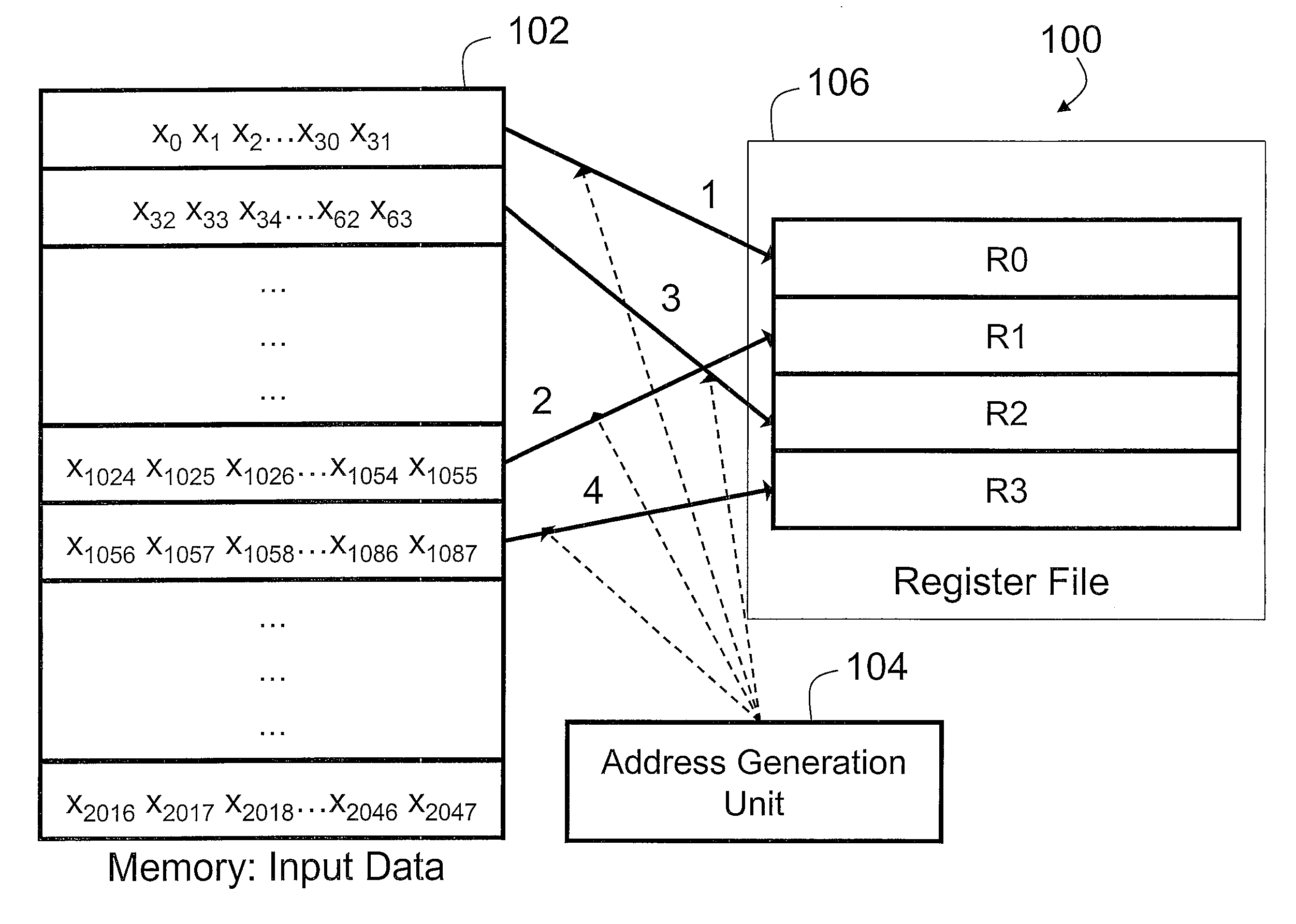
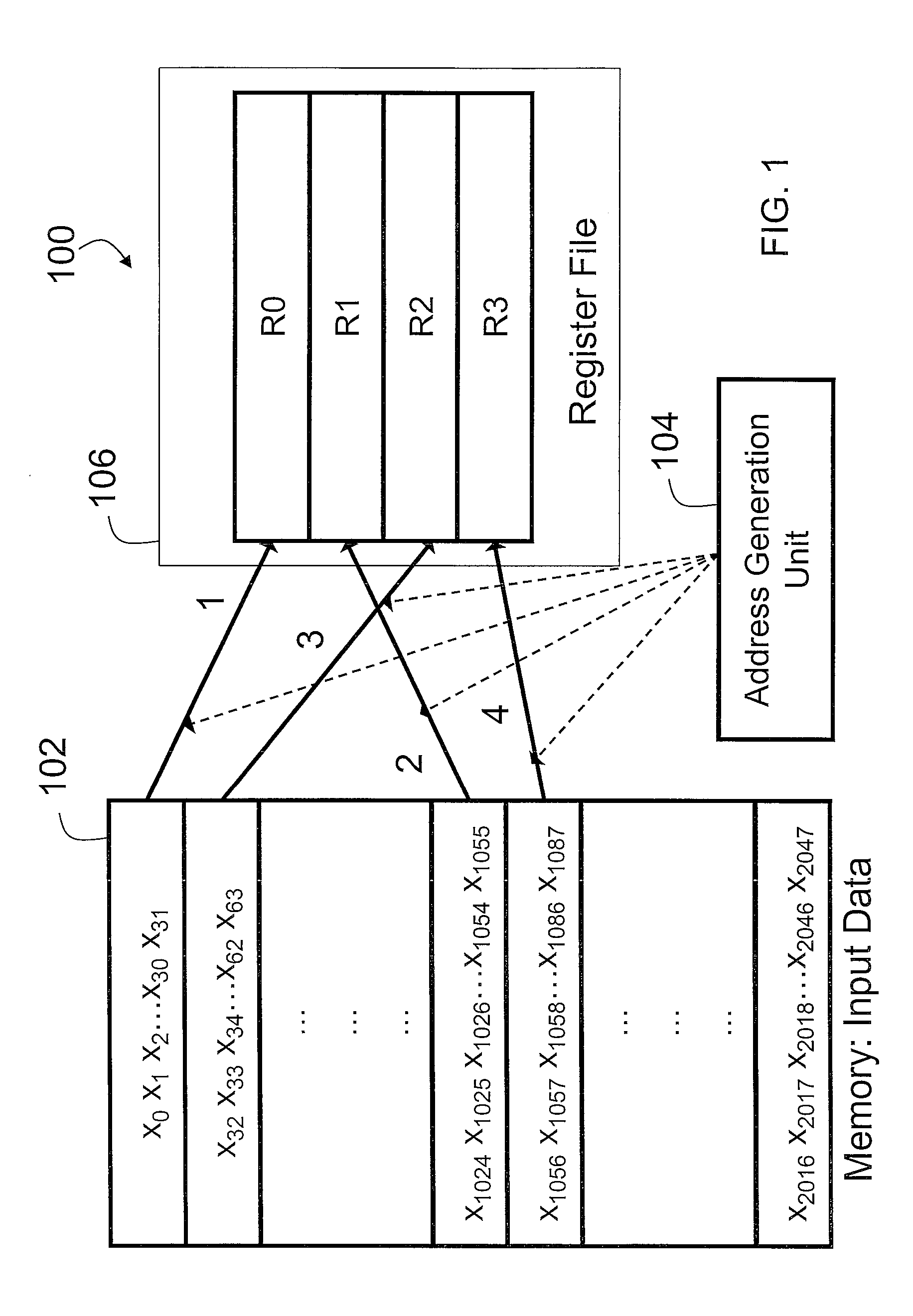
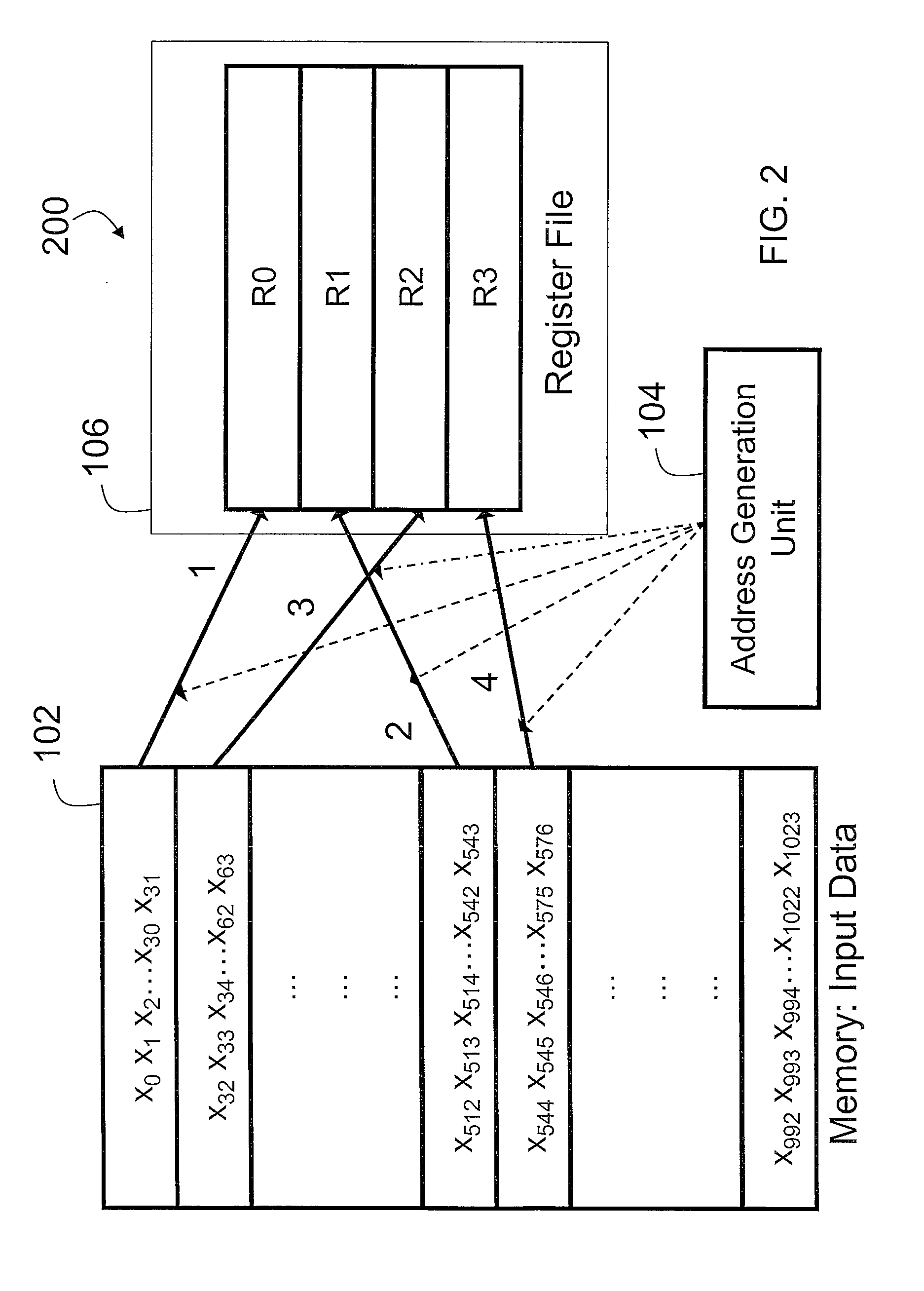
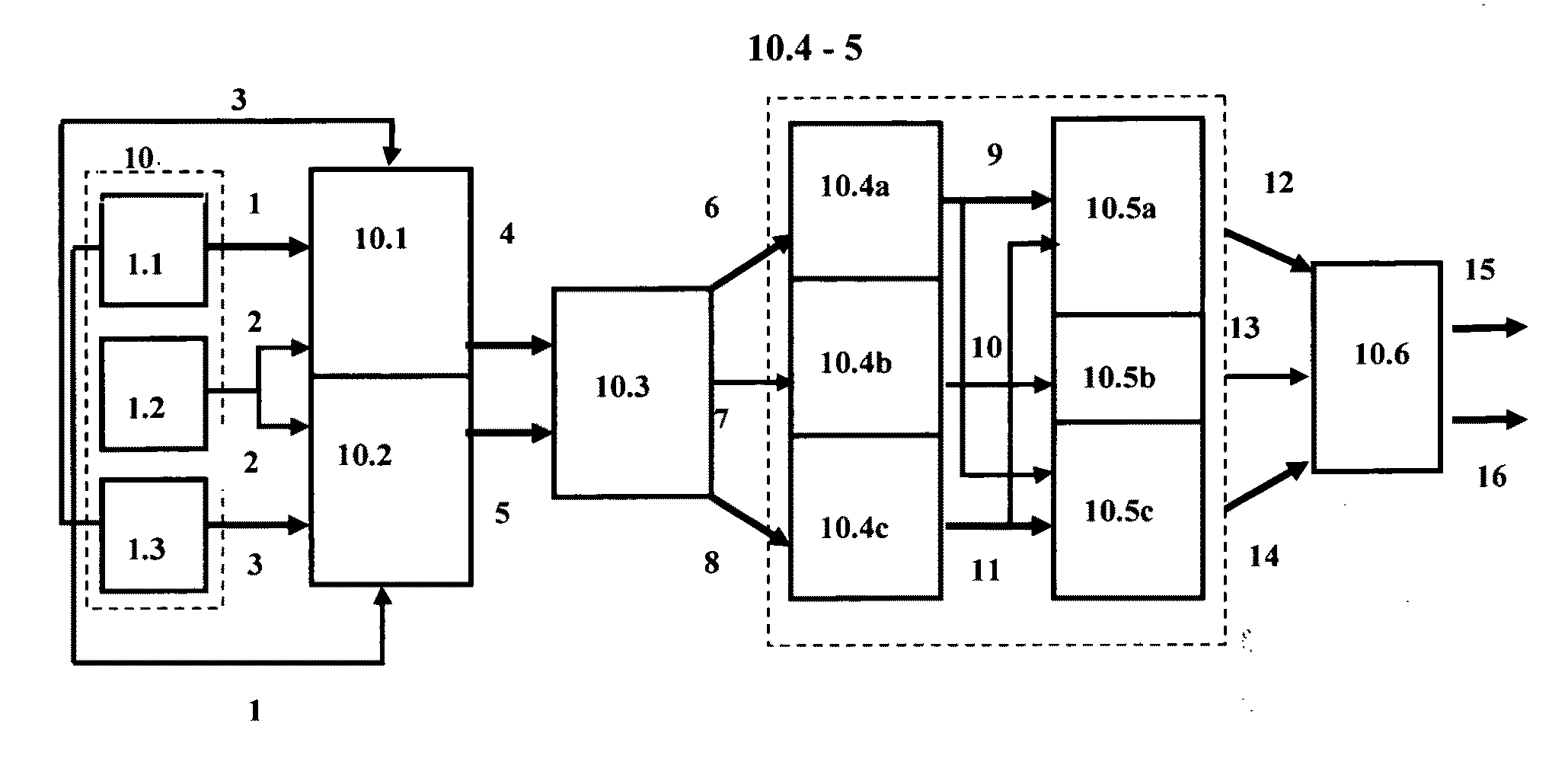
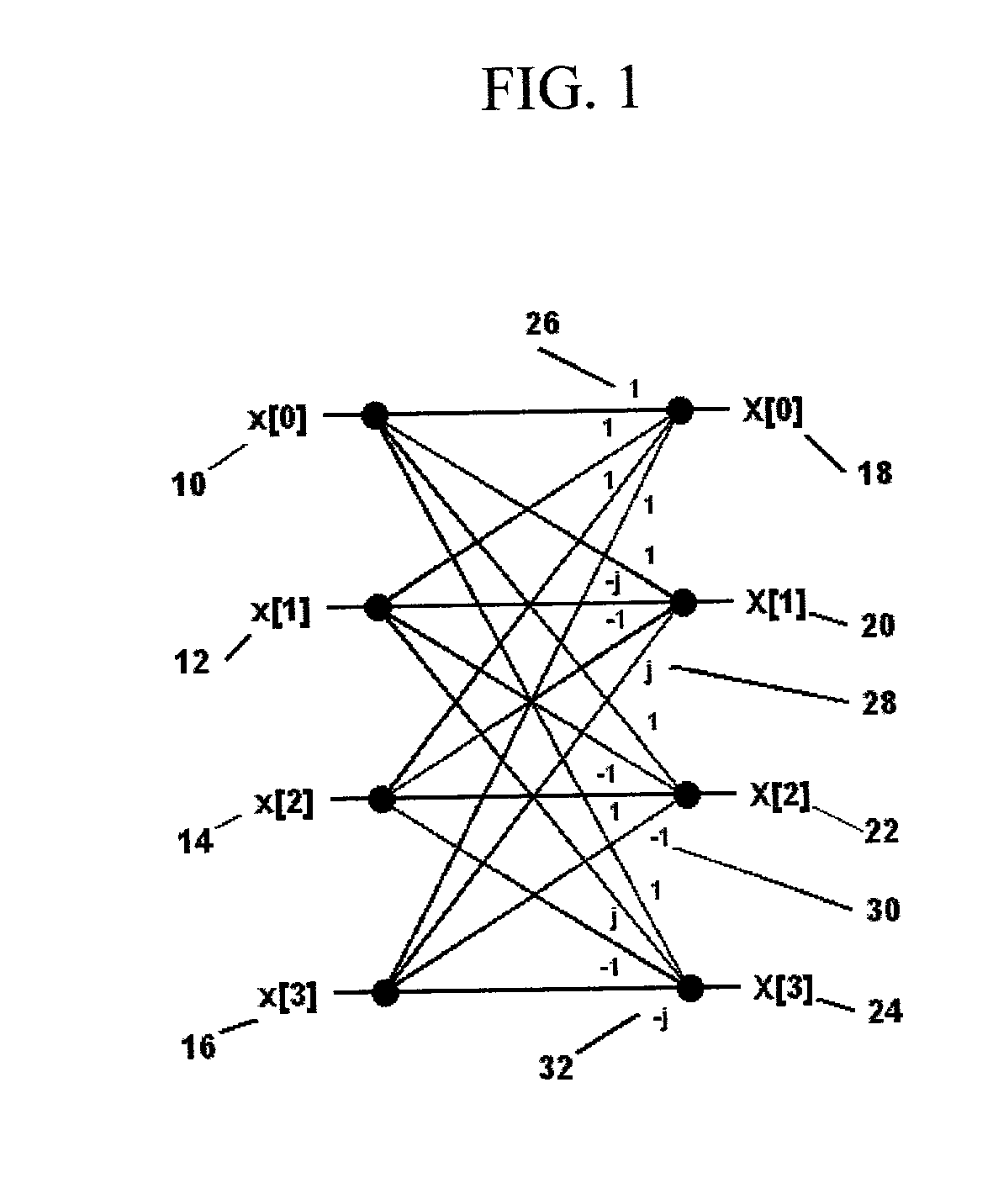
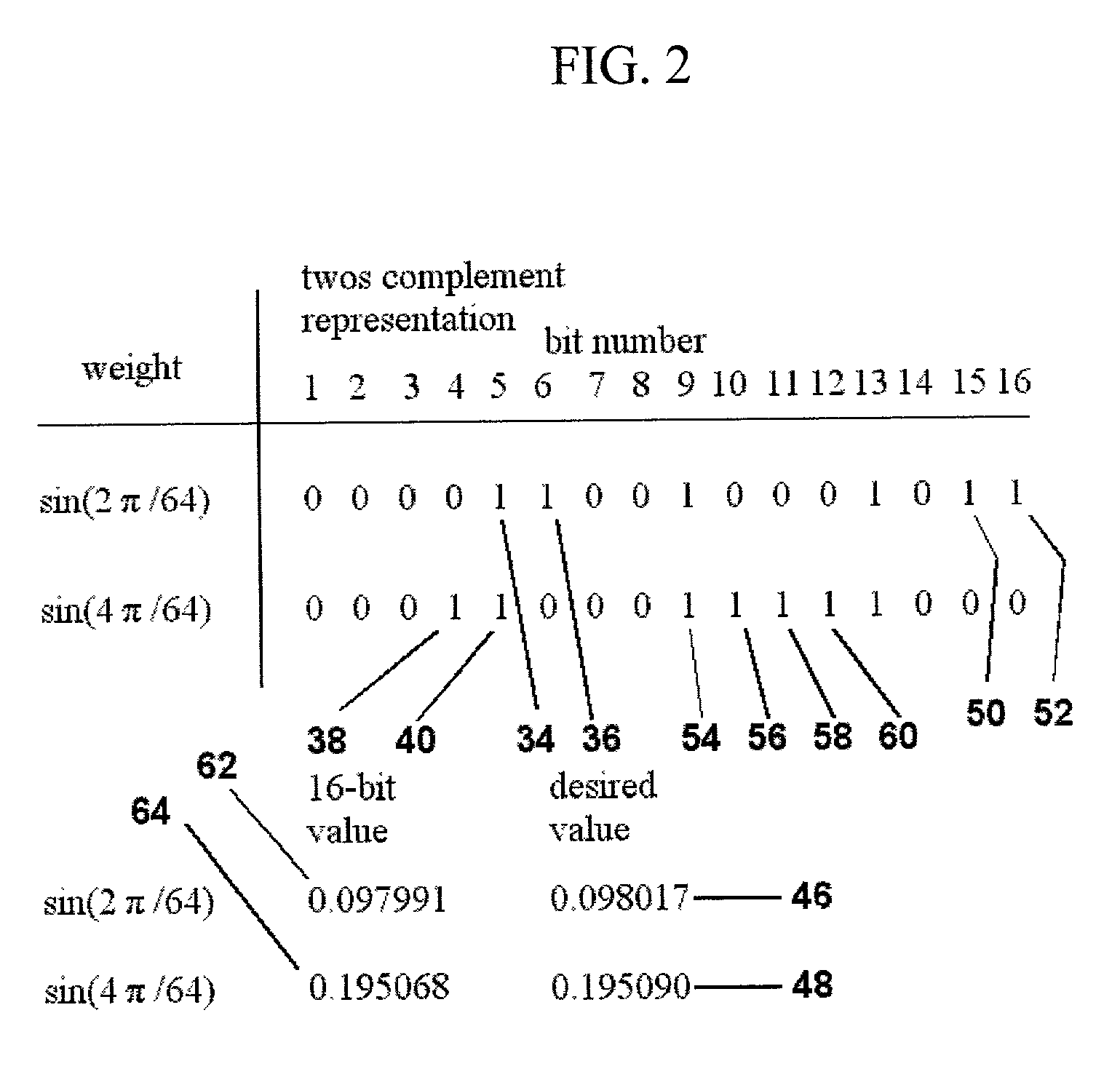
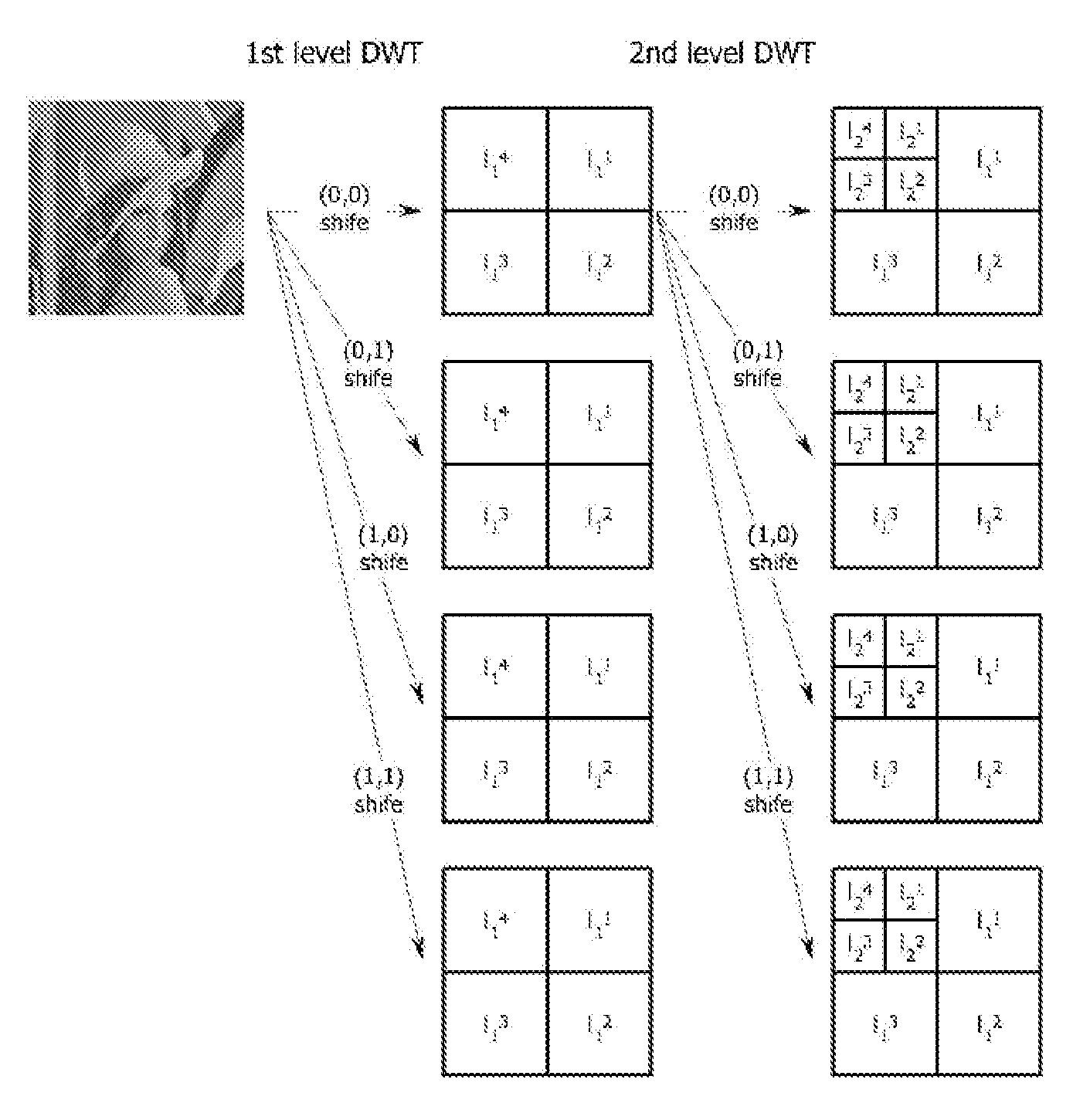
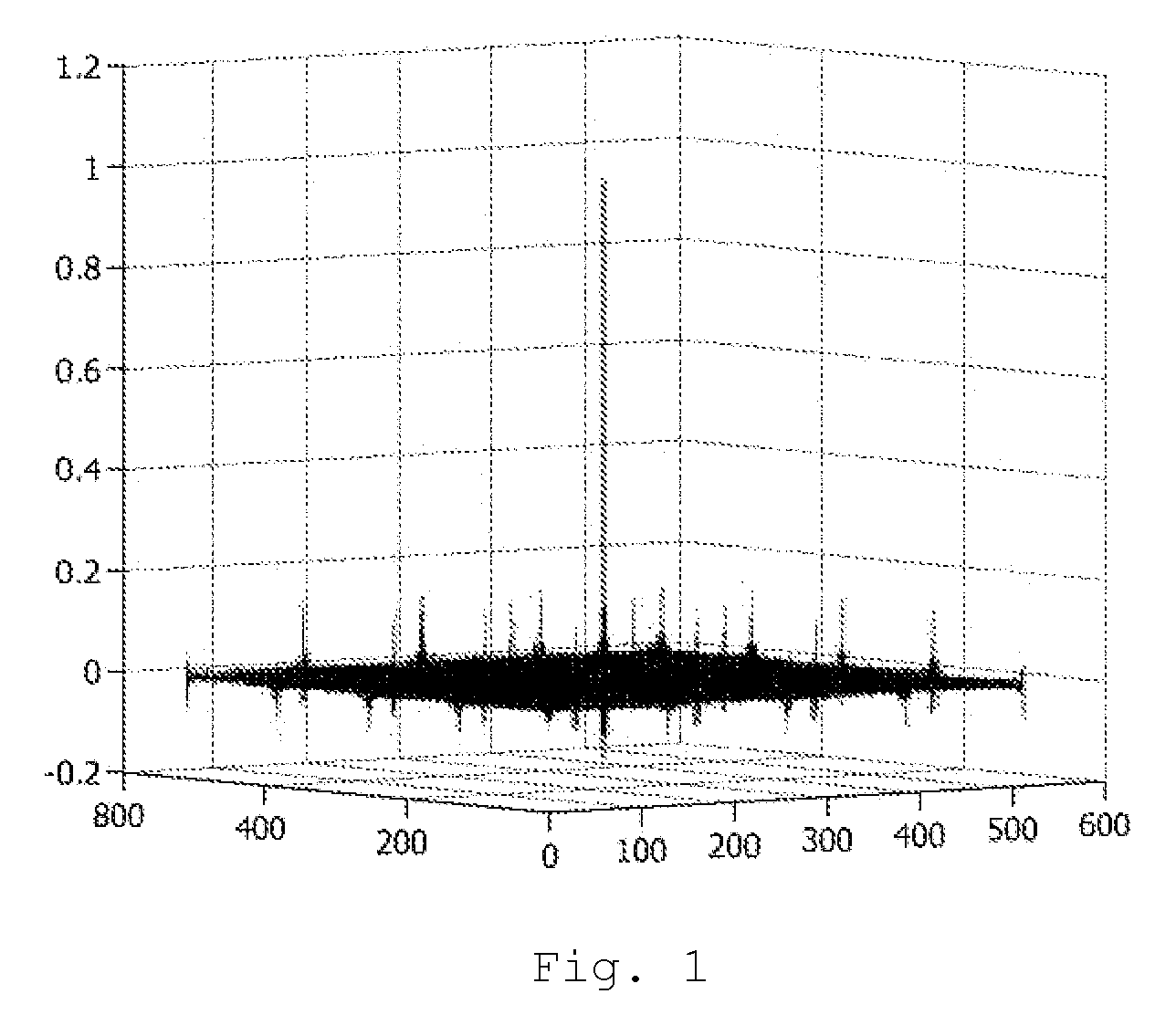
Patents
Literature
96 results about "Discrete transform" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In signal processing, discrete transforms are mathematical transforms, often linear transforms, of signals between discrete domains, such as between discrete time and discrete frequency. Many common integral transforms used in signal processing have their discrete counterparts. For example, for the Fourier transform the counterpart is the discrete Fourier transform.
