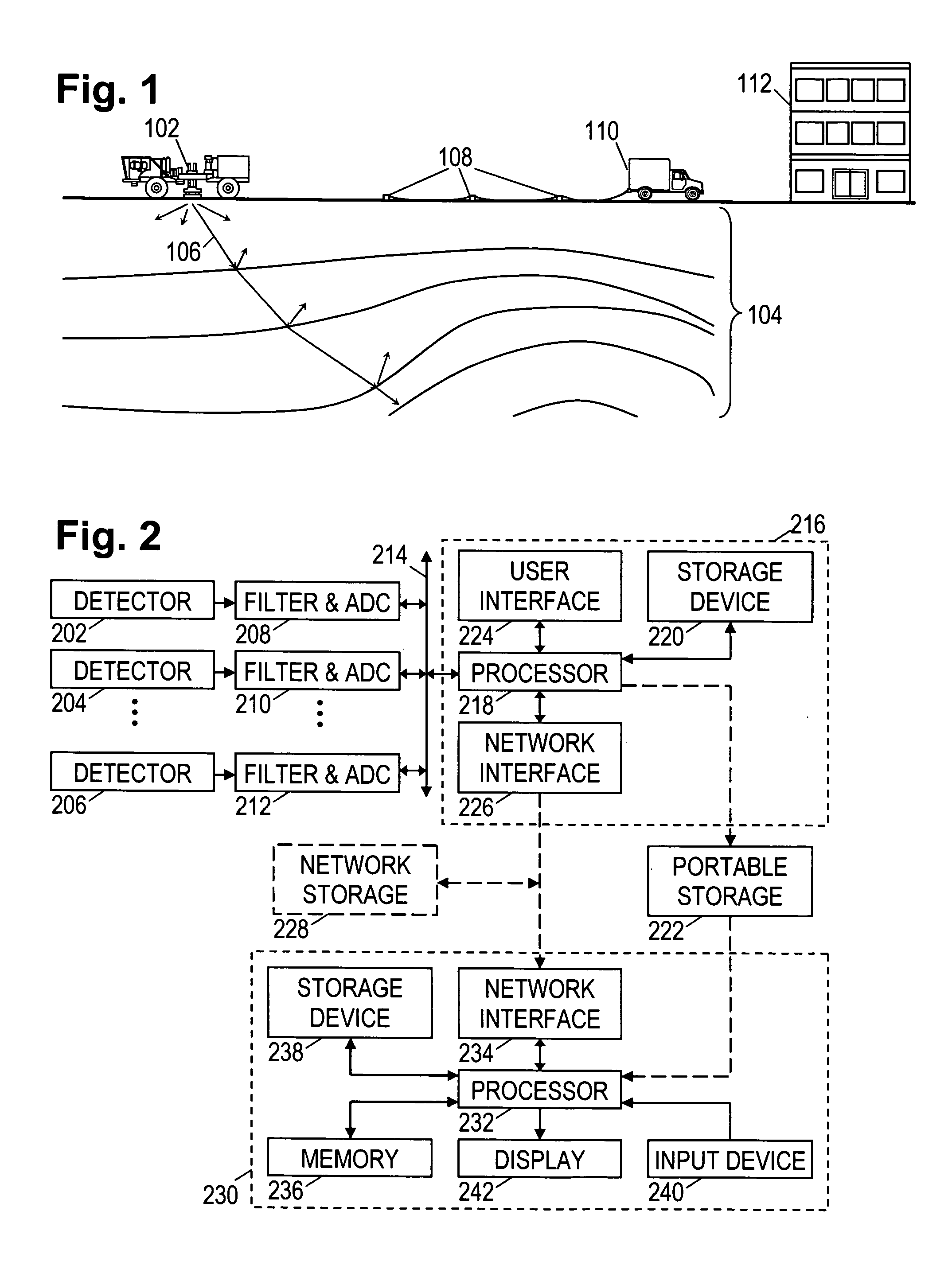
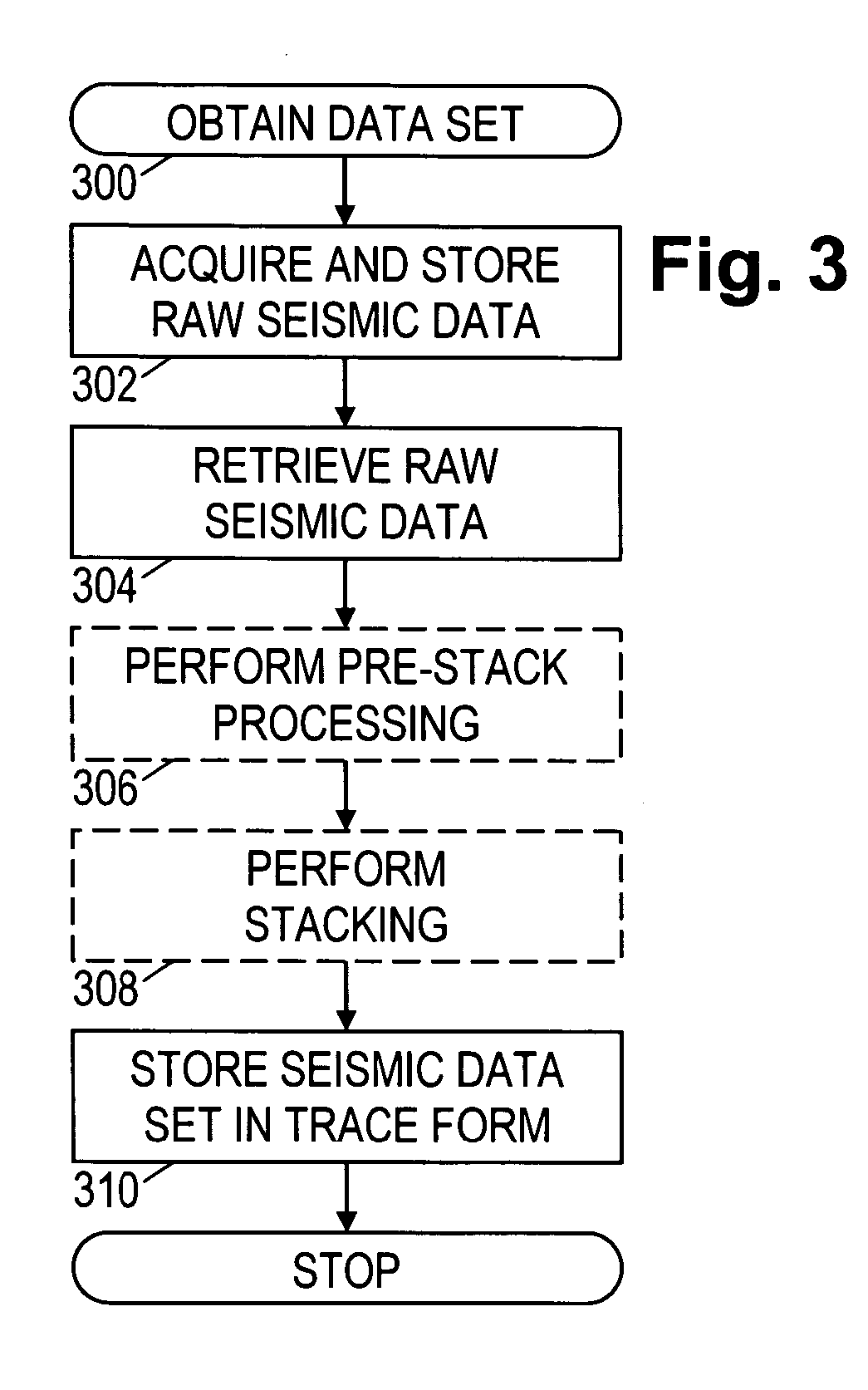
Patents
Literature
671 results about "Seismic trace" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
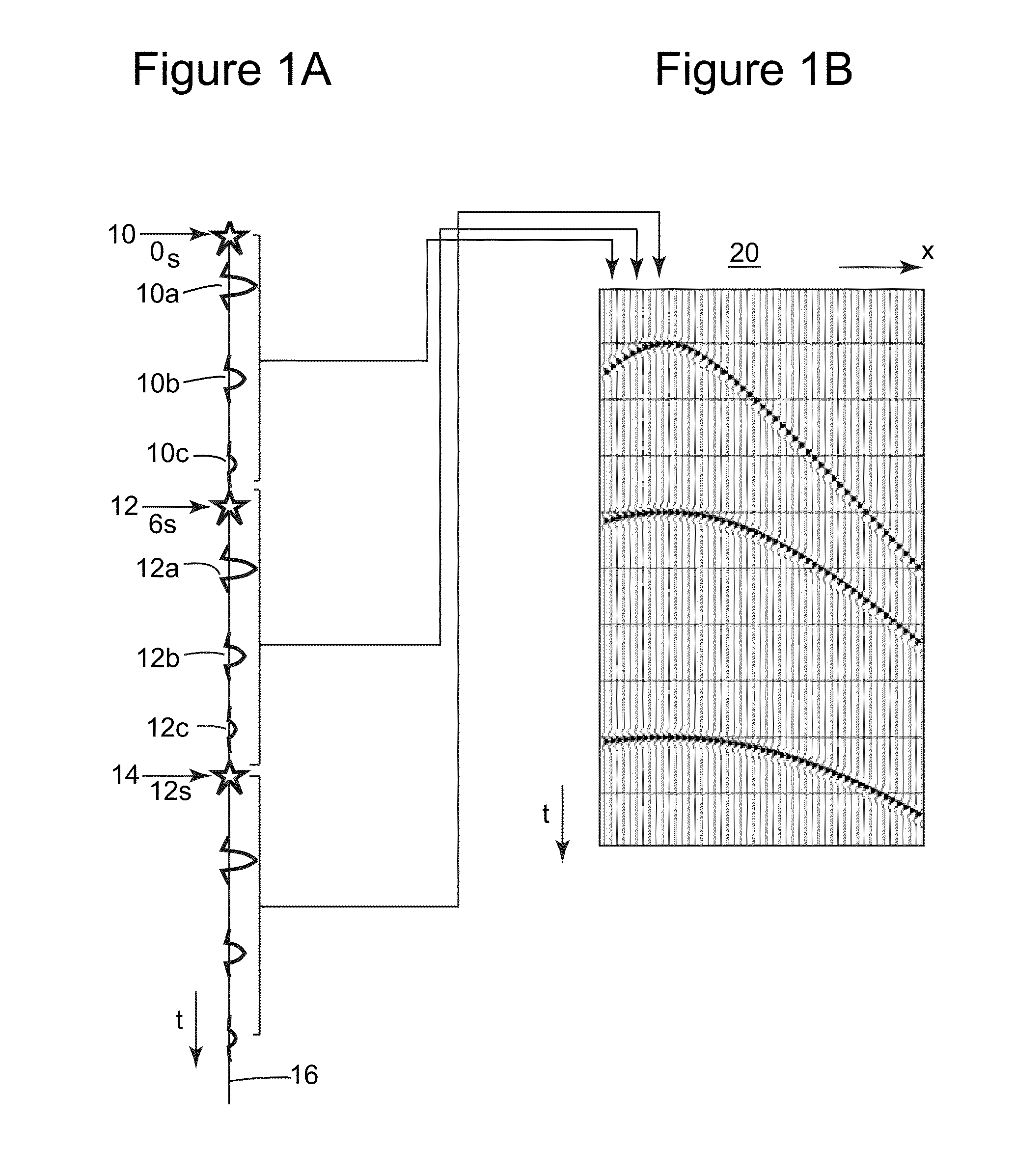
In seismology, a seismic trace refers to the recorded curve from a single seismograph when measuring ground movement. The name comes from the curve plotted by a seismograph as the paper roll rotated and the needle left a trace from which information about the subsurface could be extracted. Today's instruments record the data digitally and the word trace has come to mean the digital curve.
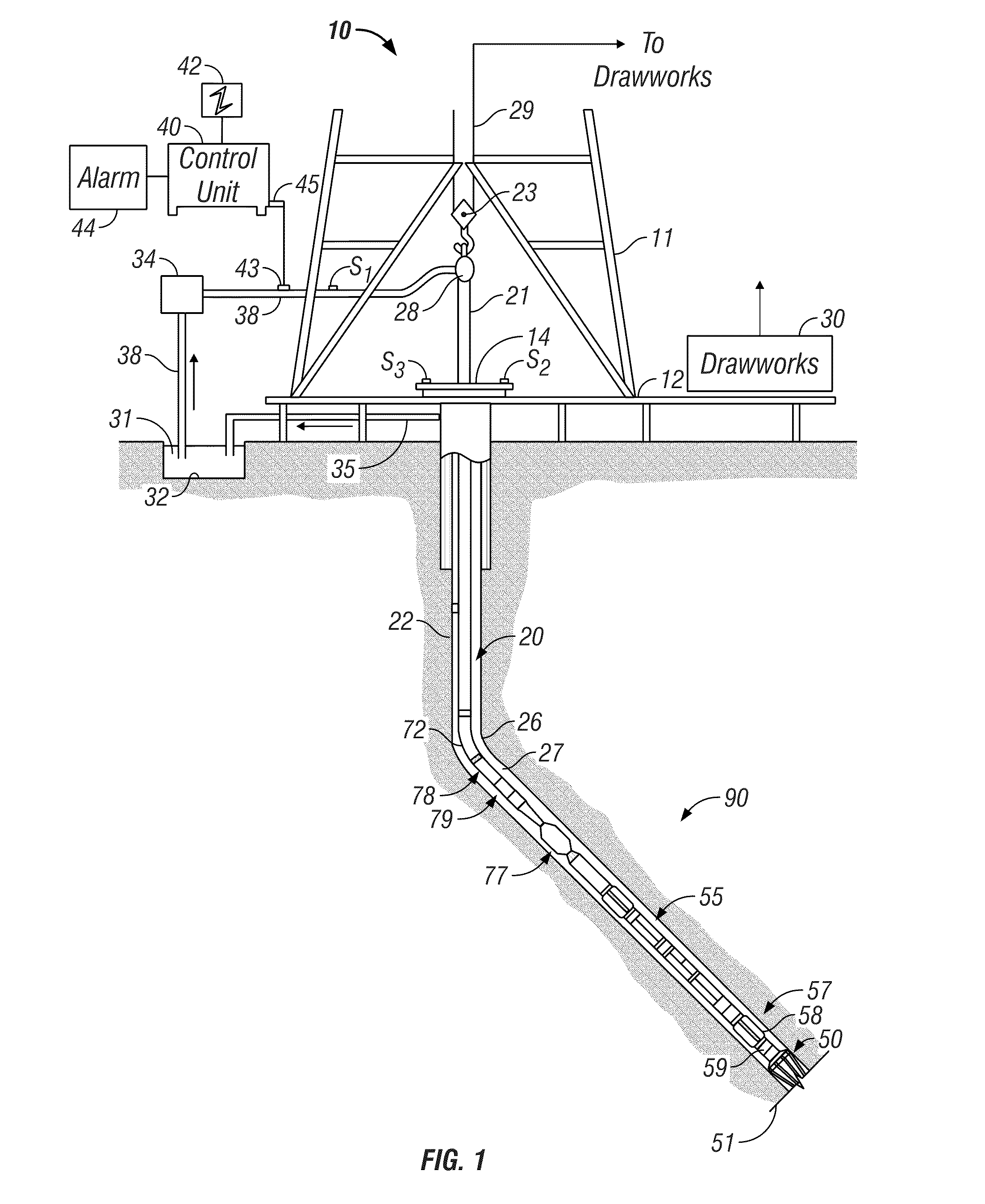
Seismic data acquisition system using acquisition stations set on the sea bottom
InactiveUS7016260B2Good synchronizationTelemetry/telecontrol selection arrangementsTransmission systemsSystems designData acquisition
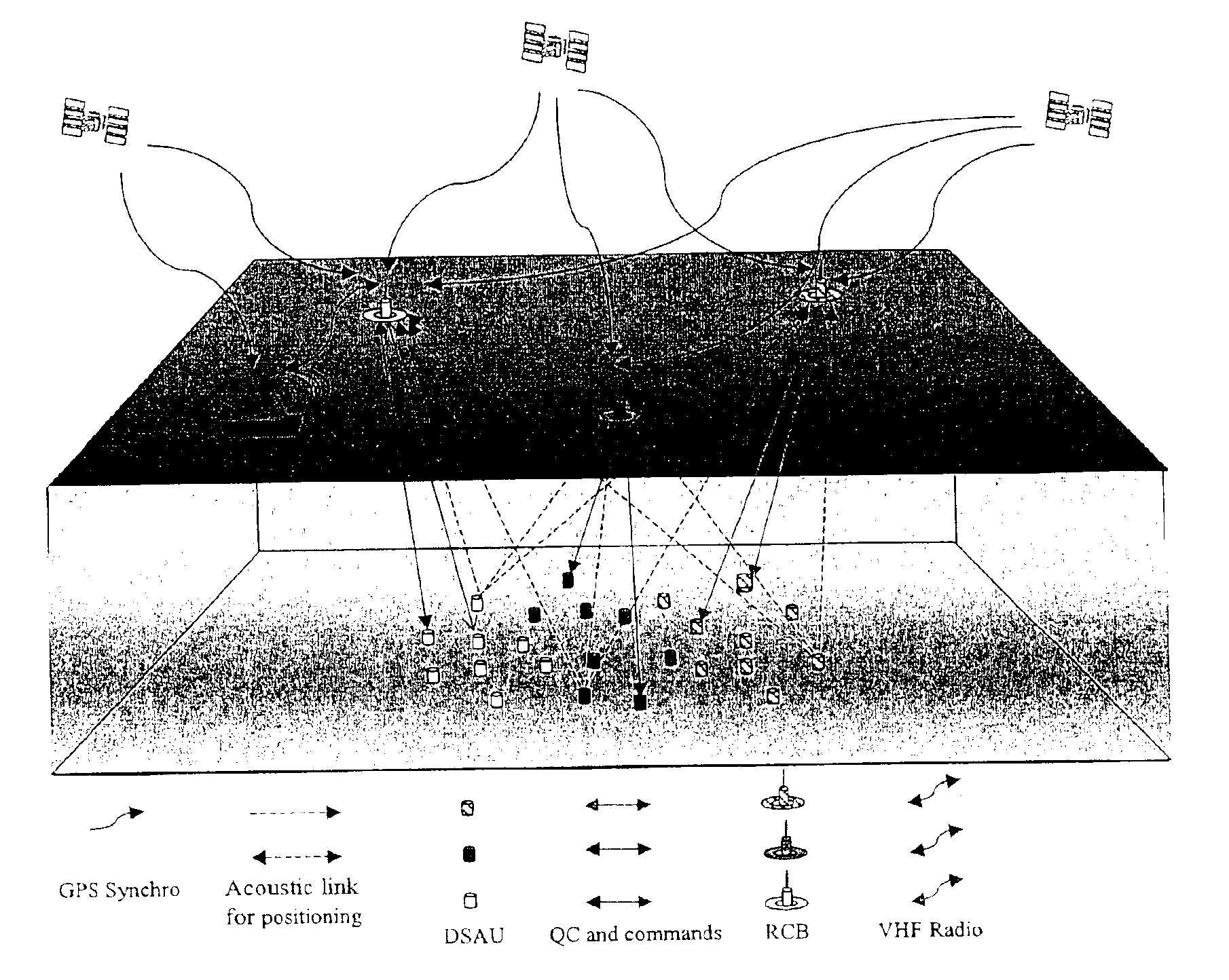
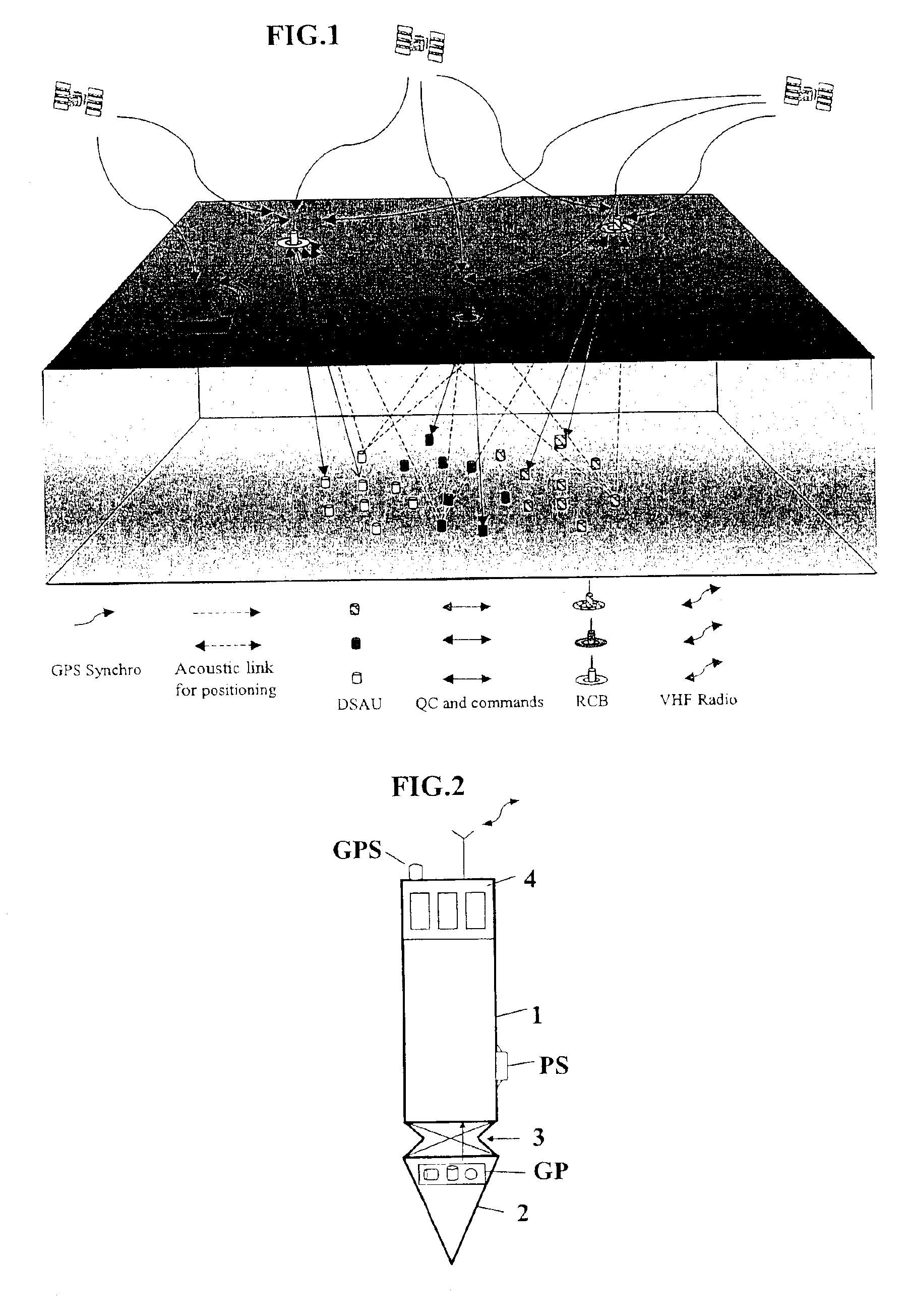
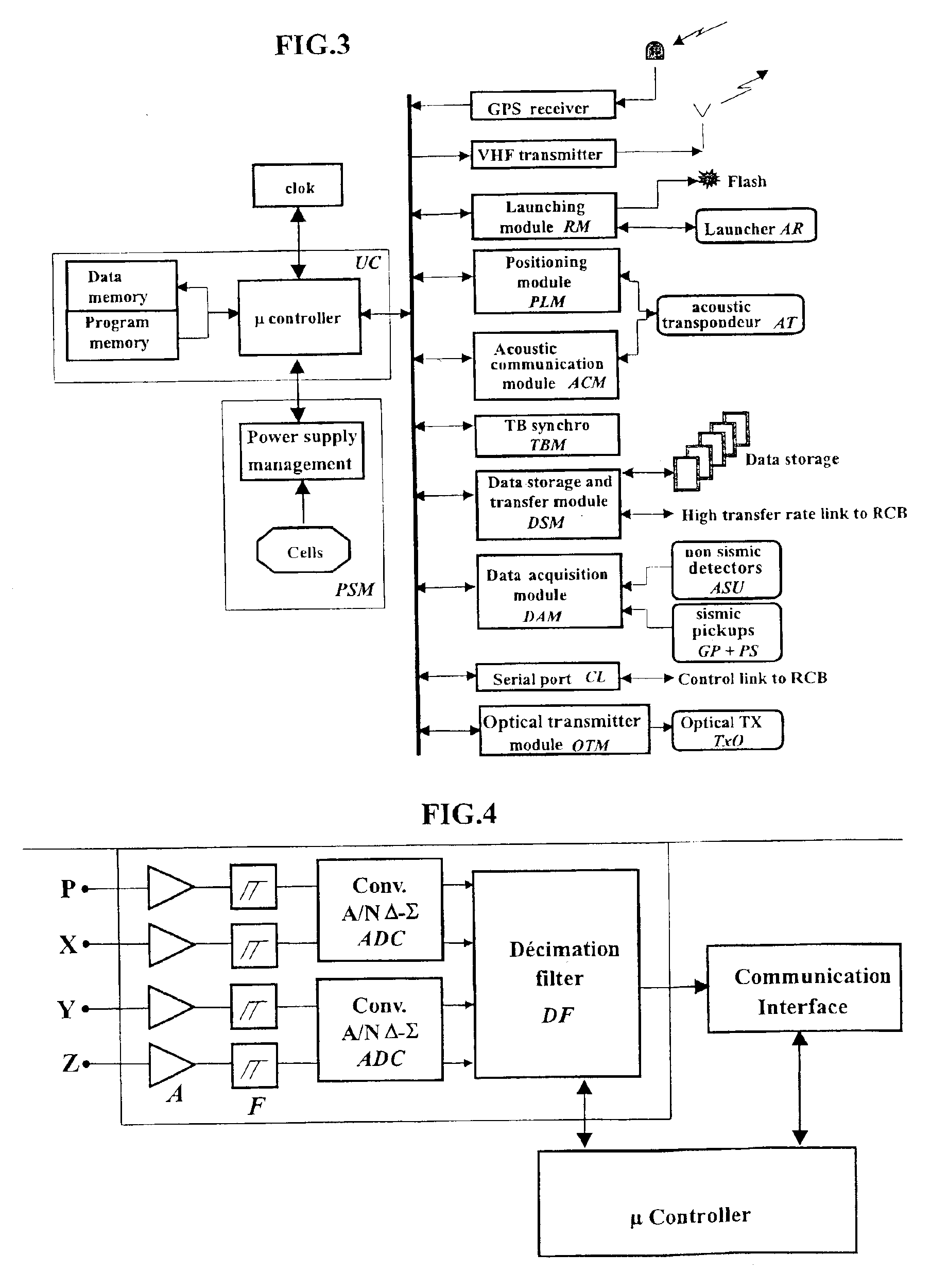
The invention is a system designed for acquisition of seismic data by means of acquisition stations set on water bottom of a water body. The system comprises acquisition stations (DSAU) combining a streamlined boom suited to penetrate the bottom and thus couple seismic receivers with the underlying formation, a sealed body for electronic data acquisition and communication modules. These acquisition stations (DSAU) are placed in the water and drop to the bottom under the effect of gravity. Relay buoys (RCB) are positioned at the surface, each with a GPS positioning module, a radio link with a central station (CCRU), on a ship for example, and modules providing acoustic communication with bottom acquisition stations (DSAU), which are used to determine the position of the stations in relation to the relay buoys and to exchange control data and seismic data (good running order data or possibly seismic traces acquired if the conditions lend themselves thereto) to provide seismic prospecting or monitoring of an underground formation.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Methods and systems for performing azimuthal simultaneous elastic inversion
