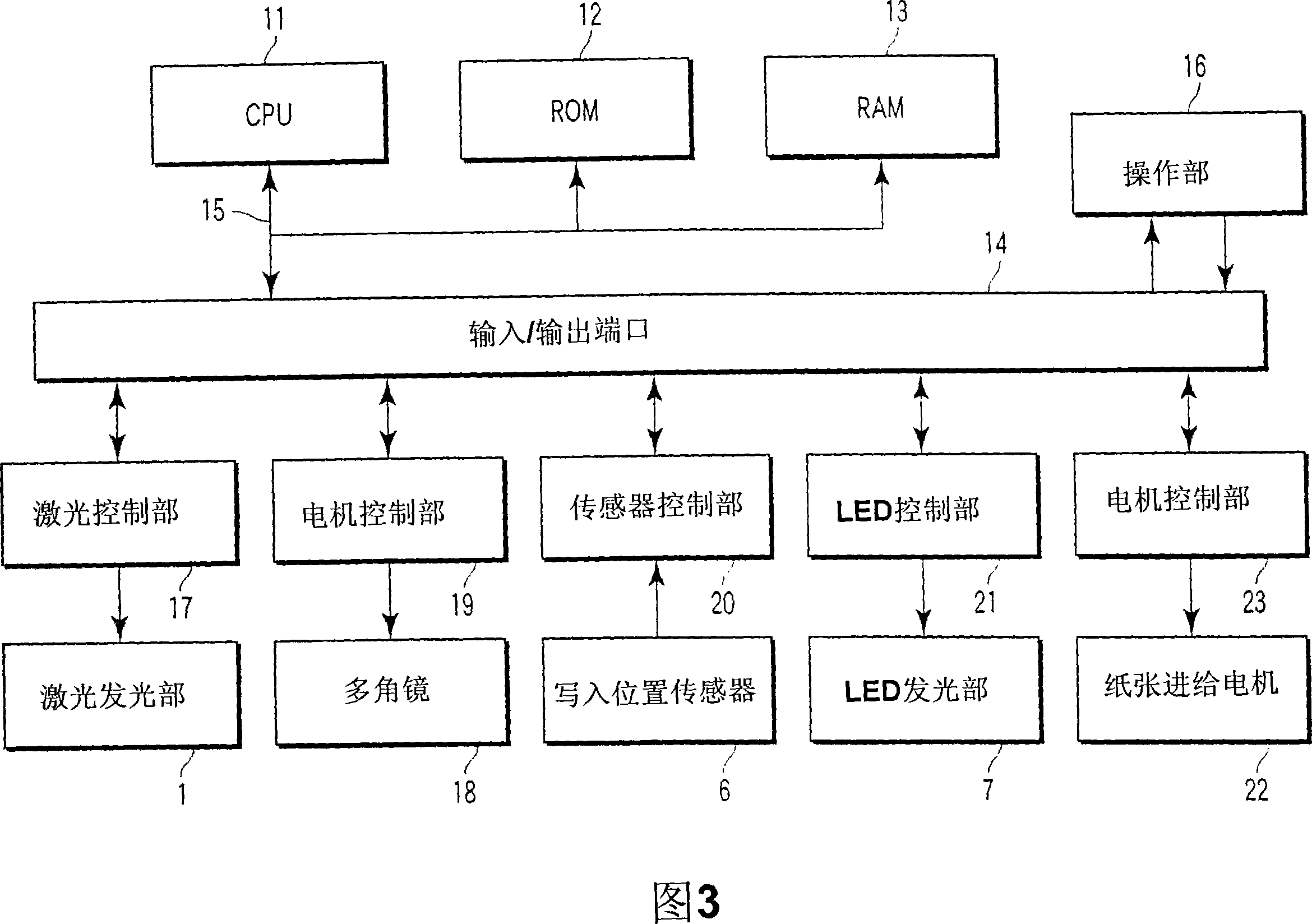
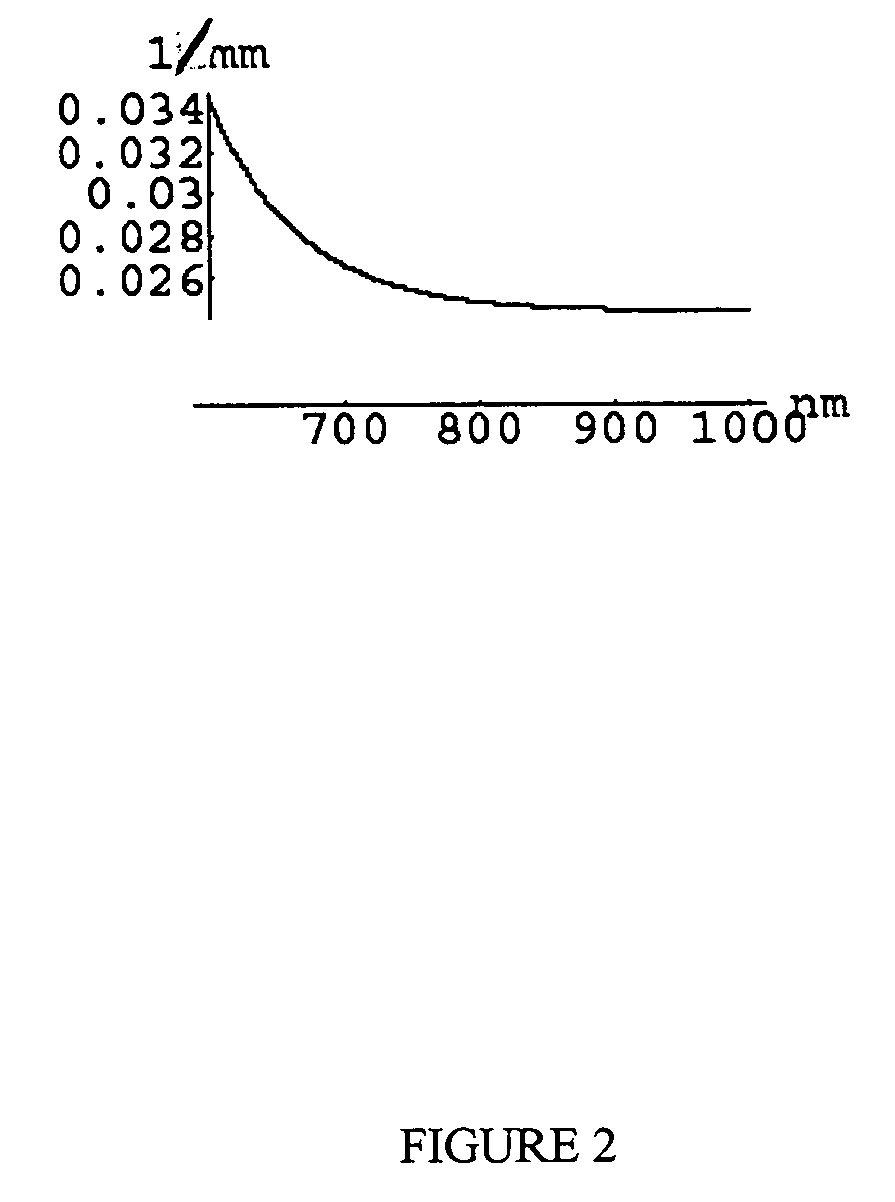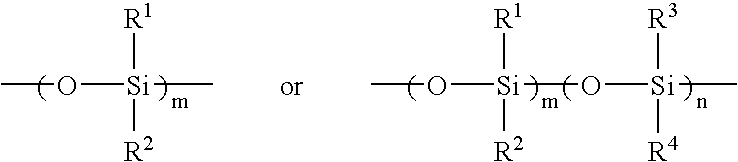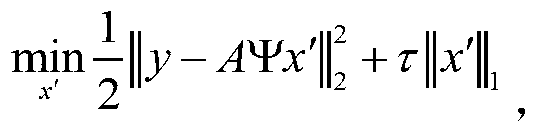Patents
Literature
62 results about "Calorescence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
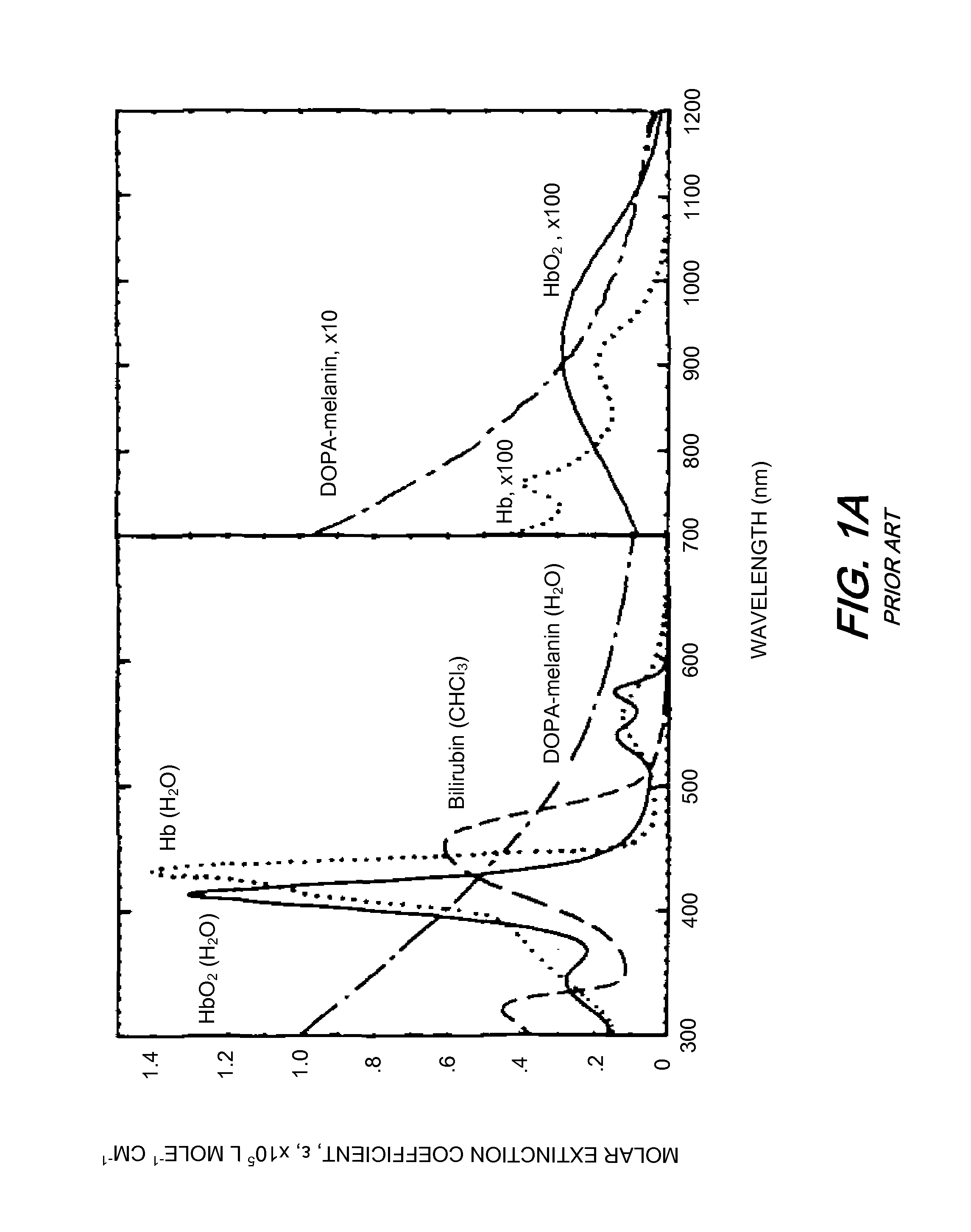
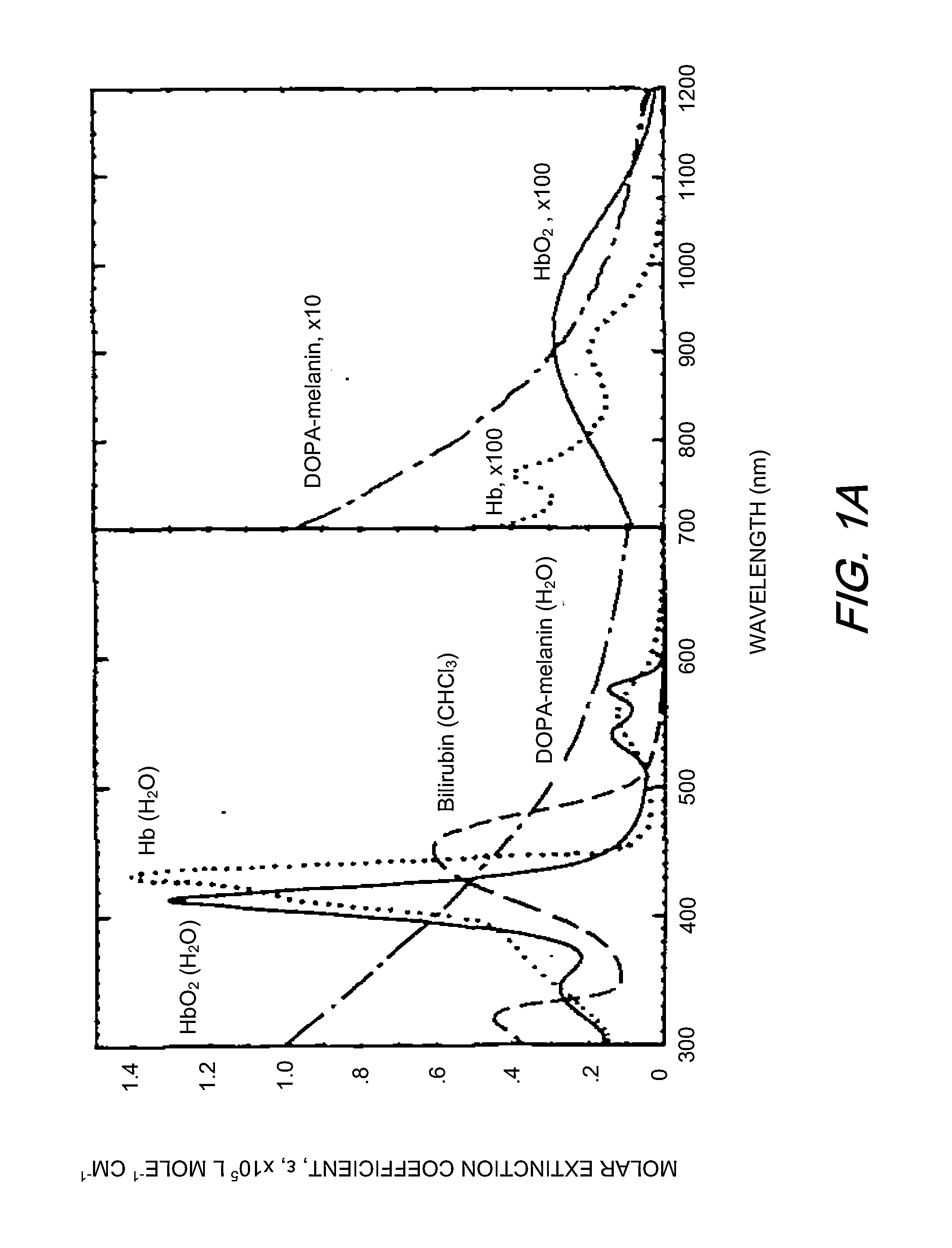
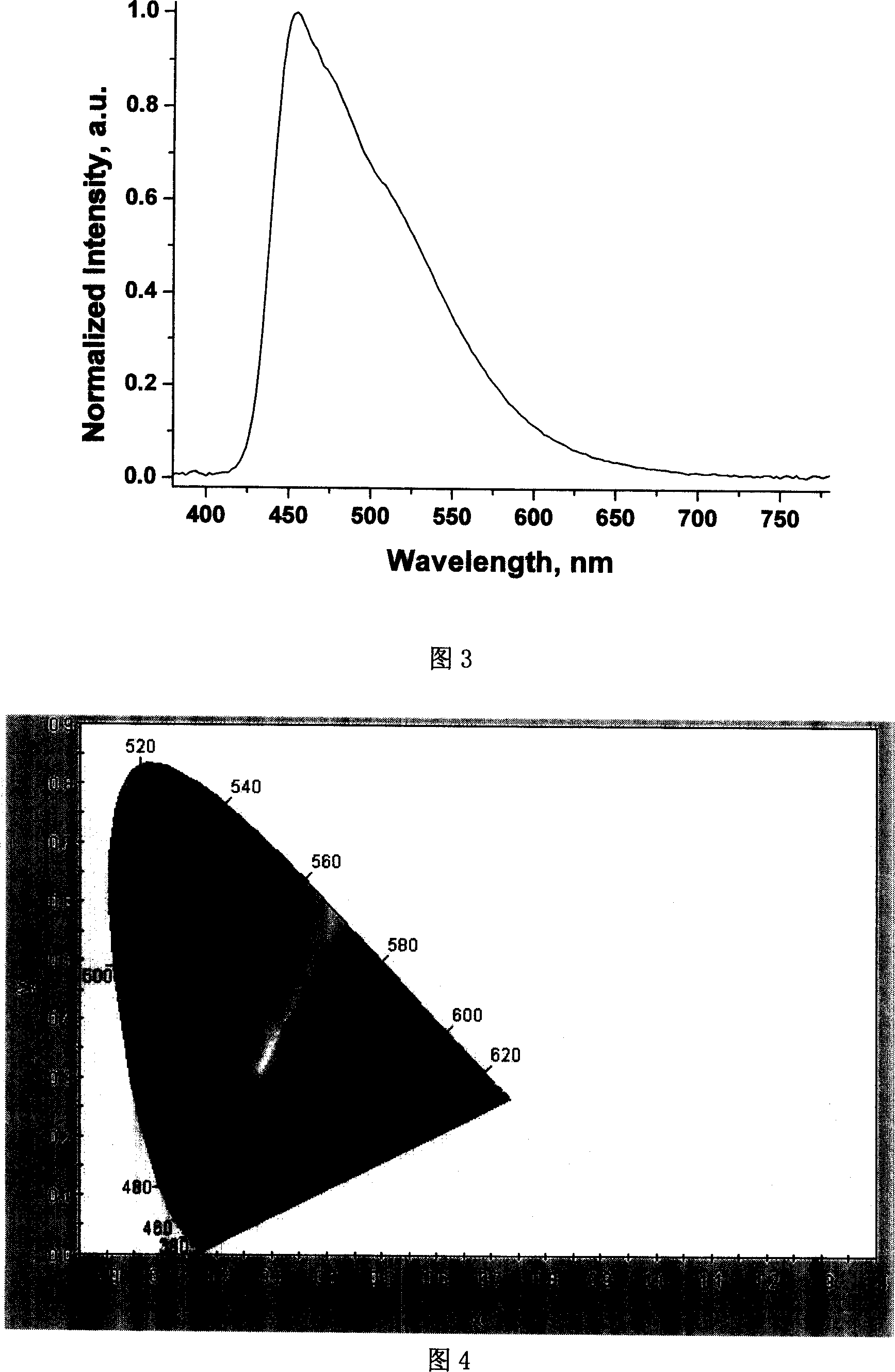
Calorescence is when matter absorbs infrared radiant energy and emits visible radiant energy in its place. For example, some kinds of flammable gas give off large amounts of radiant heat and very little visible light when burning, and if a piece of metal is placed into such a flame, the metal will become bright red-hot—which is to say the metal absorbs invisible infrared and emits visible radiation. The word calorescence was coined in 1864 on the model of the word fluorescence which had been coined in 1852. At that time, fluorescence was defined as absorption in the ultraviolet part of the spectrum followed by emission in the visible part of the spectrum. Calorescence was defined complementarily as absorption in the infrared followed by emission in the visible.
