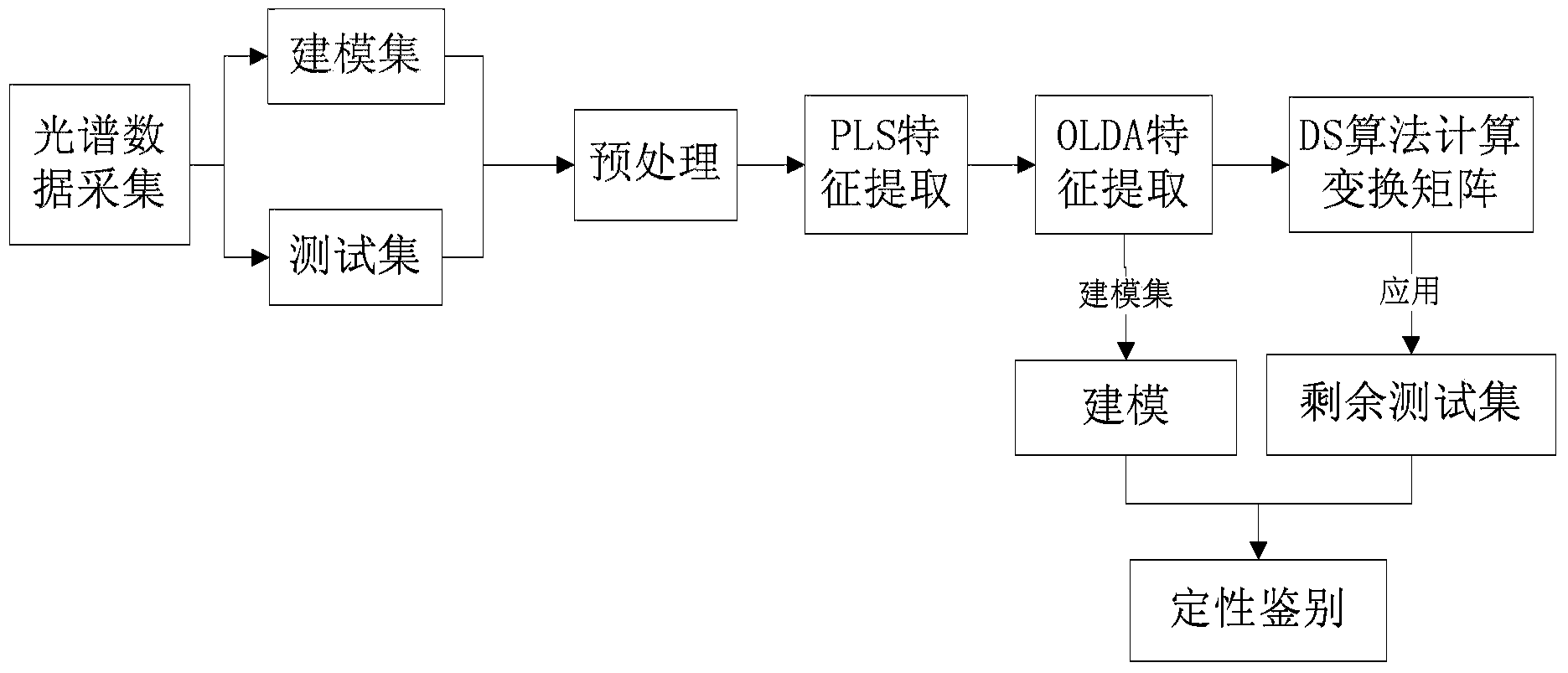
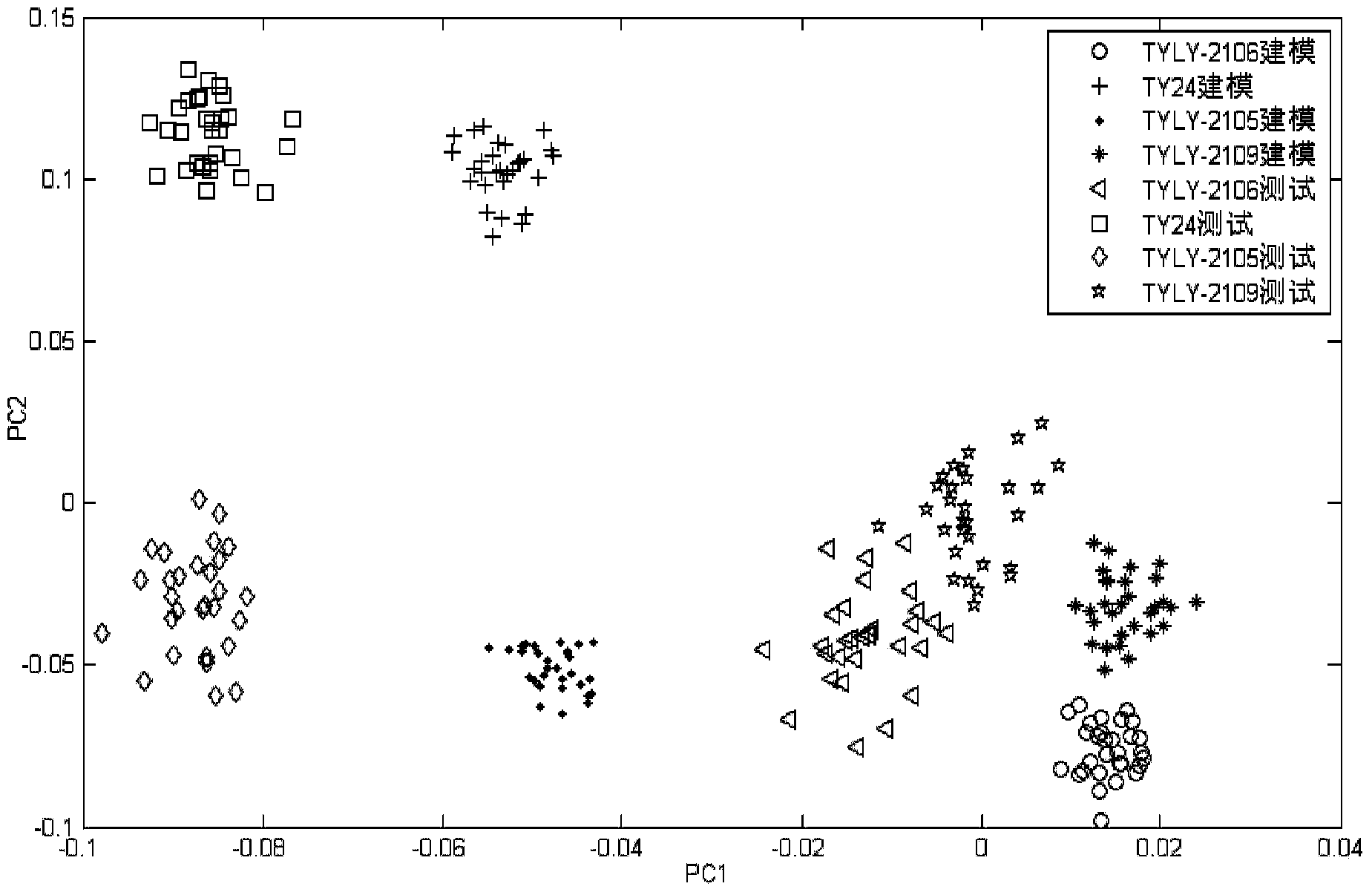
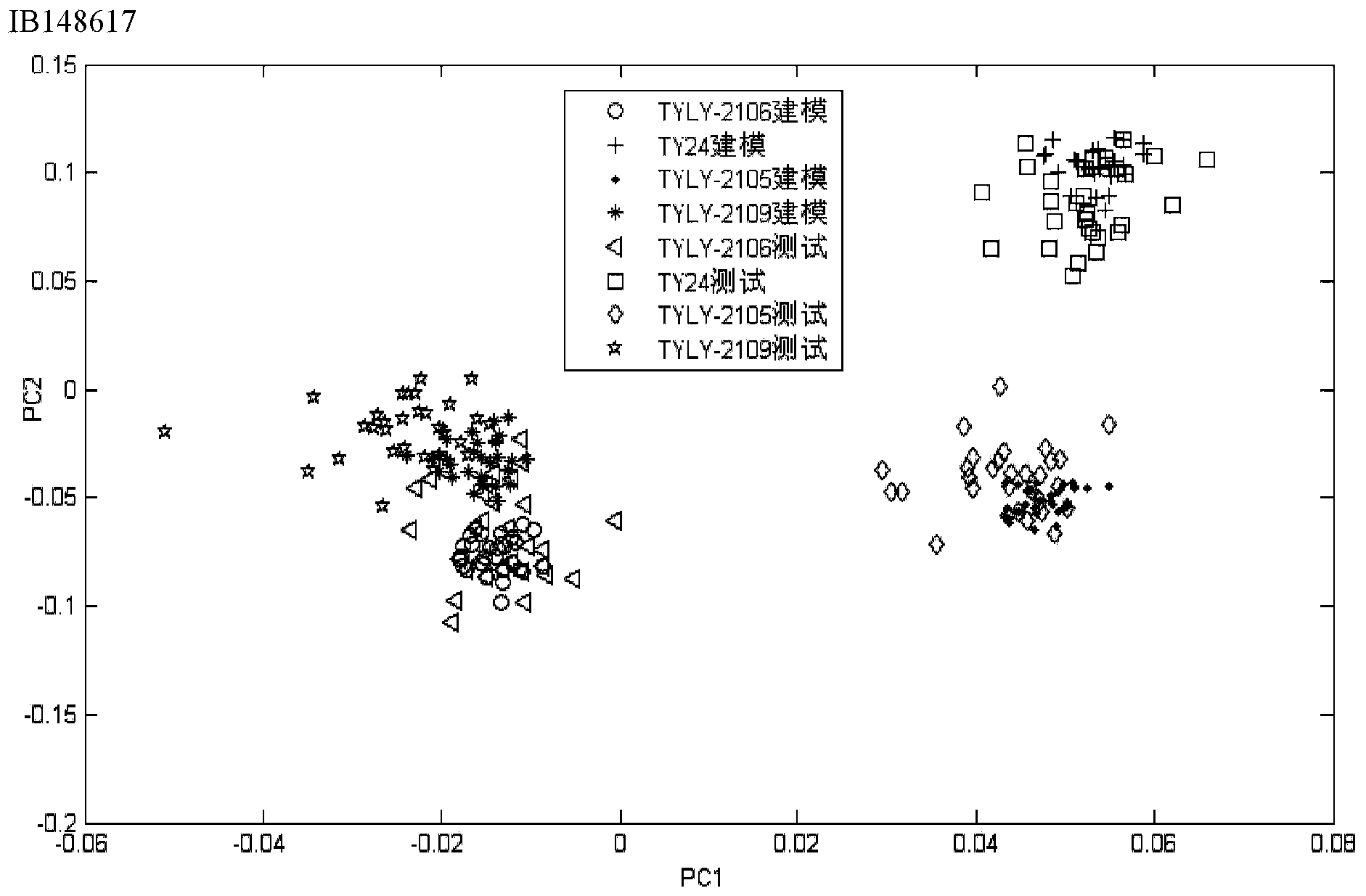
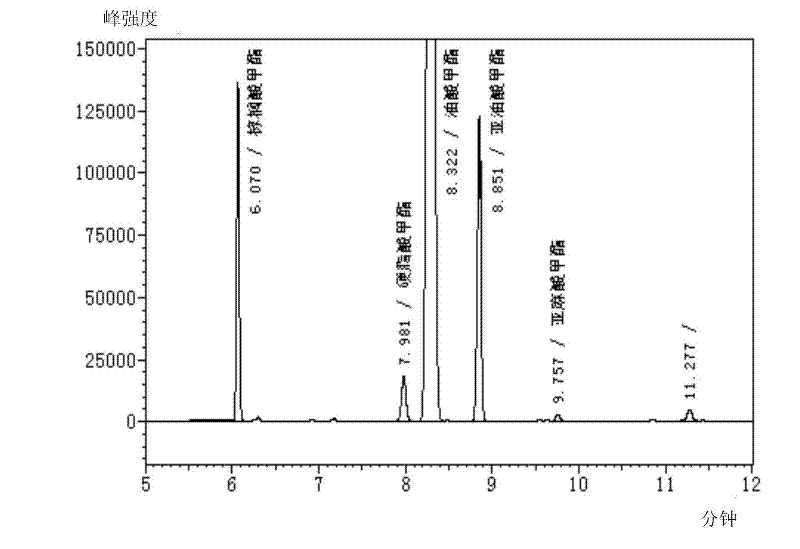
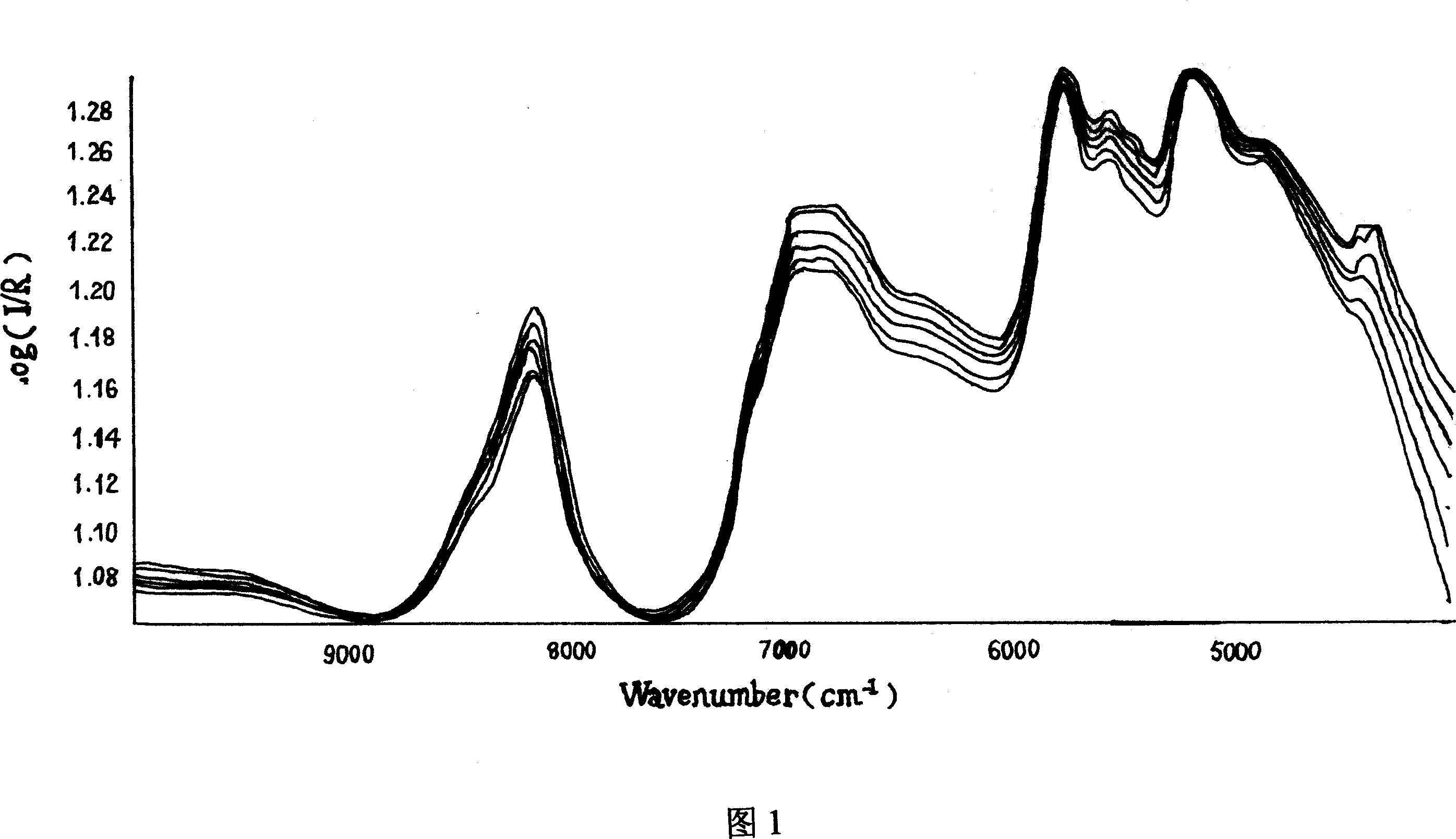
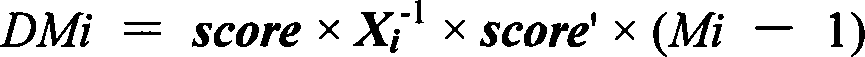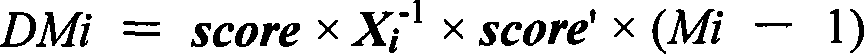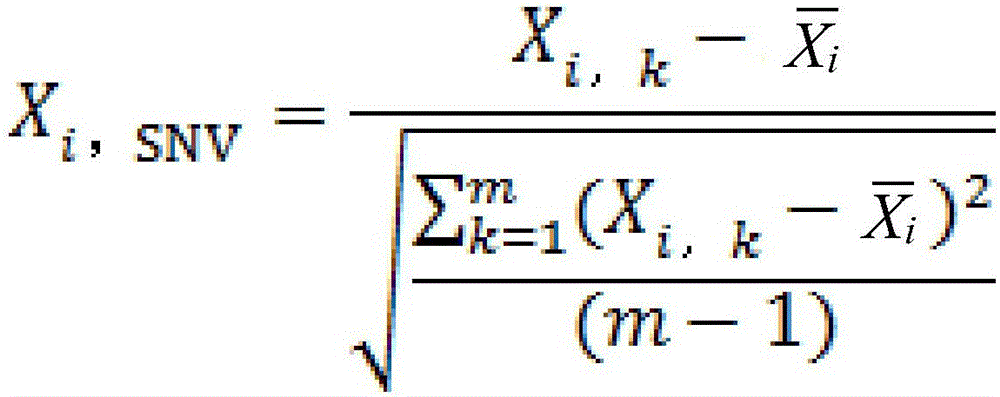Patents
Literature
1049 results about "Near infrared spectra" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
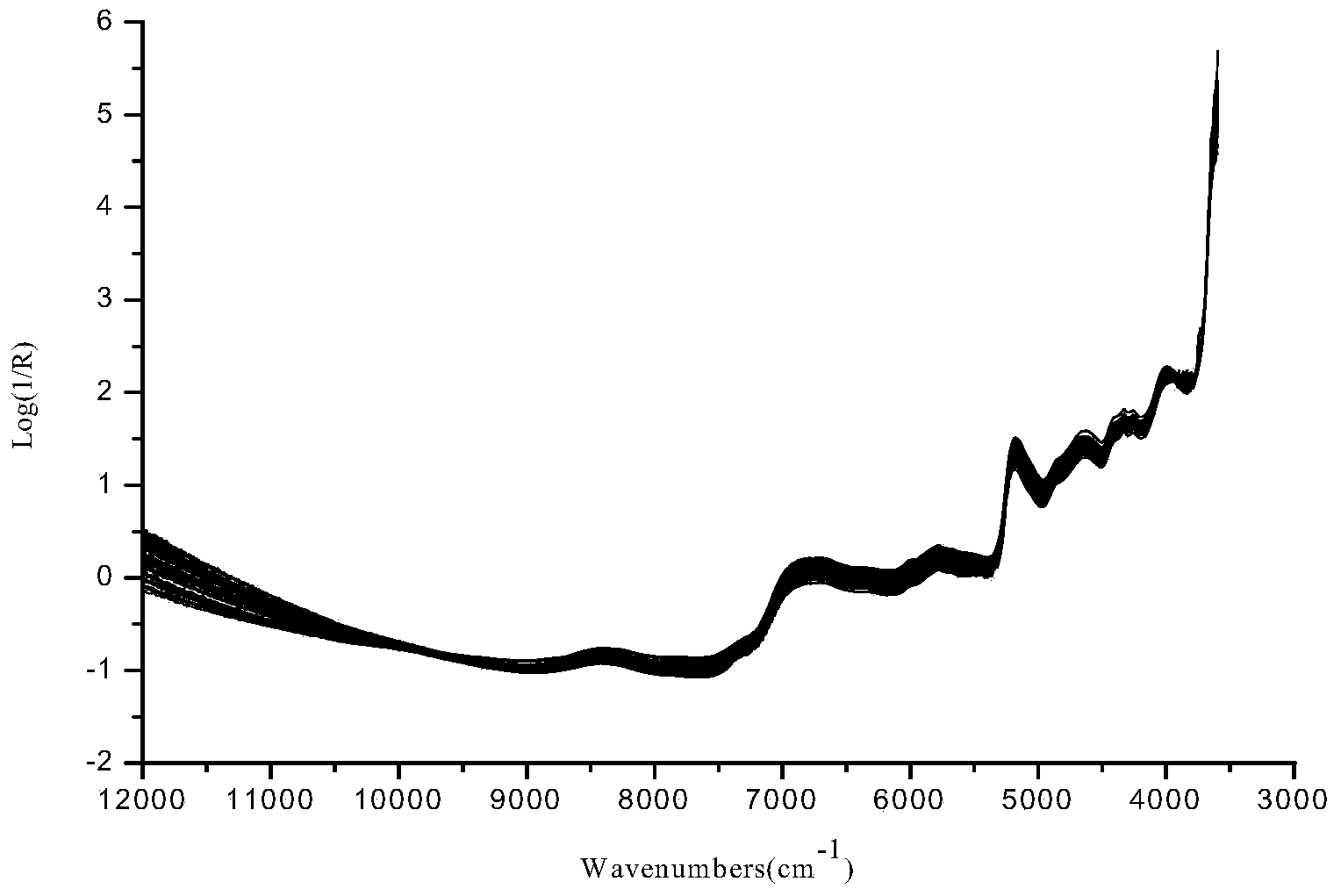
Near infrared spectroscopy (NIR) is a type of spectroscopy in which the near infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum is used as an evaluation tool. This technology is used in many different industries, including the pharmaceutical, food and agricultural industries, in certain medical diagnostic tests and in combustion and polymer science.