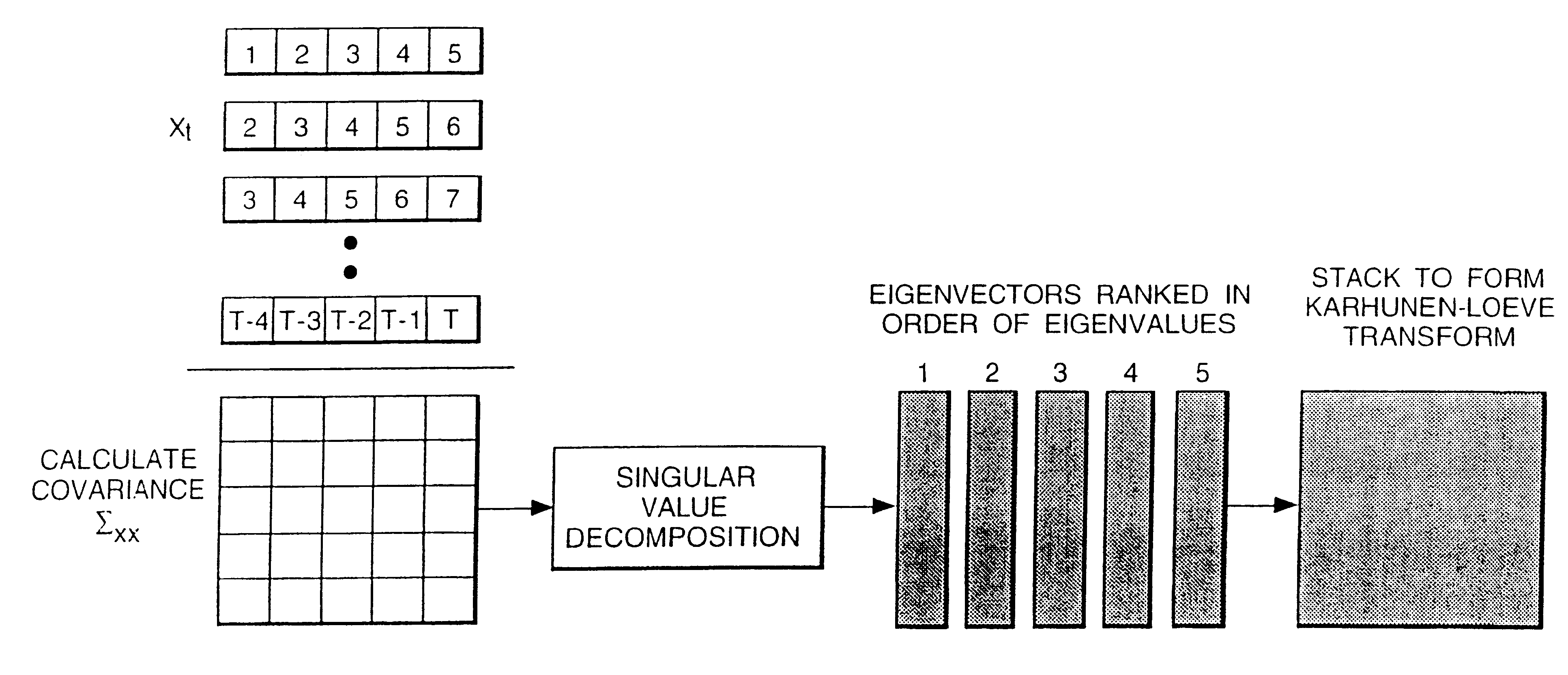
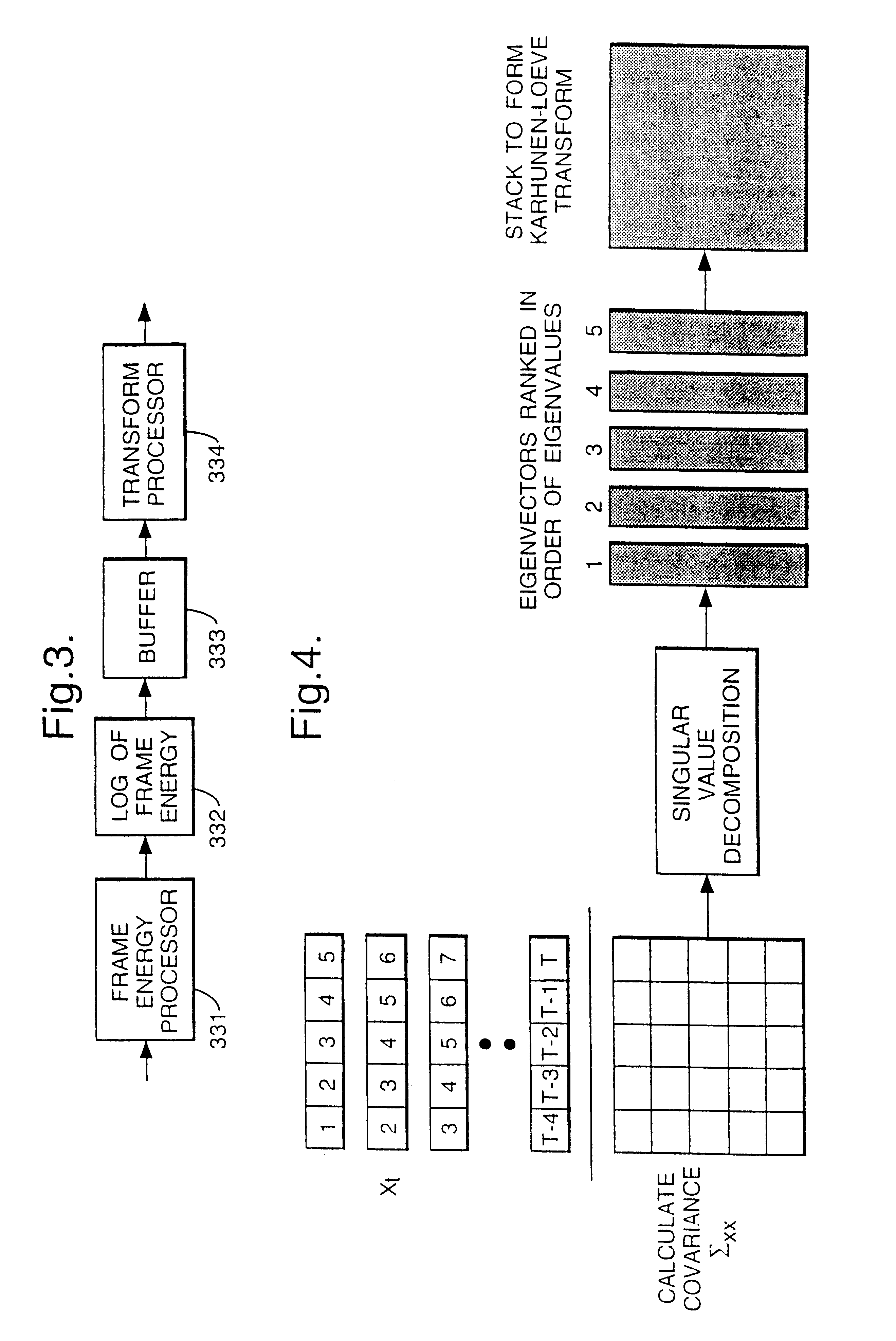
Speech transformation using log energy and orthogonal matrix
Calculate the log frame energy value of each of a pre-determined number n of frames of an input speech signal and apply a matrix transform to the n log frame energy values to form a temporal matrix representing the input speech signal. The matrix transform may be a discrete cosine transform.
Owner:BRITISH TELECOMM PLC
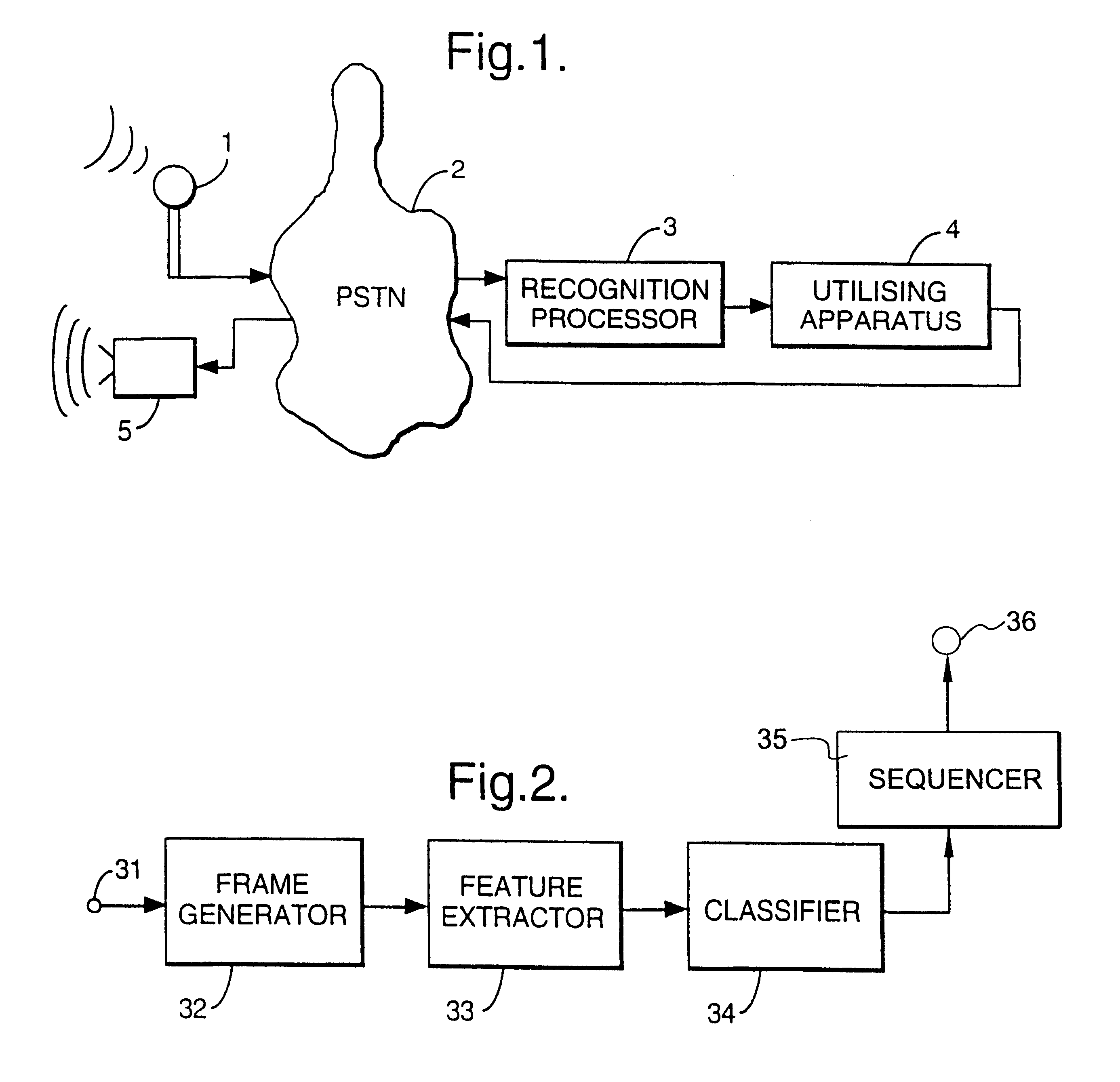
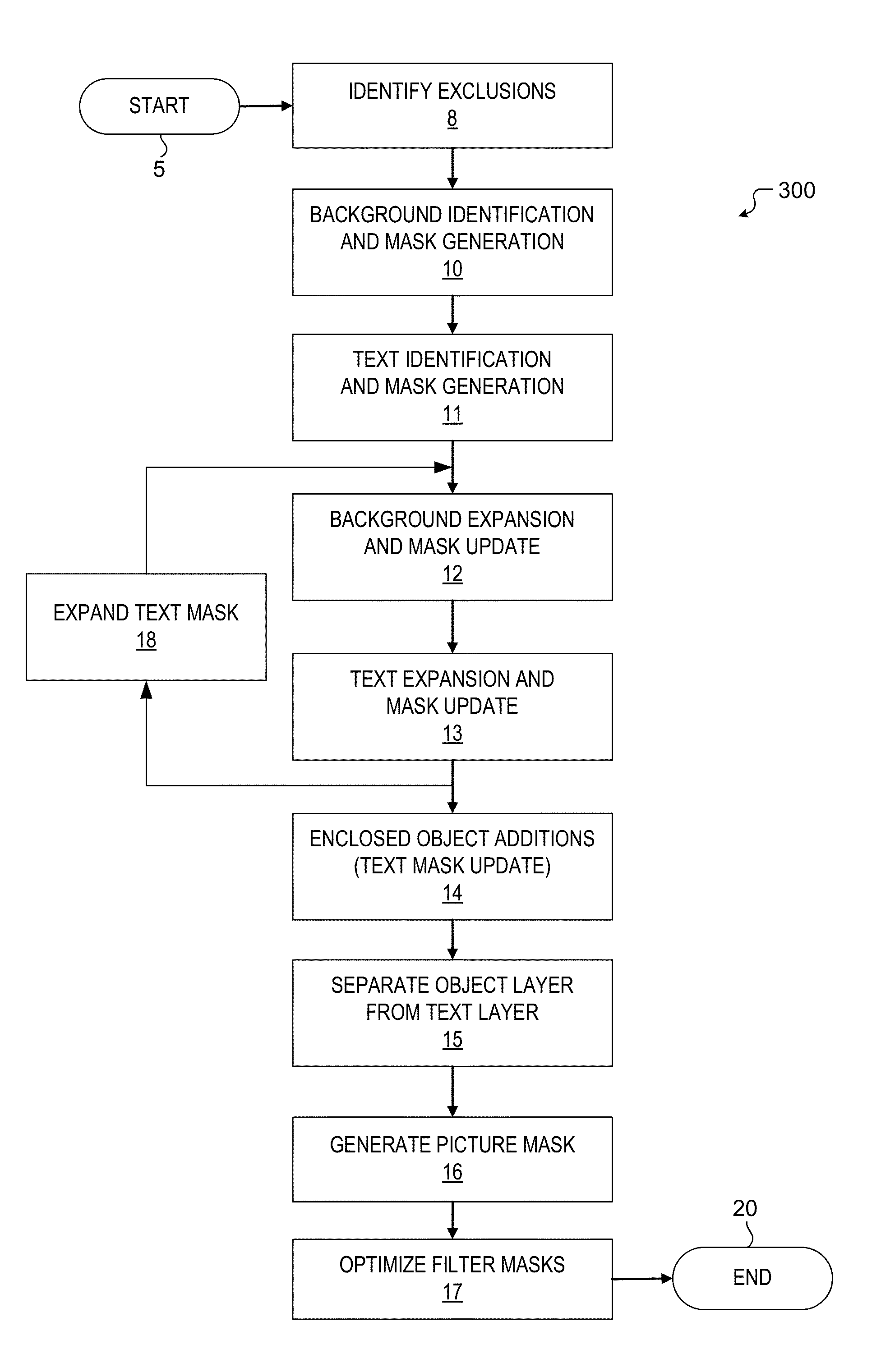
Apparatus and method for encoding an image generated in part by graphical commands
A method and apparatus for encoding an image is disclosed. A decomposition circuit comprises a set of pixel filters used to identify picture pixels, background pixels and text pixels of the image. An image encoding circuit comprises a lossy discrete transform encoder for encoding the picture pixels, a constant color lossless encoder for encoding the background pixels, and a discrete color lossless encoder for encoding the text pixels.
