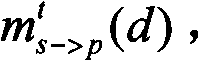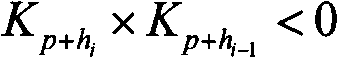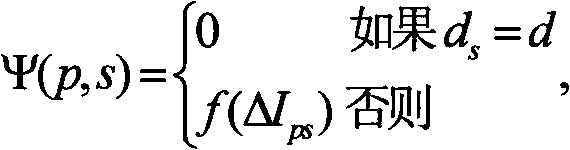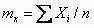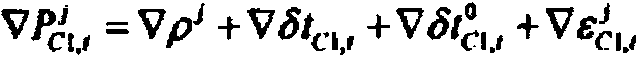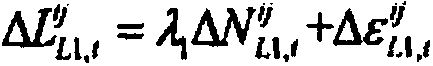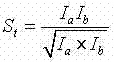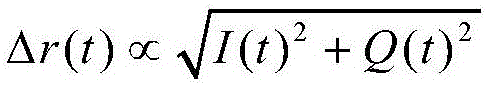Patents
Literature
471 results about "Cross correlation coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Correlation Coefficient. The correlation coefficient, sometimes also called the cross-correlation coefficient, Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC), Pearson's , the Perason product-moment correlation coefficient (PPMCC), or the bivariate correlation, is a quantity that gives the quality of a least squares fitting to the original data.
Regional depth edge detection and binocular stereo matching-based three-dimensional reconstruction method
ActiveCN101908230AStable matching costReduce mistakesImage analysis3D modellingObject pointReconstruction method
The invention discloses a regional depth edge detection and binocular stereo matching-based three-dimensional reconstruction method, which is implemented by the following steps: (1) shooting a calibration plate image with a mark point at two proper angles by using two black and white cameras; (2) keeping the shooting angles constant and shooting two images of a shooting target object at the same time by using the same camera; (3) performing the epipolar line rectification of the two images of the target objects according to the nominal data of the camera; (4) searching the neighbor regions of each pixel of the two rectified images for a closed region depth edge and building a supporting window; (5) in the built window, computing a normalized cross-correlation coefficient of supported pixels and acquiring the matching price of a central pixel; (6) acquiring a parallax by using a confidence transmission optimization method having an acceleration updating system; (7) estimating an accurate parallax by a subpixel; and (8) computing the three-dimensional coordinates of an actual object point according to the matching relationship between the nominal data of the camera and the pixel and consequently reconstructing the three-dimensional point cloud of the object and reducing the three-dimensional information of a target.
Owner:江苏省华强纺织有限公司 +1
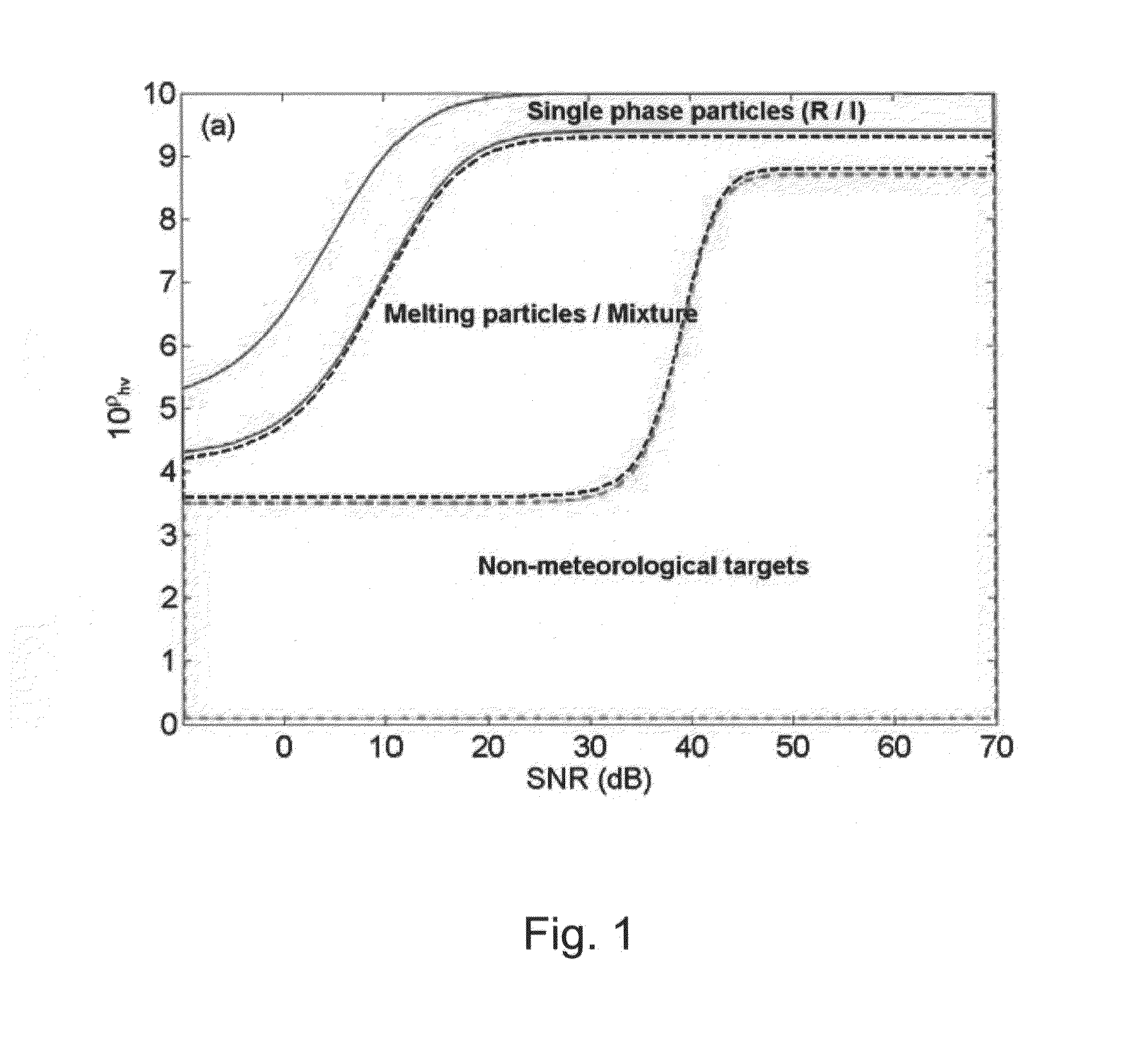
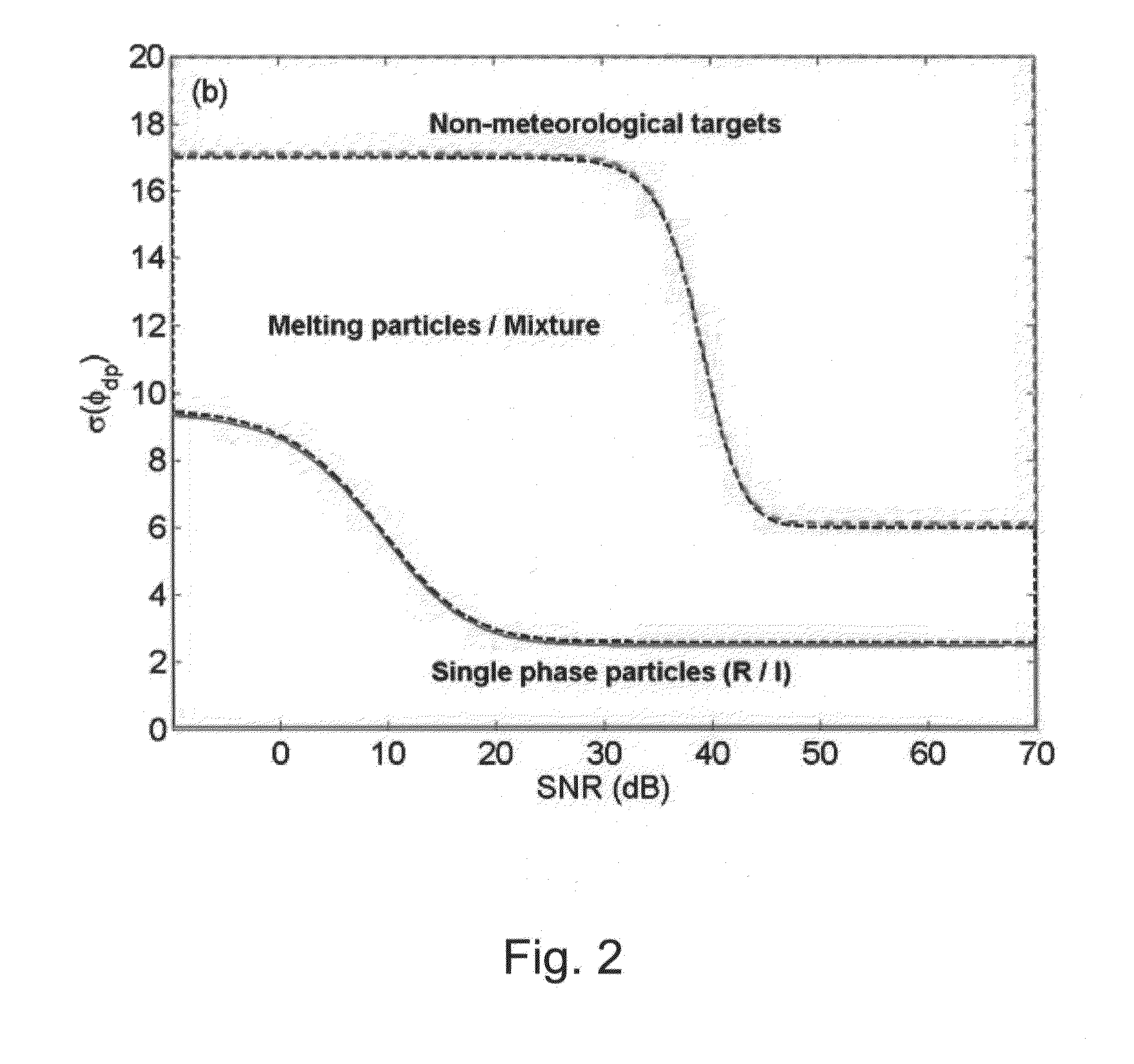
Integrated rainfall estimation method using x-band dual-polarimetric radar measurement data
ActiveUS20150145717A1Accurate estimateAccurately estimating rainfallRainfall/precipitation gaugesWeather condition predictionRainfall estimationEuclidean vector
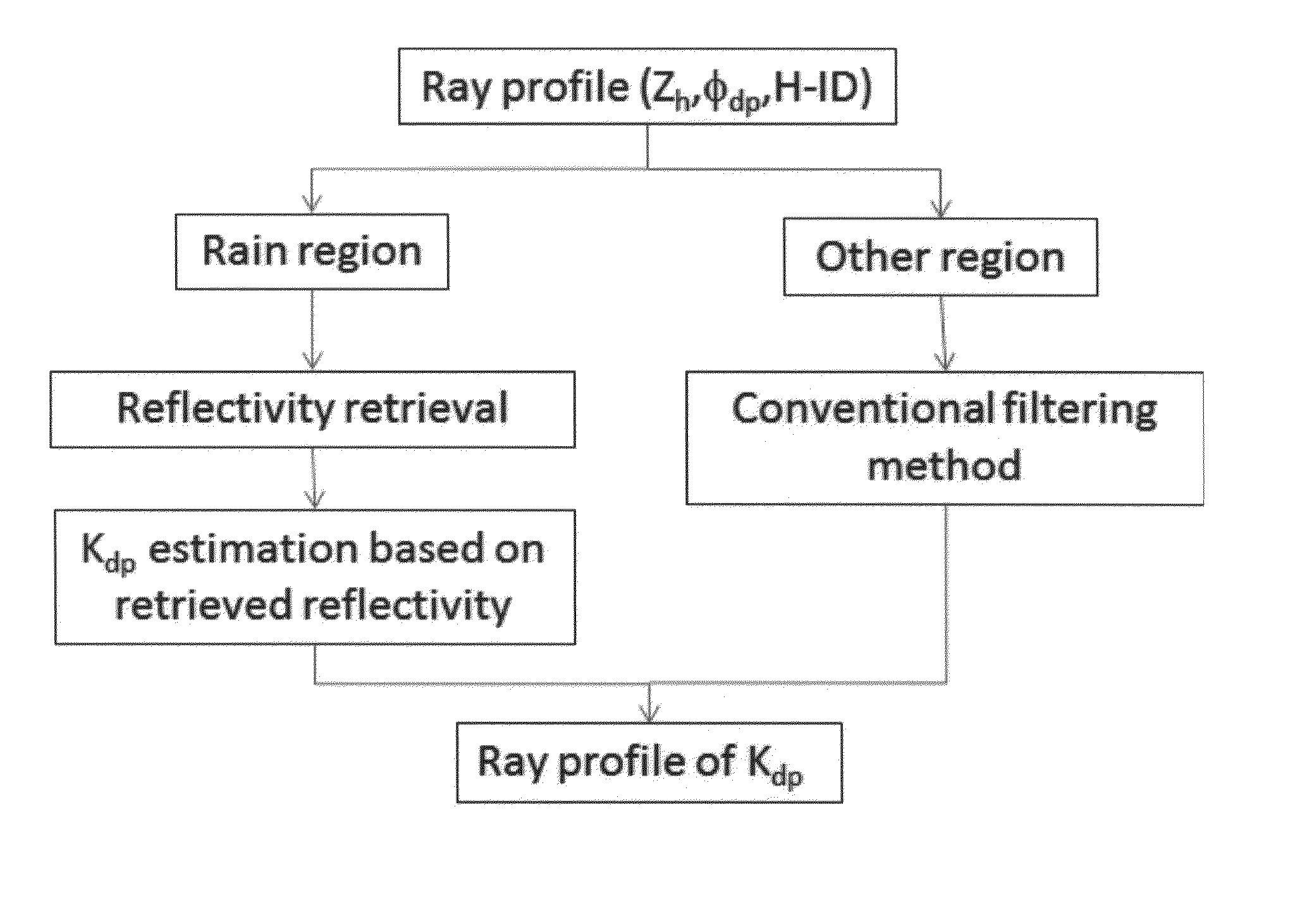
An integrated rainfall calculation method using X-band dual-polarimetric radar measurement data includes a precipitation classification step of classifying hydrometeors into four types of snow, rain / snow, rain and non-meteorological target through a fuzzy logic technique using a correlation coefficient (cross correlation coefficient, ρhv), features of a measured differential propagation phase (Ψdp(r)) or differential propagation phase (φdp) and a signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) as input variables (input feature vector); a specific differential phase calculation step of separately calculating a specific differential phase by applying a specific differential phase using a total difference of differential phase and signal-attenuation corrected reflectivity for the rain among the classified hydrometeors and applying a specific differential phase calculated using a filtering method for the other hydrometeors; and a rainfall calculation step of calculating rainfall by using a relation between the specific differential phase and the rainfall and using the separately calculated specific differential phase.
Owner:KOREA INST OF CIVIL ENG & BUILDING TECH
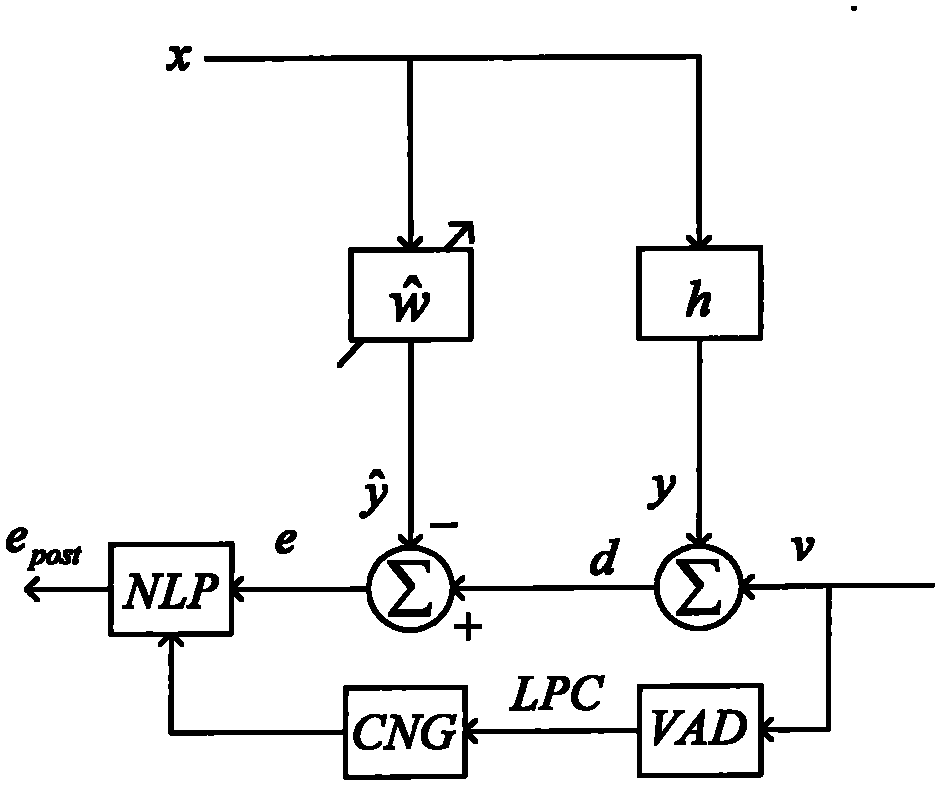
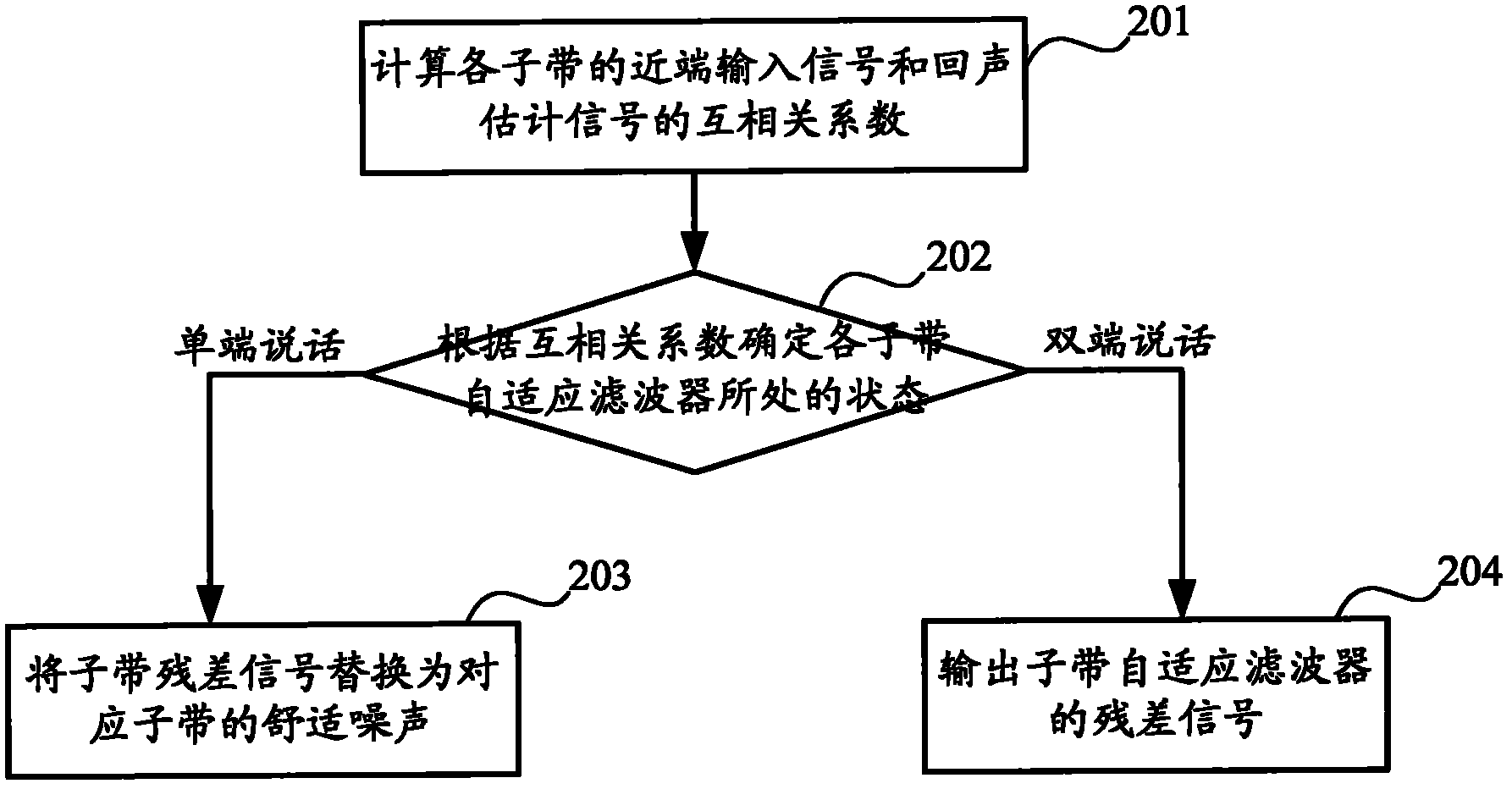
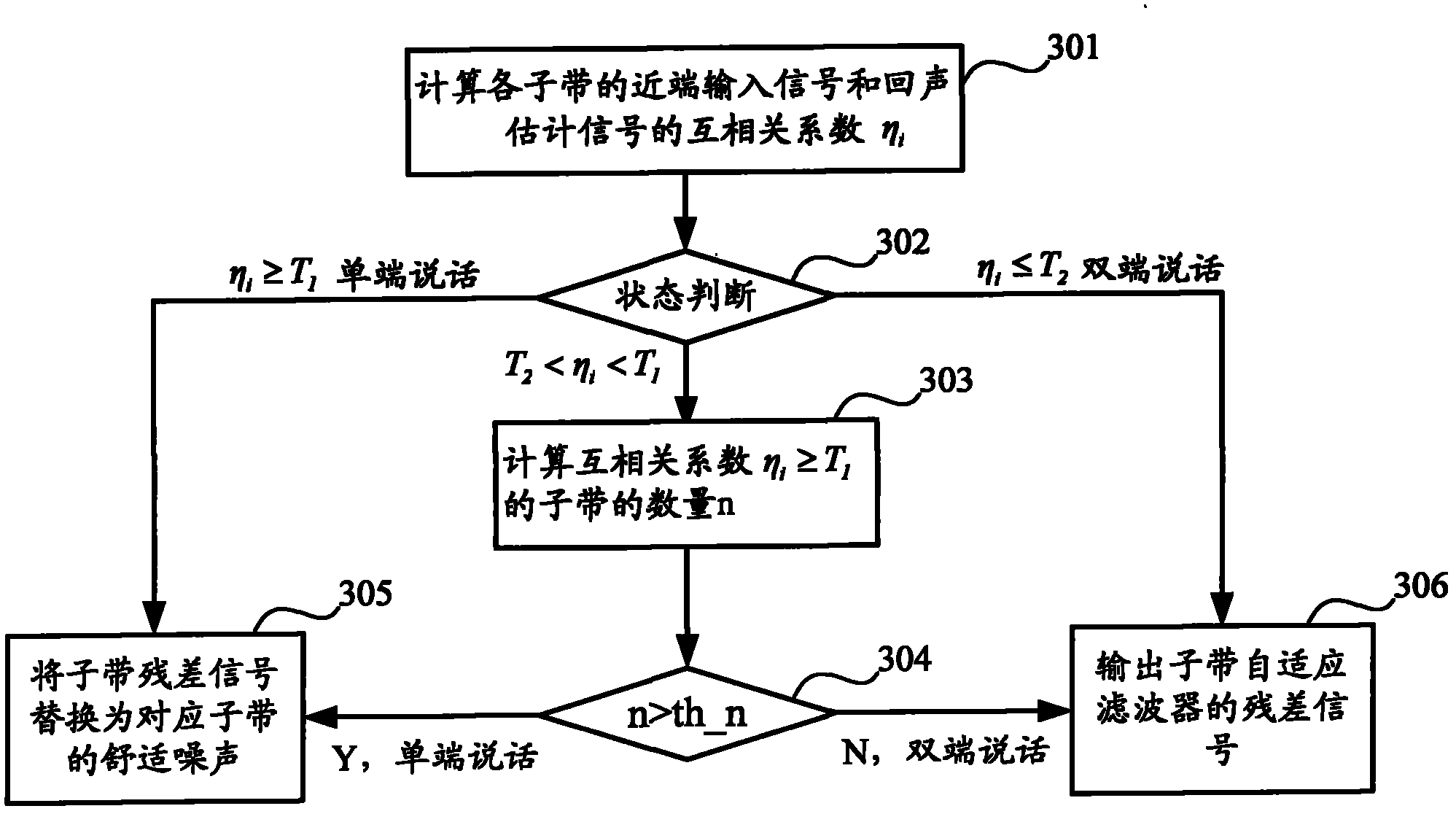
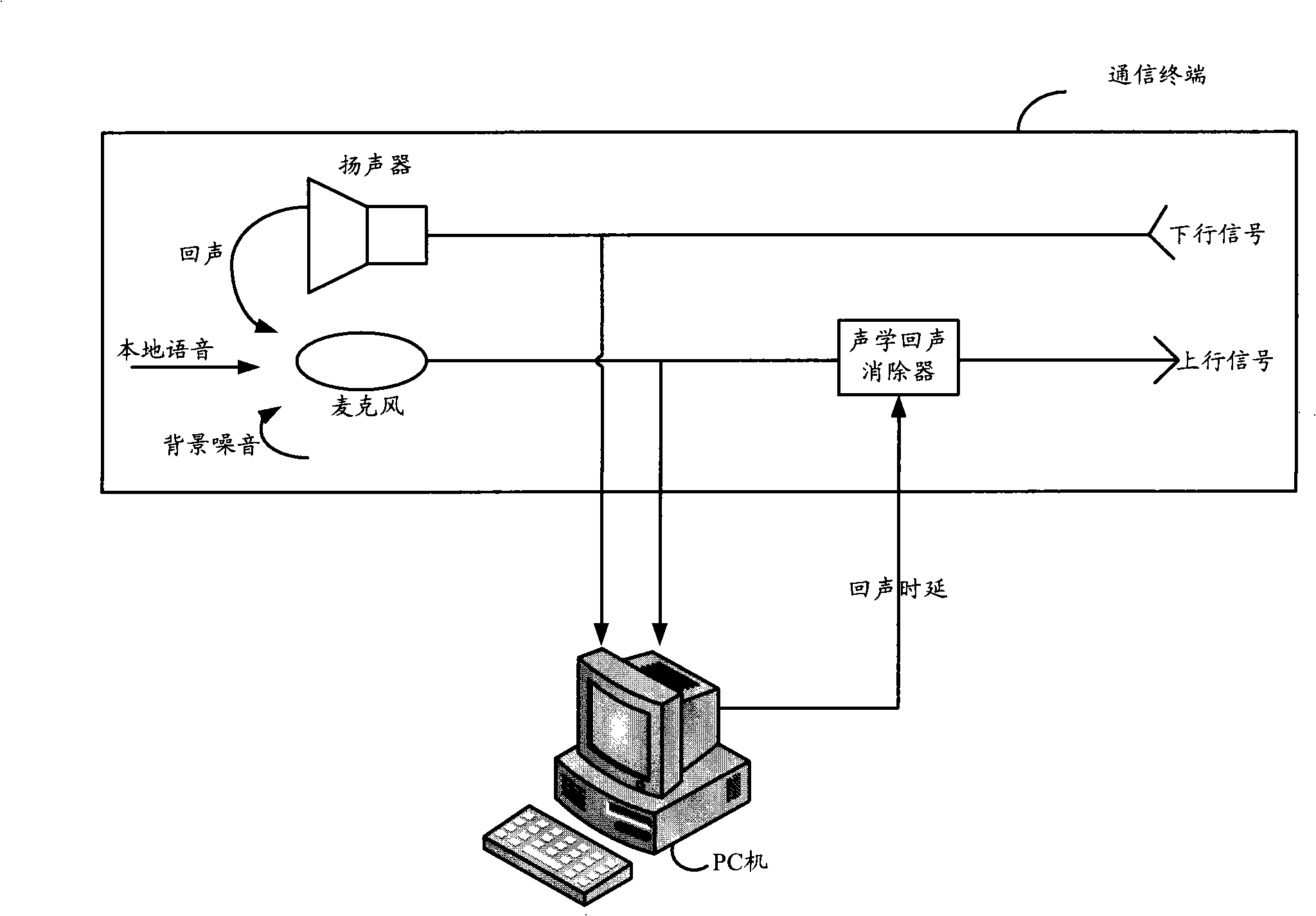
Method and device for eliminating echo
ActiveCN102065190AInhibition is effectiveEnhanced inhibitory effectTwo-way loud-speaking telephone systemsAdaptive filterSignal on
The invention discloses a method and a device for eliminating echo. The method comprises the steps of: determining the state of each subband adaptive filter respectively according to the cross correlation coefficient of an input signal on the near end of each subband and an echo estimation signal; when one end of the subband adaptive filter is in a speaking state, replacing the residual signal ofthe subband adaptive filter with comfortable noise of the subband, and outputting the replaced signal; and when both ends of the subband adaptive filter are in the speaking state, outputting the residual signal of the subband adaptive filter. In the invention, the signal processing characteristic of the subband can be fully utilized so that the residual echo can be suppressed more effectively. Inaddition, the suppression on the residual echo while both ends are in the speaking state and the protection on the voice of a person speaking on one end are enhanced, and the integral effect and the fluency of the system are improved.