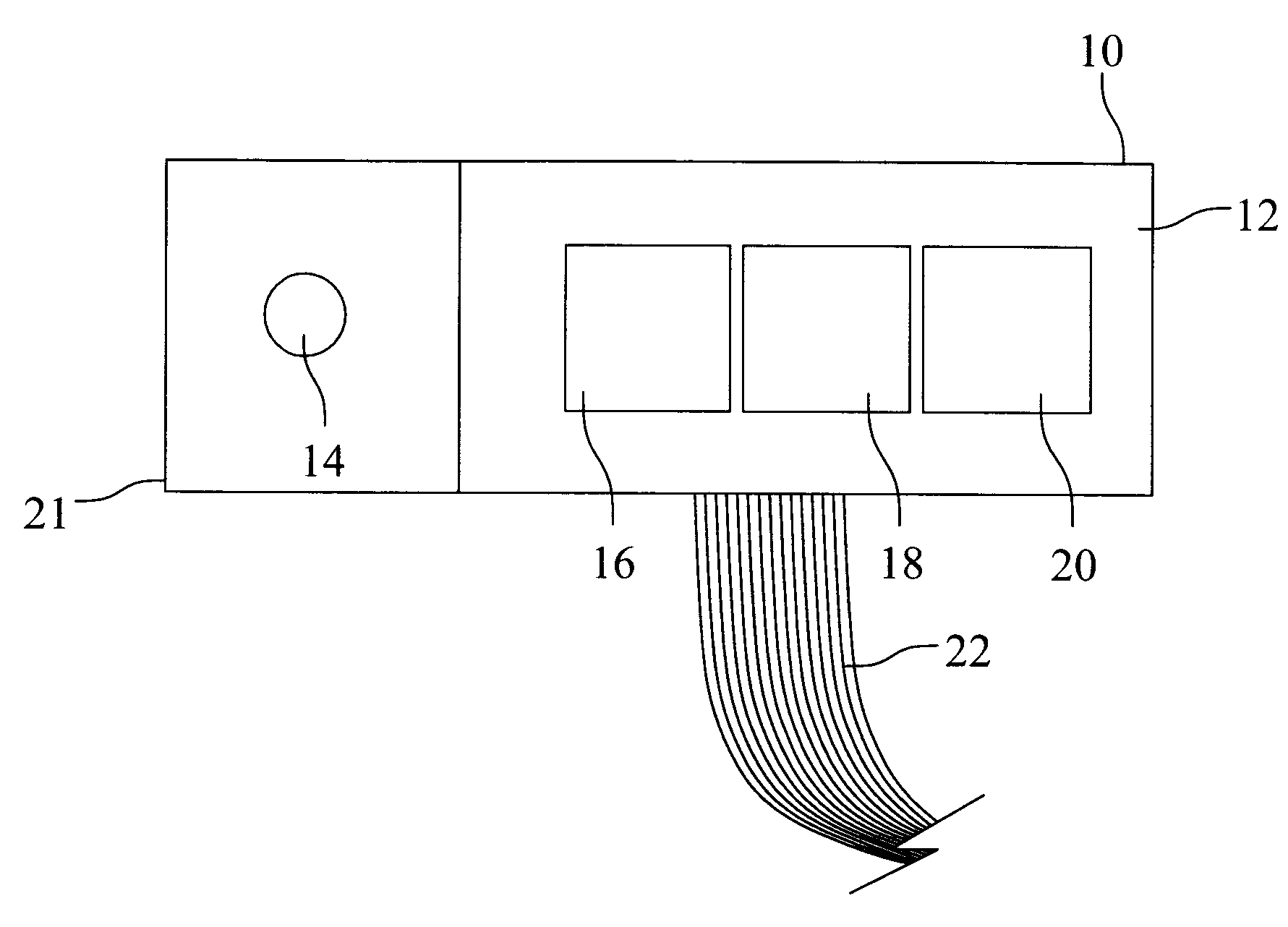
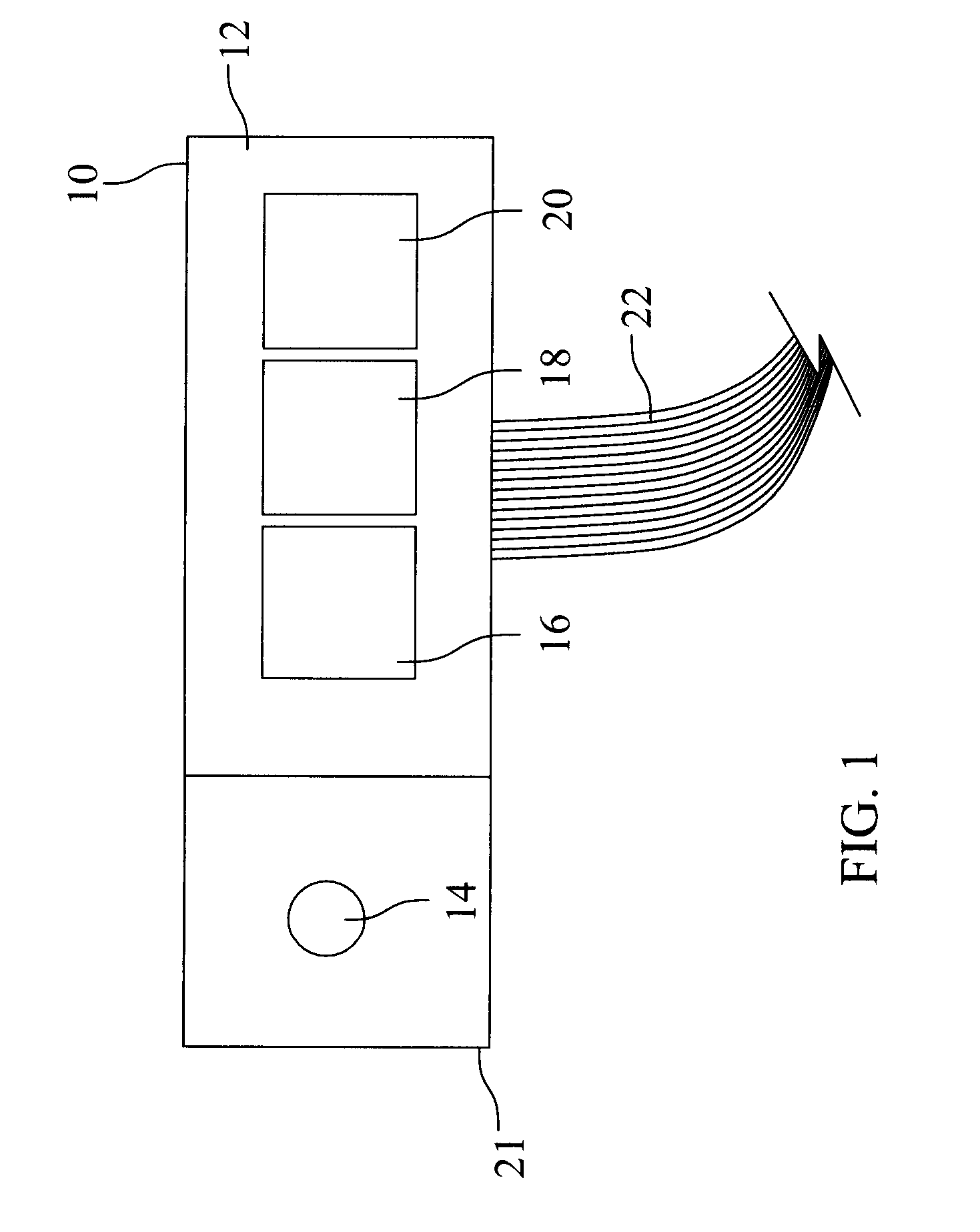
Multi-Wavelength Spatial Domain Near Infrared Oximeter to Detect Cerebral Hypoxia-Ischemia
InactiveUS20080139908A1Material analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringTissue oxygenationMulti wavelength
Methods and apparatus for measuring cerebral O2 saturation and detecting cerebral hypoxia-ischemia using multi-wavelength near infrared spectroscopy (NIRS). Near-infrared light produced by an emitter is directed through brain tissue. The intensity of the light that passes through the brain tissue is measured using photodiode detectors positioned at distinct distances from the emitter. This process is conducted for at least three wavelengths of near-infrared light. One of the wavelengths used is substantially at an isobestic point for oxy-hemoglobin and deoxy-hemoglobin, but the other two may be any wavelengths within the near-infrared spectrum (700 nm to 900 nm), so long as one of the additional wavelengths is greater than the isobestic point and the other is less than the isobestic point. Tissue oxygenation is calculated using an algorithm derived from the Beer-Lambert law. Cerebral hypoxia-ischemia may be diagnosed using the calculated tissue oxygenation value.
Owner:KURTH CHARLES DEAN
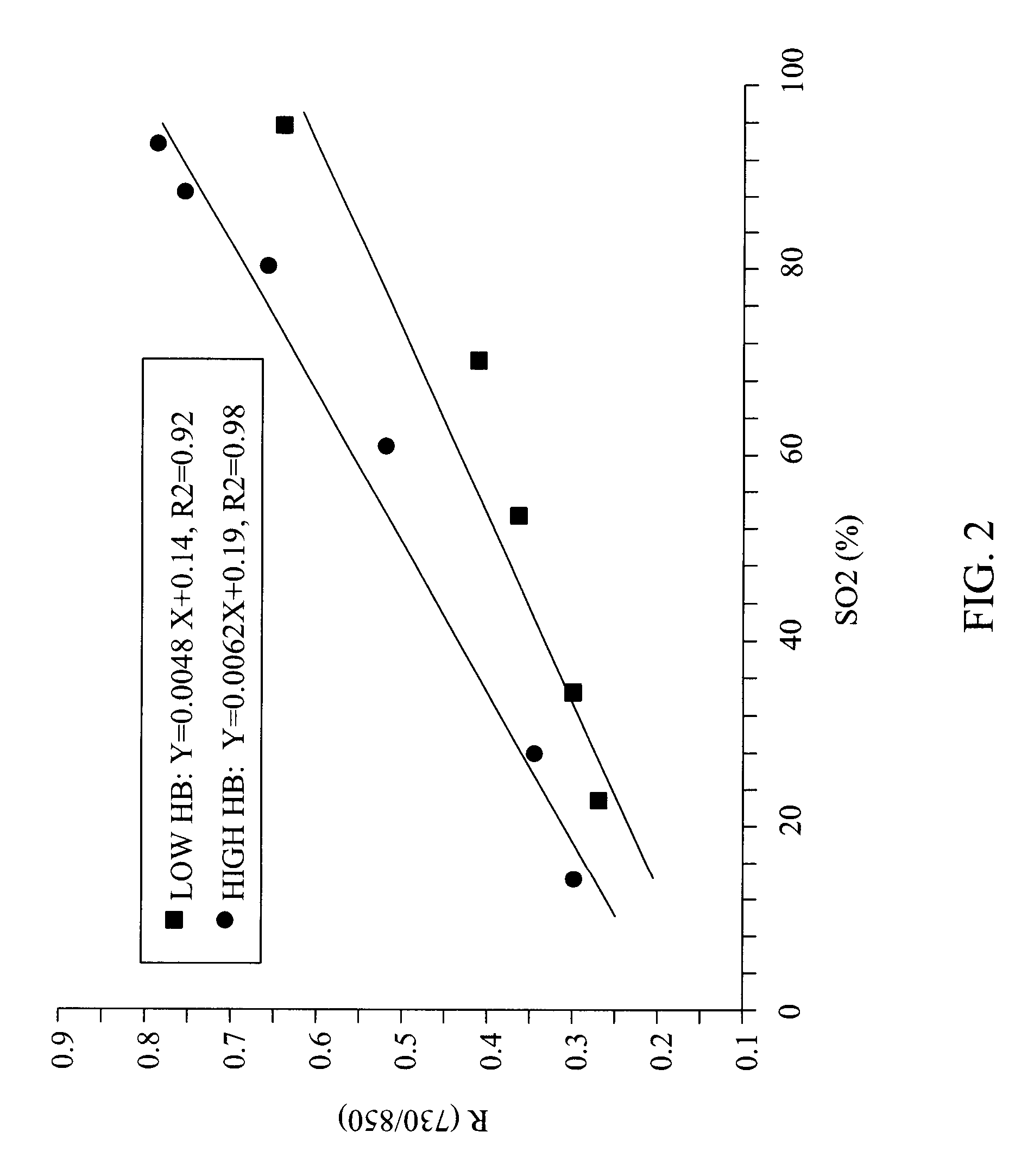
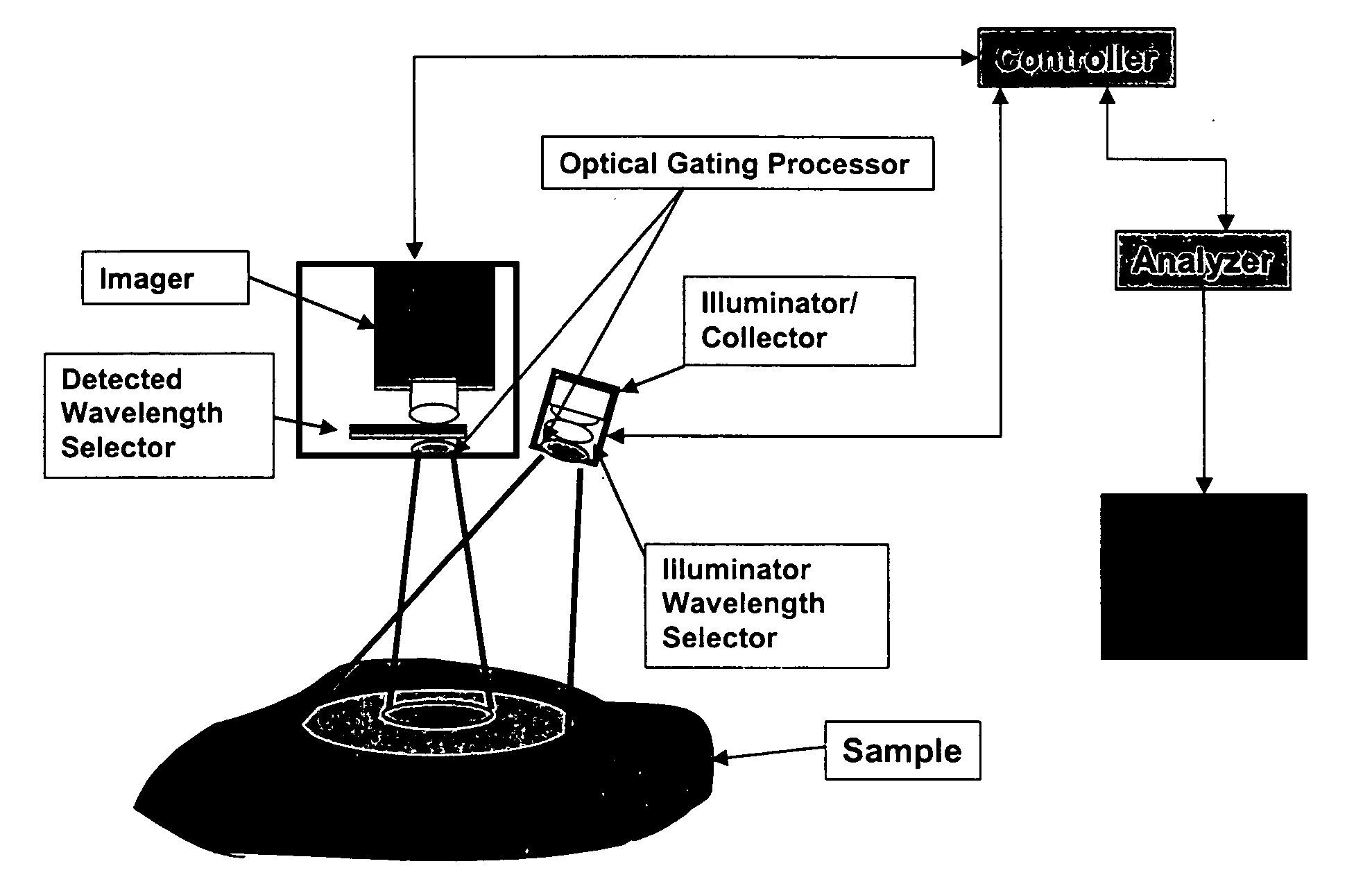
Multispectral imaging for quantitative contrast of functional and structural features of layers inside optically dense media such as tissue
InactiveUS20050273011A1Easy to measureImprove analysisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTelevision system detailsCalorescenceWavelength
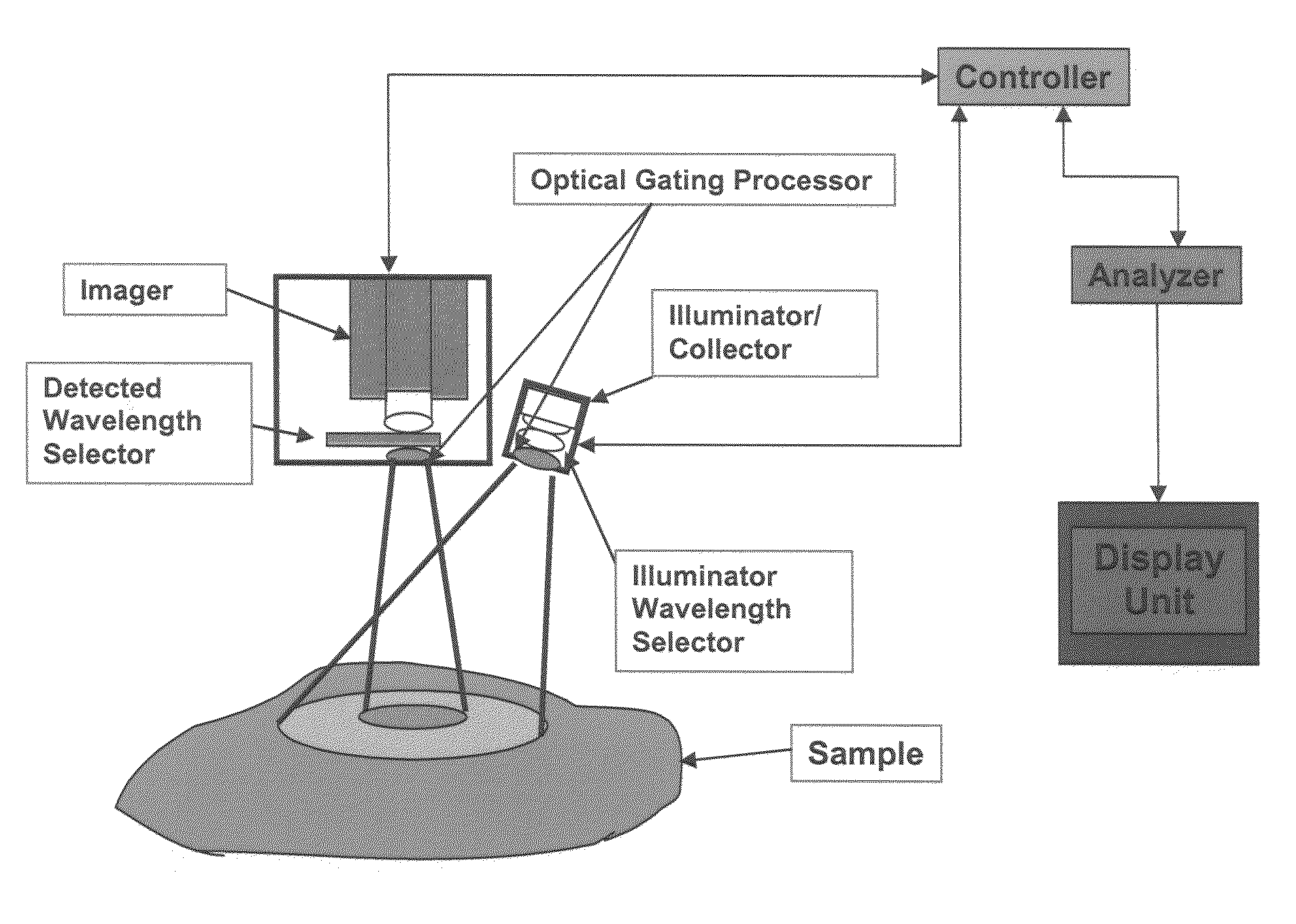
A method for the evaluation of target media parameters in the visible and near infrared is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a light source, an illuminator / collector, optional illumination wavelength selector, an optional light gating processor, an imager, detected wavelength selector, controller, analyzer and a display unit. The apparatus illuminates an in situ sample of the target media in the visible through near infrared spectral region using multiple wavelengths and gated light. The sample absorbs some of the light while a large portion of the light is diffusely scattered within the sample. Scattering disperses the light in all directions. A fraction of the deeply penetrating scattered light exits the sample and may be detected in an imaging fashion using wavelength selection and an optical imaging system. The method extends the dynamic range of the optical imager by extracting additional information from the detected light that is used to provide reconstructed contrast of smaller concentrations of chromophores. The light detected from tissue contains unique spectral information related to various components of the tissue. Using a reiterative calibration method, the acquired spectra and images are analyzed and displayed in near real time in such a manner as to characterize functional and structural information of the target tissue.
Owner:APOGEE BIODIMENSIONS
Near infra-red composite polymer-nanocrystal materials and electro-optical devices produced therefrom
InactiveUS20050002635A1Energy efficiencyChange the refractive indexSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotodetectorAbsorbed energy
The invention comprises a composite material comprising a host material in which are incorporated semiconductor nanocrystals. The host material is light-transmissive and / or light-emissive and is electrical chargetransporting thus permitting electrical charge transport to the core of the nanocrystals. The semiconductor nanocrystals emit and / or absorb light in the near infrared spectral range. The nanocrystals cause the composite material to emit / absorb energy in the near infrared (NIR) spectral range, and / or to have a modified dielectric constant, compared to the host material. The invention further comprises electro-optical devices composed of this composite material and a method of producing them. Specifically described are light emitting diodes that emit light in the NIR and photodetectors that absorb light in the same region.