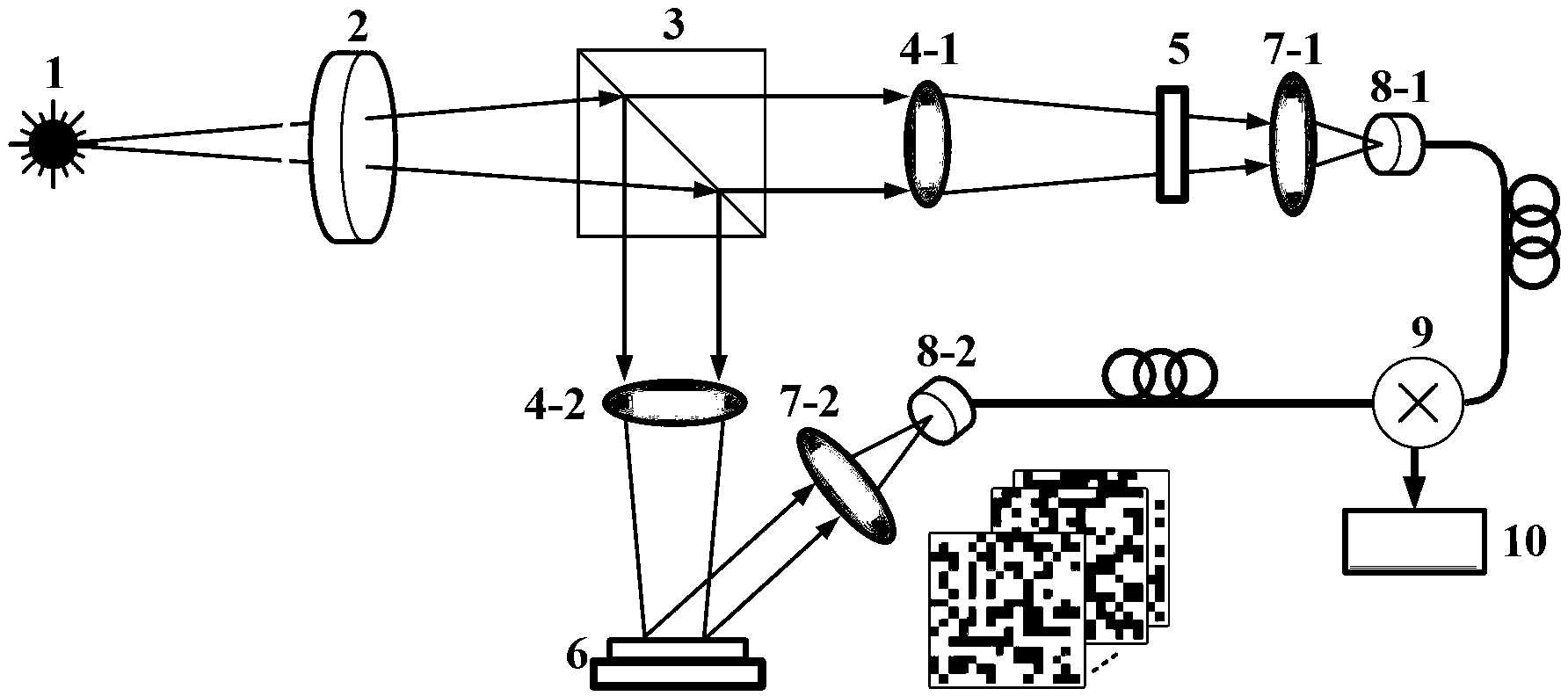
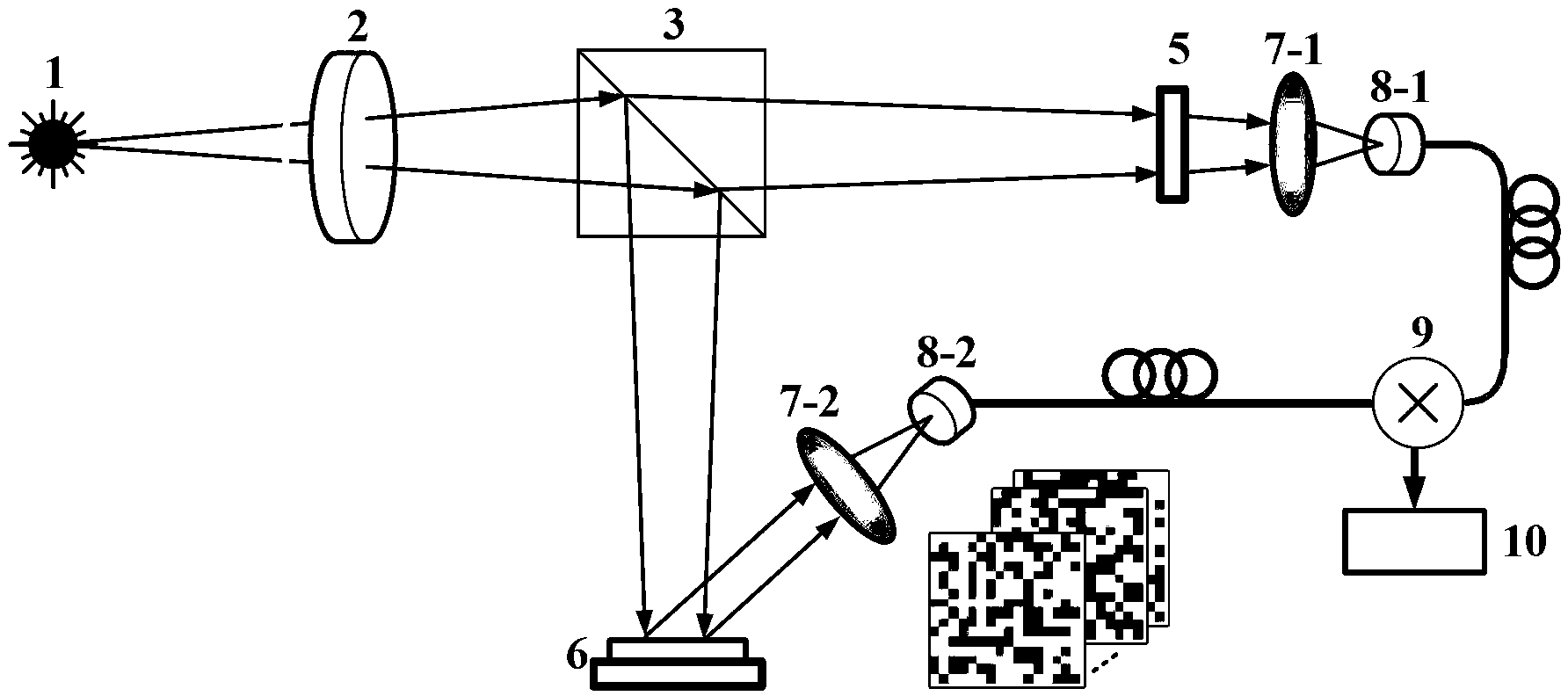
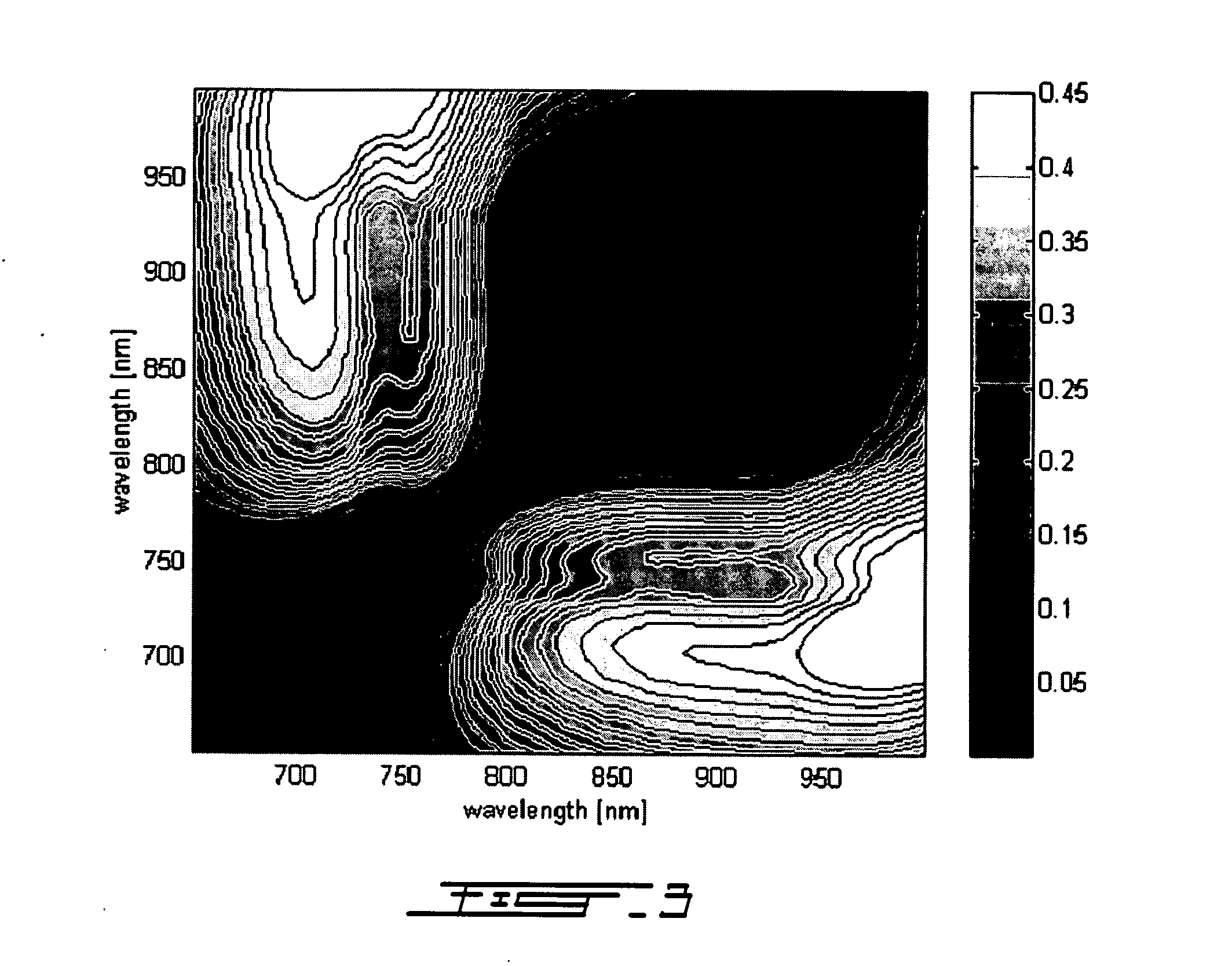
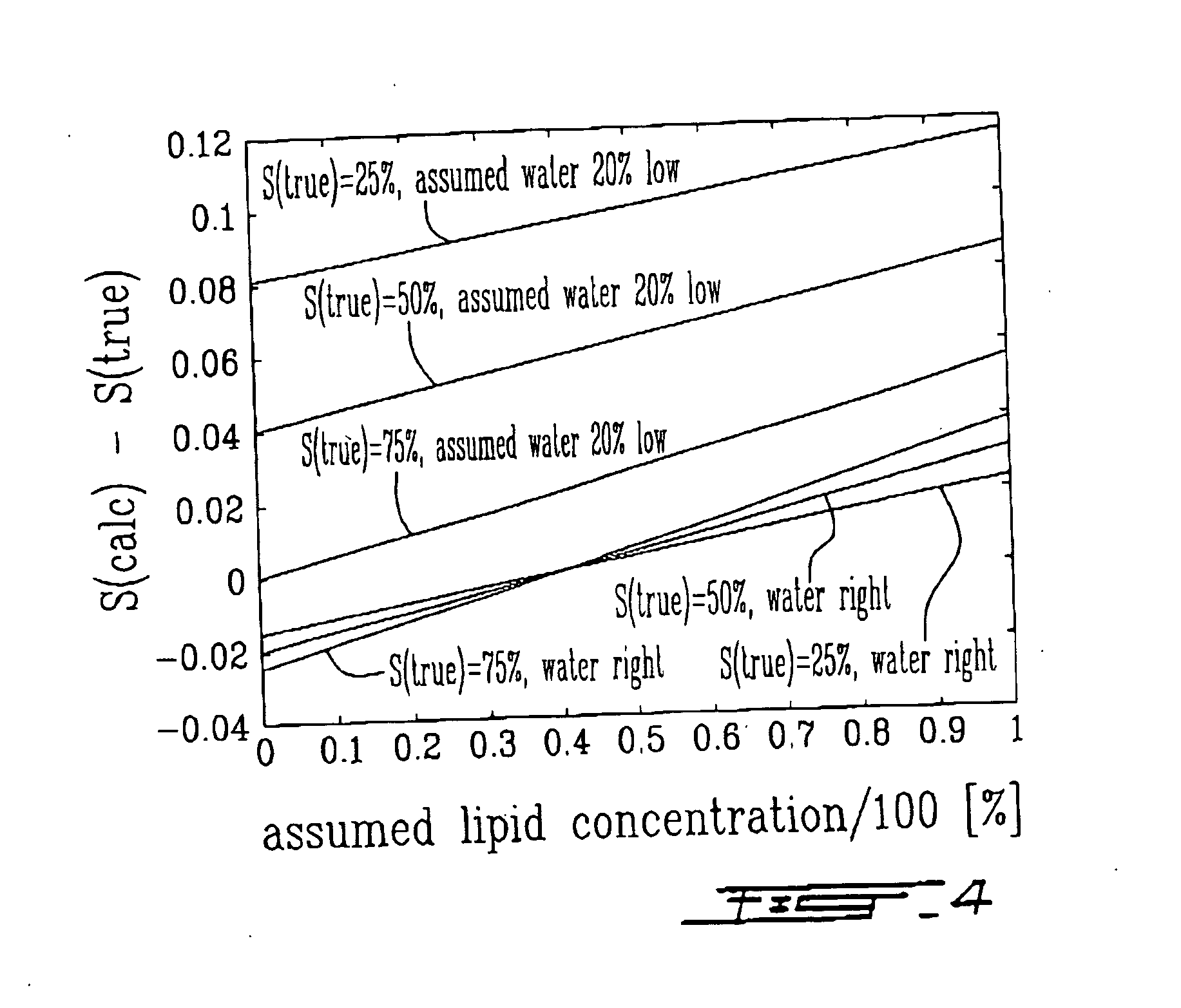
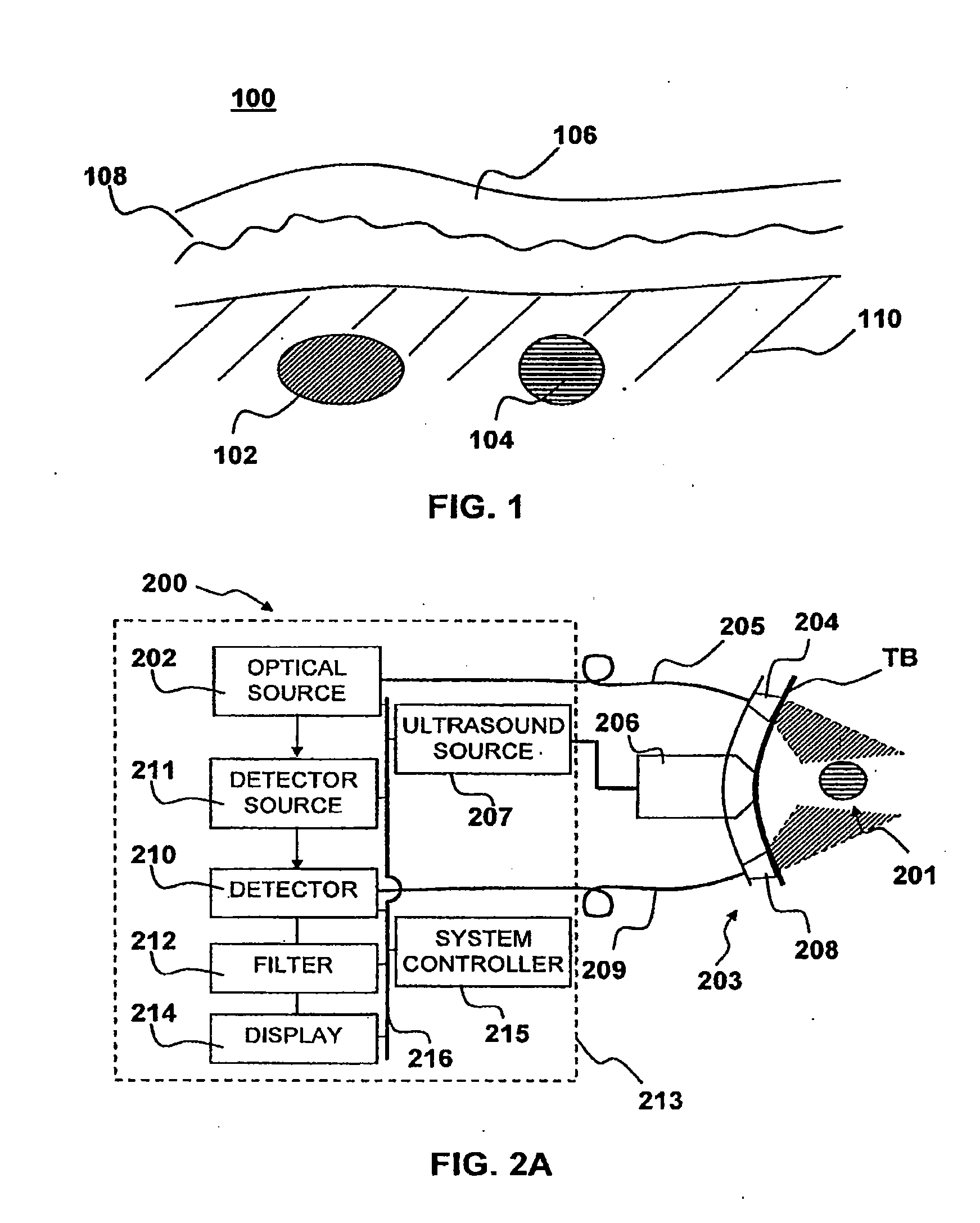
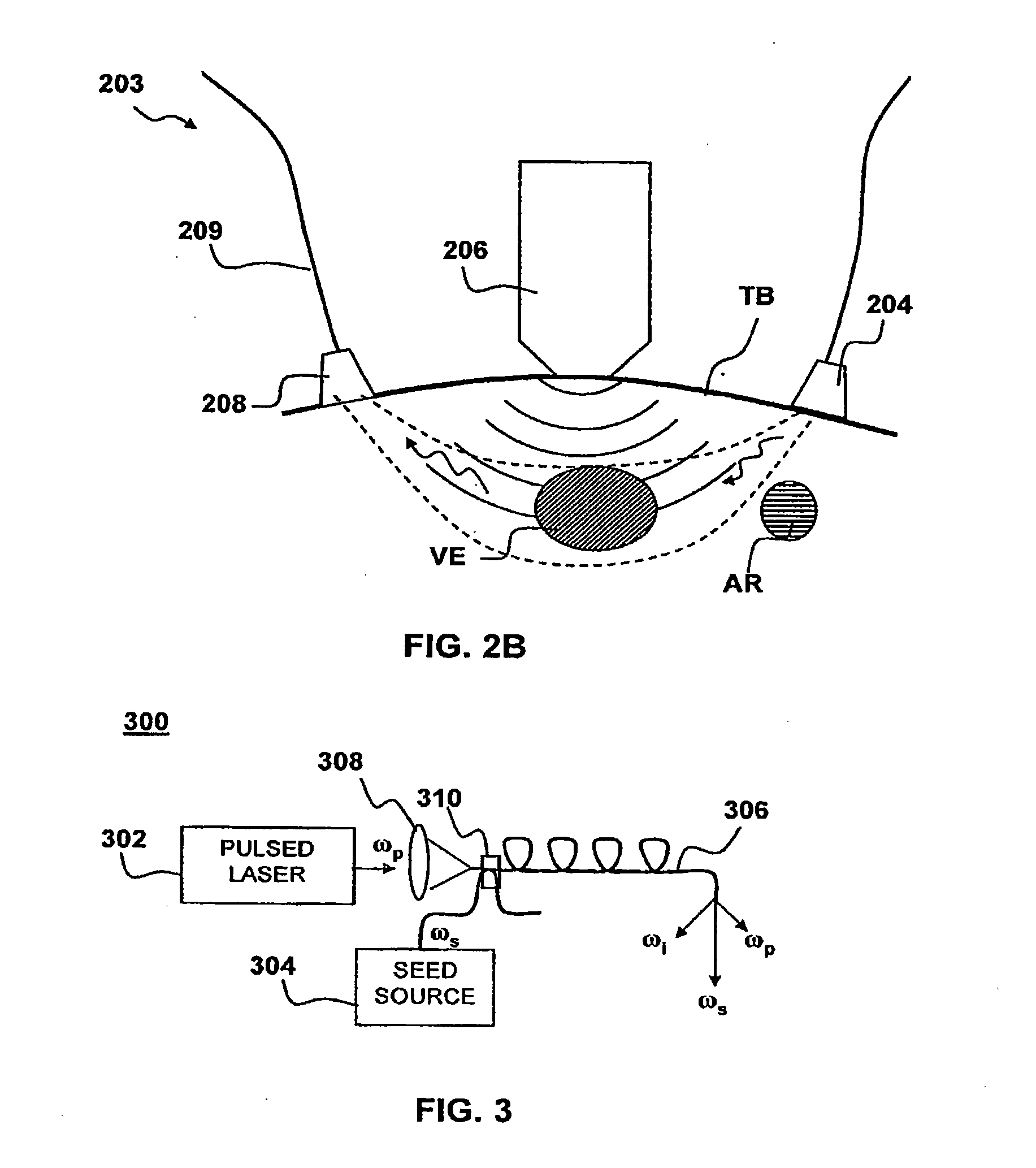
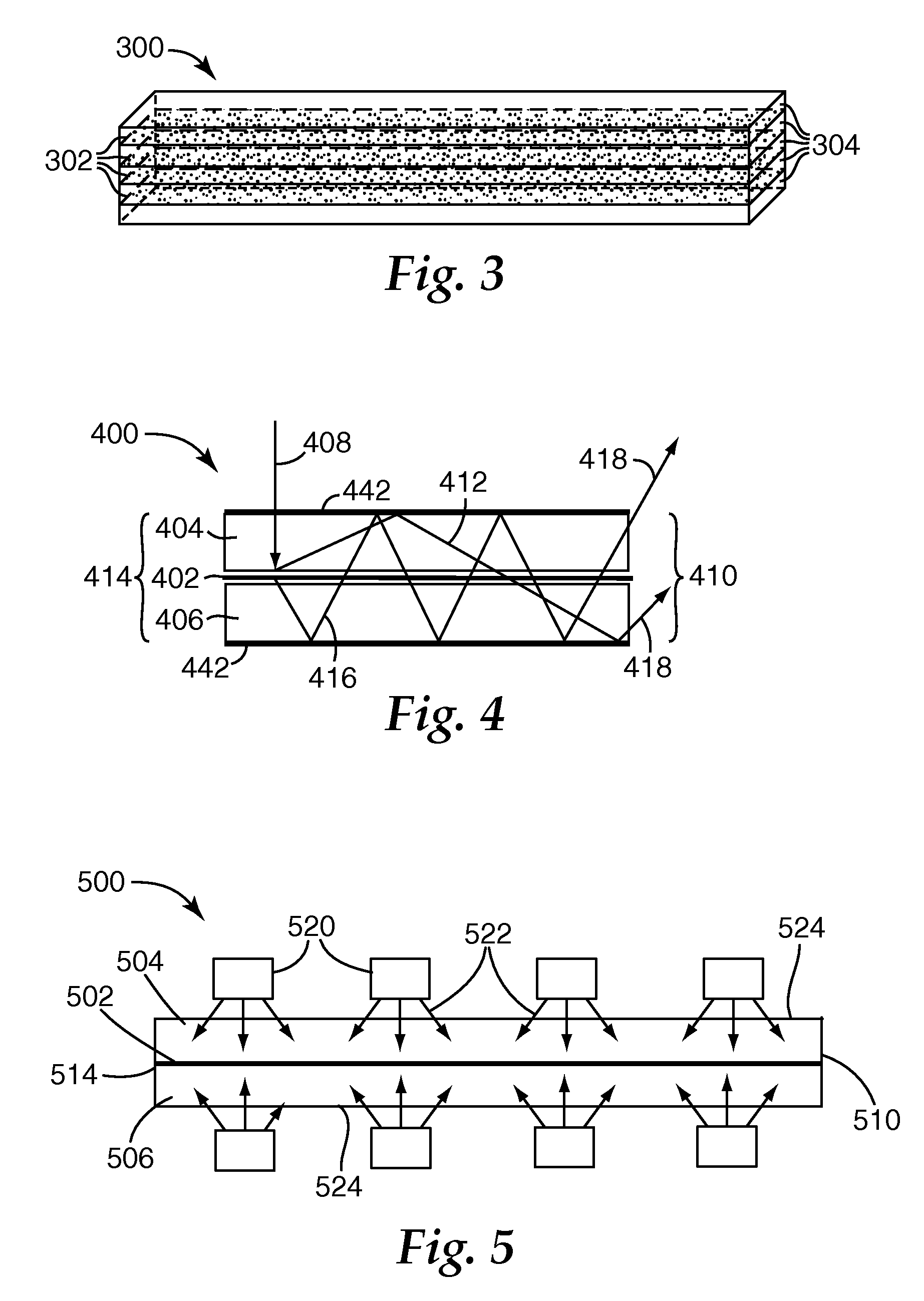
Multispectral imaging for quantitative contrast of functional and structural features of layers inside optically dense media such as tissue
InactiveUS20050273011A1Easy to measureImprove analysisUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsTelevision system detailsCalorescenceWavelength
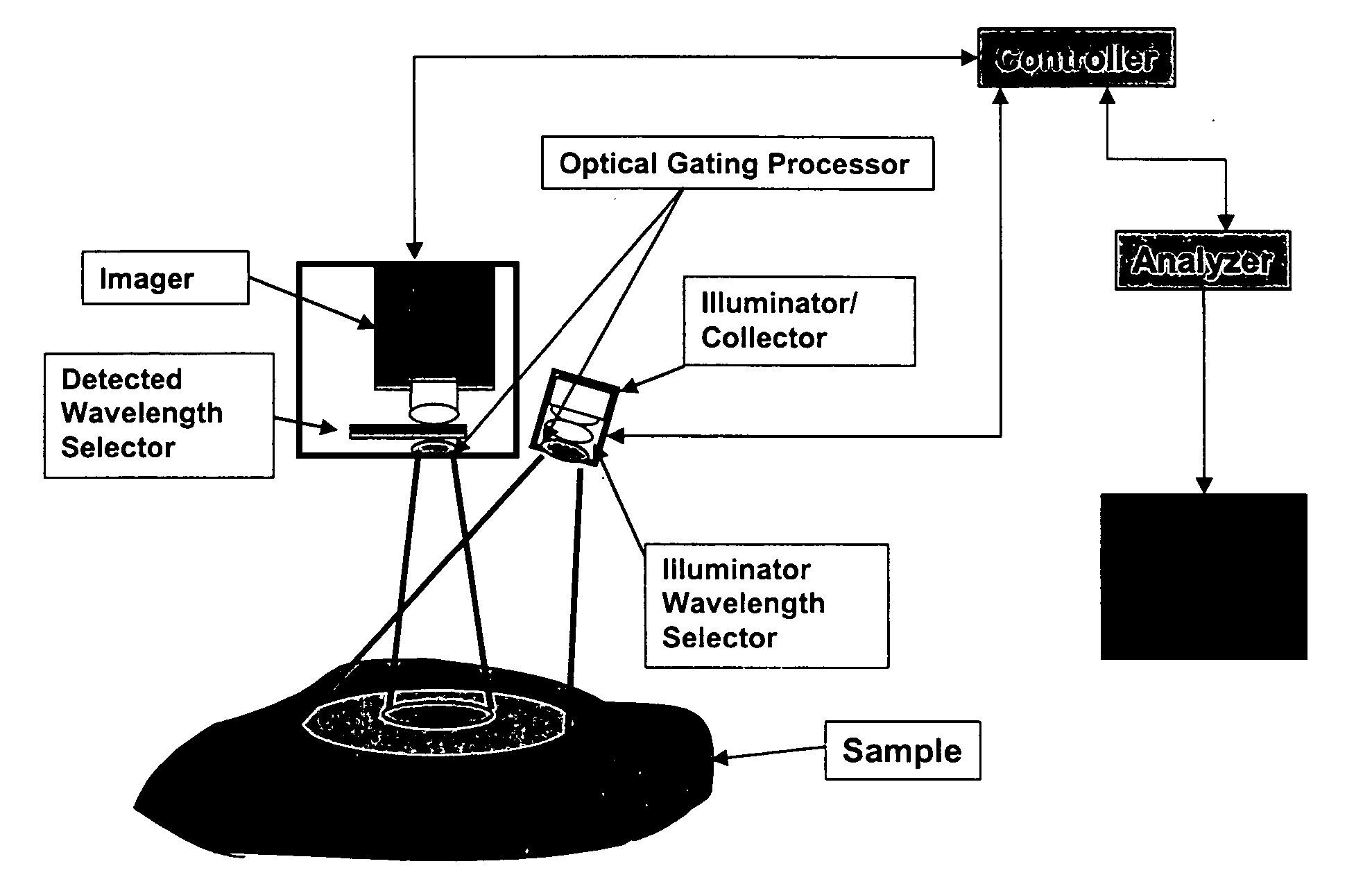
A method for the evaluation of target media parameters in the visible and near infrared is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a light source, an illuminator / collector, optional illumination wavelength selector, an optional light gating processor, an imager, detected wavelength selector, controller, analyzer and a display unit. The apparatus illuminates an in situ sample of the target media in the visible through near infrared spectral region using multiple wavelengths and gated light. The sample absorbs some of the light while a large portion of the light is diffusely scattered within the sample. Scattering disperses the light in all directions. A fraction of the deeply penetrating scattered light exits the sample and may be detected in an imaging fashion using wavelength selection and an optical imaging system. The method extends the dynamic range of the optical imager by extracting additional information from the detected light that is used to provide reconstructed contrast of smaller concentrations of chromophores. The light detected from tissue contains unique spectral information related to various components of the tissue. Using a reiterative calibration method, the acquired spectra and images are analyzed and displayed in near real time in such a manner as to characterize functional and structural information of the target tissue.