Owner:NEW H3C TECH CO LTD
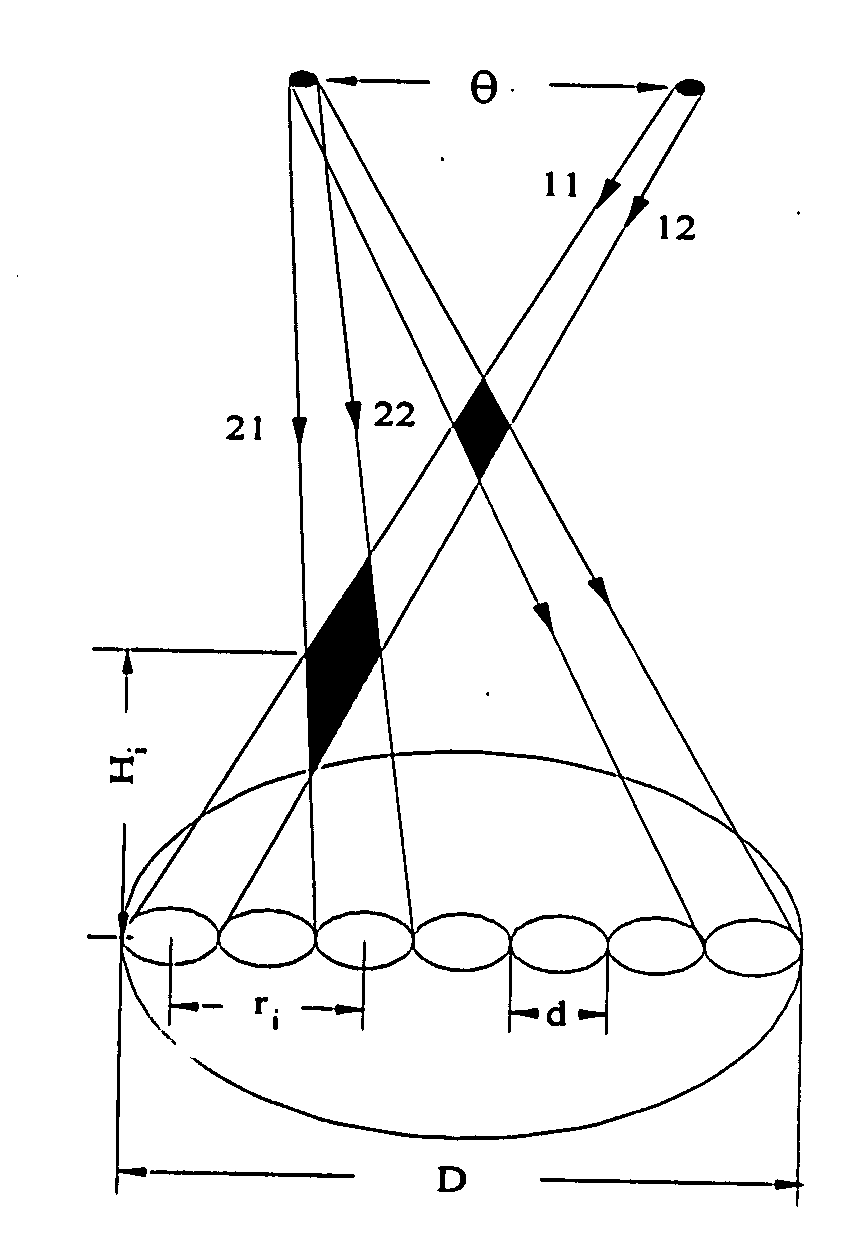
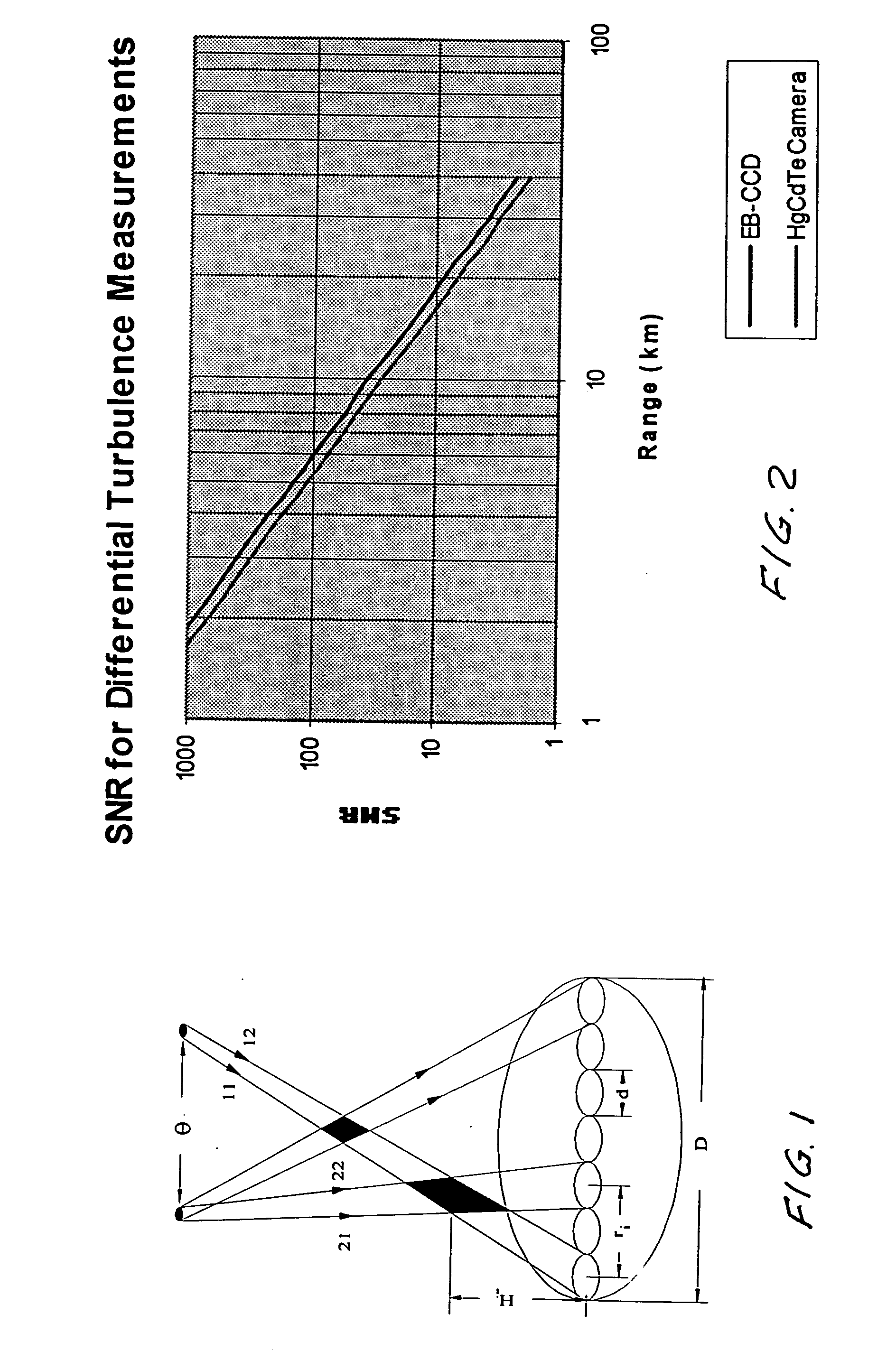
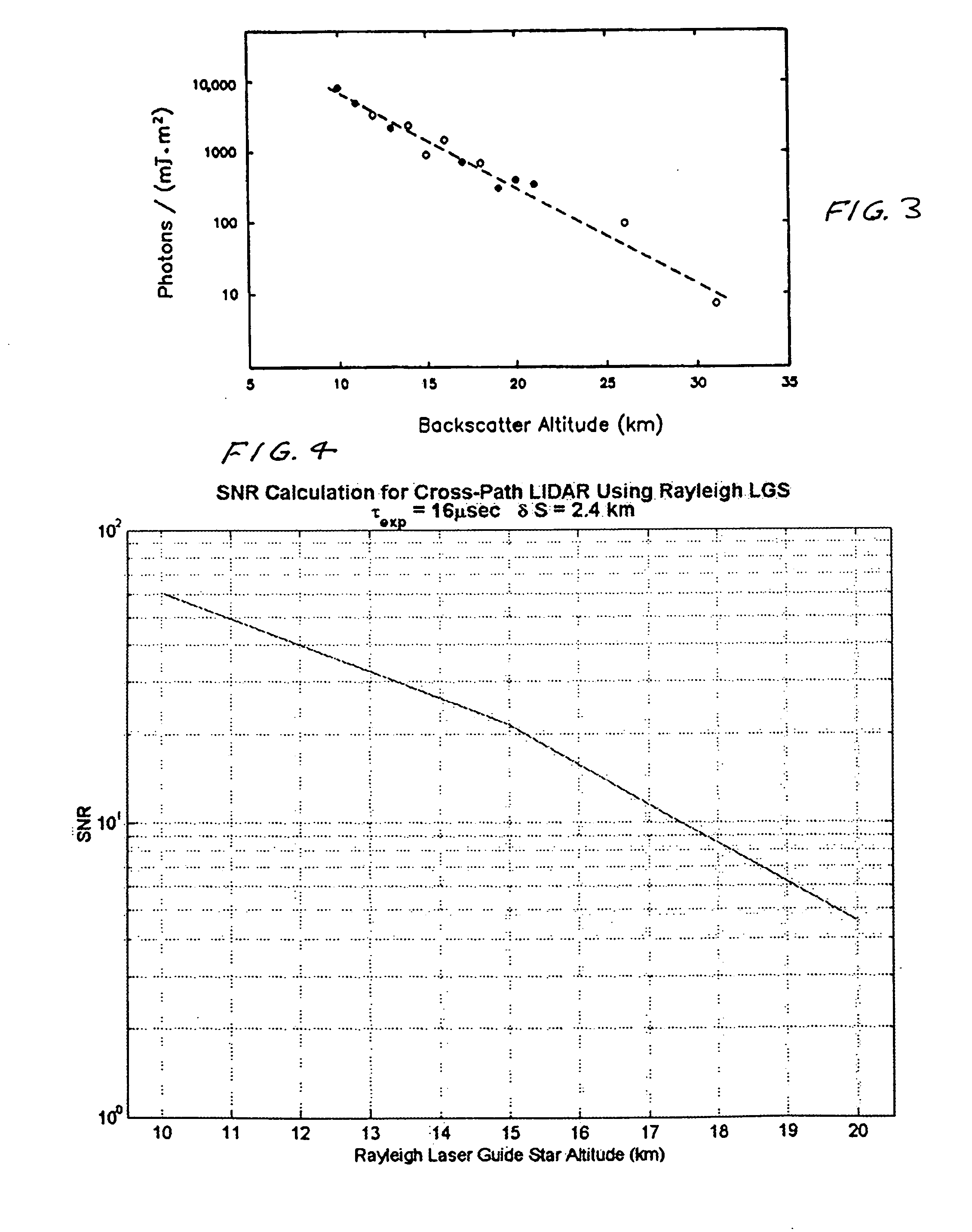
System for measuring atmospheric turbulence
InactiveUS20070077071A1Electromagnetic transmissionElectromagnetic wave reradiationWavefront sensorAngular distance
Equipment and techniques for the accurate estimates of the turbulence profile to improve the performance of adaptive optics systems designed to compensate the degradation effects of turbulence on directed energy systems, in astronomy, and in laser communication systems. The present invention is an optical turbulence profiler. The invention includes a cross-path LIDAR. The cross-path LIDAR technique uses laser guide star technology combined with a cross-path wavefront sensing method. In this method, two Rayleigh, or sodium, laser beacons separated at some angular distance are created by using a pulsed laser and a range-gated receiver. In preferred embodiments a Hartmann wavefront sensor measures the wavefront slopes from two laser guide stars. The cross-correlation coefficients of the wavefront slope are calculated, and the turbulence profile of refractive index structure characteristic Cn2(z) is reconstructed from the measured slope cross-correlations.
Owner:TREX ENTERPRISES CORP
Bearing fault diagnosis method and system device based on improved empirical wavelet transform
InactiveCN108375472AImprove the shortcomings of unreasonable segmentationAvoid mode aliasingMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionCorrelation coefficientFrequency spectrum
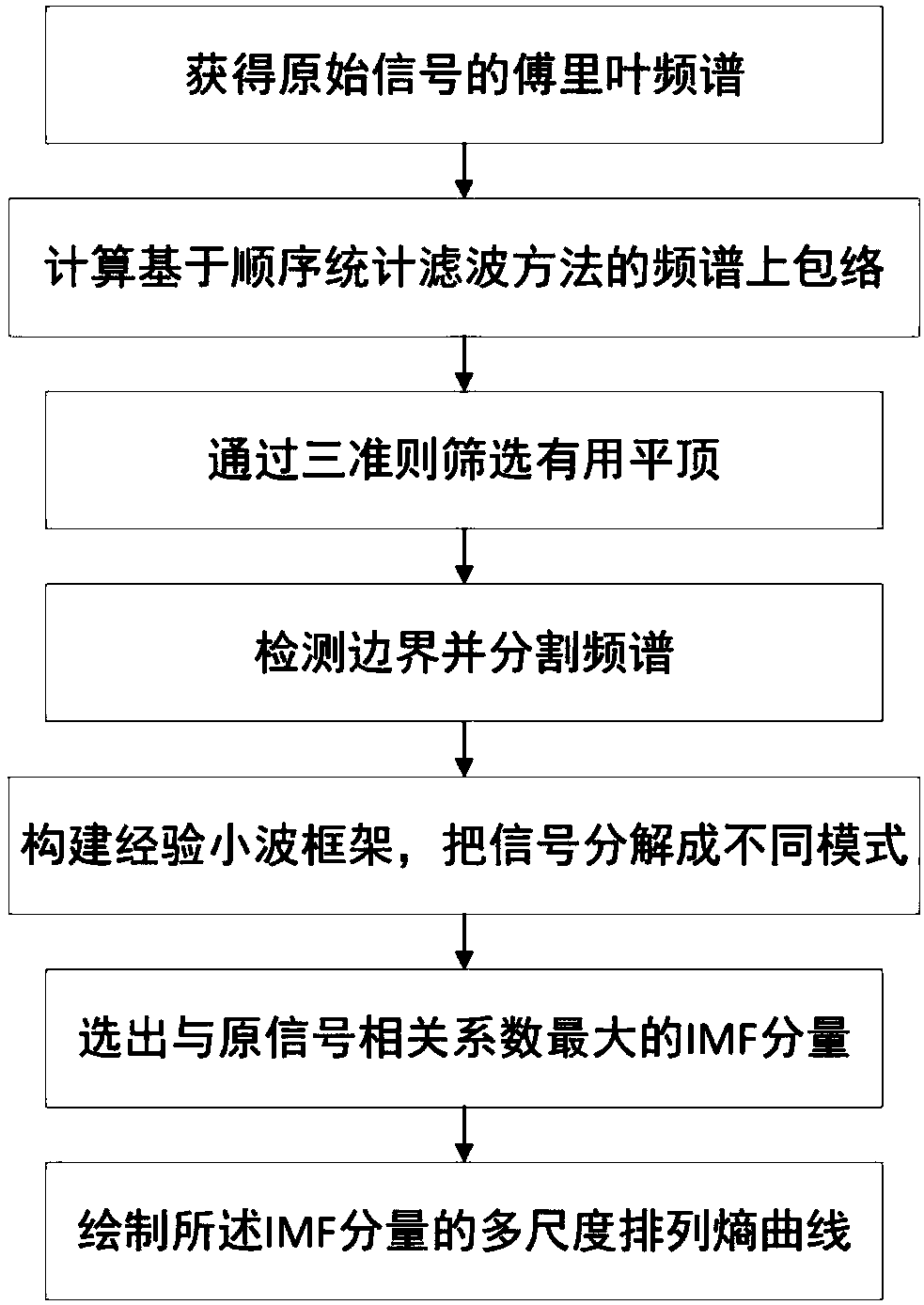
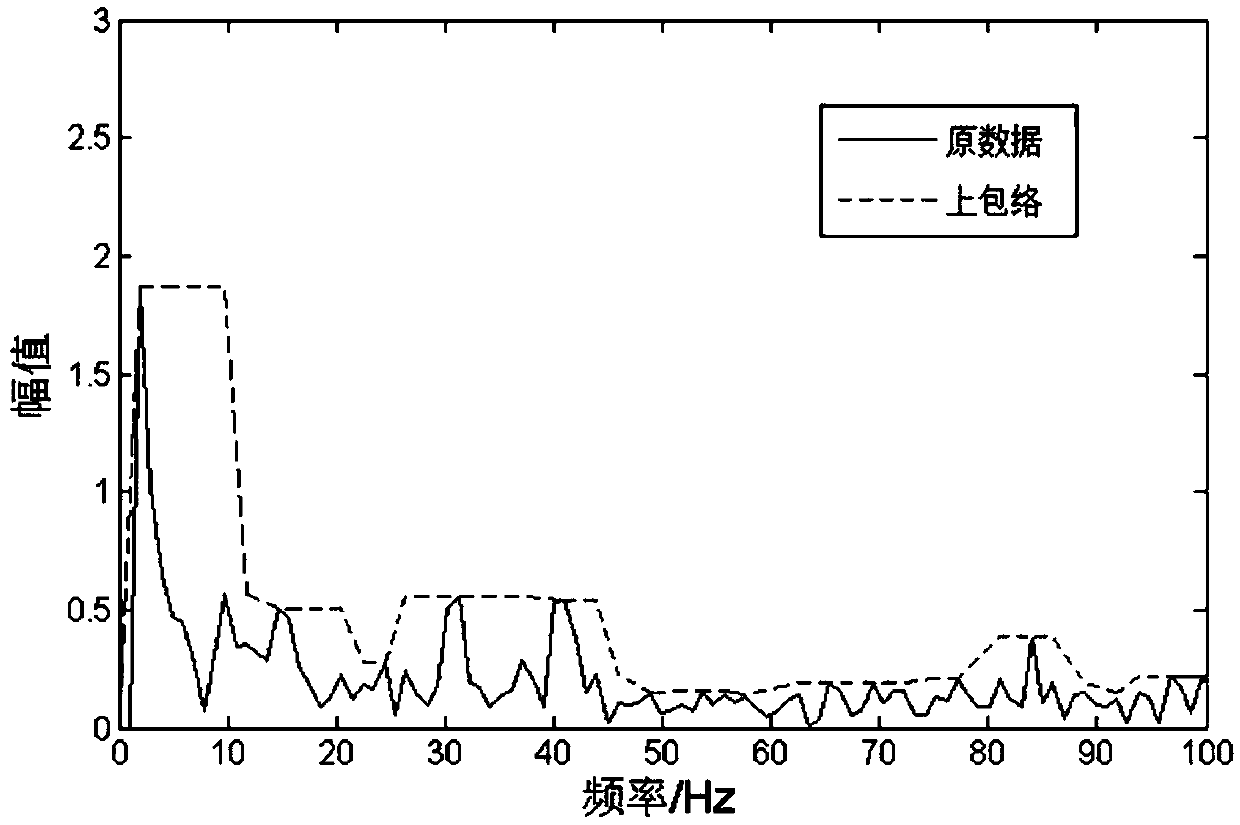
The invention provides a bearing fault diagnosis method and system device based on improved empirical wavelet transform. The method comprises: step one, collecting different fault bearing signals as analysis signals and converting a time domain waveform into a frequency domain waveform; step two, drawing an upper envelope of a frequency spectrum and transforming a frequency peak with a tight support into a flat top; step three, screening flat tops in the frequency domain based on criteria, removing meaningless flat tops, and keeping a main frequency; step four, using a minimum value between adjacent flat tops as the boundary of spectrum segmentation; step five, establishing wavelet filters respectively for segmented frequency spectrums and decomposing the signals into N mode components; step six, calculating similarity values between mode components and the original signals by using a cross-correlation coefficient and selecting a component with the highest similarity value; and step seven, taking a fault sample, calculating an IMF component with the largest correlation coefficient of the sample, calculating a multi-scale entropy of the IMF component, and drawing the multi-scale entropy curve of the sample to realize fault classification.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
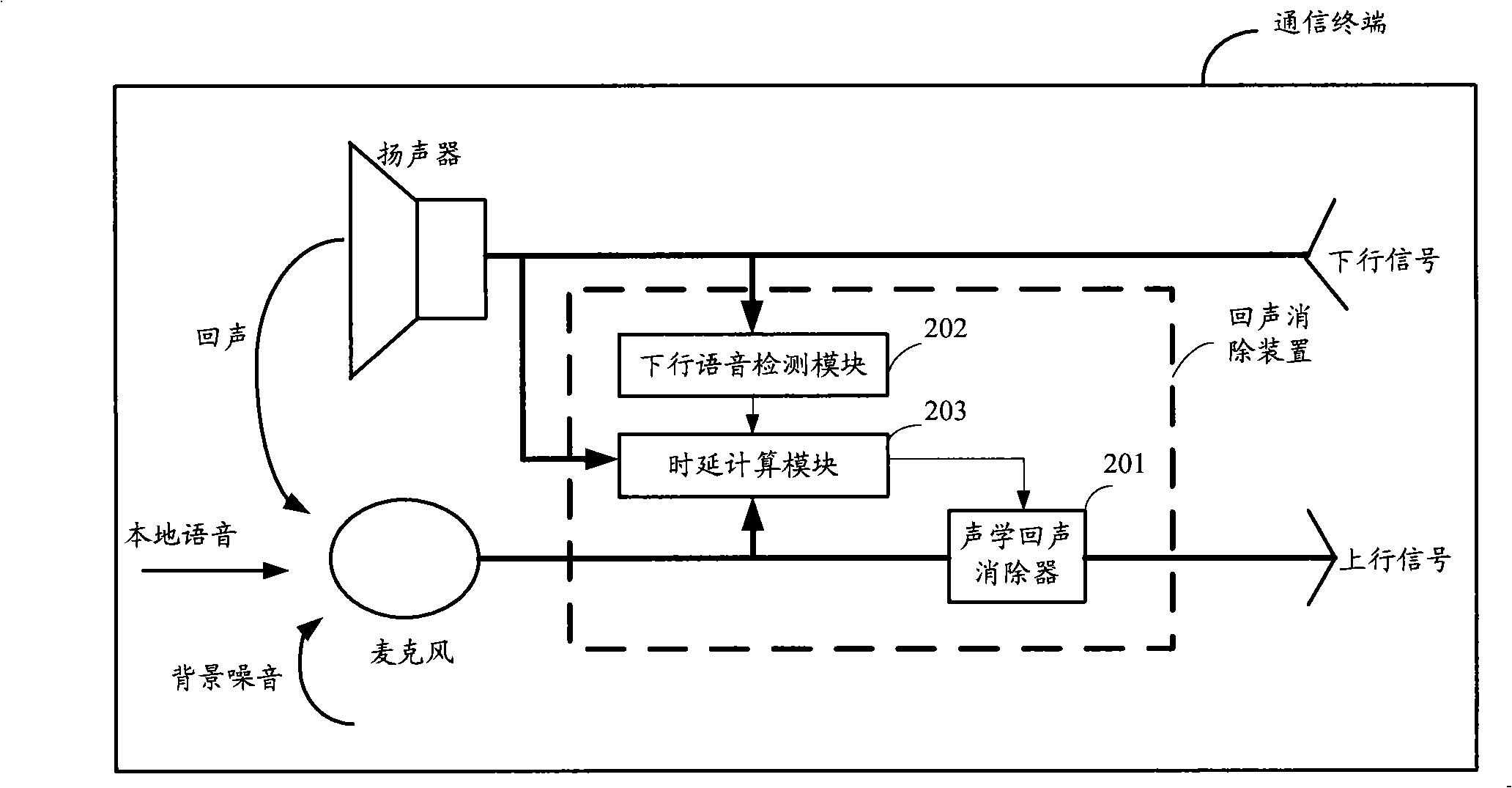
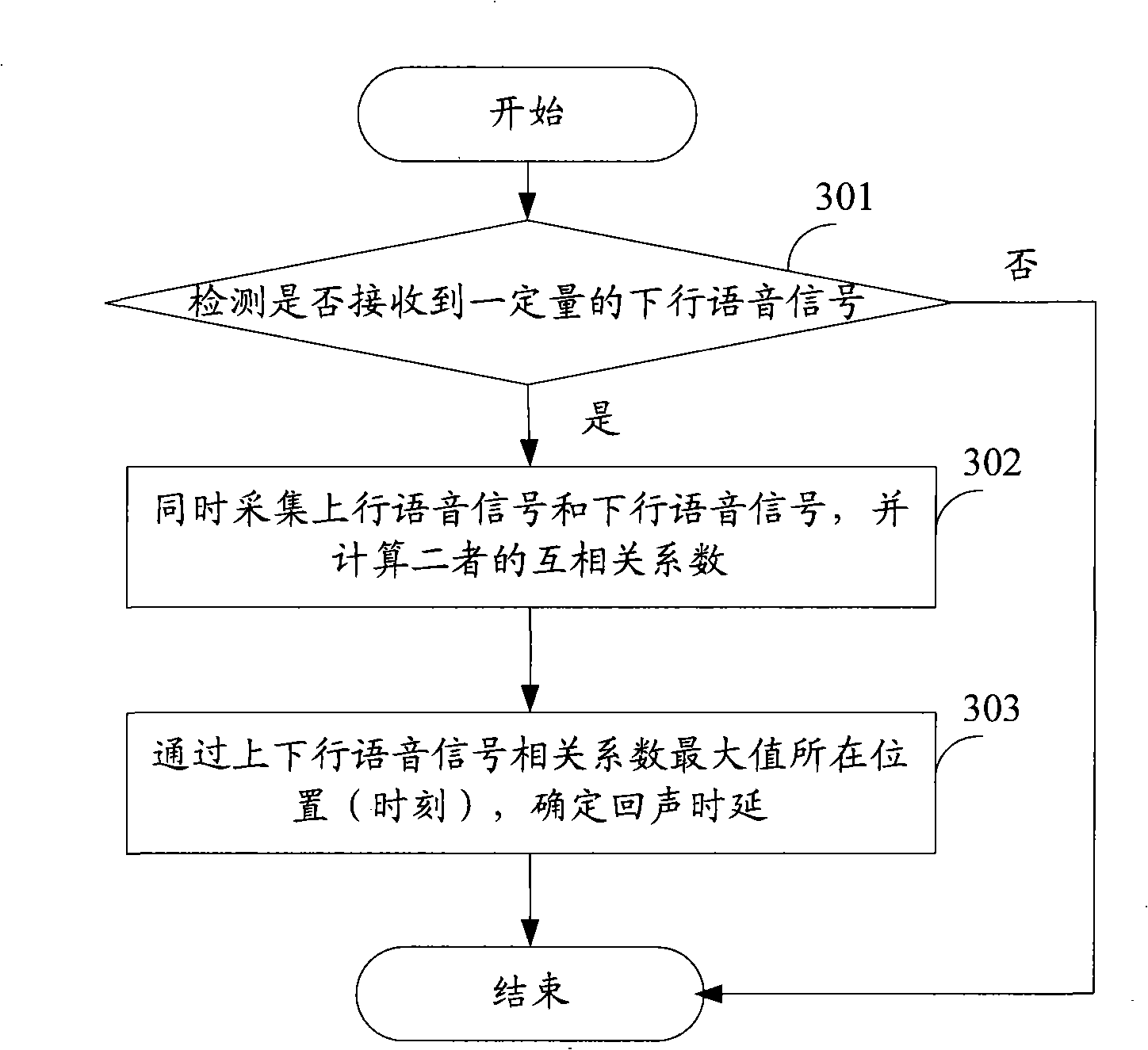
Echo elimination device, communication terminal and method for confirming echo delay time
ActiveCN101321201AAccurate Echo CancellationAvoid errorsAnti-side-tone circuitsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTime delaysComputer science
The invention discloses an echo eliminating device, comprising: an acoustic echo eliminator which receives an echo time-delay value and determine parameters according to the echo time-delay value to eliminate the echo; a downlink voice detecting module which detects whether energy of a received downlink voice signal reaches the prearranged threshold value, if so, an identifier is output; a time-delay computing module which collects the uplink, downlink voice signals, computes correlative coefficient of the uplink, downlink voice signals at the time of receiving the identifier, determines the echo time-delay value corresponding to the maximum value of the correlative coefficient, and sends the echo time-delay value to the acoustic echo eliminator. The invention not only can configure appropriate parameters for terminal by the time of leaving factory, but also can be integrated to update relevant parameters in real time for a part of the acoustic echo eliminator, thereby the invention is apt for variation of the echo time-delay owing to change of the terminal's circumstance and improves effect of echo elimination as well as reduces expenditure of system resource. Meanwhile, the invention also discloses a communication terminal including the echo eliminating device, and a method for determining the echo time-dealy.