Owner:YISSUM RES DEV CO OF THE HEBREWUNIVERSITY OF JERUSALEM LTD +1
Superparamagnetic colloidal nanocrystal structures
ActiveUS20100224823A1High magnetizationGood water dispersibilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentMagnetitePhotonics
Monodisperse colloidal nanocrystal clusters of magnetite (Fe3O4) with tunable sizes from about thirty to about three hundred nanometers have been synthesized using a high-temperature hydrolysis process. The colloidal nanocrystal clusters are capped with polyelectrolytes, and highly water soluble. Each cluster is composed of many single magnetite crystallites, thus retaining the superparamagnetic behavior at room temperature. The combination of superparamagnetic property, high magnetization, and high water dispersibility makes the colloidal nanocrystal clusters ideal candidates for various important biomedical applications such as drug delivery and bioseparation. The present invention is further directed to methods for forming colloidal photonic crystals from both aqueous and nonaqueous solutions of the superparamagnetic colloidal nanocrystal clusters with an external magnetic field applied thereto. The diffraction of the photonic crystals can be tuned from near infrared to visible and further ultraviolet spectral region by varying the external magnetic field.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
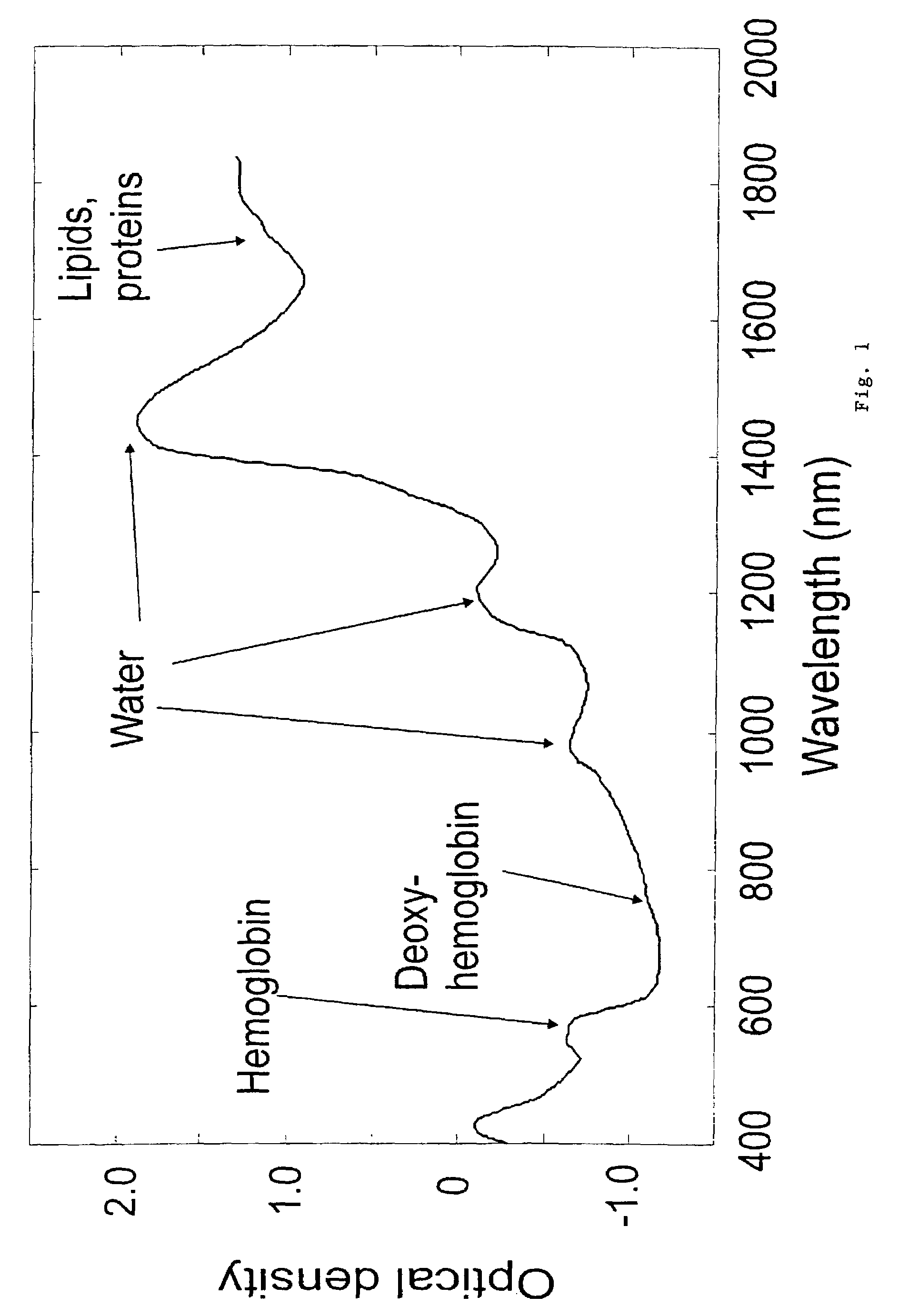
Second, third and fourth near-infrared spectral windows for deep optical imaging of tissue with less scattering
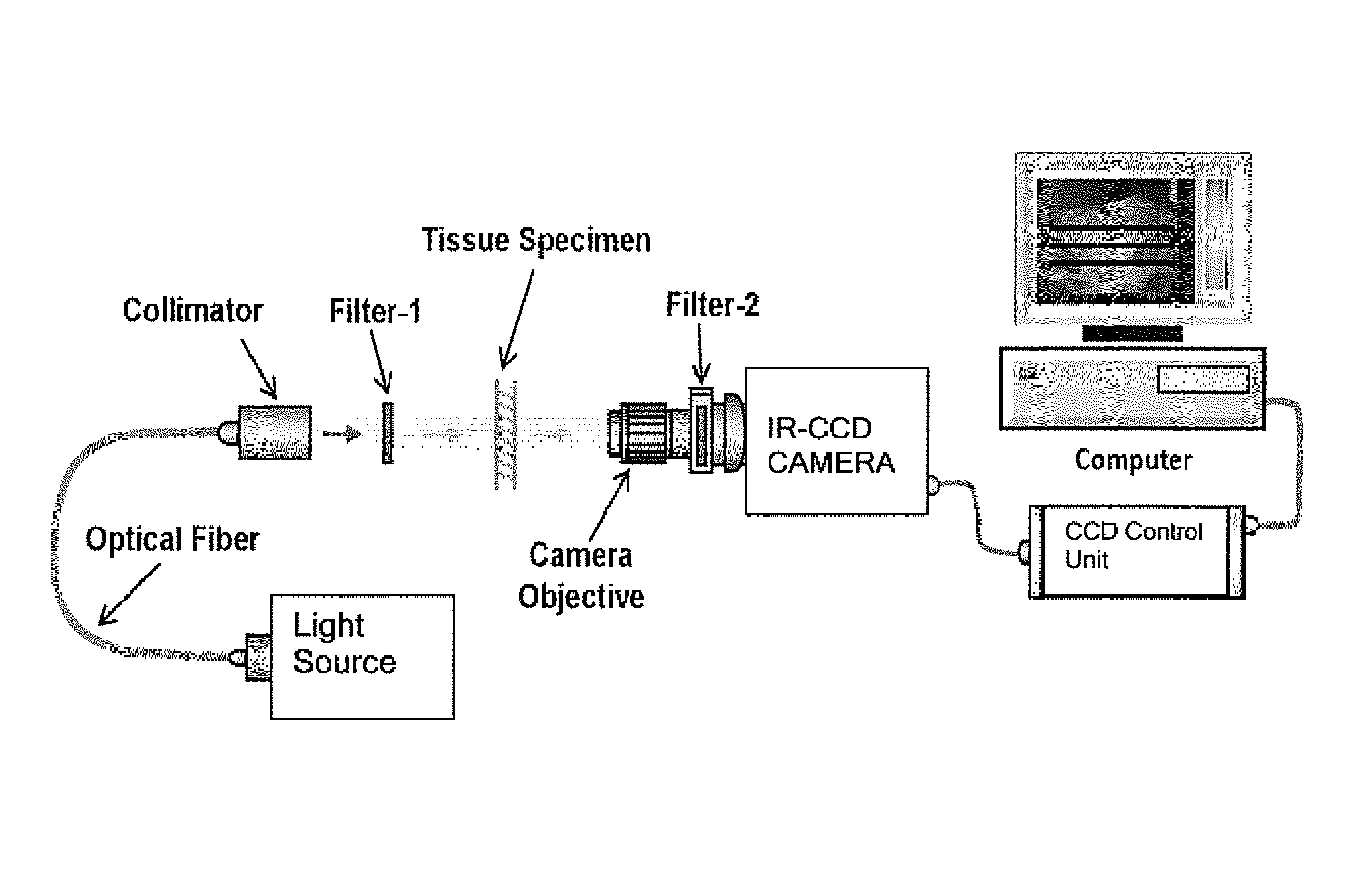
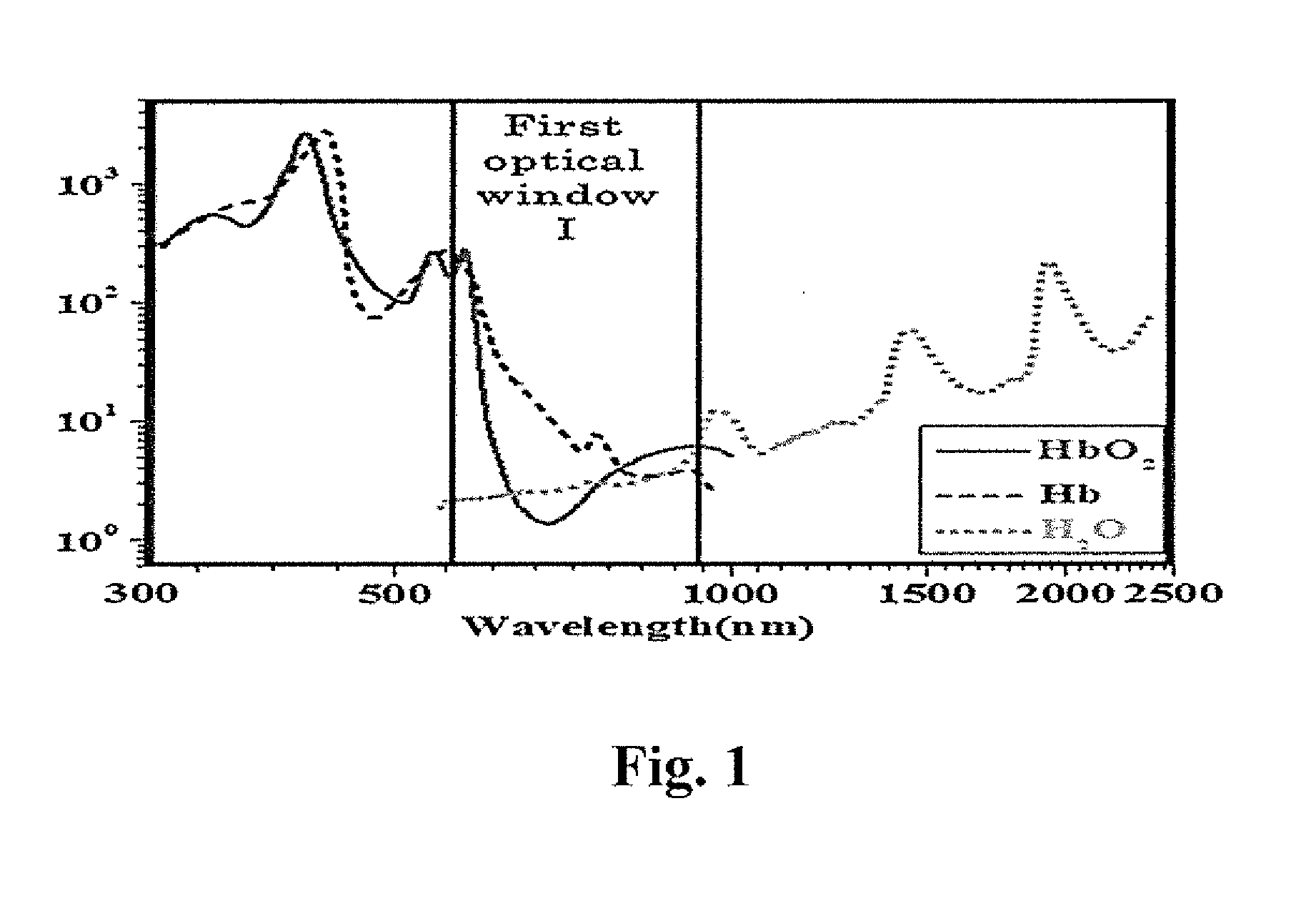
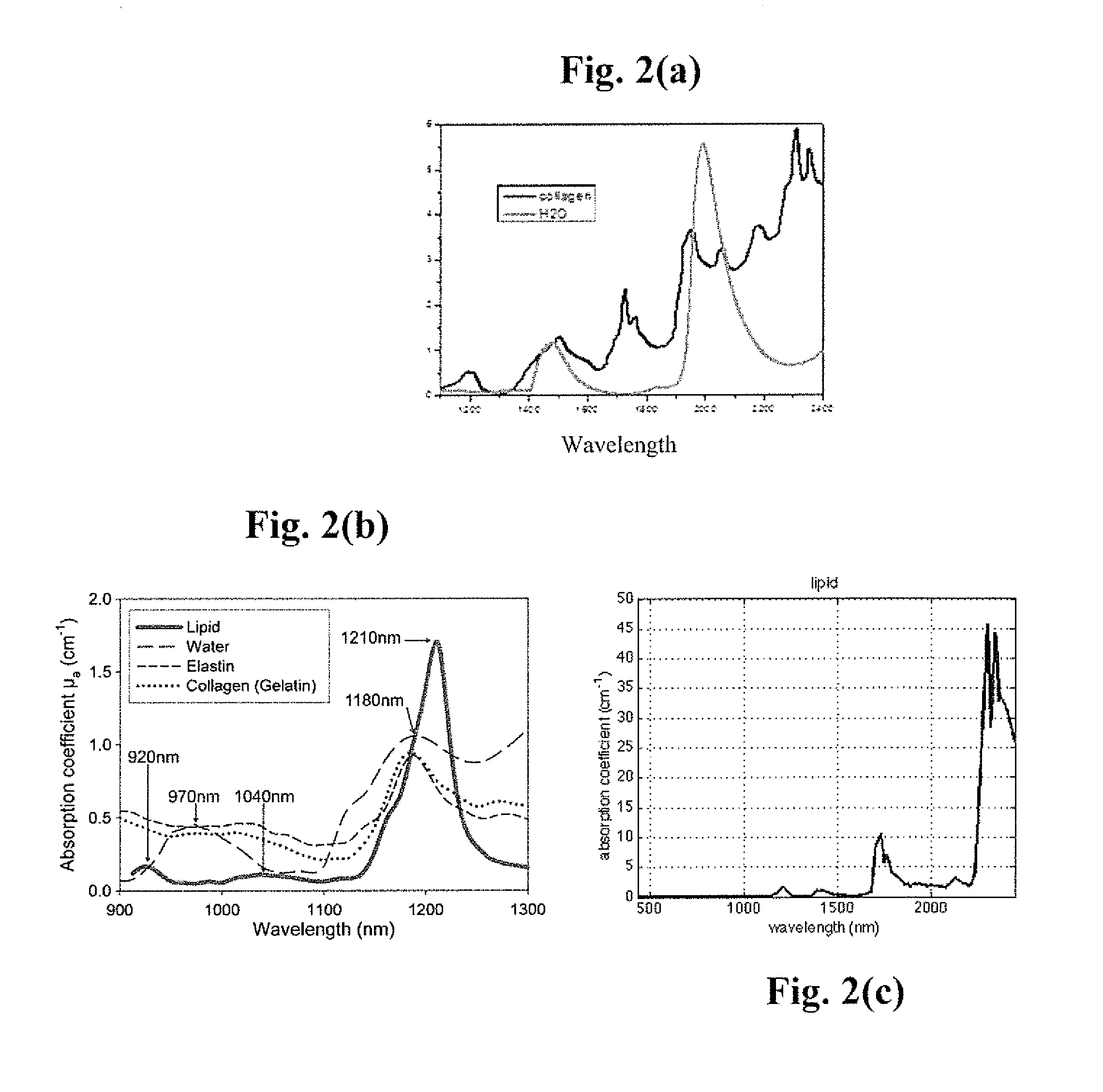
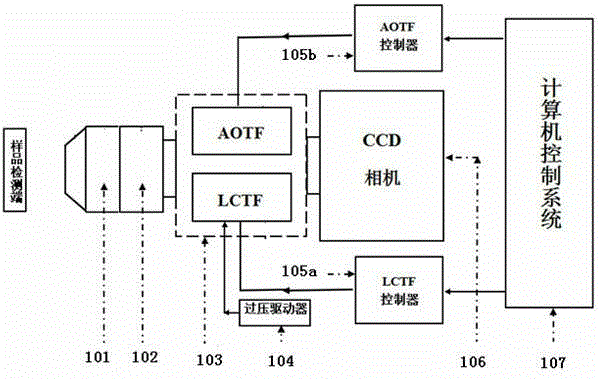
Light at wavelengths in the near-infrared (NIR) region in the second NIR spectral window from 1,100 nm to 1,350 nm and a new spectral window from 1,600 nm to 1,870 nm, known as the third NIR optical window, and fourth at 2200 cm−1 are disclosed. Optical attenuation from thin tissue slices of normal and malignant breast and prostate tissue, and pig brain were measured in the spectral range from 400 nm to 2,500 nm. Optical images of chicken tissue overlying three black wires were also obtained using the second and third spectral windows. Due to a reduction in scattering and minimal absorption, longer attenuation and clearer images can be seen in the second, third and fourth NIR windows compared to the conventional first NIR window. The second and third spectral windows will have uses in microscope imaging arteries, bones, breast, cells, cracks, teeth, and blood due to less scattering of light.
Owner:ALFANO ROBERT R
Near-infrared spectrum imaging system and near-infrared spectrum imaging method for diagnosis of depth and area of burn skin necrosis
ActiveCN103815875AFavorable guidanceAvoid painDiagnostics using spectroscopyOptical sensorsTissue proteinBurned skin
The invention provides a near-infrared spectrum imaging system for diagnosis of depth and area of burn skin necrosis. The near-infrared spectrum imaging system comprises a spectrum imager and a computer-control system. The spectrum imager acquires 1100-2500nm waveband spectral signals of burn skin necrosis tissue of a target area, the spectral signals are subjected to image analyzing and processing through the computer-control system, the depth and area of burn of the target area can be acquired through spectral matching recognition upon a spectral reflectance curve corresponding to each image element in spectral images and a standard spectral reflectance curve in a burn skin necrosis spectral database in a data module and are synthesized into three-dimensional image display of the target area. By the near-infrared spectrum imaging system, the spatial structure of skin changed due to tissue protein denaturation before and after the skin burn can be specified, so that micron-level information about boundaries of normal skin tissue and necrotic tissue and the depth of burn skin necrosis can be provided visually, and clinical diagnosis, treatment and prognosis judgment can be supportively facilitated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG DEPUSI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
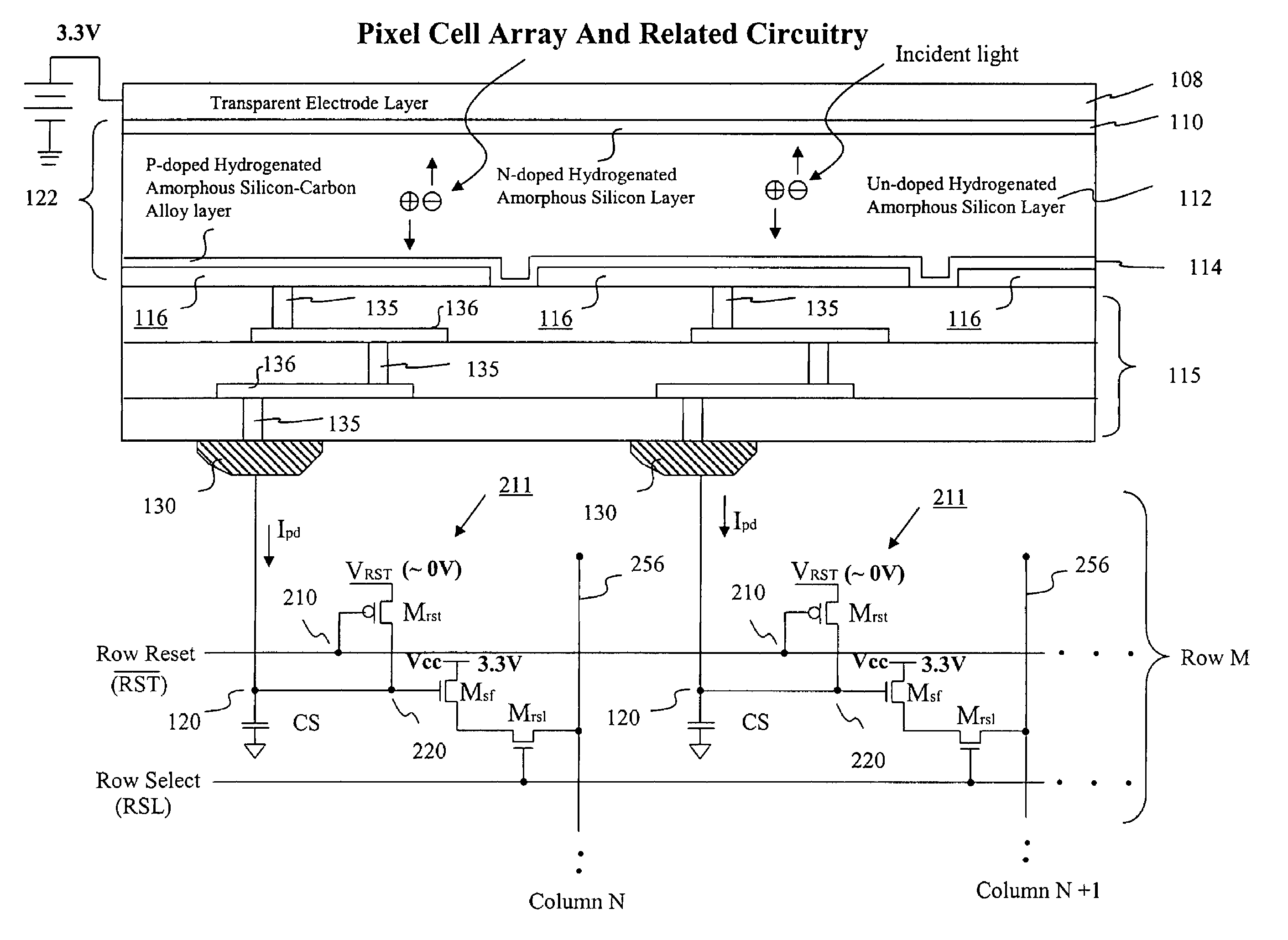
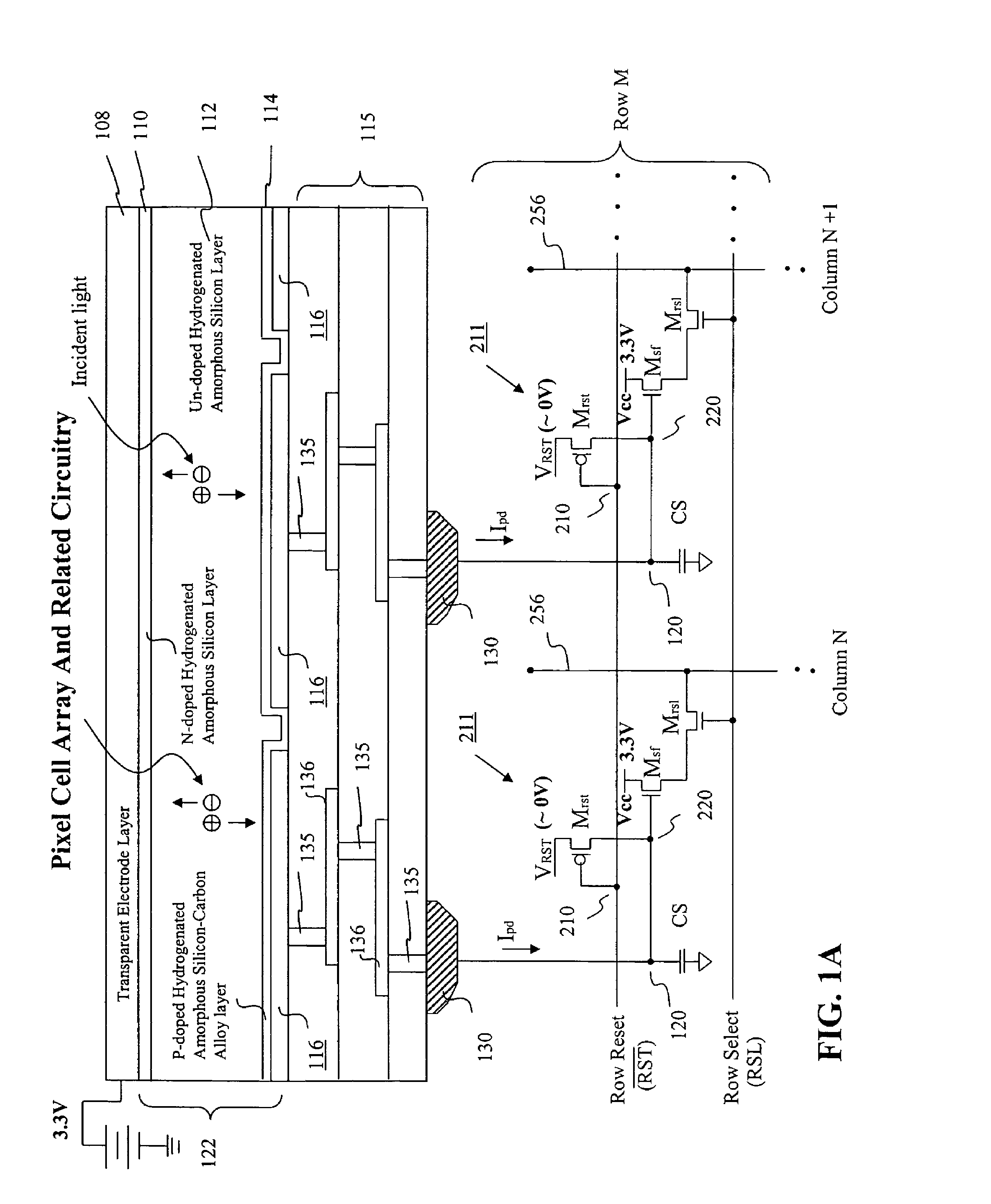
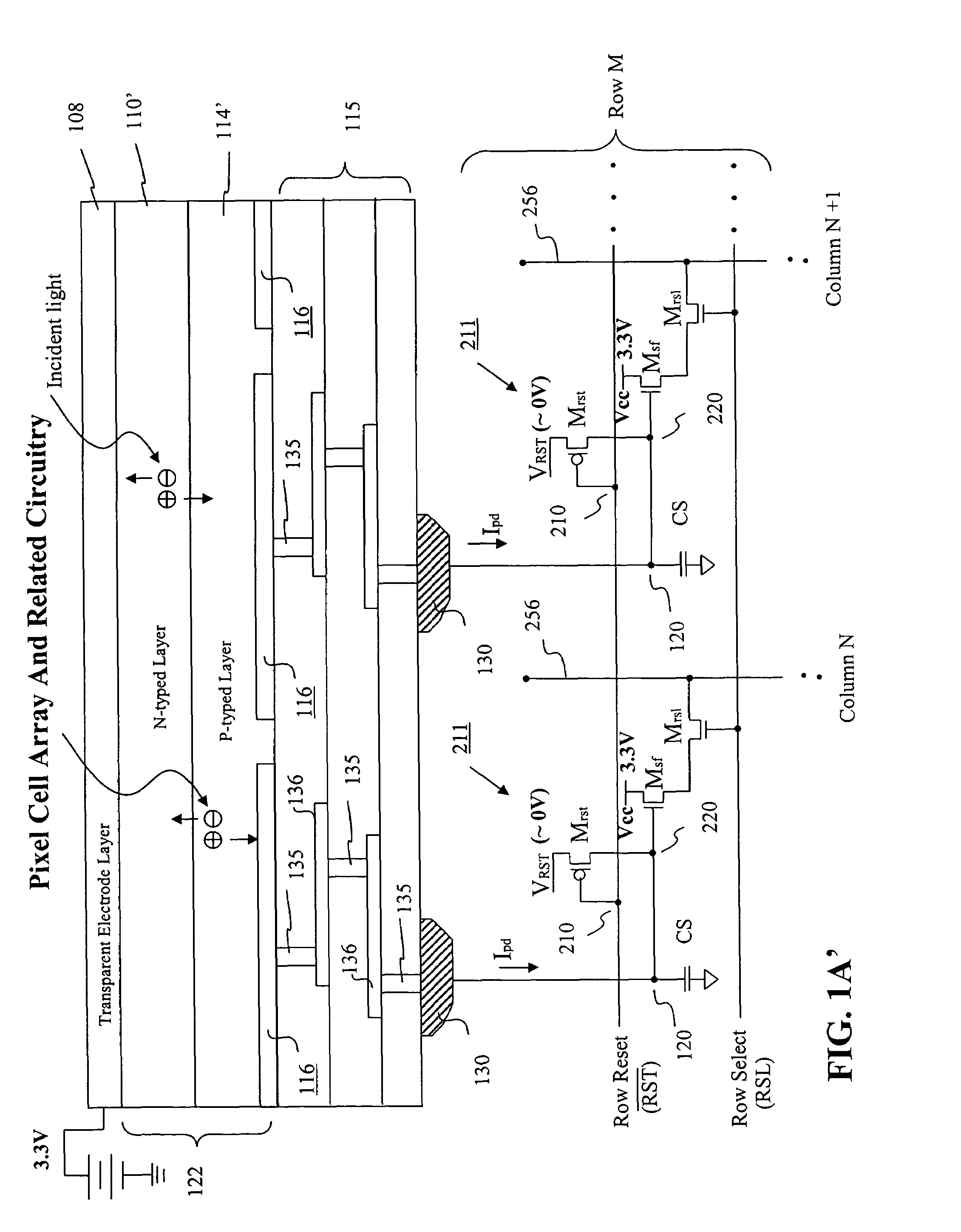
Visible/near infrared image sensor array
InactiveUS7436038B2Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayLow earth orbit
A MOS or CMOS sensor for high performance imaging in broad spectral ranges including portions of the infrared spectral band. These broad spectral ranges may also include portions or all of the visible spectrum, therefore the sensor has both daylight and night vision capabilities. The sensor includes a continuous multi-layer photodiode structure on a many pixel MOS or CMOS readout array where the photodiode structure is chosen to include responses in the near infrared spectral ranges. A preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline copper indium diselenide / cadmium sulfide photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. An alternate preferred embodiment incorporates a microcrystalline silicon germanium photodiode structure on a CMOS readout array. Each of these embodiments provides night vision with image performance that greatly surpasses the GEN III night vision technology in terms of enhanced sensitivity, pixel size and pixel count. Further advantages of the invention include low electrical bias voltages, low power consumption, compact packaging, and radiation hardness. In special preferred embodiments CMOS stitching technology is used to provide multi-million pixel focal plane array sensors. One embodiments of the invention made without stitching is a two-million pixel sensor. Other preferred embodiments available using stitching techniques include sensors with 250 million (or more) pixels fabricated on a single wafer. A particular application of these very high pixel count sensors is as a focal plane array for a rapid beam steering telescope in a low earth orbit satellite useful for tracking over a 1500-meter wide track with a resolution of 0.3 meter.