ActiveUS20110222370A1Improve stabilityReduce and constrain solution spaceSeismic signal recordingSeismic signal processingImproved methodSeismic trace
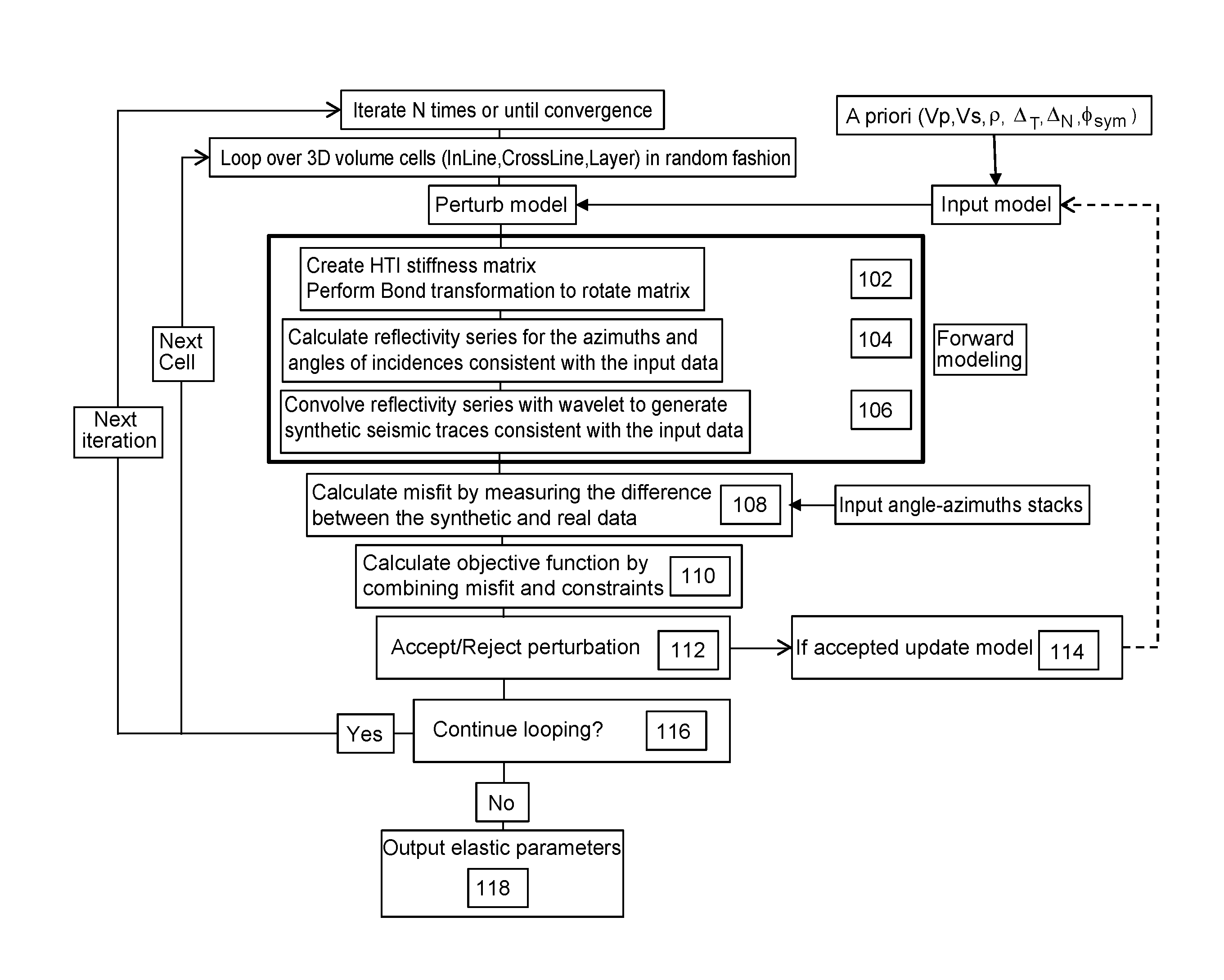
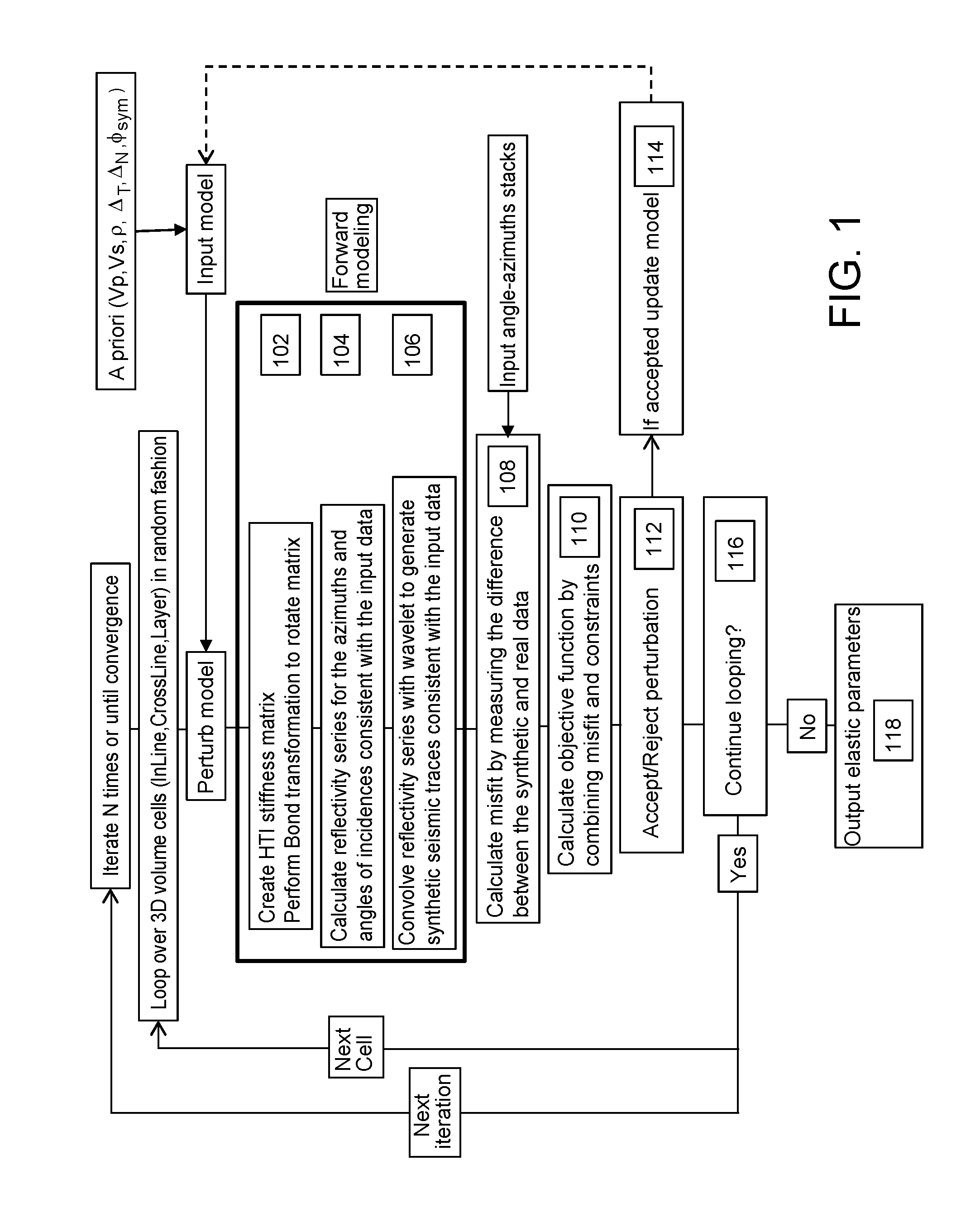
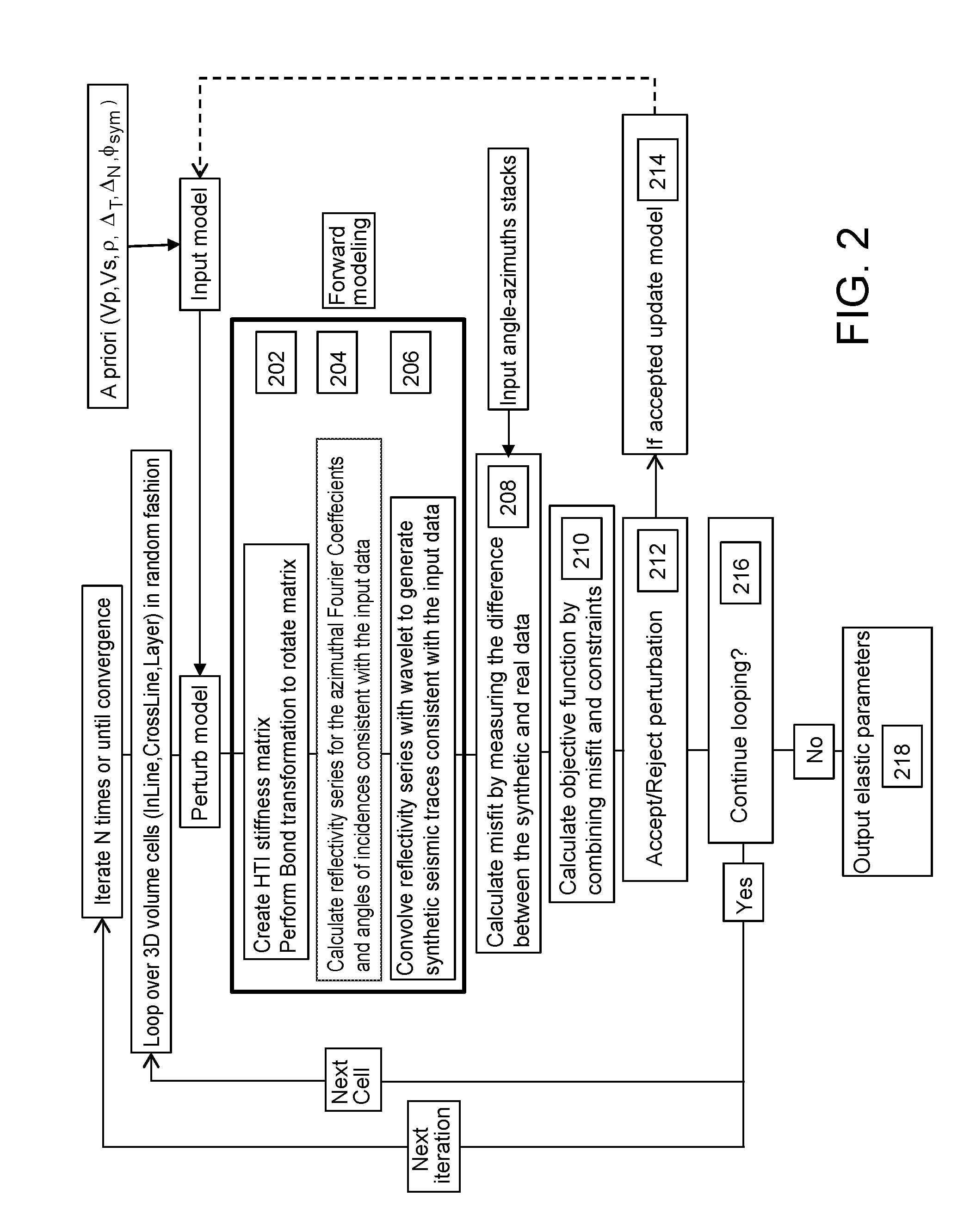
An improved method for analyzing seismic data to obtain elastic attributes is disclosed. In one embodiment, a reflectivity series is determined for at least one seismic trace of seismic data obtained for a subterranean formation, where the reflectivity series includes anisotropy properties of a formation. One or more synthetic seismic traces are obtained by convolving the reflectivity series with a source wavelet. The one or more synthetic seismic traces are inverted to obtain elastic parameters estimates. According to one aspect, the data inputs are angle-azimuth stacks. According to another aspect, the data inputs are azimuthal Fourier coefficients, un, vn.
Owner:CGG SERVICES U S
Method for identifying subsurface features from marine transient controlled source electromagnetic surveys
InactiveUS20060186887A1Water resource assessmentDetection using electromagnetic wavesControlled source electro-magneticProcess measurement
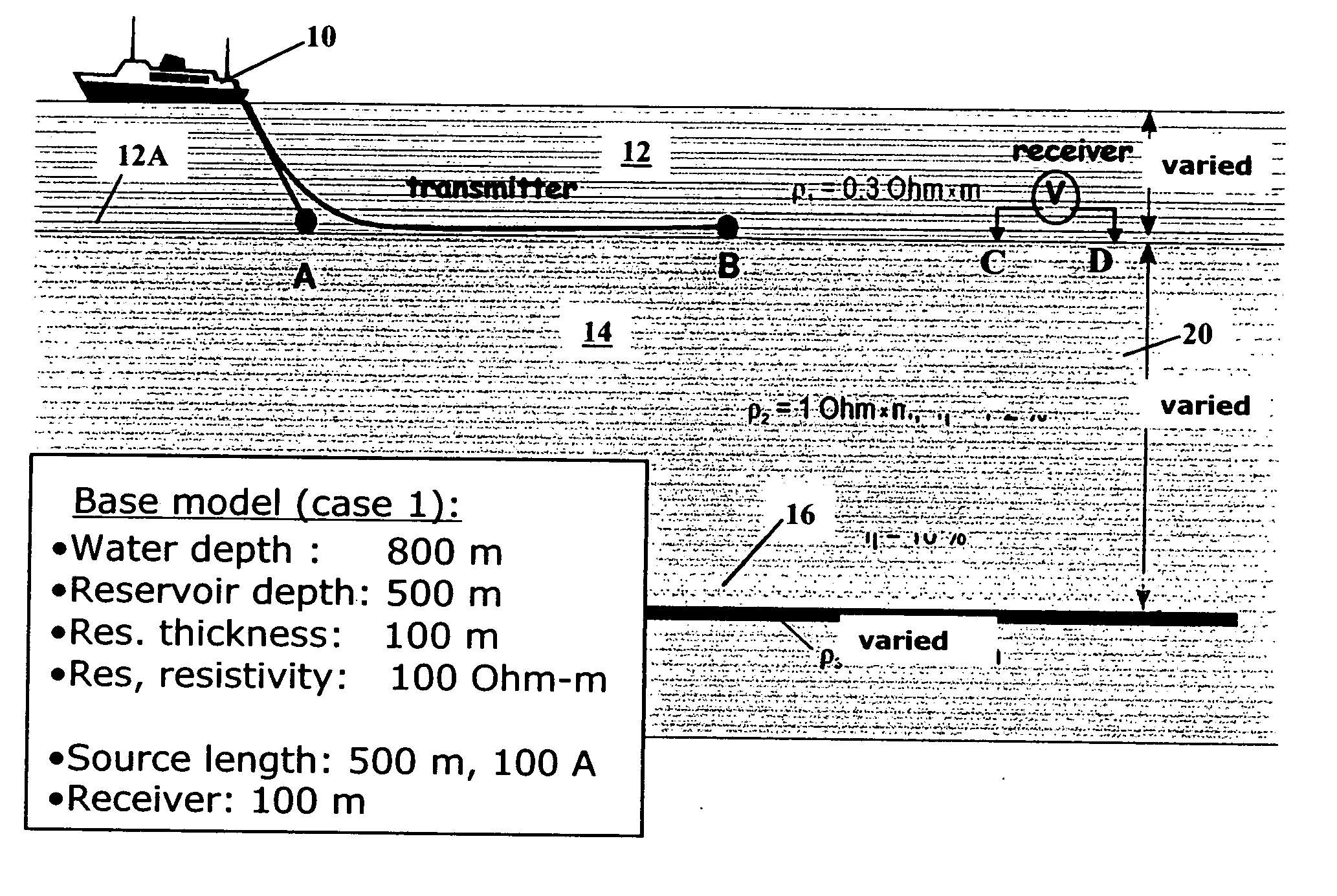
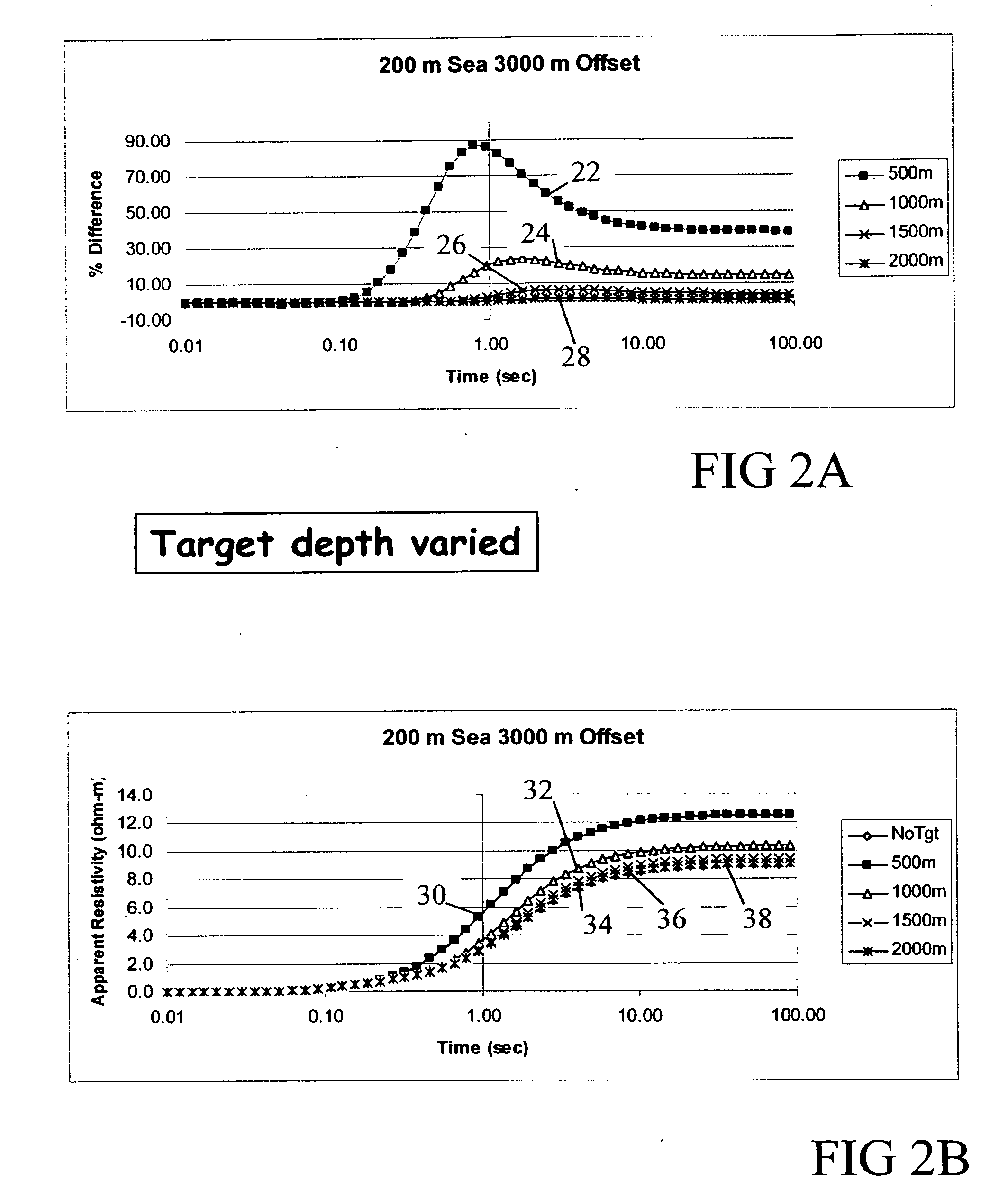
A method for identifying features in the Earth's subsurface below a body of water using transient controlled source electromagnetic measurements includes acquiring a plurality of transient controlled source electromagnetic measurements. Each measurement represents a different value of an acquisition parameter. Each measurement is indexed with respect to a time at which an electric measuring current source is switched. The plurality of measurements is processed in a seismic trace display format, in which each trace corresponds to the measurement acquired for a value of the acquisition parameter. A subsurface feature is identified from the processed measurements.