Owner:LEADCORE TECH
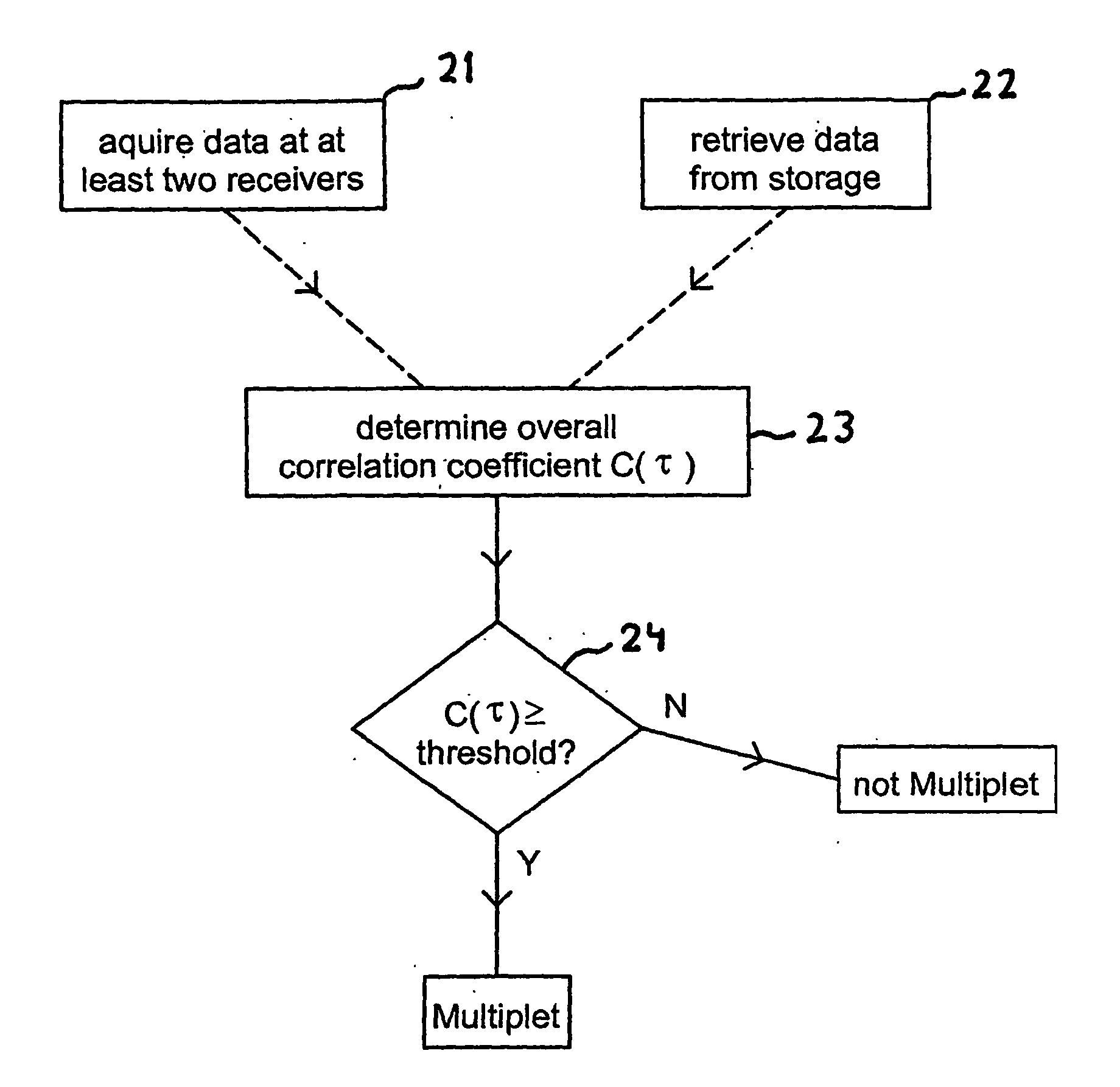
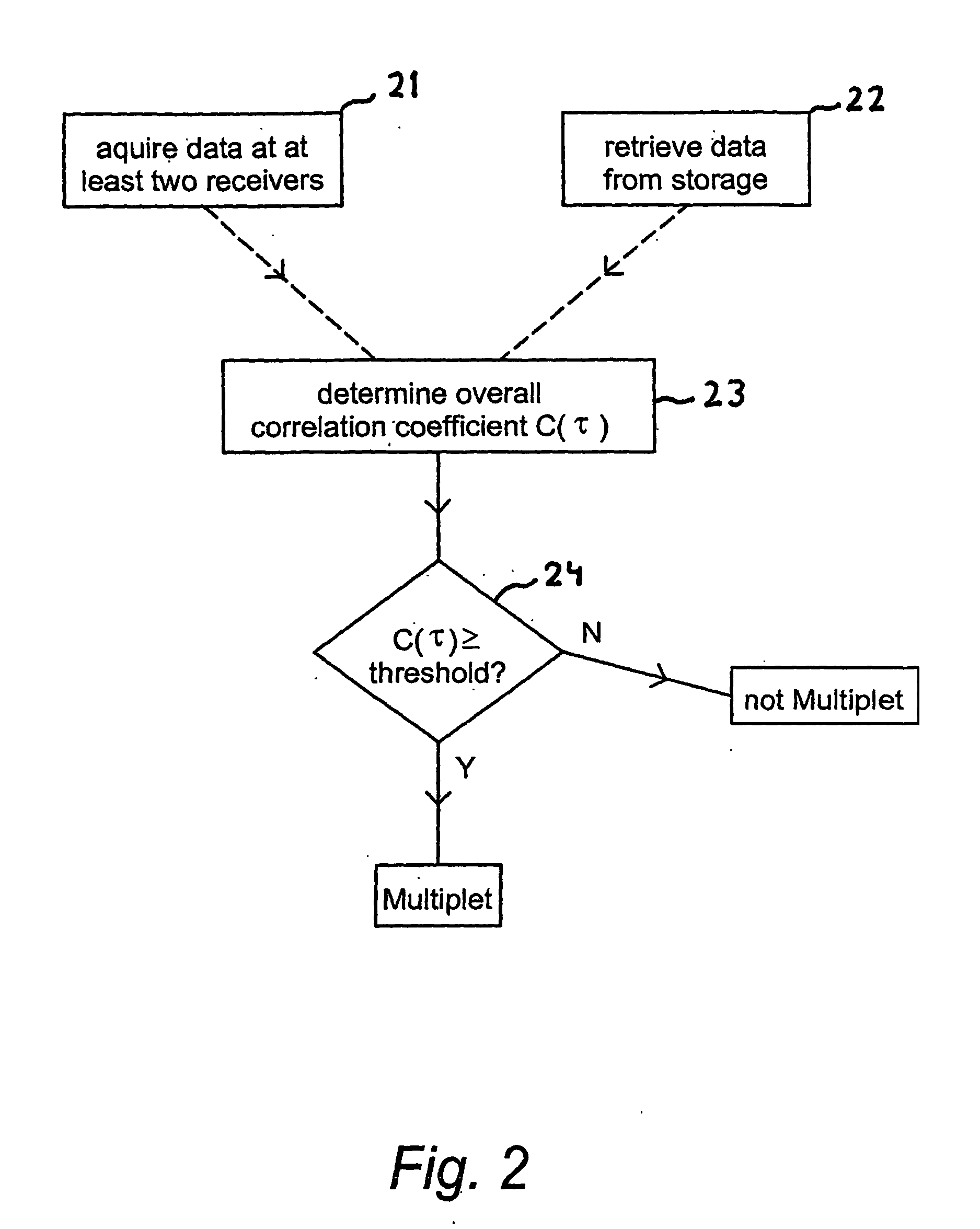
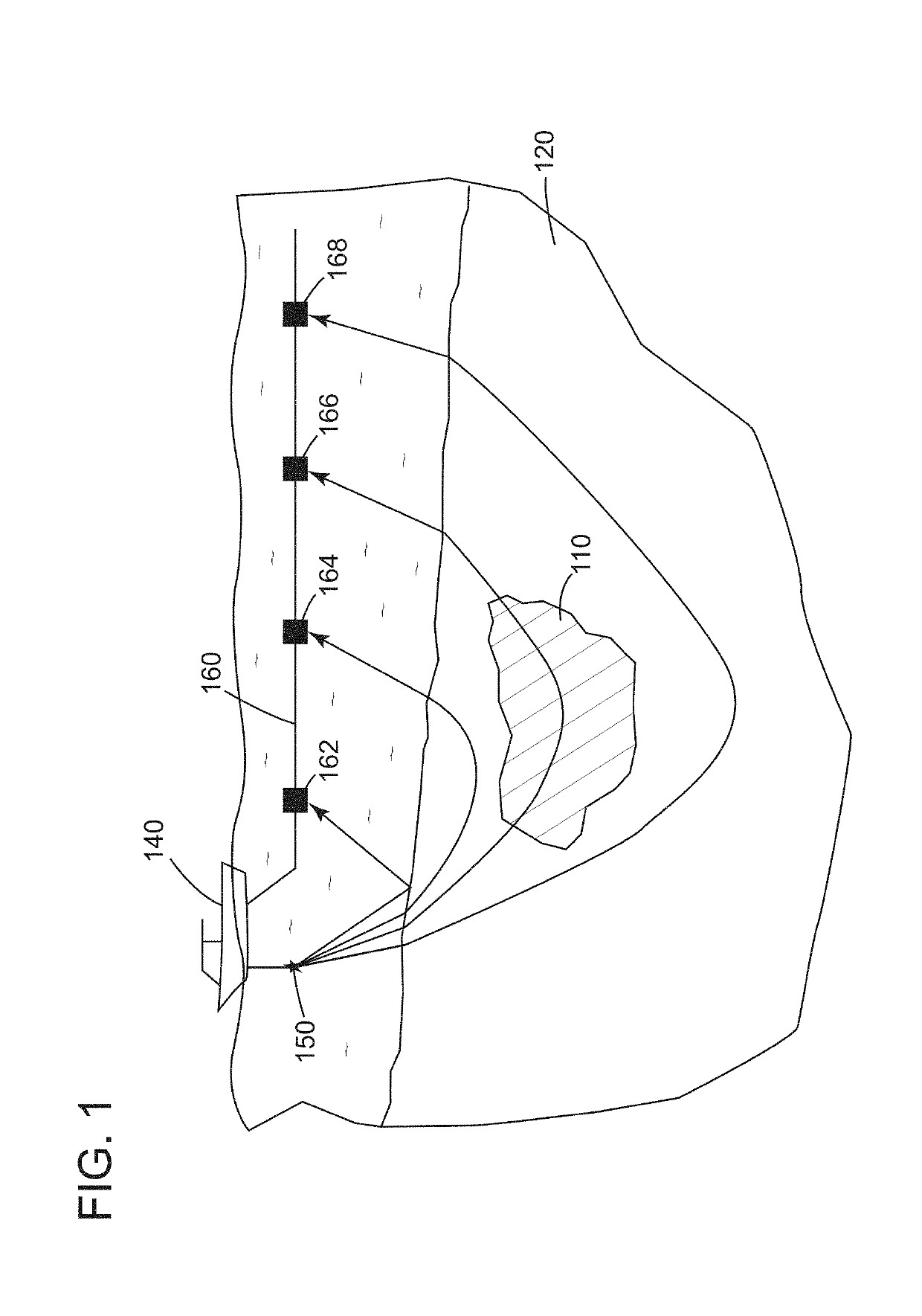
Passive seismic event detection
ActiveUS20060285438A1Reduce weightAccurate identificationSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientSeismic trace
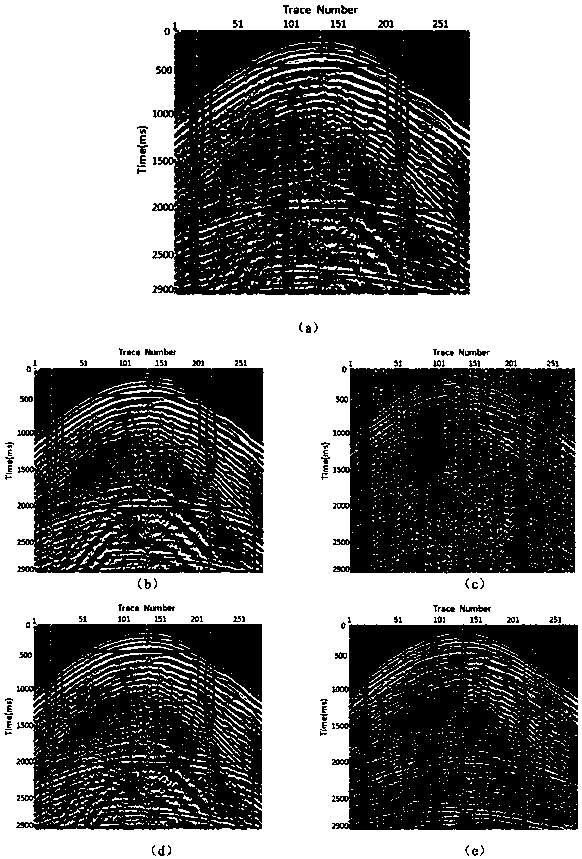
A method of identifying passive seismic events in seismic data that contains at least first seismic data traces acquired at a first seismic receiver and second seismic data traces acquired at a second receiver spatially separated from the first receiver comprises determining an overall measure of similarity for a pair of events in the seismic traces. The overall measure of similarity is indicative of similarity between the events acquired at the first seismic receiver and of similarity between the events acquired at the second seismic receiver. In one method, the overall measure of similarity is an overall cross-correlation coefficient. The overall cross-correlation coefficient is found by determining a first correlation coefficient for the pair of events from the data acquired at the first receiver and determining a second correlation coefficient for the pair of events from the data acquired at the second receiver. The overall correlation coefficient for the pair of events may be obtained from the first correlation coefficient and the second correlation coefficient by an averaging process. The overall measure of similarity may be compared with a threshold to determine whether the pair of events form a doublet. The method makes possible real-time or near-real-time identification of doublets.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
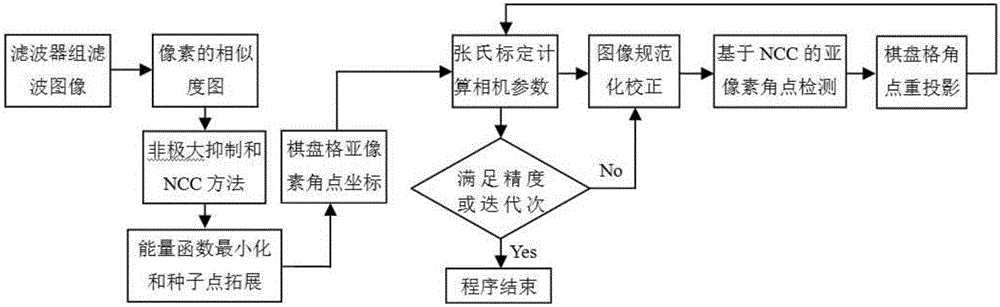
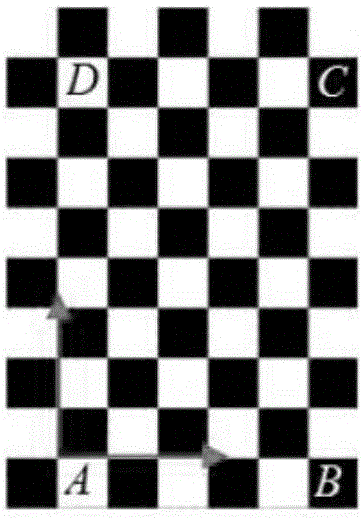
Fully automatic calibration method for high performance camera under complicated background
InactiveCN105096317AHigh precisionImage enhancementImage analysisCamera auto-calibrationCheckerboard
With an object of solving problems existing in the prior art, the invention provides a fully automatic calibration method for a high performance camera under a complicated background. The method is combined with a Robust's checkerboard corner detection method, and two groups of checkerboards corners are adopted to serve as filters on the basis of the characteristics of the corners to filter marker images. Eight filters of two types are reduced to four filters of two types, which means that the wave processing amount halves and therefore, the calibration speed increases. Further, the method utilizes a Zhang's camera calibration method to mark the camera calibration parameters. The method utilizes the marked camera calibration parameters to standardize images to be corrected, and a normalized correlation of the standardized images is calculated, and then sub-pixel precision checkerboard corners are obtained. The method then re-projects the coordinate of the checkerboard corners onto image space to obtain a precise coordinate of the corner image. The newly obtained coordinate of the corners is then substituted into the Zhang's calibration method to obtain new computed camera parameters. By repeating the above steps, a performer can obtain highly precise camera parameters. According to the embodiments of the invention, it is possible for a performer to complete automatic corner detection and camera calibration without having to resort to human-machine interactive operations.
Owner:吴晓军
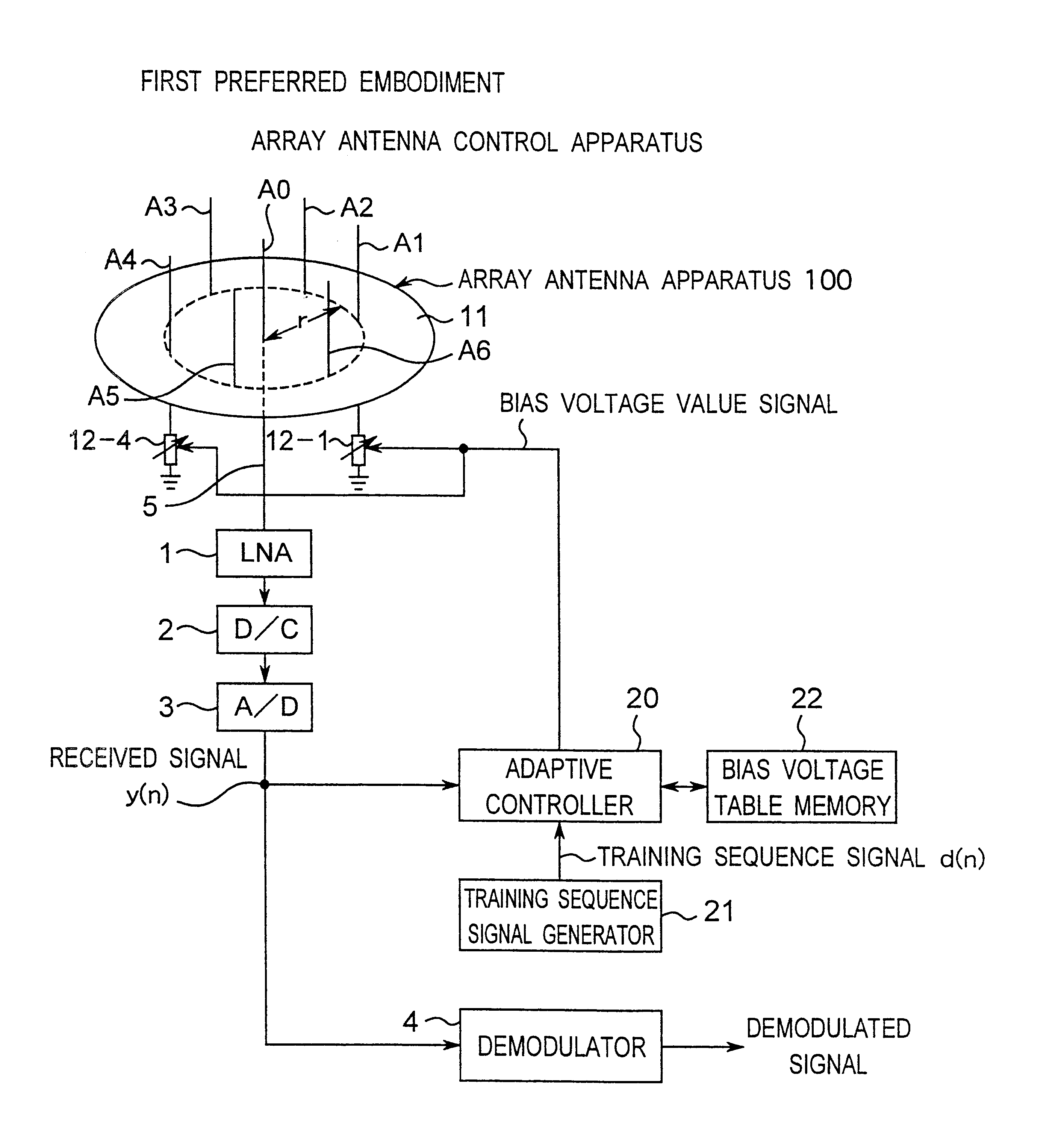
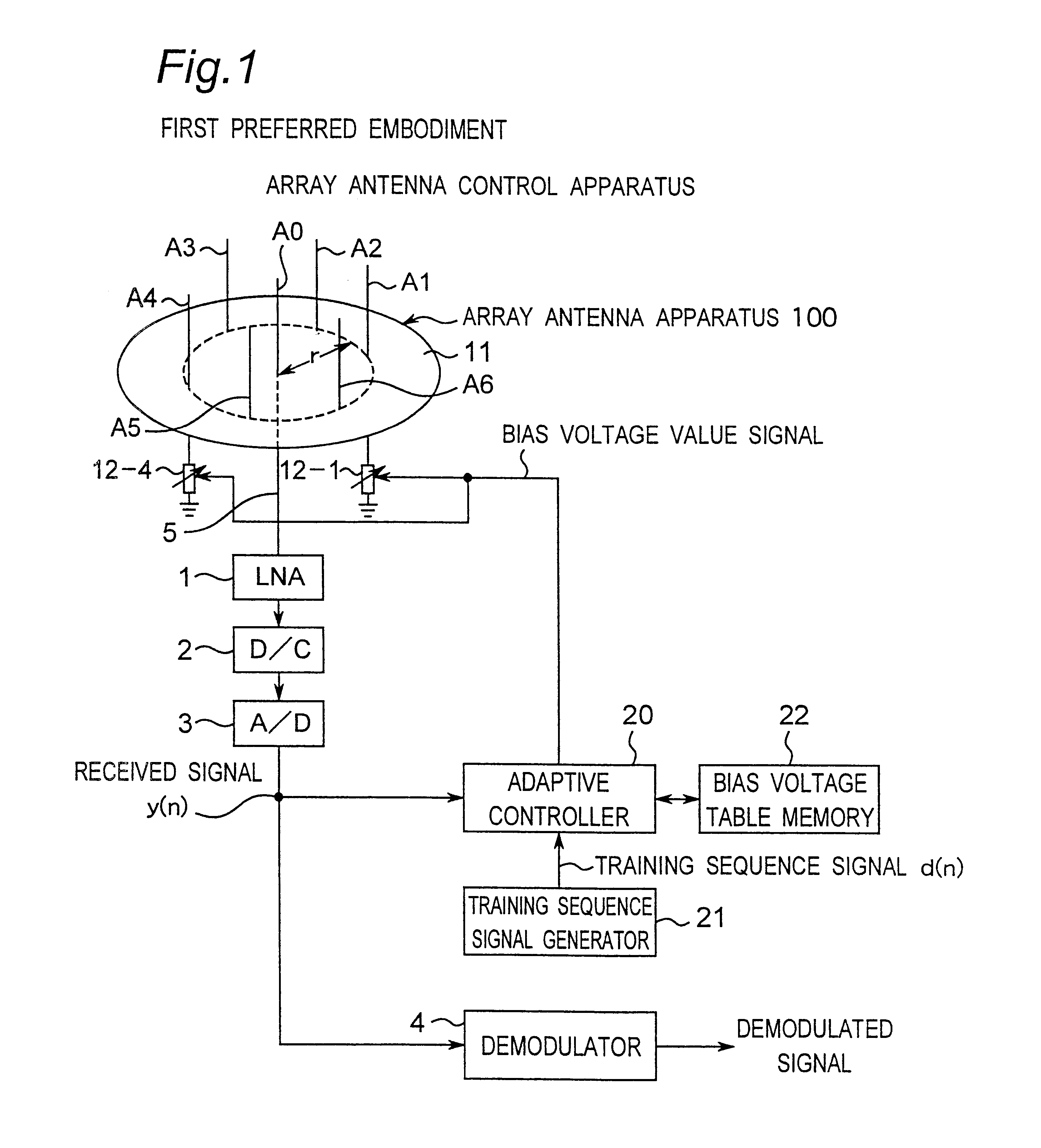
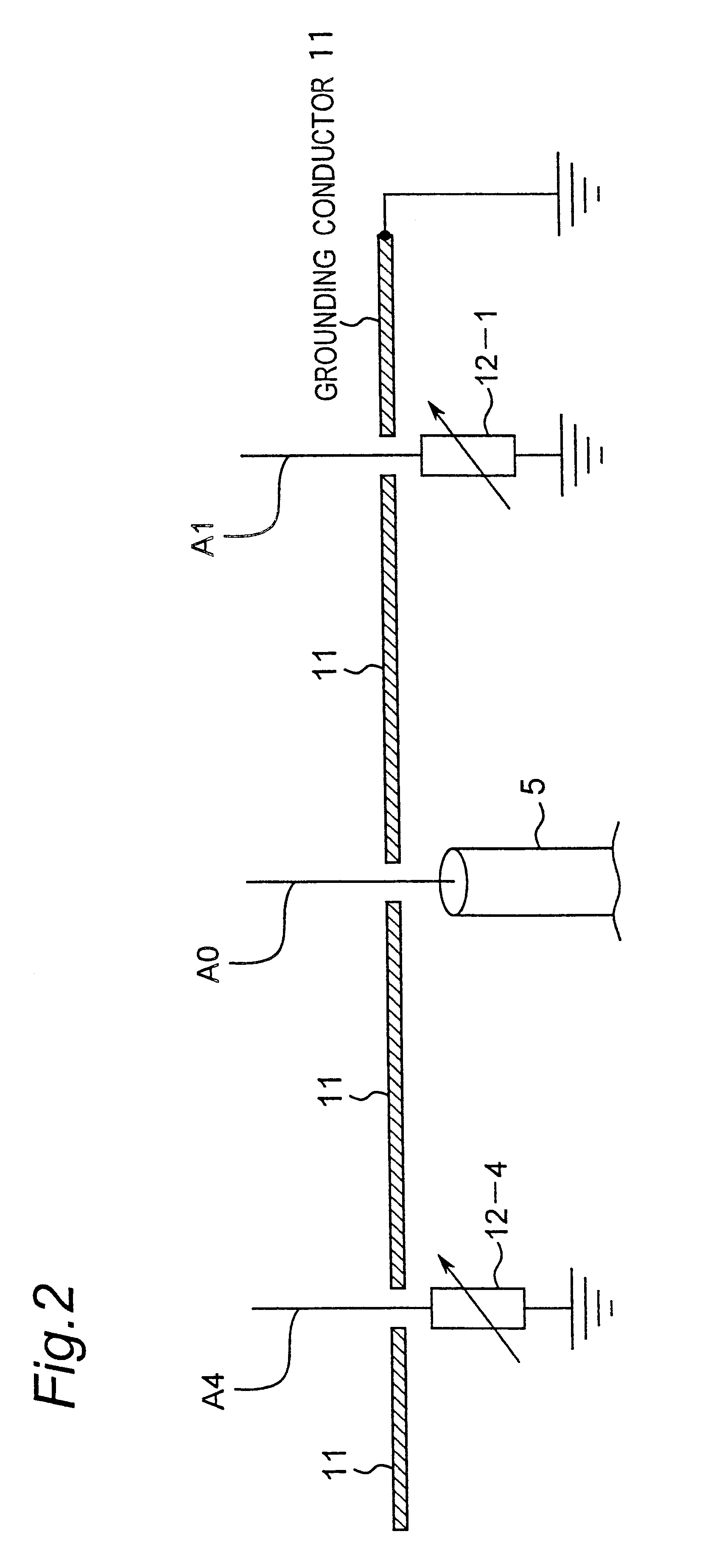
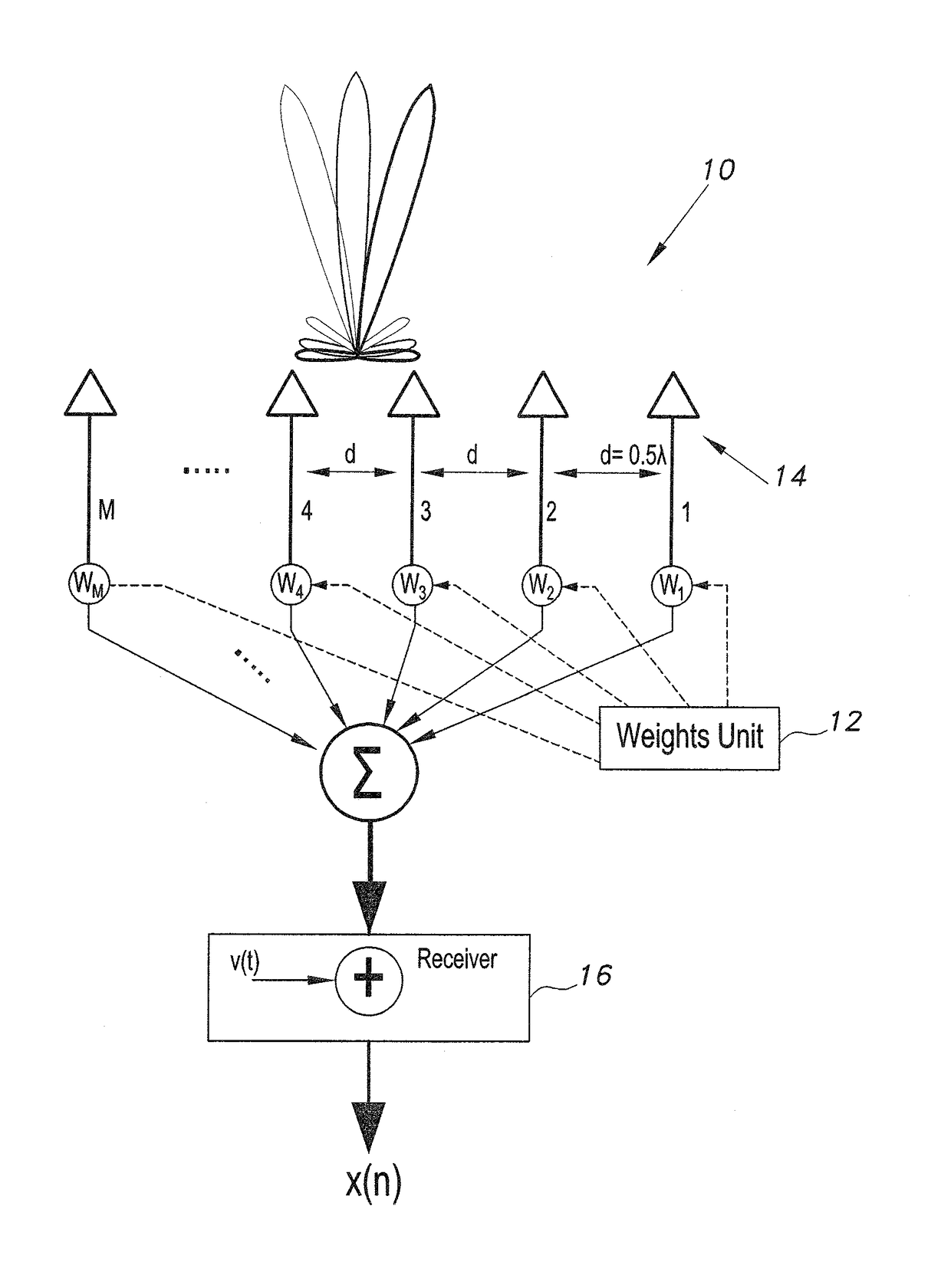
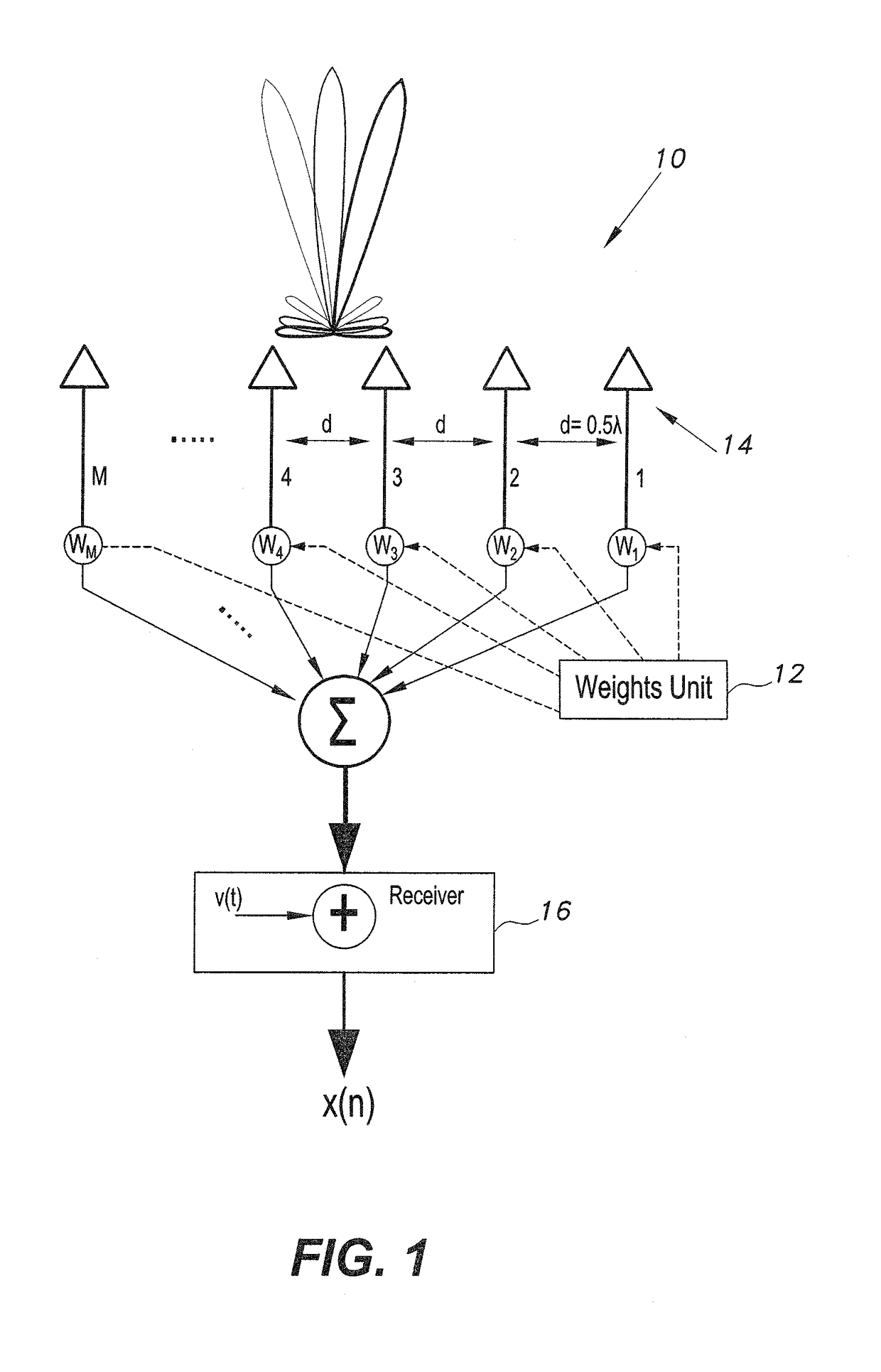
Method for controlling array antenna equipped with single radiating element and a plurality of parasitic elements
InactiveUS6677898B2Shorten convergence timeReduce the amount of calculationAntenna arraysSequence signalVoltage vector
An adaptive controller for an ESPAR antenna randomly perturbs a bias voltage vector V(n) composed of elements of bias voltage values Vm by a random vector R(n) generated by a random number generator, compares an objective function value J(n) of a cross correlation coefficient for a bias voltage vector V(n) before the perturbation with an objective function value J(n+1) of a cross correlation coefficient for a bias voltage vector V(n+1) after the perturbation, and selects and sets the bias voltage Vm corresponding to that when the cross correlation coefficient increases before and after the perturbation. Then the adaptive controller repeats the random perturbation and setting from the bias voltage of respective varactor diodes. This leads to that it is not necessary to provide a long training sequence signal, and the control process can be executed with learning so that a performance can be improved every iteration for search.