Owner:C PHOCUS
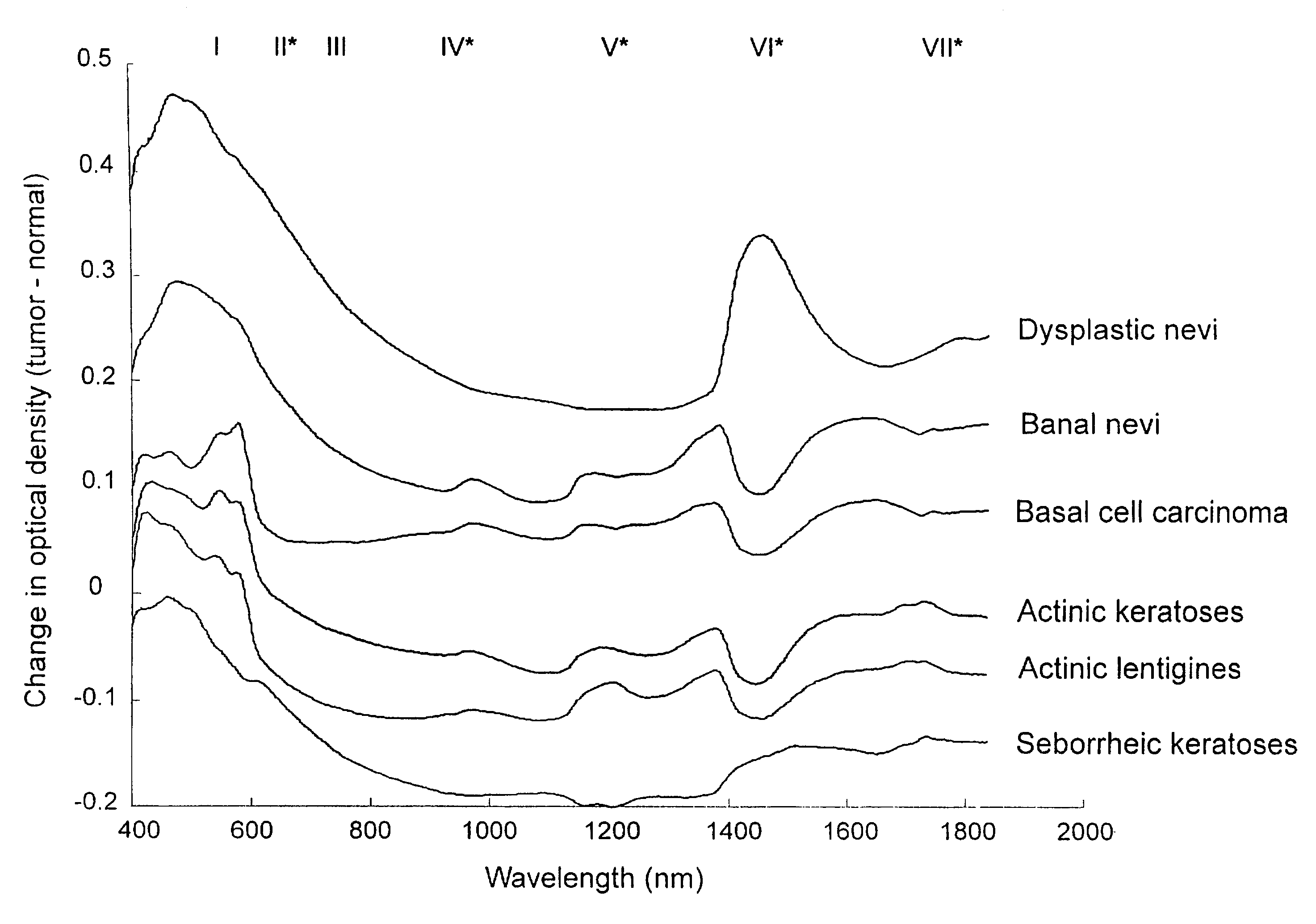
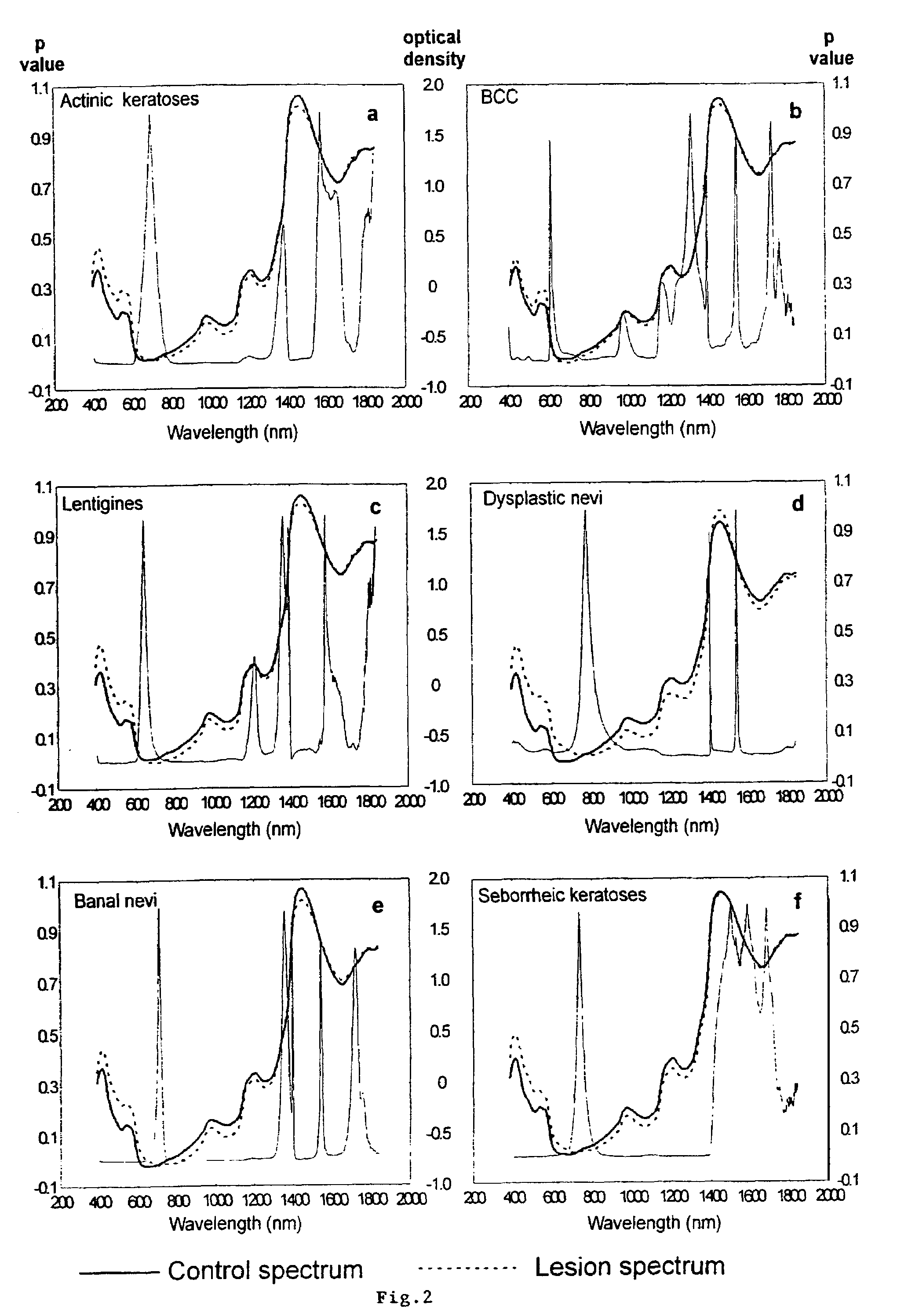
Non-invasive screening of skin diseases by visible/near-infrared spectroscopy
A non-invasive tool for skin disease diagnosis would be a useful clinical adjunct. The purpose of this study was to determine whether visible / near-infrared spectroscopy can be used to non-invasively characterize skin diseases. In-vivo visible- and near-infrared spectra (400-2500 nm) of skin neoplasms (actinic keratoses, basal cell carcinomata, banal common acquired melanocytic nevi, dysplastic melanocytic nevi, actinic lentigines and seborrheic keratoses) were collected by placing a fiber optic probe on the skin. Paired t-tests, repeated measures analysis of variance and linear discriminant analysis were used to determine whether significant spectral differences existed and whether spectra could be classified according to lesion type. Paired t-tests showed significant differences (p<0.05) between normal skin and skin lesions in several areas of the visible / near-infrared spectrum. In addition, significant differences were found between the lesion groups by analysis of variance. Linear discriminant analysis classified spectra from benign lesions compared to pre-malignant or malignant lesions with high accuracy. Visible / near-infrared spectroscopy is a promising non-invasive technique for the screening of skin diseases.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
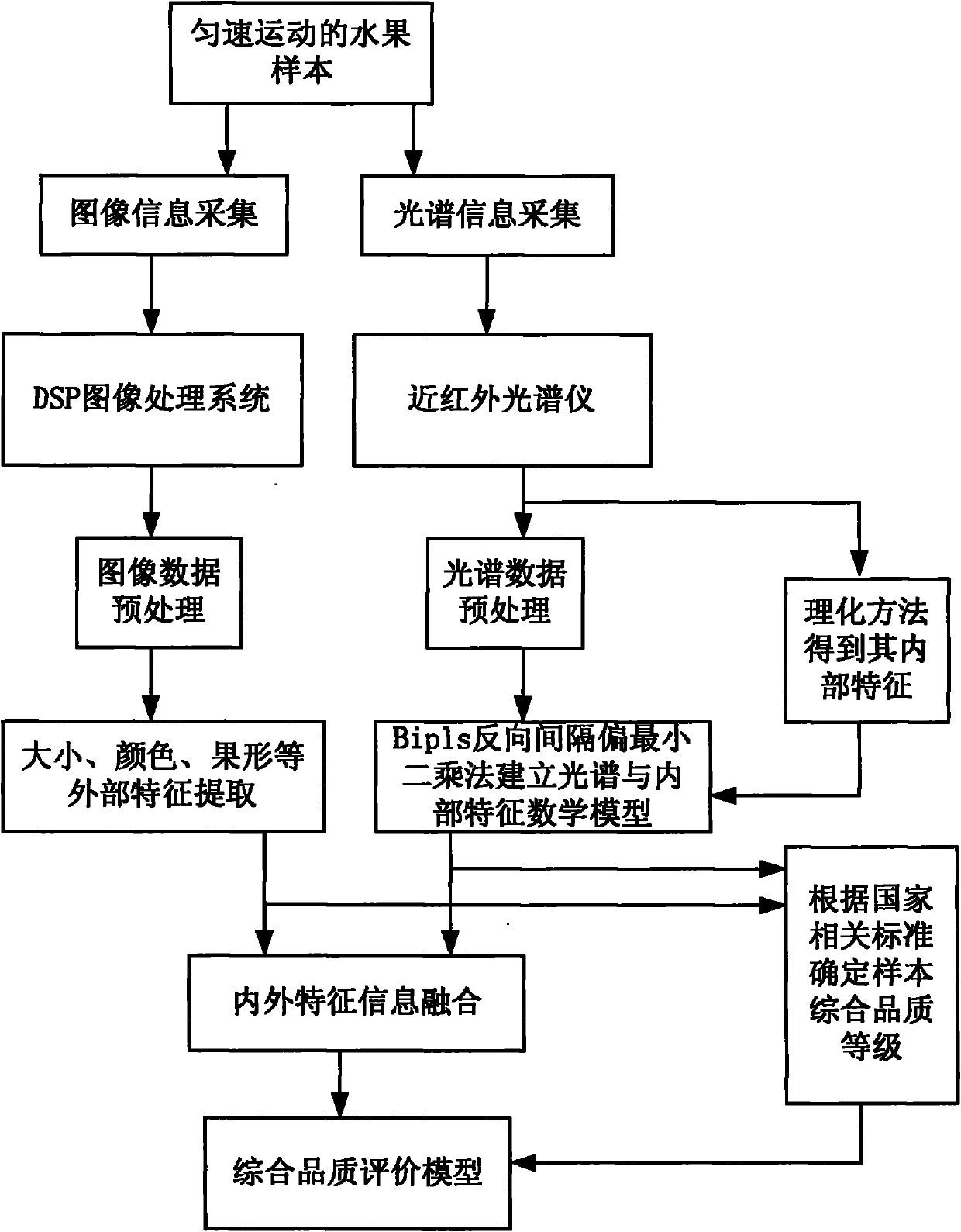
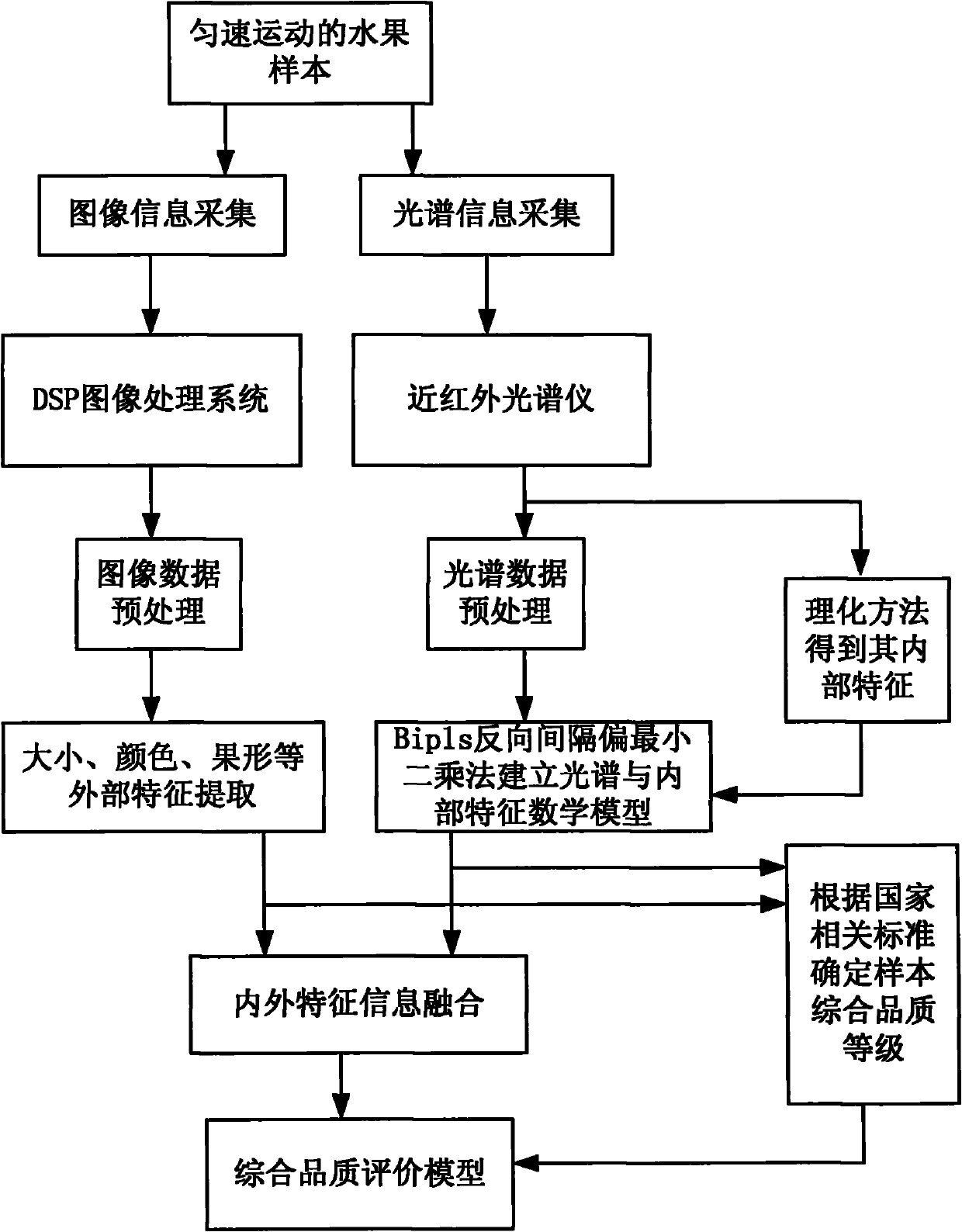
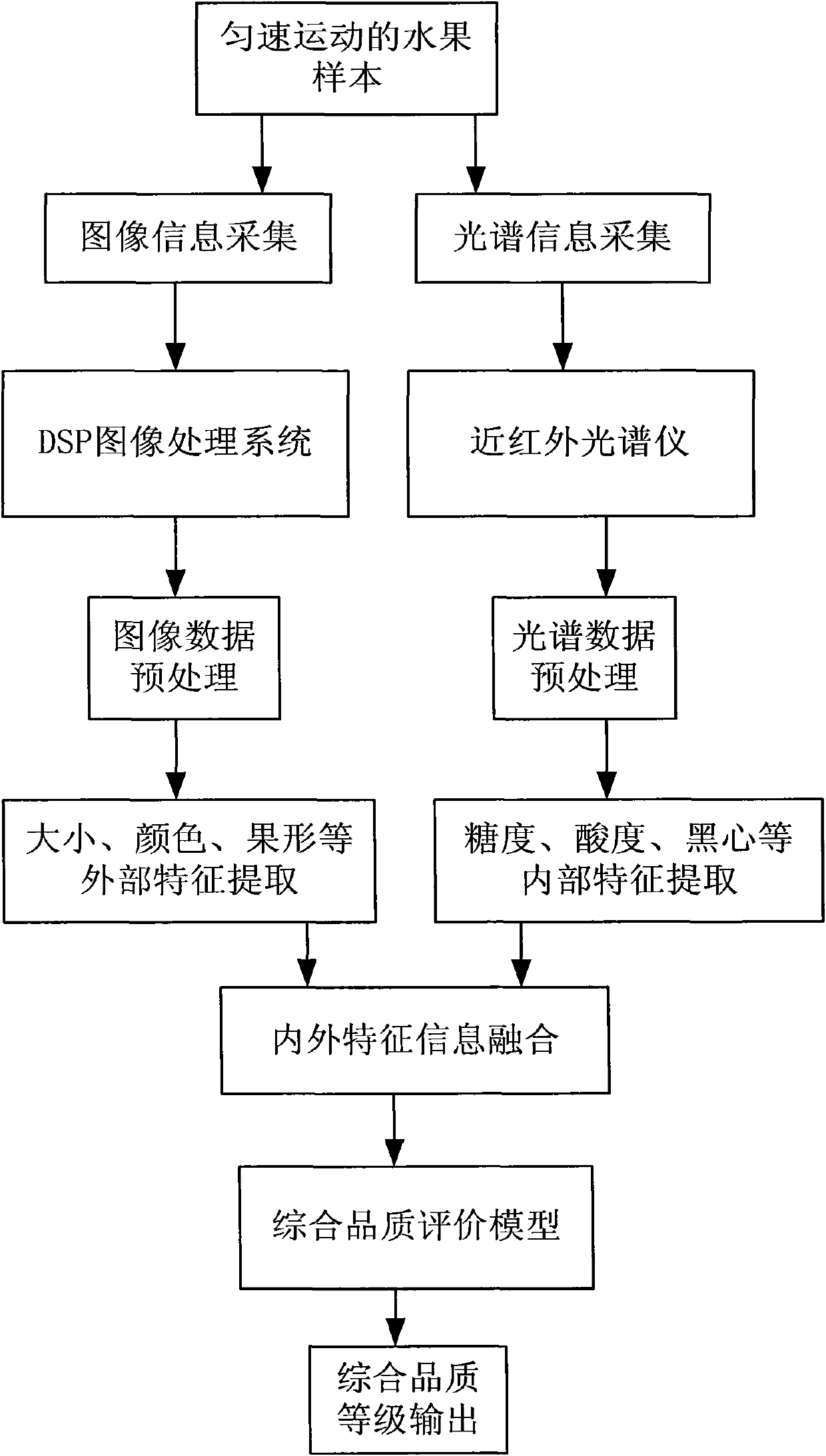
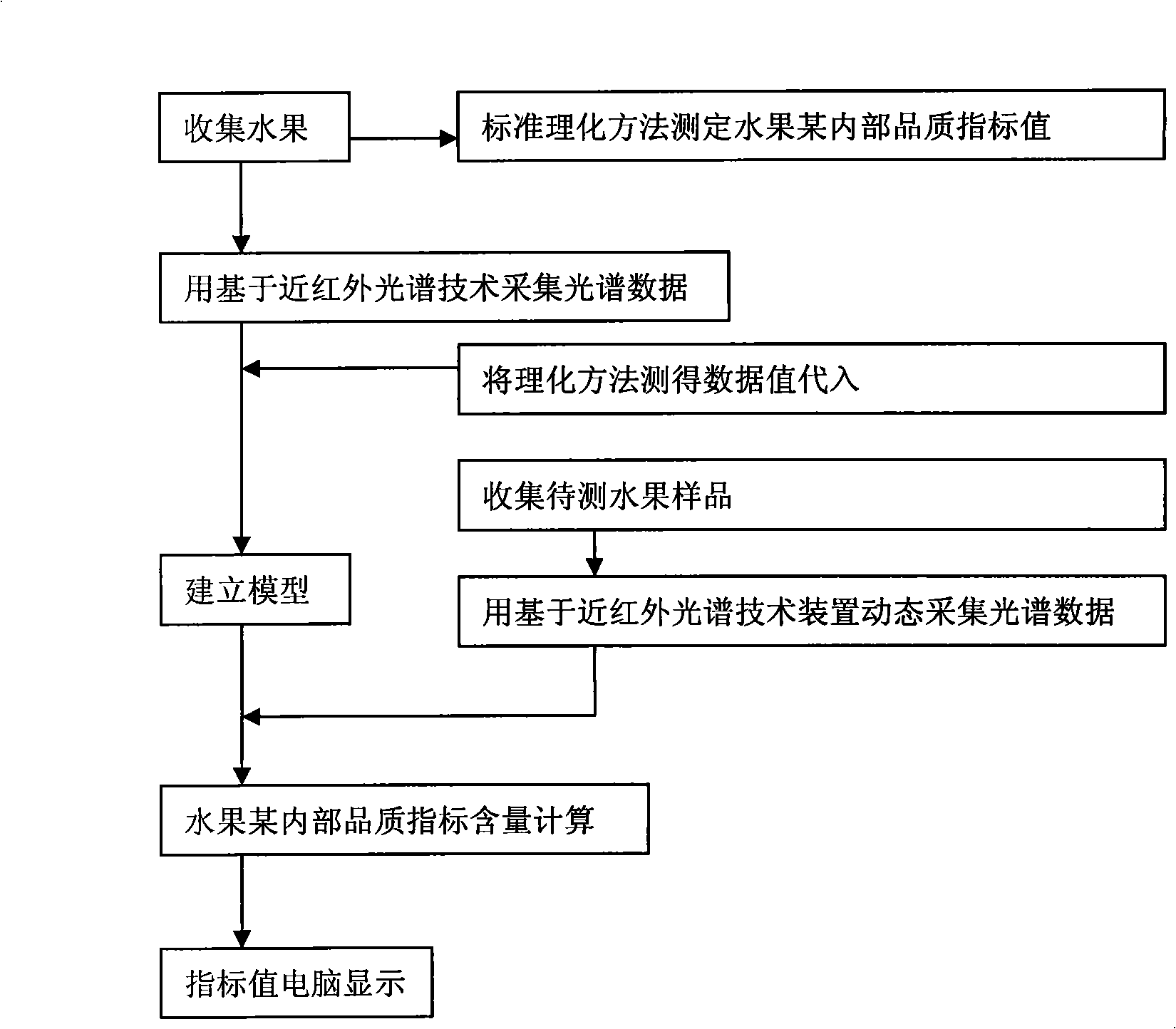
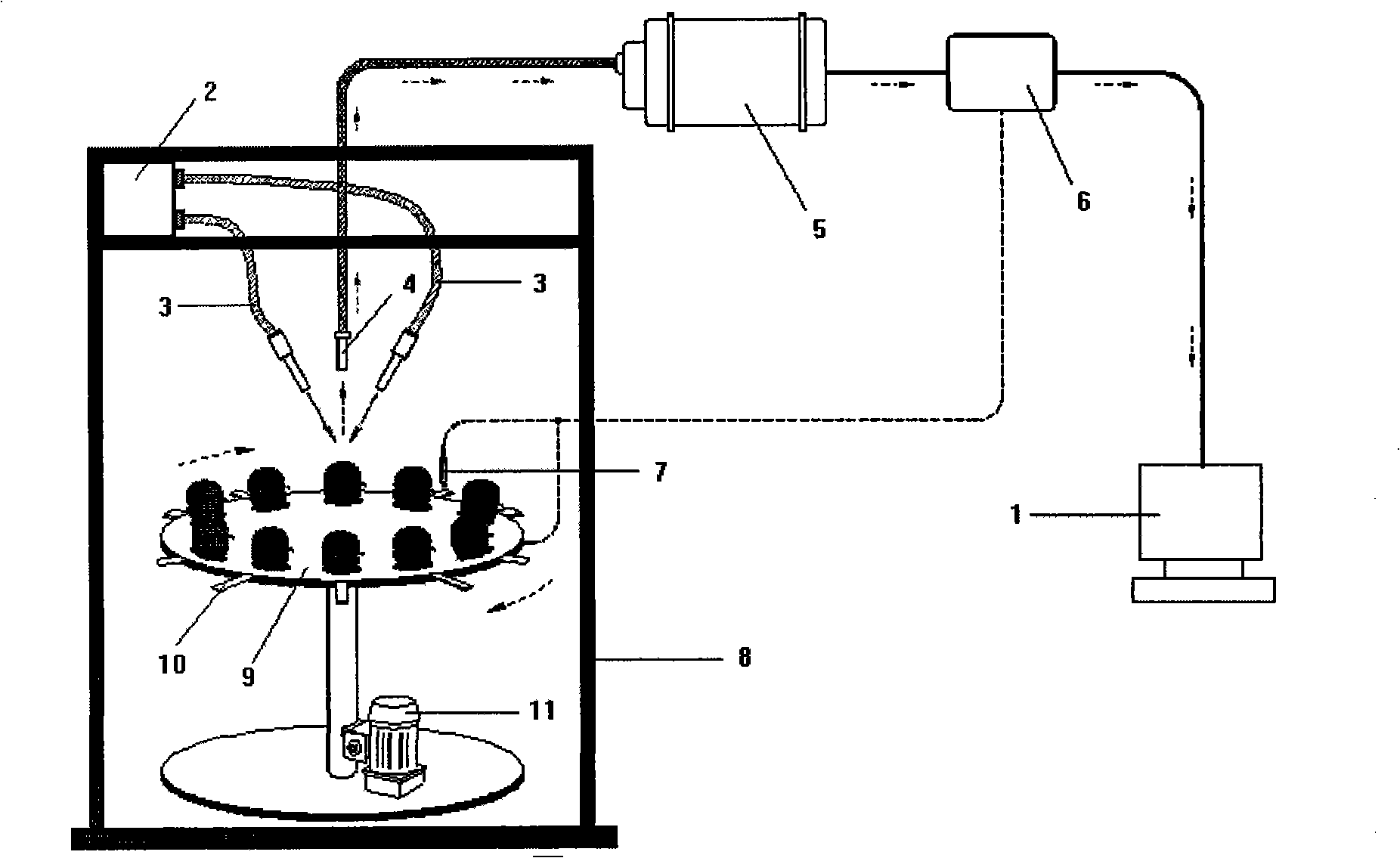
Online nondestructive testing (NDT) method and device for comprehensive internal/external qualities of fruits
InactiveCN101949686AImprove real-time performanceColor measuring devicesUsing optical meansImaging processingMathematical model
The invention discloses an online nondestructive testing (NDT) method and an online nondestructive testing (NDT) device for comprehensive internal / external qualities of fruits. The online NDT method of the invention comprises the following steps: a comprehensive quality evaluation model for the fruits is established firstly by a detection device consisting of a conveying system, a machine vision system, an Near Infrared Spectrum (NIR) system and a grading system, and the fruits performs online uniform motion through the conveying system; the machine vision system acquires the image information of the fruits and extracts the external characteristics of the fruits; the NIR system acquires the spectral information of the fruits; the grading system analyses the spectral information by a pre-established mathematical model, and extracts the internal characteristics of the fruits; and the grading system fuses the internal characteristics and the external characteristics of the fruits by a pre-established information fusion model so as to obtain the comprehensive quality level of the fruits. The method and the device of the invention can detect the internal characteristics and the external characteristics of the fruits simultaneously; a DSP high-speed image processing system is used to handle complex image information, which greatly improves the real-time characteristic of the system; and an information fusion technology is used to carry out online real-time detection on the comprehensive qualities of the fruits.