Owner:KJT ENTPR
Method for eliminating linear regular noise and multiple wave disturbance in self-adapting mode
InactiveCN101598809AEliminate interference wavesDoes not harm frequency componentsSeismic signal processingGraphicsData set
The invention relates to a method for eliminating linear regular noise of seismic prospecting and multiple wave disturbance in a self-adapting mode, aiming to provide seismic figures with high resolution for the exploration of oil fields. The method comprises the following steps: transforming seismic data sets in a field according to regular disturbance linear event virtual inclination; subtracting a seismic trace and a noise model trace to obtain a current signal value; determining the receiving probability of the noise by utilizing a probability density function and a threshold value; subtracting the separated noise from an original record to eliminate a regular interference wave; carrying out linear inverse transform on the seismic data to obtain a data set; carrying out linear inverse transform on the record with the regular interference wave being eliminated to obtain a seismic record; and carrying out separate frequency processing and noise suppressing processing. The invention dose not damage the frequency components of effective waves and has the advantages of fast operation speed, good effect for suppressing noise, suitability for pre-stack seismic data and post-stack seismic data, and the like.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Method and apparatus for seismic signal processing and exploration
InactiveUSRE38229E1Quickly seeSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsHydrocotyle bowlesioidesSeismic trace
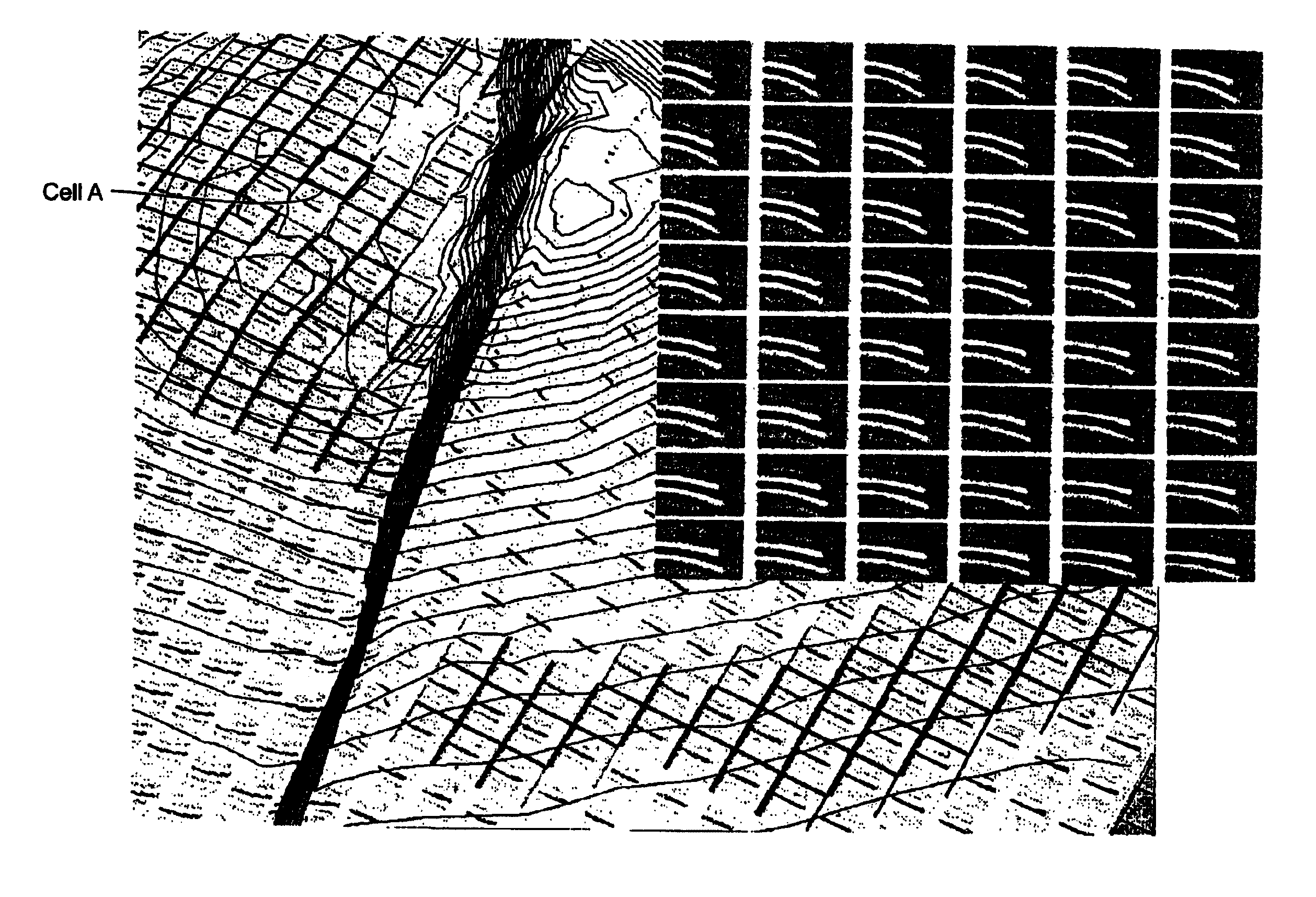
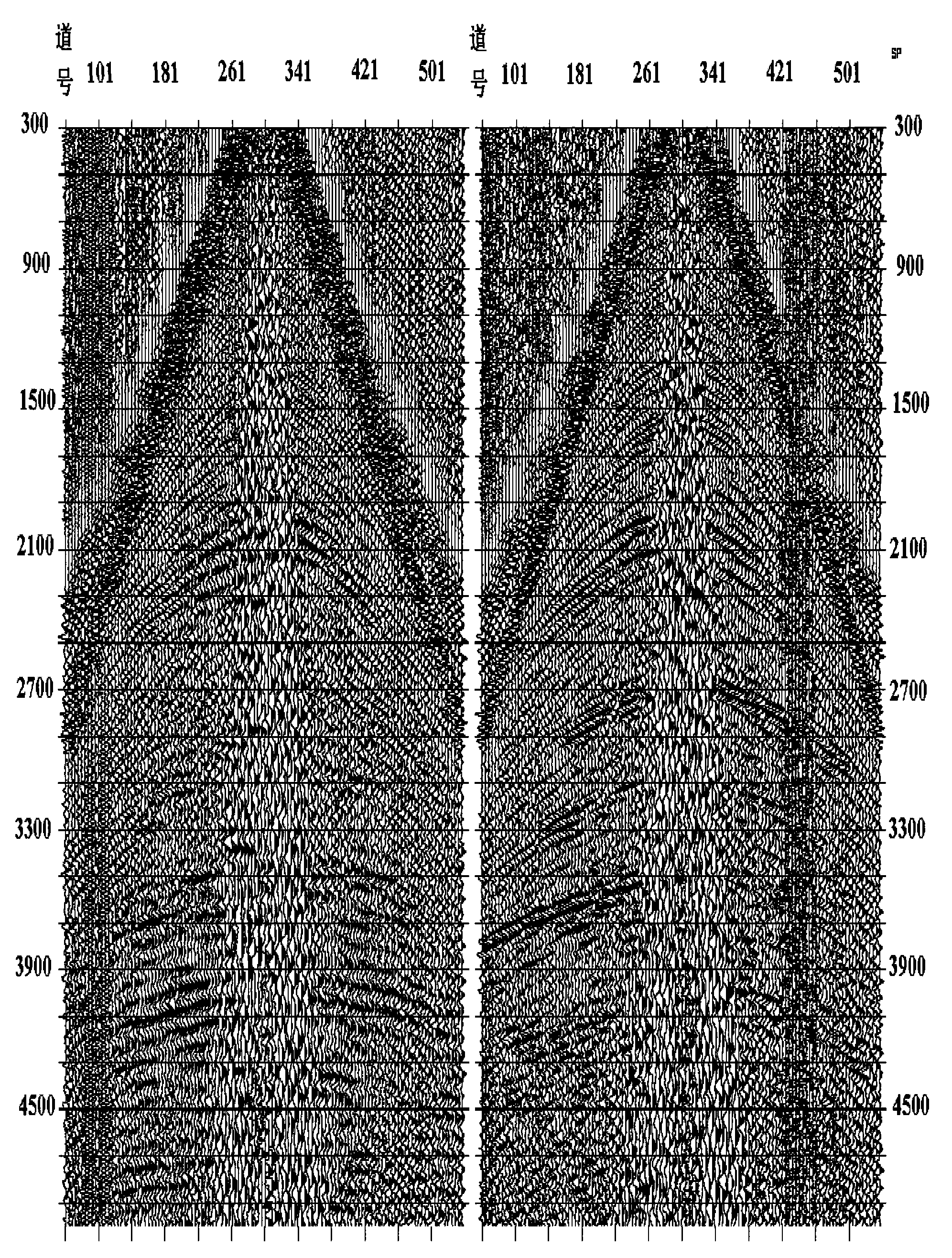
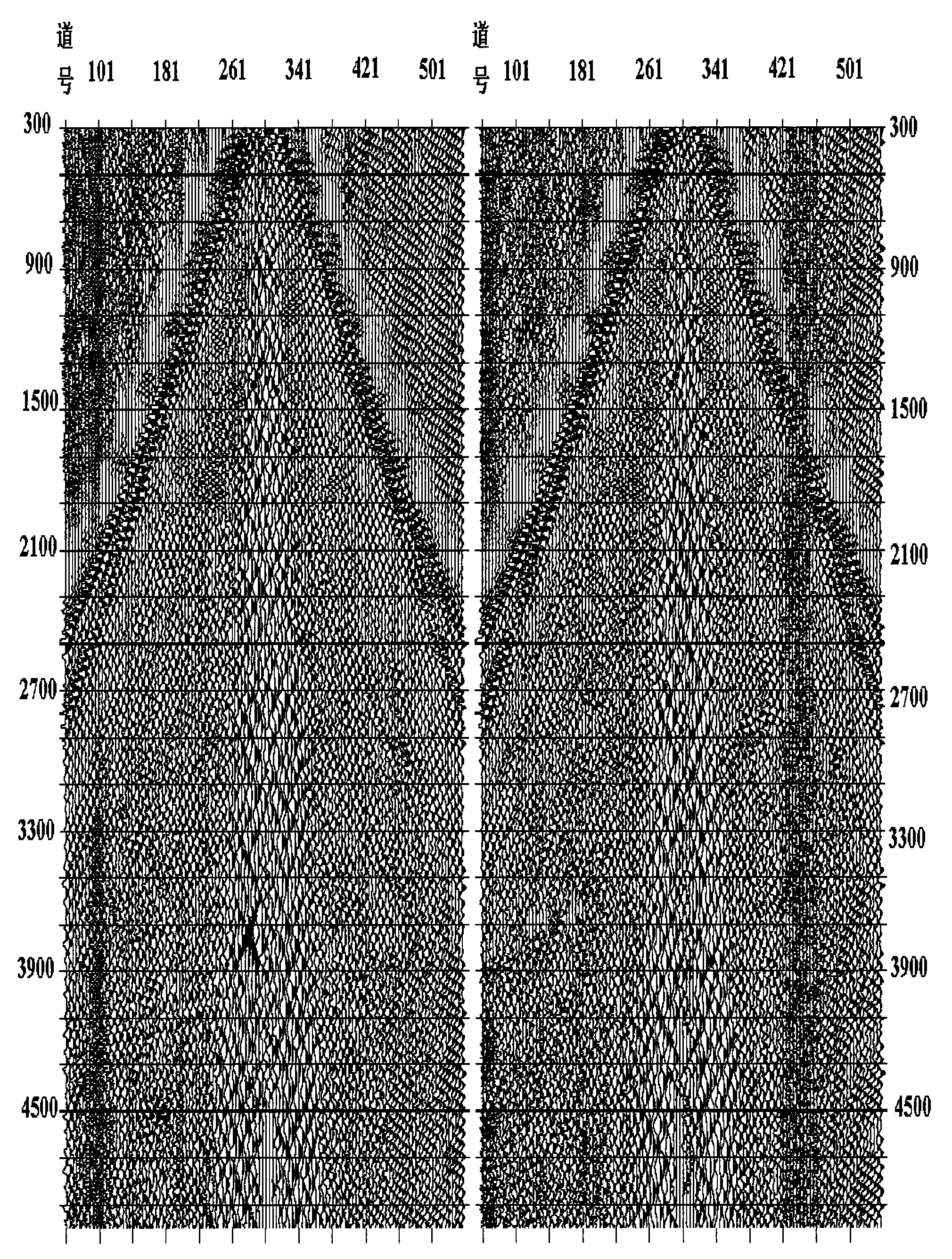
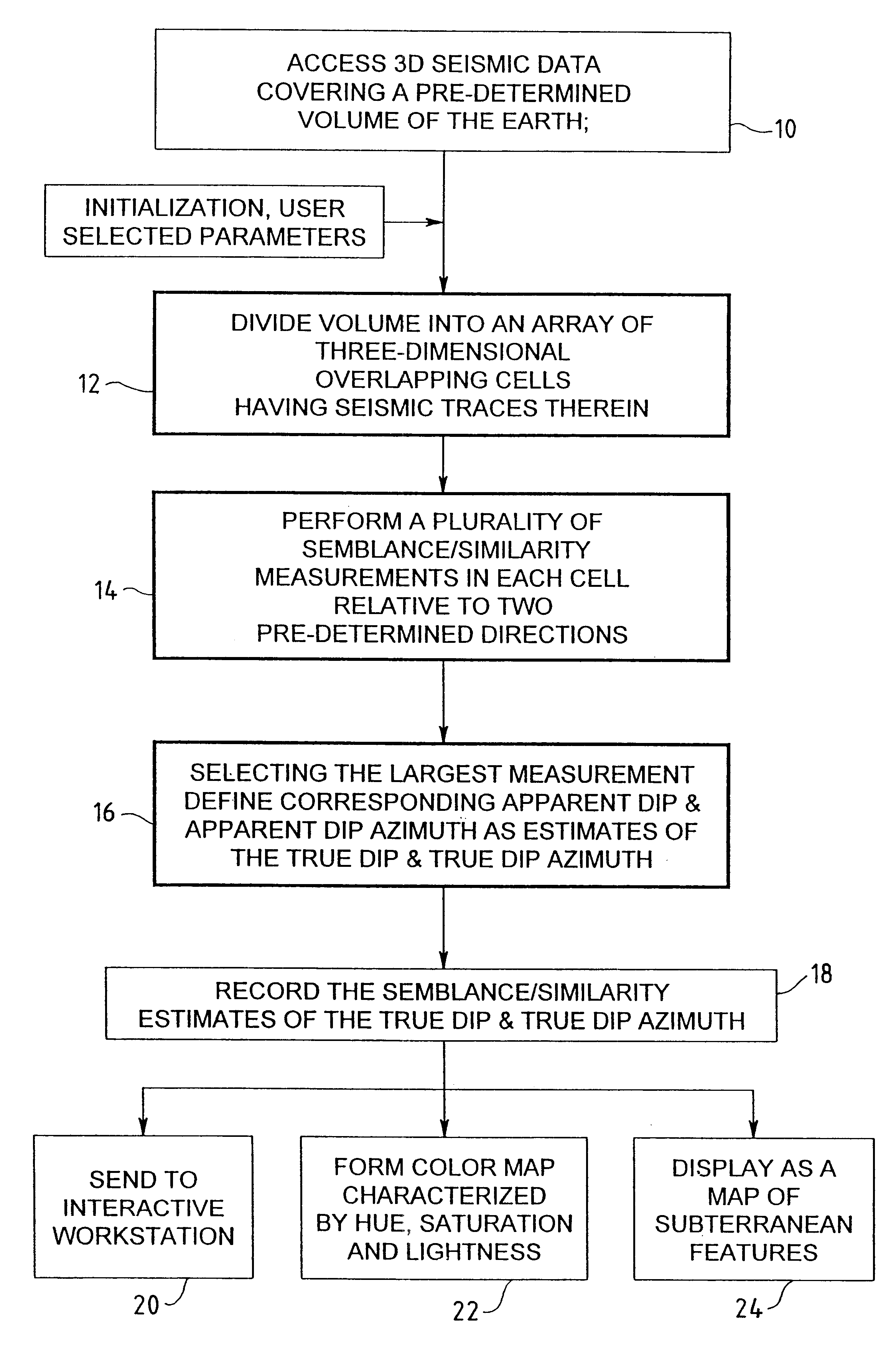
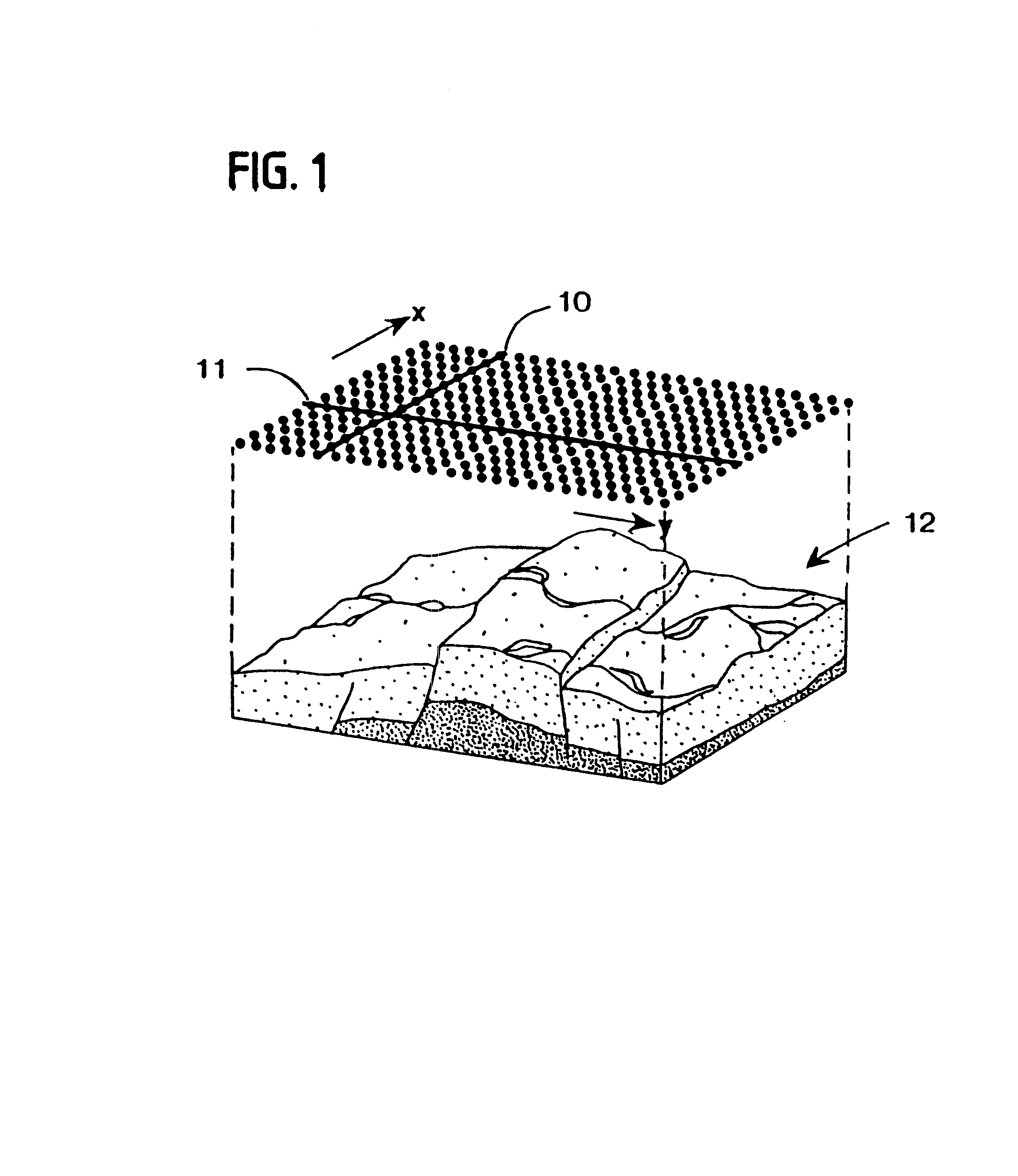
A method, a map and an article of manufacture for the exploration of hydrocarbons. In one embodiment of the invention, the method comprises the steps of: accessing 3D seismic data; dividing the data into an array of relatively small three-dimensional cells; determining in each cell the semblance / similarity, the dip and dip azimuth of the seismic traces contained therein; and displaying dip, dip azimuth and the semblance / similarity of each cell in the form a two-dimensional map. In one embodiment, semblance / similarity is a function of time, the number of seismic traces within the cell, and the apparent dip and apparent dip azimuth of the traces within the cell; the semblance / similarity of a cell is determined by making a plurality of measurements of the semblance / similarity of the traces within the cell and selecting the largest of the measurements. In addition, the apparent dip and apparent dip azimuth, corresponding to the largest measurement of semblance / similarity in the cell, are deemed to be estimates of the true dip and true dip azimuth of the traces therein. A color map, characterized by hue, saturation and lightness, is used to depict semblance / similarity, true dip azimuth and true dip of each cell; true dip azimuth is mapped onto the hue scale, true dip is mapped onto the saturation scale, and the largest measurement of semblance / similarity is mapped onto the lightness scale of the color map.
Owner:CORE LAB GLOBAL
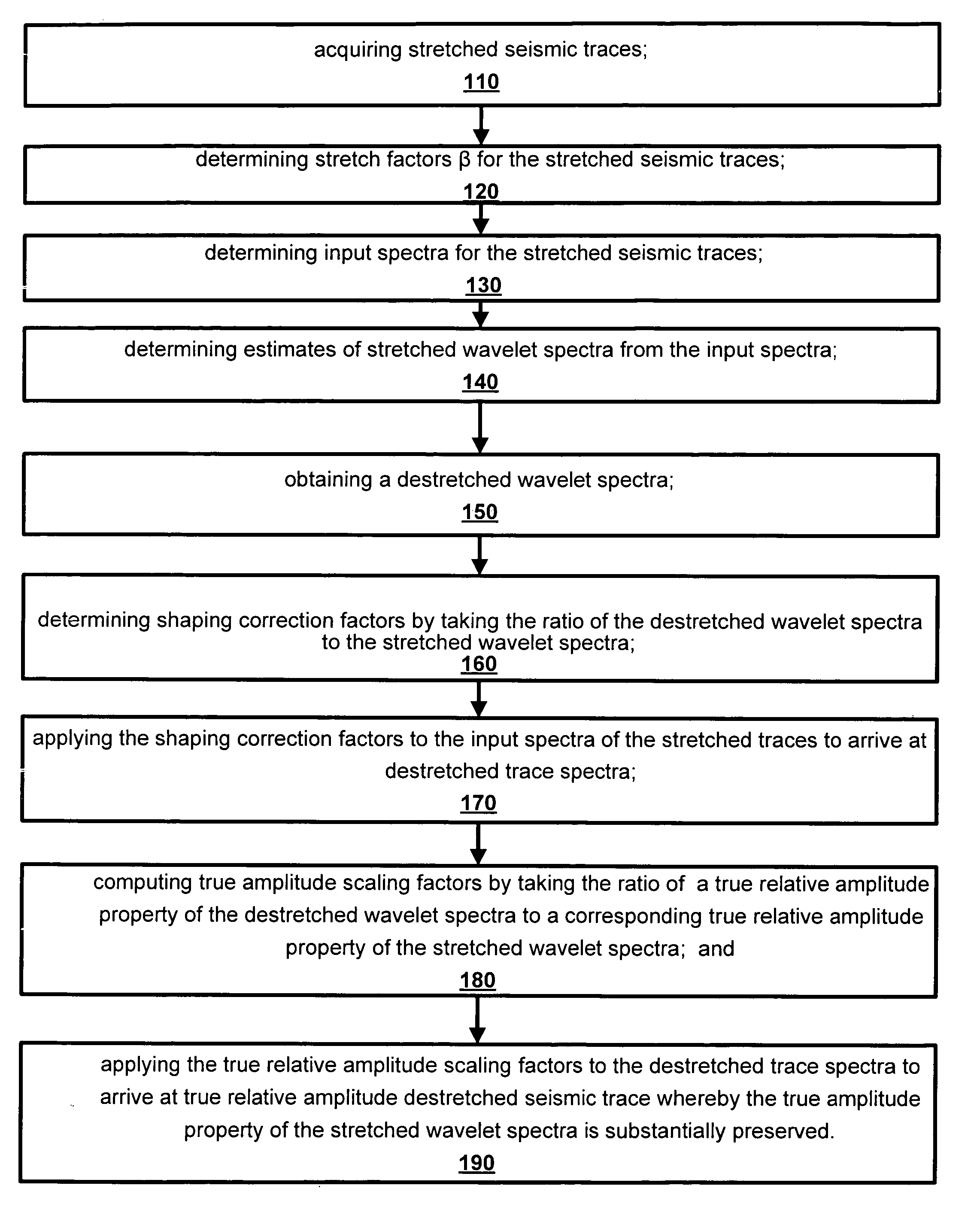
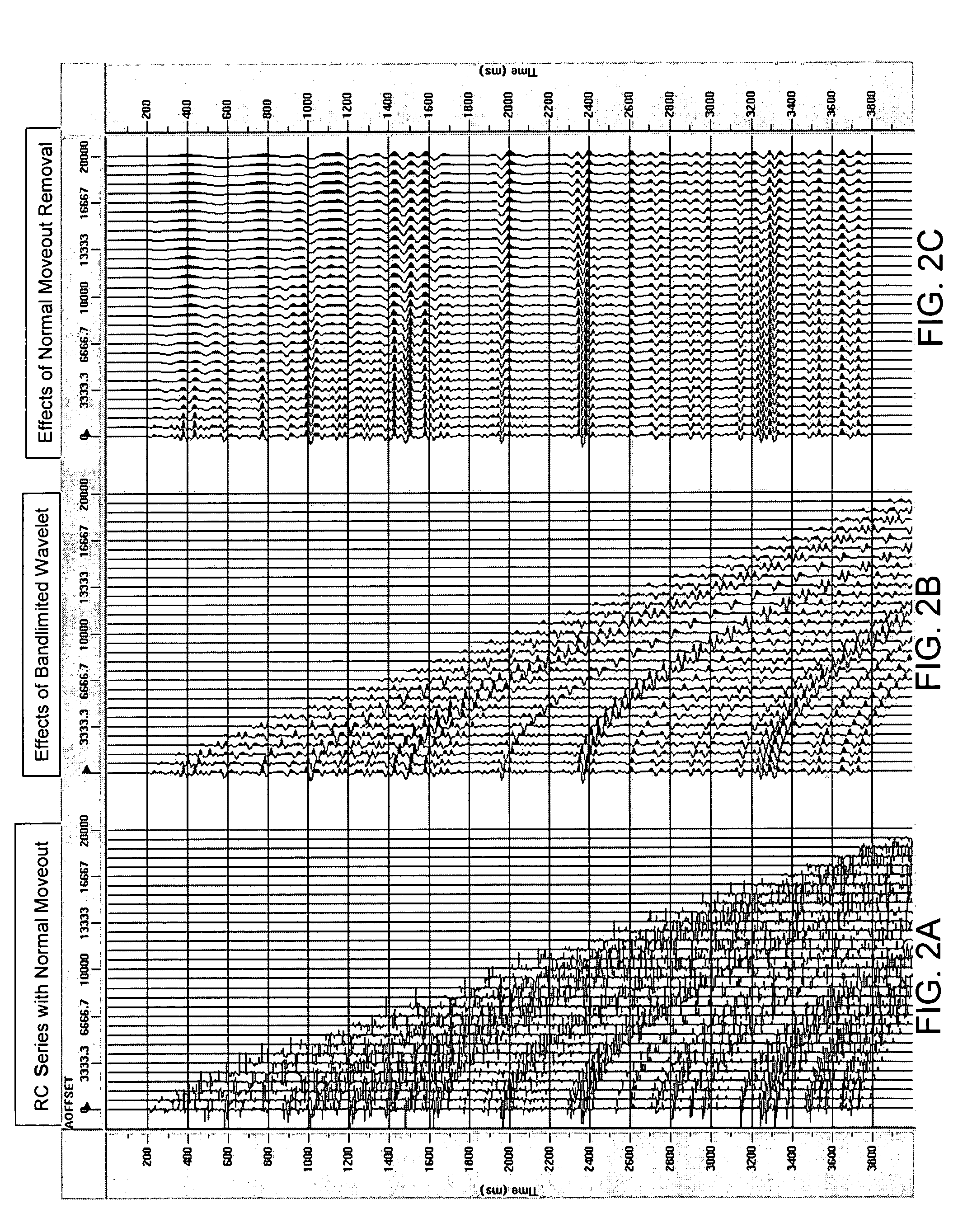
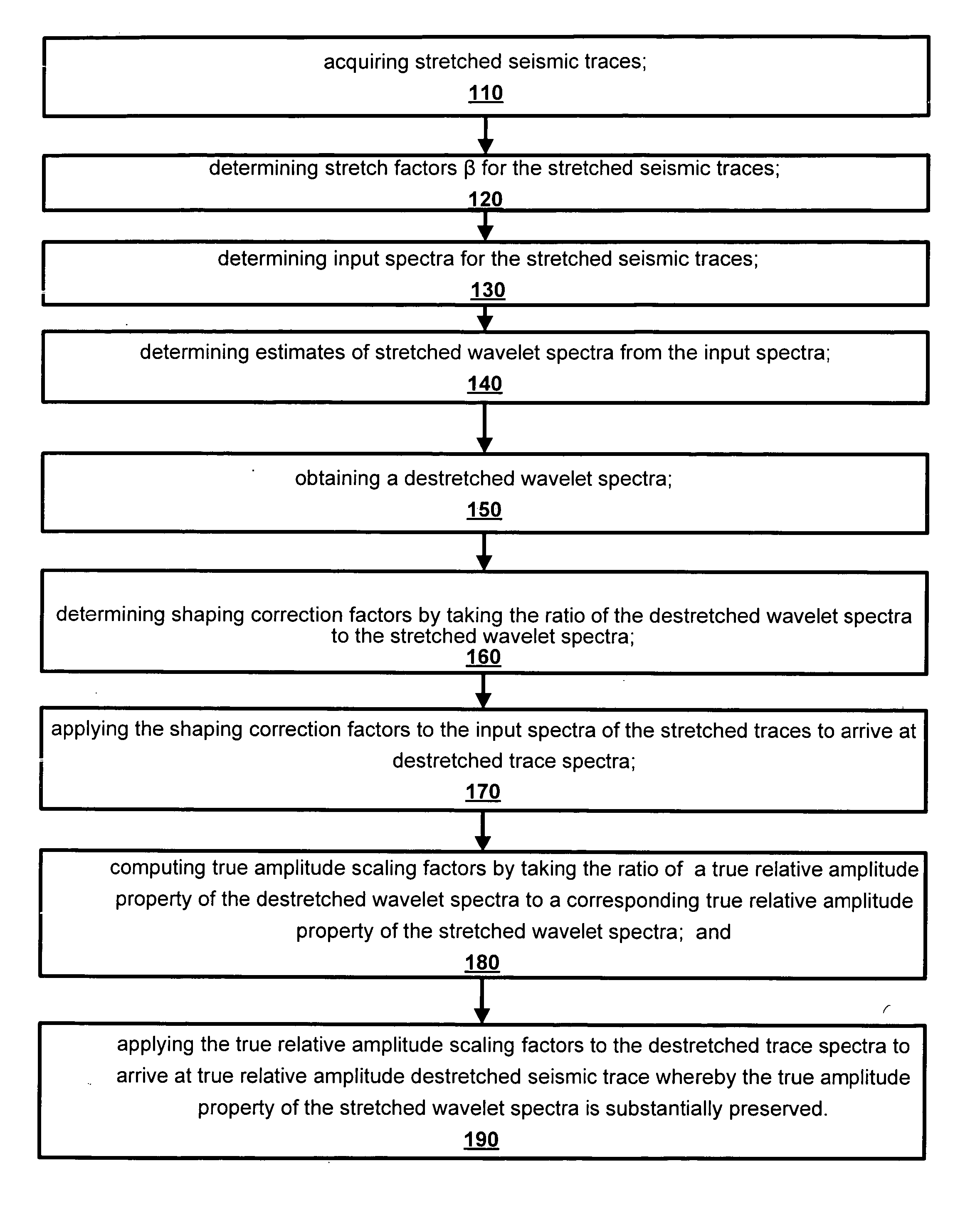
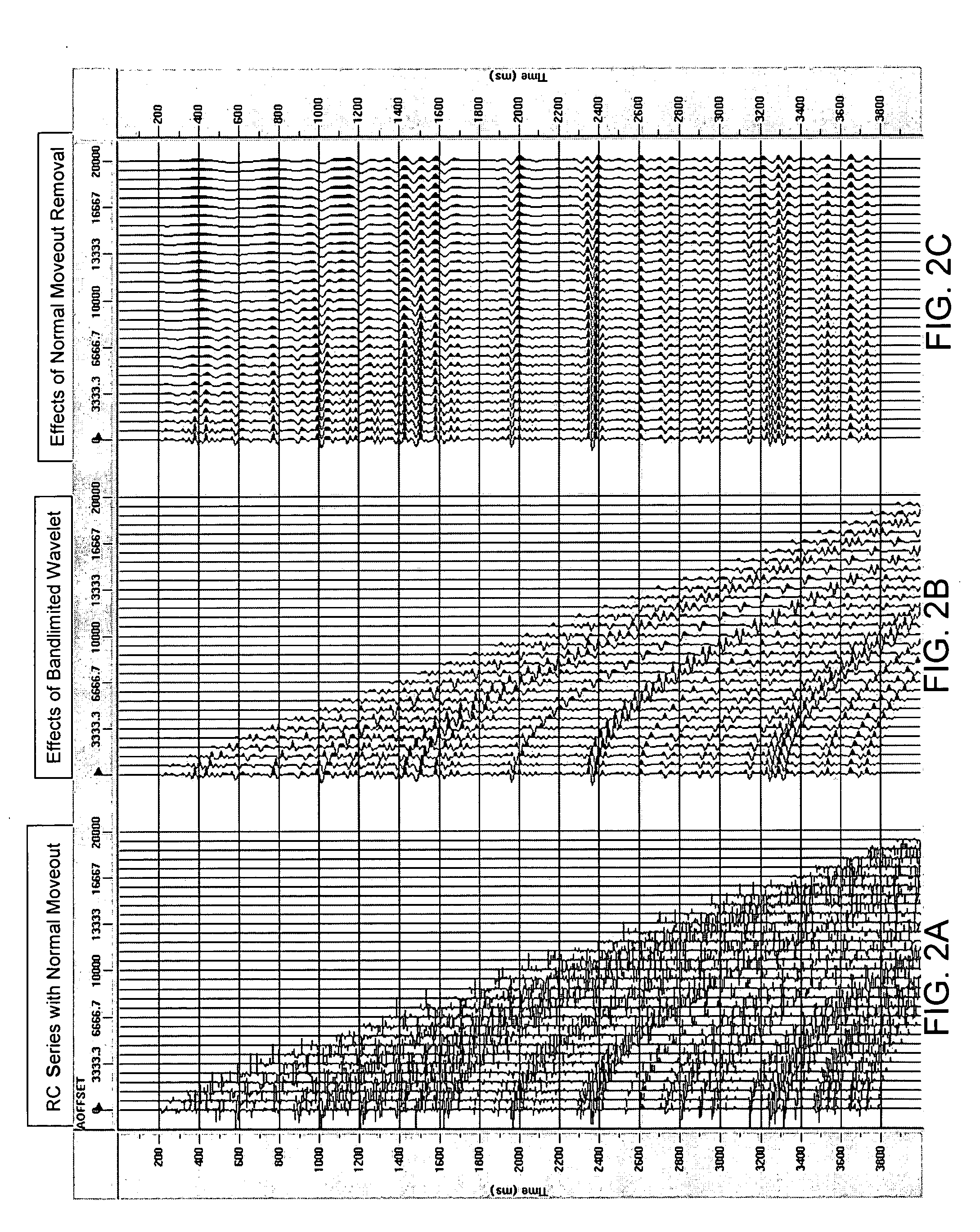
Method and apparatus for true relative amplitude correction of seismic data for normal moveout stretch effects
InactiveUS7230879B2Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsRelative magnitudeVibration amplitude
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for arriving at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces from stretched seismic traces. The method compensates for offset varying reflection interference effects due to normal moveout. Stretch factors β and also input spectra are determined for NMOR stretched seismic traces. Estimates are then made of stretched wavelet spectra from the input spectra. A destretched wavelet spectra is then obtained. Shaping correction factors are determined by taking the ratio of the destretched wavelet spectra to the stretched wavelet spectra and are applied to the input spectra of the stretched traces to arrive at a destretched trace spectra. True relative amplitude scaling factors are computed by taking the ratio of a true relative amplitude property of the destretched wavelet spectra to a corresponding true relative amplitude property of the stretched wavelet spectra. Finally, the true relative amplitude scaling factors are applied to the destretched trace spectra to arrive at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
3D prestack seismic data migration method
InactiveUS6311133B1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsTime domainSeismic trace
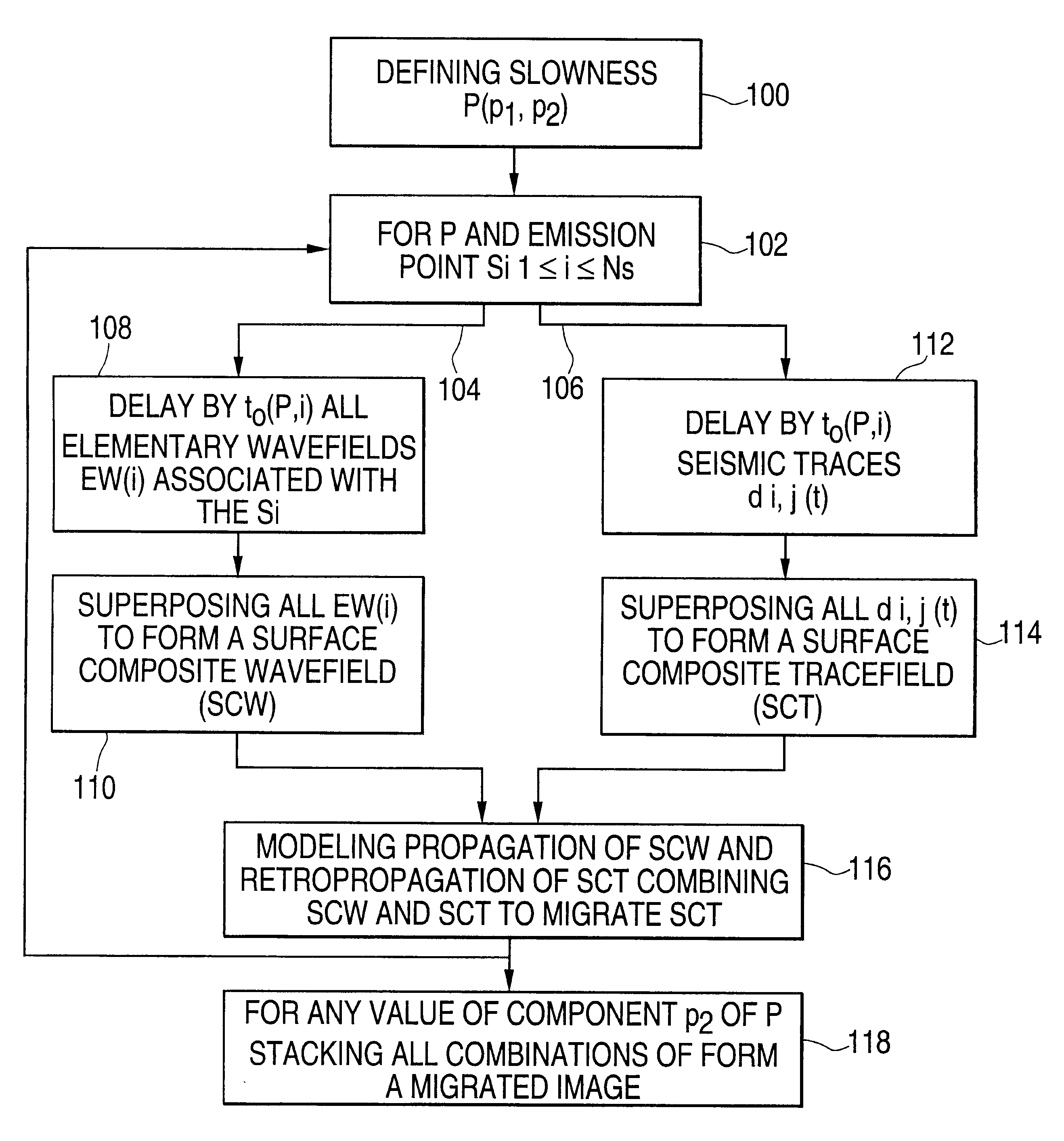
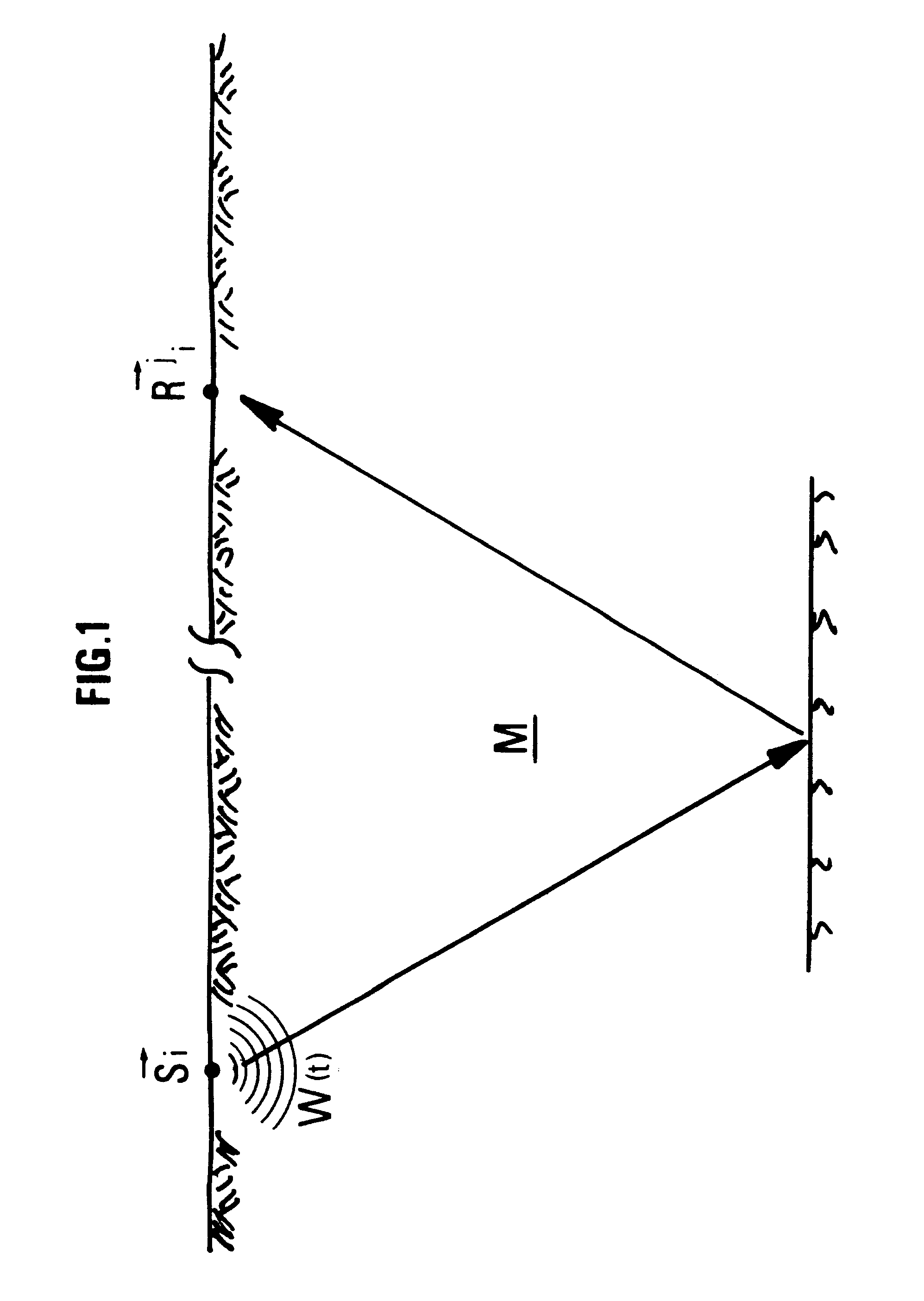
A prestack migration method allowing imaging of an underground zone, for a given velocity model of arbitrary complexity. By means of conventional wave propagation and retropropagation modelling tools, the method allows to obtain elementary migrated images associated with the values assumed by a parameter and the sum of the images obtained for the different values of the parameter (post-migration stacking), in the depth domain as well as in the time domain. This migration is obtained at an attractive price (calculation cost) because it is independent of the volume of the results calculated and of the number of seismic traces recorded. Only the volume of the zone in which the waves are propagated, the complexity of the events to be imaged and the desired accuracy have an effect on the calculation cost. Volume images are thus obtained by taking account of all the seismic traces. It is thus possible to implement a plane wave migration procedure in cases where acquisition does not allow synthesis of the subsurface response to a plane wave excitation, a response required from the outset in conventional plane wave migration algorithms. The method can be applied for imaging of geologic interfaces or heterogeneities of a part of an underground zone.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE
Seismic data interpolation system
InactiveUS7027929B2Computation timeReduce random noiseSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsReal arithmeticData set
Owner:DIVESTCO
Device and method for continuous data acquisition
InactiveUS8619497B1Seismic data acquisitionSeismology for water-covered areasSeismic traceExcitation signal
Method for generating an excitation signal for a first vibratory seismic source so that the first vibratory seismic source is driven with no listening time. The method includes a step of determining a first target spectrum for the first vibratory seismic source; a step of setting a first group of constraints for the first vibratory seismic source; and a step of generating a first excitation signal for the first vibratory seismic source based on the first group of constraints and the first target spectrum. The first seismic traces recorded with plural receivers can be identified when the first vibratory seismic source is driven with no listening time, based on the first excitation signal.
Owner:CGGVERITAS SERVICES
Visualization method for the analysis of prestack and poststack seismic data
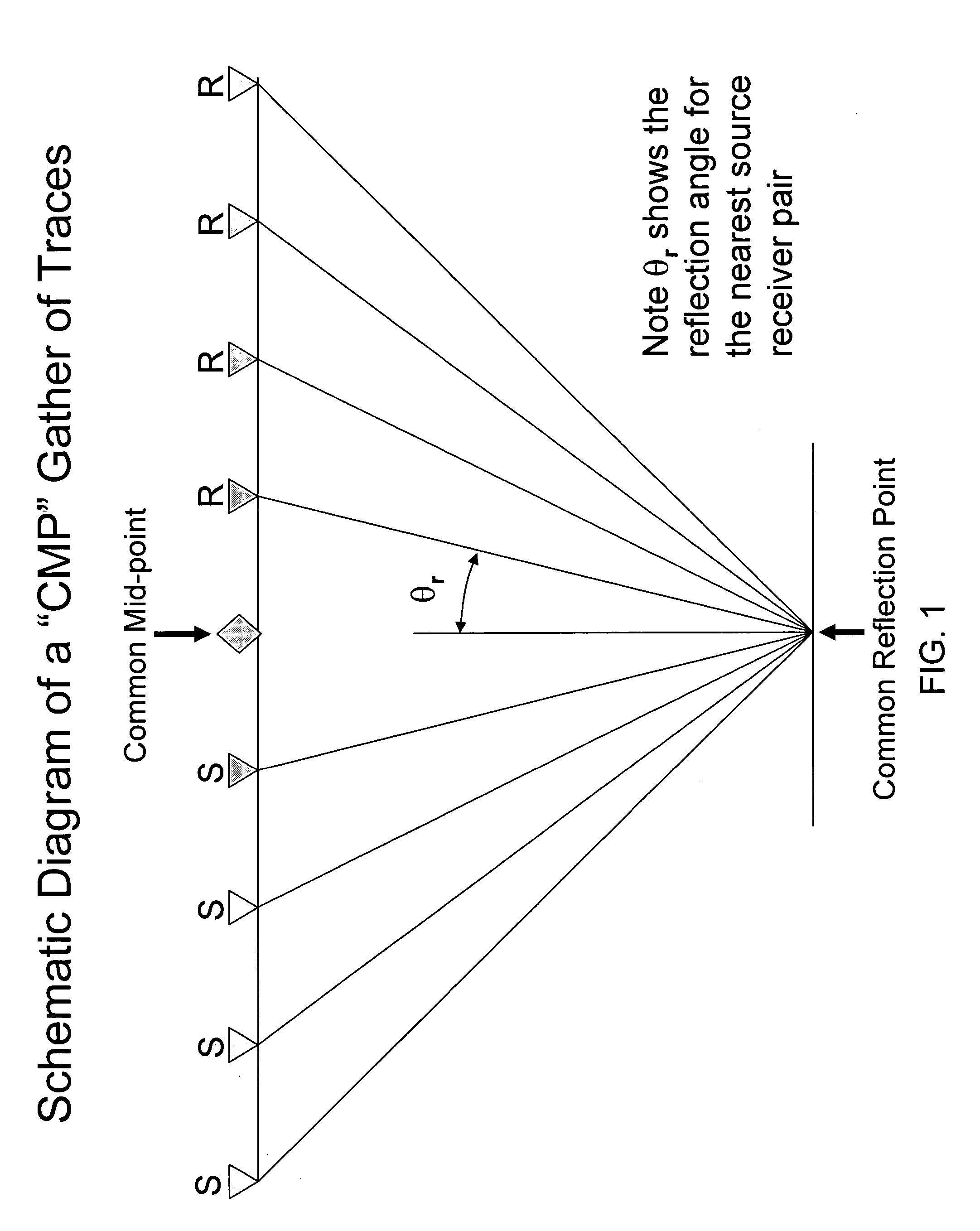
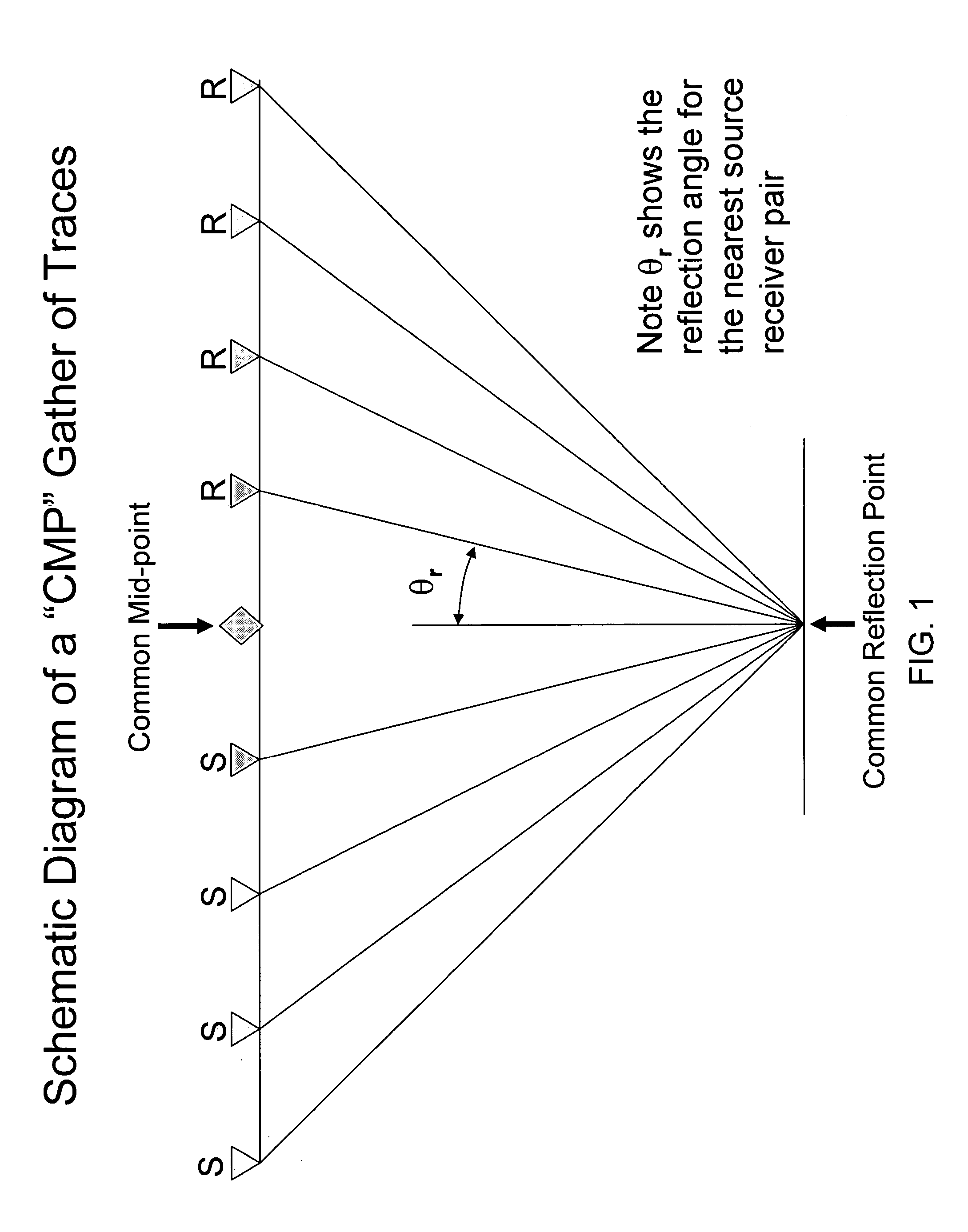
InactiveUS6989841B2Weighing apparatus using counterbalance2D-image generationDisplay deviceFinite time
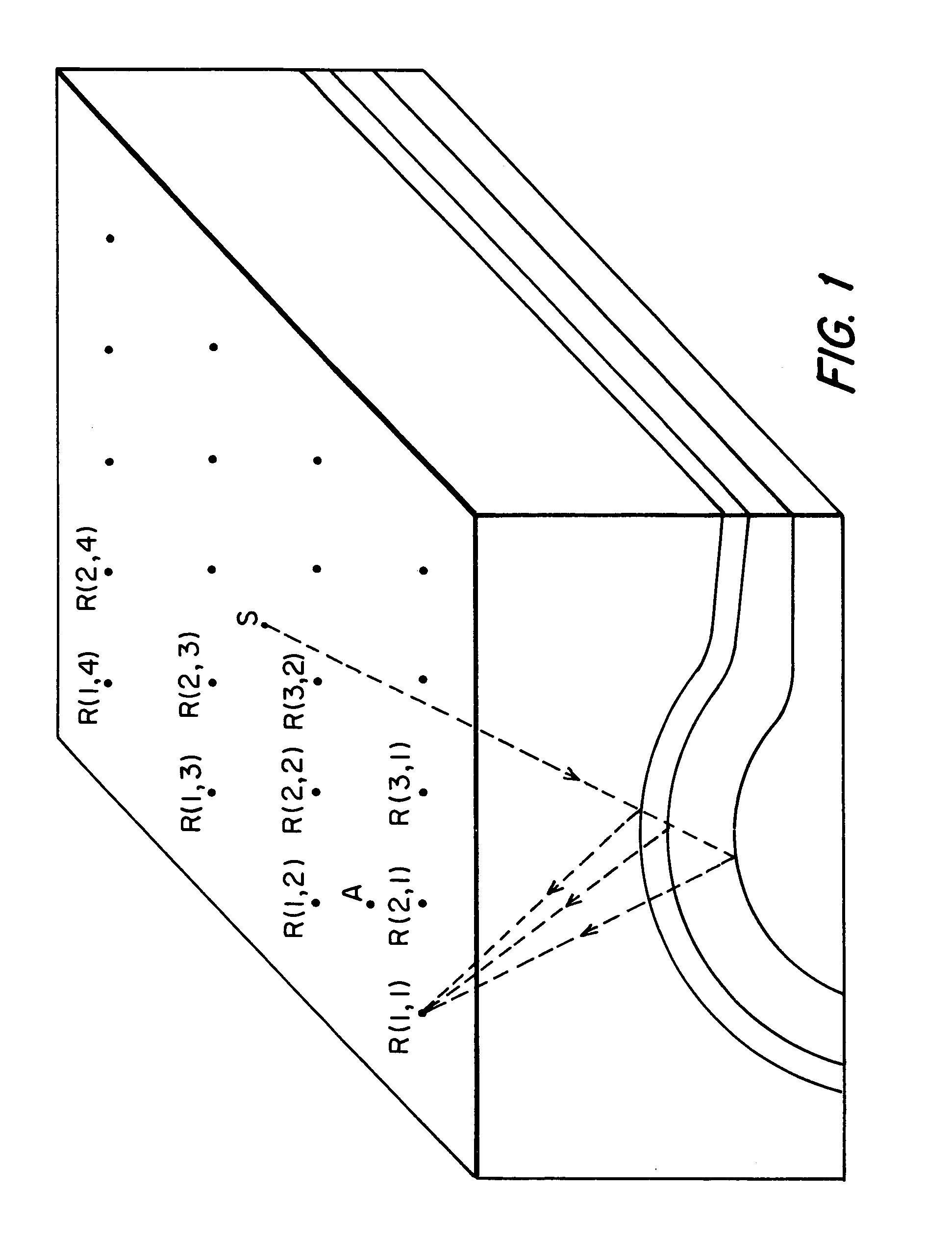
A method for presenting seismic data in a multidimensional visualization. Specifically, in the visualization technique of the current invention, seismic data is displayed in a multidimensional plan view utilizing at least four dimensions associated with the seismic data, such as for example, x, y, time / depth and offset. In the method of the invention, a plurality of time or depth windows are defined along a reflector or any other time or depth surface of interest on the prestack data as presented in standard CMP displays. In one embodiment of the invention, for each CMP gather, a window is defined around the data representing the reflector of interest. Passing through each window are individual seismic traces. The window, being defined on the seismic display, is associated with a finite time / depth segment and will contain several offsets. In addition, since each CMP gather has a constant x and y coordinate, the window is associated with specific spatial coordinates. These spatial coordinates are used to plot the window on an x-y plan view. Each window represents a segment of the seismic data associated with a reflector or other time / depth window. The data within each window can be analyzed to determine such things as, for example, the accuracy of the particular velocity model selected for data processing methods, such a migration. Furthermore, as multiple windows are plotted on the plan view, trends in the data become more prevalent to an observer. The resulting multidimensional plan view thereby permits presentation of the data utilizing at least four dimensions of the data. In another embodiment, additional information can be extracted from the multidimensional plan view by overlaying this plan view on additional representations of the data, such as for example, the underlying seismic structure. In addition, the visualization techniques could be used on poststack data to visualize several stacked traces around a point of interest.
Owner:FAIRFIELD INDUSTRIES INC
Model constraint based impedance inversion method and model constraint based impedance inversion system
ActiveCN103293551ARestoring low frequency componentsSeismic signal processingAcoustic waveSeismic trace
The invention provides a model constraint based impedance inversion method and a model constraint based impedance inversion system. The model constraint based impedance inversion method includes: acquiring log data, seismic data and acquisition matrixes of a current stratum; extracting seismic interpretation data from the seismic data; building an initial impedance model according to the log data and the seismic interpretation data; estimating seismic wavelets according to the log data and the seismic data; confirming objective function according to relationship between acoustic wave impedance and reflectance and sampling relationship when seismic traces are missing; confirming impedance sections or impedance objects of the current stratum according to the initial impedance model, estimated seismic wavelets and the objective function; and comprehensively interpreting the impedance sections and the impedance objects to acquire reservoir prediction results of the current stratum. Through model regularization, seismic data interpolation and seismic wave impedance inversion are combined organically, so that the seismic data interpolation and the seismic wave impedance inversion can be realized simultaneously.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Systems and methods of hydrocarbon detection using wavelet energy absorption analysis
InactiveUS20050043892A1Electric/magnetic detection for well-loggingSeismic signal processingData setEnergy absorption
Disclosed herein are systems and methods of hydrocarbon detection based on wavelet energy absorption analysis. One disclosed hydrocarbon detection method embodiment comprises: a) obtaining seismic trace data for a region of interest; and b) processing the seismic trace data to determine at least one wavelet energy absorption factor as a function of position within the region of interest. Another disclosed hydrocarbon detection method embodiment comprises: a) receiving from a user an indication of a region of interest in a seismic data set; and b) generating a display of wavelet energy absorption anomalies within the region of interest. One of the disclosed system embodiments comprises a memory and a processor. In this system embodiment, the memory stores hydrocarbon detection software that, when executed by the processor, configures the processor to determine at least one wavelet energy absorption factor from seismic trace data.