Owner:TERADICI CORP
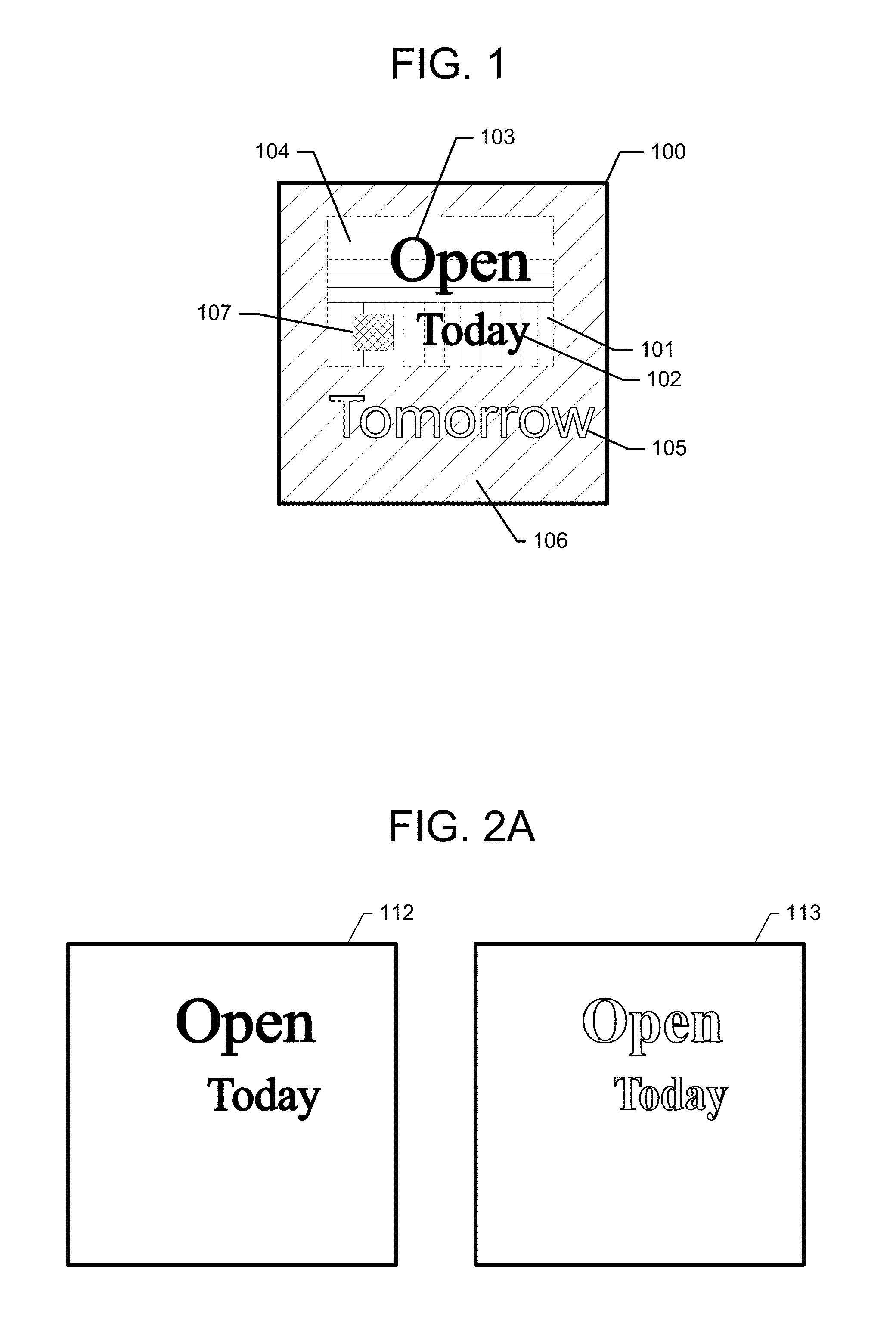
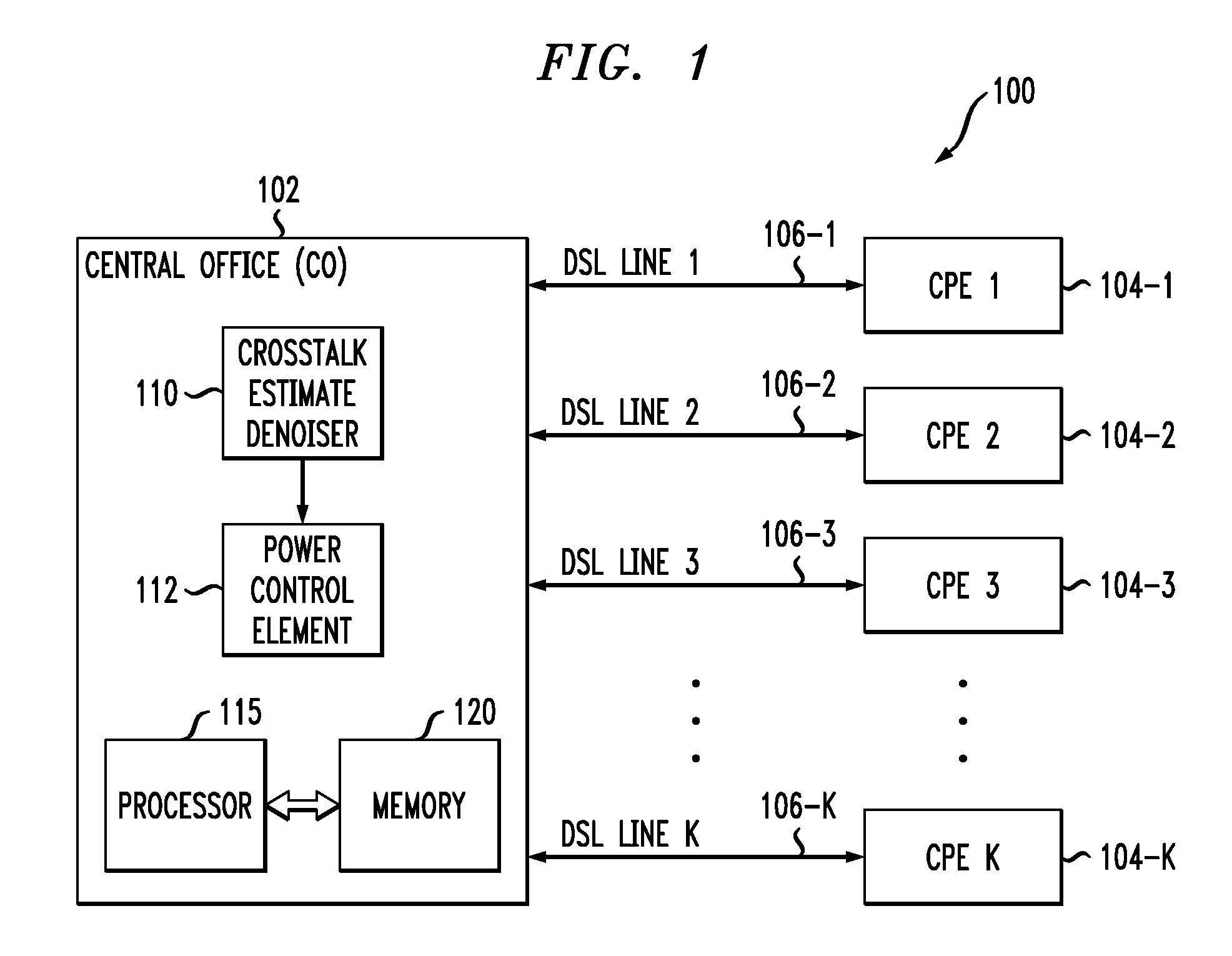
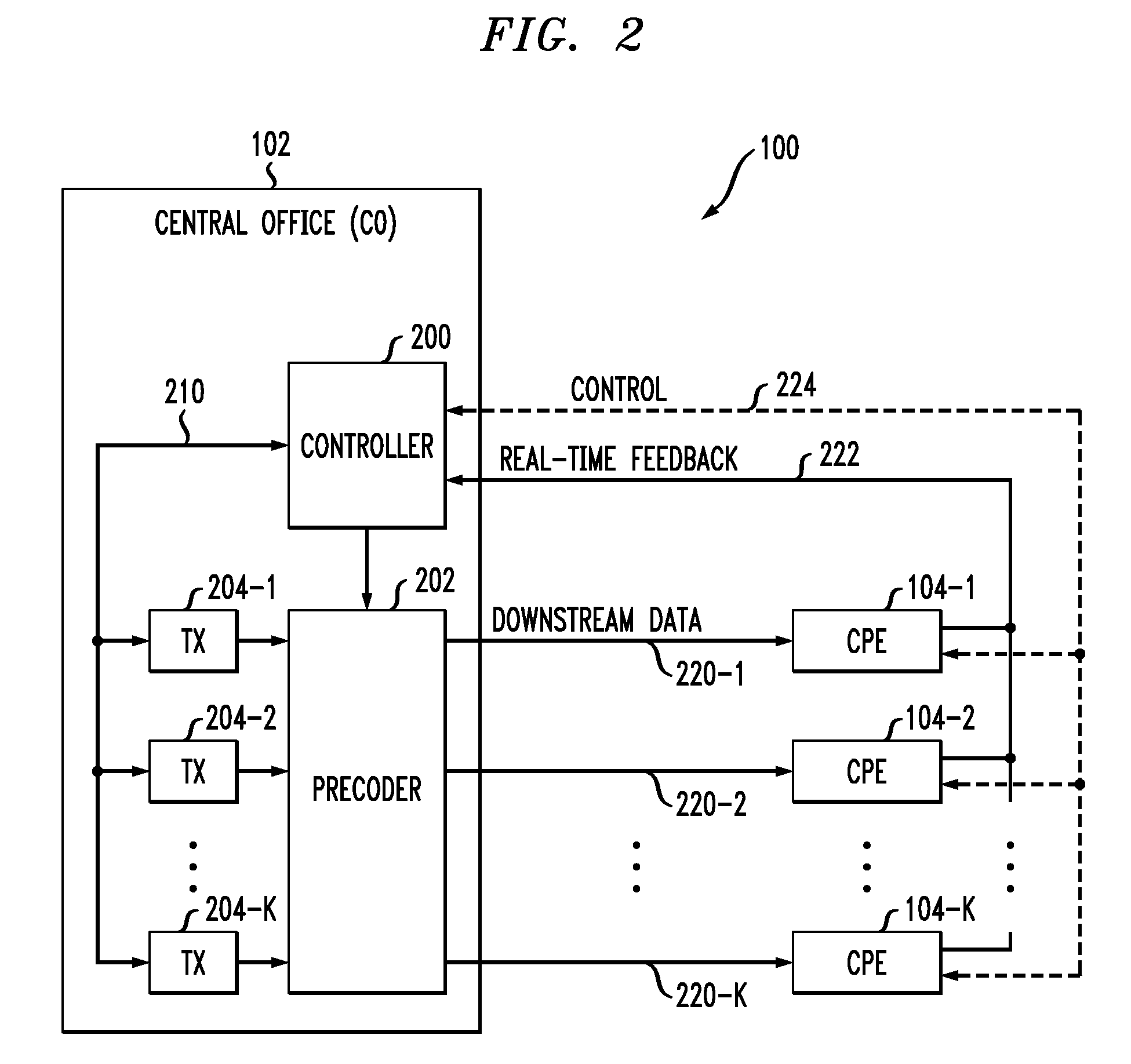
Power Control Using Denoised Crosstalk Estimates in a Multi-Channel Communication System
ActiveUS20100177855A1Reduction in average mean squared errorHigh speedError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsCommunications systemEngineering
An access node of a communication system is configured to generate denoised crosstalk estimates for respective channels of the system and to adjust power levels of signals transmitted over one or more of the channels based on the denoised crosstalk estimates. The access node obtains crosstalk estimates for the respective channels. The access node is configured to convert the crosstalk estimate for a given channel to a discrete transform domain, to substantially eliminate in the discrete transform domain one or more designated portions of the crosstalk estimate for the given channel, and to convert remaining portions of the crosstalk estimate for the given channel back from the discrete transform domain to obtain the corresponding denoised crosstalk estimate for the given channel. The access node may comprise one or more central offices of a DSL communication system.
Owner:RPX CORP
Compressive sensing
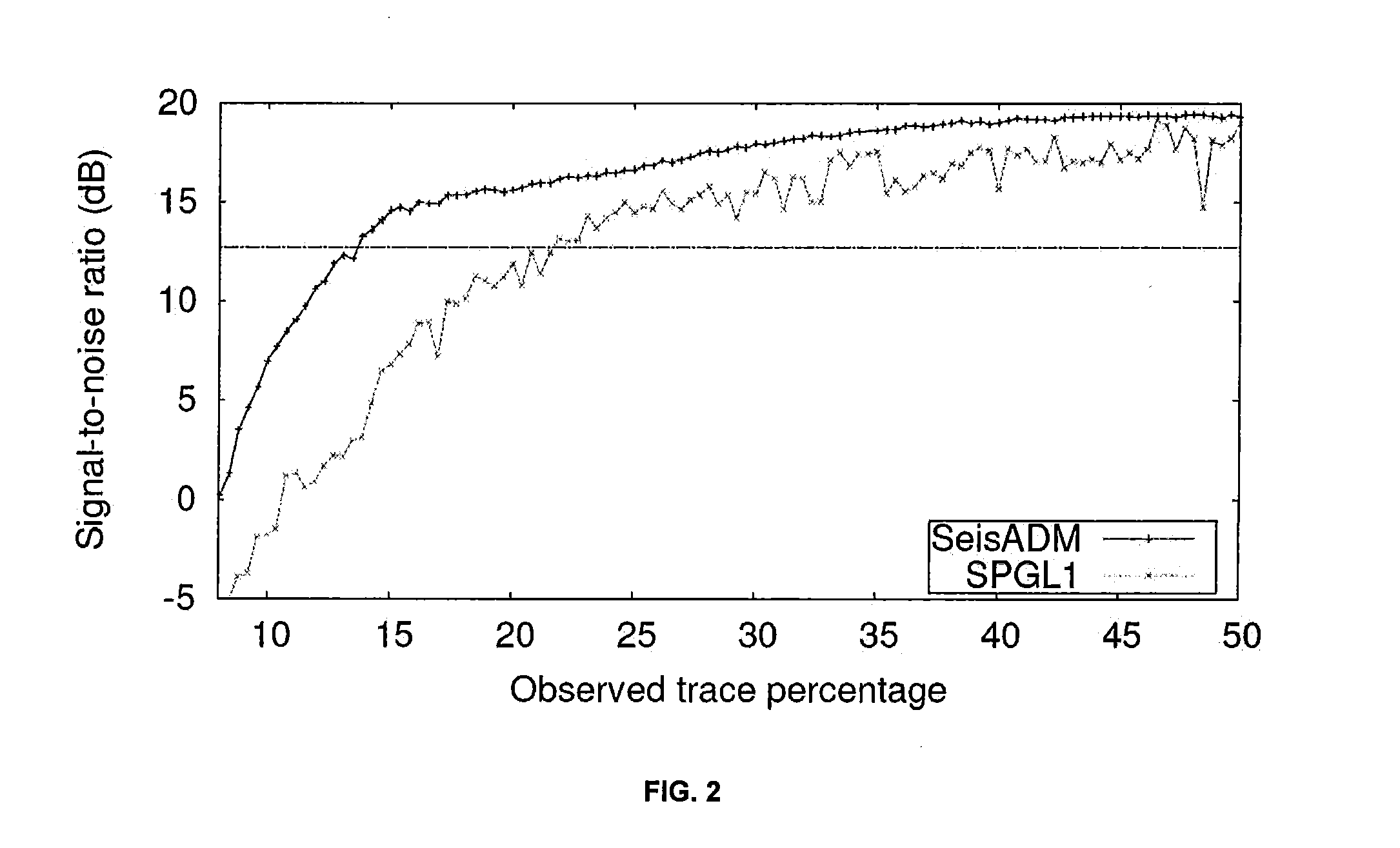
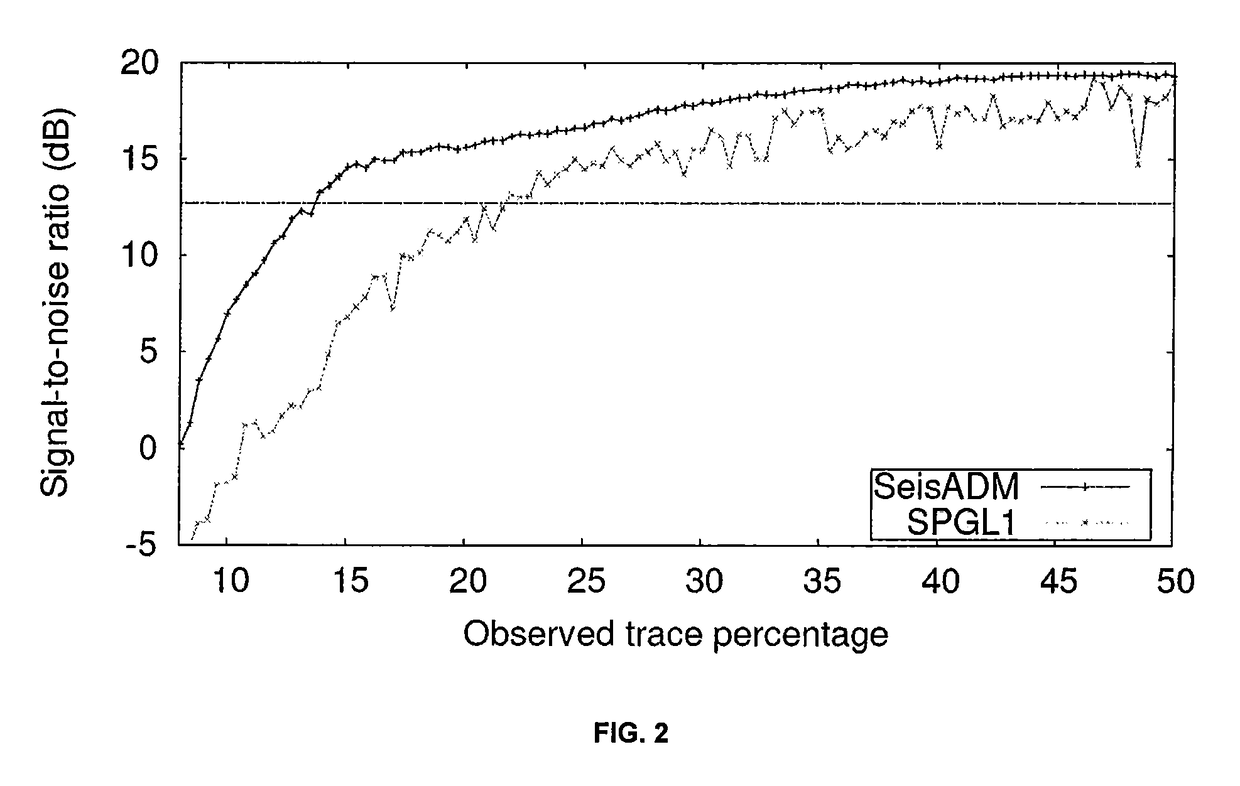
ActiveUS20150124560A1Efficient and robust algorithmLess computation timeSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic traceDiscrete transform
Computer-implemented method for determining optimal sampling grid during seismic data reconstruction includes: a) constructing an optimization model, via a computing processor, given by minu∥Su∥1 s.t. ∥Ru−b∥2≦σ wherein S is a discrete transform matrix, b is seismic data on an observed grid, u is seismic data on a reconstruction grid, and matrix R is a sampling operator; b) defining mutual coherence asμ≤CSm(logn)6,wherein C is a constant, S is a cardinality of Su, m is proportional to number of seismic traces on the observed grid, and n is proportional to number of seismic traces on the reconstruction grid; c) deriving a mutual coherence proxy, wherein the mutual coherence proxy is a proxy for mutual coherence when S is over-complete and wherein the mutual coherence proxy is exactly the mutual coherence when S is a Fourier transform; and d) determining a sample grid r*=arg minr μ(r).
Owner:SHEARWATER GEOSERVICES SOFTWARE INC
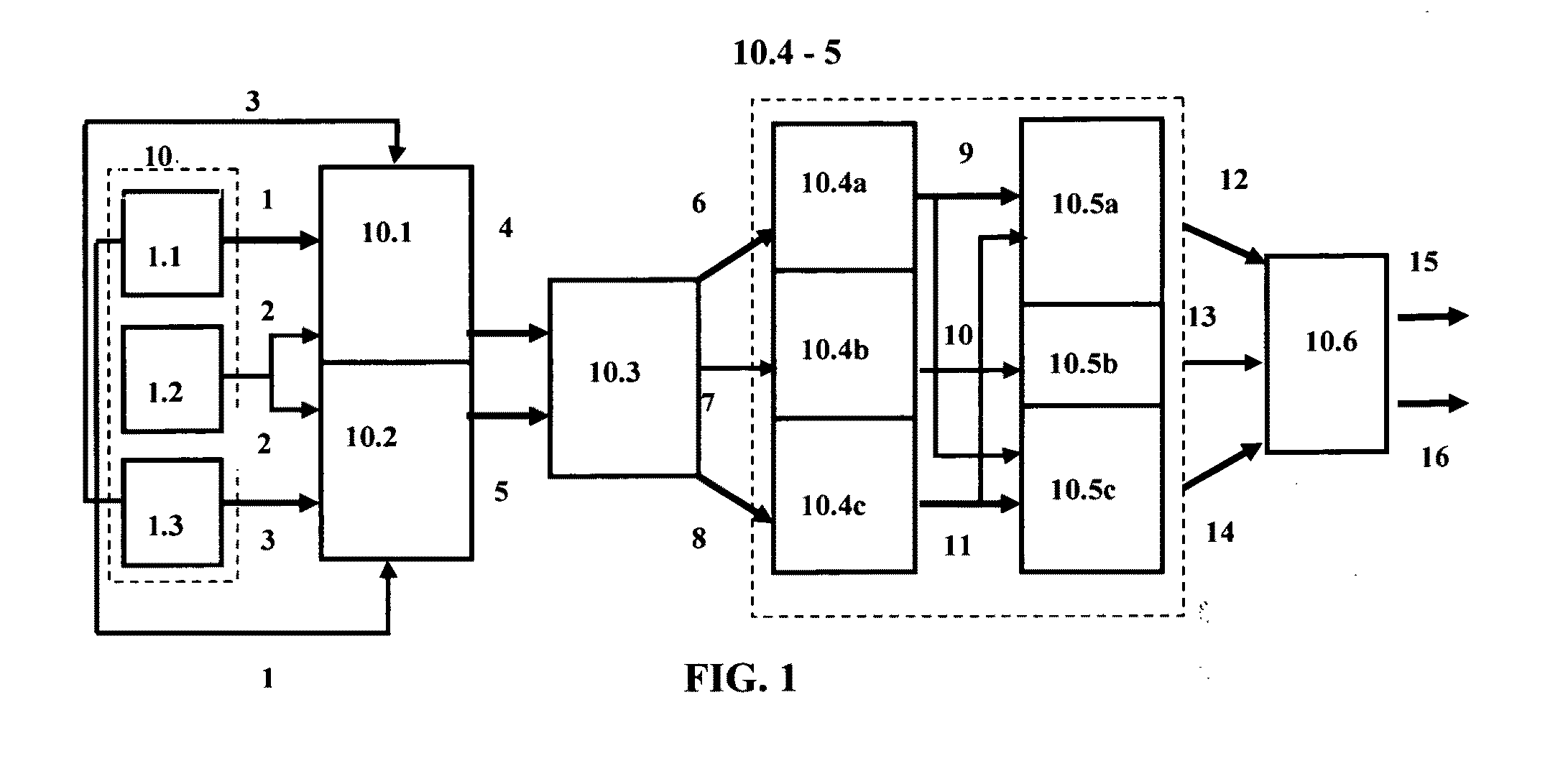
Combined IFFT and FFT system
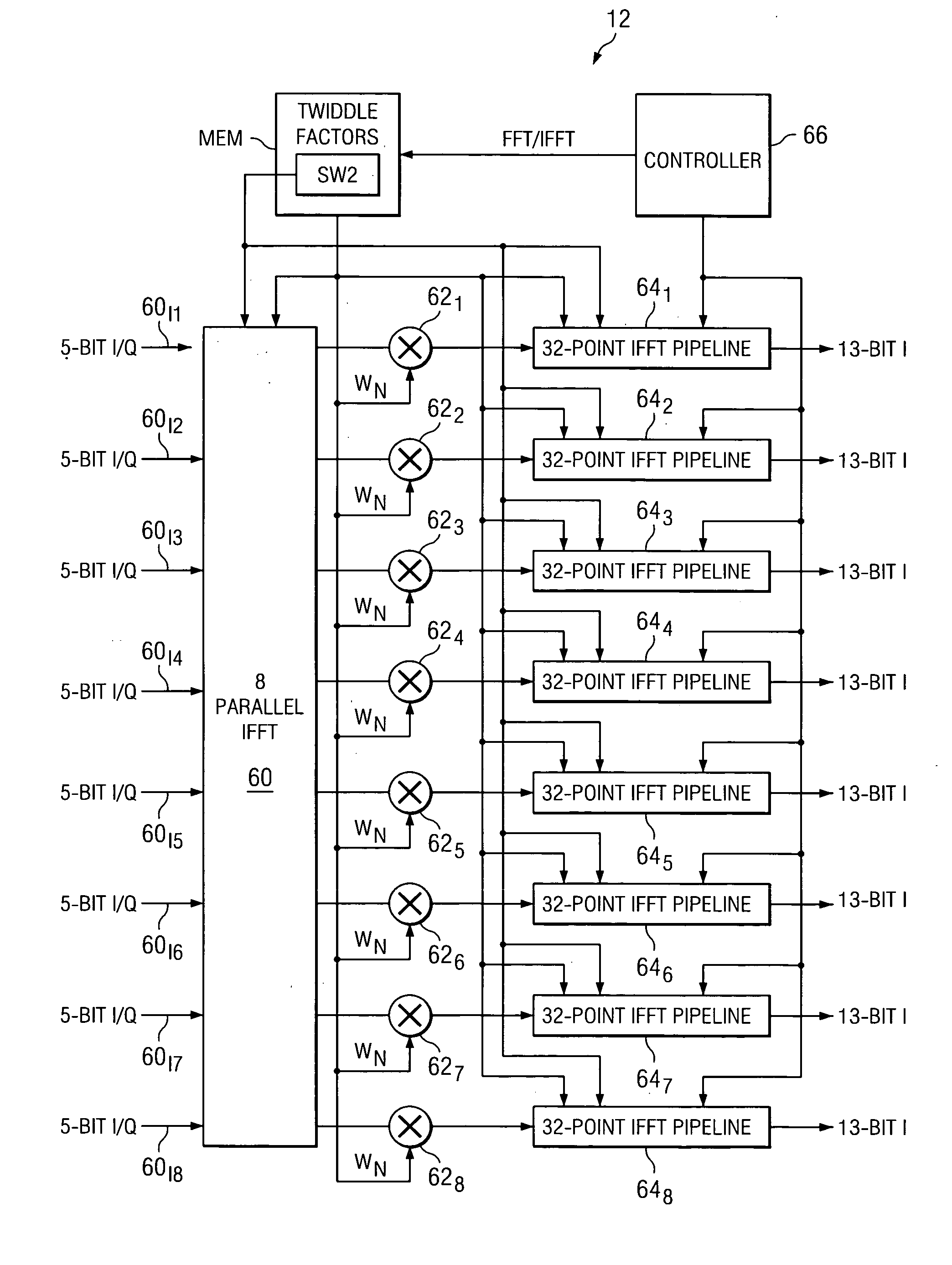
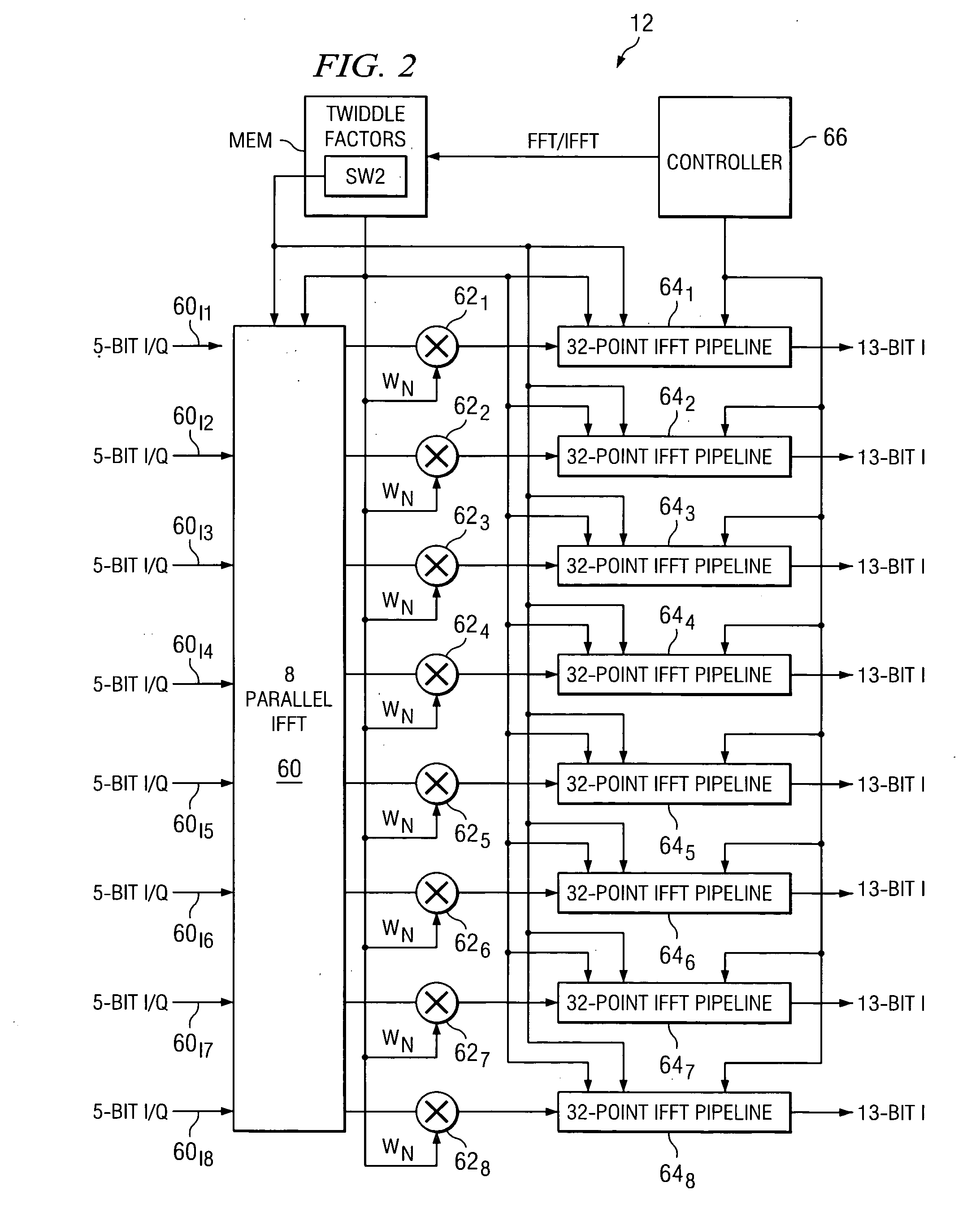
A system (12) for determining discrete transforms as between time and frequency domains. The system comprises a grid (60) comprising adders and multipliers. The grid is operable to perform in parallel an integer number P operations of a first transform function selected from one of either an IFFT or an FFT. The system also comprises the integer number of P serially-operating pipelines (641-648). Each of the pipelines is coupled to the grid and is operable to perform serially over a number of cycles an integer number S operations of the first transform. In the system, S and P are both greater than one and, in combination, the grid and the serially-operating pipelines perform the first transform type as an S×P-point transform. In a first instance at least a portion of the grid is operable to perform IFFT operations. In a second instance at least a portion of the grid is operable to perform FFT operations.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Adaptive modulation-demodulation method base on fractional order Fourier transform
InactiveCN101827060AImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionChannel state informationCurrent channel
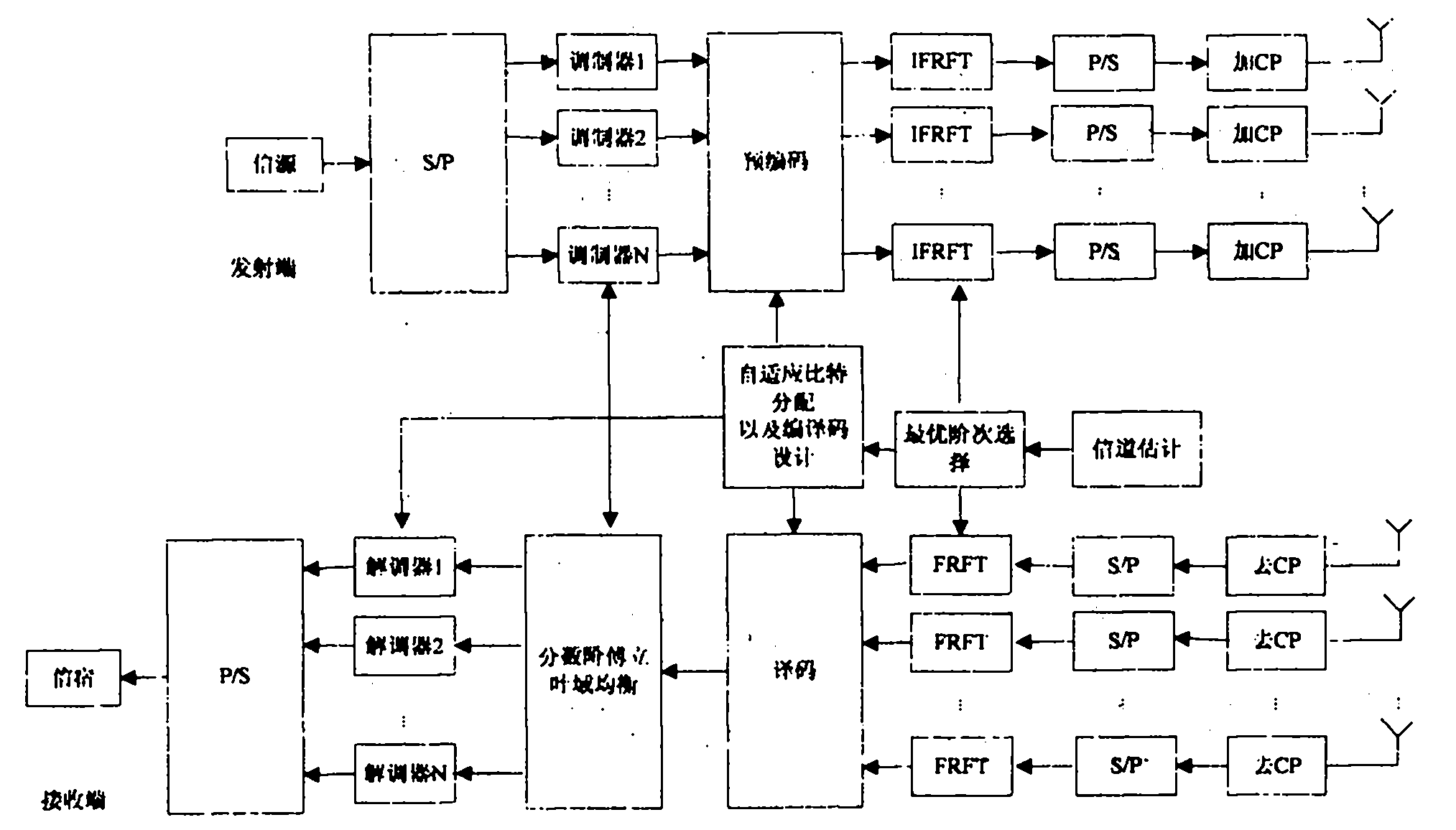
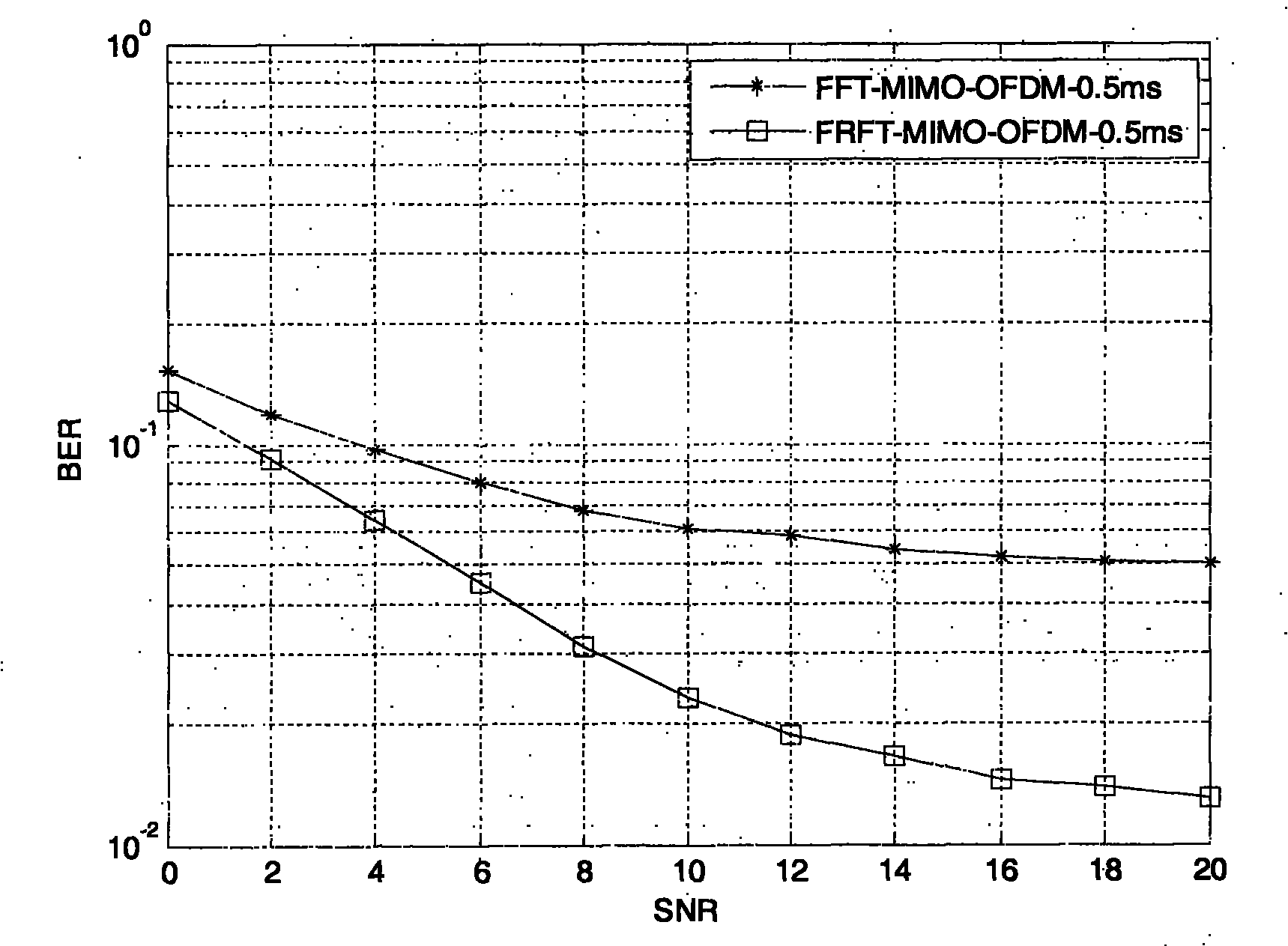