Owner:扬州福尔喜果蔬汁机械有限公司
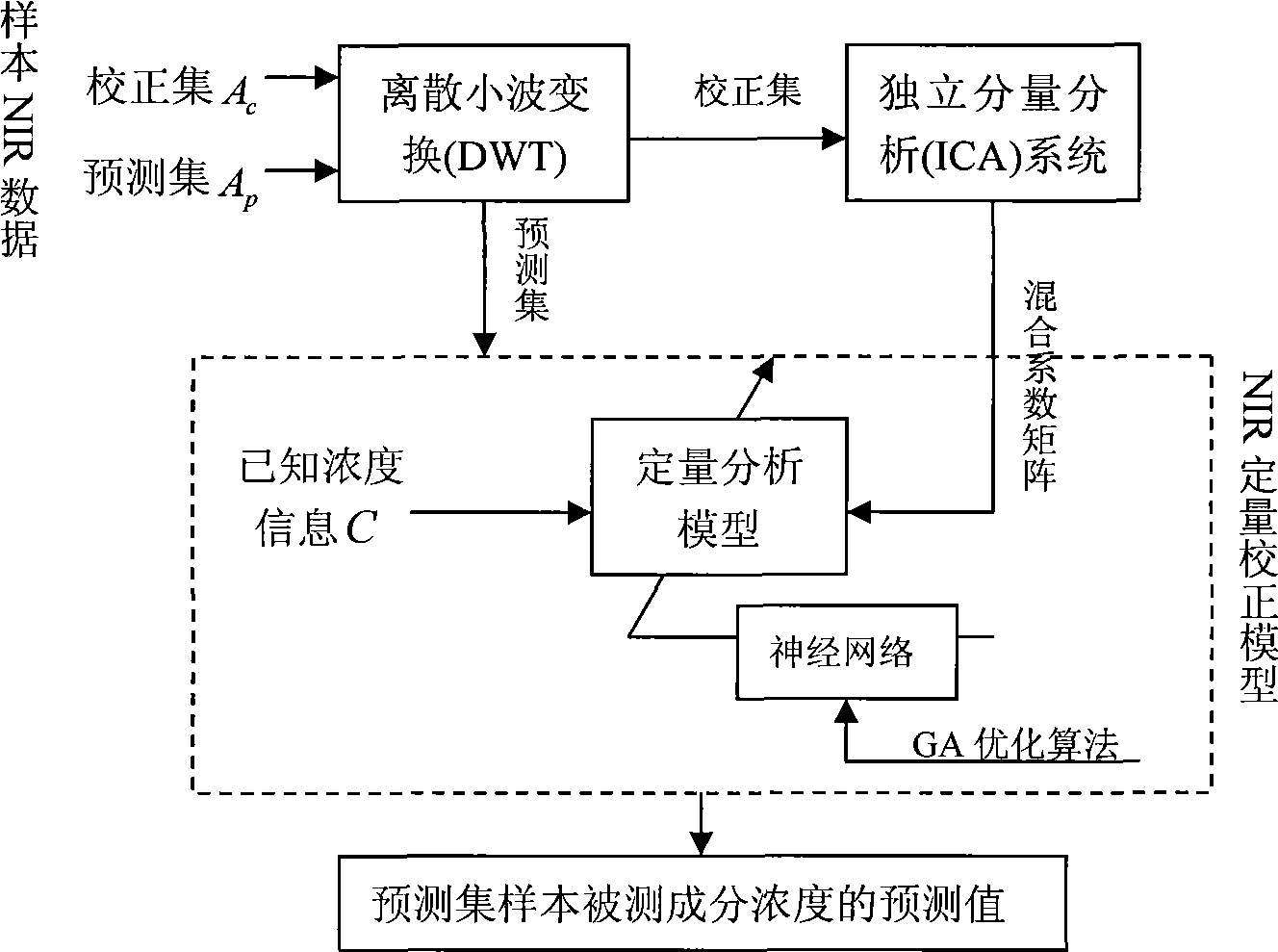
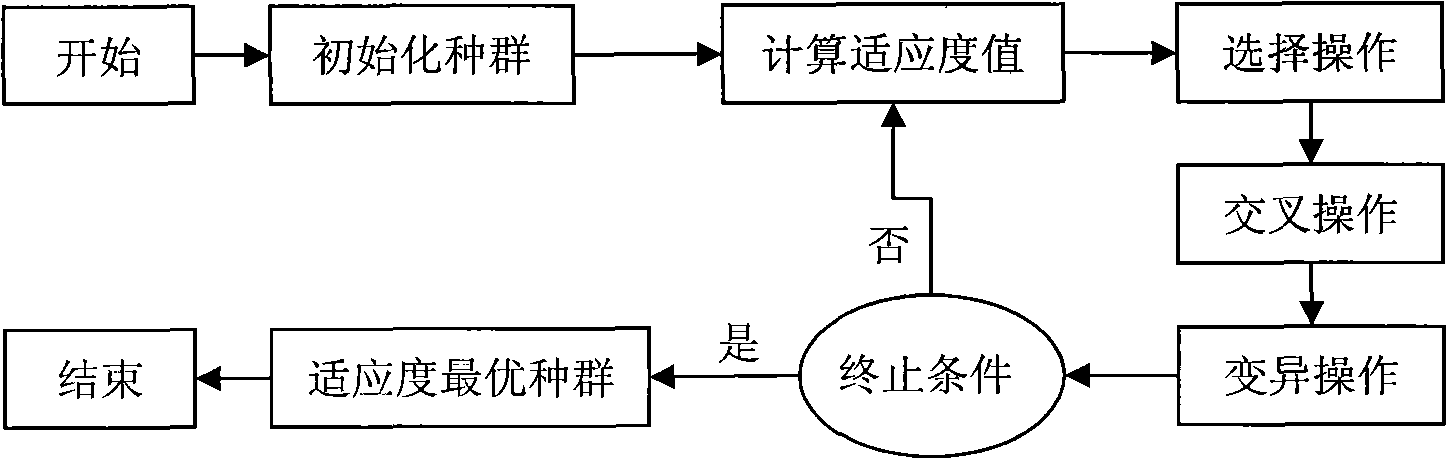
Near infrared spectrum analyzing method based on isolated component analysis and genetic neural network
InactiveCN101520412AImprove forecast accuracyRich Chemometric MethodsBiological neural network modelsColor/spectral properties measurementsInfraredMetrology
The invention discloses a near infrared spectrum analyzing method based on the isolated component analysis and genetic neural network, which comprises the following steps for the acquired near infrared spectrum: firstly, effectively compressing spectrum data by using wavelet transform; secondly, extracting an independent component and a corresponding mixed coefficient matrix of a near infrared spectrum data matrix by using an isolated component analysis method; thirdly, building a three-layer BP neutral network, using the mixed coefficient matrix of a training sample as the input and correspondingly measured component concentration matrix as the output, and optimizing a neutral network structure by adopting a genetic algorithm, and obtaining a GA-BP neutral network by the training of the training sample; fourthly, predicting and analyzing the measured component concentration of the predicted set sample by using the GA-BA neutral network. The method enriches the chemical measurement method, widens the application range of the isolated component analysis and has favorable application prospect.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
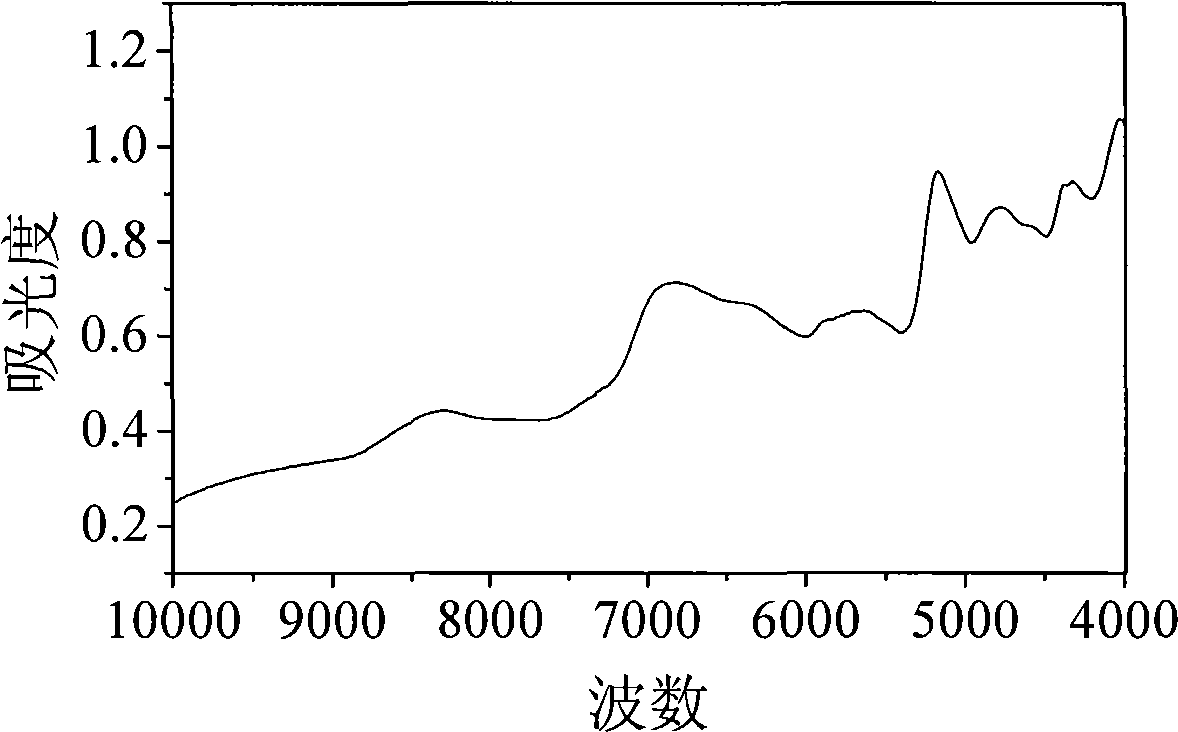
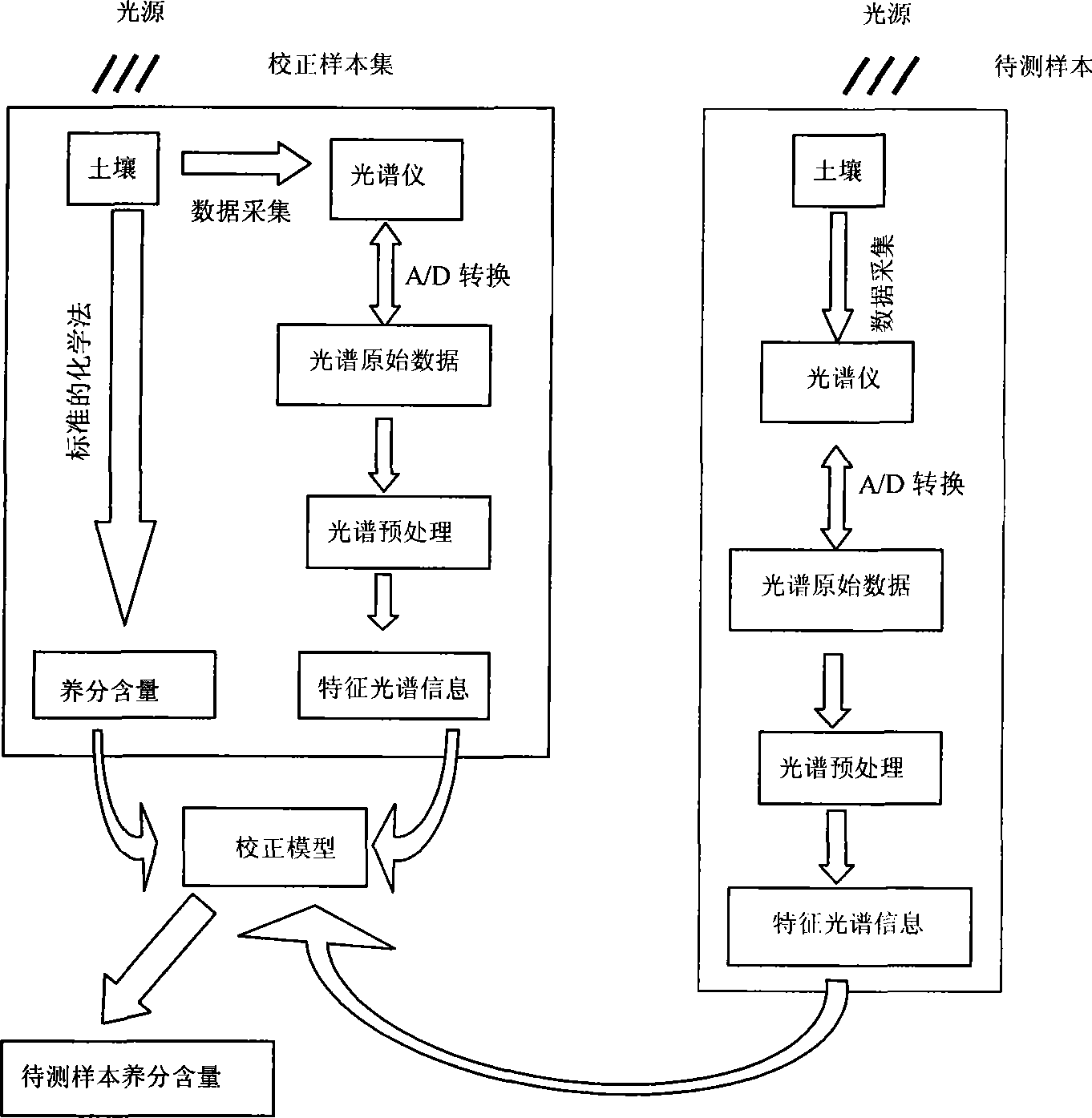
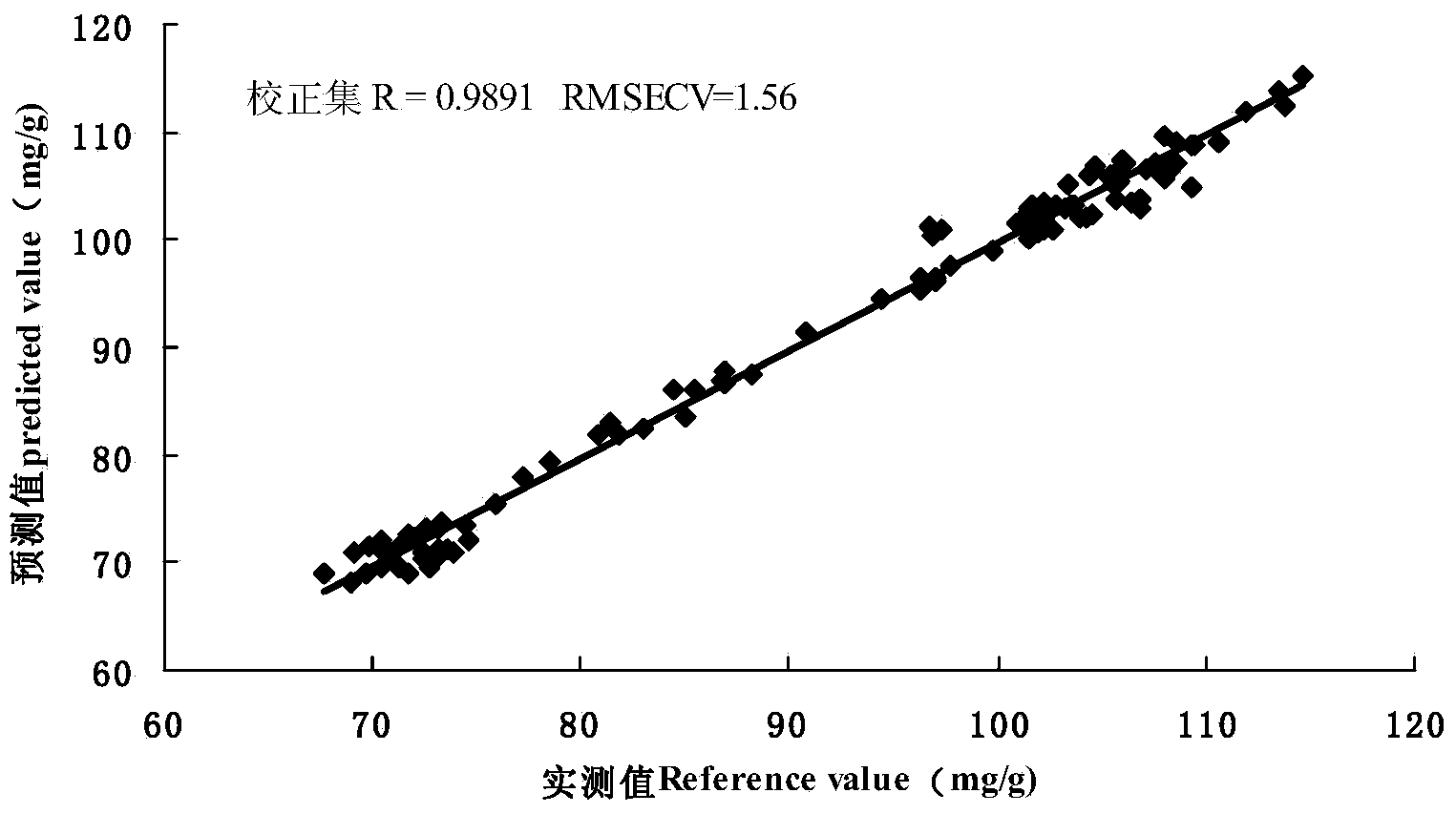
Damage-free measurement method for soil nutrient content based on near infrared spectra technology
InactiveCN101210875AShorten detection timeNo pollution in the processColor/spectral properties measurementsSoil typeMultivariate calibration
The invention discloses a nondestructive method for measuring nutrient content in soil based on near-infrared spectral technique. The method comprises two stages of calibration model construction and unknown sample measurement. The calibration model construction stage comprises the following steps of: firstly collecting samples of different soil types as a calibration sample set, scanning to obtain the near-infrared spectra of the calibration sample set, and performing spectra pretreatment to the obtained spectral data; measuring the nutrient content of the samples for model construction with GB method as standard content; and constructing a quantitive relationship between the near-infrared spectra of samples for model construction and standard nutrient content thereof using multivariate calibration algorithm to obtain a calibration model. The unknown sample measurement stage comprises the following steps of: scanning soil samples to be detected to obtain the near-infrared spectra thereof, inputting the spectral data after corresponding spectra pretreatment to the calibration model, and measuring with the calibration model to obtain the content of each nutrient. The whole process is under computer control, and the invention realizes data collection, storage, display and processing functions.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
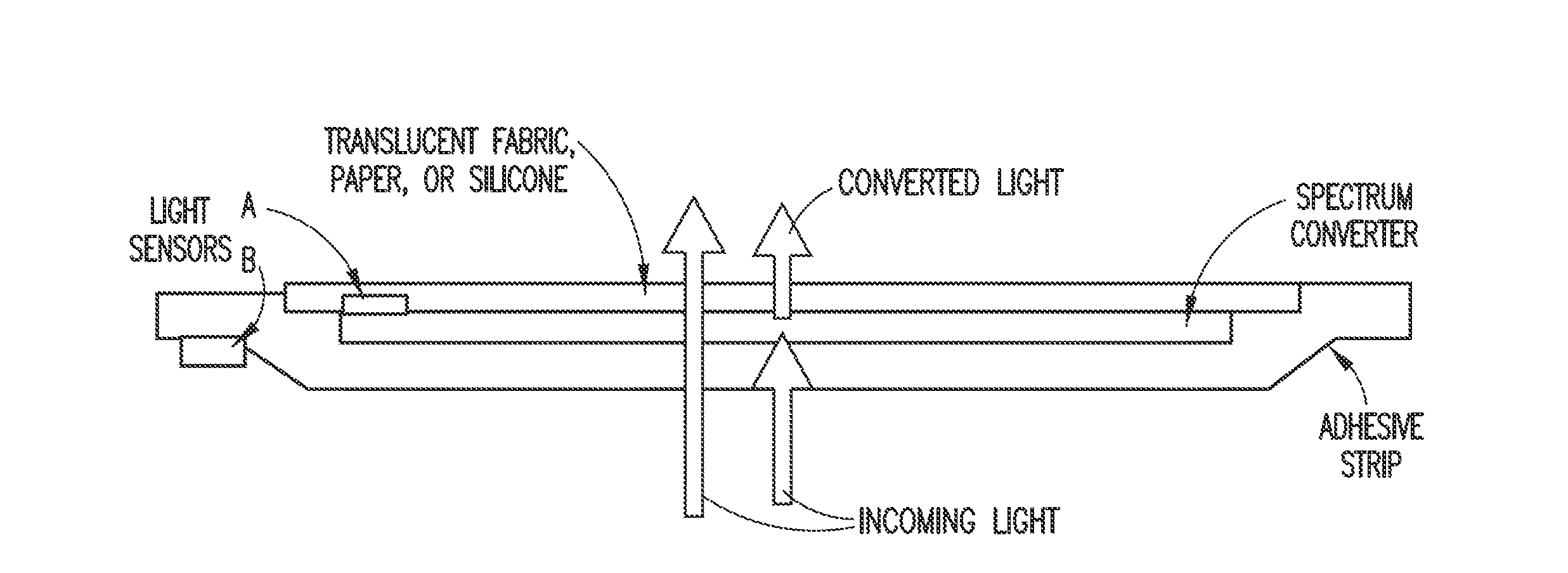
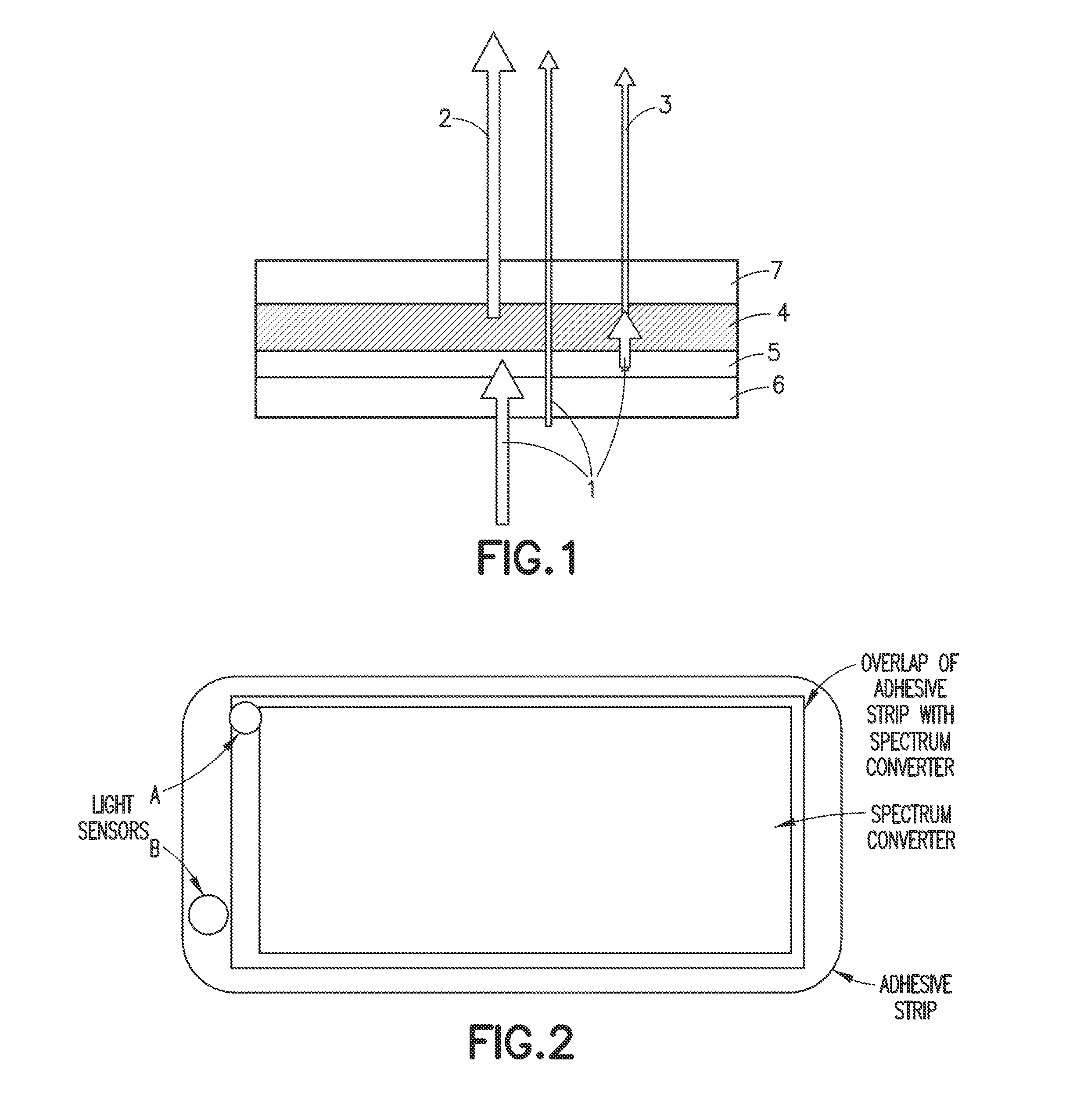
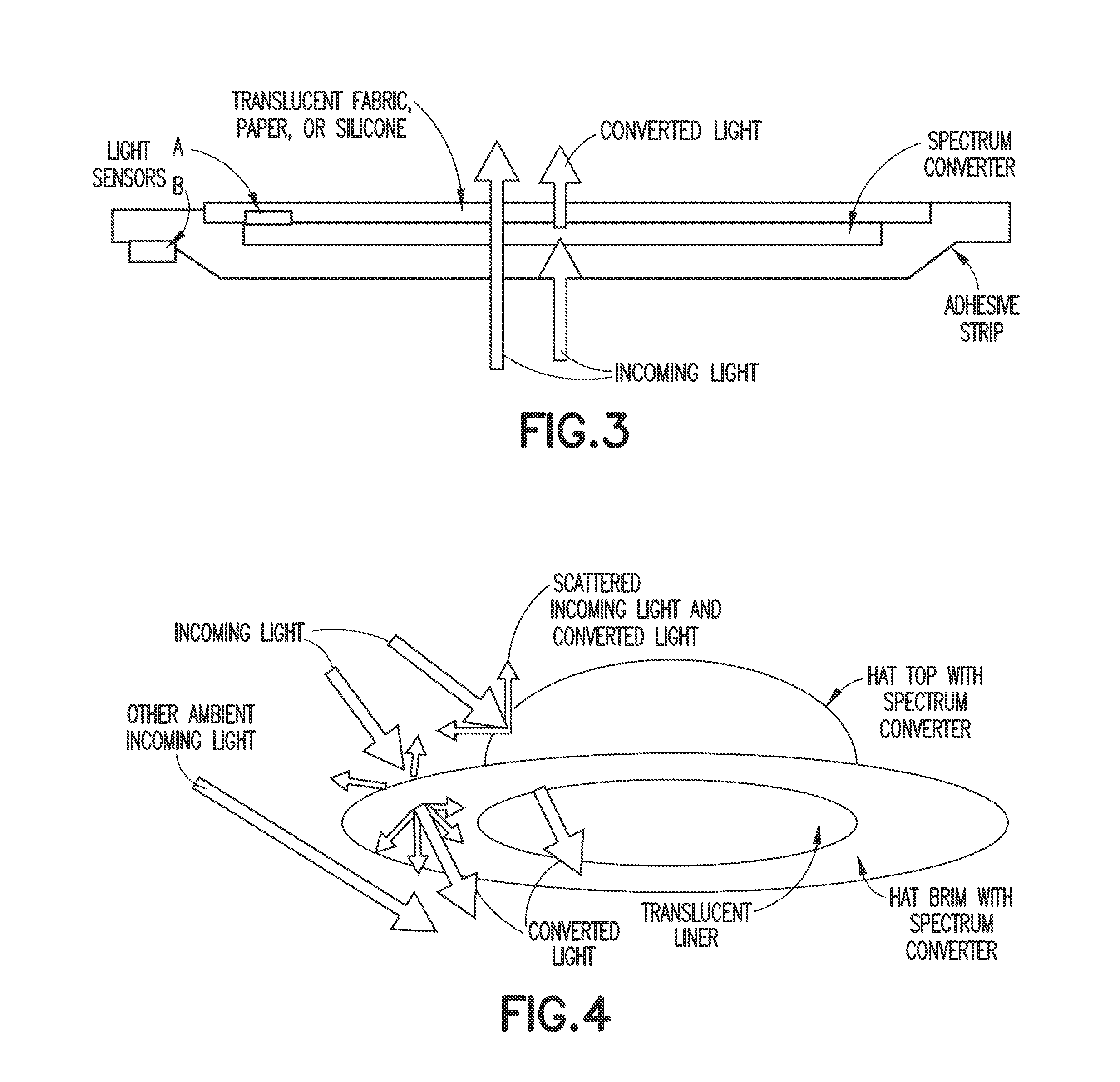
Ambient spectrum light conversion device
ActiveUS20140277294A1High quantum yieldIncrease effective strengthLuminescent dosimetersFluorescence/phosphorescenceQuantum yieldConverters
Apparatus and methods to enhance light intensity within useful red to near-infrared spectral ranges, using direct or indirect sunlight, or from other ambient white light, are described. The disclosed devices provide high quantum yield photoluminescent ambient light spectrum conversion to increase the supplied energy primarily in the 590 nm-850 nm spectral range. These devices also pass much of the incident light in the spectral range in which the device's photoluminescent materials emit light, thereby greatly increasing the effective intensity of light available in the targeted 590-850 nm wavelength range. The ambient light conversion devices of the disclosure may be incorporated in apparel, bandage-like patches, converting reflectors, large area converters, awnings, window covers, and other articles, materials, and products. The converted light may be used in therapeutic treatments, horticultural and biotechnological applications, and other applications in which the converted light outputs of the present disclosure are beneficial.