Owner:ATR ADVANCED TELECOMM RES INST INT
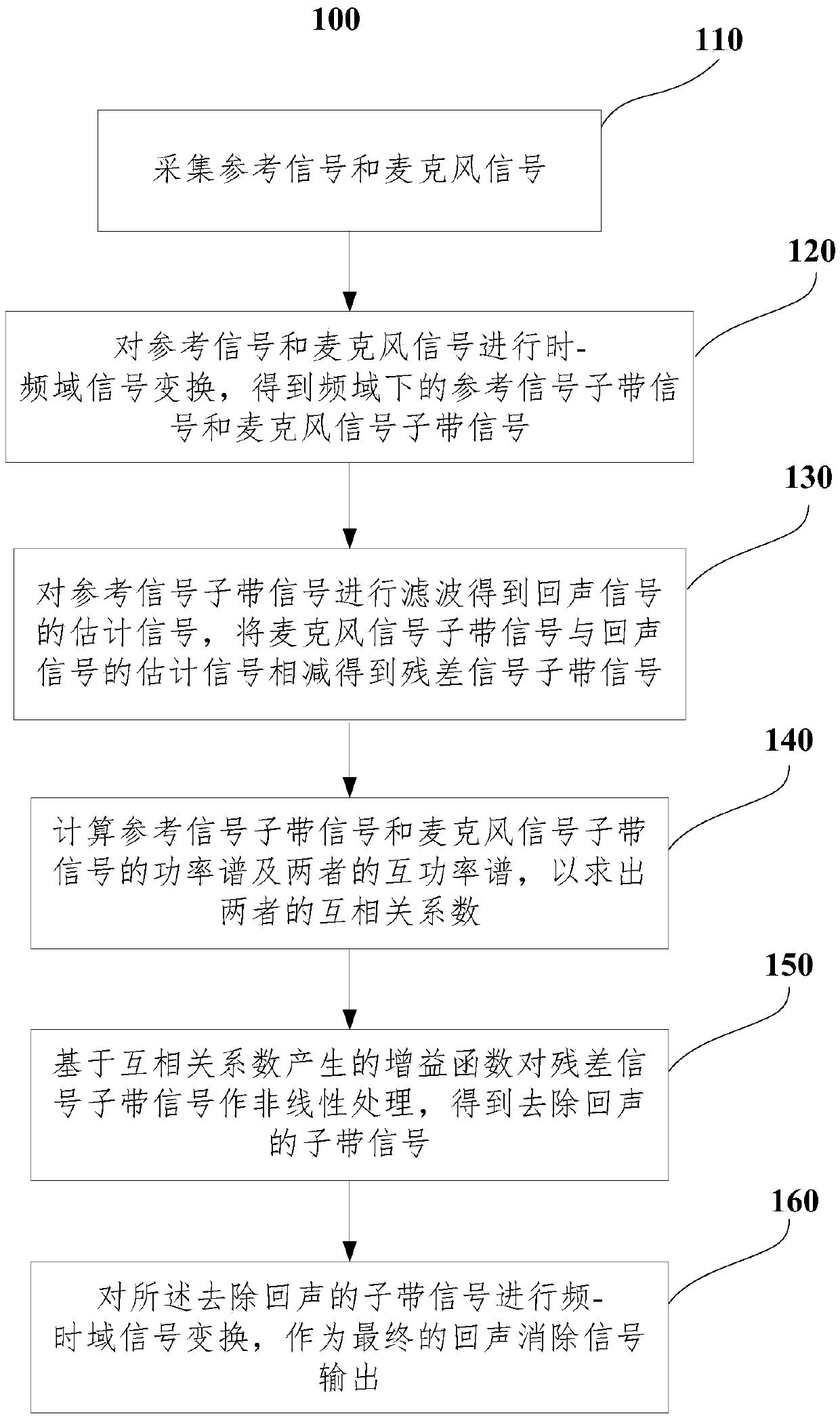
Frequency-domain echo cancellation method for speech recognition front end and computer storage medium
PendingCN109727604AReduce computationFast convergenceSpeech recognitionTime domainSpeech identification
The invention relates to an echo cancellation method and system for a speech recognition front end. The echo cancellation method mainly comprises the steps of time-frequency domain signal transformation, echo signal and residual signal estimation, sub-band signal power spectrum and cross correlation coefficient calculation, nonlinear processing based on a gain function of cross correlation coefficients, frequency-time domain transformation and the like to finally output signals without echoes. The single-channel echo cancellation method is adopted for processing frequency-domain echoes under avehicle-mounted condition or in other application scenes, and has the advantages of small calculation amount and high convergence speed.
Owner:NIO CO LTD
Wind noise suppression method used for dual-microphone digital hearing-aid
InactiveCN102254563AImprove the effect of hearing aidsWind noise reductionSpeech analysisDeaf-aid setsNoise suppressionComputer science
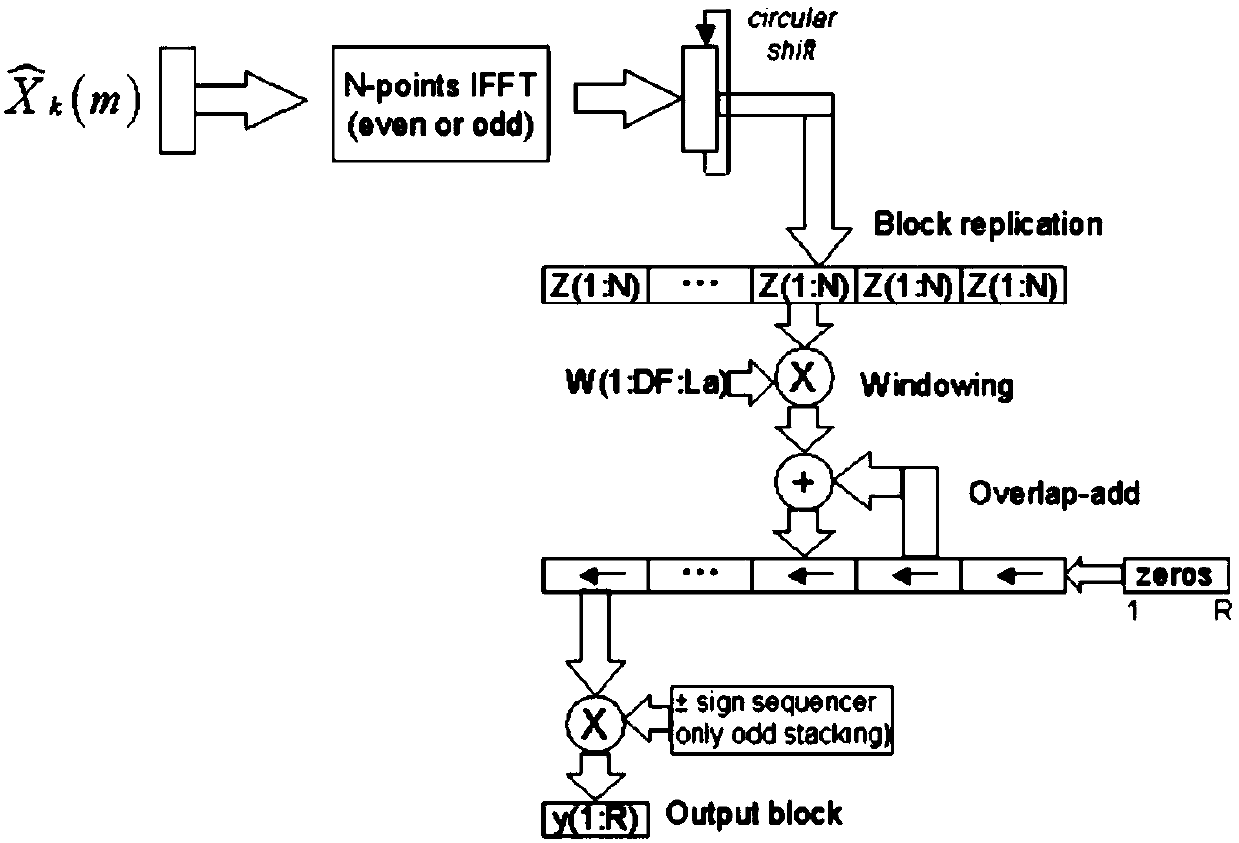
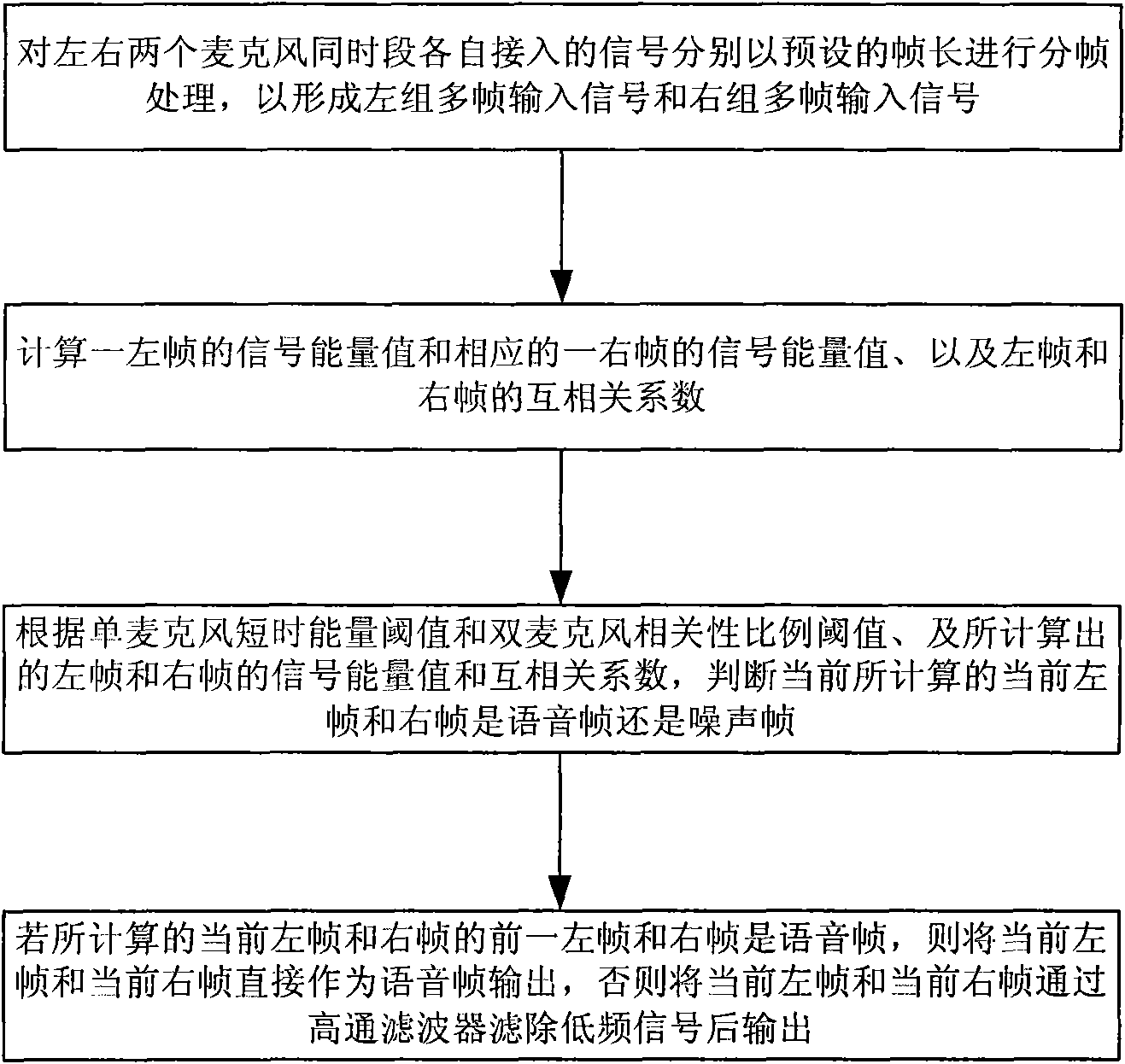
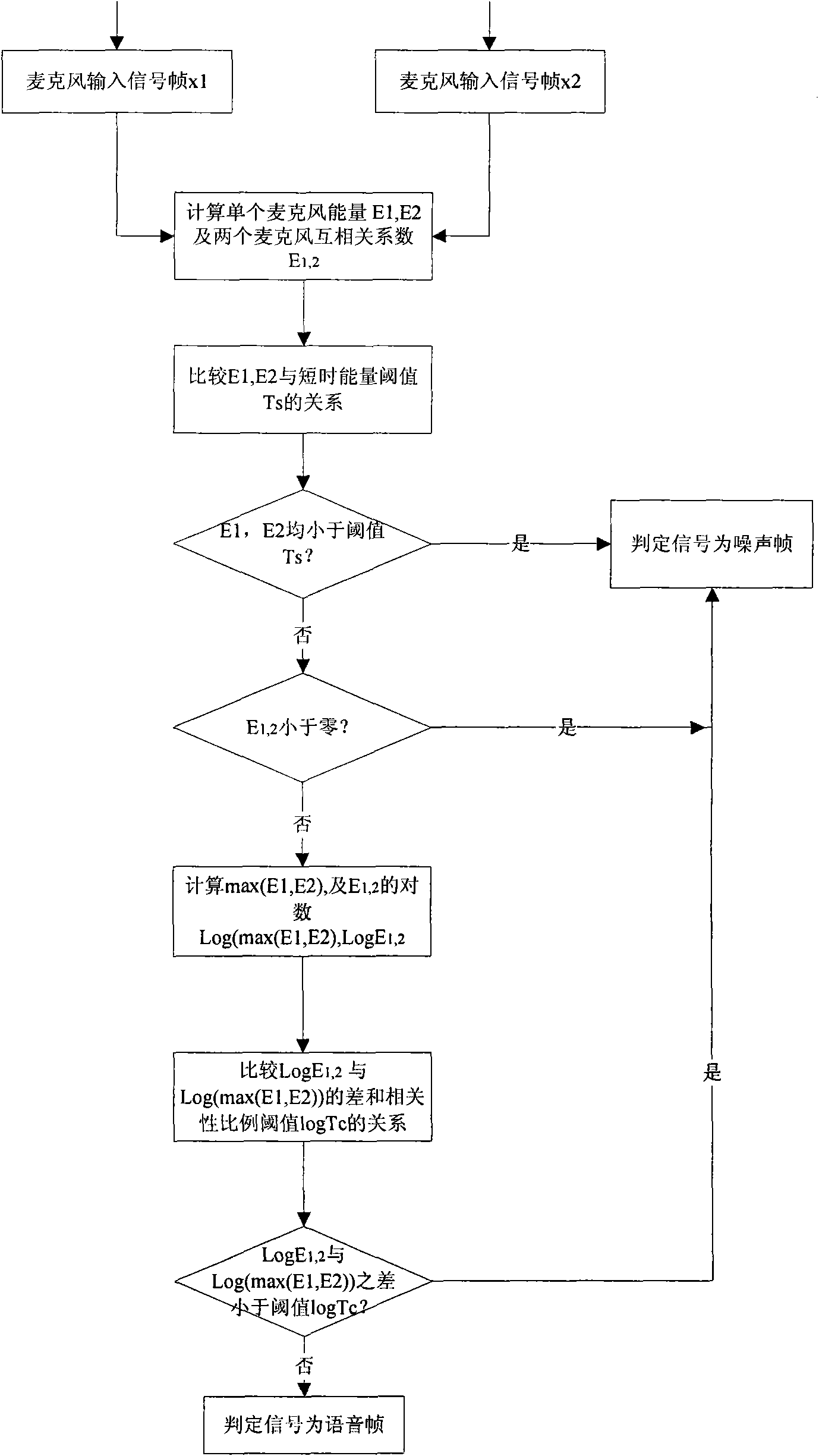
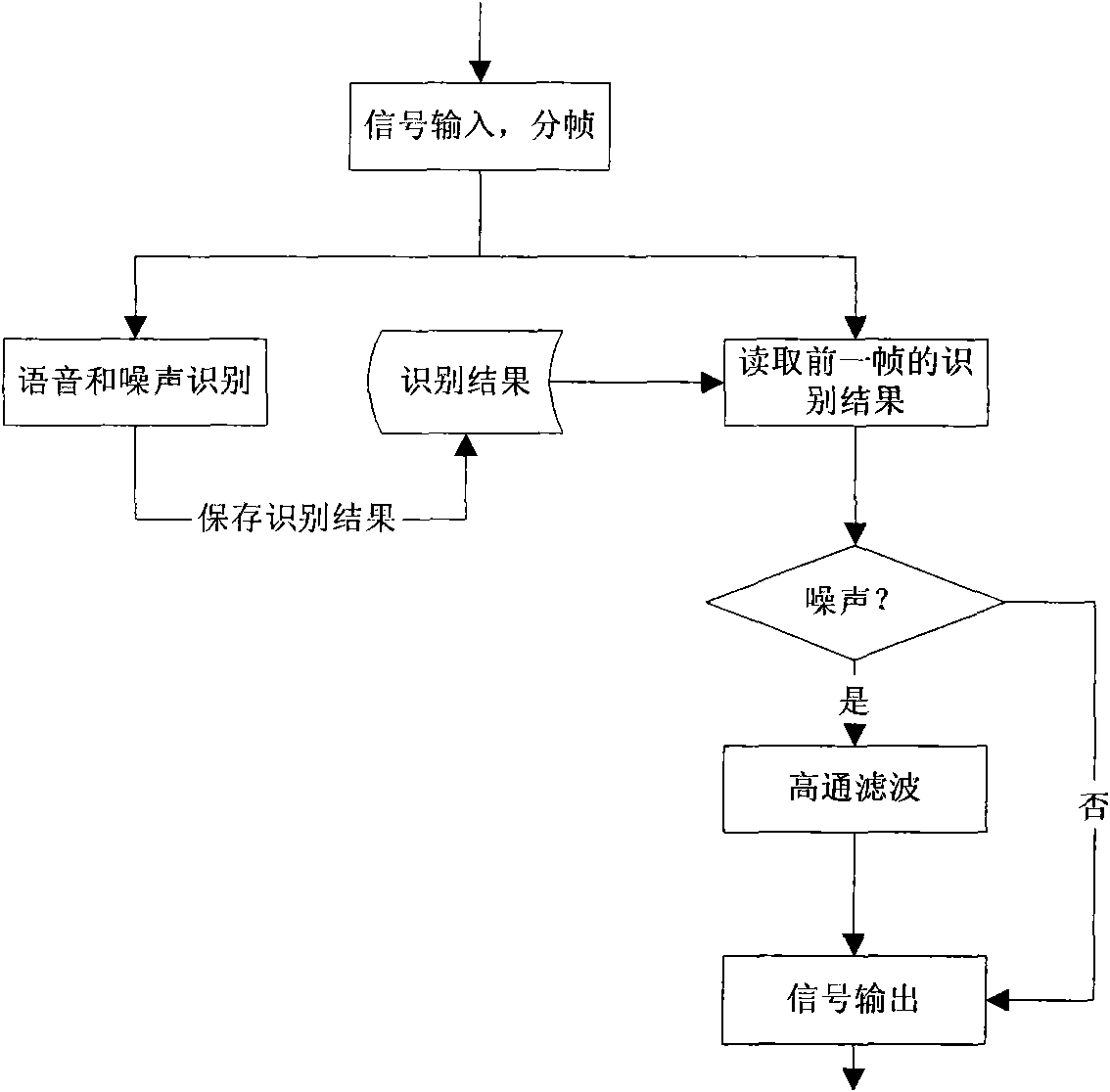
The invention relates to a wind noise suppression method used for a dual-microphone digital hearing-aid. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively carrying out framing processing on respectively accessed signals of a left microphone and a right microphone at the same time interval according to a preset frame length; then respectively calculating signal energy values of a left frame and a corresponding right frame as well as cross correlation coefficients of the left and the right frames in a left group of multiframe input signals and a right group of multiframe input signals; judging whether the current left frame and the current right frame which are calculated currently are voice frames or noise frames according to the preset single-microphone short-time energy threshold value and the preset double-microphone correlation proportion threshold value as well as the calculated respective signal energy values and the cross correlation coefficients of the left frame and the right frame, so as to be taken as the basis of a subsequent left frame and a subsequent right frame; when respective former left frame and respective former right frame of the calculated current left frame and the calculated right frame are voice frames, outputting the current left frame and the current right frame as the voice frames; and otherwise, outputting the current left frame and the current left frame through highpass filtering. Therefore, according to the invention, the wind noise is reduced, and the hearing aid effect is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI CONGWEI ACOUSTICS TECH
Gait behavior recognition method based on feature combination
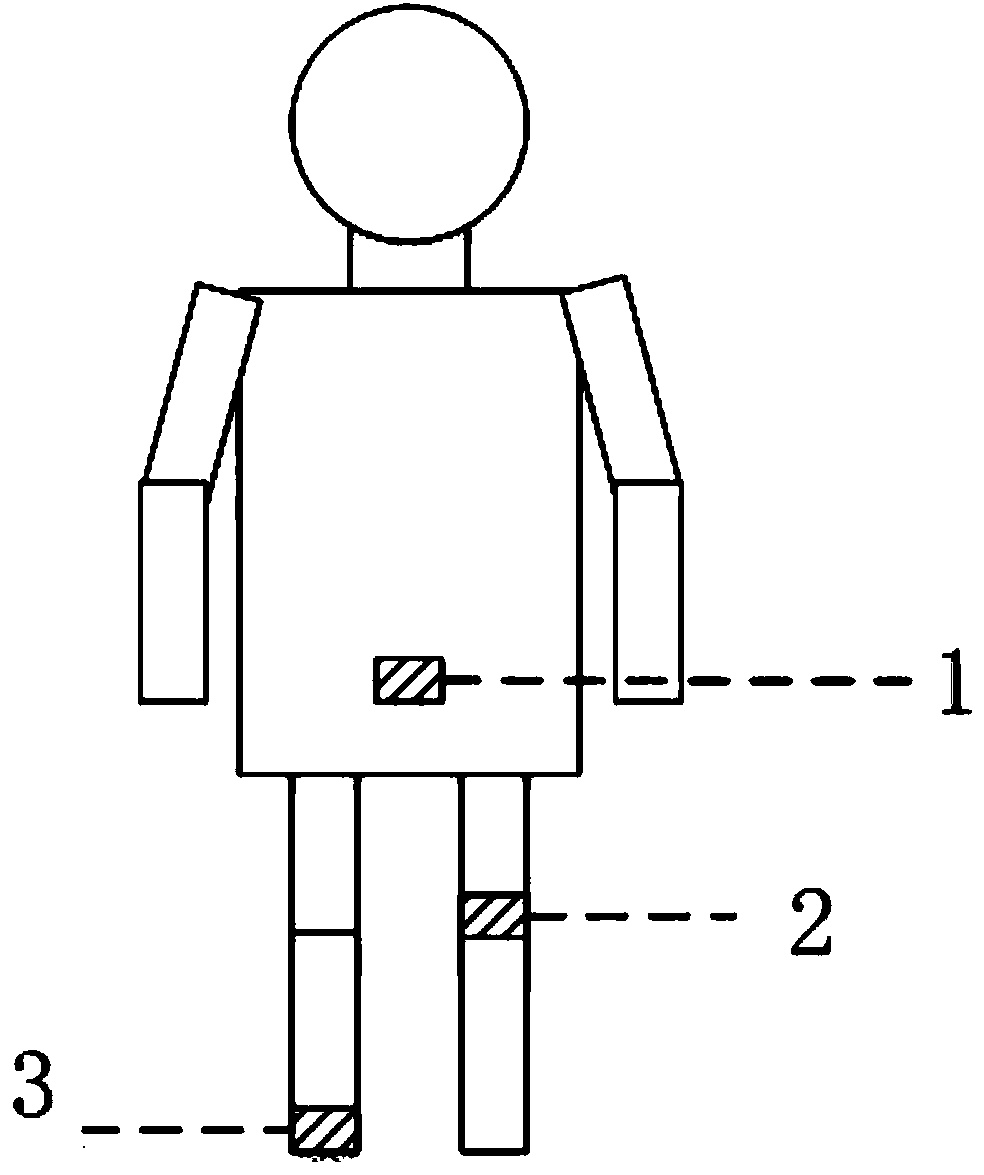
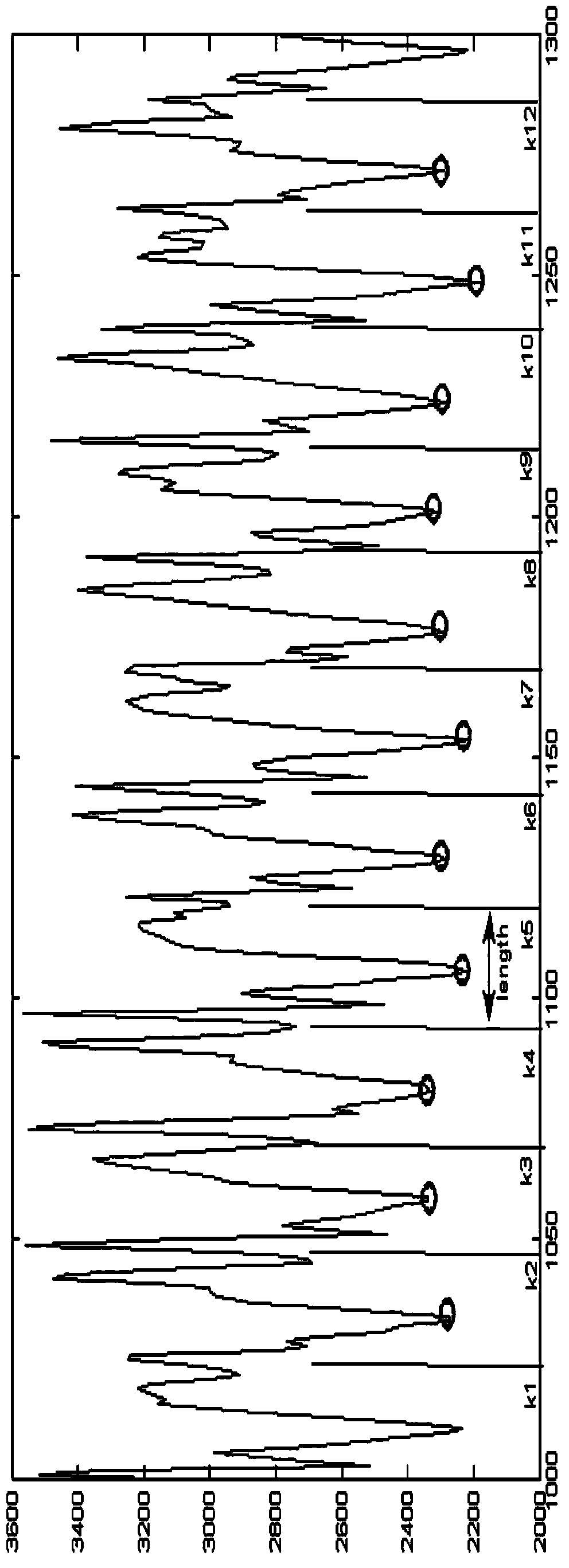
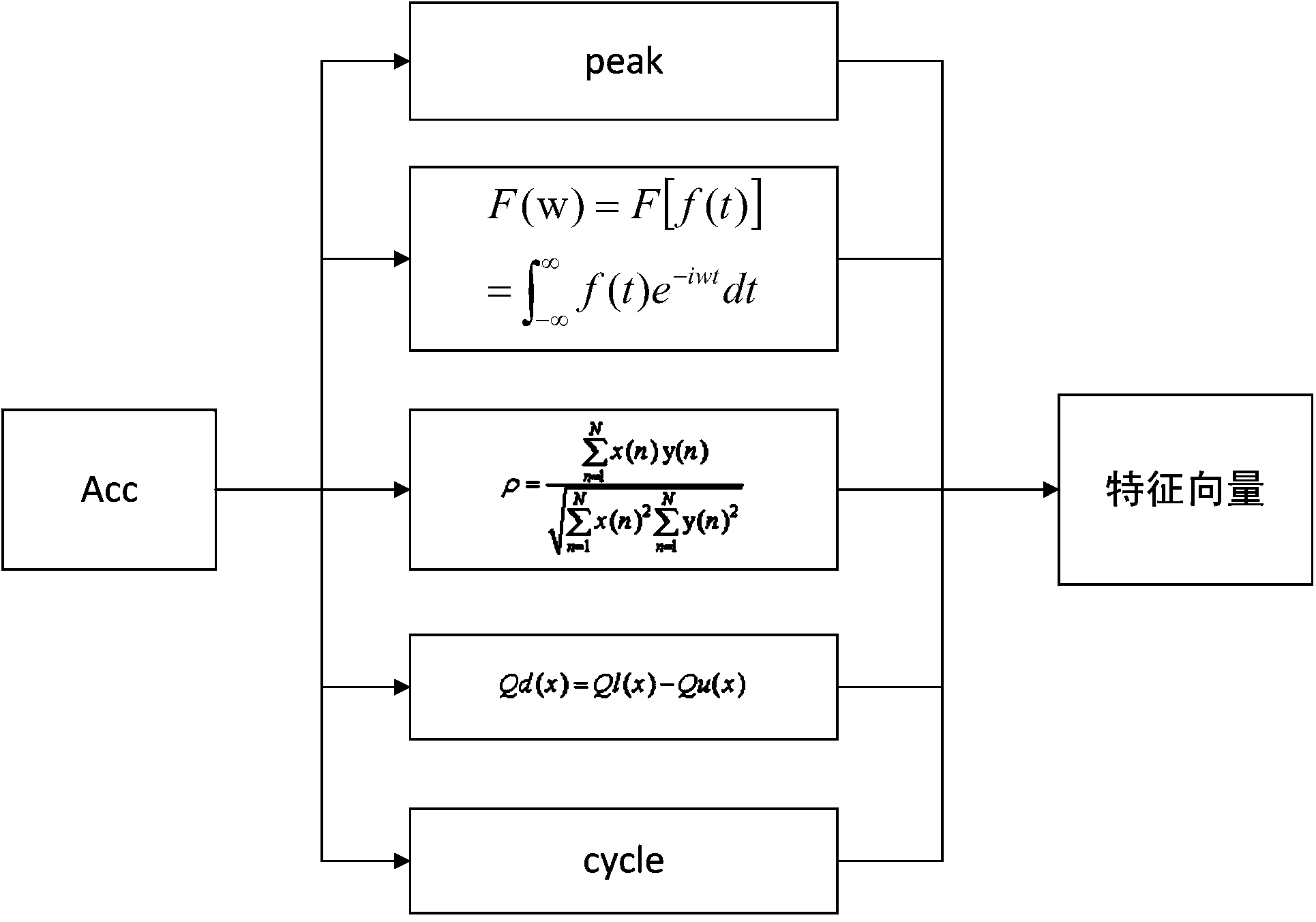
InactiveCN103886341AReduce dimensionalitySimple calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionComputation processPeak value
The invention discloses a gait behavior recognition method based on feature combination. The gait behavior recognition method based on feature combination includes the following steps that motion acceleration information of the body when a user behaves is obtained through an acceleration sensor; the peak value, frequency, gait cycle and interquartile range of each axis and the cross correlation coefficient between the different axes are calculated from the motion acceleration information; parameters are selected according to an aggregation method to form a feature vector; a sample set and the feature vectors of a gait acceleration signal to be identified serve as a training set, and a classifier is trained to have the capacity of classifying gait behaviors; all the feature vectors of the gait acceleration signal to be recognized are input to the trained classifier and given with fit categories, the fit categories of all the feature vectors are counted, and the category with the highest number of appearing times is given with the gait acceleration signal to be identified. The purposes that the calculation process is simplified, the number of dimensions of the feature vectors is decreased and the effectiveness is good are achieved.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +3