Owner:APEX SPECTRAL TECH
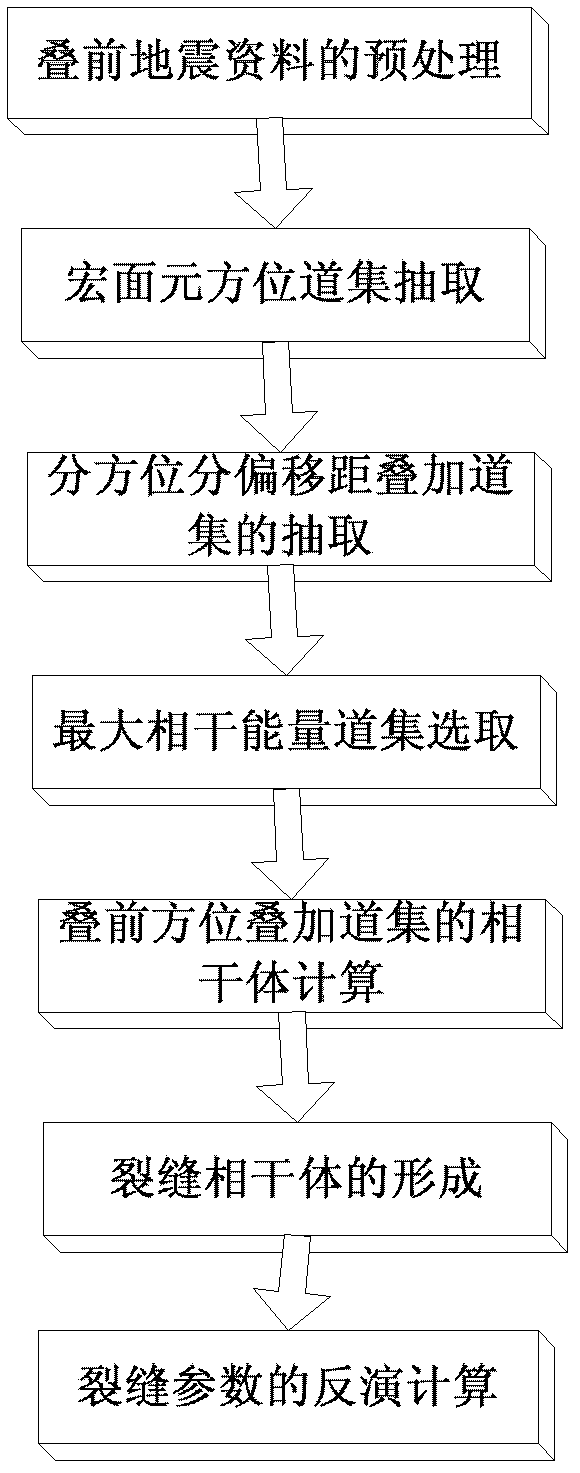
Crack detection method based on prestack coherence
The invention provides a crack detection method based on prestack coherence, which belongs to the field of oil-gas field exploration. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, processing actual prestack seismic data to obtain a prestack seismic trace gather subjected to dynamic correction; secondly, stacking separated directions and separated offset distances through utilizing the prestack direction common midpoint seismic trace gather, and obtaining separated directions and separated offset distances stacking trace gather; and carrying out covariance matrix-based coherency cube calculation on the separated directions and separated offset distances stacking trace gather obtained through stacking to obtain a crack coherency cube, carrying out crack parameter inversion calculation on the obtained crack coherency cube, and further obtaining a final crack development direction and development strength. According to the crack detection method based on prestack coherence, a coherence algorithm is introduced in the prestack seismic trace gather for the first time, and a method for recognizing faultage in a stratum with the thickness being smaller than a seismic wavelength is provided, so that the breakage or the crack in three-dimensional seismic data can be more distinct, clear and visual.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for quantificationally predicting sandstone reservoir fluid saturation by combining well and seism
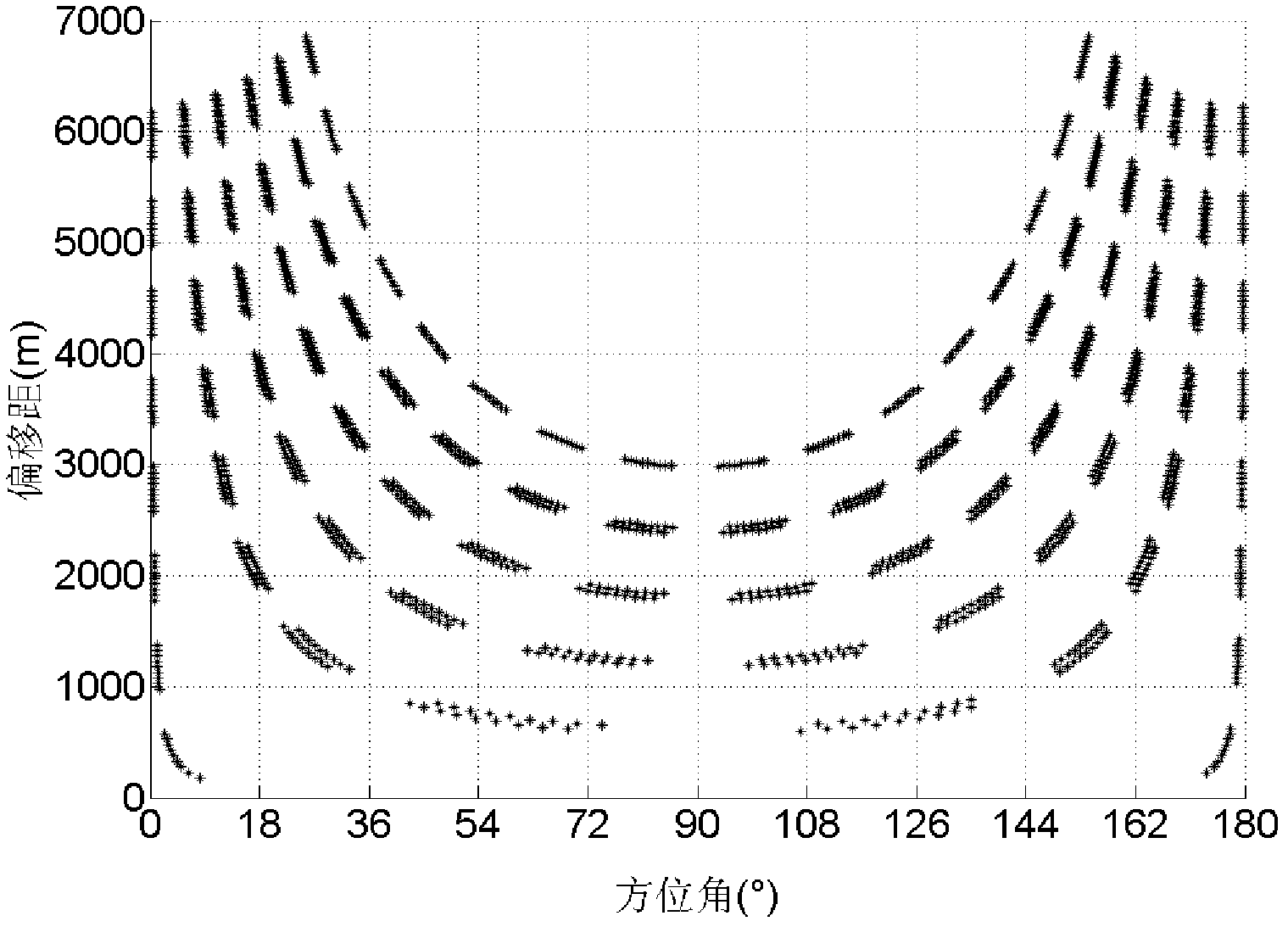
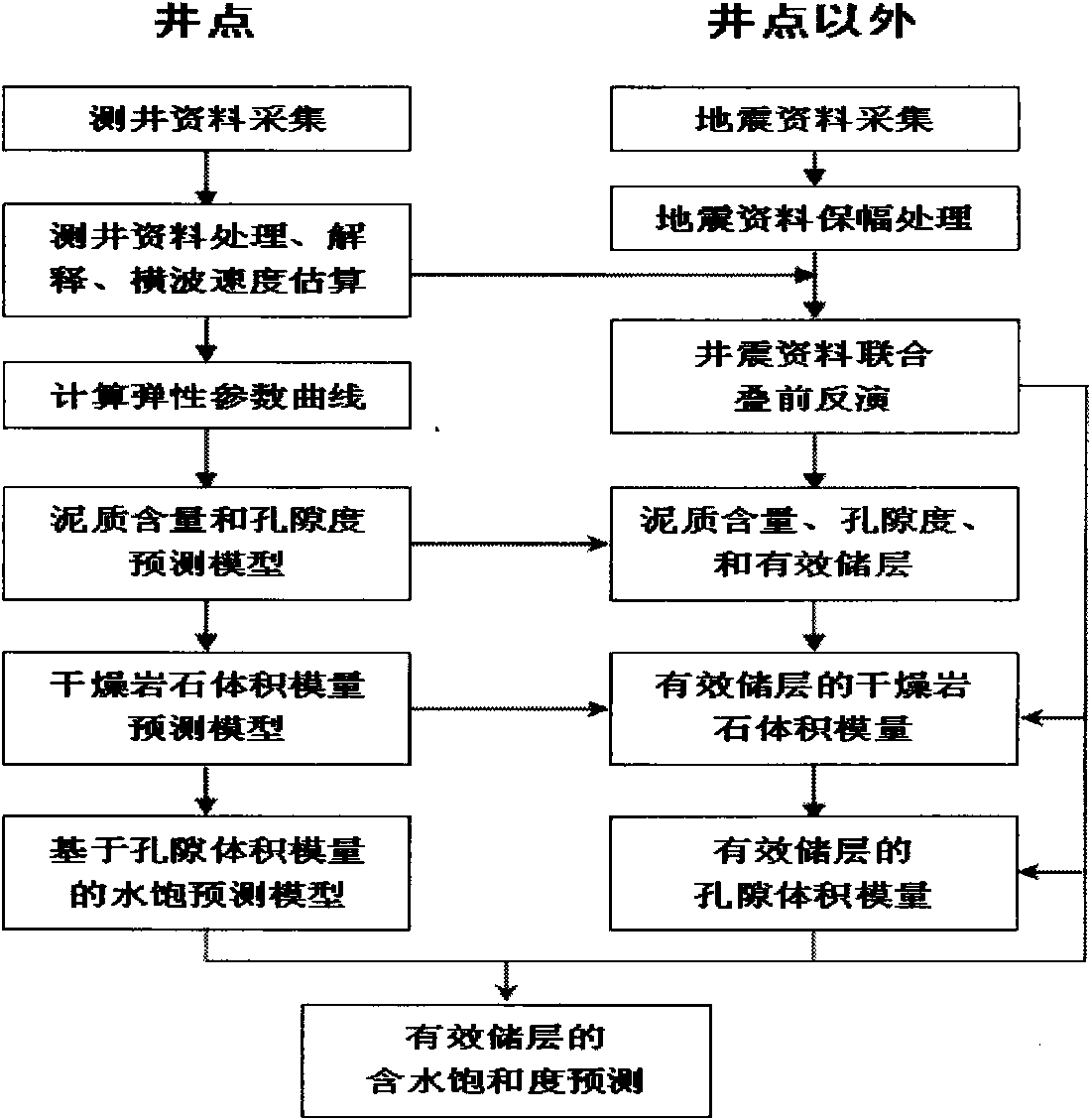
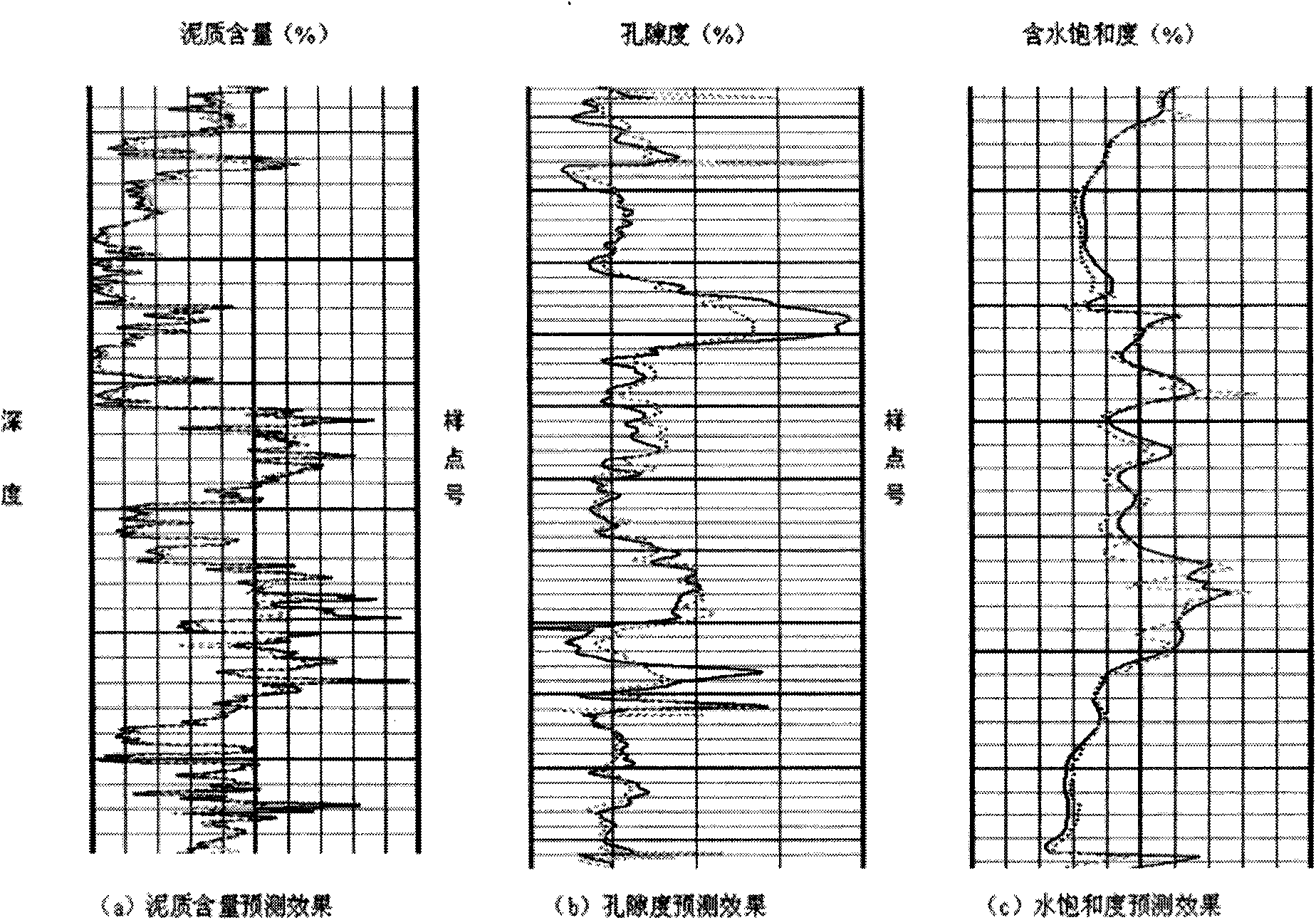
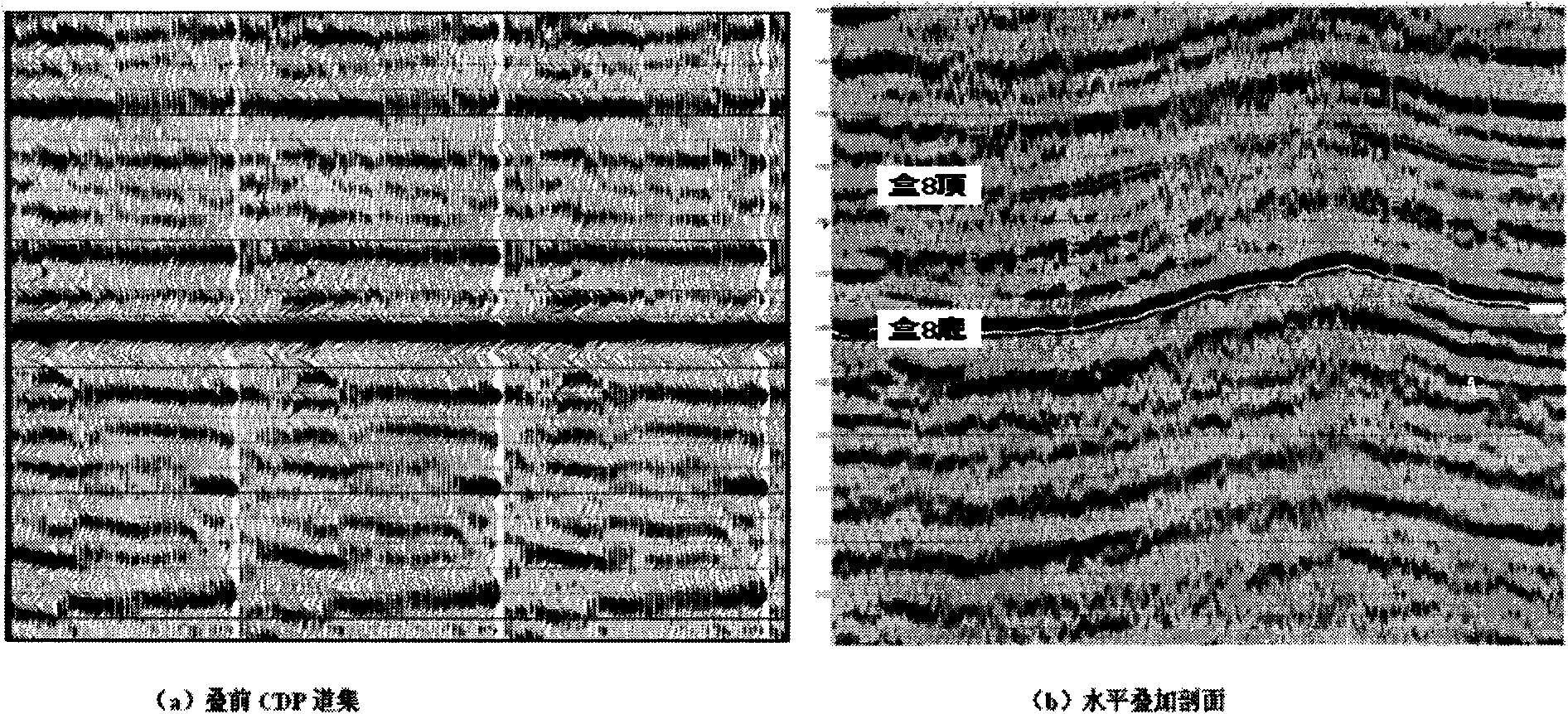
InactiveCN101887132ARealize Quantitative PredictionGood geological effectSeismology for water-loggingReservoir fluidSeismic trace
The invention discloses a method for quantificationally predicting sandstone reservoir fluid saturation by combining a well and seism in geophysical prospecting for petroleum. The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring and processing seismic data and log data to obtain each parameter curve; respectively determining the relationships among the shale content, the porosity and an elastic parameter of the well; establishing prediction models of the shale content and the porosity; calculating a pore volume modulus and a dry rock volume modulus to establish a modulus prediction model; establishing an effective reservoir water saturation prediction model; performing prestack seismic inversion by utilizing prestack seismic trace gathers and the log data to obtain an inversion data volume of each elastic parameter; calculating the dry rock volume modulus to solve the pore volume modulus by the obtained elastic inversion volume; and solving the water saturation by using the pore volume modulus. In the method, prestack seismic data and the log data are fully utilized for quantificationally predicting reservoir saturation; and good geological effects on predicting oil and gas saturation are achieved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Passive seismic event detection
ActiveUS20060285438A1Reduce weightAccurate identificationSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsCorrelation coefficientSeismic trace
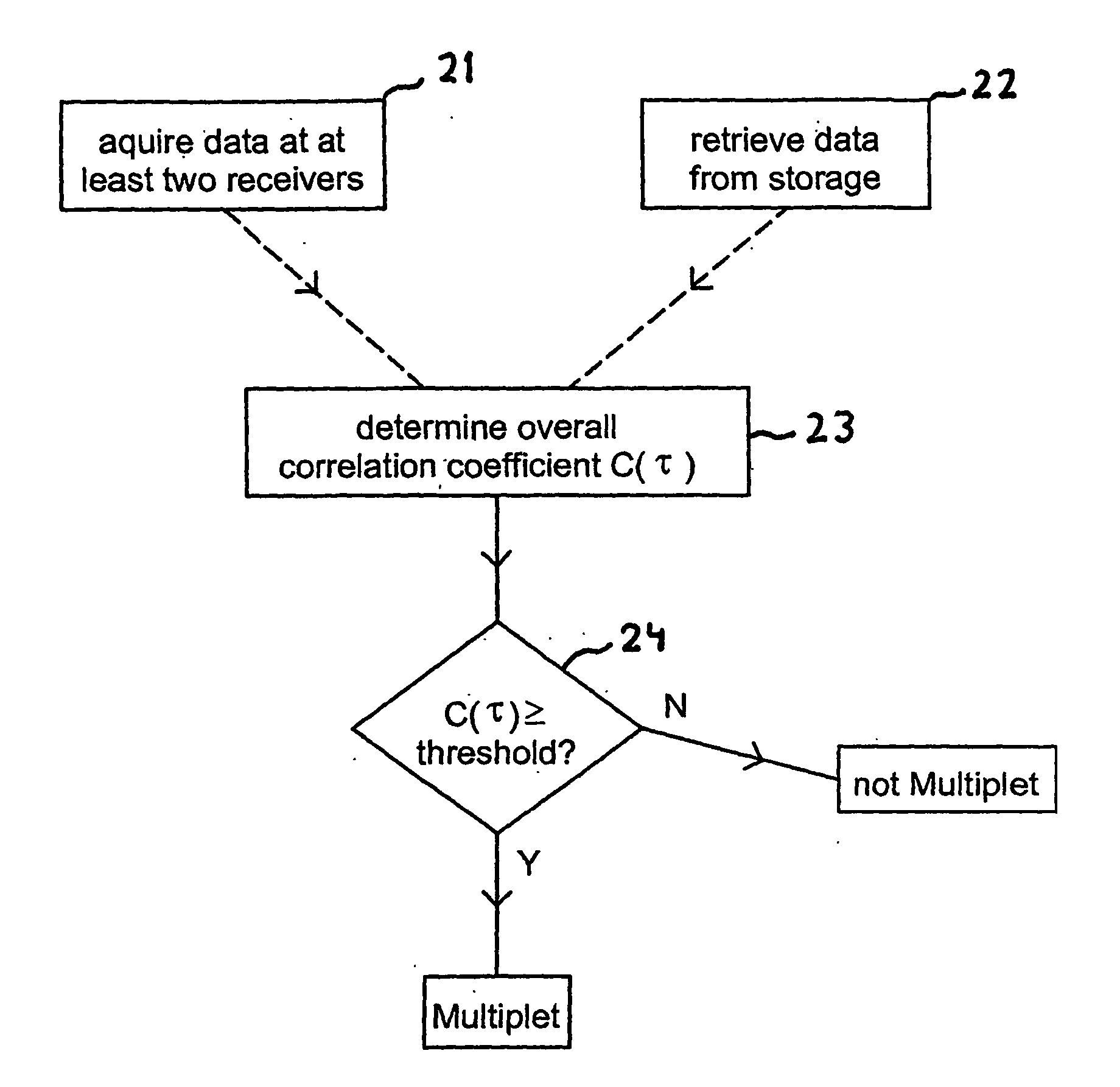
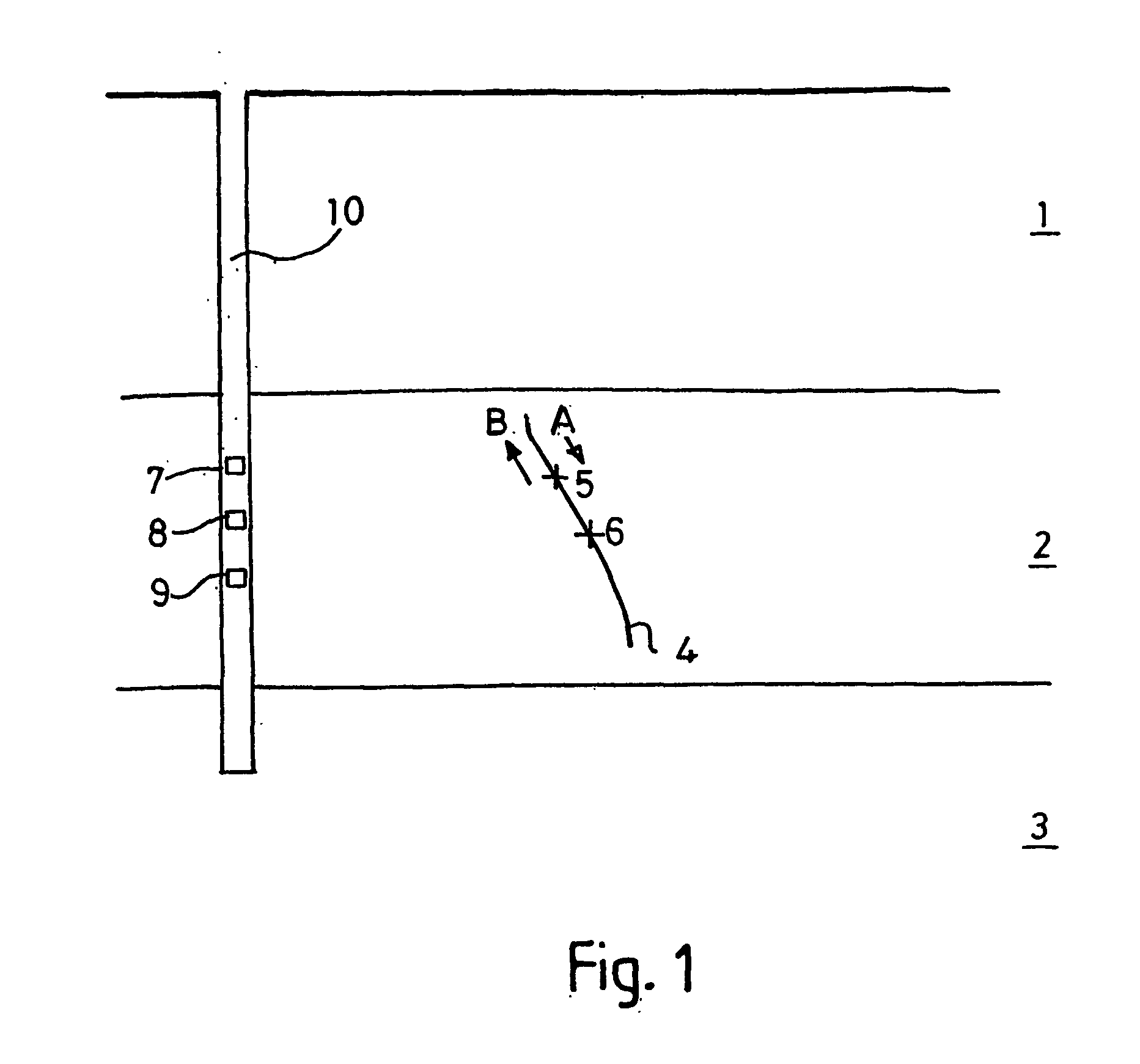
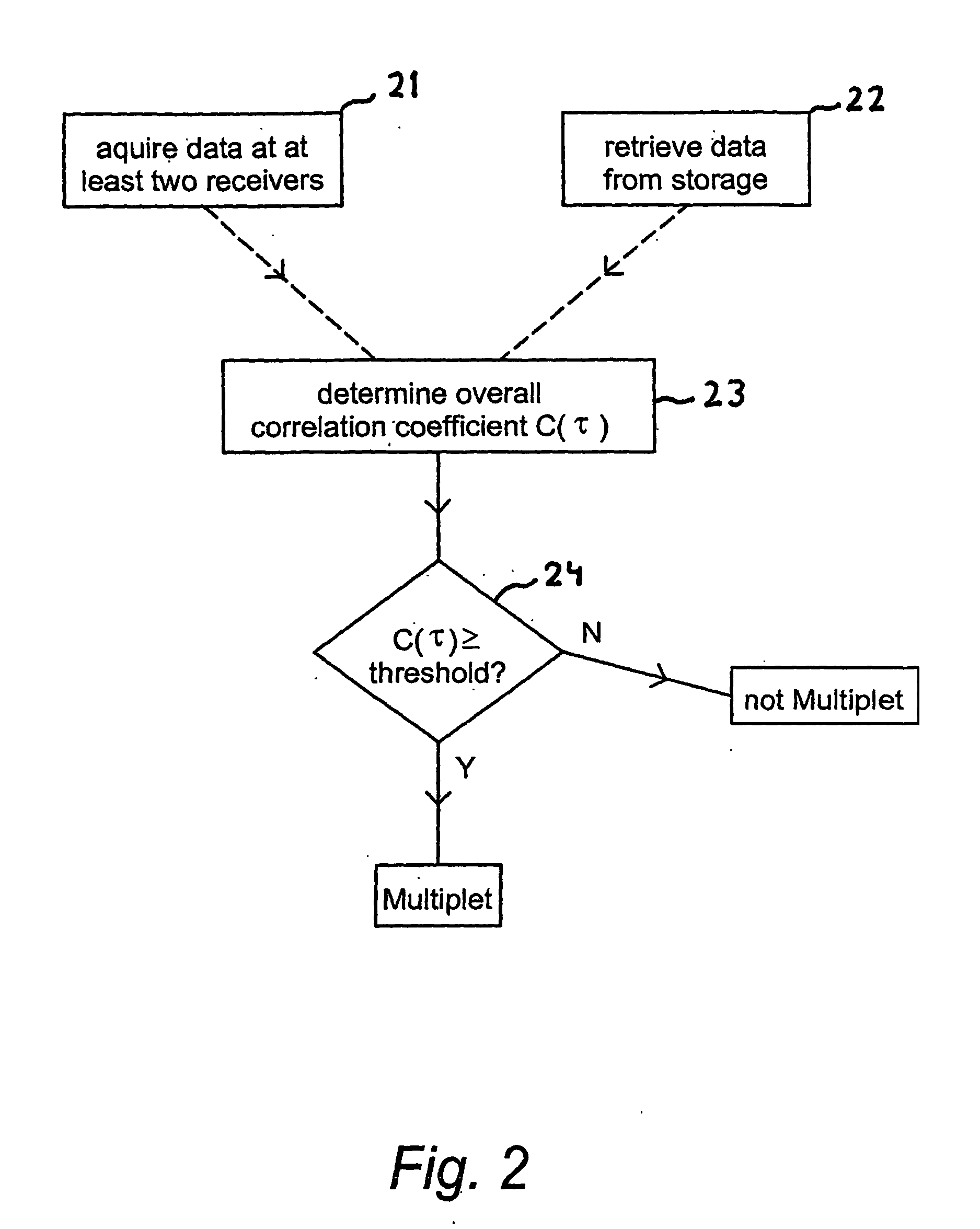
A method of identifying passive seismic events in seismic data that contains at least first seismic data traces acquired at a first seismic receiver and second seismic data traces acquired at a second receiver spatially separated from the first receiver comprises determining an overall measure of similarity for a pair of events in the seismic traces. The overall measure of similarity is indicative of similarity between the events acquired at the first seismic receiver and of similarity between the events acquired at the second seismic receiver. In one method, the overall measure of similarity is an overall cross-correlation coefficient. The overall cross-correlation coefficient is found by determining a first correlation coefficient for the pair of events from the data acquired at the first receiver and determining a second correlation coefficient for the pair of events from the data acquired at the second receiver. The overall correlation coefficient for the pair of events may be obtained from the first correlation coefficient and the second correlation coefficient by an averaging process. The overall measure of similarity may be compared with a threshold to determine whether the pair of events form a doublet. The method makes possible real-time or near-real-time identification of doublets.