Owner:JONES GARY W +1
Handheld near infrared spectrum detection system and detection method for quality of fruits and vegetables
The invention discloses a handheld near infrared spectrum detection system and a detection method for the quality of fruits and vegetables, and belongs to the field of quick detection technologies for the quality of foods or agricultural products. The handheld near infrared spectrum detection system and the detection method have the advantages that modulation light paths of a digital micro-mirror device is matched with a single-point detector and other external modules, so that the handheld, low-cost and miniaturized near infrared spectrum detection system for the quality of the fruits and vegetables can be obtained, and high-performance spectrum information can be acquired without expensive linear array detectors; characteristic wave bands are selected at first in the aspect of building fruit and vegetable quality detection models, then wave bands which do not contain information variables and are low in relevancy are removed, then a small quantity of characteristic wavelengths are selected by the id of characteristic wavelength selection processes, internal collinear relations among spectrum data are eliminated, accordingly, model calculation can be reduced, the models can be simplified, and the quality of the models can be improved; the bottleneck problems of high nondestructive detection cost for the quality of fruits and vegetables, carrying inconvenience and poor quality of existing detection models can be solved by the aid of the handheld near infrared spectrum detection system and the detection method.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
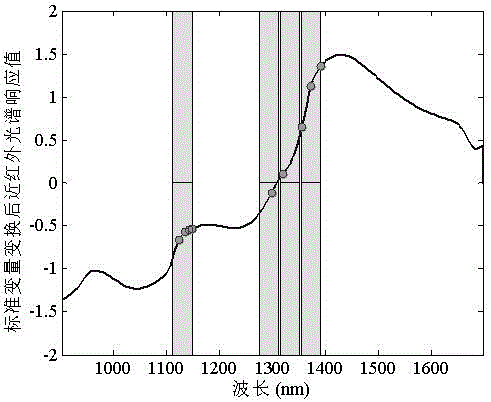
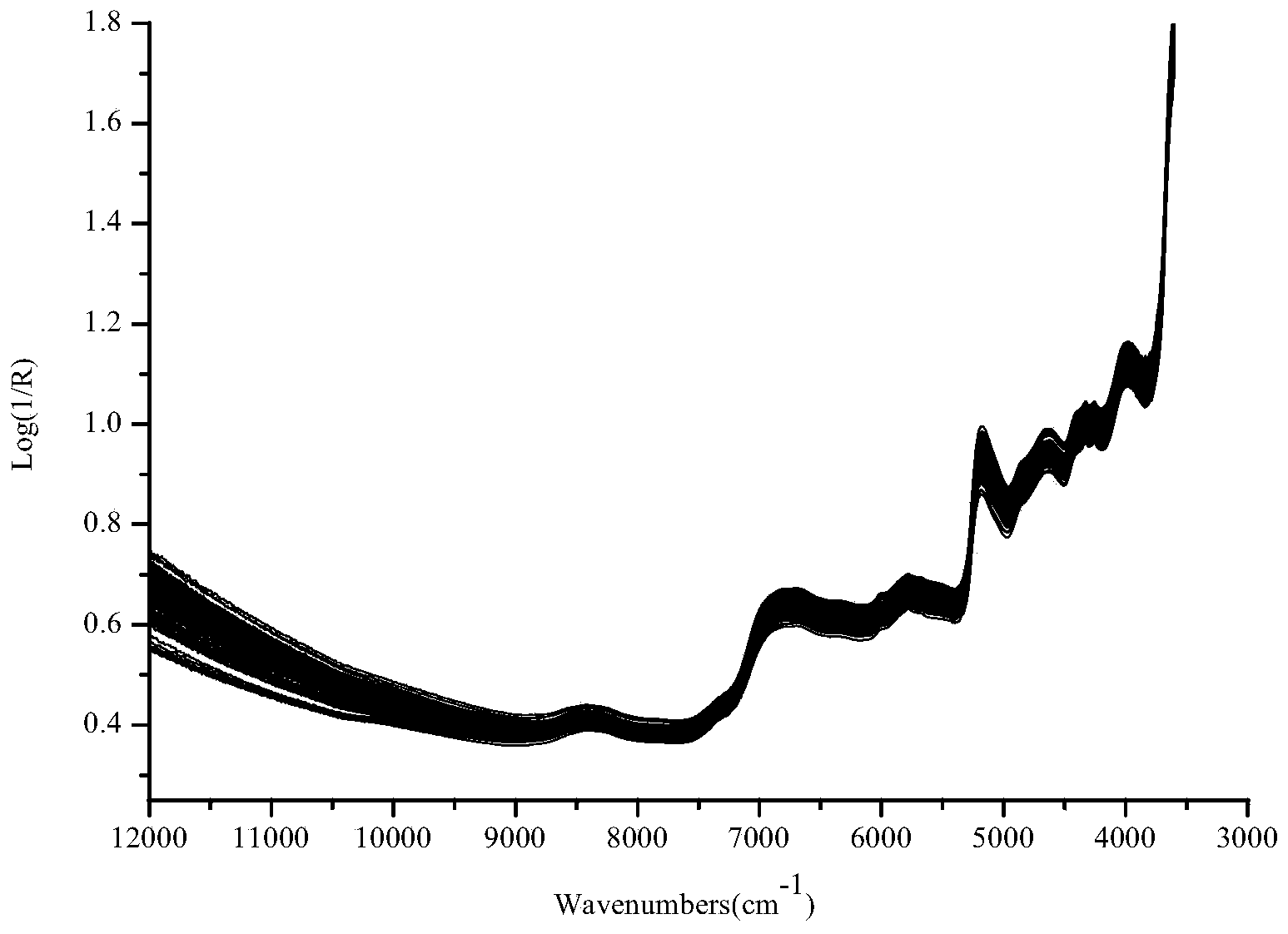
Fruit internal quality on-line checking method and apparatus based on near infrared spectra technology
InactiveCN101308086AImprove objectivityGood repeatabilityColor/spectral properties measurementsTesting foodNear infrared spectraStandardization
The invention relates to a fruit internal quality on-line detection method and an apparatus thereof. The detection method comprises: implementing the spectral scanning to the fruit to be detected and collecting a near infrared spectrum of the fruit to be detected; and putting acquired spectrum signals into a pre-established model and getting the internal quality index of the fruit to be detected. The detection apparatus includes a spectrum collection device and a computer; wherein, the spectrum collection device is used in spectral scanning to the fruit to be detected and collection of near infrared spectrum signals of the fruit to be detected so as to transmit the signals to the computer; and the computer is used for putting the received spectrum signals into the pre-established model for data analysis so as to obtain the internal quality index of the fruit to be detected. The method applies the optical detection means based on near infrared to the detection process of fruit internal quality, and can release the labor force, and the method also has advantages of high detection precision, good consistency of results and high degree of automation, and creates the conditions for the standardized classification of internal quality of fruit products.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology
InactiveCN104020129ADiscrimination scienceAccurate discriminationMaterial analysis by optical meansBlack teaAmino acid content
The invention discloses a method for discriminating fermentation quality of congou black tea based on a near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology. The method comprises: selecting a sample and performing pre-processing; using high performance liquid chromatograph to determine the content of amino acids in the sample; acquiring the spectrum of the sample, utilizing synergy interval partial least square to establish a near-infrared-spectroscopy quantitative discrimination model for amino acids, finding amino acid variation distribution, and discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea. According to the method for discriminating the fermentation quality of congou black tea based on the near-infrared-spectroscopy-combined amino acid analysis technology, pretreatment is performed on an acquired original spectrum by utilizing standard normal variable transformation (SNVT), and the amino acid near-infrared discrimination model is constructed by employing synergy interval partial least square (SiPLS). The invention provides the quantitative determining method for scientifically accurately discriminating the fermentation quality congou black tea.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
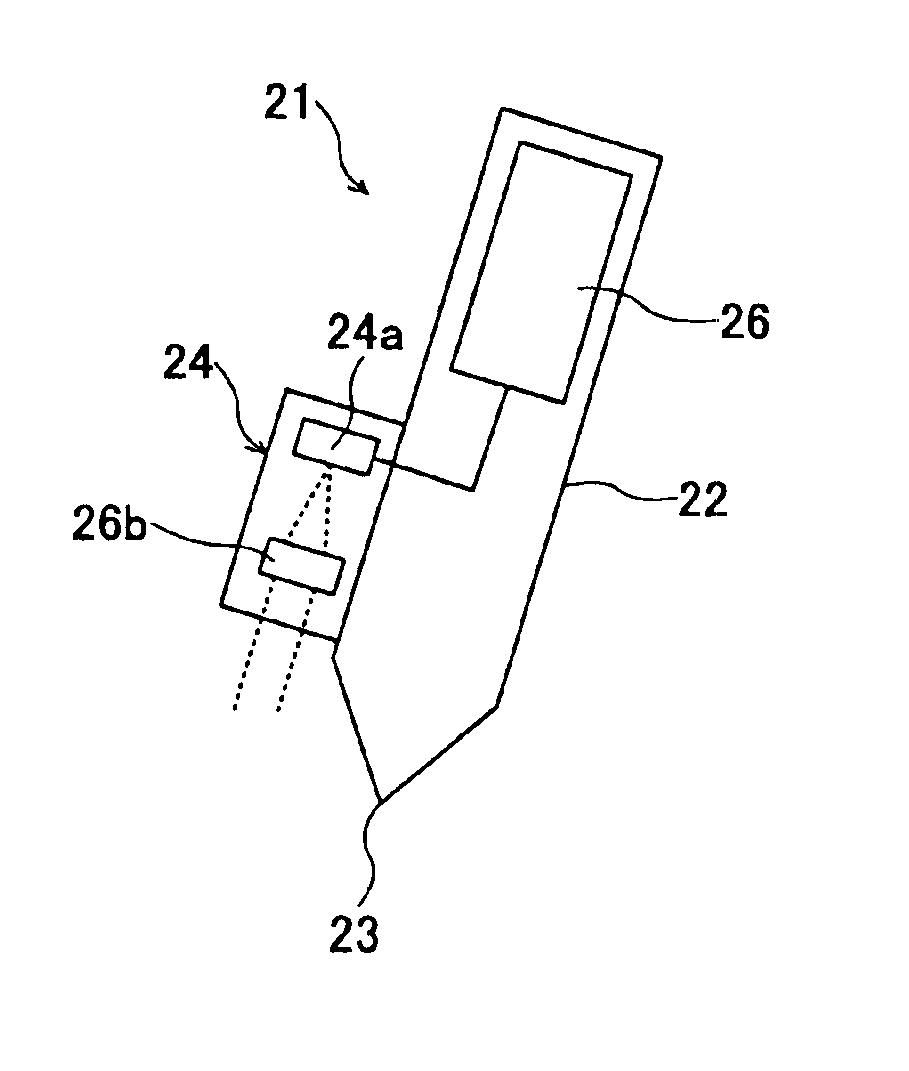
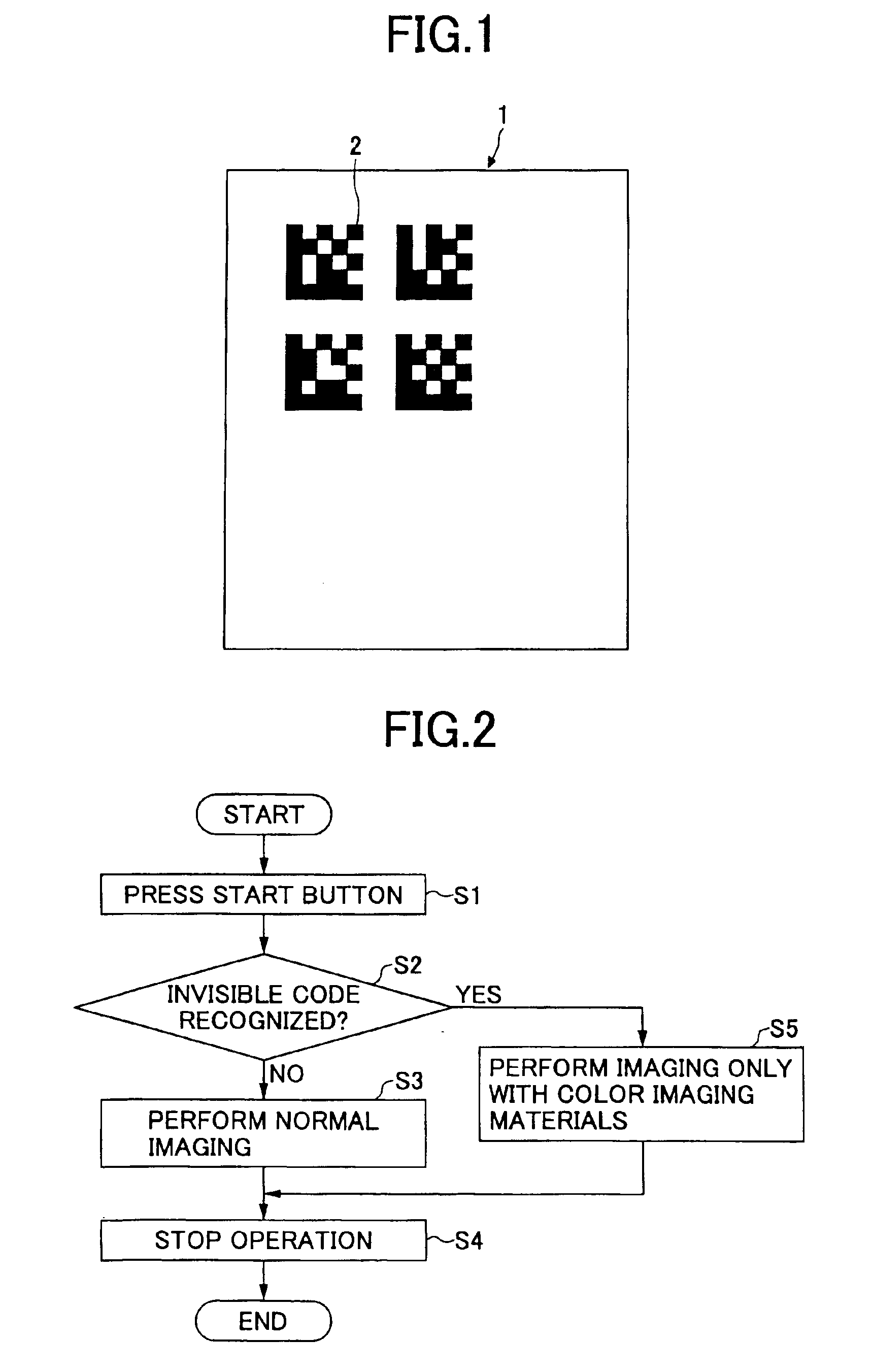
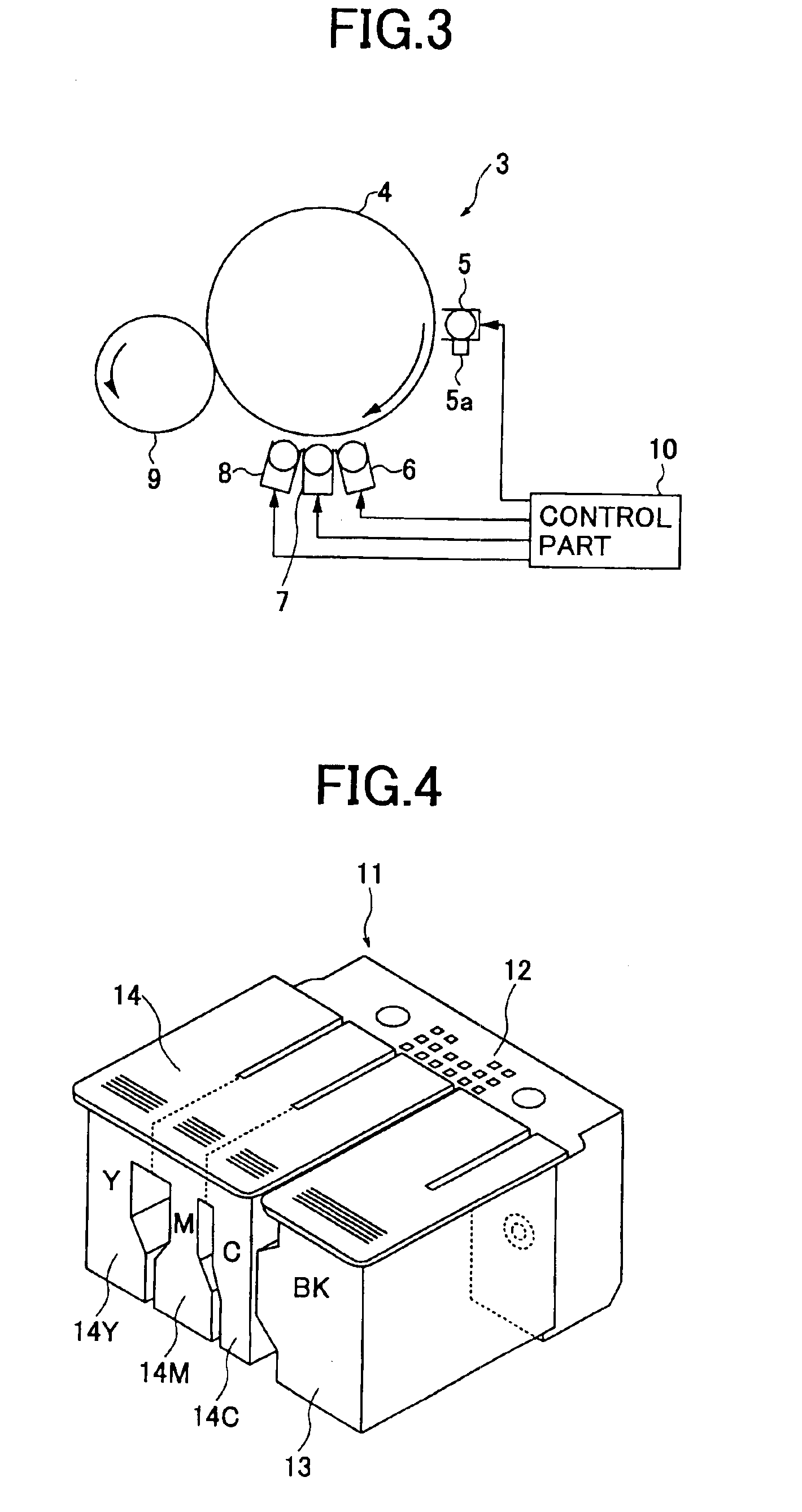
Imaging method, imaging apparatus, and image information management system
InactiveUS6935565B2Eliminate disadvantagesEasy to useElectrographic process apparatusImage data processing detailsNear infrared absorptionImaging equipment
An imaging method includes the steps of (a) determining whether an object on which an image is to be formed is an information display medium on which a code is formed with an imaging material formed of a near infrared absorbing pigment, and (b) forming the image on the object by a printer engine with an imaging material formed of a pigment absorbing no or little light in a near infrared spectral region if the step (a) determines that the object is the information display medium.
