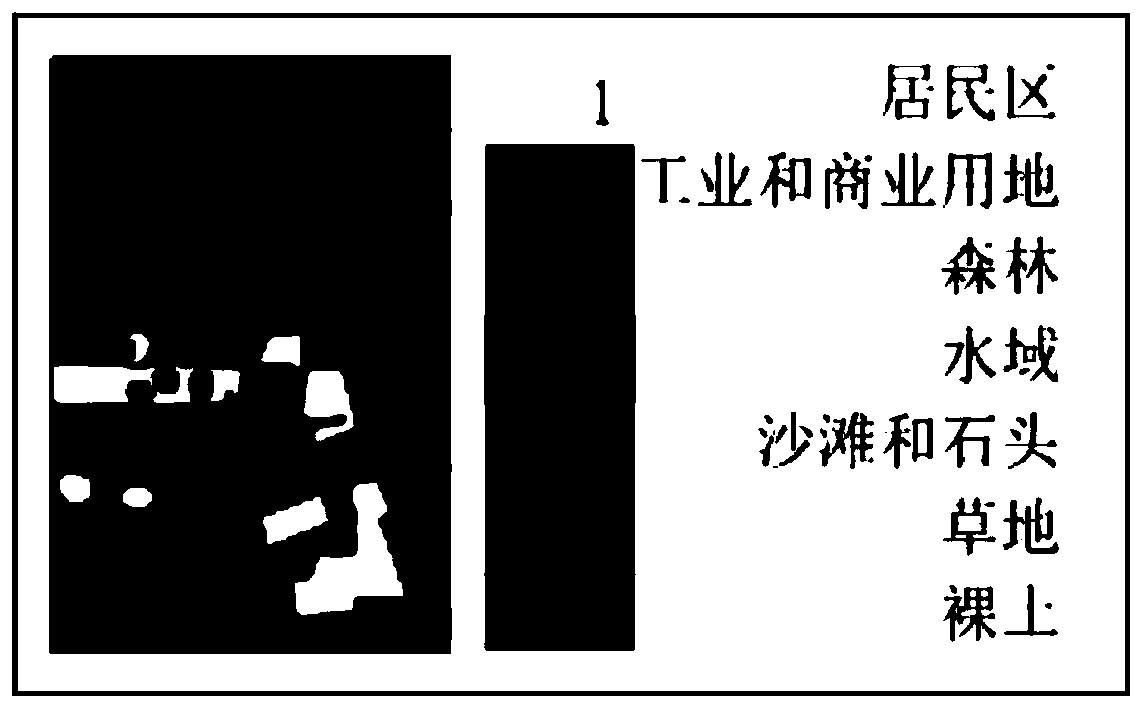
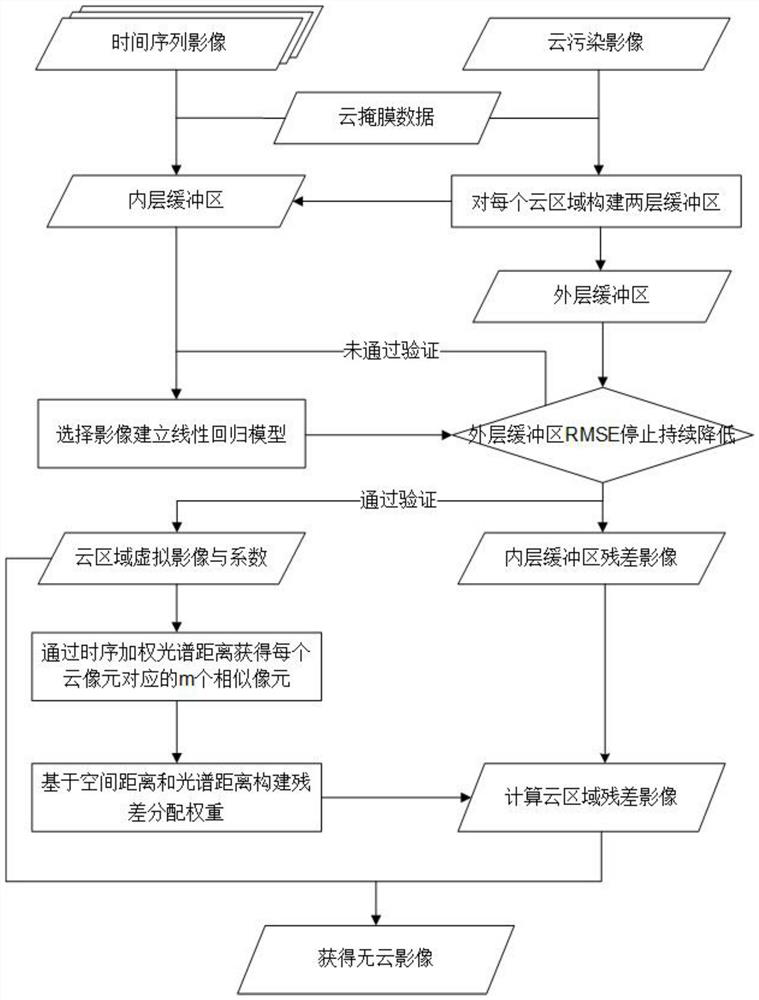
ActiveCN114298945BOvercoming precision differencesIn line with the actual situationImage enhancementImage memory managementCloud processingComputer science
The invention discloses a method for removing thick clouds from an optical satellite remote sensing image based on a virtual image. First, for the image covered by thick clouds, the cloud pixels are eliminated by using the cloud mask data. The eliminated cloud pixels are used as the target pixels to be restored, and the connected target pixels are used as the cloud regions to be restored. The cloud removal process is performed separately for each cloud area in the image. Then, the time-series weighted spectral distance is constructed, and for each target pixel, similar pixels are searched in the inner buffer. The weight is calculated by using the time-series weighted spectral distance and spatial distance between similar pixels and the target pixel, and the residuals of similar pixels are distributed to the target pixels by the method of linear weight distribution, and the residuals of the target pixels are obtained, and then the cloud area is obtained. residual image. Finally, the virtual image of the cloud area and the residual image are combined to obtain a cloud-free image of the cloud area. The invention effectively solves the problem that the optical remote sensing image cannot obtain the surface information under the condition of cloud pollution.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A Hyperspectral Image Classification Method Based on Hybrid Metrics
ActiveCN113111969BImprove reference efficiencyImprove classification accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionData setHyperspectral image classification
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on mixed metrics. The algorithm judges the degree of abnormality of the object based on the neighborhood density of the object. For k lof Any positive integer, defining the k-th distance of x as the distance between x and an object o, denoted as dis_k lof (x), where the distance between the object x and the object o is recorded as d(x, o), first use the