The invention provides an adaptive modulation-demodulation method base on fractional order Fourier transform, aiming at reducing influence caused by feedback time delay specific to an MIMO-OFDM (Multiple Input Multiple Output-Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) adaptive modulation system which has feedback time delay, and enabling the system to have better performance in a fast time-varying channel. The method has the technical scheme that inverse discrete fractional order Fourier transform is used to replace inverse discrete Fourier transform for carrying out subcarrier modulation at a transmitting terminal, discrete fractional order Fourier transform is used to replace discrete Fourier transform for carrying out subcarrier demodulation at a receiving terminal, the optimal fractional order Fourier transform order selection is carried out by channel estimation information fed back to the transmitting terminal by the receiving terminal, the deviation between the current channel state information and the feedback channel state information is reduced and the performance of the system having time delay is enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Discrete fourier transform (DFT) watermark
InactiveUS20050036613A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital dataDigital video
A Discrete Fourier Transform watermark for use with digital images / video. A Y component of a Y, U(Cb), V(Cr) digital data stream representing color components of digital video is extracted as the digital data for embedding the watermark. The digital data is then scaled to a standard size. A Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is performed on the digital data, and a magnitude domain of the Discrete Fourier Transform is computed. The watermark is embedded into selected frequency bands of the computed magnitude domain of the Discrete Fourier Transform, thereby creating a watermarked magnitude domain. The selected frequency bands comprise one or more middle frequency bands, and the middle frequency bands comprise a band of circular rings of the magnitude domain. An inverse Discrete Fourier Transform is performed on the watermarked magnitude domain to reconstruct the digital data with the embedded watermark.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
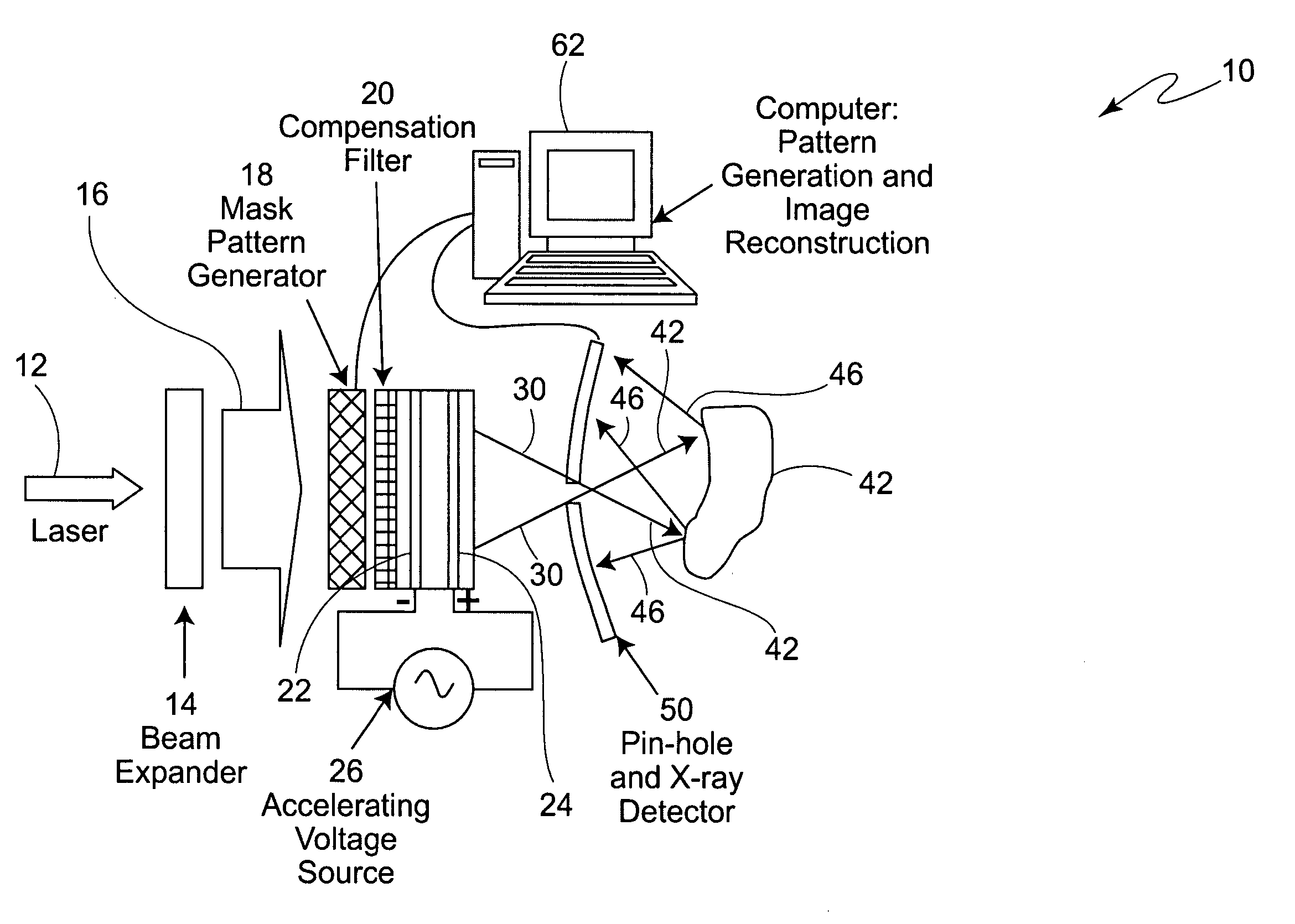
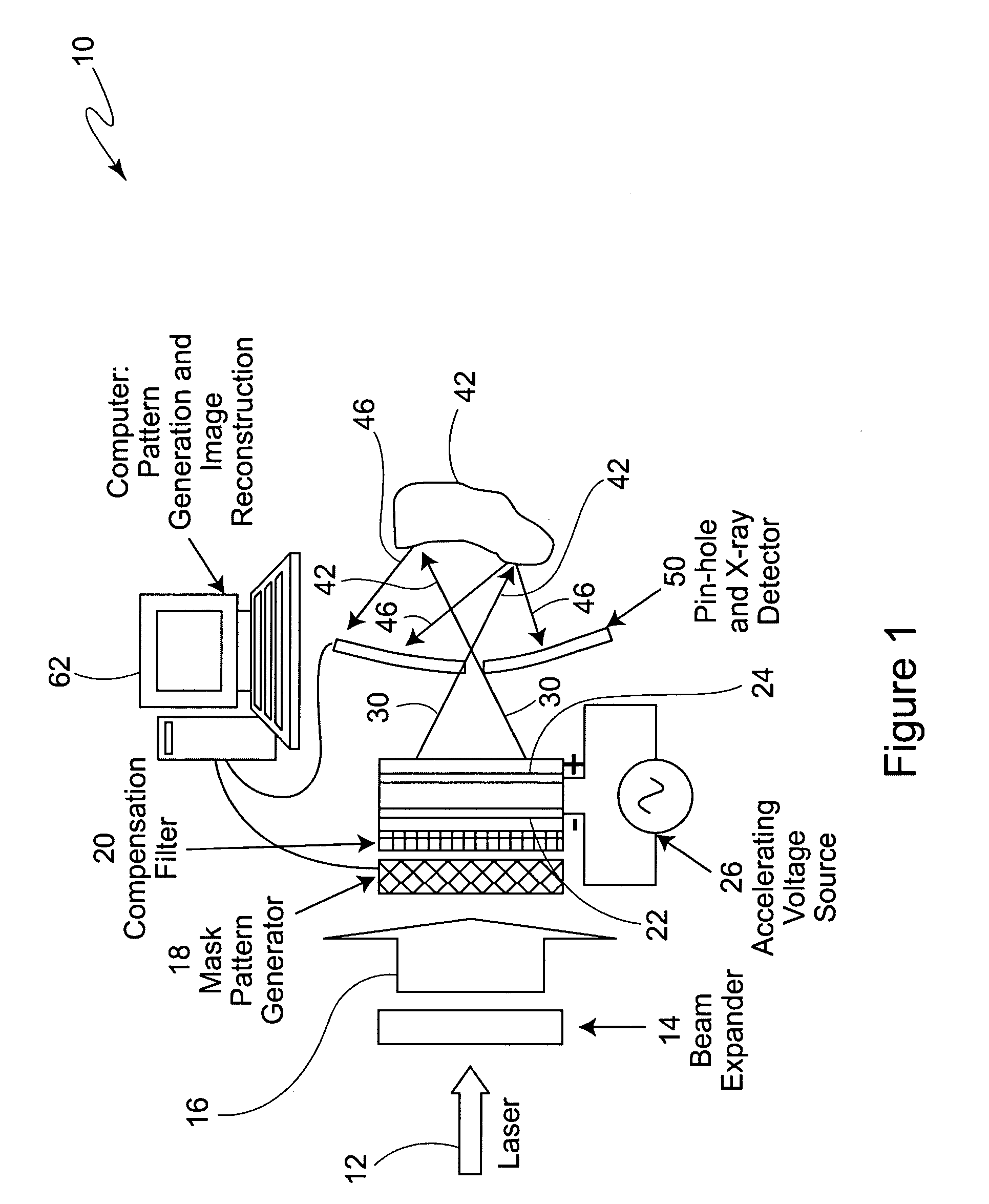
Backscatter imaging using hadamard transform masking
ActiveUS20050117701A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationCharacter and pattern recognitionHadamard transformX-ray
Backscatter imaging using Hadamard transform masking includes an area x-ray source with alternating, masked, Hadamard transform patterns. The total backscatter signal from a target for each pair of corresponding masks is recorded. The difference in signal strengths for each pair of corresponding masks is a direct measurement of the Hadamard transform coefficient for that mask. An image of the target is formed by performing an inverse discrete Hadamard transform on the complete matrix of coefficients.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
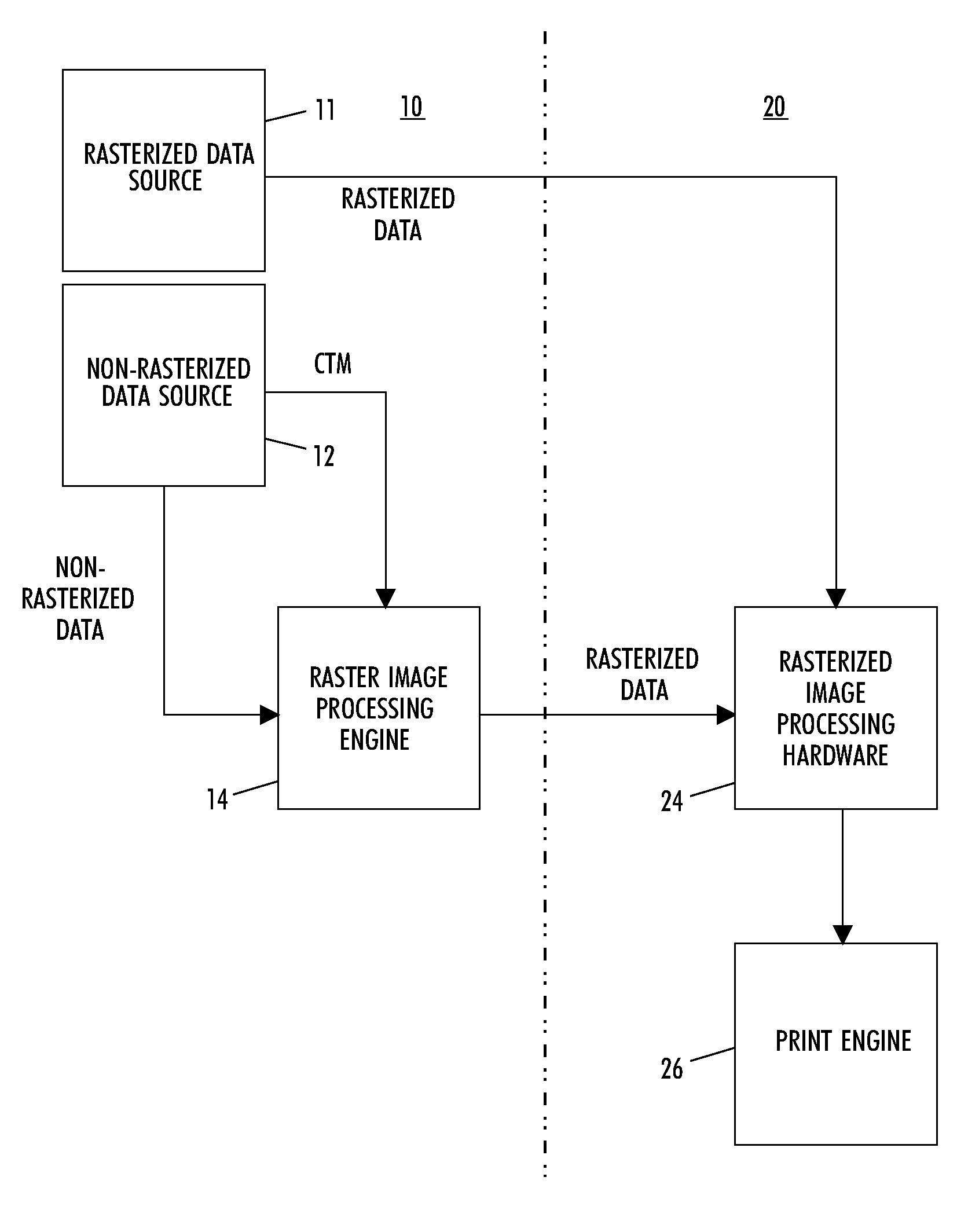
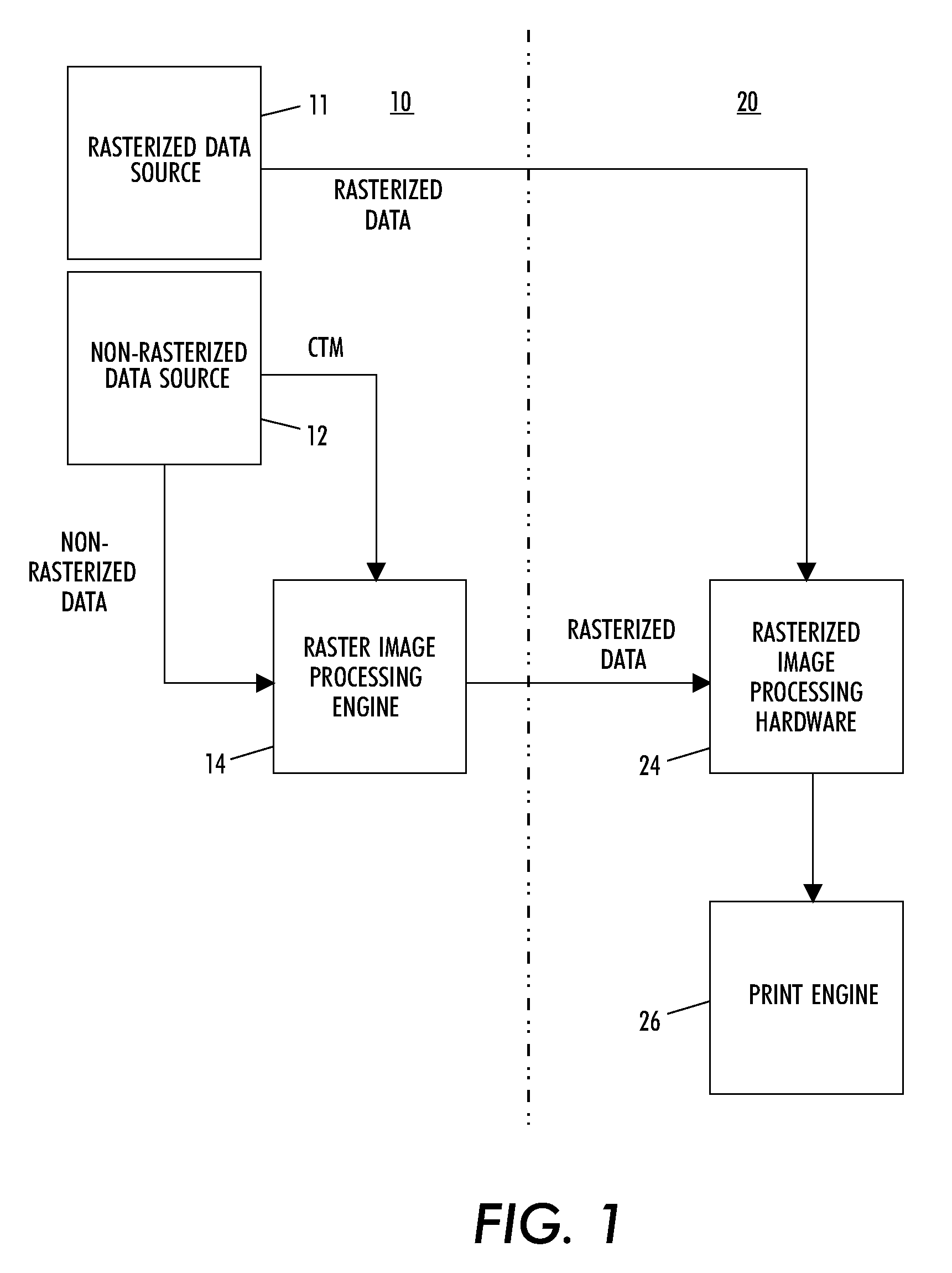
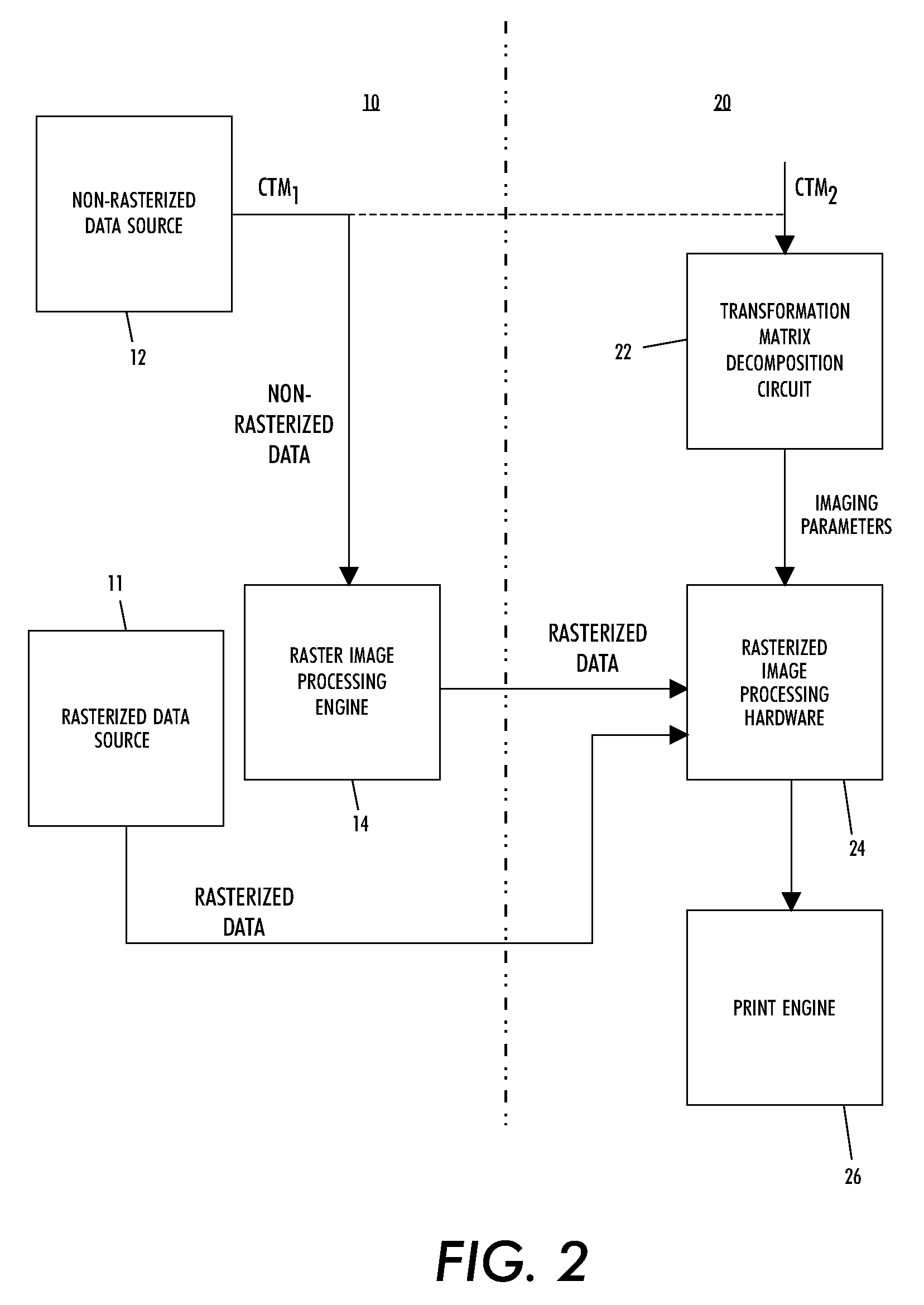
Method and system for utilizing transformation matrices to process rasterized image data
InactiveUS20100158411A1Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionTheoretical computer sciencePage description language
A method and system render rasterized data by receiving non-rasterized page description language data and a corresponding transformation matrix representing transformation operations to be performed. The non-rasterized page description language data is rasterizing to create rasterized data. The corresponding transformation matrix is decomposed into a plurality of individual transformation operation matrices and a discrete transformation operation value, from a corresponding individual transformation operation matrix, is generated for each transformation operation to be performed upon the rasterized data. The transformation operations are performed upon the rasterized data based upon the generated discrete transformation operation values.