Owner:RICOH KK
Method for detecting multivariate adulteration of edible oil based on near-infrared spectroscopy
ActiveUS20190162658A1Easy to operateShort in sample detection timeMaterial analysis by optical meansTesting foodVegetable oilSpectral database
A method for multivariate adulteration detection on an edible oil includes (1) construction of a model: S1, acquiring near-infrared spectra of edible oils; S2, establishing a near-infrared spectral database of the edible oils; S3, establishing a multivariate adulteration detection model for a type of edible oil; and (2) application of the model: acquiring spectra of a sample to be tested according to the near-infrared spectral signal acquisition method in step S1, preprocessing the obtained near-infrared spectra by using the method in step S2 to obtain near-infrared spectral data of the sample, and determining the authenticity of the sample to be tested by using the multivariate adulteration detection model for the edible oil established in step S3. The method is simple and rapid in operation, can effectively and rapidly screen the authenticity of an edible vegetable oil, and has strong practicability.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Qualitative analysis method for improving identification result on basis of near-infrared mode
ActiveCN104374738AFree from destructionNo pollution in the processMaterial analysis by optical meansAlgorithmSpectral transformation
The invention discloses a qualitative analysis method for improving an identification result on the basis of the near-infrared mode. The qualitative analysis method comprises the steps of (1) acquiring near-infrared spectral data of a sample and determining a modeling set and testing sets; (2) carrying out pretreatment, partial-least-square feature extraction and orthogonal-linear-identification feature extraction on the modeling set and the testing sets in sequence; (3) calculating a spectral transformation matrix between the modeling set and the testing sets by adopting a direct model transferring method, and correcting the remaining testing sets; (4) establishing a quantitative analysis model; and (5) carrying out quantitative identification on the remaining testing sets by utilizing the established quantitative analysis model. The qualitative analysis method disclosed by the invention is established on the basis of near-infrared quantitative analysis, and the orthogonal-linear-identification method which is used in multi-classification and two-classification problems is used in the feature extraction step; in addition, the testing sets can be corrected by the direct model transferring method, so that the model applicability caused by long-time spectral shift of the same instrument can be realized and the result of quantitative identification is improved.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for searching analog tobacco leaf based on tobacco leaf near infrared spectra
ActiveCN101251471AMaterial analysis by optical meansComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionPrincipal component analysis
The present invention relates to a similar tobacco leaves search method based on the near infrared spectrum of tobacco leaves. The near infrared spectrum of tobacco leaves is used as basic data by the present invention. Distributed sampling is first carried out to the target tobacco leaves of each species; samples are pre-treated; the near infrared spectrum of the samples is obtained by scanning the samples on a near infrared spectrometer; principal component analysis (PCA) operation is carried out to a plurality of near infrared spectra of the target tobacco leaves of each species, obtaining loading matrixes, characteristic values and standardized residual errors, so as to generate a data model of the target tobacco leaves of each species; the near infrared spectrum of an unknown tobacco leaf, and the loading matrixes in the target tobacco leaf data models are used to carry out principal component decomposition calculation to the near infrared spectrum of the unknown tobacco leaf, so as to obtain the principal component score and decomposition residual error of the unknown tobacco leaf; the principal component score of the unknown tobacco leaf and the principal component space distance of the target tobacco leaf data models are calculated, and the residual error distance between the decomposition residual error of the unknown tobacco leaf and the standardized residual errors in the target tobacco leaf data models is also calculated; the distance between the unknown tobacco leaf and the target tobacco leaves is measured through the sum square root of the principal component space distance and the residual errors; the smaller the distance is, the higher the similarity is; finally, the distances between the unknown tobacco leaf and each target tobacco leaf is compared and sorted according to the size of the distances, so as to obtain a similar tobacco leaves search result.
Owner:CHINA TOBACCO HUNAN INDAL CORP
Multispectral imaging for quantitative contrast of functional and structural features of layers inside optically dense media such as tissue
InactiveUS7920908B2Improved measurement and analysisImprove dynamic rangeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTelevision system detailsImaging modalitiesMultispectral image
A method for the evaluation of target media parameters in the visible and near infrared is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a light source, an illuminator / collector, optional illumination wavelength selector, an optional light gating processor, an imager, detected wavelength selector, controller, analyzer and a display unit. The apparatus illuminates an in situ sample of the target media in the visible through near infrared spectral region using multiple wavelengths and gated light. The sample absorbs some of the light while a large portion of the light is diffusely scattered within the sample. Scattering disperses the light in all directions. A fraction of the deeply penetrating scattered light exits the sample and may be detected in an imaging fashion using wavelength selection and an optical imaging system. The method extends the dynamic range of the optical imager by extracting additional information from the detected light that is used to provide reconstructed contrast of smaller concentrations of chromophores. The light detected from tissue contains unique spectral information related to various components of the tissue. Using a reiterative calibration method, the acquired spectra and images are analyzed and displayed in near real time in such a manner as to characterize functional and structural information of the target tissue.
Owner:APOGEE BIODIMENSIONS
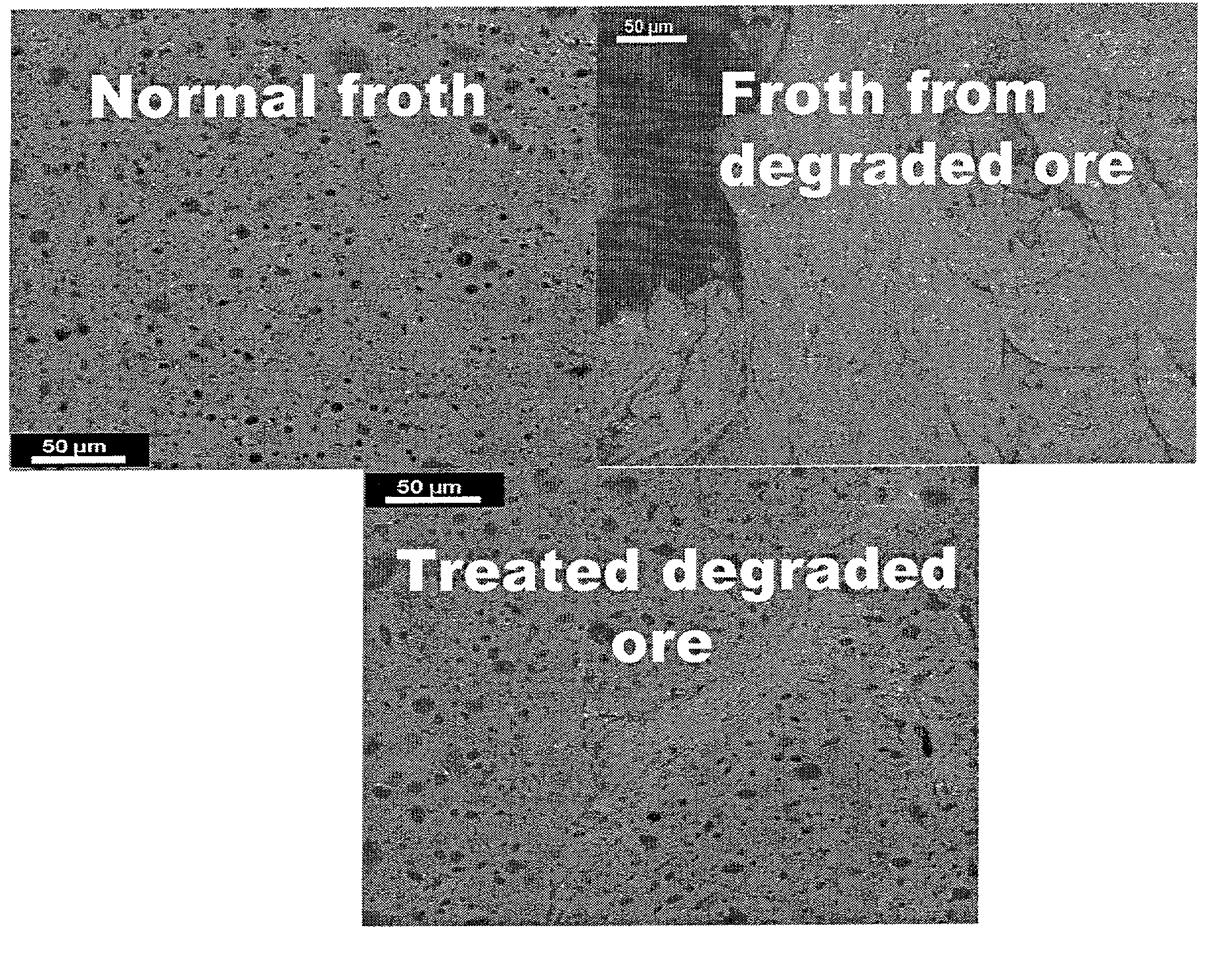
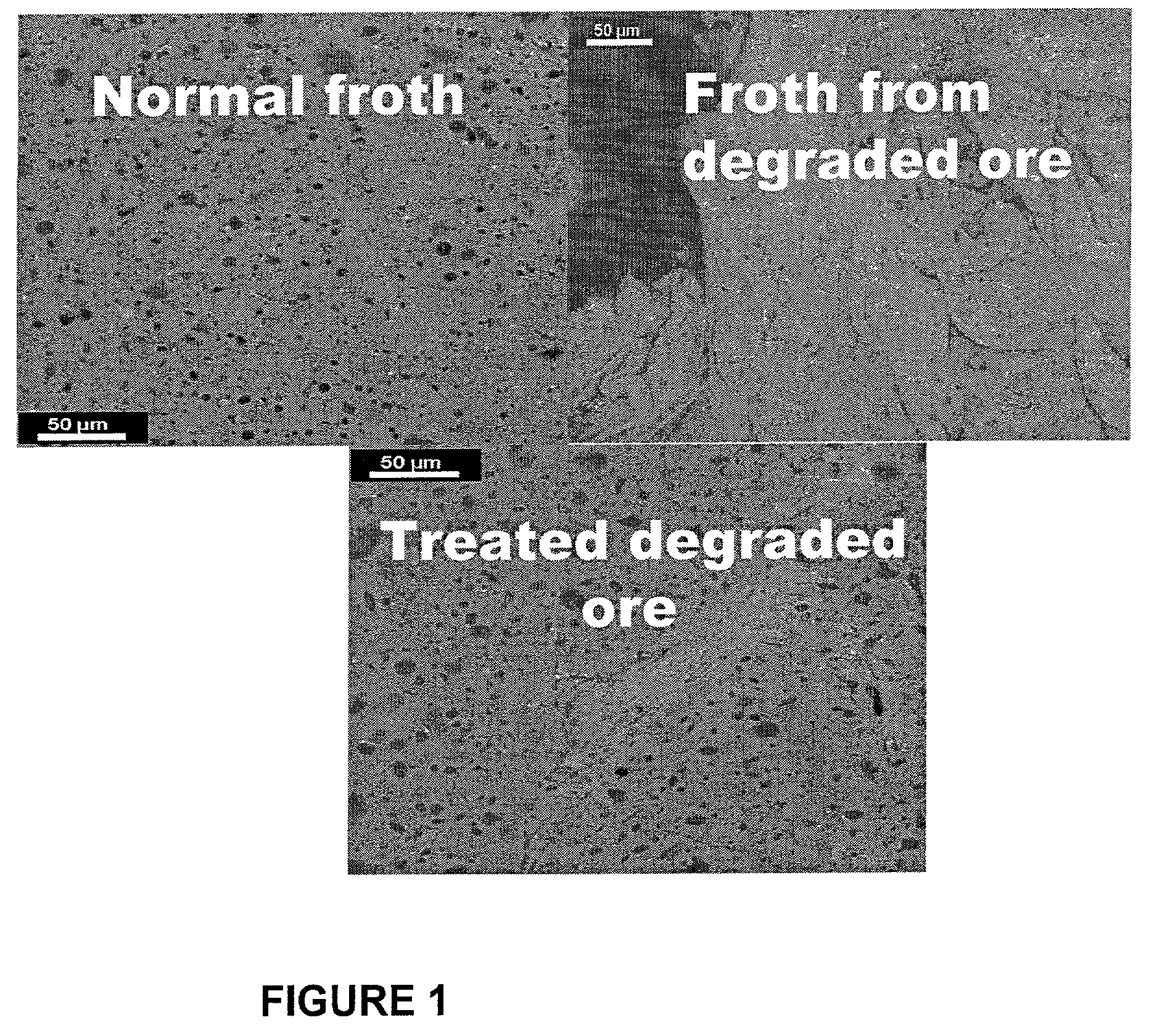
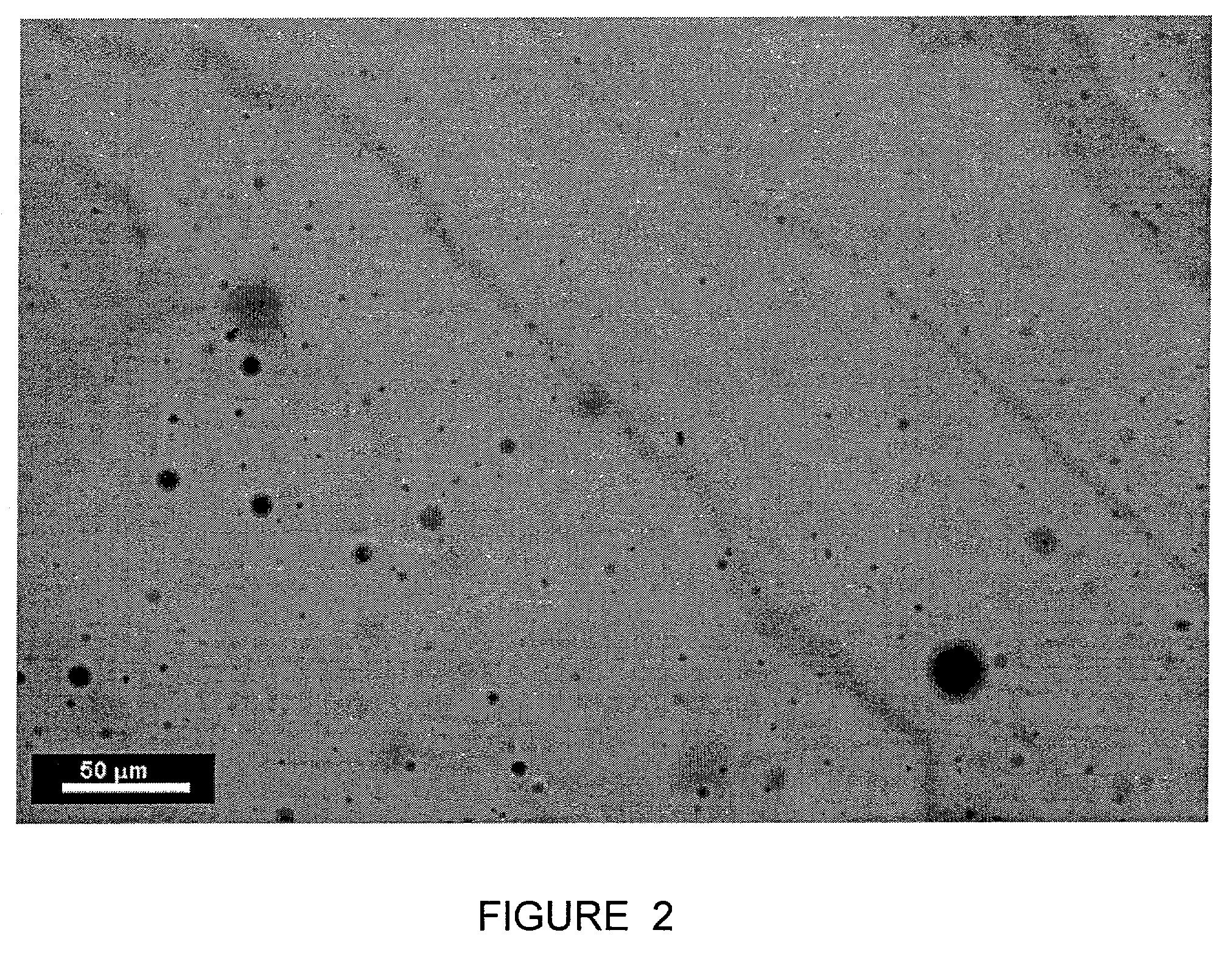
Processing of oil sand ore which contains degraded bitumen
ActiveUS7399406B2High densityRaise the ratioLiquid hydrocarbon mixture productionBiological testingWarm waterMining engineering
Methods are disclosed for identifying and treating oil sand ores having degraded bitumen. This can be done by considering the location from which the ore is mined or its history, or by microscopic examination of a bitumen froth made from the ore, or by near-infrared spectroscopy. Ore which contains degraded bitumen is treated with at least 0.05 wt / wt % alkaline material, preferably 0.1 wt. / wt % of such alkaline material, in the water addition step of a hot or warm water extraction process for the making of bitumen froth, such as the Clark process.
Owner:SUNCOR ENERGY INC
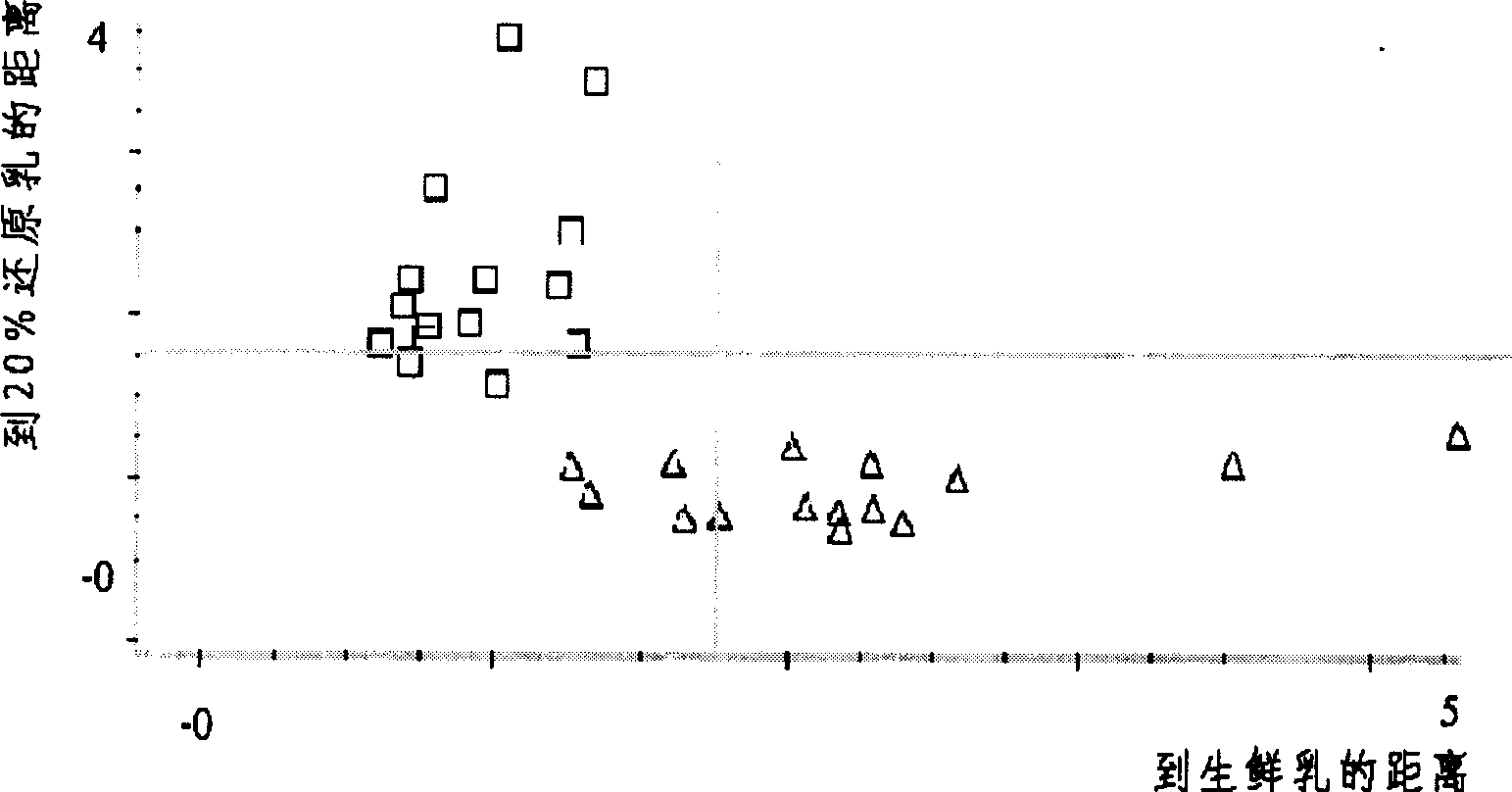
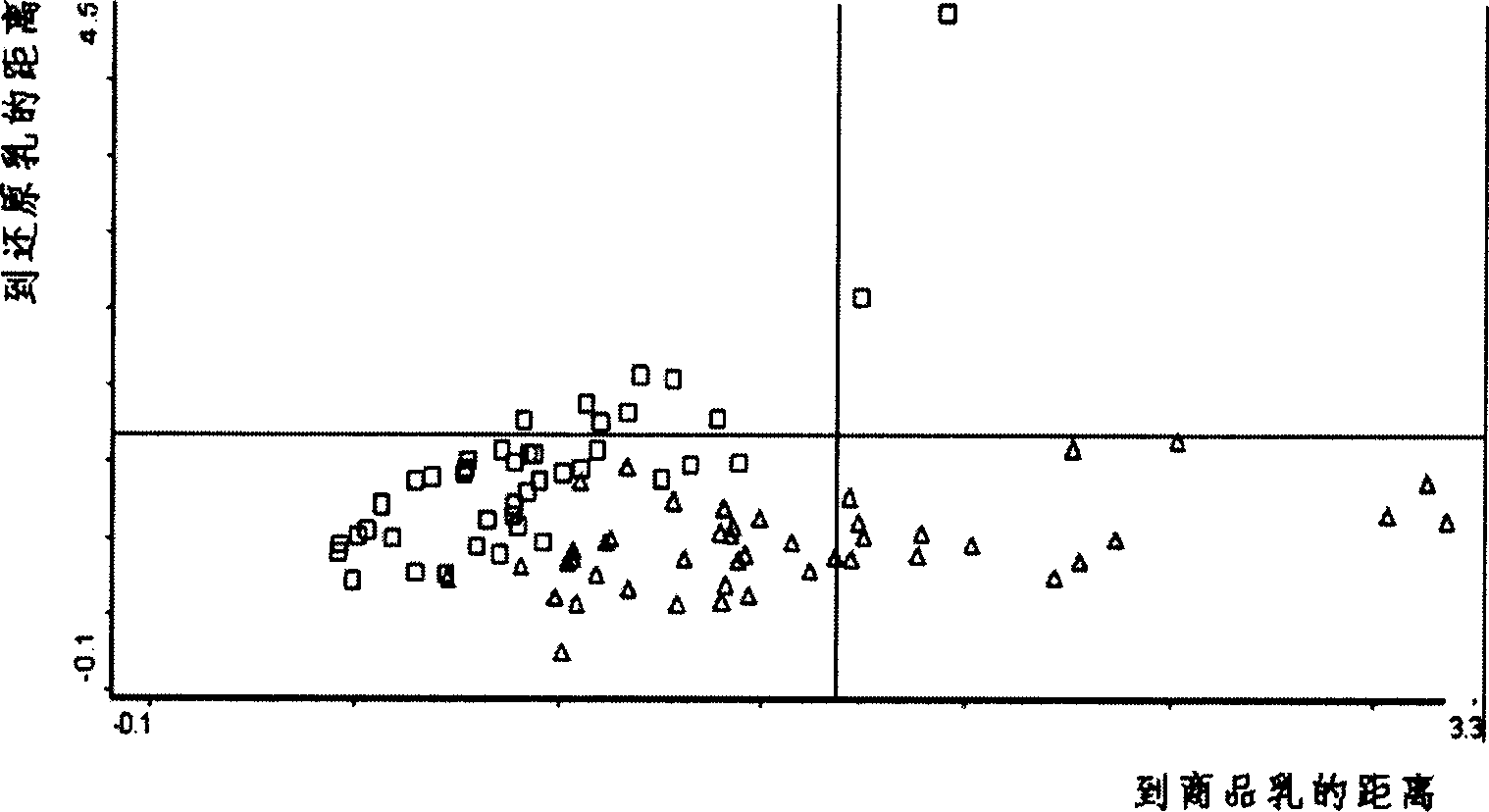
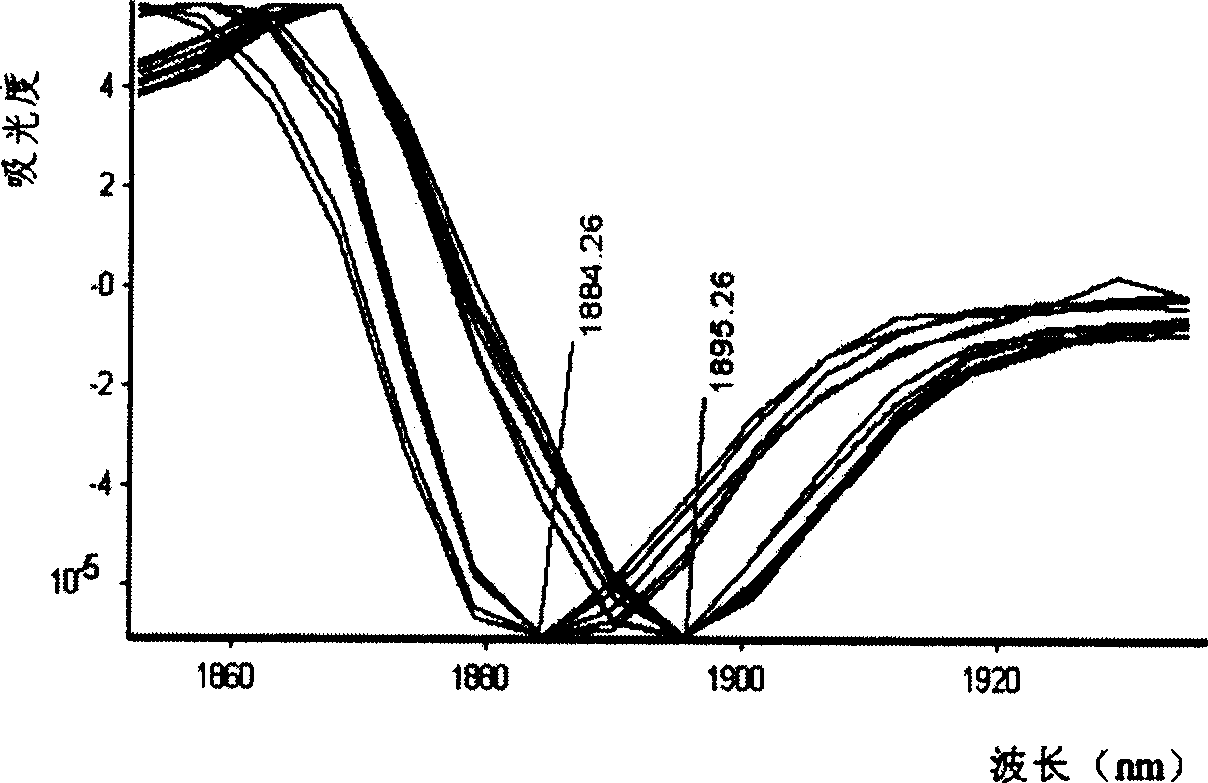
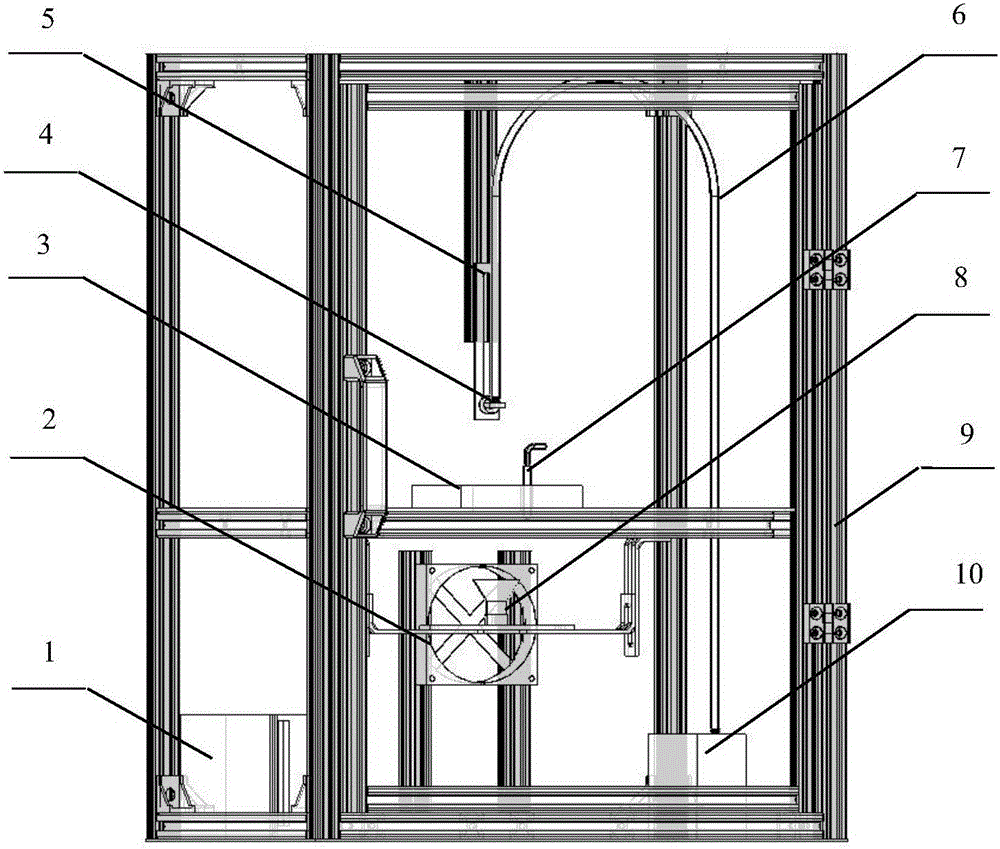
Method for identifying reductive milk in fresh milk and commodity milk by using near infrared spectrum
InactiveCN1804582ARealize authenticationImprove accuracyTesting dairy productsColor/spectral properties measurementsNear infrared spectraData treatment
The invention provides a method for using near infrared spectra to identify the reduction milk-like liquid of fresh milk and product milk, which comprises the following steps: first doing front process to the sample with known reduction milk-like liquid content, collecting the sample's near infrared spectra, establishing the qualitative or quantitative identifying model, collecting the near infrared spectra of the unknown sample to do data process and doing qualitative or quantitative identifying.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Visible/near infrared spectroscopy-based poultry infertile egg detecting method and device
InactiveCN106053358ANormal hatching effectHigh accuracy detectionColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyContact type
The invention relates to a visible / near infrared spectroscopy-based poultry infertile egg detecting method and device. The device is a poultry egg detecting device based on visible / near infrared spectroscopy. The device comprises a power source (1), a heat sink (2), an object carrying table (3), a light probe (4), a support (5), an optical fiber (6), a temperature sensor (7), a light source (8) and a detection dark box (9) and also comprises an optical signal sensor (10). The device can monitor environment temperatures in a poultry egg detection process and prevents influences of overhigh temperatures on normal incubation of poultry eggs to be detected. The adjustable probe is adopted, and the position of the light probe can be fixed without adjustment when samples of a same kind are detected, thus reducing detection time. The device adopts a non-contact detection process, overcomes disadvantages that traditional egg candling or other detecting methods need contact with poultry eggs to be detected, and avoids the problem of outside contamination caused by contact type detecting methods. The device and the method (through building an optimum mathematic model from poultry egg spectrum data and fertilization results) can detect, in high accuracy, infertile eggs and fertile eggs before incubation and can increase the production efficiency.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Near infrared spectrum based detection method for rapid discrimination of oil-tea camellia seed oil real property
ActiveCN102252972ADimension eliminationRemove order of magnitude constraintsColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectral bandsFt ir spectra
The invention discloses a near infrared spectrum based detection method for rapid discrimination of oil-tea camellia seed oil real property. The method comprises the following steps: first, a near infrared spectrometer is used to acquire spectrum data of an oil-tea camellia seed oil sample to be detected, and a near infrared spectrum scan wave number, a near infrared spectrum scan frequency and a resolution are controlled during acquisition; then data with spectral band within 5750-6000cm<-1> are selected from an acquired standard spectrum and treated with a smoothing, a first derivative processing and a self-normalization; at last the data is input into an oil-tea camellia seed oil discrimination and analysis model, and a mahalanobis distance discrimination method is employed to determine whether a sample point falls in a delimited real sample area in the oil-tea camellia seed oil discrimination and analysis model, so as to determine true or false of the sample to be detected. The detection method of the invention has advantages of simple operation, rapid detection, safety, environmental protection, and high precision.