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
Geophysical surveying
ActiveUS20140102694A1High resolutionAccurate estimateSurveySeismic data acquisitionSeismic traceSurveyor
A computer-implemented method for processing a seismic trace of a subterranean region comprising: (a) deriving a seismic wavelet for a time-window of seismic trace; (b) generating a model for the subterranean region corresponding to that time-window comprising a plurality of seismic reflectors by comparing the seismic wavelet with the time-window of the seismic trace to identify locations for the seismic reflectors, wherein the locations of the seismic reflectors are subject to a separation constraint requiring neighboring seismic reflectors to be separated by at least a minimum separation threshold which is greater than a separation corresponding to a sampling interval for the seismic trace; (c) defining a model seismic wavelet having a model seismic wavelet amplitude spectrum with a frequency bandwidth which is greater than that of the seismic wavelet amplitude spectrum determined for the time-window of the seismic trace; and (d) generating a model of the time-window of the seismic trace for the subterranean region based on the plurality of seismic reflectors of the model for the subterranean region corresponding to that time window and the model seismic wavelet.
Owner:PGS GEOPHYSICAL AS
Time-frequency decomposition earthquake-fluid recognition method
InactiveCN103235339AExact matchImprove signal-to-noise ratioSeismic signal processingFrequency spectrumDecomposition
The invention relates to the technical field of petroleum exploration, in particular to a time-frequency decomposition earthquake-fluid recognition method which includes establishing a time-frequency atom dictionary D according to Morlet wavelet function m(t)=exp[-betaXf2(t-tau)2]exp[i(2pif(t-tau)+phi)], and acquiring an initial matching atom of the Morlet wavelet function through calculation with a seismic trace and complex seismic trace method; performing matching decomposition on the seismic trace, performing iterative optimization with constraints of the time-frequency atom dictionary D in the neighborhood of the initial matching atom to acquire an optimal matching atom, stopping matching decomposition when preset conditions are achieved, and representing the initial seismic trace as a series of linear combinations of Morlet wavelet atoms; transforming the optimal matching Morlet atom into the time-frequency domain so as to acquire a time-frequency spectrum distribution of the initial seismic trace; extracting directly properties of earthquake fluid activity on a target stratum section on the time-frequency spectrum of earthquake materials; and predicting distribution range and space distribution of gas deposit according to the properties of the fluid activity. By the method, the distribution range and the space distribution of the gas deposit can be accurately predicted, so that a technical support is provided for favorable target optimization of natural gas exploration.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING) +1
Compressive sensing
ActiveUS20150124560A1Efficient and robust algorithmLess computation timeSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic traceDiscrete transform
Computer-implemented method for determining optimal sampling grid during seismic data reconstruction includes: a) constructing an optimization model, via a computing processor, given by minu∥Su∥1 s.t. ∥Ru−b∥2≦σ wherein S is a discrete transform matrix, b is seismic data on an observed grid, u is seismic data on a reconstruction grid, and matrix R is a sampling operator; b) defining mutual coherence asμ≤CSm(logn)6,wherein C is a constant, S is a cardinality of Su, m is proportional to number of seismic traces on the observed grid, and n is proportional to number of seismic traces on the reconstruction grid; c) deriving a mutual coherence proxy, wherein the mutual coherence proxy is a proxy for mutual coherence when S is over-complete and wherein the mutual coherence proxy is exactly the mutual coherence when S is a Fourier transform; and d) determining a sample grid r*=arg minr μ(r).
Owner:SHEARWATER GEOSERVICES SOFTWARE INC
Method of processing seismic data by providing surface offset common image gathers
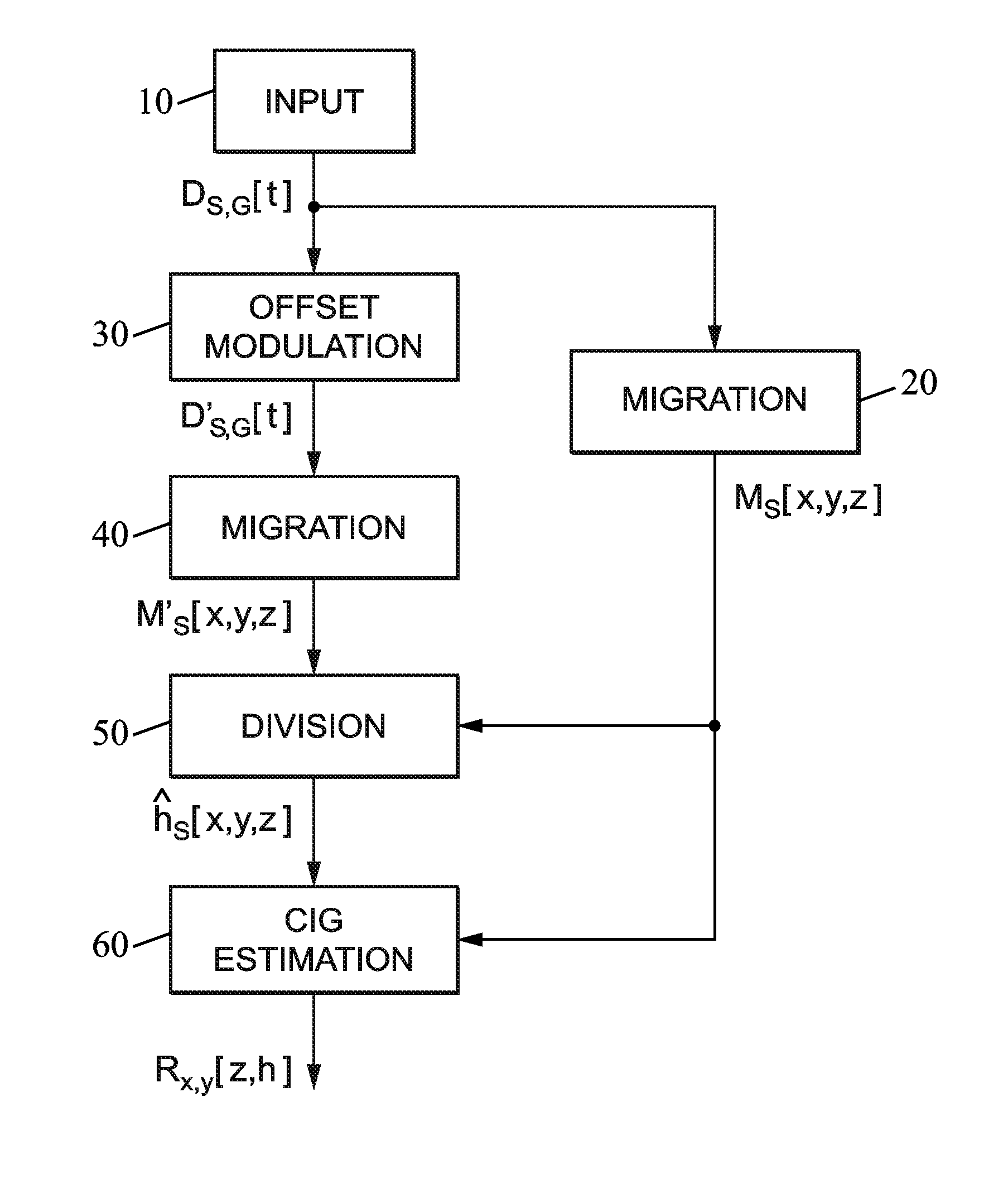
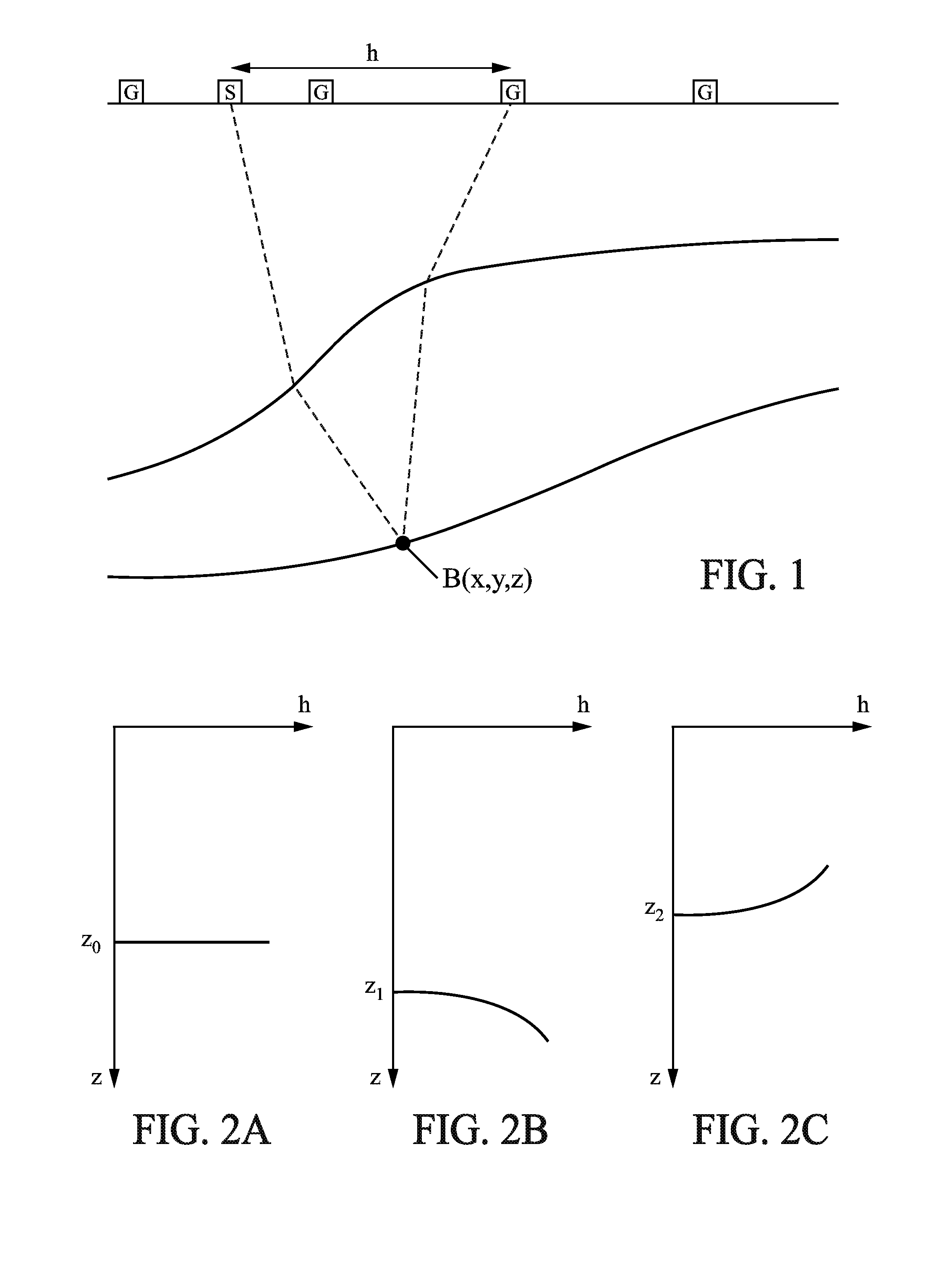
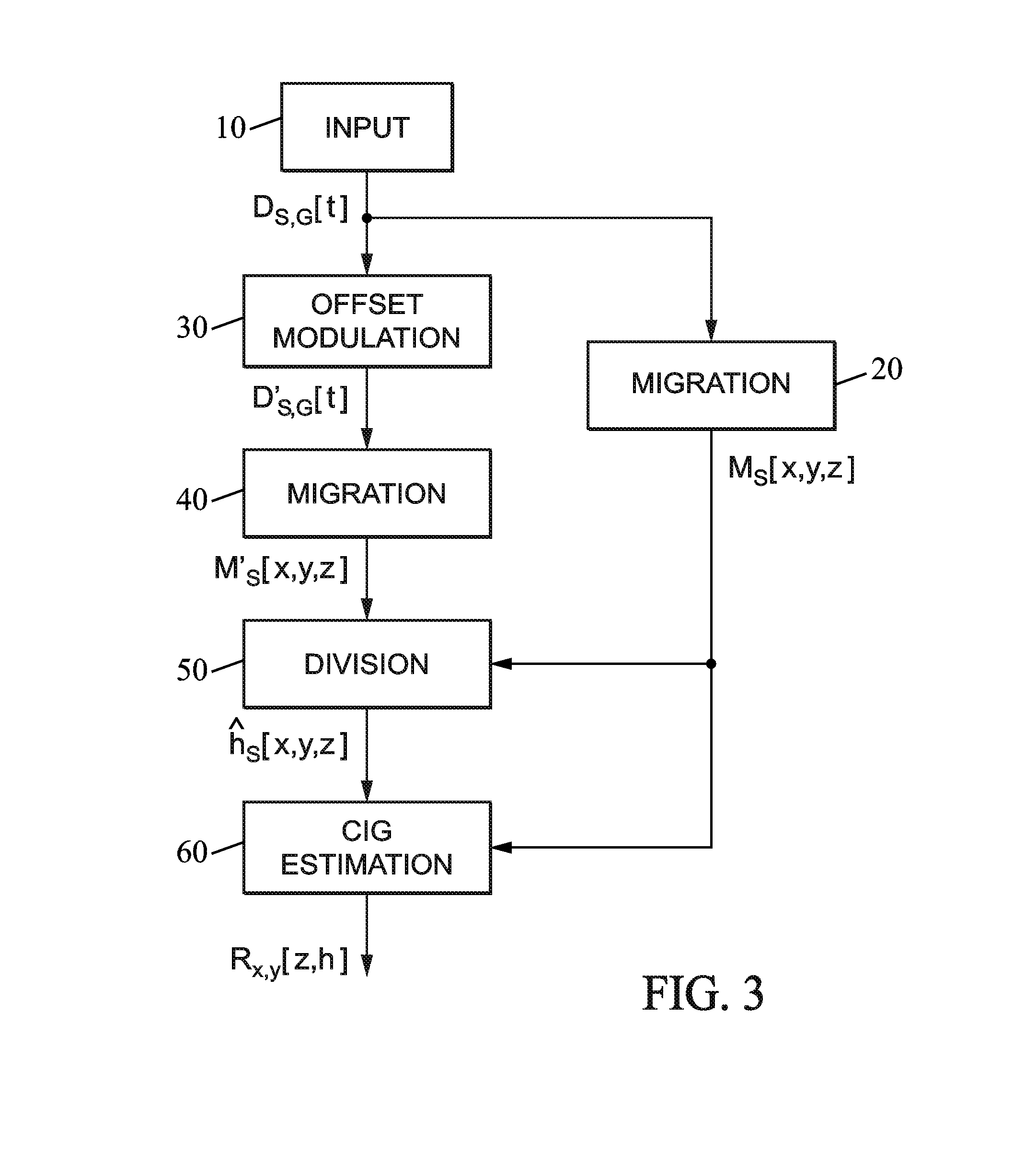
ActiveUS20140149046A1Better propagatorEasy to explainSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsSeismic traceGeophysics
The method processes input including, for each of a plurality of shots at respective source locations, seismic traces recorded at a plurality of receiver locations. Offset-modulated data are also computed by multiplying the seismic data in each seismic trace by a horizontal offset between the source and receiver locations for said seismic trace. A depth migration process is applied to the seismic data to obtain a first set of migrated data, and to the offset-modulated data to obtain a second set of migrated data. For each shot, offset values are estimated and associated with respective subsurface positions, by a division process applied to the first and second sets of migrated data.
Owner:TOTAL PUTEAUX FR
Method and apparatus for true relative amplitude correction of seismic data for normal moveout stretch effects
InactiveUS20060193205A1Seismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsRelative magnitudeNormal moveout
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for arriving at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces from stretched seismic traces. The method compensates for offset varying reflection interference effects due to normal moveout. Stretch factors β and also input spectra are determined for NMOR stretched seismic traces. Estimates are then made of stretched wavelet spectra from the input spectra. A destretched wavelet spectra is then obtained. Shaping correction factors are determined by taking the ratio of the destretched wavelet spectra to the stretched wavelet spectra and are applied to the input spectra of the stretched traces to arrive at a destretched trace spectra. True relative amplitude scaling factors are computed by taking the ratio of a true relative amplitude property of the destretched wavelet spectra to a corresponding true relative amplitude property of the stretched wavelet spectra. Finally, the true relative amplitude scaling factors are applied to the destretched trace spectra to arrive at true relative amplitude destretched seismic traces.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
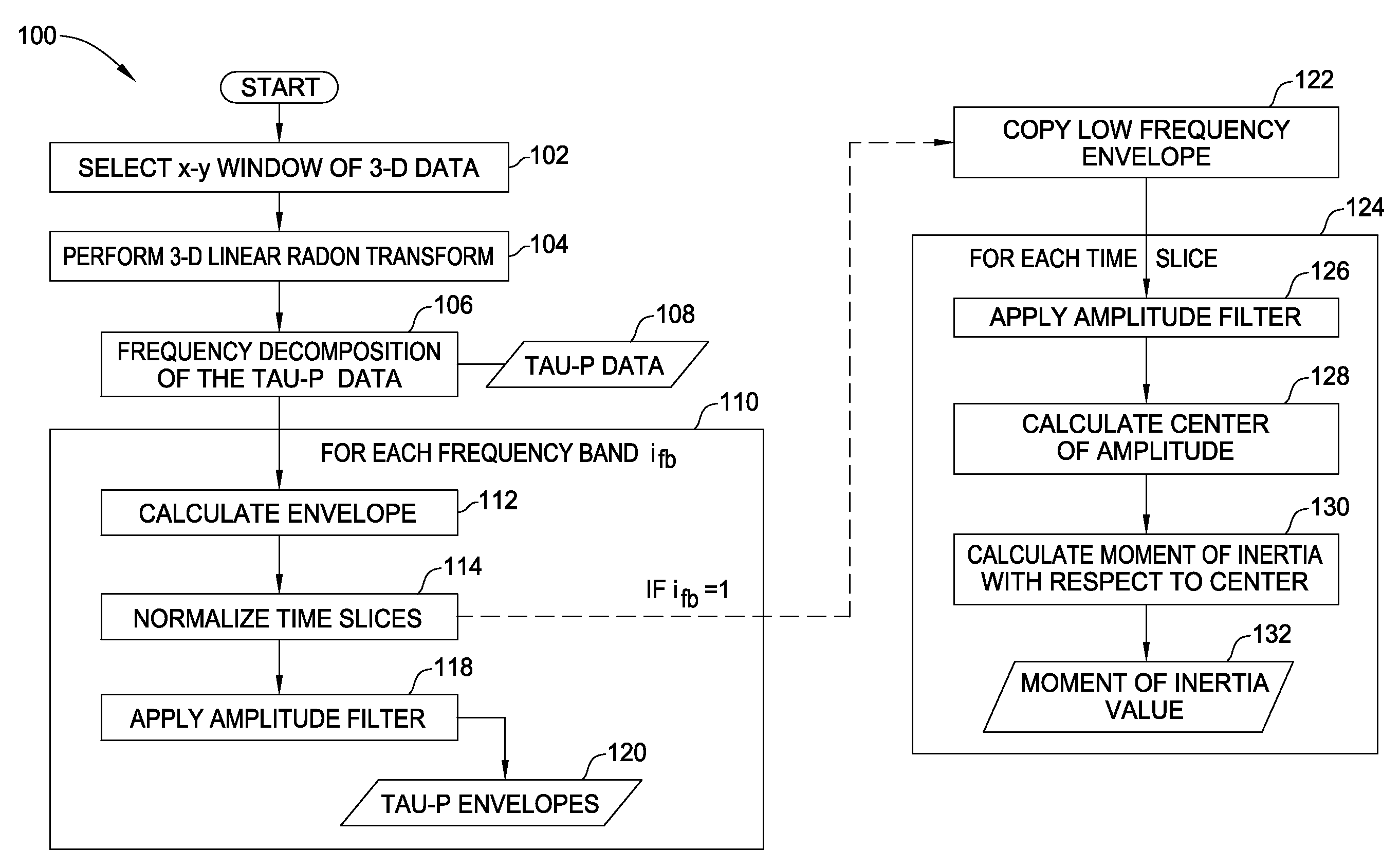
3-d tau-p interpolation
ActiveUS20090180351A1Reduce noiseRemovalSeismic signal processingSpecial data processing applicationsNoise levelEngineering
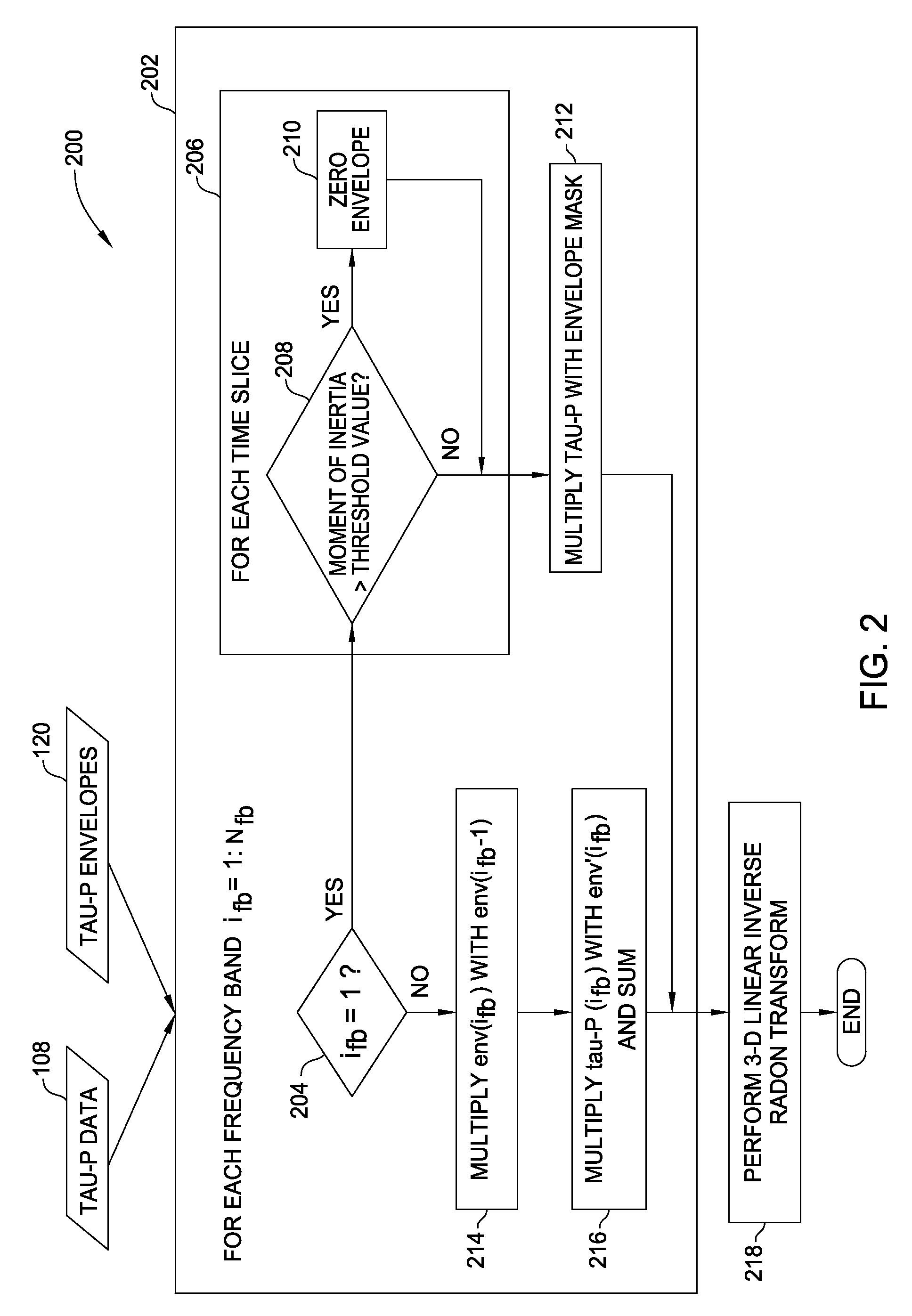
Methods and apparatus for removing noise from signal traces collected during a seismic gather, particularly removing the aliased energy in the time-slowness (tau-P) domain so that aliasing noise does not lead to high noise levels in the inverse transformed data are provided. Removal of the aliasing noise may provide for quieter seismic traces and may increase the likelihood for successful three-dimensional (3-D) tau-P interpolation and detection of seismic events.