Owner:APOGEE BIODIMENSIONS
Light adjustable lenses capable of post-fabrication power modification via multi-photon processes
InactiveUS7074840B2Unwanted changeSpectales/gogglesPhotosensitive materialsCalorescencePhotoinitiator
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
Apparatus and method for reducing follicular cell apoptosis
InactiveUS20060161226A1Decrease follicular apoptosisReducing follicular cell apoptosisLight therapyCalorescenceApoptosis
The invention provides a light emitting device having an array of light emitting diodes (LED). The array of the device is arranged to illuminate a surface area of a scalp and the LEDs exhibit a plurality of wavelengths within the near infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum between about 600-1000 nm, wherein the plurality of wavelengths synergistically combine to decrease follicular apoptosis. The array of light emitting diodes can include LEDs that are pulsed and can contain an array of light emitting diodes corresponding to about 30-200, preferably about 50-150, and more preferably about 80-120 LEDs. The light emitting device of the invention also can include a headband or a stationary mount or other mount for positioning over a target area. Also provided is a method of reducing follicular cell apoptosis. The method includes illuminating a surface area of a scalp containing a follicular hair cell for an effective period of time with an array of light emitting diodes (LED). The array of LEDs exhibit a plurality of wavelengths within the near infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum between about 600-100 nm, wherein the plurality of wavelengths synergistically combine to decrease follicular cell apoptosis. The method can include inducing an increase in nitric oxide production compared to an untreated follicular hair cell as well as inducing mitochondrial chromophore activation. An effective period of time can include about 5-30 minutes, about 10-20 minutes or about 12-18 minutes and can promote vaso perfusion of the scalp or reduction in hair loss.
Owner:MCMICKLE GEORGE R
Fluorescent volume light source with active chromphore
InactiveUS20090196046A1Point-like light sourceLight guides with fluorescent dopantsCalorescenceFluorescence
An illumination system, such as might be used for illuminating a projection system, includes at least a first source of incoherent light capable of generating light in a first wavelength range. The system includes at least one active chromophore layer, sandwiched by transparent materials into a multi-layer body. They active chromphore layer emits light in a second wavelength range, different from the first wavelength range, when illuminated by light in the first wavelength range. The multi-layer body has an extraction area and at least some of the light at the second wavelength is internally reflected within the body to the extraction area.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
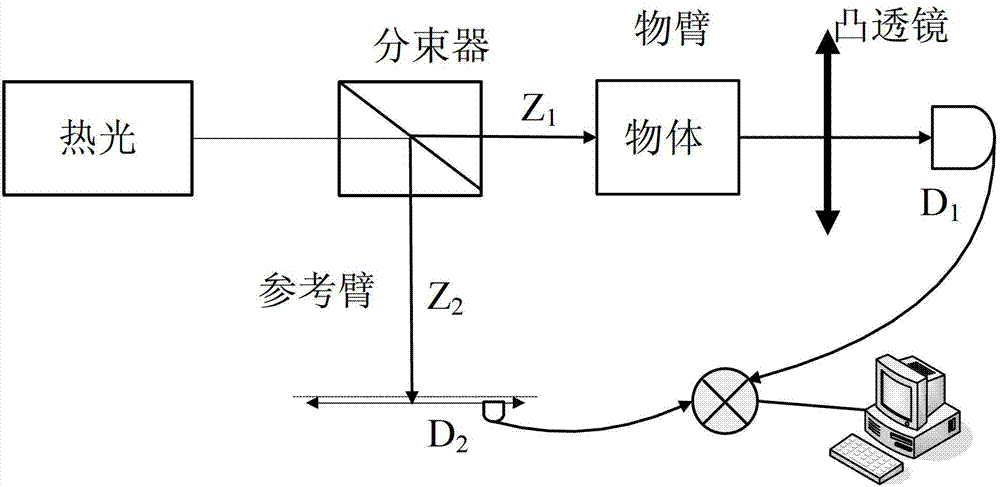
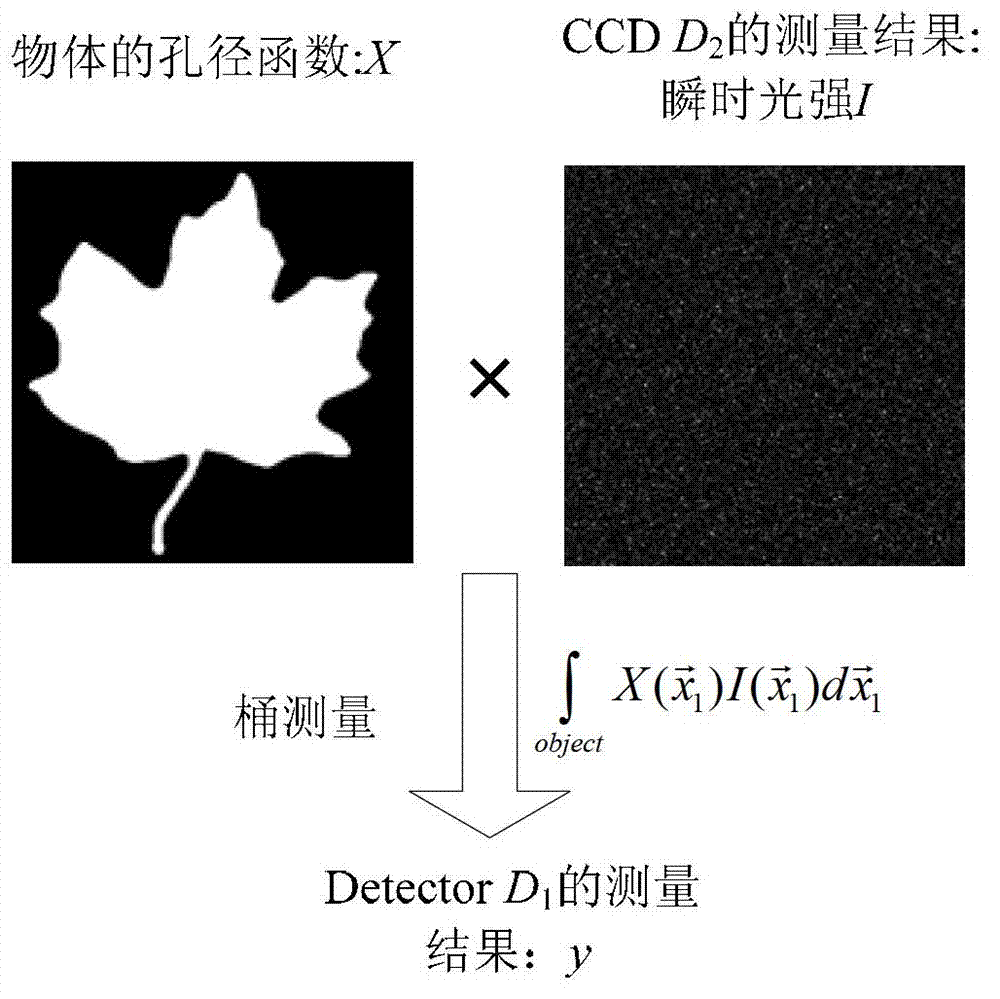
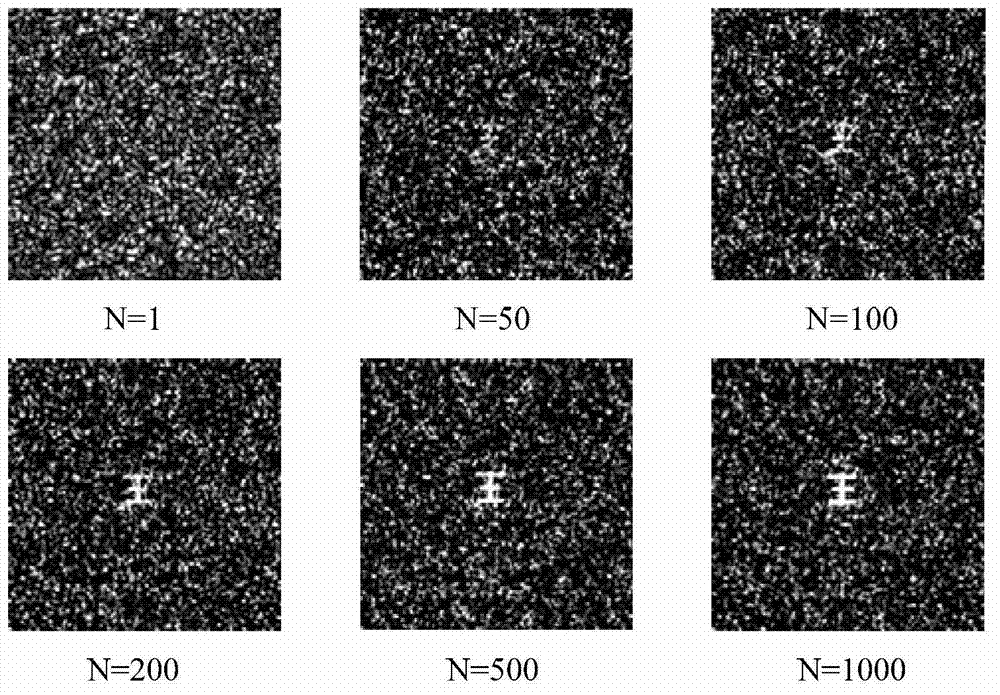
Two-dimensional compression ghost imaging system and method based on coincidence measurement
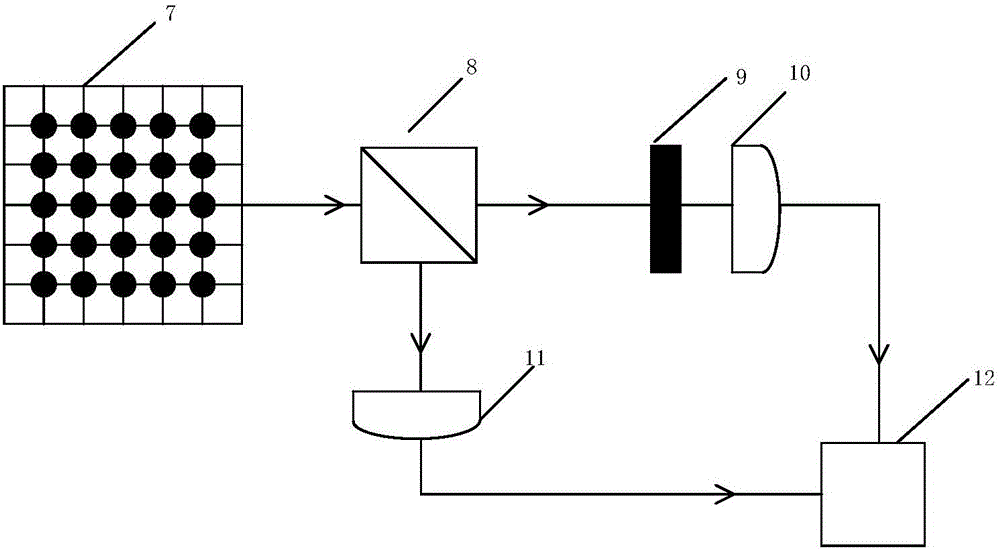
ActiveCN103323396AReduced measurement timeIncrease luminous fluxMaterial analysis by optical meansCalorescenceSpatial light modulator
The invention relates to a two-dimensional compression ghost imaging system based on coincidence measurement. The two-dimensional compression ghost imaging system comprises a laser, rotating frosted glass, an object, a spatial light modulator, a first set of convergent optical absorption lens, a second set of convergent optical absorption lens, a first point detector, a second point detector, a coincidence measurement circuit and an algorithm module, wherein laser emitted by the laser irradiates the frosted glass to produce pseudo calorescence which is divided into an object arm optical path and a reference arm optical path; on the object arm optical path, an optical field of the pseudo calorescence is spread to the object, and the total light intensity is collected through the first set of convergent optical absorption lens and the first point detector; on the reference arm optical path, the optical field of the pseudo calorescence is spread to the spatial light modulator, and after modulation, the total light intensity is collected through the second set of convergent optical absorption lens and the second point detector; the coincidence measurement circuit is used for carrying out coincidence measurement on the total light intensity of the object arm optical path and the reference arm optical path and outputting coincidence measurement values, and the algorithm module is used for reconstructing the distribution of spatial correlation coefficients according to a measurement matrix and the measurement values by applying a compression perception algorithm.