Owner:XEROX CORP
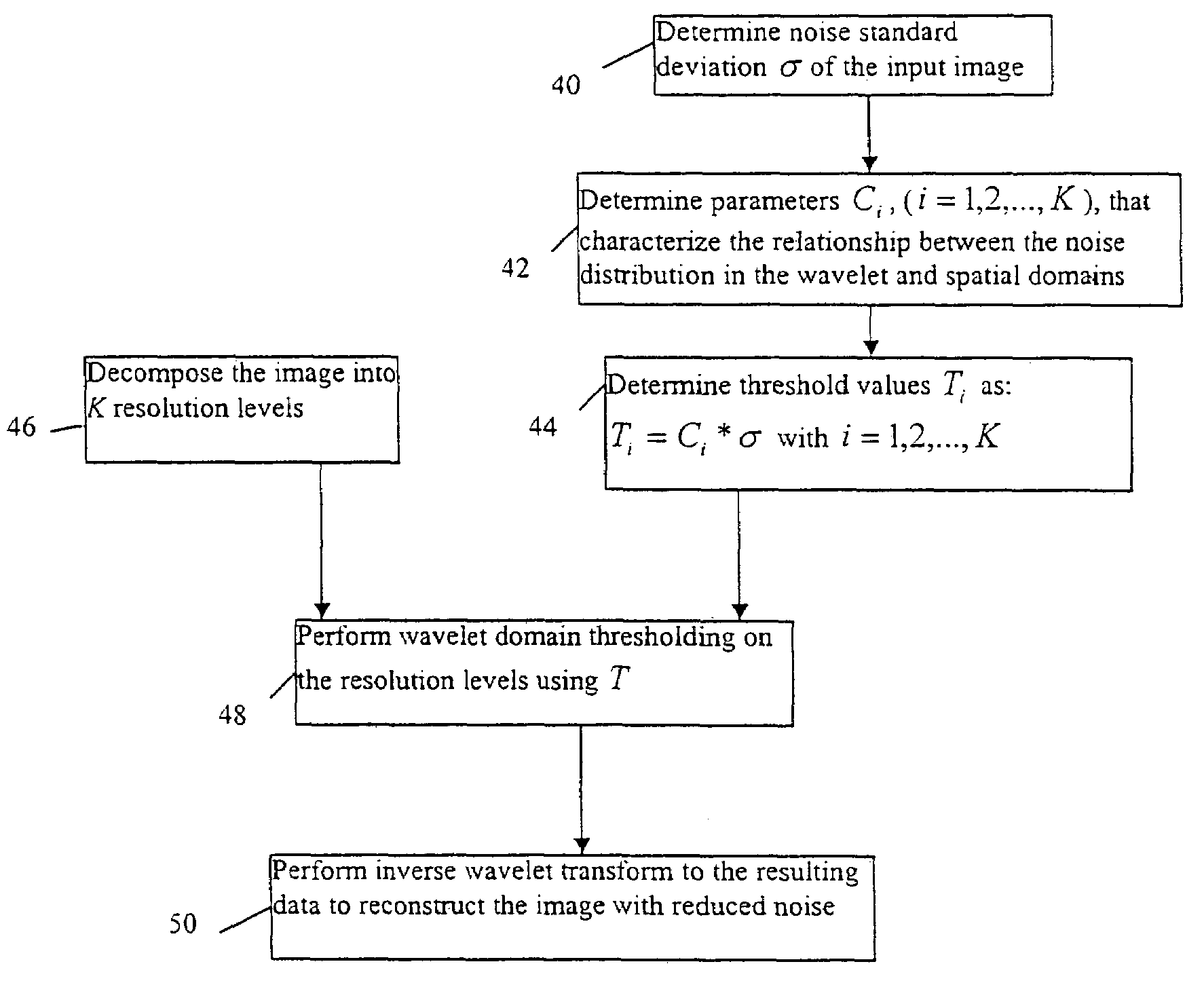
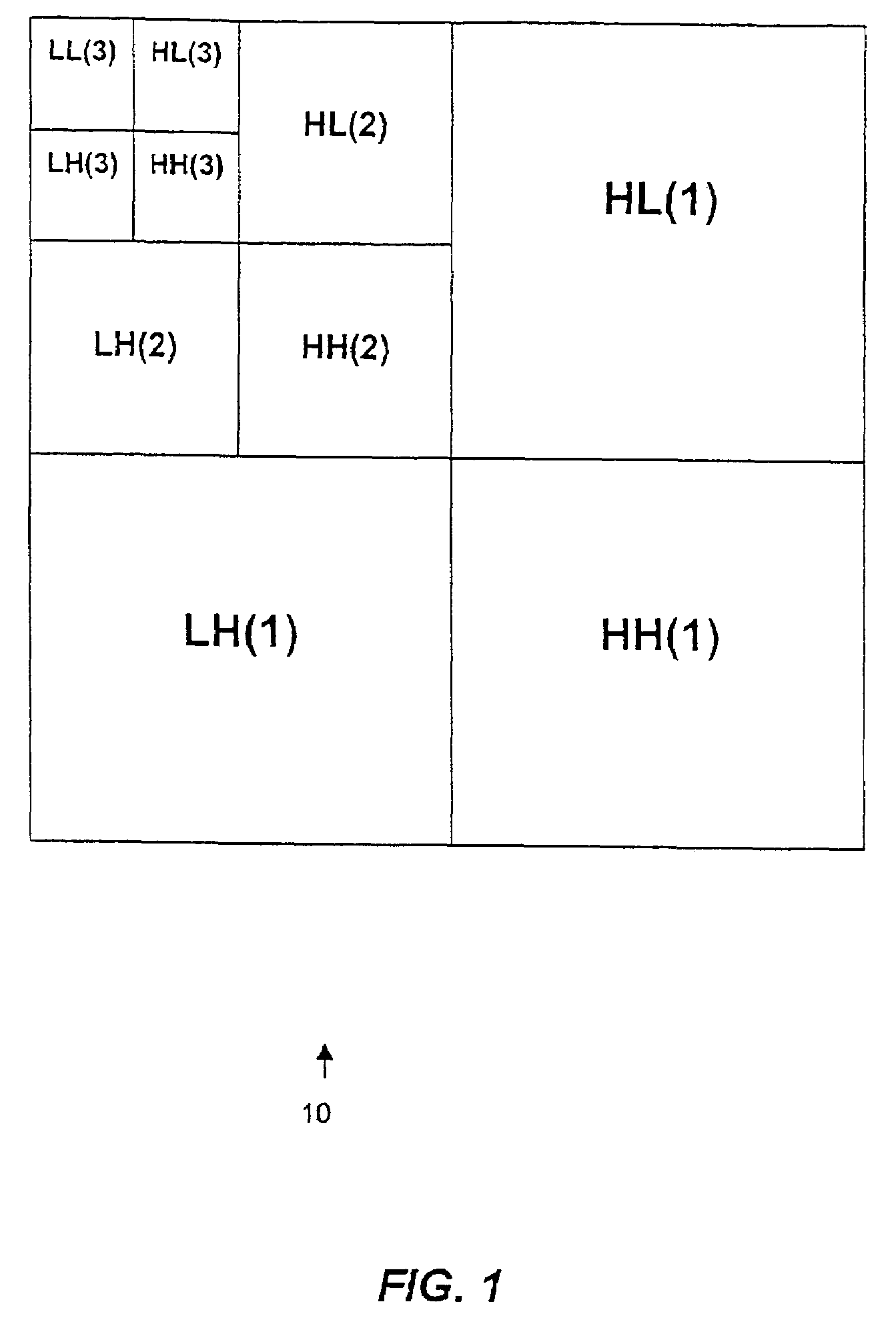
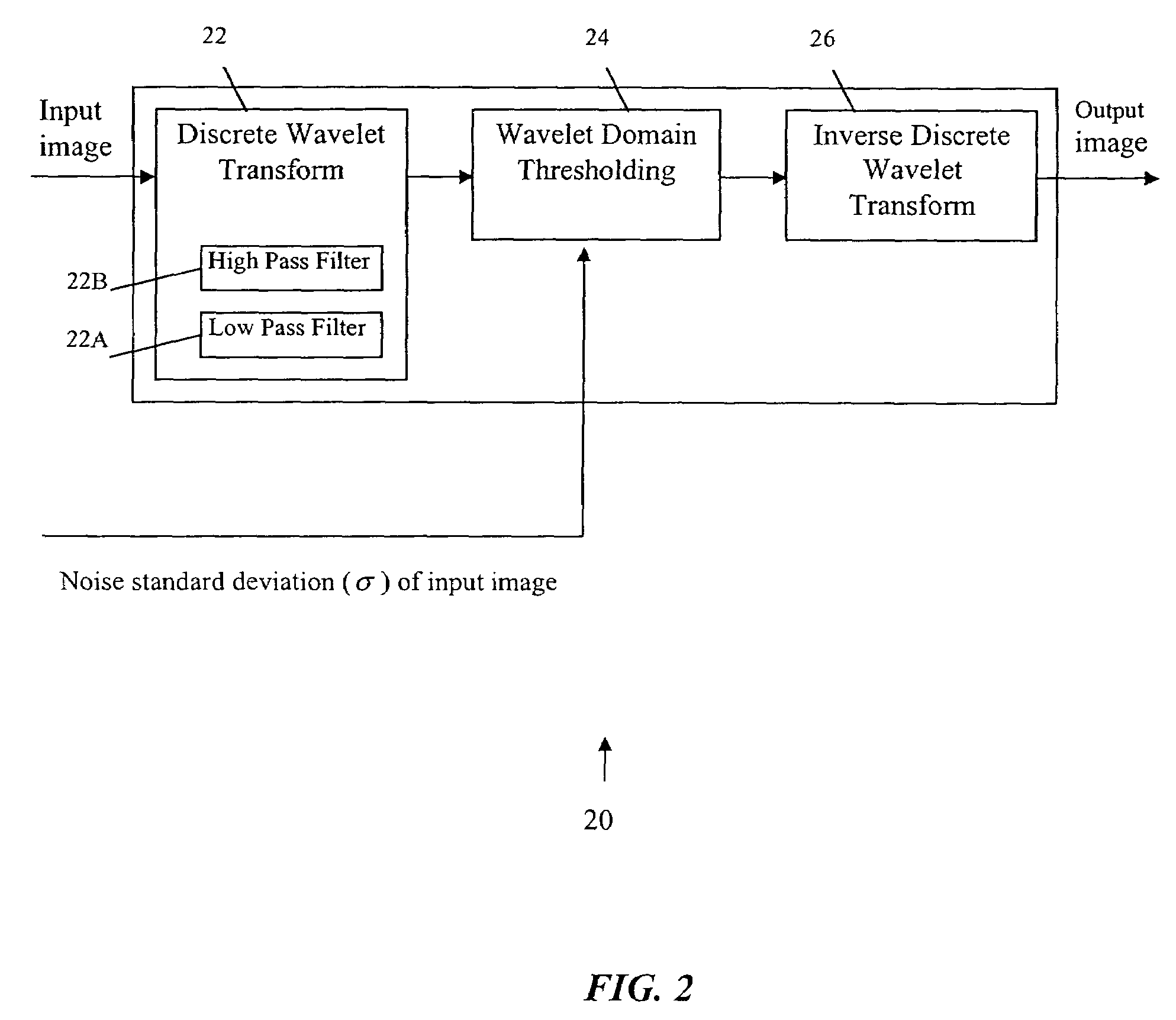
Method and apparatus for noise reduction using discrete wavelet transform
InactiveUS7260272B2Reduce noise levelReduce processImage enhancementPulse modulation television signal transmissionImage resolutionDecomposition
An improved noise reduction process by wavelet thresholding utilizes a discrete wavelet transform to decompose the image into different resolution levels. A thresholding function is then applied in different resolution levels with different threshold values to eliminate insignificant wavelet coefficients which mainly correspond to the noise in the original image. Finally, an inverse discrete wavelet transform is applied to generate the noise-reduced video image. The threshold values are based on the relationships between the noise standard deviations of different decomposition levels in the wavelet domain and the noise standard deviation of the original image.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
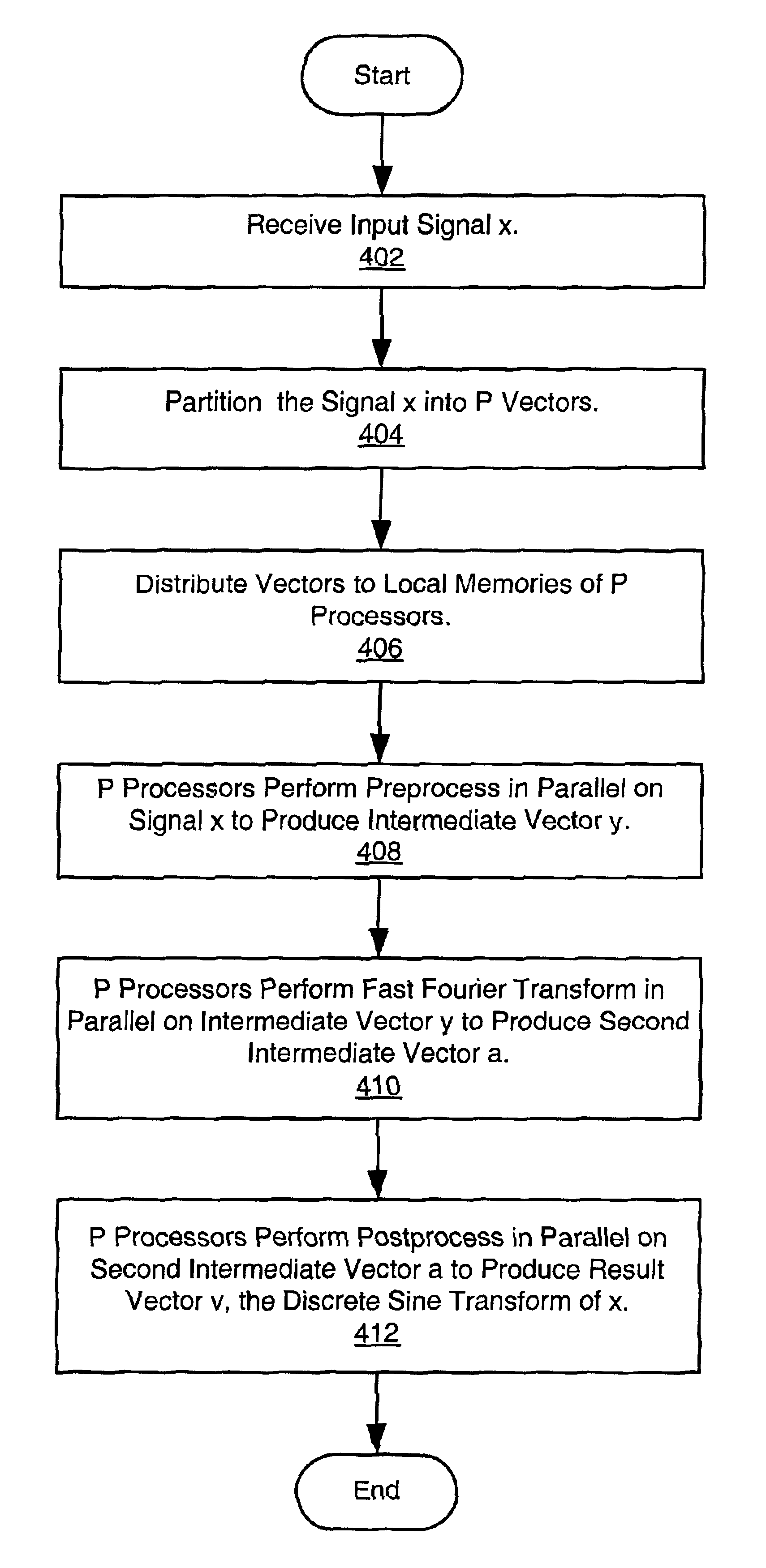
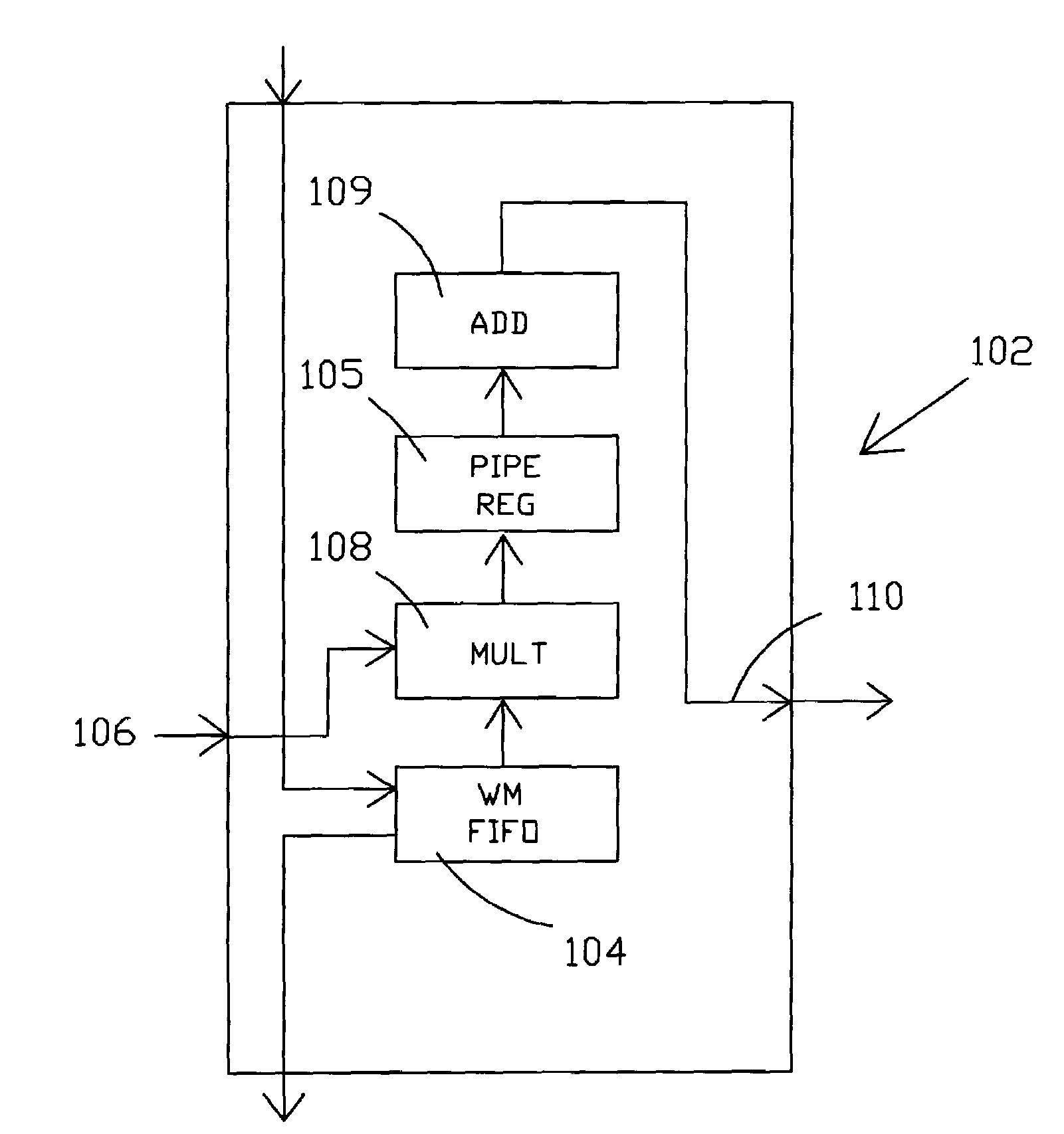
System and method for computing a discrete transform
InactiveUS6839727B2Digital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsFast Fourier transformPost processor
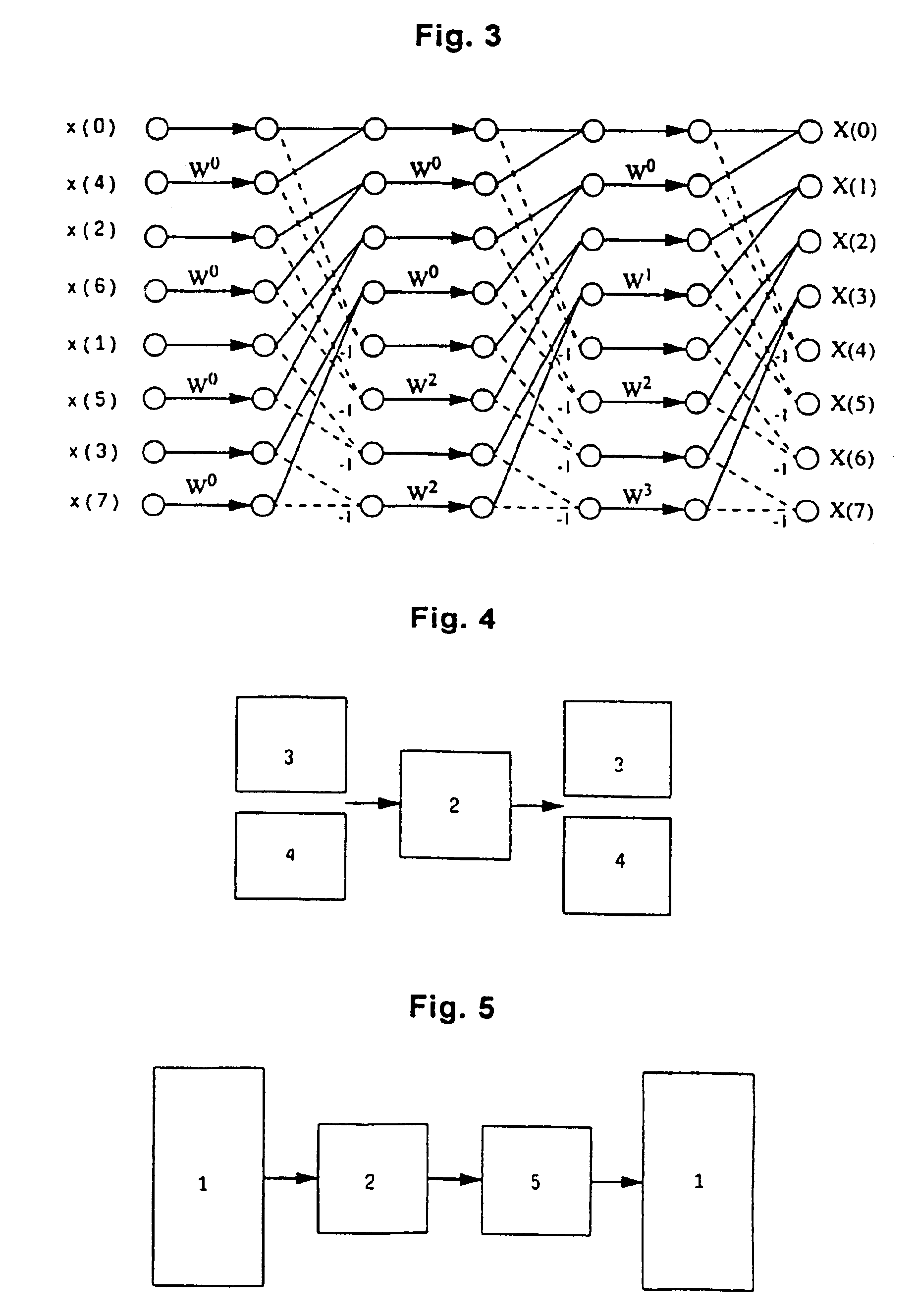
A system and method for parallel computation of Discrete Sine and Cosine Transforms. The computing system includes a plurality of interconnected processors and corresponding local memories. An input signal x is received, partitioned into P local vectors xi, and distributed to the local memories. The preprocessors may calculate a set of coefficients for use in computing the transform. The processors perform a preprocess in parallel on the input signal x to generate an intermediate vector y. The processors then perform a Fast Fourier Transform in parallel on the intermediate vector y, generating a second intermediate vector a. Finally, the processors perform a post-process on the second intermediate vector a, generating a result vector v, the Discrete Transform of signal x. In one embodiment, the method generates the Discrete Sine Transform of the input signal x. In another embodiment, the method generates the Discrete Cosine Transform of the input signal x.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Continuous extension of discrete transform for data processing
InactiveUS20060262994A1Television system detailsGeometric image transformationDiscrete cosine transformDiscrete transform
Owner:UNIV DE MONTREAL
Techniques for performing discrete fourier transforms on radix-2 platforms
ActiveUS20090313314A1Digital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsFourier transform on finite groupsDiscrete transform
A technique for performing a discrete Fourier transform (DFT) includes storing, in a single-port memory, multiple signal points. A first group of consecutive ones of the multiple signal points are fetched (from a first line of the single-port memory) to a first input register associated with a processor that includes multiple arithmetic units (AUs) that are each configured to perform multiply accumulate (MAC) operations. A second group of consecutive ones of the multiple signal points are then fetched (from a second line of the single-port memory) to a second input register associated with the processor. Selected pairs of the multiple signal points are then loaded (one from each of the first and second input registers for each pair) into the multiple arithmetic units during an initial butterfly stage. Radix-2 butterfly operations are then performed on the selected pairs of the multiple signal points (using the multiple AUs) to provide respective output elements.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Method for preprocessing vibro-sensor signals for engine diagnostics and device for carrying out thereof
InactiveUS20110224922A1Reduce diagnostic costsSimple measurement techniqueInternal-combustion engine testingFlow propertiesFiltrationEngineering
A method is provided for improved diagnostics of an internal combustion engine that includes cylinders, a crankshaft, crankshaft rotation angle sensor (CRAS), a vibro-sensor, a logic-mark sensor, each sensor produces respective signals. The method contemplates receiving the signals dividing them into a plurality of idling cycles, determining the crankshaft's position based on stochastic filtration, quasicontinuous representation of the signal, the Kalman filter, a nonlinear stochastic filter, based on CRAS characteristics and quasicontinuous representation, determining the Riesz generator basis function based on technical characteristics of the vibro-sensor, secondary discreeting of the signals with a replacement of argument, discreeting of a reciprocal function, obtaining a discrete wavelet transform, obtaining a continuous wavelet transform, obtaining a discrete wavelet transform of a reciprocal function, and producing output data. Two-dimensional arrays are divided relatively to predetermined indexes in the discrete transforms, an empirical probability distribution function is computed. Further optional diagnostic processing is provided.
