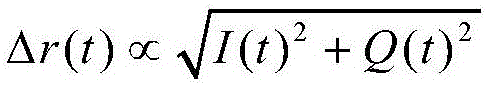Cross-correlation demodulation method for improving sensitivity of distributed optical fiber vibration sensing
A technology of sensing sensitivity and distributed optical fiber, which is applied in the direction of instruments, measuring devices, and using wave/particle radiation, can solve the problems of insufficient sensitivity, incomplete vibration information, and difficulty in accurately collecting amplitude and frequency information, and achieve improved Sensitivity and accuracy, effect of reducing error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] The specific implementation of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and examples, but the implementation and protection of the present invention are not limited thereto.
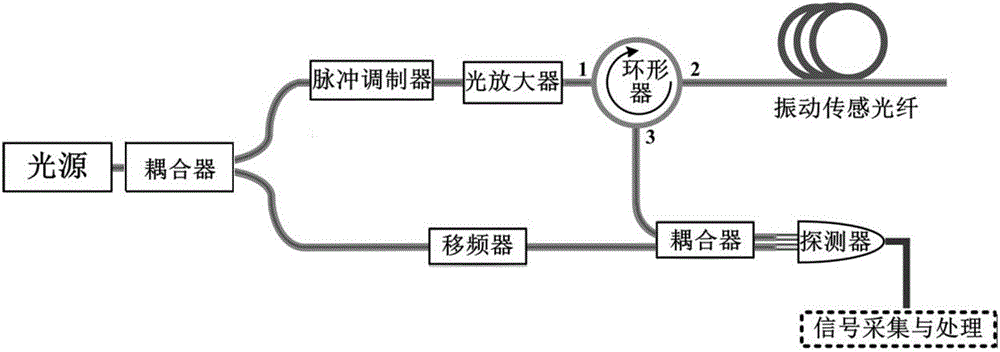
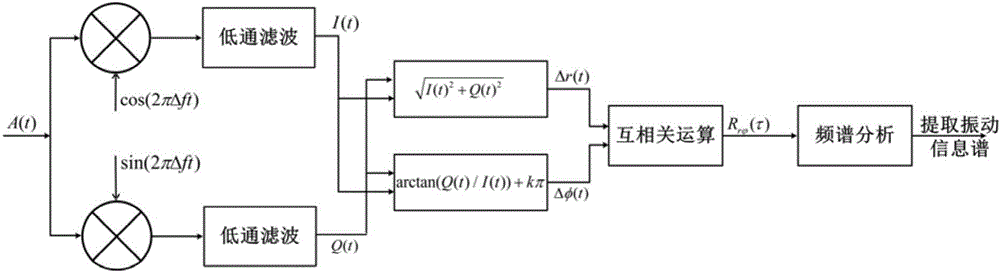
[0019] The structure of the distributed optical fiber vibration sensing system based on phase-sensitive optical time domain reflection used in this example is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the system uses a high-coherence narrow-linewidth laser as the light source, and splits the light into two paths through a coupler, one of which is modulated into an optical pulse sequence by a pulse modulator, amplified by an optical amplifier, and then injected into the vibration sensing fiber through a circulator. The Rayleigh backscattered light in the sensing fiber is transmitted back through the circulator, and is heterodyned with another local oscillator light that has been shifted by Δf through the frequency shifter. The beat frequency light sign...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com