Owner:NAT SPACE SCI CENT CAS
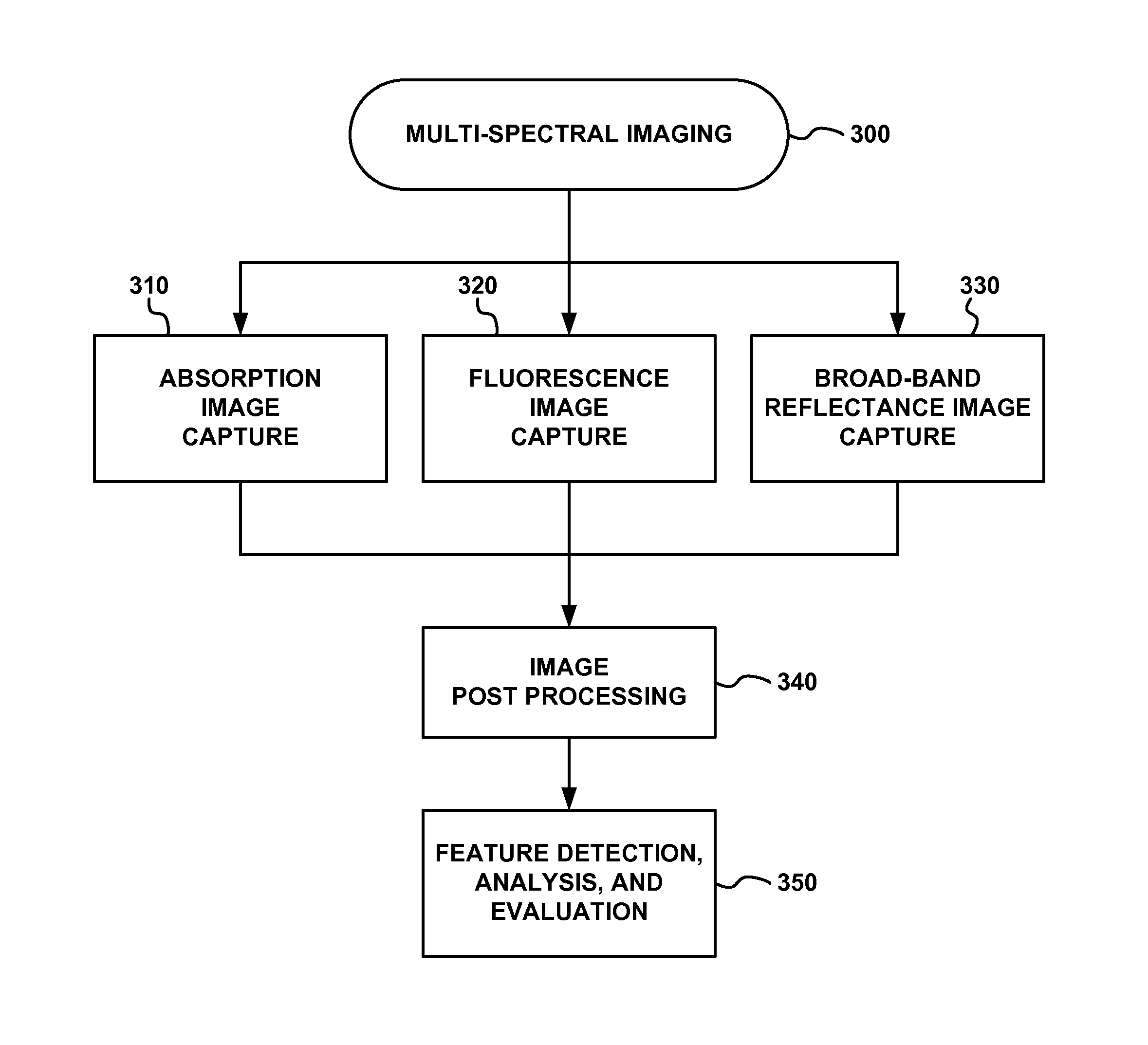
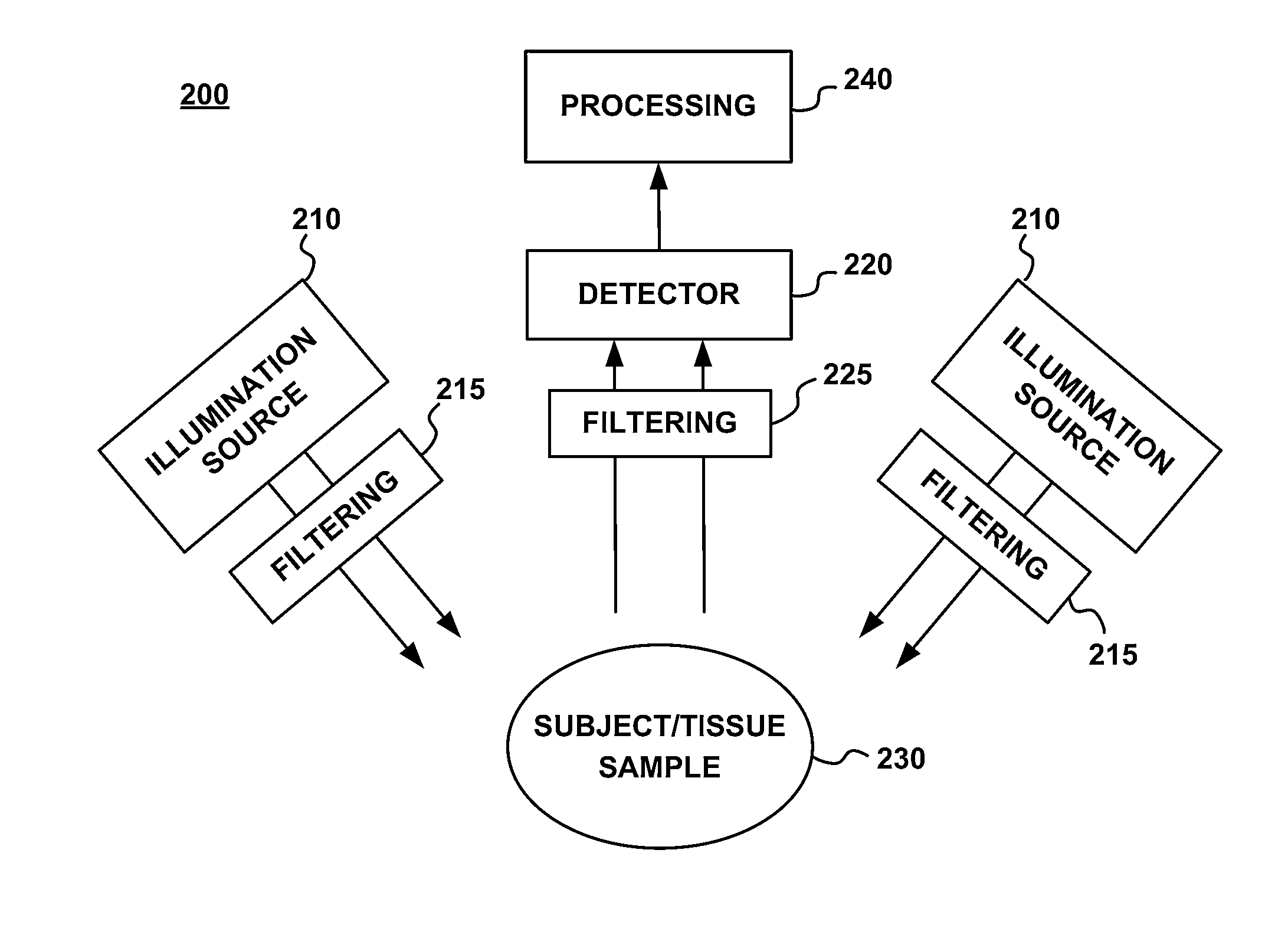
Multi-spectral tissue imaging
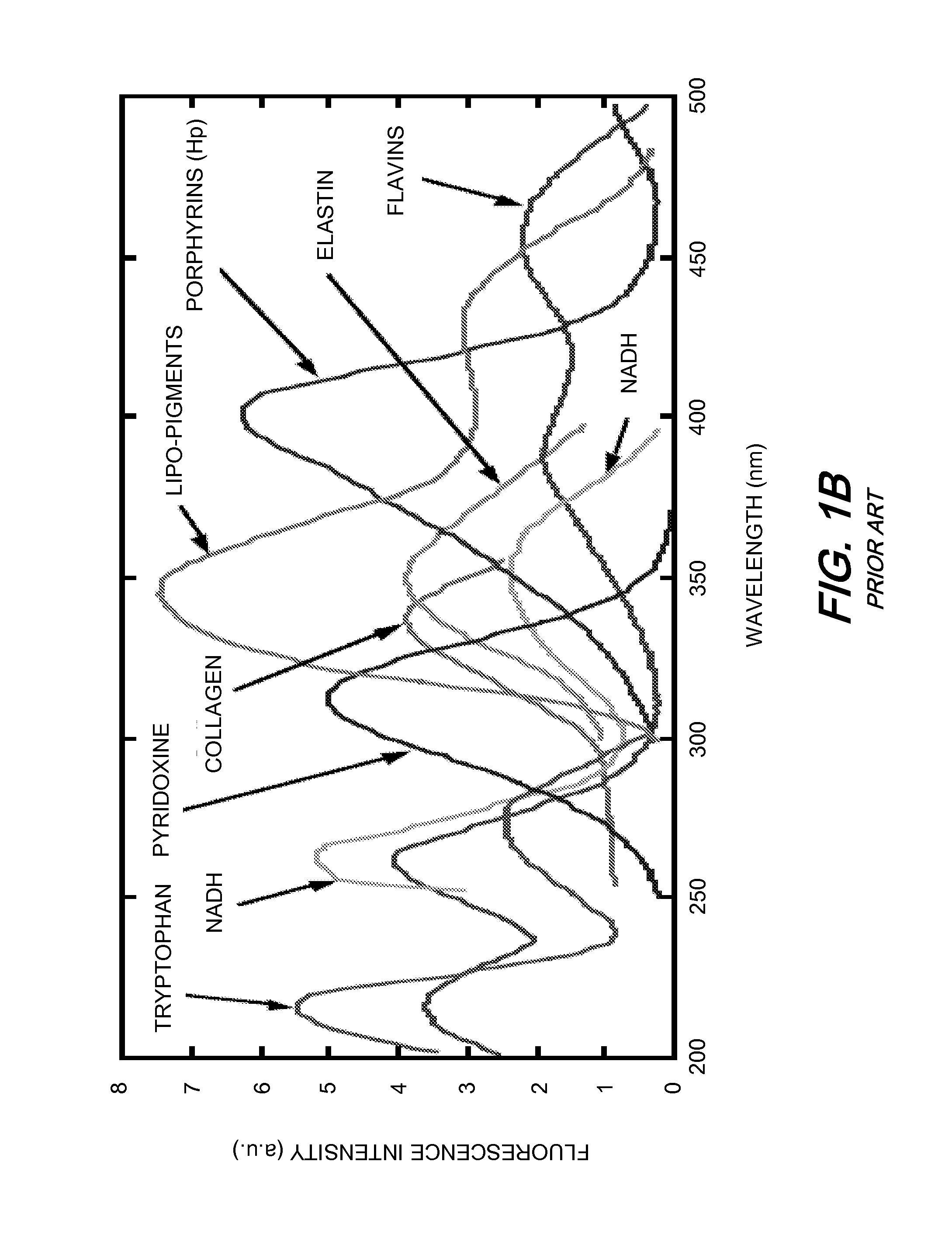
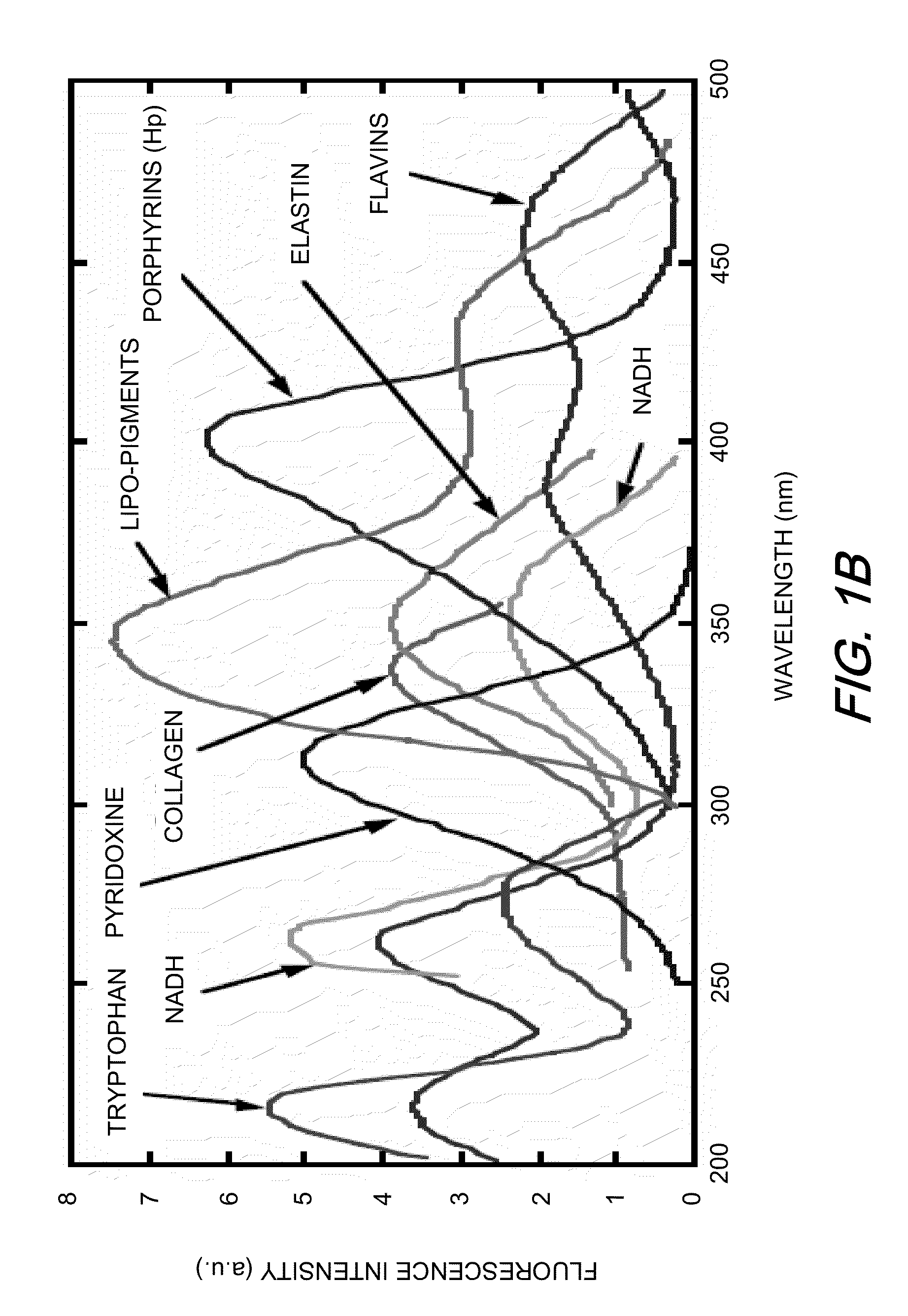
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for multi-spectral imaging of tissue to obtain information about the distribution of fluorophores and chromophores in the tissue. Using specific spectral bands for illumination and specific spectral bands for detection, the signal-to-noise ratio and information related to the distribution of specific fluorophores is enhanced as compared to UV photography, which uses a single RGB image. Furthermore, the chromophore distribution information derived from the multi-spectral absorption images can be used to correct the fluorescence measurements. The combined fluorescence, absorption, and broadband reflectance data can be analyzed for disease diagnosis and skin feature detection.
Owner:CANFIELD SCI
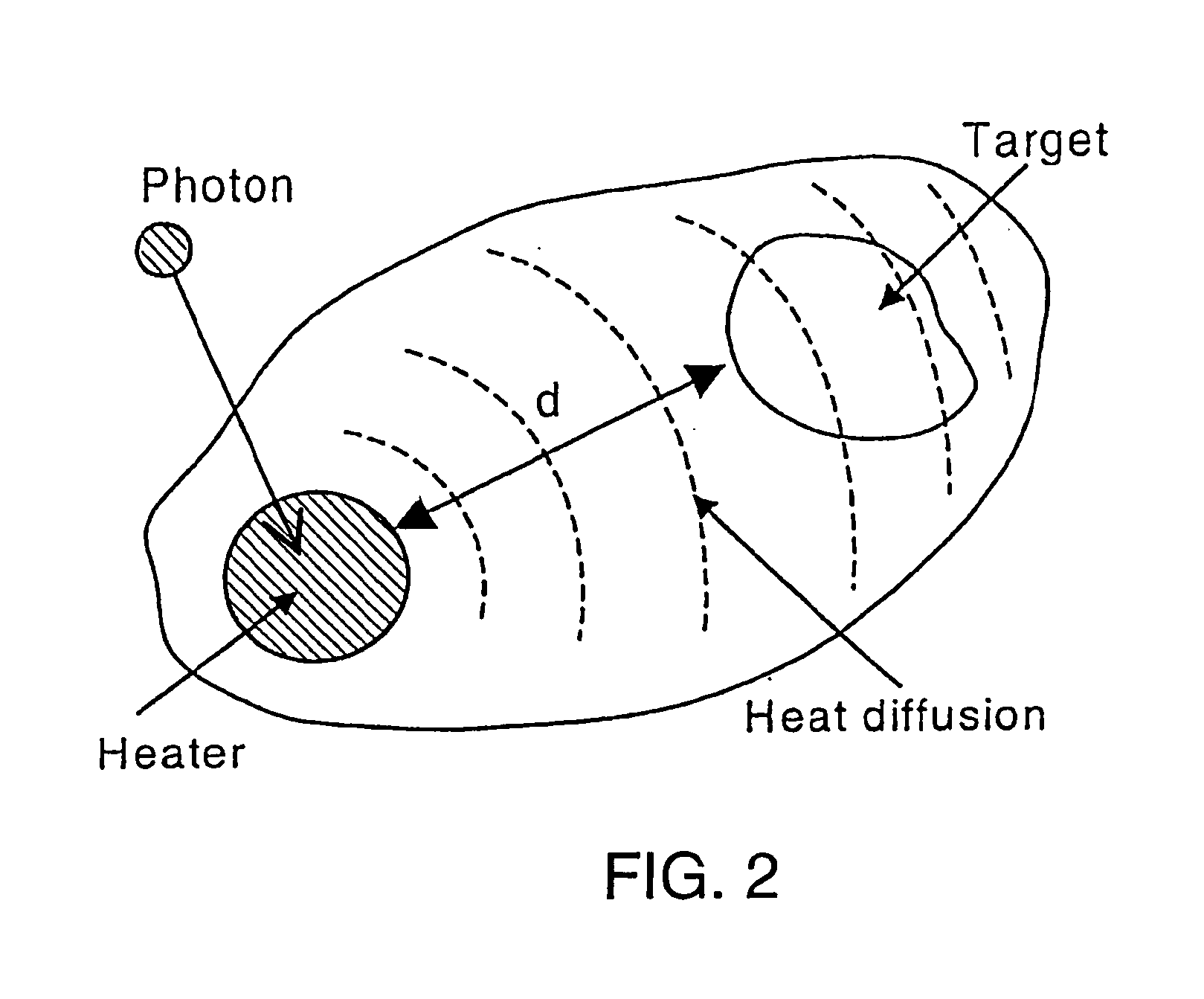
Method and Apparatus for Medical Treatment Utilizing Long Duration Electromagnetic Radiation
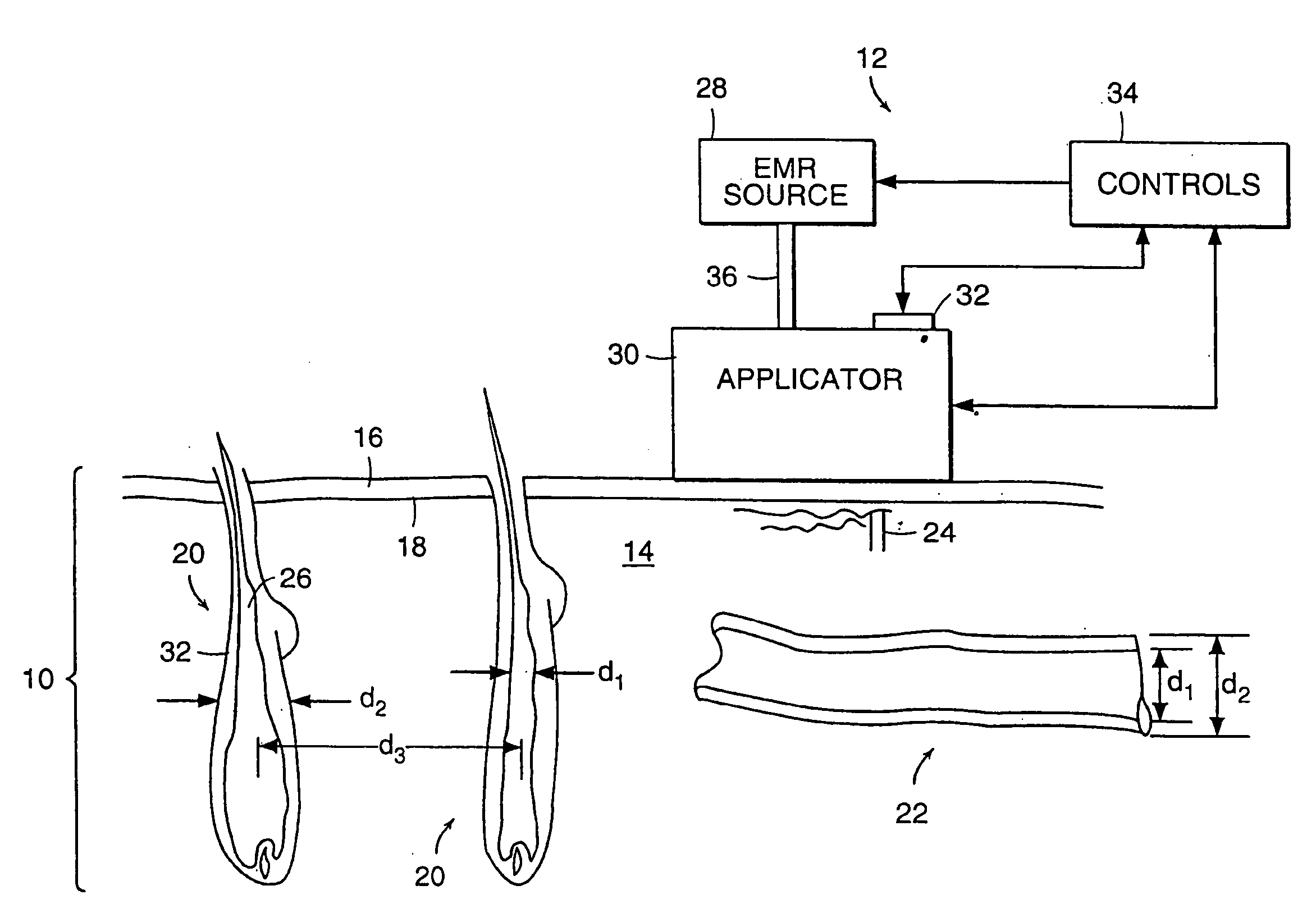
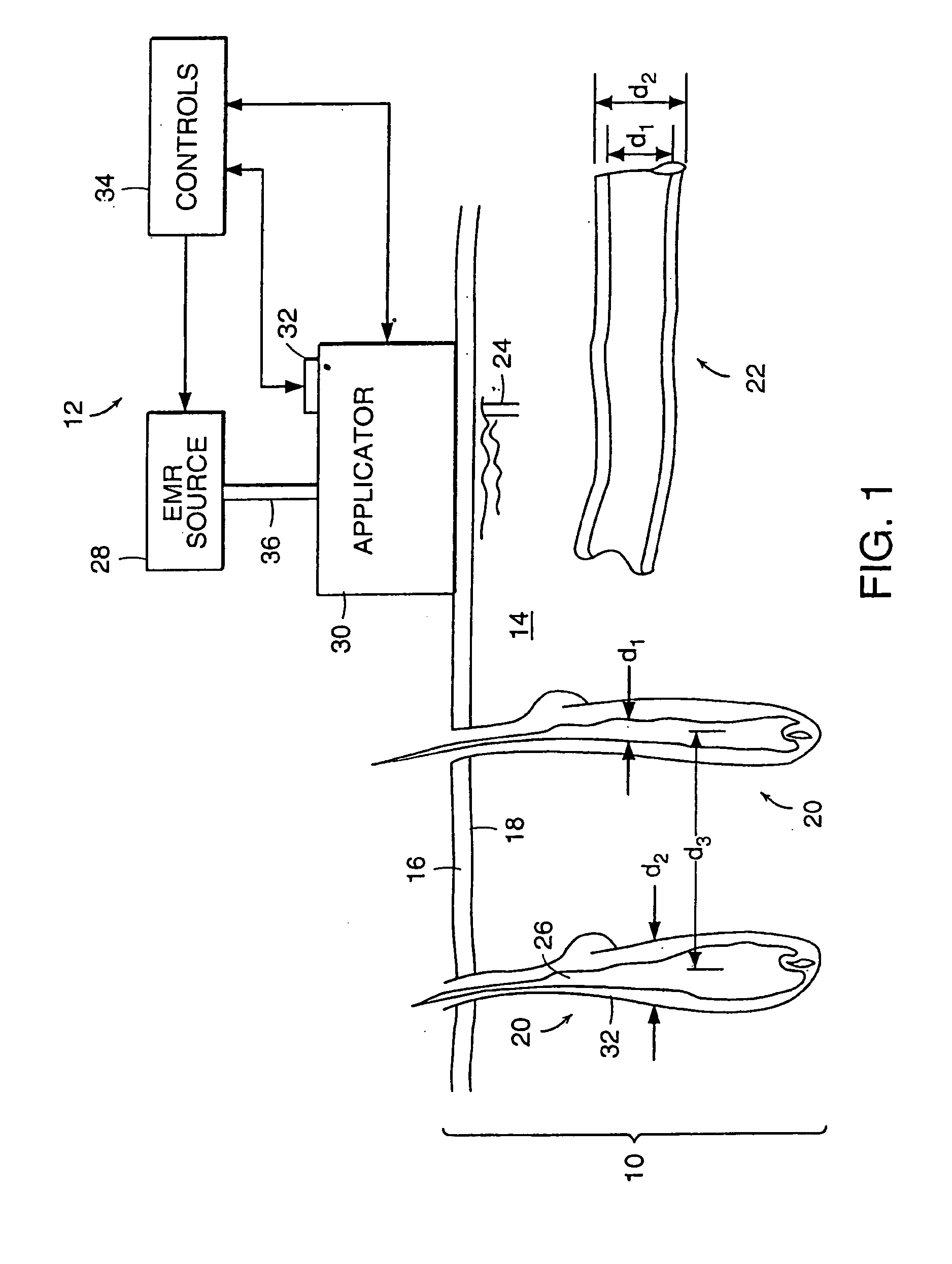
InactiveUS20110137230A1Avoid vaporizationAvoid temperature riseElectrotherapySurgical instrument detailsCalorescenceMedicine
A method and apparatus are provided for performing a medical procedure on a patient, for example a dermatological procedure, by use of electromagnetic radiation (EMR) having a relatively low peak power, and in particular a peak power low enough so as not to result in a phase change in the heater or chromophore absorbing radiation which would result in a significant reduction in its absorption, and of relatively long duration which is generally greater than, sometimes significantly greater than, the thermal relaxation time of the irradiated target.