Judging method of incompactness defect in node of concrete structure by detection by ultrasonic method
ActiveCN102012403AMultiple frequency differenceRealize quantitative descriptionAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesProcessing detected response signalAlgorithmHead wave
The invention relates to a judging method of an incompactness defect in a node of a concrete structure by detection by an ultrasonic method. On the basis of the traditional method for detecting the concrete defect by the ultrasonic method, besides an acoustic velocity and a head wave amplitude, two variable acoustic parameters, namely a complex frequency difference and a cross-correlation coefficient, are added; each acoustic parameter is processed into an acoustic parameter judging factor and each acoustic parameter judging factor is processed into a normalized comprehensive acoustic parameter judging factor; a position detecting chromatogram is drawn out according to the comprehensive acoustic parameter judging factor; and the position and range of a suspicious defect are determined according to a red area in the chromatogram. By the method, the compactness quality distribution of concrete can be directly and accurately described; errors and judgment loss caused by adoption of a single acoustic parameter for judgment can be avoided or reduced; and the difficulty in final judgment when the judgment result of the single acoustic parameter is inconsistent is also avoided. The judging method can be widely applied to the judgment of the incompactness defect in the node of the concrete structure or other complex structures.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL ENG RES INST +1
Mine microquake signal noise reduction filtering method based on VMD
ActiveCN106814396APreserve randomnessRetain propertiesSeismic signal processingDecompositionAlgorithm
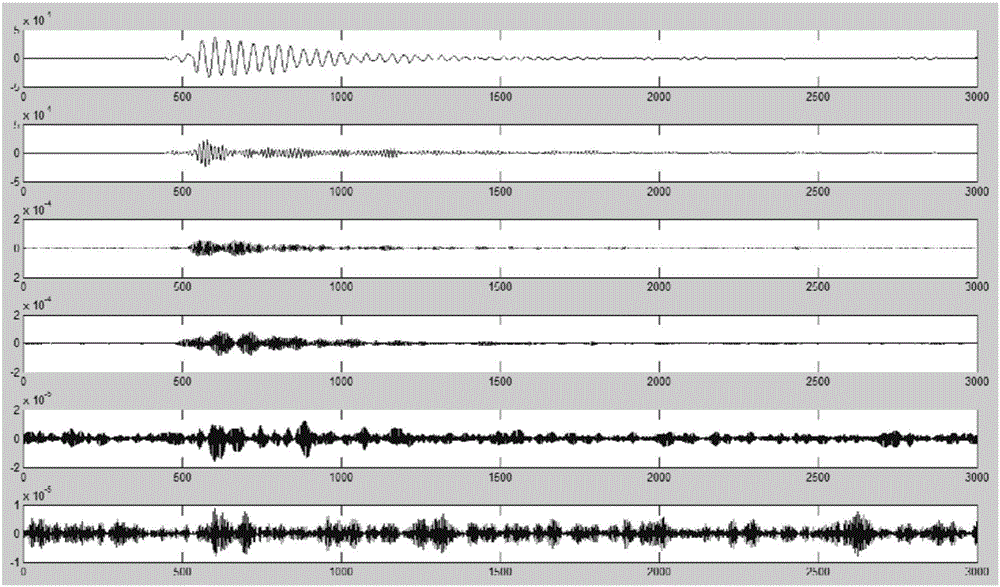
The invention discloses a mine microquake signal noise reduction filtering method based on VMD, and belongs to the signal processing technical field; the method comprises the following steps: reading a sequential sequence x (t) of noised microquake signals; carrying out VMD decomposition for the sequential sequence x (t) of the microquake signals; calculating a cross correlation coefficient between the microquake signal sequential sequence x (t) and each variation modal component uk; considering the variation modal component with the central frequency bigger than 200Hz and the cross correlation coefficient with the noised microquake signal sequential sequence x (t) smaller than 0.3 as noises, and filtering the noises; reconstructing residual variation modal components, thus obtaining noise reduction and post-filter microquake signals. The method can effectively prevent modal aliasing phenomenon, is strong in adaptability and instantaneity, and can effectively carry out noise reduction filtering treatment for the microquake signals.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
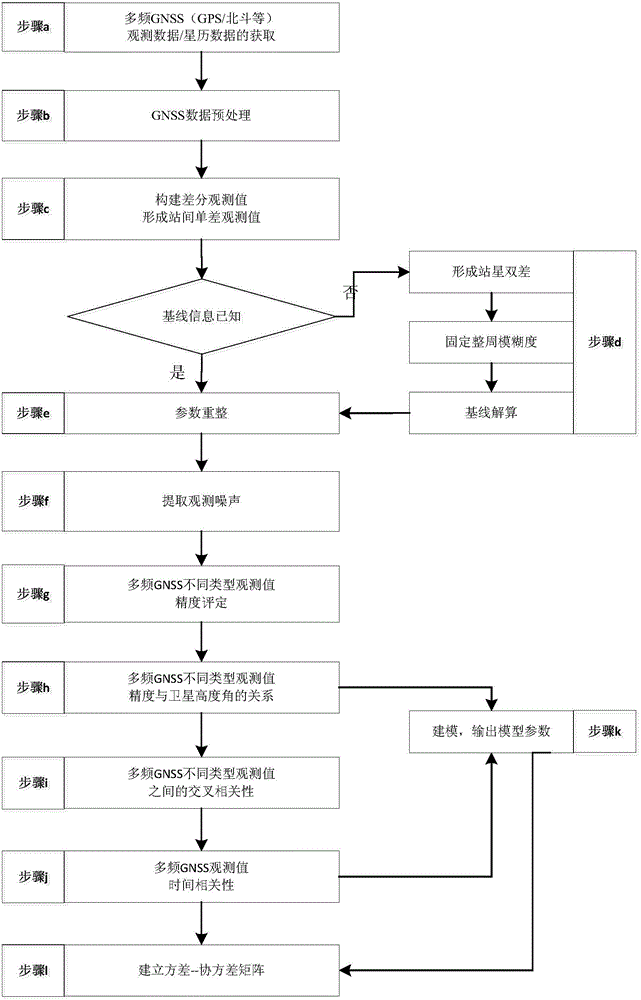
Method for modeling random characteristics of multi-frequency GNSS (global navigation satellite system) observed values
InactiveCN104102822ASimple calculationHigh speedSatellite radio beaconingSpecial data processing applicationsDouble differenceNatural satellite
The invention relates to a method for modeling random characteristics of multi-frequency GNSS (global navigation satellite system) observed values. The method comprises the following steps of acquiring multi-frequency GNSS observed data, and preprocessing the data; constructing a single difference observation equation to form an intersite single difference observed value; performing parameter reforming on the single difference observation equation according to a base line and fixed double-difference ambiguity; taking the average value of single difference observed values of single-epoch multiple satellites as the least square solution of the reformed parameter, and subtracting the least square solution from the single different observed value of each satellite to obtain single difference observation noise; calculating the accuracy of non-difference observed values of single-epoch multi-frequency GNSS different-type observed values, cross-correlation coefficients of the different-type observed values and temporal correlation coefficients of the same-type observed values by utilizing the extracted observation noise; obtaining a relation between the accuracy of the observed value of each satellite and an elevating angle; modeling, outputting model parameters and establishing a variance-covariance matrix. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simple calculating process, reliability and the like.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