Owner:KIRILLOV SERGEY +2
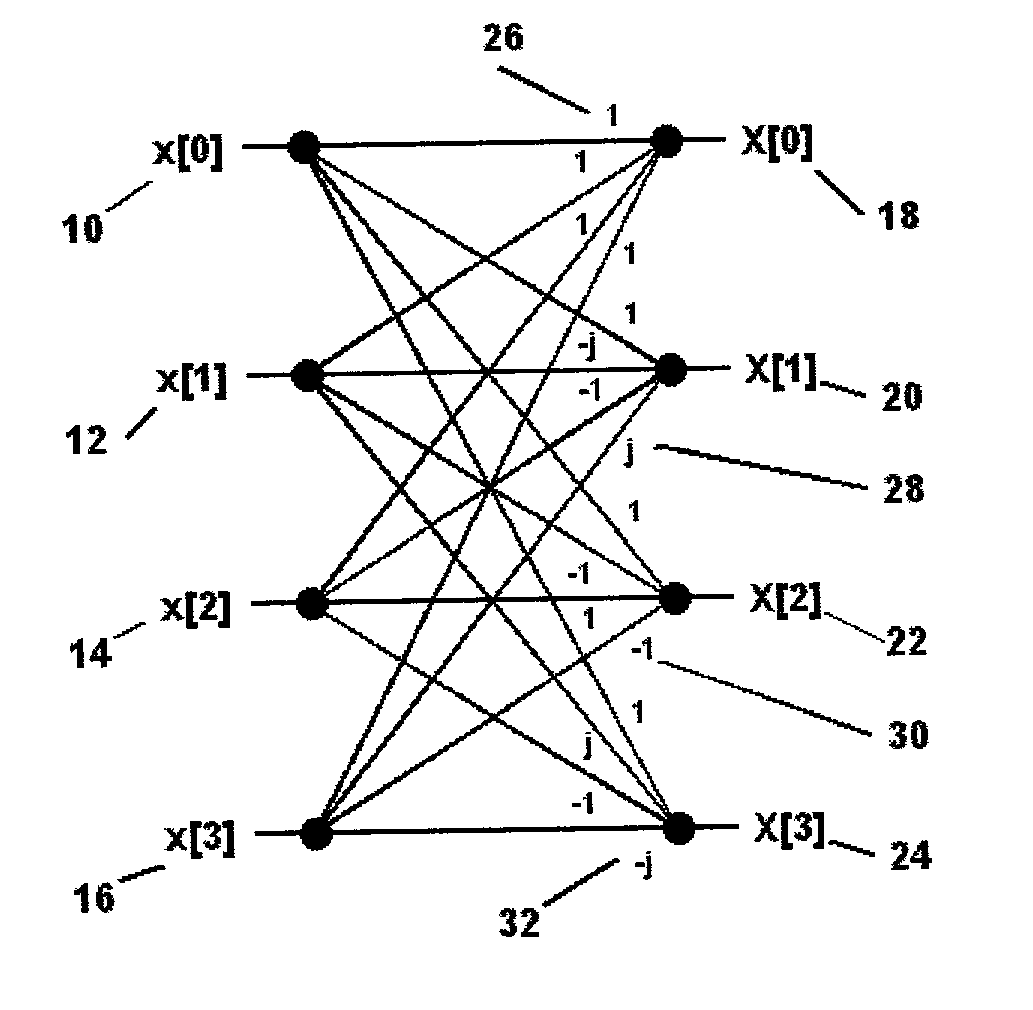
Digital systolic array architecture and method for computing the discrete Fourier transform
InactiveUS7120658B2Improve throughputLower latencyDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsDesign improvementFourier transform on finite groups
A more computationally efficient and scalable systolic architecture is provided for computing the discrete Fourier transform. The systolic architecture also provides a method for reducing the array area by limiting the number of complex multipliers. In one embodiment, the design improvement is achieved by taking advantage of a more efficient computation scheme based on symmetries in the Fourier transform coefficient matrix and the radix-4 butterfly. The resulting design provides an array comprised of a plurality of smaller base-4 matrices that can simply be added or removed to provide scalability of the design for applications involving different transform lengths to be calculated. In this embodiment, the systolic array size provides greater flexibility because it can be applied for use with any transform length which is an integer multiple of sixteen.
Owner:NASH JAMES G
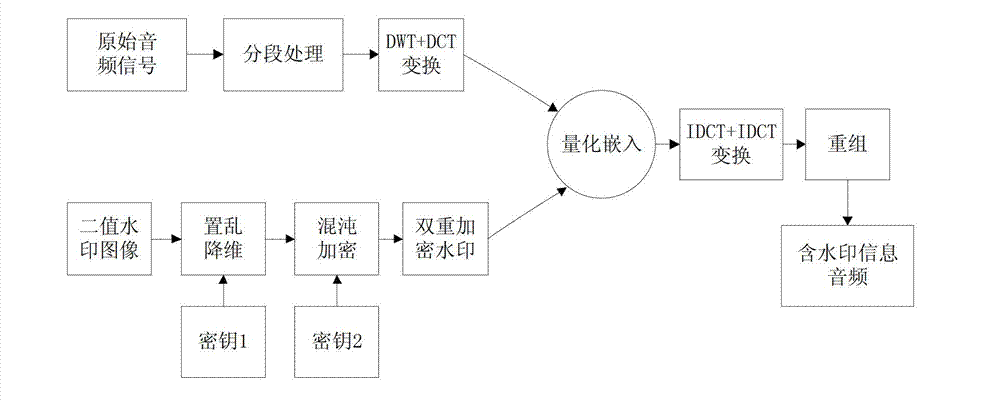
Dual encryption based discrete wavelet transform-discrete cosine transform (DWT-DCT) domain audio public watermarking algorithm
InactiveCN103208288AGuaranteed robustnessIncrease the amount of embedded informationSpeech analysisImage data processing detailsDiscrete cosine transformInverse discrete wavelet transform
The invention discloses a dual encryption based DWT-DCT domain audio public watermarking algorithm. The algorithm comprises a watermark embedding process and a watermark detection process. The watermark embedding process sequentially comprises dual encryption of a binary watermark image, segment treatment on an original voice frequency, DWT and DCT of each segment coefficient, quantization embedding, inversed discrete cosine transform (IDCT) and inversed discrete wavelet transform (IDWT) of a quantization coefficient, reorganization and obtaining of a voice frequency containing watermark information. The watermark detection process sequentially comprises segment treatment on an audio signal to be tested, DWT and DCT of each segment coefficient, summing of watermark reference values at corresponding positions of n watermark coefficient series, reconfiguration of a two-dimensional image, inverted scrambling treatment and obtaining of a restored watermark image. By the aid of the algorithm, the transparency of watermarks is effectively guaranteed, the miss ratio of watermarks is greatly reduced, and the robustness and the accuracy of the watermark detection are improved.
Owner:ZHANGZHOU INST OF TECH
Shared multiplication in signal processing transforms
InactiveUS20030074383A1Computation using non-contact making devicesComplex mathematical operationsBinary multiplierFourier transform on finite groups
A machine or method used in signal processing transforms involving computation of one or more sums each of one or more products. A first multiplier computes a first product and a first set of intermediate terms. A second multiplier computes a second product using one or more of the terms computed by the first multiplier. Because they share computations, the two multipliers can have lower implementation cost than if they function separately. The invention is particularly useful in signal processing transforms that have fixed weights, such as discrete Fourier transforms, discrete cosine transforms, and pulse-shaping filters. These transforms are multiply-intensive and are used repeatedly in many applications. Implementations of shared multiplication techniques can have reduced chip space, computation time, and power consumption relative to implementations that do not share computation. Depending on the properties of the transform being computed, shared multiplication can exploit constant numbers, variable numbers from limited sets of allowed values, and restrictions on one or both numbers in particular products.
Owner:MURPHY CHARLES DOUGLAS
Watermarking method resistant to geometric attack in wavelet transform domain
InactiveUS20090060257A1Character and pattern recognitionImage data processing detailsPeak valueComputer vision
The present invention relates, in general, to a watermarking method resistant to a geometric attack in a wavelet transform domain, and, more particularly, to technology for embedding a watermark in a discrete wavelet transform (DWT) domain, thus extracting autocorrelation (AC) peaks, which play an important part in the estimation of geometric attacks in ACF-based watermarking, and detecting watermarks using the AC peaks even after geometric distortion is applied. In the watermarking method of the present invention, a watermark pattern is embedded in subbands of a Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT) domain. An Autocorrelation Function (ACF) of a watermark is executed in the domain, thus detecting a watermark required to estimate a geometric attack. A watermark signal is detected using an undecimated wavelet transform so as to compensate for an image shift in the watermark.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Image fragile watermarking algorithm capable of realizing accurate positioning of tampered region
InactiveCN102096894APrecise positioningImage data processing detailsPattern recognitionLinear relationship
An image is easily tampered in certain application occasions, so that the real content of the image is hard to identify. Therefore, the content of the image is identified by means of tamper detection necessarily. The invention provides an image fragile watermarking algorithm capable of realizing accurate positioning of a tampered region based on discrete cosine transform. The method comprises the following steps: performing the discrete cosine transform on an original image in a partitioning way; adjusting the numerical value of the high-frequency coefficient of the image subblock discrete cosine transform to build the linear relationship of the numerical values between the two different discrete cosine transform coefficients of the same subblock; and obtaining a coefficient-adjusted image by means of the discrete cosine transform. When the content is identified, the tamper detection is realized by judging whether the set numerical value linear relation is existed between the two corresponding discrete cosine transform coefficients of each subblock of the tampered image by utilizing the reversibility of the discrete cosine transform, thus tamper detection is realized. The algorithm provided by the invention can be used for accurately positioning the tampered region of the image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Realization method for fast computation of discrete Fourier transform with non-second power points
InactiveCN103020015AMaintain propertiesNo increase in sampling pointsComplex mathematical operationsFinite fourier transformDecomposition
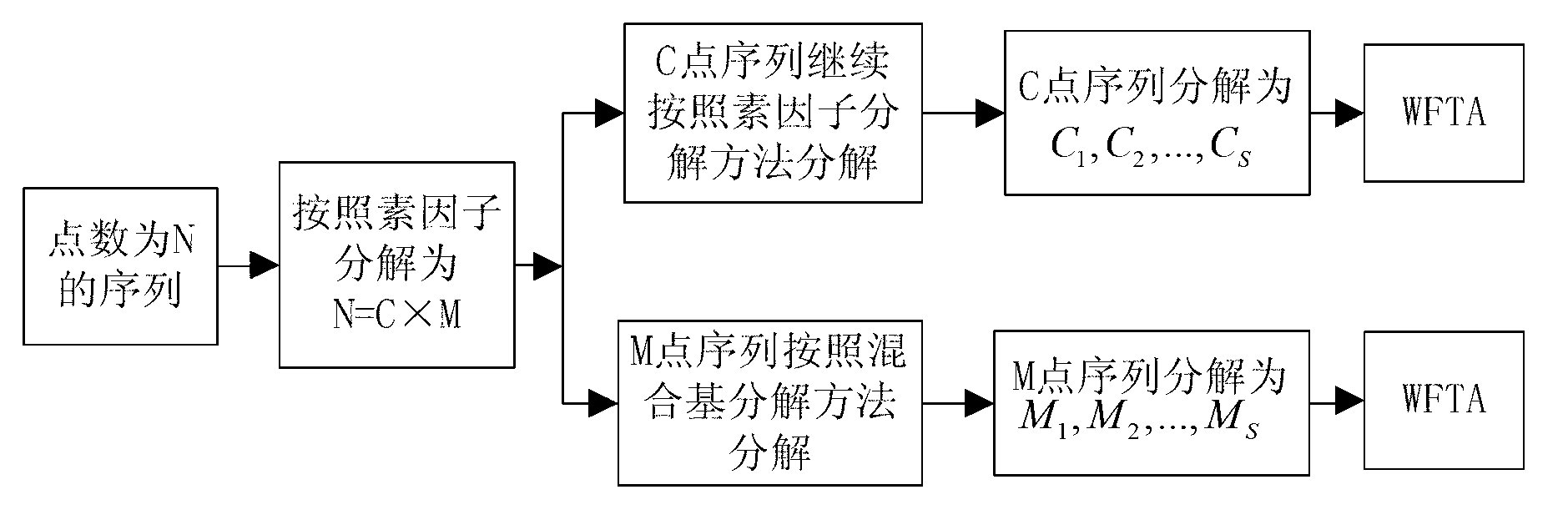
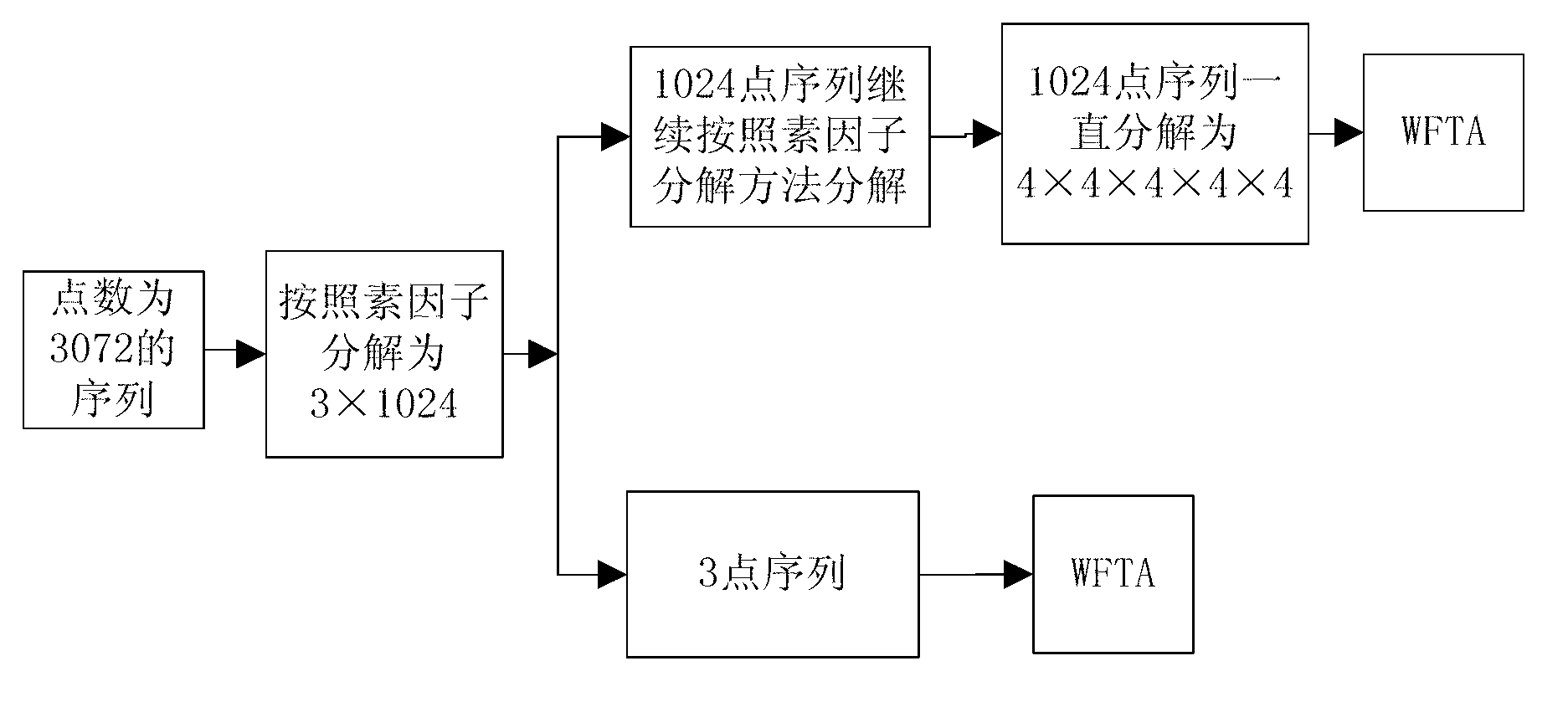
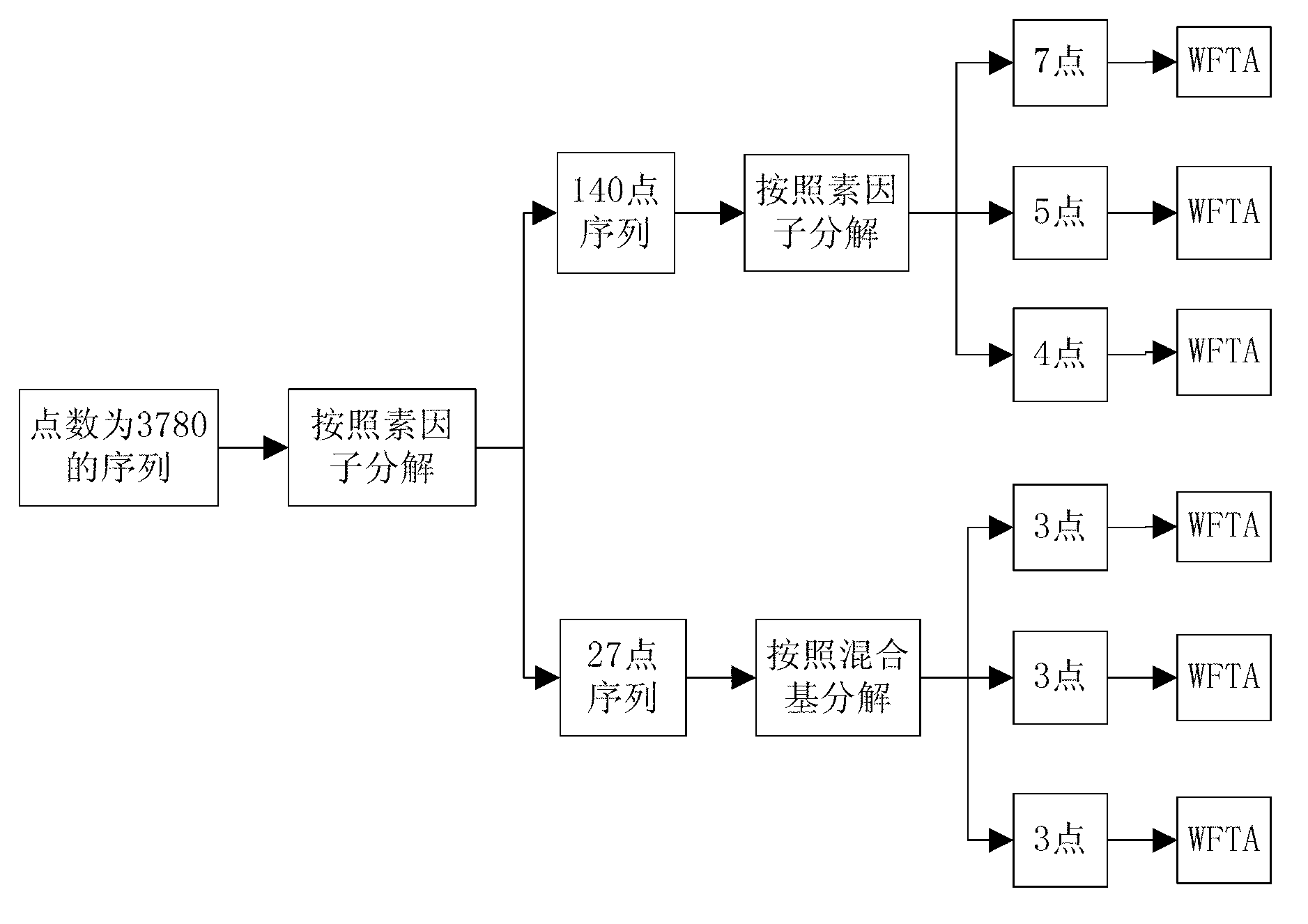
The invention discloses a realization method for fast computation of discrete Fourier transform with non-second power points. The realization method is an improvement obtained by comprehensively using a prime factor decomposition algorithm, a mixed-radix FFT (fast Fourier transform) algorithm and a WFTA (Winograd Fourier transform algorithm) decomposition method, and the sequence of non-second power points is decomposed layer by layer through common factor decomposition and prime factor decomposition. The realization method for fast computation of discrete Fourier transform with non-second power points has the characteristics of less computation, high computation efficiency and small overhead for realization.