Owner:PALOMAR MEDICAL TECH +1
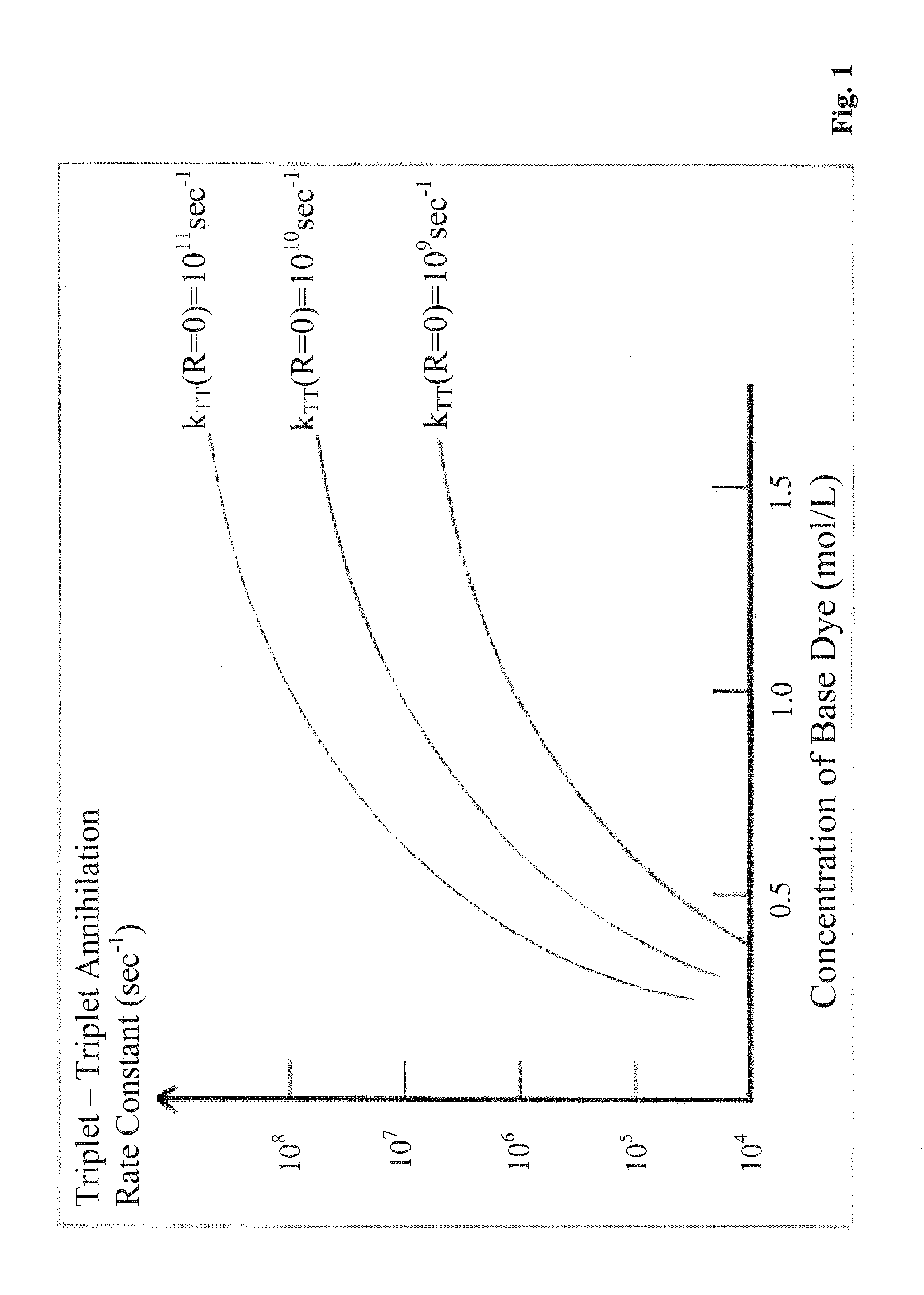
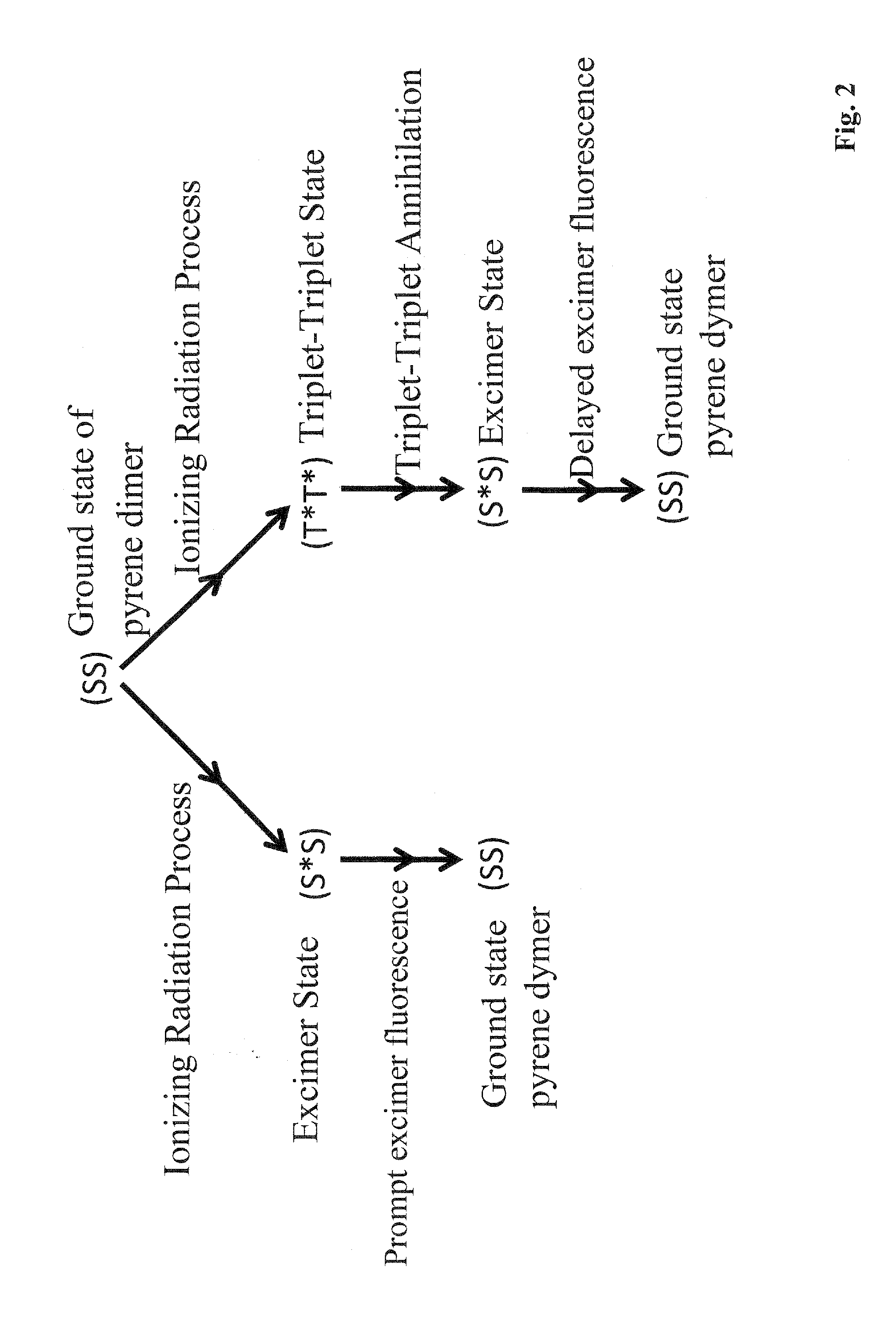
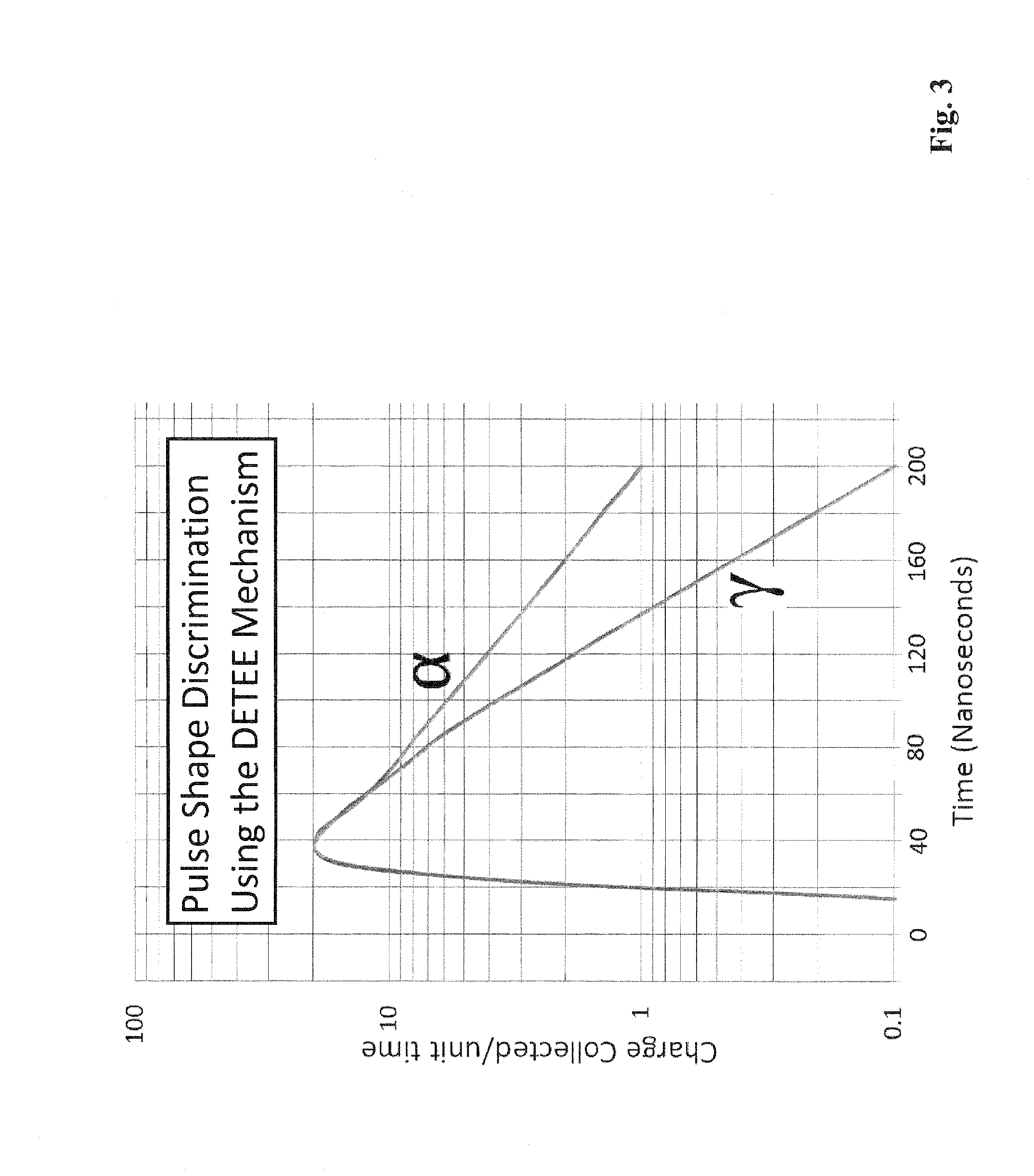
Materials, method, and apparatus for detecting neutrons and ionizing radiation
InactiveUS20120241630A1Improve solubilityImprove radiation resistanceMeasurement with scintillation detectorsMaterial analysis by optical meansCalorescenceDiffusion
Embodiments of the invention provide a scintillator material, a scintillator system, and / or a method of detecting incident radiation using a scintillator material, or scintillator system, comprising a polymer material that comprises chromophores. Additional embodiments provide a scintillator material, scintillator system, and / or a method of detecting incident radiation using a scintillator material, or scintillator system, comprising a polymer material having one, two, three, or more, organic dyes dissolved therein wherein the polymer material having the one, two, three, or more dyes dissolved therein comprises chromophores. At least one of the dyes, termed the base dye, has a concentration in the range 0.5 to 3.5 mol / L. In a specific embodiment, the base dye has a concentration in the range 1.0 to 3.0 mol / L. This base dye concentration is high enough to achieve a substantial triplet-triplet state annihilation rate despite the negligible diffusion of the dye in the rigid polymer matrix.
Owner:NANOPTICS
Carbon quantum dot/aurum cluster ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of cadmium ion and ascorbic acid
InactiveCN106047342ALow detection limitImprove detection accuracyFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsCalorescenceFluorophore
The invention discloses a carbon quantum dot / aurum cluster ratiometric fluorescent probe for detection of cadmium ion and ascorbic acid. A preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing CQDs (Carbon Quantum Dots) from alanine and histidine through a one-step hydrothermal method; performing amino-functionalization on the CQDs by using 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane, wherein the CQDs which are subjected to the amino-functionalization serve as a reference chromophore; reducing chloroauric acid through sodium borohydride by taking 11-sulfydryl undecanoic acid as a surfactant to obtain MUA-modified AuNCs (Aurum Nano Clusters), wherein the MUA-modified AuNCs serve as a main fluorophore of the ratiometric fluorescent probe; finally, coupling the CQDs and the AuNCs through an amidation reaction to obtain the CQDs / AuNCs ratiometric fluorescent probe. On the basis of static quenching and inter-filtering effects, the fluorescence of the CQDs / AuNCs can be quenched by Cd<2+>; the invention discloses the application of the CQDs / AuNCs ratiometric fluorescent probe in Cd<2+> detection. The fluorescence of the CQDs / AuNCs which is quenched by the Cd<2+> can be recovered by the ascorbic acid, so that the ratiometric fluorescent probe can also be used for the detection of AA (Ascorbic Acid). The ratiometric fluorescent probe disclosed by the invention has the lower detection limit of 32.5 nM to the Cd<2+>, has the lower detection limit of 0.105 muM to the AA, and has an application value in the detection of the cadmium ion and the ascorbic acid.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