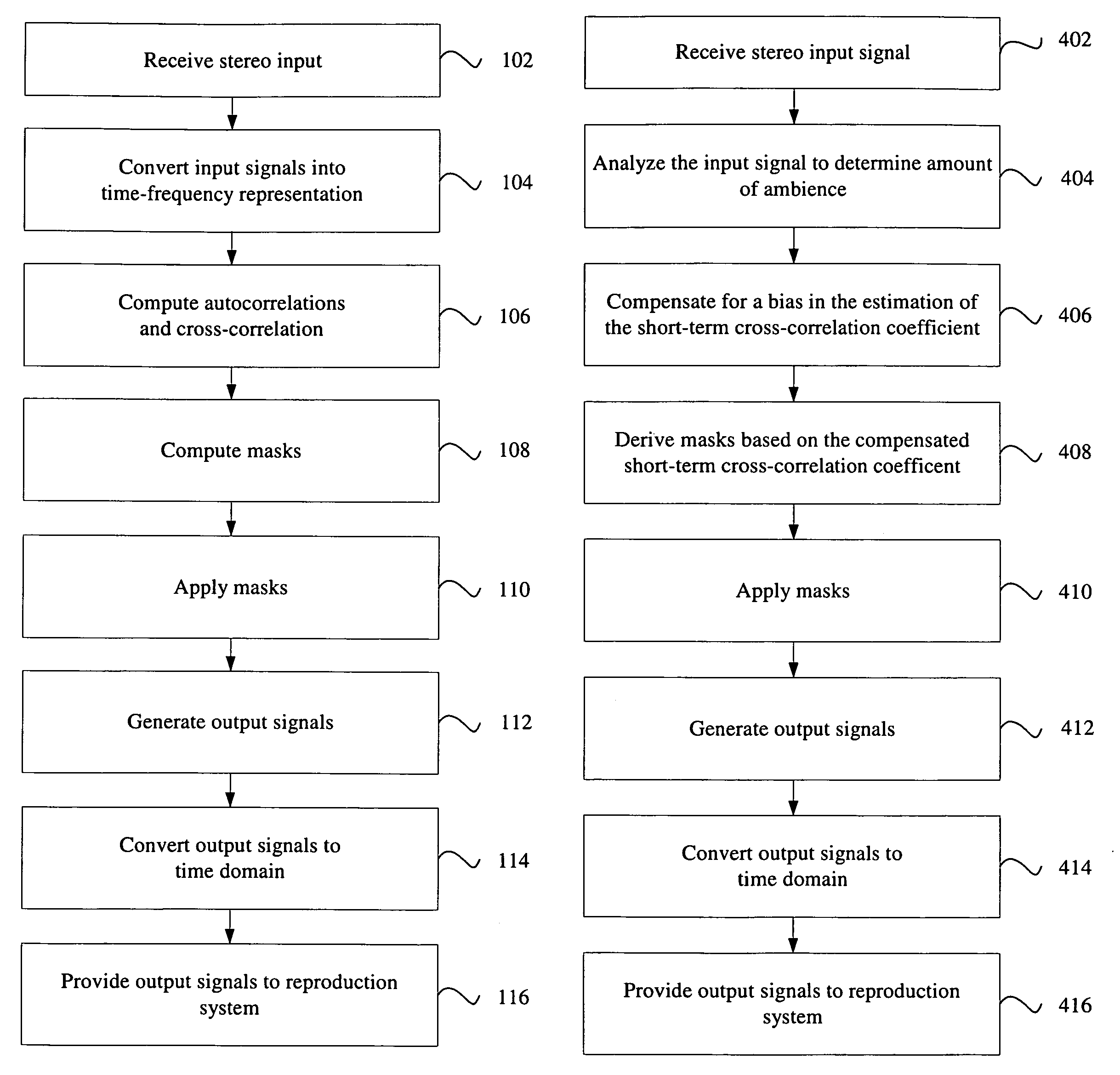
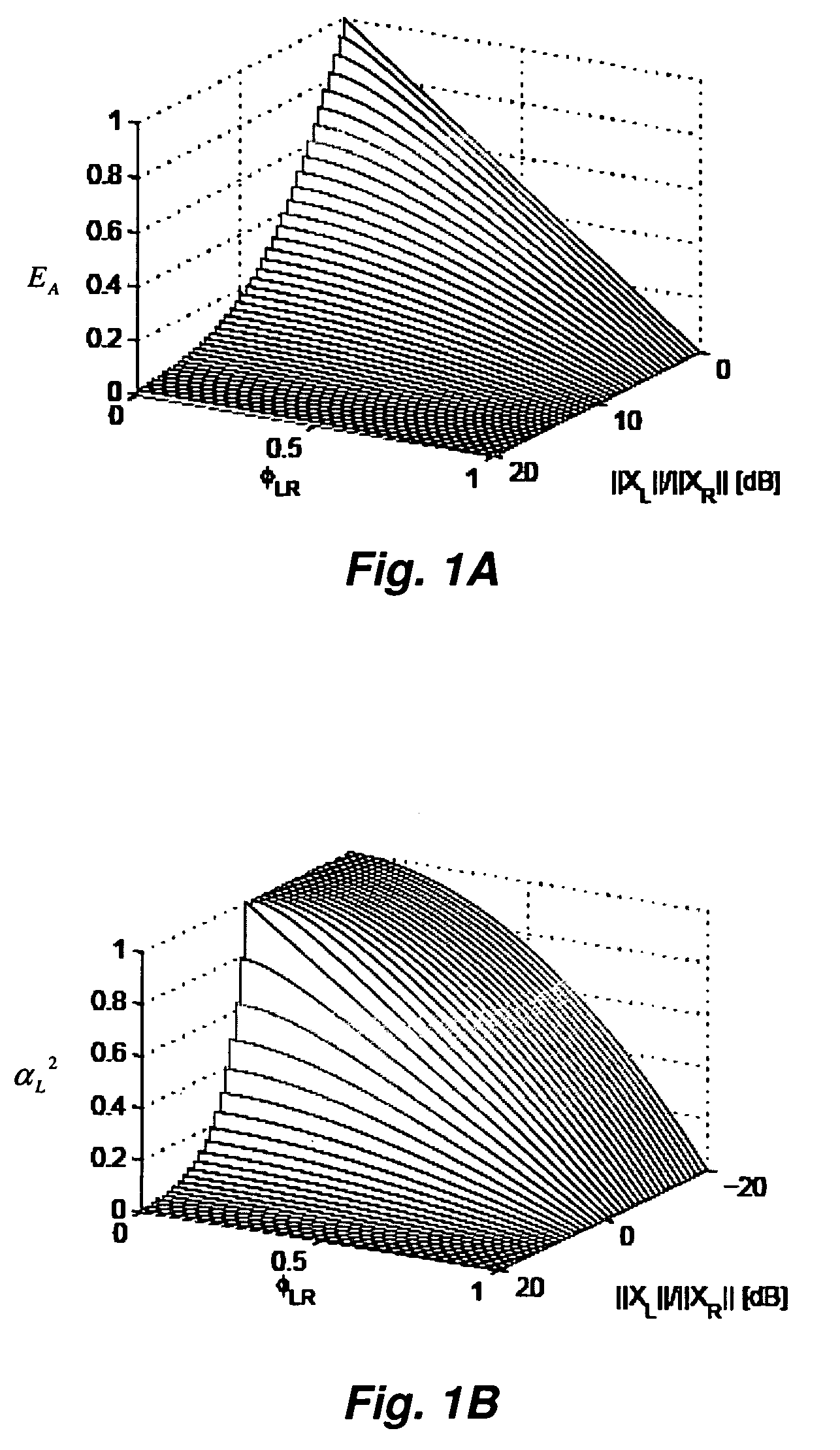
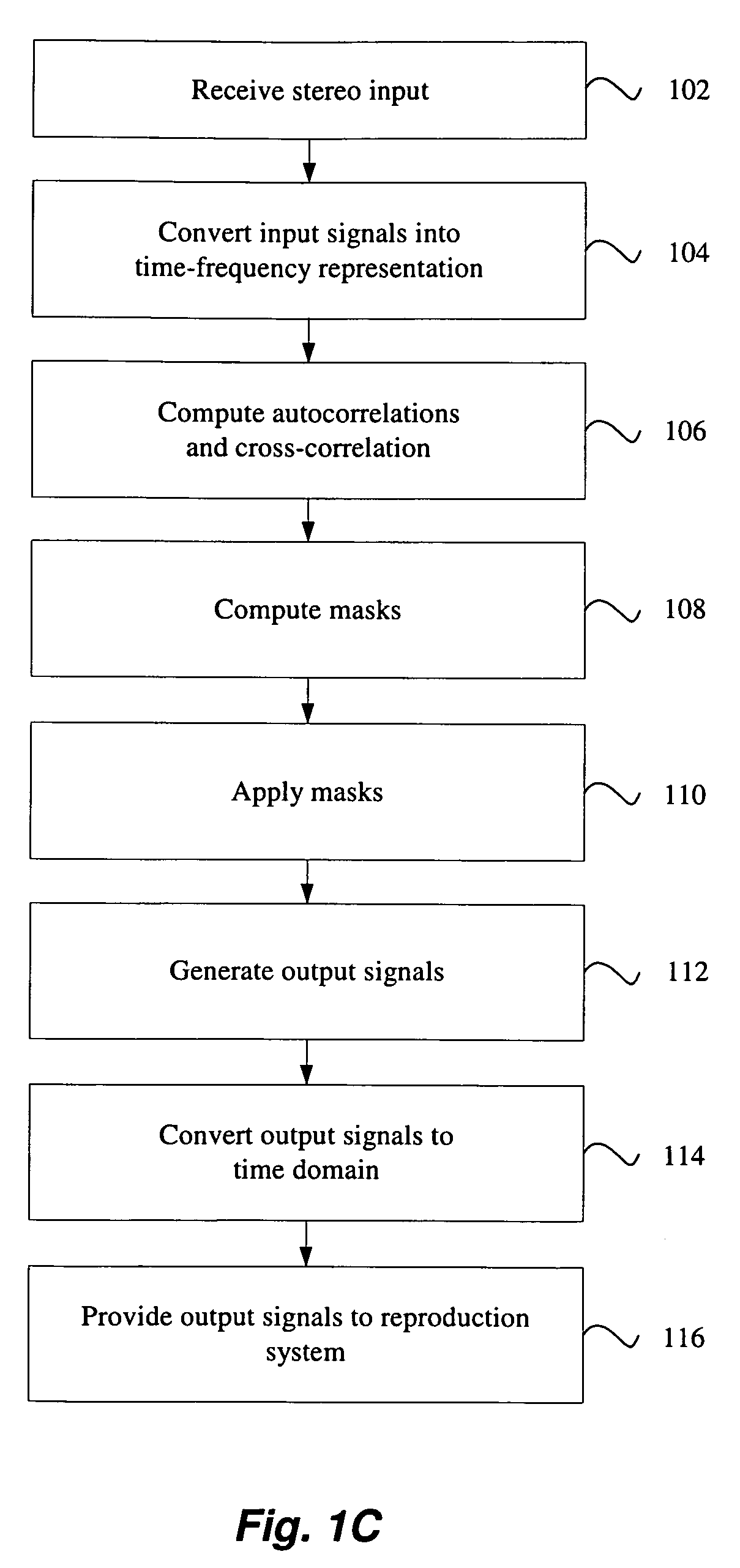
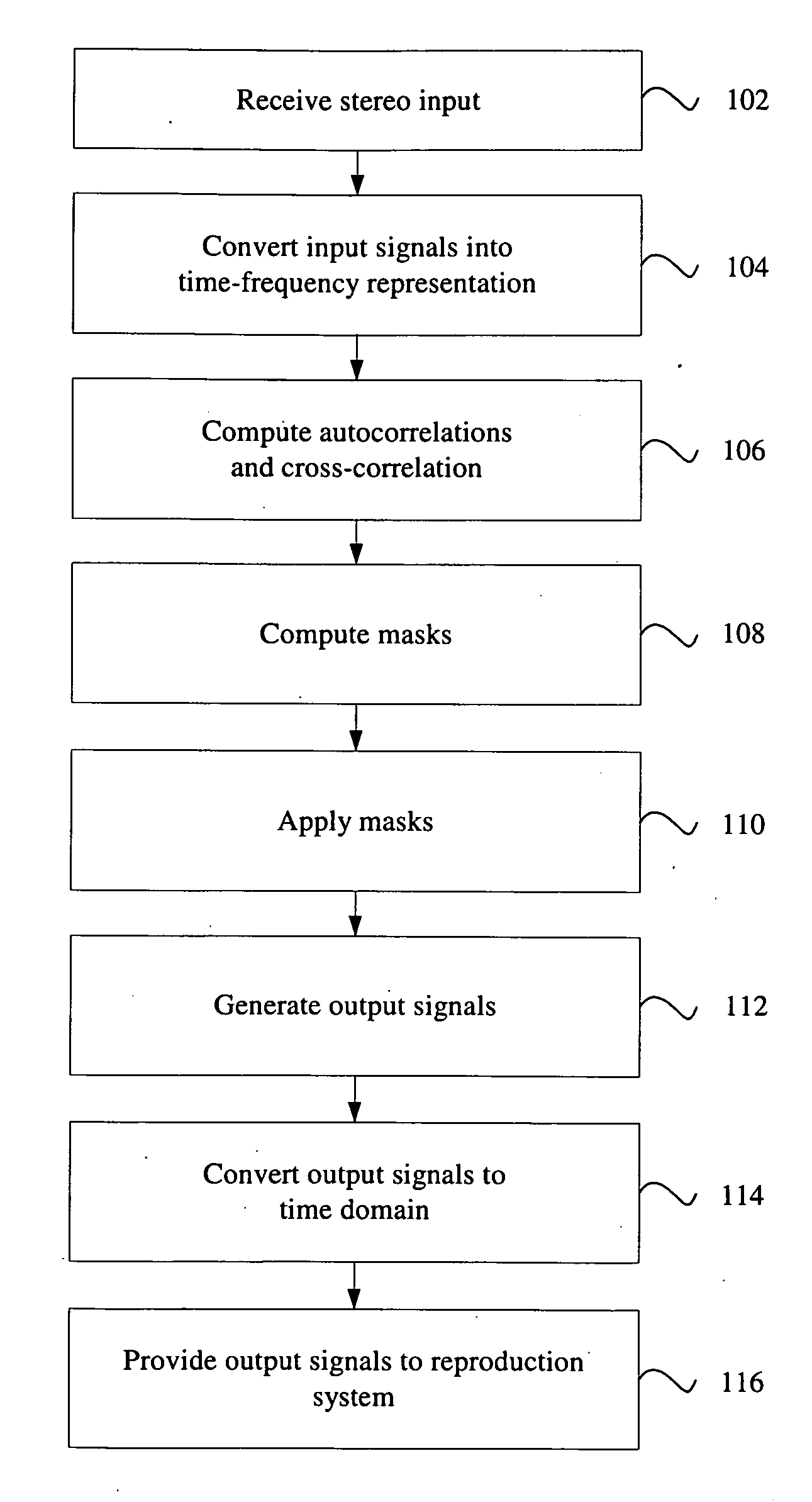
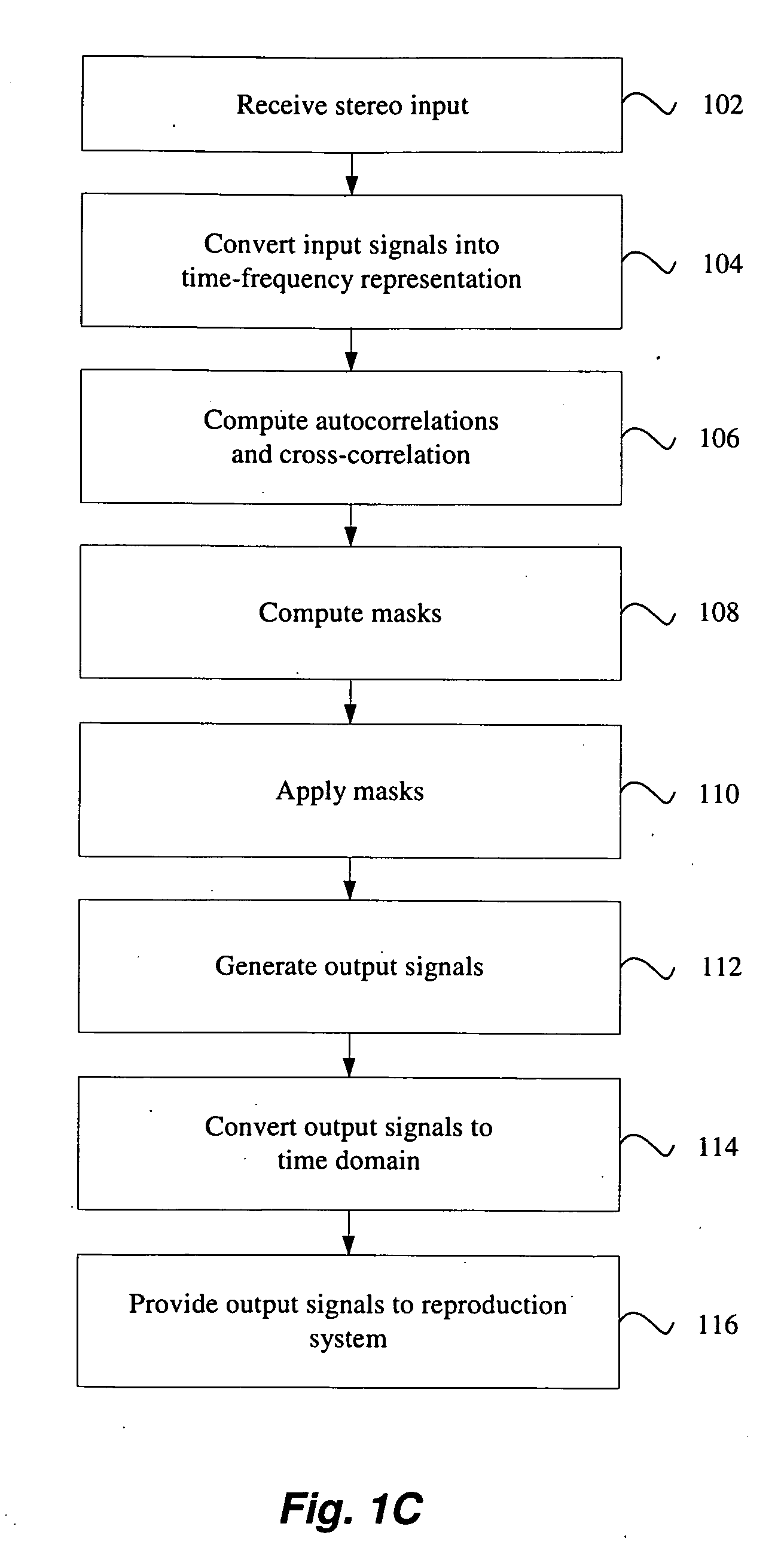
Correlation-based method for ambience extraction from two-channel audio signals
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
Method for suppressing random noise in seismic exploration based on VMD-TFPF
InactiveCN107589454AReduce random noiseImprove Spatial ConsistencySeismic signal processingProblem of timeRandom noise
The invention discloses a method for suppressing random noise in seismic exploration based on VMD-TFPF, which includes the following steps: (1) decomposing a noisy signal; (2) calculating the cross correlation coefficient, and judging modal components needing to be filtered; (3) filtering modes screened out; and (4) getting a de-noised signal through calculation. Seismic random noise can be effectively attenuated, and the effective signal amplitude can be well maintained in the filtering process. The algorithm of the scheme is easy to implement, and is of high operability. The problem of time-frequency peak filtering window size selection is avoided. The method is suitable for de-noising complex signals.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
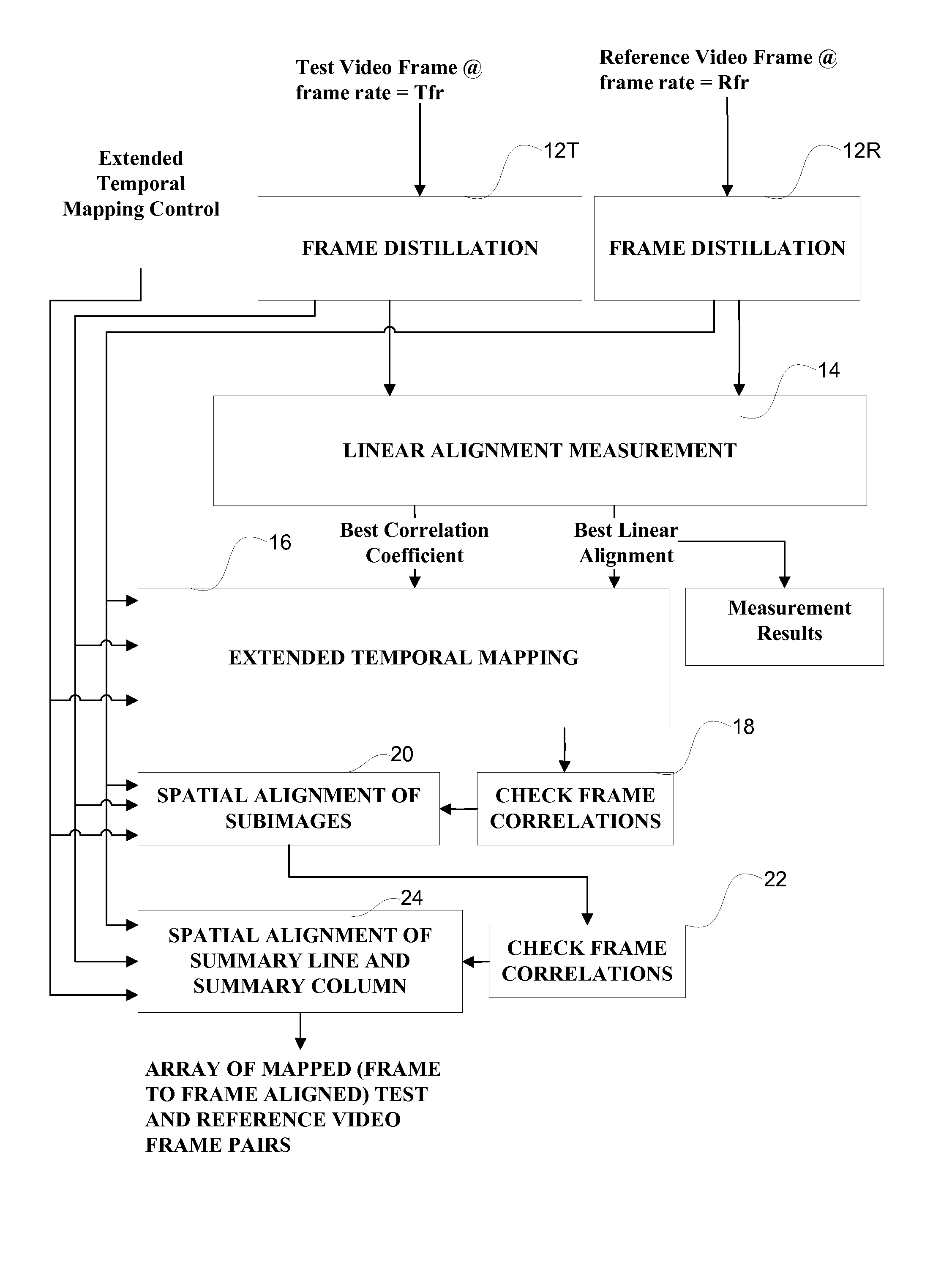
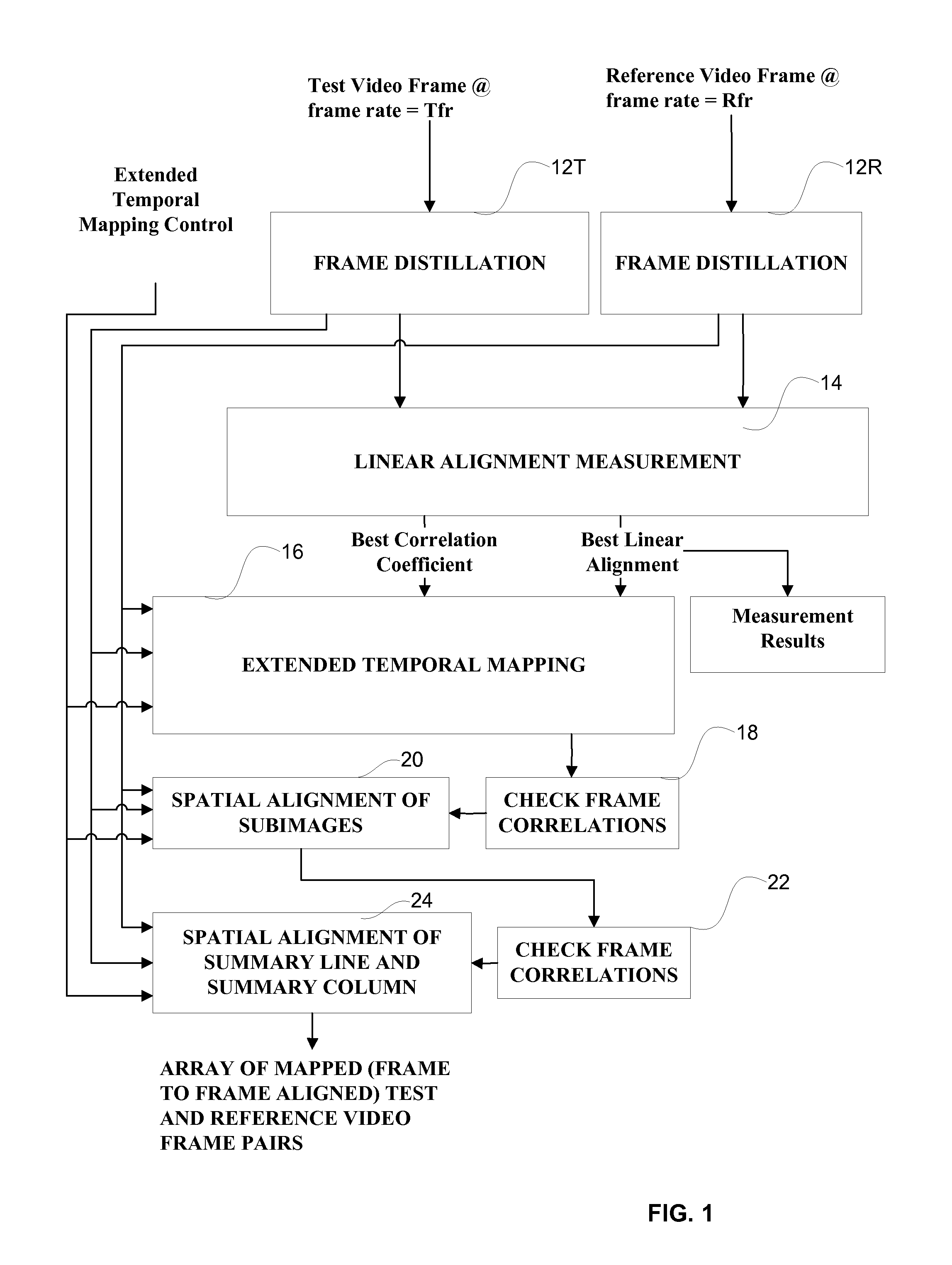
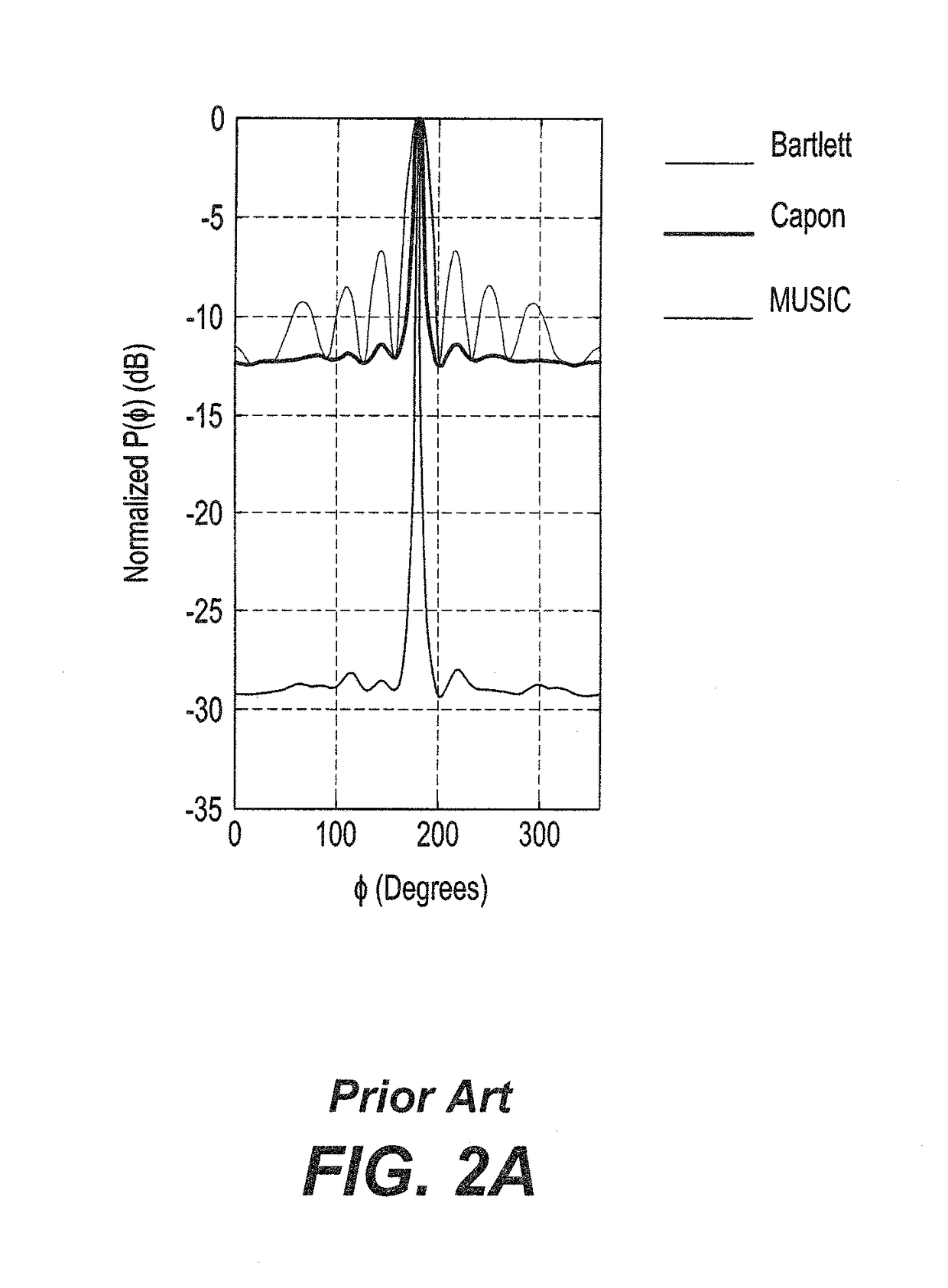
Systems and methods for robust video temporal registration
InactiveUS20080253689A1Character and pattern recognitionTelevision systemsVideo sequenceSignal parameter
A robust video temporal method for registration between test and reference video sequences without a priori knowledge of the respective signal parameters initially produces frame and subimage distillation measurements from the test and reference video sequences. The frame distillation measurements are linearly aligned using a local Pearson's cross-correlation coefficient (LPCCC) image to obtain a best alignment line, each pixel of which represents an LPCCC cross-correlation coefficient between frames of the test and reference video sequences. For each pixel of the best alignment line that is below a threshold, a vertical search is performed in the LPCCC image for a higher cross-correlation coefficient as the best cross-correlation coefficient to achieve temporal mapping between frames of the test and reference video sequences.
Owner:PROJECT GIANTS LLC
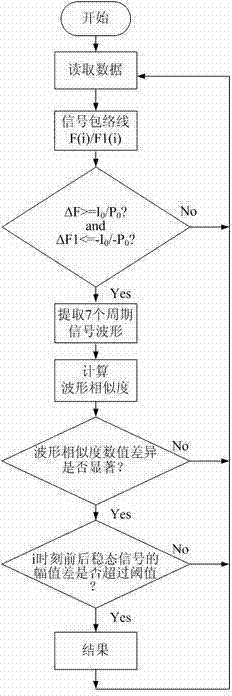
Household appliance operating state identification method based on cross correlation coefficient
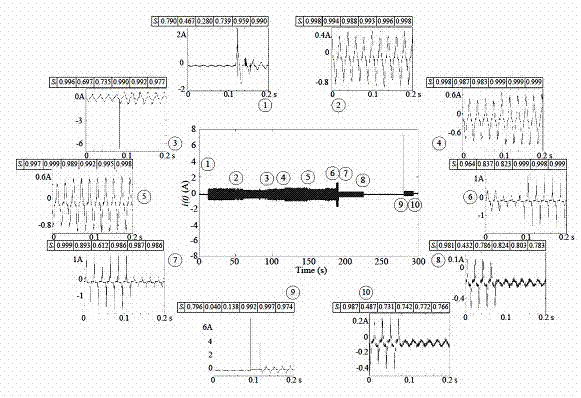
The invention relates to a household appliance operating state identification method based on a cross correlation coefficient. The identification method includes acquiring momentary currents or momentary power signals by the aid of intelligent electric meters installed at the entrance of a house to detect signal variation; based on periodicity as a unit, when signal variation exceeds a curtained threshold in a moment K, extracting signal waveforms of total seven periodicities of K-5, K-3, K, K+2, K+4, k+6 and K+8, and calculating waveform similarity between every two periodic signals in a time sequence; judging whether to start or stop the household appliances indoors by judging differences of six waveform similarity values and according to differentials of steady-state signals before and after K. The algorithm is simple and the judgment is accurate.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
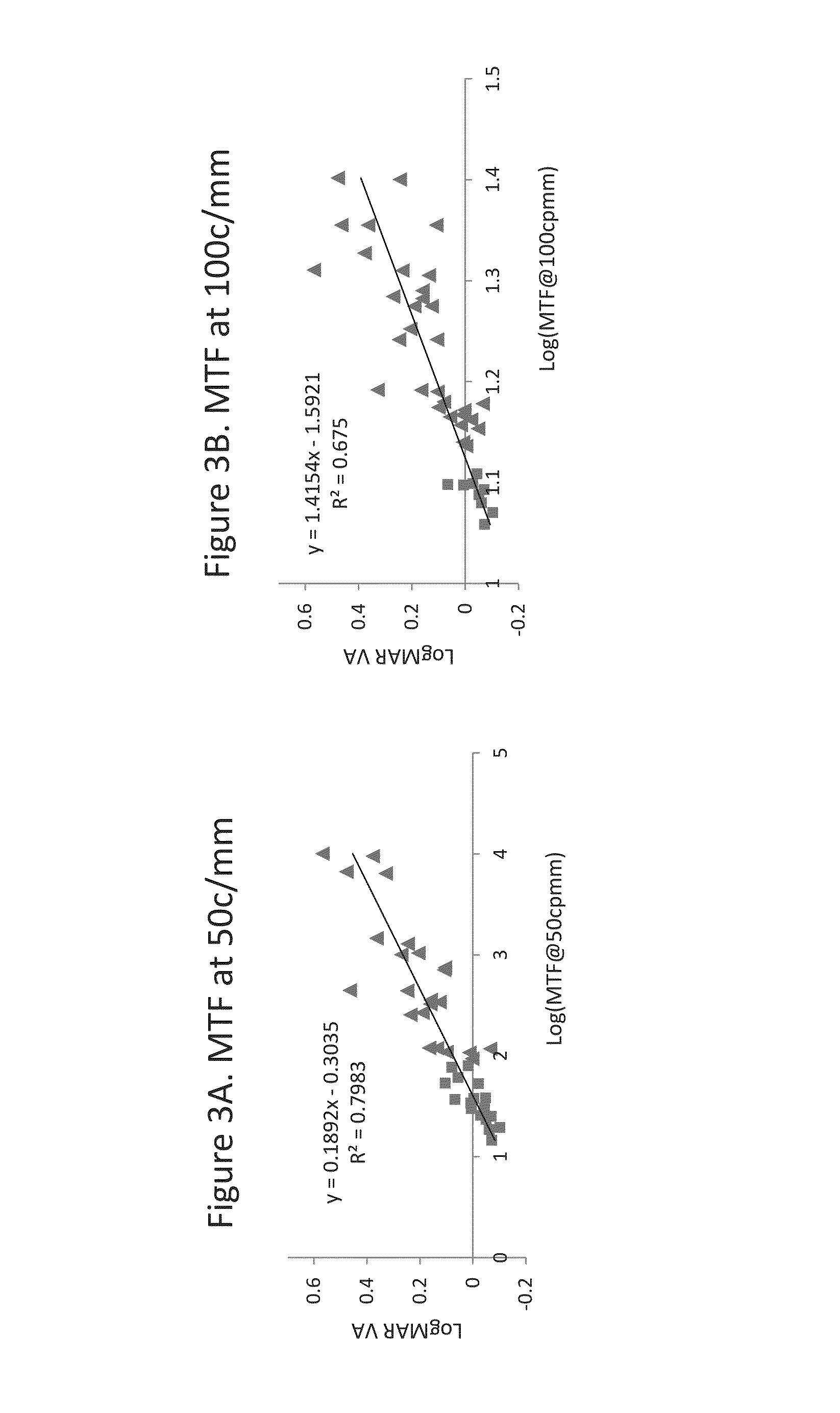
Apparatus, systems and methods for improving visual outcomes for pseudophakic patients
ActiveUS20160161364A1Easy to predictImprove performanceMedical simulationRefractive power measurementPseudophakiaComputer science
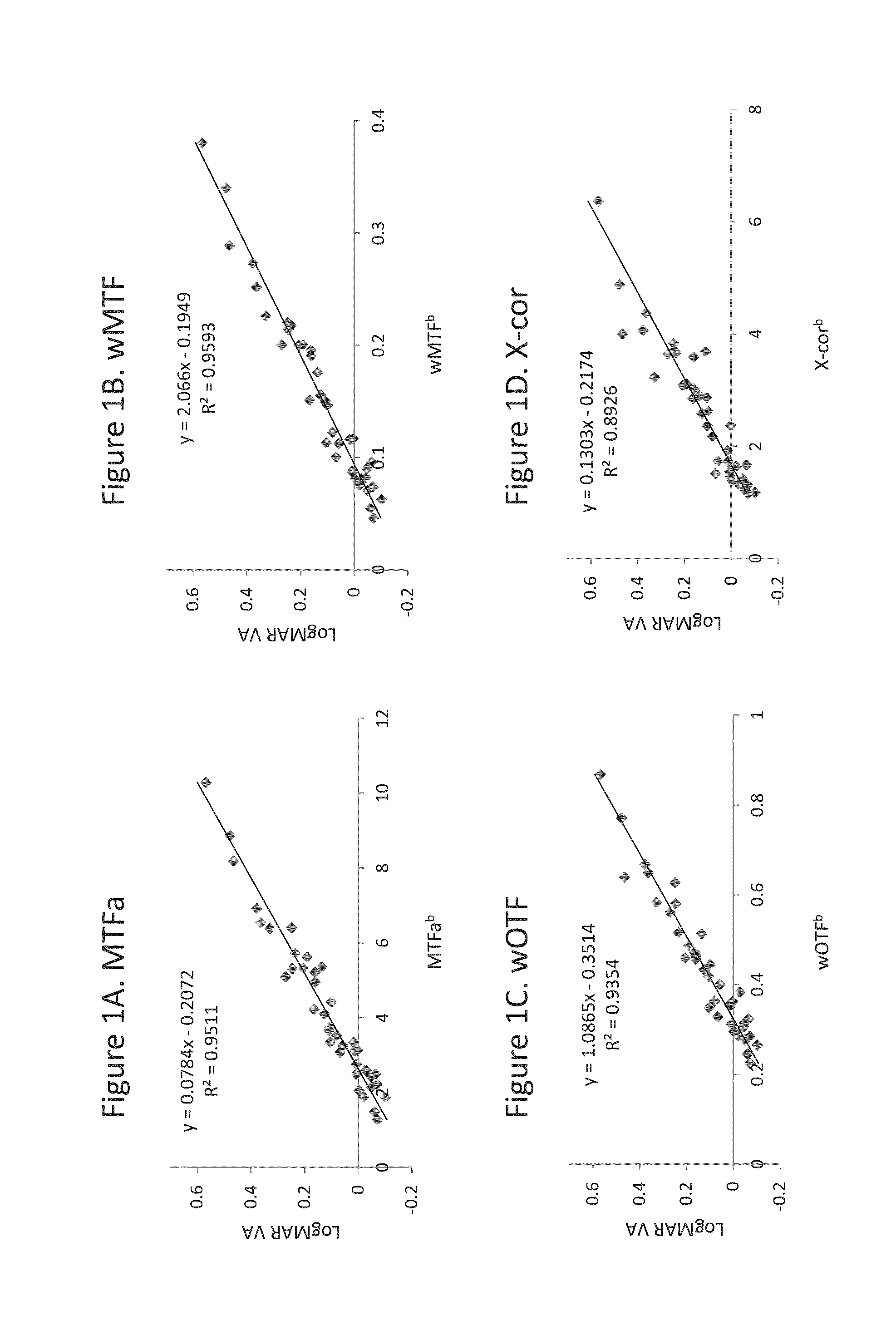
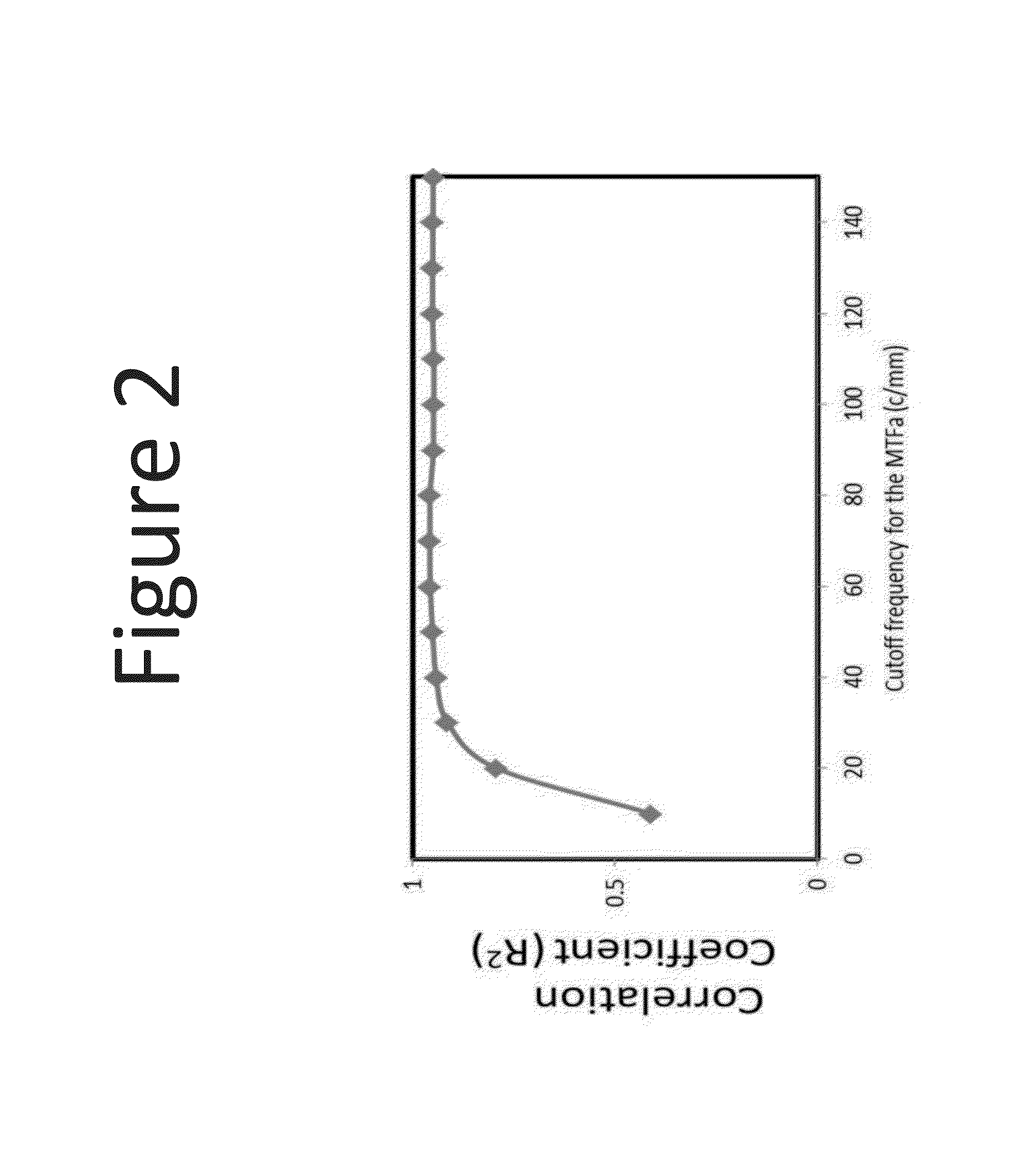
A system and method of characterizing through-focus visual performance of an IOL using metrics based on an area under the modulation transfer function for different spatial frequencies at different defocus positions of the IOL. Also disclosed is a system and method of characterizing through-focus visual performance of an IOL using a metric based on an area under a cross-correlation coefficient for an image of a target acquired by the IOL at different defocus positions of the IOL.