Owner:GUILIN KSW COMM TECH
Adaptive block length, constant converting audio frequency decoding method
The invention discloses the method used to supply the audio signal from the compressing audio code stream, it includes the below steps: the code stream can be conducted the unbinding format to distill the changing modulus and the number of the changing modulus of the every blocks; the gained changing modulus are separated into these blocks: the length of the block is equal to the power of the two, and the length of the block is more length than the times of then the number of the changing modulus of every blocks through the unbinding format; the constant length of the reverse scatter changing is used to process the reverse transform of the changing modulus after the blocking, so the transformed reversely sampling buffer is gained; the time field sampling is distilled from the gained reverse changing sampling buffer; the block through the window changing are folded by the composing window conducting the window changing to the distilled time domain sampling block. Thereinto, the numbers of the received changing modulus can be different each other.
Owner:NERO AG
Compressive sensing
ActiveUS9632193B2Lower acquisition costsData augmentationSeismic data acquisitionSeismic signal processingSeismic traceDiscrete transform
Computer-implemented method for determining optimal sampling grid during seismic data reconstruction includes: a) constructing an optimization model, via a computing processor, given by minu∥Su∥1s.t. ∥Ru−b∥2≦σ wherein S is a discrete transform matrix, b is seismic data on an observed grid, u is seismic data on a reconstruction grid, and matrix R is a sampling operator; b) defining mutual coherence asμ≤CSm(logn)6,wherein C is a constant, S is a cardinality of Su, m is proportional to number of seismic traces on the observed grid, and n is proportional to number of seismic traces on the reconstruction grid; c) deriving a mutual coherence proxy, wherein the mutual coherence proxy is a proxy for mutual coherence when S is over-complete and wherein the mutual coherence proxy is exactly the mutual coherence when S is a Fourier transform; and d) determining a sample grid r*=arg minr μ(r).
Owner:SHEARWATER GEOSERVICES SOFTWARE INC
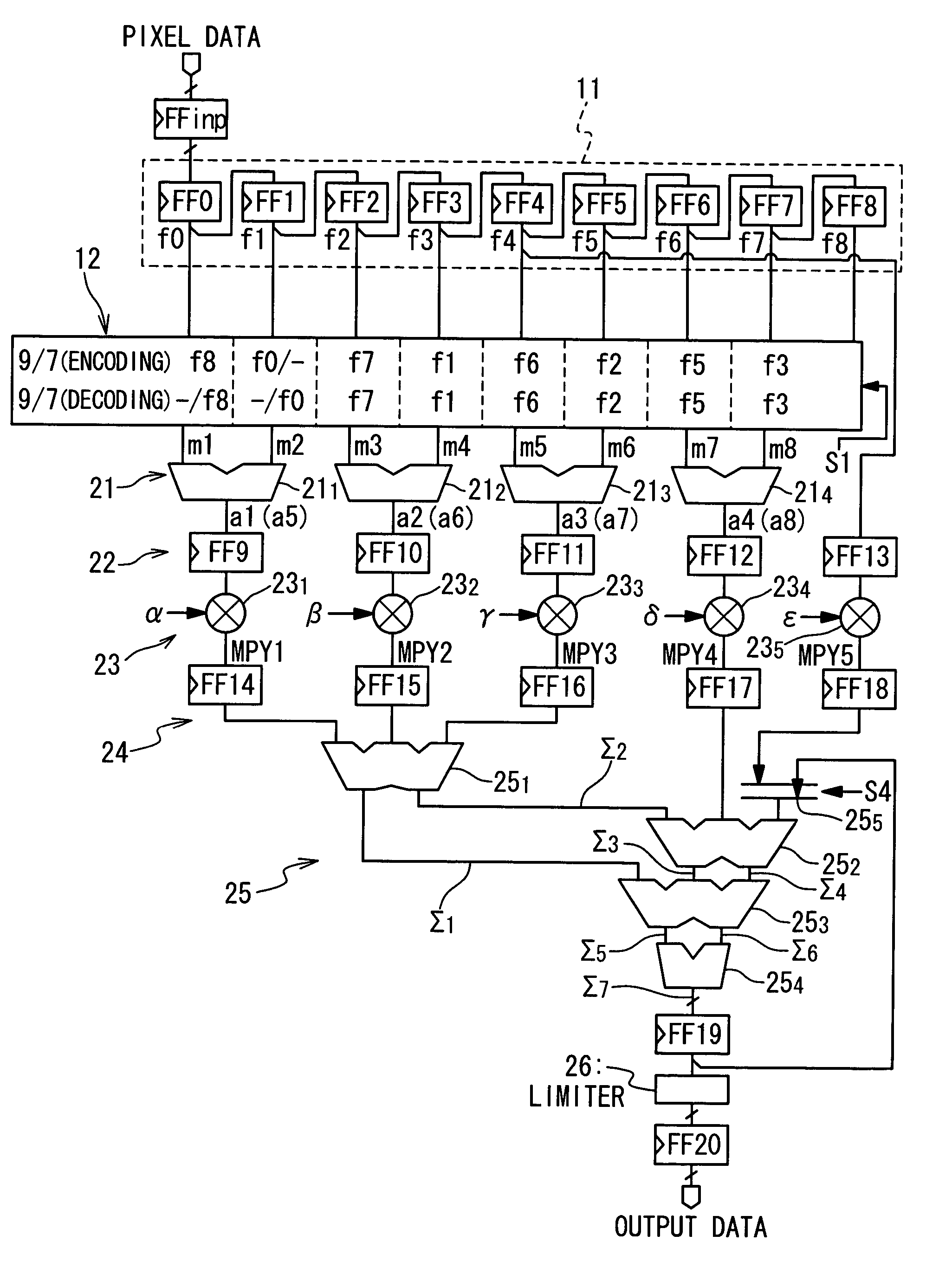
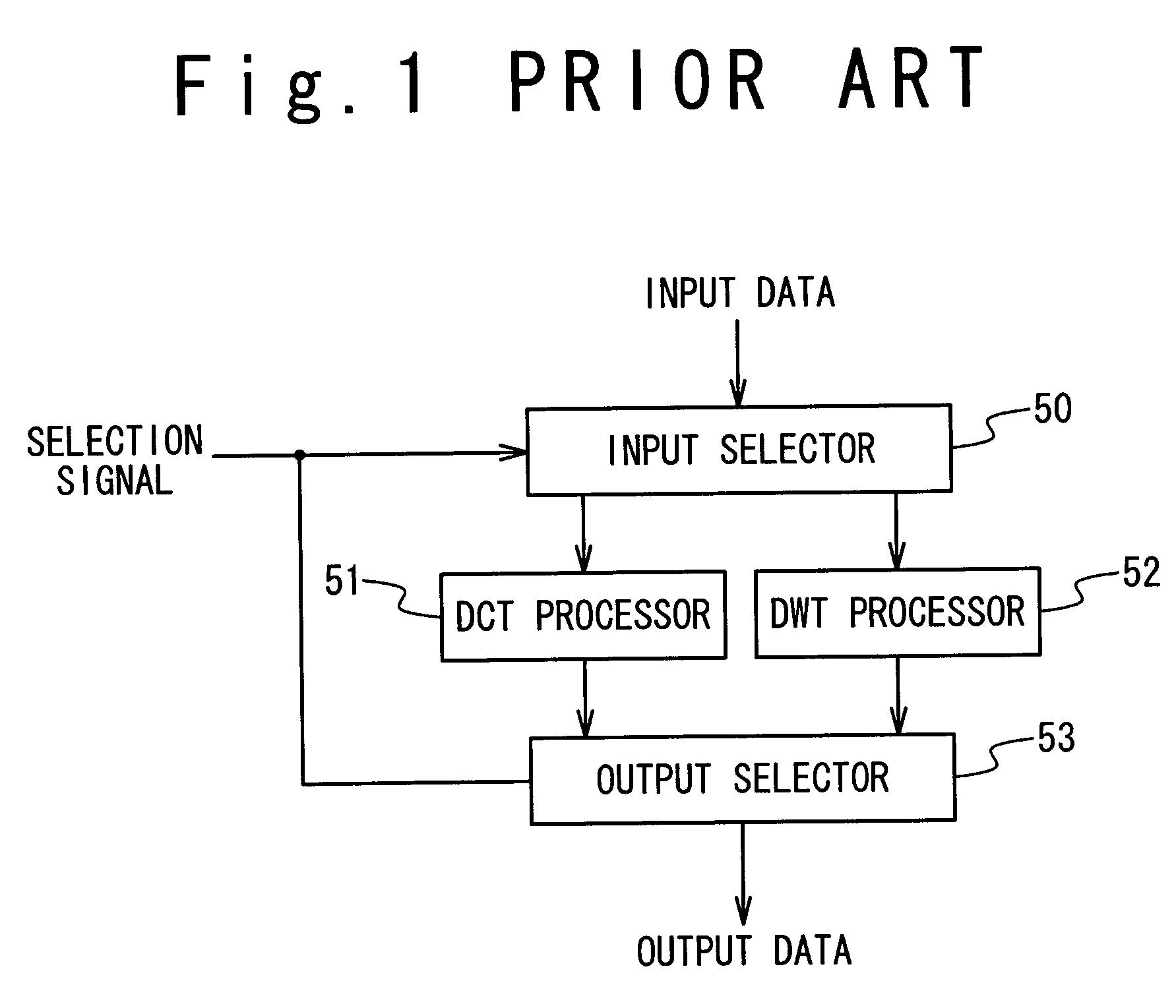
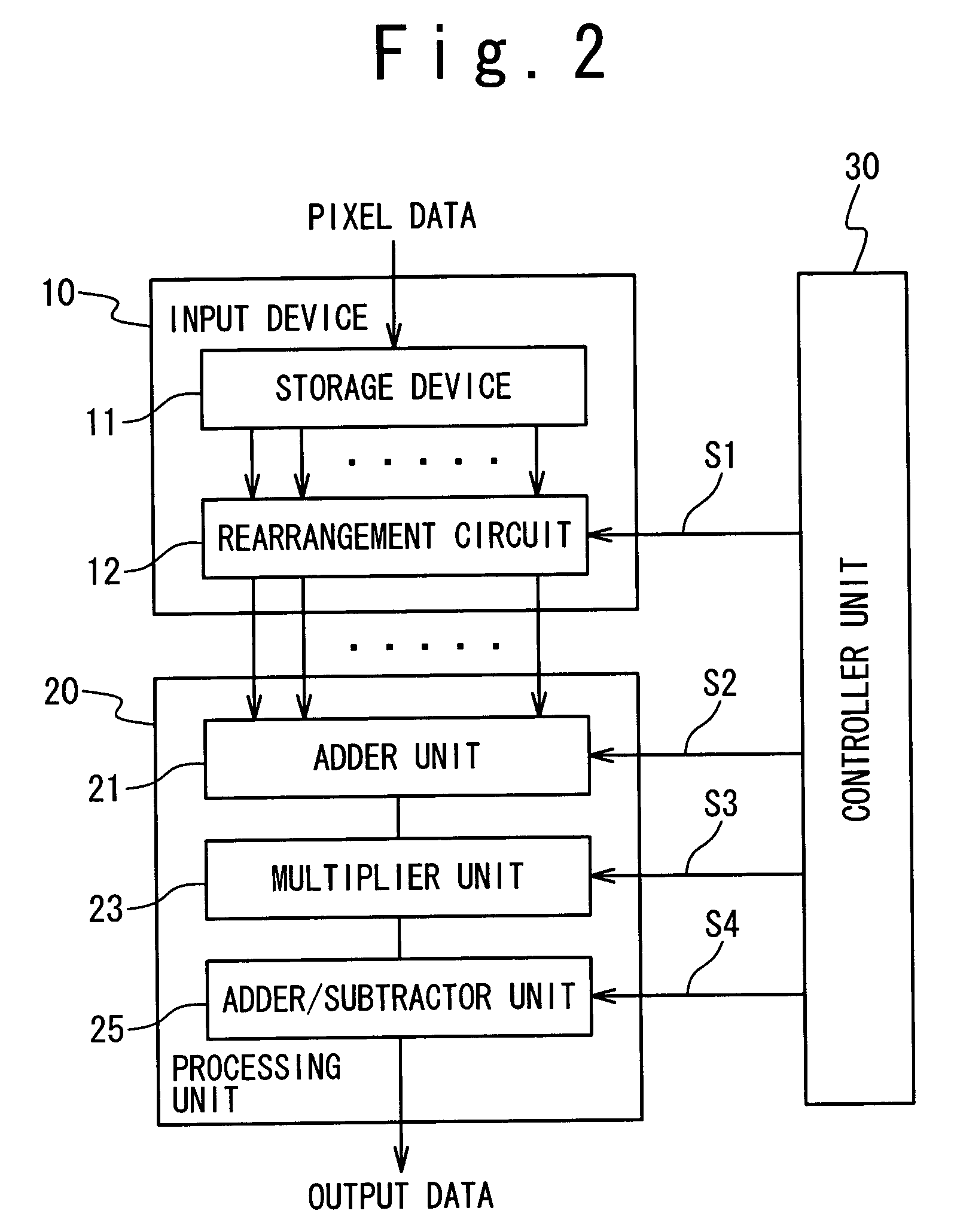
Image processing apparatus supporting both discrete cosine transform and discrete wavelet transform
ActiveUS7346640B2Reduce decreaseReduced hardware resourceCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationImaging processingDiscrete cosine transform
An image processing apparatus supporting both discrete wavelet transform and discrete cosine transform with reduced hardware resources. The image processing apparatus is composed of an input unit receiving a plurality of pixel data, a controlling unit selecting a desired transform from among discrete wavelet transform and discrete cosine transform, and providing a plurality of coefficients depending on the desired transform, and a processing unit which processes the pixel data using the plurality of coefficients to achieve the desired transform.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
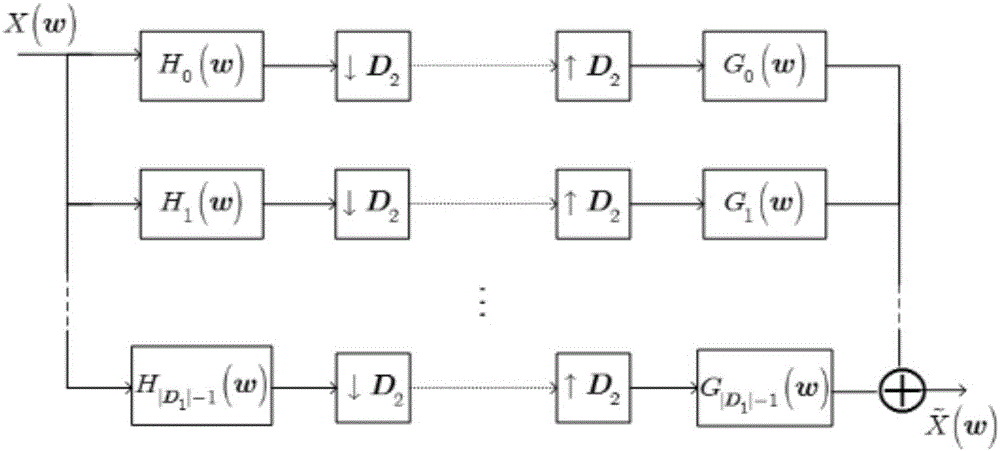
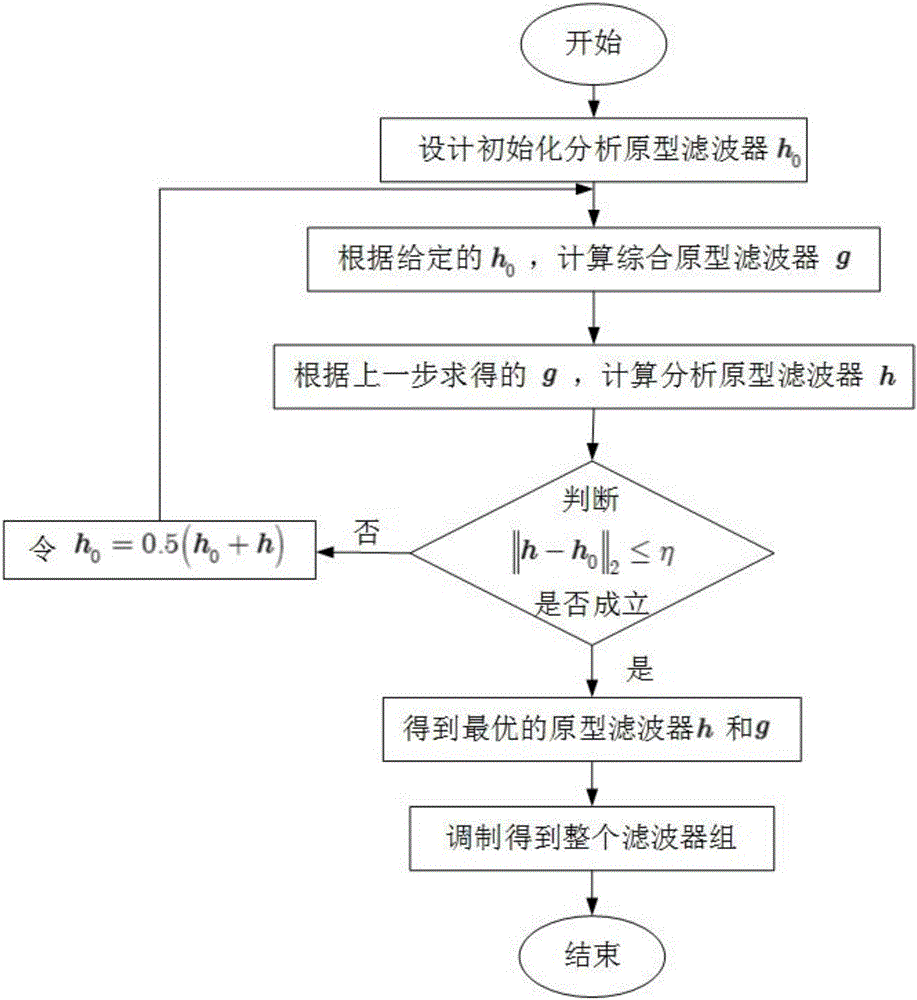
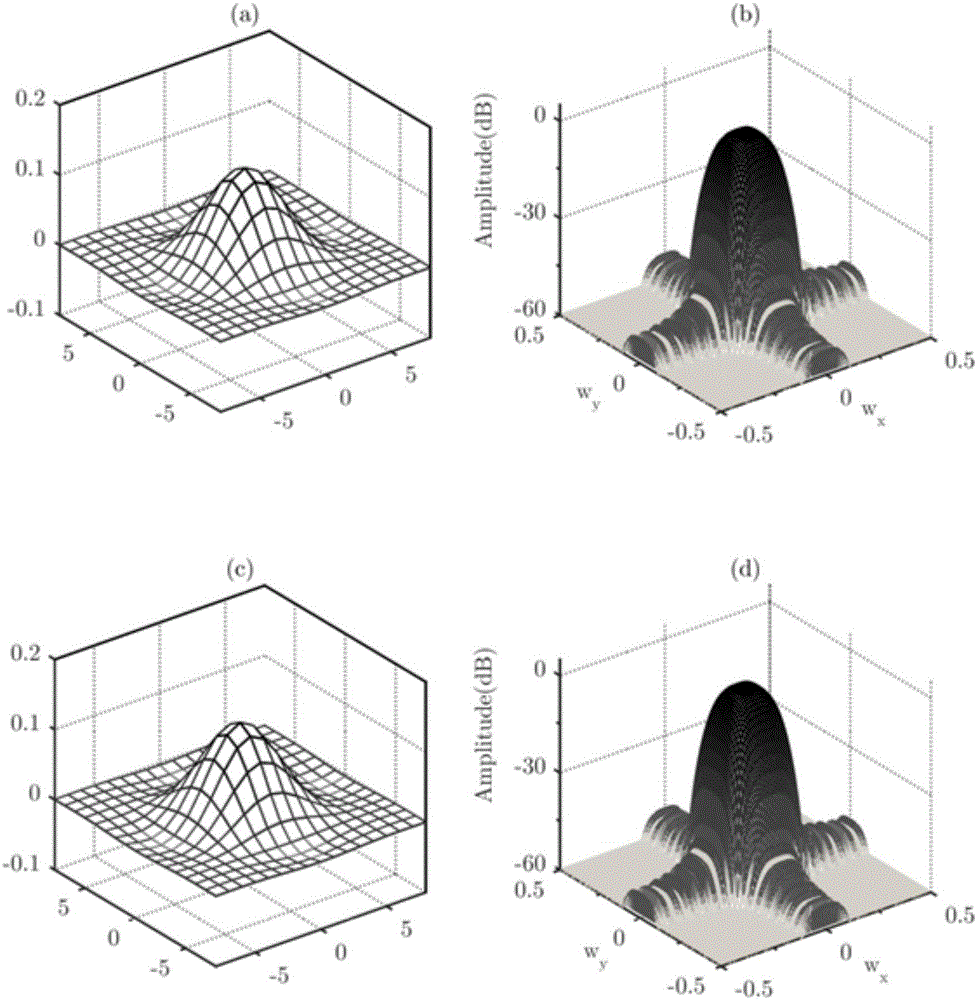
Design method of two-dimensional double prototype completely-oversampled DFT (discrete Fourier transform) modulated filter bank
InactiveCN105787204AImprove performanceRapid designCAD circuit designConstraint-based CADComputation complexityFast algorithm
The invention discloses a design method of a two-dimensional double prototype completely-oversampled DFT (discrete Fourier transform) modulated filter bank. The design of the completely-oversampled DFT modulated filter bank is realized under the condition of near perfect reconstruction. The design problem of two prototype filters is resolved into an unconstrained optimization problem, wherein an objective function is overall distortion of the filter bank, namely, a weighted sum of transmission distortion, aliasing distortion and stopband energy of the prototype filters, and the optimization problem is solved through a double-iteration mechanism according to gradient vectors of the objective function. The computation complexity is remarkably reduced according to equivalent conditions of matrix inversion and a fast algorithm of Toeplitz matrix inversion in single-step iteration. With the adoption of the method, the filter bank with better overall performance can be obtained, the computation complexity is greatly reduced, and the large-scale two-dimensional filter banks can be rapidly designed.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
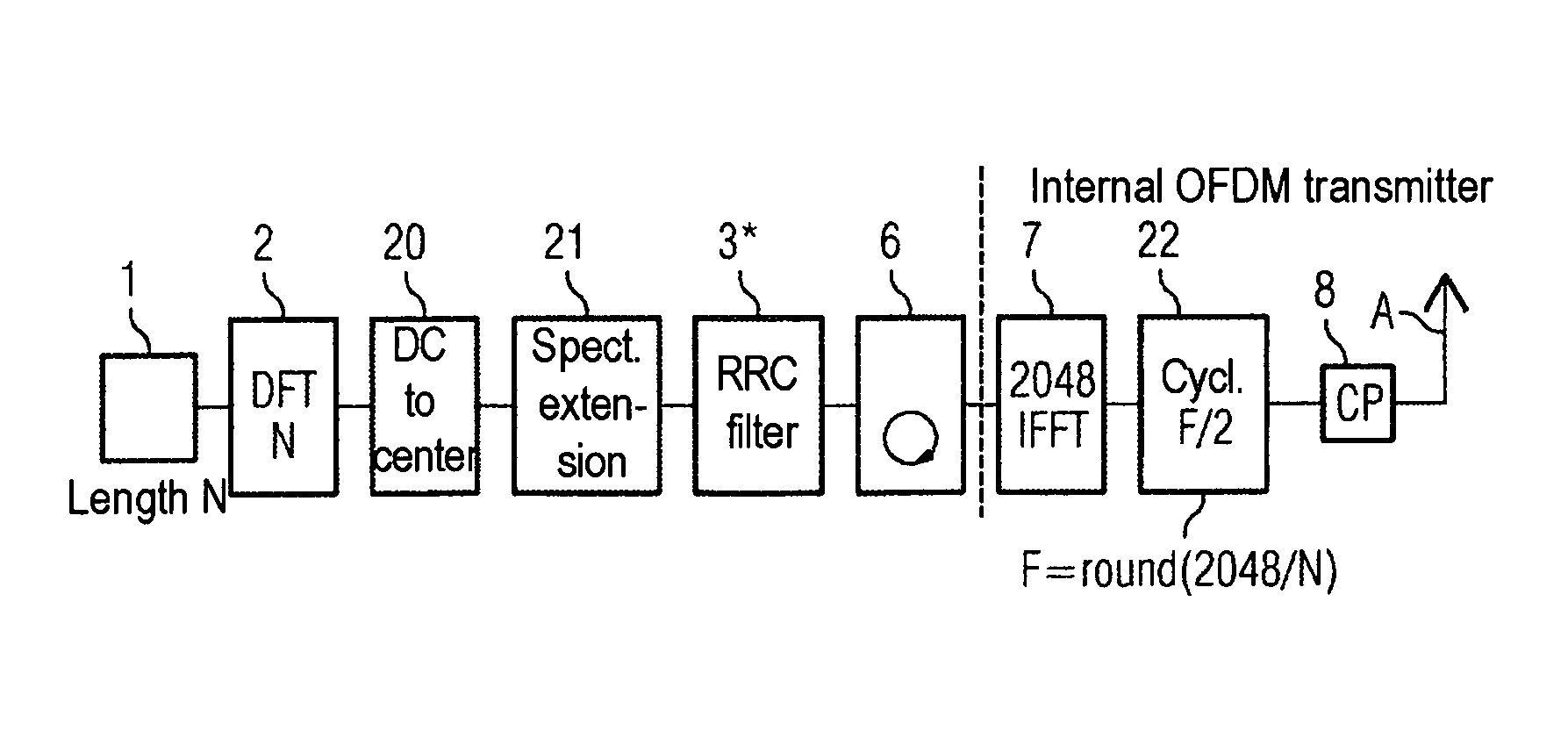
Method and/or OFDM device for SC-FDMA data transmission
ActiveUS8422572B2Less complex data processingReduce power consumptionTransmission control/equalisingFrequency-division multiplexSignal onData signal
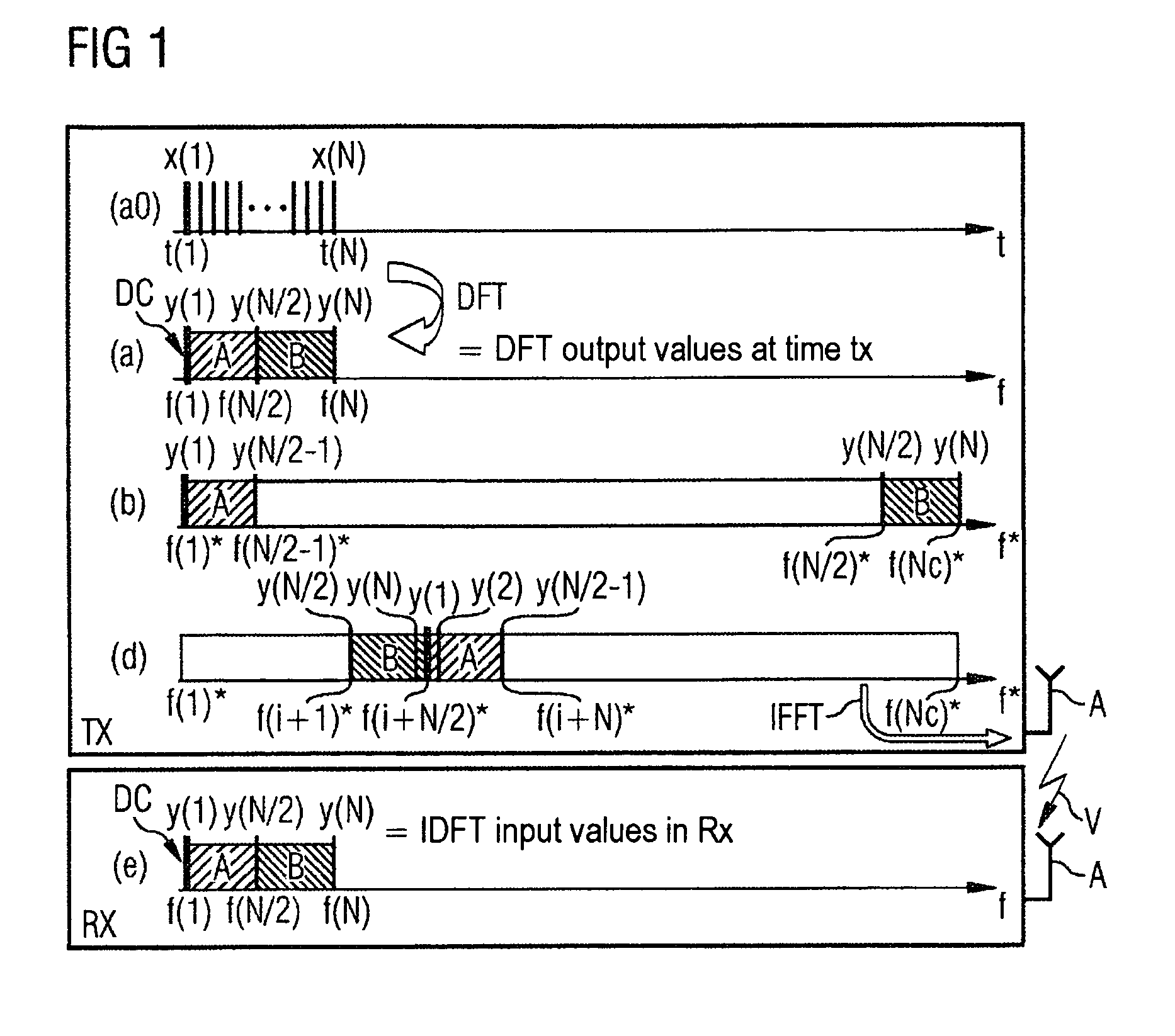
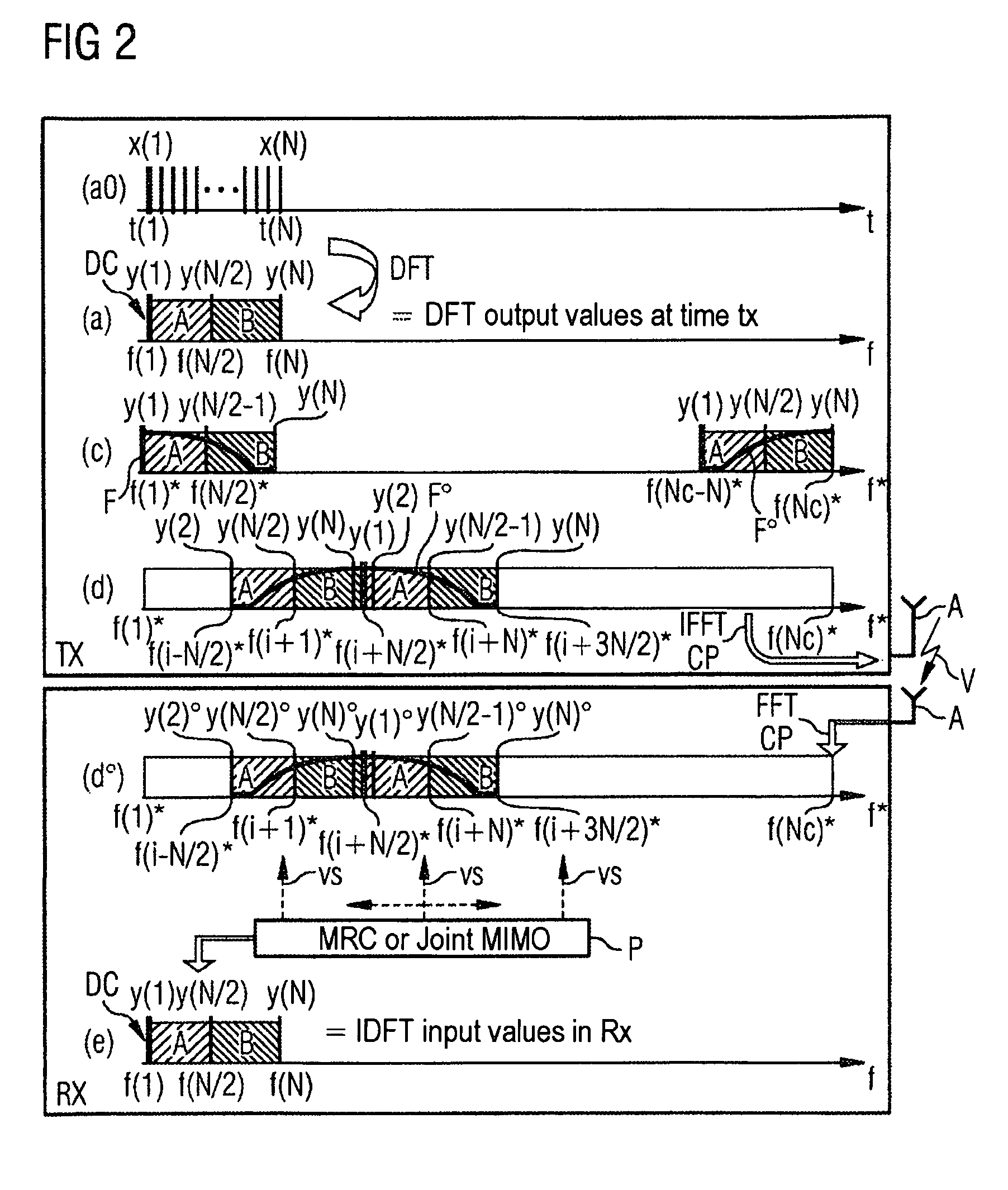
In a method and / or an OFDM device for SC-FDMA data transmission, a sequence of input data is transformed by means of a discrete transformation as transformed data signals of coded and modulated data signals on first frequency channels into a first frequency space over a first number of frequencies. The transformed data signals are mapped on second frequency channels in a second frequency space with a larger second number of frequencies. The transformed data signals on the second frequency channels are inverse-transformed using an inverse transformation. Data inversely transformed in such a way are provided for transmission. The transformed data signals are mapped into a frequency range of the second frequency channels in such a way that a constant component of the transformed data signals is mapped centrally within the frequency range.