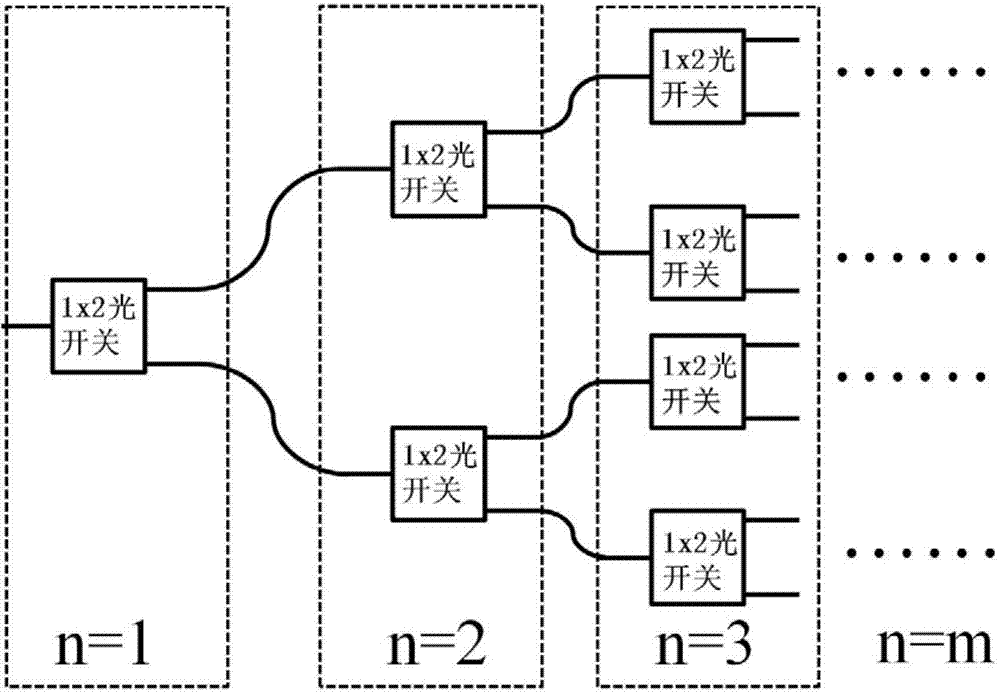
Silicon nitride waveguide calorescence switch array chip based on Mach-Zahnder structure and production method thereof
InactiveCN104849878ASimple processSuitable for mass productionNon-linear opticsCalorescenceOptical communication
The invention discloses a silicon nitride waveguide calorescence switch array chip based on a Mach-Zahnder structure and a production method thereof. The chip comprises a plurality of cascaded 1*2 Mach-Zahnder silicon nitride waveguide calorescence switch units; each unit comprises an input optical waveguide, an 1*2 branch optical waveguide, a reference arm optical waveguide, a 3dB directional coupler and two output optical waveguides. The chip is small in size, low in consumption, simple in machining process, compatible with the semiconductor CMOS process, low in cost and easy to integrate, and the application prospect in the fields of optical communication and optical interconnection is promised.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method and Apparatus for Quantification of Optical Properties of Superficial Volumes Using Small Source-to-Detector Separations
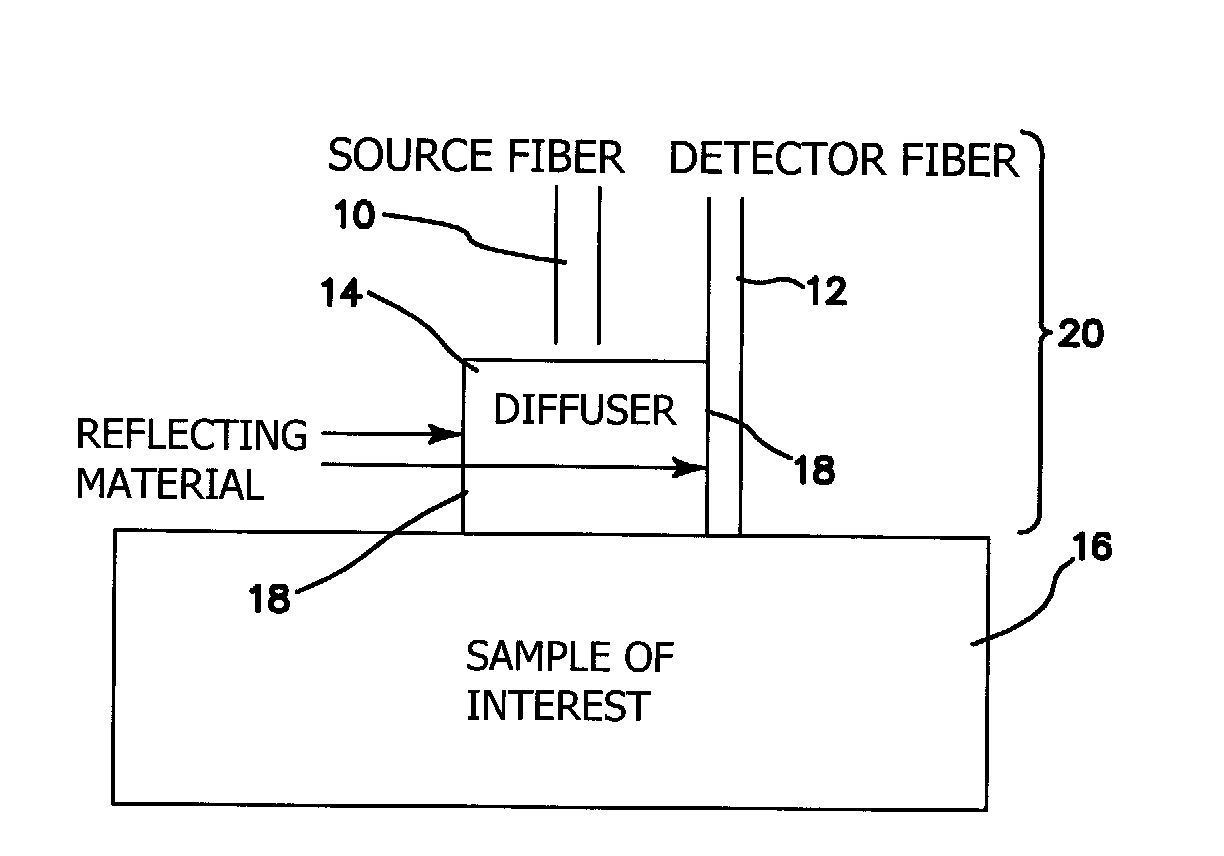
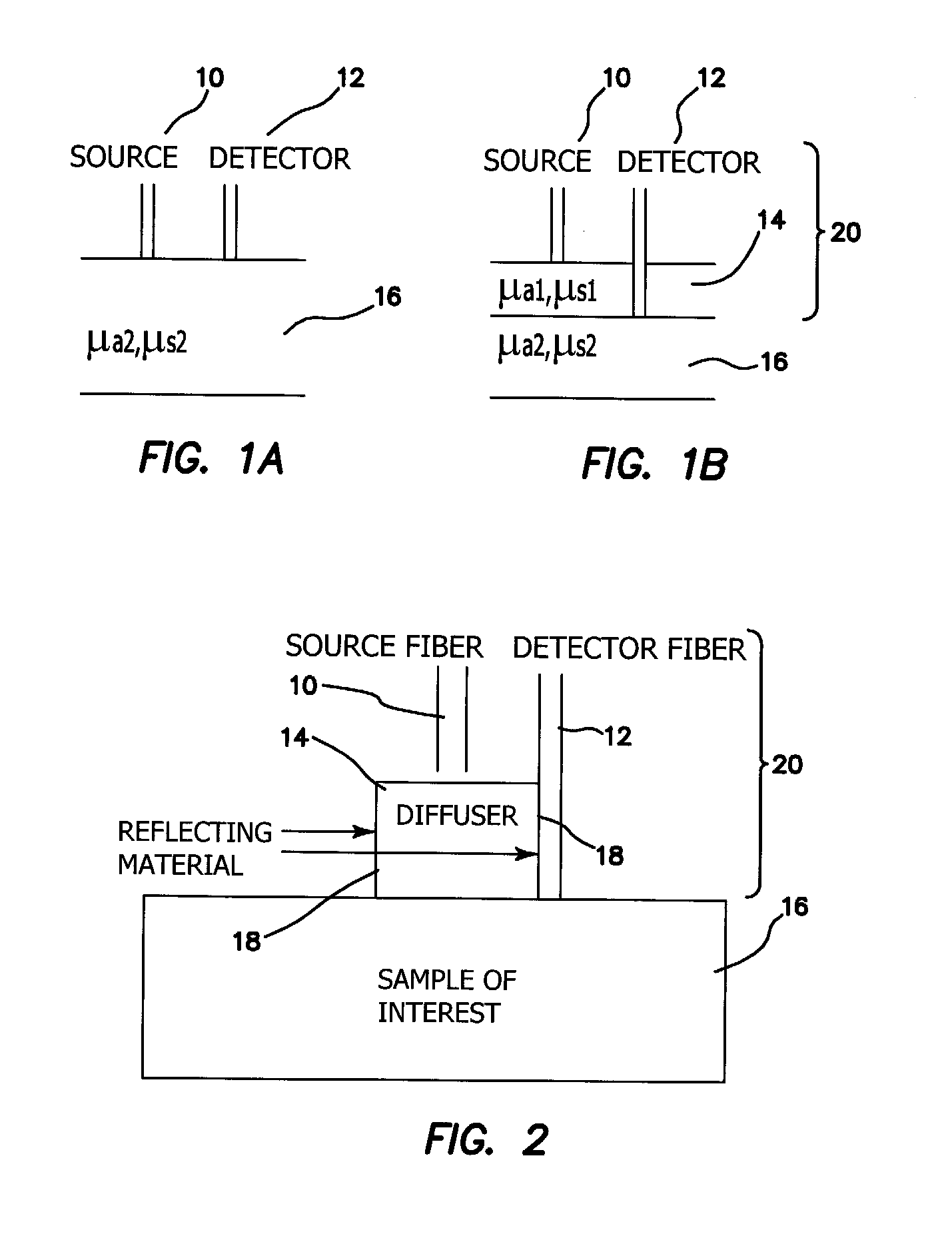
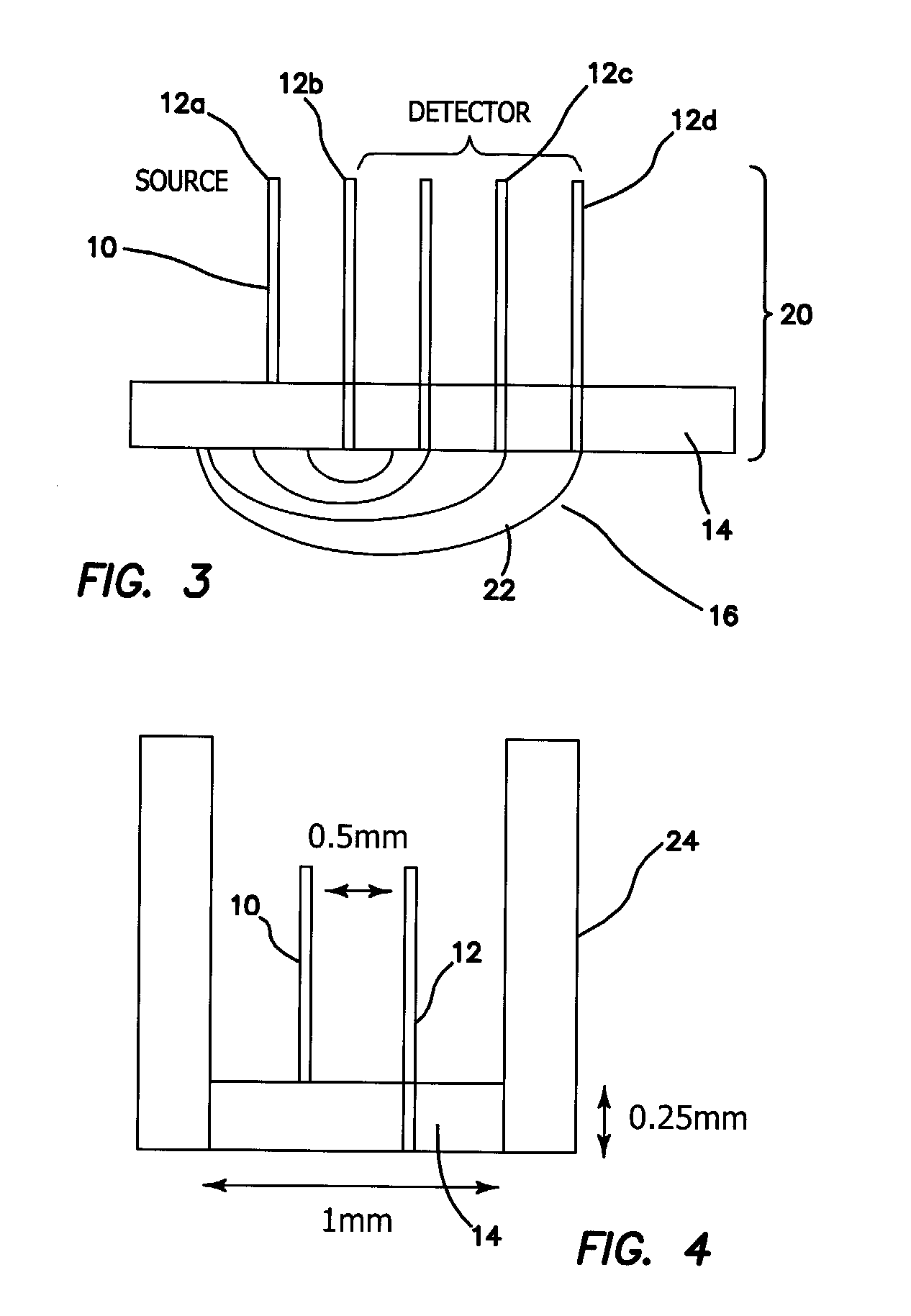
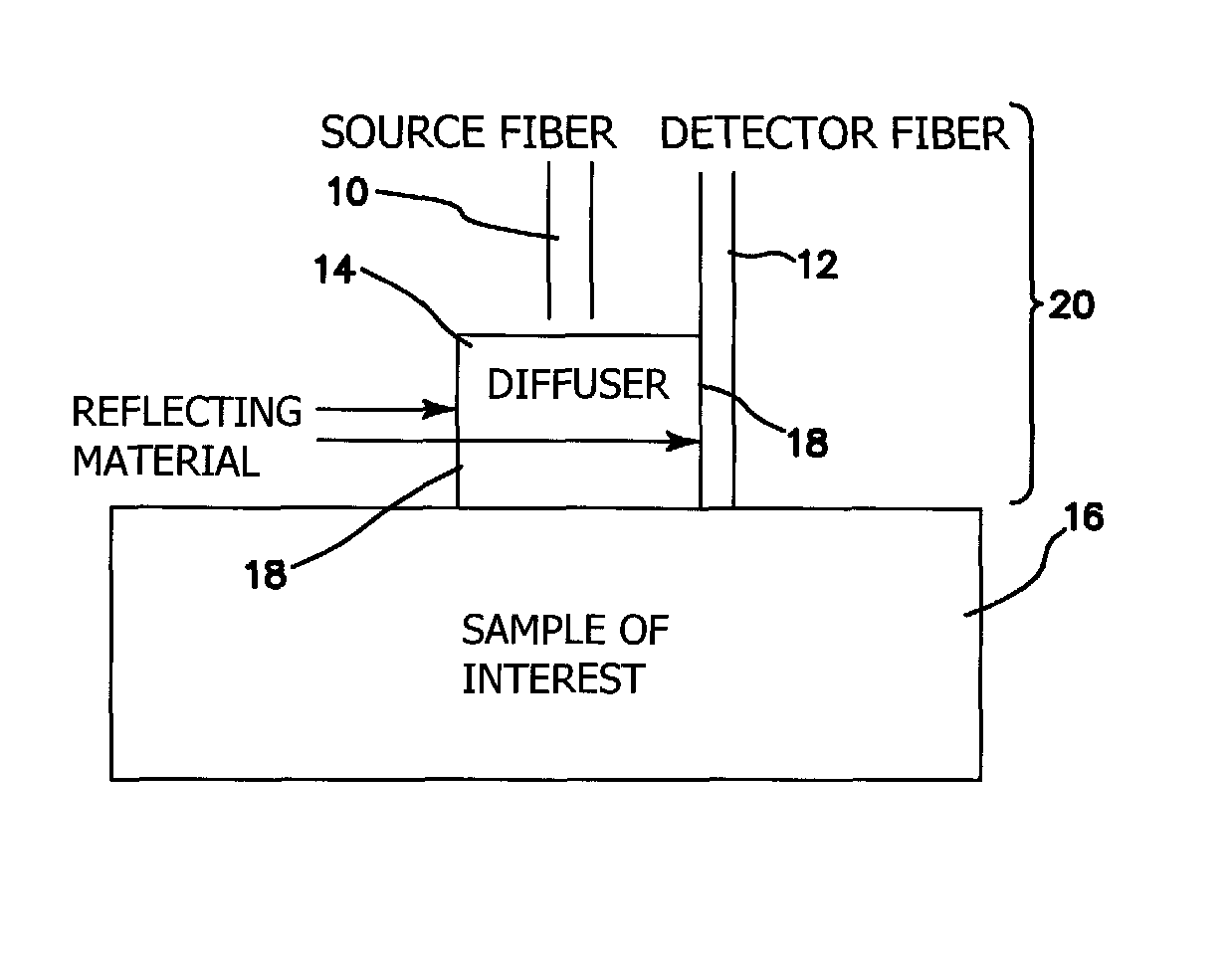
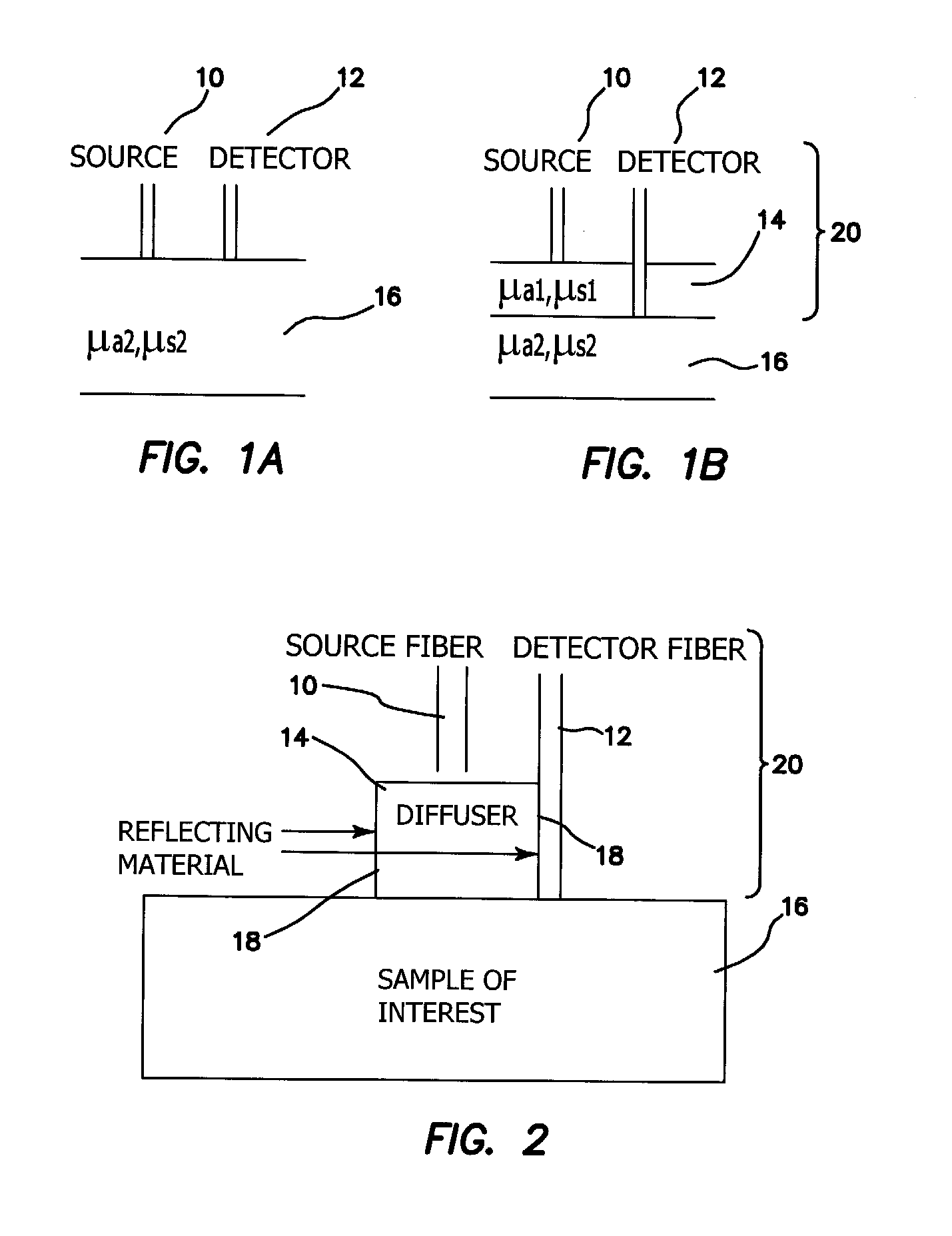
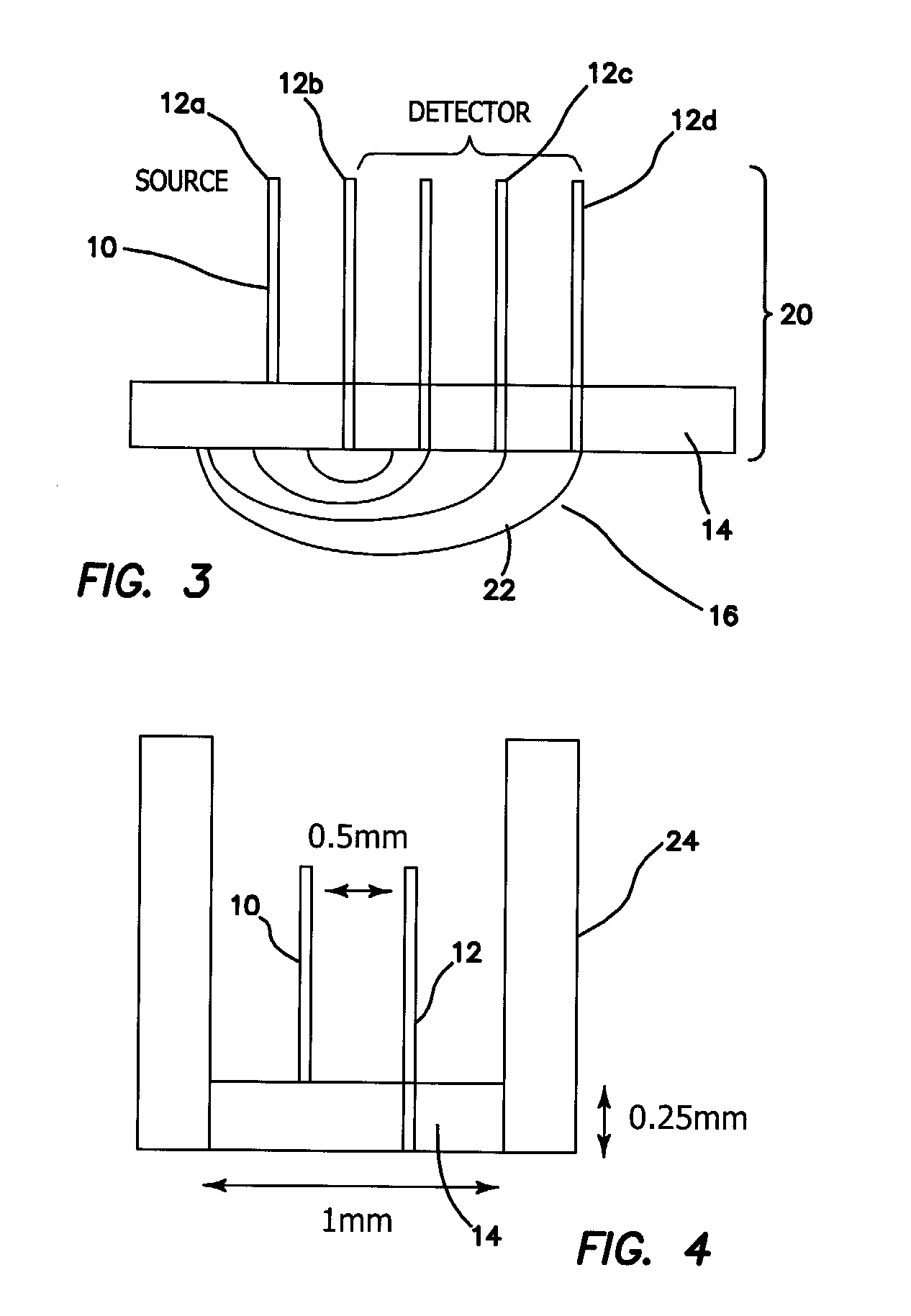
A probe for obtaining quantitative optical properties and chromophore concentrations of tissue components in tissue in-vivo at superficial depths and at source-detector separations of 5 mm or less includes a source fiber providing light to expose the tissue, a diffuser layer into which light from the source fiber is directed and then from the diffuser layer to and / or into the tissue, and a detector fiber arranged relative to the diffuser layer for detecting backscattered and / or reflected light returned from the tissue without transmission through the diffuser layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Light adjustable lenses capable of post-fabrication power modification via multi-photon processes
InactiveUS20050027031A1Unwanted changeSpectales/gogglesPhotosensitive materialsCalorescencePhotoinitiator
The invention relates to novel photoinitiators and their use in light adjustable compositions. The initiatives comprise two or more multiphoton chromophores linked by a bridging compound. The bridging compound consists of a material that is compatible with the base material of the light adjustable composition. The novel photoinitiator permit the readjustment of light adjustable material without the need for significant amounts of photoabsorbers.
Owner:RXSIGHT INC
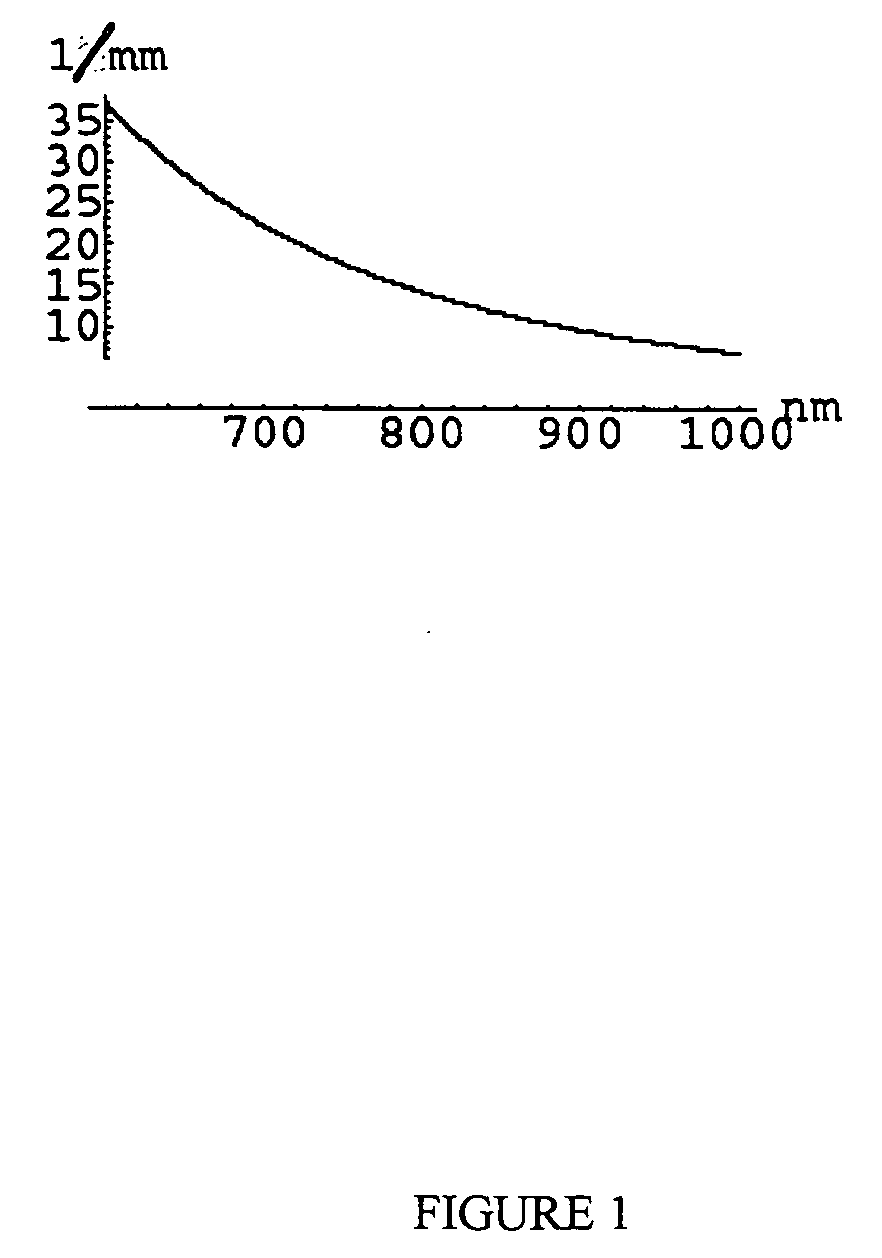
Choice of wavelengths for multiwavelength optical imaging
InactiveUS20050010113A1Improve image qualityDiagnostics using lightCalibration apparatusCalorescenceLength wave
The present invention relates to a method for wavelength selection in a multi-wavelength TPSF or CW-based optical imaging system. This consists of identifying several chromophores in a highly turbid medium and selecting optimized wavelengths whereby using these wavelengths optimizes the deduction of the chromophore concentrations. Such chromophore concentrations may be combined to deduce other properties of the turbid medium.