Owner:FAIRFIELD INDUSTRIES INC
Carbonatite oil and gas reservoir crack earthquake detection method
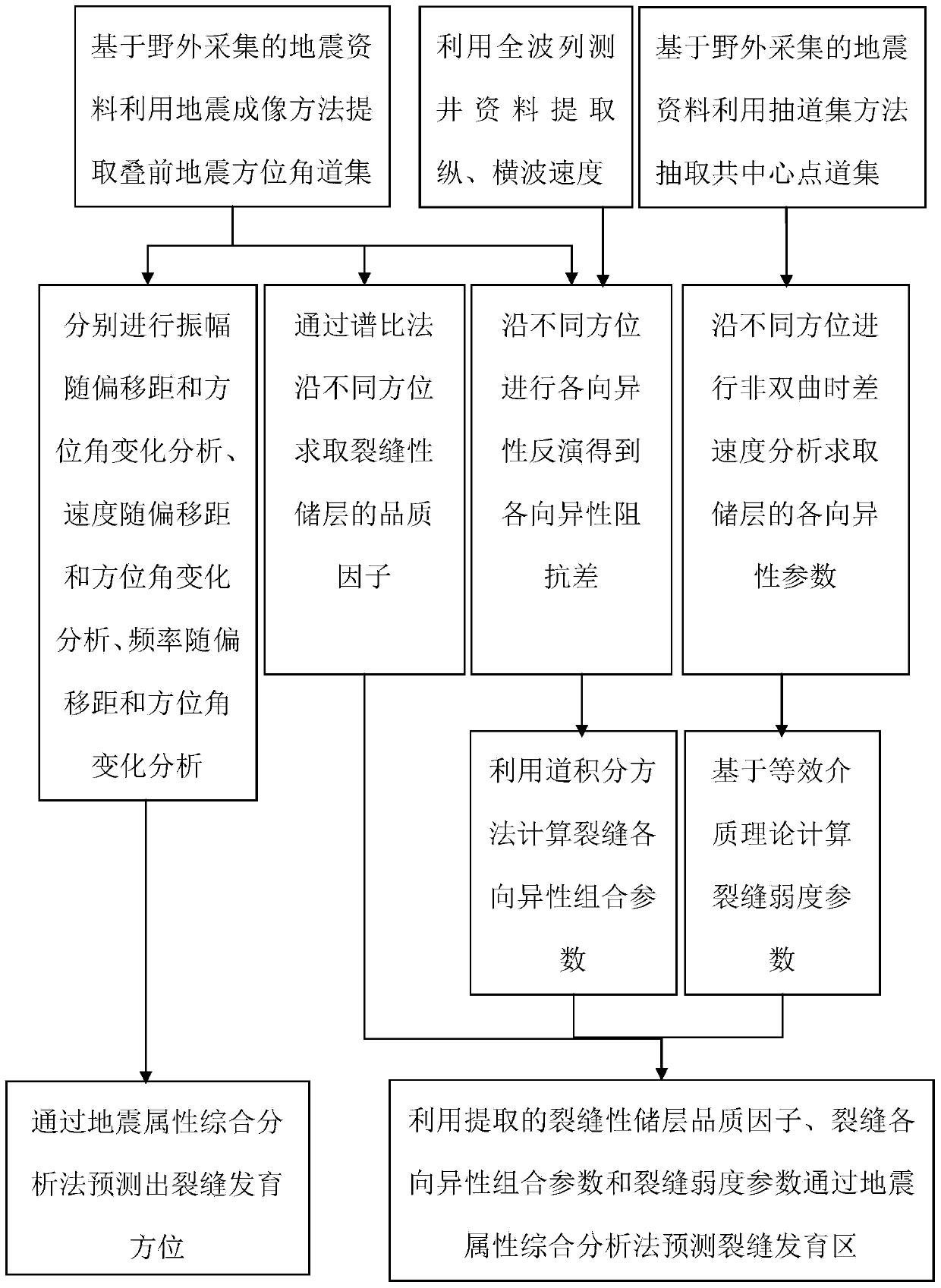
InactiveCN103424776AAccurate estimateFull use of amplitudeSeismic signal processingEarthquake detectionEllipse
The invention belongs to the field of exploration geophysics, and particularly relates to a carbonatite oil and gas reservoir crack earthquake detection method. The method comprises the steps of: carrying out amplitude versus offset and azimuth angle analysis, speed versus offset and azimuth angle analysis, frequency versus offset and azimuth angle analysis respectively based on pre-stack seismic azimuth angle dataset, further carrying out ellipse fitting respectively to obtain a crack development azimuth angle, and predicting a crack development azimuth through a seismic attribute comprehensive analysis way; carrying out quality factor parameter extraction, anisotropic parameter inversion and non-hyperbolic moveout velocity analysis respectively based on pre-stack seismic trace dataset and shear wave velocity data, and predicting a reservoir crack development region by comprehensively utilizing the parameters above through a seismic attribute comprehensive analysis way. The carbonatite oil and gas reservoir crack earthquake detection method can give more comprehensive consideration to the geology of the reservoir and the physic characteristics of the globe, and the estimated crack azimuth and the predicted crack development region are more exact.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Zero-offset seismic trace construction
ActiveUS20100002539A1Improve extrapolationImprove interpolationSeismology for water-covered areasData setSeismic trace
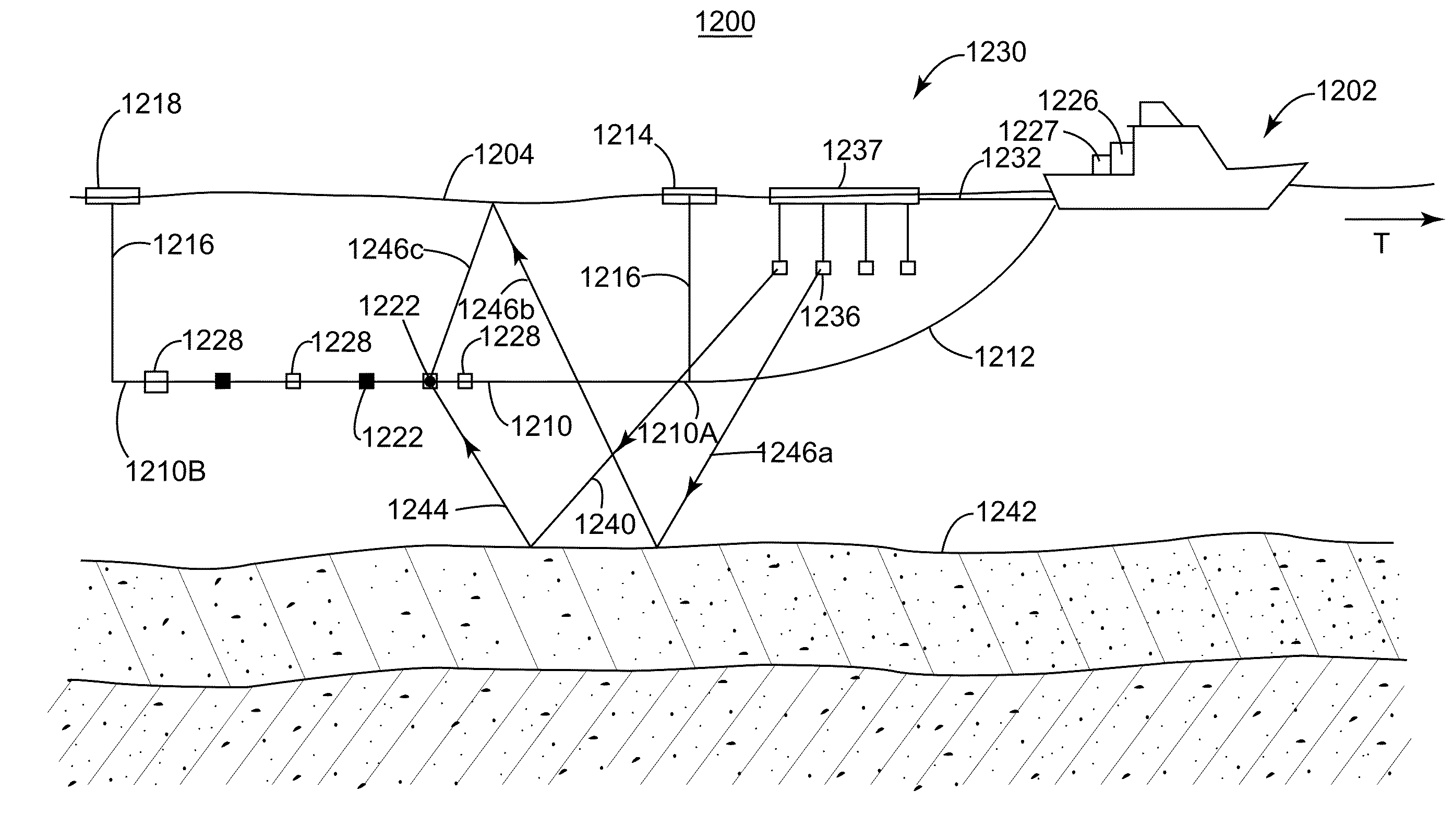
Described are methods for obtaining seismic signals representative of properties of the earth's interior, including the steps of obtaining near-field acoustic signals recorded in the vicinity of a seismic source (13), muting from the near-field acoustic signals at least partly signals representing direct arrivals from the seismic source (13), and using a remaining part of the obtained signals as estimate of a zero-offset data set. The zero-off set data set can then be used to interpolate data from conventional acquisition location, such as streamers (11), to locations closer to the source (13).
Owner:WESTERNGECO LLC
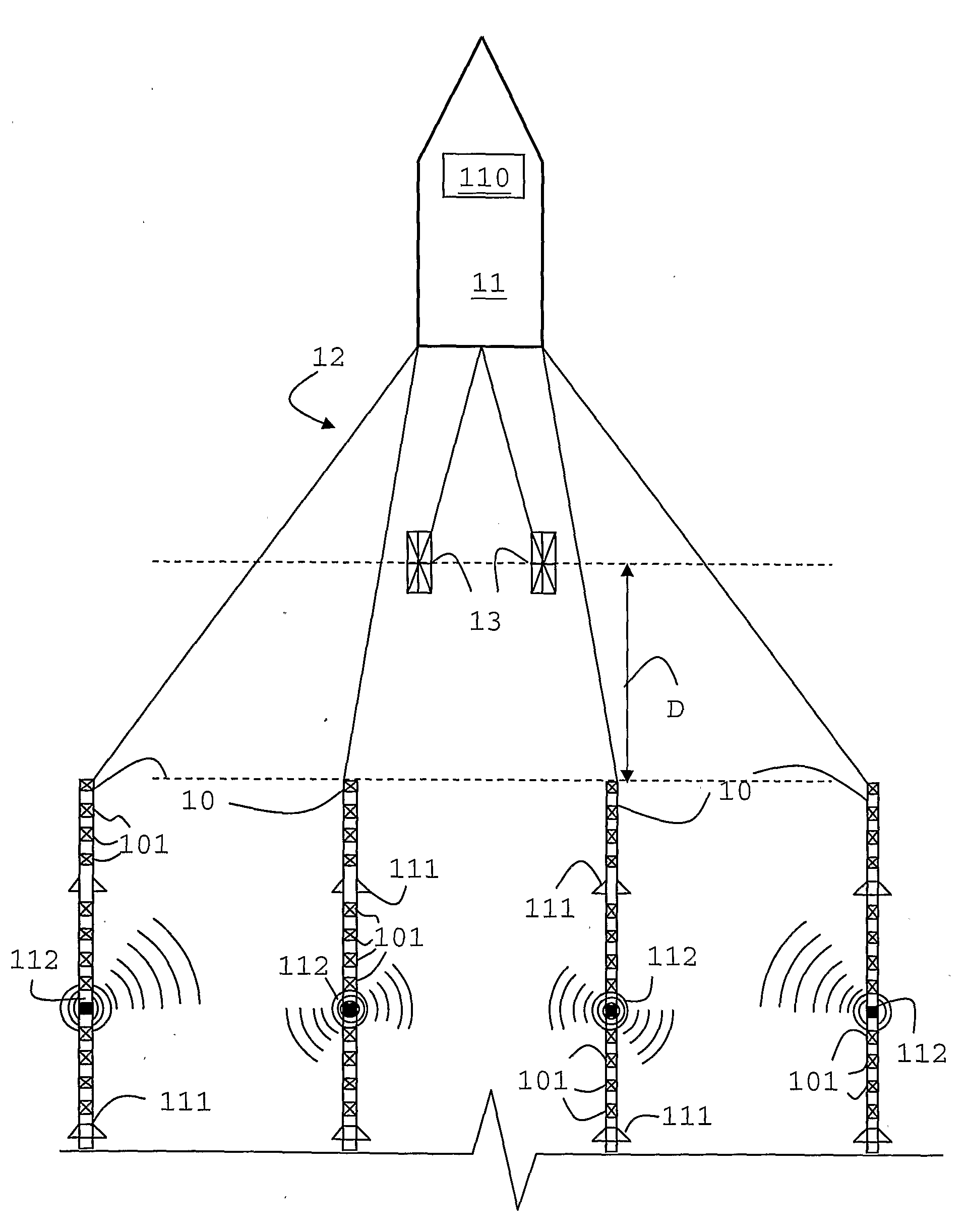
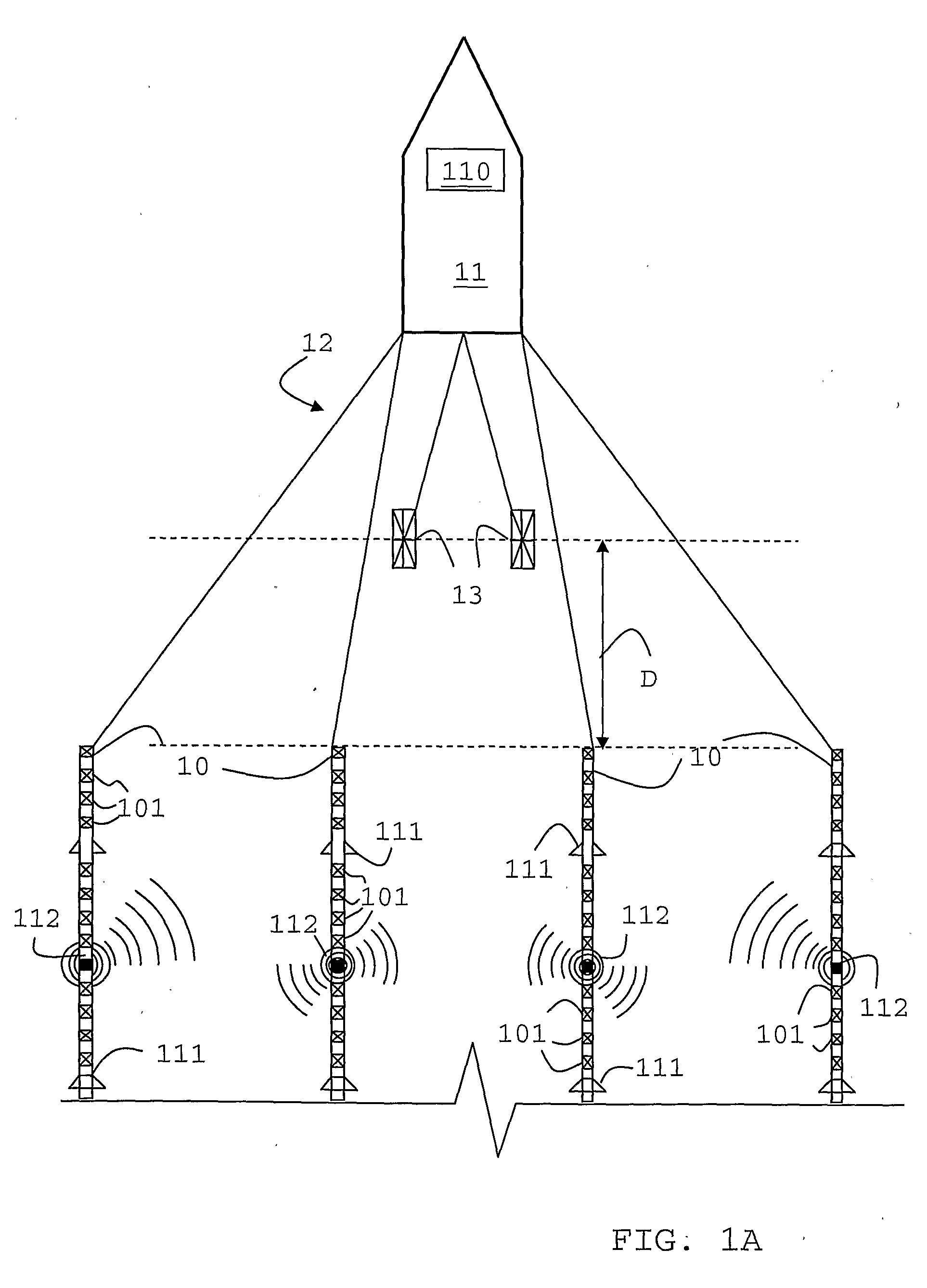
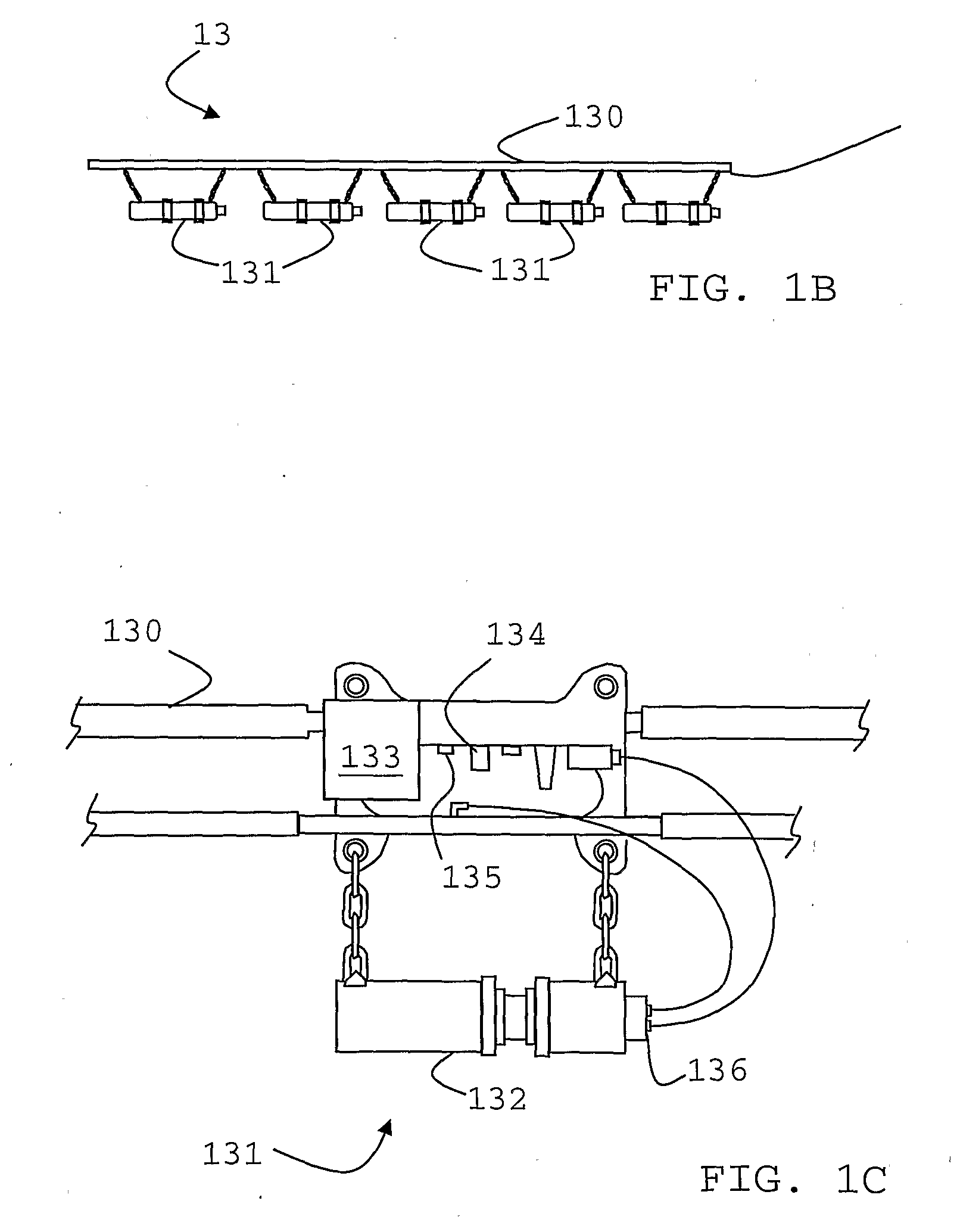
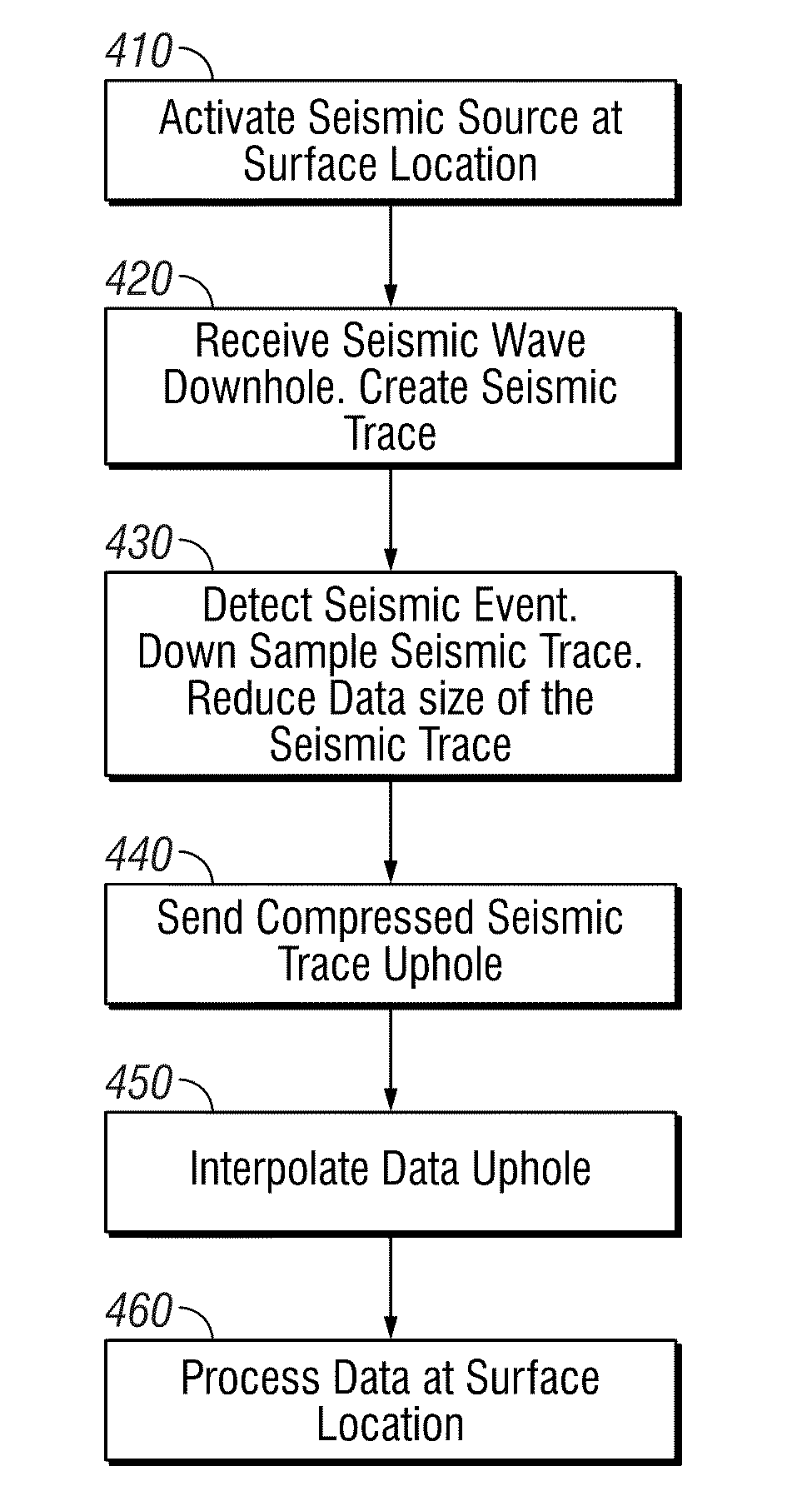
Sending a Seismic Trace to Surface After a Vertical Seismic Profiling While Drilling Measurement
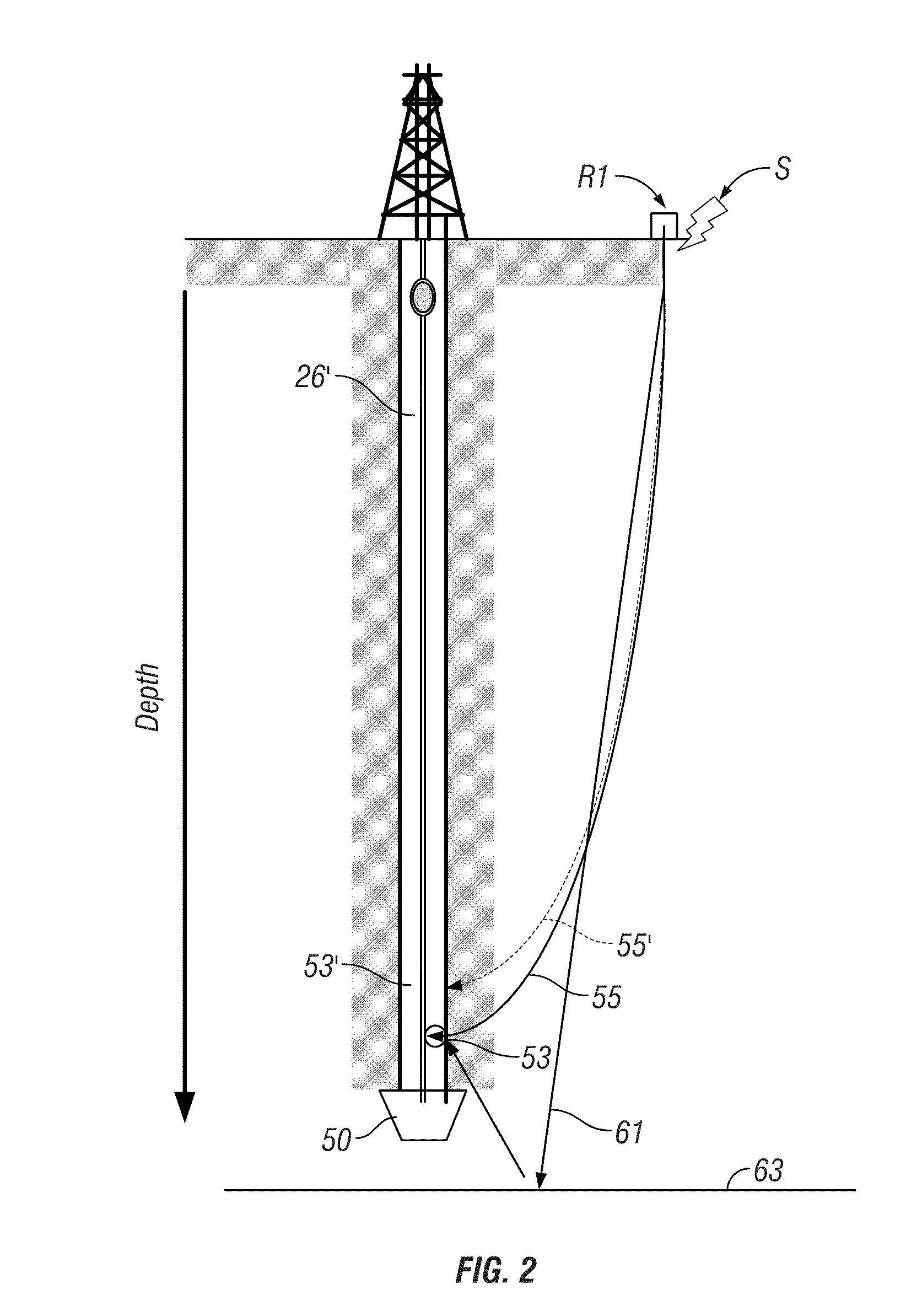
ActiveUS20100315901A1Seismic signal processingSeismology for water-loggingVertical seismic profileWell drilling
A system, method and computer-readable medium for acquiring seismic data, which includes activating a seismic source at a surface location; defining a seismic trace of a seismic wave received at a downhole location on a bottomhole assembly in a borehole in response to the activation of the seismic source; compressing the seismic trace; and recording the compressed seismic trace to a storage medium.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Device and method for de-blending simultaneous shot data
InactiveUS20140303898A1Remove cross-talk noiseRemove noiseSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic traceGeophysics
Device, medium and method for de-blending seismic data. The method for de-blending seismic data associated with a subsurface of the earth includes receiving initial seismic traces recorded by plural sources; de-blending, in a processor, the initial seismic traces to generate de-blended seismic traces; and generating an image of the subsurface based on the de-blended seismic traces. The initial seismic traces include uncontaminated portions corresponding to time intervals substantially free from cross-talk from other sources, and the uncontaminated portions are used to remove cross-talk noise on other initial seismic traces.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
Reservoir wave impedance prediction method based on dipole wave
ActiveCN102650701AHigh-resolutionHigh precisionSeismic signal processingDatabase analysisImage resolution
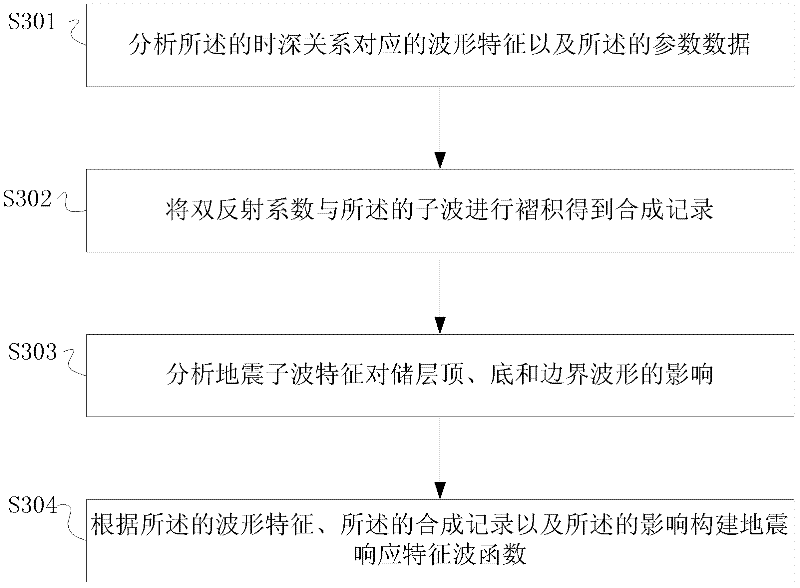
The invention provides a reservoir wave impedance prediction method based on dipole wave, which comprises the following steps that: logging data is analyzed to acquire the corresponding parameter data of the seismic response characteristics of a reservoir; well seismic calibration is carried out according to the logging and seismic data so as to extract wavelets and determine the time-depth relationship; the seismic response characteristic wave function of impedance changes is constructed according to the parameter data, the wavelets and the time-depth relationship; the way integral characteristics of the logging data are extracted according to the seismic response characteristic wave function to form a seismic response model database; the seismic data beside a well is analyzed according to the seismic response model database to work out an impedance interpretation spectrum of the seismic data beside the well; a seismic trace is analyzed according to the seismic response model database to work out a data body wave impedance spectrum; and the wave impedance is predicted according to the seismic response model database, the impedance interpretation spectrum and the data body wave impedance spectrum. According to the reservoir wave impedance prediction method based on the dipole wave, the wave impedance of the reservoir is predicted through the seismic characteristics and wave impedance change rules based on the analysis to the logging data, so that the precision in predicting the wave impedance of the reservoir and the resolution to thin reservoirs are improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for improving seismic data resolution ratio for well control