Owner:NOKIA SIEMENS NETWORKS GMBH & CO KG +1
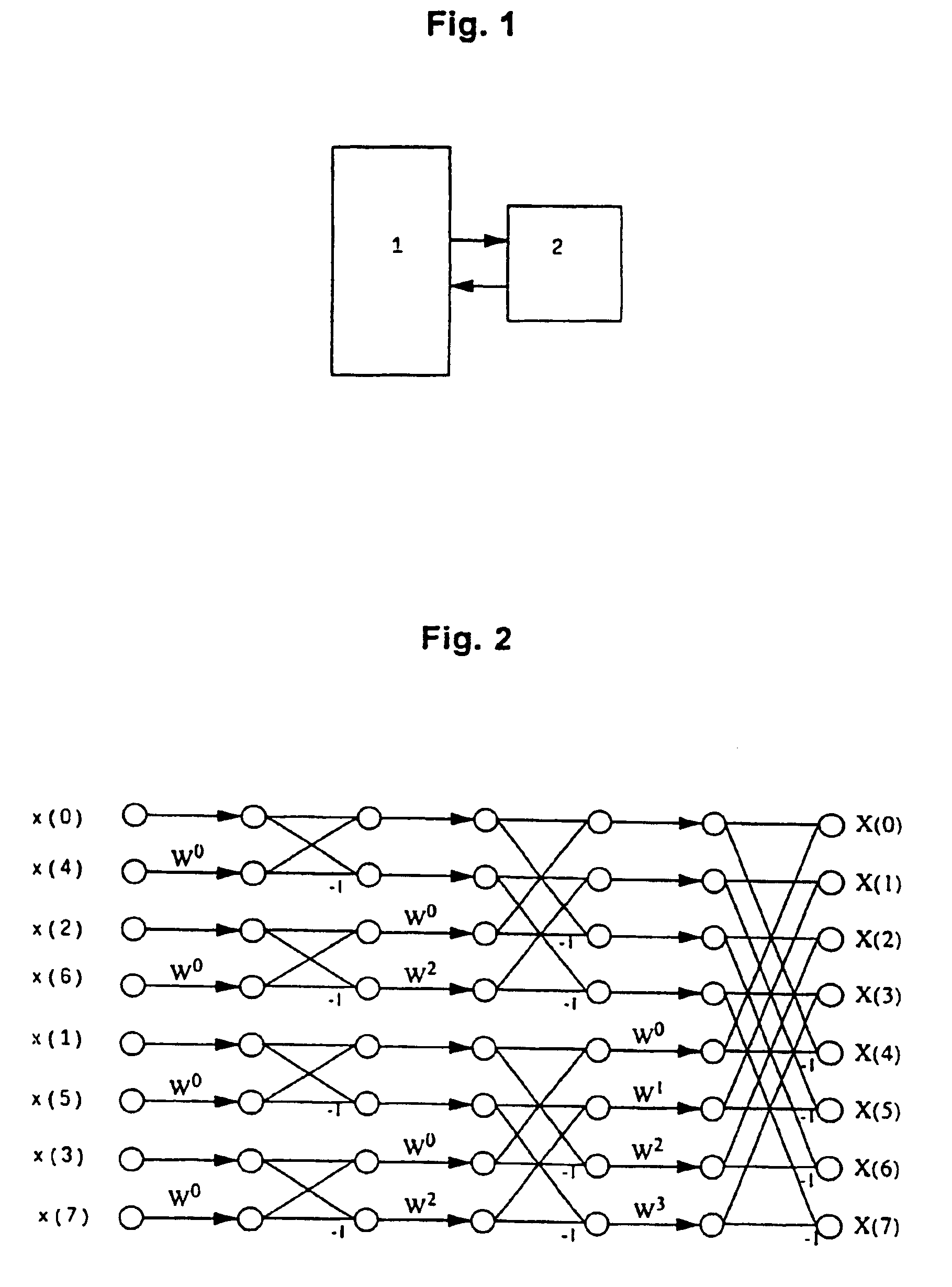
Method and device for calculating a discrete orthogonal transformation such as FFT or IFFT
InactiveUS6904445B1Quick calculationFacilitates addressingCode conversionComplex mathematical operationsOrthogonal transformationDiscrete transform
The invention comprises a method for calculating an orthogonal discrete transform on the basis of the DIT method in prescribed intermediate steps with the following steps: the data are read from a memory organized on page-for-page basis; the intermediate step prescribed by the transform is carried out; the resulting data are stored in a buffer memory; and the resulting data are written page-for-page from the buffer memory to the memory organized on a page-for-page basis. Suitable discrete orthogonal transforms are FFT, IFFT, DCT, IDCT and transforms of similar structure.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Fixed-Coefficient Variable Prime Length Recursive Discrete Fourier Transform System
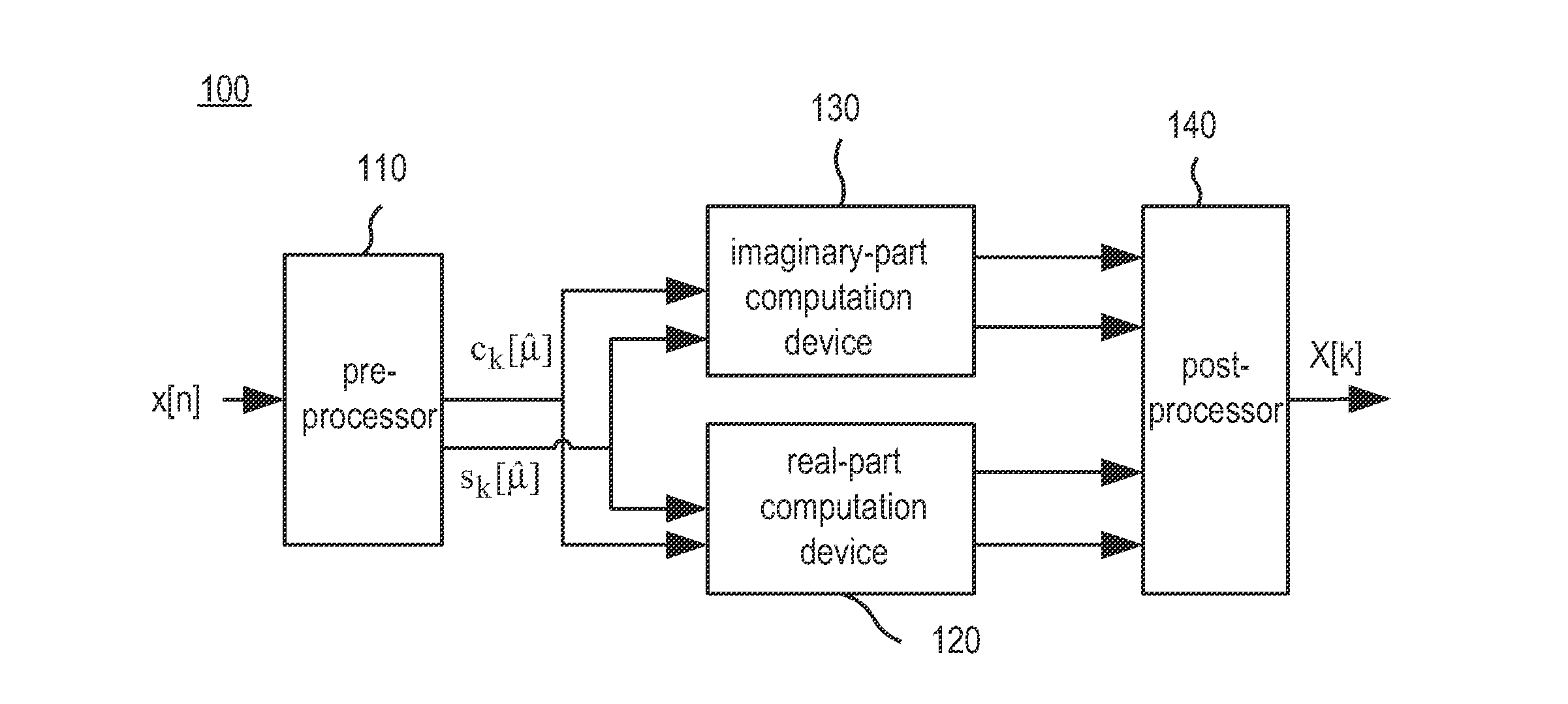
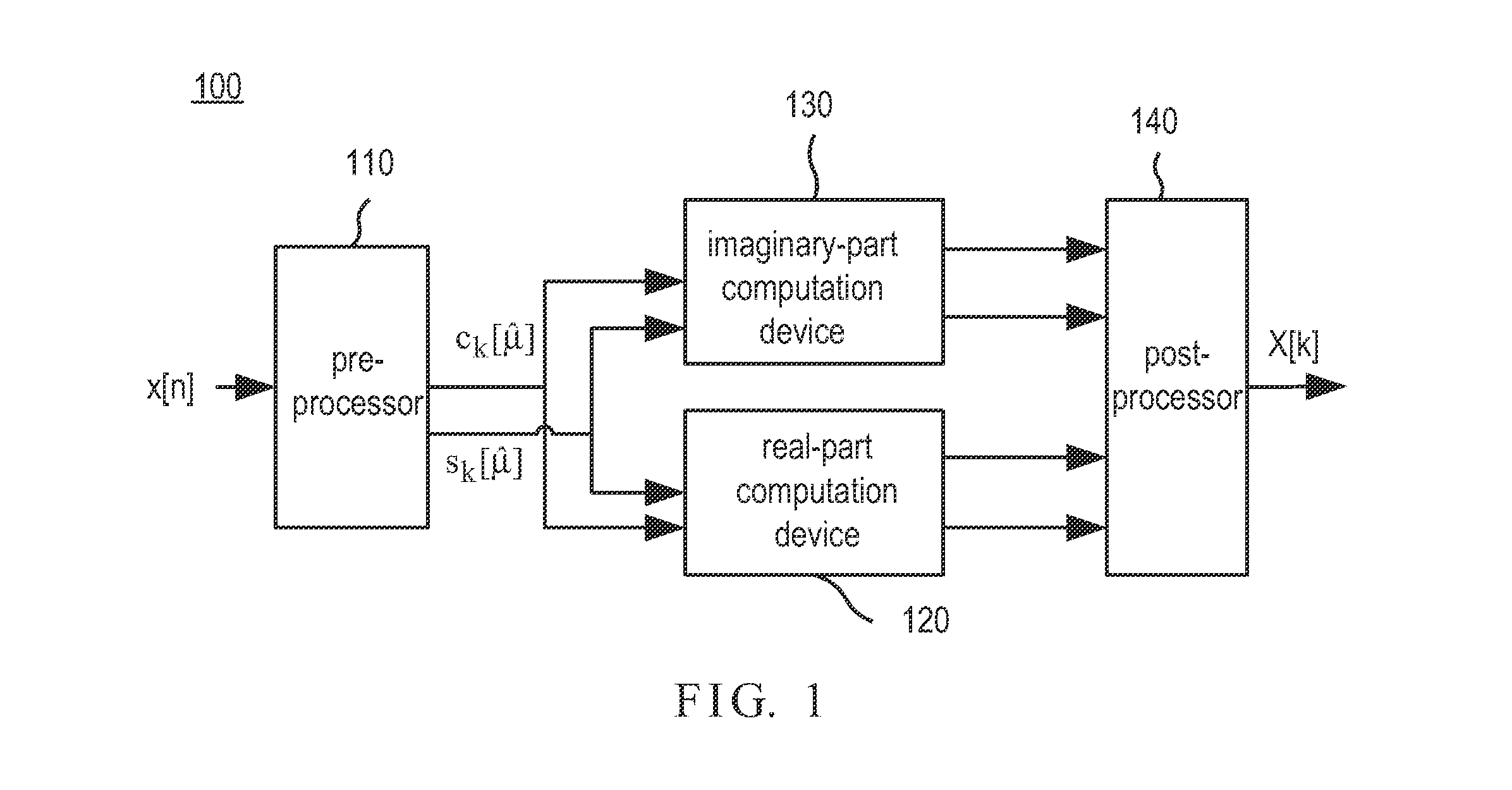
InactiveUS20130173680A1Reduce complexityDataDigital computer detailsComplex mathematical operationsInverse discrete fourier transformFourier transform on finite groups
A fixed-coefficient variable prime length recursive discrete Fourier transform system includes a pre-processing device, a real-part computation device, an imaginary-part computation device and a post-processing device. The pre-processing device receives N digital input signals and performs order permutation operation to generate first and second temporal signals, wherein N is a prime number. The real-part computation device receives the real part of the first and second temporal signals and performs discrete cosine / sine transform to generate third and fourth temporal signals. The imaginary-part computation device receives the imaginary part of the first and second temporal signals and performs discrete cosine / sine transform to generate fifth and sixth temporal signals. The post-processing device receives the third, fourth, fifth and sixth temporal signals to perform order permutation and addition operations for generating N digital output signals, wherein the N digital output signals are the discrete Fourier transform of the N digital signals.
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
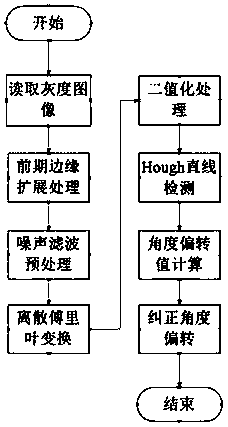
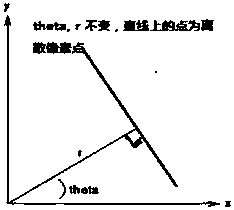
Fourier transform-based text image deflection correction method
PendingCN108121983AEasy to identifyImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionFast Fourier transformDiscrete transform
The invention discloses a Fourier transform-based text image deflection correction method. Mainly, an angular deflection value is analyzed from a frequency domain of a text image through discrete Fourier transform, thereby realizing deflection correction of the text image.
Owner:蓝盾信息安全技术有限公司
SPEED fast magnetic resonance imaging method based on discrete cosine transform
ActiveCN103728581AImprove sparsityQuality improvementMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsData acquisitionDiscrete cosine transform
The invention discloses a SPEED fast magnetic resonance imaging method based on discrete cosine transform. The SPEED fast magnetic resonance imaging method based on discrete cosine transform mainly includes the steps of k space data collection, zero fill Fourier reestablishment, discrete cosine transform, discrete cosine transform domain double-layer sparse ghost model determining, overlapped ghost separation based on LSE, discrete cosine inverse transformation, registering and summation of a plurality of ghost sub-images and image reconstruction. By means of the SPEED fast magnetic resonance imaging method, discrete cosine transform can be used for SPEED data sparse representation and improve image sparseness, and accordingly quality of a SPEED reconstructed image is improved.
Owner:镇江利达信息科技有限公司
Discrete cosine neural-network fuzzy noise reduction method for nuclear detection data
ActiveCN103176219AEasy to identifyImprove signal-to-noise ratioBiological neural network modelsNuclear radiation detectionPattern recognitionFrequency spectrum
The invention belongs to the field of nuclear detection processing in nuclear technique exploration, in particular to a discrete cosine neural-network fuzzy noise reduction method for nuclear detection data, and aims to effectively reduce noise in gamma spectrum data. The method includes the steps: subjecting spatial data formed by nuclear detection signal data to discrete cosine transform to obtain frequency spectrum data in a discrete cosine domain; subjecting the nuclear detection data to filtering and inverse discrete cosine transform in the discrete cosine domain to obtain primary noise reduction result; establishing a neural network, inputting a sample by using the nuclear detection signal data as nodes in the neural network, and estimating parameters of a membership function in the neutral network by means of least squares back-propagation to obtain final noise reduction result output by the neural network. The method is capable of well recognizing noise signals, network model parameters are regulated and optimized according to noise signal features, the noise in the signal data is reduced effectively, and signal-to-noise ratio of the nuclear detection data is increased greatly.
Owner:BEIJING RES INST OF URANIUM GEOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com