Owner:SOFTSCAN HEALTHCARE GROUP
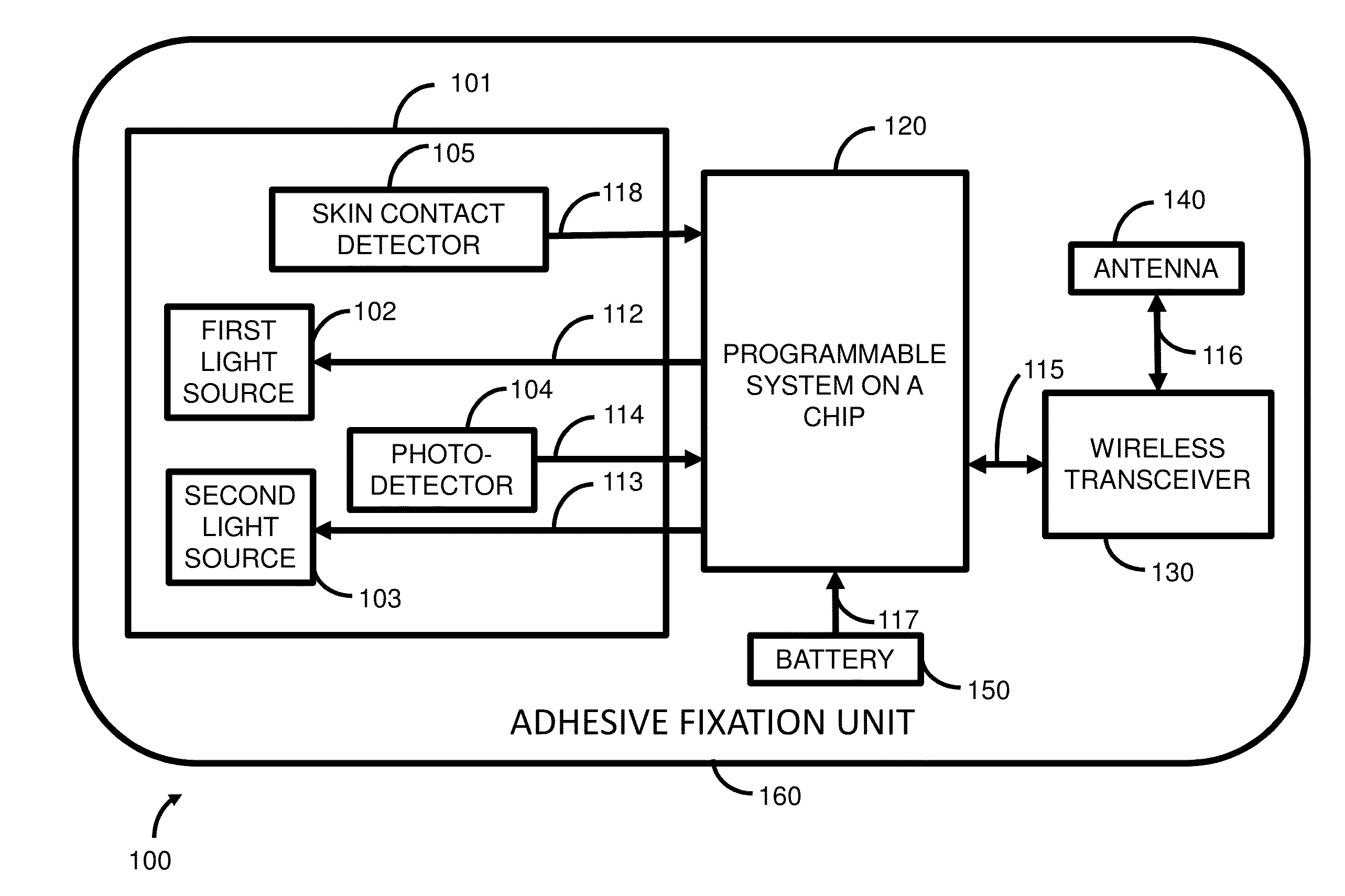
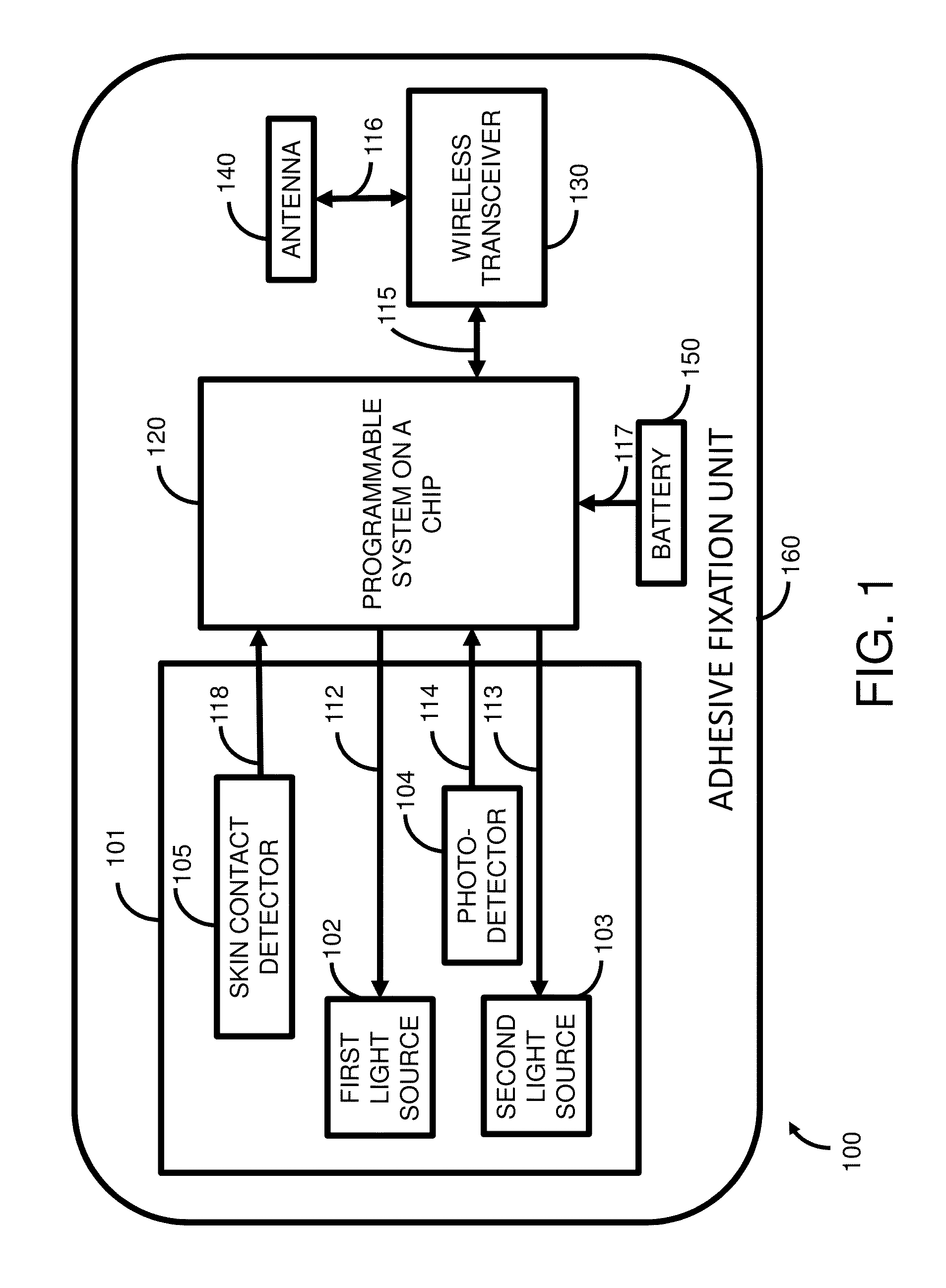
Wireless disposable shock trauma monitoring device
InactiveUS20130096401A1Small sizeEasy to useDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCalorescencePhotodetector
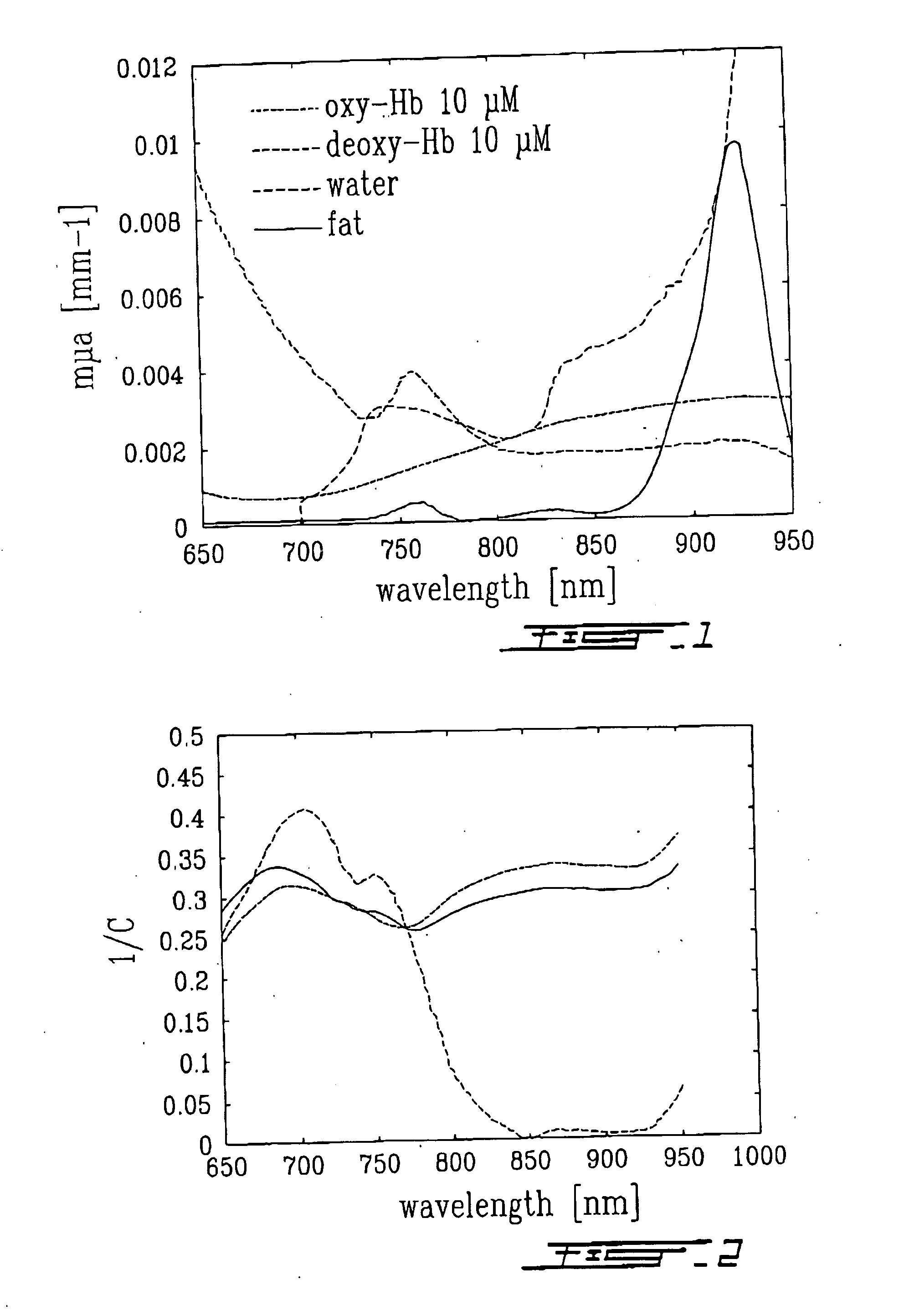
Apparatus for monitoring oxygen saturation levels in tissue for a miniature wireless disposable optical tissue oximeter to are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a sensor contains a first light source, a second light source, a photodetector, and a skin contact detector. Once skin contact is detected, the first light source emits light in the near infrared region, and the second light source emits light in the visible red region. The emitted light passes through a transparent layer of an adhesive fixation unit, and enters the underlying tissue, where a portion of the light is absorbed by tissue chromophores, including oxygenated hemoglobin and deoxygenated hemoglobin, and reflected back out of the tissue into the photodetector. The oxygen saturation of the tissue under the sensor is then calculated. The oxygen saturation measurements are wirelessly transmitted to a remote display device, such as a smartphone running a smartphone software application which receives the measurements and displays them in numeric, graphical, and audible form. In addition, the smartphone software application may relay the data to the Internet for remote viewing on a web site or remote transfer to a hospital patient data system.
Owner:INNOVAMEDIX
Device and method for converting incident radiation into electrical energy using an upconversion photoluminescent solar concentrator
InactiveUS20120031466A1High energyHigh refractive indexPV power plantsPhotometryCalorescenceElectricity
Device and method for converting incident radiation into electrical energy using an upconversion photoluminescent solar concentrator is disclosed. An upconversion photoluminescent solar concentrator device includes a waveguide. The waveguide has a waveguide medium. An upconversion chromophore is in contact with the waveguide medium. The upconversion chromophore is configured to absorb an incident photon. The upconversion chromophore is also configured to emit an emitted photon. The emitted photon has higher energy than the incident photon. A photovoltaic device absorbs the emitted photon, generating electricity.
Owner:BRUER GARRETT
Silicon waveguide refractive index calorescence adjusting structure
InactiveCN103018929ALarge adjustment rangeRegulated low power consumptionNon-linear opticsCalorescenceElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a silicon waveguide refractive index calorescence adjusting structure, which sequentially comprises a substrate, a lower cladding, a waveguide layer, an upper cladding and an electrode layer from bottom to top; the waveguide layer is in a ridge shape, a central area of the ridge shape is a lightly-doped intrinsic area I, and flat areas on two sides of the ridge shape are respectively heavily-doped areas; and two sides of the upper cladding are respectively provided with a metal through hole, and the heavily-doped areas of the waveguide layer are connected with the electrode layer through the through hole. After an external power supply is electrified, the waveguide layer produces heat, the temperature in a waveguide core area is increased, and the refractive index is increased, so that the calorescence adjusting effect is realized. The waveguide layer is used as hot resistance to produce the heat, and the heat source directly acts on a light field, so that compared with a traditional calorescence adjusting structure adopting a metal resistance, the silicon waveguide refractive index calorescence adjusting structure has characteristics of lower power consumption and shorter response time.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Apparatus and method for non-invasive and minimally-invasive sensing of parameters relating to blood
InactiveUS20100152559A1Improve accuracyDiagnostics using lightOrgan movement/changes detectionCalorescenceNon invasive
Medical diagnostic system, apparatus and methods are disclosed. Optical transmitters generate radiation-containing photons having a specific interaction with at least one target chromophore in a target structure, preferably a blood vessel such as the interior jugular vein. The optical transmitters transmit the radiation into at least a first area including a substantial portion of the target structure and into a second area not including a substantial portion of the target structure. Optical receivers detect a portion radiation scattered from at least the first area and the second area. A processor estimates oxygenation, pH or cardiac output based on the scattered radiation detected from the first area, and the scattered radiation from the second area.
Owner:SKYLINE BIOMEDICAL
Multi-spectral tissue imaging
Apparatus and methods are disclosed for multi-spectral imaging of tissue to obtain information about the distribution of fluorophores and chromophores in the tissue. Using specific spectral bands for illumination and specific spectral bands for detection, the signal-to-noise ratio and information related to the distribution of specific fluorophores is enhanced as compared to UV photography, which uses a single RGB image. Furthermore, the chromophore distribution information derived from the multi-spectral absorption images can be used to correct the fluorescence measurements. The combined fluorescence, absorption, and broadband reflectance data can be analyzed for disease diagnosis and skin feature detection.
Owner:CANFIELD SCI
Ultraviolet radiation absorbing polyethers
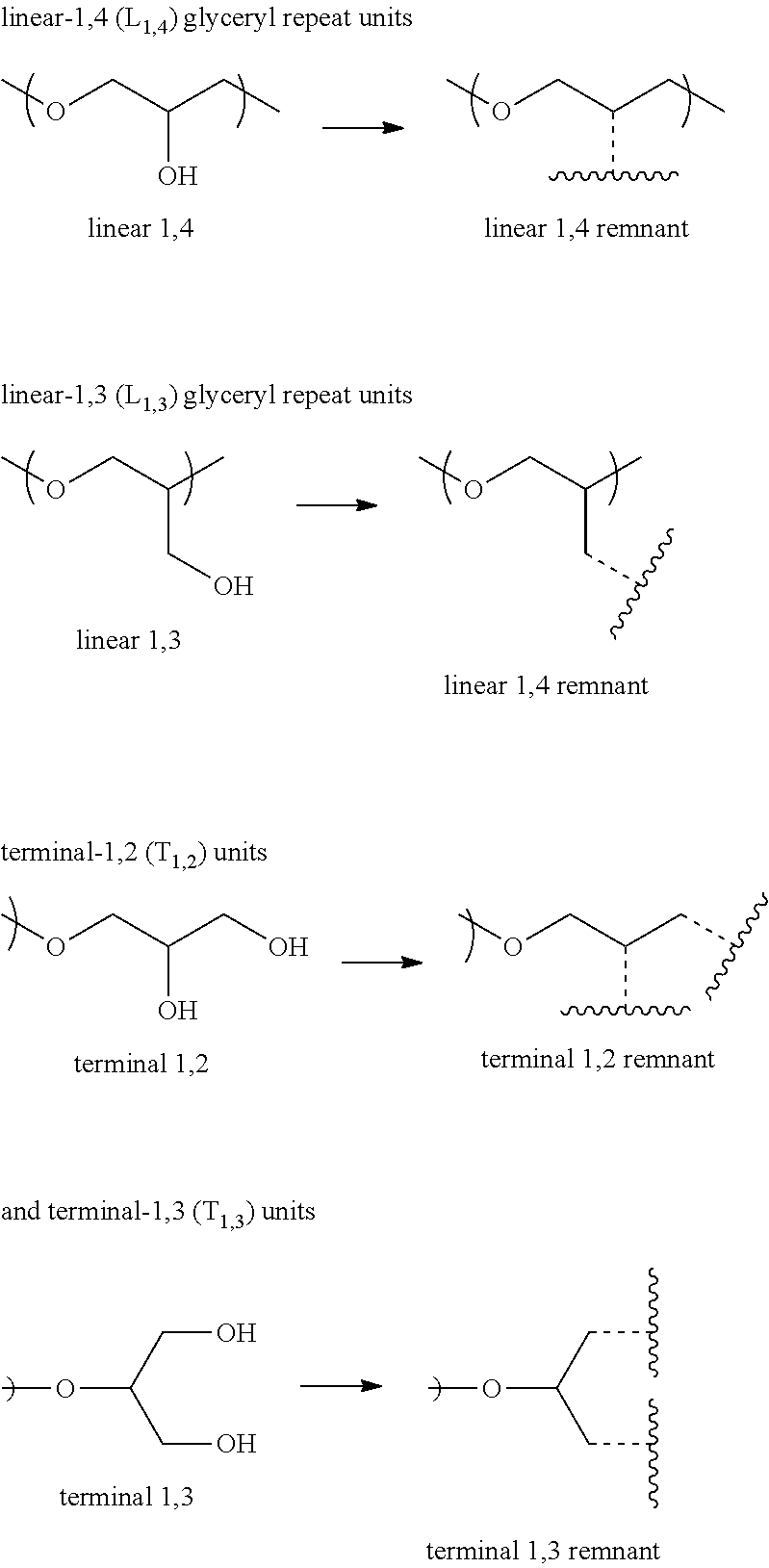
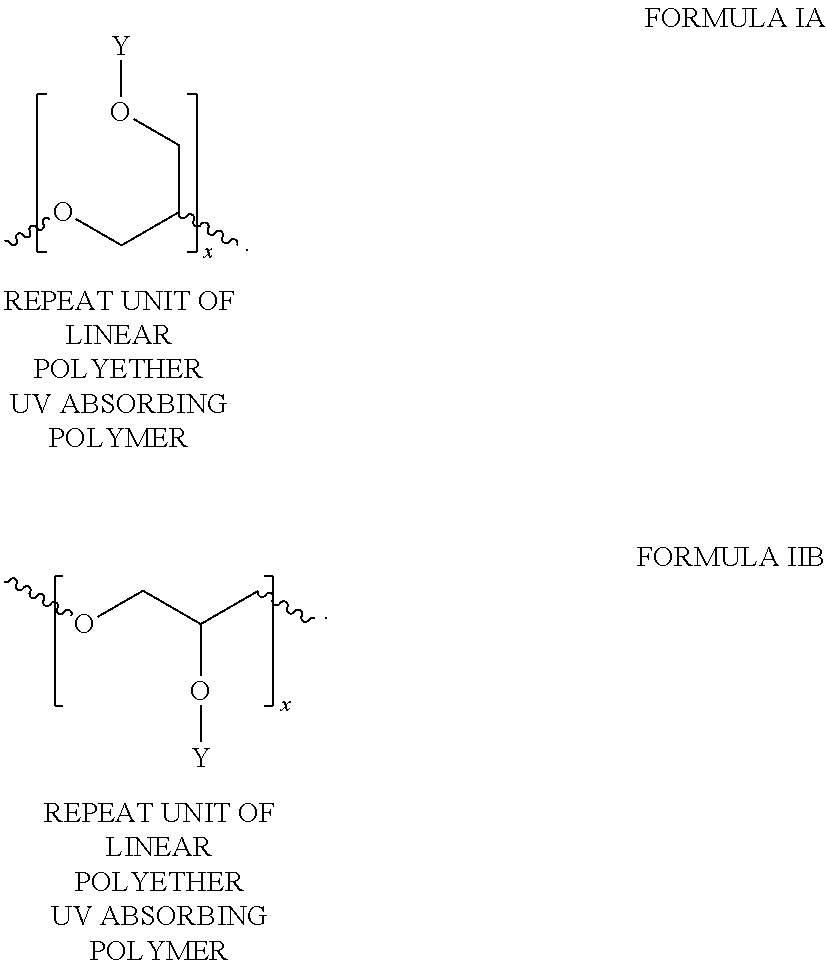
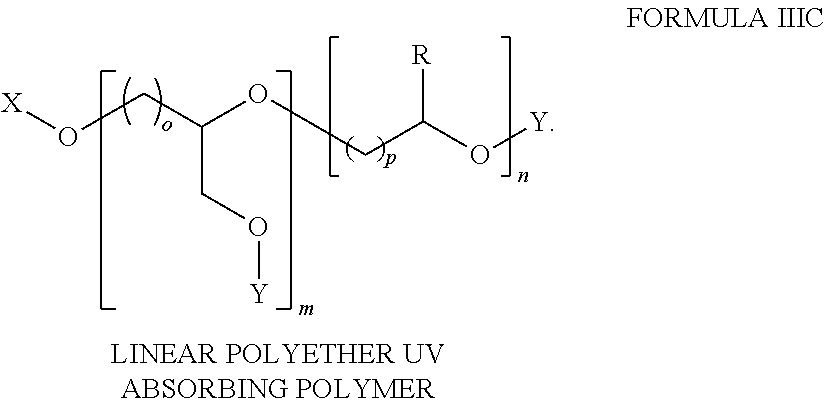
ActiveUS20140004061A1Provide protectionCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCalorescenceUltraviolet
A polymer composition comprising a linear ultraviolet radiation absorbing polyether that comprises a chemically bound UV-chromophore.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
Synthesis and luminescent characteristics of novel phosphorus containing light-emitting polymers
InactiveUS20020193522A1Additional drawbackOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesCalorescenceElectronic transmission
The present invention relates to a kind of synthesis and luminescent characteristic of novel phosphorus containing light-emitting polymers, especially one improving the luminescence efficiency of the synthesis light-emitting polymers. According to the method of the present invention, the electron-transporting chromophores are introduced into an emission polymer to increase its electron affinity. Further, several phosphorus-containing emission chromophores are synthesized and incorporated with electron-transporting chromophores finally resulting in the novel phosphorus chromophores emitting blue light as expected, improving thermal stability of resulting polymers such that the absorption peaks of these polymers are restricted to a stable range.
