Silicon waveguide refractive index calorescence adjusting structure
A refractive index, light adjustment technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of slow speed, limited adjustment range, large adjustment power consumption, etc., to achieve large adjustment range, short response time, and adjustment power consumption. low effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
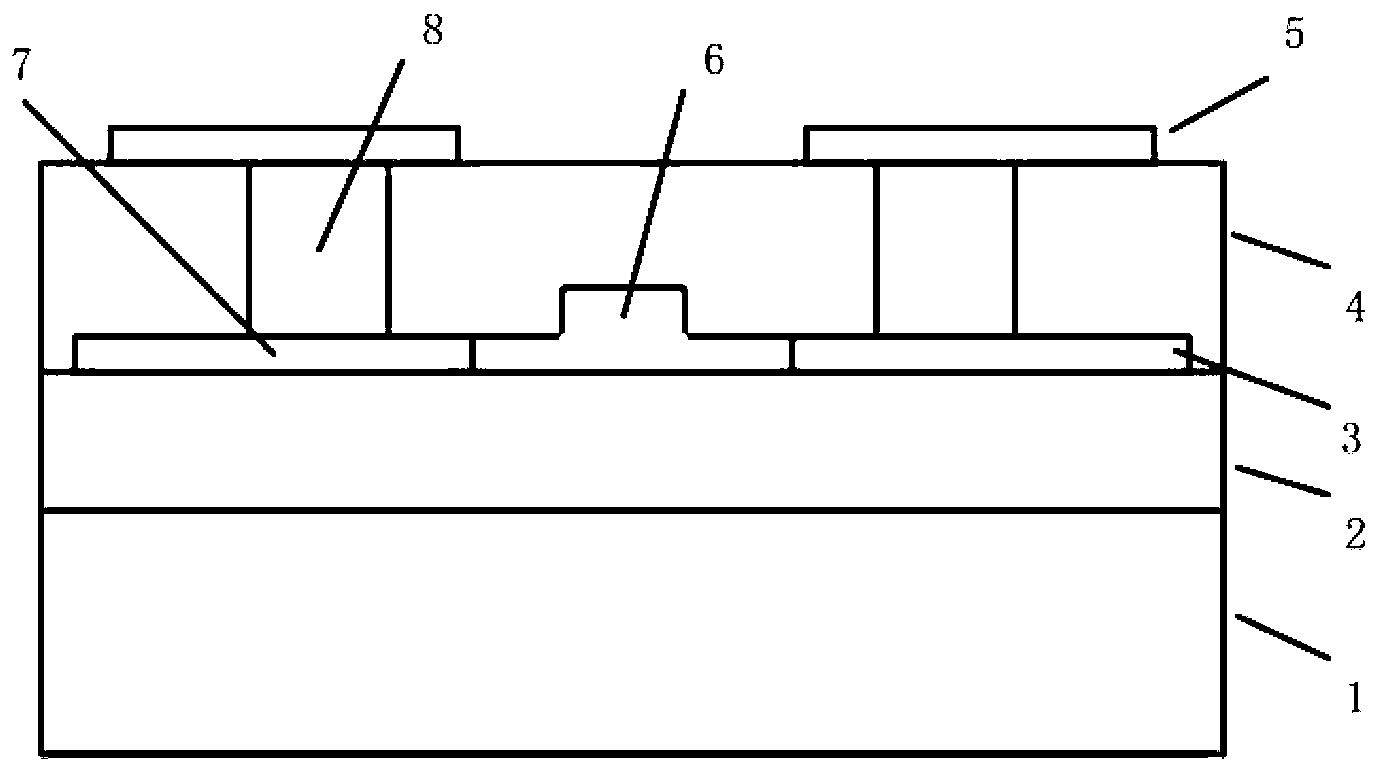
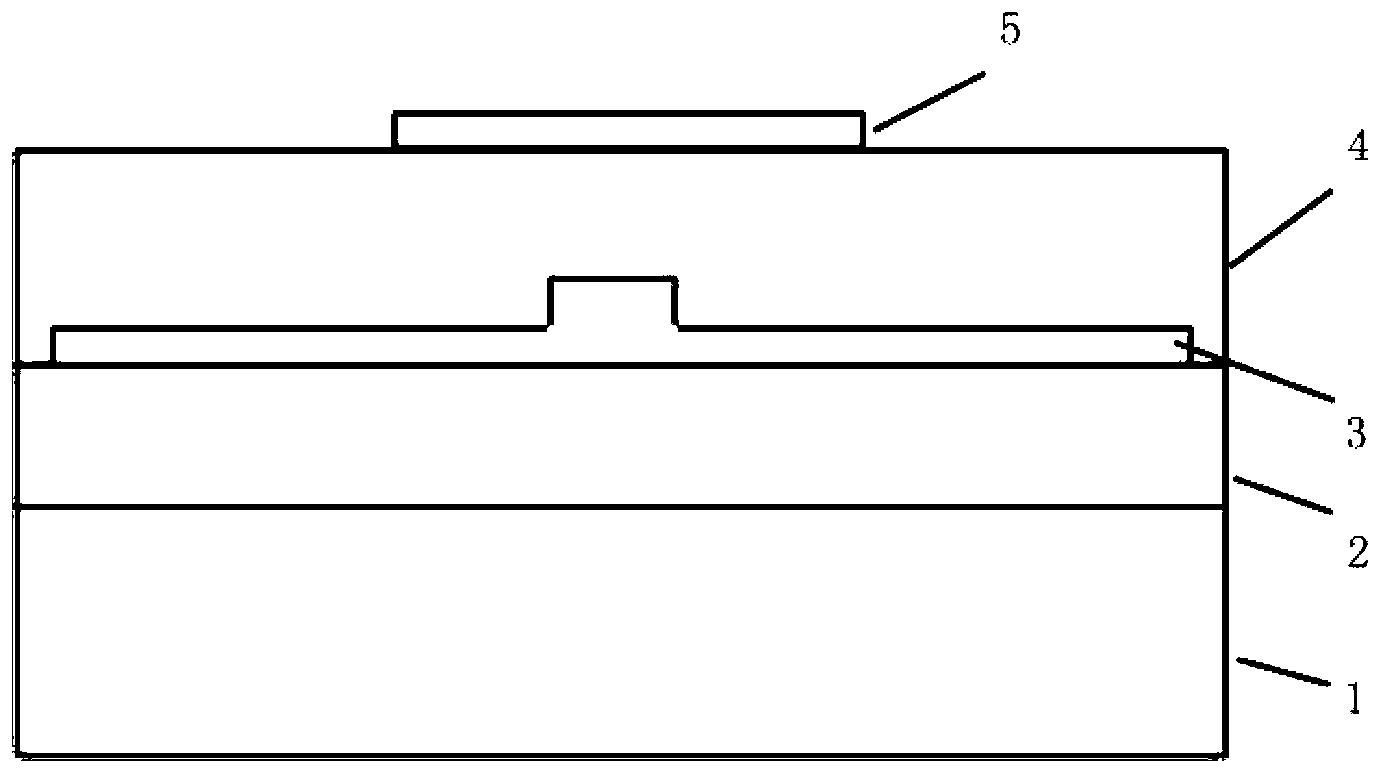
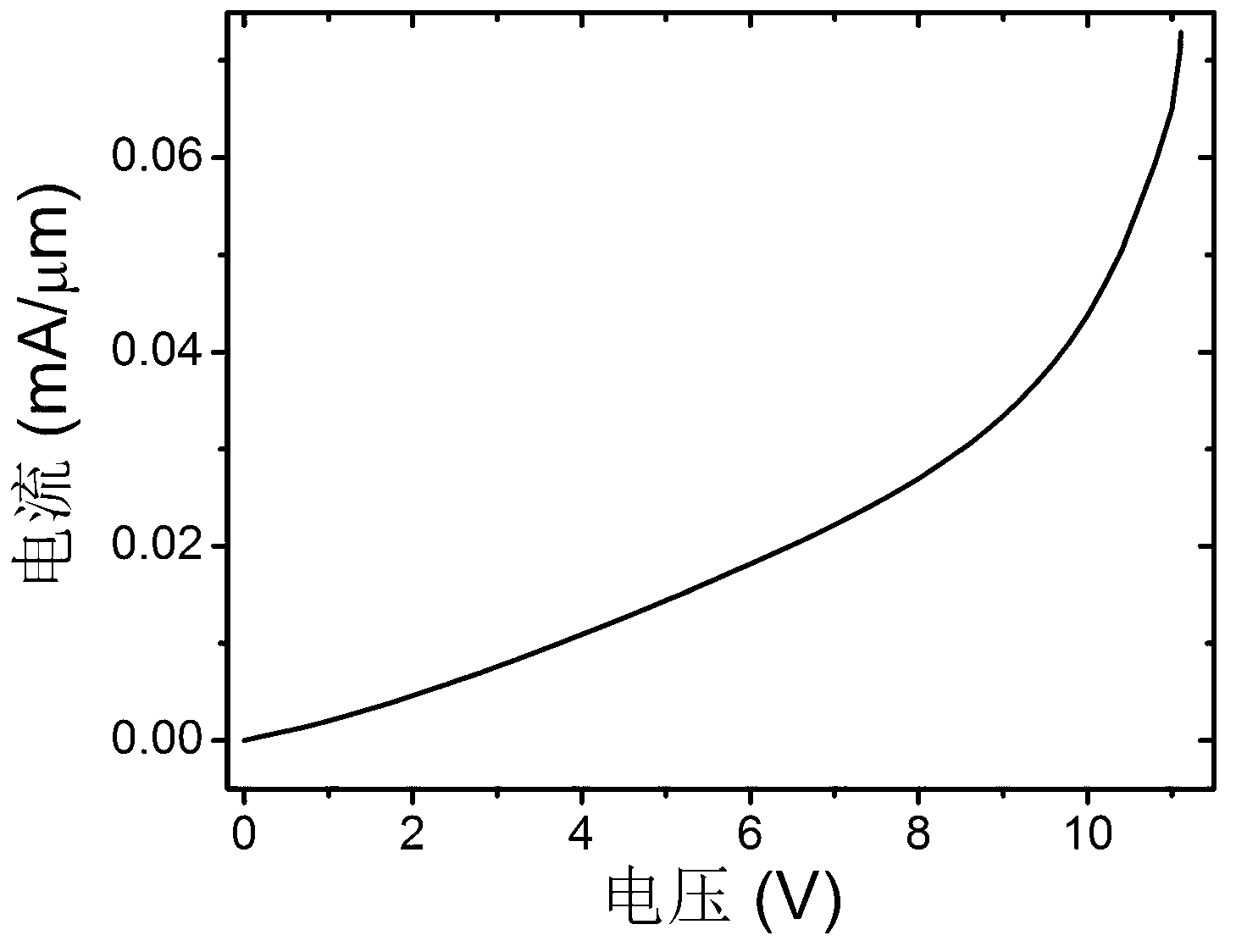
[0032] In this embodiment, the thickness of the lower cladding layer 2 is 2 μm; the width of the ridge of the waveguide layer 3 is 500 nm, the height of the inner ridge is 220 nm, and the height of the outer ridge is 60 nm; the thickness of the upper cladding layer 4 is 1.5 μm. The heavily doped region 7 is p-type doped with a width of 4μm and a doping concentration of 10 20 cm -3 ; Lightly doped intrinsic i-region 6 doping concentration 10 15 cm -3 The edge of the heavily doped region 7 is separated from the edge of the waveguide core region by 300 nm; the width of the through hole is 1 μm; a p-i-p thermal resistance structure is formed. The relationship between voltage and current of this p-i-p thermal resistance structure is as image 3 As shown, after the voltage increased to ~9.5V, the resistance continued to decrease as the voltage increased. When an external voltage of 4V is applied, the temperature distribution diagram of the structure after stabilization is as follows ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com