Owner:AMO GRONINGEN
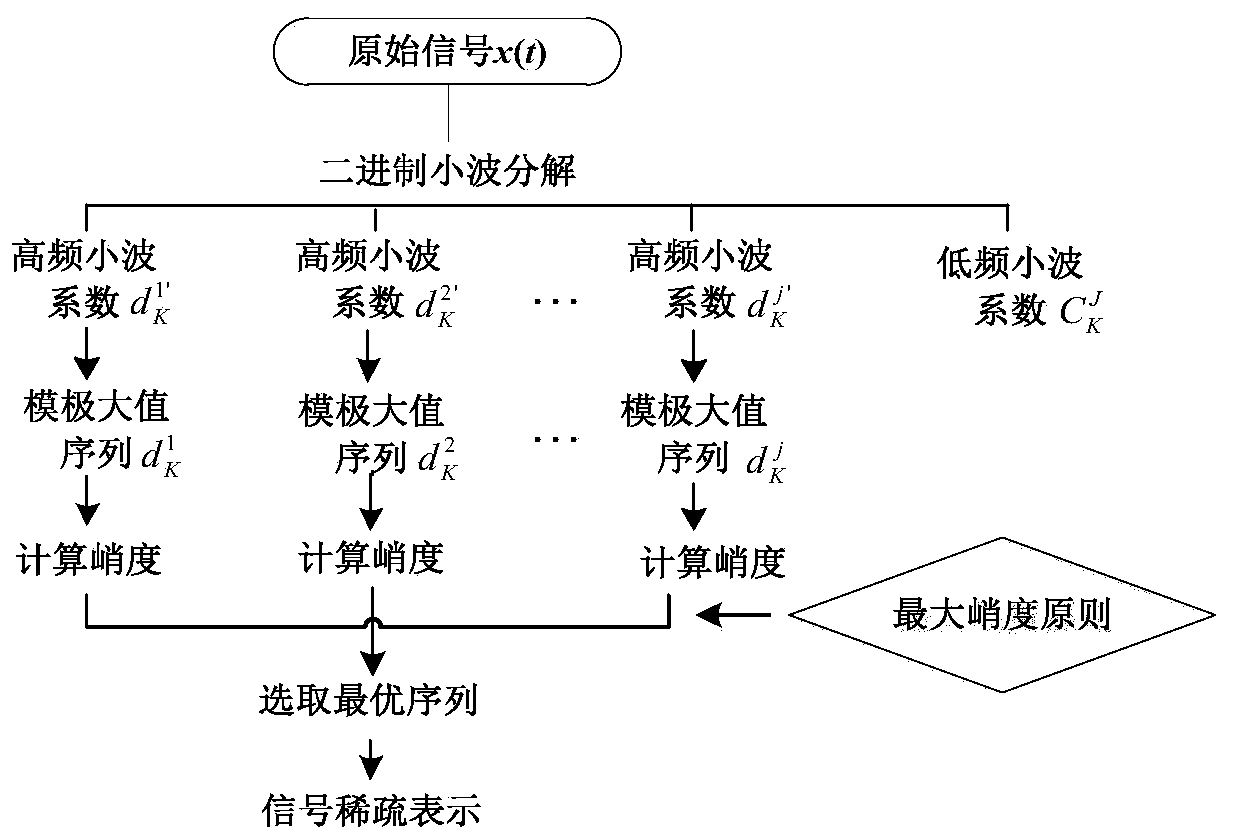
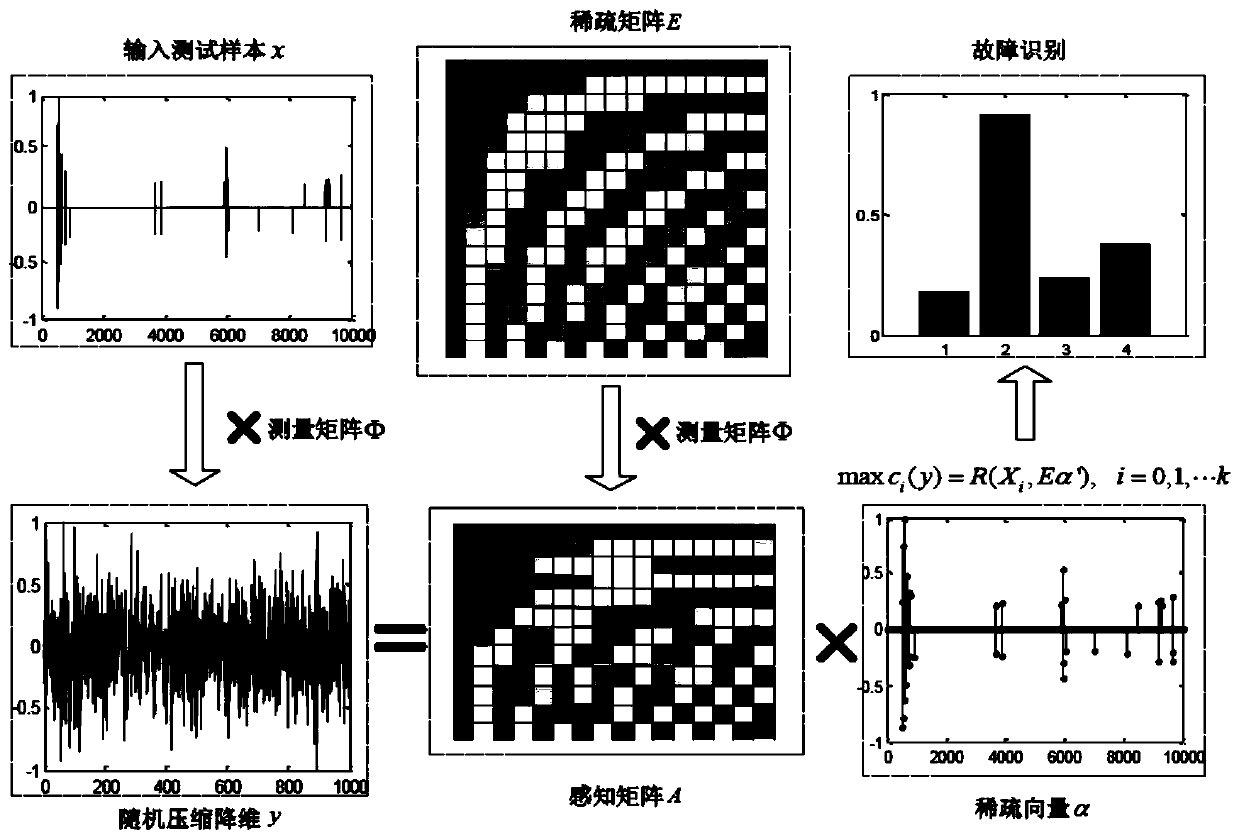
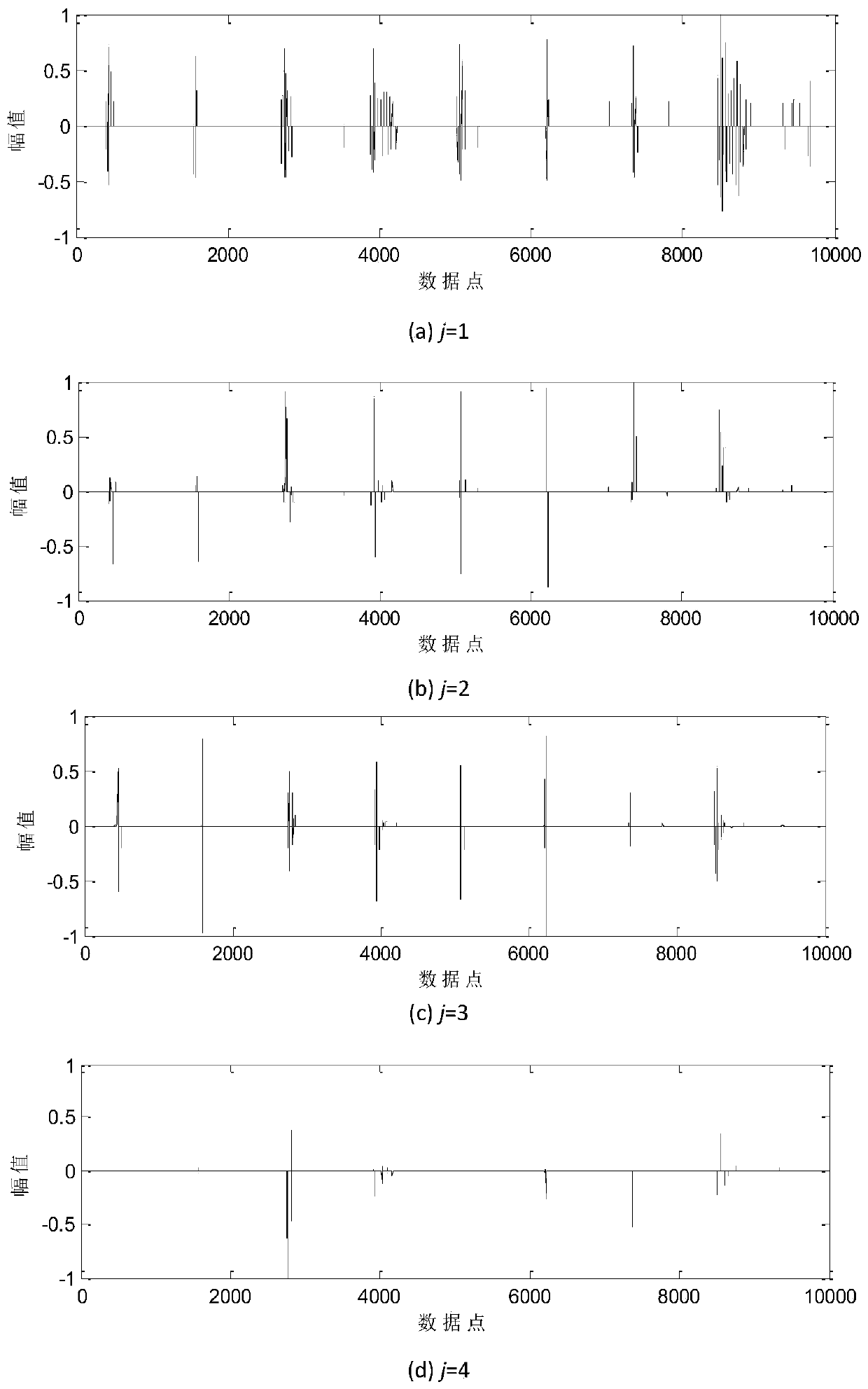
Improved self-adaptive sparse sampling fault classification method
InactiveCN109993105AReduce redundant informationReduce complexityMachine bearings testingCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsTime shifting
An improved self-adaptive sparse sampling fault classification method belongs to the technical field of fault diagnosis. A traditional sparse classification method is improved. Firstly, a wavelet module maximum value and a kurtosis method are used for carrying out feature enhancement processing on signals, and on the premise that signal sparsity is guaranteed, a unit matrix is adopted to replace aredundant dictionary. Secondly dimension reduction is carried out on data by adopting a Gaussian random measurement matrix, thereby reducing redundant information in the signal, and reserving effective and small amount of data. Then, a sparse coefficient is solved by adopting a sparsity adaptive matching pursuit (SAMP) algorithm, and the compressed signal is reconstructed; and finally, a cross correlation coefficient is adopted as a judgment basis of the category of the fault, so that an improved adaptive sparse sampling fault classification method is provided. Experimental verification proves that redundant information in signals is effectively reduced, the influence of time shift deviation on fault type judgment is avoided, meanwhile, the operation complexity is reduced, and the calculation speed and the reconstruction precision are improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Wideband radar detecting method for correcting correlation matrix based on high resolution target distance image
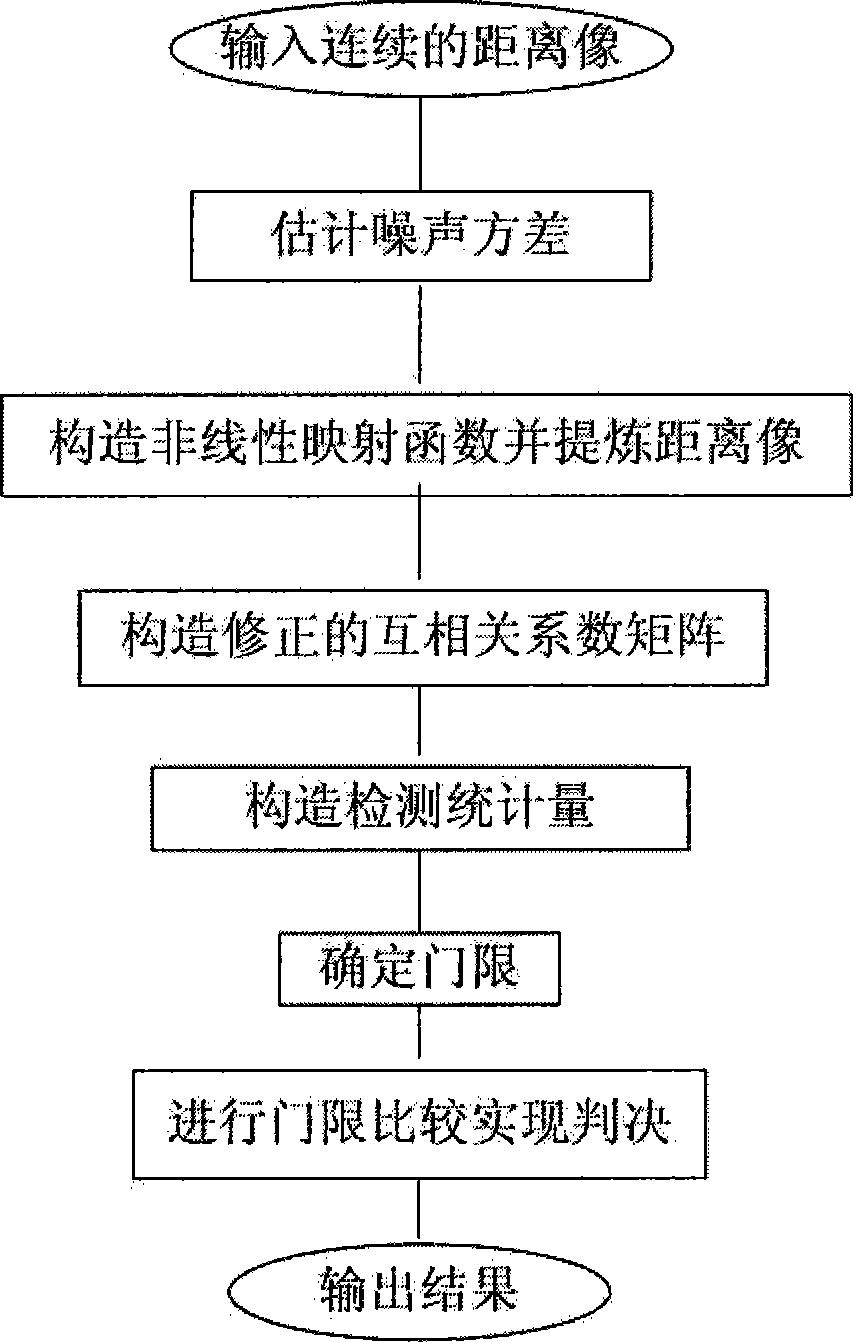
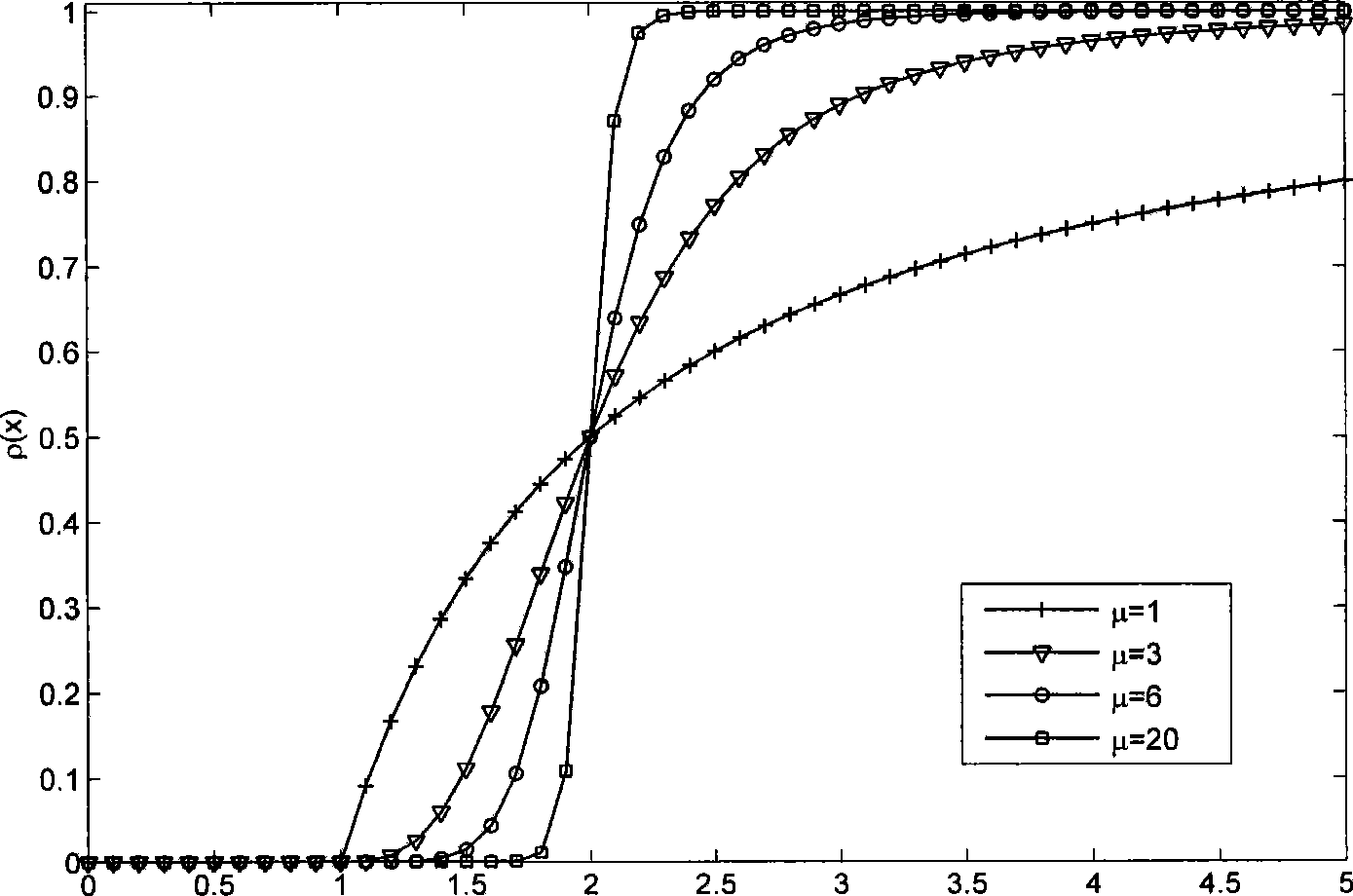
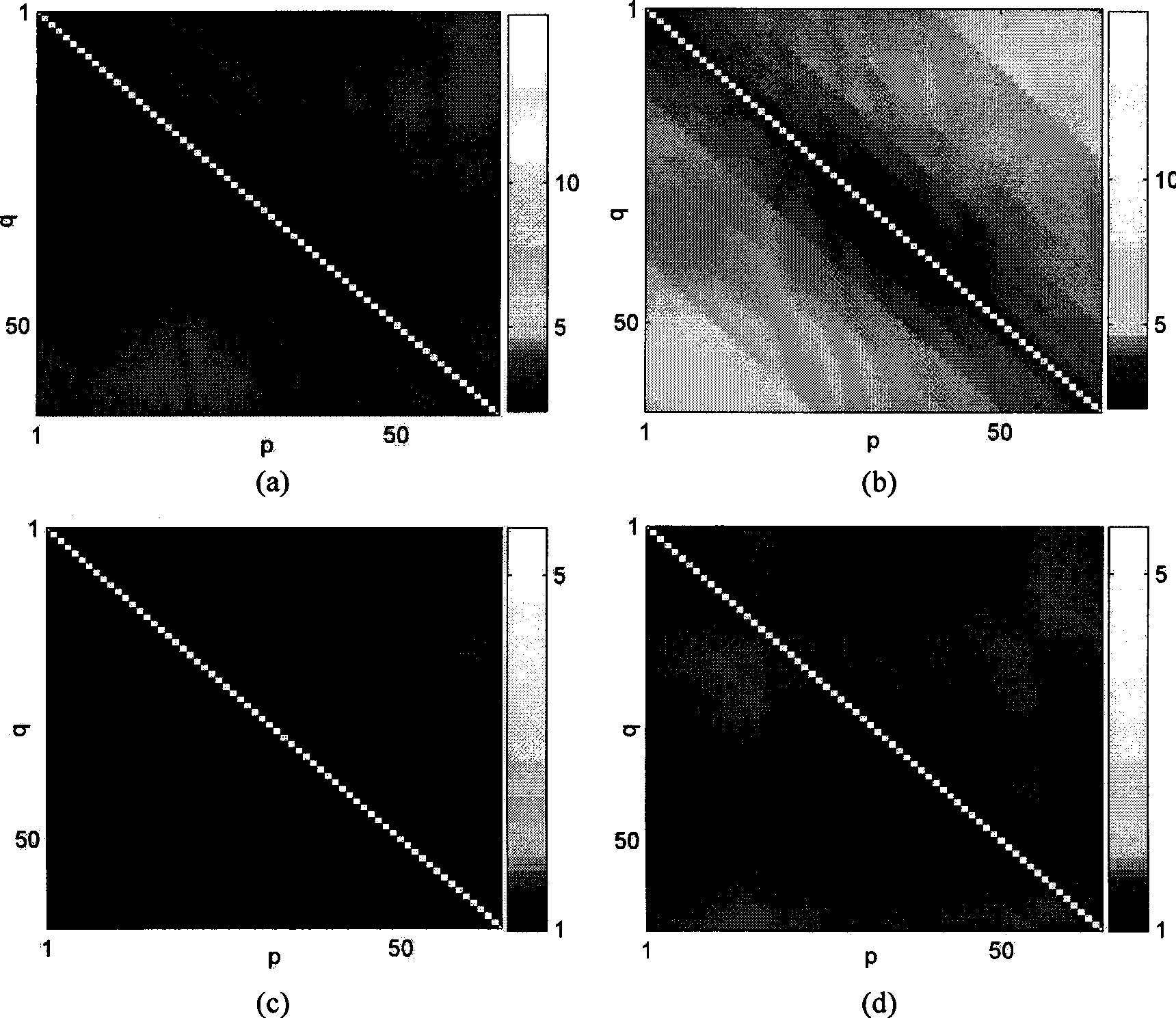
InactiveCN101509972AImprove object detection performanceRealize accumulationRadio wave reradiation/reflectionLinear contractionCurrent noise
The invention provides a method for detecting a broadband radar on the basis of continuous high-resolution target distance image-correction correlation matrix, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) standard deviation estimation is carried out to the noise of distance images that contain noise; (2) based on the standard deviation, a set of non-linear contraction mapping is established, and then the distance images that contain noise are refined according to the contraction mapping, thus obtaining refined multi-pulse distance images; (3) based on the multi-pulse distance images, cross correlation coefficient between every two refined distance images is calculated, thus obtaining a corrected cross correlation coefficient matrix; (4) the cross correlation coefficient matrixes are accumulated to establish the detecting statistic value, and the detecting threshold of current noise variance is set; (5) the detecting statistic value and the detecting threshold are compared to judge whether the target exists. The method has the advantages of cross distance unit detection and multi-pulse accumulation and is used for detecting a non-cooperative target under unknown prior information condition.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and system for restraining interference and combining diversity
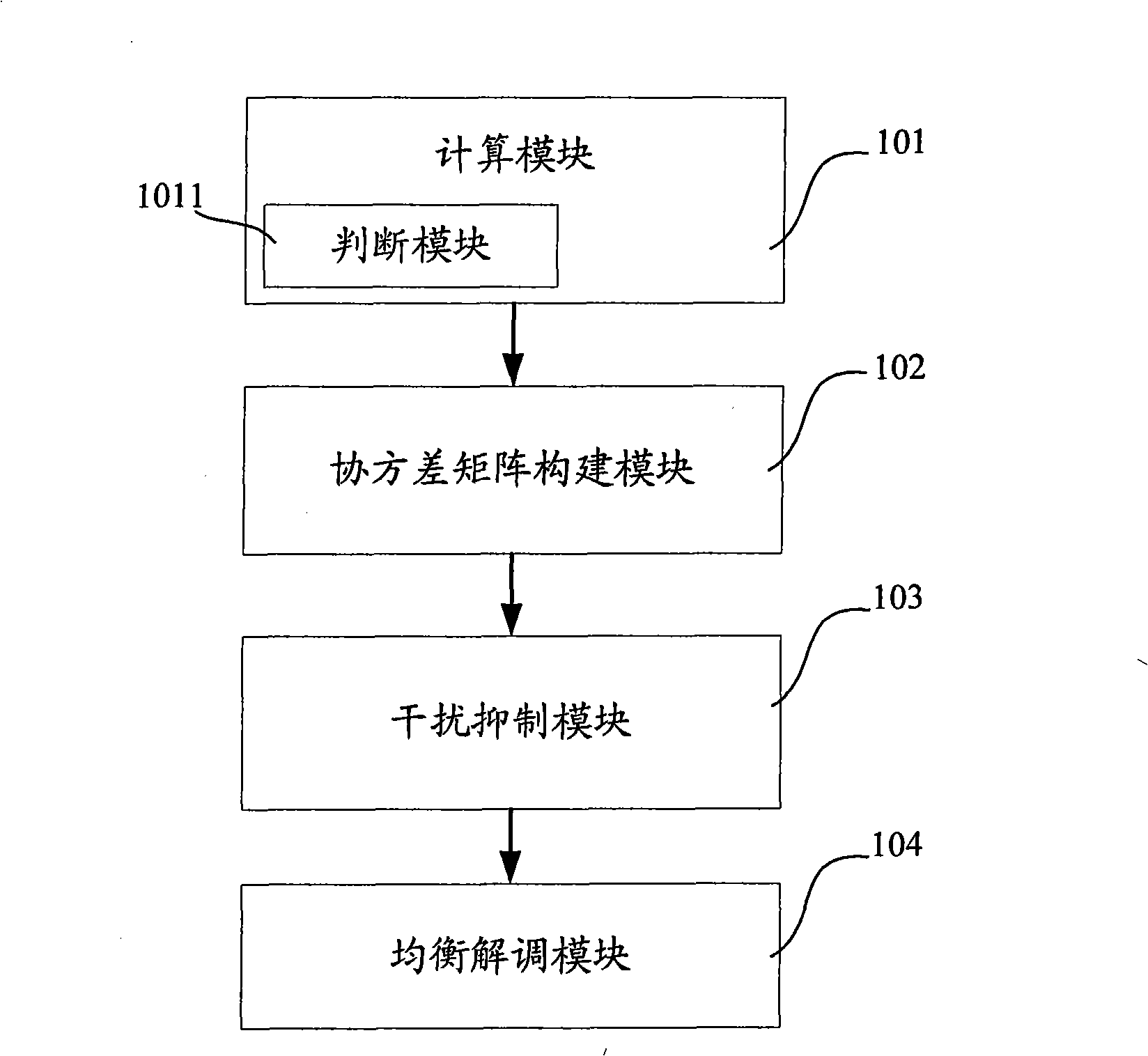
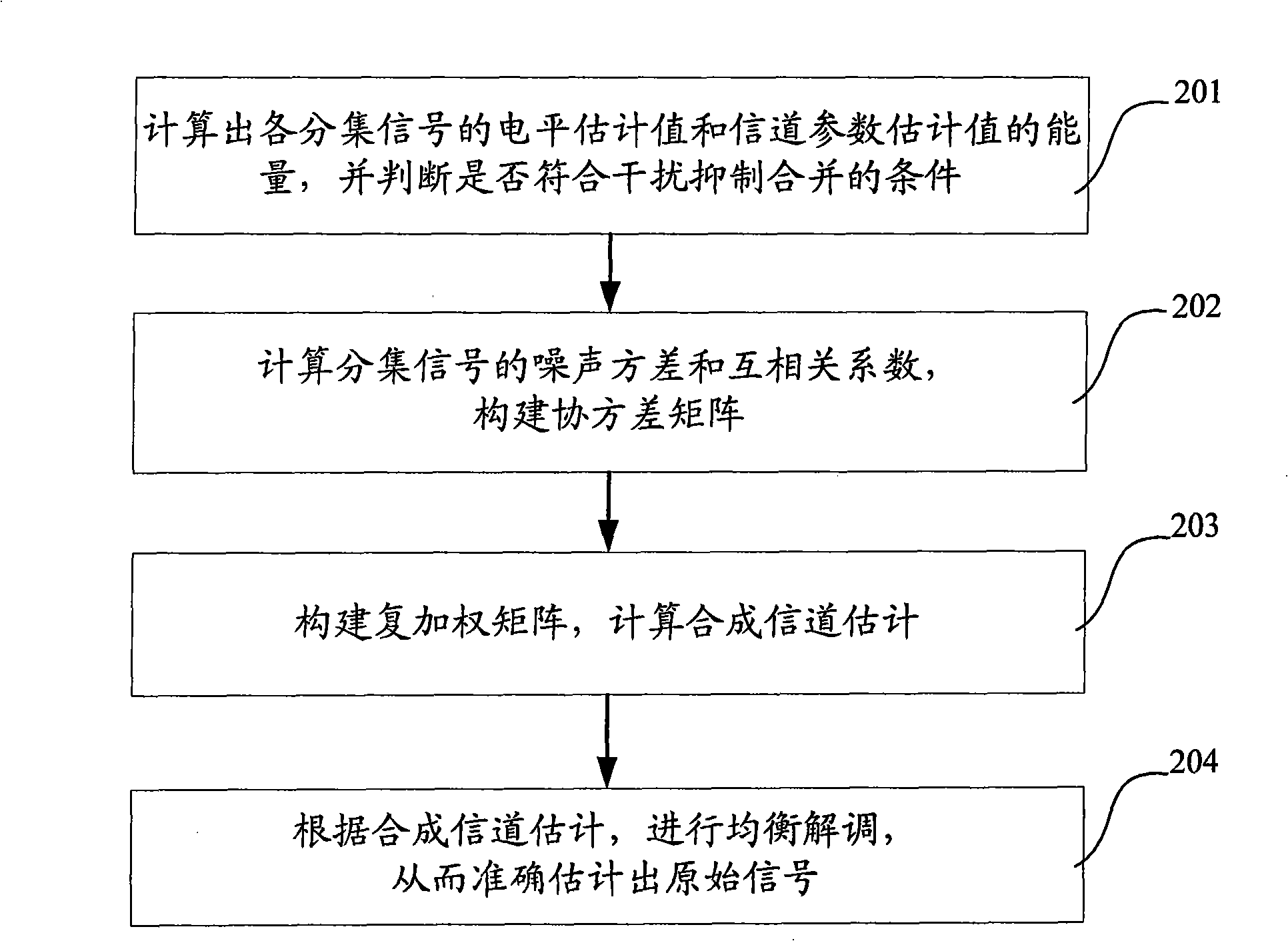
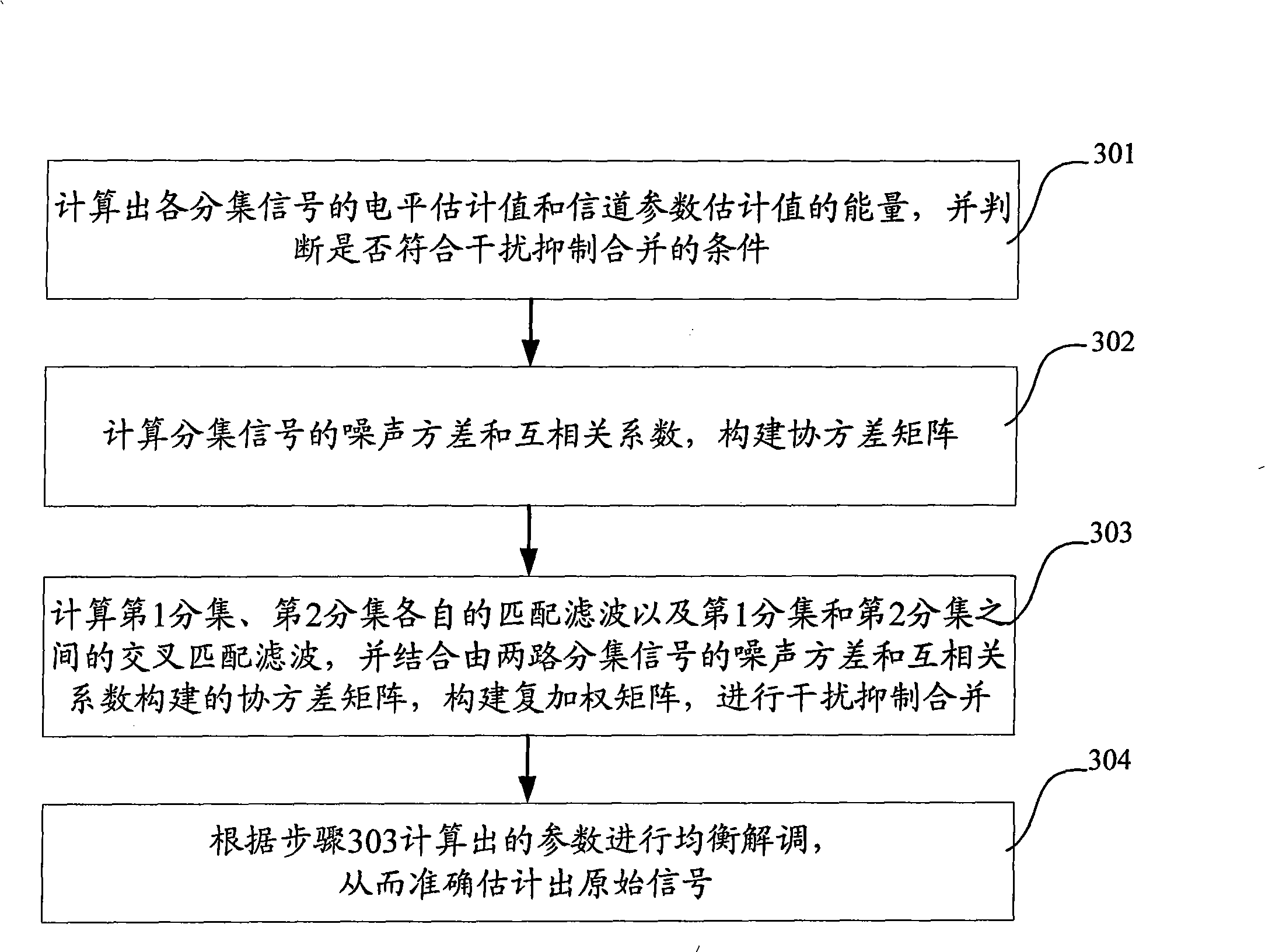
ActiveCN101330358AImprove receiver sensitivityExpand coverageTransmitter/receiver shaping networksError prevention/detection by diversity receptionConducted InterferenceEngineering
The invention discloses an interference suppression diversity and combination method which comprises the steps of calculating the capacities of a level estimation value of a diversity signal and a channel parameter estimation value; calculating the noise variance and cross correlation coefficient of the diversity signal to construct a covariance matrix; constructing a weighted matrix according to the covariance matrix to conduct interference, suppression and combination; and conducting equal demodulation according to a result of the interference, suppression and combination. The invention also discloses an interference suppression diversity and combination system which comprises a calculation module, a covariance matrix construction module, an interference suppression module and an equal demodulation module. The method greatly reduces the complexity of a system, improves the receiving sensitivity of a receiver, and enlarges the coverage of a base station, thereby providing an interference suppression diversity and combination technical proposal which has the advantages of low complexity, high estimation accuracy and easy realized engineering.