Owner:SUN YIH MIN
Ultrasonic ghost imaging method and device based on principle of calorescence ghost imaging
InactiveCN106526602AImprove image qualityQuality improvementAcoustic wave reradiationCalorescenceBeam splitter
The invention provides an ultrasonic ghost imaging method and device based on the principle of lens-free calorescence ghost imaging, which belongs to the field of target imaging detection. Ultrasonic wave emitted by an ultrasonic emission source is divided into two beams through an acoustic beam splitter. The ultrasonic wave transmitted through an object to be imaged is received by an ultrasonic wave barrel detector. An ultrasonic CCD detector is used to receive an ultrasonic beam emitted by the ultrasonic emission source. A correlator is used to calculate the second order correlation function of the ultrasonic sound intensity detected by two ultrasonic detectors. Coincidence measurement is carried out on two ultrasonic signals to acquire the image of the object to be imaged. According to the invention, the ultrasonic wave is introduced into ghost imaging as a wave source; a new ultrasonic ghost imaging method is realized; the imaging method has a great anti-perturbation characteristic; and compared with traditional ultrasonic imaging, the imaging method can realize lensless imaging, and has the advantages of high resolution, high image quality and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Fluorescent volume light source with active chromphore
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Self-adaptation morphological filtering system and method applied to calorescence correlation imaging
The invention discloses a self-adaptation morphological filtering system and a method applied to calorescence correlation imaging. The method includes the following steps: binarization processing on related images to form binary system grayscale images; corrosion on the binary system grayscale images through a morphological filter by utilizing structural elements in certain sizes to remove spots produced by the related images, and therefore pixels on object boundaries can be eliminated; median filtering on the corroded binary system grayscale images so as to remove noise; and closed operation and expansion operation on the binary system grayscale images to achieve the purpose of regaining original images. By means of the self-adaptation morphological filtering system and the method applied to the calorescence correlation imaging, good imaging effect comparing with images of lowpass filtering, average filtering and median filtering is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI DIANJI UNIV
LED package for uniform color emission
ActiveUS20120211778A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCalorescencePhosphor
A light emitting diode package for one or more light emitting diodes mounted on a substrate. A frame is disposed on at least a portion of the substrate and substantially surrounds, but does not contact, the light emitting diode. The frame is substantially transparent to light emitted from the light emitting diode and includes one or more first wavelength converting materials. The wavelength converting materials, which may be one or more phosphors, convert at least a portion of light emitted at the emission wavelength to different wavelength. A cover covers the light emitting diode within the frame. The cover layer includes one or more second wavelength converting materials differing from the first one or more wavelength converting materials in wavelength converting material concentration or in converted light wavelength or in combinations of wavelength converting materials.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Method for producing electric-melting zirconia used for turquoise pigment and glaze
ActiveCN101703958ANarrow particle size distributionThe particle size distribution range is reasonableGrain treatmentsZirconium oxidesCalorescenceAtmospheric pressure
The invention relates to a method for producing electric-melting zirconia used for turquoise pigment and glaze, which is characterized in that: in a process of fine crushing, a feed particle size D50 is controlled between 20 and 25mu m, the working air pressure of a nozzle of a jet mill is 0.8MPa, a cyclonecluster is adjusted to 45Hz, a grader is adjusted to 18Hz, and the size distribution after the crushing meets the conditions that: D10 is not less than 3mu m, D50 is kept between 14 and 15mu m, and the difference between D90 and D10 is not more than 30mu m. The method has the advantages that: the narrow size distribution range of zirconia powder is realized, and reasonable grain size distribution is realized; and the electric-melting zirconia is favorable for color development of the turquoise pigment and glaze compared with the traditional electric-melting zirconia, comprehensively improves the blue degree of corresponding pigment and glaze, reduces a brightness value, makes the pigment develop more bright and vivid color in the glaze, and improves the beautifulness of corresponding ceramic products. The electric-melting zirconia after reasonable particle size control and adjustment can improve the high temperature resistance of the turquoise pigment and glaze more obviously than the electric-melting zirconia which is not controlled, and still can keep bright tone at the temperature higher than 1,200DEG C so as to promote the application to high temperature pigments.
Owner:BENGBU ZHONGHENG NEW MATERIALS SCI & TECH CO LTD
Near-white organic electroluminescent material and its prepring method
InactiveCN1935935AReduce self-quenchingReduce luminous intensityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesCalorescenceLuminous intensity
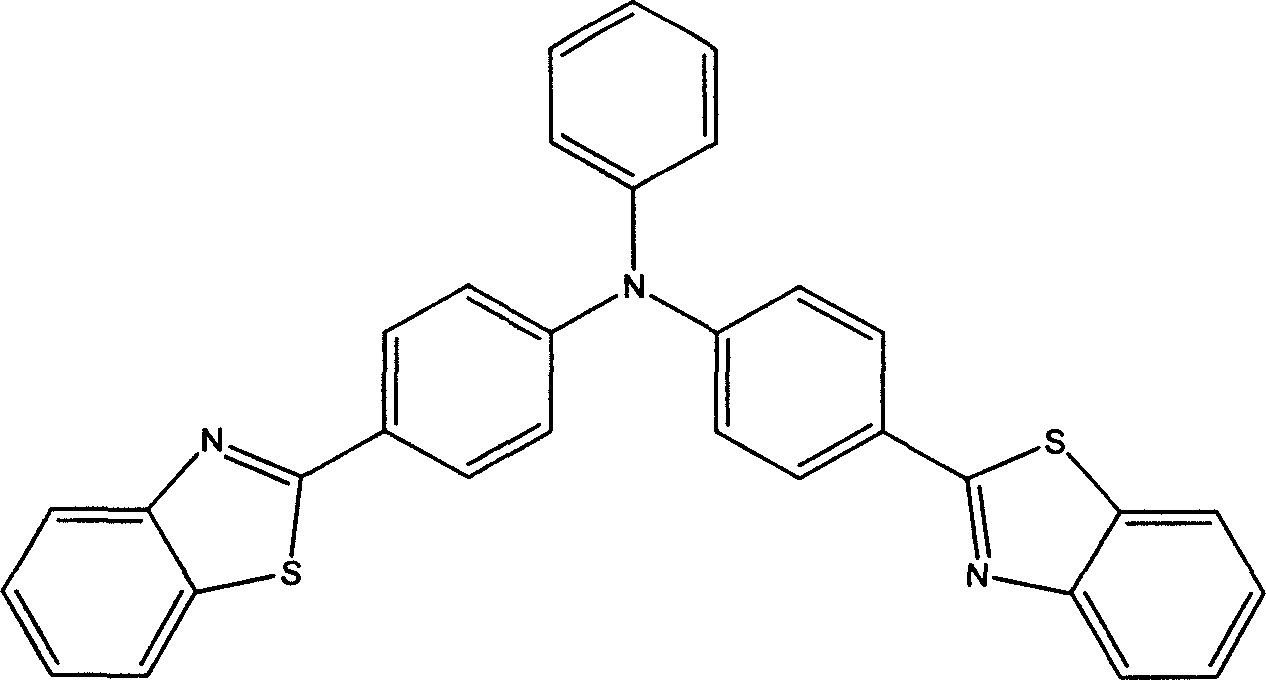
The invention relates to organic electroluminescence luminous close white luminescent material and the preparing method. The material has basic structure of the tri-aromatic amine which has extensibility in three-dimensional space to reduce agglomeration among molecule and luminescent material self quenching, many different chromophoric group-benzothiazole which can increase luminous intensity for molecule which has better electron transmission characteristic, can produce formless film with high thermal stability and good uniformity. Thus the material can be used to make close white organic electroluminescence device or panchromatic one with other materials. It has wide application prospect in other optoelectronic device.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
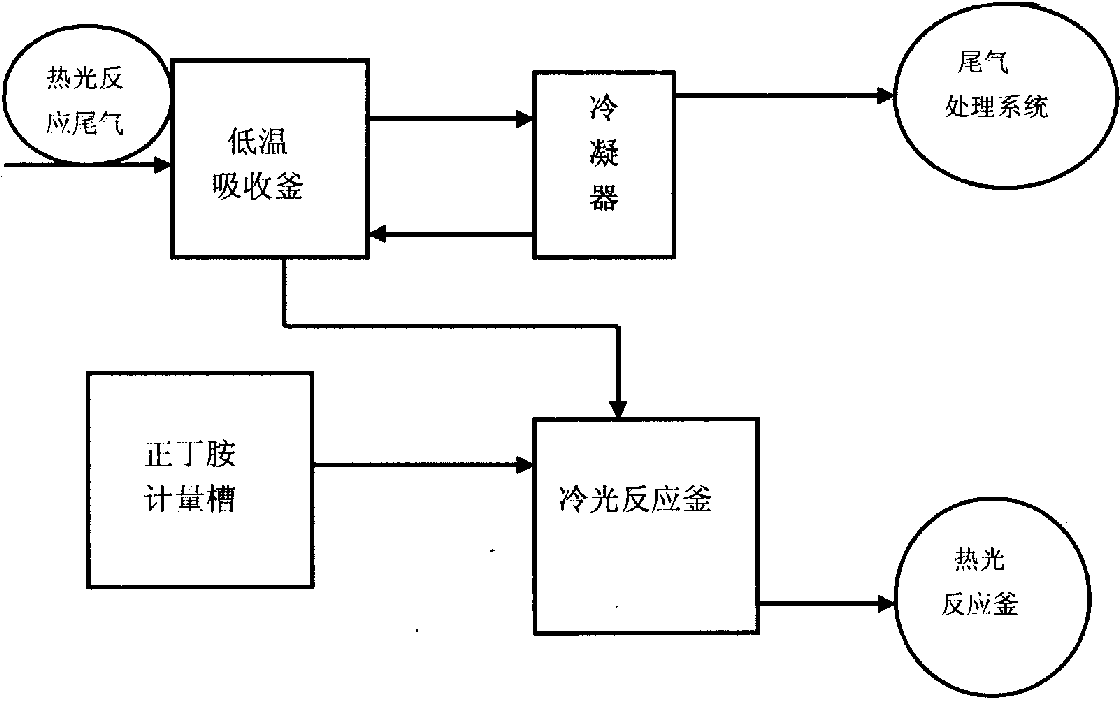
Recycling method for phosgene in tail gas generated in calorescence reaction for synthesizing normal-butyl isocyanate
ActiveCN103638688ATake advantage ofMaximize utilizationDispersed particle separationVapor condensationCalorescenceN-butylisocyanide
The invention relates to a recycling method for phosgene in tail gas generated in calorescence reaction for synthesizing normal-butyl isocyanate. The recycling method comprises the steps of continuously cooling and absorbing the tail gas generated in the calorescence reaction for synthesizing the normal-butyl isocyanate through a low temperature solvent, and condensing the tail gas through a condenser, wherein the non-condensing gas directly enters a tail gas processing system; preparing normal-butyl acyl chloride from the solvent containing the phosgene with certain quality concentration through cold light reaction, metering the phosgene-containing solvent, shifting the solvent into a cold light kettle, dropwise adding n-butylamine at -8 DEG C to -2 DEG C, after the dropwise adding, keeping the temperature for 1 hour so as to obtain the n-butylamine acyl chloride; and resolving the n-butylamine acyl chloride in a calorescence reaction kettle to obtain the normal-butyl isocyanate. The method provided by the invention has the advantages that the phosgene is utilized to the greatest extent, the load of the tail gas generated in the normal-butyl isocyanate calorescence reaction in a tail gas processing system and the alkali charge during tail gas processing are reduced, the production cost of the product is reduced, and the purpose of saving and recycling resources is achieved.
Owner:HUNAN GOFAR FINE CHEM IND TECH CO LDT
Method and apparatus for quantification of optical properties of superficial volumes using small source-to-detector separations
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Information recording apparatus for thermosensitive medium
A recording apparatus for recording information in a thermosensitive medium which has a photothermal conversion layer having a light wavelength absorption property and a coloring layer colored by the heat generated by the photothermal conversion layer comprises a first light source that emits a light beam for writing information to a scanning position in a main scanning direction in the thermosensitive medium, and a second light source that emits a light of lower energy density than the light beam emitted by the first light source to the scanning position in the main scanning direction in the thermosensitive medium or to the vicinity thereof. The first light source and the second light source emit lights having wavelengths within the range of the absorption property of the photothermal conversion layer respectively to form recording dots of one line in the main scanning direction in a noncontact manner with the thermosensitive medium.
Owner:TOSHIBA TEC KK
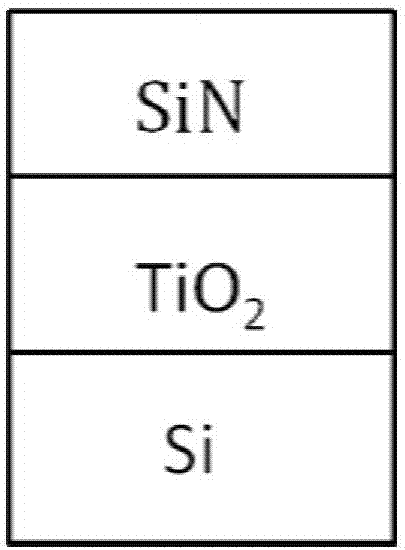
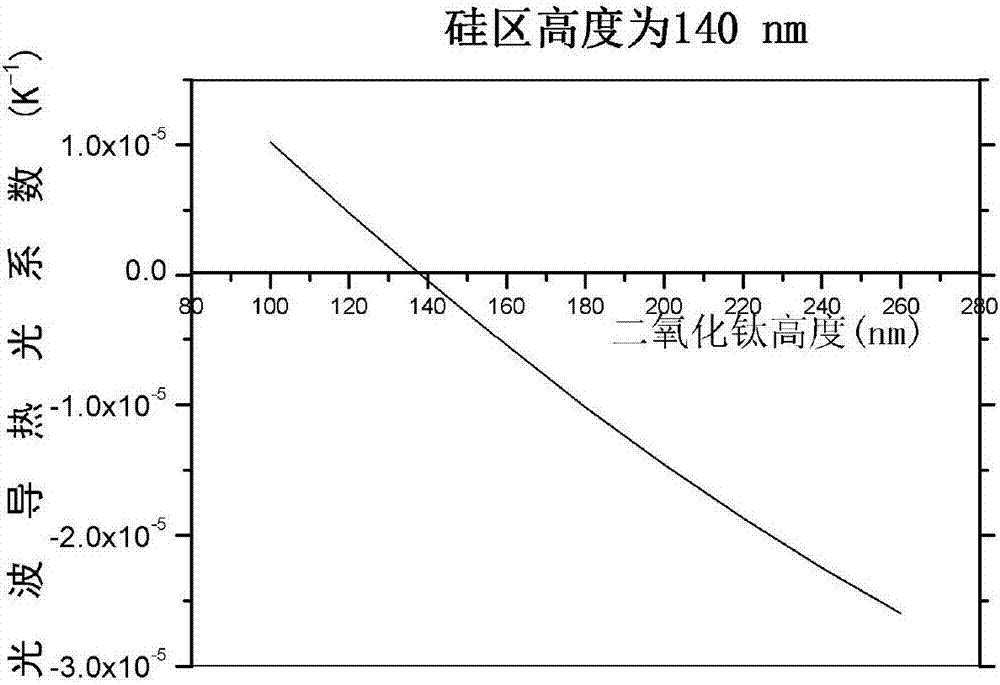
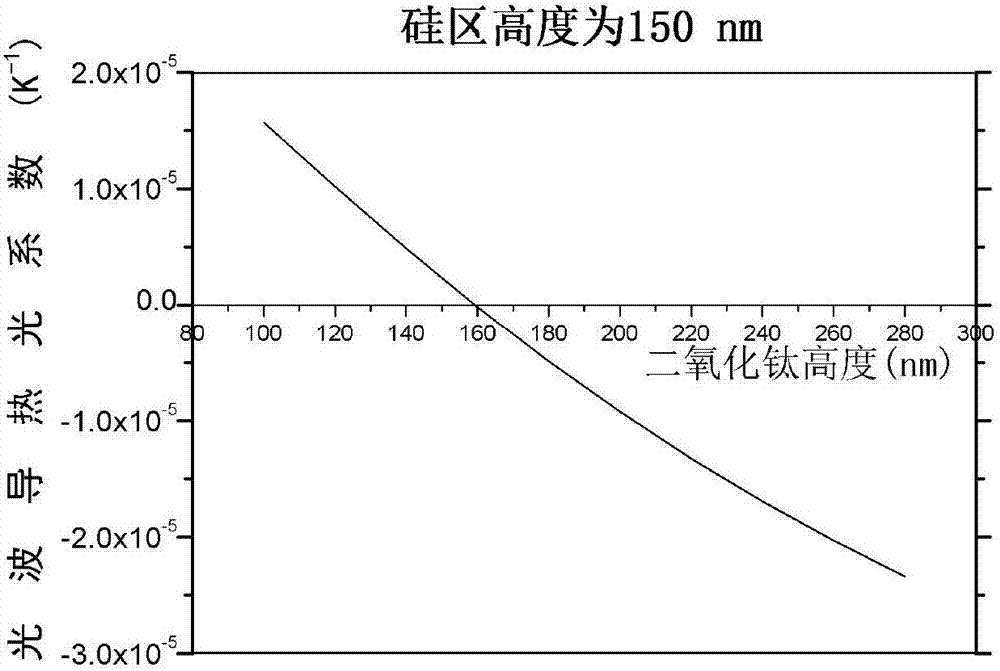
Broadband temperature-insensitive optical waveguide device
The invention discloses a broadband temperature-insensitive optical waveguide device, which comprises a core area and a cladding in mutual lamination, wherein the core area adopts silicon; the cladding adopts titanium dioxide; the other surface of the cladding is provided with a coverage layer; and the coverage layer adopts a material with a positive calorescence coefficient. The light intensity limiting factor of each structure layer in the optical waveguide is influenced by the wavelength, after the wavelength become larger, an evanescent field of the light transmitted in the optical waveguide becomes larger, and correspondingly, the light intensity limiting factor in the cladding becomes larger. Thus, corresponding to different wavelengths, the light intensity limiting factor in each layer changes, as the wavelength become larger, the total calorescence coefficient of the optical waveguide does not monotonously change along with the temperature, a curve similar to a parabolic change is formed, and temperature insensitivity in a broad wavelength range can be realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com