labeled data set to train the classifier, and use the classifier to classify the unlabeled samples; judge the unlabeled samples Confidence, adding high confidence unlabeled samples to the set of labeled samples; use k‑NN to select the k closest to the labeled sample knn Neighboring samples are not marked, and the spatial distance and LOF distance are introduced while calculating the spectral distance between samples. And the adaptive method is used to determine the input parameters of k-NN and LOF, which effectively improves the efficiency of the algorithm's parameter search and effectively improves the classification accuracy of the classification algorithm. The classification performance of the proposed algorithm on these datasets is better than that of similar algorithms.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
A Segmentation Method of Hyperspectral Remote Sensing Image Based on Spectral Curve Spectral Distance
ActiveCN109377507BSuppress oversegmentationImprove reliabilityImage enhancementImage analysisSpectral curveSpectral distance
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing image segmentation method based on spectral curve spectral distance. Firstly, a neighborhood spectral curve spectral distance model of a target pixel is constructed; Hilbert transform is used to obtain parity filtering results through convolution operations, and Use the square root of the square sum of the parity filtering results as local energy to construct an edge feature enhancement model; combine the two to obtain an edge feature enhancement model based on neighborhood spectral features, which is used to obtain edge feature enhancement results; use the edge feature enhancement results as gradient data Input the watershed segmentation algorithm and optimize the watershed segmentation algorithm to achieve high-precision segmentation of remote sensing images, which can effectively suppress the over-segmentation phenomenon of hyperspectral remote sensing images, and solve the problem of weak and false edge features in hyperspectral remote sensing images affecting remote sensing image segmentation Resulting technical issues.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com