Owner:ZTE CORP
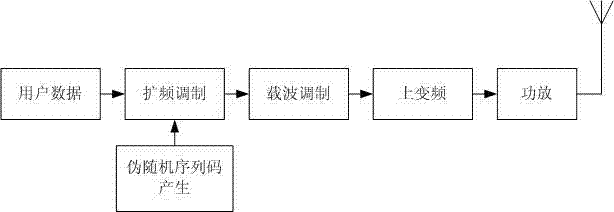
Method for realizing multi-user spread spectrum broadcasting station based on parallel interference cancellation algorithm
InactiveCN102684737AImprove capacity utilizationImprove frequency band utilizationError preventionBroadcastingData transmission
The invention provides a method for realizing a multi-user spread spectrum broadcasting station based on parallel interference cancellation algorithm, which can realize data transmission between a plurality of users and a receiver at the same time under the same frequency. The parallel interference cancellation algorithm is realized on a receiver; and before the algorithm is realized, a code synchronization module of the receiver outputs a spreading code of the current phase position, and a despreading module outputs a primary despreading signal. The parallel interference cancellation algorithm comprises the following steps: firstly, a spreading code is utilized to despread the primary despreading signal for the second time and the cross correlation coefficients of different user spreading codes are worked out at the same time; secondly, all secondary spread spectrum signals that interfere with users are multiplied and added with the corresponding cross correlation coefficients respectively to obtain interference signals; thirdly, the interference signals are subtracted from baseband digital signals to obtain baseband signals without interference; and finally, code synchronization, despreading and carrier synchronization demodulation are performed to the baseband signals without interference so as to obtain the current user data. According to the invention, the processes are carried out concurrently, so that radio station communication and data transmission between a plurality of users and the receiver can be realized in the same frequency band at the same time.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
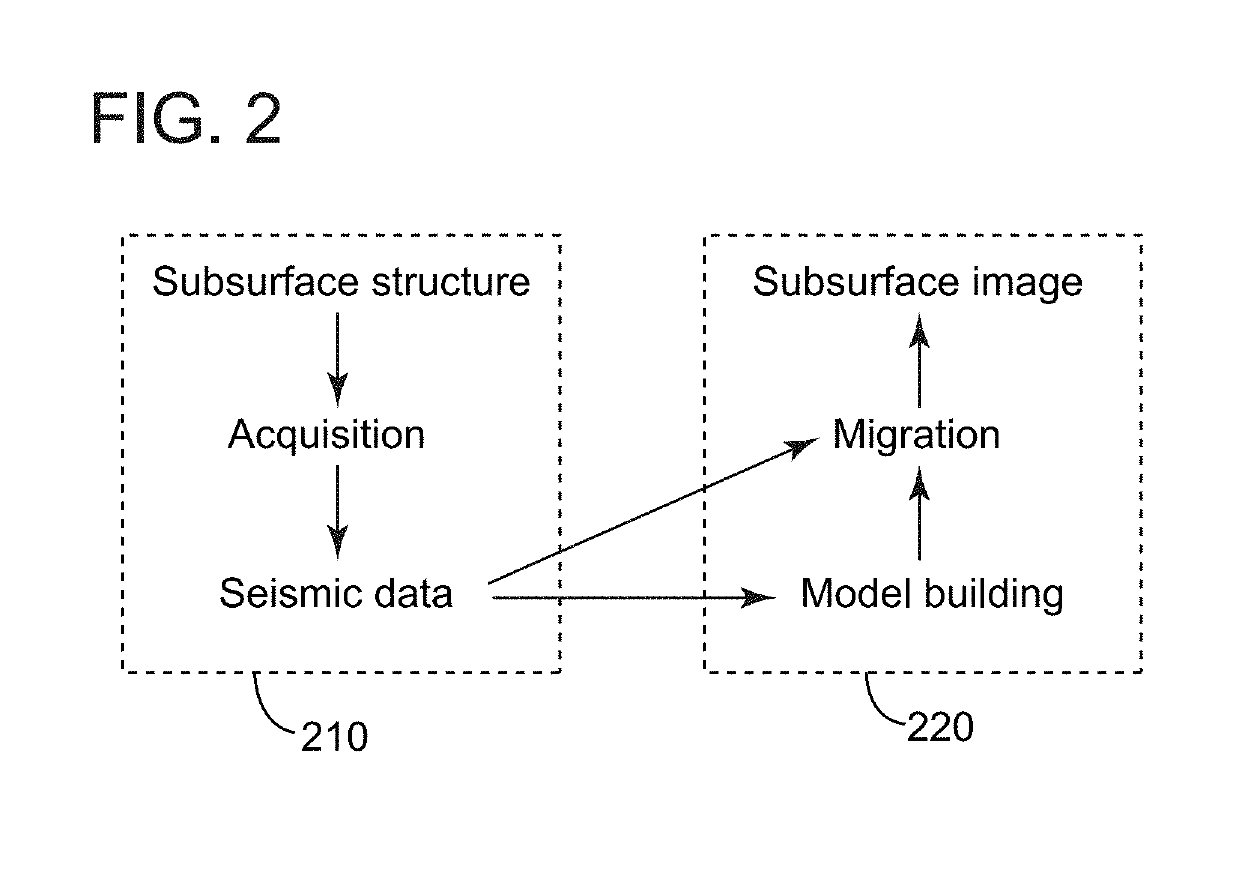
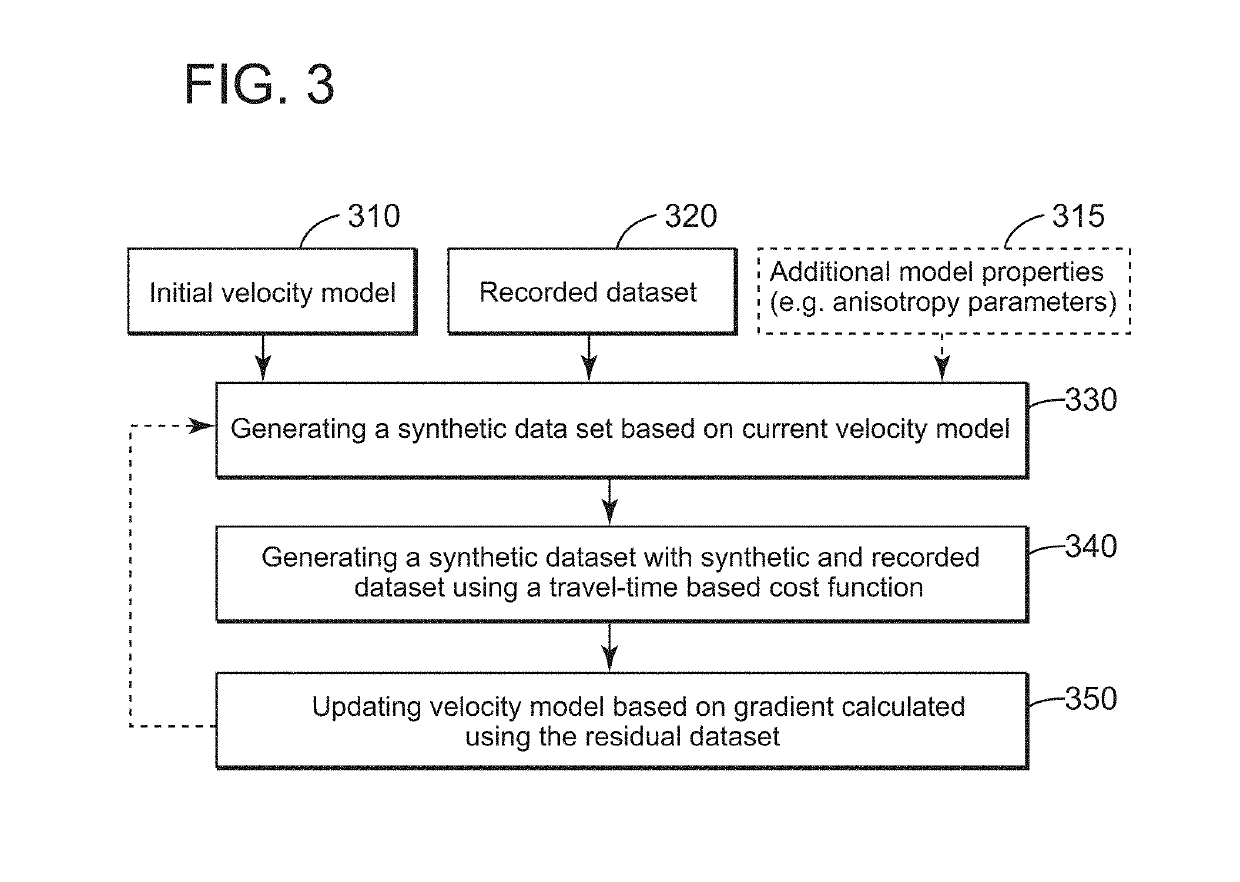
Methods using travel-time full waveform inversion for imaging subsurface formations with salt bodies
Methods and devices use improved FWI techniques for seismic exploration of subsurface formations including salt bodies using a travel-time cost function. In calculating the travel-time cost function, time-shifts may be weighted using cross-correlation coefficients of respective time-shifted recorded data and synthetic data generated based on current velocity model. The improved methods enhance the resulting image while avoiding cycle-skipping and issues related to amplitude difference between synthetic and recorded data.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SAS
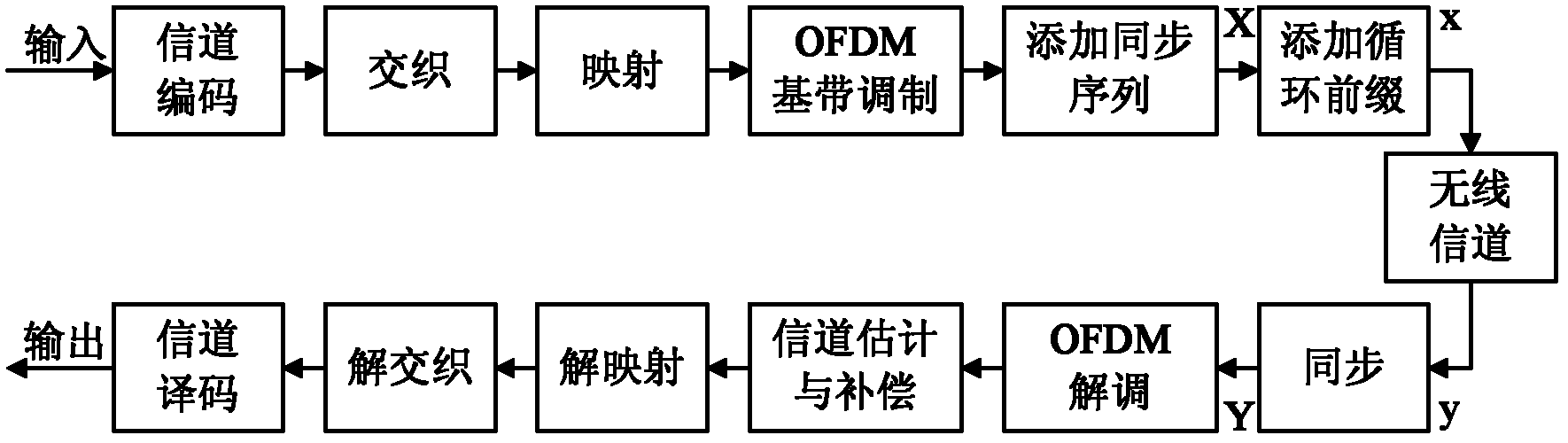
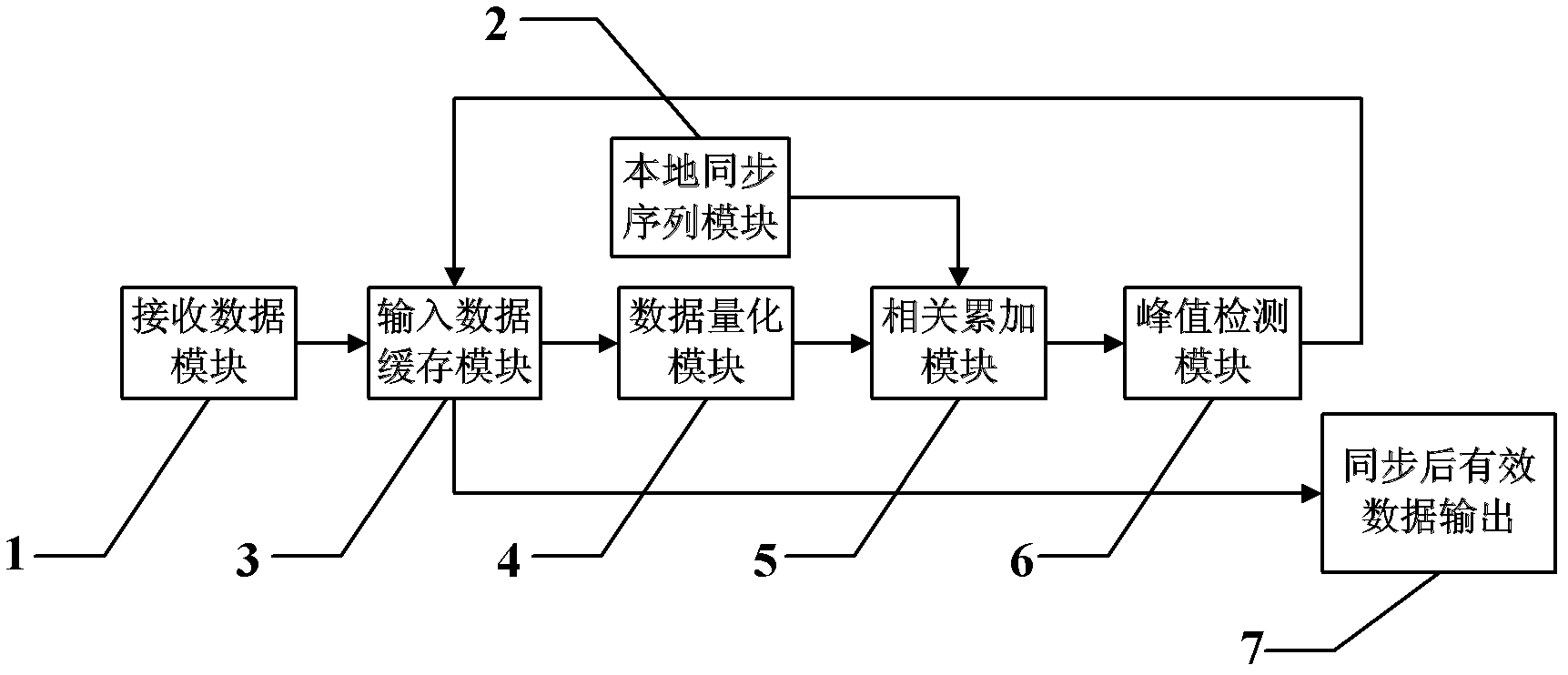
A Timing Synchronization Method for Receivers in OFDM Wireless Communication System
InactiveCN102291351APinpoint the starting positionActive Timing SynchronizationMulti-frequency code systemsFast Fourier transformTime domain
The invention, aiming at an OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) wireless communication system, provides a timing synchronization algorithm which can be easily and simply implemented in a receiver. A 62-point frequency domain ZC (Zadoff-Chu)sequence is generated by a generation formula of a frequency domain ZC sequence, two ends of the generated sequence are added with 33 zeros, then, three zeros are inserted between neighboring points so as to expand the sequence to have 512 points, and synchronization sequence obtained by performing IFFT (Inverse Fast Fourier Transform) is usedas a synchronizing signal of the OFDM wireless communication system; the receiver firstly quantifies the received synchronization sequence, then, performs conjugated correlation with a local synchronization sequence, and simultaneously, calculates a cross correlation coefficient amplitude based on sum of absolute values of a real part and an imaginary part. In this way, the correlation operation and the cross correlation coefficient amplitude calculation only contain addition and subtraction, use of a multiplying unit is avoided, operation complexity is greatly reduced, processing efficiency is improved and resource is saved, so that the timing synchronization of the receiver can be implemented easily and simply, and can be implemented more effectively on receiver hardware.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Method and apparatus for simple angle of arrival estimation
The method and apparatus for angle of arrival estimation are used for estimating the angle of arrival of a received signal by a switched beam antenna array and a single receiver. The switched beam antenna array first collects an omnidirectional signal to be used as a reference signal. A main beam thereof is then switched to scan an angular region of interest. The collected signals from the switched beams are cross-correlated with the reference signal. The cross-correlation coefficient is the highest at the true angle of arrival and relatively negligible otherwise. The collected signal from each beam angle is cross-correlated with the omnidirectional reference signal to determine the angle of arrival of the received signal.
Owner:QATAR UNIVERSITY
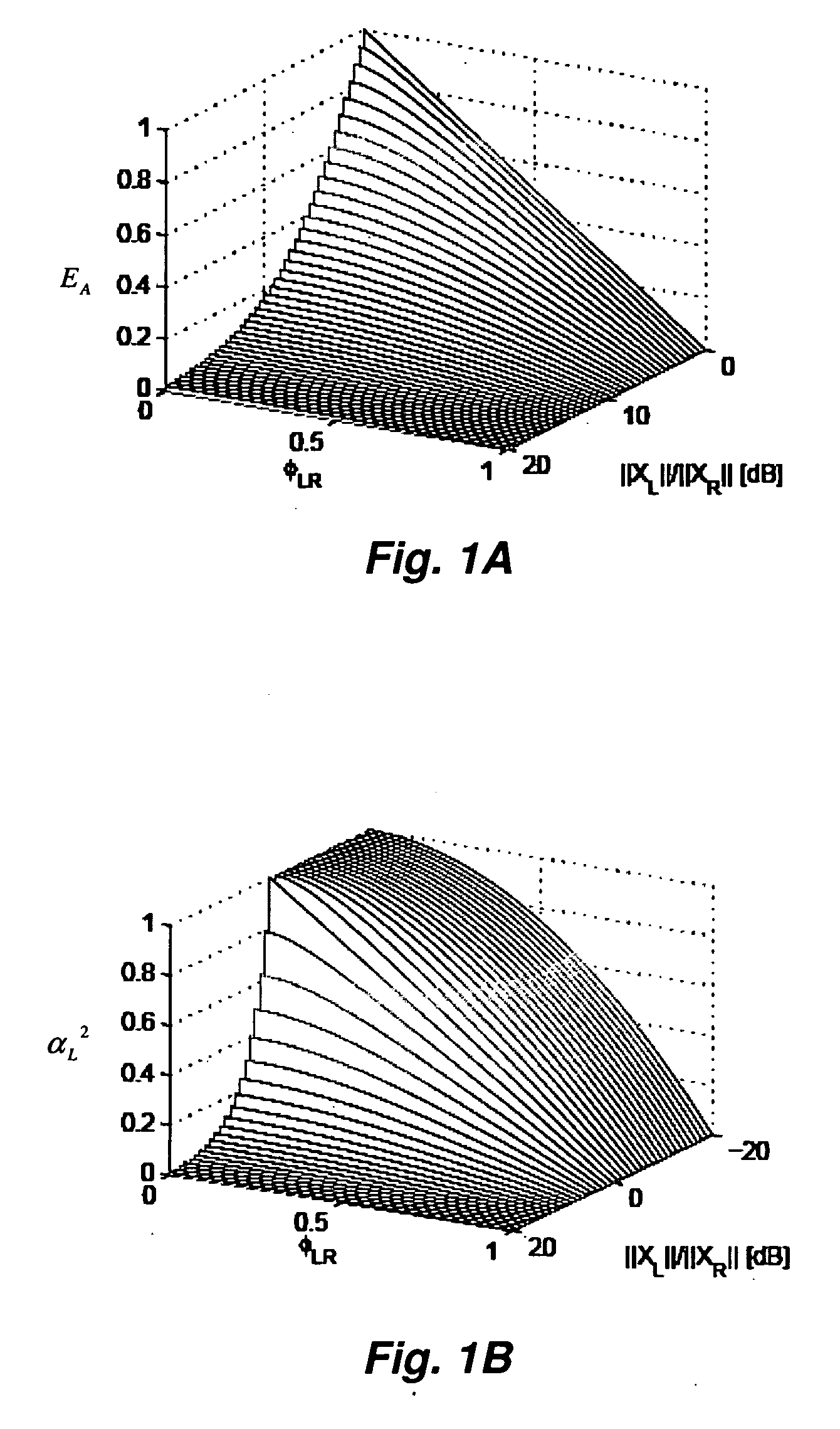
Correlation-based method for ambience extraction from two-channel audio signals
A method of ambience extraction includes analyzing an input signal to determine the time-dependent and frequency-dependent amount of ambience in the input signal, wherein the amount of ambience is determined based on a signal model and correlation quantities computed from the input signals and wherein the ambience is extracted using a multiplicative time-frequency mask. Another method of ambience extraction includes compensating a bias in the estimation of a short-term cross-correlation coefficient. In addition, systems having various modules for implementing the above methods are disclosed.
Owner:CREATIVE TECH CORP
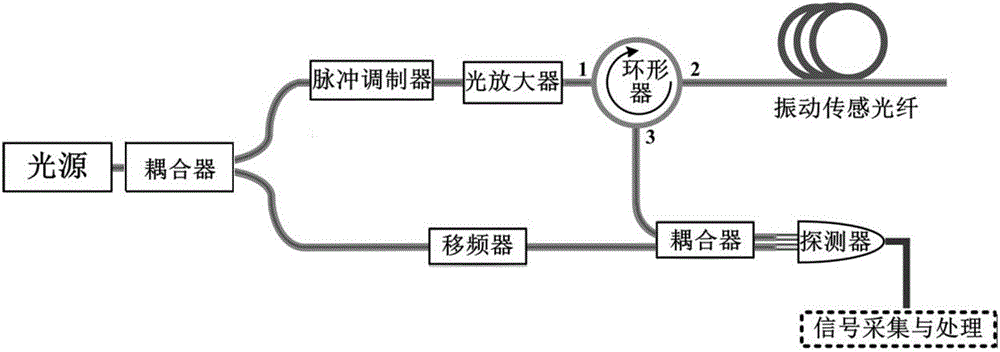
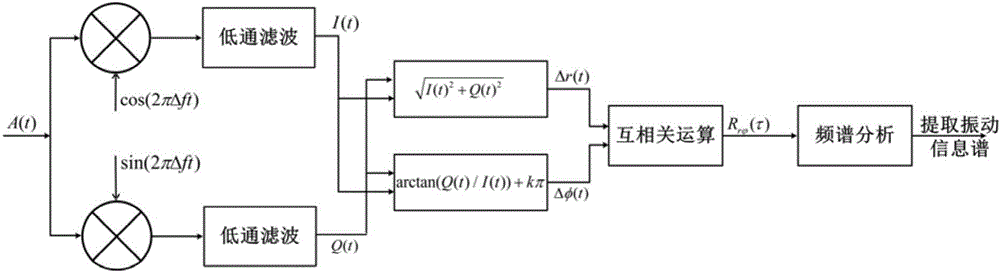
Cross-correlation demodulation method for improving sensitivity of distributed optical fiber vibration sensing
ActiveCN106679790AReduce mistakesHigh sensitivitySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementUsing wave/particle radiation meansFrequency spectrumDemodulation
The invention belongs to the field of distributed optical fiber vibration sensing technology, and provides a cross-correlation demodulation method for improving the sensitivity of distributed optical fiber vibration sensing. The method uses the orthogonal demodulation method for carrier frequency removal and low pass filtering of a heterodyne coherent beat frequency signal collected by a distributed optical fiber sensing system, and then amplitude and phase information are obtained; the cross correlation coefficient of the amplitude and the phase information is obtained based on cross-correlation operation. Spectrum analysis is conducted on the basis of the correlation signal, and information related to vibration is extracted more sensitively and accurately.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Three-dimensional fault line selection method based on random resonance and transient current signal
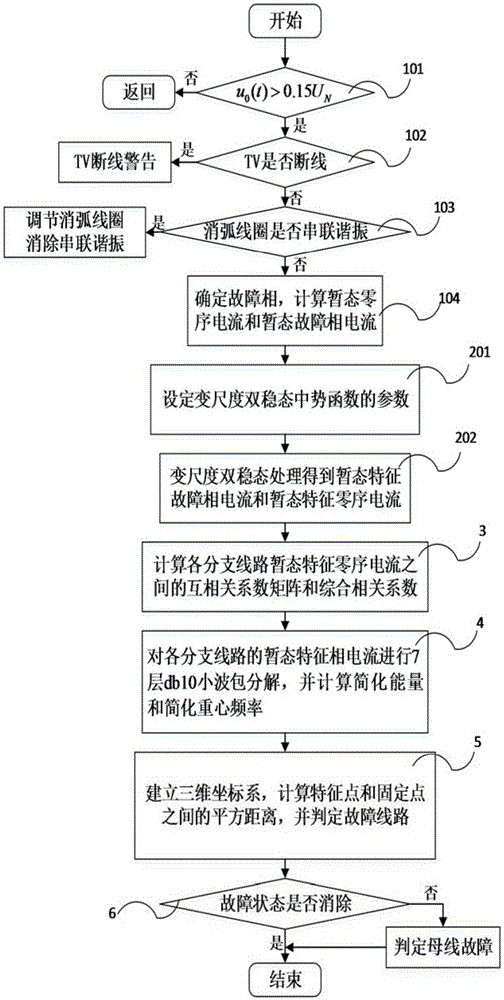
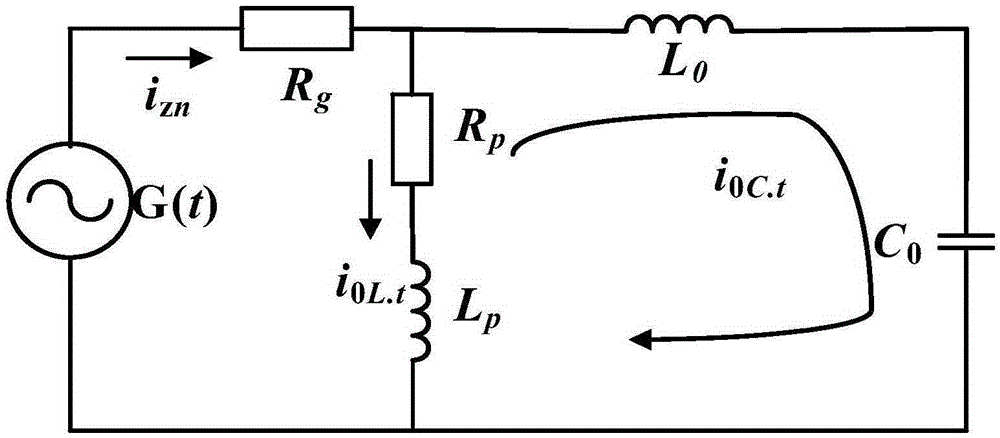
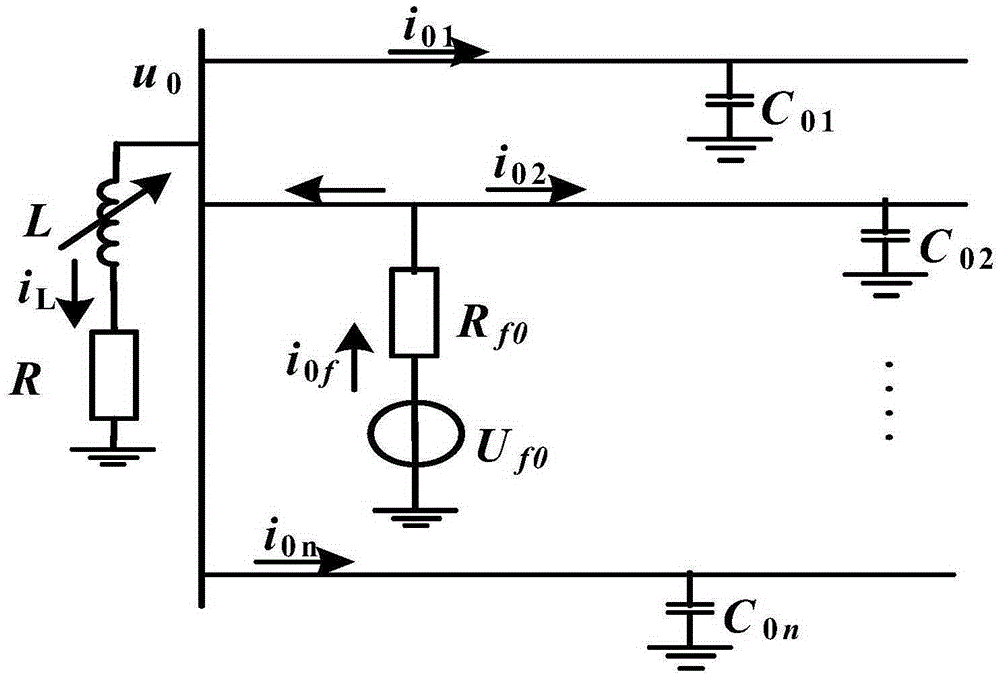
ActiveCN105259471AImprove reliabilityImprove line selection accuracyFault locationPhase currentsGravity center
The invention relates to a three-dimensional fault line selection method based on random resonance and a transient current signal. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) after a power distribution network is faulted, recording the zero-sequence current iZn(t) and the fault phase current iXn(t) of each branch line fault, and computing transient zero-sequence current izn(t) and transient fault phase current ixn(t); (2) performing variable-scale bistable treatment on the transient zero-sequence current izn(t) and transient fault phase current ixn(t); (3) computing a cross correlation coefficient matrix M and an integrated correlation coefficient Mn among the transient characteristic zero-sequence current iczn(t) of the branch lines and selecting the line ln with the minimum Mn; (4) performing seven-layer db10 wavelet packet decomposition on the transient characteristic phase current icxn(t) of each branch line and computing simplified energy E*sn and simplified gravity center frequency f*gn; and (5) forming a three-dimensional coordinate system by using the simplified gravity center frequency f*gn as a horizontal ordinate, the simplified energy E*sn as a vertical coordinate, and a polarity parameter value as a longitudinal coordinate. Compared with a method in the prior art, the method is high in reliability and is not liable to suffer from external interference.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com