Owner:HUNAN AGRI PRODS PROCESSING INST
Method for quickly on-line detection of traditional Chinese medicine Kuhuang injection effective ingredient using near infra red spectrum
InactiveCN101078685AColor/spectral properties measurementsTesting medicinal preparationsReal time analysisHplc method
The invention discloses a method for measuring effective component content in kuhuang injection on line by near-infrared spectroscopy quickly. Effective components in kuhuang injection mainly comprise aloe-emodin, rhein, emodin, chrysophanol, physcion, sophocarpine and matrine so on. Near-infrared absorption spectroscopy collecting kuhuang injection make data of effective component content relate with near-infrared spectroscopy by HPLC method. Calibration model is built by partial least-squares regression method. Quick on-line measurement for effective component in injection can be accomplished. Studying result shows that near-infrared spectroscopy analyzing method can measure effective component in kuhuang injection effectively. The method is provided with simple pretreatment for sample, quick measurement and measuring multiple components at the same time. It can be used in on-line analysis and on-line quality control in tcm manufacture process.
Owner:常熟雷允上制药有限公司
Method for detecting urea-doped milk based on synchronous-asynchronous two-dimensional near-infrared related spectra
ActiveCN104316491AHigh spectral resolutionHigh selectivityMaterial analysis by optical meansSpecial data processing applicationsNear infrared spectraMulti dimensional
The invention relates to a method for detecting urea-doped milk based on synchronous-asynchronous two-dimensional near-infrared related spectra. The method comprises the following steps: 1, preparing pure milk for experiments and urea-doped milk; 2, respectively scanning the near-infrared spectra of the pure milk for experiments and the urea-doped milk; 3, calculating to obtain the normalization synchronous-asynchronous two-dimensional near-infrared related spectrum matrix of the pure milk for experiments and the normalization synchronous-asynchronous two-dimensional near-infrared related spectrum matrix of the urea-doped milk; 4, building a discrimination model with a categorical variable matrix by a multi-dimensional partial least squares; 5, scanning and calculating unknown sample milk to obtain the synchronous-asynchronous two-dimensional near-infrared related spectrum matrix of the unknown sample milk, and substituting into the discrimination model to obtain whether urea is doped or not. Similarity and difference information of a to-be-analyzed system, changing with external interference, are fully utilized, and the influence of the single adoption of synchronous spectrum or asynchronous spectrum matrix redundant information on the model is overcome. The method is simple and scientific, and the analysis efficiency and the discriminating accuracy are high.
Owner:天津市浓昇农业科技有限公司
Quick edible oil variety identification method based on multisource spectral feature fusion
ActiveCN105806824AComprehensive Internal Characteristic InformationStrong complementarityRaman scatteringFt ir spectraPhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a quick edible oil variety identification method based on multisource spectral feature fusion. The method comprises the steps of selecting an unknown variety of edible oil sample to be identified, acquiring a Raman spectrum chart and a near infrared spectrum chart, preprocessing the Raman spectrum chart and the near infrared spectrum chart to obtain a preprocessed Raman spectrum chart and a preprocessed near infrared spectrum chart, conducting feature extraction on the preprocessed Raman spectrum chart and the preprocessed near infrared spectrum chart to obtain a Raman characteristic variable and a near infrared characteristic variable, conducting spectral characteristic fusion on the Raman characteristic variable and the near infrared characteristic variable to obtain a characteristic fusion spectrum chart, and conducting variety identification on the unknown variety of edible oil sample by means of an optimized qualitative model. The method is safe and quick, detection is convenient, identification accuracy is high, and practical value and popularization value are high.
Owner:WUHAN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
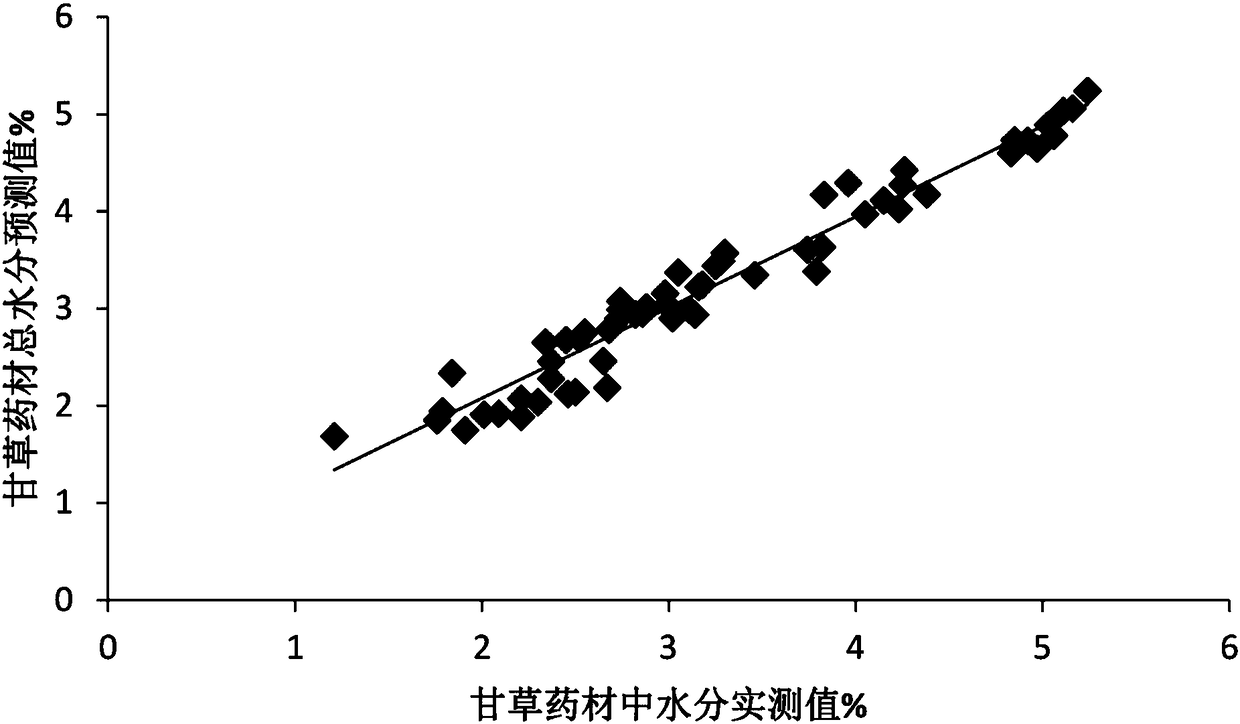
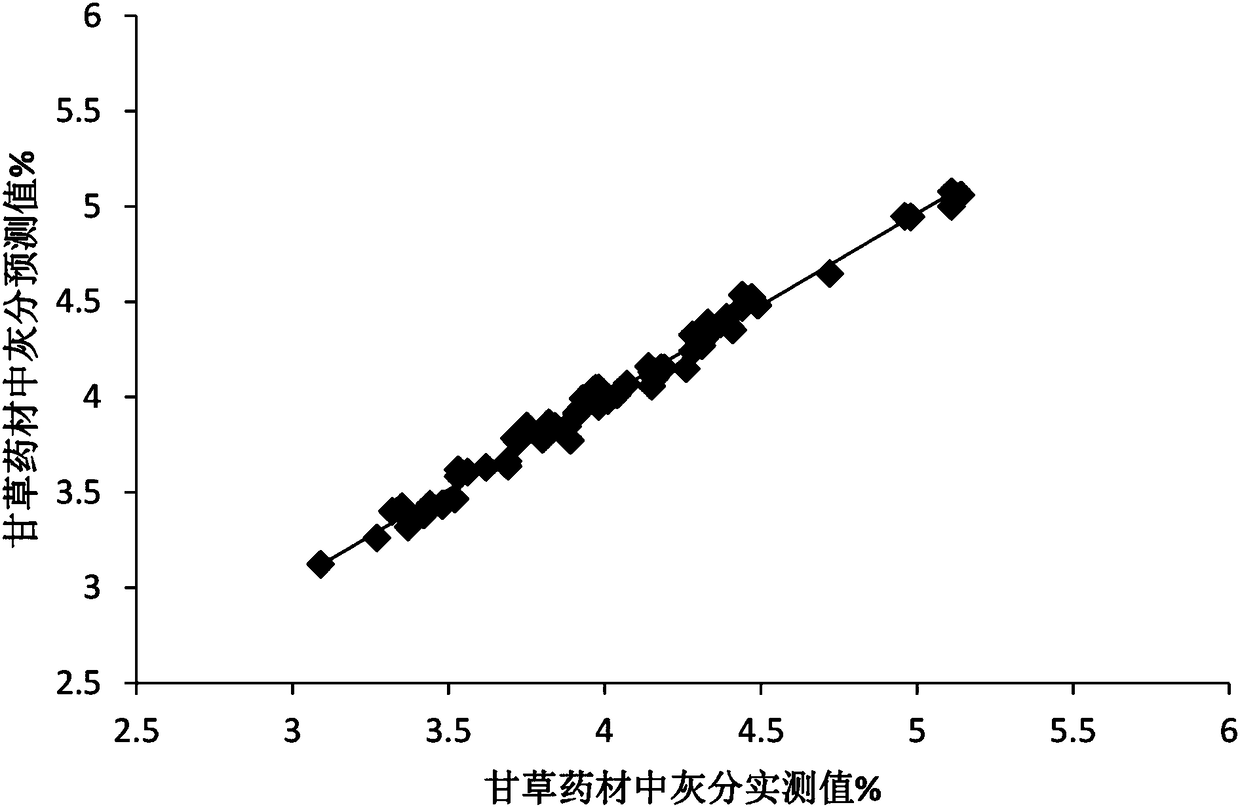
Near infrared quantitative analysis model for radix glycyrrhizae medicinal material and detection method and standard
InactiveCN108519348AQuality judgmentMeet detectionMaterial analysis by optical meansPretreatment methodMultivariate calibration
The invention belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicinal materials analysis and detection and the technical field of near infrared spectroscopic analysis and detection and relatesto a near infrared quantitative analysis model for a radix glycyrrhizae medicinal material, an establishment method and a detection method and standard for the radix glycyrrhizae medicinal material.The establishment method for the model comprises the following steps: collecting a radix glycyrrhizae medicinal material sample; measuring the content of a quality control index component of the radixglycyrrhizae medicinal material; acquiring a near infrared spectrum; preprocessing the original near infrared spectrum and determining an optimal preprocessing method and a modeling spectrum waveband; establishing a near infrared quantitative calibration model for the near infrared spectrum and a corresponding measured value of the content of the quality control index component of the radix glycyrrhizae medicinal material by use of a multivariate calibration method; verifying the near infrared quantitative calibration model. The detection method for the radix glycyrrhizae medicinal material comprises the following steps: acquiring and importing a near infrared spectrum of a radix glycyrrhizae sample into the quantitative calibration model and predicting the content of the quality controlindex component. According to the method, the radix glycyrrhizae medicinal material can be nondestructively detected rapidly, and the authenticity and the quality of the medicinal material can be qualitatively and quantitatively detected rapidly.
Owner:NINGXIA MEDICAL UNIV
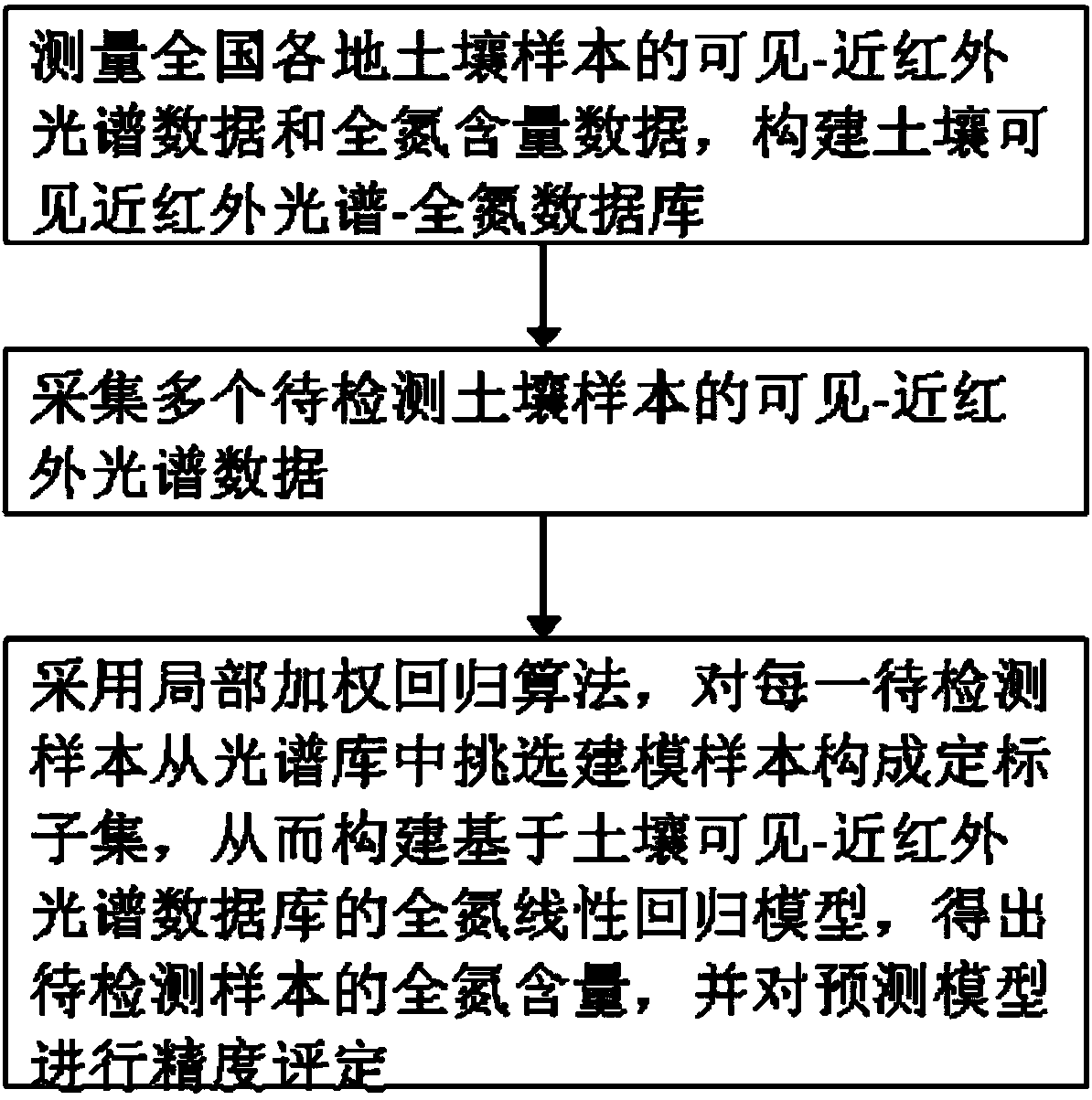
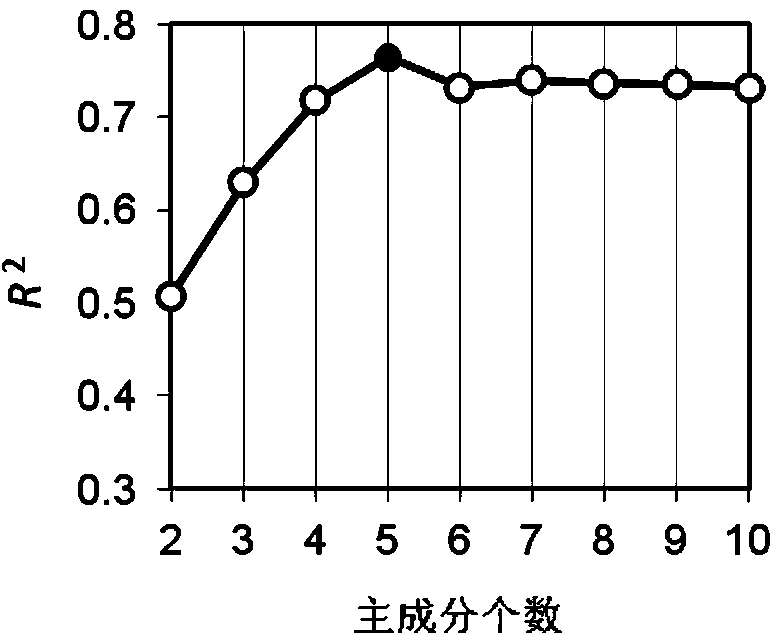
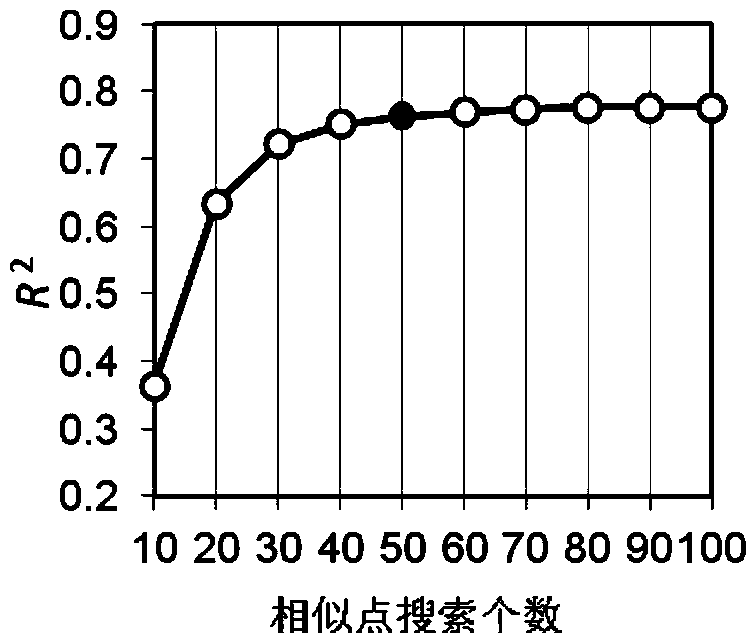
Soil total nitrogen real-time detection method based on soil visible-near infrared spectrum library
InactiveCN103884661ASolve the repeatabilitySolve the problem that the data format is not uniform and cannot be sharedColor/spectral properties measurementsSpecial data processing applicationsSoil sciencePredictive methods
The invention discloses a soil total nitrogen real-time detection method based on a soil visible-near infrared spectrum library. The soil total nitrogen real-time detection method comprises the following steps: measuring data of visible-near infrared spectrums and data of total nitrogen contents of soil samples across the country to establish a soil visible near infrared spectrum-total nitrogen database; collecting the data of the visible-near infrared spectrums of a plurality of soil samples to be detected; selecting model establishing sample from the spectrum library for each sample to be detected to form a calibration subset by using a local weighted regression algorithm to establish a total nitrogen linear regression model based on the soil visible-near infrared spectrum database to obtain the total nitrogen contents of the samples to be detected, and evaluating accuracy of a prediction model. Compared with the conventional method for establishing a prediction model by merely using all the soil sample spectrums in the region, the prediction model established by the method is excellent in stability and universality, so that the prediction capability is significantly improved and the defects that the soil spectrums are repeatedly collected, the data format is non-uniform and is incapable of being shared, and the established models are incapable of being universally used can be avoided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for measuring density of Huoli Wood using near infrared spectrum
InactiveCN1936537AQuick analysisWeighing by removing componentScattering properties measurementsWater dischargeDiffuse reflection
This invention relates to a method for testing density of alive stumpage wood with near infrared spectrum including: selecting not less than 120 bug-free wood samples, controlling the temperature of the samples at 20-25deg.C, dividing them into five regions of moisture rate of 3-30%, 30-80%, 80-30%, 130-200%, 200-300% and collecting the diffuse reflection near infrared spectrums of the woods, applying a water discharge method to test the volume when the sample is full of water, applying a drying method to test the absolute weight of the sample to compute the water ratio and density of the woods, setting up a pretest model of moisture, setting up density correction models separately for five regions of water rate and utilizing the set-up models to analyze the density of unknown samples.
Owner:INST OF WOOD INDUDTRY CHINESE ACAD OF FORESTRY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com