ActiveCN102937720AClear overlapping relationshipThe overlapping relationship is accurateSeismic signal processingHorizonEqualization
The invention provides a method for improving a seismic data resolution ratio for well control. The method for improving the seismic data resolution ratio for well control comprises the steps of calculating reflection coefficients at all well positions; calculating deconvolution operators at all well positions according to reflection coefficients at all well positions; conducting reverse distance weighted three-dimensional spatial interpolation on all deconvolution operators to obtain deconvolution operators of all seismic traces in a three-dimensional space; and conducting convolution processing on original seismic trace data according to deconvolution operators of all seismic traces, and obtaining three-dimensional data volumes through phase correction and trace equalization. The method for improving the seismic data resolution ratio for well control solves the problems that seismic data in the prior art are low in resolution ratio and high in limitation of application range, and the method has the advantages that a plurality of weakened horizon information is strengthened, information of structures such as faults is clear and the superimposing relationship of horizons is clear and accurate.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method and device for automatically identifying abnormal seismic traces
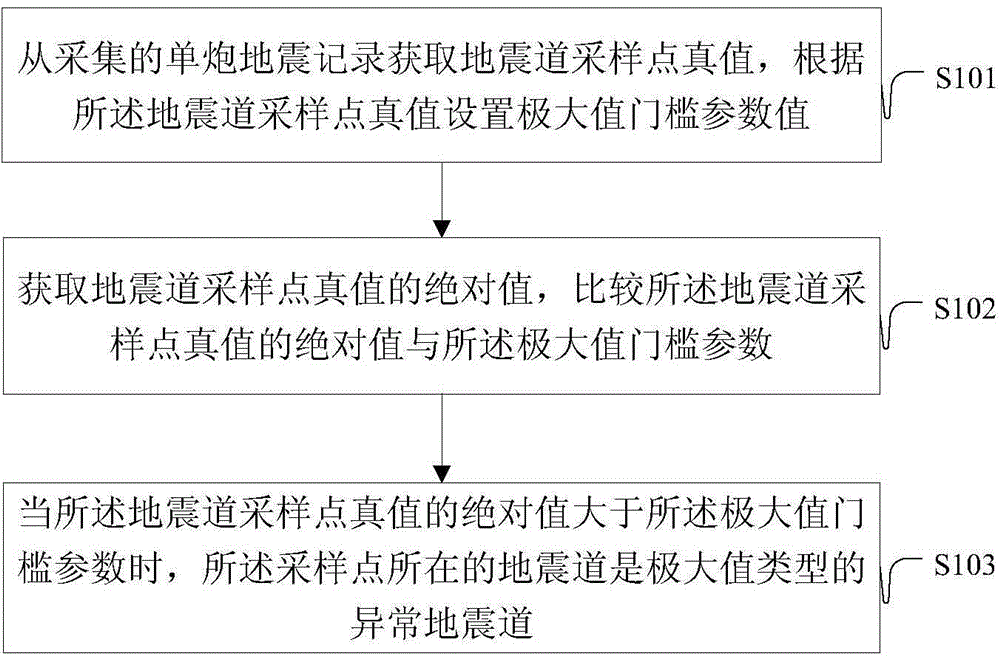
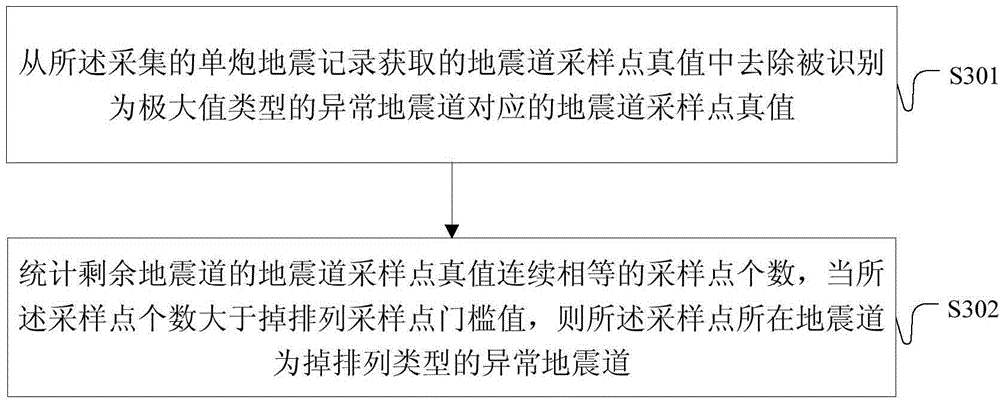
ActiveCN104459779AAccurate identificationAccurate automatic identificationSeismic signal processingTruth valueSeismic trace
The embodiment of the invention provides a method and device for automatically identifying abnormal seismic traces. The method includes the steps that true values of seismic trace sampling points are obtained from collected single-explosion seismic records, and a maximum value threshold parameter value is set according to the true values of the seismic trace sampling points; absolute values of the true values of the seismic trace sampling points are obtained and compared with the maximum value threshold parameter value; when the absolute values of the true values of the seismic trace sampling points are larger than the maximum value threshold parameter value, the seismic traces where the sampling points are located are the maximum-value-type abnormal seismic traces. By means of the technical scheme, the accuracy for identifying the abnormal seismic traces can be greatly improved.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
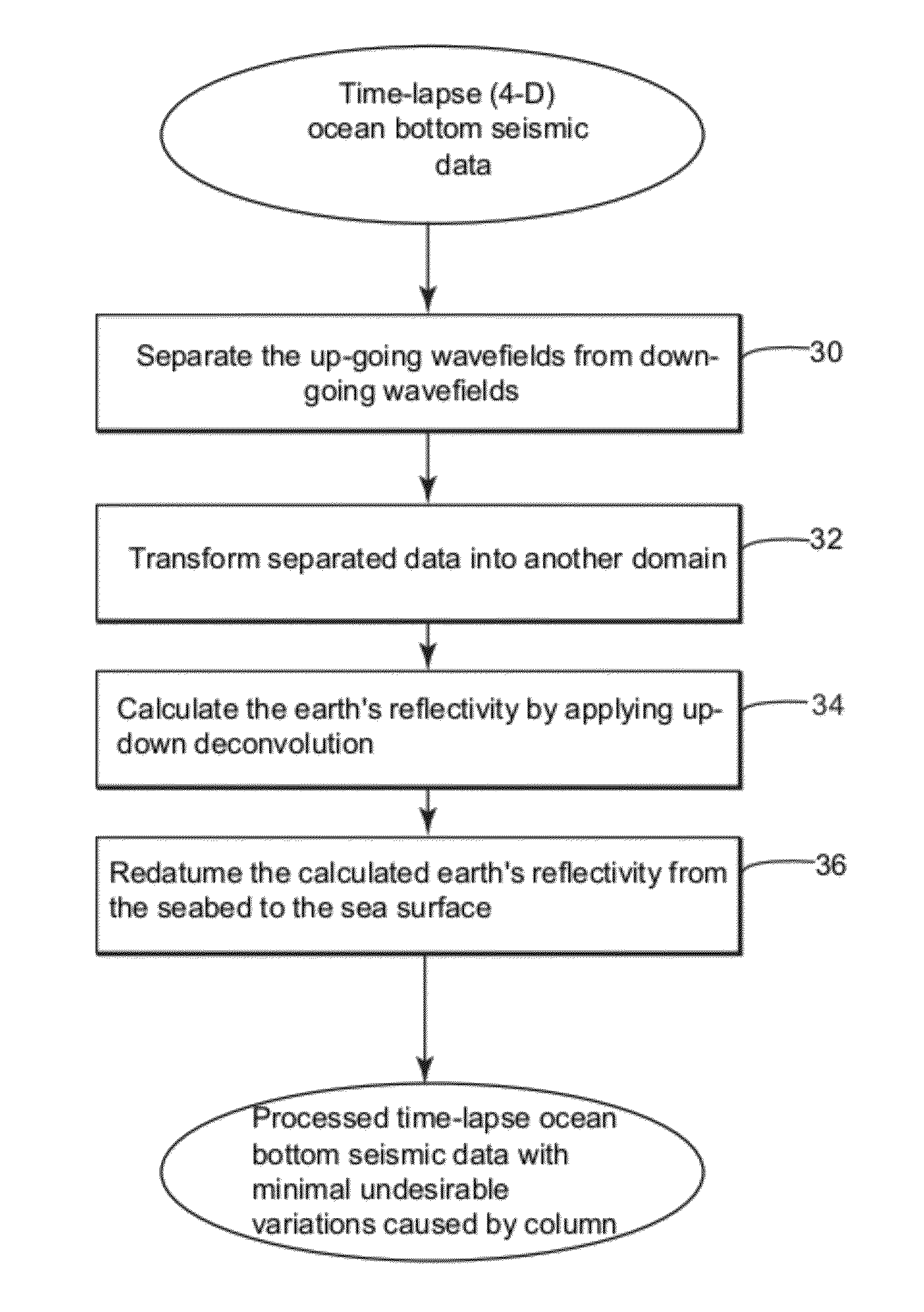
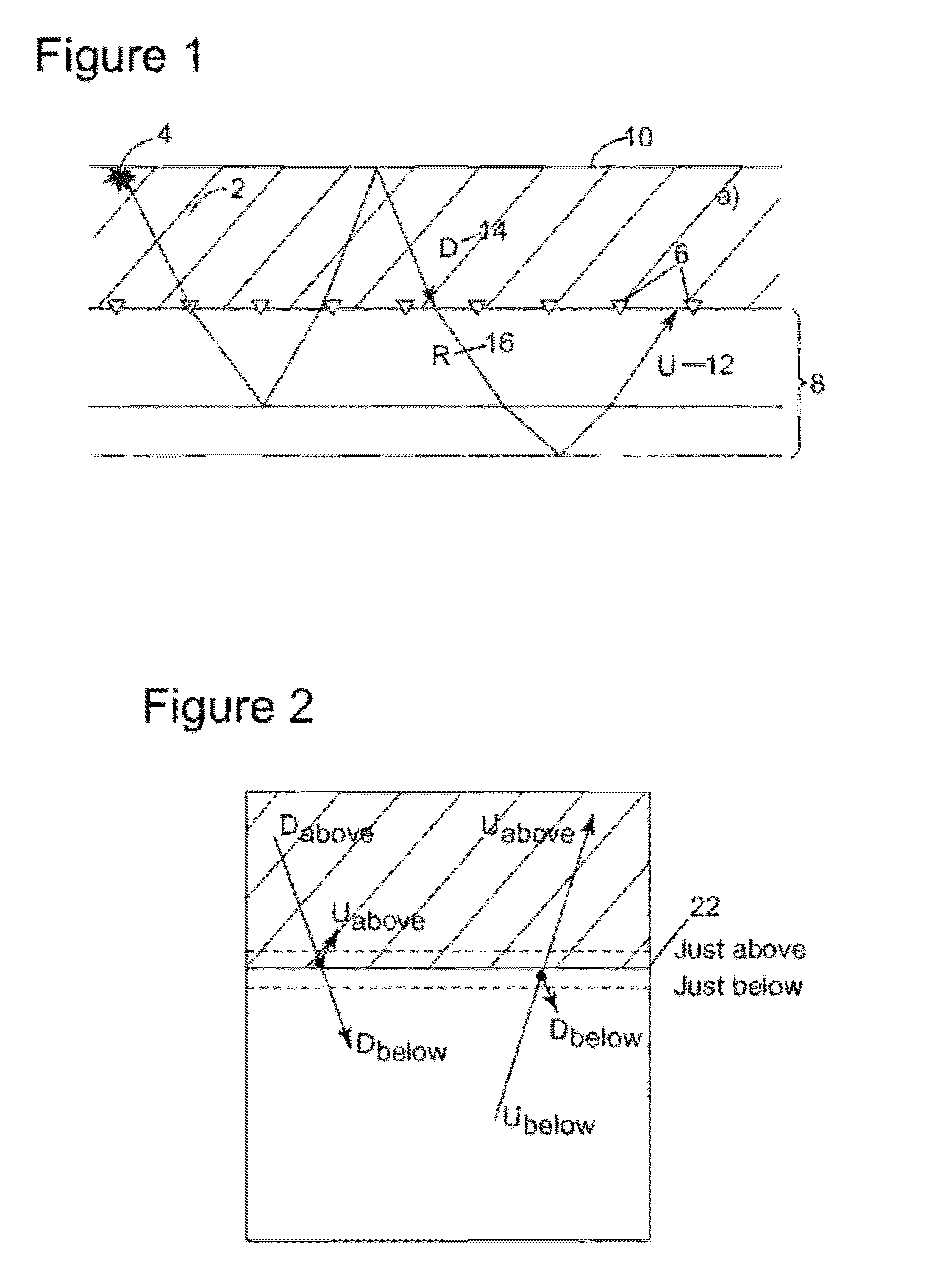
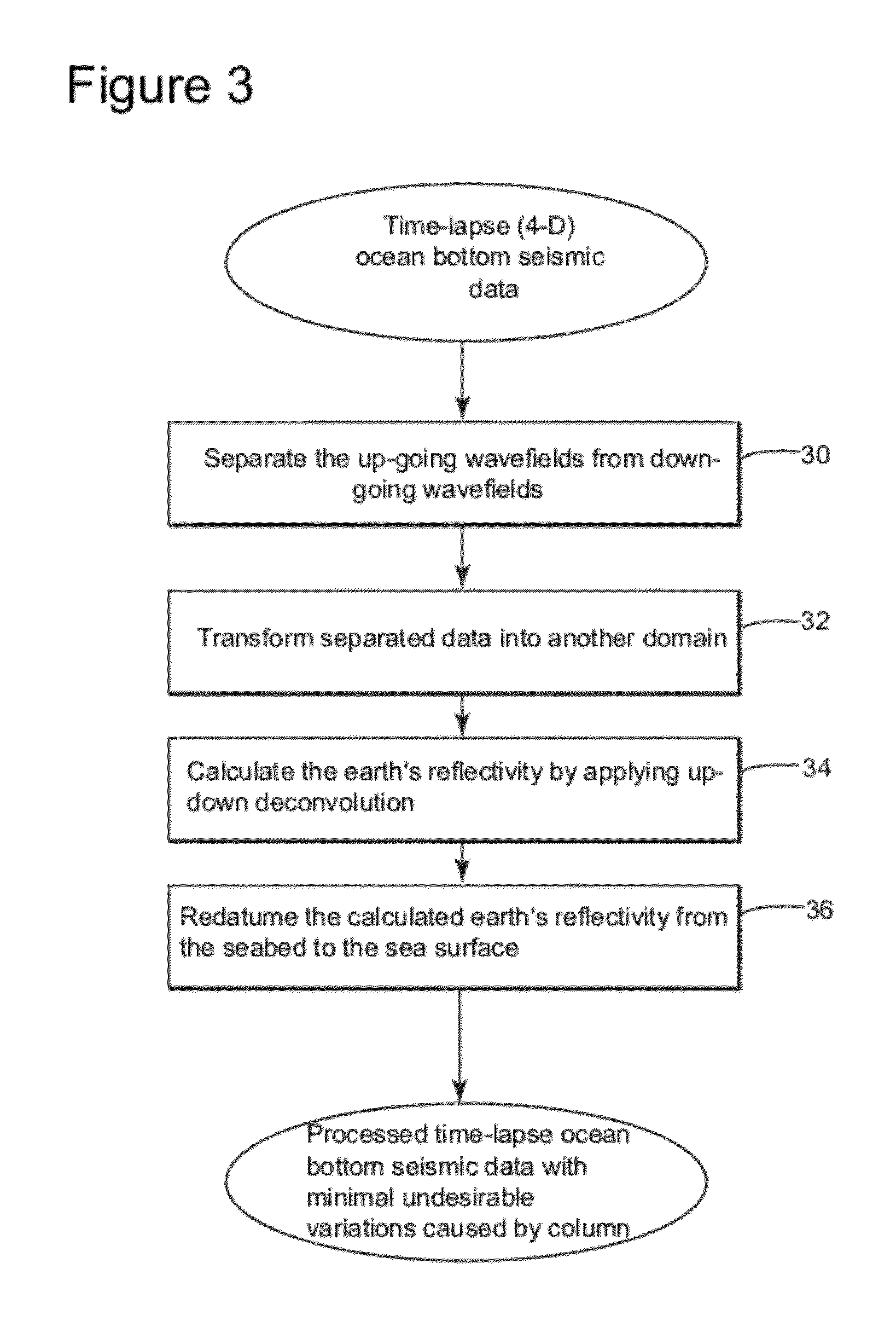
Methods and systems to eliminate undesirable variations in time-lapse seismic surveys
Device and method for processing 4-dimensional (4-D) seismic traces. The method includes receiving at least two vintages of seismic traces recorded by seismic receivers for a same subsurface area, wherein said seismic receivers are located at the ocean floor; applying up-down deconvolution to each of said vintages of seismic traces to obtain a representation of a reflectivity of said subsurface area from each vintage of seismic traces; and redatuming the up-down deconvolution result of each vintage from the ocean floor to a desired water depth of the ocean to reduce one or more changes in said seismic traces associated with water layer variations between recordings of said series of seismic traces. The redatumed seismic data is used to generate one or more images representing characteristics of said subsurface area.
Owner:CGGVERITAS SERVICES
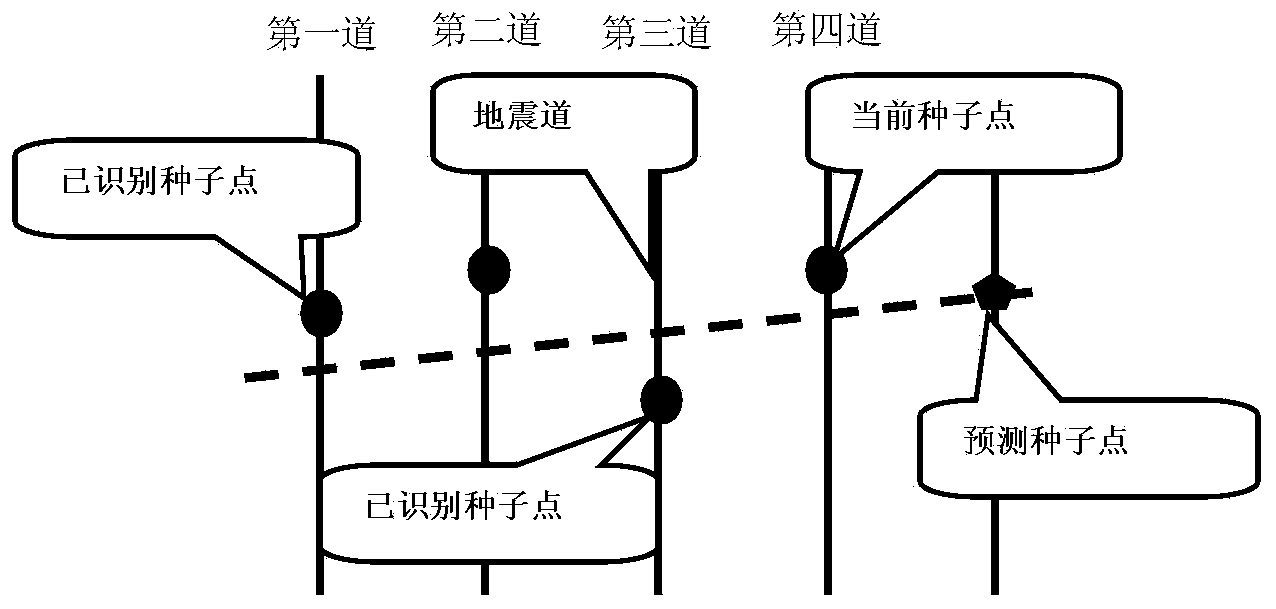
Geologic horizon automatic tracking method and device
An embodiment of the invention provides a geologic horizon automatic tracking method and device. The method comprises the steps that a target horizon seed point is preset on seismic data; the target horizon seed point is taken as a current seed point, and geologic horizon automatic tracking is performed in the following manner: a seed point is determined to be a prediction seed point in the geologic horizon automatic tracking direction in a search range on a seismic trace set adjacent to the current seed point, and seismic wave group information of the prediction seed point is extracted; seismic wave group information of the current seed point is extracted, and the similarity of the seismic wave group information of the prediction seed point and the seismic wave group information of the current seed point is determined, if the similarity is larger than or equal to a preset value, the prediction seed point is set to be a new current seed point, and otherwise, a seed point selected from seed points in a seed point search range is set to be a new current seed point for continuous search. According to the scheme, the anti-noise capacity of geologic horizon automatic tracking and the horizon tracking accuracy are improved.
Owner:BGP OF CHINA NAT GASOLINEEUM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com